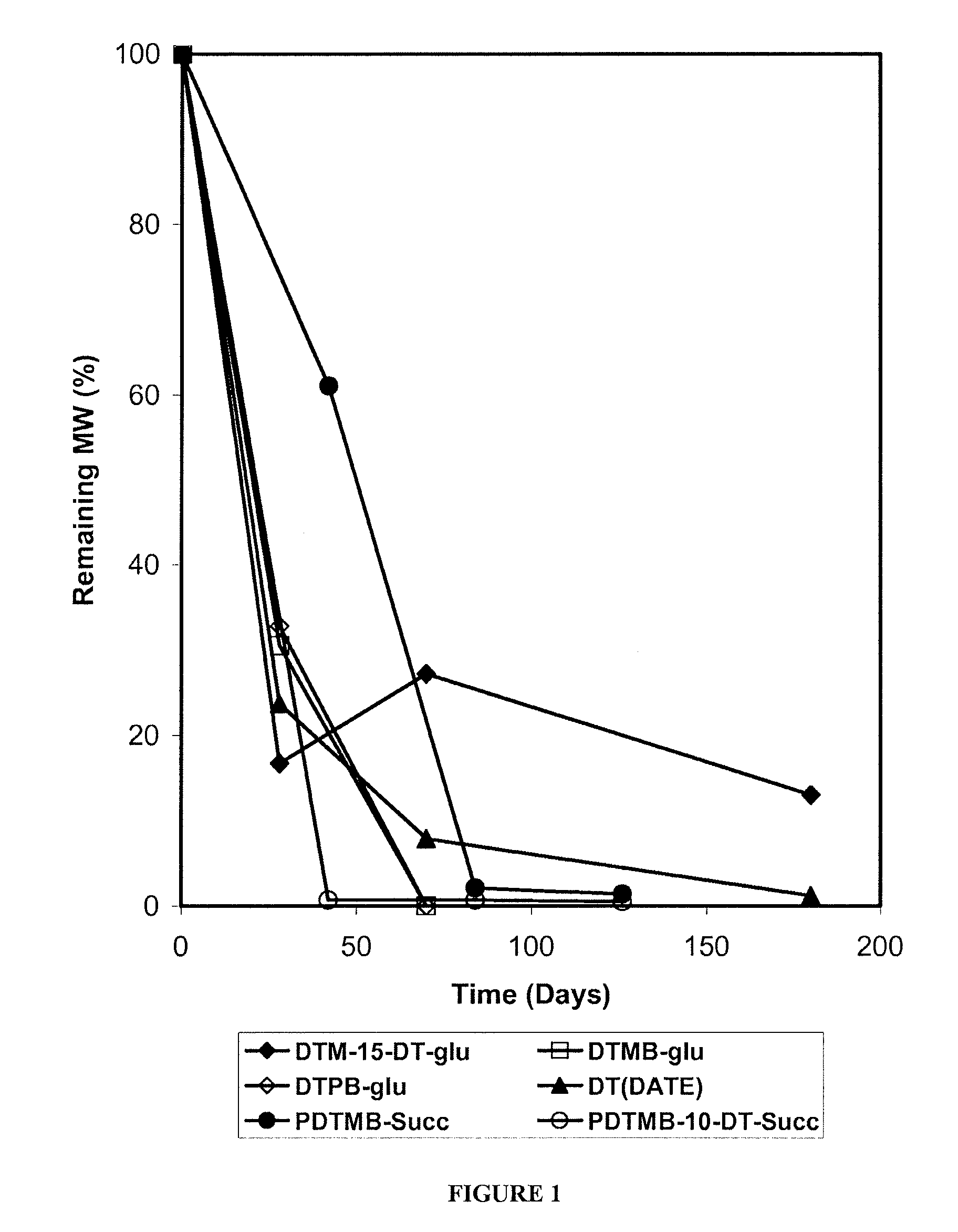
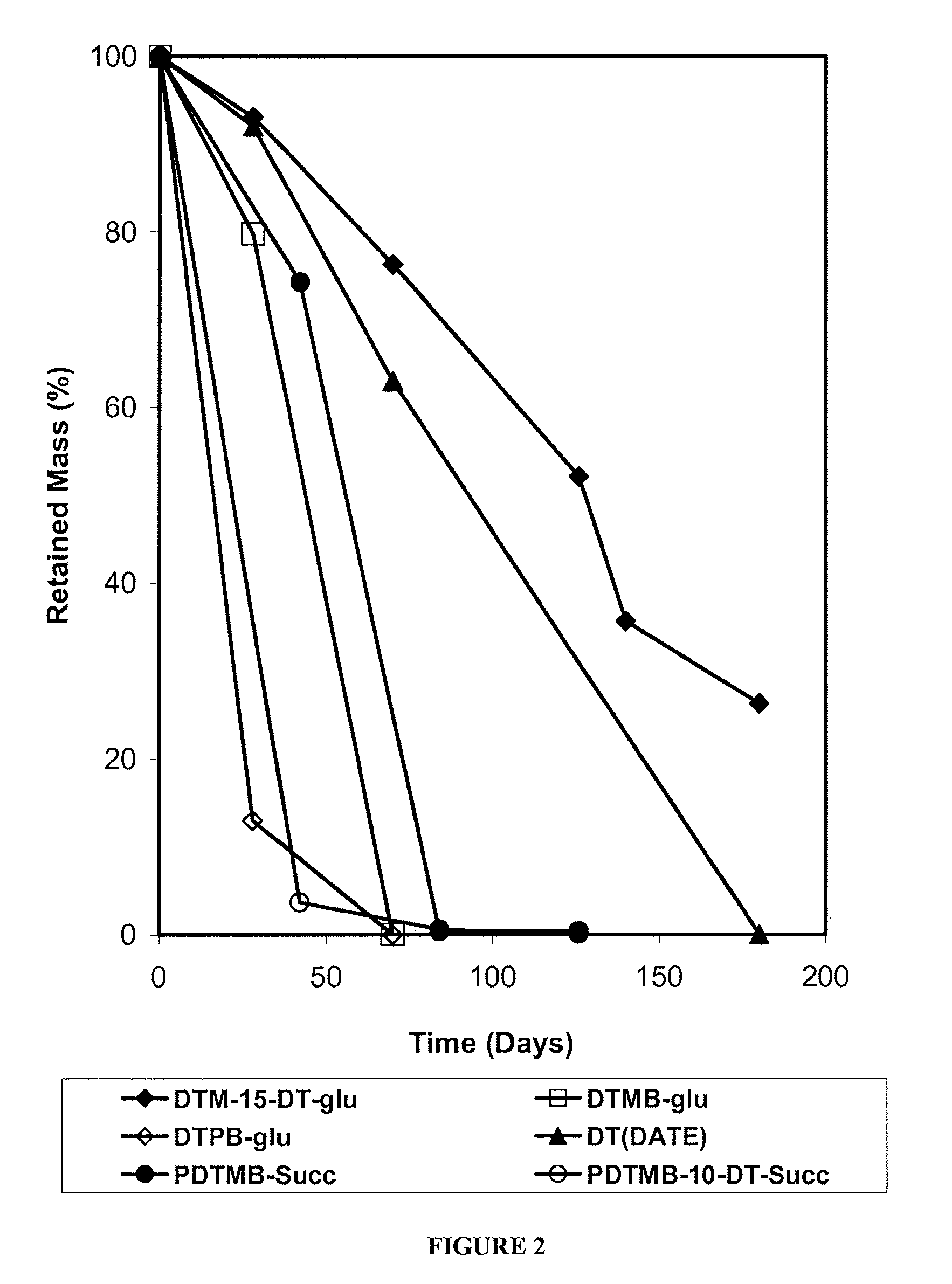
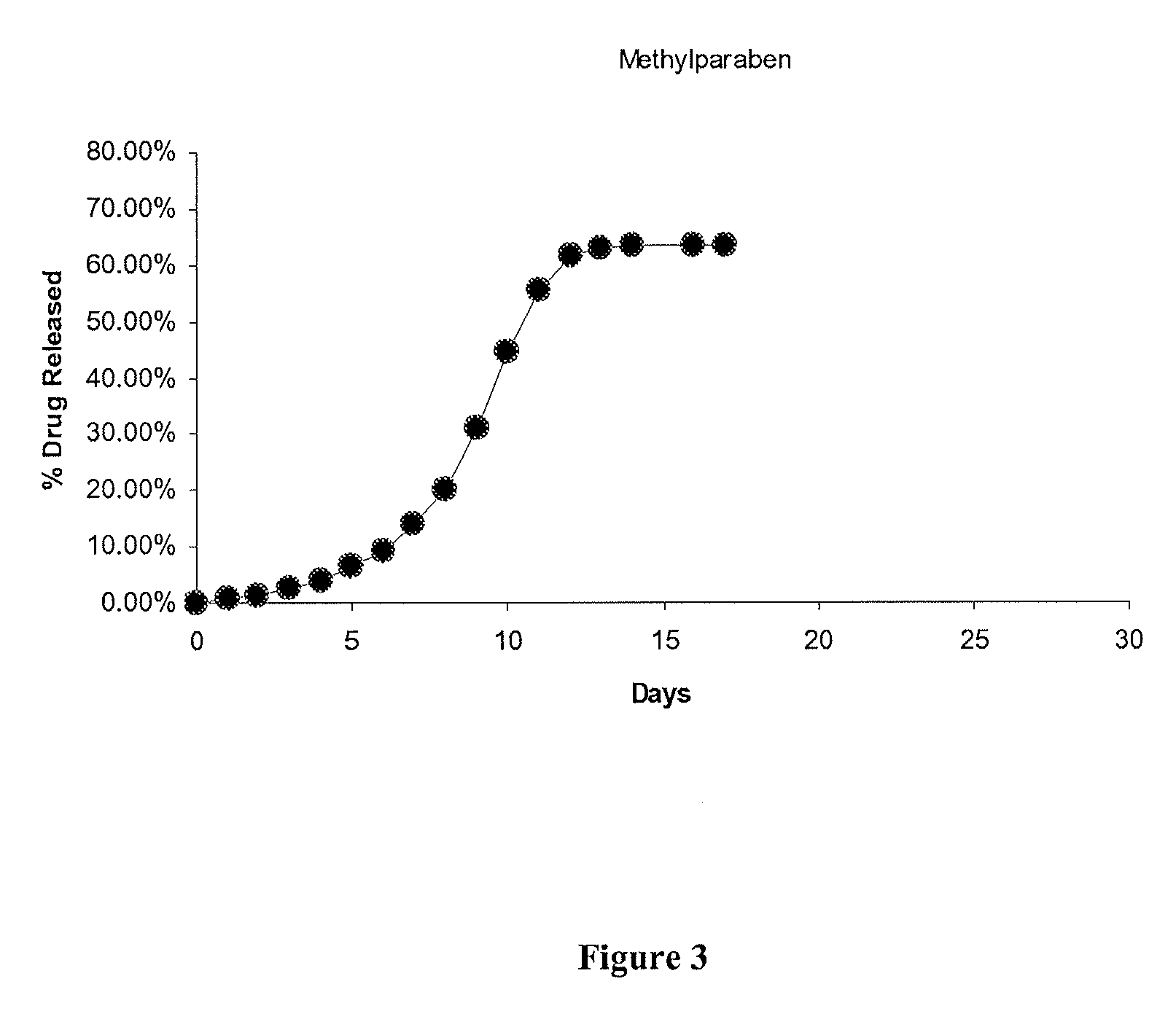
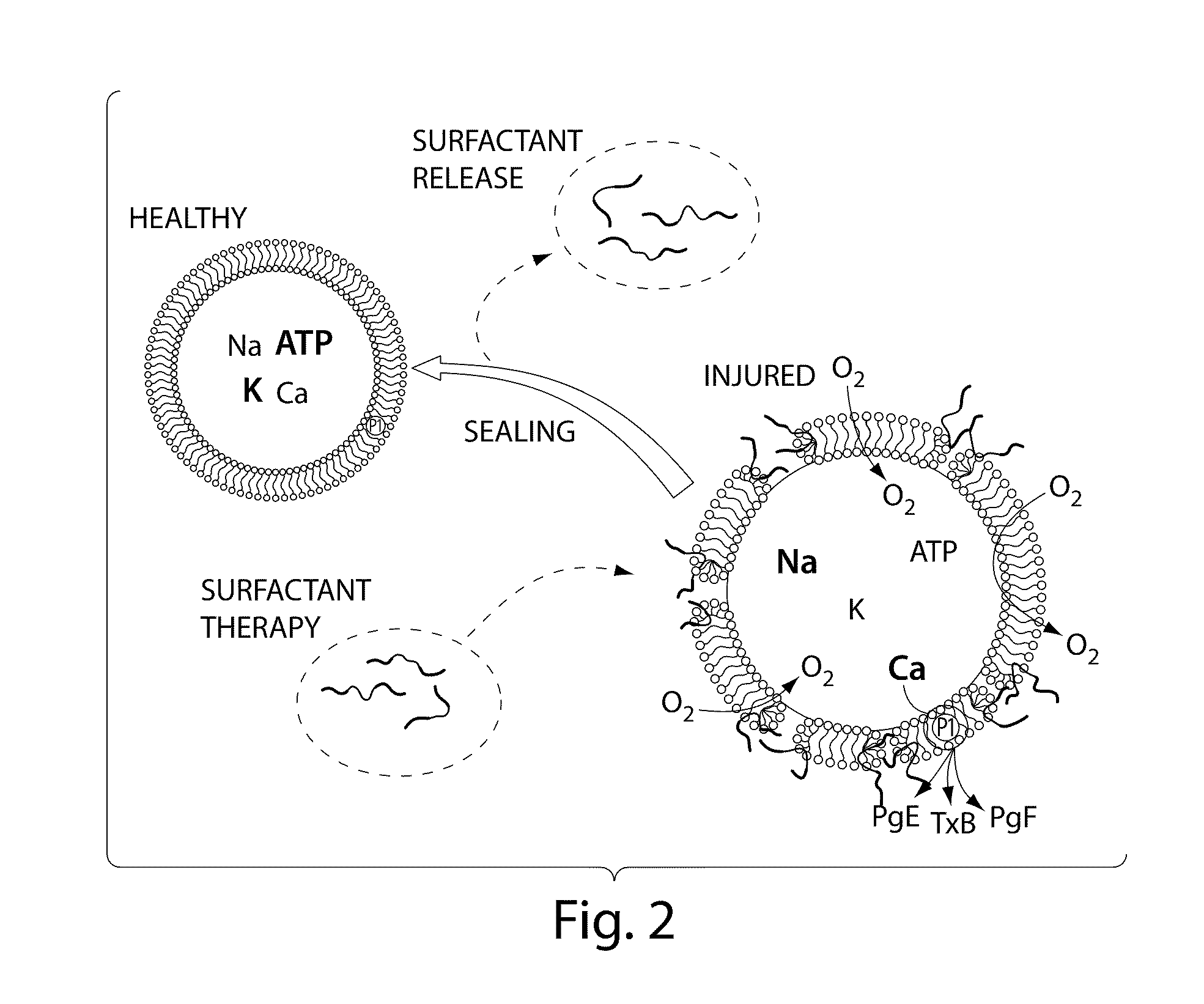
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
171 results about "Resorption" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Resorption is the absorption into the circulatory system of cells or tissue, usually by osteoclasts.
