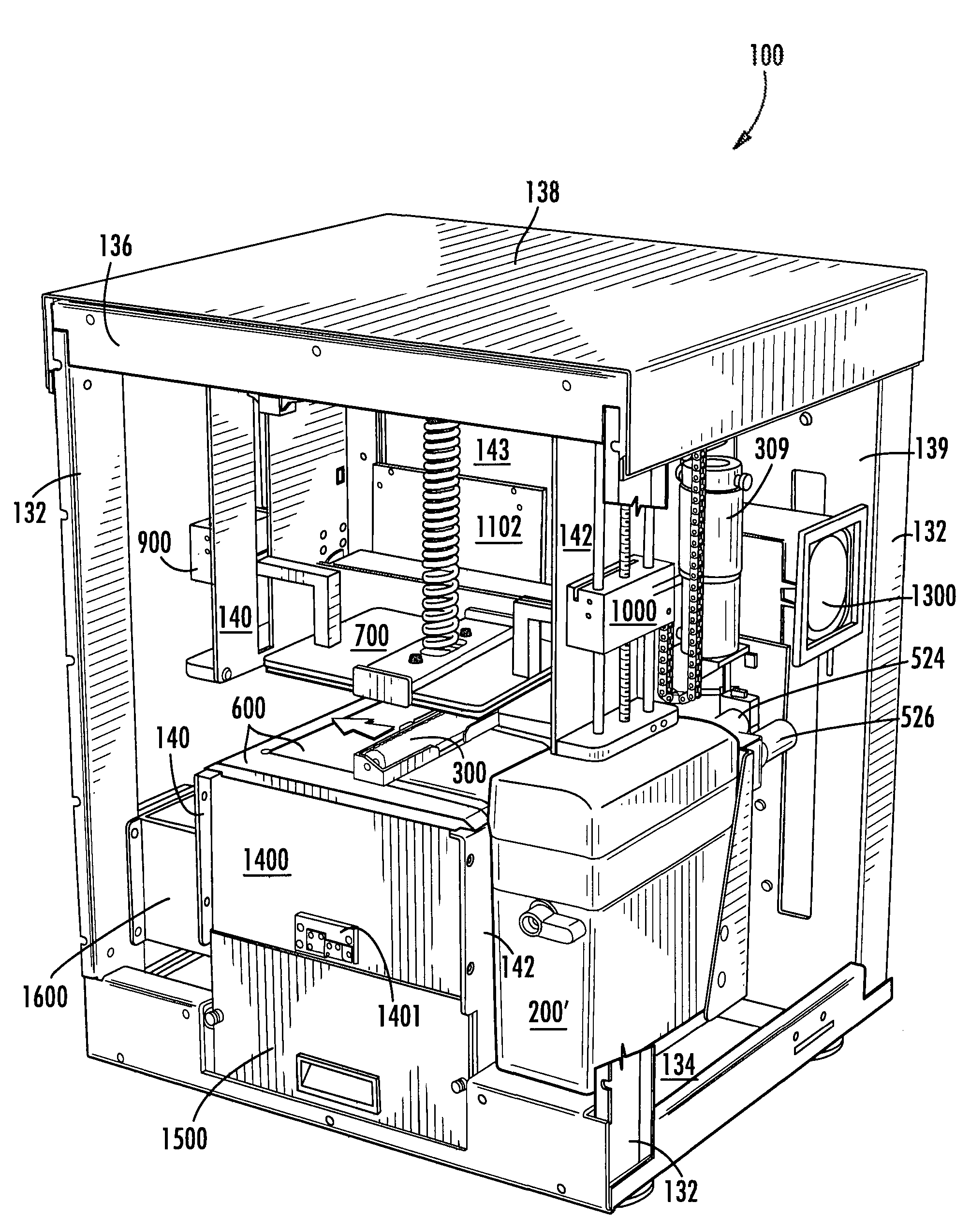
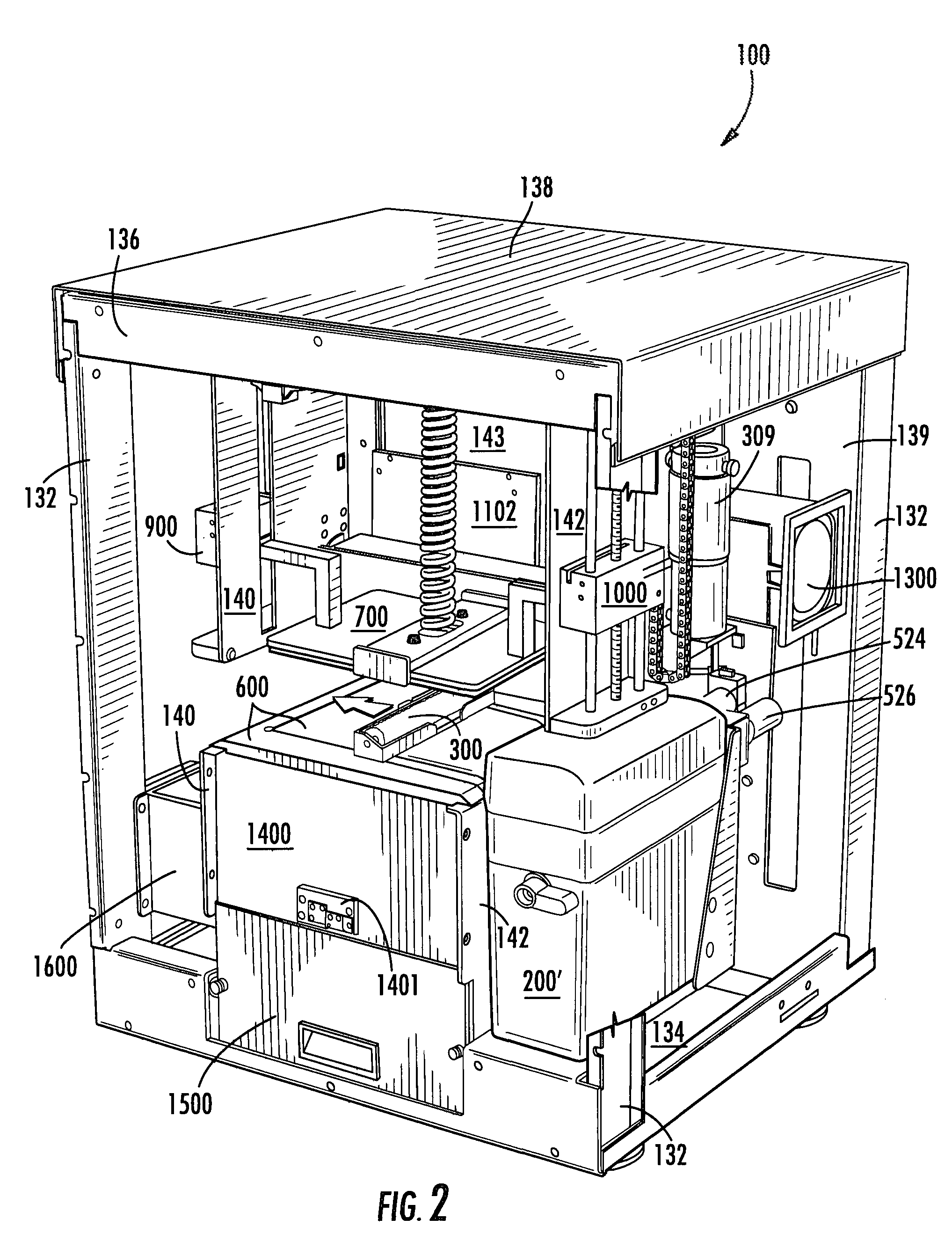
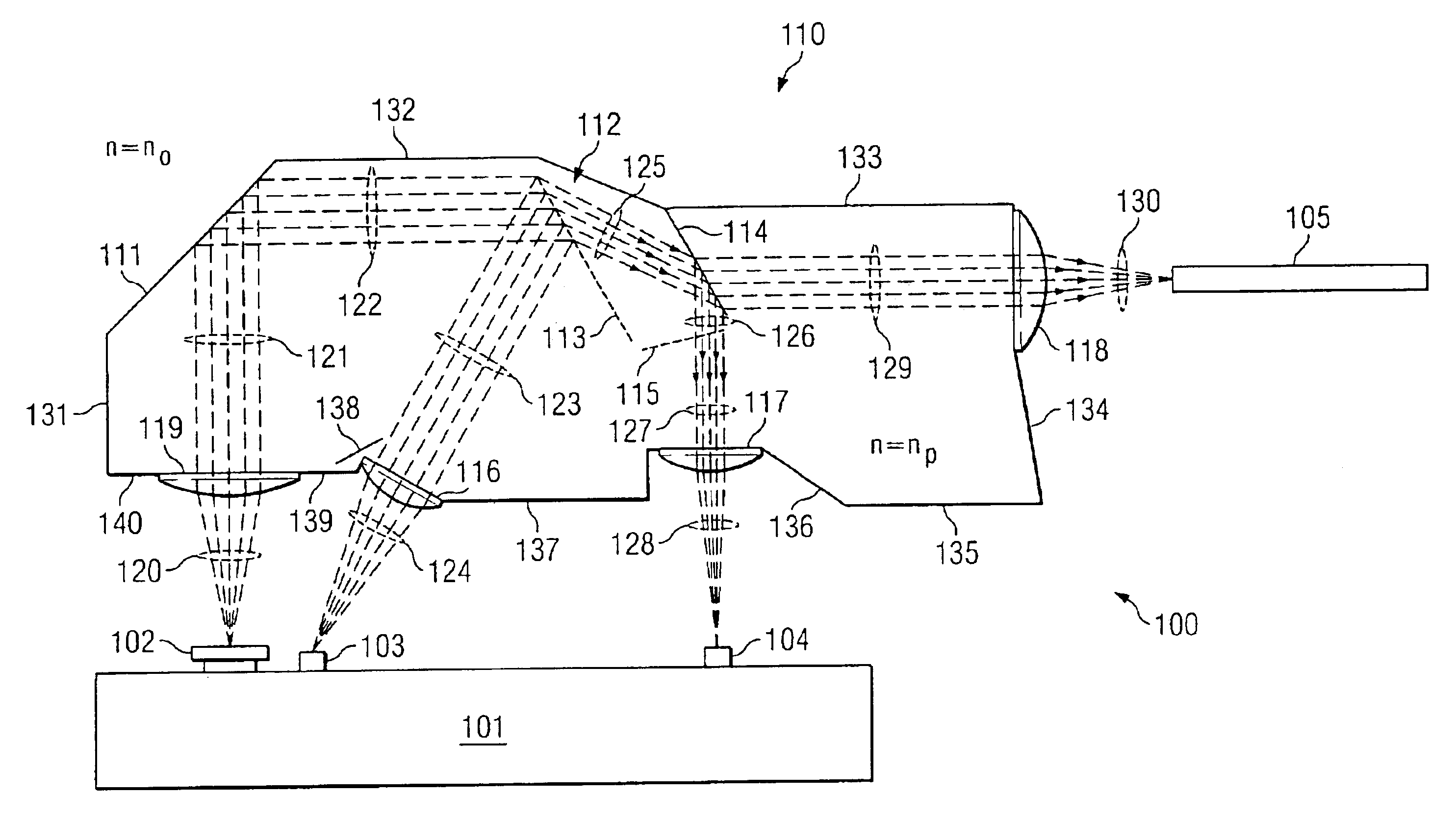
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
15341 results about "Injection moulding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Injection moulding is a manufacturing process for producing parts by injecting molten material into a mould. Injection moulding can be performed with a host of materials mainly including metals (for which the process is called die-casting), glasses, elastomers, confections, and most commonly thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers. Material for the part is fed into a heated barrel, mixed (Using a helical shaped screw), and injected (Forced) into a mould cavity, where it cools and hardens to the configuration of the cavity. After a product is designed, usually by an industrial designer or an engineer, moulds are made by a mould-maker (or toolmaker) from metal, usually either steel or aluminium, and precision-machined to form the features of the desired part. Injection moulding is widely used for manufacturing a variety of parts, from the smallest components to entire body panels of cars. Advances in 3D printing technology, using photopolymers which do not melt during the injection moulding of some lower temperature thermoplastics, can be used for some simple injection moulds.
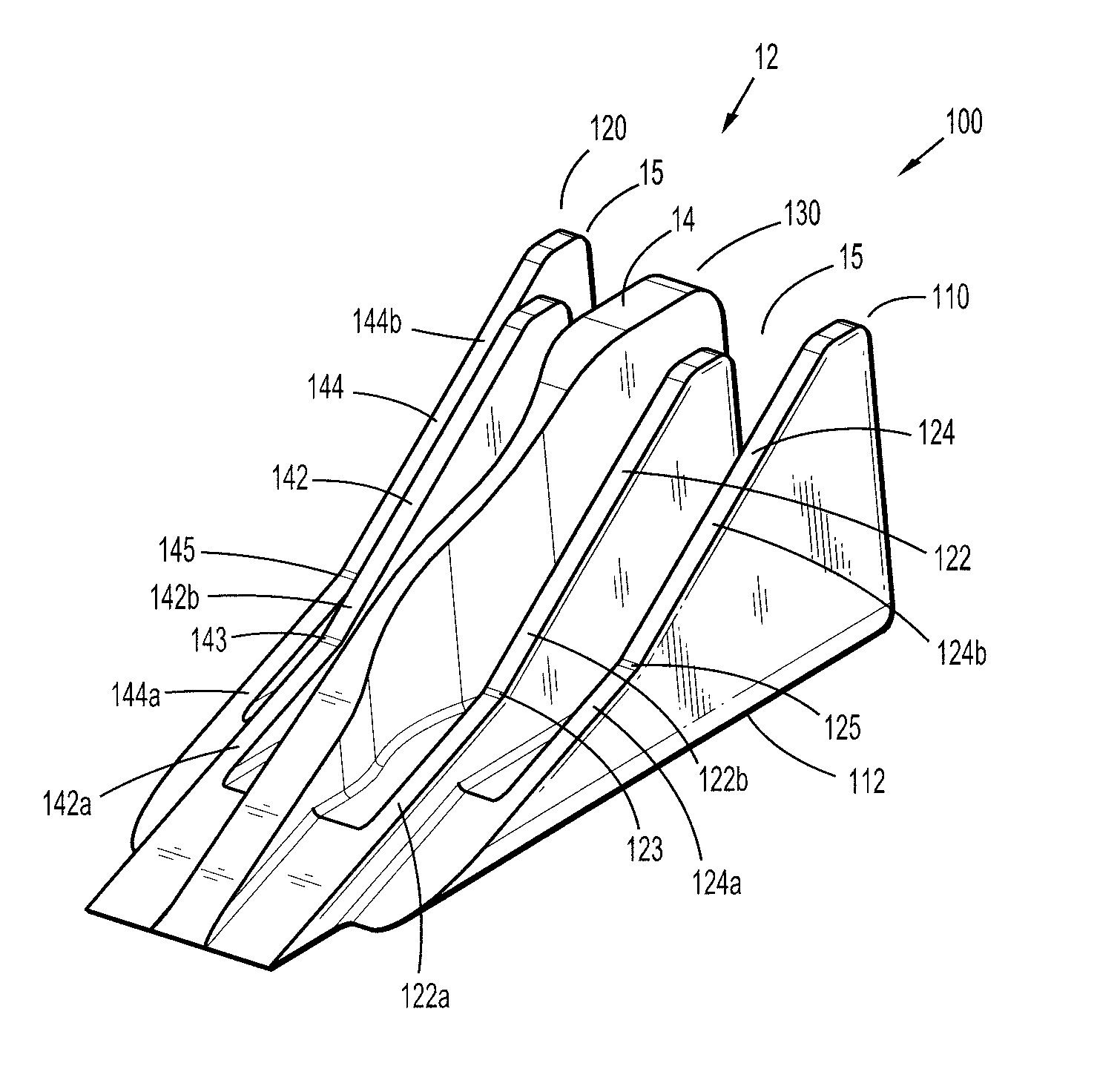
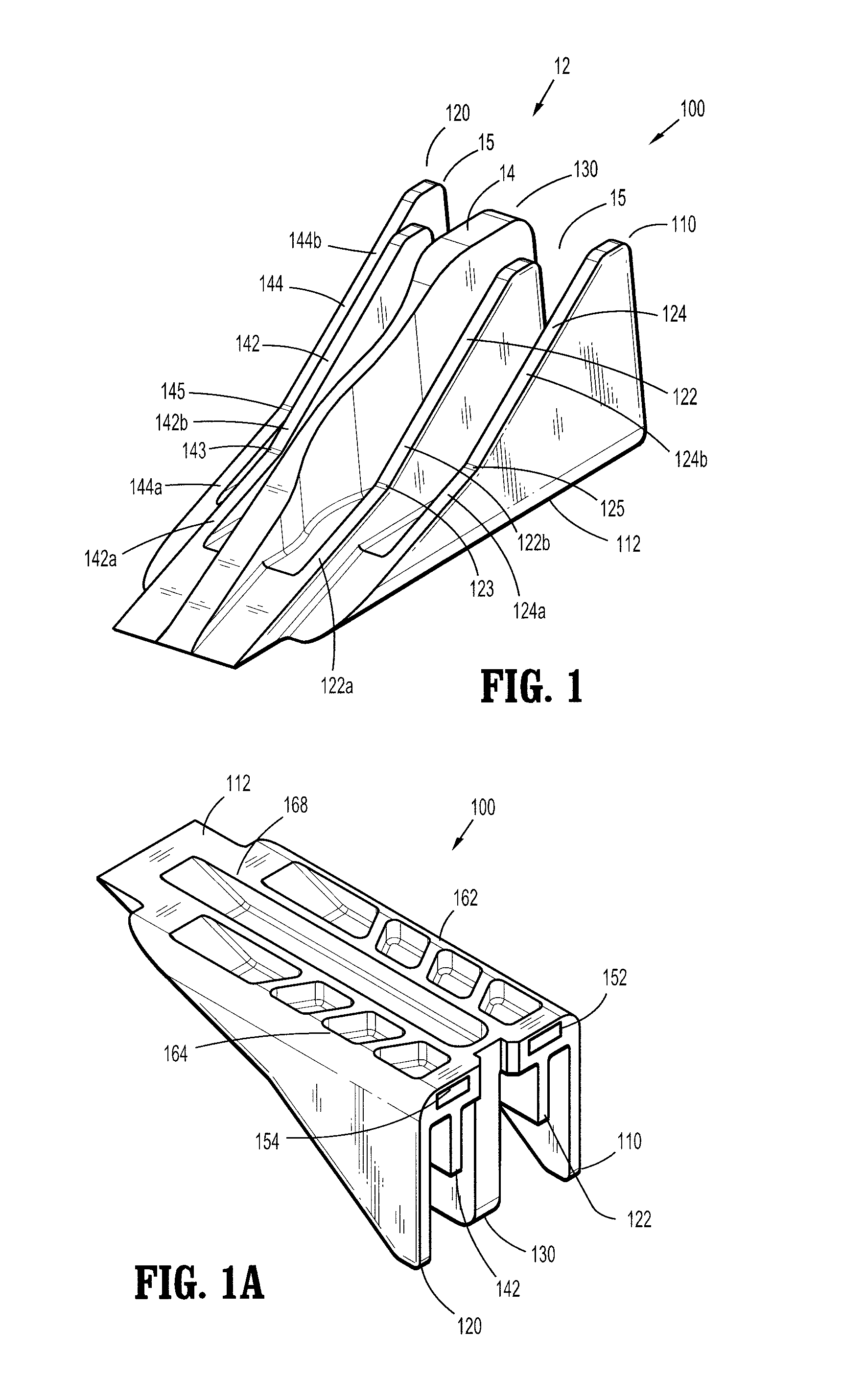
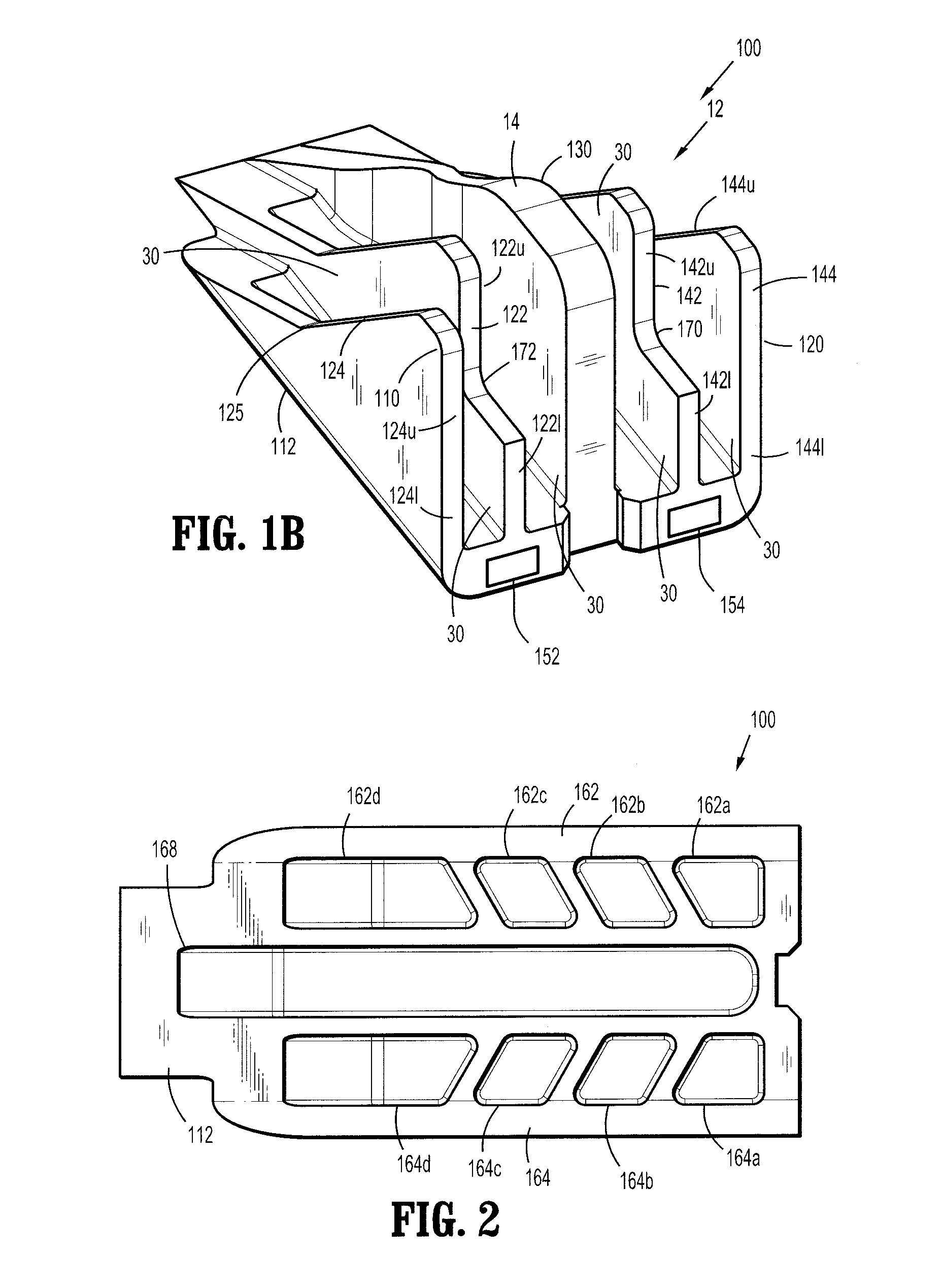
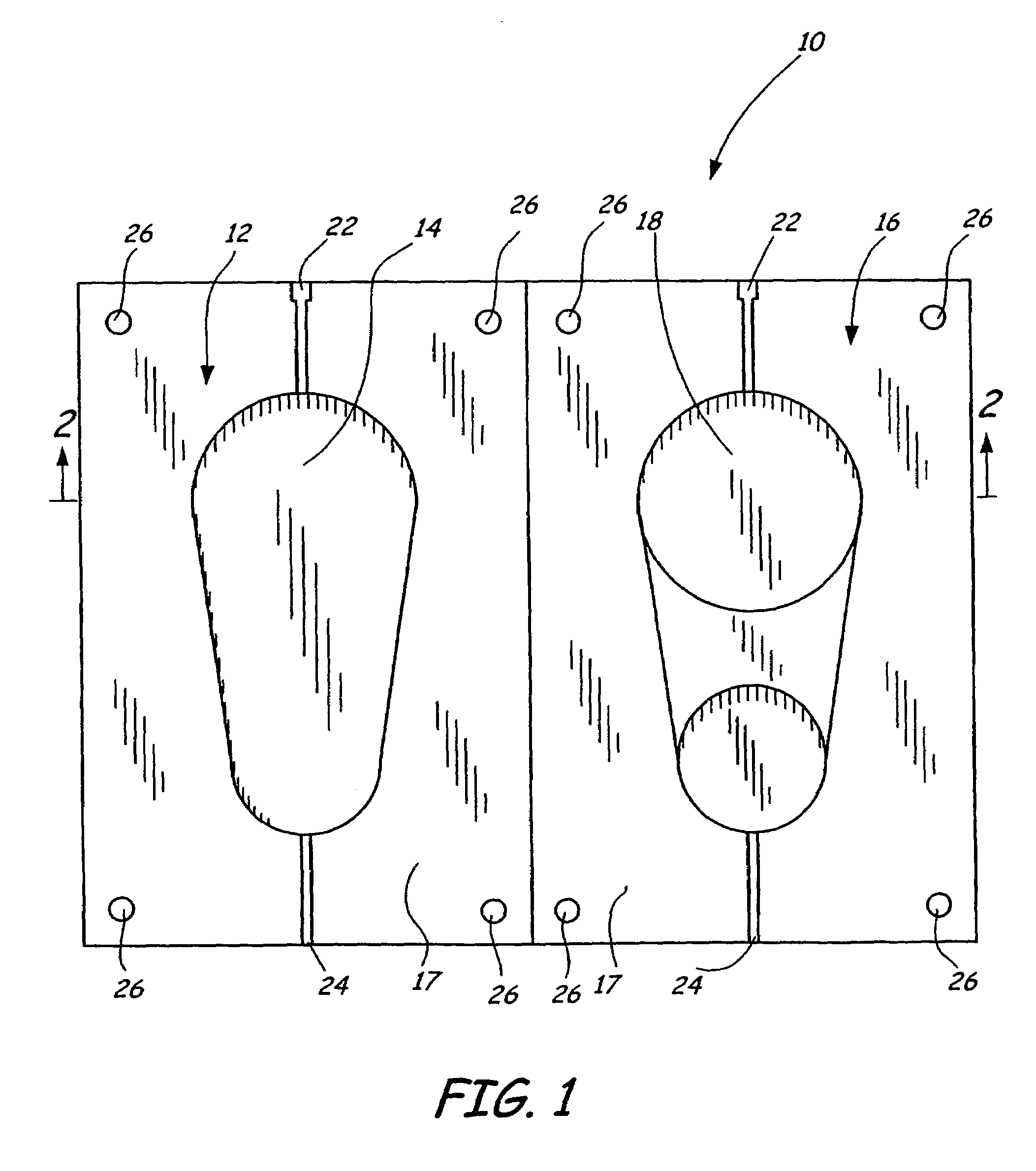
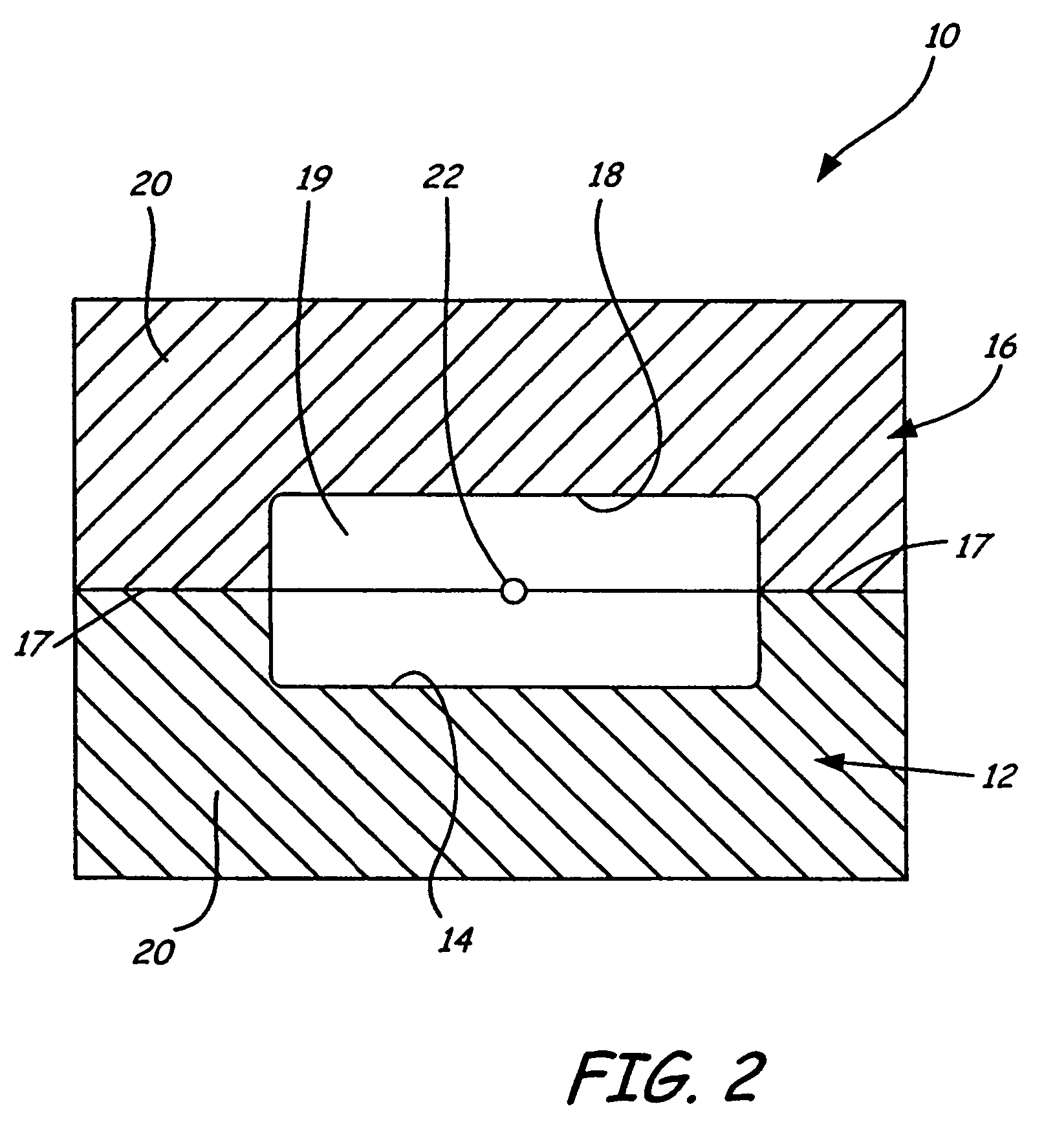
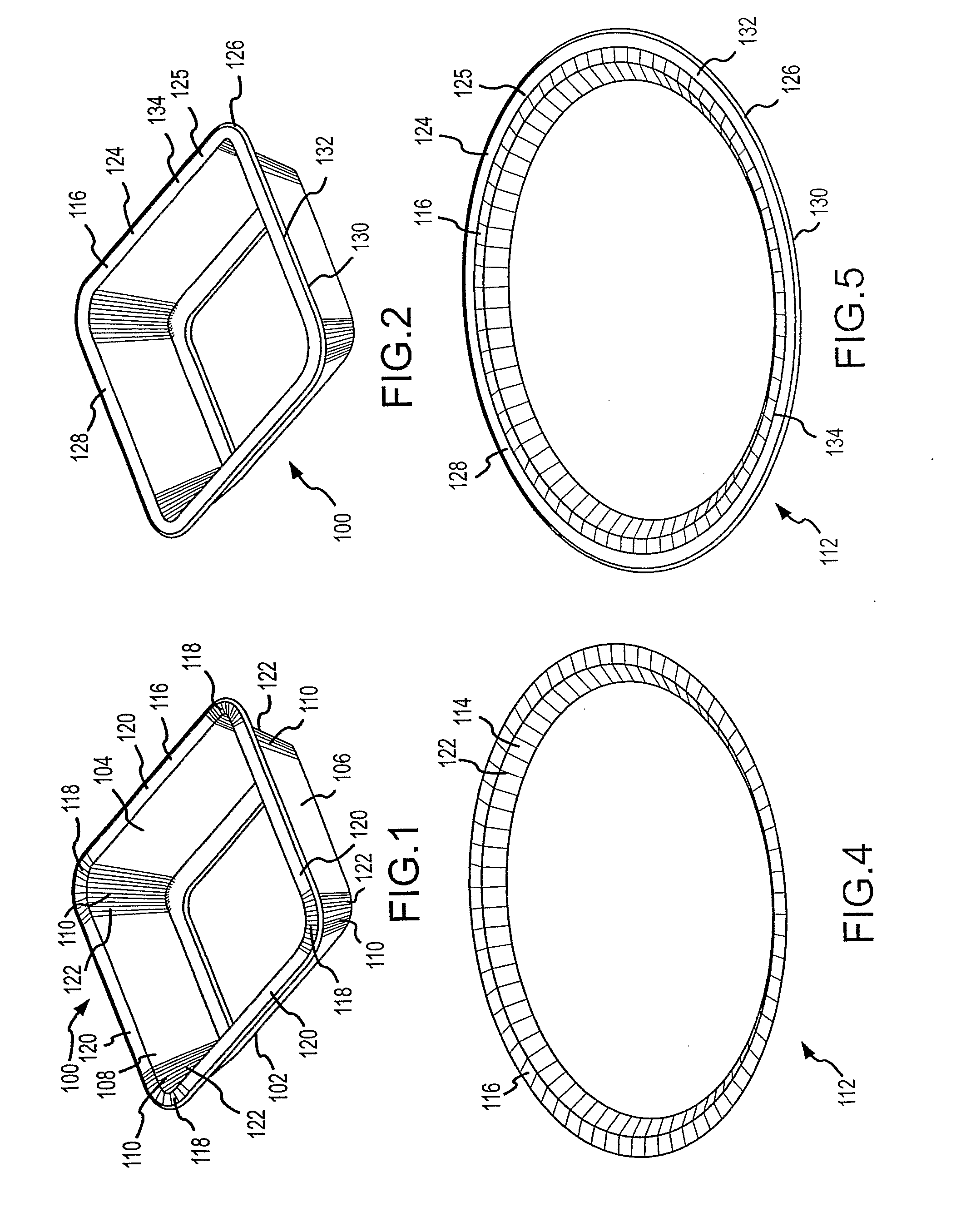
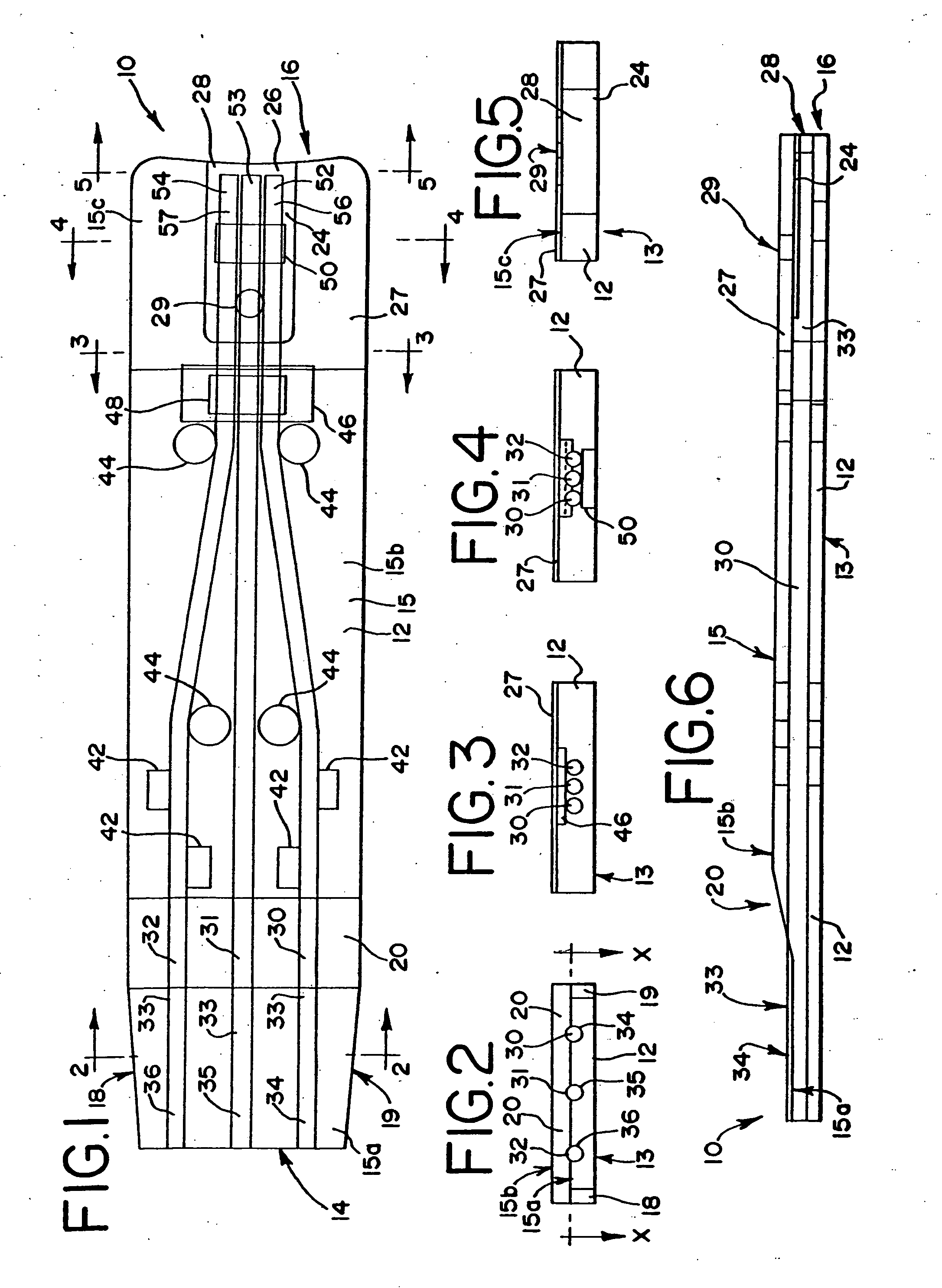
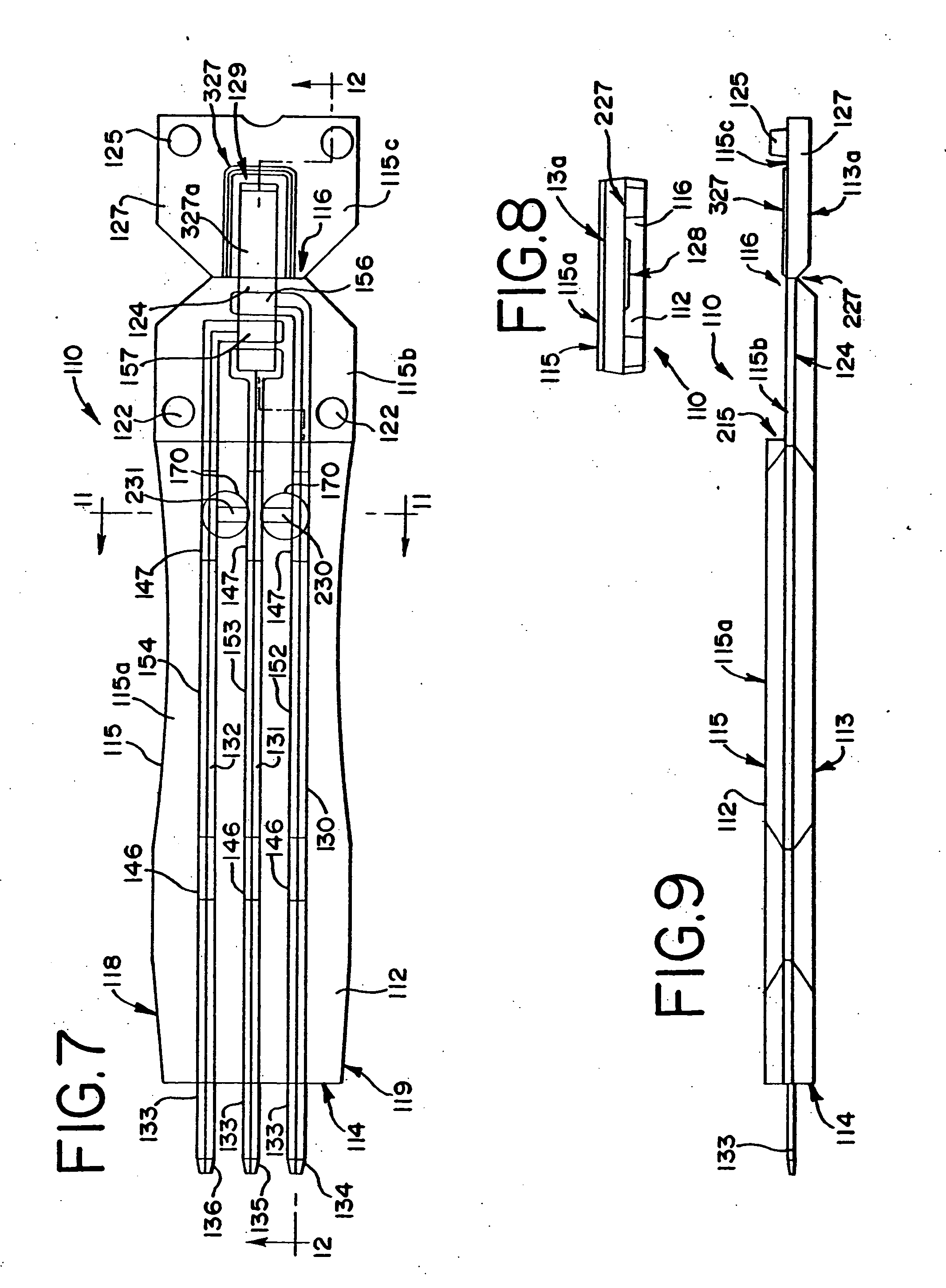
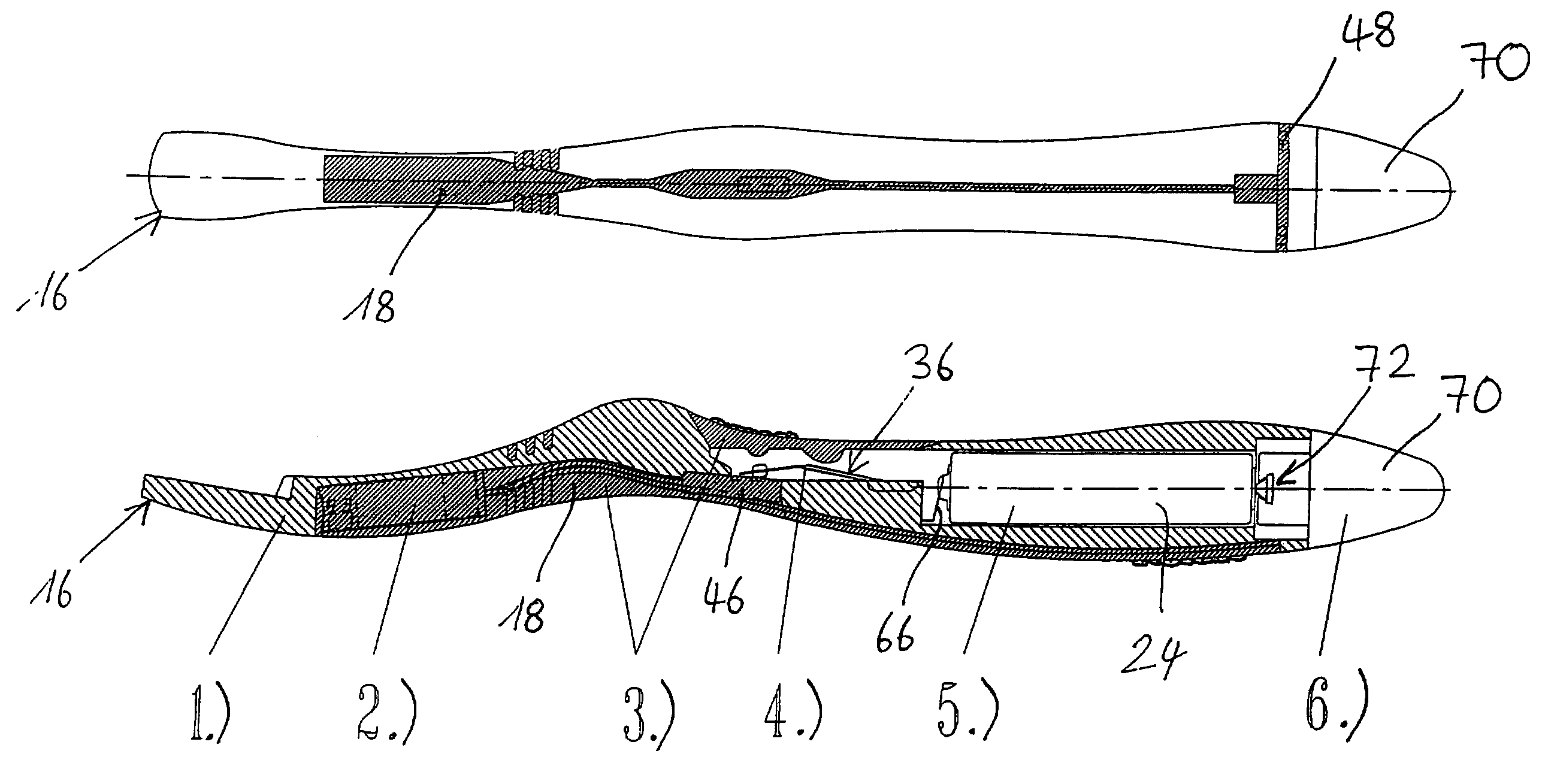
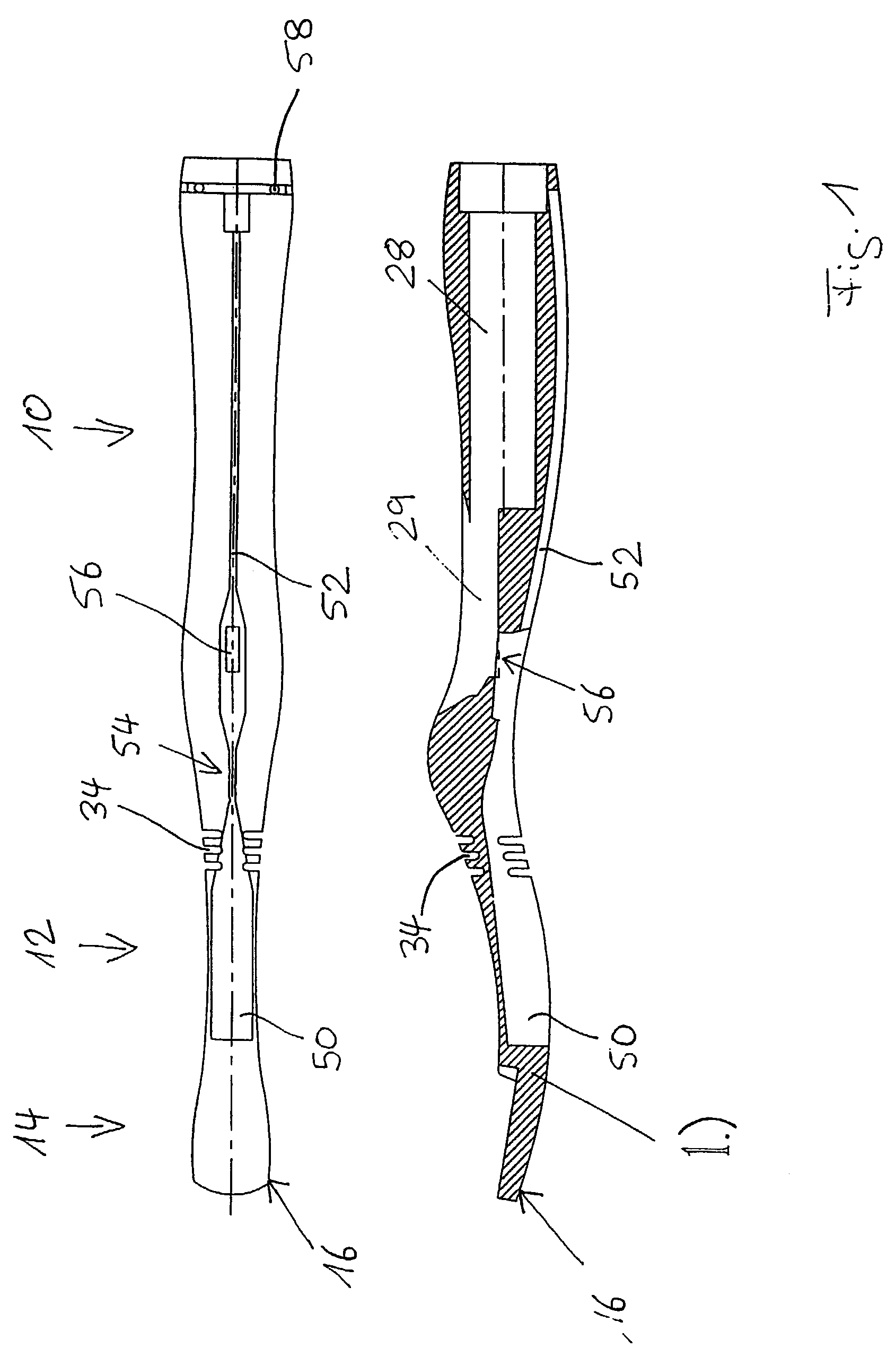
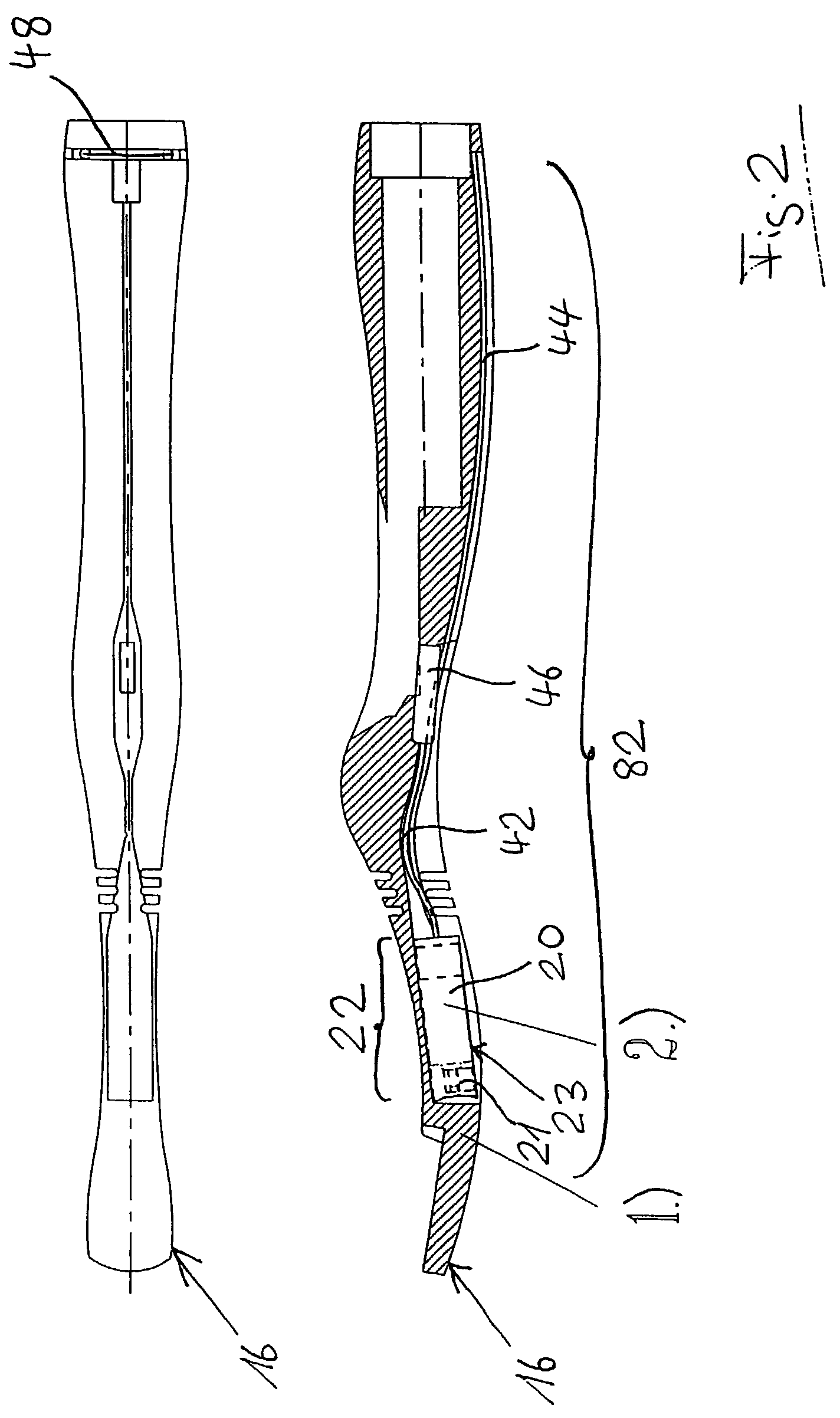
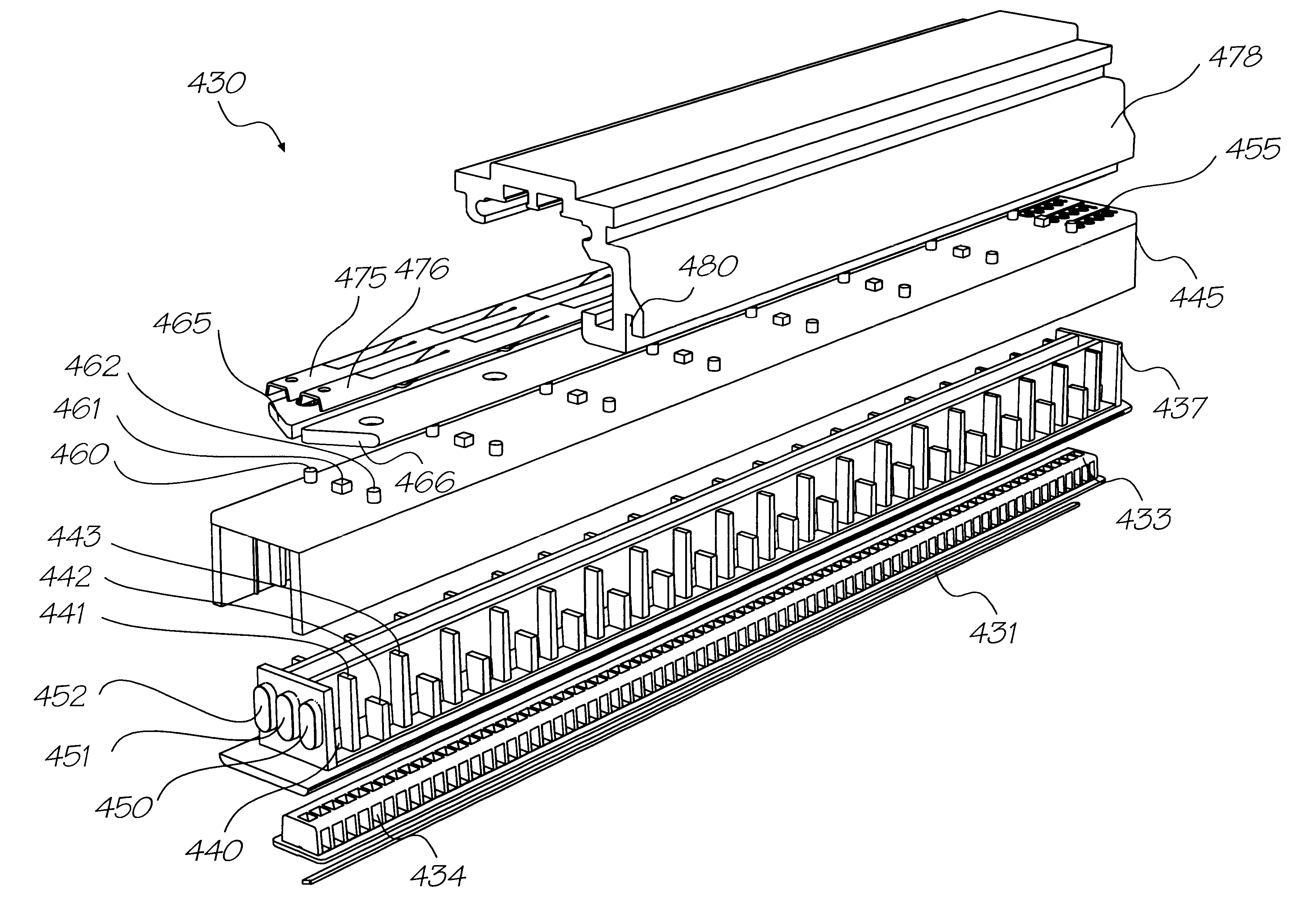
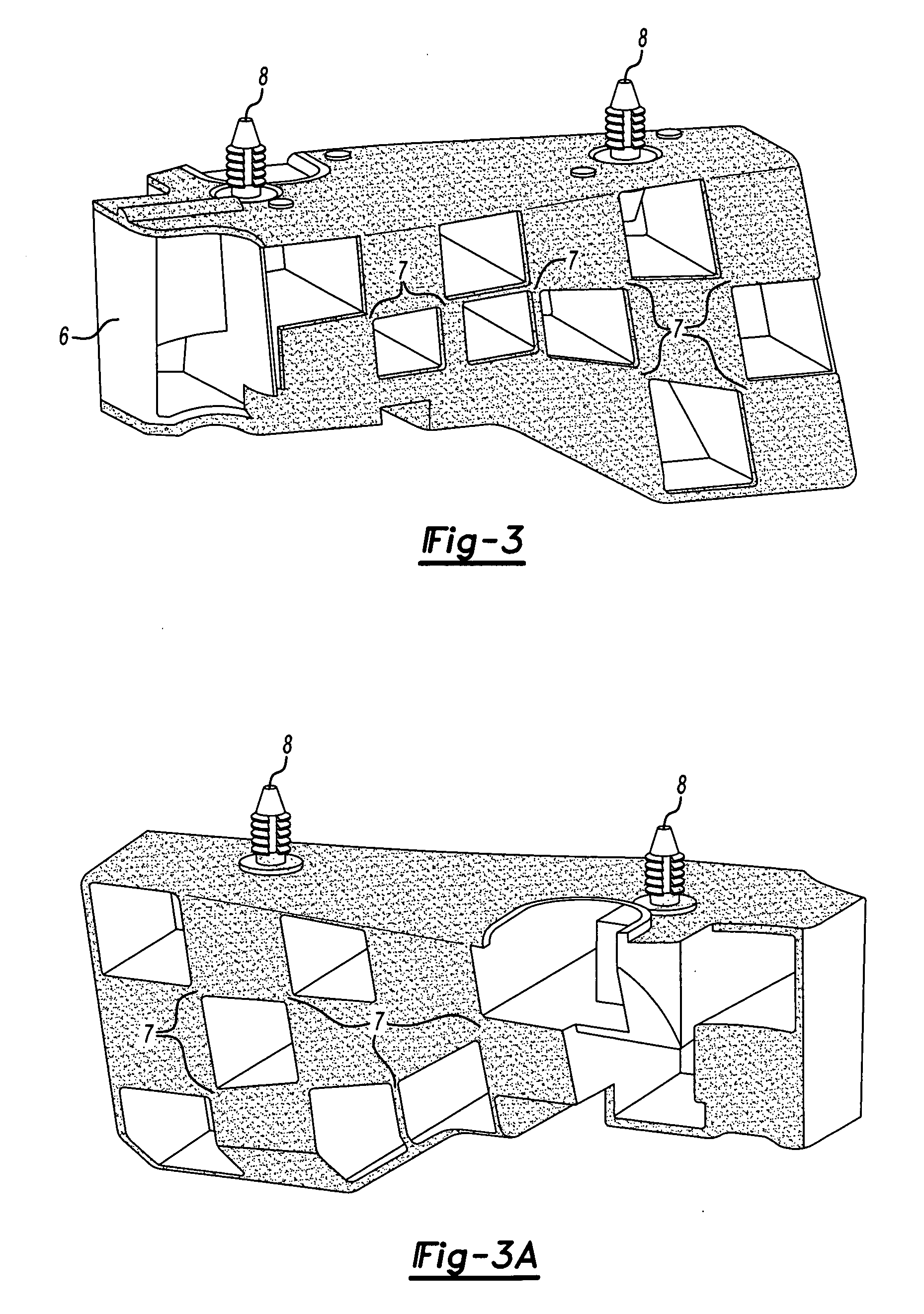
Actuation sled having a curved guide member and method
