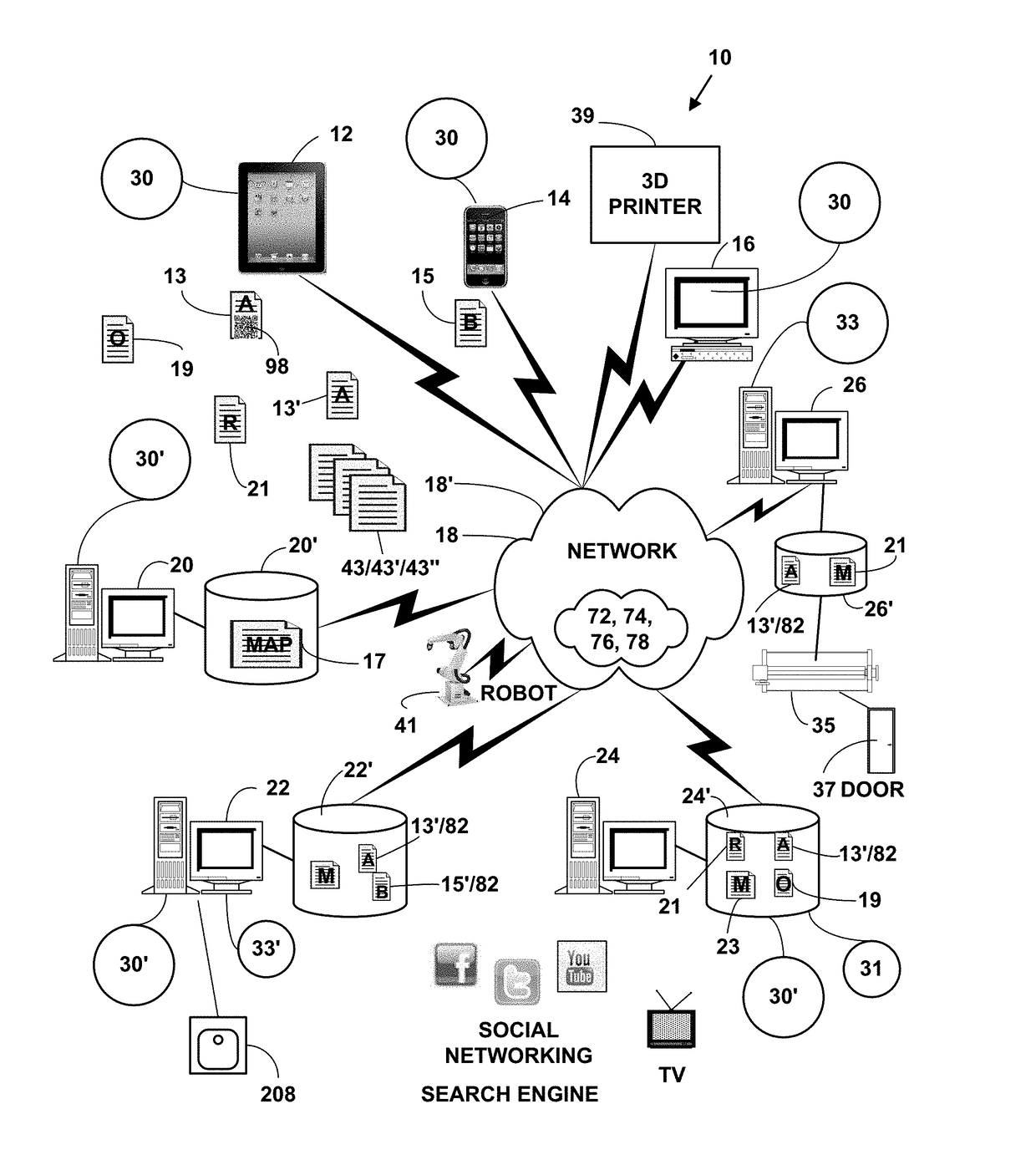
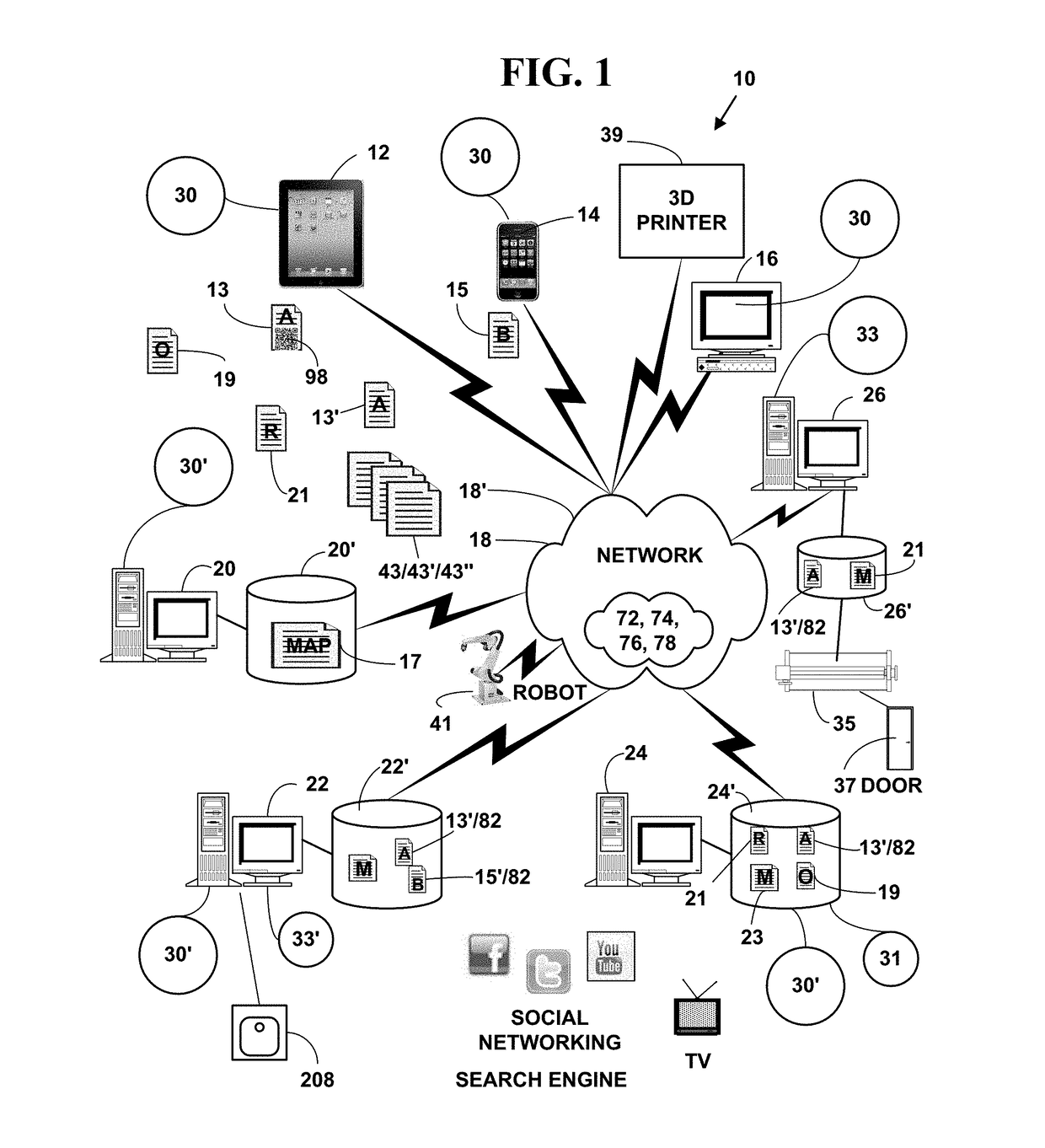
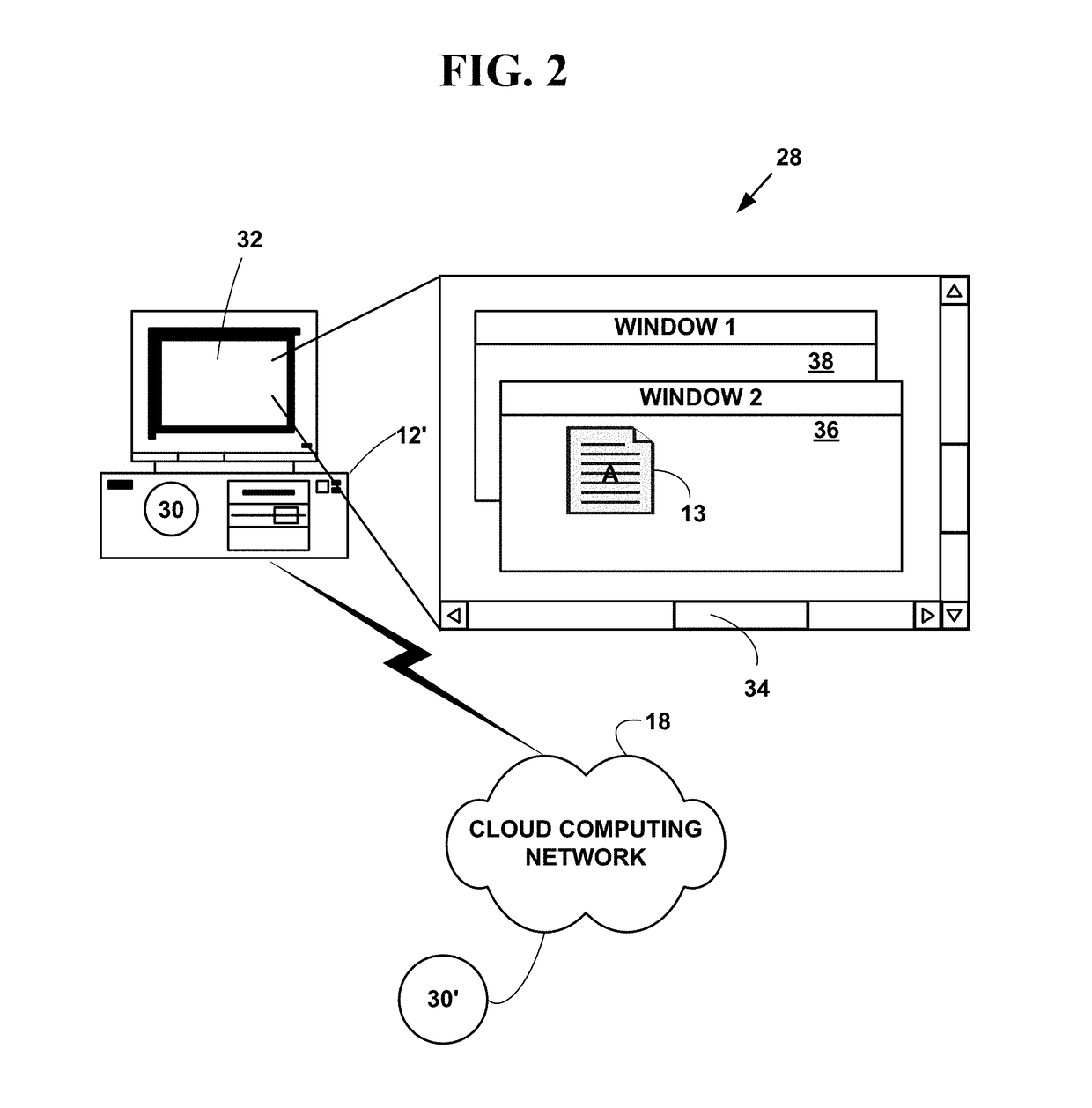
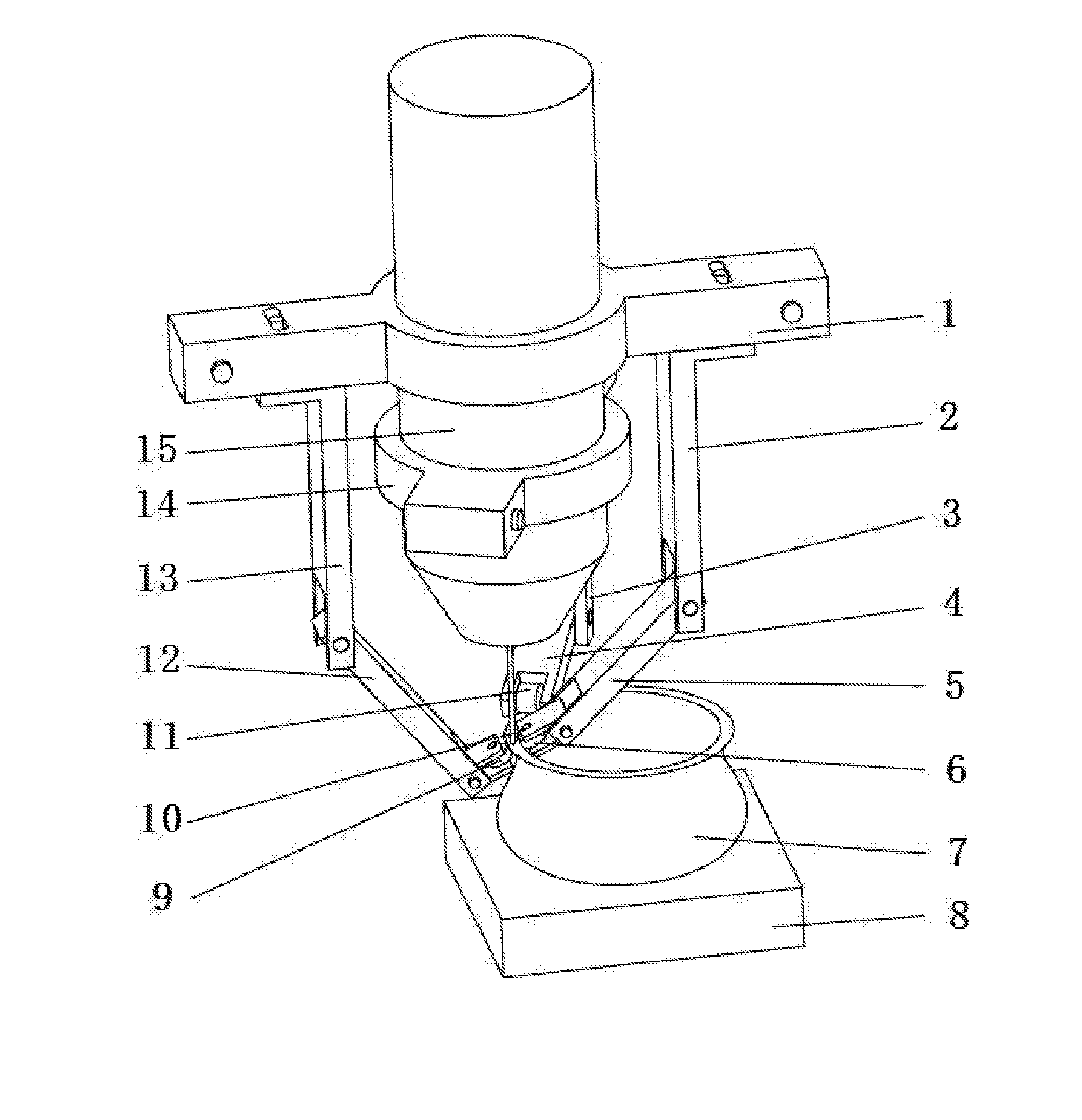
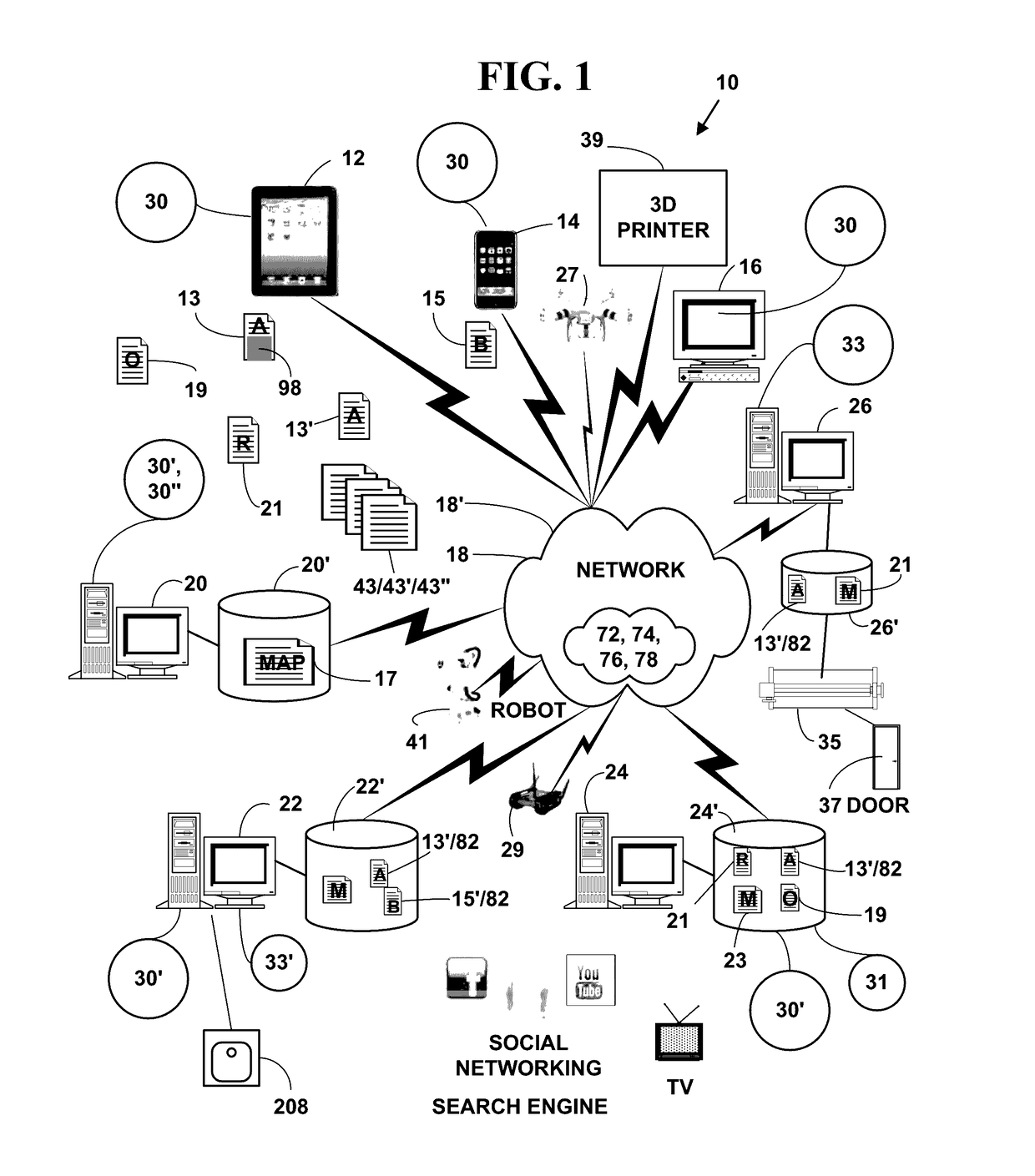
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2787 results about "3D modeling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In 3D computer graphics, 3D modeling is the process of developing a mathematical representation of any surface of an object (either inanimate or living) in three dimensions via specialized software. The product is called a 3D model. Someone who works with 3D models may be referred to as a 3D artist. It can be displayed as a two-dimensional image through a process called 3D rendering or used in a computer simulation of physical phenomena. The model can also be physically created using 3D printing devices.
