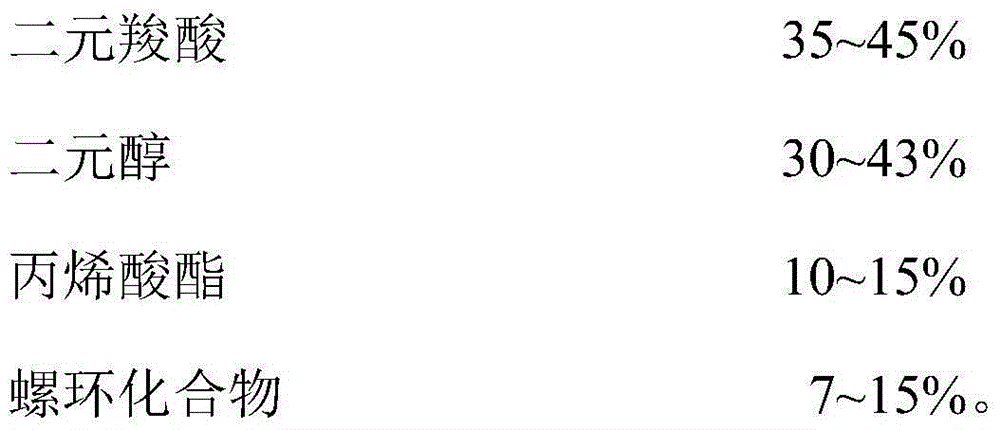Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
400 results about "Fused deposition modeling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
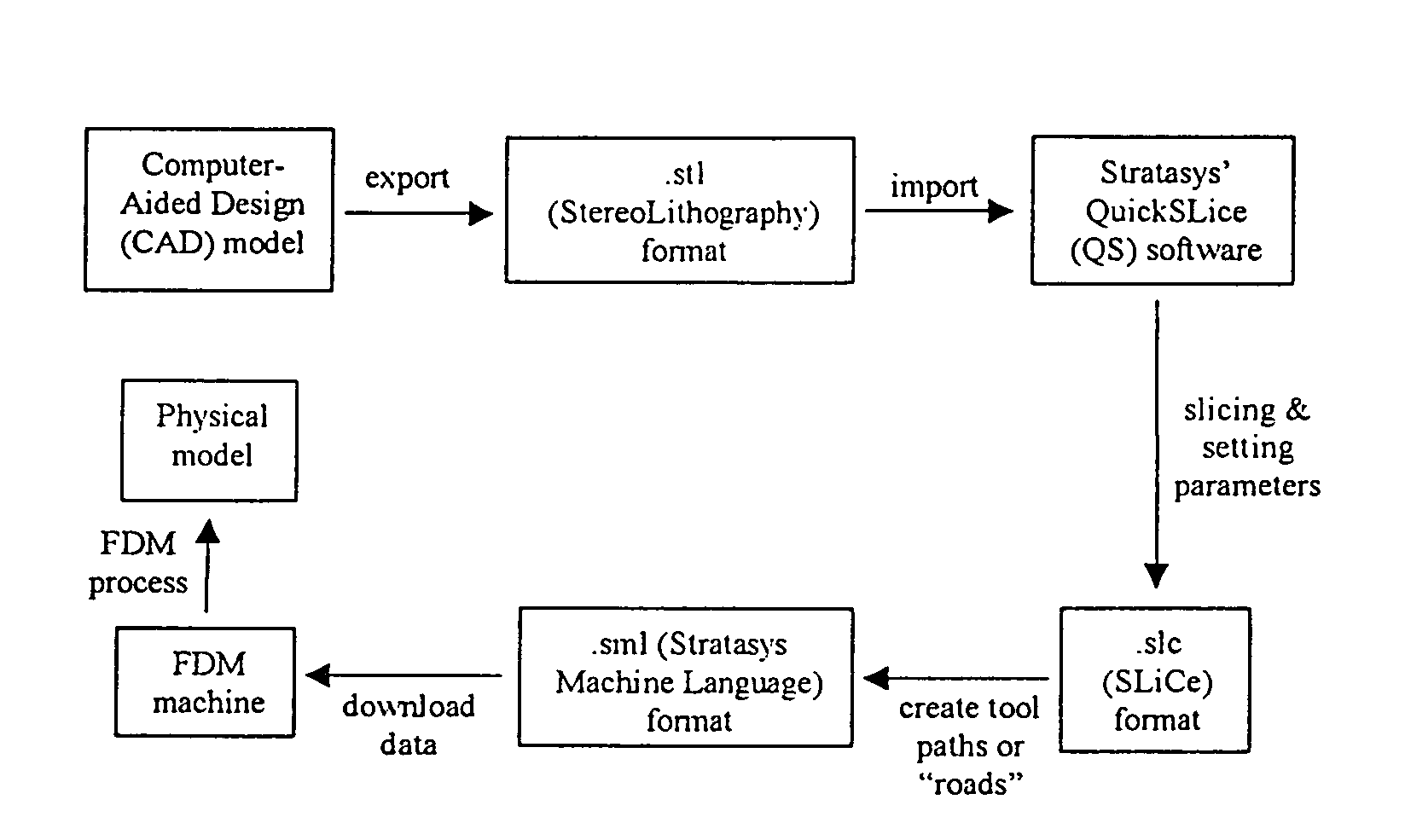
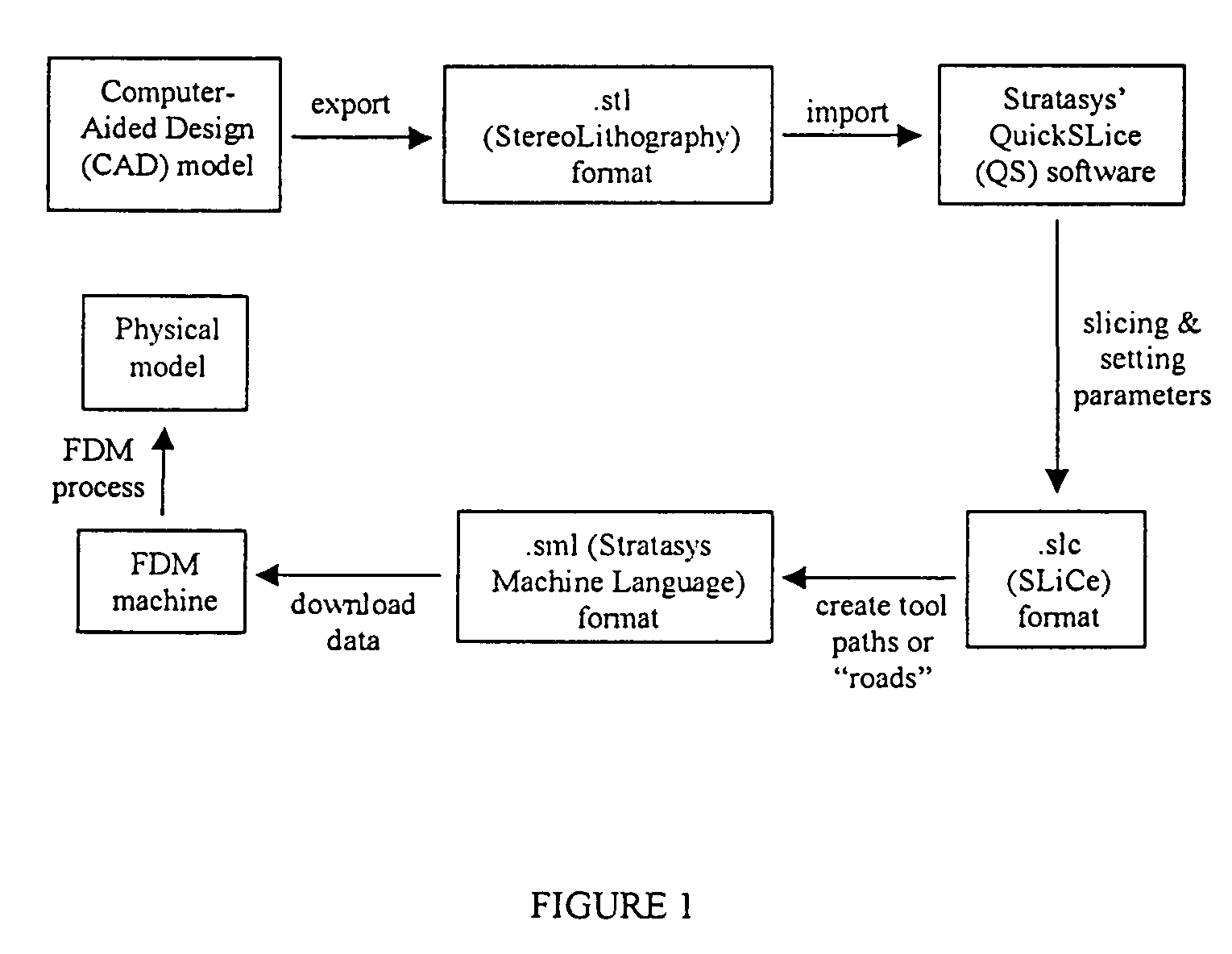
Fused deposition modeling is an additive manufacturing technology commonly used for modeling, prototyping, and production applications. FDM works on an "additive" principle by laying down material in layers; a plastic filament or metal wire is unwound from a coil and supplies material to produce a part. The technology was developed by S. Scott Crump in the late 1980s and was commercialized in 1990. The term fused deposition modeling and its abbreviation to FDM are trademarked by Stratasys Inc. The exactly equivalent term, fused filament fabrication, was coined by the members of the RepRap project to give a phrase that would be legally unconstrained in its use. It is also sometimes called Plastic Jet Printing.