An apparatus for injection molding includes at least one mold part having at least one surface. The mold part includes at least one mold part having at least one substantially central, sloping, non-linear surface, the at least one mold part including at least one shaped portion. The mold part further includes at least one substantially closed cavity region disposed within the at least one substantially central, sloping, non-linear surface. The mold part further includes at least one gate disposed on a base portion of the mold part for providing fluid communication to the at least one cavity region, the base portion having a plurality of recesses / depressions extending longitudinally along the length of the mold part. Additionally, at least one flow restrictor may be positioned on the mold part for initially directing flow of injected fluid to the at least one shaped portion.
Owner:COVIDIEN LP
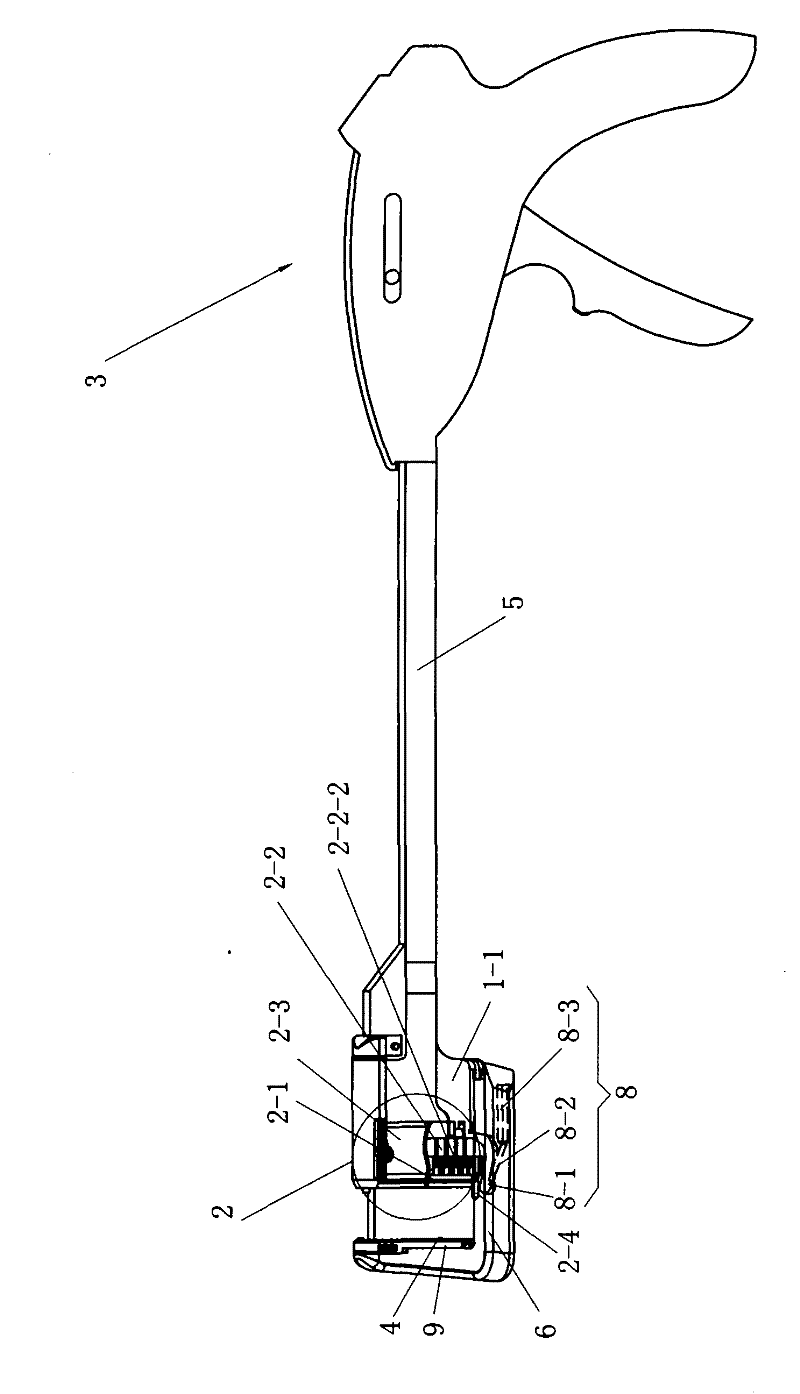
Arc-shaped cutting anastomat
The invention relates to an arc-shaped cutting anastomat comprising an anastomosis nail shaping mechanism, a nail pushing assembly, a trigger handle, a nail supporting seat, a base of the nail supporting seat, a knife cushioning ring and two splints, wherein the nail pushing assembly comprises a cutting knife, a nail pushing sheet, a nail bin and a guide post; the end of the nail pushing sheet and both sides of the cutting knife are respectively provided with a plurality of inner nail pushing dental sheets which are near the cutting knife and a plurality of outer nail pushing dental sheets which are far away from the cutting knife; the cutting knife and the nail pushing sheet are injected and molded at a time to be fixed together; the outer side of the each outer nail pushing dental sheeton the nail pushing sheet is provided with a reinforcing rib; the inner side of each nail pushing dental sheet on the nail pushing sheet is provided with a reinforcing rib; both ends of the first guide surfaces of the nail pushing dental sheets are respectively connected with the first contact surfaces and the second contact surfaces of the nail pushing dental sheets through concave arc-shaped connecting surfaces, and both ends of the second guide surfaces thereof are respectively connected with the first contact surfaces and the second contact surfaces through the concave arc-shaped connecting surfaces; and the first contact surfaces and the second contact surfaces are respectively in contact with the inner walls of the nail pushing dental sheet holes of the nail bin. The invention has the advantages of good trigger anastomosis shaping effect and high safety.
