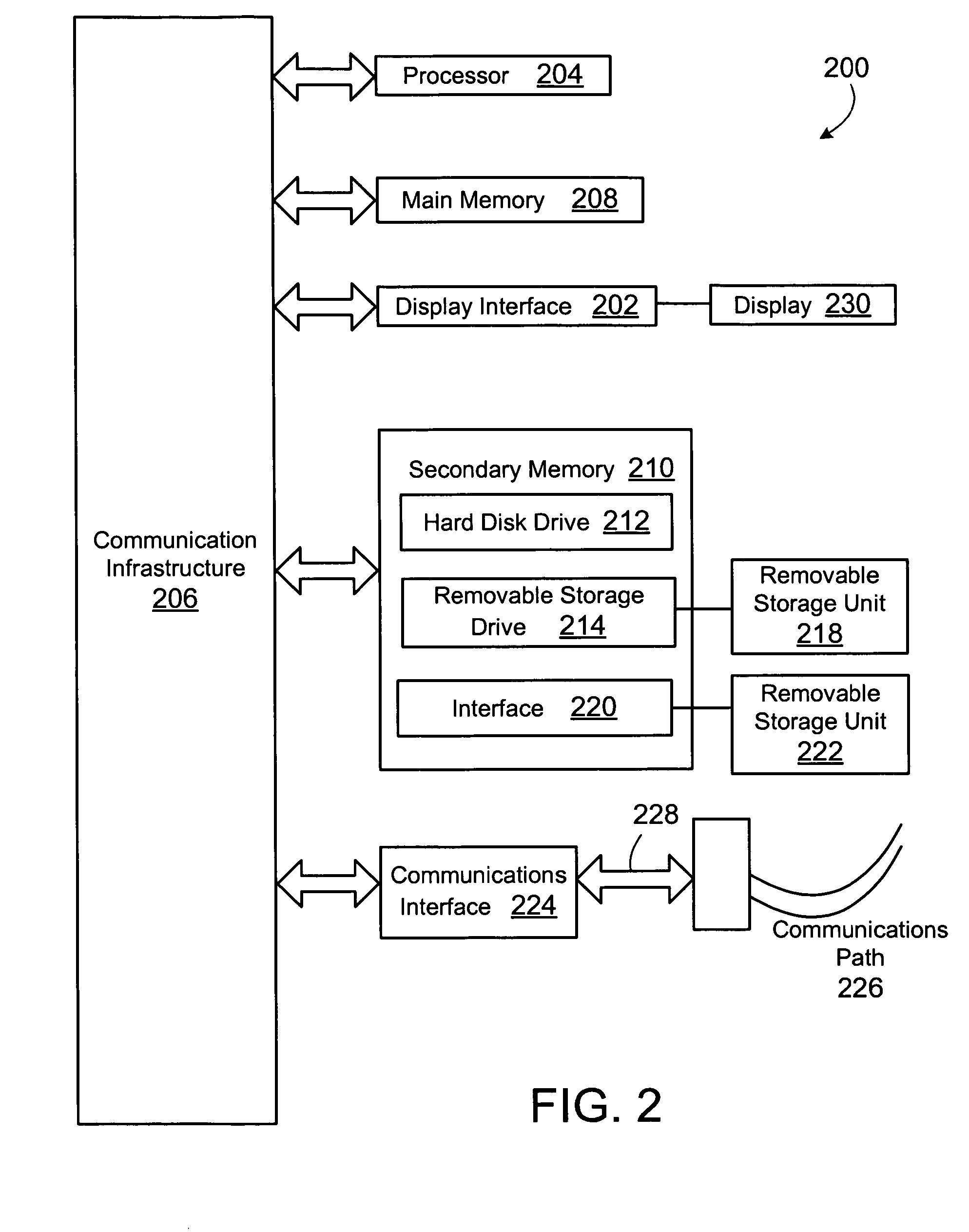
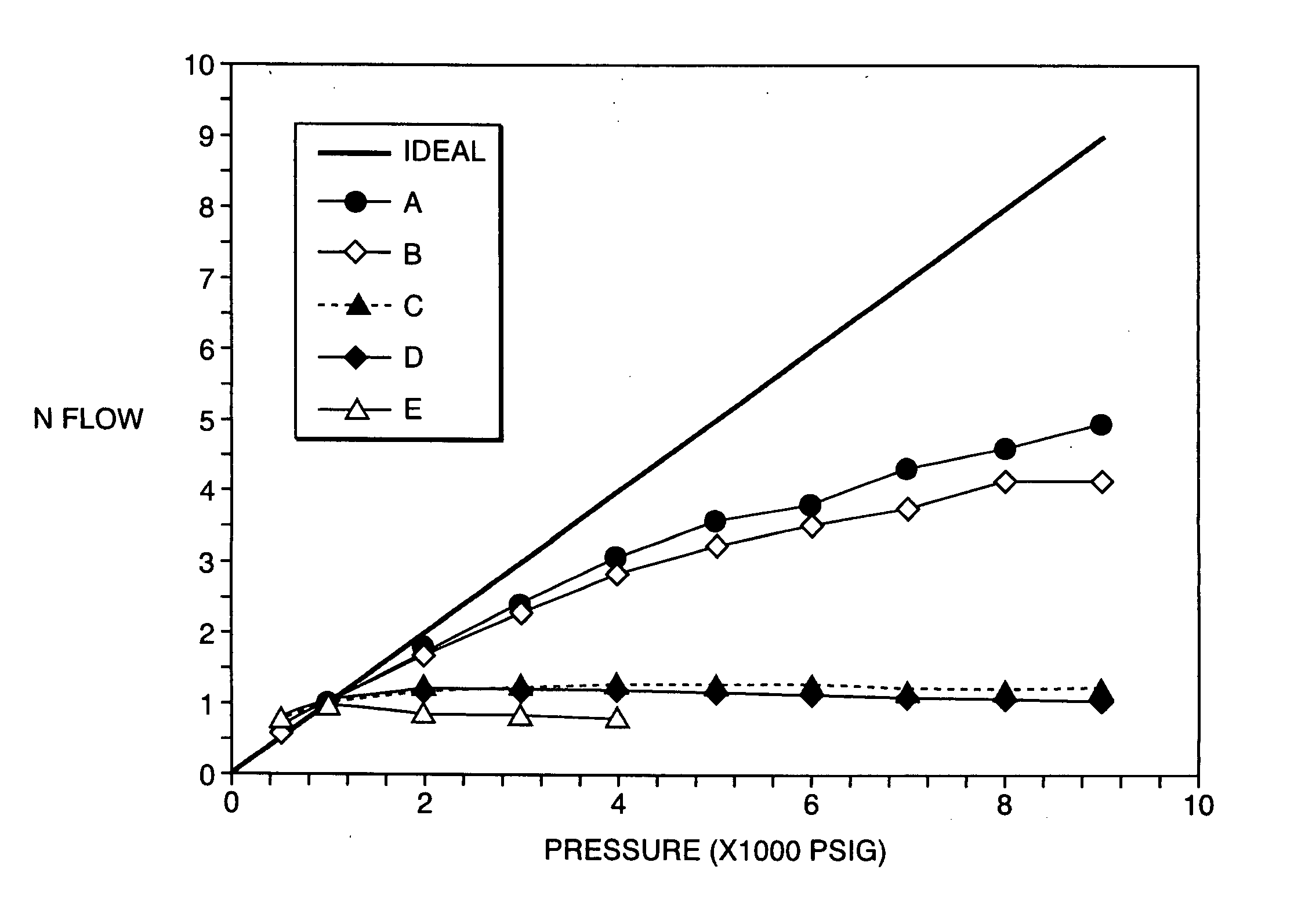
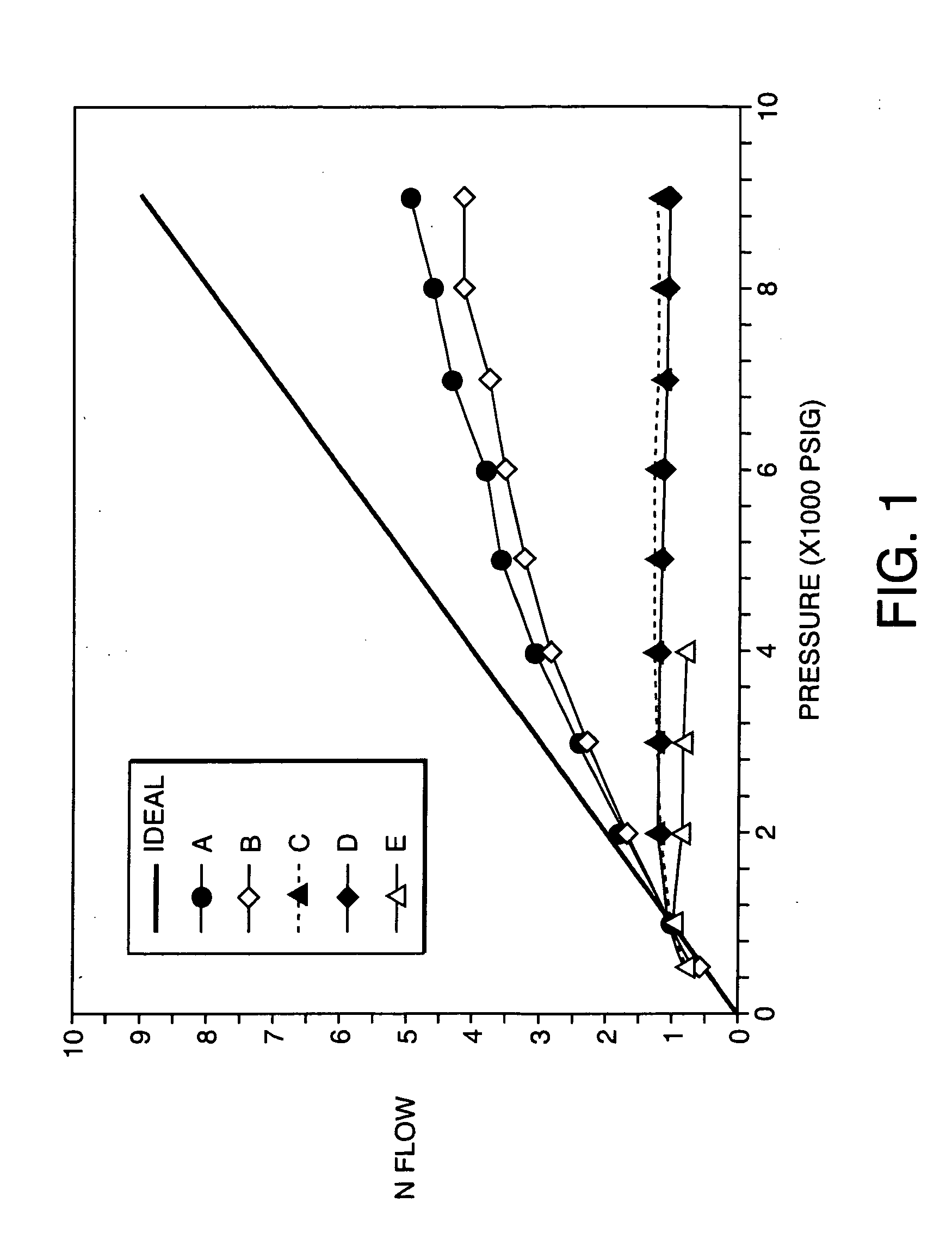
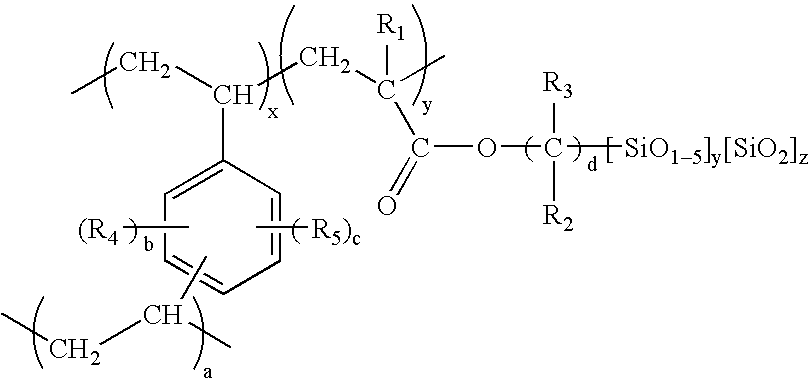
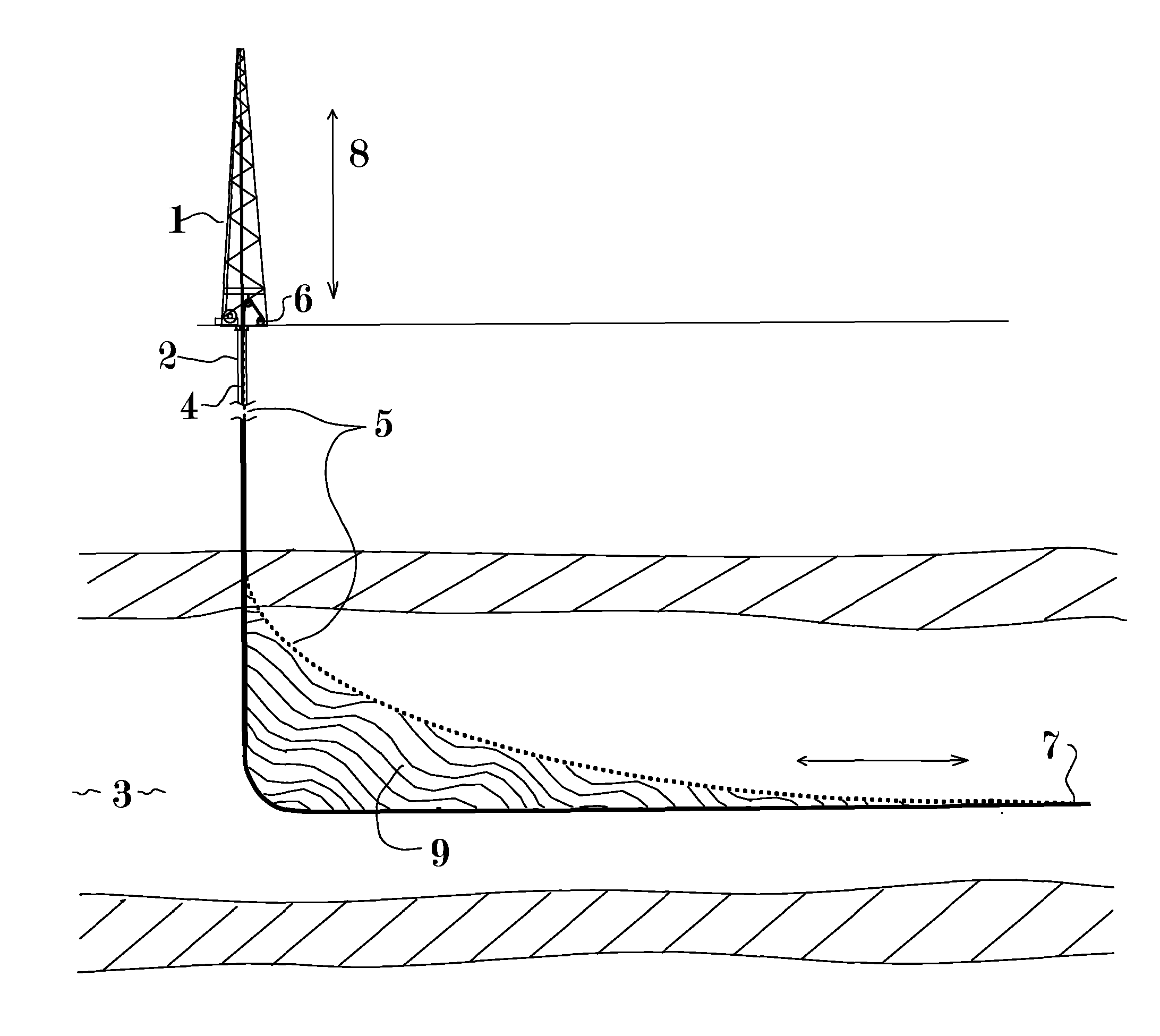
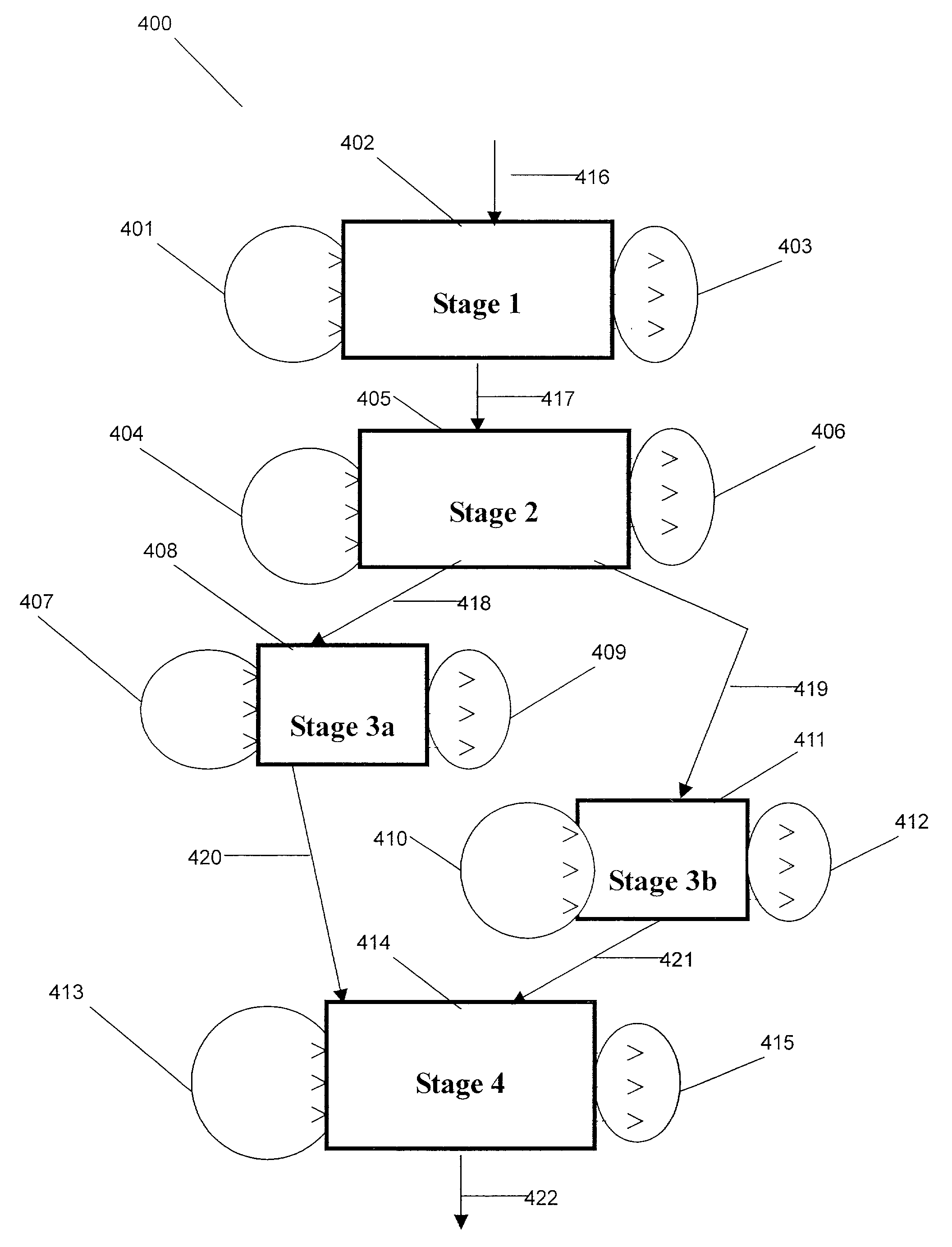
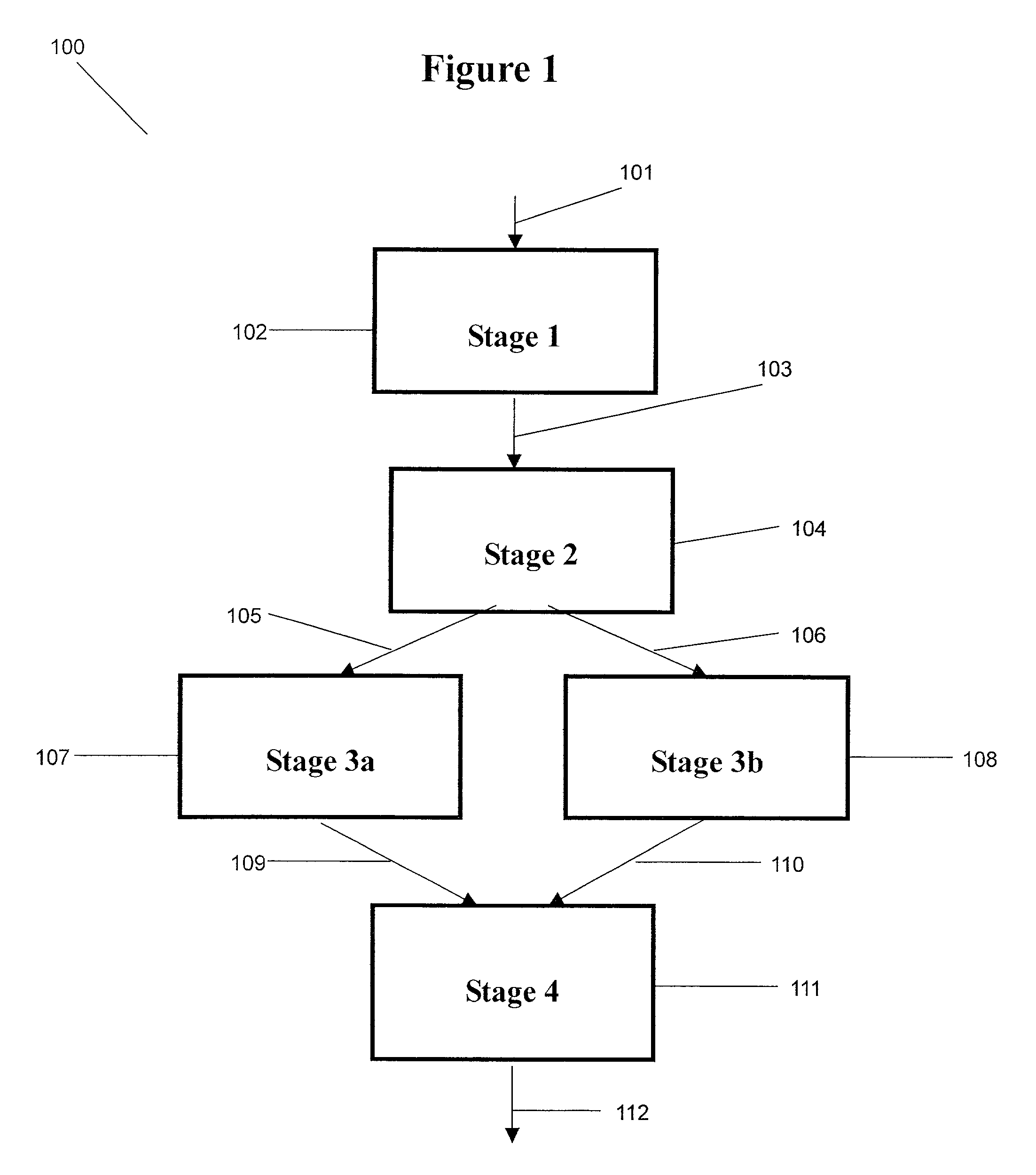
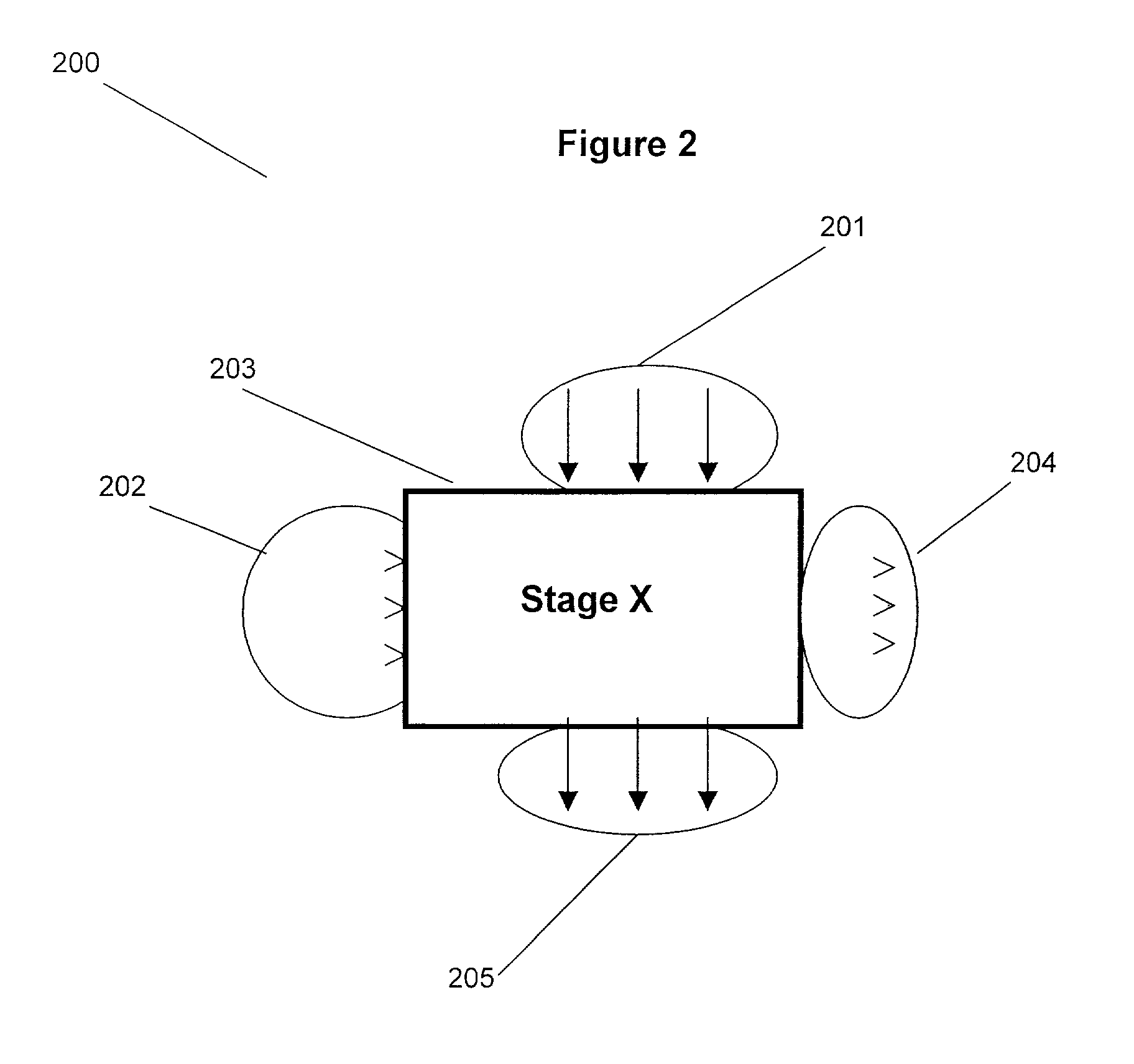
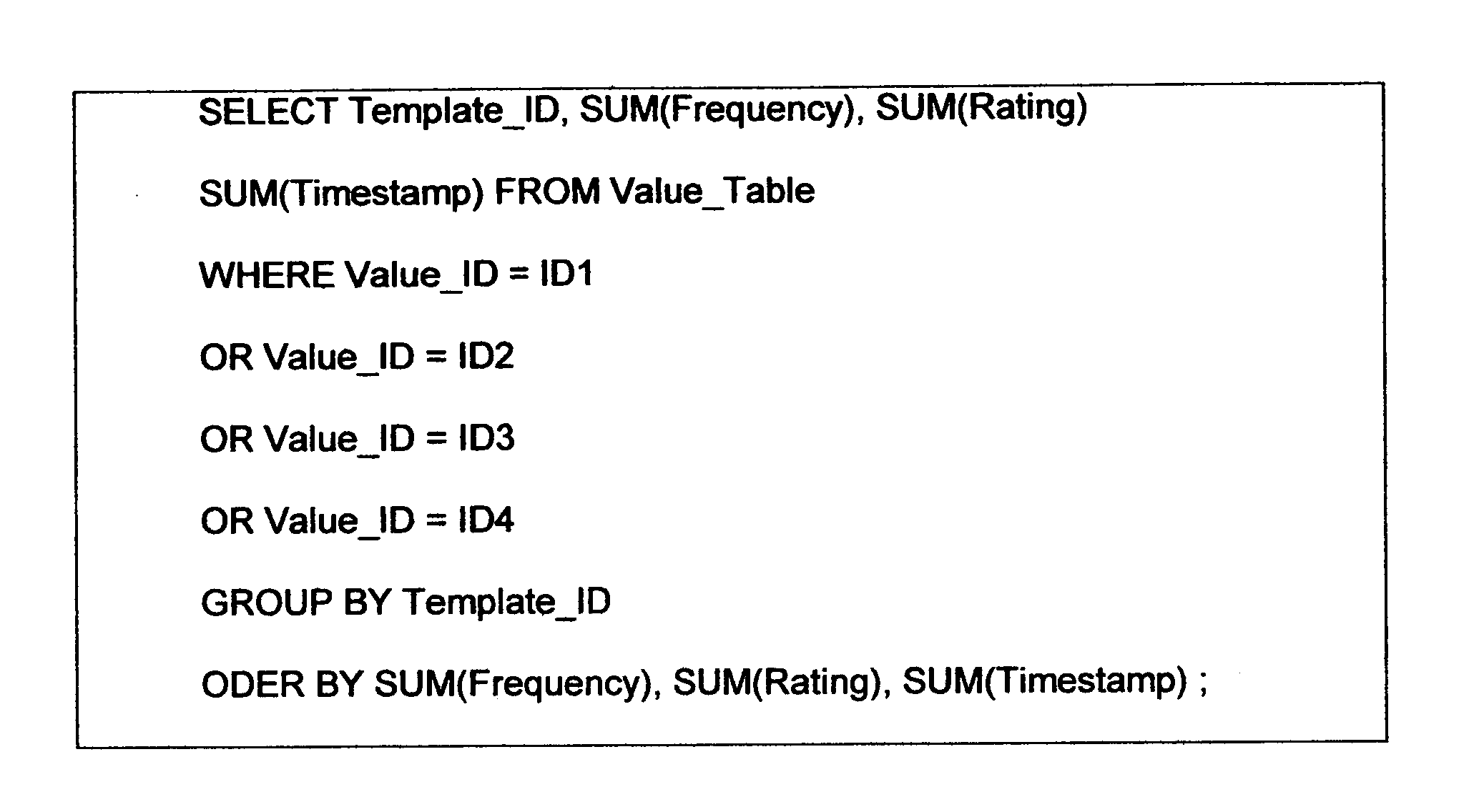
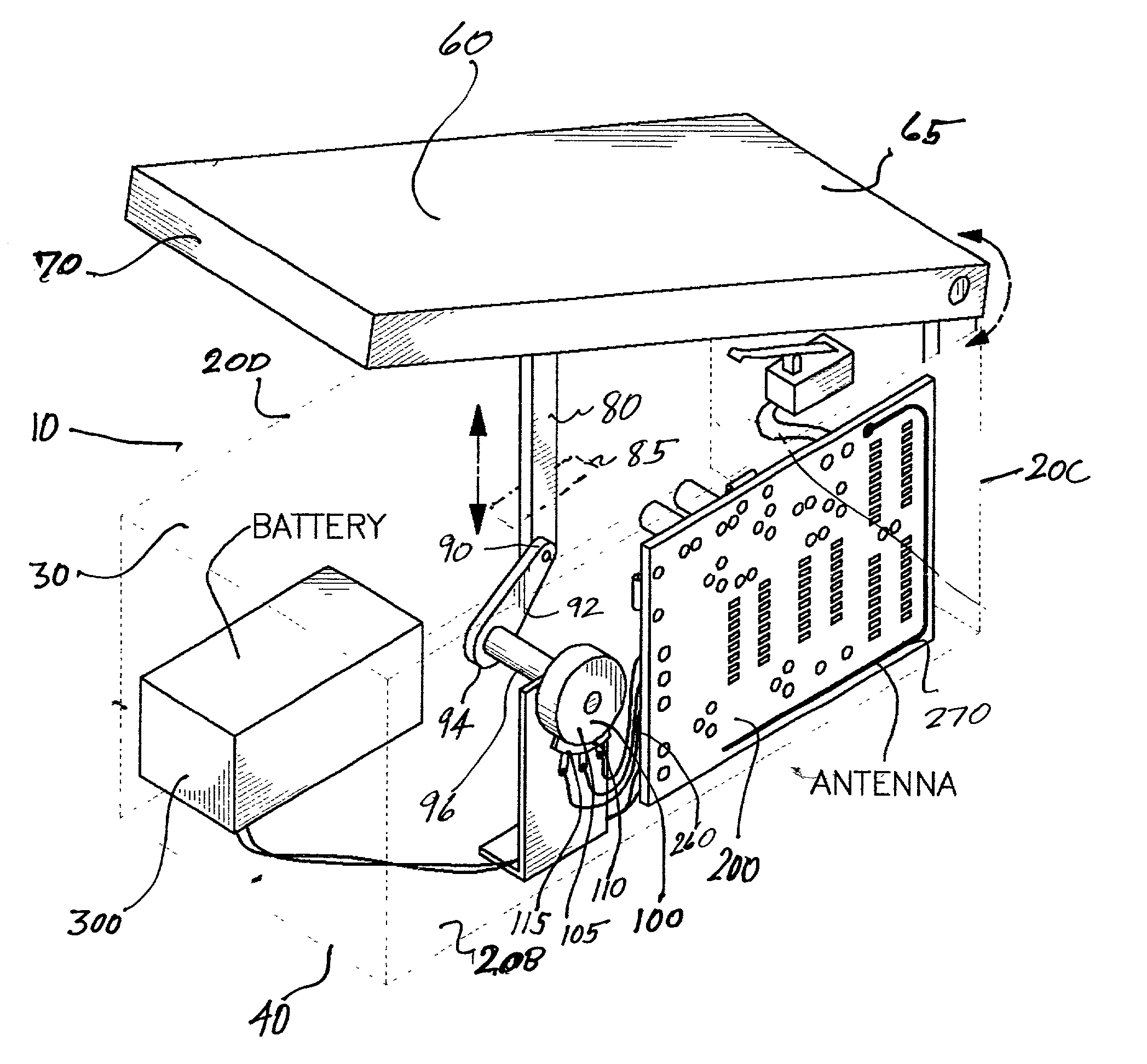
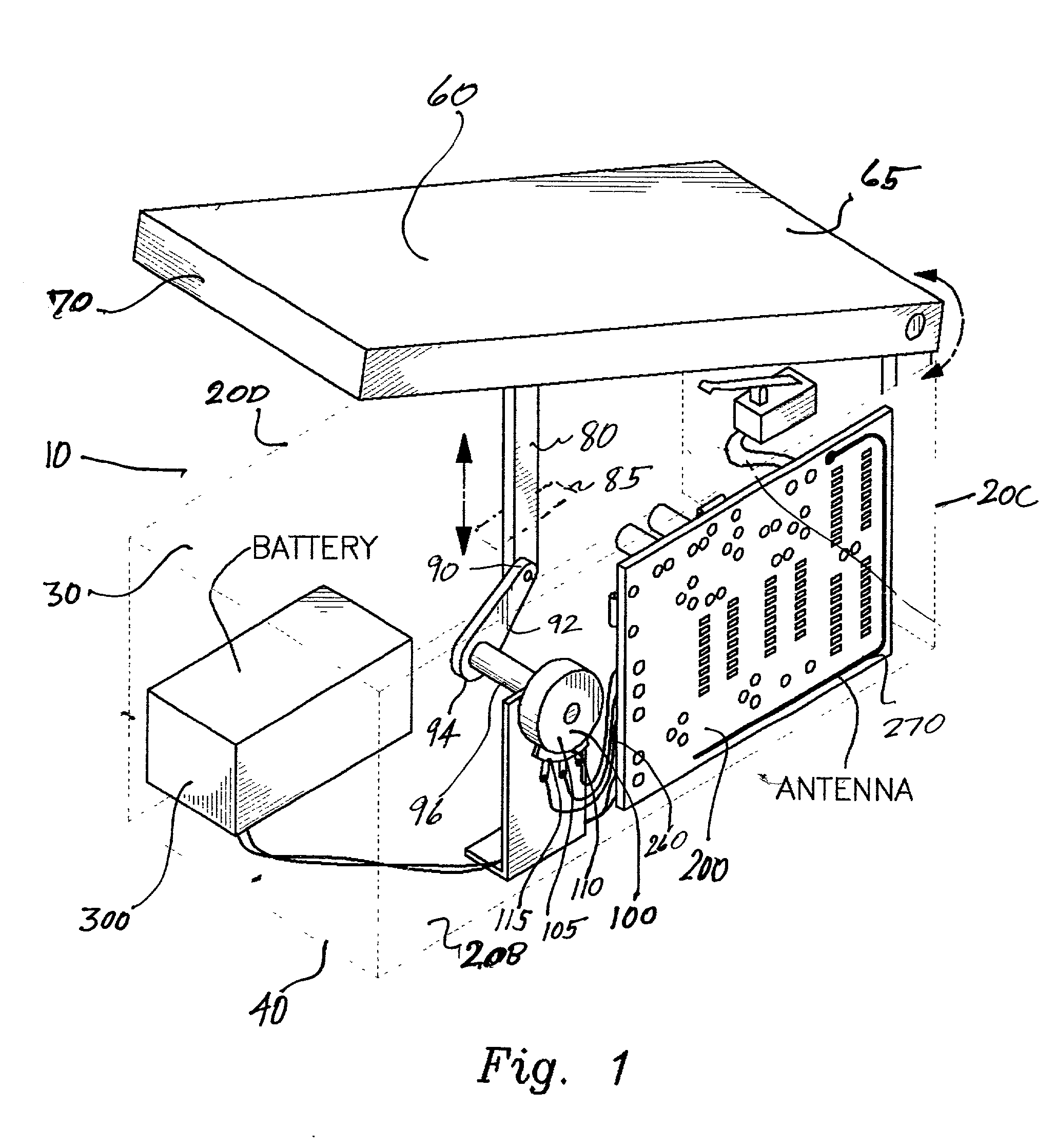
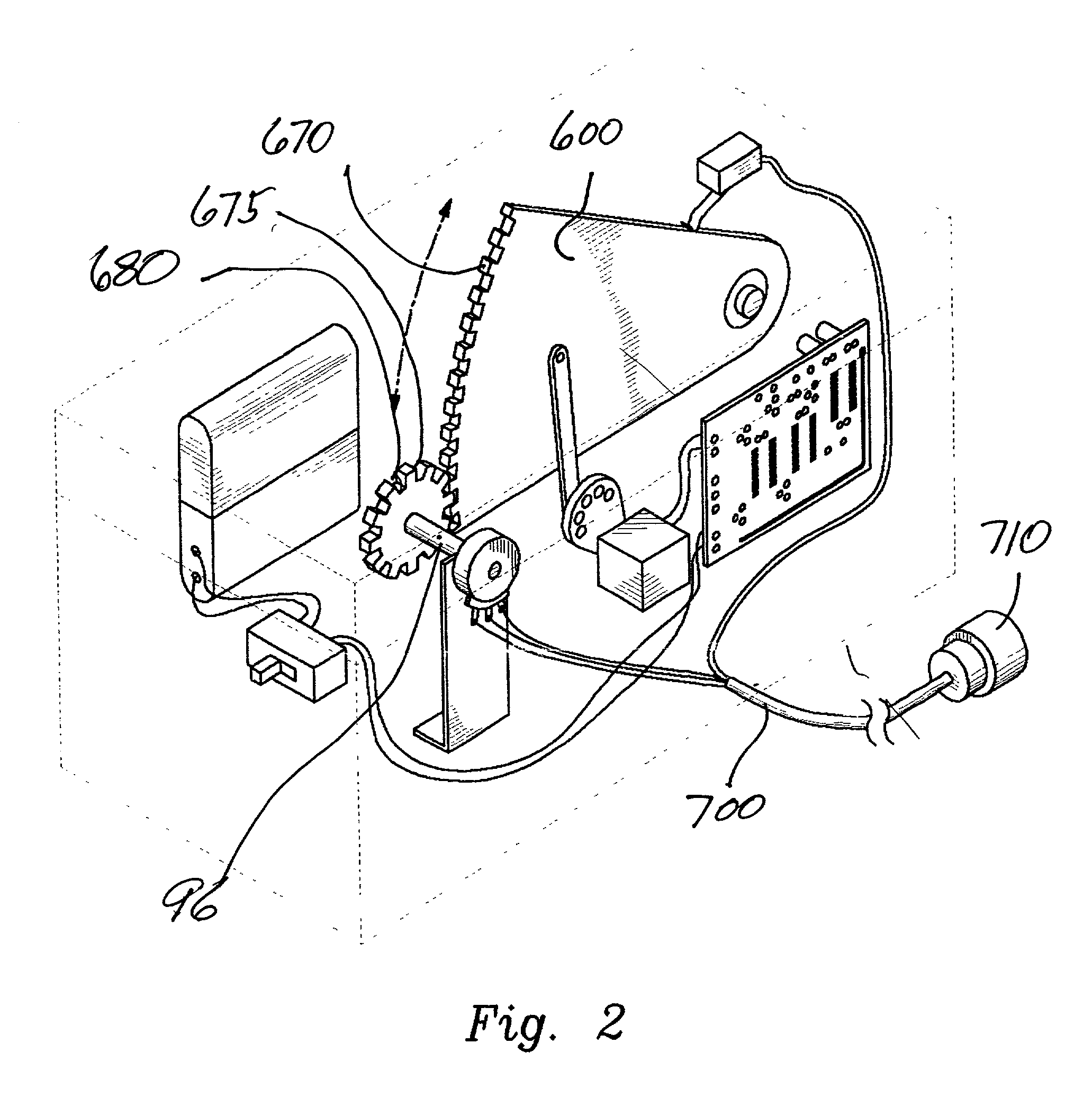
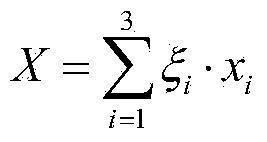Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
141 results about "Patent application" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A patent application is a request pending at a patent office for the grant of a patent for an invention described in the patent specification and a set of one or more claims stated in a formal document, including necessary official forms and related correspondence. It is the combination of the document and its processing within the administrative and legal framework of the patent office.
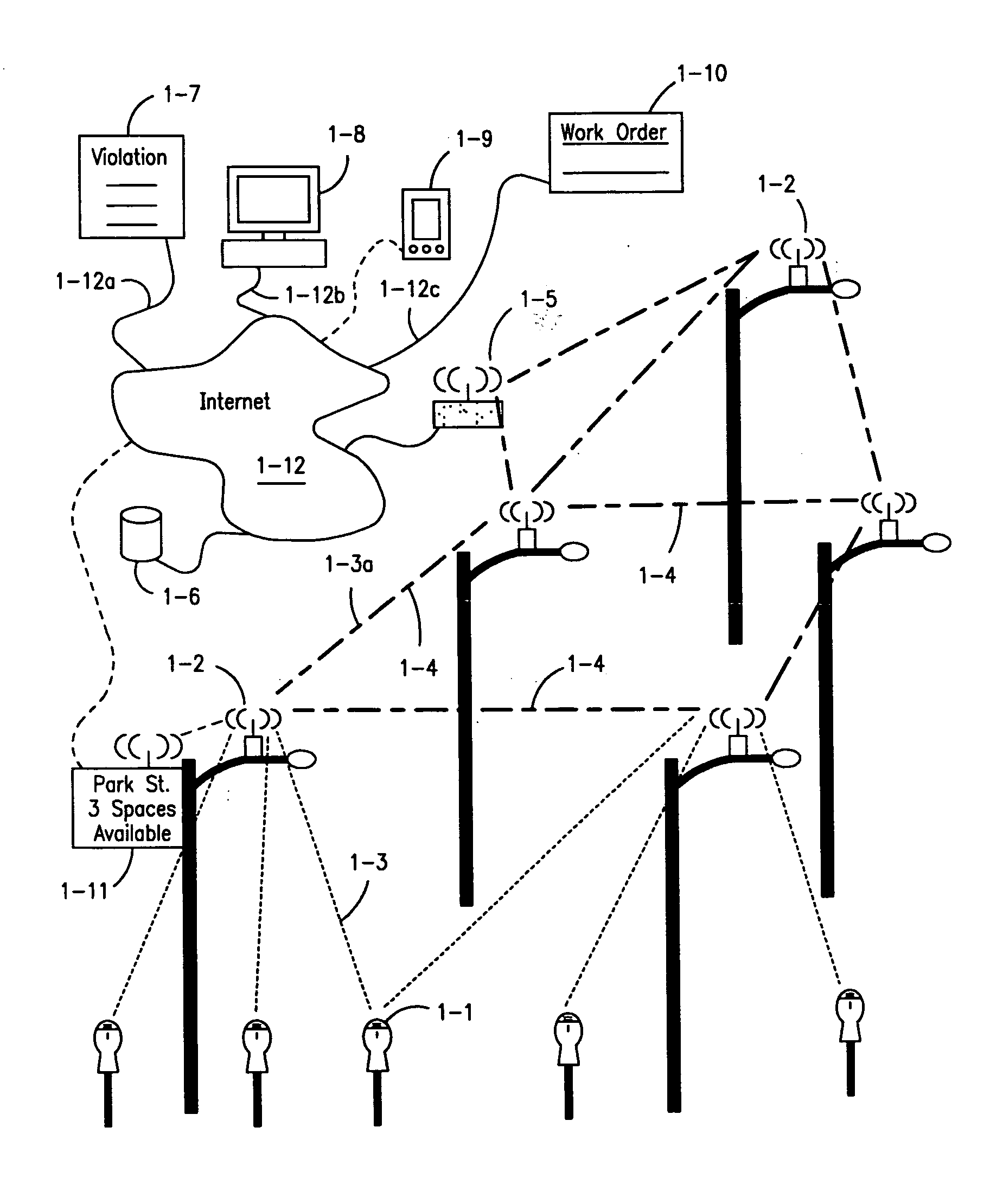
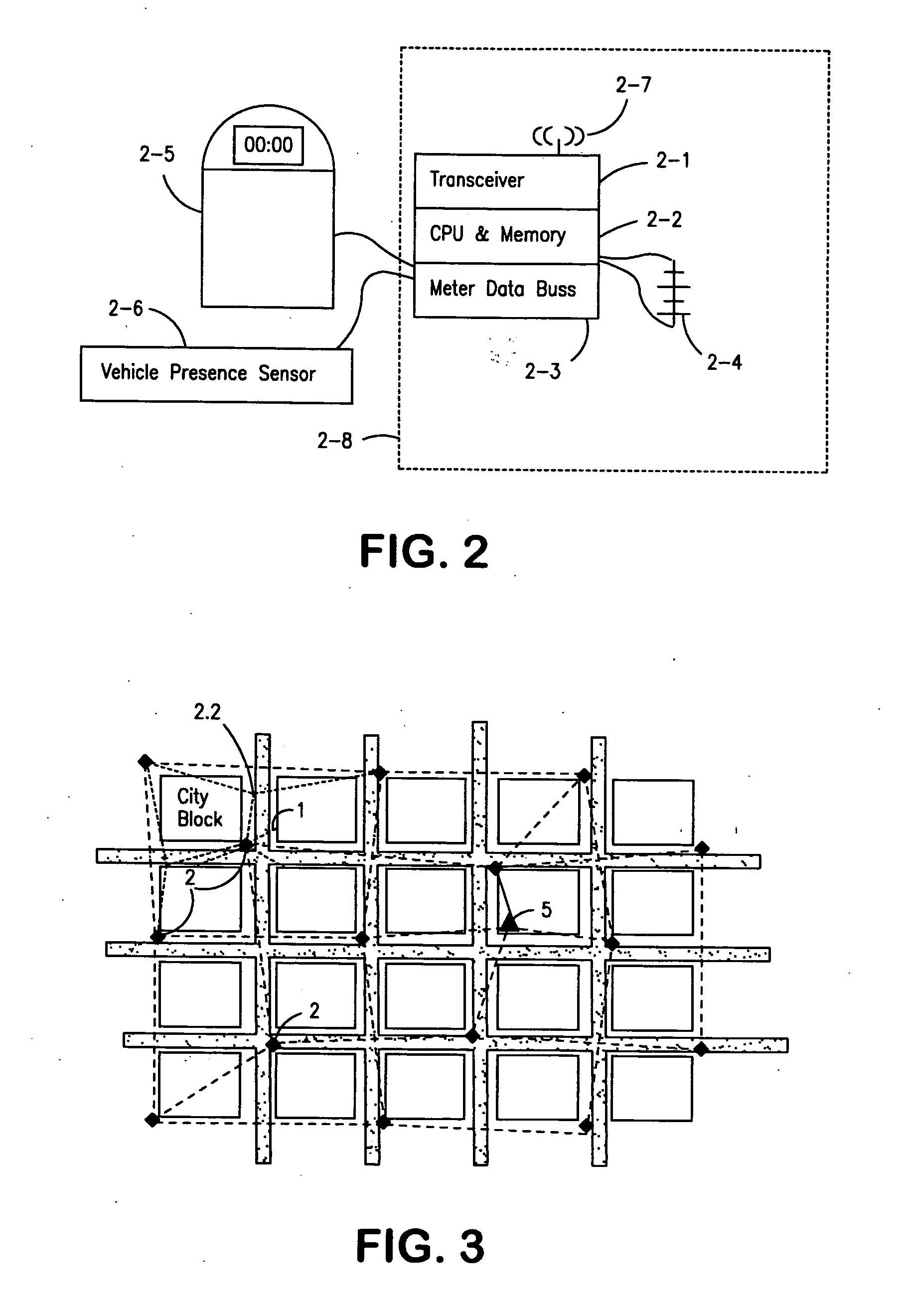
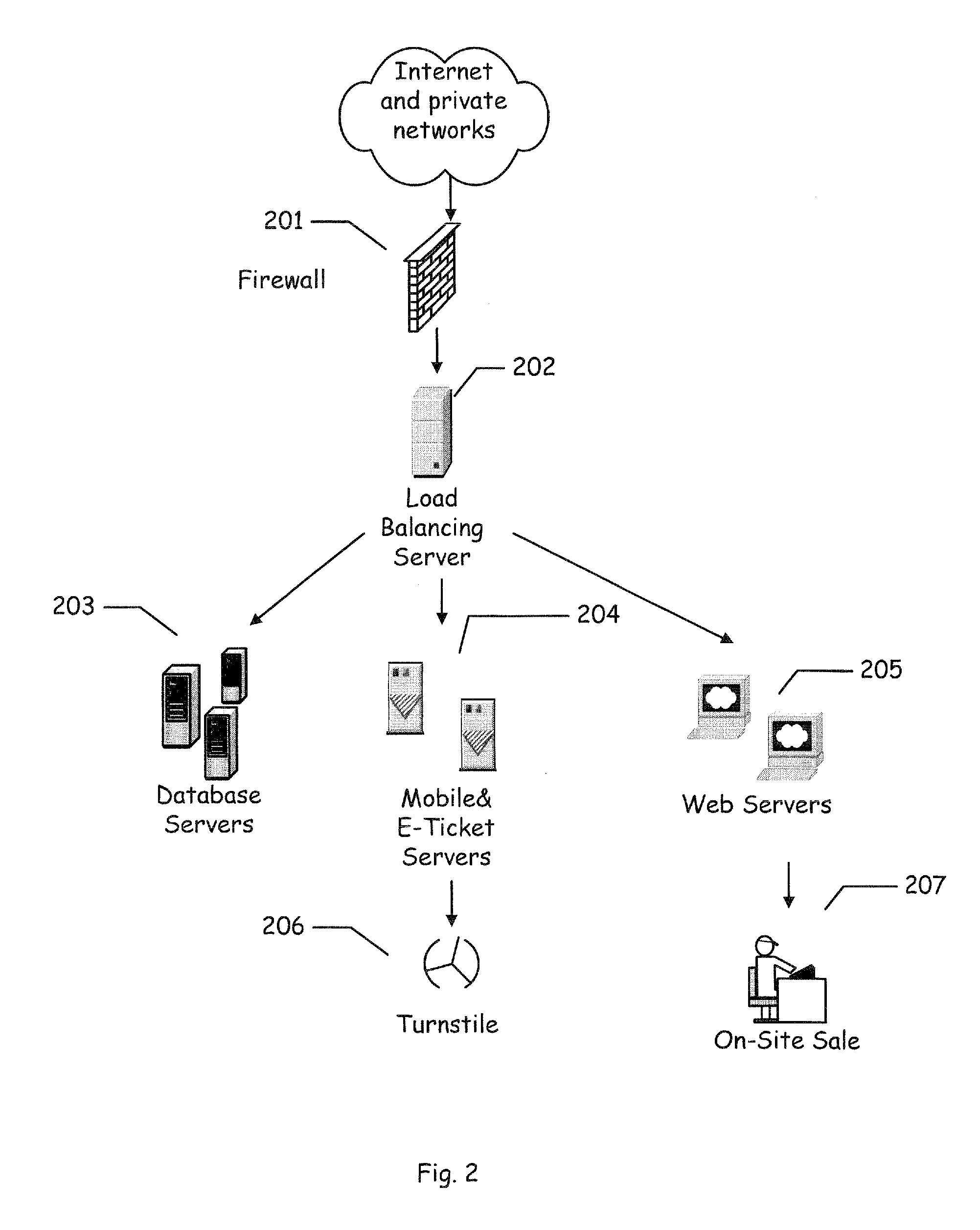
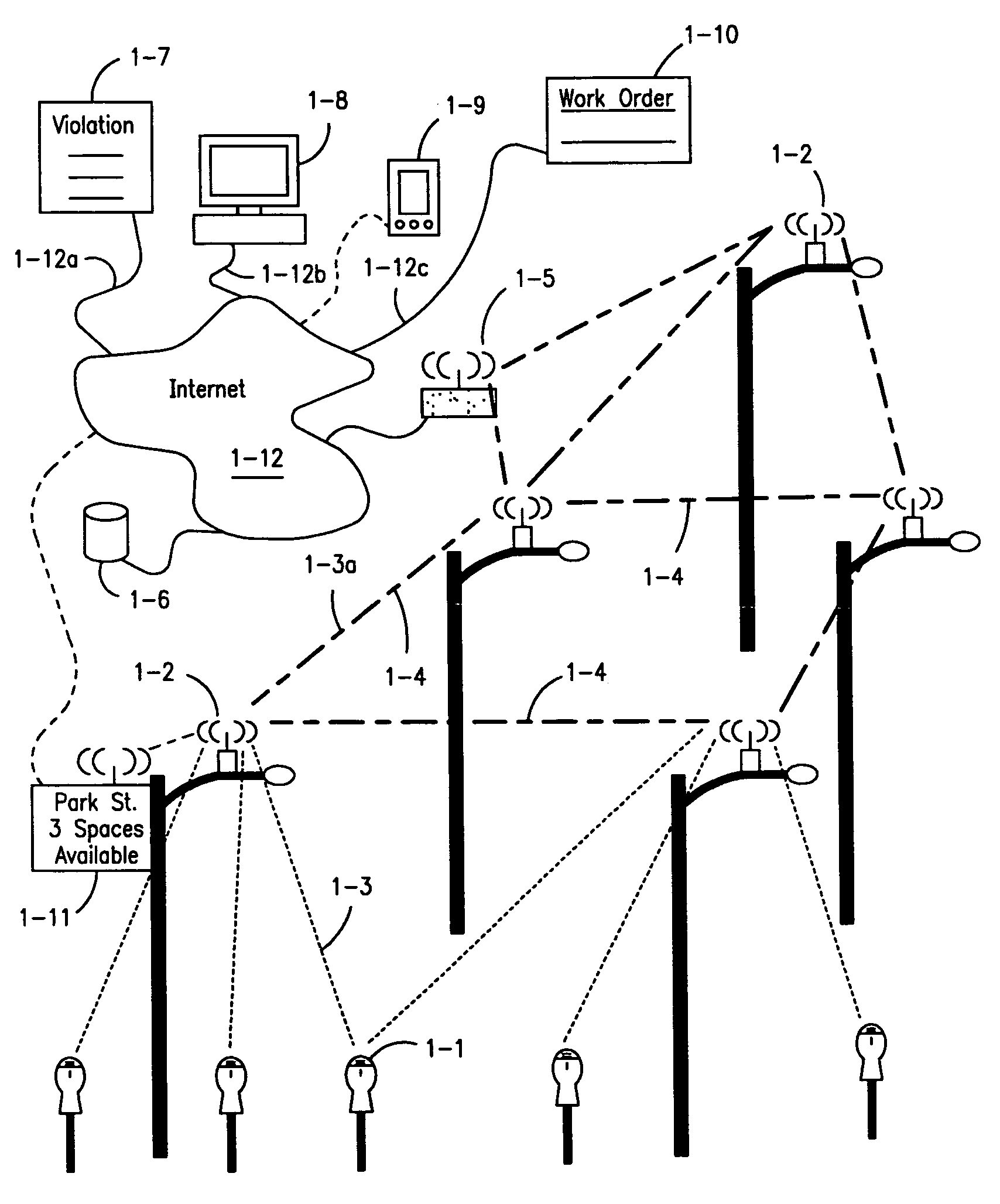
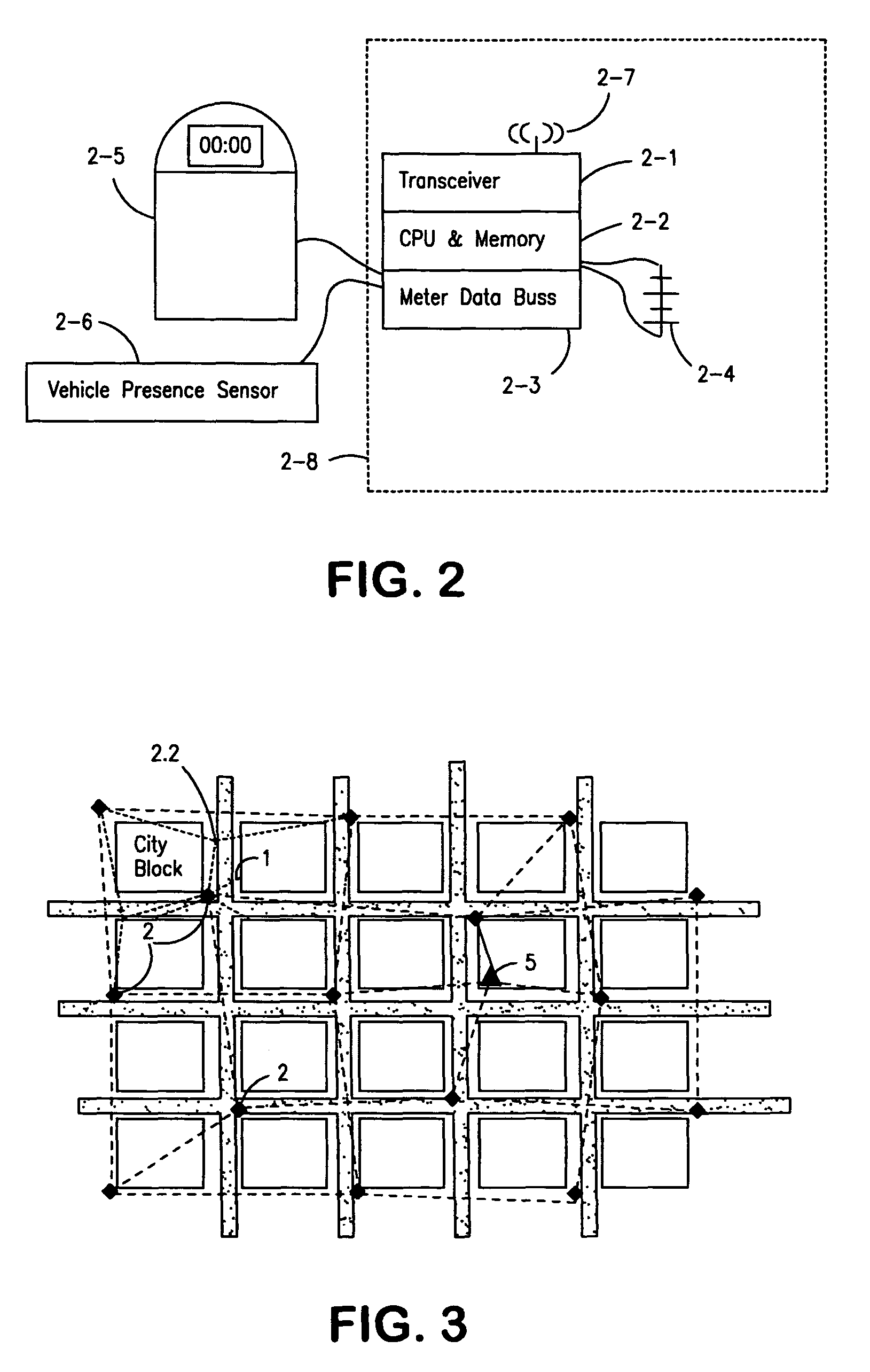
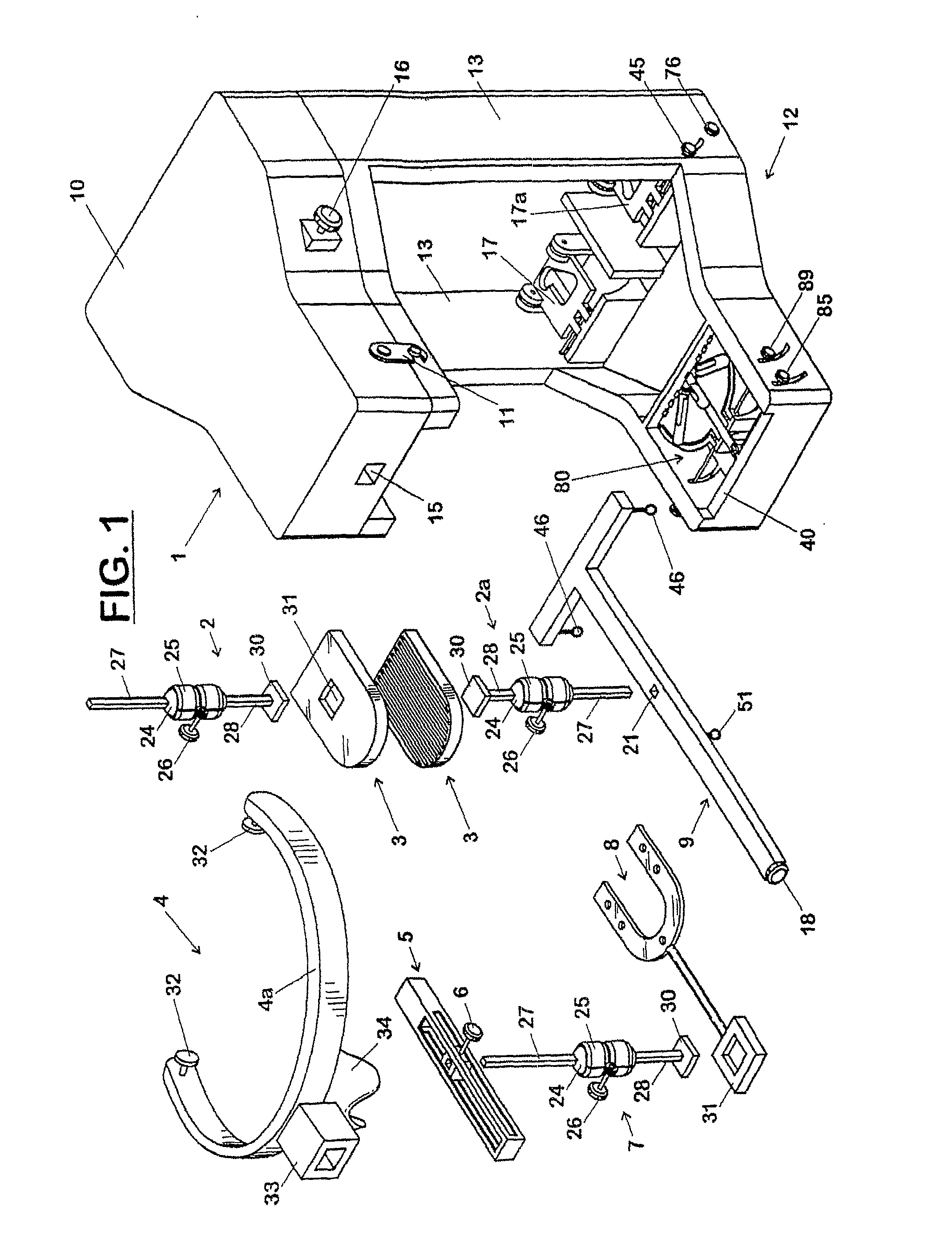
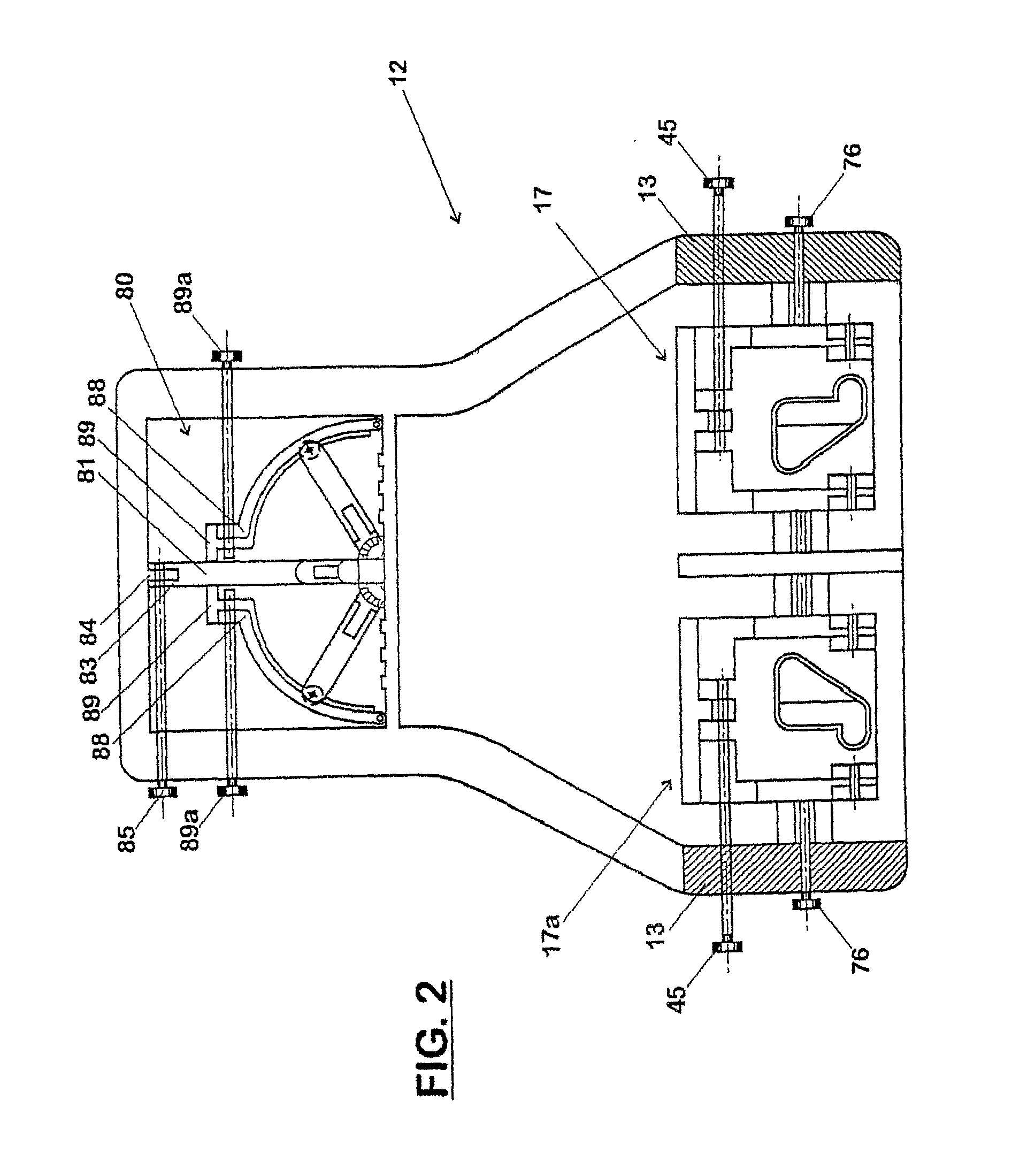
Parking system employing rem techniques
ActiveUS20080291054A1Low efficiencyAllocation is accurateTicket-issuing apparatusTransmission systemsVehicle detectorSoftware analytics
The system described is an integrated parking management system which makes use of patented vehicle detectors to collect and transmit data, essentially in near real time, as to all events happening as to single or multiple parking spaces (e.g. current and historic use, length of time of occupancy of current occupant) to a central clearing device for which patent application has been made which serves as a logic core and repository, making use of proprietary software, analyzing, displaying and distributing the data so developed as to a parking plant and all of its components to allow