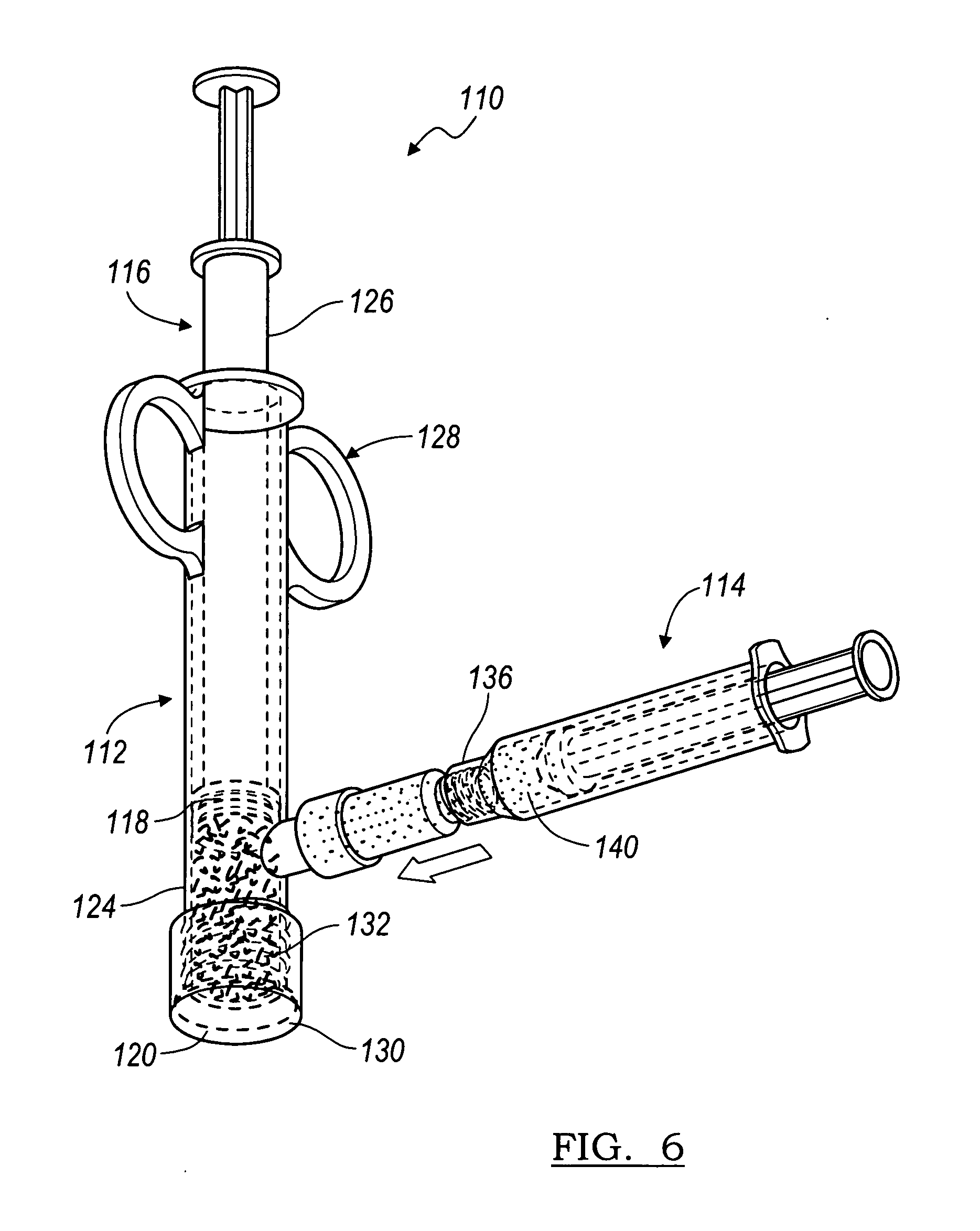
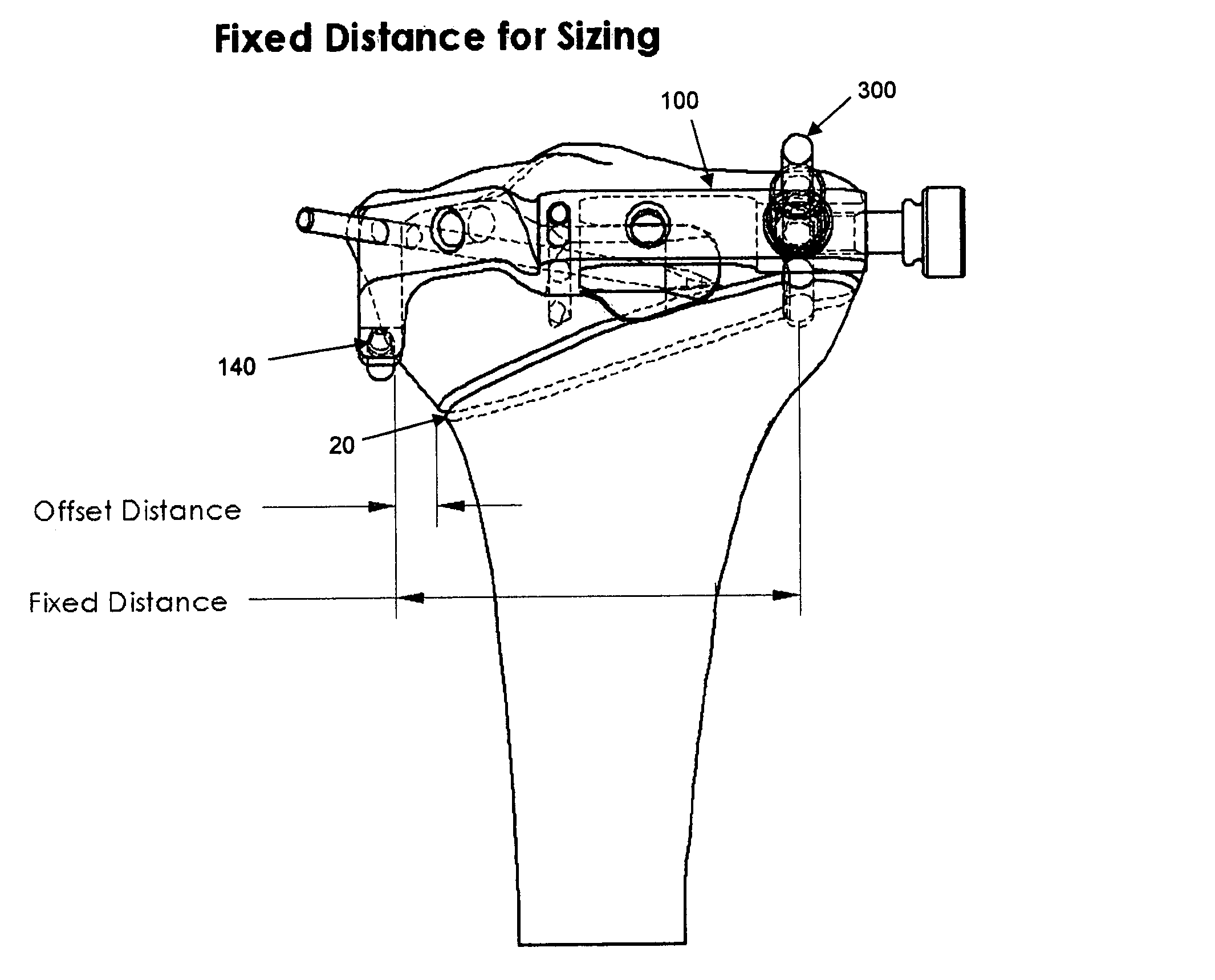
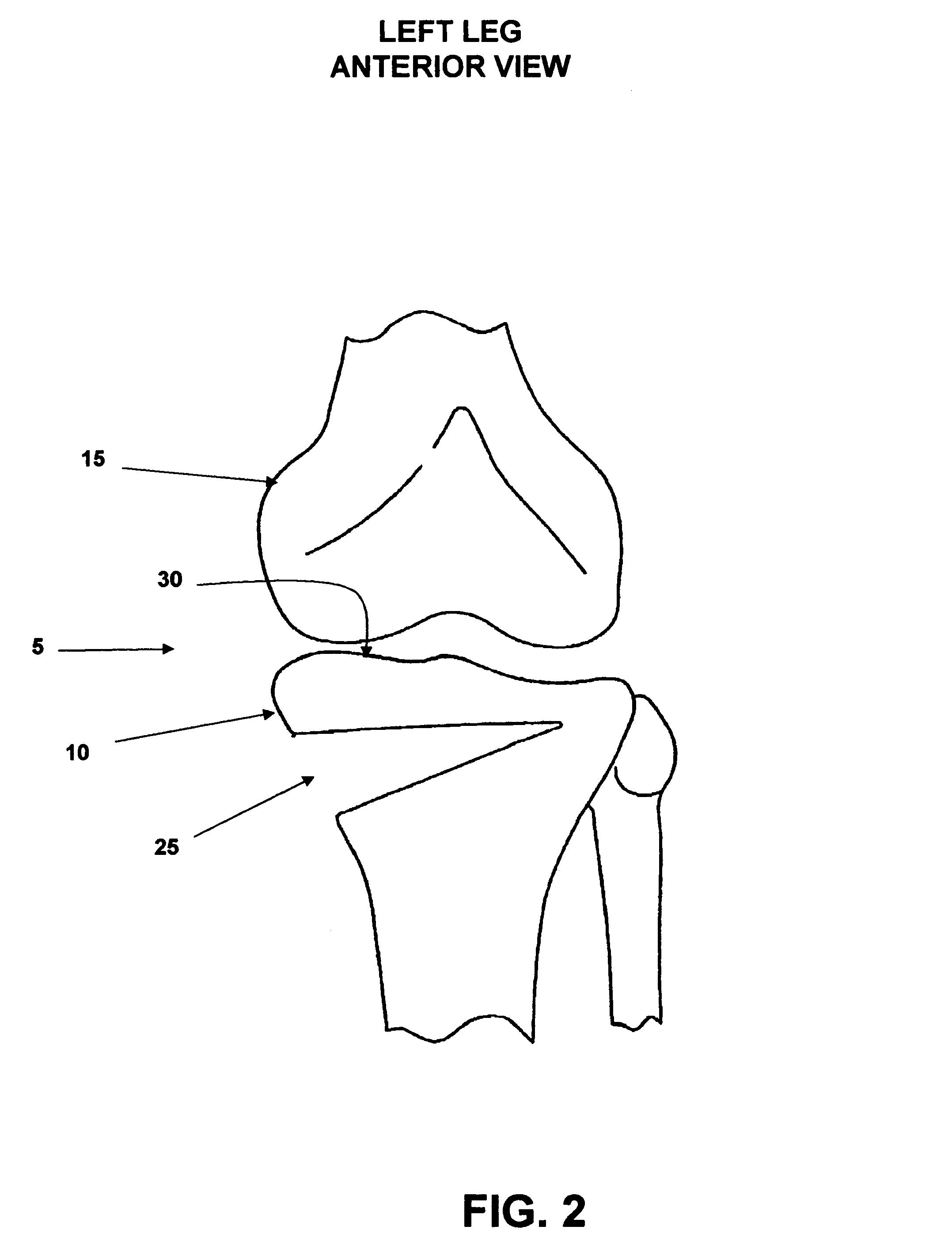
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
628 results about "Bone surface" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
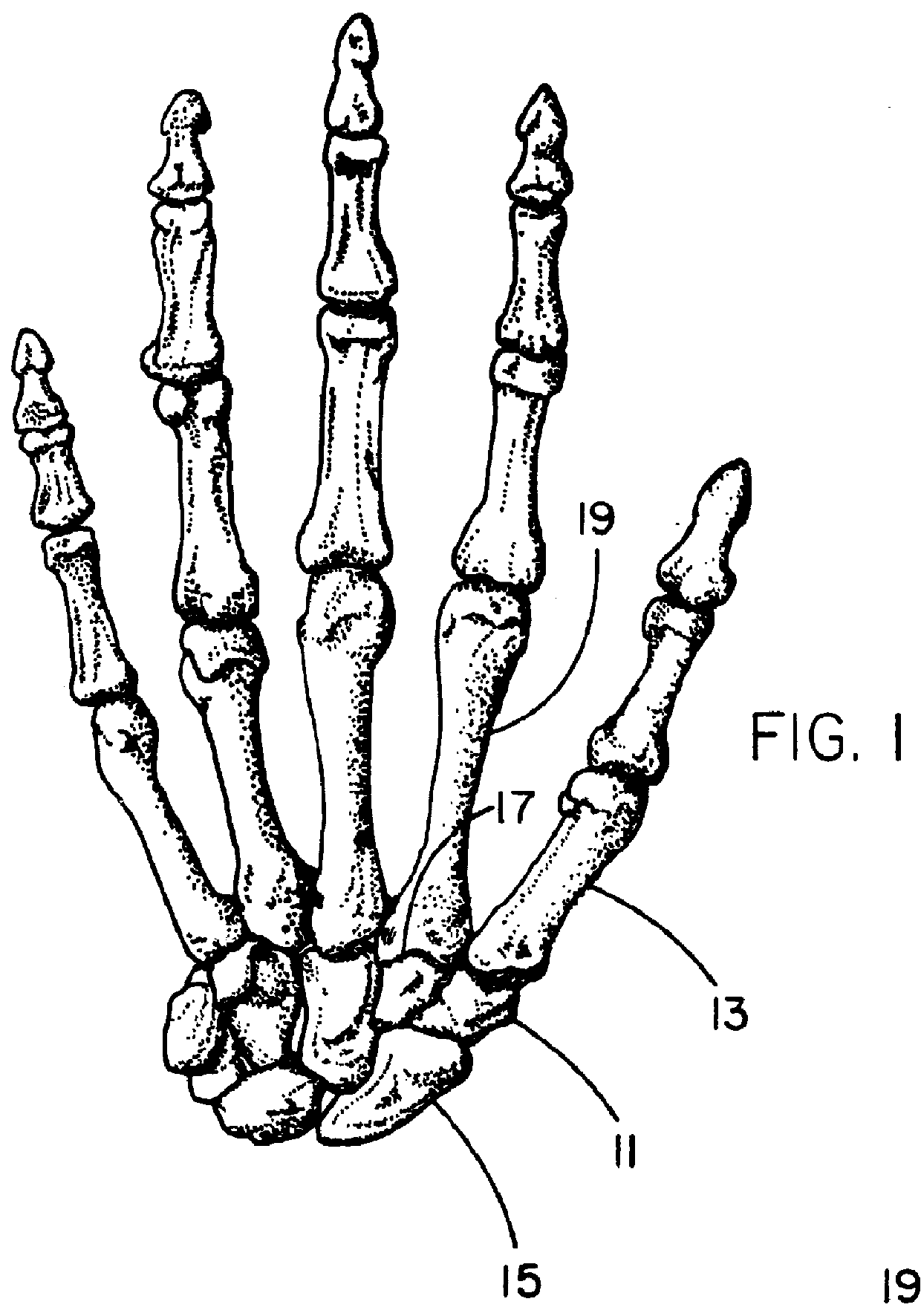
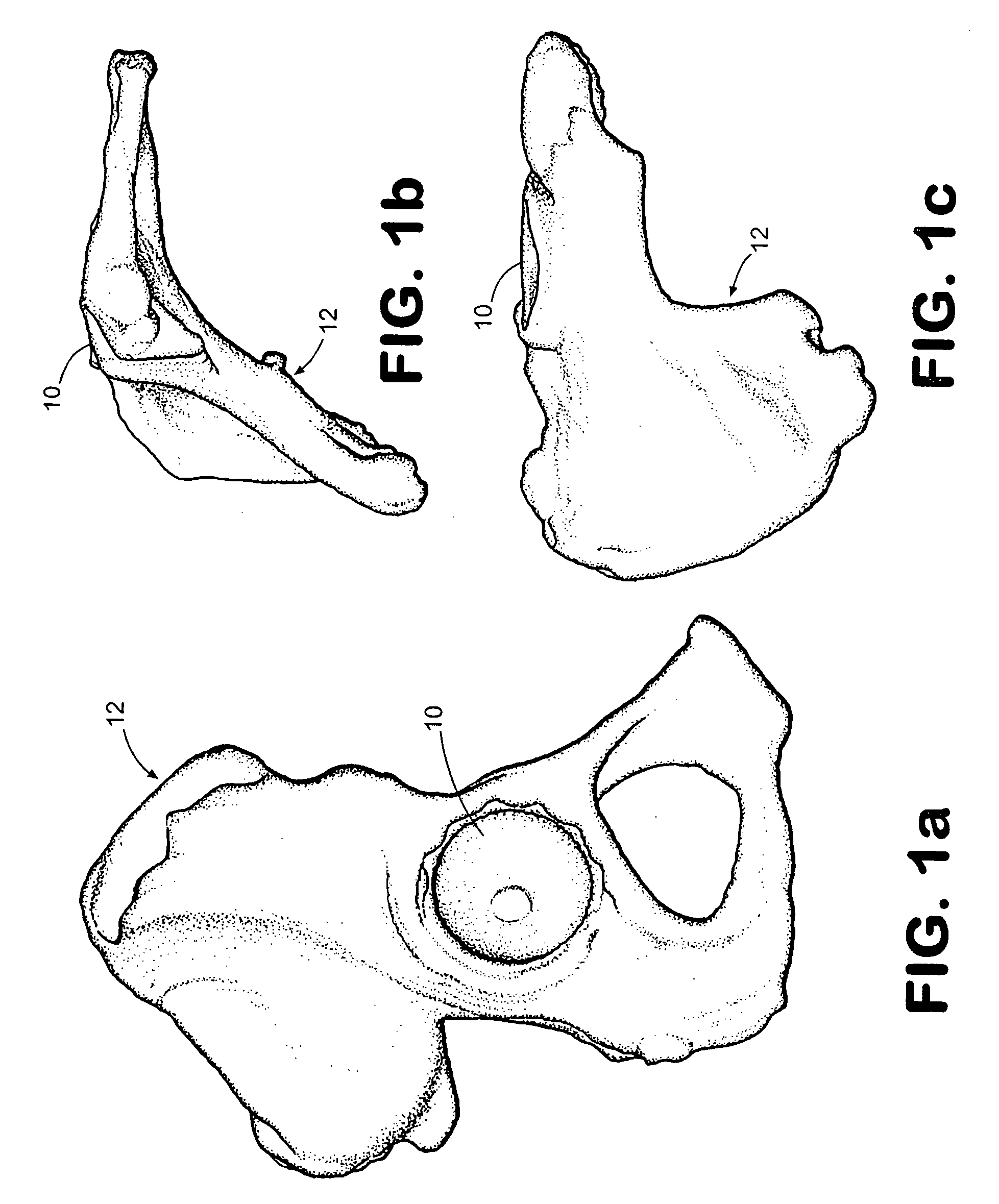
Almost every bone in your body is made of the same materials: The outer surface of bone is called the periosteum (say: pare-ee-OSS-tee-um). The next layer is made up of compact bone. Within the compact bone are many layers of cancellous (say: KAN-sell-us) bone, which looks a bit like a sponge.
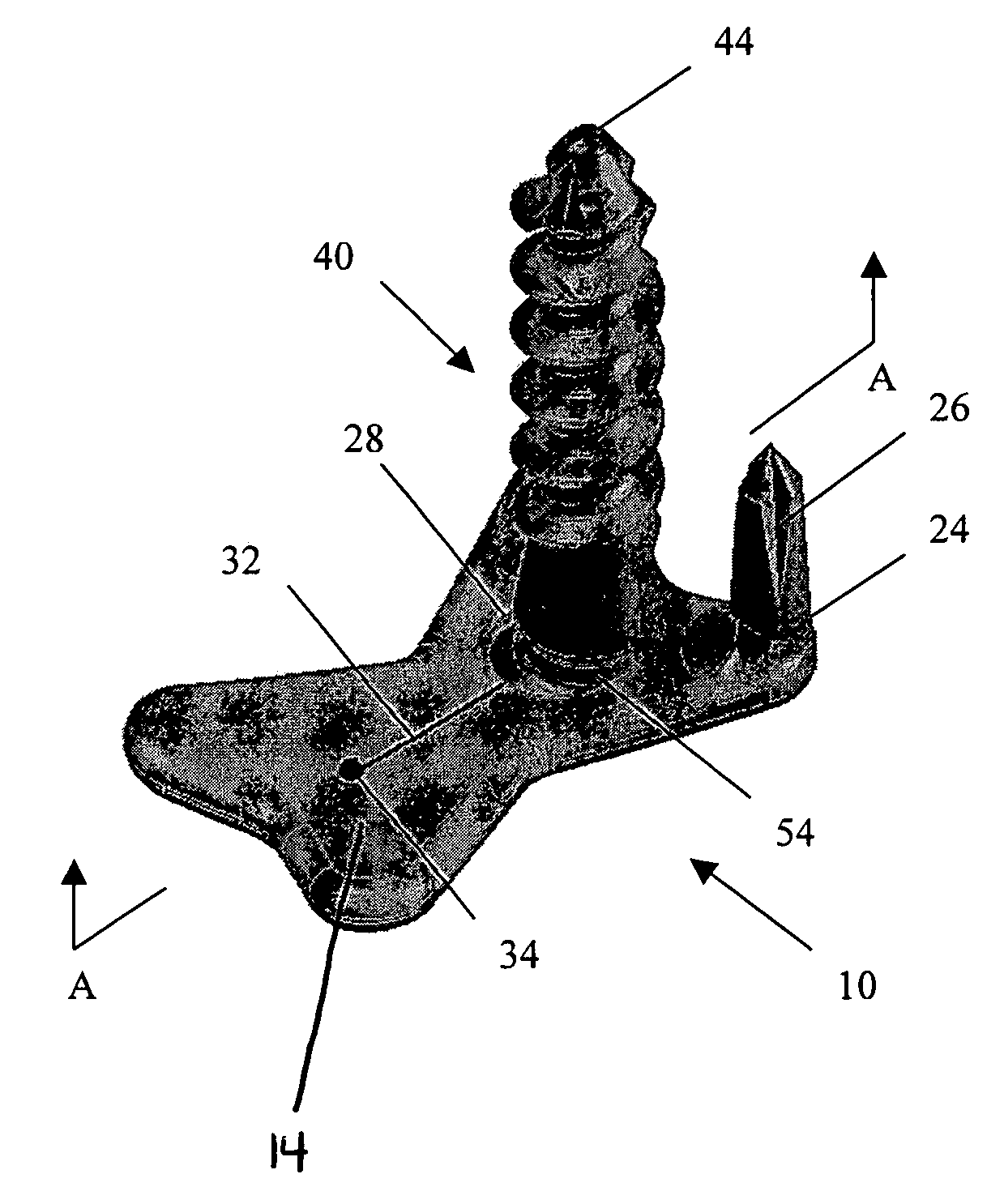
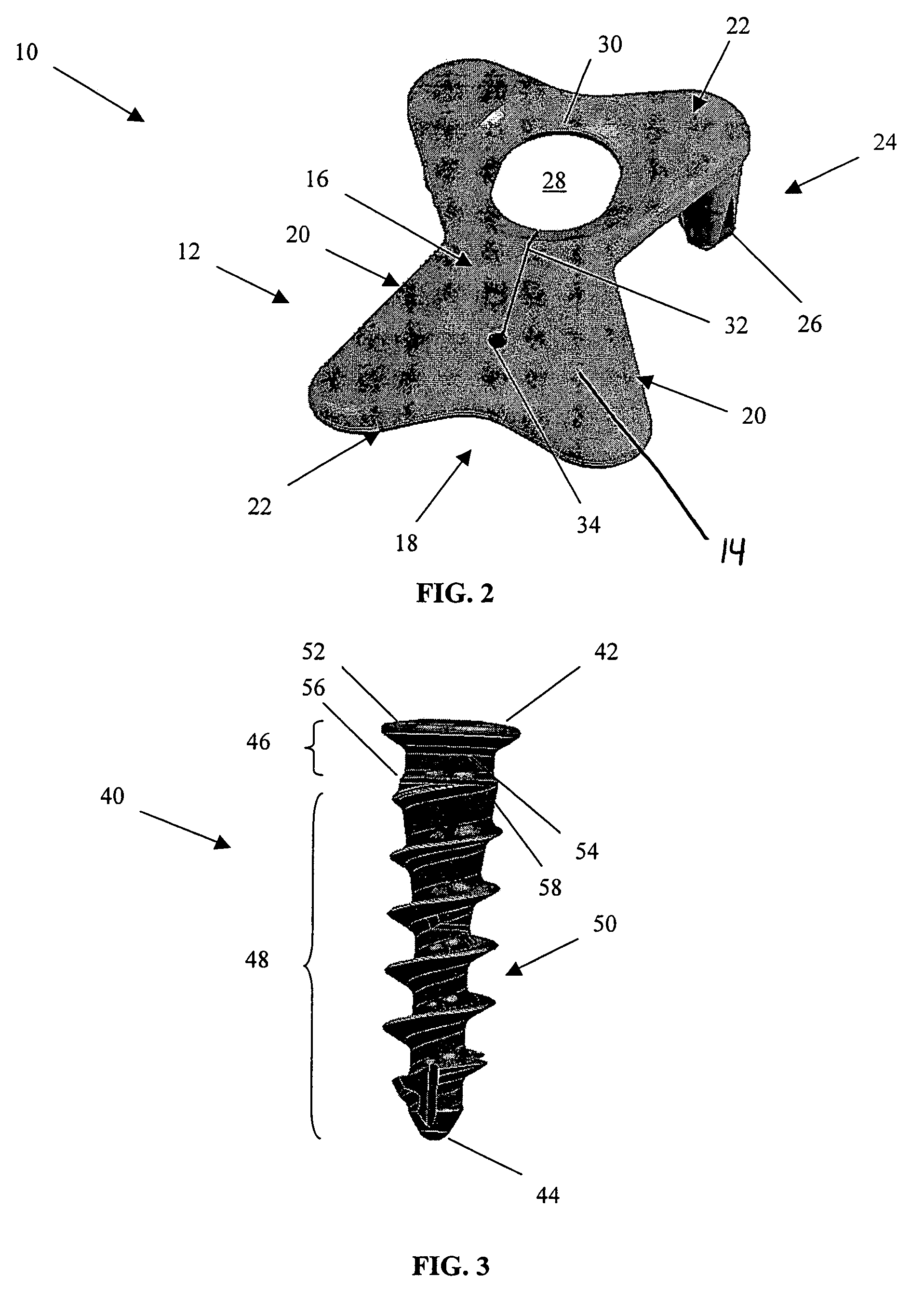
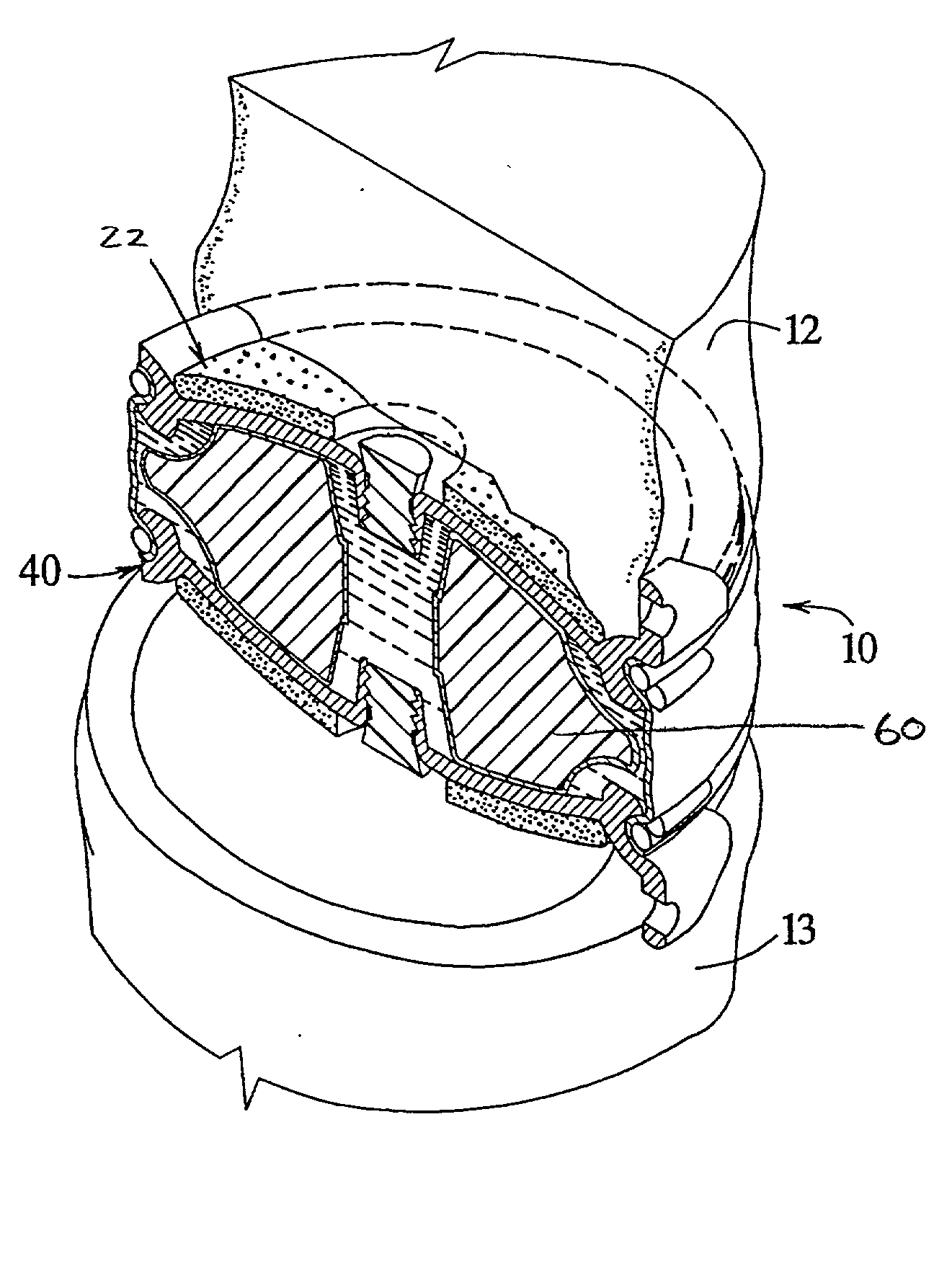
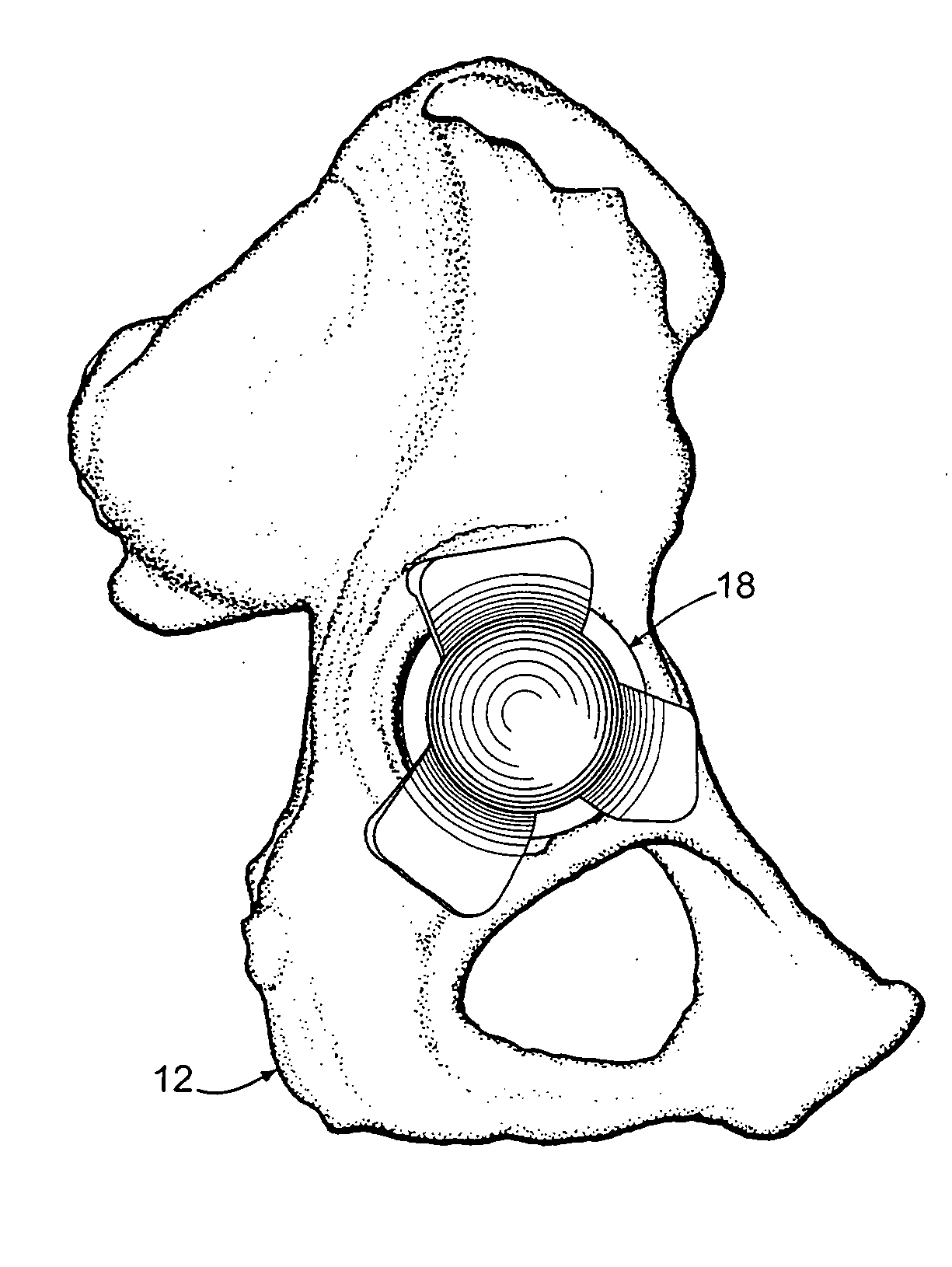
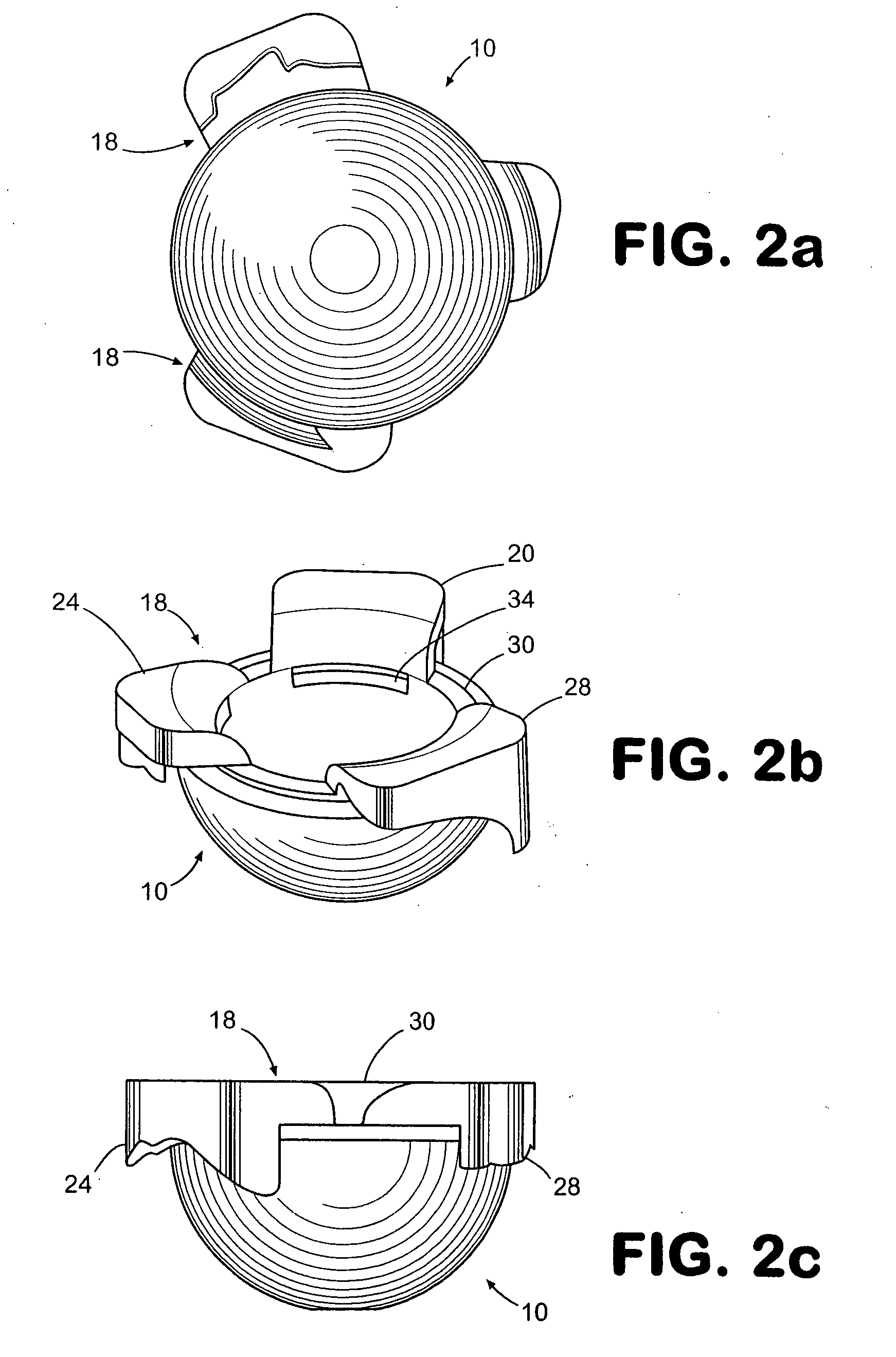
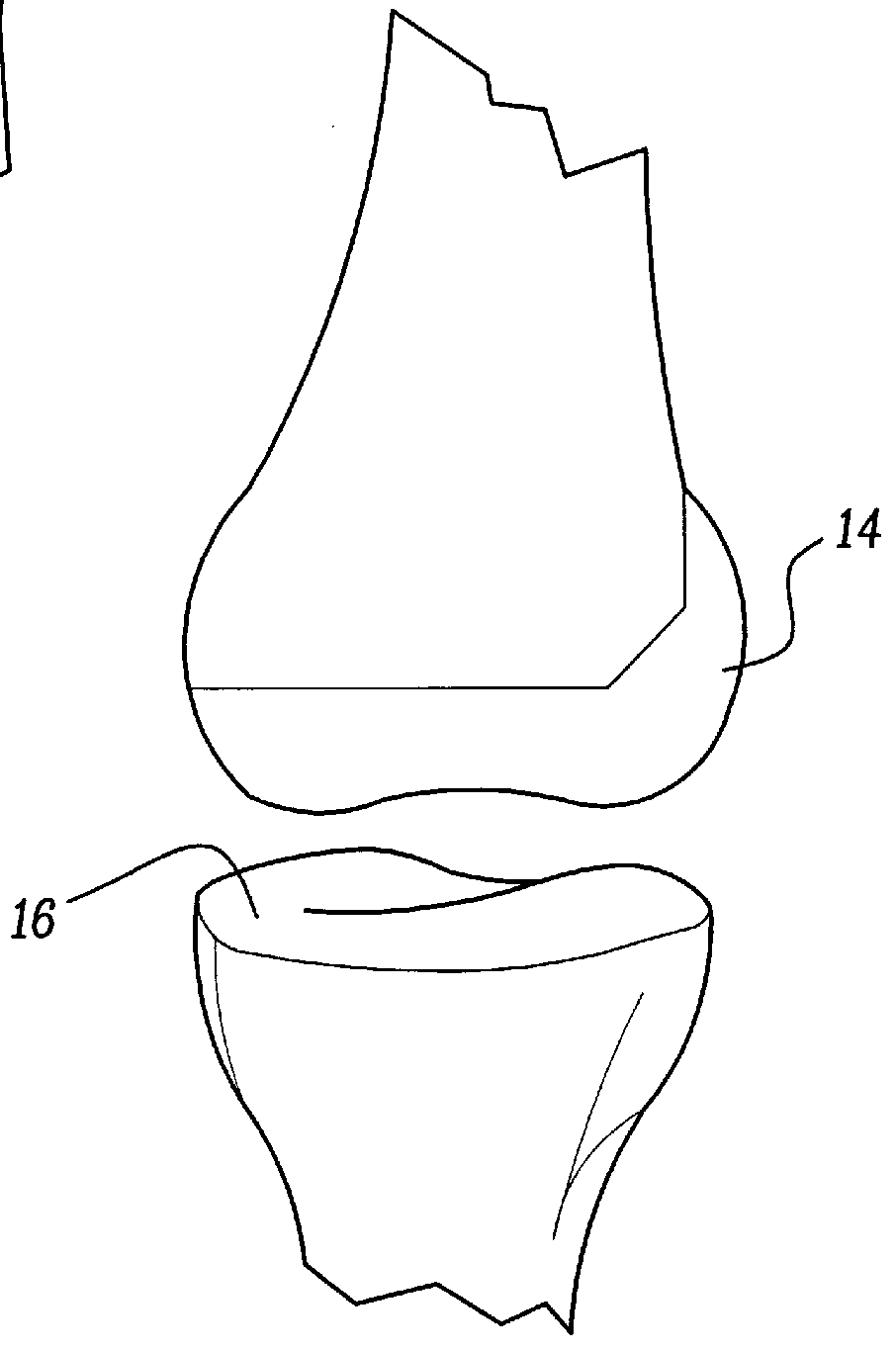
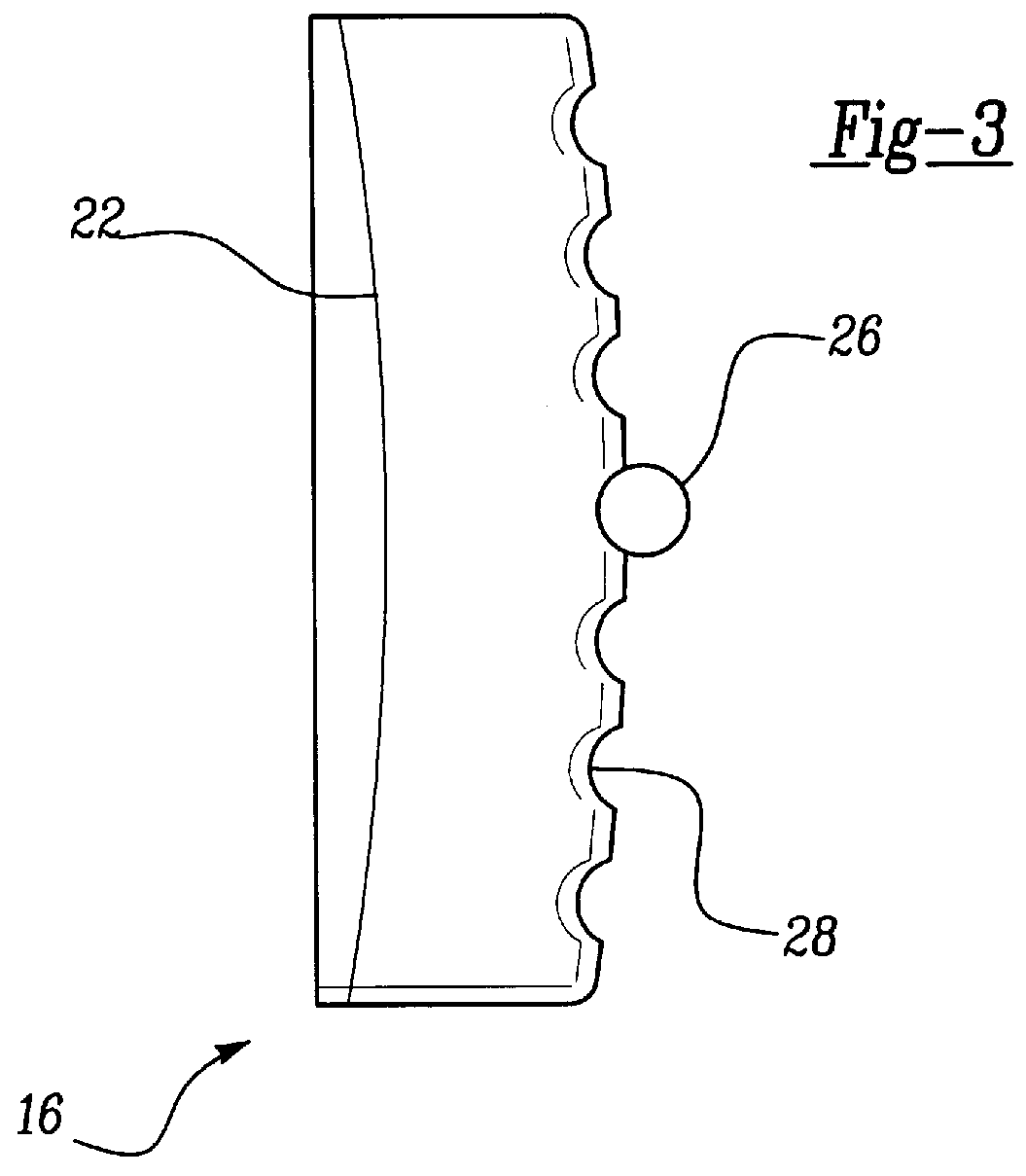
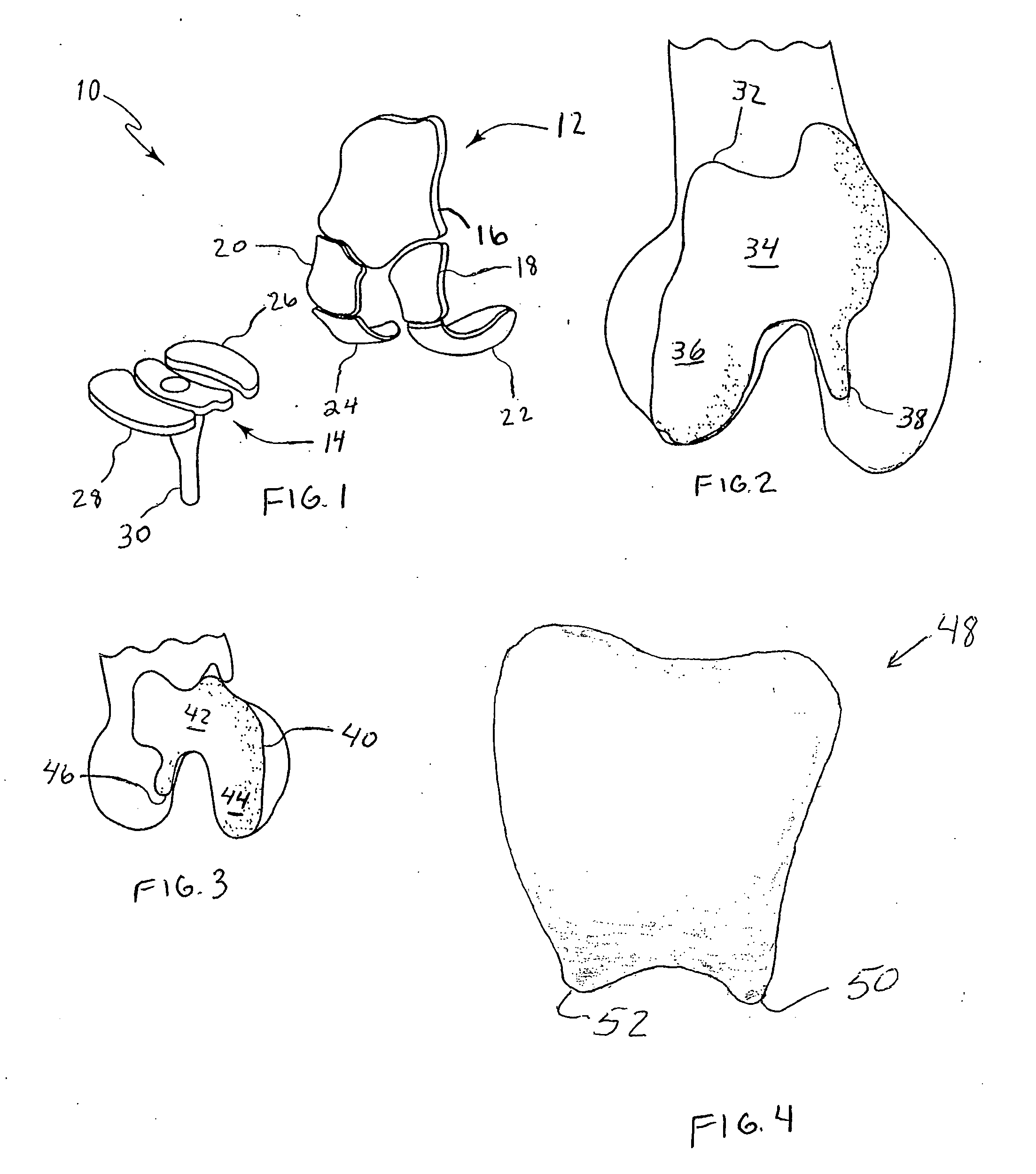
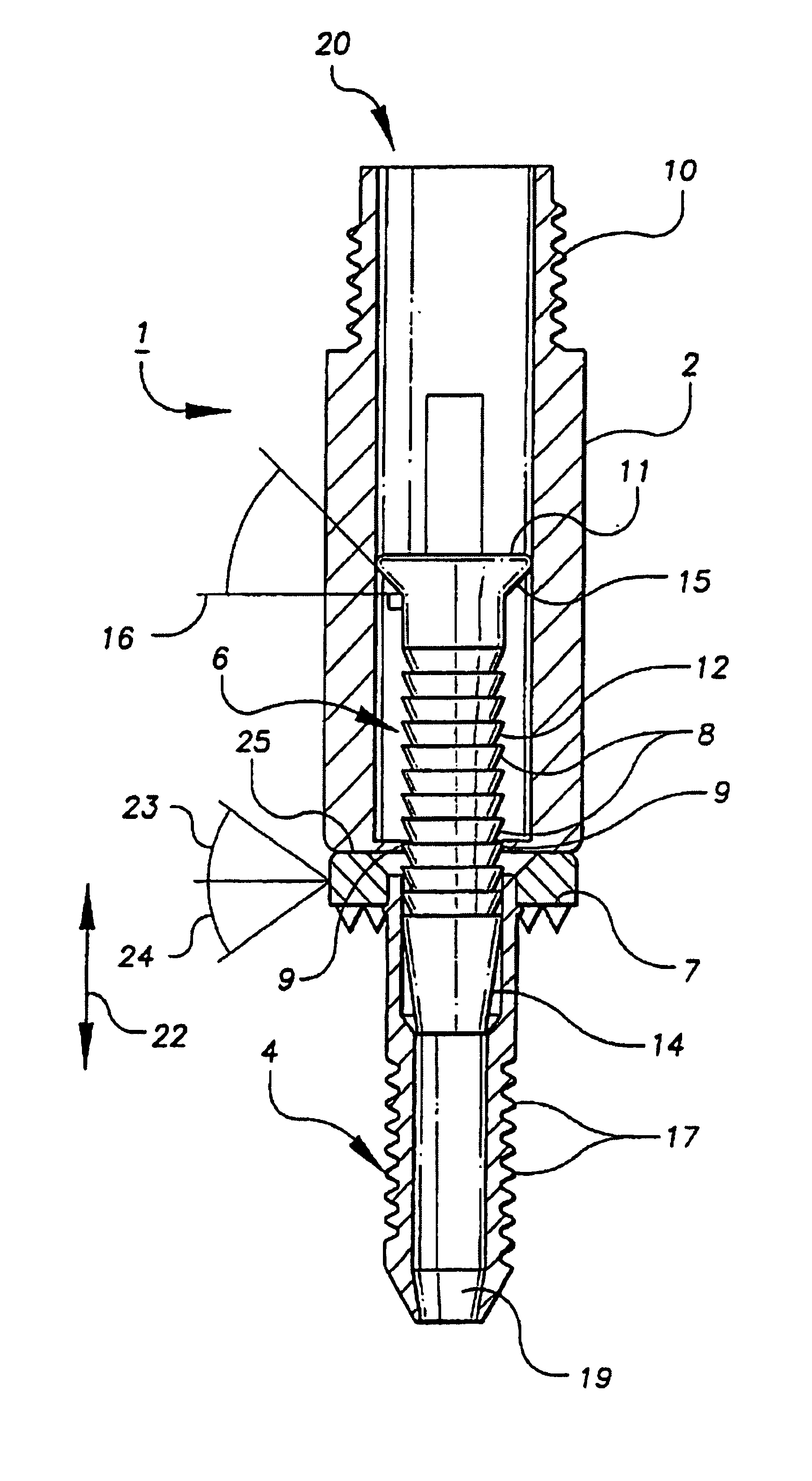