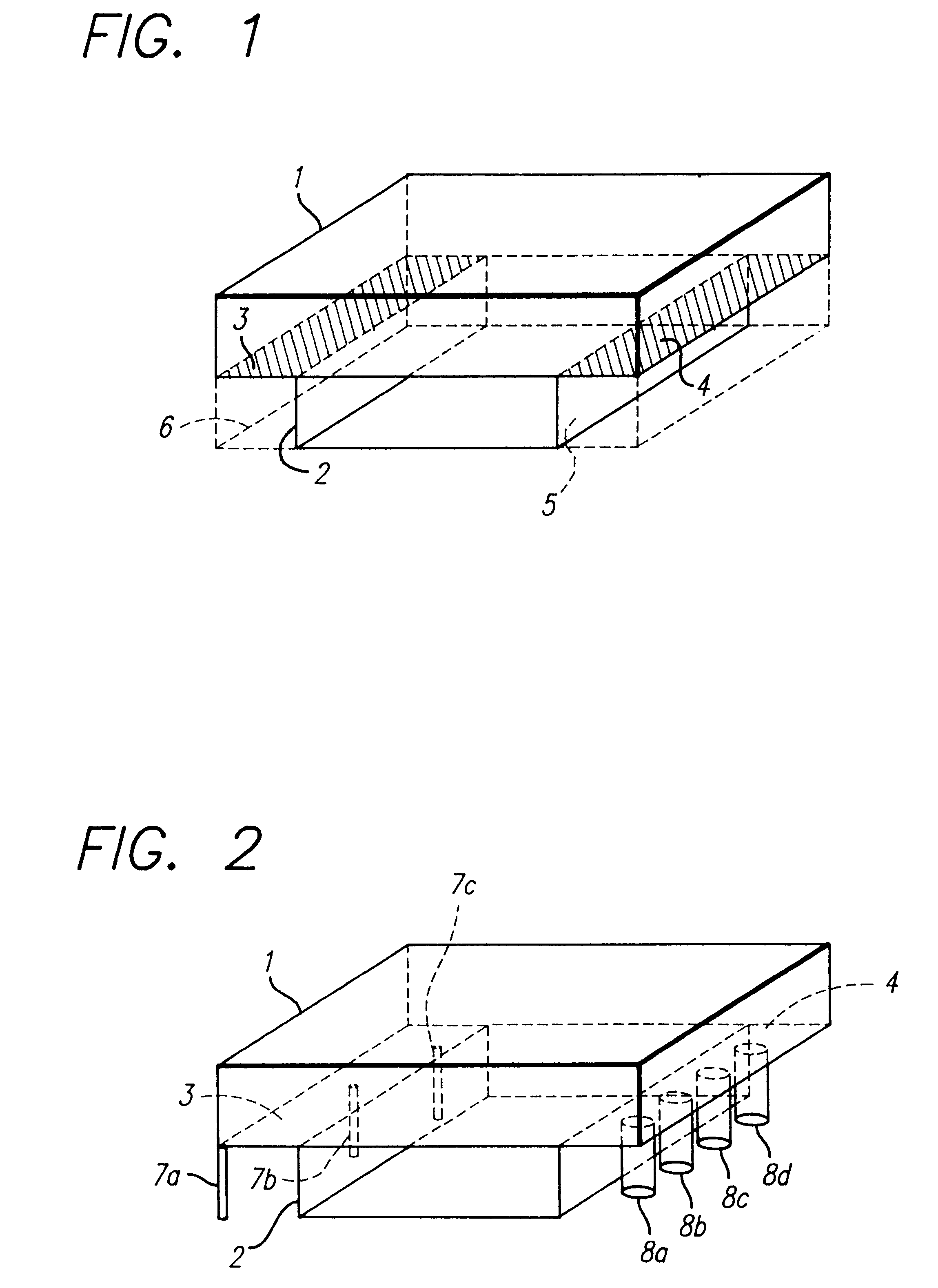
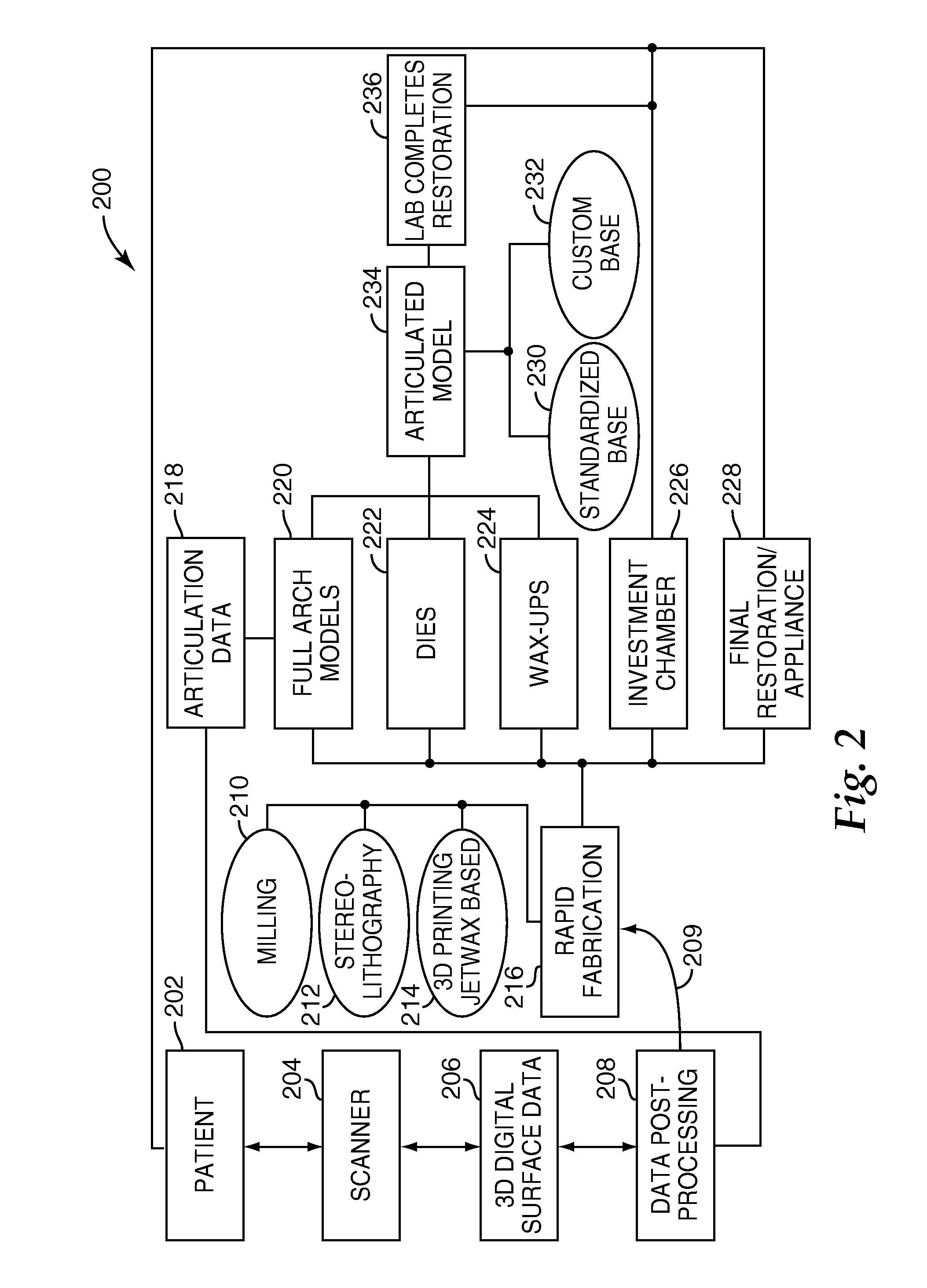
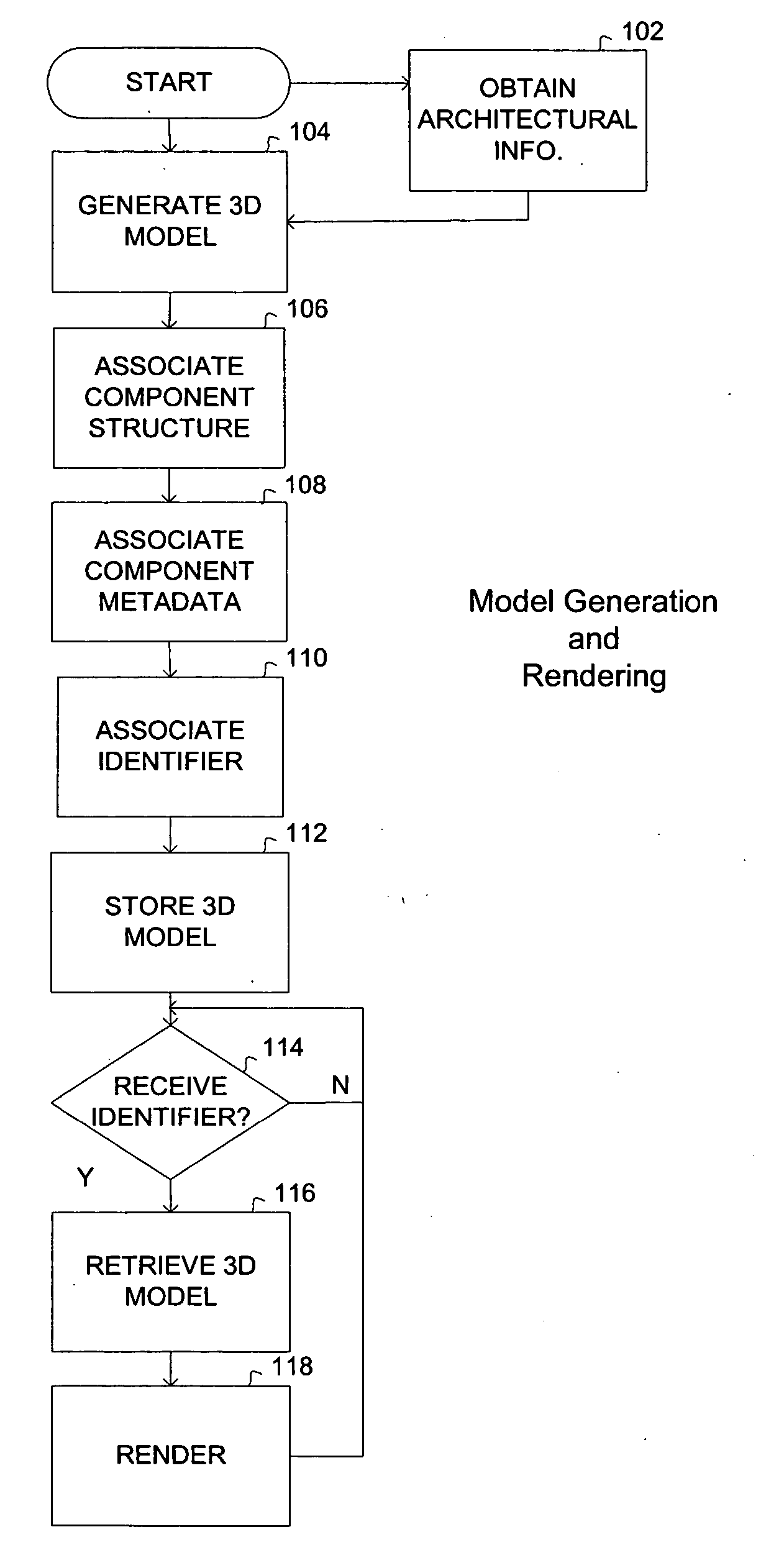
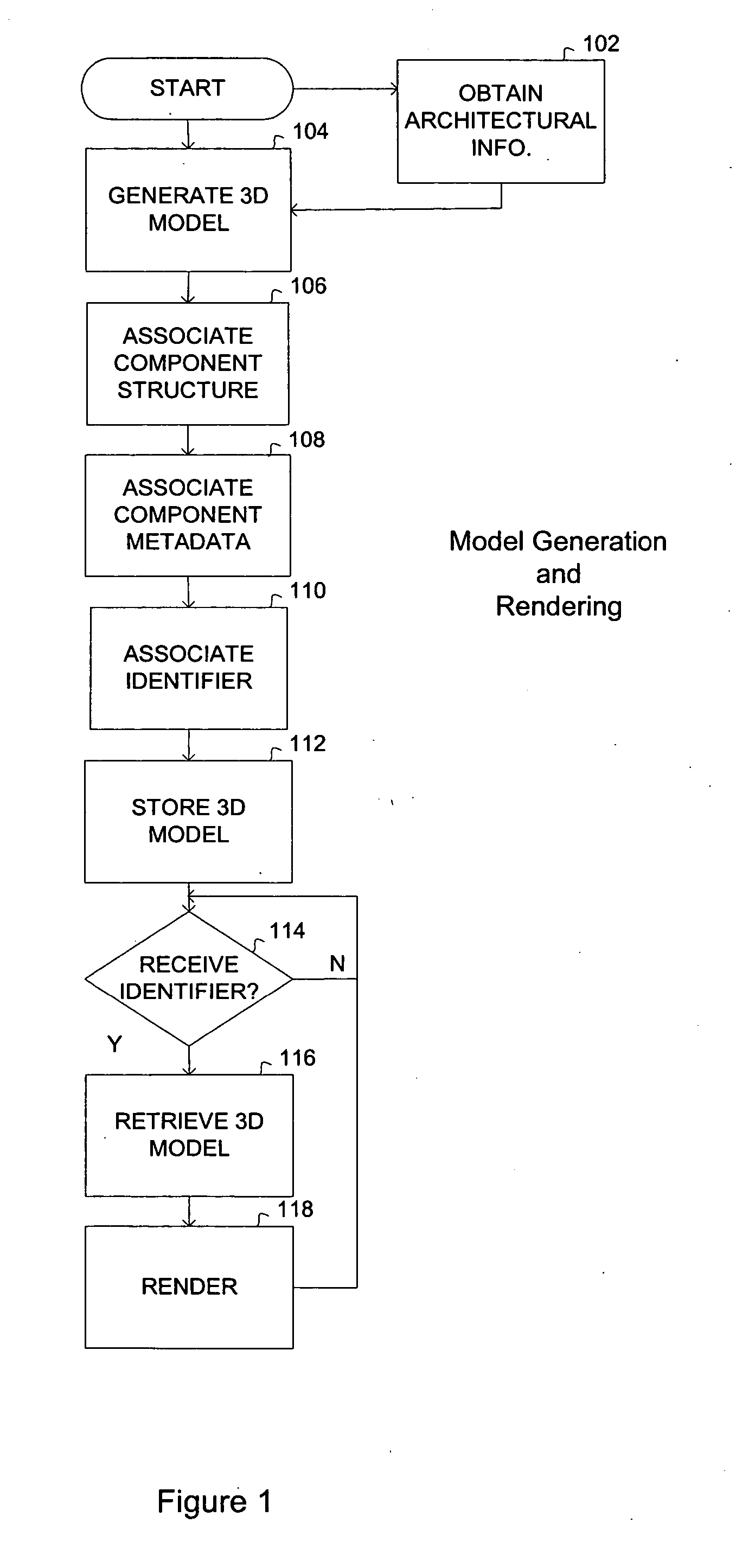
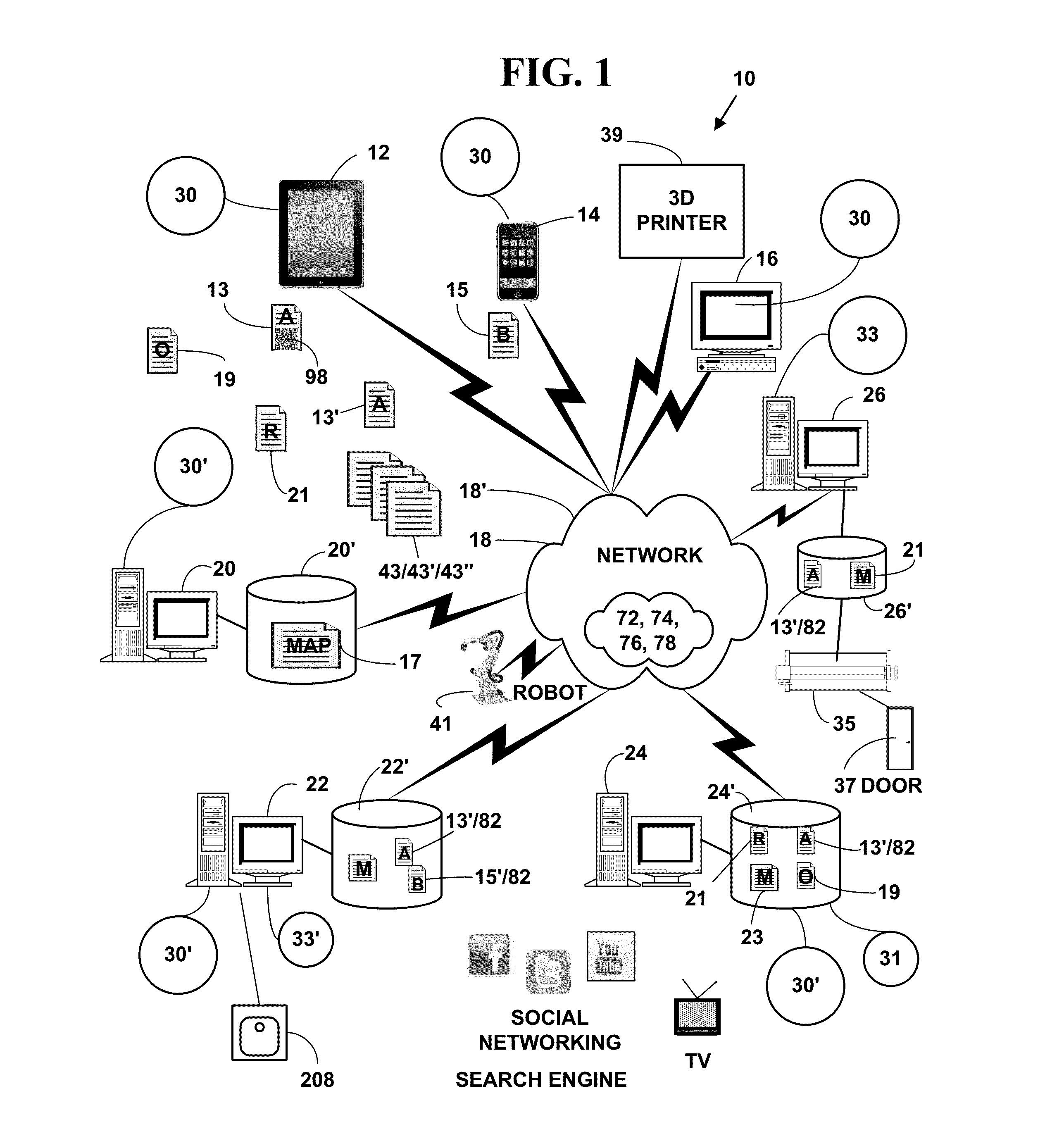
Selective deposition modeling method and apparatus for forming three-dimensional objects and supports
InactiveUS6193923B1Easy to disassembleMinimal damageAdditive manufacturing apparatusCeramic shaping apparatusEngineeringSelective deposition
A variety of support structures and build styles for use in Rapid Prototyping and Manufacturing systems are described wherein particular emphasis is given to Thermal Stereolithography, Fused Deposition Modeling, and Selective Deposition Modeling systems, and wherein a 3D modeling system is presented which uses multijet dispensing and a single material for both object and support formation.
Owner:3D SYST INC
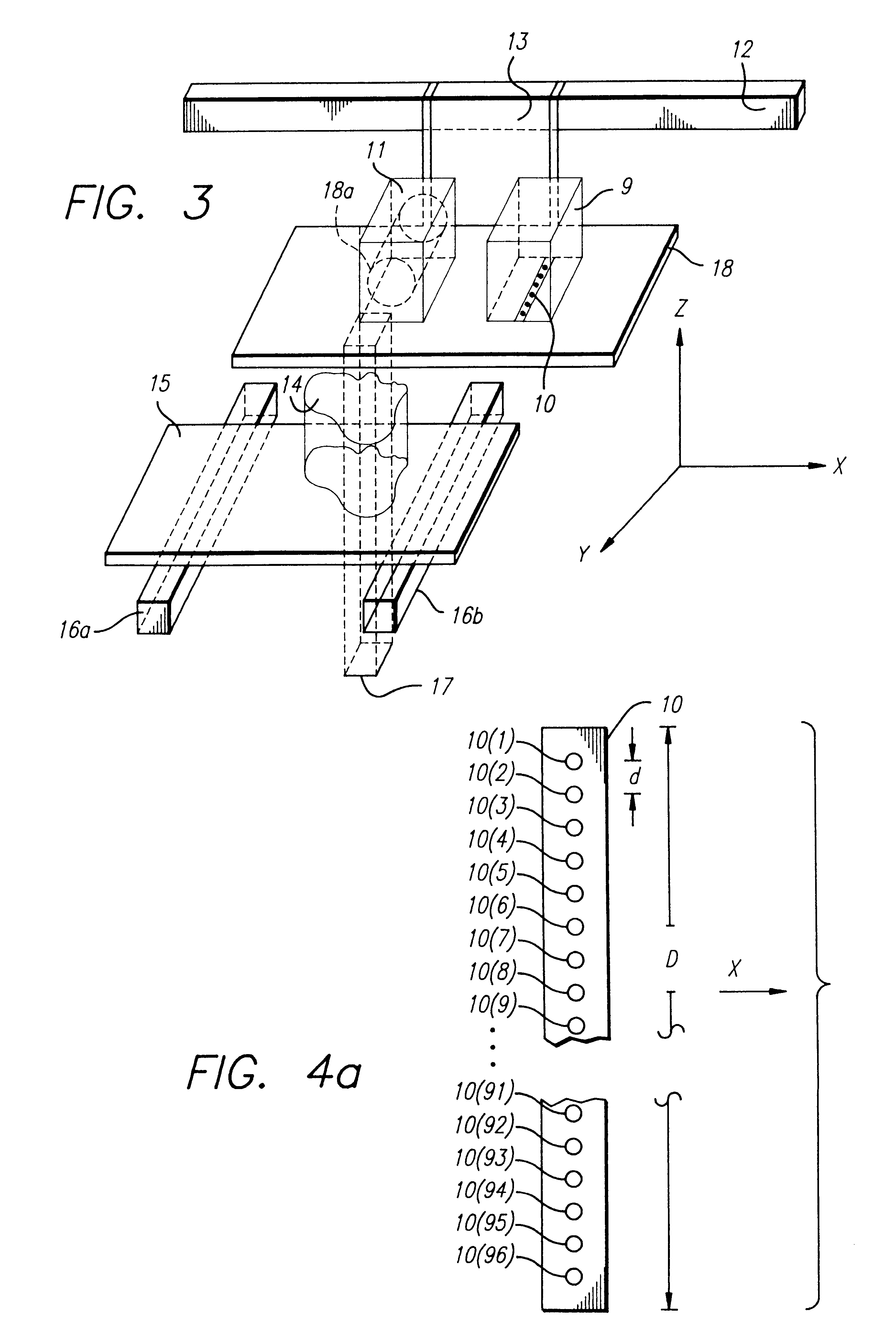
System and method for accurate printing of three dimensional models utilizing adjustment parameters
InactiveUS7209797B2Quality improvementAdditive manufacturing apparatusMeasurement apparatus componentsDimensional modeling3D modeling
A system and method for building three dimensional objects may adjust data used to build the objects to, for example, improve quality or correct for defects. A printer may, for example, accept data representing the object and modify the data according to an adjustment parameter; the printer may build the object according to the parameter. The parameter may be, for example, fixed in the printer, user entered, and / or calculated by the printer. In one embodiment, a support pedestal may be built of deposited material before the object is built.
