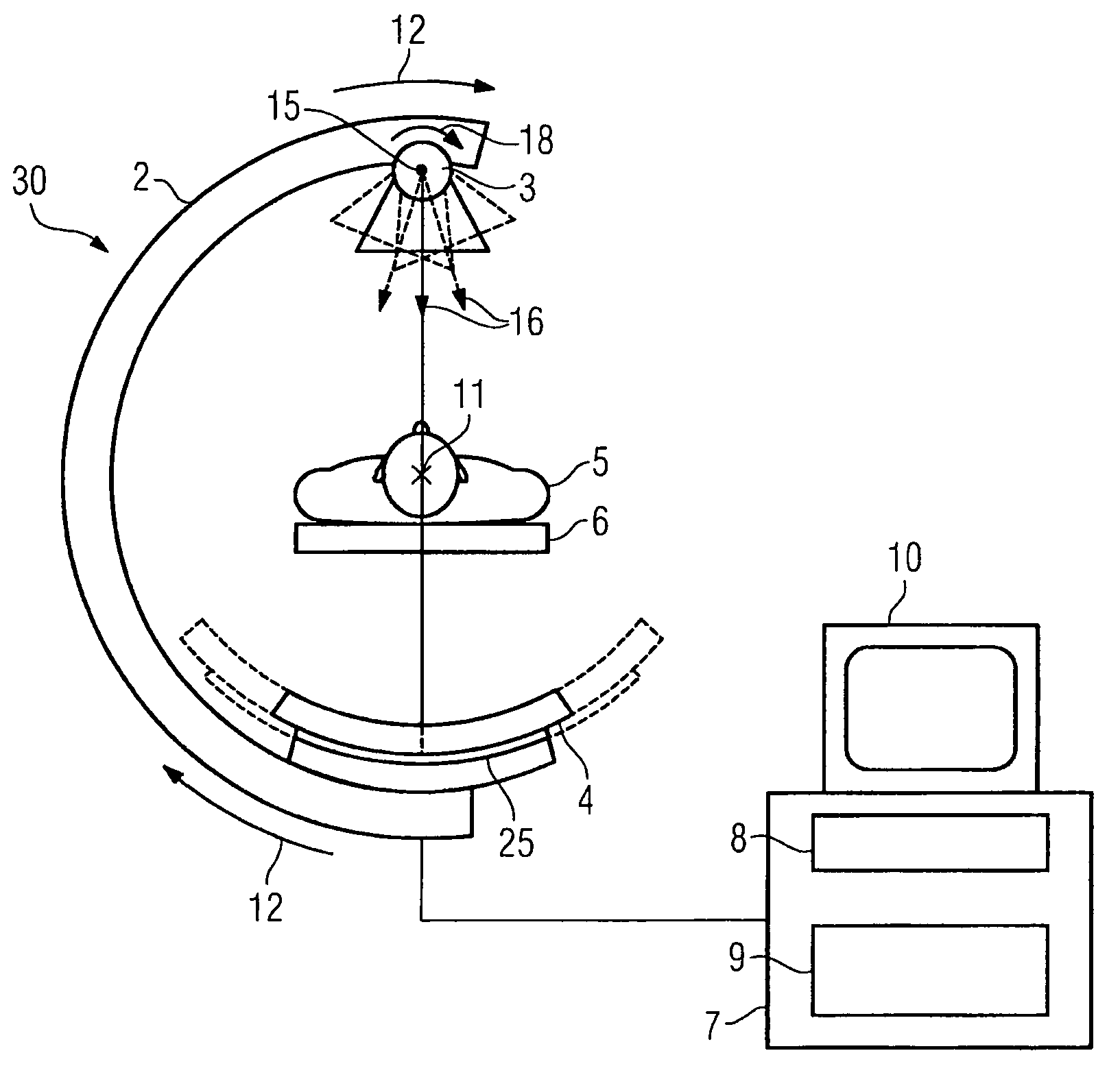
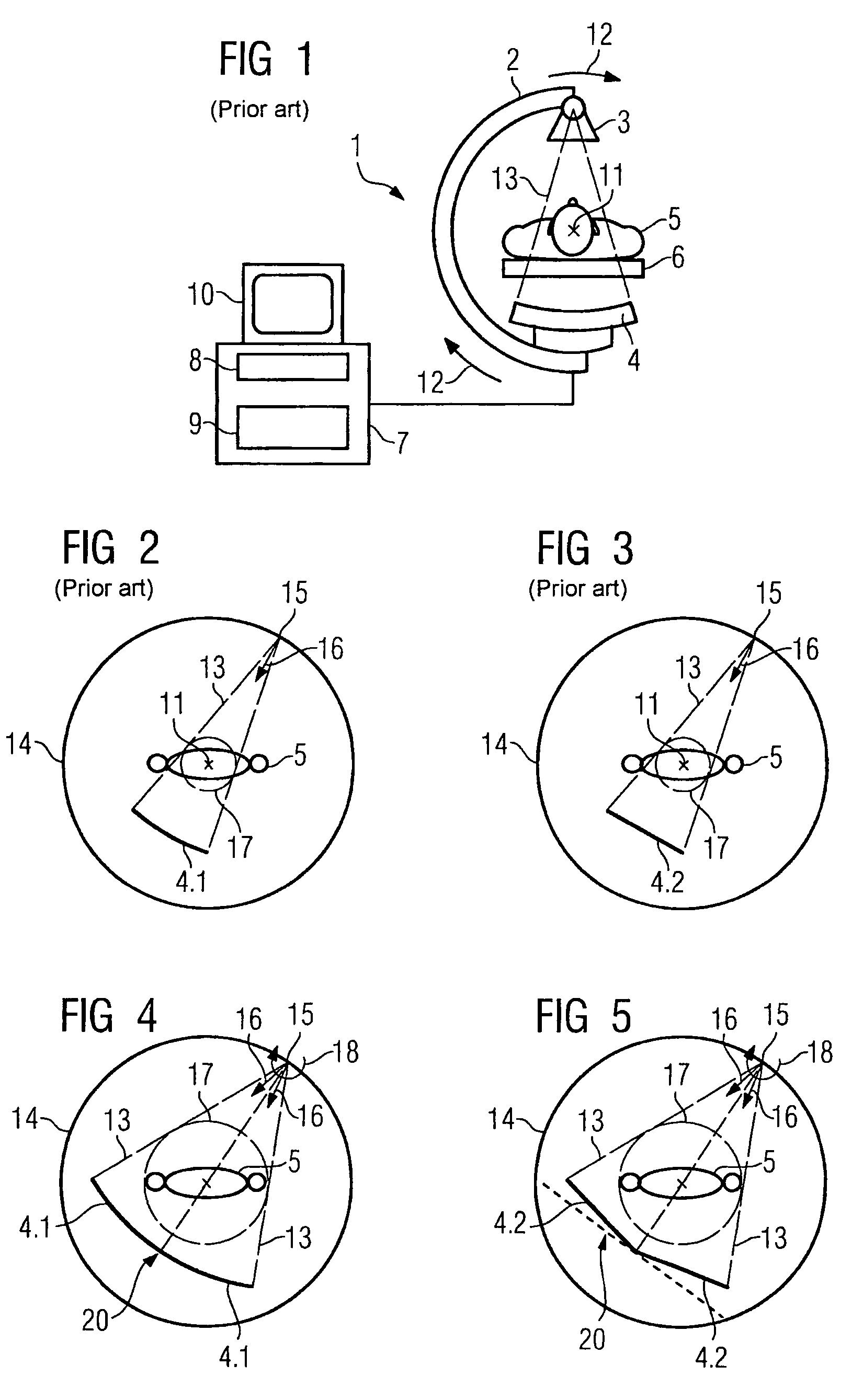
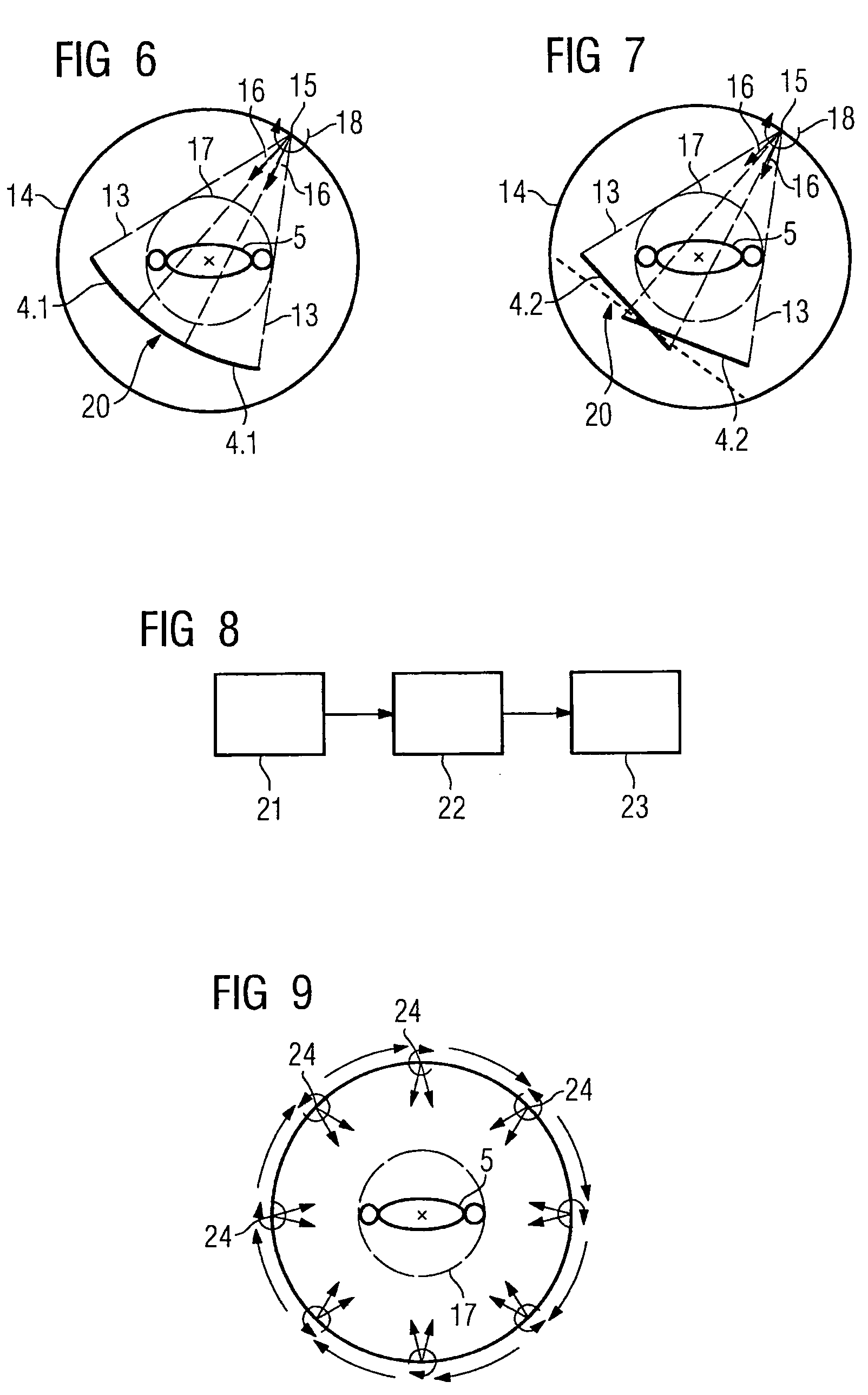
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3740 results about "Voxel" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
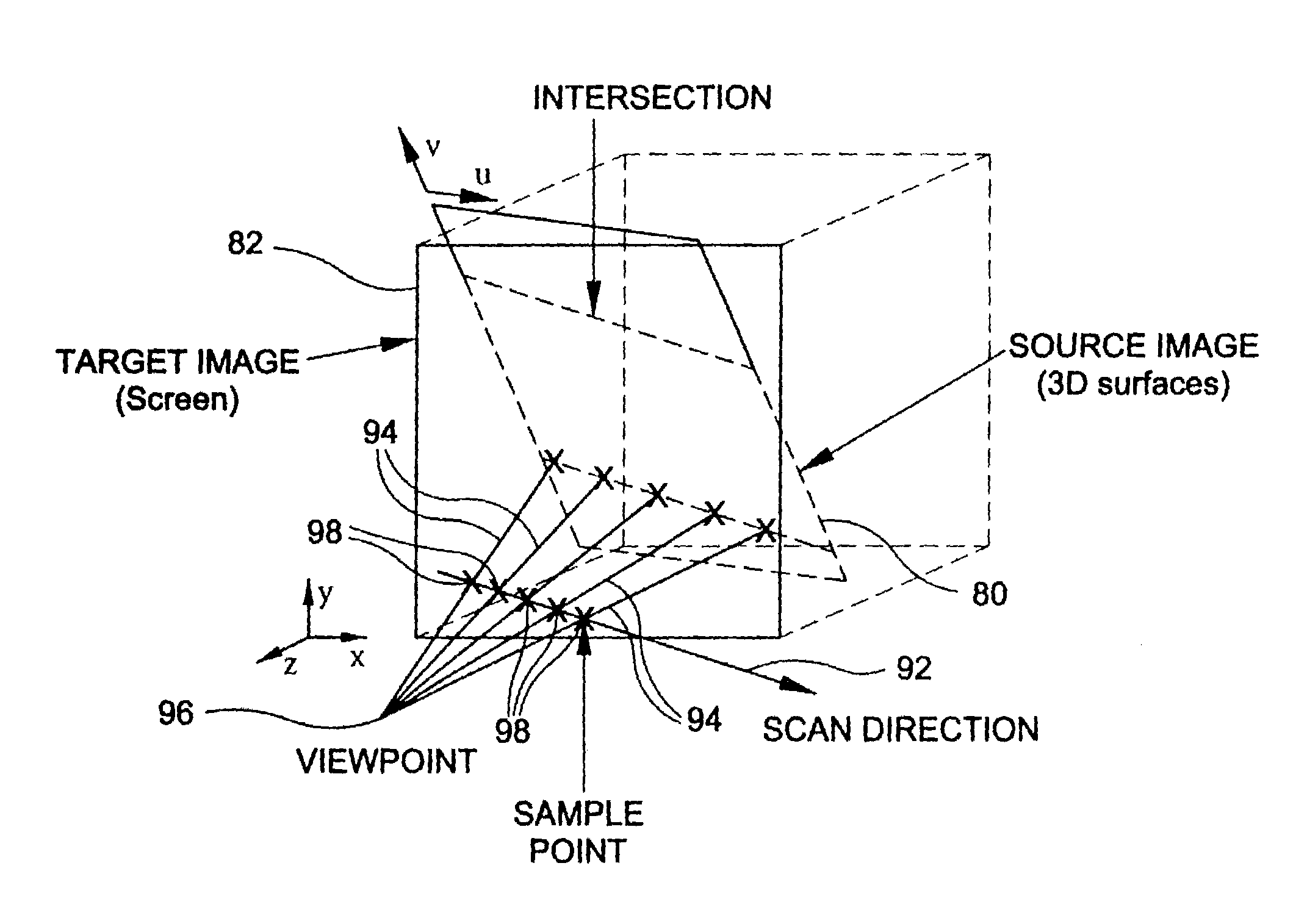
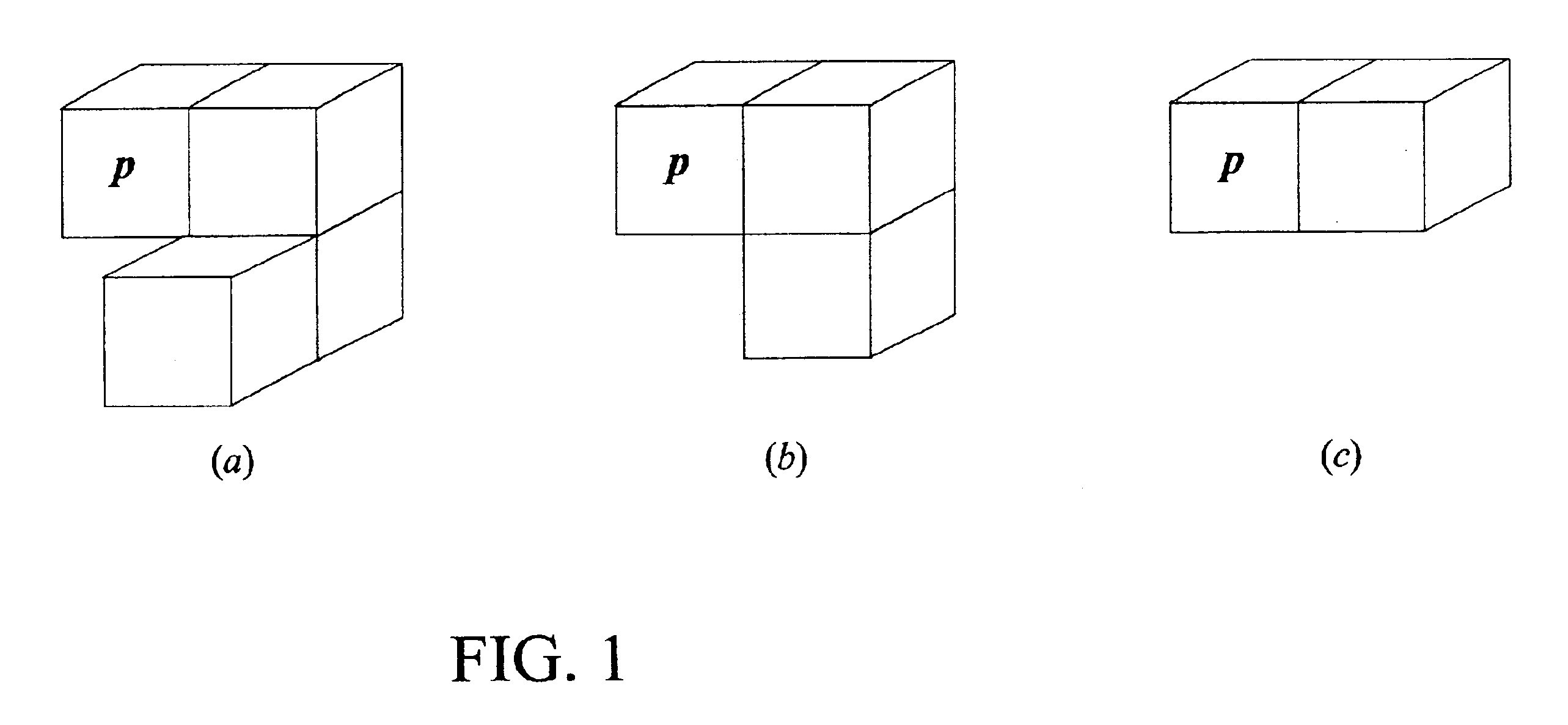
A voxel represents a value on a regular grid in three-dimensional space. As with pixels in a 2D bitmap, voxels themselves do not typically have their position (coordinates) explicitly encoded with their values. Instead, rendering systems can infer the position of a voxel based upon its position relative to other voxels (i.e., its position in the data structure that makes up a single volumetric image). In contrast to pixels and voxels, polygons are often explicitly represented by the coordinates of their vertices (points). A direct consequence of this difference is that polygons can efficiently represent simple 3D structures with lots of empty or homogeneously filled space, while voxels excel at representing regularly sampled spaces that are non-homogeneously filled.
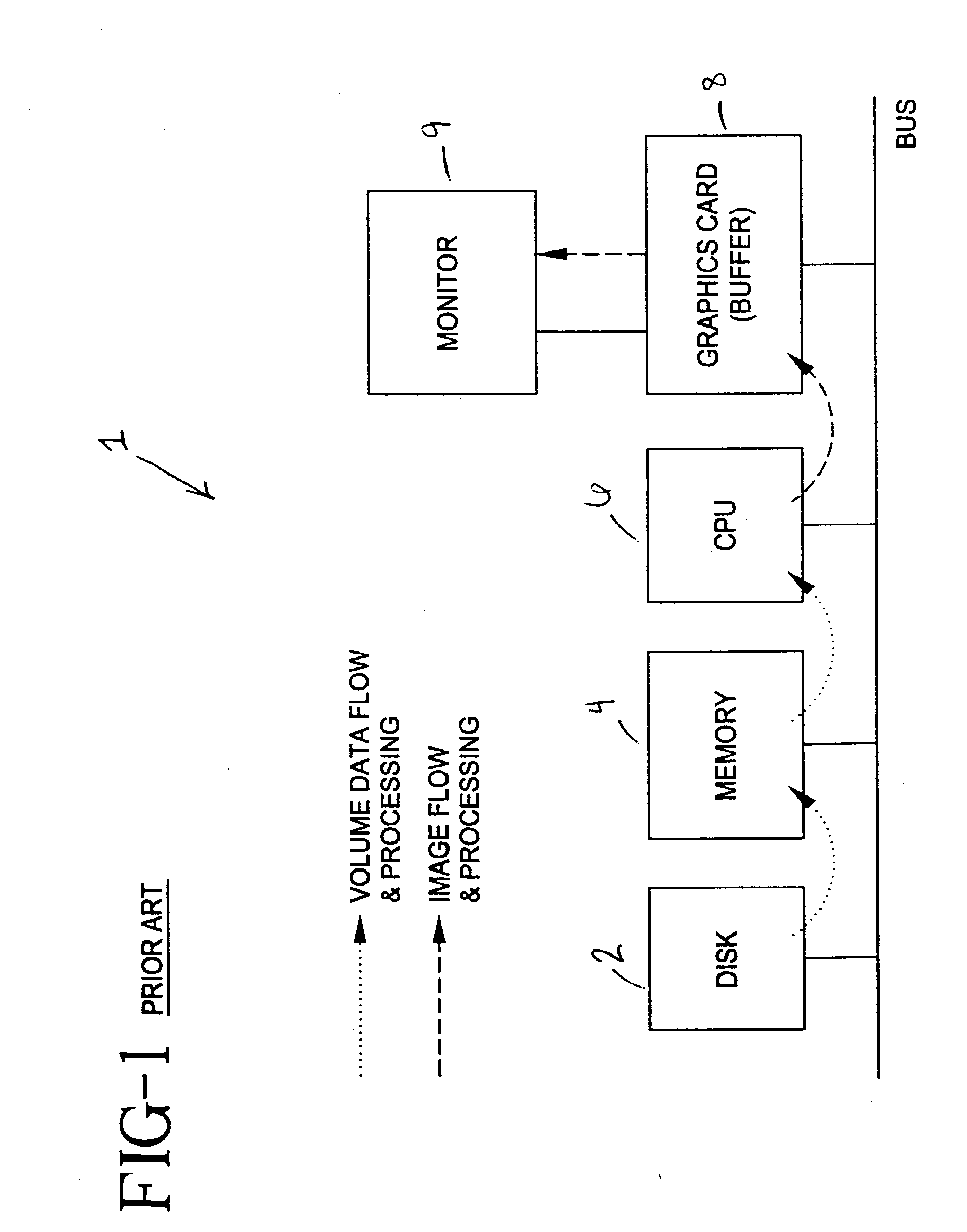
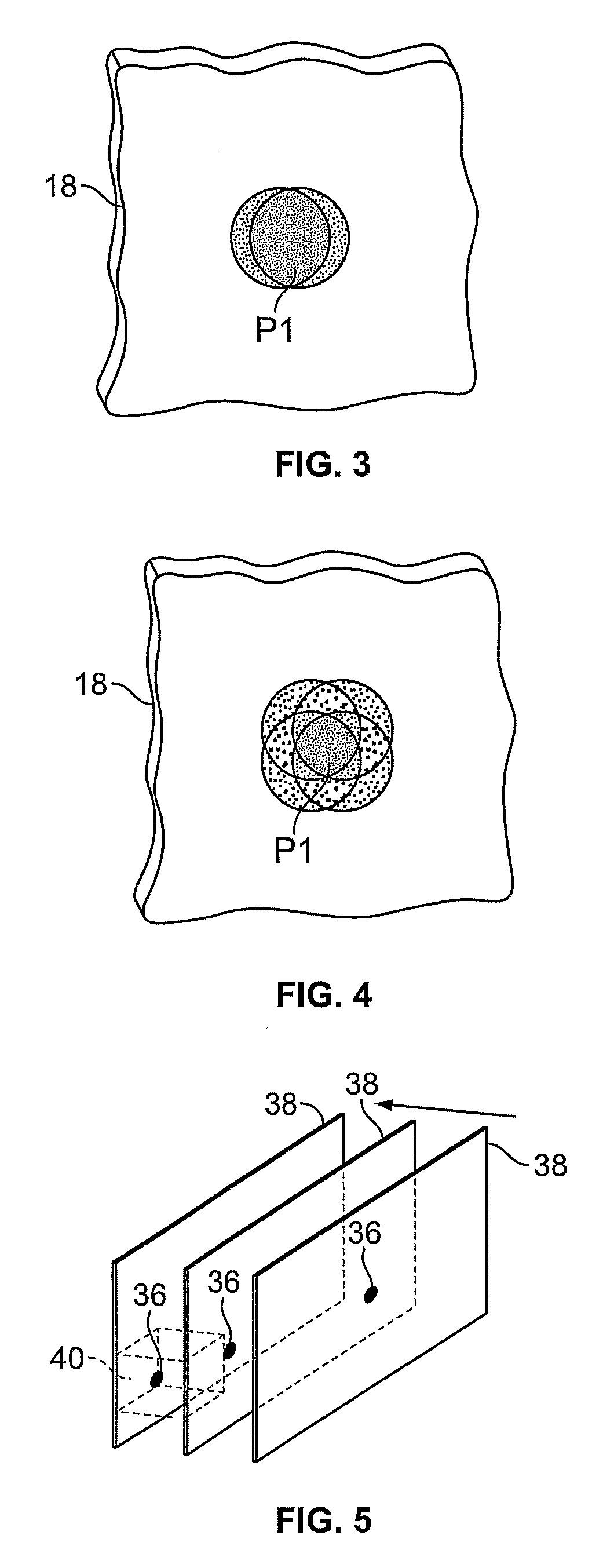
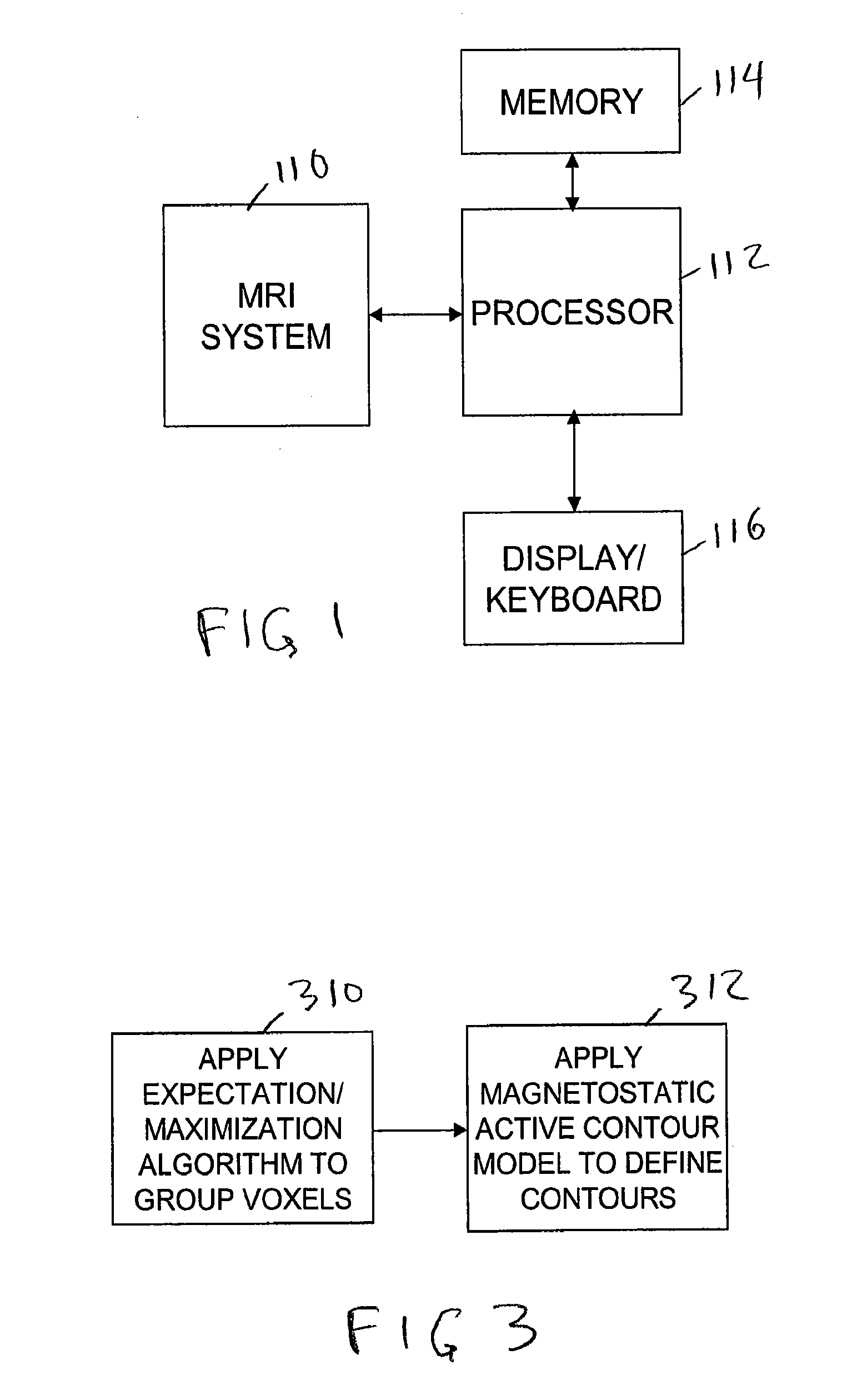
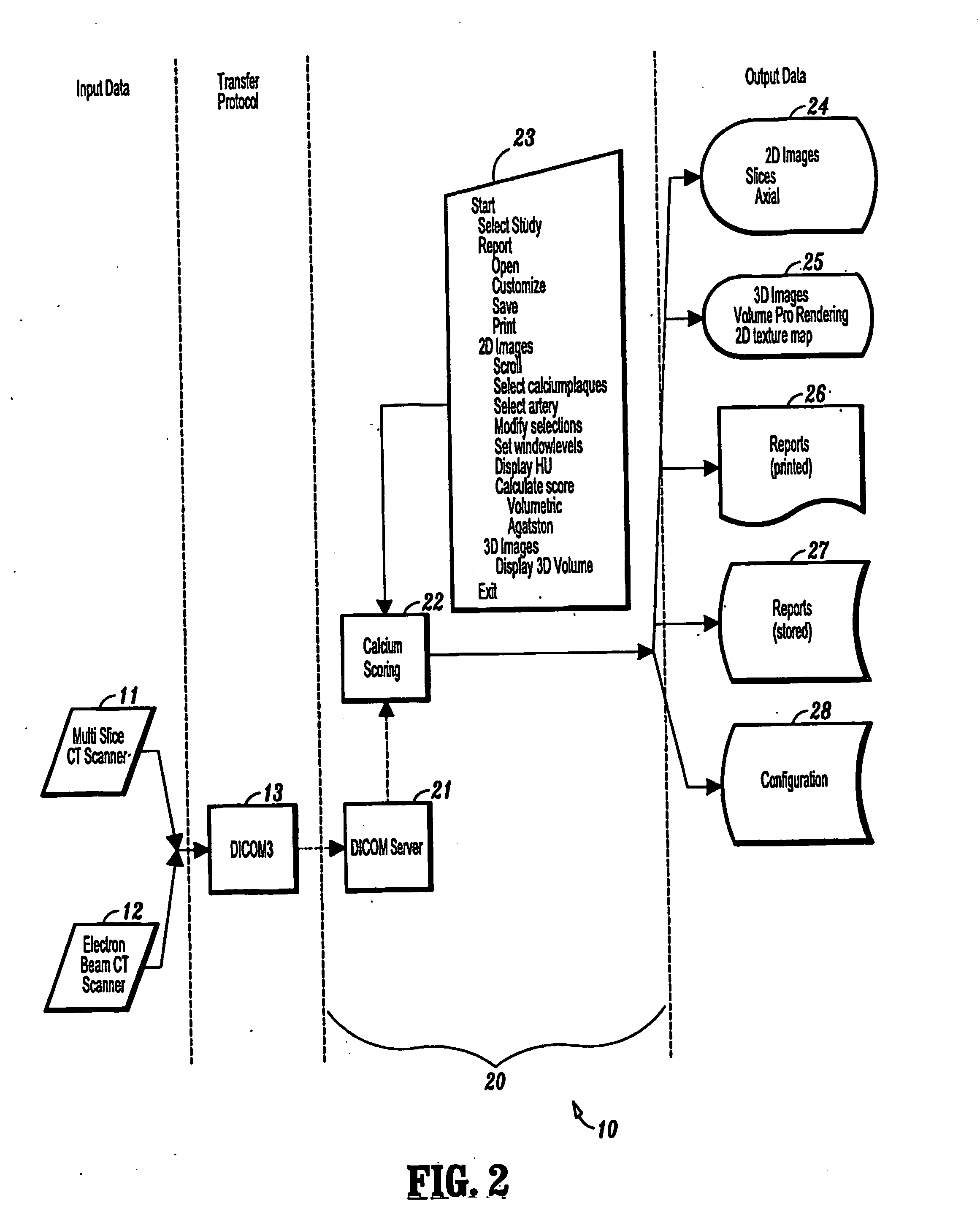
Apparatus and method for volume processing and rendering
InactiveUS7133041B2Improve performanceImprove image quality3D-image rendering3D modellingVoxelGlobal illumination
An apparatus and method for real-time volume processing and universal three-dimensional rendering. The apparatus includes a plurality of three-dimensional (3D) memory units; at least one pixel bus for providing global horizontal communication; a plurality of rendering pipelines; at least one geometry bus; and a control unit. The apparatus includes a block processor having a circular ray integration pipeline for processing voxel data and ray data. Rays are generally processed in image order thus permitting great flexibility (e.g., perspective projection, global illumination). The block processor includes a splatting unit and a scattering unit. A method for casting shadows and performing global illumination in relation to light sources includes sweeping a two dimensional array of rays through the volume can also be implemented with the apparatus. A method for approximating a perspective projection includes using parallel projection.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
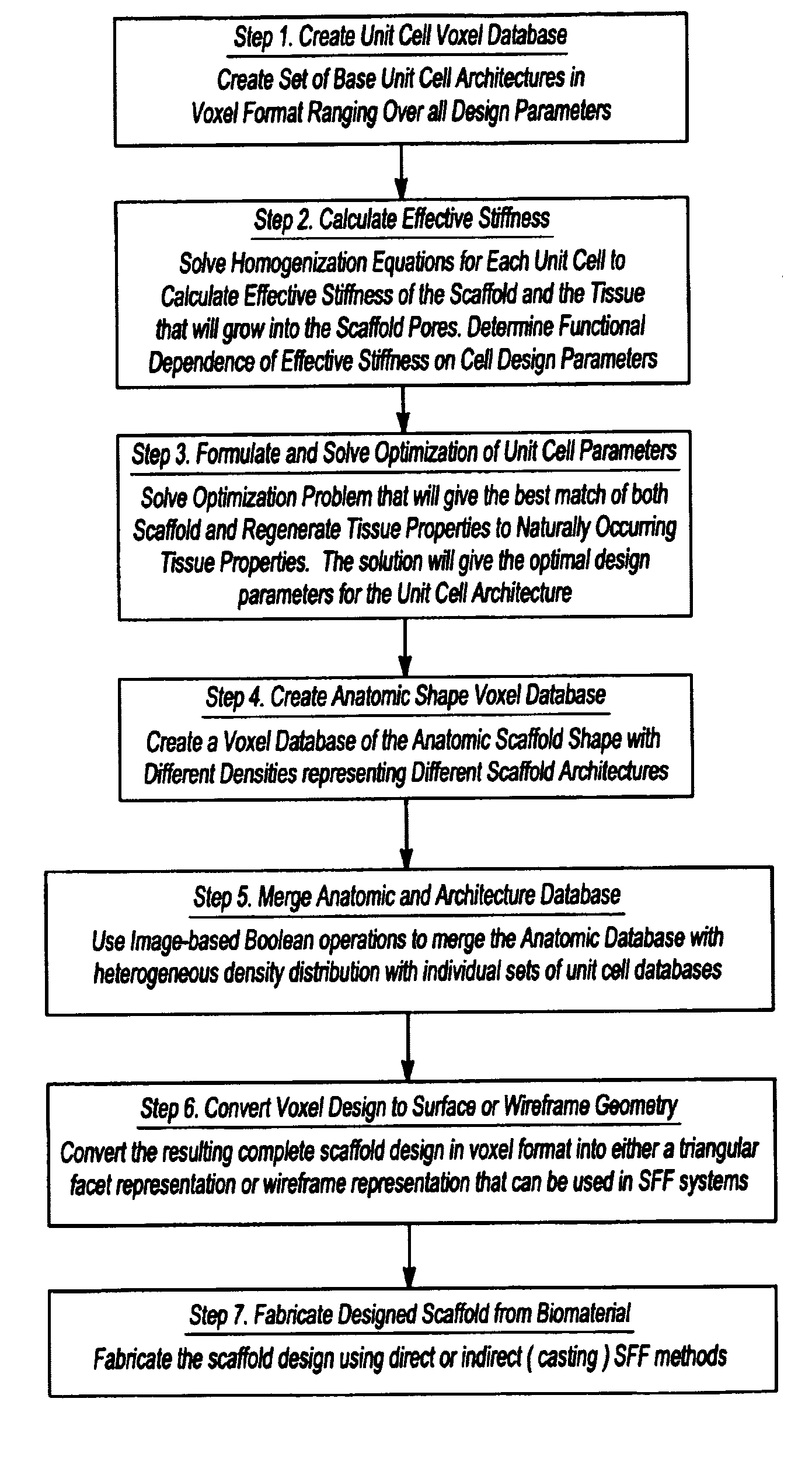
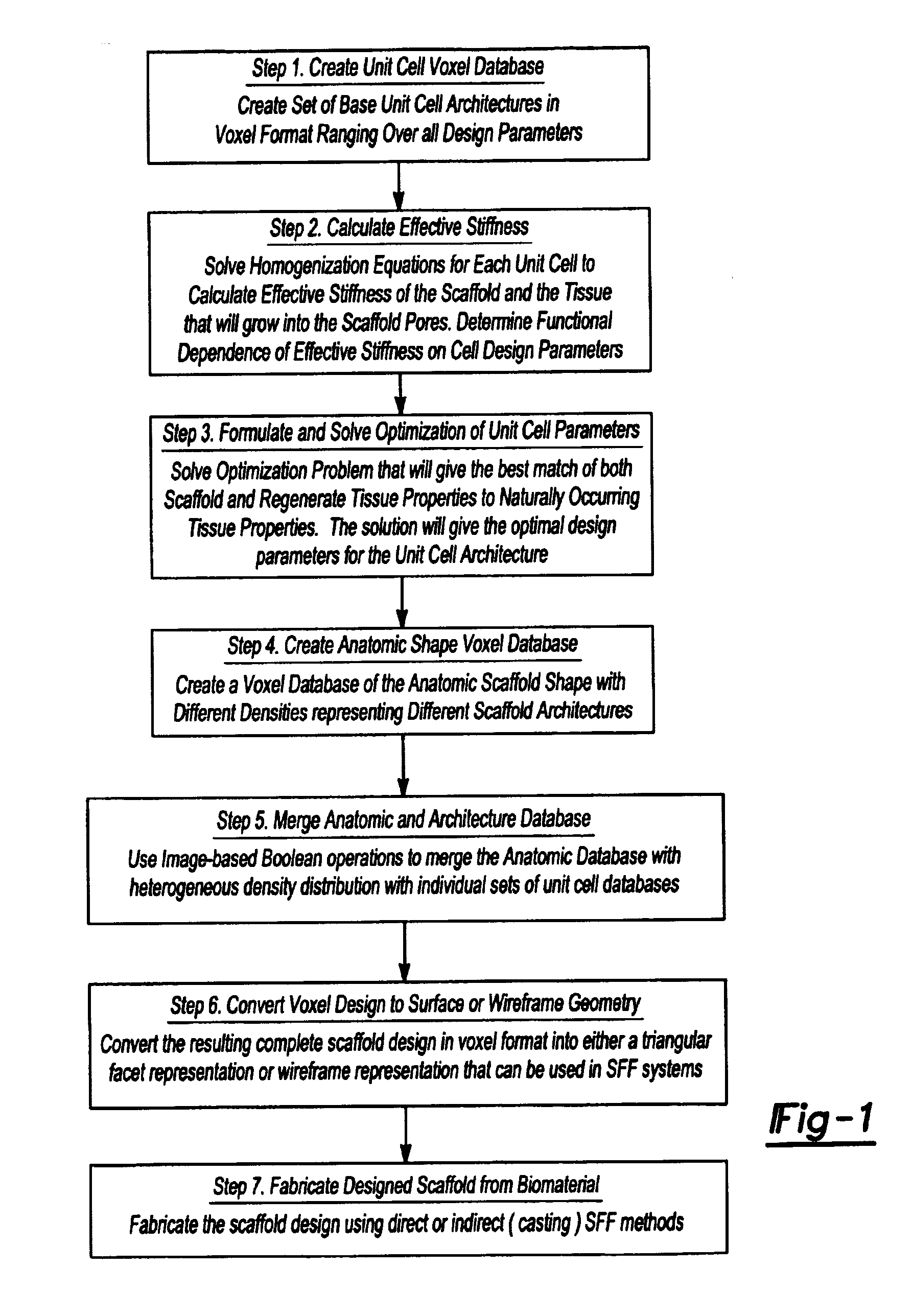
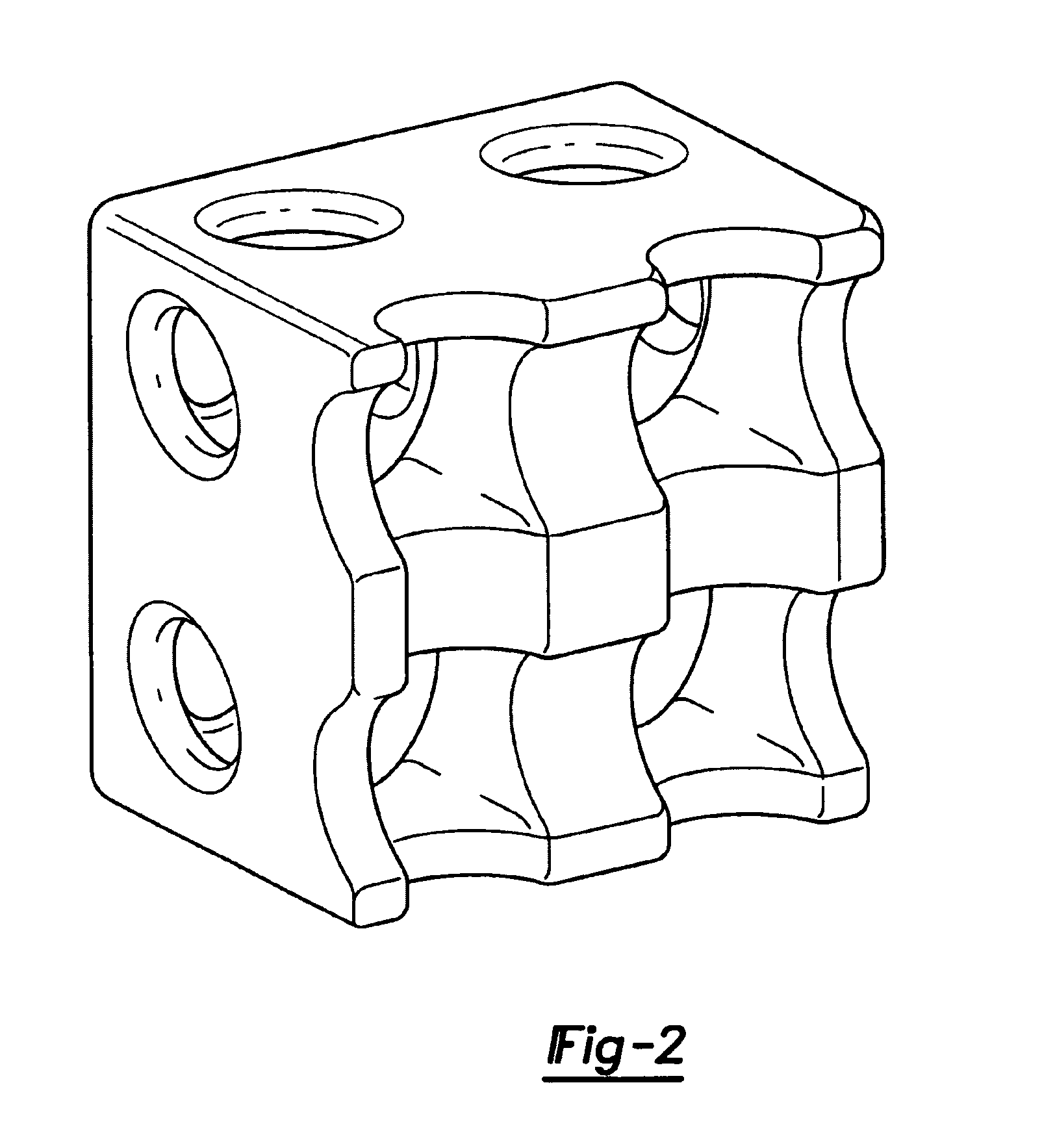
Design methodology for tissue engineering scaffolds and biomaterial implants
