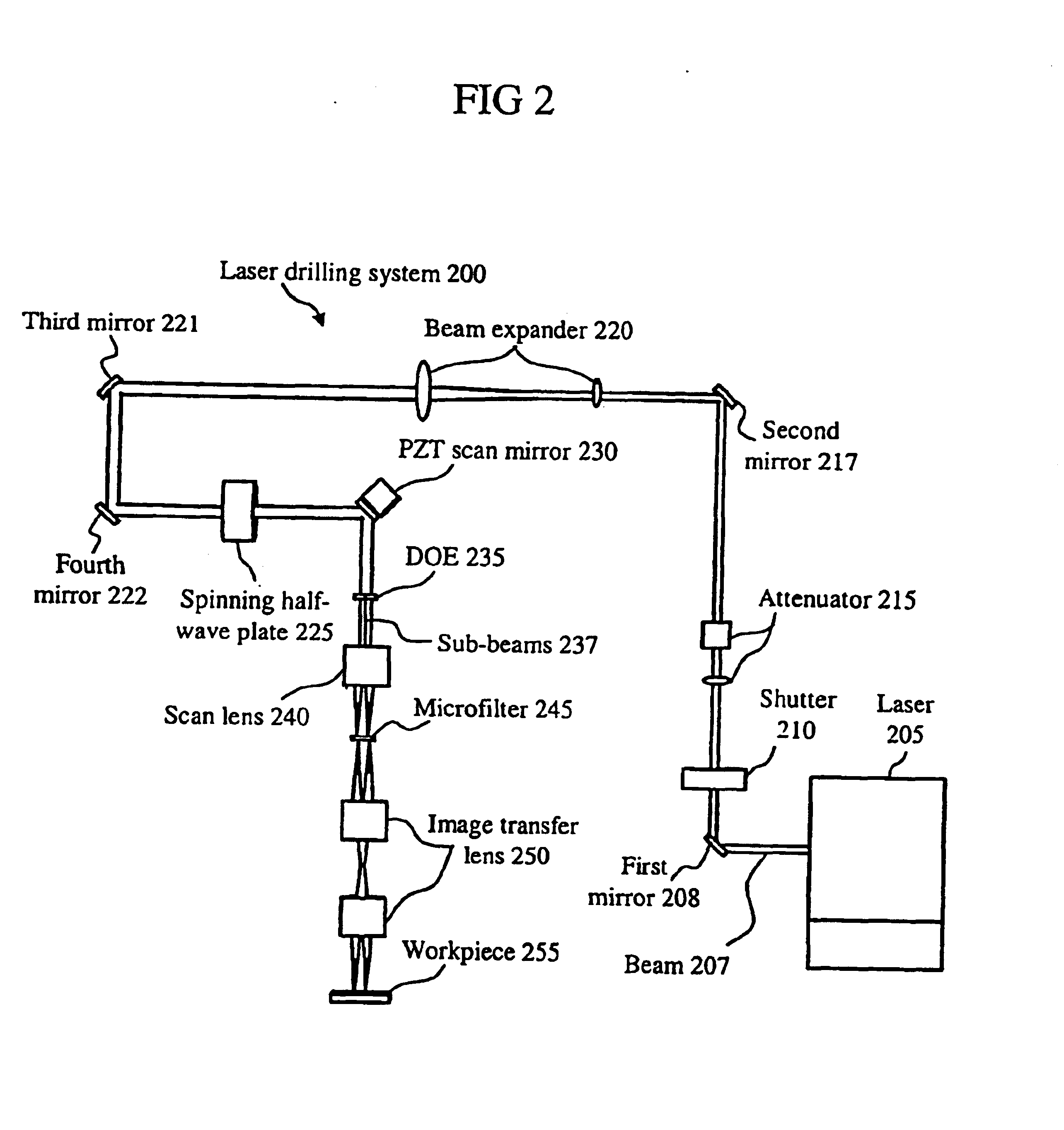
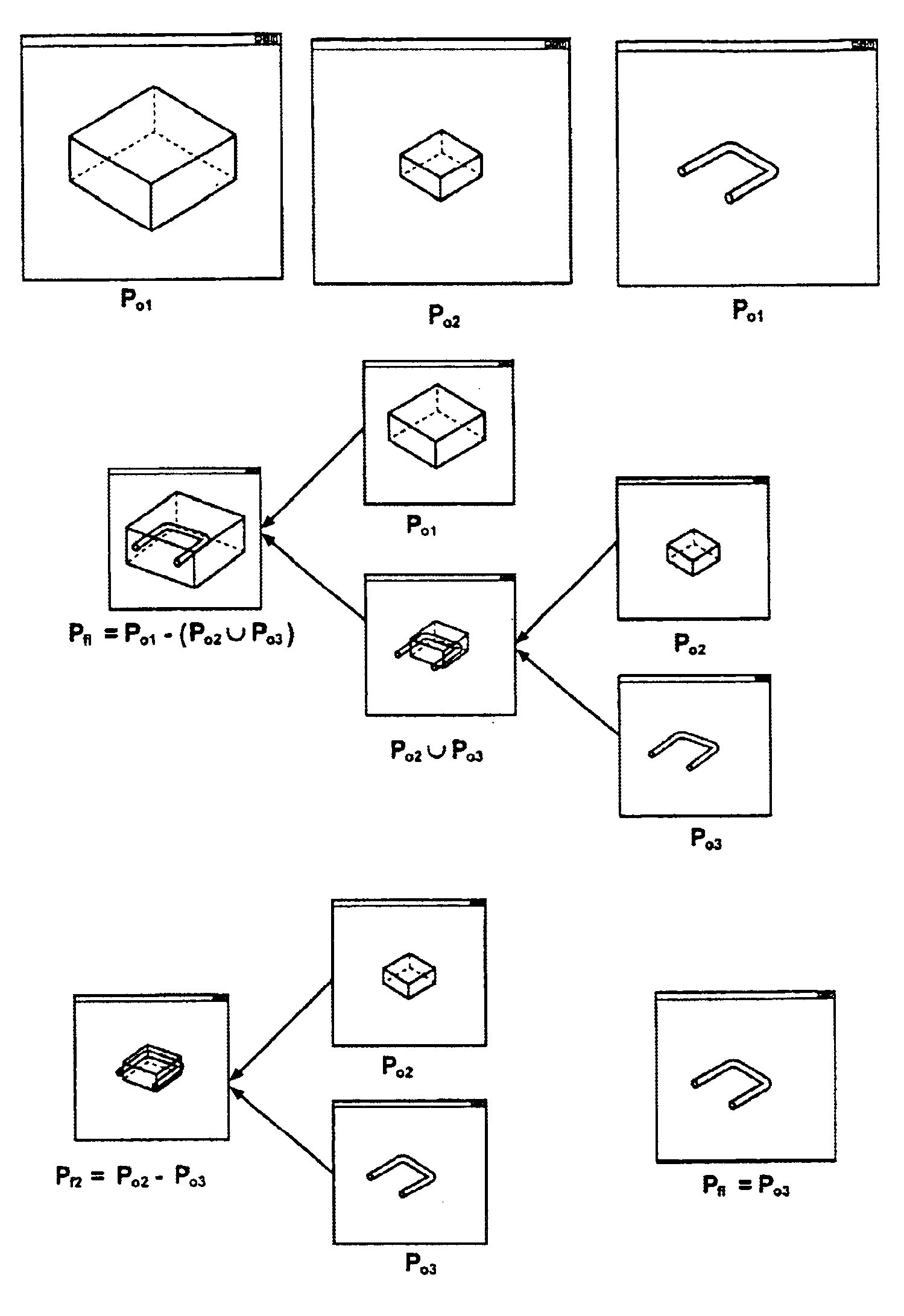
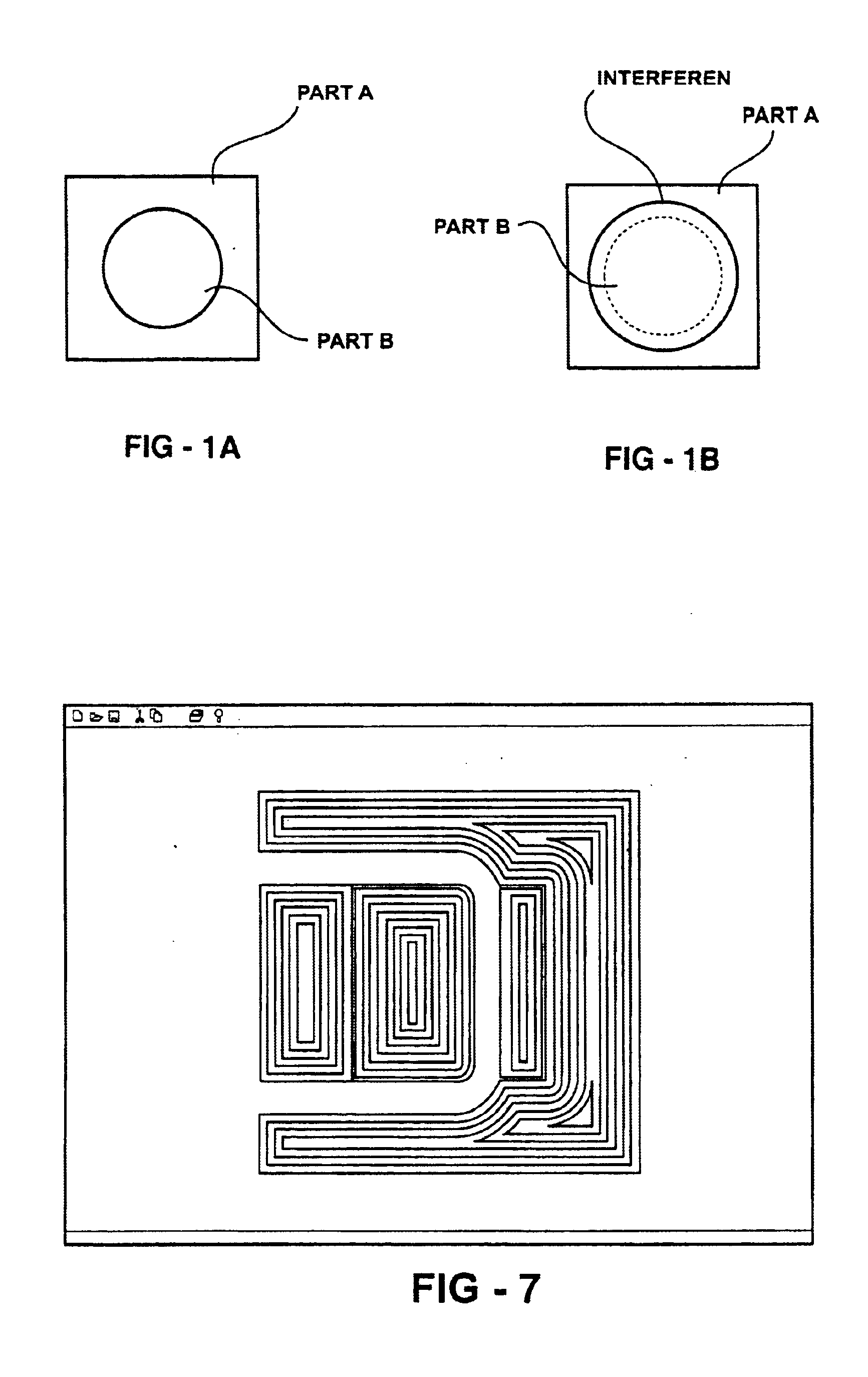
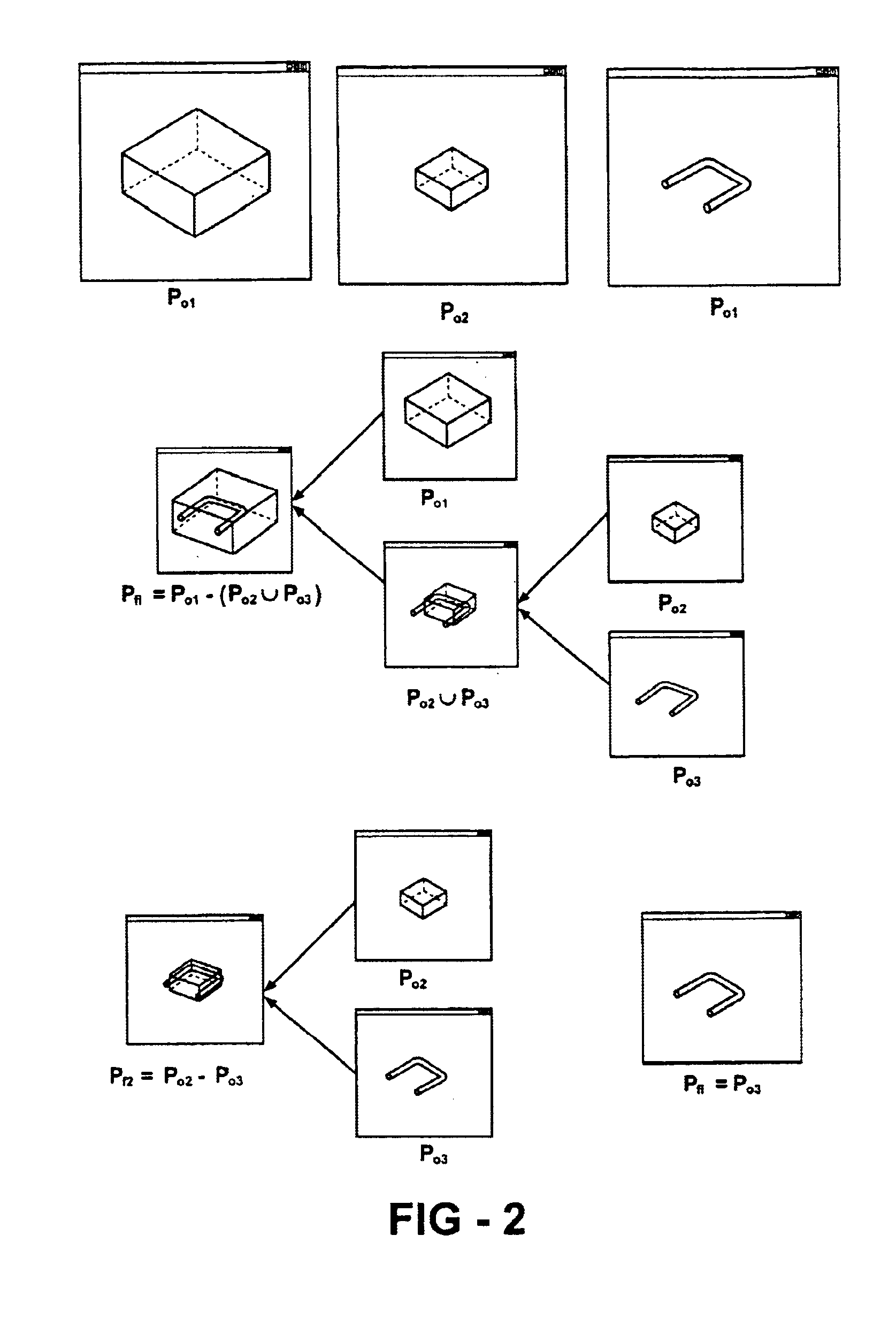
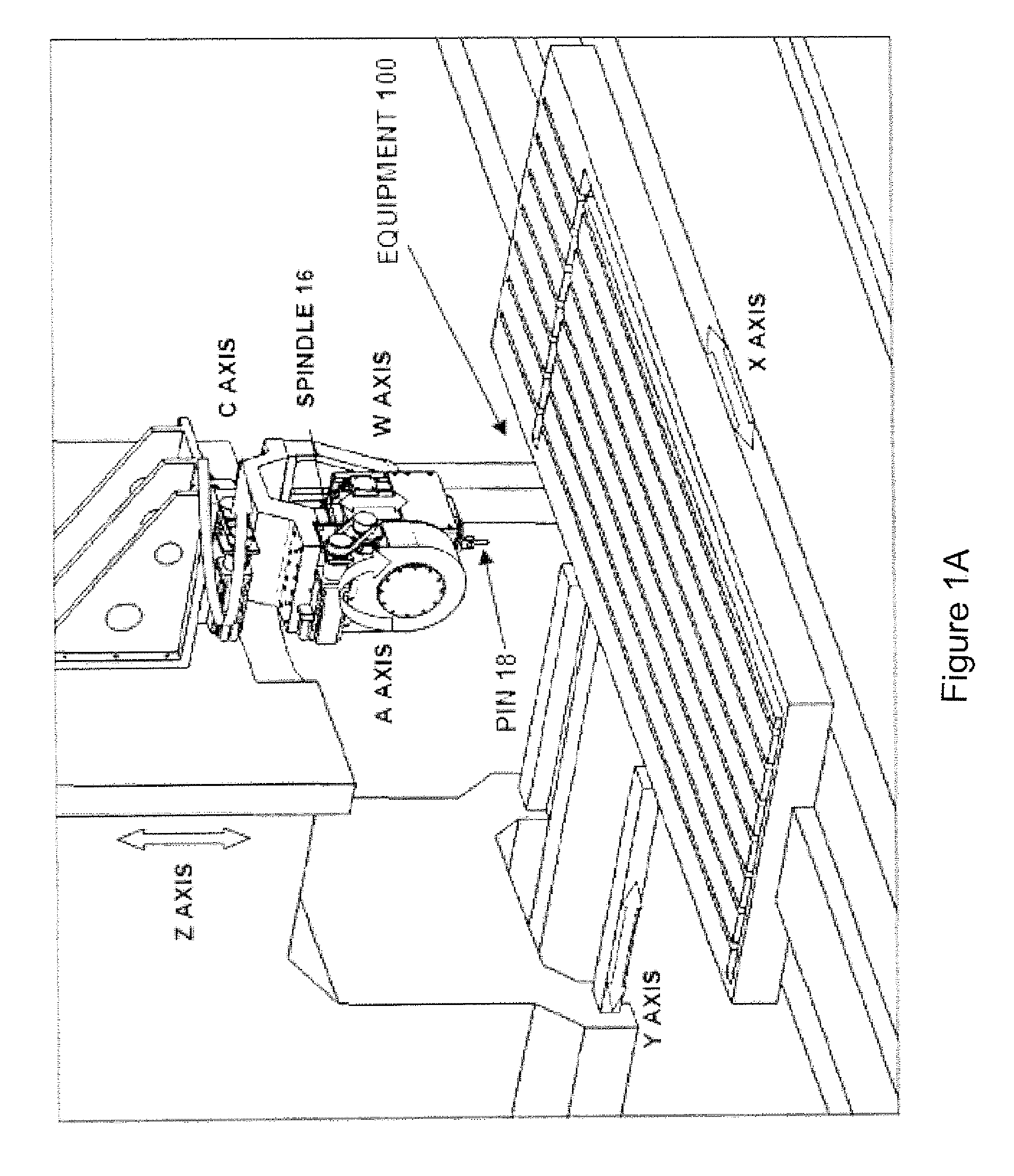
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1112 results about "Tool path" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Path tool. The path tool allows you to see the ideal paths that workers will take from their homes to their workplaces, or from workplaces to homes. Once the path tool is selected, simply click on a home or workplace to show the paths that workers will take.