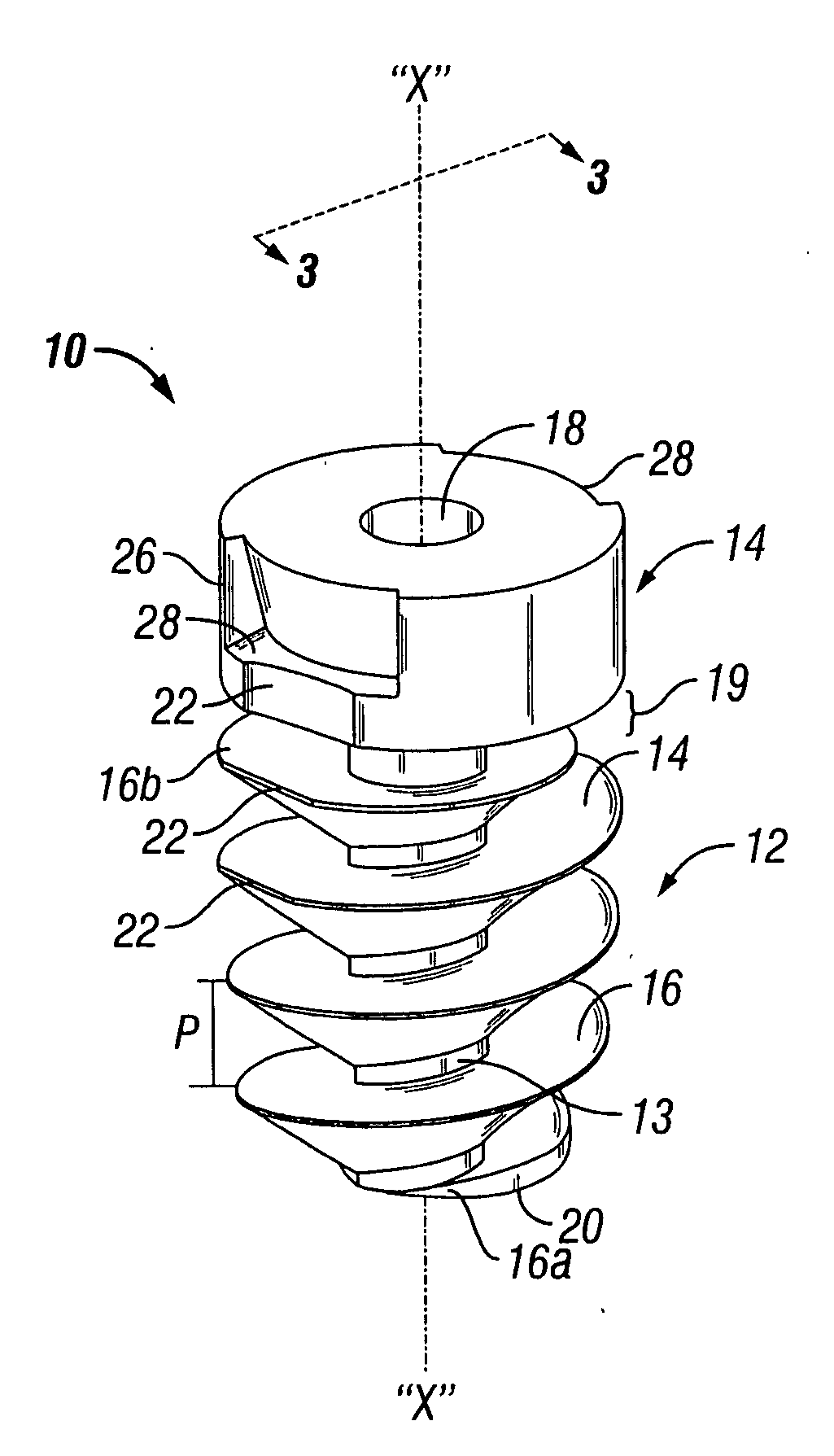
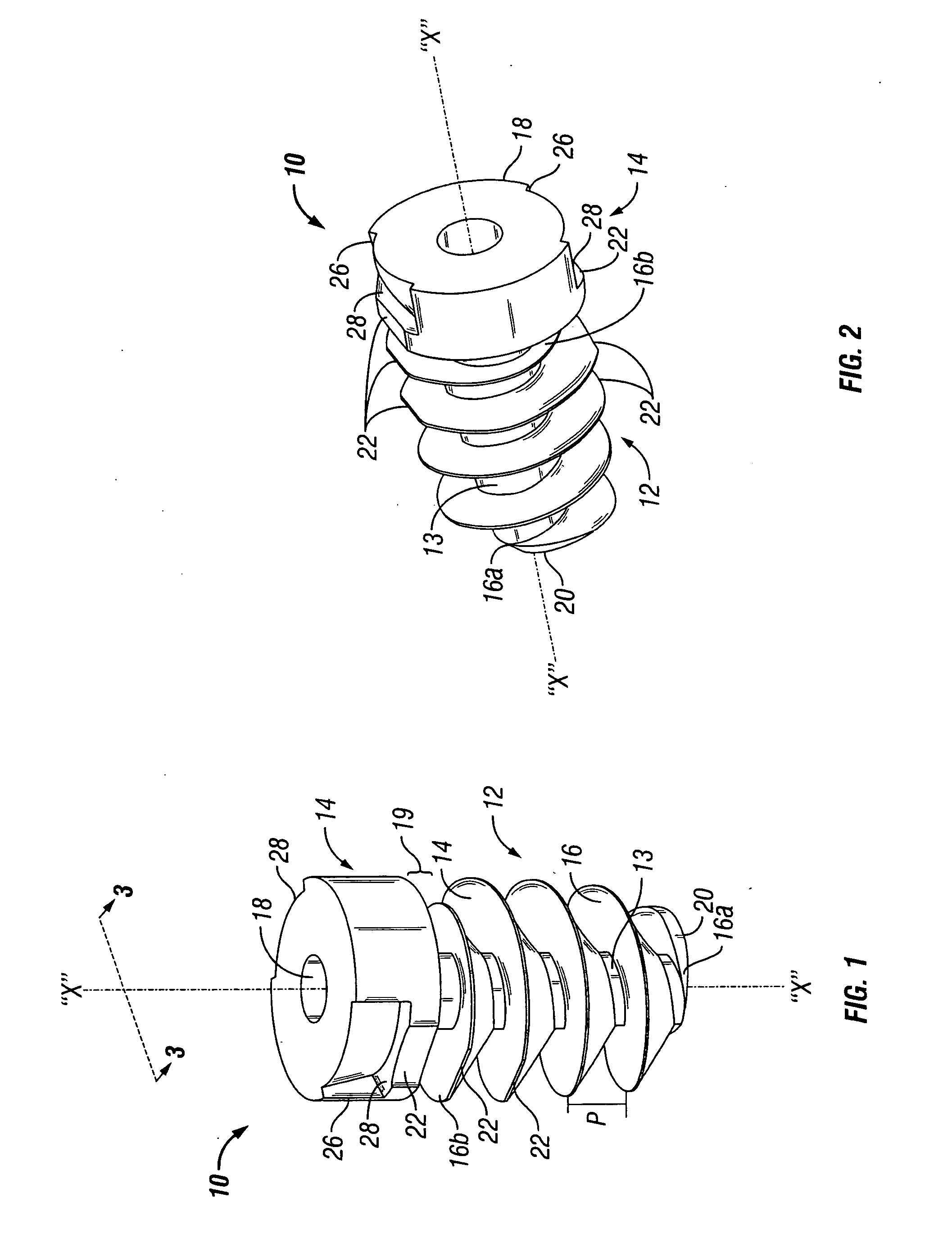
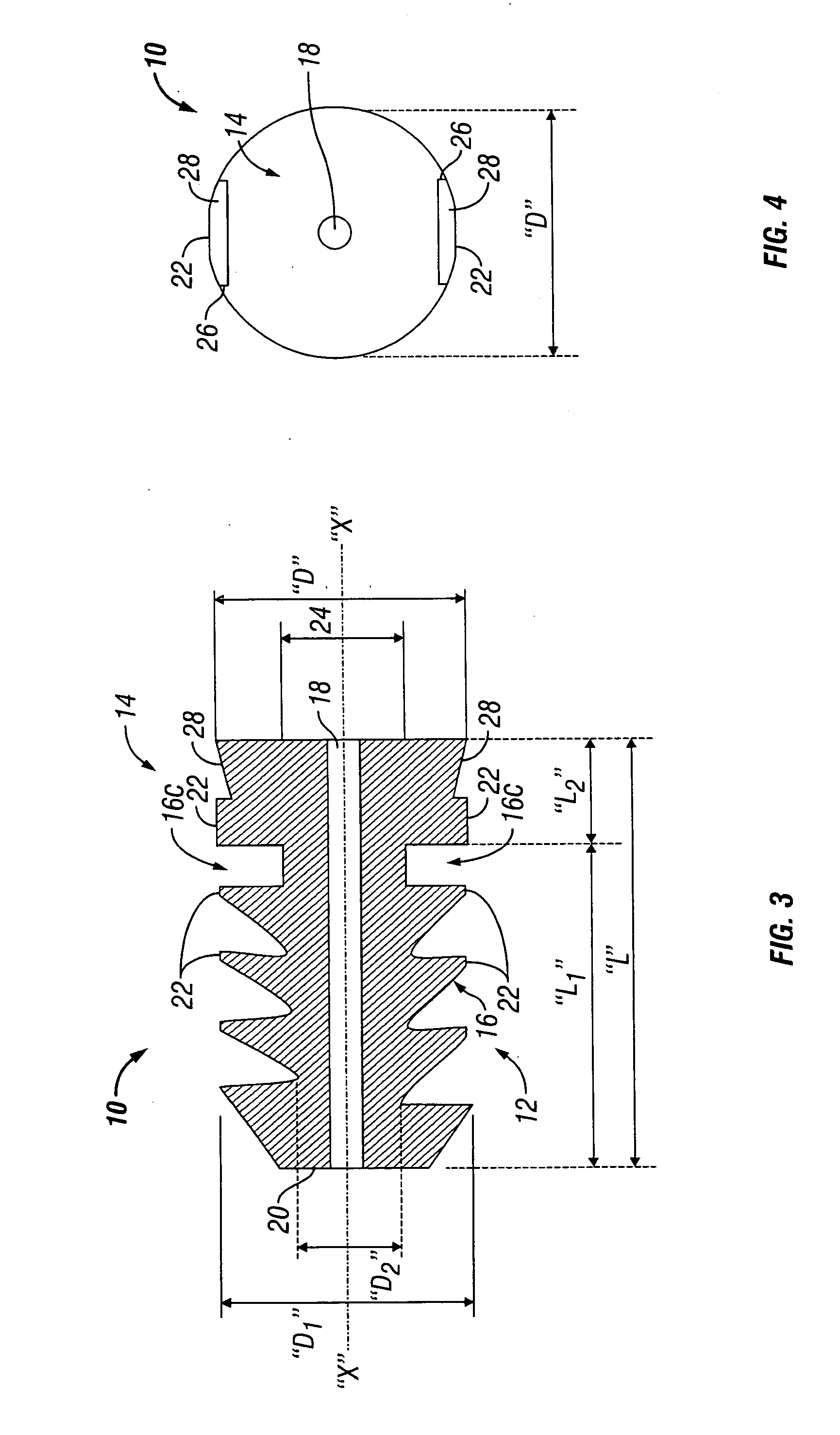
Surgical fastener with predetermined resorption rate
ActiveUS20050267478A1Reduce the amount requiredMinimize formationSuture equipmentsLigamentsTime rangeIn vivo
A resorbable screw fastener and a method of firing with an applicator capable of applying a surgical fastener to tissue in order to form tissue connection to secure objects to tissue, the fastener including a body portion having a helical thread, a head portion disposed at the proximal end of the body portion. The resorbable screw fastener is 100% resorbed in vivo during a period of time ranging from about 14 days to about one year after implantation.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Implant device for cartilage regeneration in load bearing articulation regions
An implant device for cartilage regeneration in loading-bearing regions uses the osteochondral defect model. The implant is formed of resorbable polymeric materials. The implant is designed such that load is transmitted from the articulating surface of the bone platform through the implant to the entire area of subchondral bone of the bone platform. Application of load in this manner results in reduced subchondral bone resorption, leading to joint stabilization and maintenance of normal joint biomechanics. The implant allows for the incorporation therein of a resorbable scaffold or matrix material. The present implant solves the current inability to regenerate cartilage in load-bearing articulating surfaces using engineered scaffold devices.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
Resorbable interposition arthroplasty implant
InactiveUS6017366AImprove permeabilityAvoid collisionFinger jointsWrist jointsTrapezium BoneSurgical department
A resorbable implant for interposition arthroplasty which is intended to fill a void between two adjacent bone ends, providing a cushion between the bone ends to prevent impingement of the bone ends while providing time for tissue to infiltrate into the space occupied by the implant. It has a protracted resorption time of preferably at least three months to allow time for the proliferation of load-bearing host fibrous tissue in place of the resorbed implant material. The implant preferably is porous with a pore size of greater than about 80 microns in order to enhance infiltration of fibrous tissue. The implant has a modulus in the range of 0.8 to 20 MPa which is soft enough to allow it to conform to surface irregularities of the adjacent bone surfaces while being hard enough to maintain a desired separation between those bones while tissue infiltration replaces the resorbable implant material. The implant may be preformed to the desired shape or alternatively may be formable by the surgeon by methods such as carving with a scalpel. A preferred application for the implant is as a trapezium bone replacement.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
Implantable biomimetic prosthetic bone
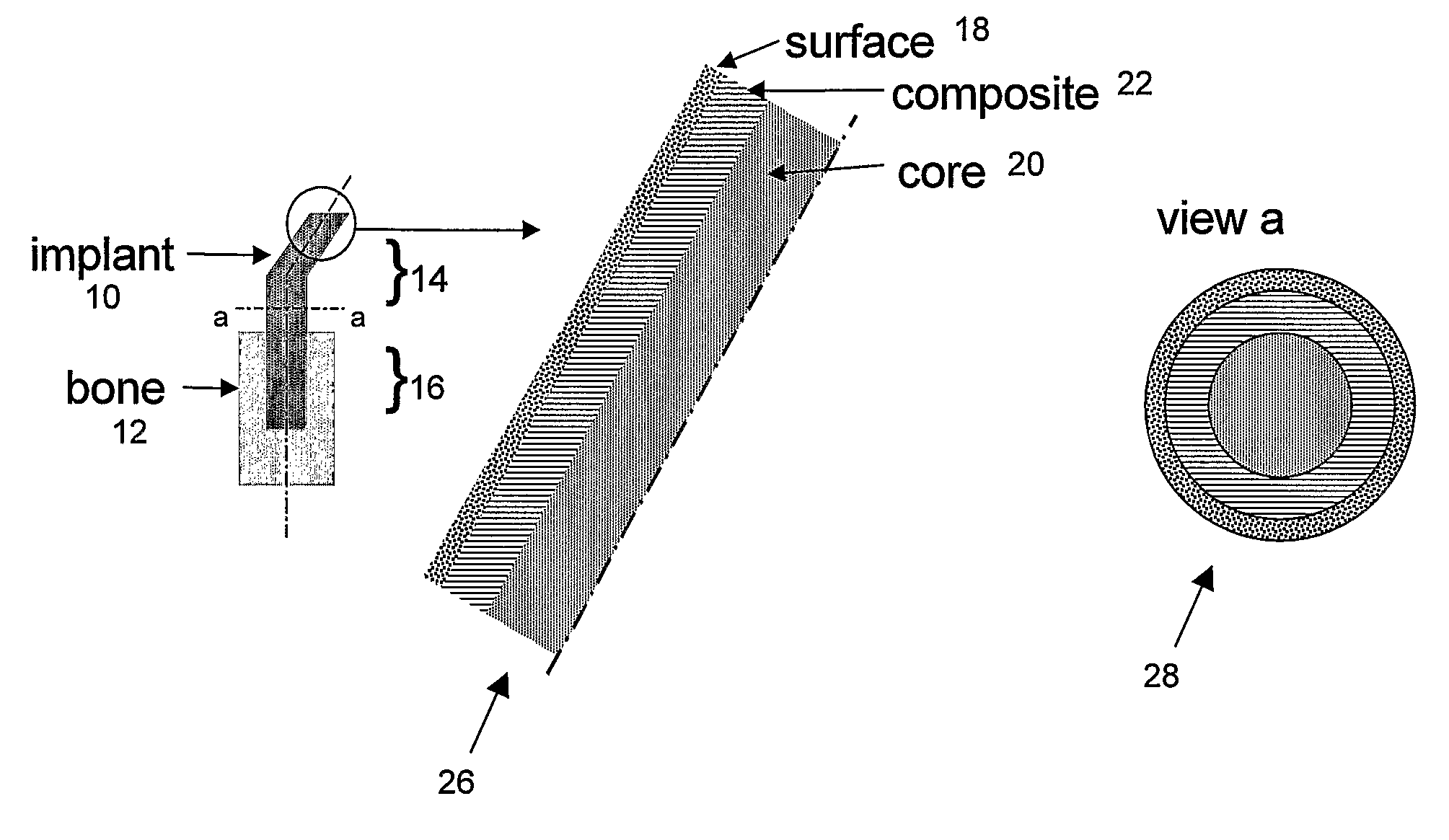
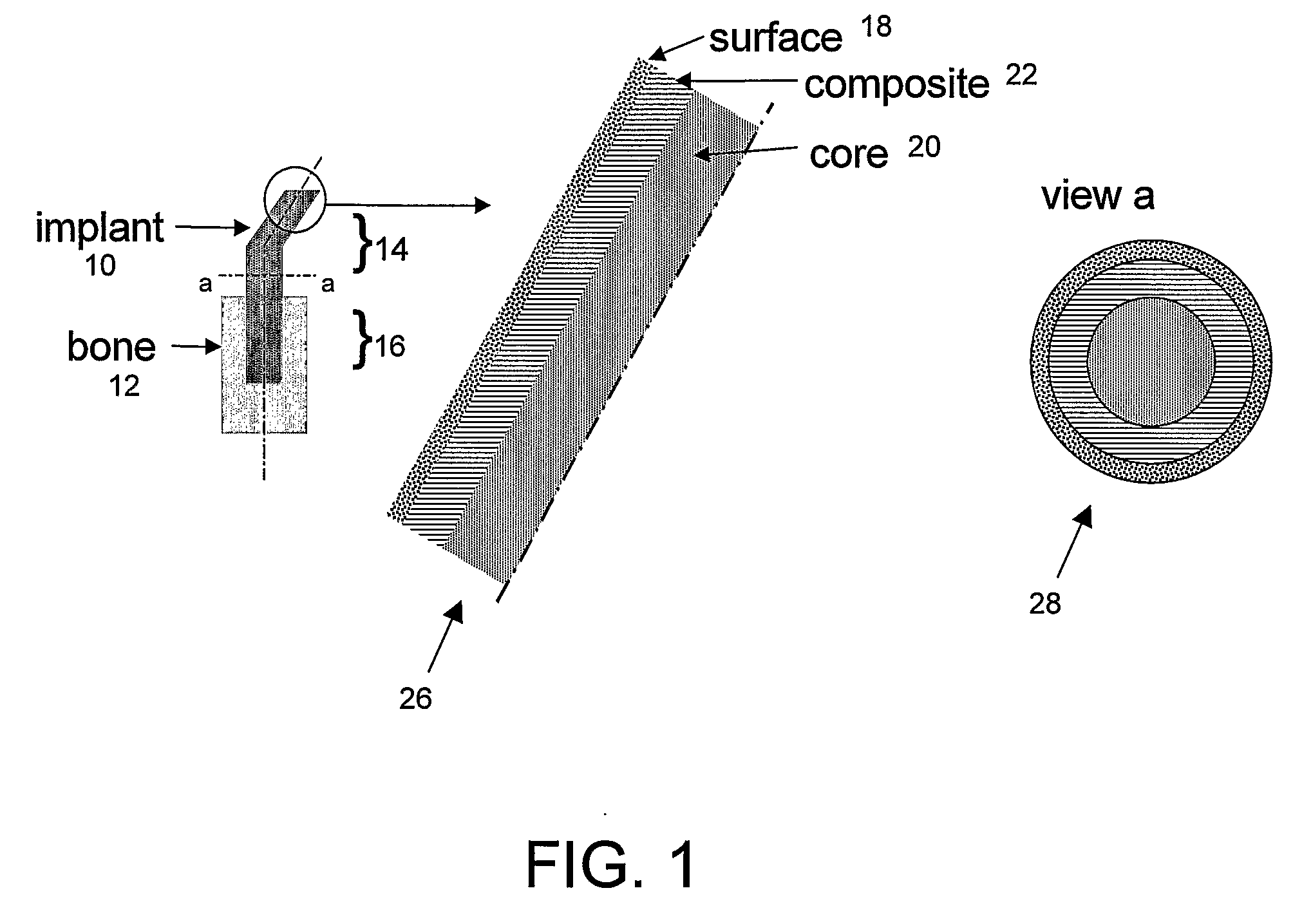
InactiveUS20090177282A1Reduce riskMolten spray coatingLamination ancillary operationsNormal boneFiber-reinforced composite
