Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
10053 results about "Blind hole" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
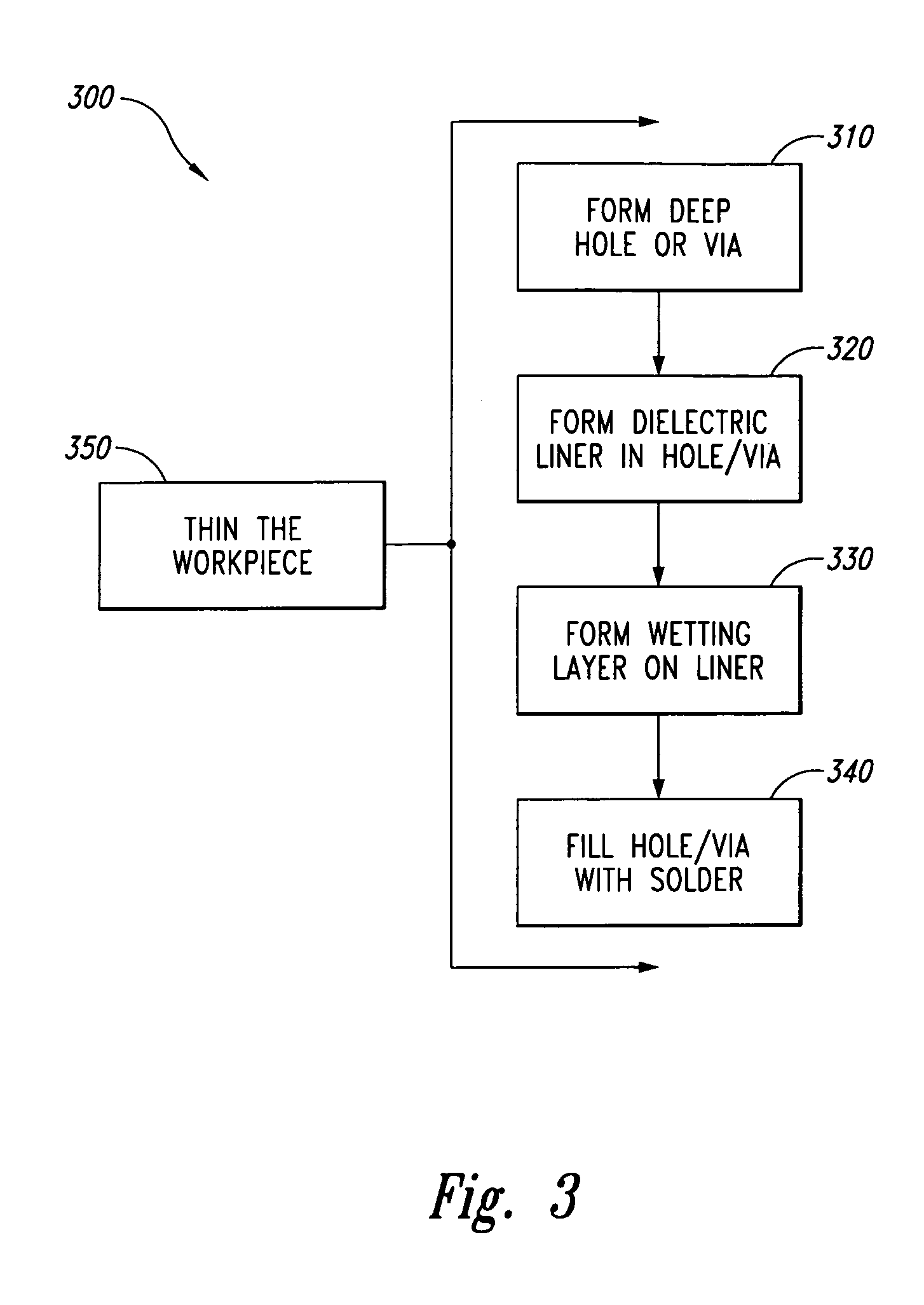
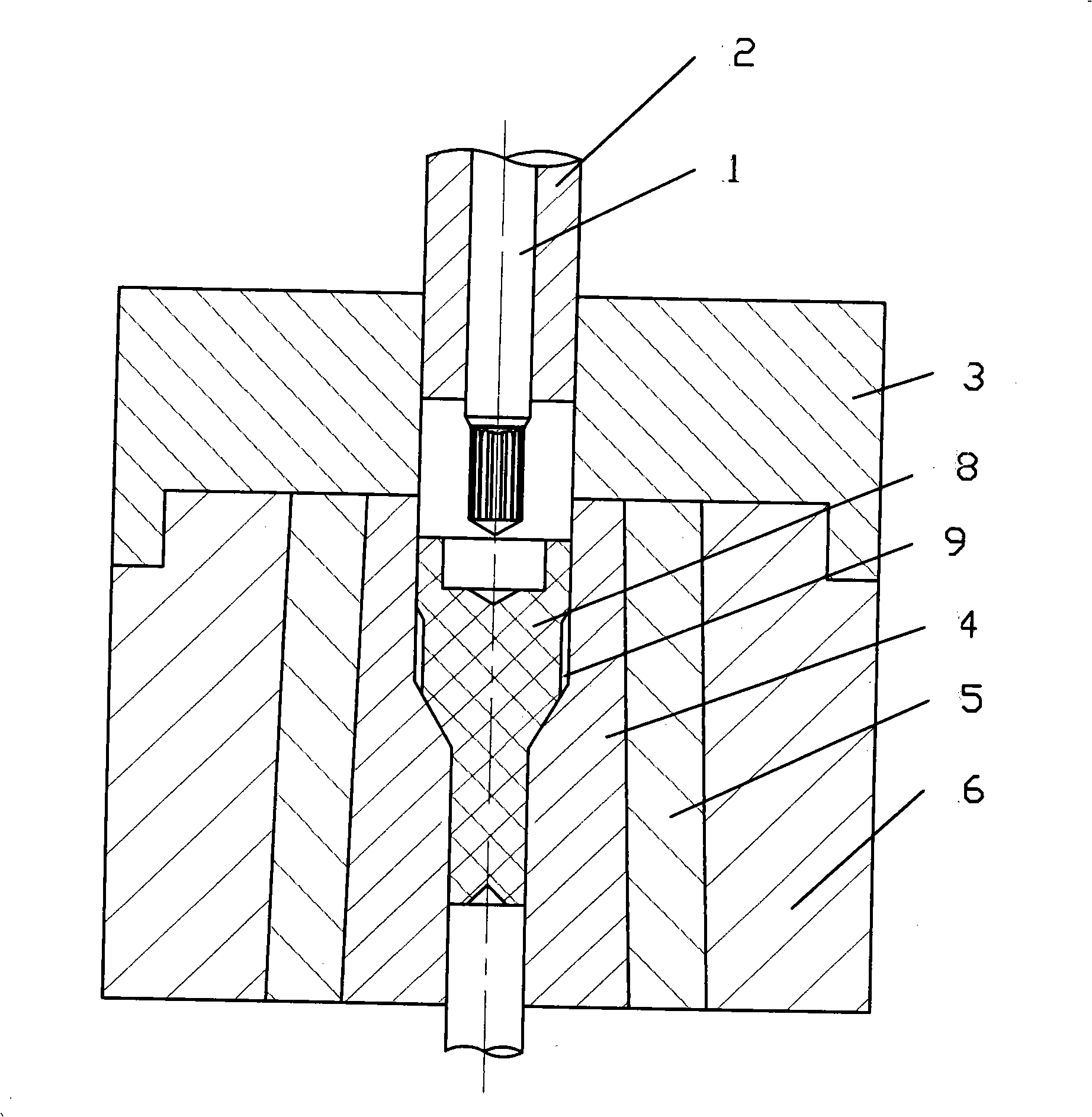
A blind hole is a hole that is reamed, drilled, or milled to a specified depth without breaking through to the other side of the workpiece. A through hole is a hole that is made to go completely through the material of an object. In other words, a through hole is a hole that goes all the way through something. ...
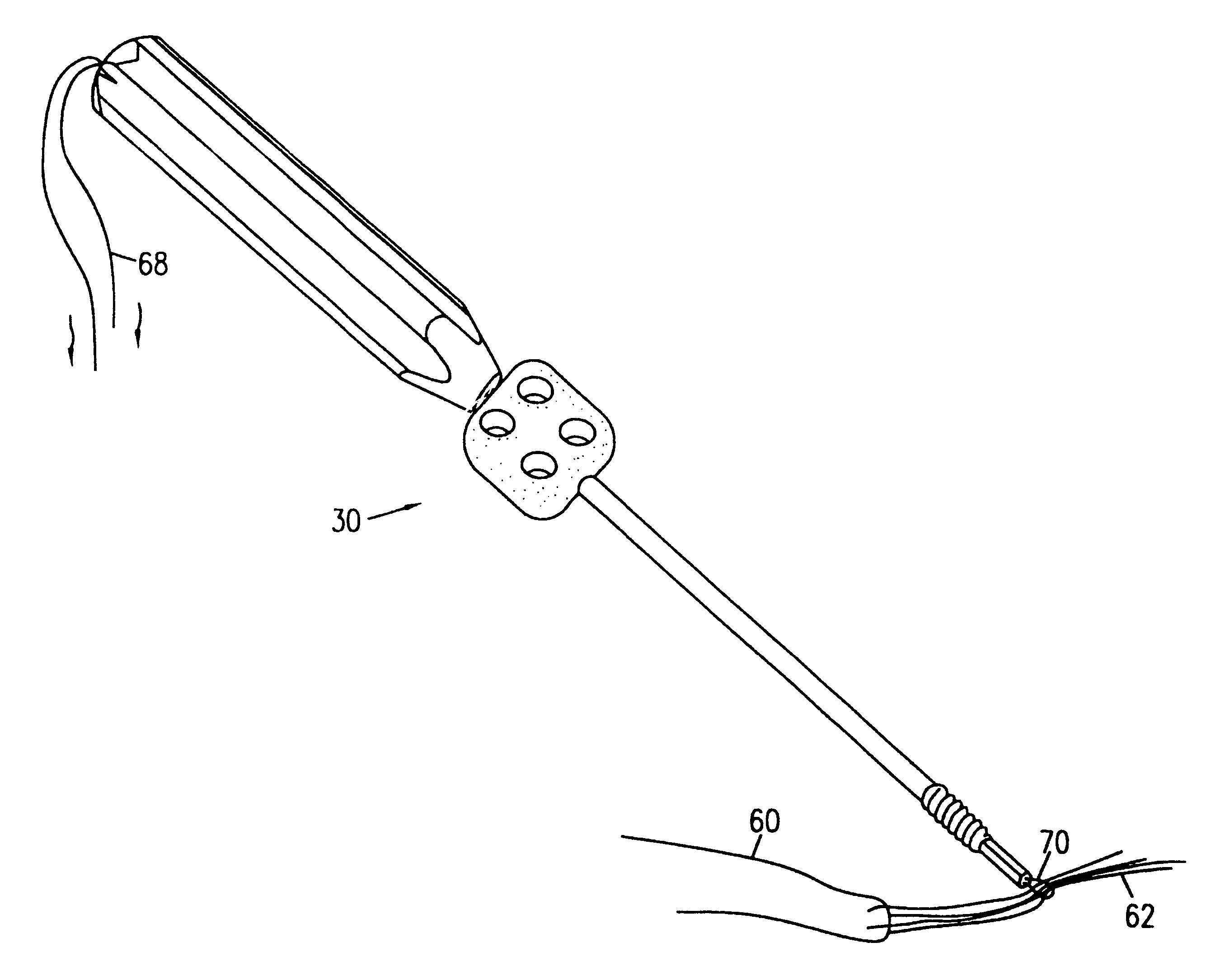
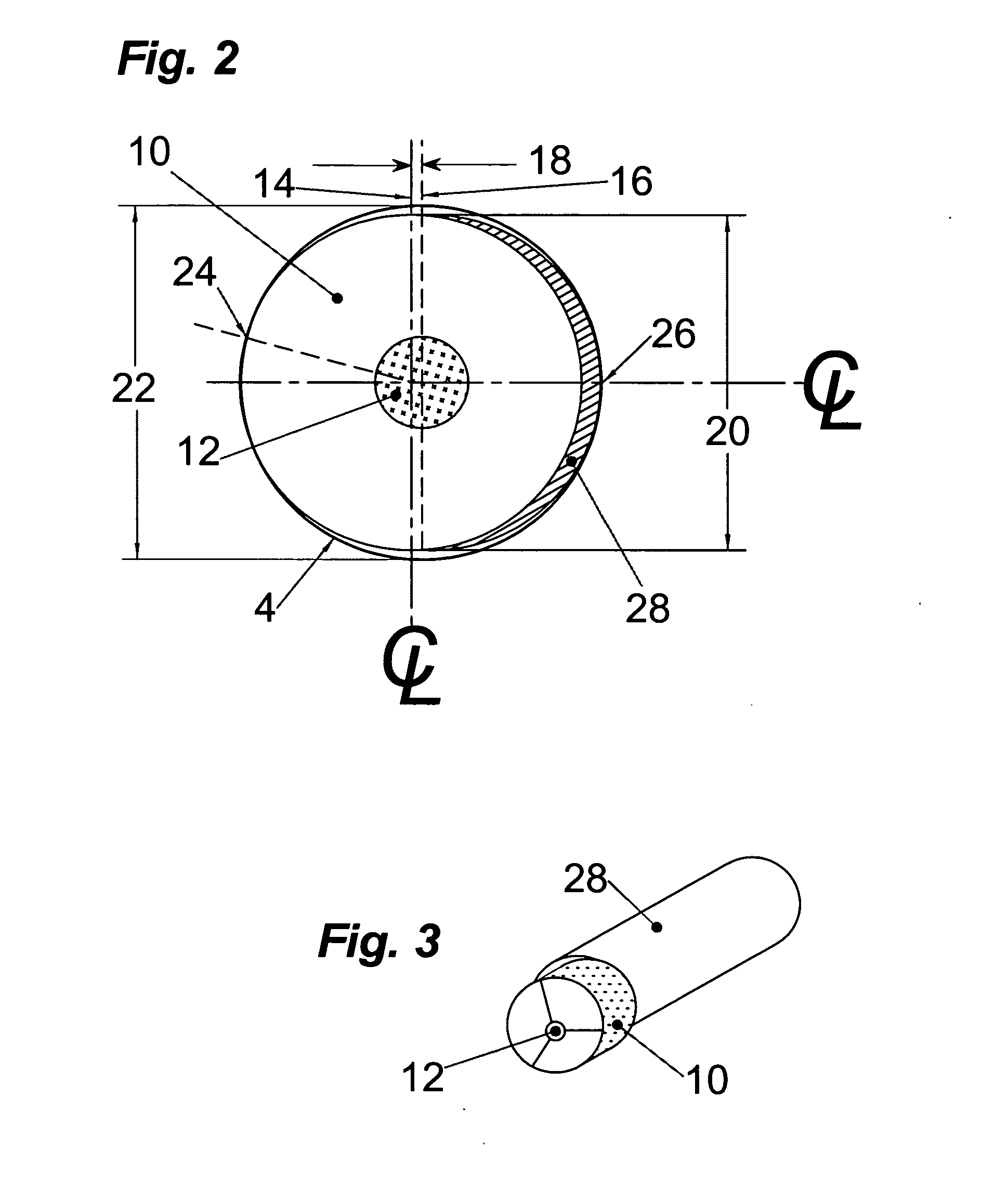
Graft fixation using a screw or plug against suture or tissue
InactiveUS6544281B2Excellent pull-out strengthHigh strengthSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisDistal portionSurgical department
A method for securing soft tissue to bone with excellent pull-out strength which does not require the surgeon to tie suture knots to secure the tissue to the bone. A blind hole or socket is created in the bone at the location the graft is to be secured. Preferably, suture is then passed through the graft at desired points. A cannulated driver is pre-loaded with a cannulated plug or screw slidably disposed onto the distal portion of the driver. In a preferred embodiment, a separate piece of suture is passed through the cannula of the driver with a loop end of that suture exposed at the distal end of the driver. The ends of the suture attached to the graft are fed through the suture loop at the end of the driver. Alternatively, the graft itself may be fed through the suture loop, in which case it is not necessary to attach suture through the graft. In another embodiment, the suture loop exposed at the distal end of the cannula of the driver may be omitted, and the sutures attached to the graft may then be fed through the driver cannula from the distal end to position the graft relative to the driver. The driver is inserted into the hole with the screw or plug just outside the hole. Tension is then placed on the suture. Once adequate tension is achieved on the suture, the driver is pressed into the hole, which engages the first thread or bump of the screw or plug on the bone. The screw or plug is then fully advanced into the hole using the driver. When the screw or plug is fully inserted, the suture loop is freed and the driver is removed. The loose ends of the sutures protruding from the anchor site can be cleaned up by clipping them short.
Owner:ARTHREX
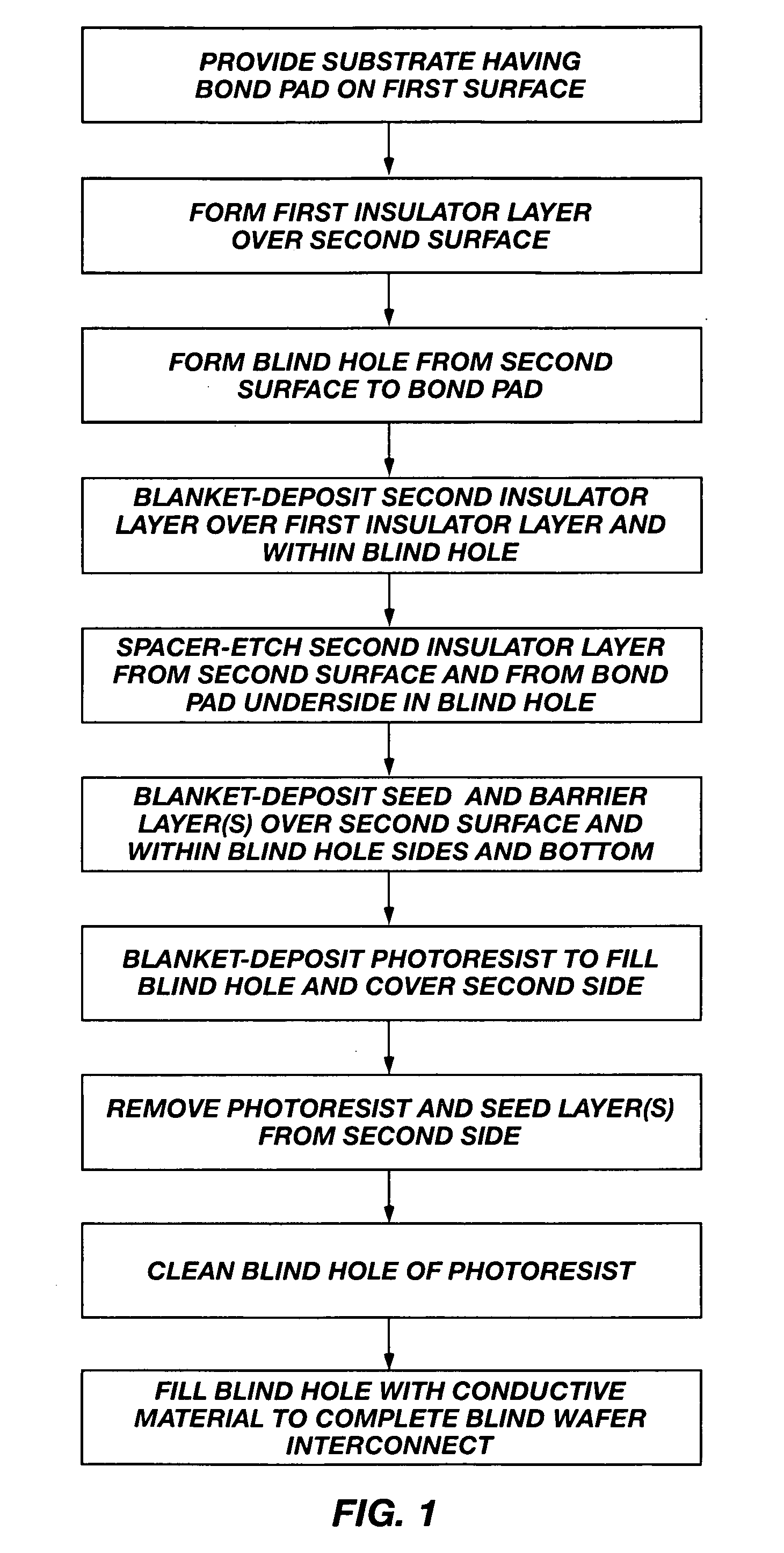
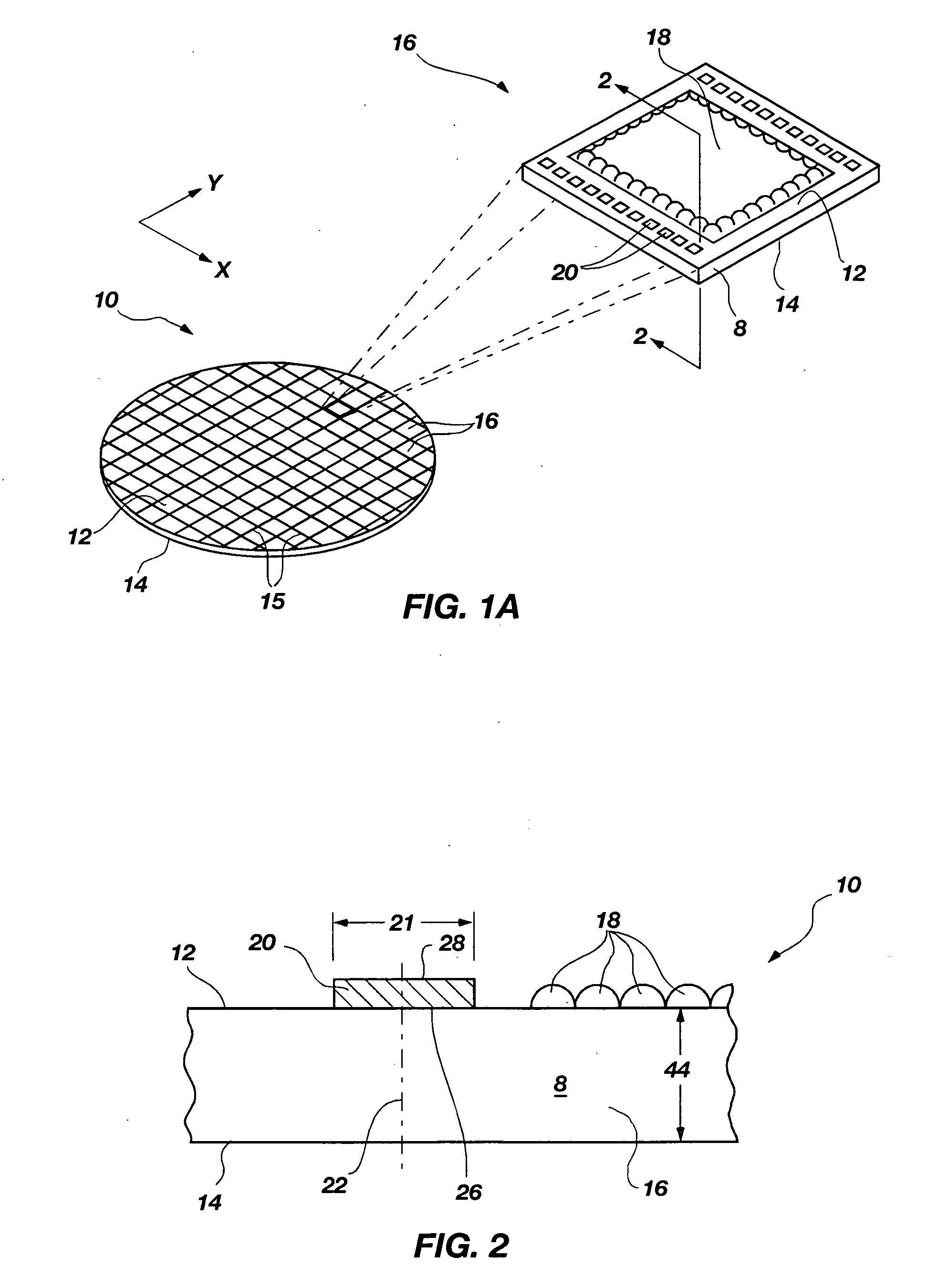
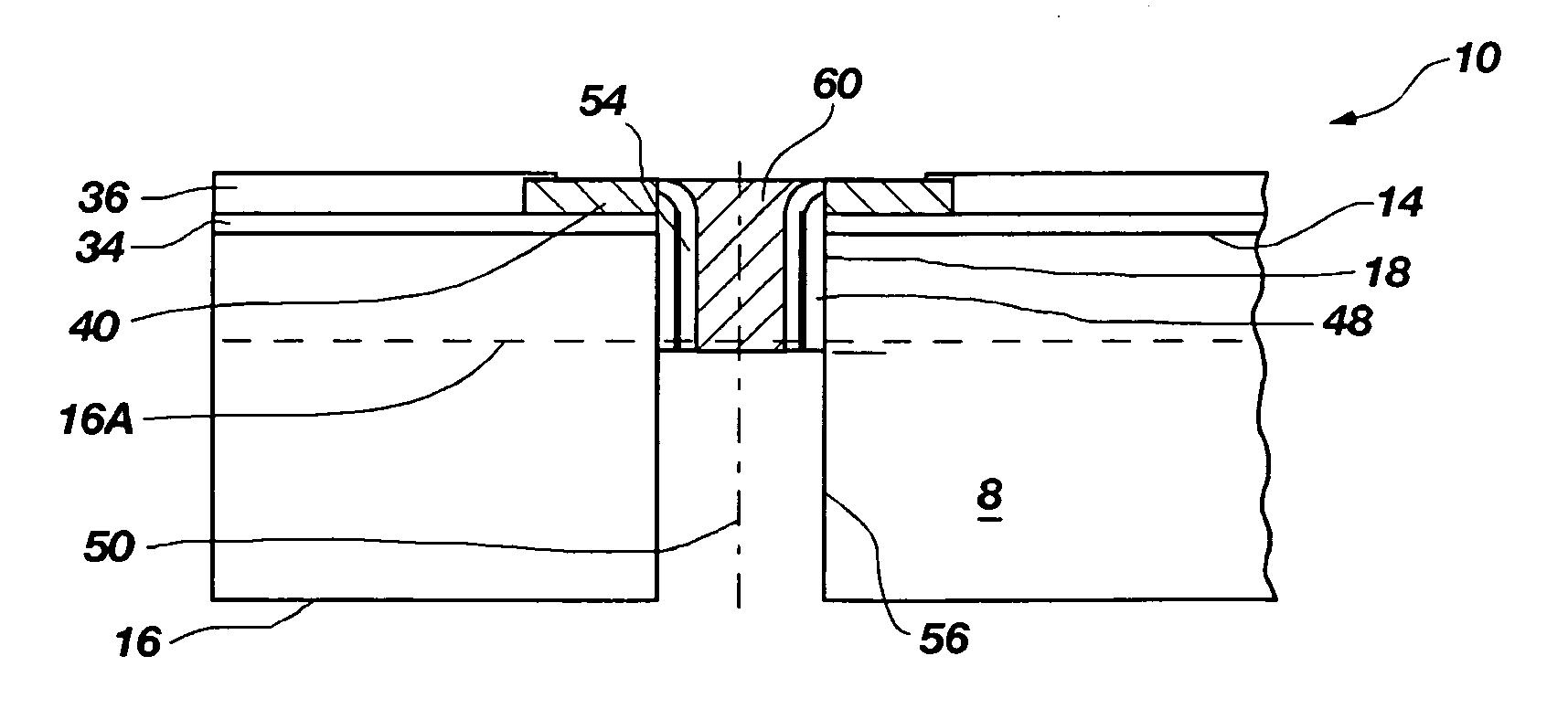
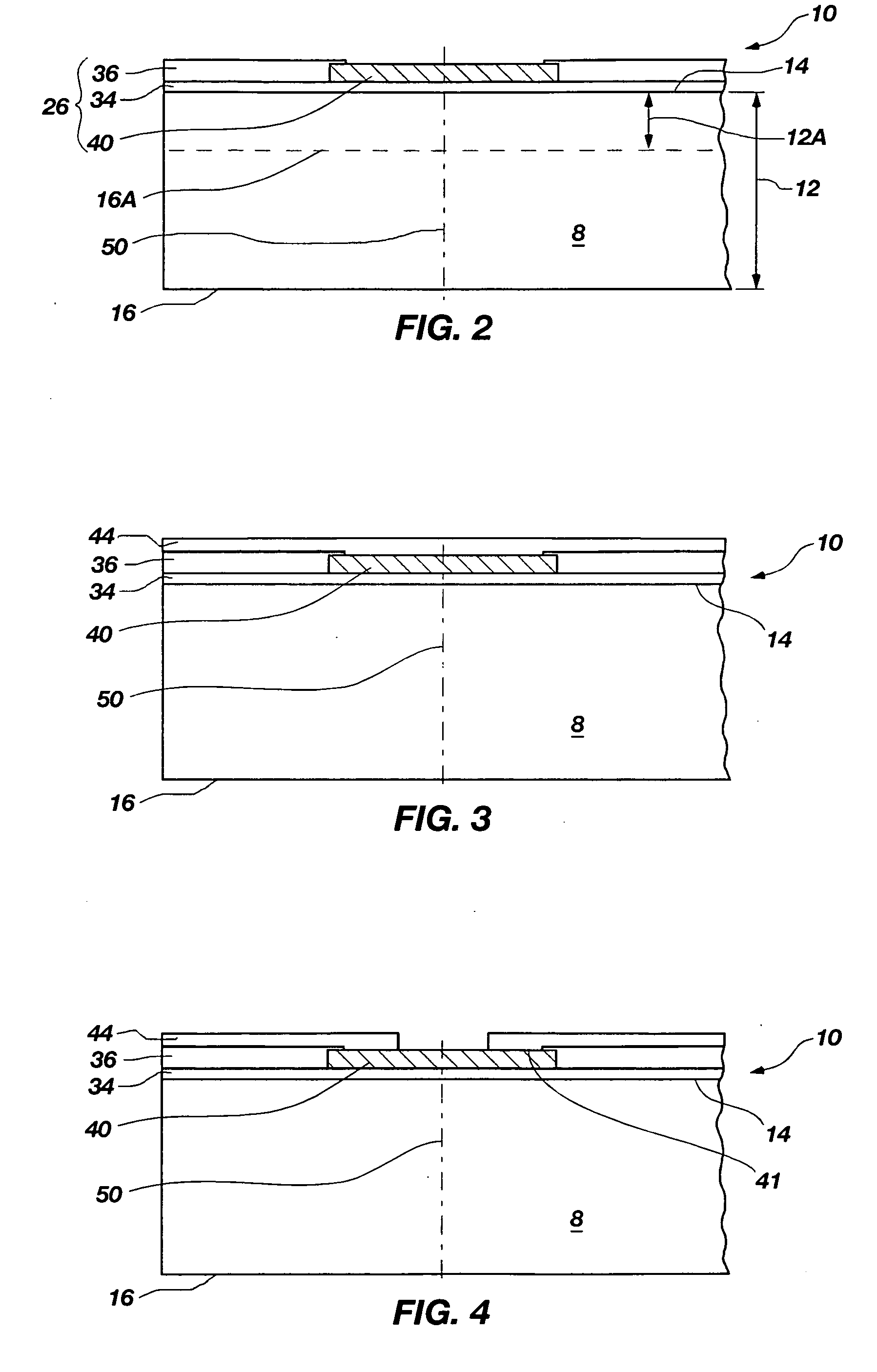
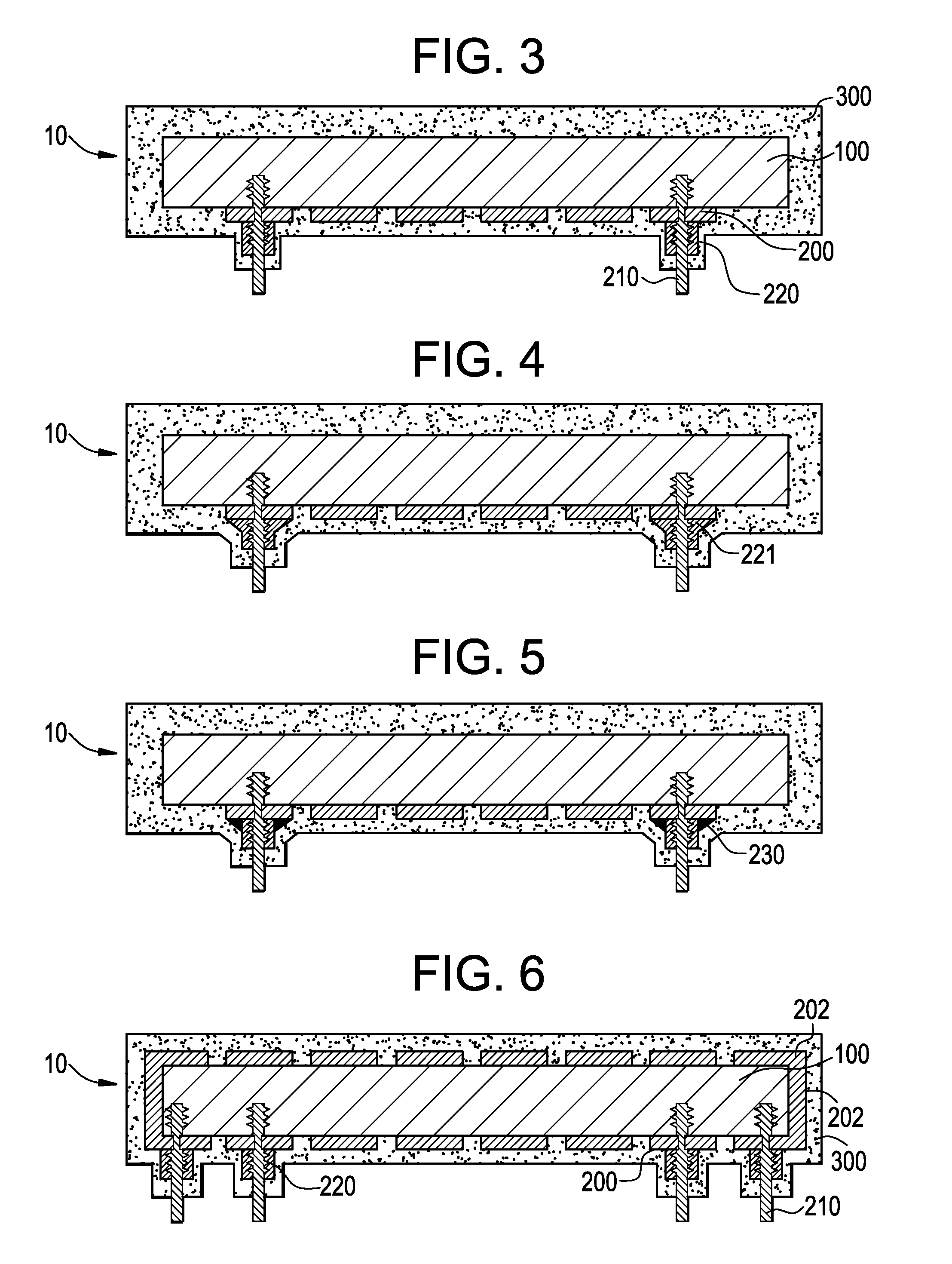
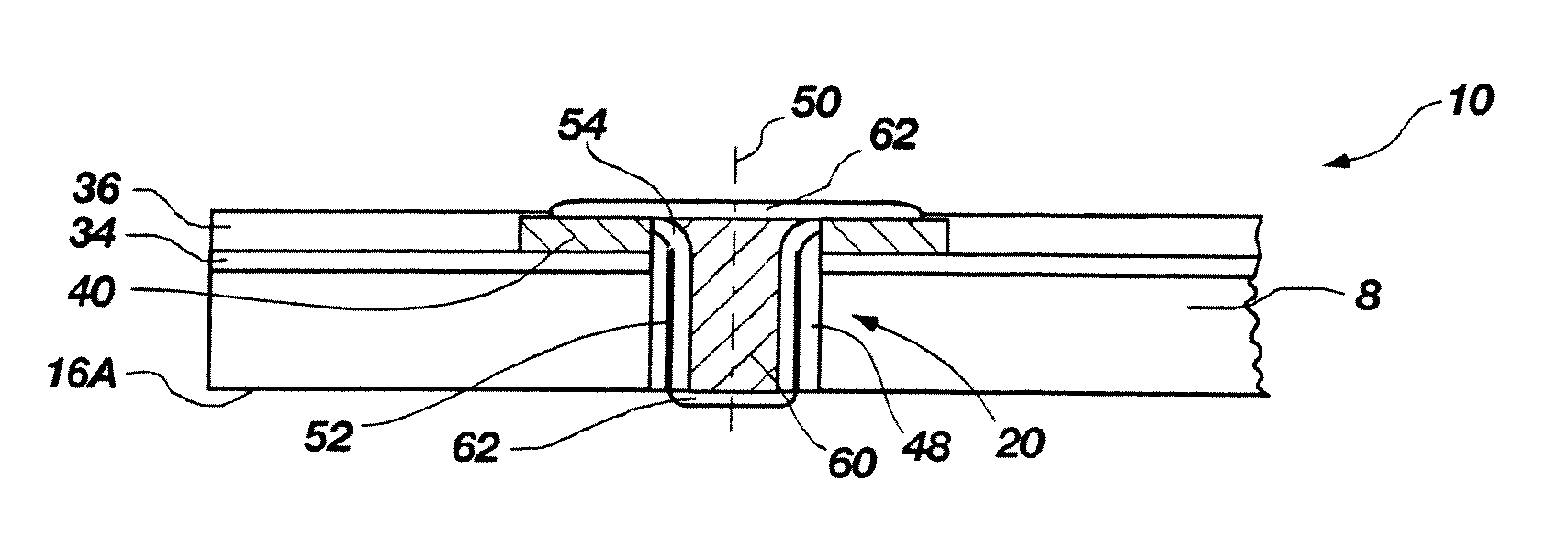
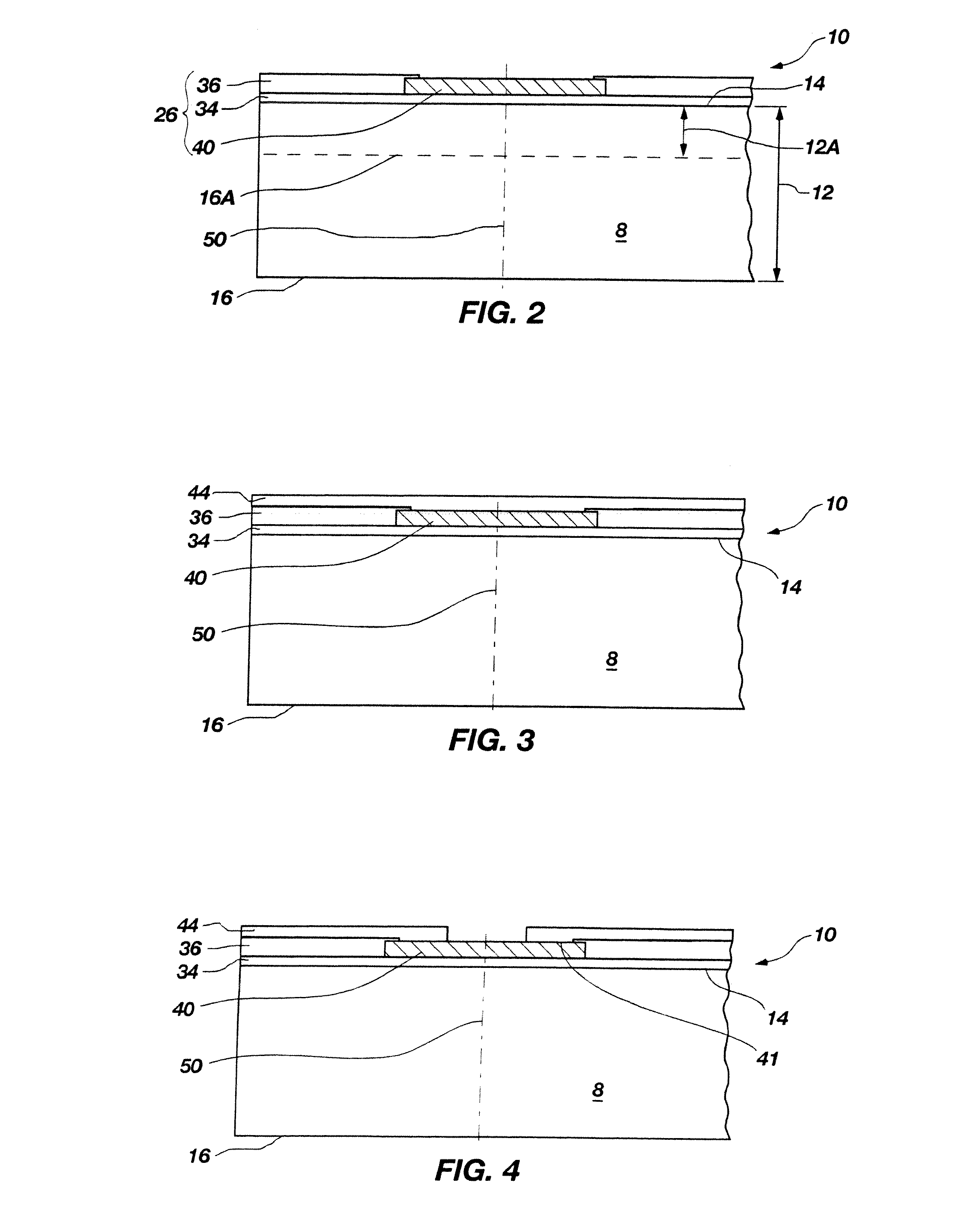
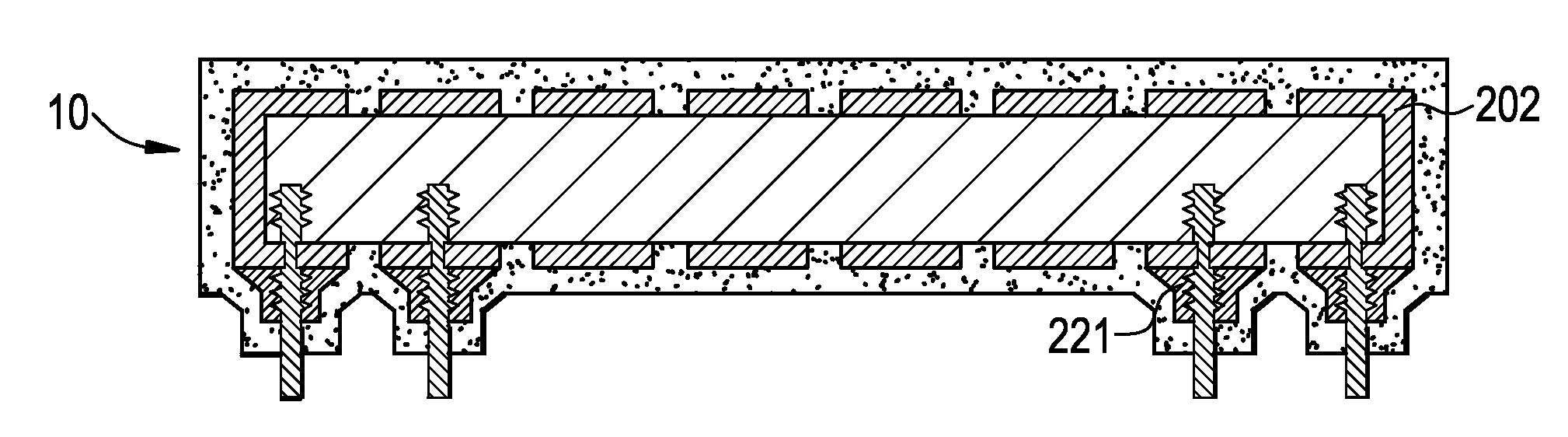
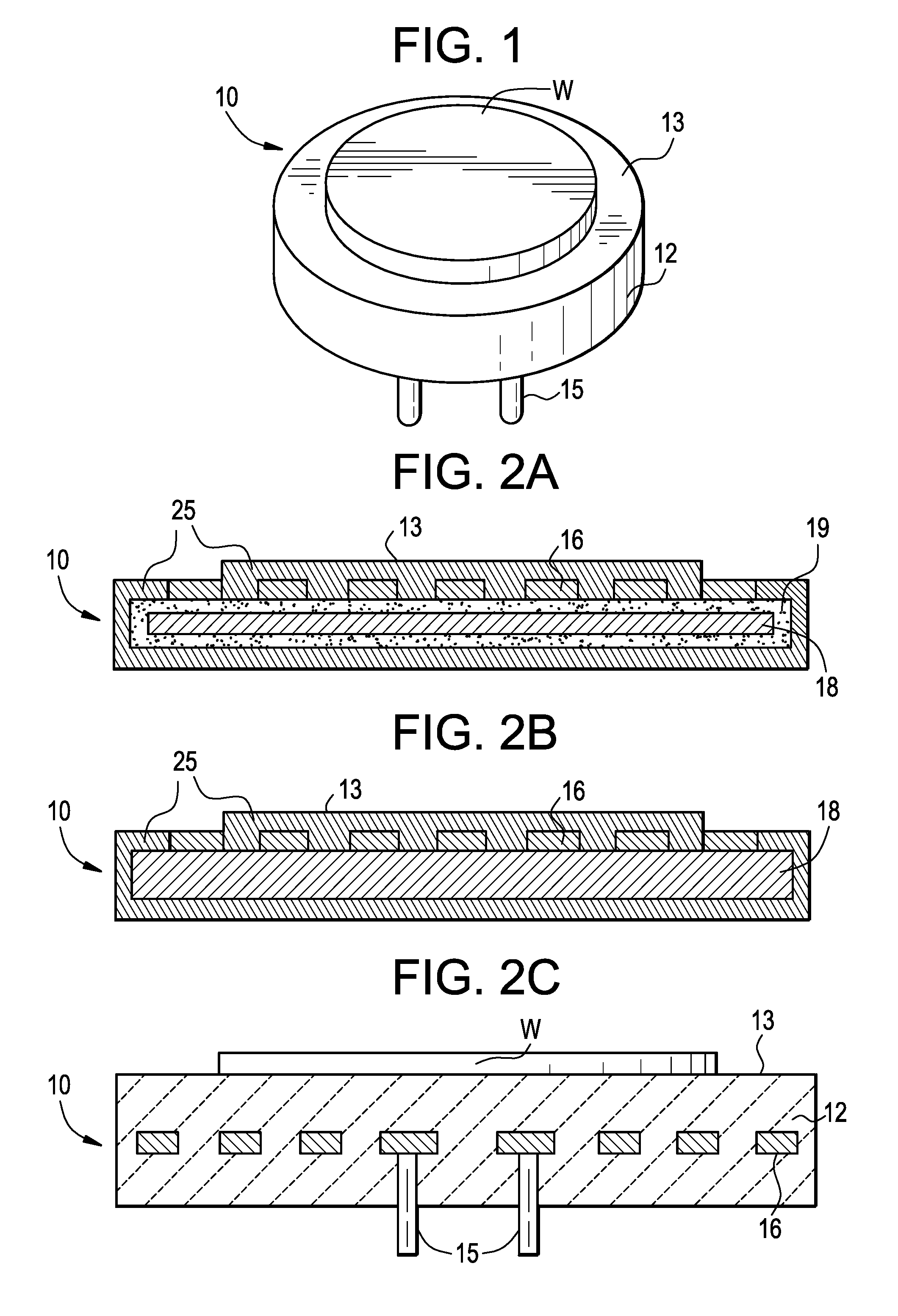
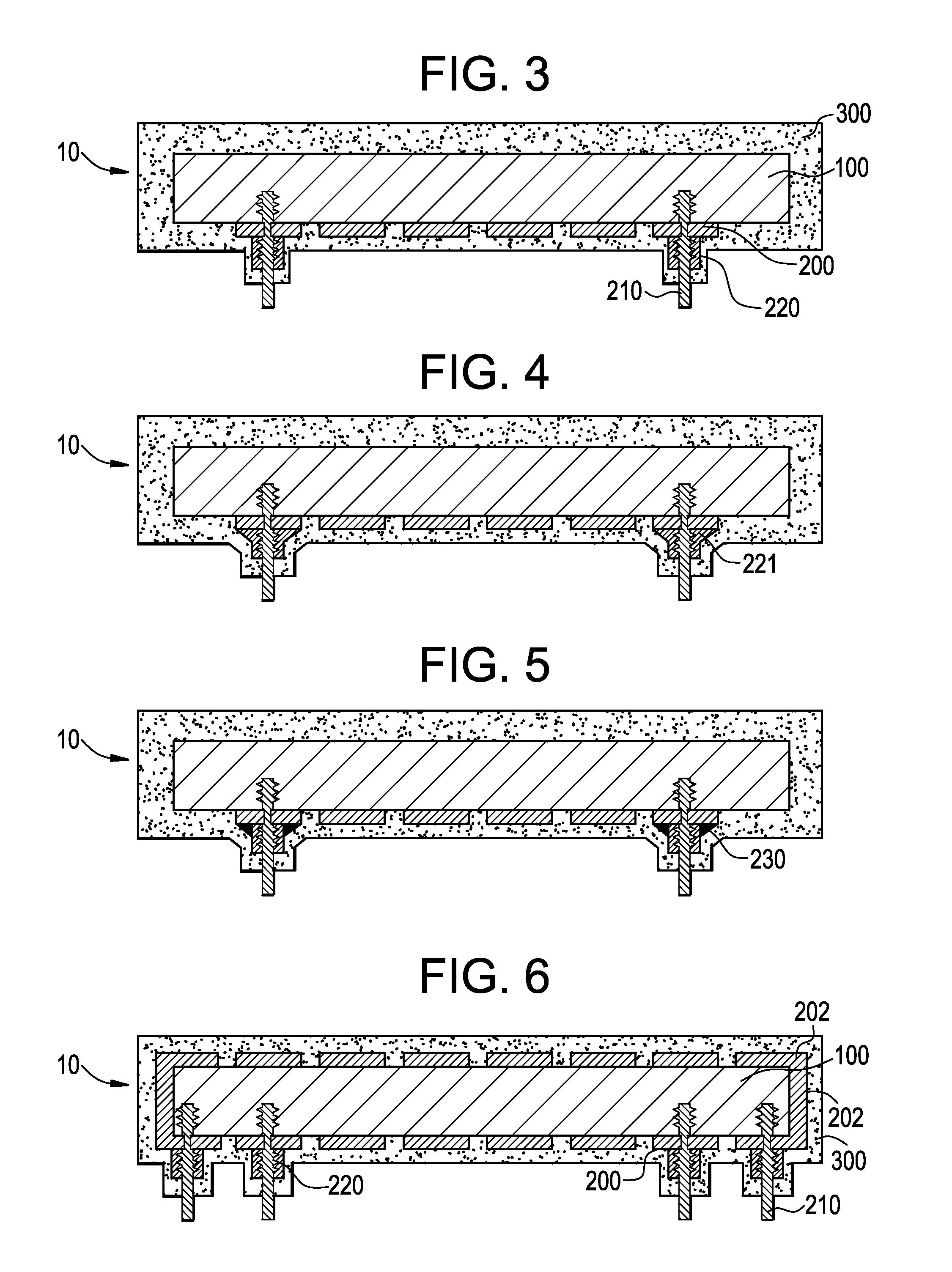
Methods of forming blind wafer interconnects, and related structures and assemblies
InactiveUS20070045780A1Reduce expensesReduce processing timeSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesResistSolder ball