A design methodology is provided for creating biomaterial scaffolds optimized for in vivo function with any 3D anatomic shape. The method creates all designs using voxel based design techniques. It also provides for optimization of implant and scaffold microstructure to best match functional and biofactor delivery (including cells, genes and proteins) requirements. The voxel based design techniques readily allow combination of any scaffold or implant microstructure database with any complex 3D anatomic shape created by CT or MRI scanners. These designs can be readily converted to formats for layered manufacturing or casting.
Owner:HOLLISTER SCOTT J +2
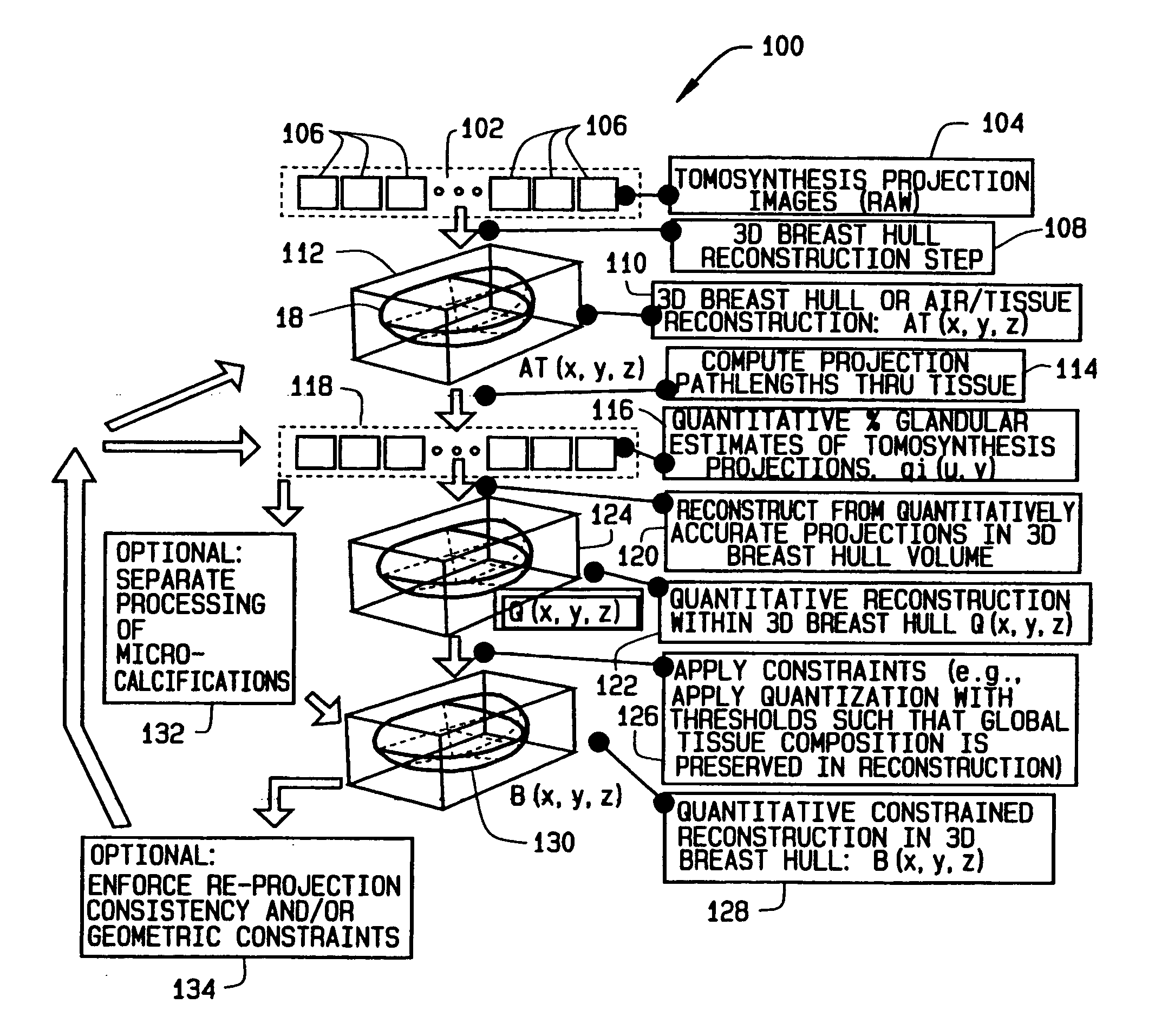
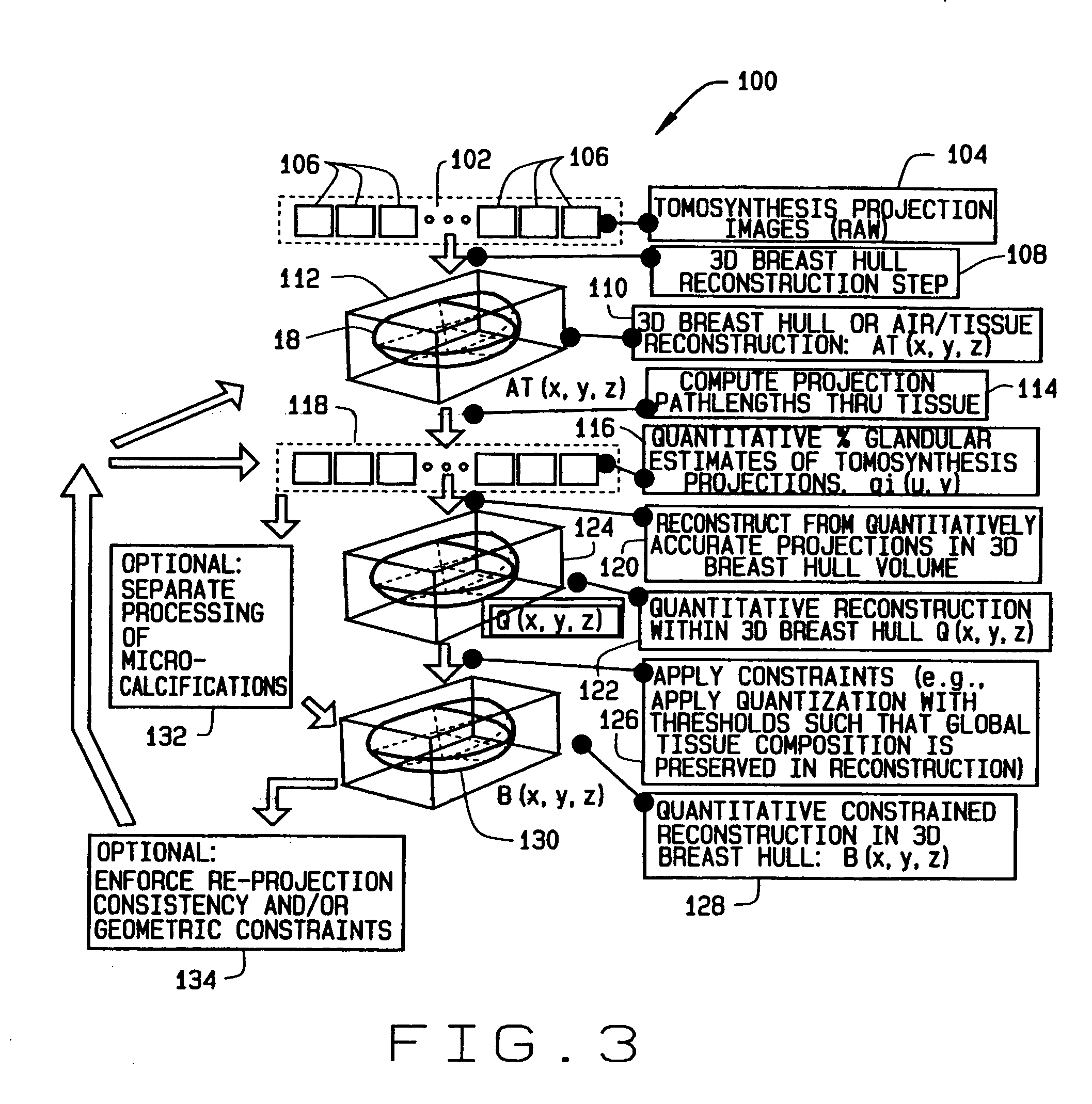
Methods and apparatus for reconstruction of volume data from projection data
ActiveUS20050135664A1Reconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionTomosynthesisVoxel
Some configurations of method for reconstructing a volumetric image of an object include obtaining a tomosynthesis projection dataset of an object. The method also includes utilizing the tomosynthesis projection dataset and additional information about the object to minimize a selected energy function or functions to satisfy a selected set of constraints. Alternatively, constraints are applied to a reconstructed volumetric image in order to obtain an updated volumetric image. A 3D volume representative of the imaged object is thereby obtained in which each voxel is reconstructed and a correspondence indicated to a single one of the component material classes.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
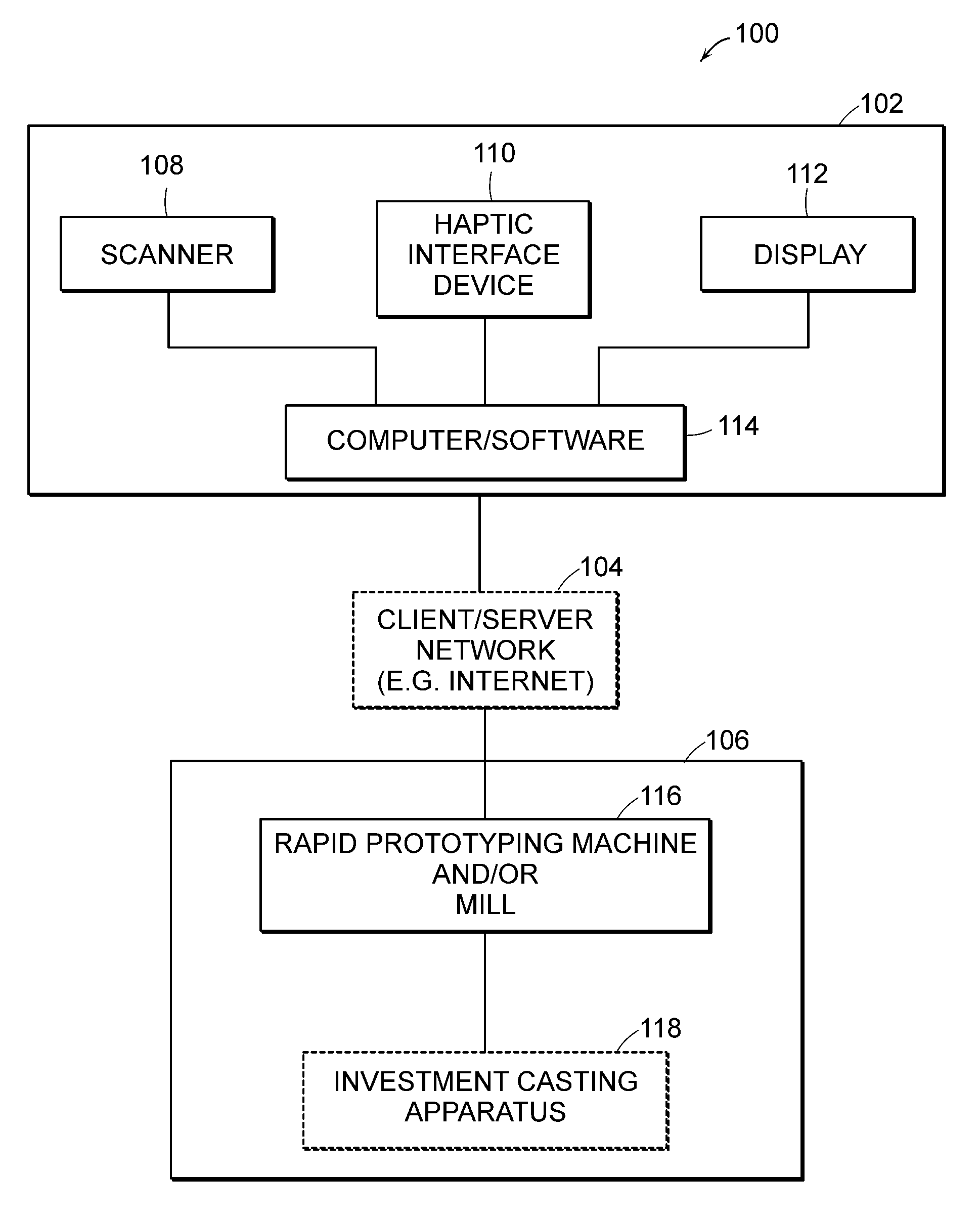
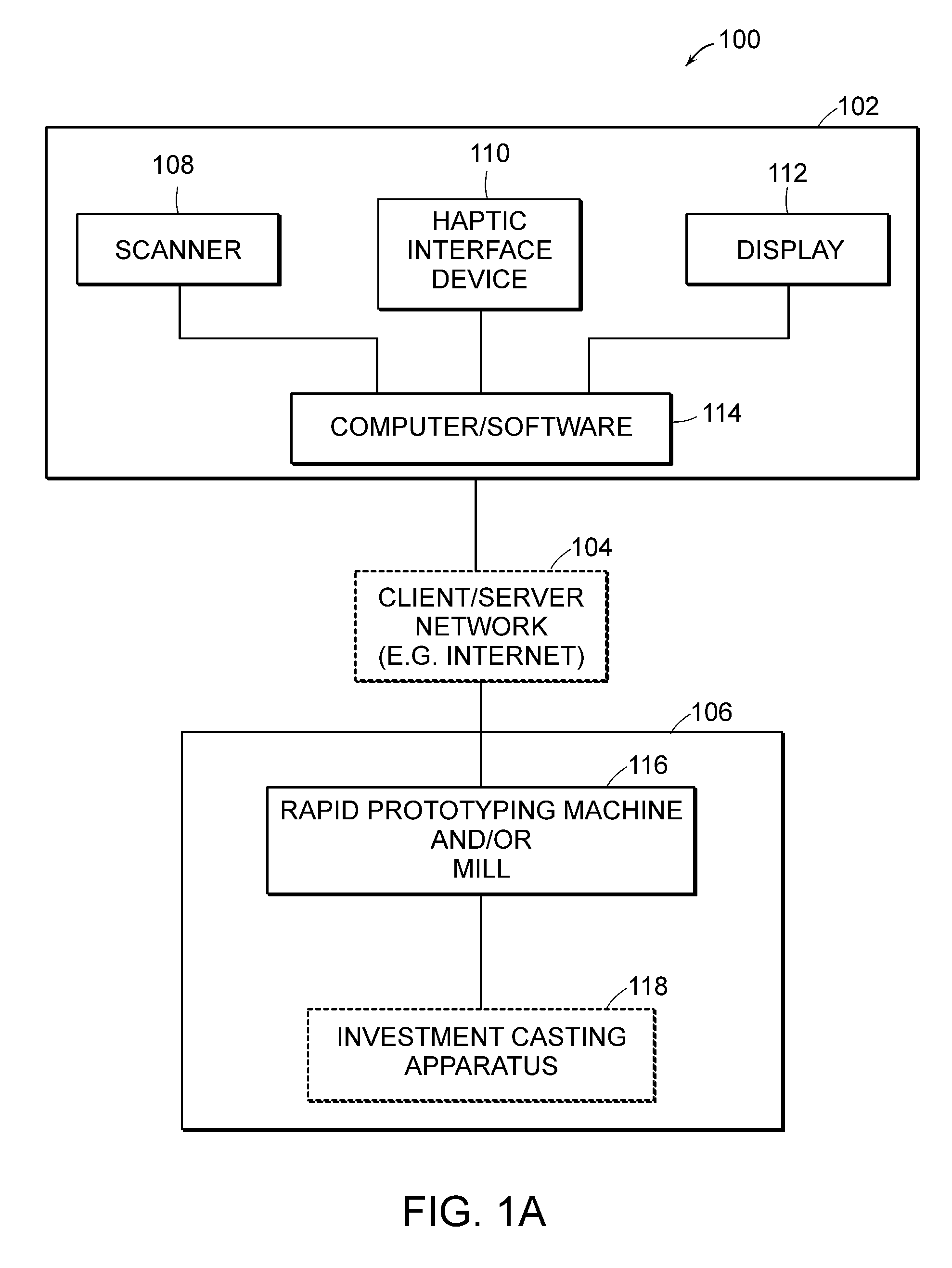
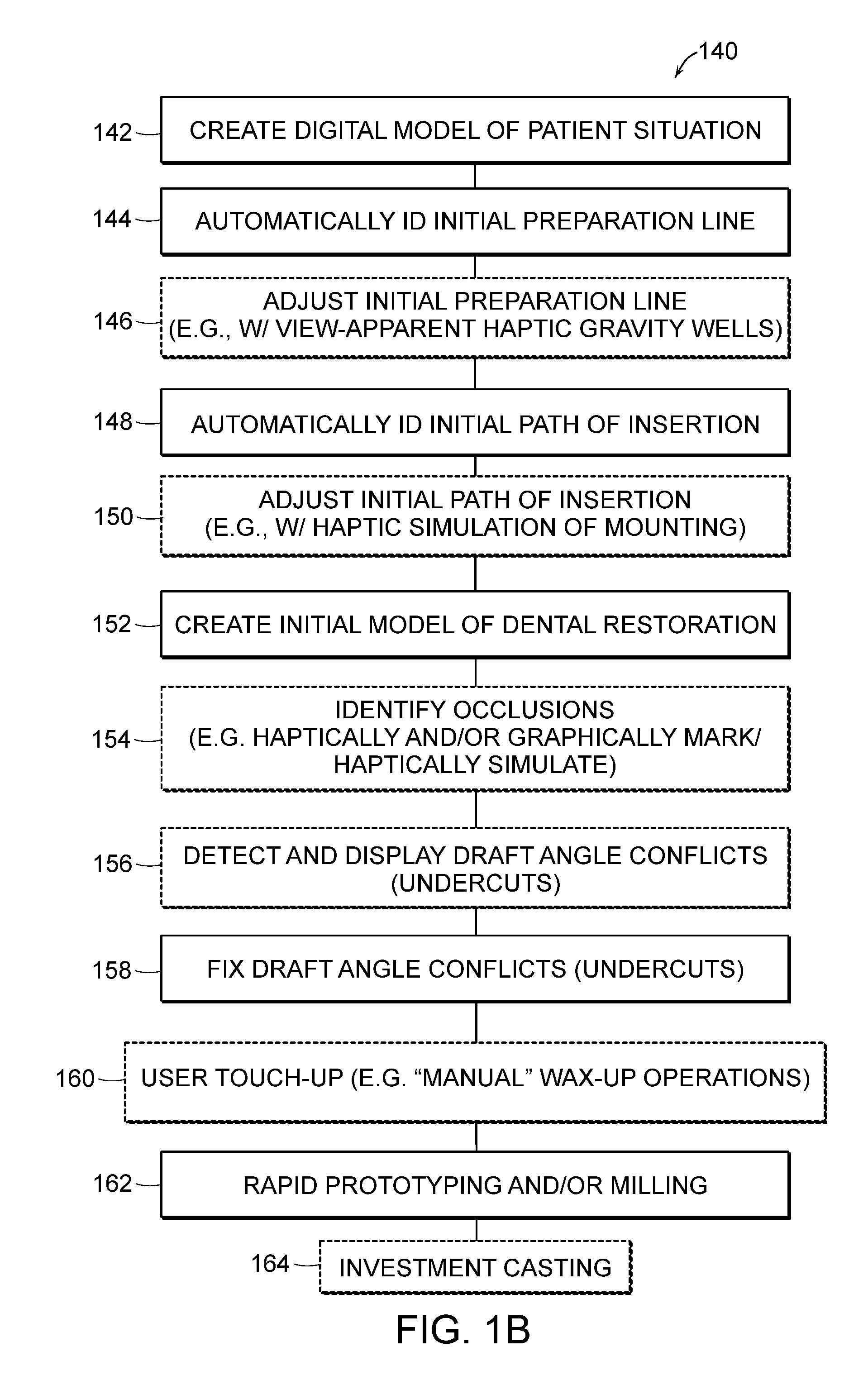
Systems for haptic design of dental restorations
InactiveUS20080261165A1Big advantageEasy to useAdditive manufacturing apparatusOthrodonticsVoxelInvestment casting
The invention provides systems for integrated haptic design and fabrication of dental restorations that provide significant advantages over traditional practice and existing computer-based systems. The systems feature technical advances that result in significantly more streamlined, versatile, and efficient design and fabrication of dental restorations. Among these technical advances are the introduction of voxel-based models; the use of a combination of geometric representations such as voxels and NURBS representations; the automatic identification of an initial preparation (prep) line and an initial path of insertion; the ability of a user to intuitively, haptically adjust the initial prep line and / or the initial path of insertion; the automatic identification of occlusions and draft angle conflicts (e.g., undercuts); the haptic simulation and / or marking of occlusions and draft angle conflicts; and coordination between design output and rapid prototyping / milling and / or investment casting.
