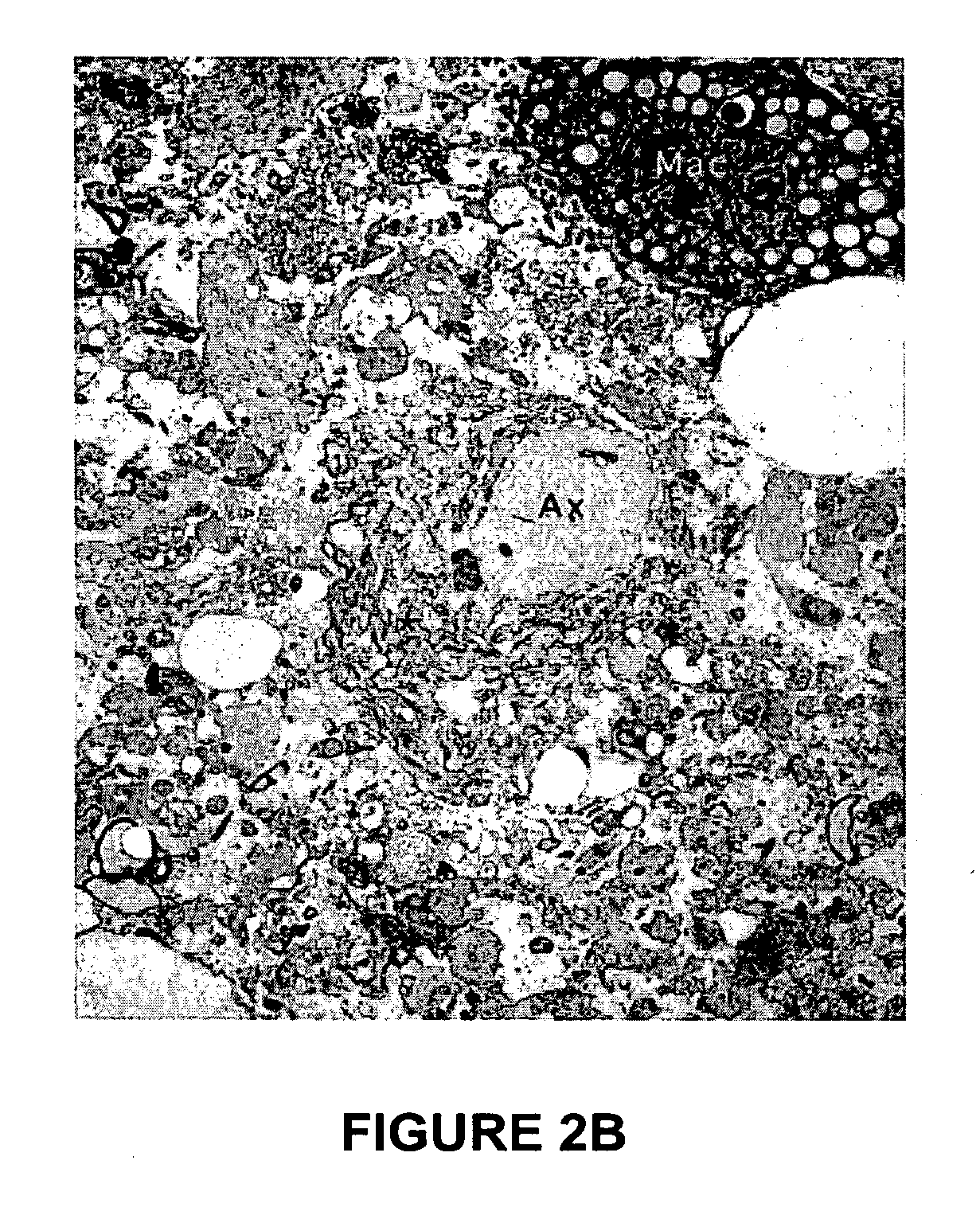
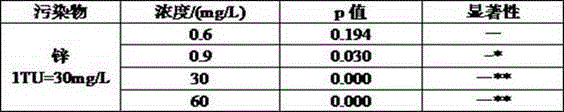
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
677 results about "Zebrafish" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The zebrafish (Danio rerio) is a freshwater fish belonging to the minnow family (Cyprinidae) of the order Cypriniformes. Native to South Asia, it is a popular aquarium fish, frequently sold under the trade name zebra danio (and thus often called a "tropical fish" although both tropical and subtropical). The zebrafish is also an important and widely used vertebrate model organism in scientific research, for example in drug development, in particular pre-clinical development. It is also notable for its regenerative abilities, and has been modified by researchers to produce many transgenic strains.
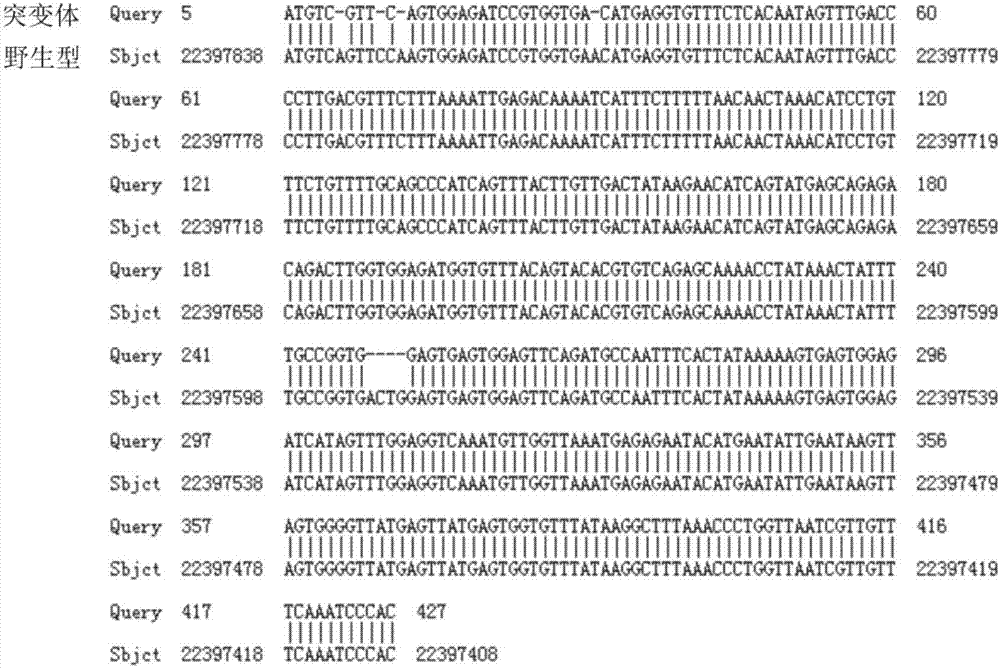
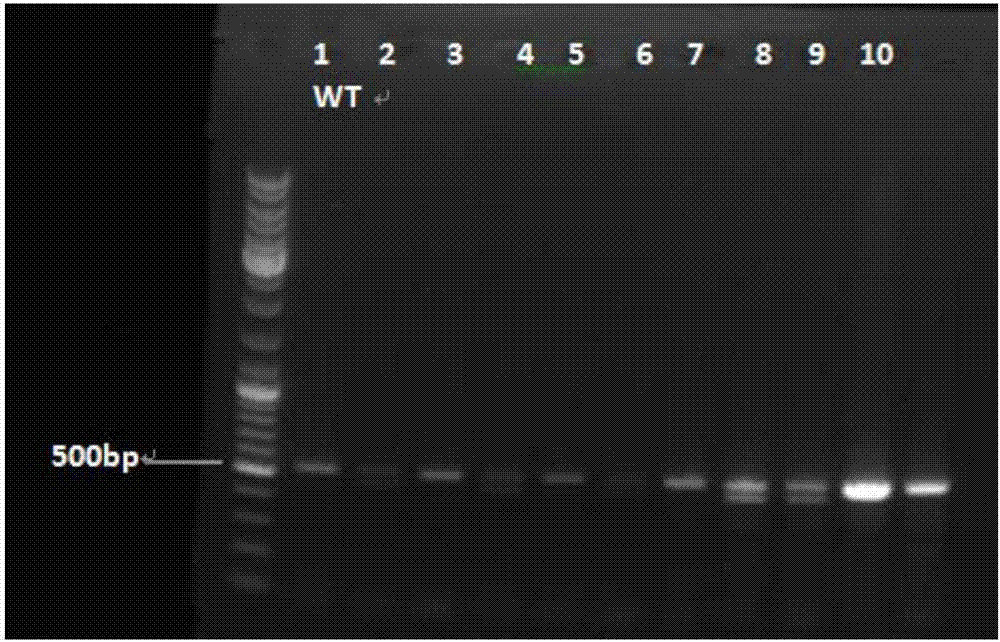
Preparation method of zebrafish with hepcidin gene knocked out by use of CRISPR / Cas9 technology
The present invention mainly relates to formation of zebrafish with hepcidin gene knocked out, by the use of CRISPR / Cas9 technology, a unique PAM region is designed, so that the hepcidin gene in the zebrafish is knocked out, and other genes are not accidentally injured. The first case of hepcidin knockout transgenic animal model zebrafish has great significance, the hepcidin is a major factor in the regulation of iron, once the hepcidin is knocked out, an animal model can be successfully molded into an iron overload animal model, the human factor intervention can be excluded, the hepcidin has great significance to iron expression researches, meanwhile compared with the traditional gene knockout technology, the CRISPR / Cas9 technology has low toxicity, high accuracy, high efficiency, short success cycle and other characteristics, and the hepcidin gene can be faster knocked out.
