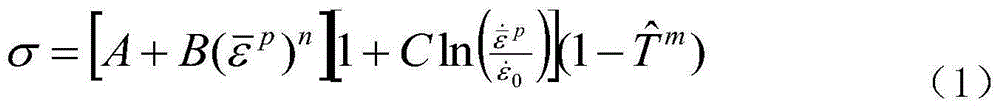Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1605 results about "Finite element simulation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Microfluidic large scale integration
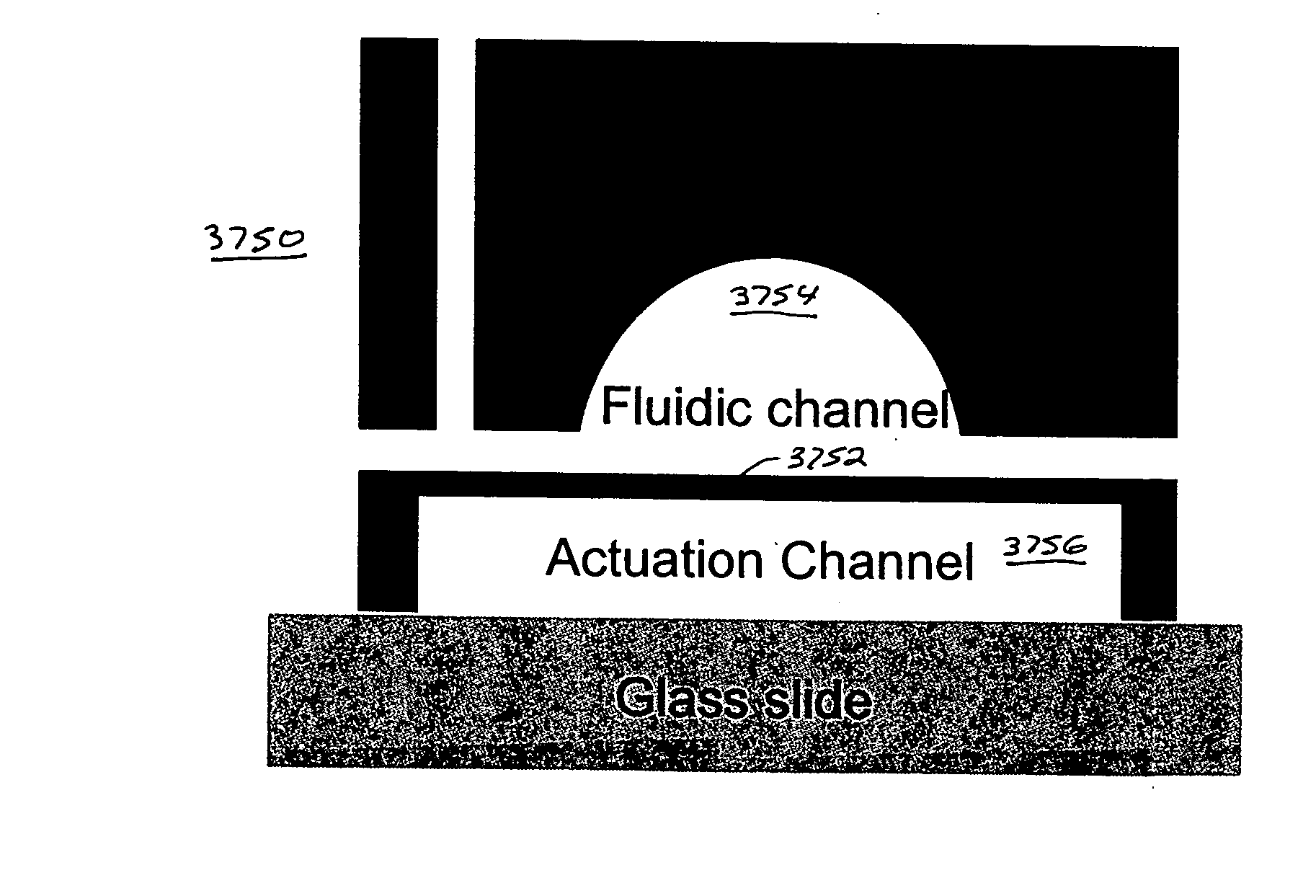
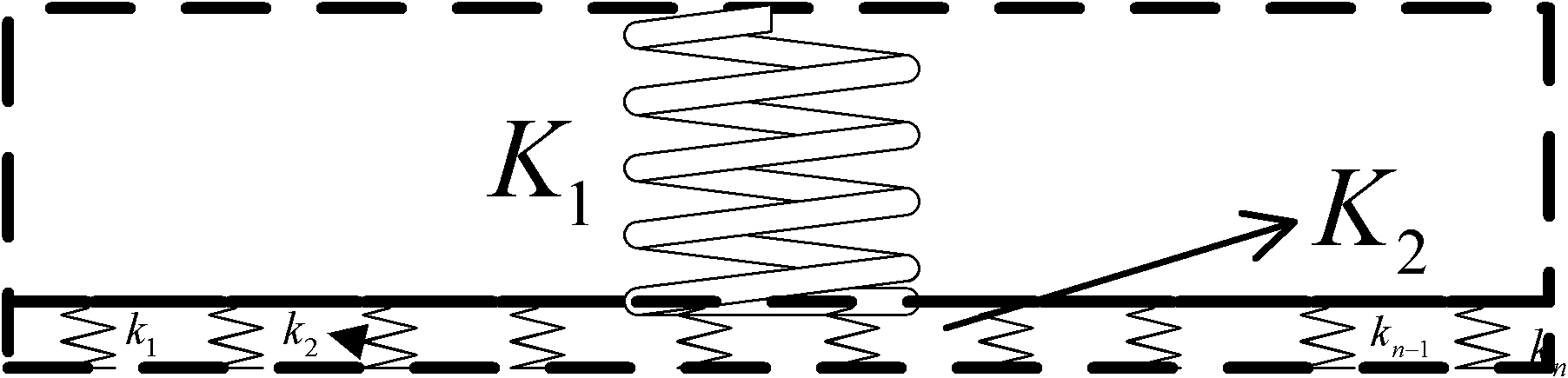
InactiveUS20050072946A1Operating means/releasing devices for valvesCircuit elementsElastomerFlow resistivity
Using basic physical arguments, a design and method for the fabrication of microfluidic valves using multilayer soft lithography is presented. Embodiments of valves in accordance with the present invention feature elastomer membrane portions of substantially constant thickness, allowing the membranes to experience similar resistance to an applied pressure across their entire width. Such on-off valves fabricated with upwardly- or downwardly-deflectable membranes can have extremely low actuation pressures, and can be used to implement active functions such as pumps and mixers in integrated microfluidic chips. Valve performance was characterized by measuring both the actuation pressure and flow resistance over a wide range of design parameters, and comparing them to both finite element simulations and alternative valve geometries.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
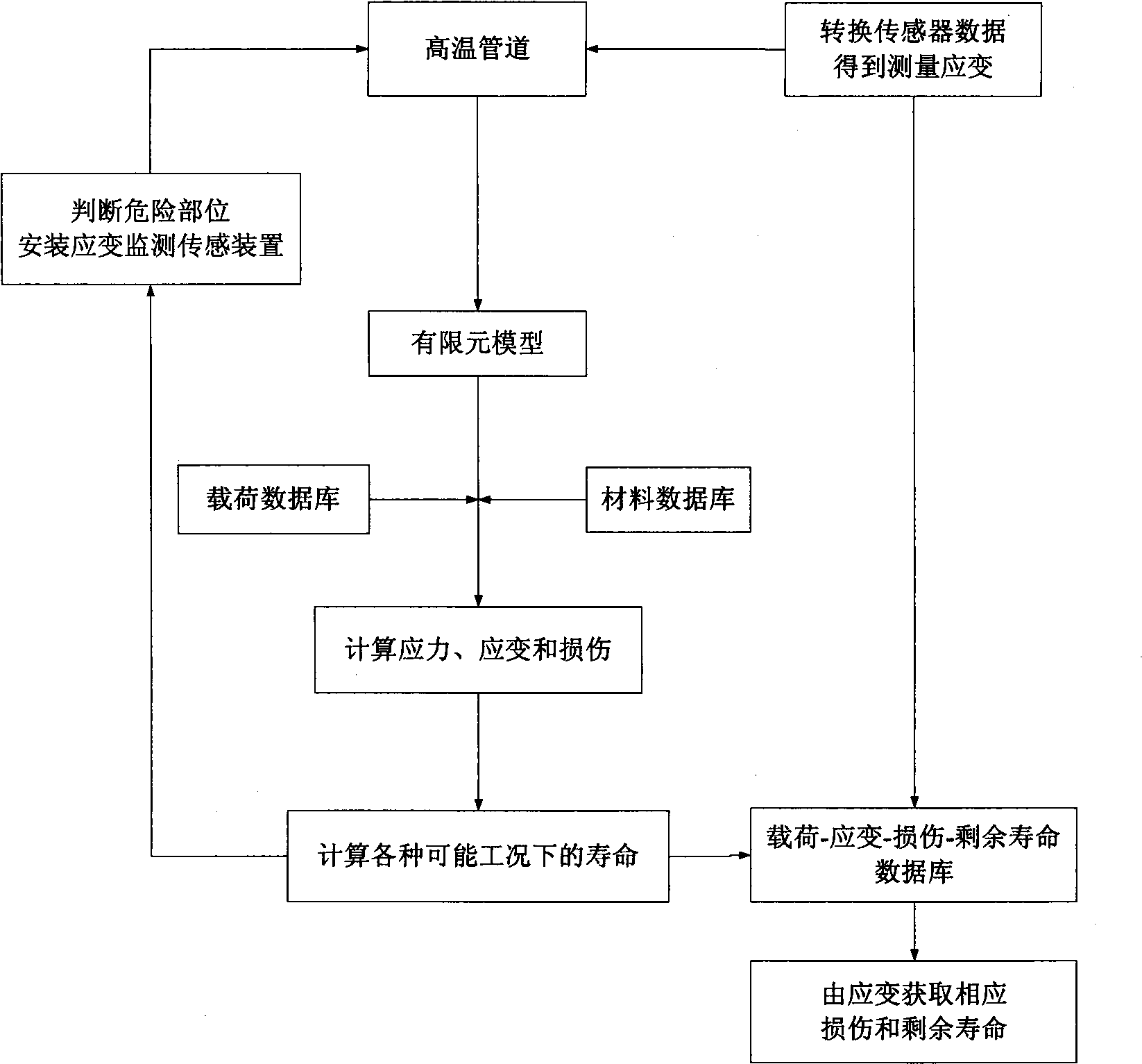
On-line prediction method for high-temperature pipe damage and longevity
InactiveCN101509855AGuaranteed real-time monitoringExtend your lifeMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesSpecial data processing applicationsElement analysisPredictive methods
The invention relates to an online predicting method of damage and service life of a high temperature pipeline. The method comprises the following implementing steps of: (1) carrying out finite element simulation analysis of damage and coupling to the high temperature pipeline; (2) finding out important monitoring parts according to the analysis results, arranging a sensor and monitoring the strain of the sensor; (3) carrying out finite element analysis (including analytical subprogram of a constitutive equation) for different working conditions and establishing database with damage, strain and residual life and strain; and (4) carrying out online inquiry and comparison to strain values detected online and the value of the load working condition and the data in the database so as to obtain the assessment value of corresponding damage and residual life. The online predicting method has the advantages of being capable of carrying out real-time monitoring to the high temperature pipeline in operation while production is carried out normally, reflecting the deformation and damage of the important parts and key parts in time, making correct estimation to the use life and residual life of the pipeline, being beneficial to guaranteeing safe production, adjusting the production load, planning maintenance reasonably and effectively prolonging the service life of production equipment.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
ABAQUS-based finite element simulation method of correcting welding deformation through ultrasonic shot-peening
The invention discloses an ABAQUS-based finite element simulation method of correcting welding deformation through ultrasonic shot-peening. The method includes: firstly, utilizing the finite element software ABAQUS to simulate the welding process of a certain-sized aluminum alloy sheet to obtain the distribution of the welding residual stress and the deformation;and secondly, reading in a stress force and deformation grid and performing the simulative computation of a shot-peening shape correction process on the basis of the welding stress and deformation. The ABAQUS-based finite element simulation method of correcting the welding deformation through the ultrasonic shot-peening takes the limits that the complexity of mechanism of the shot-peening process and the influence of various variable factors result in great difficulties in optimizing shot-peening process parameters and the method which purely relies on experimental data and experience consumes much time and money into consideration, so that the ABAQUS-based finite element simulation method is introduced to assist the selection of the ultrasonic shot-peening process parameters and the strain of the stress and the change of the deformation are analyzed to explain the mechanism of the shape correction.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Modeling method for two-dimensional variable-curvature process model of section bar part
ActiveCN102968524ARapid designCorrectly designedSpecial data processing applicationsModel methodComputer science
The invention belongs to the technical field of aircraft manufacturing and relates to a modeling method for a two-dimensional variable-curvature process model of a section bar part. Through dispersing a contour line, the contour line is dispersed into a plurality of line segments and arc segments. By adopting finite element simulation, the recurrent magnitude of every dispersed segment is calculated; a compensated part contour curve is obtained through multiple iteration compensation; and the part contour curve is used for defining the process model of the part. The modeling method for the two-dimensional variable-curvature process model of the section bar part has the beneficial effects the process model of the section bar part can be rapidly and accurately designed, and a design used for a stretch bending mould is provided to craft personnel.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
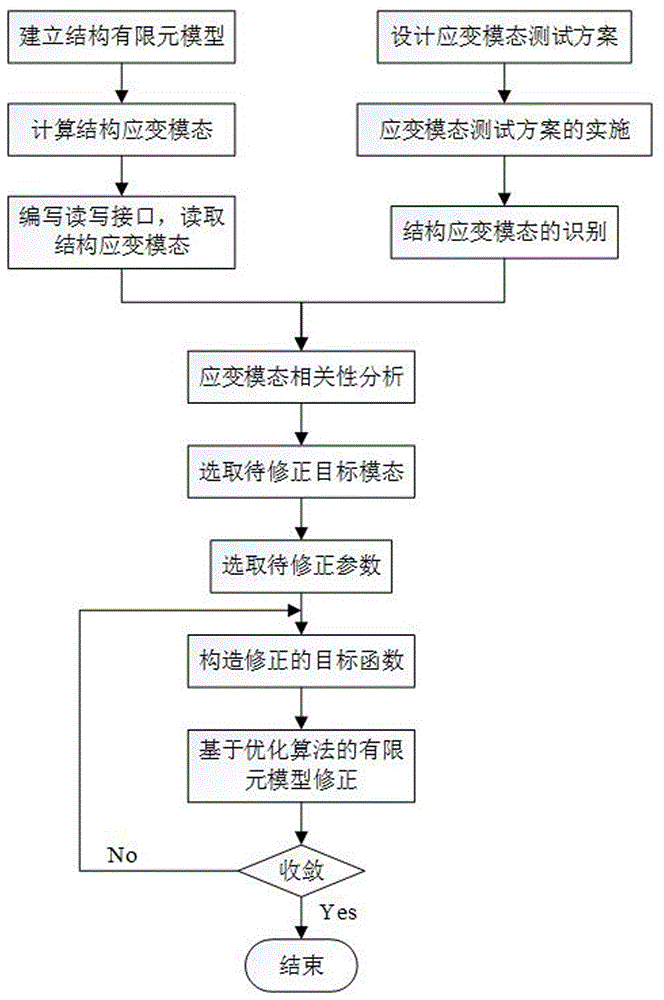
Model updating method based on strain modal shape correlation
InactiveCN106529055ASimple structureDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelStructural dynamics
The invention discloses a model updating method based on strain modal shape correlation. The specific steps are as follows: step 1), establishing a finite element model of a structure and analyzing the finite element model; step 2), performing experimental design and analysis; step 3), extracting a finite element simulation strain mode; step 4), performing correlation analysis: adopting a model confidence factor, and analyzing the correlation between the finite element model and the strain modal shape of an experimental test; step 5), selecting a mode to be modified; step 6), selecting a parameter to be identified; step 7), constructing a modification target; and step 8), performing modified iteration. According to the model updating method based on the strain modal shape correlation provided by the invention, by selecting an appropriate unit type, the obtained finite element model of the structure provides a reference model for strain response calculation; by selecting an appropriate strain mode to be modified, parameters to be modified and an optimum design method, the modified finite element model can better reflect the strain response of the structure; and the accurate finite element model is beneficial to the subsequent structural dynamic optimization design based on the finite element model, and the development of structural health monitoring and structural response prediction and so on.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Copper-alloy pipe-material casting-milling technology parameter designing and optimizing method
InactiveCN1979496AOptimizing Graphical Result ExpressionAvoid breakingPhysical realisationSpecial data processing applicationsNerve networkMachining deformation
The invention discloses a method for designing and optimizing cast-rolling process parameters of copper alloy tubing, using database as design basic, using nerve network as design method of process parameters and indexes, and using genetic algorithm as process parameter optimizing means, integrating nerve network, genetic algorithm, finite element simulation, experiment design, CAD parameterized design and database technique into the process design and parameter optimization, designing and optimizing the cast-rolling process parameters of the copper alloy tubing. And the invention has high automation degree, and can be applied to machining deformation of copper alloy tubing, and make personnel short of special knowledge able to make accurate and standard machining process.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Optimization design method of composite material wing panel
ActiveCN106156449AImprove work efficiencyShorten the design cycleGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationElement modelEngineering
The invention discloses an optimization design method of a composite material wing panel. The optimization design method comprises the following steps: (1) carrying out finite element simulation modeling on the main structure of a wing; (2) applying a load and boundary condition to a finite element wing box section model; (3) calculating an integral wing box finite element model, and extracting the internal load of a structure; (4) designing a layup library, and calculating the laminate attributes of all layers in the layup library to obtain a rigidity matrix and an equivalent elastic modulus; (5) aiming at the calculation requirements of different structural unit initial dimensions and different failure modes of a skin stringer to carry out secondary distribution calculation on the load; (6) calculating the design allowable value of each structure failure mode of the panel; (7) calculating the safety margin of each BAY of a panel structure; (8) setting a maximum slope rate of panel layup arrangement and an adjacent area laminate throwing layer, setting the Poisson ratio difference value coefficient and the stiffness ratio of the stringer and the skin, and regulating the layer if a design range is not met; (9) if the design does not meet weight requirements, requiring to circularly carrying out the steps (1) to (8) to regulate the lay and the dimension until structure weight requirements are met. According to the method, the design and optimization working efficiency of the integral panel of the composite material is improved, and research and development cost is saved.