Owner:SENSABLE TECH
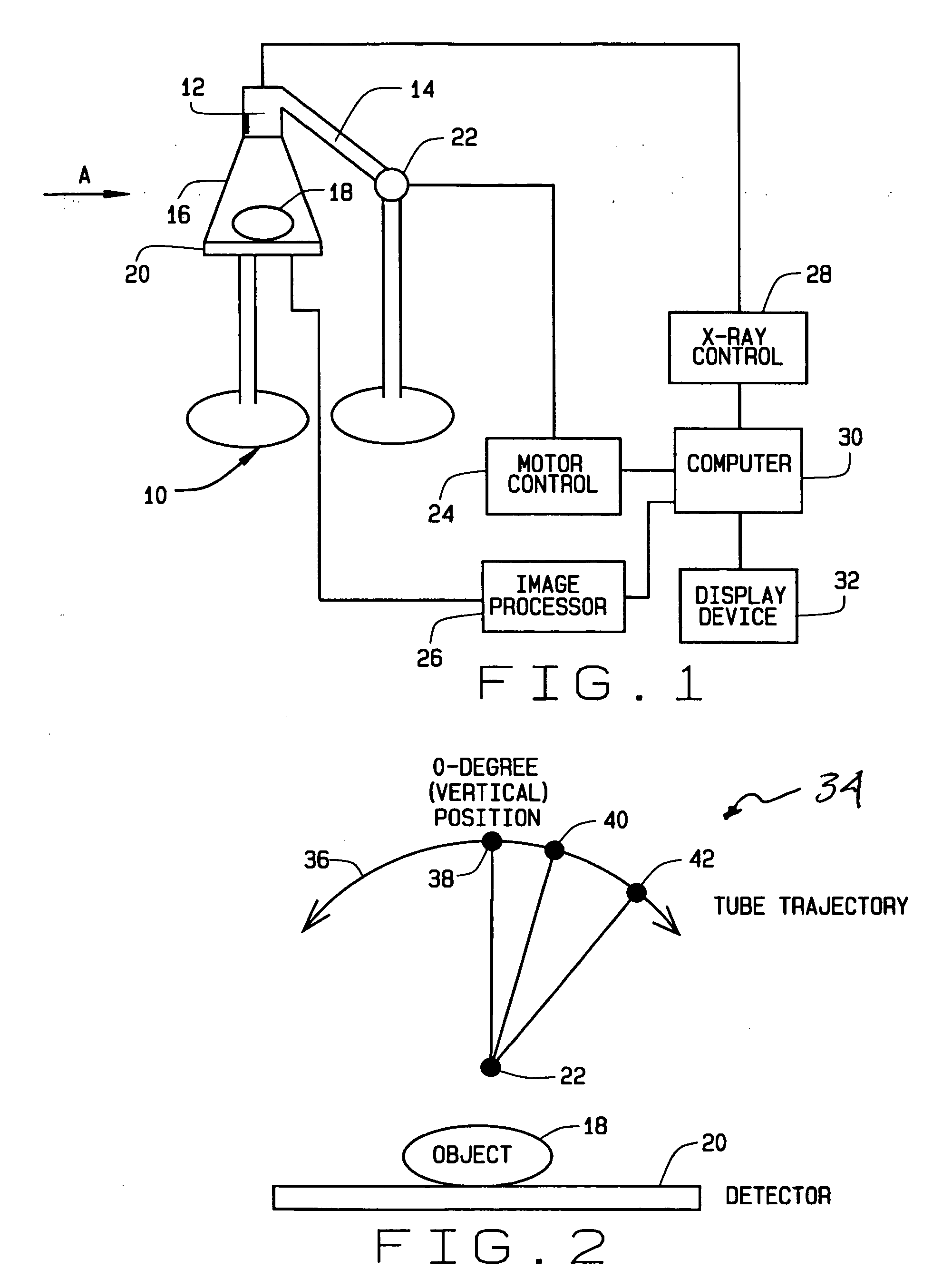
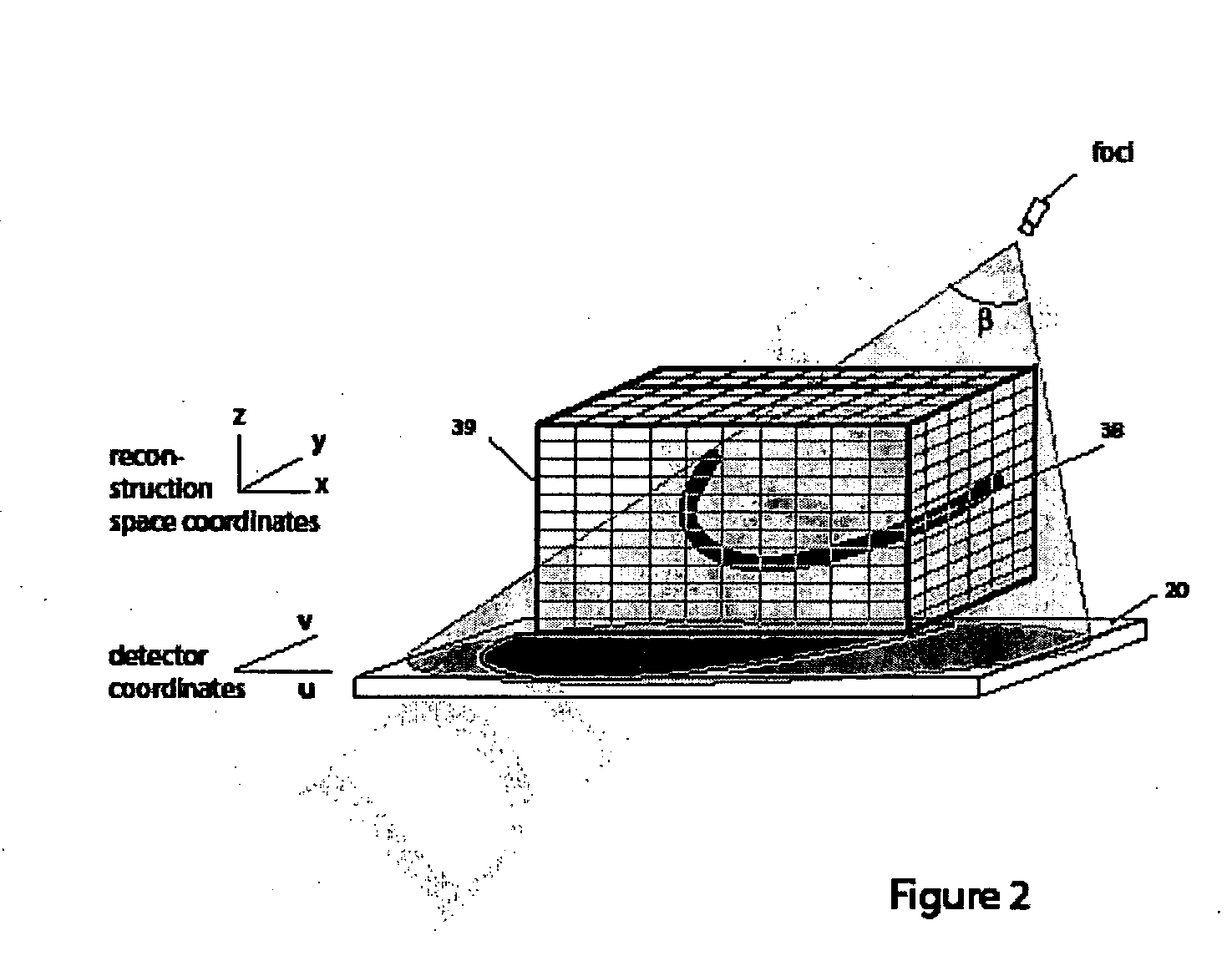
Method for reconstructing a three-dimensional image volume and x-ray devices
InactiveUS7711083B2Improve executionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingVoxelProjection image
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
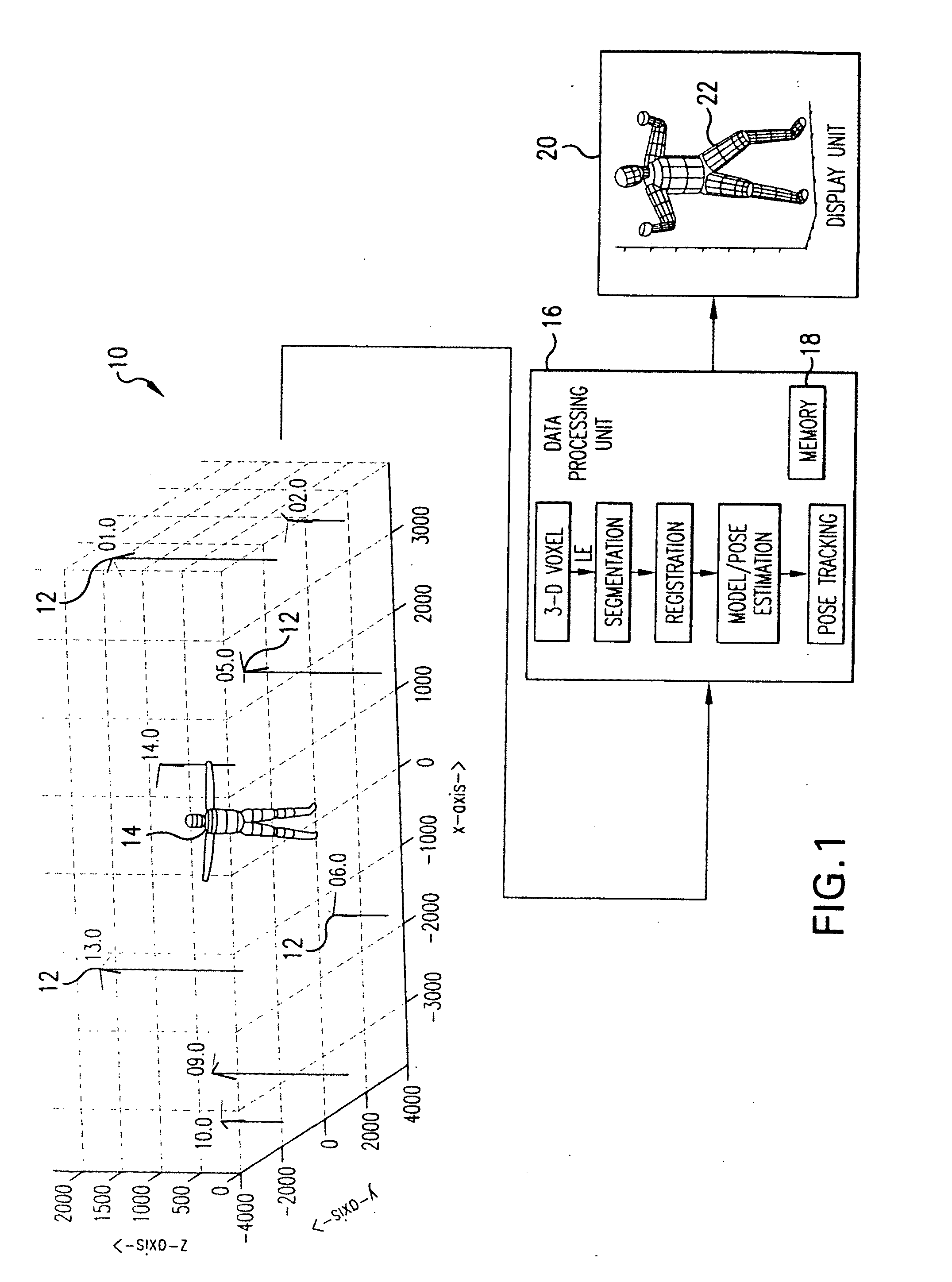
Method and system for markerless motion capture using multiple cameras
InactiveUS20090232353A1Accurate estimateAccurate presentationImage enhancementDetails involving processing stepsProbabilistic methodVoxel
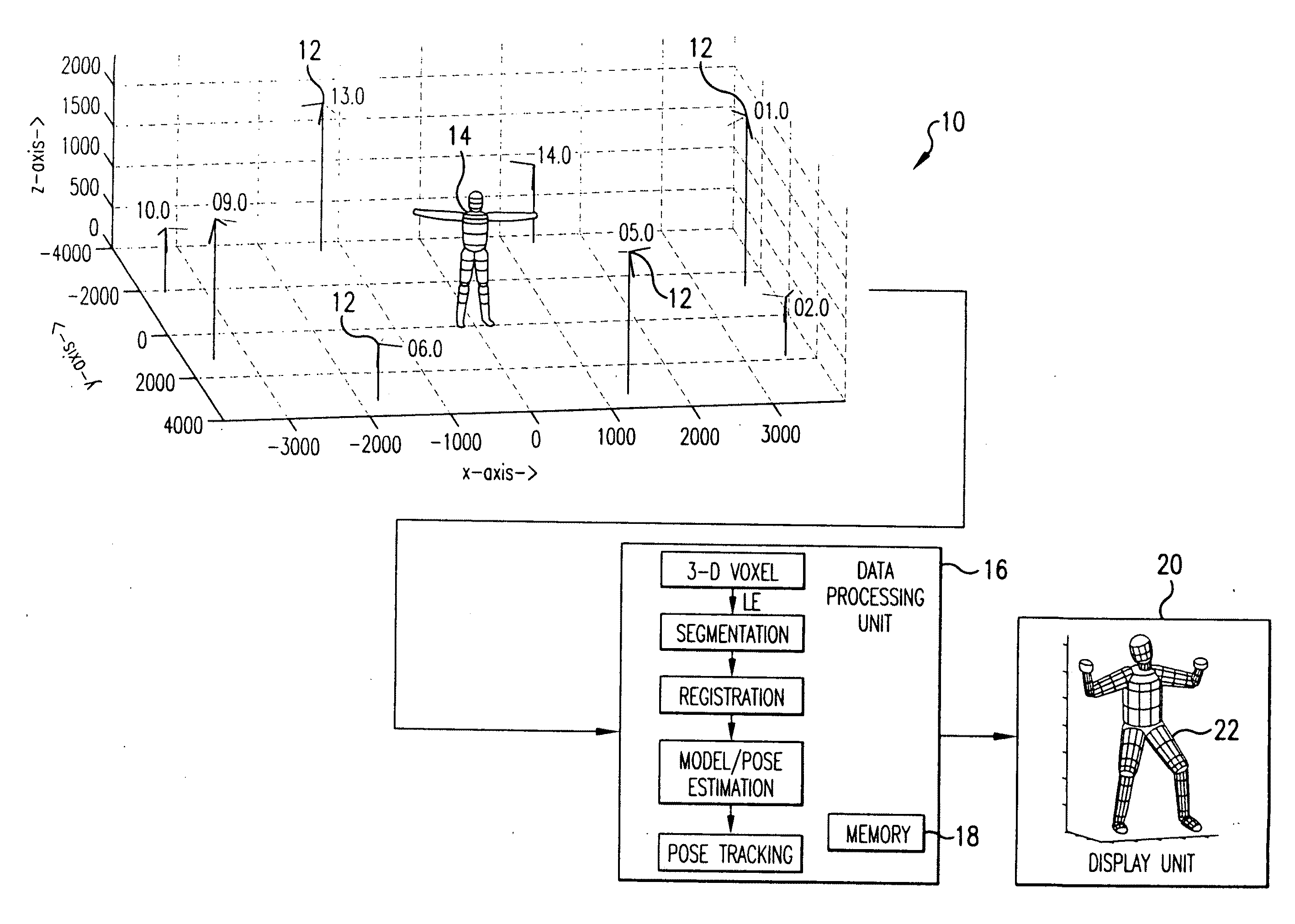
Completely automated end-to-end method and system for markerless motion capture performs segmentation of articulating objects in Laplacian Eigenspace and is applicable to handling of the poses of some complexity. 3D voxel representation of acquired images are mapped to a higher dimensional space (k), where k depends on the number of articulated chains of the subject body, so as to extract the 1-D representations of the articulating chains. A bottom-up approach is suggested in order to build a parametric (spline-based) representation of a general articulated body in the high dimensional space followed by a top-down probabilistic approach that registers the segments to an average human body model. The parameters of the model are further optimized using the segmented and registered voxels.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
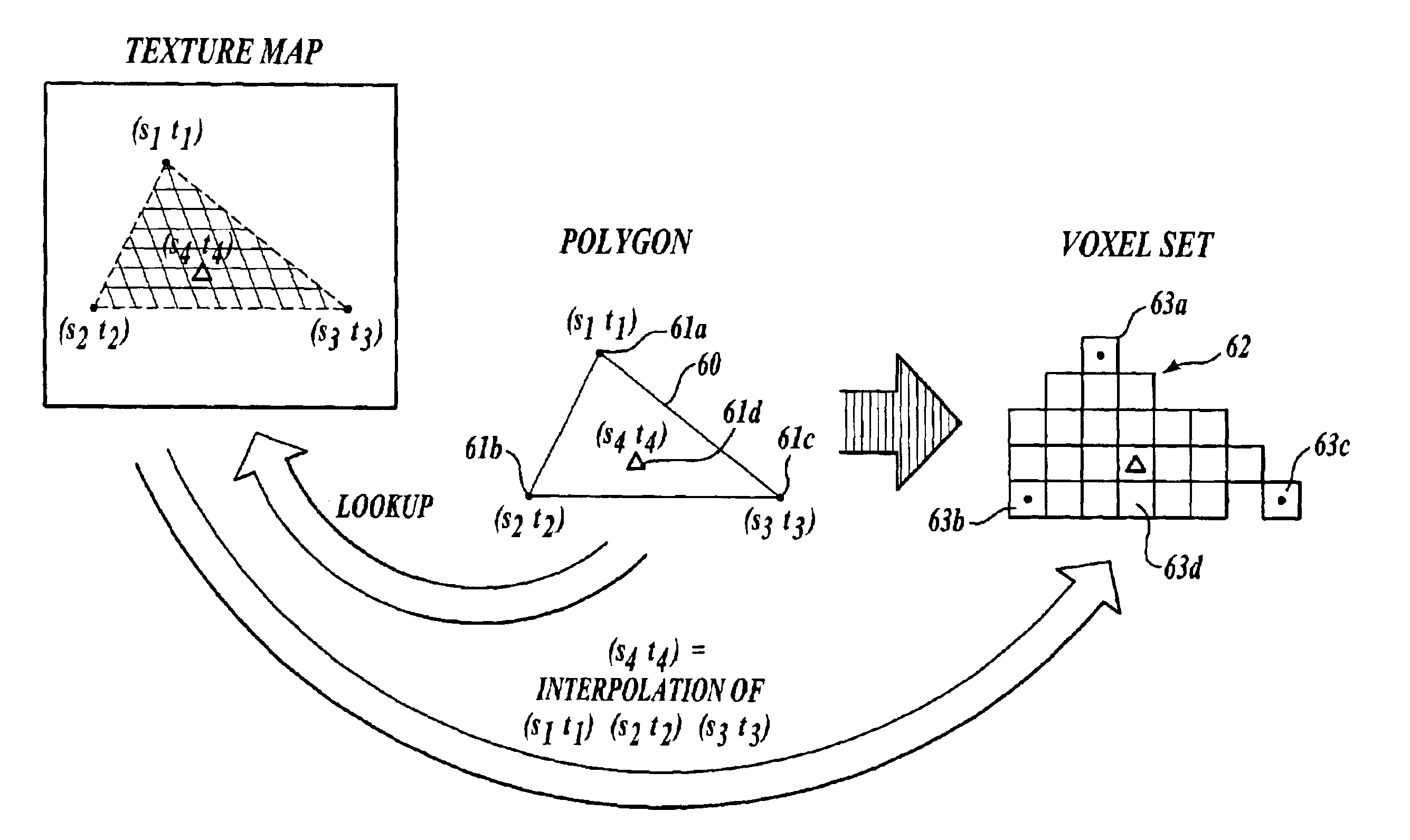
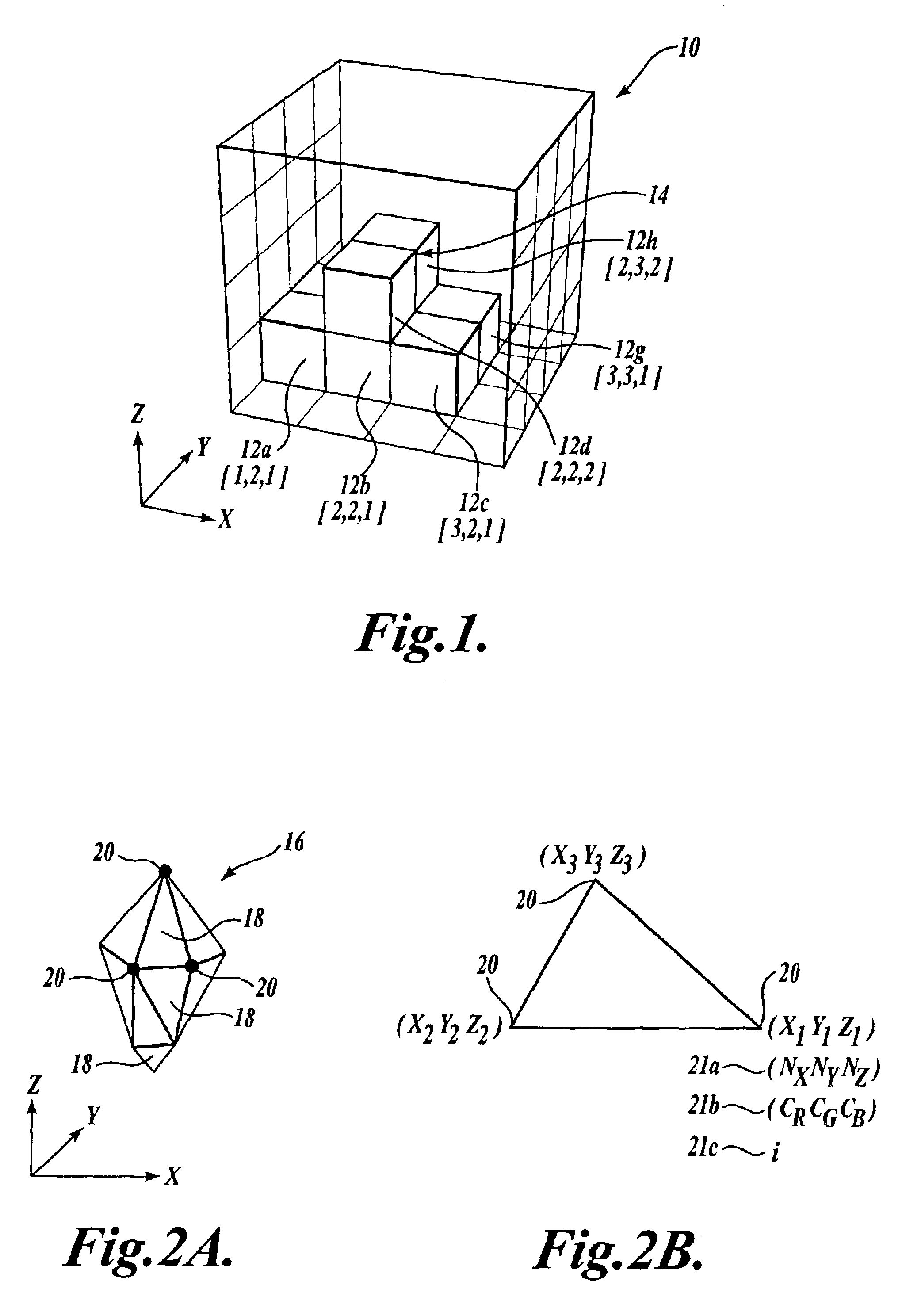
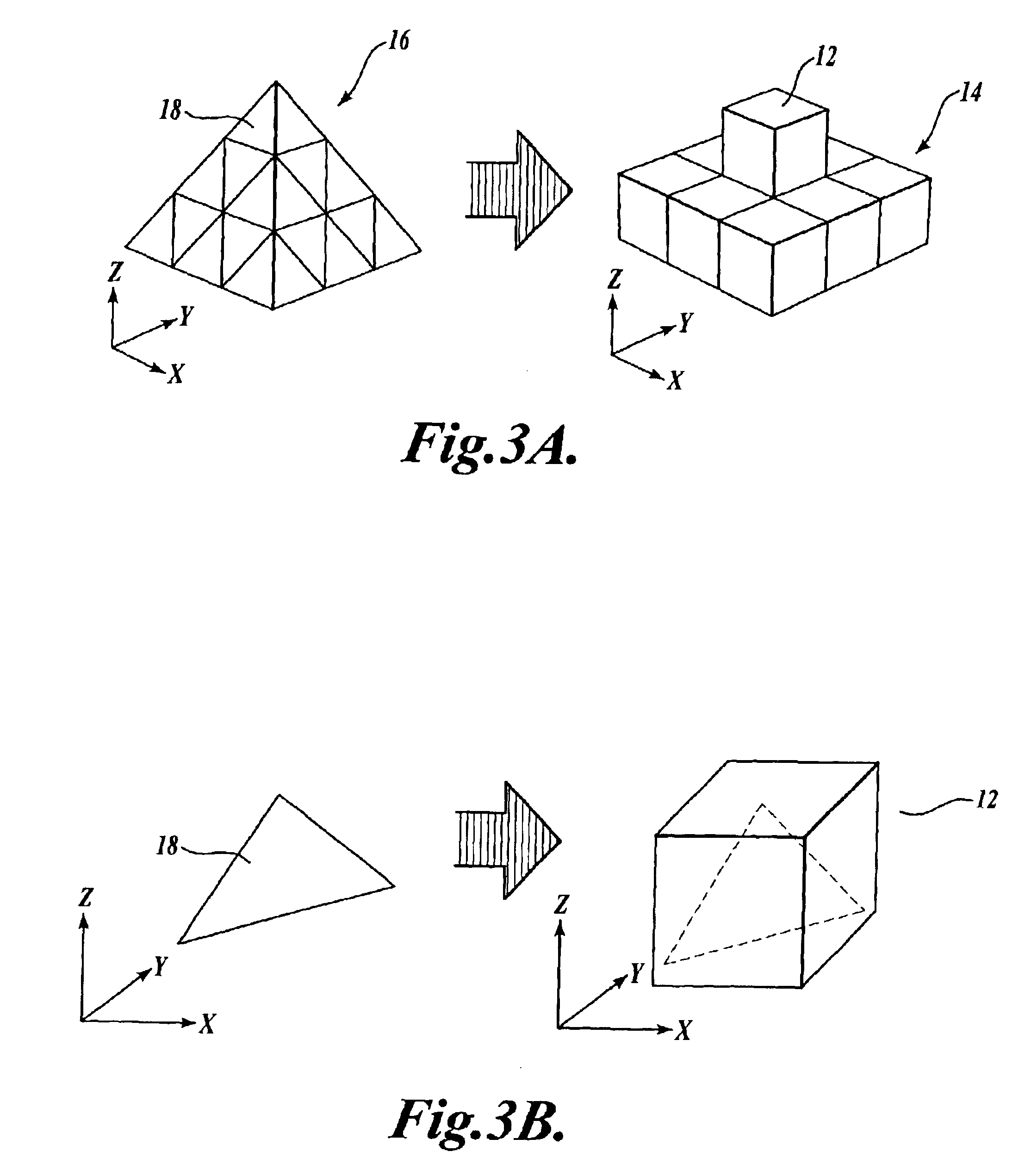
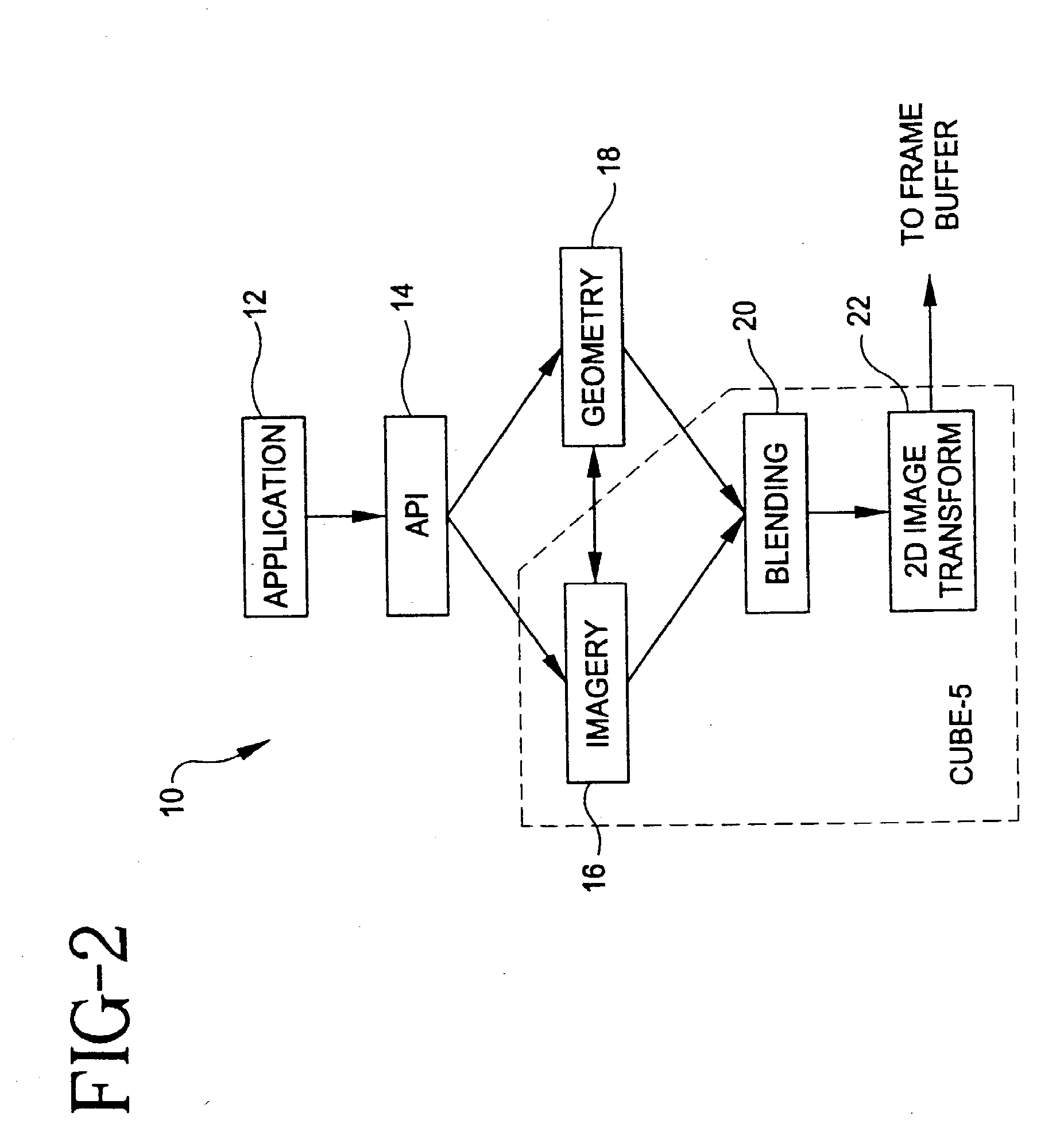
Method and apparatus for transforming polygon data to voxel data for general purpose applications
InactiveUS6867774B1Efficient conversionHigh resolution3D-image rendering3D modellingGeneral purposeScan conversion
A method and apparatus are provided for transforming 3D geometric data, such as polygon data (16) formed of polygons (18), into volumetric data (14) formed of voxels (12). According to the method, 3D geometric data to be converted to voxel data are acquired, and the resolution of a final voxel grid to be produced is obtained (e.g., user-defined). Then, each geometric unit (e.g., a polygon) in the 3D geometric data is mapped (or scan converted) to an imaginary voxel grid having a higher resolution than the resolution of the final voxel grid. Next, with respect to the geometric units that are mapped to the imaginary voxels in the imaginary voxel grid dividing one final (actual) voxel into smaller sub-volumes, a weighted average of the attribute values (color, normal, intensity, etc.) is obtained. The weighted average is stored as the attribute value of the final voxel.
Owner:MCLOUD TECH USA INC
Volume analysis and display of information in optical coherence tomography angiography
ActiveUS9713424B2Solve the slow scanning speedHigh transparencyImage enhancementImage analysisVoxelData set
Computer aided visualization and diagnosis by volume analysis of optical coherence tomography (OCT) angiographic data. In one embodiment, such analysis comprises acquiring an OCT dataset using a processor in conjunction with an imaging system; evaluating the dataset, with the processor, for flow information using amplitude or phase information; generating a matrix of voxel values, with the processor, representing flow occurring in vessels in the volume of tissue; performing volume rendering of these values, the volume rendering comprising deriving three dimensional position and vector information of the vessels with the processor; displaying the volume rendering information on a computer monitor; and assessing the vascularity, vascular density, and vascular flow parameters as derived from the volume rendered images.