Methods for forming blind wafer interconnects (BWIs) from the back side of a previously thinned substrate structure such as a semiconductor wafer to the underside of a bond pad on its active surface includes the formation of a blind hole from the back side, application of a passivating layer therein, anisotropically etching to remove passivation material from the blind hole bottom, blanket-depositing at least one conductive layer within the blind hole and over the back side, blanket-depositing a resist in the blind hole and over the back side, planarizing the back side to remove resist and the at least one conductive layer, removing resist from the blind hole, and filling the blind hole with solder or other conductive material or a dielectric material. Variations in the methods include formation of a conductive pad adjacent the back side surface, disposition of a solder ball or other conductive structure on the BWI, or forming an end thereof in the form of an extended slug protruding from the back side (for ball-less attachment) as the outer terminus of the BWI.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
Methods for forming through-wafer interconnects, intermediate structures so formed, and devices and systems having at least one solder dam structure
ActiveUS20070045779A1Conveniently attachedEliminate cross-contaminationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesVitrificationDevice material
A method for forming through-wafer interconnects (TWI) in a substrate of a thickness in excess of that of a semiconductor die such as a semiconductor wafer. Blind holes are formed from the active surface, sidewalls thereof passivated and coated with a solder-wetting material. A vent hole is then formed from the opposite surface (e.g., wafer back side) to intersect the blind hole. The blind hole is solder filled, followed by back thinning of the vent hole portion of the wafer to a final substrate thickness to expose the solder and solder-wetting material at both the active surface and the thinned back side. A metal layer such as nickel, having a glass transition temperature greater than that of the solder, may be plated to form a dam structure covering one or both ends of the TWI including the solder and solder-wetting material to prevent leakage of molten solder from the TWI during high temperature excursions. Intermediate structures of semiconductor devices, semiconductor devices and systems are also disclosed.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
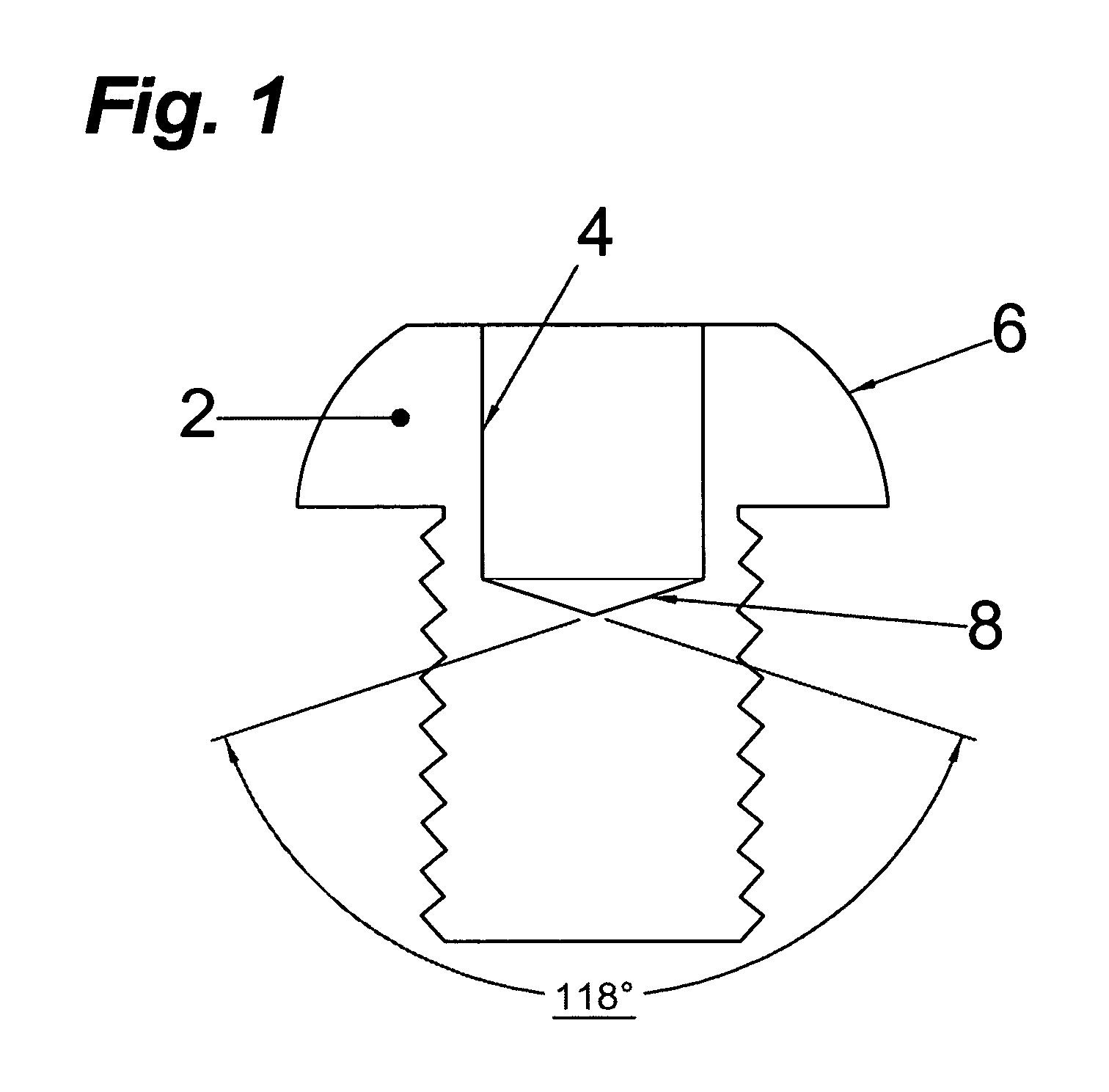
Torque-setting, tamper-resistant fastener and method and tool for use with same
A fastener includes a round, blind hole or pocket in its head. Installation and removal of the fastener is accomplished with a tool containing an eccentric segment on the end of a shaft. When rotated within the pocket, the eccentric segment displaces laterally relative to the shaft to provide a friction grip to the lateral wall of the pocket. The strength of the grip is proportional to the applied torque. Eccentric displacement allows rotation but prevents the tool from spinning out of the fastener thereby eliminating cam-out and surface damage resulting from contact with a spinning tool tip. The eccentric head of the tool can be made disposable and to shear off when a predetermined torque is reached. The smooth-sided round hole offers no purchase for commonly available tools; making the fastener tamper-resistance. In another embodiment, the fastener includes a raised portion in the pocket. A tool having a complementary opening shears off the raised portion at a predetermined torque.