Owner:AVIC SAC COMML AIRCRAFT
Method for controlling machining accuracy of large integrated thin-walled parts based on finite element analysis
InactiveCN104077442AReduce machining accuracyShorten the processing cycleSpecial data processing applicationsElement analysisMachining deformation
The invention discloses a method for controlling the machining accuracy of large integrated thin-walled parts based on finite element analysis. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, extracting local structural features of the large integrated thin-walled part; 2, performing finite element simulative analysis on local structural features to obtain an optimized cutting technology; 3, numerically modeling a large integrated workblank, and loading an initial internal stress; 4, protocoling a tool path, namely protocoling the machining sequence of the feature structures; 5, performing simulative analysis on the integrated structure to obtain a predicted deformation result under the condition of process technology; 6, regulating and optimizing a clamp scheme to control machining deformation. The method adopts finite element simulation, can analyze and predict in advance before the actual machining of the parts, and thereby corresponding machining strategy is adjusted, machining deformation is effectively controlled, production cycle of the parts is shortened, and production cost is reduced.
Owner:NANJING CHENGUANG GRP +1
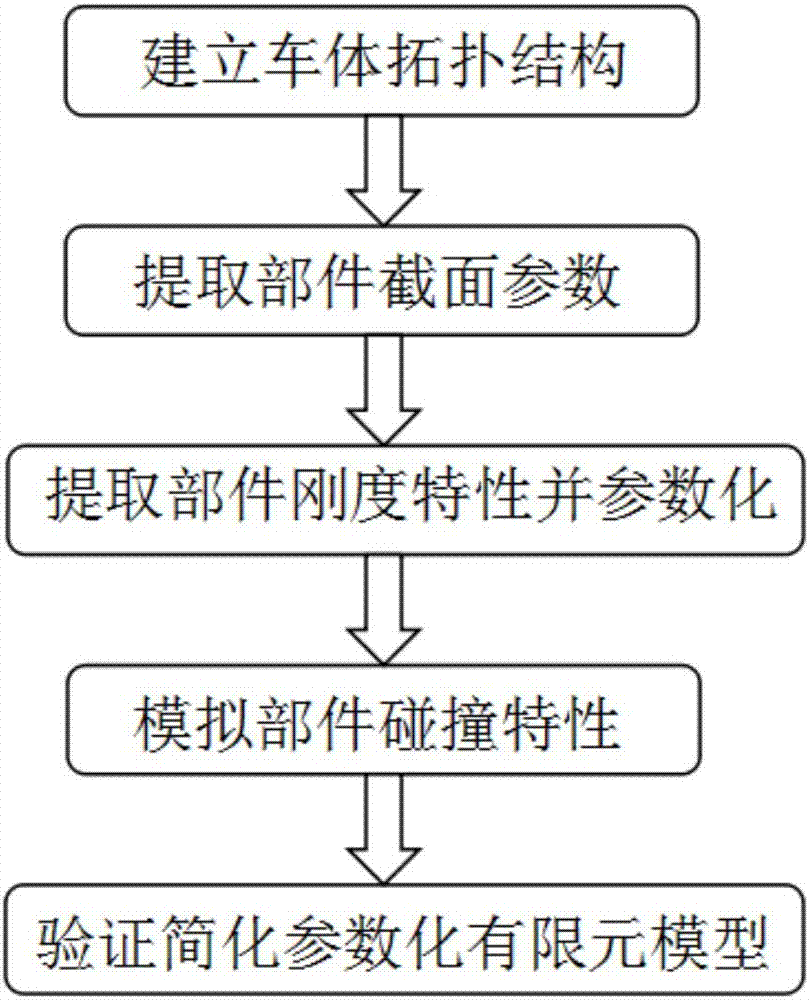
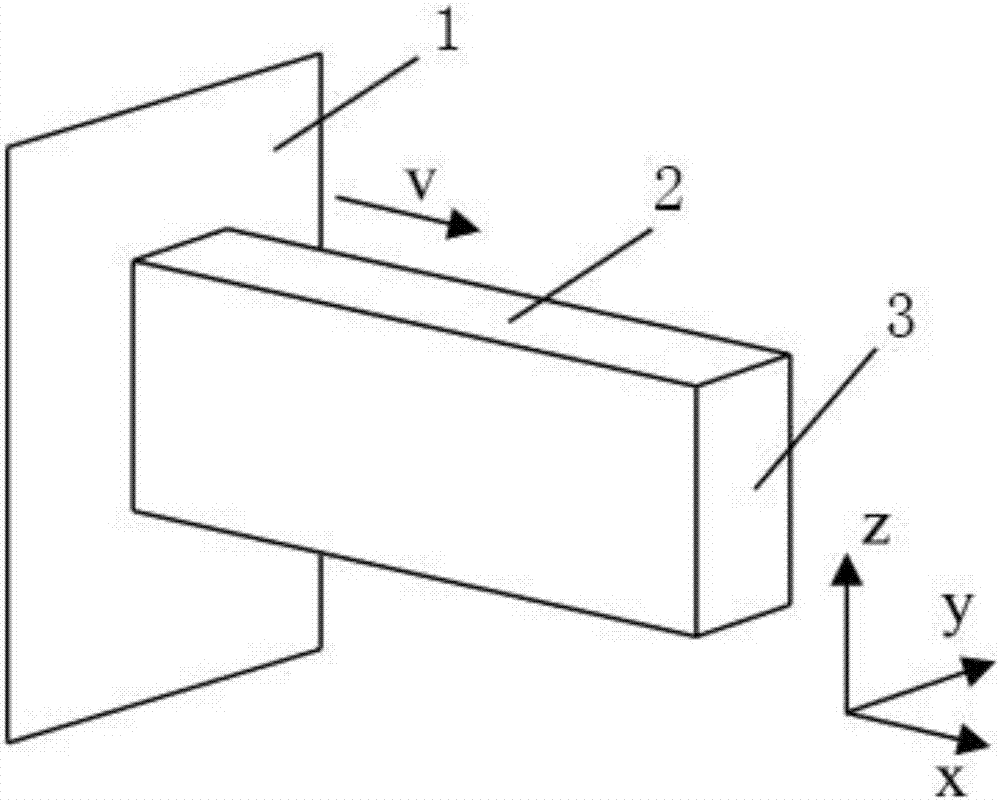
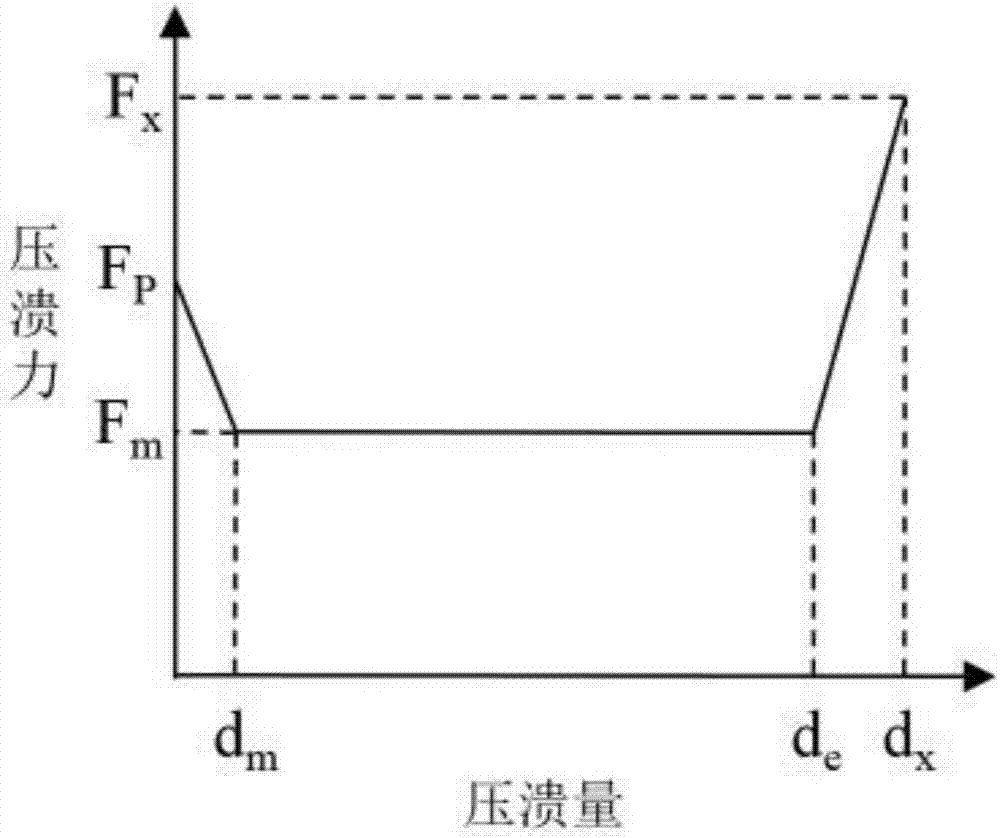
Method for building simplified parametric finite element model of car collision
InactiveCN107256289AQuick calculationEasy to modifyDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelLS-DYNA
The invention discloses a method for building a simplified parametric finite element model of car collision, and aims to solve the problem of consumption of a large amount of modification and calculation time due to adoption of a conventional detailed finite element model in car body structure anti-collision design and improvement in the prior art. The method comprises the following steps of 1) establishing a topological structure of a car body: (1) obtaining a detailed finite element model of a car; (2) building a one-dimensional unit topological model of the car body; and (3) building a topological structure model of the car body; 2) extracting cross section parameters of parts; 3) extracting stiffness characteristics of the parts and performing parameterization: (1) extracting crushing stiffness characteristics and performing parameterization; (2) building finite element simulation models of the crushing parts by utilizing Hypermesh software and performing calculation by utilizing LS-DYNA software to obtain a crushing force-crushing quantity curve; and (3) simplifying the crushing force-crushing quantity curve according to an absorbed energy equality principle and performing parameterization; 4) simulating collision characteristics of the parts; and 5) verifying the simplified parametric finite element model.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
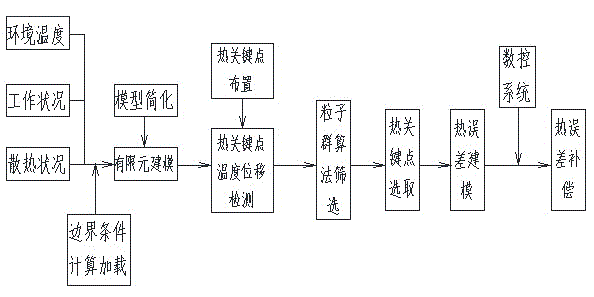
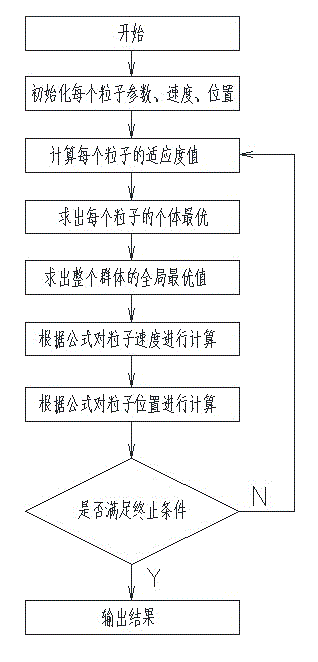
Numerical control machine tool thermal error compensating method
ActiveCN105022344AReduce thermal errorsImprove machining accuracyProgramme controlComputer controlNumerical controlMeasurement point
The invention discloses a numerical control machine tool thermal error compensating method. The method comprises the following steps of making a finite element simulation analysis geometric model of a numerical control machine tool main shaft structure and simplifying the geometric model; loading a proper boundary condition according to the working state and the working environment of the main shaft structure; performing thermodynamics and statics finite element simulation analysis on the simplified geometric model; selecting temperature and thermal deformation values of a certain number of points from the analysis result; screening the data through a particle swarm optimization algorithm; selecting optimum four-point temperature values as the numerical control machine tool thermal error compensating parameters and making an error compensating model to achieve numerical control machine tool thermal error compensation. On the basis of finite element simulation analysis, the method adopting the particle swarm optimization algorithm to acquire key temperature points for thermal error compensation and using the temperature measuring values of the key temperature points as the numerical control machine tool thermal error compensating basis makes the selection of thermal error temperature measuring points simplified. The machine tool thermal errors are effectively alleviated. The machine tool processing precision is further improved.