all parties (including prospective users) who are concerned with the various aspects of a parking plant and its components (e.g. determination as to availability of spaces, maintenance and repair of meters, collection of revenues and enforcement of parking regulations) not only to access and make passive use of the information developed, in near real time, to permit them to identify what's happening to the plant and its components as to their own particular interest in such plant and so maximize the efficient use both of the resources of the plant and their own resources directed to the particular aspect of their interface with the plant and its components but also to access and make active use of such information for whatever purpose and in whatever fashion using whatever means of access they may wish. While others have made claim to certain of the individual functions described, e.g. vehicle detection, nobody has identified or patented
Owner:INNOVAPARK
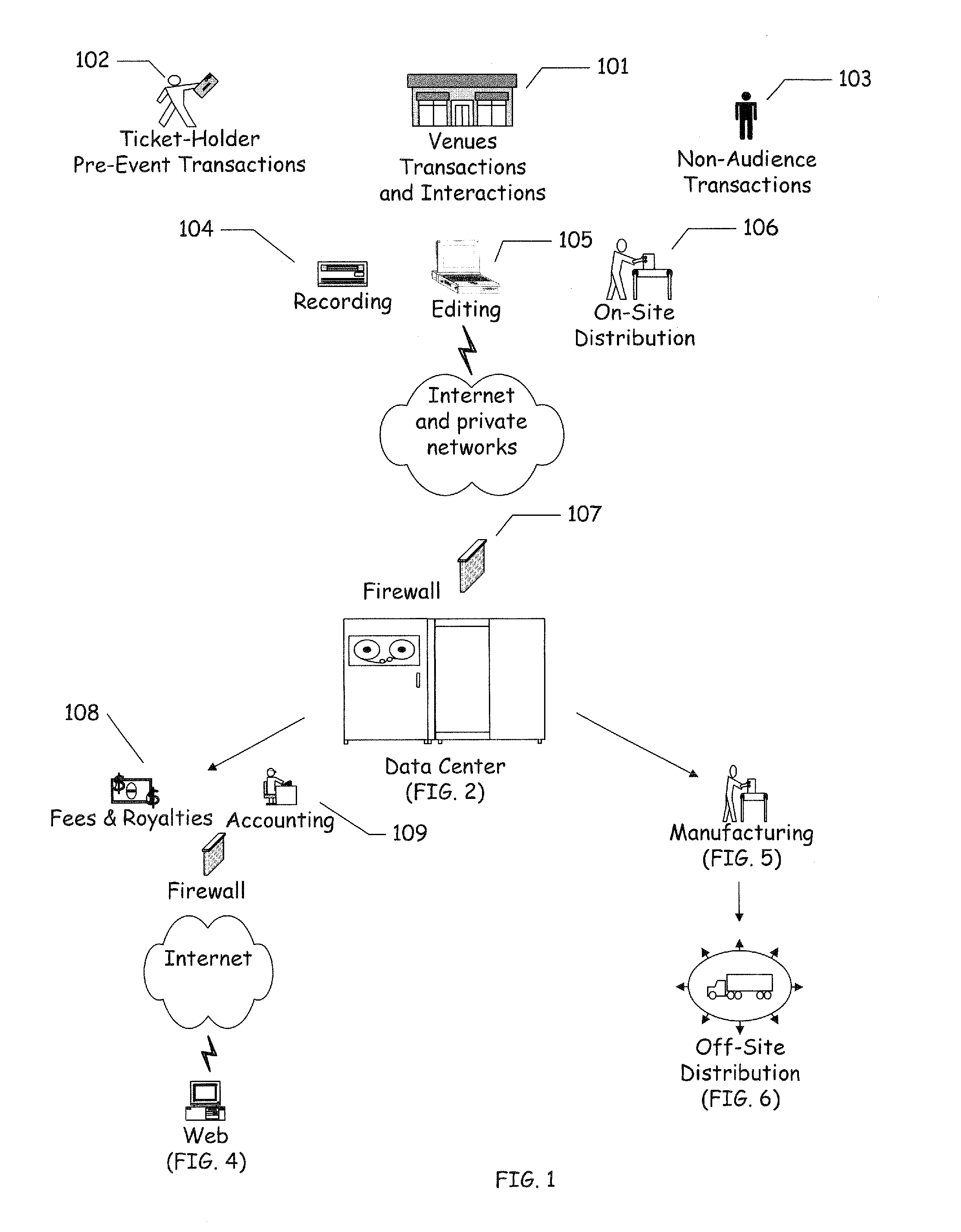
Electronic System and Apparatuses Coupling Ticketing on Mobile Devices with Event Sponsorship and Interaction
The instant disclosure is a continuation in part of this inventor's previously disclosed US and PCT patent applications that claim operating systems, apparatuses and mobile phone devices for live event and common carrier electronic ticketing, event interaction and the end-to-end production, editing, authenticated distribution and management of event-associated Recordings. It now adds placement of at least one of a logo, message, icon, ad or public service announcement on an electronic ticket, entry pass, admission / placed bet or other receipt and on event-related Recordings as a technological production solution for global brands and program sponsors that is independent of placing ads on search engine Websites and their links.
Owner:GURVEY AMY R
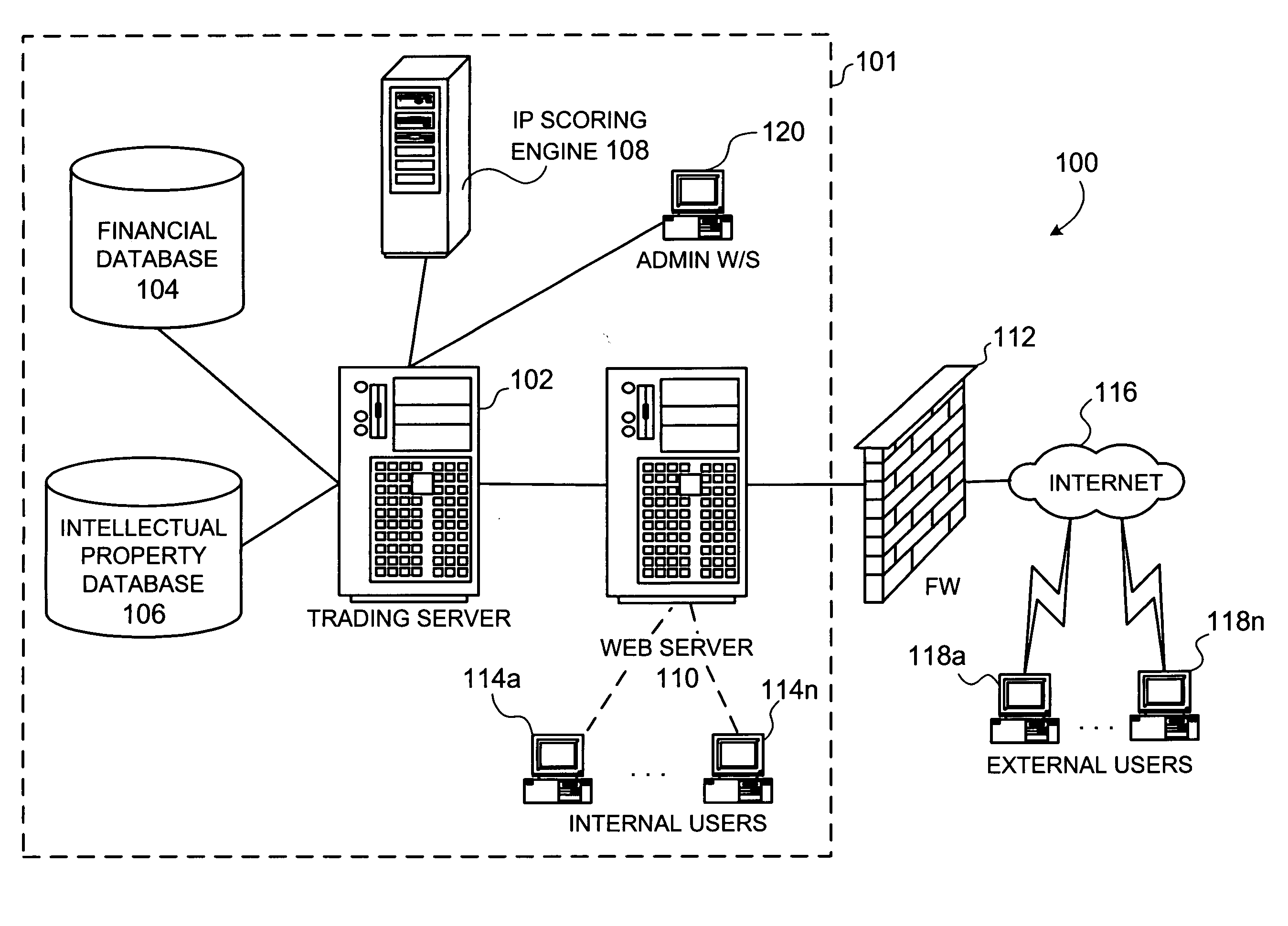
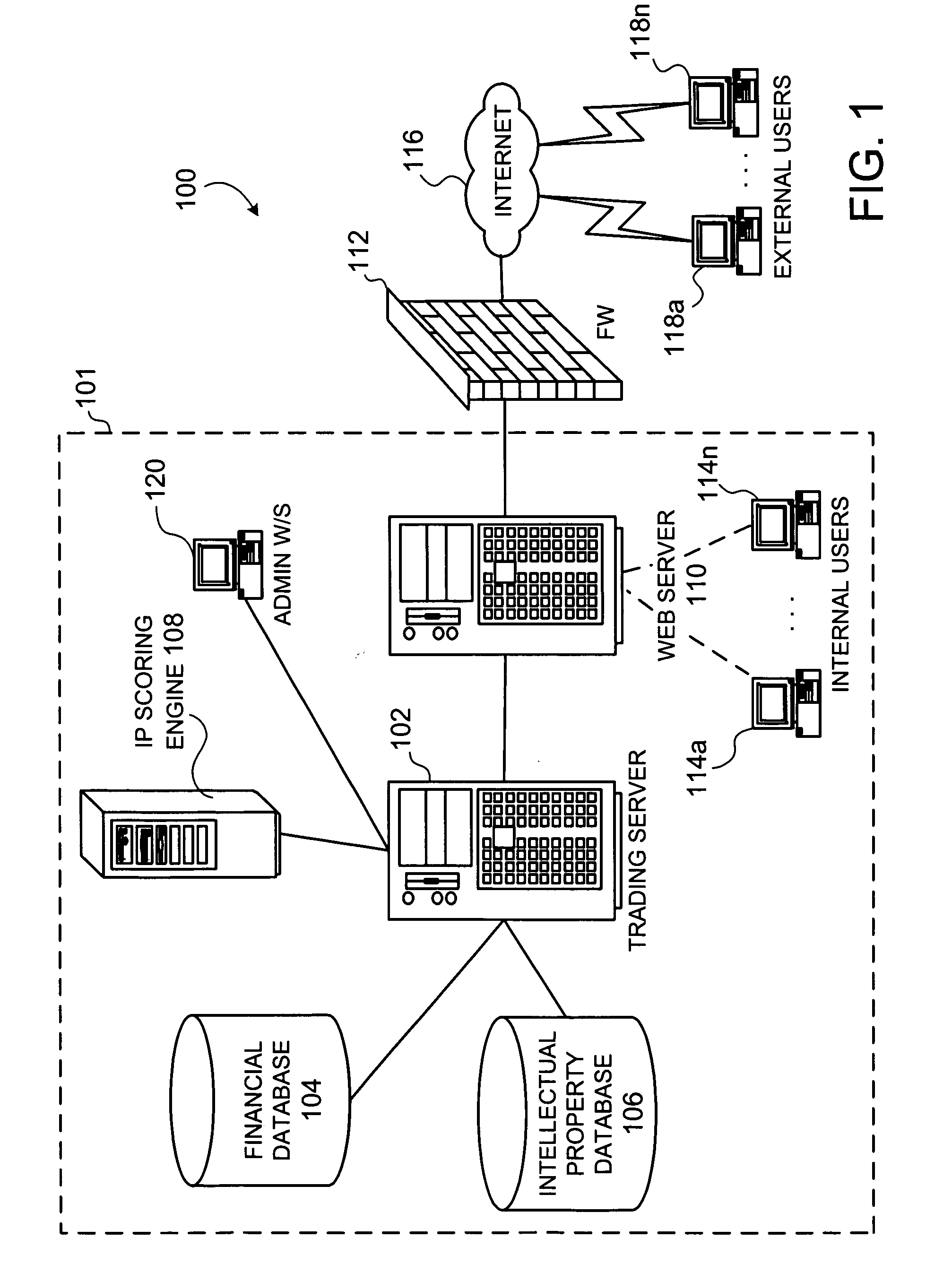
Methods for creating and valuating intellectual property rights-based financial instruments
InactiveUS20060100948A1Enhanced and advantageous methodBetter hedgingFinanceGraphicsGraphical user interface
