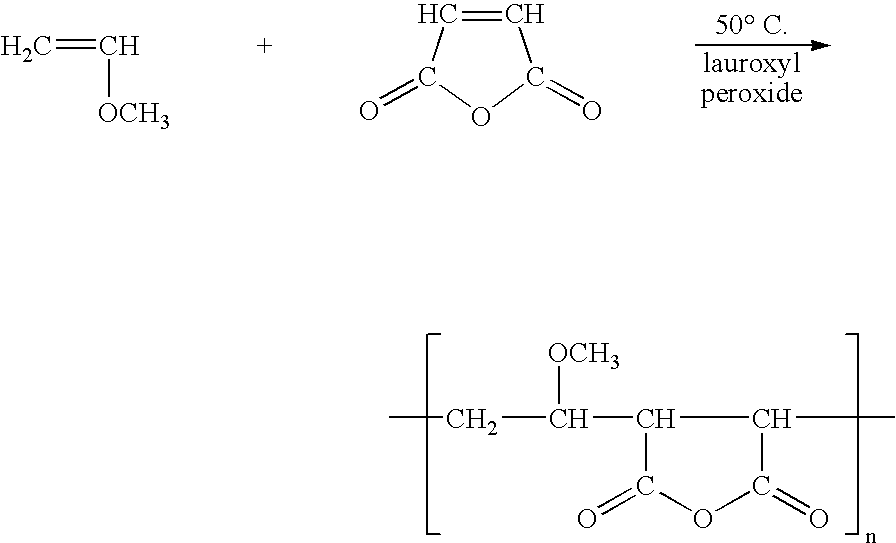
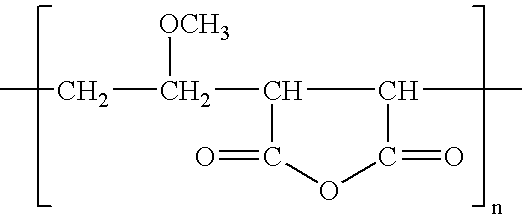
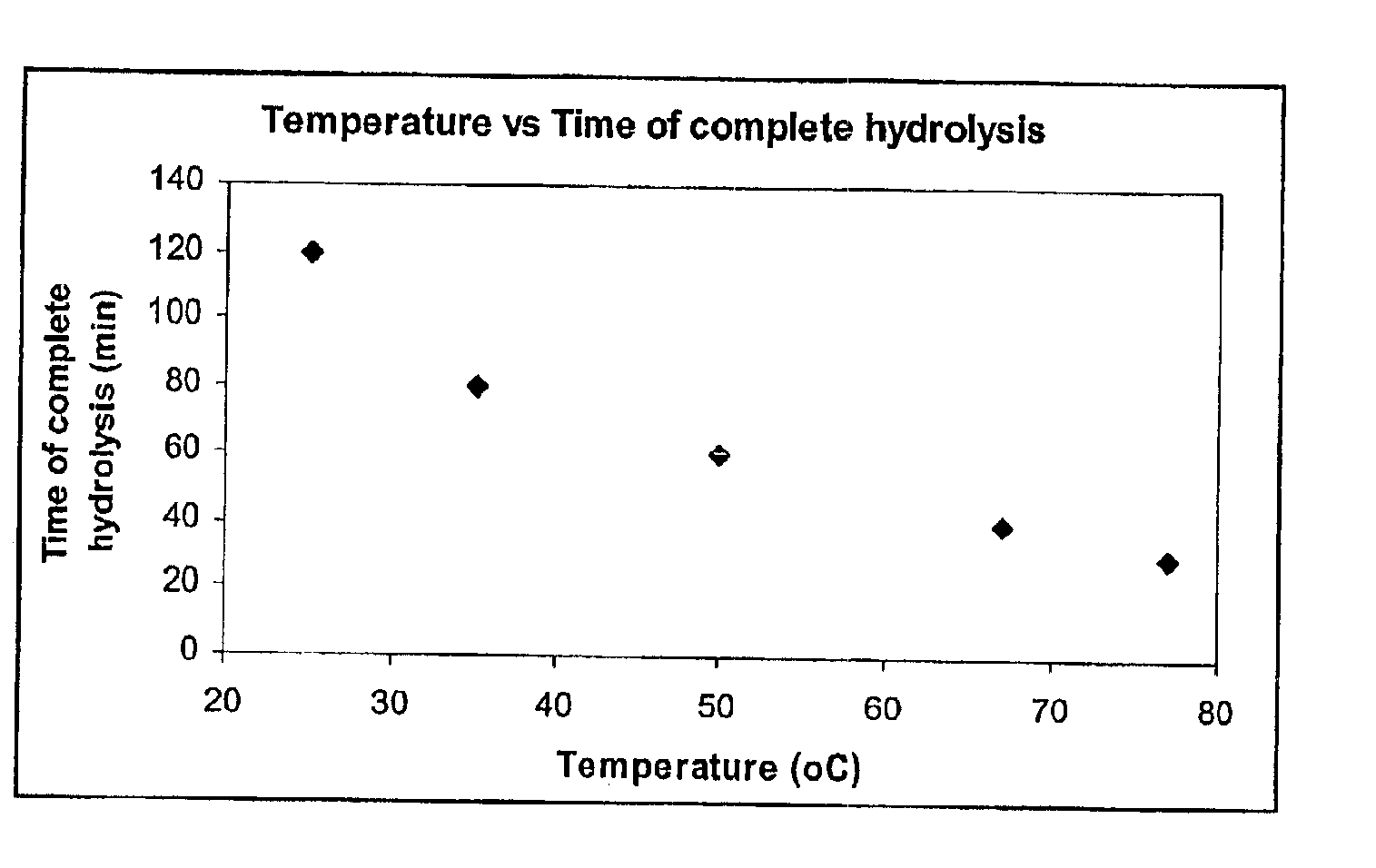
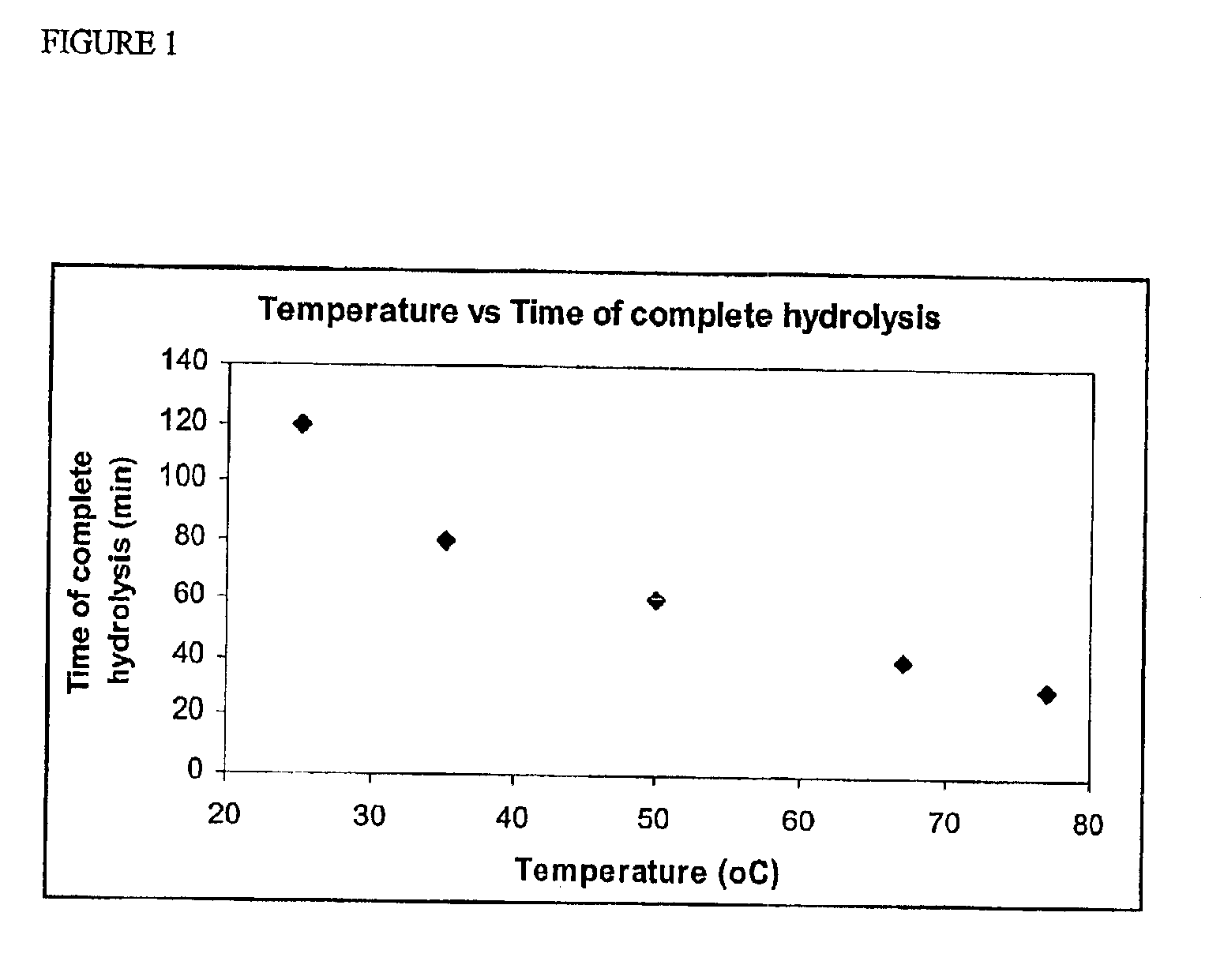