Owner:CHANGZHOU JIANRUIBAO MEDICAL DEVICES
Composite polymer based cartridge case having an overmolded metal cup, polymer plug base assembly
A cup and plug assembly of a base for a polymer based ammunition cartridge case body includes a cylindrical sleeve joined to the base. The base includes a plug molded over a cup. The cup includes a first annular cup portion extending in a first direction from a web formed therein and a second annular cup portion extending in a second direction from the web opposite to the first direction. The plug having a first annular portion that completely encompasses an outer circumferential surface of the cup and a second annular portion that extends from the first annular portion. The second annular portion of the plug completely covering an inner surface of the first annular cup portion of the cup. The cup preferably being formed from a metal or a suitable non-metal and the plug being formed from a suitable polymer that is injection molded over the cup.
Owner:TRUE VELOCITY IP HLDG LLC
Method for making memory cards and similar devices using isotropic thermoset materials with high quality exterior surfaces
InactiveUS7225537B2Shorten the timeQuality improvementPrinted circuit assemblingLine/current collector detailsEngineeringInjection moulding
Memory Cards containing Integrated Circuits and other electronic components (e.g. resistors) in a variety of form factors having high quality external surfaces of polycarbonate, synthetic paper (e.g. Teslin), or other suitable material (e.g. PVC) can be made through use of injection molded thermoplastic material or thermosetting material that becomes the core layer of said Memory Cards and similar devices. The object of the invention is to provide the following properties to Memory Cards: rapid production cycle, high volume manufacturing throughput, security, electronics protection, better tamper resistance, durability, and highly reliable complex electronics encapsulation, achieved through a process utilizing low temperature and low pressure.