Owner:徐又佳
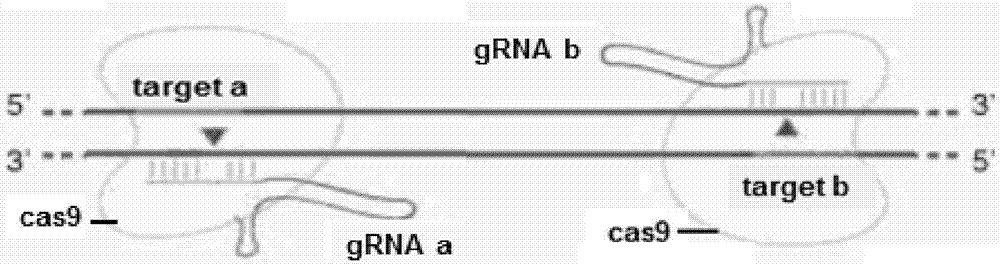
Crispr/Cas9-induced scale-missing zebra fish mode and establishment method
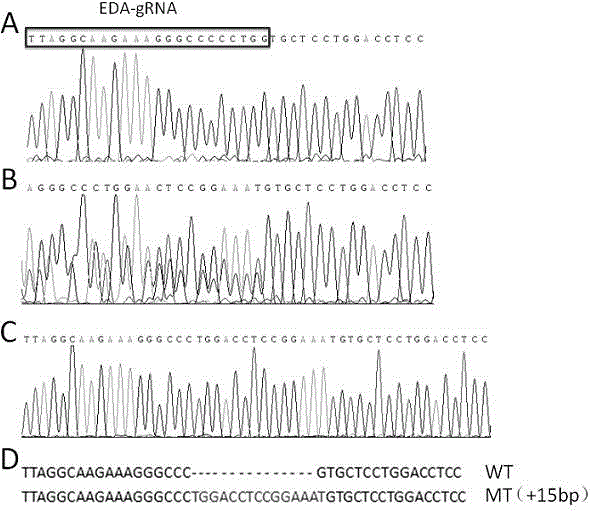
The invention relates to a Crispr / Cas9-induced scale-missing zebra fish mode. The mode is scale-missing zebra fish containing EDA gene exon 4-locus base insertion. Meanwhile, the invention also discloses an establishment method and the application of the Crispr / Cas9-induced scale-missing zebra fish mode. The established scale-missing zebra fish mode has a great application value in functional research of related genes of appendages of the skin, screening of medicines for treating ectoderm dysplasia such as human baldness, and the like.
Owner:CHINA ACAD OF SCI NORTHWEST HIGHLAND BIOLOGY INST
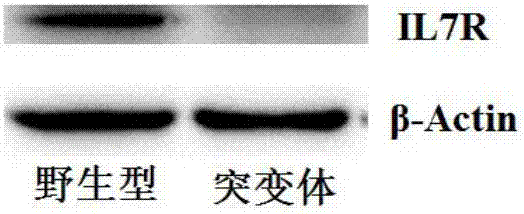
Preparation of IL7R gene-deleted zebra fish mutant and application thereof
ActiveCN107058320AConvenient for in vivo experimental researchGenetic stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementPeptidesDeveloping nervous systemMutant
The invention discloses an IL7R gene-deleted zebra fish mutant and a preparation method thereof. The construction of the IL7R gene-deleted zebra fish mutant is realized through a CRISPR / Cas9 technology. Moreover, the invention also discloses application of the IL7R gene-deleted zebra fish mutant; a mutant model provided by the invention can be used for studying an effect of IL7R in the nervous system development and myelination.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Method for obtaining bmp2a gene knocked-out zebra fish through CRISPR/Cas9
The invention discloses a method for obtaining bmp2a gene knocked-out zebra fish through CRISPR / Cas9. A novel gRNA sequence is designed between a first exon and an intron of BMP2a, the gRNA sequence is GGAGCCCATCACTAGACTCTTGG, and enzyme digestion is HinfI. Compared with a traditional gene knockout technology, the CRISPR / Cas9 technology has the advantages of low toxicity, high accuracy, high efficiency, short success cycle and the like. Therefore, the BMP2a gene can be theoretically knocked out faster.
Owner:WUXI NO 2 PEOPLES HOSPITAL
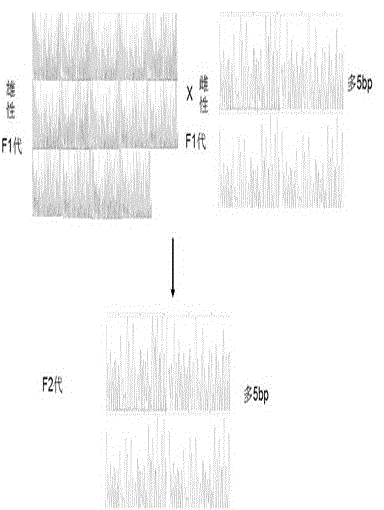
Method for breeding tcf25 gene deletion type zebra fish through gene knockout
InactiveCN107988268AEfficient and More Precise SilenceEasy to makeHydrolasesMicroinjection basedDiseaseGenotype Analysis
The invention relates to the technical field of gene knockout, and particularly discloses a method for breeding a tcf25 gene deletion type zebra fish through gene knockout. The method comprises the steps of through a CRISPR / Cas9 gene editing technology, designing an appropriate targeting gene locus on a tcf25 gene of the zebra fish, synthesizing in vitro to obtain specific sgRNA and Cas9-mRNA, microinjecting into a cell of the zebra fish, and after culturing an embryo for 60h, selecting the embryo for carrying out genotyping, so that the effectiveness of the selected locus is verified. The method provided by the invention is lower in off-target rate, removes the tcf25 gene through interference, is beneficial to further revealing the whole process of cardiac morphogenesis and a molecular mechanism regulating the process through researching functions through a genetics means, and is of great importance on understanding a cardiac disease pathology and researching and developing a new therapeutic schedule medically.
Owner:HUNAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
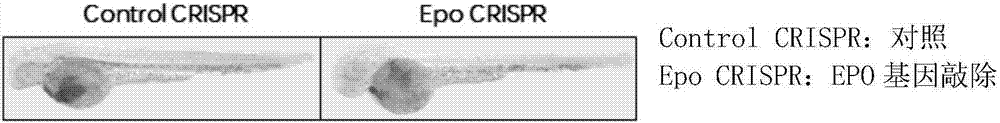
Method, primer and plasmid for constructing EPO gene knockout zebrafish animal model and preparation method of primer and plasmid
ActiveCN107217075ADeepen the understanding of the roleHigh gene knockout success rateHydrolasesStable introduction of DNAEscherichia coliExon