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
551results about How to "Reduce dirt" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
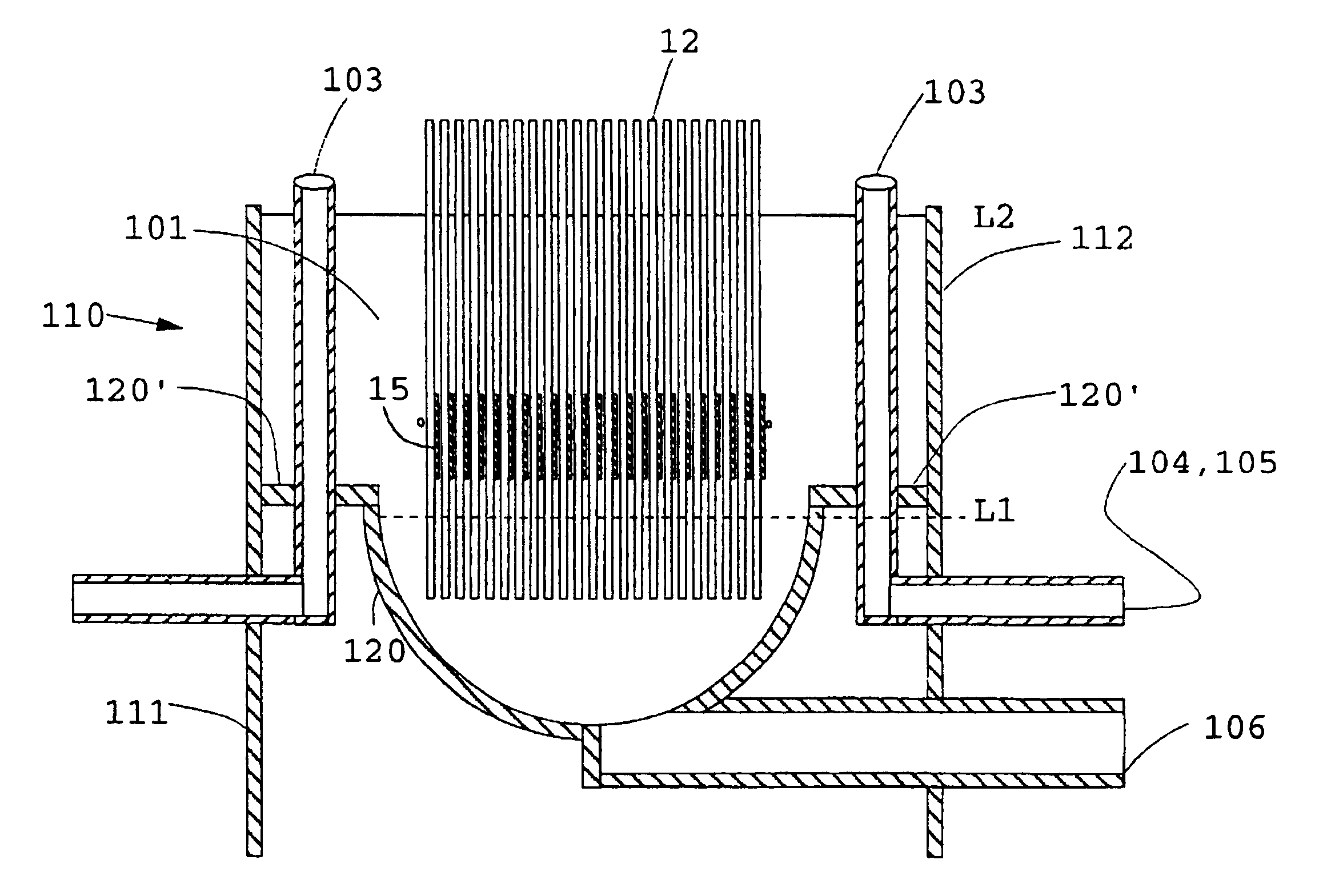
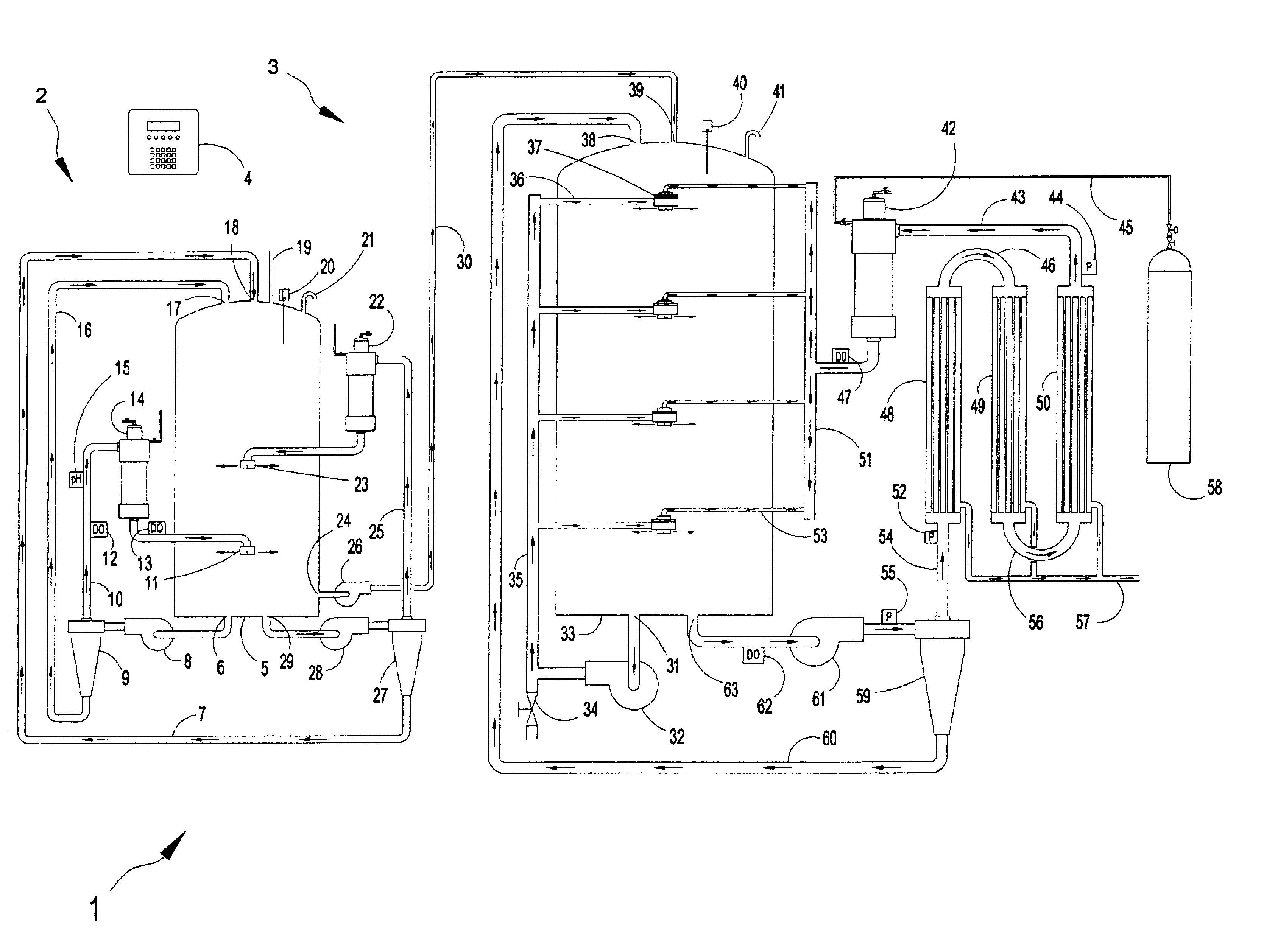
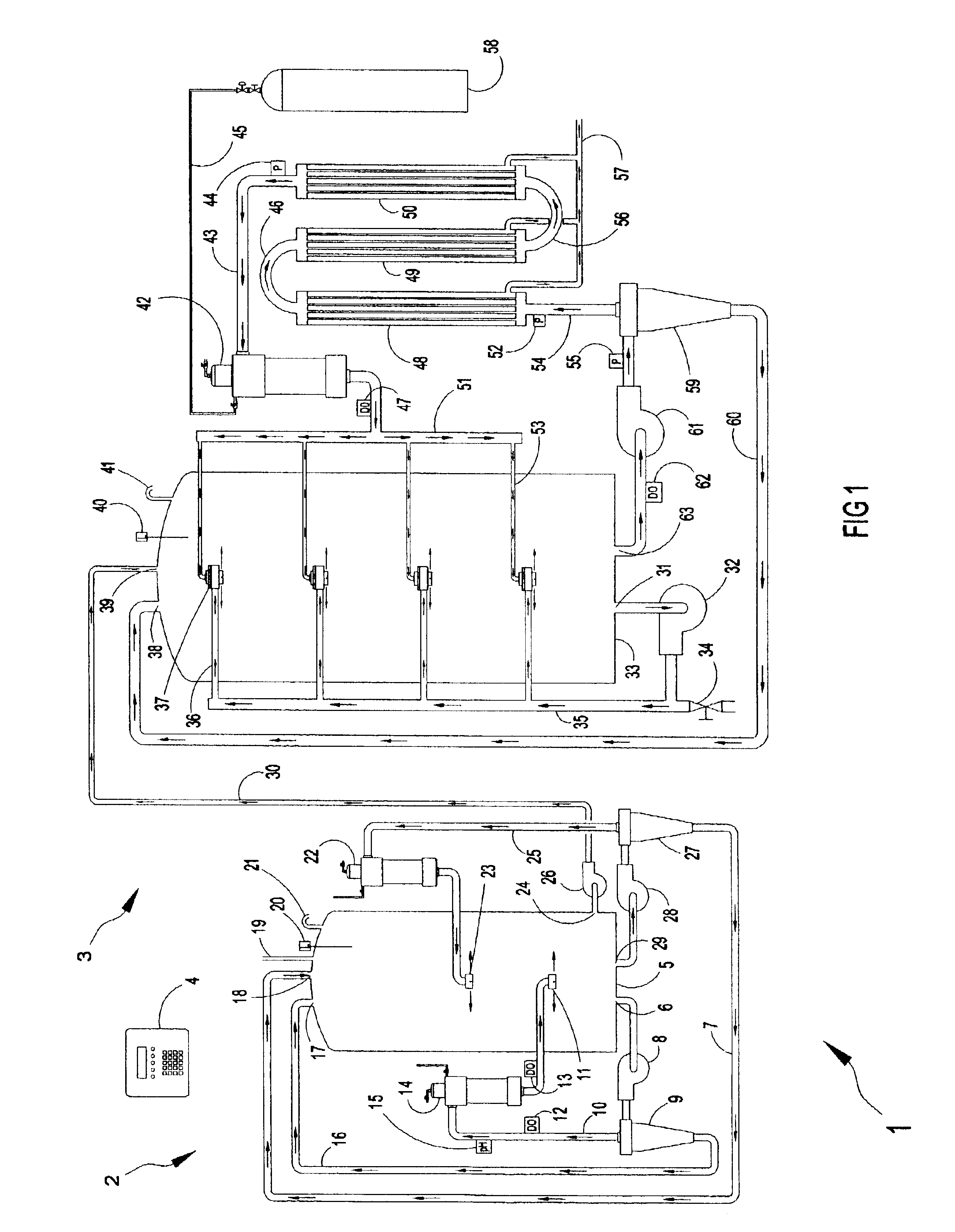
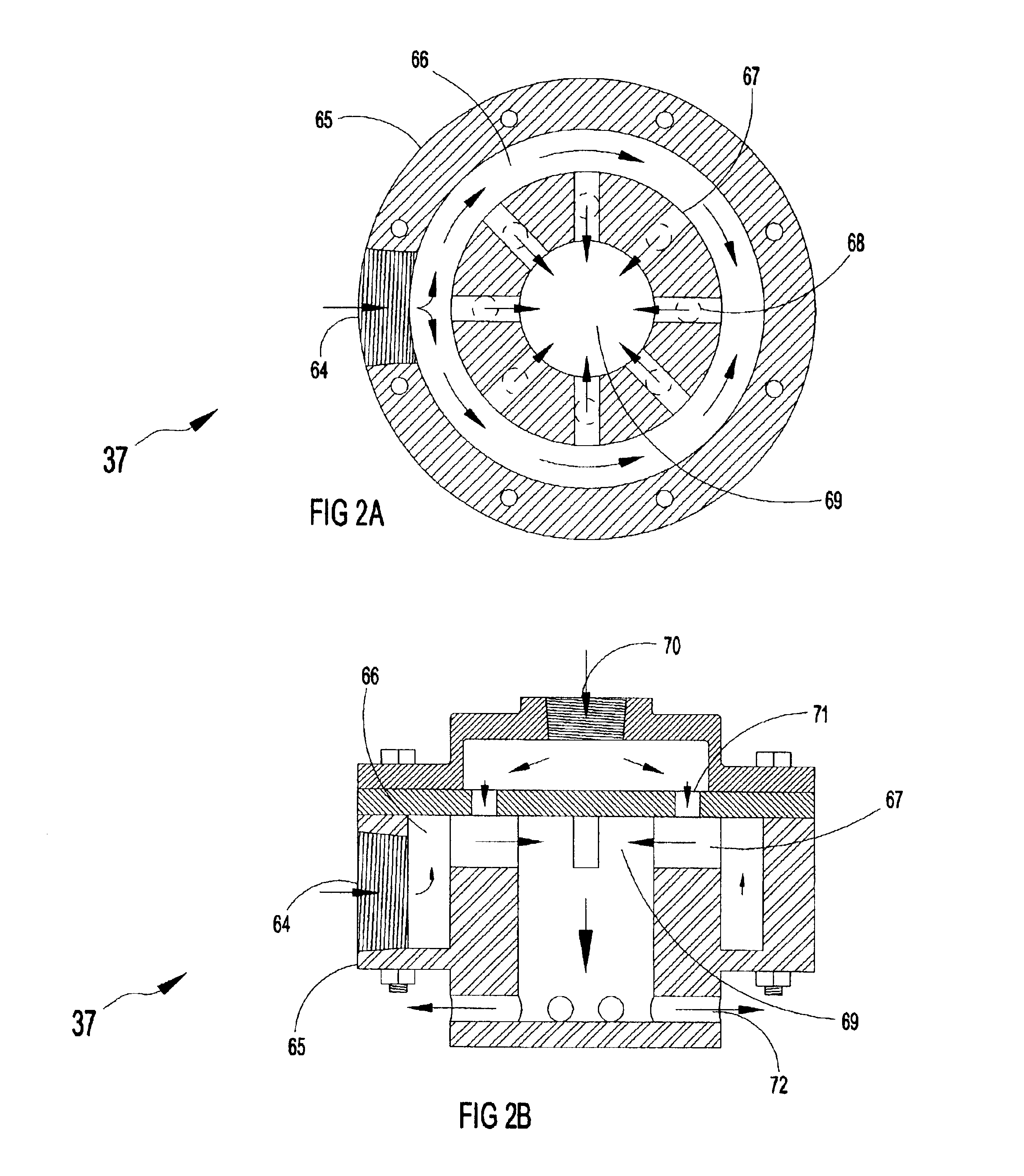
