Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1990results about "Mutant preparation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
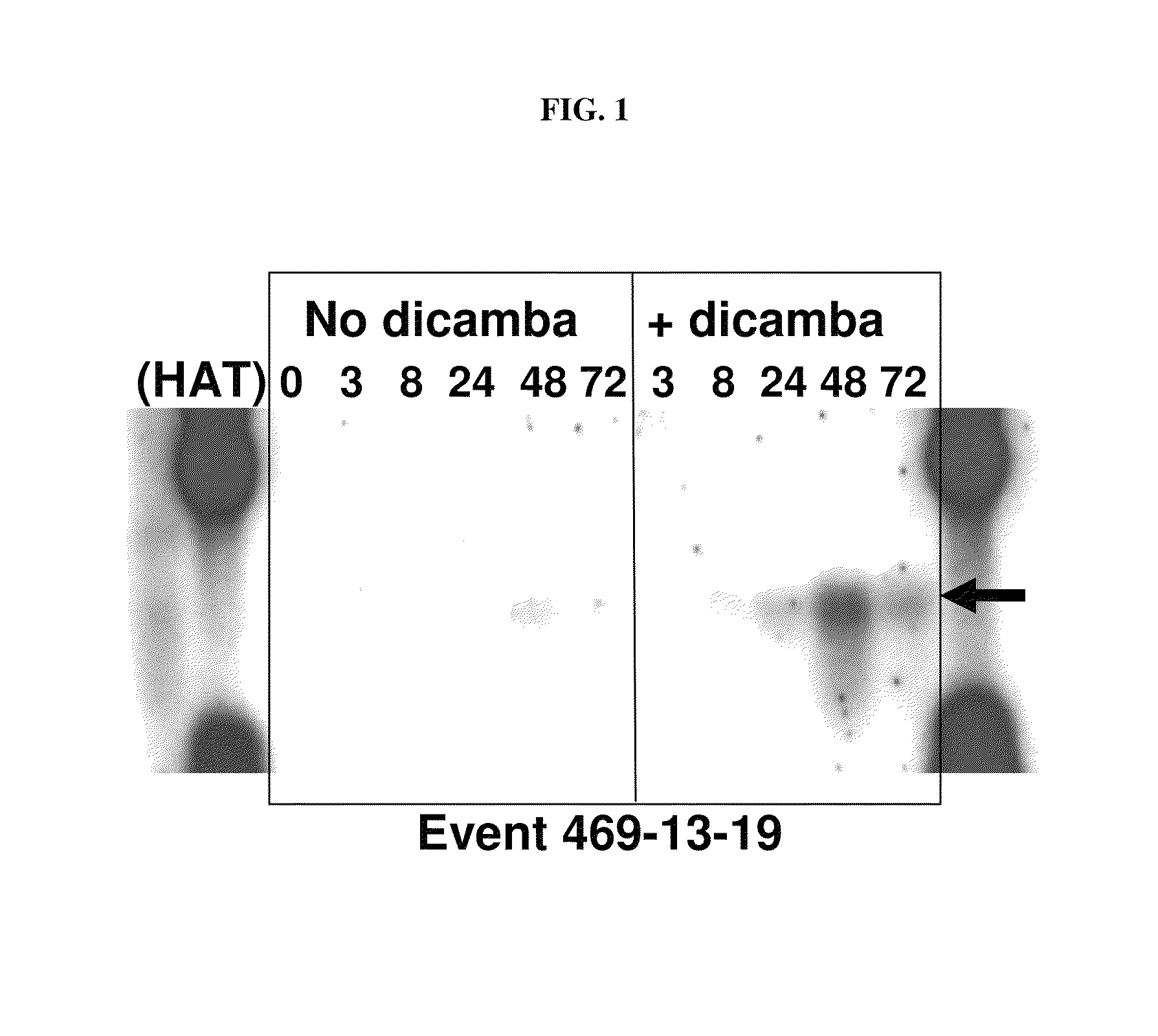
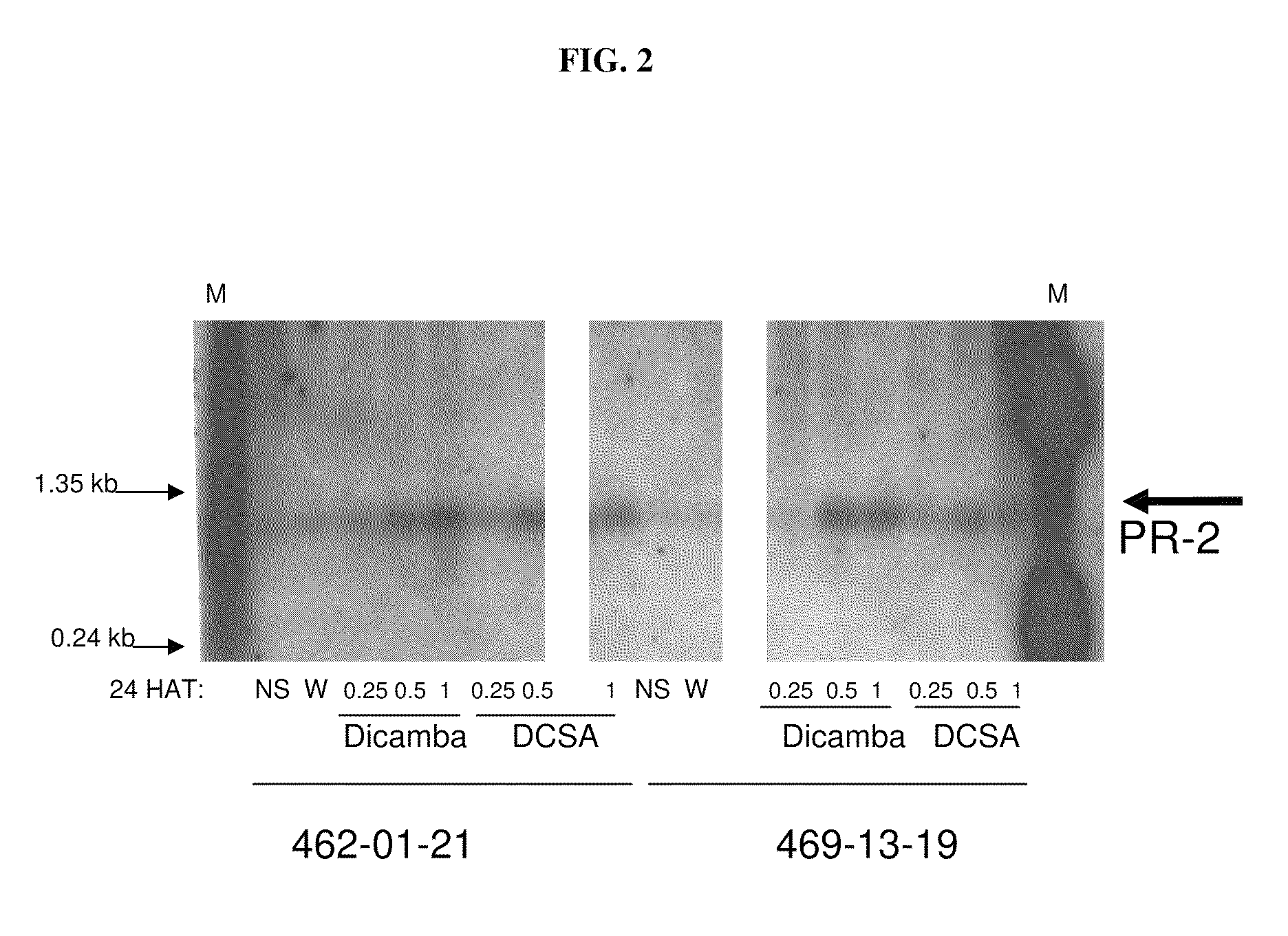
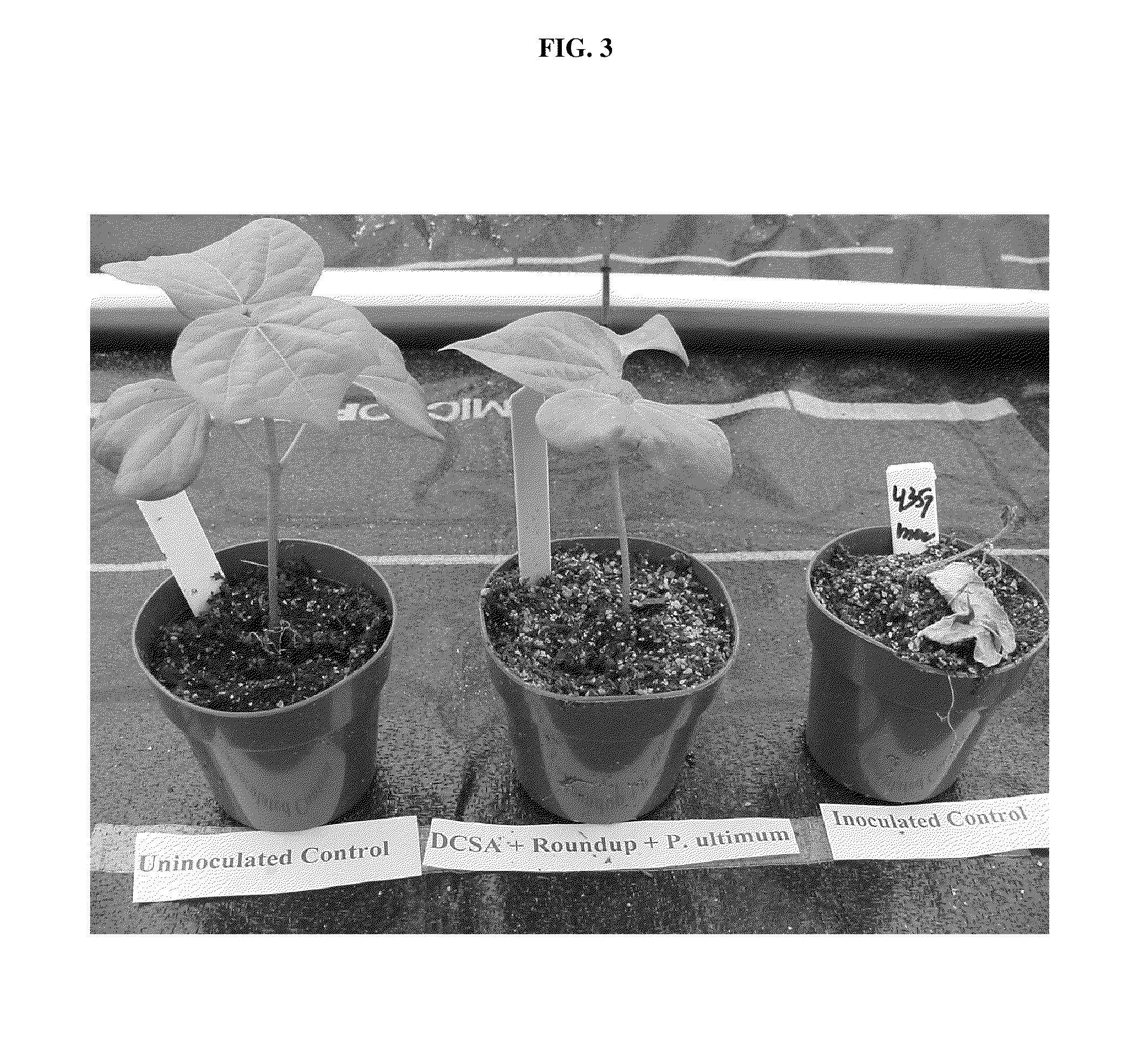
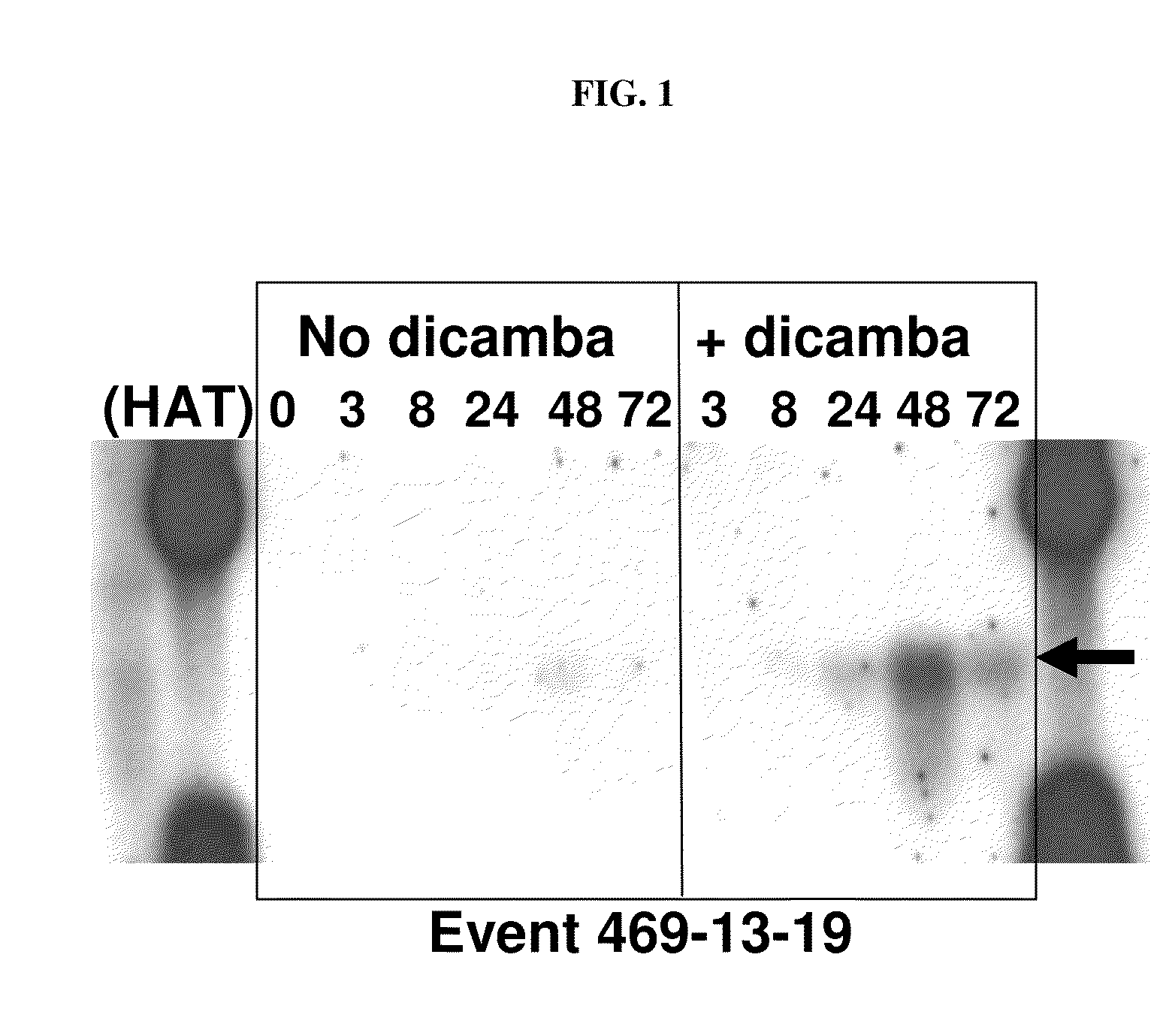
Methods and compositions for improving plant health
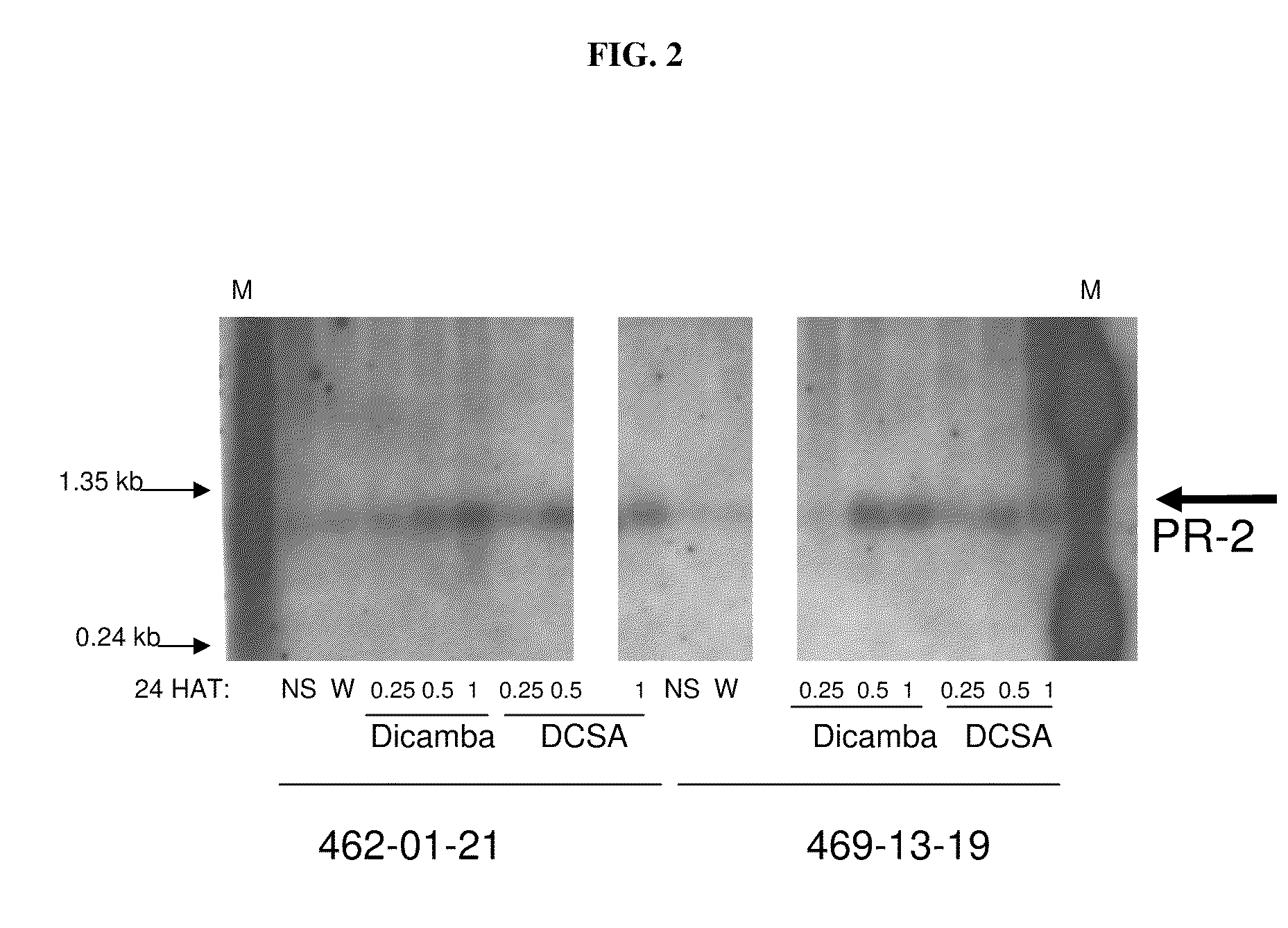
The present invention provides methods and compositions for improving plant health. In particular, application of dicamba or another substrate of DMO, or metabolites thereof including DCSA, to a plant confers tolerance to, or defense against, abiotic or biotic stresses such as oxidative stress including herbicide application, and plant disease, and enhances crop yield. Such application may be in combination with the application of another herbicide such as glyphosate.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Herbicide resistance in plants
InactiveUS6222100B1Confers resistanceEffectively combat weed problemBiocideSeed and root treatmentPlant tissueNovel gene
This invention is directed to the production of plants, plant tissues and seeds which are resistant to inhibition by an herbicide which normally inhibits the growth and development of those plants, plant tissues and plant seeds. In particular this invention is directed to altered acetohydroxyacid synthase enzymes which are resistant to inhibition by herbicides which normally inhibit the activity of the synthase before such alteration. This invention further relates to genes encoding such enzymes, and to processes for utilizing these novel genes and enzymes. Further products of the invention include plants, plant tissues and seeds which exhibit resistance to such herbicides resulting from expression of genes encoding herbicide resistant acetohydroxyacid synthase enzyme.