Bone tissue at the interface of a bone implant is shielded from stresses found in normal bone because of the higher stiffness or rigidity in the implant versus in bone. The resulting “stress shielding” of the bone by the implant eventually results in resorption of bone at the bone-implant interface and ultimately necessitates replacement of the bone implant. To overcome these problems, an implantable biomimetic prosthetic bone having a porous surface, a fiber-reinforced composite structure, and a polymer-based core is disclosed. The prosthetic bone is a good match for structure, stiffness, viscoelastic properties, specific weight and overall structure as real bone or host tissues adjacent to the prosthetic bone. The prosthetic bone may be formed as a total hip prosthesis.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
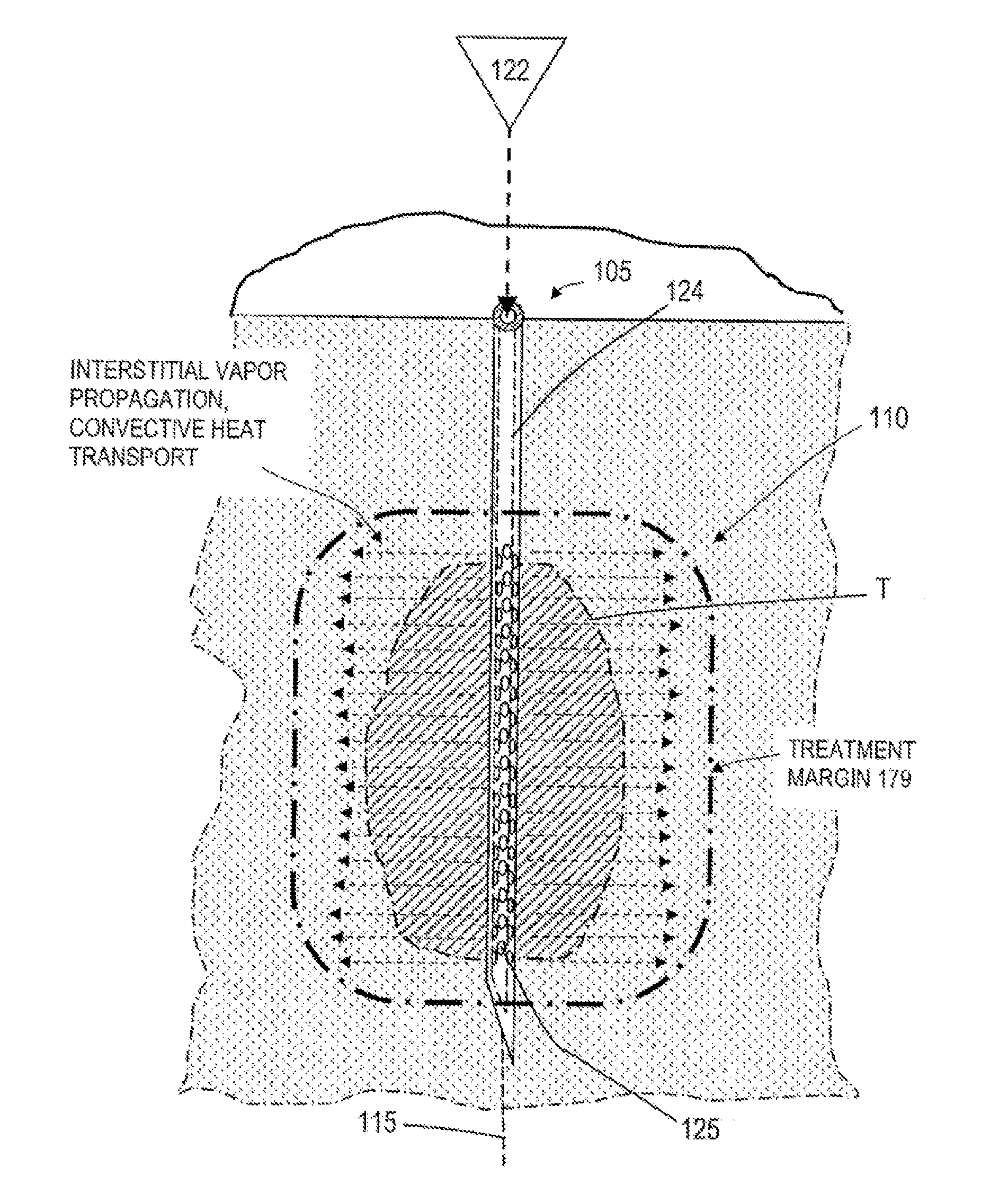
Medical systems and methods for ablating and absorbing tissue
ActiveUS20100262133A1Prevent drynessAvoid reabsorptionSurgical instruments for heatingBiological activationTarget tissue
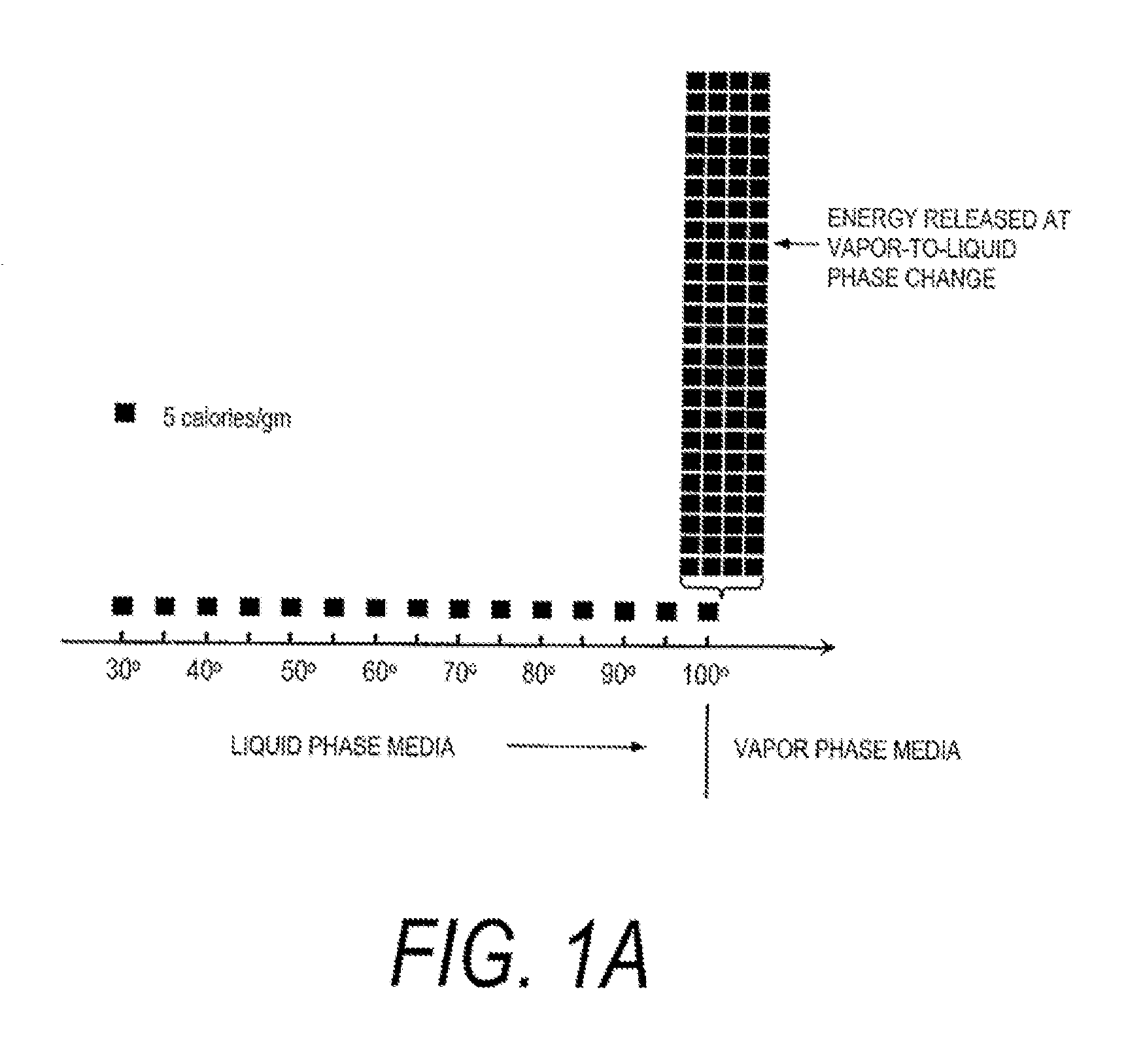
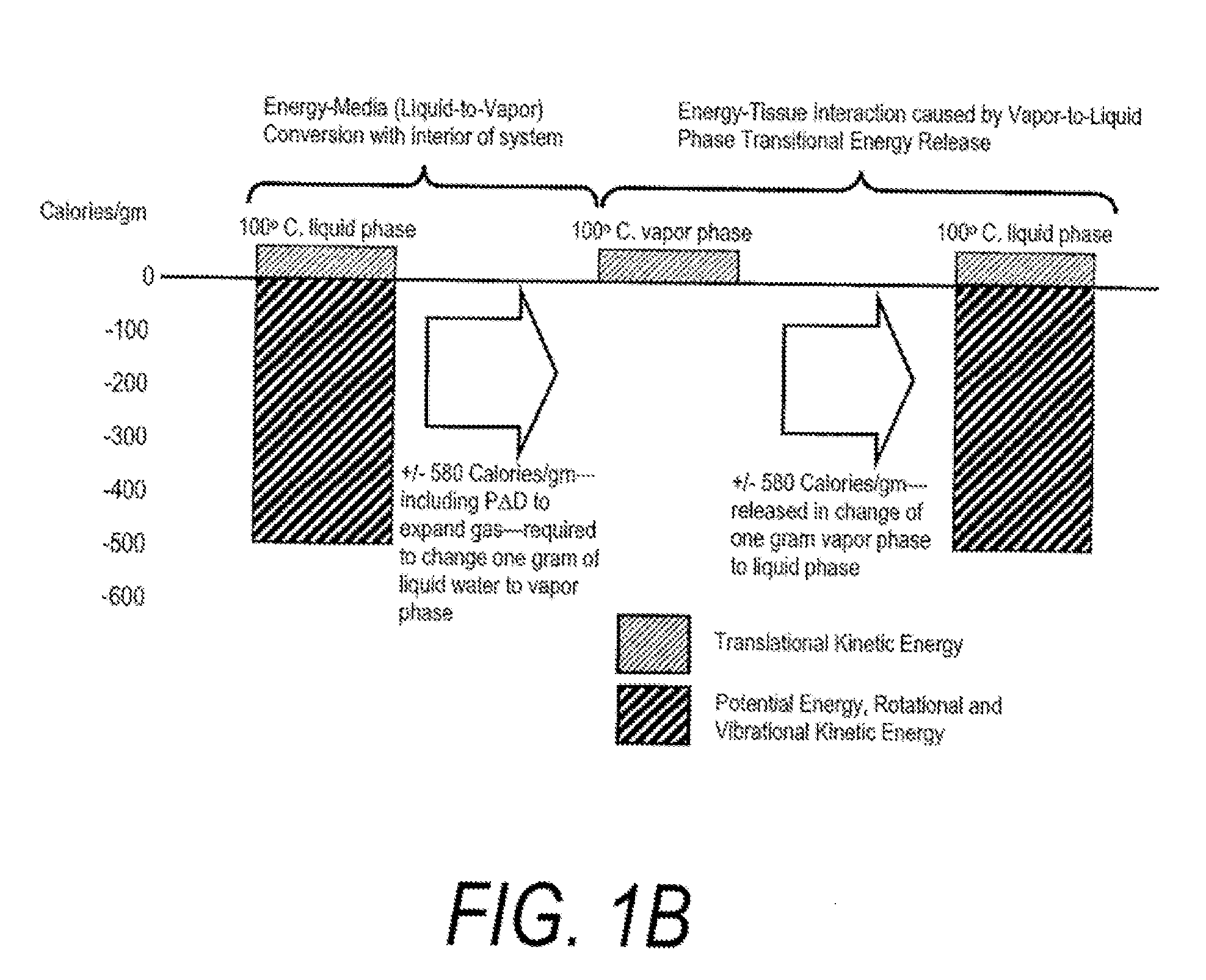
Methods, devices, and systems are described herein for applying energy to tissue for ablation of tissue while allowing the tissue to be resorbed within the body. Such methods, devices, and systems control application of energy to maintain a temperature of target tissue above an ablation temperature, being dependent upon the activation time, and below a transformation temperature, also being dependent upon the activation time, where the transformation prevents or hinders resorption of the treated tissue by the body.
Owner:TSUNAMI MEDTECH
Controlling resorption of bioresorbable medical implant material
InactiveUS20020138154A1Different and fast resorption rateAnti-incontinence devicesCatheterPorosityBody fluid
The resorption of a medical implant can be controlled with the use of particles embedded in a resorbable bulk material forming the implant or portion thereof. The implant can be removed from a body of a mammal by natural biological mechanisms after use. The resorption of the implant can involve swelling and / or hydrolyzing of the particles within the implant upon contact with a body fluid such that porosity and flow of fluid within the bulk material of the implant is increased. Resorption of the implant may also involve the use of particles with magnetic properties embedded within the implant such that an applied magnetic field causes the particles to vibrate within the bulk material thereby increasing the porosity and thus the flow of fluid, hence facilitating resorption of the implant. The resorption rate of the implant can be controlled by modulating swelling, hydrolysis, or movement of the embedded particles.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Dialysis solution for peritoneal dialysis
InactiveUS6284140B1Easy to degradeDwell timeBiocideSolvent extractionHydroxyethyl starchUltrafiltration
The present invention relates to dialysis solutions for peritoneal dialysis, containing hydroxyethyl starch as the osmotically-active substance, electrolytes and, optionally, conventional additives, where the hydroxyethyl starch has a molecular weight Mw in the range from 10,000 to 150,000, a substitution MS in the range from 0.10 to 0.40, a substitution DS in the range from 0.09 to 0.35 and a substitution ratio C2 / C6>=8. With this peritoneal dialysis solution it is possible, with an outstanding ultrafiltration, to maintain a longer dwell time, for example the dialysis solution can be utilized for a period of 12 hours in the CAPD without replacement. In addition, the inventive dialysis solution is also particularly advantageous for patients with residual kidney function. The resorption of the osmotically active substance is clearly diminished and even after a dwell time of 12 hours it amounts to a maximum of 60-70%.
Owner:FRESENIUS AG
Calcium phosphate cement composition and a method for the preparation thereof
