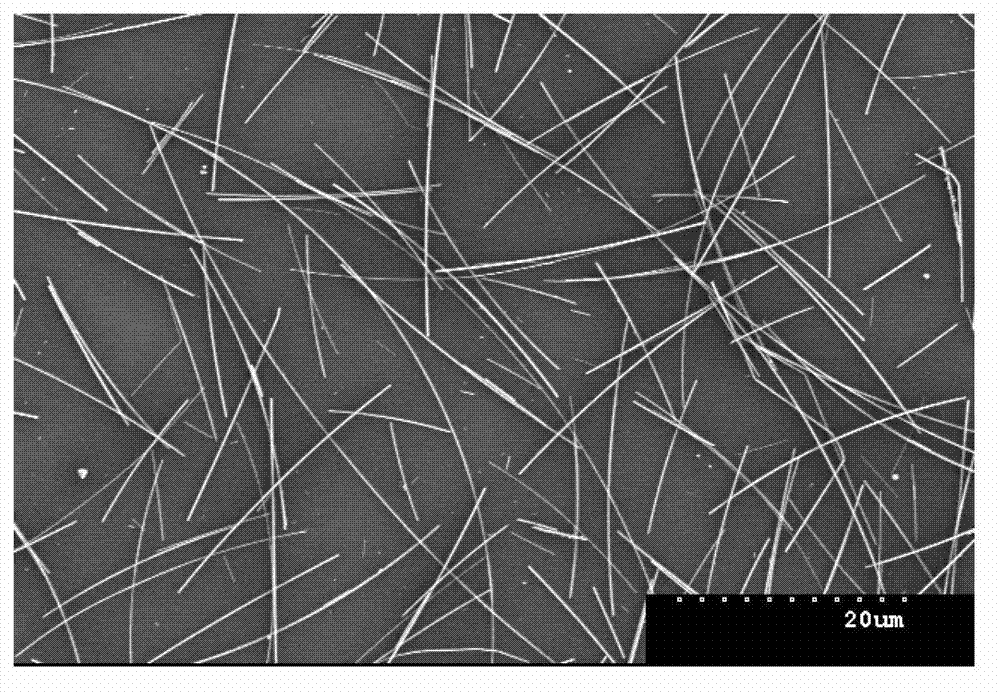
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
9076 results about "High volume manufacturing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
High-volume manufacturing is the same as mass production: fabricating large quantities of goods in short periods of time. Goods that are produced in high volume often have little or no variation. For example, an auto-parts manufacturer might create thousands of units the exact same part to send to automobile factories.
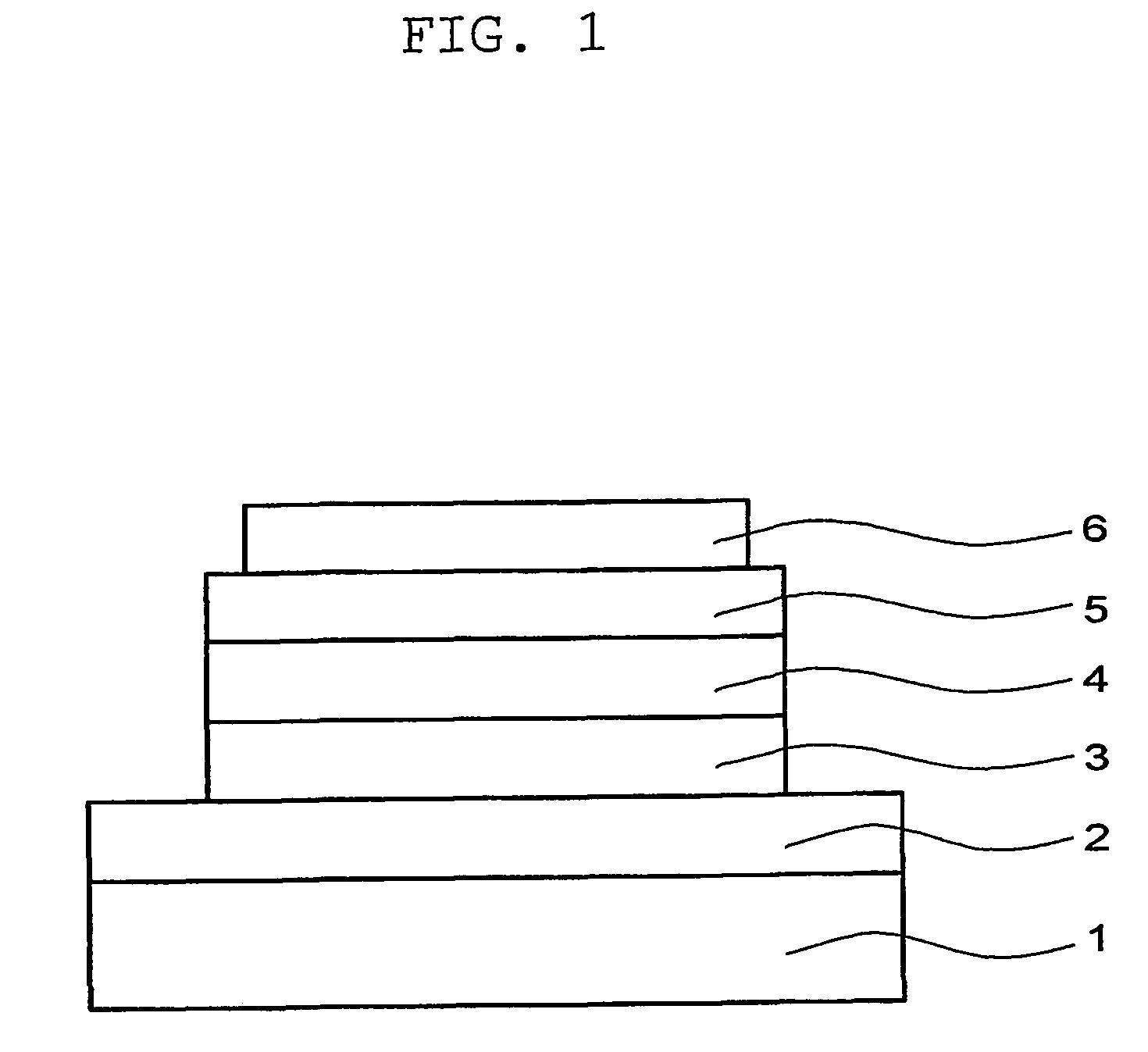
Light emitting material and organic light-emitting device
InactiveUS7396598B2High efficiency of light emissionKeep energy smallDischarge tube luminescnet screensGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsFluorescenceTriplet state
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
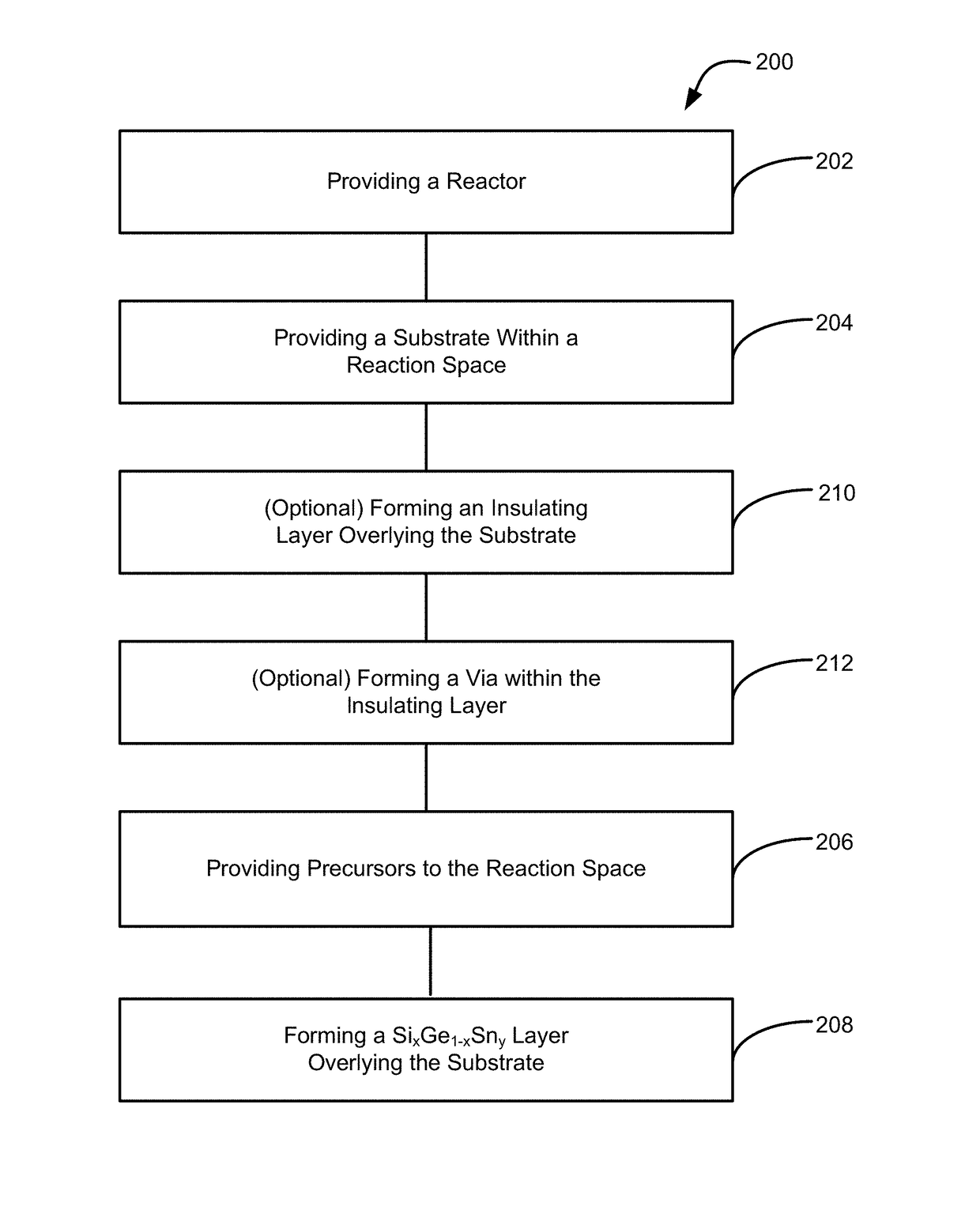
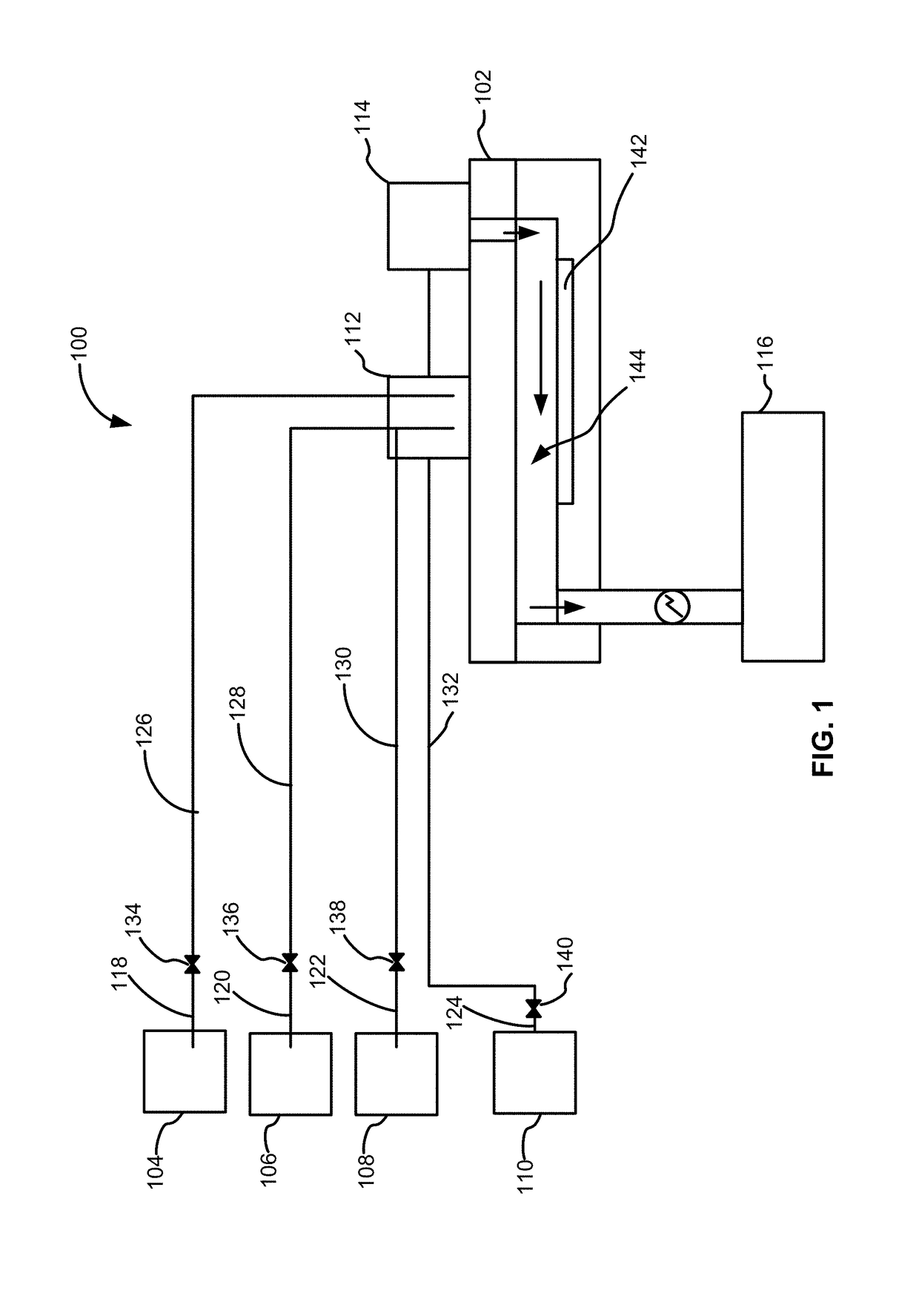
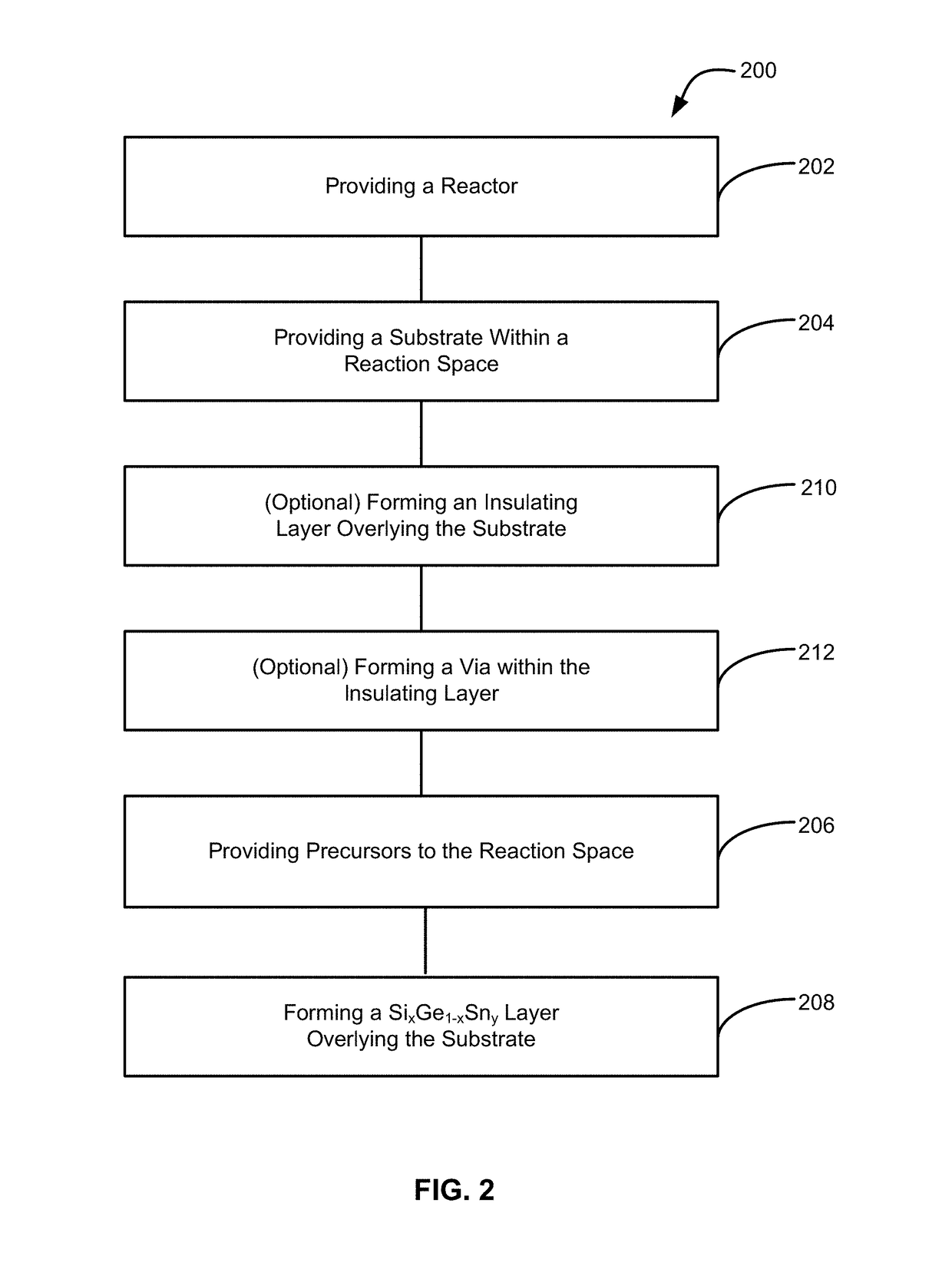
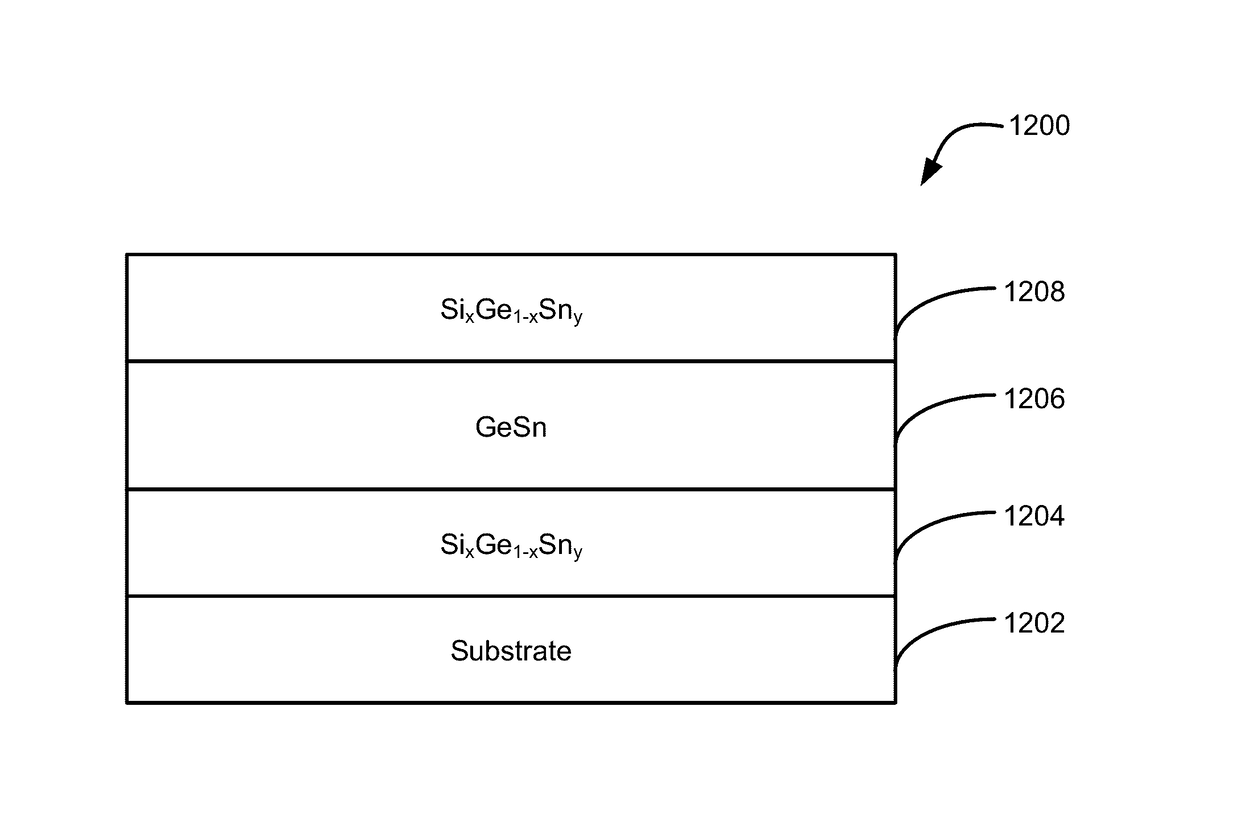
Methods of forming silicon germanium tin films and structures and devices including the films
ActiveUS9905420B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHigh volume manufacturingChemical vapor deposition
Methods of forming silicon germanium tin (SixGe1-xSny) films are disclosed. Exemplary methods include growing films including silicon, germanium and tin in an epitaxial chemical vapor deposition reactor. Exemplary methods are suitable for high volume manufacturing. Also disclosed are structures and devices including silicon germanium tin films.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Method for preparing graphene compounds and graphene oxide compounds with high efficiency
The invention relates to a method for preparing graphene compounds and graphene oxide compounds with high efficiency, relating to the method for preparing the graphene compounds and the graphene oxide compounds. The invention solves the problems of easy composition of graphene or graphene oxide per se and many process steps, higher cost and difficult dispersedness for preparing the graphene compounds and the graphene oxide compounds by the traditional method at the same time. The invention adopts a mechanical stripping method to obtain the graphene compounds and the graphene oxide compounds. In the invention, an automatic machine is utilized, solid particles are used for assisting stripping, the contact area and the stripping number of the stripping process are greatly increased, and carbon material powder experiences a lot of stripping processes through the action of shear and impact, thereby obviously improving the stripping efficiency and achieving the purpose of uniform dispersedness to the composites. The method is suitable for industrial mass production of the graphene compounds and the graphene oxide compounds.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