Owner:FLESHER ROBERT W
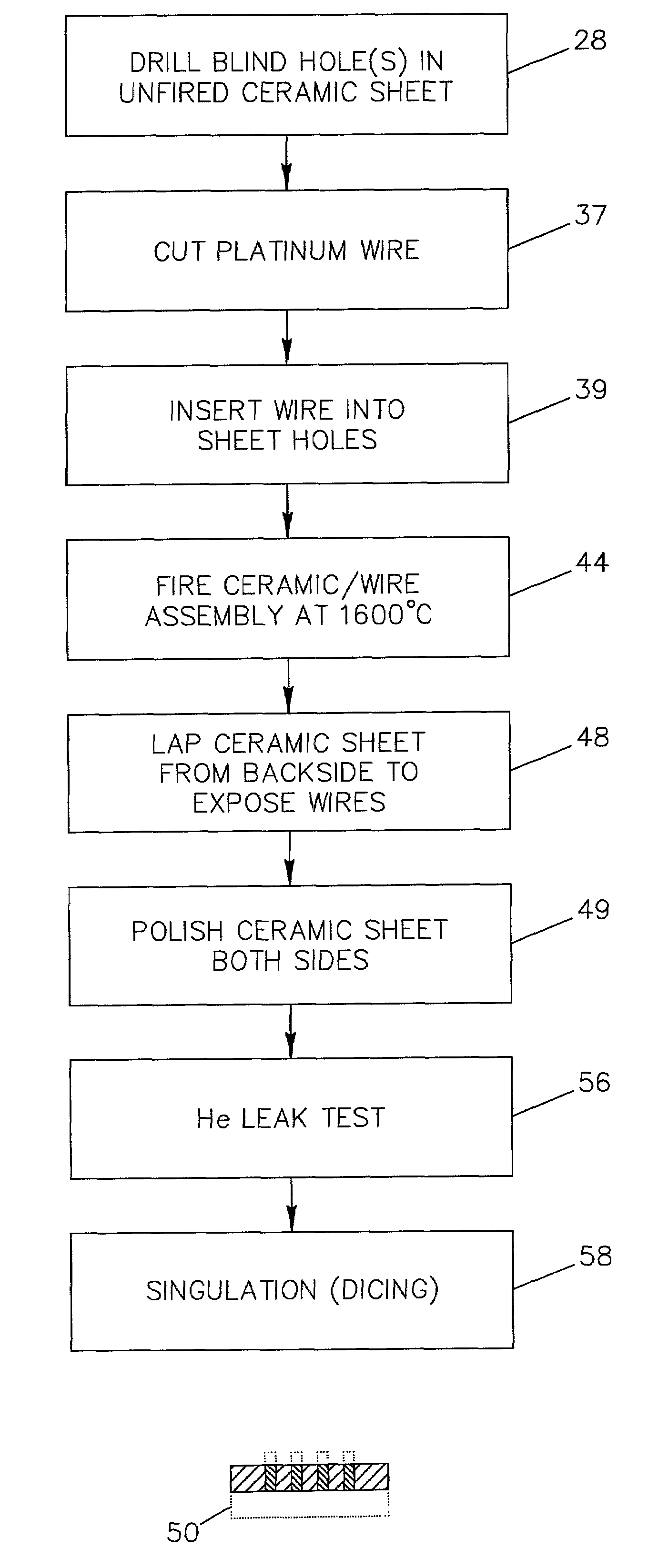
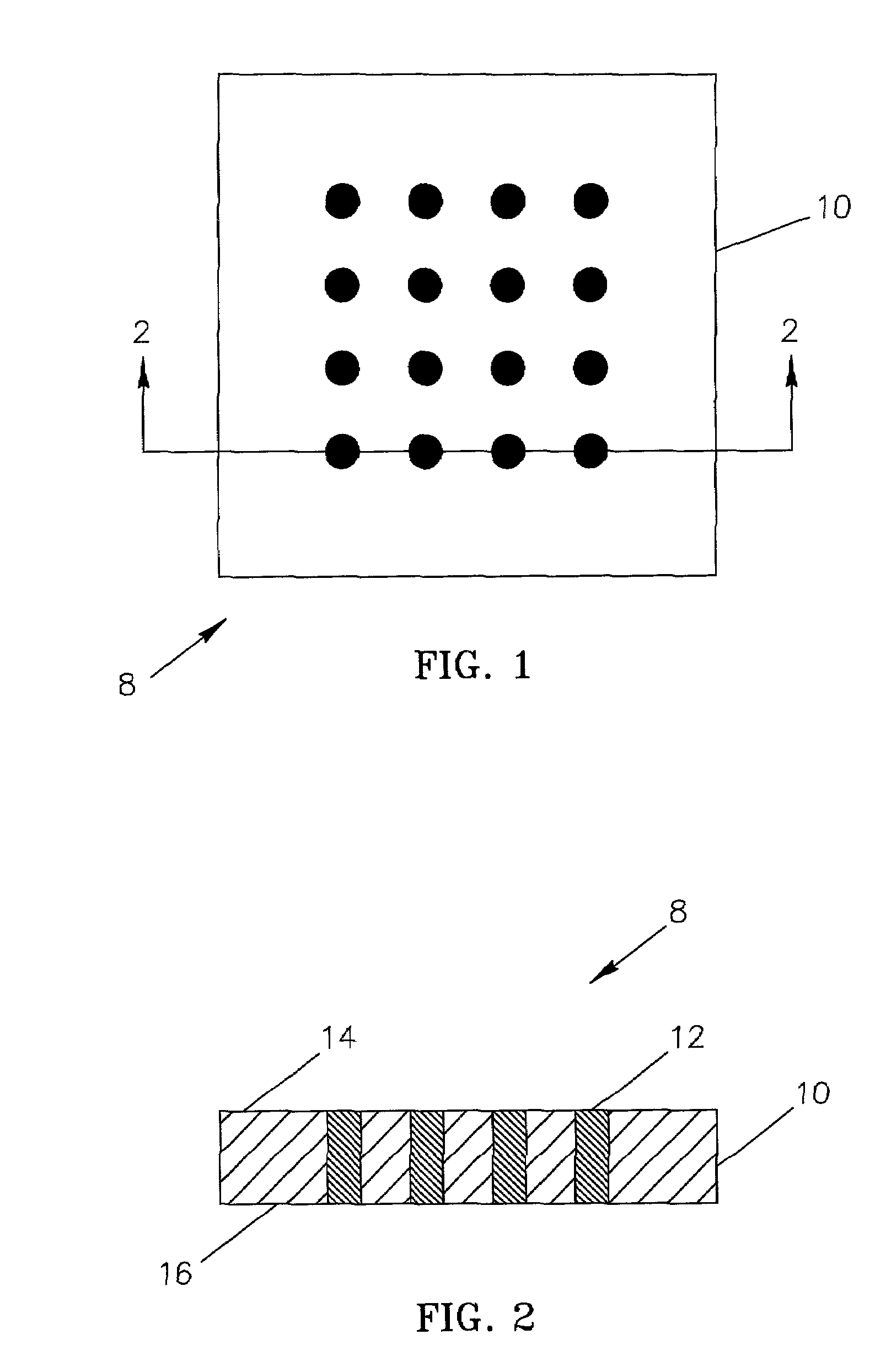
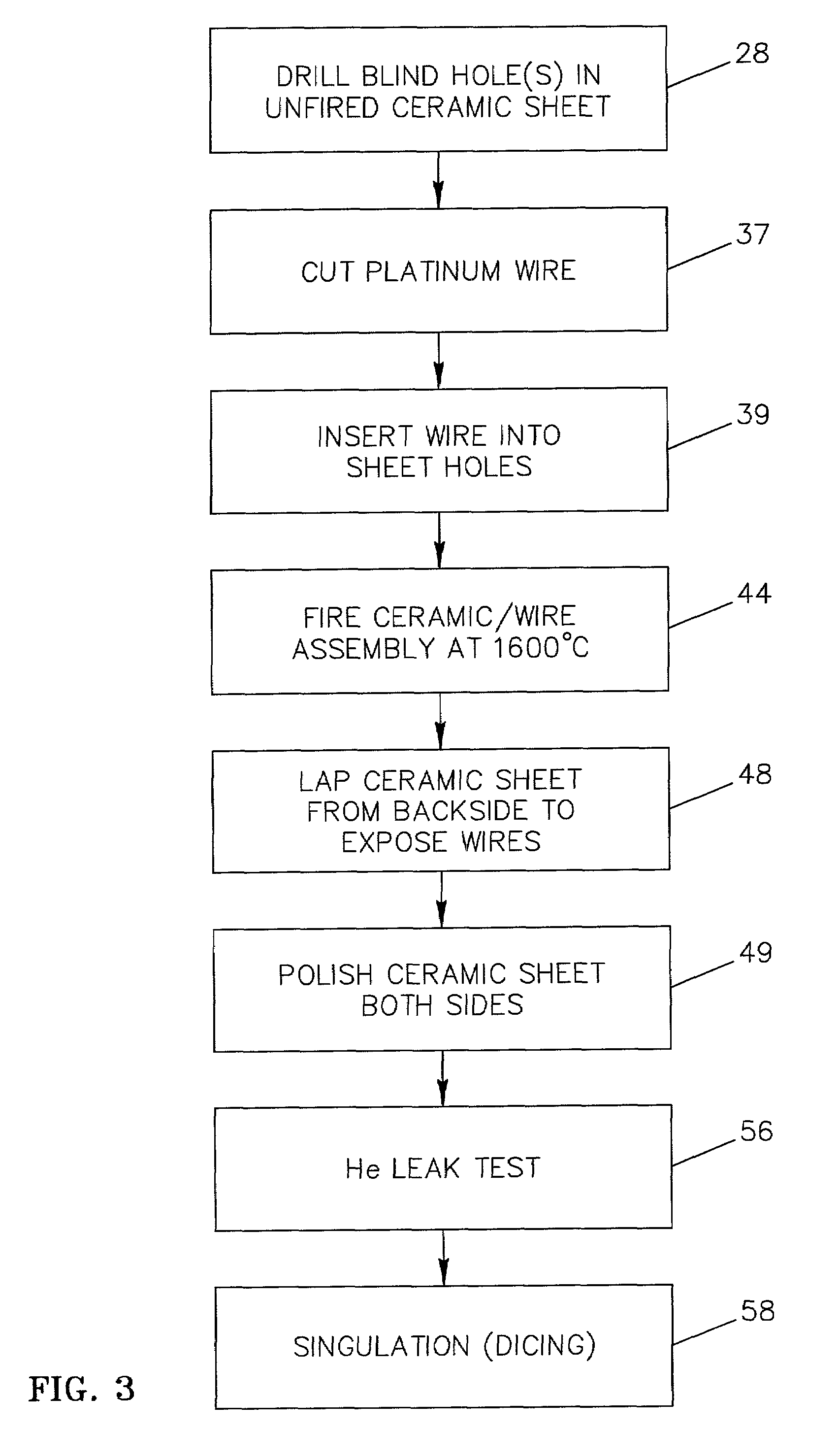
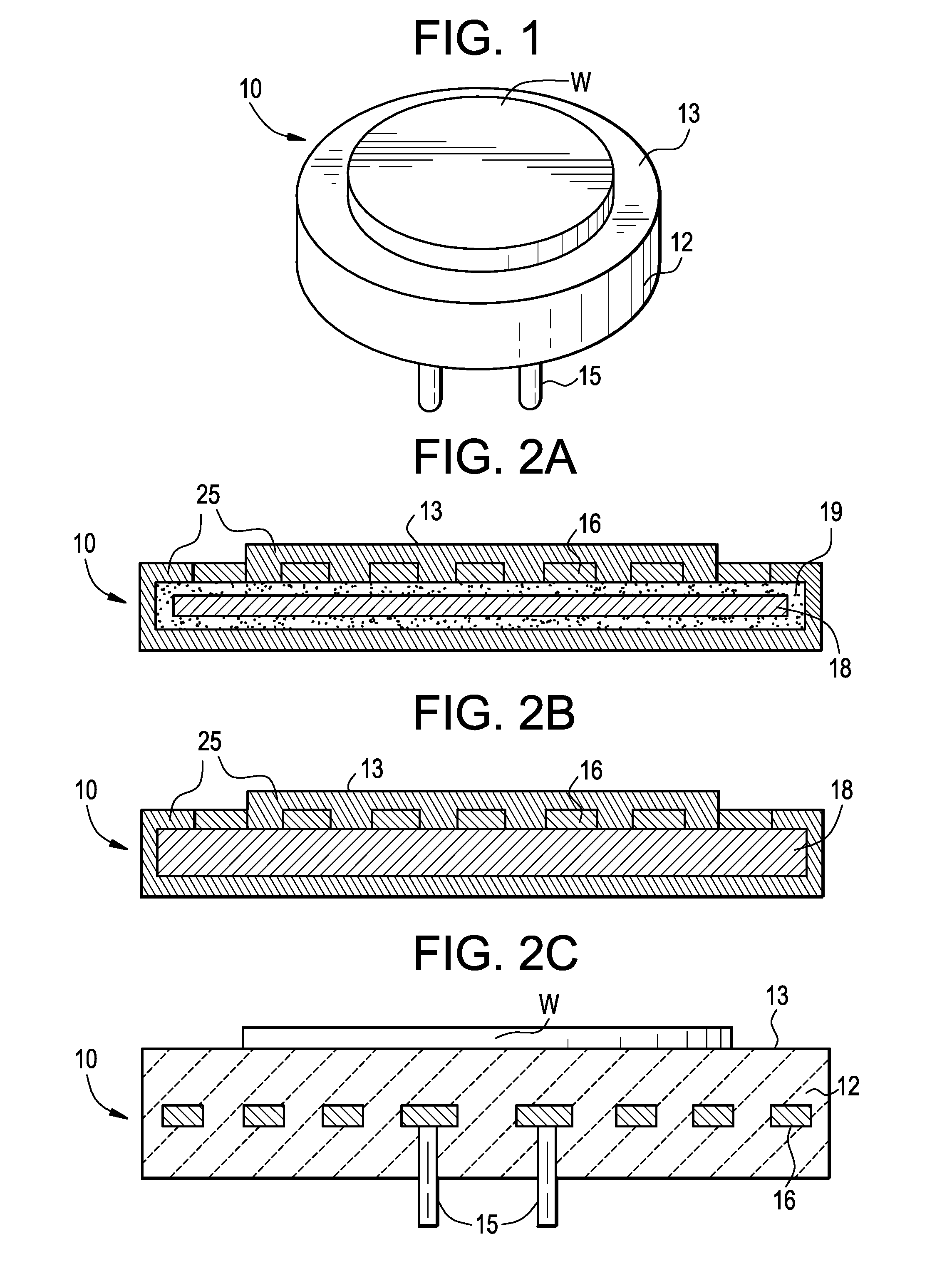
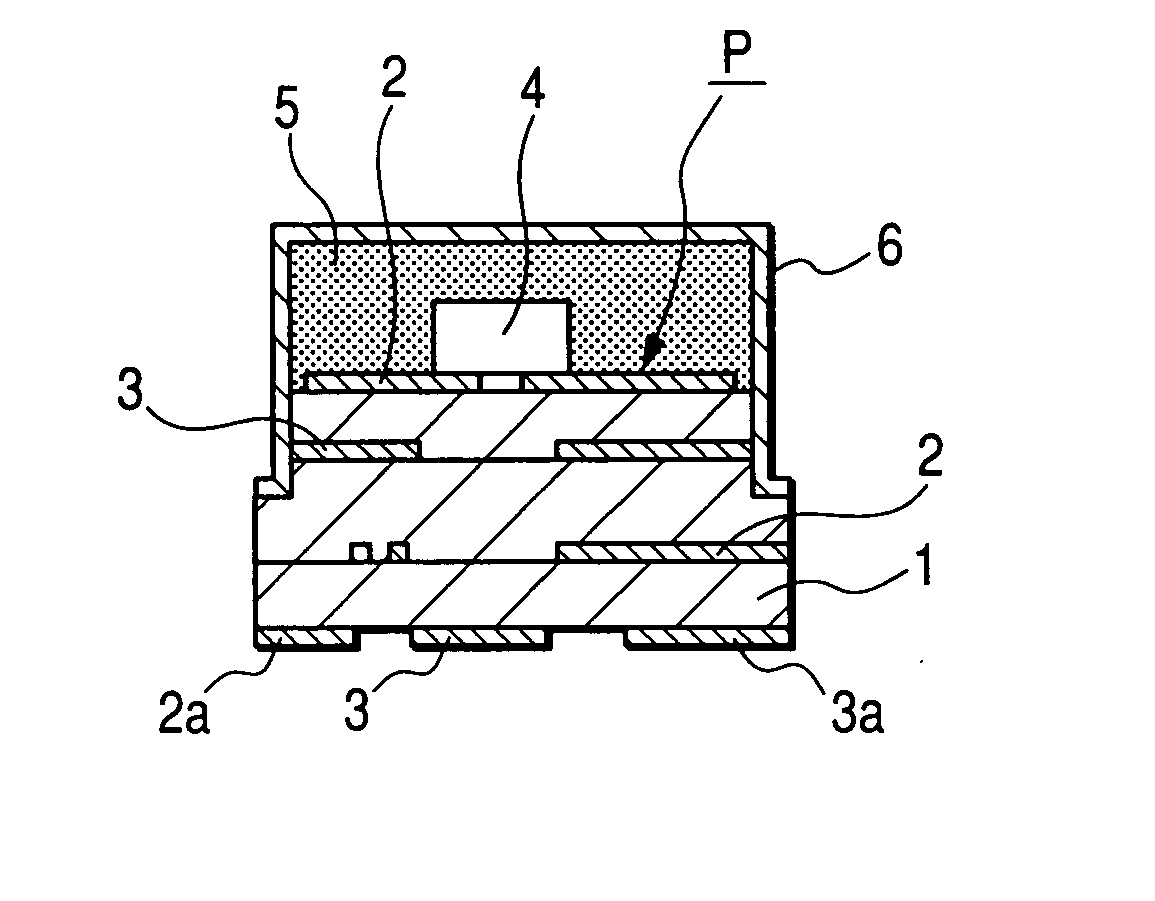
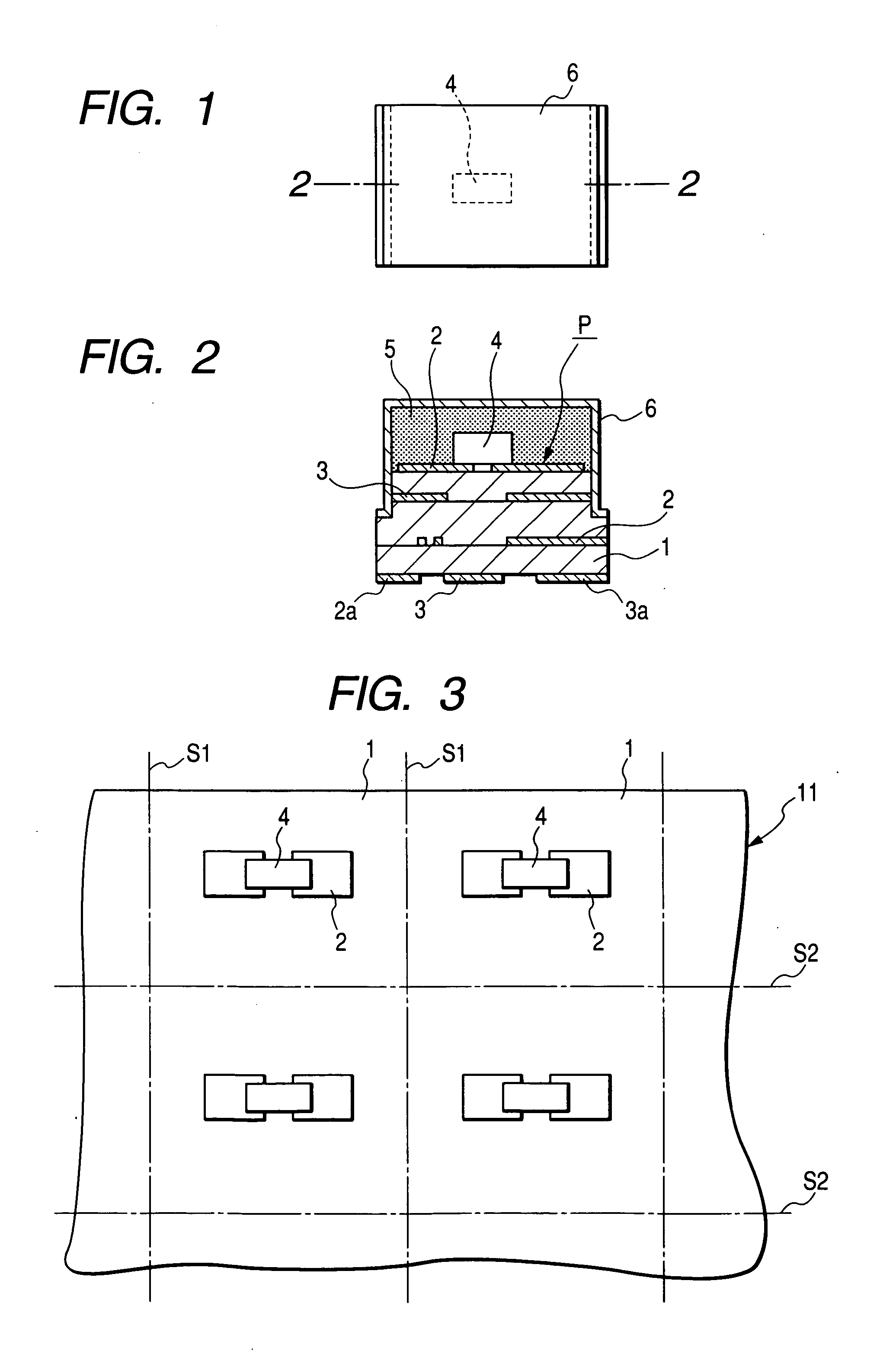
Method and apparatus for providing hermetic electrical feedthrough
A method and apparatus suitable for forming hermetic electrical feedthroughs in a ceramic sheet having a thickness of ≦40 mils. More particularly, the method yields an apparatus including a hermetic electrical feedthrough which is both biocompatible and electrochemically stable and suitable for implantation in a patient's body. The method involves:(a) providing an unfired, ceramic sheet having a thickness of ≦40 mils and preferably comprising >99% aluminum oxide;(b) forming multiple blind holes in said sheet;(c) inserting solid wires, preferably of platinum, in said holes;(d) firing the assembly of sheet and wires to a temperature sufficient to sinter the sheet material but insufficient to melt the wires; and(e) removing sufficient material from the sheet lower surface so that the lower ends of said wires are flush with the finished sheet lower surface.
Owner:SECOND SIGHT MEDICAL PRODS
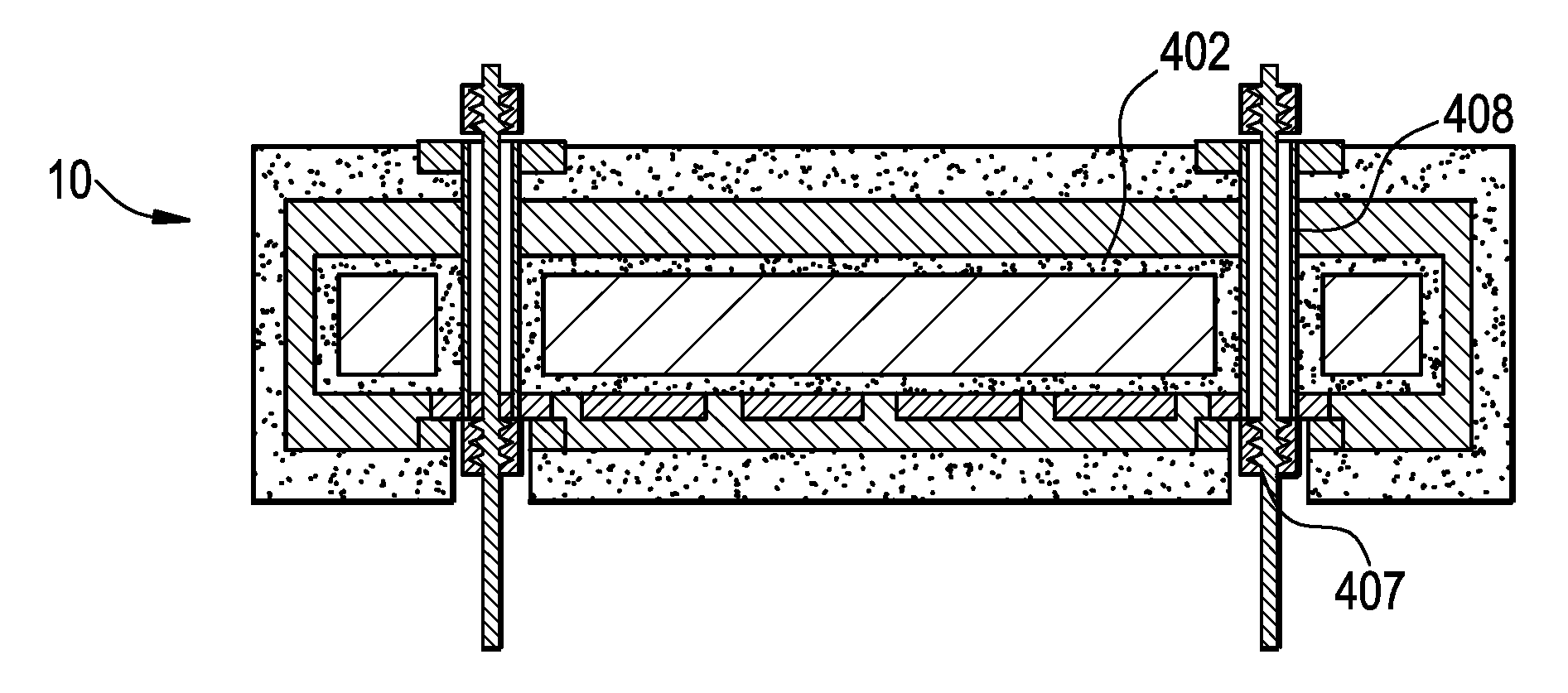
Corrosion resistant wafer processing apparatus and method for making thereof
InactiveUS20080016684A1Line/current collector detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical connectionWadding
A wafer processing apparatus characterized by having corrosion resistant connections for its electrical connections, gas feed-through channels, recessed areas, raised areas, MESA, through-holes such as lift-pin holes, threaded bolt holes, blind holes, and the like, with the special configurations employing connectors and fillers having excellent chemical resistant properties and optimized CTEs, i.e., having a coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) that closely matches the CTE of the base substrate layer, the electrode(s), as well as the CTE of coating layer. In one embodiment, a nickel plated molybdenum insert is employed.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Novel magnetic mechanical anti-theft lock
The invention provides a novel magnetic mechanical anti-theft lock which comprises a wafer type key, a lock core rotor and a lock shell, and the wafer type key comprises a wafer; at least six magnetic blocks are arranged in the wafer, and the lock core rotor is a T-shaped cylinder on the appearance, and matches with the lock shell in a contacting way; a second magnetic spring blind hole and a magnetic spring are arranged in the position where the lock core rotor corresponds to the magnetic blocks, and the magnetic spring and the corresponding magnetic block are mutually repellent in terms of magnetism; an iron spring is respectively arranged in the position where the lock shell corresponds to the magnetic spring, and part of the iron spring convexly extends to the blind hole of the second magnetic spring; the bottom of the iron spring is also connected with a return spring, and the lock core fixing hole accommodates the narrow part of the lock core rotor. As the lock core of the lock has no key hole, destruction by tools such as a bolt driver, a screwdriver and the like can be prevented; besides, the key of the lock can not be easily duplicated, and the lock has multiple anti-theft functions, elegant appearance, strong invisibility and higher security.
Owner:泉州市科安盾智能锁业有限公司
Method of manufacturing shielded electronic circuit units
InactiveUS7478474B2Printed circuit assemblingMagnetic/electric field screeningEngineeringElectronic component
A metallic film and a grounding pattern are surely connected to each other so as to achieve electrical shield of an electronic circuit unit. In an electronic circuit unit, the metallic film is provided on a top surface of a sealing resin portion for burying an electronic component, the side surfaces of the sealing resin portion that are opposite to each other, and the side surfaces of the multi-layered substrate that are opposite to each other. The metallic film is connected to the grounding patterns that are provided on the top surface of the multi-layered substrate or between the laminated layers of the multi-layered substrate. Therefore, it is possible to achieve a superior electrical shielding effect through the metallic film, as compared with the related art. Since the metallic film is formed on the side surfaces of the sealing resin and the side surfaces of the multi-layered substrate, when the metallic film is formed by a plating method, the blind hole may not be provided in the related art. Therefore, it is possible to achieve the superior circulation of the plating liquid, which results in sure connection between the sure connection between the grounding pattern and the metallic film.