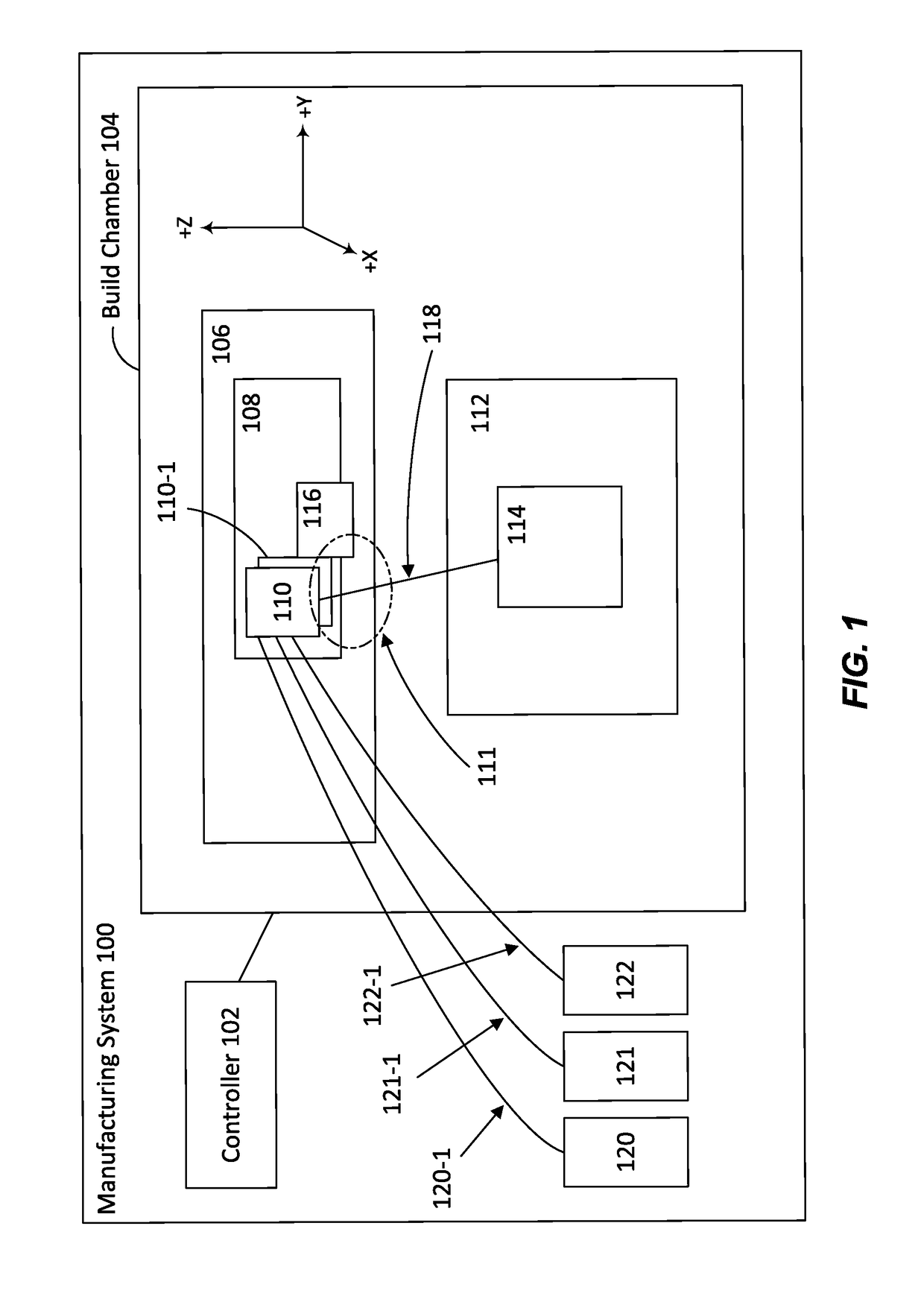
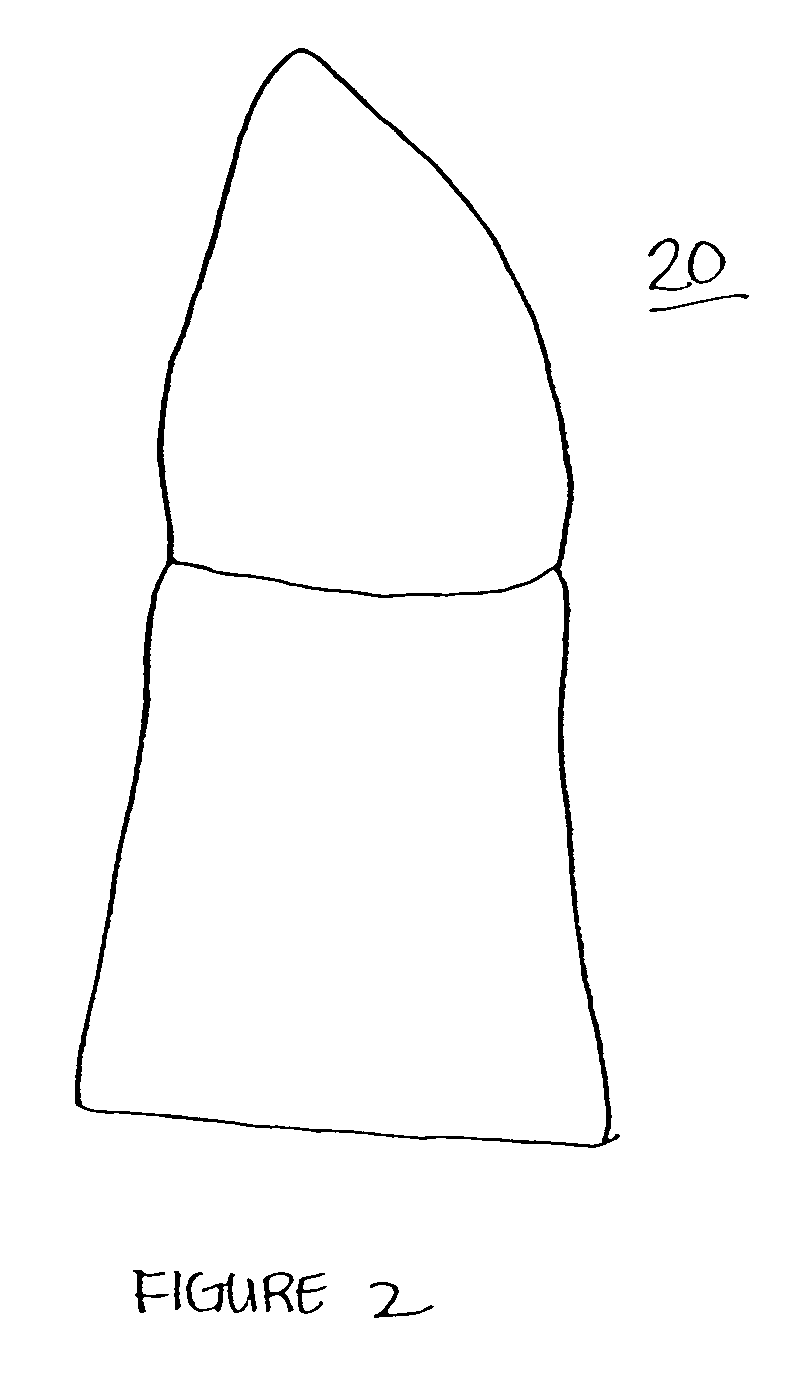
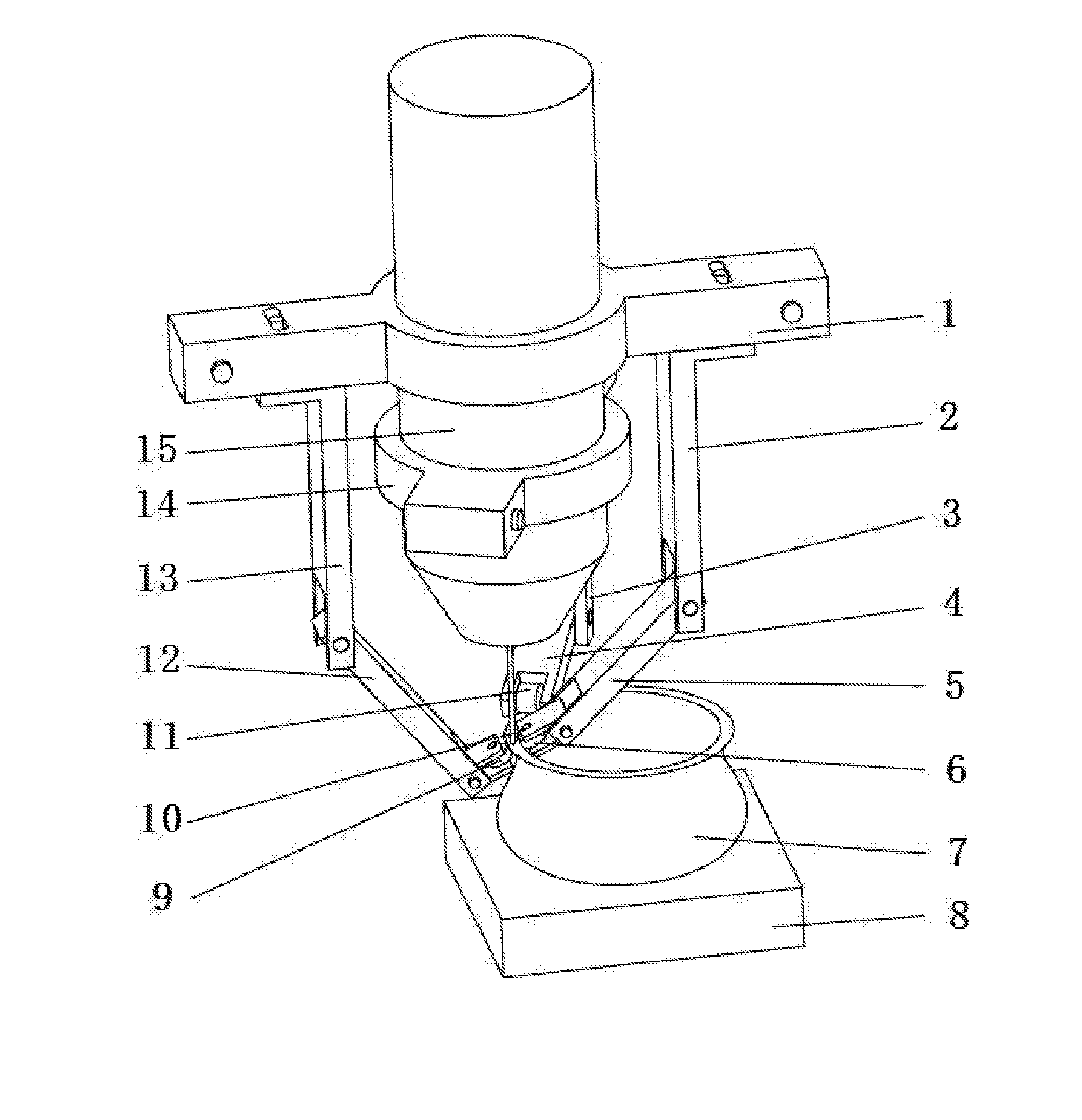
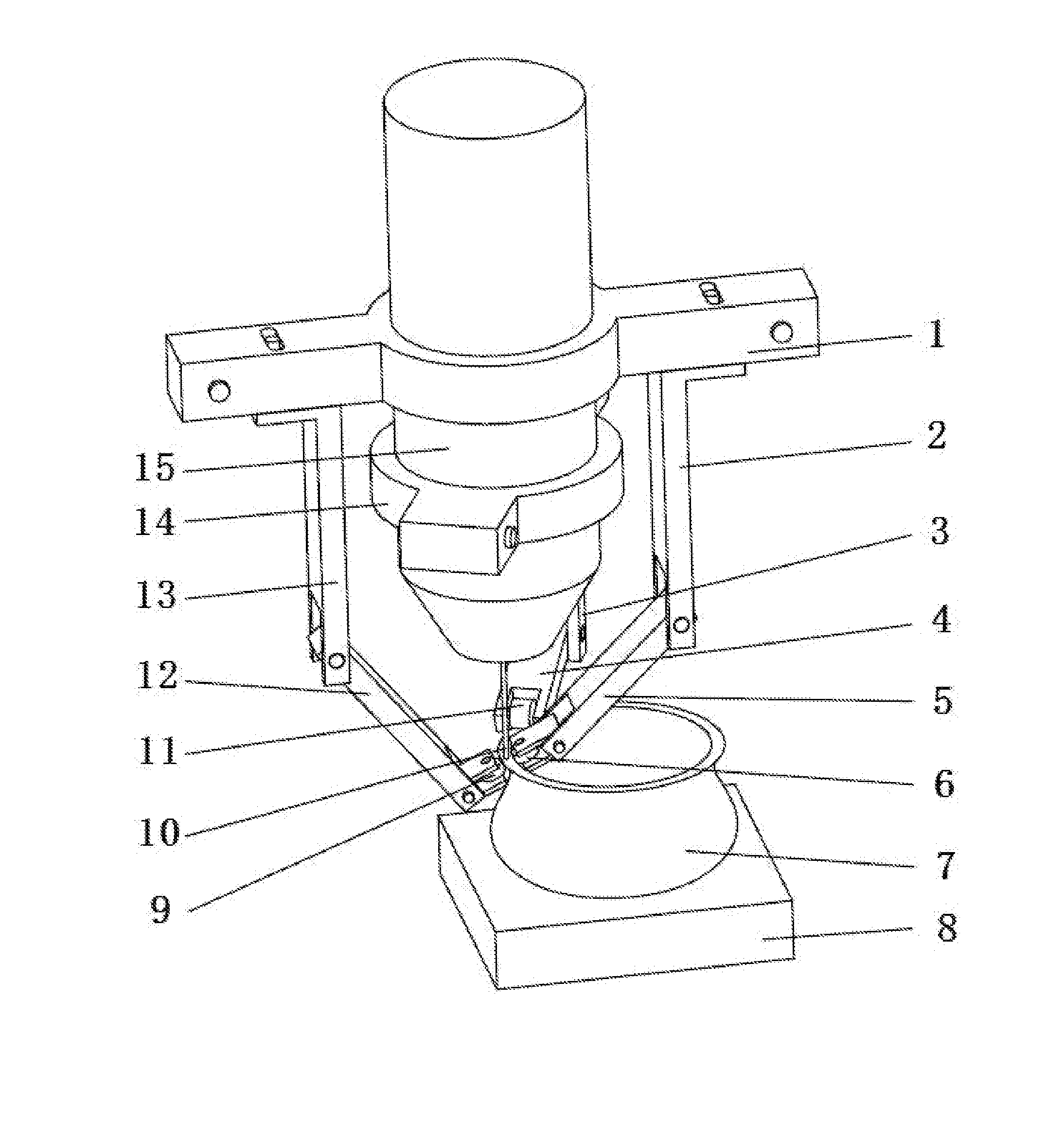
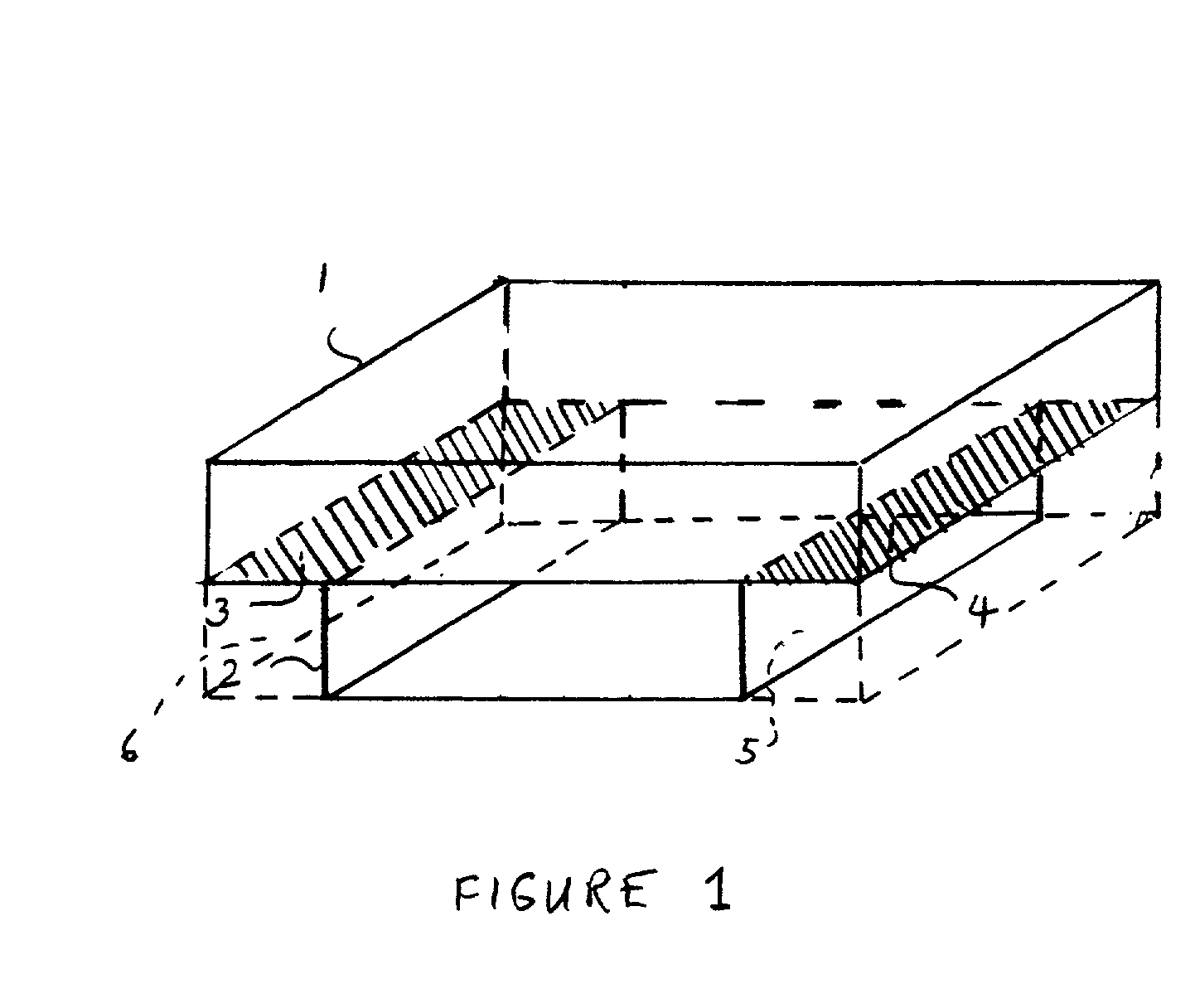
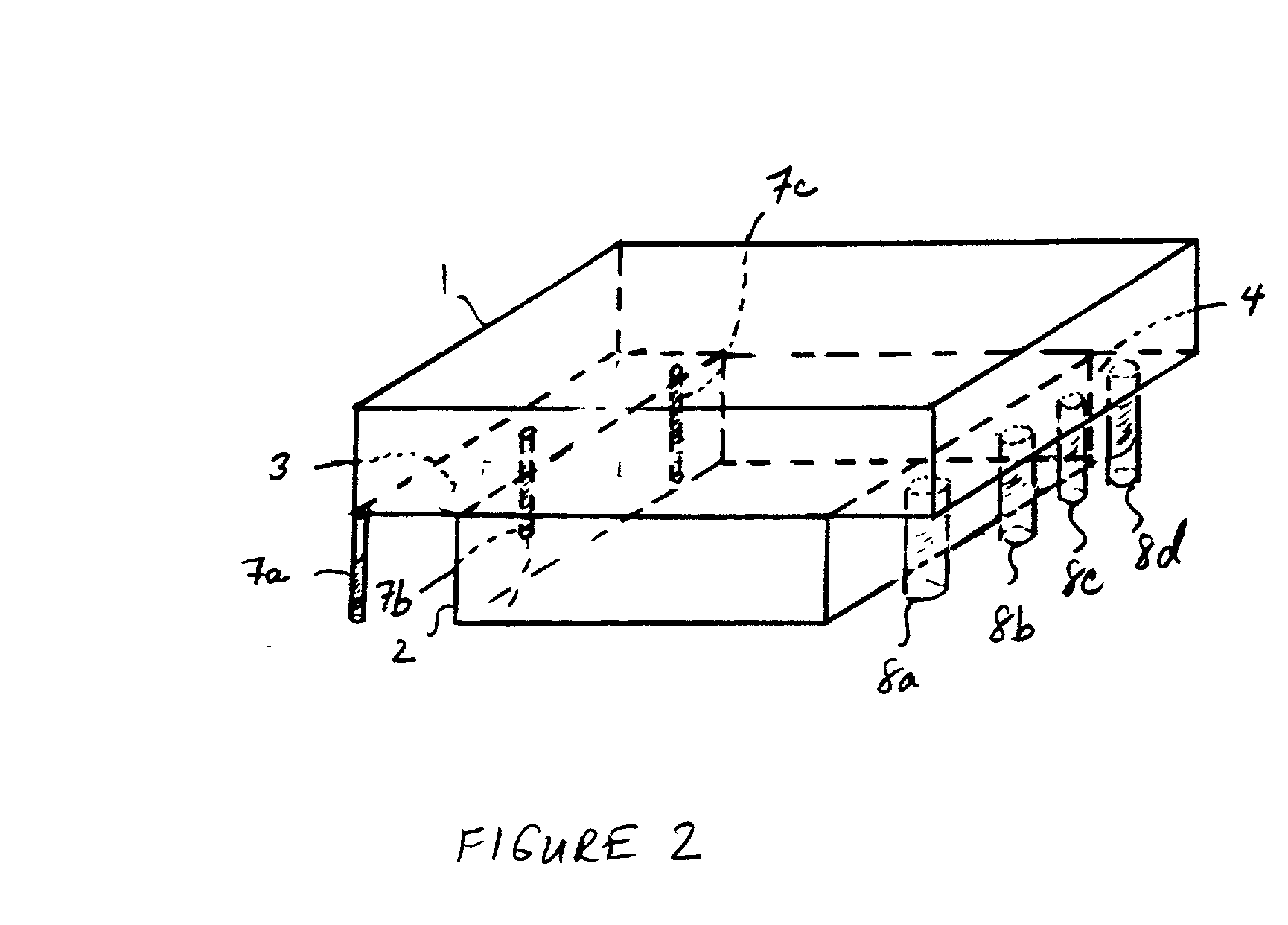
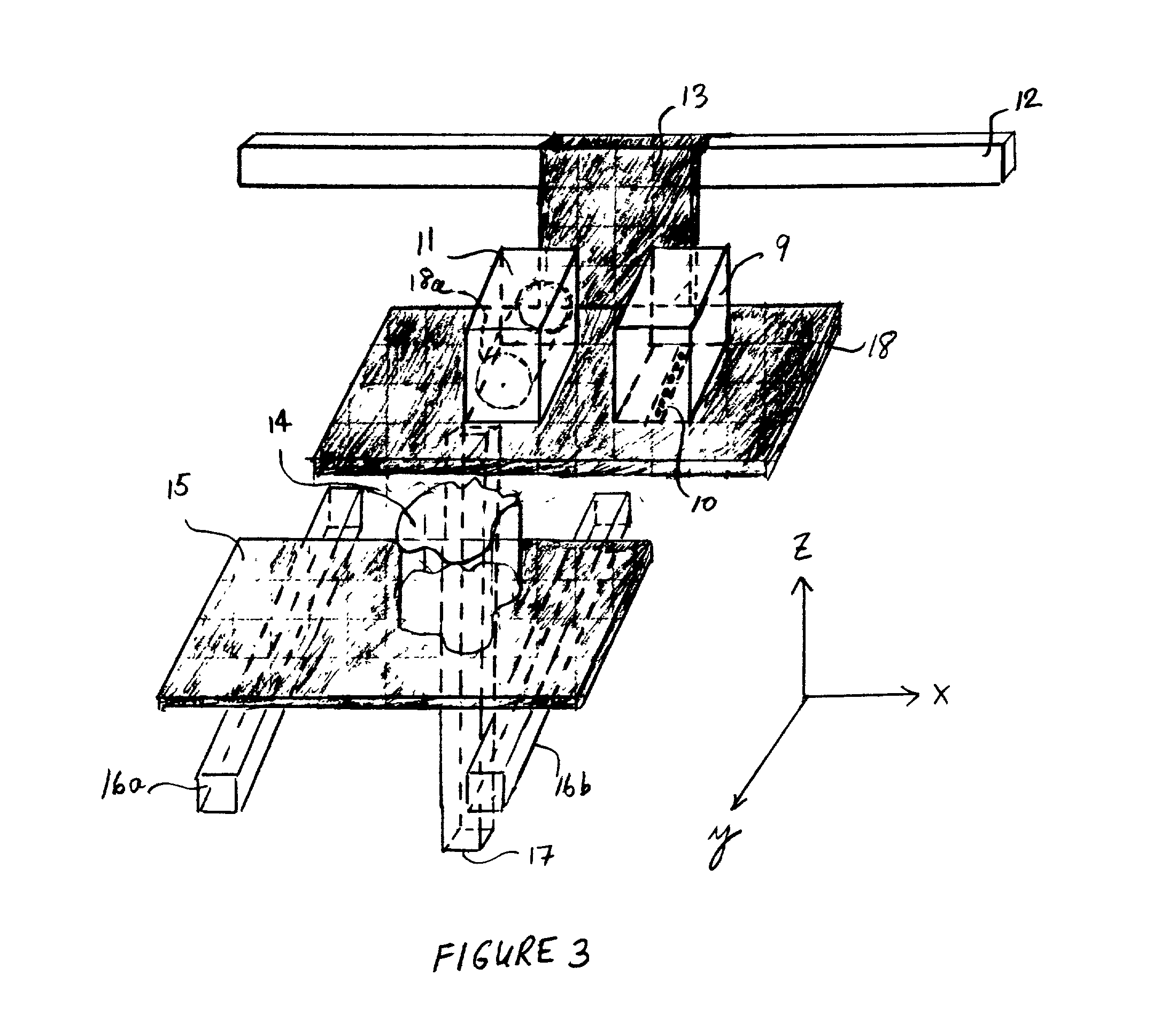
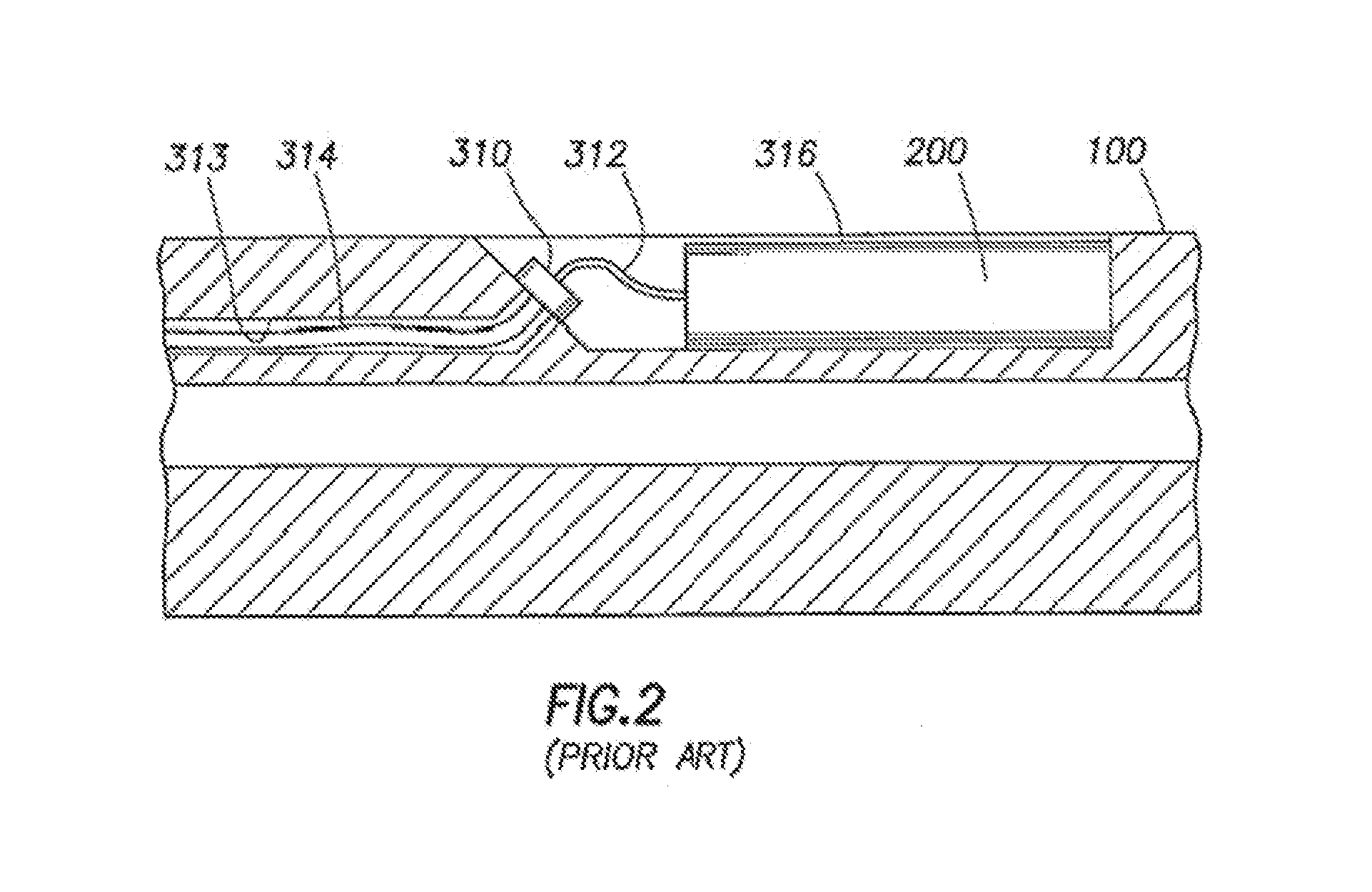
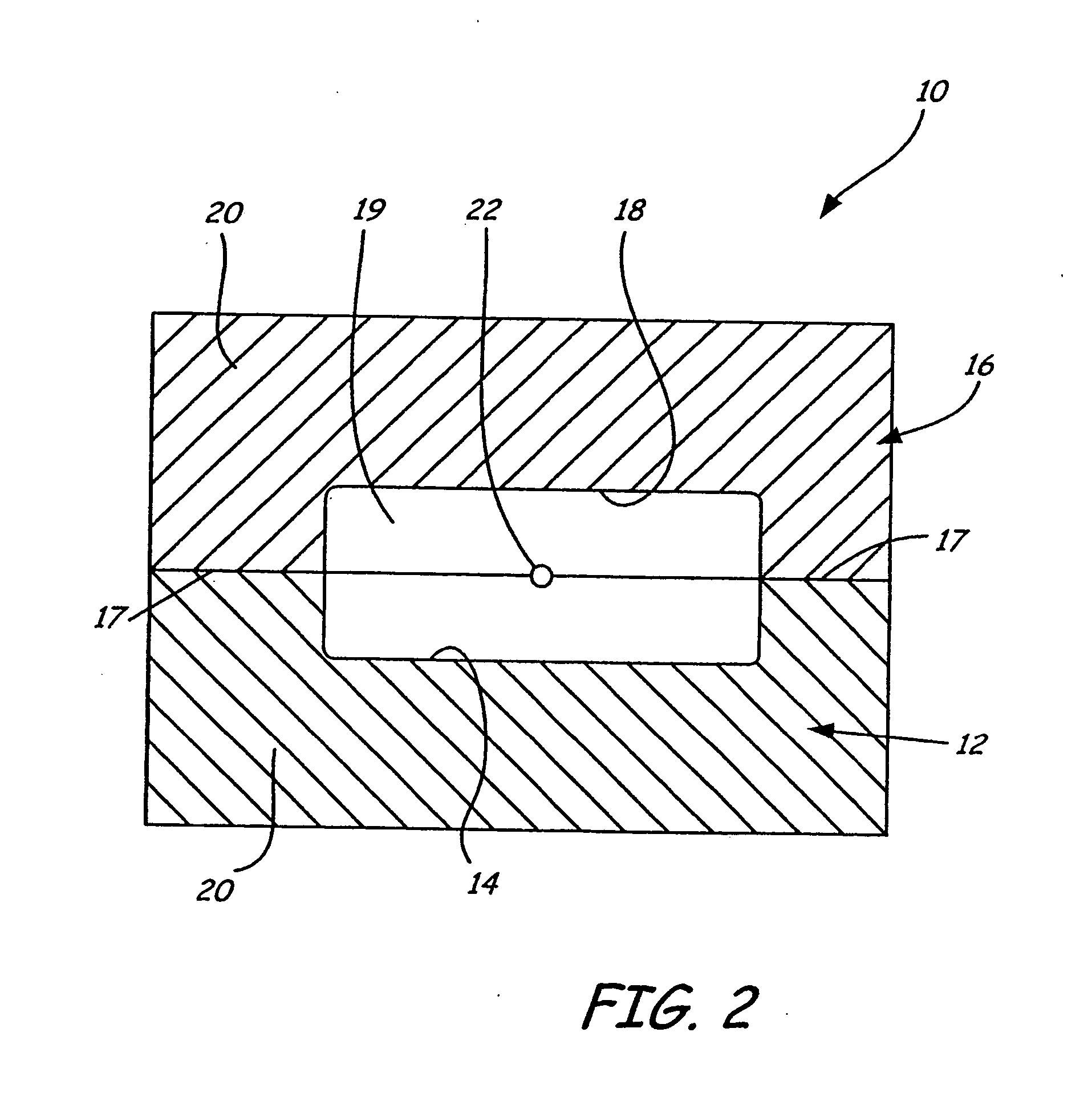
Selective deposition modeling method and apparatus for forming three-dimensional objects and supports
InactiveUS6193923B1Easy to disassembleMinimal damageAdditive manufacturing apparatusCeramic shaping apparatusEngineeringSelective deposition
A variety of support structures and build styles for use in Rapid Prototyping and Manufacturing systems are described wherein particular emphasis is given to Thermal Stereolithography, Fused Deposition Modeling, and Selective Deposition Modeling systems, and wherein a 3D modeling system is presented which uses multijet dispensing and a single material for both object and support formation.