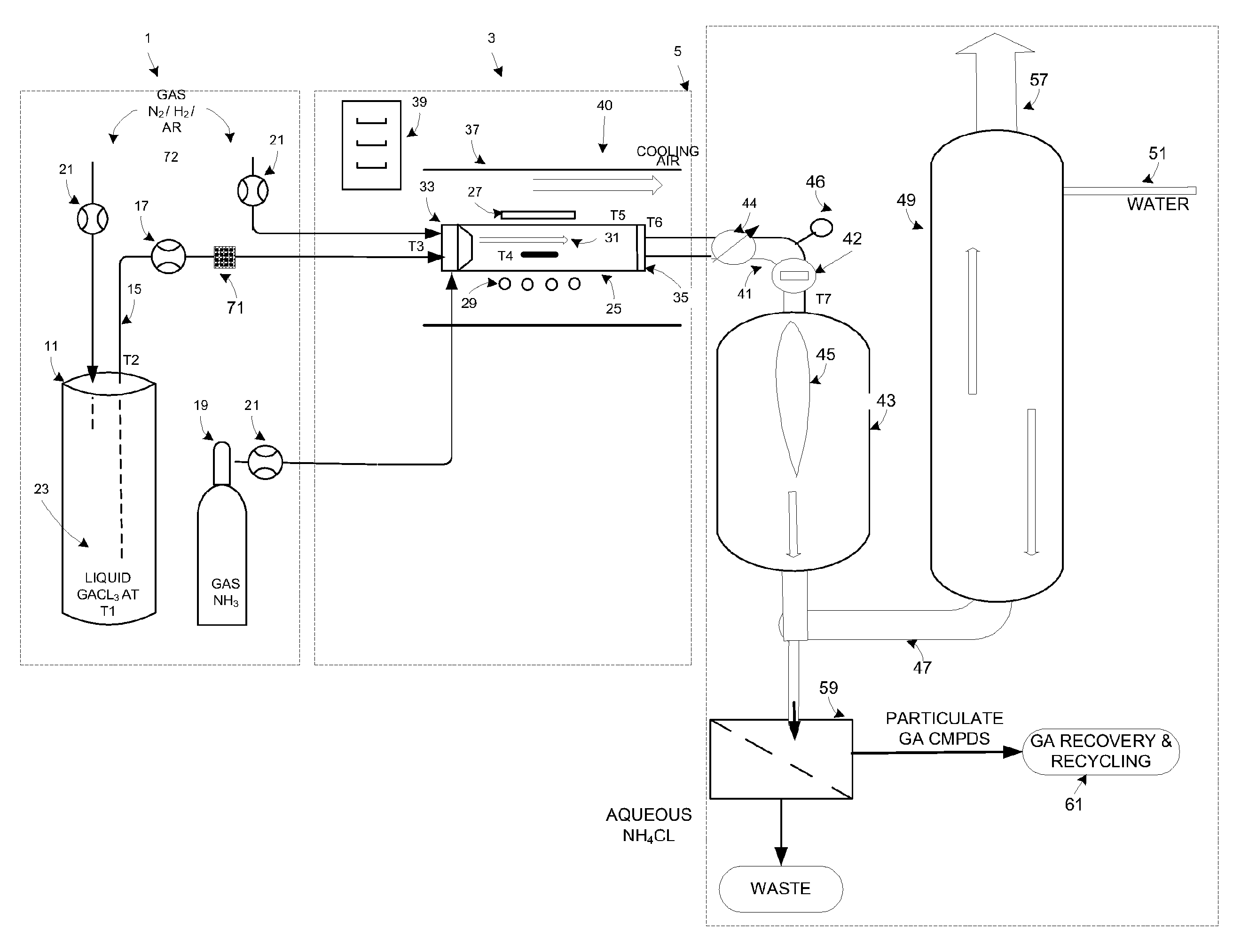
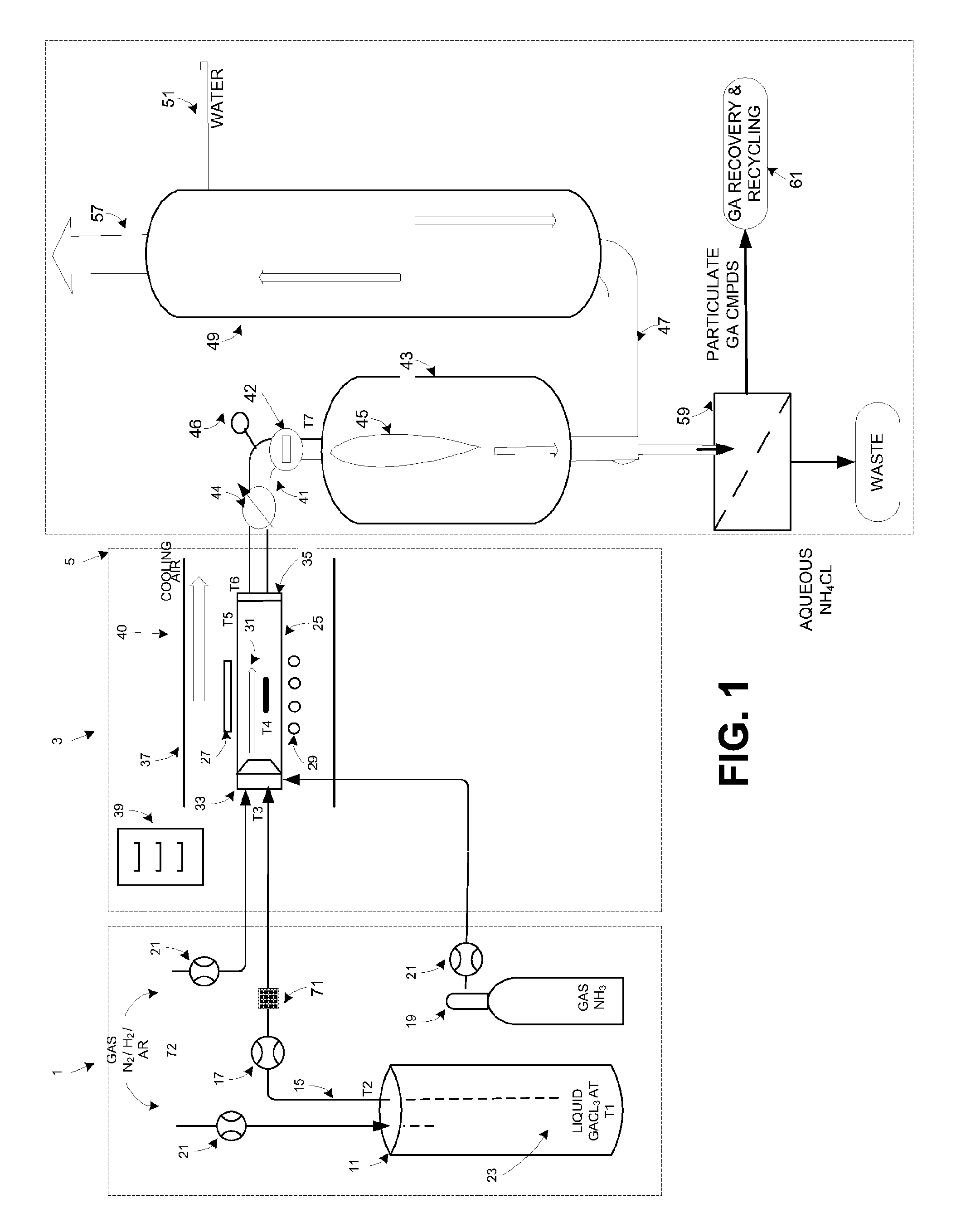
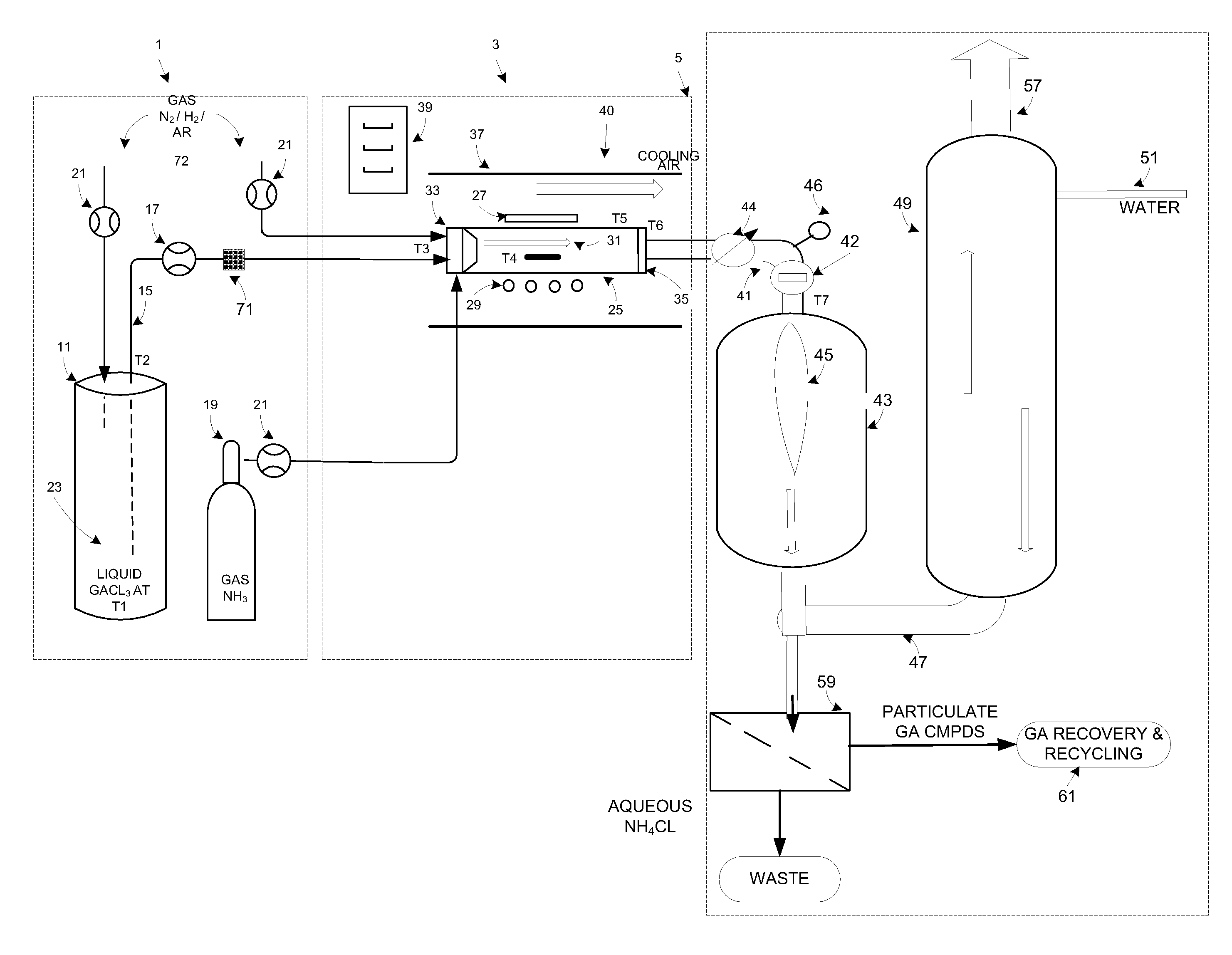
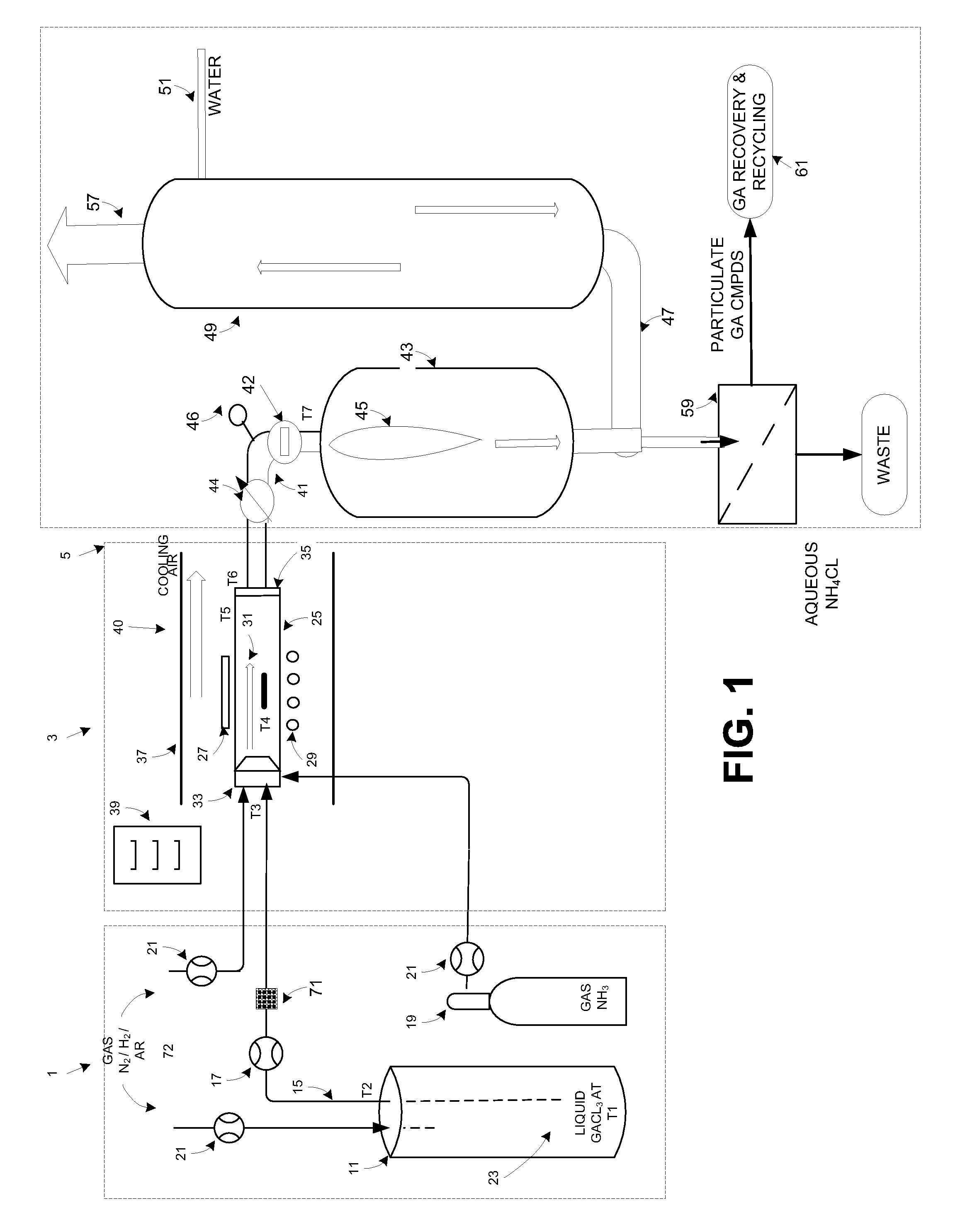
High volume delivery system for gallium trichloride
InactiveUS20090223441A1High manufacturing processEasy to prepare in large batchesPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh volume manufacturingSemiconductor materials
The present invention is related to the field of semiconductor processing equipment and methods and provides, in particular, methods and equipment for the sustained, high-volume production of Group III-V compound semiconductor material suitable for fabrication of optic and electronic components, for use as substrates for epitaxial deposition, for wafers and so forth. In preferred embodiments, these methods and equipment are optimized for producing Group III-N (nitrogen) compound semiconductor wafers and specifically for producing GaN wafers. Specifically, the precursor is provided at a mass flow of at least 50 g Group III element / hour for a time of at least 48 hours to facilitate high volume manufacture of the semiconductor material. Advantageously, the mass flow of the gaseous Group III precursor is controlled to deliver the desired amount.
Owner:S O I TEC SILICON ON INSULATOR THECHNOLOGIES
Method for making memory cards and similar devices using isotropic thermoset materials with high quality exterior surfaces
InactiveUS7225537B2Shorten the timeQuality improvementPrinted circuit assemblingLine/current collector detailsEngineeringInjection moulding
Memory Cards containing Integrated Circuits and other electronic components (e.g. resistors) in a variety of form factors having high quality external surfaces of polycarbonate, synthetic paper (e.g. Teslin), or other suitable material (e.g. PVC) can be made through use of injection molded thermoplastic material or thermosetting material that becomes the core layer of said Memory Cards and similar devices. The object of the invention is to provide the following properties to Memory Cards: rapid production cycle, high volume manufacturing throughput, security, electronics protection, better tamper resistance, durability, and highly reliable complex electronics encapsulation, achieved through a process utilizing low temperature and low pressure.