Owner:MGI PHARMA
High threonine producing lines of Nicotiana tobacum and methods of producing
InactiveUS7173170B2Improve the level ofImproved taste and aromaMutant preparationFermentationNicotiana tabacumThreonine
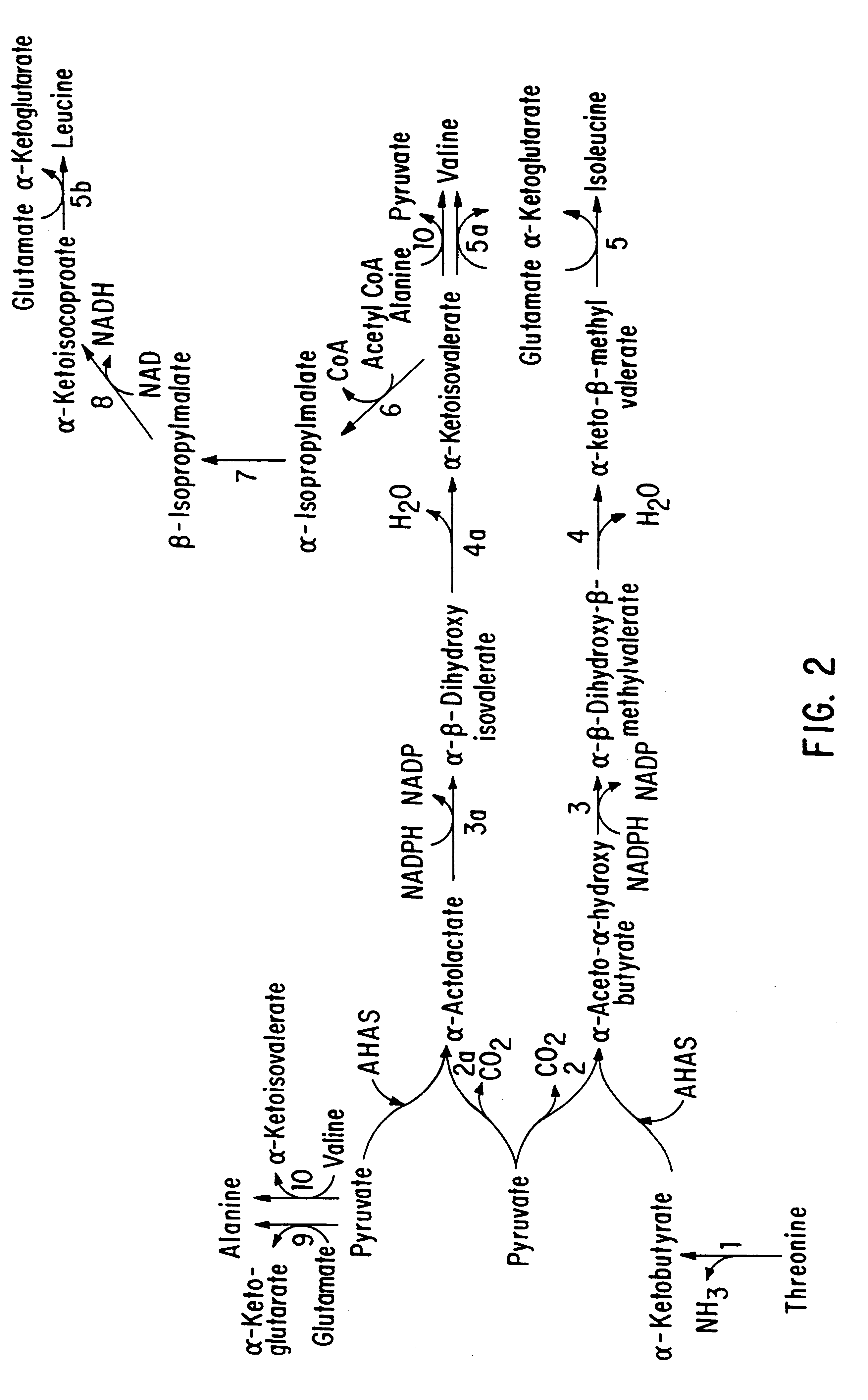
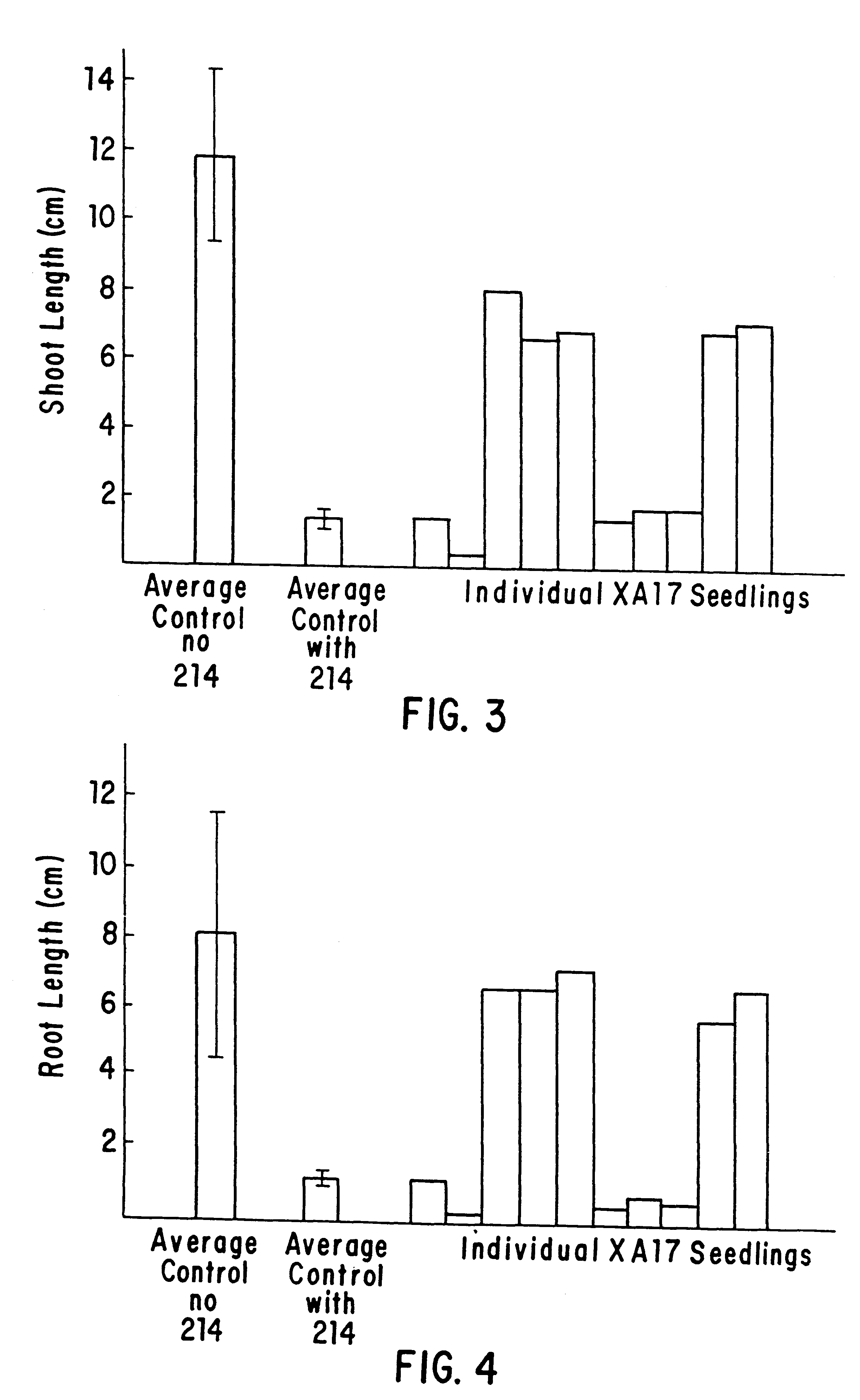
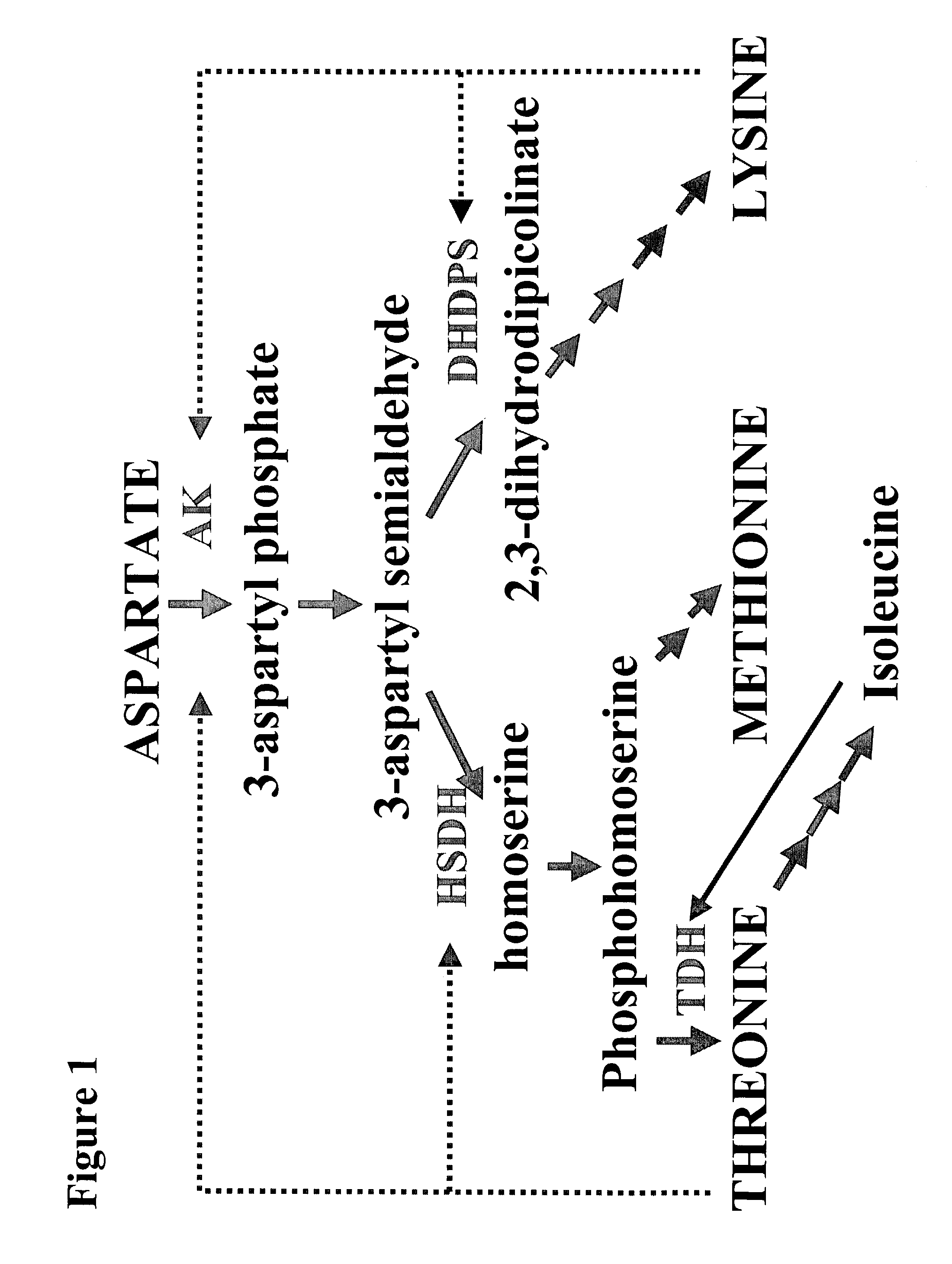
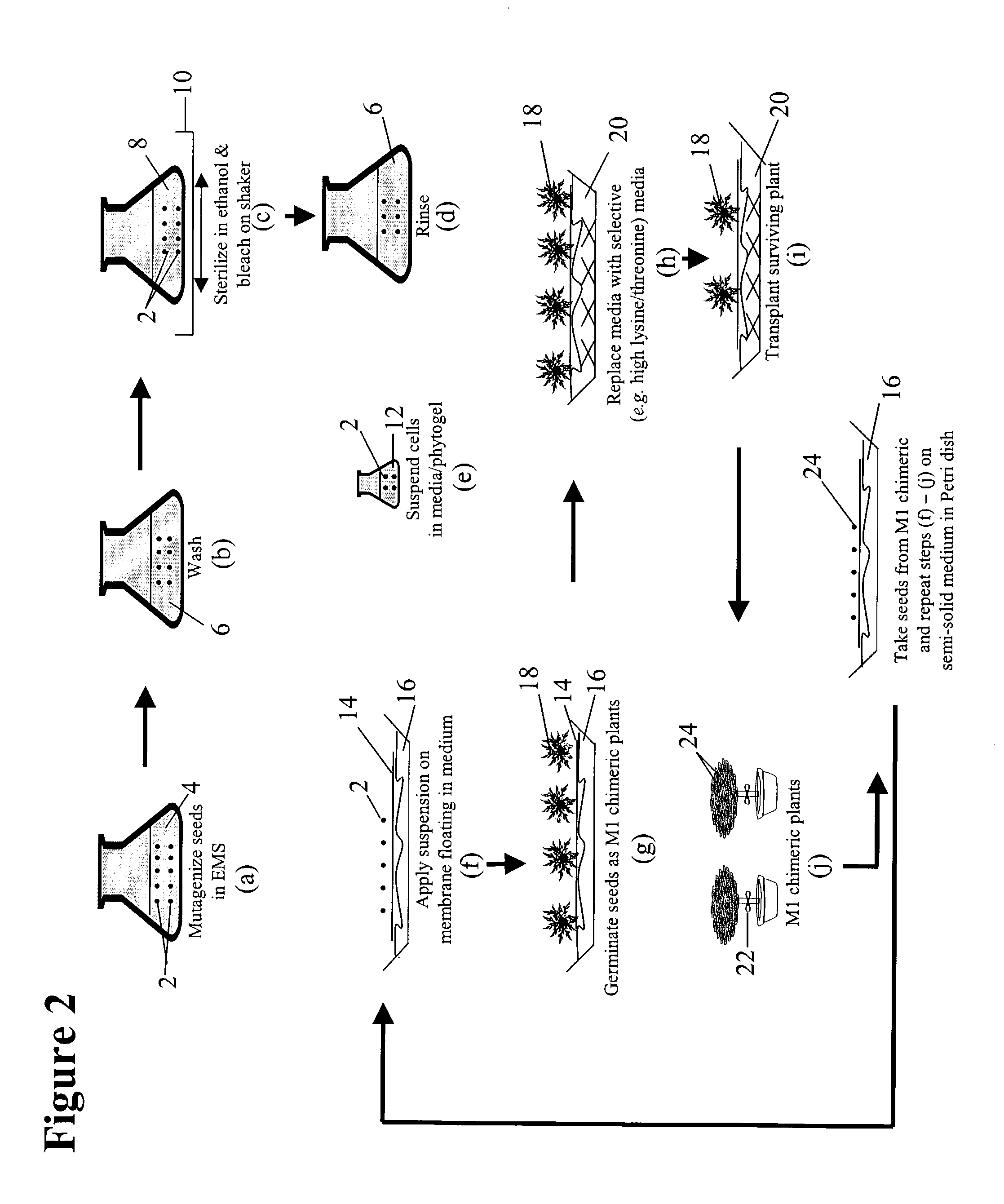
The present invention provides a method for producing plants with a desired phenotypic trait which comprises subjecting plants to mutagenesis, screening chimeric progeny for plants having the desired phenotypic trait, and propagating the survivors. In an embodiment, the phenotypic trait comprises an altered amino acid content. Preferably, the technique is used to generate Nicotiana tobacum plant lines having an increase in at least one amino acid. In a preferred embodiment, the invention provides improved Nicotiana tobacum plant lines producing at least 1.35 nmole of threonine per milligram of dry plant weight. These plants are useful for improving the flavor and aroma of the tobacco.
Owner:REYNOLDS TECH
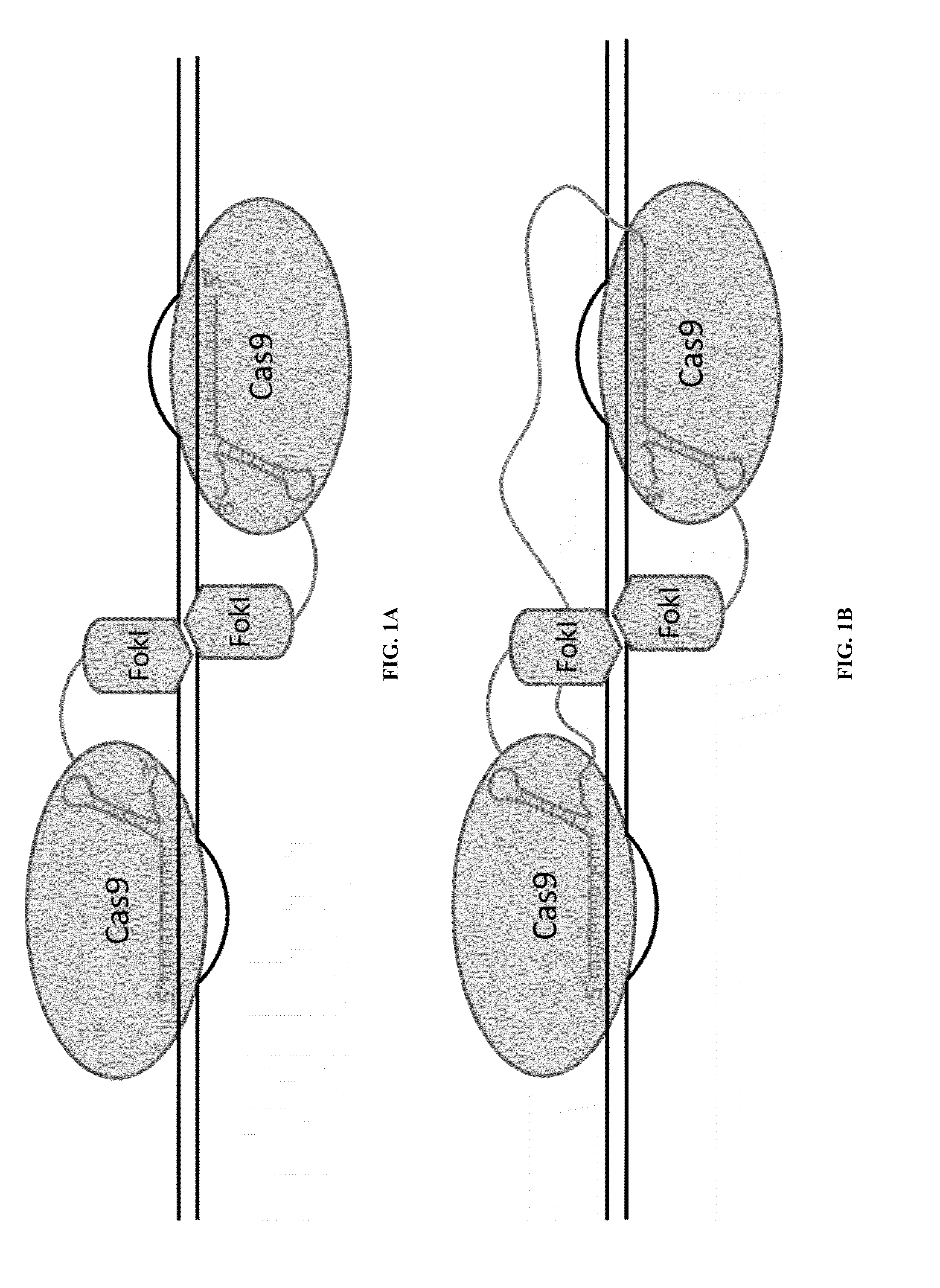
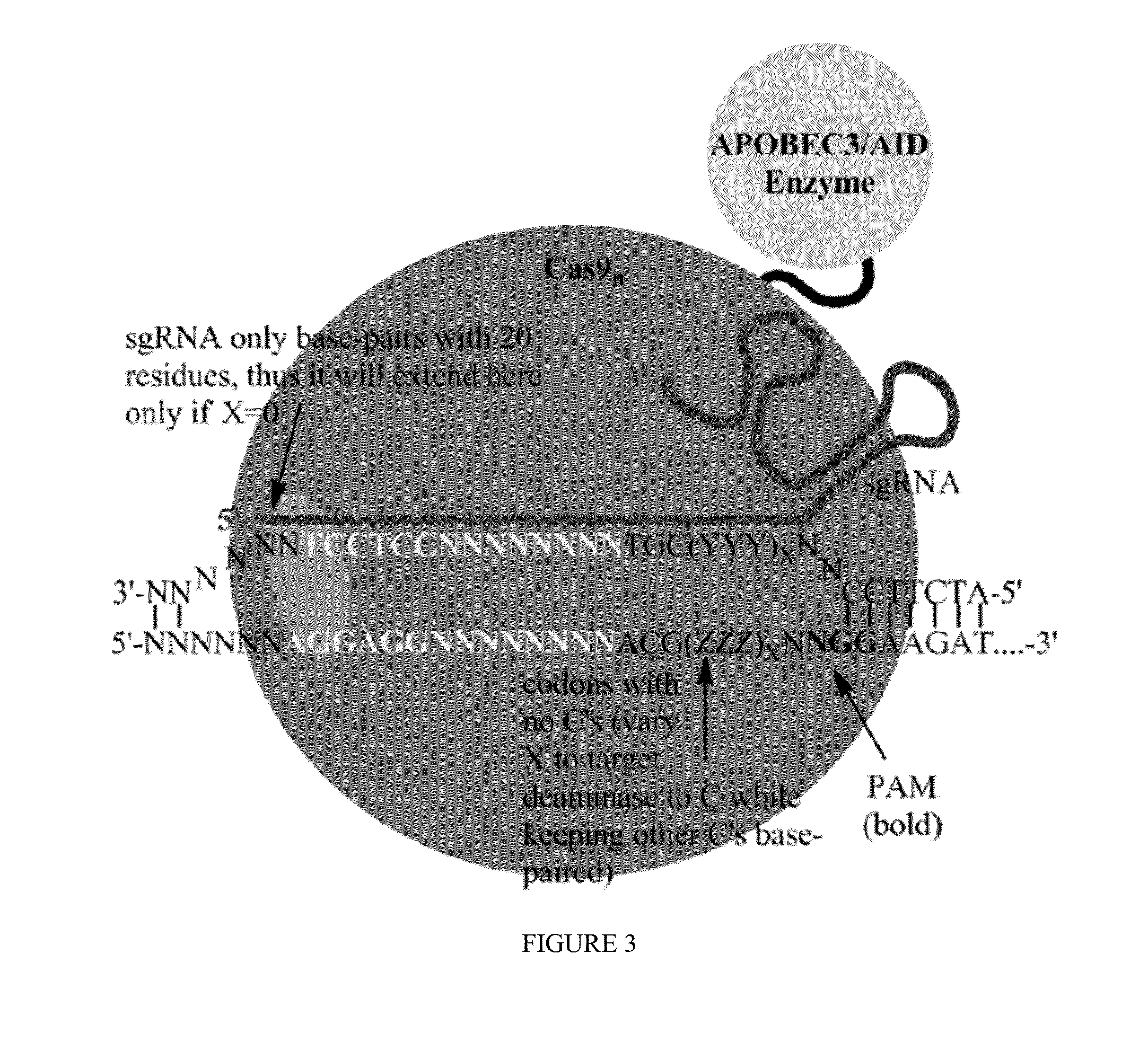
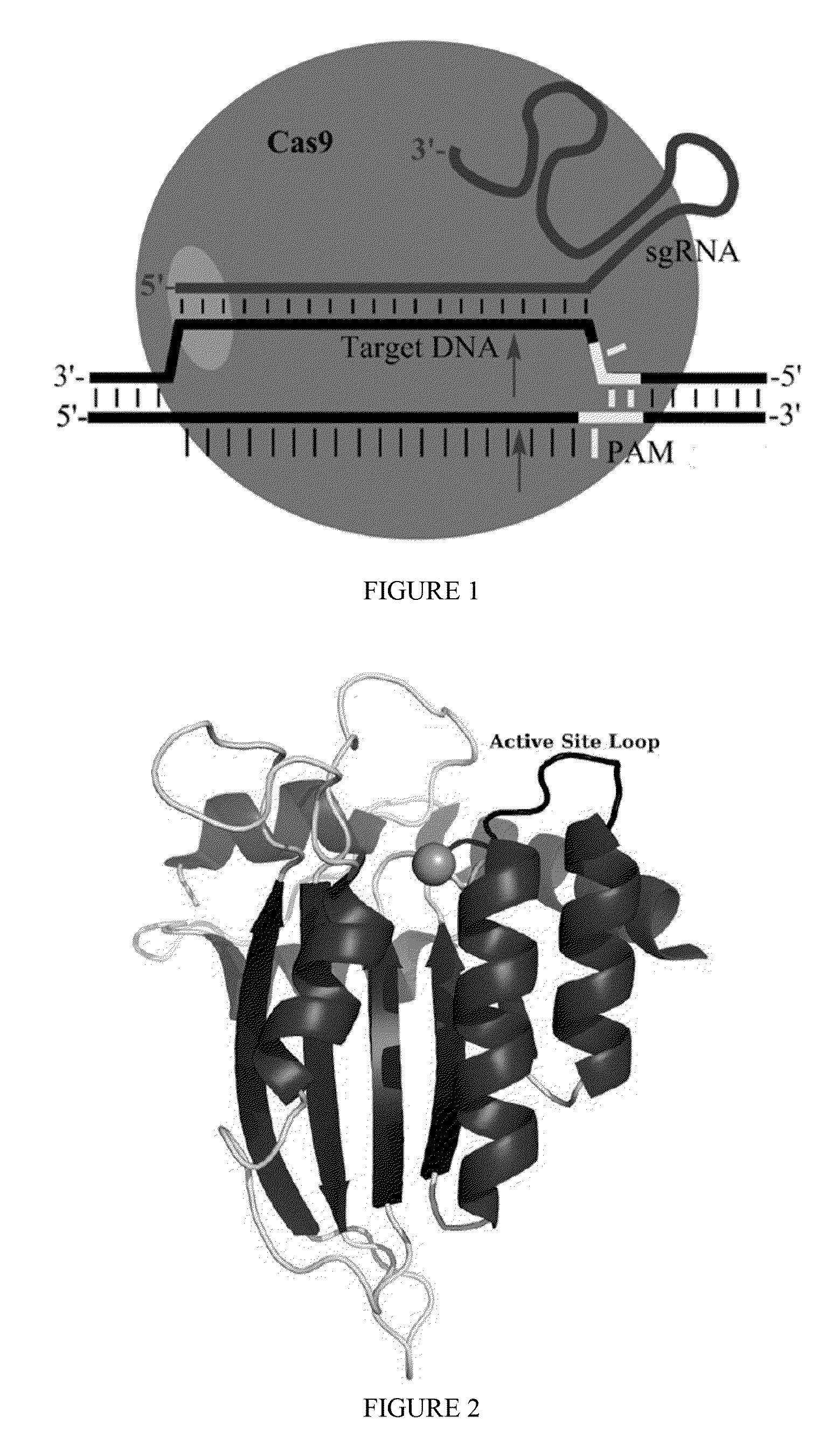
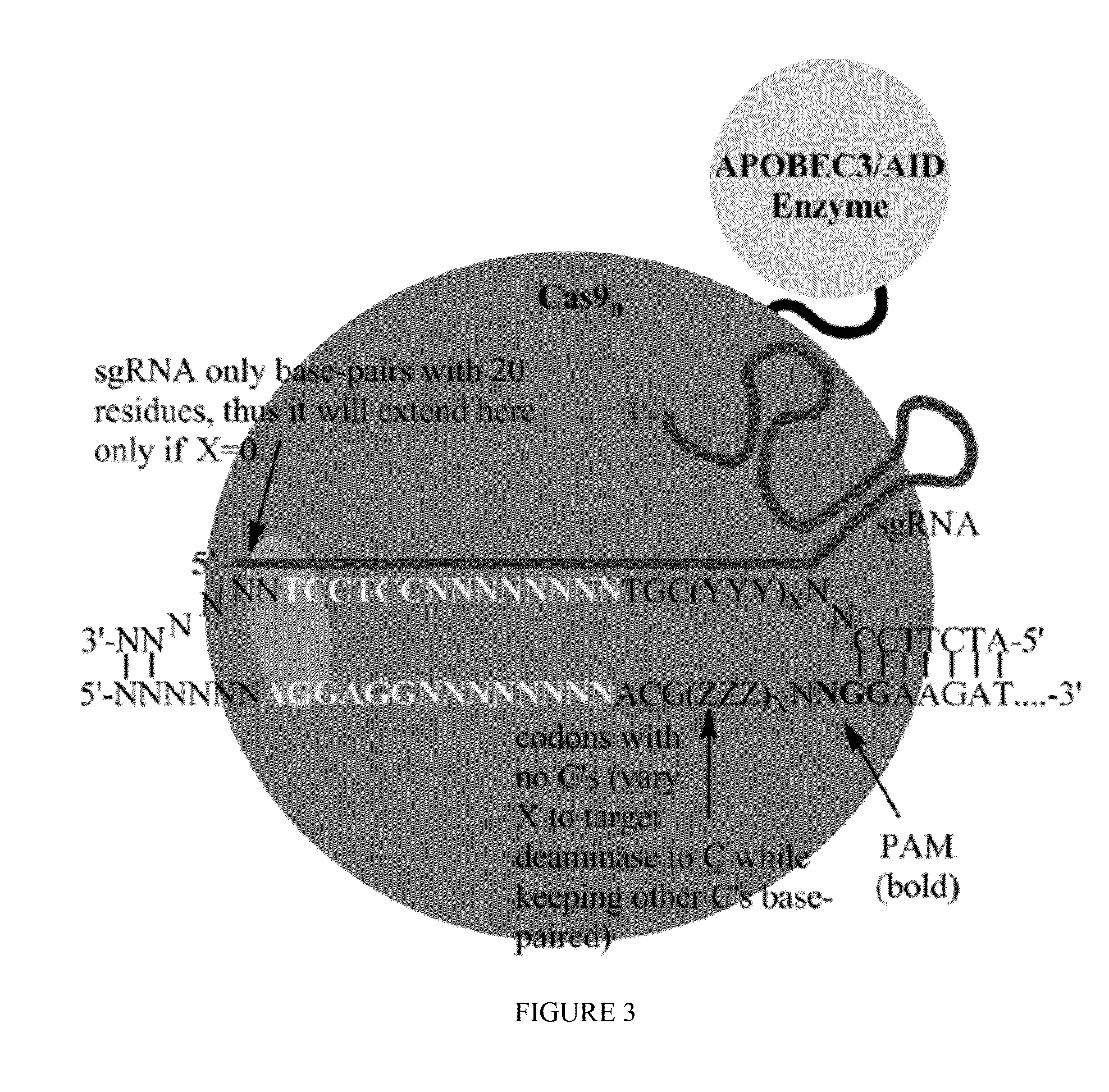
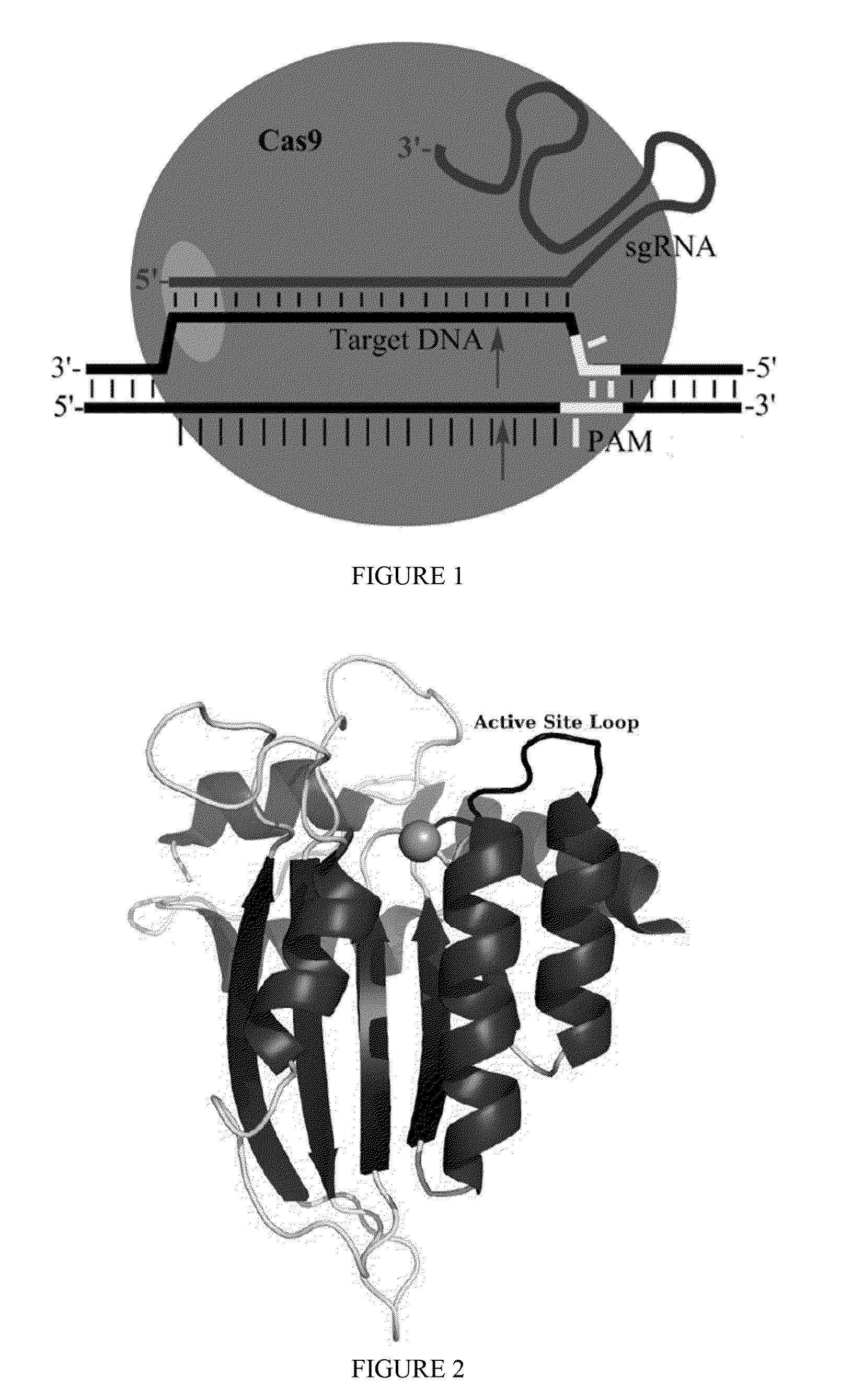
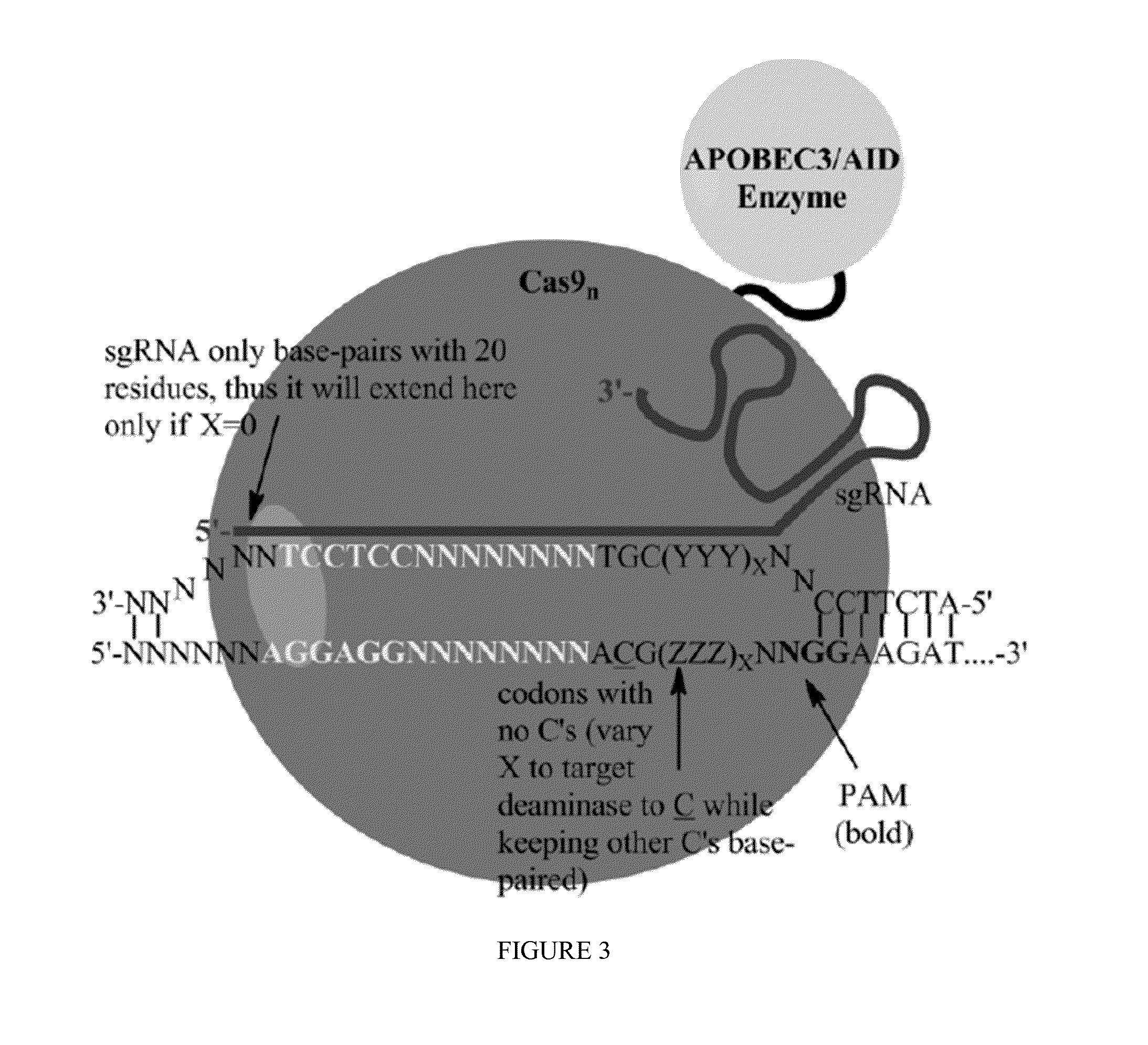
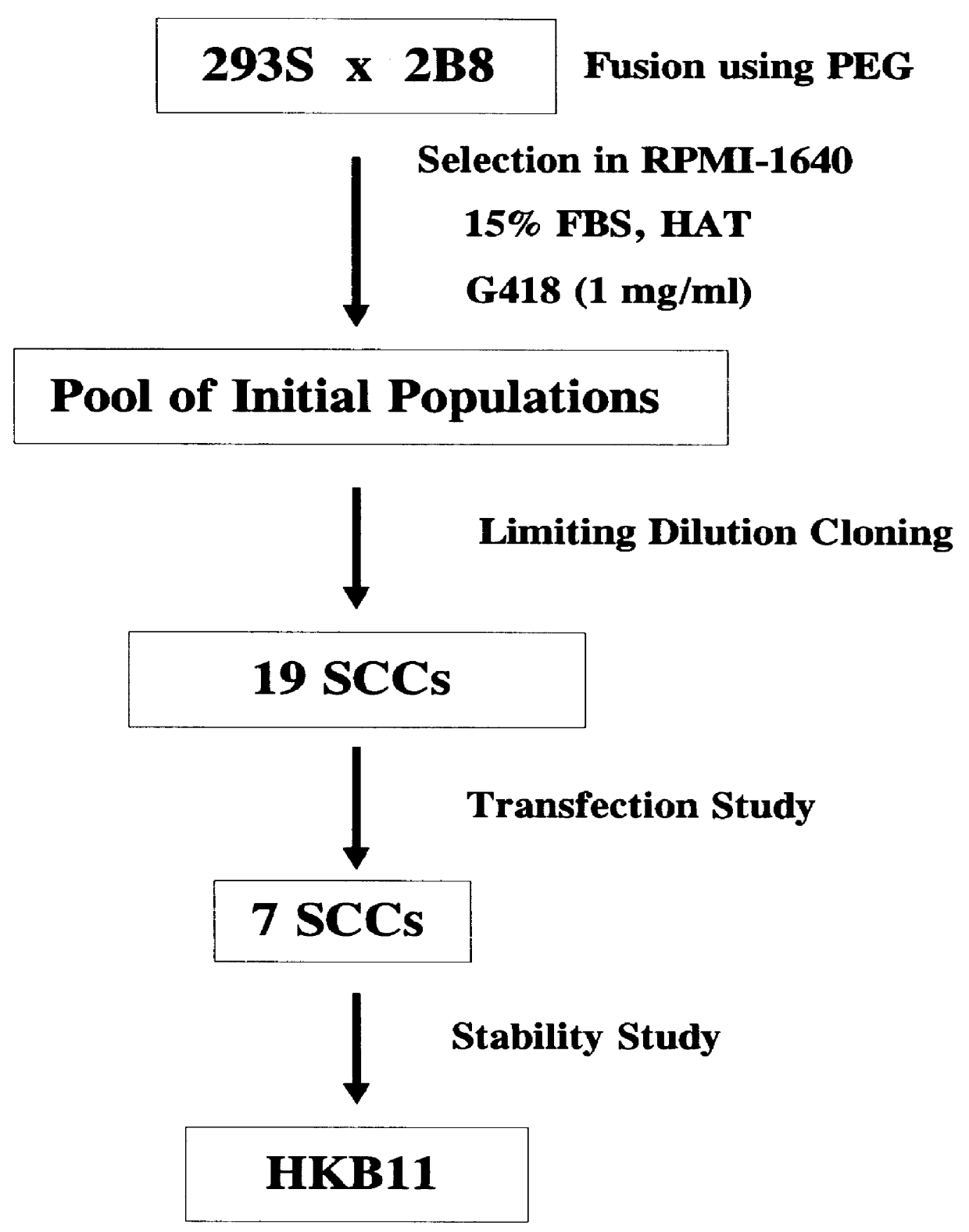
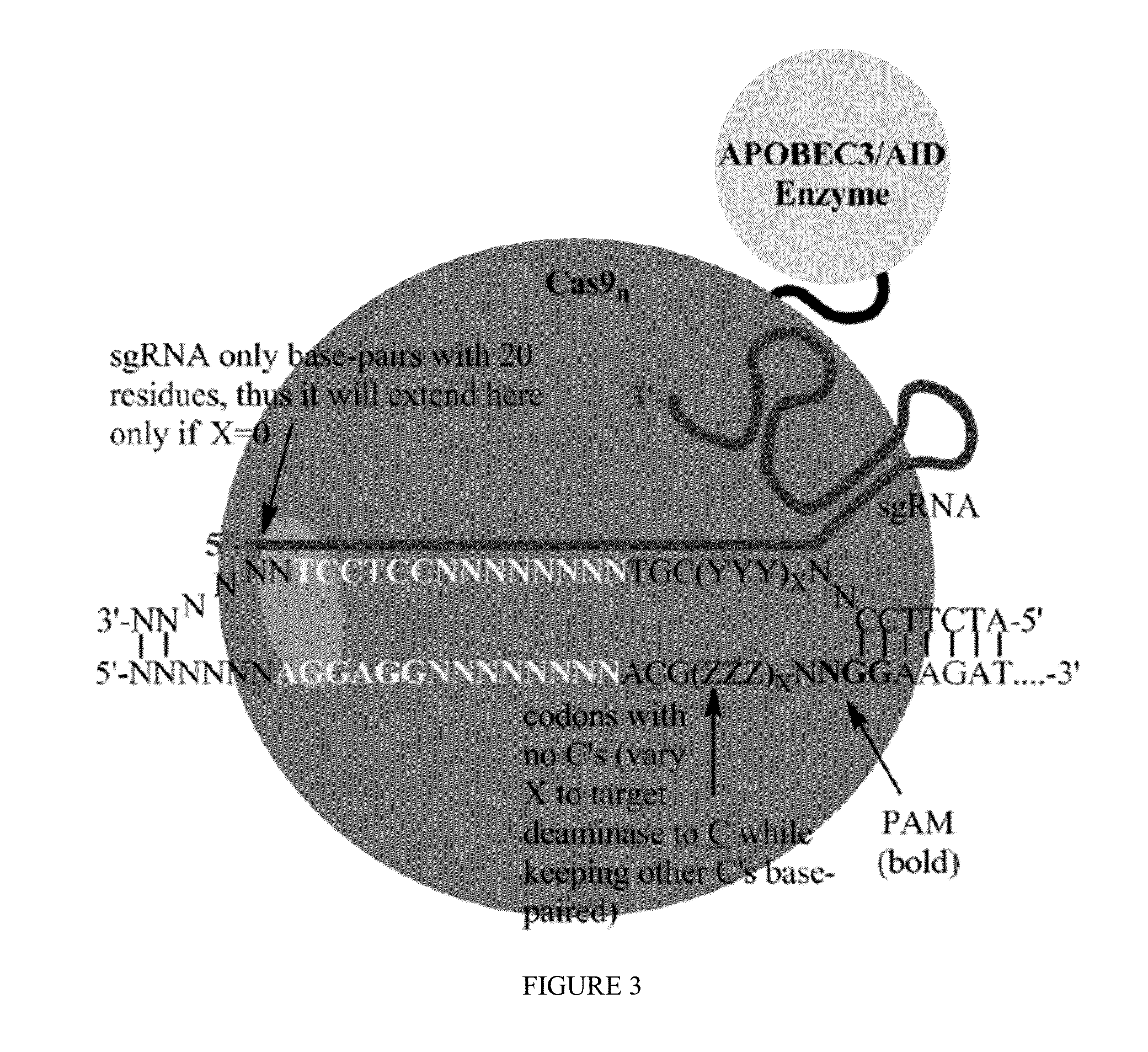
Fusions of cas9 domains and nucleic acid-editing domains
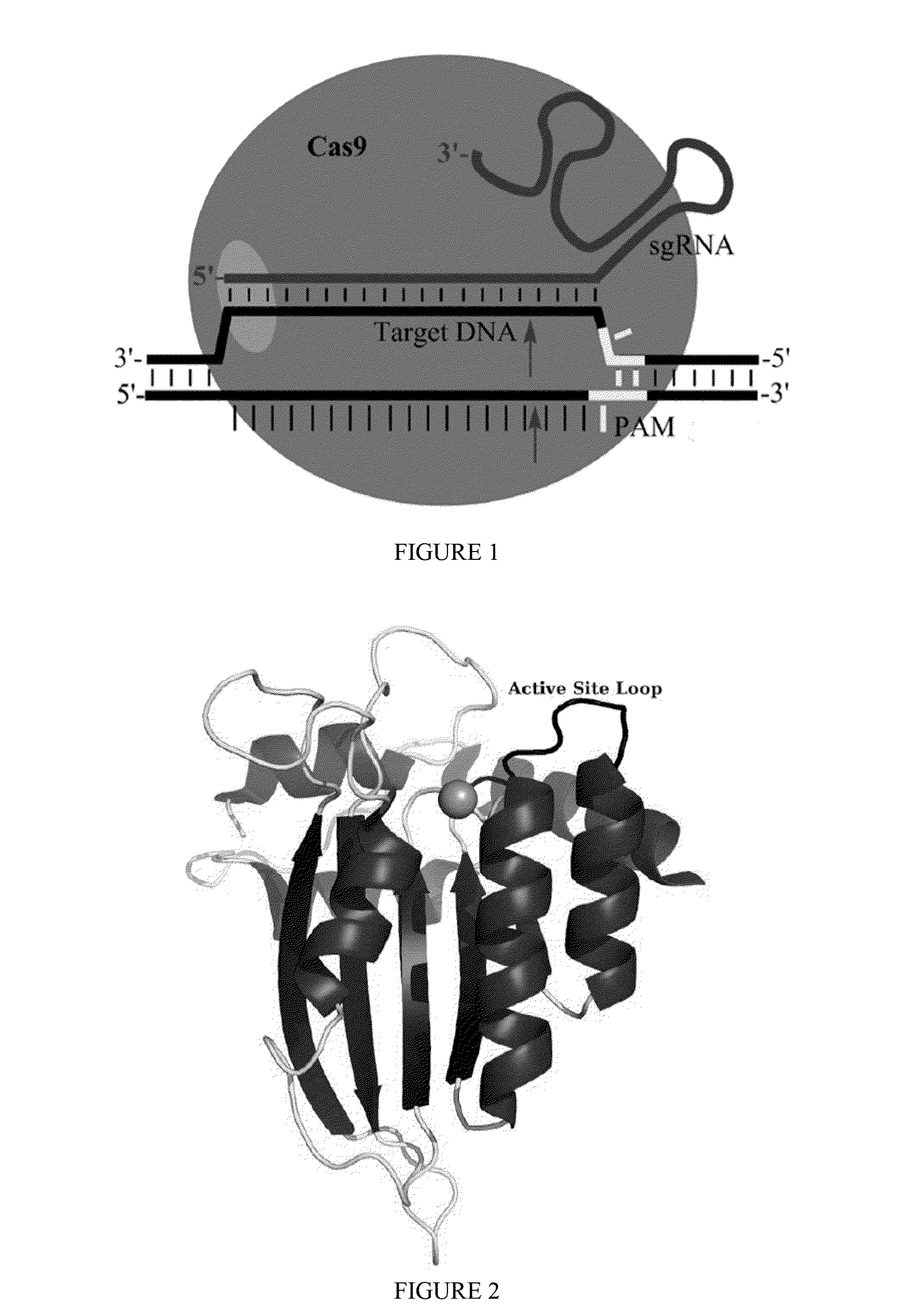
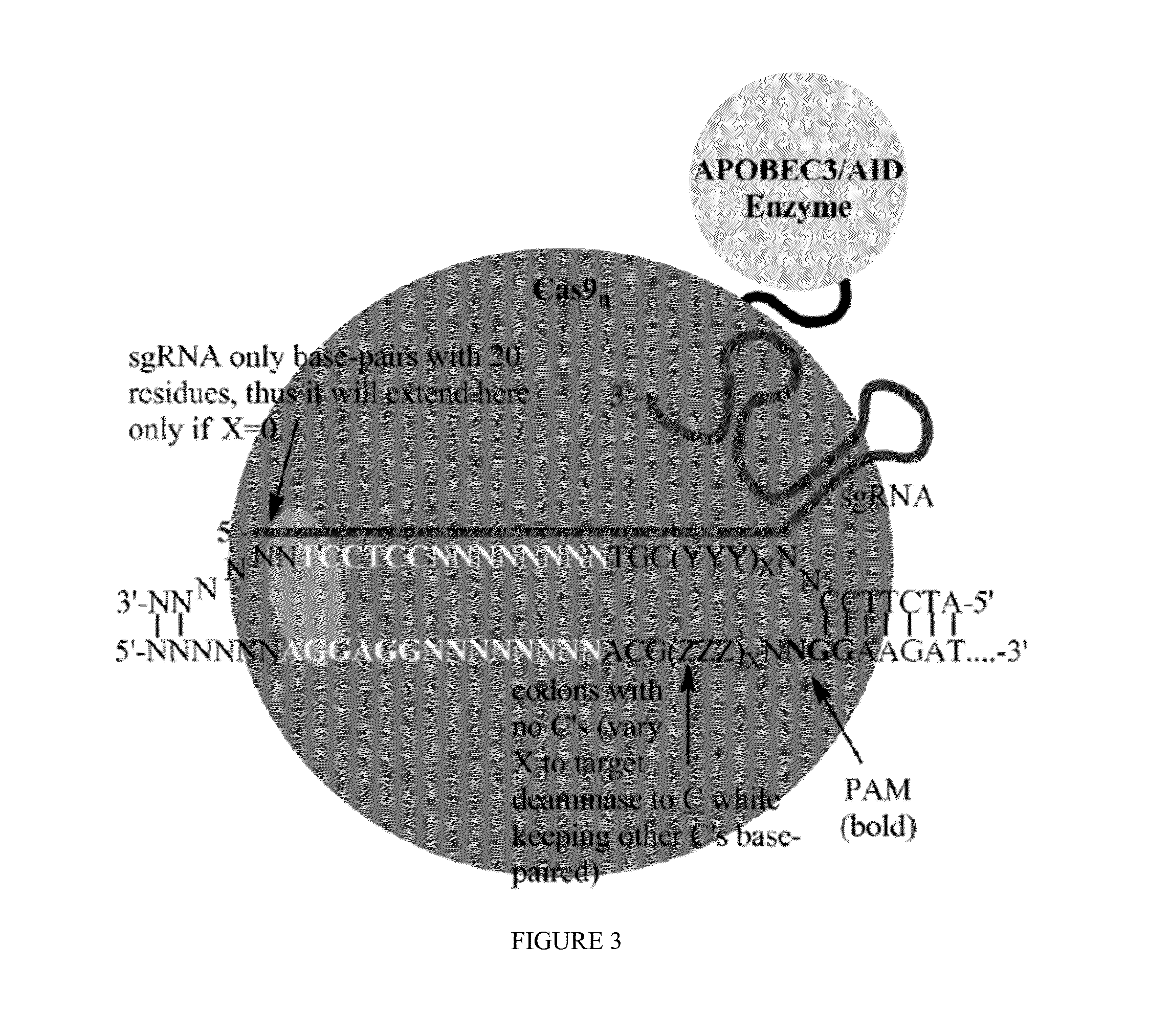
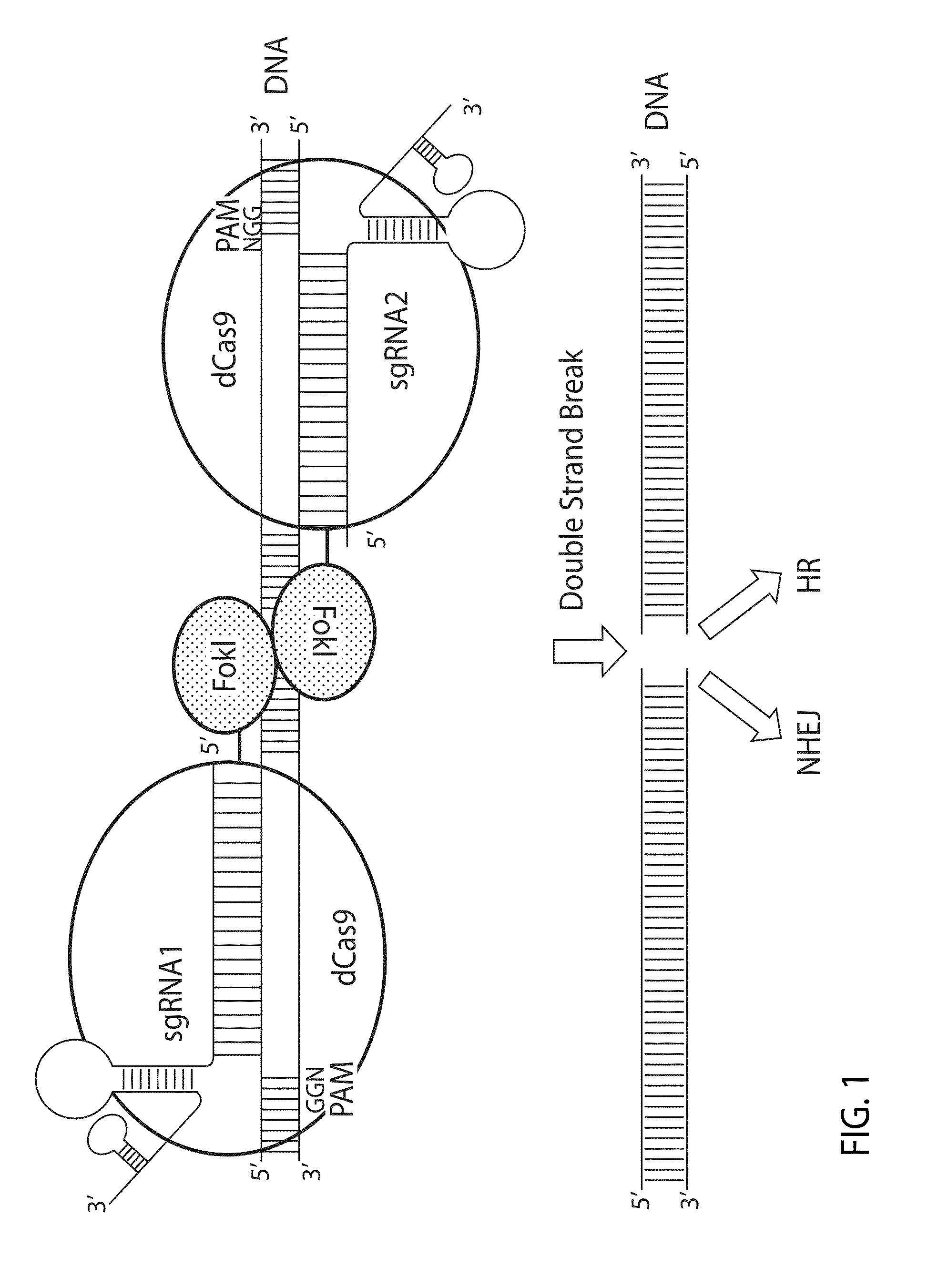
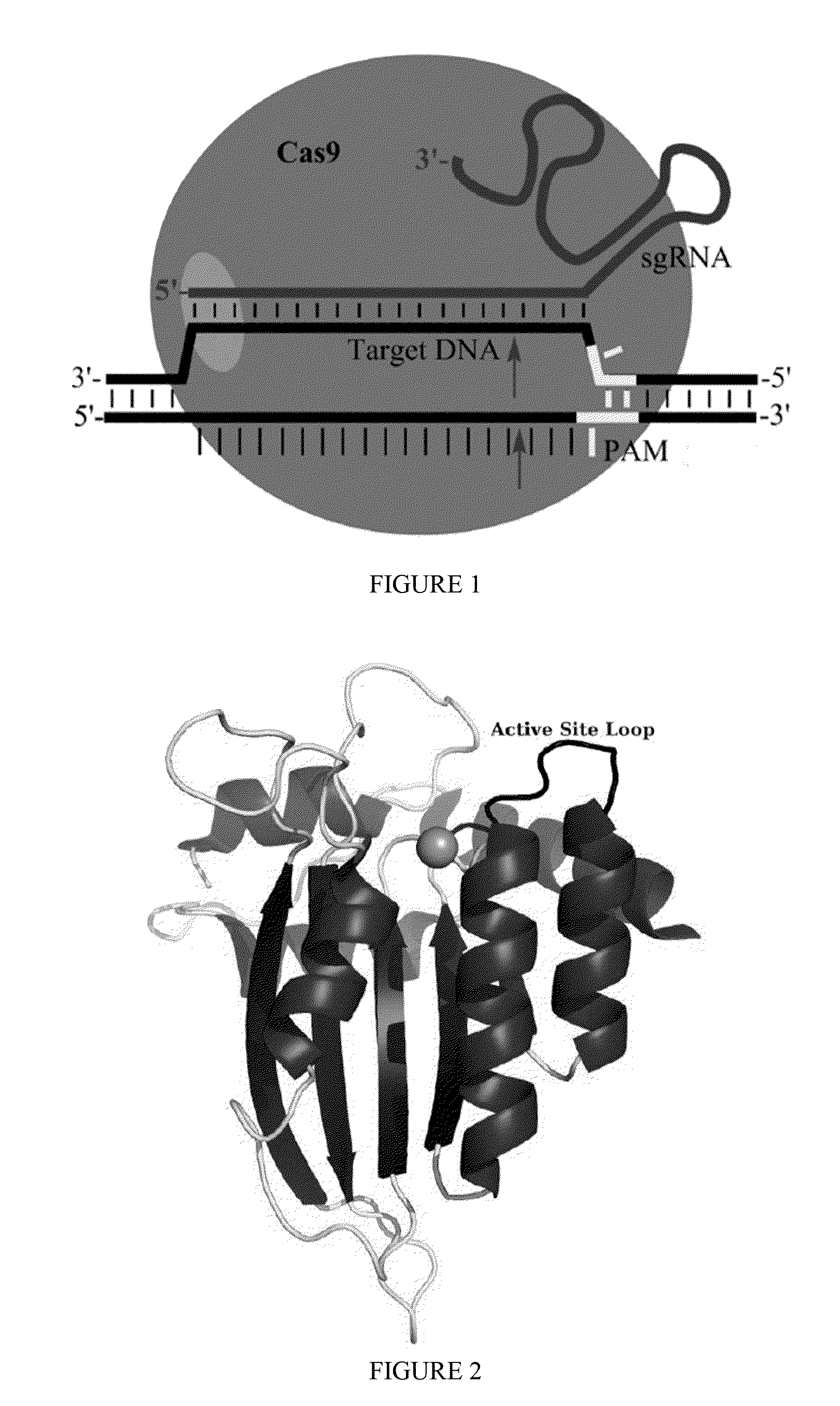
Some aspects of this disclosure provide strategies, systems, reagents, methods, and kits that are useful for the targeted editing of nucleic acids, including editing a single site within the genome of a cell or subject, e.g., within the human genome. In some embodiments, fusion proteins of Cas9 and nucleic acid editing enzymes or enzyme domains, e.g., deaminase domains, are provided. In some embodiments, methods for targeted nucleic acid editing are provided. In some embodiments, reagents and kits for the generation of targeted nucleic acid editing proteins, e.g., fusion proteins of Cas9 and nucleic acid editing enzymes or domains, are provided.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Controlled electroporation and mass transfer across cell membranes