Owner:3D SYST INC
Selective deposition modeling method and apparatus for forming three-dimensional objects and supports
InactiveUS6270335B2Less distortionReduce the risk of bridgingAdditive manufacturing apparatusConfectioneryEngineeringSelective deposition
Owner:3D SYST INC
Layered deposition bridge tooling
InactiveUS7255821B2Additive manufacturing apparatusAdditive manufacturing with liquidsFilling materialsInjection molding machine
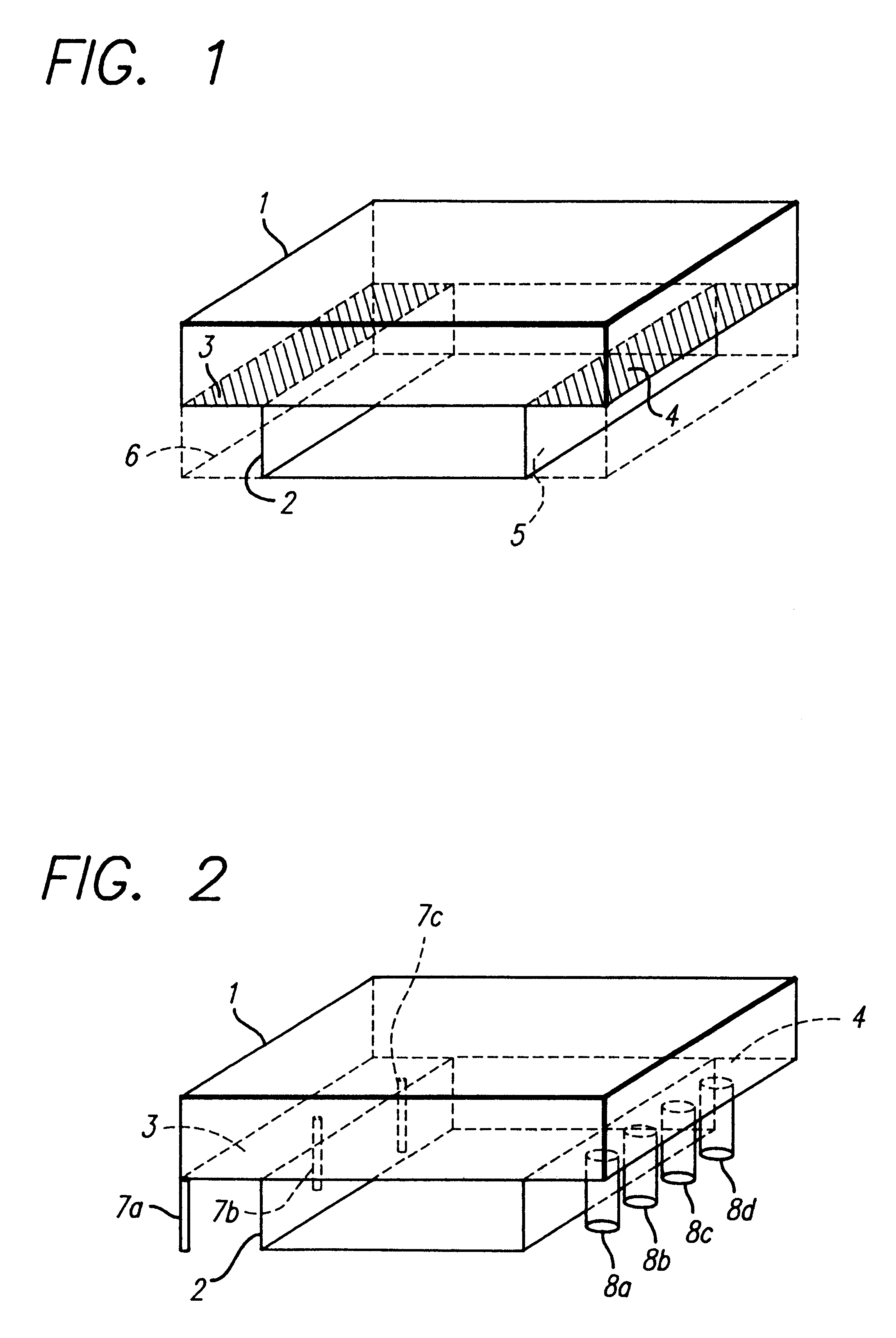
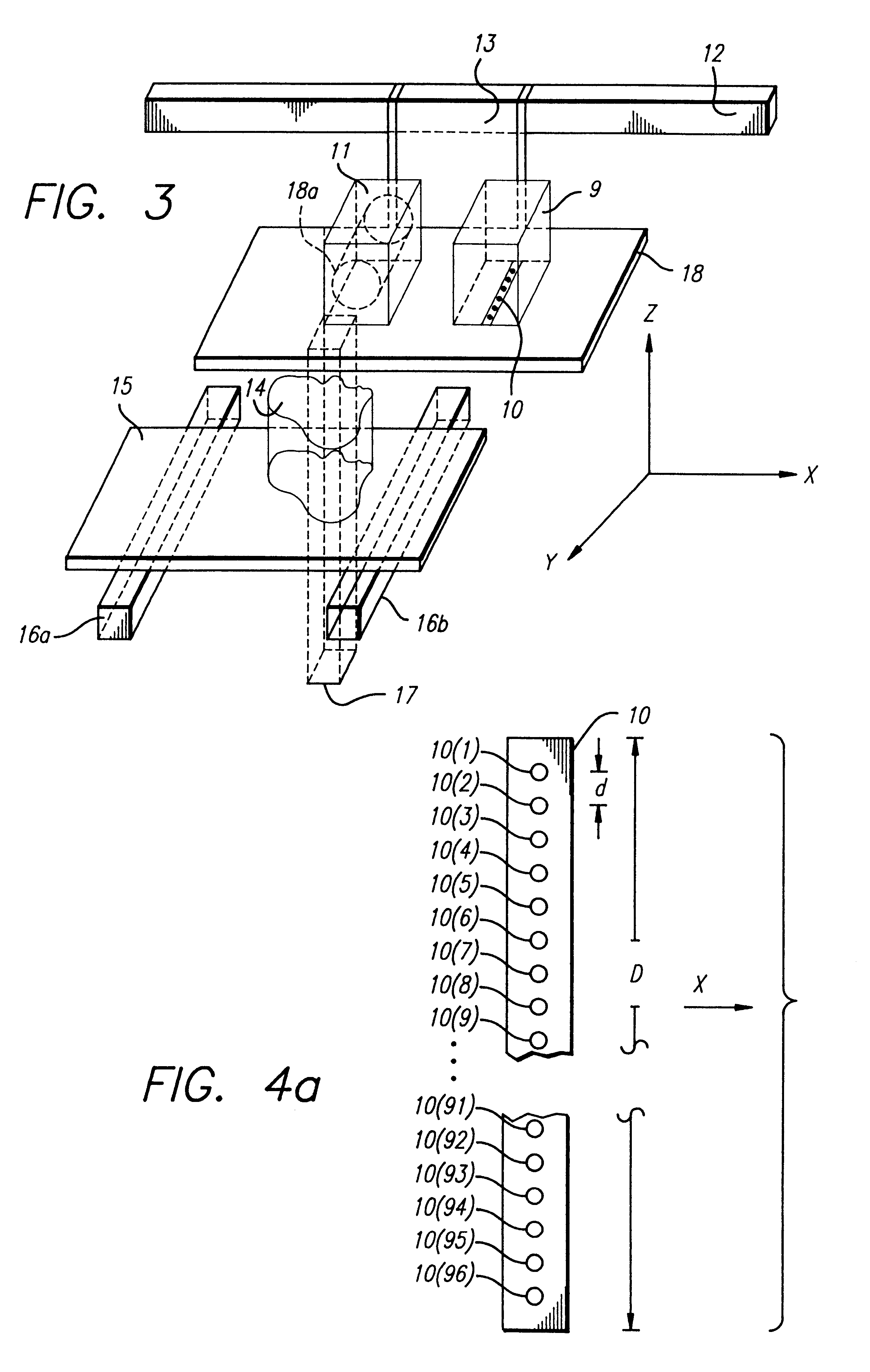
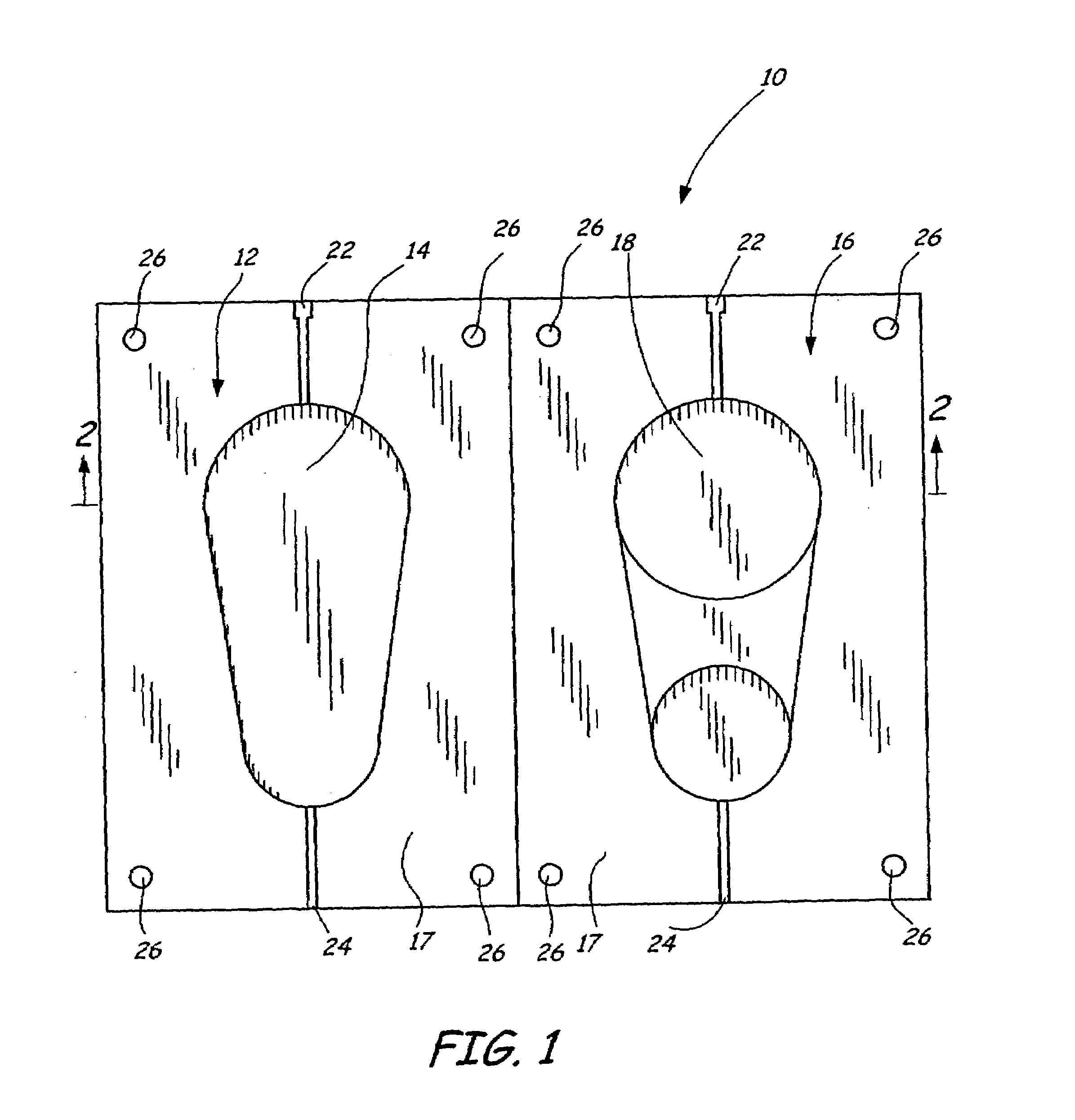
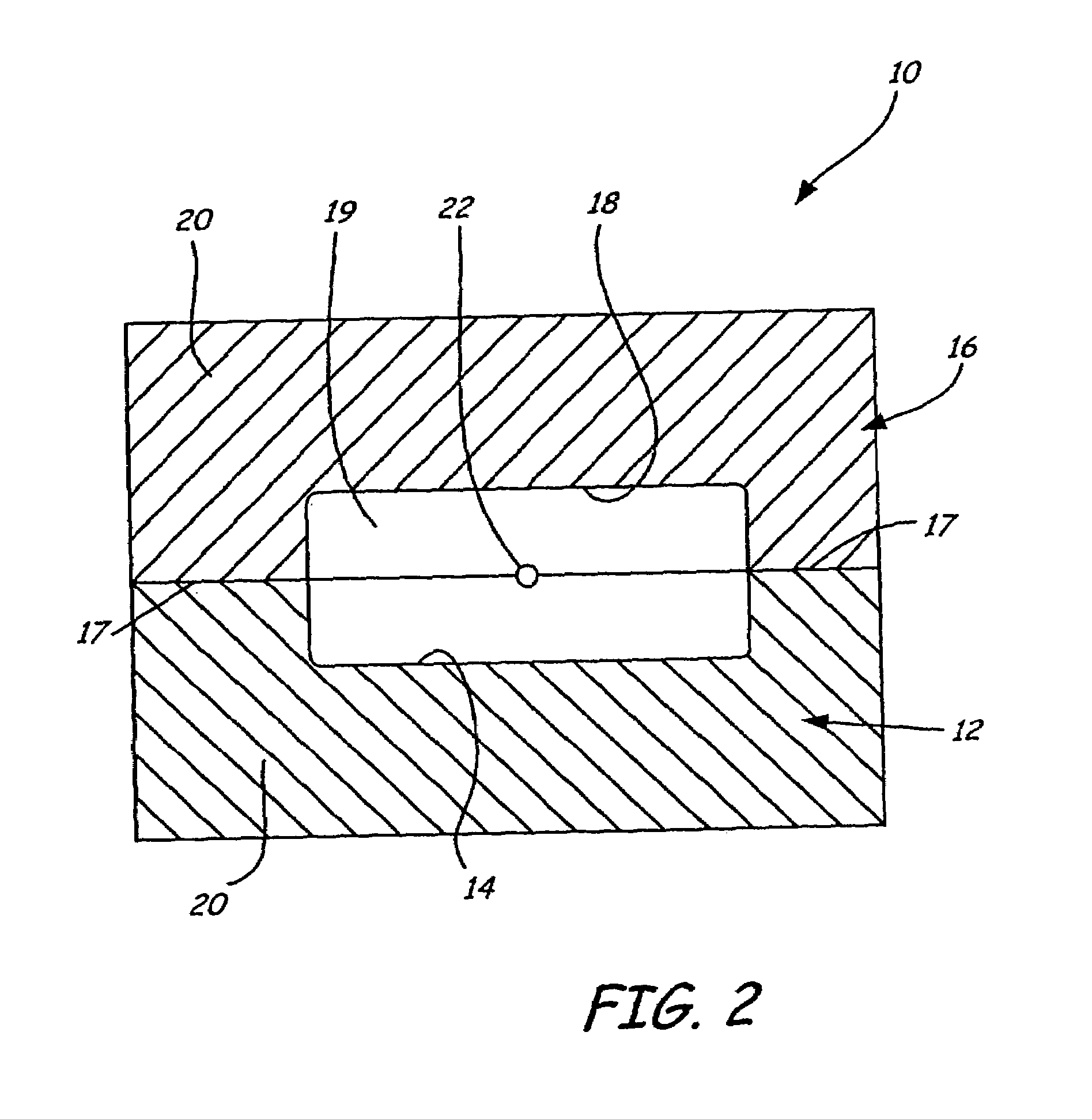
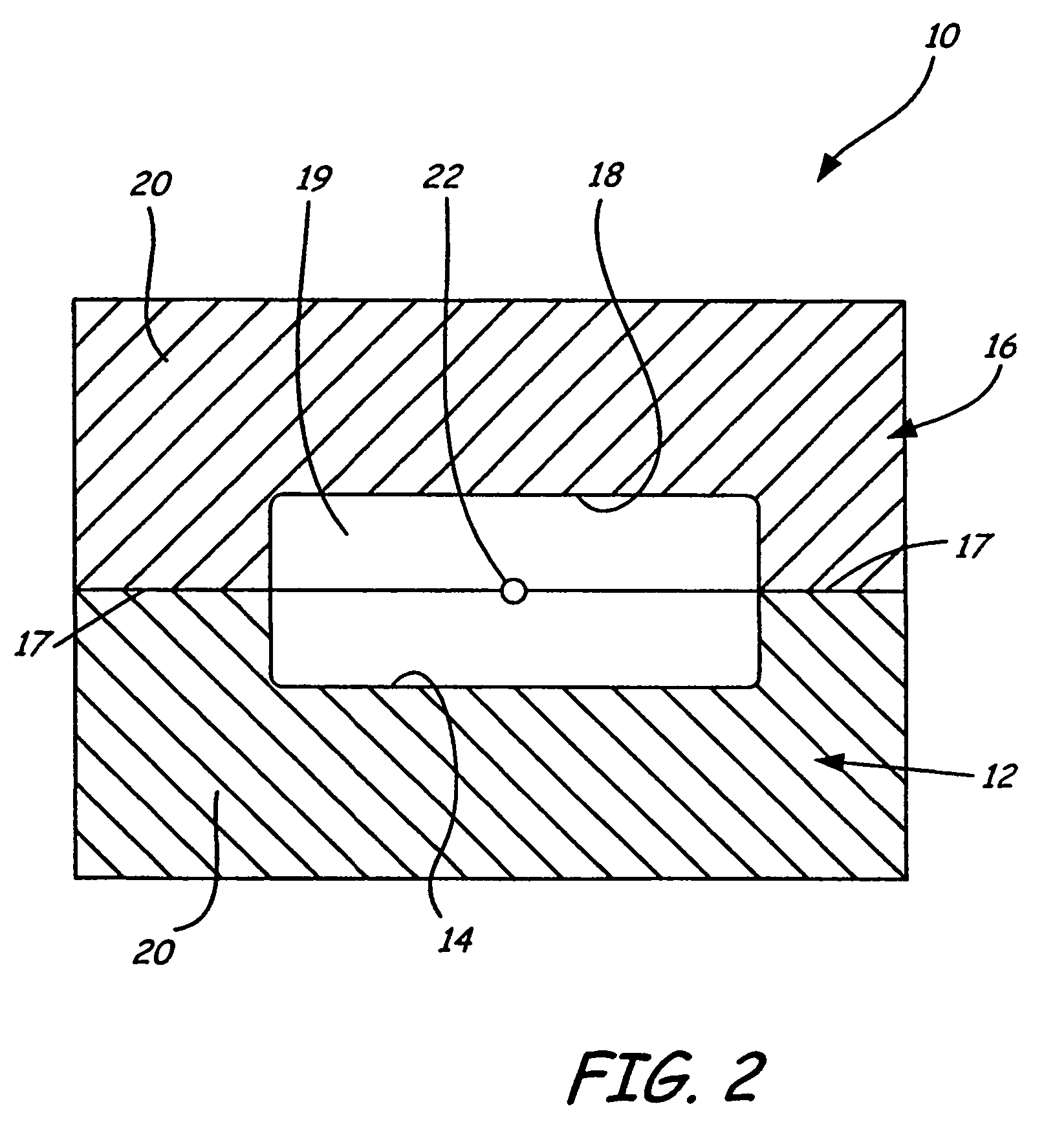
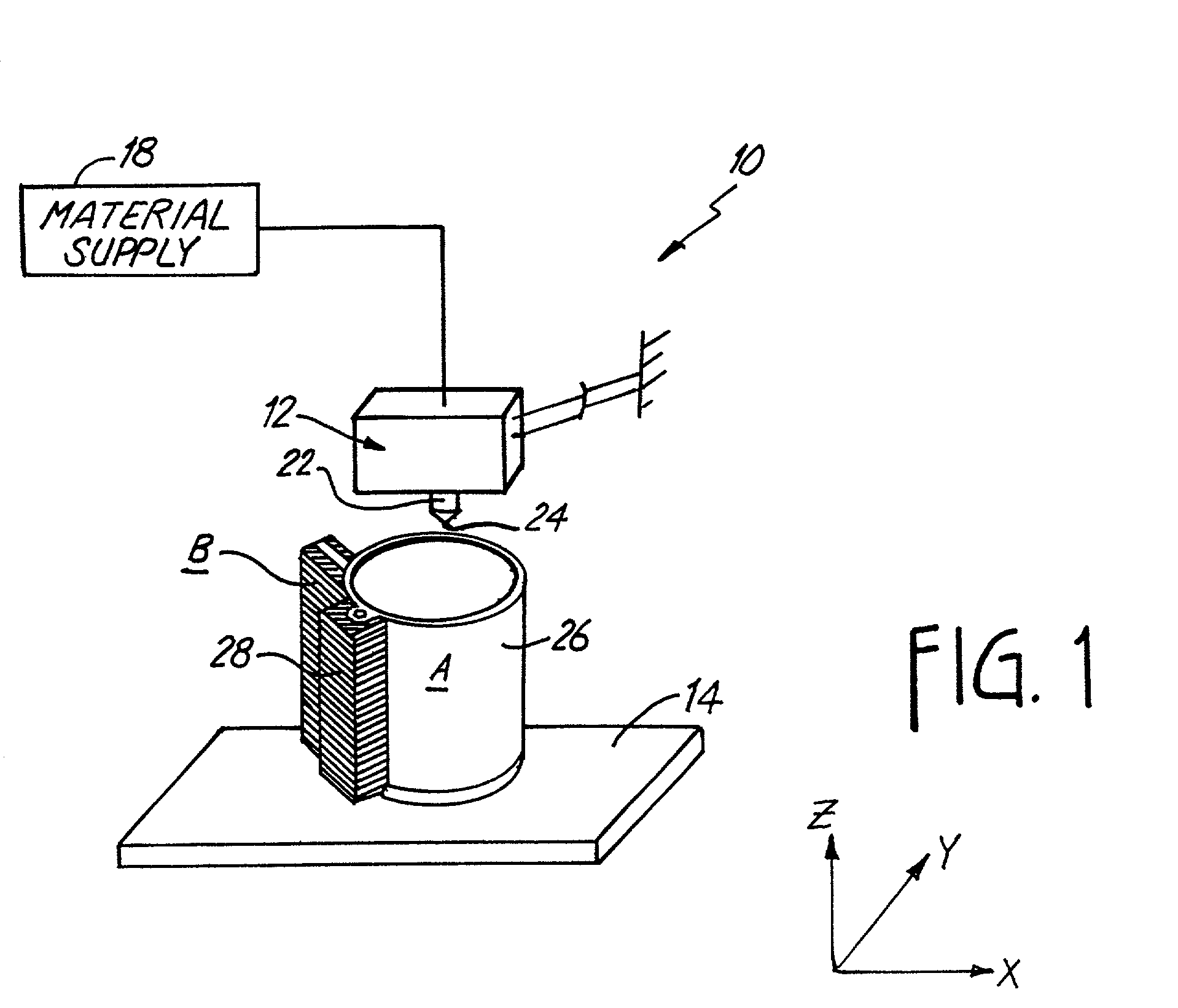
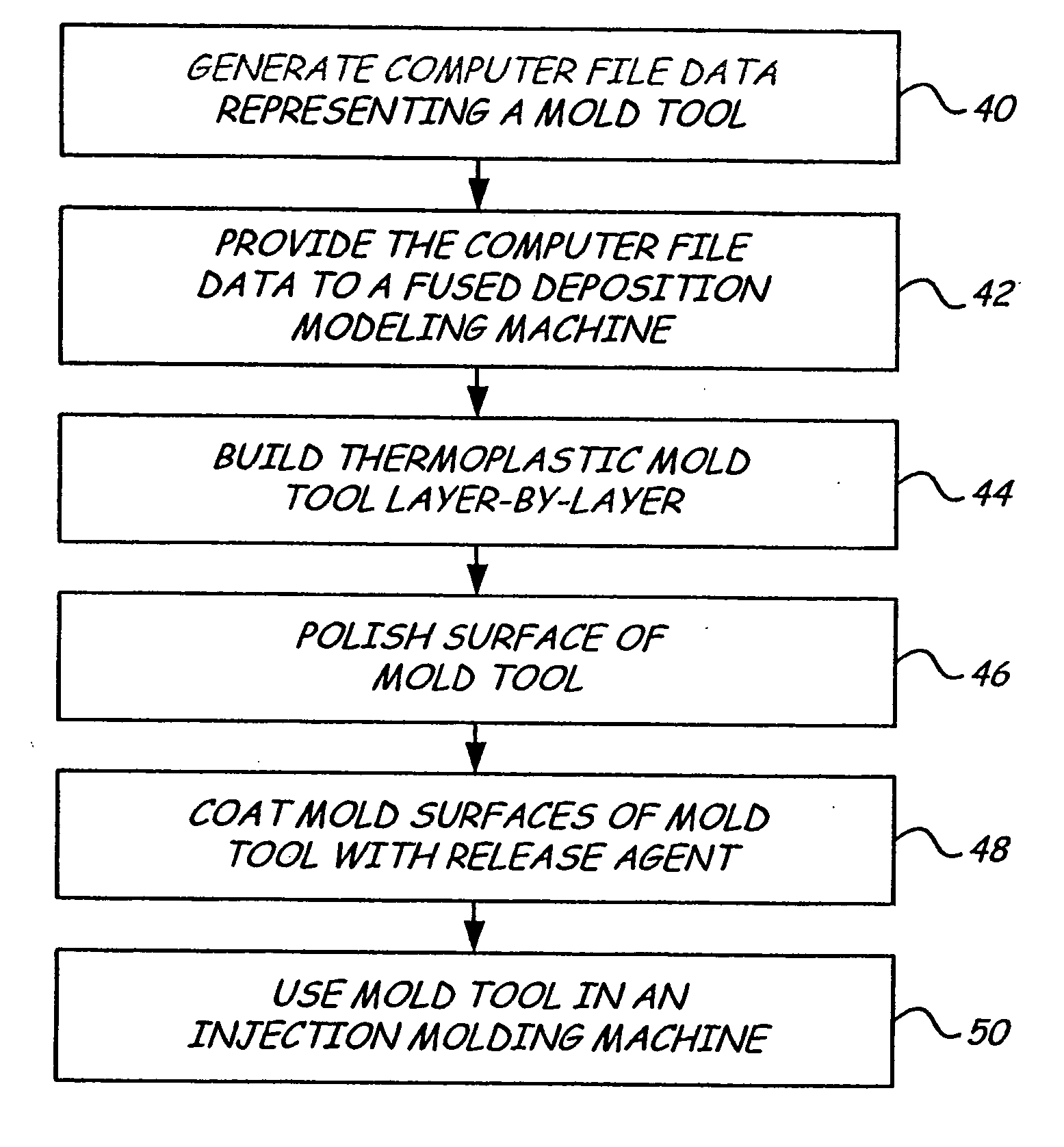
Disclosed is a method for making a prototype plastic injection molded part from a mold tool (10) built by fused deposition modeling. The mold tool (10) is built by depositing roads of a molten thermoplastic resin in layers in a predetermined pattern defined by computer file data representing the inverse of the desired prototype molded part, and is used in an