Owner:STRATASYS LTD
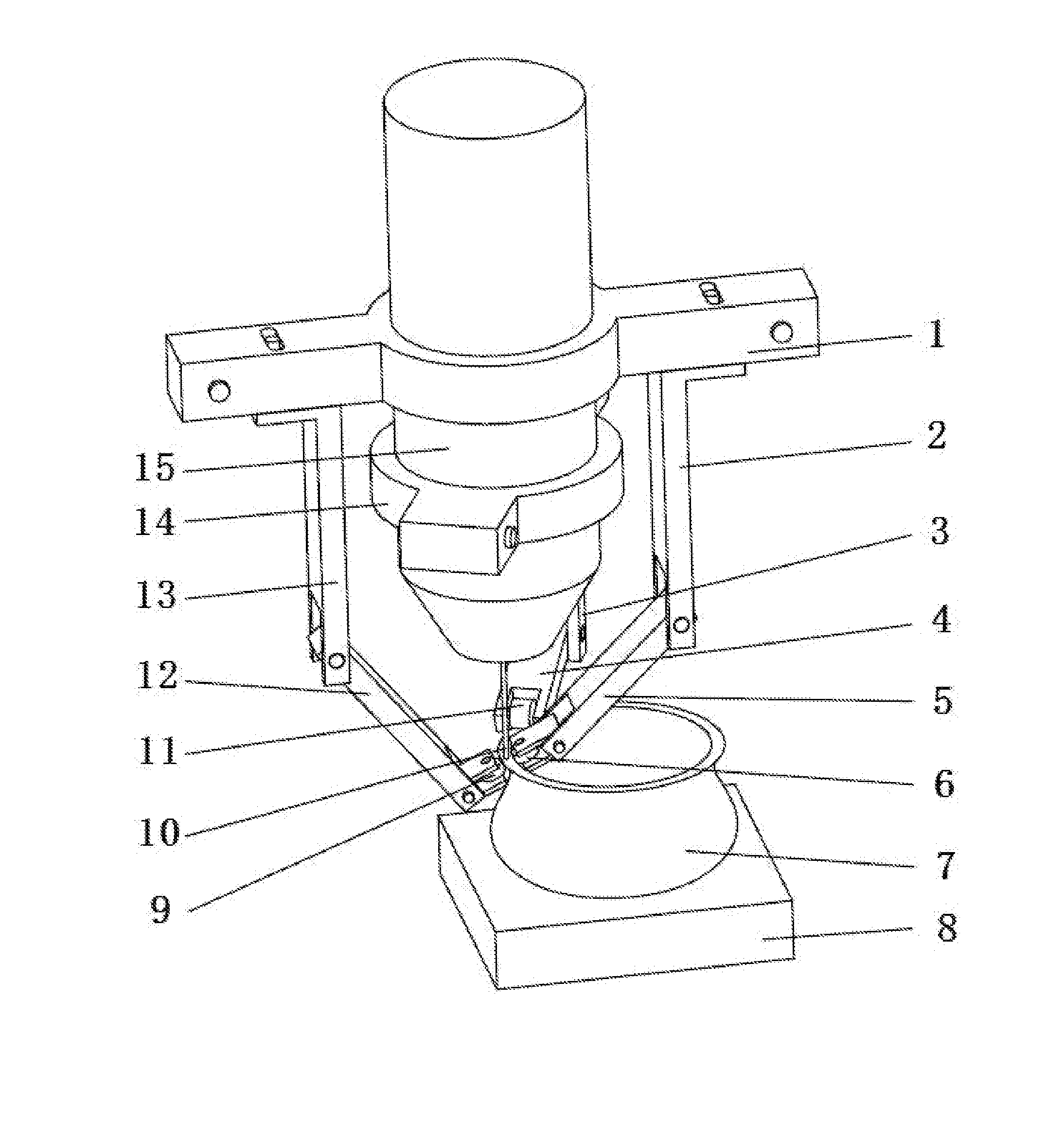
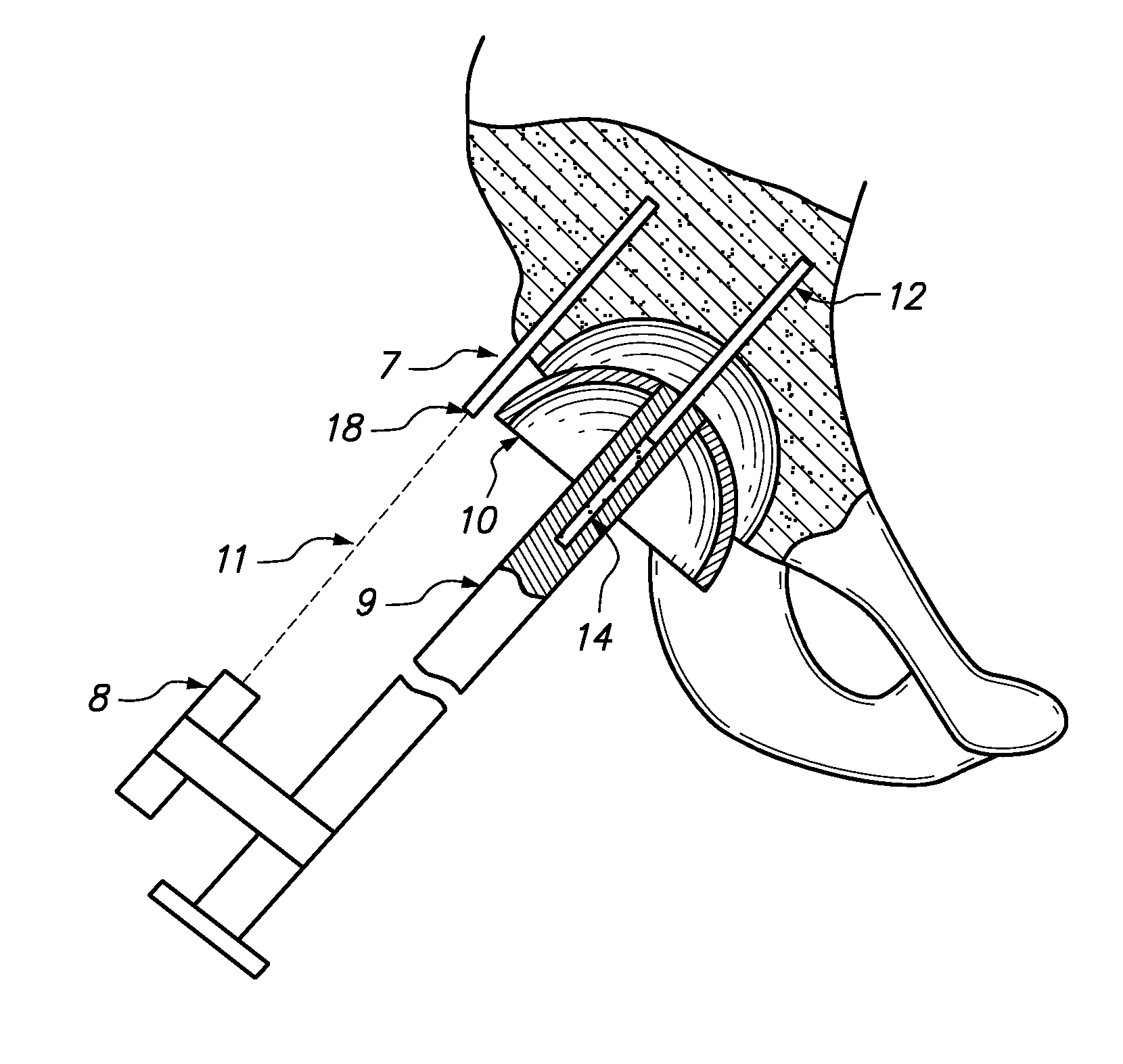
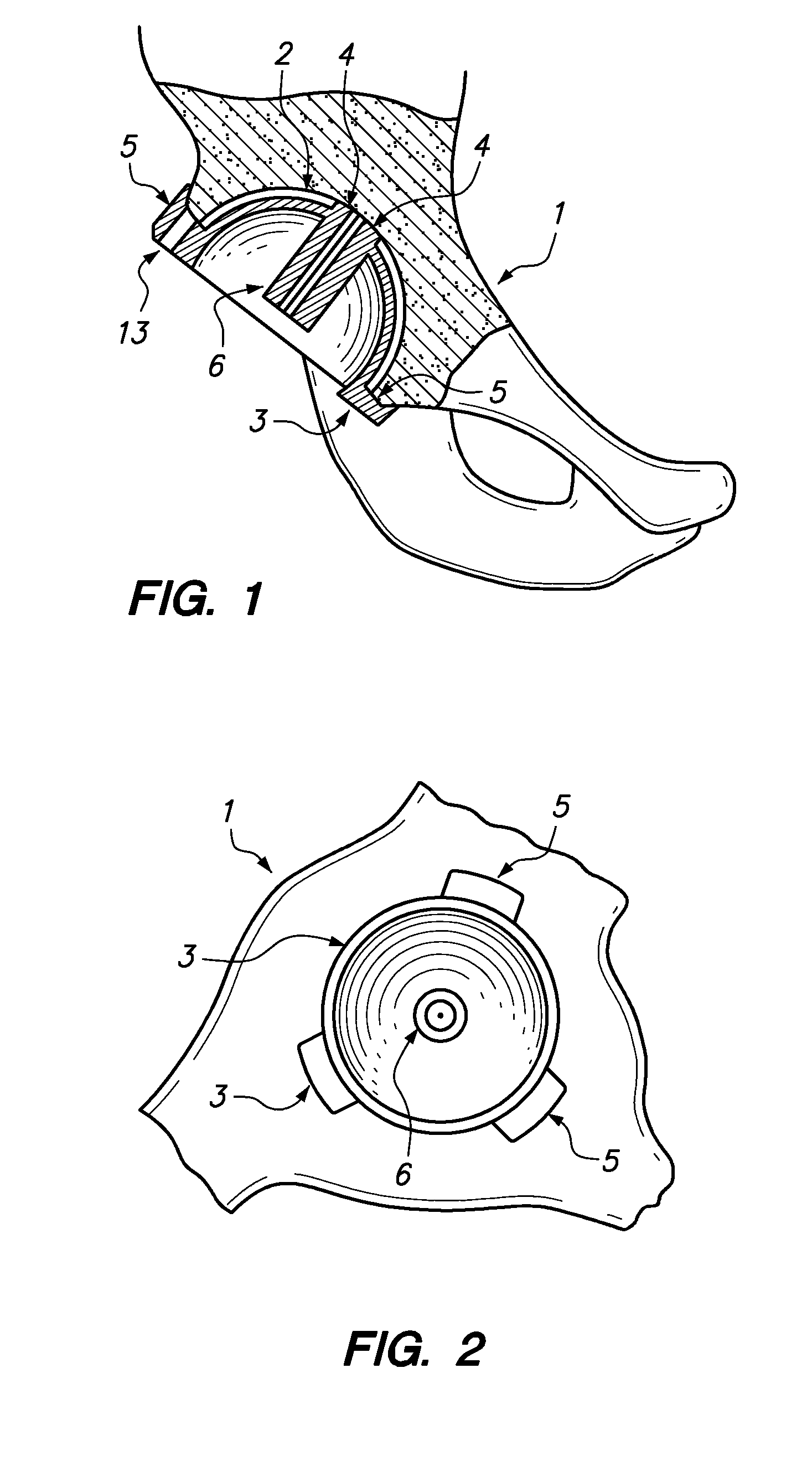
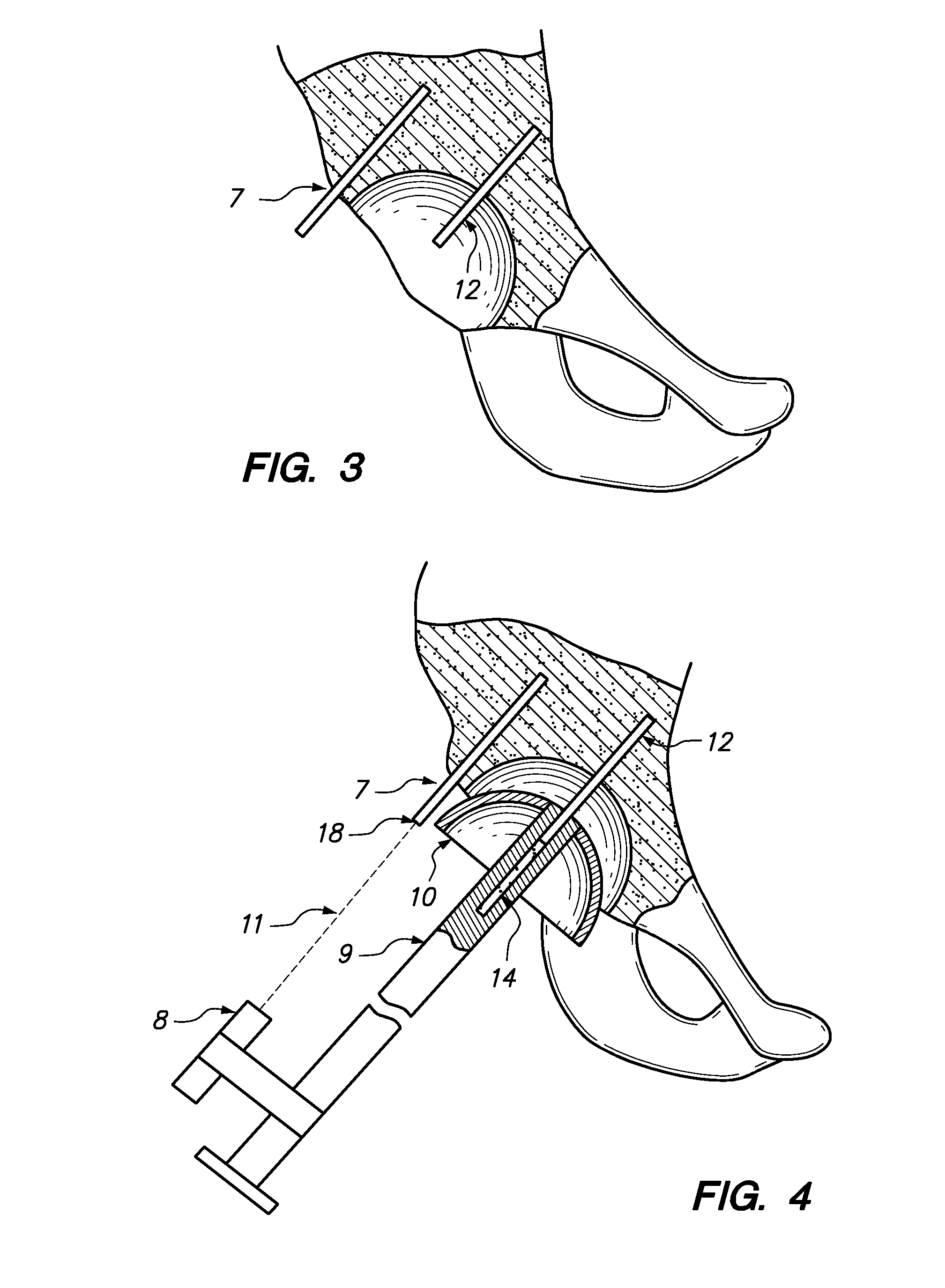
Device and method for achieving accurate positioning of acetabular cup during total hip replacement
InactiveUS20100274253A1DiagnosticsComputer-aided planning/modellingMedical imaging dataHip resurfacing
A method and device are provided in order to achieve optimal or desired orientation of an acetabular cup for total hip replacement or hip resurfacing. The method and device utilize preoperative medical imaging such as CT or MRI scans, 3D computer modeling and a patient-specific alignment jig created from medical imaging data such as CT or MRI data and computer 3D modeling. The device allows accurate placement of a drill hole to establish an acetabular axis, and placement of an acetabular cup perpendicular to the axis.
Owner:URE KEITH J
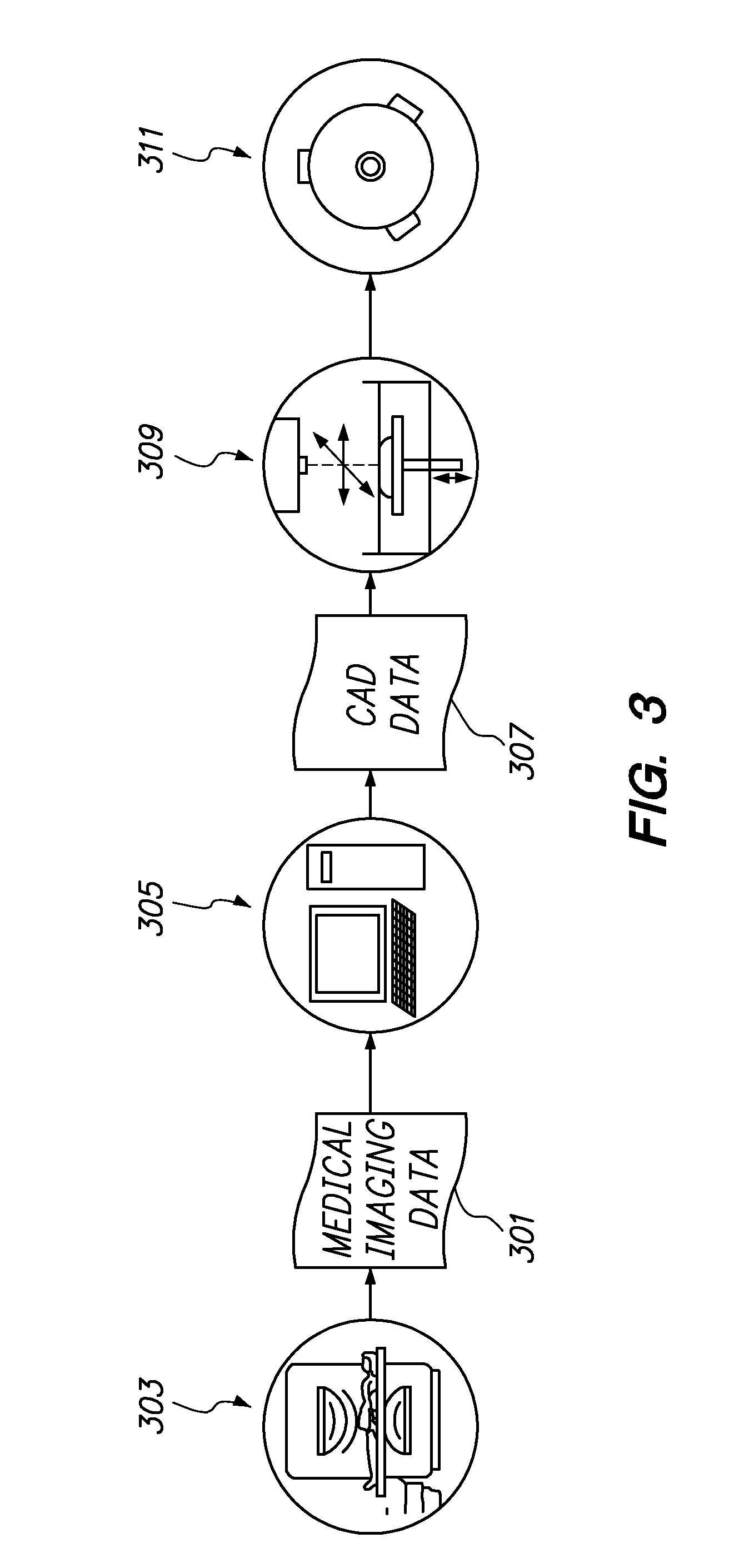
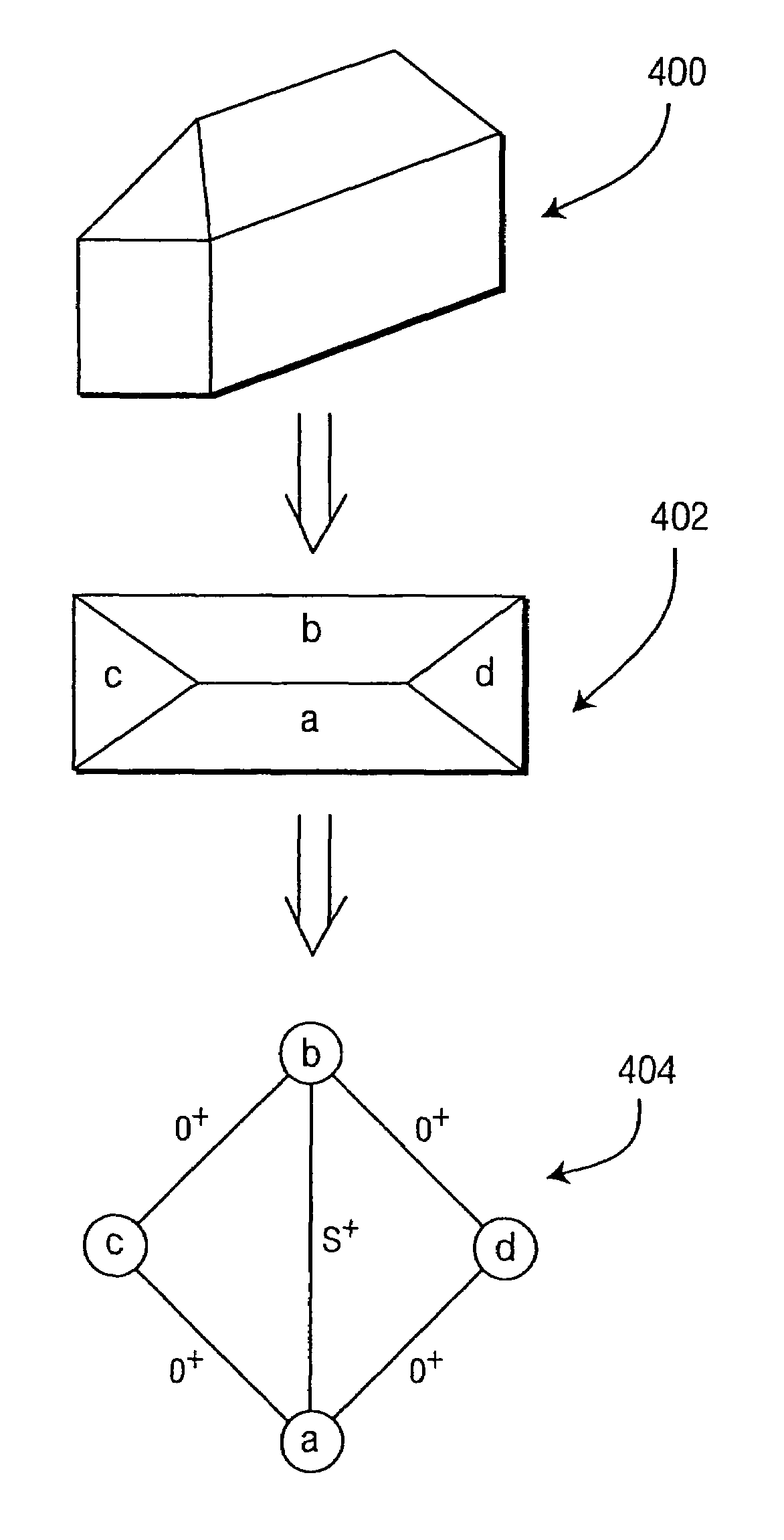
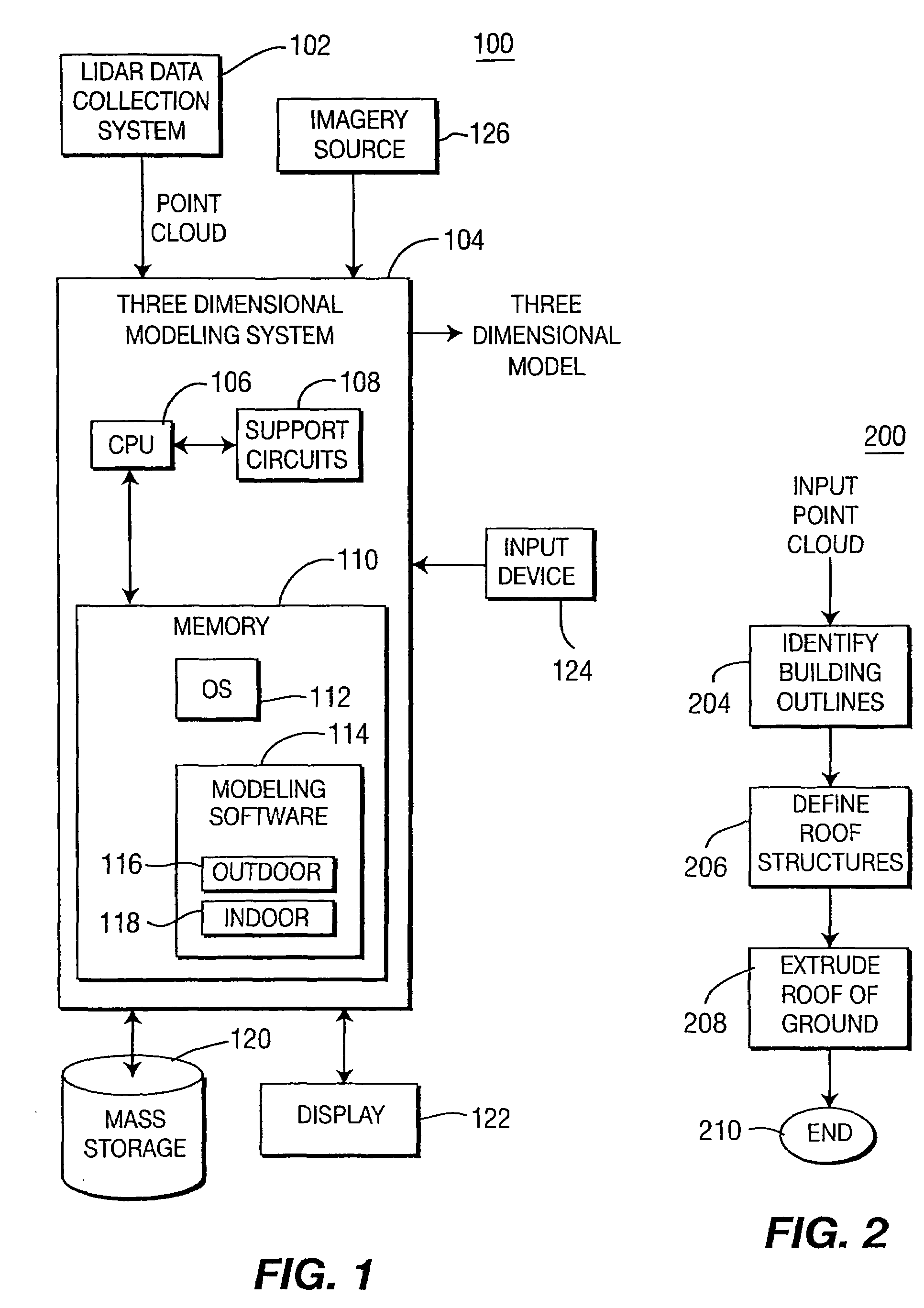
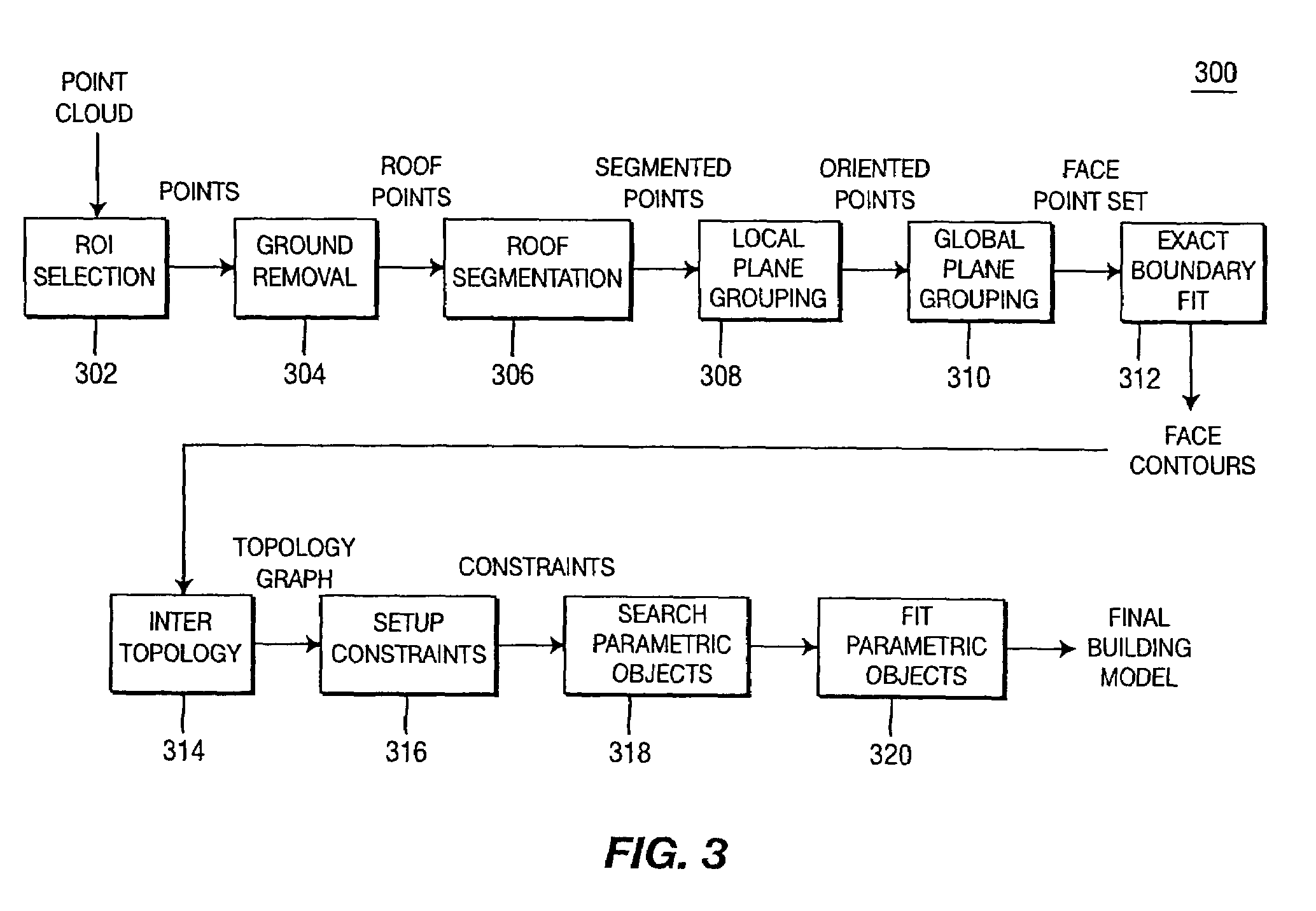
Method for generating a three-dimensional model of a roof structure
A method and apparatus for automatically generating a three-dimensional computer model from a “point cloud” of a scene produced by a laser radar (LIDAR) system. Given a point cloud of an indoor or outdoor scene, the method extracts certain structures from the imaged scene, i.e., ceiling, floor, furniture, rooftops, ground, and the like, and models these structures with planes and / or prismatic structures to achieve a three-dimensional computer model of the scene. The method may then add photographic and / or synthetic texturing to the model to achieve a realistic model.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
Selective deposition modeling method and apparatus for forming three-dimensional objects and supports
InactiveUS6270335B2Less distortionReduce the risk of bridgingAdditive manufacturing apparatusConfectioneryEngineeringSelective deposition
Owner:3D SYST INC
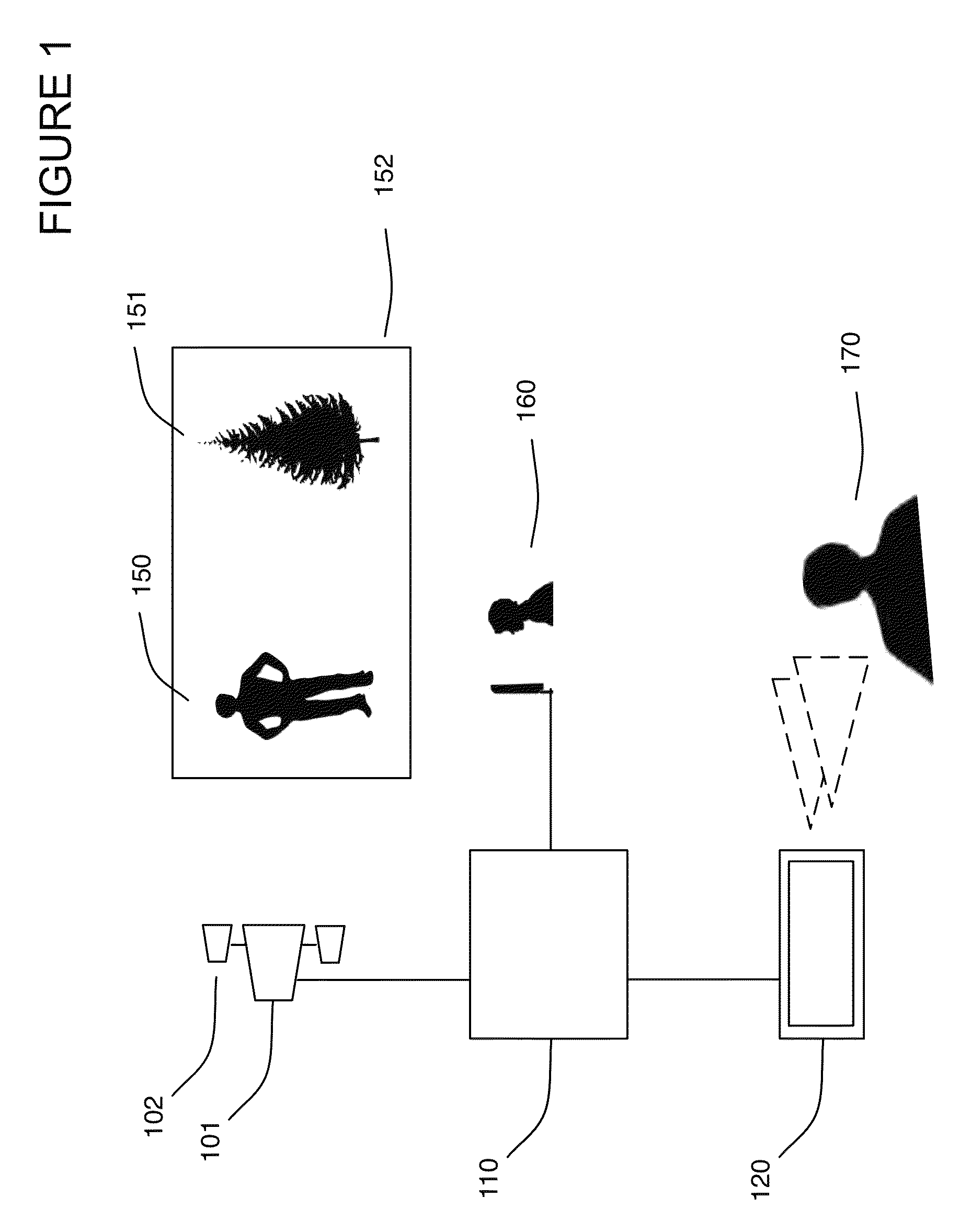
Estimation of object properties in 3D world
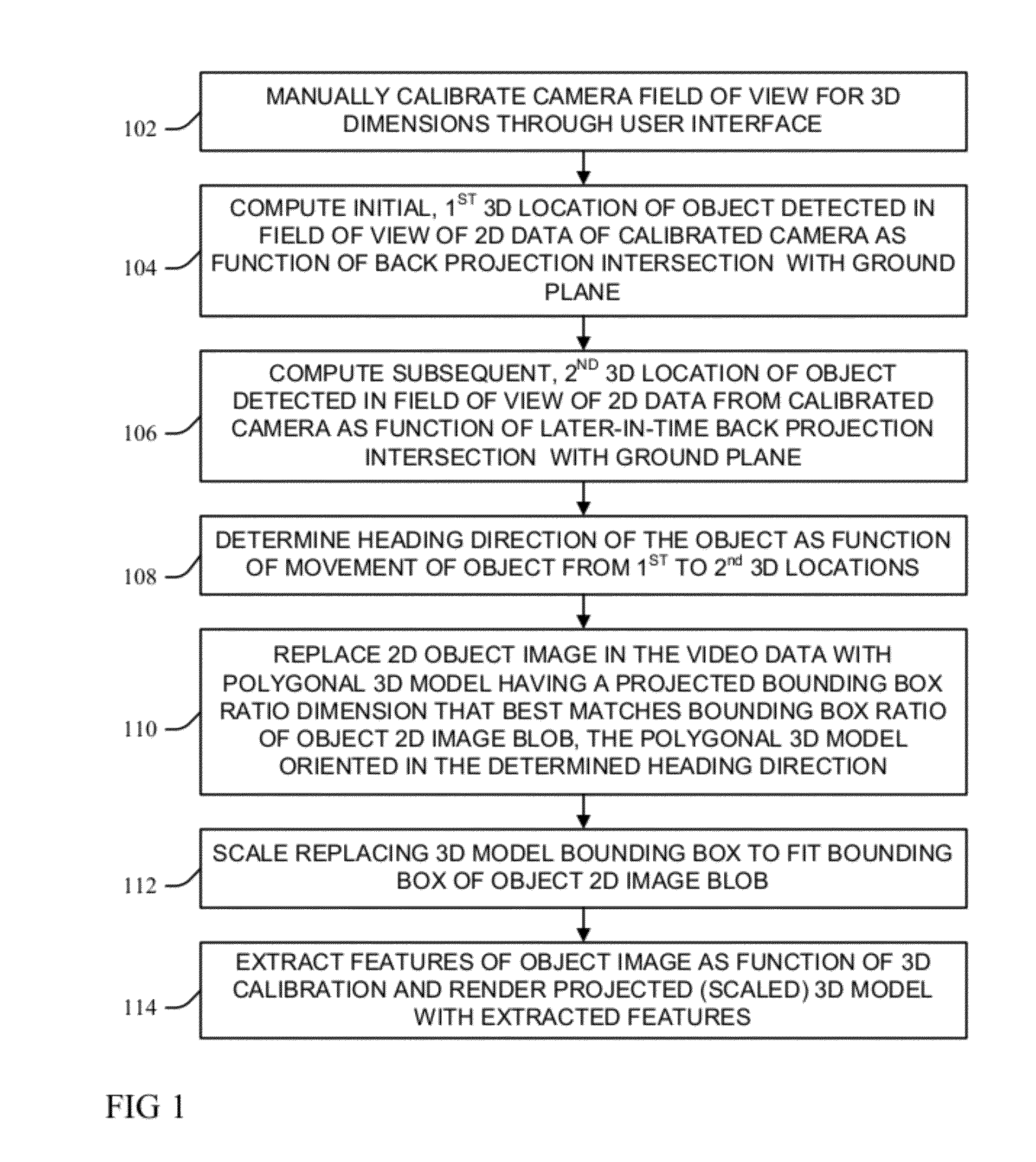
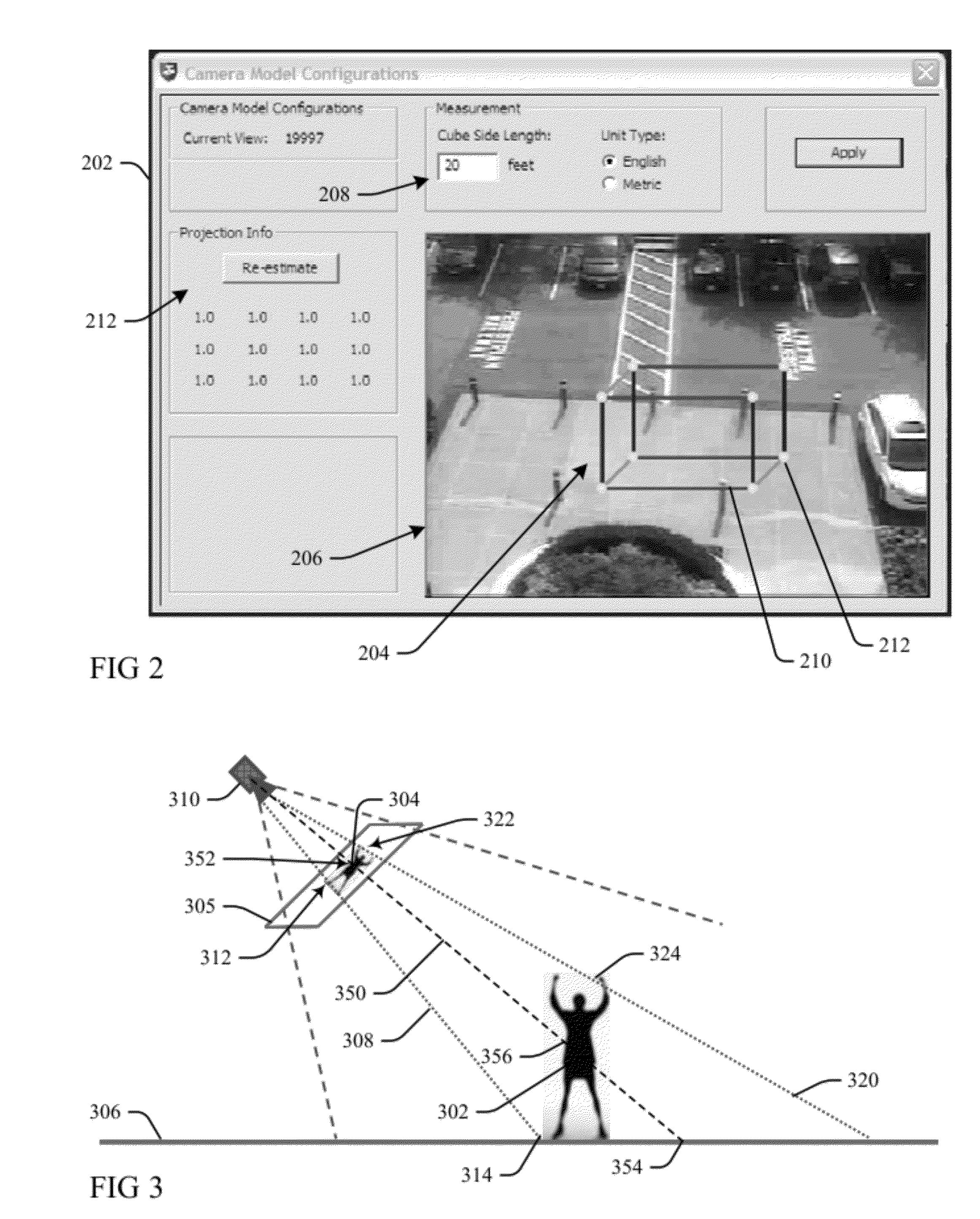