Owner:SPAIDE RICHARD F
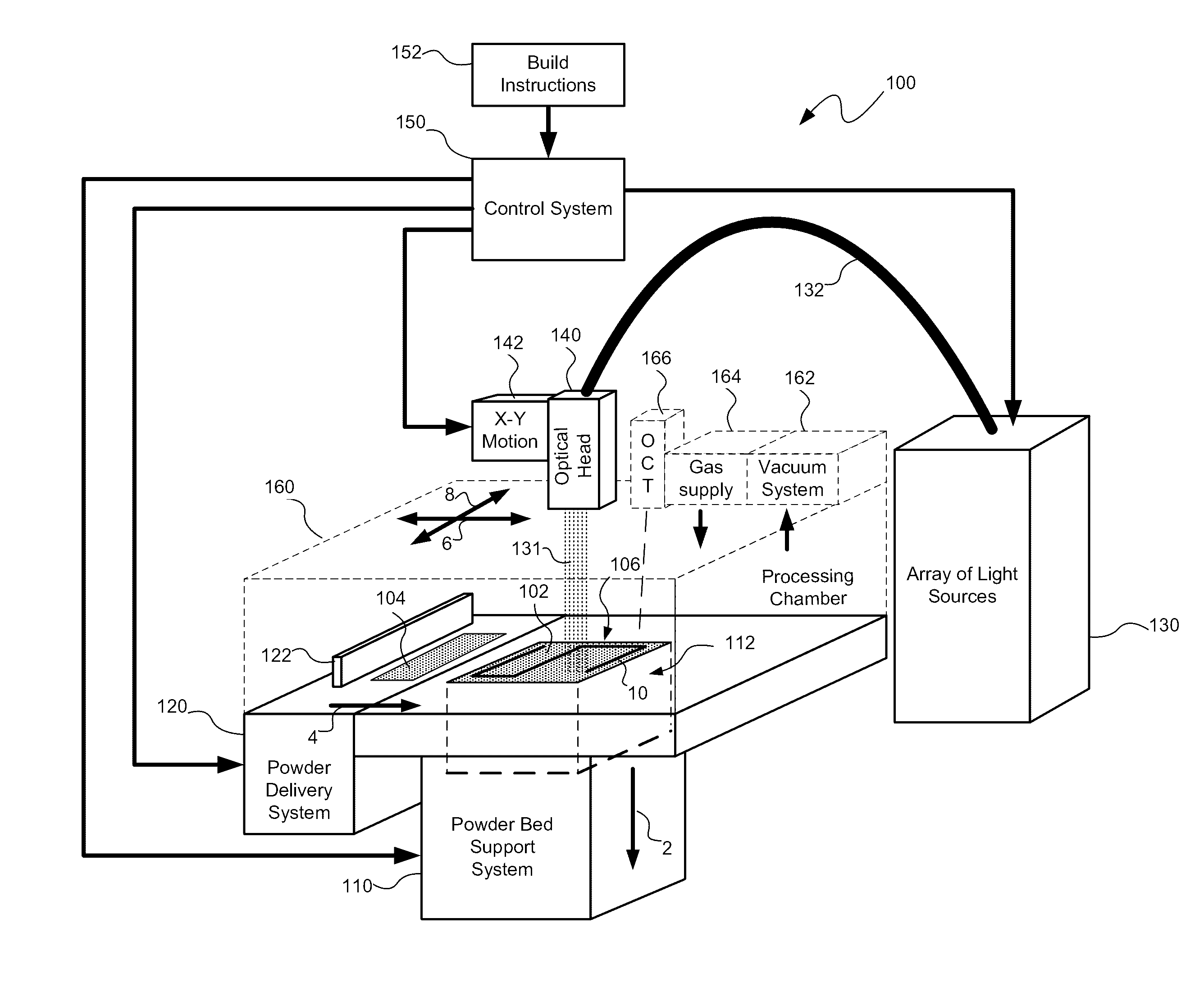
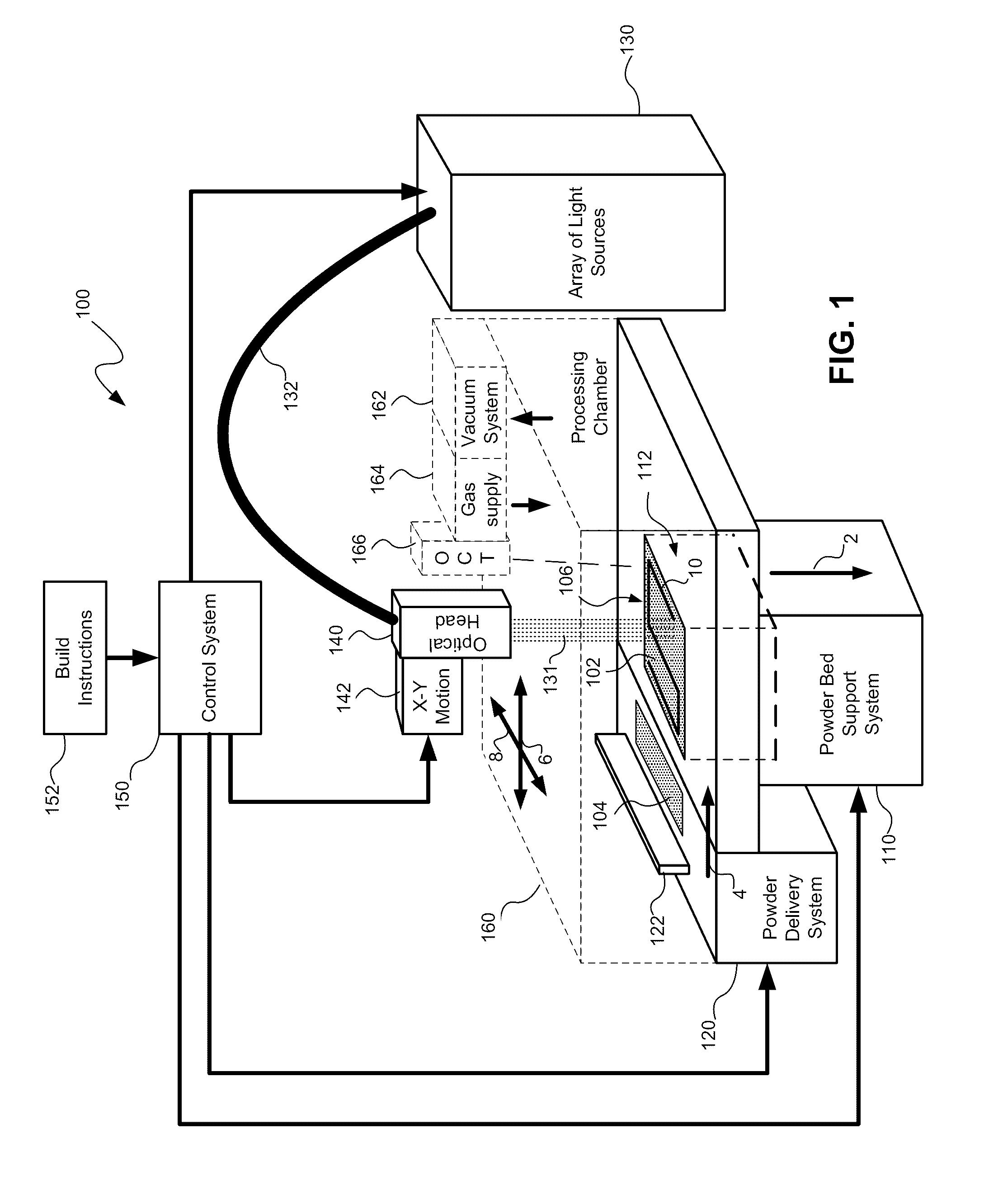
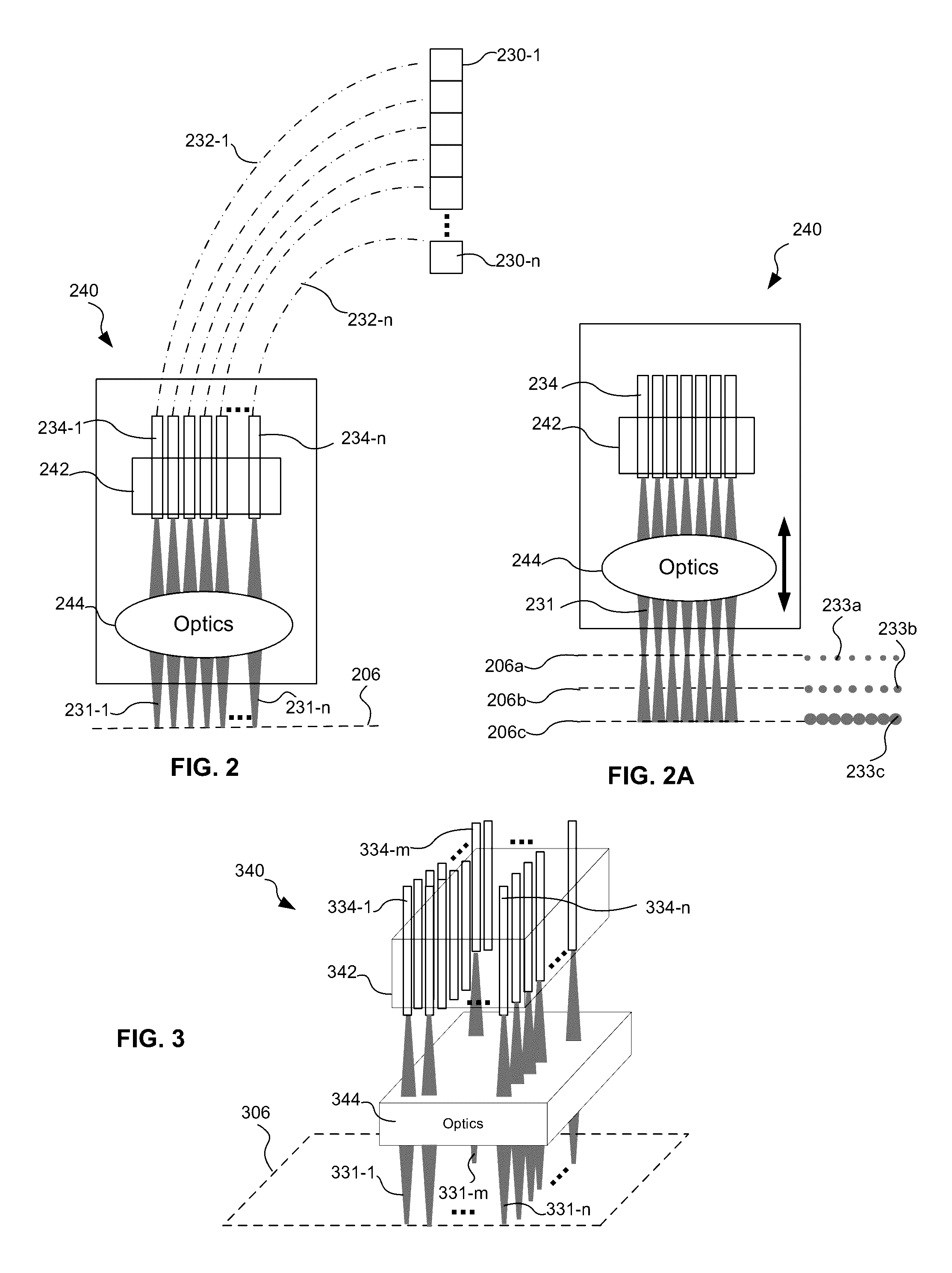
Multiple beam additive manufacturing
Systems and methods for multiple beam additive manufacturing use multiple beams of light (e.g., laser light) to expose layers of powder material in selected regions until the powder material fuses to form voxels, which form build layers of a three-dimensional structure. The light may be generated from selected light sources and coupled into an array of optical fibers having output ends arranged in an optical head in at least one line such that multiple beams are sequentially directed by the optical head to the same powder region providing multiple beam sequential exposures (e.g., with pre-heating, melting and controlled cool down) to fuse the powder region. The multiple sequential beams may be moved using various techniques (e.g., by moving the optical head) and according to various scan patterns such that a plurality of fused regions form each build layer.
Owner:IPG PHOTONICS CORP
Apparatus and Method for Real-Time Volume Processing and Universal Three-Dimensional Rendering
InactiveUS20070206008A1Increase flexibilityImprove performance3D-image rendering3D modellingVoxelGlobal illumination
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
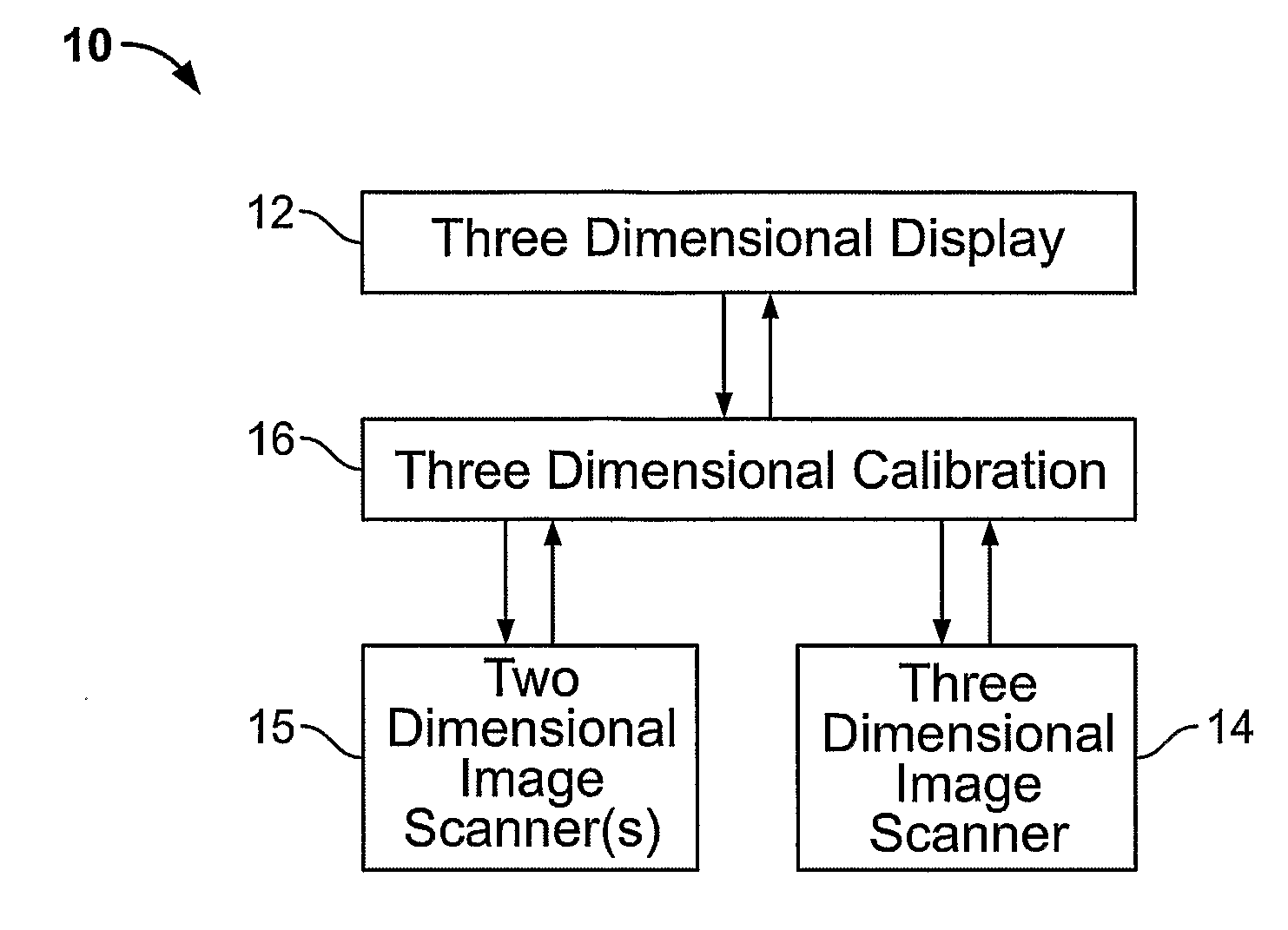
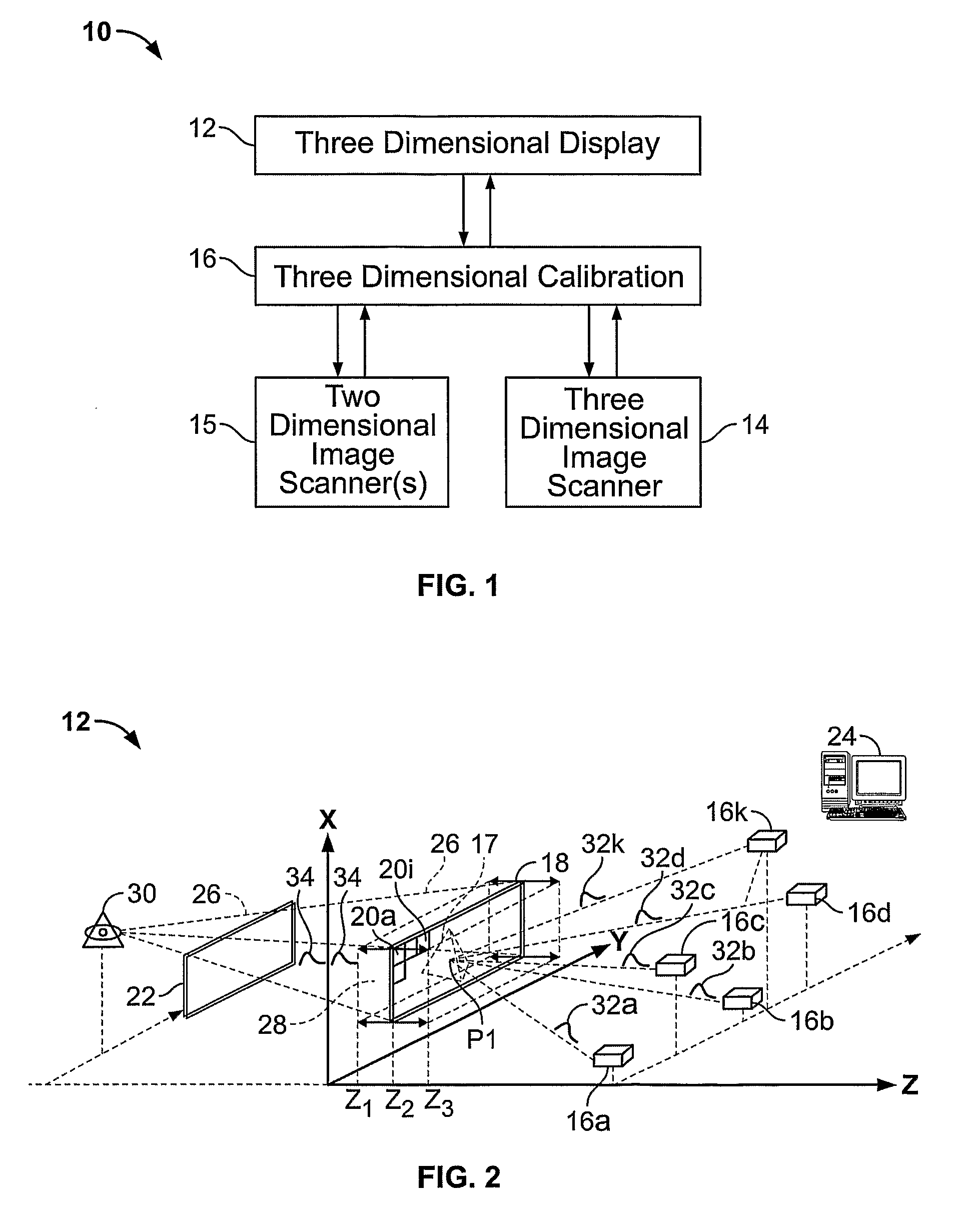
Three-Dimensional Imaging System Using Optical Pulses, Non-Linear Optical Mixers And Holographic Calibration
A three dimensional imaging system is disclosed which includes a three dimensional display (12), three-dimensional calibration equipment (16), and one or more two-dimensional (15) or three dimensional (14) image scanners. The three-dimensional display (12) uses optical pulses (32a-32k) and a non linear optical mixer (18) to display a three-dimensional image (17). The three-dimensional image (17) is generated in voxels of the display volume (28) as the optical mixer (18) sweeps the display volume (28). The three-dimensional calibration equipment (16) uses a hologram projected proximal to a desired object (164) to calibrate optical imaging devices (162a-162c) and to simplify the combination of the images from one or more optical imaging devices (162a-162c) into three-dimensional information. The three-dimensional image scanner (14) employs optical pulses (136, 138) and a non-linear optical mixer (128) to acquire three-dimensional images of a desired object (134). The three-dimensional image scanner (14) captures both the shape and color of a desired object (134).
Owner:STEVENS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
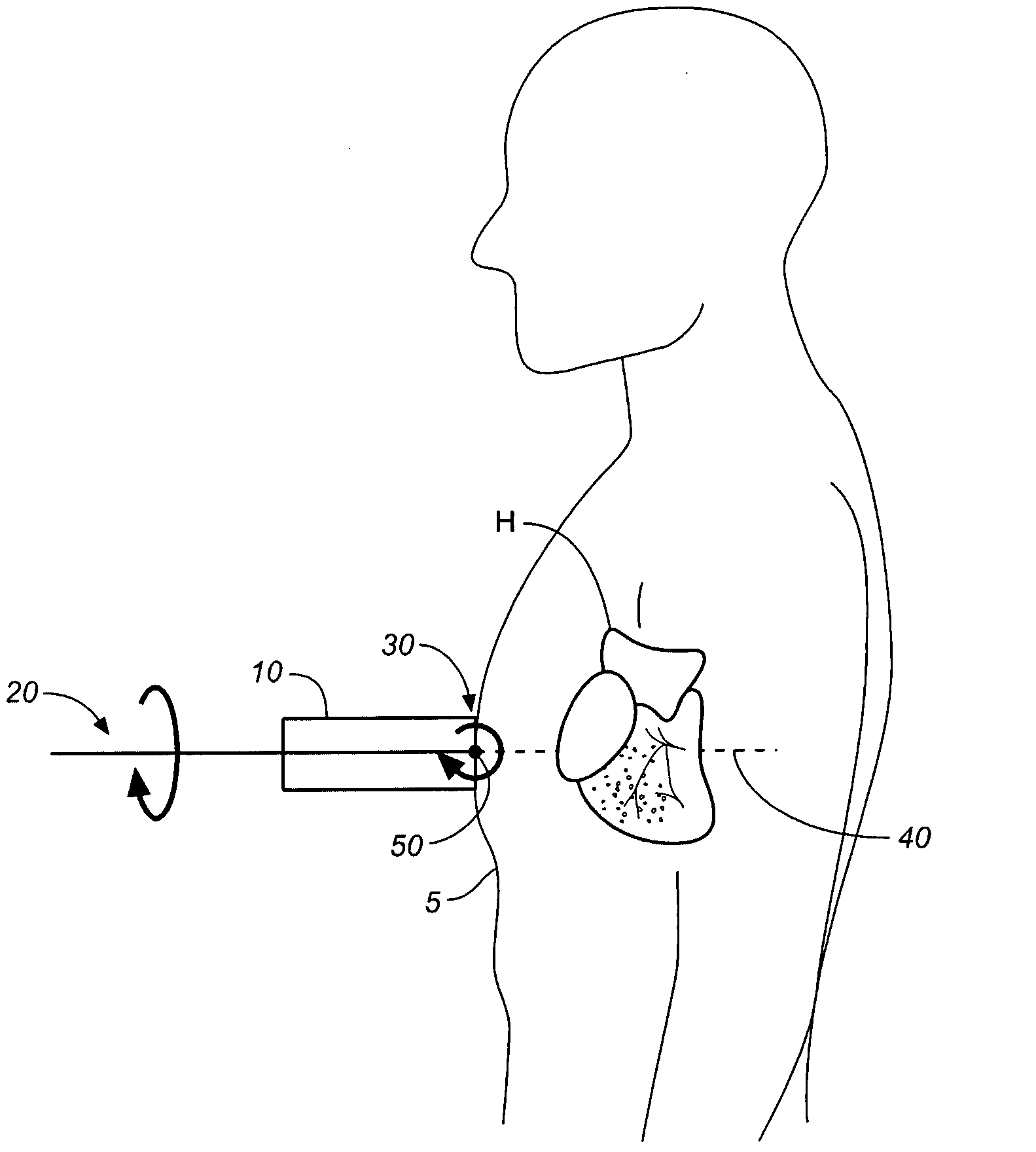
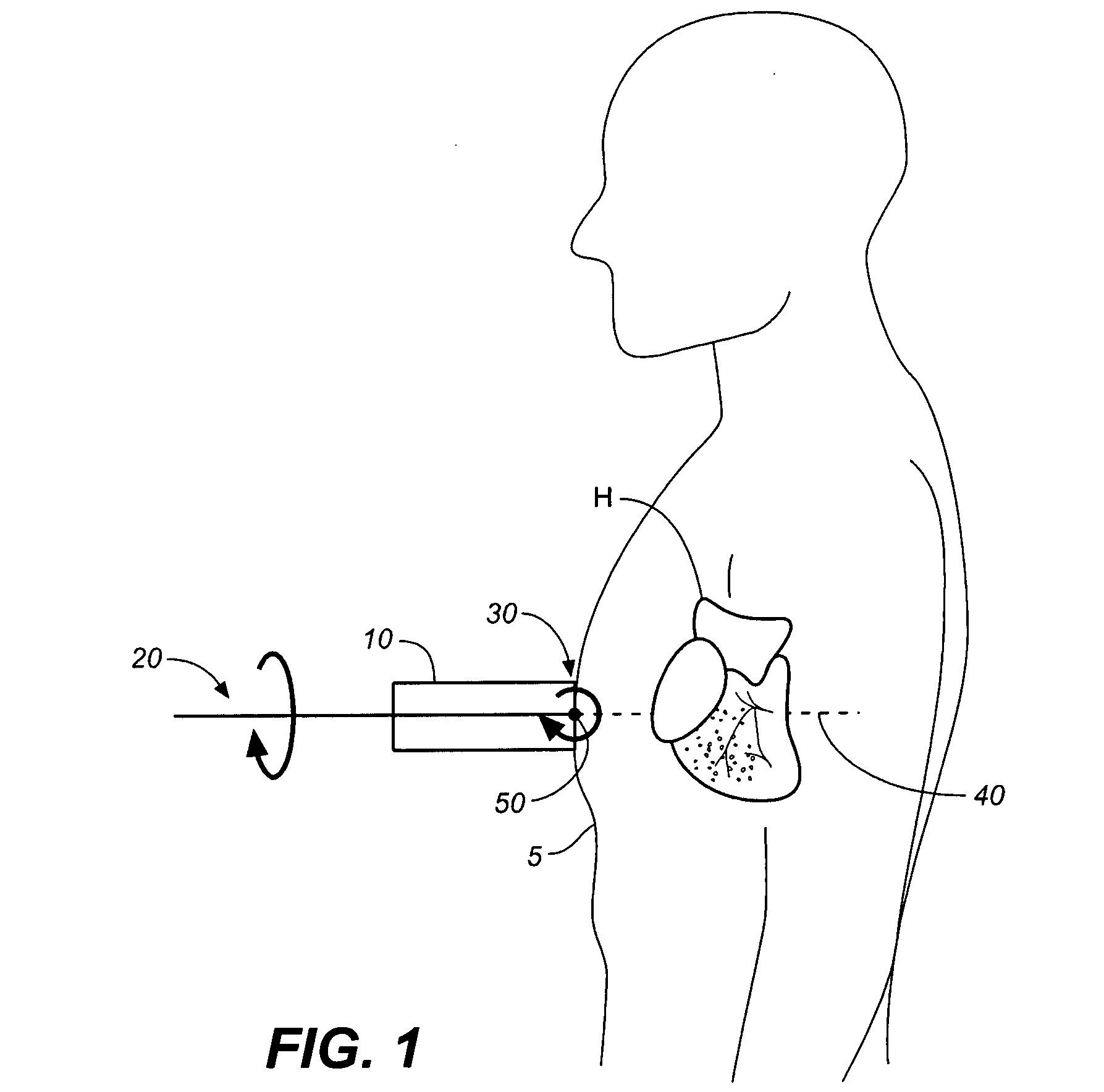
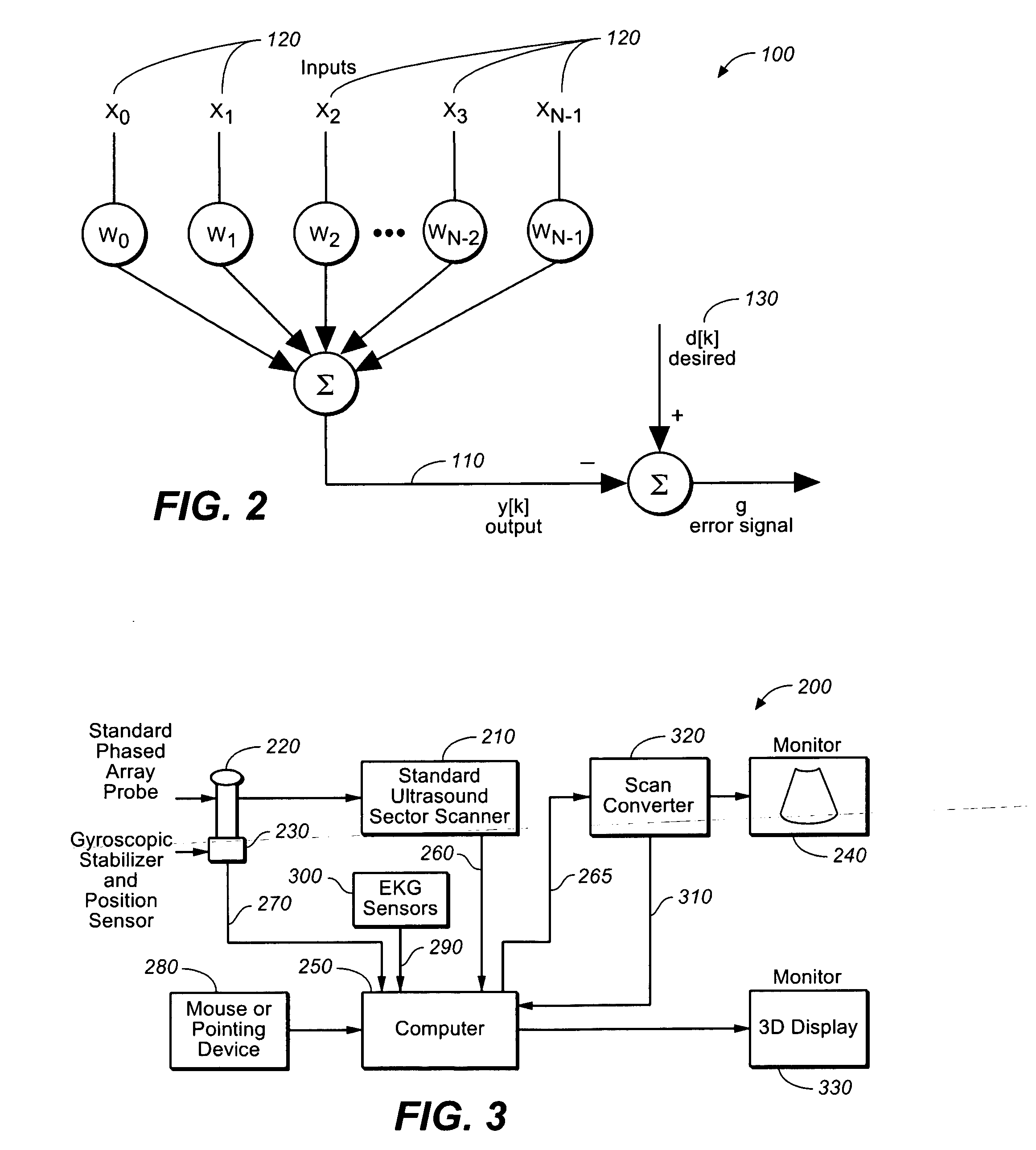
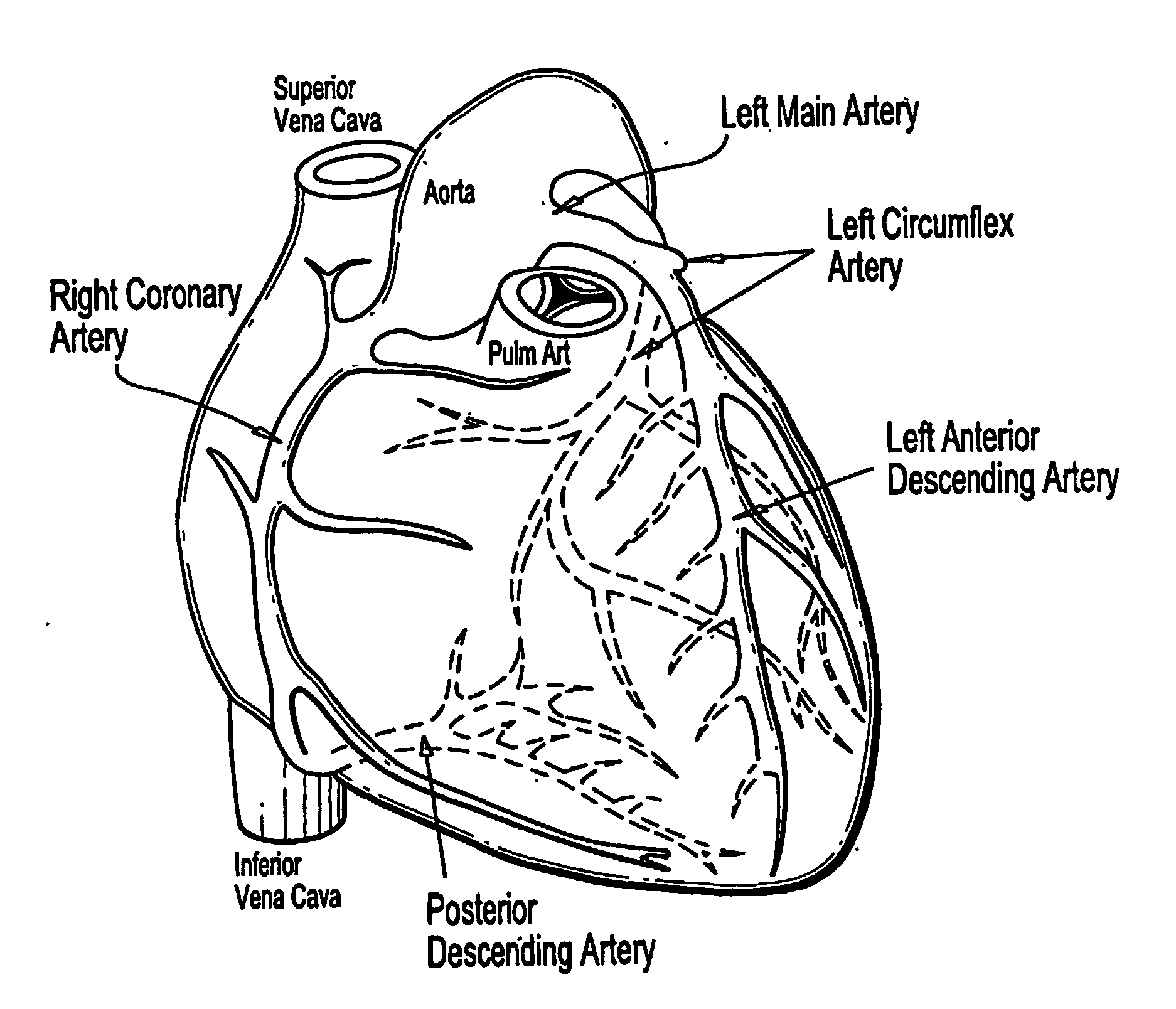
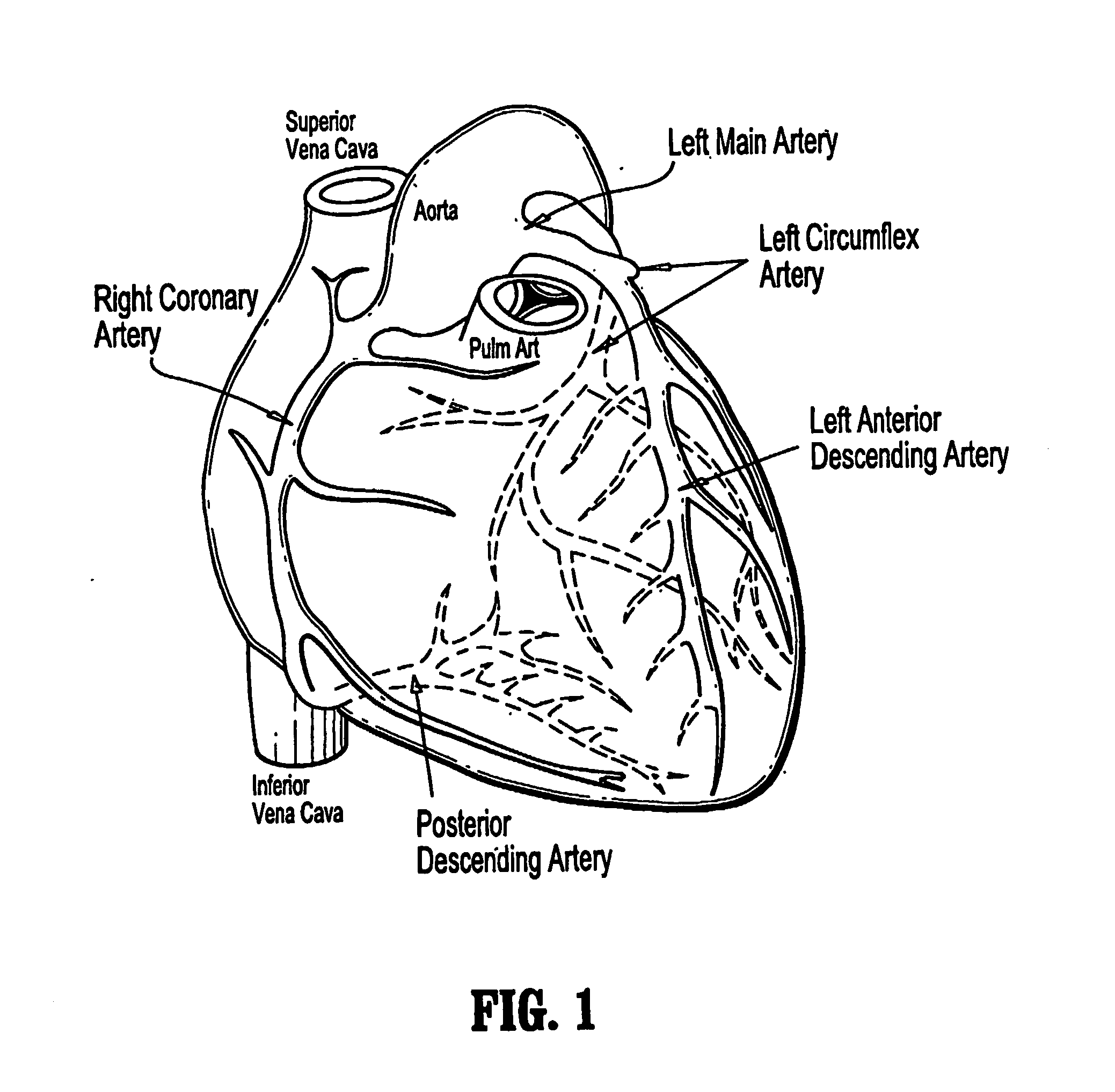
Method and apparatus to visualize the coronary arteries using ultrasound
ActiveUS20070238999A1Improved three dimensional imageReduce noiseImage enhancementImage analysisBLOOD FILLEDScreening techniques
A non-invasive screening technique for visualizing coronary arteries which overcomes the problems of visualizing the curved arteries by projecting the three dimensional volume of the arteries onto a two dimensional screen. Blood filled areas, and in particular, the coronary arteries and veins, are highlighted to contrast them with other nearby tissues using non-linear classification and segmentation techniques. Data is gathered as a sequence of 2D slices stored as a 3D volume. Software is employed to interpolate voxels intermediate to the slices. Wiener filtering or LMS spatial filtering can be implemented on each 2D scan to improve lateral resolution and reduce noise prior to the use of the scan data with the classification and segmentation algorithms. A traditional handheld ultrasound probe is employed to enable the technician to locate the area of interest, but a gyroscopic stabilizer is added to minimize unwanted variation on two axes of rotation while scanning through angles on the third axis of rotation.