Owner:CARDXX
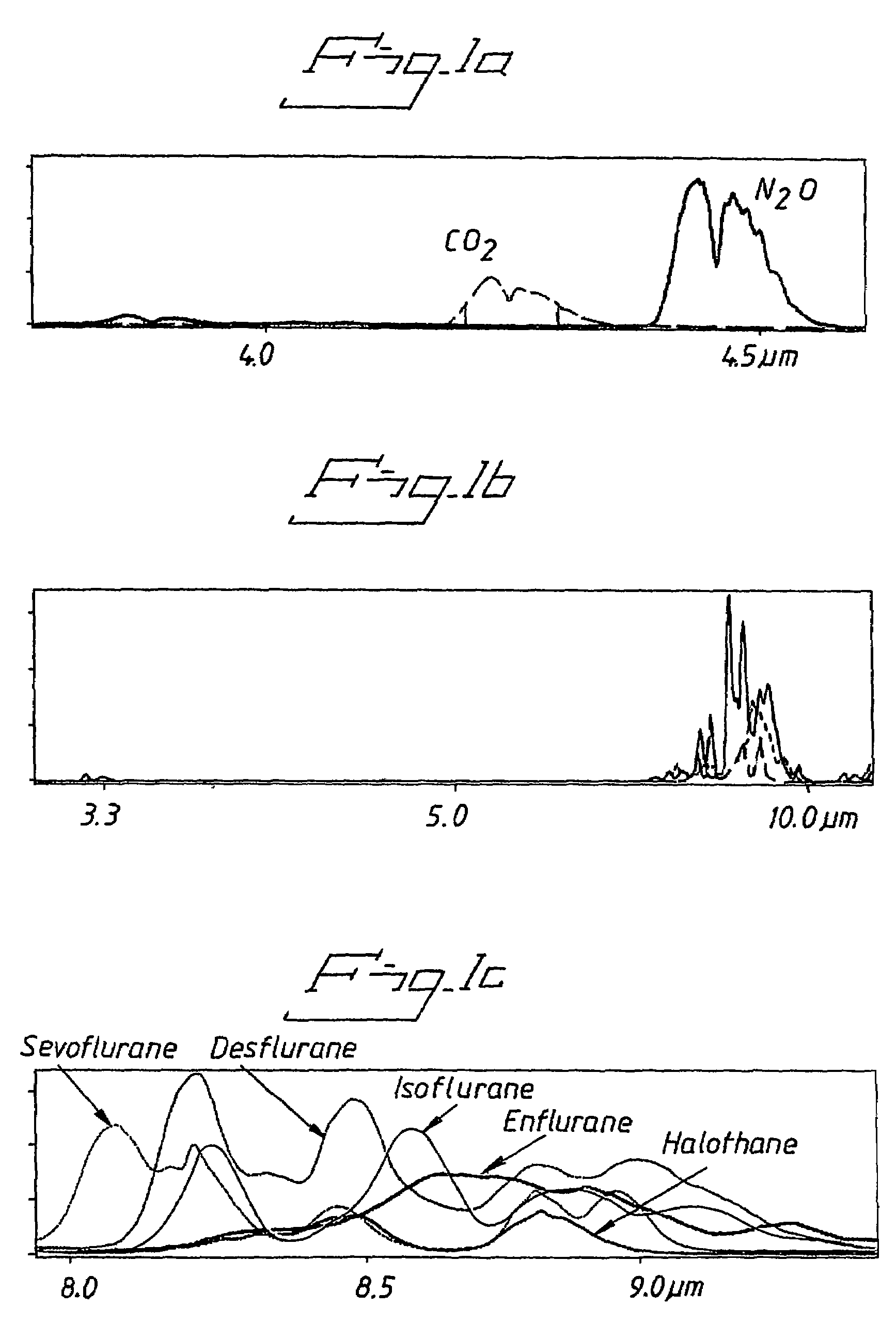
Air gas analyzer window and a method for producing such a window
ActiveUS7629039B2Uniform material thicknessSatisfactory transmission propertyLayered productsRespiratory organ evaluationPlastic materialsLight beam
A window for use in an adapter for an IR gas analyser for analysing breathing gases, where the gases flow through a through-penetrating passageway in the adapter, which includes windows disposed on opposite sides of the passageway so as to enable an IR beam to be sent through the windows and through the passageway containing said breathing gases. Each window is a one-piece structure comprised of plastic material and has a round basic shape that includes a surrounding edge and a central part which is sunken in relation to the surrounding edge and which forms the window through which the IR beams or rays shall be able to pass. A method of producing such a window, by injection moulding a thermoplastic material in a mould where injection of the plastic material is also disclosed.
Owner:PHASEIN
Orthopaedic devices with plastic injection molded onto fabric
InactiveUS6024712AReliable rapid lacingEfficient methodNon-surgical orthopedic devicesBandagesOrthopaedic deviceCombined use
The present invention pertains to an orthopedic support having a flexible inner member and an exo-skeleton that is molded directly onto the flexible inner member. In one particular embodiment, a versatile, multi-medium orthopedic ankle support assembly has an inner fabric support for extending at least partially around an injured part of the anatomy and for providing basic support for the injury. A plastic exo-support is injection molded into said fabric support and supplies supplemental support for resisting motion of the injured part in undesired directions. The fabric support has a main body portion for extending at least part way around the injured part of the anatomy and has edges to be secured together after the fabric support is fitted to the injured part. The invention is not limited to ankle braces, of course, as the general principle of molding an exo-skeleton onto a flexible inner member may be used in conjunction with numerous different supports. An efficient method for constructing an orthopedic support includes the steps of first placing a sheet of flexible material across a mold, cutting the sheet, injection molding the exo-structure onto the sheet material in the mold, and securing the sheet into an orthopedic support.
Owner:ROYCE MEDICAL PRODS +1
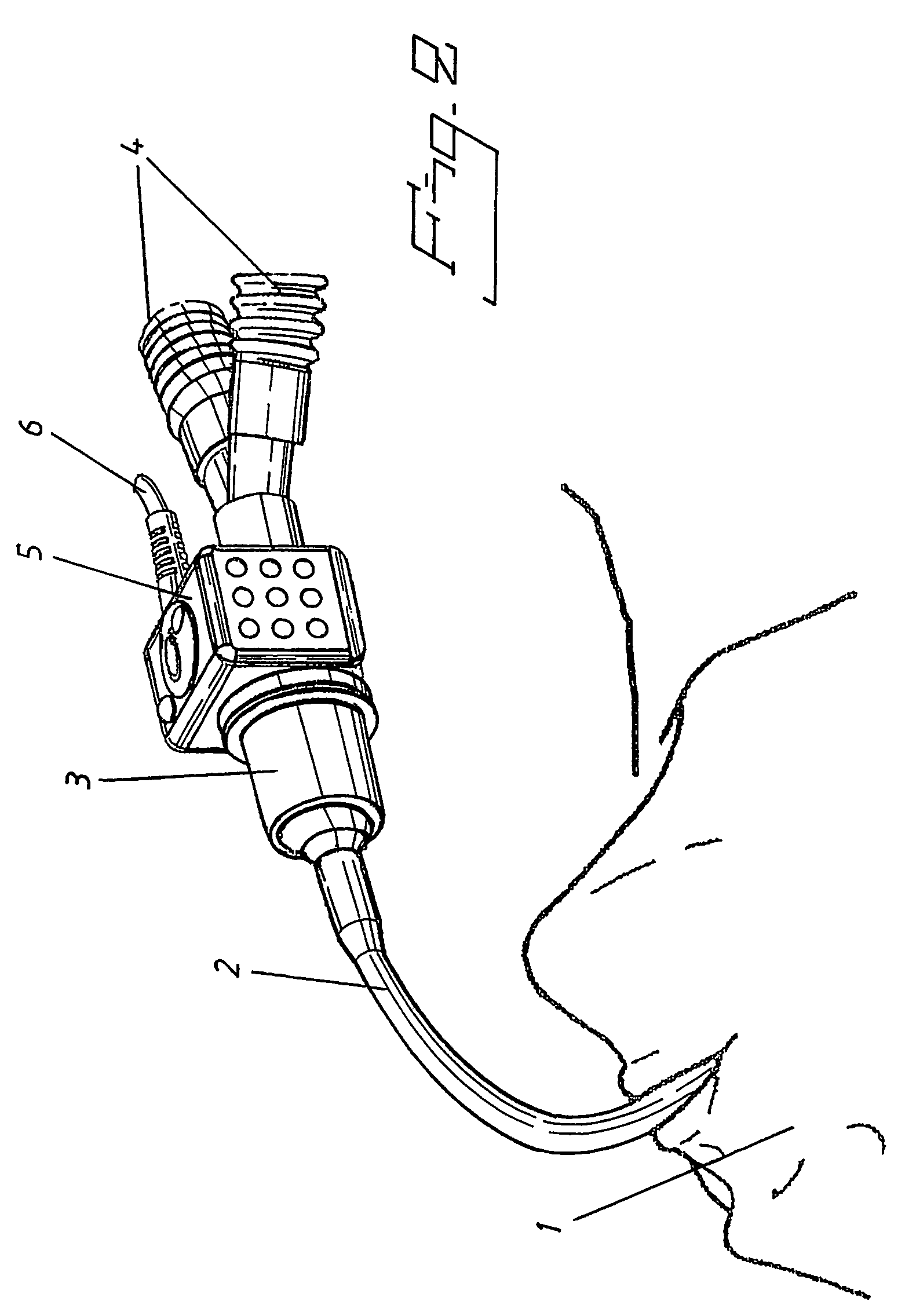
Catheter assemblies and injection molding processes and equipment for making the same
InactiveUS20050033237A1Increased complexityExtension of timeMouldsInfusion syringesMulti materialCatheter hub
Various single-part catheter assemblies, multi-part integrated catheter assemblies, and methods and apparatus for making the same are disclosed. The single-part catheter assemblies include a catheter hub integrally formed with a catheter tube for insertion into the bloodstream of a patient. The multi-part integrated catheter assemblies include a catheter hub integrally formed to a catheter tube for insertion into the bloodstream of a patient. The catheter assemblies of the invention may be injection molded in a single step or in multiple steps by injecting flows of molten plastic into a cavity of molds provided herein such that the flows converge into an even distribution about the circumference of the sleeve. The mold may have a core pin designed to fit into the cavity. Through the use of the even distribution of flows, the core pin may be seated within the cavity in an untensioned manner. The catheter assemblies of the invention may be produced of a single material or of multiple materials.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Thermally conductive thermoplastic
InactiveUS6162849AImprove thermal conductivityImprove mechanical propertiesPlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsMixingThermoplasticPolymer science
This invention relates to a thermally conductive moldable polymer blend comprising a thermoplastic polymer having a tensile at yield of at least 10,000 psi; at least 60% by weight of a mixture of boron nitride powders having an average particle size of at least 50 microns; and a coupling agent. The composition displays a thermal conductivity of at least about 15 W / m DEG K and it is capable of being molded using high speed molding techniques such as injection molding.
Owner:FERRO CORP
Molded/integrated touch switch/control panel assembly and method for making same
InactiveUS6897390B2Overcomes shortcomingSimple manufacturing processStampsContact surface shape/structureEngineeringInjection moulding
Touch switches are integrated with thermoformable, injection molded, and other substrates to yield integrated touch switch / control panel assemblies. The ensuant assemblies can include ridges, depressions, anchors, overlaps, rivets and bezels or other housings. They can have any combination of flat and curved surfaces. Further, such assemblies can be incorporated into components of other assemblies, such as automobiles.
Owner:TOUCHSENSOR TECH
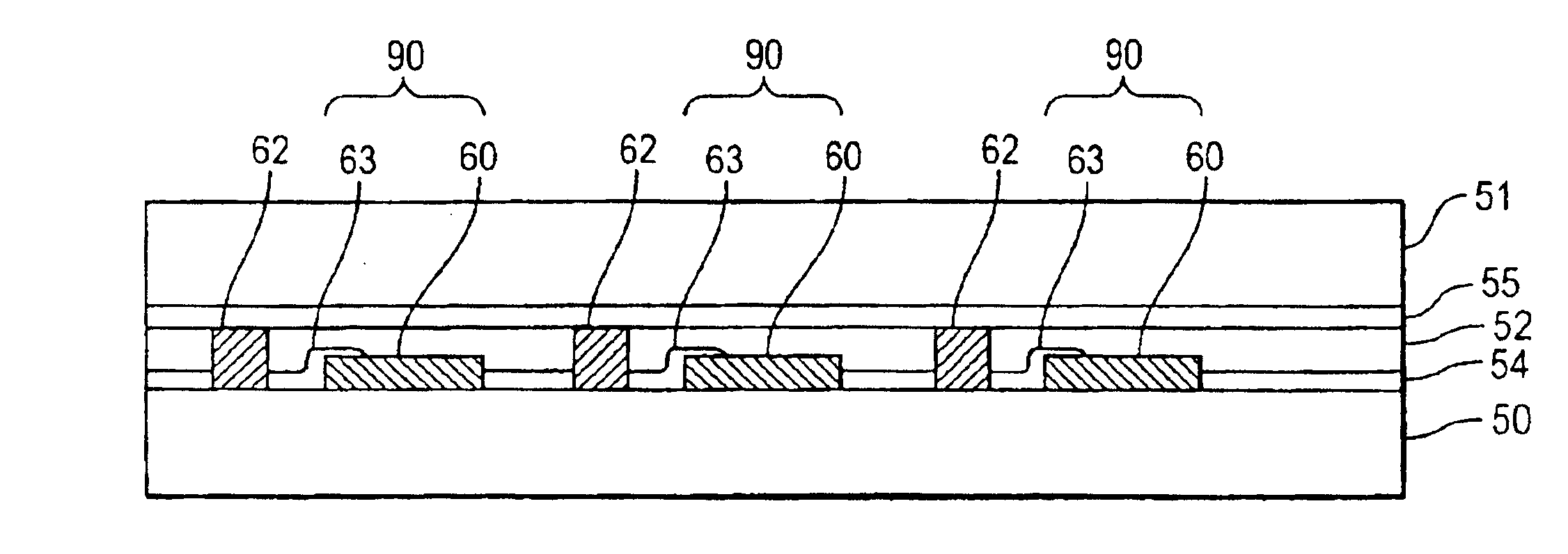
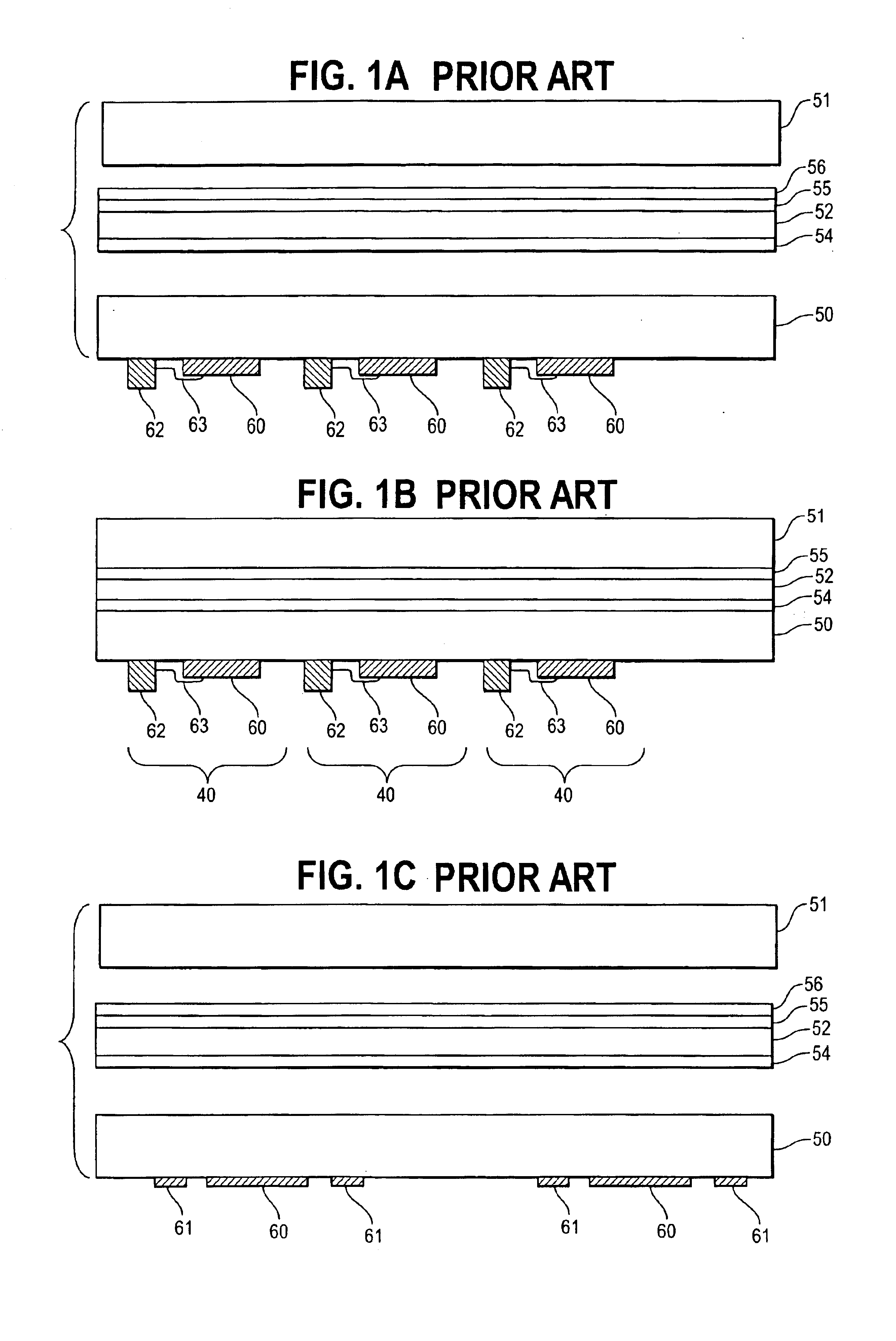
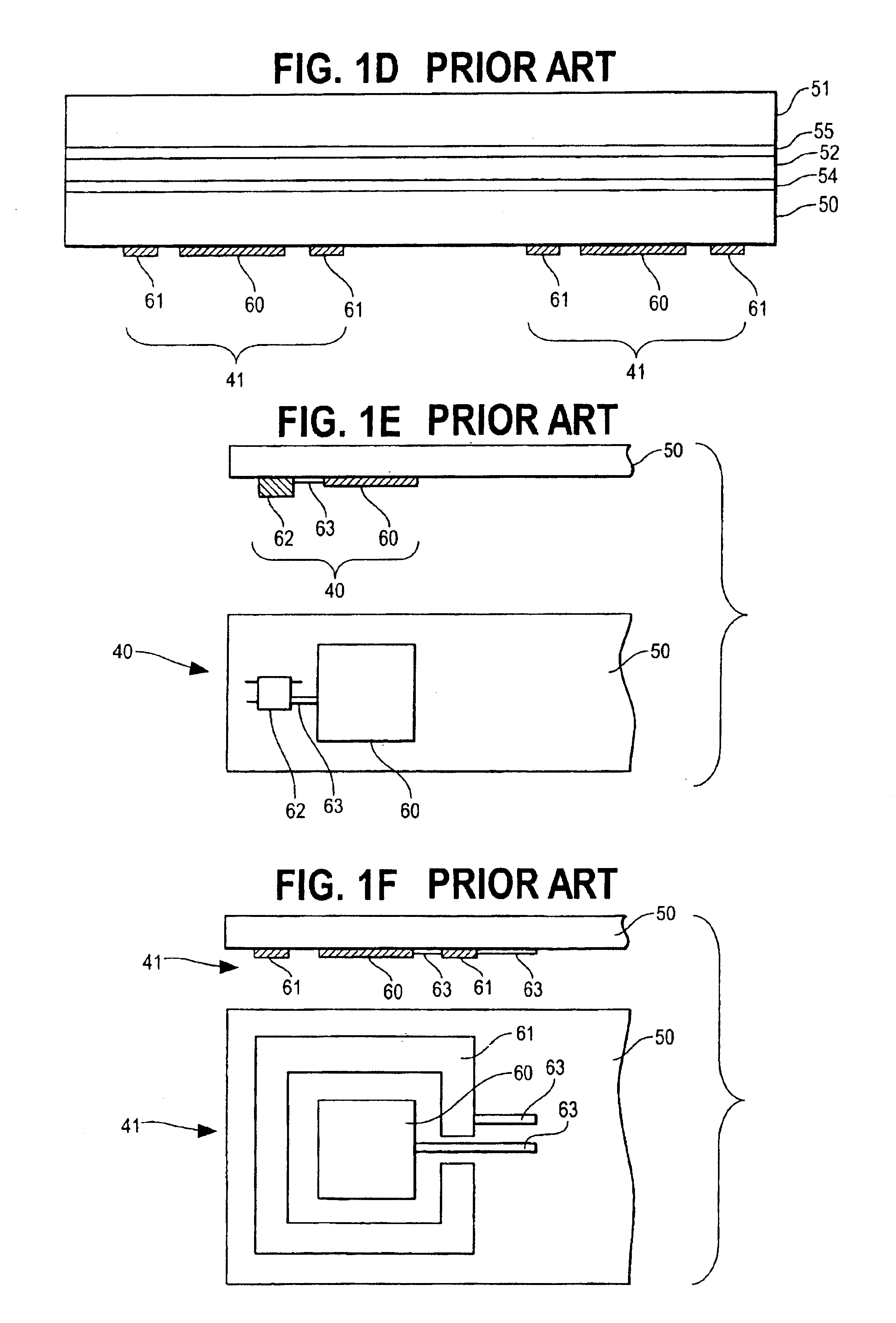
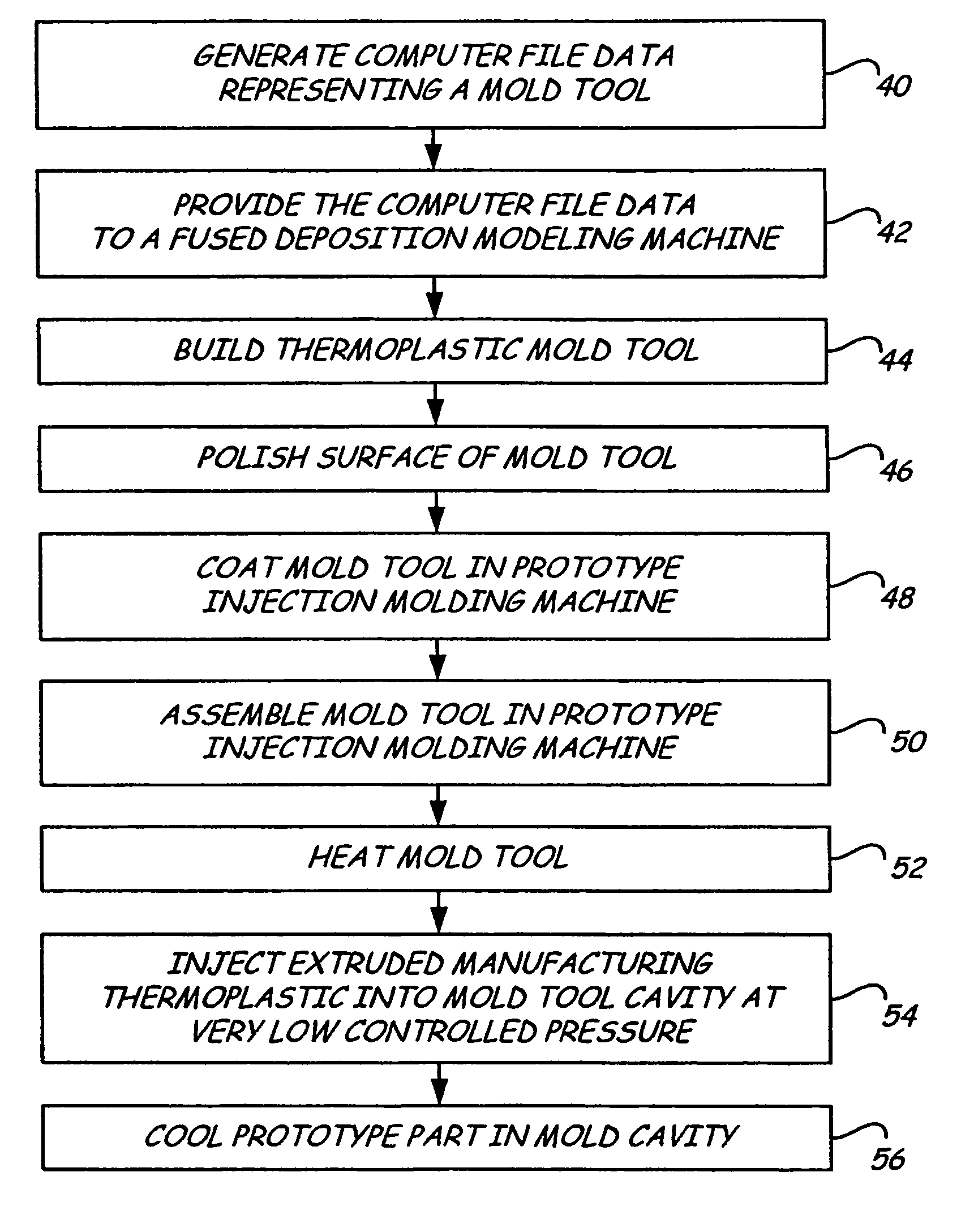
Rapid prototype injection molding
InactiveUS7125512B2Additive manufacturing apparatusMechanical vibrations separationInjection mouldingRapid prototyping
Owner:STRATSYS INC
Liquid crystalline thermosets from ester, ester-imide, and ester-amide oligomers
InactiveUS6939940B2Low viscosityLow dielectric constantLiquid crystal compositionsLiquid crystallineEnd-group
Main chain thermotropic liquid crystal esters, ester-imides, and ester-amides were prepared from AA, BB, and AB type monomeric materials and were end-capped with phenylacetylene, phenylmaleimide, or nadimide reactive end-groups. The resulting reactive end-capped liquid crystal oligomers exhibit a variety of improved and preferred physical properties. The end-capped liquid crystal oligomers are thermotropic and have, preferably, molecular weights in the range of approximately 1000-15,000 grams per mole. The end-capped liquid crystal oligomers have broad liquid crystalline melting ranges and exhibit high melt stability and very low melt viscosities at accessible temperatures. The end-capped liquid crystal oligomers are stable for up to an hour in the melt phase. These properties make the end-capped liquid crystal oligomers highly processable by a variety of melt process shape forming and blending techniques including film extrusion, fiber spinning, reactive injection molding (RIM), resin transfer molding (RTM), resin film injection (RFI), powder molding, pultrusion, injection molding, blow molding, plasma spraying and thermo-forming. Once processed and shaped, the end-capped liquid crystal oligomers were heated to further polymerize and form liquid crystalline thermosets (LCT). The fully cured products are rubbers above their glass transition temperatures. The resulting thermosets display many properties that are superior to their non-end-capped high molecular weight analogs.