Owner:上海电气自动化集团有限公司
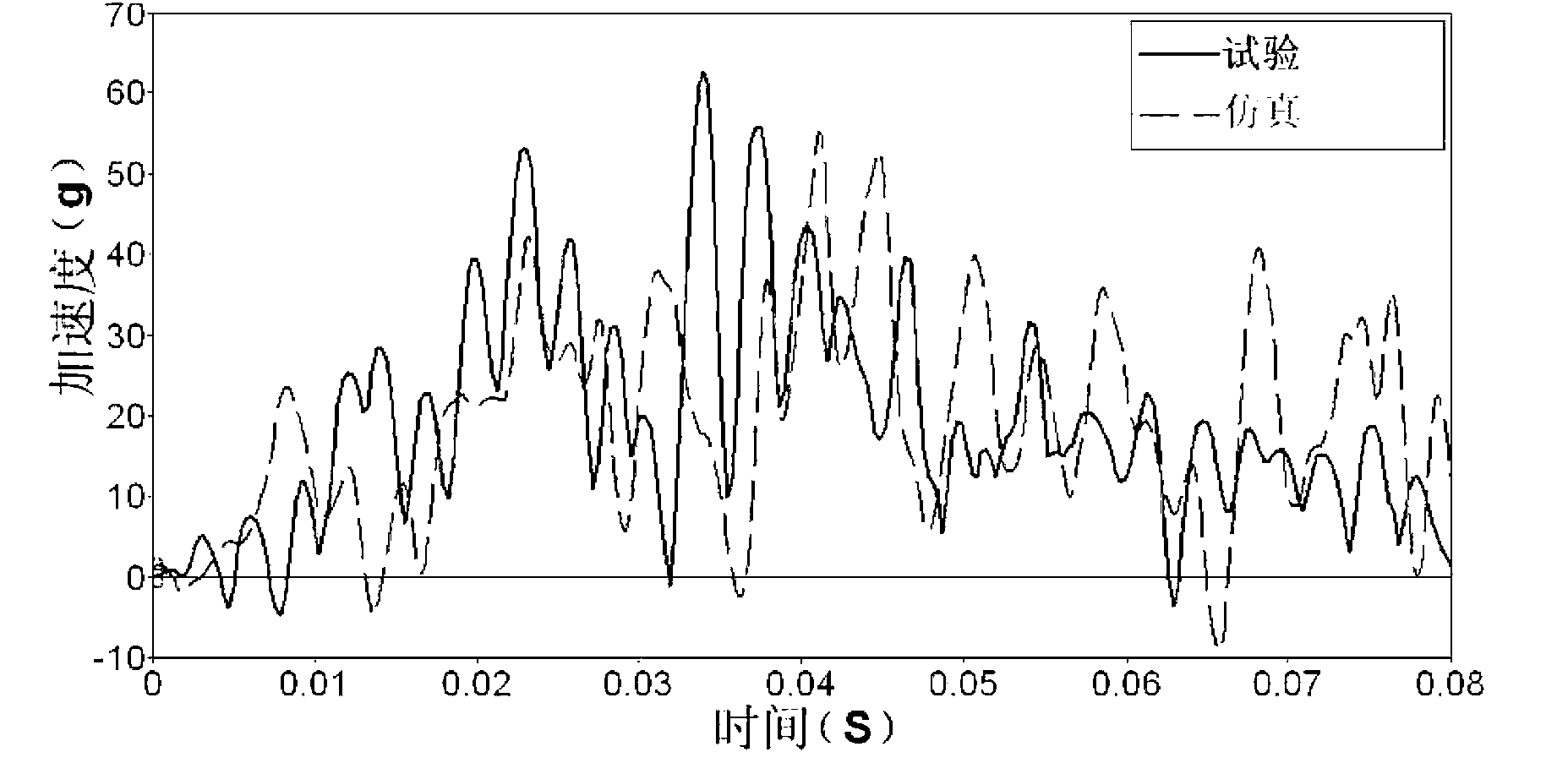
Finite element simulation
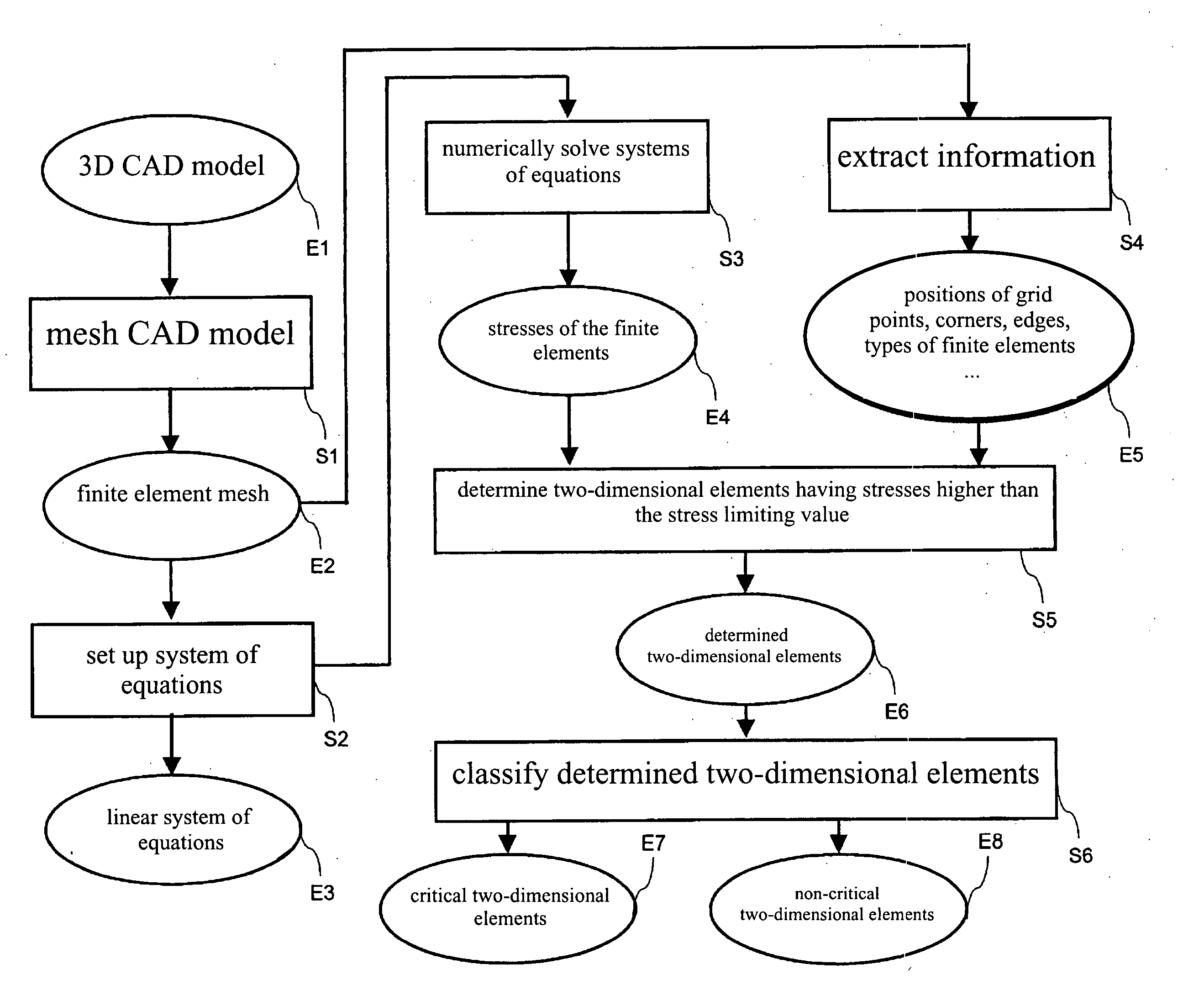
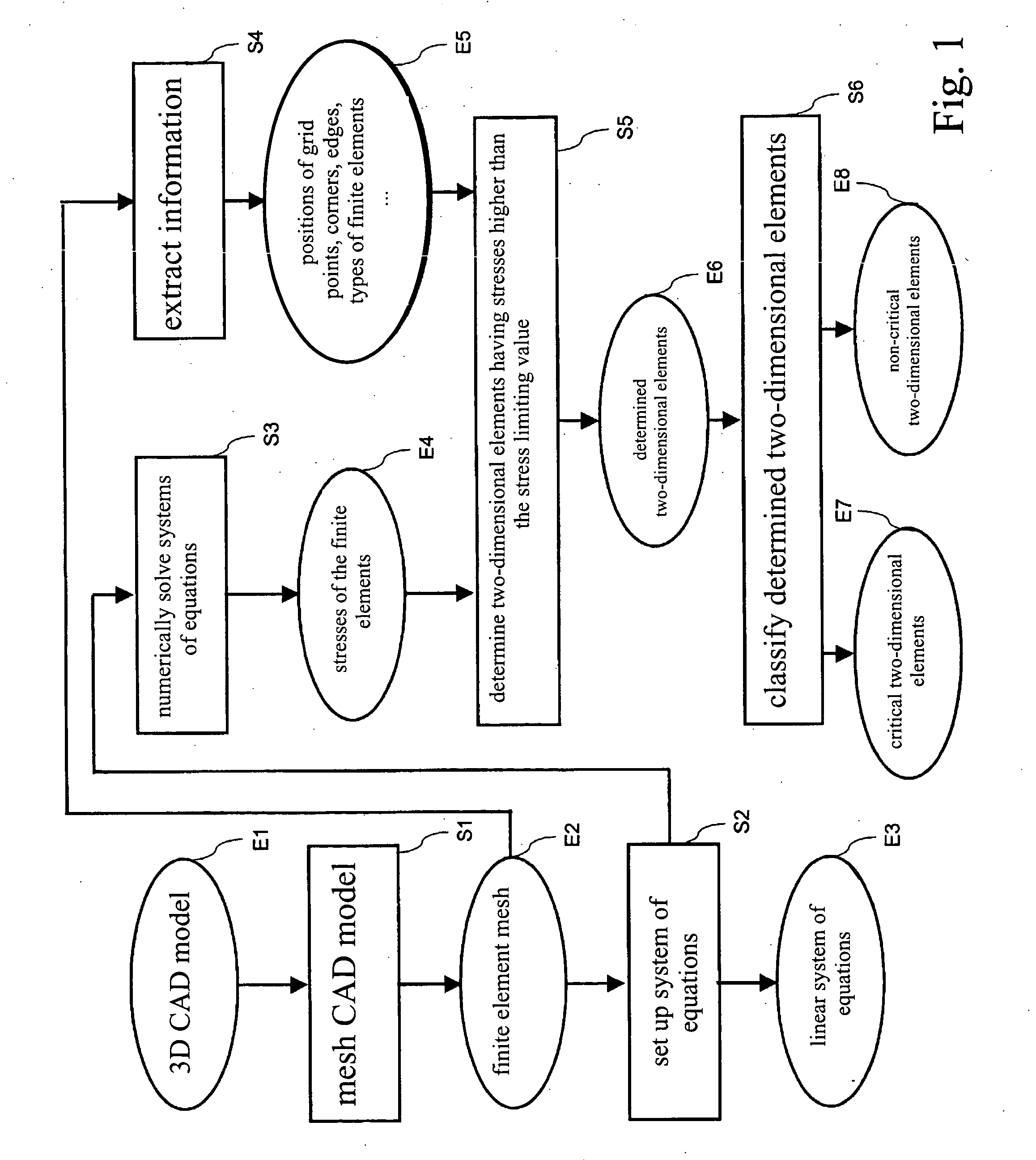
ActiveUS20050171745A1Improving critical classificationGeometric CADComputation using non-denominational number representationIndustrial systemsEngineering
A method for automatic evaluation of a finite element simulation for an industrial system such as a motor vehicle body includes predefining an electronic design model of the industrial system and generating finite elements for the model. The stresses occurring in the finite elements are determined using a finite element simulation. Each finite element, which is a two-dimensional element and not a rigid object element and whose stress exceeds a predefined stress limiting value, is determined. For each determined two-dimensional element which is not a triangle, an element limiting value is determined on the basis of the stress limiting value. Each determined two-dimensional element is classified as critical if its computed stress exceeds the established element limiting value. The method enables identification of areas of the industrial system having a high stress and reduces the effect of inaccuracies that occur on the evaluation of the finite element simulation due to the approximation of the vehicle body by finite elements.
Owner:CHEMTRON RES
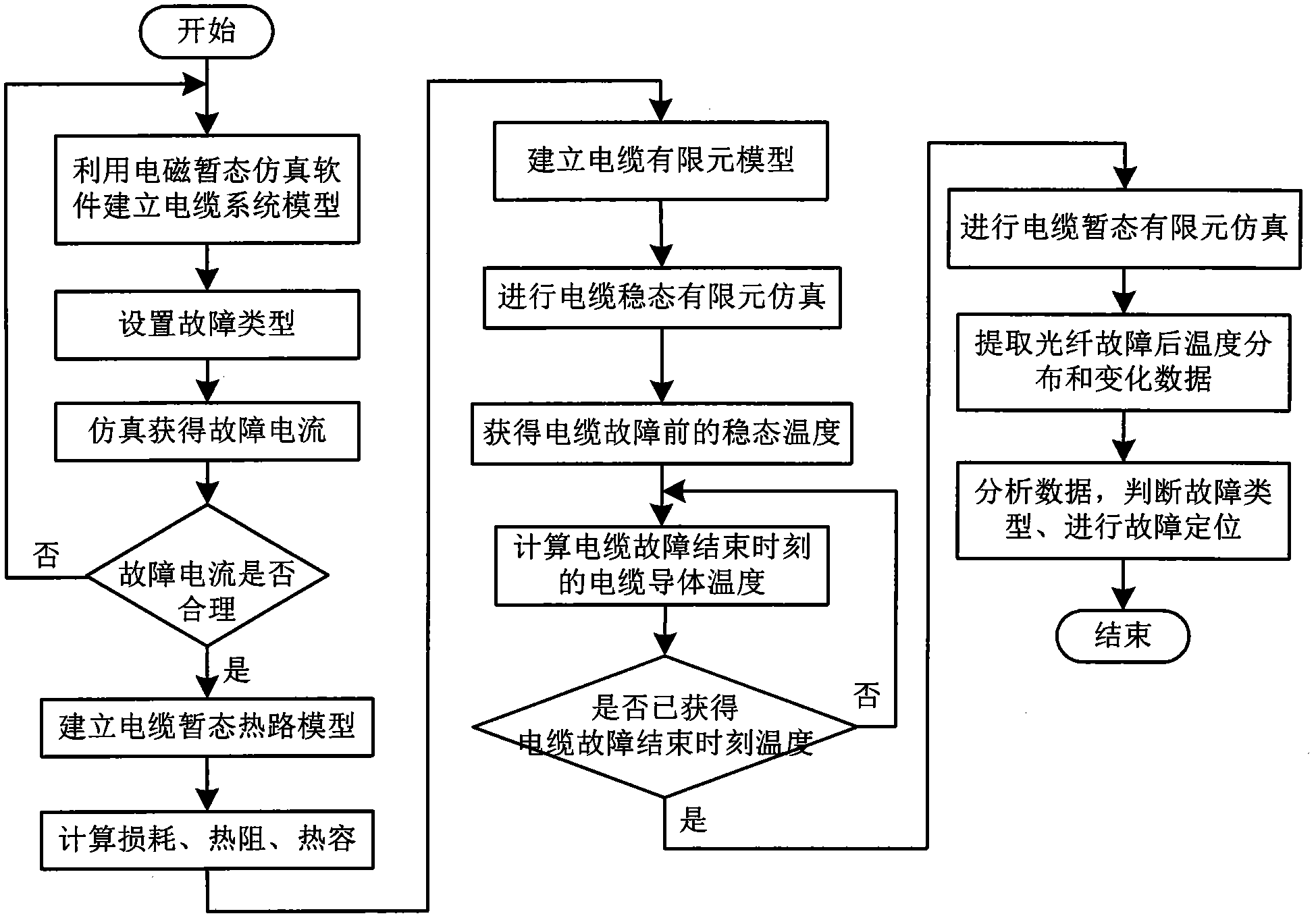
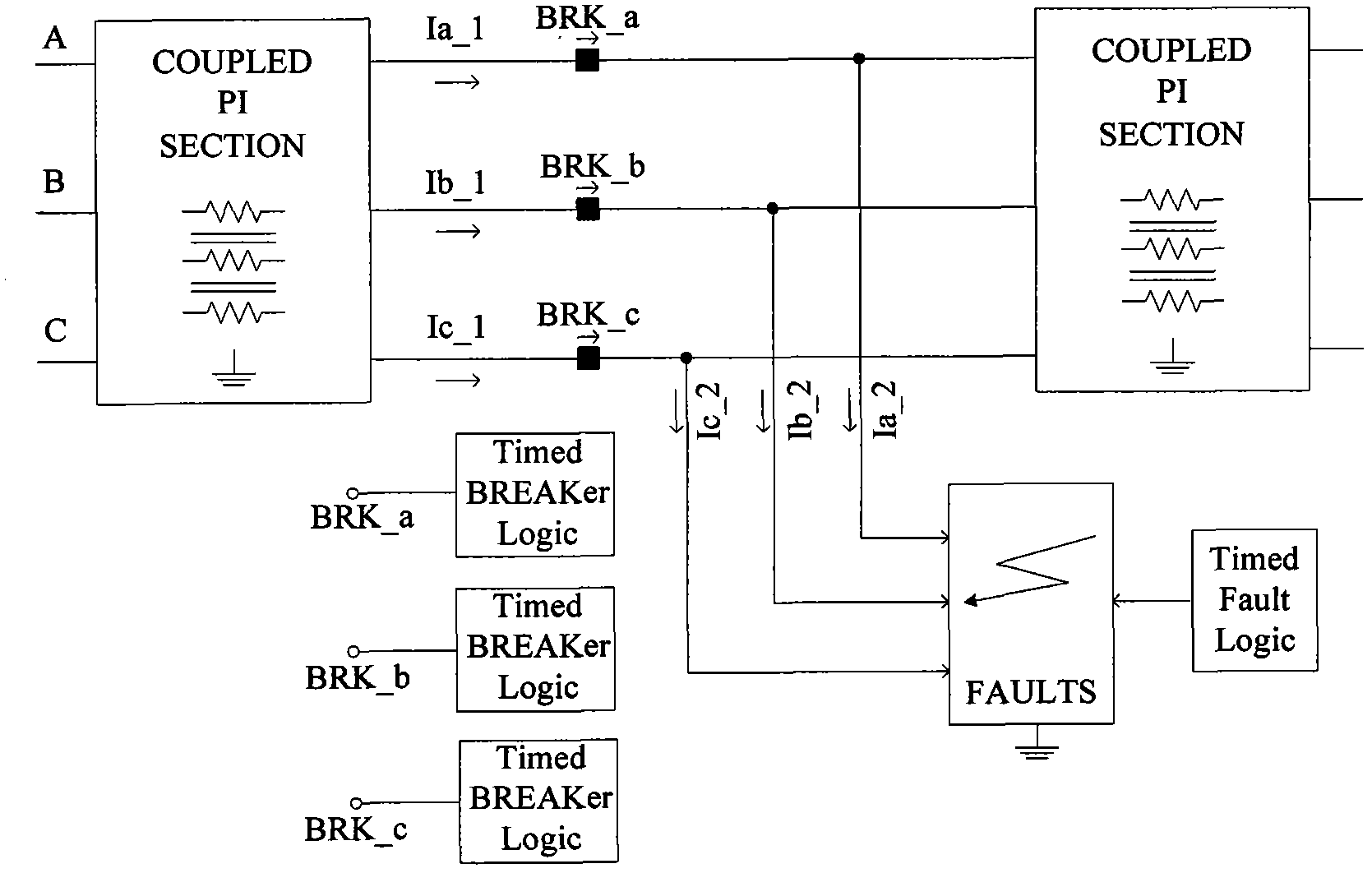
Distributive optical fiber temperature measurement based cable electrical failure simulation analysis method
ActiveCN103728539AFull failure dataComprehensive Failure DataFault locationTransient stateElement model
The invention belongs to the field of cable electrical failure simulation analysis and particularly relates to a distributive optical fiber temperature measurement based cable electrical failure simulation analysis method. The method comprises building a cable failure model, setting line parameters, determining failure types, performing failure simulation and obtaining the current value during the failure through electromagnetic transient simulation software; building a cable transient thermal path model according to IEC 60287 standards, and calculating the cable transient temperature during the failure; building a cable and temperature measurement optical fiber thermodynamic finite element model through finite element simulation software, and simulating the steady temperature field distribution before the failure and the transient temperature field distribution and changes after the failure of the cable and the temperature measurement optical fiber; obtaining cable electrical failure recognition and location criteria according to the temperature distribution and change rule of the temperature measurement optical fiber in simulation results. According to the method, the problems of poor accuracy, difficulties in experiment and the like during cable electrical failure analysis through temperature measurement optical fiber temperature distribution data are solved. The method has the advantages of being flexible in failure setting, high in work efficiency and the like.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
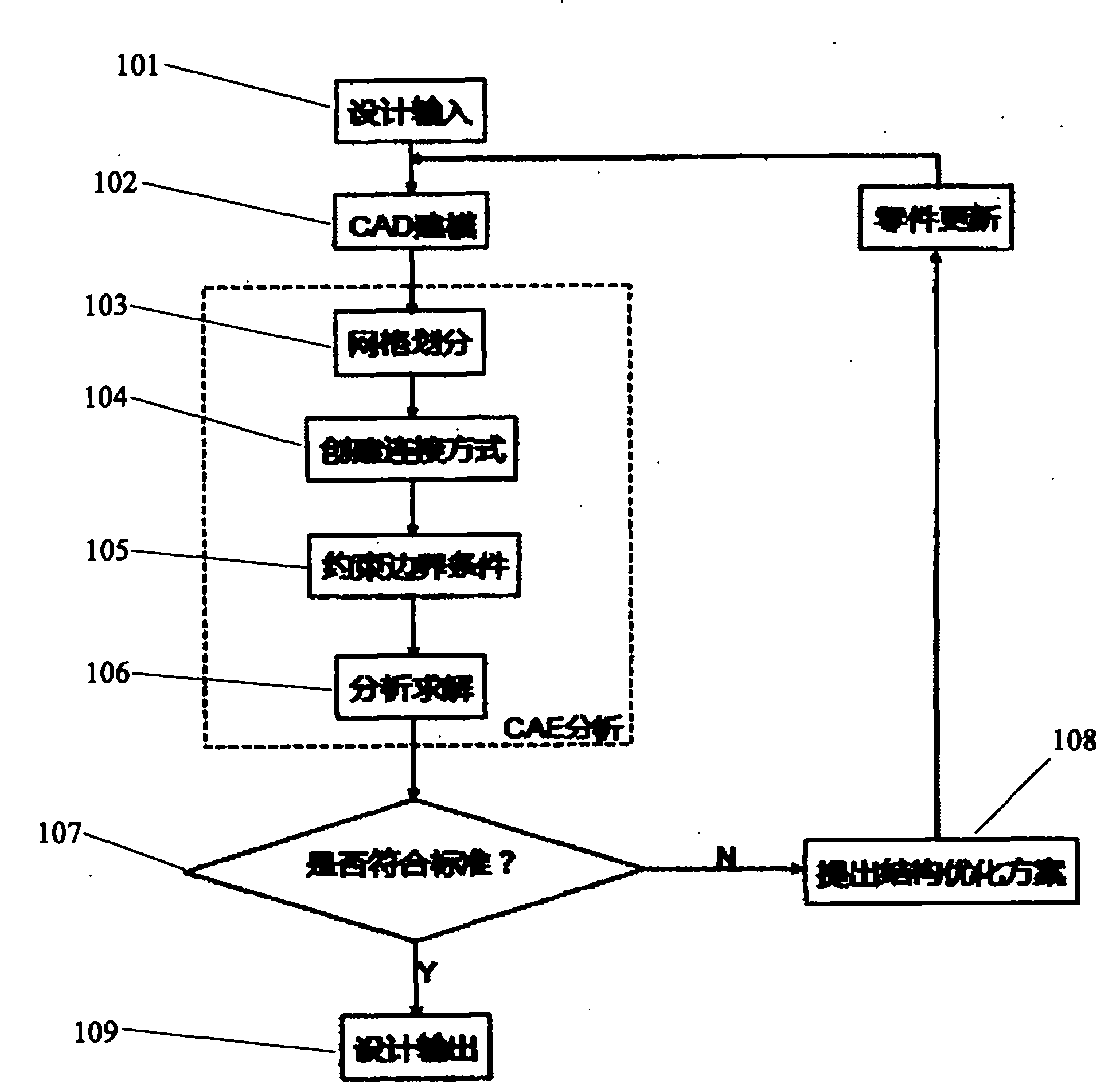
Optimization design method for sagging problem of car door based on CAE (Computer Aided Engineering) structural analysis
InactiveCN101916322AShort cycleShorten the timeSpecial data processing applicationsComputer Aided DesignElement model
The invention discloses an optimization design method for the sagging problem of a car door based on CAE structural analysis, which comprises the steps of: obtaining a design input condition from total arrangement and configuration of a car body; creating a CAD (Computer Aided Design) model by modeling software; dividing grids of the CAD model; simulating actual conditions to create a connection relationship; simulating a boundary constraint condition during an actual test of a car door assembly; carrying out solution analysis on a finite element model generated finally; comparing a result obtained by finite element simulation operation with an industry standard; if an obtained conclusion is lower than the industry standard, providing a structural optimization design; and if the obtained conclusion is higher than the industry standard, completing final design output. The method not only enhances the inspection accuracy, but also greatly reduces the period of a whole repair part so as to shorten the time of developing the whole car. Structural errors can be corrected in time by CAE analysis in early design, thereby reducing the cost of developing the whole car.