Systems, methods and computer program products for creating and valuating intellectual property rights-based financial instruments, including patent futures, options, swaps, and the like, are disclosed. In an embodiment, the present invention provides a “patent derivative” to allow investors (e.g., venture capitalist) to hedge their risk in investing in a high-technology, start-up company with no issued patents, but with one or more pending patent applications. The system includes databases for IP rights and financial information, as well as a central processing trading server that is accessible via internal and external workstations. The workstations provide a graphical user interface to enter a series of inputs and receive information (i.e., output) concerning such a financial instrument. The method and computer program product involve collecting the series of inputs affecting the value of the financial instrument and applying a pricing model modified to account for some aspect of potential intellectual property (e.g., patent) rights.
Owner:RAYMOND MILLIEN
System for providing a binding cost for foreign filing a patent application
InactiveUS20090307577A1Easy to useQuick fixOffice automationResourcesIntellectual propertyApplication software
Information relating to intellectual property, across one or more intellectual property applications having various types of intellectual property data, can be provided and / or accessed in an integrated manner. Commonality(ies) are determined between disparate intellectual property applications, that may be applied by the intellectual property applications in accessing the intellectual property information. Responsive to a user request, which may include a specified commonality, stored information regarding the disparate data corresponding to the disparate intellectual property applications is retrieved. The commonality is utilized in bridging the gap to the intellectual property data for the disparate intellectual property applications. The bridging is provided by use of a commonality and by an IP engine.