Owner:NASA
Injection molding of polymeric material
Injection molding systems and methods useful for making microcellular foamed materials are provided as well as microcellular articles. Pressure drop rate and shear rate are important features in some embodiments, and the invention provides systems for controlling these parameters in an injection molding system. Another aspect involves an injection molding system including a nucleator that is upstream of a pressurized mold. Another aspect involves an extrusion system with the reciprocating screw for forming a single phase solution of non-nucleated blowing agent and polymeric material. Another aspect involves very thin walled microcellular material and very thin walled polymeric material. Another aspect provides a method for producing high weight reductions in very thin-walled parts with surfaces that have no noticeable differences from non-foamed parts.
Owner:TREXEL
Disposable Cap for Endoscope
InactiveUS20070213591A1Manufactured easily and economically and convenientlyReduce necessitySurgeryEndoscopesPlastic materialsInjection moulding
A cap, which is detachably connectable to an optical head of an endoscope, has a tubular housing, which is manufactured by injection molding from translucent plastic material. The housing includes a rear open end and a frontal end closed by a frontal face and an antiglare ring for preventing a viewer of the optical head from viewing parasitic reflections. The antiglare ring is embedded within the frontal face of the cap and said optical head can view an object of interest through a portion of the frontal face which is confined by the antiglare ring. The antiglare ring is provided with at least one discontinuity region through which the plastic material can flow during injection molding of the cap.
Owner:STRYKER GI
Container Having a Rim or other Feature Encapsulated by or Formed From Injection-Molded Material
ActiveUS20070267374A1Strengthen and stabilizeProvide supportClosure lidsTurning machine accessoriesHermetic sealEngineering
Owner:GRAPHIC PACKAGING INT
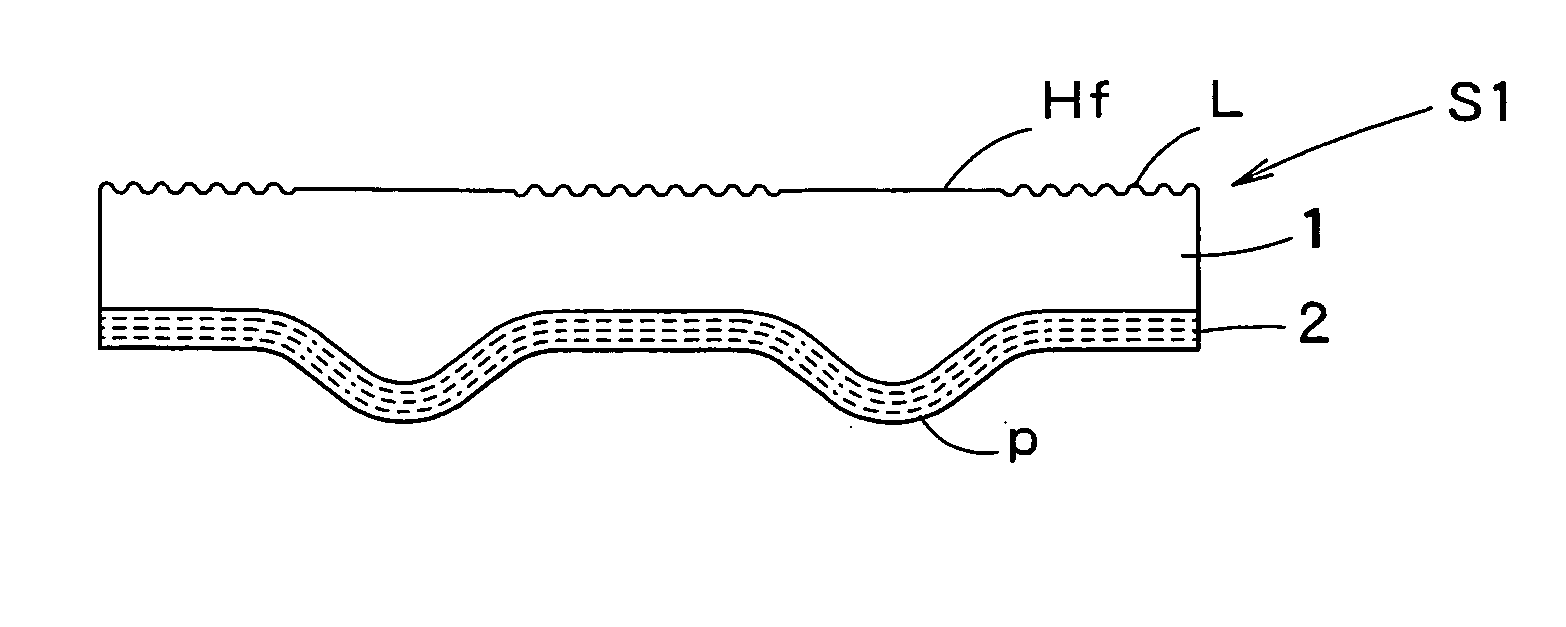
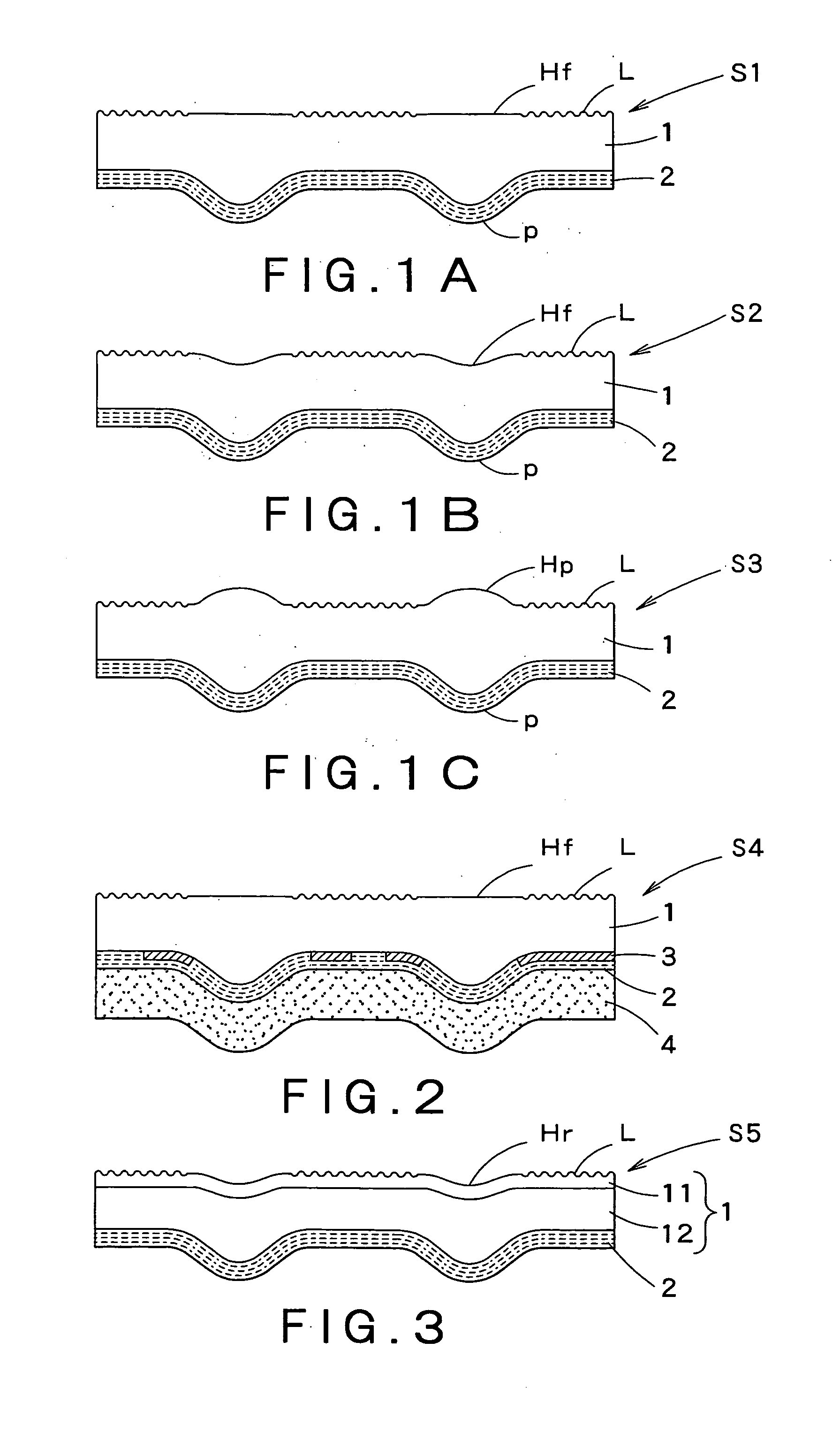
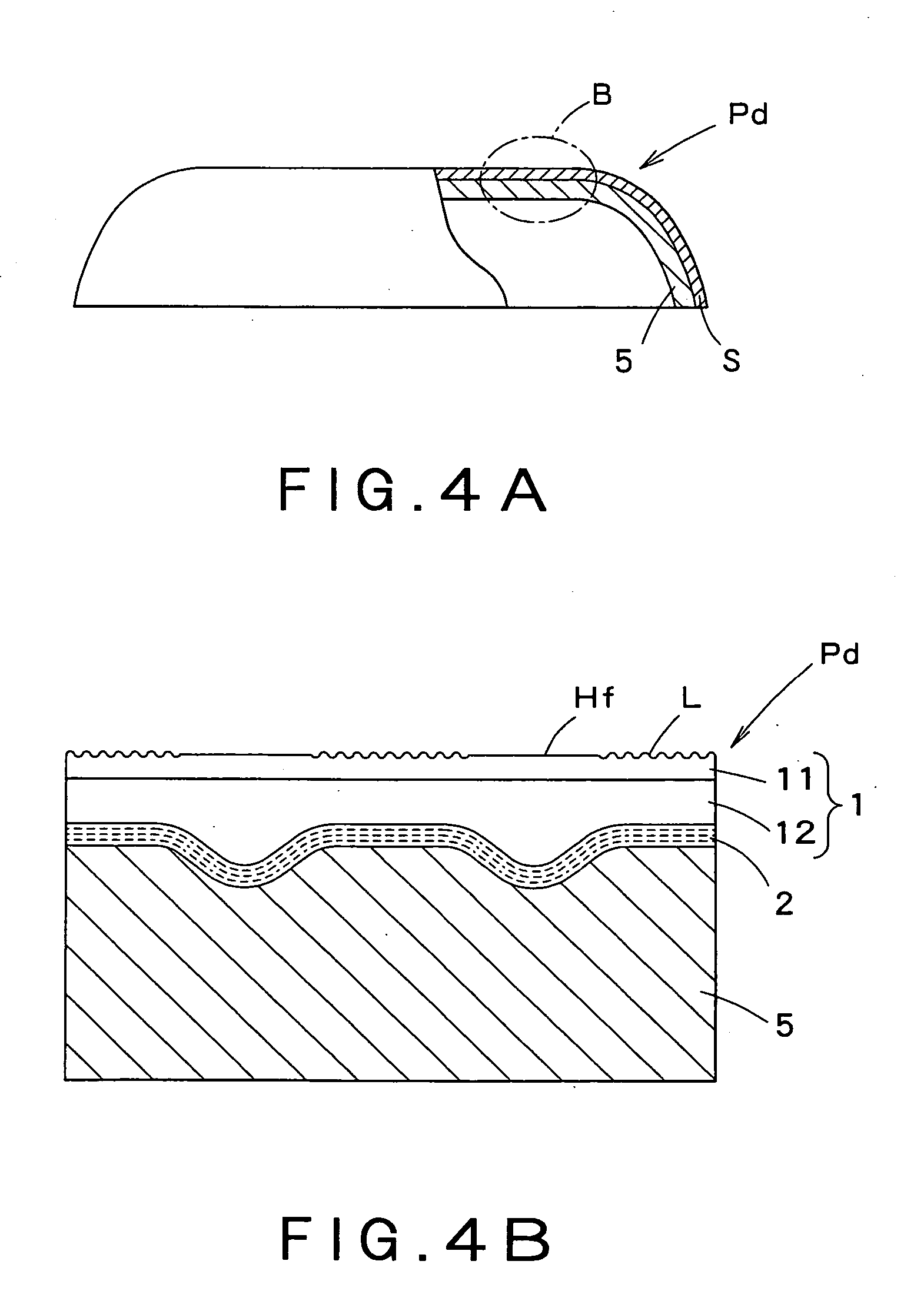
Decorating sheet, decorating molded article and in-mold decorating injection molding
ActiveUS20070026197A1Easy to manufactureOrnamental structuresSpecial ornamental structuresShell moldingEngineering
A decorating sheet comprises a transparent resin substrate sheet 1 and a glossy layer 2 laminated to the back surface of the transparent resin substrate sheet 1, and the front surface of the transparent resin substrate sheet 1 is divided into high-gloss portions H and low-gloss portions L. The transparent resin substrate sheet 1 is thick at the high-gloss portions and thin at the low-gloss portions, and, owing to these portions, the decorating sheet can provide a pattern that is visually sensed as if it were a three-dimensional pattern. This transparent resin substrate sheet 1 is composed of two layers, a crystalline resin layer 11 and a non-crystalline resin layer 12. A decorated molded product Pd can be obtained by laminating this decorating sheet to a resin molded product 5.
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
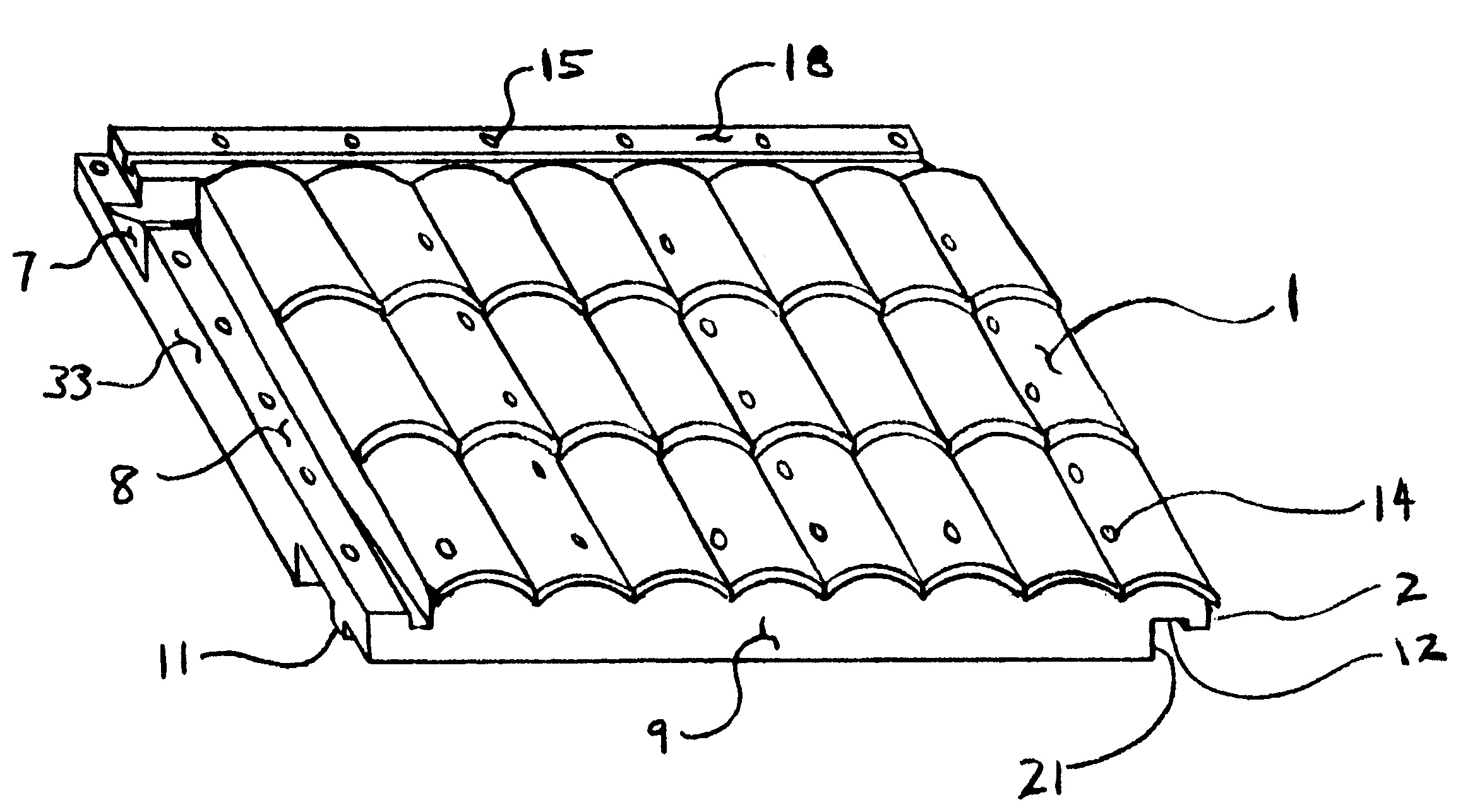
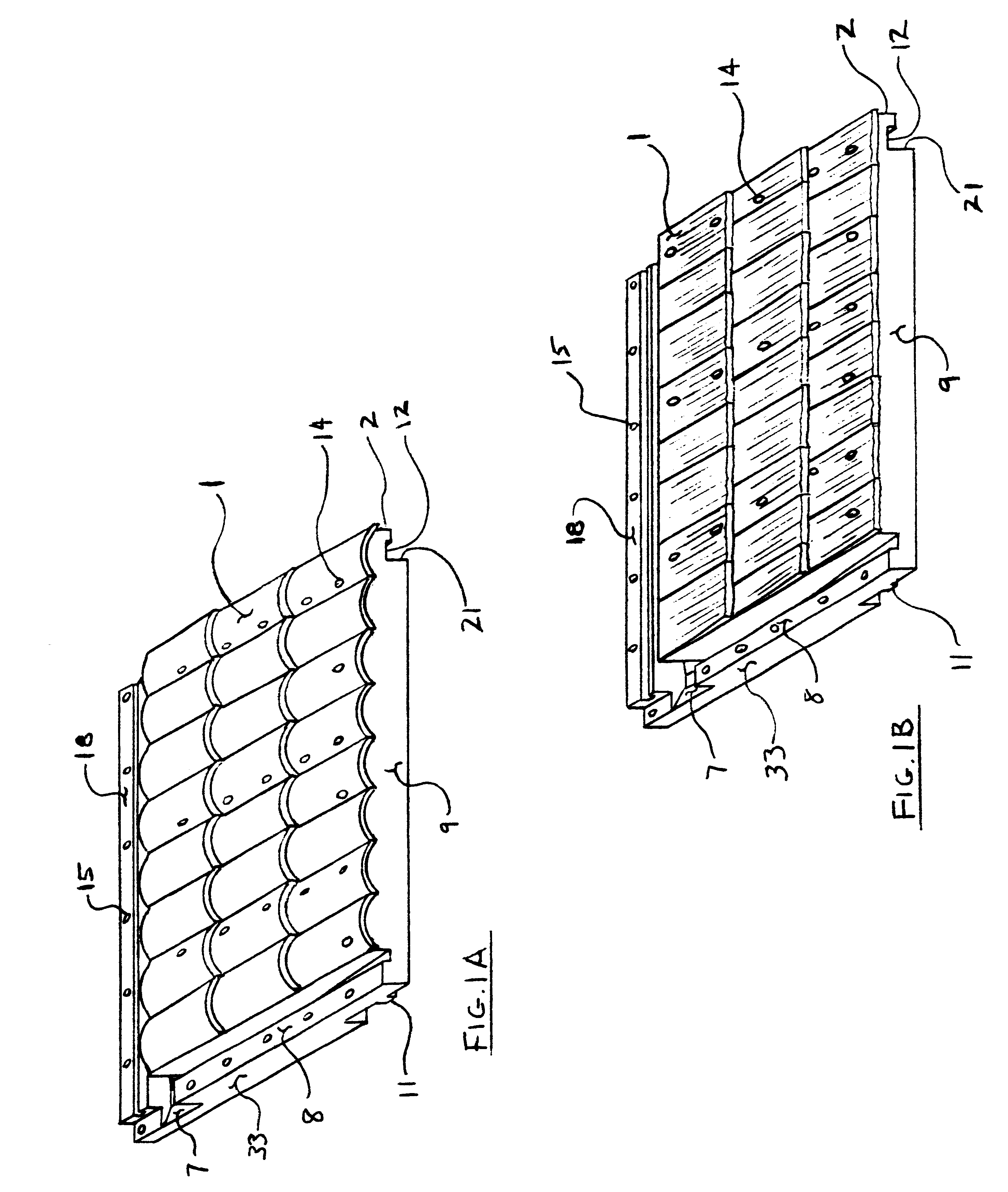
Roofing panel system and method for making same
InactiveUS6282858B1Eliminate needSimple and accurate methodRoof covering using tiles/slatesWallsFiberglass meshWater channel
An injection molded rigid roof panel system for constructing pitched roof structures of the type affixed directly to roof trusses or rafters and needing no structural or supporting sheathing surface or moisture barrier. Comprised of no less than (23) standard roof panel components of varying shapes, sizes, colors and exposed surfaces replicating conventional roofing surfaces. Panels overlap, underlap and interlock by means of an array of shoulders, locating ribs and clearance channels creating a unitized roof system utilizing integral seals at the seams, subsurface water channels and self sealing, threaded fasteners whose molded-in, counter-bored holes are further sealed by composite plugs. Panels are produced by mixing, extruding and pelletizing a compound of over 60% recycled materials and encapsulating a semi-rigid fiberglass mesh sheet in the panels during the injection molding process producing a roofing product that is fire retardant, impervious to moisture, insects, ultraviolet rays and winds in excess of 130 mph.