The invention provides a method, primer and plasmid for constructing an EPO gene knockout zebrafish animal model and a preparation method of the primer and the plasmid, and belongs to the field of biomedicine. The method includes the steps of 1) establishment of an EPO gene knockout zebrafish CRISPR oligomer sequence plasmid; and 2) establishment and culture of the EPO gene knockout zebrafish animal model on the basis of CRISPR gene knockout technology; wherein the step 1) comprises 1-1) design and synthesis of the primer aiming at an EPO exon 2 region target sequence and 1-2) synthesis of the Escherichia coli plasmid containing the EPO target sequence. The method for constructing the EPO gene knockout zebrafish animal model can be used to construct the EPO gene knockout zebrafish animal model, and facilitates further understanding and research of EPO.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF MEDICAL COLLEGE OF XIAN JIAOTONG UNIV
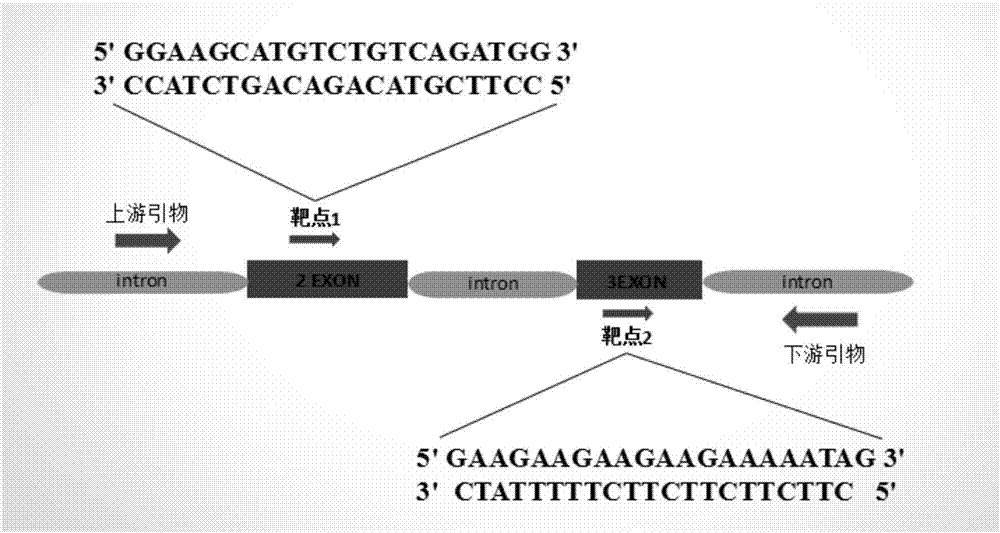
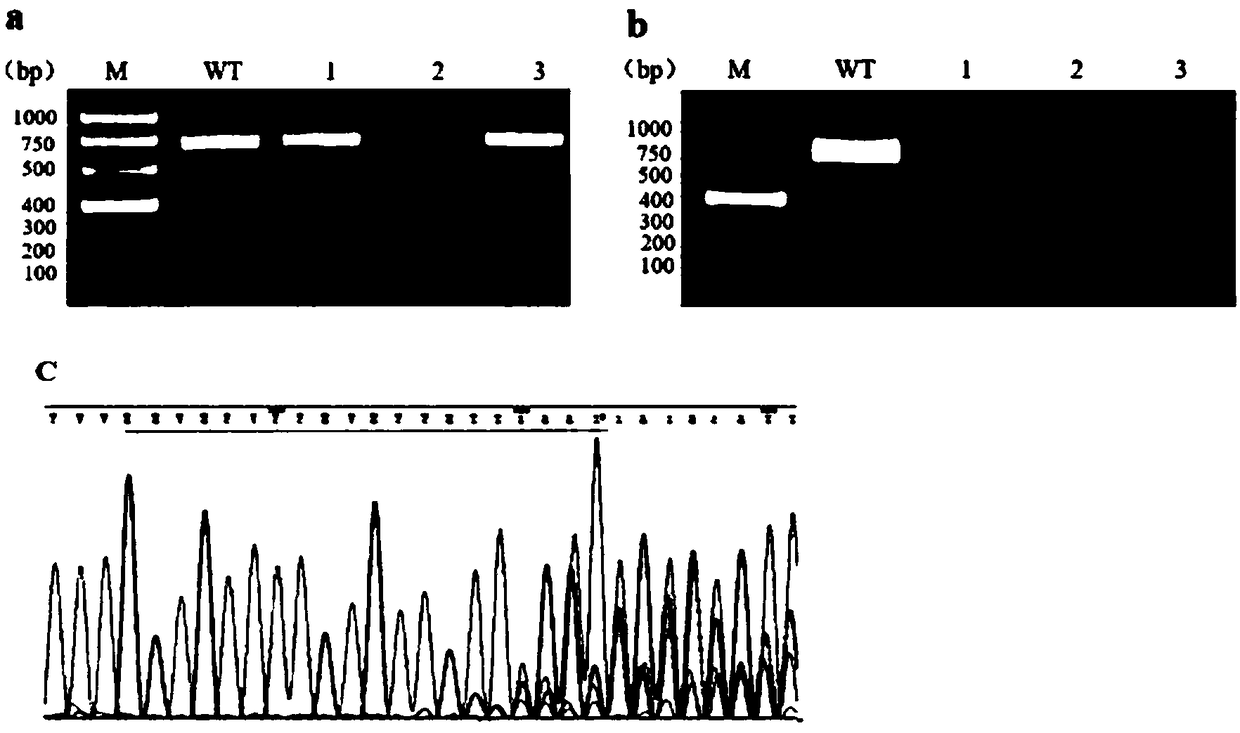
Preparation method of zebrafish notch1b gene mutant
PendingCN108707629AGenetic background is clear and cleanFacilitate in-depth researchHydrolasesStable introduction of DNAPUC19Embryo
The invention discloses a preparation method of a zebrafish notch1b gene mutant. The preparation method includes: determining positions of knock-out target spots of the notch1b gene; utilizing pUC19-gRNA scaffold plasmid as a template, and performing PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification with primers T7-notch1b-sfd and tracr rev; subjecting a PCR product to purification and in-vitro transcription to obtain gRNA (guide ribose nucleic acid); introducing the gRNA and Cas9mRNA into a cell-stage embryo of zebrafish, and culturing to obtain the notch1b gene mutant stable in inheritance. Thepreparation method has the advantages that by the aid of the CRISPR / Cas9 (clustered regularly interspersed short palindromic repeats, CRISPR / CRISPR-associated genes, cas gene) technology, and by meansof selecting a specific section of targeting domain, the notch1b gene in the zebrafish is knocked out, other genes are protected from being 'injured accidentally', the zebrafish without the Notch1b gene is formed, and great significance is achieved on study of Notch signal channels.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
Ferroportin1 nucleic acids and proteins
Positional cloning has been carried out to identify the gene responsible for the hypochromic anemia of the zebrafish mutant weissherbst. The gene, ferroportin1, encodes a novel multiple-transmembrane domain protein, expressed in the yolk sac. Zebrafish ferroportin1 is required for the transport of iron from maternally-derived yolk stores to the circulation, and functions as an iron exporter when expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Human and mouse homologs of the ferroportin1 gene have been identified. The invention includes isolated polynucleotides, vectors and host cells comprising nucleotide sequences encoding Ferroportin1 proteins and variants thereof, including those having iron transport function. The invention also includes polypeptides encoded by ferroportin1 genes and variants of such polypeptides, and fusion polypeptides comprising a Ferroportin1 or a portion thereof. Methods to produce a Ferroportin1, methods to produce antibodies to a Ferroportin1 and methods to identify agents binding to a Ferroportin1, which can be inhibitors or enhancers of Ferroportin1 iron transport activity, are also described. Inhibitors of Ferroportin1 activity can be used in a therapy for hemochromatosis.
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP
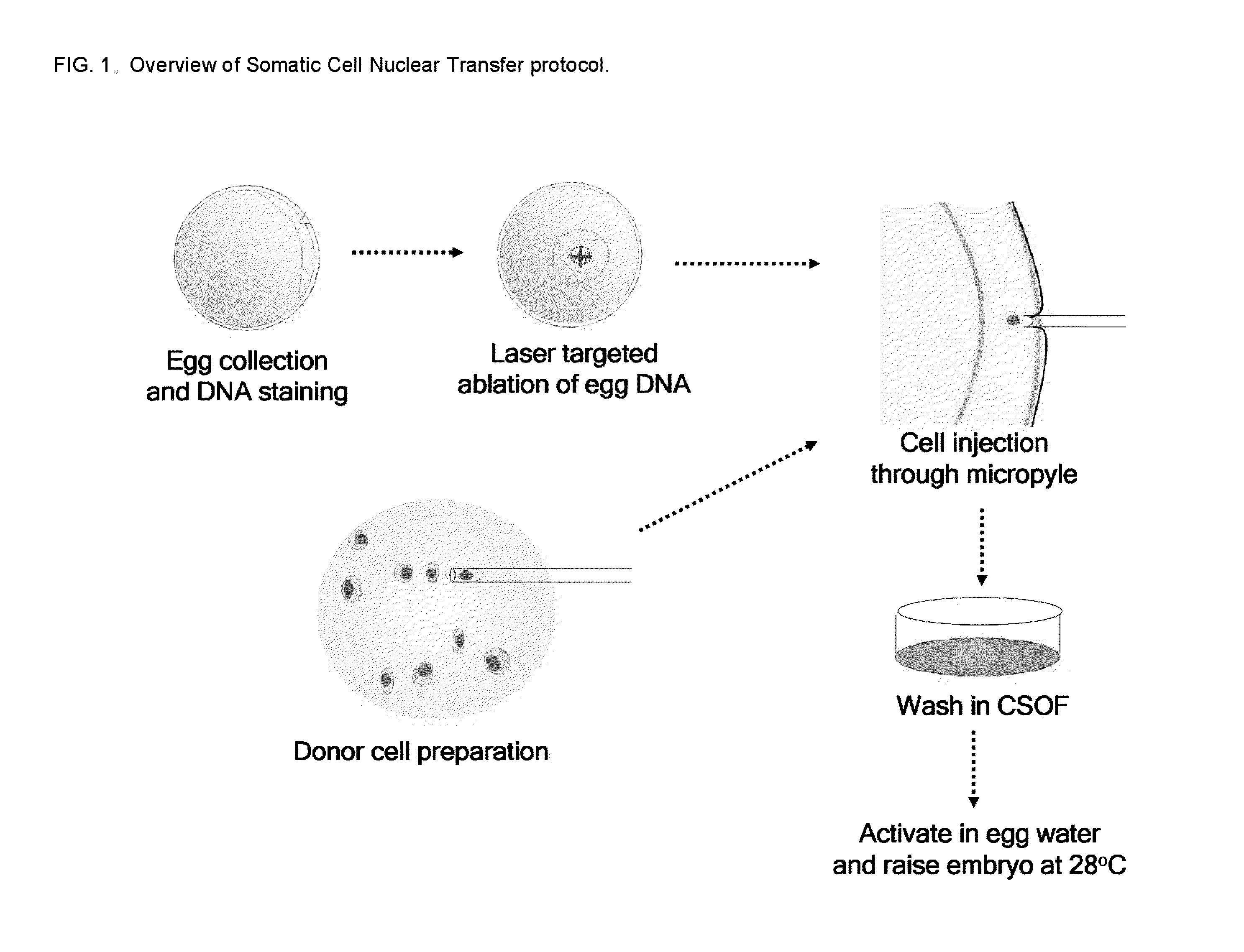
Efficient Somatic Cell Nuclear Transfer In Fish
InactiveUS20100037330A1Easy to useEasy to modifyMutant preparationTissue cultureSomatic cellSomatic cell nuclear transfer
The present disclosure provides methods of producing enucleated cells by photoablation. Such enucleated cells may be used as recipient cells for Somatic Cell Nuclear Transfer and cloning. The nuclear donor and / or enucleated recipient cells may be any fish cells, such as zebrafish, koi, or medaka fish cells. Such methods may be used to efficiently produce transgenic fish including by way of example zebrafish, koi, and medaka fish.