Owner:MAUI IMAGING
Method and apparatus for monitoring and quantitatively evaluating tumor perfusion
InactiveUS20030211036A1Deeper understandingNo adverse effect on general well-beingImage analysisIn-vivo radioactive preparationsVoxelResonance
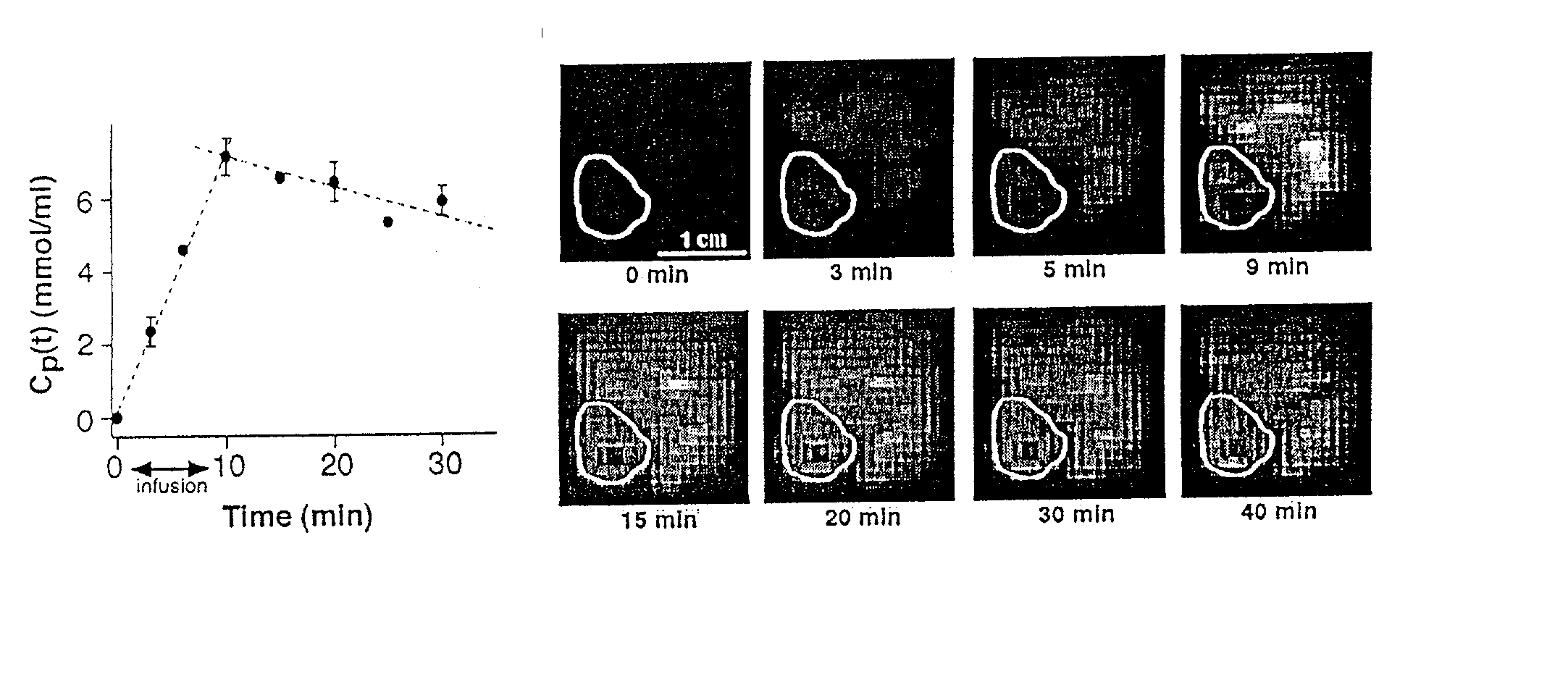
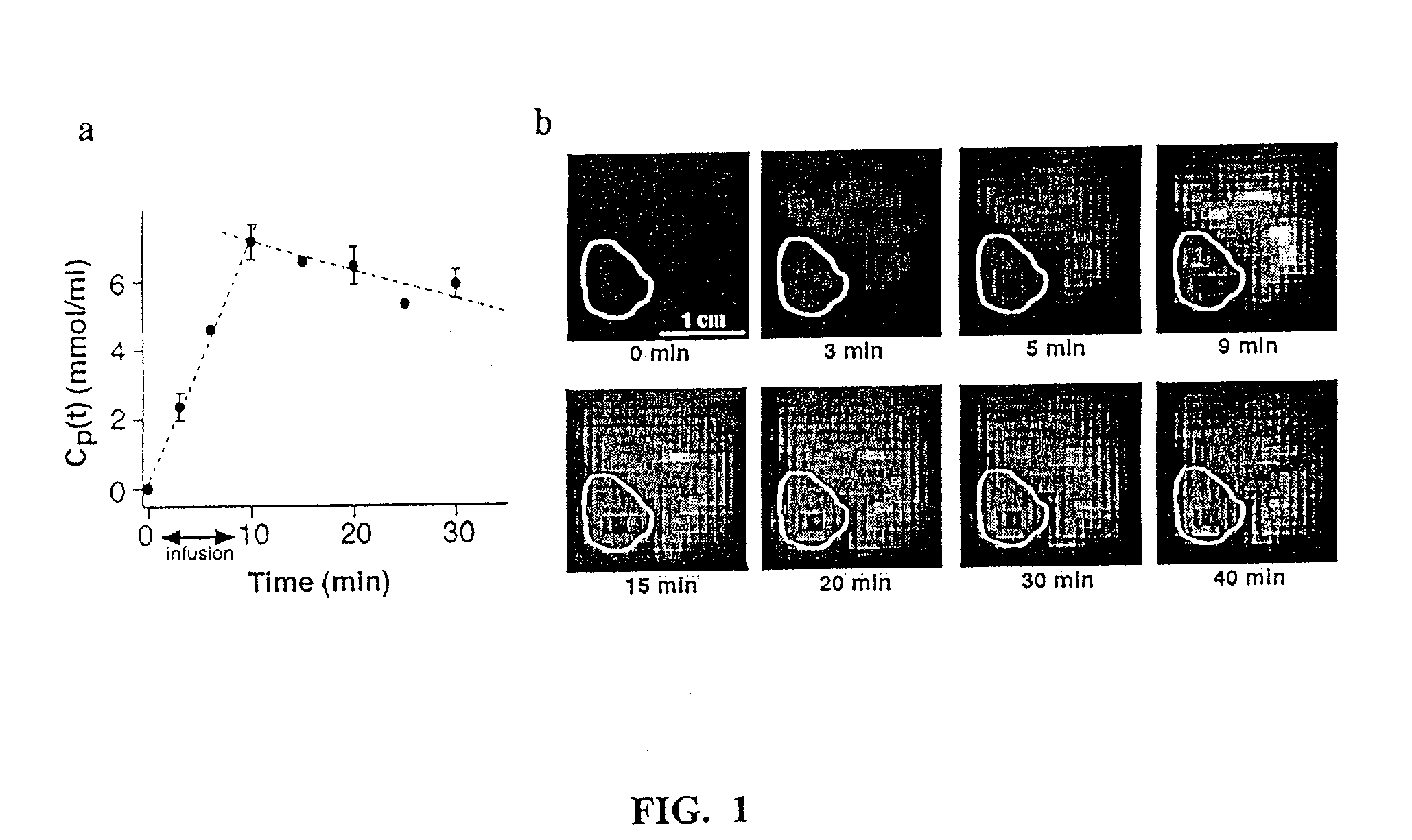
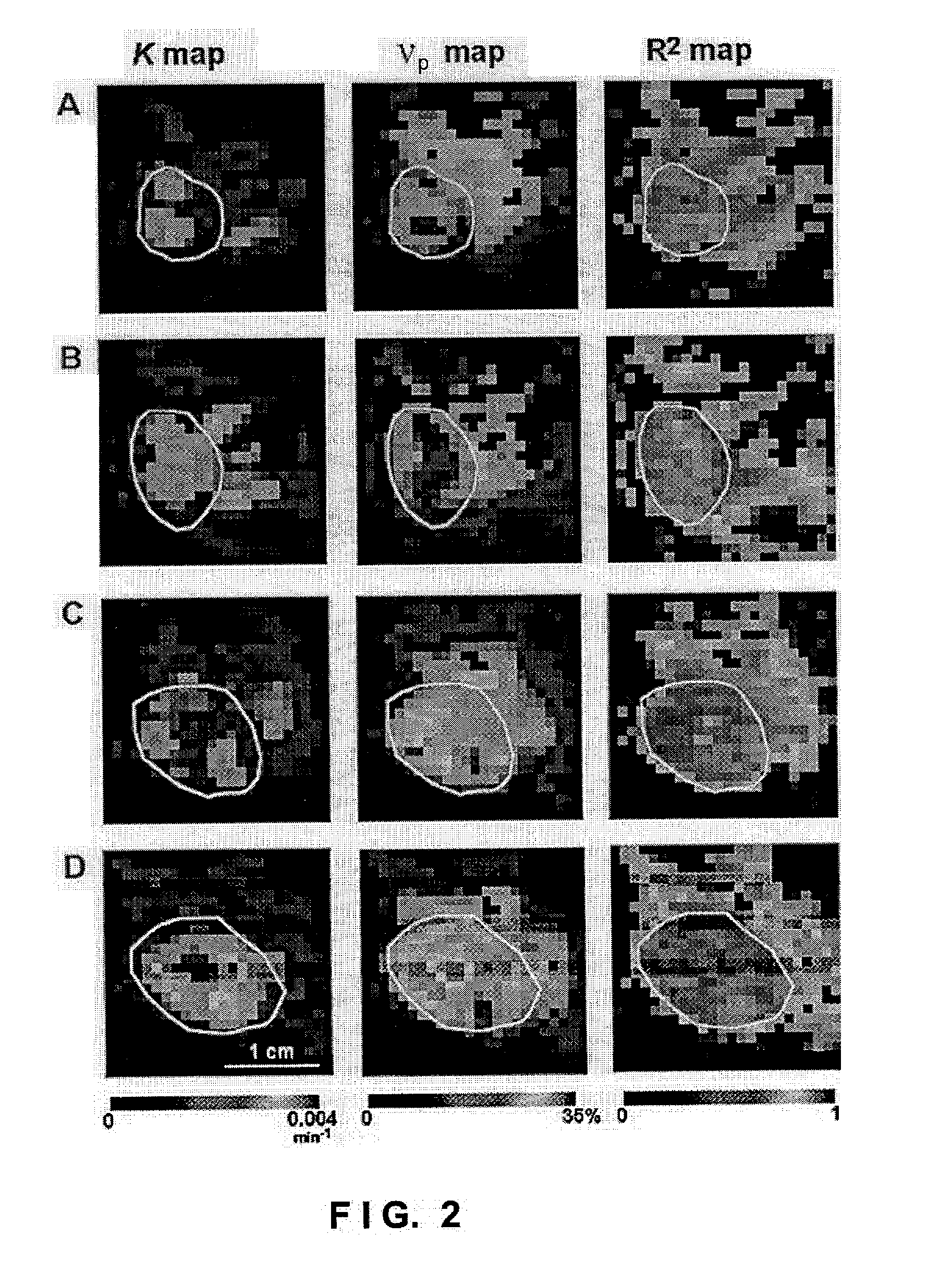
Method and apparatus for monitoring a patient having a tumor to determine perfusion tumor heterogeneity wherein a solution containing a tracer, preferably a <2>H-saline solution is infused into the patient's bloodstream at a predetermined slow rate to effect perfusion into the tumor. An MRI machine is adjusted to acquire a set of dynamic <2>H magnetic resonance images of the tumor. The <2>H-images are obtained before infusion, during infusion and post infusion. First, the obtained images are processed to quantitatively determine perfusion per voxel of the images. Next, maps of perfusion parameters are generated to indicate spatial distribution of tumor perfusion. The maps are displayed in color code and analyzed.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD AT THE WEISZMANN INST OF SCI
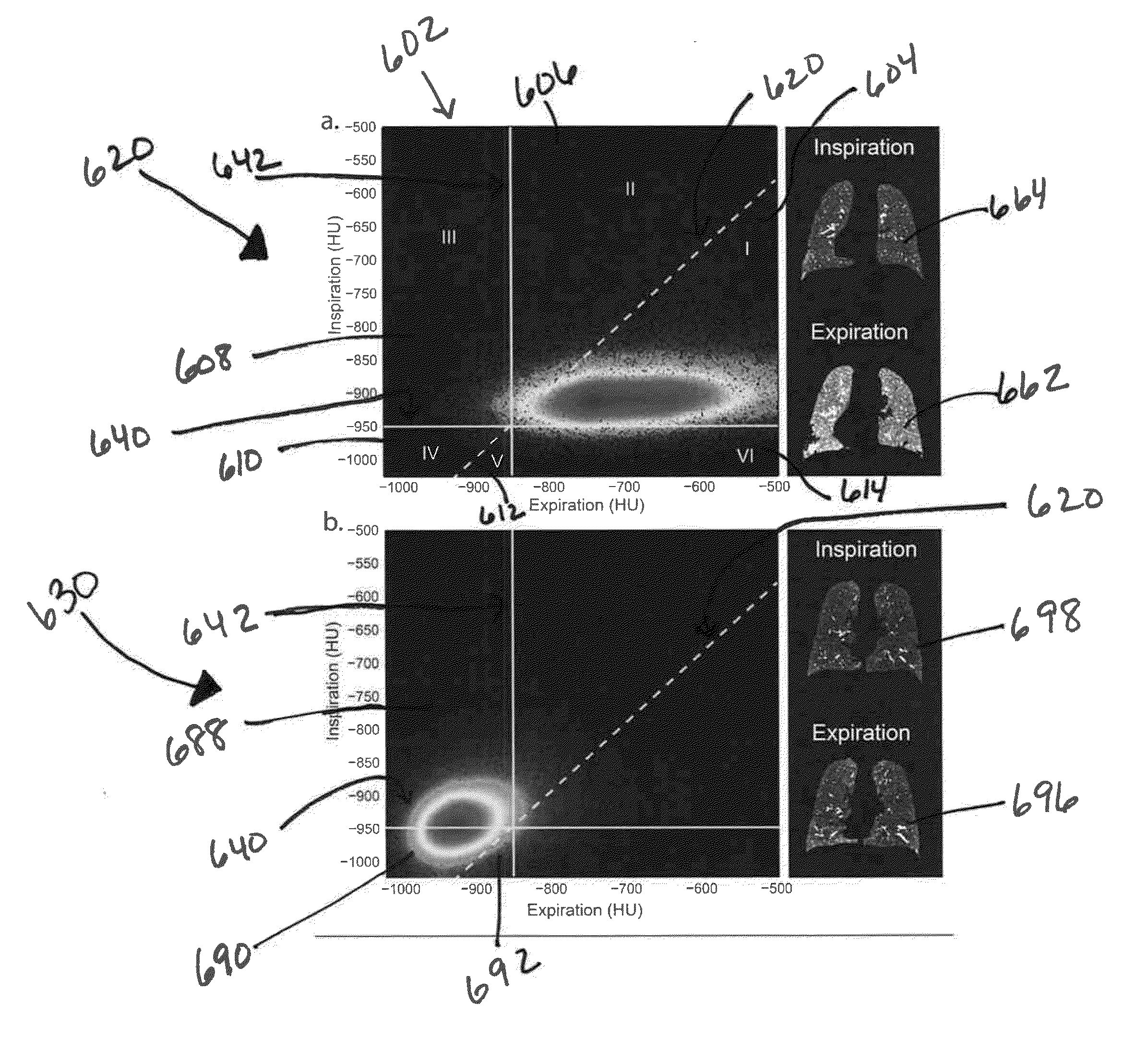
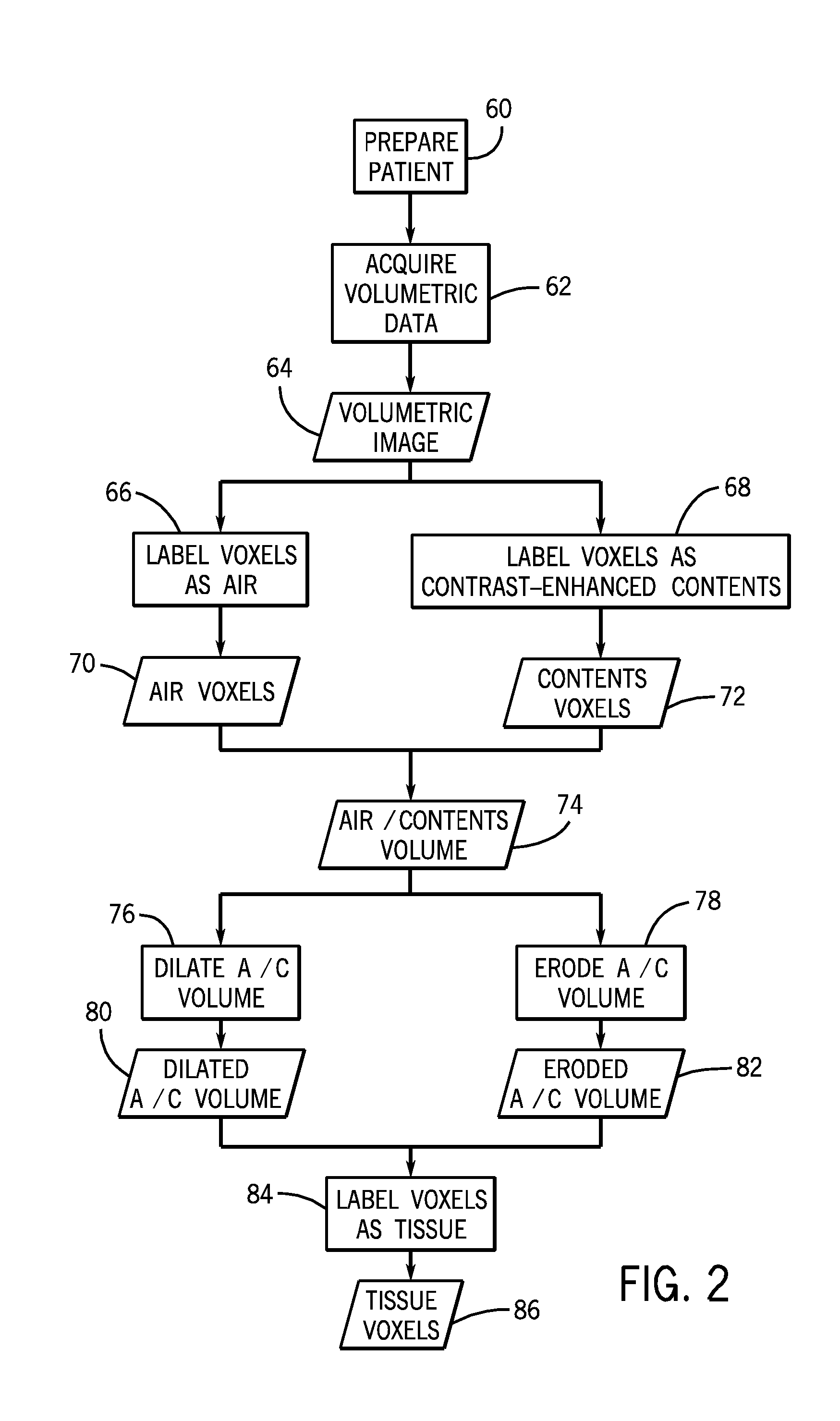
Tissue Phasic Classification Mapping System and Method
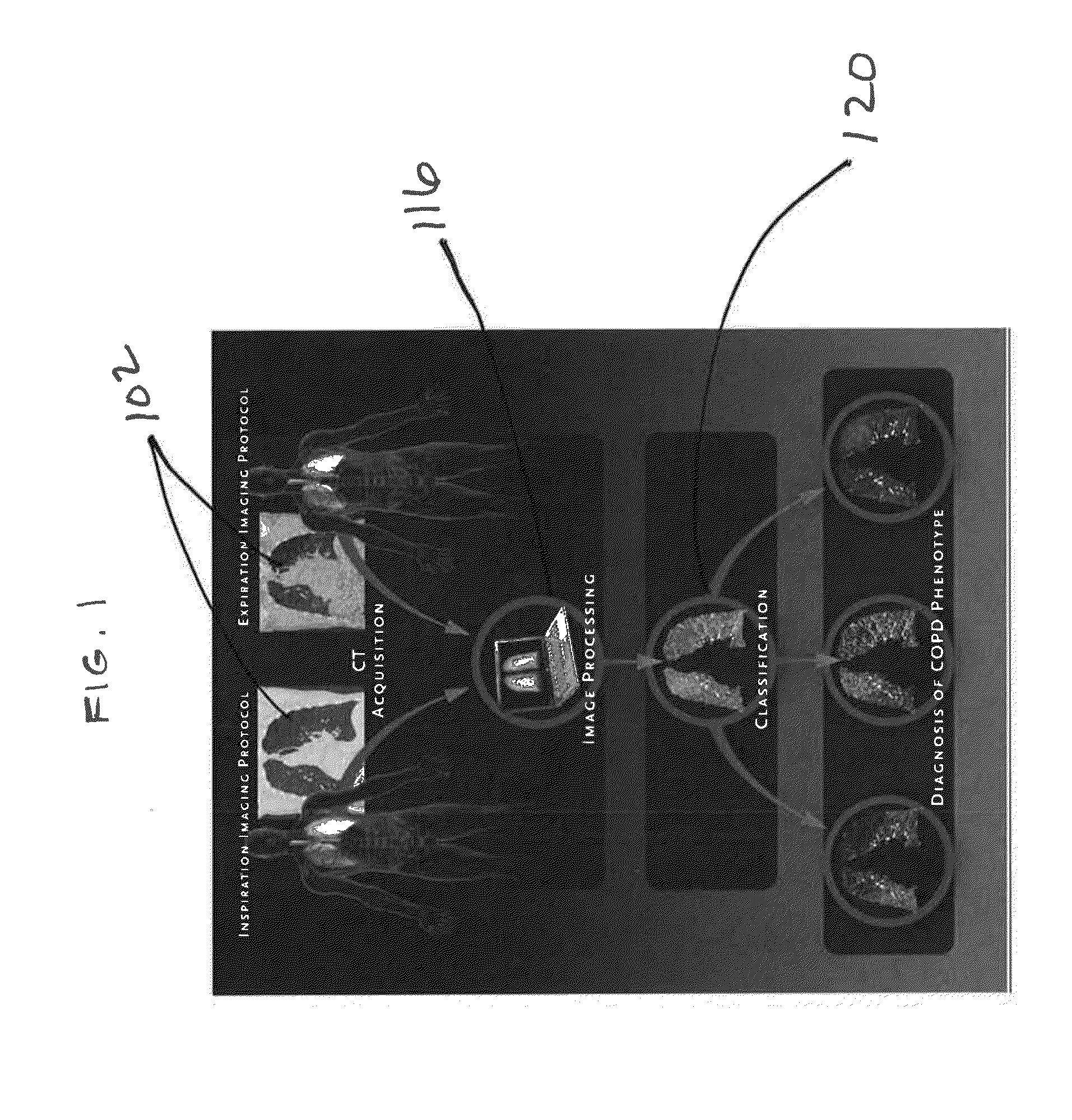
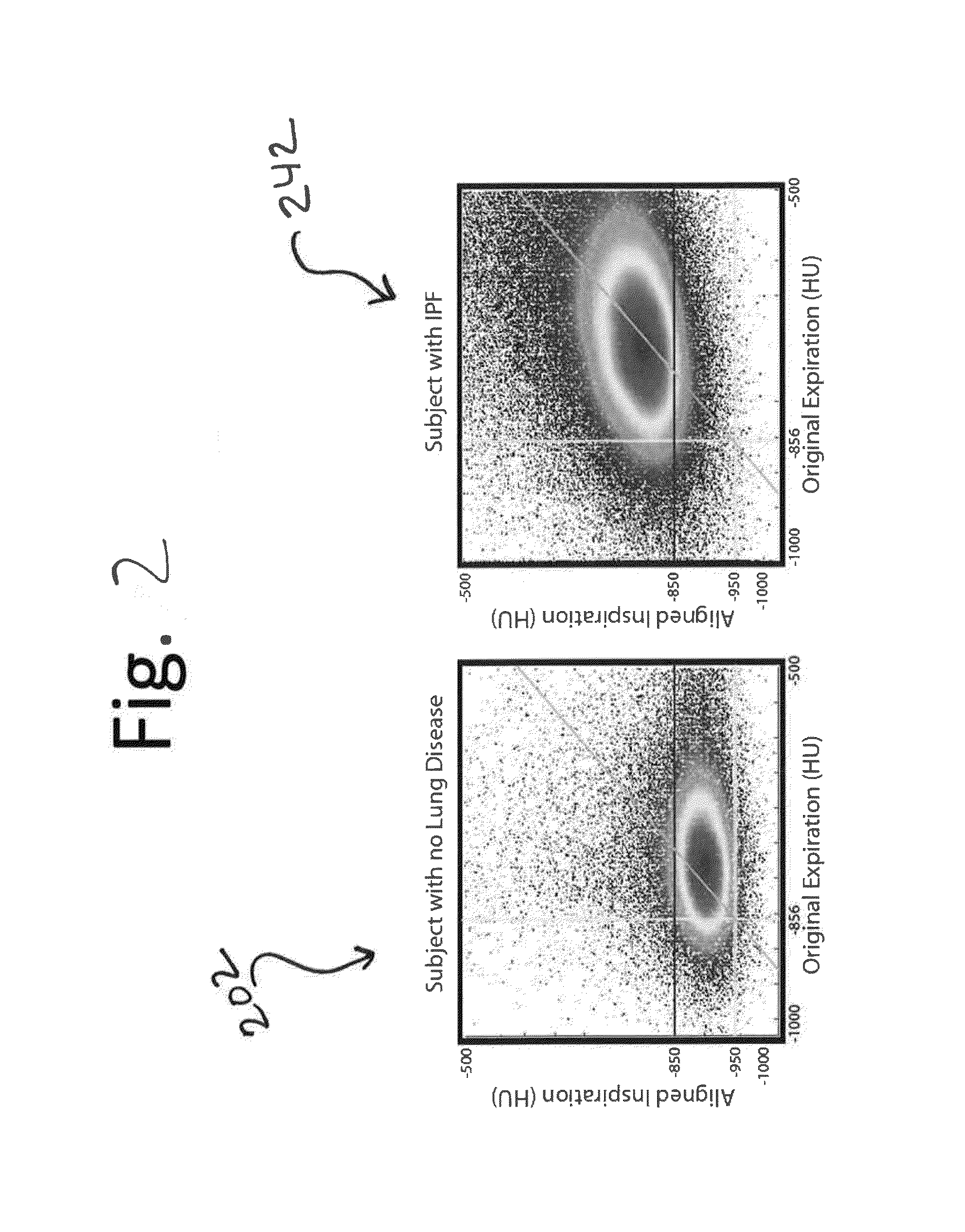
A voxel-based technique is provided for performing quantitative imaging and analysis of tissue image data. Serial image data is collected for tissue of interest at different states of the issue. The collected image data may be deformably registered, after which the registered image data is analyzed on a voxel-by-voxel basis, thereby retaining spatial information for the analysis. Various thresholds are applied to the registered tissue data to identify a tissue condition or state, such as classifying chronic obstructive pulmonary disease by disease phenotype in lung tissue, for example.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
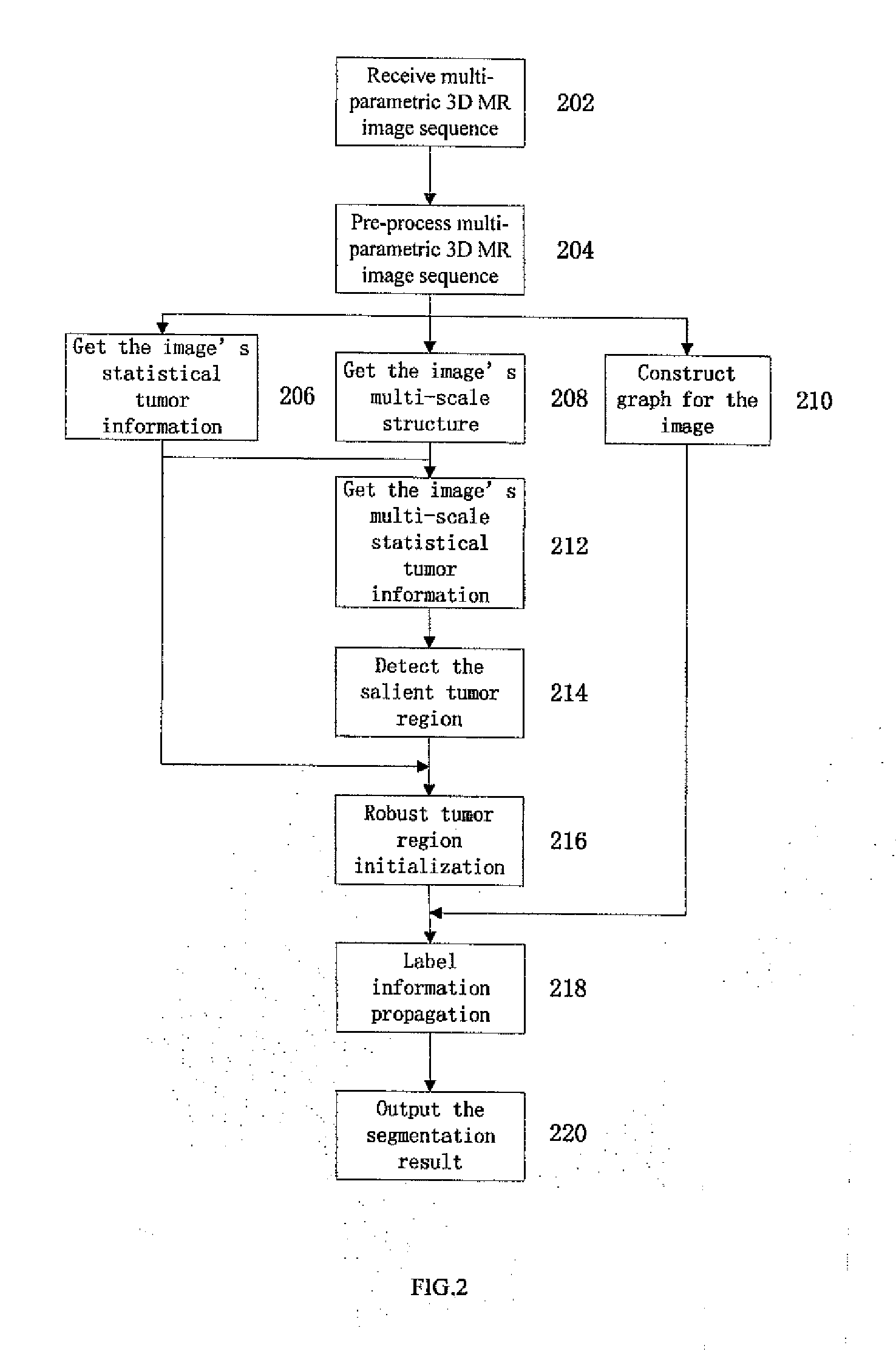
Method for brain tumor segmentation in multi-parametric image based on statistical information and multi-scale struture information
InactiveUS20130182931A1Accurate and reliable tumor segmentationPerformance degradation can be reducedImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionVoxel
A method for brain tumor segmentation in multi-parametric 3D magnetic resonance (MR) images, comprising: determining, for each voxel in the multi-parametric 3D MR image sequence, a probability that the voxel is part of brain tumor; extracting multi-scale structure information of the image; generating multi-scale tumor probability map based on initial tumor probability at voxel level and multi-scale structure information; determining salient tumor region based on multi-scale tumor probability map; obtaining robust initial tumor and non-tumor label based on tumor probability map at voxel level and salient tumor region; and generating a segmented brain tumor image using graph based label information propagation. The present invention is capable of achieving statistical reliable, spatially compact, and robust tumor label initialization, which is helpful to the accurate and reliable tumor segmentation. And the label information propagation framework could partially alleviate the performance degradation caused by image inconsistency between images to be segmented and training images.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
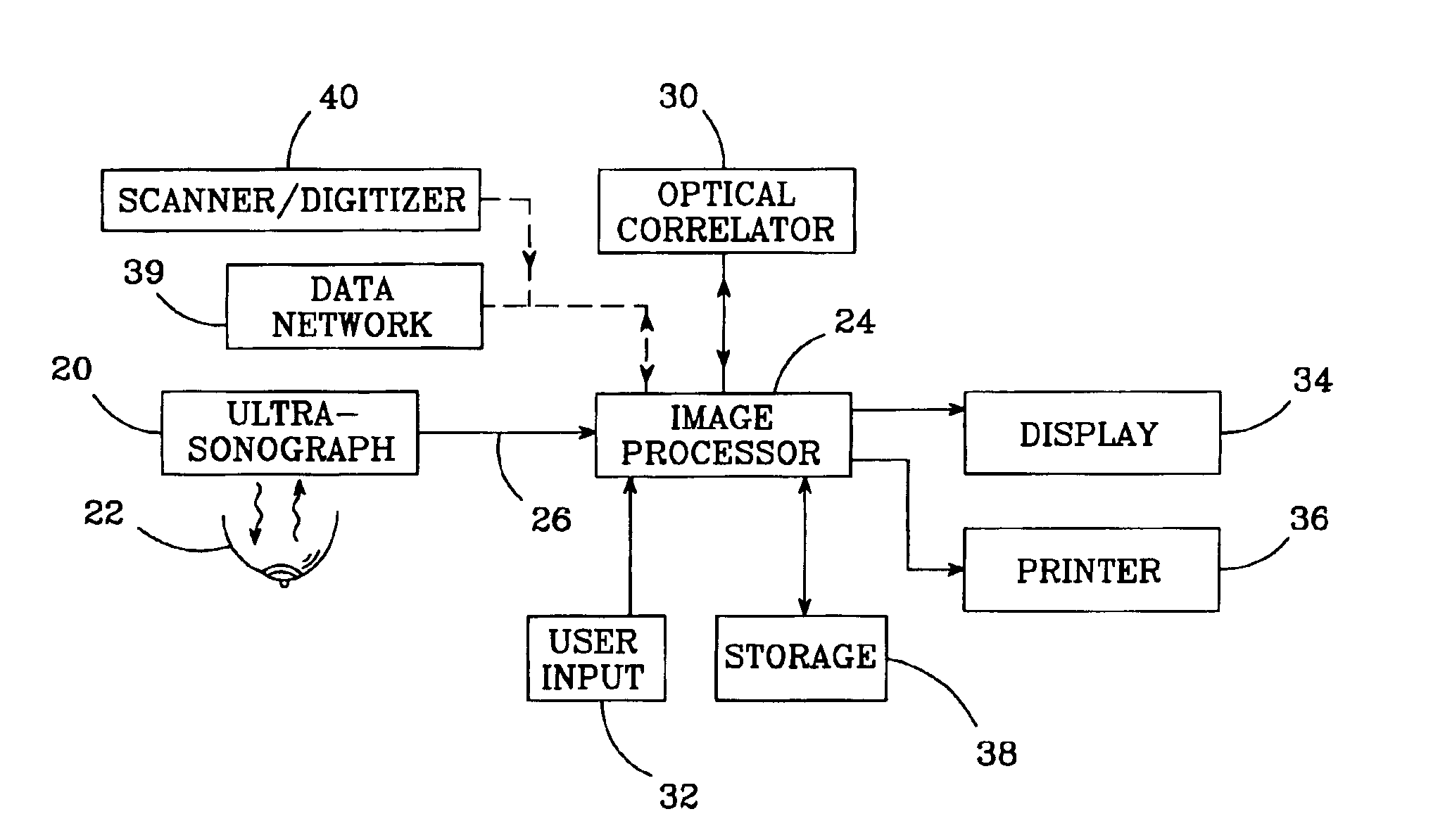
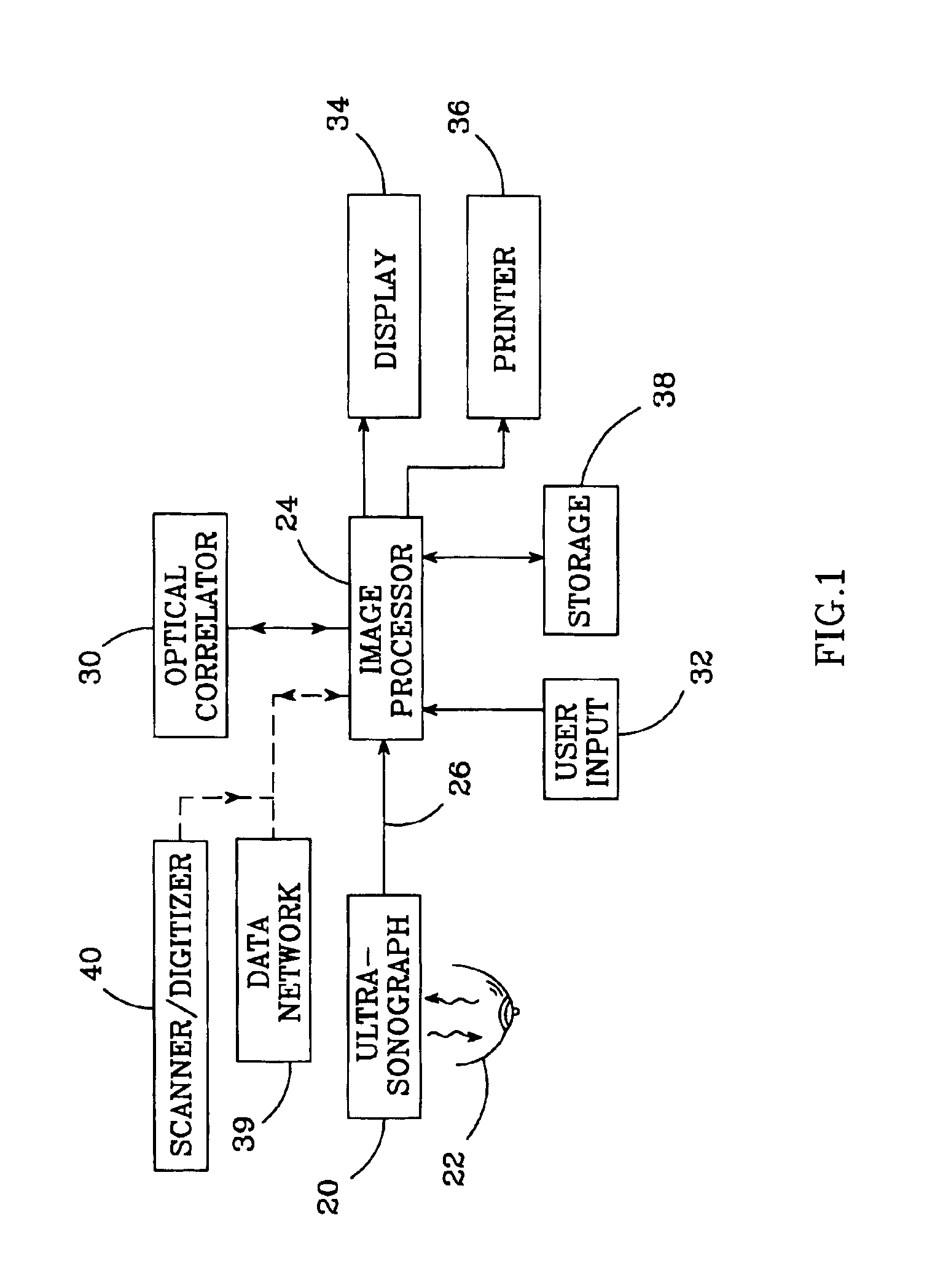
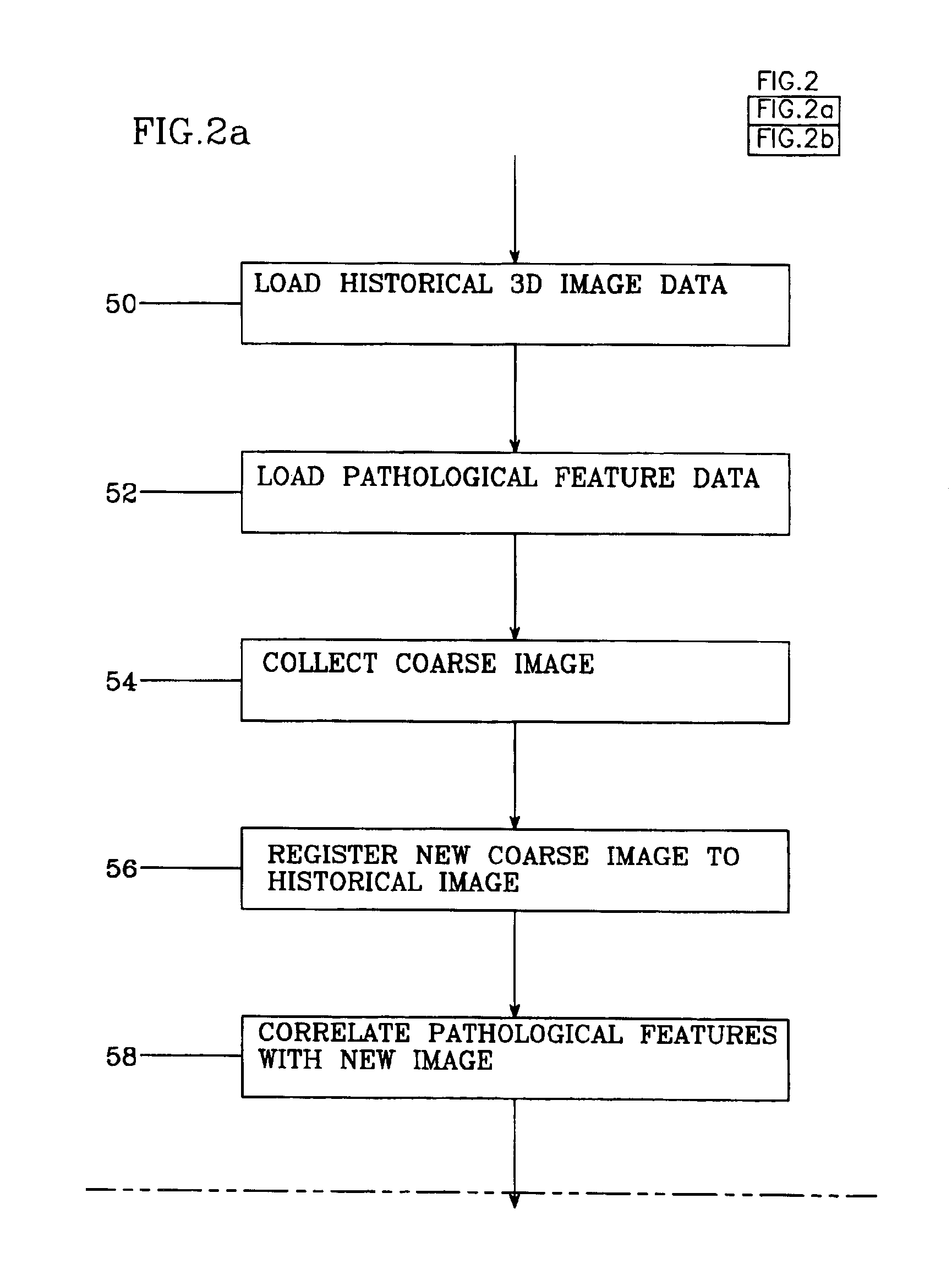
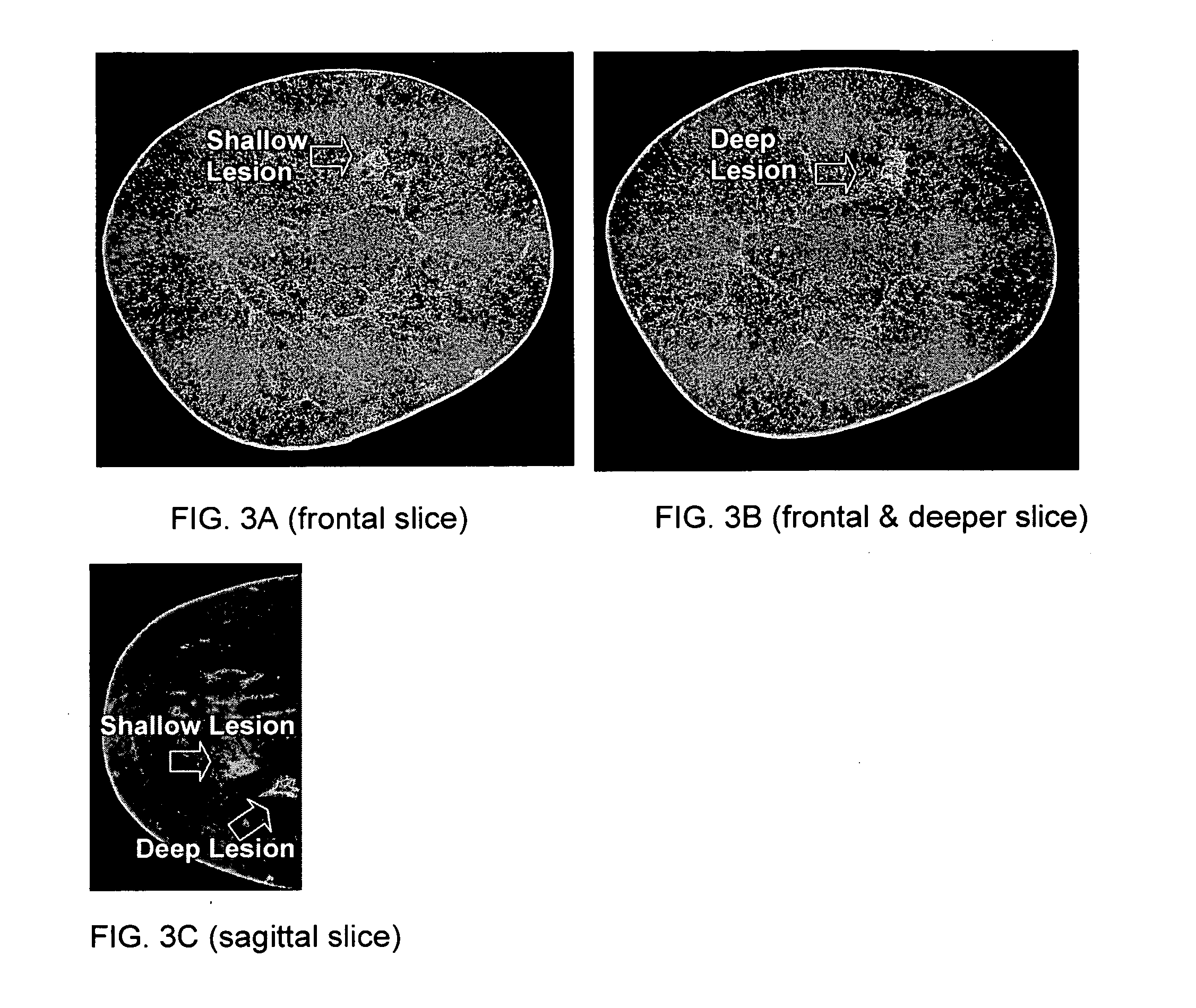
Historical comparison of breast tissue by image processing
