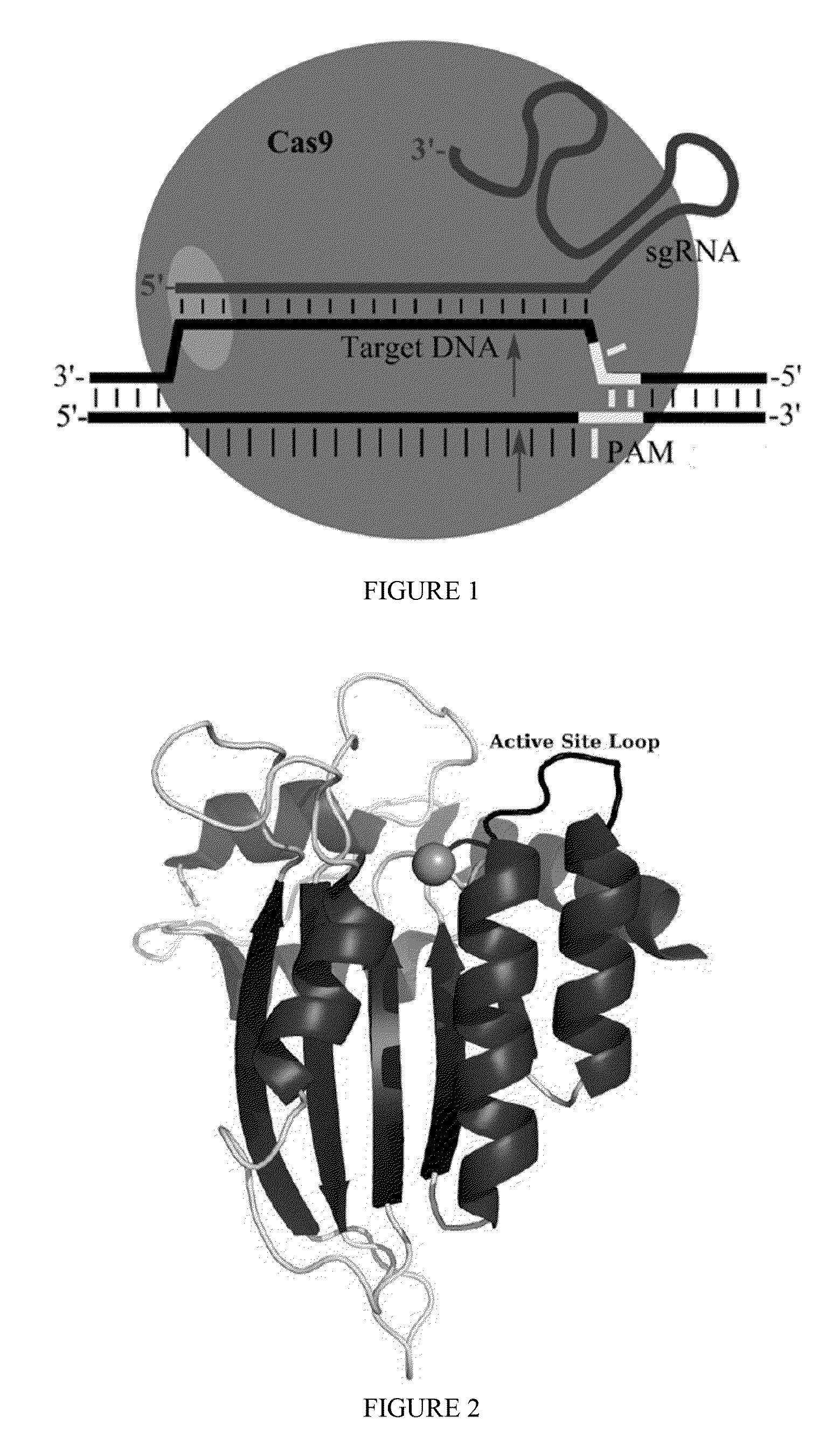
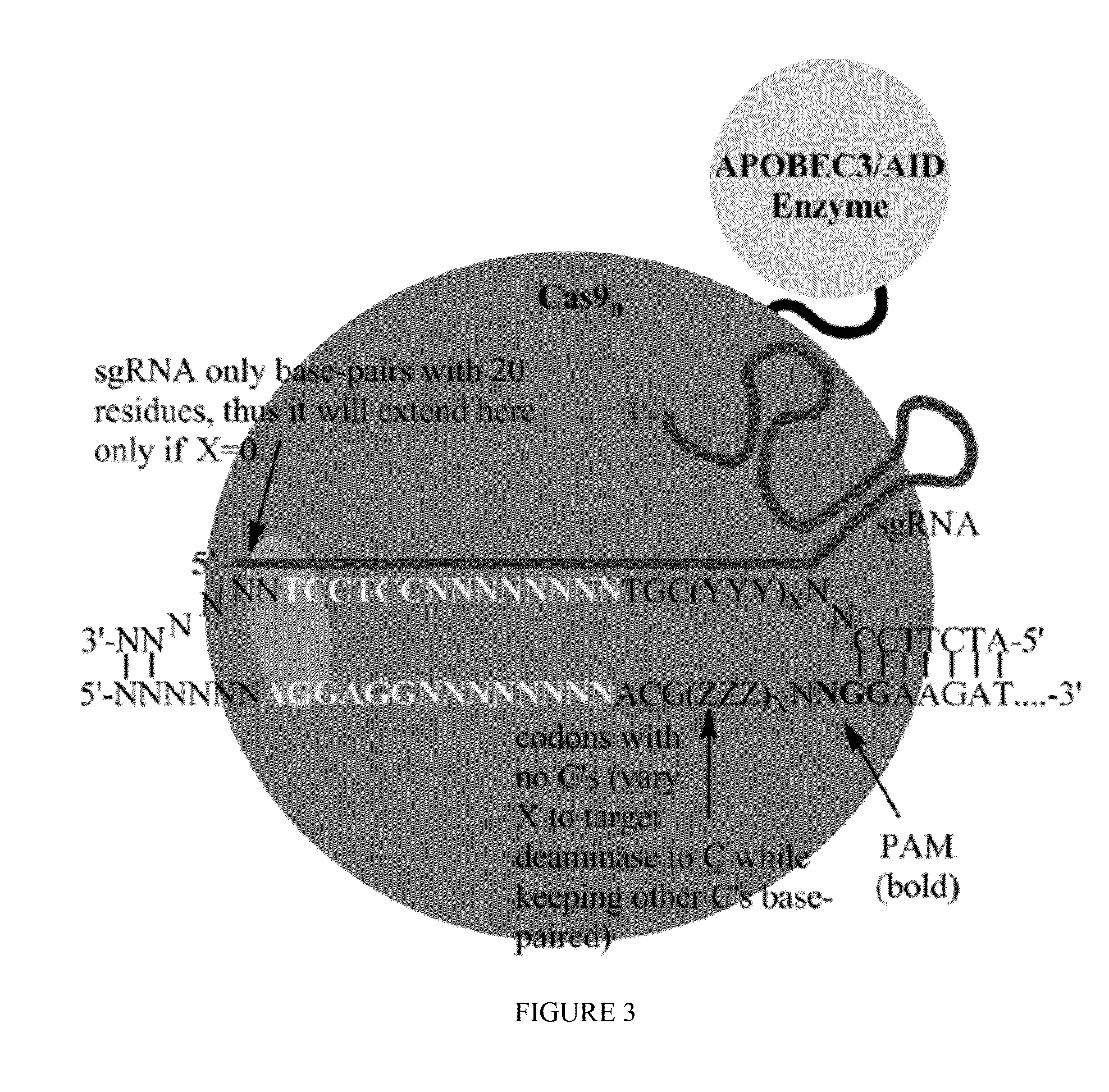
Methods for correcting alpha-antitrypsin point mutations
a technology of alpha-antitrypsin and point mutation, which is applied in the field of methods for correcting alpha-antitrypsin point mutations, can solve the problems of no genome engineering tools, however, that enable the manipulation of a single nucleotide, change in the sequence of either the chimera or the genome,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Fusion Proteins
[0120]Exemplary Cas9:deaminase fusion proteins are provided below:
[0121]Cas9: Human AID Fusion (C-Terminal)
(SEQ ID NO: 30)MDSLLMNRRKFLYQFKNVRWAKGRRETYLCDKKYSIGLAIGTNSVGWAVITDEYKVPSKKFKVLGNTDRHSIKKNLIGALLFDSGETAEATRLKRTARRRYTRRKNRICYLQEIFSNEMAKVDDSFFHRLEESFLVEEDKKHERHPIFGNIVDEVAYHEKYPTIYHLRKKLVDSTDKADLRLIYLALAHMIKFRGHFLIEGDLNPDNSDVDKLFIQLVQTYNQLFEENPINASGVDAKAILSARLSKSRRLENLIAQLPGEKKNGLFGNLIALSLGLTPNFKSNFDLAEDAKLQLSKDTYDDDLDNLLAQIGDQYADLFLAAKNLSDAILLSDILRVNTEITKAPLSASMIKRYDEHHQDLTLLKALVRQQLPEKYKEIFFDQSKNGYAGYIDGGASQEEFYKFIKPILEKMDGTEELLVKLNREDLLRKQRTFDNGSIPHQIHLGELHAILRRQEDFYPFLKDNREKIEKILTFRIPYYVGPLARGNSRFAWMTRKSEETITPWNFEEVVDKGASAQSFIERMTNFDKNLPNEKVLPKHSLLYEYFTVYNELTKVKYVTEGMRKPAFLSGEQKKAIVDLLFKTNRKVTVKQLKEDYFKKIECFDSVEISGVEDRFNASLGTYHDLLKIIKDKDFLDNEENEDILEDIVLTLTLFEDREMIEERLKTYAHLFDDKVMKQLKRRRYTGWGRLSRKLINGIRDKQSGKTILDFLKSDGFANRNFMQLIHDDSLTFKEDIQKAQVSGQGDSLHEHIANLAGSPAIKKGILQTVKVVDELVKVMGRHKPENIVIEMARENQTTQKGQKNSRERMKRIEEGIKELGSQILKEHPVENTQLQNEKLYLYYLQNGRDMYVDQELDIN...
example 2
Correction of a PI3K Point Mutation by a Cas9 Fusion Protein
[0128]An A3140G point mutation in exon 20 of the PI3KCA gene, resulting in an H1047R amino acid substitution in the PI3K protein is corrected by contacting a nucleic acid encoding the mutant protein with a Cas9:AID (SEQ ID NO: 30) or a Cas9:APOBEC1 (SEQ ID NO: 92) fusion protein and an appropriately designed sgRNA targeting the fusion protein to the mutation site in the encoding PI3KCA gene. The A3140G point mutation is confirmed via genomic PCR of the respective exon 20 sequence, e.g., generation of a PCR amplicon of nucleotides 3000-3250, and subsequent sequencing of the PCT amplicon.
[0129]Cells expressing a mutant PI3K protein comprising an A3140G point mutation in exon 20 are contacted with an expression construct encoding the Cas9:AID (SEQ ID NO: 30) or a Cas9:APOBEC1 (SEQ ID NO: 92) fusion protein and an appropriately designed sgRNA targeting the fusion protein to the mutation site in the antisense strand of the encod...
example 3
Correction of a Presenilin 1 Point Mutation by a Cas9 Fusion Protein
[0130]An A->G point mutation in codon 143 of the presenilin1 (PSEN1) gene, resulting in an I143V amino acid substitution in the PSEN1 protein is corrected by contacting a nucleic acid encoding the mutant PSEN1 protein with a Cas9:AID (SEQ ID NO: 30) or a Cas9:APOBEC1 (SEQ ID NO: 92) fusion protein and an appropriately designed sgRNA targeting the fusion protein to the mutation site in the encoding PSEN1 gene. See, e.g., Gallo et. al., J. Alzheimer's disease. 2011; 25: 425-431 for a description of an exemplary PSEN1 I143V mutation associated with familial Alzheimer's Disease. The A->G point mutation is confirmed via genomic PCR of the respective PSEN1 sequence, e.g., generation of a PCR amplicon of about 100-250 nucleotides around exon 143, and subsequent sequencing of the PCT amplicon.
[0131]Cells expressing the mutant PSEN1 protein are contacted with an expression construct encoding the Cas9:AID (SEQ ID NO: 30) or a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| nucleic acid- | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| nucleic acid-editing | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| nucleic-acid- | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com