Owner:MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Ferroportin1 nucleic acids and proteins
Positional cloning has been carried out to identify the gene responsible for the hypochromic anemia of the zebrafish mutant weissherbst. The gene, ferroportin1, encodes a novel multiple-transmembrane domain protein, expressed in the yolk sac. Zebrafish ferroportin1 is required for the transport of iron from maternally-derived yolk stores to the circulation, and functions as an iron exporter when expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Human and mouse homologs of the ferroportin1 gene have been identified. The invention includes isolated polynucleotides, vectors and host cells comprising nucleotide sequences encoding Ferroportin1 proteins and variants thereof, including those having iron transport function. The invention also includes polypeptides encoded by ferroportin1 genes and variants of such polypeptides, and fusion polypeptides comprising a Ferroportin1 or a portion thereof. Methods to produce a Ferroportin1, methods to produce antibodies to a Ferroportin1 and methods to identify agents binding to a Ferroportin1, which can be inhibitors or enhancers of Ferroportin1 iron transport activity, are also described. Inhibitors of Ferroportin1 activity can be used in a therapy for hemochromatosis.
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP
New method for screening anti-liver injury medicament by using model organism zebra fish
InactiveCN101810866AHigh modeling success rateImprove work efficiencyInorganic active ingredientsDigestive systemLiver tissueOperability
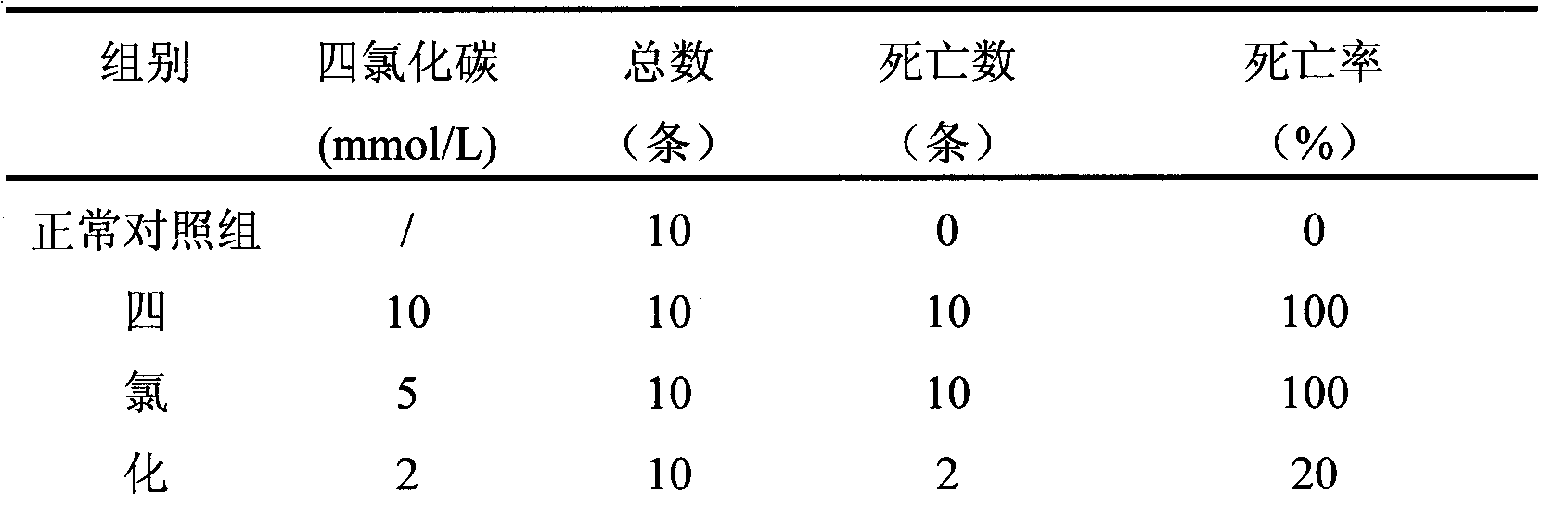
The invention discloses a new method for screening an anti-liver injury medicament by using a model organism zebra fish. The method comprises the following steps: continuously molding the zebra fish serving as a molding object for 3 days by using preferred carbon tetrachloride at the concentration of 1mmol / L to obtain the zebra fish of a liver injury model, and then evaluating the anti-liver injury activity of different receptor medicaments by using ALT and AST levels in the liver tissue of the zebra fish and the pathological change condition of the liver tissue of the zebra fish. Experimental results show that the new method for screening the anti-liver injury medicament by using the model organism zebra fish has high molding success rate, can simulate an in vivo environment to perform quick screening, and has the advantages of strong operability, accurate experimental results, little amount of required reacceptance medicament, strong repeatability, low cost, wide application range, capability of performing batch screening experiments and high work efficiency.
Owner:JIANGSU PROVINCE INST OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
Zebrafish Assay
InactiveUS20040133114A1Improve throughputGuaranteed predictive effectVectorsDiagnostic recording/measuringAssayBiomedical engineering
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Mode creature method for medicament toxicity research
A method for studying toxicity of drugs by using model organism zebra fish comprises the following steps of: selecting 100 to 200 adult zebra fishes, respectively disposing in bottles containing a solution of 30 to 50 mL, keeping the temperature in the bottles substantially constant at 22 to 25 DEG C, randomly grouping, each group containing 10 to 20 fishes, wherein the solution in one of the groups is pure water (blank), the solutions in other groups are medicinal solutions with different concentrations, and 0.5% to 2% dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) can be added to assist dissolving a drug that has poor water solubility, when an additional solvent comparison group prepared by adding 0.5% to 2% DMSO into the pure water is needed; recording the death number of zebra fishes in the medicinal solutions of different concentrations within 24 h, and calculating the death rate (%); calculating median lethal dose-LD50 by Bliss method according to the experiment result; and representing the acute toxicity by the value of LD50. According to the method, the LD50s of zebra fish of triptolide, matrine and emodin are respectively 5.39*10<-3>, 112.3 and 1.08*10<3> mug / mL. The method can objectively reflect the toxicity of drugs.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Animal model systems for viral pathogenesis of neurodegeneration, autoimmune demyelination, and diabetes
InactiveUS20060130161A1Nervous disorderPeptidesProgressive multifocal leukoencephalopathyAutoimmune disease
Provided are non-human animal model systems for viral pathogenesis of neurodegeneration, autoimmune demyelination, and autoimmune diseases such as diseases of the central nervous system, including multiple sclerosis (MS), and diabetes. Such non-human animal model systems may be suitably employed for the study of diseases such as MS and diabetes and for the identification and characterization of candidate therapeutic compounds and compositions for the treatment of such diseases. Also provided herein are markers and methods for the detection, in patients susceptible to autoimmune disease, of autoimmune diseases of the central nervous system such as progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) following treatment with one or more therapeutic agent as exemplified herein by the therapeutic agent natalizumab. Exemplary animal model systems comprise marmosets infected with a herpesvirus such as HHV6-A and HHV6-B, transgenic mouse and zebrafish animal model systems wherein the transgene encodes CD46, and methods for monitoring the risks of patients having MS, diabetes and other auto-immune disorders treated with anti-adhesion molecules such as natalizumab.
Owner:CARANTECH
Method of screening compounds
InactiveUS20050155087A1Altered phenotypeEliminate needNervous disorderOrganic chemistryBiological bodyHuman phenotype
The present invention is directed to a novel, target-blind approach to drug discovery. The concept is to model human phenotypes in a teleost, such as a zebrafish, and then screen compounds, e.g., small molecules, for their ability to alter the phenotype. Because the screen is performed with a whole vertebrate organism and uses a phenotype as the output, the need to first identify target genes is eliminated. This approach is powerful because a single screen can theoretically detect drugs affecting any target relevant to the phenotype being observed, even if those targets are not yet characterized.