injection molding machine without the addition of any reinforcement fill material or layers to create the prototype part. The disclosed method provides prototype plastic injection molded parts within a twenty-four hour time period.
Owner:STRATSYS INC
Rapid prototype injection molding
InactiveUS7125512B2Additive manufacturing apparatusMechanical vibrations separationInjection mouldingRapid prototyping
Owner:STRATSYS INC
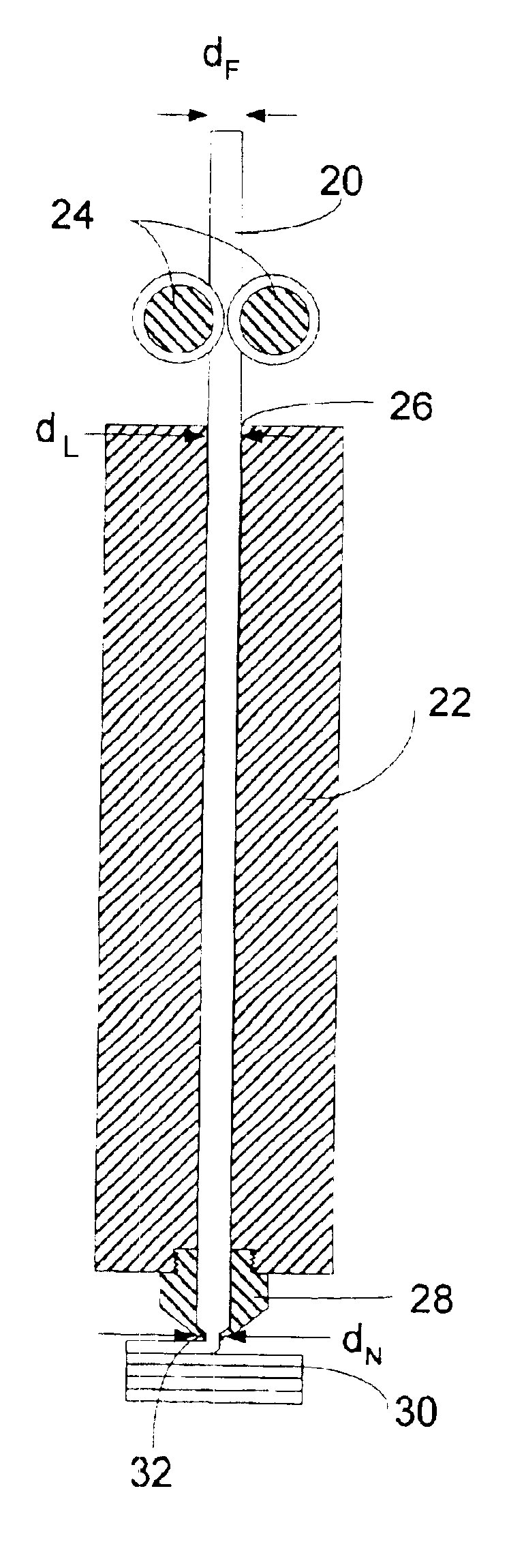
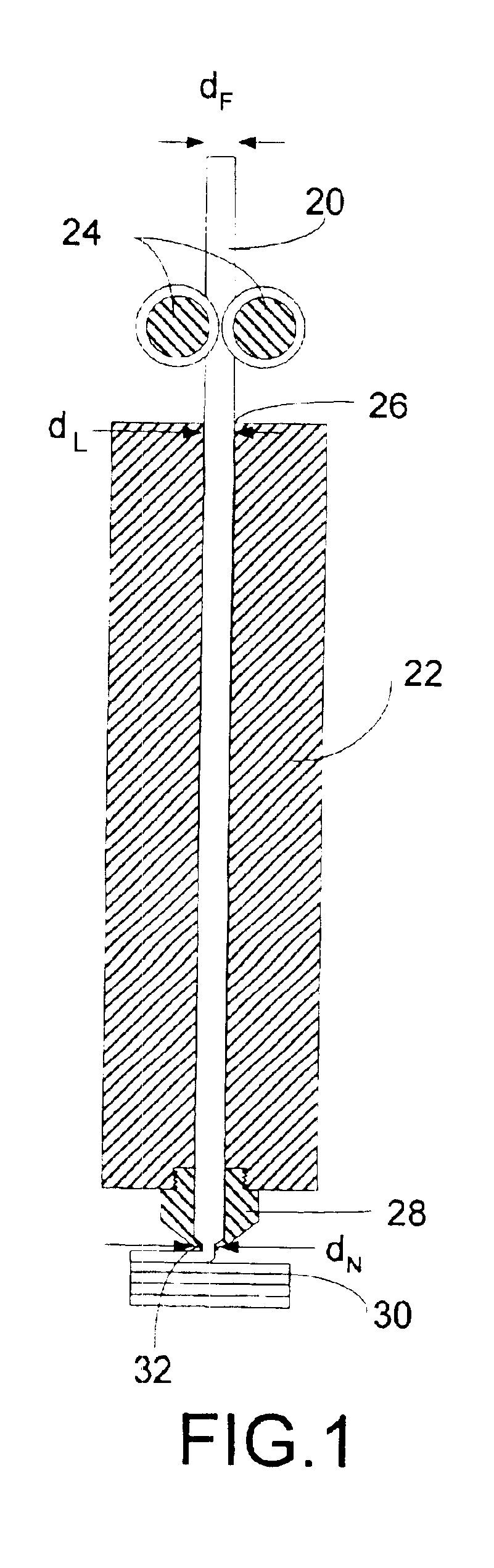
High-precision modeling filament
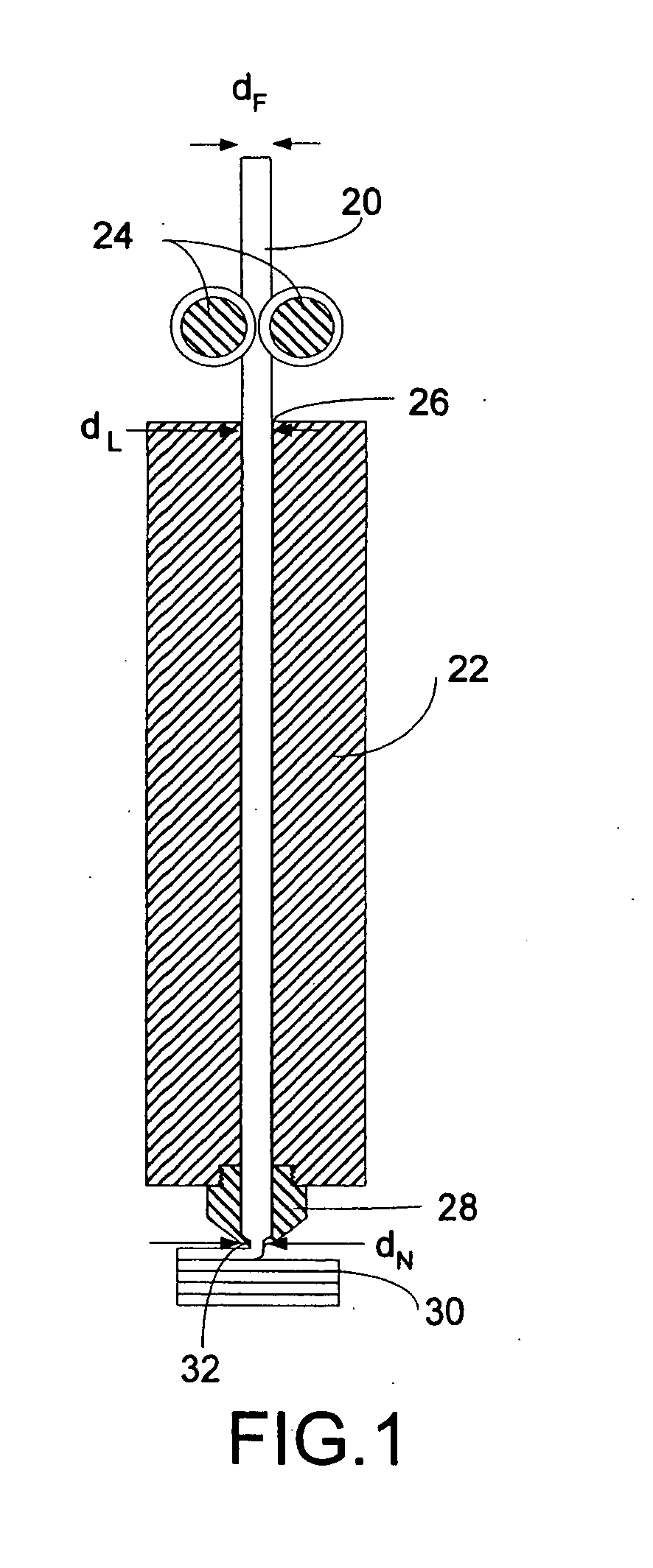
Disclosed is a modeling filament for use as feedstock in a fused deposition modeling liquifier, and a method for manufacturing the filament. The diameter and standard deviation of the filament are controlled to meet various tolerance requirements of jam resistance, slip resistance, model strength, liquifier overflow prevention and hysteresis-free transient response. Standard deviation of the filament diameter is matched to a filament target diameter. The resulting filament is used to form high-quality models.