Owner:CARDXX
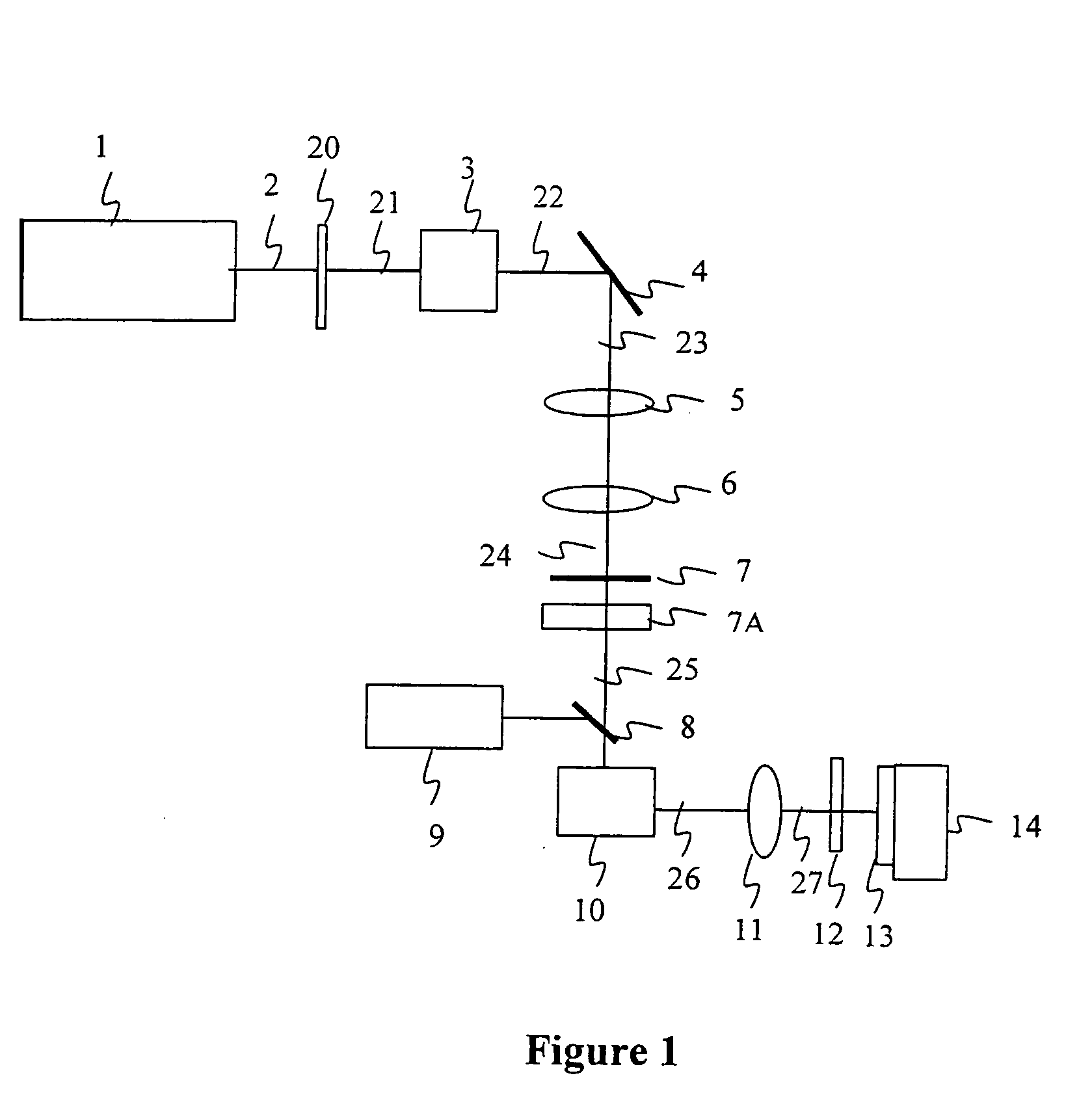
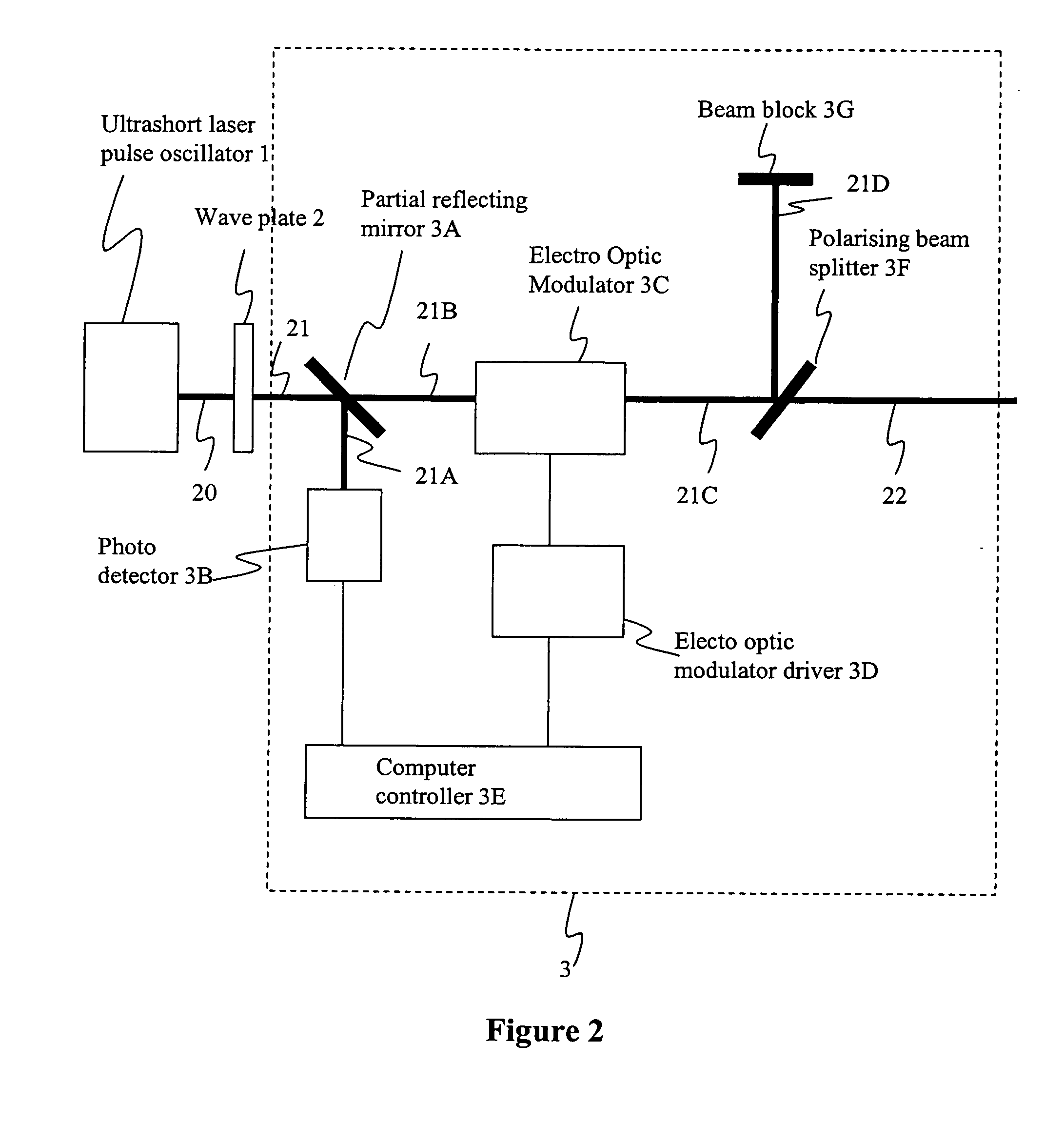
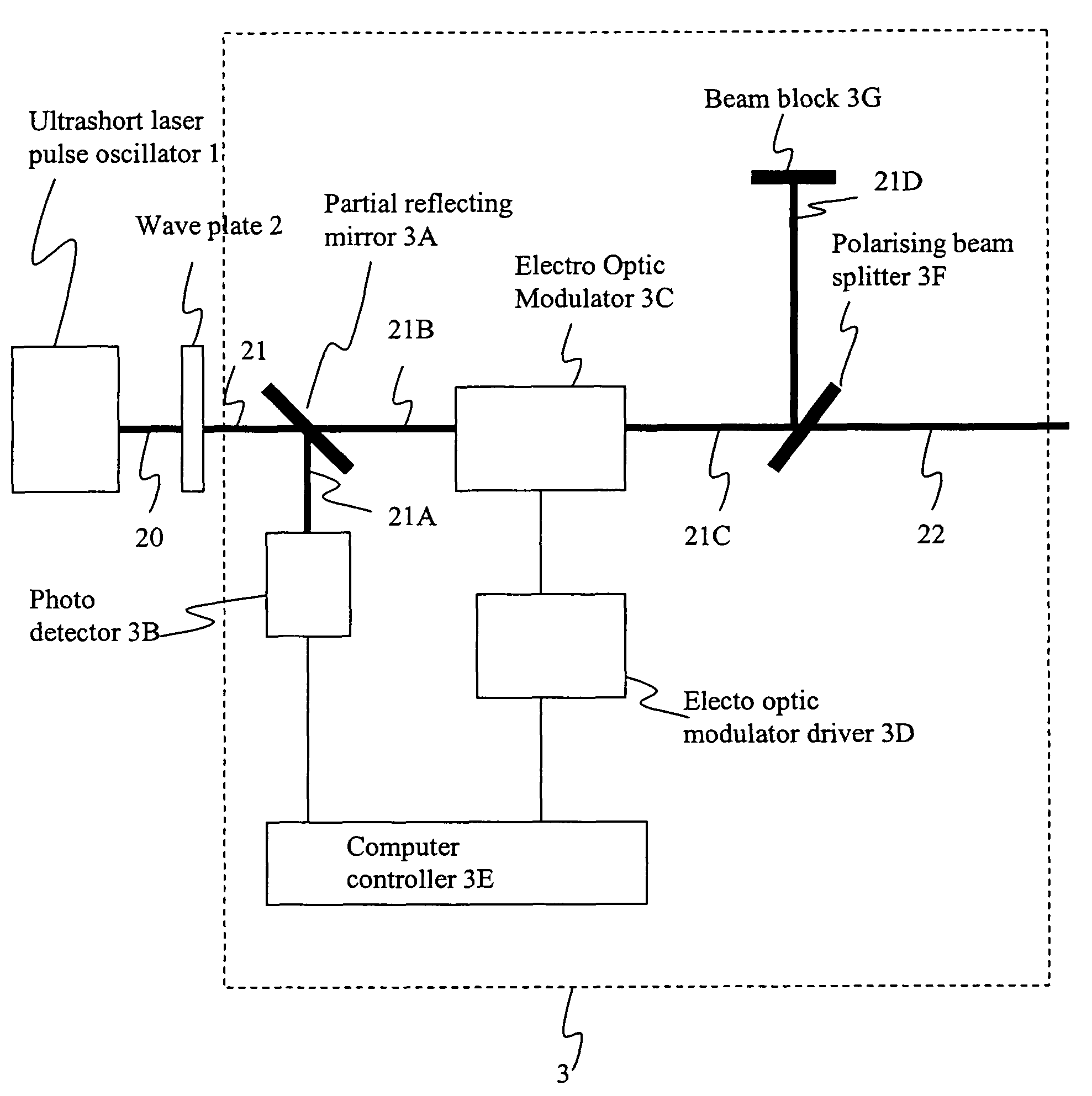
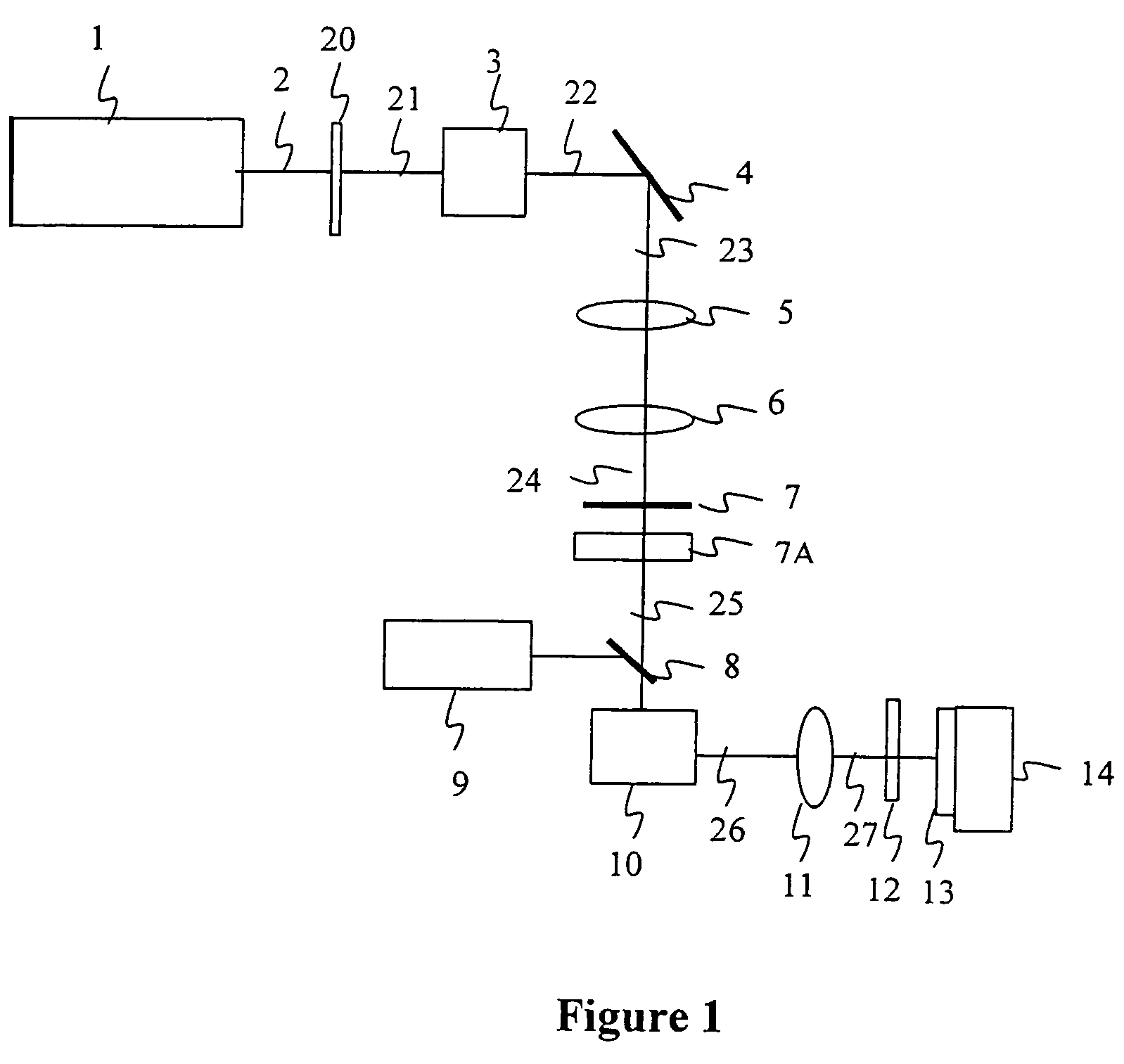
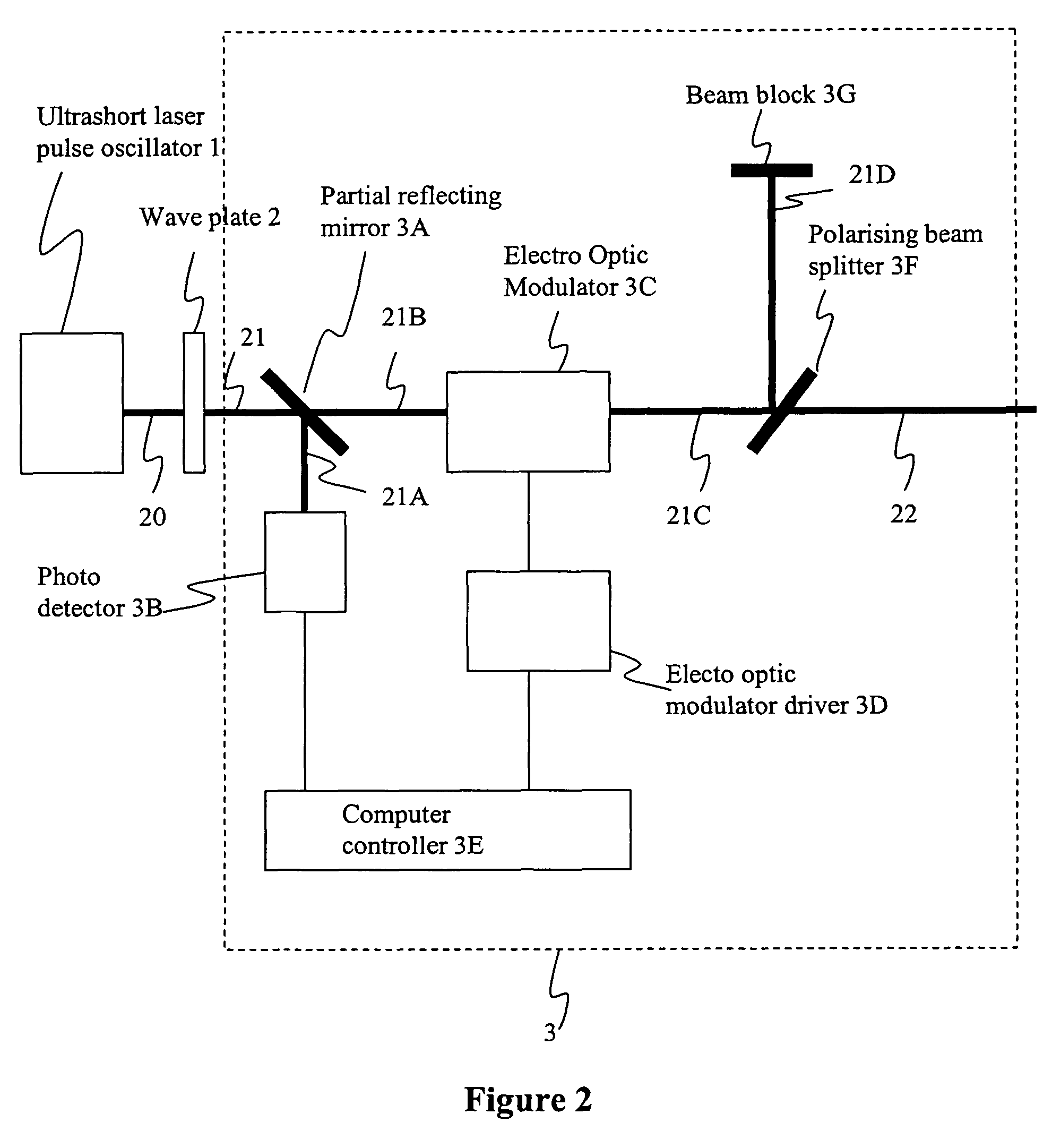
Method and apparatus for dicing of thin and ultra thin semiconductor wafer using ultrafast pulse laser
InactiveUS20050274702A1Improve inner wall qualityImprove surface qualityWelding/soldering/cutting articlesMetal working apparatusPicosecond laserFacula
The present invention relates to the apparatus, system and method for dicing of semiconductor wafers using an ultrafast laser pulse of femtosecond and picosecond pulse widths directly from the ultrafast laser oscillator without an amplifier. Thin and ultrathin simiconductor wafers below 250 micrometer thickness, are diced using diode pumped, solid state mode locked ultrafast laser pulses from oscillator without amplification. The invention disclosed has means to avoid / reduce the cumulative heating effect and to avoid machine quality degrading in multi shot ablation. Also the disclosed invention provides means to change the polarization state of the laser beam to reduce the focused spot size, and improve the machining efficiency and quality. The disclosed invention provides a cost effective and stable system for high volume manufacturing applications. An ultrafast laser oscillator can be a called as femtosecond laser oscillator or a picosecond laser oscillator depending on the pulse width of the laser beam generated.
Owner:LASERFACTURING
Method for preparing graphene or graphene oxide by using high-efficiency and low-cost mechanical stripping
InactiveCN101817516AImprove stripping efficiencyLight in massHigh volume manufacturingSolid particle
The invention provides a method for preparing graphene or graphene oxide by using high-efficiency and low-cost mechanical stripping and relates to a preparation method of the graphene or the graphene oxide, solving the problems that the traditional micro-mechanical stripping method has low efficiency and can not be used for large-batch production. The method comprises the following step of separating carbon materials by utilizing solid particles and a liquid working medium (or gas working medium) and adopting mechanical stripping to obtain the graphene or the graphene oxide, wherein the carbon materials comprise graphite powder, expanded graphite, expandable graphite or graphite powder oxide. By using automatic machinery and using a great deal of solid particles for assisting stripping processes, the invention greatly increases the contact areas and the stripping times of the stripping processes, the carbon materials are subject to a great amount of stripping processes in a short time through the shearing and impacting functions of the solid particles on the carbon materials, and thereby the method obviously improves the stripping efficiency, has low cost and is suitable for the industrial and large-batch production of the graphene or the graphene oxide.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
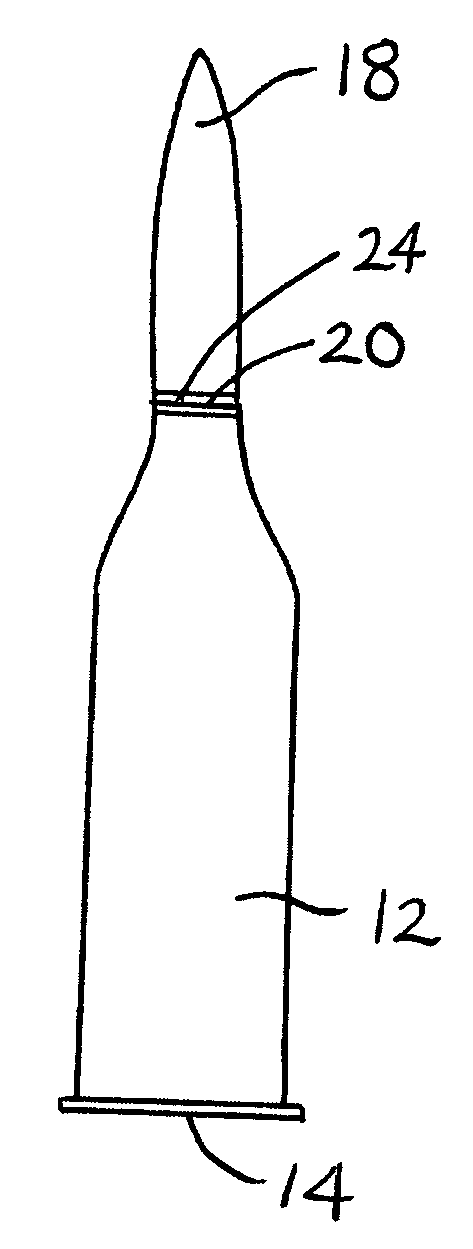
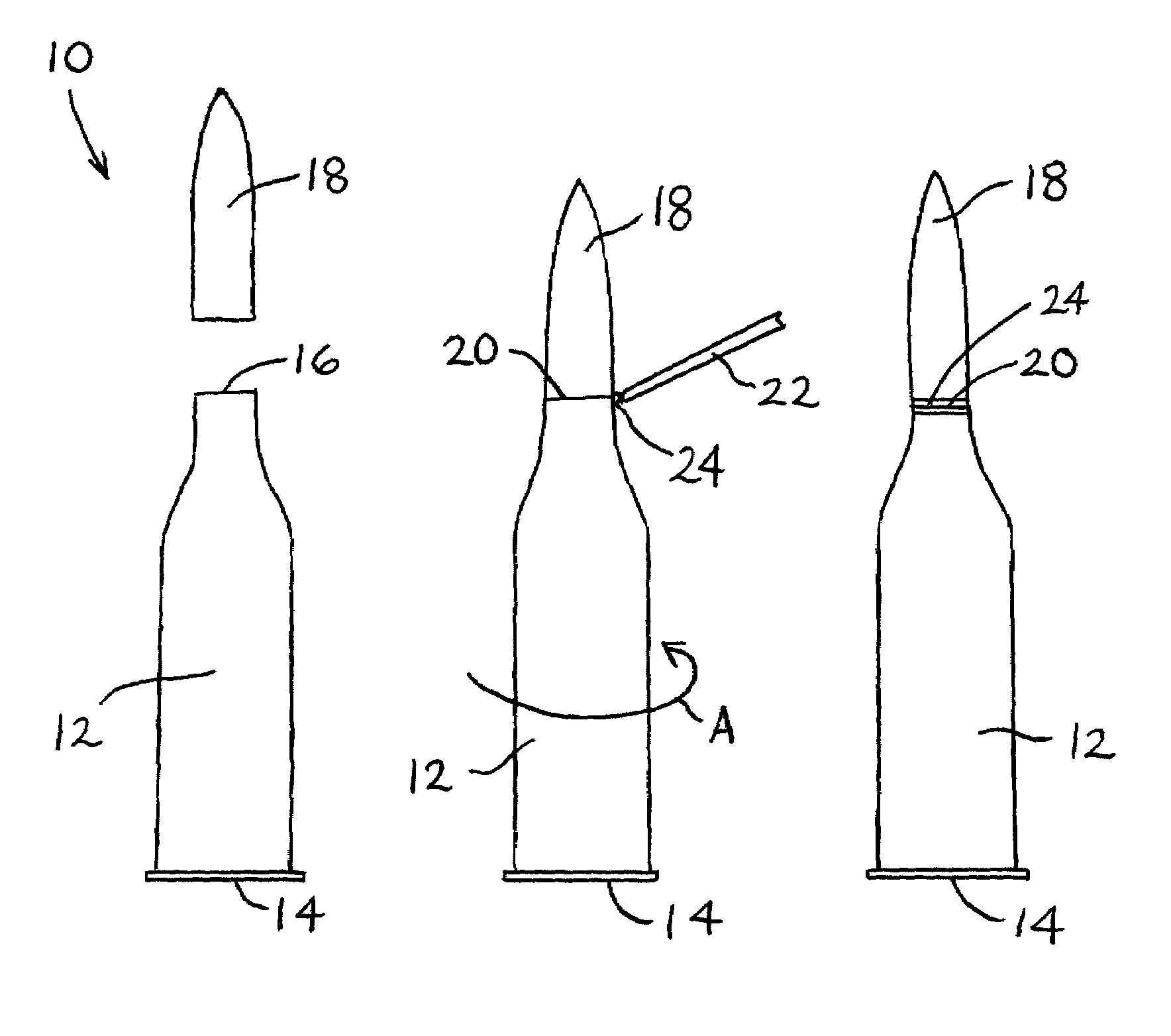
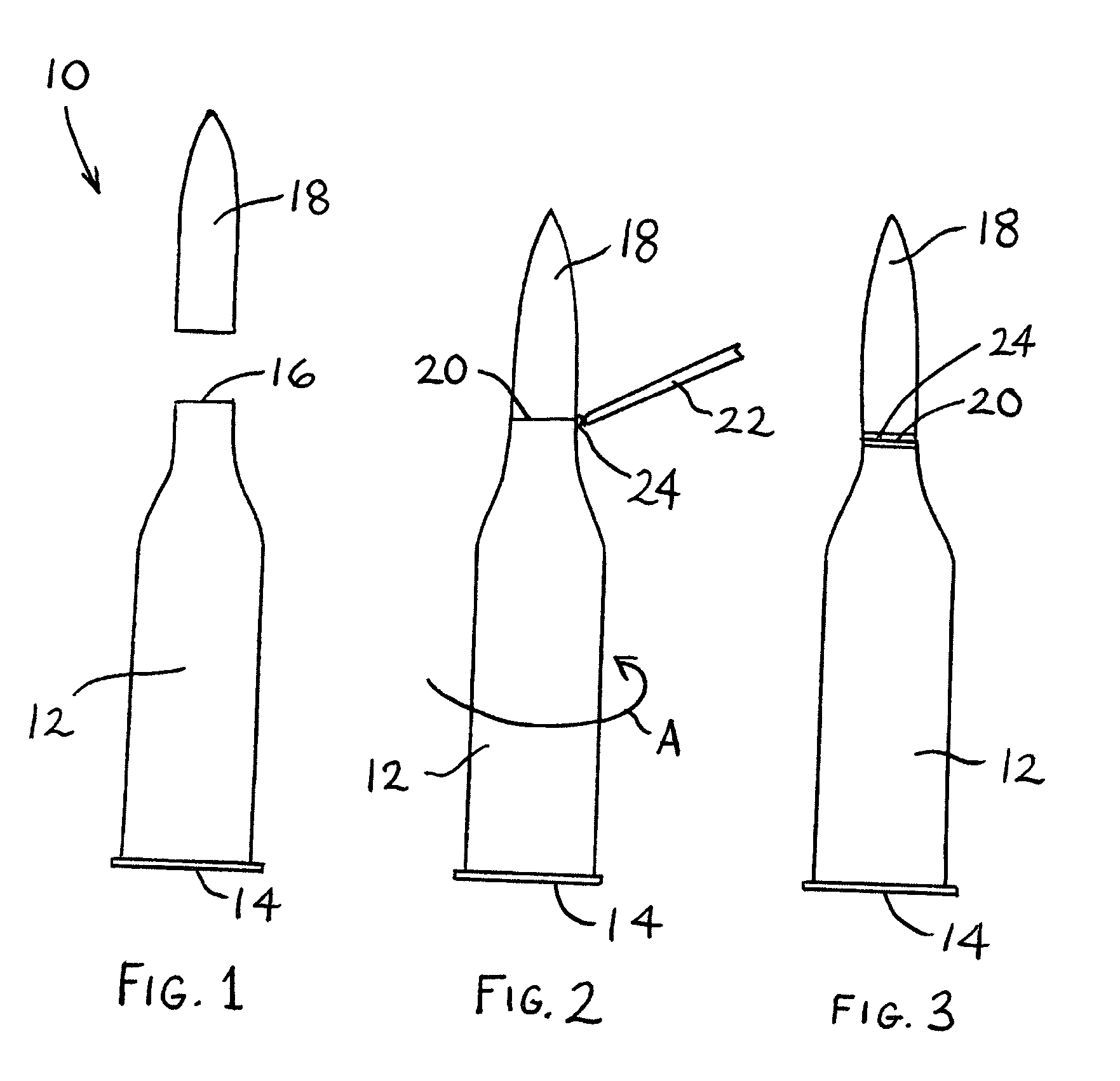
Ammunition articles comprising light-curable moisture-preventative sealant and method of manufacturing same
A process for manufacturing an ammunition article, including: (a) providing a cartridge including a projectile disposed in a casing and presenting a joint between the projectile and the casing; (b) applying to the joint a sealingly effective amount of a light-curable sealant composition; and (c) exposing the applied sealant composition to curingly effective light. The resulting ammunition article is sealed at the projectile / casing joint against moisture incursion, and such article is amenable to high-speed, high-volume production by the method of the invention.