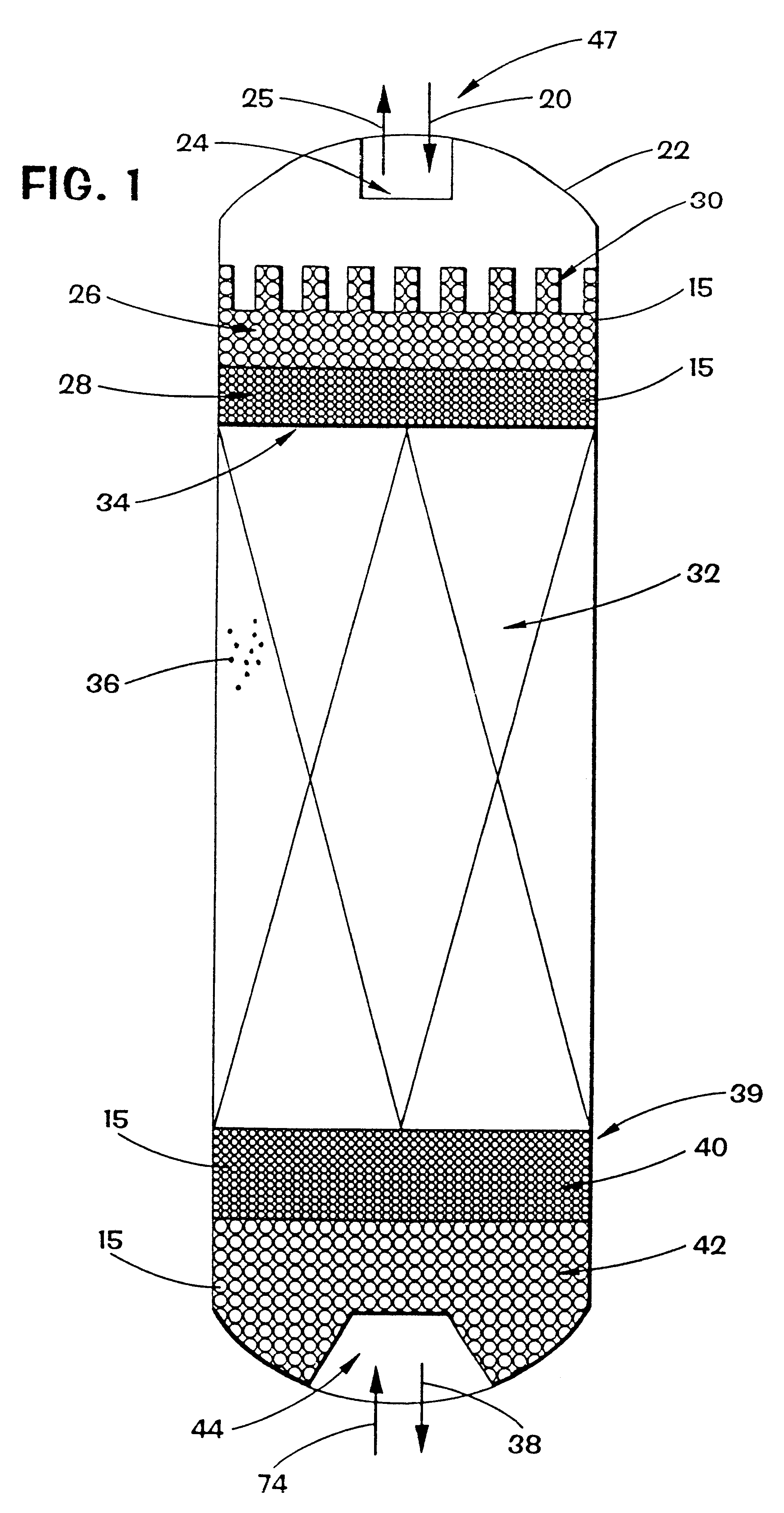
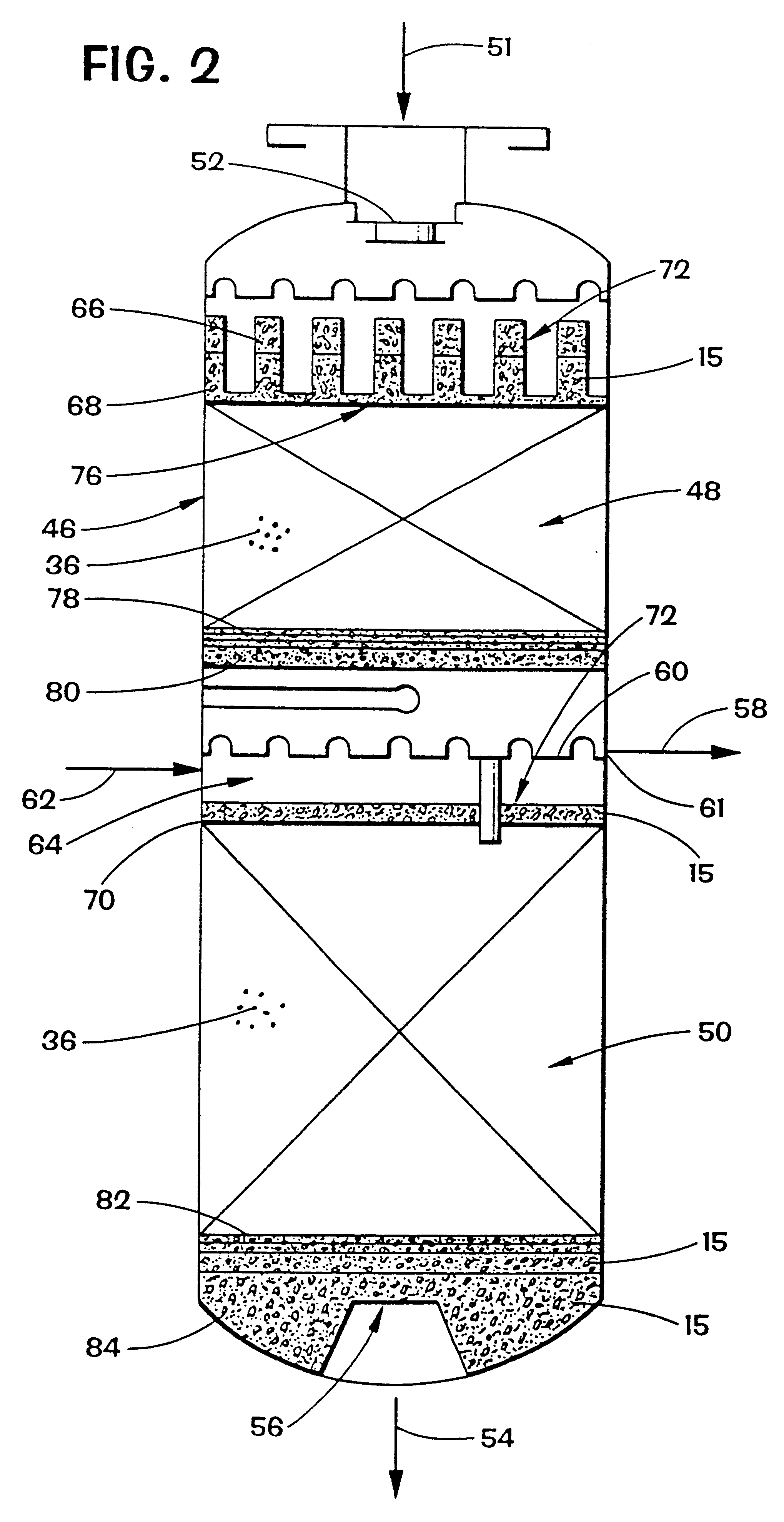
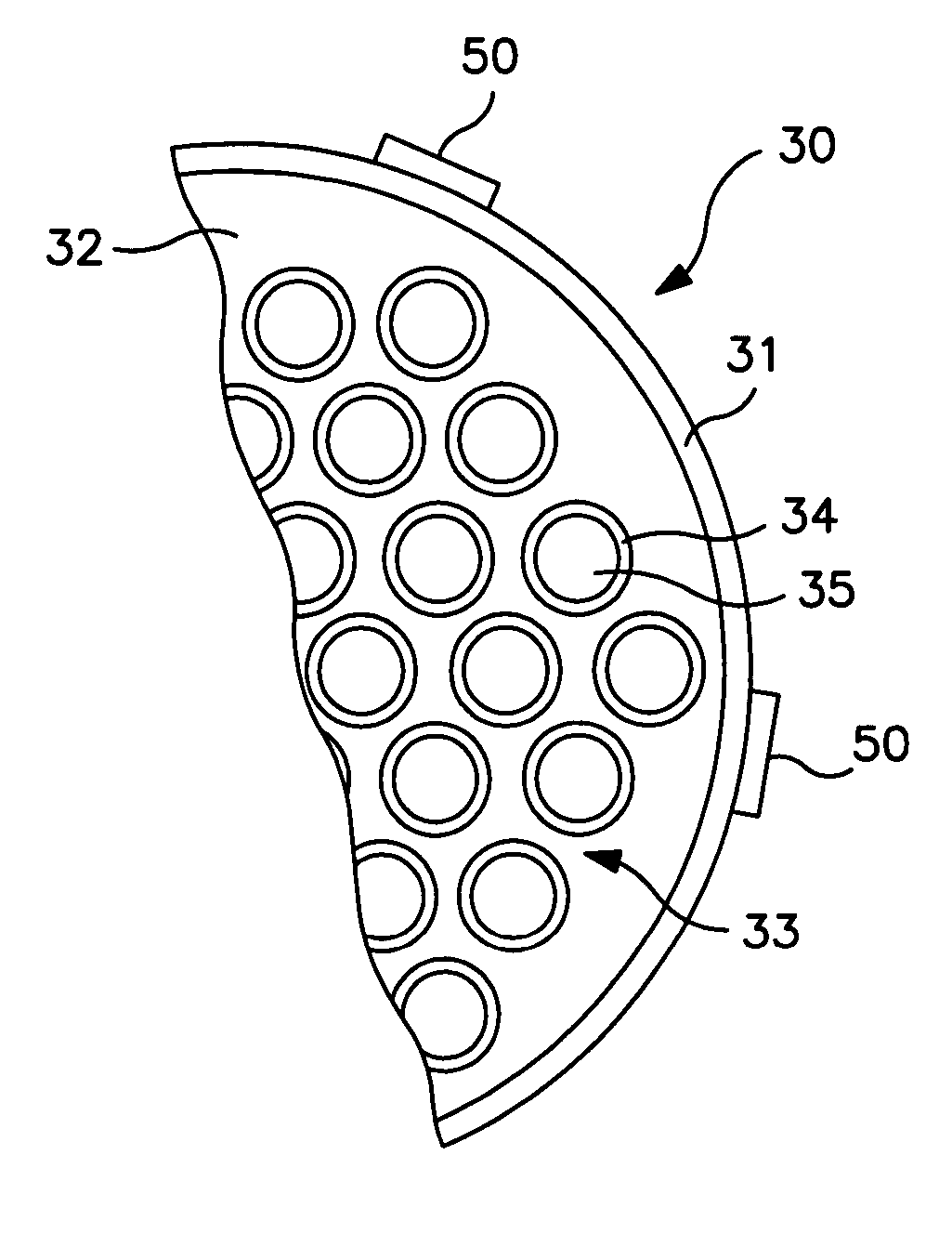