Owner:SWICK ANDREW C
Thermoplastic composite material, and preparation method and application thereof
The invention belongs to the field of polymer composite materials, and discloses a thermoplastic composite material, and a preparation method and an application thereof. The composite material is composed of the components of, by weight: 1-99 parts of a prepreg and 1-99 parts of a thermoplastic composition or thermoplastic resin. The preparation method comprises the steps that: the 1-99 parts of thermoplastic composition or thermoplastic resin is added into a feeding hopper of an injection molding machine, and is mixed with the 1-99 parts of prepreg already in an injection mold; and injection molding is carried out. The invention also discloses an application of the thermoplastic composite material in car bumpers, car door inner panels, car bumper beams, cars toe-boards, car hood, car rear lift door, building templates, biogas digesters, train sidings, train wall panels, or train roof panels. The composite material provided by the invention has the advantages of smooth outer surface, high gloss, good appearance, excellent mechanical performance, high strength, and good impact resistance.
Owner:HEFEI GENIUS NEW MATERIALS
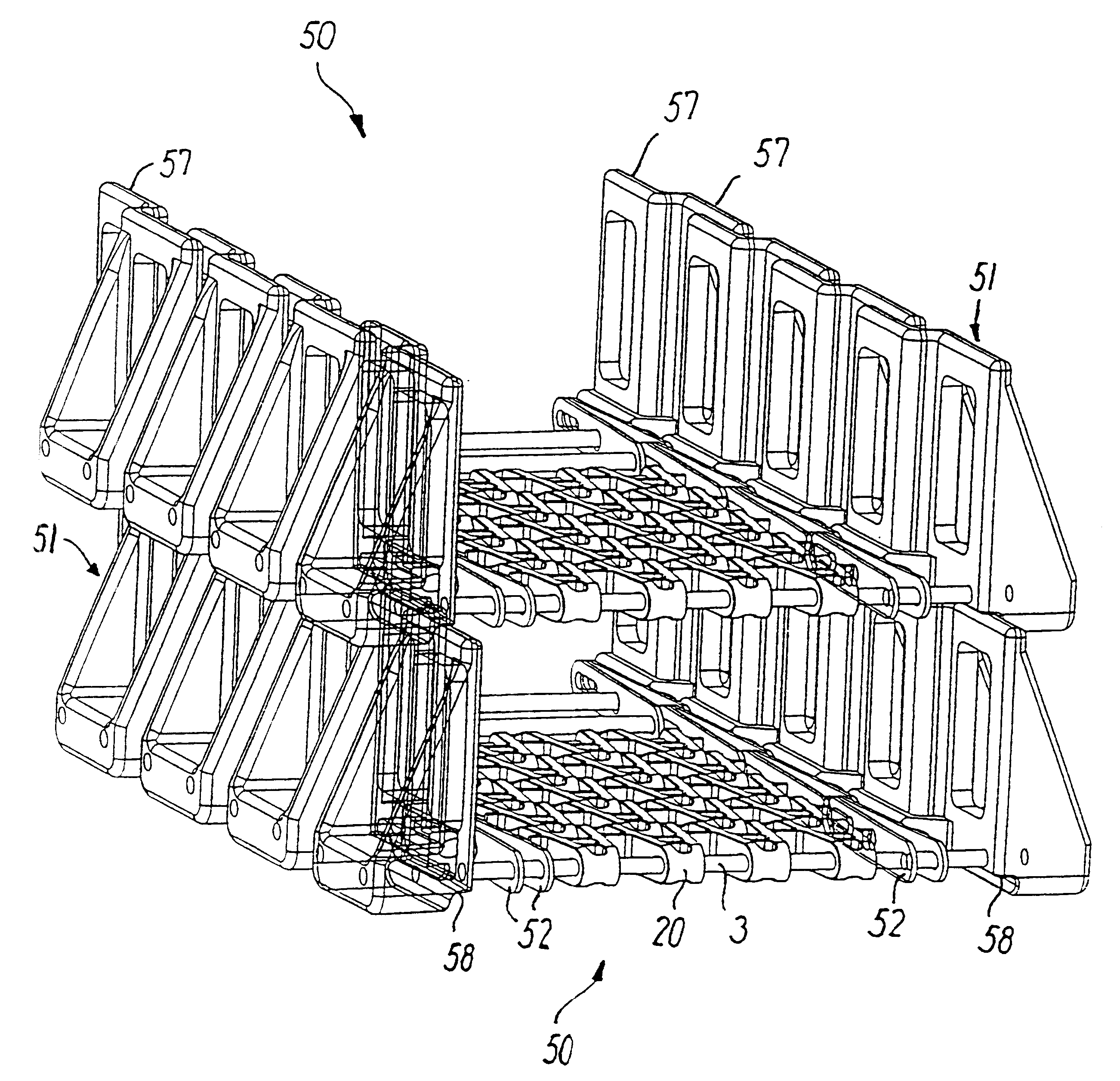
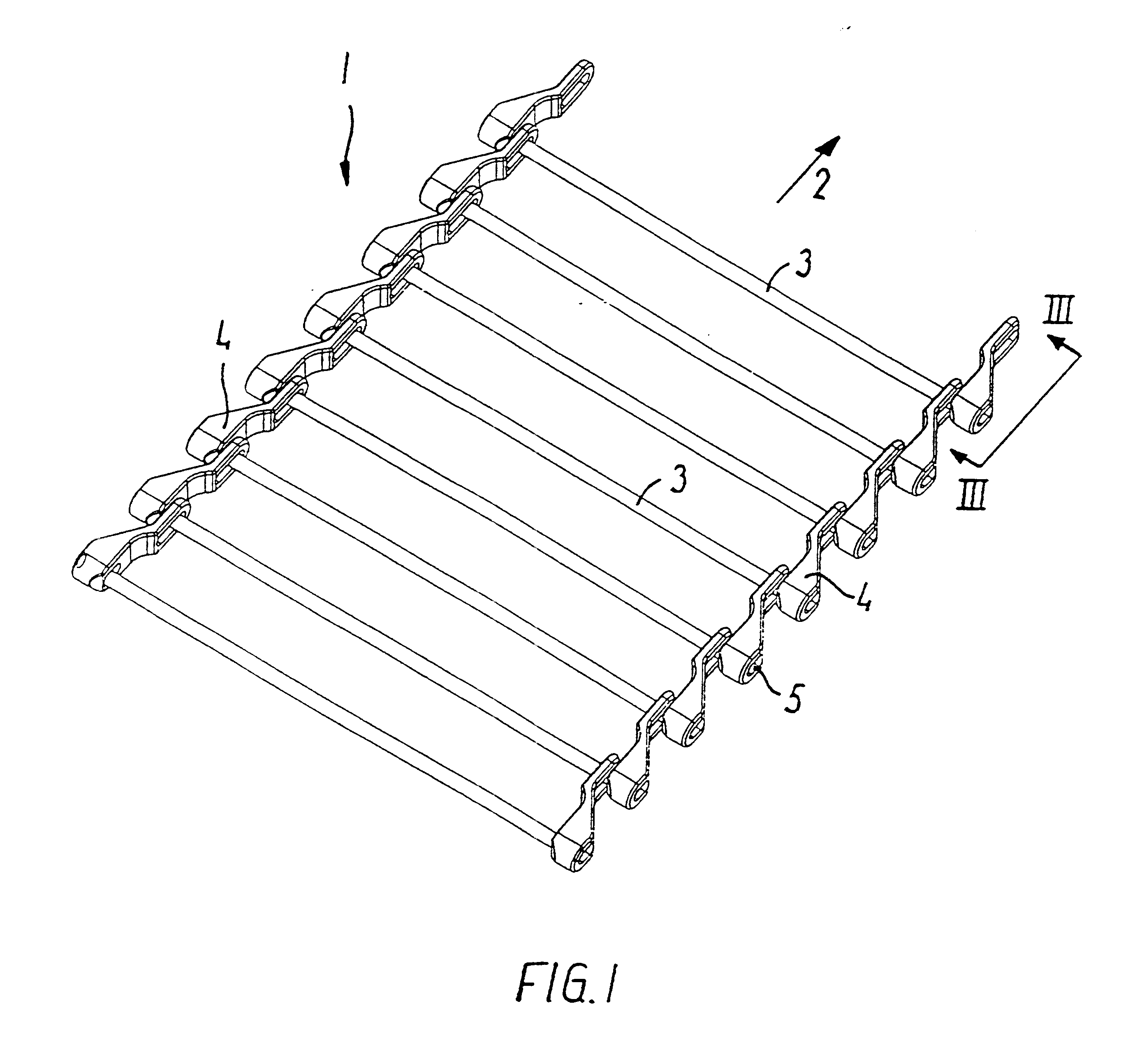
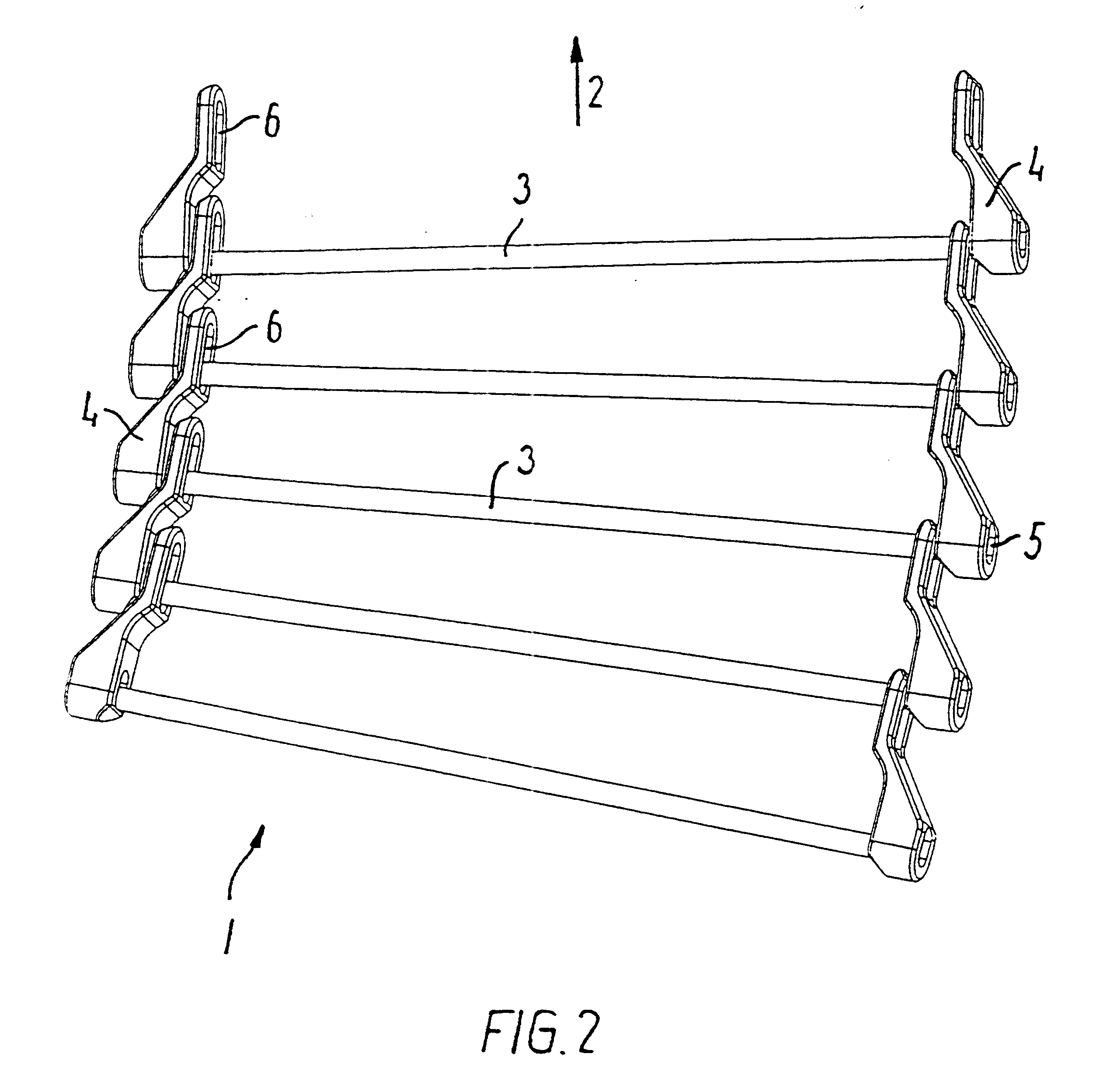
Transport band for conveying along a spiral path
A conveyor belt (1) is composed of a number of identical links in the formation of an endless belt, where each link comprises at least one axle (3) arranged transversely in relation to the direction of travel (2), and an outer link (4) at each side in engagement with the axle. Each outer link comprises an elongated hole for the adjacent link's axle, so that the belt can be driven in a curve in the plane of the belt. Each outer link has at least one securing hole for a transverse axle, where the coupling-together between the axle (3 and the outer link (4) is effected by a separable snap-lock. The outer link is moulded as a one-piece unit in a suitable plastic material, preferably by injection moulding. The outer links (4) can also be configured in a larger version for the construction of conveyor belts for operation in self-stacking helical systems.
Owner:UNI CHAINS INT +1
Method of making sensor
InactiveUS20050067737A1Improve performanceMaterial electrochemical variablesElectron transfer mediatorCompound (substance)
Owner:RAPPIN CRAIG +2
Personal hygiene device
ActiveUS7240390B2Reduce riskFulfil requirementsCarpet cleanersBrush bodiesEngineeringInjection moulding
The invention relates to a process for producing a toothbrush having a body, which comprises a handle region, a head region and a neck region located between the handle region and the head region, and having functional elements which are arranged, at least in part, within the body and comprise an electrically operated functional unit and an electric supply device which has an energy store and is intended for the functional unit, in the case of which the body is produced, by injection molding, from at least one hard component, which serves as a reinforcement, and at least one soft component, and at least some of the functional elements, during the production of the body, are encapsulated, at least in part, directly by the plastic which forms the soft component.
Owner:TRISA HLDG AG
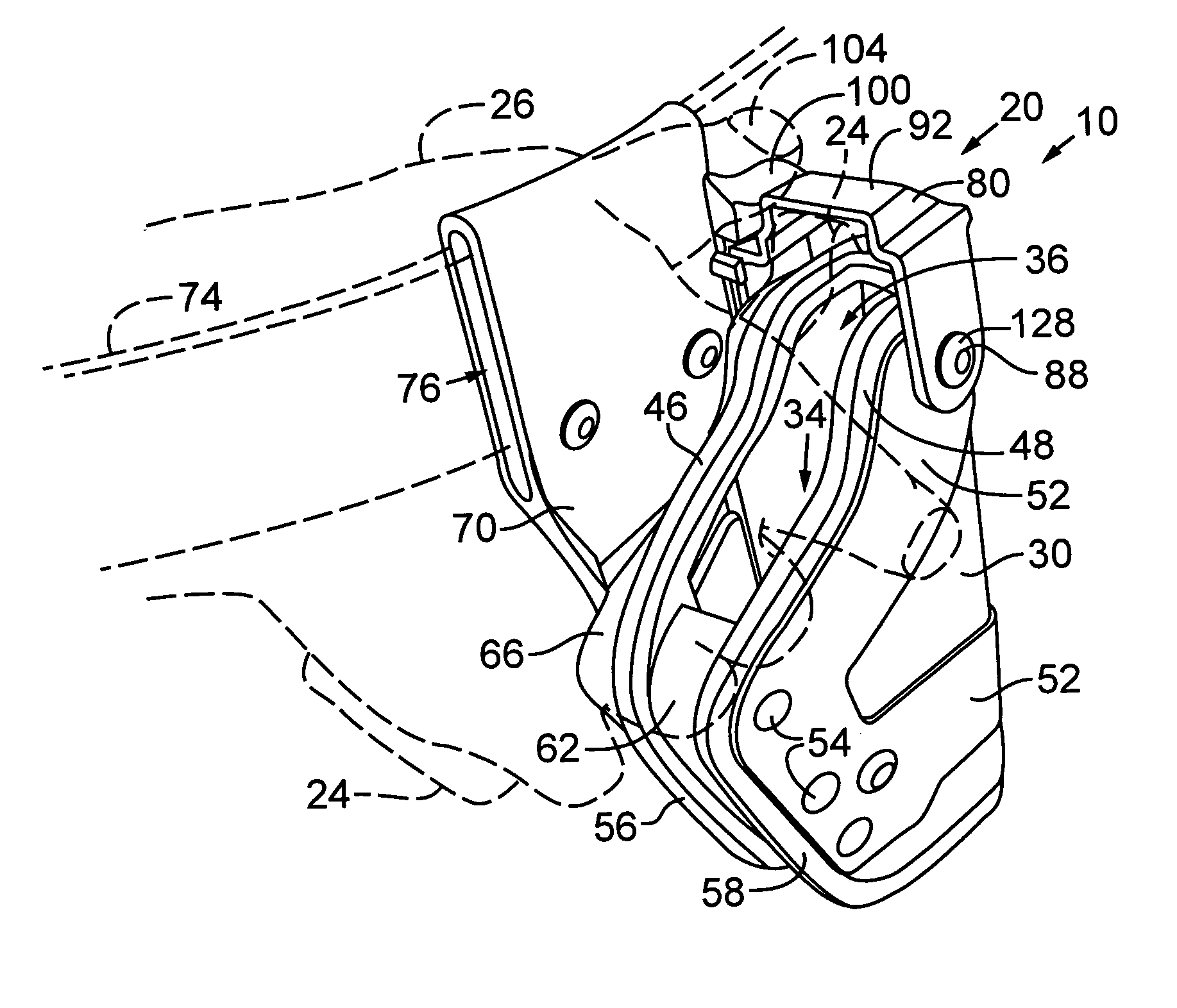
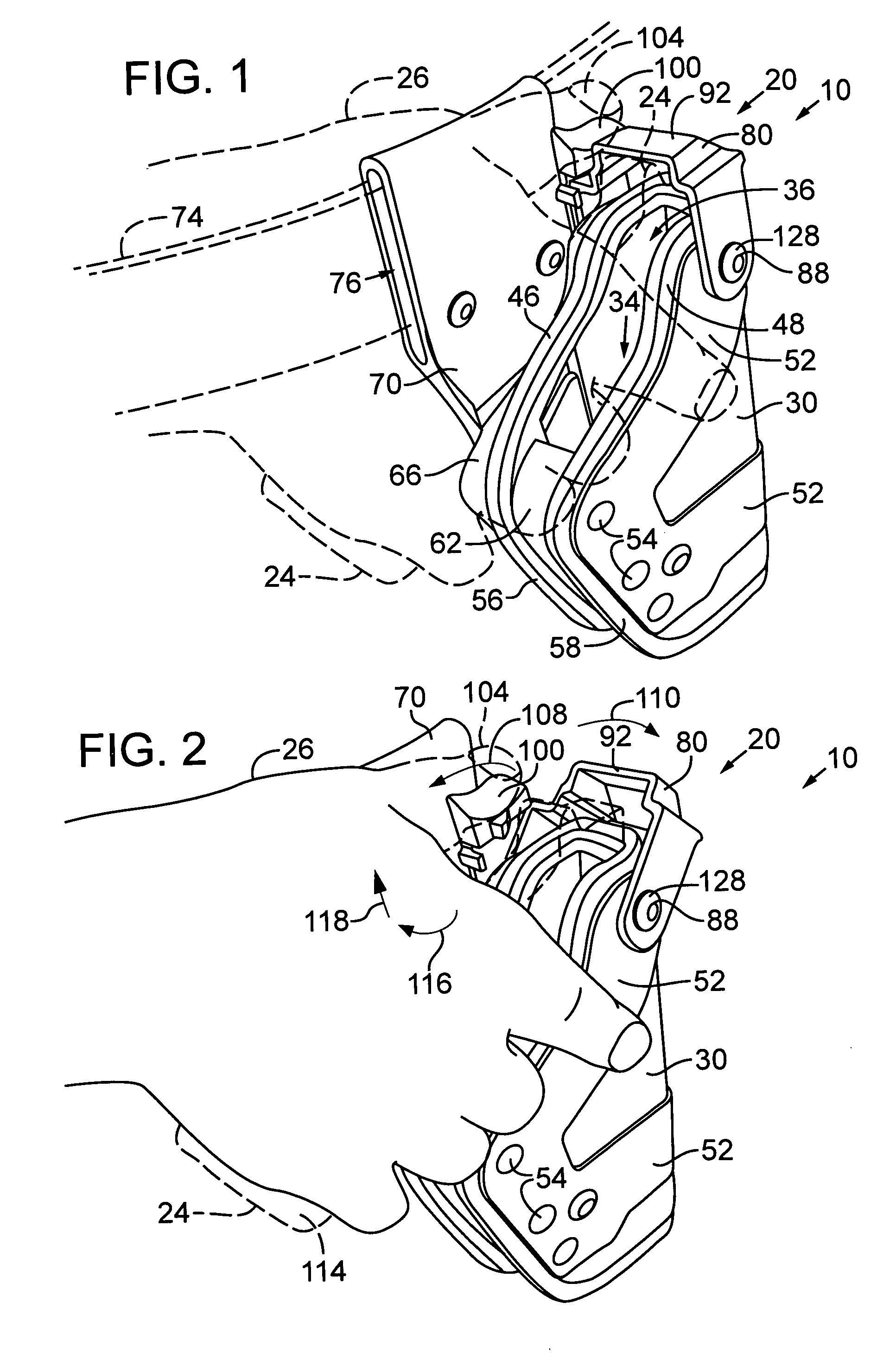
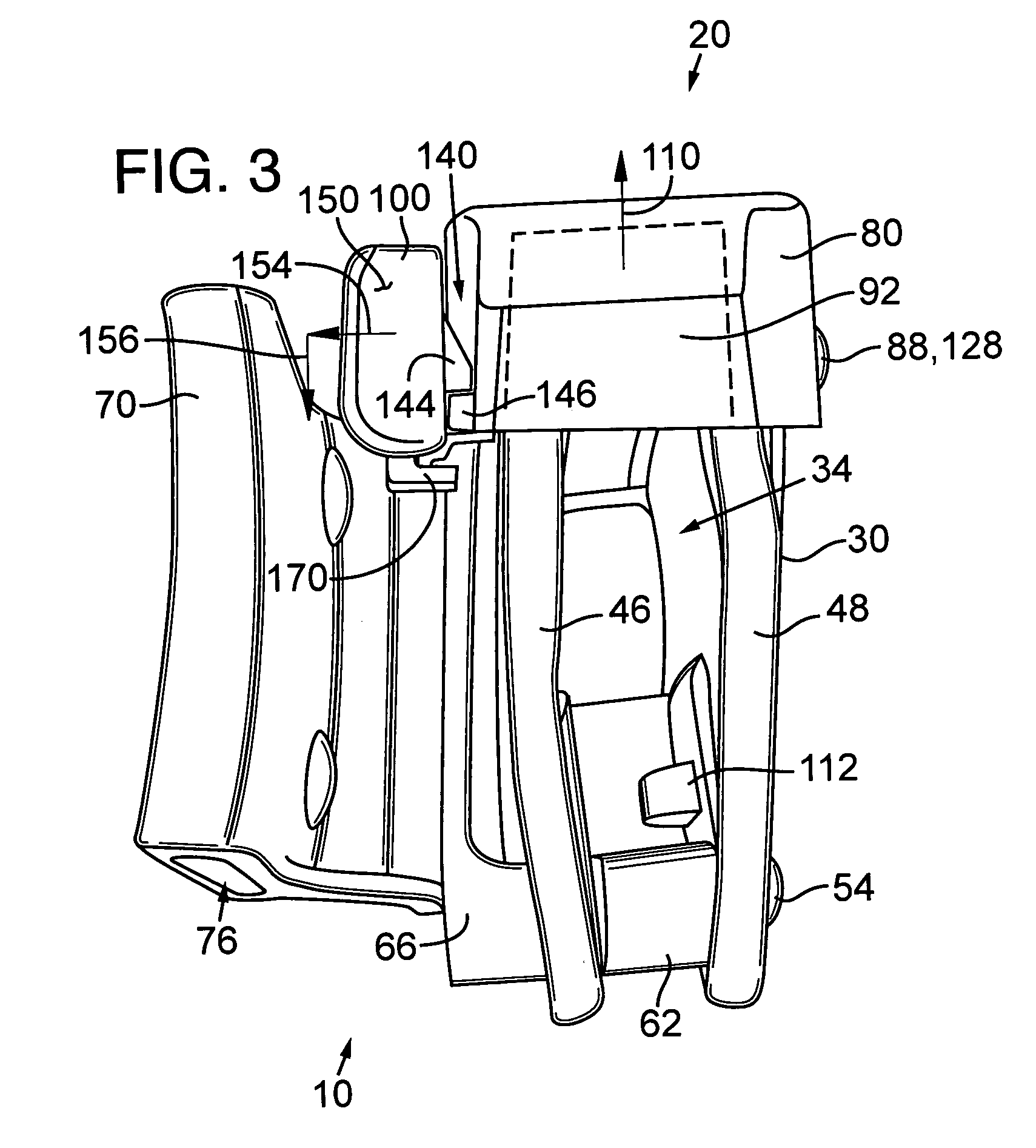
Security hood for handgun holsters and the like
InactiveUS20050035163A1Prevent openingImprove security levelTravelling carriersArms wearablesHOOD assemblyEngineering
A security hood assembly for a holster includes a hood that is movably supported in association with a holster body so that the hood extends over a portion of a holstered handgun or other service item when the hood in a closed position, to prevent unauthorized removal of the service item. A lever may be operably coupled to the hood for driving the hood toward an open position, to allow the service item to be removed from the holster. In some embodiments, a latch mechanism releasably engages when the hood is in the closed position to prevent the hood from being opened through direct manipulation of the hood. The hood is preferably formed of a substantially rigid material, such as injection molded plastic. Holsters including the security hood assembly may also include internal retention devices, hood biasing mechanisms, and electronic devices responsive to opening of the hood.