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP
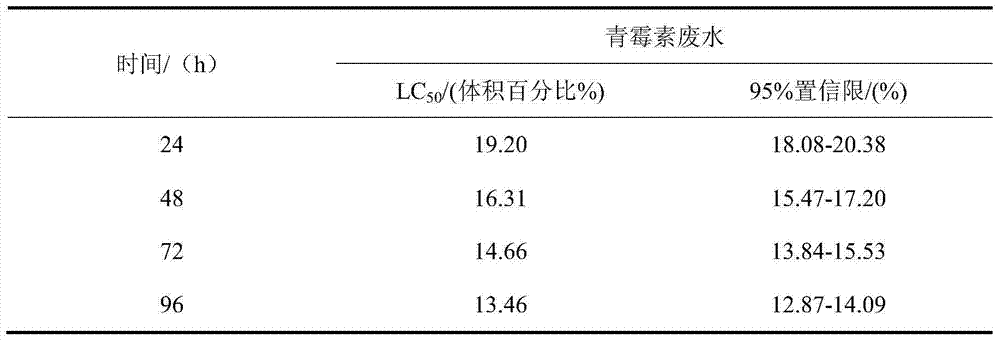
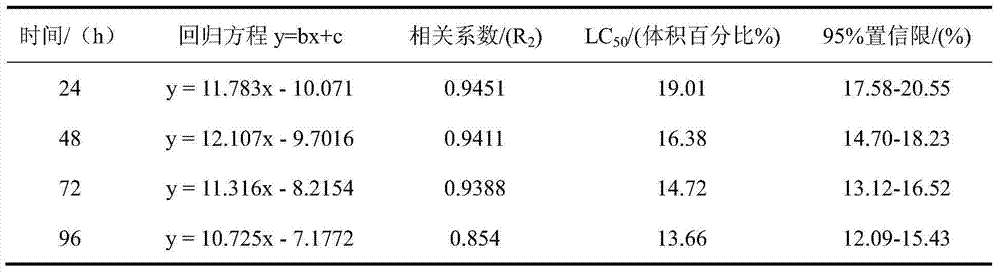
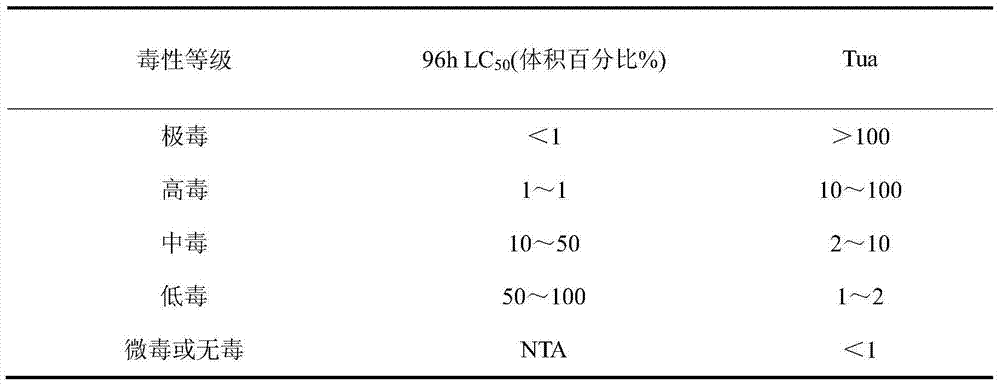
Method for testing typical antibiotics wastewater toxicity by using zebra fishes
InactiveCN103616489ASolve conventional physical and chemical indicatorsTesting waterAcute toxicity testingMalondialdehyde
The invention belongs to the field of environmental toxicology, and relates to a method for testing typical antibiotics wastewater toxicity by using zebra fishes. According to the method, zebra fishes are used as to-be-tested organisms, and are exposed in typical antibiotics wastewater, the short-term or long-term toxic effect of the typical antibiotics wastewater to the zebra fishes is quantitatively tested through analyzing the acute toxicity and subacute toxicity of the typical antibiotics wastewater to the zebra fishes, the acute toxicity is described by using the 96h medium lethal concentration (96h LC50) (typical antibiotics wastewater percent by volume percent), and the subacute toxicity is described by fish body biochemical indexes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity, peroxidase (POD) activity and malondialdehyde (MDA) content. By adopting the method, the toxicity characteristics and toxicity levels of the typical antibiotics wastewater can be analyzed, tested and quantitatively described, and the problem that conventional physicochemical indexes can not reflect biotoxicity of the typical antibiotics wastewater can be solved, and results obtained by analyzing, testing and describing can be used as biotoxicity monitoring and evaluating indexes of the typical antibiotics wastewater.
Owner:HEBEI UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Automated systems and methods for screening zebrafish
InactiveUS20100119119A1Facilitate toxicology studyRapid and automated and extensive compound screeningBiological material analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionZoologyComputer science
Systems and methods for screening zebrafish comprising, a storage device for at least temporarily storing an image of a zebrafish to be screened; a zebrafish atlas; and an operating device that automatically screens the zebrafish at least in part by automatically comparing one or more anatomical features of the zebrafish to one or more standards.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Methods of screening agents for activity using teleosts
InactiveUS20070143865A1Compounds screening/testingLuminescence/biological staining preparationActive agentAngiogenesis growth factor
The present invention provides methods of screening an agent for activity using teleosts. Methods of screening an agent for angiogenesis activity, toxic activity and an effect cell death activity in teleosts are provided. Methods of screening an agent for an activity in the brain or central nervous system in zebrafish are provided. The invention further provides high throughput methods of screening agents in multi-well plates.
Owner:PHYLONIX PHARMA
Wnt16 gene deletion type zebra fish
InactiveCN106191110AShorten the growth cycleGood medical researchNucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionLiving bodyGenome
The invention discloses a wnt16 gene deletion type zebra fish. Compared with the prior art, specific genes in the genome of a living body can be muted more efficiently and precisely; moreover, the manufacturing is simple, the cost is lower, multiple sites on target genes can be sheared at the same time, and any number of single gene can be muted. The wnt16 gene deletion type zebra fish can be applied to research related with gene and skeleton growth and other research for finding whether deletion of wnt16 gene is related with growth of other organs such as heart or not, and thus the wnt16 gene deletion type zebra fish has a good medical research value. At the same time, the growth period of zebra fishes without wnt16 gene is obviously shortened, and the wnt16 gene deletion type zebra fish also has a good commercial value therefore.
Owner:HUNAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
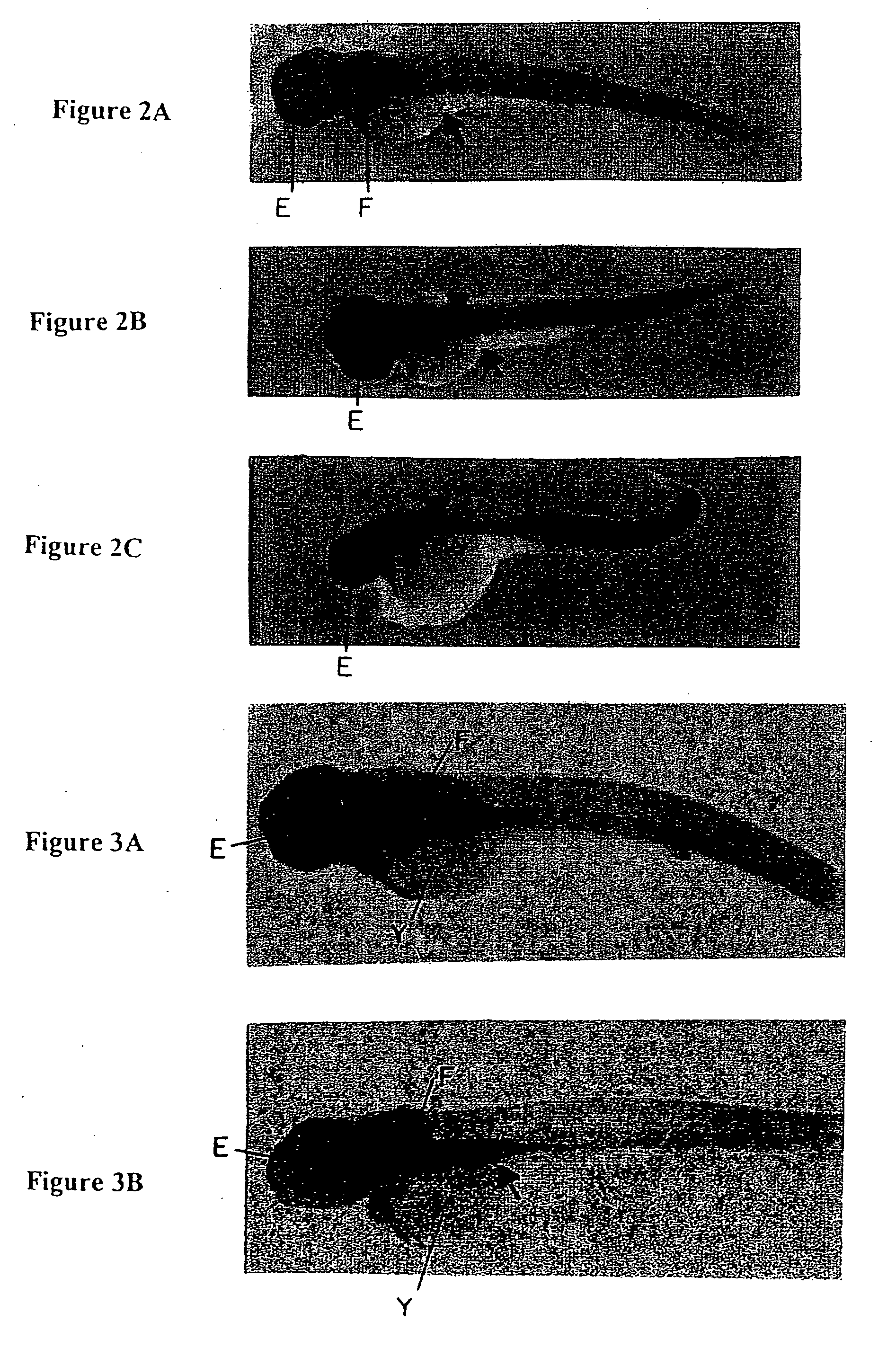
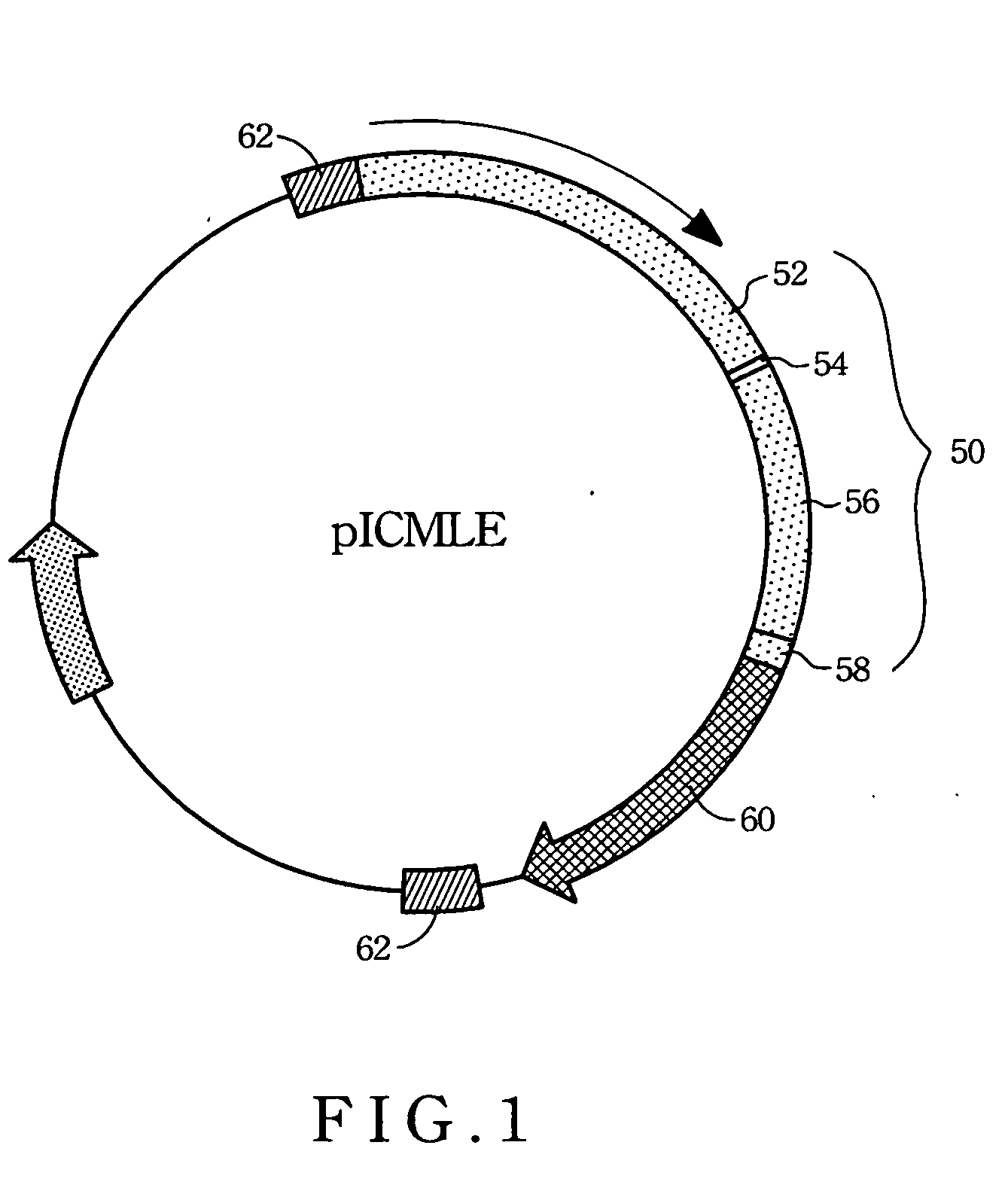
Method for producing heart-specific fluorescence of non-human eukaryotic animals
A method of expressing in vivo heart-specific fluorescence in transgenic line of zebrafish is developed, which provides a research model for studying heart-related gene functions and performing gene therapies in the future. The method comprises the following steps. Firstly, a plasmid is constructed. This plasmid construct includes the upstream regulatory region, the exon 1, the intron 1, and the exon 2 of cmlc2 gene, cDNA of GFP, wherein the cmlc2 gene and GFP cDNA form a cassette, and inverted terminal repeats from adeno-associated virus are flanked at both sides of this cassette. The plasmid construct is linearized and microinjected into one-celled zebrafish fertilized eggs. Lastly, the heart-specific fluorescent expressed zebrafish are selected and the germline-transmitting transgenic strain is generated.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
Zebrafish models of acute myelogenous leukemia
InactiveUS20070186288A1High activityImprove stabilityVectorsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsChronic myelogenous leukemiaAML - Acute myeloid leukaemia
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Method of creating zebra fish peristalsis model and screening prokinetic medicaments
ActiveCN103301480AEasy to manufactureFast preparationIn-vivo testing preparationsHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsFluorescence microscope