Owner:上海奕代汽车技术有限公司
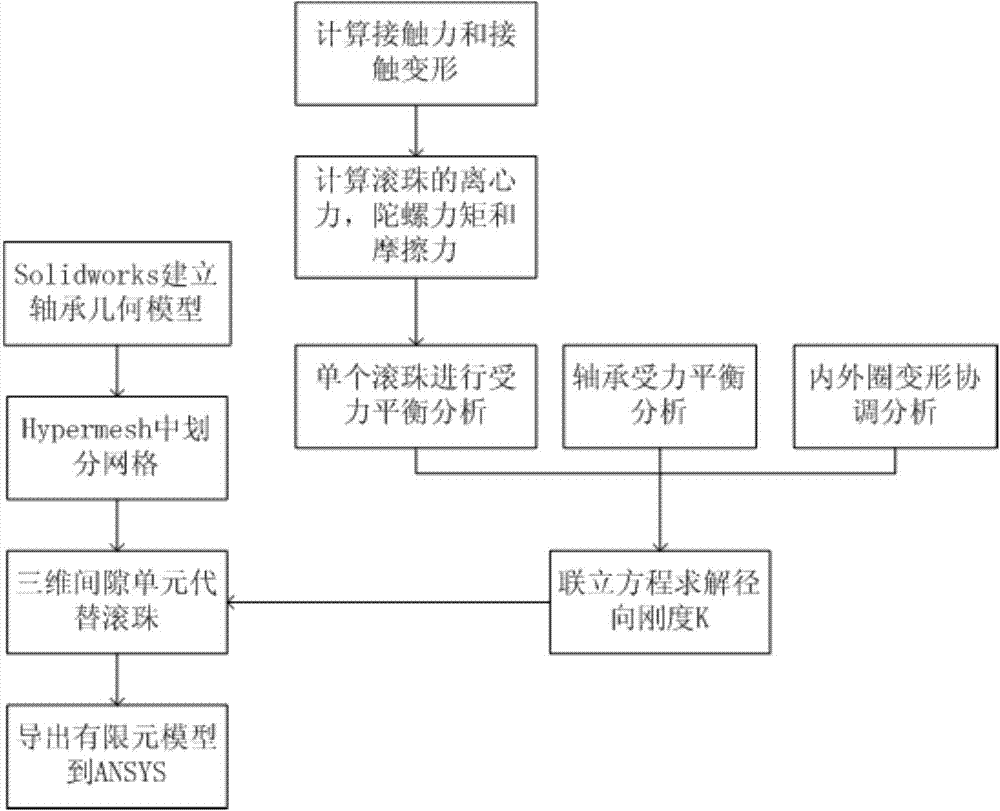
Bearing simplifying method in finite element simulation analysis
InactiveCN104239654AThe result is close to the realSimple calculationSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelElement analysis
The invention discloses a bearing simplifying method in finite element simulation analysis. According to the method, a three-dimensional gap unit is used for simplifying finite element analysis of an angular contact bearing, and a three-dimensional model of the bearing is drawn in three-dimensional mapping software solidworks. The bearing model is imported into finite element pre-processing software Hypermesh. An outer ring and an inner ring of the bearing are divided into hexahedral meshes. The outer ring and the inner ring of the bearing are connected through the three-dimensional gap unit. The spring stiffness K in the gap unit is worked out through a bearing radial stiffness calculation program. The finite element model is exported from the Hypermesh, then the finite element model is imported into engineering simulation software ANSYS, and mechanical calculation is conducted. According to the method, the calculation amount of finite element analysis can be simplified, the efficiency can be increased, and the calculation accuracy cannot be damaged.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Simulation method for residual stress prediction of micro-milling nickel-based superalloy
ActiveCN105117547AEasy to predictAchieve forecastSpecial data processing applicationsMilling cutterScanning electron microscope
The invention provides a simulation method for residual stress prediction of micro-milling nickel-based superalloy, belongs to the field of finite element simulation cutting, and relates to a finite element simulation method for residual stress prediction analysis in the cutting processing process of difficult-to-process materials of the nickel-based superalloy. According to the simulation method, the finite element simulation method is used; the elastic-plastic constitutive relationship of materials is considered; and a Johnson-Cook fracture failure criterion is used for judging the failure, so that residual stress prediction values under different cutting parameters can be obtained. A micro-milling cutter for experiments is shot into a picture through a scanning electron microscope; the picture is drawn into a micro-milling cutter solid model through software; a three-dimensional processed workpiece model is built; and the model is subjected to lattice division. The method has the advantages that the surface residual stress can be measured, and the residual stress in the depth direction can also be measured, so that the problem of measurement difficulty of the residual stress in the depth direction in the measurement process is solved. The cost is reduced, and the labor is saved. In a prediction model, the cutting parameters are variable; and the prediction on the surface residual stress of the difficult-to-process materials is effectively realized.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
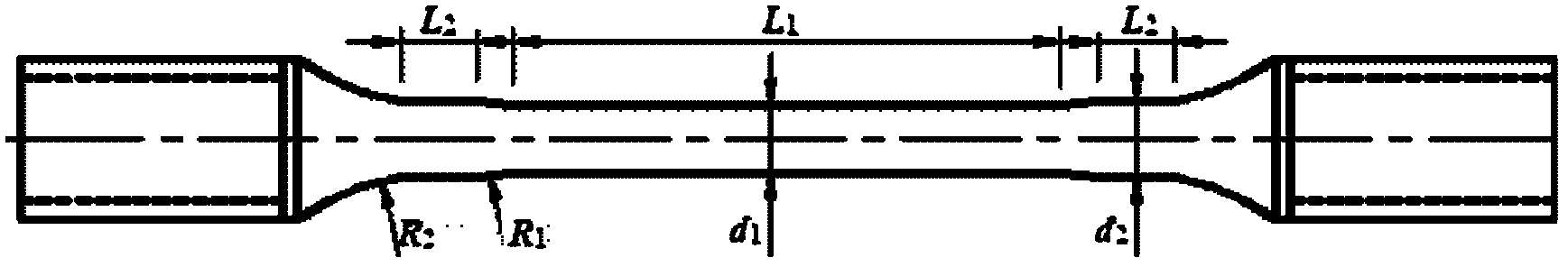
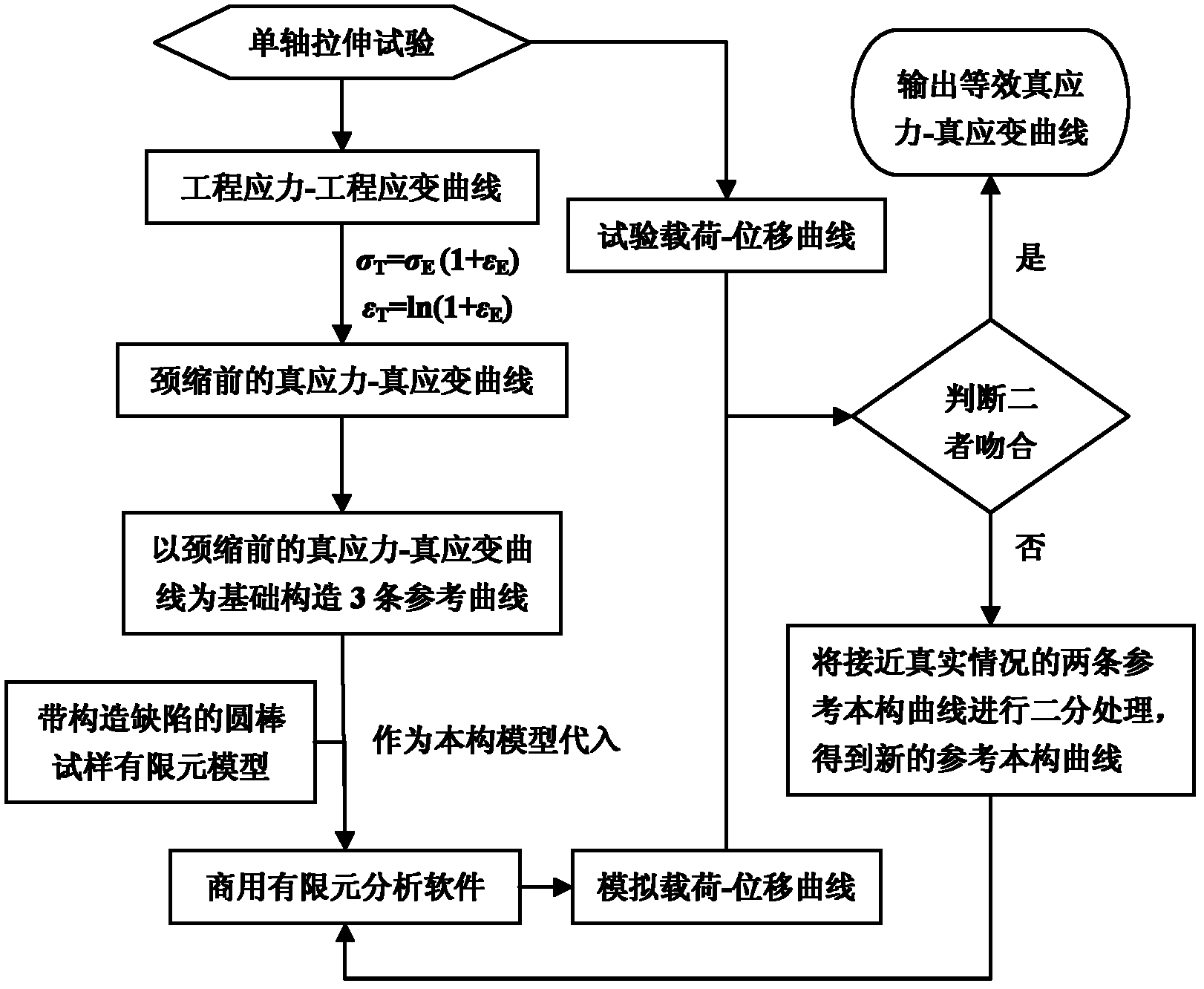
Single-shaft tensile overall true stress-true strain curve testing technique
InactiveCN102221503AEfficient measurementMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesFracture mechanicsEngineering structures