Owner:ALPS ALPINE CO LTD
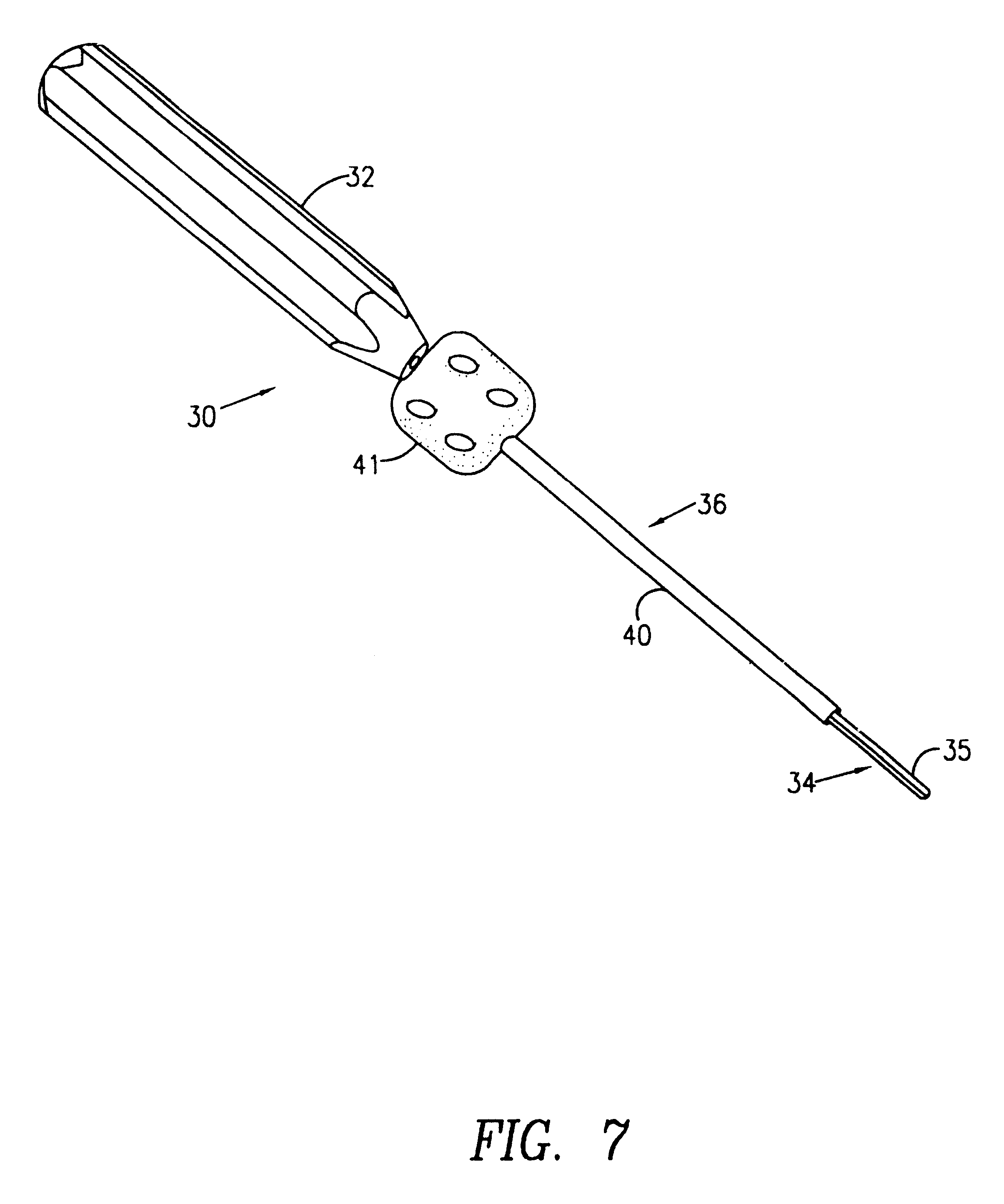
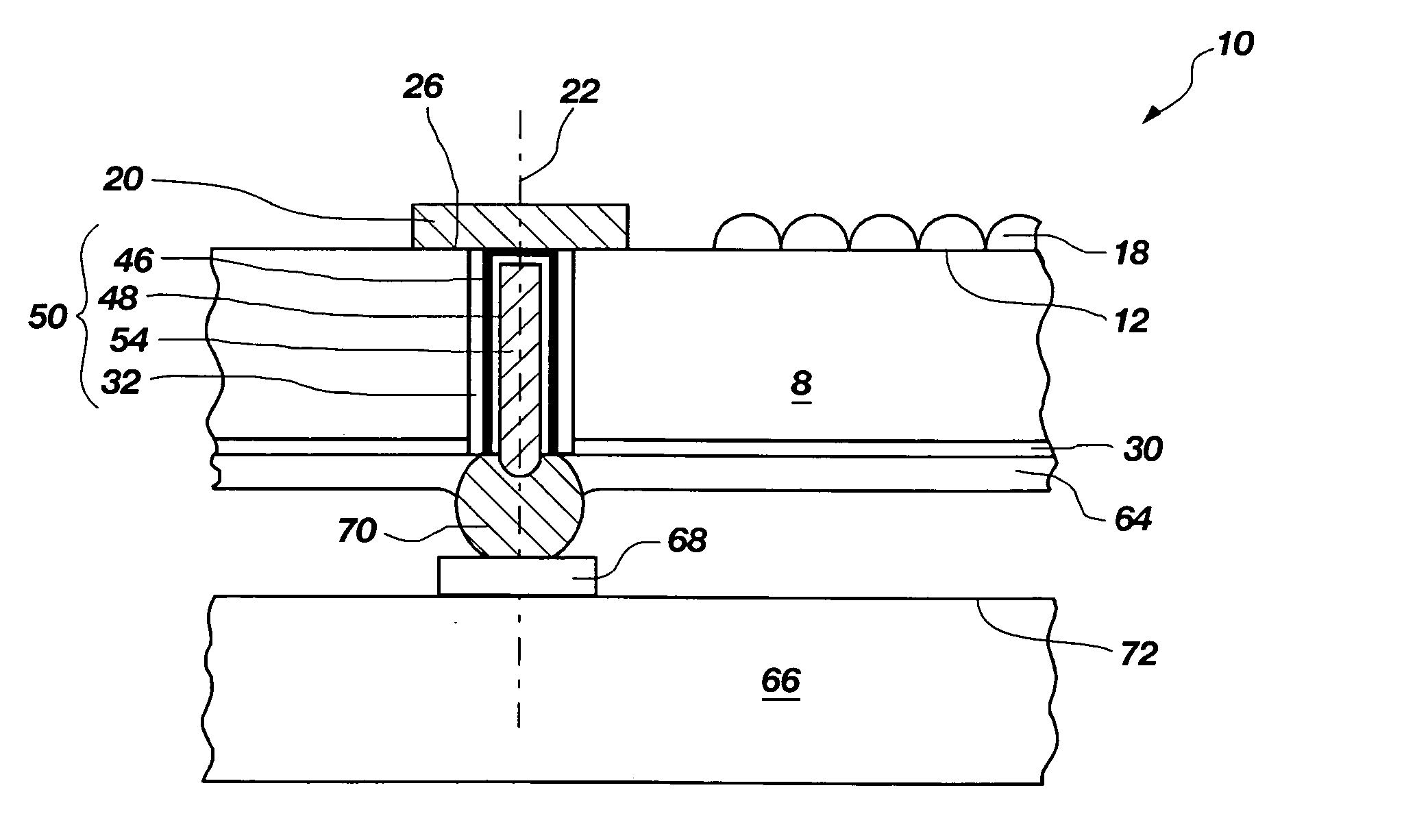
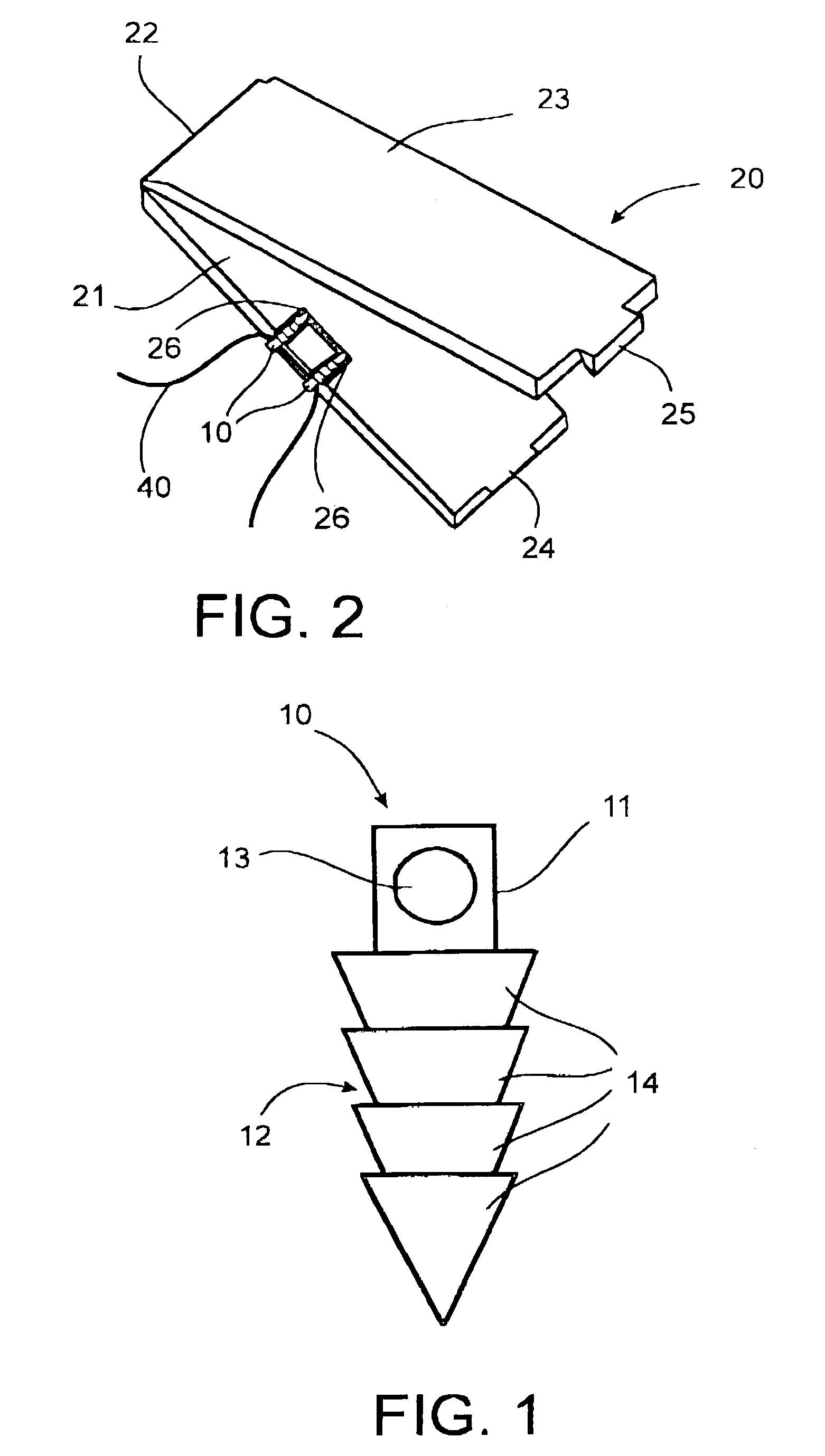
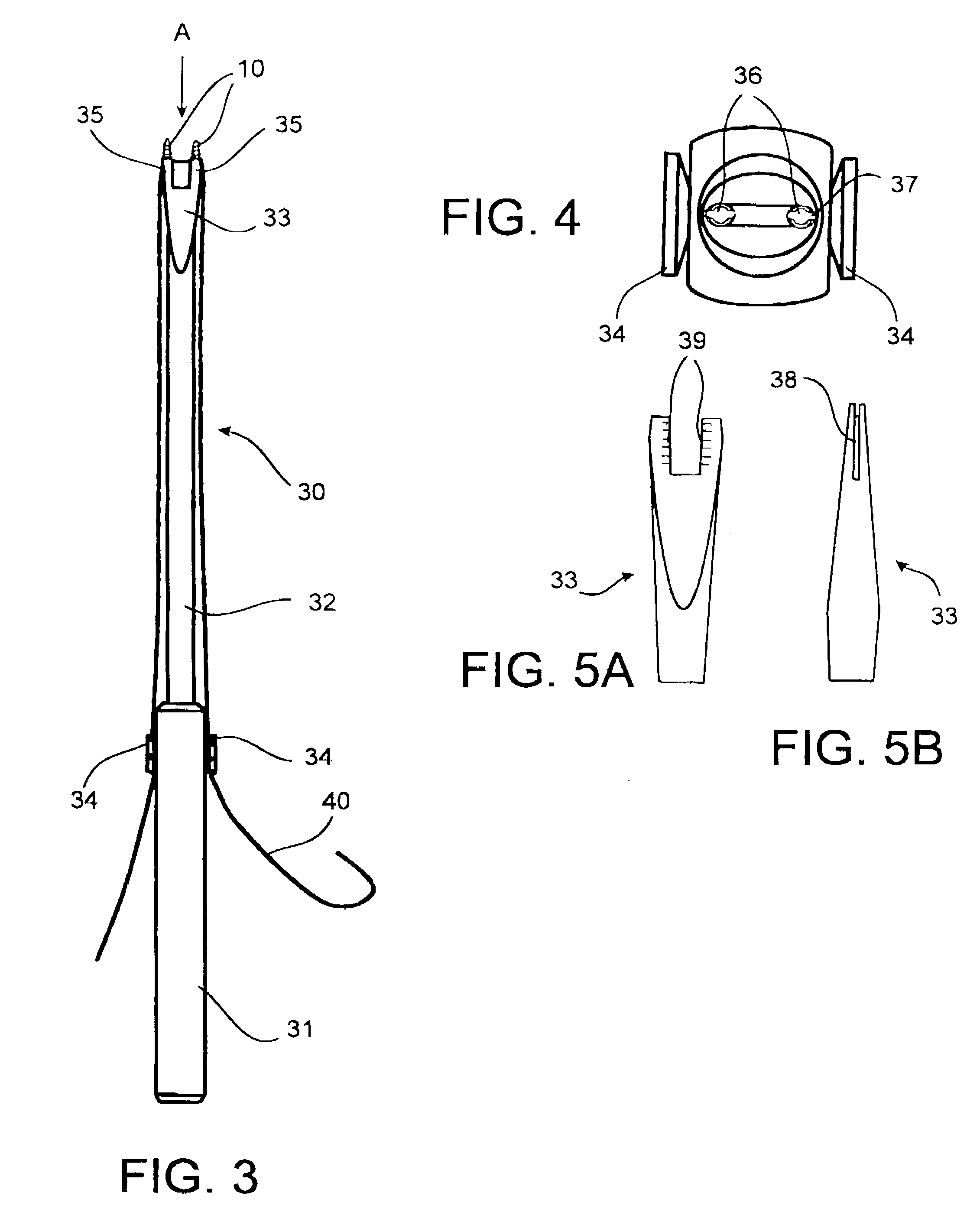
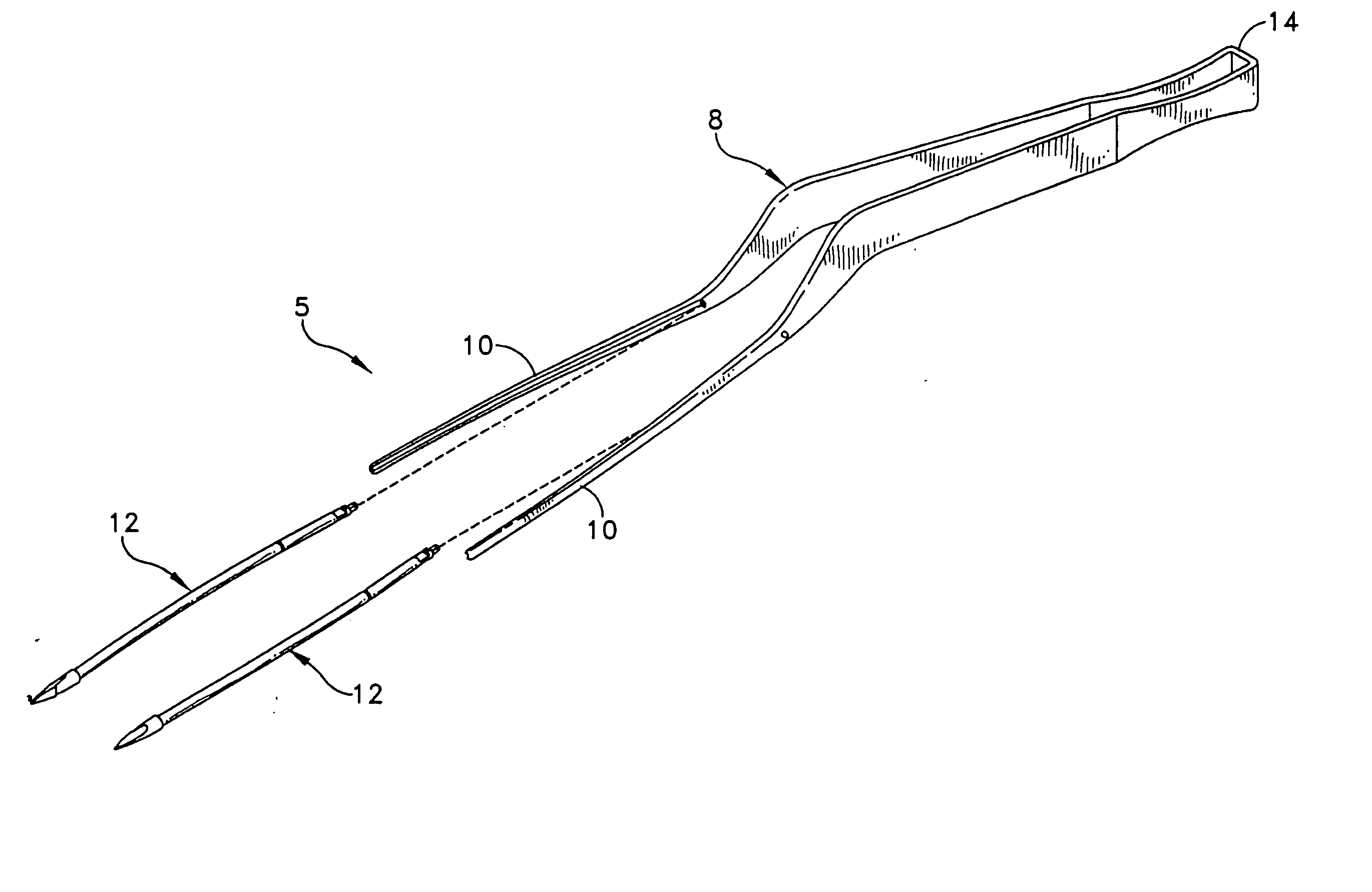
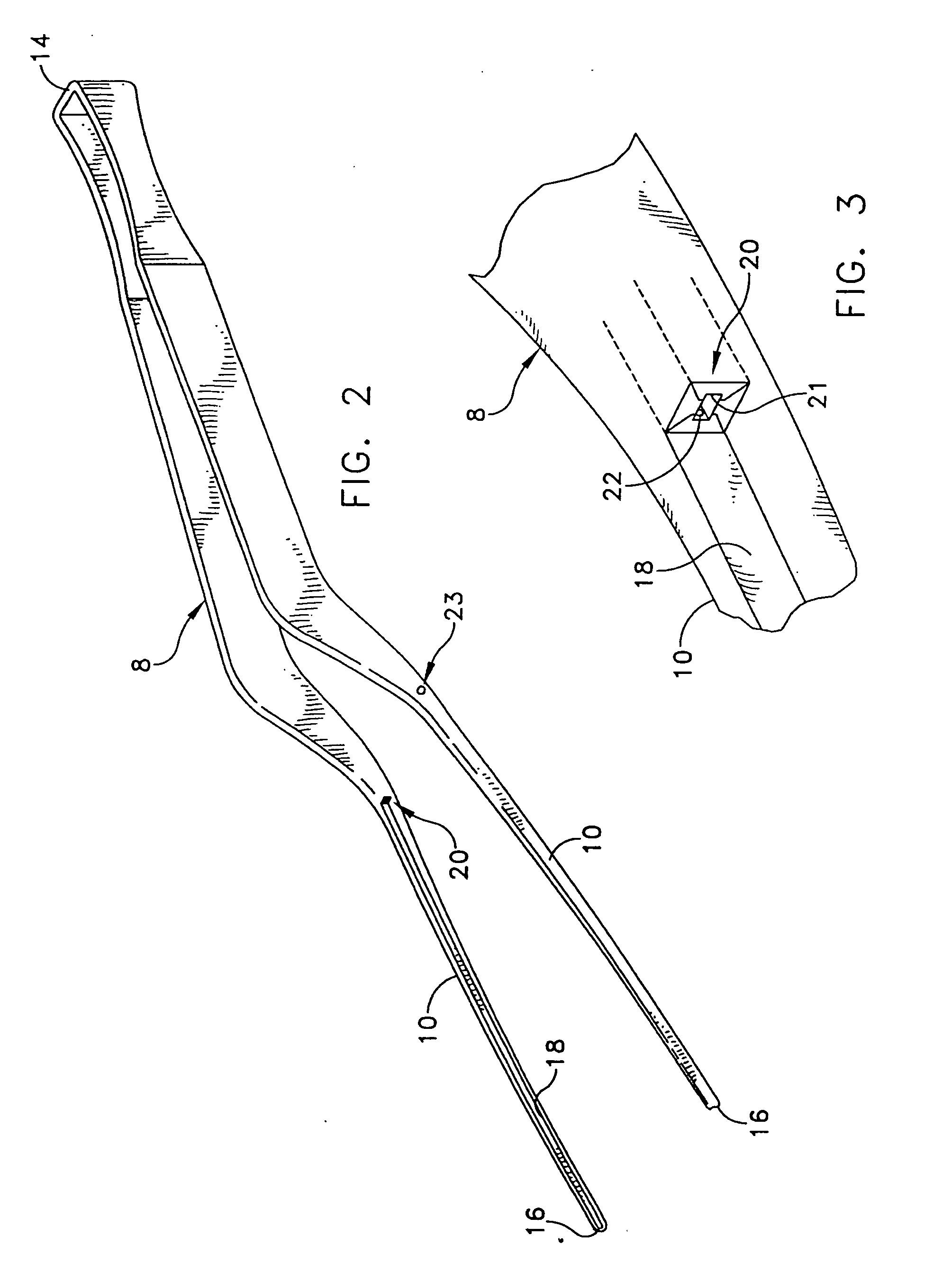
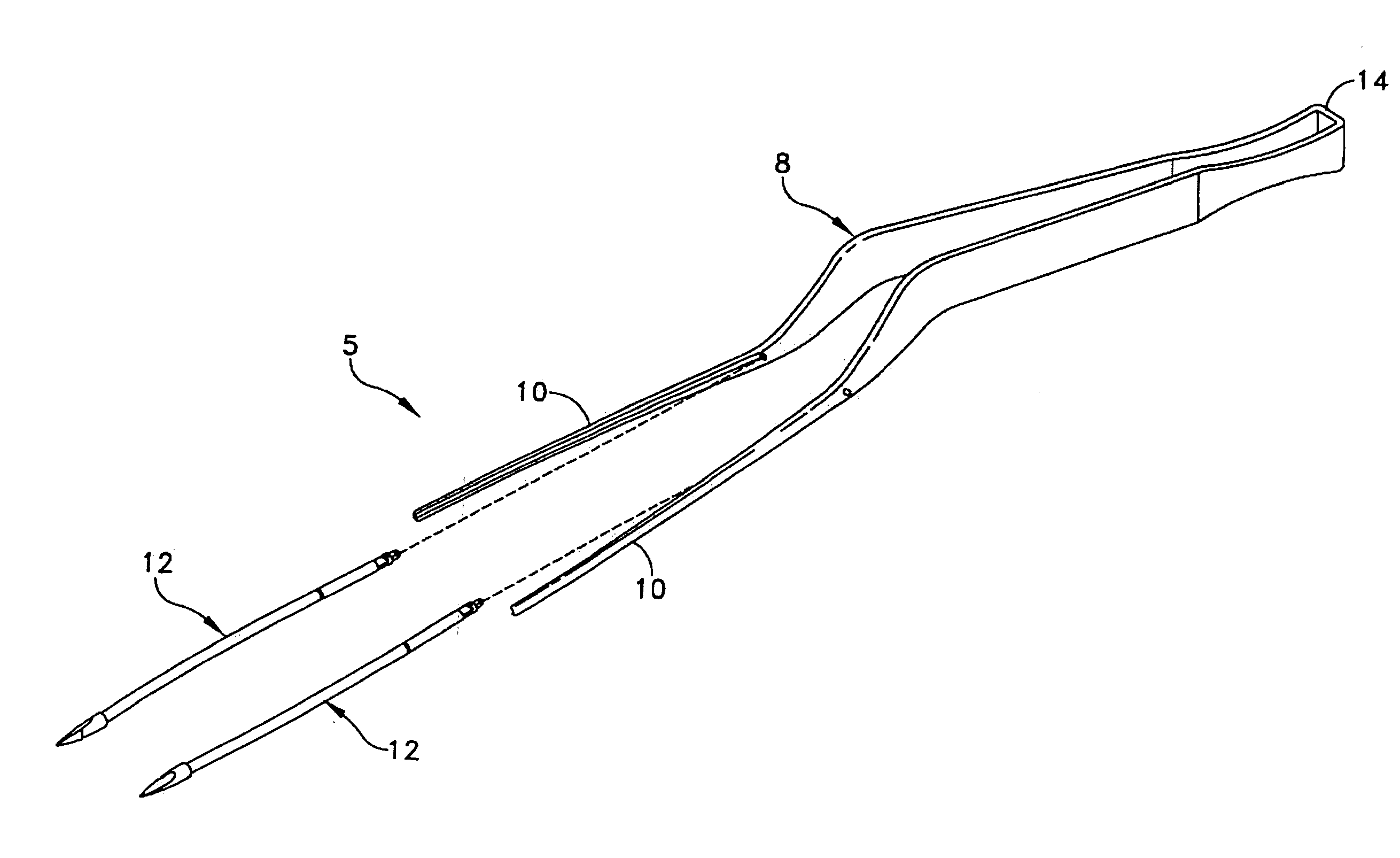
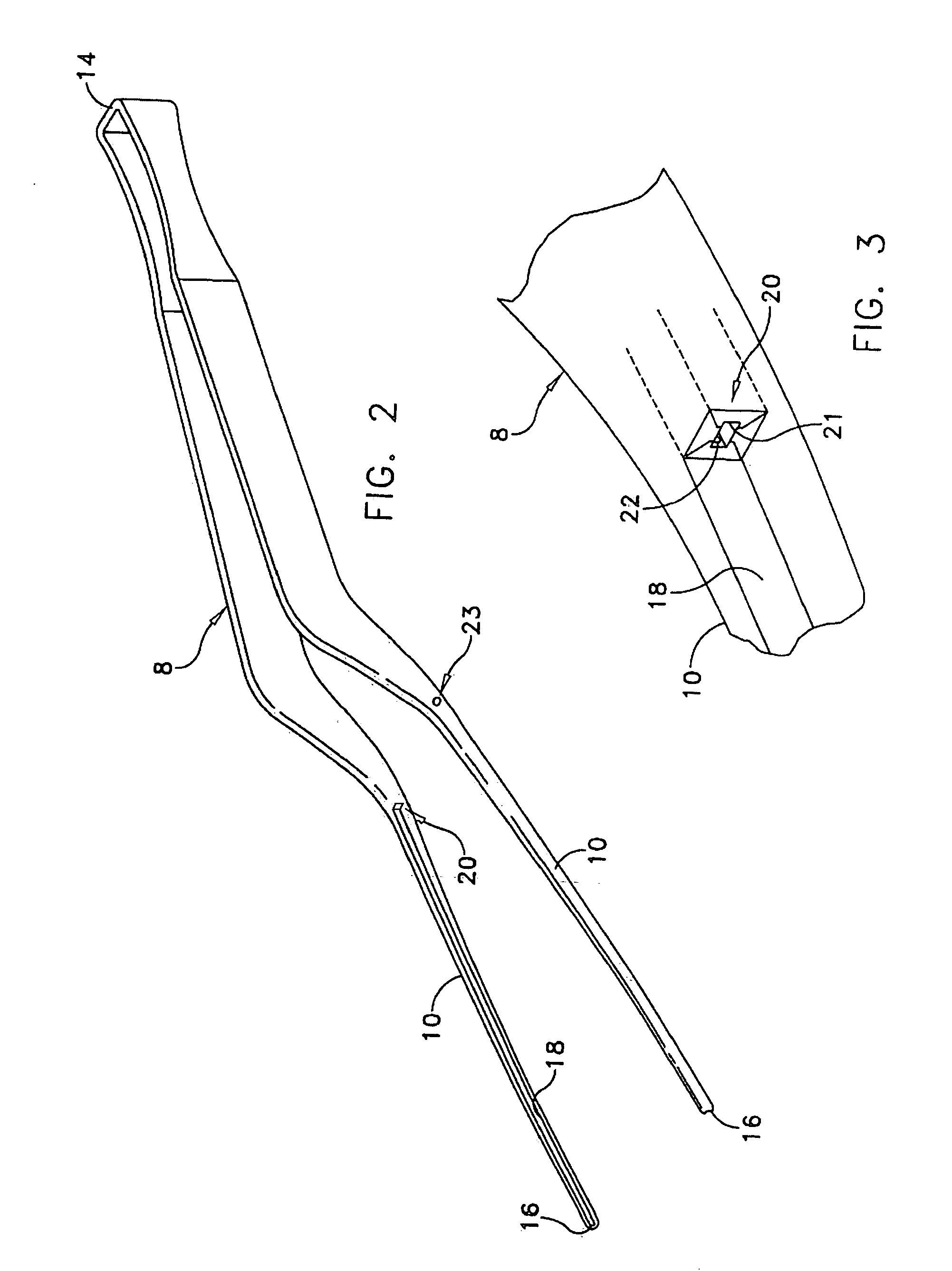
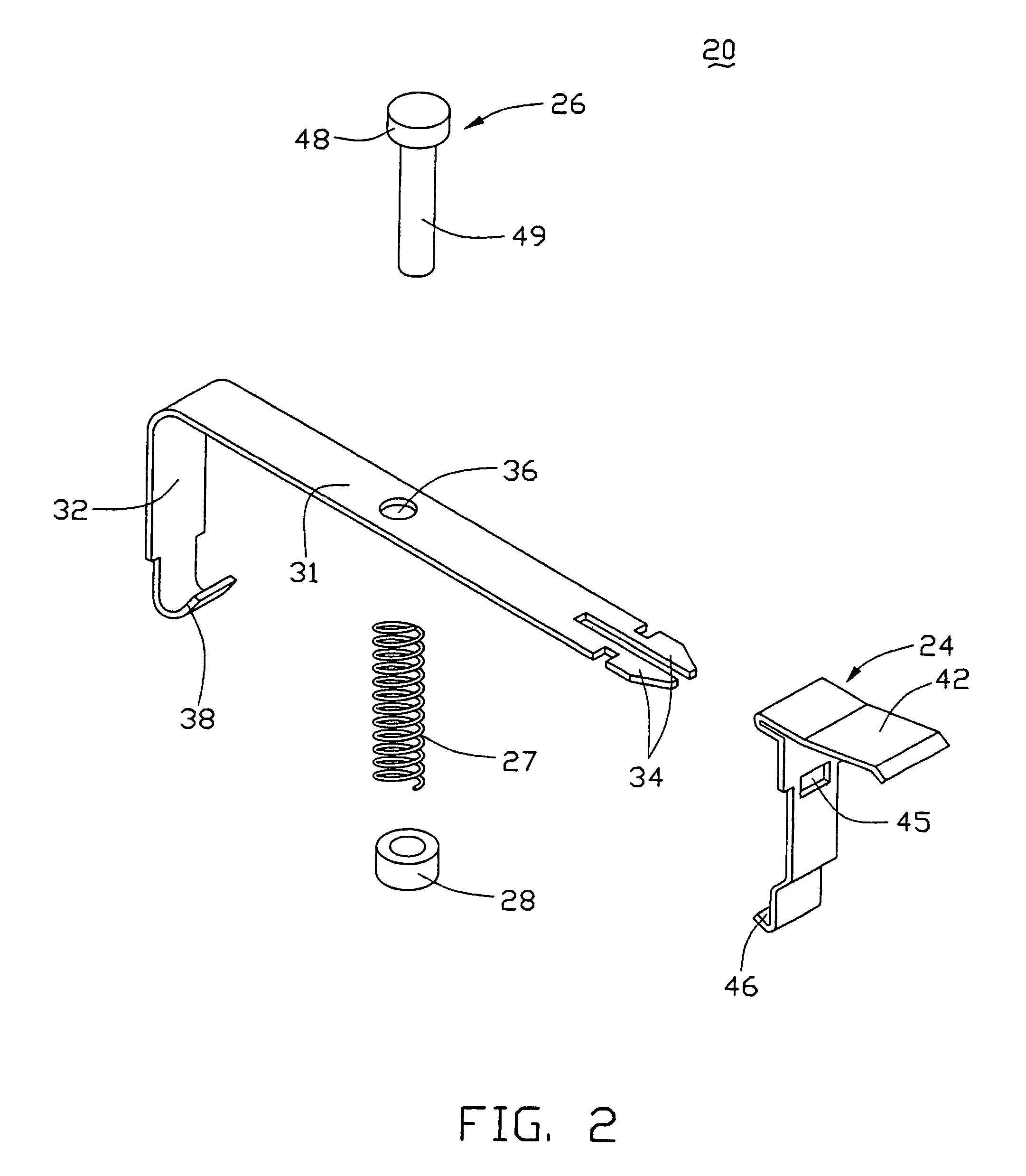
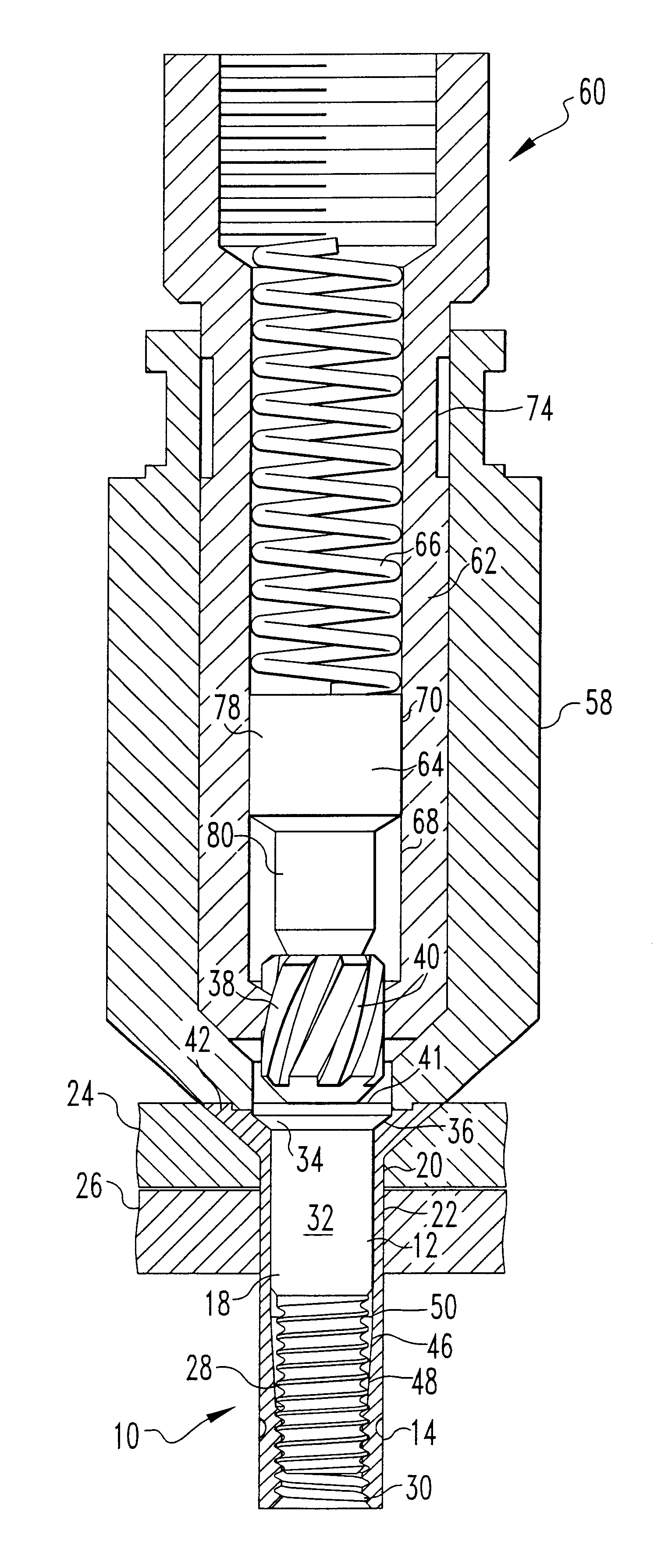
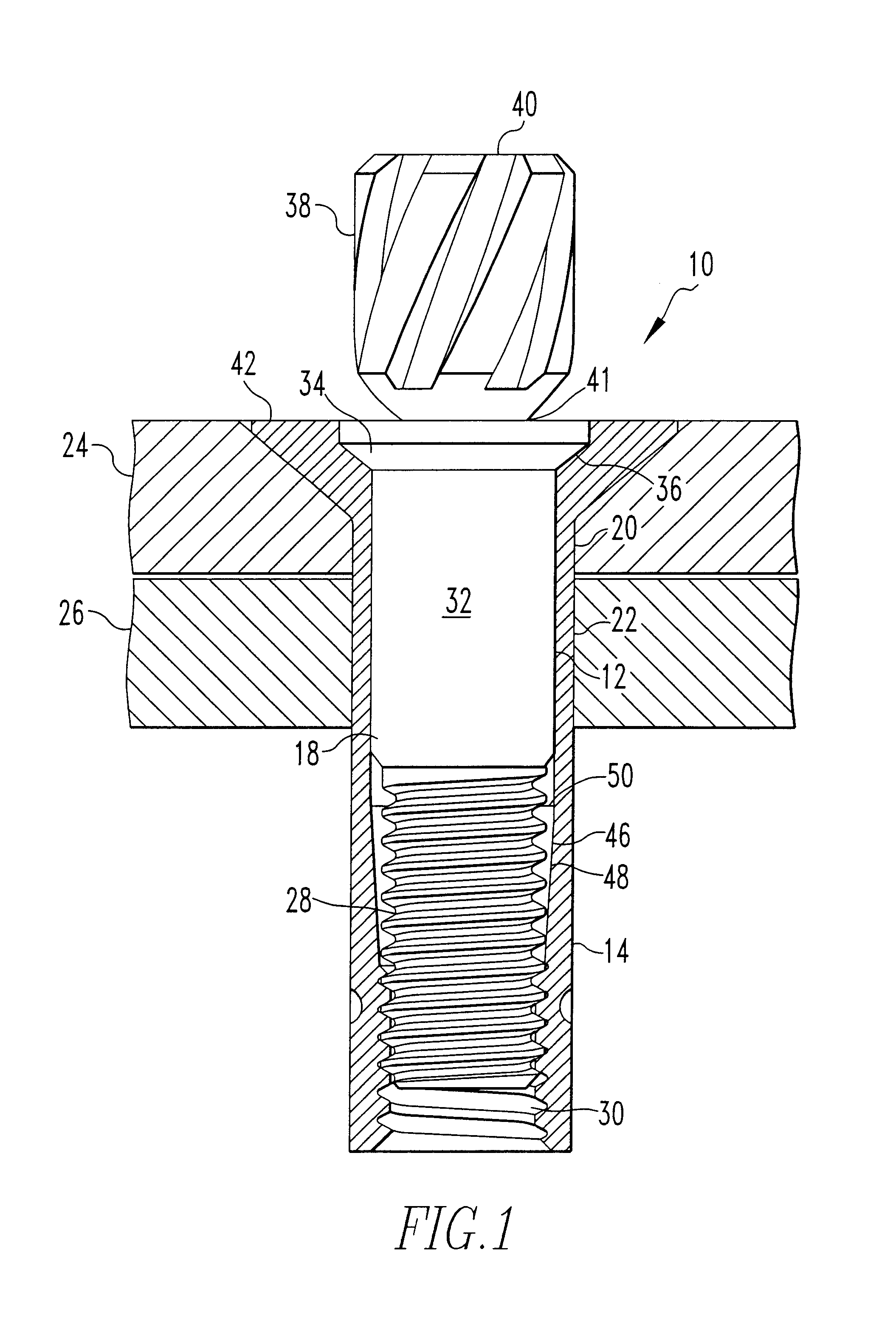
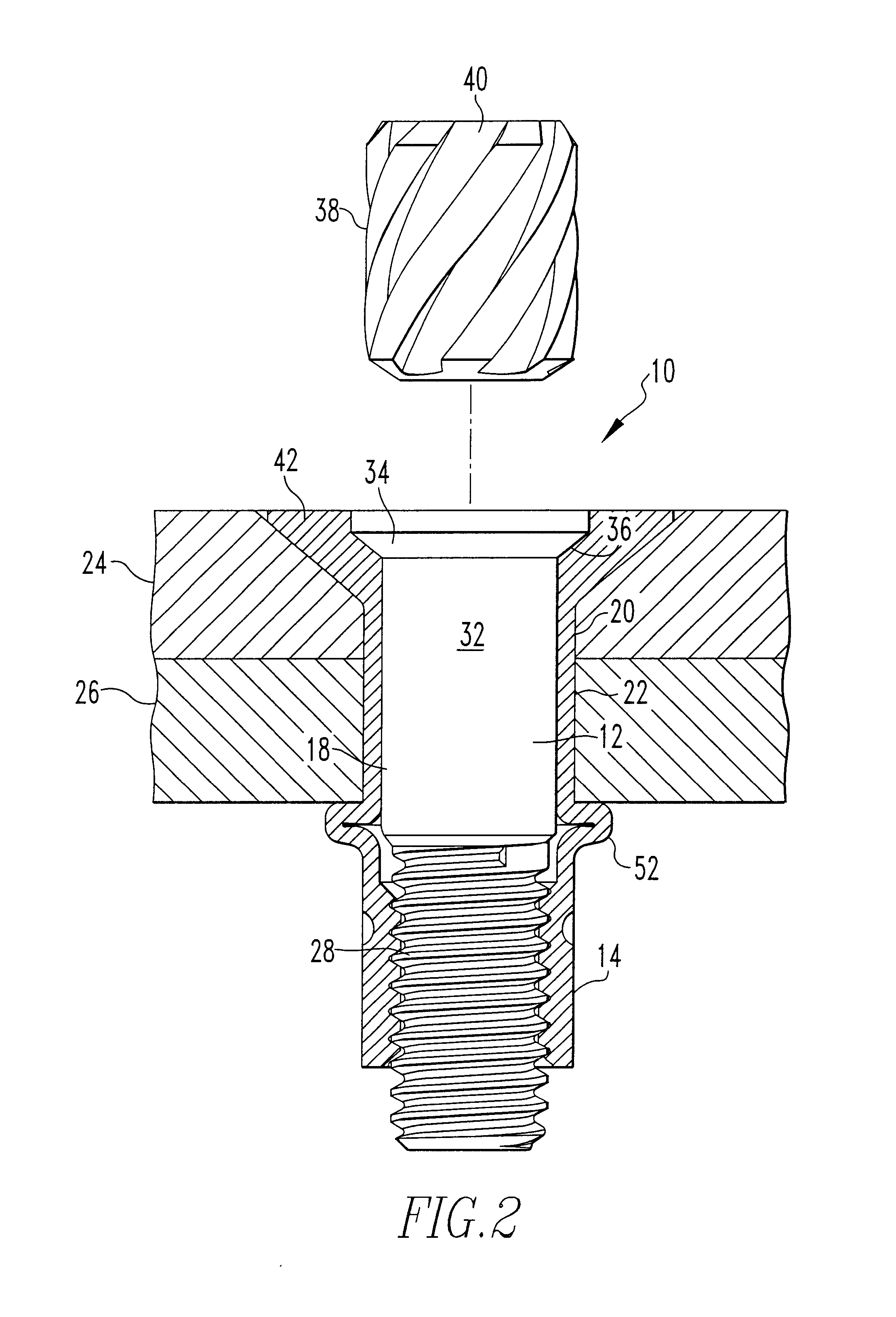
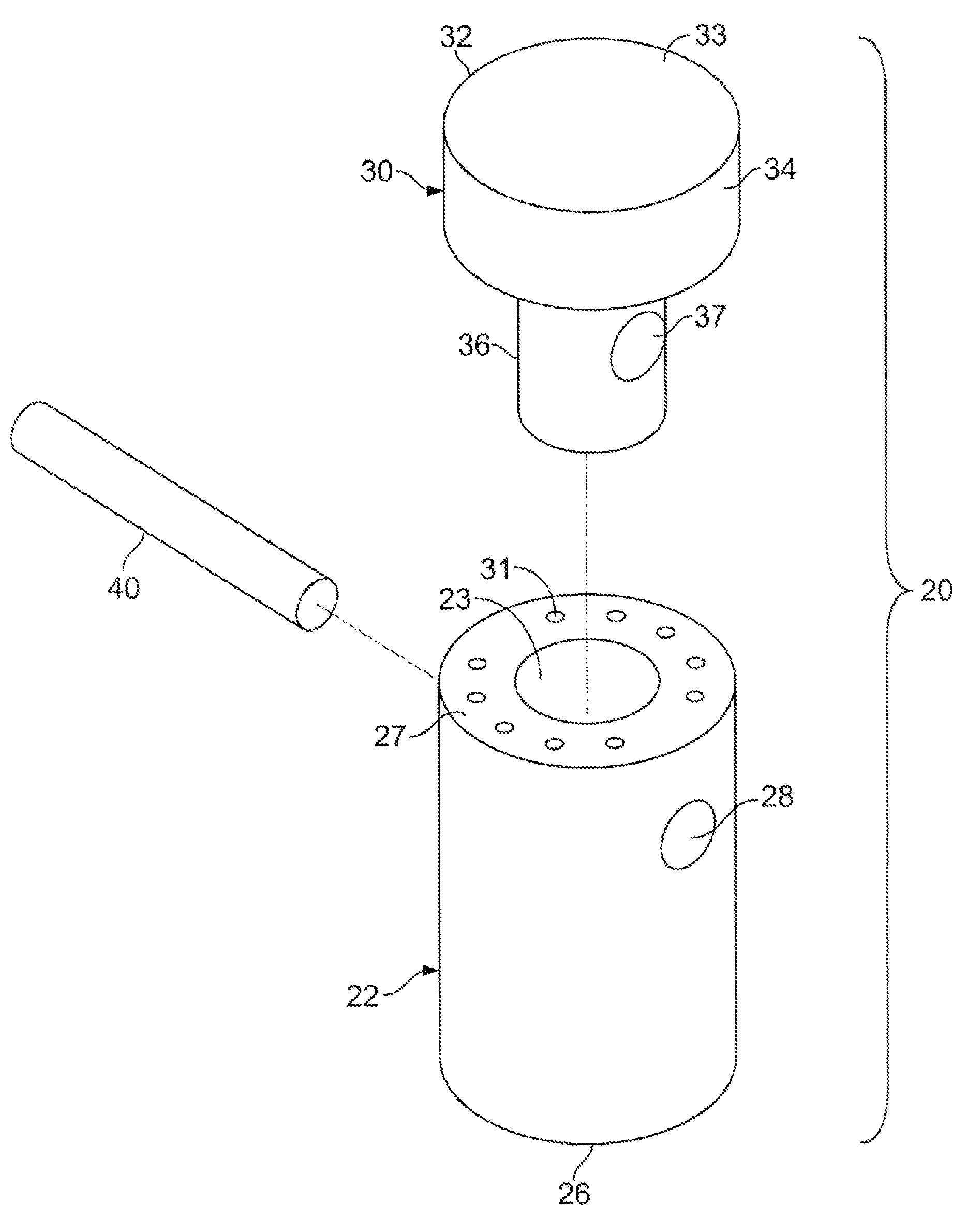
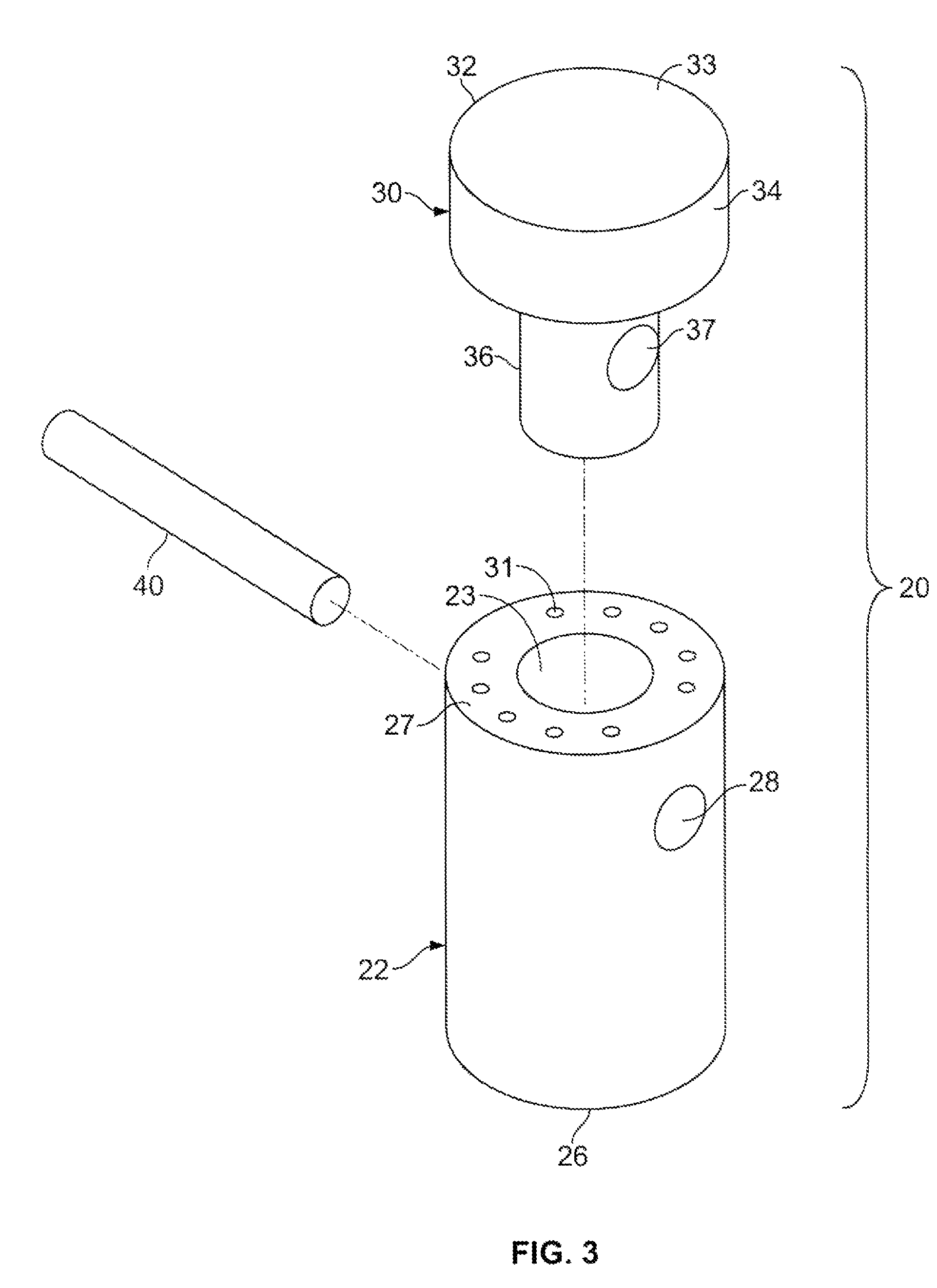
Method for fixing a soft tissue on a bone
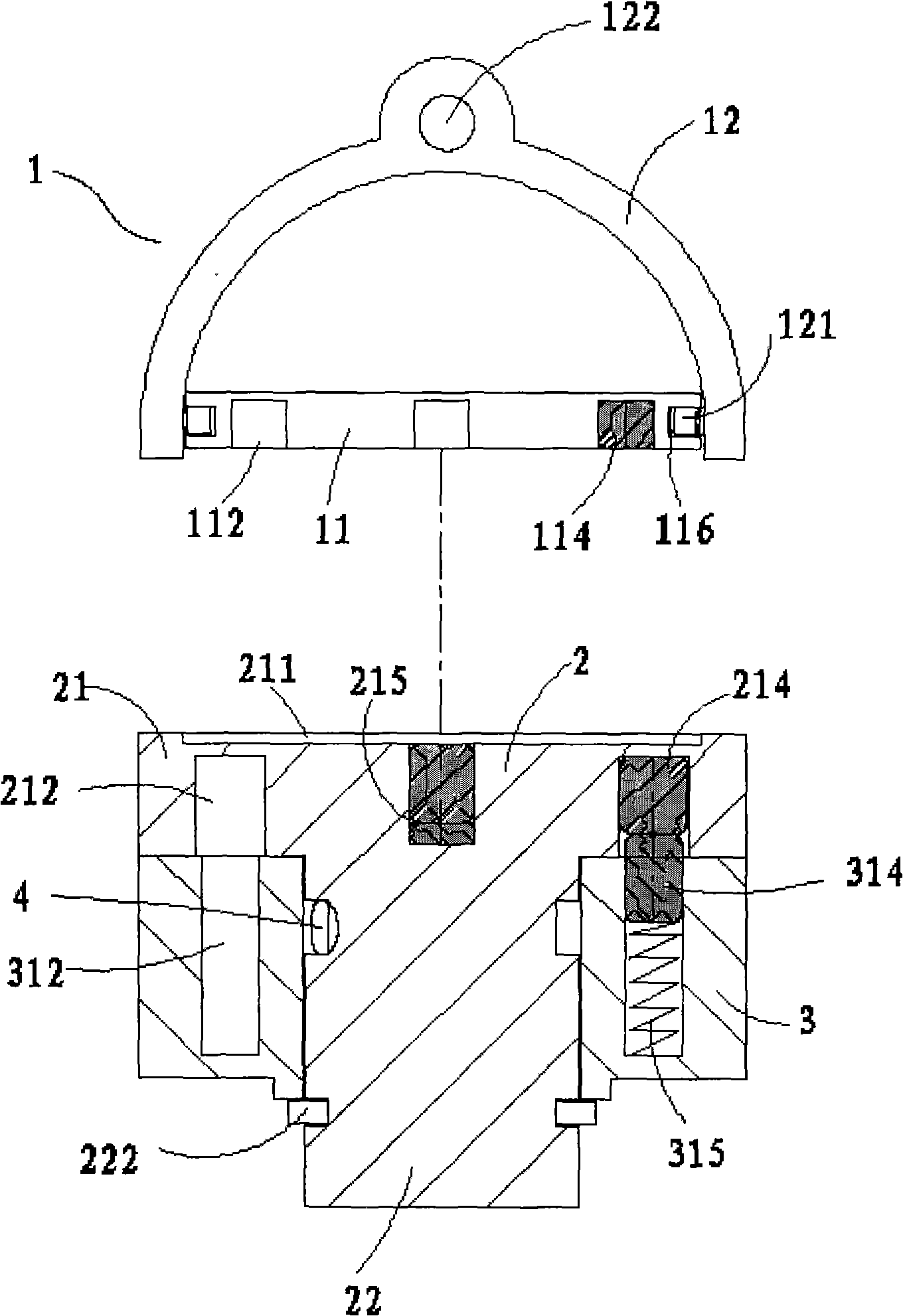
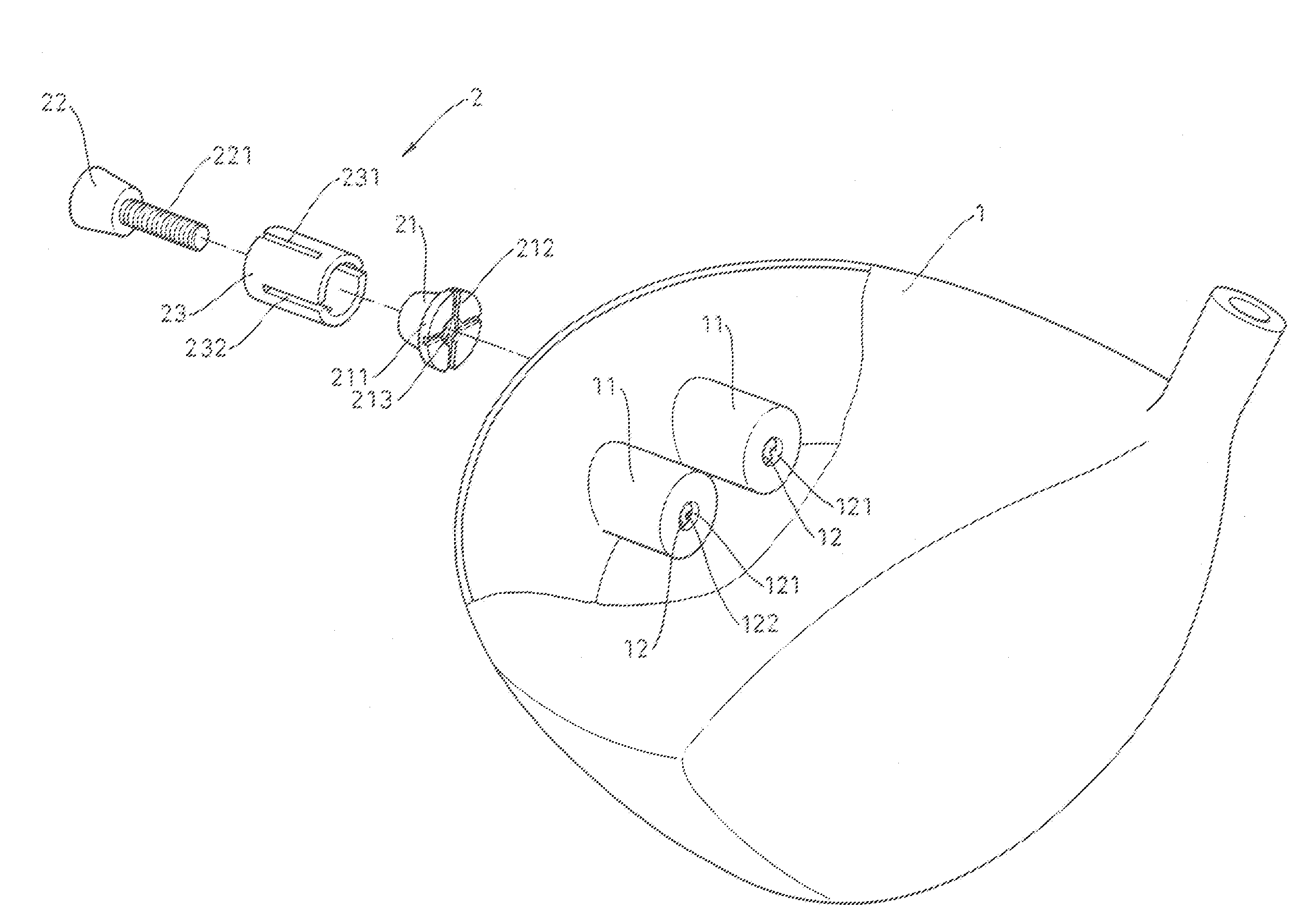
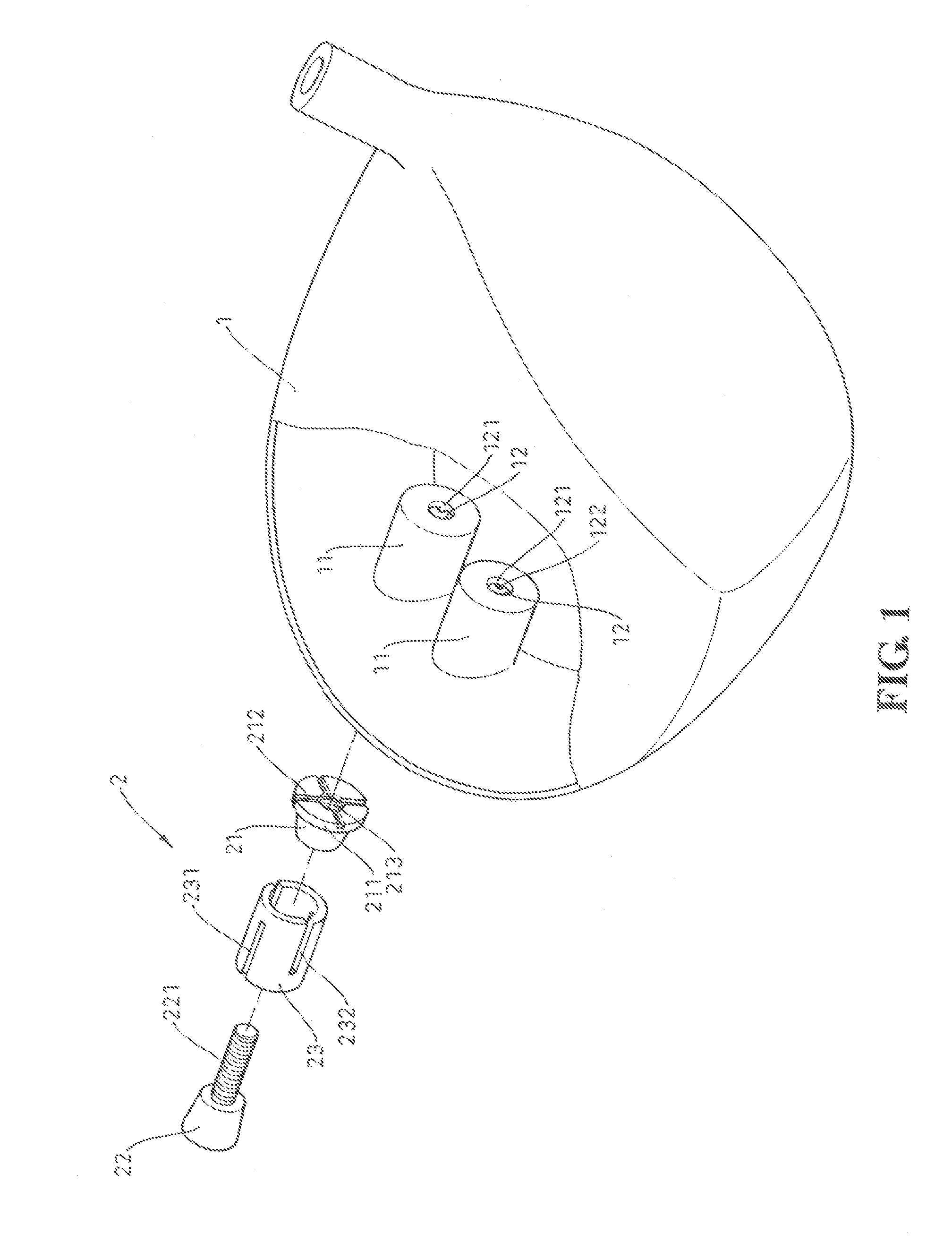
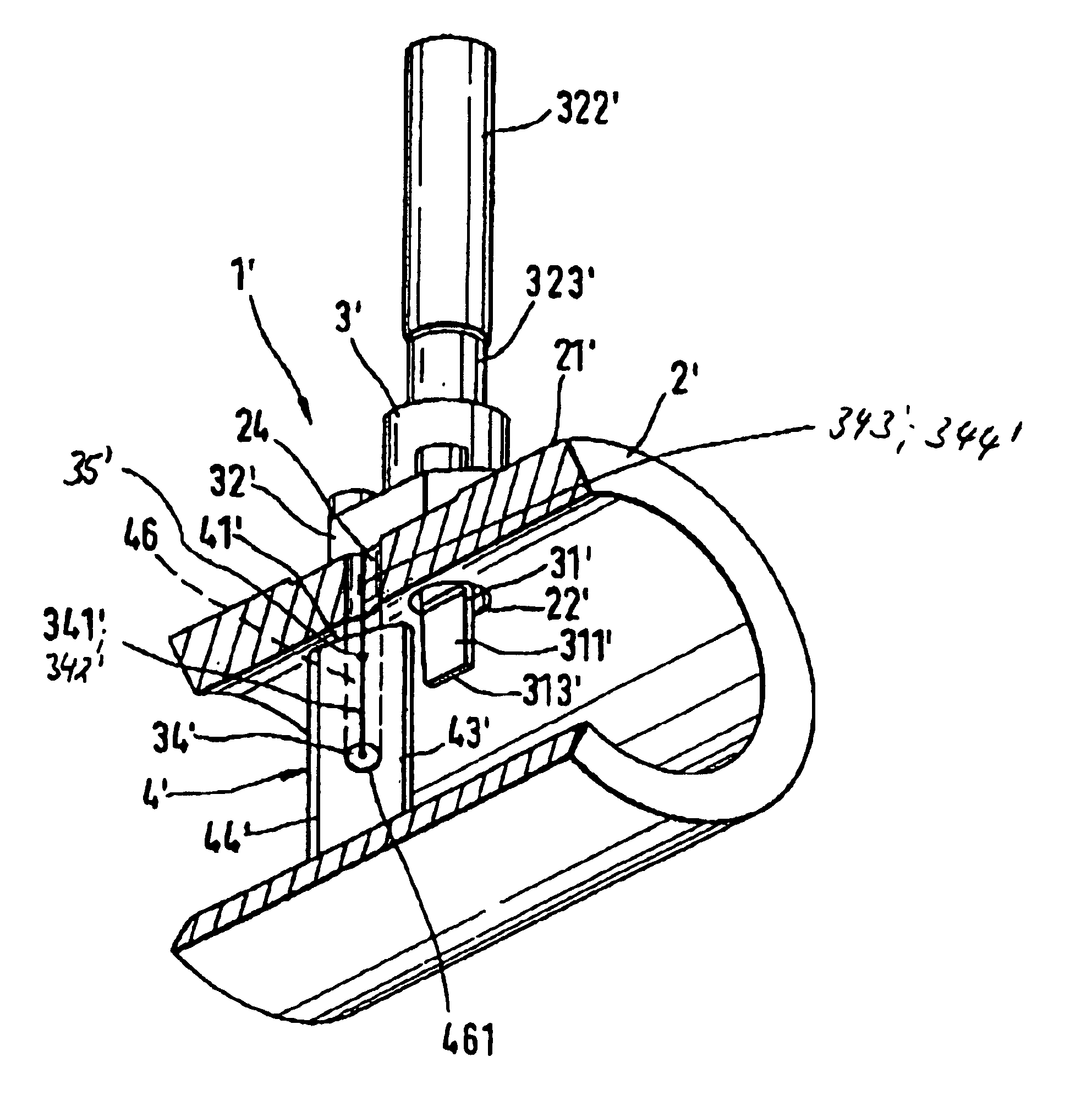
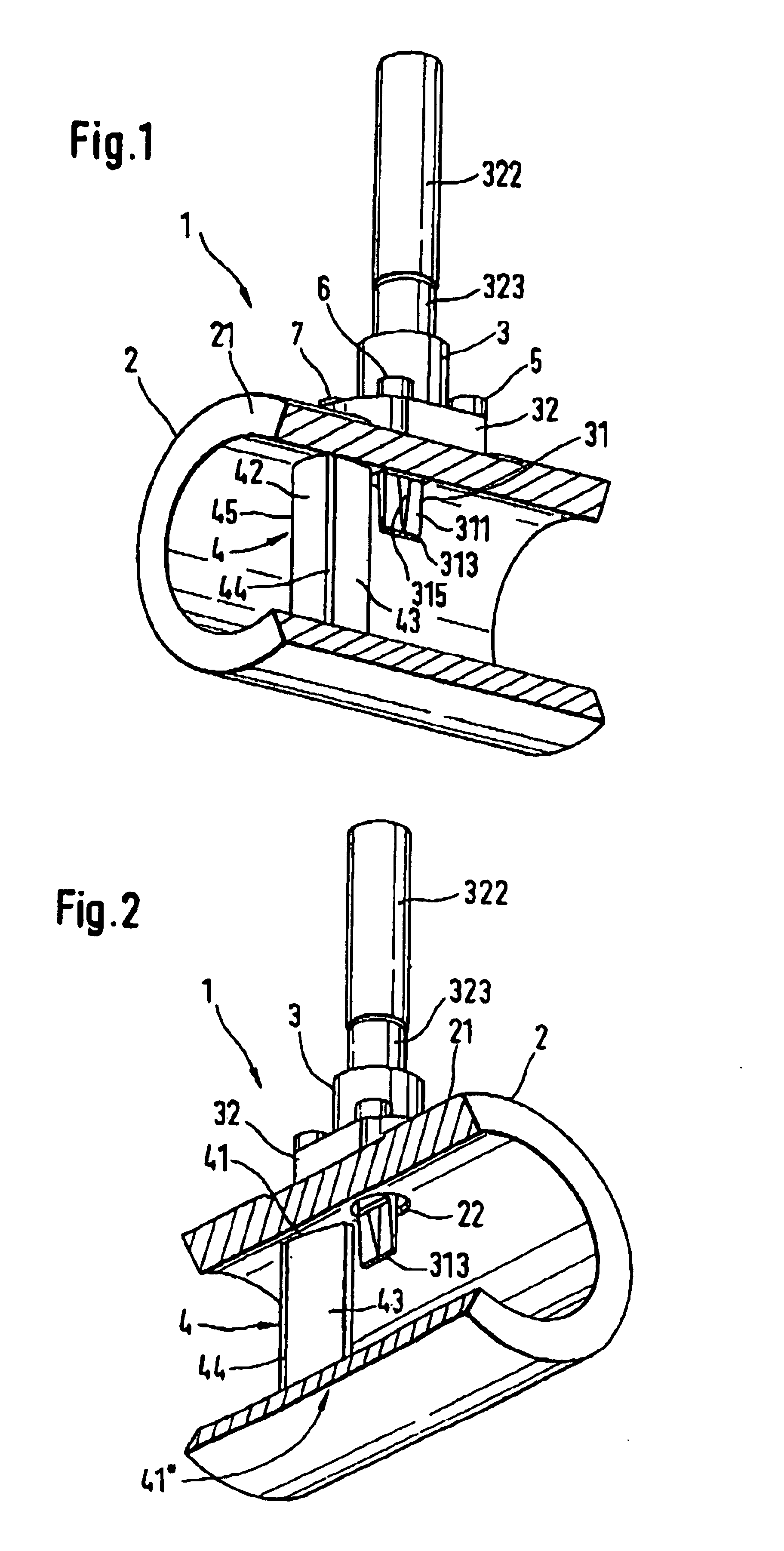
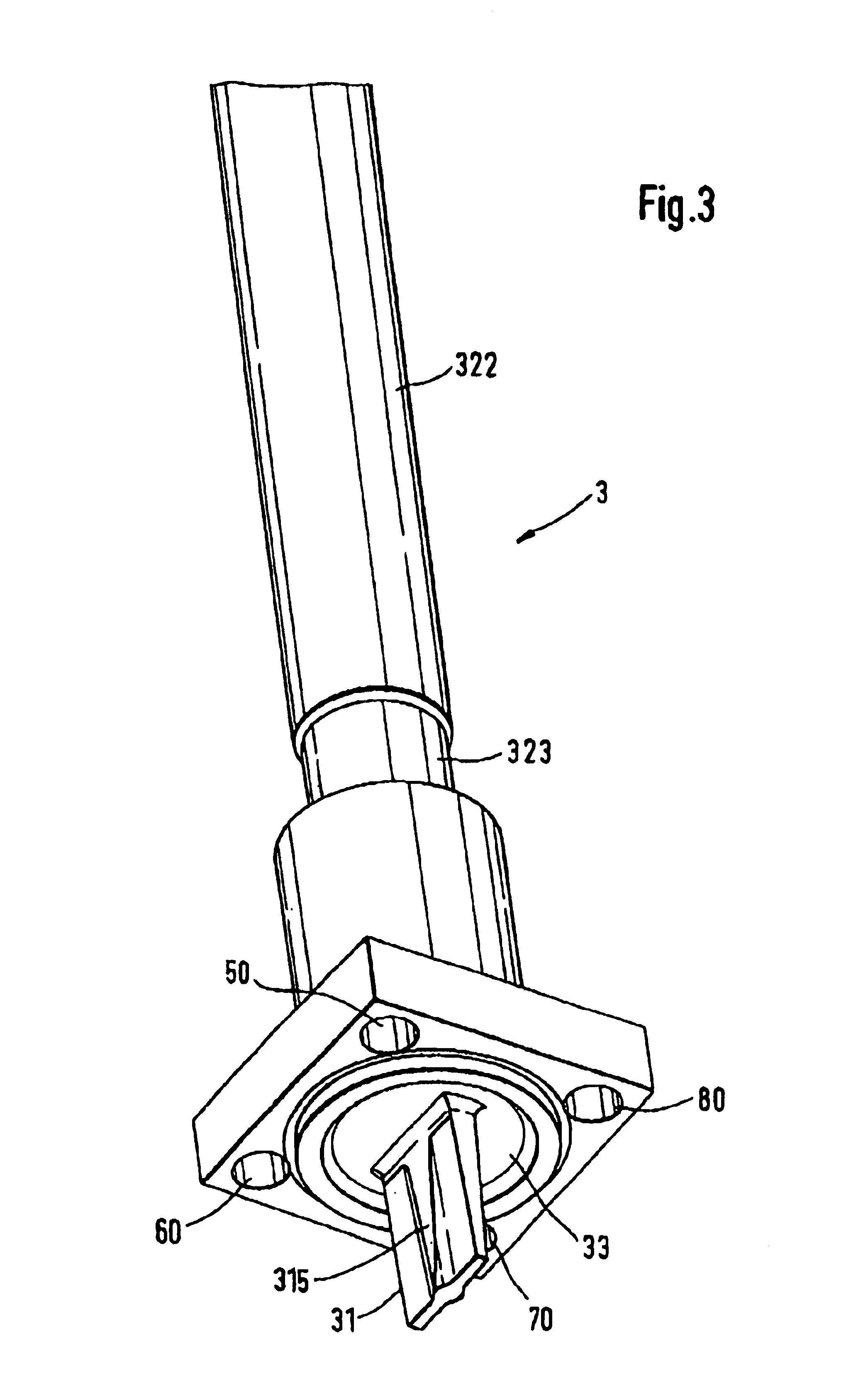
The invention concerns a set for fixing a soft tissue, such as a ligament or tendon on a bone, comprising two nails (10) and a member for positioning and setting (30) the nails in the superimposed soft tissue and bone. The two nails comprise a first cylindrical upper portion and a second lower portion formed by a stepped coaxial superposition of inverted cones. The cylindrical portion is provided with a hole for passing through a suture (40) designed to constitute a way for maintaining the soft tissue in position on the bone during healing. The positioning and setting member (3) comprises a handle (31) wherein is nested a cylindrical rod (32) including an end (33). The U-shaped end comprises two branches (35) provided with a blind cylindrical bore designed to receive the cylindrical part of the nails (10). When the nails are secured to the member (30), the suture (40) is maintained by the stop elements (34) of the handle (31).