Owner:LEE EUGENE M
Porous inorganic/organic homogenous copolymeric hybrid materials for chromatographic separation and process for the preparation thereof
InactiveUS20050230298A1Ion-exchange process apparatusComponent separationChromatographic separationPolymer science
Owner:WATERS TECH CORP
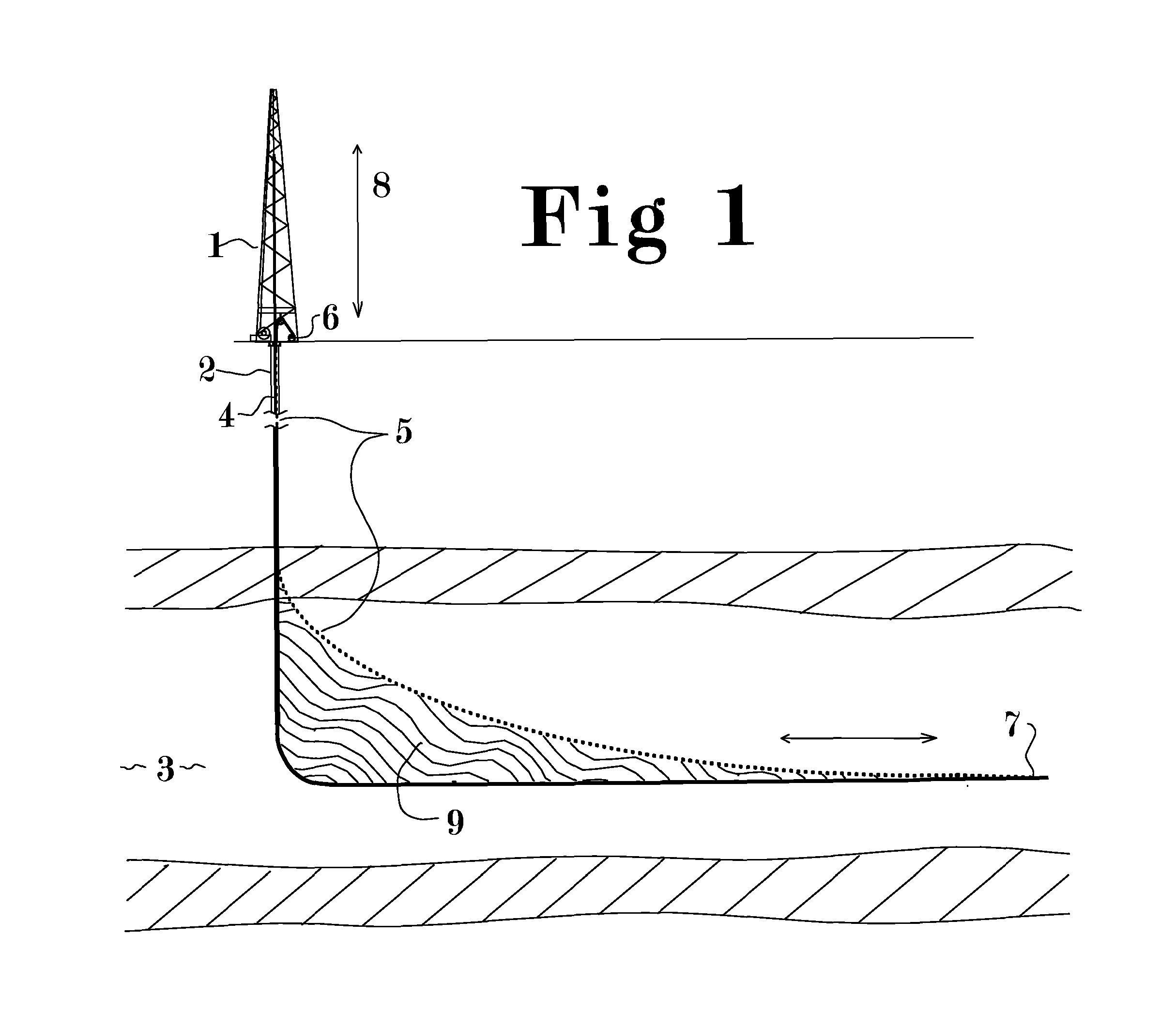
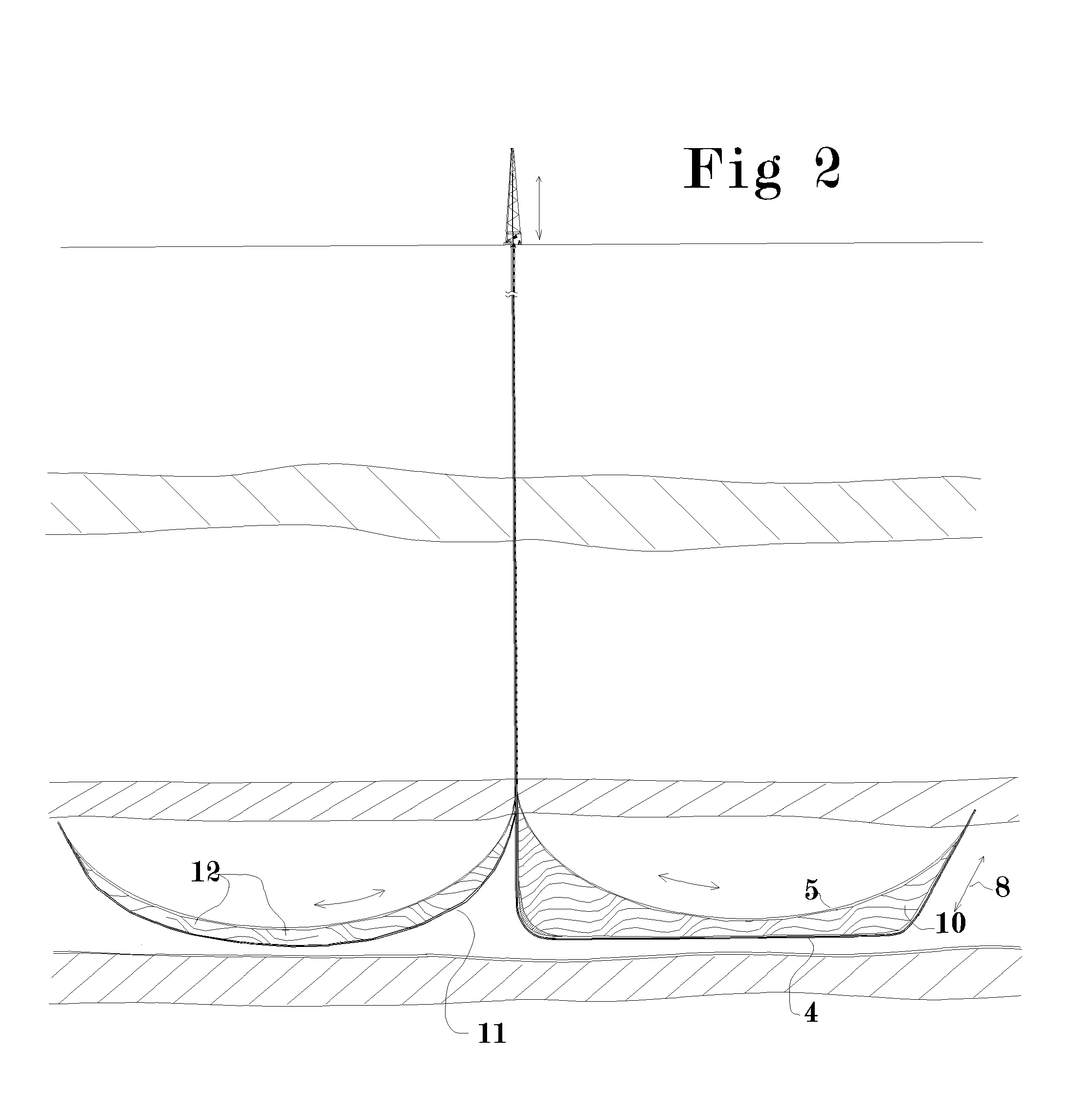
Method and Apparatus for Increasing Well Productivity
InactiveUS20110247816A1Increase productivityRate of flow of resources between the formation and the well is substantially increasedEarth drilling toolsFluid removalEnvironmental issueFlow limitation
This patent application discloses method and apparatus to cut an extended slot connecting a well to a substantial cross section of a desired producing formation whereby material can flow freely between the formation and the wellbore and at least partially overcome the flow limitations of low permeability formations without the environmental issues associated with hydraulic fracturing. It is further disclosed that the connection between said slot and the formation may be further enhanced by explosive or combustive processes that rapidly generate gas pressure within the large surface area of the slot, thereby changing its characteristics and forcing open additional fractures into the cross section of formation exposed to the slot. The method may significantly increase the recoverable percentage of natural gas from low permeability deposits such as shale and coal.
Owner:CARTER JR ERNEST E
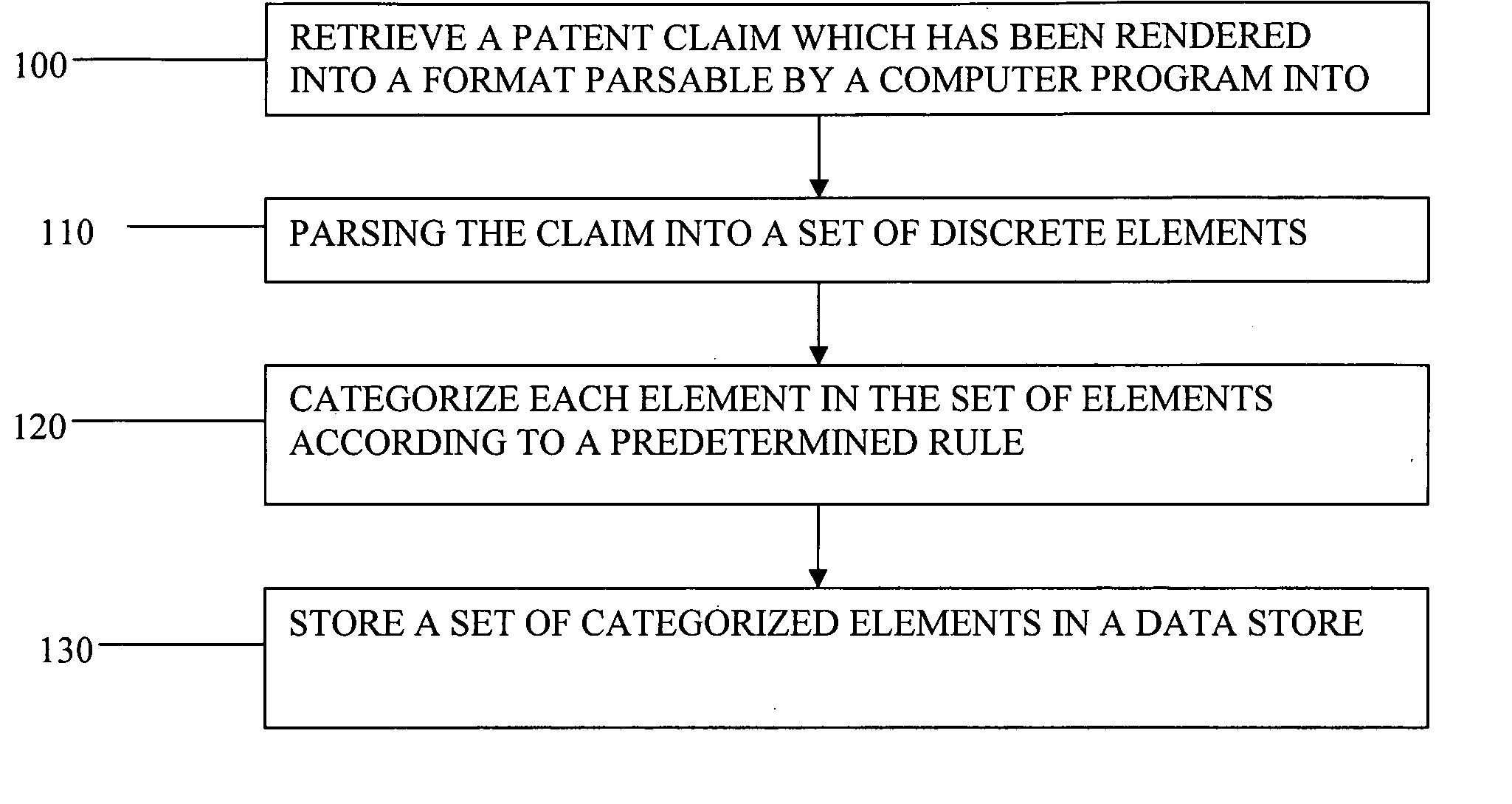
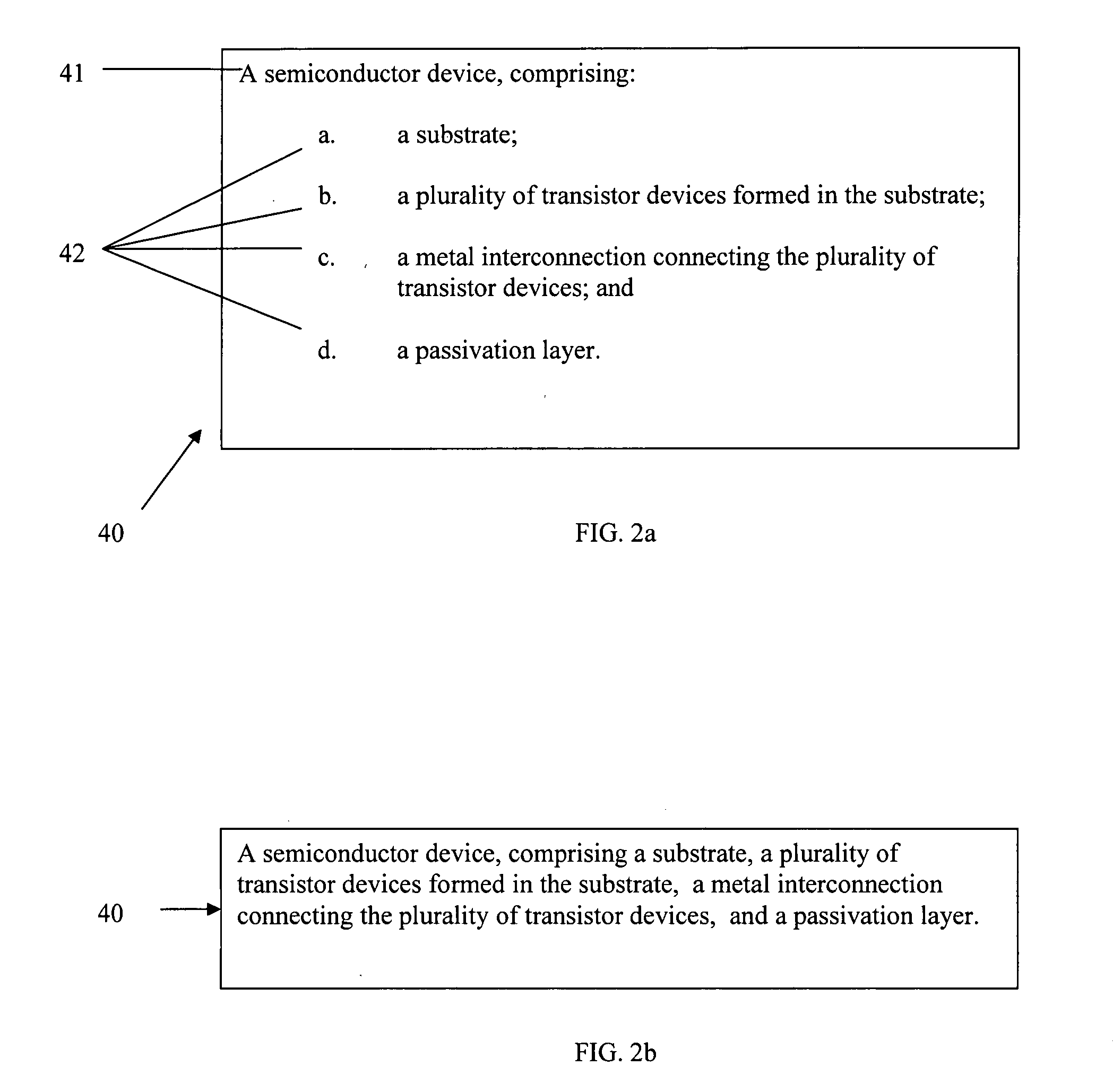
Automatic patent claim reader and computer-aided claim reading method
A method of analyzing a claim in a patent or patent application is disclosed, comprising retrieving a patent claim which has been rendered into a format parsable by a computer program into a computer memory; parsing the claim into a set of discrete elements; categorizing each element in the set of elements according to a predetermined rule; and storing a set of categorized elements in a data store. A parsing program executable in a computer may be used to parse the patent claim and, optionally, to identify one or more keyword sets in the parsed claim. A rating program may also be used to assign a rating weight to each categorized element. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract which will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
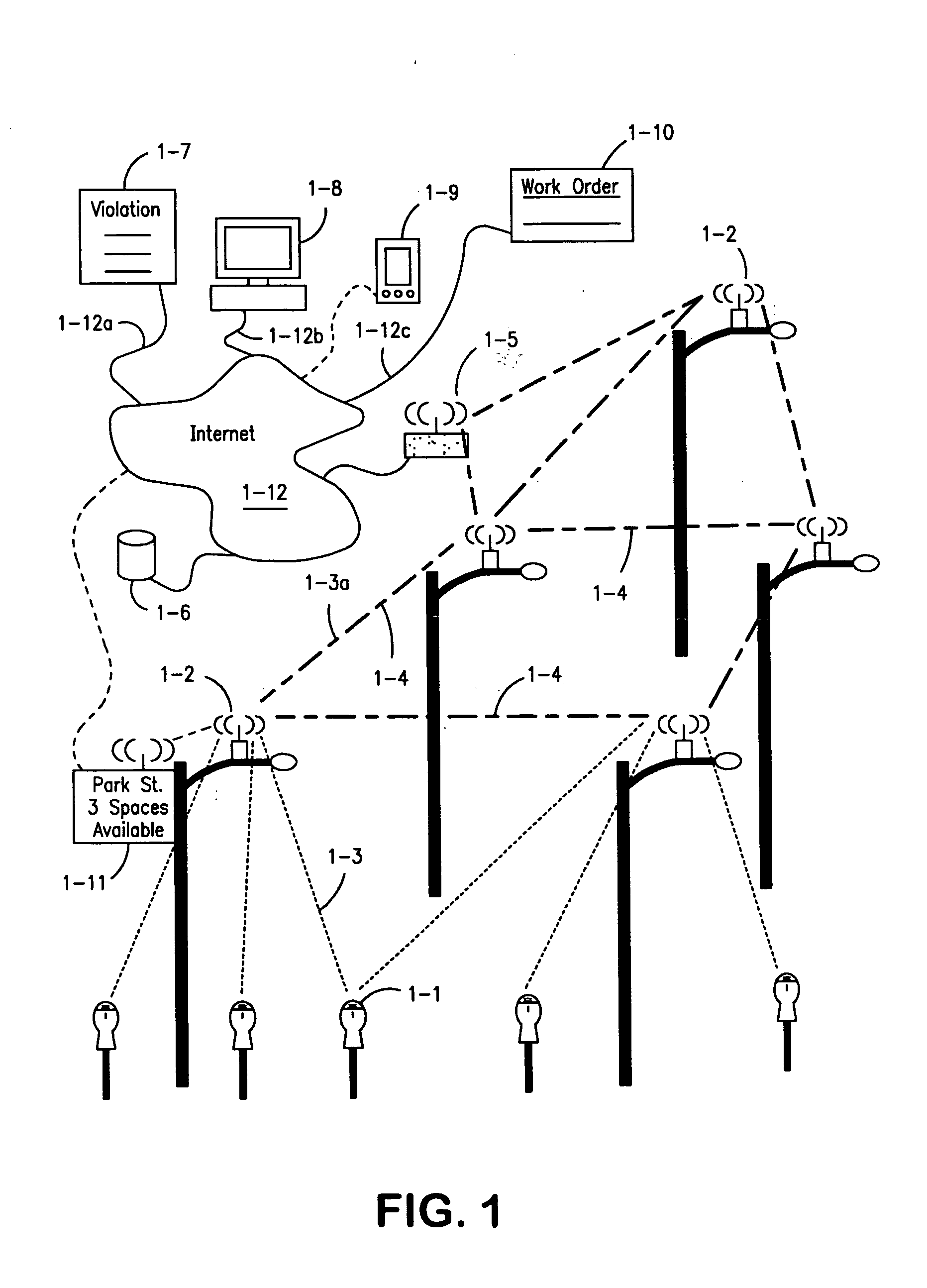
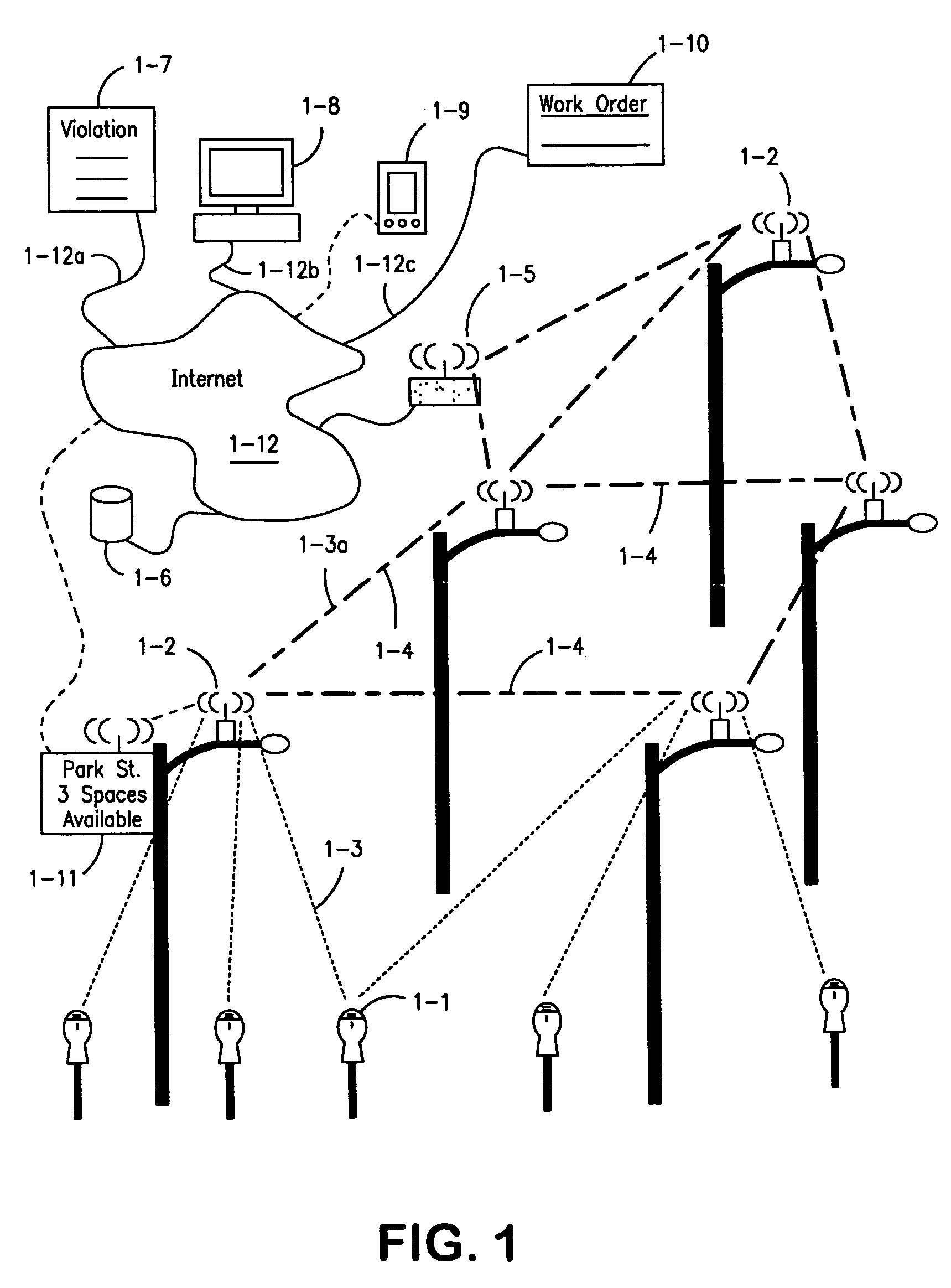
Parking system employing rem techniques
The system described is an integrated parking management system which makes use of patented vehicle detectors to collect and transmit data, essentially in near real time, as to all events happening as to single or multiple parking spaces (e.g. current and historic use, length of time of occupancy of current occupant) to a central clearing device for which patent application has been made which serves as a logic core and repository, making use of proprietary software, analyzing, displaying and distributing the data so developed as to a parking plant and all of its components to allow all parties (including prospective users) who are concerned with the various aspects of a parking plant and its components (e.g. determination as to availability of spaces, maintenance and repair of meters, collection of revenues and enforcement of parking regulations) not only to access and make passive use of the information developed, in near real time, to permit them to identify what's happening to the plant and its components as to their own particular interest in such plant and so maximize the efficient use both of the resources of the plant and their own resources directed to the particular aspect of their interface with the plant and its components but also to access and make active use of such information for whatever purpose and in whatever fashion using whatever means of access they may wish. While others have made claim to certain of the individual functions described, e.g. vehicle detection, nobody has identified or patented.
Owner:INNOVAPARK
Strategic method for process control
InactiveUS7461040B1Increase productivityImprove efficiencySpeech analysisSound input/outputData setValidation methods
A strategic method for process control wherein the method includes, for a predetermined process juncture, the steps of: (A) defining an interconnection cell having associated therewith (i) at least one set of input data or at least one set of process control parameters, and (ii) at least one set of output data; (B) assigning at least one boundary value to at least one set of the sets associated with the defined interconnection cell; (C) using the assigned at least one boundary value, forming a plurality of discrete respective set combinations, and (D) for the interconnection cell, processing data from the plurality of respective formed set combinations into respective corresponding data record clusters.The strategic method for process control is a continuation-in-part of a Knowledge-Engineering Protocol-Suite, (U.S. patent application Ser. No. 09 / 588,681 filed on 7 Jun. 2000) incorporated herein by reference, that generally includes methods and systems, apparatus for search-space organizational validation, and appurtenances for use therewith. The protocol-suite includes a search-space organizational validation method for synergistically combining knowledge bases of disparate resolution data-sets, such as by actual or simulated integrating of lower resolution expert-experience based model-like templates to higher resolution empirical data-capture dense quantitative search-spaces. The protocol-suite includes facile algorithmic tools for use with the method.
Owner:ADA ANALYTICS ISRAEL
Thinking search engines
InactiveUS20070219980A1Digital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsDatasheetEngineering
The invention describes Thinking Search Engines, a novel search technology that uses the data representation, problem solving and learning from experience techniques of Thinking Machines of U.S. patent application Ser. No. 11 / 204,346 by the author. Thinking Search Engines process documents and obtain their subjects in terms of the entities, templates, problems, concerns, solutions, and protocols that they describe whether or not these subjects are explicitly mentioned. They provide an initial ranking of search results by estimating the relative amount of information that each document contains for each of its subjects. During a search session, the machine records various data such as the address of the client machine, the files requested for each search query, the sequence, the elapsed time prior to each request, and the type of action that follows a request in the Session Information Table. Whenever a search session expires, its data is processed to populate the Experience Table of the Thinking Database. In turn, the experience data is used to tune the ranking of resulting files. The Thinking Search Engine also generates sponsoring links that are useful to users without competing with the products and services of the hosting site. Matching topics for sponsoring links are obtained by selecting from the Protocol Table of the Thinking Database all protocols and templates that use those of the hosting sites. Then the protocols and templates of the hosting site are eliminated to avoid competition. The remaining ones are the matching criteria for generating sponsoring links.
Owner:SONGFACK POLYCARPE
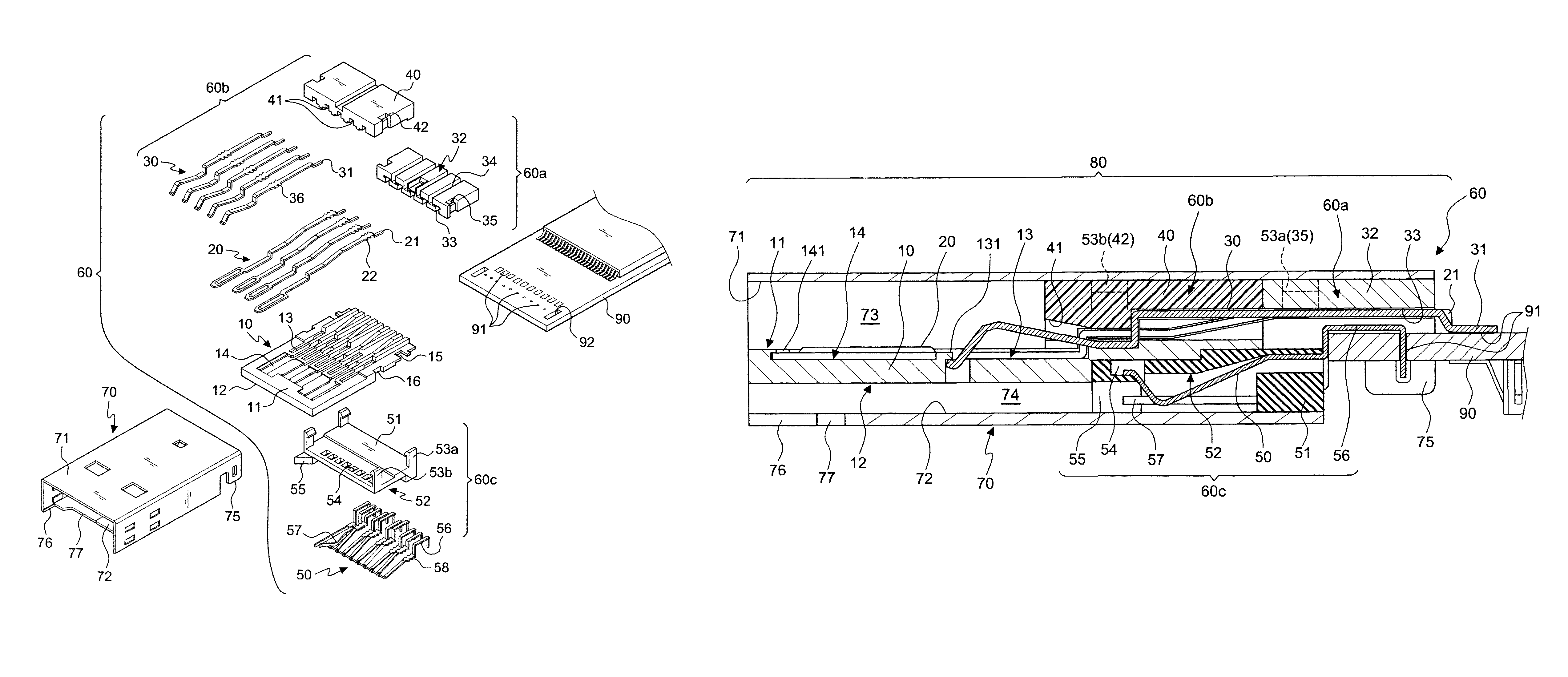
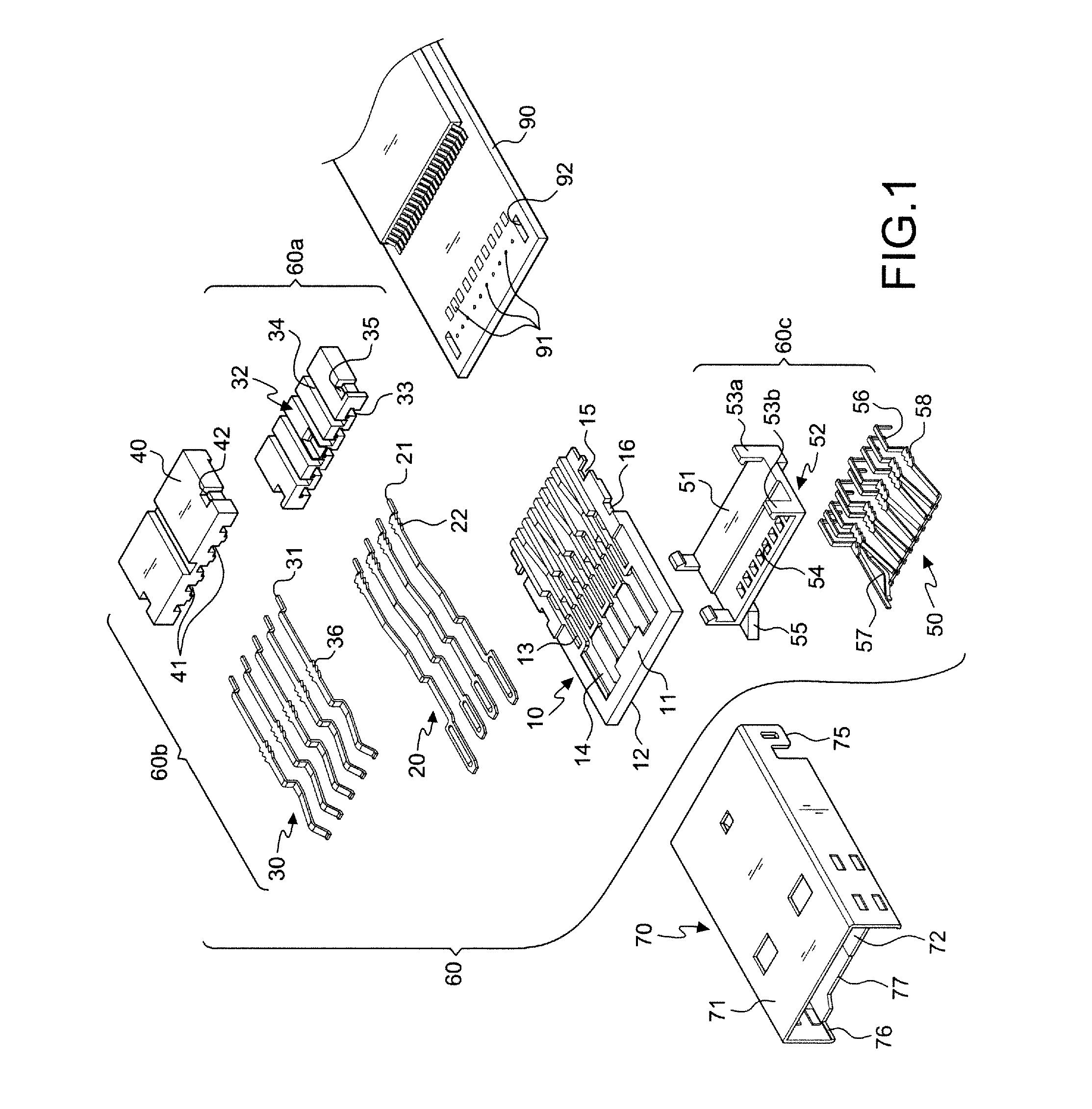
Combined structure of a USB plug with a built-in card-reading slot
InactiveUS8167658B1Convenient and modularized manufacturingConvenient and modularized and assemblySensing by galvanic contactsTwo-part coupling devicesElectricityEngineering
A combined structure of a USB plug with a built-in card-reading slot, and more particular, a combined structure for the patent application U.S. Pat. No. 7,575,481 that permit a convenient manufacturing and meets different needs. An isolation base is provided in cooperation with two or three different isolation pieces which are joined by a hooked connection to create a module. The isolation pieces are each provided with an engaging slot. It is possible to choose the desired terminal set of certain type to achieve the predetermined functions of a certain USB specification. A metal housing meeting the specification of USB A-type plug dimensions encloses the compound connection module, thereby creating a first slot for the electric connection with the female connector of USB 2.0 or USB 3.0. Meanwhile, a second slot is provided for the insertion of the thin-type Micro SD / T-Flash memory card. Accordingly, a USB plug with a built-in card-reading slot is created. Moreover, the USB plug is an independent connection element that allows for a convenient connection with circuit boards or electronic products having different functions. As a result, the requirements of different electronic products are fulfilled.