The invention discloses a single-shaft tensile overall true stress-true strain curve testing technique. According to the technique, a single-shaft tensile test is performed on a round rod sample, and an equivalent true stress-true strain curve which can really reflect the tensile overall deformation characteristics of a material can be solved through finite element simulation iteration. The testing technique disclosed by the invention can realize the overall equivalent true stress-true strain curve of the single-shaft tensile until fracture of the material, can be used for the deformation analysis of a large structure and the fracture mechanics analysis of a component comprising cracks and has important engineering values for promoting the theory development of mechanics, the optimization design of an engineering structure and the material performance evaluation.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Microfluidic large scale integration
InactiveUS8220494B2Operating means/releasing devices for valvesCircuit elementsElastomerFlow resistivity
Using basic physical arguments, a design and method for the fabrication of microfluidic valves using multilayer soft lithography is presented. Embodiments of valves in accordance with the present invention feature elastomer membrane portions of substantially constant thickness, allowing the membranes to experience similar resistance to an applied pressure across their entire width. Such on-off valves fabricated with upwardly- or downwardly-deflectable membranes can have extremely low actuation pressures, and can be used to implement active functions such as pumps and mixers in integrated microfluidic chips. Valve performance was characterized by measuring both the actuation pressure and flow resistance over a wide range of design parameters, and comparing them to both finite element simulations and alternative valve geometries.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
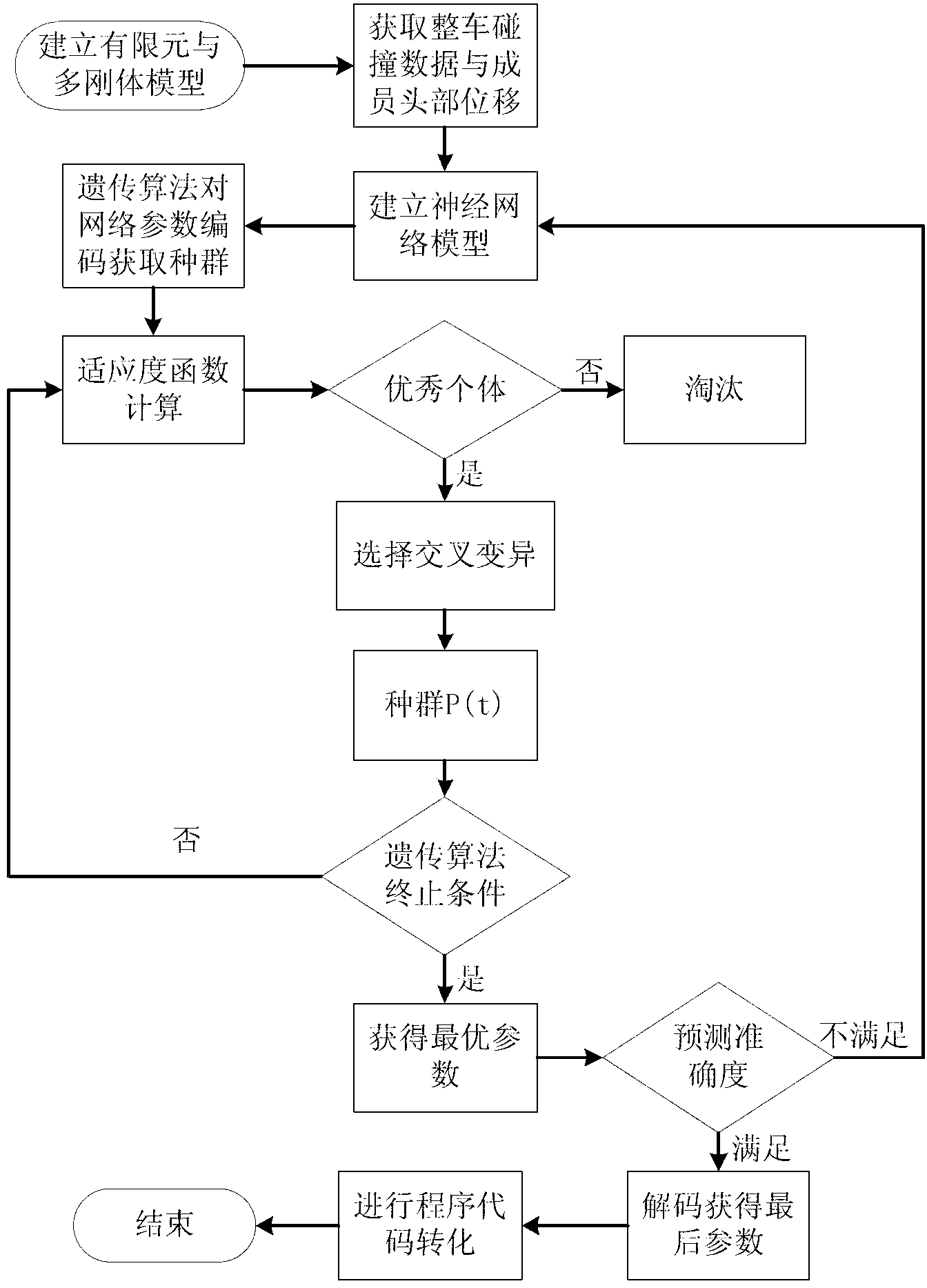
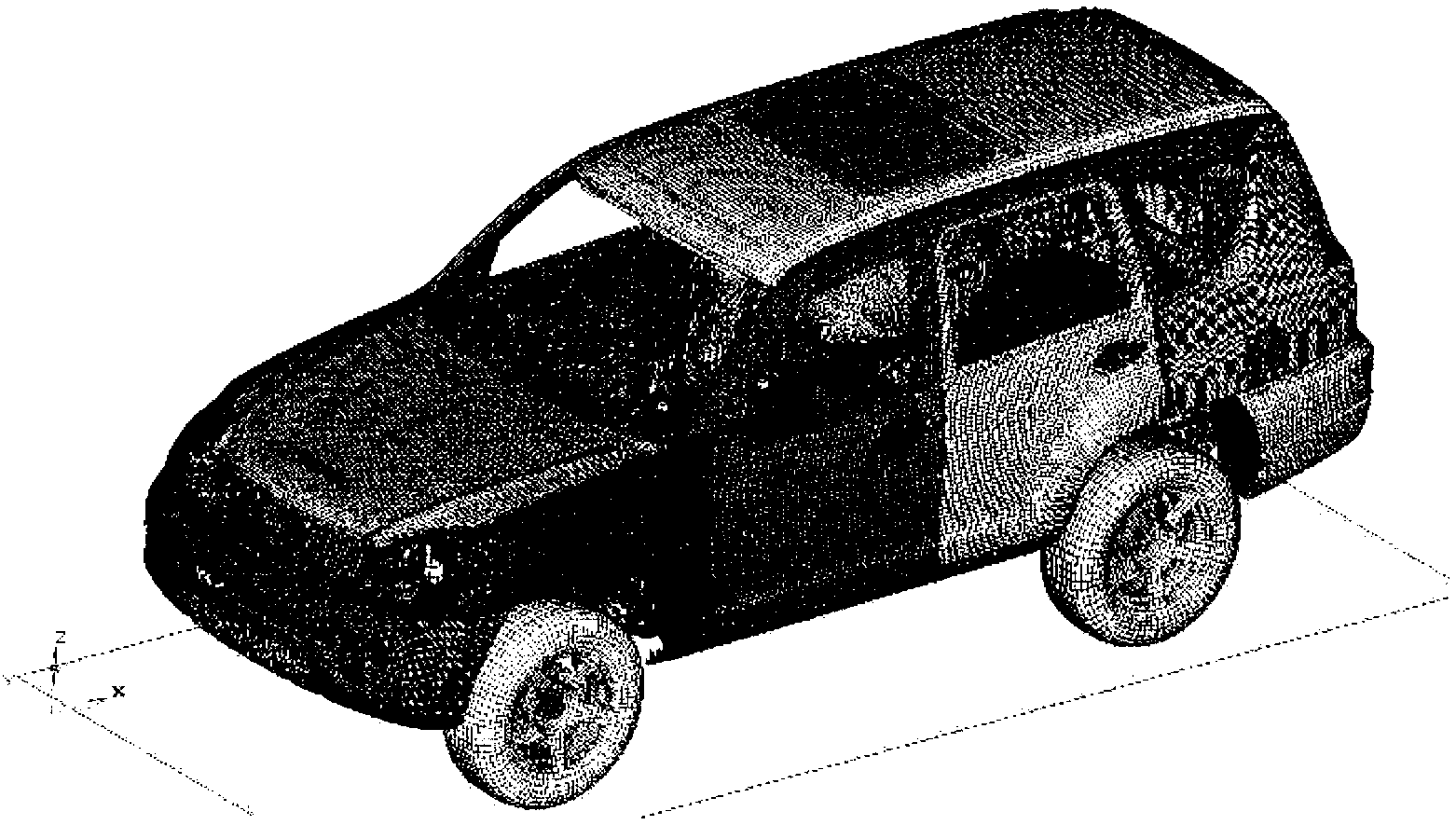
Air bag detonation control method based on genetic neural network
The invention discloses an air bag detonation control method based on a genetic neural network, which is set up based on a genetic neural network model. The method comprises the steps that a finite element simulation model of a certain automobile type is established according to the certain automobile type; acceleration data of a complete automobile and response data of a passenger at different impact speeds are obtained by using the simulation model; a multilayer neural network model is established by taking the acceleration data of the complete automobile as an input parameter, and the impact speeds and head displacement of the passenger as output parameters; neural network parameters are optimized by a genetic algorithm; an optimal neural network parameter is obtained; an optimal network model is subjected to program writing, and input to a controller; and the controller performs real-time processing on the acceleration data input by an acceleration sensor of the automobile, and outputs a predicted impact speed and the optimal ignition time within an effective time range. The intelligent air bag detonation control method is high in accuracy and timeliness, safe and reliable.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
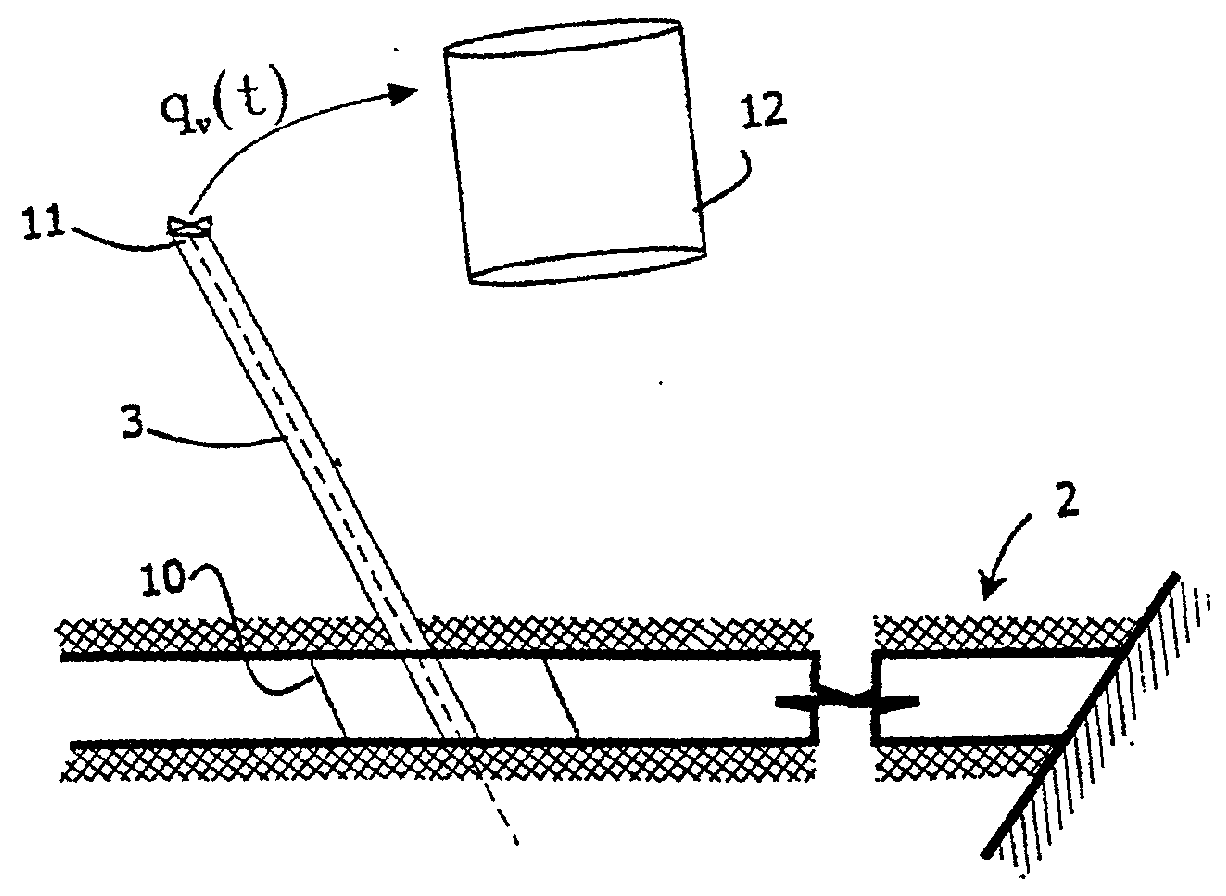
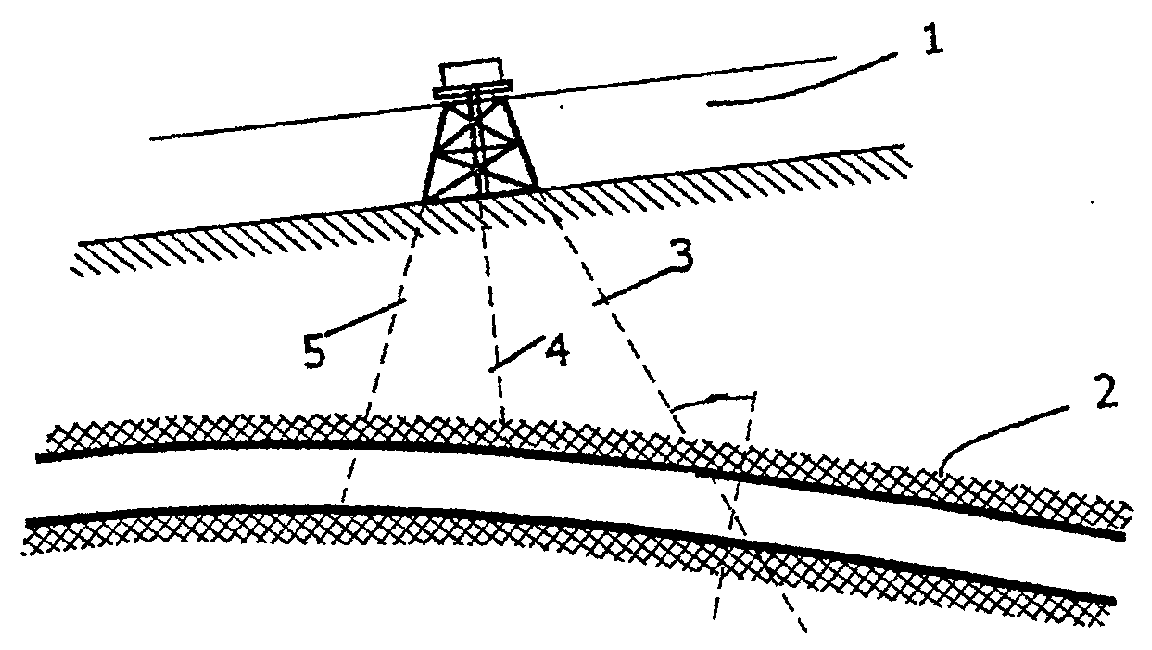
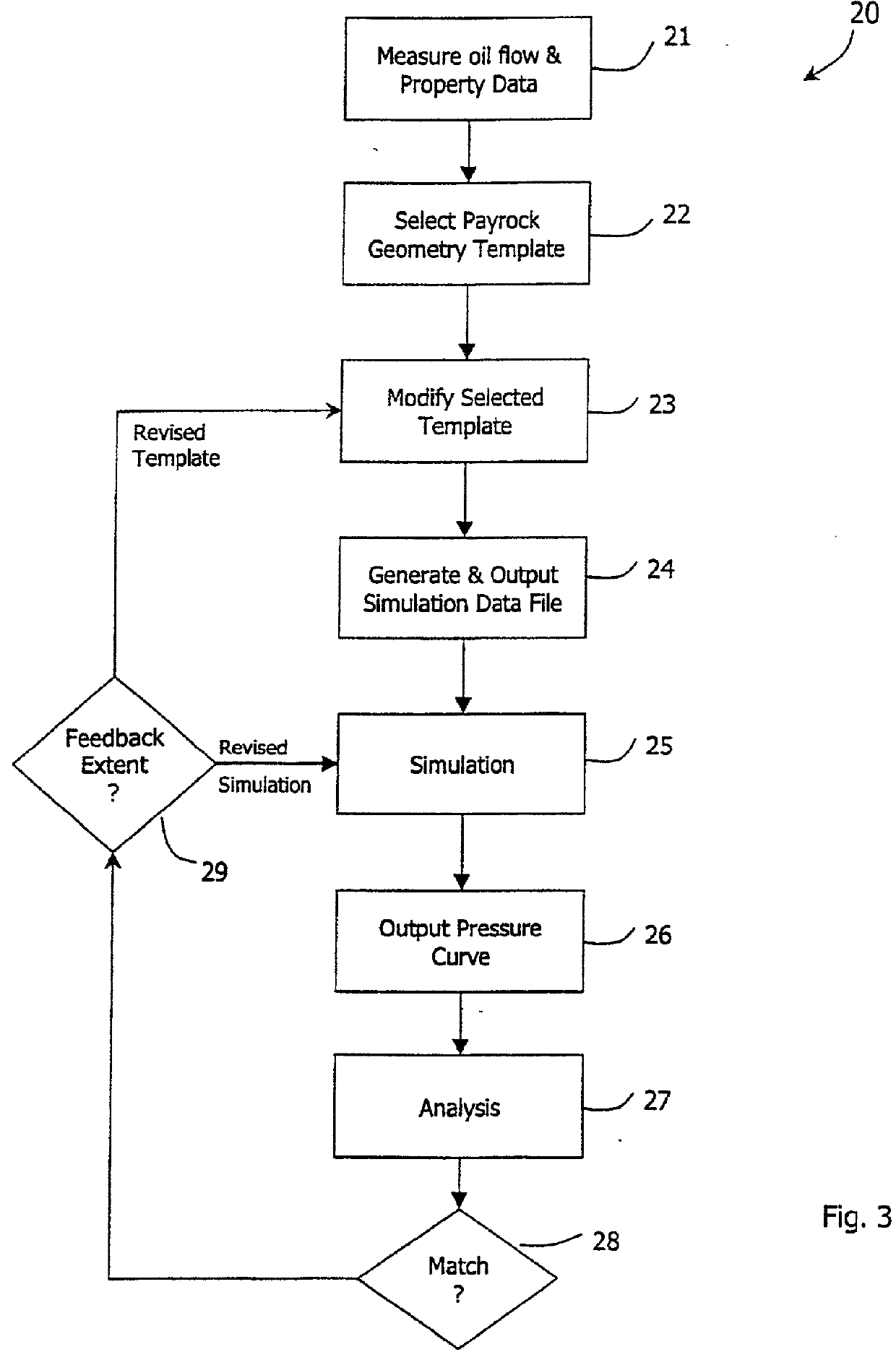
Hydrocarbon reservoir testing
InactiveUS20010056339A1Simulation is accurateLess engineer time requirementElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingPermeability/surface area analysisComputer scienceBase line
A reservoir in a payrock (2) is analyzed using finite element simulation. A reservoir engineer selects an appropriate model from a set of template models, each comprising a set of polygons (51) in plan and layers (53) in elevation. The polygons are defined in objects instantiated from classes by control points and the layers as depth values of control points. A pattern object sweeps rotationally about a wellbore in a wellbore polygon to define a pattern of elements, fewer in number with distance from the wellbore. A polygon object also sweeps linearly from a generator line in the direction of a base line. The generator and a base lines correspond to polygon boundaries. Finite element simulation is performed with the model so derived.