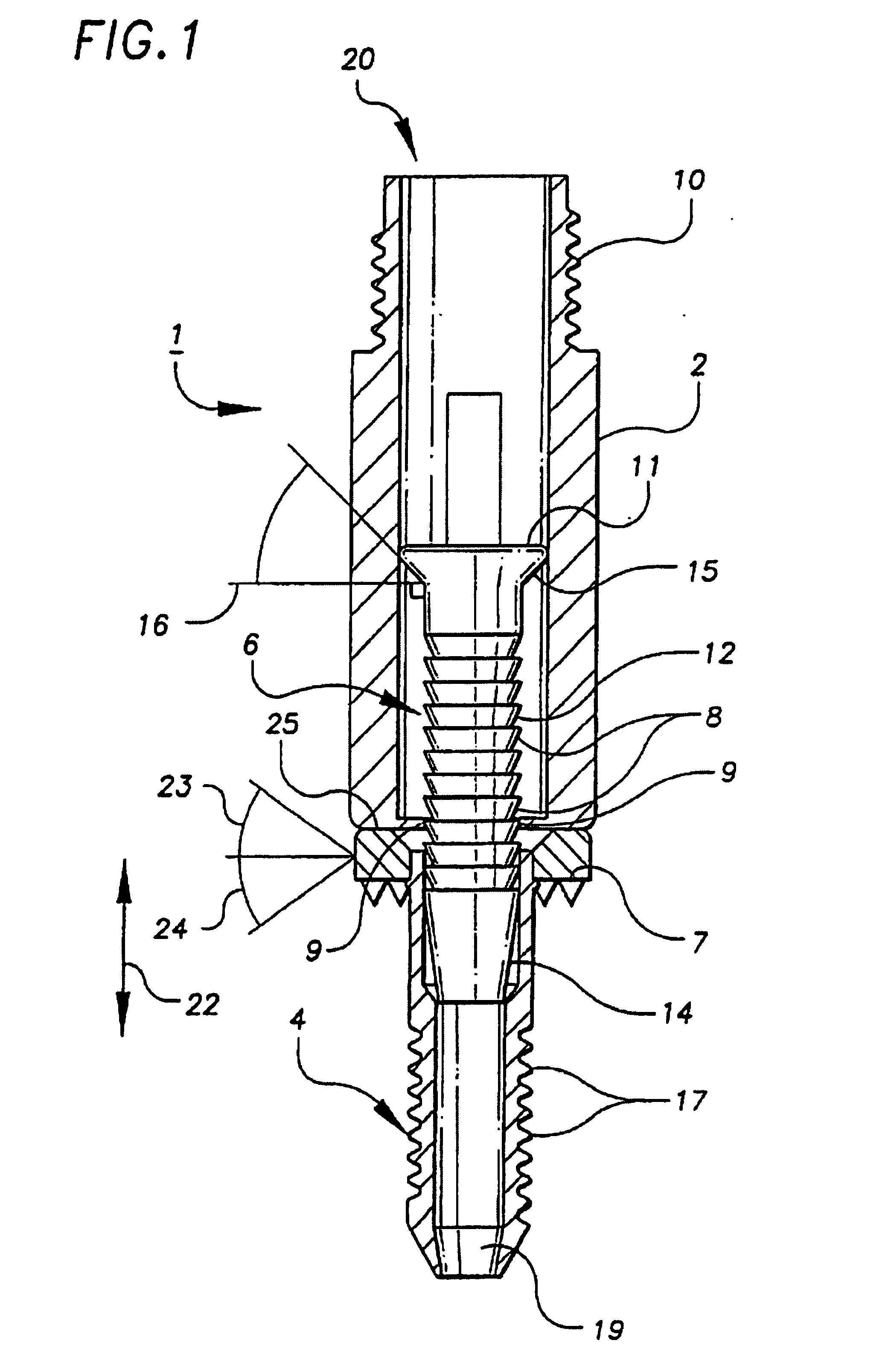
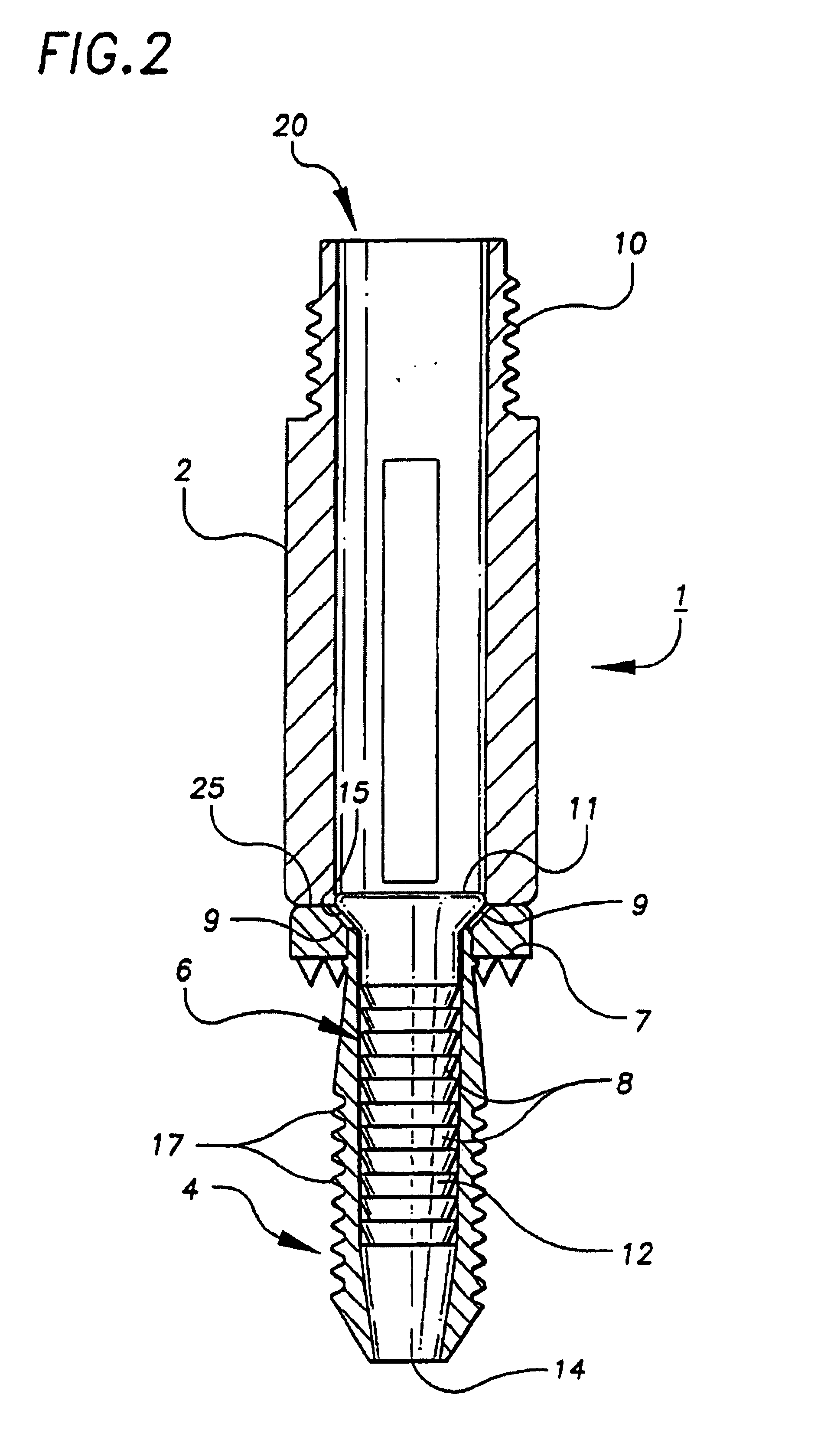
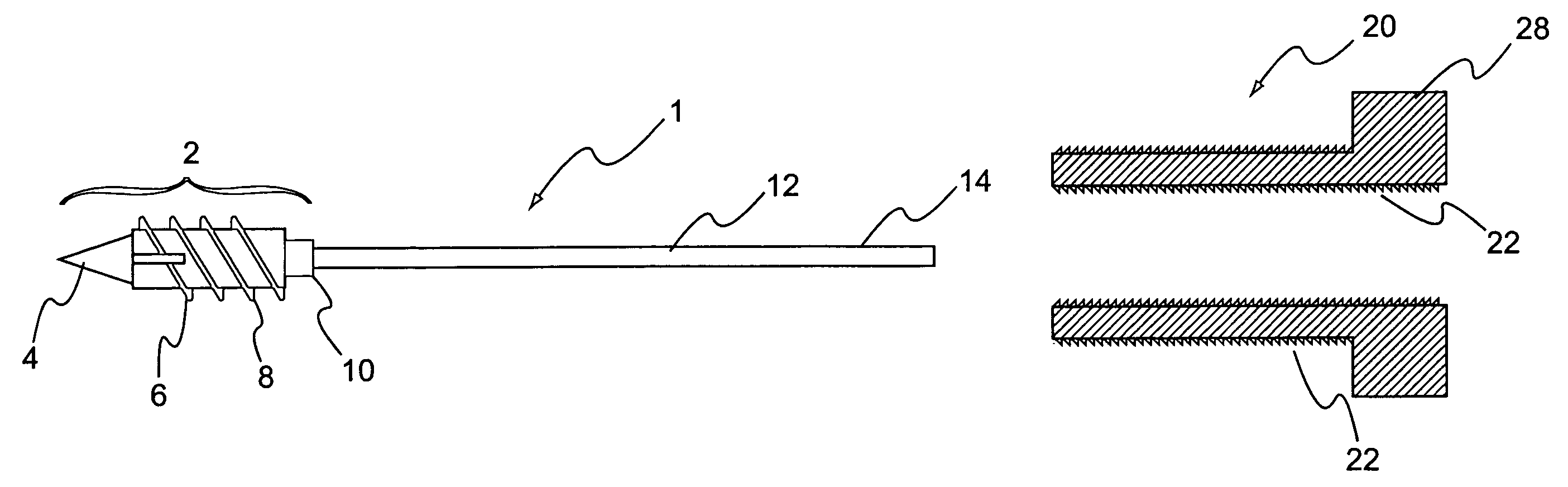
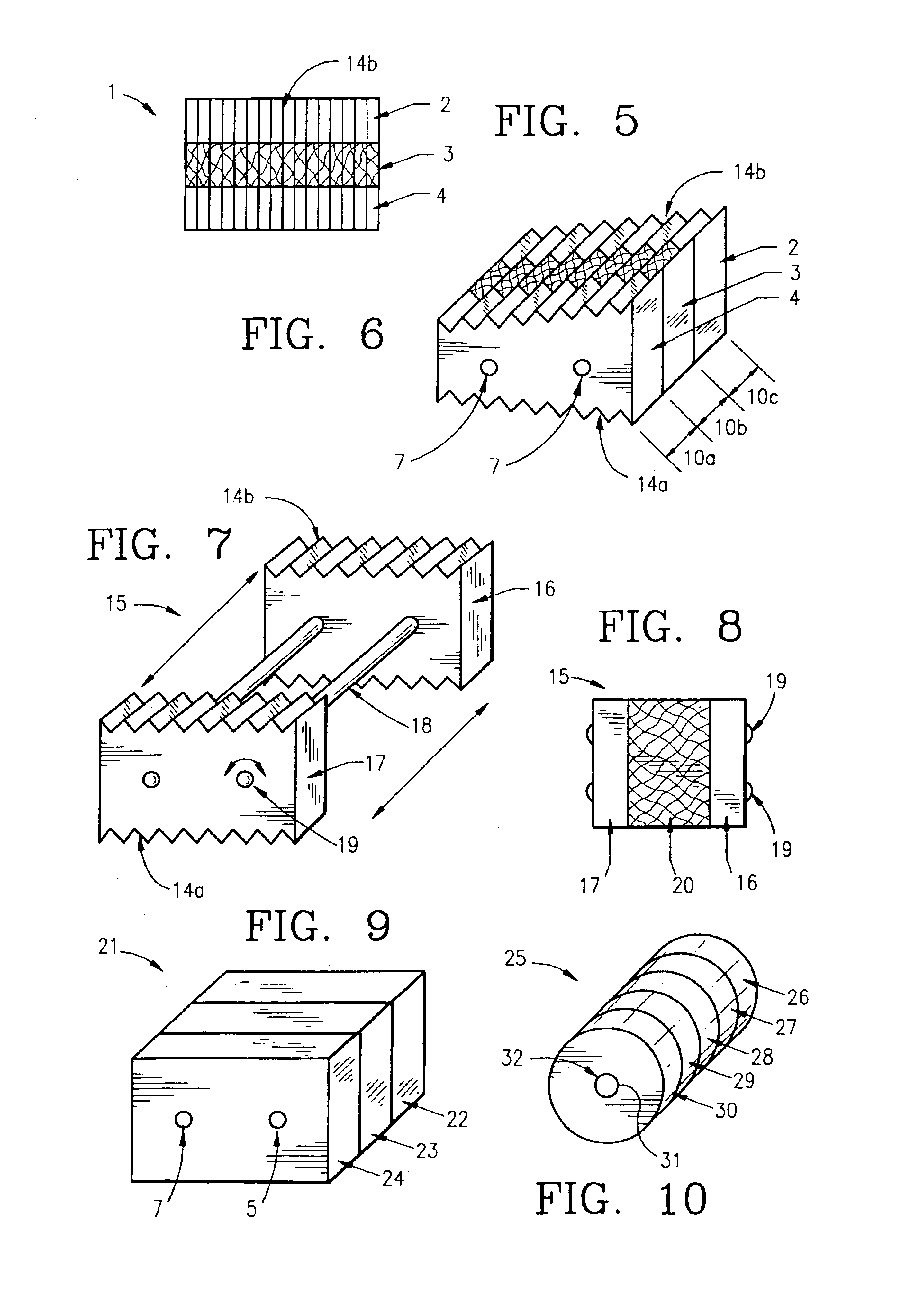
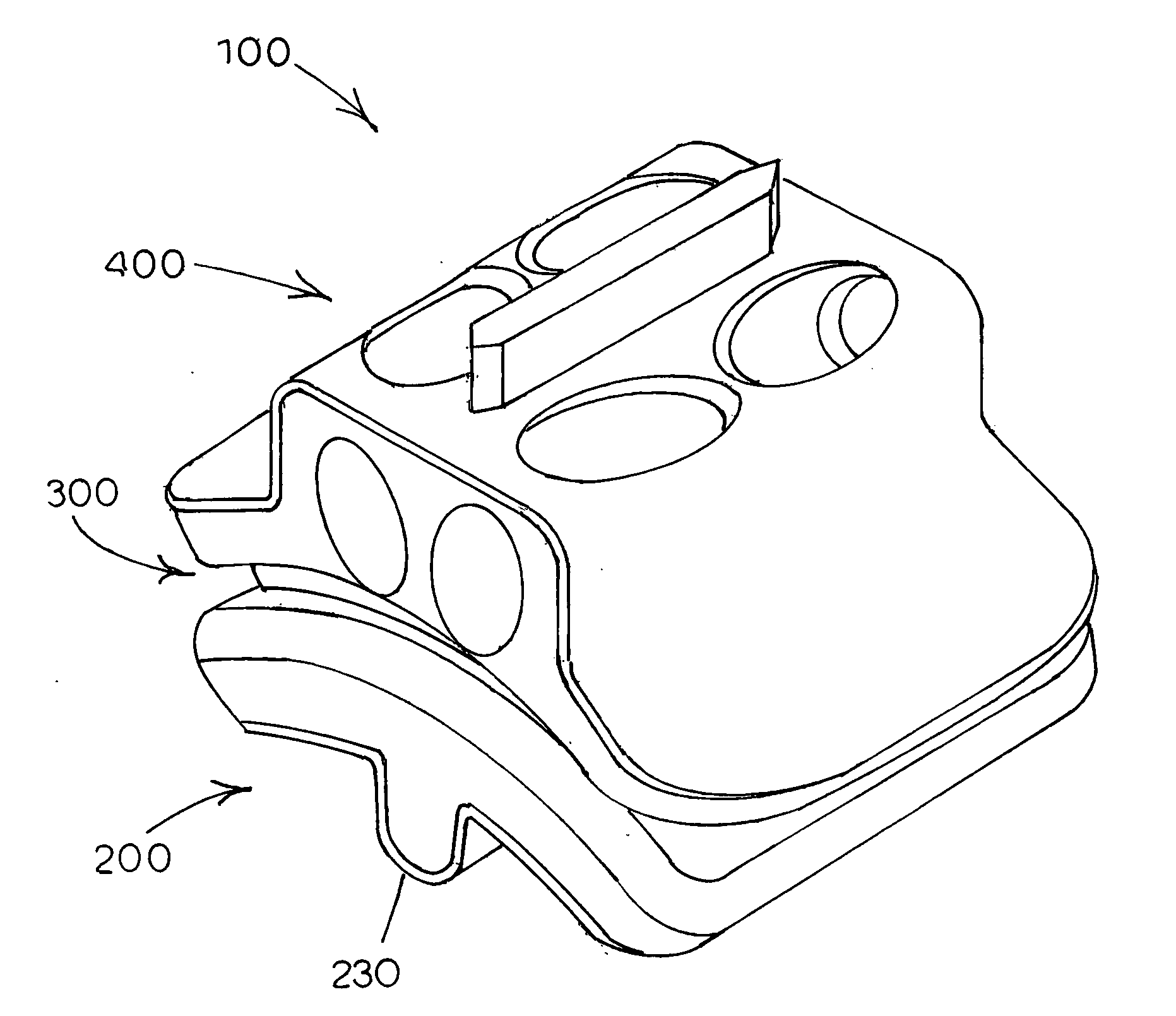
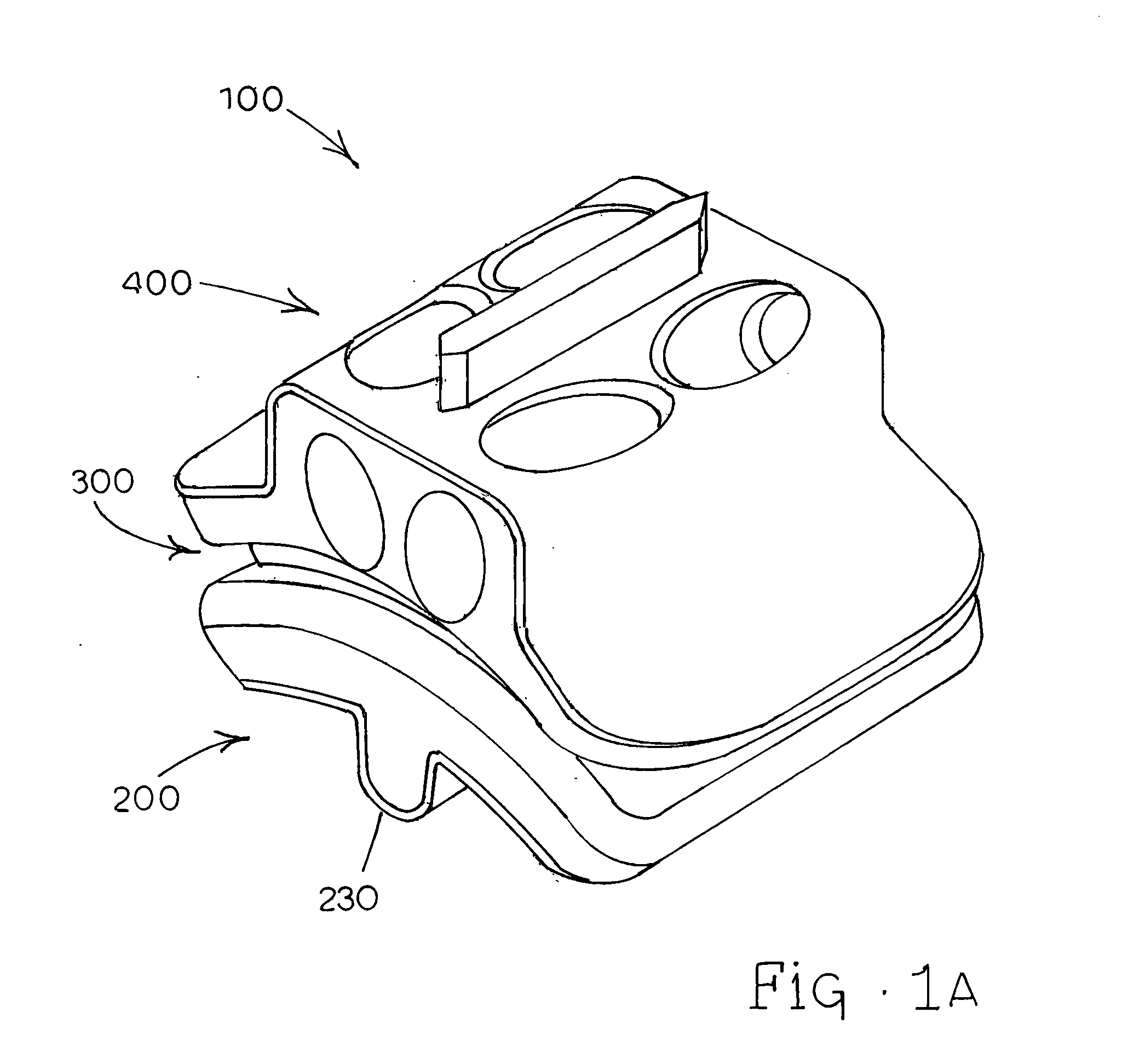
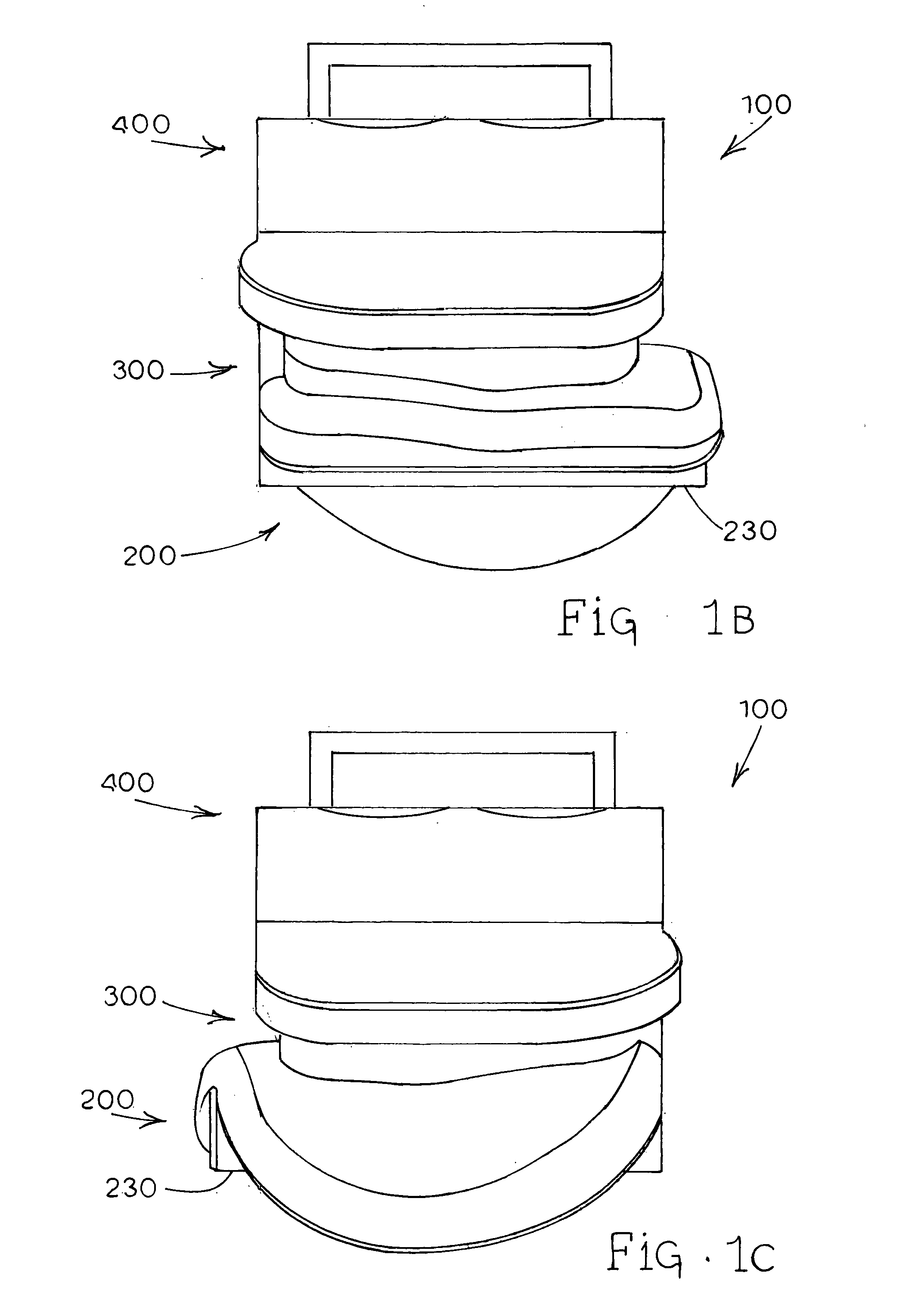
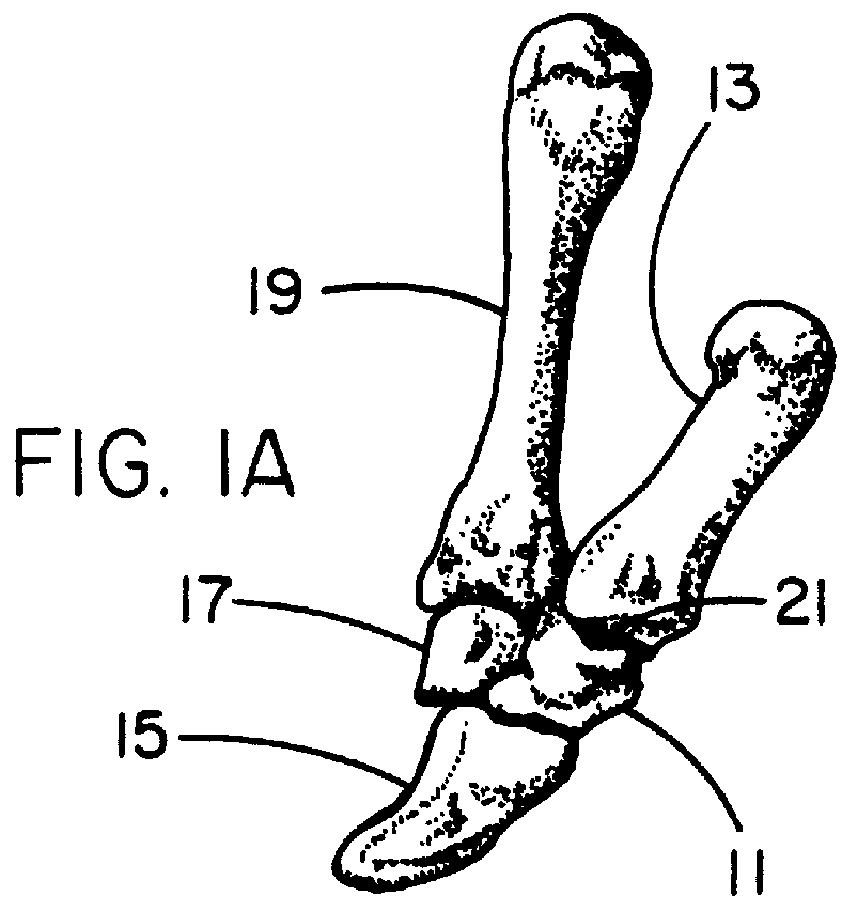
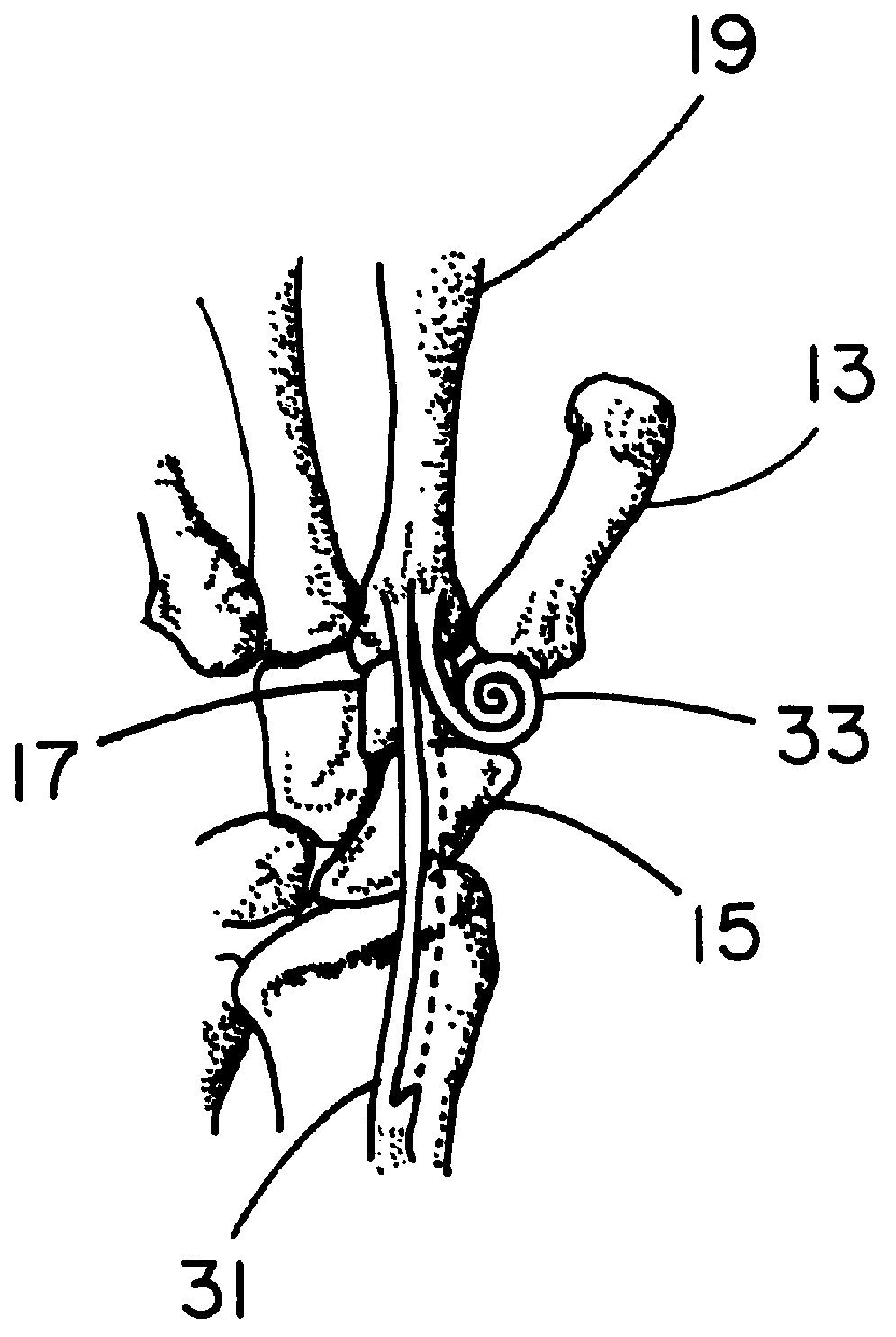
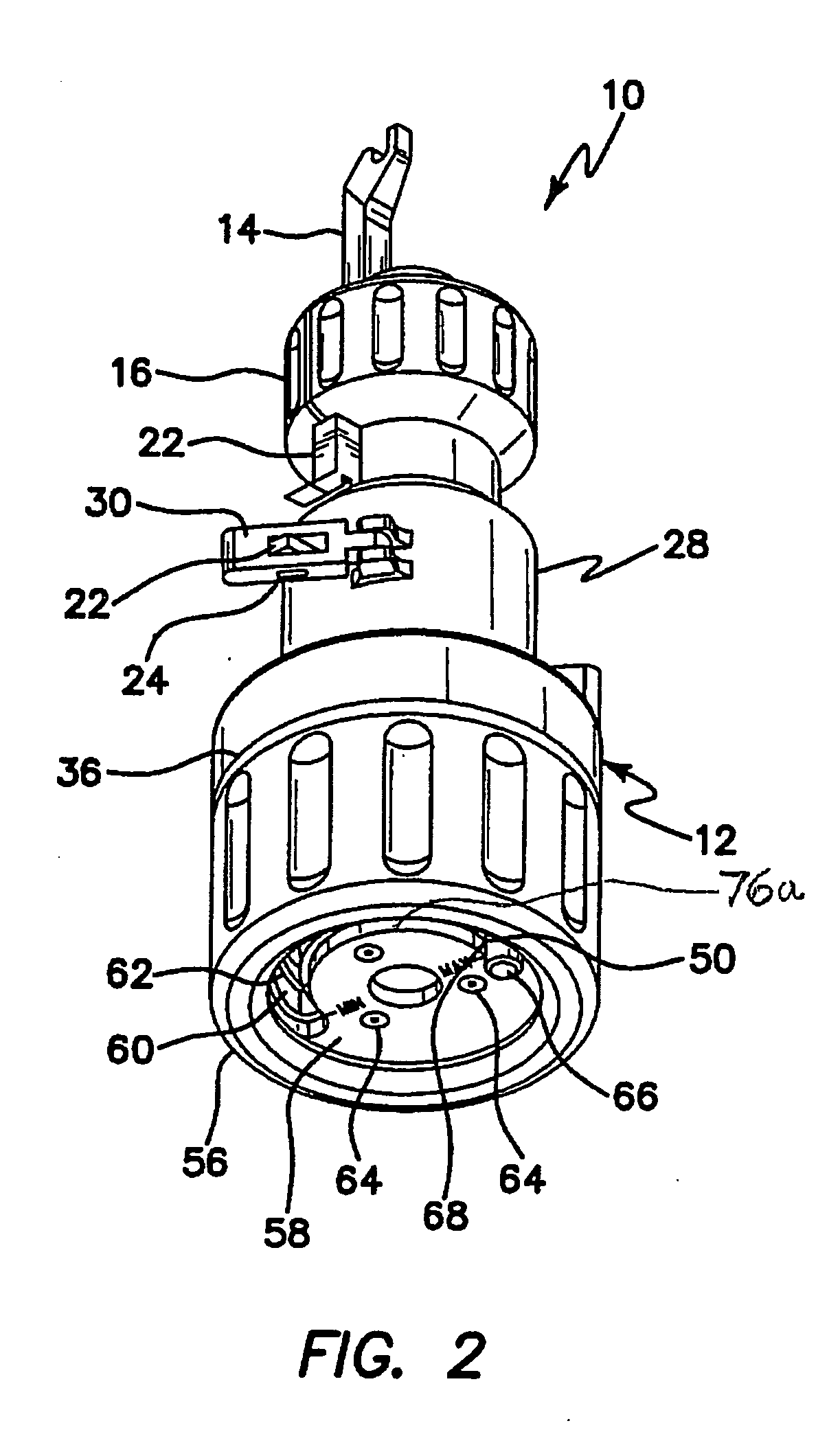
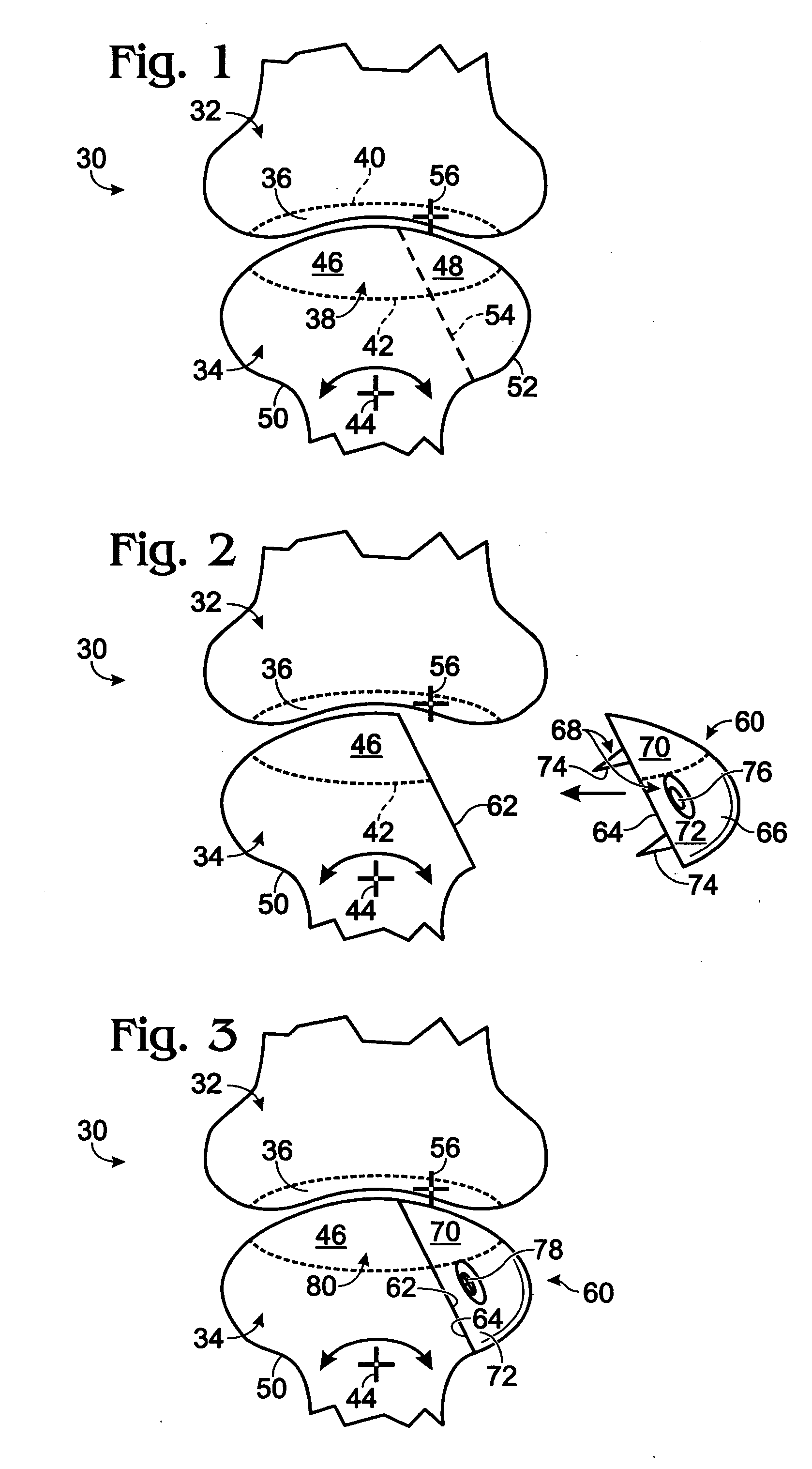
Anterior buttress staple
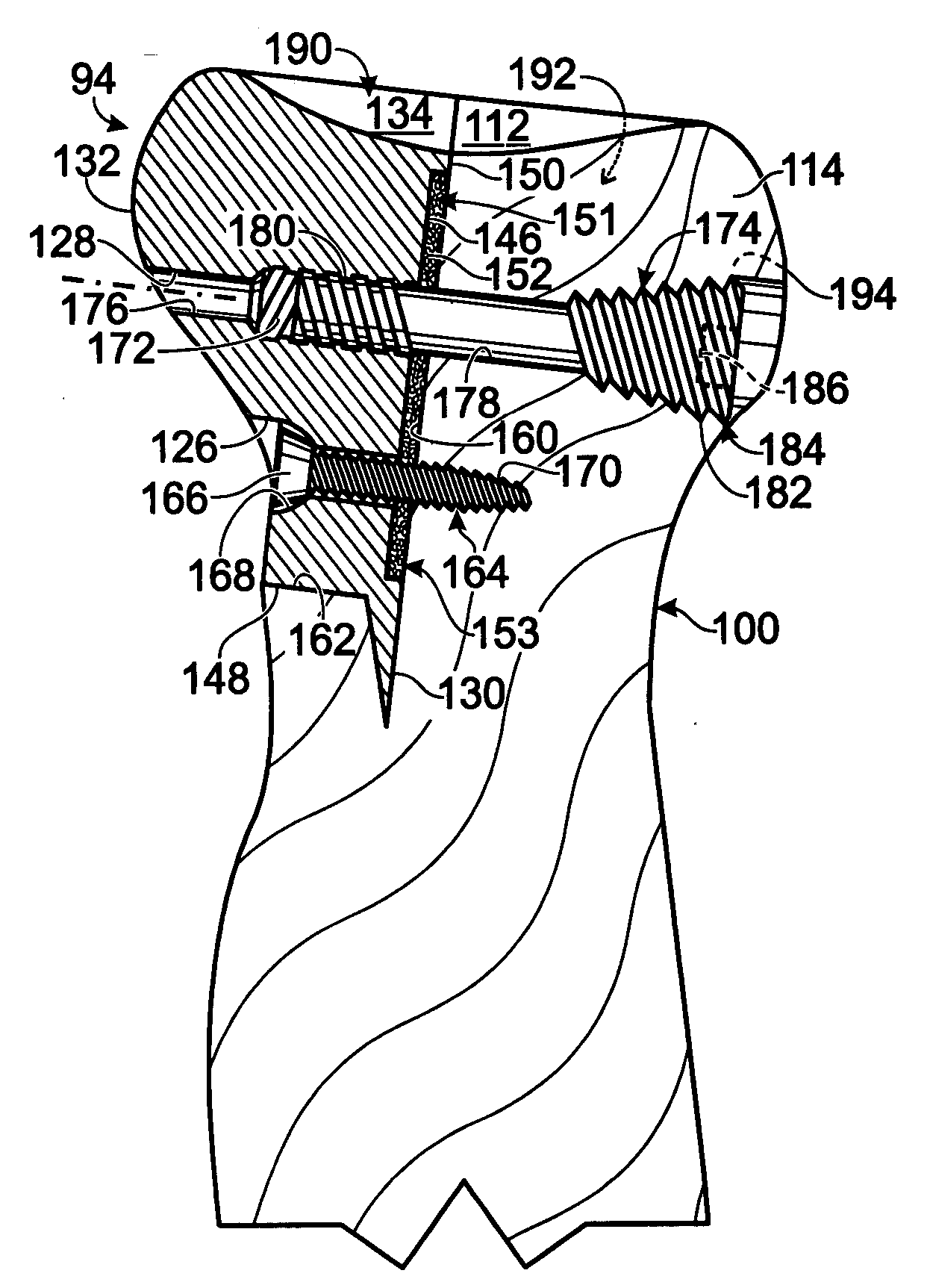
An anterior buttress staple and screw system is provided that can be used to hold an implant such as a disc prosthesis in place and thereby prevent its migration out of the spinal column. The buttress staple comprises a screw locking plate having a screw locking design that prevents the screw from backing up and away from the plate. The screw is configured to provide an interference fit with the screw locking plate, and can be used as a staple removal tool during revision surgery when the screw locking plate needs to be lifted from the bone surface on which it is attached.