An image processing system and method visually documents and displays changes between historical and later mammographic images, preferably in three dimensions. A composite image is created which visually emphasizes temporal differences between the historical and later images. Preferably three-dimensional, digitized images, displayable in various projections, are stored for archival purposes on computer readable media. An image processor preferably exploits an optical correlator to register the historical and later images accurately and provide correlation values as temporal scalars of the differences. The registered images are then compared, voxel-by-voxel, to detect temporal differences. The composite image is displayed with synthetic colors or other visual clues to emphasize apparent changes (for example, tumor growth or shrinkage).
Owner:LITTON SYST INC +1
Tissue classification in medical images
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
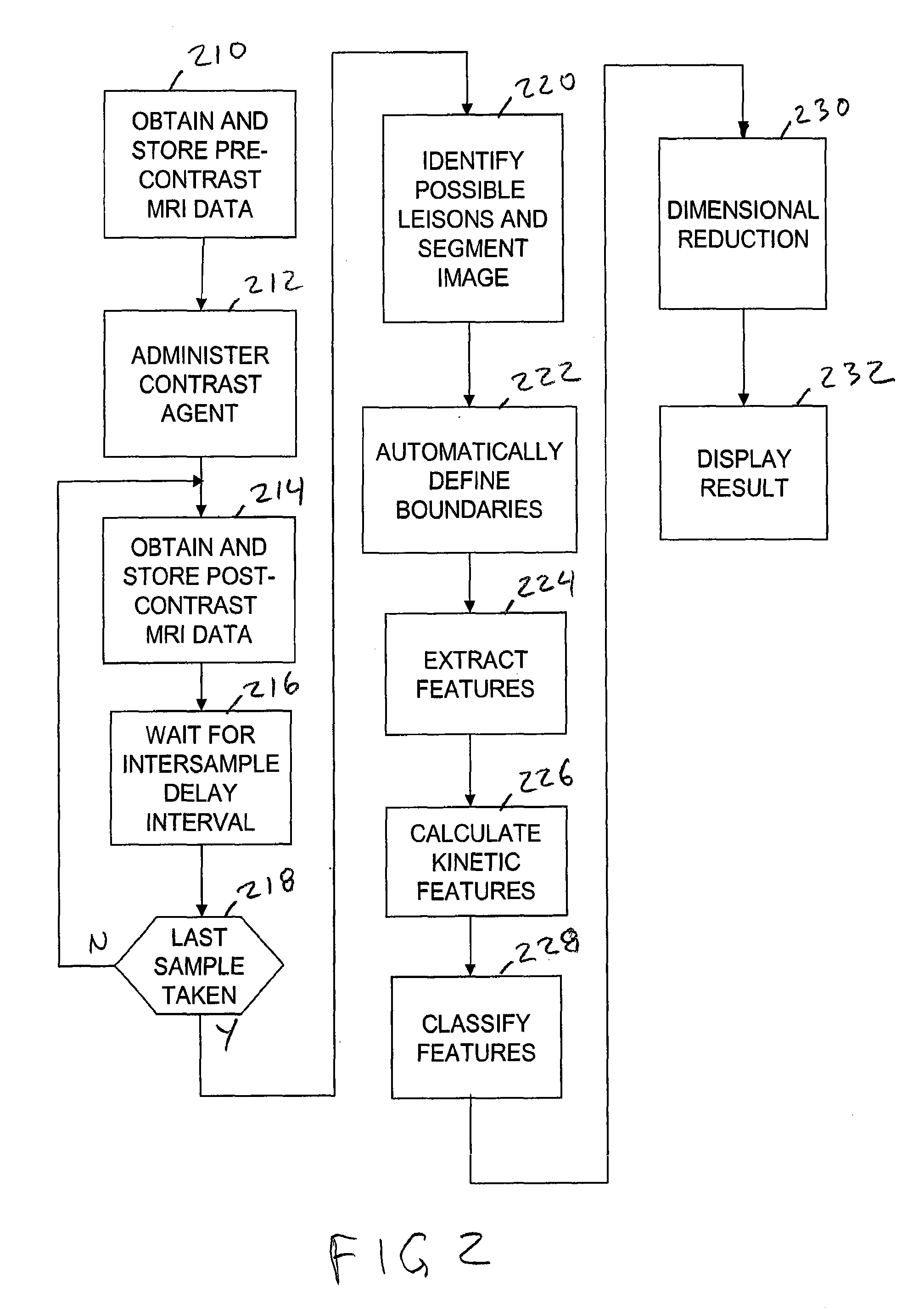
System and method for automated segmentation, characterization, and classification of possibly malignant lesions and stratification of malignant tumors
A method and apparatus for classifying possibly malignant lesions from sets of DCE-MRI images includes receiving a set of MRI slice images obtained at respectively different times, where each slice image includes voxels representative of at least one region of interest (ROI). The images are processed to determine the boundaries of the ROIs and the voxels within the identified boundaries in corresponding regions of the images from each time period are processed to extract kinetic texture features. The kinetic texture features are then used in a classification process which classifies the ROIs as malignant or benign. The malignant lesions are further classified to separate TN lesions from non-TN lesions.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Imaging system and methods for cardiac analysis
InactiveUS20110206247A1Efficiently and accurately detect and viewLess tediousImage enhancementImage analysisGraphicsHuman anatomy
Imaging systems and methods for viewing medical images of human anatomy and, in particular, to a 3-dimensional imaging system that allows a user to efficiently and accurately detect and view coronary artery calcification as displayed graphically on a computer screen. In one aspect, a method for displaying medical images comprises obtaining an image dataset comprising anatomical image data (step 50), automatically grouping connected components in the image data to form groups of connected components (steps 50-57), and displaying the groups of connected components are distinguishable in the displayed image (58-59). The image dataset may comprise a volume data set and the groups of connected components comprise regions of neighboring voxels that share a similar property. The image dataset may comprise a 2-dimensional data set and the groups of connected components comprise regions of neighboring pixels that share a similar property. Different groups of connected components may be displayed in different colors and / or different opacities or certain groups may not be displayed at all.
Owner:VIATRONIX
Displaying image data using automatic presets
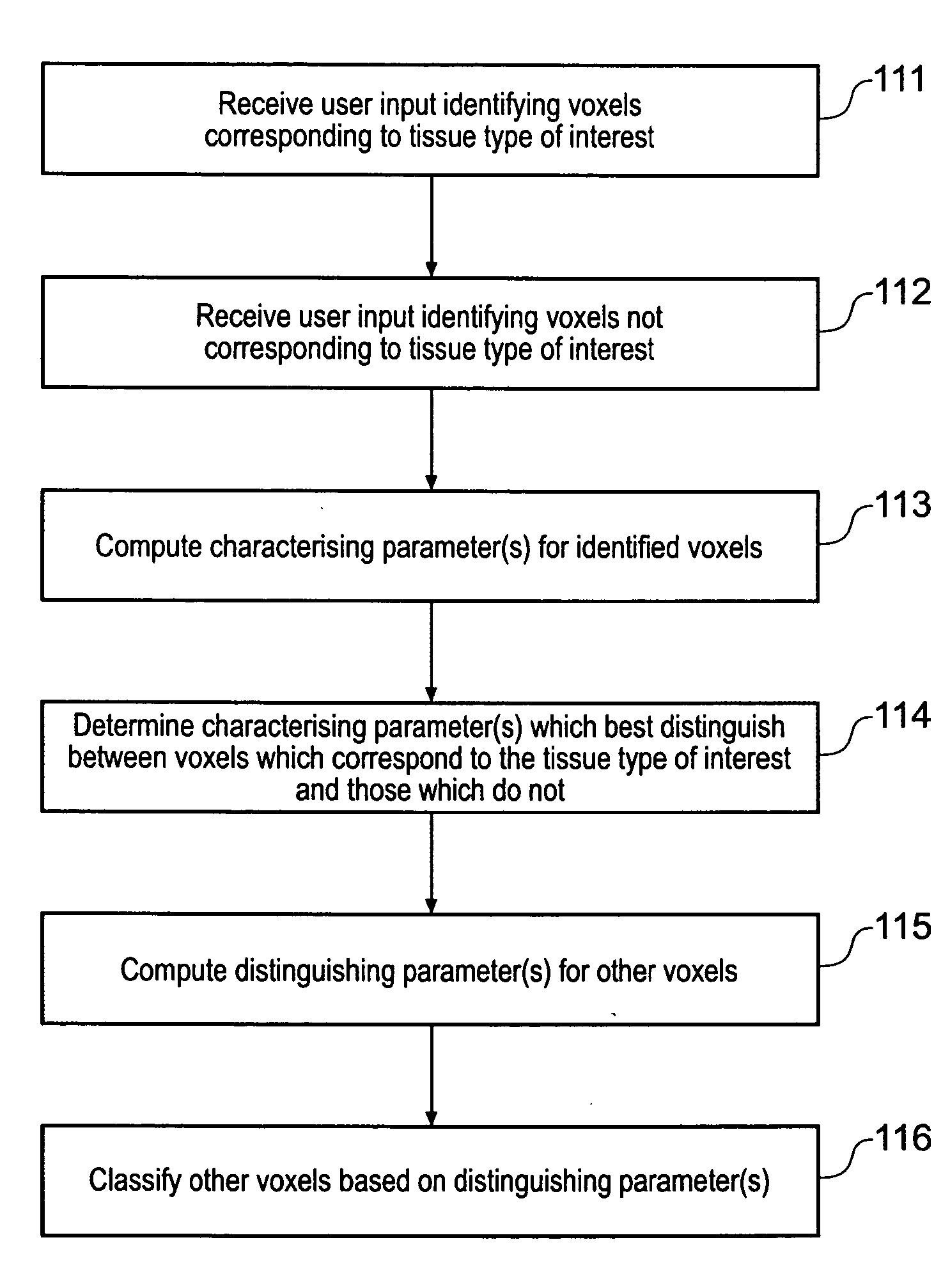
InactiveUS20050017972A1Easy and intuitiveAccurate classificationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementPattern recognitionVoxel
A computer automated method that applies supervised pattern recognition to classify whether voxels in a medical image data set correspond to a tissue type of interest is described. The method comprises a user identifying examples of voxels which correspond to the tissue type of interest and examples of voxels which do not. Characterizing parameters, such as voxel value, local averages and local standard deviations of voxel value are then computed for the identified example voxels. From these characterizing parameters, one or more distinguishing parameters are identified. The distinguishing parameter are those parameters having values which depend on whether or not the voxel with which they are associated corresponds to the tissue type of interest. The distinguishing parameters are then computed for other voxels in the medical image data set, and these voxels are classified on the basis of the value of their distinguishing parameters. The approach allows tissue types which differ only slightly to be distinguished according to a user's wishes.