Owner:BEACON ADHESIVES INC
Methods of forming silicon germanium tin films and structures and devices including the films
ActiveUS20170154770A1Low throughput timeSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHigh volume manufacturingChemical vapor deposition
Methods of forming silicon germanium tin (SiGexGe1−xSny) films are disclosed. Exemplary methods include growing films including silicon, germanium and tin in an epitaxial chemical vapor deposition reactor. Exemplary methods are suitable for high volume manufacturing. Also disclosed are structures and devices including silicon germanium tin films.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
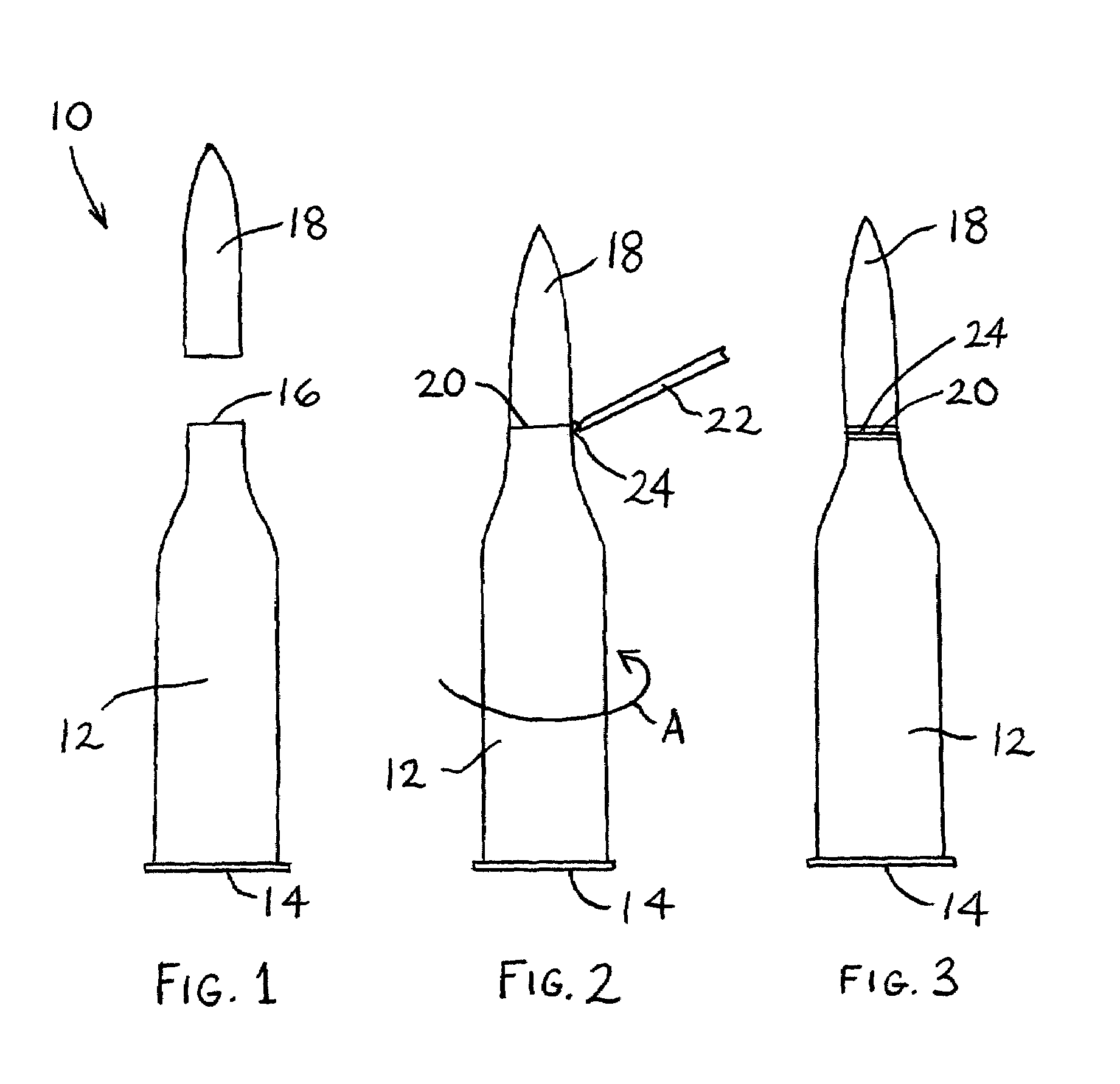
Ammunition articles comprising light-curable moisture-preventative sealant and method of manufacturing same
ActiveUS20050056183A1Ammunition projectilesAmmunition testingHigh volume manufacturingProcess engineering
A process for manufacturing an ammunition article, including: (a) providing a cartridge including a projectile disposed in a casing and presenting a joint between the projectile and the casing; (b) applying to the joint a sealingly effective amount of a light-curable sealant composition; and (c) exposing the applied sealant composition to curingly effective light. The resulting ammunition article is sealed at the projectile / casing joint against moisture incursion, and such article is amenable to high-speed, high-volume production by the method of the invention.
Owner:BEACON ADHESIVES INC
Method and apparatus for dicing of thin and ultra thin semiconductor wafer using ultrafast pulse laser
InactiveUS7804043B2Minimize heating effectImprove machine qualityWelding/soldering/cutting articlesMetal working apparatusPicosecond laserBeam polarization
The present invention relates to the apparatus, system and method for dicing of semiconductor wafers using an ultrafast laser pulse of femtosecond and picosecond pulse widths directly from the ultrafast laser oscillator without an amplifier. Thin and ultrathin semiconductor wafers below 250 micrometer thickness, are diced using diode pumped, solid state mode locked ultrafast laser pulses from oscillator without amplification. The invention disclosed has means to avoid / reduce the cumulative heating effect and to avoid machine quality degrading in multi shot ablation. Also the disclosed invention provides means to change the polarization state of the laser beam to reduce the focused spot size, and improve the machining efficiency and quality. The disclosed invention provides a cost effective and stable system for high volume manufacturing applications. An ultrafast laser oscillator can be a called as femtosecond laser oscillator or a picosecond laser oscillator depending on the pulse width of the laser beam generated.
Owner:LASERFACTURING
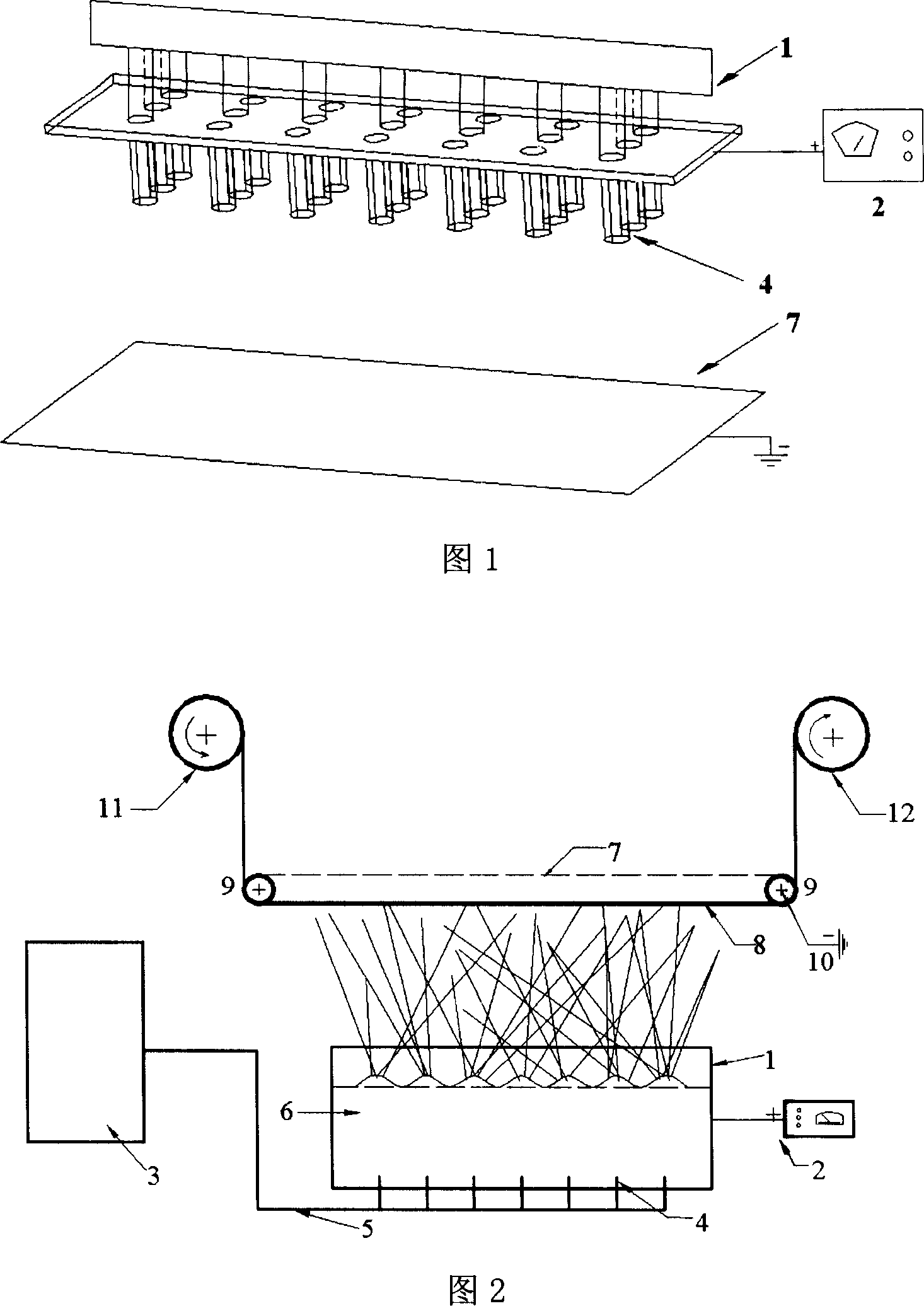
Jet type electrostatic spinning equipment capable of producing Nano fiber in bulk
InactiveCN101003916AThe need for large-scale productionNo frequent replacementSpinnerette packsFilament/thread formingFiberHigh volume manufacturing
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
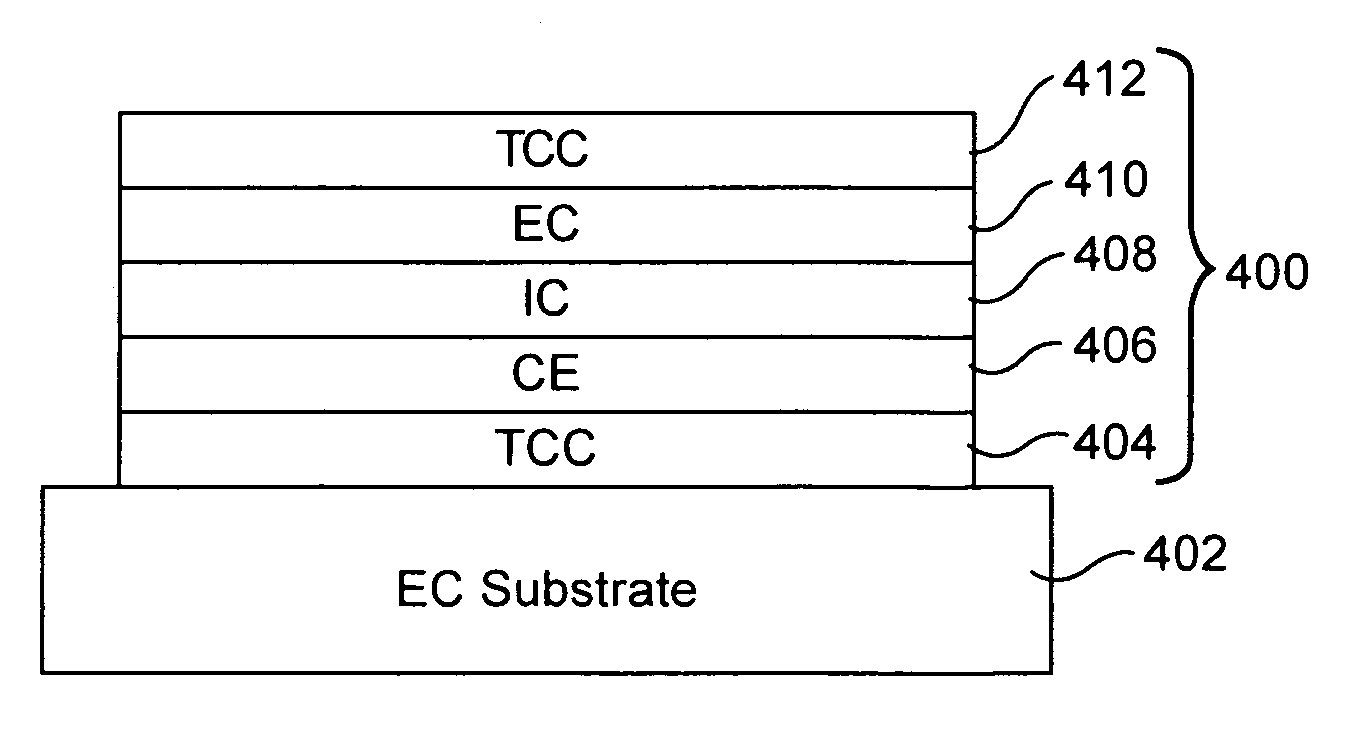
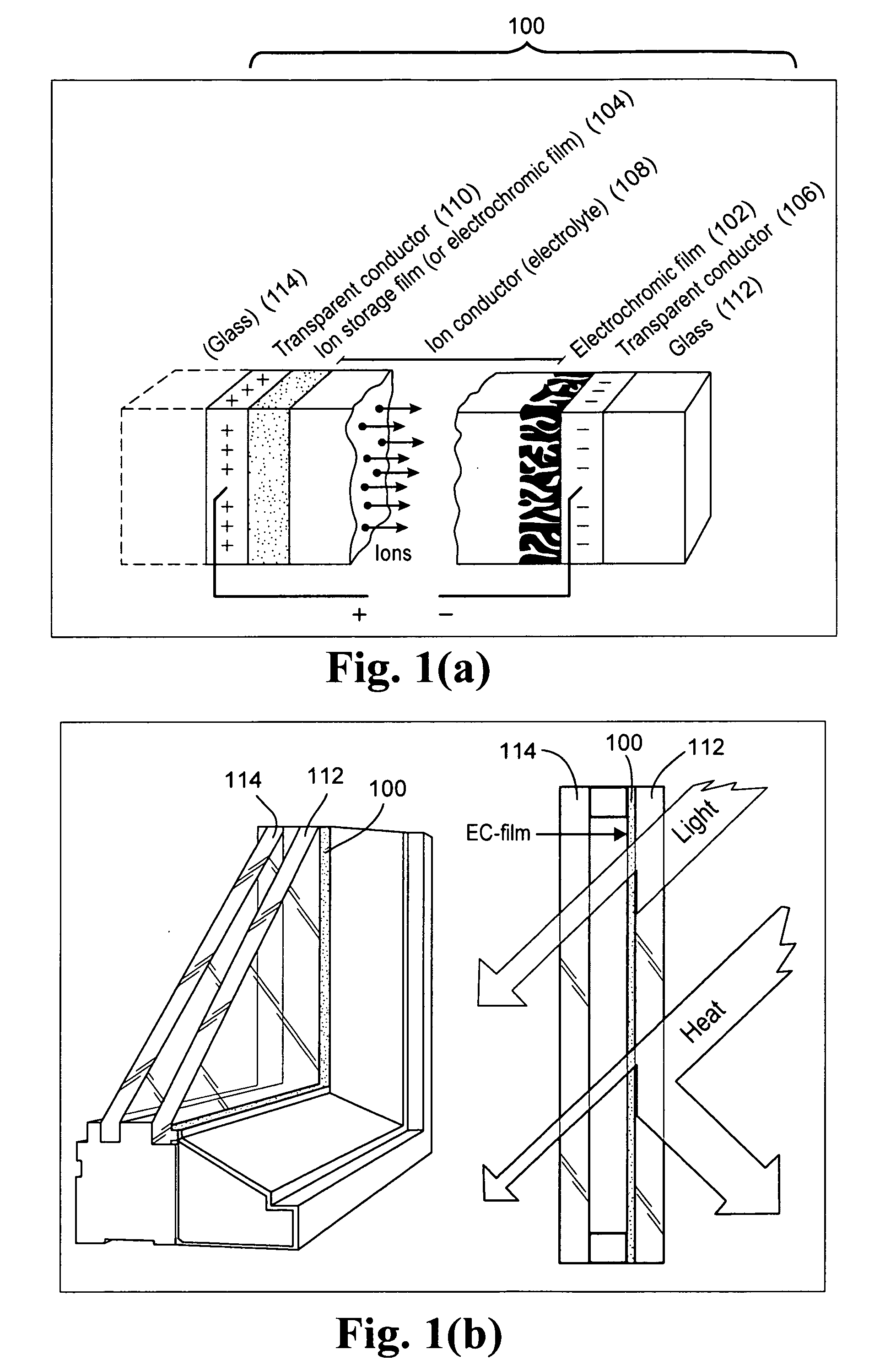
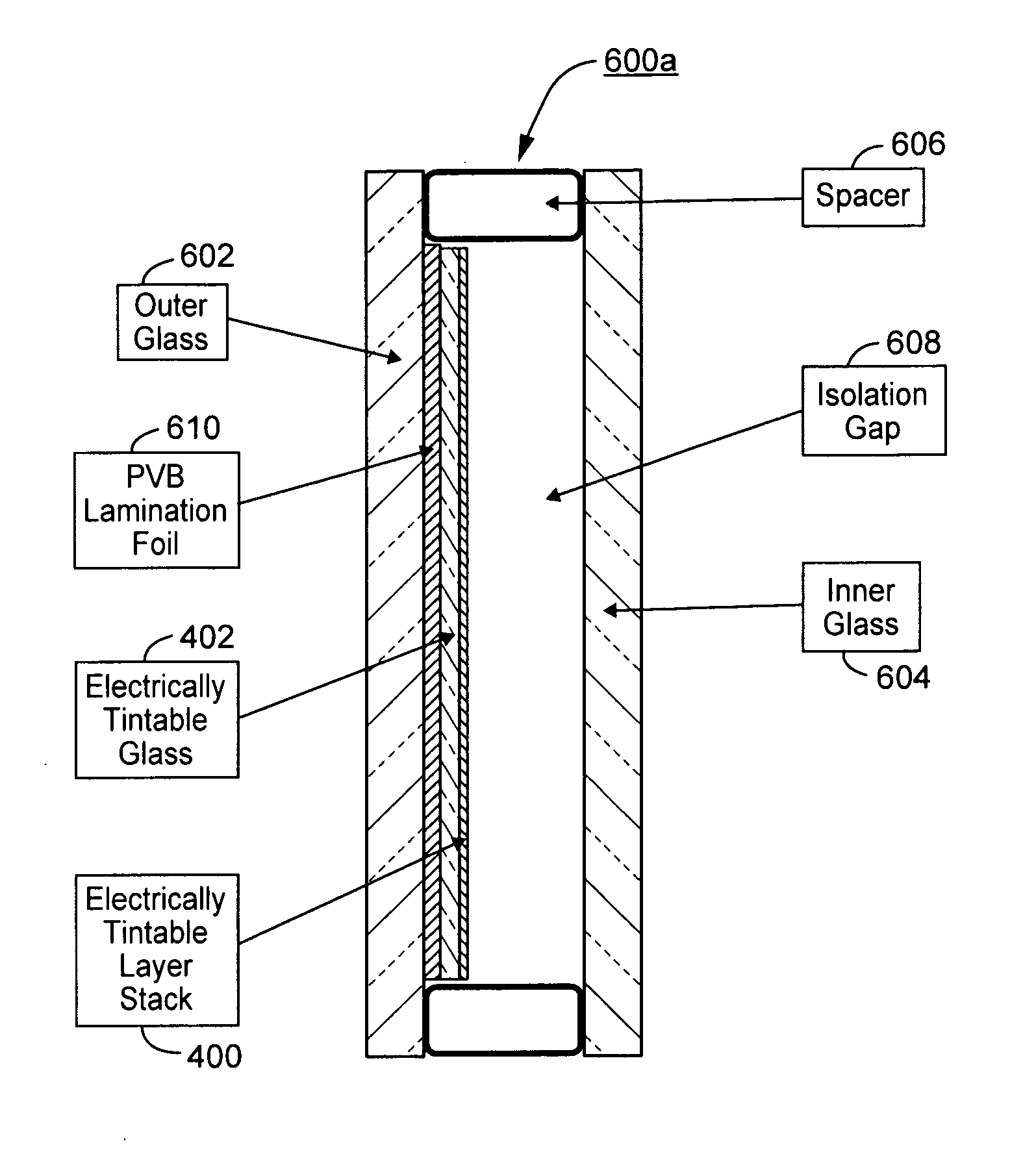
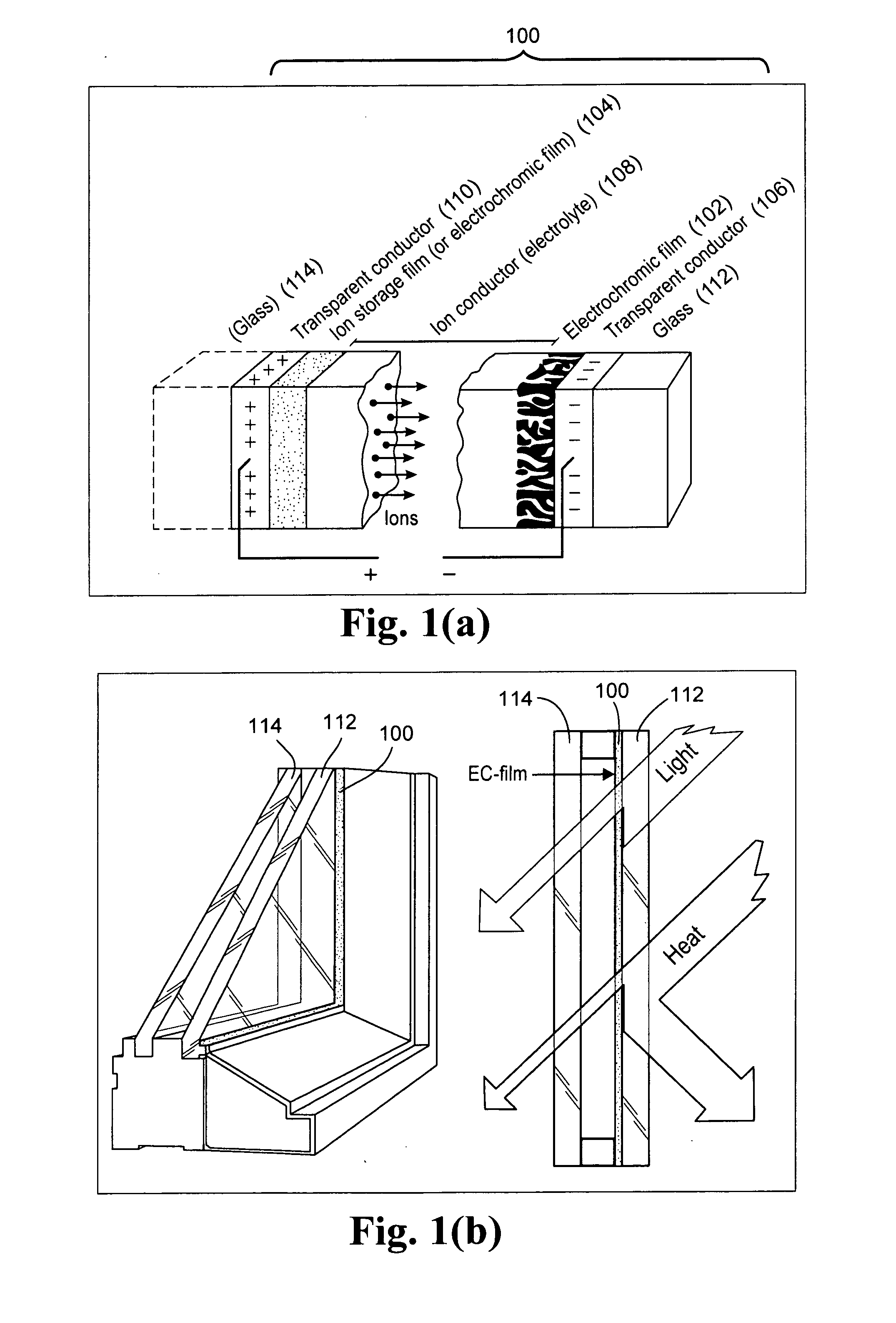
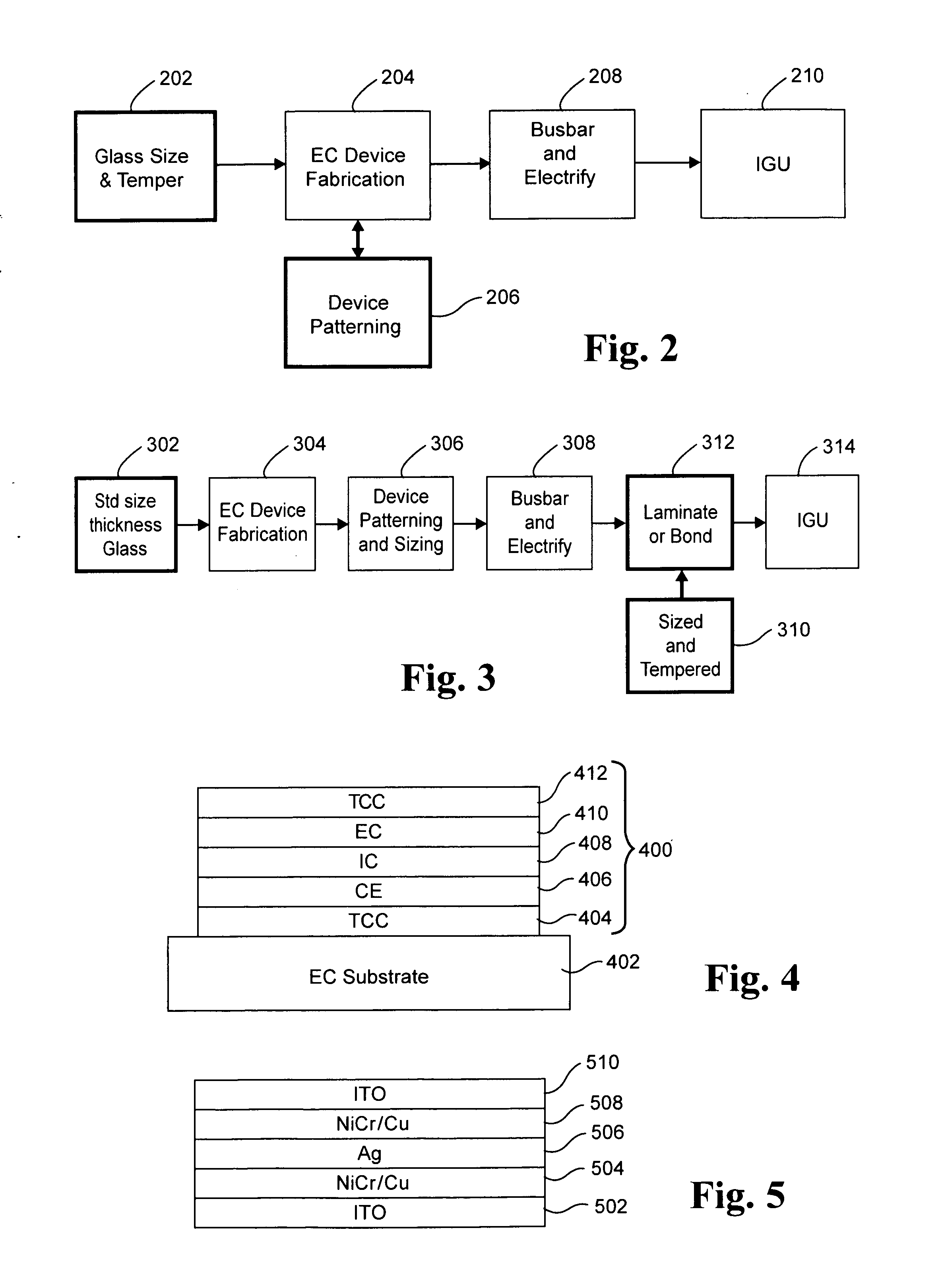
Electrochromic devices, assemblies incorporating electrochromic devices, and/or methods of making the same
ActiveUS20110048614A1Great visible transmissionGood lookingLamination ancillary operationsLight protection screensElectricityProcess integration
Certain example embodiments of this invention relate to electrochromic (EC) devices, assemblies incorporating electrochromic devices, and / or methods of making the same. More particularly, certain example embodiments of this invention relate to improved EC materials, EC device stacks, high-volume manufacturing (HVM) compatible process integration schemes, and / or high-throughput low cost deposition sources, equipment, and factories.
Owner:GUARDIAN GLASS LLC
Electrochromic devices, assemblies incorporating electrochromic devices, and/or methods of making the same
ActiveUS20110051221A1Great visible transmissionGood lookingLight protection screensGlass/slag layered productsElectricityProduction rate
Certain example embodiments of this invention relate to electrochromic (EC) devices, assemblies incorporating electrochromic devices, and / or methods of making the same. More particularly, certain example embodiments of this invention relate to improved EC materials, EC device stacks, high-volume manufacturing (HVM) compatible process integration schemes, and / or high-throughput low cost deposition sources, equipment, and factories.
Owner:GUARDIAN GLASS LLC
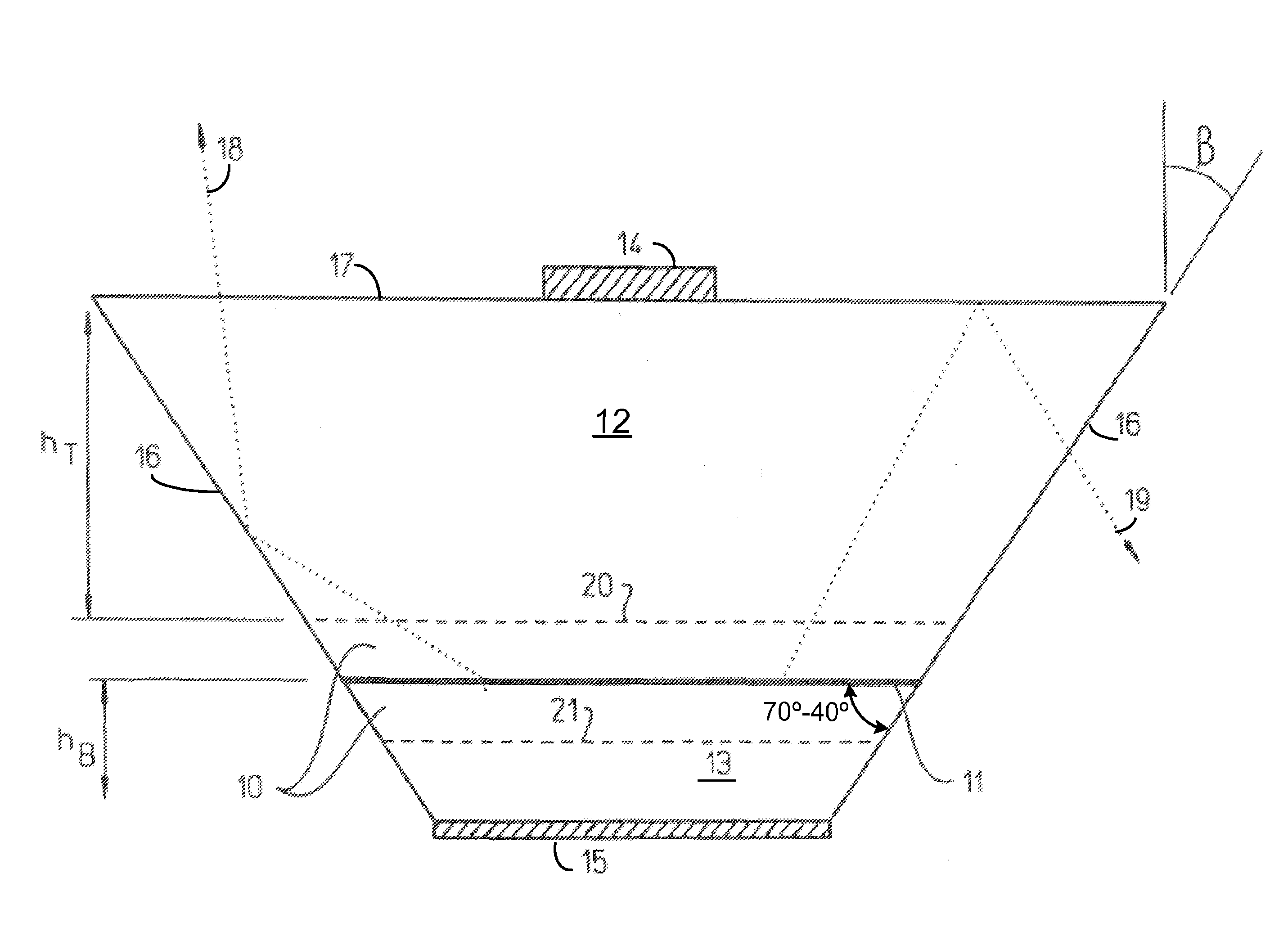
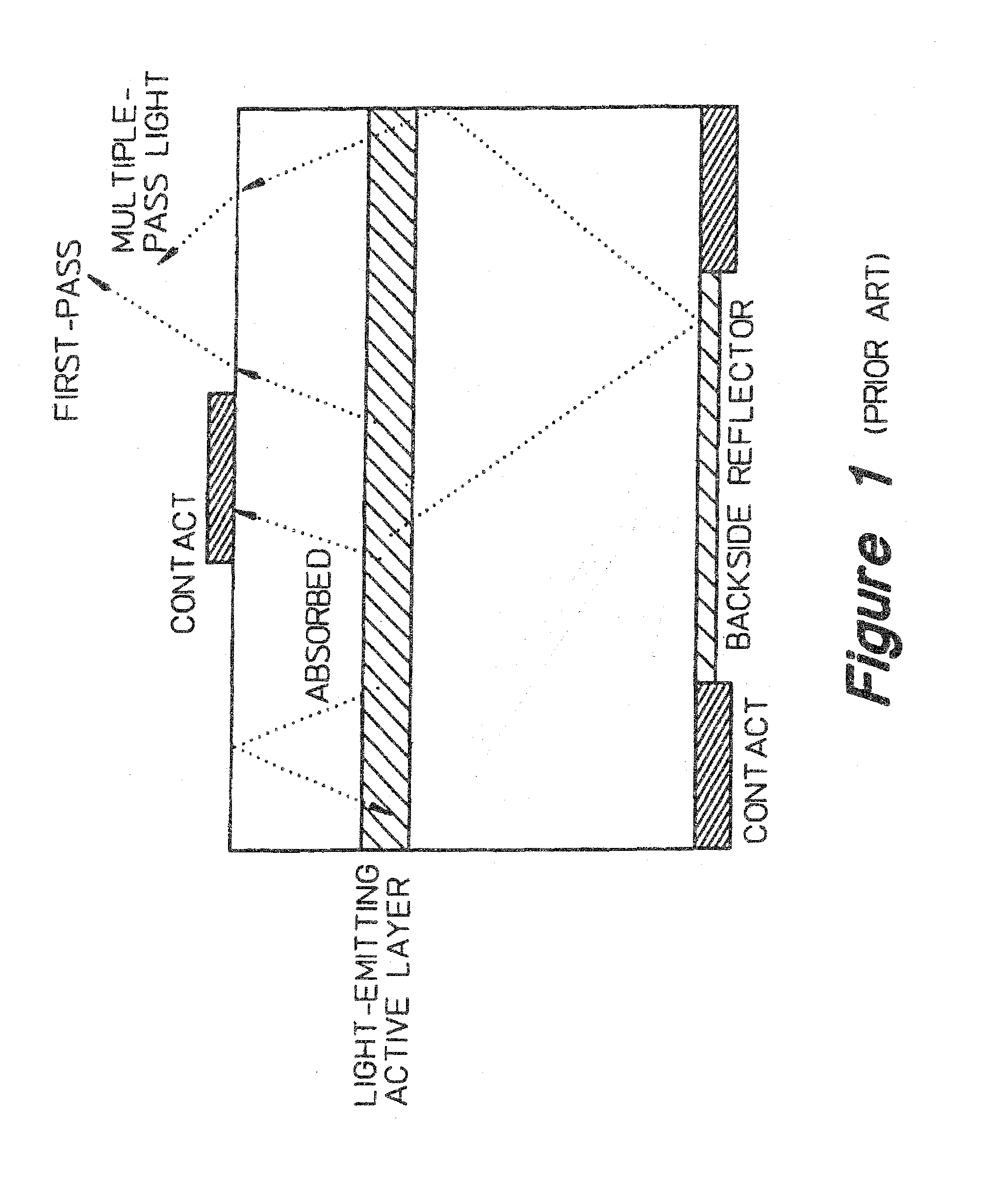
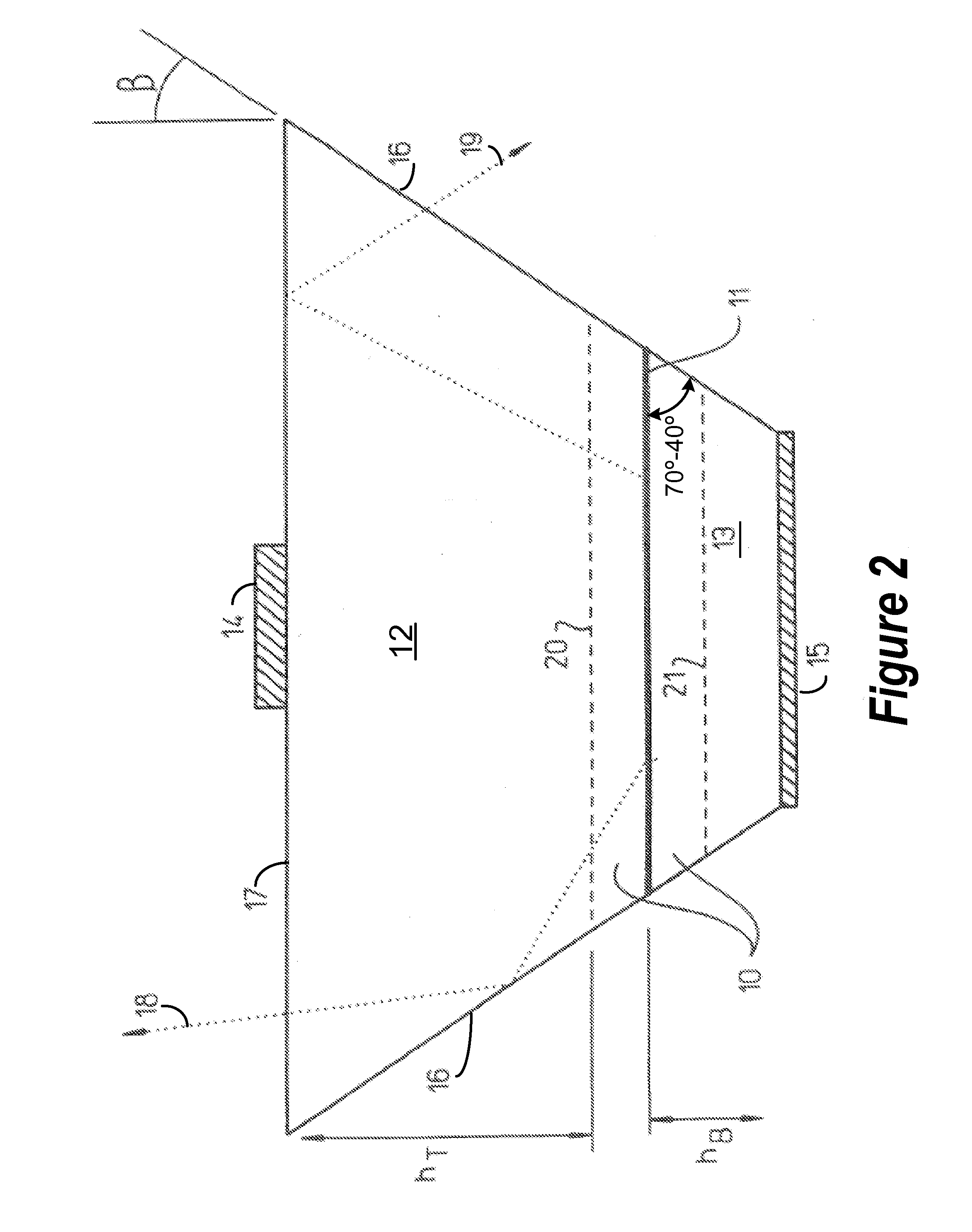
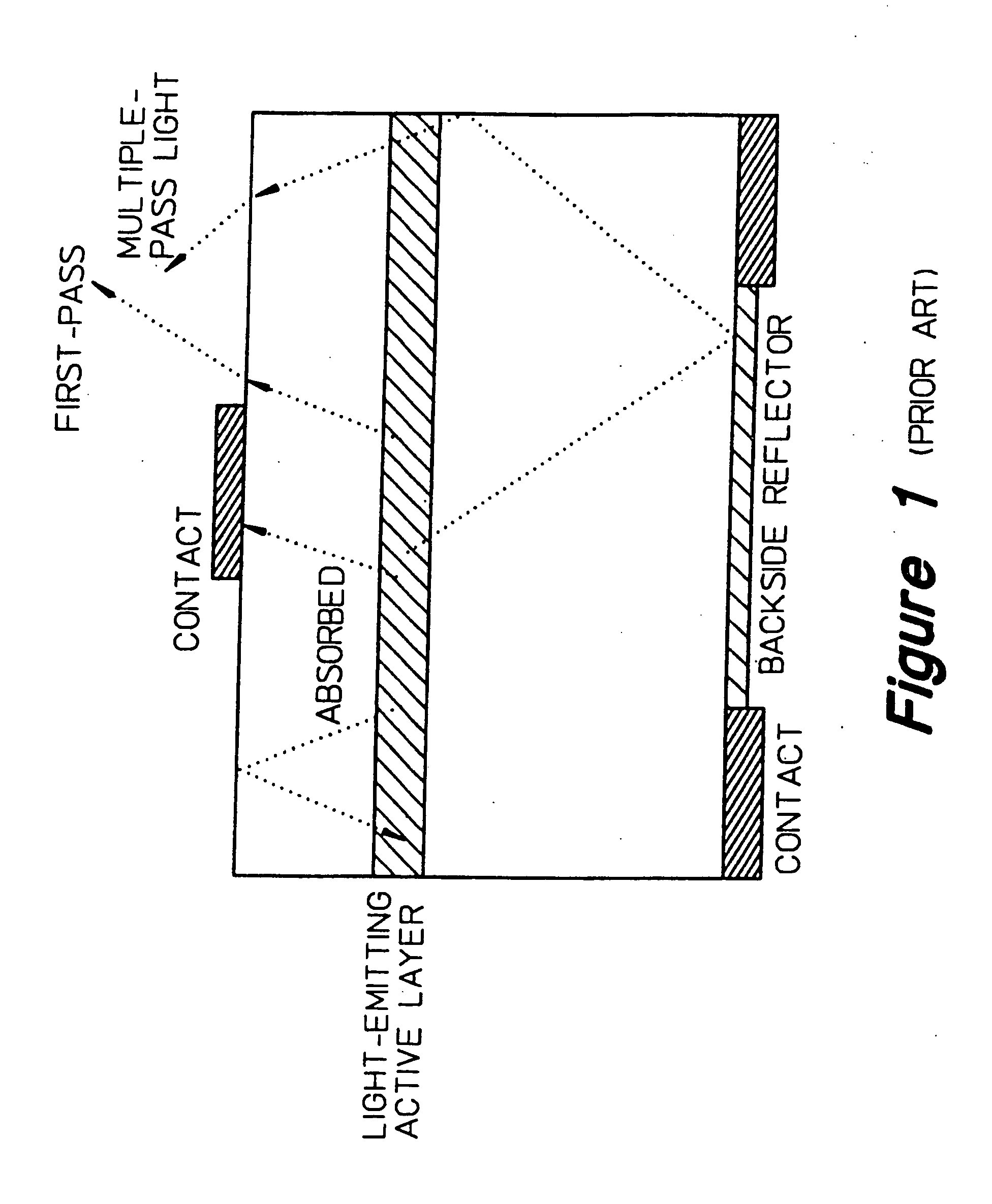
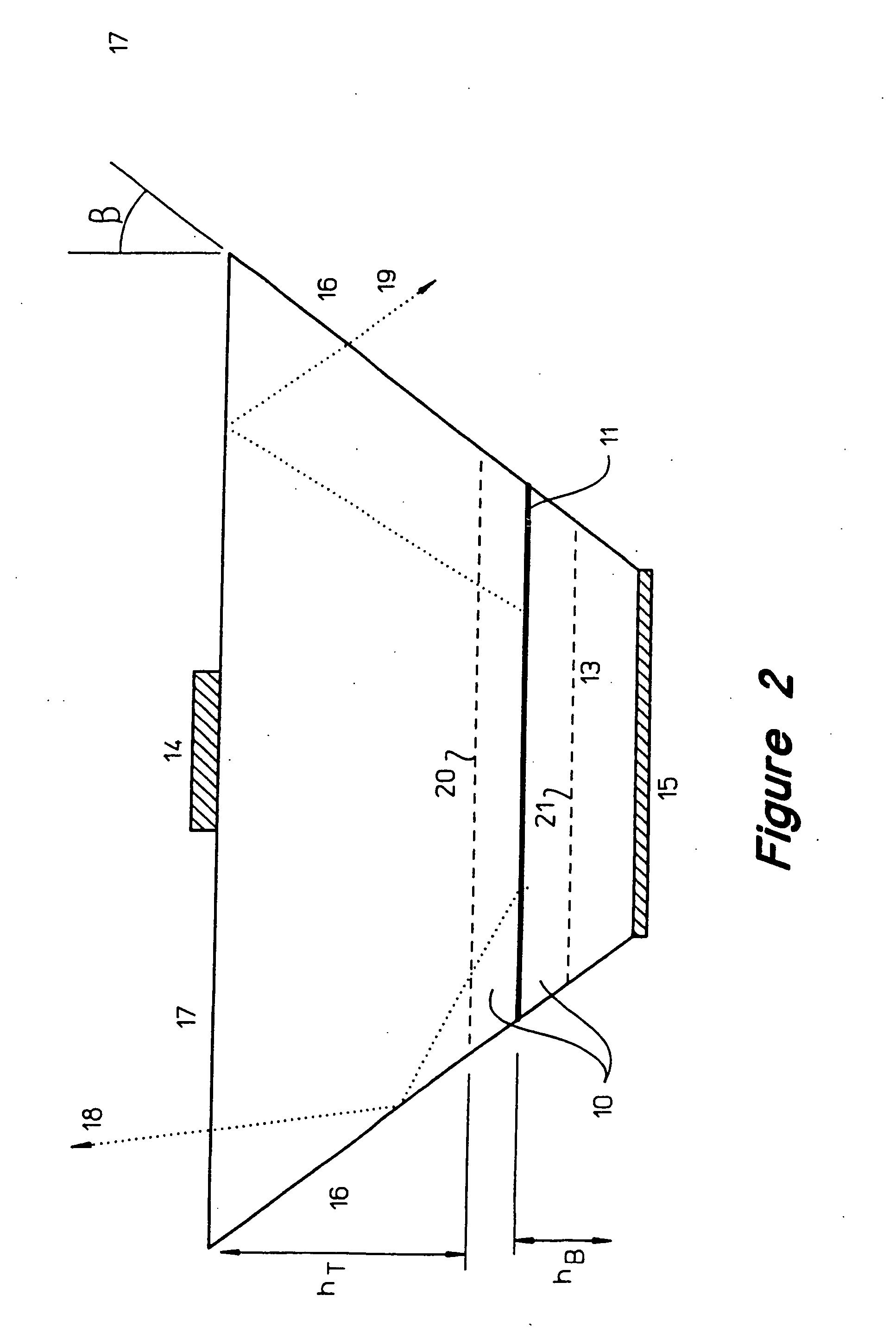