Owner:DEPUY ACROMED INC
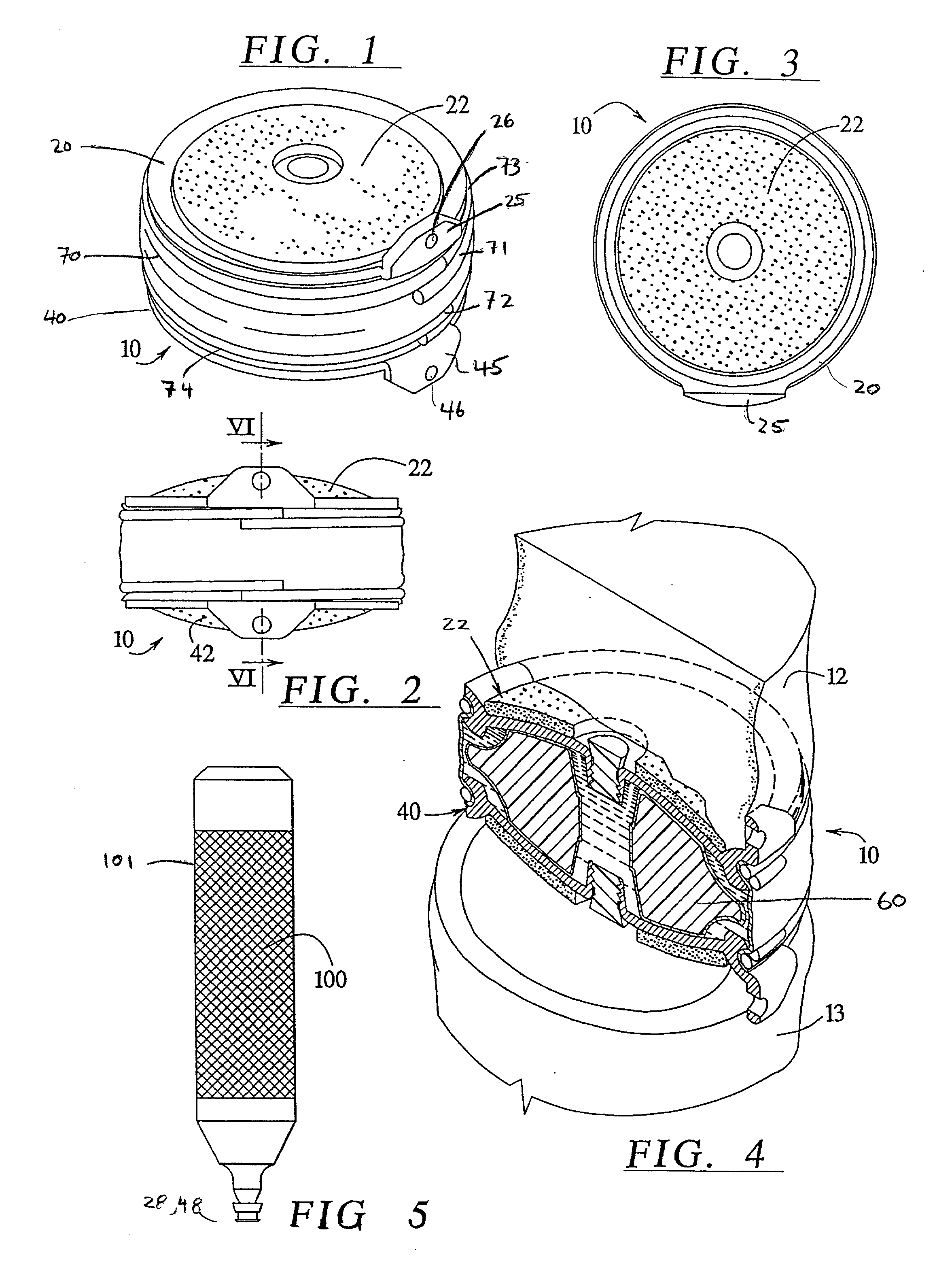
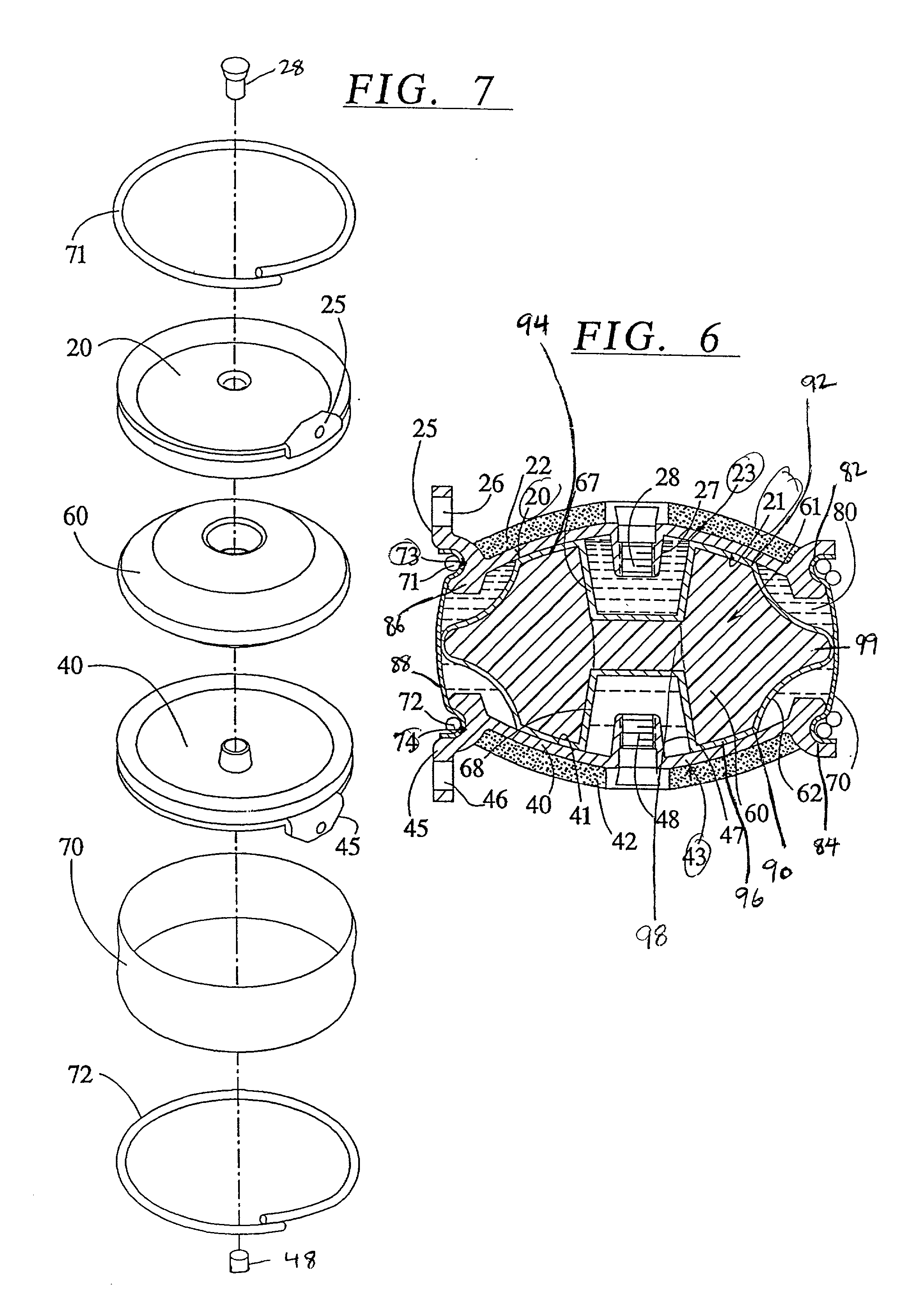
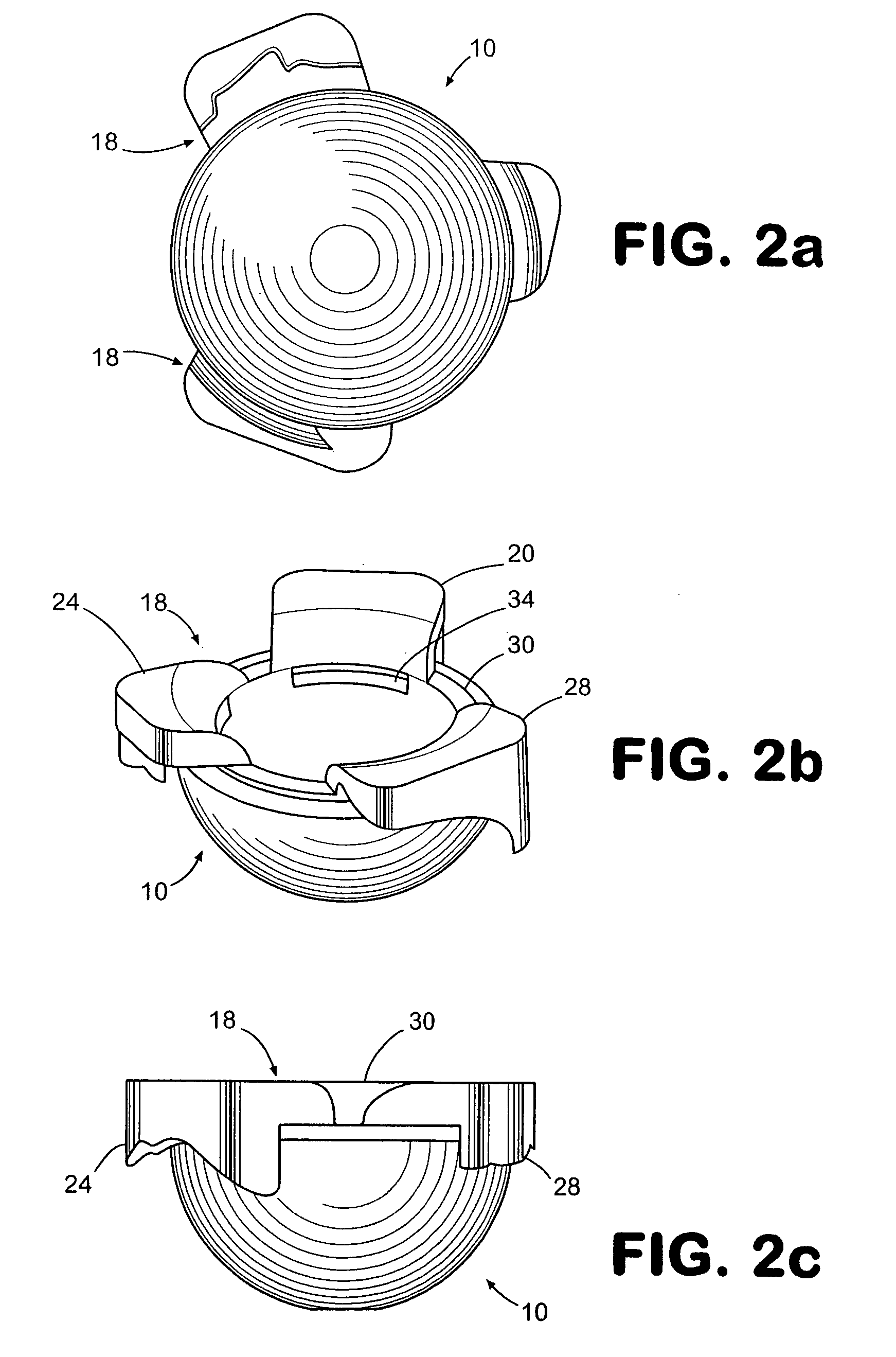
Implantable joint prosthesis
InactiveUS20020035400A1Improve wear resistanceImprove tribological propertiesDiagnosticsJoint implantsRange of motionIntervertebral disc
The invention relates to a surgical implant that provides an artificial diarthroidal-like joint, suitable for use in replacing any joint, but particularly suitable for use as an intervertebral disc endoprosthesis. The invention contains two rigid opposing shells, each having an outer surface adapted to engage the surfaces of the bones of a joint in such a way that the shells are immobilized by friction between their outer surfaces and the surfaces of the bone. These outer surfaces are sufficiently rough that large frictional forces strongly resist any slippage between the outer surface and the bone surfaces in the joint. They may be convex, and when inserted into a milled concavity, are immediately mechanically stable. Desirably, the outer surfaces of the shells are adapted to allow for bony ingrowth, which further stabilizes the shells in place. The inner surfaces of the shells are relatively smooth, and adapted to slide easily across a portion of the outer surface of a central body disposed between the shells. The central body has a shape that cooperates with the shape of the inner surface of the shell so as to provide a range of motion similar to that provided by a healthy joint. A flexible sheath extends between edges of the opposing shells. The inner surface of this sheath, together with the inner surfaces of the rigid shells, defines a cavity encasing the central body. At least a portion of this cavity is filled with a fluid lubricant, further decreasing the frictional force between inner surfaces of the shell and the surface of the central body.