Owner:STRATSYS INC
Dental restorations formed by solid free-form fabrication methods
InactiveUS6994549B2Manufacture of restorationAdditive manufacturing apparatusImpression capsFree formThin layer
Solid free form fabrication techniques such as fused deposition modeling and three-dimensional printing are used to create a dental restoration. Three-dimensional printing comprises inkjet printing a binder into selected areas of sequentially deposited layers of powder. Each layer is created by spreading a thin layer of powder over the surface of a powder bed. Instructions for each layer may be derived directly from a CAD representation of the restoration. The area to be printed is obtained by computing the area of intersection between the desired plane and the CAD representation of the object. All the layers required for an aesthetically sound restoration can be deposited concurrently slice after slice and sintered / cured simultaneously. The amount of green body oversize is equivalent to the amount of shrinkage which occurs during sintering or curing. While the layers become hardened or at least partially hardened as each of the layers is laid down, once the desired final shaped configuration is achieved and the layering process is complete, in some applications it may be desirable that the form and its contents be heated or cured at a suitably selected temperature to further promote binding of the powder particles.
Owner:JENERICPENTRON
System and method for cutting material in continuous fiber reinforced additive manufacturing
ActiveUS20170144375A1Additive manufacturing with liquids3D object support structuresEngineeringKnife blades
Methods, apparatus, and systems for cutting material used in fused deposition modeling systems are provided, which comprise a ribbon including one or more perforations. Material is passed through at least one perforation and movement of the ribbon cuts the material. A further embodiment comprises a disk including one or more blade structures, each forming at least one cavity. Material is passed through at least one cavity and a rotational movement of the disk cuts the material. A further embodiment comprises a slider-crank mechanism including a slider coupled to a set of parallel rails of a guide shaft. The slider moves along a length of the rails to cut the material. Yet another embodiment comprises one or more rotatable blade structures coupled to at least one rod. The rotation of the blade structures causes the blade structures to intersect and cut extruded material during each rotation.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Use and production of coated filaments for extrusion-based 3D printing processes
ActiveUS20140134335A1Additive manufacturing apparatusFilament manufacturePolymer sciencePrinting press
Owner:EVONIK OPERATIONS GMBH
Solid free-form fabrication methods for the production of dental restorations
Solid free form fabrication techniques such as fused deposition modeling and three-dimensional printing are used to create a shell or die used in the manufacture of a dental restoration. Three-dimensional printing includes ink-jet printing a binder into selected areas of sequentially deposited layers of powder. Each layer is created by spreading a thin layer of powder over the surface of a powder bed. Instructions for each layer may be derived directly from a CAD representation of the restoration. The area to be printed is obtained by computing the area of intersection between the desired plane and the CAD representation of the object. All the layers required for an aesthetically sound shell can be deposited concurrently slice after slice and sintered / cured simultaneously.
Owner:PENTRON LAB TECH
High-precision modeling filament
InactiveUS6866807B2Improve accuracyQuality improvementAdditive manufacturing apparatusMouldsHysteresisEngineering
Disclosed is a modeling filament for use as feedstock in a fused deposition modeling liquifier, and a method for manufacturing the filament. The diameter and standard deviation of the filament are controlled to meet various tolerance requirements of jam resistance, slip resistance, model strength, liquifier overflow prevention and hysteresis-free transient response. Standard deviation of the filament diameter is matched to a filament target diameter. The resulting filament is used to form high-quality models.
Owner:STRATSYS INC
Method for manufacturing metal parts and molds and micro-roller used therefor
ActiveUS20130197683A1Formability of complexImprove accuracyArc welding apparatusAdditive manufacturing with liquidsNumerical controlWire rod
A method for manufacturing parts and molds by: 1) slicing a three-dimensional CAD model of a part or mold; 2) planning a modeling path according to slicing data of the three-dimensional CAD model, whereby generating numerical control codes for modeling processing; and 3) performing fused deposition modeling of powders or wire material of metal, intermetallic compounds, ceramic and composite functional gradient materials by layer using a welding gun on a substrate layer via a numerical control gas shielded welding beam or laser beam according to a track specified by the numerical control code for each layer. A micro-roller or a micro-extrusion unit is installed at a contact area between melted and softened areas. The micro-roller or the micro-extrusion unit synchronously moves along with fused deposition area, which results in compressing and processing of the fused deposition area during the fused deposition modeling.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
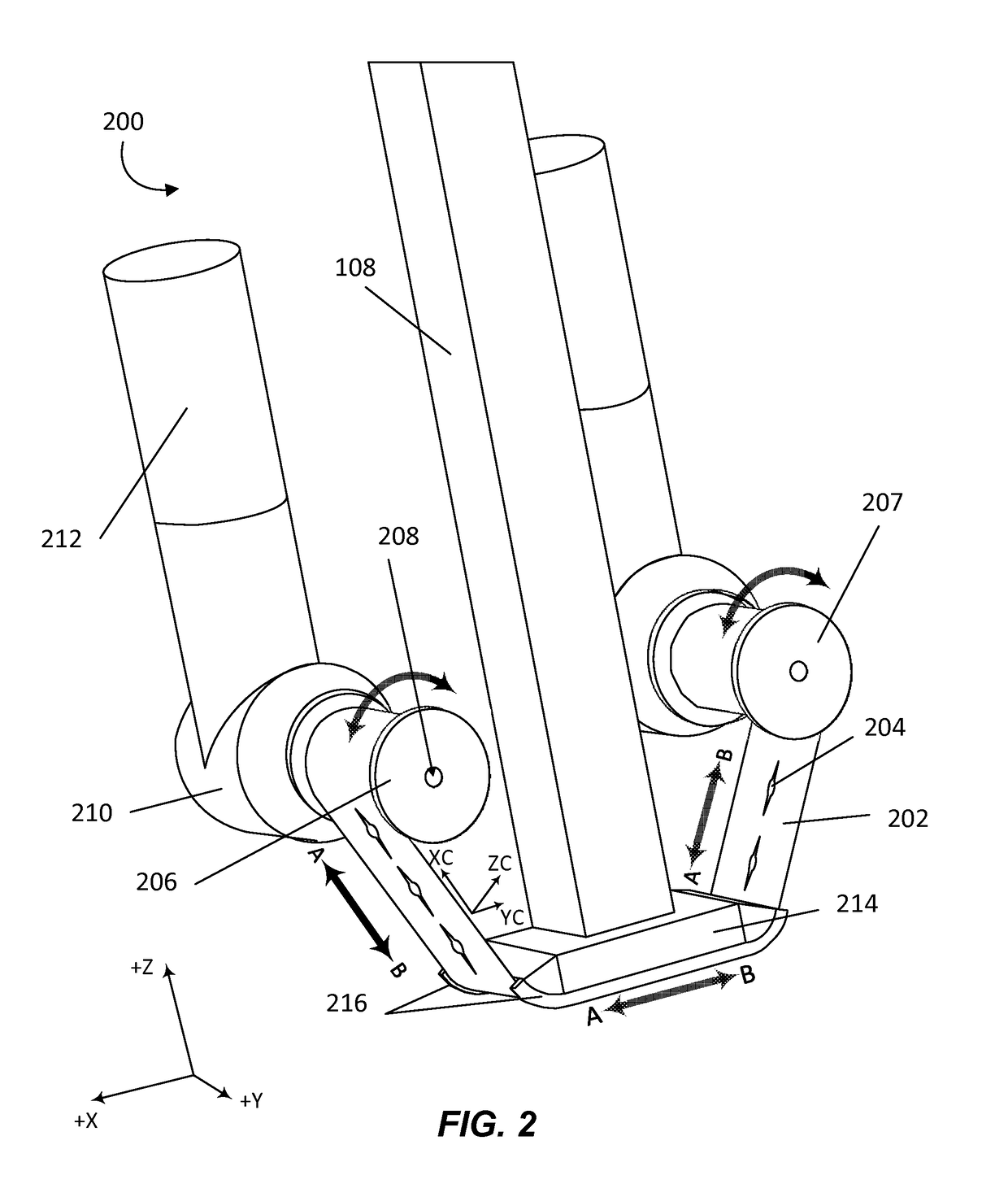
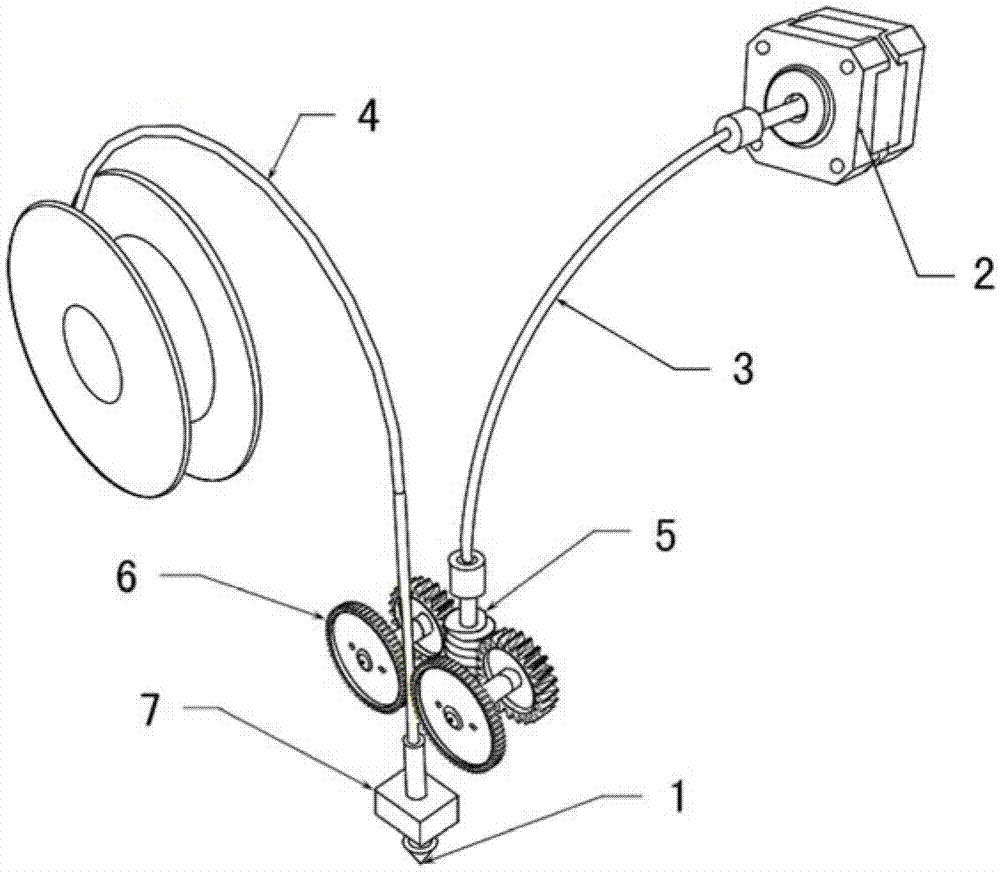
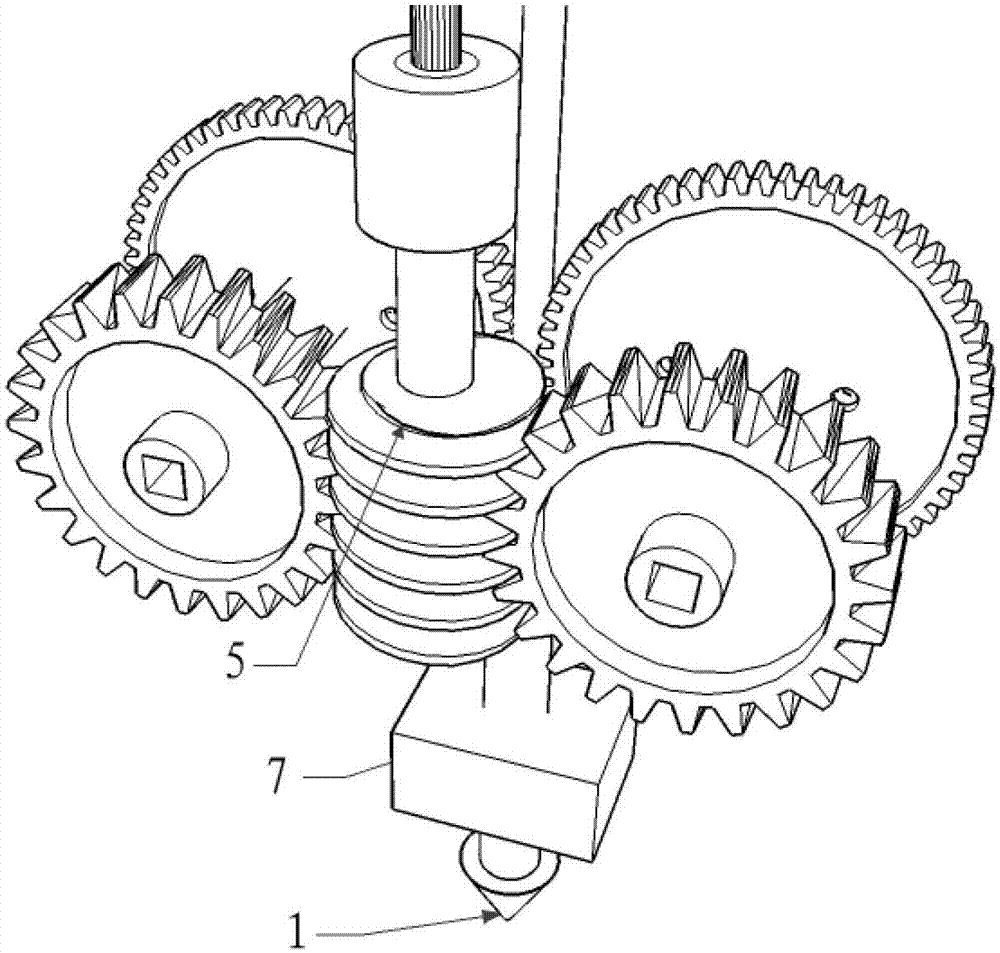
Extrusion device applied to fused deposition modeling high speed 3D (Three Dimensional) printer
The invention relates to an extrusion device applied to a fused deposition modeling high speed 3D (Three Dimensional) printer, which belongs to the technical field of 3D printing. The extrusion device comprises an extrusion nozzle, a wire feeding module and a stepping motor, wherein the wire feeding module conveys a printing wire to the extrusion nozzle for extruding under the drive of the stepping motor. The wire feeding module and the extrusion nozzle form a printing travelling mechanism, the stepping motor is fixedly arranged on the high speed 3D printer, an output shaft of the stepping motor is connected to the wire feeding module via a motor driving flexible shaft, and the stepping motor does not follow up the motion of the printing travelling mechanism, so that the whole weight of the printing travelling mechanism is reduced effectively and the printing travelling mechanism can run fast, and simultaneously the extrusion precision and the even extrusion pressure of the extrusion device are ensured. The extrusion device which is applied to a fused deposition modeling high speed 3D printer and provided by the invention has a simple structure and a convenient use-pattern and is low in cost.