Light extraction from a semiconductor light emitting device via chip shaping
InactiveUS7268371B2Precise positioningReasonable degreeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesHigh volume manufacturingActive layer
A method for designing semiconductor light emitting devices is disclosed wherein the side surfaces (surfaces not parallel to the epitaxial layers) are formed at preferred angles relative to vertical (normal to the plane of the light-emitting active layer) to improve light extraction efficiency and increase total light output efficiency. Device designs are chosen to improve efficiency without resorting to excessive active area-yield loss due to shaping. As such, these designs are suitable for low-cost, high-volume manufacturing of semiconductor light-emitting devices with improved characteristics.
Owner:PHILIPS LUMILEDS LIGHTING CO LLC
Fabrication of high efficiency, high quality, large area diffractive waveplates and arrays
InactiveUS20110262844A1Quality improvementLow costPhotomechanical exposure apparatusHologram recording materialOptical polarizationImage quality
The objective of the present invention is providing a method for fabricating high quality diffractive waveplates and their arrays that exhibit high diffraction efficiency over large area, the method being capable of inexpensive large volume production. The method uses a polarization converter for converting the polarization of generally non-monochromatic and partially coherent input light beam into a pattern of periodic spatial modulation at the output of said polarization converter. A substrate carrying a photoalignment layer is exposed to said polarization modulation pattern and is coated subsequently with a liquid crystalline material. The high quality diffractive waveplates of the present invention are obtained when the exposure time of said photoalignment layer exceeds by generally an order of magnitude the time period that would be sufficient for producing homogeneous orientation of liquid crystalline materials brought in contact with said photoalignment layer. Compared to holographic techniques, the method is robust with respect to mechanical noises, ambient conditions, and allows inexpensive production via printing while also allowing to double the spatial frequency of optical axis modulation of diffractive waveplates.
Owner:BEAM ENG FOR ADVANCED MEASUREMENTS
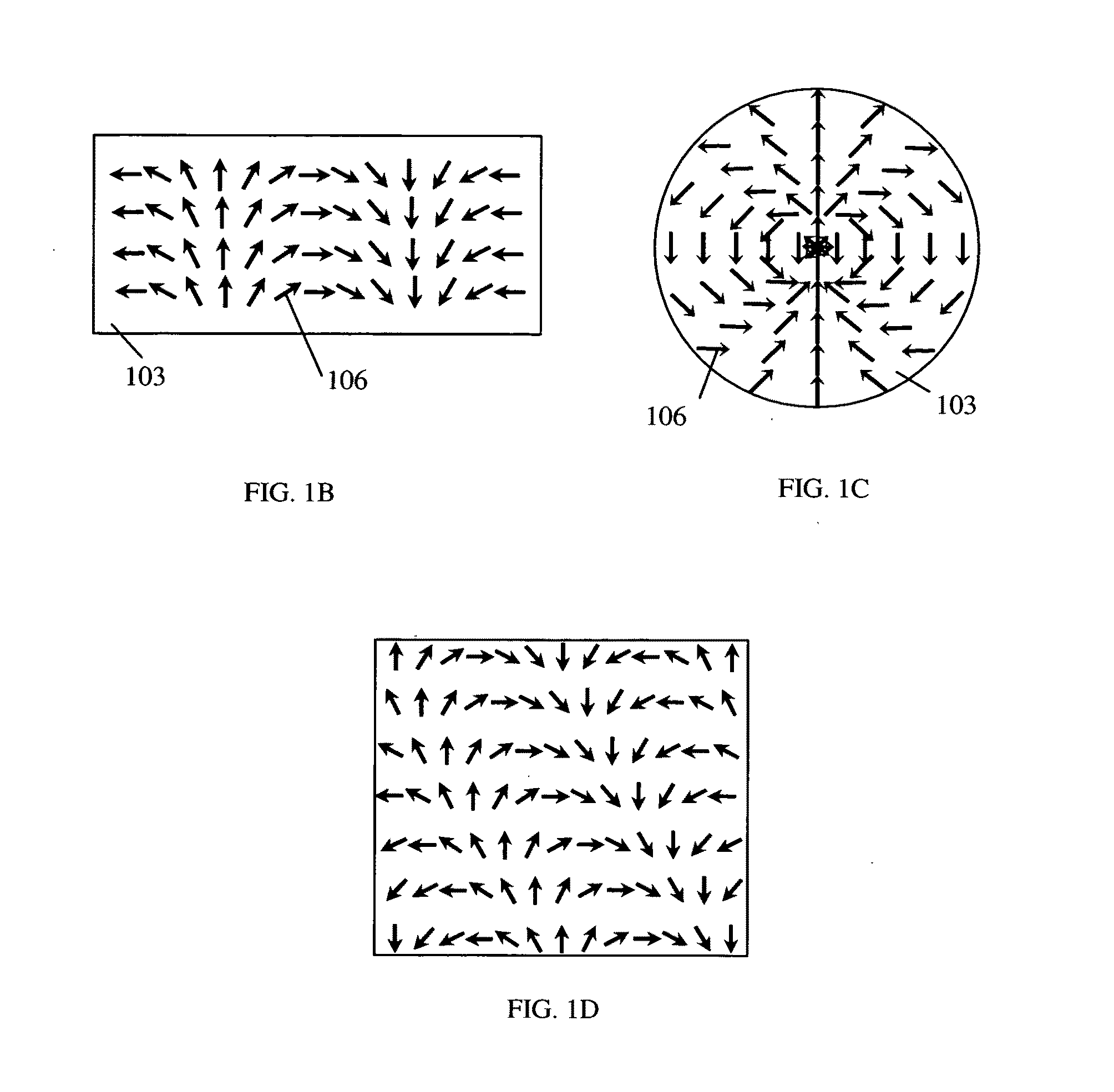
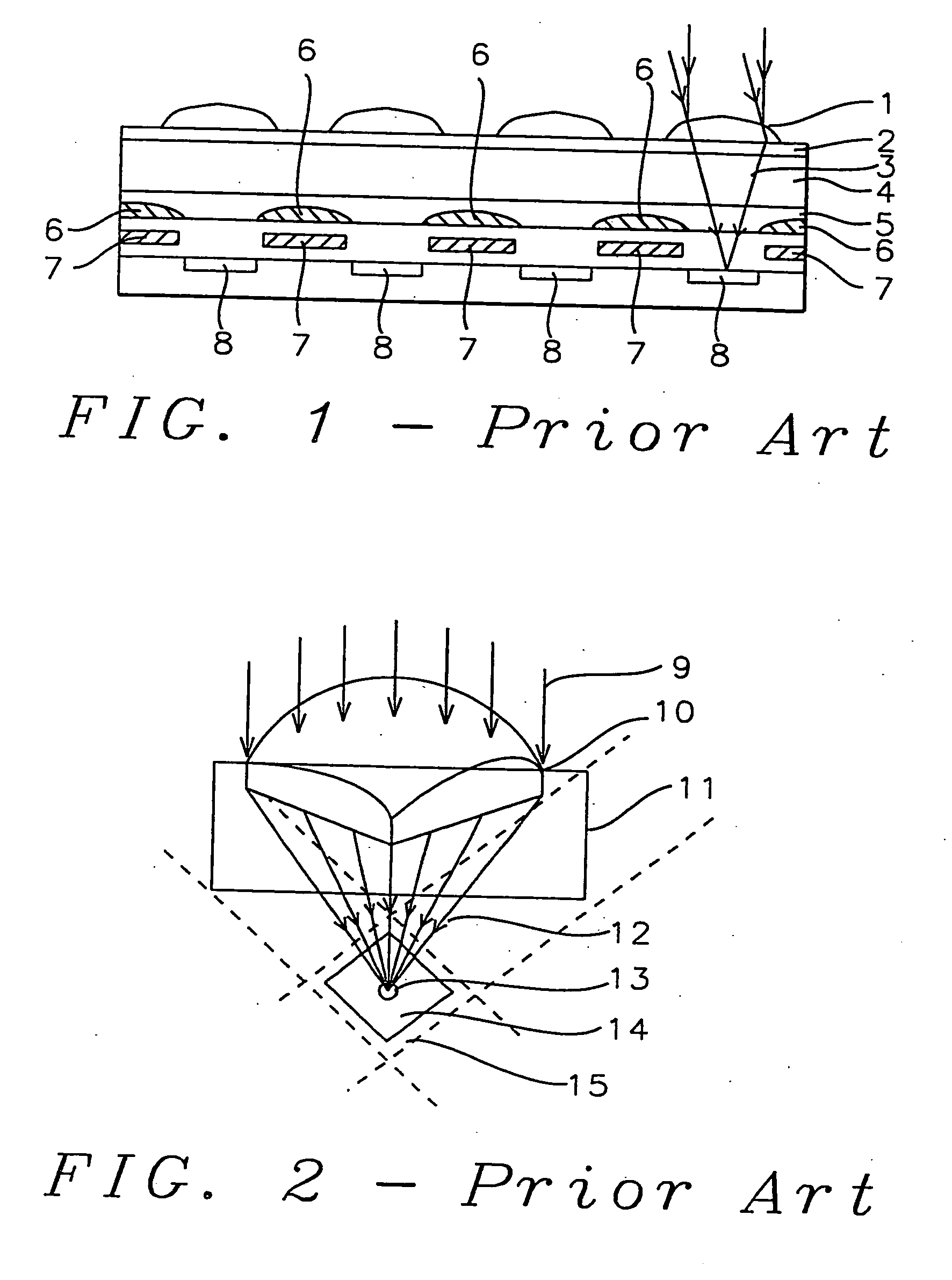
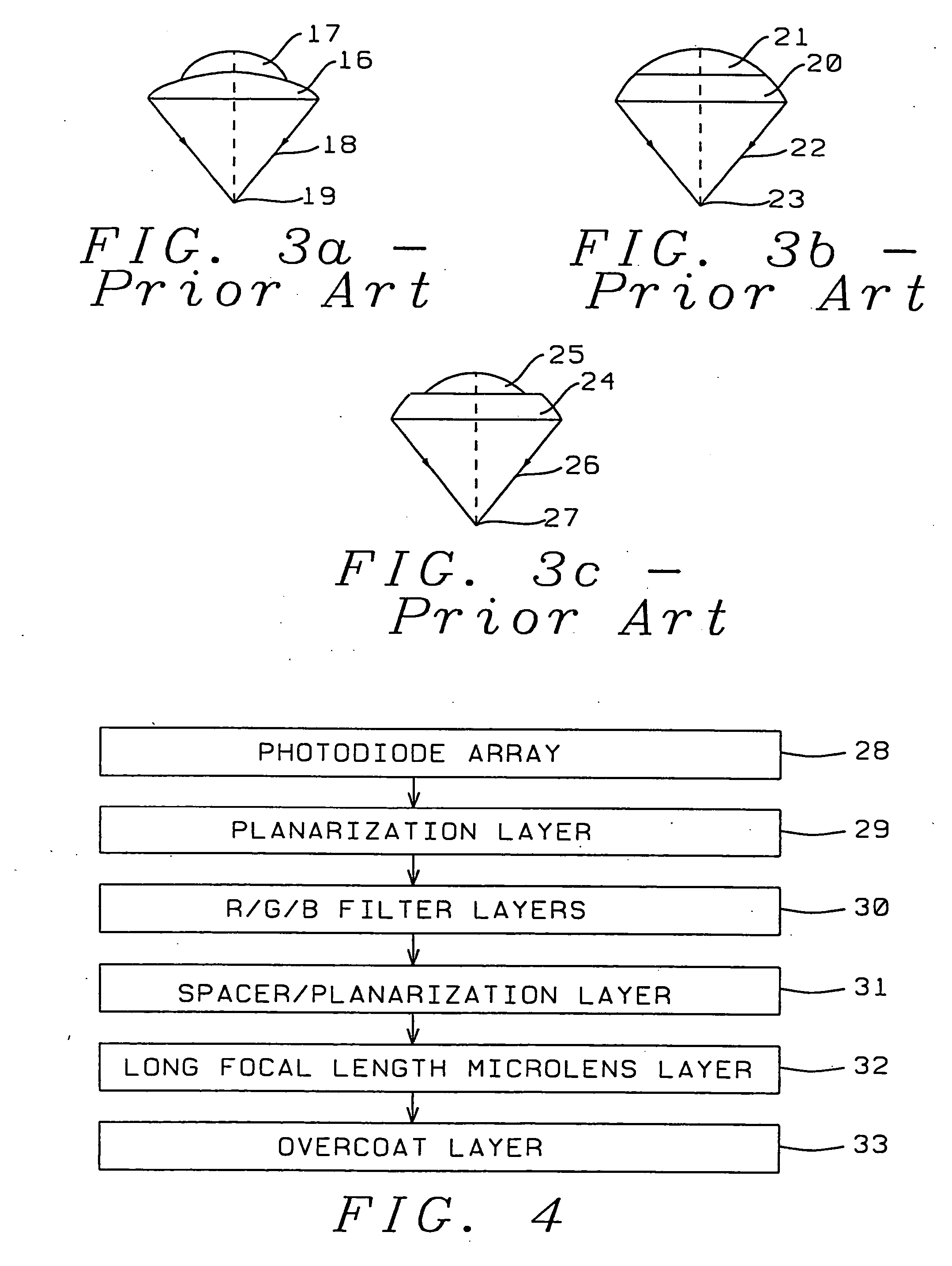
High transmittance overcoat for microlens arrays in semiconductor color imagers
InactiveUS20050041296A1Improve focus performanceHigh light transmittanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCMOSHigh volume manufacturing
A transmittance overcoat with effectively planar top surface and specified optical and materials properties is applied above a microlens layer to extend the focal length and enhance the performance of long focal length microlenses for semiconductor array color imaging devices. The geometrical optics design factors and microelectric fabrication sequence to achieve optimized long focal length microlens performance are disclosed. The principal advantages of the adaptive process taught in the present invention is shown to enable real-time compensation adjustments for process and material variations. The overcoat process enables simplified single-layer integrated microlens optics for low-cost, high volume manufacturing of CMOS and CCD color video cameras.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
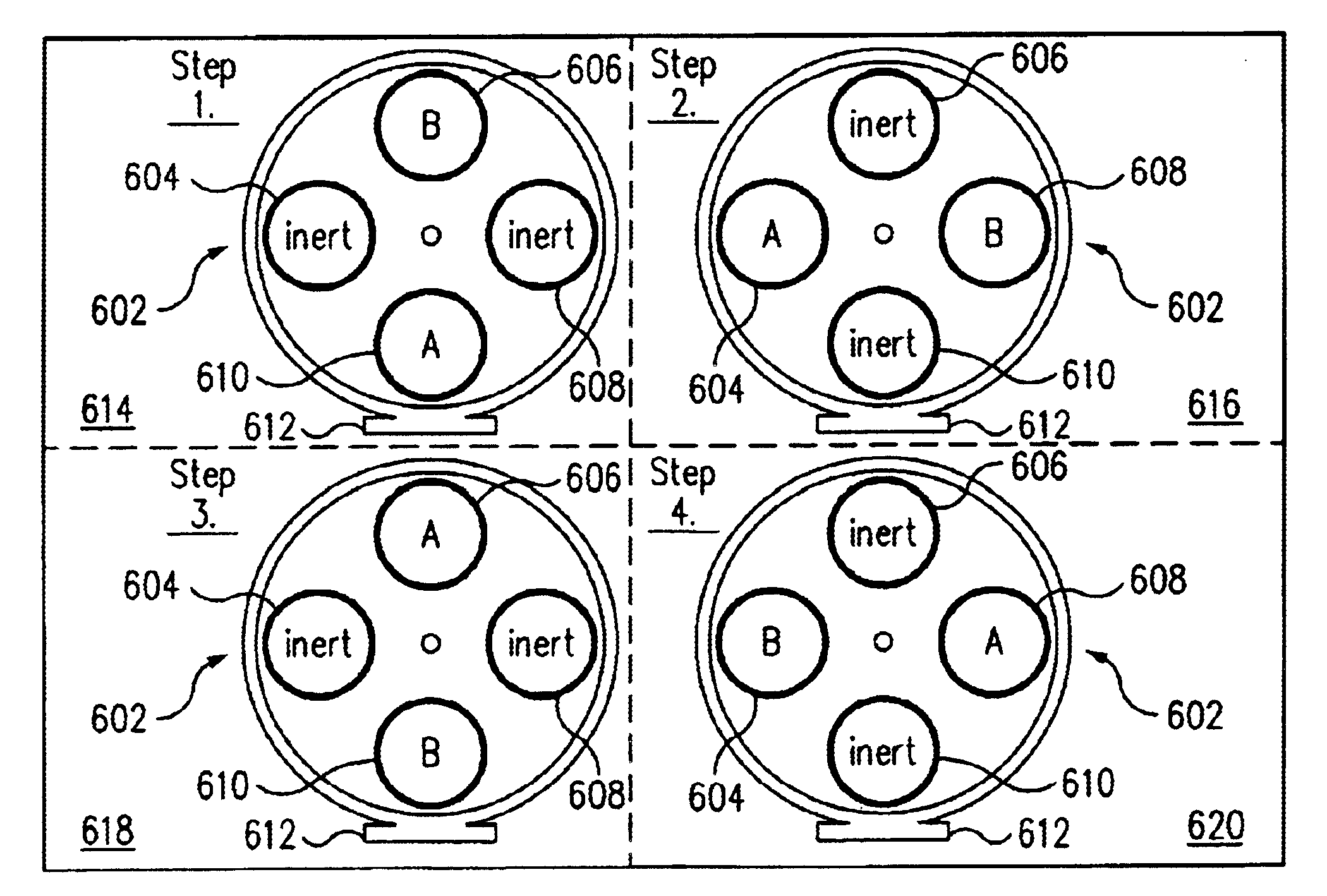
Atomic layer deposition systems and methods
InactiveUS6902620B1Polycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh volume manufacturingGas phase
Atomic layer deposition systems and methods are disclosed utilizing a multi-wafer sequential processing chamber. The process gases are sequentially rotated among the wafer stations to deposit a portion of a total deposition thickness on each wafer at each station. A rapid rotary switching of the process gases eliminates having to divert the process gases to a system vent and provides for atomic layer film growth sufficient for high-volume production applications. Conventional chemical vapor deposition can also be performed concurrently with atomic layer deposition within the multi-wafer sequential processing chamber.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
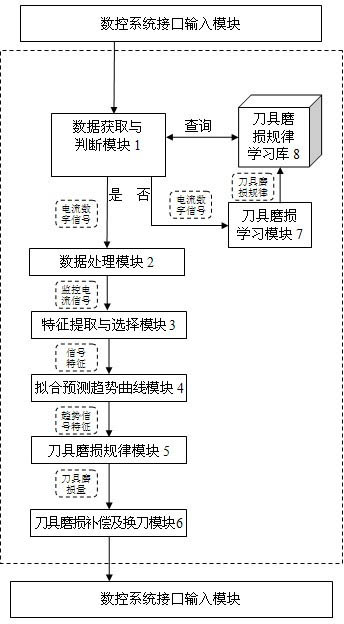
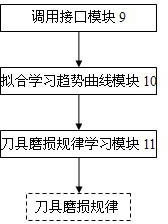
Tool wear monitoring system capable of realizing self-learning in numerical control machining state
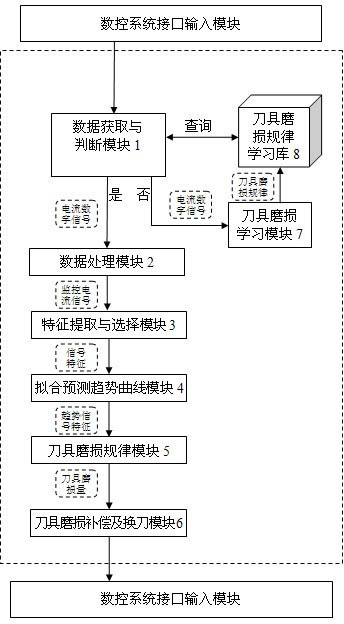
InactiveCN102073300ACutting Condition MonitoringReal-time monitoring of cutting statusProgramme controlComputer controlData acquisitionEngineering