InactiveUS20060121610A1High levelImprove efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsControl mannerCell membrane
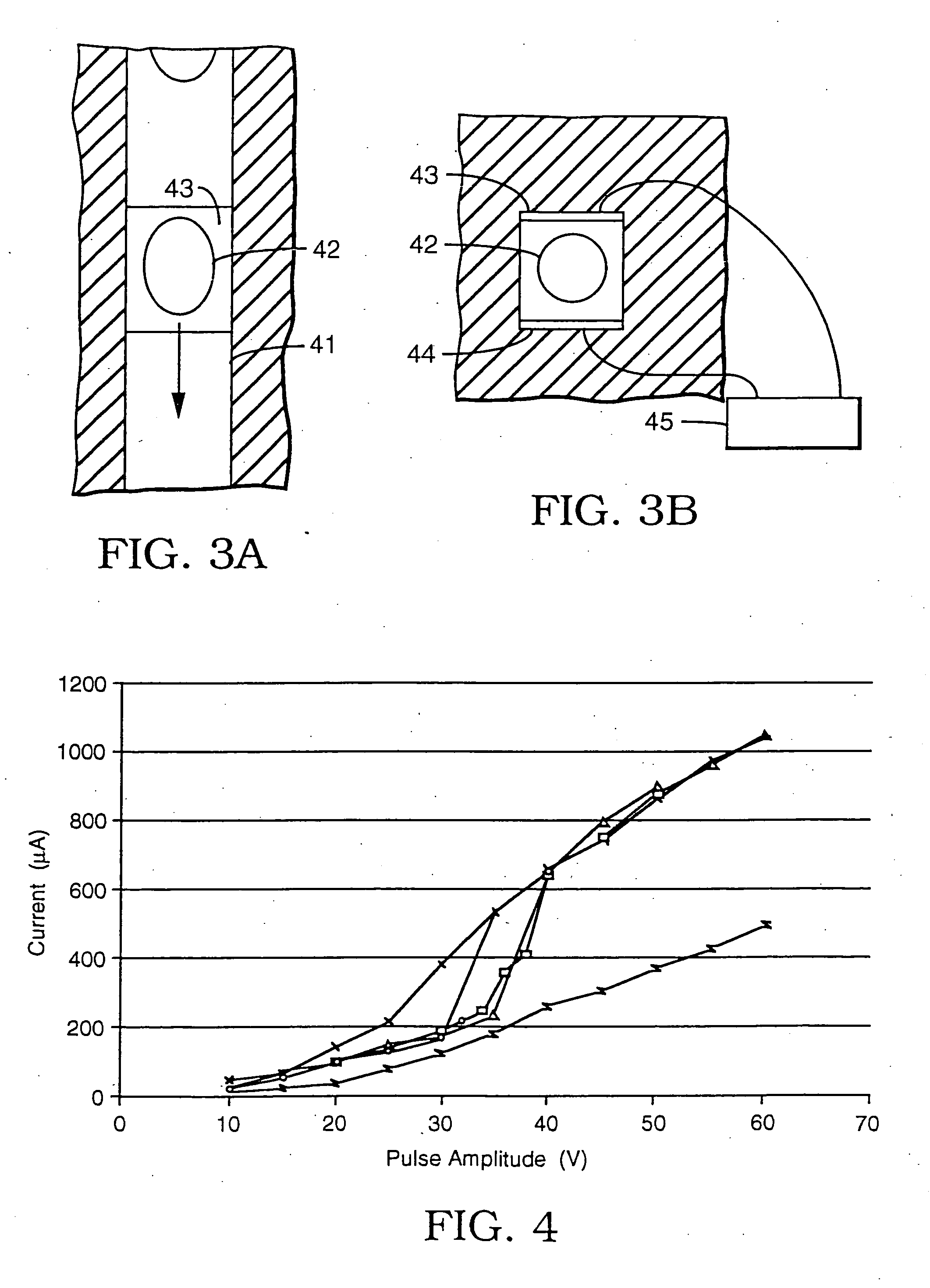
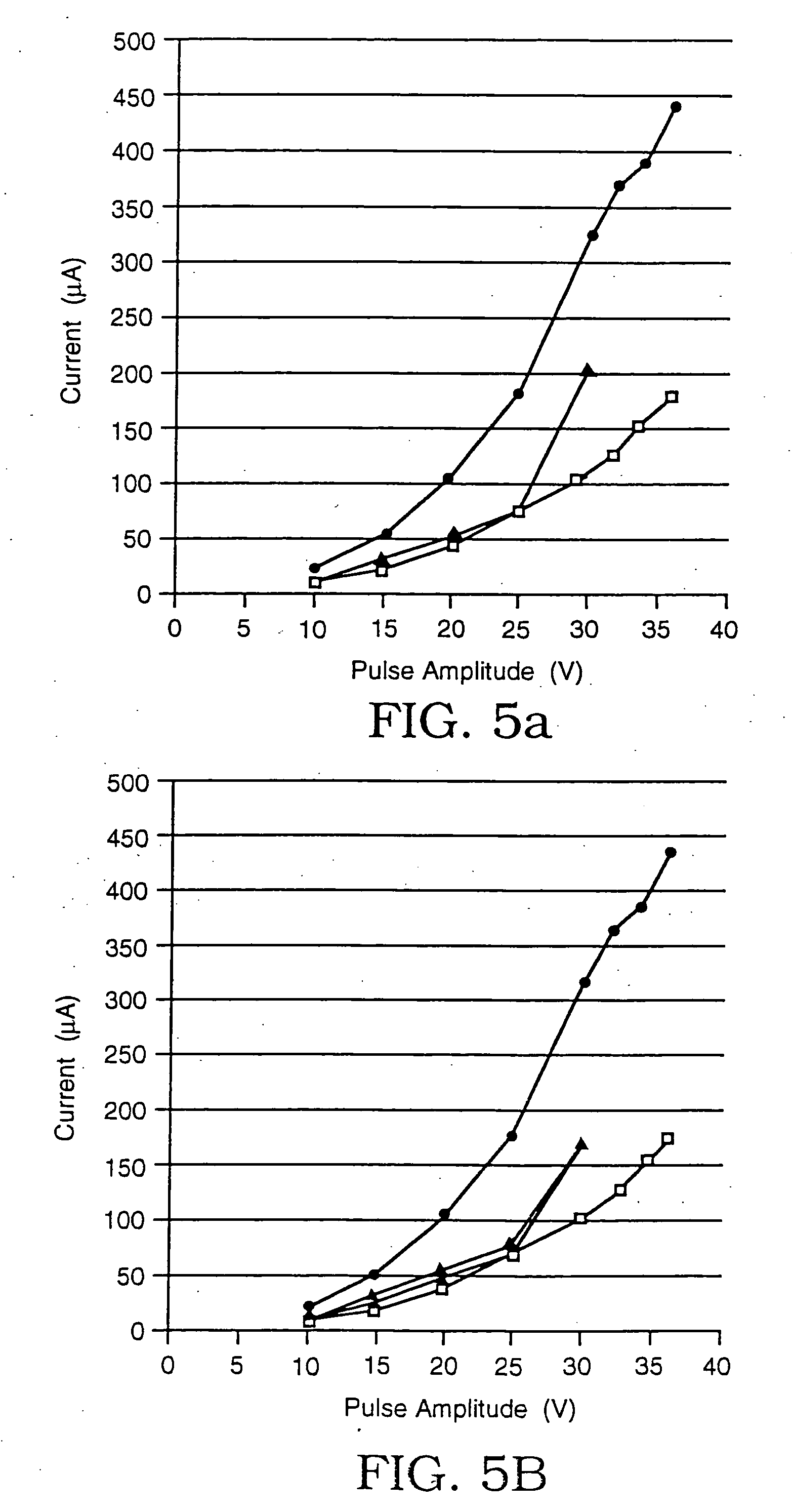
Electroporation is performed in a controlled manner in either individual or multiple biological cells or biological tissue by monitoring the electrical impedance, defined herein as the ratio of current to voltage in the electroporation cell. The impedance detects the onset of electroporation in the biological cell(s), and this information is used to control the intensity and duration of the voltage to assure that electroporation has occurred without destroying the cell(s). This is applicable to electroporation in general. In addition, a particular method and apparatus are disclosed in which electroporation and / or mass transfer across a cell membrane are accomplished by securing a cell across an opening in a barrier between two chambers such that the cell closes the opening. The barrier is either electrically insulating, impermeable to the solute, or both, depending on whether pore formation, diffusive transport of the solute across the membrane, or both are sought. Electroporation is achieved by applying a voltage between the two chambers, and diffusive transport is achieved either by a difference in solute concentration between the liquids surrounding the cell and the cell interior or by a differential in concentration between the two chambers themselves. Electric current and diffusive transport are restricted to a flow path that passes through the opening.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Crispr/cas system-based novel fusion protein and its applications in genome editing
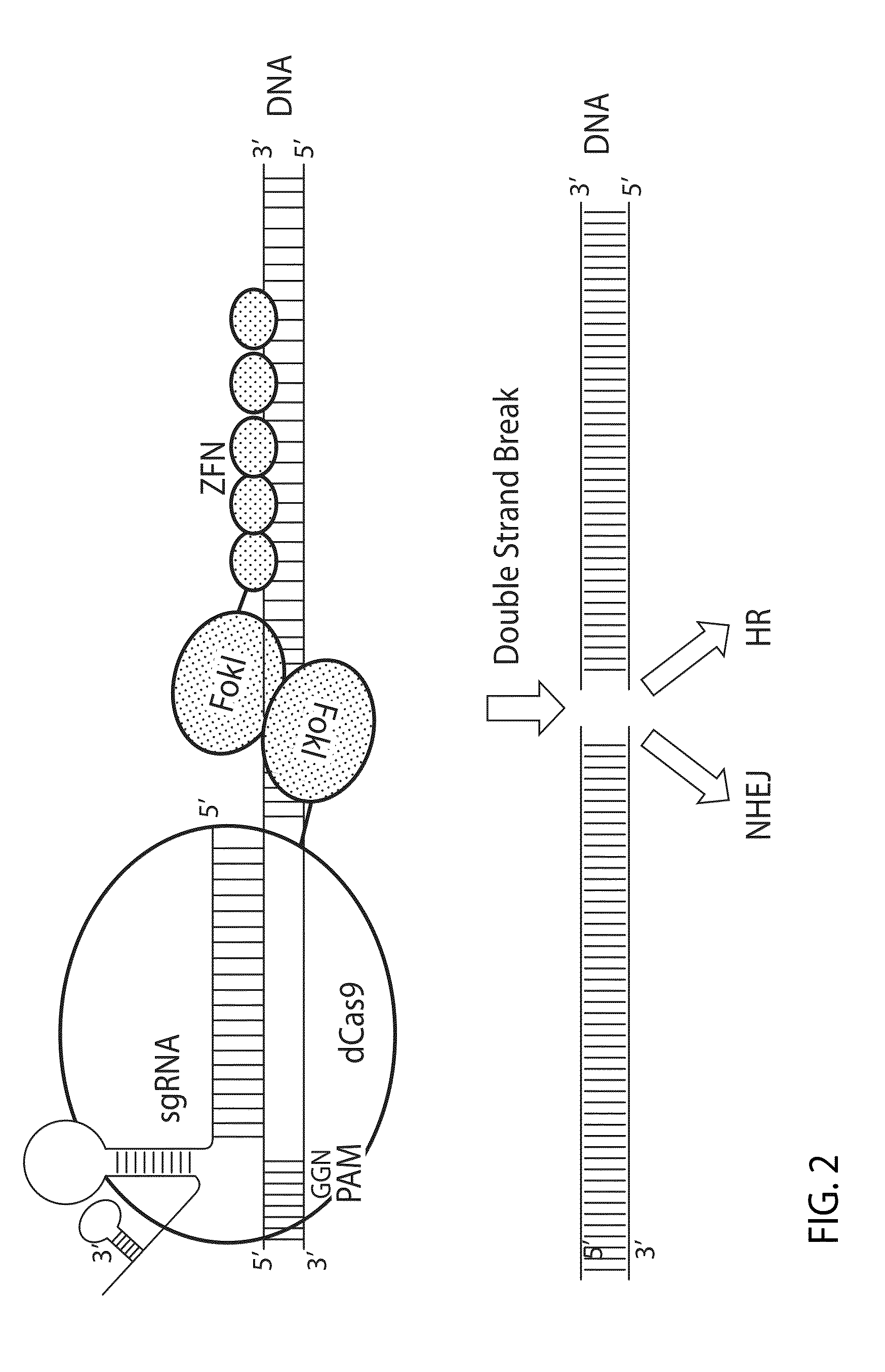
An inactive CRISPR / Cas system-based fusion protein and its applications in gene editing are disclosed. More particularly, chimeric fusion proteins including an inCas fused to a DNA modifying enzyme and methods of using the chimeric fusion proteins in gene editing are disclosed. The methods can be used to induce double-strand breaks and single-strand nicks in target DNAs, to generate gene disruptions, deletions, point mutations, gene replacements, insertions, inversions and other modifications of a genomic DNA within cells and organisms.
Owner:SAGE LABS
Herbicide resistance in plants