Owner:PANOWIN TECH
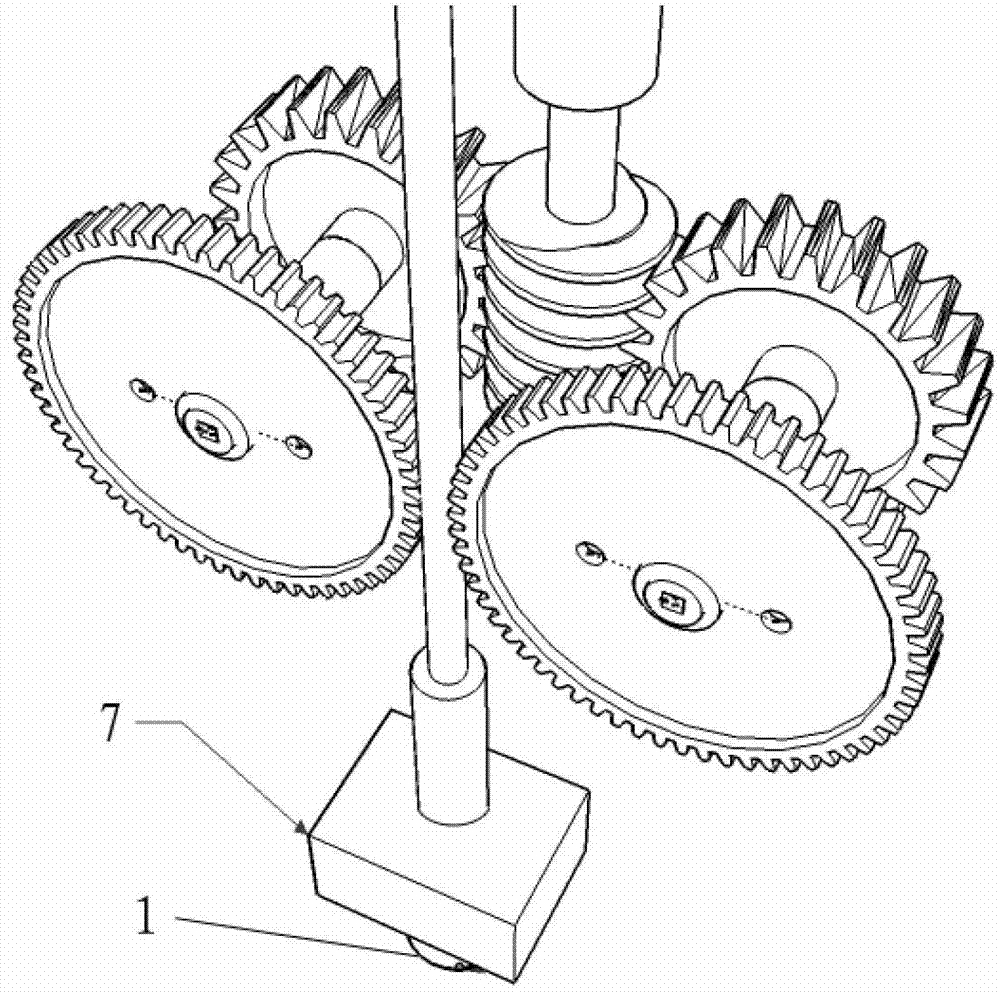
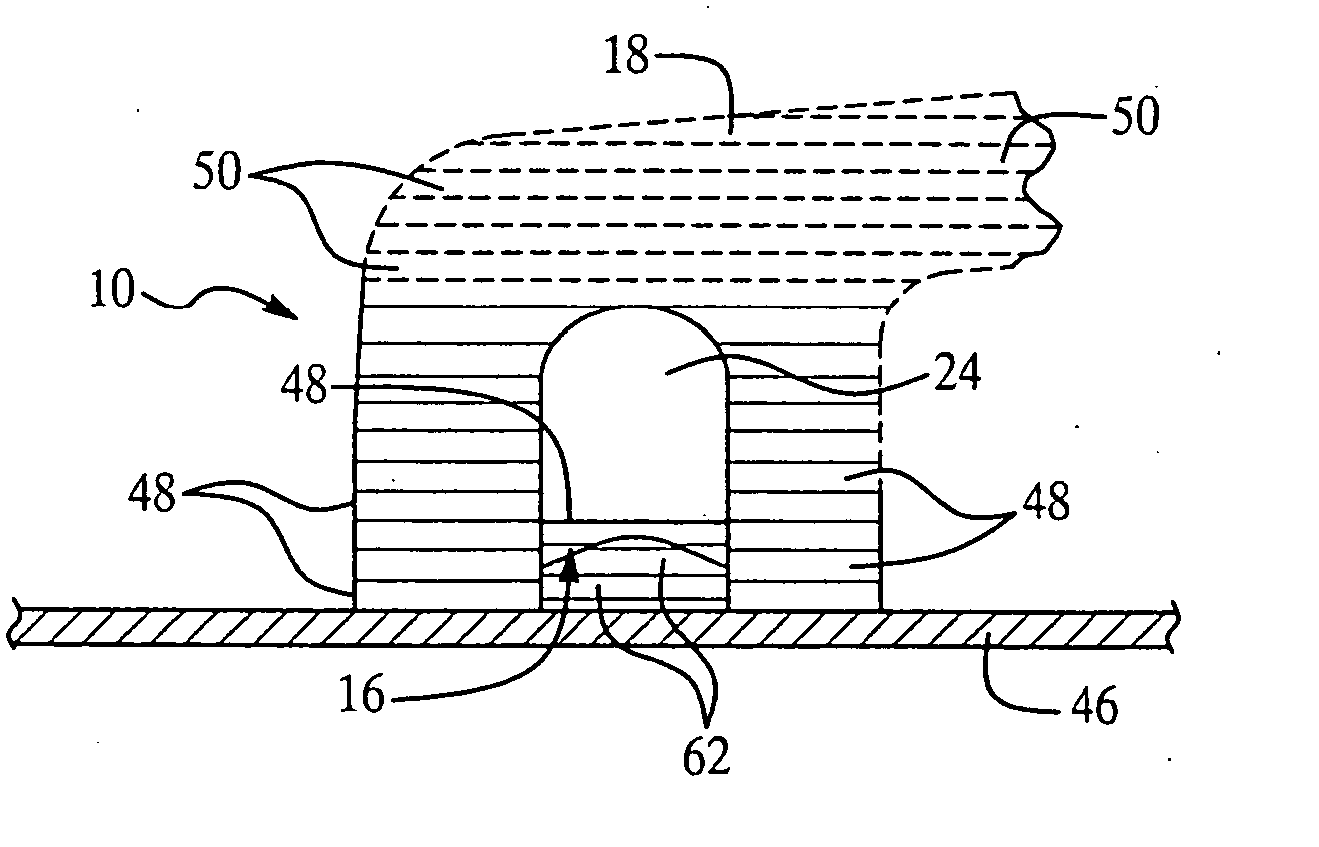
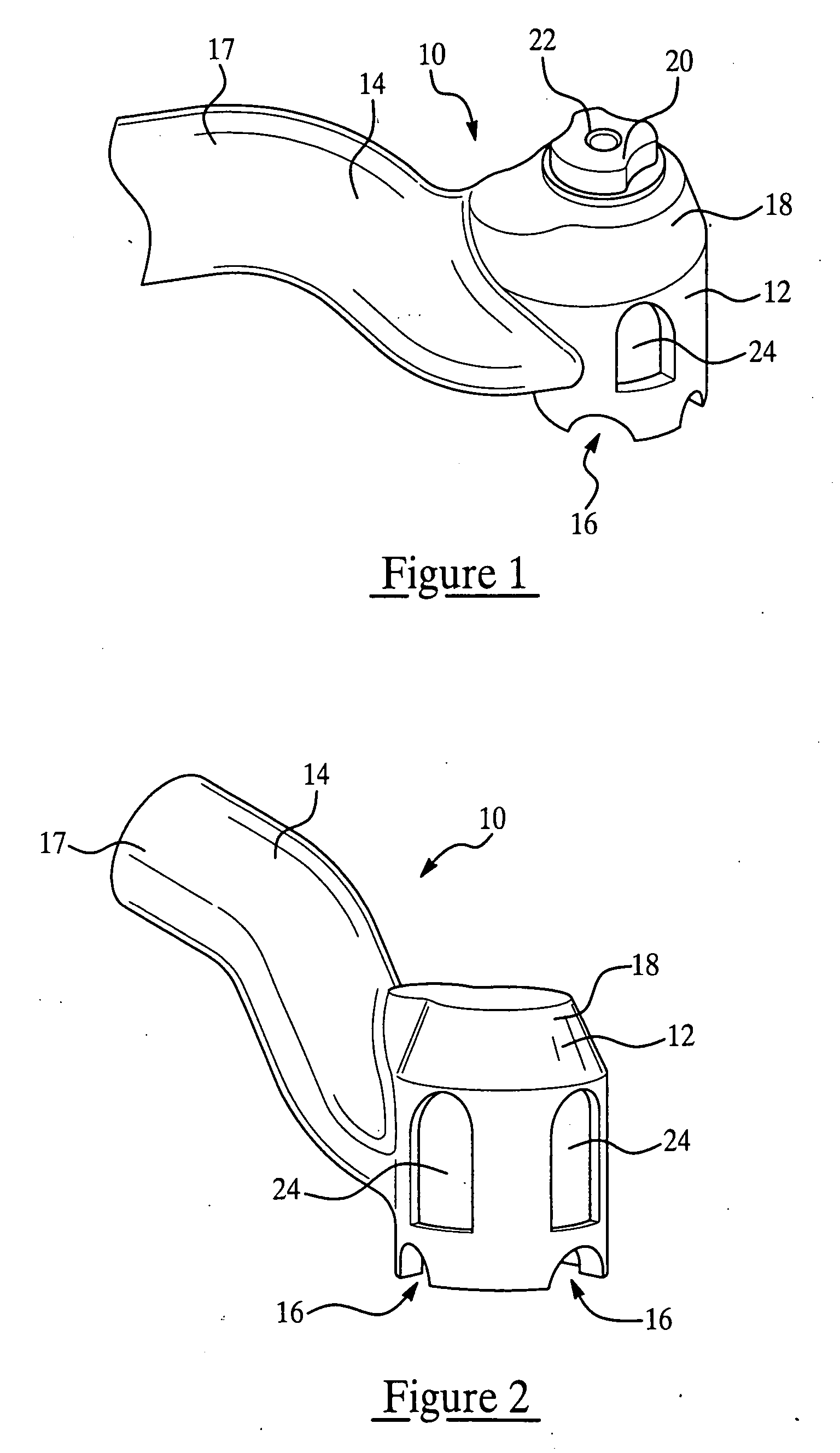
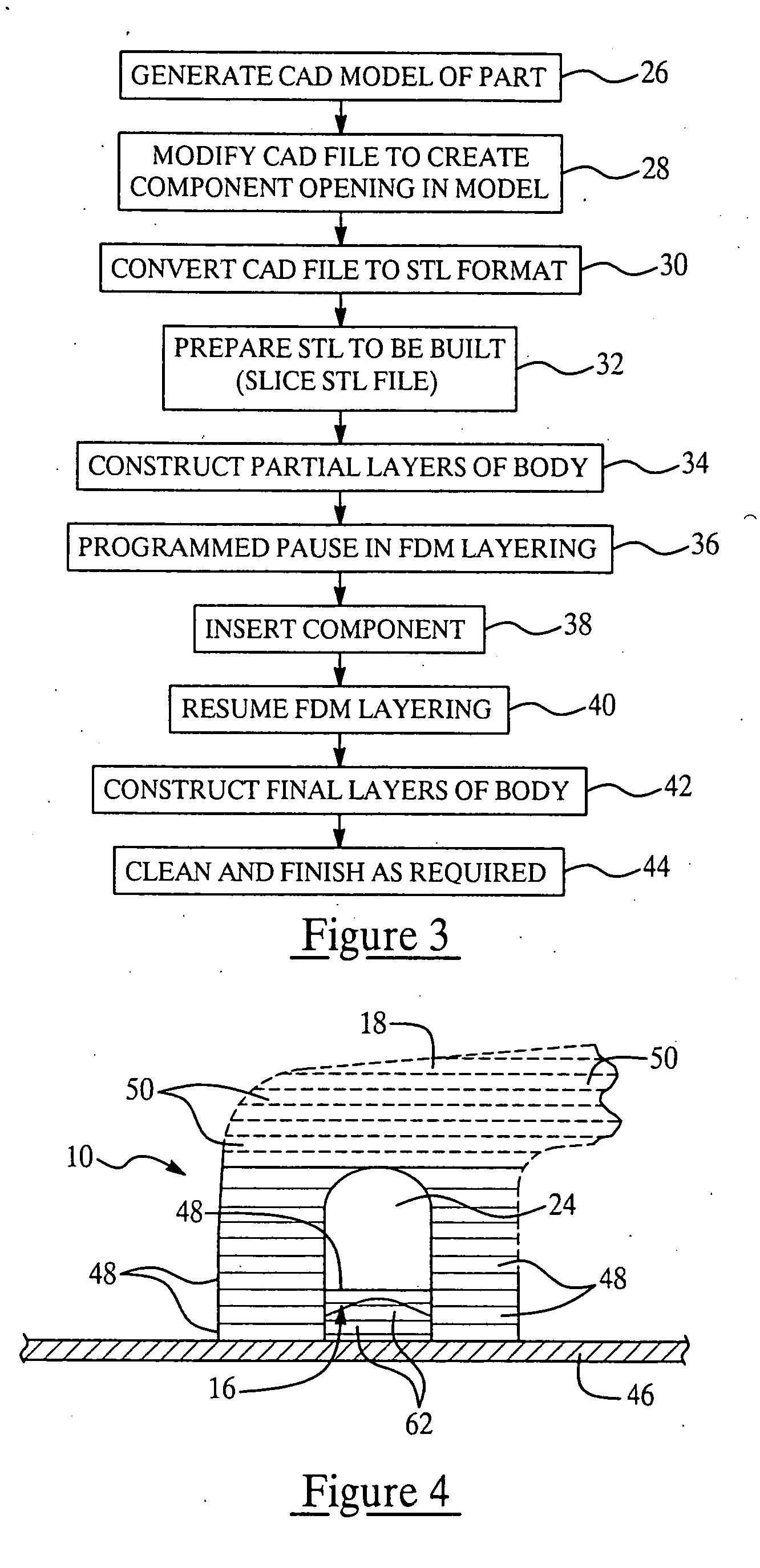
Rapid part fabrication employing integrated components
InactiveUS20070071902A1Additive manufacturing apparatusLiquid surface applicatorsFree formEngineering
A part having an integrated, discrete component is produced by direct digital manufacturing and rapid, solid free-form fabrication techniques. A CAD file representing the part is modified to include an opening in the body of the part in which the component is to be inserted. The fabrication is performed by additive layering of a thermoplastic material, preferably using fused deposition modeling or stereolithography. The layering process is interrupted to allow the component to be inserted in the partially formed part, following which additional layers are added which secure the component in the part in place and complete the physical structure of the part.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Selective deposition modeling method and apparatus for forming three-dimensional objects and supports
InactiveUS20010003004A1Less distortionAdditive manufacturing apparatusConfectioneryEngineeringSelective deposition
Owner:3D SYST INC
Three-dimensional bioresorbable scaffolds for tissue engineering applications
InactiveUS8071007B1Biocompatibility hardHard integrationAdditive manufacturing apparatusCeramic shaping apparatusBiocompatibility TestingHard tissue
The invention relates to the use of Fused Deposition Modeling to construct three-dimensional (3D) bioresorbable scaffolds from bioresorbable polymers such as polycaprolactone (PCL), or from composites of bioresorbable polymers and ceramics, such as polycaprolactone / hydroxyapatite (PCL / HA). Incorporation of a bioresorbable ceramic to produce a hybrid / composite material support provides the desired degradation and resorption kinetics. Such a composite material improves the biocompatibility and hard tissue integration and allows for increased initial flash spread of serum proteins. The basic resorption products of the composite also avoids the formation of an unfavorable environment for hard tissue cells due to a decreased pH. The scaffolds have applications in tissue engineering, e.g., in tissue engineering bone and cartilage.
Owner:OSTEOPORE INT PTE
Addititve manufacturing of components for downhole wireline, tubing and drill pipe conveyed tools
InactiveUS20130310961A1Additive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyDirect metal laser sinteringSelective laser sintering
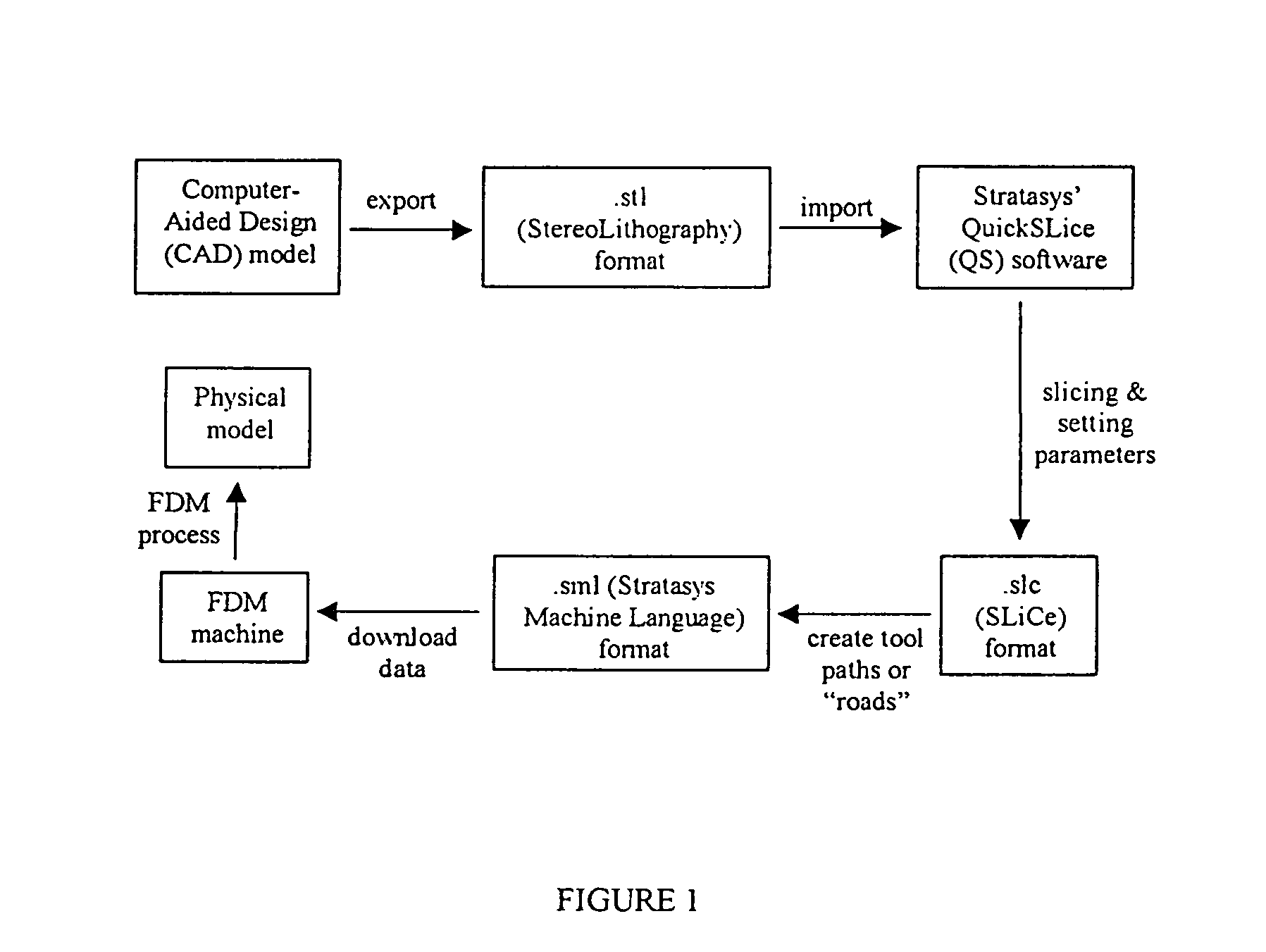
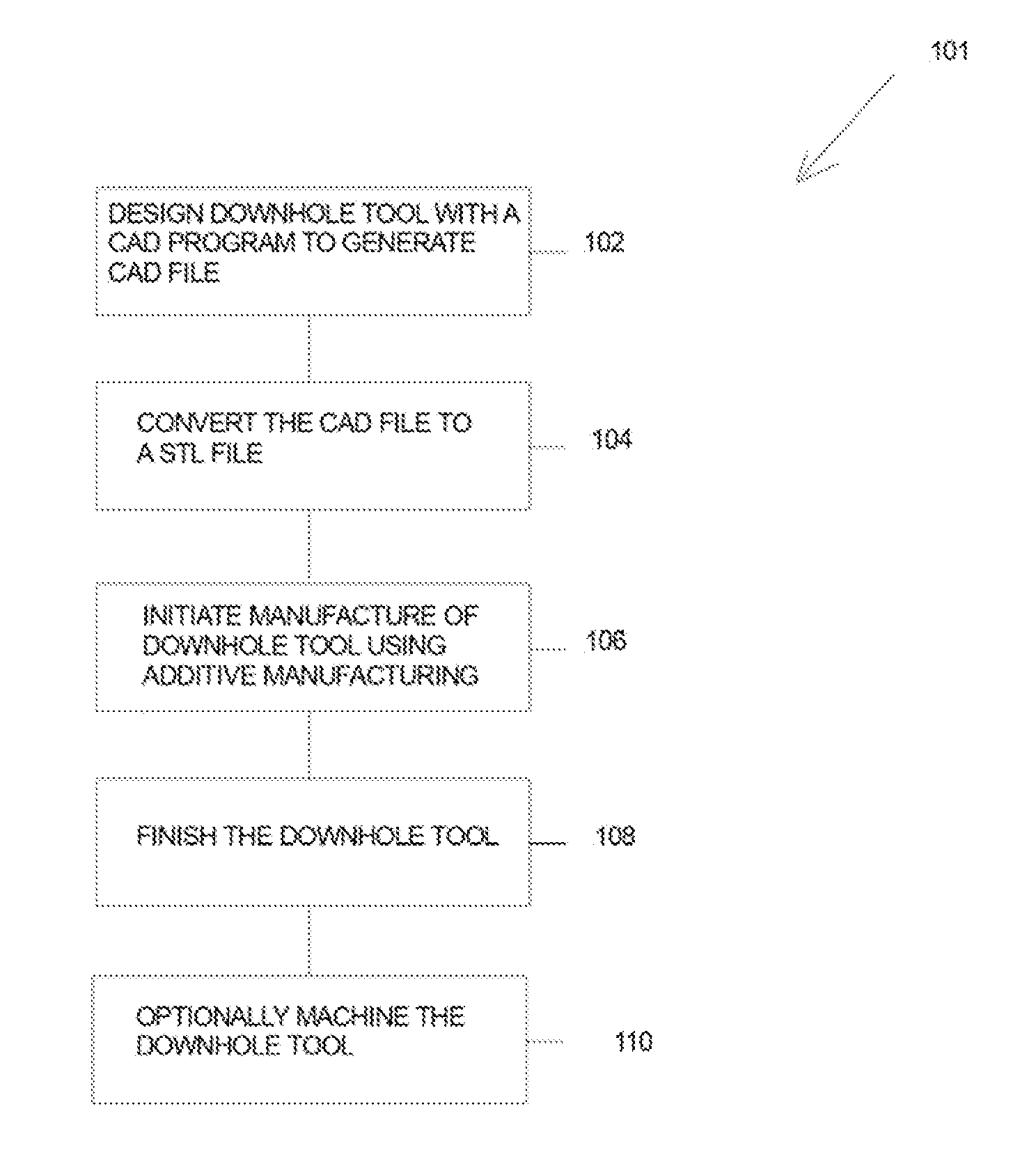
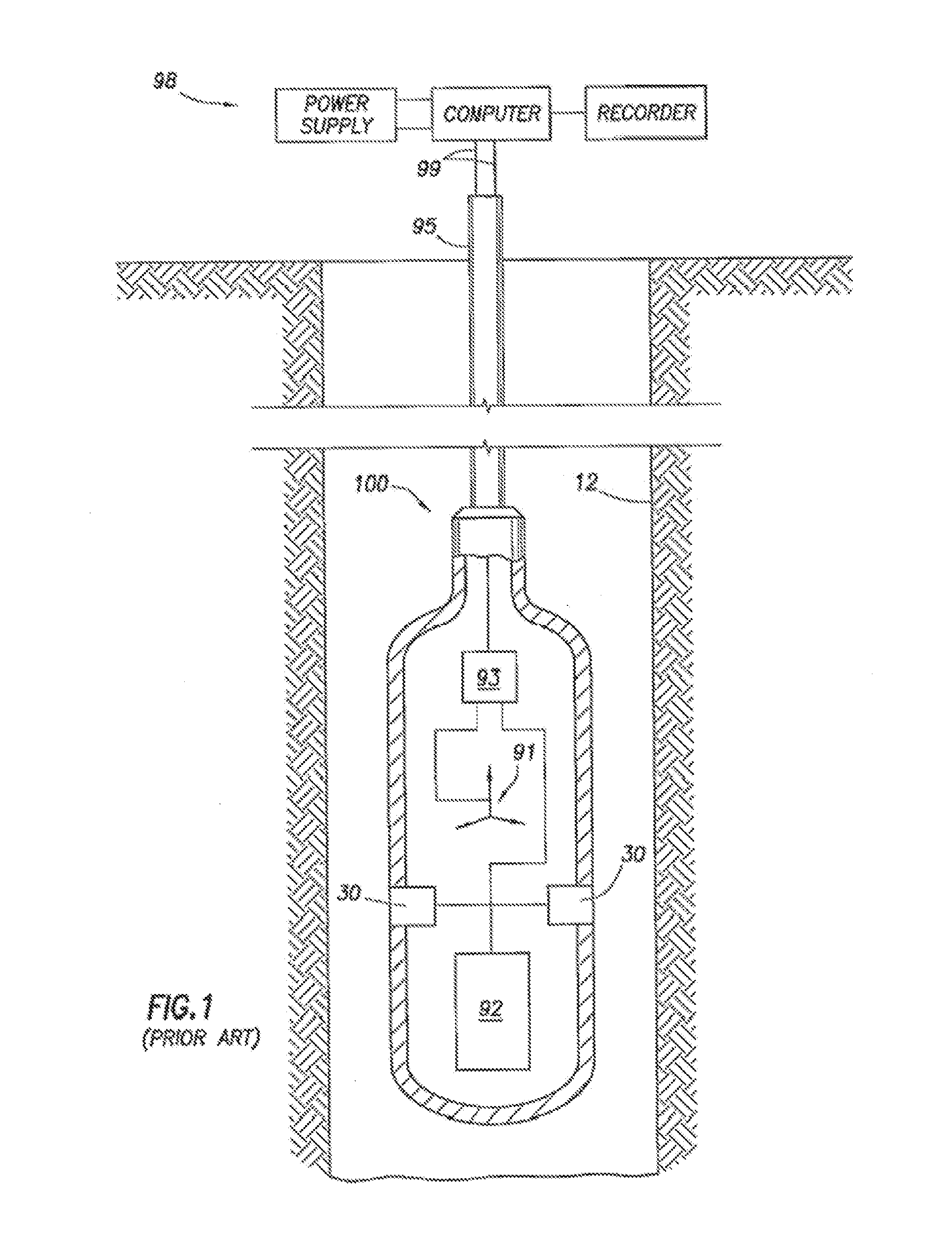
Additive manufacturing may be used to manufacture components of downhole tools conveyed by downhole wireline, tubing, drill pipe and / or the like. A method in accordance with one or more aspects of the disclosure uses starting materials to incorporate one or more feedthroughs, passages, channels, chambers and the like in a downhole tool structure during the formation of the structure. A CAD may be made and then converted to a STL file, and then stereo lithography, selective laser sintering, fused deposition modeling, direct metal laser sintering and / or electron beam melting may be used to form the downhole tool. Subtractive manufacturing may be performed on the downhole tool after the downhole tool is formed by additive manufacturing.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
A thermoplastic material used for three-dimensional printing and an application method thereof
InactiveCN104163634ABroaden the field of 3D printing preparationBroaden the field of preparationCeramic shaping apparatusPolymer scienceMetallic materials
A thermoplastic material used for three-dimensional printing is disclosed. The thermoplastic material comprises inorganic powder and thermostatic resin. The weight of the inorganic powder is 60-99.9% of the total weight. The weight of the thermostatic resin is 0.1-40% of the total weight. The inorganic powder is ceramic powder or metal powder or ceramic-metal composite powder. An application method of the thermostatic material is also disclosed. The thermoplastic material and the application method provide more printing material choices for the three-dimensional printing technology, and achieve preparation of a three-dimensional structure of a ceramic material, a metal material, or ceramic-metal composites by utilization of the fused deposition modeling three-dimensional printing technology.