Owner:LIU CHEN YA
Method and apparatus for signaling to a mobile device which set of training sequence codes to use for a communication link
ActiveUS20110170482A1Cross-correlation ratioCriteria allocationSignal allocationTelecommunicationsTelecommunications link
The present patent application improves DARP by allowing multiple users on one time slot (MUROS). It comprises means and instructions for signaling training sequence set information to a remote station, comprising receiving signaling from a remote station indicating if a new set of training sequences is supported, and using a channel description to signal the training sequence set to be used by the remote station for a communication channel being established.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Patent application for a computer motional command interface
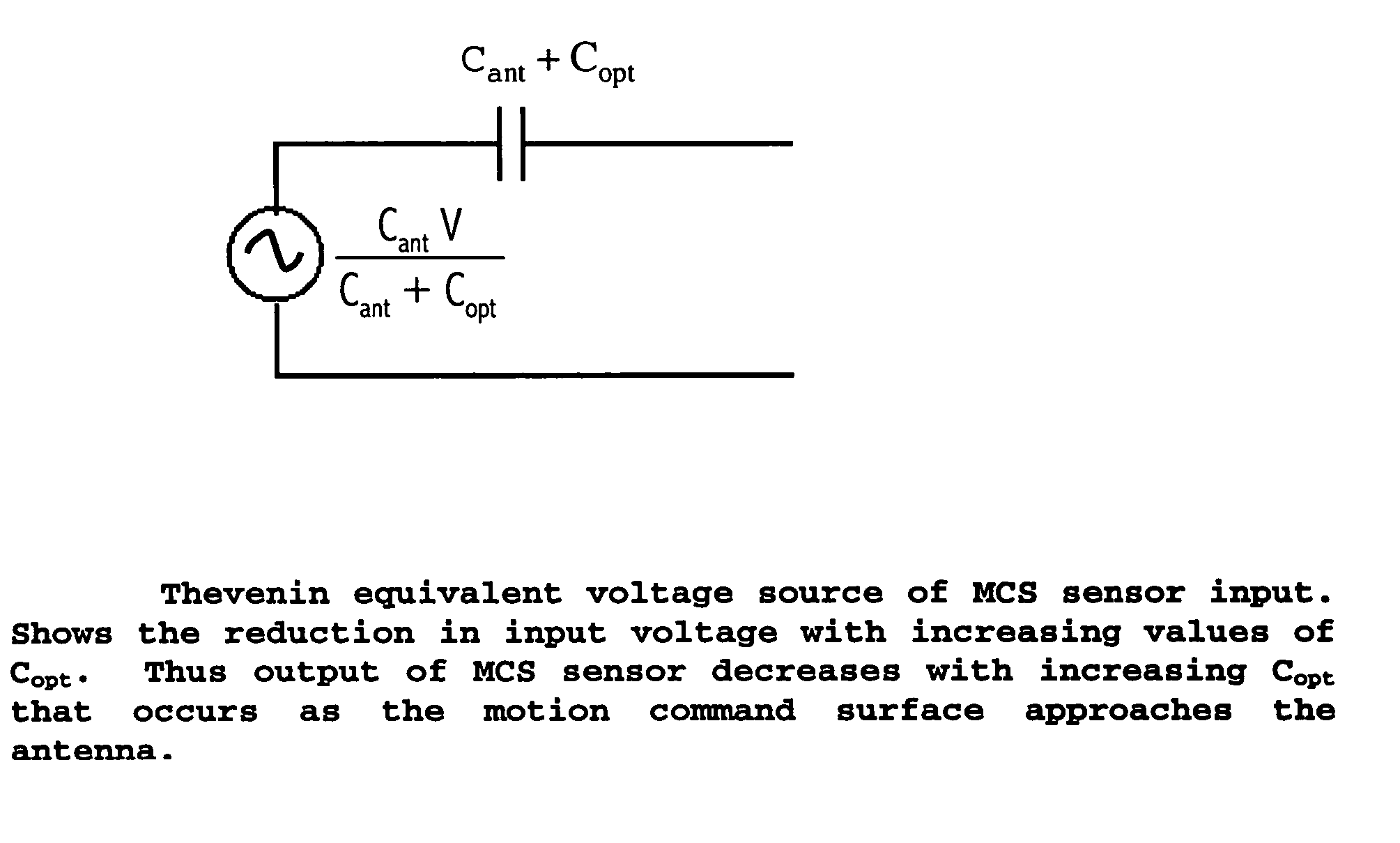
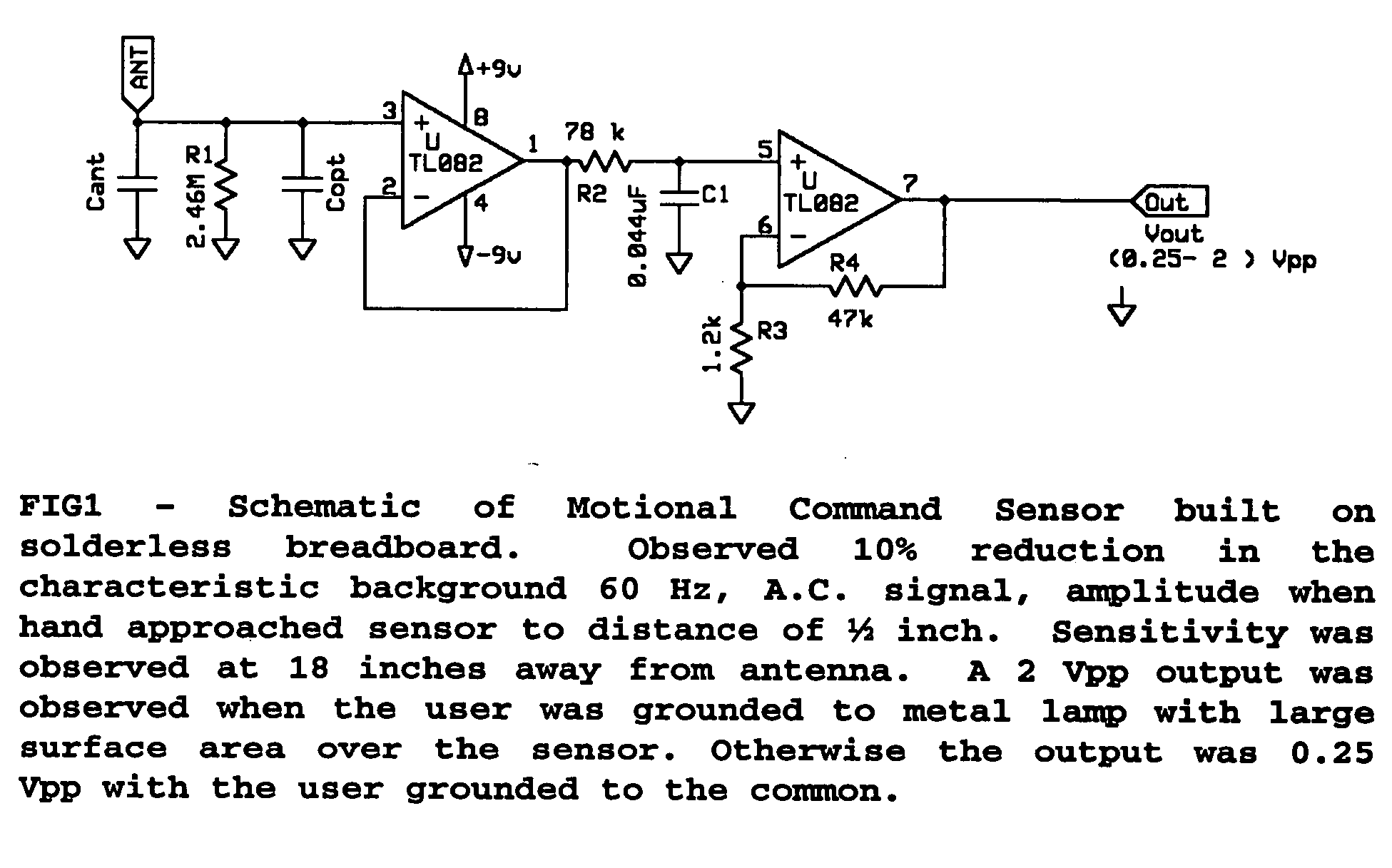
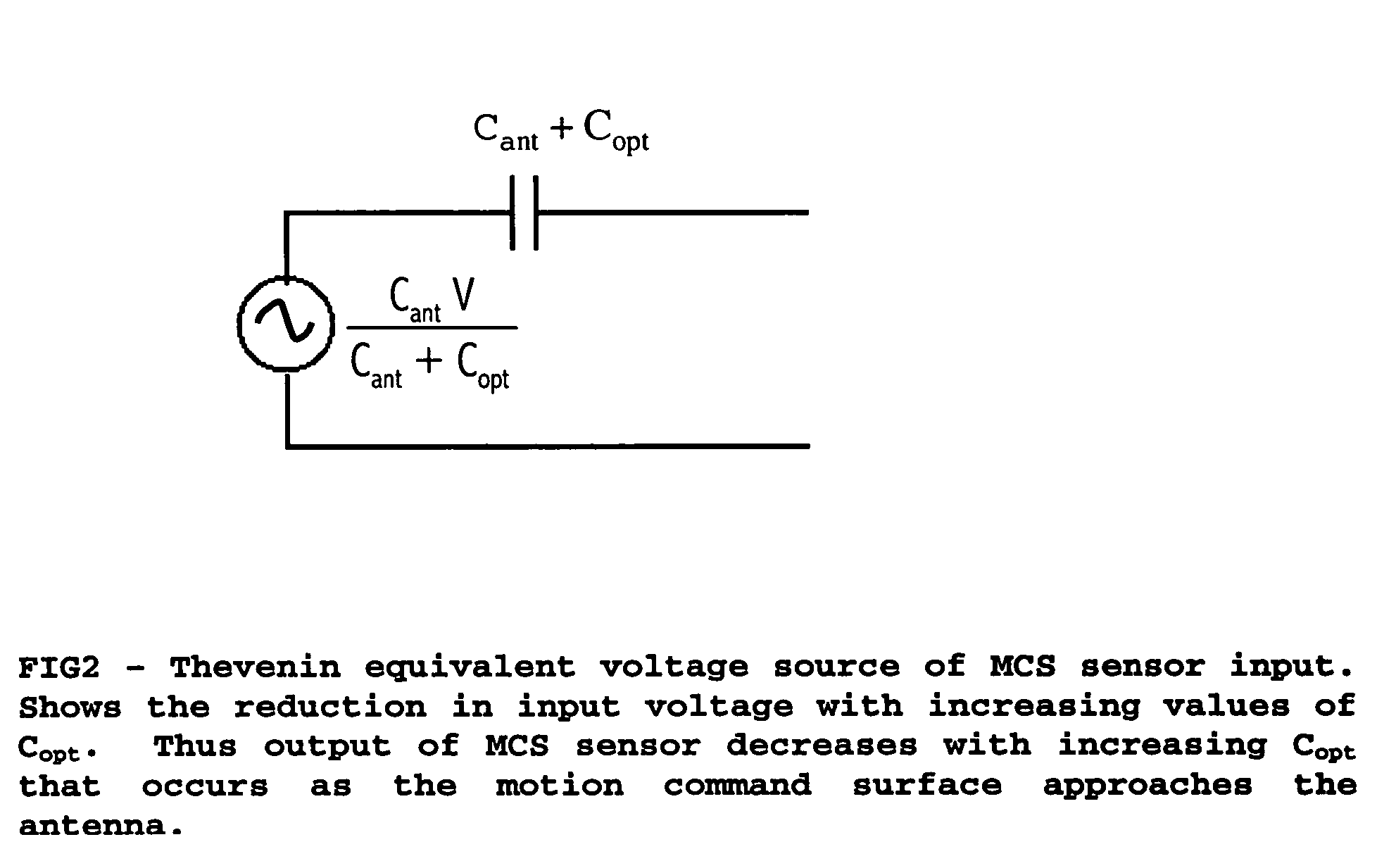
InactiveUS20040251918A1Increasing personal realismLess tediumInput/output for user-computer interactionResistance/reactance/impedenceBody movementComputer science
A method and apparatus is described for interacting with electronic devices via motional commands. The method uses perturbations of the background quasistatic electric fields. The apparatus measures perturbations in electric potential relative to the background. Body movement is recognized by comparing changes in signals in time with signals collected from training sets for specified motional commands or gestures. Upon recognizing the commands, the apparatus issues the predetermined response to the motion.
Owner:CEHELNIK THOMAS G
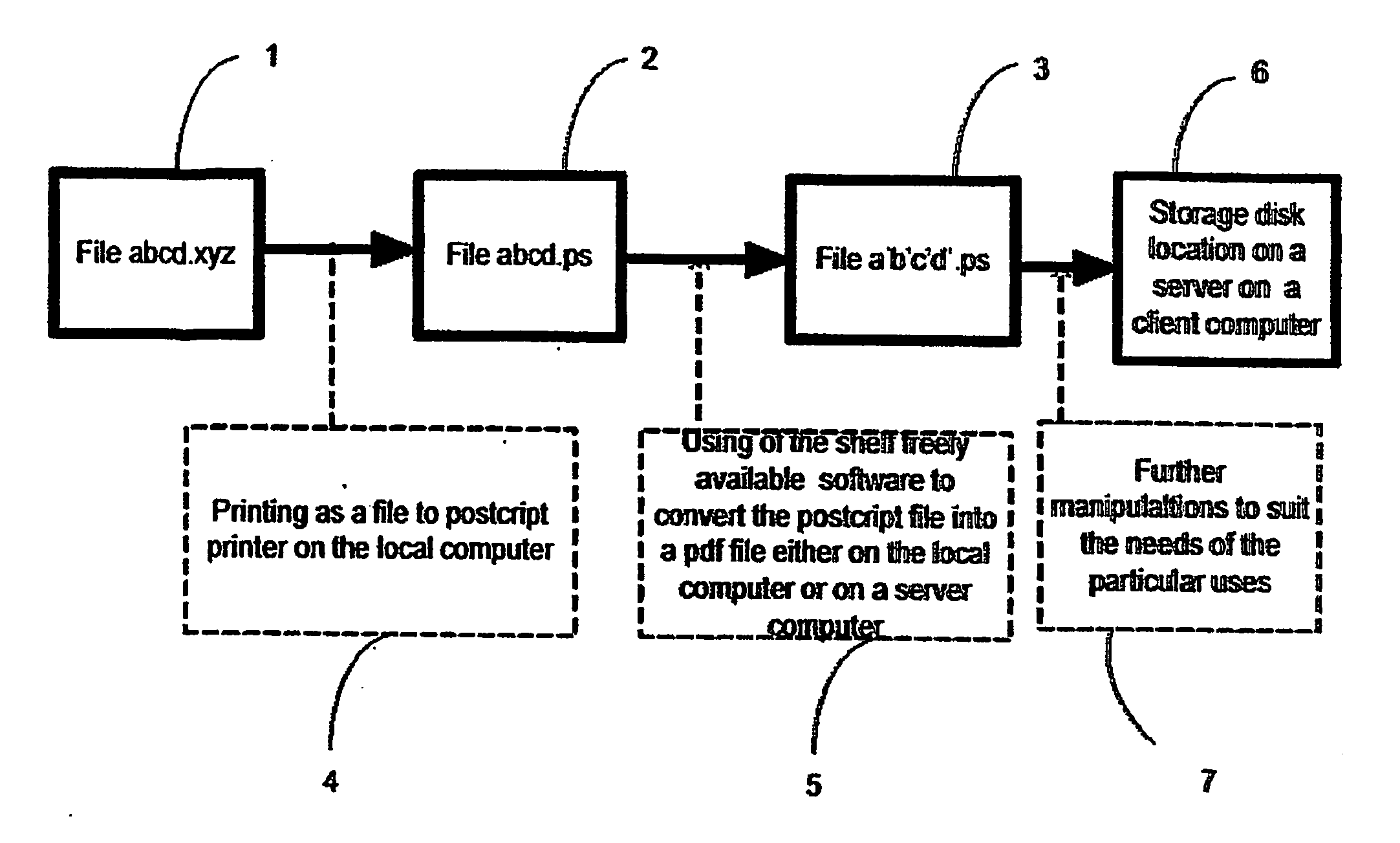
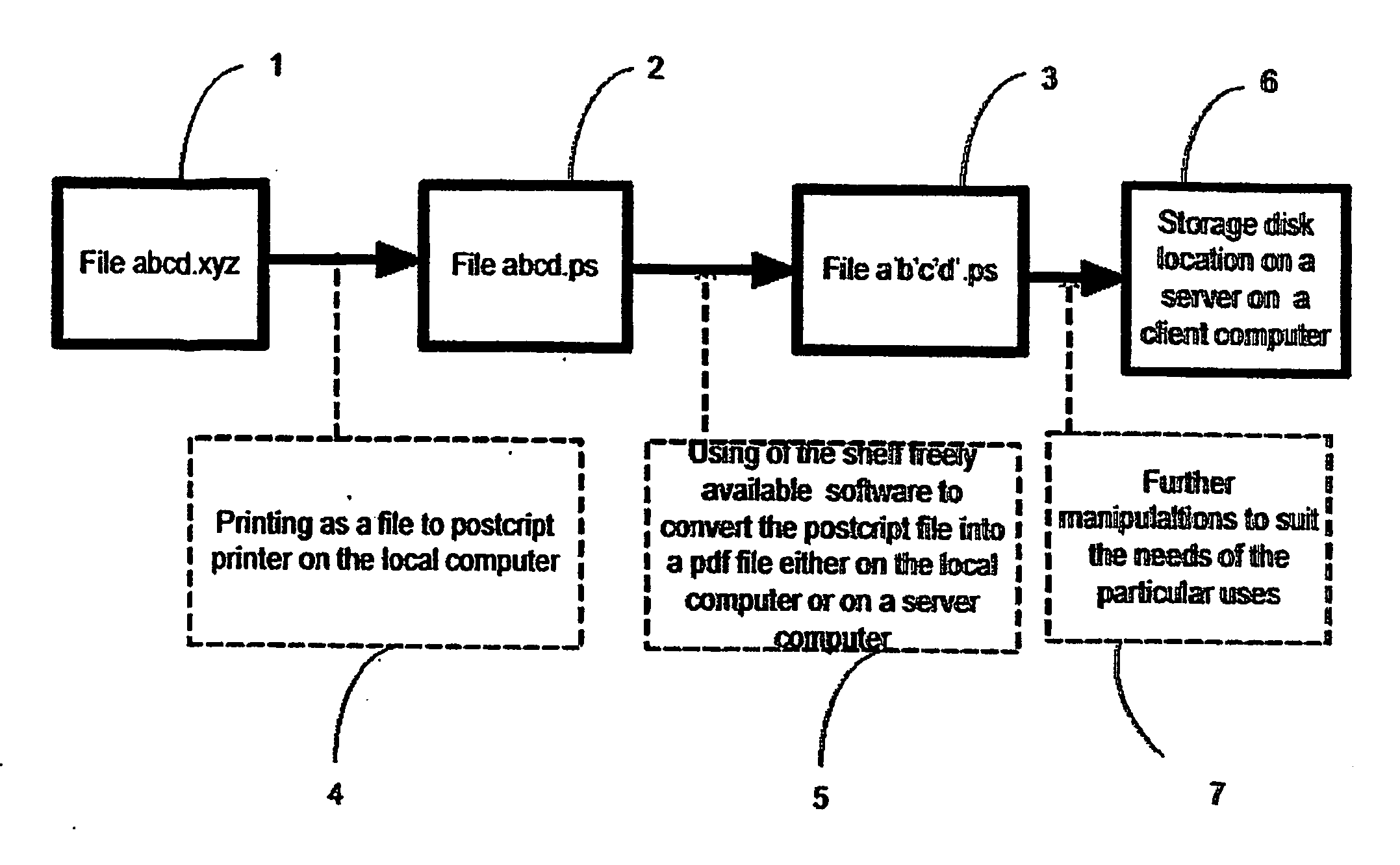
Online method and system for converting any file in any format into a pdf file for various uses
InactiveUS20060187478A1Improve convenienceImprove simplicityDigital output to print unitsPaper documentClient-side
A method and system for enabling the conversion of the printable content of any file document in any file format type (1) from a client computer to a Portable Document Format (PDF) file (2) created on a central server. The system allows for secure sharing or subsequent electronic submission of the converted document (2). The system also provides improved technology for an alternative method for online printing and online document submission for various applications including proposal submissions, patent application submissions and online mail submissions.
Owner:PHIL KONGTCHEU
Steering for independent suspension system
Disclosed herein is a novel steering system specifically designed to operate in conjunction with the powered version of the extreme-travel independent suspension system that is disclosed in the U.S. patent application Ser. No. 14 / 087,552. Based on a steering mechanism commonly found in off-road racing trucks built around Ford's twin I-beam front suspension system, this novel steering system comprises a type of swingset steering linkage structure. Unique features of this novel steering system include a right-angle bellcrank and swingset arm whereby the vertical bellcrank arm functions like the swingset arm. This novel steering system utilizes front or rear driver and passenger tie rods operating in coincidence with their counterpart suspension links to control the directional orientation of the steering or non-steering knuckles with minimal bump steer or change in toe throughout suspension travel, respectively.