Owner:SPINAL DYNAMICS CORP
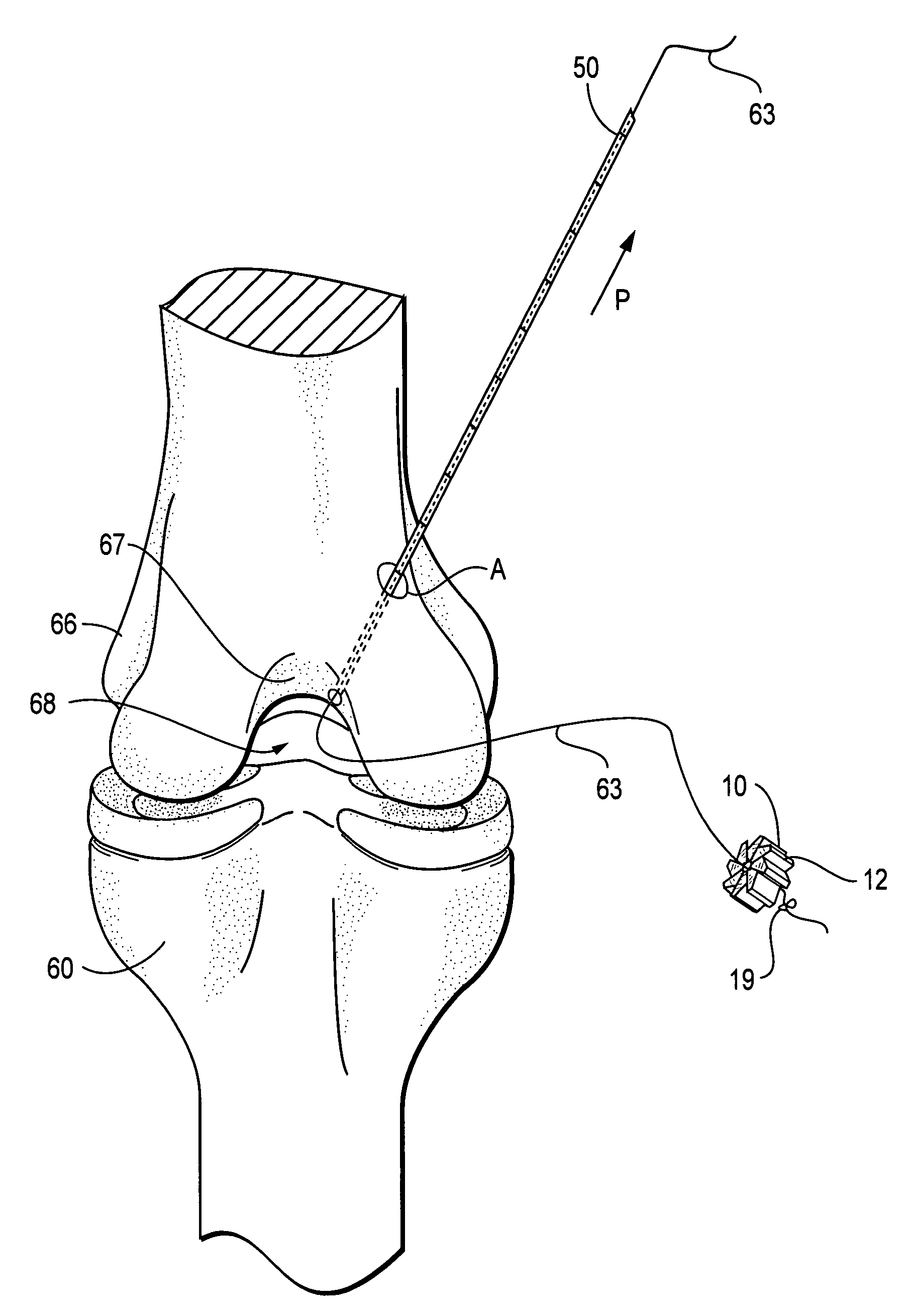
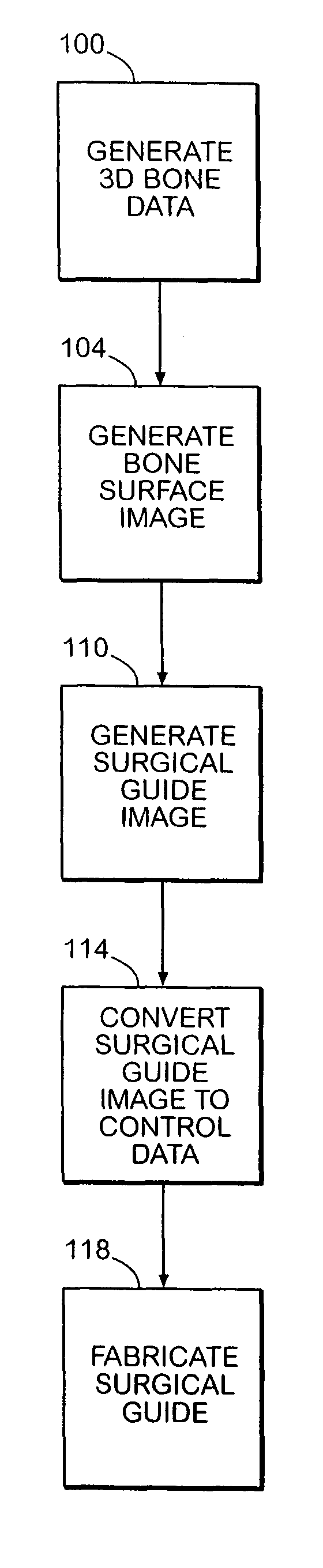
System and method of designing and manufacturing customized instrumentation for accurate implantation of prosthesis by utilizing computed tomography data
ActiveUS20050148843A1Quickly and accurately attachesPrecise positioningPerson identificationJoint implantsMedicineControl data
A method and system may be used to design and control the manufacture of a surgical guide for implanting a prosthetic component. The system includes a bone surface image generator, a surgical guide image generator, and a surgical guide image converter. The bone surface image generator receives three dimensional bone anatomical data for a patient's bone and generates a bone surface image. The surgical guide image generator generates a surgical guide image from the bone surface image and an image of a prosthesis imposed on the bone surface image. The supporting structure of the generated surgical guide image conforms to the surface features of the three dimensional bone surface image. The surgical guide image is converted by surgical guide image converter into control data for operating a machine to form a surgical guide that corresponds to the surgical guide image.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
Total joint arthroplasty system
ActiveUS20090131941A1Precise alignmentImprove visualizationMedical simulationProgramme controlJoint arthroplastyTotal hip arthroplasty
A method and system for performing a total joint arthroplasty procedure on a patient's damaged bone region. A CT image or other suitable image is formed of the damaged bone surfaces, and location coordinate values (xn,yn,zn) are determined for a selected sequence of bone surface locations using the CT image data. A mathematical model z=f(x,y) of a surface that accurately matches the bone surface coordinates at the selected bone spice locations, or matches surface normal vector components at selected bone surface locations, is determined. The model provides a production file from which a cutting jig and an implant device (optional), each patient-specific and having controllable alignment, are fabricated for the damaged bone by automated processing. At this point, the patient is cut open (once), the cutting jig and a cutting instrument are used to remove a selected portion of the bone and to provide an exposed planar surface, the implant device is optionally secured to and aligned with the remainder of the bone, and the patient's incision is promptly repaired.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Implantable joint prosthesis
ActiveUS20020128715A1Increased durabilityImprove stabilityDiagnosticsJoint implantsIntervertebral discSurgical implant
The invention relates to a surgical implant that provides an artificial diarthroidal-like joint, suitable for use in replacing any joint, but particularly suitable for use as an intervertebral disc endoprosthesis. The invention contains two rigid opposing shells, each having an outer surface adapted to engage the surfaces of the bones of a joint in such a way that the shells are immobilized by friction between their outer surfaces and the surfaces of the bone. These outer surfaces are sufficiently rough that large frictional forces strongly resist any slippage between the outer surface and the bone surfaces in the joint. They may be convex, and when inserted into a milled concavity, are immediately mechanically stable. Desirably, the outer surfaces of the shells are adapted to allow for bony ingrowth, which further stabilizes the shells in place. The inner surfaces of the shells are relatively smooth, and adapted to slide easily across a portion of the outer surface of a central body disposed between the shells. The central body has a shape that cooperates with the shape of the inner surface of the shell so as to provide a range of motion similar to that provided by a healthy joint. A flexible sheath extends between edges of the opposing shells. The inner surface of this sheath, together with the inner surfaces of the rigid shells, defines a cavity encasing the central body. At least a portion of this cavity is filled with a fluid lubricant, further decreasing the frictional force between inner surfaces of the shell and the surface of the central body.
Owner:COMPANION SPINE LLC
System and method for manufacturing arthroplasty jigs having improved mating accuracy
ActiveUS20100023015A1Facilitate arthroplasty implantsDiagnosticsComputer-aided planning/modellingSacroiliac jointOrthodontics
Disclosed herein is a method of defining a mating surface in a first side of an arthroplasty jig. The mating surface is configured to matingly receive and contact a corresponding patient surface including at least one of a bone surface and a cartilage surface. The first side is oriented towards the patient surface when the mating surface matingly receives and contacts the patient surface. The method may include: a) identifying a contour line associated with the patient surface as represented in a medical image; b) evaluating via an algorithm the adequacy of the contour line for defining a portion of the mating surface associated with the contour line; c) modifying the contour line if the contour line is deemed inadequate; and d) employing the modified contour line to define the portion of the mating surface associated with the contour line.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
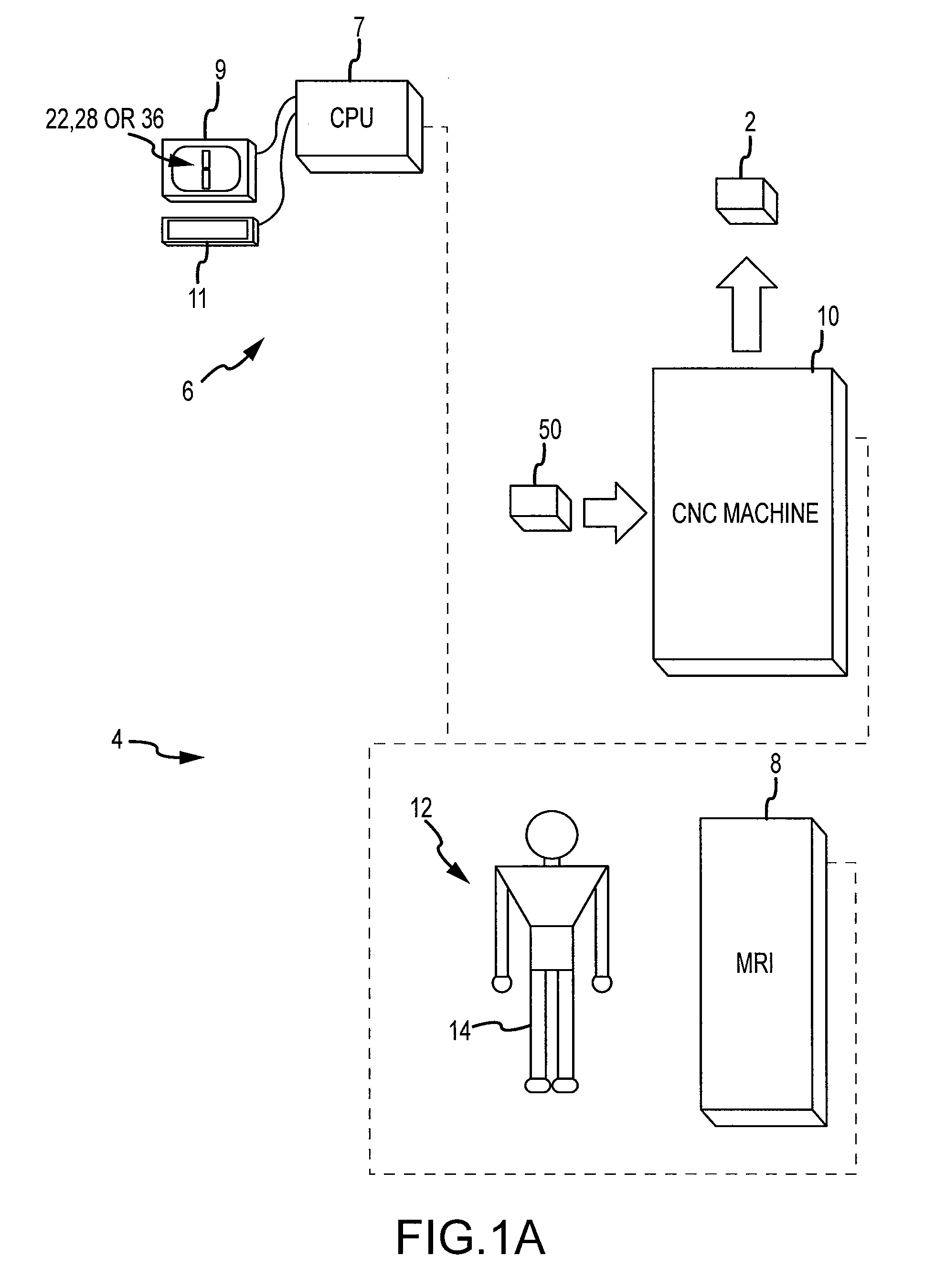
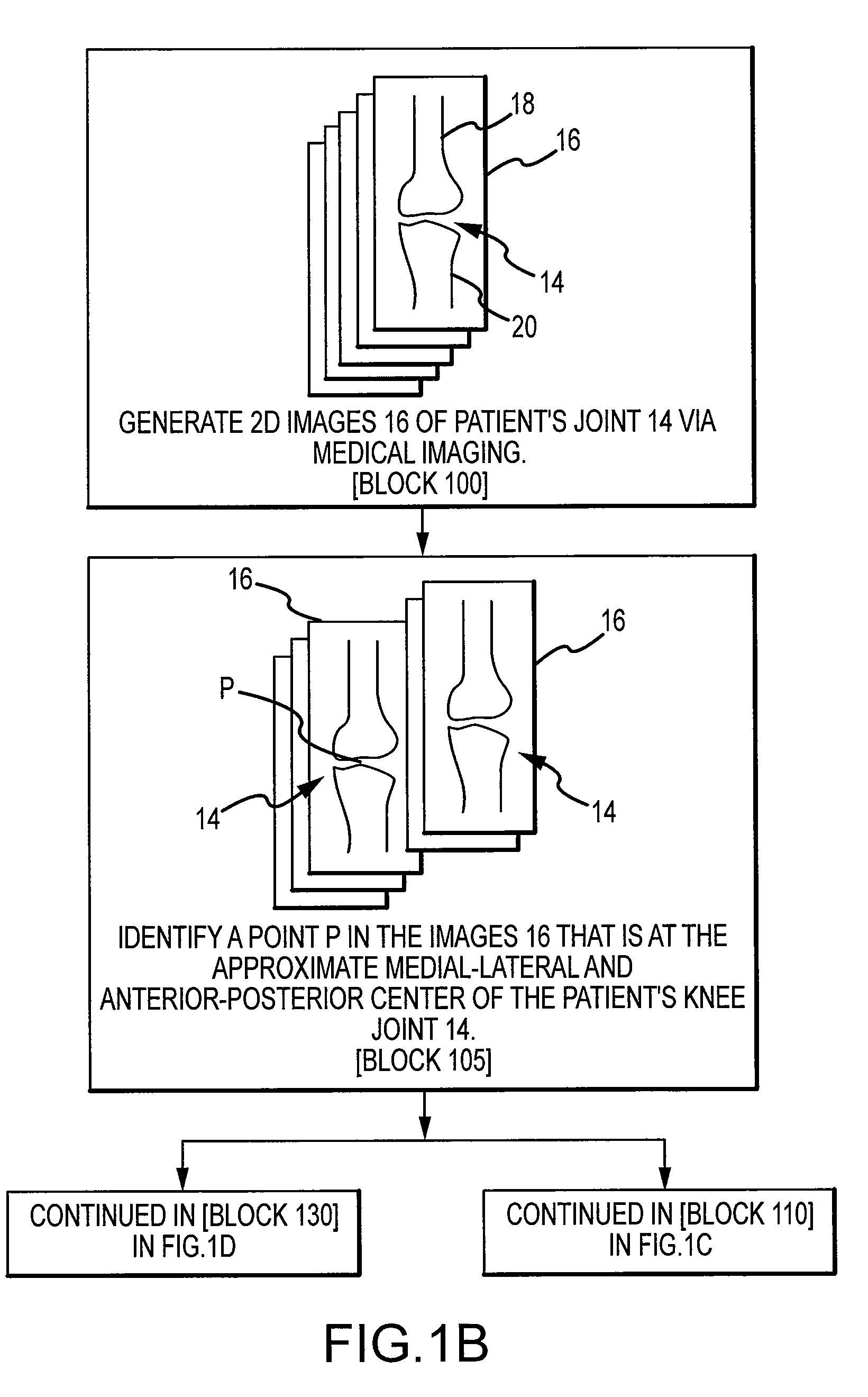
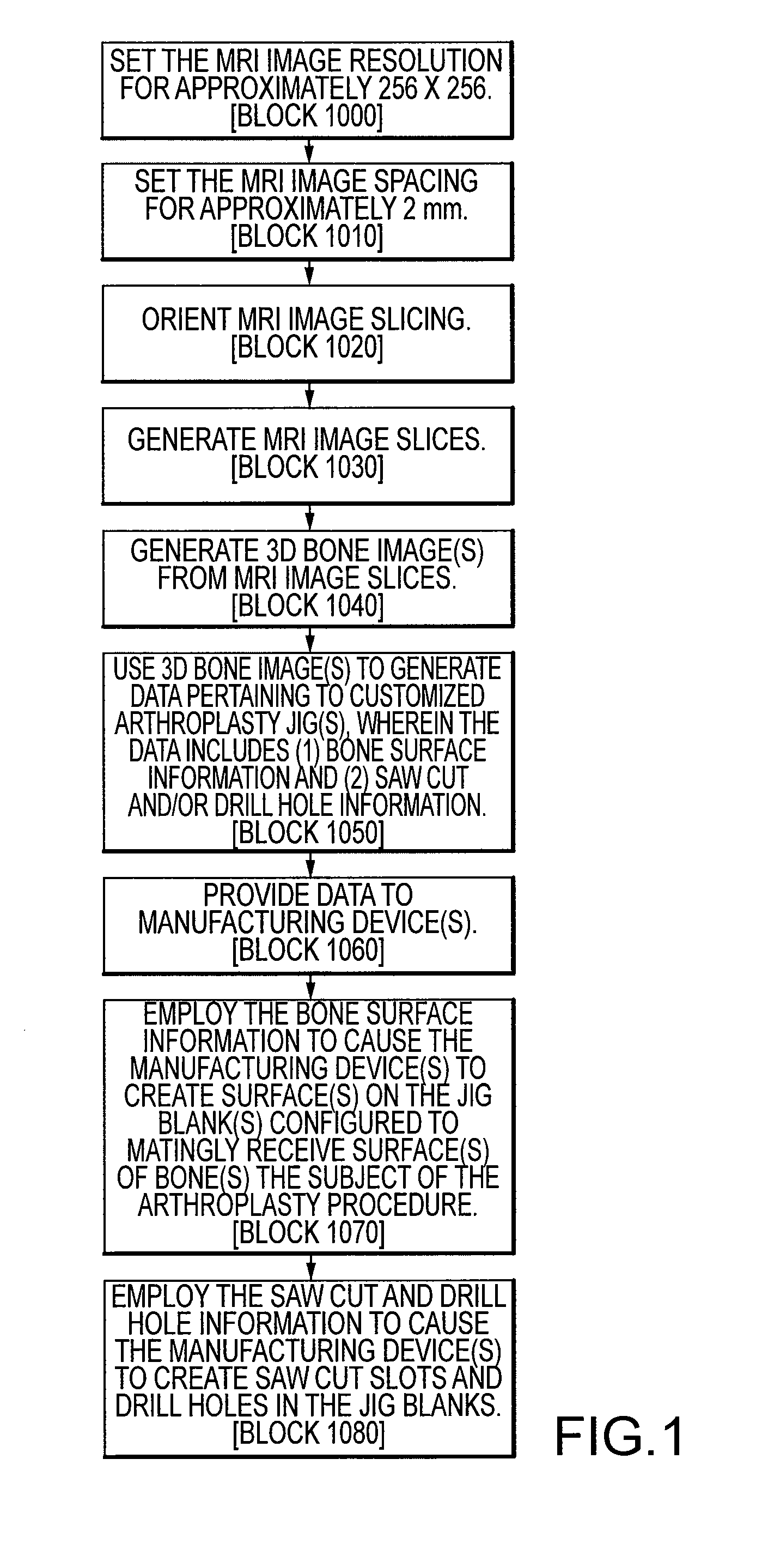
Generating MRI images usable for the creation of 3D bone models employed to make customized arthroplasty jigs
ActiveUS20090138020A1Character and pattern recognitionComputer-aided planning/modellingMri imageSacroiliac joint
Disclosed herein is a method of creating a customized arthroplasty jig. The method may include: generating two-dimensional MRI images of a patient's joint area to undergo arthroplasty; electronically orienting the two dimensional MRI image slices to account for the patient's joint area being randomly physically oriented in a scanning area of a MRI machine; generating a three-dimensional bone image of at least a portion of a bone of the patient's joint area from the generated two-dimensional MRI images; using the three-dimensional bone image to generate data pertaining to the customized arthroplasty jig, wherein the data includes bone surface information; providing the data to at least one manufacturing device; and employing the bone surface information to cause the at least one manufacturing device to create a surface on the arthroplasty jig configured to matingly receive a surface of the bone.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Joint and Cartilage Diagnosis, Assessment and Modeling
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Surgical suture staple and attachment device for securing a soft tissue to a bone
A surgical suture staple and an application appliance for the secure and permanent attachment of a soft tissue to a bone provides a staple having a first and second metal or composite pin which will not adversely affect the bone within which it is attached, the first and second pin connected by a synthetic fiber suture. At least one suture is swedged into each first pin near an upper pin head and either swedged into or adjustably attached through the second pin also near an upper pin head, the first and second pins further comprising an extendable securing means which prevents the first and second pin from being removed from the bone within which it is implanted and a depression within the upper pin head receiving the driving end of an application appliance. The first and second pins are driven into a bone slightly below the bone surface on each side of a soft tissue being anchored to the bone, the suture securing the soft tissue with or without penetration.
Owner:JORDAN CHRISTOPHER
Method of implanting a uni-condylar knee prosthesis
The invention relates generally to a method for implanting a uni-condylar knee prosthesis. The method includes steps for preparing the bone surfaces of both the femoral and tibial effected compartments. The femoral compartment is prepared by making a distal cut, a posterior cuts and a posterior chamfer cut. Holes that correspond to posts on the femoral component are also prepared. The tibial compartment is prepared using a cutting guide and following the sclerotic bone formation on the proximal tibia. At least one hole is prepared in the sloped cut tibial surface to use for alignment when cementing the tibial component that has an alignment peg.
Owner:BIOMET MFG CORP
Systems and methods for compartmental replacement in a knee
A kit for a prosthesis system includes a plurality of first components, each of the plurality of first components for replacing one of a plurality of first surface portions of a bone, a second component for replacing a second surface portion of the bone and a resilient connector for connecting at least one of the plurality of first components to the second component. In accordance with one method, components from a prosthesis system kit used to replace adjacent portions of a bone surface are assembled ex vivo.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Noninvasive diagnostic system
InactiveUS20120029345A1Physical therapies and activitiesUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasonic sensorProximate
A device for acquiring data and diagnosing a musculoskeletal injury. The device includes a semi-flexible housing, at least one ultrasonic transducer, a positional localizer, and a transmission system. The semi-flexible housing is positioned proximate a portion of the musculoskeletal system of a patient and supports the at least one ultrasonic transducer and the positional localizer. The at least one ultrasonic transducer is configured to acquire an ultrasonic data indicative of a bone surface. The positional localizer is positioned at a select location relative to the at least one ultrasonic transducer and tracks movement of the housing. The transmission system transmits the ultrasonic data of the at least one ultrasonic transducer and the movement data of the positional localizer to a data analyzer for analysis and diagnosis.