Owner:VOXAR
Local Alignment and Positioning Device and Method
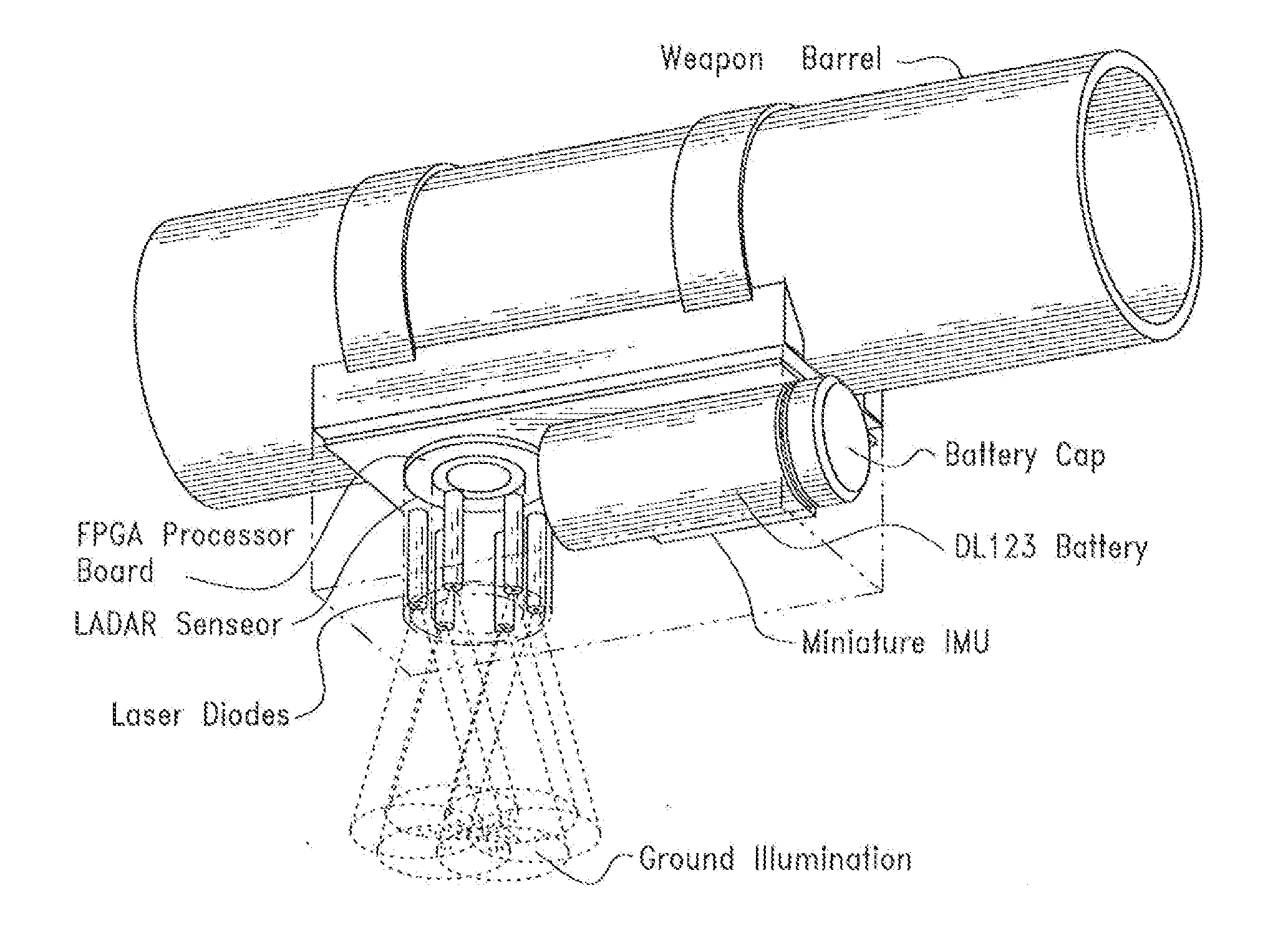
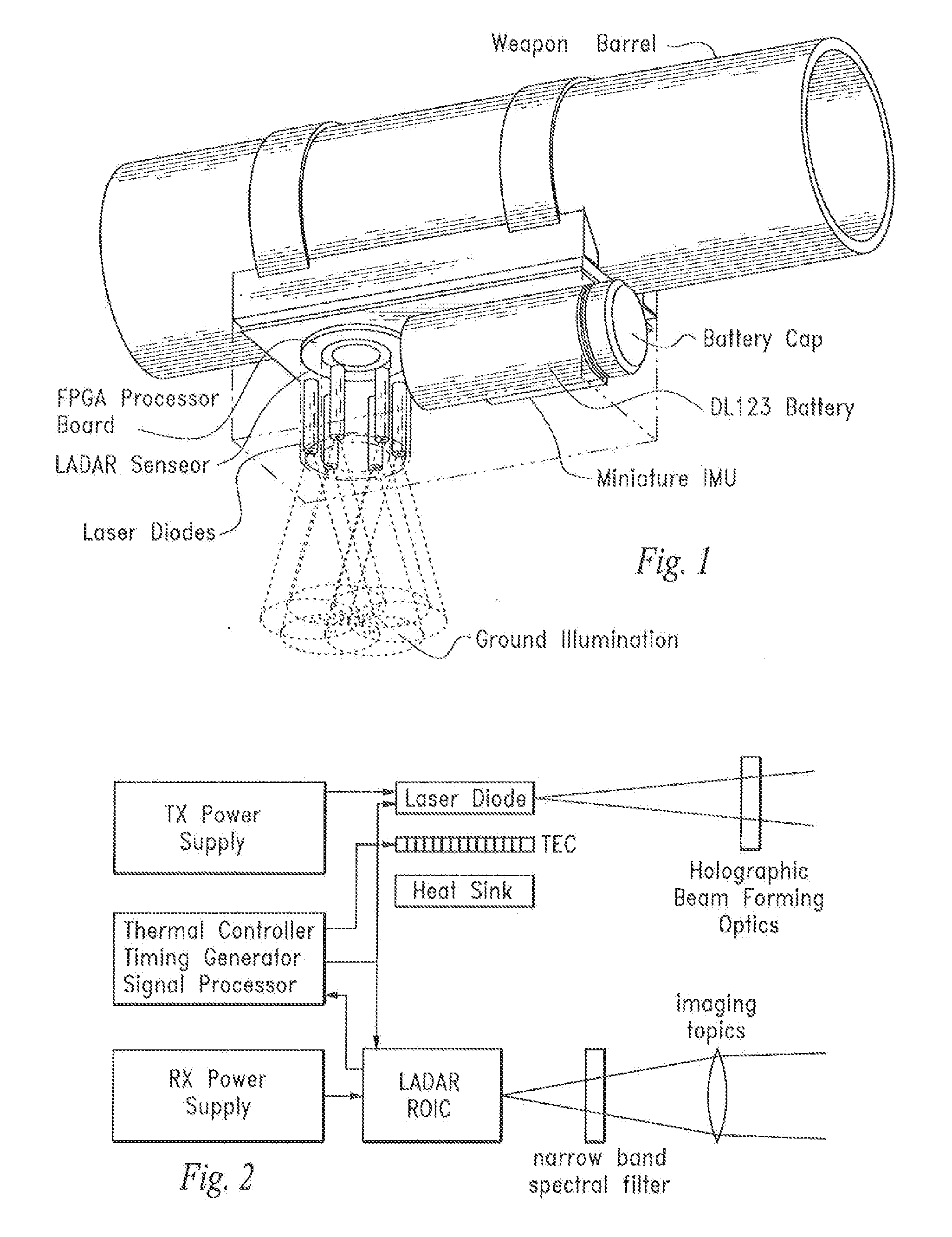
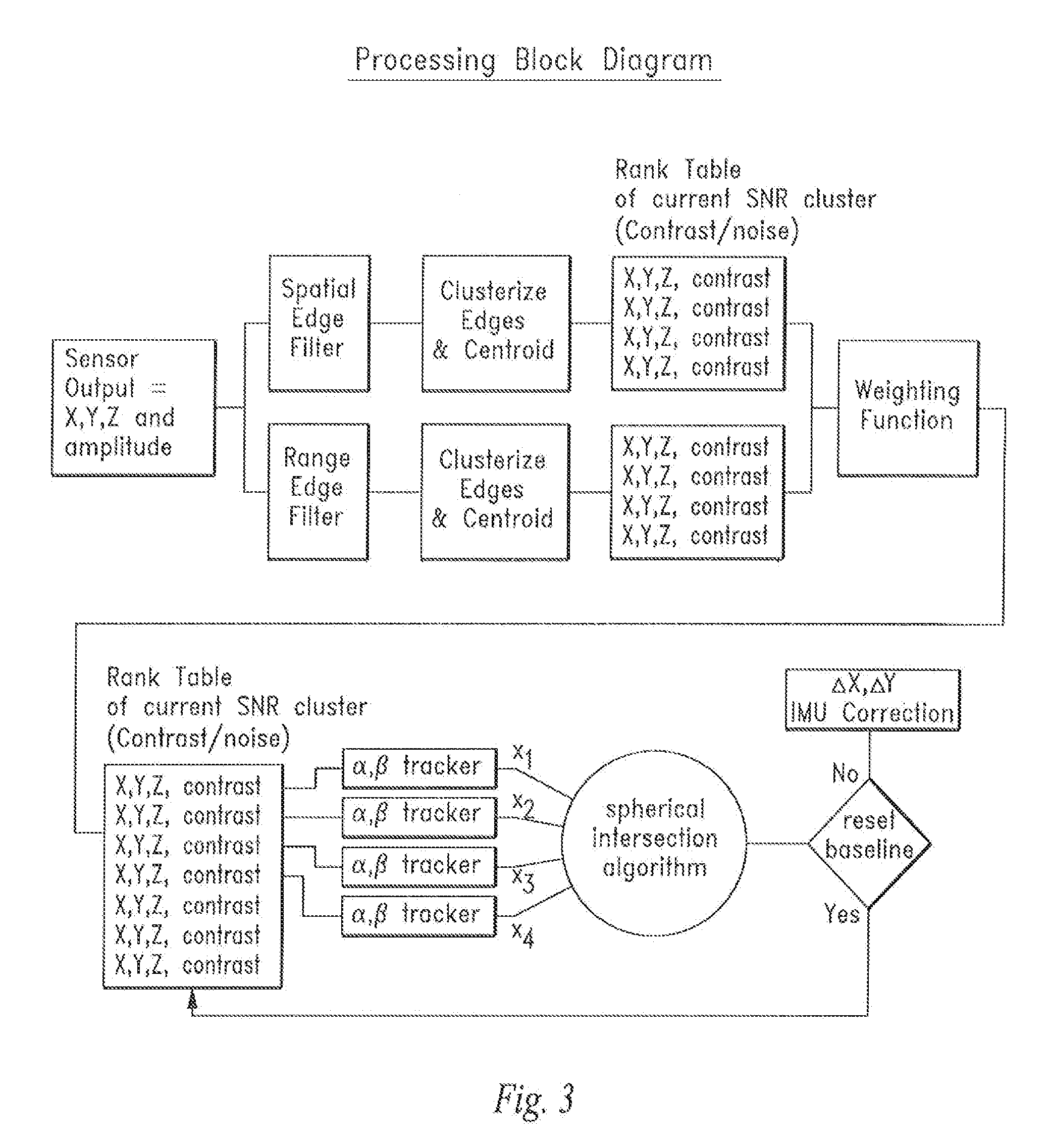
InactiveUS20140293266A1Accurate measurement rangeAccurate measurementOptical rangefindersWeapon control systemsTerrainVoxel
A device and method that uses terrain features having one or more predetermined characteristics or weights in an electronic image date frame or set of frames such as a LIDAR voxel set of image data frames for use as system reference points which are, in turn, used in one or more trilateration calculations performed in electronic circuitry to determine a position or ego-motion of the device.
Owner:PFG IP
Method and system for image processing and assessment of blockages of heart blood vessels
InactiveUS20080317310A1Assessing blockages in blood vesselsReduce resolutionImage enhancementImage analysisVoxelImaging processing
One embodiment discloses a computerized method of assessing deposits and / or blockages in blood vessels in a human, specifically in a human heart. The method may include inputting patient data and creating a computerized interactive model of a heart based on the patient data. Patient data may include a plurality of images of a least a portion of a human heart. Images may include three-dimensional images. An image may be divided into regions. A property of a region may be assessed. A property may include intensity of brightness of a region or a portion of a region. A region may include one or more voxels or one or more pixels. A method may include comparing a property of a region of a heart from a first image to a second image. The first image and the second image may include equivalent regions acquired during different time periods.
Owner:PHI HEALTH +1
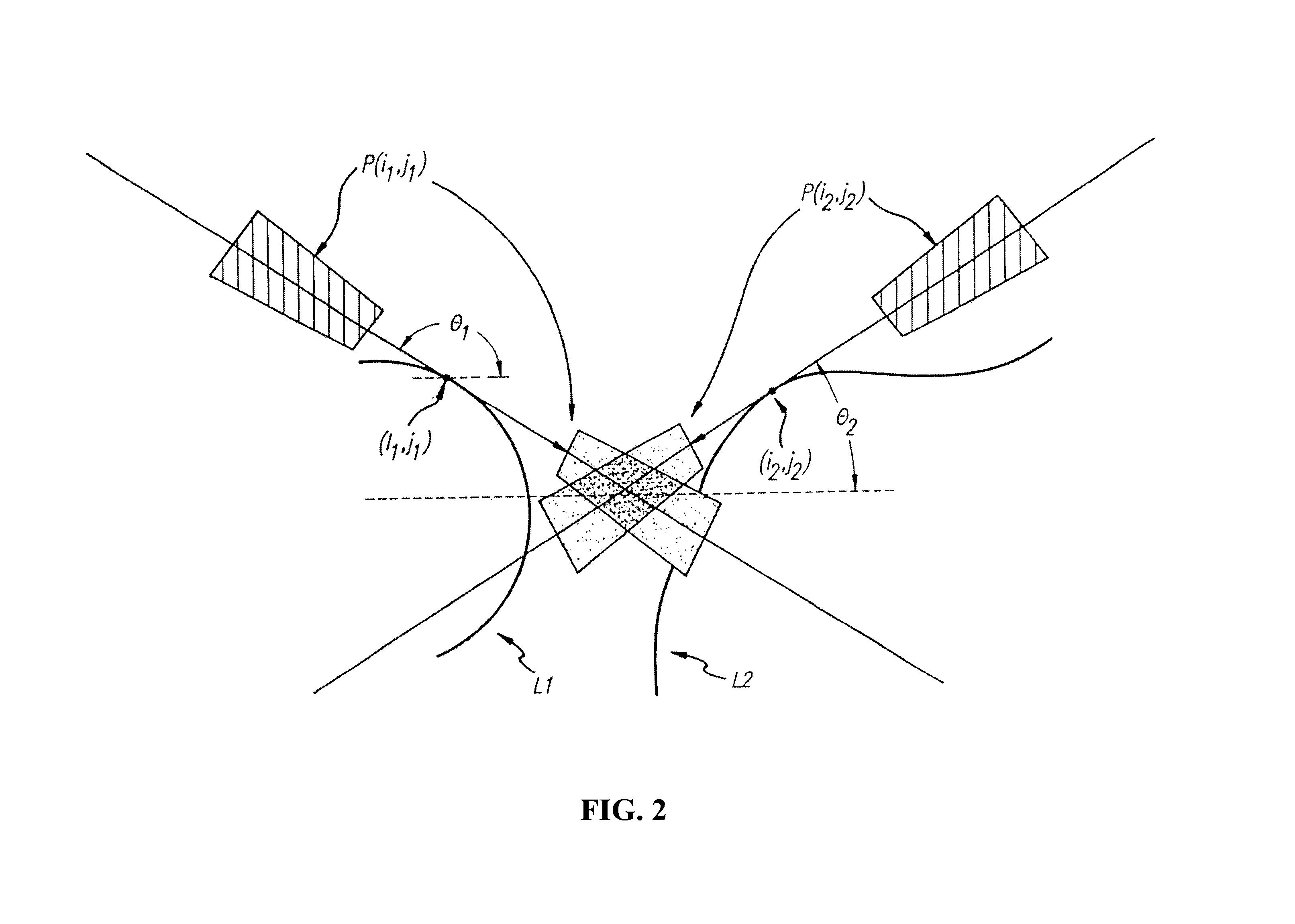
Methods and apparatus for back-projection and forward-projection
ActiveUS20050152590A1Few computational resourceAddressing slow performanceReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationVoxelProjection image
The invention provides improvements in reconstructive imaging of the type in which a volume is reconstructed from a series of measured projection images (or other two-dimensional representations) generated by projection of a point x-ray source (or other radiation source), positioned at a distinct focus, through the volume to a plane at which the respective projection image is acquired (“detector plane”). In one aspect, the improvements are with respect to back-projecting a two-dimensional representation lying in the detector plane (representing, for example, a difference between an originally-acquired measured projection image and a subsequently-generated estimate thereof) to generate three-dimensional representation (which can be used, for example, to update an estimate of the volume). According to this aspect, for each of one or more slices of the 3D representation parallel to the projection plane and for each distinct focus at which a projection is generated, the following steps are performed in connection with the back-projection: (i) warping the first 2D representation to generate a second 2D representation by applying to the first 2D representation a selected linear mapping, where that selected linear mapping would map, in order to match dimensions of the respective slice within the 3D representation, a region defined by projection, at the respective focus, of comers of that slice onto the detector plane, and (ii) incrementing values of each of one or more voxels of the respective slice by an amount that is a function of a value of a correspondingly indexed pixel of the second 2D representation. A related aspect provides improvements with respect to forward-projecting, as well as in iterative (and non-iterative) methodologies that incorporate both back-projection and forward-projection.
Owner:PME IP
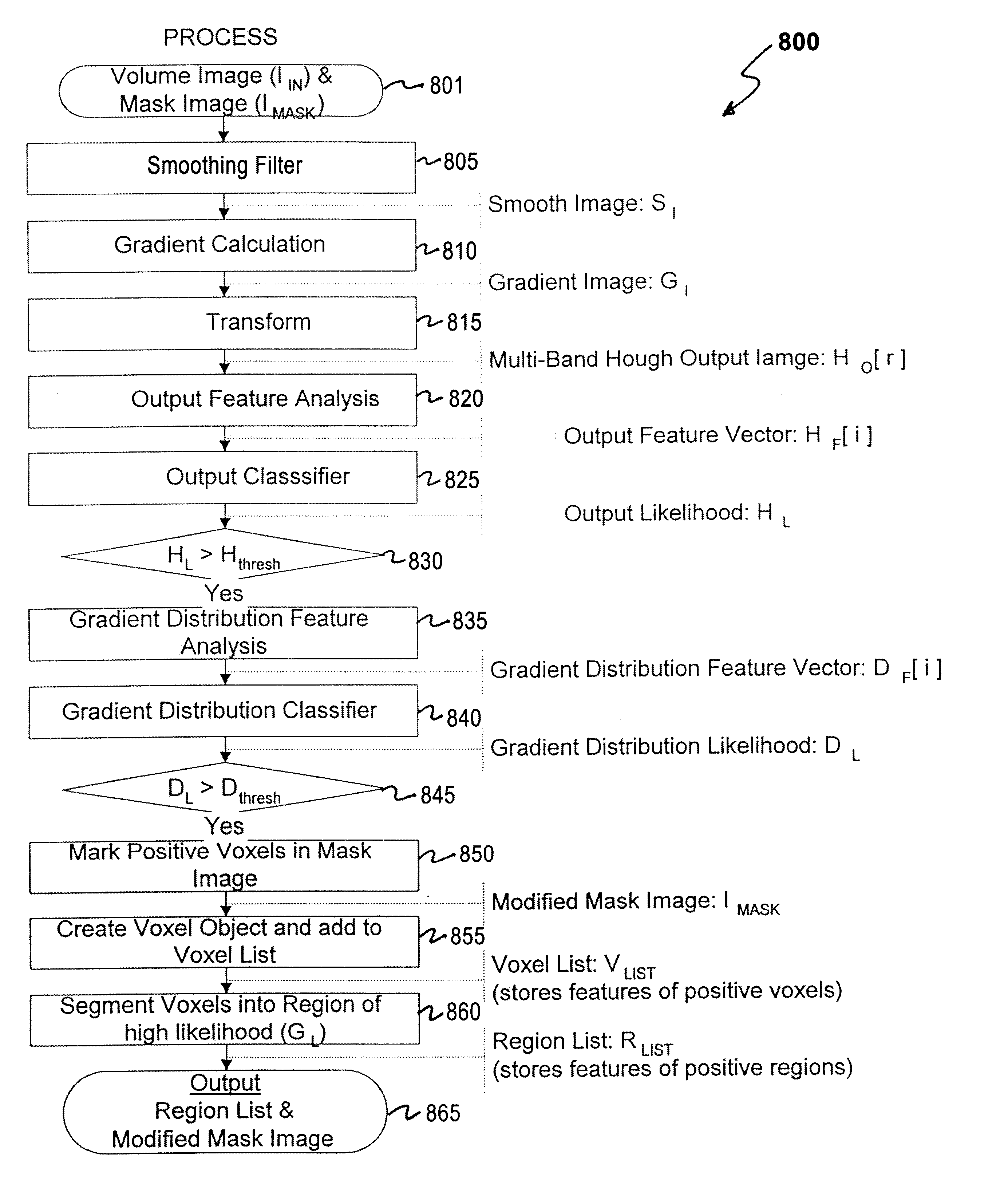
Density nodule detection in 3-D digital images
InactiveUS6909797B2Quickly highlightReduce sensitivityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationImage analysisVoxelRapid scan
An algorithm is quickly scans a digital image volume to detect density nodules. A first stage is based on a transform to quickly highlight regions requiring further processing. The first stage operates with somewhat lower sensitivity than is possible with more detailed analyses, but operates to highlight regions for further analysis and processing. The transform dynamically adapts to various nodule sizes through the use of radial zones. A second stage uses a detailed gradient distribution analysis that only operates on voxels that pass a threshold of the first stage.
Owner:MEVIS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS
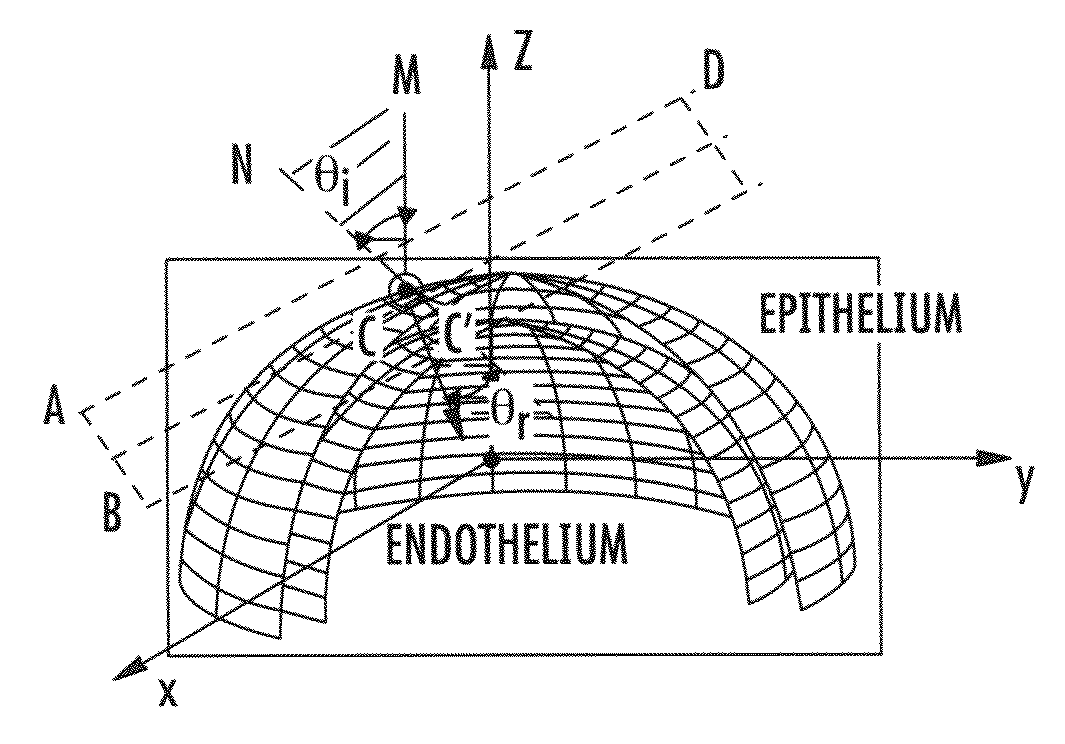
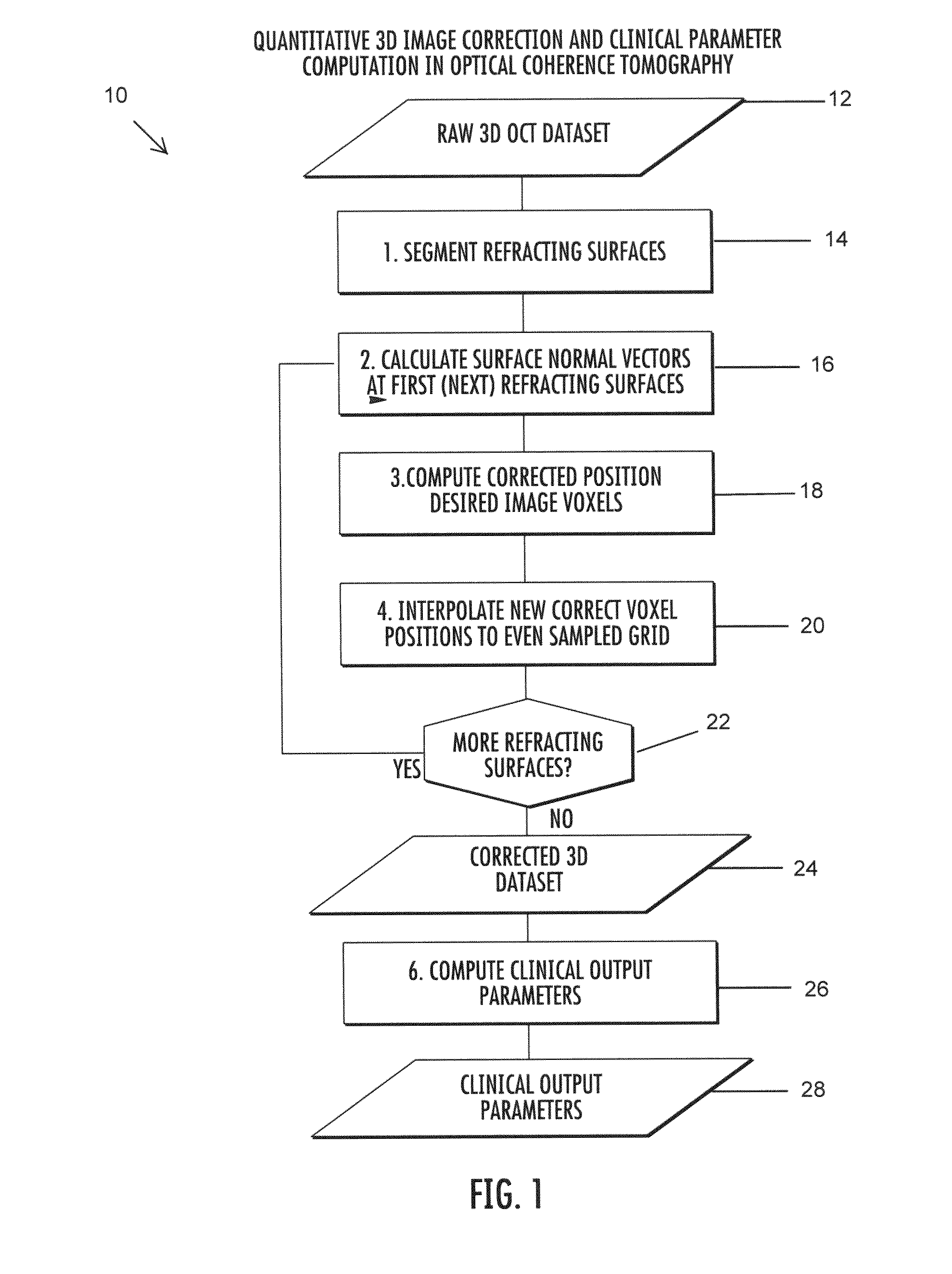
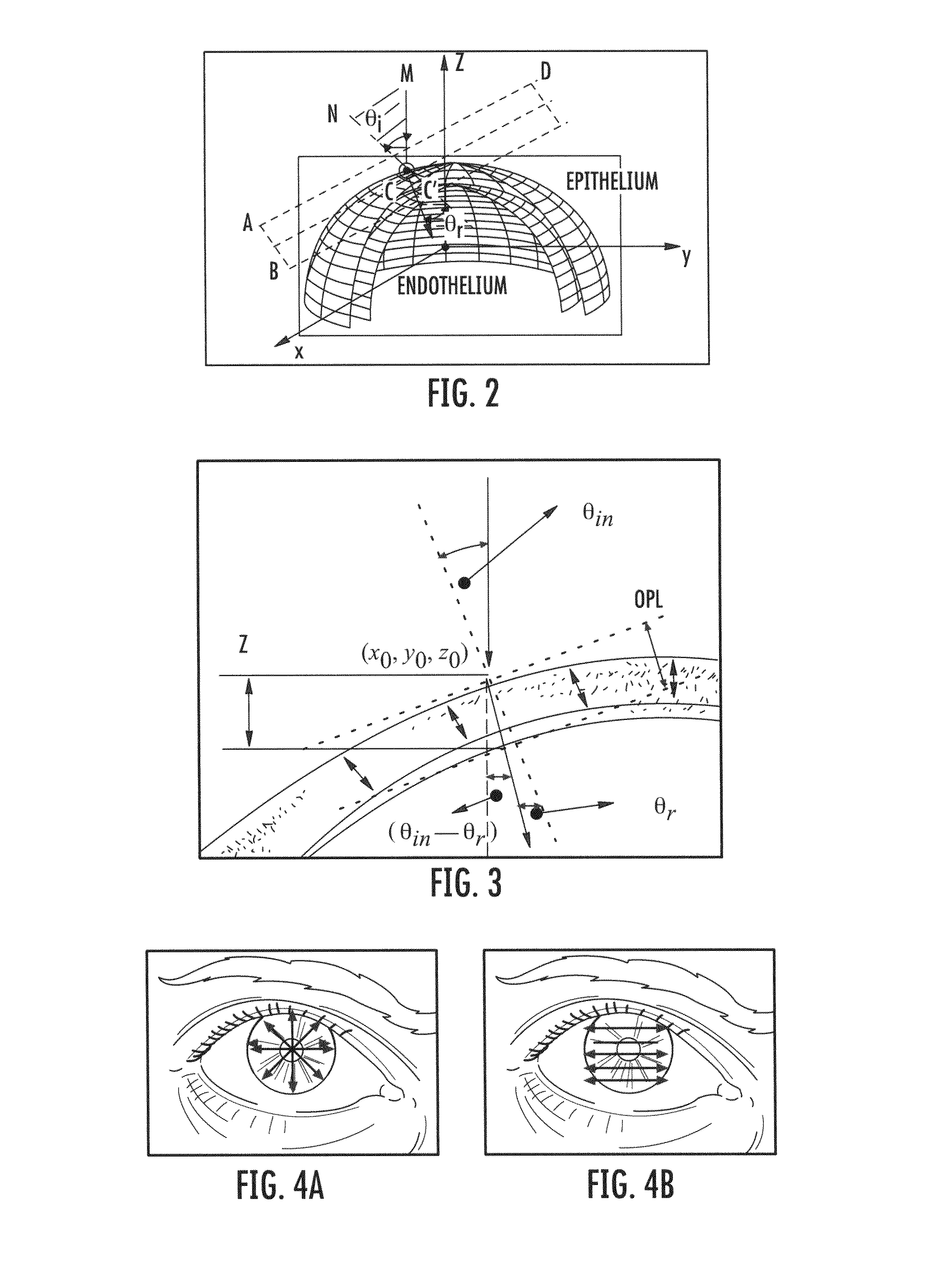
Methods and computer program products for quantitative three-dimensional image correction and clinical parameter computation in optical coherence tomography
Methods and computer program products for quantitative three-dimensional (“3D”) image correction in optical coherence tomography. Using the methods and computer program products, index interface (refracting) surfaces from the raw optical coherence tomography (“OCT”) dataset from an OCT system can be segmented. Normal vectors or partial derivatives of the curvature at a refracting surface can be calculated to obtain a refracted image voxel. A new position of each desired refracted image voxel can be iteratively computed. New refracted corrected voxel positions to an even sampling grid can be interpolated to provide corrected image data. In some embodiments, clinical outputs from the corrected image data can be computed.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Surgical Assistance System
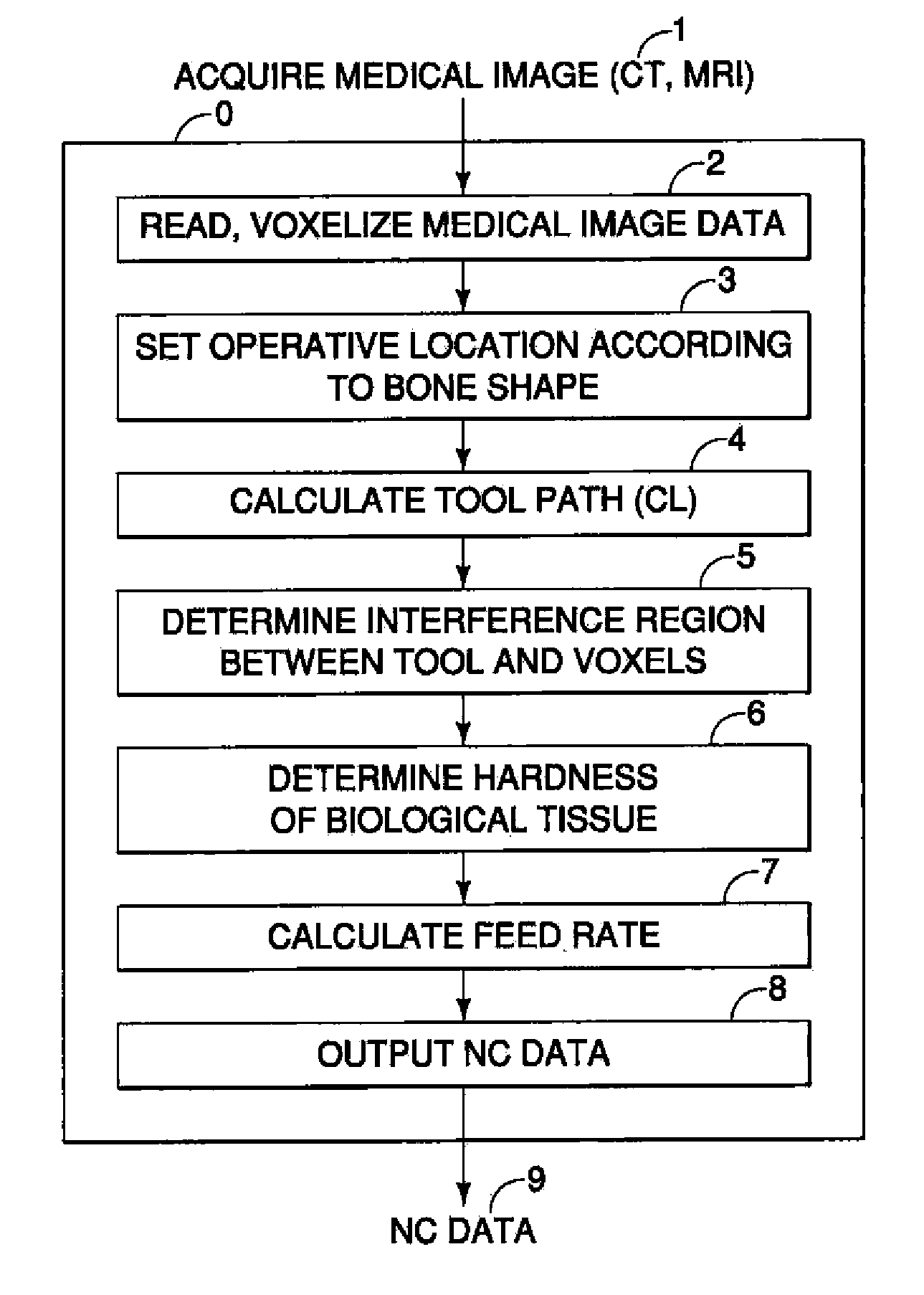
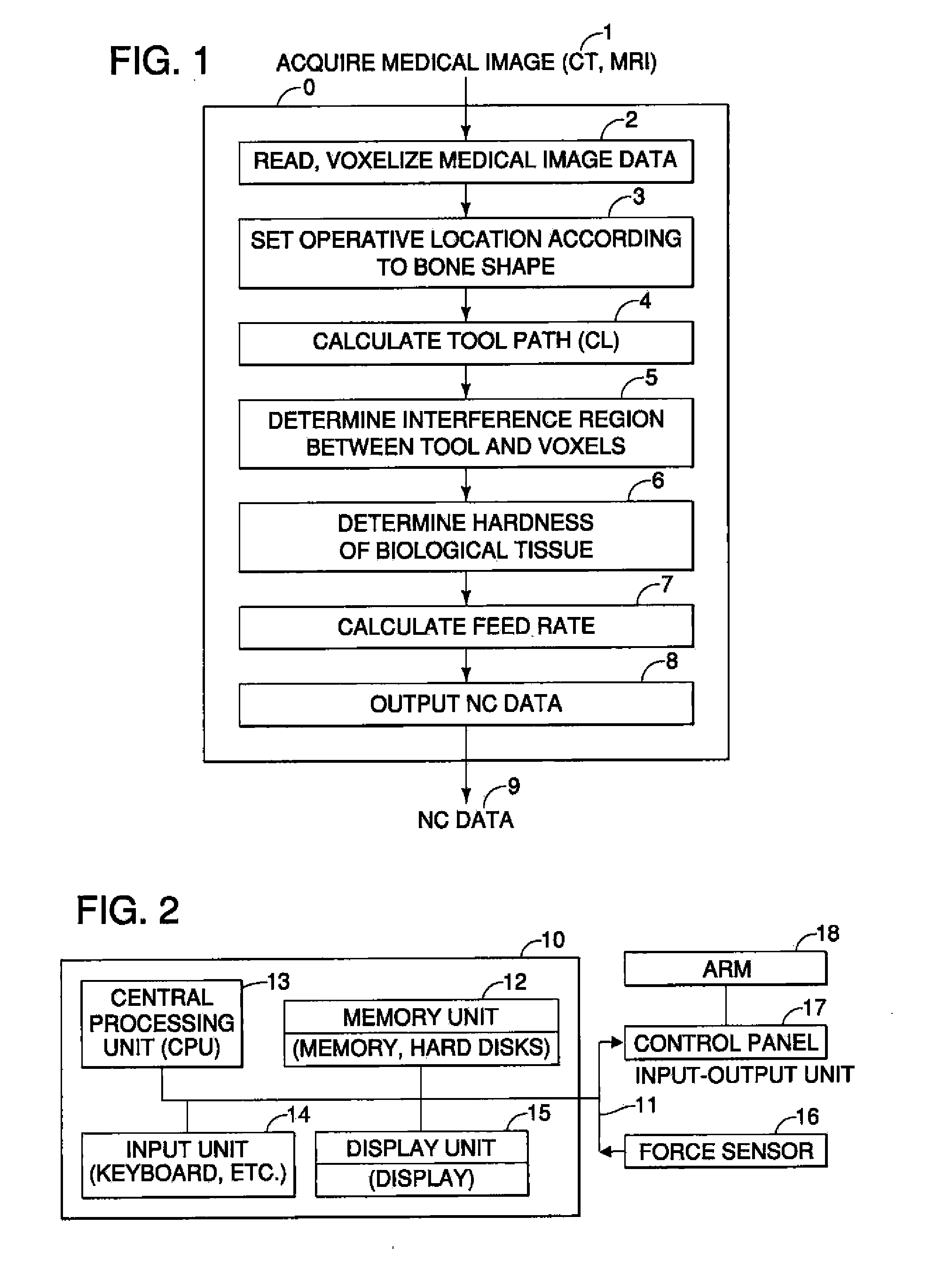
InactiveUS20110306985A1Precise resectionMinimal invasivenessDiagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsSurgical operationVoxel
A surgical assistance system for operating on biological tissue using a surgical tool attached to an arm of an automatically-controlled surgical instrument so that an optimal feed rate of the tool is calculated and outputted to the surgical instrument, the system including: a device for storing and voxelizing medical image data obtained from a biological tissue subject to surgery; a device for setting an operative location based on the shape of the biological tissue; a device for calculating a tool path along which the tool travels to perform surgery at an operative location; a device for determining the region of interference between the tool and the voxels; a device for determining the hardness of the biological tissue in the interference region; a device for calculating an optimal tool feed rate corresponding to the hardness; and a device for outputting the feed rate obtained by the calculations to the surgical instrument.