The invention belongs to the field of drug screening and particularly relates to a method of creating a zebra fish peristalsis model and screening prokinetic medicaments. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) selecting the zebra fish; (2) inducing the model and treating the compound; (3) quantitatively analyzing through a fluorescence microscope. A fluorescent dye is applied in the invention for the first time to research the gastrointestinal peristalsis conditions, the new research method is a great complement for the existing research models, and the peristalsis model has important value in high throughput screening of the prokinetic compounds due to the maneuverability, non-invasion, simplicity and quickness.
Owner:HANGZHOU HUANTE BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
Lactobacillus rhamnosus NX-2 and application thereof in preparation of uric acid reducing drugs
ActiveCN111826315AInhibitory activityLower uric acid levelsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesLactobacillus rhamnosusXanthine
The invention discloses lactobacillus rhamnosus NX-2 and an application thereof in preparation of uric acid reducing drugs, and belongs to the technical field of microorganisms. The lactobacillus rhamnosus NX-2 disclosed by the invention has a preservation number of CGMCC No.20110. Non-inactivated and inactivated fermentation supernate, bacterial suspension and cell disruption material supernate of the lactobacillus rhamnosus NX-2 have uric acid reducing effects on a zebrafish high-uric-acid model, and can inhibit the activity of xanthine oxidase in the body of a high-uric-acid zebrafish. Thelactobacillus rhamnosus NX-2 disclosed by the invention has a huge potential application prospect in the aspect of preparing medicines for treating and / or preventing hyperuricemia.
Owner:广东南芯医疗科技有限公司 +2
Building method and application of zebra fish hyperlipidemia model
InactiveCN102907357ATrue reflection absorptionTrue reflection distributionClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaDiseaseYolk
The invention relates to a building method of a zebra fish hyperlipidemia model and application of the animal model to hyperlipidemia disease research and lipid-lowering drug screening. The building method of the zebra fish hyperlipidemia model mainly includes the steps of zebra fish selection, feeding of zebra fish by yolk powder, histochemical staining or fluorescent staining, image analysis and / or microwell plate analysis and statistical analysis. The building method has the advantages of simplicity, convenience, rapidity, economy, high efficiency, high throughput and the like, and the model can be used for hyperlipidemia disease research and lipid-lowering drug screening. The building method and application of the zebra fish bacterial infection model are of great significance to acceleration of research and development on lipid-lowering drugs and improvement on treatment of patients suffering from hyperlipidemia.
Owner:HANGZHOU HUANTE BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
Method for screening mitochondria targeted compounds by using zebra fish
ActiveCN101968484AOvercome costsImprove throughputMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorPreparing sample for investigationStainingChemical compound
Owner:南京新环检测科技有限公司
Zebra fish behavior induction and analytical method and system
InactiveCN102172225AClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaAnalysis methodVisual perception
The invention relates to a zebra fish behavior induced and analytical method and system. The system comprises a visual stimulus device, a camera and an analytical system, wherein, the visual stimulus device can at least induce the eye movement reaction behavior and optomotor reaction behavior of zebra fish; the camera is used for shooting the behavior of the zebra fish, so as to acquire video data; the analytic system carries out behaviouristics analysis on the input video data so as to obtain the behavior data of the eye movement reaction and optomotor reaction of the zebra fish. The method and system provided by the invention can be used for analyzing the eye movement reaction and the optomotor reaction of the grown-up zebra fish as well as the eye movement reaction of the infant zebra fish.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
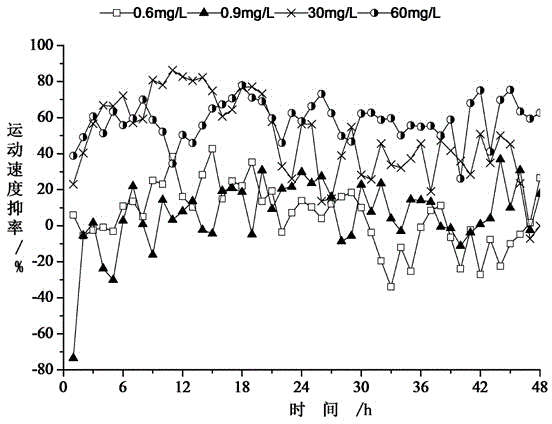
Method for determining biotoxicity of water quality based on zebrafish movement velocity change
InactiveCN104833784AImprove timelinessIncreased sensitivityGeneral water supply conservationTesting waterAcute toxicity testingWater quality
The invention discloses a method for determining biotoxicity of water quanlity based on movement velocity change of zebrafish. The method comprises the following steps: domesticating zebrafish; carrying out acute toxicity test on the domesticated zebrafish and calculating the 48 hour medial lethal concentration; and carrying out behavior test on the domesticated zebrafish, determining the movement velocity change of the zebrafish and judging the biotoxicity of water quality. With movement velocity of the zebrafish in a water environment as a biomarker, the biotoxicity of pollutants is evaluated; the movement behavior of the zebrafish in the water environment is tracked and captured; the movement track of the zebrafish is visually observed at any time; the speed index is determined in real time; quantitative evaluation for determining the biotoxicity of water quality by employing the zebrafish movement velocity change is realized; water quality fluctuation is displayed within a short period of time; the biological monitoring and early warning timeliness, sensitivity and accuracy are improved; a technical support is provided for sudden water body pollution; and the water supply quality safety is ensured.