Owner:JOINTVUE LLC
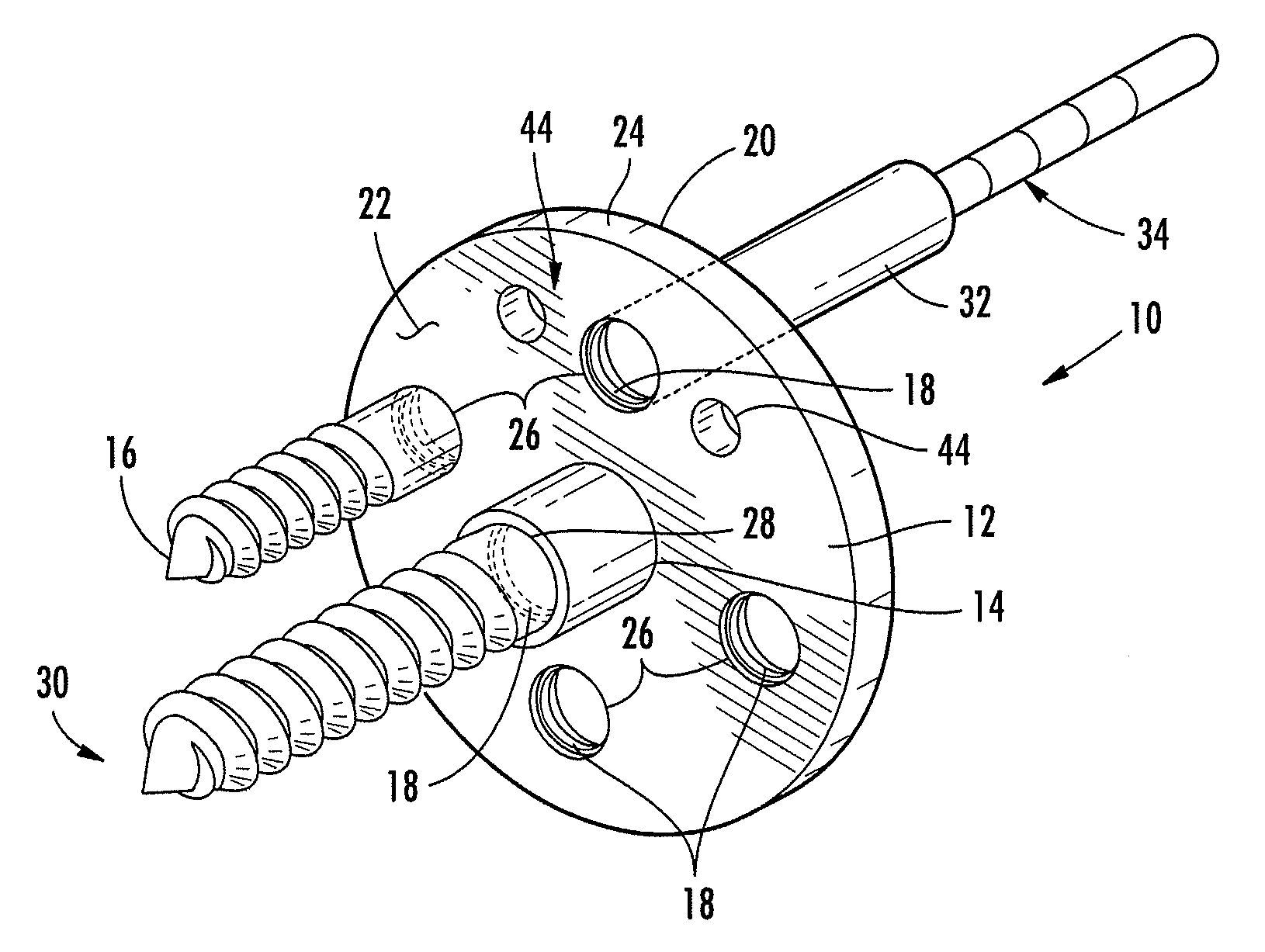
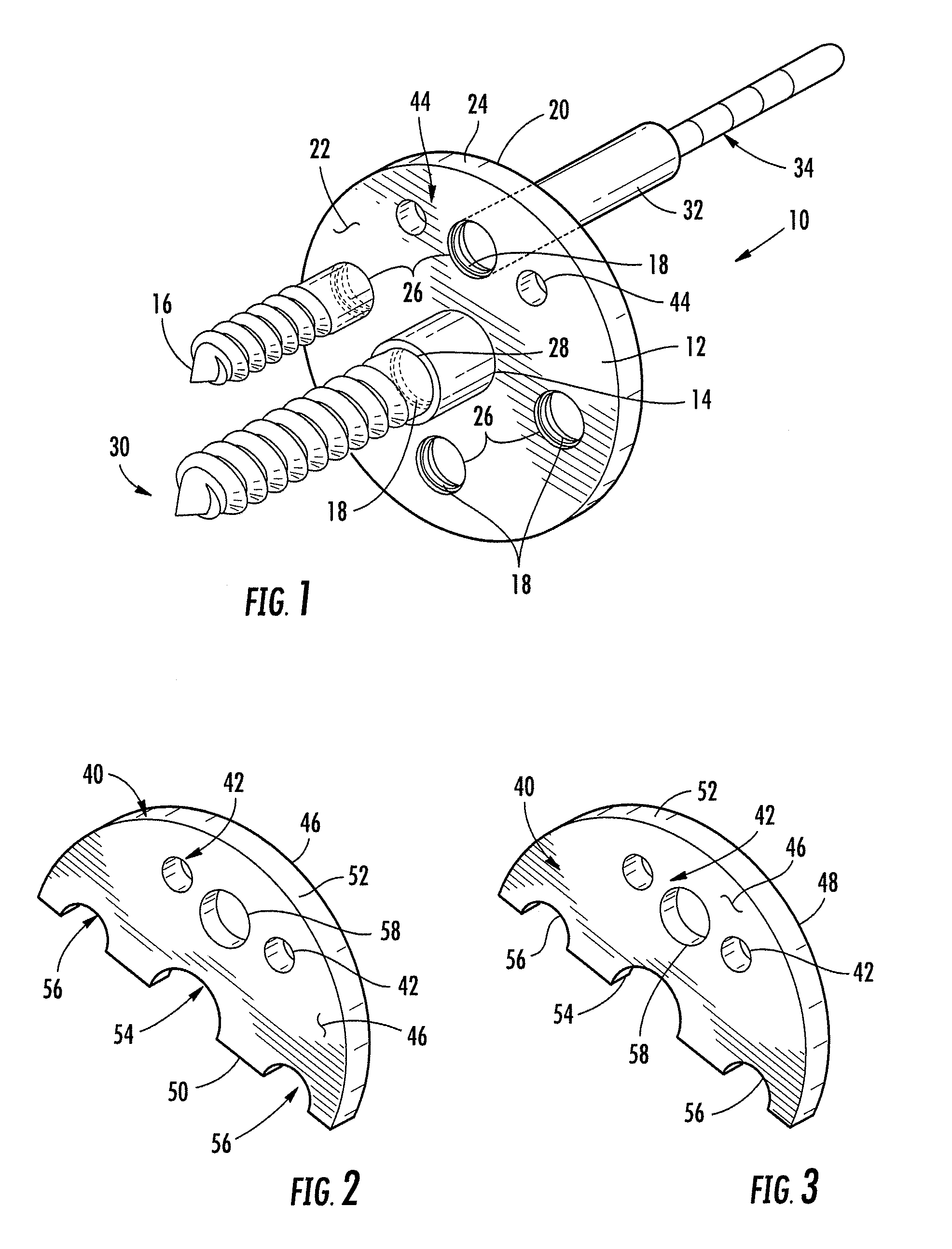
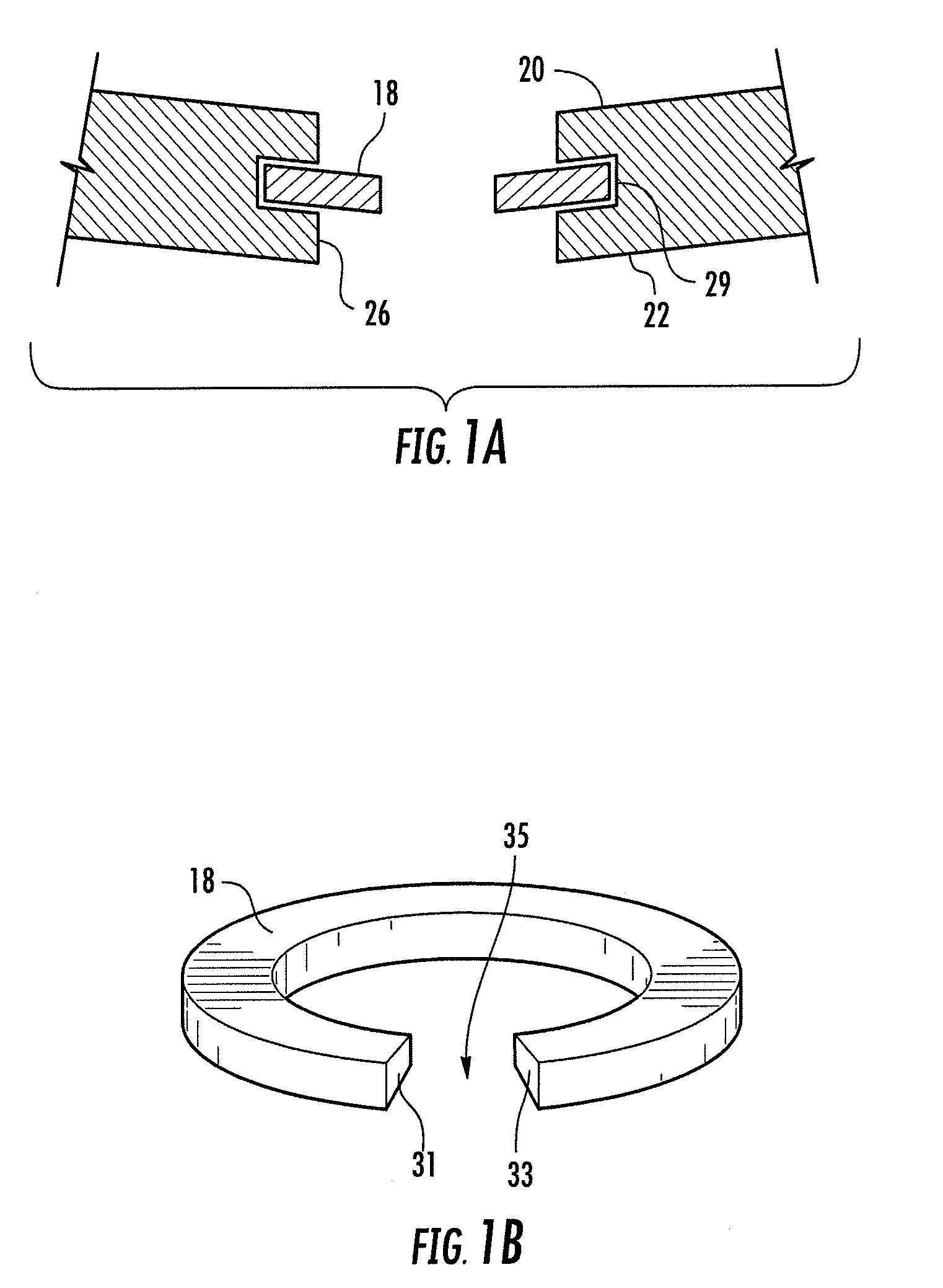
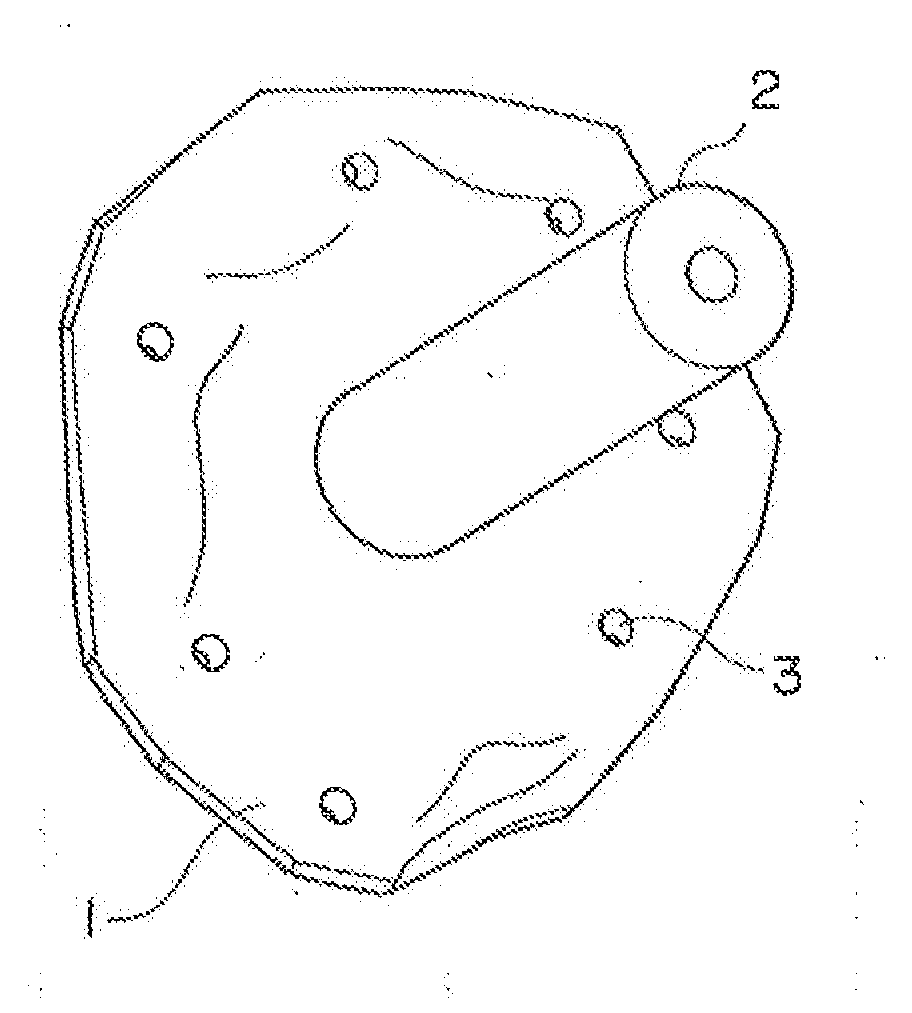
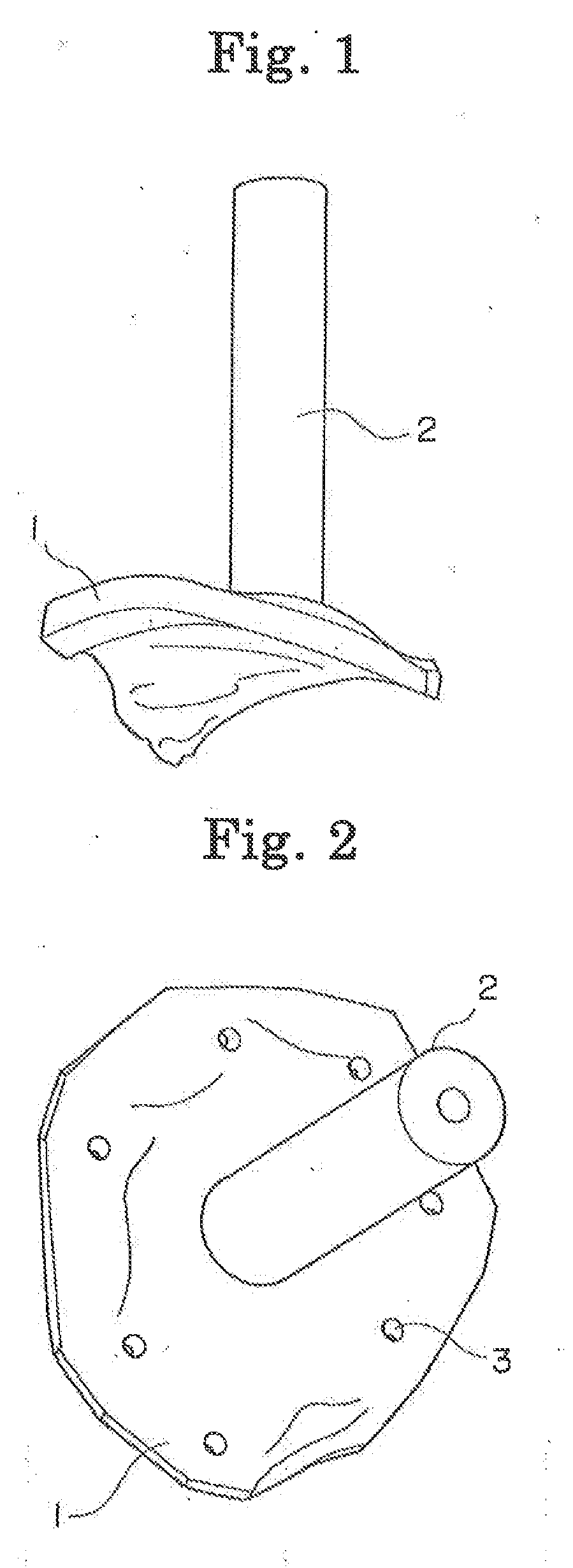
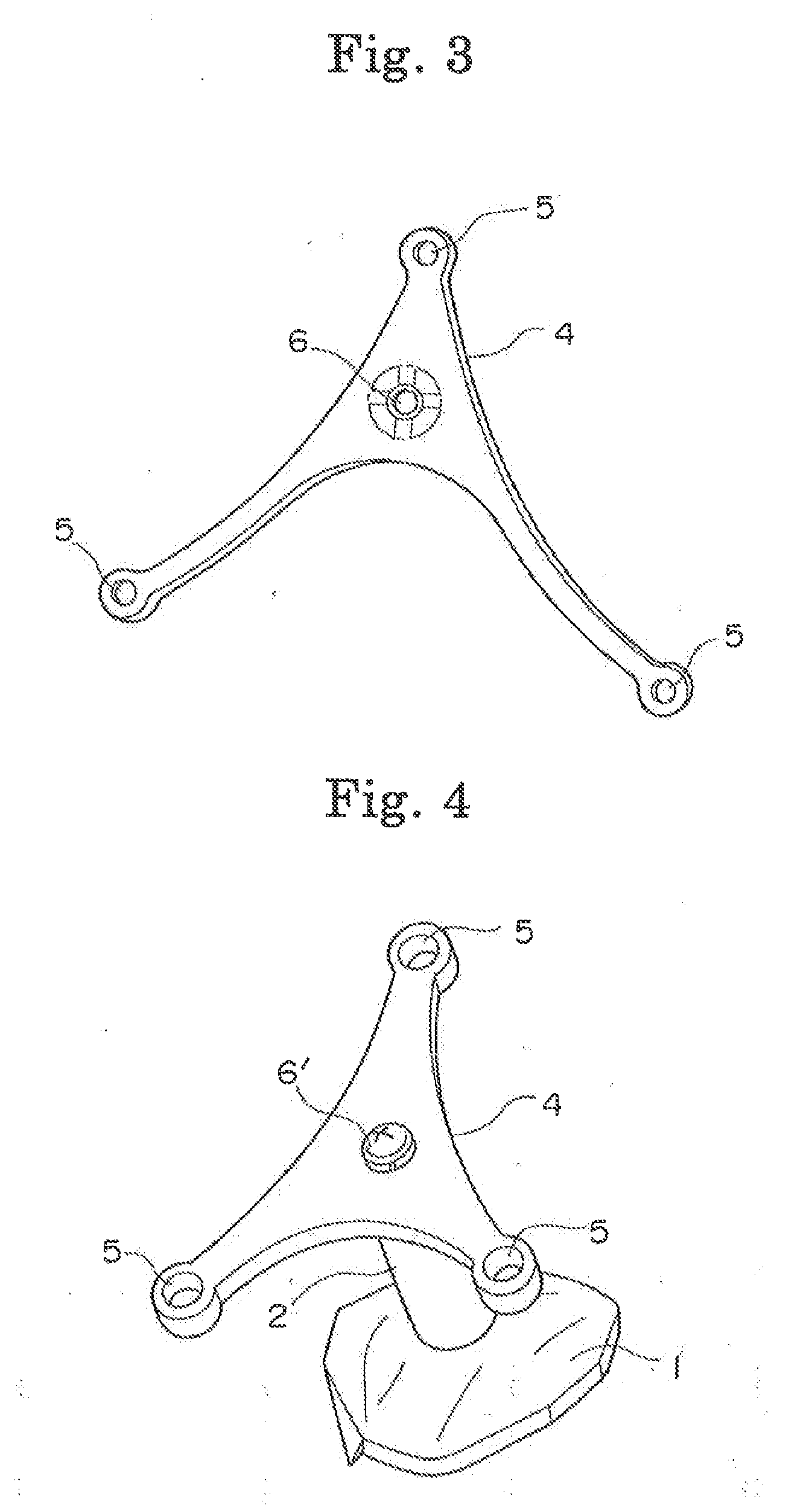
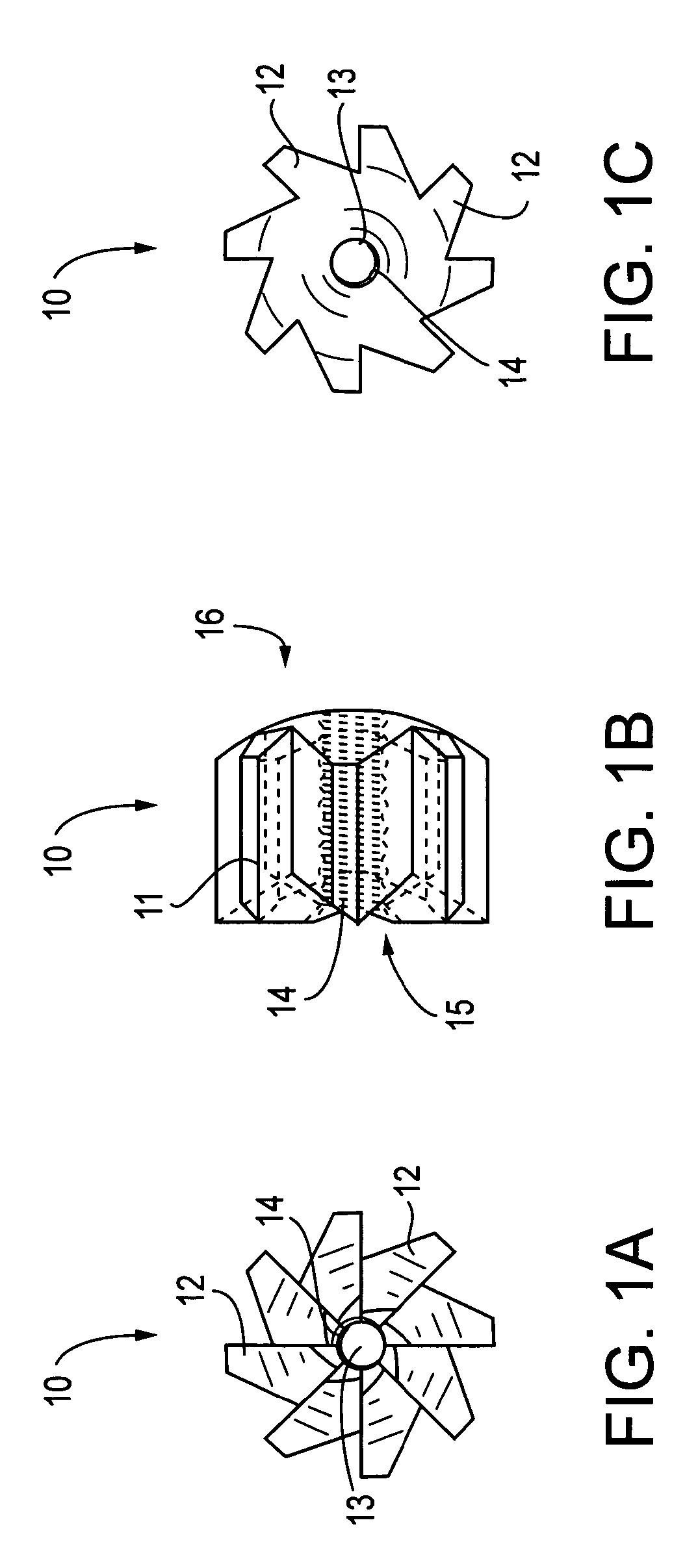
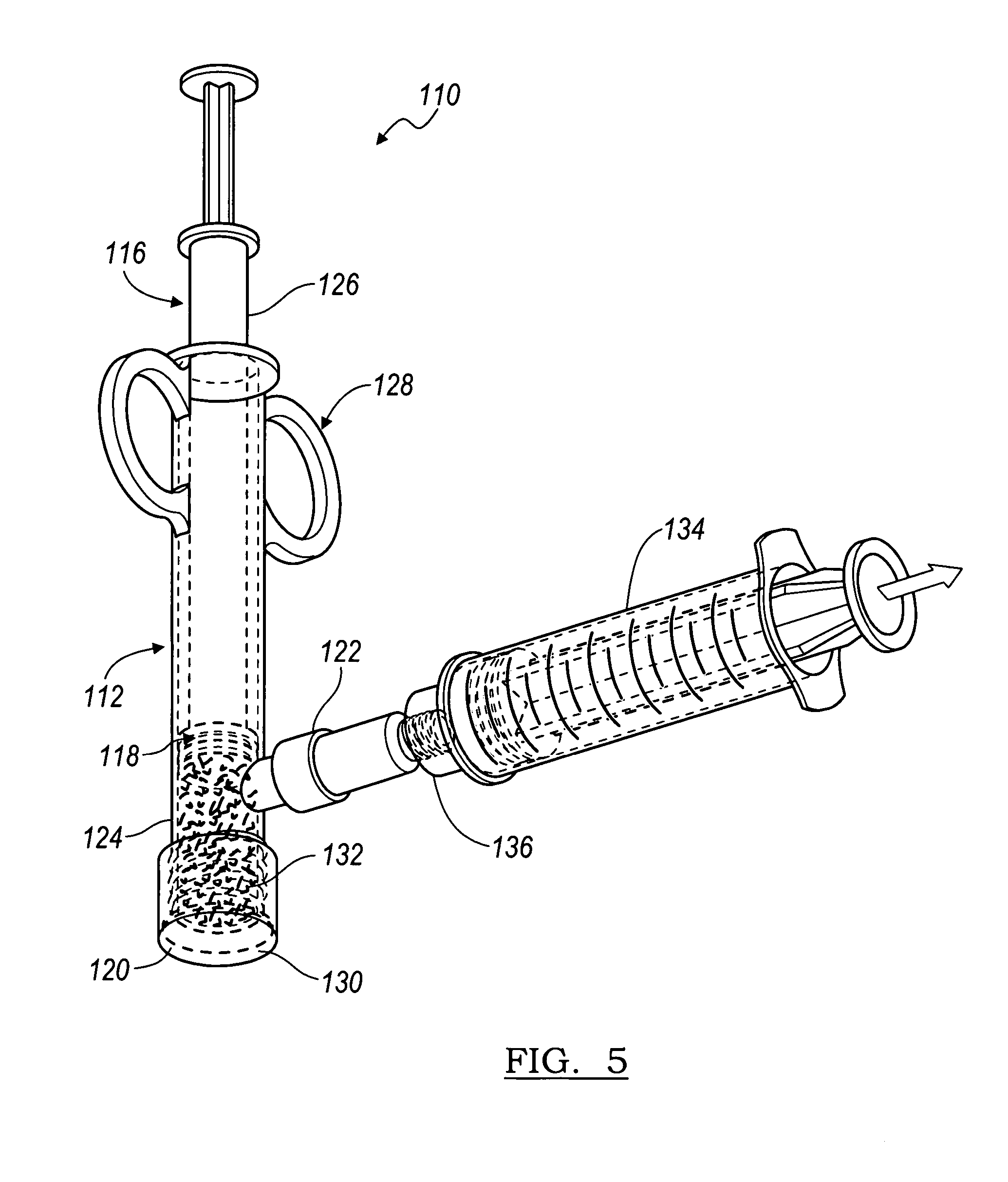
Bone anchor and deployment device therefor
A rivet-like bone anchor has a floating washer at its head that can adapt to an angled bone surface and, thereby, better secure a tissue thereto. The anchor includes a rivet, an expandable sleeve, and a washer. The rivet includes a head and an elongate body having proximal and distal ends, the head being mounted on the proximal end of the elongate body. The expandable sleeve has an inner bore adapted to receive the rivet body. The washer “floats” at a proximal end of the sleeve. As the rivet is inserted into sleeve, the sleeve expands into an interference fit with the bone. The head of the rivet, moreover, forces the floating washer into contact with the tissue at an angle that conforms to that of the underlying bone surface. A deployment tool permits the anchor to be deployed without application of unnecessary counterforce. The tool includes an outer tube, the distal end of which can hold the anchor housing, e.g., via a screw fit. A rod, which is slidably disposed within the bore of the tube, can be used to push the rivet into the expandable sleeve so that the sleeve expands into the bone, so that the floating washer is forced into position against the bone surface, and so that anchor is broken away from the housing. This can be effected, for example, by squeezing the distal ends of the outer tube and the rod together, e.g., in the manner that the end of a syringe is squeezed.
Owner:INNOVASIVE DEVICES
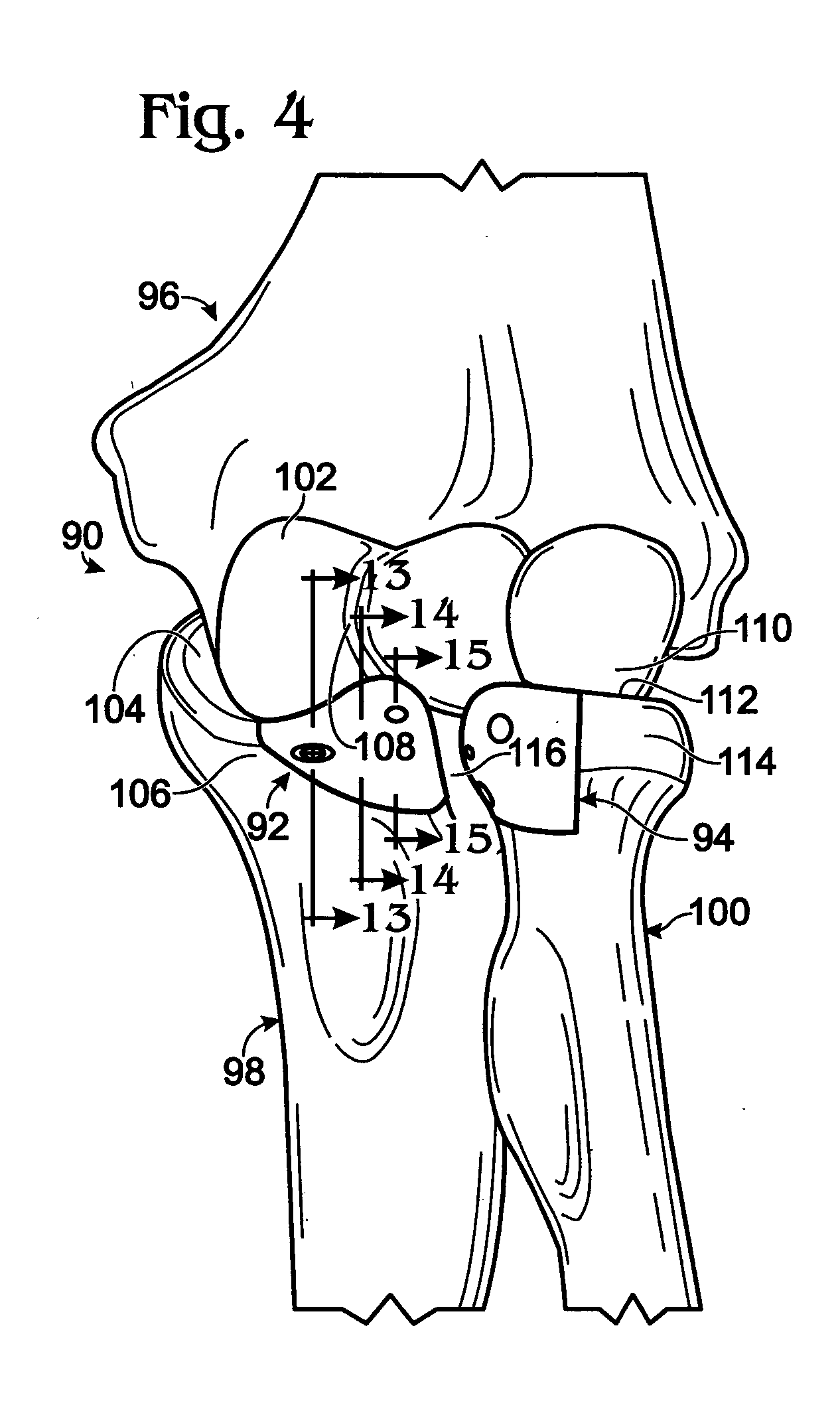
System and method for the fixation of bone fractures
The invention facilitates the fixation of bone fractures. In a particular embodiment, the head component includes a tip, cutting threads and mating threads which are inserted into the far cortex of the bone. A wire extends from the head component and exits from the near cortex. A cap device having a sawtooth inner surface is threaded over the wire having an inverse sawtooth outer surface such that the cap is restricted from backwards movement. Tension is then applied to the wire while the cap is tightened against or within the bone surface to thereby apply an appropriate amount of pressure between the surfaces of the fracture. The excess wire beyond the cap can then be removed.