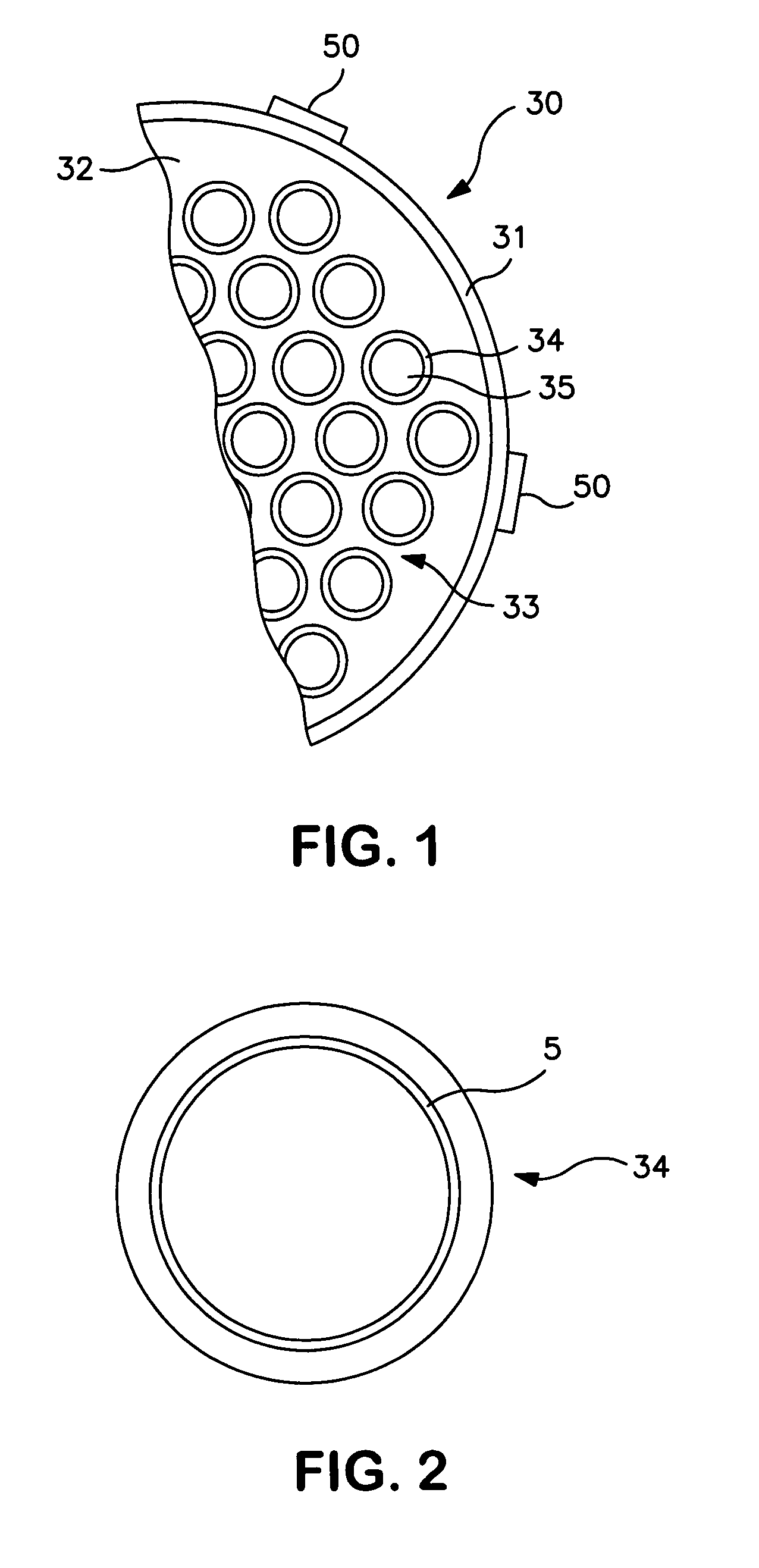
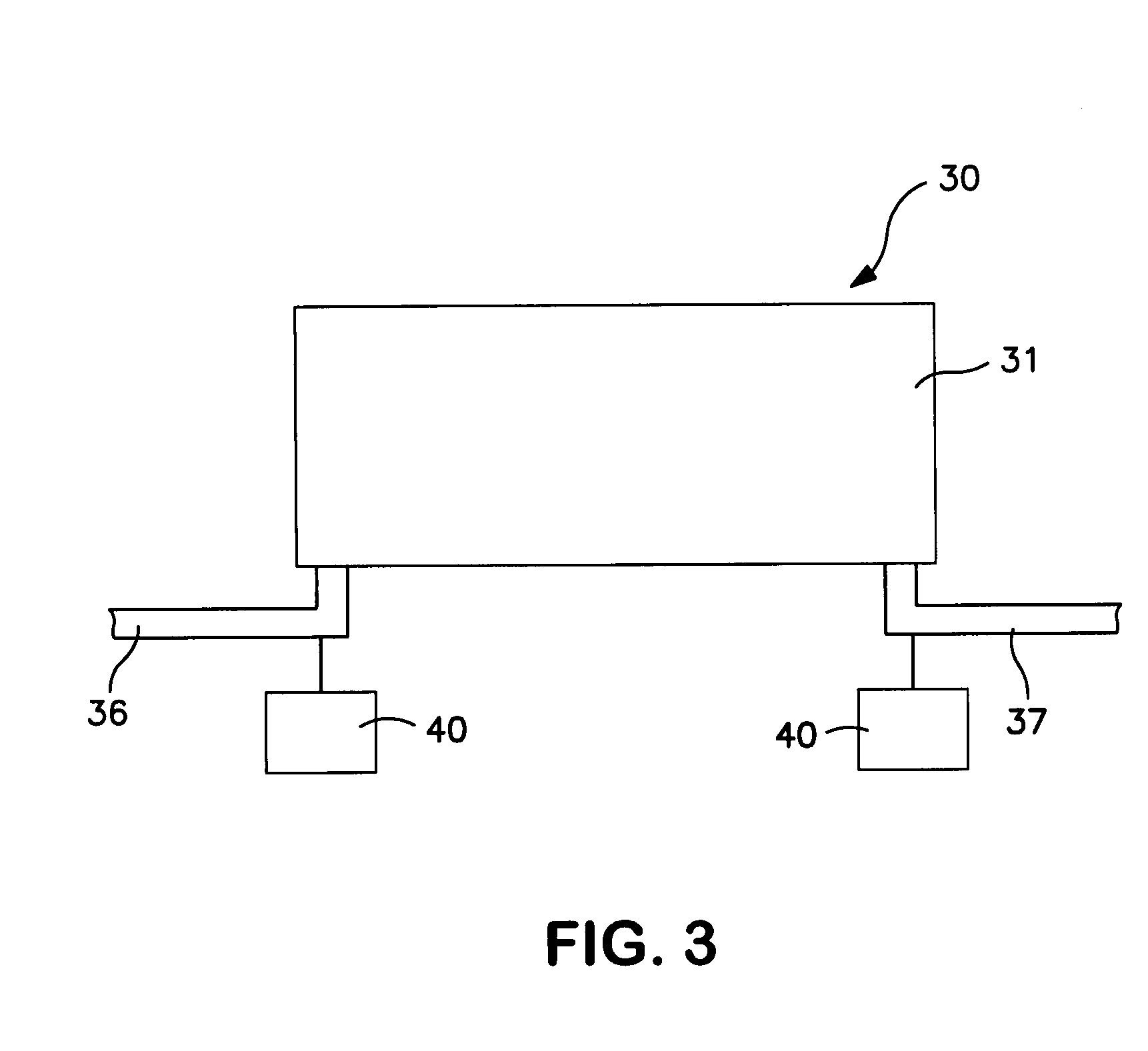
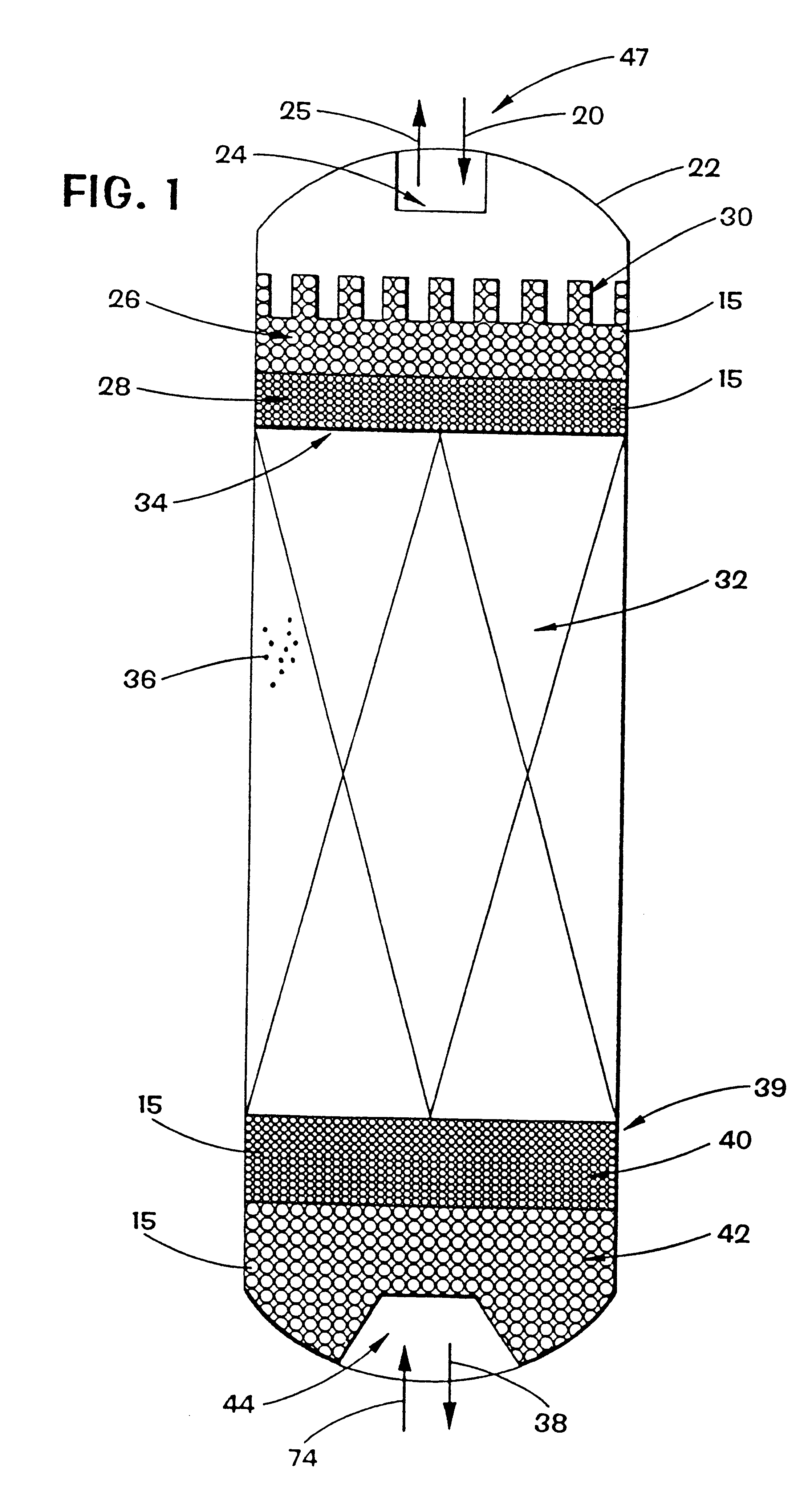
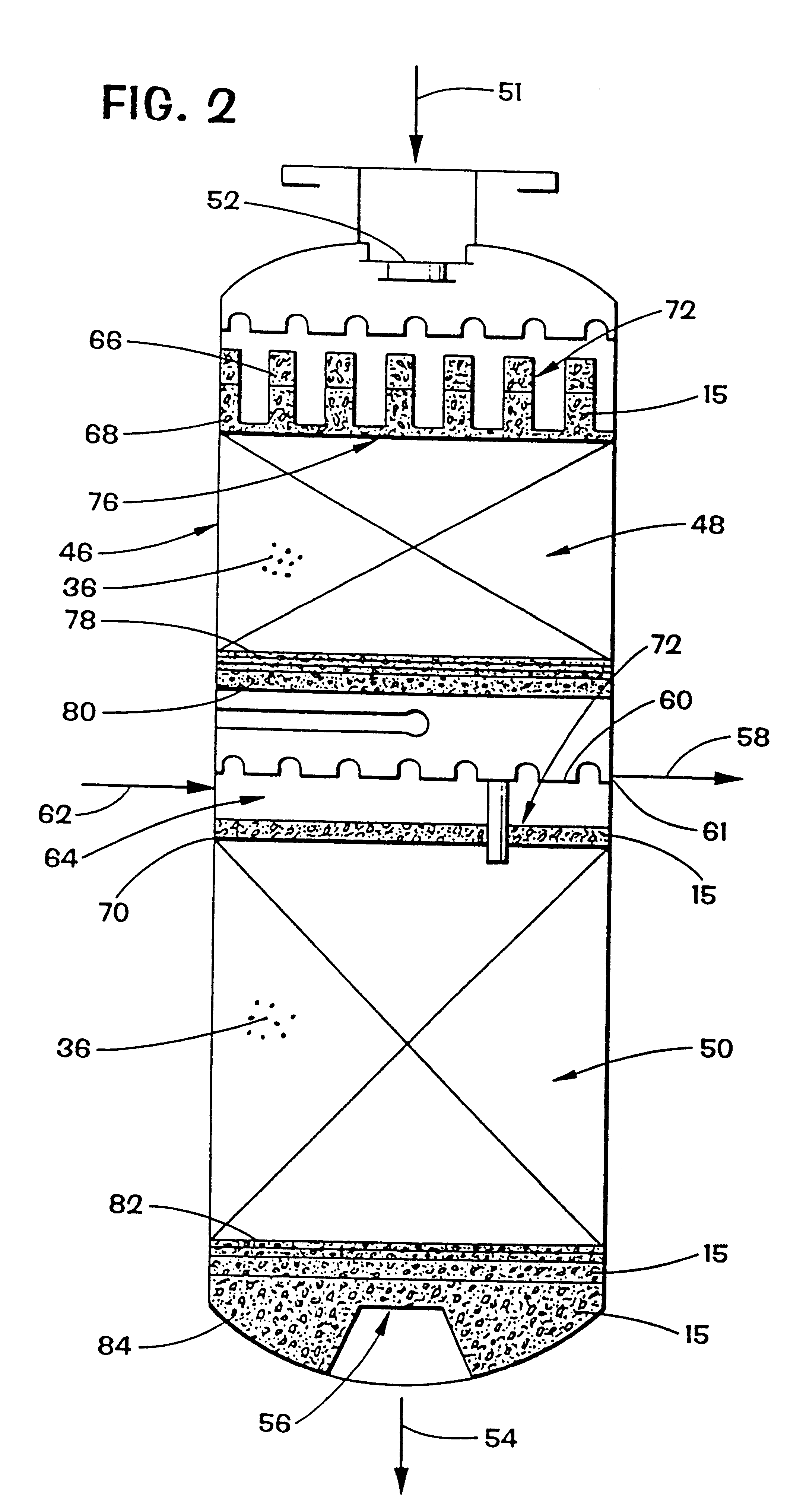