Owner:MD SUPPLY S A R L
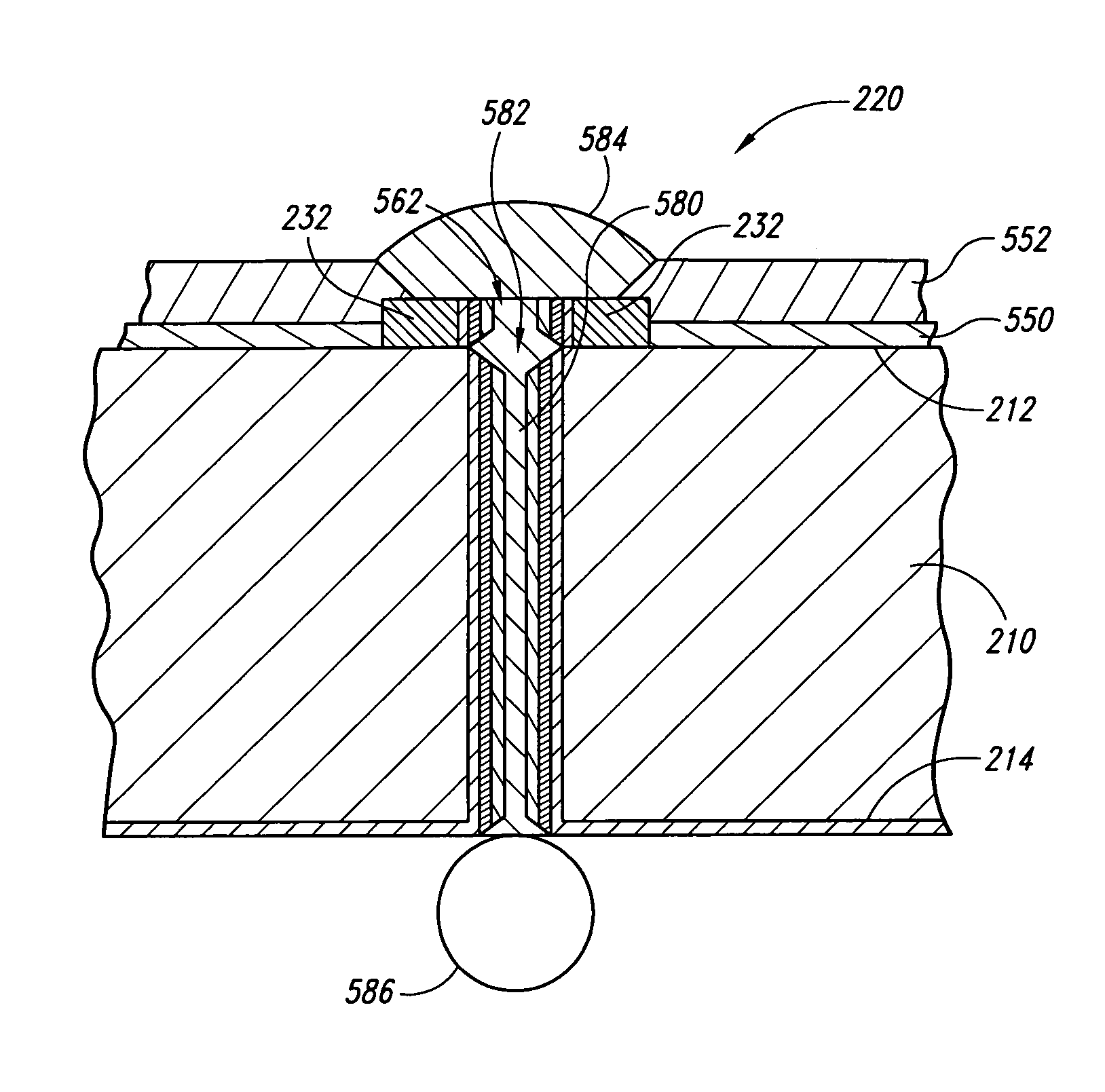
Methods for forming interconnects in microelectronic workpieces and microelectronic workpieces formed using such methods
ActiveUS7271482B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringIntegrated circuit
Methods for forming interconnects in microelectronic workpieces and microelectronic workpieces having such interconnects are disclosed herein. One aspect of the invention is directed toward a method for manufacturing a microelectronic workpiece having a plurality of microelectronic dies. The individual dies include an integrated circuit and a terminal electrically coupled to the integrated circuit. In one embodiment, the method includes forming an opening in the workpiece in alignment with the terminal. The opening can be a through-hole extending through the workpiece or a blind hole that extends only partially through the substrate. The method continues by constructing an electrically conductive interconnect in the workpiece by depositing a solder material into at least a portion of the opening and in electrical contact with the terminal. In embodiments that include forming a blind hole, the workpiece can be thinned either before or after forming the hole.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Heat pipe for cautery surgical instrument
A heat pipe for a cautery surgical instrument such as a surgical forceps including a pair of elongate arms joined at an end so as to provide for resilient compressible movement of the arms between a normally open position and a squeezed closed position. The heat pipe provides for conduction of heat away from an electrode tip, and comprises an evaporator portion having a first diameter and a condenser portion spaced away from the evaporator end, and that transitions from the first diameter to at least one smaller diameter section. A socket is disposed within each arm of the forceps, and includes a longitudinal blind hole that is sized so as to releasably receive the smaller diameter section of the condenser portion, and a catch for engaging a portion of the arm.
Owner:THERMAL
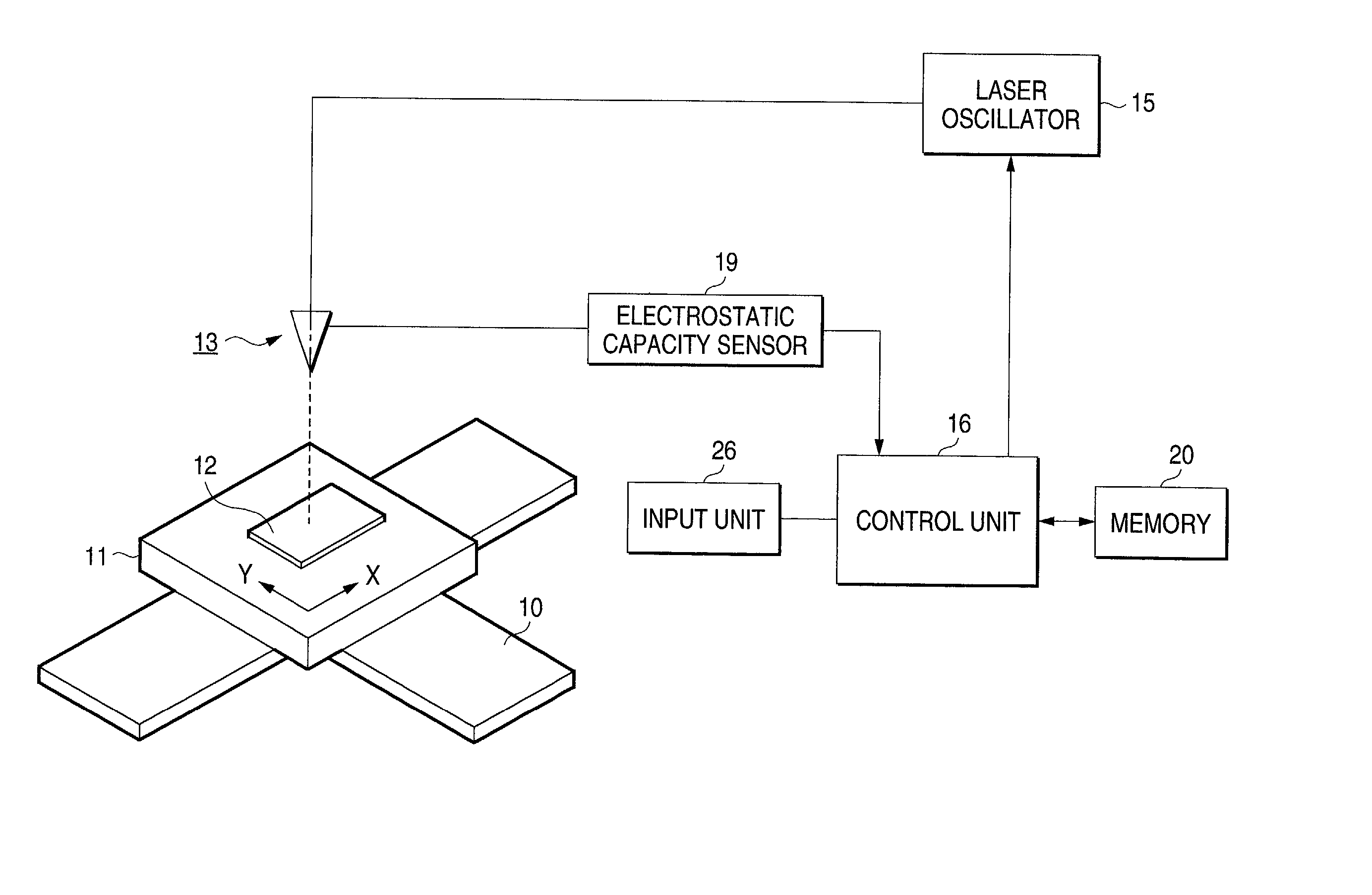
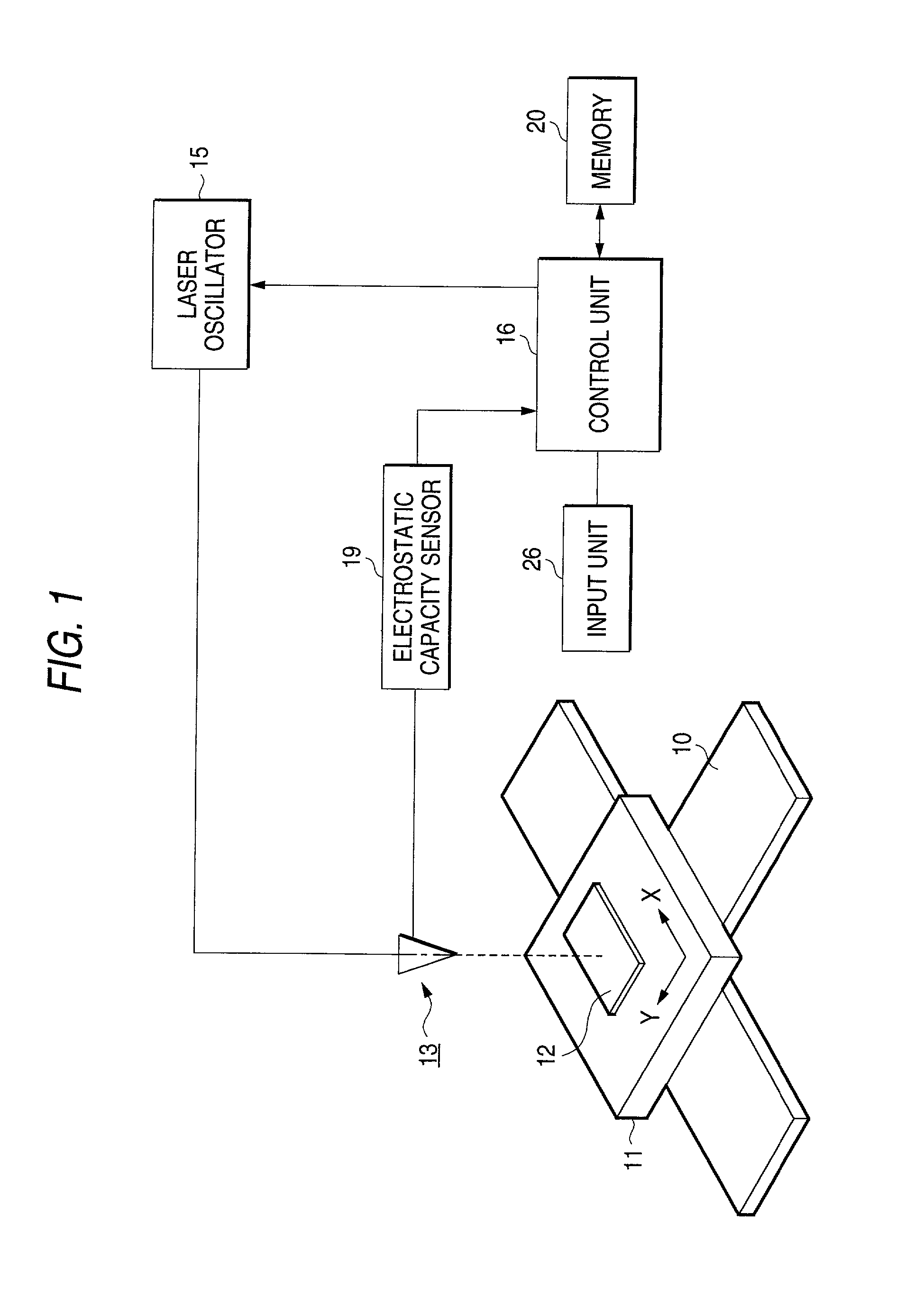
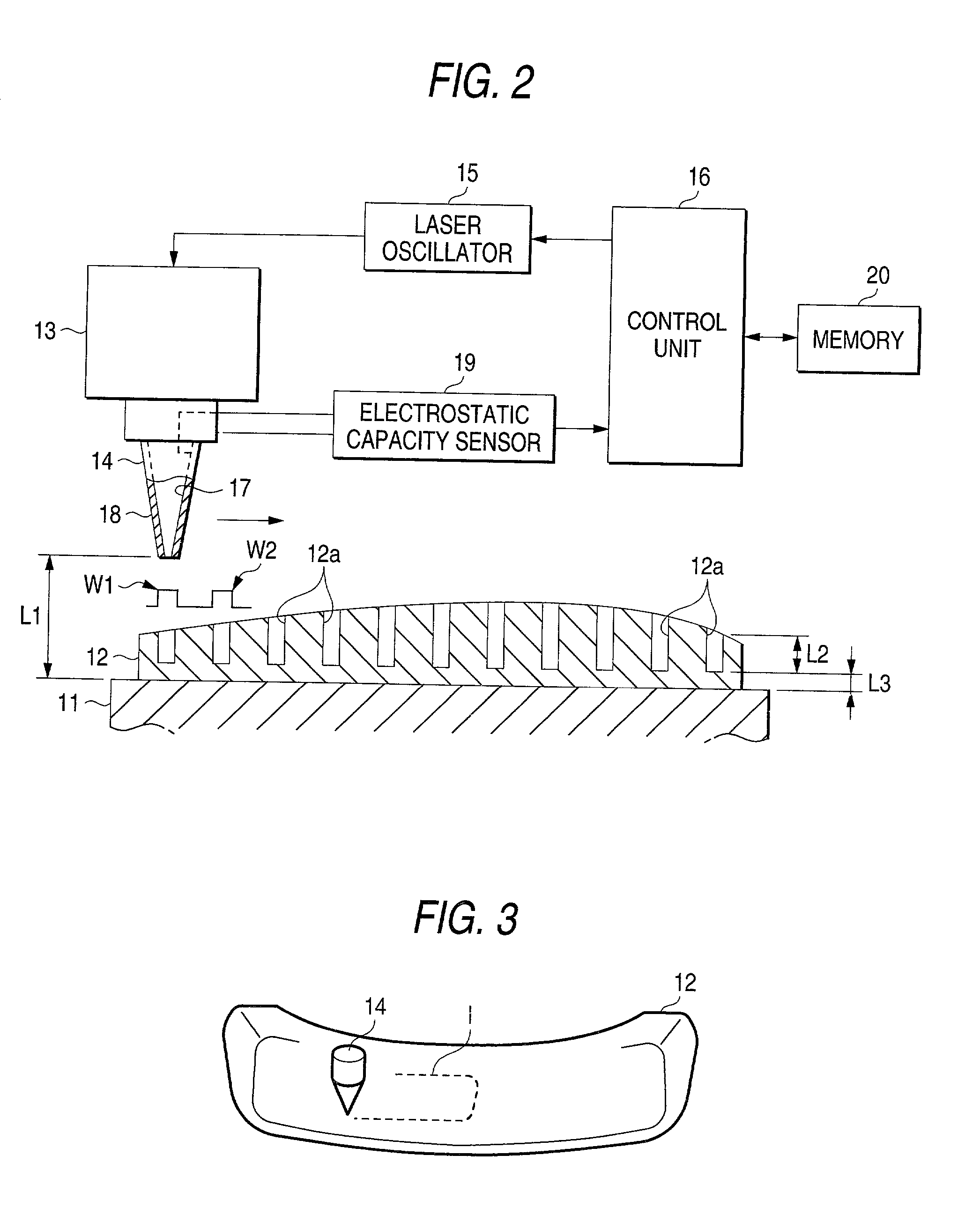
Laser beam machining apparatus and laser beam machining method
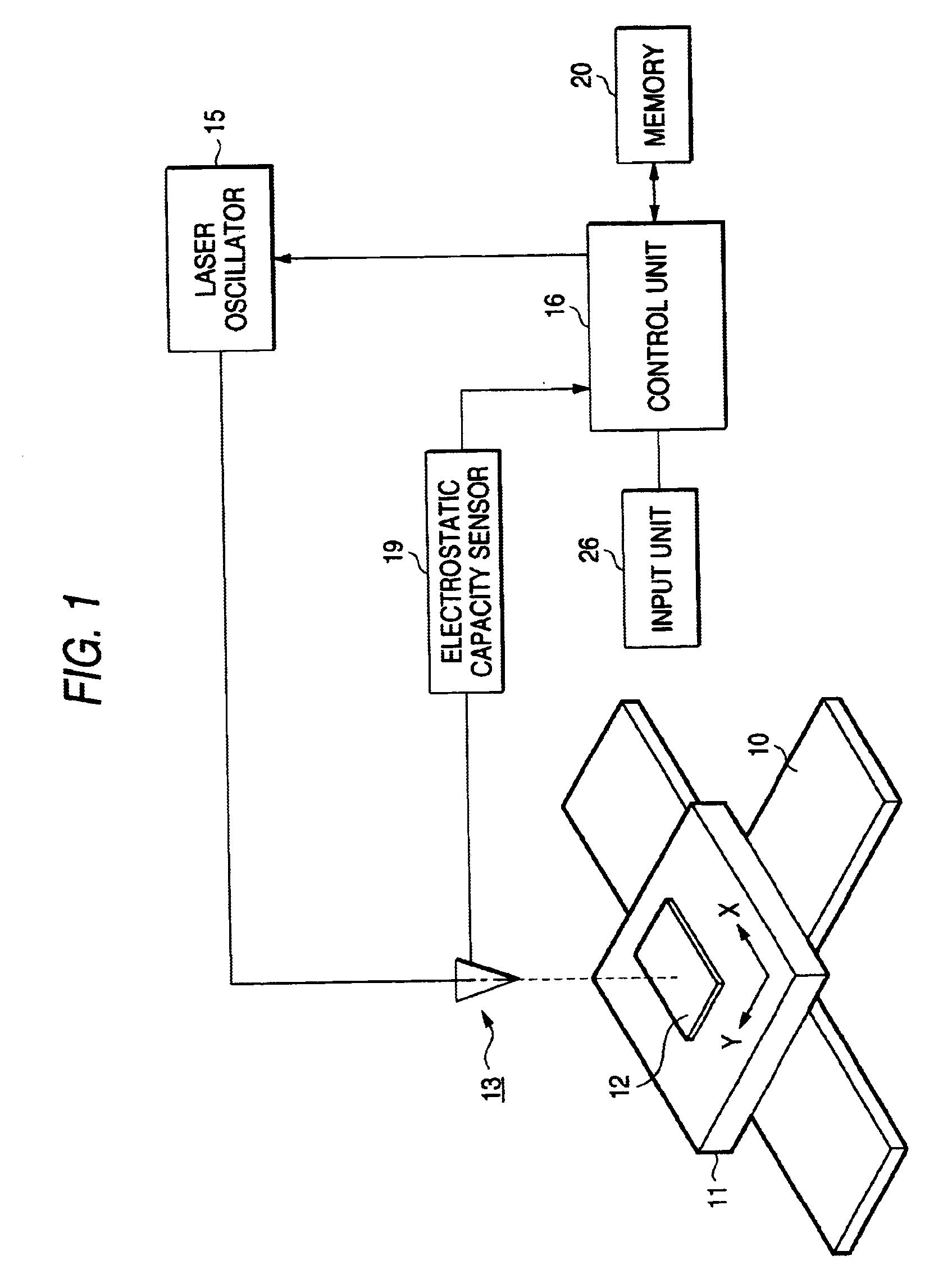
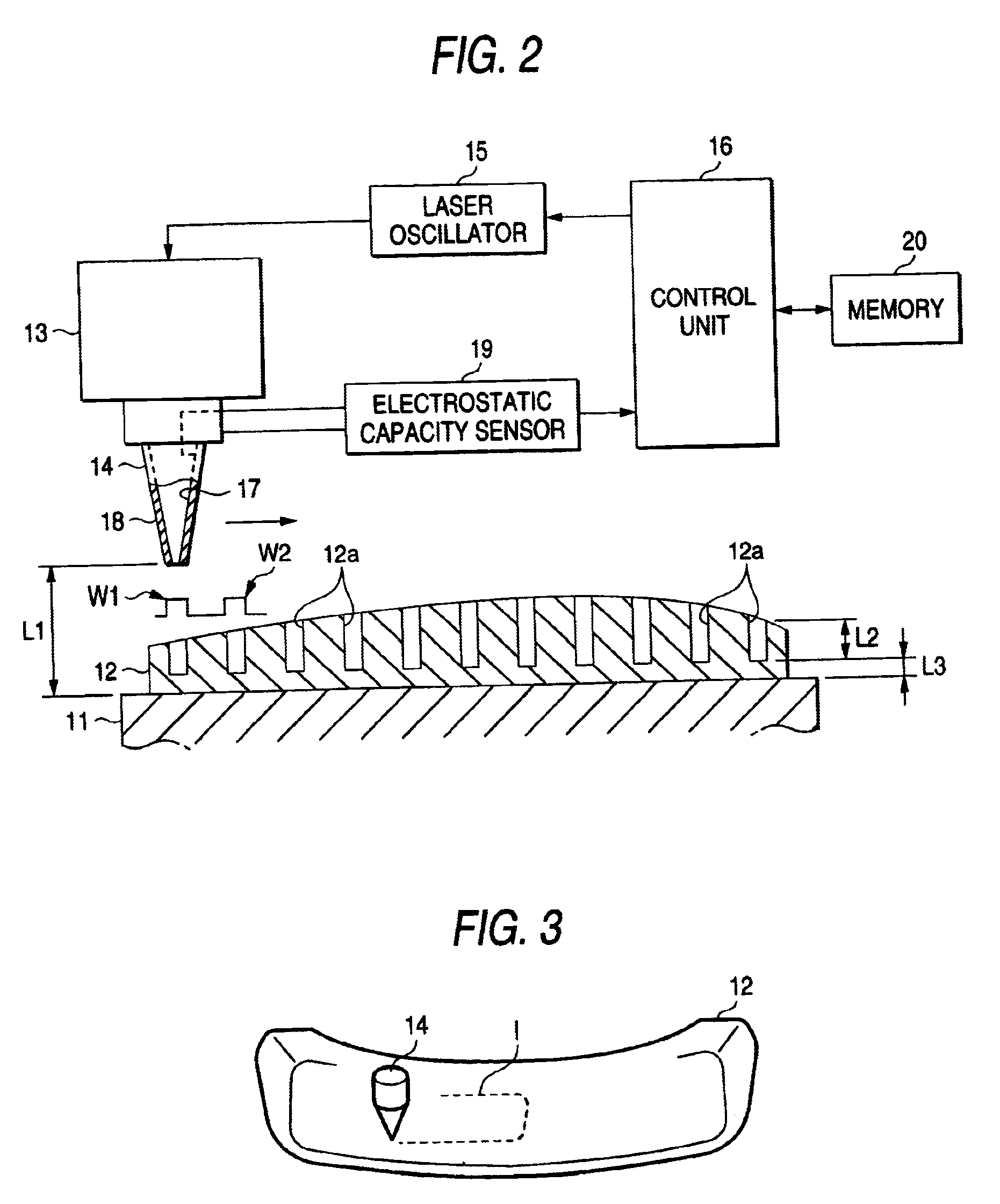
InactiveUS20030000927A1Pedestrian/occupant safety arrangementLaser beam welding apparatusLaser NozzleSpray nozzle
A laser beam machining apparatus forms blind holes at predetermined intervals in a workpiece by intermittently irradiating a laser beam from a laser nozzle to the workpiece while the laser nozzle and the workpiece being moved relatively. During the time the workpiece is subjected to machining, the electrostatic capacity between the support member and the laser nozzle is detected by an electrostatic capacity sensor while the workpiece made of conductive material is supported on the support member. The irradiation output power is controlled by a control unit which operates to vary the number of output pulses from the laser nozzle each time one hole is formed according to the result detected in response to variation in the thickness of the workpiece.