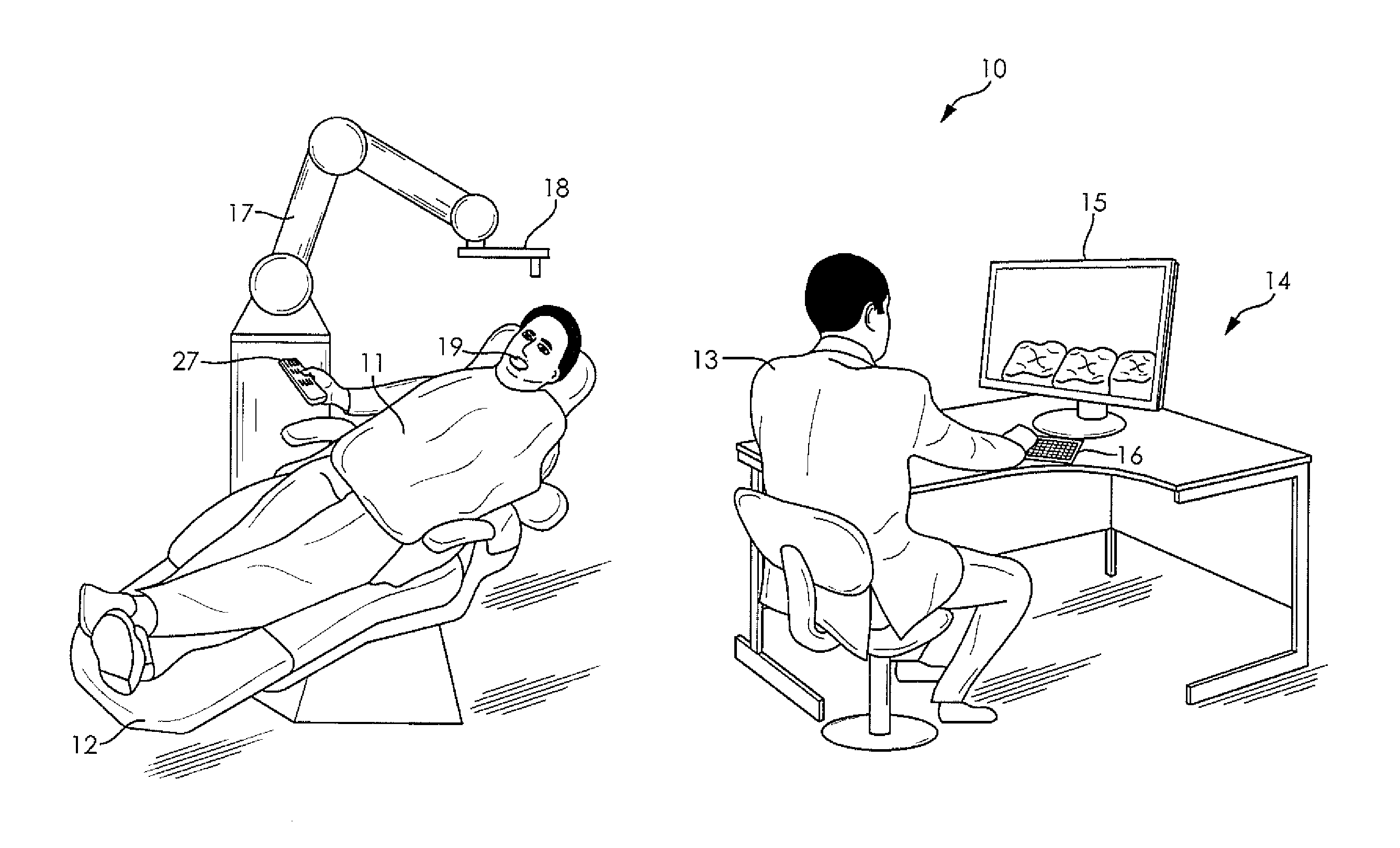
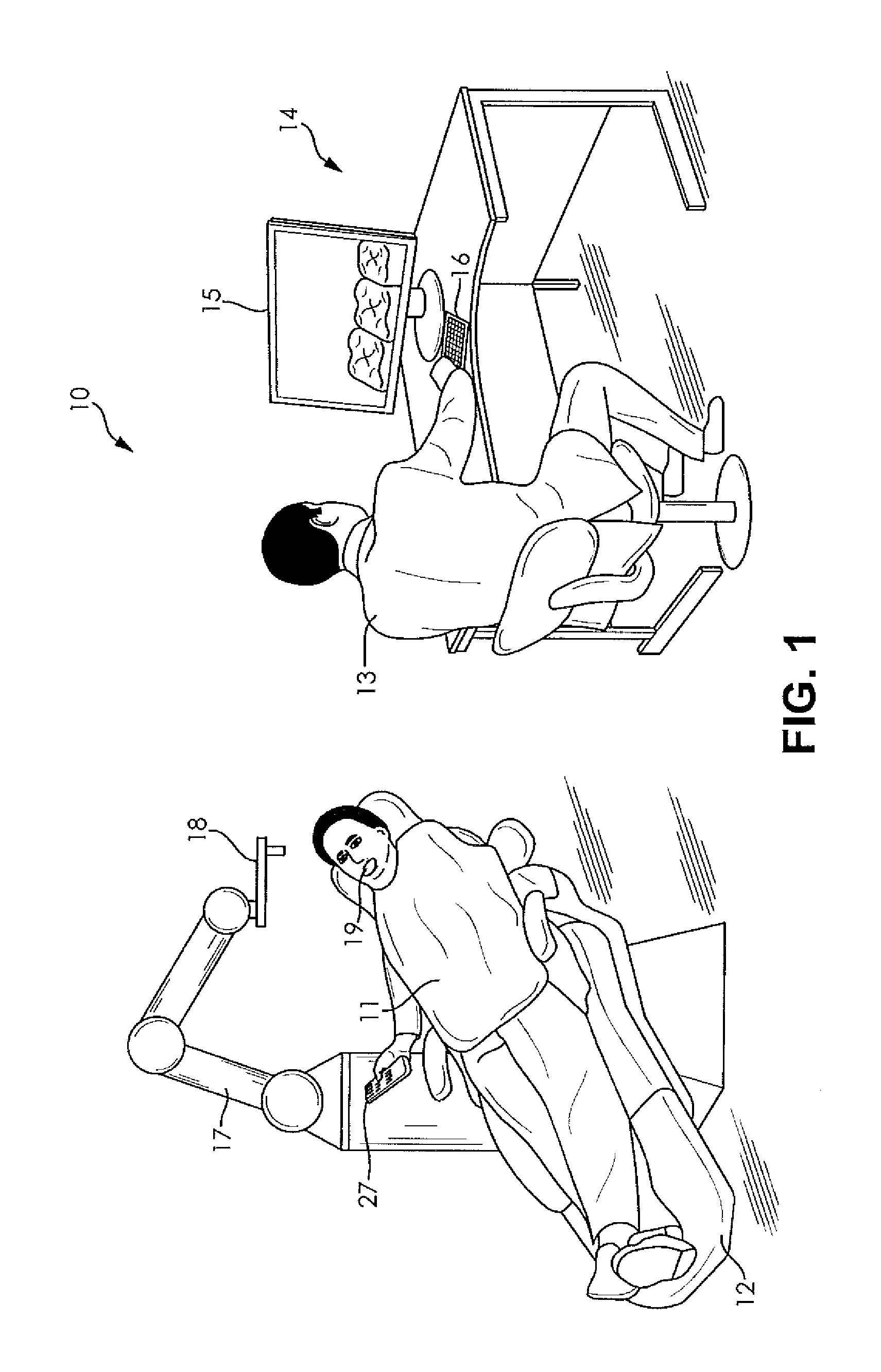
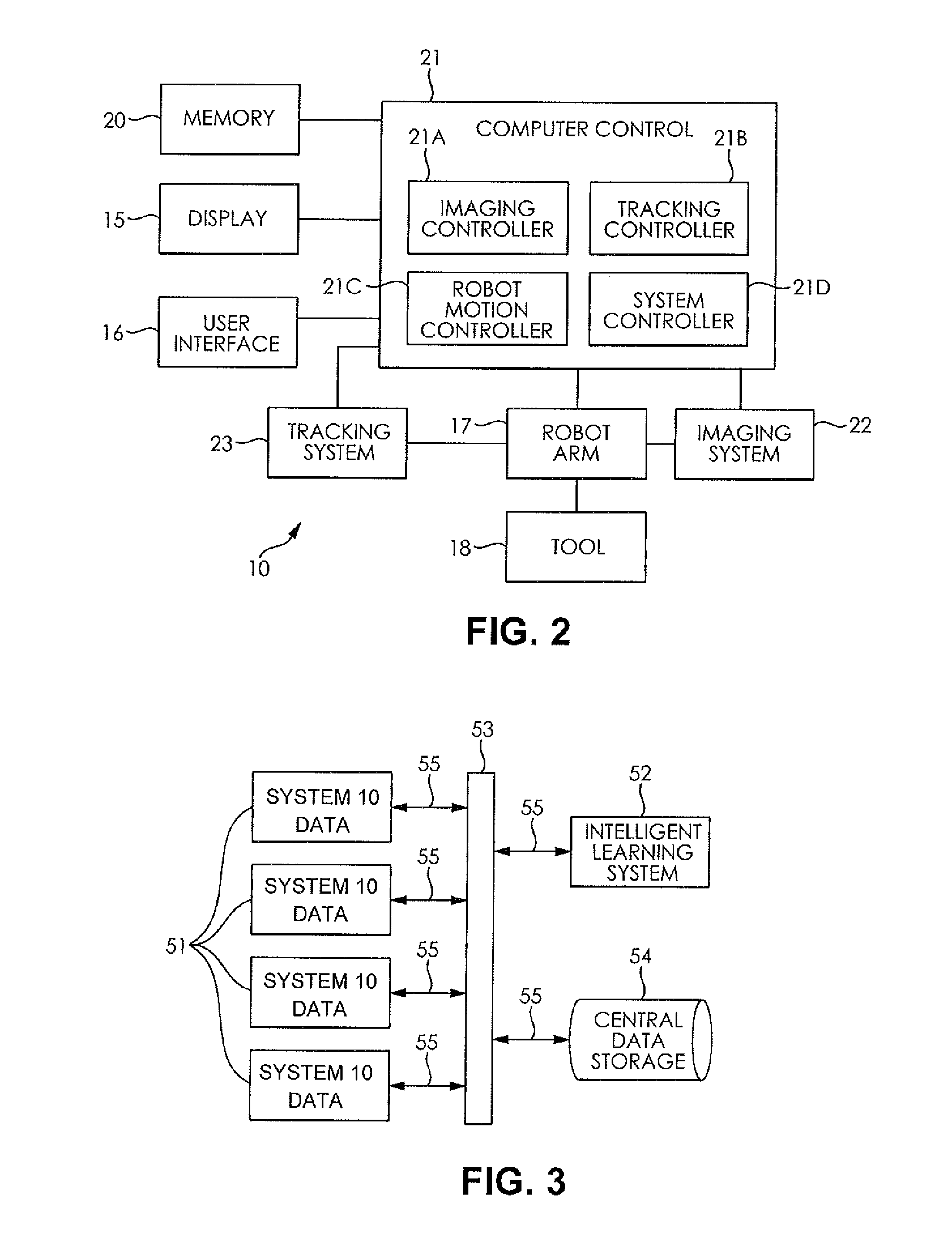
System and method for automating medical procedures
ActiveUS20150057675A1Most comfortMinimum durationDental implantsDiagnosticsDisplay deviceVisual perception
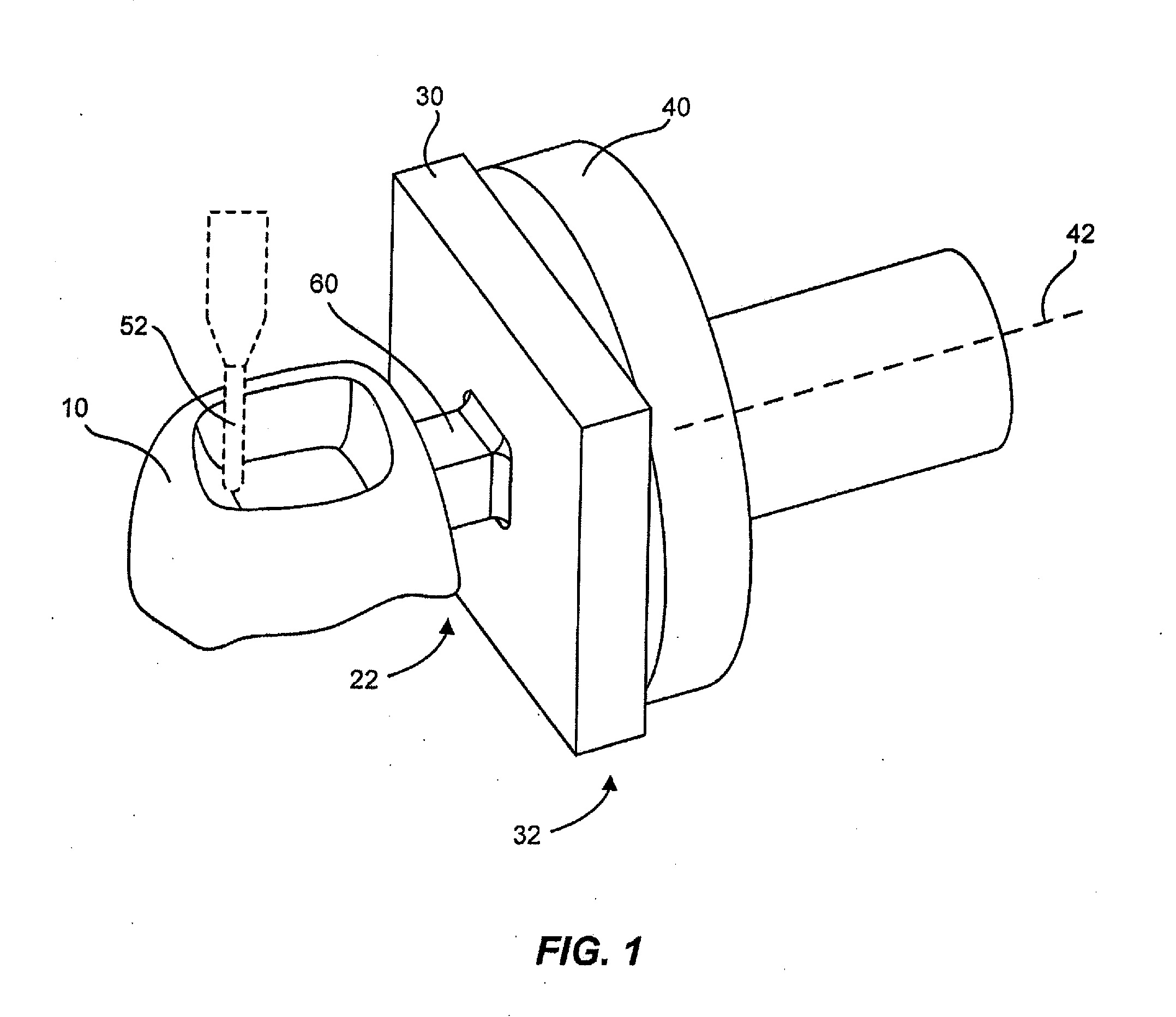
A system and a method for automating a medical process including a memory storing a software program, a computer connected to the memory for running the software program, a display connected to the computer for generating a visual representation of output data generated by the computer running the program, a user interface connected to the computer for obtaining image data representing a configuration of a patient treatment space and fixed markers in the treatment space and storing the image data in the memory, a robot arm connected to the computer, and a medical tool mounted on the robot arm wherein when a human inputs a selected treatment procedure into the computer, the computer runs the software program to generate a tool path based upon the treatment procedure and the image data, and the computer operates the robot arm to move the medical tool along the tool path without human guidance, and wherein the data generated during the treatment procedure is stored, analyzed, and shared among collaborating computer systems.