Owner:KEPLER RES & DEV
Method for predicting and analyzing cutting deformation of thin-walled structural parts
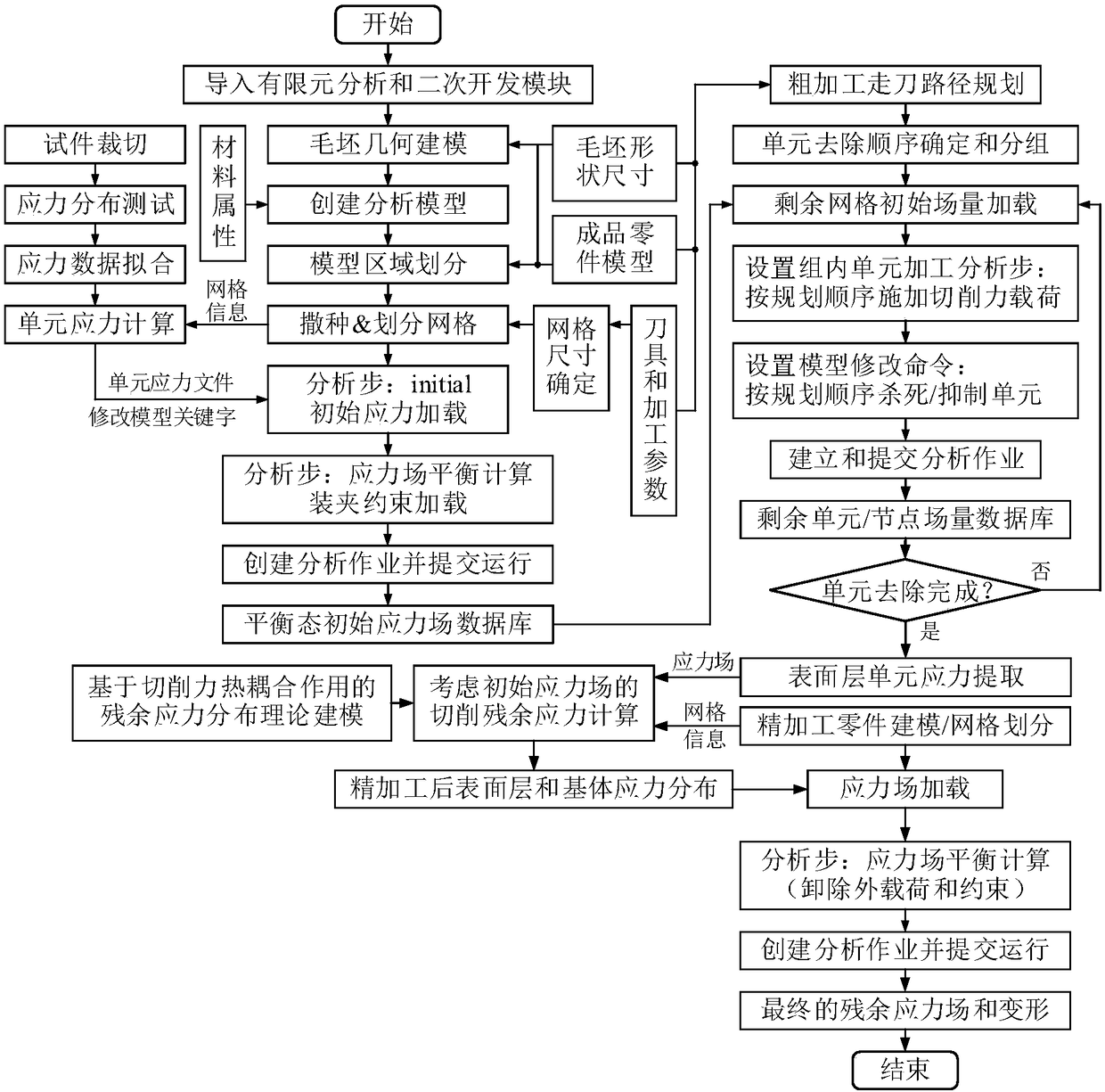
ActiveCN108182325ASimulation results are accurateImprove efficiencyGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationStress distributionSurface layer
The invention discloses a method for predicting and analyzing cutting deformation of thin-walled structural parts. Based on combination of finite element simulation analysis and cutting force thermalcoupling theoretical modeling, the evolution process of blank structural parts with initial residual stress in an internal stress field during the coarse and fine cutting process to better reflect theimpact of body residual stress distribution of the structural parts after coarse processing on cutting residual stress distribution of a finish machining surface layer, and the impact of stress release of the structural parts after completion of the whole cutting process on processing deformation, and finally the prediction of machining residual stress and machining deformation can be achieved.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
Finite-element-based machine tool important part residual stress multi-process continuous modeling simulation method
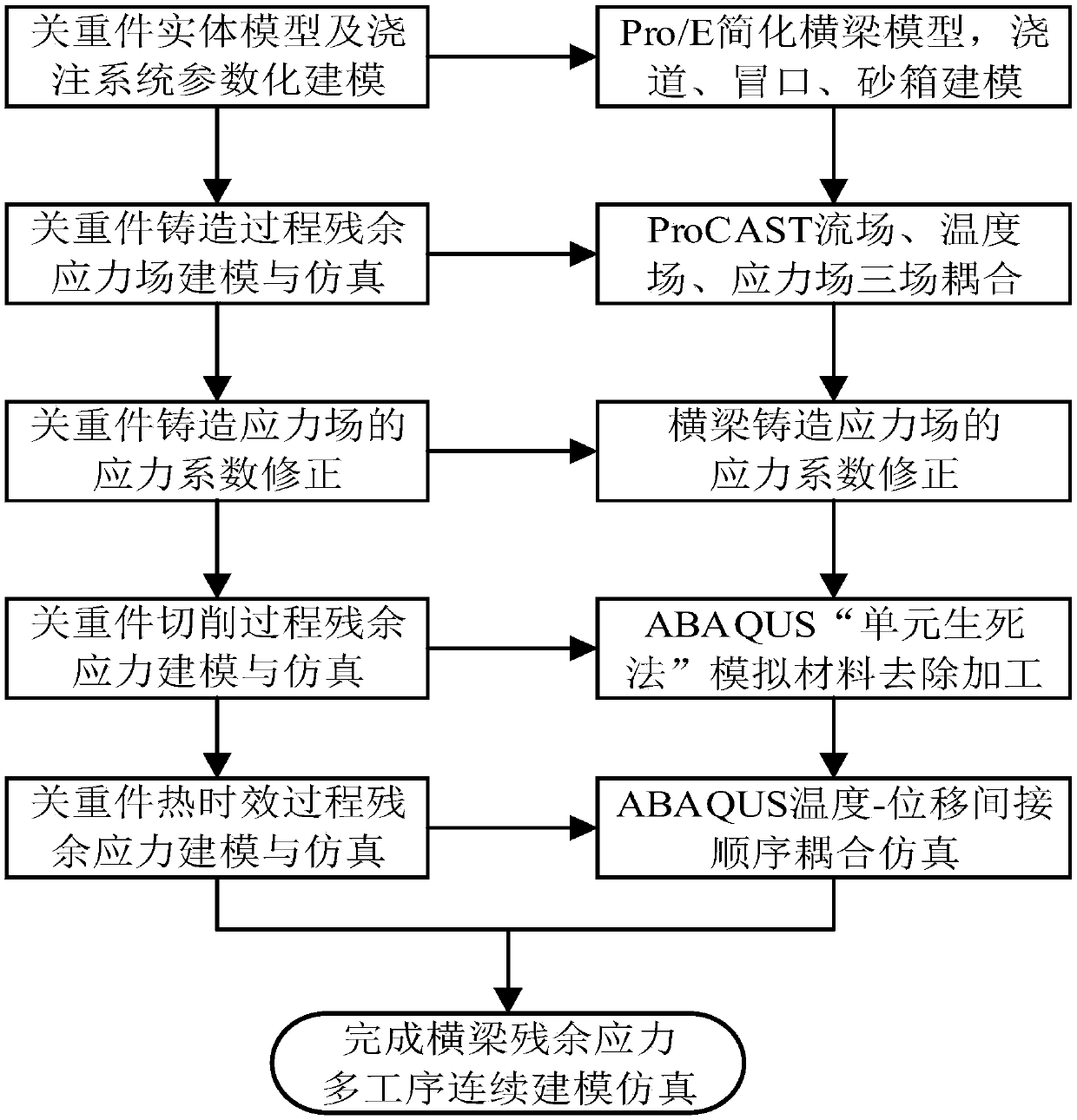
ActiveCN108304657AEnable continuous simulationImprove calculation accuracyDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsMethod testMATLAB
The invention discloses a finite-element-based machine tool important part residual stress multi-process continuous modeling simulation method. The method comprises the steps of important part model simplification and casting system three-dimensional modeling, important part casting process finite element simulation, important part casting stress field coefficient correction, important part machining residual stress simulation, and important part thermal aging process residual stress finite element simulation. Accordingly, multi-process continuous simulation of casting, cutting and thermal aging processes are implemented; a blind hole method test measurement value serves as a reference, a stress value of an important part casting simulation corresponding point is extracted, a test value ofthe corresponding point and a correction coefficient with the minimum simulation value error are fitted by applying a least square method through MATLAB, and then the whole casting stress field datais corrected; the calculation accuracy of finite element simulation is improved, and the technical purpose that the casting stress field obtained after a beam is corrected is guided into an ABAQUS accurately is achieved.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Control method for compensating location torque of permanent-magnet motor by injecting current harmonics
InactiveCN101515780ANo additional costSmall positioning torqueElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsHarmonic analysisEngineering
The invention discloses a control method for compensating location torque of permanent-magnet motor by injecting current harmonics; in the method, harmonic current is injected to interact with the fundamental wave permanent magnetic potential to generate an additional torque component, so that the additional torque can be equal to the amplitude of the fundamental wave and the ultra-harmonics component in the directional torque and the phase positions thereof are opposite and can be offset, thus achieving the aim of compensating the location torque. In the method, firstly harmonic analysis is carried out on the location torque of the permanent-magnet motor by using finite element simulation result or observed data and adopting the Fourier series approximation approaching method; secondly the aero load counter electromotive force of the permanent-magnet motor is analyzed and the corresponding mathematical expression is written out; and finally the injected harmonic current is worked out according to the principle that additional torque and location torque can offset each other.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method for testing cutting and bonding friction characteristics with point-contact opened-closed type pin-disc friction system
The invention relates to a method for testing cutting and bonding friction characteristics with a point-contact opened-closed type pin-disc friction system which is structured by a friction test platform transformed by a lathe. Aiming at the research requirements on the cutting friction problem and through the design of a pin-disc structure and the combination of lathe space motion trail, an opened-closed type system can be structured, and the cutting friction under an extreme working condition can be simulated; and an acting force of a contact interface can be measured by utilizing a Kistler piezoelectric force meter, a tangential force component caused by material elasticplastic deformation can be removed by combining a finite element simulation method, and thus a bonding friction factor can be obtained. The method disclosed by the invention is mainly used for testing and analyzing the friction characteristic of cutters in the cutting process. A main body of equipment is common equipment in a manufacturing laboratory, and has the advantages of good rigidity, simple structure, easy implementation and the like.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY +1
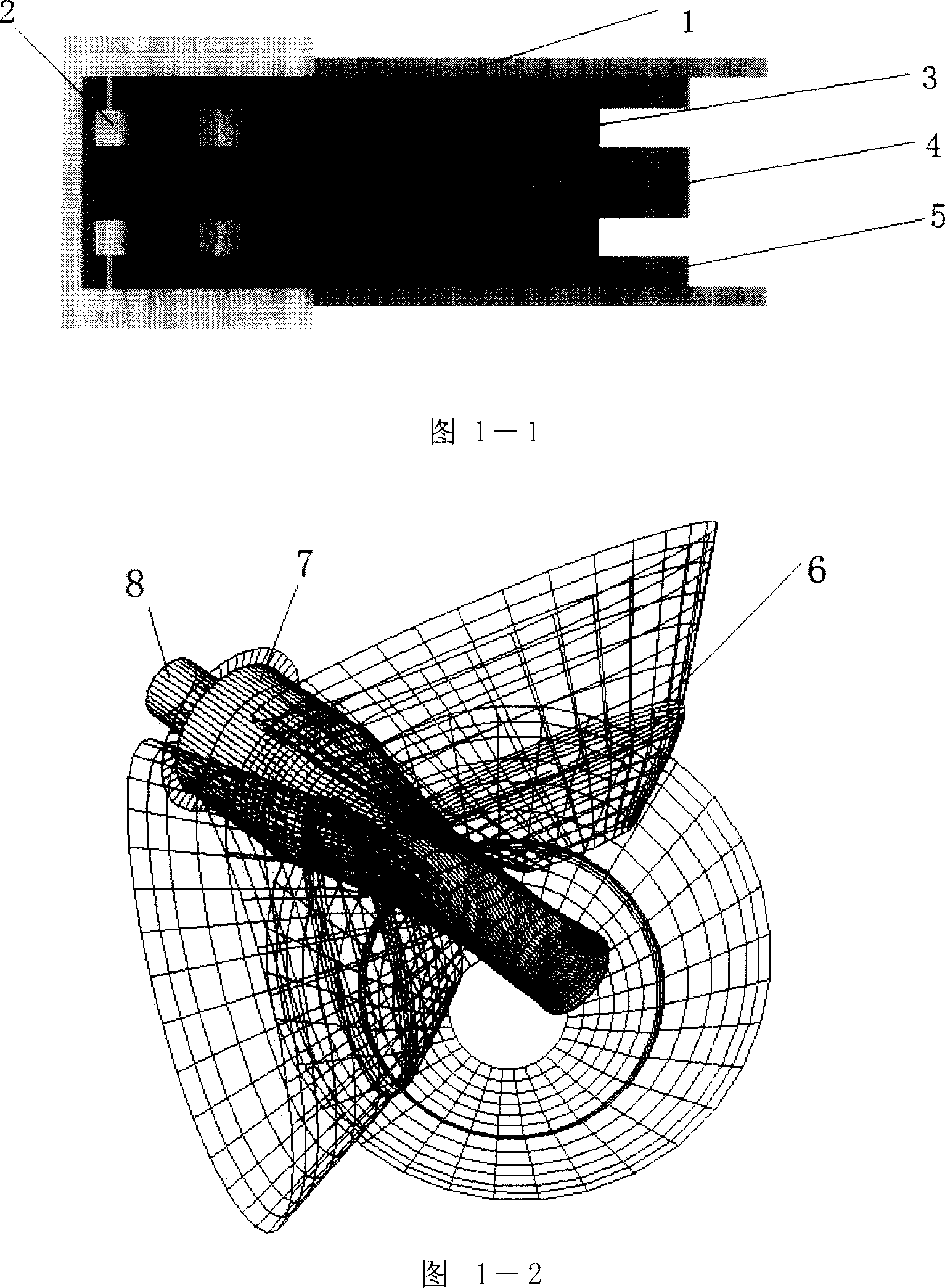
Manufacturing technique of digitally customizing orthopedic implants
InactiveCN103150442AFit closelyReduced chance of internal fixation failureSpecial data processing applicationsGraphicsBond properties
The invention discloses a manufacturing technique of digitally customizing an orthopedic implant, which comprises the steps of scanning a fracture part of a fracture patient, obtaining injured fracture data, introducing the injured fracture data into 3D (three dimensional) medical finite element simulation software for processing, obtaining a 3D figure of the fracture part, reconstructing and resetting fracture part, introducing 3D figure data after medical 3D reconstruction and resetting into 3D industrial design software, designing a primary orthopedic implant according to a surgical requirement and experience, obtaining 3D figure data of the primary orthopedic implant, introducing the 3D figure data of the primary orthopedic implant into the 3D medical finite element simulation software to conduct virtual assembly with the fracture part after the medical 3D reconstruction and resetting, confirming a position and a direction of a screw hole of the primary orthopedic implant according to a resetting condition of the fracture part, introducing 3D figure data of a final orthopedic implant into a quick forming machine to accumulate to a practical orthopedic implant, and obtaining the finished orthopedic implant. The manufacturing technique can design specially and achieve high-precision resetting and internal fixation according to different fracture shapes, and the manufactured orthopedic implant is good in surface bonding property and reasonable in thickness.