Owner:SHANDONG JIANZHU UNIV +1
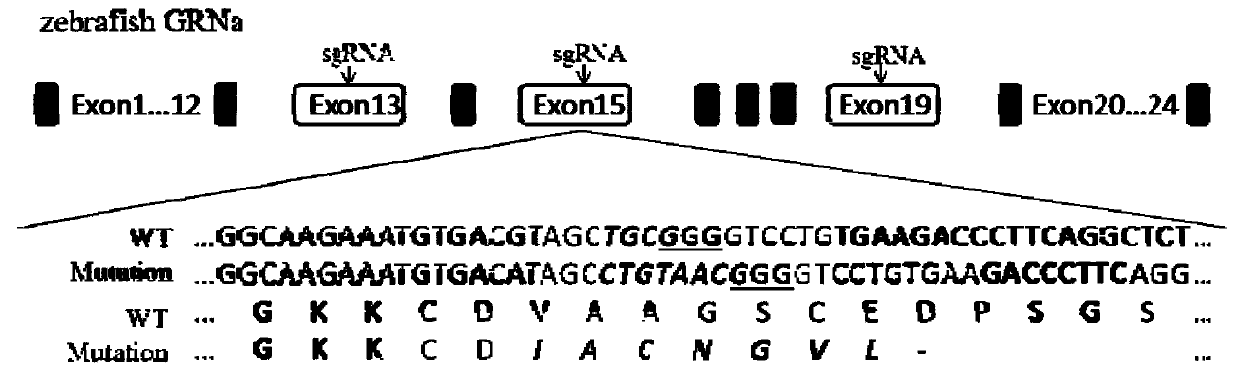
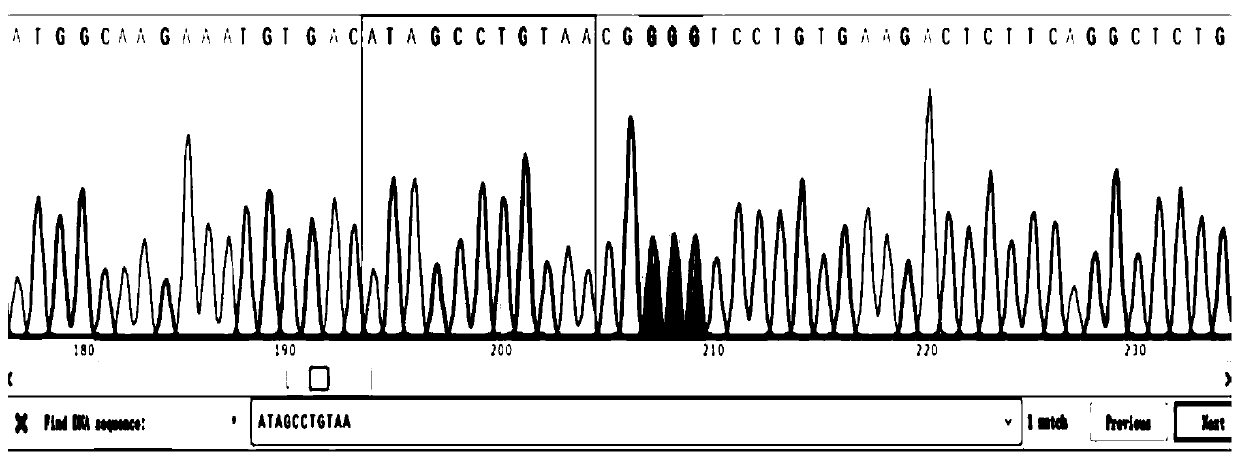
GRNa gene knockout zebrafish mutant and preparation method thereof
PendingCN110904103AOvert pathological phenotypeMicroinjection basedStable introduction of DNABiotechnologyStaining
The invention relates to a preparation method of a GRNa gene knockout zebrafish strain, which comprises the following steps: screening sgRNA of a target GRNa gene, constructing a eukaryotic expressionvector carrying Cas9 and sgRNA expression elements, screening a positive zebrafish founder, and screening first filial generation and second filial generation. The expression condition of the GRNa gene is identified and the obtained GRNa gene knockout zebrafish strain is proved to normally mate and lay eggs and can be stably inherited to filial generations after being mutually intercrossed for more than three generations of the GRNa gene knockout zebrafish strain. And genome, mRNA and protein levels prove that the GRNa gene is hardly expressed. The invention can be used as a tool for zfGRNa gene research. Related experiments such as HE staining and immunohistochemistry prove that the GRNa gene knockout zebrafish strain shows an obvious pathological phenotype and can be used for researching mechanisms of GRNa in diseases such as nervous system diseases and metabolic diseases and screening related drugs; the invention can also be applied to scientific research and economic culture of zebrafish, and has good commercial value.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
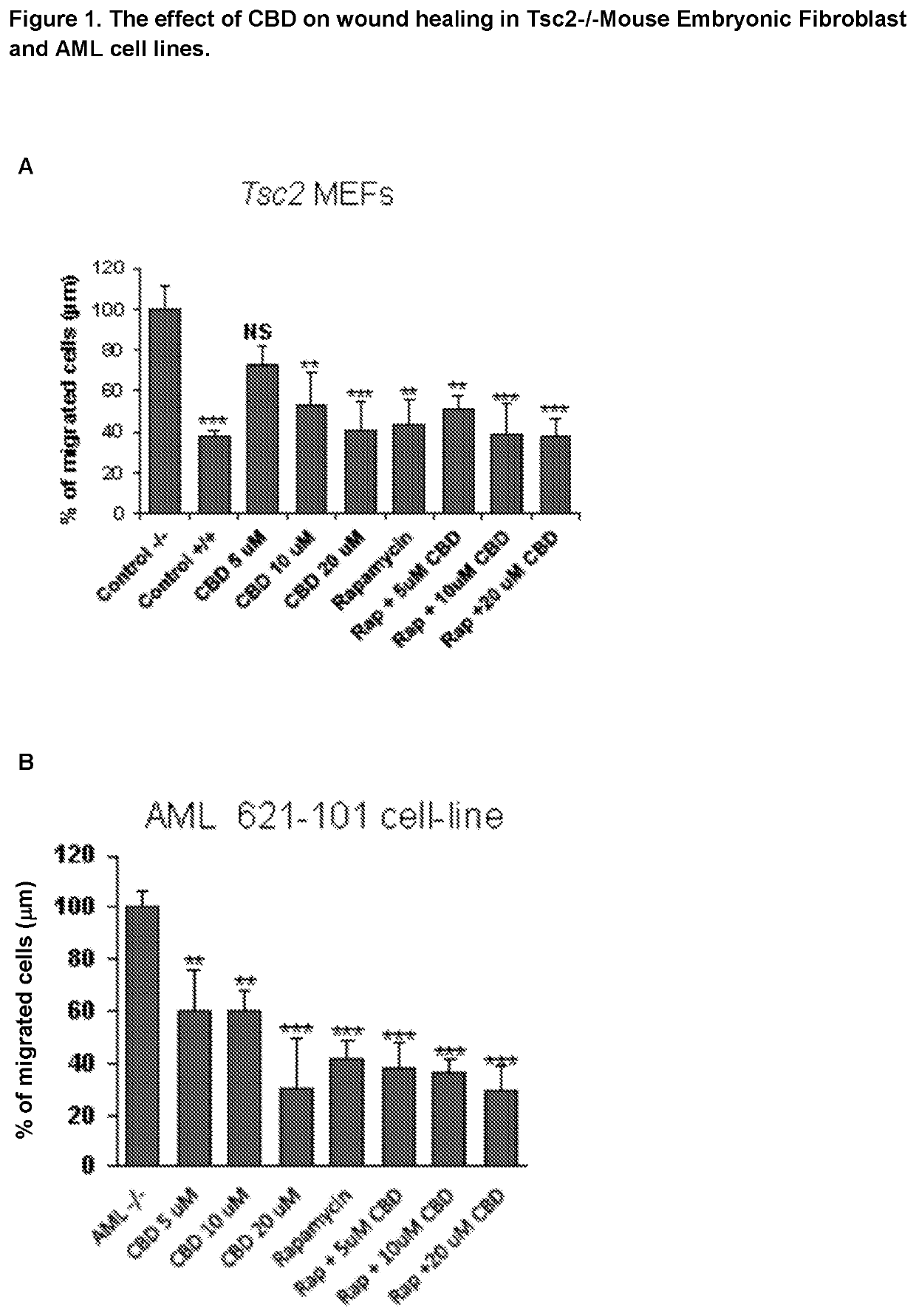
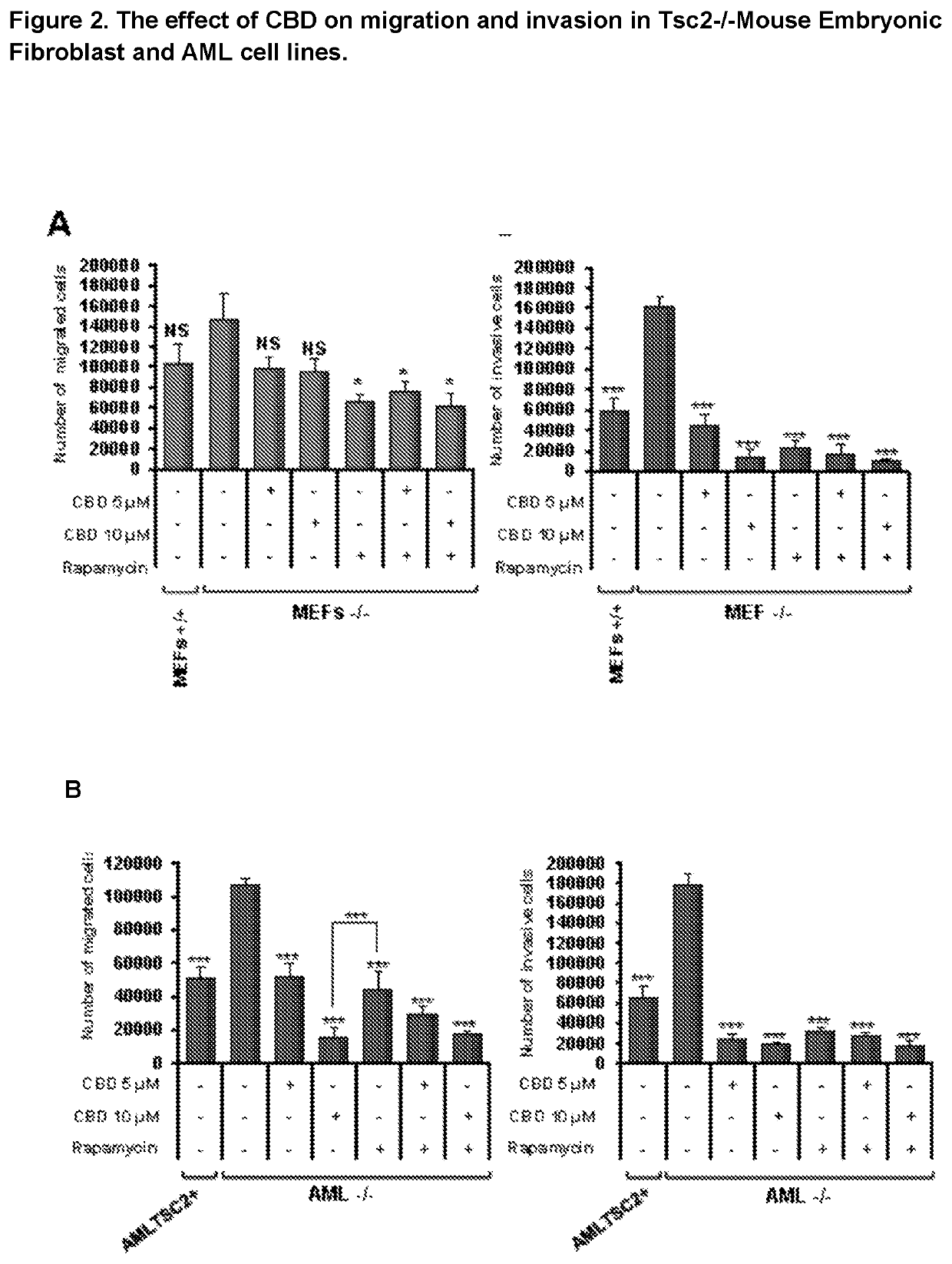
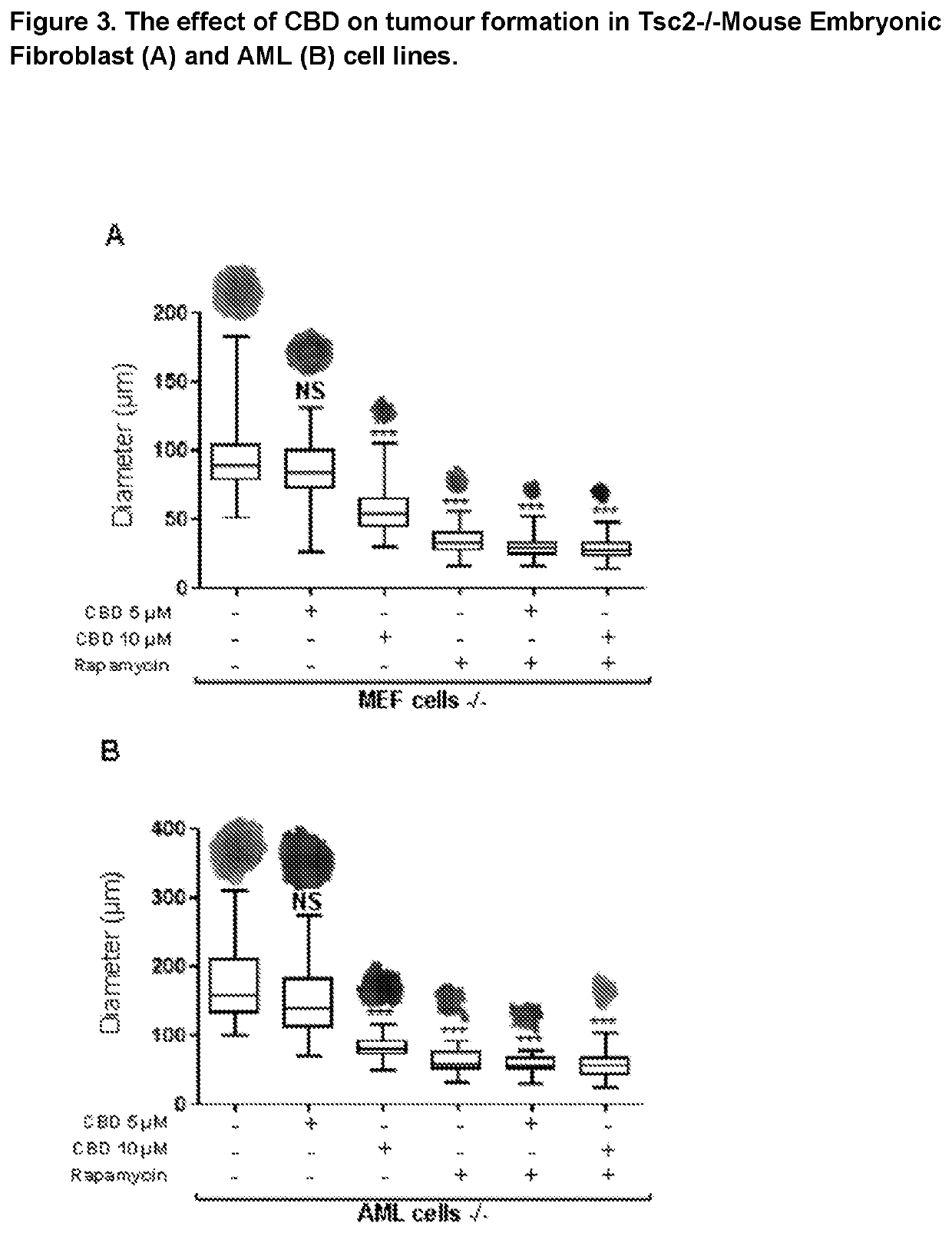
Use of cannabidiol in the treatment of tuberous sclerosis complex
InactiveUS20200206153A1Prevent and reduce tumourReduce doseHydroxy compound active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsBenign tumoursDisease