Owner:NAKASHIMA MEDICAL +1
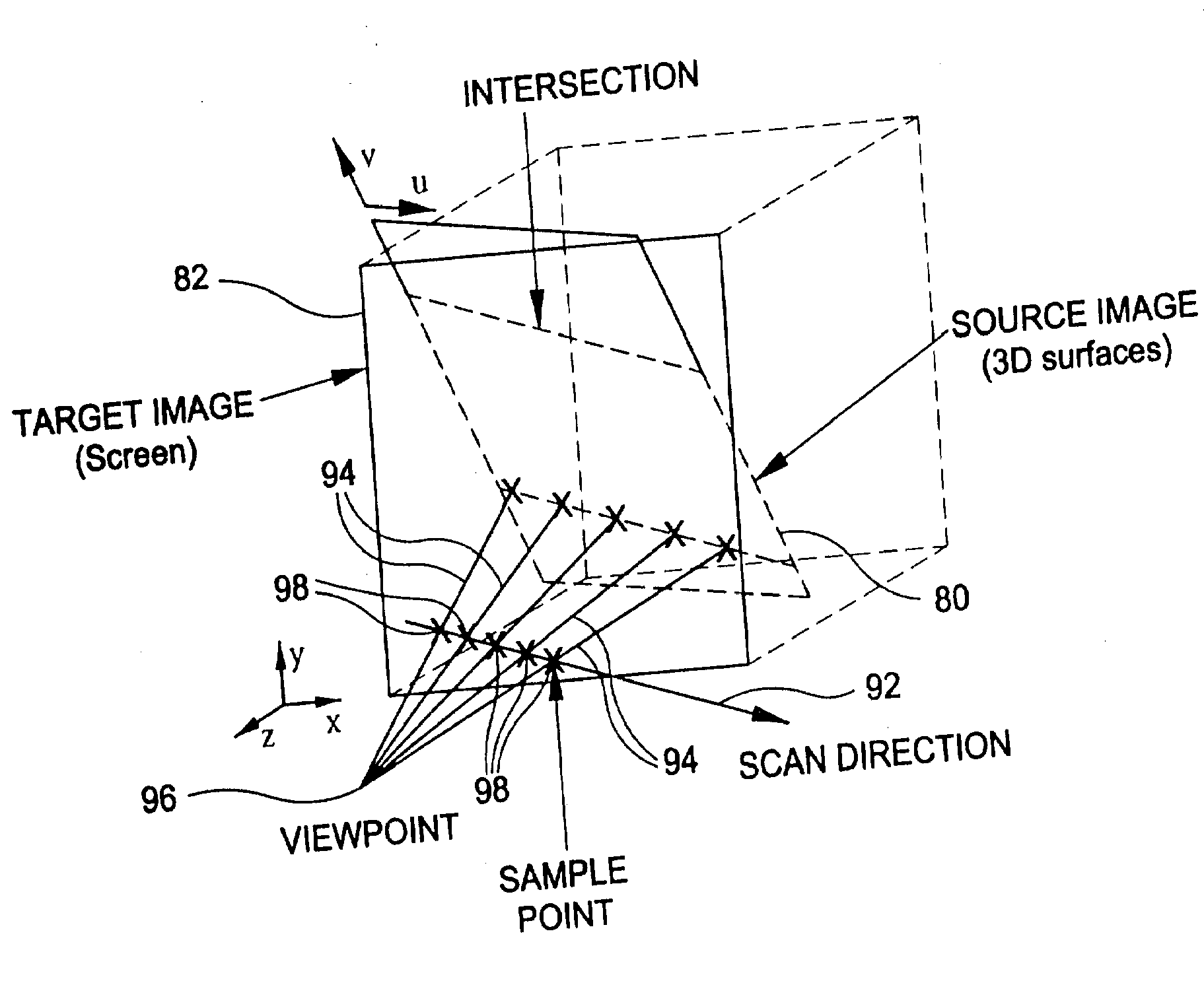
Methods, systems, and computer program products for processing three-dimensional image data to render an image from a viewpoint within or beyond an occluding region of the image data
InactiveUS20090103793A1Good voxel resolutionSensitive to contrastCharacter and pattern recognition3D-image renderingVoxelViewpoints
Methods, systems, and computer program products for processing three-dimensional image data to render an image from a viewpoint within or beyond an occluding region of the image data are disclosed. According to one method, a set of three-dimensional image data is accessed. The image data includes image data for a surface of interest and image data for a region occluding the surface of interest from a desired viewpoint. The viewpoint may be within or beyond the occluding region. A plurality of rays is cast from the viewpoint to the surface. Along each ray, an occlusion determination is made independent from a volume rendering transfer function definition to render voxels within the occluding region as transparent or partially transparent. The volume rendering transfer function is applied along a portion of each ray outside of the occluding region to render voxels defining surface of interest as visible. The voxels that define the surface are displayed as visible. The voxels within the occluding region are shown in a transparent or partially transparent manner.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
Digital topological analysis of trabecular bone MR images and prediction of osteoporosis fractures
The invention provides method, system and device for determining trabecular bone structure and strength by digital topological analysis, and offers, for the first time, a demonstration of superior associations between vertebral deformity and a number of architectural indices measured in the distal radius, thus permitting reliable and noninvasive detection and determination of the pathogenesis of osteoporosis. A preferred embodiment provides imaging in three dimension of a region of trabecular bone, after which the 3D image is converted into a skeletonized surface representation. Digital topological analysis is applied to the converted image, and each image voxel is identified and classified as a curve, a surface, or a junction; and then associated with microarchitectural indices of trabecular bone to quantitatively characterize the trabecular bone network. The invention is applicable in vivo, particularly on human subjects, or ex vivo.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
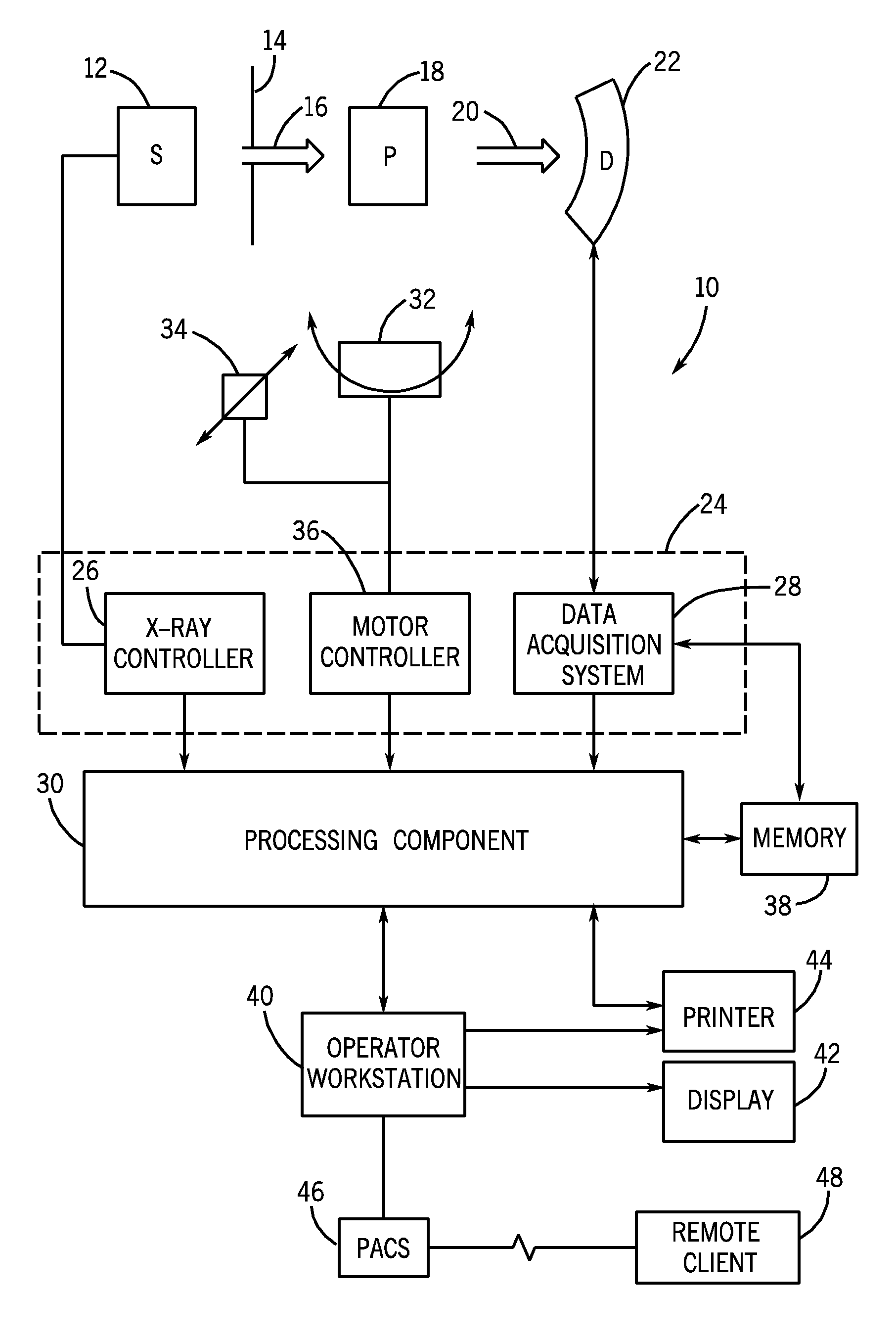
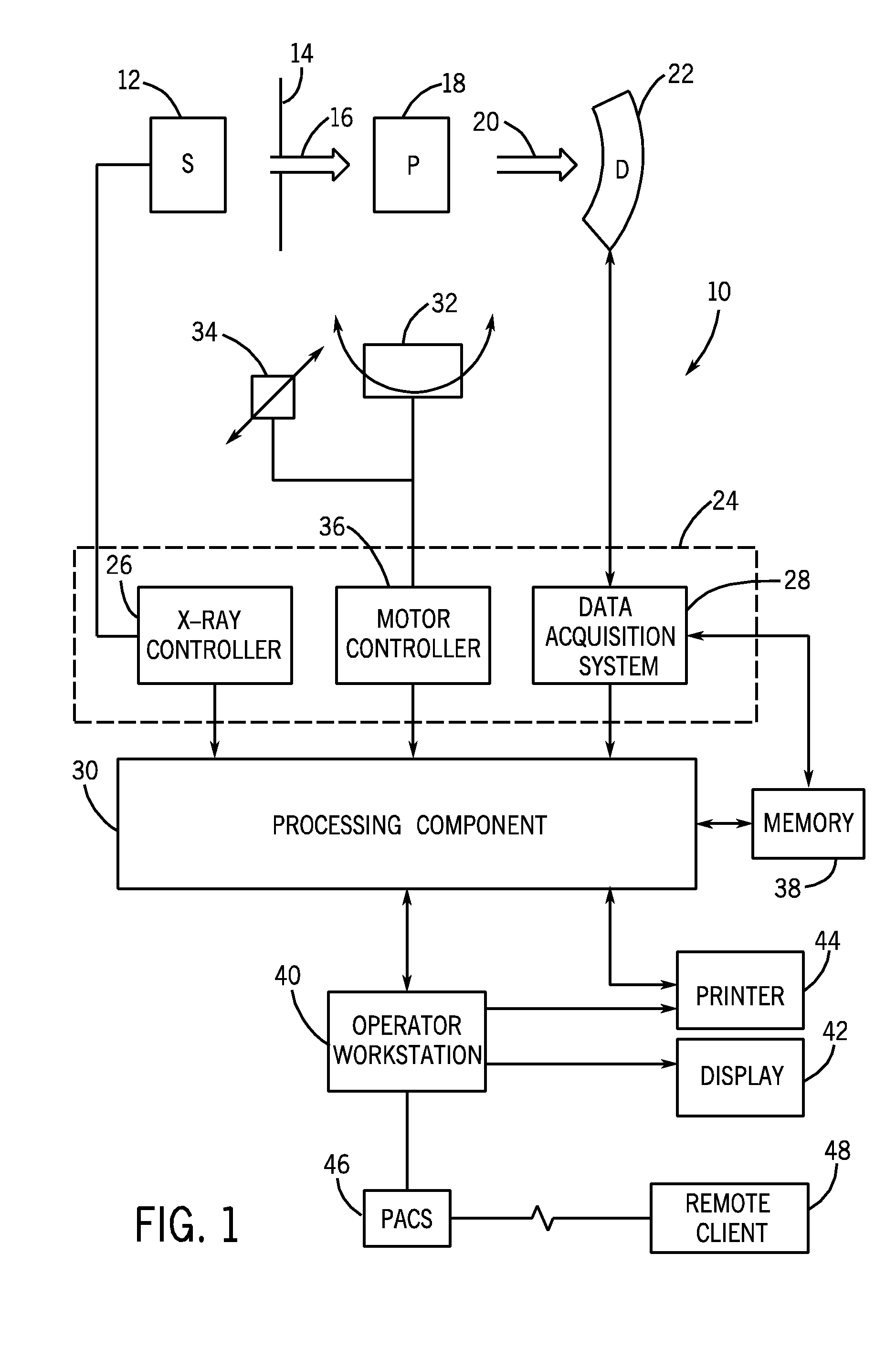
Contrast-enhanced cone beam X-ray imaging, evaluation, monitoring and treatment delivery
ActiveUS20070269000A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingVoxelData set
A method of imaging a patient's uncompressed region of interest using X-ray cone beam computed tomography or cone beam digital tomography comprises the step of introducing an effective amount of a contrast agent to the uncompressed region of interest. A system for imaging a patient's uncompressed region of interest using cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) or cone beam digital tomography (CBDT) comprises an X-ray source transmitting an X-ray to the uncompressed region of interest, an image acquisition system acquiring a plurality of two-dimensional projection images data for a CBCT or CBDT data set with at least one of the projection images acquired in 35 milliseconds or less, and a processor generating a three-dimensional computed tomography image data set resolving voxels with dimensions of 0.4 mm or less in at least two orthogonal directions.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS +2
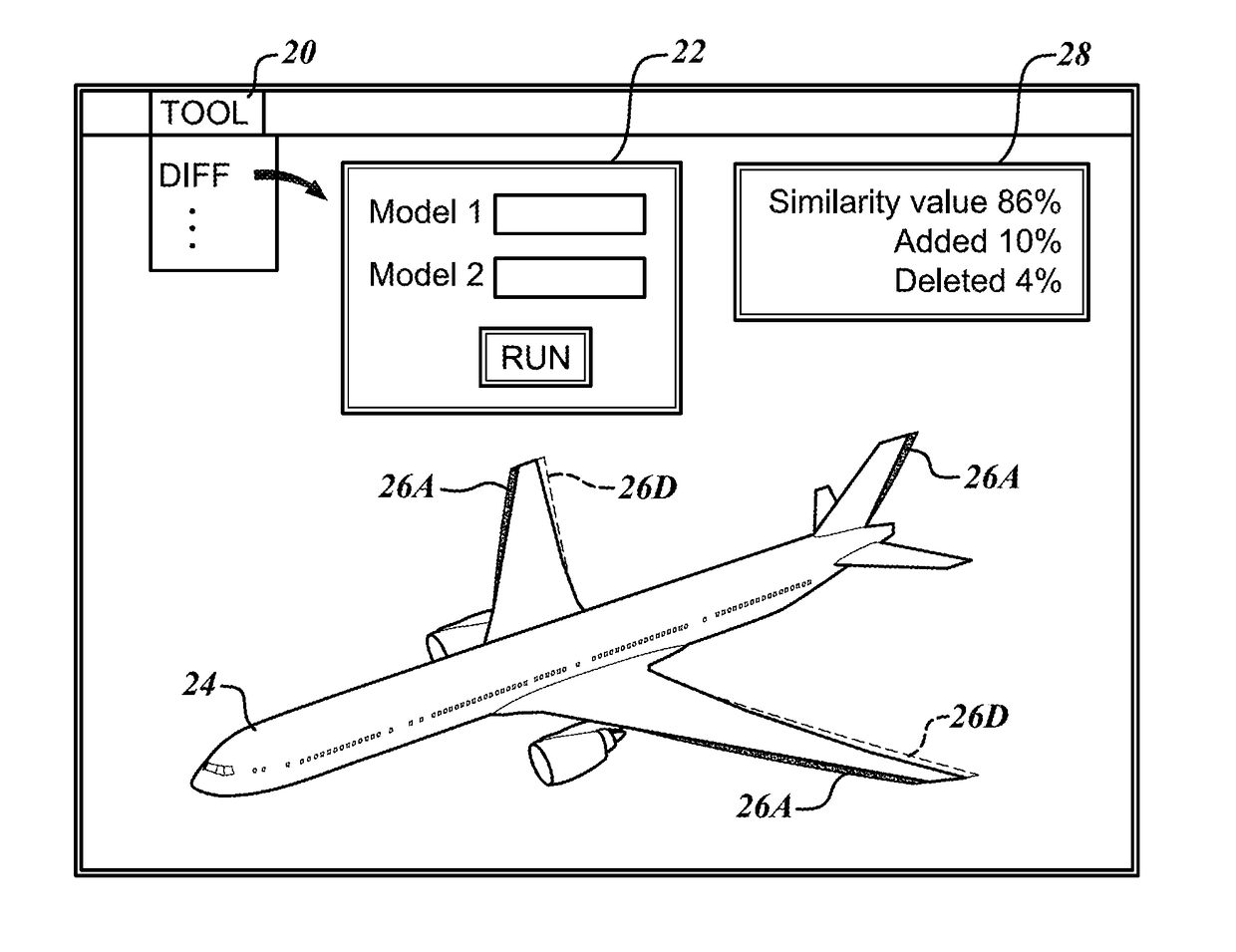
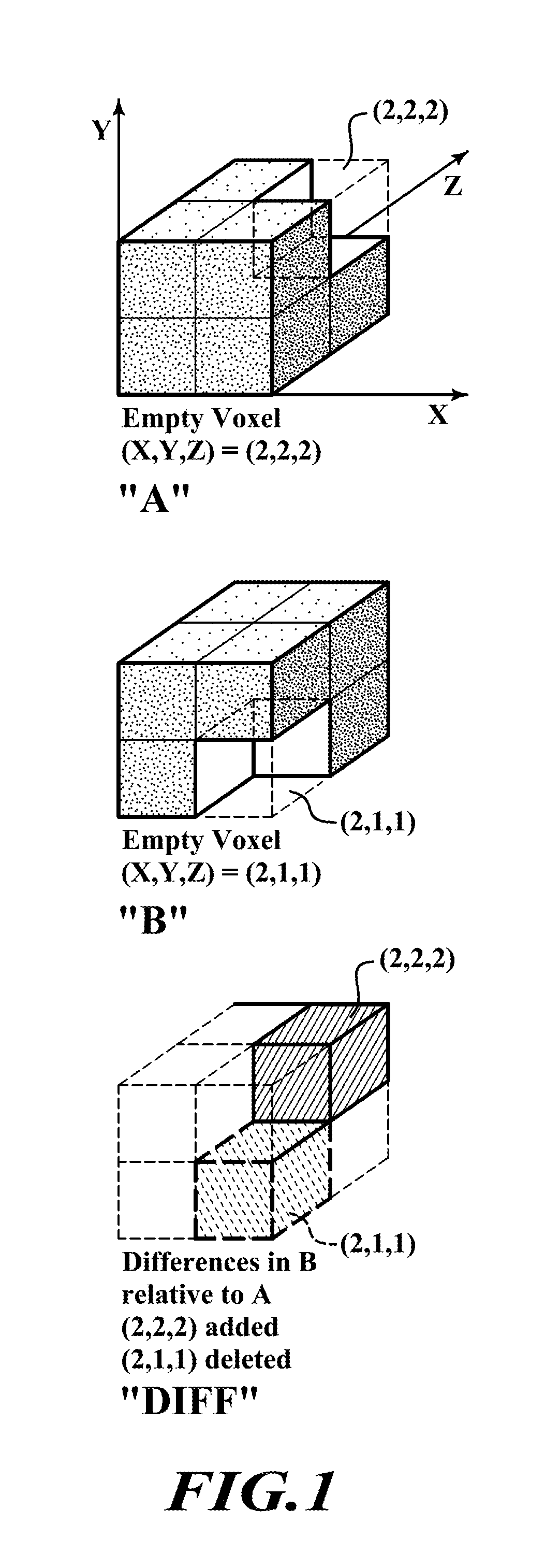
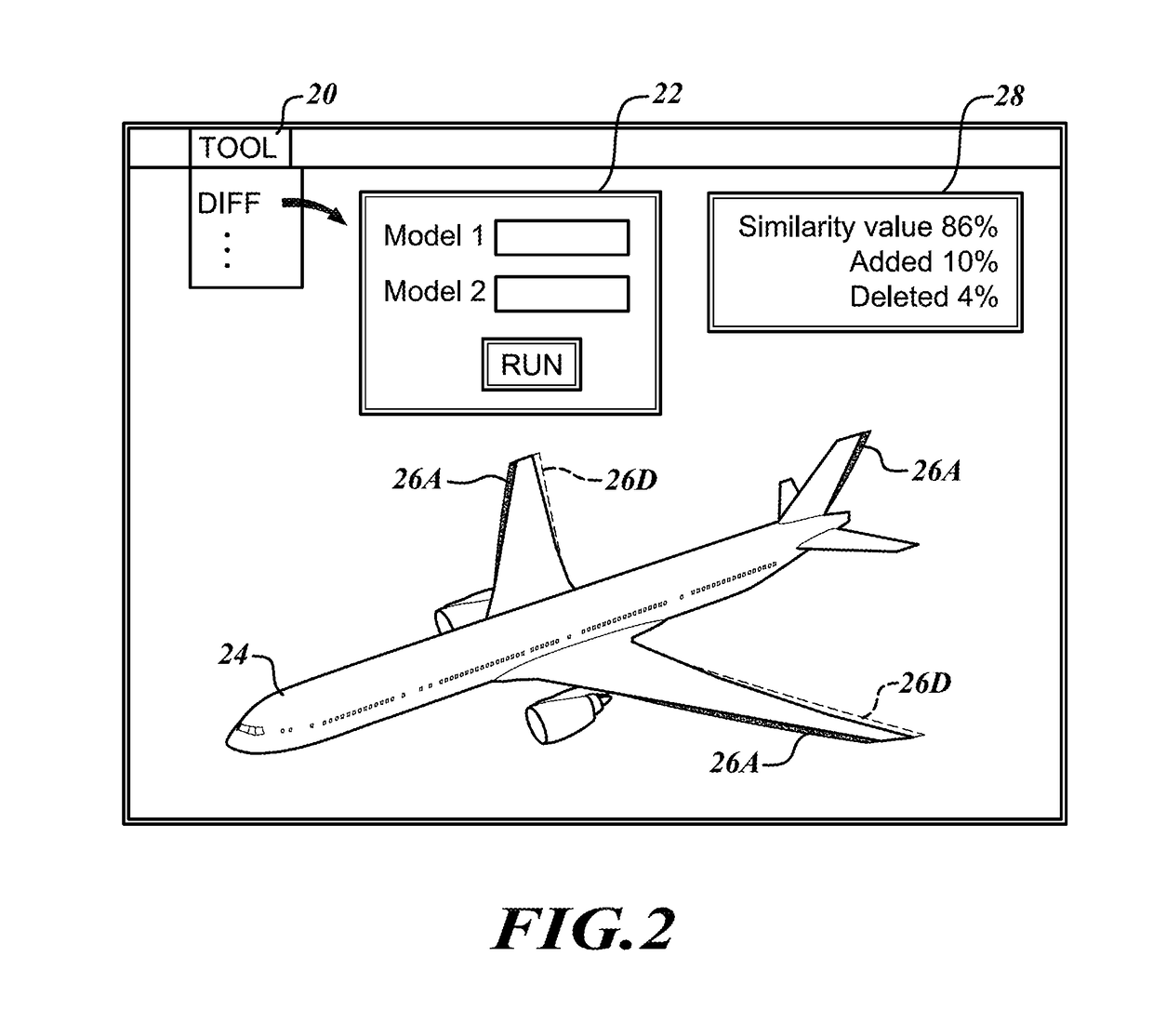
System, computer-readable medium and method for 3D-differencing of 3D voxel models
System, computer-readable medium and method are provided for differencing (diffing) first and second sets of 3D voxel data to identify differences that may exist between the two sets. The system includes a 64-bit processor, a memory, and a display. The memory is loaded with the two sets of 3D voxel data arranged in a 64-tree data structure, wherein an occupied or empty state of each voxel is indicated by 1 bit. The processor executes a 3D voxel diffing algorithm including steps of: (i) aligning the first and second sets of 3D voxel data; (ii) making a one-to-one comparison between each voxel in the first set and a corresponding voxel in the second set to create a diff model that records differences found between the first and second sets; and (iii) displaying the content of the diff model on the display.
Owner:NGRAIN CANADA CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com