Objects within two-dimensional (2D) video data are modeled by three-dimensional (3D) models as a function of object type and motion through manually calibrating a 2D image to the three spatial dimensions of a 3D modeling cube. Calibrated 3D locations of an object in motion in the 2D image field of view of a video data input are computed and used to determine a heading direction of the object as a function of the camera calibration and determined movement between the computed 3D locations. The 2D object image is replaced in the video data input with an object-type 3D polygonal model having a projected bounding box that best matches a bounding box of an image blob, the model oriented in the determined heading direction. The bounding box of the replacing model is then scaled to fit the object image blob bounding box, and rendered with extracted image features.
Owner:KYNDRYL INC
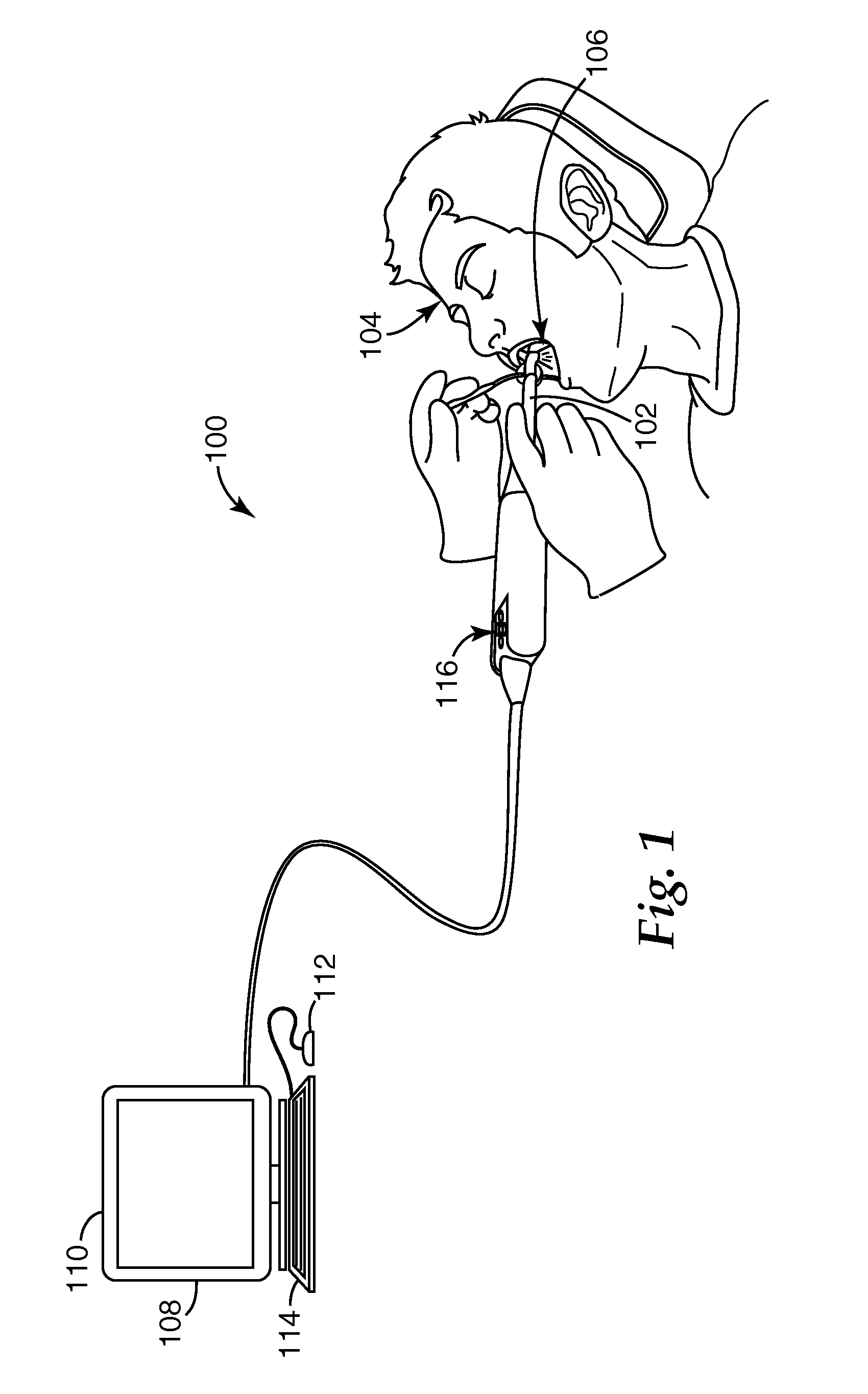
Video-assisted margin marking for dental models
InactiveUS20100281370A1Simple production processSpeed up the processInput/output for user-computer interactionImpression capsInteractive modelingAmbiguity
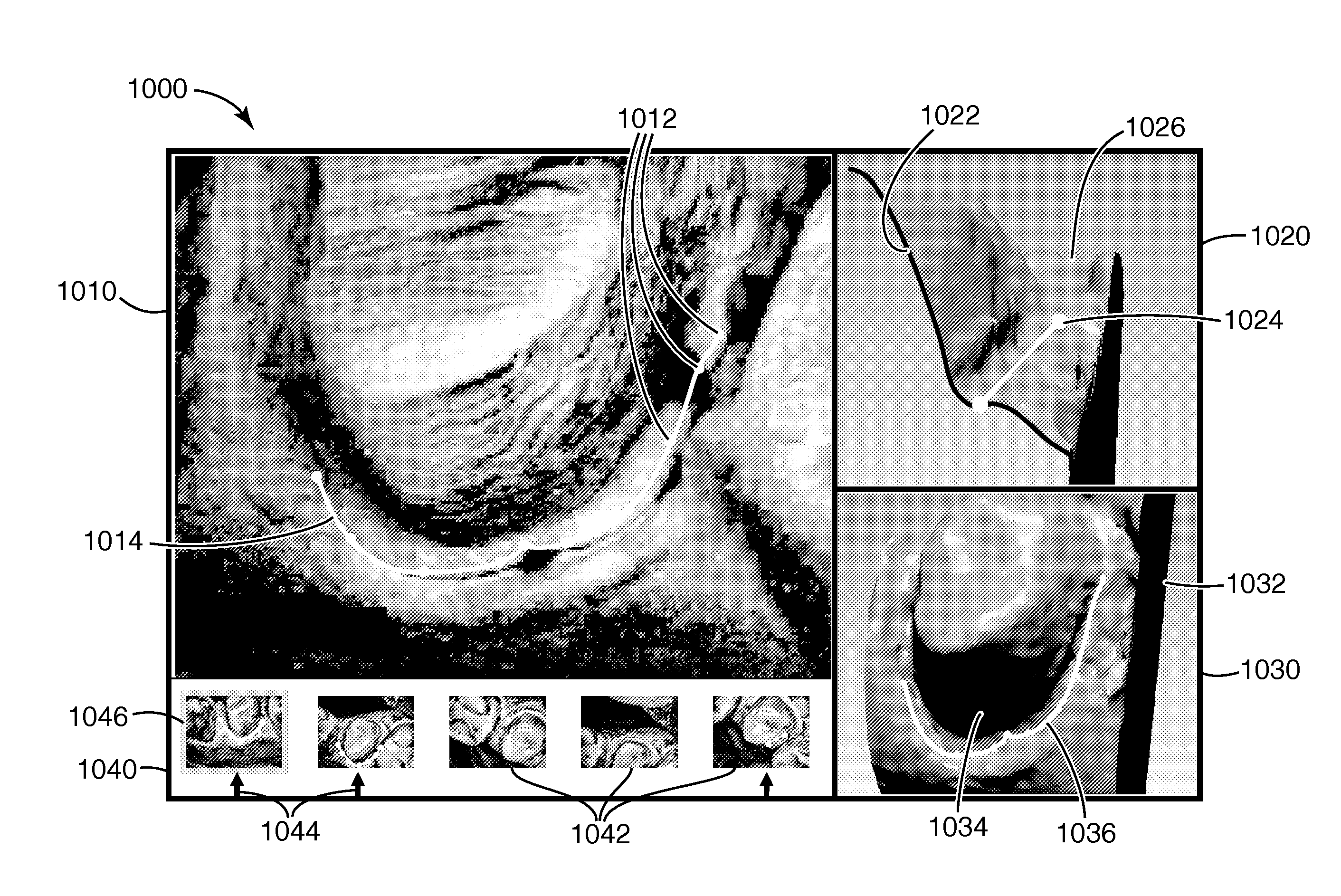
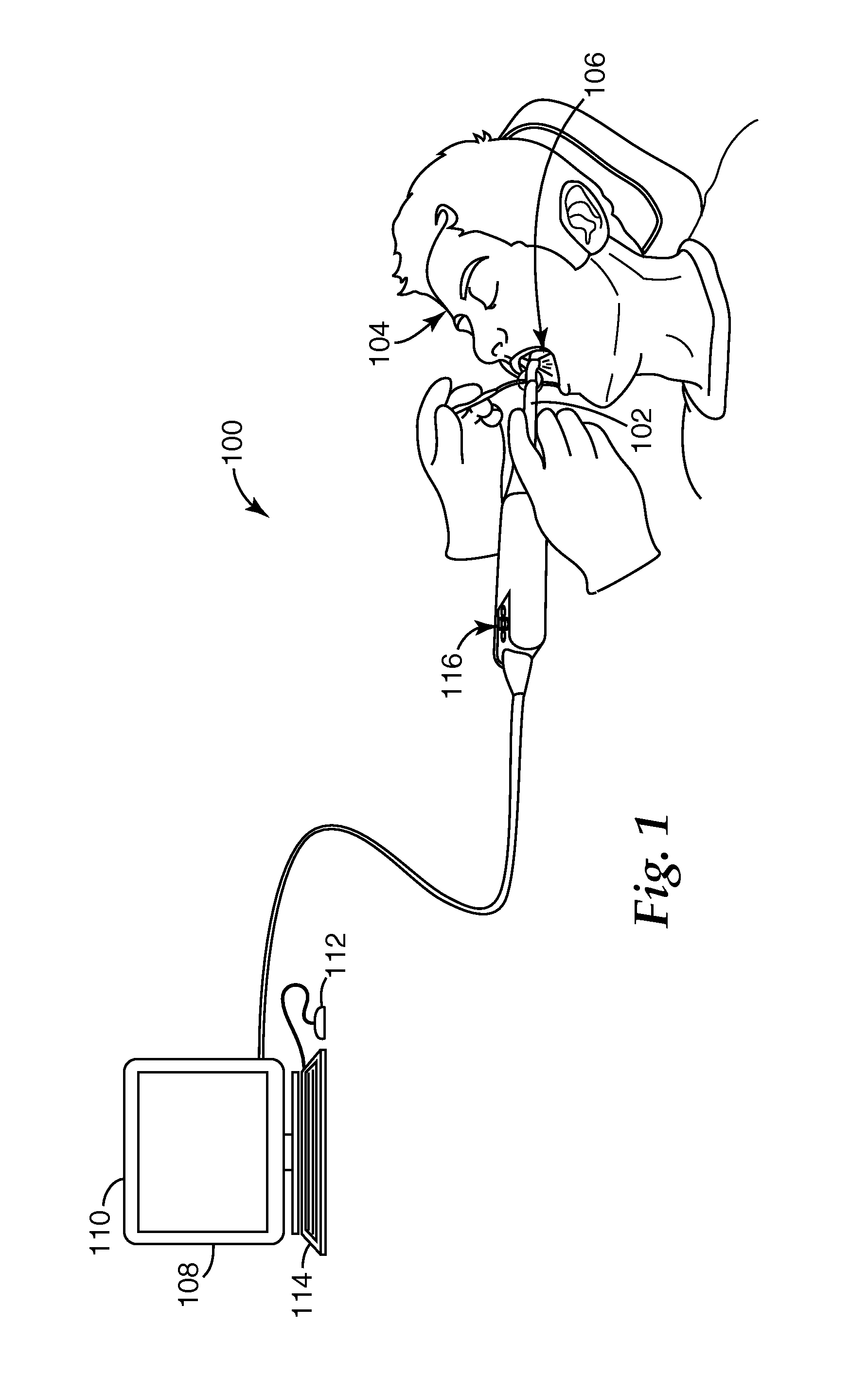
Tools are described for preparing digital dental models for use in dental restoration production processes, along with associated systems and methods. Dental modeling is improved by supplementing views of three-dimensional models with still images of the modeled subject matter. Video data acquired during a scan of the model provides a source of still images that can be displayed alongside a rendered three-dimensional model, and the two views (model and still image) may be synchronized to provide a common perspective of the model's subject matter. This approach provides useful visual information for disambiguating surface features of the model during processing steps such as marking a margin of a prepared tooth surface for a restoration. Interactive modeling tools may be similarly enhanced. For example, tools for margin marking may synchronize display of margin lines between the still image and the model so that a user can interact with either or both of the visual representations, with changes to a margin reflected in both displays.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
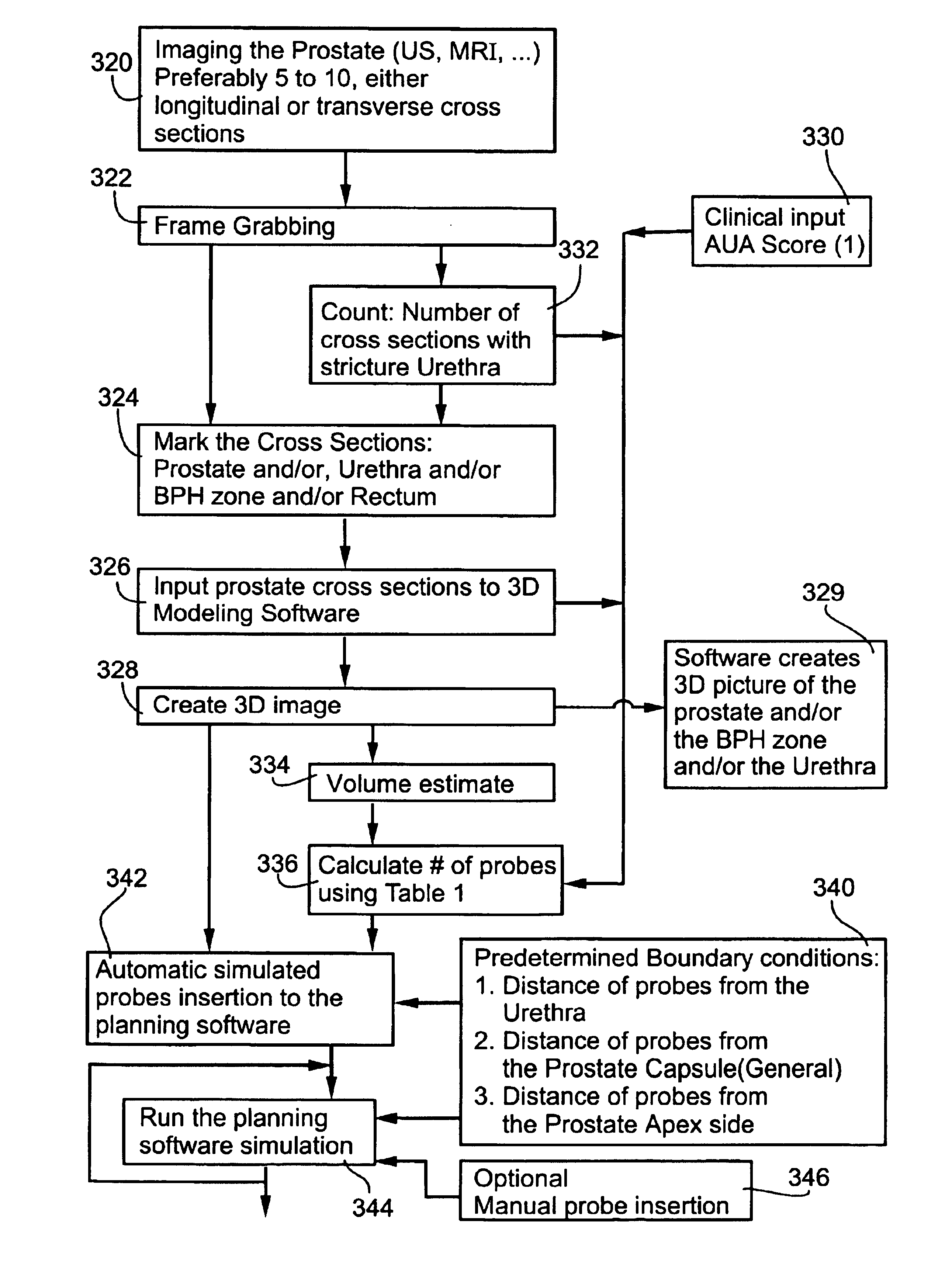
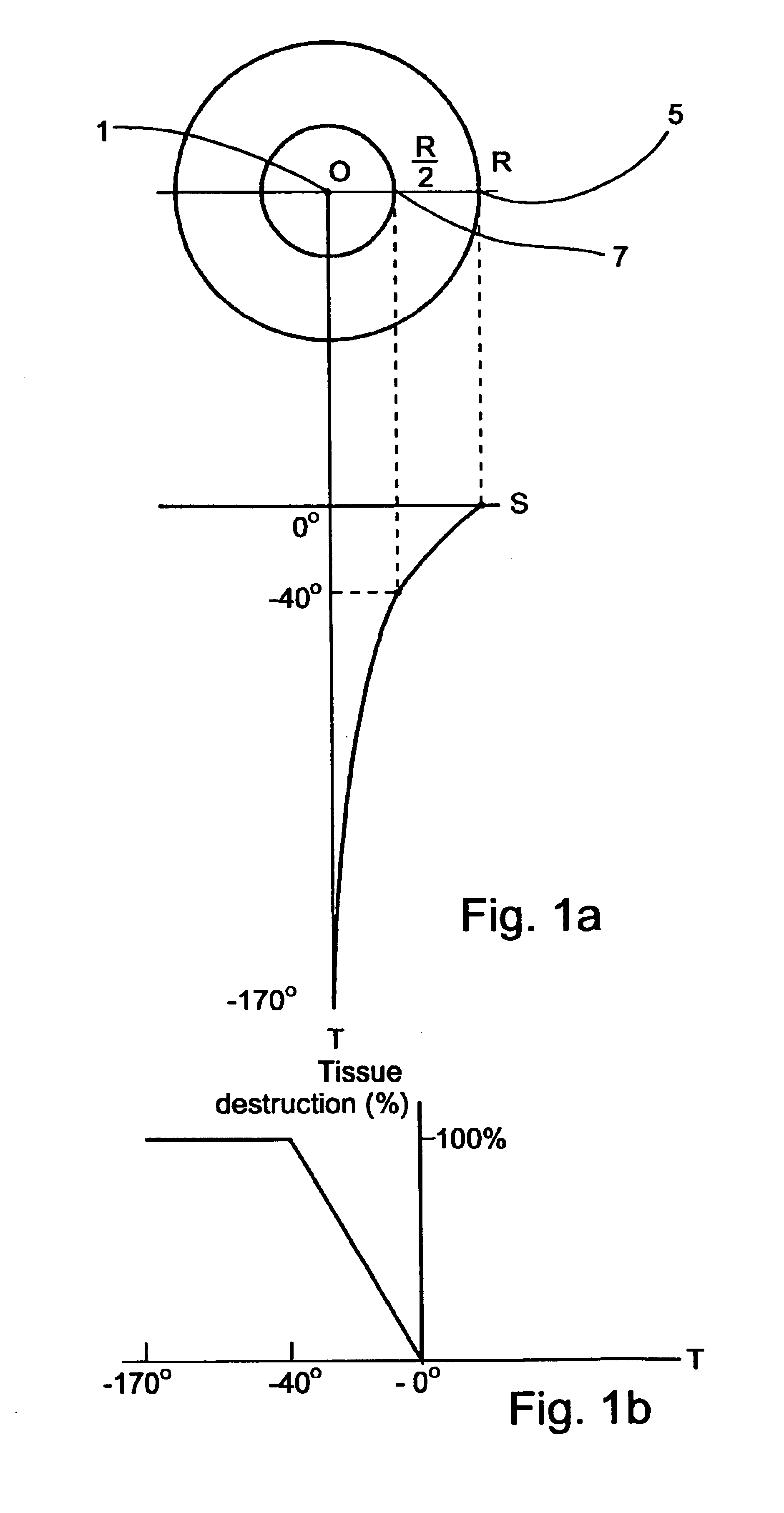
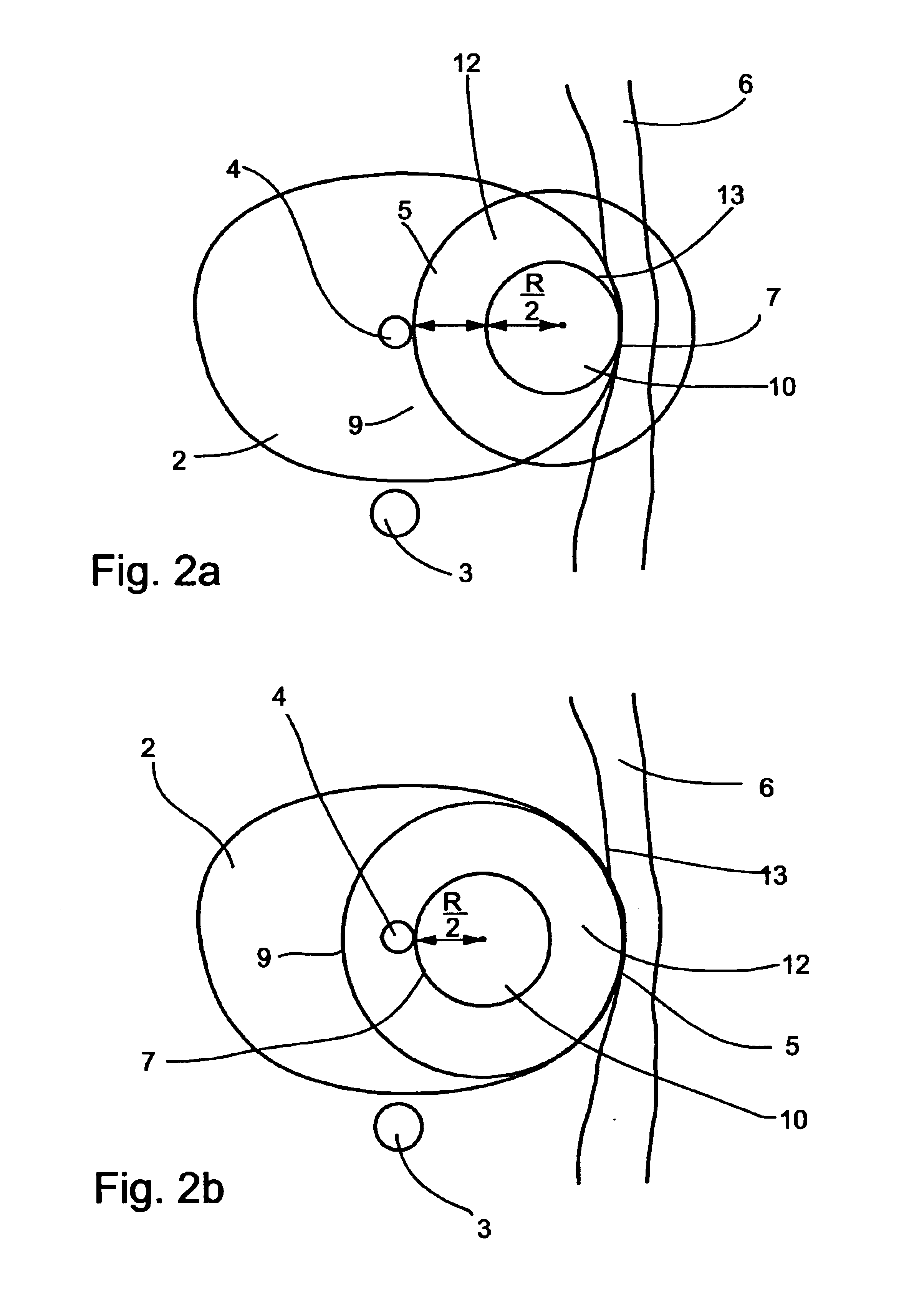
Planning and facilitation systems and methods for cryosurgery
InactiveUS6905492B2Effective planningEasy to interveneOrgan movement/changes detectionCatheterDiagnostic Radiology ModalityImaging modalities