Owner:CHANGZHOU WASTON MEDICAL APPLIANCE CO LTD
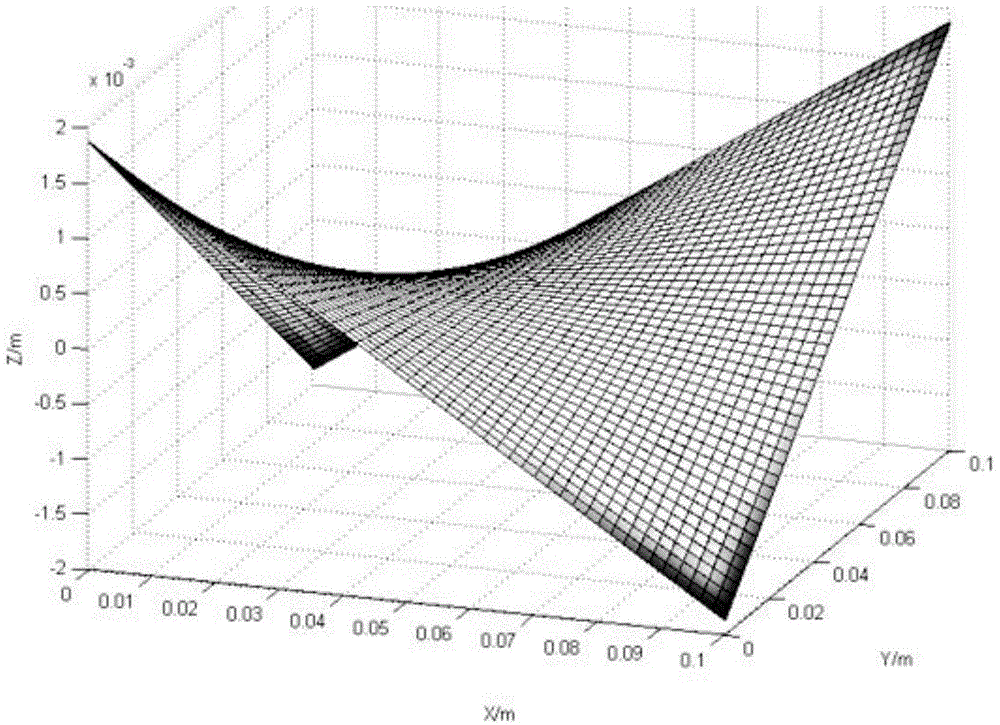
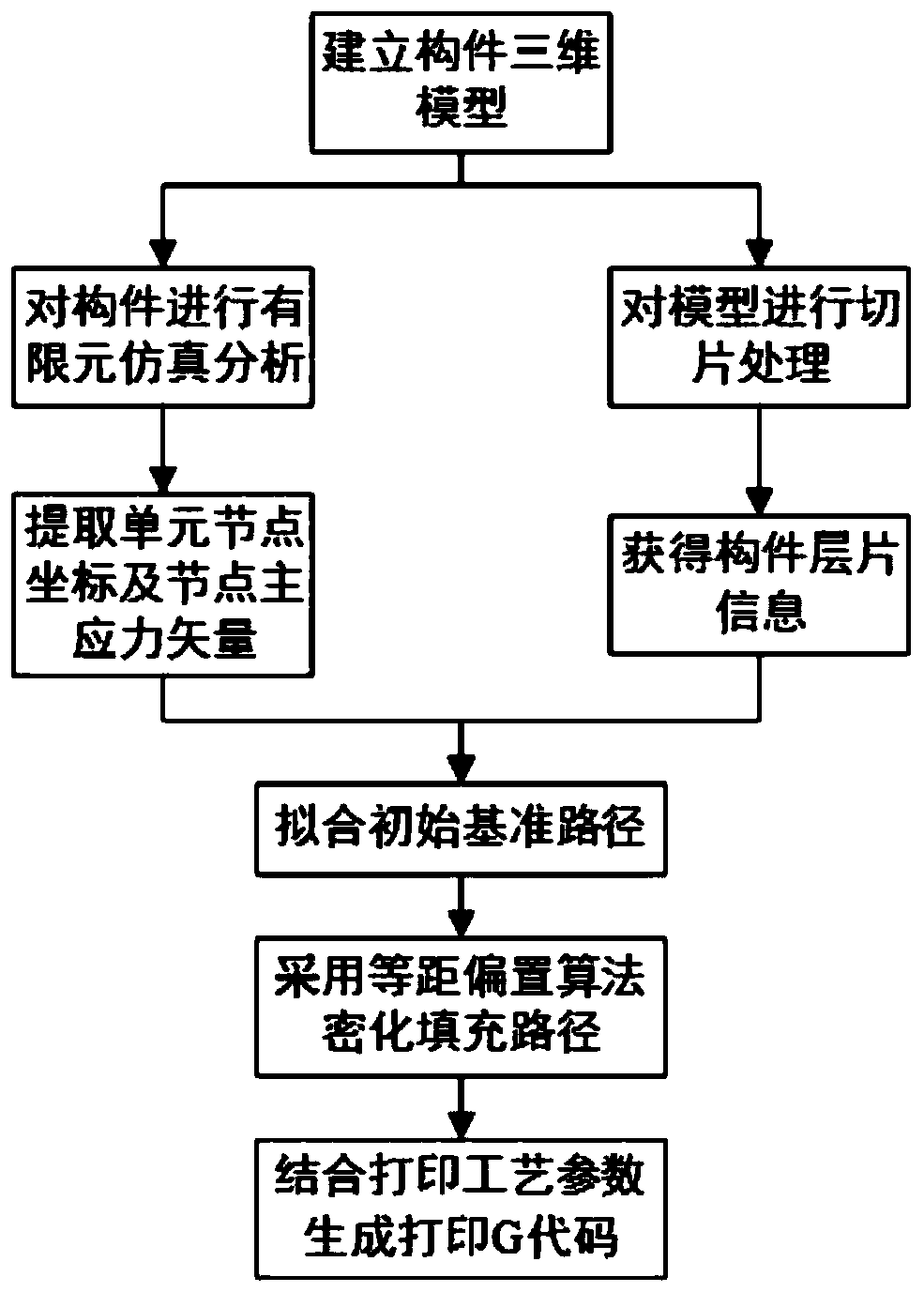
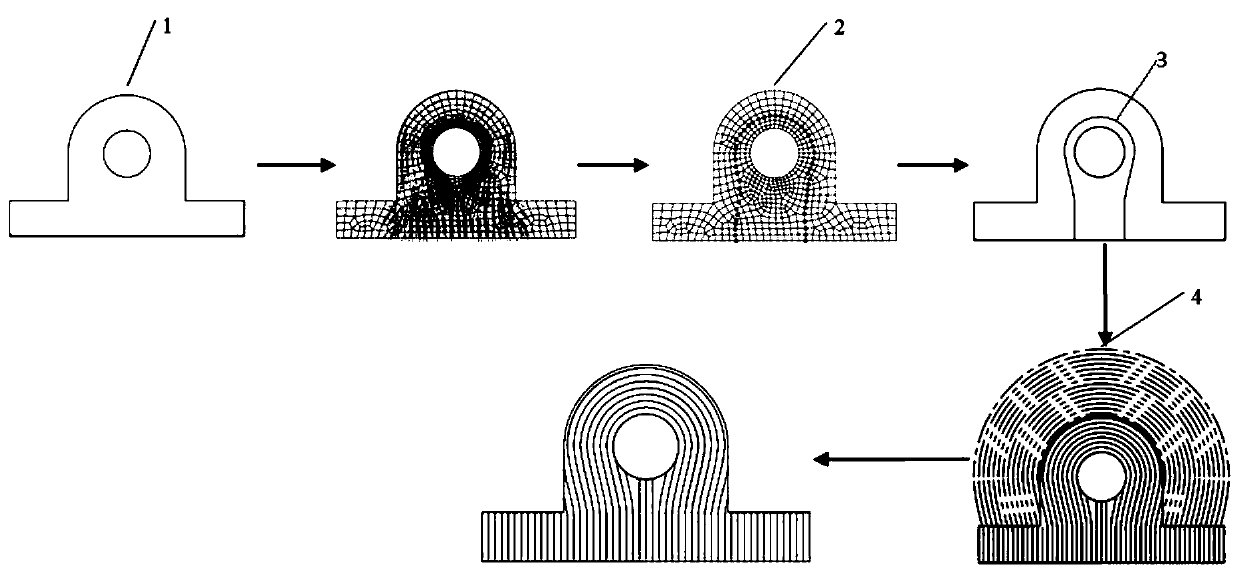
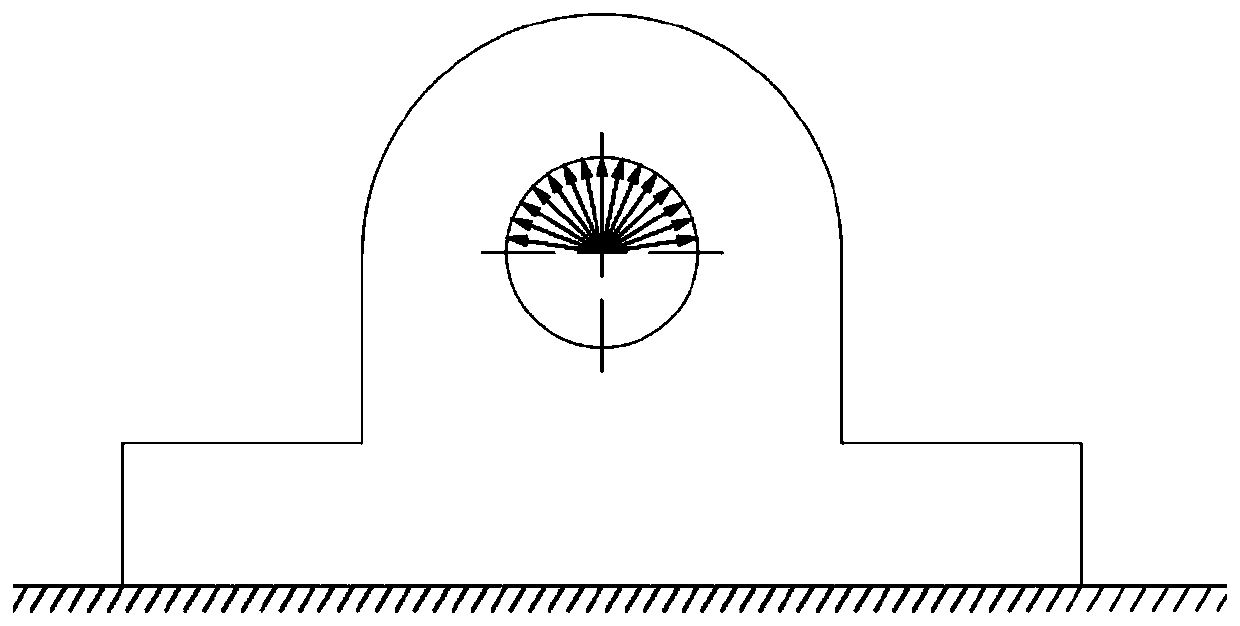
Laser 3D printing finite element simulation method
InactiveCN108399307AReduce manufacturing costIncrease productivityAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyEngineeringLine structure
The invention discloses a laser 3D printing finite element simulation method. The method includes: establishing a three-dimensional geometrical model with a substrate area and stack layer areas, wherein the stack layer areas comprise one or more layer structures sequentially stacked on the substrate layer, and the layer structures are formed by line structures representing printing routes; respectively setting material parameters for the substrate area and the stack layer areas to enable the substrate area and the stack layer areas to obtain physical properties of corresponding materials; setting temperature and heat radiating surfaces of the substrate layer, and setting contact surfaces of the substrate area and the stack layer areas or contact surfaces of the stack layer areas as convection and radiation surfaces; dividing the line structures into a plurality of analysis step structures, adopting a birth-death element setting method to sequentially activate each analysis step structure according to the printing routes, sequentially performing analogue simulation, and correcting parameters according to simulation results, so that reference and theoretical support is provided for parameter setting in practical laser 3D printing.