Owner:MICHAELS OF OREGON
Ink supply arrangement for a portable ink jet printer
Owner:SILVERBROOK RES PTY LTD +1
Wood plastic composite material
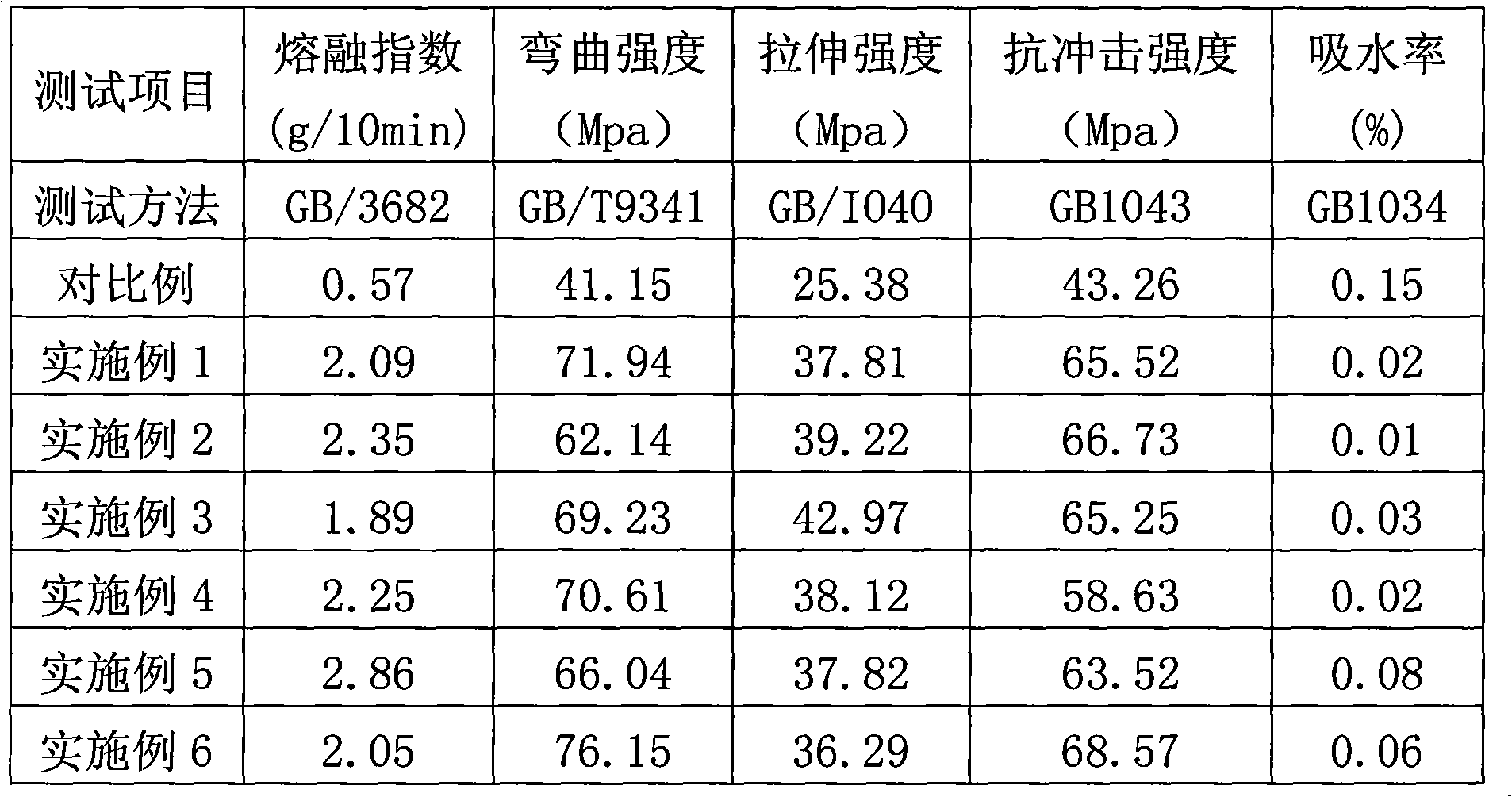
The invention relates to a wood plastic composite material comprising the following materials in parts by weight: 100 parts of wood meals, 20-80 parts of waste plastics, 5-50 parts of waste rubbers, 10-60 parts of high-melt index thermoplastic resins, 1-12 parts of surface active agents, 2-8 parts of lubricating agents, 0.1-4 parts of cross-linking agents, 0.1-4 parts of antioxygens and 0.05-1.5 parts of processing agents, wherein the grain diameter of the wood meals ranges from 10 meshes to 325 meshes; the flow velocity of the high-melt index thermoplastic resins is higher than 20 g / 10 minutes; the cross-linking agents are peroxides, thus the invention improves the dispersibility and the flowability of the wood meals contained in the composite and the compatibility of plastics by adding the high-melt index thermoplastic resins, can not only better utilize the resources, but also enhances the mechanical strength (such as tensile strength, bending strength, impact strength, and the like) of the composite material by adding the waste rubbers, has the advantages of good processing property, low water absorption rate, good stability of products, and the like and is suitable for injection moulding and beneficial to market promotion.
Owner:东莞市启原实业有限公司
Injection molding method for neutral and acidic-group containing (meth)acrylate copolymers
InactiveUS20020160042A1Reduce contentOrganic dyesPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsMeth-Additive ingredient
The invention relates to a process for producing mouldings by injection moulding, the steps in the process being A) Melting a mixture made from a) a (meth)acrylate copolymer composed of from 40 to 100% by weight of free-radical-polymerized C1-C4-alkyl esters of acrylic or methacrylic acid and from 0 to 60% by weight of (meth)acrylate monomers having an anionic group in the alkyl radical, where the copolymer comprises b) from 0.1 to 3% by weight of a release agent, and, where appropriate, the mixture may comprise c) from 0 to 50% by weight of a drier, d) from 0 to 30% by weight of a plasticizer, e) from 0 to 100% by weight of additives or auxiliaries, f) from 0 to 100% by weight of an active pharmaceutical ingredient, g) from 0 to 20% by weight of another polymer or copolymer, where the amounts given for components b) to g) are based on the (meth)acrylate copolymer a) and the mixture prior to melting has a content of more than 0.5% by weight of low-boiling constituents with vapour pressure of at least 1.9 bar at 120° C., B) Devolatilizing the mixture in the thermoplastic state at temperatures of at least 120° C., thereby lowering to not more than 0.5% by weight the content of the low-boiling constituents with vapour pressure of at least 1.9 bar at 120° C., C) Injecting the molten and devolatilized mixture into the mould cavity of an injection mould, the temperature of the mould cavity being below the glass transition temperature of the (meth)acrylate copolymer by at least 10° C., cooling the molten mixture, and removing the resultant moulding from the mould.
Owner:PFIZER INC +1
Solid imaging apparatus and method
ActiveUS7614866B2Reduce viscosityImprove bindingLiquid surface applicatorsConfectioneryAir entrainmentHigh intensity
Owner:3D SYST INC
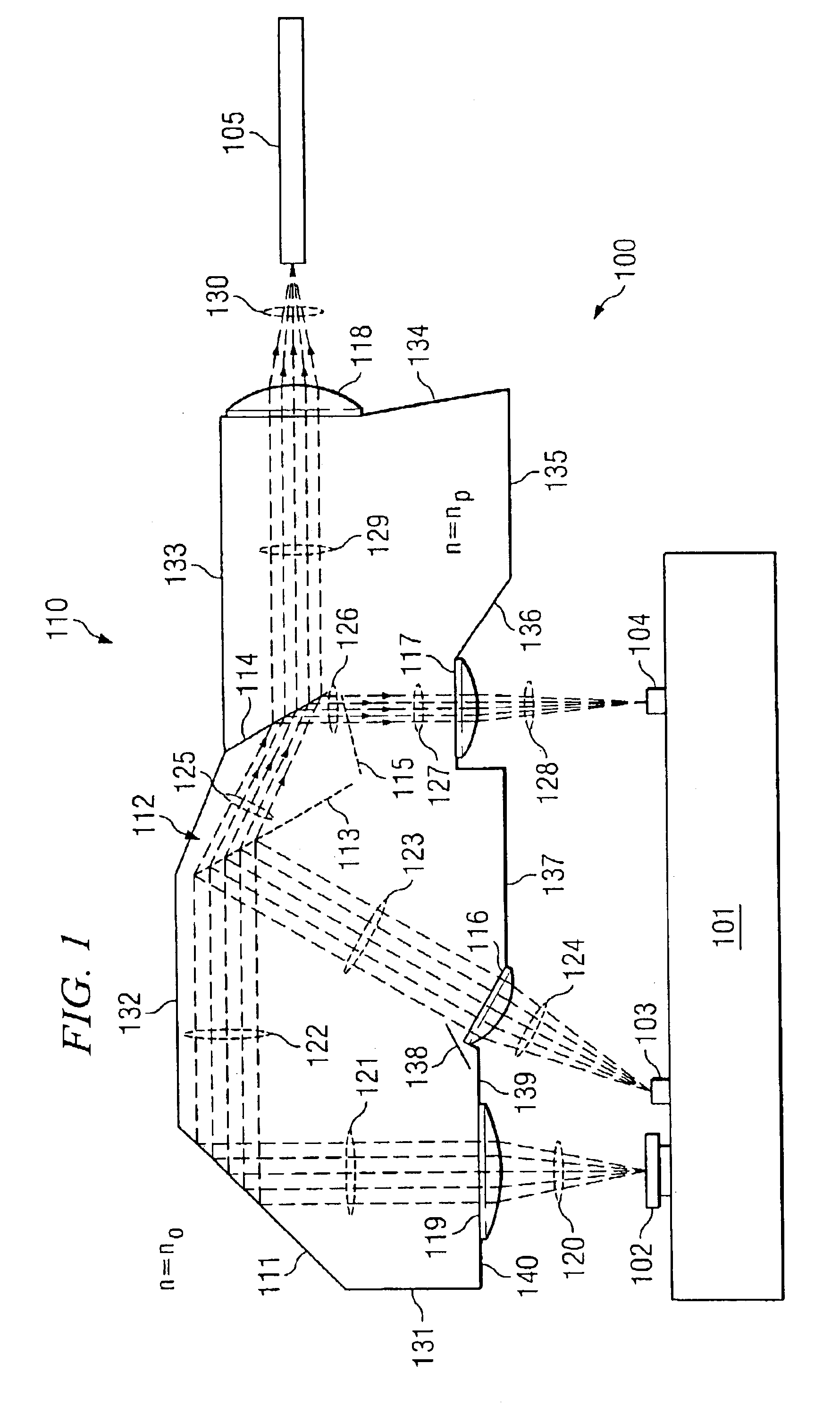
Small form factor all-polymer optical device with integrated dual beam path based on total internal reflection optical turn
InactiveUS6888988B2Low costUse minimizedCoupling light guidesNon-linear opticsTotal internal reflectionOptical Module
A monolithic optical module of injection-molded high temperature polymeric resin combines an optical turn of typically 90 degrees together with dual or triple beam paths. No additional piece parts are necessary for achieving the optical turn, since this occurs by total internal reflection (TIR), and no additional piece parts are necessary for dual monitoring, which is realized by means of an air-gap functioning as a dual beam-splitter plate. The monolithic optical module further includes integrally surfaces for accurate alignment of the module with external optical elements, and can additionally include integral optical elements, for example lenses and thin film coatings.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Overmoulding
In the overmoulding of an article channels are provided in the surface of the article to guide the flow of the overmoulding material, in addition holes may be provided across the article to enable flow of the overmoulding material to the side of the carrier remote from the point of injection. The techniques are particular useful in the overmoulding of articles having a lattice or honeycomb structure particularly when produced by injection moulding. When the overmoulding material is foamable the overmoulded articles may be used as acoustic baffles or structural reinforcement for automobiles.