InactiveUS6211438B1Confers resistanceEffectively combat weed problemMutant preparationVector-based foreign material introductionPlant tissueNovel gene
This invention is directed to the production of plants, plant tissues and seeds which are resistant to inhibition by an herbicide which normally inhibits the growth and development of those plants, plant tissues and plant seeds. In particular this invention is directed to altered acetohydroxyacid synthase enzymes which are resistant to inhibition by herbicides which normally inhibit the activity of the synthase before such alteration. This invention further relates to genes encoding such enzymes, and to processes for utilizing these novel genes and enzymes. Further products of the invention include plants, plant tissues and seeds which exhibit resistance to such herbicides resulting from expression of genes encoding herbicide resistant acetohydroxyacid synthase enzyme.
Owner:MGI PHARMA
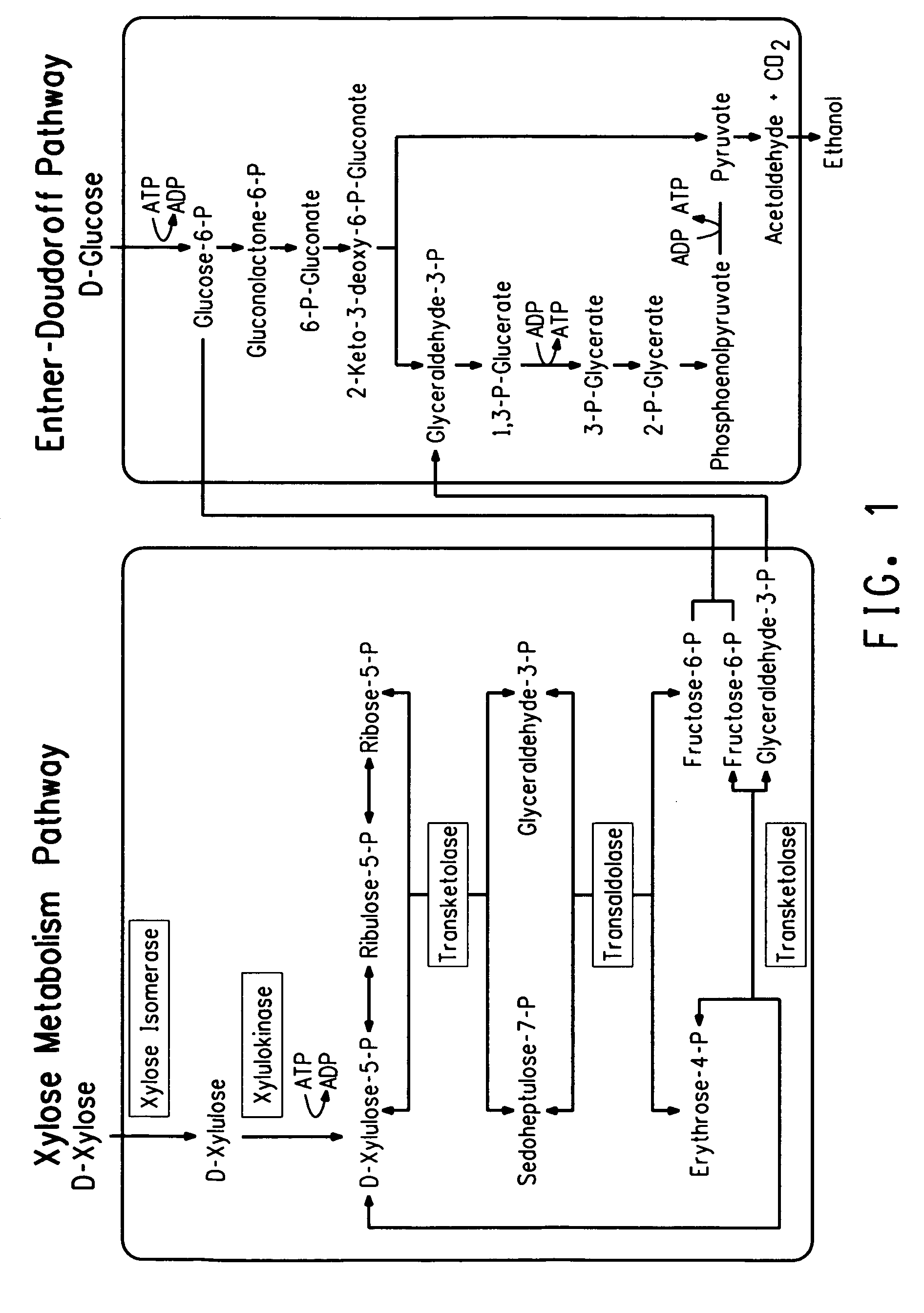
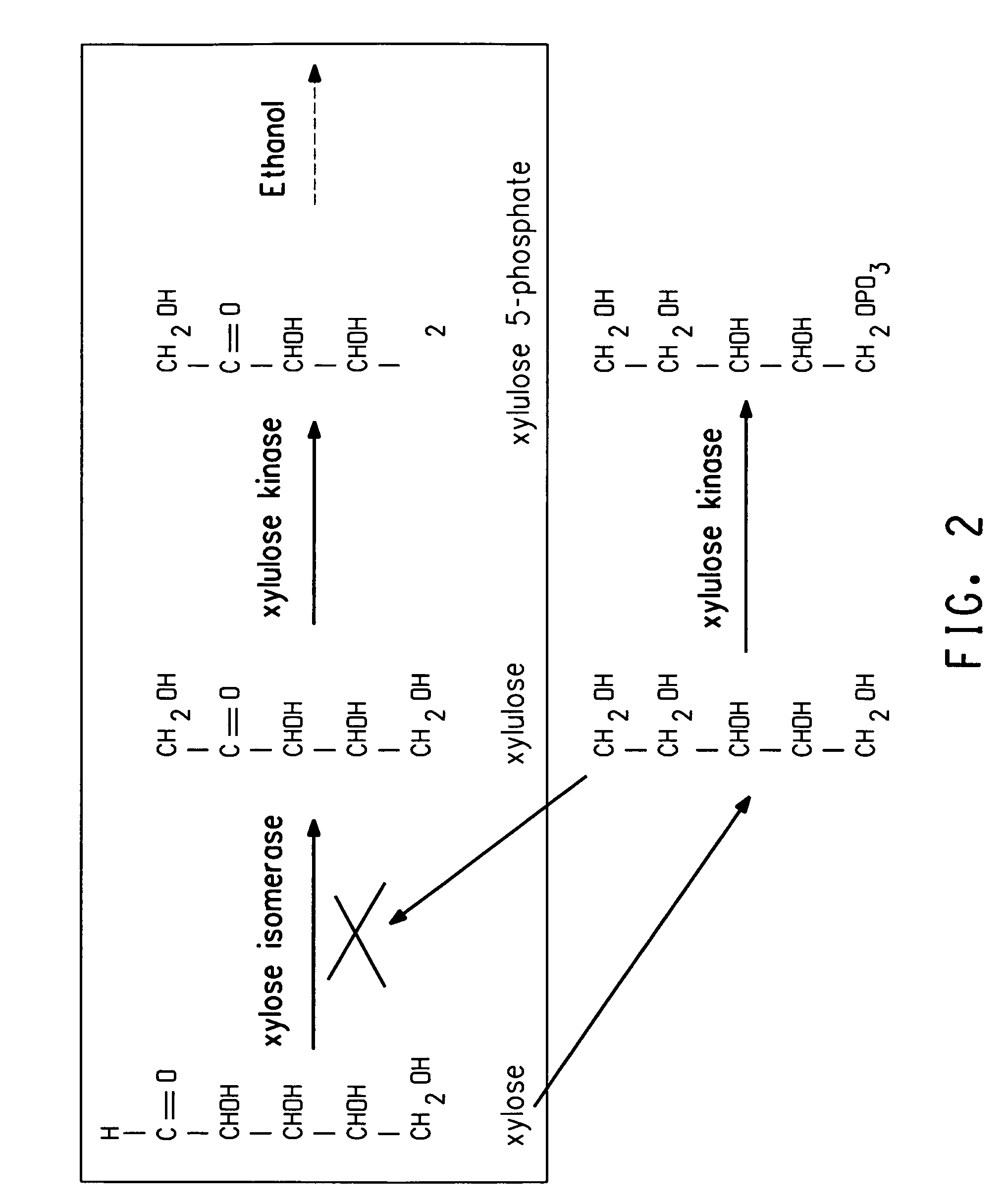
Xylitol synthesis mutant of xylose-utilizing zymomonas for ethanol production
InactiveUS7741119B2Reduce productionIncreased ethanol productionBacteriaUnicellular algaeFructoseOxidoreductase Gene
A strain of xylose-utilizing Zymomonas was engineered with a genetic modification to the glucose-fructose oxidoreductase gene resulting in reduced expression of GFOR enzyme activity. The engineered strain exhibits reduced production of xylitol, a detrimental by-product of xylose metabolism. It also consumes more xylose and produces more ethanol during mixed sugar fermentation under process-relevant conditions.
Owner:SUSTAINABLE TECH CORP +1
Cas9-recombinase fusion proteins and uses thereof
ActiveUS20150071898A1Strong specificityReduce the possibilityFusion with DNA-binding domainBacteriaSite-specific recombinationResearch setting
Some aspects of this disclosure provide compositions, methods, and kits for improving the specificity of RNA-programmable endonucleases, such as Cas9. Also provided are variants of Cas9, e.g., Cas9 dimers and fusion proteins, engineered to have improved specificity for cleaving nucleic acid targets. Also provided are compositions, methods, and kits for site-specific recombination, using Cas9 fusion proteins (e.g., nuclease-inactivated Cas9 fused to a recombinase catalytic domain). Such Cas9 variants are useful in clinical and research settings involving site-specific modification of DNA, for example, genomic modifications.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