ActiveUS6929692B2Good water solubilityIncreased formationOther chemical processesBone implantChemical synthesisCalcium biphosphate
The invention describes a new calcium phosphate cement powder, whose composition can best be described over the Ca / P molar ratio range of 1.35 to 1.40, most preferably 1.39, and whose two components were prepared by wet chemical synthesis procedures. One component is chemically-synthesized, bi-phasic alpha-TCP (Ca3(PO4)2, 95 wt %)+HA (Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2, 5 wt %) powder, while the second component is again a chemically-synthesized, single-phase DCPD (CaHPO4·2H2O) powder. A setting solution (Na2HPO4·2H2O) is used to form a self-setting calcium phosphate cement from the powder mixture. This cement can be used as bone filler or bone substitute in applications, which require higher rates of resorption.
Owner:DR AHMET CUNEYT TAS
Controlling resorption of bioresorbable medical implant material
InactiveUS6913765B2Avoids pain and sufferingReduces medical expense and lost productivityAnti-incontinence devicesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismPorosityMedicine
The resorption of a medical implant can be controlled with the use of particles embedded in a resorbable bulk material forming the implant or portion thereof. The implant can be removed from a body of a mammal by natural biological mechanisms after use. The resorption of the implant can involve swelling and / or hydrolyzing of the particles within the implant upon contact with a body fluid such that porosity and flow of fluid within the bulk material of the implant is increased. Resorption of the implant may also involve the use of particles with magnetic properties embedded within the implant such that an applied magnetic field causes the particles to vibrate within the bulk material thereby increasing the porosity and thus the flow of fluid, hence facilitating resorption of the implant. The resorption rate of the implant can be controlled by modulating swelling, hydrolysis, or movement of the embedded particles.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Joint treating method
InactiveUS7128763B1Stimulate and promote formationKeep movingJoint implantsArticular surfacesFibrocartilage
A method for treating a non-weight bearing arthritic joint involves resecting at least one of the opposed joint surfaces to expose a cancellous bone surface. A bioresorbable implant is mounted to one of the joint surfaces so that the resected joint surface rubs against the surface of the implant. This causes the fibroblast to change into fibrocartilage at the resected bone surface as the implant is resorbed thereby effectively replacing the implant with fibrocartilage during such resorption.
Owner:BLATT GERALD
Intervertebral implant
InactiveUS6843805B2Increase contactFacilitate primary bone growthInternal osteosythesisBone implantIntervertebral diskBiomedical engineering
The present invention relates to an intervertebral implant for fusion of vertebrae. The implant has top and bottom surfaces configured and dimensioned to contact end plates of the vertebrae and a jacket forming a side surface of the implant and having a three-dimensional texture for promoting initial stability. The implant is made of a porous ceramic material. The implant according to this invention is characterized in that upon primary fusion during the resorption process, it equalizes the distance (corresponding to intervertebral disk height) between two vertebrae while providing adequate fusion and is resorbed by the body after a certain amount of time.