Systems and methods for planning a cryoablation procedure and for facilitating a cryoablation procedure utilize integrated images displaying, in a common virtual space, a three-dimensional model of a surgical intervention site based on digitized preparatory images of the site from first imaging modalities, simulation images of cryoprobes used according to an operator-planned cryoablation procedure at the site, and real-time images provided by second imaging modalities during cryoablation. The system supplies recommendations for and evaluations of the planned cryoablation procedure, feedback to an operator during cryoablation, and guidance and control signals for operating a cryosurgery tool during cryoablation. Methods are provided for generating a nearly-uniform cold field among a plurality of cryoprobes, for cryoablating a volume with smooth and well-defined borders, thereby minimizing damage to healthy tissues.
Owner:GALIL MEDICAL
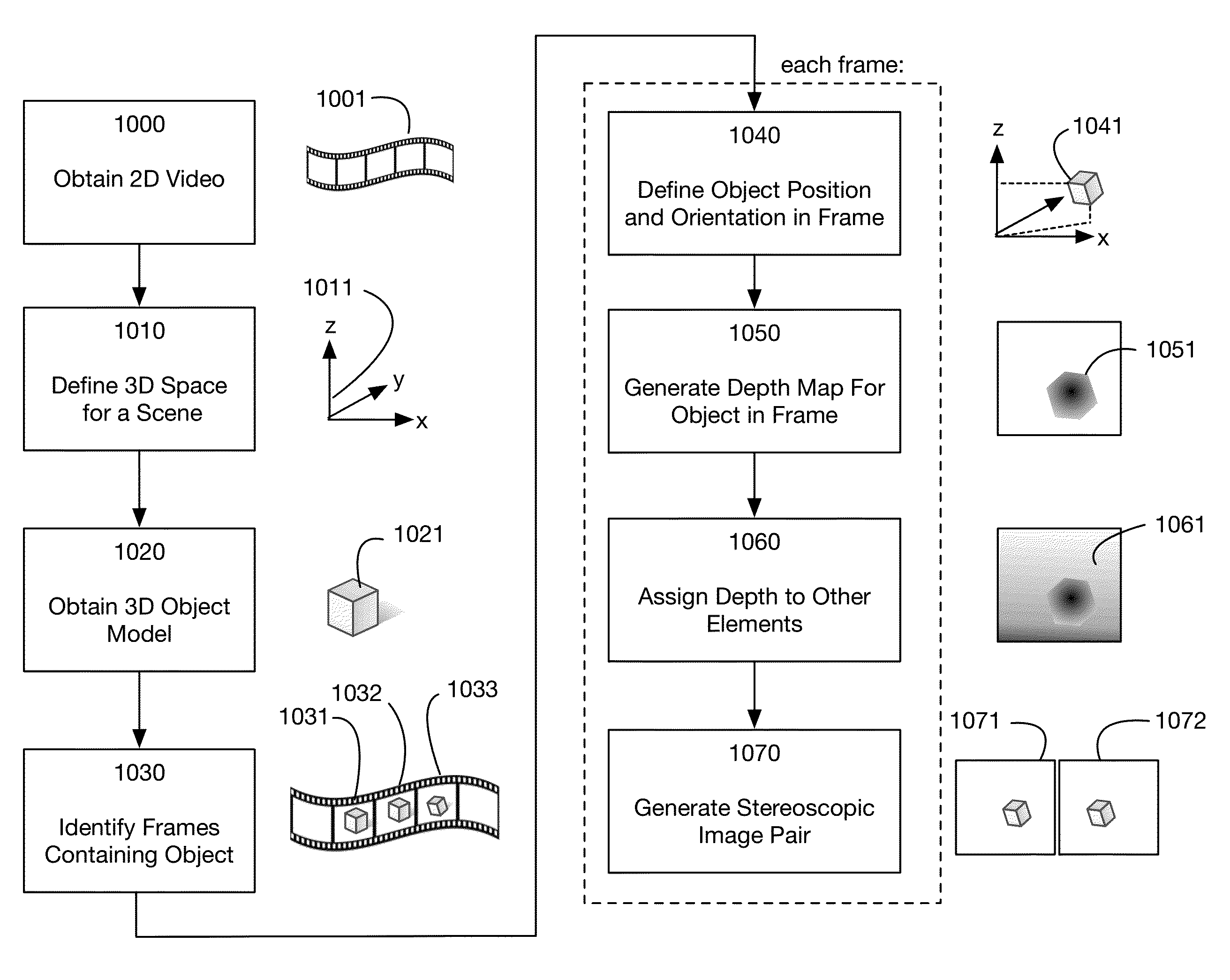
Method of converting 2D video to 3D video using 3D object models
InactiveUS9438878B2Quick conversionIncrease flexibilityImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature trackingDegrees of freedom
Method for converting 2D video to 3D video using 3D object models. Embodiments of the invention obtain a 3D object model for one or more objects in a 2D video scene, such as a character. Object models may for example be derived from 3D scanner data; planes, polygons, or surfaces may be fit to this data to generate a 3D model. In each frame in which a modeled object appears, the location and orientation of the 3D model may be determined in the frame, and a depth map for the object may be generated from the model. 3D video may be generated using the depth map. Embodiments may use feature tracking to automatically determine object location and orientation. Embodiments may use rigged 3D models with degrees of freedom to model objects with parts that move relative to one another.
Owner:LEGEND FILMS INC
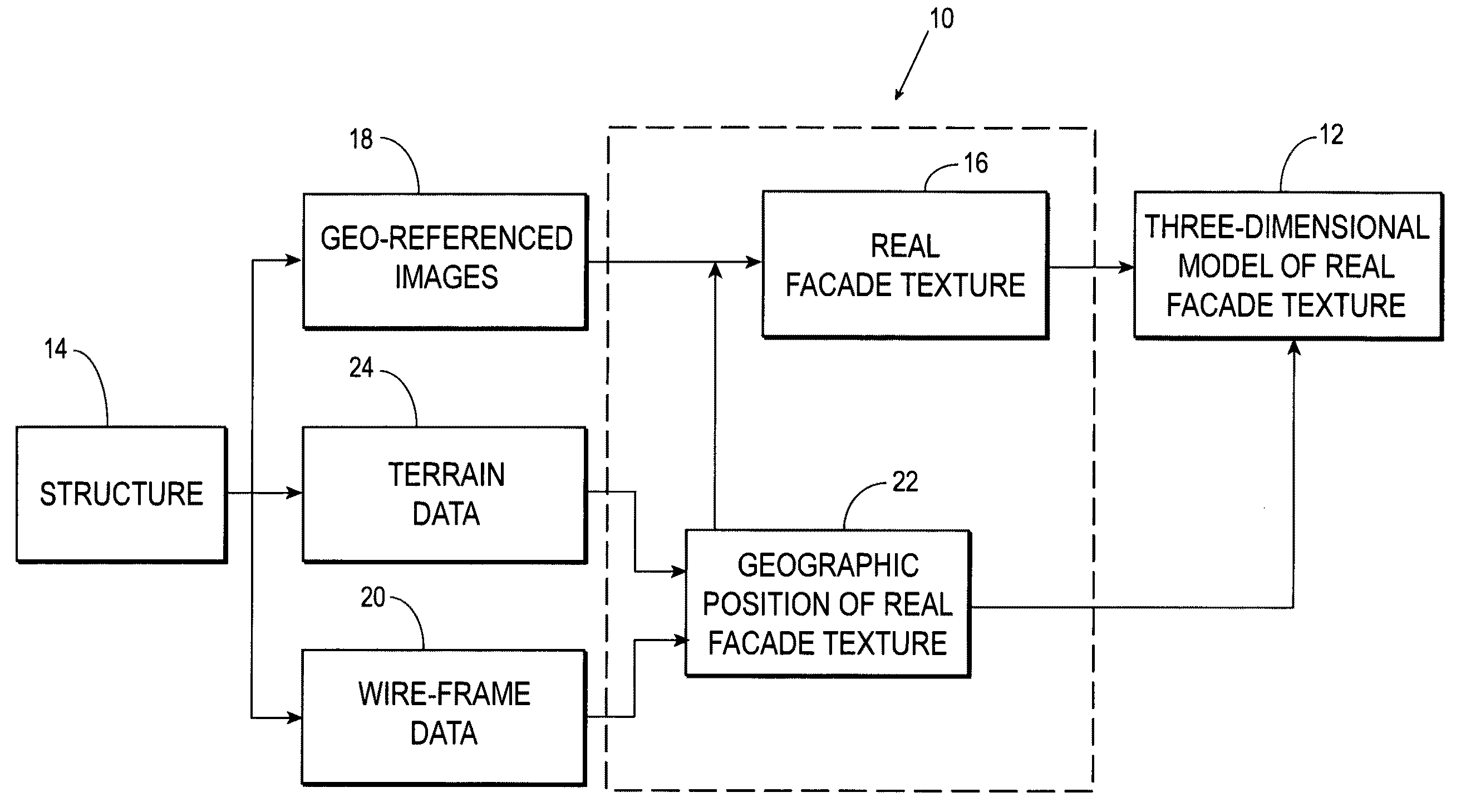
Systems and methods for rapid three-dimensional modeling with real facade texture
Owner:PICTOMETRY INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION
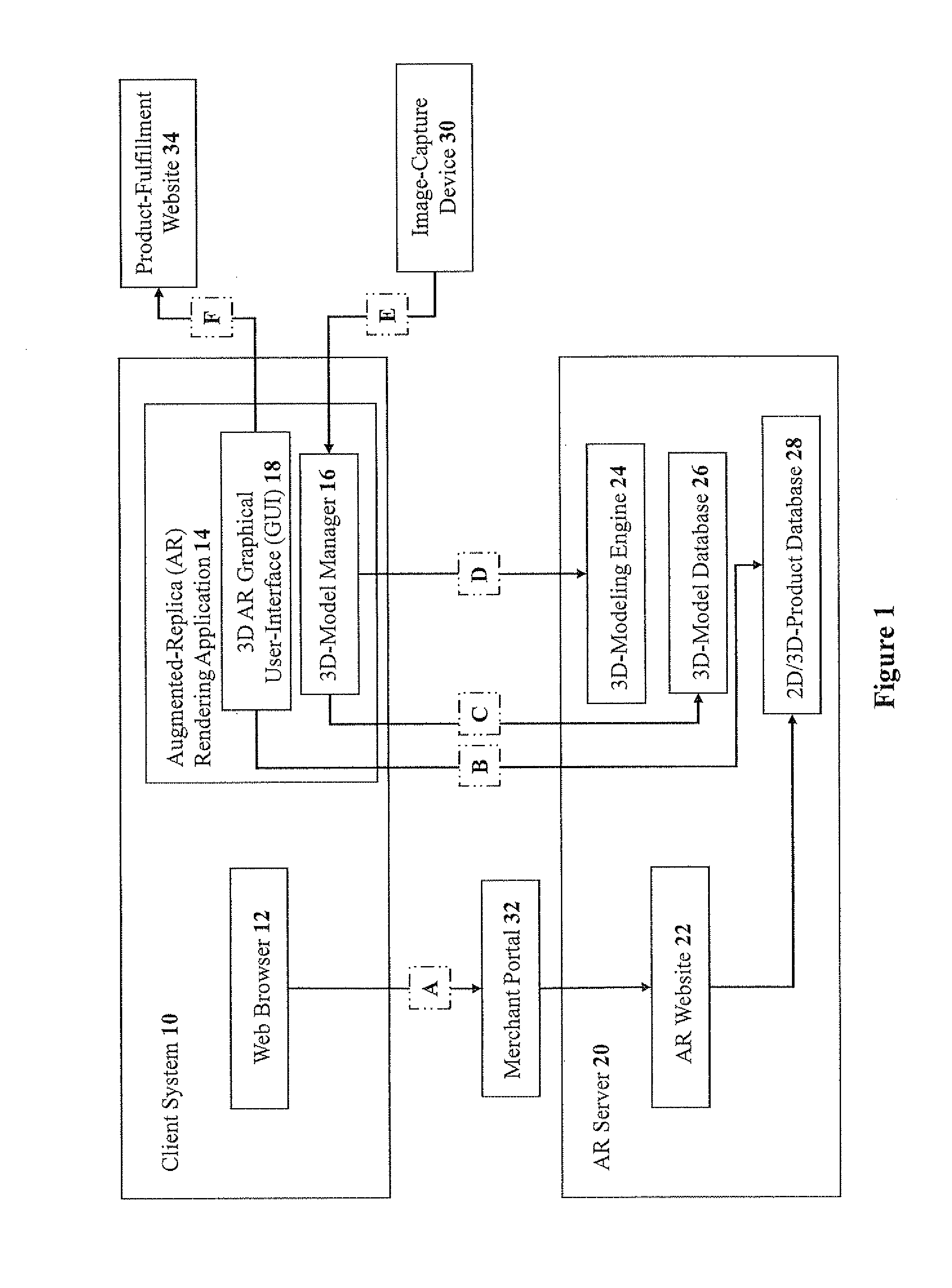
Methods and systems for three-dimensional rendering of a virtual augmented replica of a product image merged with a model image of a human-body feature
ActiveUS20110234581A1Time and cost-effectiveSpectales/gogglesCharacter and pattern recognitionHuman body3D modeling
A system for rendering a merged virtual 3D augmented replica of a 3D product image and a 3D model image of a body part. A 3D modeling engine transforms an acquired 2D image of a body part into a 3D augmented replica thereof. A GUI enables the merging, displaying and manipulating of the 3D product image and the 3D augmented replica of a body part.