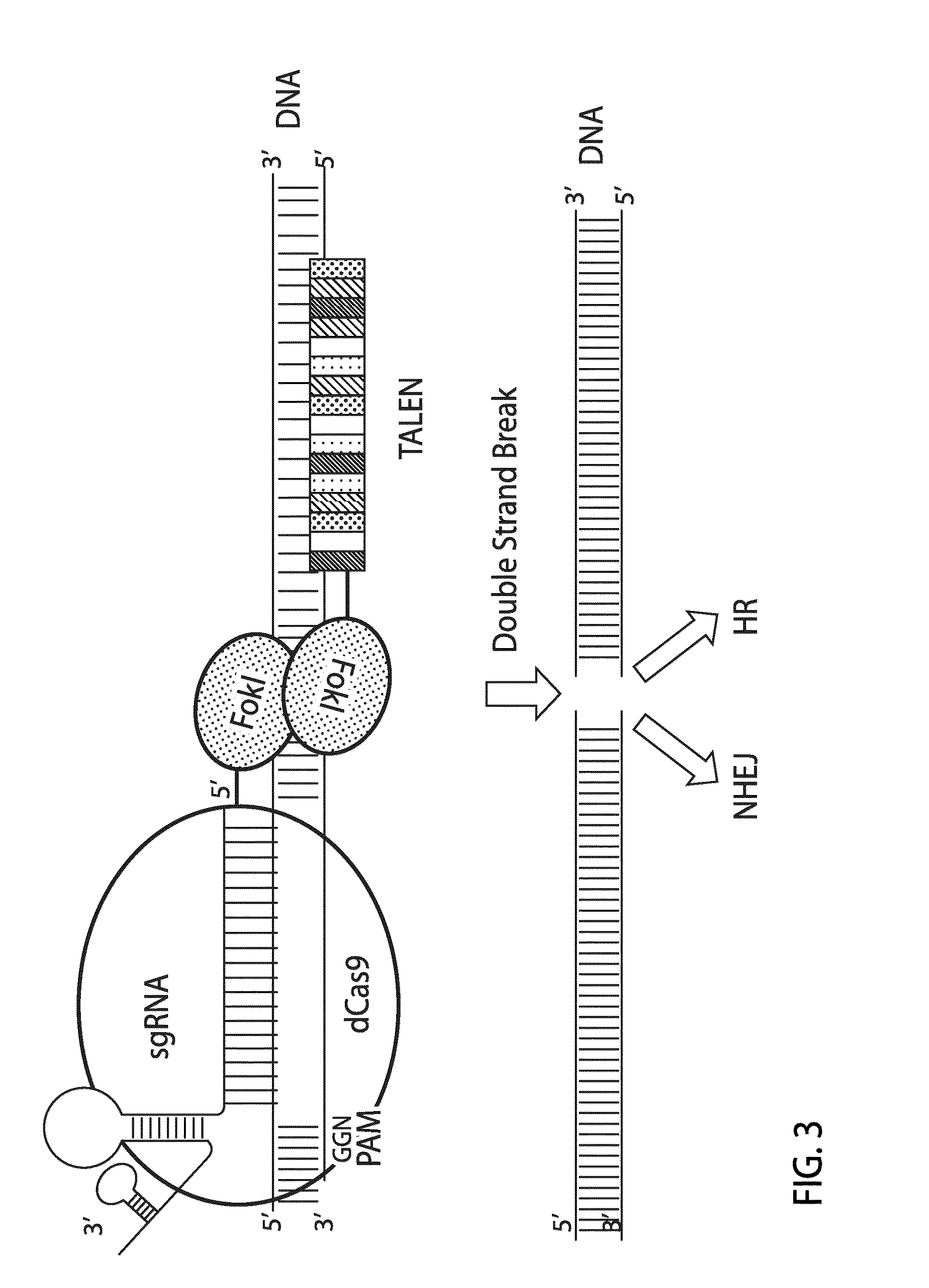
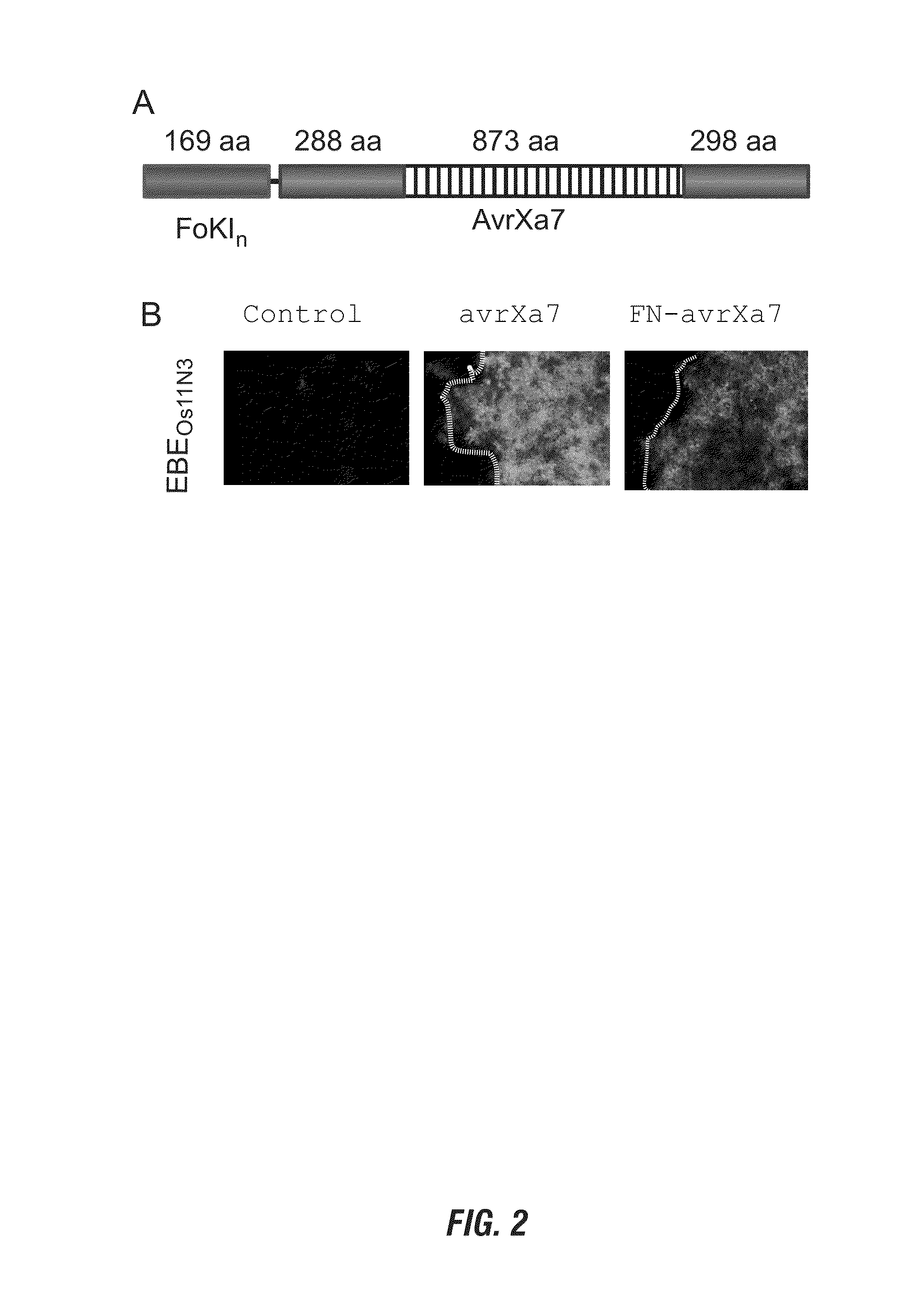
Nuclease activity of tal effector and foki fusion protein
The present invention provides compositions and methods for targeted cleavage of cellular chromatin in a region of interest and / or homologous recombination at a predetermined site in cells. Compositions include fusion polypeptides comprising a TAL effector binding domain and a cleavage domain. The cleavage domain can be from any endonuclease. In certain embodiments, the endonuclease is a Type IIS restriction endonuclease. In further embodiments, the Type IIS restriction endonuclease is FokI.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Corn plants and products with improved oil composition
InactiveUS6248939B1Increase contentHigh oleic acid producing characteristicsMutant preparationAnimal feeding stuffChemical compositionComponents of crude oil
This invention relates to corn (Zea mays L.) seed and grain having a significantly higher oleic acid content than conventional corn by virtue of heritable genes for increased oil and oleic acid content and / or lowered levels of linoleic acid. The present invention also relates to the production of high oil, high oleic grain, its oil, its progeny and its use.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Electromagnetic activation of gene expression and cell growth
InactiveUS20050059153A1Accelerating cell cycleReduce inflammationElectrotherapyMutant preparationAngiotensin receptorA-DNA
The invention is directed to a method for accelerating the cell cycle by delivering to a cell an effective amount of electromagnetic energy. The invention also provides a method for activating a cell cycle regulator by delivering to a cell an effective amount of electromagnetic energy. Also provided by the invention is a method for activating a signal transduction protein; a method for activating a transcription factor; a method for activating a DNA synthesis protein; and a method for activating a Receptor. A method for inhibiting an angiotensin receptor as well as a method for reducing inflammation also are provided by the present invention. The invention also is directed to a method for replacing damaged neuronal tissue as well as a method for stimulating growth of administered cells.