Owner:ORTHOIP
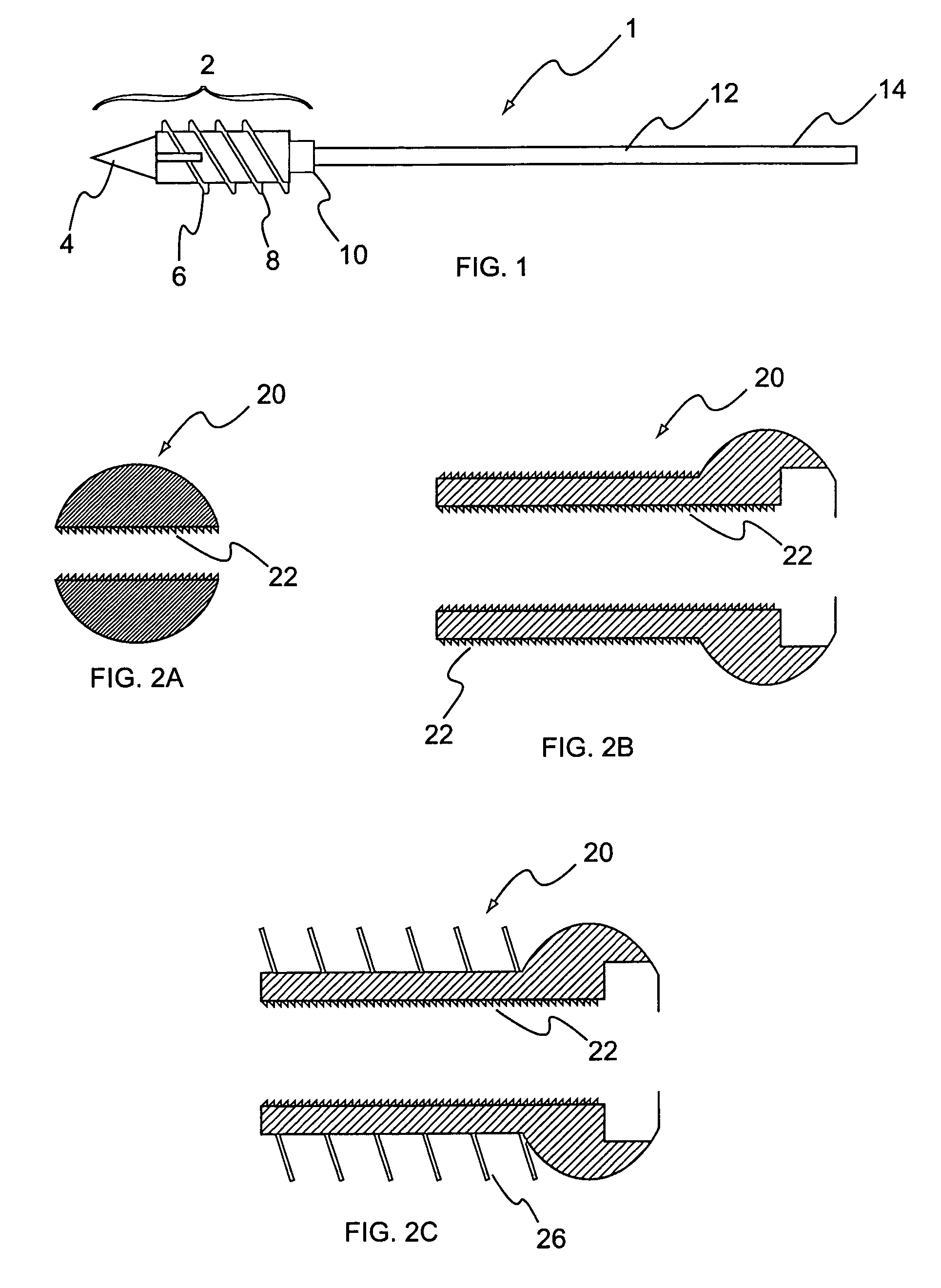
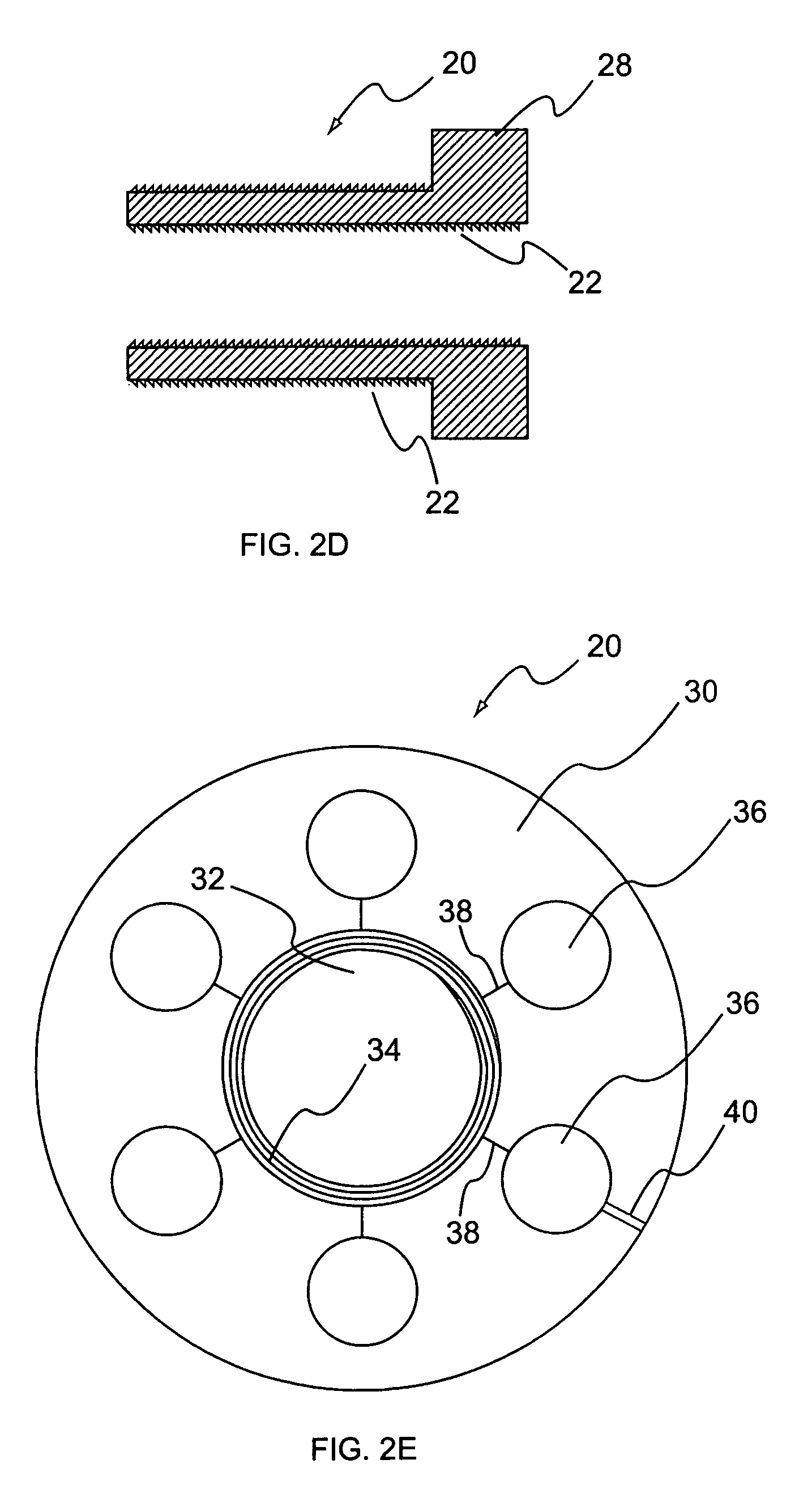
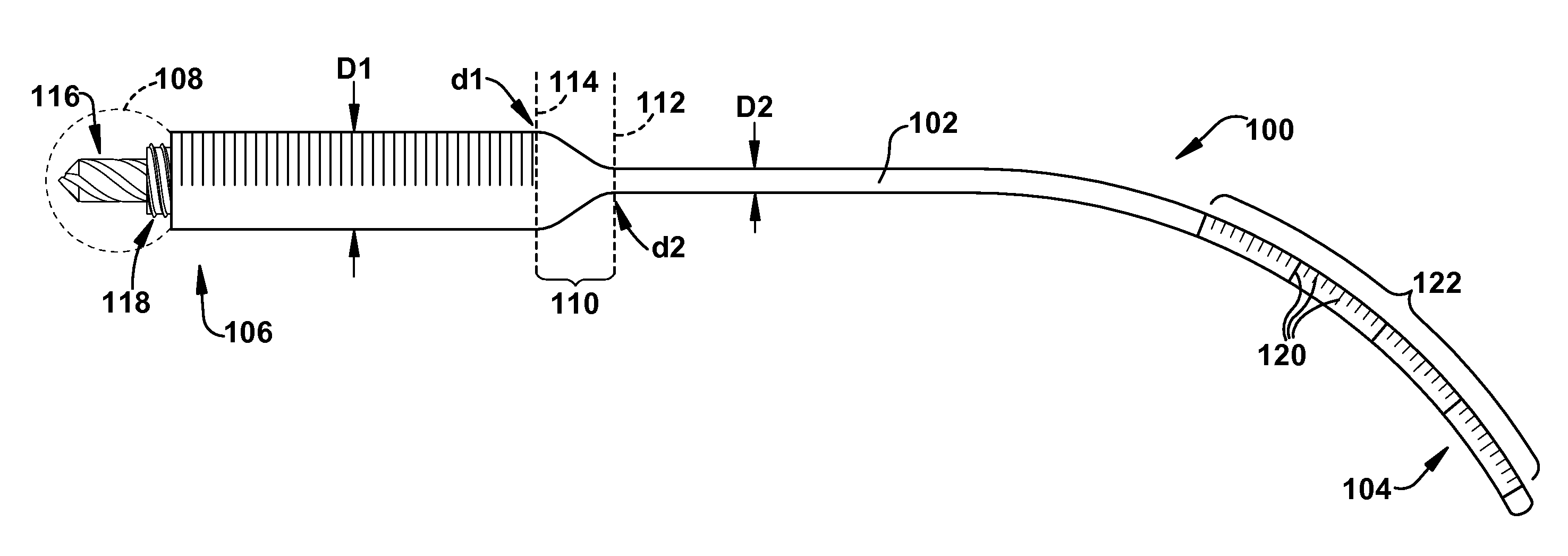
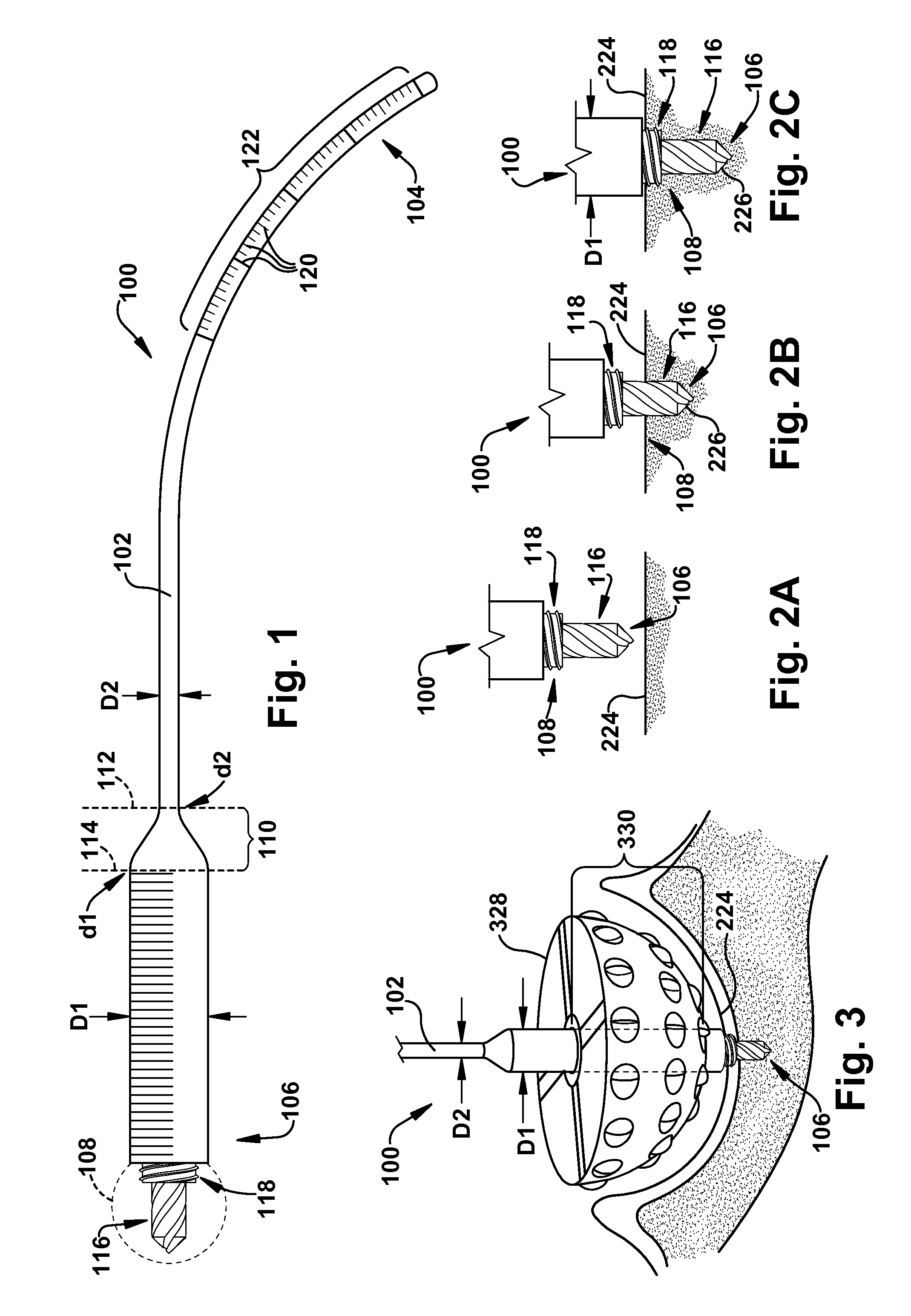
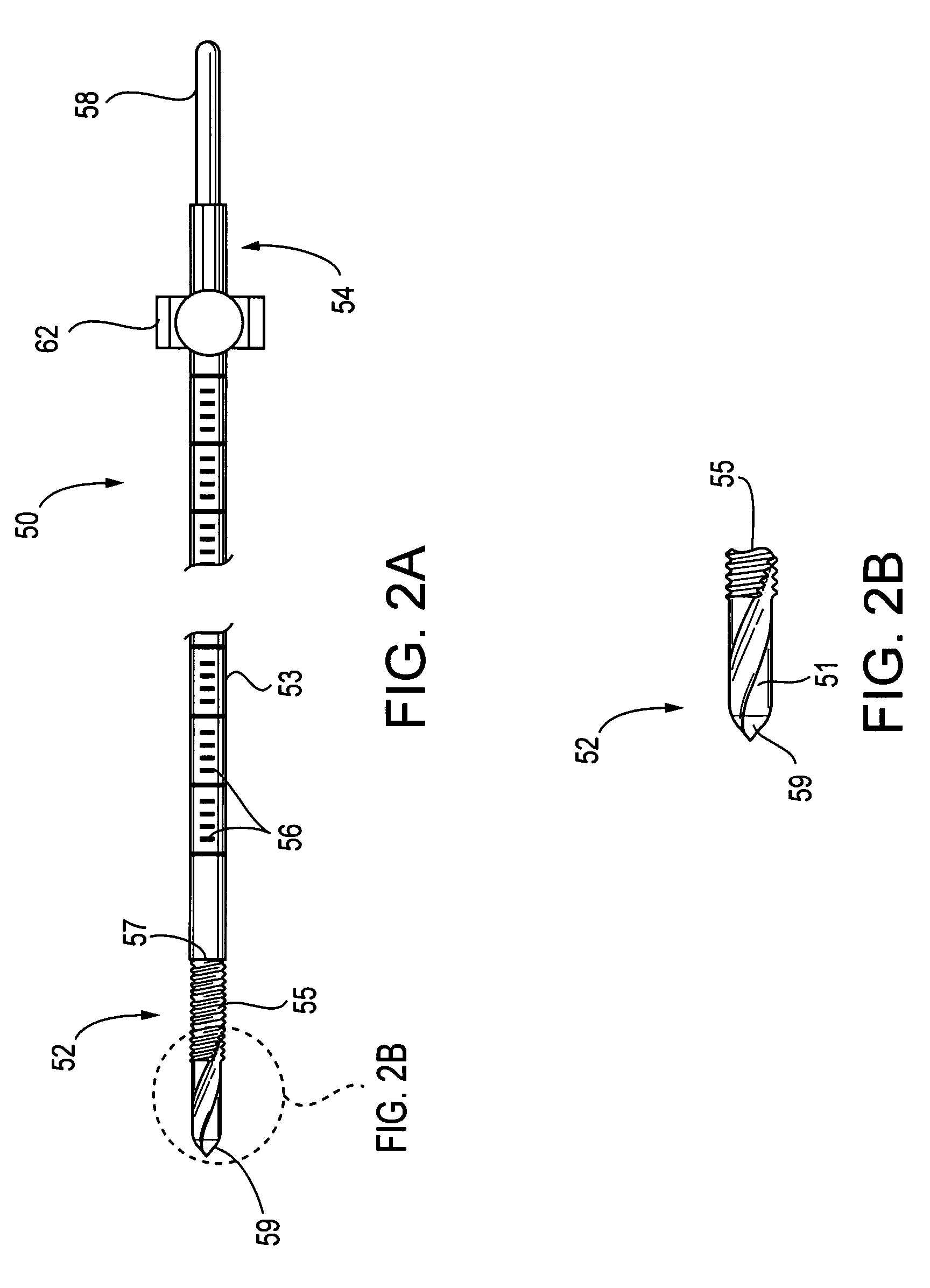
Method and apparatus for insertion of an elongate pin into a surface
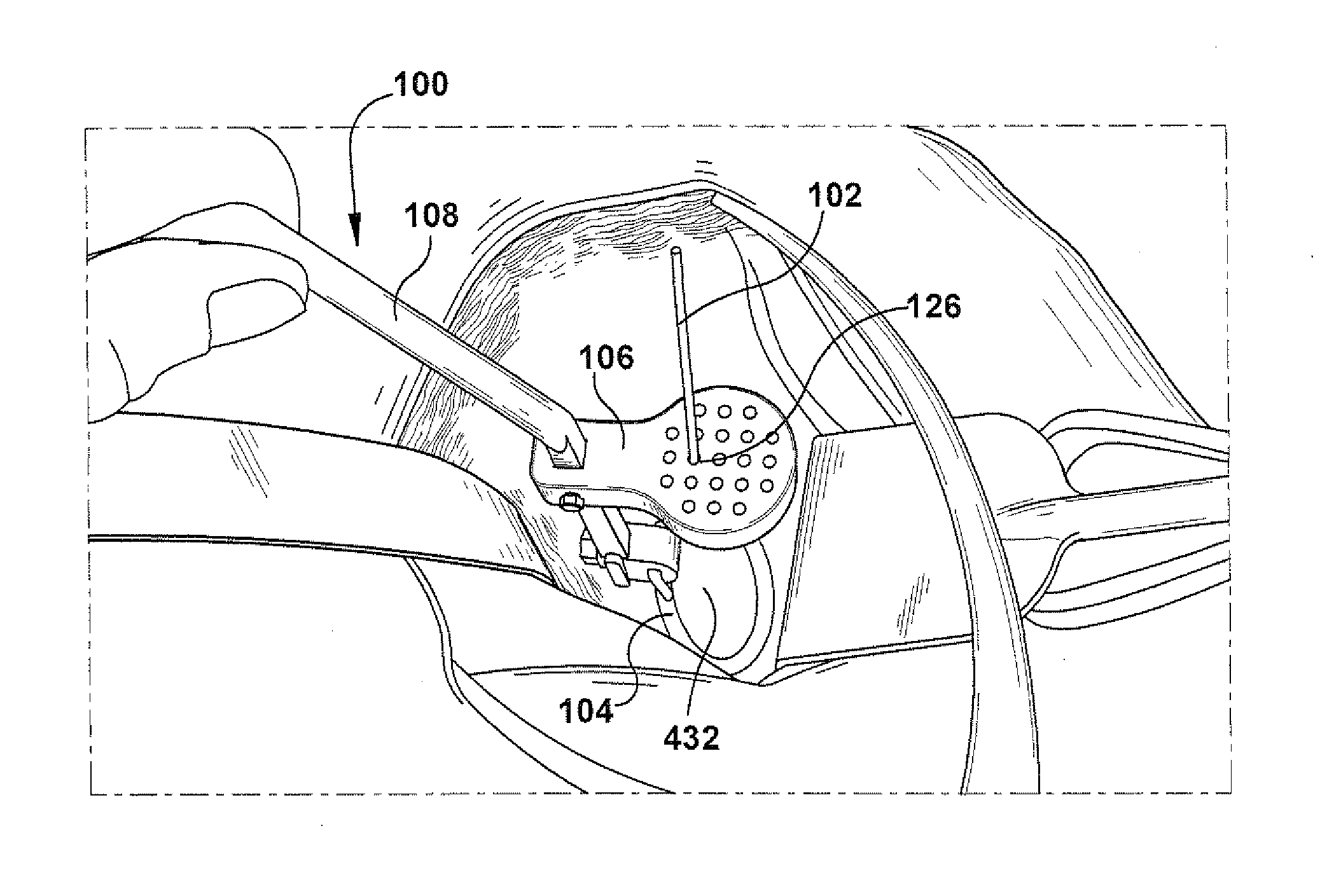
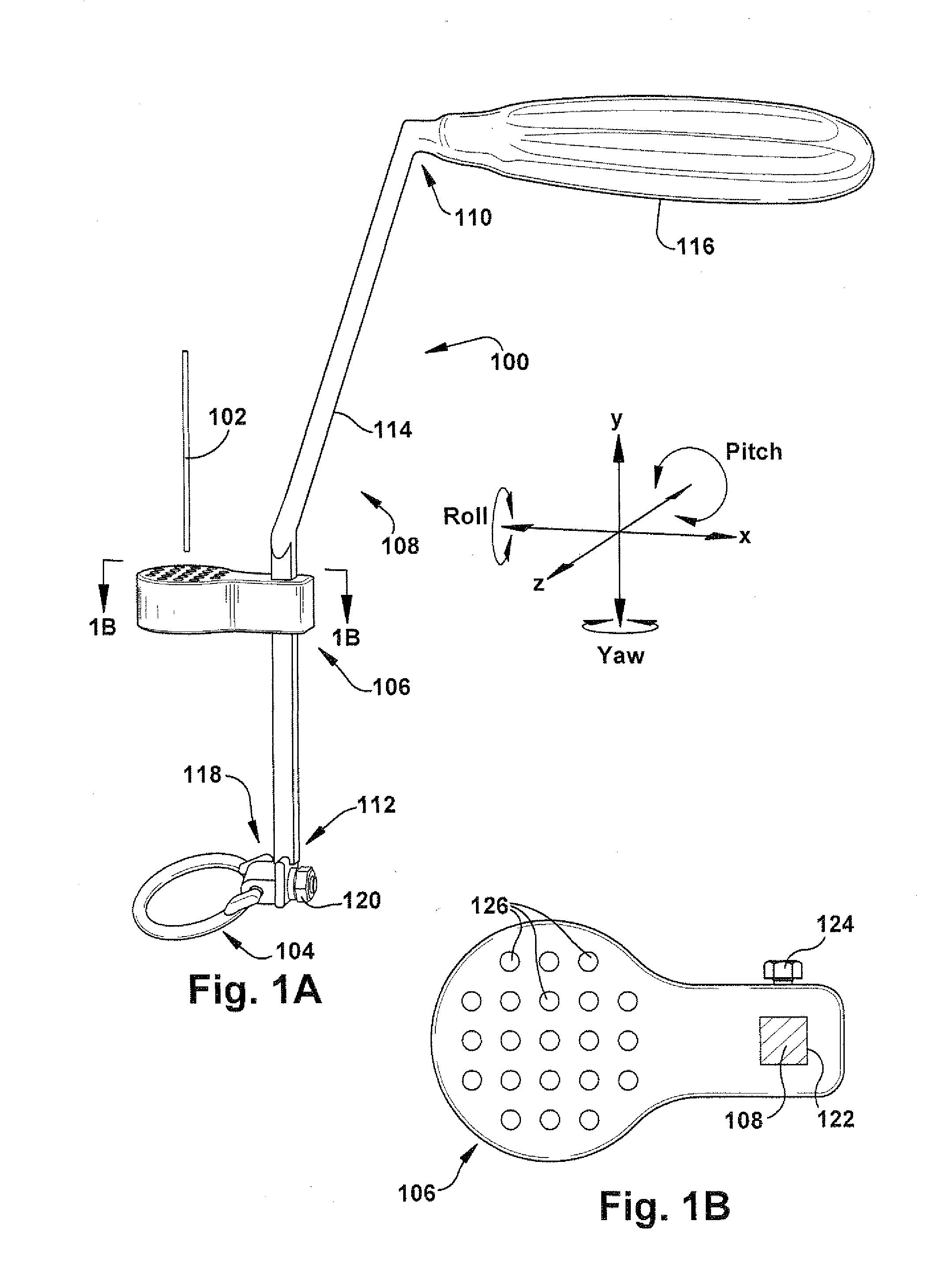
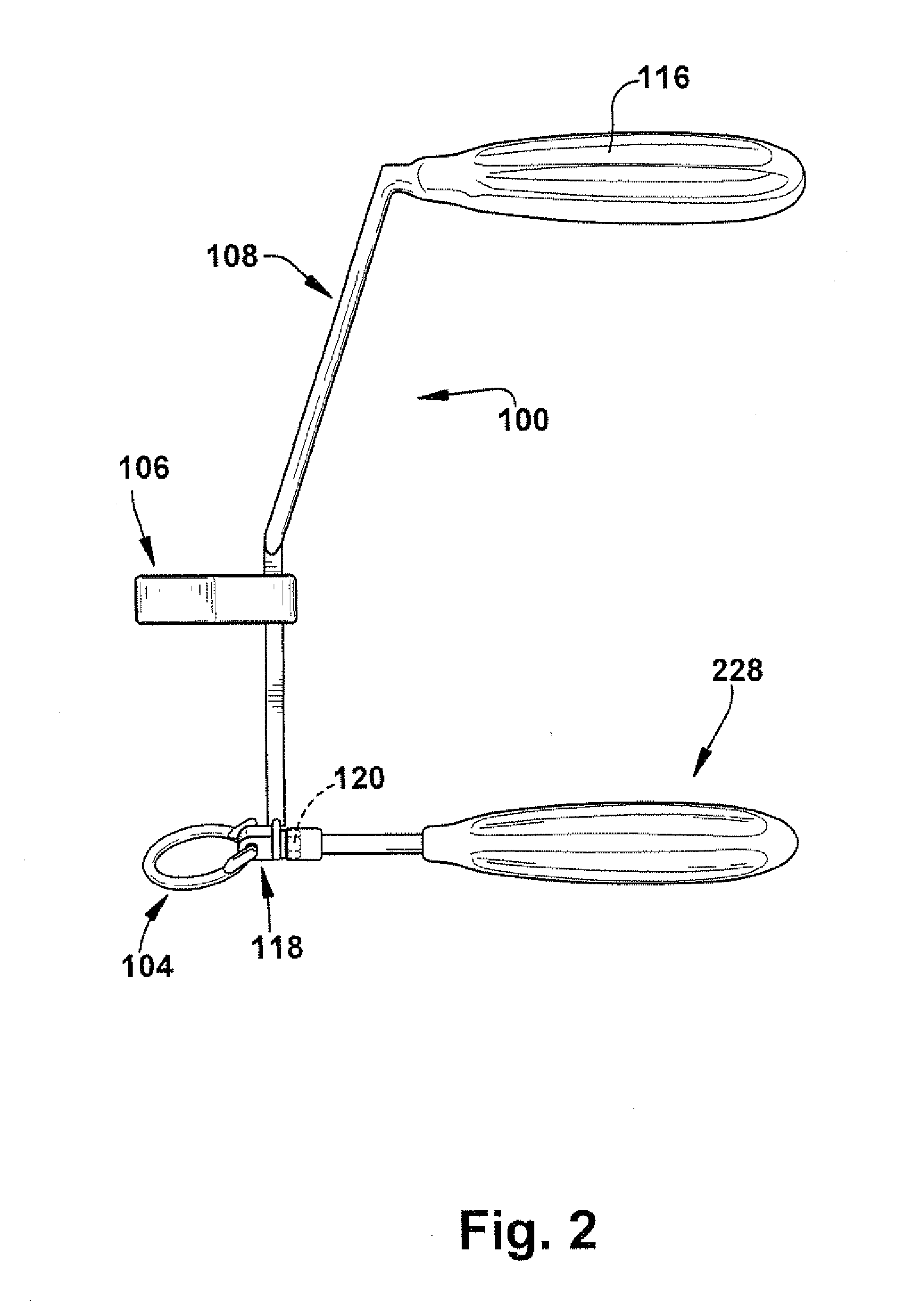
A trajectory structure is configured for contact with a surface to dictate an insertion trajectory of a pin relative to the surface. A location structure is configured to allow longitudinal passage of at least a portion of the pin therethrough to dictate an insertion location of the pin relative to the surface. An elongate handling rod is connected to the trajectory structure and the location structure. The handling rod supports the trajectory structure and the location structure for manipulation by a user. The handling rod spaces the trajectory structure and the location structure longitudinally apart. The trajectory structure is connected to the handling rod for trajectory adjustment in at least two degrees of freedom relative to the handling rod. The insertion trajectory of the pin insertion is substantially dependent upon the trajectory adjustment. A method for inserting an elongate guide pin into a bone surface is also provided.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
Prosthetic implant and method of implantation
A prosthetic implant useful in a cementless application is disclosed. The implant may include a curved bone facing surface and one or more pegs or keels. Preferably, the implant is implanted on a bone surface that has been prepared so as to allow for a snap fit between the implant and the bone.