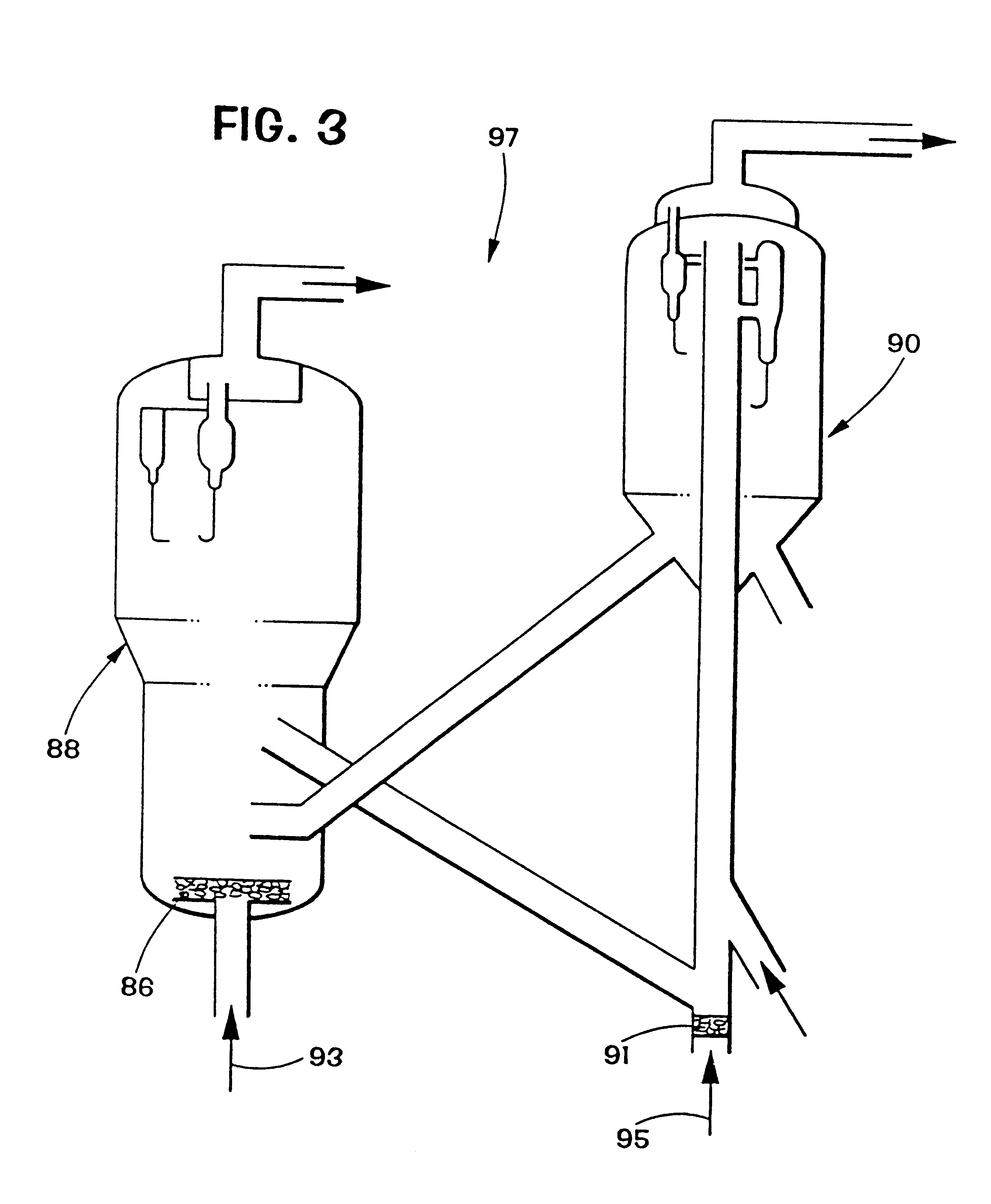
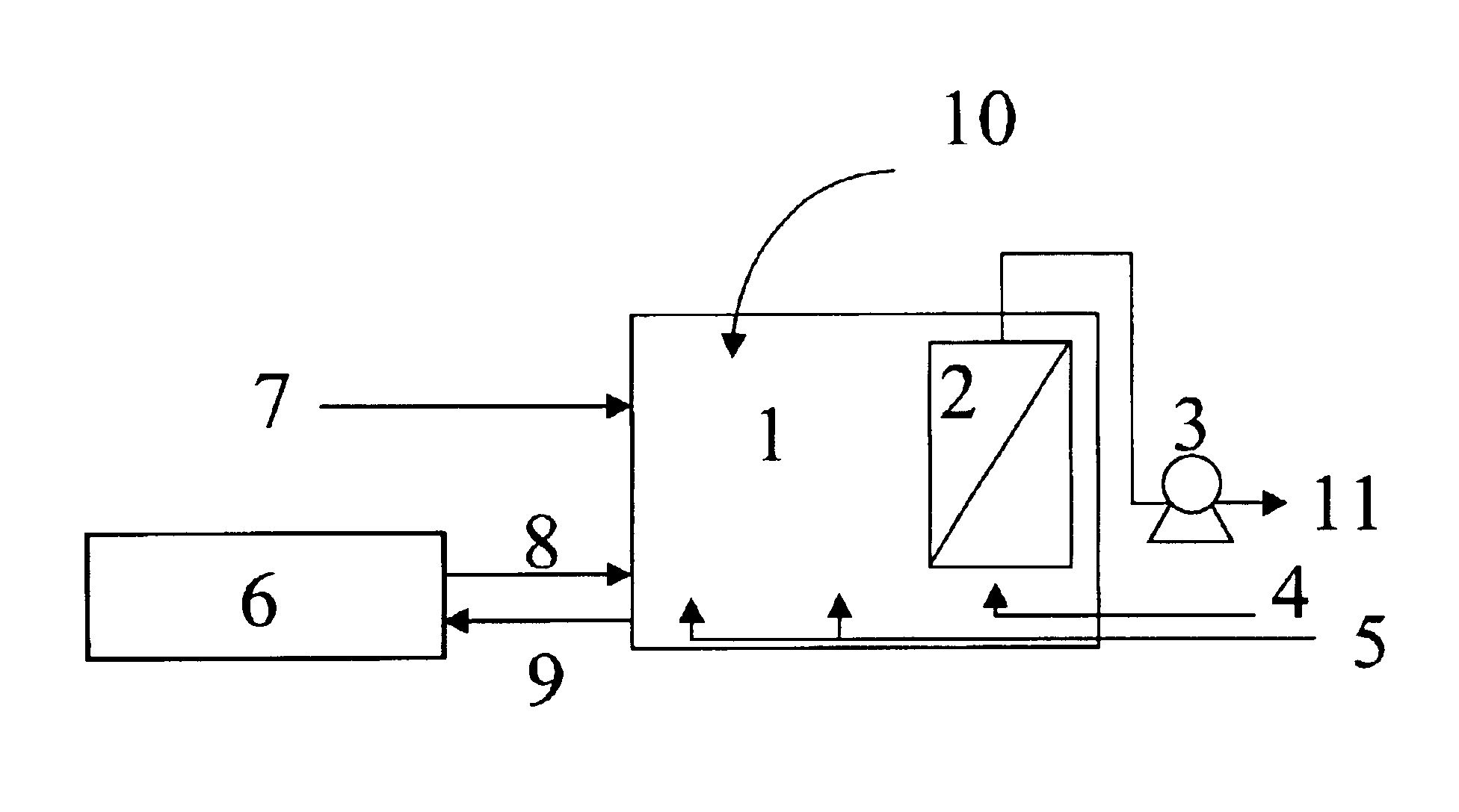
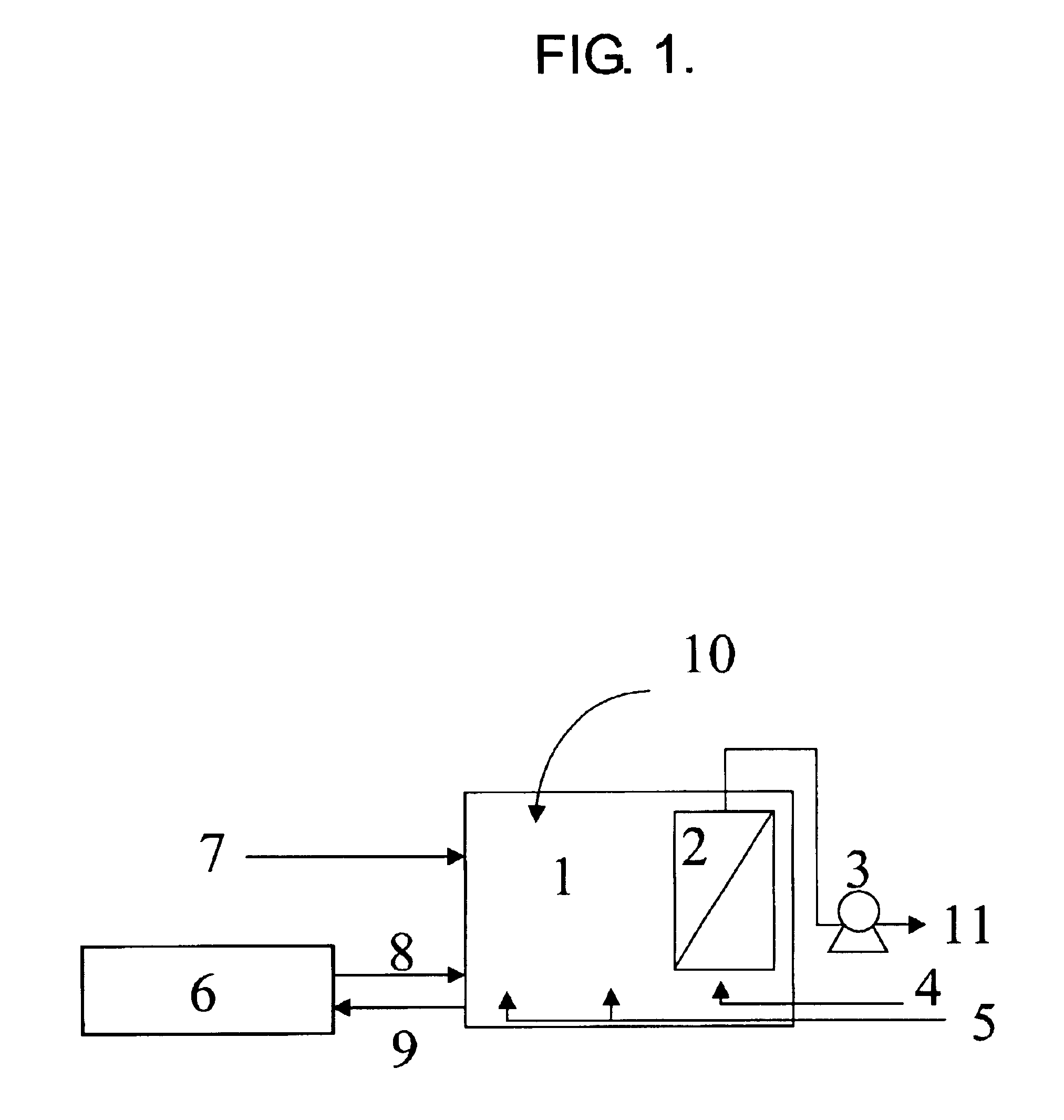
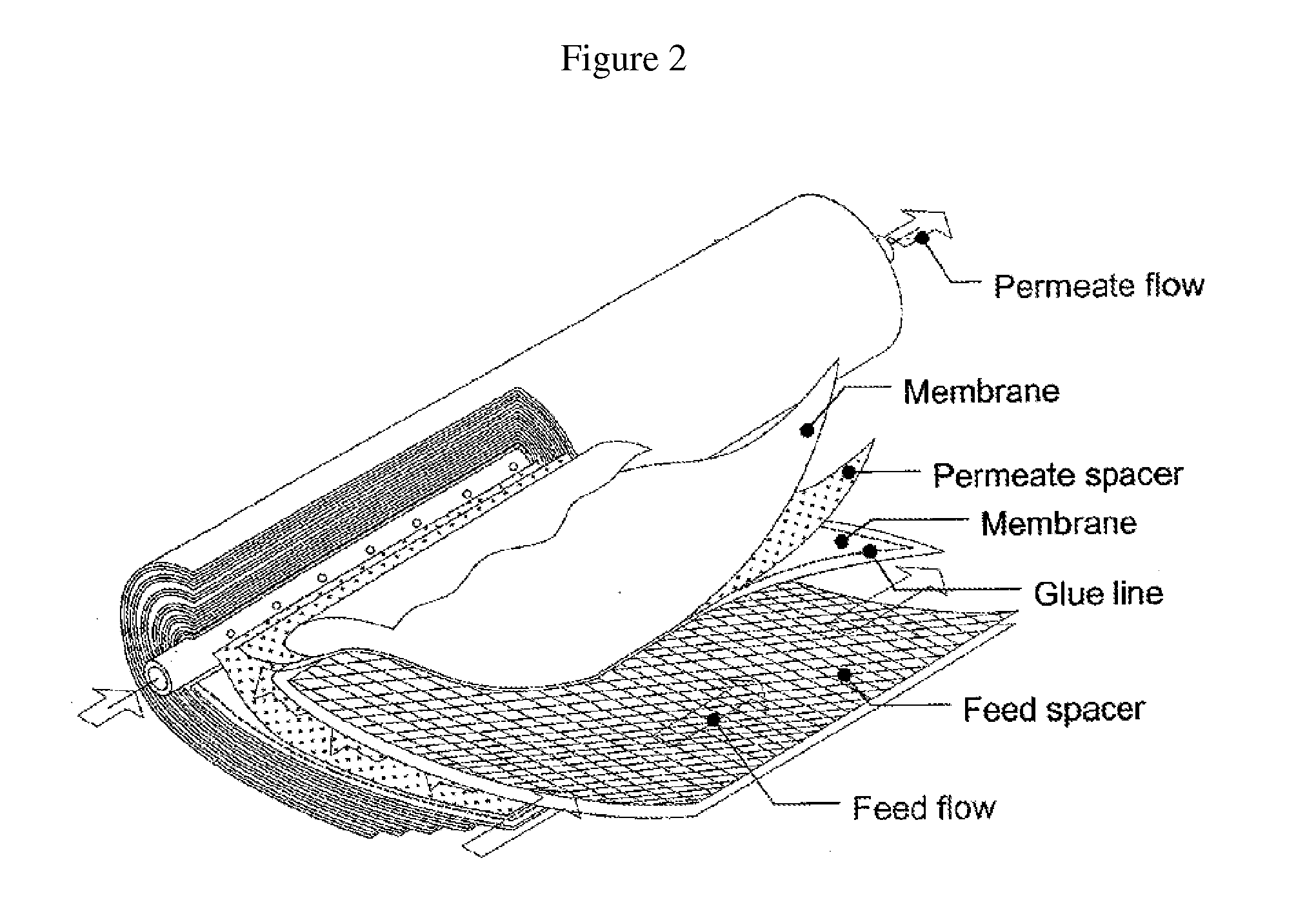