Owner:BANDY RONALD SCOTT
Method of separating, identifying and characterizing cracks in 3D space
ActiveUS20170372470A1Accurate calculationAccurate representationImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionVoxel
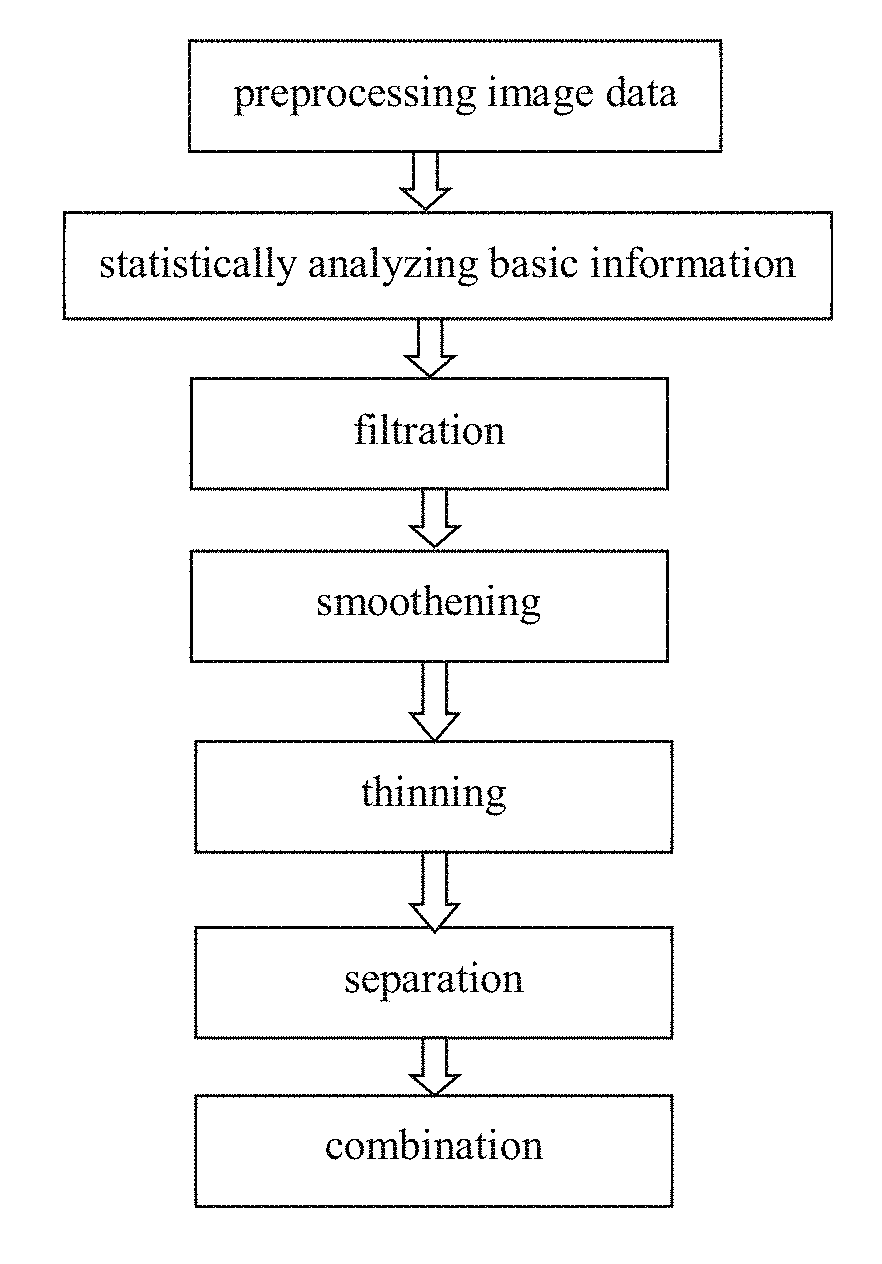
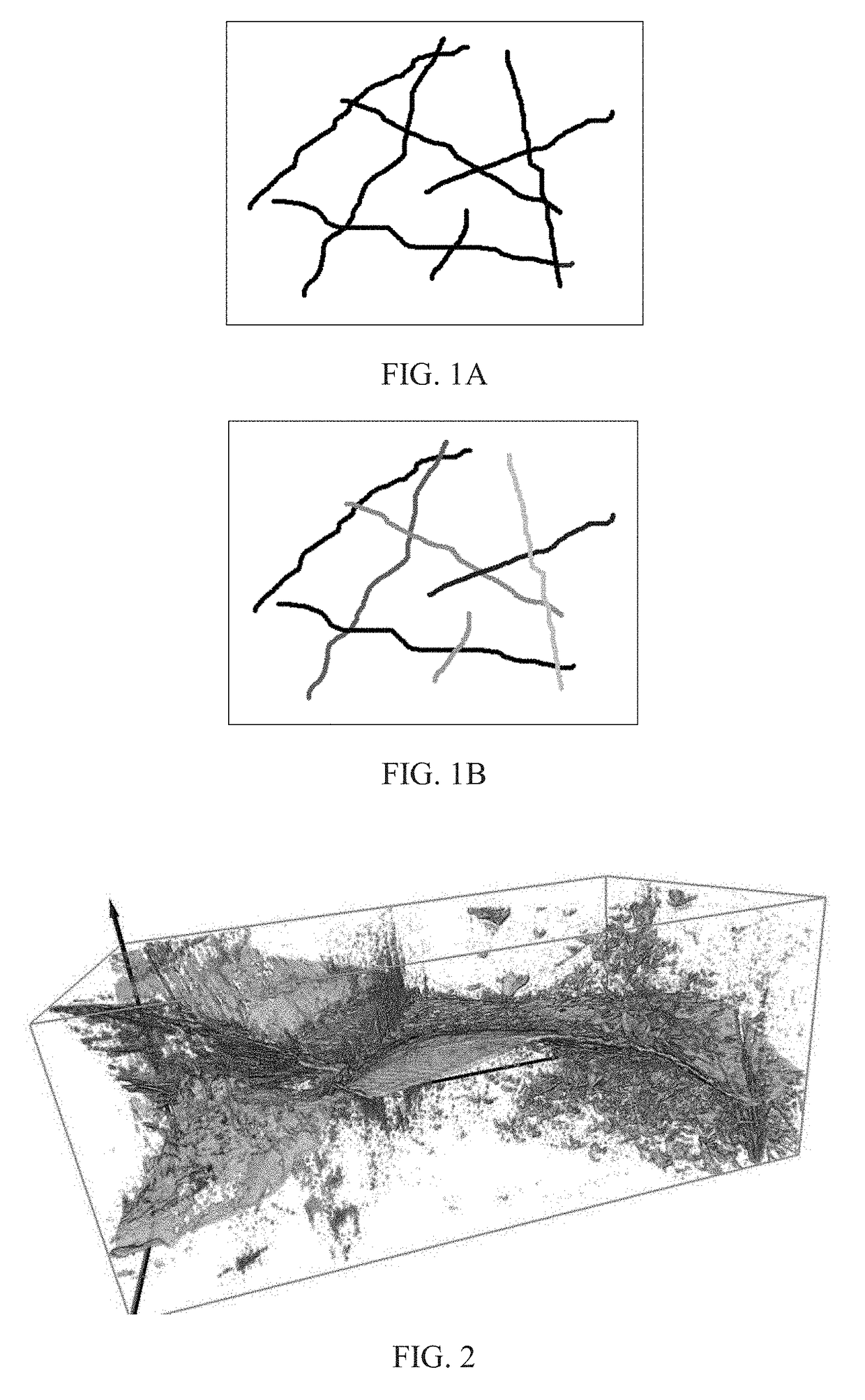
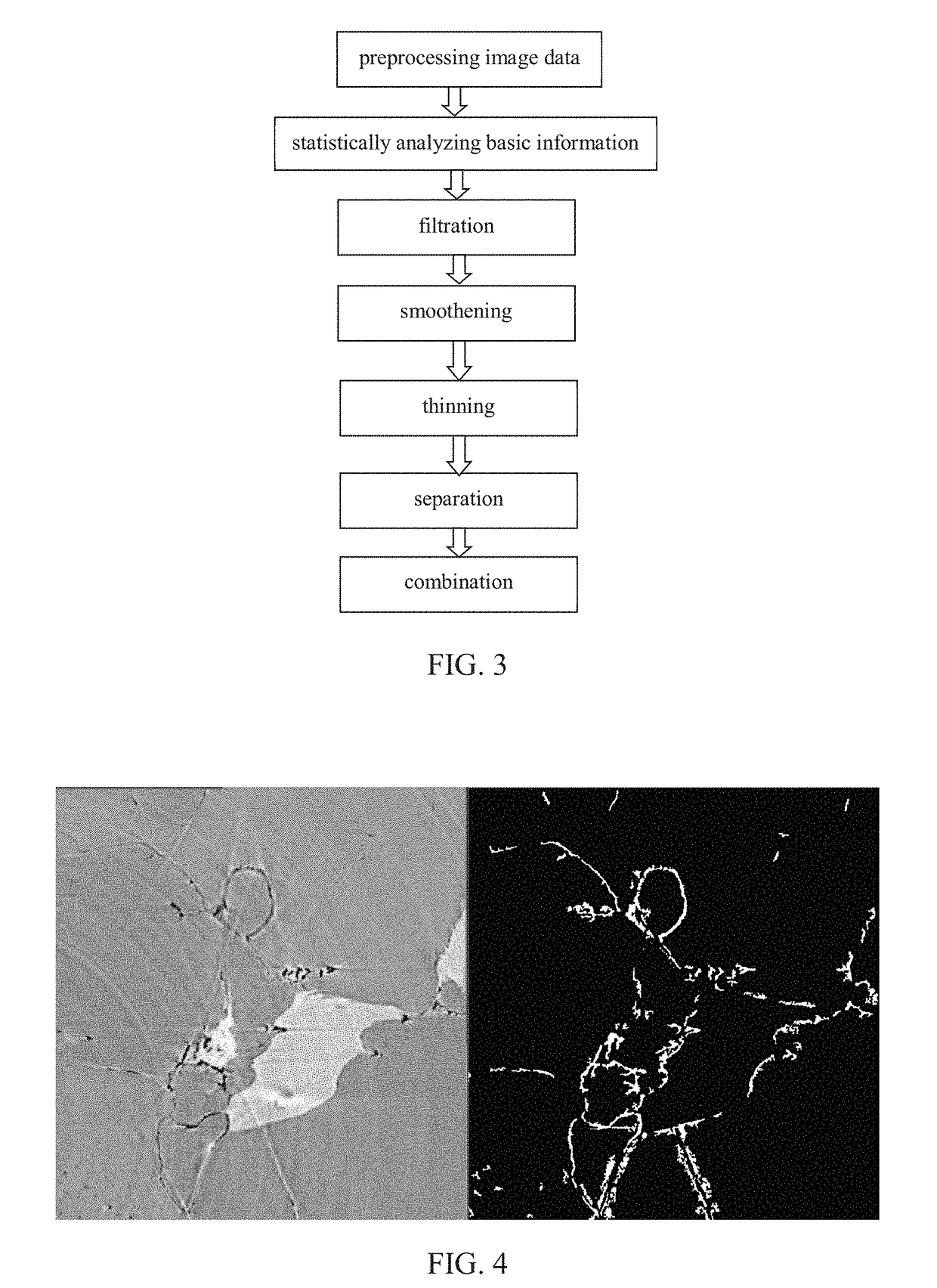
The present invention discloses a method of separating, identifying and characterizing cracks in 3D space, which processes as follows to a volumetric image, so as to perform the separation, identification and the characterization of the cracks in the 3D space: 1) preprocessing digital image; 2) statistically analyzing basic information of the digital image: the basic information of the image includes porosity, connectivity of each pore, statistics of pore size, and position, size, orientation and anisotropy of each pore-structure; 3) filtration: removing non-crack structure in the image; 4) smoothening: smoothening and mending the image; 5) thinning: thinning the void structure into a thickness d (d can be any value, but more appropriate to be 2 to 3 voxels generally) in a direction with shortest extension in the 3D space; 6) separation: separating intersected cracks in a crack network by breaking the connections; 7) combination: combining those elongated cracks that are disconnected in the last step, merging tiny structures that are formed during the separation to a nearby large cluster, and restoring cracks to the thickness before thinning, and eventually giving out the characterization of the cracks. In the following expression, the wording “void” is used more, emphasizing the “empty” gap in the image rather than the rock solid. In this patent application, it is mainly for the case where the void appears in a state of crack, not excluding the case where the void appears in a state of small pore.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
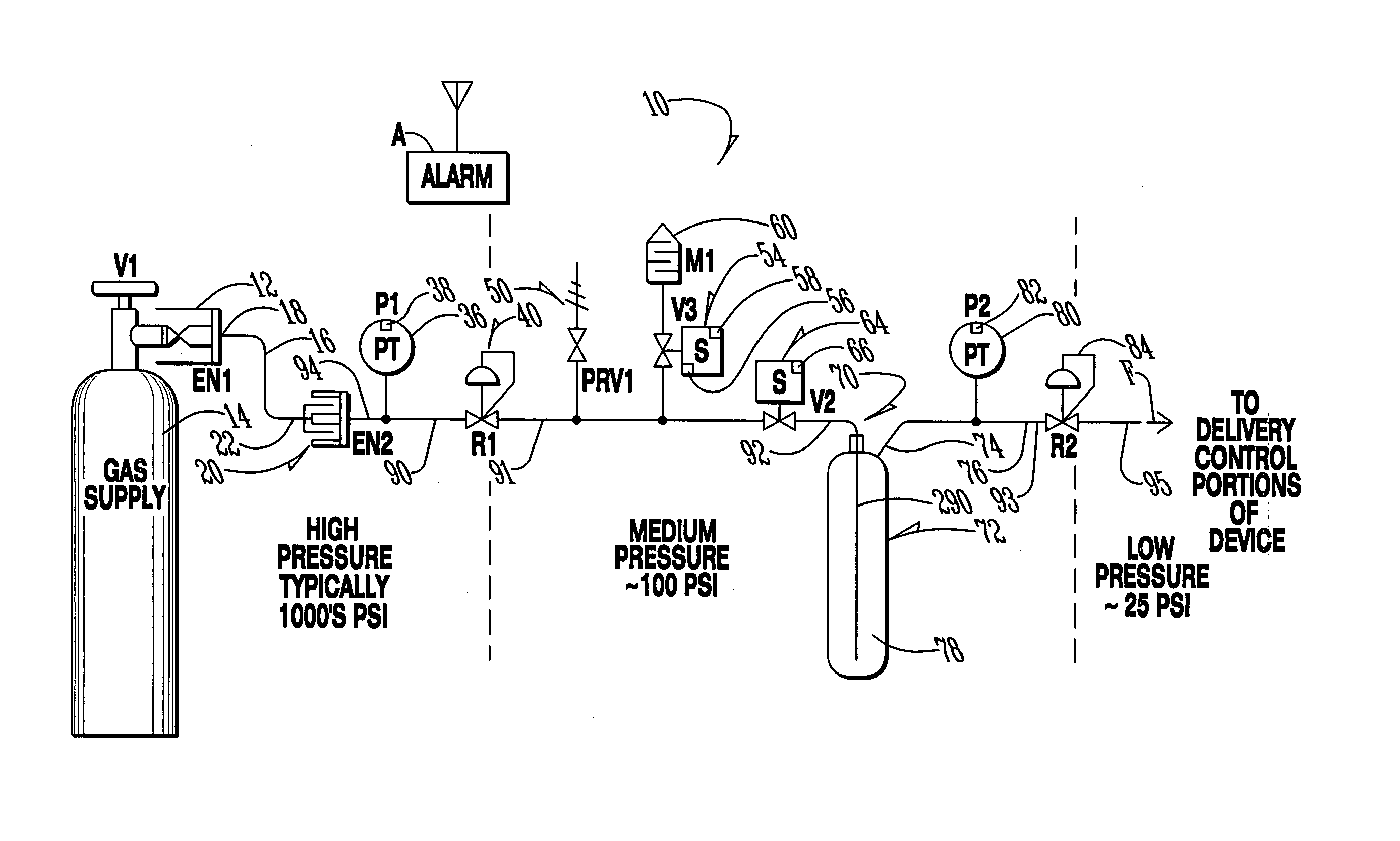
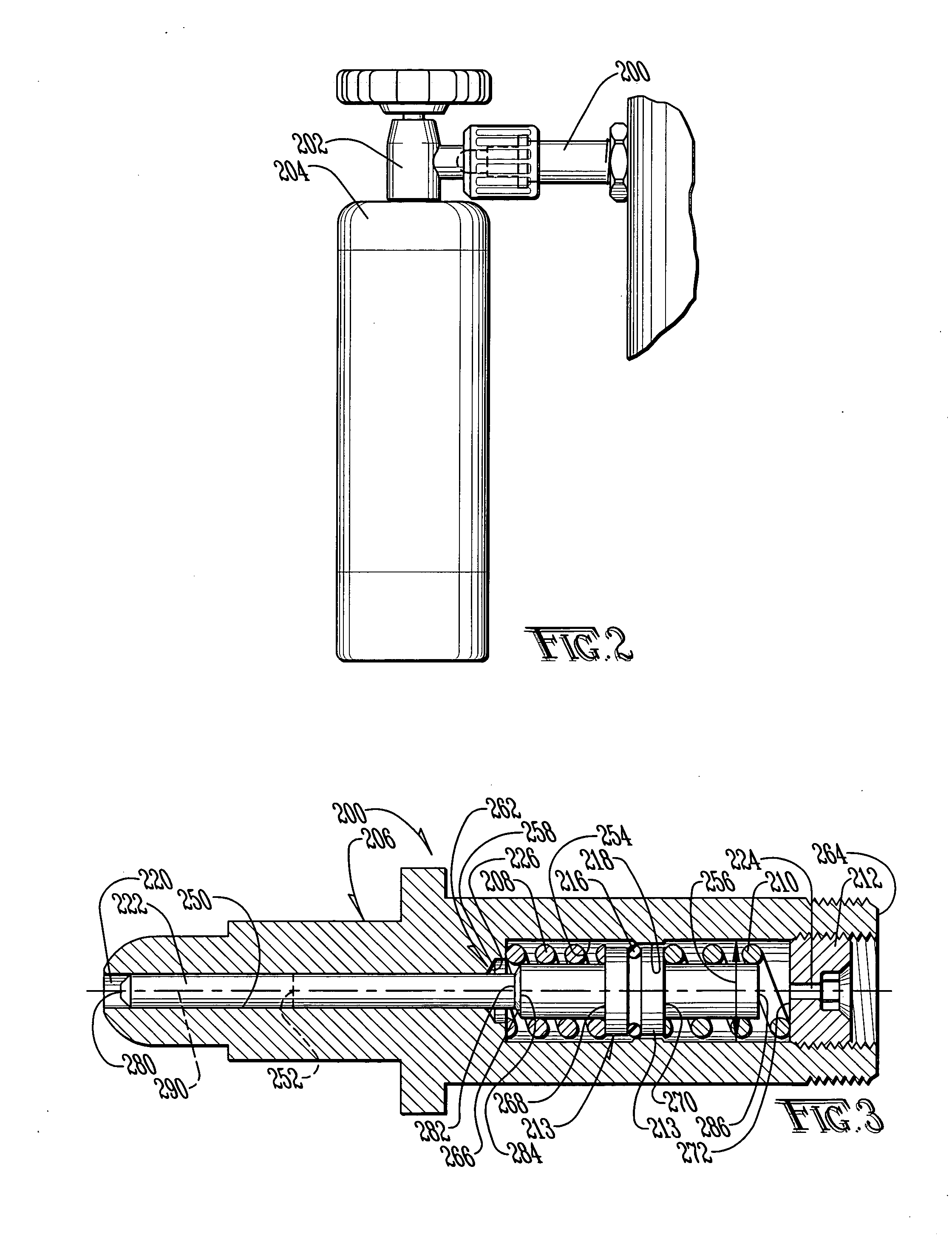
Method for purging a system for use in administrating therapeutic gas to a patient
InactiveUS20050004511A1Efficiently effectively purgingThe process is simple and effectiveRespiratory masksMedical devicesMedicineSystem usage
A system that controls and manages administration of a therapeutic gas, such as NO, O2, or the like, to a patient is purged using a method that conserves purge gas. The system was fully disclosed in U.S. patent applications Ser. No. 09 / 688,229, filed on Oct. 16, 2000 and Ser. No. 10 / 351,755 filed on Jan. 27, 2003 and includes an equalizing valve and a reservoir.
Owner:PULMONOX TECH
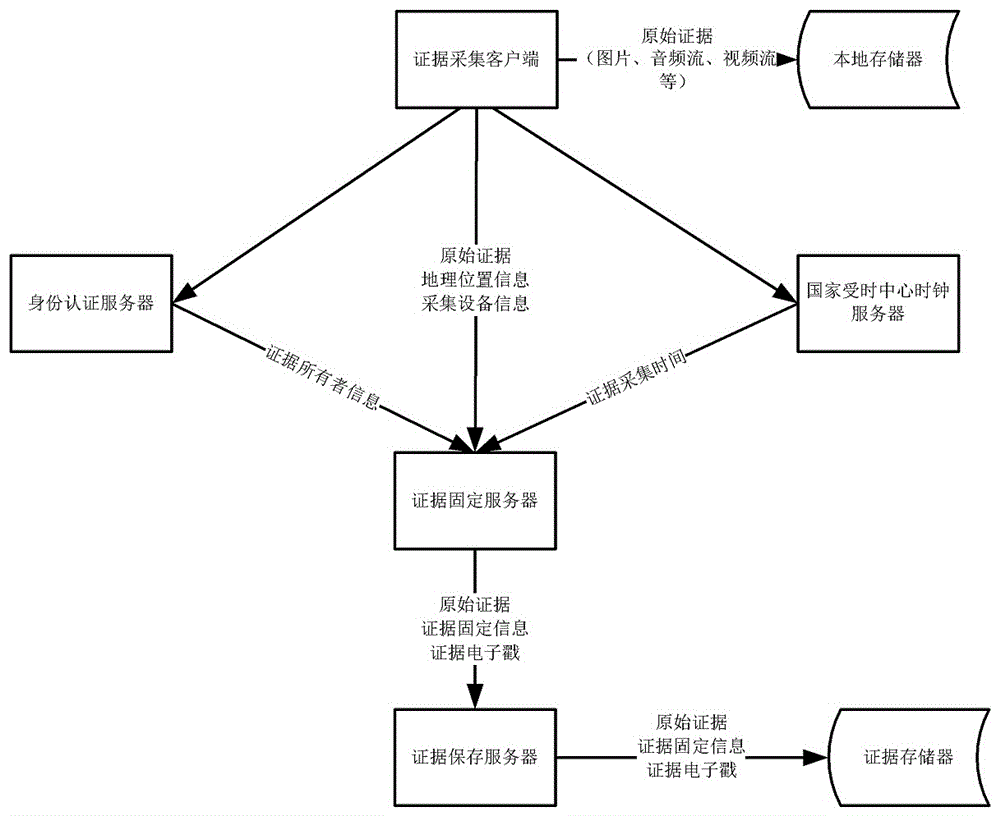
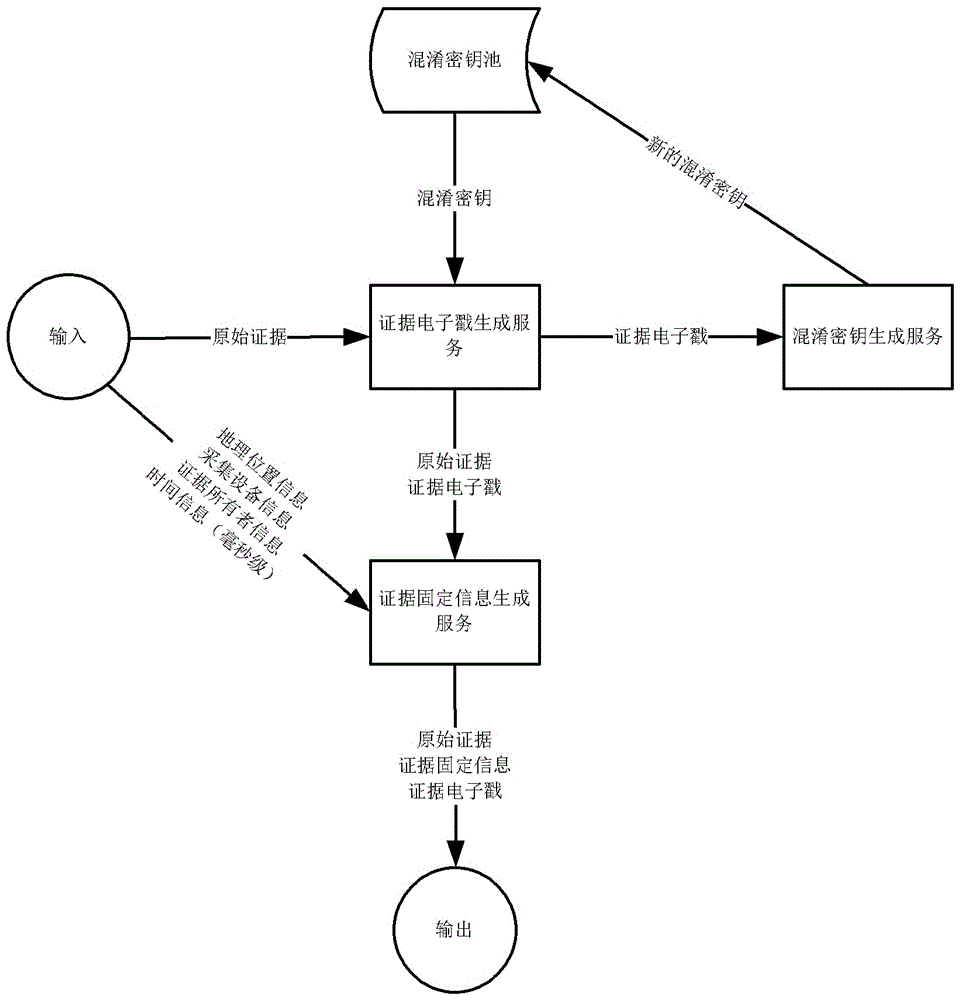
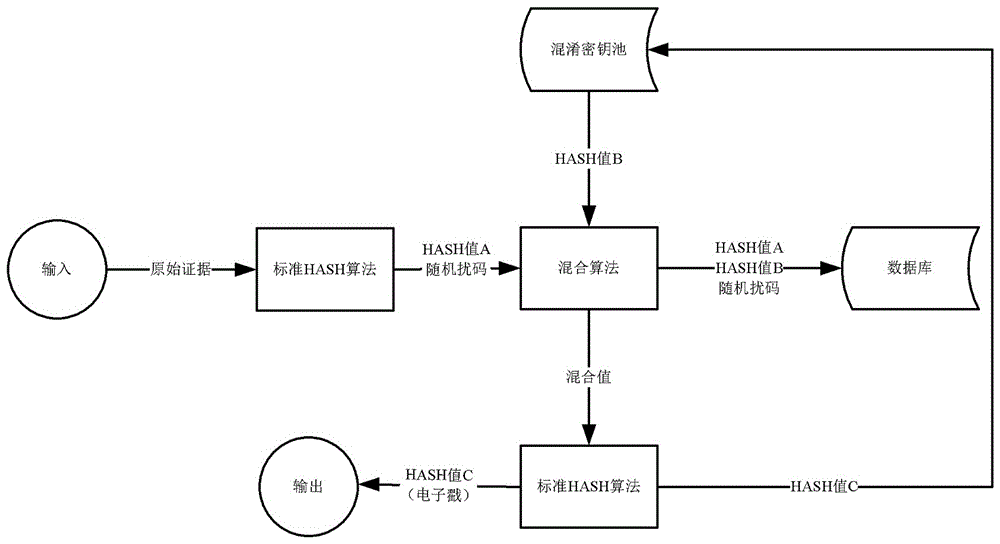
System and method for real-time collection and fixing of electronic evidence
InactiveCN106657049AIncrease the difficulty of crackingLarge amount of informationClosed circuit television systemsData acquisition and loggingReal time acquisitionPatent application
The invention discloses a method for real-time collection and fixing of an electronic evidence. The method comprises the following steps: a client collects an original evidence in a real-time manner through collection equipment; the client uploads the original evidence in a real-time manner to an evidence fixing server; and the evidence fixing server generates an electronic evidence stamp according to the original evidence, and saves the electronic evidence stamp in a storage device. The invention further discloses a system for real-time collection and fixing of the electronic evidence, which comprises the collection equipment, the evidence fixing server, an evidence saving server, and the storage device. The method and system provided by the invention has the advantages that the idea of ''real-time collection and real-time fixing'' is adopted to ensure that the electronic evidence, if tampered after the collection, cannot be successfully validated, so that legal effects of the electronic evidence can be effectively guaranteed.
Owner:重庆法记云网络科技有限责任公司
Apparatus to control output of a welding machine
InactiveUS20020144979A1Guaranteed uptimeImprove methodElectric discharge heatingArc welding apparatusPower flowControl theory
The mechanism which is the subject of this patent application is centered on a control device adapted to facilitate the control and regulation of the electrical current or the gaseous intake and mixture for a welding machine, thereby regulating the output of the welding machine, such mechanism including a foot-operated pedal member, which, in turn, is mechanically linked to electromechanical means activated by radio transmission means to regulate such electrical current input or the gaseous output.