Owner:STRYKER CORP
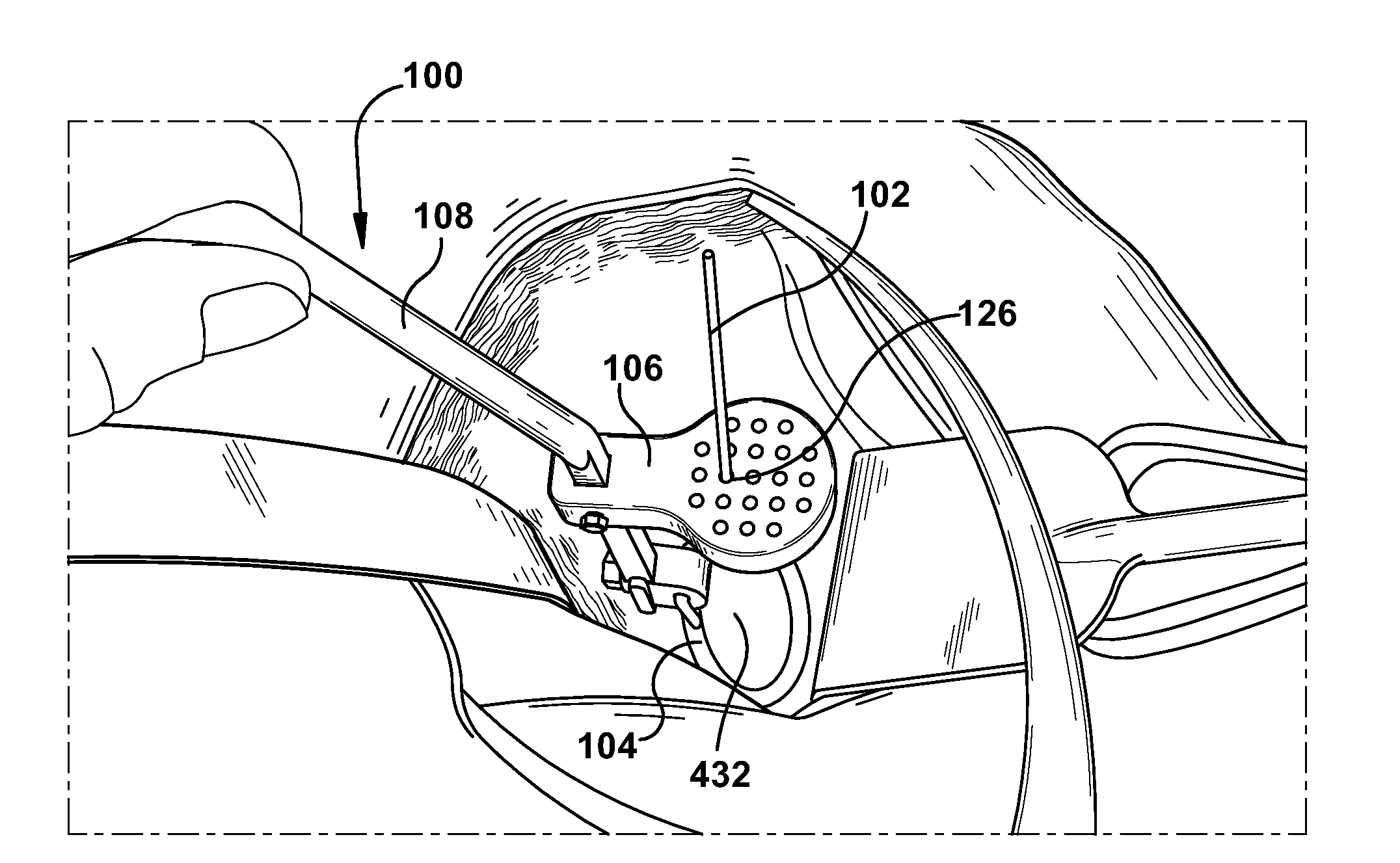
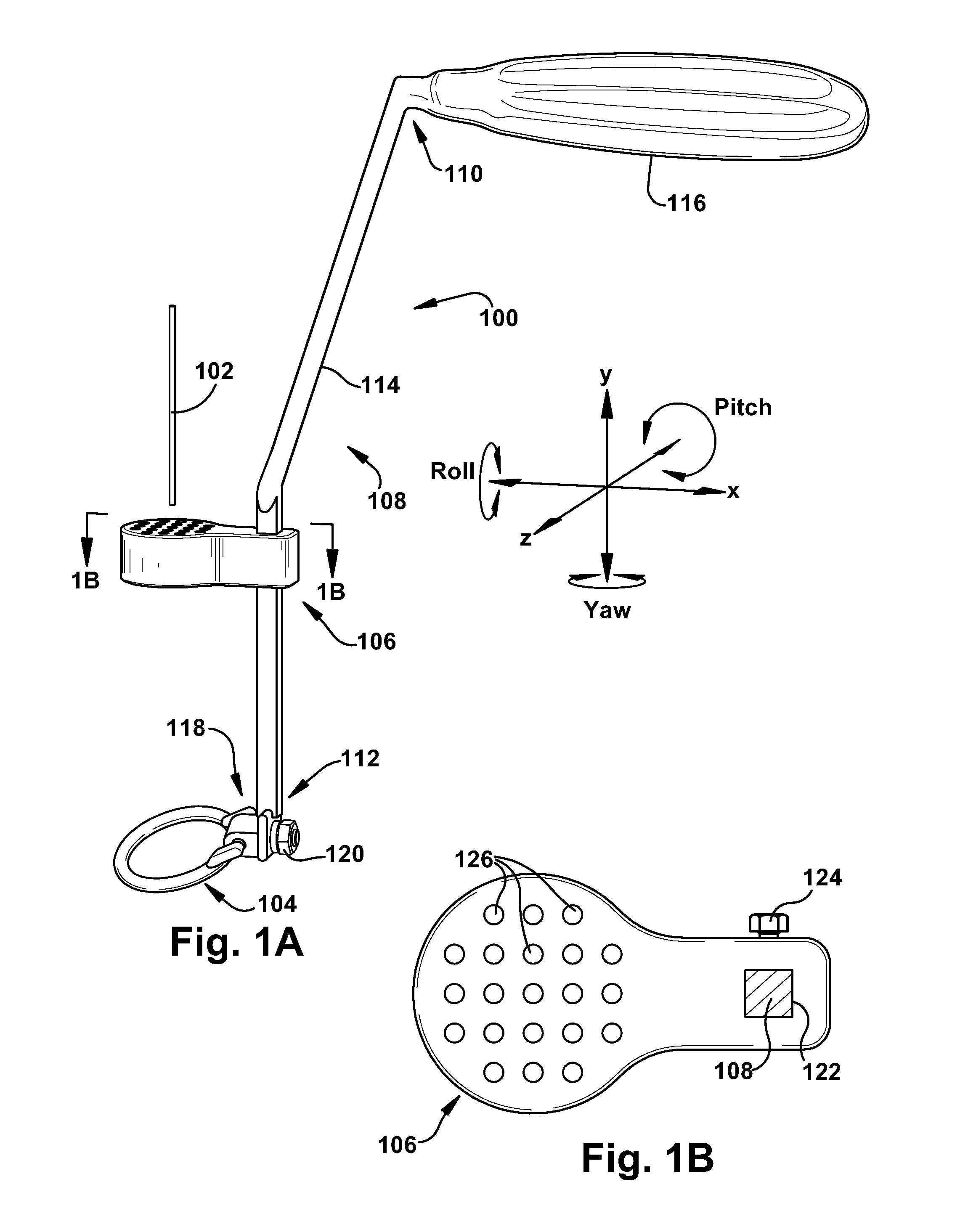
Method and apparatus for providing a relative location indication during a surgical procedure
An orthopedic guidewire includes an elongate guidewire body having longitudinally spaced proximal and distal guidewire ends. An engaging feature is located at the distal guidewire end and is configured to selectively engage a bone surface. At least one of a variable diameter and a variable stiffness are along a portion of the guidewire body spaced apart from the engaging feature. A method of providing a relative location indication during a surgical procedure utilizing the orthopedic guidewire is also included.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
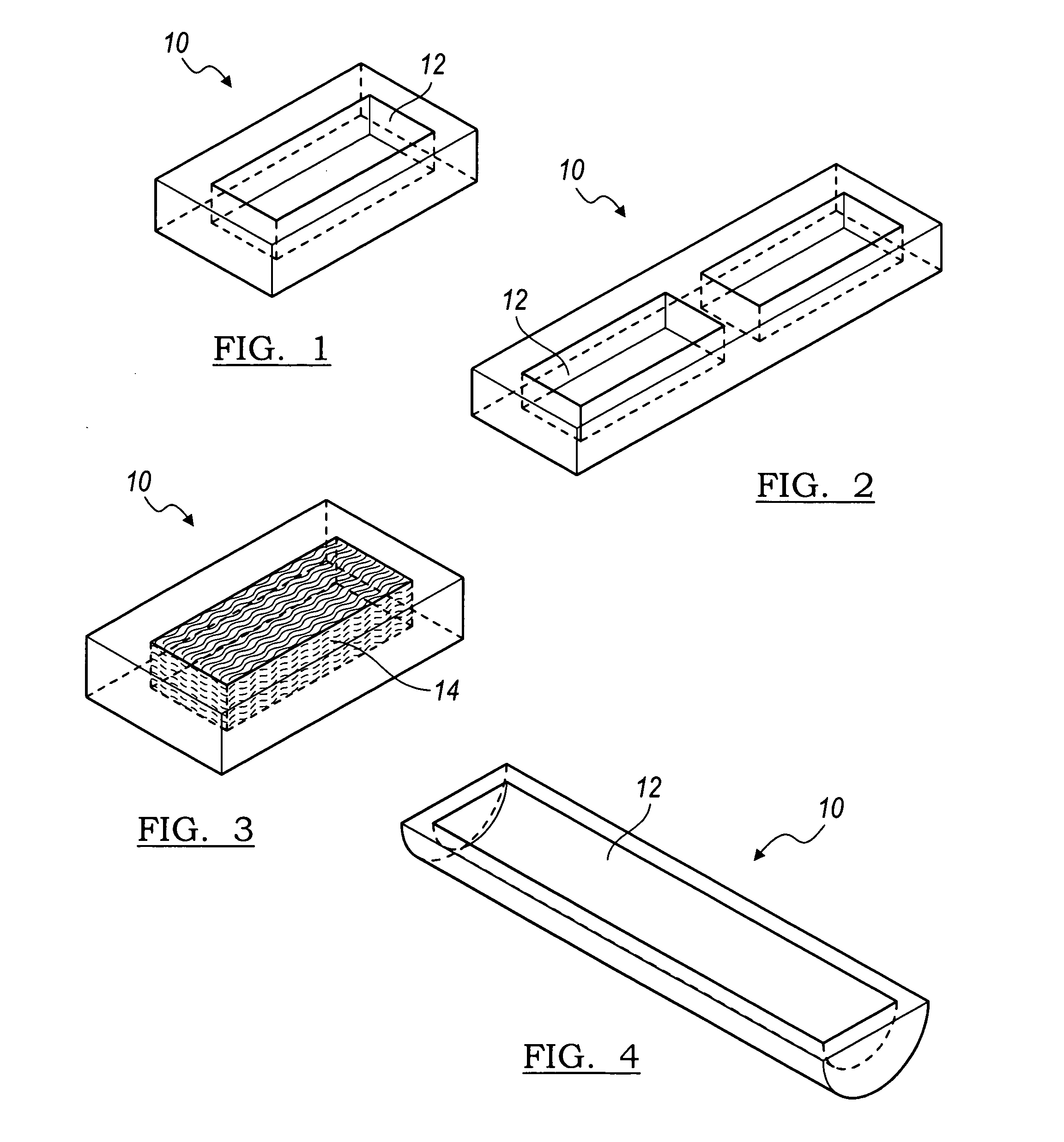
Composite bone graft, method of making and using same
InactiveUS6902578B1Avoid significant donor site morbidityHigh mechanical strengthBone implantJoint implantsDiseaseOssicular Prosthesis Implantation
The invention is directed to a composite bone graft for implantation in a patient, and methods of making and using the composite bone graft, along with methods for treating patients by implanting the composite bone graft at a site in a patient. The composite bone graft includes two or more connected, discrete, bone portions, and includes one or more biocompatible connectors which hold together the discrete bone portions to form the composite bone graft. The composite bone graft may include one or more textured bone surfaces. The textured surface preferably includes a plurality of closely spaced protrusions, preferably closely spaced continuous protrusions. The composite bone graft is useful for repairing bone defects caused by congenital anomaly, disease, or trauma, in a patient, for example, for restoring vertical support of the anterior and / or posterior column. Implantation of the composite bone graft results in improved graft stability and osteoinductivity, without a decrease in mechanical strength. The composite bone graft does not shift, extrude or rotate, after implantation. The present composite bone graft can be appropriately sized for any application and can be used to replace traditional non-bone prosthetic implants.
Owner:LIFENET HEALTH
Base plate system for shoulder arthroplasty and method of using the same
Embodiments of the present invention provide systems and methods for use in a replacing a joint having a prepared bone surface. A base plate system according to one embodiment includes a base plate comprising a plurality of locking screw holes defined therethrough and first and second opposing surfaces, wherein the second surface is configured to be positioned adjacent to the prepared bone surface. The system also includes a central peg extending outwardly from the second surface of the base plate and configured to engage the prepared bone surface and a plurality of locking screws configured to be inserted within a respective locking screw hole and engage the prepared bone surface. In addition, the system includes a plurality of locking washers disposed within a respective locking screw hole and configured to receive a respective locking screw and lock the locking screw at a desired angle with respect to the base plate.
Owner:GROH GORDON I
Modular total ankle prosthesis apparatuses, systems and methods, and systems and methods for bone resection and prosthetic implantation
Ankle prosthesis apparatuses, systems and methods are provided as disclosed herein. Additionally, systems and methods for bone resection and implantation of prosthetics are provided, including surgical techniques and related instrumentation. An ankle prosthesis apparatus can include a talar component having a lower surface with a bone fixation portion for fixation to a talus bone and an upper surface designed for articulation with a bearing component. The bearing component can have a lower surface for articulation with the talar component and an upper surface for articulation with a tibial component. The tibial component can have a lower surface for articulation with the bearing component and an upper surface with a bone fixation portion for fixation to a tibia bone and / or a fibula bone. The bearing component can have a protrusion on its upper surface adapted for engagement with a recess on the tibial component to allow desired rotational and translational movement. Methods and systems can be used to prepare a bone surface for implantation of a prosthesis including determining a location for a curved cut line on the bone surface and drilling a series of holes tangent to the curved cut line to create a curved bone resection surface. Methods and systems can be used for the implantation of an ankle joint prosthesis including the use of an alignment guide, tibia and talus drill guides, tibia and talus saw guides, and tibia and talus broach guides, all components of which can be placed on and removed from a plurality of alignment anchor pins throughout the implantation procedure. A method for medially to laterally implanting an ankle joint prosthesis can include exposing tibia and talus bones from the medial side, resection of the tibia and talus bones, broaching the tibia and talus bones, and positioning and affixing the ankle joint prosthesis components.
Owner:INTEGRA LIFESCI
Resorbable interposition arthroplasty implant
InactiveUS6017366AImprove permeabilityAvoid collisionFinger jointsWrist jointsTrapezium BoneSurgical department
A resorbable implant for interposition arthroplasty which is intended to fill a void between two adjacent bone ends, providing a cushion between the bone ends to prevent impingement of the bone ends while providing time for tissue to infiltrate into the space occupied by the implant. It has a protracted resorption time of preferably at least three months to allow time for the proliferation of load-bearing host fibrous tissue in place of the resorbed implant material. The implant preferably is porous with a pore size of greater than about 80 microns in order to enhance infiltration of fibrous tissue. The implant has a modulus in the range of 0.8 to 20 MPa which is soft enough to allow it to conform to surface irregularities of the adjacent bone surfaces while being hard enough to maintain a desired separation between those bones while tissue infiltration replaces the resorbable implant material. The implant may be preformed to the desired shape or alternatively may be formable by the surgeon by methods such as carving with a scalpel. A preferred application for the implant is as a trapezium bone replacement.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
Suture management and tensioning devices and methods for soft tissue reconstruction or bone-to-bone fixation
ActiveUS20080154260A1Convenient introductionSimplifying retention of sutureSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsBone fixationSoft tissue reconstruction
Owner:CAYENNE MEDICAL INC
Method for manufacturing registration template
InactiveUS20140096369A1Precise alignmentShorten the timeDiagnostic markersInstruments for stereotaxic surgeryTomographyOptical tracking
A method for manufacturing a registration template for use in medical navigation system-guided surgery, comprising: producing a registration template having a surface, which precisely surface-bonds to a surface of a bone at a surgical target site of a patient, and having three or more registration points, from stereoscopic surface data ensuring precise surface bonding to the surface of the bone at the surgical target site of the patient, based on stereoscopic surface data created from tomography information on the bone of the surgical target site of the patient; and providing a pedestal (4) for mounting optical tracking balls (7), which are used for three-dimensional position detection for a medical navigation system, at the center of the registration points. By using the template having curves surfaces which three-dimensionally precisely and intimately contact the bone surface of the patient, high-precision registration can be performed, and an operator's man-hours immediately before surgery in an operating room can be reduced to shorten the surgery time.
Owner:ONO
Method and apparatus for insertion of an elongate pin into a surface
A trajectory structure is configured for contact with a surface to dictate an insertion trajectory of a pin relative to the surface. A location structure is configured to allow longitudinal passage of at least a portion of the pin therethrough to dictate an insertion location of the pin relative to the surface. An elongate handling rod is connected to the trajectory structure and the location structure. The handling rod supports the trajectory structure and the location structure for manipulation by a user. The handling rod spaces the trajectory structure and the location structure longitudinally apart. The trajectory structure is connected to the handling rod for trajectory adjustment in at least two degrees of freedom relative to the handling rod. The insertion trajectory of the pin insertion is substantially dependent upon the trajectory adjustment. A method for inserting an elongate guide pin into a bone surface is also provided.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
Prosthesis for partial replacement of an articulating surface on bone
Systems, including apparatus, methods, and kits, for replacing a portion of an articulating bone surface with a surface region of a partial prosthesis.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
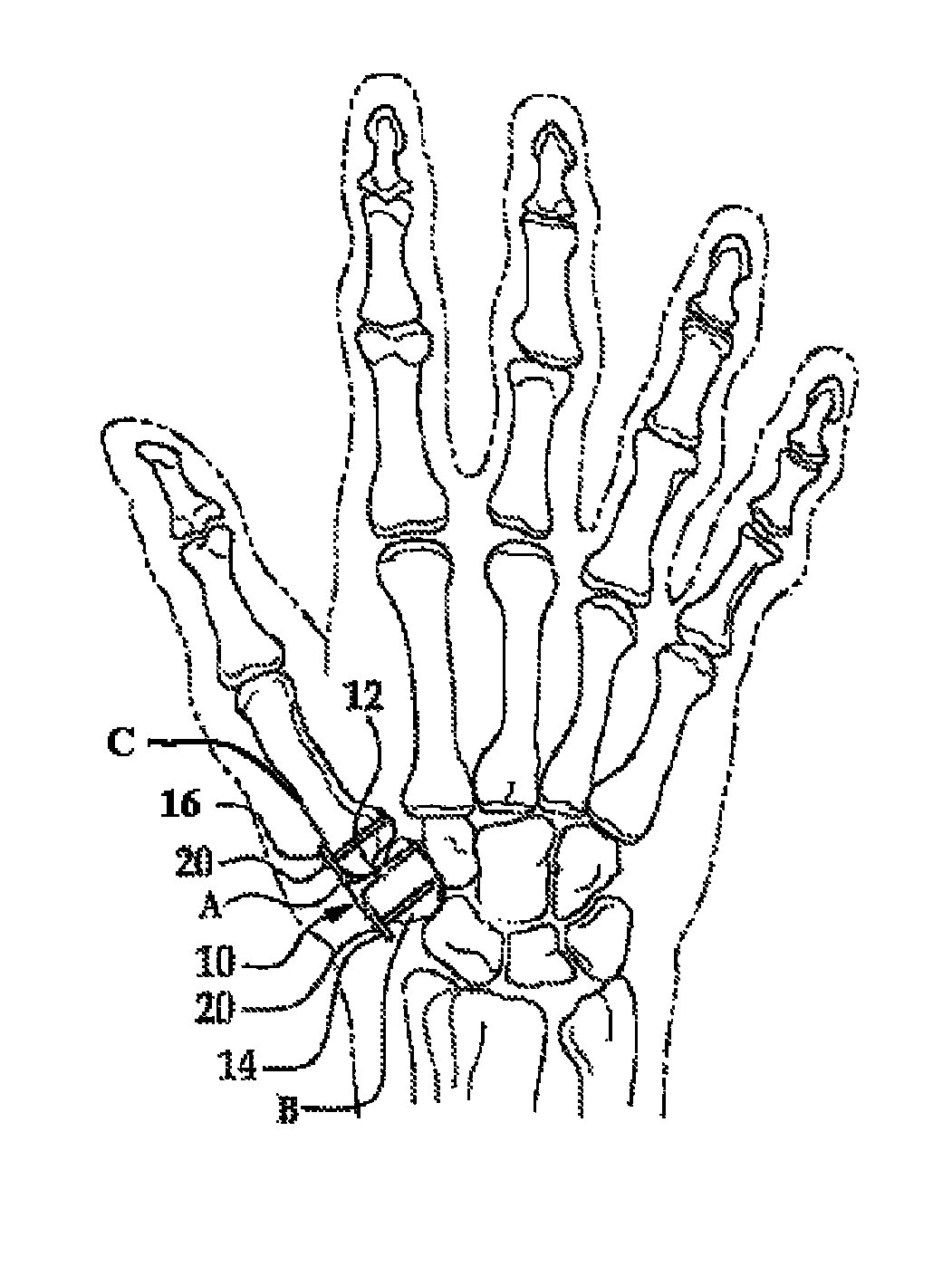
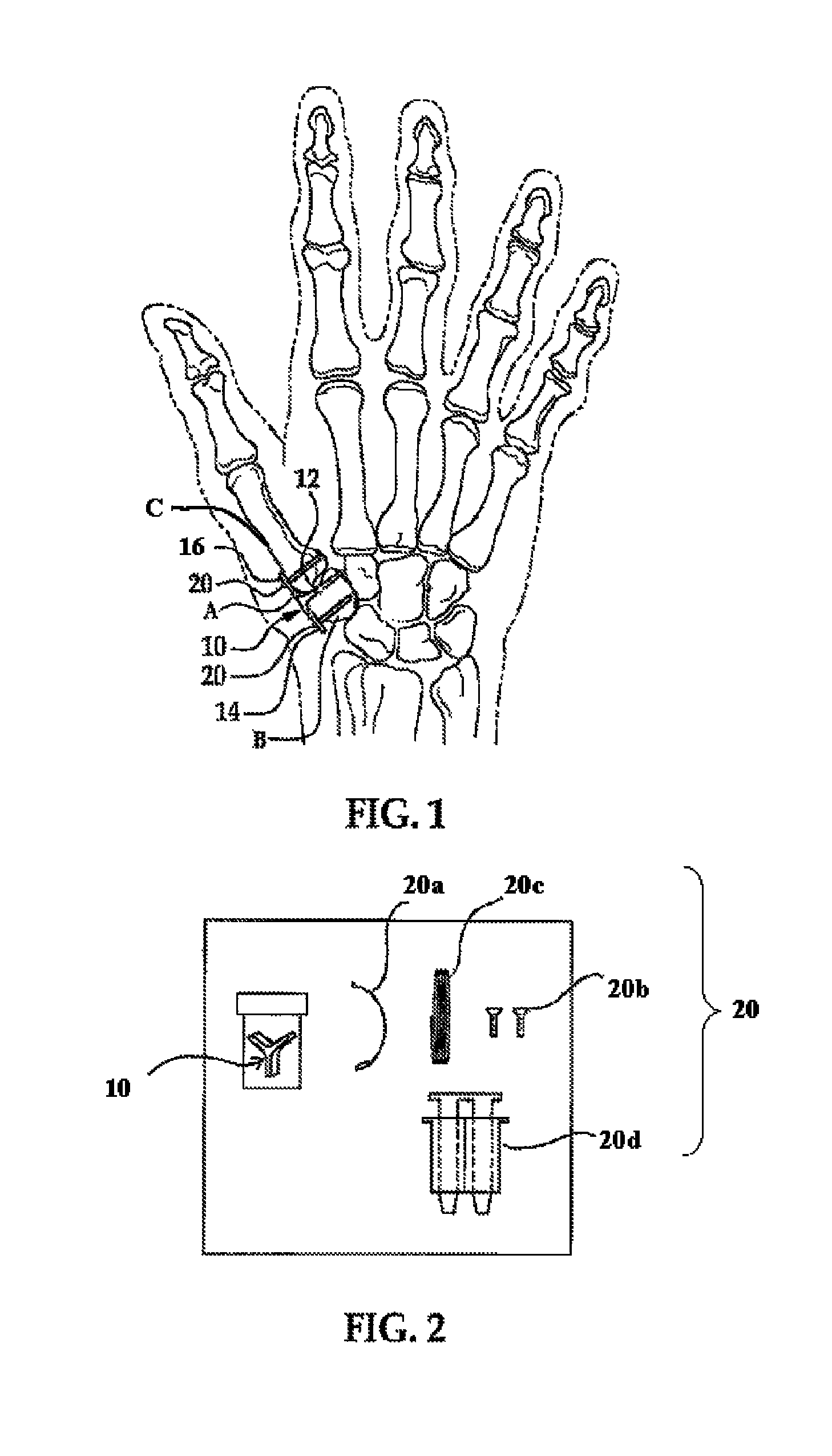
Surgical technique using a contoured allograft cartilage as a spacer of the carpo-metacarpal joint of the thumb or tarso-metatarsal joint of the toe
A spacer for implantation into a subject is provided that includes a sterilized piece of cartilaginous allograft tissue. The piece forms a Y-shape with a base adapted to insert within a first carpo-metacarpal joint or carpo-metatarsal joint of the subject, and has a first arm adapted to secure to a trapezium bone adjoining the joint, and a second arm adapted to secure to a proximal metacarpal or metatarsal bone adjoining the joint. A procedure for implanting the spacer includes exposing a target joint and abrading a bone surface interior to the joint to induce surface bleeding. The spacer base is then inserted into the joint. The spacer first arm is adhered to the first bone of the joint and the spacer second arm is adhered to the second bone of the joint. A kit is also provided for surgical implantation of the spacer.
Owner:SHAPIRO PAUL S
ACL reconstruction technique using retrodrill
Methods and apparatus for arthroscopic tenodesis using sockets in bone created by retrograde cutting. A cannulated pin is drilled through bone and into a joint space in the normal, antegrade direction, guided by a drill guide. A strand provided through the cannulated pin is used to draw a retrodrill cutter into the joint space. The retrodrill cutter is threaded onto the cannulated pin, which is turned for retrograde cutting of a socket into the bone. The method is used to form a pair of sockets in the joint, which accept the respective ends of a replacement graft. The graft is brought into position in the joint space using loops formed in the strands, in a manner similar to introduction of the retrodrill cutter. The reconstruction is completed by securing suture attached to the graft ends with a button implant installed at the bone surface.
Owner:ARTHREX
System and method of designing and manufacturing customized instrumentation for accurate implantation of prosthesis by utilizing computed tomography data
ActiveUS8175683B2Quickly and accurately attachesPrecise positioningPerson identificationCharacter and pattern recognitionProsthesisControl data
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
Method and apparatus for repairing bone
InactiveUS20060280803A1Not easily dislodgedIncrease resistanceBone implantUnknown materialsDemineralized boneAnimal subject
Formed compositions for application to a bone surface of a human or animal subject, comprising: a bone material; and a carrier comprising denatured demineralized bone, where the composition is formed into a shape suitable for administration to the bone. Methods are provided for making formed compositions for application to a bone surface of a human or animal subject comprise mixing a demineralized bone and water; heating the mixture to form a carrier; mixing the carrier with bone to form a moldable composition; and molding the moldable composition to produce a formed composition. Several apparatuses are provided in which to hydrate the formed bone composition. Methods of hydrating a formed bone composition are also provided.
Owner:BIOMET MFG CORP
Method and apparatus for performing an open wedge, high tibial osteotomy
An apparatus and method for performing an open wedge osteotomy. The apparatus includes devices for forming an open wedge osteotomy in bone, including a keyed-wedge implant. The method includes the steps of forming a cut in a bone, forming a keyhole in the bone surface at the proximal end of the cut, and positioning a keyed wedge-shaped implant into the cut formed into the bone.
Owner:ARTHREX INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com