The invention discloses a tool wear monitoring system capable of realizing self-learning in a numerical control machining state. The structure of the system is that: a tool wear rule learning library stores learned tool wear rules; a data acquisition and judgment module provides a servo drive current digital signal for a data processing module to perform format conversion and store the signal as a monitoring current signal; a characteristic extraction and selection module selects signal characteristics strongly correlated with tool wear; a fitted predicted trend curve module establishes a signal characteristic-tool machining service life relationship curve; a tool wear rule module obtains the learned tool wear rules from the tool wear rule learning library, and substitutes the trend signal characteristics into the learned tool wear rules to obtain a tool wear extent; and a tool wear compensation and tool replacement module makes a tool wear compensation and tool replacement decision according to the tool wear extent, and provides the tool wear compensation and tool replacement decision for a numerical control system interface input module. The system is applied to the condition offluctuating cutting parameters in mass production, and can achieve relatively higher accuracy under the condition of constant cutting parameters.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
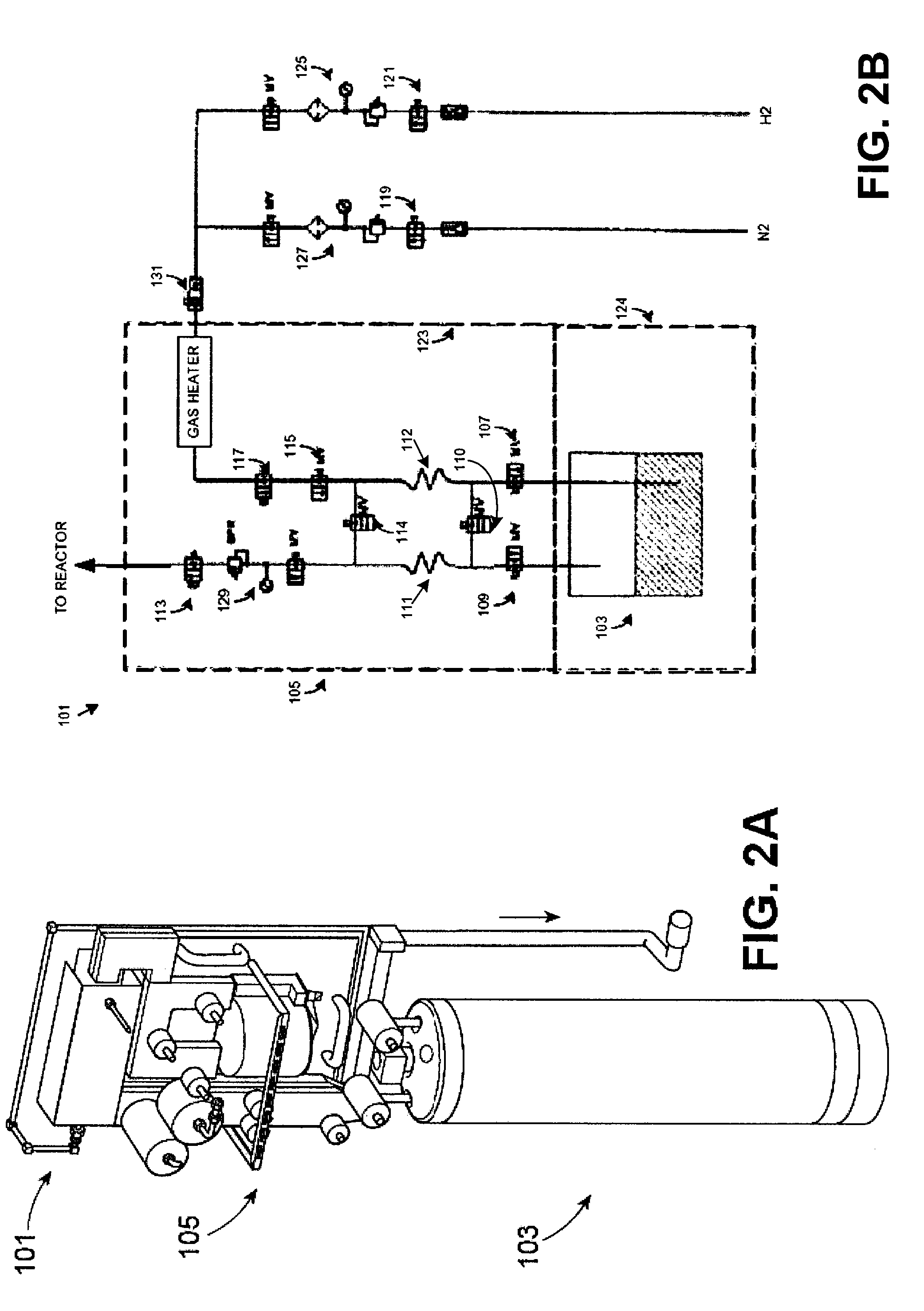
Methods for high volume manufacture of group iii-v semiconductor materials
InactiveUS20090223442A1Long operating timeEfficient depositionPolycrystalline material growthFrom chemically reactive gasesHigh volume manufacturingSemiconductor materials
The present invention is related to the field of semiconductor processing equipment and methods and provides, in particular, methods for the sustained, high-volume production of Group III-V compound semiconductor material suitable for fabrication of optic and electronic components, for use as substrates for epitaxial deposition, for wafers and so forth. In preferred embodiments, these methods are optimized for producing Group III-N (nitrogen) compound semiconductor wafers and specifically for producing GaN wafers. Specifically, the method includes reacting an amount of a gaseous Group III precursor as one reactant with an amount of a gaseous Group V component as another reactant in a reaction chamber under conditions sufficient to provide sustained high volume manufacture of the semiconductor material on one or more substrates, with the gaseous Group III precursor continuously provided at a mass flow of 50 g Group III element / hour for at least 48 hours.
Owner:S O I TEC SILICON ON INSULATOR THECHNOLOGIES
Inductively coupled plasma reactor for producing nano-powder
InactiveUS20050258766A1Inhibit growthAvoid adsorptionNanostructure manufactureElectric discharge tubesGas passingInduction plasma technology
Disclosed herein is a high-frequency induction plasma reactor apparatus for producing nano-powder, which is configured to continuously manufacture nano-powder in large quantities using solid-phase powder as a starting raw material and to manufacture high-purity nano-powder by completely vaporizing the material powder. The high-frequency induction plasma reactor apparatus comprises an upper body and a cover. The upper body is provided with a reaction pipe receiving a reactor extending vertically inside thereof, a high-frequency coil surrounding the outer periphery of the reaction pipe and a ceramic inner wall provided inside the reaction pipe. The ceramic inner wall is formed with a plurality of gas passing bores and defines a gas movement passage with the inner side wall of the reaction pipe therebetween for allowing the inflow of argon gas from the outside into the reactor. The cover is mounted to the upper end of the reactor and adapted to seal the reactor. The cover is provided with a powder injection tube communicating with the reactor.
Owner:NPC CO LTD
Light extraction from a semiconductor light emitting device via chip shaping
InactiveUS20060011935A1Improve external quantum efficiencyPrecise positioningSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesHigh volume manufacturingActive layer
A method for designing semiconductor light emitting devices is disclosed wherein the side surfaces (surfaces not parallel to the epitaxial layers) are formed at preferred angles relative to vertical (normal to the plane of the light-emitting active layer) to improve light extraction efficiency and increase total light output efficiency. Device designs are chosen to improve efficiency without resorting to excessive active area-yield loss due to shaping. As such, these designs are suitable for low-cost, high-volume manufacturing of semiconductor light-emitting devices with improved characteristics.
Owner:PHILIPS LUMILEDS LIGHTING CO LLC
Composite of aluminum alloy and resin composition and process for producing the same
InactiveUS20060257624A1Mass productivityMold shrinkage factor should be smallSynthetic resin layered productsRecord information storagePolytetramethylene terephthalateHigh volume manufacturing