The present invention relates to the use of cannabidiol (CBD) for the treatment of tumours associated with Tuberous Sclerosis Complex (TSC). In particular the CBD was able to decrease the number and size of marker cells, pS6, in a zebrafish model of TSC. This is5 suggestive of a disease modifying effect whereby treatment with CBD could result in the reduction or prevention of the benign tumours that occur in TSC patients. Preferably the CBD used is in the form of a highly purified extract of cannabis such that the CBD is present at greater than 98% of the total extract (w / w) and the other components of the extract are characterised. In particular the cannabinoid tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) has been substantially 10 removed, to a level of not more than 0.15% (w / w) and the propyl analogue of CBD, cannabidivarin, (CBDV) is present in amounts of up to 1%. Alternatively, the CBD may be a synthetically produced CBD. In use the CBD is given concomitantly with one or more other drugs used in the treatment of TSC. Such drugs may include rapamycin and / or everolimus.
Owner:GW RES LTD
Bifidobacterium animalis NX-6 and application thereof in preparation of lipid-lowering and weight-losing medicines
The invention discloses bifidobacterium animalis NX-6 and application thereof in preparation of lipid-lowering and weight-losing medicines, and belongs to the technical field of microorganisms. The preservation number of the bifidobacterium animalis NX-6 disclosed by the invention is CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No. 20114. The uninactivated and inactivated fermentation supernate, bacterial suspension and cell disrupted supernate of novel bifidobacterium animalis NX-6 show good effects of slowing down weight and body length increase, improving body mass index(BMI) and reducing fat area percentage on zebrafish, and have a potential weight losing effect; triglyceride (TG) and total cholesterol (TC) in a zebrafish hyperlipidemia model body can be obviously reduced, and a good hypolipidemic effect is shown. The novel bifidobacterium animalis NX-6 disclosed by the invention has a huge potential application prospect in the aspect of preparing medicines fortreating and / or preventing obesity and hyperlipidemia.
Owner:广东南芯医疗科技有限公司 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com