Owner:NO 55 INST CHINA ELECTRONIC SCI & TECHNOLOGYGROUP CO LTD
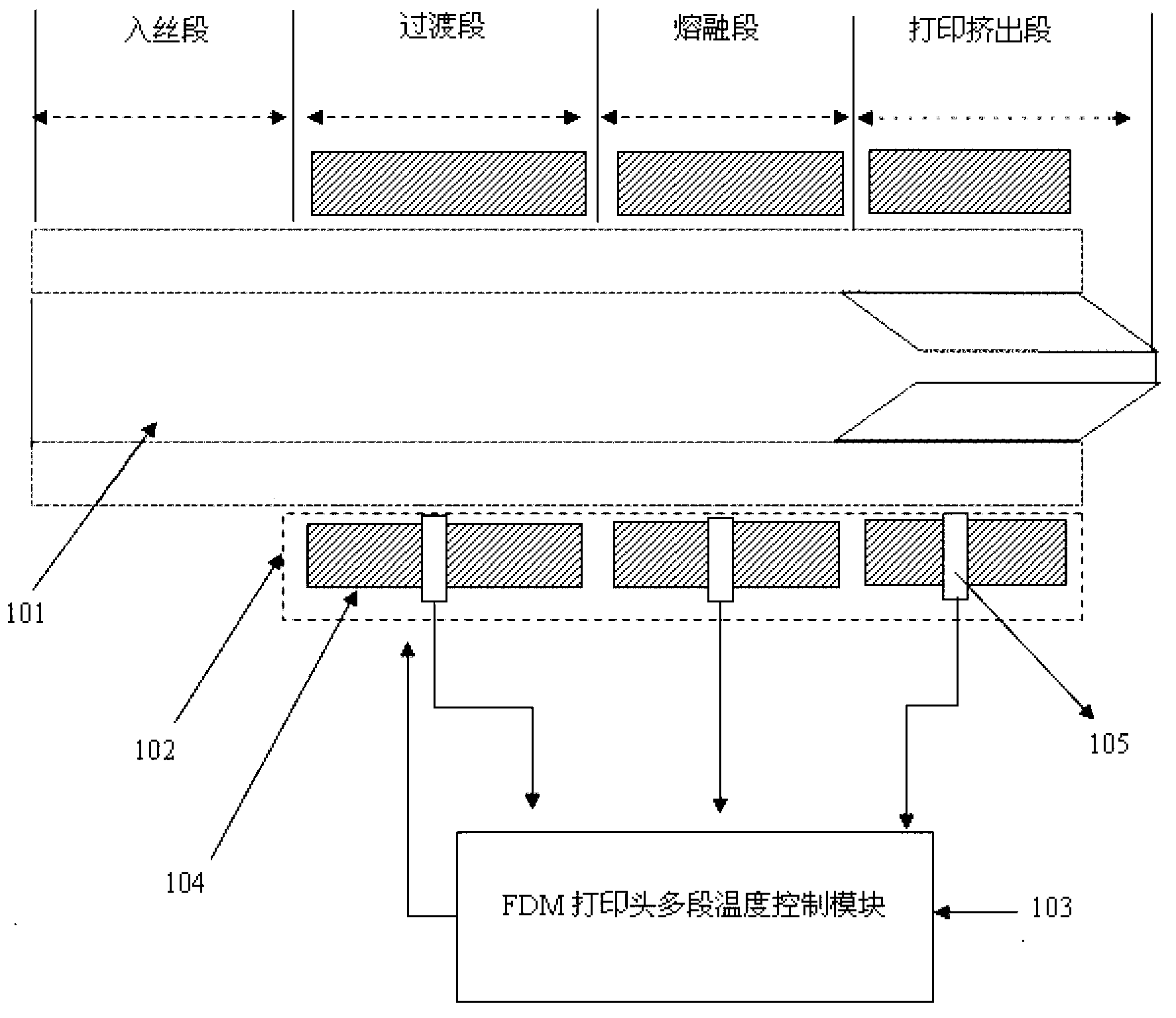
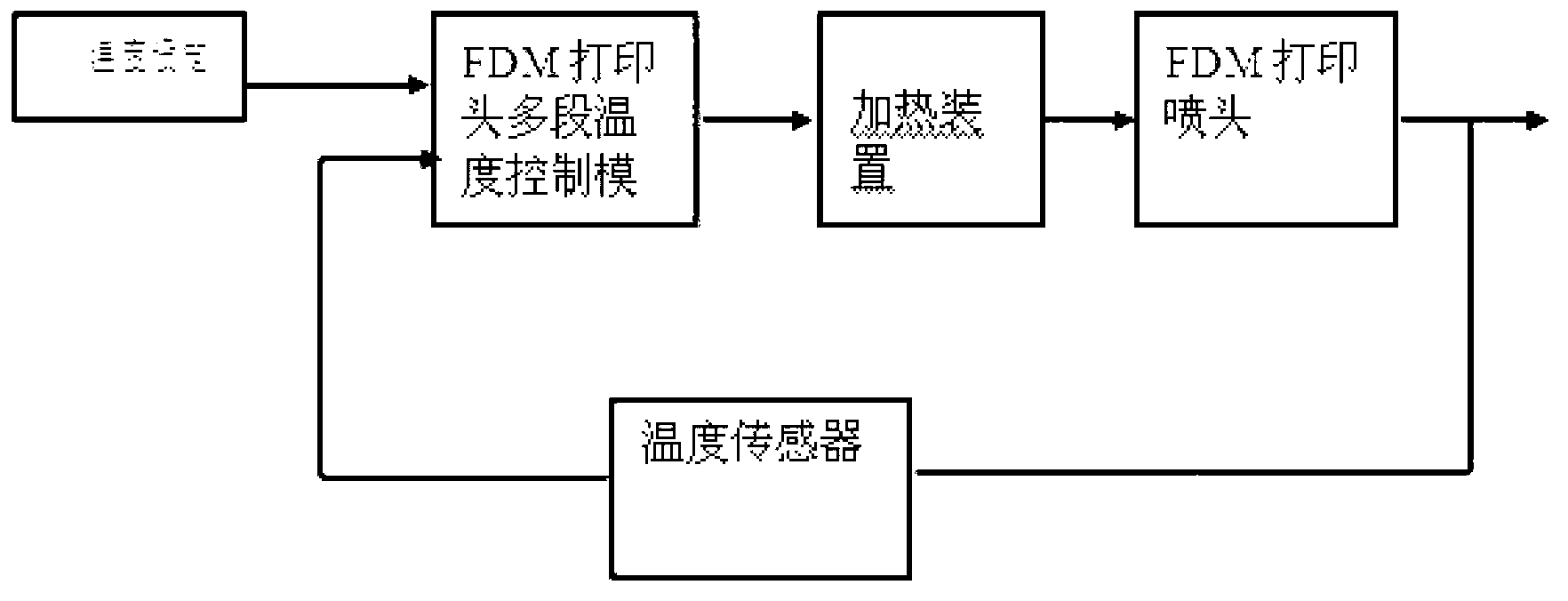
Multistage-temperature-control-based fused deposition modeling (FDM) type 3D printing sprayer and temperature control method
The invention relates to a 3D printing technology, and aims at providing a multistage-temperature-control-based fused deposition modeling (FDM) type 3D printing sprayer and a temperature control method. The multistage-temperature-control-based FDM 3D printing sprayer comprises a printing sprayer body and a heating device arranged at the outer part of the printing sprayer body, and is characterized in that a forming chamber inside the printing sprayer body is divided into four parts of a fuse feeding section, a transition section, a fusion section and a printing and extruding section; the heating device is divided into three sections which are correspondingly arranged at the outer sides of the transition section, the fusion section and the printing and extruding section of the forming chamber, and each section of the heating device comprises an electric heater and a temperature sensor which are independent and is respectively connected with a multistage temperature control module of an FDM type printing sprayer through a signal wire. The multistage-temperature-control-based FDM type 3D printing sprayer is capable of realizing the corresponding gradient control of temperatures of all sections of the printing sprayer and ensuring that an FDM printing material is always kept in a printable state, and can not cause the problems of layer collapse, damage and blockage due to overhigh or overlow temperature due to the adoption of single temperature control; and meanwhile, the blockage and the fracture of a wire of a conventional printing head are avoided, and the quality of formed products is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
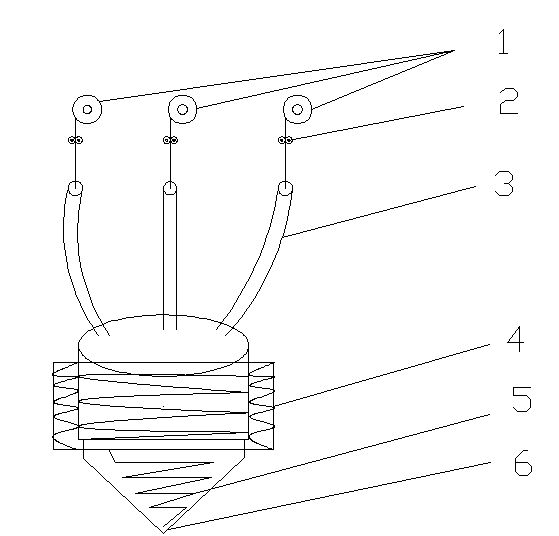
Colored 3D (Three Dimensional) printing equipment using fused deposition modeling method
InactiveCN103895228ARich printing applicationsCan only print monochromeAdditive manufacturing apparatus3D object support structuresControl systemColored
The invention provides colored 3D (Three Dimensional) printing equipment using a fused deposition modeling method. The colored 3D printing equipment comprises three sets of feeding mechanisms for filamentary raw materials with red, yellow and blue base colors, a material mixing heater (4), a static / dynamic pipeline material mixer (5), a replaceable type printing nozzle (6), a three-dimensional motion molding platform (7) with a heating function and an equipment control system, wherein the feeding mechanisms are composed of a discharging scroll (1), a stepping type motor feeding machine (2) and a feeding guide pipe (3). The colored 3D printing equipment is characterized in that a three-primary-color principle is utilized, namely the red, yellow and blue colors are mixed according to a proper ratio to obtain nearly all colors in the natural world; thermoplastic raw material fused wires or powder with the red, yellow and blue colors can be heated and mixed according to different ratios to form different colored printing materials, and then the fused deposition modeling (FDM) method is used for carrying out 3D printing to obtain a colored product. The colored 3D printing equipment has the beneficial effects that the disadvantage that a current colored 3D printing equipment using the fused deposition modeling method only can be used for printing a single-color or double-color product is overcome; the post-period coloring and processing time of the product is shortened, the working efficiency is improved and a 3D printing application is enriched.
Owner:王利民
Method for three-dimensional modeling
InactiveUS7314591B2Easy to disassembleImprove thermal stabilityProgramme controlAdditive manufacturing apparatusResistDimensional modeling
A three-dimensional model and its support structure are built by fused deposition modeling techniques, wherein a thermoplastic material containing silicone is used to form the support structure and / or the model. The thermoplastic material containing silicone exhibits good thermal stability, and resists build-up in the nozzle of an extrusion head or jetting head of a three-dimensional modeling apparatus. The silicone contained in a support material acts as a release agent to facilitate removal of the support structure from the model after its completion.
Owner:STRATSYS INC
Layered deposition bridge tooling
InactiveUS20060001190A1Solve Porosity InsufficiencyAdditive manufacturing apparatusAdditive manufacturing with liquidsFilling materialsInjection molding machine
Disclosed is a method for making a prototype plastic injection molded part from a mold tool (10) built by fused deposition modeling. The mold too (10)l is built by depositing roads of a molten thermoplastic resin in layers in a predetermined pattern defined by computer file data representing the inverse of the desired prototype molded part, and is used in an injection molding machine without the addition of any reinforcement fill material or layers to create the prototype part. The disclosed method provides prototype plastic injection molded parts within a twenty-four hour time period.