Owner:KOMATSU IND CORP
Cooling Element for electrosurgery
A cooling member for a cautery surgical instrument such as a surgical forceps including a pair of elongate arms joined at an end so as to provide for resilient compressible movement of the arms between a normally open position and a squeezed closed position. The cooling member provides for conduction of heat away from an electrode tip, and comprises an first portion having a first diameter and a second portion spaced away from the first portion, and that transitions from the first diameter to at least one smaller diameter section. A socket is disposed within each arm of the forceps, and includes a longitudinal blind hole that is sized so as to releasably receive the smaller diameter section of the second portion, and a catch for engaging a portion of the arm.
Owner:THERMAL
Methods for forming through-wafer interconnects and devices and systems having at least one dam structure
ActiveUS20070262424A1Conveniently attachedEliminate cross-contaminationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesVitrificationDevice material
A method for forming through-wafer interconnects (TWI) in a substrate. Blind holes are formed from a surface, sidewalls thereof passivated and coated with a conductive material. A vent hole is then formed from the opposite surface to intersect the blind hole. The blind hole is solder filled, followed by back thinning of the vent hole portion of the wafer to a final substrate thickness to expose the solder and conductive material at both the active surface and the thinned back side. A metal layer having a glass transition temperature greater than that of the solder may be plated to form a dam structure covering one or both ends of the TWI. Intermediate structures of semiconductor devices, semiconductor devices and systems are also disclosed.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Shielded electronic circuit unit and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20060266547A1Improve shielding effectPrinted circuit assemblingMagnetic/electric field screeningEngineeringElectronic component
A metallic film and a grounding pattern are surely connected to each other so as to achieve electrical shield of an electronic circuit unit. In an electronic circuit unit, the metallic film is provided on a top surface of a sealing resin portion for burying an electronic component, the side surfaces of the sealing resin portion that are opposite to each other, and the side surfaces of the multi-layered substrate that are opposite to each other. The metallic film is connected to the grounding patterns that are provided on the top surface of the multi-layered substrate or between the laminated layers of the multi-layered substrate. Therefore, it is possible to achieve a superior electrical shielding effect through the metallic film, as compared with the related art. Since the metallic film is formed on the side surfaces of the sealing resin and the side surfaces of the multi-layered substrate, when the metallic film is formed by a plating method, the blind hole may not be provided in the related art. Therefore, it is possible to achieve the superior circulation of the plating liquid, which results in sure connection between the sure connection between the grounding pattern and the metallic film.
Owner:ALPS ALPINE CO LTD
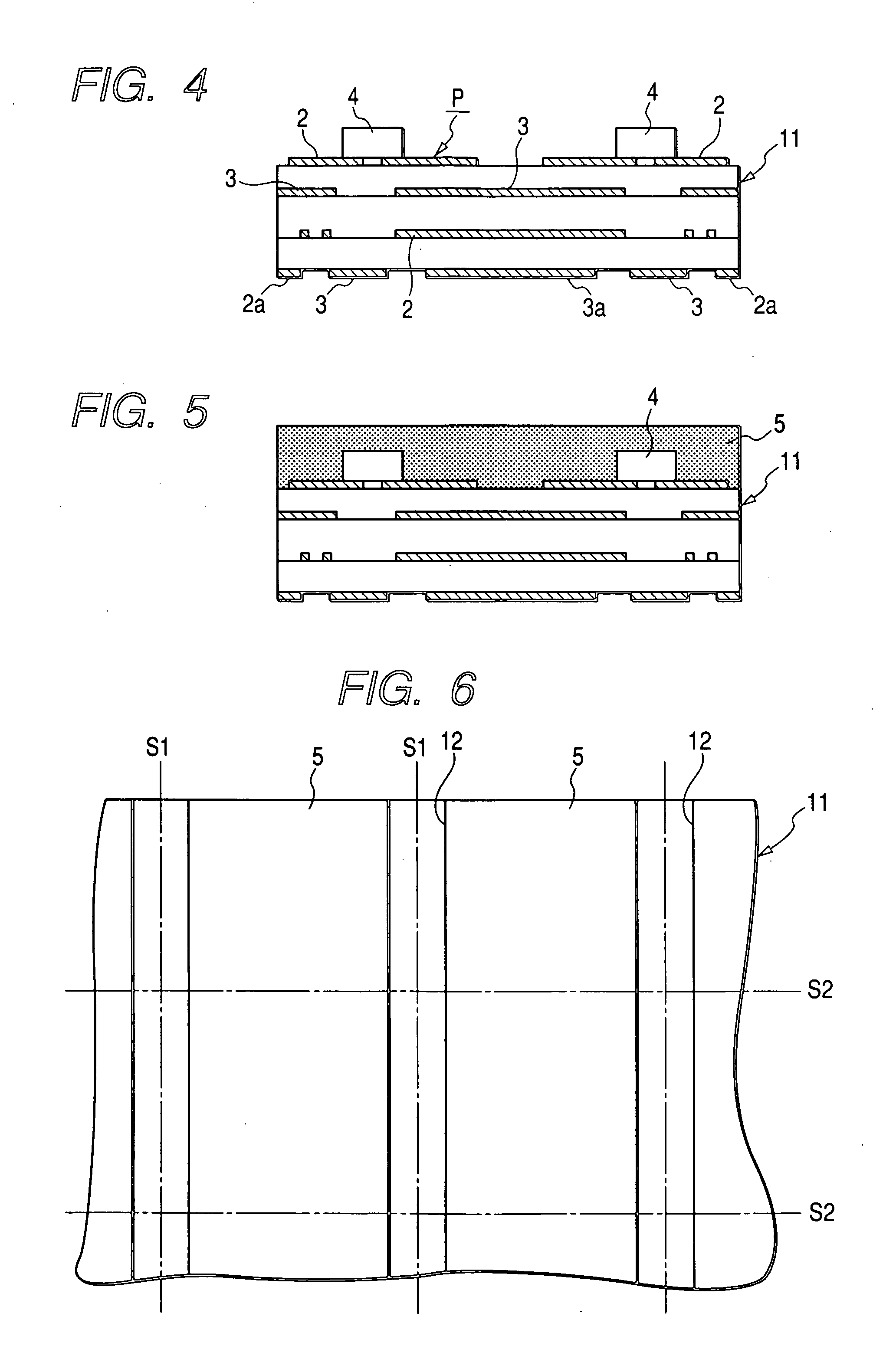
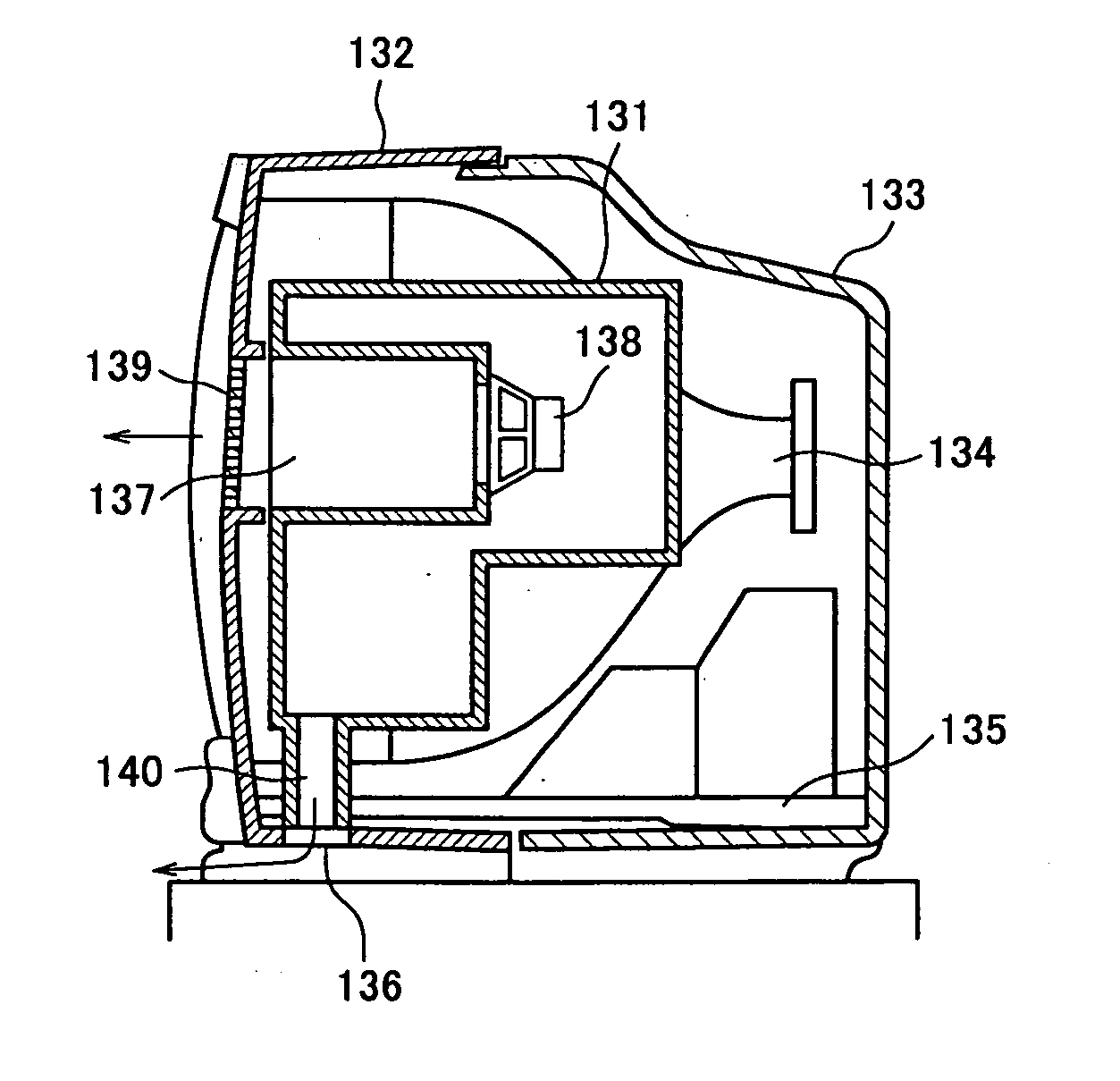
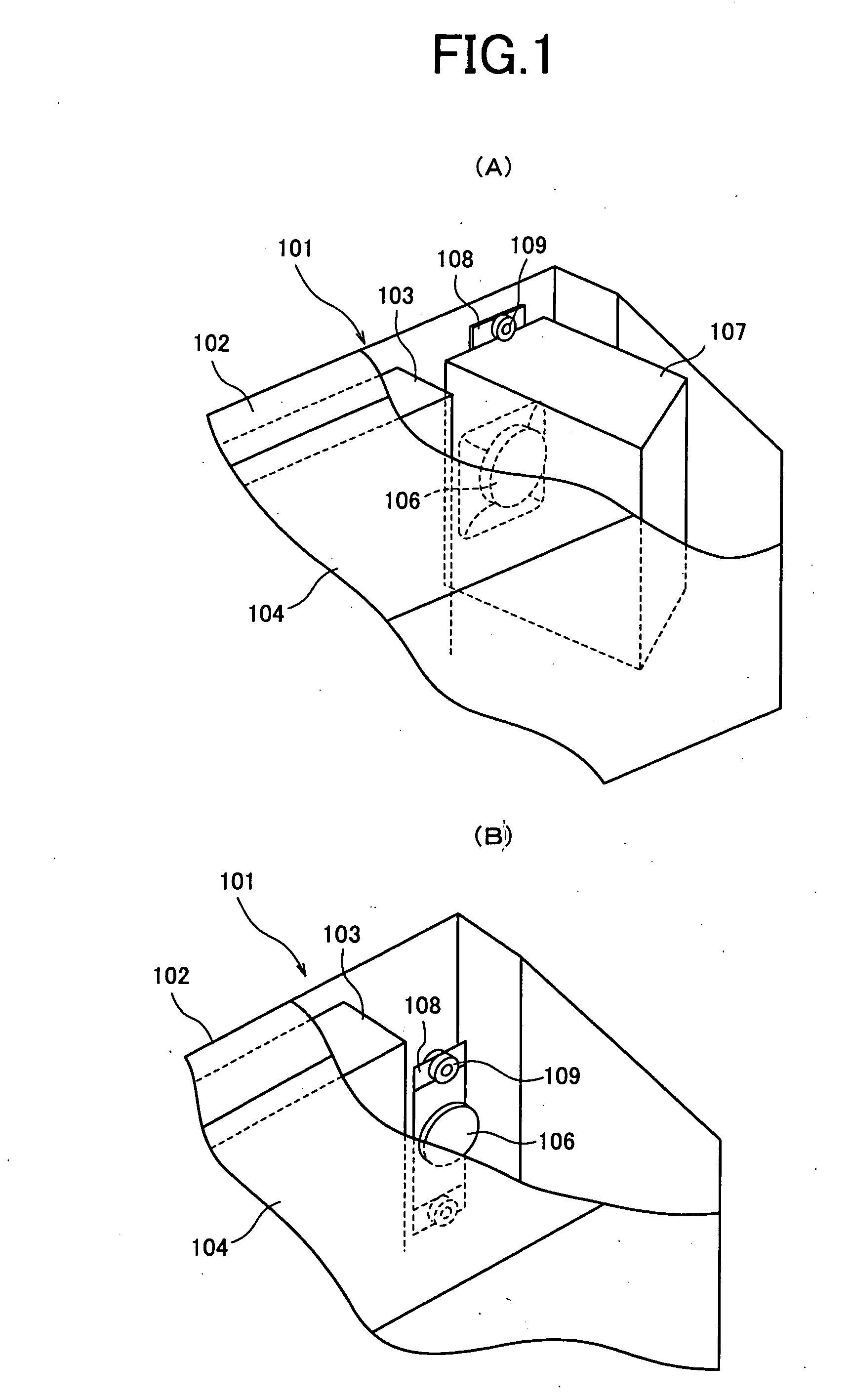
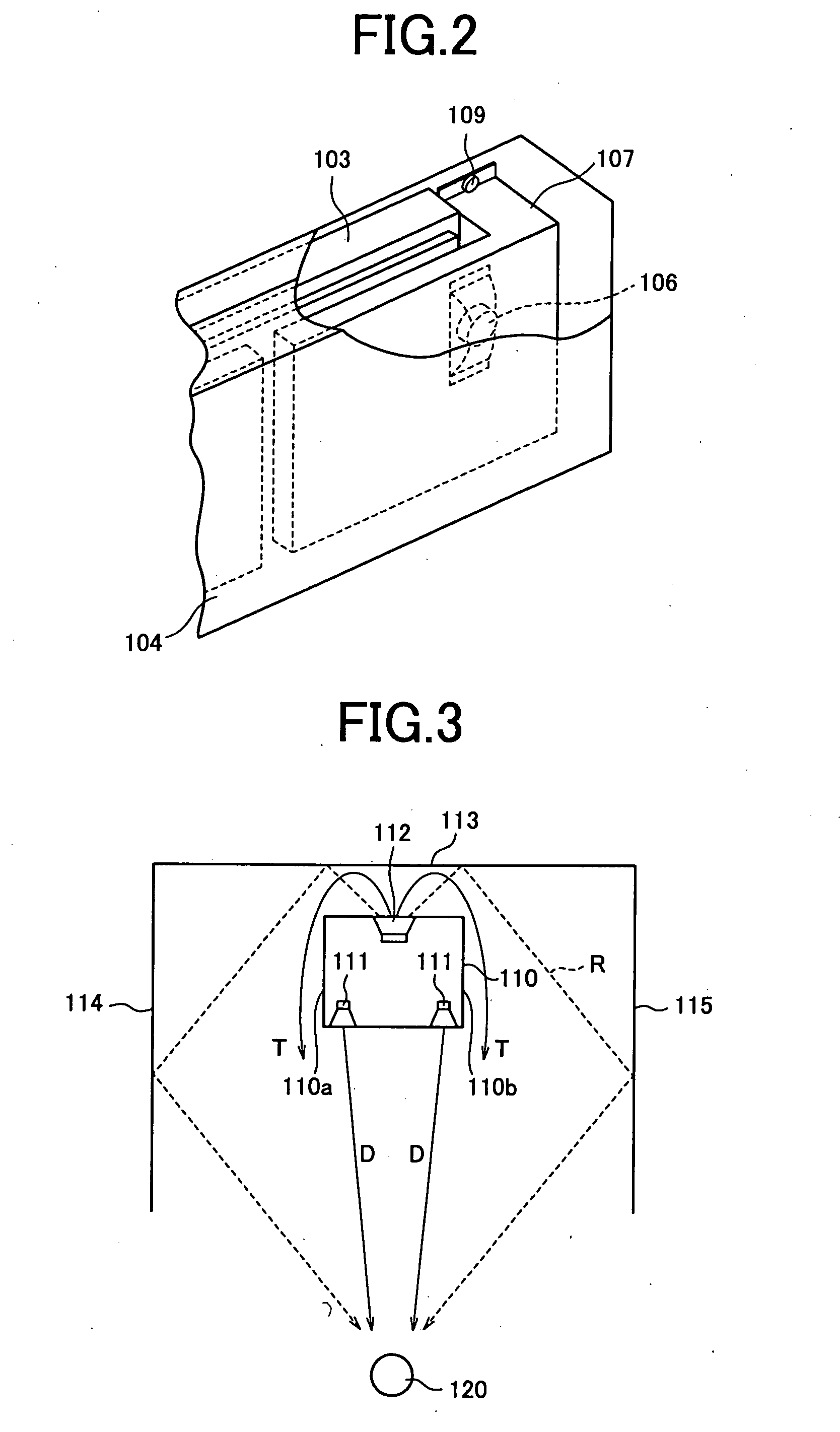
Image display device
InactiveUS20050129263A1Improve low frequency sound qualityQuality improvementTelevision system detailsColor television detailsEngineeringWoofer
An image display device (10) has a main display body (1) provided with a thin display unit (2), a low-frequency loudspeaker (woofer) (3) and two middle and high frequency loudspeakers (tweeters) (4a, 4b) and a stand (8) supporting the main display body (1). The stand (8) has a base (6) being just opposite at its top surface to a duct outlet of the woofer (3) , thereby sound emitted from the duct can be constantly absorbed by and reflected from the base and provided with the stable quality without influence of the floor's material. A housing containing the first loudspeaker and a pair of the second loudspeakers has a plurality of through holes formed in a first area corresponding to an aperture of each loudspeaker (3, 4a, 4b) and a plurality of blind holes formed in a second area surrounding the first area, wherein the second area for the first loudspeaker is different in peripheral shape and / or size from the second area for each of the second pair of loudspeakers. The above arrangement can attain an improved sound field expanding effect by using one woofer and two tweeters, attaining the sophisticated design of the loudspeaker system.
Owner:SHARP KK
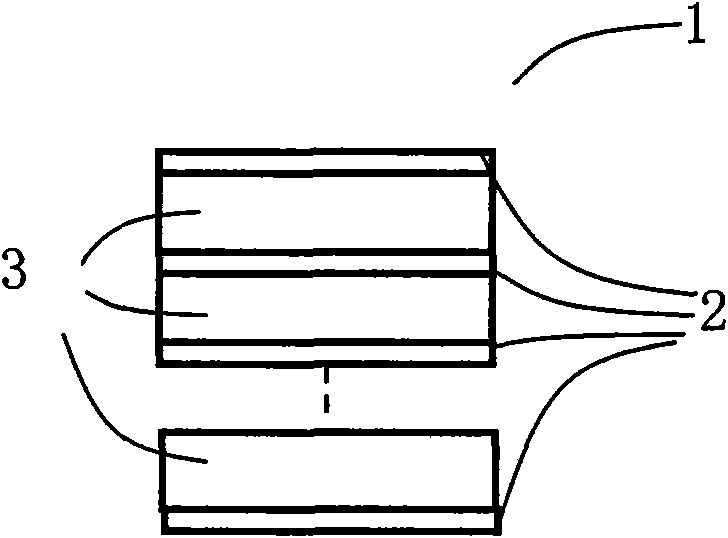
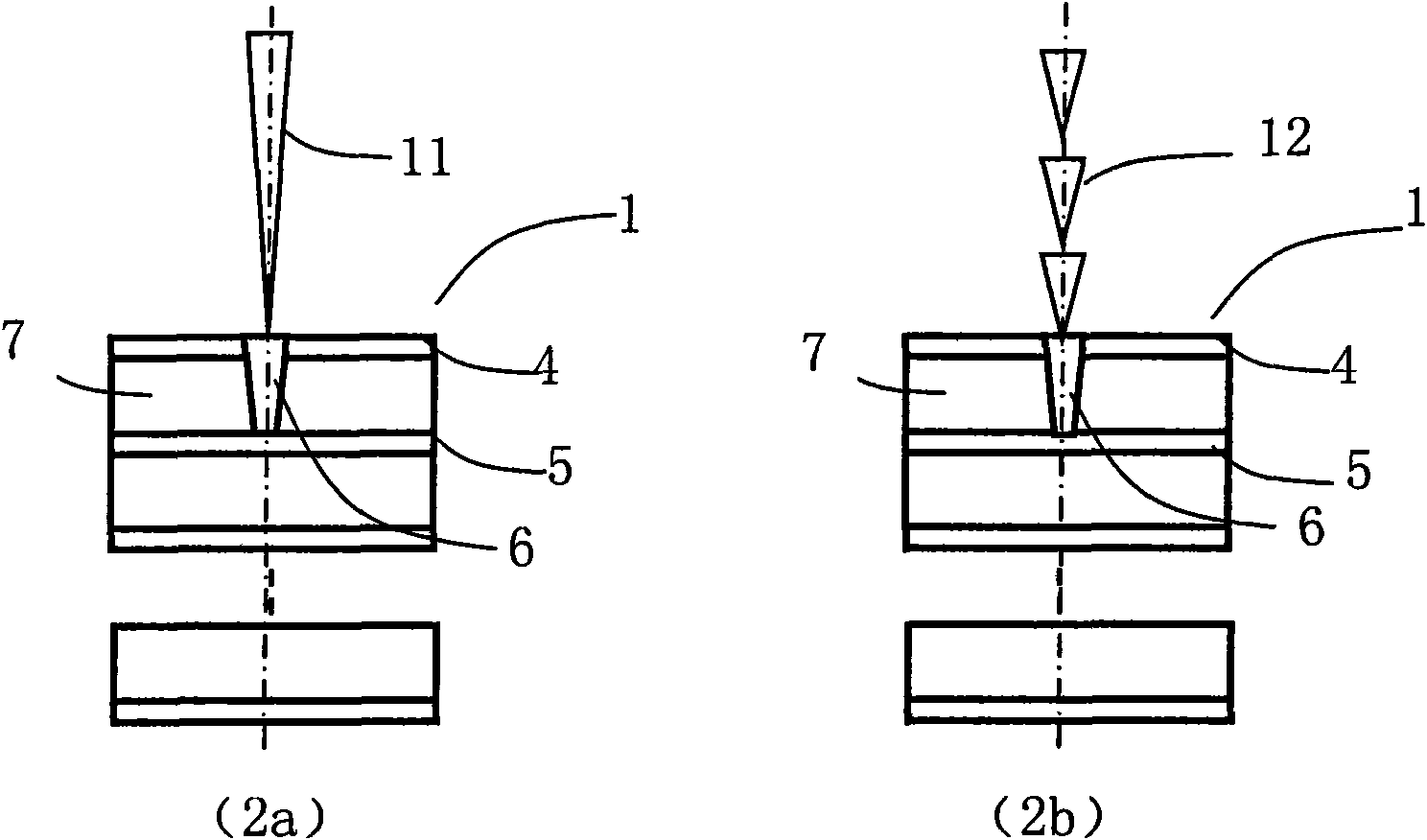
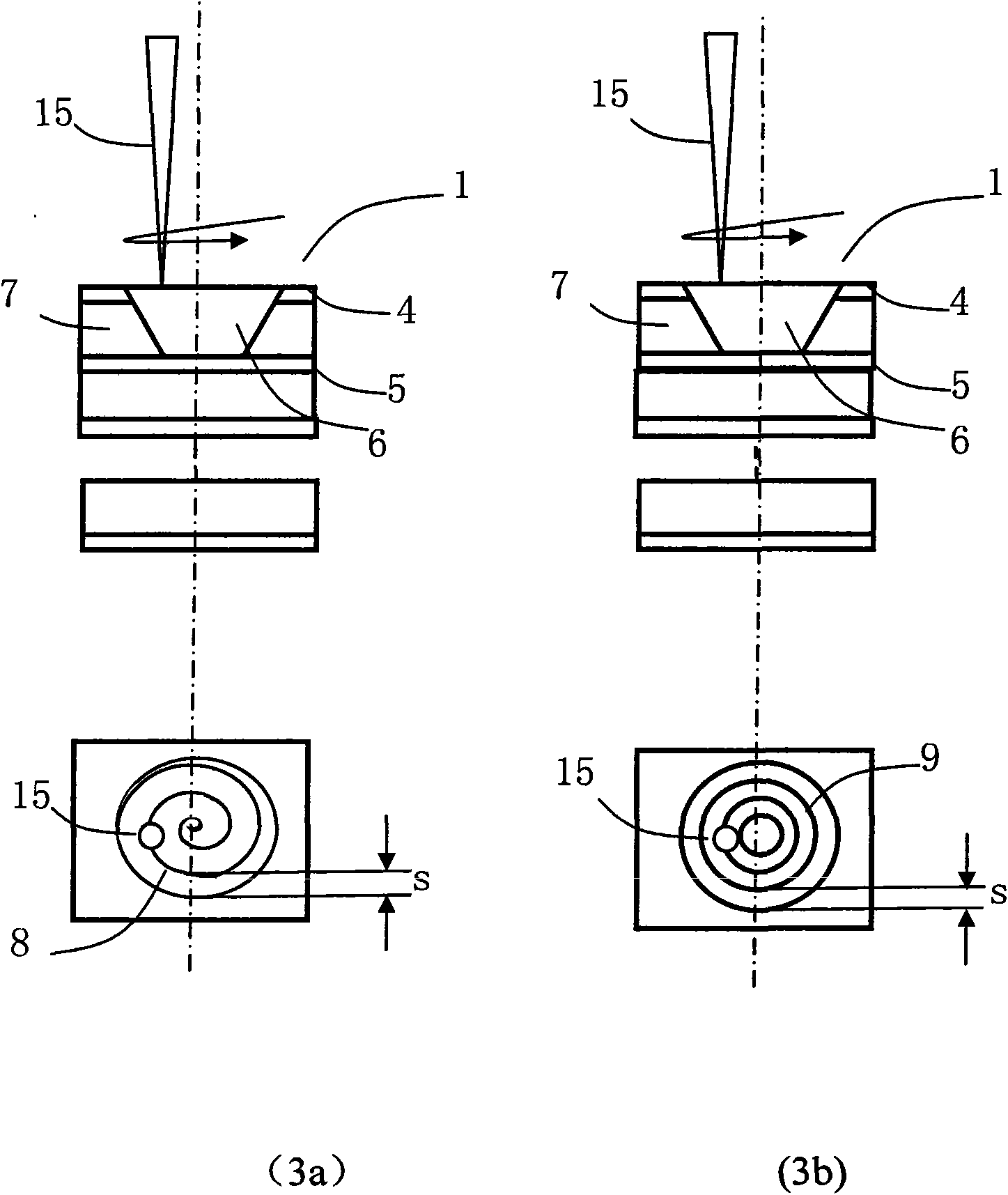
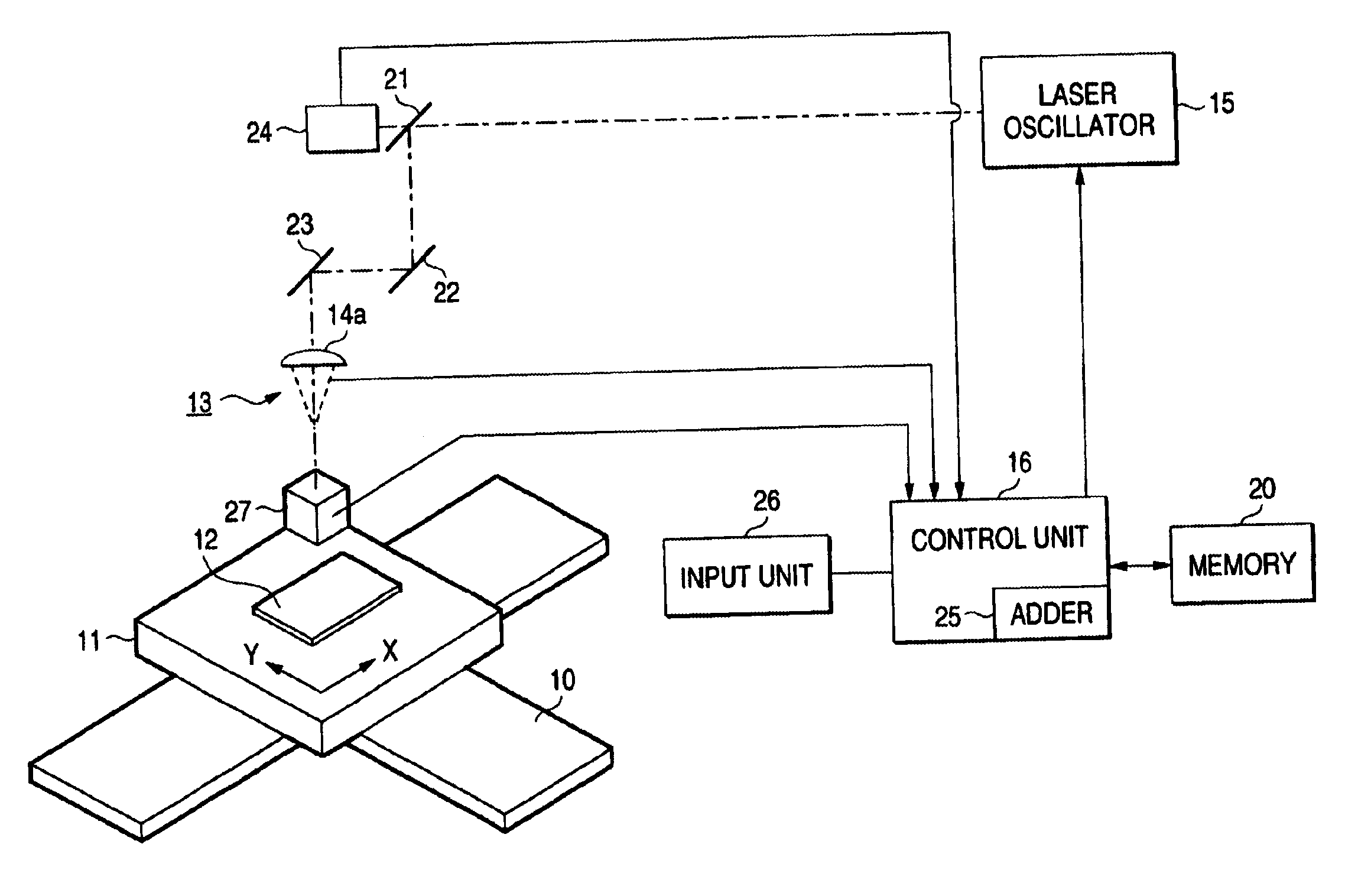
Method for processing blind hole by laser
InactiveCN101610643AAvoid Scanning RequirementsRemove distortionConductive material mechanical removalLaser beam welding apparatusUv laserLaser processing
The invention discloses a method for processing a blind hole by laser. The method combines fixed point UV laser impulse and UV laser spiral line or concentric circle scanning and is used for one-step blind hole processing or multi-step blind hole processing on multilayer circuit board. The method divides the UV laser blind hole drilling process into two parts, namely a part with an area near the circle center of the blind hole not more than UV laser spot diameter and a part with an area more than the UV laser spot diameter. Fixed point UV laser impulse is adopted to drill the blind hole, so as to remove material in the region with an area near the circle center not more than UV laser spot diameter; then UV laser spiral line or centric circle scanning method is adopted to move outside, so as to remove the material in the region with an area near the circle center more than UV laser spot diameter until meeting set blind hole size; and one-step blind hole or multi-step blind hole processing is drilled by UV laser through two steps or more steps. The method can ensure processing quality consistency of each blind hole, can greatly reduce bottom unevenness of the blind hole, and also can improve margin quality of blind hole processing.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Laser beam machining apparatus and laser beam machining method
InactiveUS6680459B2Pedestrian/occupant safety arrangementLaser beam welding apparatusLaser NozzleSpray nozzle
A laser beam machining apparatus forms blind holes at predetermined intervals in a workpiece by intermittently irradiating a laser beam from a laser nozzle to the workpiece while the laser nozzle and the workpiece being moved relatively. During the time the workpiece is subjected to machining, the electrostatic capacity between the support member and the laser nozzle is detected by an electrostatic capacity sensor while the workpiece made of conductive material is supported on the support member. The irradiation output power is controlled by a control unit which operates to vary the number of output pulses from the laser nozzle each time one hole is formed according to the result detected in response to variation in the thickness of the workpiece.