Owner:SYNTHES USA
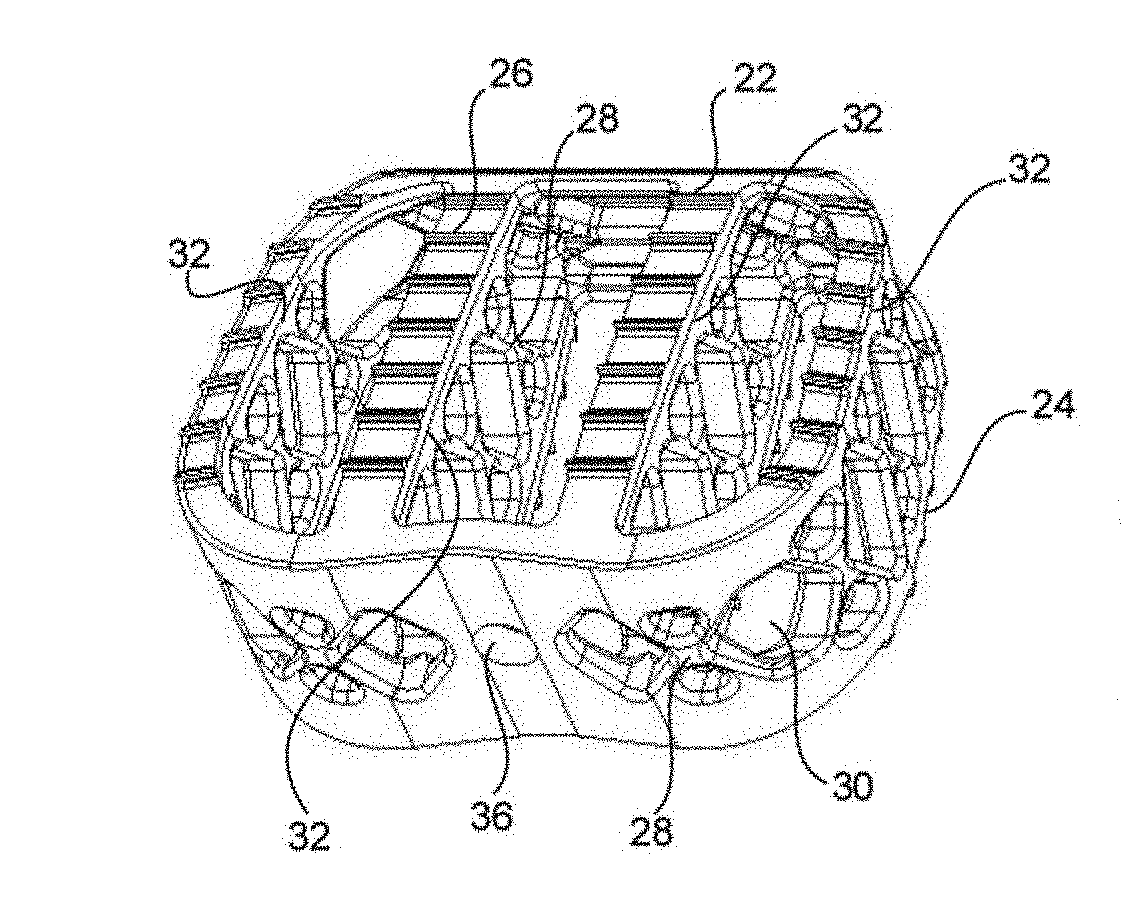
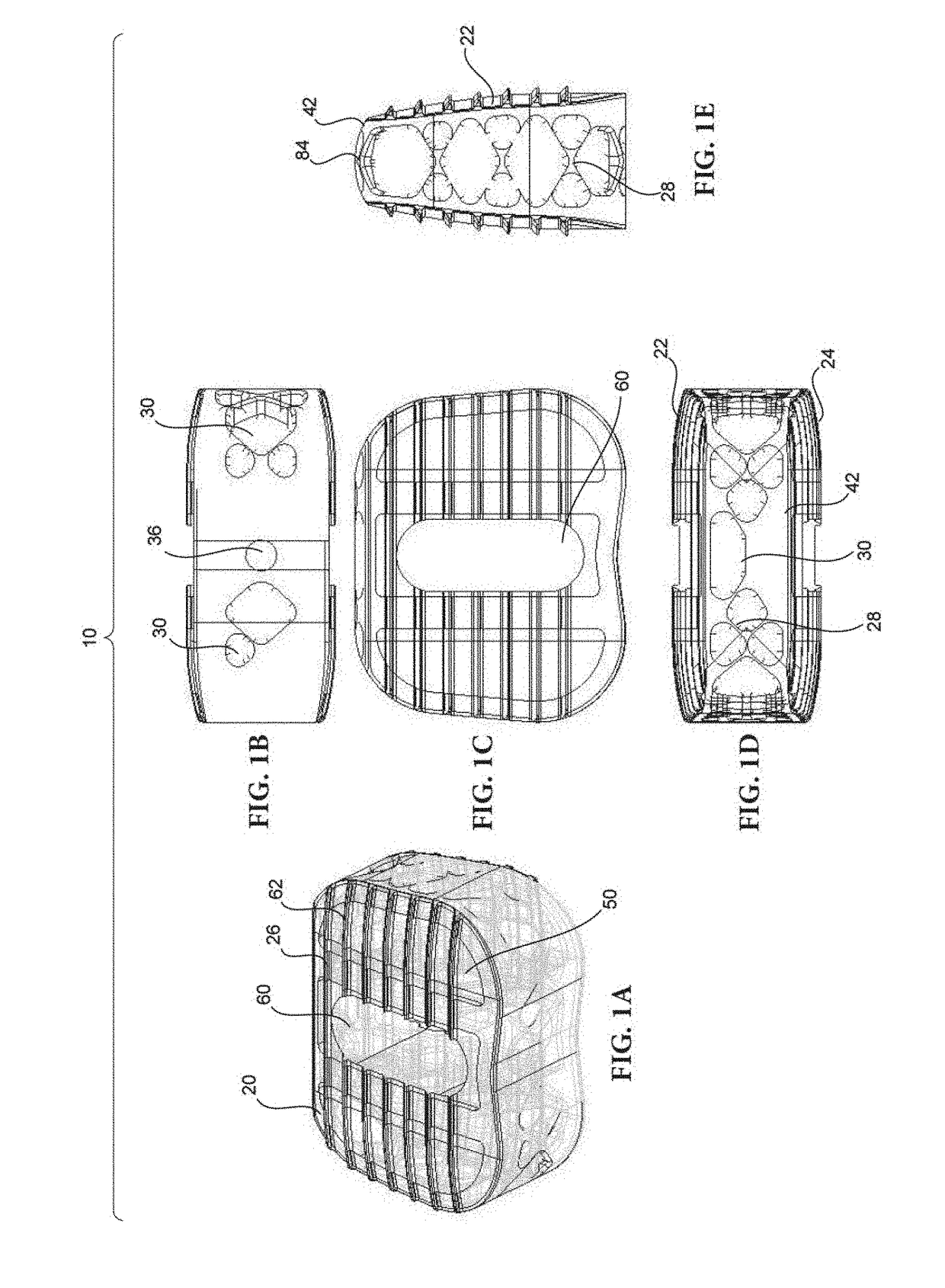
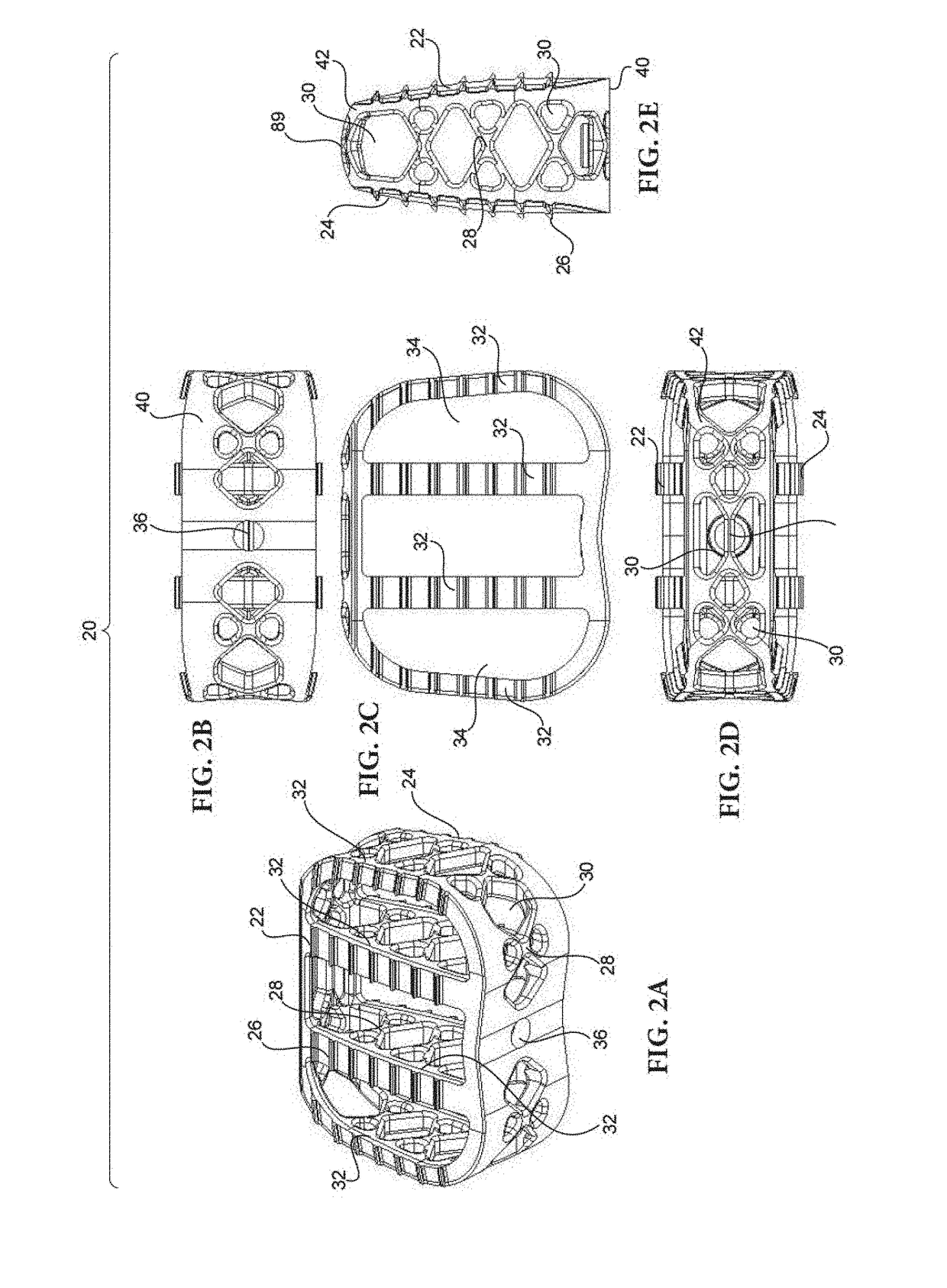
Partially resorbable implants and methods
ActiveUS20170182222A1Reduce stress peaksReduce and eliminate subsidenceSpinal implantsTissue regenerationSide effectPost implantation
Implants including non-resorbable frameworks and resorbable components, as well as methods of use thereof are disclosed. The embodiments include different combinations of a non-resorbable framework (in some case structural and in other cases non-structural), and a resorbable component embedded within and / or around the framework (again, in some cases structural and in other cases non-structural). The disclosed implants provide an efficient means of providing structural support for the vertebral bodies post-implantation, as well as encouraging resorption of the implant and fusion of the associated vertebral bodies without negative side effects and / or failure, such as subsidence of the implant or cracking / fracturing of a portion of the implant when implanted.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC
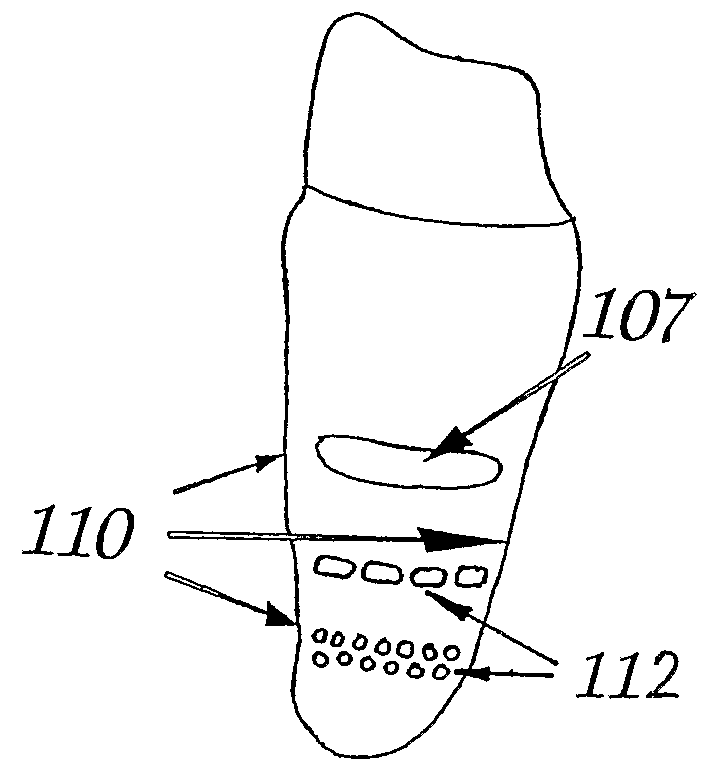
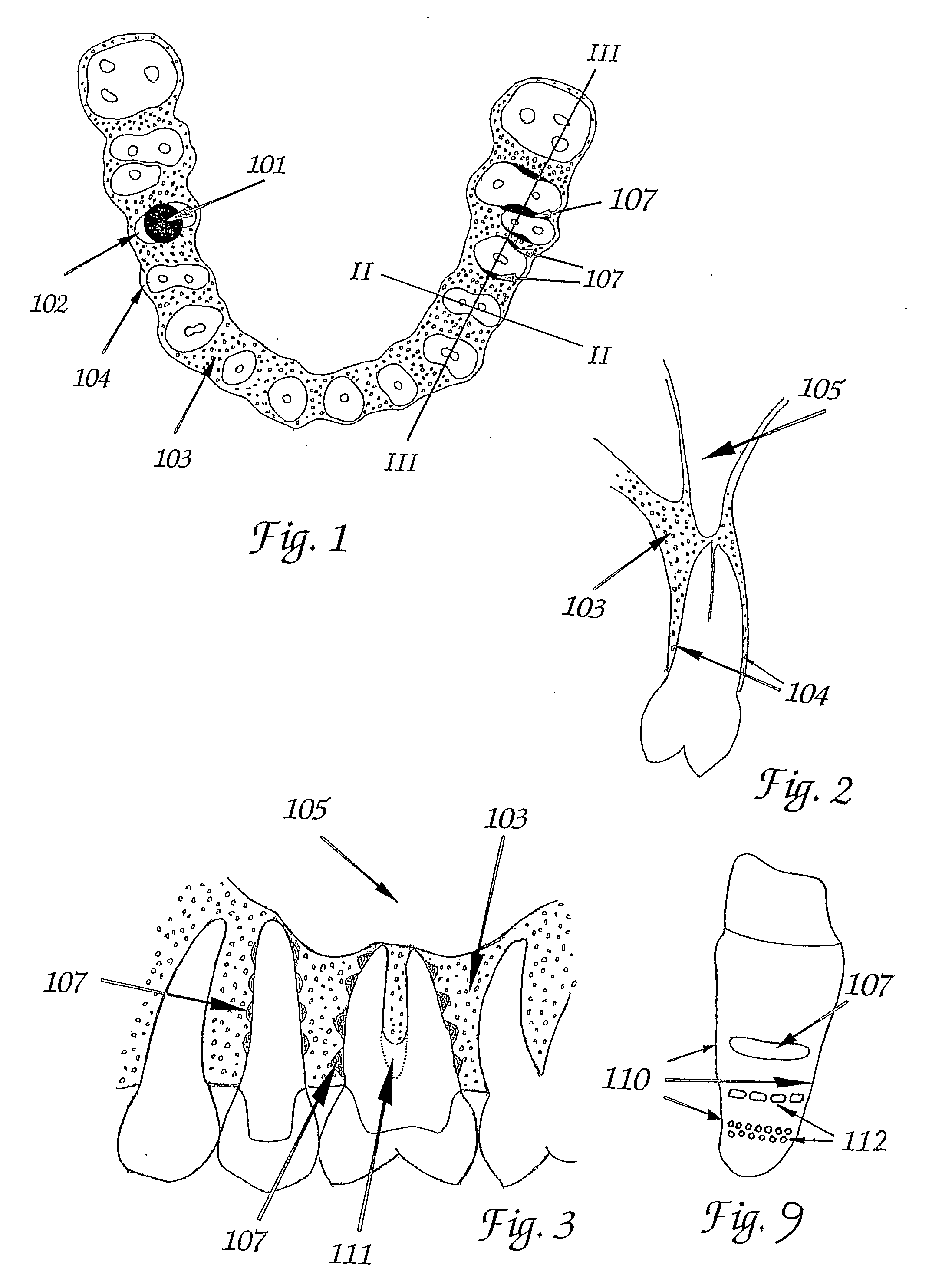
Tooth Implant
ActiveUS20090092944A1Short maintenance periodMinimal traumaDental implantsExtract toothThin cortical bone
The invention concerns a non rotation-symmetric but root-analogue or tooth socket-analogue dental implant of the same size and shape as the root of the extracted tooth with macro retentions protruding from the implant surface (107, 113, 116).Macro retentions (107, 113, 116) are strictly limited to surface areas of the implant in the interdental space next to spongy and thick bone and in case of the last molar, facing the bone at the end of the tooth row. The diameter of the dental implant in transverse direction next to the thin cortical bone buccal and lingual / palatinal is identical to the alveolar bone or preferably stands back to avoid any pressure induced resorption and fracture of the thin cortical bone layer, respectively, at any cost.