A composite characterized by comprising an aluminum alloy shaped item having a surface roughness of 5 to 50 μm or more, the surface provided with 1 μm or less fine depressions or protrusions, and a thermoplastic resin composition composed mainly of a polyphenylene sulfide or polybutylene terephthalate resin whose average of lengthwise and crosswise linear expansion coefficients is in the range of 2 to 4×10−5° C.−1, the thermoplastic resin composition penetrating and anchored in the depressions or protrusions. The thermoplastic resin composition is not easily detached from the aluminum alloy shaped item. Thus, in, for example, electronic equipments and household electrical appliances, the advantage of metallic cage body can be reconciled with the advantage of synthetic resin structure. This composite can ensure high production efficiency and is suitable for mass production. Further, morphology and structure designing thereof can be accomplished freely.
Owner:TAISEI PLAS CO LTD
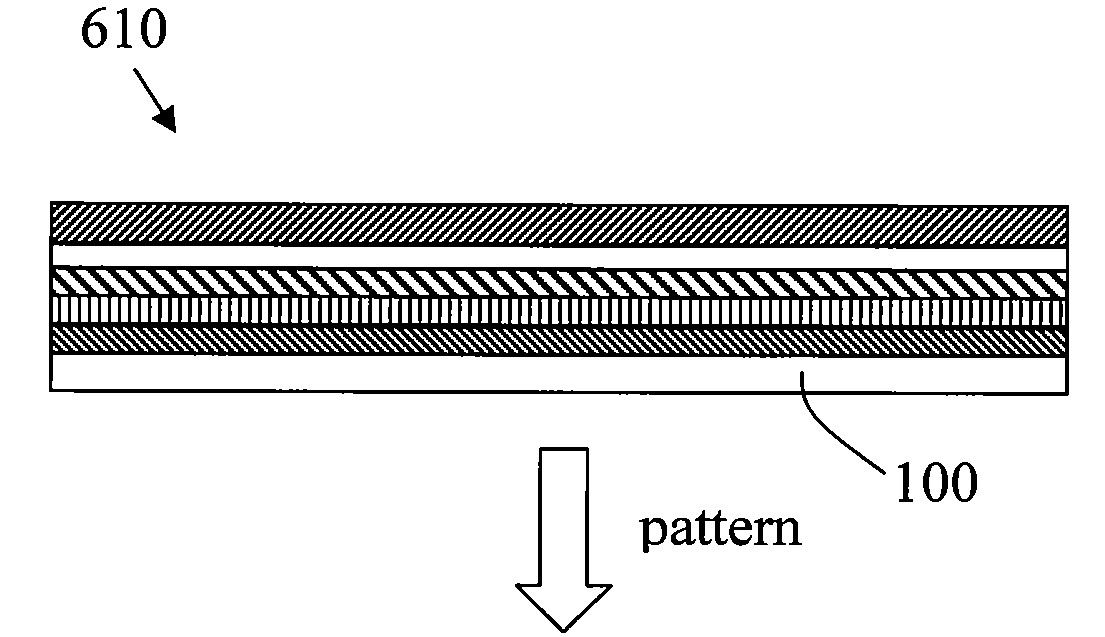
Method for high volume manufacturing of thin film batteries
ActiveUS20090148764A1Improve manufacturabilityLow costFinal product manufacturePrinted batteriesHigh volume manufacturingEngineering
Concepts and methods are provided to reduce the cost and complexity of thin film battery (TFB) high volume manufacturing by eliminating and / or minimizing the use of conventional physical (shadow) masks. Laser scribing and other alternative physical maskless patterning techniques meet certain or all of the patterning requirements. In one embodiment, a method of manufacturing thin film batteries comprises providing a substrate, depositing layers corresponding to a thin film battery structure on the substrate, the layers including, in order of deposition, a cathode, an electrolyte and an anode, wherein at least one of the deposited layers is unpatterned by a physical mask during deposition, depositing a protective coating, and scribing the layers and the protective coating. Further, the edges of the layers may be covered by an encapsulation layer. Furthermore, the layers may be deposited on two substrates and then laminated to form the thin film battery.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC +1
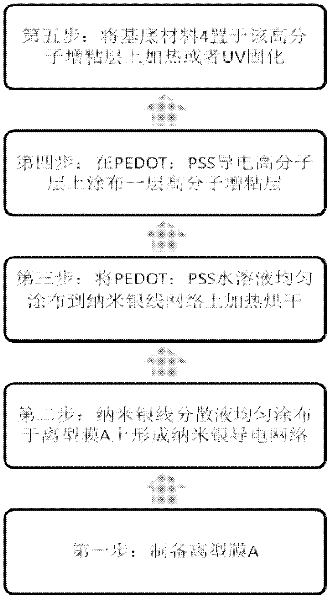
Nanometer silver transparent electrode material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102522145AEasy to manufactureTo prevent the phenomenon of insulationConductive layers on insulating-supportsCable/conductor manufactureElectricityHigh volume manufacturing
The invention discloses a nanometer silver transparent electrode material and a preparation method thereof. The nanometer silver transparent electrode material comprises the following four layers of structures: 1 a nanometer silver wire network, 2 poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT): an electricity conductive high molecular layer formed by evenly coating PSS aqueous solution, 3 a high molecular material tackifying layer and 4 a substrate. The nanometer silver wire transparent electrode is high in light transmitting rate, low in resistance, good in adhesion between the electricity conductive layer and the substrate, high in surface flatness degree, simple in preparation process and convenient for large-scale production and overcomes the shortcomings of being complex in a process for preparing the nanometer silver wire transparent electrode through a transfer method and not suitable for large-scale production.
Owner:JIANGSU NANOWELL ADVANCED MATERIALS SCI&TECH
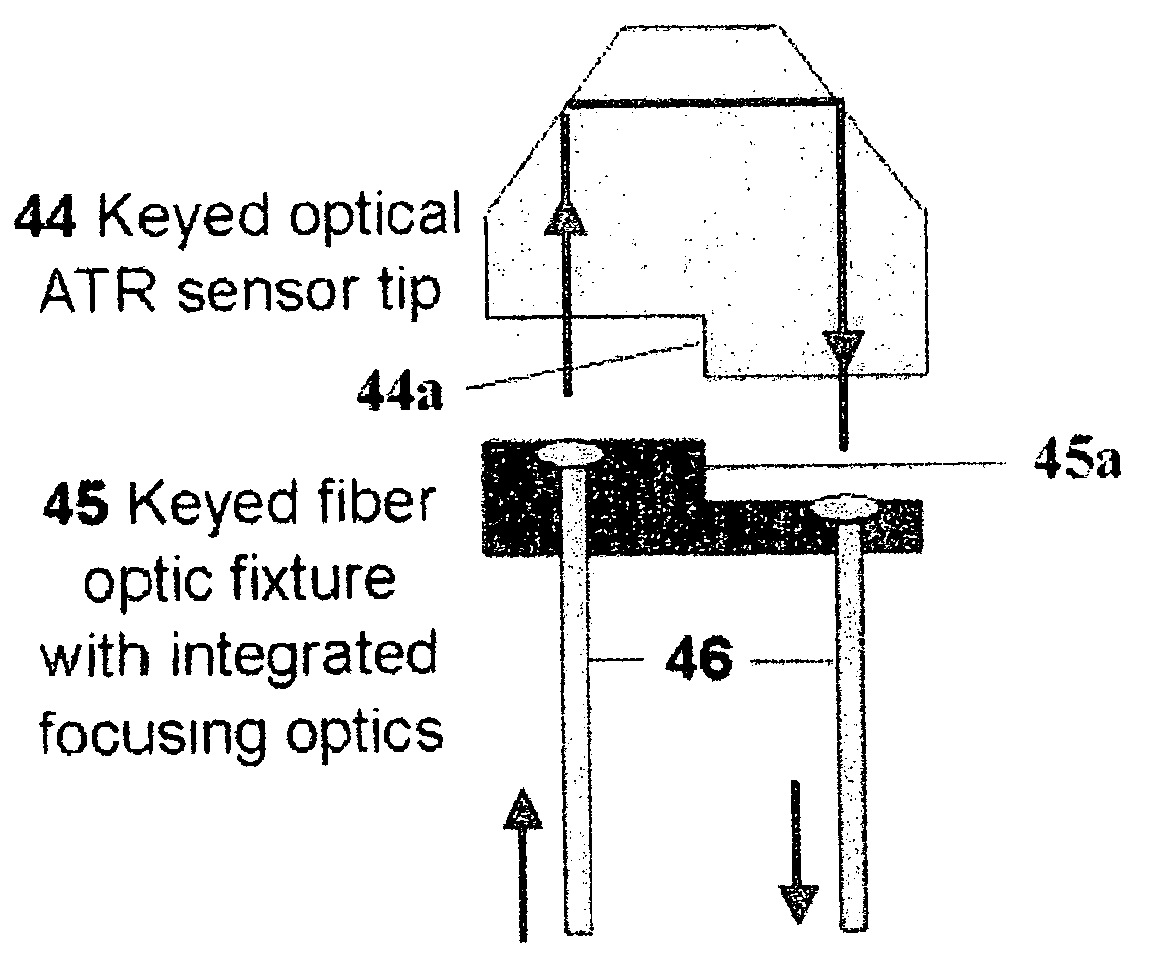
Low-cost on-line and in-line spectral sensors based on solid-state source and detectors combinations for monitoring lubricants and functional fluids
ActiveUS7339657B2Good surface protectionReduce dirtRadiation pyrometryPhotometryFluorescenceSpectral responsivity
A series of optical spectral sensors is based on a combination of solid-state sources (illumination) and detectors housed within an integrated package that includes the interfacing optics and acquisition and processing electronics. The focus is on low cost and the fabrication of the sensor is based on techniques that favor mass production. Materials and components are selected to support low-cost, high volume manufacturing of the sensors. Spectral selectivity is provided by the solid-state source(s) thereby eliminating the need for expensive spectral selection components. The spectral response covers the range from the visible (400 nm) to the mid-infrared (25,000 nm / 25.0 μm), as defined by the availability of suitable low-cost solid-state source devices. A refractive optical system is employed, primarily in an internal reflection mode, allowing a selection of sample handling tools, including, but not restricted to internal reflectance and transmittance. A secondary channel allowing for light scattering or fluorescence methods is an option. The targeted applications of the sensing devices are for lubricants and functional fluids in the heavy equipment, automotive and transportation industries. A source reference channel is included to provide measurement stability and temperature compensation.