Owner:BRACHIUM
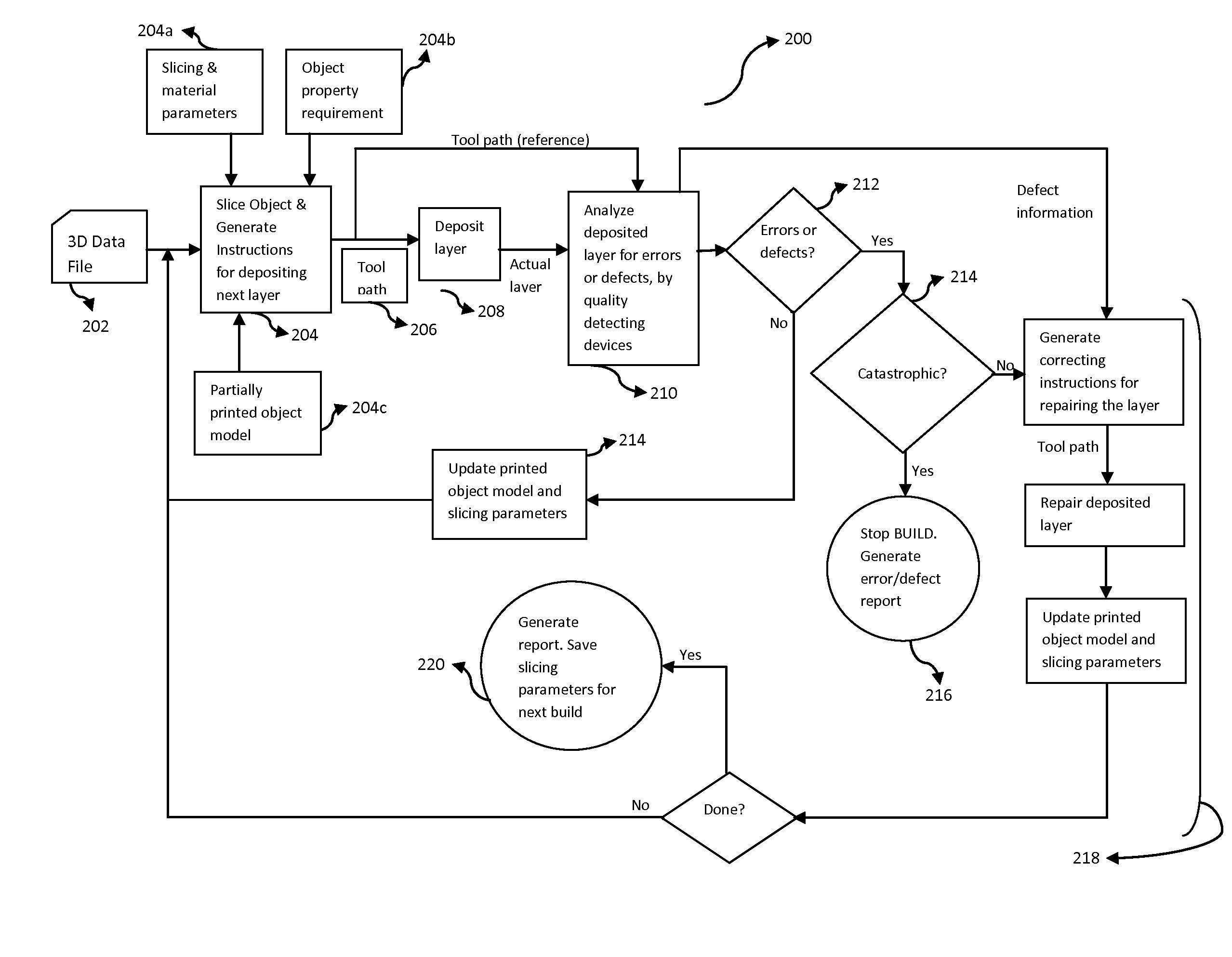
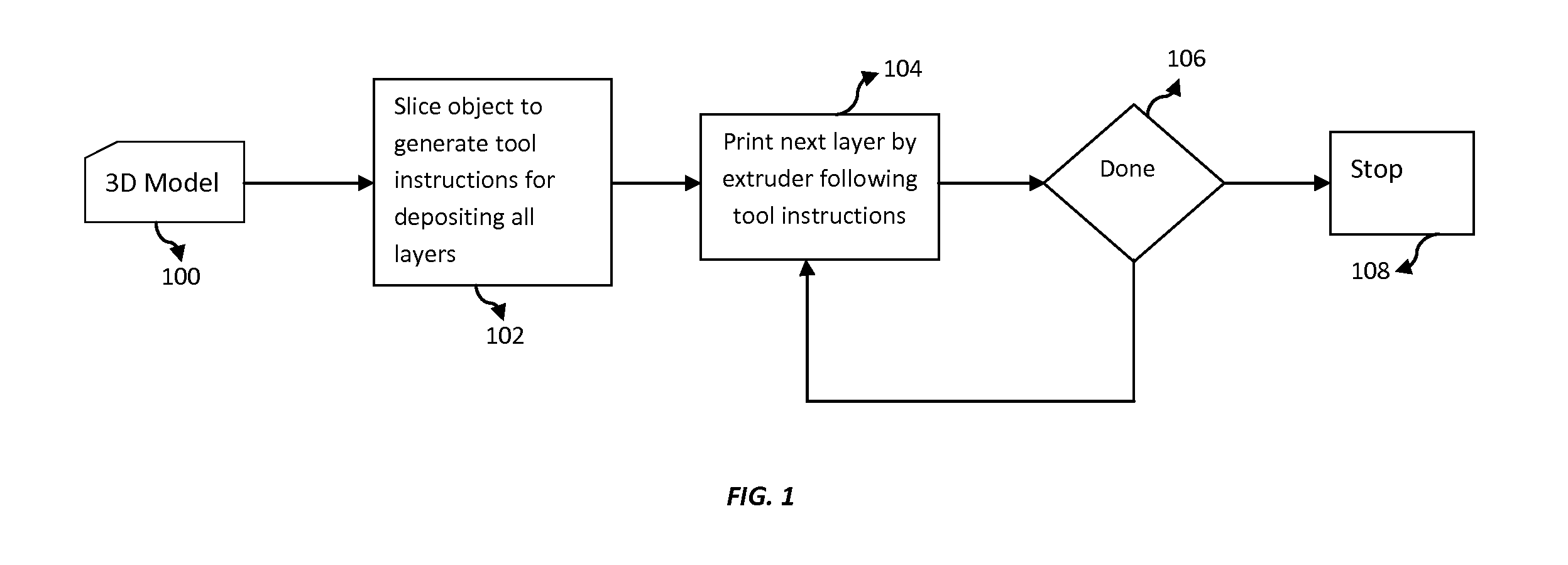
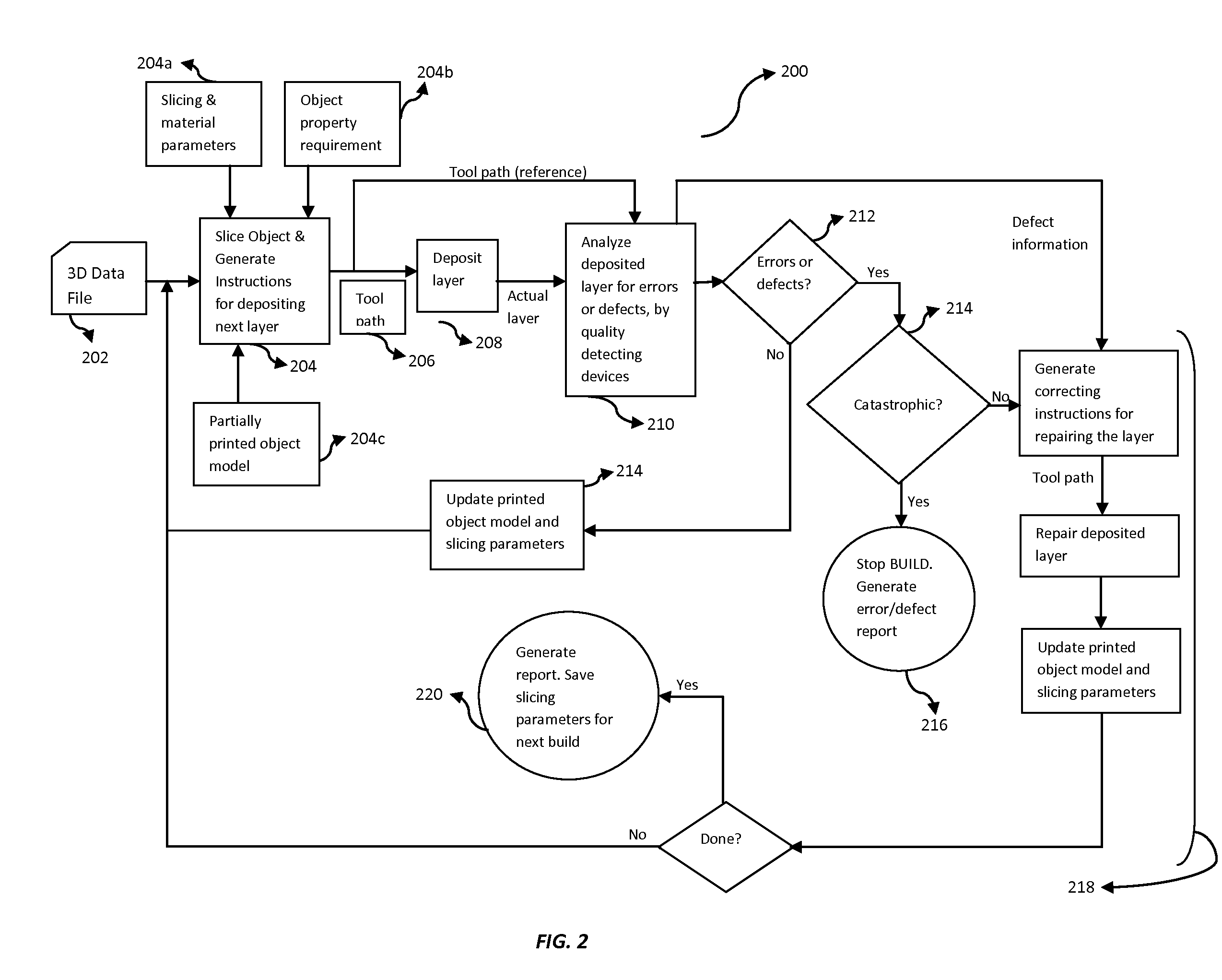
Method to monitor additive manufacturing process for detection and in-situ correction of defects
ActiveUS20160236414A1Minimize presenceProgramme controlAdditive manufacturing apparatusStructural geometryEngineering
The present invention provides a system and a method for real time monitoring and identifying defects occurring in a three dimensional object build via an additive manufacturing process. Further, the present invention provides in-situ correction of such defects by a plurality of functional tool heads possessing freedom of motion in arbitrary planes and approach, where the functional tool heads are automatically and independently controlled based on a feedback analysis from the printing process, implementing analyzing techniques. Furthermore, the present invention provides a mechanism for analyzing defected data collected from detection devices and correcting tool path instructions and object model in-situ during construction of a 3D object. A build report is also generated that displays, in 3D space, the structural geometry and inherent properties of a final build object along with the features of corrected and uncorrected defects. Advantageously, the build report helps in improving 3D printing process for subsequent objects.
Owner:AREVO INC
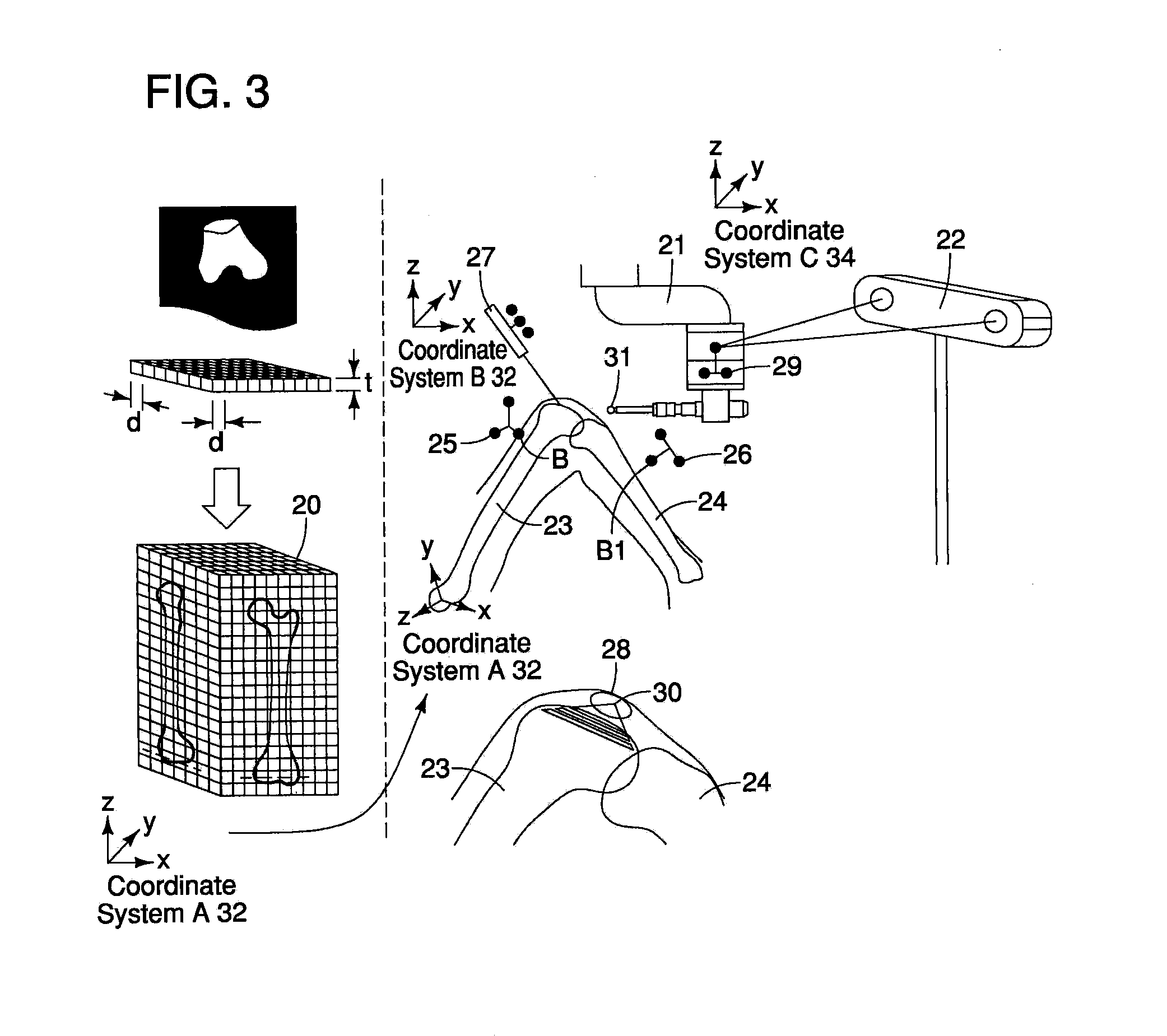
Surgical Assistance System
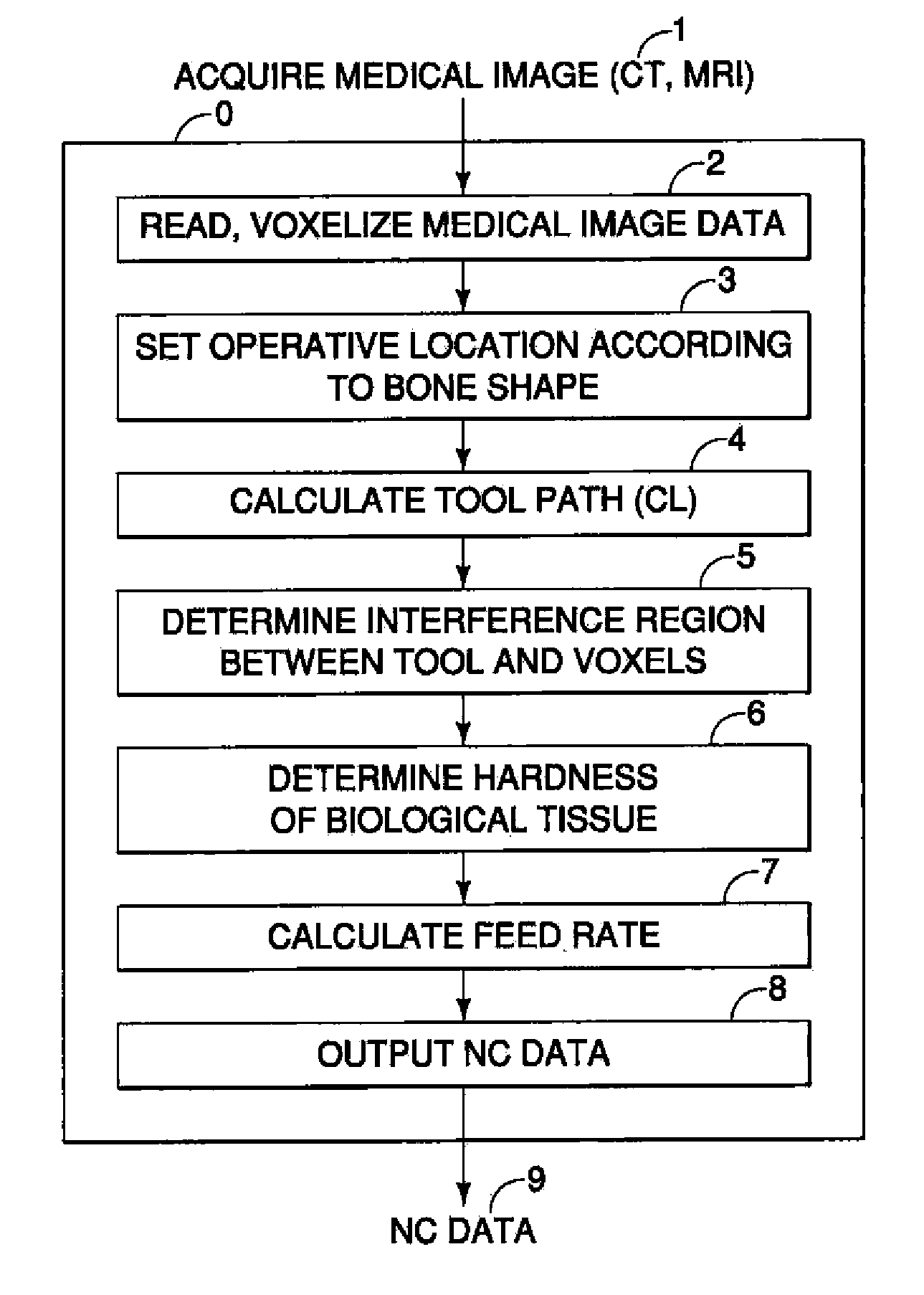
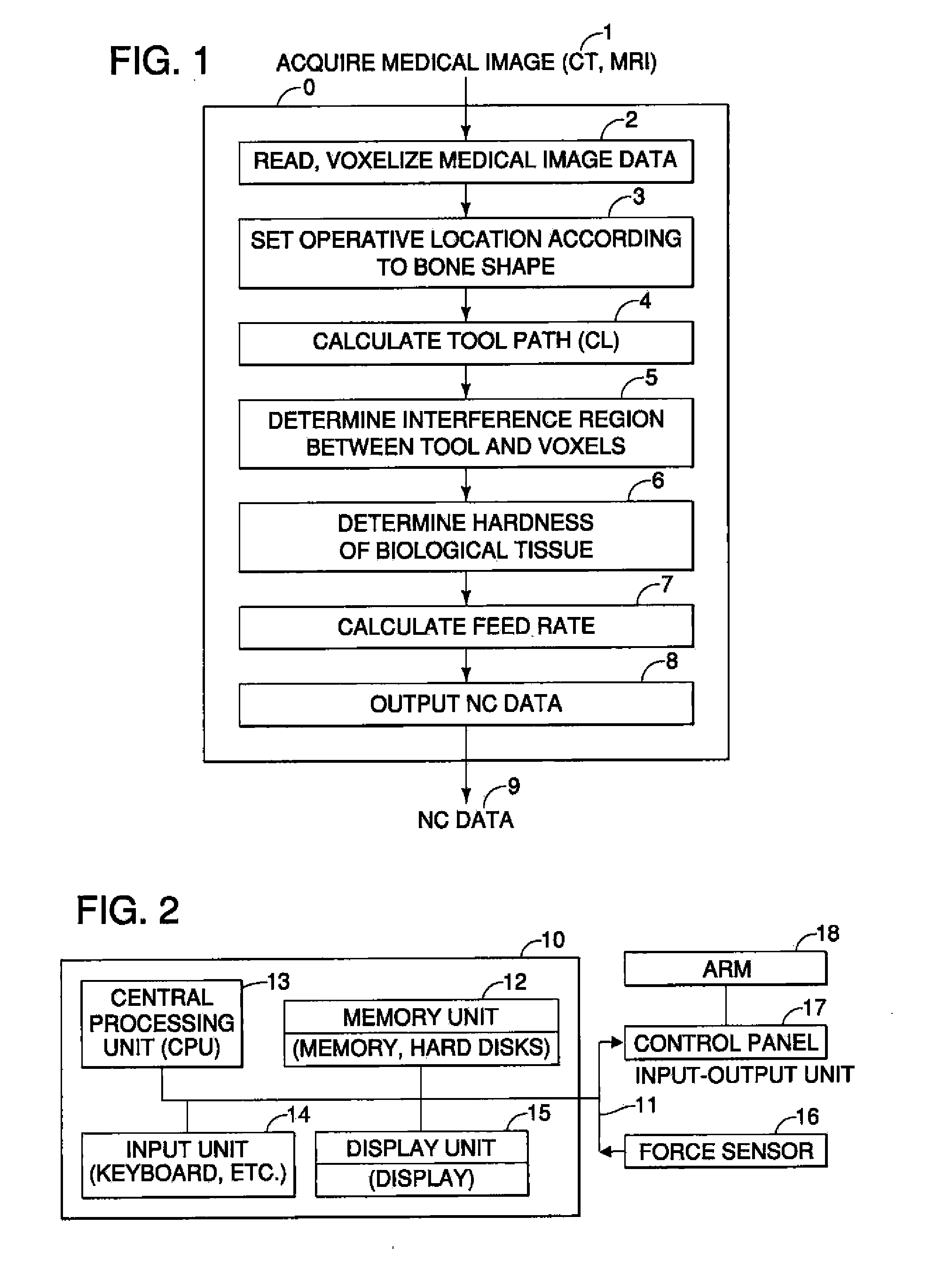
InactiveUS20110306985A1Precise resectionMinimal invasivenessDiagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsSurgical operationVoxel
A surgical assistance system for operating on biological tissue using a surgical tool attached to an arm of an automatically-controlled surgical instrument so that an optimal feed rate of the tool is calculated and outputted to the surgical instrument, the system including: a device for storing and voxelizing medical image data obtained from a biological tissue subject to surgery; a device for setting an operative location based on the shape of the biological tissue; a device for calculating a tool path along which the tool travels to perform surgery at an operative location; a device for determining the region of interference between the tool and the voxels; a device for determining the hardness of the biological tissue in the interference region; a device for calculating an optimal tool feed rate corresponding to the hardness; and a device for outputting the feed rate obtained by the calculations to the surgical instrument.