Owner:PIRKER WOLFGANG
Three-dimensional bioresorbable scaffolds for tissue engineering applications
InactiveUS8071007B1Biocompatibility hardHard integrationAdditive manufacturing apparatusCeramic shaping apparatusBiocompatibility TestingHard tissue
The invention relates to the use of Fused Deposition Modeling to construct three-dimensional (3D) bioresorbable scaffolds from bioresorbable polymers such as polycaprolactone (PCL), or from composites of bioresorbable polymers and ceramics, such as polycaprolactone / hydroxyapatite (PCL / HA). Incorporation of a bioresorbable ceramic to produce a hybrid / composite material support provides the desired degradation and resorption kinetics. Such a composite material improves the biocompatibility and hard tissue integration and allows for increased initial flash spread of serum proteins. The basic resorption products of the composite also avoids the formation of an unfavorable environment for hard tissue cells due to a decreased pH. The scaffolds have applications in tissue engineering, e.g., in tissue engineering bone and cartilage.
Owner:OSTEOPORE INT PTE
Implantable prosthesis
A prosthetic device including biologically compatible and preferably fully resorbable materials includes a tissue infiltratable portion and a second portion. The two portion may have different rates of resorption. The ingrowth portion may include a plurality of openings to encourage tissue ingrowth and vascularization. The second portion may be stronger than the ingrowth portion and provide a location for fixation of the device. The portion may be attached using resorbable adhesives, sutures or other constructs to render a fully resorbable prosthesis.
Owner:CR BARD INC
Implant device for cartilage regeneration in load bearing articulation regions
An implant device for cartilage regeneration in loading-bearing regions uses the osteochondral defect model. The implant is formed of resorbable polymeric materials. The implant is designed such that load is transmitted from the articulating surface of the bone platform through the implant to the entire area of subchondral bone of the bone platform. Application of load in this manner results in reduced subchondral bone resorption, leading to joint stabilization and maintenance of normal joint biomechanics. The implant allows for the incorporation therein of a resorbable scaffold or matrix material. The present implant solves the current inability to regenerate cartilage in load-bearing articulating surfaces using engineered scaffold devices.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
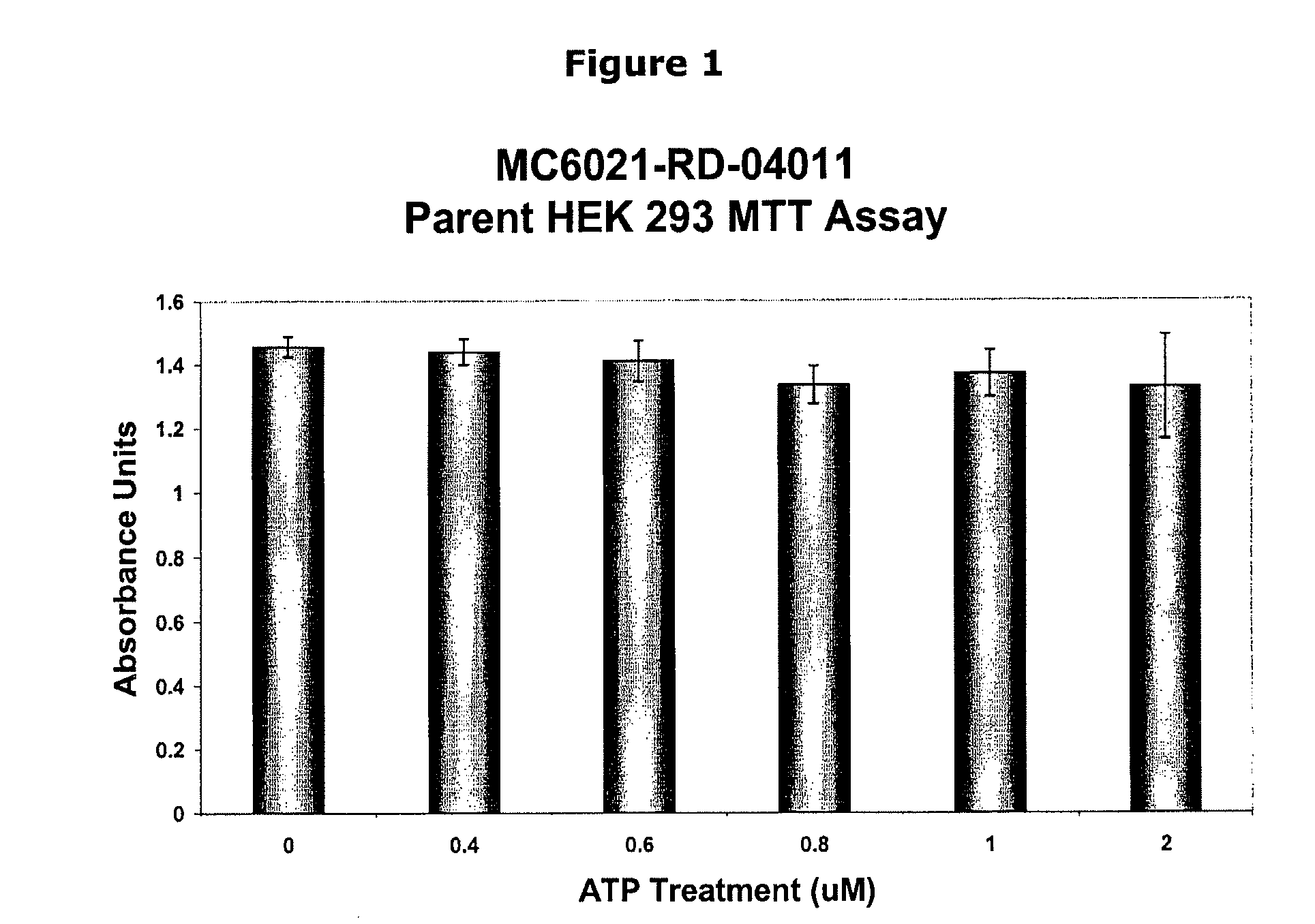
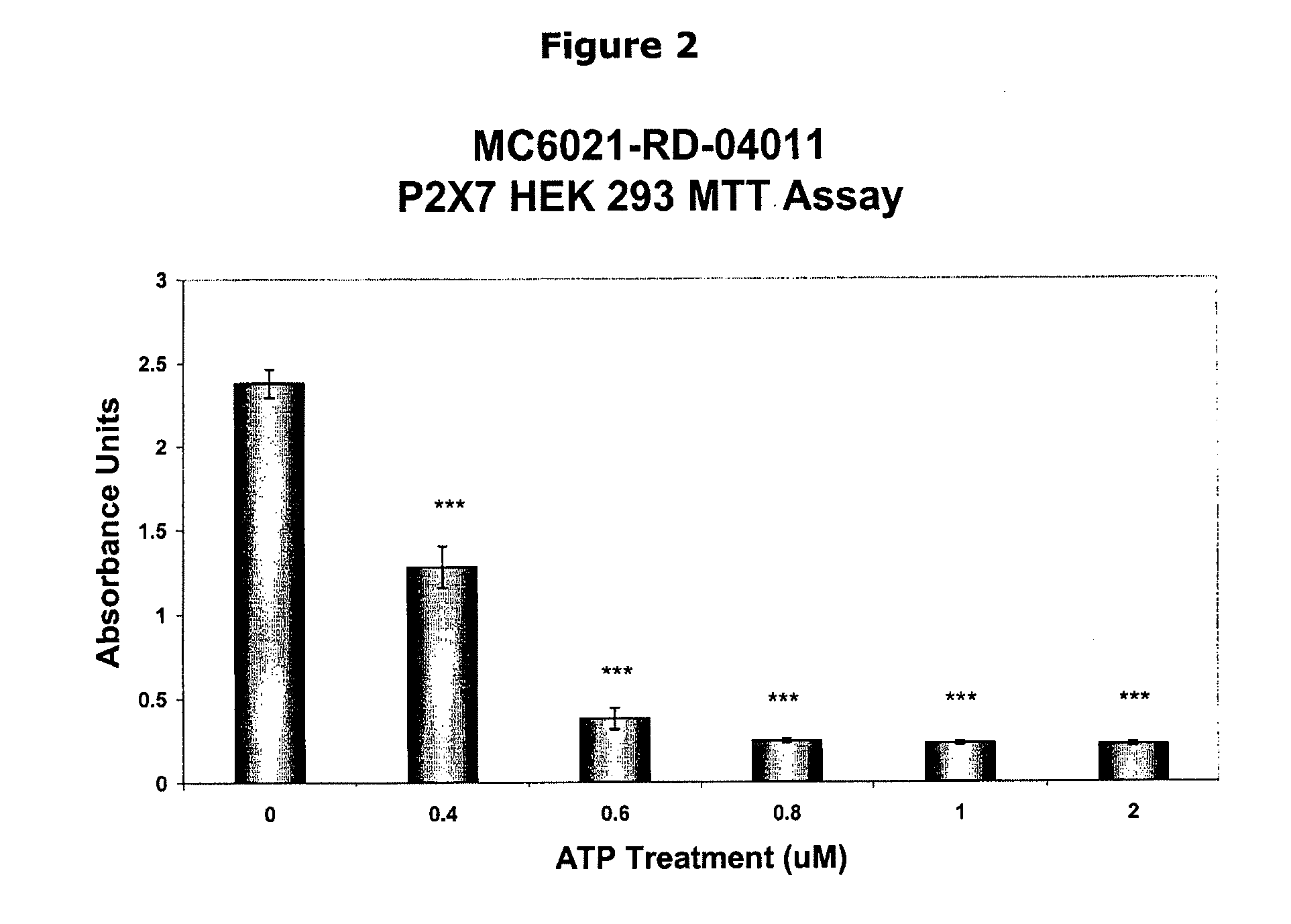
Inhibition of atp-mediated, p2x7 dependent pathways by pyridoxal-5-phosphate and vitamin b6 related compounds
InactiveUS20090215727A1Improve the level ofOrganic active ingredientsBiocideBone formationProstate cancer
P5P can be used as effective treatments for the modulation of P2X7, IL-1β, and inflammation response, and for diseases in which prevention of P2X7-dependent pathways or prevention of release of IL-1β is desirable, such as epithelial cancer, leukemia, brain tumors, spinal cord injury, tuberculosis, Alzheimer's Disease, neurodegenerative diseases, autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease, diabetes, including type I diabetes, prostate cancer, and osteoporosis, bone formation and resorption.