Owner:SENTELLIGENCE
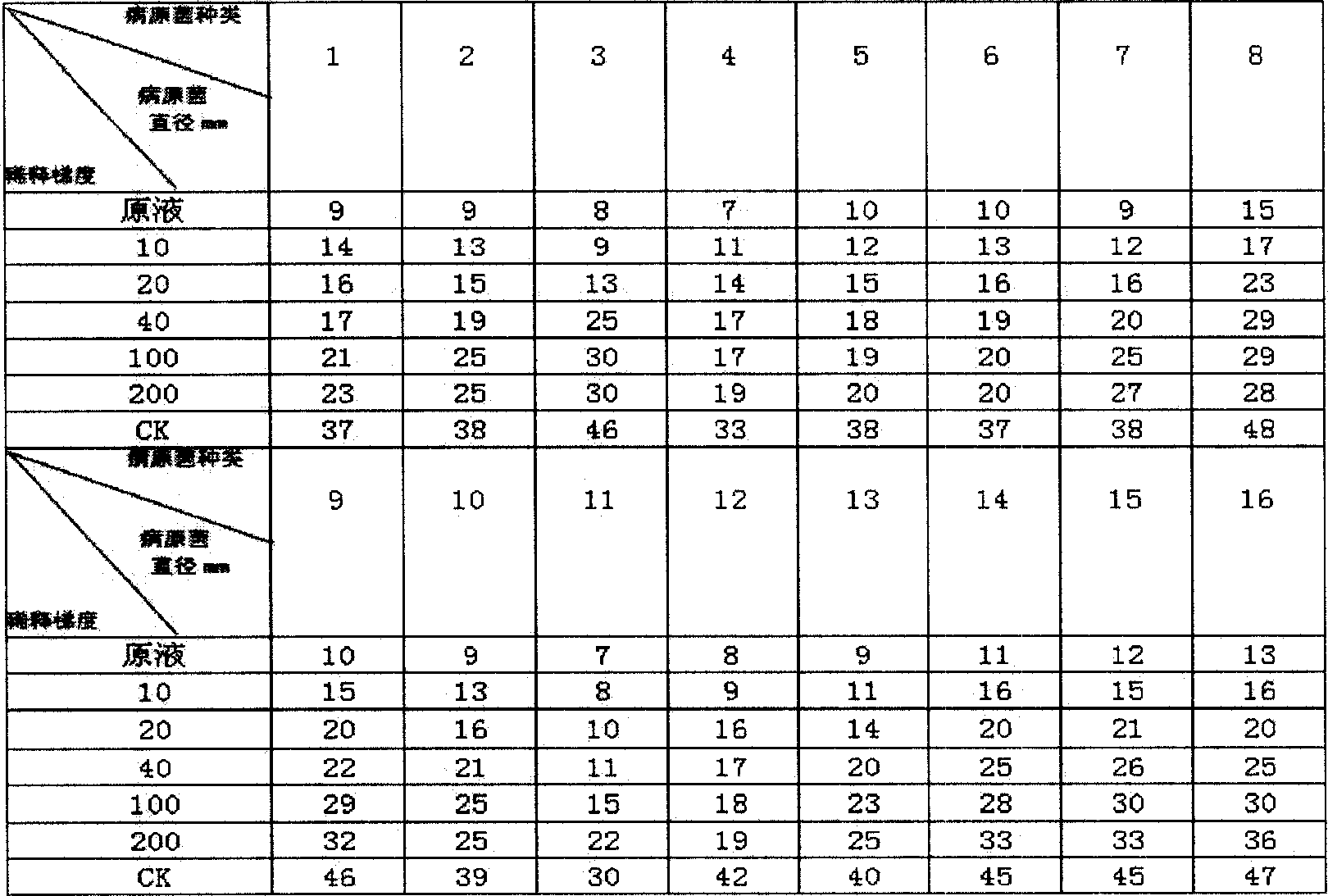
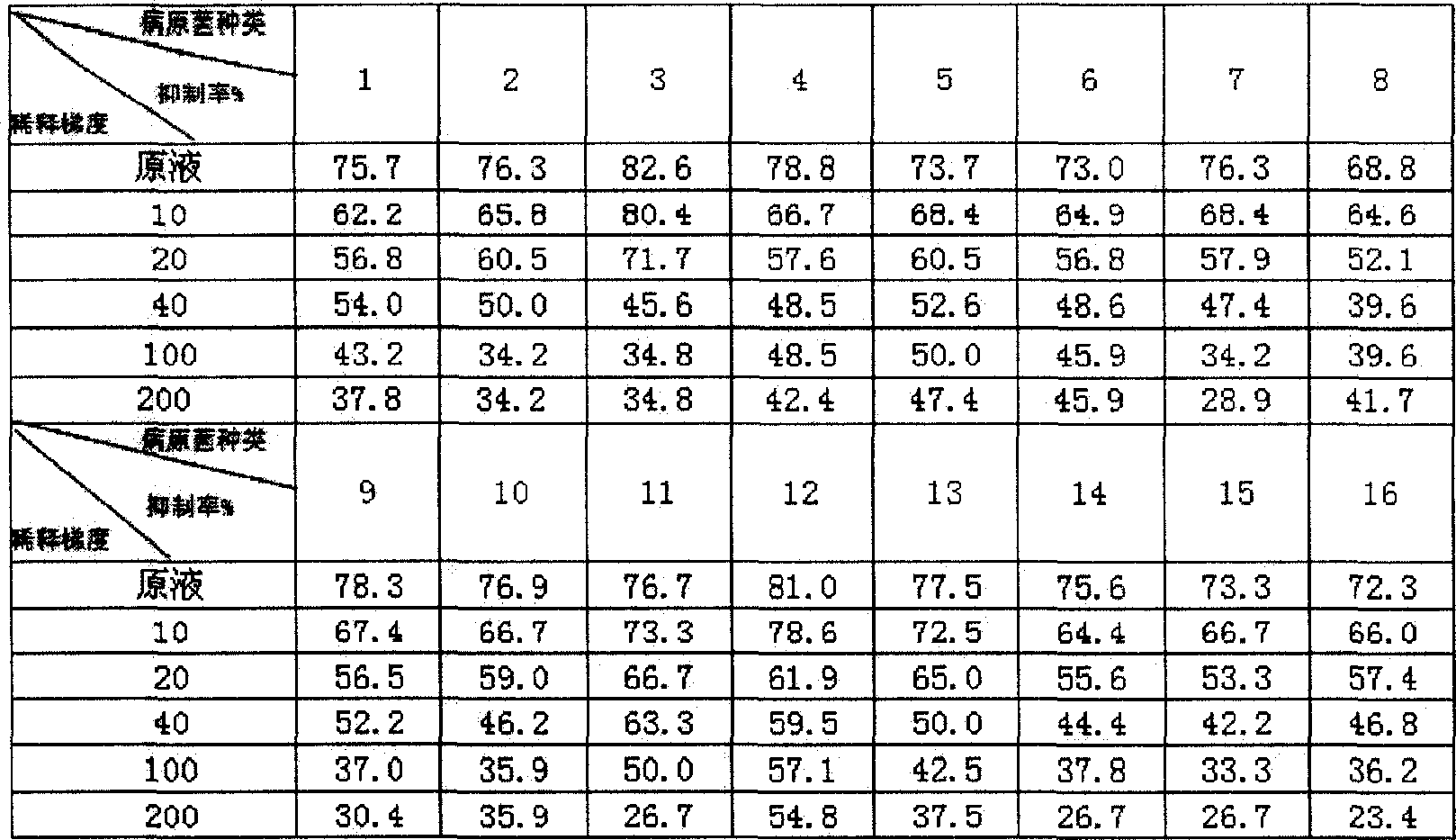
Bacillusamyloliquefaciens strain and application thereof
The invention relates to a strain of lys-starch bacillus as well its application. The bacterium is separated from the soil on eggplant fields, anning district, Lanzhou, Gansu. The bacterium is identified to be Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. It's preserved in the Chinese typical culture preserving center (CCTCC) with a preserving name of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens I7 and preserving code of M206027. The broth of M206027 and M206027strain, non-cell culture fluid of M206027 strain's broth, and the monomer extracted from the M206027strain, M206027 broth or its non-cell culture fluid can be used in the biological control of peach anthracnose bacterium, pear nigrities artis bacterium, apple brown rot bacterium, Fusarium acuminatum, Fusarium oxysporum, Fusarium semitectum, chilli black rot bacterium, cucumber blight bacterium, tomato early blight bacterium, eggplant early blight bacterium, dry thread Pyrenomycetes, wheat foot rot bacterium, potato thread Pyrenomycetes, potato early blight bacterium, potato late blight bacterium and watermelon downy mildew bacterium. It's easy to get the material of the invention and easy to operate; besides, it can be widely used in full scale production.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
Method of preparing silver nanowire by utilization of hydrothermal method
InactiveCN103084584AImprove processing stabilityLow sensitivity to process parametersNanotechnologyMetal chlorideHigh volume manufacturing
The invention relates to a method of preparing silver nanowire by utilization of a hydrothermal method. The steps including: directly mixing ethylene glycol PVP solution which contains metal chloride with the concentration of 0.01M-2MPVP and the concentration of 1*10M-1*10-2M with ethylene glycol silver nitrate solution with the concentration of 0.01M-1M at normal temperature, stirring the mixed solution to be uniformed mixed, obtaining mixed reaction mother solution; the volume ratio of ethylene glycol silver nitrate solution to ethylene glycol PVP solution is 1:1-10:1; the molar ratio of silver nitrate to the PVP in the mixed reaction mother solution is 1:10-10:1, and the molar ration of silver nitrate to metal chloride is 10:1-104:1; putting the mixed reaction mother solution into an reaction kettle, warming the mixed reaction mother solution to 160 DEG C - 180 DEG C to carry out reduction reaction, the silver salt in the mother solution is restored, and silver nanowire is obtained. The method of preparing silver nanowire by utilization of the hydrothermal method has the advantage of being simple and high-efficient, no need of being preheated when the preliminary reaction is carried out at the normal temperature, easy to control of reaction conditions, and especially applicable to mass production.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
High numerical aperture objective lens manufacturable in wafer form
A composite micro-lens for use in an optical or magneto-optical information storage system, made up of one or more lens elements which, when coupled in assembly, provide a desired numerical aperture. The design may provide, if necessary, a photo resist lens, a shaped ball lens, or one or more contoured surfaces within the composite construction to correct for aberrations. The composite lens designed in this manner allowing for the use of wafer-level assembly processes to provide high volume production capabilities. It is further intended that this micro-lens design support integration in an optical or magneto-optical head design.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
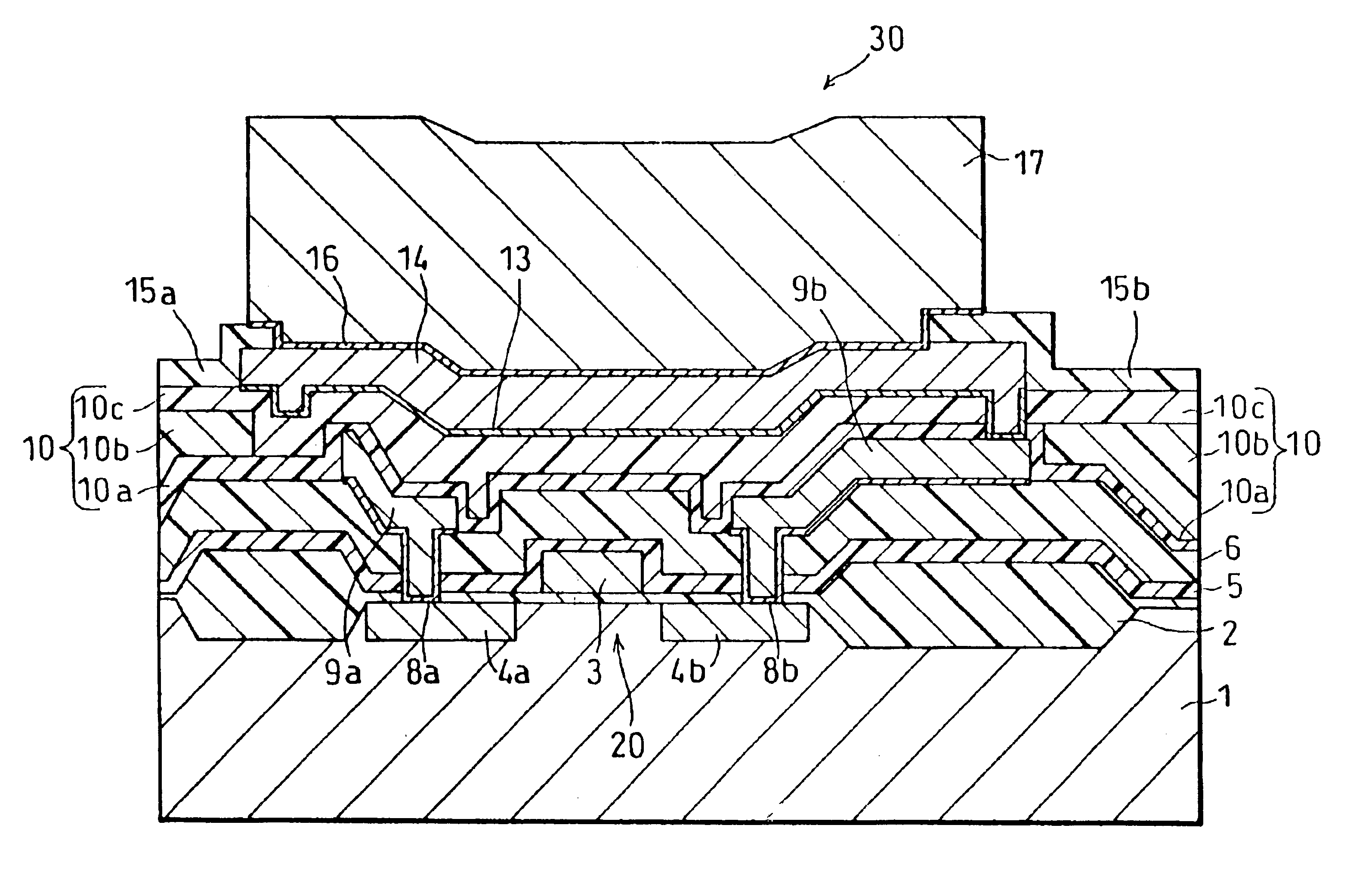
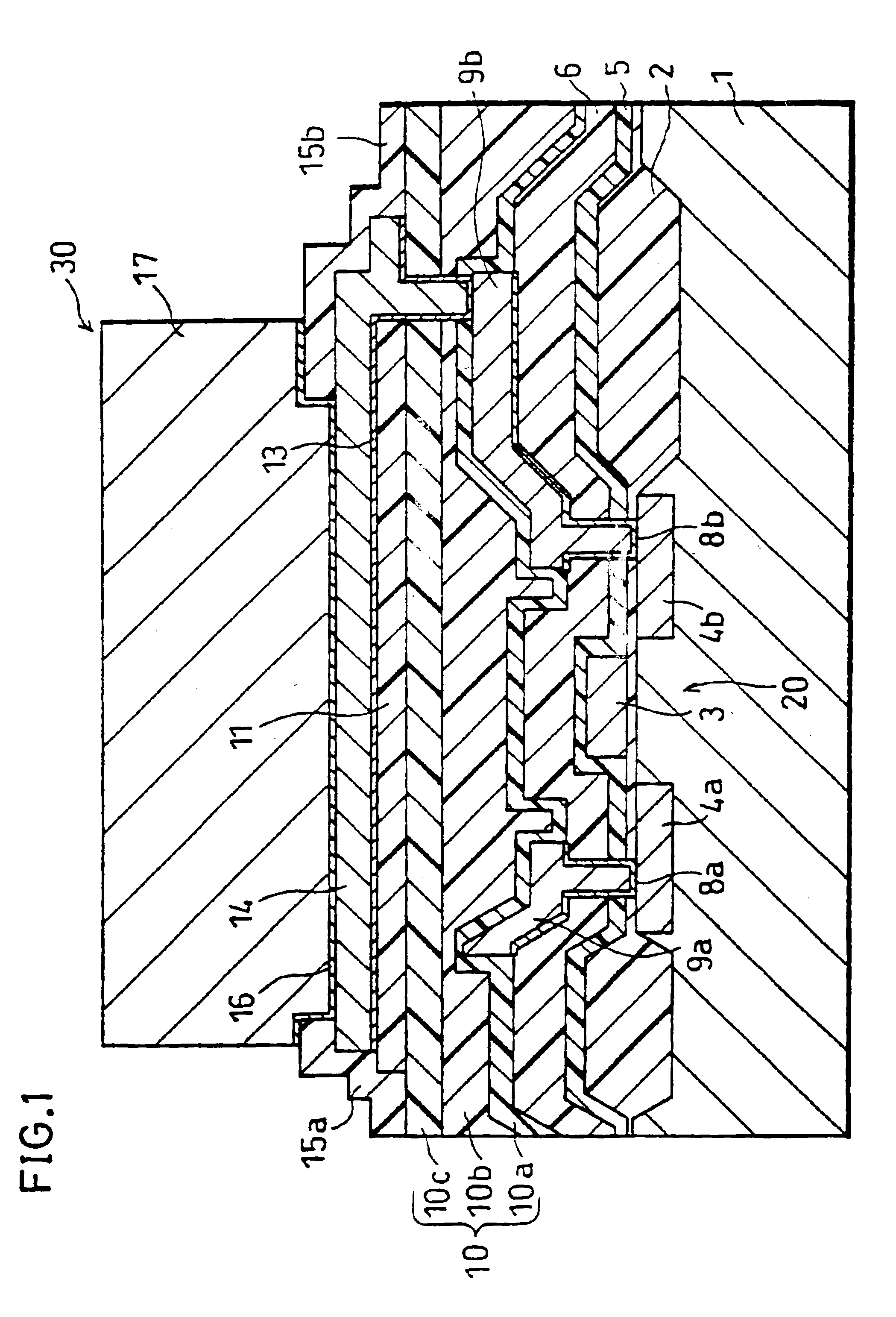
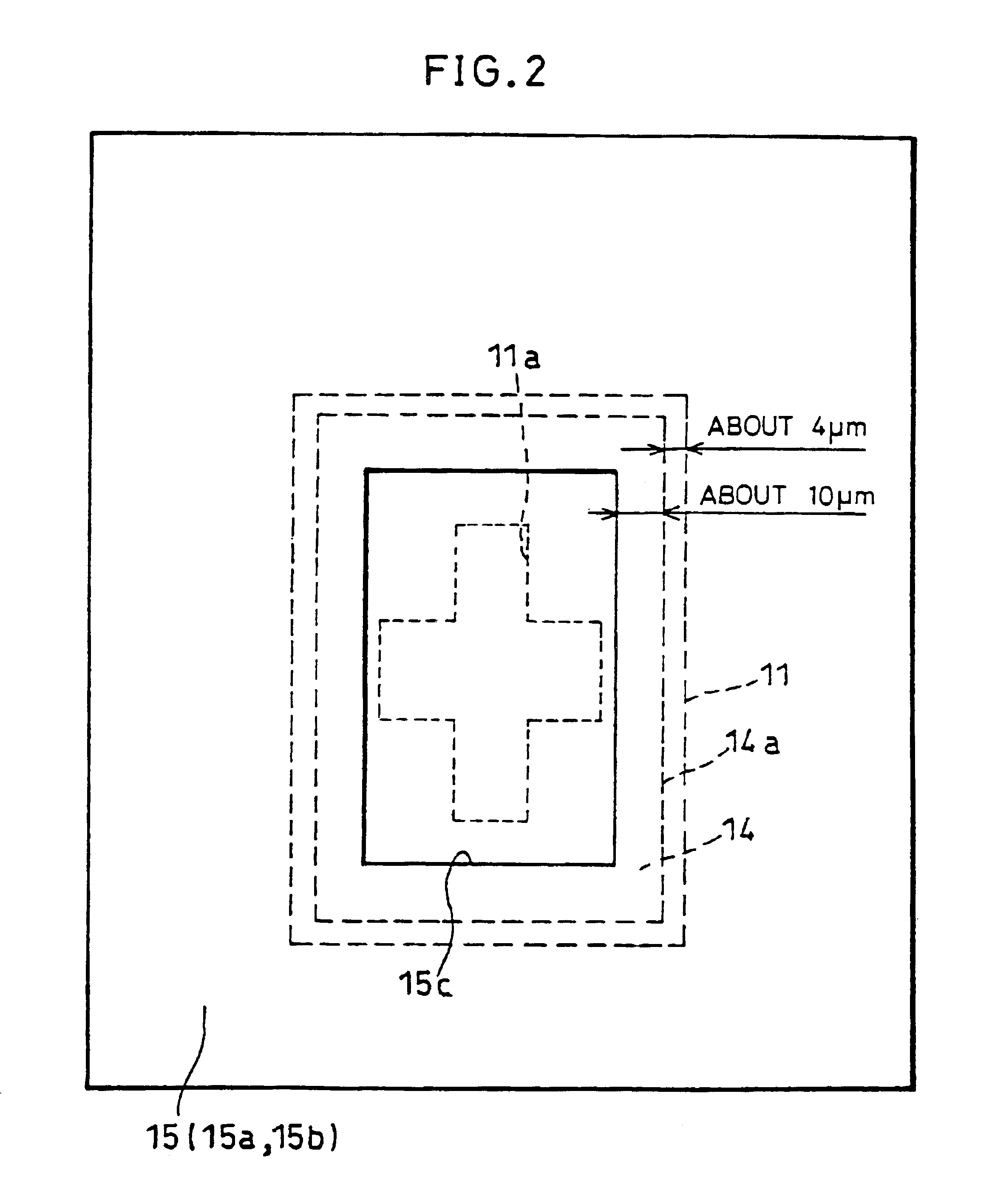
Semiconductor device having active element connected to an electrode metal pad via a barrier metal layer and interlayer insulating film
InactiveUS6864562B1Prevent peelingBreakdown of partSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesHigh volume manufacturingDevice material
A semiconductor device of the present invention has (1) an active element provided on a semiconductor substrate, (2) an interlayer insulating film formed so as to cover the active element, (3) a pad metal for an electrode pad which is provided on the interlayer insulating film, (4) a barrier metal layer which is provided on the active element with the interlayer insulating film therebetween, so that the pad metal is formed on the barrier metal layer, and (5) an insulating layer having high adherence to the barrier metal layer, the insulating layer being provided between the interlayer insulating film and the barrier metal layer. With this arrangement, the adherence between the barrier metal layer, the insulating film and the interlayer insulating film is surely improved, and even in the case where an external force is applied to the electrode pad upon bonding or after bonding, the barrier metal layer hardly comes off the part thereunder. Therefore, the breakdown of a level difference compensating film, and the exfoliation of the barrier metal layer from the interlayer insulating film can be prevented, while the semiconductor device of the area pad structure featuring lower costs, high quality, and high liability is constantly mass-produced. Besides, the yield of the semiconductor device is surely improved.
Owner:SHARP KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com