Owner:NAKASHIMA MEDICAL +1
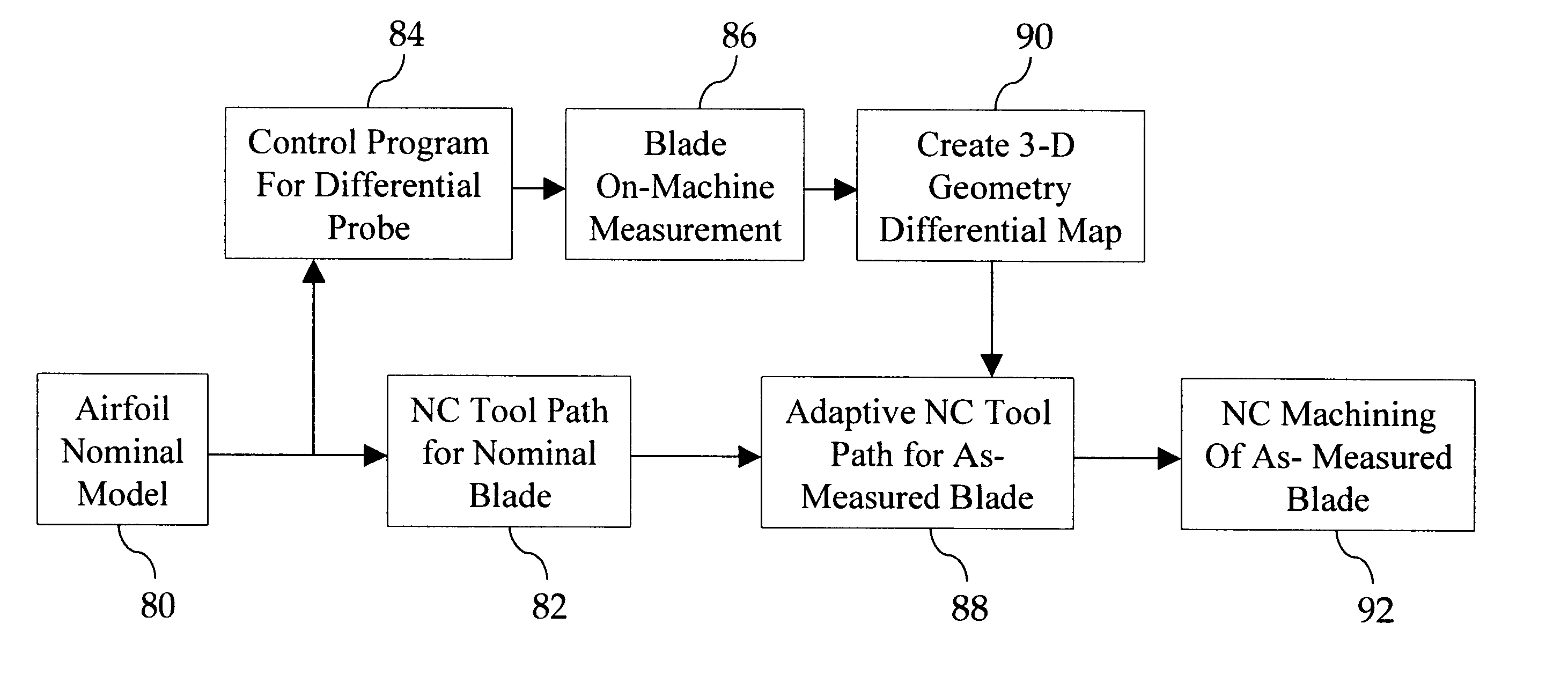
Systems and methods for automated sensing and machining for repairing airfoils of blades
InactiveUS6912446B2AdaptableEasy maintenanceProgramme controlTurbinesNumerical controlData acquisition
A method for repairing an airfoil comprising creating a nominal numerically-controlled tool path based on a nominal shape of the airfoil, measuring the airfoil using a displacement sensor, capturing differences in the airfoil shape as compared to the nominal shape, creating a three-dimensional map by synchronizing x, y and z coordinates and readings from the sensor, modifying the tool path based on the three-dimensional map, and machining the airfoil. A system for measuring and machining an airfoil comprising a computer operable for data acquisition and numerically-controlled tool path generation, a numerically-controlled machine, a cutting tool holder comprising a plurality of cutting tools, and a displacement-sensing probe.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Laser net shape manufacturing using an adaptive toolpath deposition method
A method is disclosed for laser cladding a substrate, comprising providing the substrate; depositing a first determined variable bead width of a material along a toolpath upon the substrate; depositing a second adjacent determined variable bead width of a material along the toolpath which overlaps the first determined variable bead width of deposited material; continuing to deposit a plurality of overlapping predetermined adjacent variable bead widths of a material until a first material layer is complete; forming a second material layer by depositing a plurality of overlapping predetermined variable bead widths of a material on top of the first material layer; and continuing to deposit material layers on top of deposited material layers until the cladding is complete; wherein the variable bead width of the deposited material is controlled by a computer having a plurality of input parameters to maintain an approximately constant percent of bead width overlap.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and apparatus for determining and guiding the toolpath of an orthopedic surgical robot
ActiveUS20130035696A1Enhance safety and accuracy and efficiencyDiagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsSurgical operationSurgical robot
A surgical robot system for cutting bone, the surgical robot system comprising:a surgical robot having an end effector;a cutter attached to the end effector;position determining means for determining the position of a bone which is to be cut vis-à-vis the surgical robot;pre-plan means for storing a pre-planned cut of the bone and instructing the surgical robot to cut bone in accordance with the same;a display for displaying the pre-planned cut of the bone; andinput means for enabling a user to deactivate the pre-plan means and to enable manual control of the cutter by the user.
Owner:THINK SURGICAL
Ruled surface impeller tool path planning and processing method
InactiveCN101271326ASolving the Problems of Five-Axis MachiningHigh degree of automationProgramme controlComputer controlImpellerNumerical control
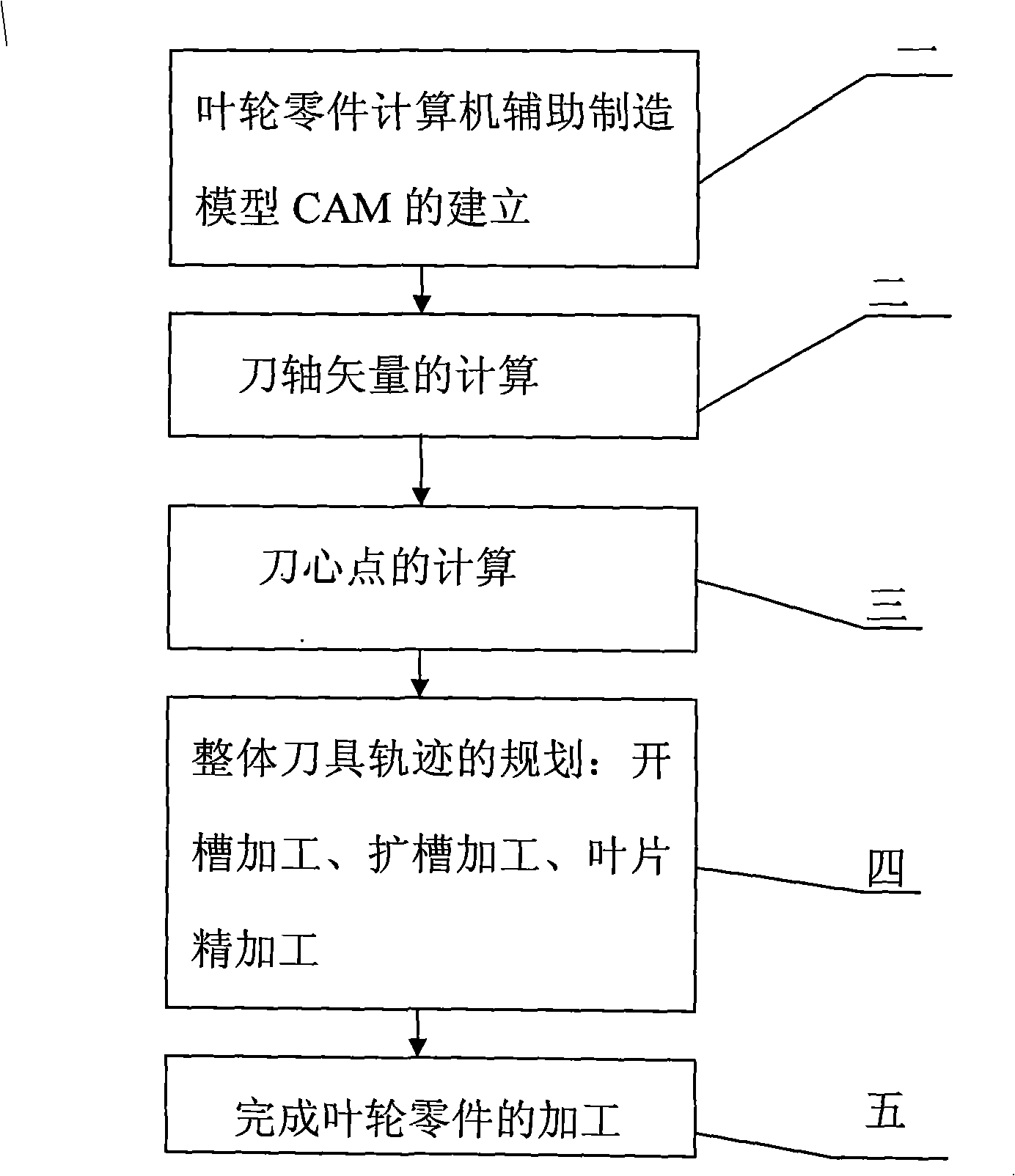
A path planning processing method of a ruled surface impeller cutter relates to a cutter path planning processing method. The invention solves the problems of the prior numerical control processing method of an impeller part, the problem are that a whole processing technology for processing a integral type ruled surface impeller is not proposed, the calculating method of the point of a knife centre or the point of a knifepoint is not given, the processing cutting efficiency is low, the operation is complex and the degree of automation is low and the five-axis processing of the ruled surface impeller can not be realized etc. The main steps of the method are the establishment of the calculator assistant manufacturing model CAM of an impeller part, the calculation of the vector of a cutter shaft, the calculation of the point of the knife centre, the planning of whole cutter path and the achievement of the processing of the impeller part. The method of the invention solves the problem of the five-axis processing of the ruled surface impeller and has the advantages of high processing cutting efficiency, easy operation and high degree of automation The ruled surface impeller processed by the method has the characteristics of orderly linage of flow passage, symmetrical structure and the uniform distribution of cutter path at the surface of the flow passage, thus reducing the workload of subsequent polishing processing greatly.