Owner:REGENESIS BIOMEDICAL
Microbial production of nuclease resistant DNA, RNA, and oligo mixtures
Owner:FRAYNE CONSULTANTS
Methods for correcting caspase-9 point mutations
Some aspects of this disclosure provide strategies, systems, reagents, methods, and kits that are useful for the targeted editing of nucleic acids, including editing a nucleic acid encoding a mutant Caspase-9 protein to correct a point mutation associated with a disease or disorder, e.g., with neuroblastoma. The methods provided are useful for correcting a Caspase-9 point mutation within the genome of a cell or subject, e.g., within the human genome. In some embodiments, fusion proteins of Cas9 and nucleic acid editing enzymes or enzyme domains, e.g., deaminase domains, are provided. In some embodiments, reagents and kits for the generation of targeted nucleic acid editing proteins, e.g., fusion proteins of Cas9 and nucleic acid editing enzymes or domains, are provided.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Methods of treatment using electromagnetic field stimulated stem cells
InactiveUS20050084962A1High proliferation ratePromote differentiationMutant preparationArtificial cell constructsElectricityMesenchymal stem cell
Methods of modifying stem cells, in particular mesenchymal stem cells, using electric or electromagnetic fields. In one embodiment, the present invention provides methods of modulating a mesenchymal stem cell activity, the method comprising administering electric stimulation to mesenchymal stem cells in vitro. In another embodiment, the present invention provides methods for the treatment of a human or other mammal subject in need thereof, comprising providing an in vitro culture comprising mesenchymal stem cells, administering an electric stimulation to the in vitro culture, and implanting the mesenchymal stem cells into the mammal subject. In another embodiment, the present invention provides methods for the treatment of a human or other mammal subject, the method comprising implanting mesenchymal stem cells into the mammal subject, and administering an electric stimulation to the mesenchymal stem cells in situ. The present invention also comprises compositions comprising mesenchymal stem cells treated with electric stimulation.
Owner:EUROPEAN BIOINFORMATICS INSTITUTE
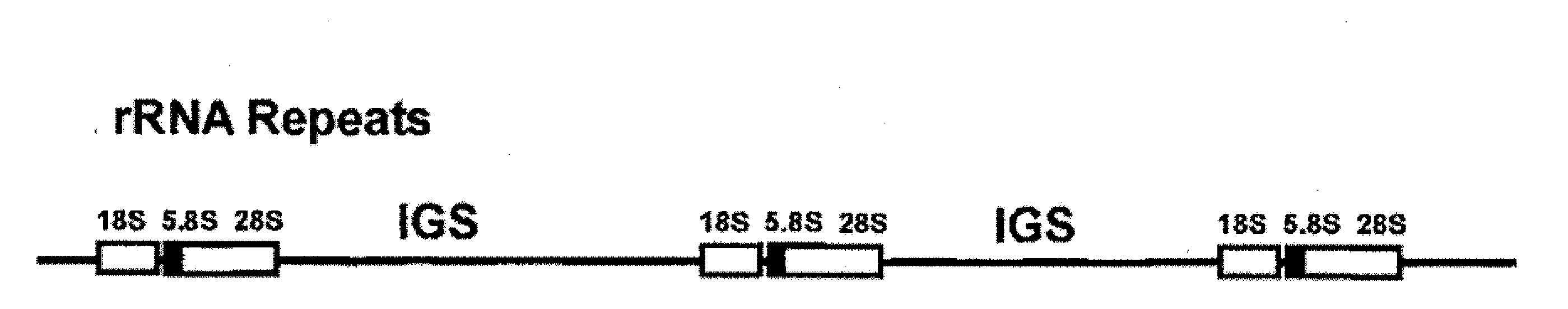
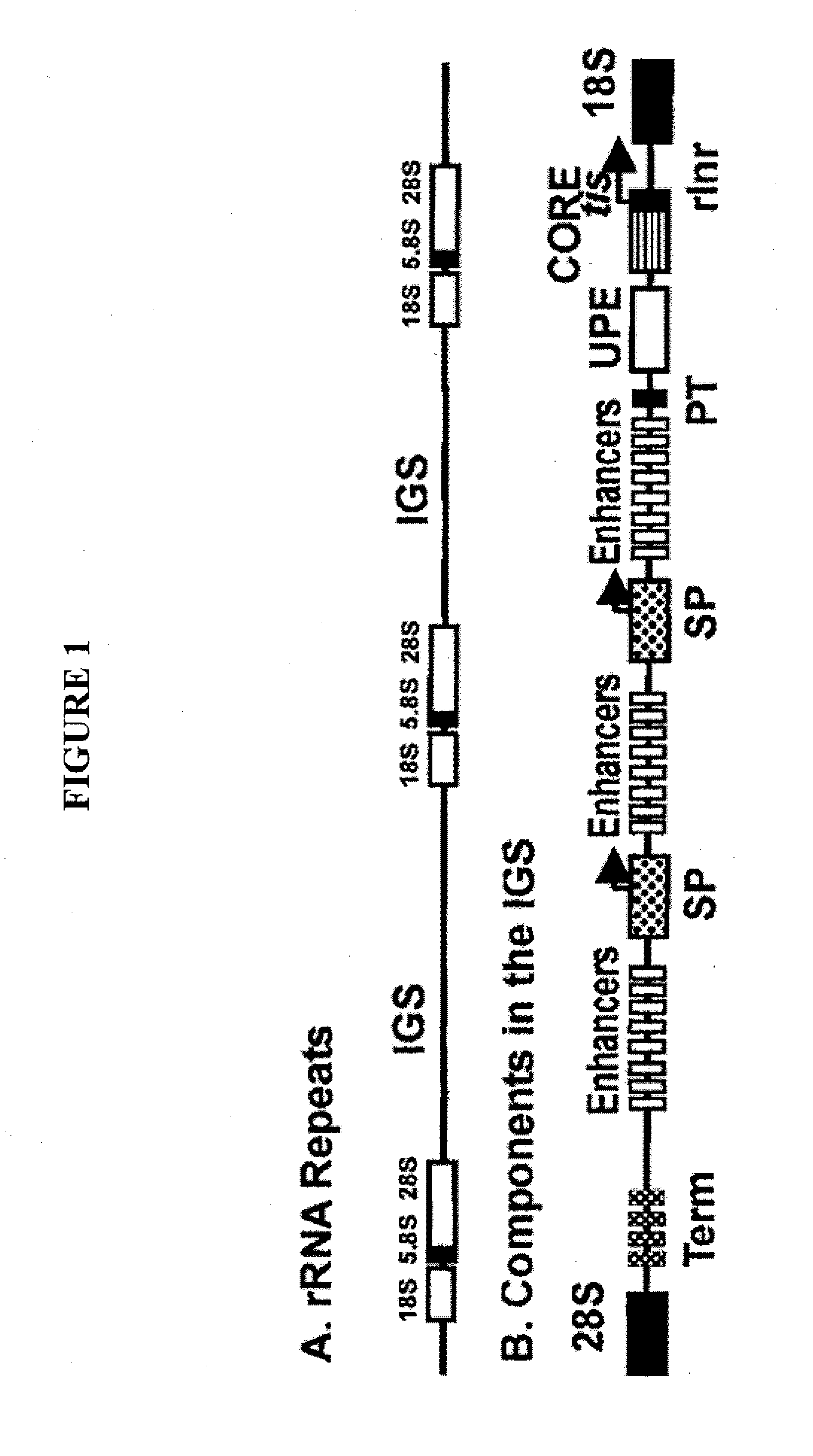
Nuclear based expression of genes for production of biofuels and process co-products in algae
Various embodiments provide, for example, vectors, expression cassettes, and cells useful for transgenic expression of nucleic acid sequences. In various embodiments, vectors can contain nuclear-based sequences of unicellular photosynthetic bioprocess organisms for the production of food- and feed-stuffs, oils, biofuels, starches, raw materials, pharmaceuticals or fine chemicals.
Owner:KUEHNLE AGROSYST
Methods and compositions for improving plant health
ActiveUS20090105077A1Improve efficiencyGood for healthBiocidePlant growth regulatorsMetaboliteGlyphosate
The present invention provides methods and compositions for improving plant health. In particular, application of dicamba or another substrate of DMO, or metabolites thereof including DCSA, to a plant confers tolerance to, or defense against, abiotic or biotic stresses such as oxidative stress including herbicide application, and plant disease, and enhances crop yield. Such application may be in combination with the application of another herbicide such as glyphosate.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Herbicide resistant rice
InactiveUS6274796B1Growth inhibitionGood flexibilityBiocideMutant preparationRice plantsAcetohydroxy Acid Synthetase
Rice plants are disclosed with two separate, but synergistic mechanisms for resistance to herbicides that normally inhibit a plant's acetohydroxyacid synthase (AHAS) enzyme. The herbicide resistance of plants with both resistance mechanisms is substantially greater than one would expect from a simple combination of the two types of resistance. The first of the two resistance mechanisms is a metabolic pathway that is not fully understood, but that does not itself involve a mutant AHAS enzyme. The second resistance mechanism is a mutant AHAS enzyme, an enzyme that shows direct resistance to levels of herbicide that normally inhibit the enzyme, in both in vivo and in vitro assays. Besides controlling red rice, many AHAS-inhibiting herbicides also effectively control other weeds that are common in rice fields. Several of these herbicides have residual activity, so that a treatment controls both existing weeds as well as weeds that sprout later. No herbicide currently available for use on rice has residual activity against a broad spectrum of weeds including red rice. With effective residual activity against red rice and other weeds, rice producers now have a weed control system superior to those currently used.
Owner:BOARD OF SUPERVISORS OF LOUISIANA STATE UNIV & AGRI & MECHANICAL COLLEGE
Process for Chromosomal Engineering Using a Novel Dna Repair System
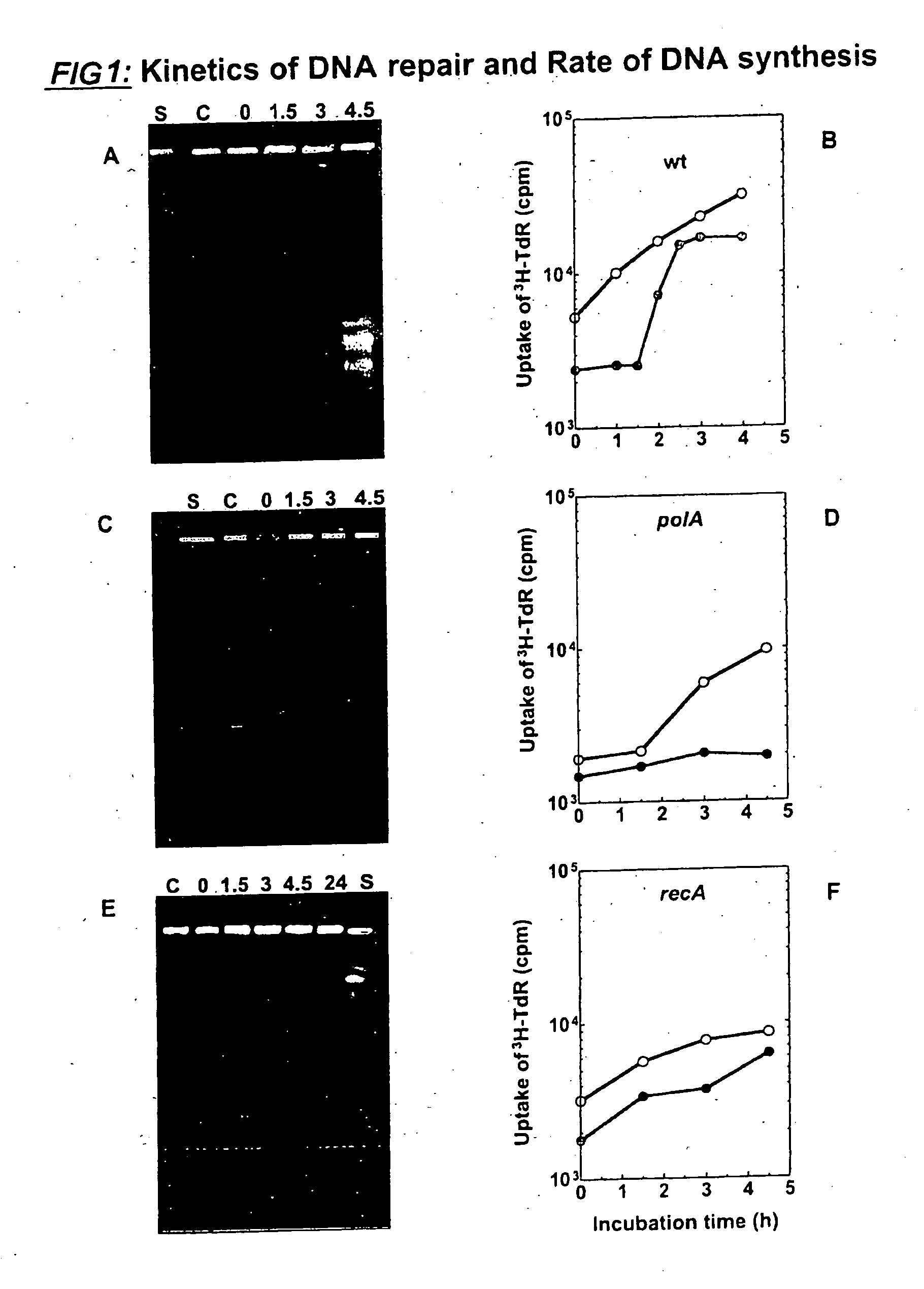
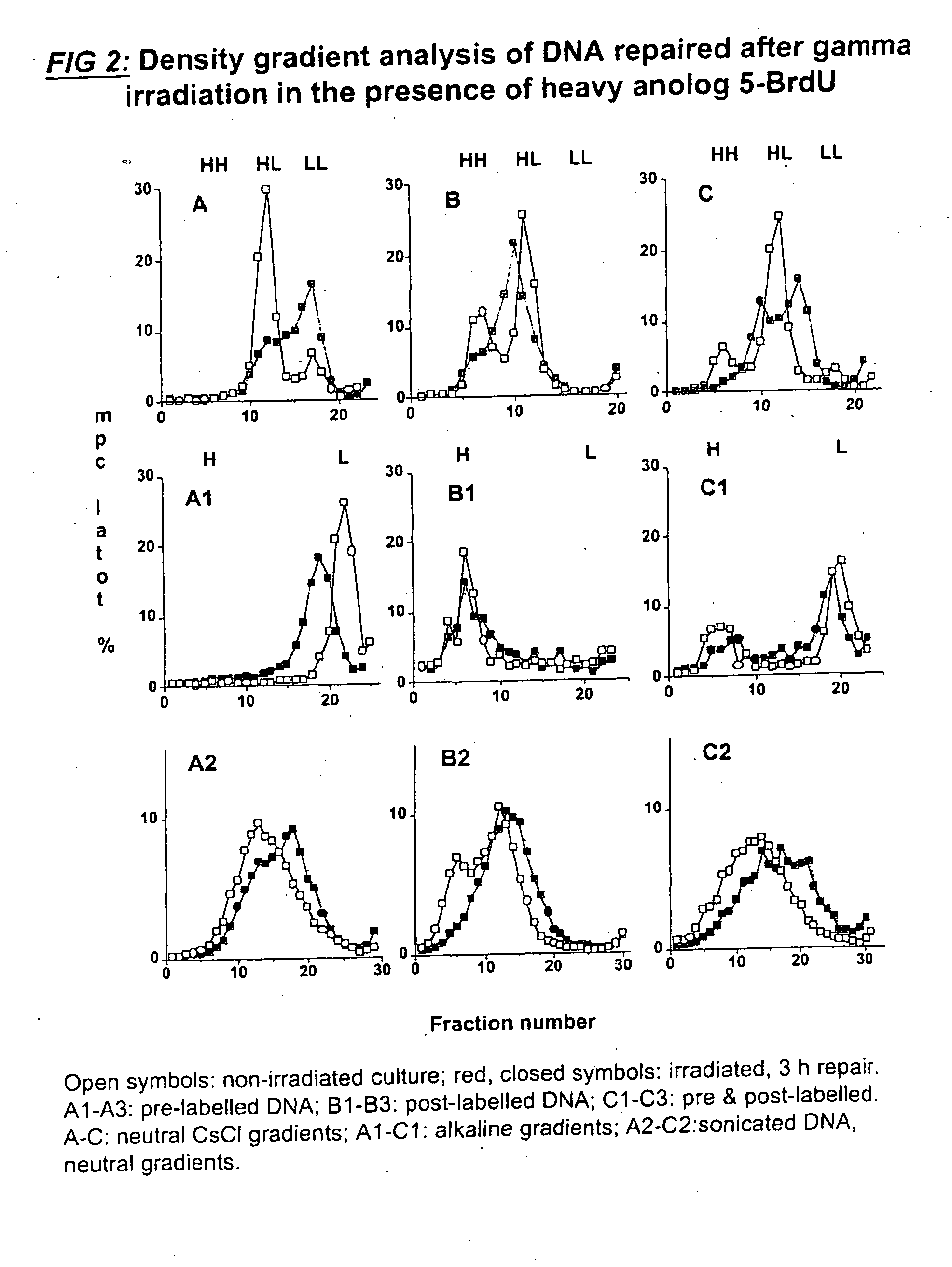
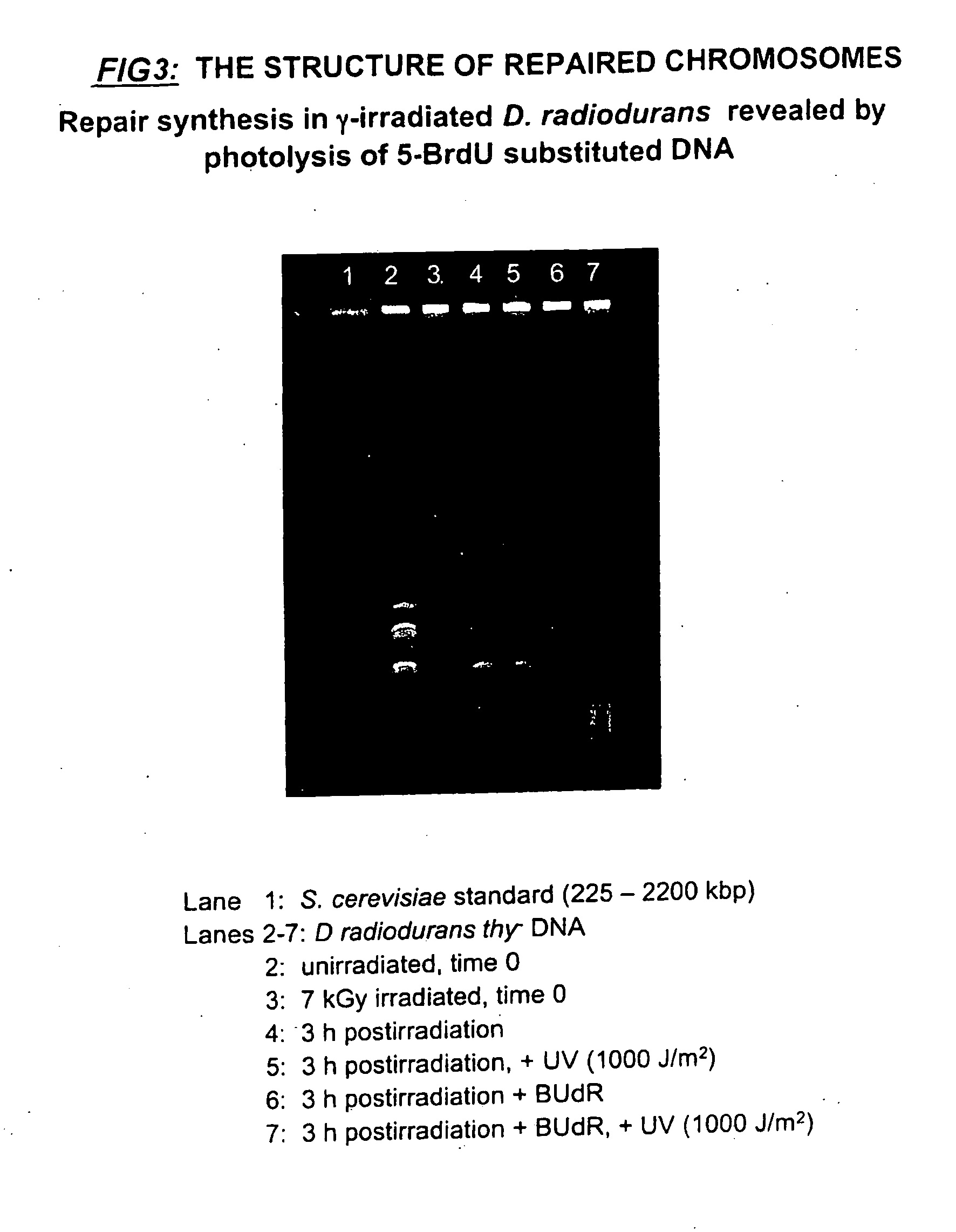
This invention relates to chromosomal engineering via DNA repair process. The process of the invention comprises the steps of: 1) submitting at least one source of biological activity, e.g. Deinococcus radiodurans, to radiation, desiccation and / or chemical treatment liable to damage the DNA, so as to substantially shatter its chromosomes into short fragments; 2) annealing complementary single strand tails extended by the synthesis templated on partially overlapping DNA fragments of said shattered chromosomes; 4) converting the resulting long linear DNA intermediates into intact circular chromosomes, by means of a RecA dependent homologous recombination; whereas at least one foreign source of genetic material, e.g. DNA, can be introduced during steps 2 and / or 3; and 4) optionally separating and collecting the recombined chromosomes thus obtained.