Owner:KOMATSU IND CORP
Methods of forming blind wafer interconnects, and related structures and assemblies
InactiveUS20070257373A1Reduce expensesShorten the timeSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringConductive materials
Methods for forming blind wafer interconnects (BWIs) from the back side surface of a substrate structure to the underside of a bond pad on the opposing surface includes the formation of a blind hole from the back side surface, forming a passivating layer therein, removing passivation material from the blind hole bottom, depositing at least one conductive layer within the blind hole, and filling the blind hole with solder or other conductive material or a dielectric material.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
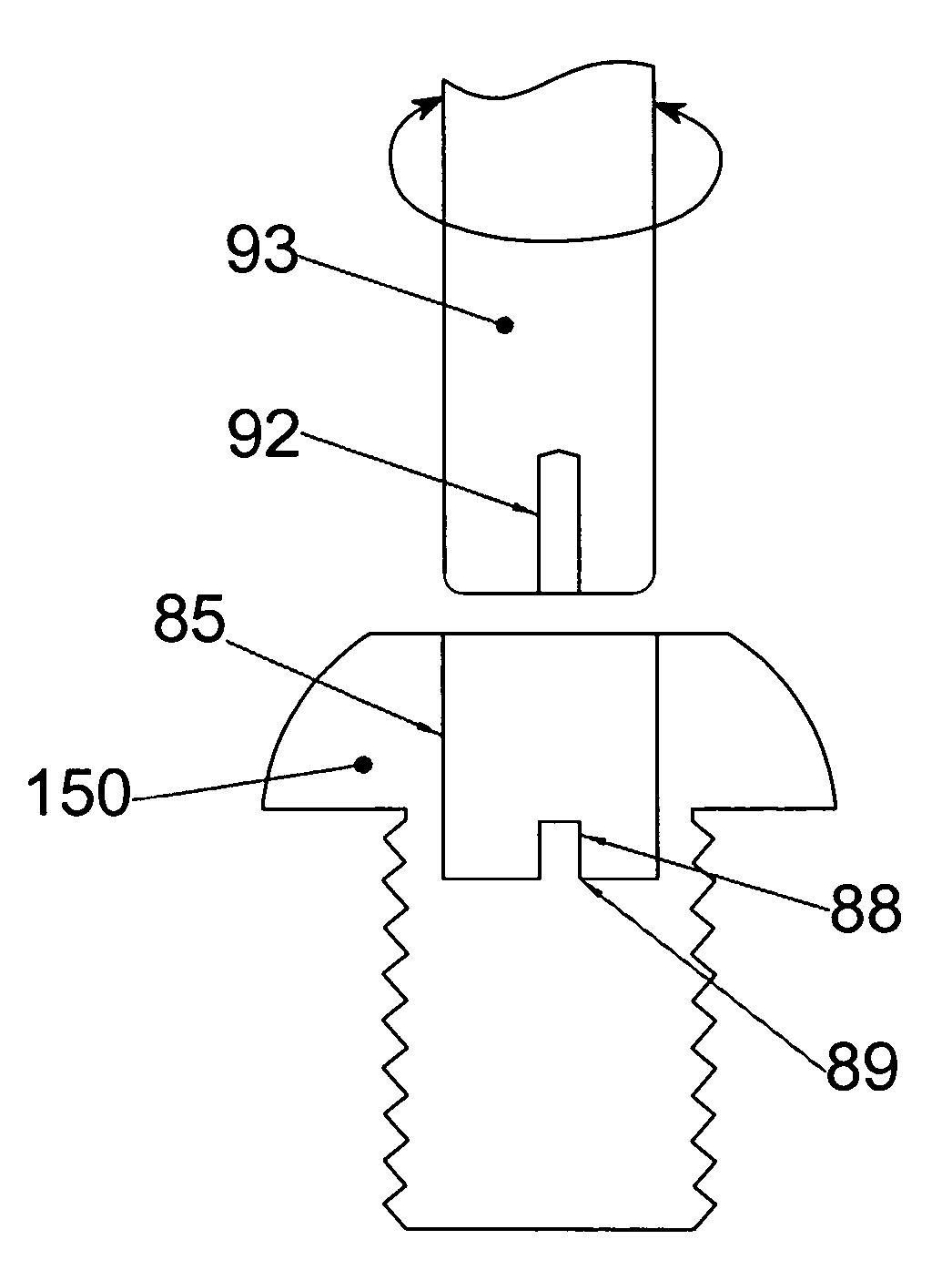
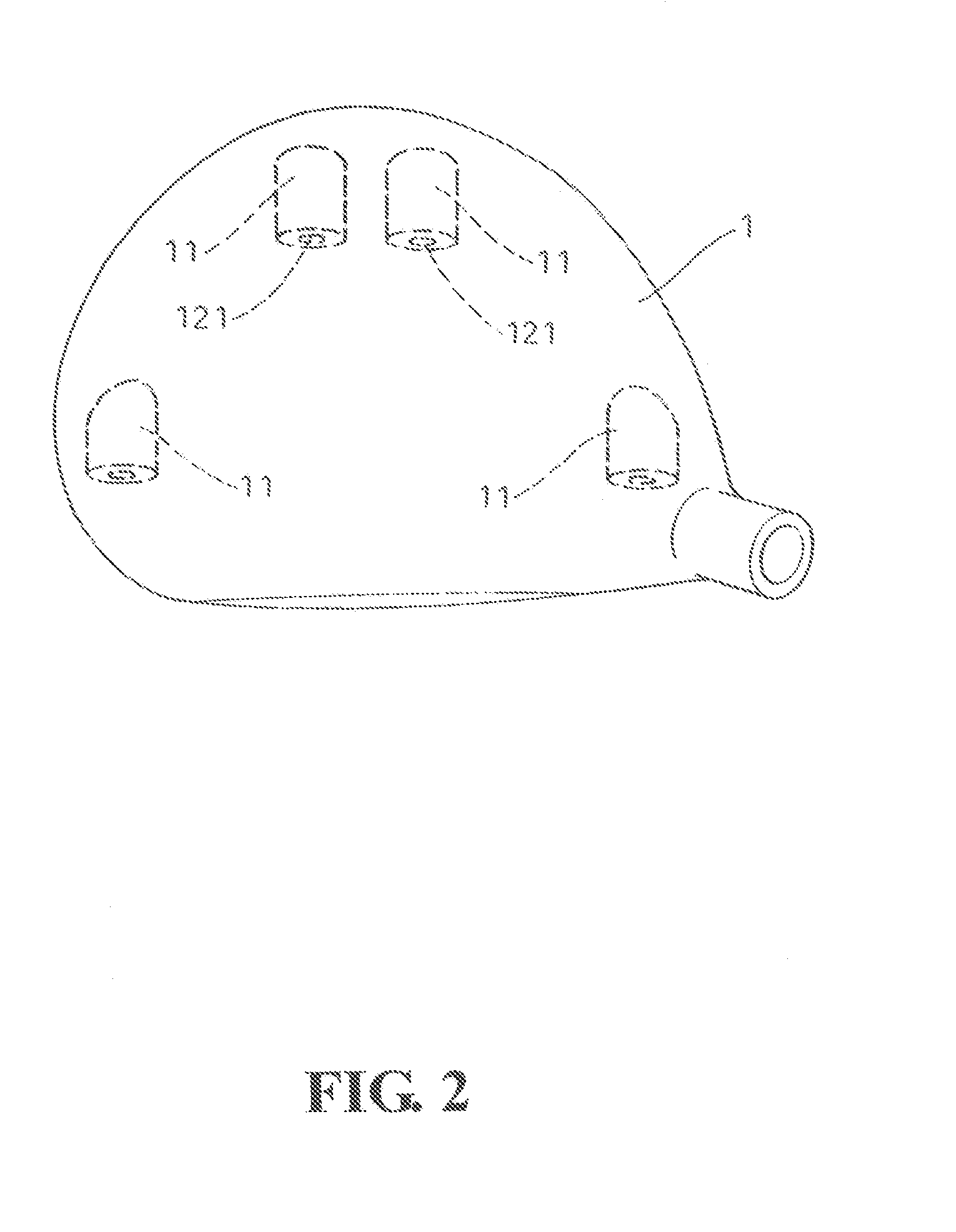
Weight adjustable golf club head
The club head contains a number of blind holes arranged at appropriate places other than the hitting surface of the club head. Each blind hole is for the accommodation of a weight member. Each weight member contains at least a weight element and a fastening element. The fastening element has a threaded rod extending from the bottom of a cone-shaped head. The fastening element is squeezed into an end of the weight element with the threaded rod penetrating through the weight element and into the club head for fixation. On the other hand, the circumference of the weight element has a number of slits so that the cone-shaped head of the fastening element can force the wall of the weight element to press tightly against the hole to further enhance the fixation.
Owner:HSIAO PEN LONG
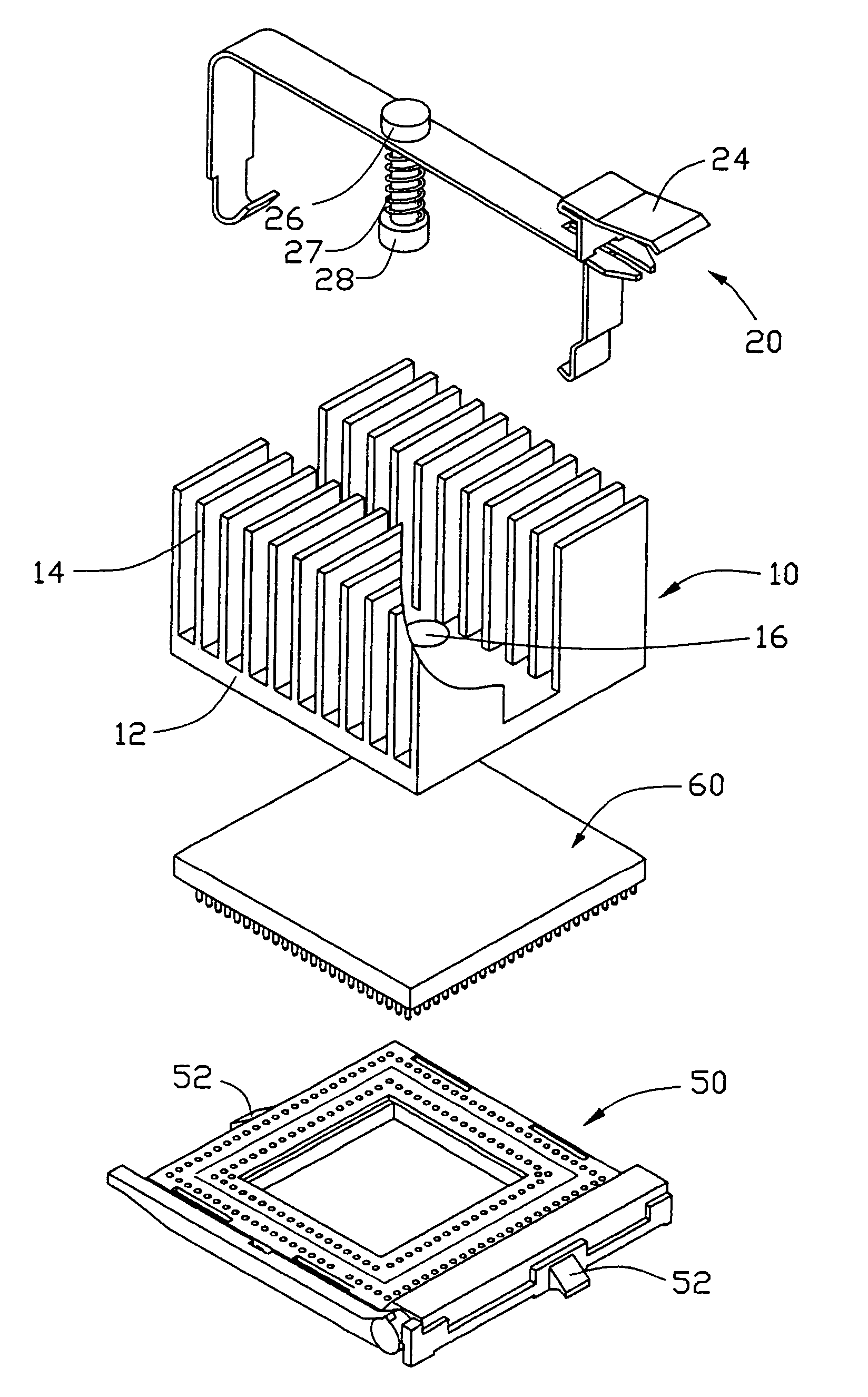
Heat sink clip with pressing post
InactiveUS7009843B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringHeat spreader
A heat sink clip (20) includes a main body, a post (26), and a spring (27). The main body includes a longitudinal portion (31), first and second locking arms (32, 24) extending downwardly from opposite ends of the longitudinal portion. The longitudinal portion defines a through aperture (36) in a middle thereof. Two hooks (38, 46) are respectively formed at free ends of the first and second locking arms for engagement with catches (52) of a socket (52). The post has a pressing portion at a bottom thereof for being fittingly received in a blind hole (16) of a heat sink (10). The post extends through the through aperture of the longitudinal portion. The resilient element is disposed around the post below the longitudinal portion.
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD
Blind fastener and nose assembly for installation of the blind fastener
InactiveUS6868757B2Reduce wall thicknessNot significantly weaken the sleeveRivetsLoad modified fastenersNoseBlind hole
A blind fastener for securing a plurality of workpieces is provided that has a sleeve, and a pin member. In an alternate embodiment, the blind fastener has a sleeve, a pin member and a nut. The sleeves have a head with a plurality of rearwardly sloping recesses disposed therein. The recesses are adapted to be engaged with a plurality of rearwardly sloping nibs disposed on one end of a nose secured to an installation tool. The pin members have a splined head adapted to be engaged with a splined driver secured to an installation tool. Use of the splined head on the pin member, the splined driver, rearwardly sloping recesses on the sleeve, and rearwardly sloping nibs on the nose eliminates camming out of the nibs from the recesses during installation of the blind fastener. A nose assembly for installation of the blind fastener is also provided.
Owner:HUCK INT INC
Vortex flow sensor for measuring fluid flow through a flow tube
InactiveUS6910387B2Improve thermal conductivityEasy to measureVolume/mass flow by dynamic fluid flow effectIndirect mass flowmetersTwo temperatureEngineering
The vortex flow sensor is designed to measure the mass flow rate, the volumetric flow rate, or the flow velocity of a fluid flowing in a flow tube having a tube wall, and has two temperature sensors arranged in such a way that the vortex flow sensor may also be used with fluids which would corrode the temperature sensors. A bluff body in the flow tube sheds vortices and thus causes pressure fluctuations. A vortex sensor device responsive thereto is fitted downstream of the bluff body in a hole provided in the wall of the flow tube. The vortex sensor device comprises a sensor vane extending into the fluid. The temperature sensors are disposed in a blind hole of the sensor vane. Alternatively, the temperature sensor may be disposed in blind hole of the bluff body.
Owner:ENDRESS HAUSER FLOWTEC AG
Method for mounting diamond, diocroma or the like in jadeite or jade
A method for inlaying the diamond or zircon onto jadeite includes such steps as blanking, drilling one or more blind or through holes, installing inlaying nail, cutting the inlaying nail, inlaying the diamond or zircon to said inlaying nail, wrapping the edge of inlaid diamond or zircon by an expanding sleeve made of gold alloy or stainless steel, grinding and polishing.
Owner:李杰城
Tamper-resistant fastener and method and tool for use with same
A fastener includes a round, blind hole or pocket in its head. Installation and removal of the fastener is accomplished with a tool containing an eccentric segment on the end of a shaft. When rotated within the pocket, the eccentric segment displaces laterally relative to the shaft to provide a friction grip to the lateral wall of the pocket. The strength of the grip is proportional to the applied torque. Eccentric displacement allows rotation but prevents the tool from spinning out of the fastener thereby eliminating cam-out and surface damage resulting from contact with a spinning tool tip. The eccentric head of the tool can be made disposable and to shear off when a predetermined torque is reached. The smooth-sided round hole offers no purchase for commonly available tools; making the fastener tamper-resistance. In another embodiment, the fastener includes a raised portion in the pocket. A tool having a complementary opening shears off the raised portion at a predetermined torque.
Owner:FLESHER ROBERT W
Two piece cancellous construct for cartilage repair
ActiveUS7837740B2Guaranteed functionEasily placed in defect areaBone implantTissue regenerationInterference fitChondral defect
The invention is directed toward a cartilage repair assembly comprising a shaped allograft two piece construct with a demineralized cancellous cap and a mineralized cylindrical base member defining a blind bore with a through going transverse bore intersecting the blind bore. The demineralized cancellous cap has a cylindrical top portion and a smaller diameter cylindrical stem extending away from the top portion which fits into the blind bore of the mineralized base member. The cap stem defines a transverse through going bore which is aligned with the through going bore of the base member to receive a cylindrical cortical pin holding the cap within the base member. The shaped structure is dimensioned to fit in a drilled bore in a cartilage defect area so that the assembly engages the side wall of the drilled bore in an interference fit.
Owner:MUSCULOSKELETAL TRANSPLANT FOUND INC
Corrosion resistant wafer processing apparatus and method for making thereof
InactiveUS20080006204A1Vacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingElectrical connectionThermal expansion
A wafer processing apparatus characterized by having corrosion resistant connections for its electrical connections, gas feed-through channels, recessed areas, raised areas, MESA, through-holes such as lift-pin holes, threaded bolt holes, blind holes, and the like, with the special configurations employing connectors and fillers having excellent chemical resistant properties and optimized CTEs, i.e., having a coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) that closely matches the CTE of the base substrate layer, the electrode(s), as well as the CTE of coating layer. In one embodiment, a filler composition comprising a glass-ceramic material is employed.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Tap
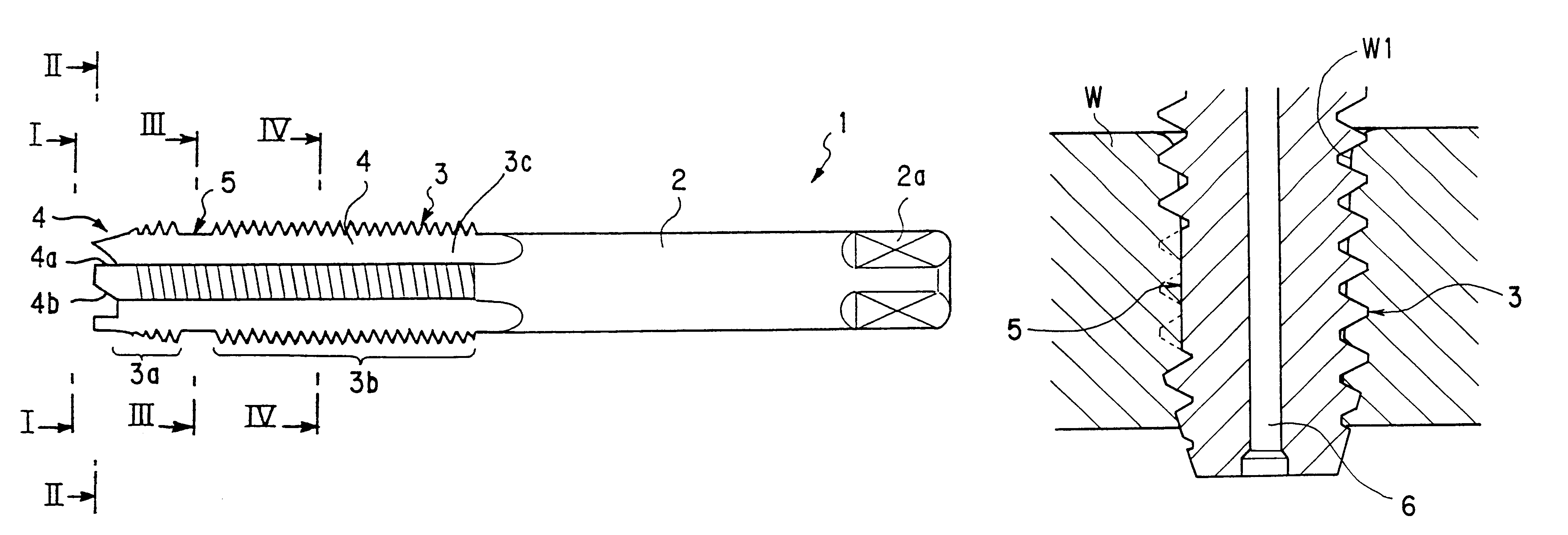
InactiveUS6499920B2Reduce processing timeImprove productivityThread cutting toolsWood turning toolsFluteEngineering
A cutting tap comprises a threaded portion including a lead whose thread diameter gradually decreases toward a front end of the lead, a complete thread portion continued from the lead, and four flutes arranged at equal intervals in a circumferential direction. In the cutting tap, a first cutting edge portion for processing a prepared hole is formed at a front end surface of the lead, and a second cutting edge portion for finishing a minor diameter of an internal thread is formed in a part of an outer periphery of the complete thread portion, the second cutting edge portion being one or more pitches long. The cutting tap can perform processing of a prepared hole, tapping, and finishing of a minor diameter by a single step, and can also perform tapping even if a prepared hole for an internal thread is a blind hole or the like and does not have enough space.
Owner:TANOI MFG CO LTD
Cold-forging technique of gear shaft
InactiveCN101332488ALow flow resistanceReduce the bearing unit extrusion forceForging/hammering/pressing machinesMetallic material coating processesGear wheelPre stress
The invention relates to a cold forging technology for a gear shaft; the cold forging technology is characterized in that a new technology of the cold forging forming of the inside and outside and split flow forging, a volume split flow space is arranged between the gear shaft diameter and a concave die, the metal flow resistance is reduced and the unit extruding force carried by the die is lowered by split flow; high-strength die steel and split structure are adopted to produce a gear hole forming die; the concave die is produced by adopting three-layer sleeve prestressed structure so as to improve the compression resistance of the die; a punch is made from an alloy steel material and used for the cold forging and precision forming of a complex gear form blind hole, which improves the forming quality and production efficiency of the gear hole, and lowers the consumption of the raw materials markedly. The cold forging technology of the invention has the advantages of achieving the smooth forming of the gear form blind hole, improving the production efficiency greatly, and improving the quality of the gear hole and the qualification rate of the product markedly.
Owner:SHANGHAI DONGFU COLD FORGING MFG
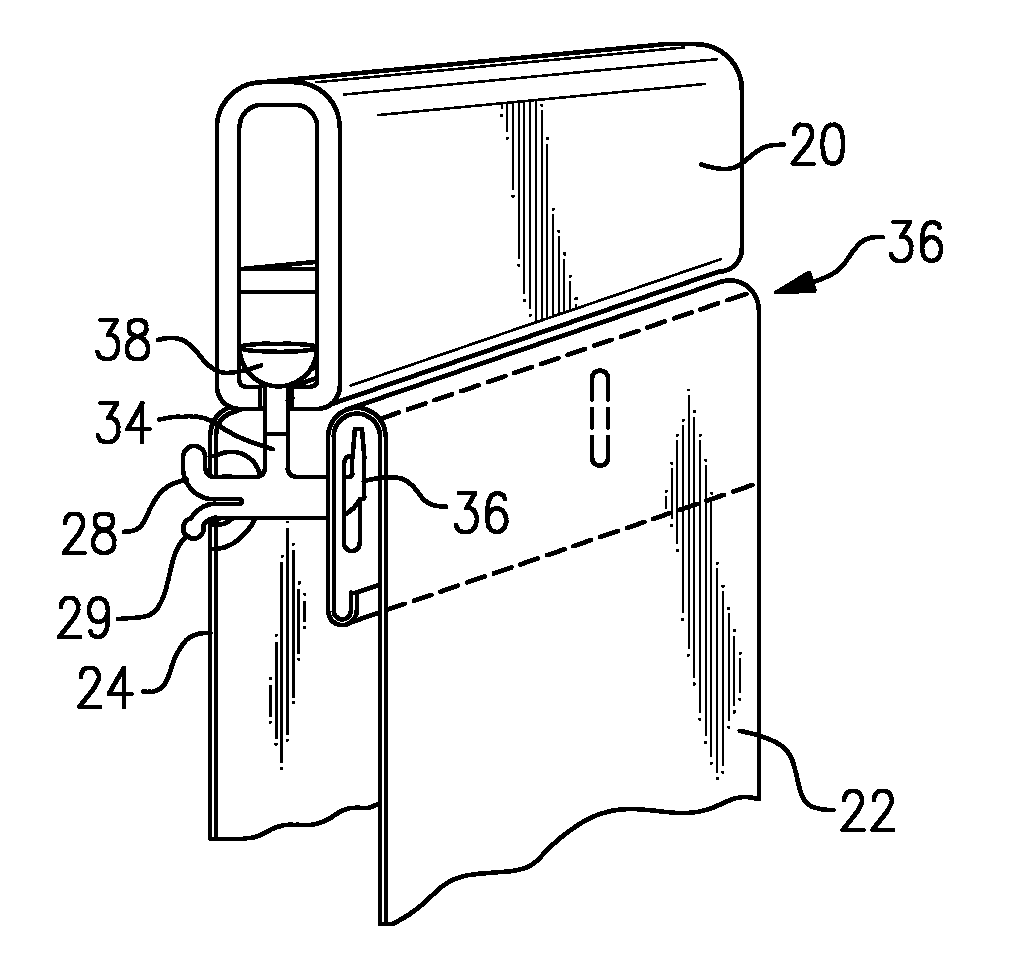
Shower curtain rail and glide assembly
A shower curtain and support system employs an elongated rail supported at the shower or tub. The rail extrusion can be an extrusion with an inverted U profile, with an open slot or slots at its base. There are glides, e.g., nylon members with a ball, hemisphere, or other wide head portion and shaft that projects out through the slot from the open interior of the rail. The glides have one or two hook structures for attaching to a fabric curtain and a vinyl curtain liner. In one preferred version, there is a liner hook and spring retaining arm on one side that fits into the grommet at the top of the liner. On the other side is a short arm with a button that fits into a button hole on the cloth or fabric curtain. The curtain has blind button holes or grommets at its upper hem, so that the hook structure, e.g., button, does not show.
Owner:KARTRI SALES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com