Owner:哈尔滨工大宏图橡塑科技有限公司
Method and apparatus for brittle materials processing
InactiveUS20100252540A1Avoids chipping and crackingExcessive heat build can be avoidedLaser detailsWelding/soldering/cutting articlesLaser processingOptoelectronics
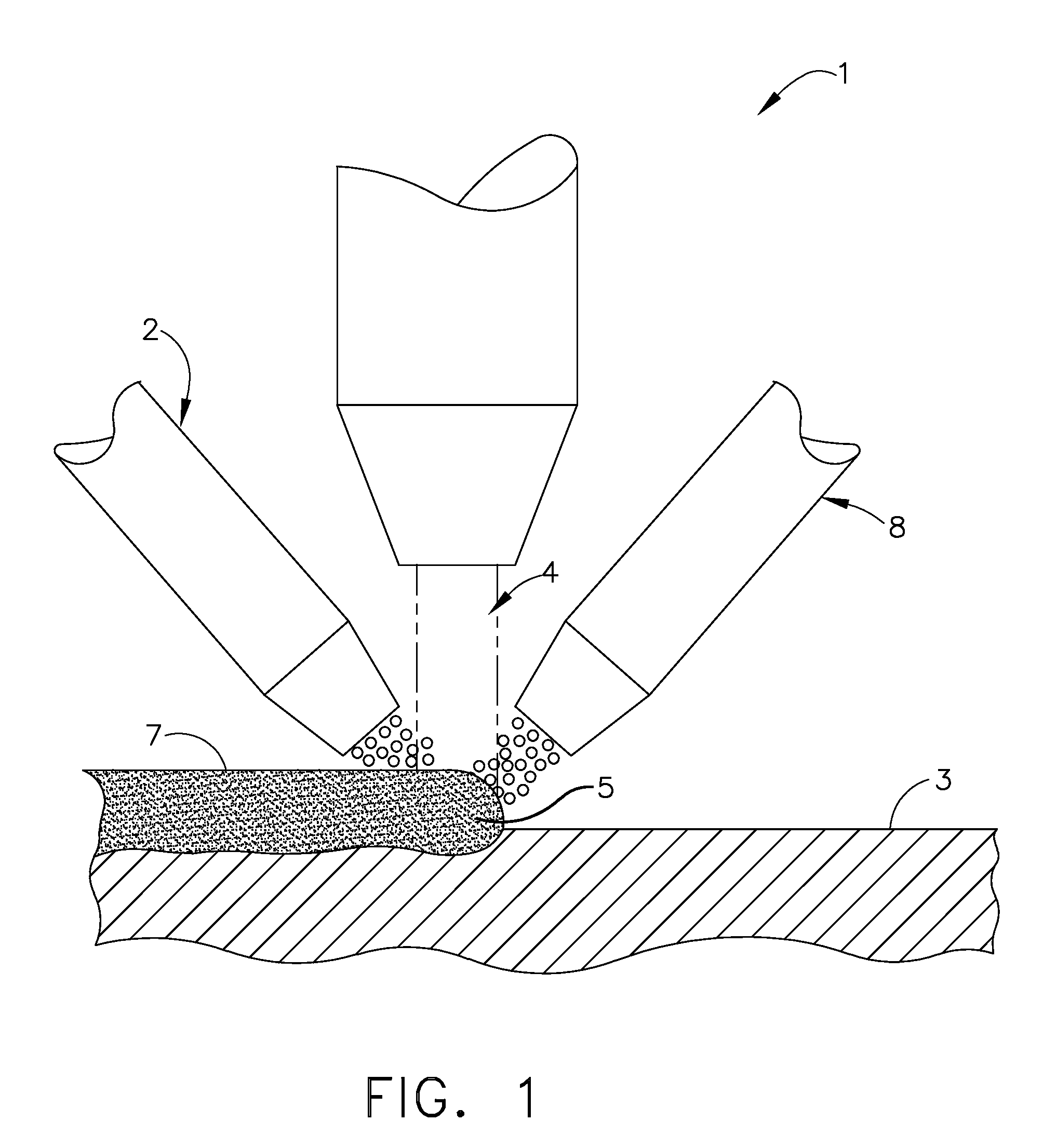
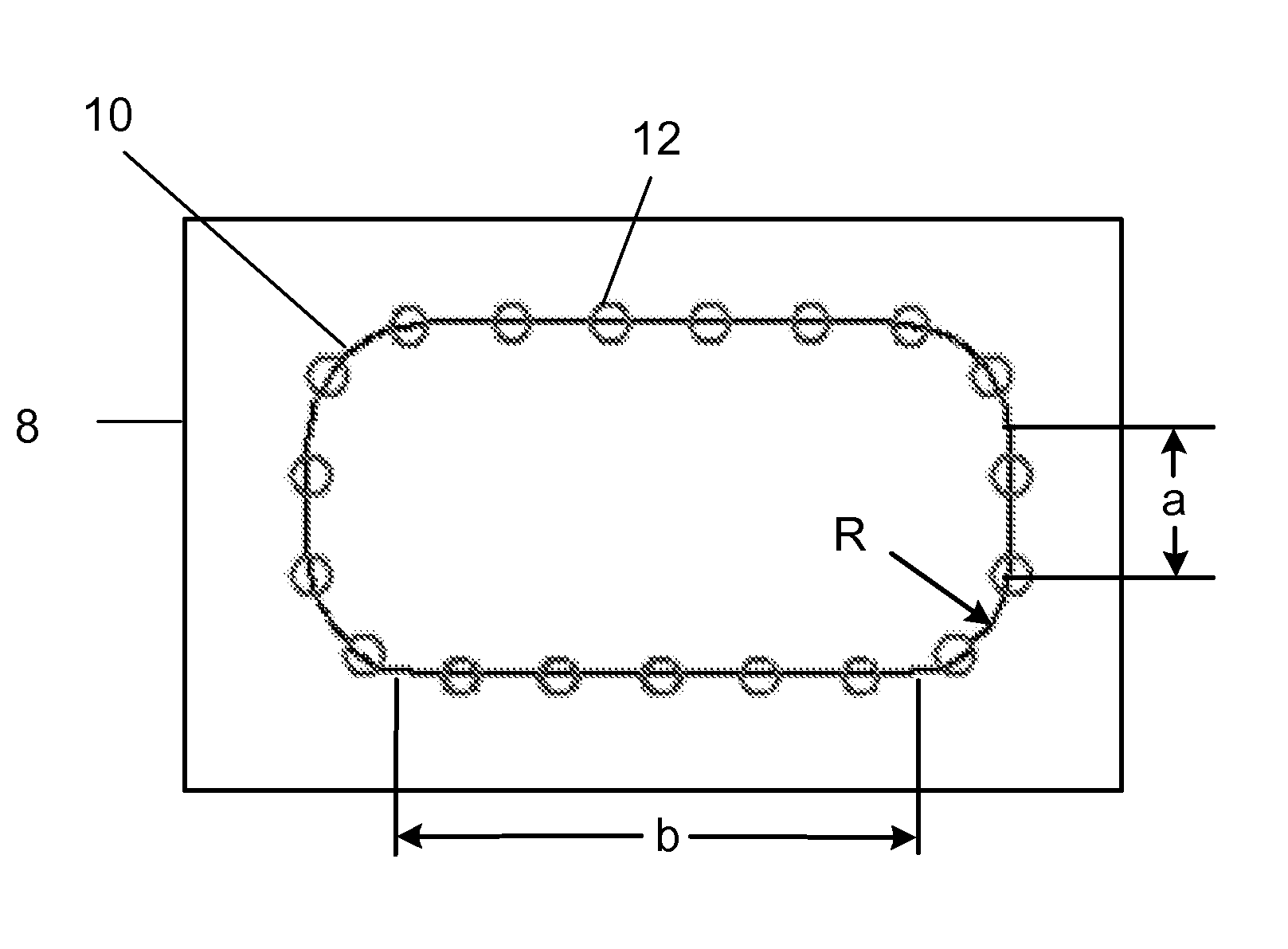
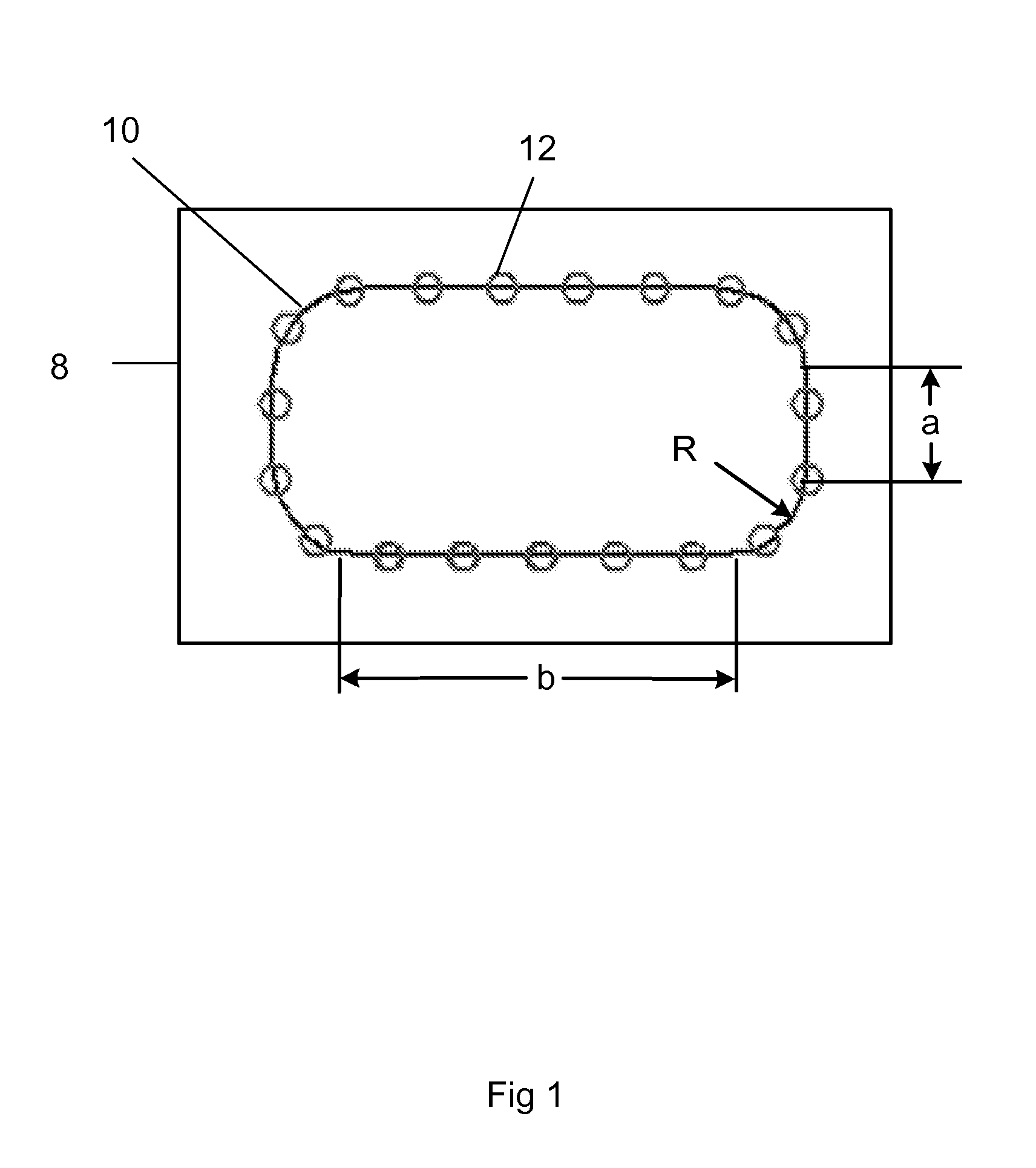
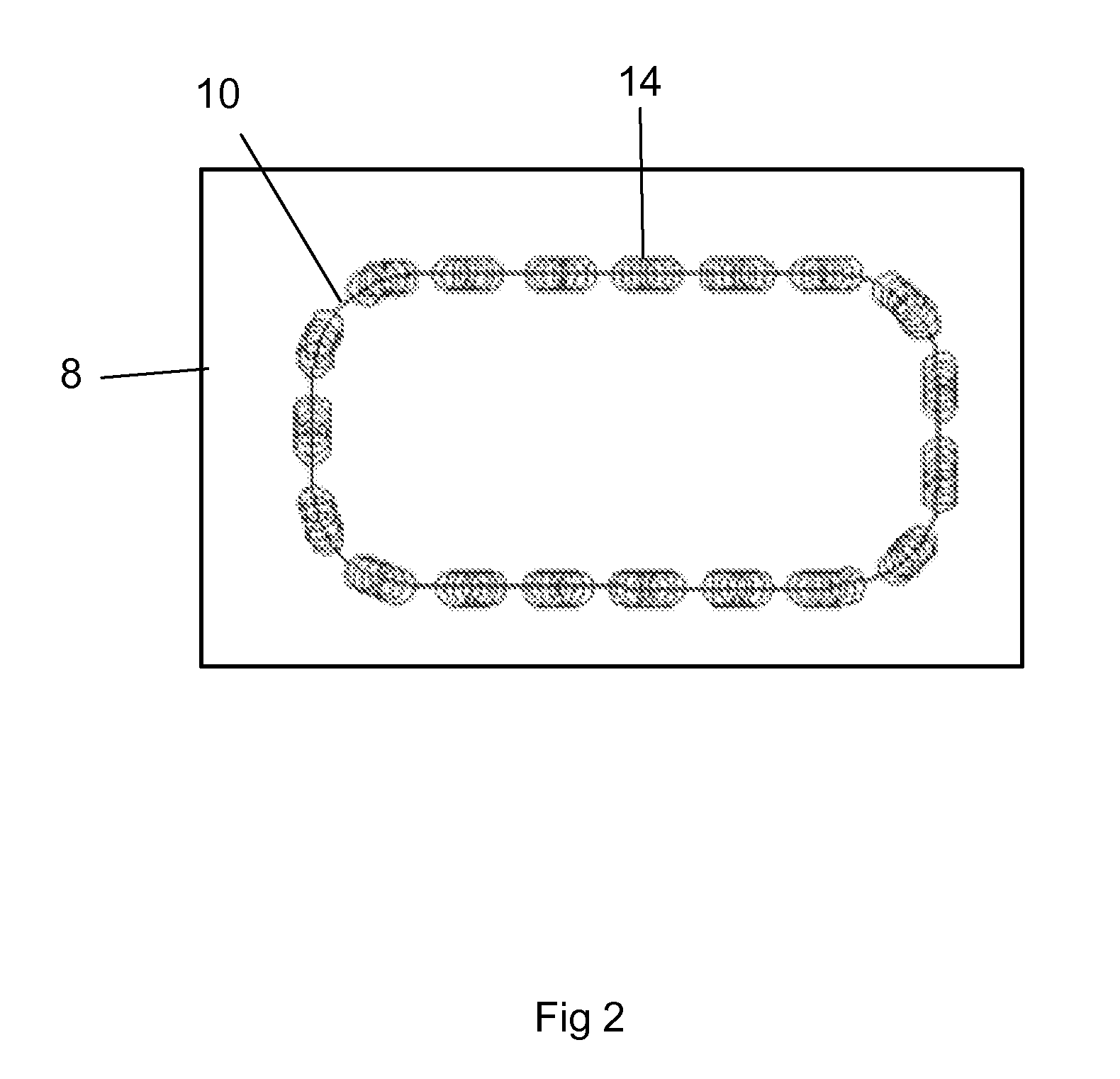
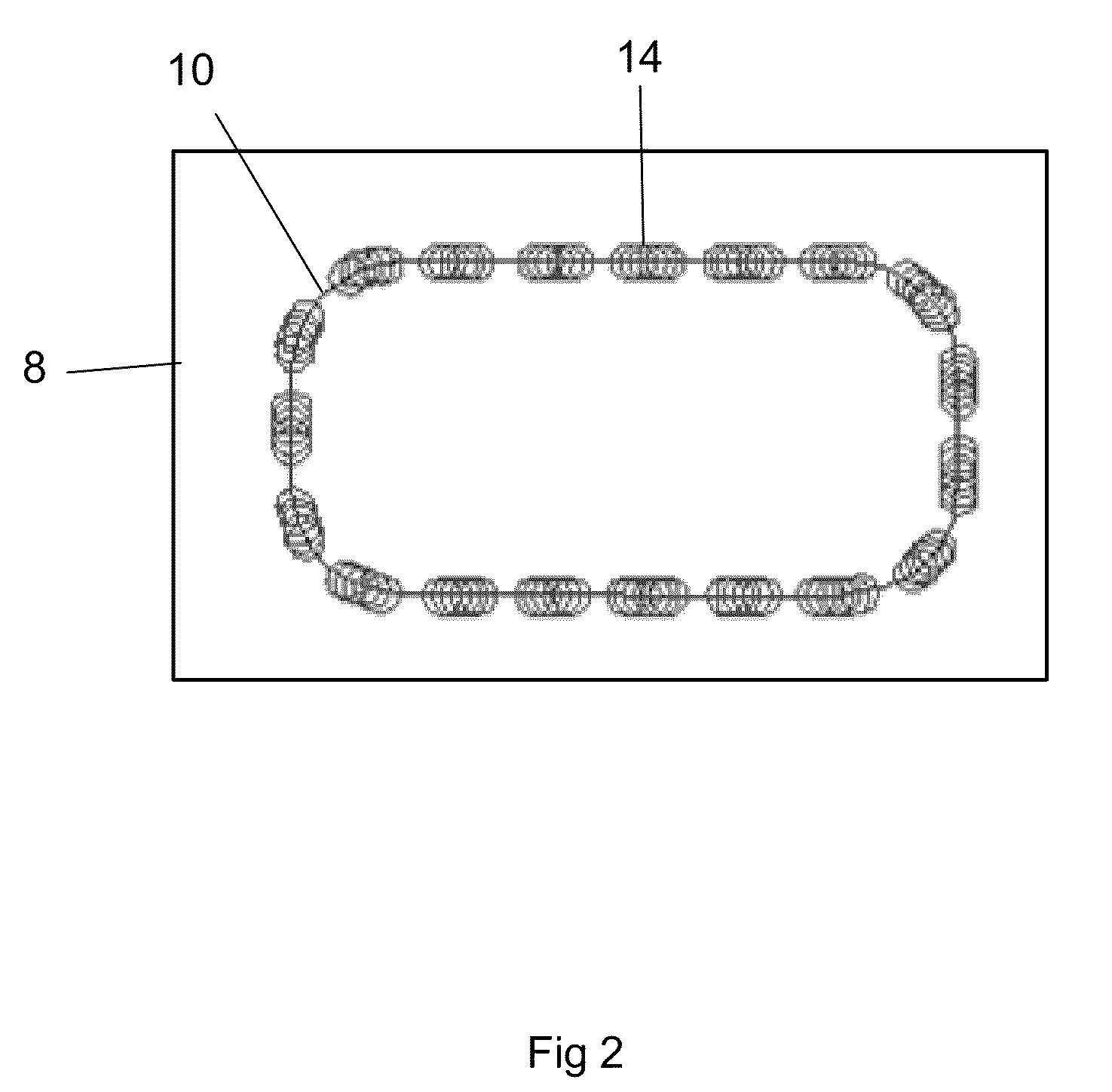
An improved method for laser machining features in brittle materials 8 such as glass is presented, wherein a tool path 10 related to a feature is analyzed to determine how many passes are required to laser machine the feature using non-adjacent laser pulses 12. Laser pulses 12 applied during subsequent passes are located so as to overlap previous laser spot locations by a predetermined overlap amount. In this way no single spot receives excessive laser radiation caused by immediately subsequent laser pulses 12 being applied adjacent to a previous pulse location.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
Method for improved brittle materials processing
InactiveUS20100252959A1Avoid chippingAvoid crackingLaser detailsDecorative surface effectsLaser processingOptoelectronics
An improved method for laser machining features in brittle materials such as glass is presented, wherein a tool path related to a feature is analyzed to determine how many passes are required to laser machine the feature using non-adjacent laser pulses. Laser pulses applied during subsequent passes are located so as to overlap previous laser spot locations by a predetermined overlap amount. In this way no single spot receives excessive laser radiation caused by immediately subsequent laser pulses being applied adjacent to a previous pulse location.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
Method of laser milling using constant tool path algorithm
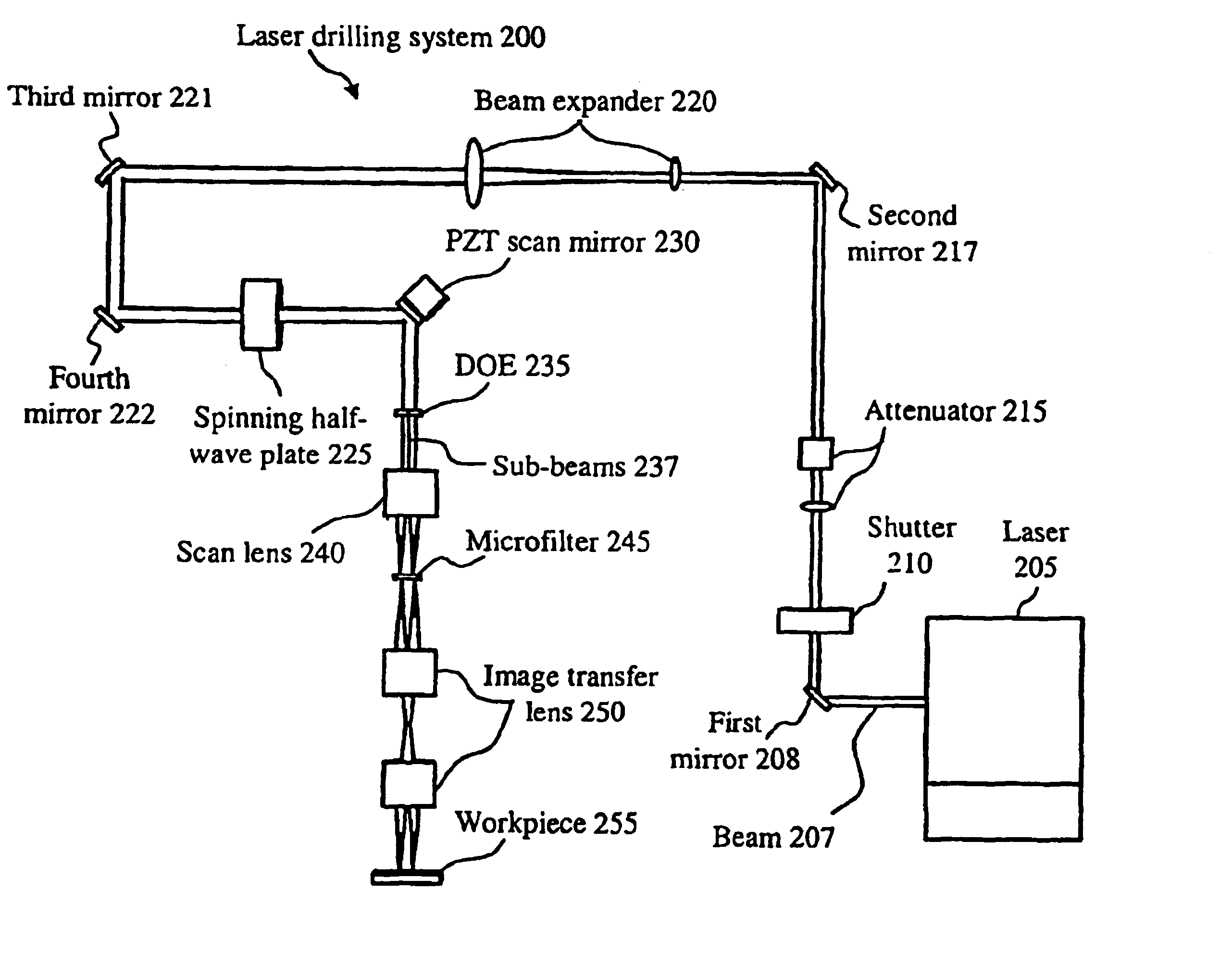
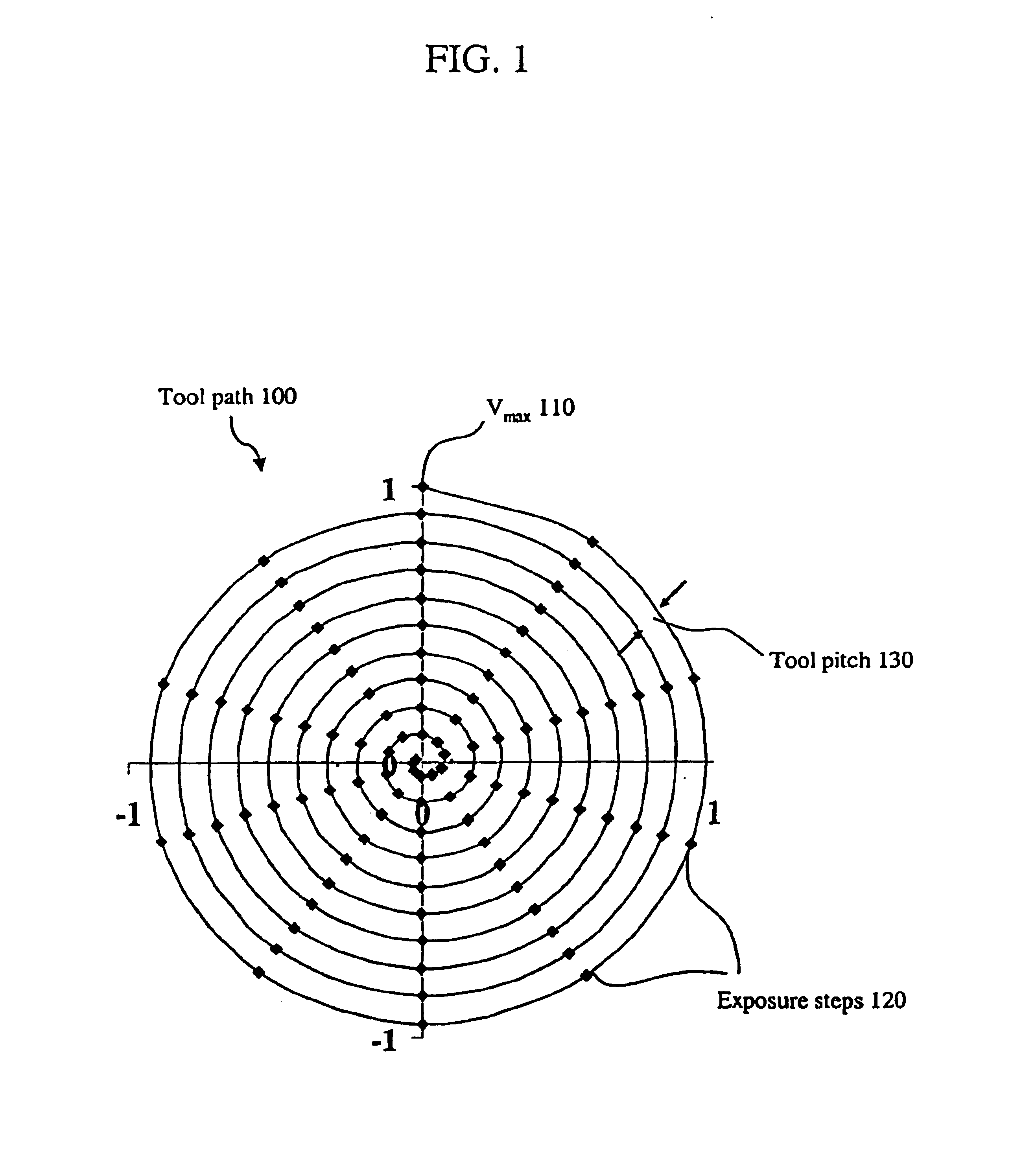
InactiveUS6897405B2Quality improvementGood repeatabilityPrinted circuit manufacturePrintingPicosecond laserLight energy
A method of creating a milled structure in a fixed material using a moving laser beam is disclosed, where a picosecond laser provides short pulses of light energy to produce required exposure steps, where a variable rate of laser beam movement conducts the milling upon the material, where the laser beam tool path directs the milling process to produce a milled hole of high quality and repeatability, and where the knowledge of how to measure these 3 quantities is returned as feedback into the laser system. The present invention is further embodied as a spiral milled tool path structured to achieve the customer specified tapered hole shape. The constant arc speed tool path is required to produce tapered holes to customer specification.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Spray gun track planning method for free-form surface spraying robot
ActiveCN102527554AReduce planning timeSimple calculationSpraying apparatusSpecial data processing applicationsNumerical controlFree form
The invention discloses a spray gun track planning method for a free-form surface spraying robot. According to the spray gun track planning method disclosed by the invention, the characteristic that a numerical control processing process is very similar to the spaying process is utilized, so that the motion track of a spray gun can be obtained by little calculation on the basis of the tool path. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, dividing the sprayed surface in three-dimensional modeling software into a plurality of areas with regular shape, generating m equidistant tool paths and deriving the equidistant tool paths into standard APT (Automatic Programming Tools) files by using a five-axis numerical control machining method; extracting tool motion information contained in the APT files, extending the obtained tool points, processing the corner parts into circular arc transition to generate a spray gun path point sequence and then solving a spray gun posture sequence on the path point sequence; and interpolating the spray gun posture sequence to generate a complete motion track of the spray gun. According to the spray gun track planning method disclosed by the invention, accurate control over the track of the spray gun can be realized and the high praying quality is ensured; and the spray gun track planning method is simple in calculation process and calculation amount.