Owner:AR ES TECH
Fast multilevel imagination and reality occlusion method at actuality enhancement environment
InactiveCN102129708AMeet real-time requirementsStrengthen the occlusionSteroscopic systems3D-image renderingDimensional modelingParallel processing
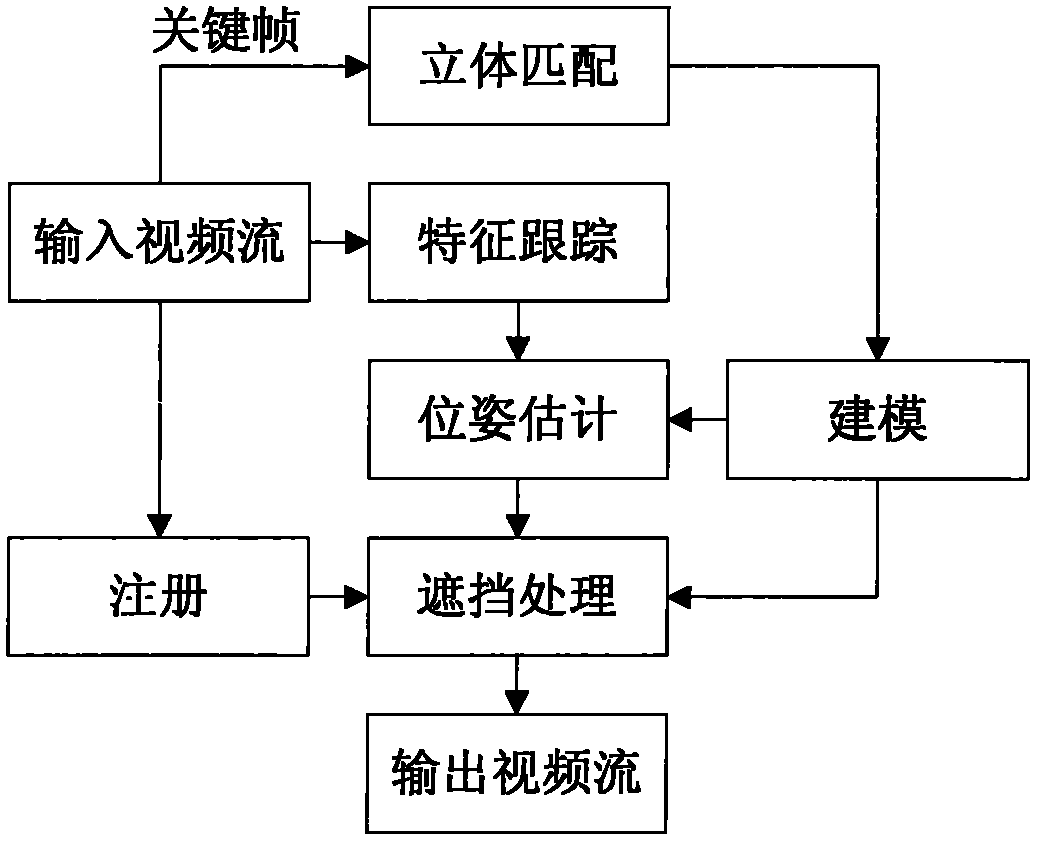
The invention relates to a fast multilevel imagination and reality occlusion method at an actuality enhancement environment, comprising the following steps of: acquiring videos of a real scene by using a two-path video camera; extracting a pair of keyframes from a two-path video stream at set intervals to carry out the resolving of a dense depth map, building a three-dimensional model of a real object participating in occlusion, and extracting sparse feature points; tracking the sparse feature points of all middle frames of the two-path video stream, and estimating the posture of a current camera by combining with the positions of the sparse feature points in an image; acquiring the three-dimensional information of the real object according to a model built for the last time; moving and rotating the model of the real object according to the posture of the current camera; carrying out depth relation comparison by utilizing the three-dimensional information of the recently regulated real object with a registered three-dimensional virtual object; and respectively processing the three-dimensional tracking of the middle frames and the three-dimensional reconstruction of the keyframes in parallel at different threads. The invention is suitable for unknown and variable environments without modeling in advance and can meet the requirements for real time.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
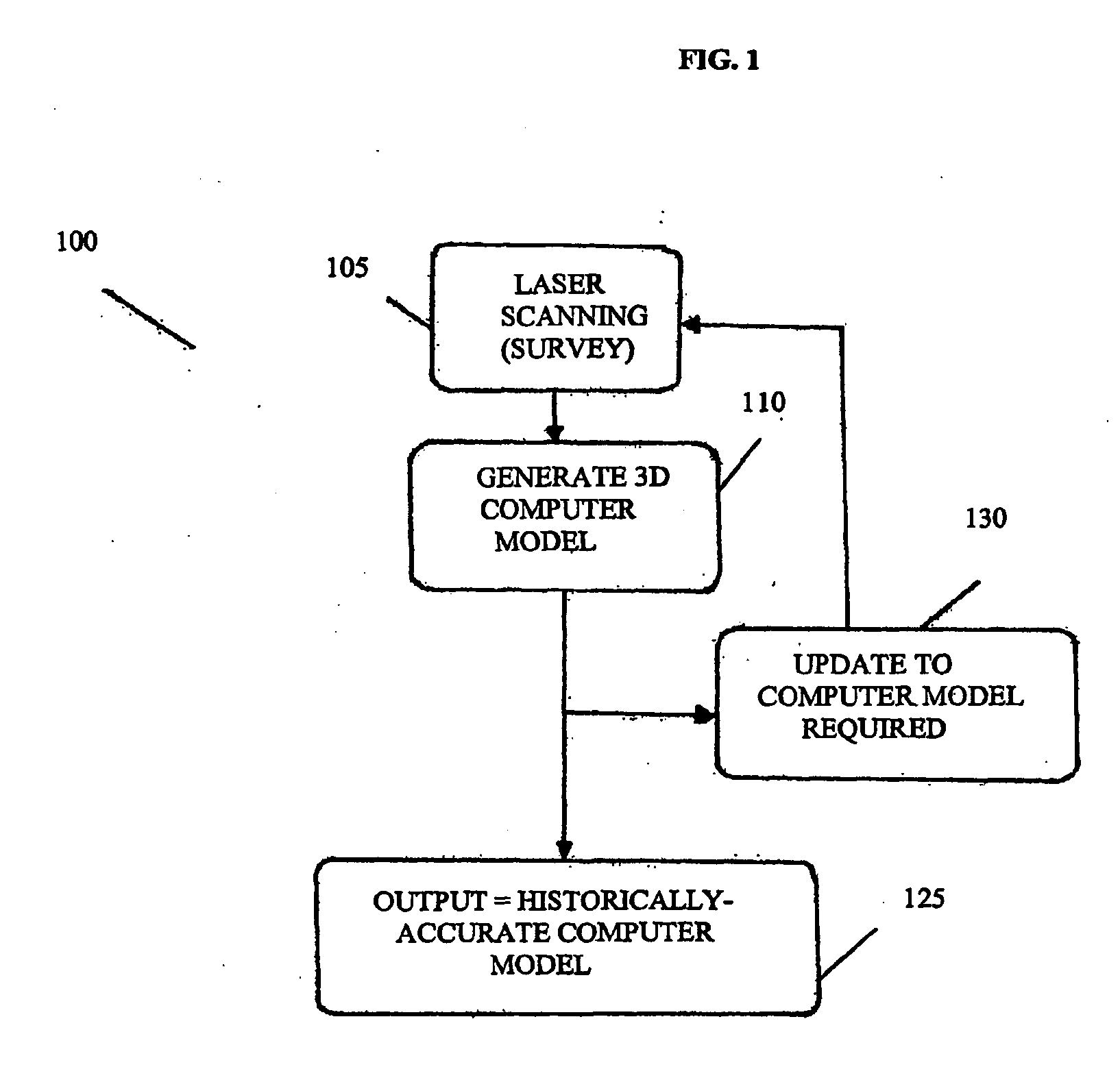
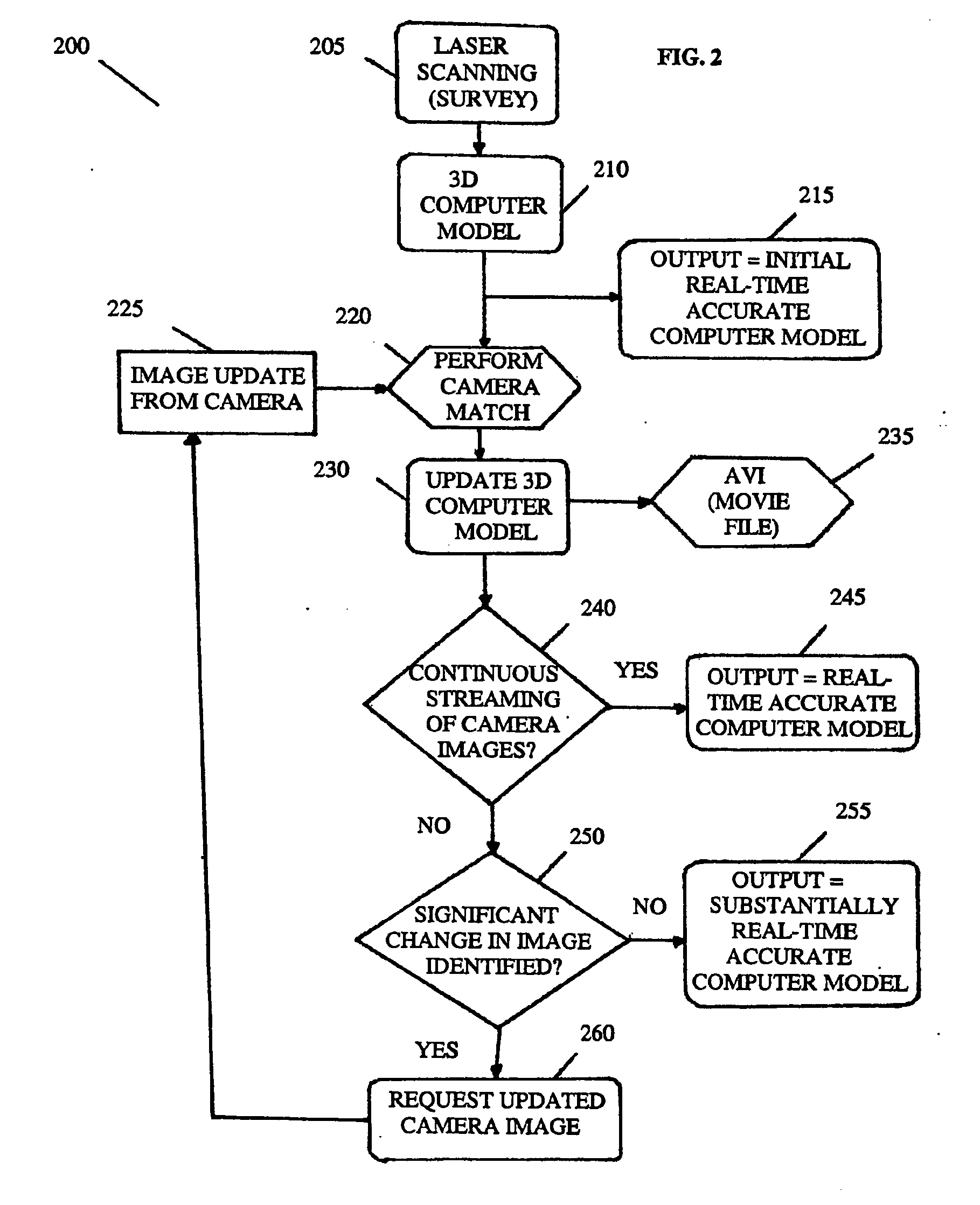
Adaptive 3D image modelling system and apparatus and method therefor
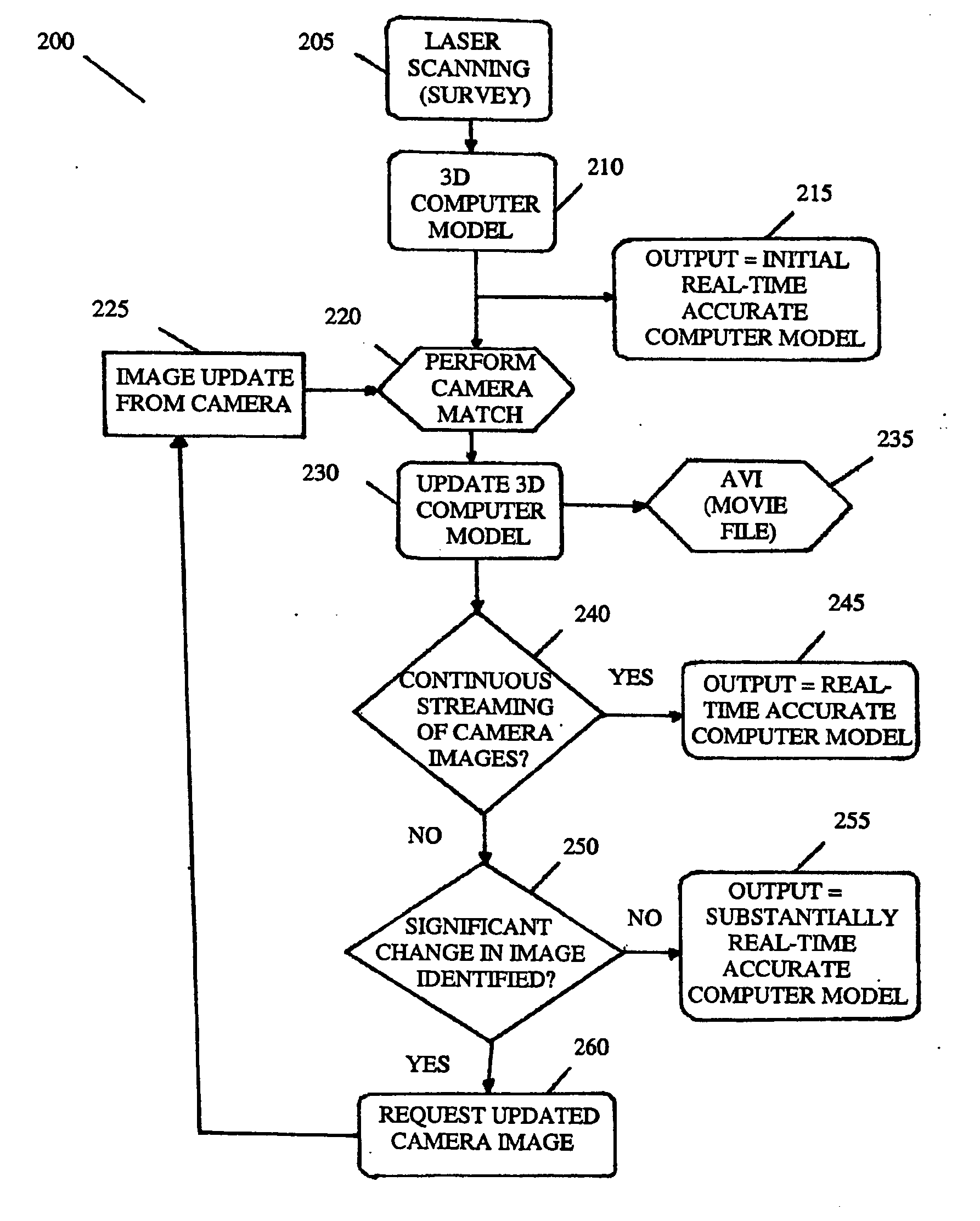
A system which resolves accuracy problems with 3D modeling techniques by using a 3D computer model that is updated using views provided by, say, a camera unit or camera system. The 2D images provided by matching the perspective view of an image within the model to that of an image of the environment. The 3D computer model can therefore be updated remotely, using 2D data.
Owner:MARZELL LAURENCE
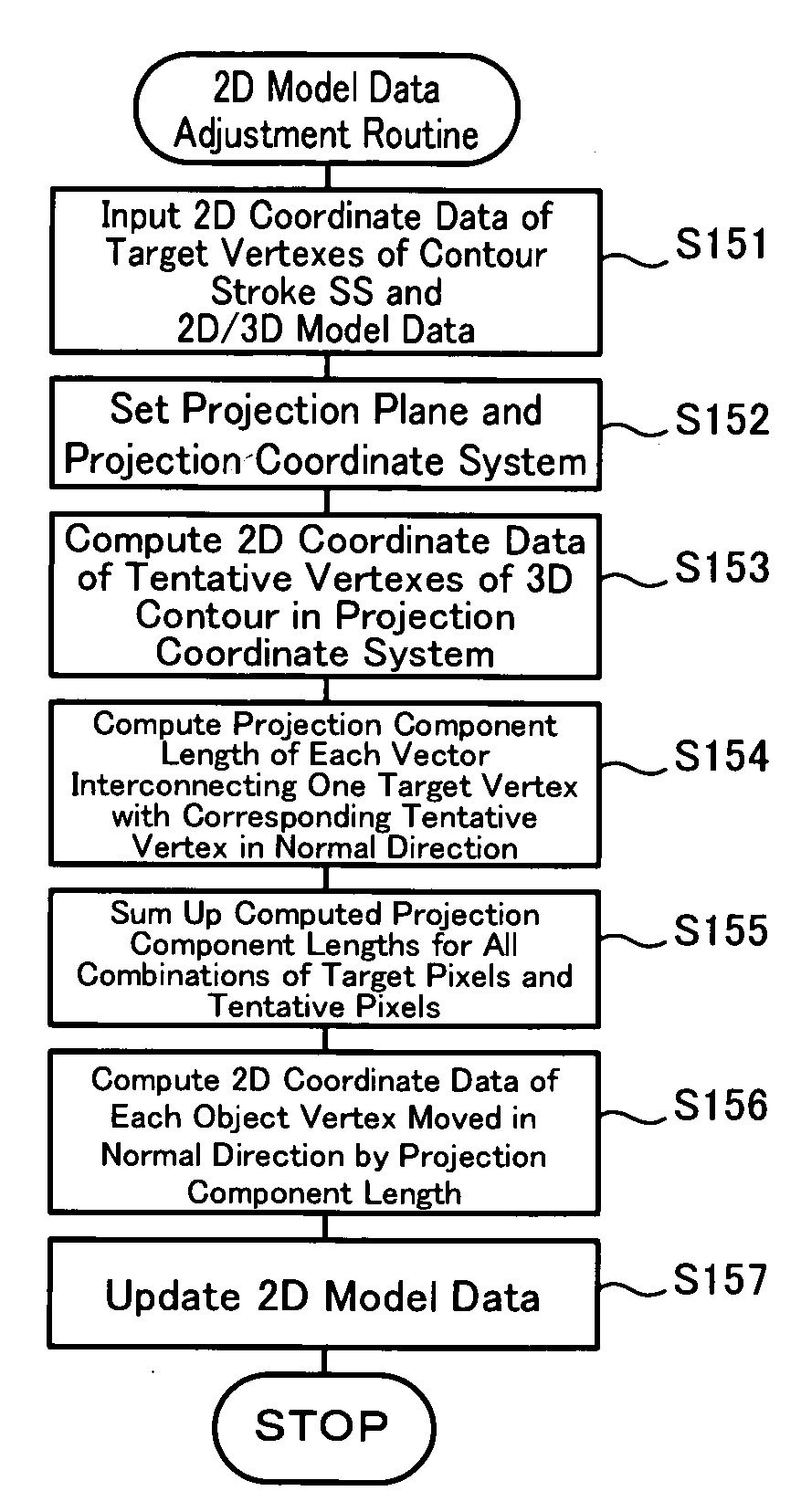
Three-dimensional shape conversion system, three-dimensional shape conversion method, and program for conversion of three-dimensional shape
InactiveUS20090040224A1Improve accuracyAdequately consistentSpecial data processing applications3D-image renderingThree dimensional shapeDimensional modeling
In a computer 20 with a three-dimensional shape conversion program installed therein, a coordinate processing unit 21 obtains two-dimensional coordinate data of a contour stroke SS input through the user's operation of a mouse 50 or another suitable input unit. A 2D / 3D modeling unit 22 performs two-dimensional modeling based on the obtained two-dimensional coordinate data and thereby generates two-dimensional model data regarding a two-dimensional pattern, while performing three-dimensional modeling based on the generated two-dimensional model data and generates three-dimensional model data regarding a three-dimensional shape obtained by expanding the two-dimensional pattern. A 2D model data regulator 23 adjusts the two-dimensional model data to make a corresponding contour of the three-dimensional shape defined by the three-dimensional model data substantially consistent with the input contour stroke SS.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO
Synchronized views of video data and three-dimensional model data
ActiveUS20110050848A1Simple production processSpeed up the processTelevision system detailsImpression capsInteractive modelingSubject matter
Tools are described for preparing digital dental models for use in dental restoration production processes, along with associated systems and methods. Dental modeling is improved by supplementing views of three-dimensional models with still images of the modeled subject matter. Video data acquired during a scan of the model provides a source of still images that can be displayed alongside a rendered three-dimensional model, and the two views (model and still image) may be synchronized to provide a common perspective of the model's subject matter. This approach provides useful visual information for disambiguating surface features of the model during processing steps such as marking a margin of a prepared tooth surface for a restoration. Interactive modeling tools may be similarly enhanced. For example, tools for margin marking may synchronize display of margin lines between the still image and the model so that a user can interact with either or both of the visual representations, with changes to a margin reflected in both displays.