Owner:MEDICURE INT INC
Glass scaffolds with controlled resorption rates and methods for making same
InactiveUS7005135B2Promote bone growthEconomical and simple methodPot furnacesGlass furnace apparatusFiberDissolution
The present invention relates to resorbable glass scaffolds for use in biological applications and methods for making same. Specifically, these scaffolds are composed of phosphate glass fibers, where the rate of dissolution into biological fluids is controlled by the length of time the glass is held above its melt temperature prior to spinning the fiber.
Owner:ADVANCED TECH & REGENERATIVE MEDICINE
Orthopedic fusion plate having both active and passive subsidence controlling features
ActiveUS20060167457A1Deleterious effectPrevent movementInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsEngineeringTongue and groove
An orthopedic fusion plate device has a rigid perimetral frame which embraces a pair of plates retained within the frame by a tongue and groove mechanism so that the plates can move in only a single dimension, toward and away from another. The device is intended to mitigate the effects of bone graft resorption and settling through either active or passive mechanisms.
Owner:SUDDABY LOUBERT
Bone enhancing composite
InactiveUS20060147547A1Reduce morbidityIncrease capacityAntibacterial agentsBiocideBiological propertyMedicine
A bone-enhancing composite material comprising synthetic apatite and at least one supplementary bioactive agent selected from a biocompatible polymer and an anti-resorption agent added ab initio, methods of preparing said composite and uses thereof are provided. The physical and biological properties of the composite are controlled by the addition of specific supplementary bioactive agents as well as optional therapeutic agents. The composite may be used as a powder, a paste or an implant.
Owner:PROCHON BIOTECH
Three-dimensional bioresorbable scaffolds for tissue engineering applications
ActiveUS7968026B1Good biocompatibilityImproves hard tissue integrationAdditive manufacturing apparatusMouldsBiocompatibility TestingHard tissue
The invention relates to the use of Fused Deposition Modeling to construct three-dimensional (3D) bioresorbable scaffolds from bioresorbable polymers such as polycaprolactone (PCL), or from composites of bioresorbable polymers and ceramics, such as polycaprolactone / hydroxyapatite (PCL / HA). Incorporation of a bioresorbable ceramic to produce a hybrid / composite material support provides the desired degradation and resorption kinetics. Such a composite material improves the biocompatibility and hard tissue integration and allows for increased initial flash spread of serum proteins. The basic resorption products of the composite also avoids the formation of an unfavorable environment for hard tissue cells due to a decreased pH. The scaffolds have applications in tissue engineering, e.g., in tissue engineering bone and cartilage.
Owner:OSTEOPORE INT PTE
Glass scaffolds with controlled resorption rates and methods for making same
The present invention relates to resorbable glass scaffolds for use in biological applications and methods for making same. Specifically, these scaffolds are composed of phosphate glass fibers, where the rate of dissolution into biological fluids is controlled by the length of time the glass is held above its melt temperature prior to spinning the fiber.
Owner:ADVANCED TECH & REGENERATIVE MEDICINE
Resorption-controllable medical implants
InactiveUS7261734B2Avoids pain and sufferingReduces medical expense and lost productivitySurgeryCatheterBody fluidBiomedical engineering
Bioresorbable medical implants are designed to have different resorption rates over time or over the topography of the implants. The resorption of the medical implants are controlled by including layers having differing resorption rates. The layers resorb sequentially over time through sequential exposure to body fluids. A resorption-controllable medical implant includes a series of two or more layers. The first layer includes a first bioresorbable material. The second layer includes a second bioresorbable material and resorbable particles of a first kind dispersed within the second bioresorbable material. Additional layers of bioresorbable material alone or including resorbable particles may be added to slow or speed resorption and achieve desired control over the resorption of the implant. Resorbable particles can be added in differing amounts or kinds in various segments of the implant to provide topographically differing resorption rates.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Osteoinductive bone graft injectable cement
ActiveUS20120100225A1Sufficient load bearingFoster de novo bone growthSurgical adhesivesPeptide/protein ingredientsFiberMedicine
Osteoconductive bone graft materials are provided. These compositions contain injectable cements and demineralized bone matrix fibers. The combination of these materials enables the filling of a bone void while balancing strength and resorption.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
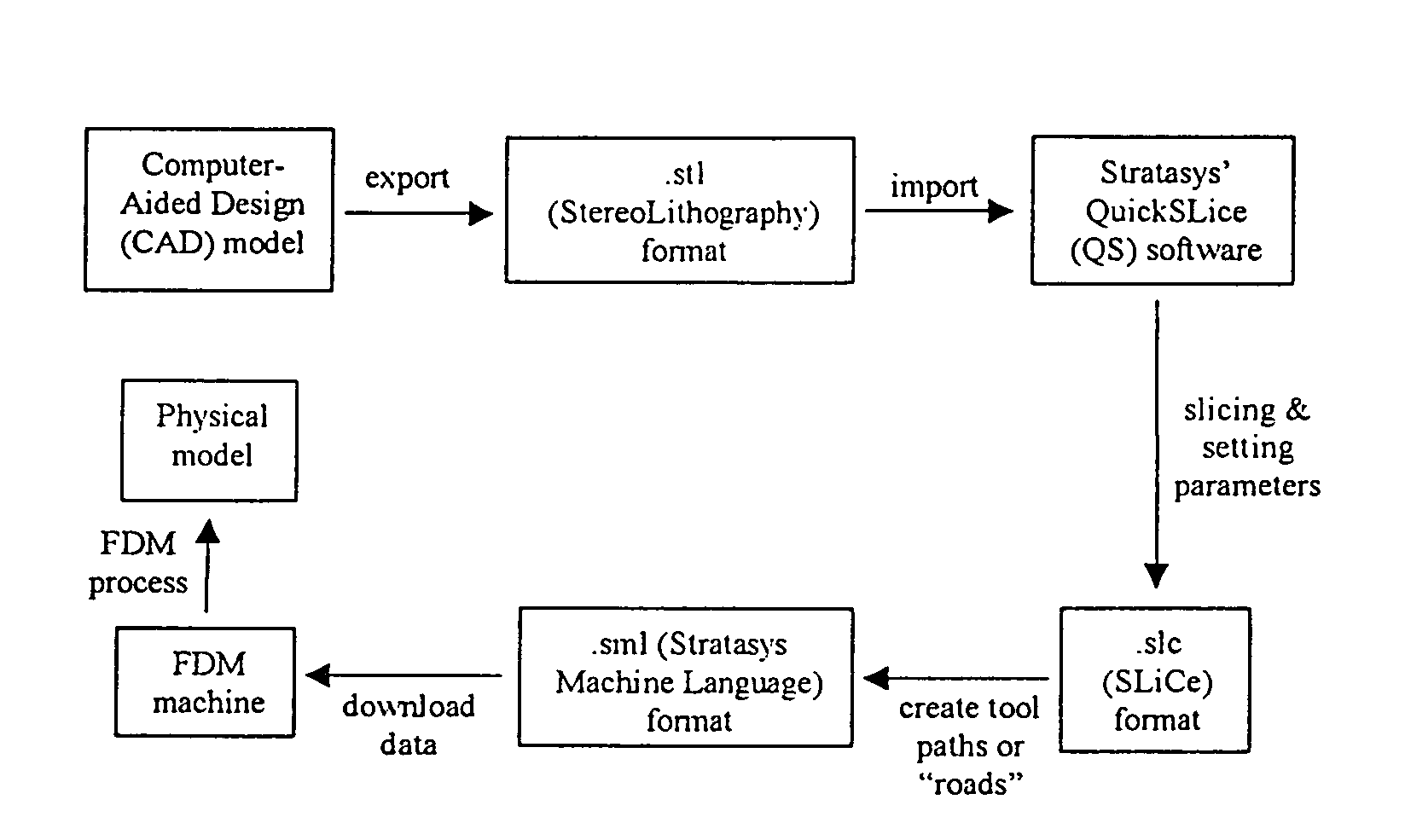
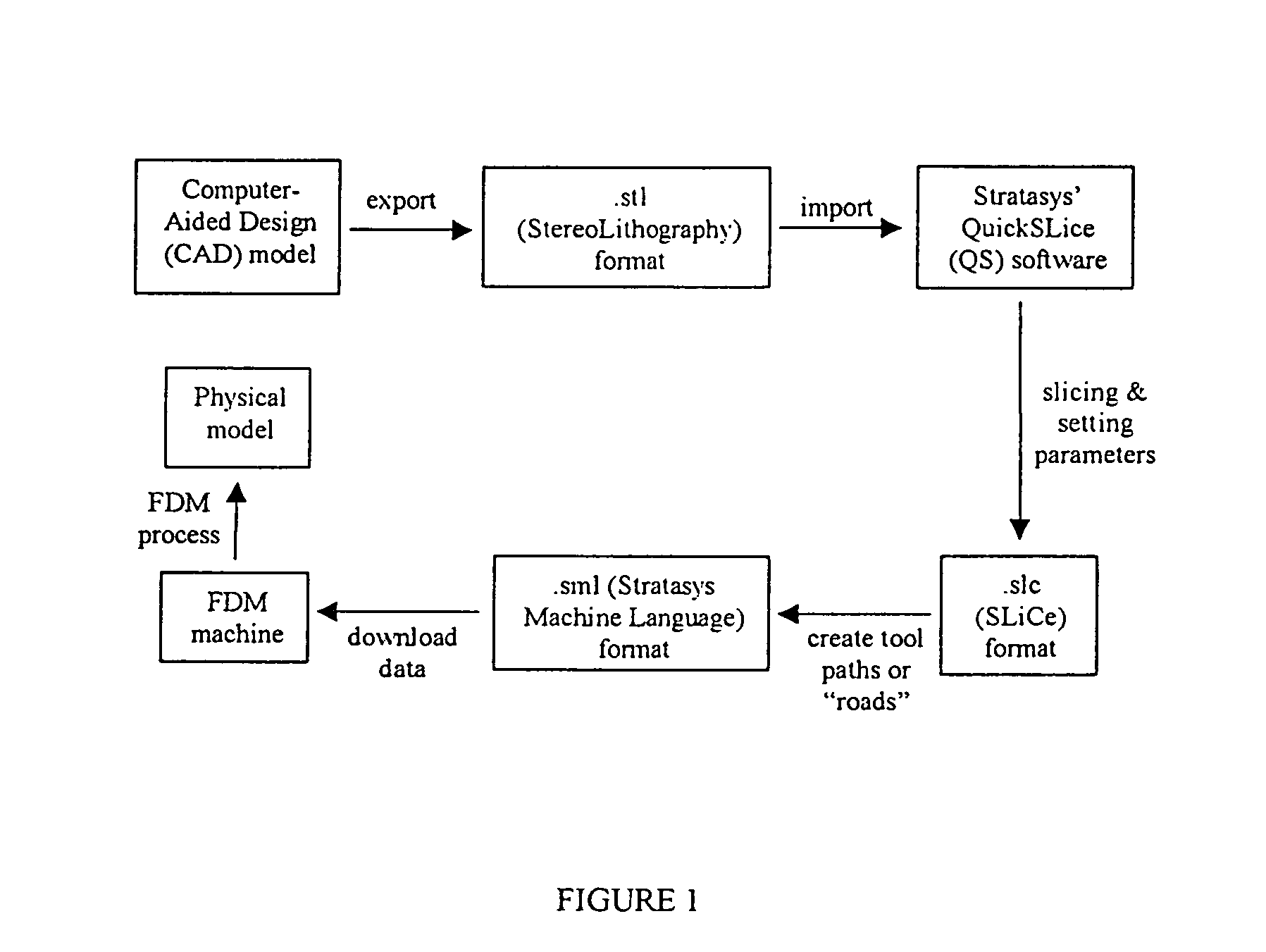
Manufacturing process, such as three dimensional printing, including binding of water-soluble material followed by softening and flowing and forming films of organic-solvent-soluble material
InactiveUS20070009606A1Effectively osteoinductiveHigh porosityAdditive manufacturing apparatusPhotosensitive materialsManufacturing technologyAdditive ingredient
The invention includes biostructures which may be characterized as having substantially all of the organic-solvent-soluble material in the form of a network of irregularly shaped perforated films. The biostructure may further include particles of a substantially-insoluble material, which may be a member of the calcium phosphate family. The biostructure may be osteoconductive. The biostructure may further contain an Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient or other bioactive substance. The API may be a substance which stimulates the production of bone morphogenetic protein, such as Lovastatin or related substances, thereby making the biostructure effectively osteoinductive. One or more of the polymers may have a resorption rate in the human body such as to control the release of the API. Methods of manufacture are also disclosed.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +1
Phenyl Ester Side Chains to Increase Polymer Resorptivity
The present invention relates to polymers modified to increase their resorbability. In particular, the polymers of the invention have phenyl ester side chains which are good leaving groups and which thereby increase the resorption rate of the polymer relative to the same polymer, for example, bearing a comparable amount of an alkyl ester side chain. Such polymers are generally water insoluble, but when modified are able to solublize drugs and upon degradation and resorption, release those in a physiological environment in a controlled and / or sustained manner.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Method of preventing fat graft resorption by administering fat-derived cells and poloxamer P 188
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Graft prosthetic composite for proximal humerus
A proximal humeral prosthesis includes a humeral head having a distal end and a proximal end adapted to be coupled to a glenoid cavity of a scapula; a humeral stem core having an outer surface, a distal end, and a proximal end adapted to be coupled to the distal end of the humeral head; a humeral stem graft having an inner surface adapted to be coupled to at least a portion of the outer surface of the humeral stem core, a distal end, a proximal end, and an outer surface including at least one tendon attachment site; and an intramedullary stem having a proximal end adapted to be coupled to the distal end of the humeral stem core and a distal end adapted to be coupled to at least one bone of a skeleton. The prosthesis can be rendered modular and can further include a spacer segment. Resorption of bone from the humeral stem graft can be inhibited by compression of the humeral stem graft. Further, the prosthesis can include sites for attachment of soft tissues to the prosthesis, soft tissues for attachment to soft or bony tissues of the recipient, or both, which can improve function of the shoulder joint.