Owner:清研同创机器人(天津)有限公司
Multi-material toolpath generation for direct metal deposition
A method of modeling multiple material parts for additive manufacturing processes such direct metal deposition operates within the constraints of a single material CAD system. Each material is modeled separately as a single or multiple solid part, under the assumption that there are no internal multiple materials; that is, no voids for other material parts. The parts are ordered from the outer most geometry to the innermost geometry and Boolean operations are performed to calculate the final volume for each part. In use of the invention, should any design changes occur, only the parts as originally defined need to be modified, and the method is reapplied. The method is applicable to the generation of CAM cutting paths for 2½-D and 3-D geometries by pocket machining with spiral-in, spiral-out, and arbitrary direction raster tool paths using stock material with and without reflection, depending upon the geometry. Single- and multi-material files may be merged one toolpath file, and commands may be embedded for closed- or open-loop control of the fabrication process.
Owner:DM3D TECH
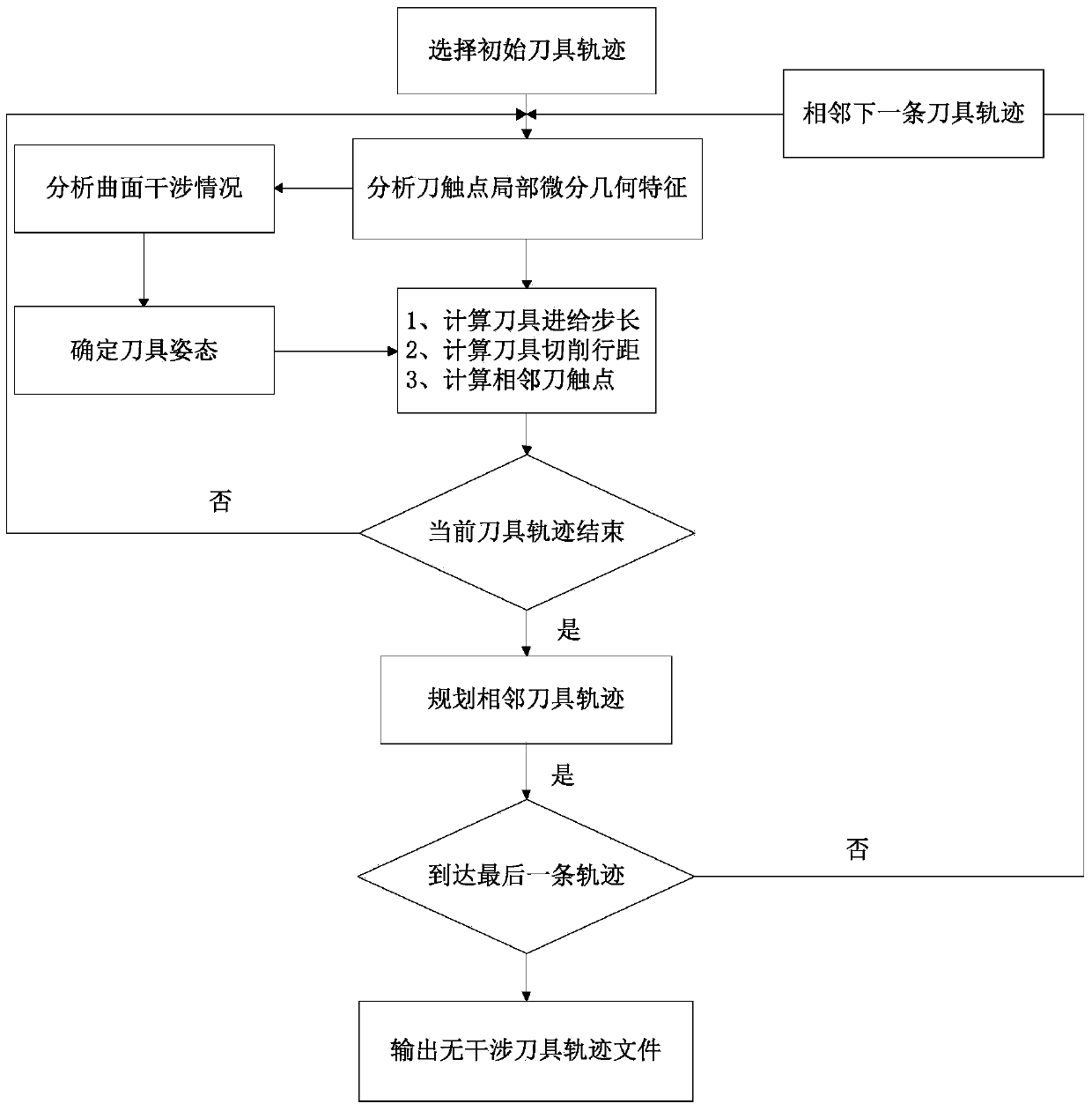
Method for planning smooth and non-interference tool route of 5-axis numerical control machining
ActiveCN101109944AShorten the timeAvoid repeated adjustmentsNumerical controlNumerical controlCircular disc
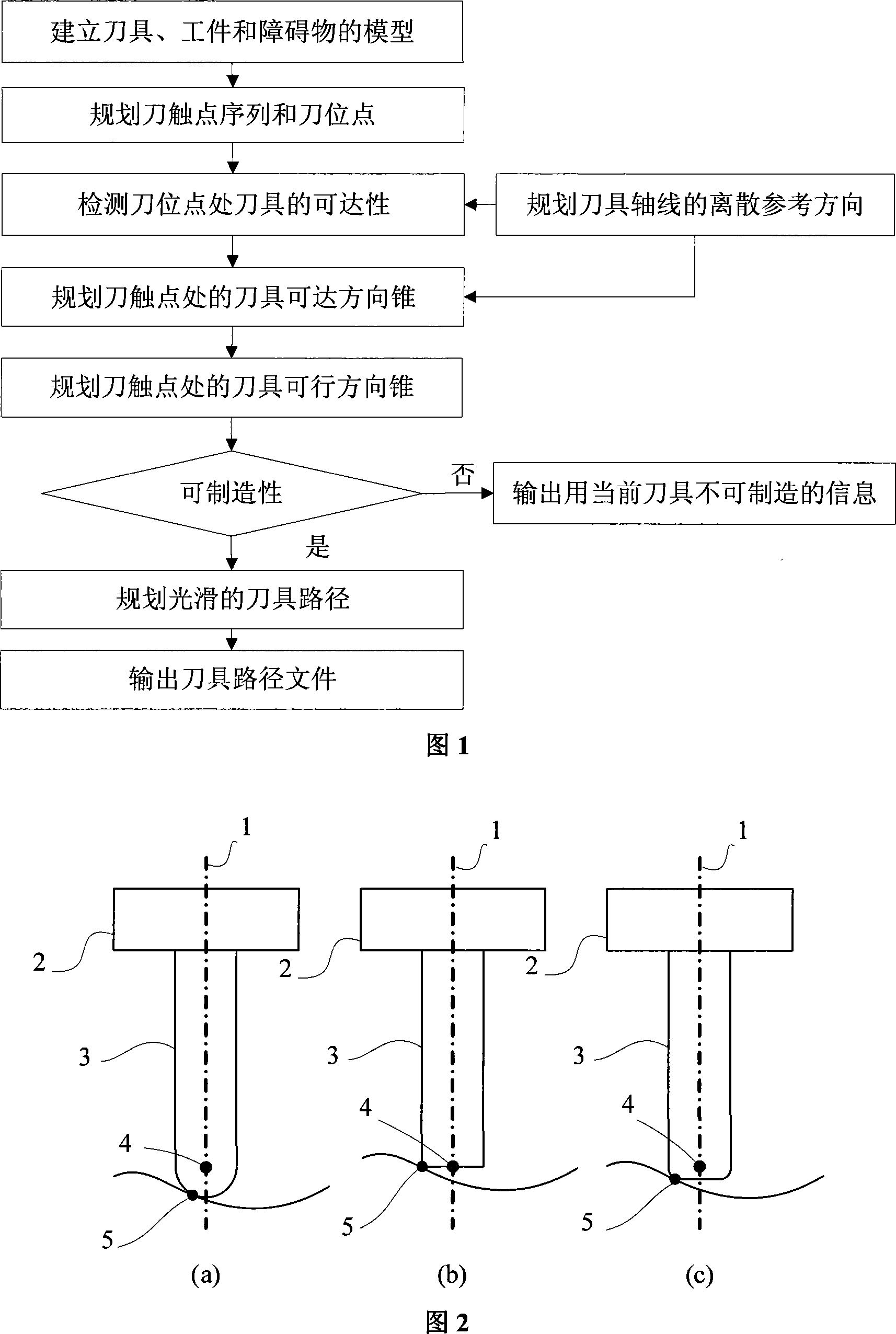
The utility model relates to a five-axle digital controlled tool path planning method of which the processing is smooth and free of interference as well as the analysis on the producibility of the components. Firstly, the geometrical models for the cutting tools, the work pieces and the obstacles are established. Along the negative direction of the scattered reference direction, griding the obstacle and the disc of the cutting tool turning circle cylindrical surface at the cutter spacing point. Based on the test in depth, the visual information can be obtained to judge the accessibility of the cutting tool along the scattered reference direction. Also, the directional cone for the attainability of the cutting tool can be planned at the cutting tool contact. Based on the continuity constraint of the direction and the restriction of the processing surroundings, the cone for the feasible direction can be calculated and the producibility can be judged. If the producibility is available, the smooth and the non-interference tool path can be planed in the directional cone as per the principle of the minimum change of direction in the tool path so as to output the tool path document. The utility model has a high computational efficiency and a simple programming, so as to be suitable to the wantonly rendered geometrical models such as the polygon grid and the free curved surface. Also, the interference of the clip and the toolbar can be avoided.
Owner:CHENGDU USEFUL TECH CO LTD
Tool path data generation apparatus for NC machine tool and numerical controller provided with it
InactiveUS7269471B2Effective reflectionProgramme controlAutomatic control devicesNumerical controlData memory
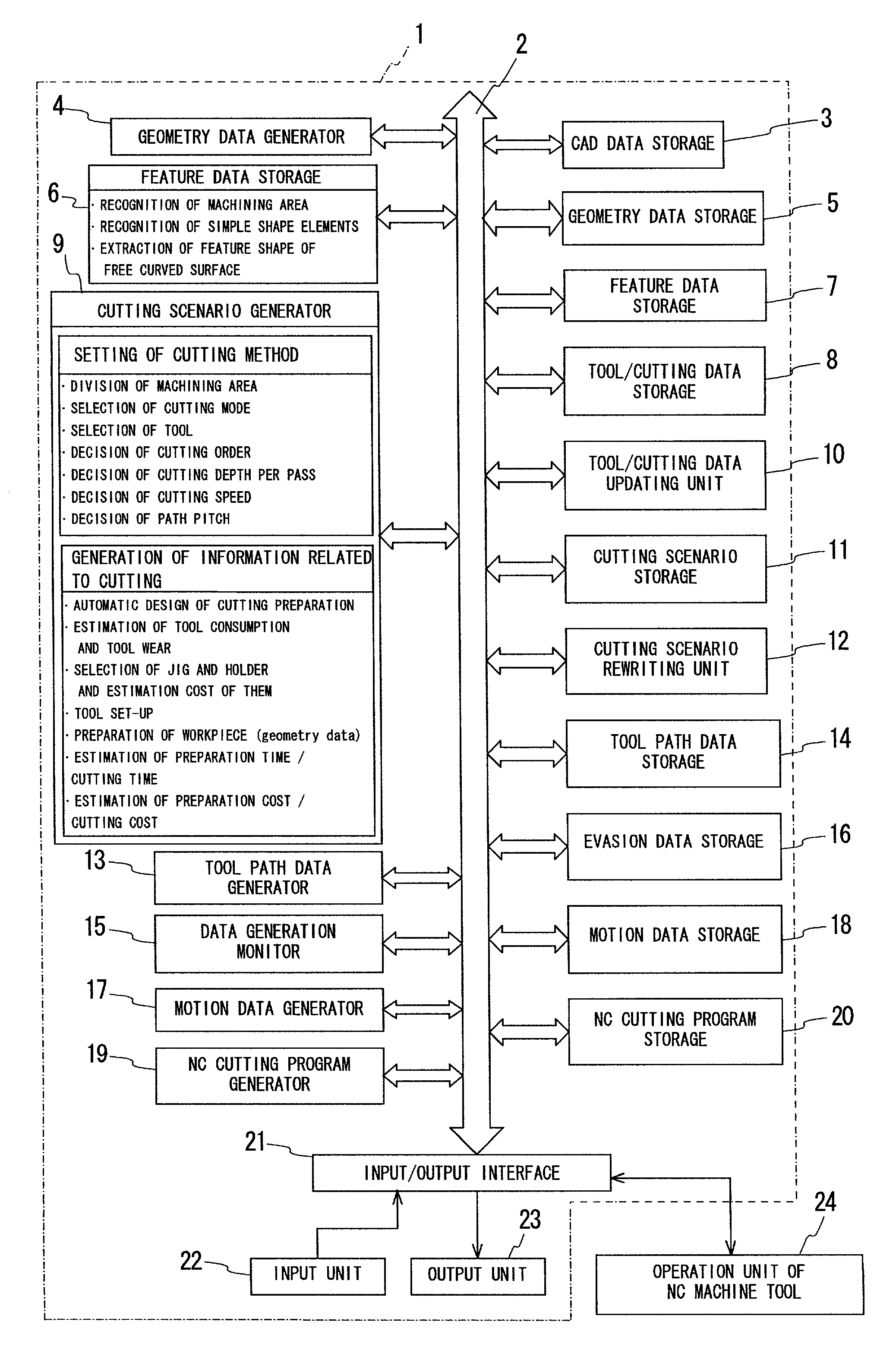
Tool path data generation apparatus (41) that can speedily and securely generate tool path data on the basis of CAD data. The tool path data generation apparatus (41) includes a feature data extractor (6) to extract features in relation to at least a three-dimensional shape of a workpiece, a tool / cutting data storage (8) to store a cutting mode etc. in accordance with a feature shape, a cutting method setting unit (9) to set an optimal cutting method for each feature shape on the basis of the extracted feature data and the stored tool / cutting data, and a tool path data generator (13) to generate tool path data on the basis of set cutting method. An operator doesn't have to input any data in generating tool path data, therefore tool path data can be speedily generated.