Owner:DEINOVE SA
Rice containing endophytic bacteria and method of producing it
InactiveUS7084331B2Improve the level ofIncrease productionBacteriaUnicellular algaeRice plantsBacteroides
The present invention provides a rice plant that shows enhanced growth and increased seed production, which also enables reduction of the use of chemical fertilizers.In the present invention, a nitrogen-fixing endophytic bacterium is isolated from bacteria symbiotically inhabiting natural plants, the isolated endophytic bacterium is artificially proliferated and then artificially inoculated into rice plants, and thus, the nitrogen-fixing endophytic bacteria are allowed to infect to rice plants.
Owner:SOC FOR TECHNO INNOVATION OF AGRI FORESTRY & FISHERIES +1
Methods for correcting alpha-antitrypsin point mutations
InactiveUS20150166984A1Nervous disorderFusion with DNA-binding domainHuman DNA sequencingObstructive Pulmonary Diseases
Some aspects of this disclosure provide strategies, systems, reagents, methods, and kits that are useful for the targeted editing of nucleic acids, including editing a nucleic acid encoding a mutant α-antitrypsin protein to correct a point mutation associated with a disease or disorder, e.g., with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) disease. The methods provided are useful for correcting an α-antitrypsin point mutation within the genome of a cell or subject, e.g., within the human genome. In some embodiments, fusion proteins of Cas9 and nucleic acid editing enzymes or enzyme domains, e.g., deaminase domains, are provided. In some embodiments, reagents and kits for the generation of targeted nucleic acid editing proteins, e.g., fusion proteins of Cas9 and nucleic acid editing enzymes or domains, are provided.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
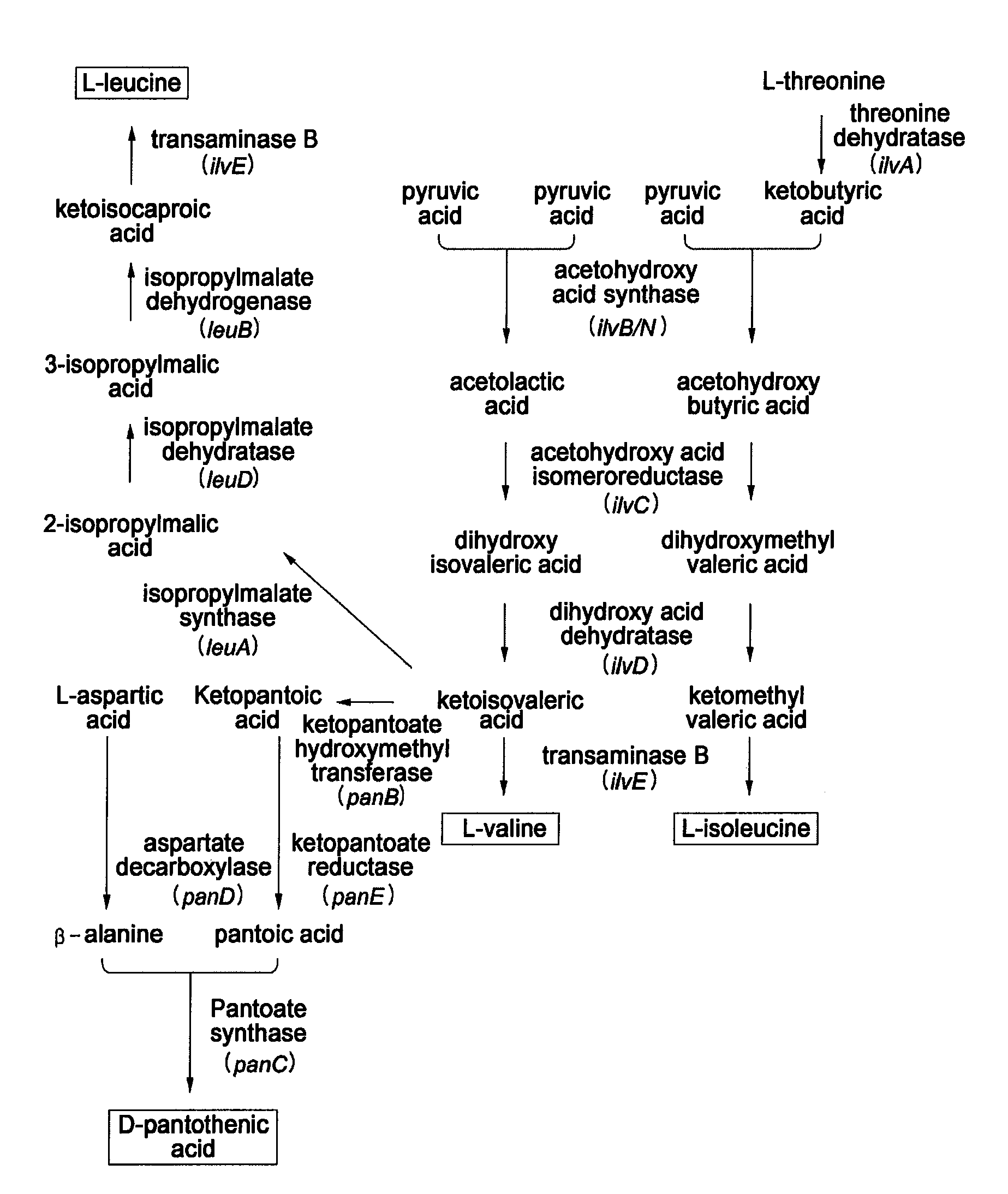
Microorganism having enhanced L-valine productivity and method for producing L-valine using the same
The present invention relates to a microorganism having an enhanced L-valine productivity and a method for producing L-valine using the same. More particularly, the present invention relates to a Corynebacterium glutamicum mutant strain that has resistance to L-valine and derivatives thereof so as to have an enhanced L-valine productivity, and a method for producing L-valine using the same.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Methods and compositions for producing double allele knock outs
The present invention provides a method and compositions utilizing the CRISPR system to disrupt a target gene in eukaryotic cells to produce double allele knock outs. The method finds use in producing afucosylated antibodies with enhanced ADCC activity.
Owner:LARIX BIOSCI
Continuous directed evolution of proteins and nucleic acids
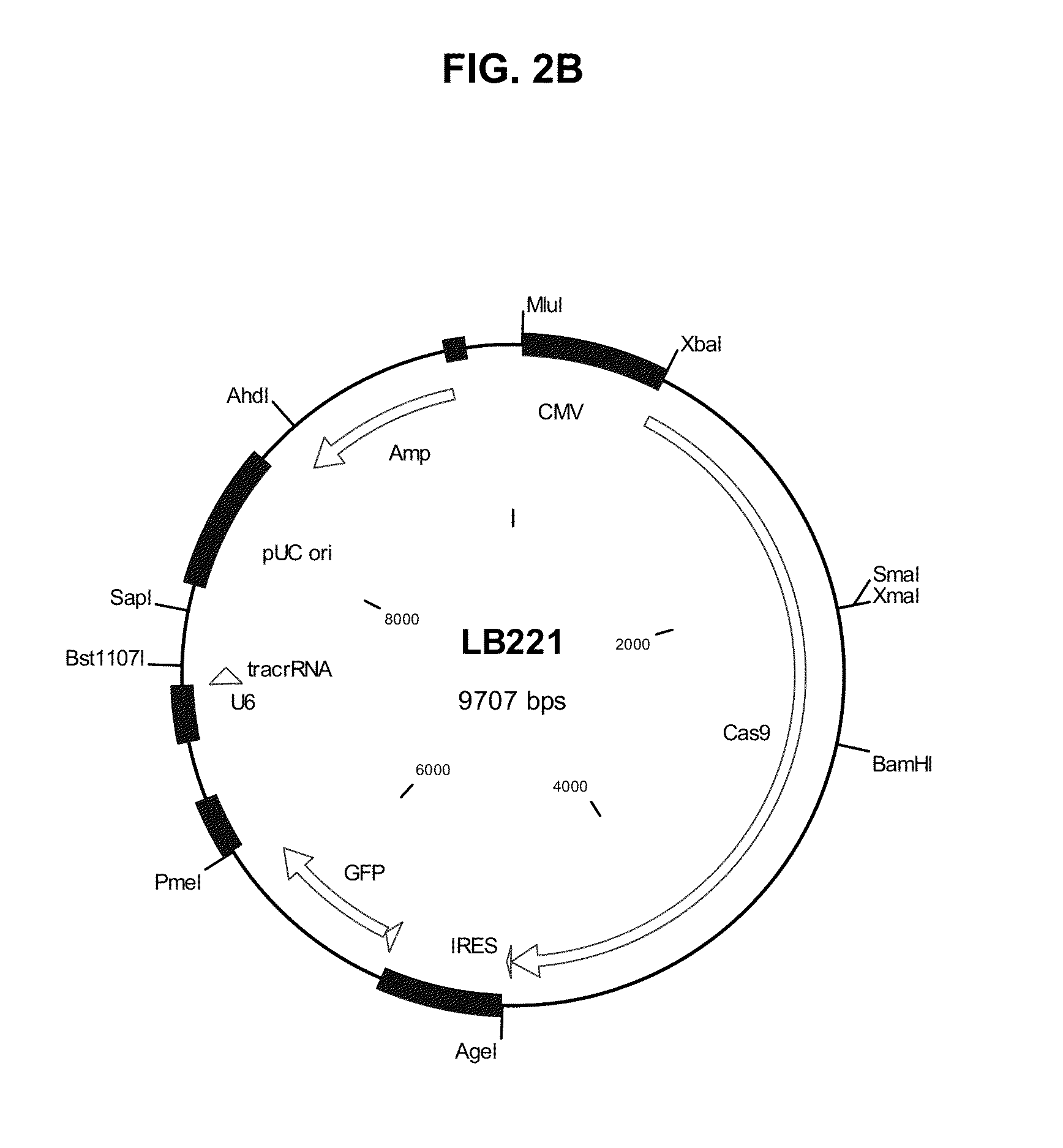
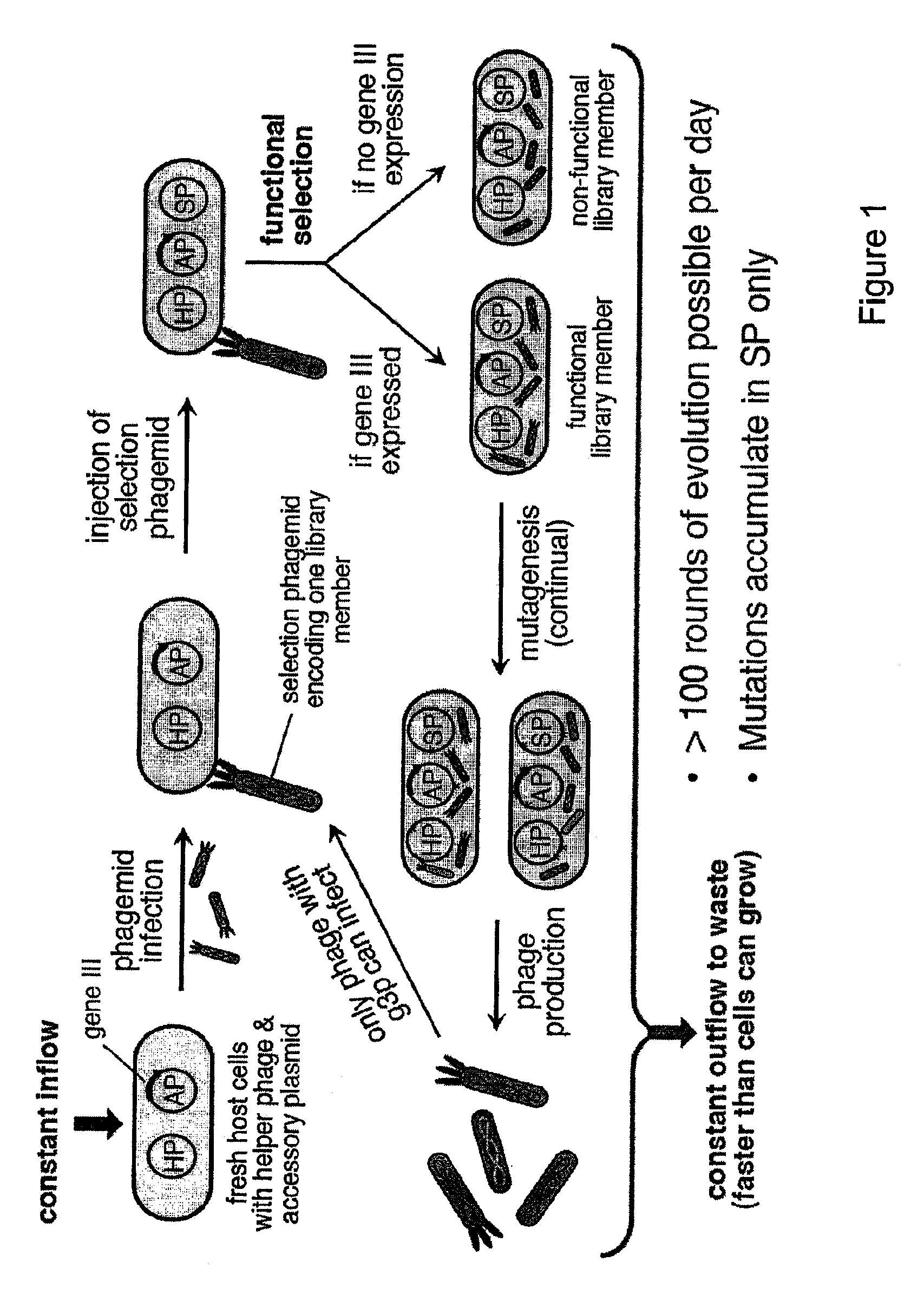
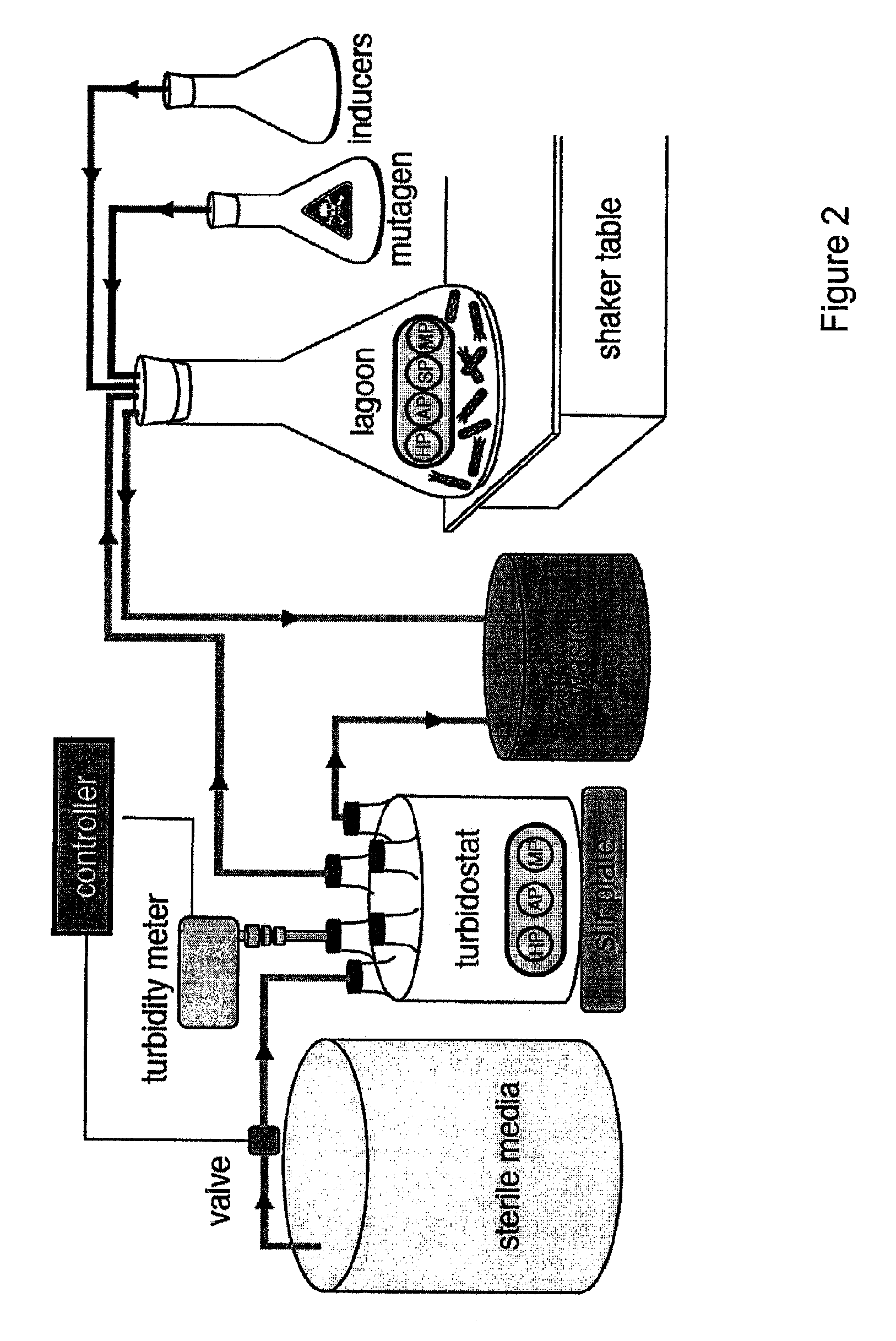
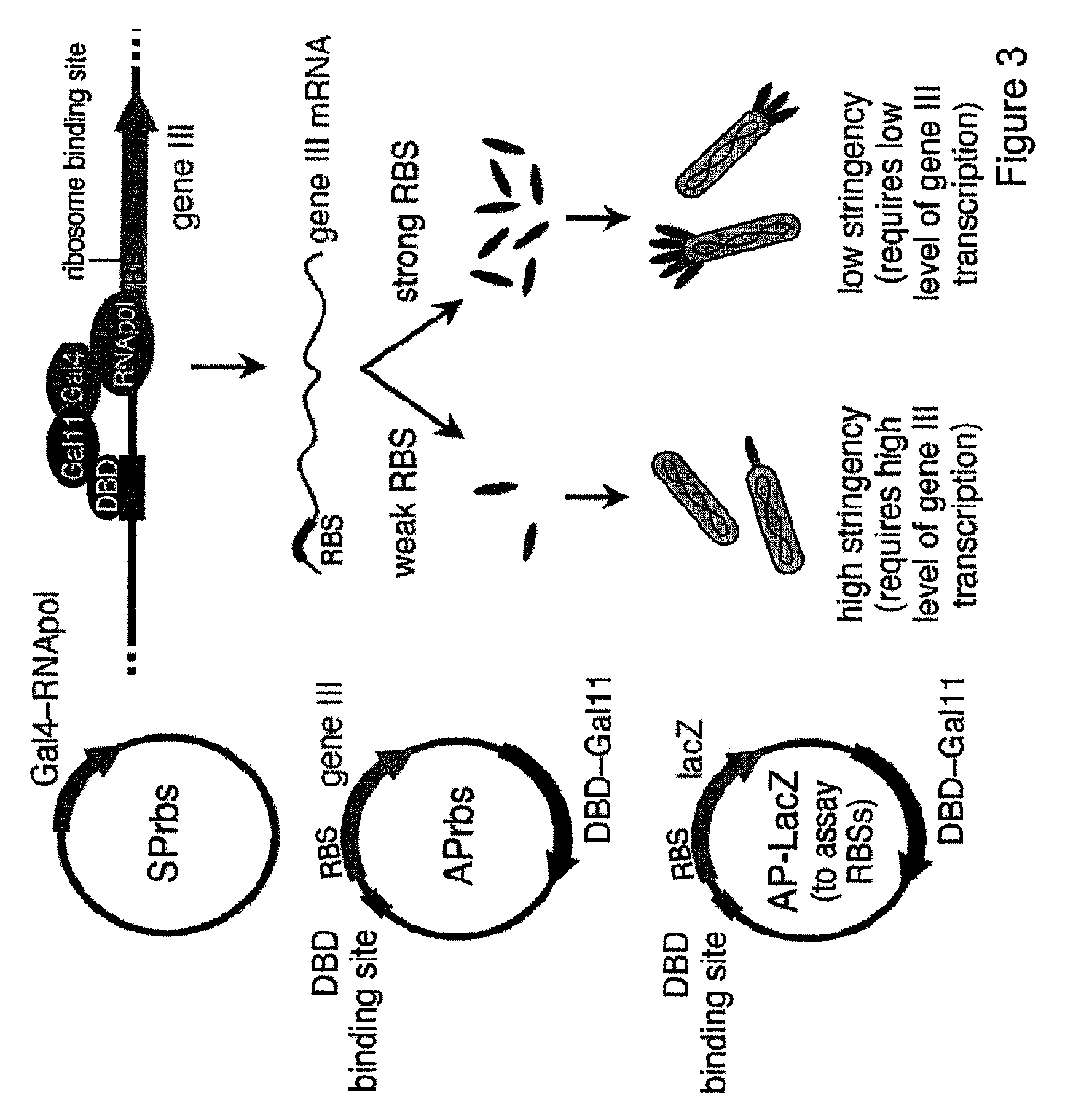
ActiveUS9023594B2Microbiological testing/measurementMutant preparationCell biologyDirected evolution
The present invention discloses generalizable methods of evolving nucleic acids and proteins utilizing continuous directed evolution. The invention discloses methods of passing a nucleic acid from cell to cell in a desired function-dependent manner. The linkage of the desired function and passage of the nucleic acid from cell to cell allows for continuous selection and mutation of the nucleic acid.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Methods for correcting presenilin point mutations
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
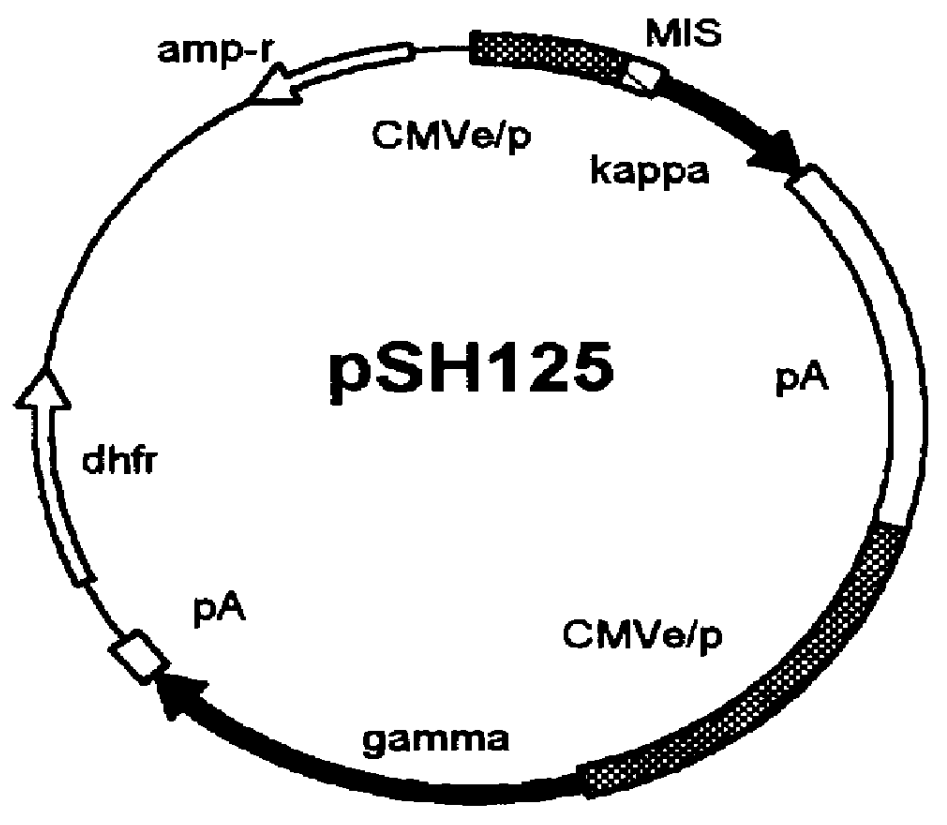
Human hybrid host cell for mammalian gene expression
InactiveUS6136599AEasily transfectedEasy to adaptGenetically modified cellsMutant preparationHeterologousMammal
Human / human hybrid cells were made via fusion of human embryonic kidney cells (293S) and modified Burkitt's lymphoma cells (2B8). The fusion cells are useful as host cells for the recombinant expression of mammalian genes. The advantages of using these hybrid clones of human kidney- and B-cells, called HKBs, for mammalian gene expression, include (i) the cells are negative for immunoglobulin expression, (ii) the cells grow easily in plasma protein-free medium (with or without the addition of recombinant insulin) as suspension cultures in a shake flask or in a fermenter (iii) the cells are very susceptible for transfection of DNA, and (iv) the cells secrete high levels of heterologous recombinant proteins, such as recombinant monoclonal antibodies, soluble ICAM-1, rIL-4, and rFVIII.