Owner:MEDIT CORP
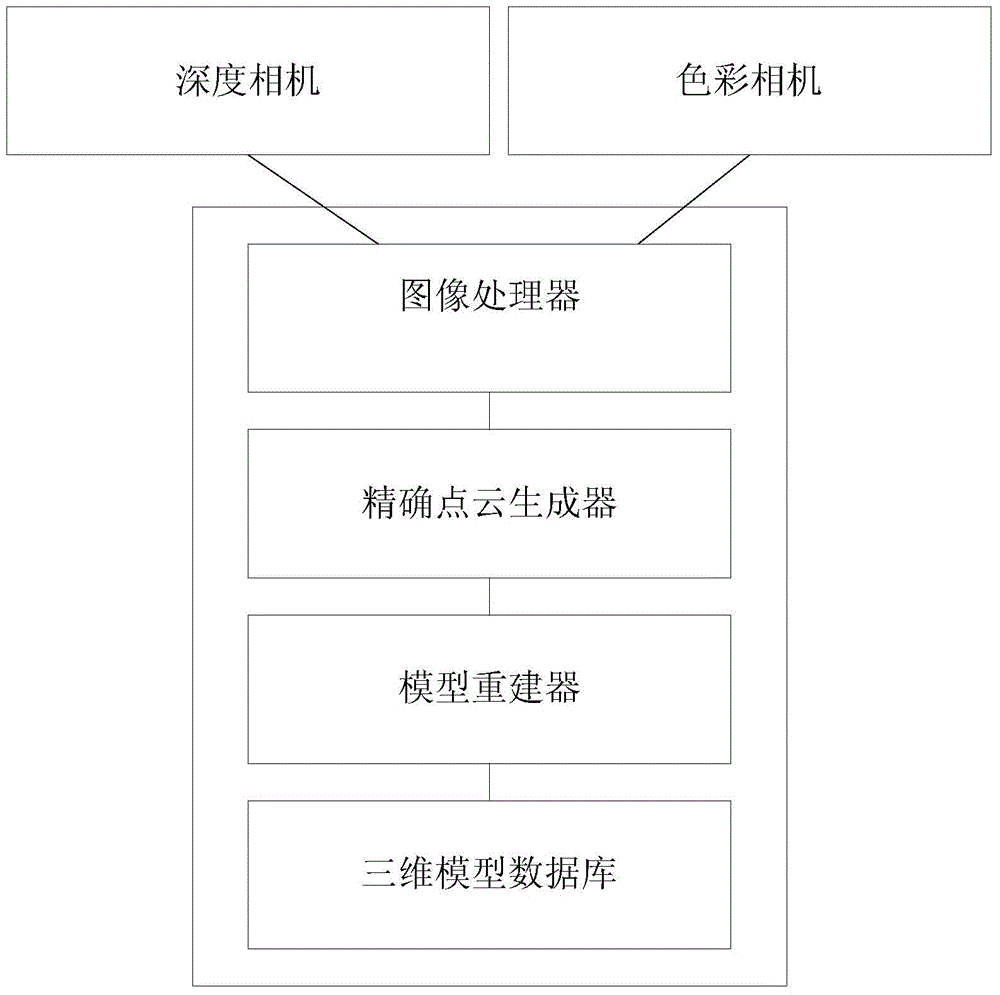
Three-dimensional model reconstruction method and system
InactiveCN104599314AReduce motion blurReduce data redundancyImage analysis3D modellingPoint cloudMultiple frame
The invention relates to a three-dimensional model reconstruction method and system. The method comprises the following steps: S1, performing image acqusition on a target by using at least one depth camera to acquire a depth image of the target; S2, preprocessing the acquired depth image; S3, acquiring dense point cloud data according to the depth image of the target to reconstruct a target depth information point cloud grid; S4, combining and registering the multiple frames of reconstructed depth images to obtain a three-dimensional model. By implementing the method and the system, the accurate three-dimensional model of the target can be acquired without manually marking the target.
Owner:SHENZHEN ORBBEC CO LTD
Method and system for creating 3D models from 2D data for building information modeling (BIM)
ActiveUS9817922B2Computer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsSimulationHigh dimensional
A method and system for creating three dimensional (3D) models from two dimensional (2D) data for building information modeling (BIM). The method and system allow new, 2D, 3D and higher dimensional models to be created for existing 3D modeling programs (e.g., AUTODESK REVIT, AUTOCAD, VECTORWORKS, MICROSTATION, ARCHICAD, etc.). The new models are used to enhance and extend existing 3D modeling programs. The new models can also be used to directly create physical objects (e.g., windows, doors, etc.) represented by the new models with robots, 3D printers and manufacturing machines.
Owner:ANGULERIS TECH
Method and system for GPS enabled model and site interaction and collaboration for BIM and other design platforms
A method and system for GPS enabled model and site interaction for Building Information Modeling (BIM) and other design platforms. Collaboration information for actual physical objects at physical locations is automatically collected and associated with virtual objects in virtual object models in a three-dimensional (3D) object modeling programs for a selected project or new virtual objects that did not previously exist are created in the 3D modeling program and associated with the actual physical objects that have been physically added to at a project site. The method and system allows two-way real-time and static collaboration between native and new composite XD (e.g., 3D, or lower or higher dimensional) object models from within existing 3D modeling BIM programs (e.g., AUTODESK REVIT, AUTOCAD, VECTORWORKS, etc.) and the actual physical objects at the actual physical locations.
Owner:ANGULERIS TECH
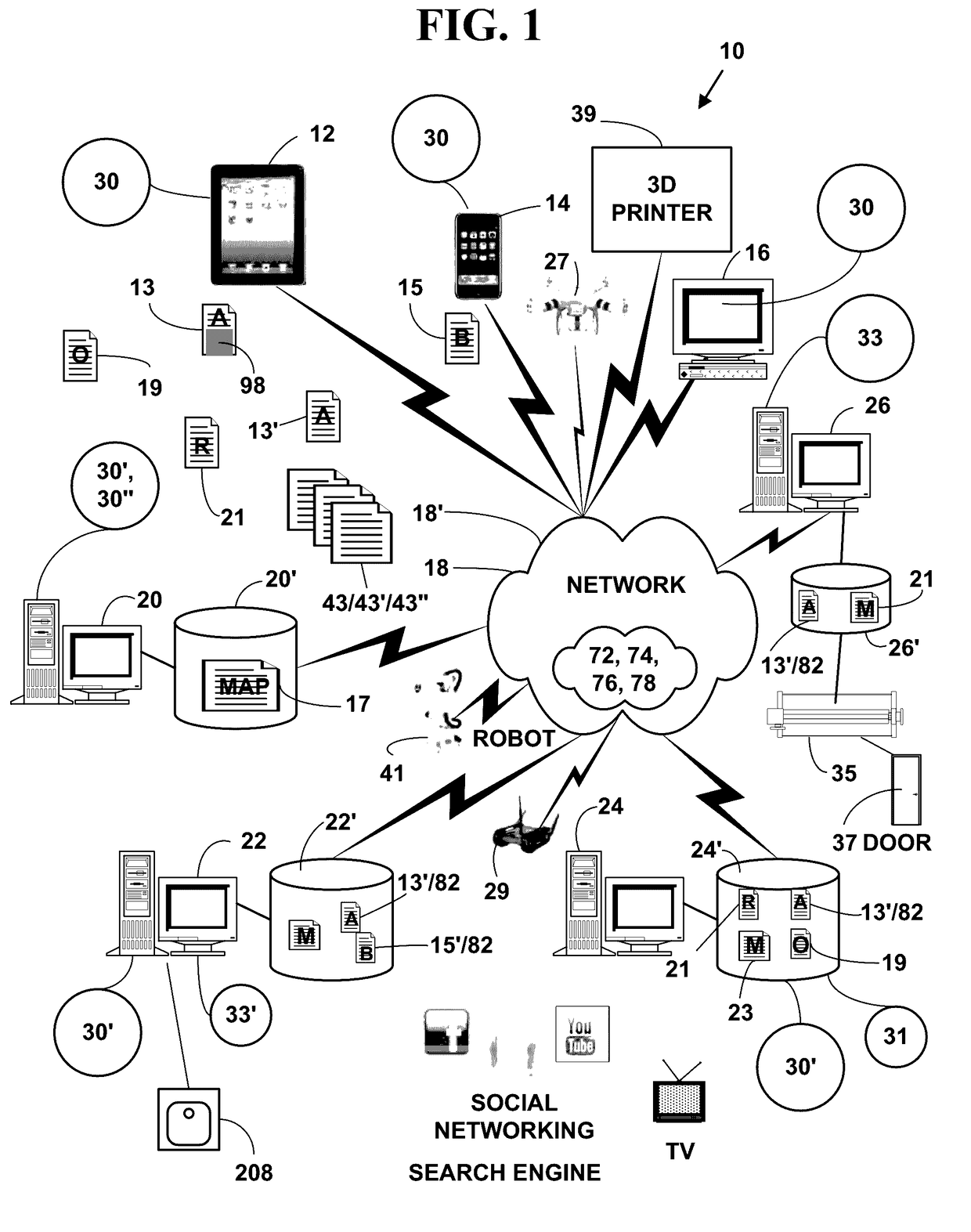
Systems and methods for 3D modeling and asset management
A 3D modeling system is configured to generate a 3D model from a plurality of architectural, engineering and construction information related to a physical asset being model. The 3D model is based on component models that are associated with specific geometry, geo-positioning, lighting, acoustics, and other real world features or characteristics. The 3D model can also be turned into a digital asset by associating it with critical information related to the physical asset and storing the 3D model and the associations in a database for retrieval and management of the digital asset.
Owner:SATELLIER SCREAMPOINT
Method and system for creating composite 3D models for building information modeling (BIM)
A method and system for creating composite three dimensional (3D) models for building information modeling (BIM). The method and system provides the creation of new composite 3D and higher dimensional models from plural different 3D models from plural different manufacturers for existing 3D modeling (e.g., AUTODESK REVIT, AUTODESK INVENTOR, AUTOCAD, SKETCHUP, VECTORWORKS, MICROSTATION, ARCHICAD, SOLIDWORKS, PROE, etc.) The new composite 3D models are used to enhance and extend existing 3D modeling programs. The new models can also be used to directly create new physical objects (e.g., windows, doors, etc.) that never existed before with robots, 3D printers and manufacturing machines.
Owner:ANGULERIS TECH
Method for manufacturing metal parts and molds and micro-roller used therefor
ActiveUS20130197683A1Formability of complexImprove accuracyArc welding apparatusAdditive manufacturing with liquidsNumerical controlWire rod
A method for manufacturing parts and molds by: 1) slicing a three-dimensional CAD model of a part or mold; 2) planning a modeling path according to slicing data of the three-dimensional CAD model, whereby generating numerical control codes for modeling processing; and 3) performing fused deposition modeling of powders or wire material of metal, intermetallic compounds, ceramic and composite functional gradient materials by layer using a welding gun on a substrate layer via a numerical control gas shielded welding beam or laser beam according to a track specified by the numerical control code for each layer. A micro-roller or a micro-extrusion unit is installed at a contact area between melted and softened areas. The micro-roller or the micro-extrusion unit synchronously moves along with fused deposition area, which results in compressing and processing of the fused deposition area during the fused deposition modeling.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
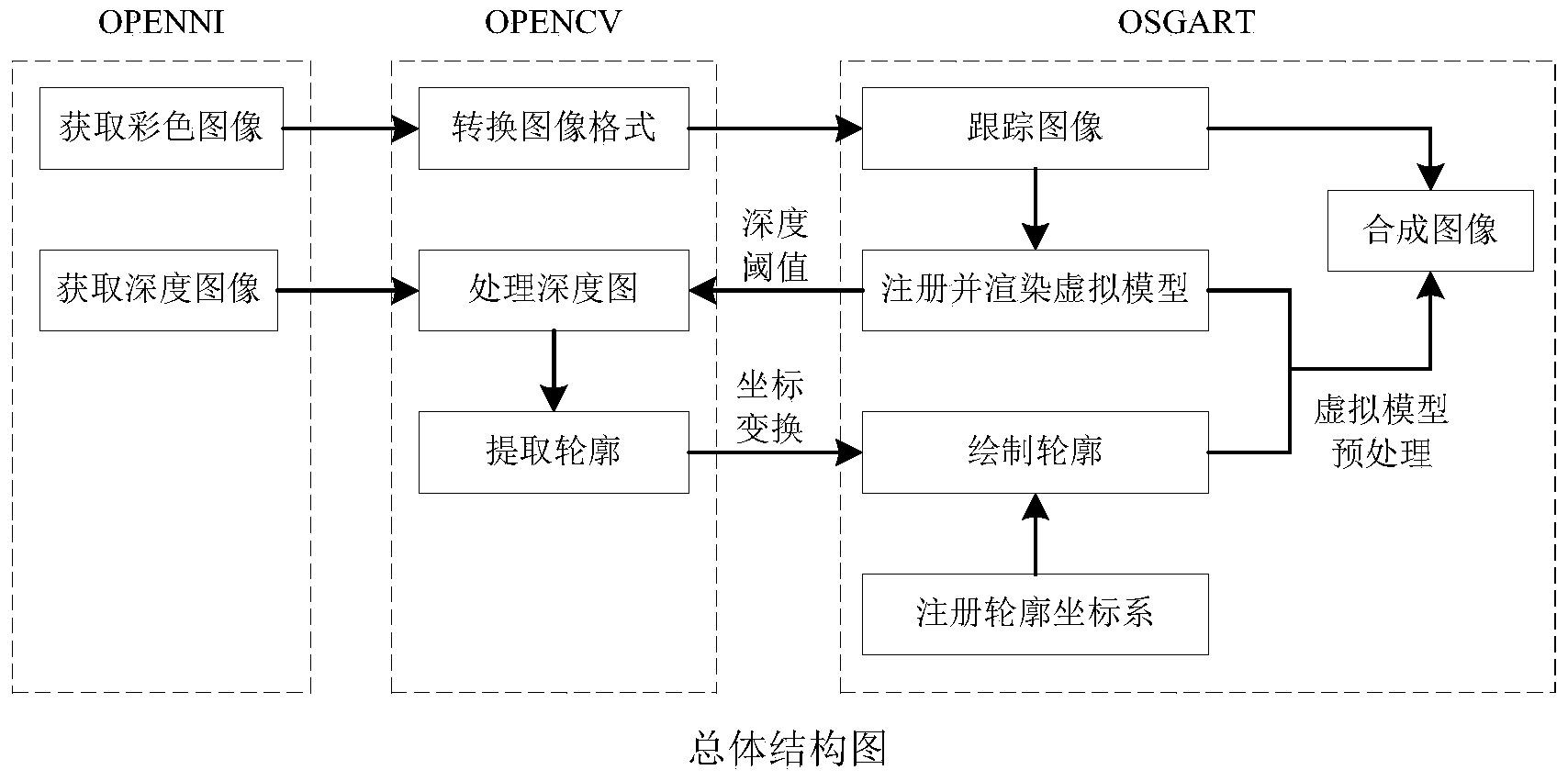
Virtual reality occlusion handling method, based on virtual model pretreatment, in augmented reality system
InactiveCN103489214AMeet real-time requirementsGood virtual and real occlusion effectImage analysis3D-image renderingOcclusion effectColor image
The invention relates to a virtual reality occlusion handling method, based on a virtual model pretreatment, in augmented reality system. The method comprises the steps of utilizing a depth camera KINECT to obtain a color image and a gray level image representing depth information; converting the color image into a bitmap image capable of being identified and tracked by an augmented reality occlusion system and registering a virtual model in a three-dimension mode; combining the three-dimensional registration position of the virtual model and the self depth of the virtual model to conduct threshold treatment on the gray level image and extracting the peripheral contour of a real object; in the render scene of the virtual model, registering a contour coordinate system in a three-dimensional mode; switching a two-dimensional outline vertex coordinate system into a three-dimensional coordinate corresponding to the actual size, drawing in the contour coordinate system, and using a re-drawn contour as a three-dimensional model to shield the virtual model; combining the color image and the treated virtual model, filling a real object image into an outline internal area, namely, the occlusion part of the virtual model, so as to obtain a virtual reality occlusion effect. According to the method, pre-modeling and comparing the depth information of the virtual model pixel by pixel are not needed, so that the method is suitable for environments with unknown changes and can meet instantaneity requirements.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
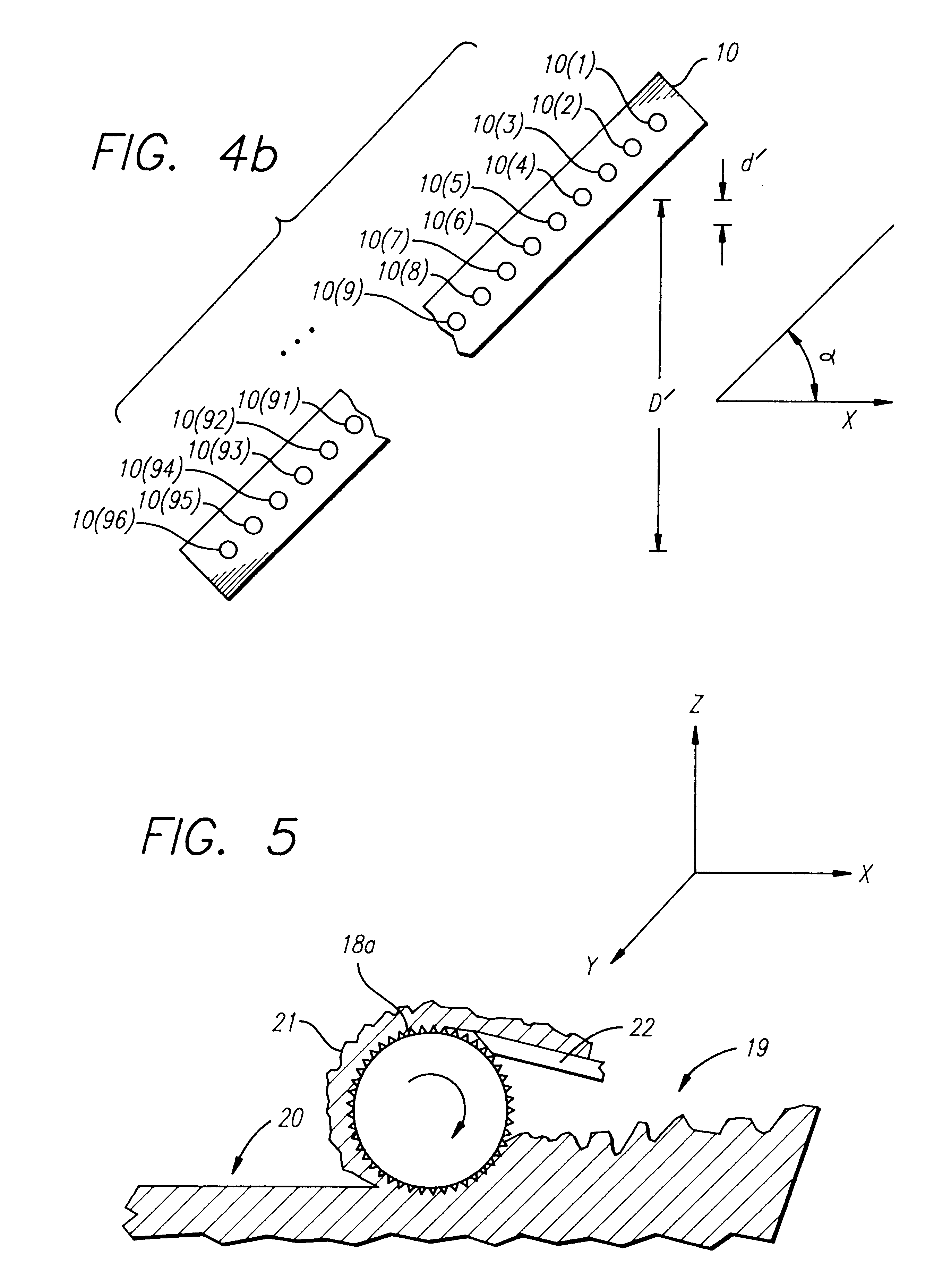
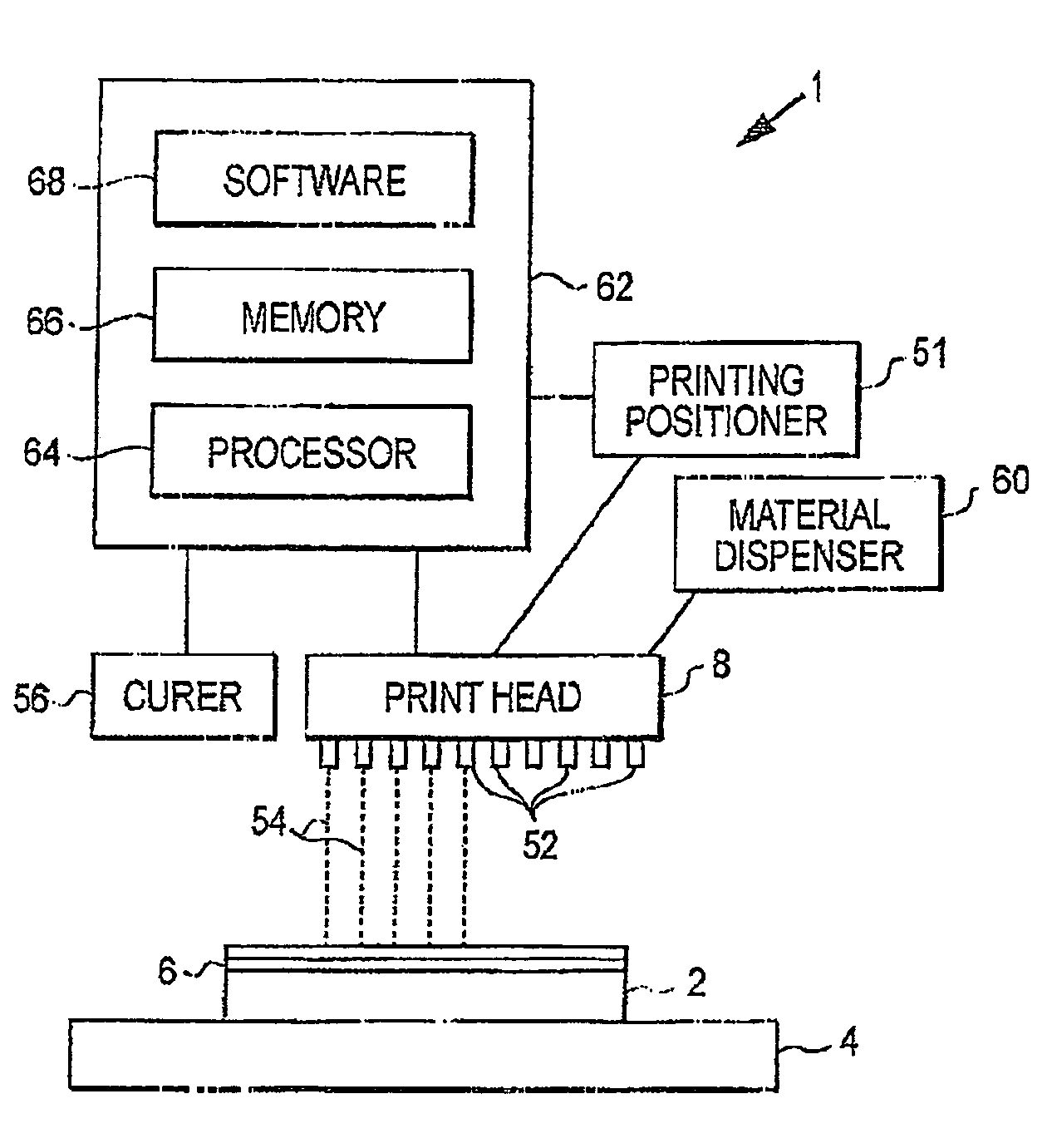
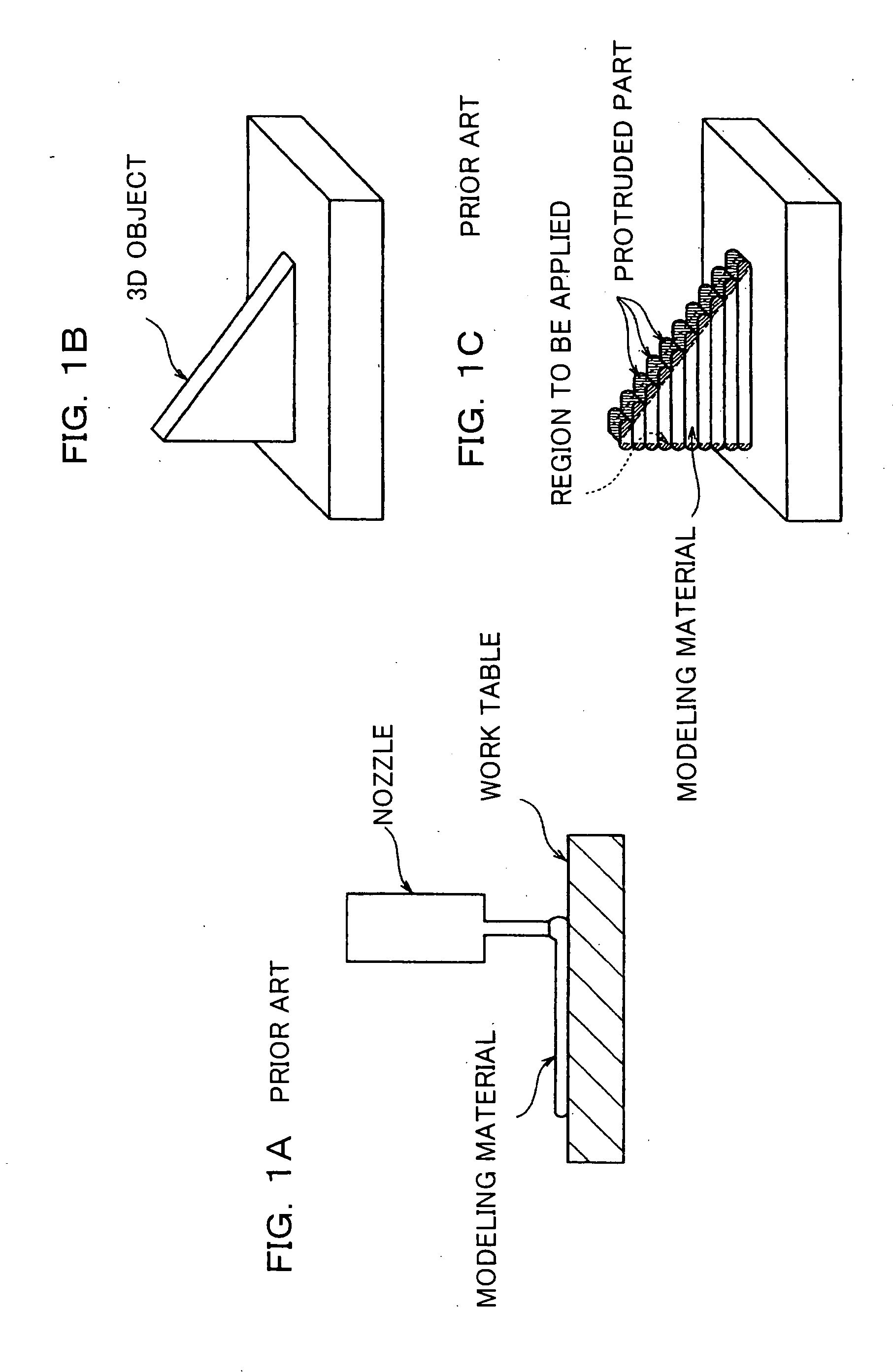
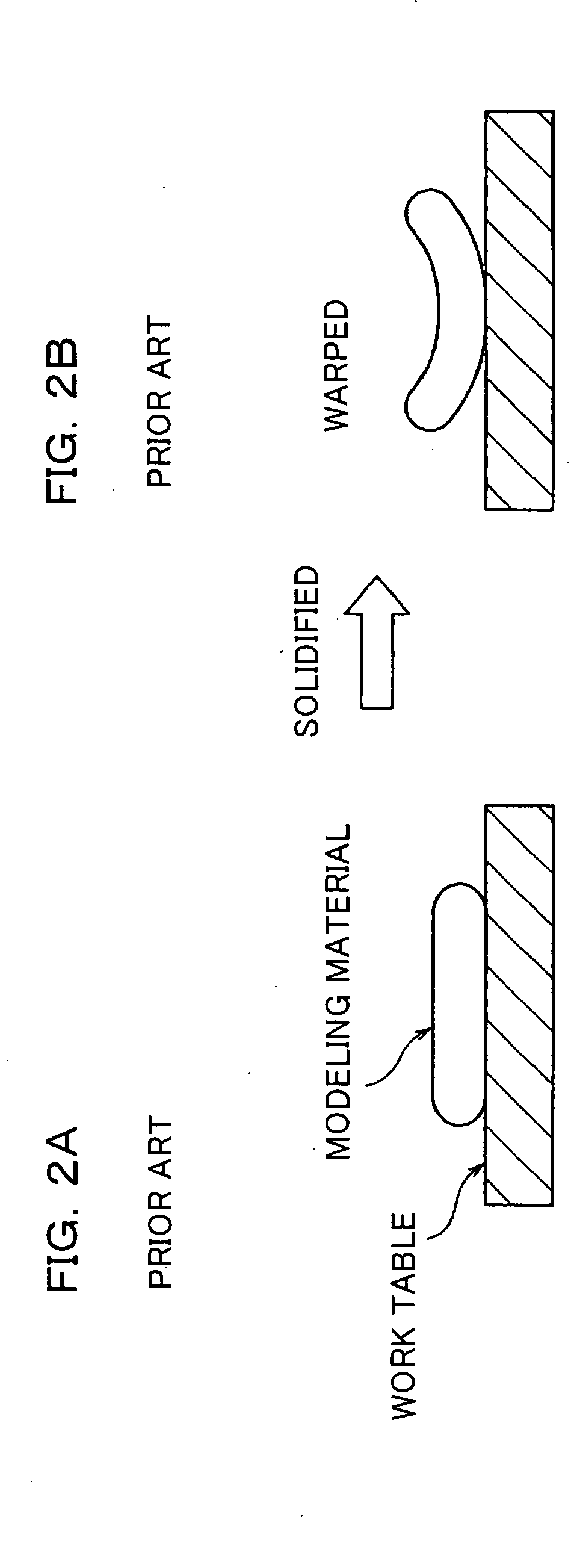
3D modeling device and 3D modeling method for supplying material with high precision
A 3D modeling device performs repeatedly a step of cutting a subsidiary material layer formed of a subsidiary material and cutting a modeling material layer formed of a modeling material. The 3D modeling device comprises at least one of a subsidiary material supplying device which discharges the subsidiary material drop by drop from an outlet positioned apart from a region in which the subsidiary material is to be applied at a predetermined distance, and a modeling material supplying device which discharges the modeling material drop by drop from an output positioned apart from a region in which the modeling material is to be applied at a predetermined distance. Since the material can be applied with high precision, a high-quality 3D molded object is provided.