Owner:ZEPHYROS INC
Method for preparing magnetic filling with biological affinity, hydrophilicity and activity for water treatment
InactiveCN1522972AEasy to grow and compactGood compatibilitySustainable biological treatmentBiological water/sewage treatmentInjection molding machineInjection moulding
The present invention relates to a preparation method of biological affinity hydrophilic active magnetic seed filling material for treating water. It is characterized by that said method includes the following steps: mixing biological affinity substance, hydrophilic substance, magnetic powder and active carbon or magnetic powder and calcium carbonate in the high-molecular base material, and adding dispersion lubricating agent, uniformly stirring them, placing them into injection moulding machine, utilizing filling mould to make extrusion moulding and magnetizing, so as to obtain the invented filling material. It has biological affinity and hydrophilicity, at the same time can induce microbial activity and enzyme activity, and can raise oxygen utilization rate in water and water treatment efficiency.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
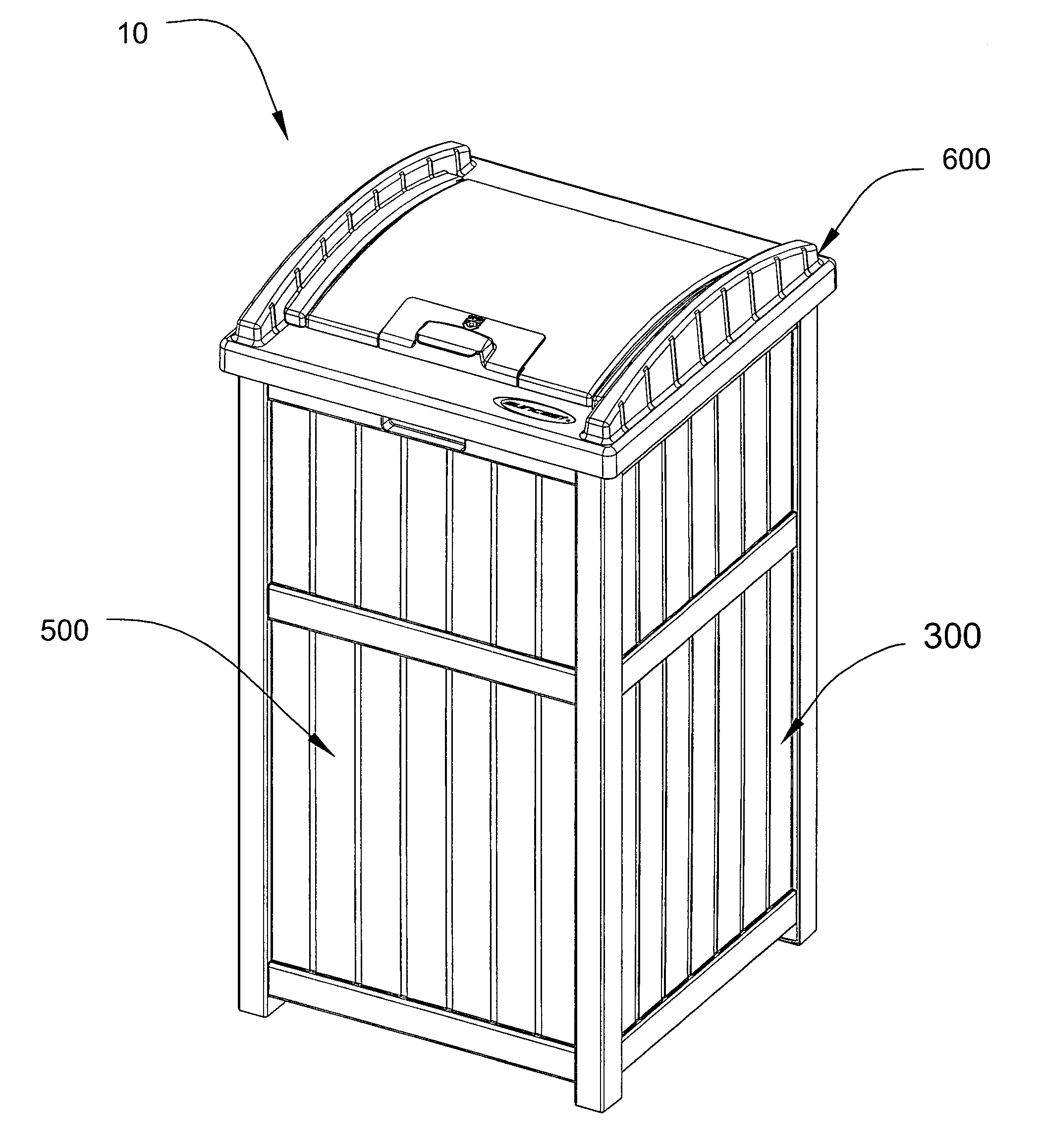
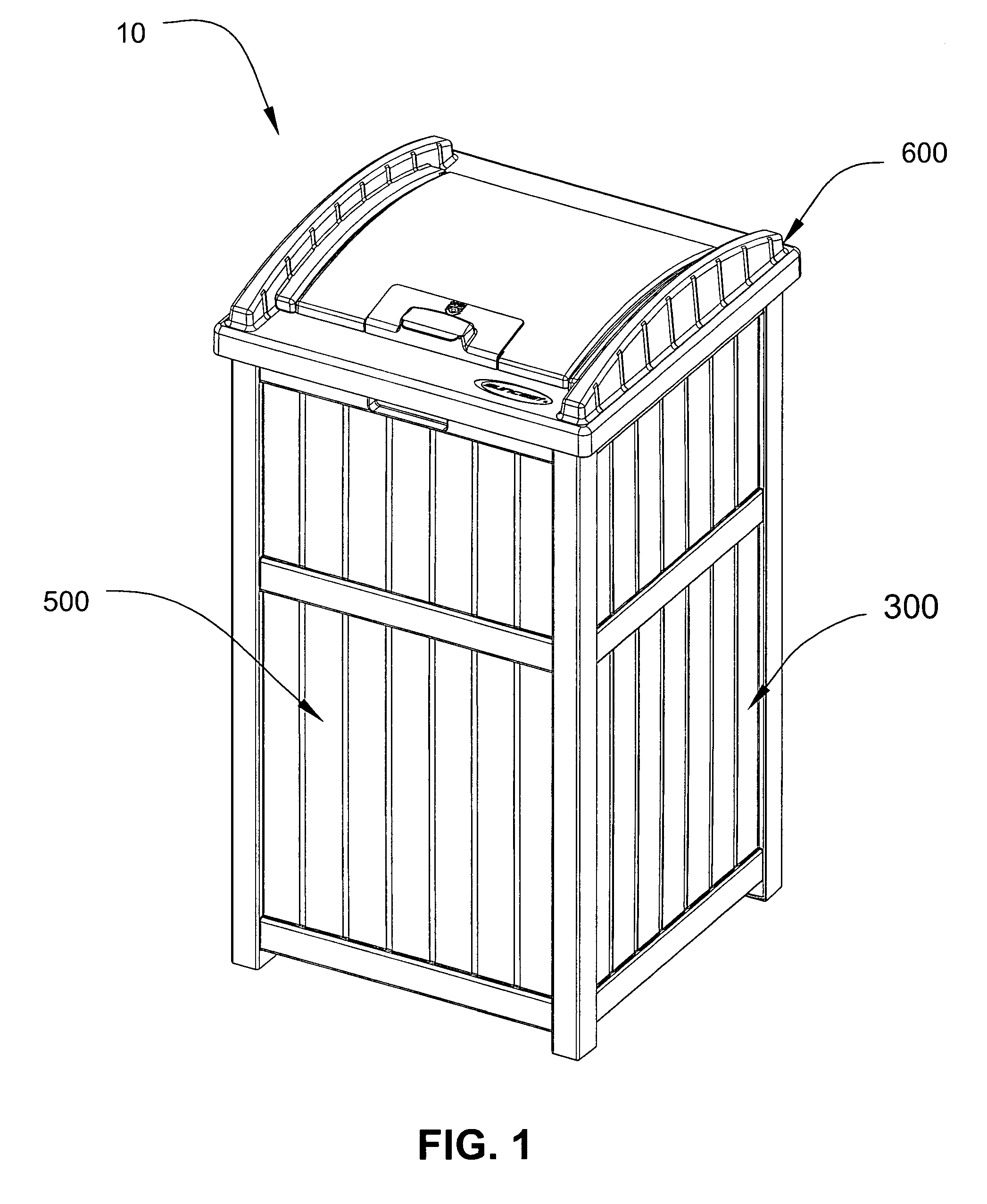
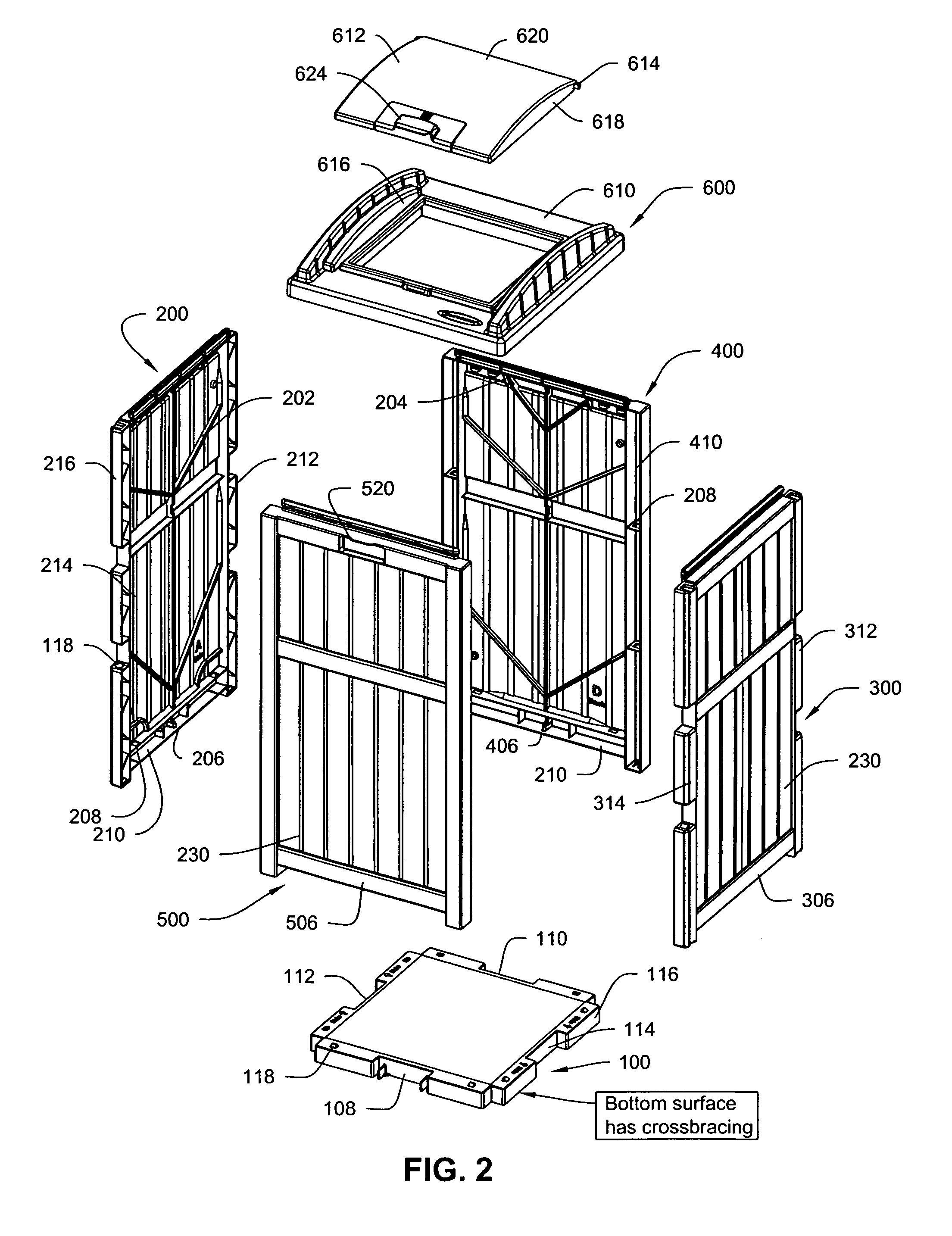
Secure trash container assembly
Owner:SUNCAST
Injection molding method for manufacturing plastic parts
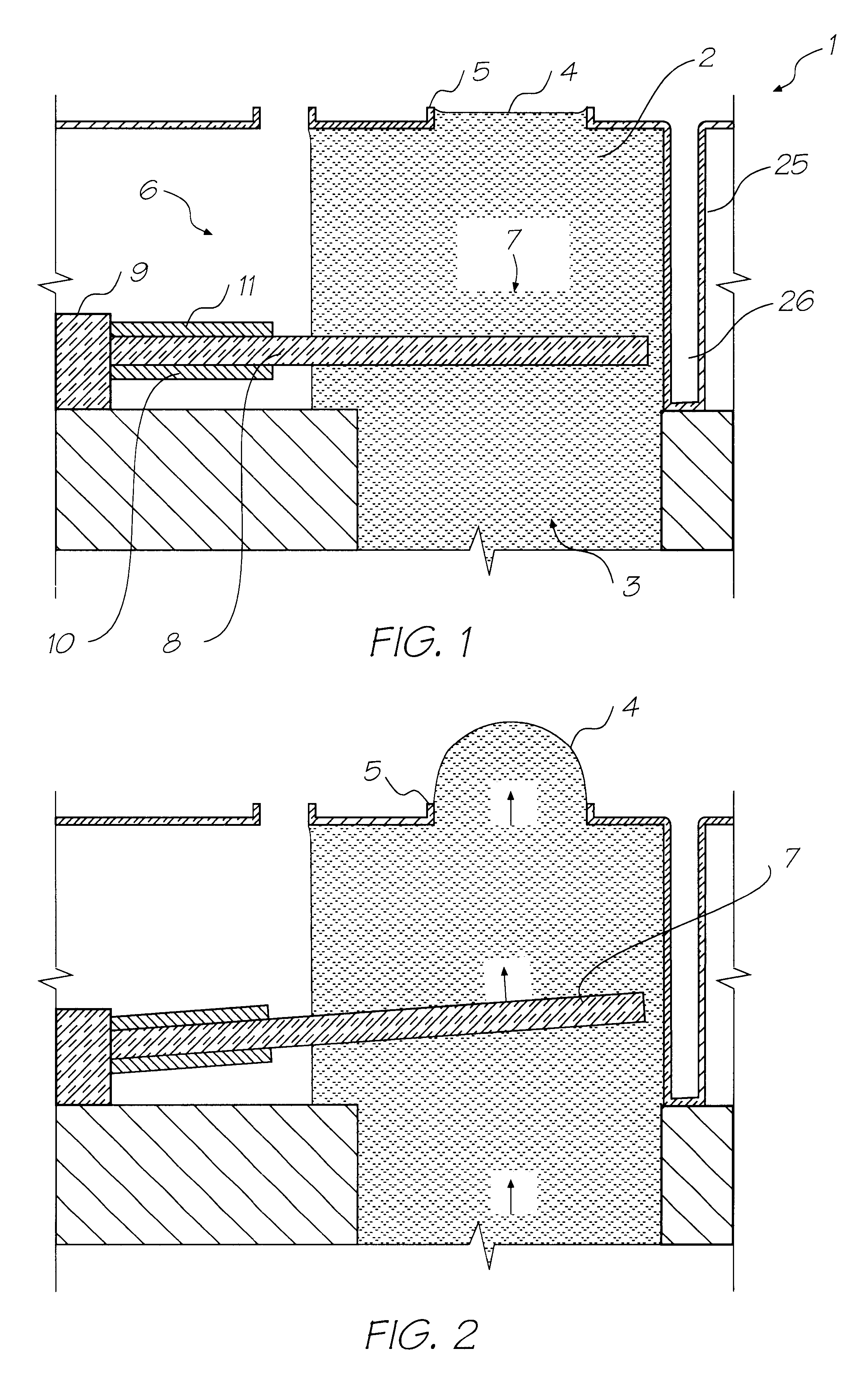
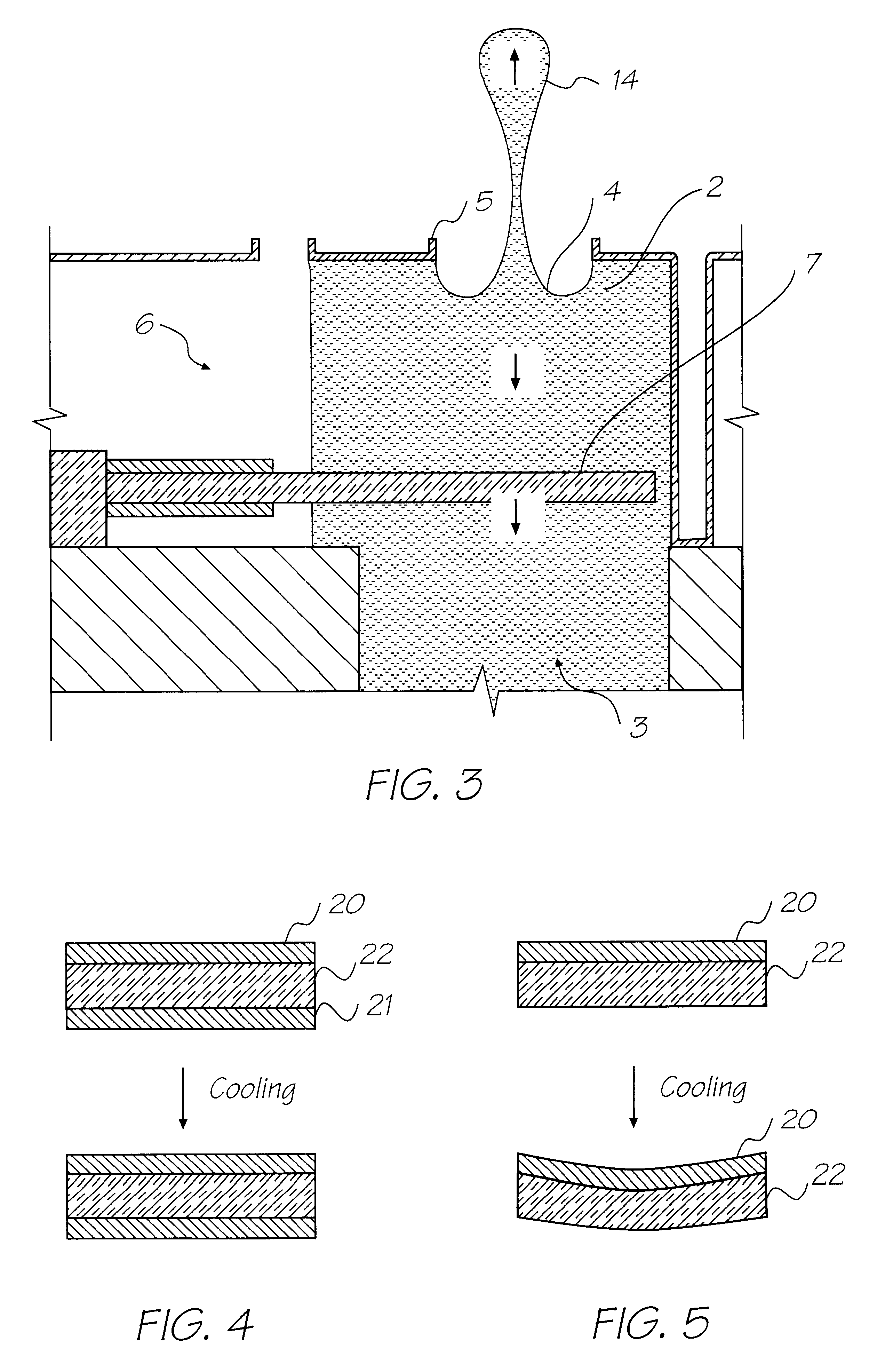
InactiveUS20060068206A1Quality improvementImprove replicationMouldsLayered productsInjection pointSingle injection
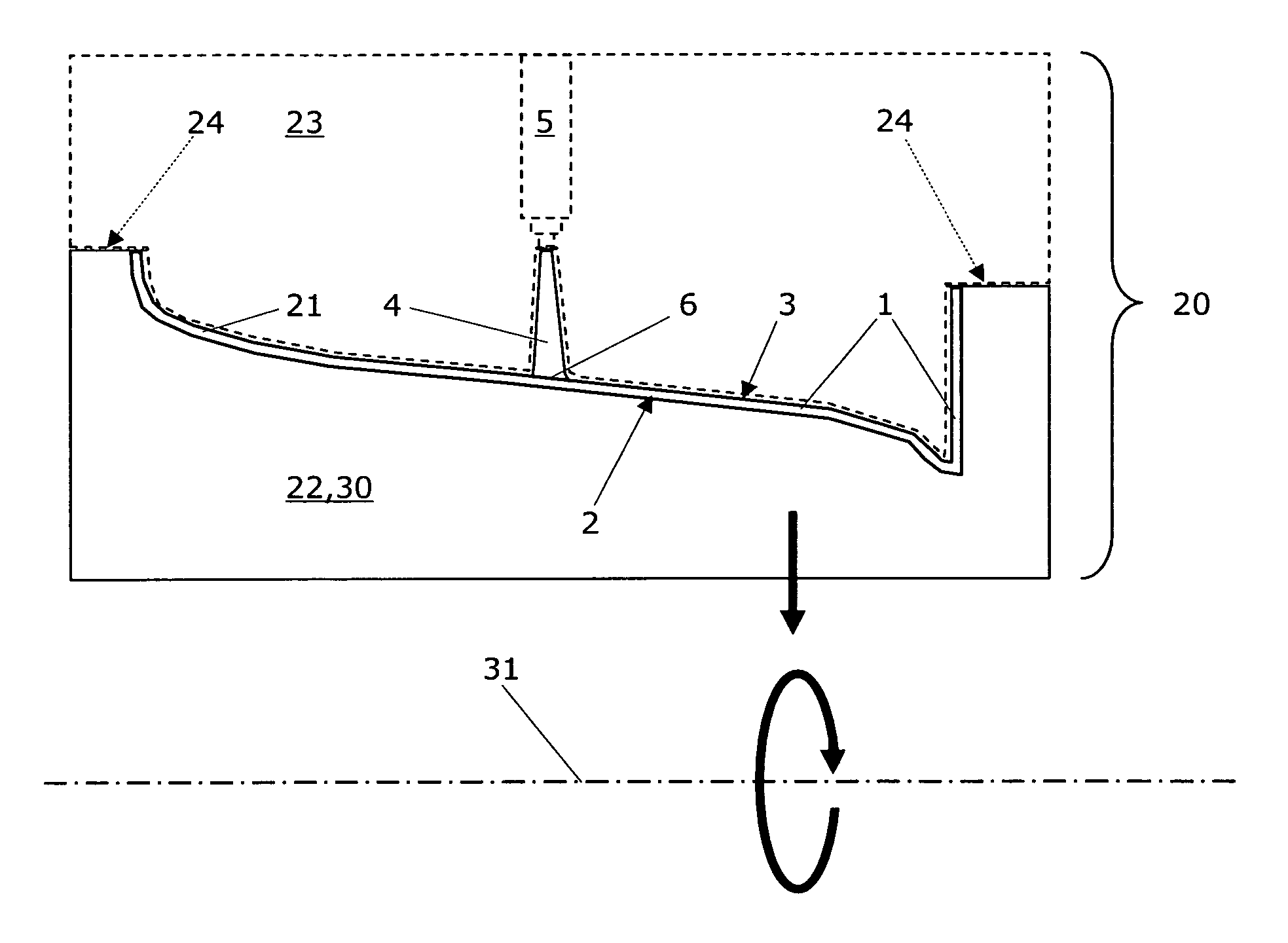
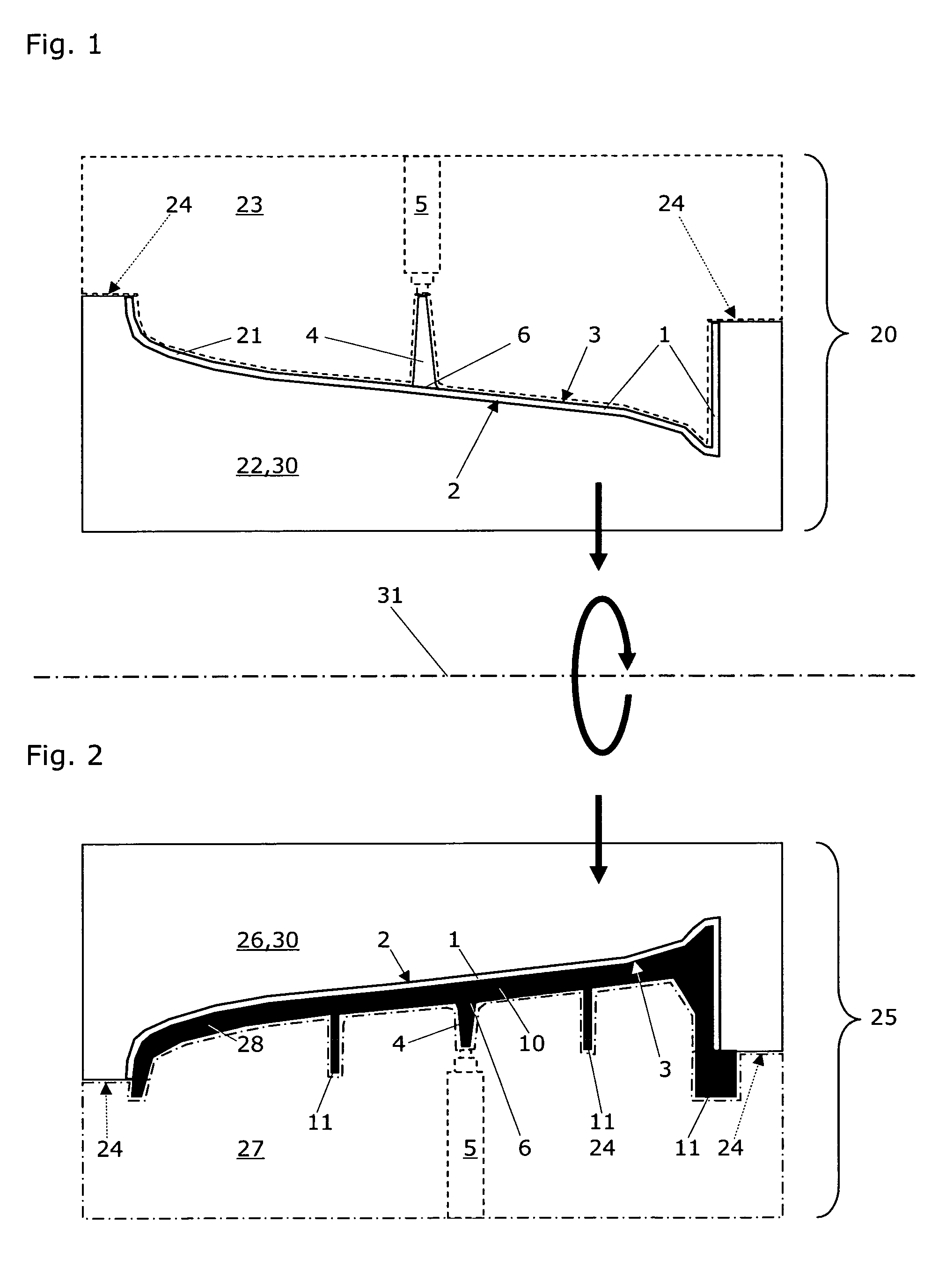
Disclosed is an injection molding method for manufacturing plastic parts from thermoplastically processible plastic molding materials with at least one exposed part (1) and at least one functional part (10), whereby the plastic molding material for the exposed part (1) comprises a transparent or translucent matrix with added effect pigments, and whereby the functional parts (10) can exhibit different physical and / or chemical plastic properties to the exposed parts (1). The injection molding method comprises the following steps: a) injection molding and solidification of the plastic molding material of the at least one exposed part (1) with an exposed surface (2) and a core surface (3) facing away from the latter in a first mold (20) with a first cavity (21); b) opening of the first mold (20) along a parting line or plane (24); c) closing of a second mold (25) with the at least one exposed part (1) in a second cavity (28); d) injection molding and solidification of the plastic molding material of the functional part (10) on the core surface (3) of the at least one exposed part (1); and e) opening of the second mold (25) and removal of the part. The injection molding method according to the invention is characterized in that for each exposed part (1)—to prevent irregularities such as flow marks and / or knit lines—a single injection nozzle (5) positioned to optimize the flow or at least two injection nozzles in a cascaded injection molding method are used, and that the plastic molding material for the exposed part (1) comprises at least one transparent polymer. The corresponding plastic parts manufactured by injection molding exhibit an exposed surface (2) and a core surface (3) facing away from the latter with at least one injection point (6), whereby the functional part (10) of the plastic part is injection molded onto the core surface (3) of the previously solidified exposed part (1).
Owner:EMS CHEM AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com