Owner:FEDORCAK MICHAEL R
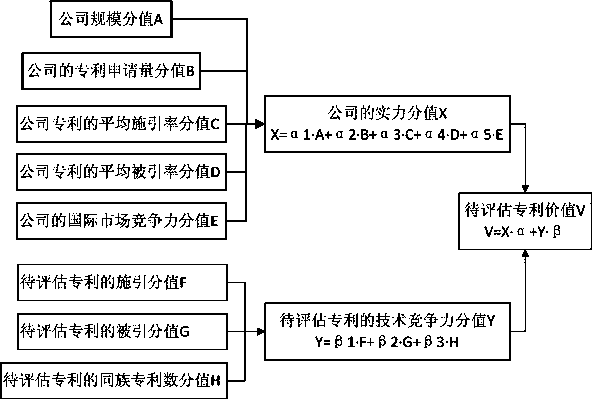
Patent value assessment method
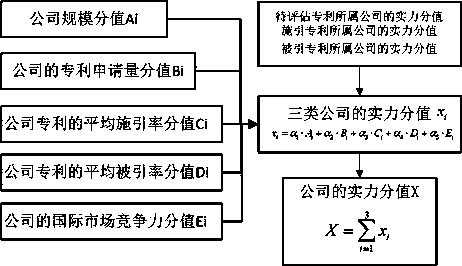
The invention discloses a patent value assessment method. The influences on the patent value from the strength value of a patentee company and the technical competitiveness value of a patent to be assessed are considered respectively, and then weighted summation is carried out; when the strength value of the patentee company is calculated, the factors of the company scale value, the application number of patents of the company, the average cited rate of the patents of the company, the average citing rate of the patents of the company, the average same-class patent number of the patents of the company and the like are included; the strength of the company owning the patent right of the patent citing the patent to be assessed and the strength of the company owning the patent right of the patient cited by the assessed patent are considered; when the technical competitiveness value of the patent to be assessed is calculated, the number of the cited patients by the patient to be assessed, the number of times of being cited by patents and the number of same-class patents of the patient to be assessed are considered. Comprehensive and accurate searching based on the DWPI database is carried out, the value of each patent in the DWPI database can be calculated, high effectiveness is obtained, and the patent value assessment method can be applied to assessment of patent value.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
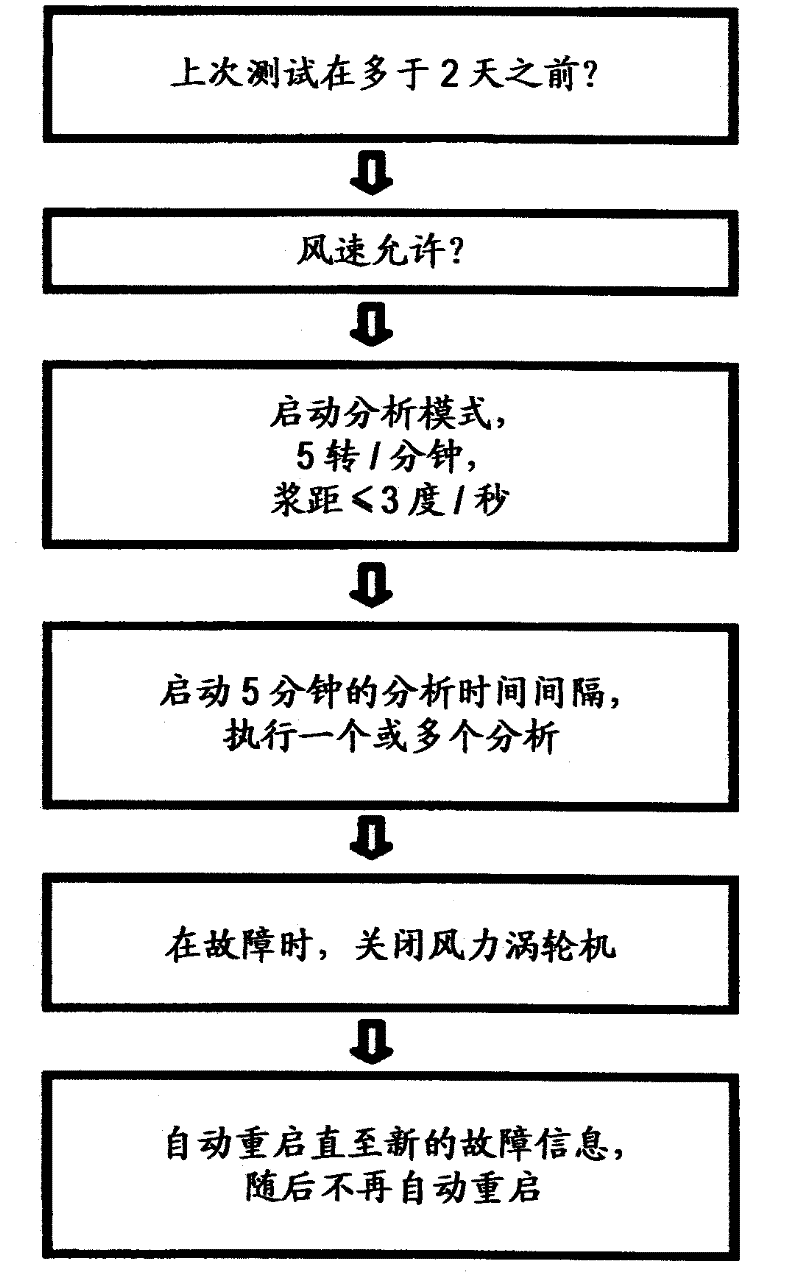
Method for monitoring wind turbines
Owner:SUZLON ENERGY LTD
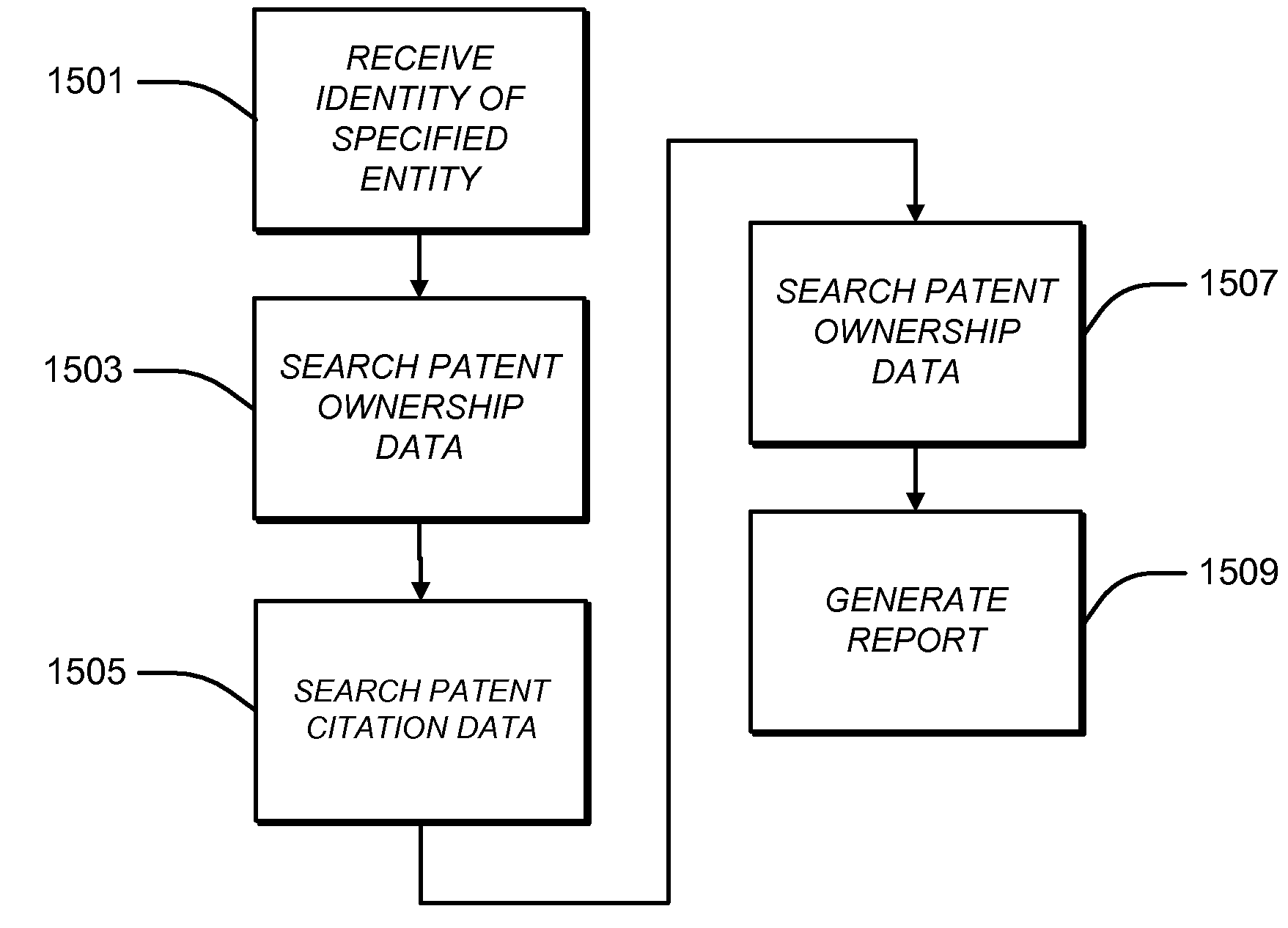
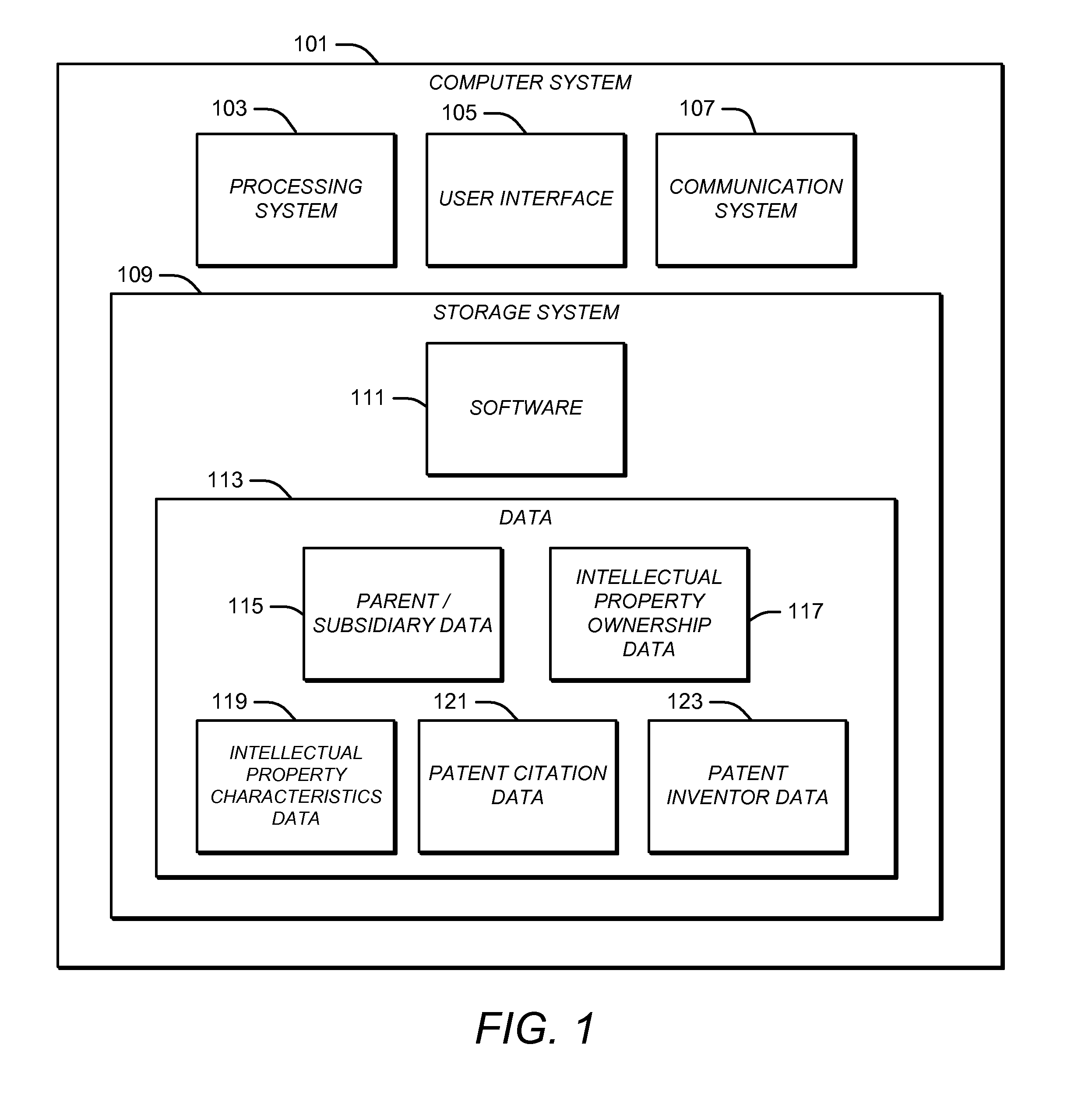
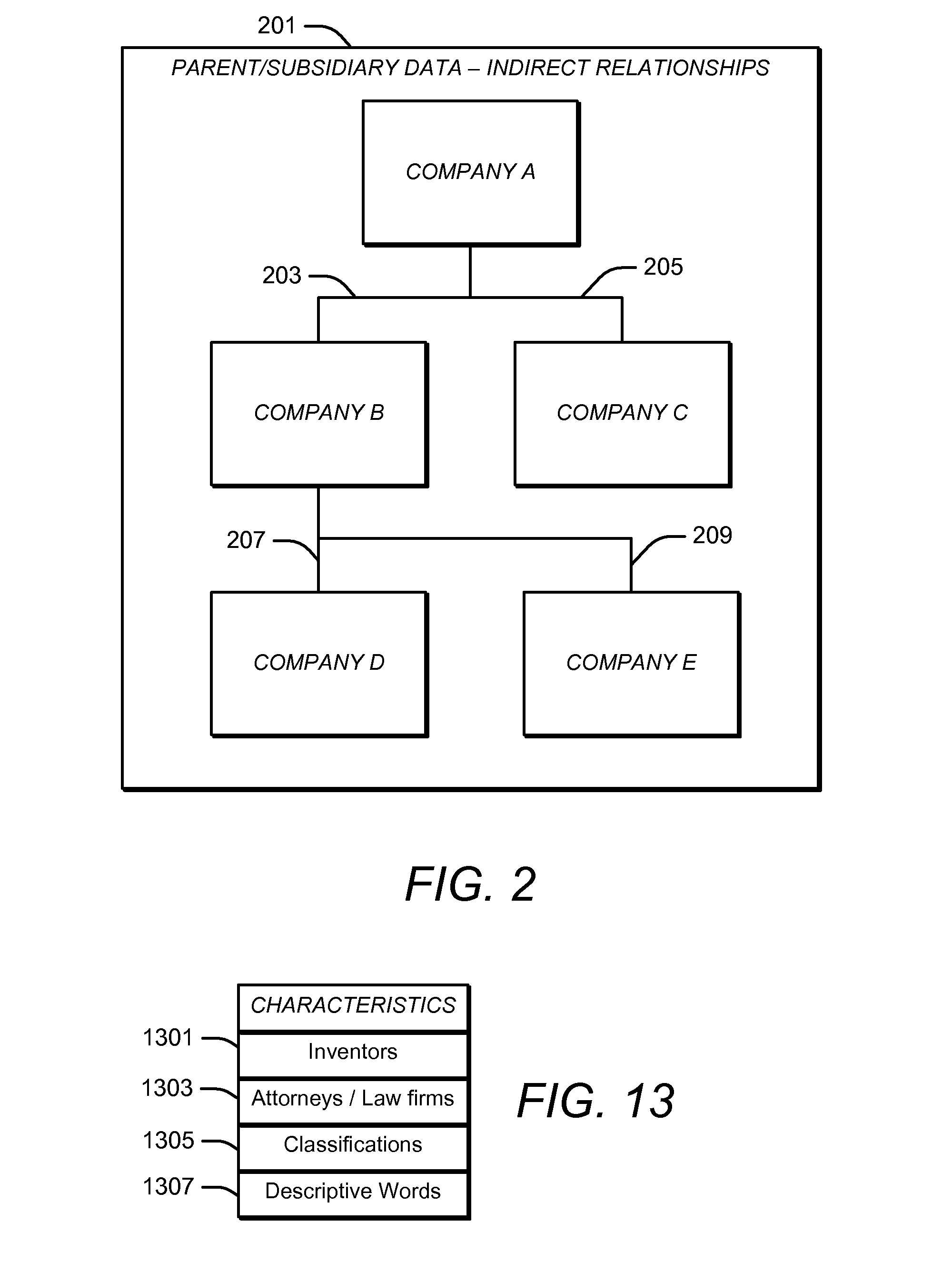
Automated Identification of Competitors
A computer system may be configured with software that performs an automated process for identifying likely competitors of a specified entity. The process may include receiving information indicative of the identity of the specified entity. The process may include searching patent ownership data for patents and / or patent applications that are owned by the specified entity. The patent ownership data may be indicative of the identity of owners of patents and / or patent applications. The process may include searching patent citation data for patents and / or patent applications that are cited by and / or that cite to the patents and / or patent applications that are owned by the specified entity. The patent citation data may be indicative of the identity of patents and / or patent applications that cite to or are cited by other patents and / or patent applications. The process may include searching the patent ownership data for the owners of the cited and / or citing patents and / or patent applications and generating a report identifying the owners of the cited and / or citing patents and / or patent applications.
Owner:MDB CAPITAL GROUP
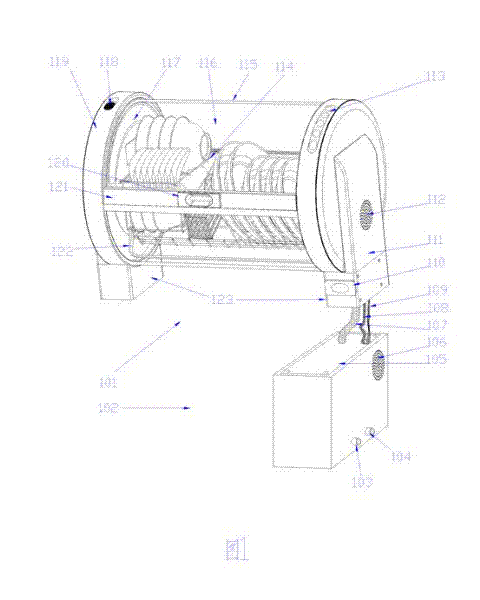
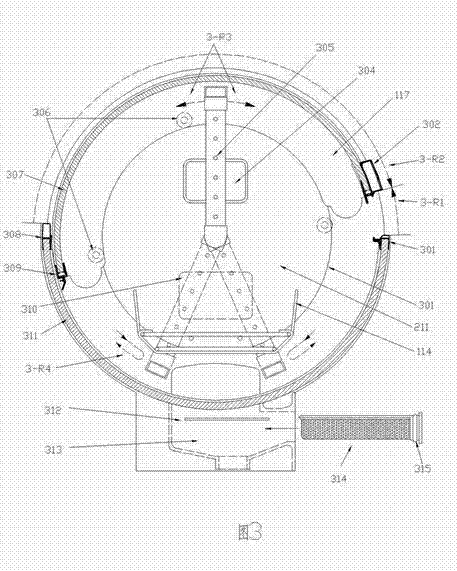
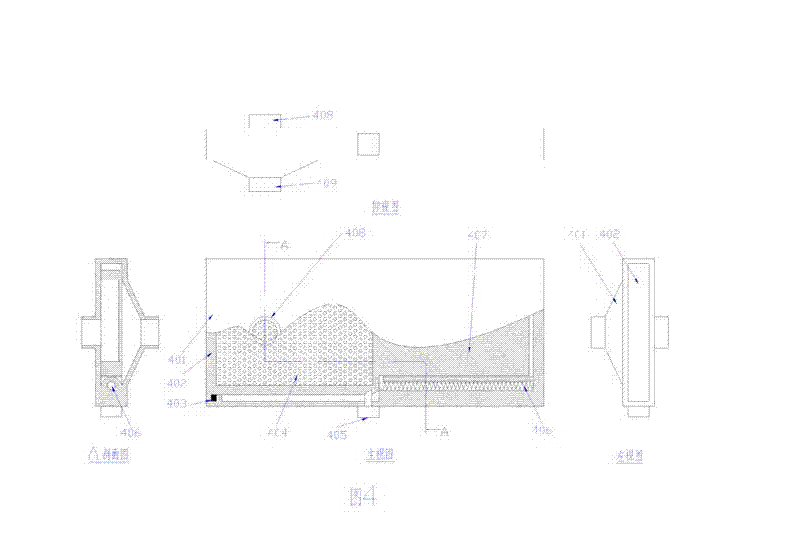
Horizontal table type dish washing machine
InactiveCN102362804ATo achieve the purpose of useDrying solid materials with heatTableware washing/rinsing machinesSynchronous motorWater circulation
The invention belongs to a divisional application of the patent application of a split type disinfection dish washing machine with the application number being 200810187050.X. A washing cavity of the horizontal table type dish washing machine disclosed by the invention consists of an embedded push-pull door and a transverse washing groove with an upward groove opening, wherein the embedded push-pull door can retract into the washing groove so that a washing box is opened, or the arc-shaped push-pull door is rotated out of the washing groove to form the washing cavity with the washing groove so that the washing box is closed. A dish rack is arranged in the washing cavity, the dish rack is fixed at fixing points arranged at the two side surfaces of the washing cavity for erecting the bottom of the washing cavity, and the water circulation flowing and the push-pull door embedding are convenient. A cross arm jet pipe is arranged in the washing cavity and is in an n or m shape, the high-pressure water inlet end of the cross arm jet pipe is connected with a rotary sealing joint, the other end of the cross arm jet pipe realizes the transmission connection with a synchronous motor, and the synchronous motor drives the cross arm jet pipe to realize the reciprocating rotary spraying around the dishes in a way of spraying in a large surrounding range.
Owner:陆丰科
Method for creating a data file
InactiveUS20060277217A1Easily decideNew dataFile/folder operationsSpecial data processing applicationsData fileElectronic equipment
A function for creating a new file by editing and synthesizing one or more data files such as pictures, movies, and music, is very promising function and provides a new possibility to the portable electronic devices. However, in the existing technology, the user may be bothered with selecting items for a new data file from a lot of items stored in the portable electronic device. In this patent application, an invention that may be used for easy-selection of items in such cases will be disclosed.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Efficient Multiple Prediction In Two and Three Dimensions
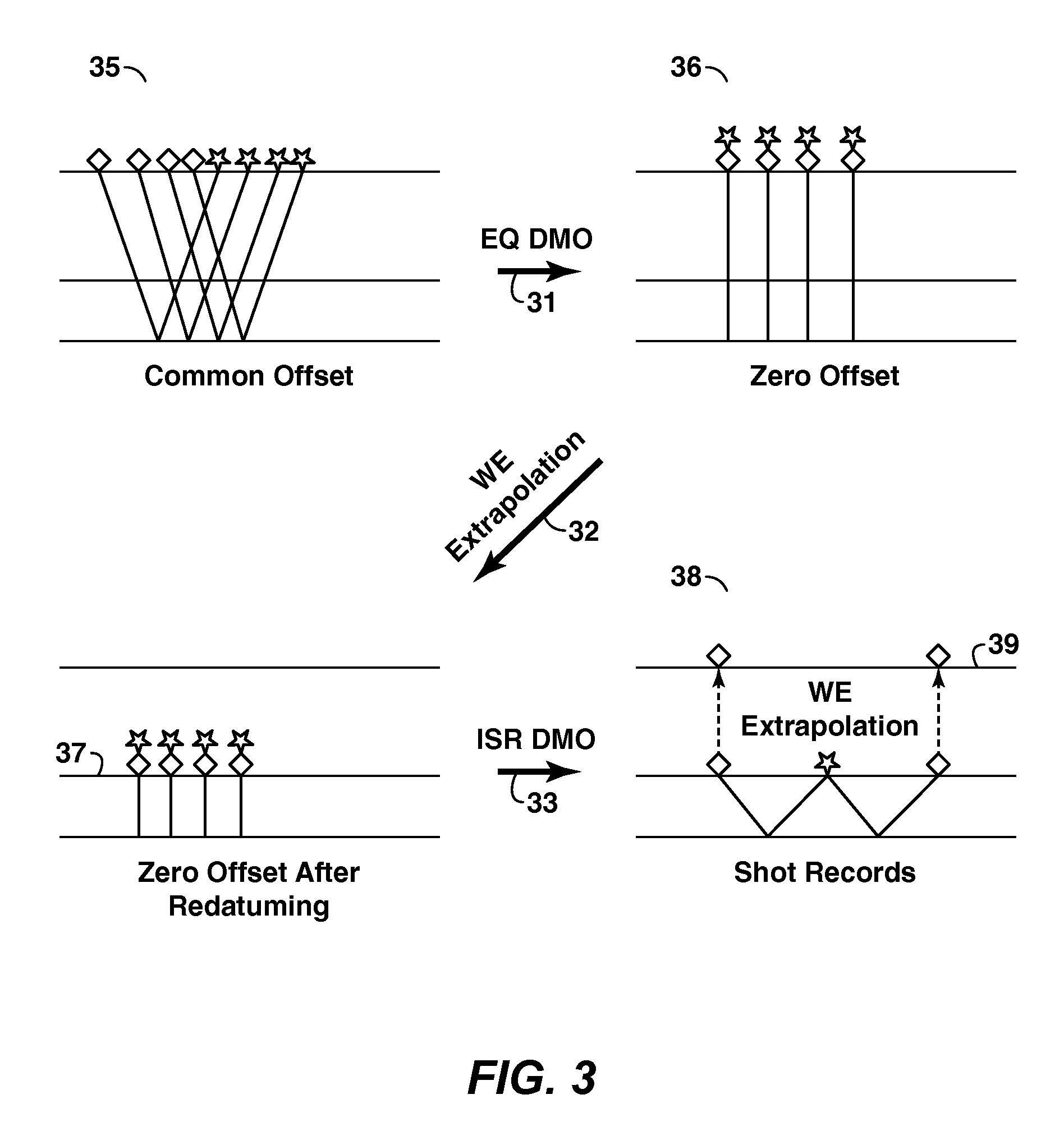
A method is disclosed that uses (a) source-receiver reciprocity and (b) a method such as ISR DMO (U.S. Patent Application Publication No. 2006 / 0098529) that allows reconstruction of densely sampled gathers at arbitrary surface locations, to efficiently predict multiple reflections, either surface related or interbed multiples, in seismic data. For each reconstructed gather and each output (field) trace, two traces are extracted corresponding to the field source and receiver positions of the output trace, then they are convolved and the convolution result is added (summed) to that obtained by applying this procedure to previously reconstructed gathers. The efficiency results from the fact that the convolutions are performed by looping over all traces for each “bounce” point, with the outer loop being over bounce points. Once all the reconstructed gathers are processed, multiple predictions are obtained for the whole survey by conventional means.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Sgc stimulators
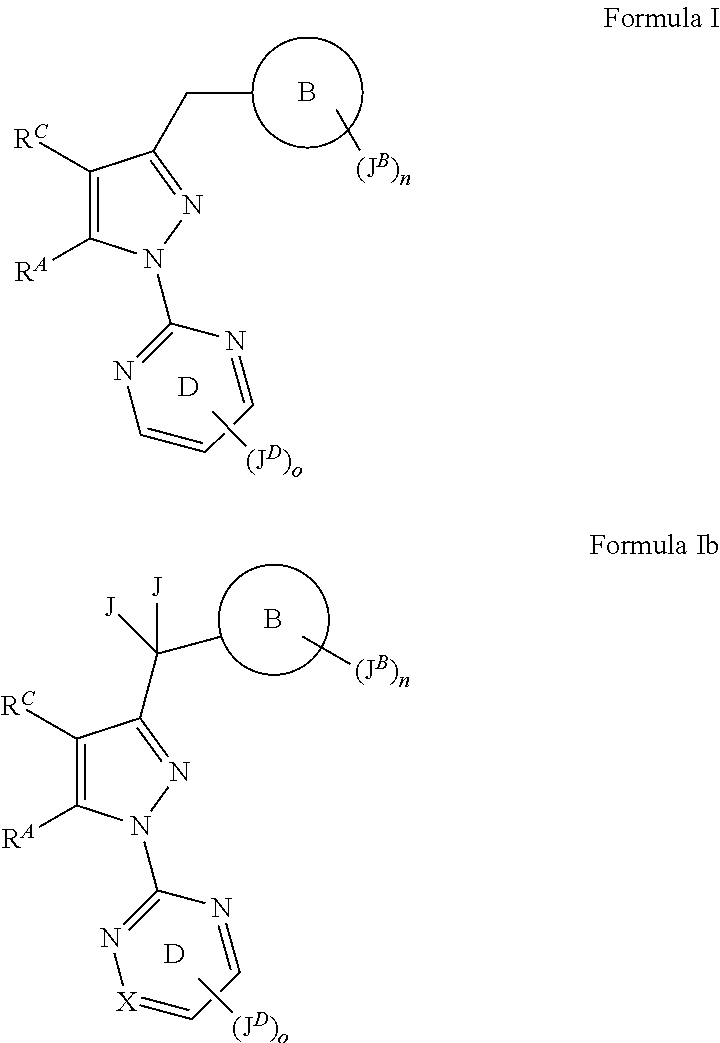
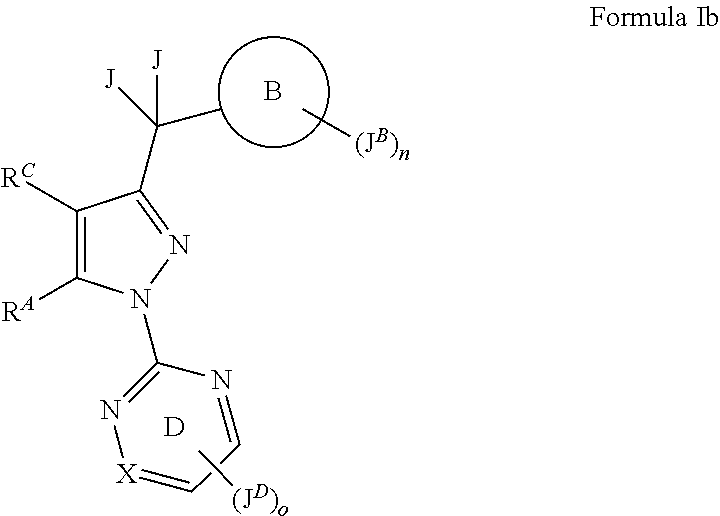
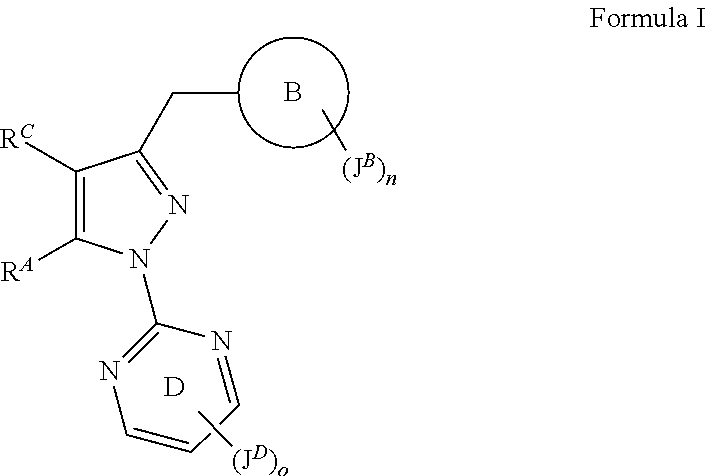
The present patent application discloses at least the compounds according to Formula I or Formula Ib shown below, or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof,wherein ring B, JB, n, JD, J, o, X, RC and RA are as described herein.