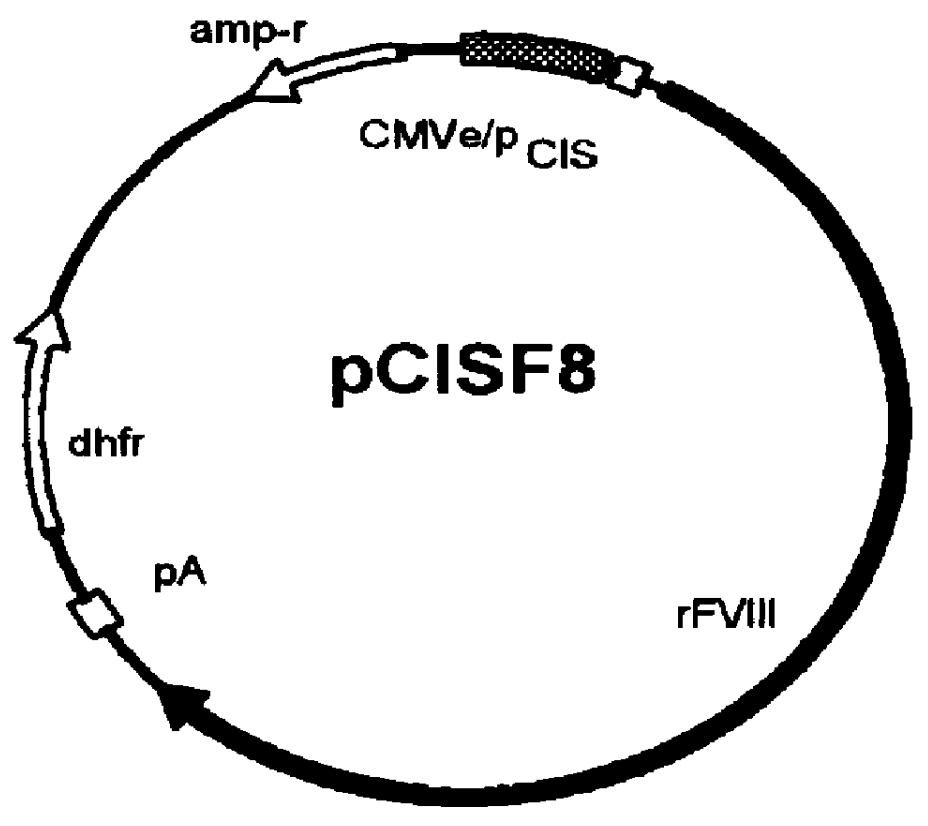
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC +1
Attenuated negative strand viruses with altered interferon antagonist activity for use as vaccines and pharmaceuticals
InactiveUS6669943B1Impaired ability to antagonizeAvoiding and minimizing side effectSsRNA viruses negative-senseVirus peptidesNegative strandPharmaceutical drug
Owner:AVIR GREEN HILLS BIOTECH RES DEVMENT TRADE +1
Electrodes coated with treating agent and uses thereof
InactiveUS6713291B2Rapidly ready for useShort pulse widthBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiological cellCoated electrodes
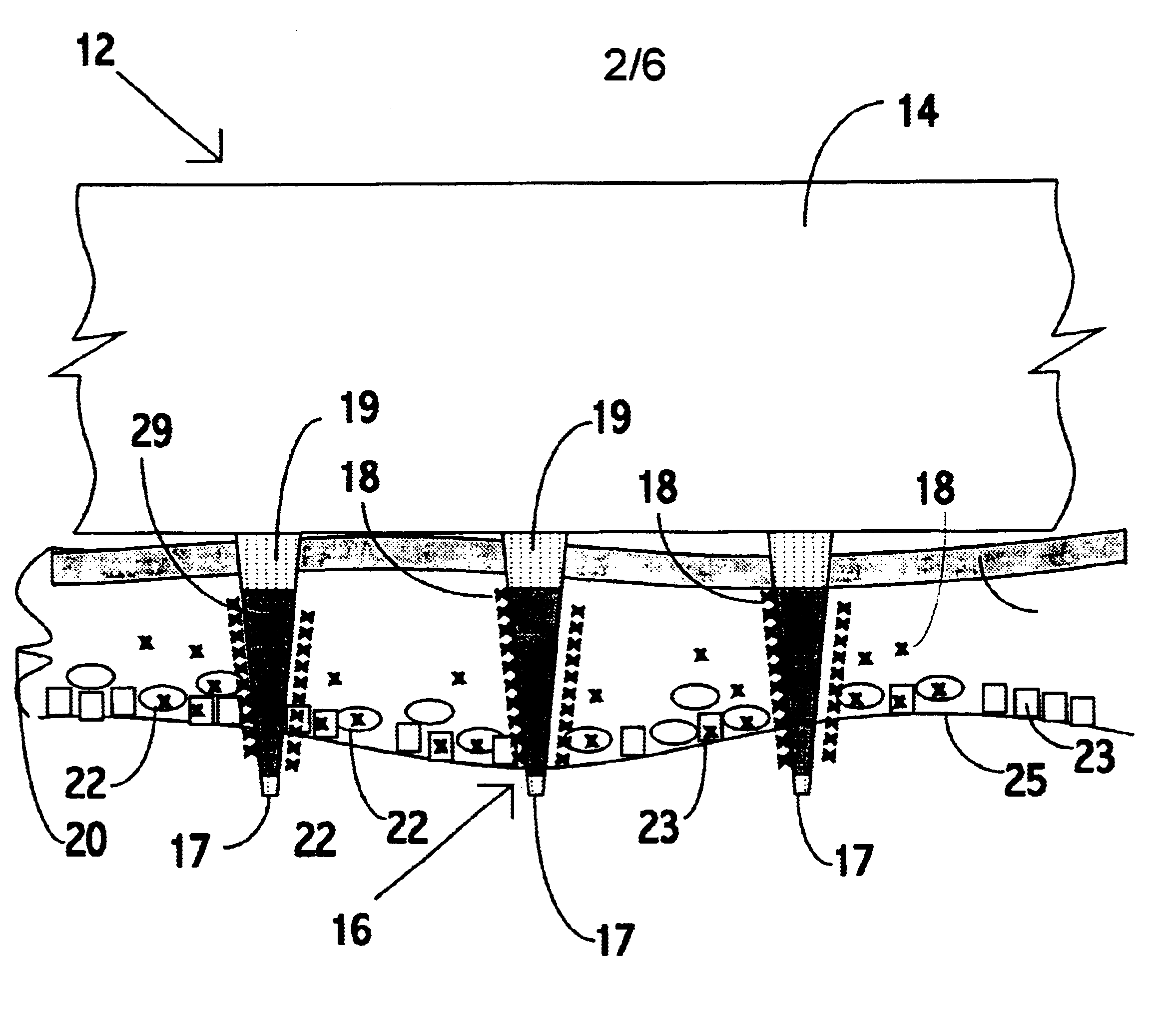
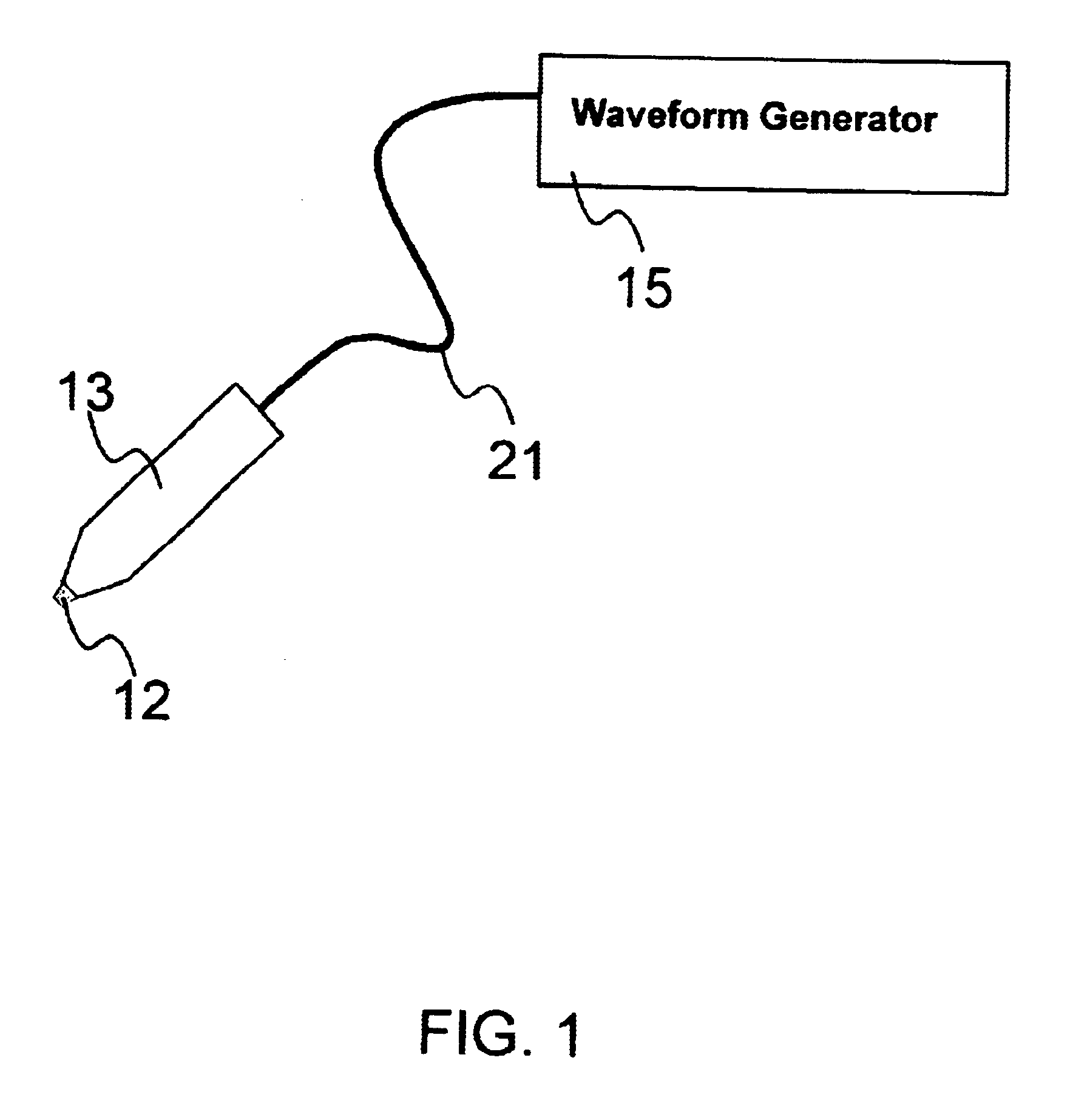
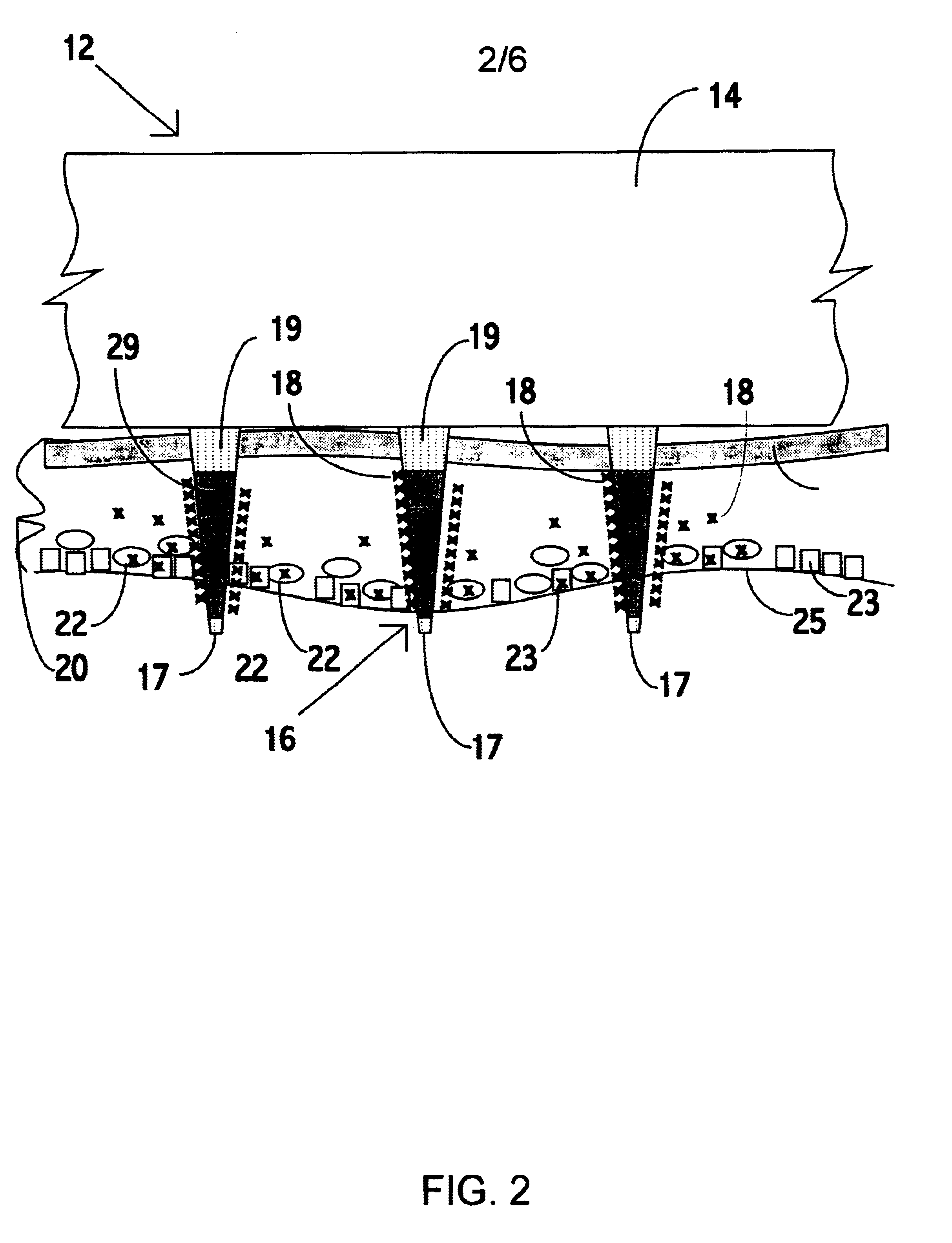
An object of the invention is to provide a method for delivery of macromolecules into biological cells in the tissues of a patient and includes the steps of: (a) providing electrodes (16) in an electrode assembly (12), wherein the electrodes have fixed electrode surfaces (42) which are coated with at least one static layer of electrode releasable molecules (44) to be delivered; (b) providing a waveform generator (15) for generating electric fields; (c) establishing electrically conductive pathways between the electrodes (16) and the waveform generator (15); (d) locating the electrodes (16) such that the biological cells are situated therebetween, and (g) providing electric fields in the form of pulse waveforms from the waveform generator (15) to the electrodes (16), such that molecules in the at least one static layer of the electrode releasable molecules (44) on the electrodes (16) are delivered into the biological cells. The electrode releasable molecules (44) can be either electric field separable molecules and / or solvent separable material. Another object of the invention is to provide an apparatus for carrying out the method of the invention. The static-coated electrode assembly (12) can be provided in a sterile package (24), from which the electrode assembly (12) is removed prior to use. The statically-coated electrode assembly (12) can be in a form of a disposable assembly (12) which is removable and replaceable from an electrode assembly holder (13).
Owner:CELLECTIS SA
Methods for correcting pi3k point mutations
Some aspects of this disclosure provide strategies, systems, reagents, methods, and kits that are useful for the targeted editing of nucleic acids, including editing a nucleic acid encoding a mutant PI3KCA protein to correct a point mutation associated with a disease or disorder, e.g., with a neoplastic disorder. The methods provided are useful for correcting a PI3KCA point mutation within the genome of a cell or subject, e.g., within the human genome. In some embodiments, fusion proteins of Cas9 and nucleic acid editing enzymes or enzyme domains, e.g., deaminase domains, are provided. In some embodiments, reagents and kits for the generation of targeted nucleic acid editing proteins, e.g., fusion proteins of Cas9 and nucleic acid editing enzymes or domains, are provided.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com