Owner:ROLAND DG CORP
Device and method for achieving accurate positioning of acetabular cup during total hip replacement
A method and device are provided in order to achieve desired orientation of an acetabular cup for total hip replacement or hip resurfacing. The method and device utilize preoperative CT, MRI or other scans, 3D computer modeling and a patient specific alignment jig created from CT, MRI or other data and computer 3D modeling. The device allows accurate placement of a drill hole to establish an acetabular axis and placement of an acetabular cup perpendicular to the axis.
Owner:URE KEITH J
Method and system for creating 3D models from 2d data for building information modeling (BIM)
ActiveUS20150248503A1Computer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsSimulationHigh dimensional
A method and system for creating three dimensional (3D) models from two dimensional (2D) data for building information modeling (BIM). The method and system allow new, 2D, 3D and higher dimensional models to be created for existing 3D modeling programs (e.g., AUTODESK REVIT, AUTOCAD, VECTORWORKS, MICROSTATION, ARCHICAD, etc.). The new models are used to enhance and extend existing 3D modeling programs. The new models can also be used to directly create physical objects (e.g., windows, doors, etc.) represented by the new models with robots, 3D printers and manufacturing machines.
Owner:ANGULERIS TECH
Method and system for creating composite 3D models for building information modeling (BIM)
A method and system for creating composite three dimensional (3D) models for building information modeling (BIM). The method and system provides the creation of new composite 3D and higher dimensional models from plural different 3D models from plural different manufacturers for existing 3D modeling (e.g., AUTODESK REVIT, AUTODESK INVENTOR, AUTOCAD, SKETCHUP, VECTORWORKS, MICROSTATION, ARCHICAD, SOLIDWORKS, PROE, etc.) The new composite 3D models are used to enhance and extend existing 3D modeling programs. The new models can also be used to directly create new physical objects (e.g., windows, doors, etc.) that never existed before with robots, 3D printers and manufacturing machines.
Owner:ANGULERIS TECH
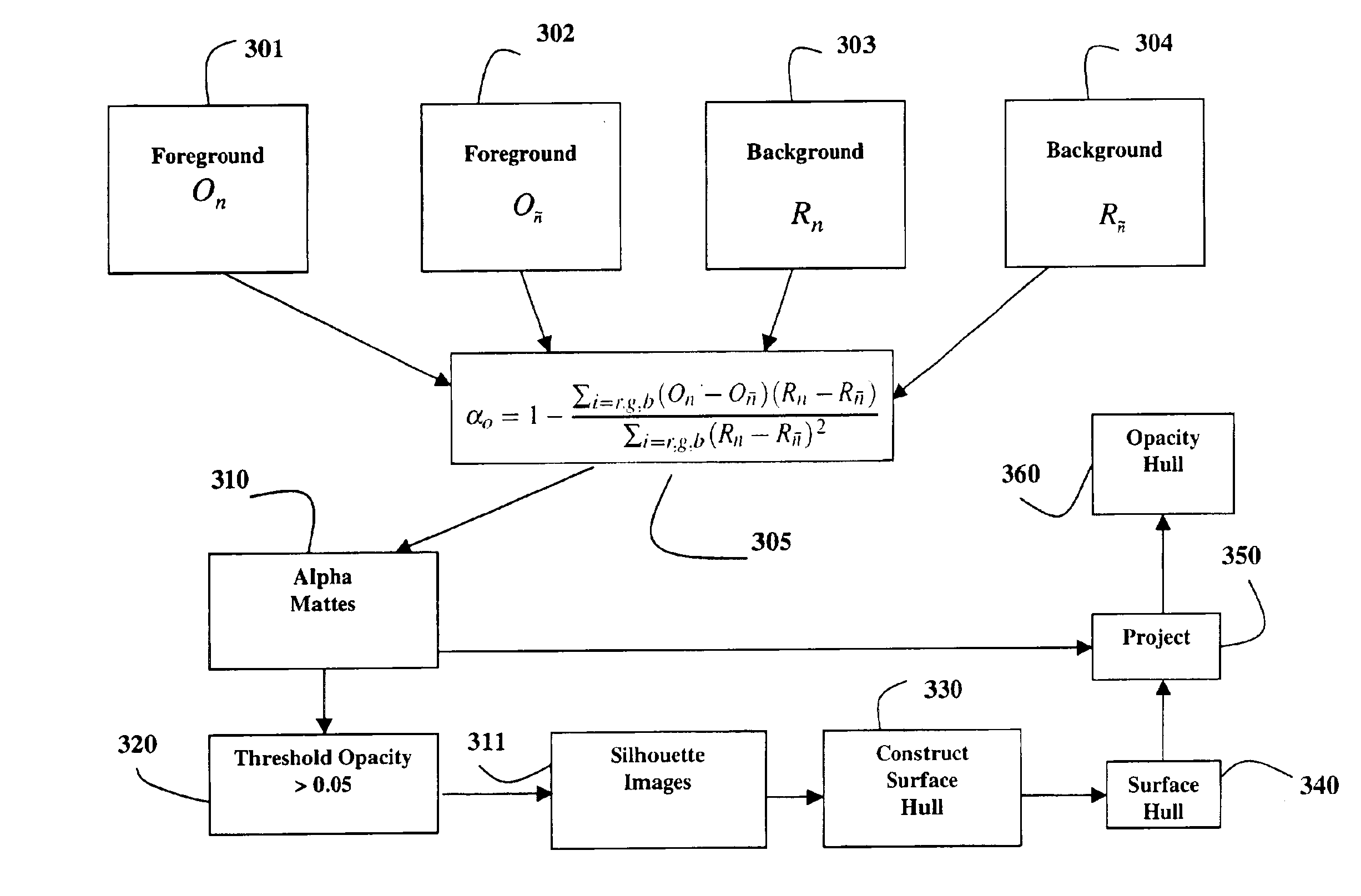
Image-based 3D modeling rendering system
InactiveUS6903738B2Easy to useSimple setup3D-image rendering3D modellingMultiple viewpoint3D modeling
A method models a three-dimensional object by first acquiring alpha mattes of the object for multiple viewpoints. The alpha mattes are then projected onto a surface hull completely enclosing the object to construct an opacity hull storing opacity values of the surface of the object. The object is illuminated for various lighting conditions while images are acquired. The images are projected onto the opacity hull to render the object under arbitrary lighting conditions for arbitrary viewpoints.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Method and system for native object collaboration, revision and analytics for BIM and other design platforms
A method and system for native object collaboration, revision and analytics for Building Information Models (BIM) and other design platforms. The method and system provide X-dimensional (XD) models for building information modeling (BIM) with collaboration and analytics. The method and system allows real-time and static collaboration on native and new composite XD (e.g., 3D, or lower or higher dimensional) object models from within existing 3D modeling BIM programs (e.g., AUTODESK REVIT, AUTOCAD, VECTORWORKS etc.). Collaboration analytics are collected and displayed.
Owner:ANGULERIS TECH
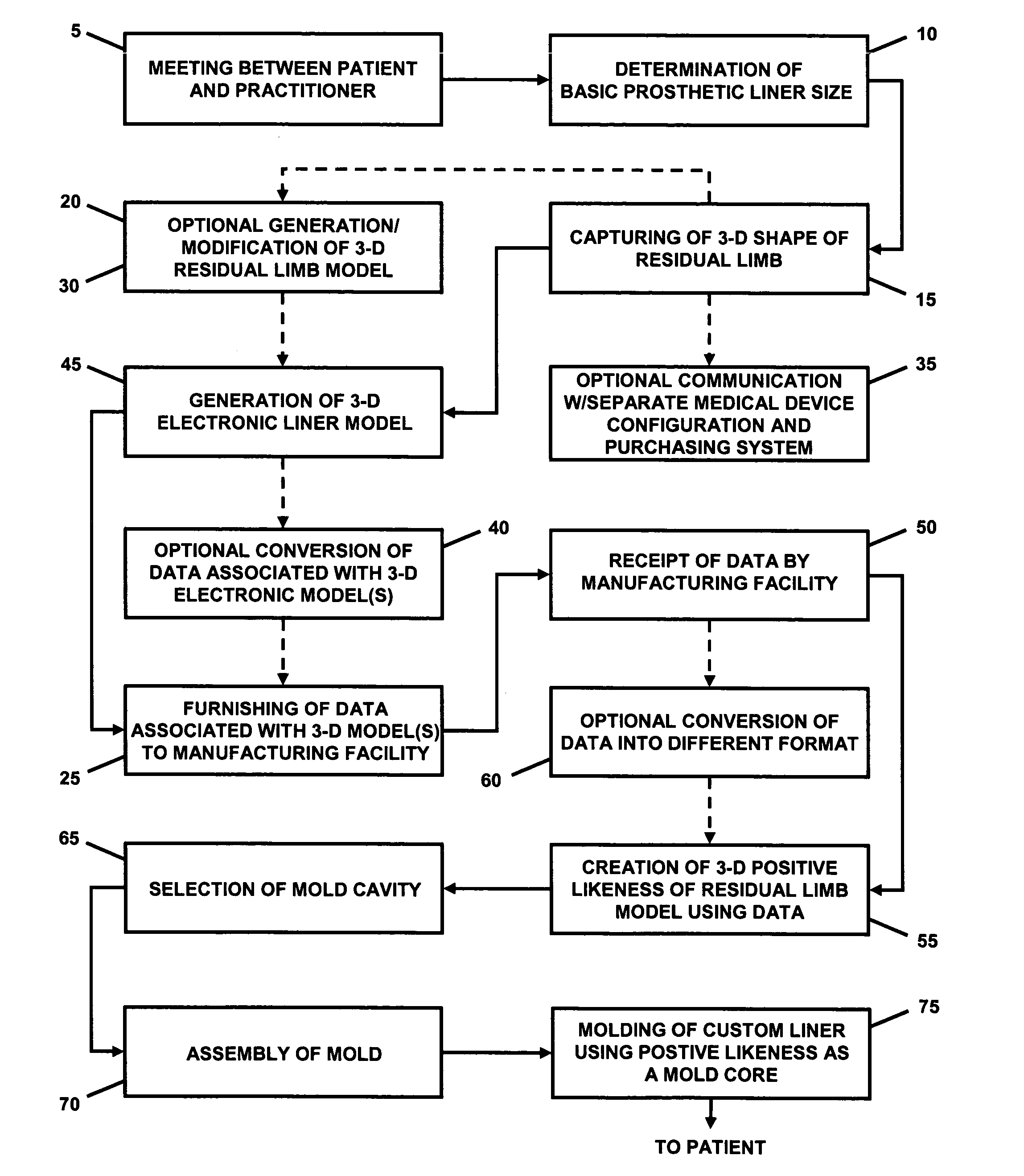
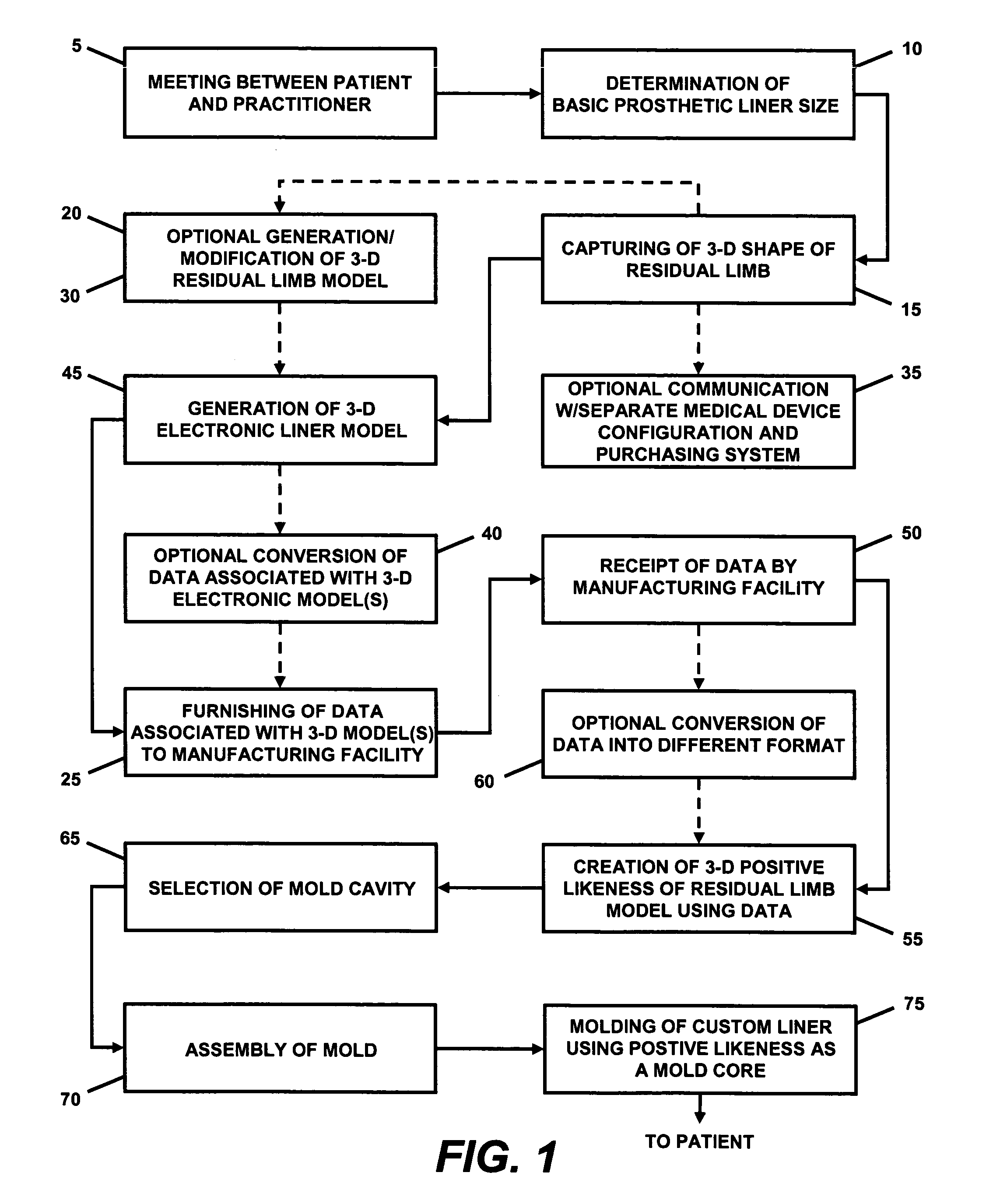
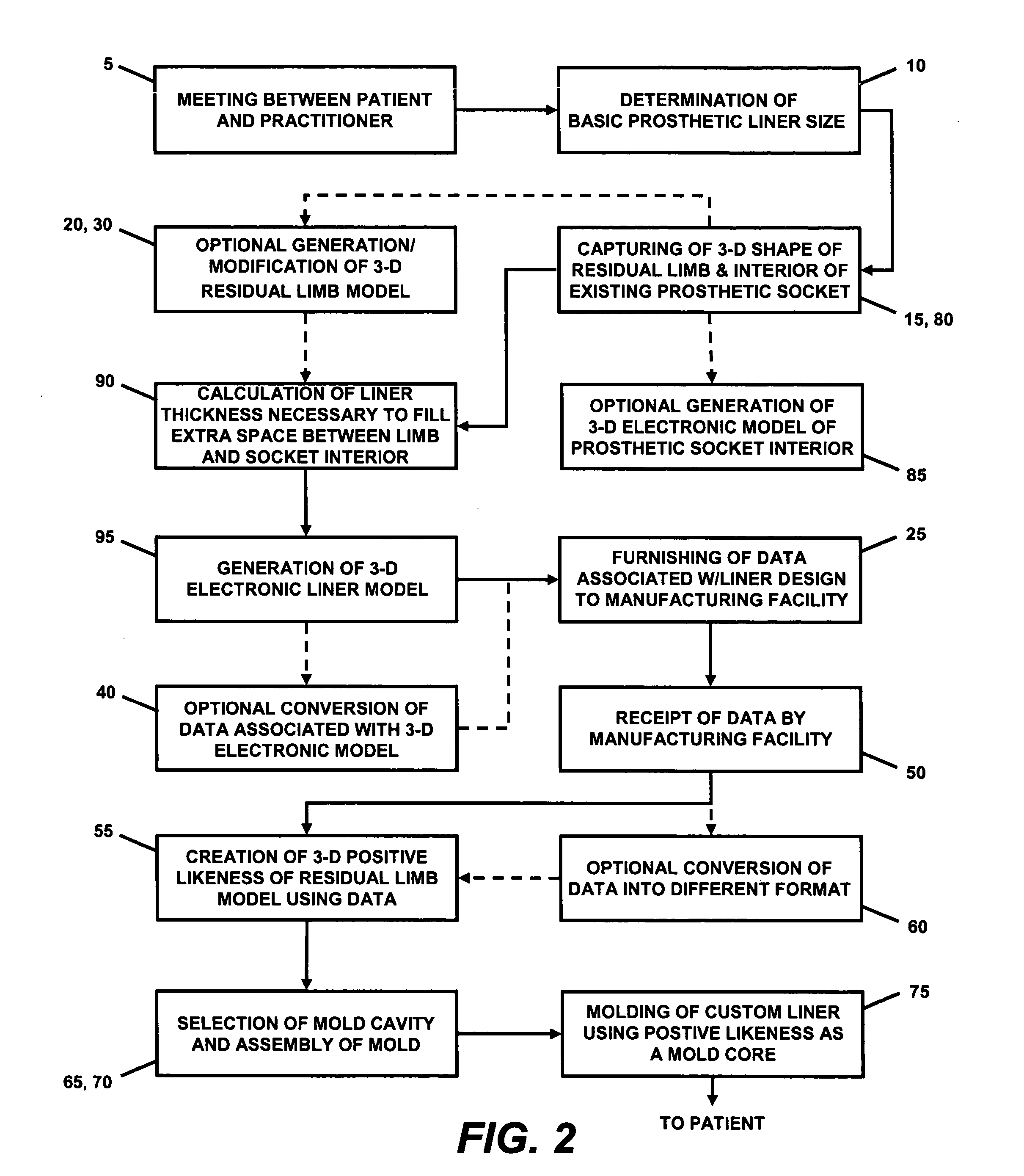
Custom prosthetic liner manufacturing system and method
ActiveUS20050119777A1Good for scrollingEasy doffingProgramme controlDigital data processing detailsResidual limbDevice prosthetic
A system and method for manufacturing a custom prosthetic liner. The system may include a shape capture device for capturing the shape of a residual limb. The captured shape may be used to generate a 3-dimensional electronic liner model using a processor and specialized software. A 3-dimensional electronic model of the residual limb may also be produced. Preferably, an interface is provided that allows a user of the system to alter the shape and / or size of the 3-dimensional model(s) to allow the subsequently-produced liner to accommodate particular features of the residual limb. Data associated with at least the resulting 3-dimensional liner model is provided to a manufacturing facility equipped to produce a custom liner therefrom. The data may be remotely transmitted to the manufacturing facility. A positive likeness of the residual limb is created from the data associated with the 3-dimensional model(s), and is subsequently used as a mold core in the liner molding process.
Owner:WILLOWWOOD GLOBAL LLC
Automated metrology and model correction for three dimensional (3D) printability
A system and a method automate metrology, measurement, and model correction of a three dimensional (3D) model for 3D printability. Slices of the 3D model are received or generated. The slices represent 2D solids of the 3D model to be printed in corresponding print layers. Medial axis transforms of the slices are calculated. The medial axis transforms represent the slices in terms of corresponding medial axes. A local feature size at any point along a boundary of the slices is determined as the shortest distance from the point to a corresponding medial axis.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com