Owner:DALIAN JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY
CH4169 alloy forging piece grain size analysis and predication method
The invention relates to the field of high-temperature alloy forging, and particularly relates to a CH4169 alloy forging piece grain size analysis and predication method. The CH4169 alloy forging piece grain size analysis and predication method comprises the following steps: carrying out a near isothermal forging experiment on a CH4169 alloy sub-size double-cone test sample; carrying out finite element simulation on a near isothermal forging experiment process to obtain forging thermal parameters of the test sample; determining the grain size and determining forging thermal parameter values according to a finite element calculation result; drawing a contour map of the relation of the grain size and the forging thermal parameters according to the obtained grain size and forging thermal parameters; carrying out the finite element simulation on an actual production process of a CH4169 alloy forging piece, and counting the forging thermal parameters; and determining the grain size of a part to be analyzed and predicated by utilizing the drawn contour map of the grain size and the forging thermal parameters. According to the CH4169 alloy forging piece grain size analysis and predication method, the established contour map of the relation of the grain size and the CH4169 alloy forging thermal parameters is used for analyzing and predicating the grain size in the CH4169 alloy forging piece, and the method is convenient to use and has the high predication accuracy.
Owner:重庆两航金属材料有限公司
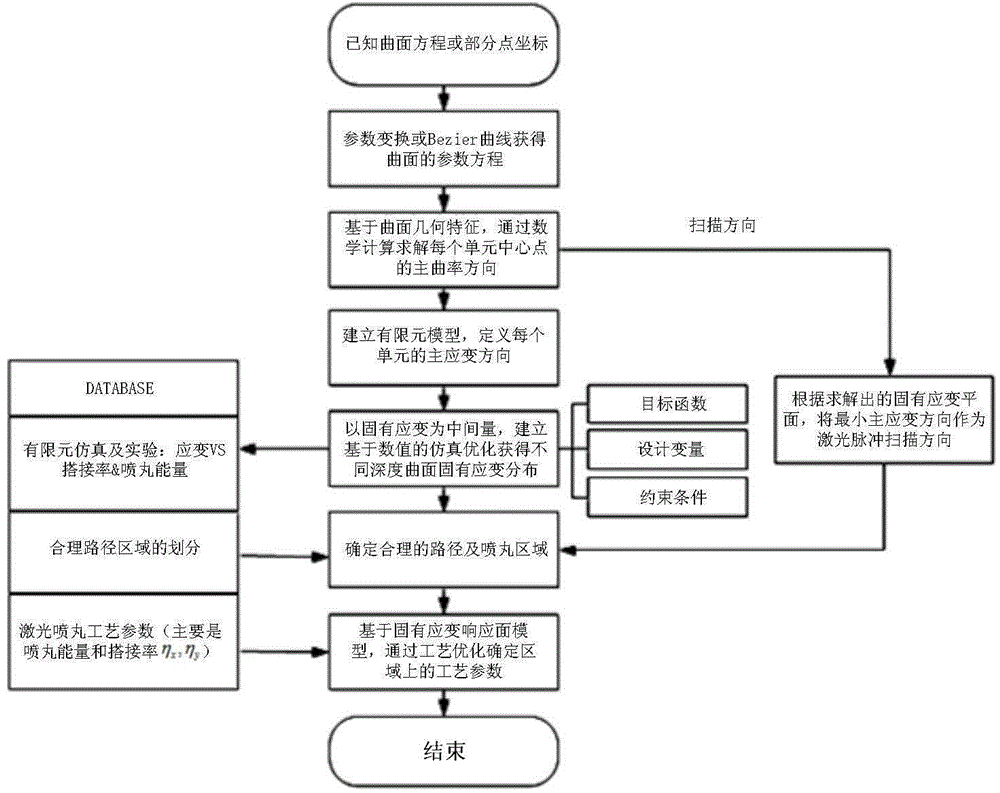
Method for determining laser peening forming process parameter of complex curved-surface-shaped workpiece
ActiveCN104899345AImprove fatigue resistanceAccelerated corrosionSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelStrain response
The invention provides a method for determining a laser peening forming process parameter of a complex curved-surface-shaped workpiece. The method comprises the following steps: according to a curved surface parameter equation of the workpiece, carrying out geometrical characteristic analysis on the curved surface of the workpiece to calculate a main strain direction so as to obtain a laser pulse scanning direction in laser peening forming; establishing a workpiece bending deformation finite element model which takes depth-direction inherent strain distribution as a deformation source, and optimizing an inherent strain field to obtain the inherent strain distribution of different positions of the workpiece along the depth direction, wherein an inherent strain direction is the main strain direction; and according to inherent strain response surface models under different laser peening forming process parameters and the inherent strain of different positions of the workpiece along the depth direction, optimizing the laser peening forming process parameters, and obtaining an optimal laser peening forming process parameter corresponding to different inherent strain fields on the surface of the workpiece. A non-elastic deformation problem can be converted into an elastic deformation problem to improve the efficiency and the precision of finite element simulation.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
3D printing path planning method of continuous fiber reinforced composite material
ActiveCN110001067AImprove mechanical propertiesImprove performanceAdditive manufacturing apparatusManufacturing data aquisition/processingStress distributionFiber-reinforced composite
The invention relates to a 3D printing path planning method of a continuous fiber reinforced composite material, and belongs to the cross field of composite materials and additive manufacturing. According to the 3D printing path planning method of the continuous fiber reinforced composite material, finite element simulation technology is utilized to simulate and analyze the stress distribution ofan element under the action of a load, and a printing path of continuous fiber reinforced composite material additive manufacturing is planned according to the stress distribution direction and transmission characteristics of the element and the characteristics of fiber continuity. Compared with a traditional path planning method, the orientation of the continuous fibers can be adjusted pertinently, the bearing capacity of the element is improved to the maximum extent, the usage amount of fiber materials is reduced, the manufacturing cost of the continuous fiber reinforced composite material is reduced, and the high performance, high efficiency, high precision and low cost 3D printing forming of the continuous fiber reinforced composite material are achieved.
Owner:ADVANCED MFG TECH CENT CHINA ACAD OF MASCH SCI & TECH
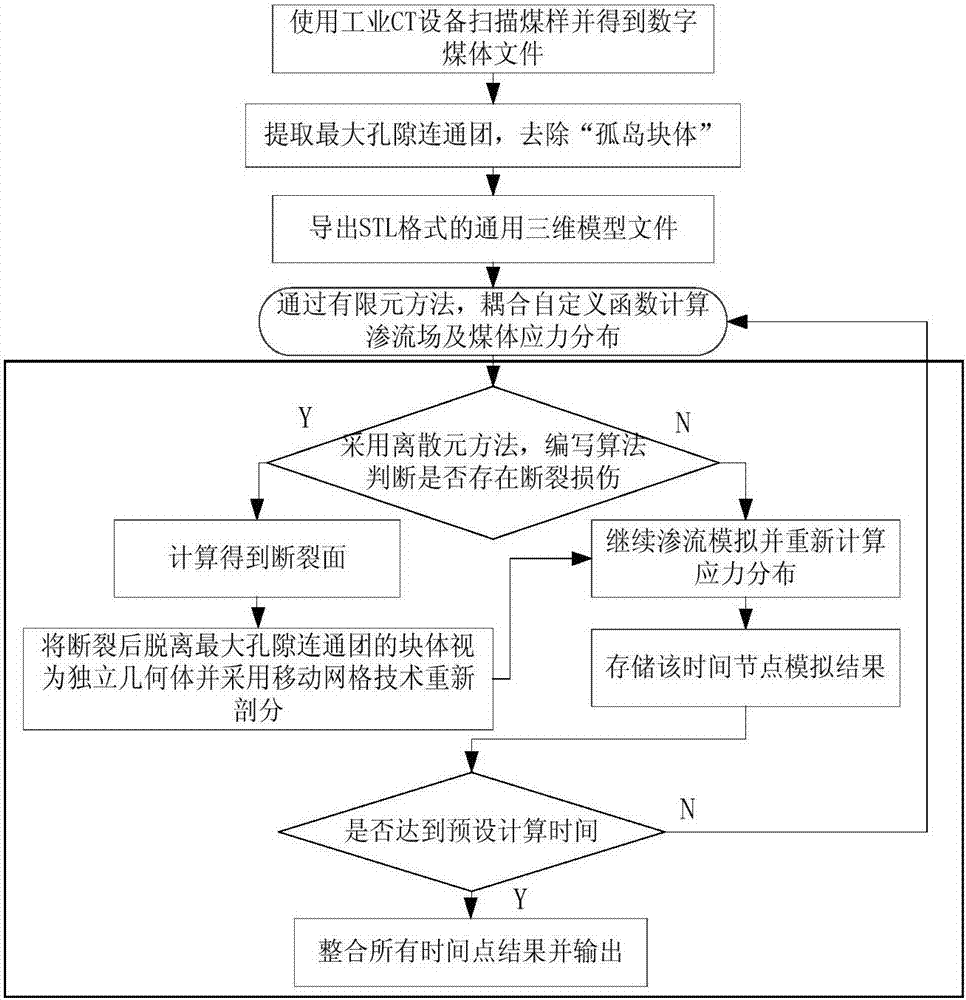
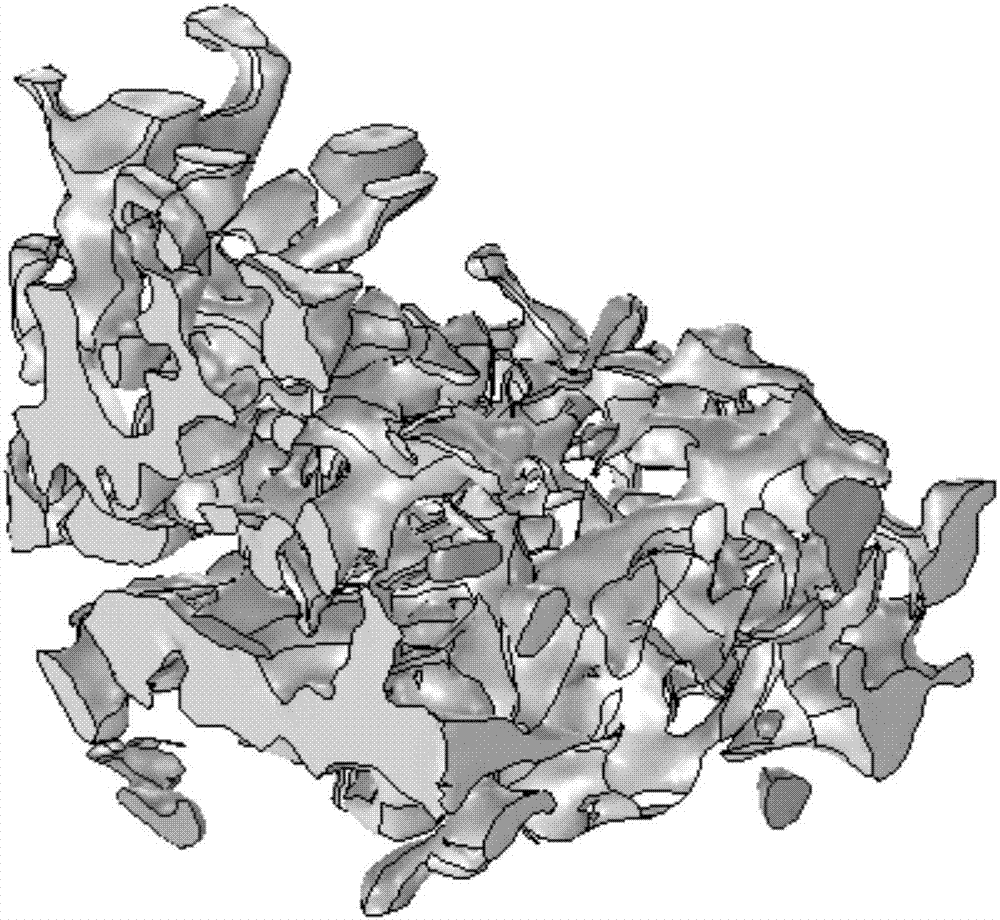
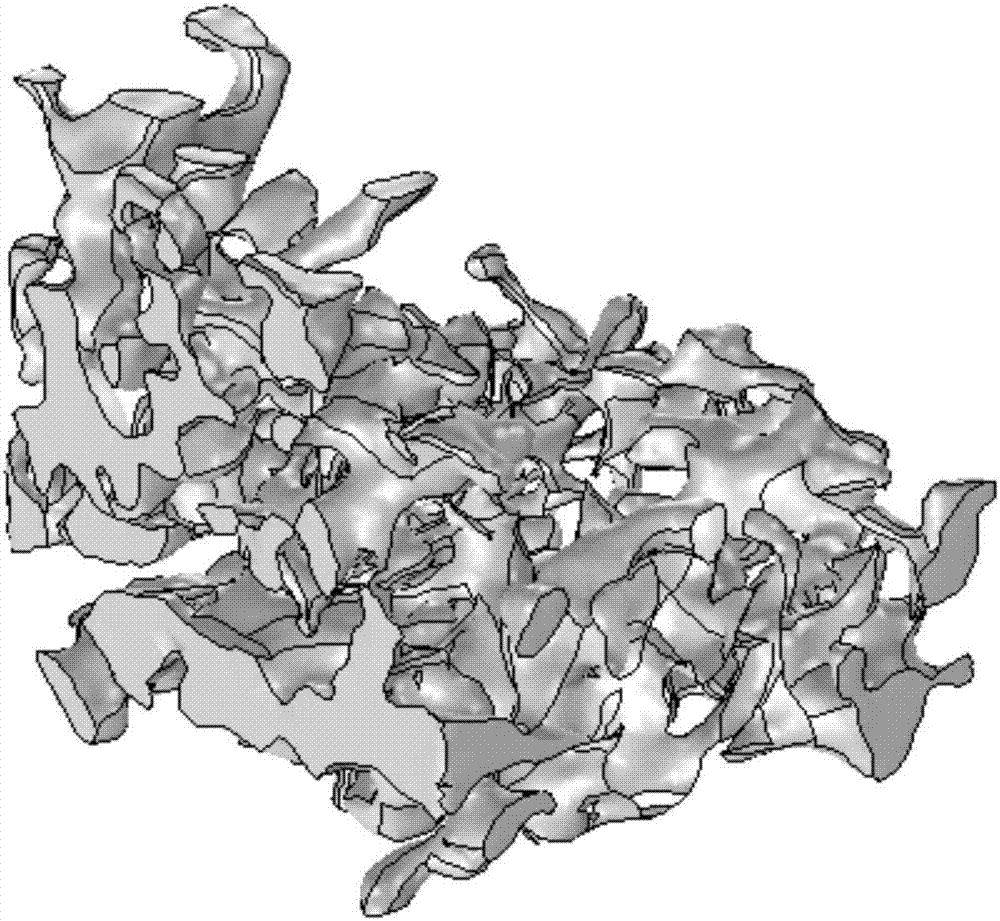
Seepage simulation method for constructing coal body based on finite element-discrete element CT (Computer Tomography)
ActiveCN106960070AFracture RealizationUniversally applicableDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsPorous mediumMobile grid
The invention discloses a seepage simulation method for constructing a coal body based on finite element-discrete element CT (Computer Tomography). The method comprises the following steps: performing industrial CT scanning to obtain a three-dimensional data body of the coal body, performing three-dimensional reconstruction, and removing an ''island block'' to obtain a general three-dimensional geometric model which can be called by simulation software; writing a coal body fracture discrimination algorithm by a discrete element simulation method, and determining whether the coal body is deformed, even fractured under the action of hydraulic pressure stress; meanwhile, realizing migration of coal body fragments formed after fracture in the coal body along with moisture flow based on an finite element simulation method by a mobile grid method; and performing numerical simulation of a moisture seepage pressure field, a seepage speed field and a coal body moisture increment at the same time in order to reveal deformation and fracture phenomena of the coal body and a migration rule of moisture in a water injection process of a porous medium coal bed to the maximum extent.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for determining rigidity of bolt connecting piece
ActiveCN102063552AAvoid errorsSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringFinite element simulation
The invention discloses a method for determining rigidity of a bolt connecting piece, which comprises the steps of: establishing a macroscopic finite element simulation model and a microscopic finite element simulation model of a bolt connecting piece; dividing the rigidity of the bolt connecting piece into a matrix rigidity of the bolt connecting piece and a faying face rigidity of the bolt connecting piece, which are connected in series to obtain the rigidity of the whole bolt connecting piece, wherein the faying face rigidity of the bolt connecting piece is obtained by the parallel connection of rigidities of all contact micro-convex bodies; carrying out application of boundary conditions of the combined macroscopic and microscopic finite element simulation models and simulation calculation for the bolt connecting piece; and calculating the rigidity of the bolt connecting piece on the basis of the results of the simulation calculation and the established rigidity models of the boltconnecting piece.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com