Owner:ZIMMER INC
Method for fostering bone formation and preservation
ActiveUS20050256047A1Rapid bone formationShorten the lengthPeptide/protein ingredientsChiropractic devicesSufficient timeBlood concentration
A method of inducing bone formation in a subject in need of such inducement comprises the steps of mechanically inducing an increase in osteoblast activity in the subject and elevating blood concentration of at least one bone anabolic agent in the subject. The method steps may be performed in any order, but in sufficient time proximity that the elevated concentration of the anabolic agent and the mechanically induced increase in osteoblast activity overlaps. The method may additionally comprise providing the subject with an elevated blood concentration of at least one antiresorptive agent, wherein the elevated concentration is sufficient to prevent resorption of new bone growth produced due to the osteoblast activity. Use of the method permits targeting of specific bones of the subject for bone production and preservation, faster bone production and earlier discontinuation of bone anabolic pharmaceuticals. Kits adapted for performing the method are provided.
Owner:UNIGENE LABORATORIES +1
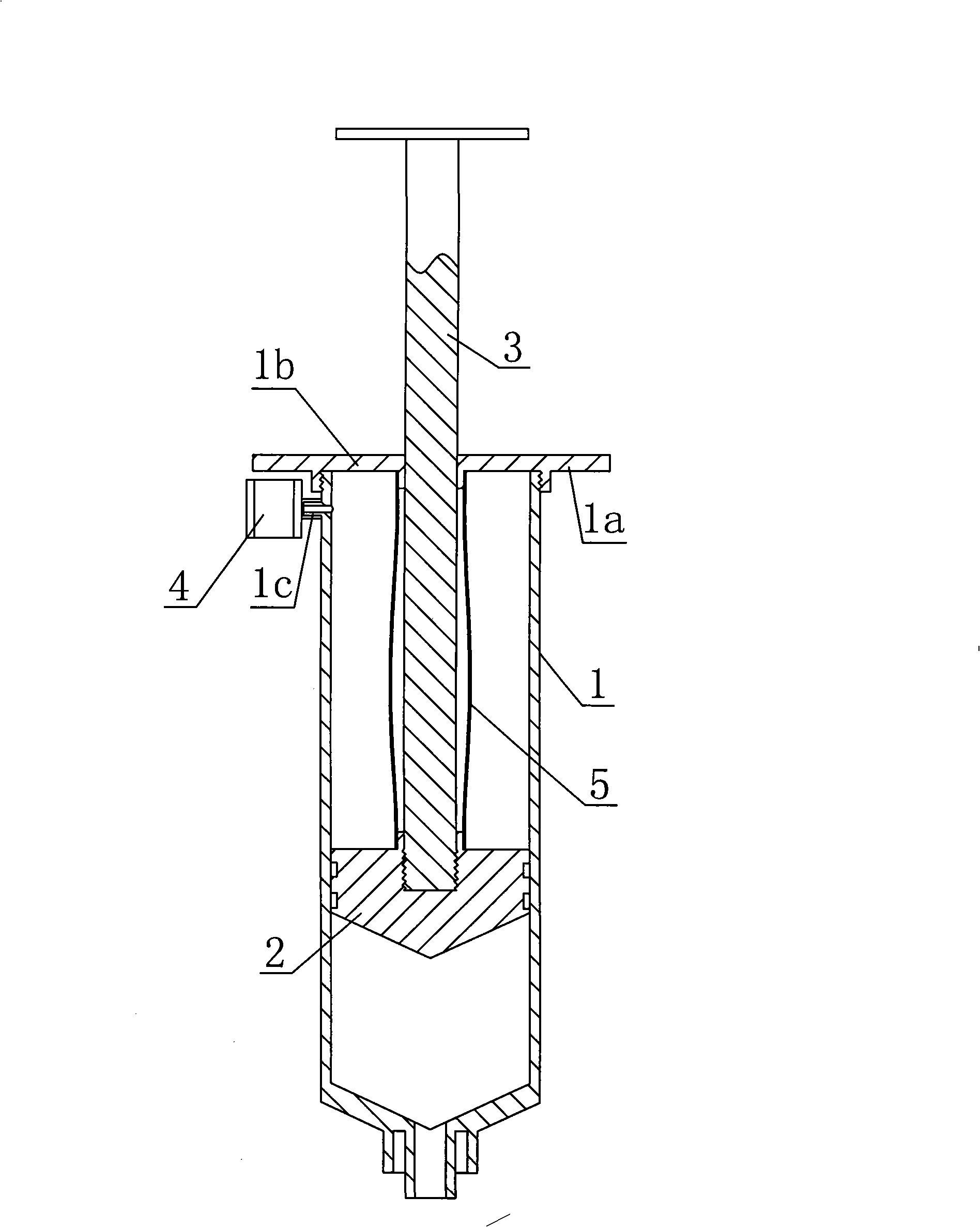
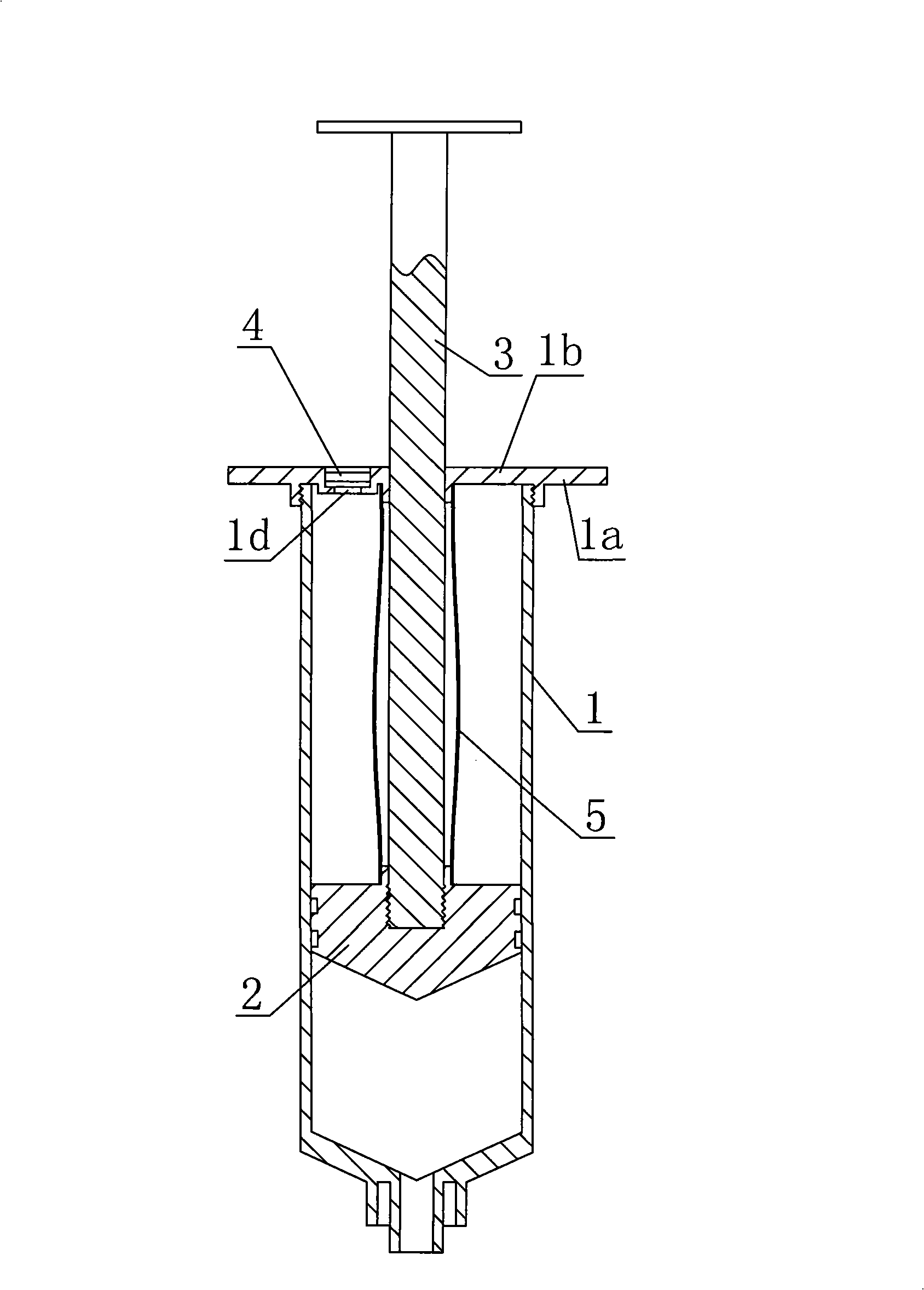
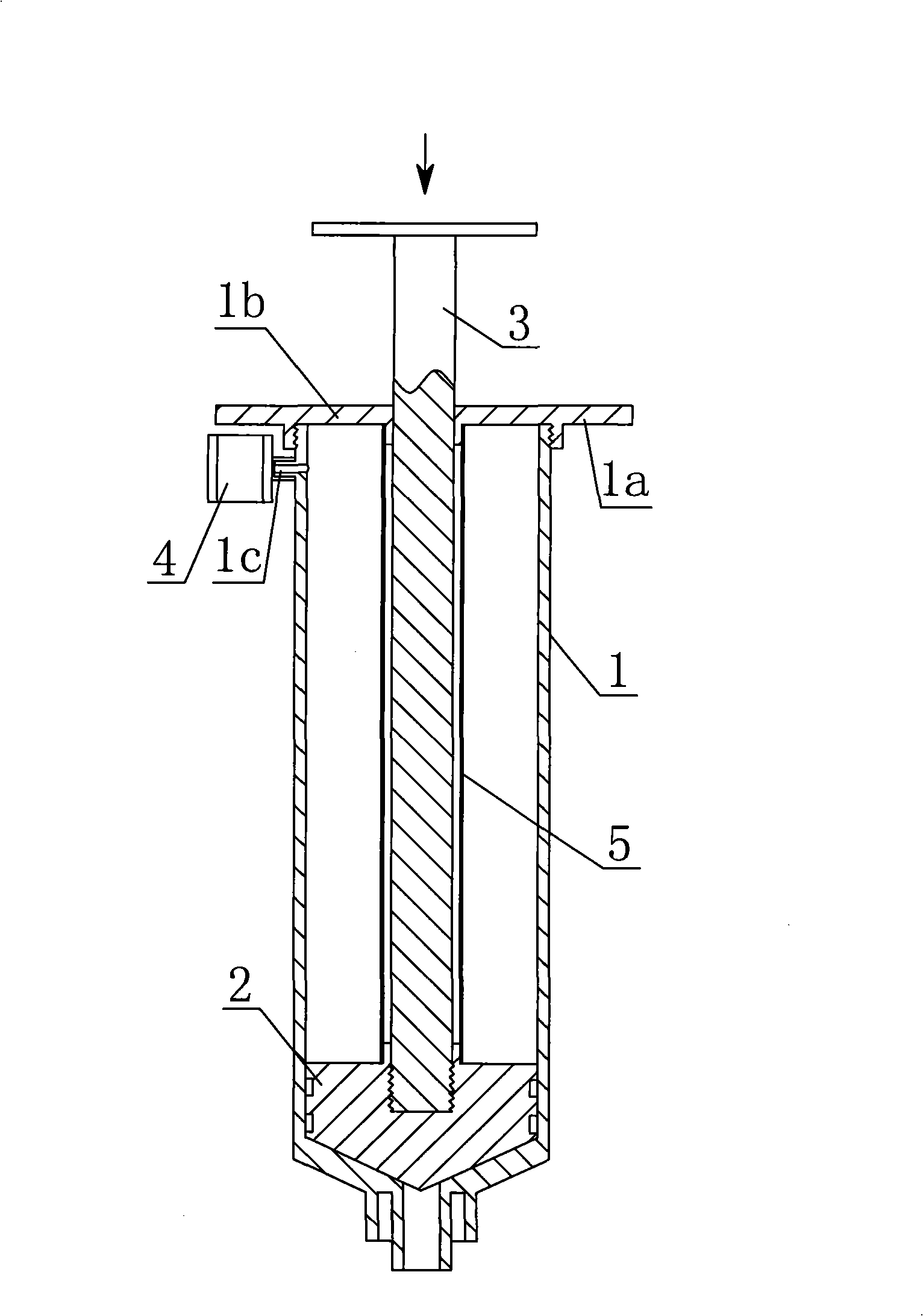
Automatic resorption type antipollution medicine adding syringe
InactiveCN101264359ARealize automatic suctionGreat suctionInfusion syringesIntravenous devicesBiochemical engineeringAir filter
The invention discloses an automatic resorption typed pollution prevention injector for adding medicine, comprising a syringe, a swing plate arranged at the rear end of the syringe, a piston arranged in the syringe, and a guide cover arranged at the rear end of the syringe. The injector is characterized in that: a cylindrical push rod is drilled through the middle of the guide cover and is connected with the piston, an air filter is connected with the rear end of the syringe, the air filter is communicated with the intracavity of the syringe; wherein, an elastic piamater sleeve is arranged on the external periphery of the cylindrical push rod between the guide cover and the piston, the natural length of the elastic piamater sleeve is shorter than the stroke of the piston in the syringe; the automatic resorption typed pollution prevention injector is used for blending injected medical solution. The injector has the advantages of labor saving and convenient use.
Owner:陈庆强
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com