Owner:DMG MORI SEIKI CO LTD +1
Performing high-speed events ''on-the-fly'' during fabrication of a composite structure by automated fiber placement
An apparatus and method are provided for performing a high-speed event, such as a cut / add of a tow, in an automated fiber placement process, by initiating the high-speed event prior to a fiber placement head reaching a location along a tool path of the fiber placement head at which it is desired to have the high-speed event completed.
Owner:INGERSOLL MACHINE TOOLS
Method for Machining a Dental Prosthesis
InactiveUS20120148985A1Reduce the possibilityRaise the possibilityTooth crownsArtificial teethProsthesisEngineering
A method for machining a dental prosthesis that reduces the likelihood of forming tool failure includes machining a workpiece to form a top surface and a side surface of the dental prosthesis, machining a connector between a proximal end of the dental prosthesis and a proximal end of the workpiece, and machining a bottom surface of the dental prosthesis with a spiral tool path.
Owner:JUNG YUNOH +1
Method and apparatus for generating a tool path for a robotic orthopedic surgical procedure
ActiveUS20130035690A1Minimizes soft tissue traumaMinimizing required surgical accessMedical simulationMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesComputer scienceSoft tissue
A method for generating an improved tool path for cutting a bone so as to minimize soft tissue trauma, wherein the method comprises:accessing an image of the bone which is to be cut;accessing an image of a pre-determined cutting pattern;superimposing the image of the pre-determined cutting pattern against the image of the bone;calculating the intersection of the pre-determined cutting pattern and the bone using the superimposed images of the pre-determined cutting pattern and the bone; andgenerating a tool path based upon the intersection of the pre-determined cutting pattern and the bone so as to minimize soft tissue trauma by leaving a thin perimeter of bone at the boundary of the bone cut when the boundary of the bone cut is adjacent to a bone surface.
Owner:THINK SURGICAL
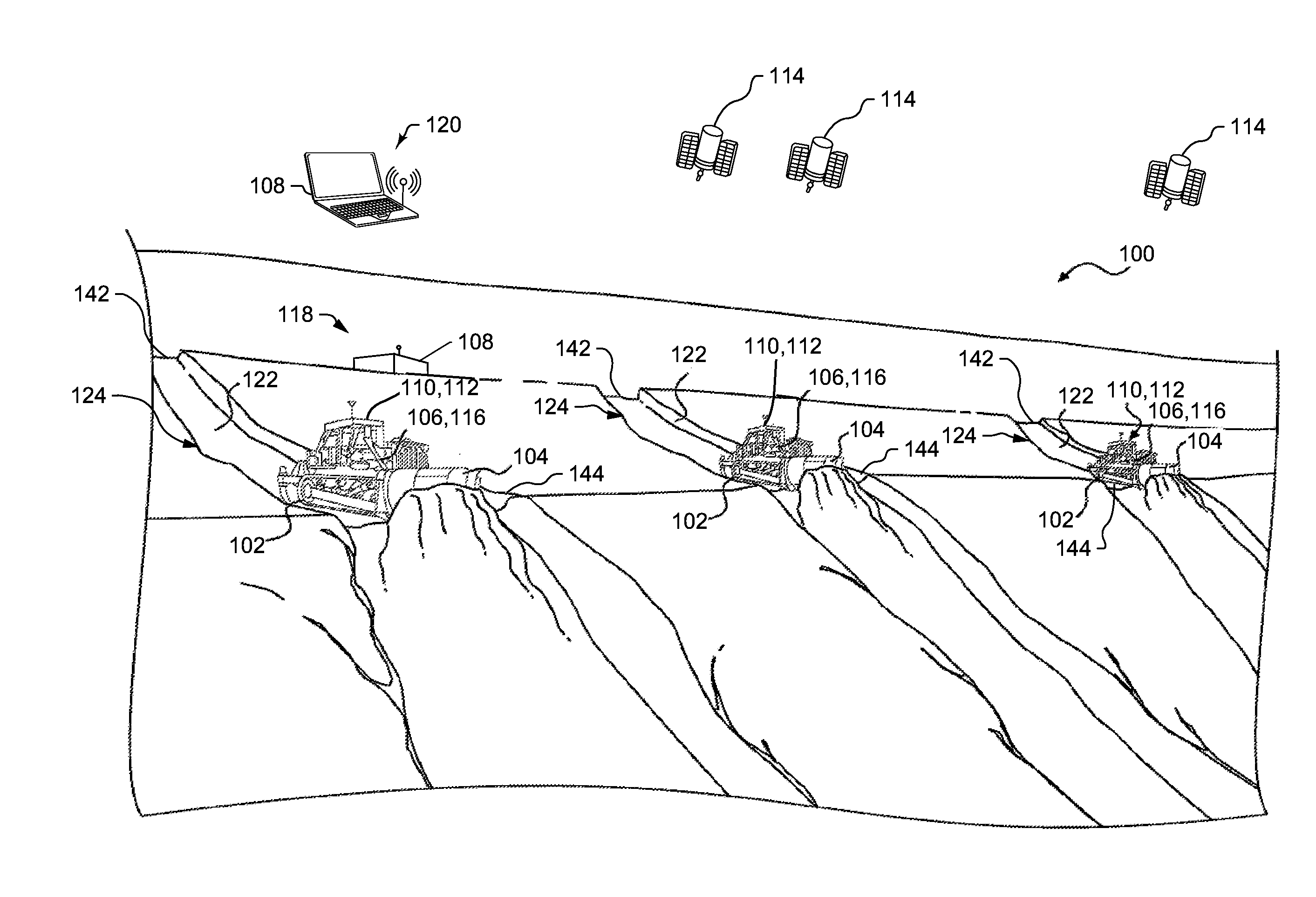
Systems and Methods for Constrained Dozing
A computer-implemented method for determining an implement path for a machine implement at a worksite is provided. The computer-implemented method may include identifying a work surface and a pass target of the worksite, defining a loading profile based on one or more curves constrained to the work surface and the pass target, defining a carry profile based on the loading profile and the pass target, and designating the loading profile and the carry profile as the implement path.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
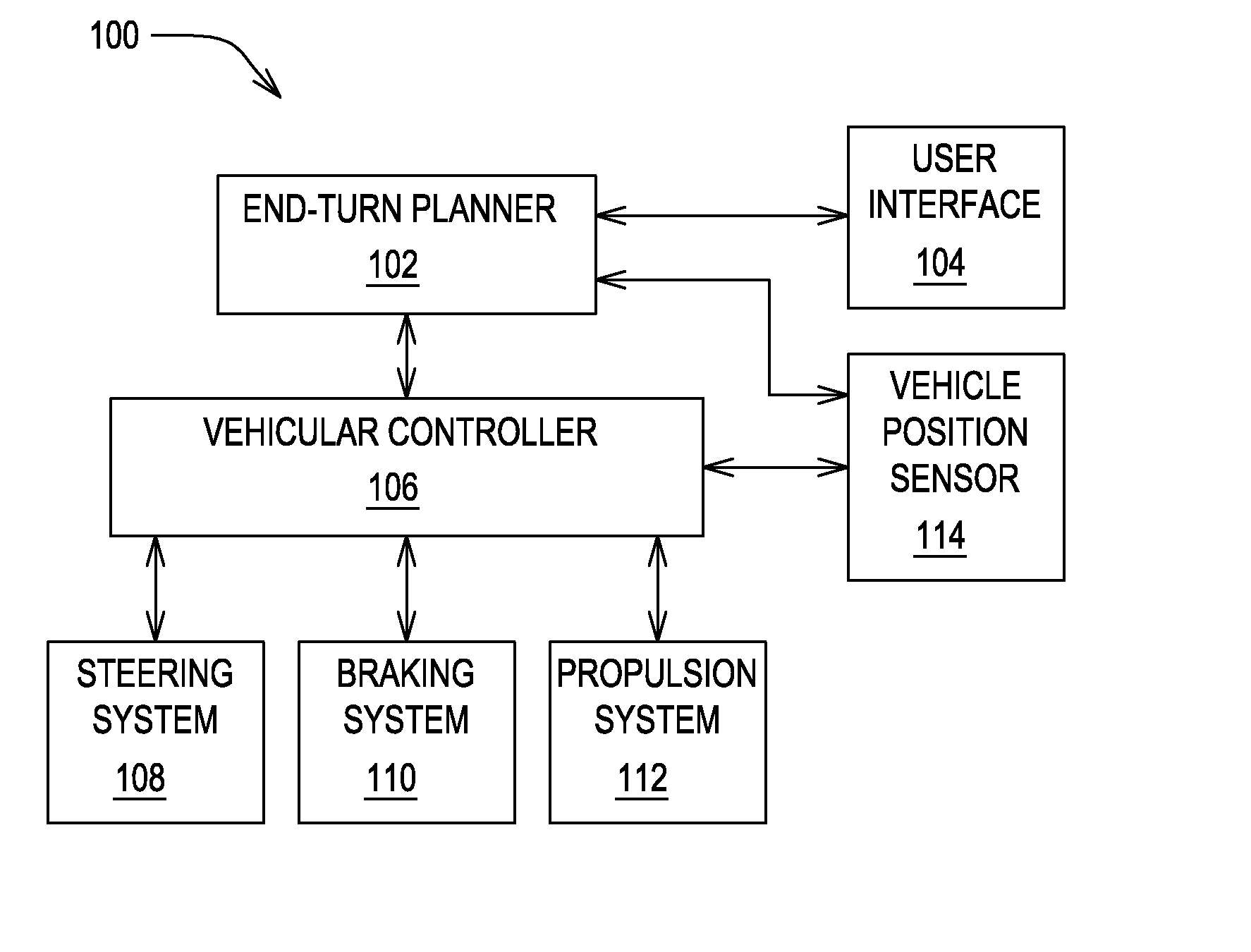
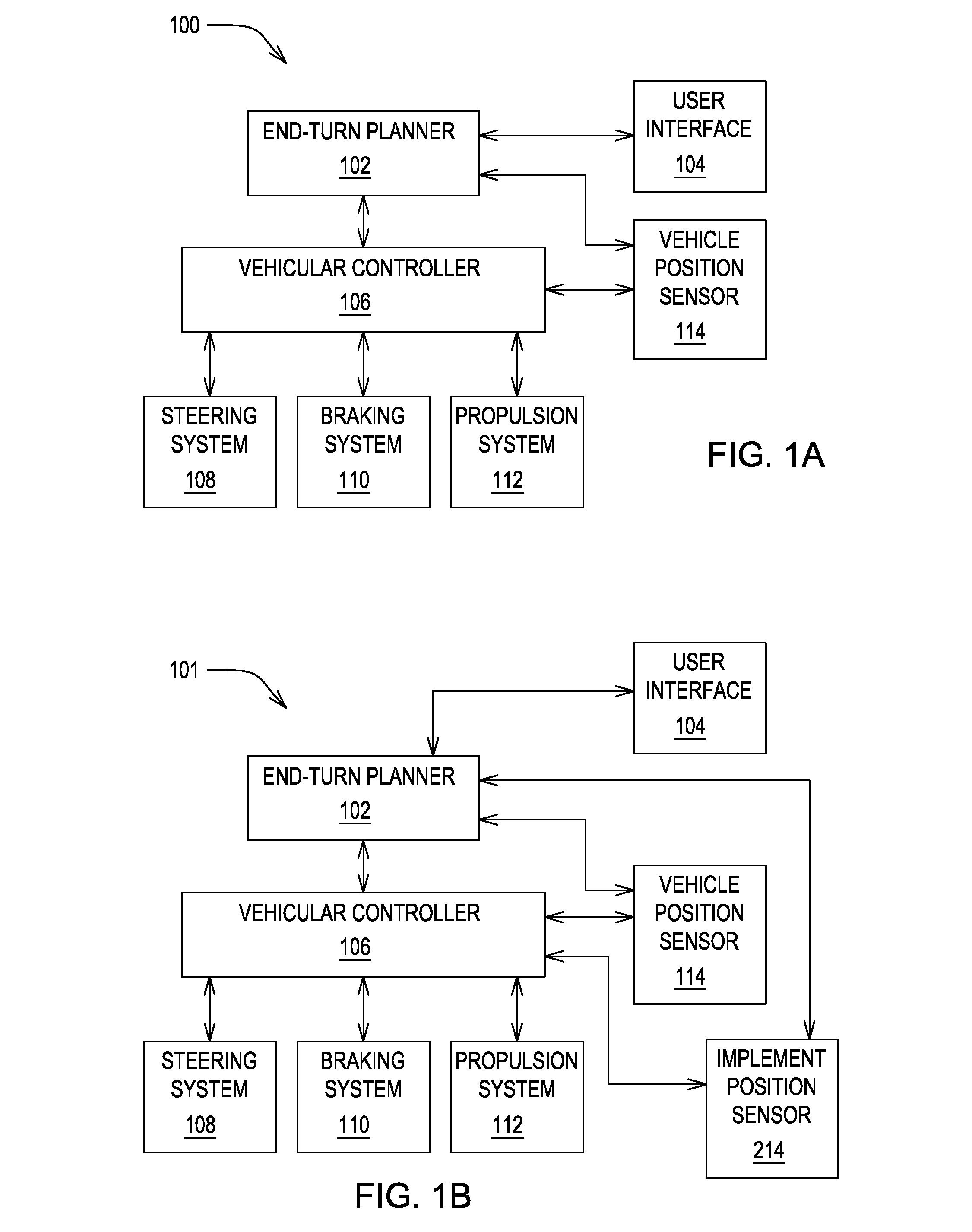
Method and system for generating end turns
ActiveUS20090037041A1External condition input parametersGuiding agricultural machinesEngineeringPosition sensor
A method and system for controlling a vehicle comprises a boundary establisher for establishing a boundary of a work area. A vehicle position sensor (e.g., a location-determining receiver) determines a position of the vehicle. A planner module plans a raw turn of a vehicle to be executed in accordance with a model turn pattern if the position of the vehicle has traversed the boundary. An adjustment module may adjust the raw turn of the vehicle to a compensated turn such that an implement coupled to the vehicle follows an implement path that substantially tracks the model turn pattern.
Owner:DEERE & CO
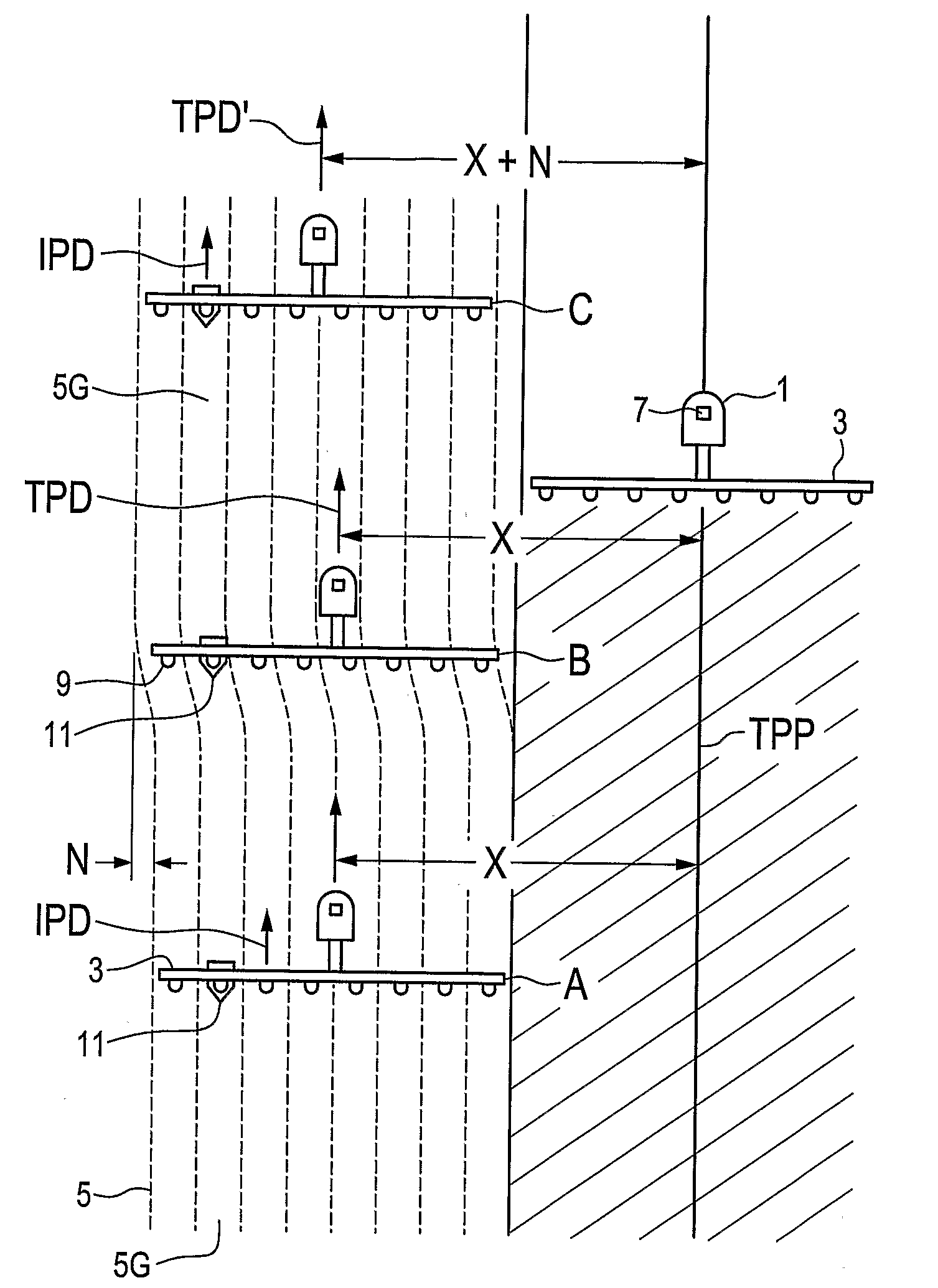
Guiding Agricultural Implements
InactiveUS20100017075A1Analogue computers for trafficGuiding agricultural machinesEngineeringDirect control
A system and method of guiding a vehicle moving an implement along crop rows in a field includes using an external guidance apparatus to receive external vehicle location signals and guide the vehicle along a desired vehicle path in response to the vehicle location signals. The position of a guide crop row location relative to the implement is also sensed and linked to the external guidance apparatus such that the external guidance apparatus is operative to laterally adjust the desired vehicle path to maintain the implement substantially on a desired implement path relative to the crop rows. The vehicle path can be directly controlled with respect to the crop rows, or row location information can be linked to the external guidance apparatus through a field guidance apparatus that is operative to shift the implement laterally relative to the vehicle.