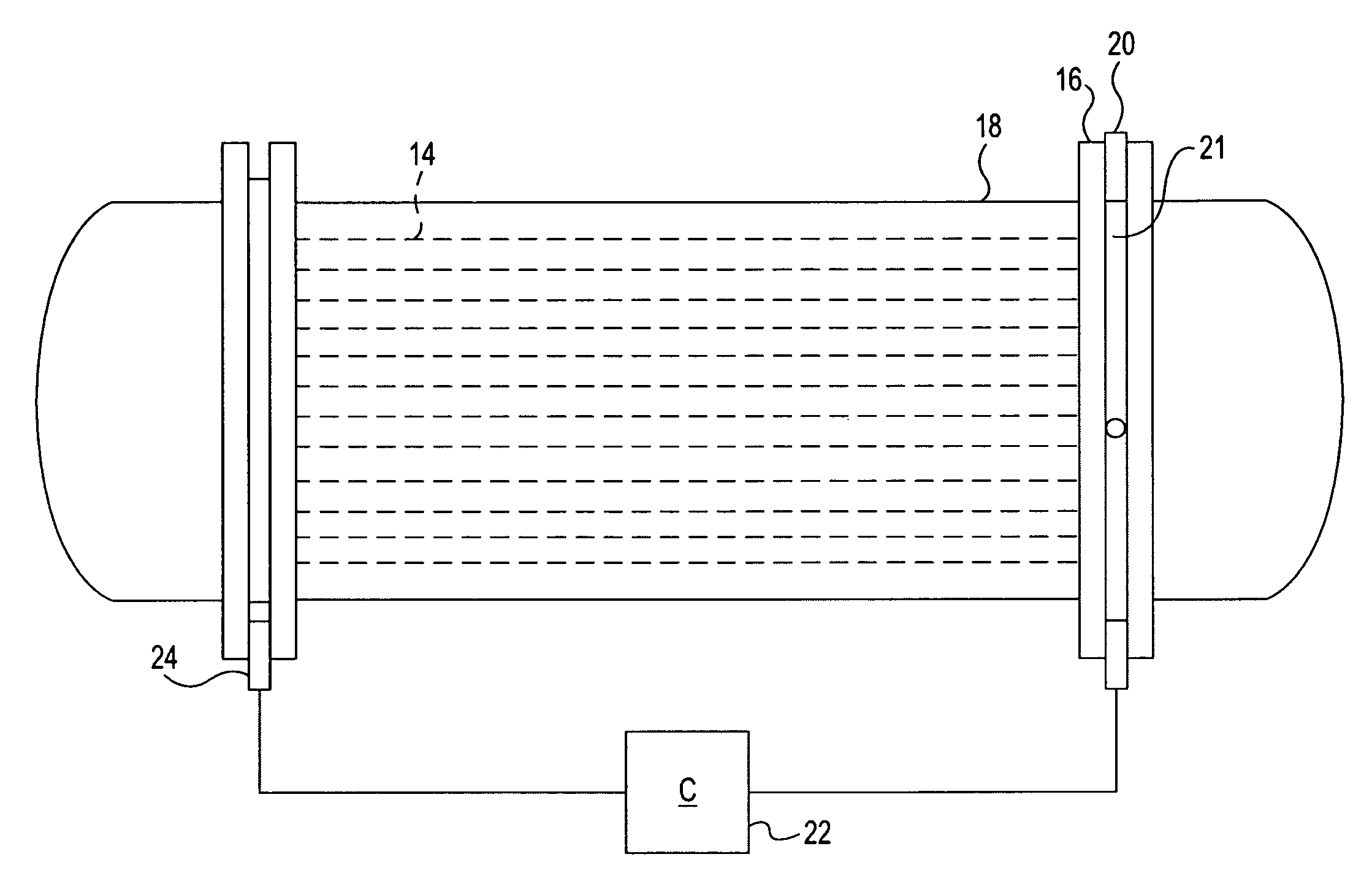
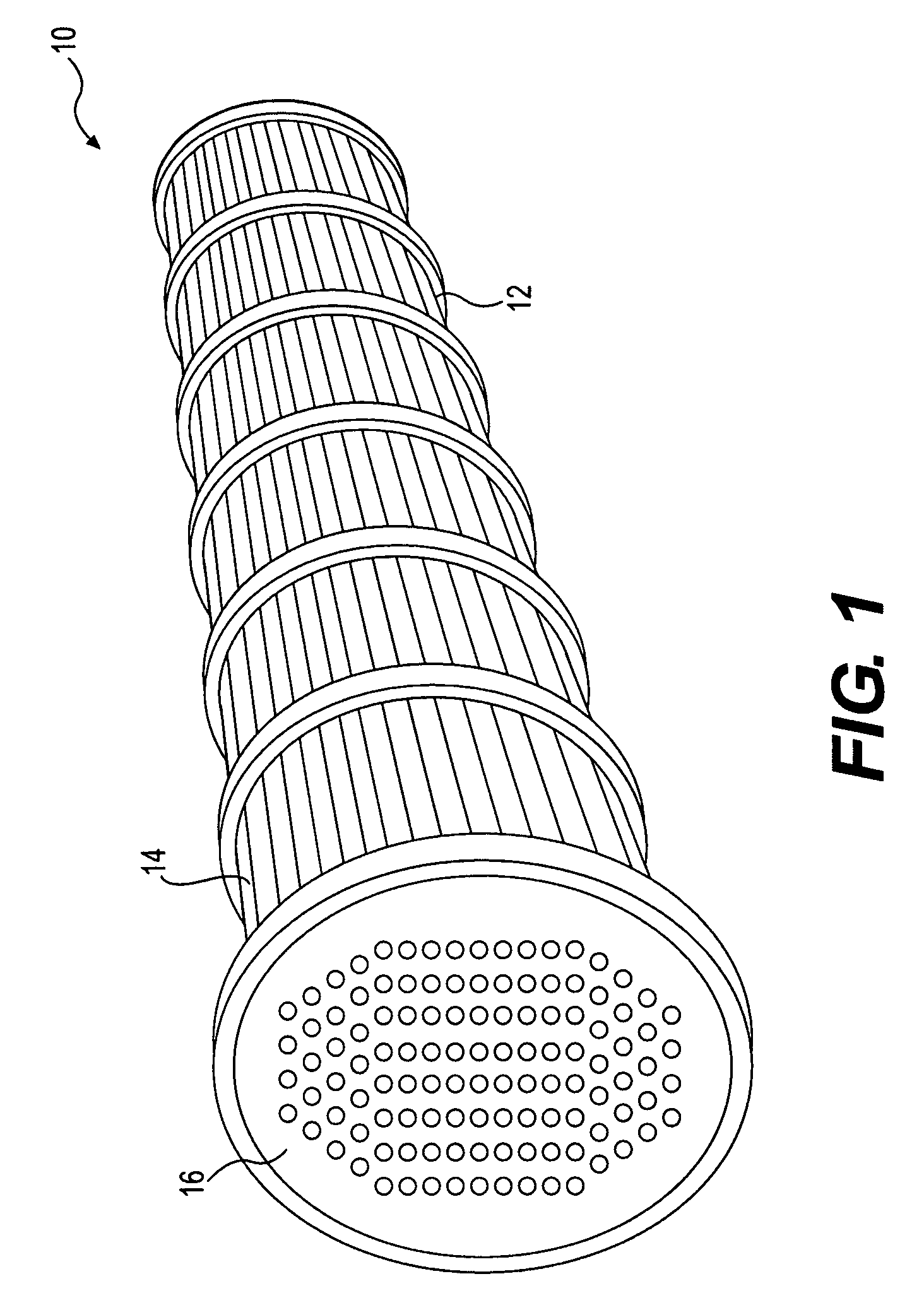
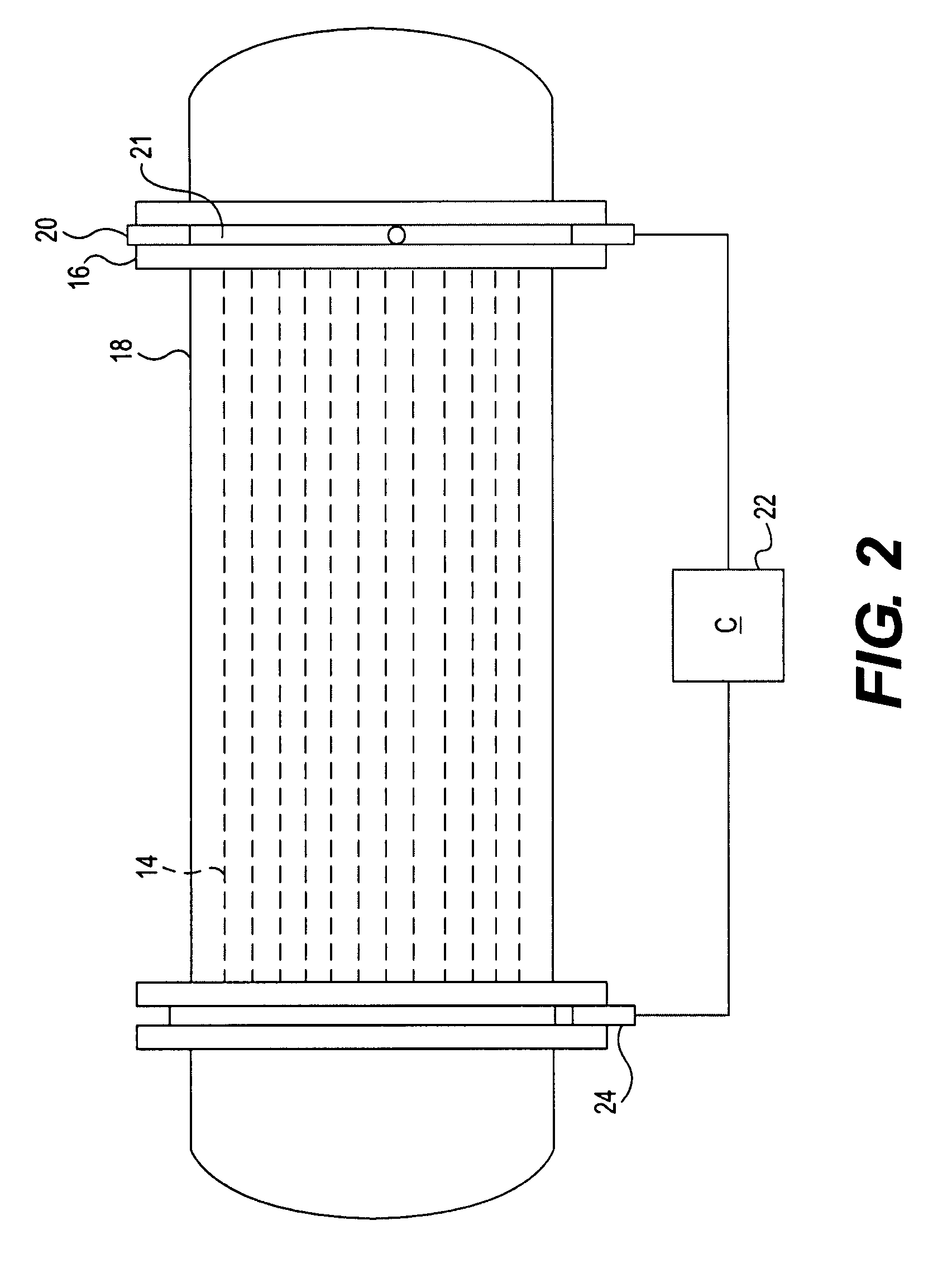