Owner:CYCLERION THERAPEUTICS INC
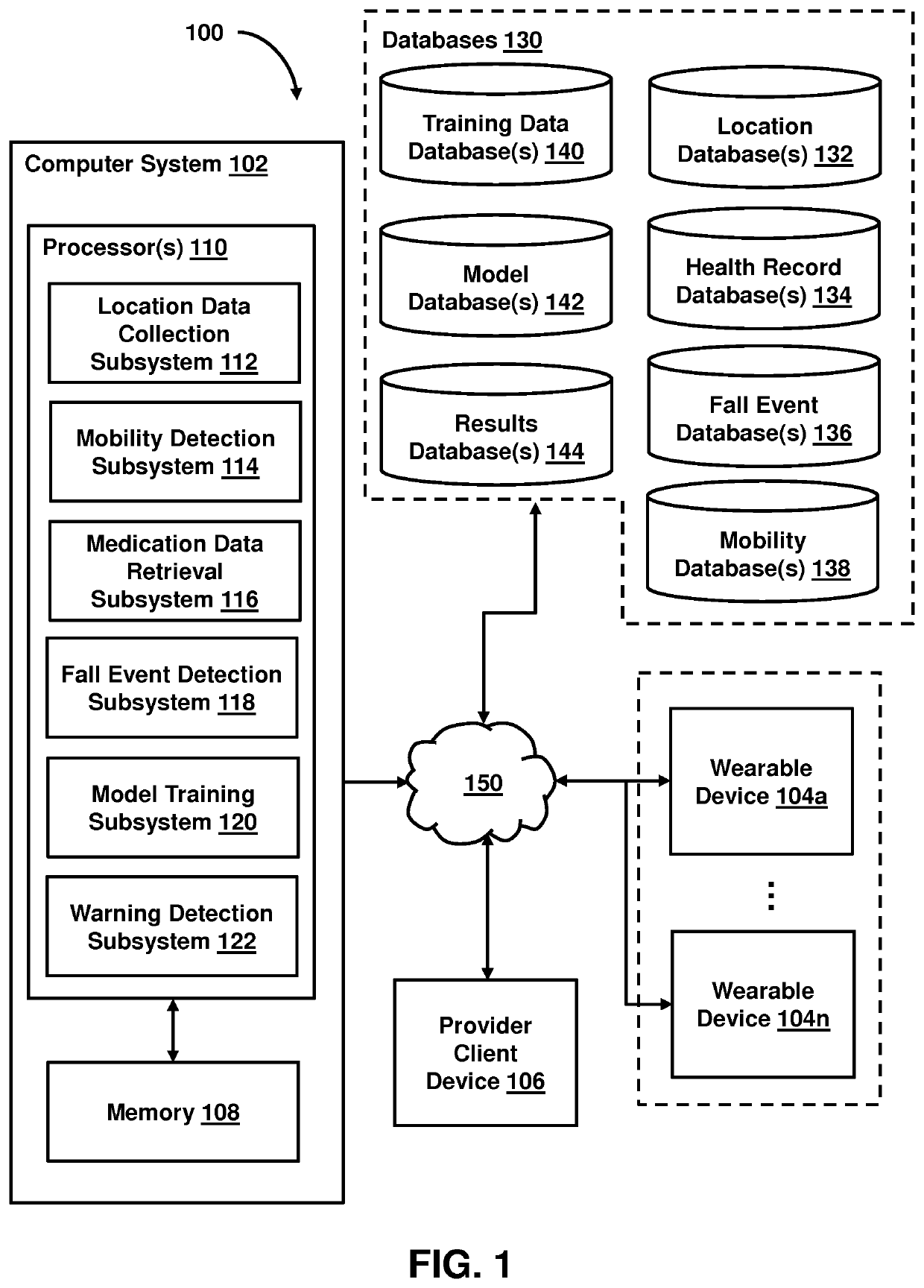
System and method for detecting adverse medication interactions via a wearable device
PendingUS20210358637A1Easy to trainPhysical therapies and activitiesMedical data miningMedication interactionPharmaceutical drug
The present patent application relates detecting adverse medication interactions using a wearable device. In some embodiments, fall event data of a patient is obtained, the fall event data including a set of fall events experienced by the patient during a first time period. Medication data associated with the patient is also capable of being obtained. The medication data indicates a set of medications taken or prescribed to be taken by the patient during the first time period. Training data is configured to be generated for a prediction model based on the fall event data and the medication data, and the training data is capable of being provided to the prediction model. The prediction model is configured to estimate, based on the training data, a dependency between one or more medications and a risk of experiencing a fall event.
Owner:LIFELINE SYST INC +1
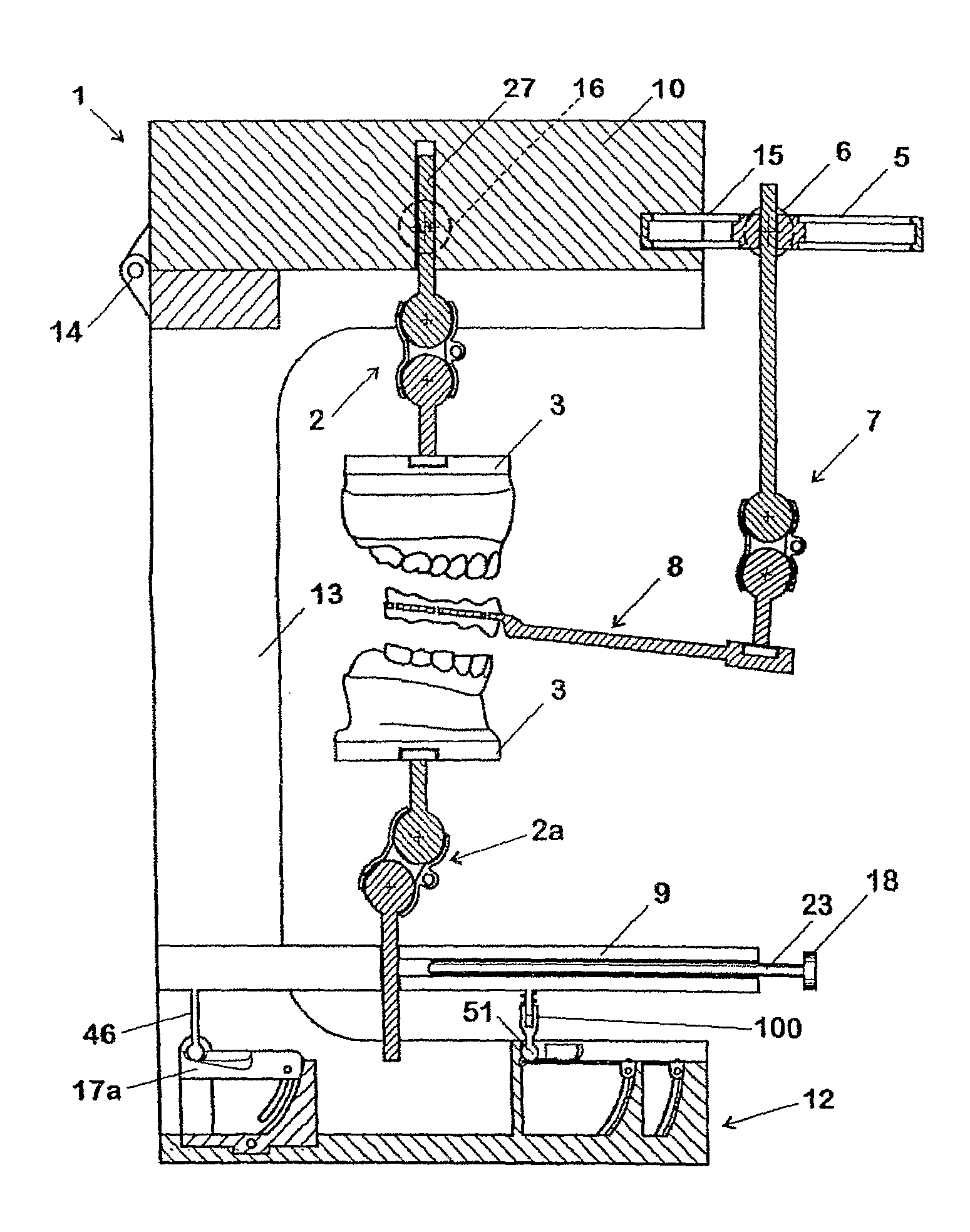
Dental articulator for positioning the arcades without the use of plaster
InactiveUS20120295219A1Improve fidelitySlow dynamicDental articulatorsEducational modelsDental ArticulatorsCombined use
This patent application refers to a mechanical equipment that, when used in conjunction with a device to determine the position of the superior arcade of the patient, based on landmarks on the skull of the same, allows accurate reproduction of the position of the dental arches, represented by plaster models and simulation of mandibular movements. These models are connected to the equipment, through a unique positioning mechanical system, eliminating the use of plaster to fix the same. The patent, now required, includes features of the equipment currently called “articulator” and “face-bow” and adds new features in an unprecedented and innovative way. The set of the equipment is light weighted, and easy to handle, allowing up to 50% reduction in the time required for assembly and adjustments when compared to the equipment market, and its guide system makes the reproduction of mandibular movements very accurate, avoiding errors in diagnosis and treatment.
Owner:MONTEIRO GERAS JORGE AVELINO +1
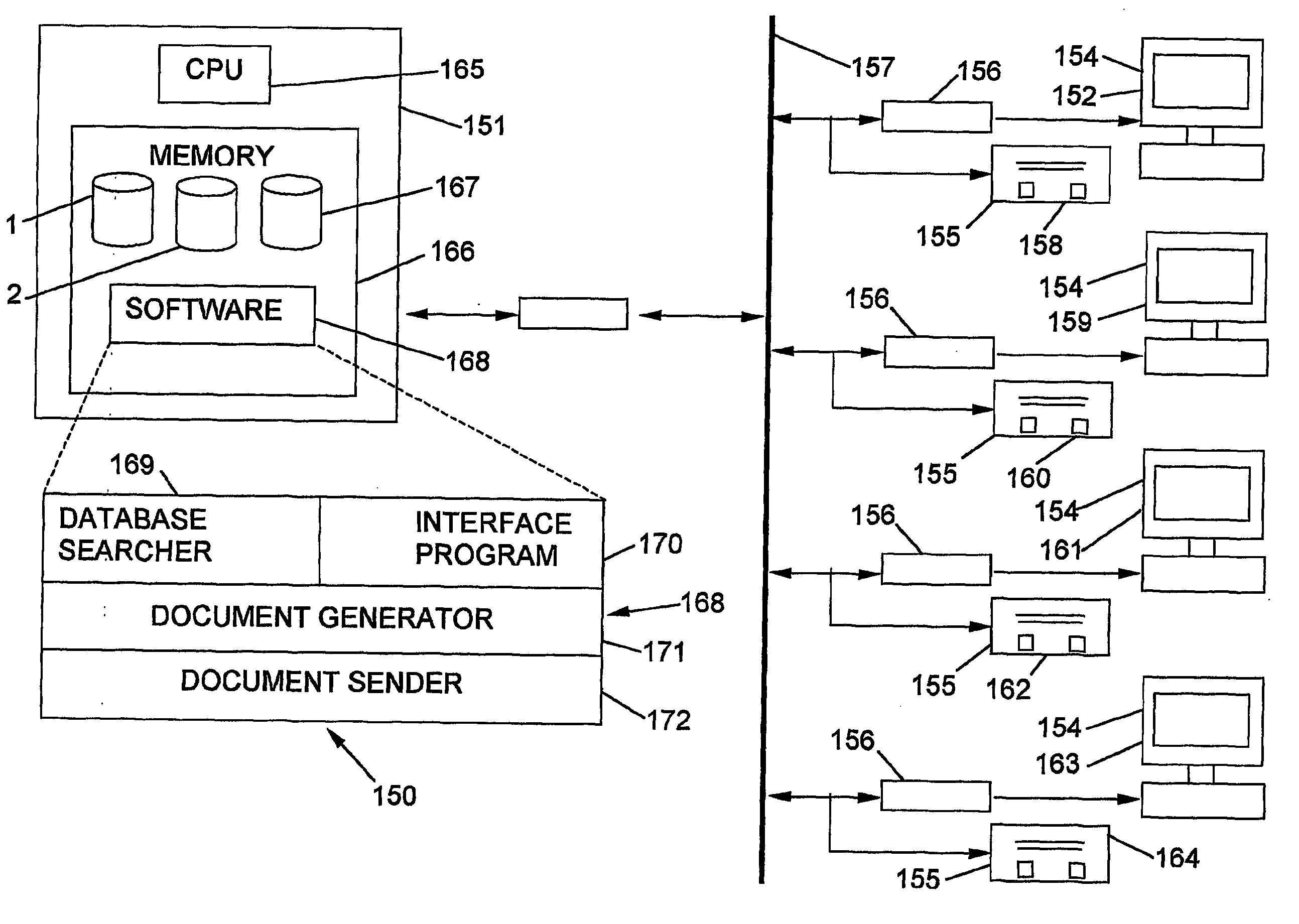
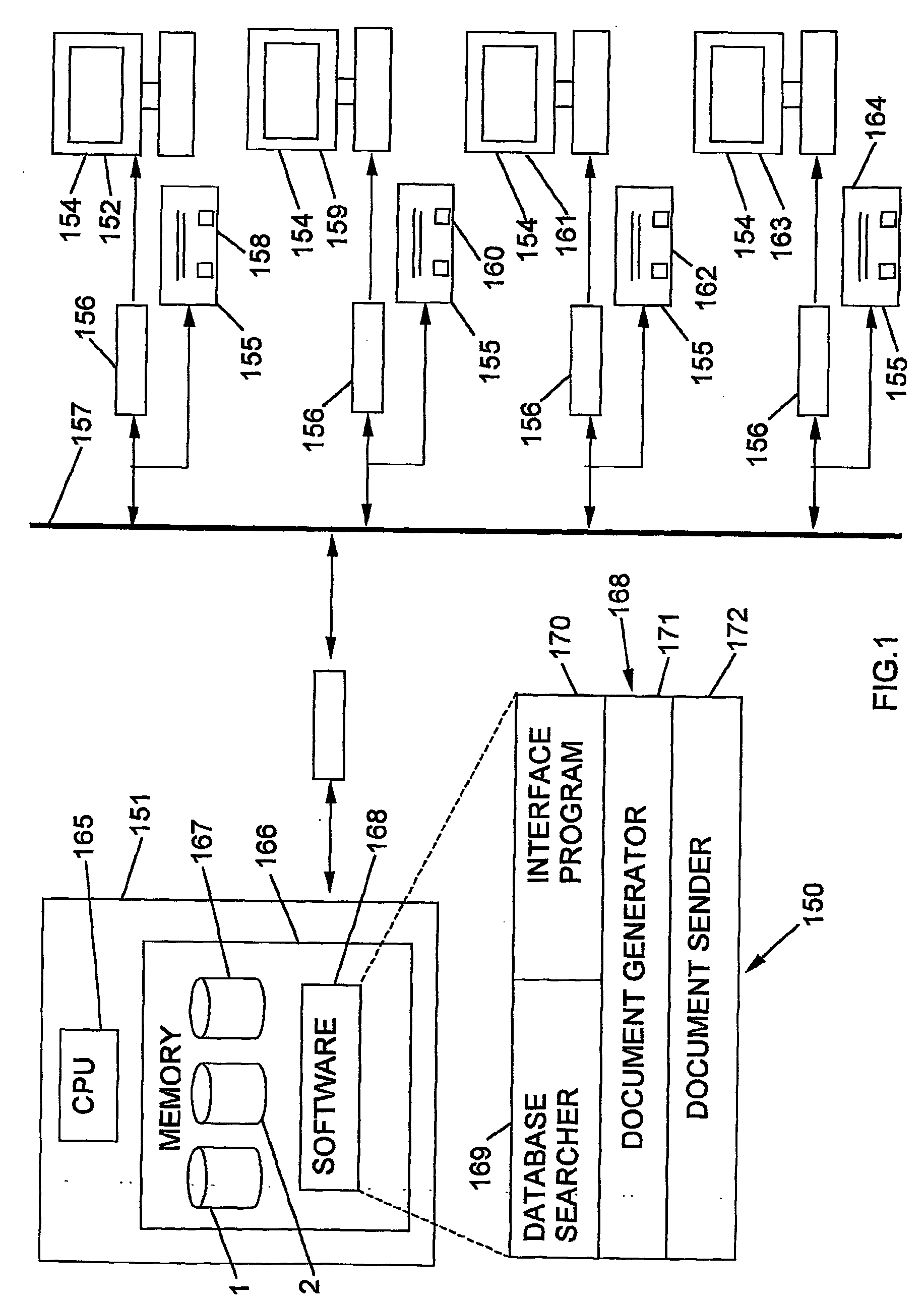
System and method of attracting and lodging pct national phase applications
InactiveUS20040030673A1Digital data processing detailsOffice automationDocumentation generatorComputerized system
A computer implemented system and method of attracting and lodging PCT national phase patent applications. The computer system for lodging a PCT national phase application with a patent office has an interface which is adapted to receive a national phase filling instruction. The interface is in communication with a document generator which is adapted to generate a national phase entry message. The generator is in communication with a document sender which is adapted to send the national phase entry message to the patent office. When the interface receives a national phase filing instruction the document generator generates the national phase entry message and the document sender sends the message to the patent office thereby lodging the PCT national phase application.
Owner:INOVIA HOLDINGS PTY LTD
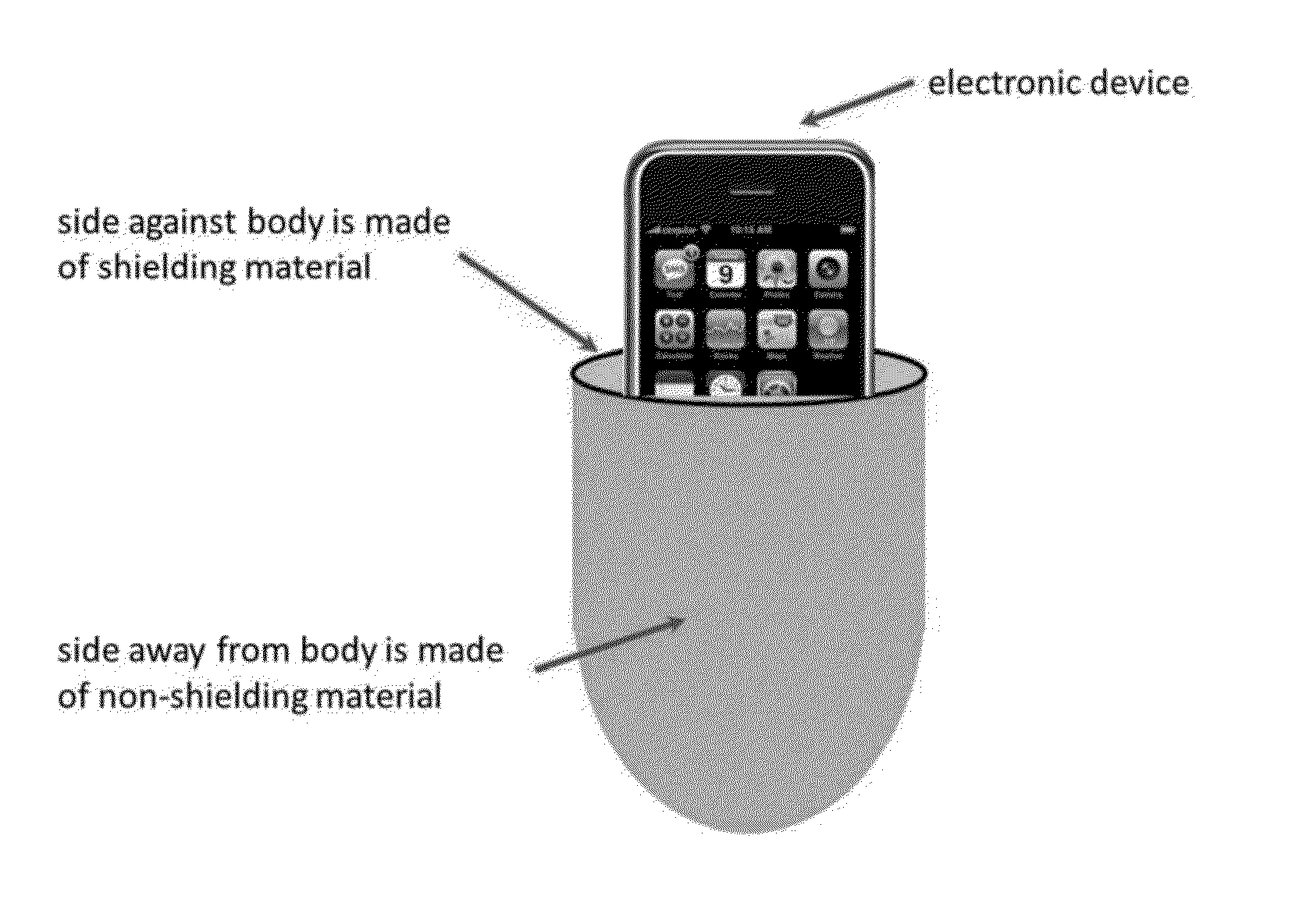
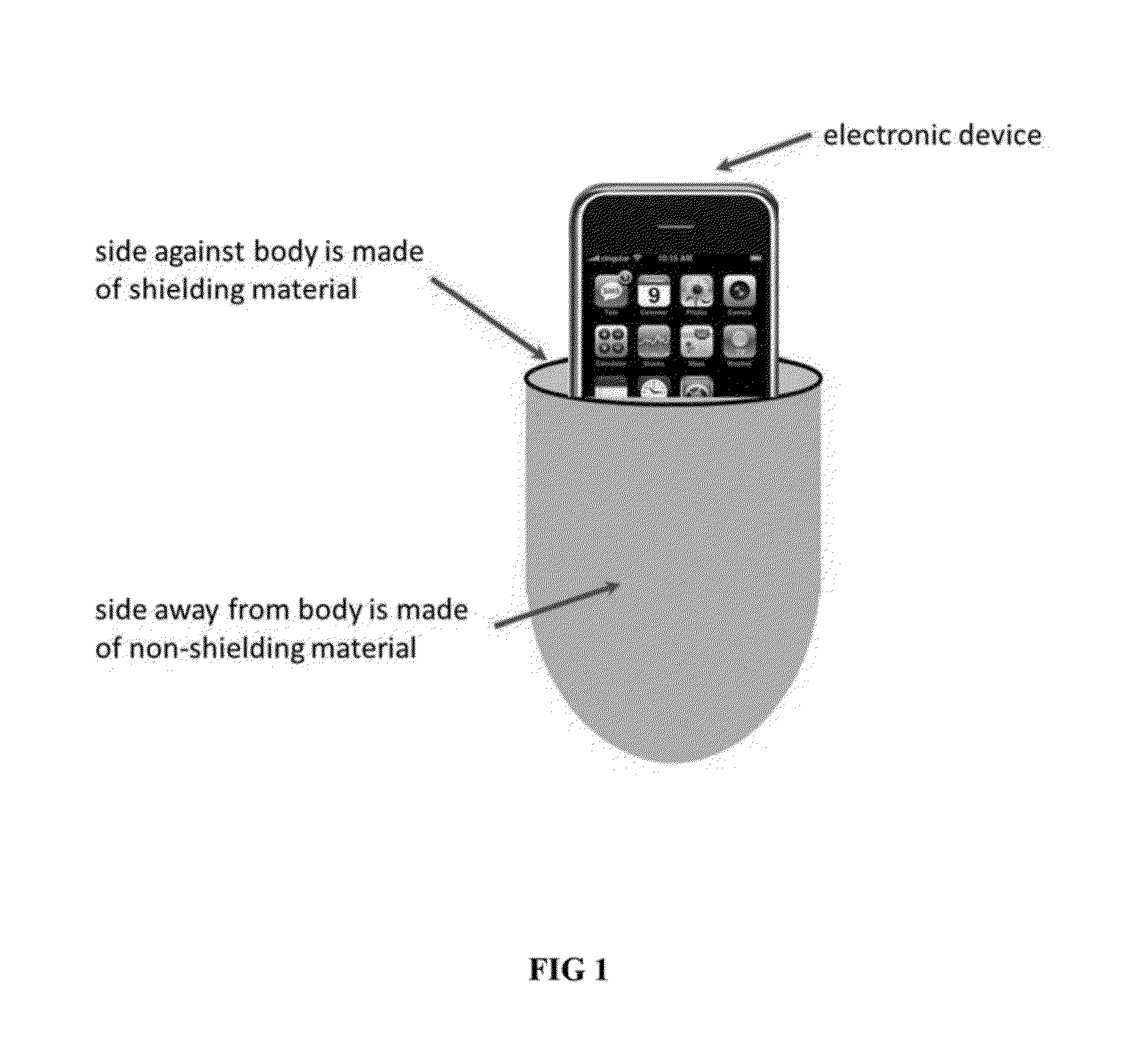
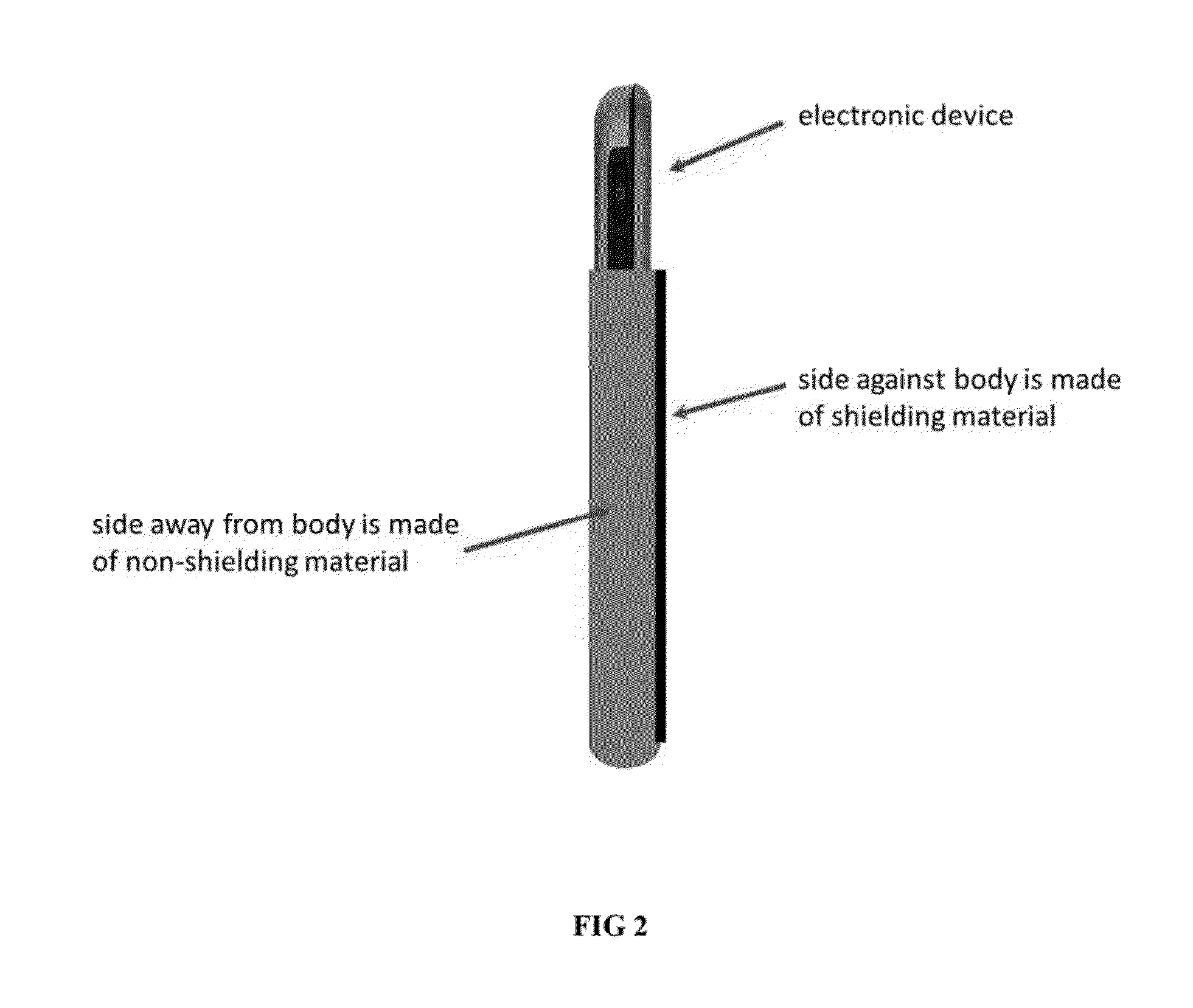
Thin Pocket Liner and Pad for Protection Against Electromagnetic Exposure when Carrying and/or Using Electronic Devices
InactiveUS20130220694A1Reduces human exposure to long term electromagnetic energyReduce exposureOther accessoriesTransmissionPatent applicationEngineering
This patent application is associated with the provisional patent applications No. 61 / 634,254 and No. 61 / 634,255 which claims the filing date of Feb. 27, 2012. This patent application is for a device which can be described as a pocket liner (and pad) designed to protect individuals from close contact to electromagnetic exposure when they carry (or using) their electronic devices close to their bodies. Studies have shown that exposure to excess electromagnetic radiation has harmful effects to humans. This device is designed to protect the user from those effects by significantly reducing exposure to electromagnetic energy from personal electromagnetic devices with minimal interference to the normal operation of the electronic device. In some realizations, the device is designed to also protect users from thermal exposure.
Owner:WITTMAN HOLLOWAY SUSAN KAY +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com