Owner:STRAW TRACK MFG
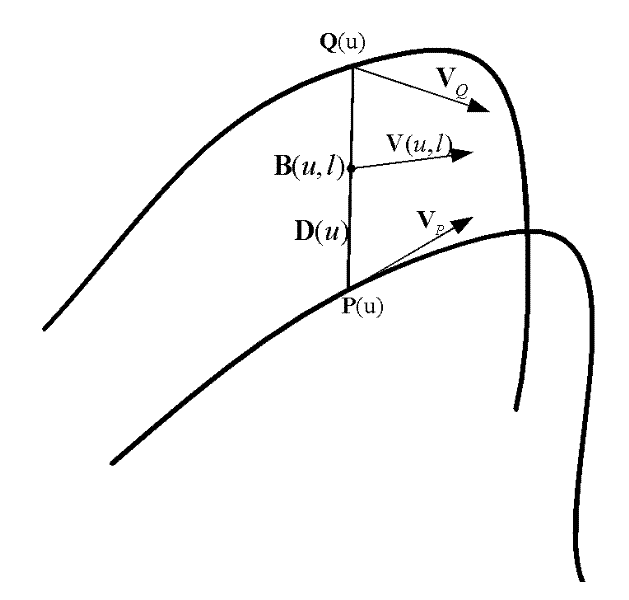
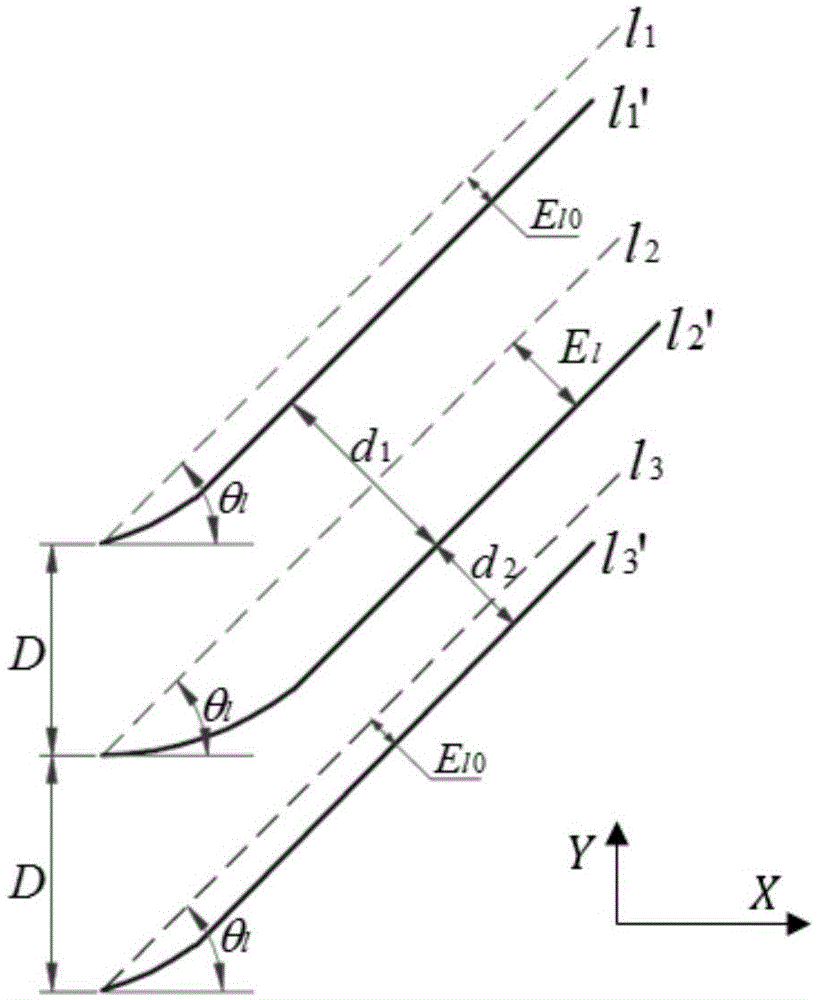
Velocity Planning Method of Double Nurbs Tool Trajectory in Five-axis NC Machining
ActiveCN102298358AOvercome technical difficulties affecting machining accuracyImprove computing efficiencyProgramme controlComputer controlNumerical controlCurrent velocity
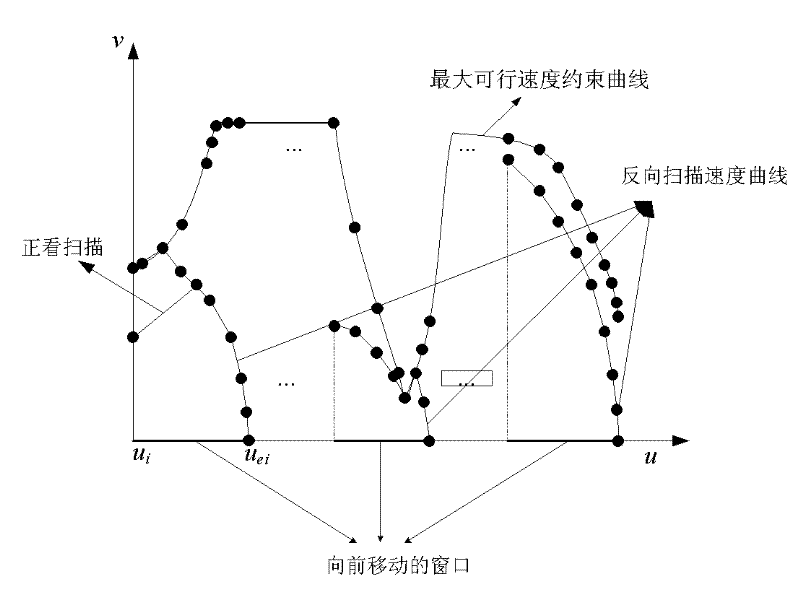
The invention discloses a NURBS (Non-Uniform Rational B-Splines) tool path speed planning method for five-axis numerical control machining. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, creating synthesized constraints oriented to double NURBS cure tool path route interpolation, synthesizing the constraints to solve a maximum speed and an acceleration of the tool in a moving process, and establishing a synthesized constraint space in a machine tool interpolation process; 2, performing bidirectional speed planning based on window scanning, taking the current speed as basis, scanning forwardsfrom a window start pint to a window tail end in a viable speed domain to obtain a feeding speed of a current period. The method ensures that the path is machined with the highest speed under a condition of meeting the requirements on servo capability and machining performance of the machine tool, and implements a high-quality and high-efficiency machining process.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV +1
Five-axis side milling machining process parameter design method
InactiveCN102129232AAccurate transient cutting thicknessImprove accuracyNumerical controlNumerical controlAnalytical expressions
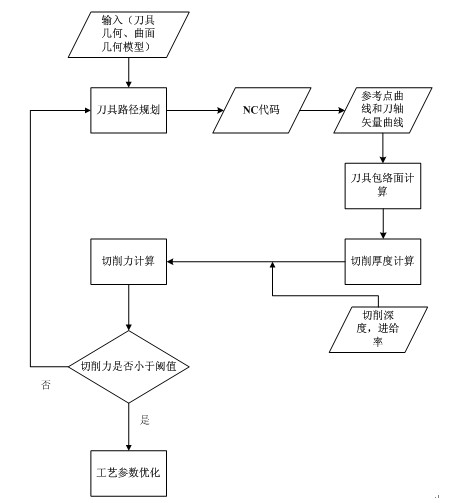
The invention discloses a five-axis side milling machining process parameter design method, belongs to the technology of numerical control (NC) machining, and solves the problem that real machining conditions cannot be reflected in cutting force calculation in the conventional process parameter design method. The method comprises the following steps of: tool path planning, cutting force calculation and process parameter optimization; in the tool path planning step, an NC code is generated by using computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) software; in the cutting force calculation step, first, a continuous tool path is generated from the NC code; then, a cutting thickness is obtained; and finally, the cutting force is calculated according to the cutting thickness; and in the process parameter optimization step, whether the calculated cutting force is not greater than a design threshold is judged; if the calculated cutting force is not greater than the design threshold, the NC code, the cutting depth and a feed rate are taken as input parameters; and otherwise, an NC code is regenerated. In the method, the real machining conditions are reflected by utilizing a tool enveloping surface analytical expression and the obtained transient cutting thickness is more accurate, so that the accuracy of the calculation of the cutting thickness and the cutting force is improved, and reliable assurance is provided for precisely and efficiently machining a spatial curved surface.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Interference-free tool path generation method in machining of transitional surfaces by flat-end milling cutter
InactiveCN103744349AImprove processing efficiencyReduce surface roughnessNumerical controlMilling cutterPath generation
The invention discloses a method for generating interference-free flat-end milling cutter process path along the ridge direction of transitional surfaces. The method comprises the following steps: (1) initial machining tool path is set, a tool is processing along the ridges of transitional surfaces, a current tool contact is calculated to obtain effective curvature of the machining tool at the tool contact; (2) curvature interference analysis of transitional surface machining is carried out according to the effective curvature of the machining tool at the tool contact, tool bottom interference is analyzed, and the angle of the tool is deflected at the tool contact to obtain interference-free tool posture; (3) parameter calculation is carried out on the adjusted tool path so as to obtain step-length and cut row distance; and (4) adjacent tool path lines are calculated, including calculation of adjacent tool contacts and calculation of tool location data, and interference-free tool path is finally obtained. By the method, automatic planning of interference-free tool path can be realized; large cut row distance is obtained; cutting efficiency is high; machining surface roughness is low; surface fairness is good; and problems of low cutting efficiency, poor machining surface quality and the like by machining of a ball-end milling cutter are solved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
System and method for steering of an implement on sloped ground
A target steering angle is detected, where the target steering angle is associated with an implement steering system for tracking a planned implement path. A data processor determines whether or not the implement steering angle is at or near a maximum steering angle toward a lateral upslope of ground. The data processor determines whether the implement is aligned with the planned implement path. A controller or data processor adjusts a target vehicle steering angle of the vehicle to guide the implement toward the lateral upslope in alignment with the planned implement path such that the implement tracks the planned implement path if the implement steering angle is at or near the maximum steering angle.
Owner:DEERE & CO
Method for controlling machining accuracy of large integrated thin-walled parts based on finite element analysis
InactiveCN104077442AReduce machining accuracyShorten the processing cycleSpecial data processing applicationsElement analysisMachining deformation
The invention discloses a method for controlling the machining accuracy of large integrated thin-walled parts based on finite element analysis. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, extracting local structural features of the large integrated thin-walled part; 2, performing finite element simulative analysis on local structural features to obtain an optimized cutting technology; 3, numerically modeling a large integrated workblank, and loading an initial internal stress; 4, protocoling a tool path, namely protocoling the machining sequence of the feature structures; 5, performing simulative analysis on the integrated structure to obtain a predicted deformation result under the condition of process technology; 6, regulating and optimizing a clamp scheme to control machining deformation. The method adopts finite element simulation, can analyze and predict in advance before the actual machining of the parts, and thereby corresponding machining strategy is adjusted, machining deformation is effectively controlled, production cycle of the parts is shortened, and production cost is reduced.
Owner:NANJING CHENGUANG GRP +1
Process and apparatus for generating control data for controlling a tool on a machine tool comprising at least 5 axes
ActiveUS20100204814A1Increased tool wearHigh surface finishGrinding feed controlAutomatic grinding controlControl dataEngineering
A process and an apparatus for generating control data for controlling a tool on a machine tool comprising at least 5 axes for the production of a predetermined finished part having a base body and at least one flank section protruding from the base body, finished part geometry data of the predetermined finished part geometry of the finished part being generated by means of fundamental geometry parameters and path data being generated by means of the finished part geometry data, the path data indicating the tool path along the surface of the flank section over which the tool has to travel with what tool orientation relative to the workpiece to remove material from the workpiece, the tool orientation of the tool corresponding to an orientation of a axis of rotation of the tool and the tool rotating about the axis of rotation of the tool to remove material from the workpiece.
Owner:DECKEL MAHO PFRONTEN GMBH
Method for directly generating tool path based on measured data
InactiveCN102608954AAvoid problems with radius compensationAvoid cumbersomeComputer controlSimulator controlNumerical controlPoint cloud
The invention discloses a method for directly generating a tool path based on measured data. The method comprises the following steps of: biasing a point cloud curved surface by means of directly biasing points; establishing a reference curved surface according to the shape and size of biased point cloud and planning the tool path on the reference curved surface; projecting a tool path point on the reference curved surface to the biased point cloud so as to obtain initial tool location information by employing a directed projection method; fitting the projection point by using a segmented triple Bezier curve, re-sampling the projection point by employing an equal arc length method to generate a self-adaptive tool path so as to improve the machining precision; and correcting the sampling point by employing point-based local neighboring orthogonal projection to improve to precision so as to obtain the final tool location point information. The numerical control machining tool path is directly generated by the measured data, a complex process of reconstructing a curved surface model is avoided, reverse engineering and a numerical control technique are effectively integrated, the manufacturing efficiency and precision are improved, and automation is conveniently realized.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Method for detecting diameter of outer wall of tapered case of aviation engine on line
InactiveCN102927952AGuaranteed accuracyReduce manufacturing costMeasurement devicesNumerical controlAviation
The invention discloses a method for detecting the diameter of an outer wall of a tapered case of an aviation engine on line. According to the method, a five-coordinate numerical control milling center with a Renishaw MP10 trigger-type measuring head is equipped, tapered case parts and a mounting seat on the surface of a tapered case are equipped; a fine adjustment ring gauge of the used measuring head is measured on line; a point contact-type measurement mode is adopted; a machine tool siemens control system Sinumeric 840 D on-line measurement technology is adopted; and an on-line measurement quick tool path amendment and error compensation generation technology is adopted. The method has a broad application prospect; and by the on-line measurement technology, a numerically-controlled machine tool is impelled to form a machining and detecting integrated numerical control machining unit. By the method, the traditional manufacturing mode that a design characteristic is equipped with a set of measurement tool in the current industry is changed, the manufacturing cost of the tool is saved, repair labor-hour is saved, and first-pass yield of product processing is improved, so that the development period and the production cost of new products are reduced.
Owner:SHENYANG LIMING AERO-ENGINE GROUP CORPORATION
Curved surface tool path contour error compensation method based tool location point correction
ActiveCN104615083AHigh precisionCalculation stableProgramme controlComputer controlEstimation methodsControl system
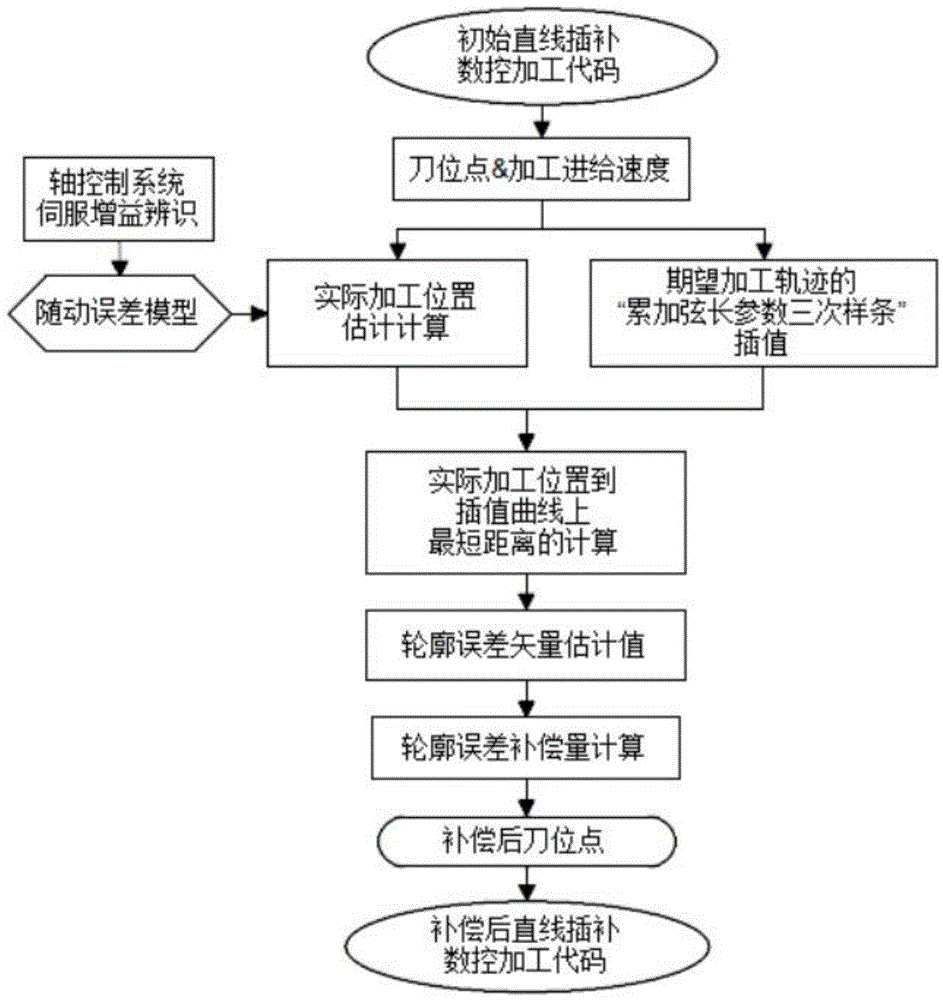
The invention belongs to the field of numerical control machine tool dynamic error compensation and relates to a novel contour error estimation method, particularly to a curved surface tool path contour error compensation method based tool location point correction. The method comprises, on the basis of identifying the servo gain of a machining feed shaft control system, estimating practical machining points off line according to a following error model and linear interpolation machining codes; estimating contour error vectors according to a method similar to accumulated chord length parametric cubic spline of ideal tool paths; computing the contour error compensation according to the components of the contour error vectors on every axis to obtain compensated tool location points and further to generate linear interpolation numerical control machining codes for practical machining. The curved surface tool path contour error compensation method based tool location point correction can improve the dynamic precision of a numerical control machine tool and is high in precision, stable in computation, free from online measurement, easy to implement and wide in application range.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Friction stir welding spindle downforce and other control techniques, systems and methods
InactiveUS20100072261A1Welding/cutting auxillary devicesAuxillary welding devicesElectricityButt joint
Friction stirred welding equipment, developed according to requirements of high reliability, robustness, precision and low cost, weld lap and butt joints in complex surfaces with fixed pin tool under controlled downforce. Exemplary equipment comprises a control force orbital spindle, wherein a coaxial sensor measures the downforce and simultaneously the axial electrical actuator corrects axial tool position along the welding, by a direct axial force system control, in order to maintain controlled downforce according to previously set parameters. The equipment sets up, monitors and controls the spindle rotation speed, welding speed, acceleration speed and downforce and can record in a database the downforce and tool welding position during the welding. The exemplary equipment may also comprise a laser system that scans the backing surface before welding and corrects original tool path, in order to provide an offset tool path and precision alarm system to get a safe welding, avoiding tool collision with the backing.
Owner:EMBRAER SA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com