Owner:STRATSYS INC
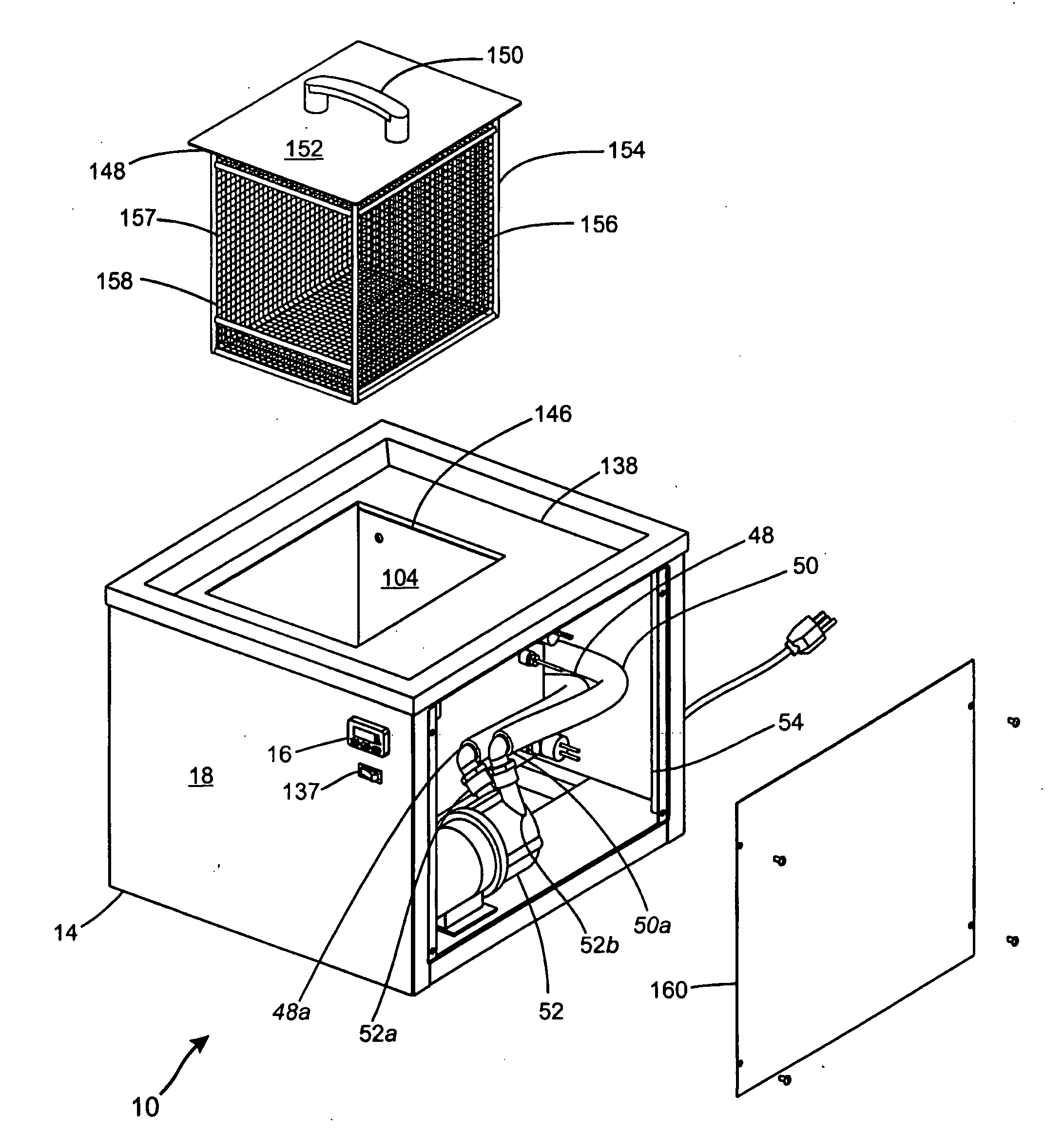
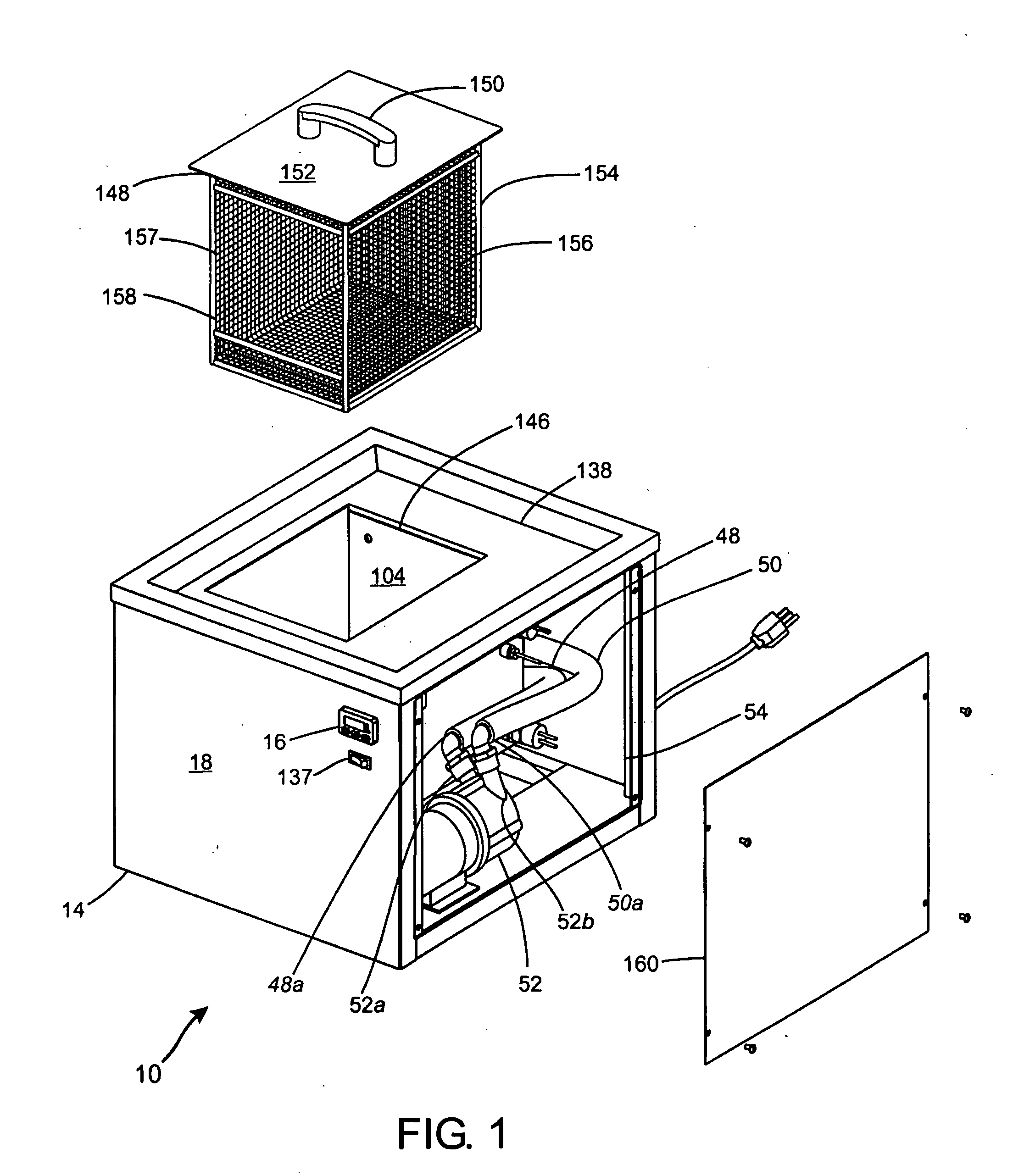
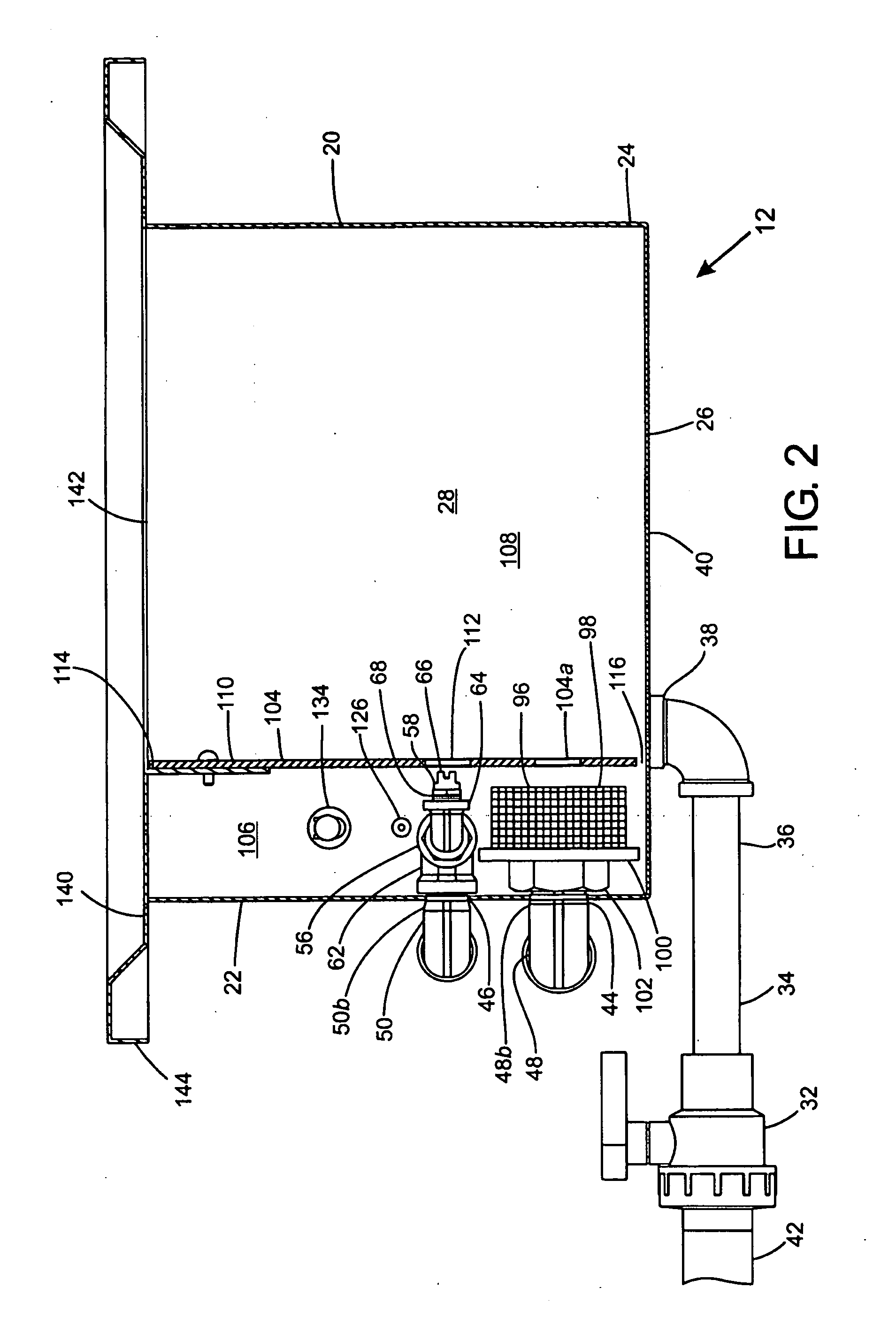
Removing Soluble Support Material From Rapid Prototype Part
ActiveUS20090241997A1Additive manufacturing apparatusHollow article cleaningFused deposition modelingBiomedical engineering
A container has been devised for use with a rapid prototype part making machine, specifically of the type having Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) capabilities. The container includes a liner that has an exterior surface and that is expandable to define a mouth portion and a volume for receiving, via the mouth portion, a rapid prototype part having soluble support material deposited on the rapid prototype part. An inlet port is formed on the exterior surface and is in fluid communication with the volume. An outlet port is formed on the exterior surface and is in fluid communication with the volume. A sealing arrangement is configured and arranged to selectively substantially prevent egress of an aqueous cleaning solution from the mouth portion of the liner. The inlet port is configured to introduce the aqueous cleaning solution into the volume to remove the soluble support material from the rapid prototype part.
Owner:TAFOYA DAVID JONATHAN
Method for preparing biodegradable polymer self-expansion type intravascular stent based on 3D printing technology
InactiveCN105771003AImprove long-term patencyAvoid axial shorteningSurgeryPharmaceutical delivery mechanismBiocompatibility TestingBiodegradable polymer
The invention relates to a method for preparing a biodegradable polymer self-expansion type intravascular stent based on 3D printing technology.The method includes the specific steps of synthesizing polylactic acid-based shape-memory polyurethane / Fe304 nanocomposite material with good biocompatibility and biodegradability, and making the composite material into the intravascular stent through the Fused Deposition Modeling technology.In addition, in order to increase the blood vessel endothelium repair speed, sirolimus, heparin, endothelial growth factors or the like are selectively introduced to the stent surface through electrostatic spinning.A 'time'dimension is added for the shape-memory function of the base material, and combined with the 3D printing technology, a 4D forming concept is given to the stent.By means of the magnetocaloric effect of Fe304, shape recovery of the shape-memory polymer can be remotely excited, so that the intravascular stent expands automatically, balloon dilatation is not required during stent implantation, axial shortening during balloon dilatation and radial resilience during withdraw of the stent are avoided, and damage of blood vessels is reduced to a minimum level.In addition, the introduction of Fe304 solves the problem that a polymer stent has poor development.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Mass production of shells and models for dental restorations produced by solid free-form fabrication methods
InactiveUS20050110177A1Improve bindingAdditive manufacturing apparatusImpression capsFree formThin layer
Solid free form fabrication techniques such as fused deposition modeling and three-dimensional printing are used to create a shell used in the manufacture of a dental restoration. Three-dimensional printing includes ink-jet printing a binder into selected areas of sequentially deposited layers of powder. Each layer is created by spreading a thin layer of powder over the surface of a powder bed. Instructions for each layer may be derived directly from a CAD representation of the restoration. The area to be printed is obtained by computing the area of intersection between the desired plane and the CAD representation of the object. All the layers required for an aesthetically sound shell can be deposited concurrently slice after slice and sintered / cured simultaneously. While the layers become hardened or at least partially hardened as each of the layers is laid down, once the desired final shaped configuration is achieved and the layering process is complete, in some applications it may be desirable that the form and its contents be heated, cooled or cured at a suitably selected temperature to further promote the integrity of solid free-form structures.
Owner:PENTRON LAB TECH
Three-dimensional bioresorbable scaffolds for tissue engineering applications
ActiveUS7968026B1Good biocompatibilityImproves hard tissue integrationAdditive manufacturing apparatusMouldsBiocompatibility TestingHard tissue
The invention relates to the use of Fused Deposition Modeling to construct three-dimensional (3D) bioresorbable scaffolds from bioresorbable polymers such as polycaprolactone (PCL), or from composites of bioresorbable polymers and ceramics, such as polycaprolactone / hydroxyapatite (PCL / HA). Incorporation of a bioresorbable ceramic to produce a hybrid / composite material support provides the desired degradation and resorption kinetics. Such a composite material improves the biocompatibility and hard tissue integration and allows for increased initial flash spread of serum proteins. The basic resorption products of the composite also avoids the formation of an unfavorable environment for hard tissue cells due to a decreased pH. The scaffolds have applications in tissue engineering, e.g., in tissue engineering bone and cartilage.
Owner:OSTEOPORE INT PTE
No-mold fusion stacking manufacture method of parts or mold
InactiveCN101362272AReduce or eliminate dropReduce or eliminate droolingWelding/cutting auxillary devicesArc welding apparatusNumerical controlMelting tank
The invention relates to a method for die-free fused deposition modeling of a part or a die, which belongs to the method of die-free modeling, and solves the problems of falling, flowing and collapsing of fusing material in the process of support-free and die-free fused deposition modeling of the existing method. The method comprises the following steps: (1) hierarchy slicing processing is performed to the three-dimensional CAD model of the part or the die; (2) a computer generates numerical control codes required by the shaping of each hierarchy according to the hierarchy slicing data and the characteristics of the slicing size and shape of each hierarchy; and (3) numerically controlled gas-shielded welding arc or laser bean is adopted to fuse and shape the fusing material on the base plate in sequence according to the numerical control codes of each hierarchy, until the requirements on the size and the surface of the part or the die are met; simultaneously, electromagnetic field acting on the fusing material in the melting bath is generated through an electromagnetic device. By adopting the method, the part or the die made of metal, intermetallic compound, metal ceramics, ceramics and functionally gradient material can be quickly obtained with low cost and high quality.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Material and method for three-dimensional modeling
Owner:STRATSYS INC
Copolyester thermoplastic material used for three-dimensional printing, and preparation and application thereof
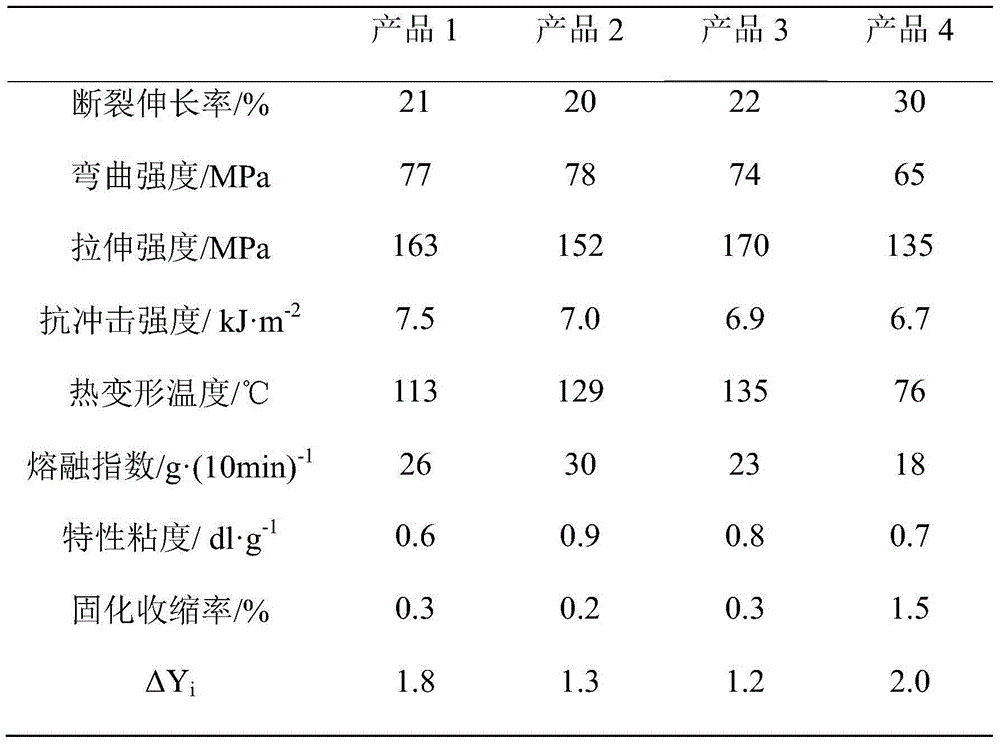
The invention provides a copolyester thermoplastic material used for three-dimensional printing and preparation and application thereof. The copolyester thermoplastic material is mainly prepared from monomers of the raw materials consisting of, by mass, 35 to 48 parts of dicarboxylic acid, 30 to 43 parts of dihydric alcohol, 8 to 15 parts of acrylate and 7 to 15 parts of a spiro-compound through copolymerization in the presence of a catalyst. The invention has the following main beneficial effects: the copolyester high-molecular material prepared in the invention has good mechanical properties and machinability, is a good thermoplastic material and has a wide application scope; high temperature resistance and moisture resistance of the material are substantially improved compared with those of traditional products, and the material has good weatherability; the material has small shrinkage, adhesion among different layers is strong, a product manufactured from the material does not suffer interlayer stripping and warping, so the material is an ideal three-dimensional printing material and is especially applicable to fused deposition modeling (FDM) technology.
Owner:HANGZHOU FIRST APPLIED MATERIAL CO LTD
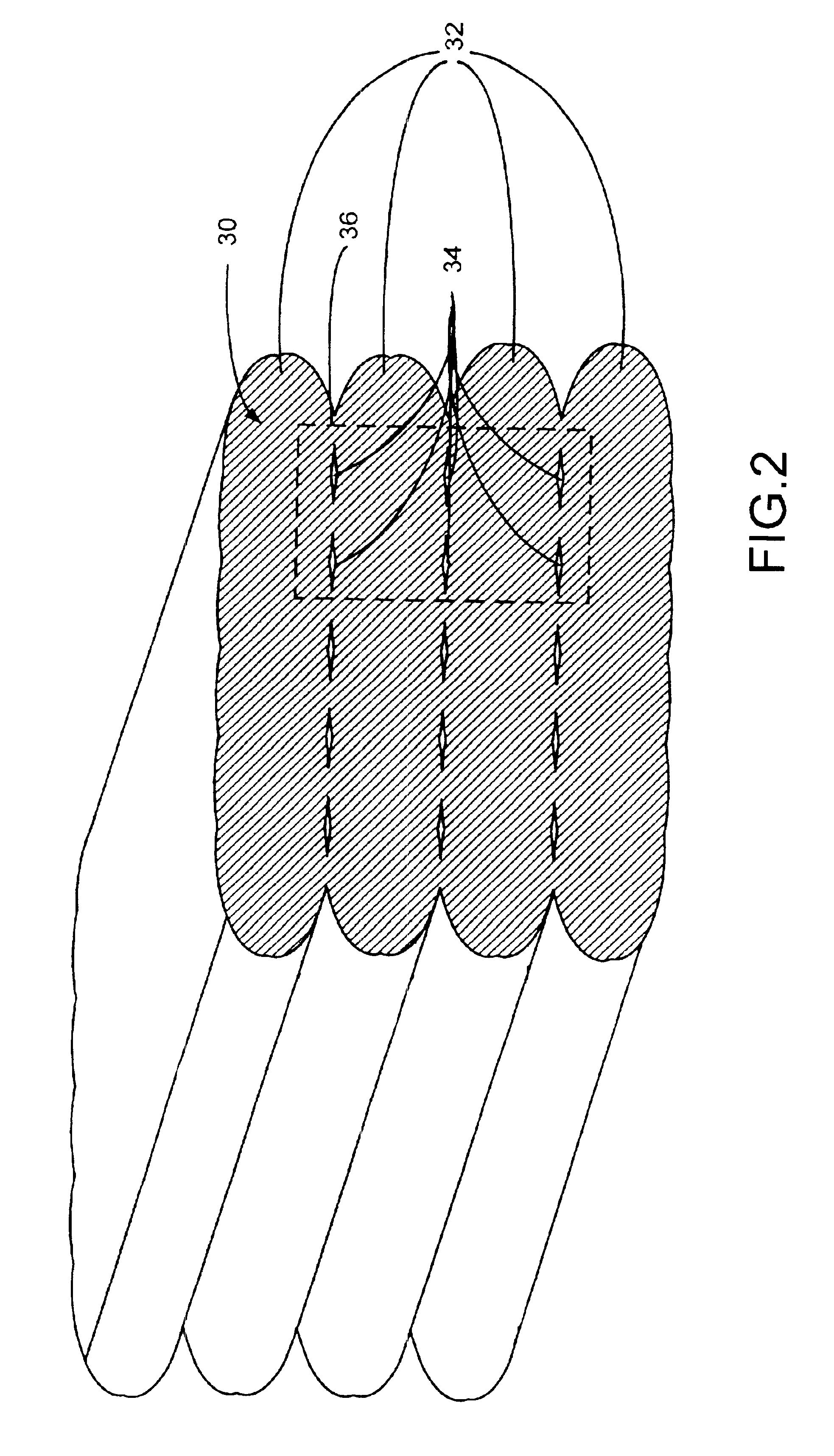
Supporting module for fused deposition modeling three-dimensional printing and generating method of supporting module
InactiveCN105058798AReduce the difficulty of dismantlingReduce spacingAdditive manufacturing apparatusFixation pointComputer module
The invention discloses a supporting module for fused deposition modeling three-dimensional printing and a generating method of the supporting module. The supporting module is used for supporting the suspended portion of a model needing three-dimensional printing. The supporting module comprises multiple supporting units arranged at intervals to provide multiple fixation points for the suspended portion. Compared with an original supporting module, the supporting module can be more easily removed from the suspended portion of the model while the supporting performance is kept.
Owner:PANOWIN TECH
Six-channel aggregation-fusion type squeezing nozzle for fused deposition modeling type color three-dimensional printer
ActiveCN104742364AHigh thermal efficiency utilizationImprove energy efficiencyComputer printingControl system
The invention discloses a six-channel aggregation-fusion type squeezing nozzle. The squeezing nozzle is provided with six thread inlets and one thread outlet and is suitable for a fused deposition modeling type (FDM) all-true color three-dimensional printer control system capable of achieving precision printing. Raw material printing threads of each color can be fused without a temperature difference in a nozzle aggregation fusion mixing and stirring cavity in a process of printing a color three-dimensional stereoscopic workpiece, the colored threads are extruded, a thread outlet caliber can be changed, and printing, all true color and high precision can be achieved. Accordingly, the mechanical strength of the printed workpiece reaches the mechanical strength index of the material, maintenance and replacement are convenient, resources are saved, energy consumption is reduced, the cost is reduced, and the nozzle is simple in structure, stable and reliable.
Owner:辽宁重彩立体打印机有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com