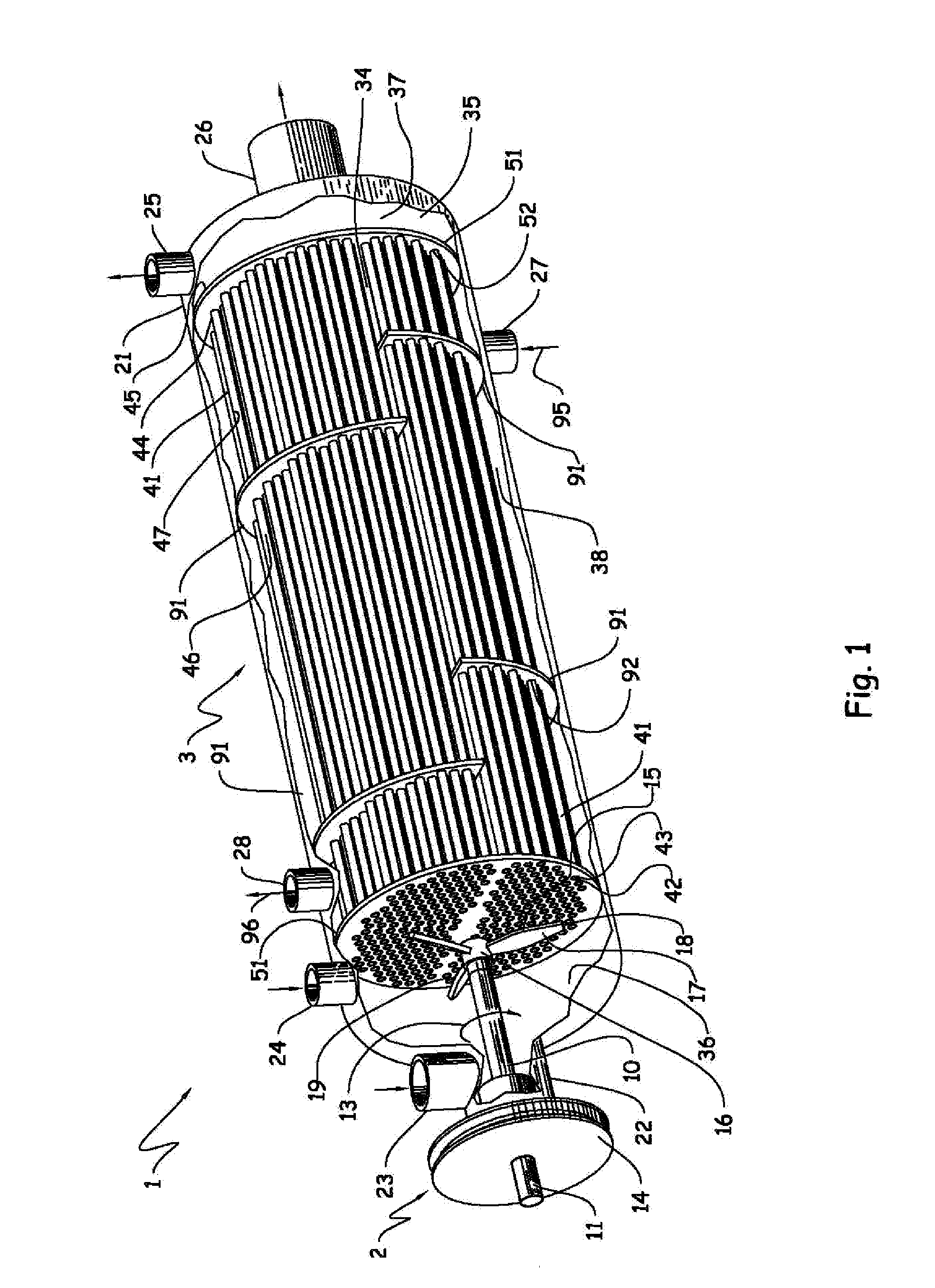
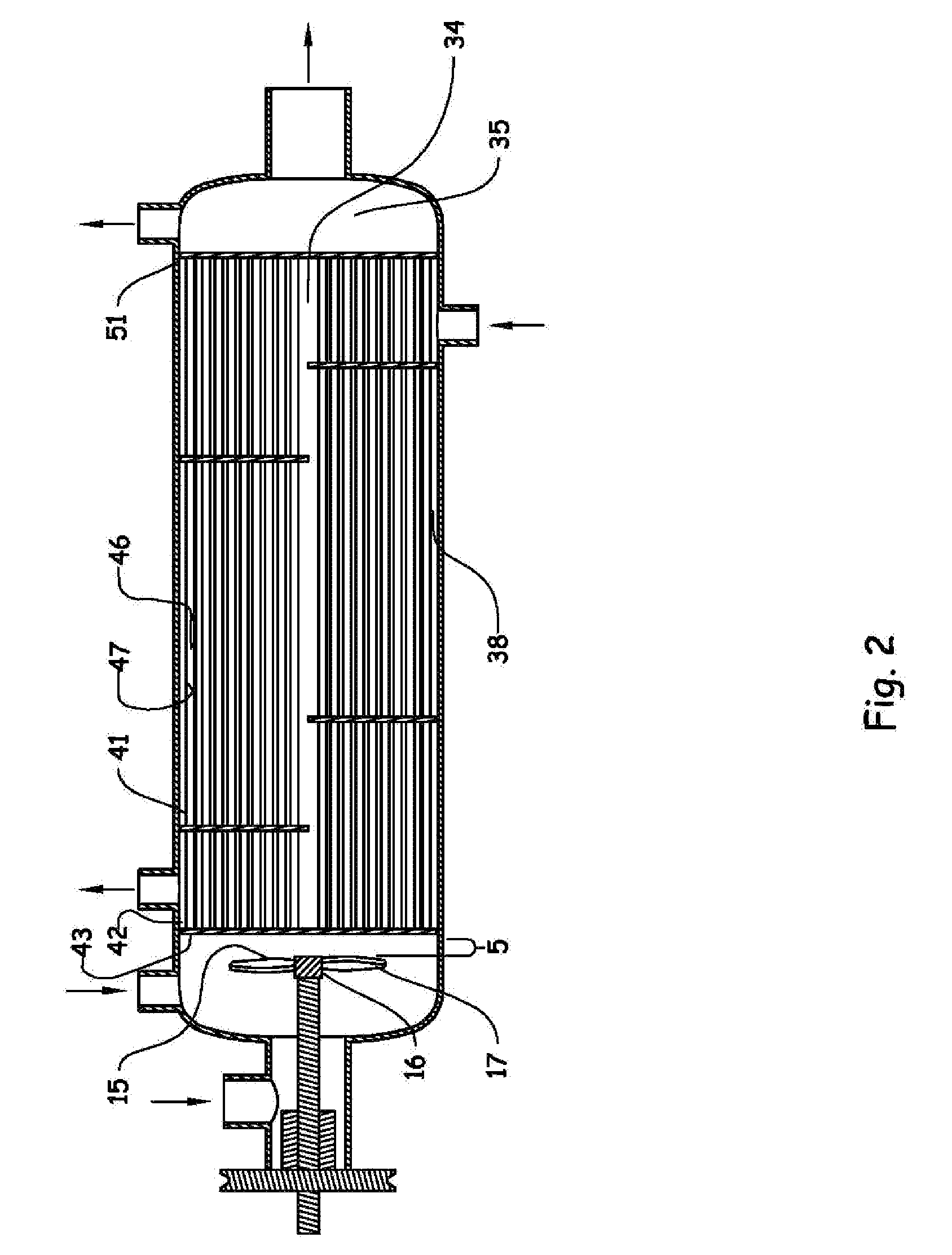
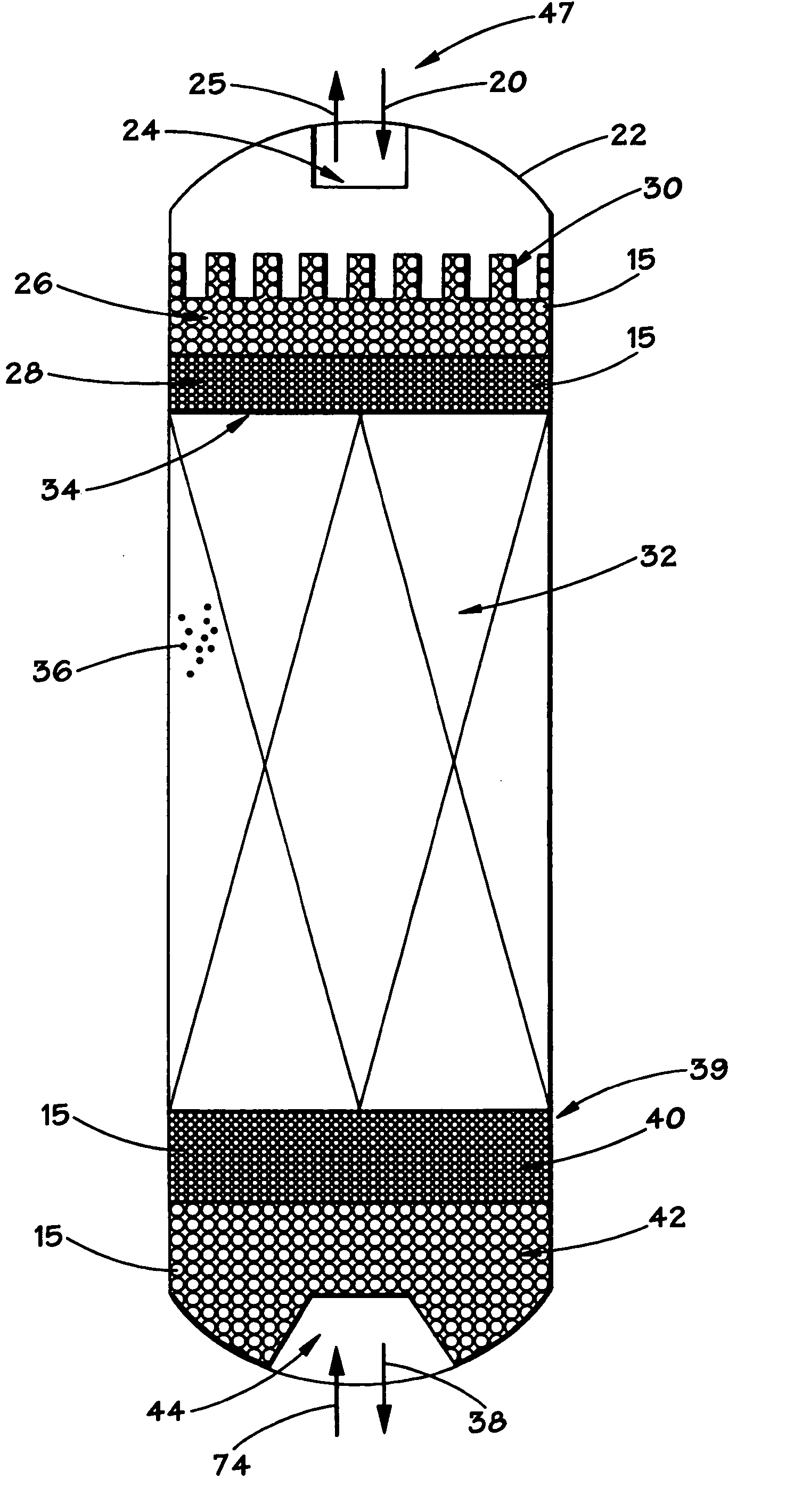
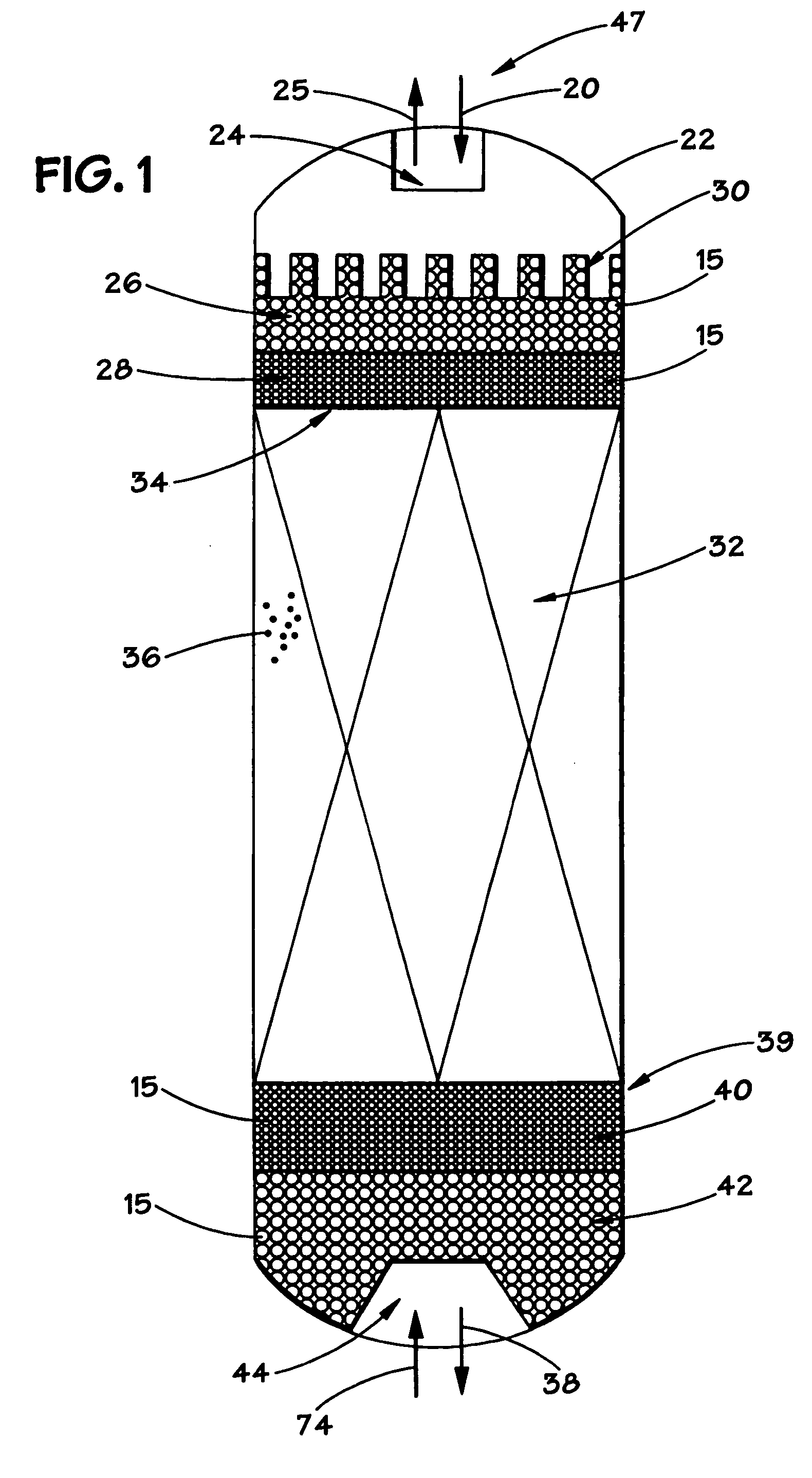
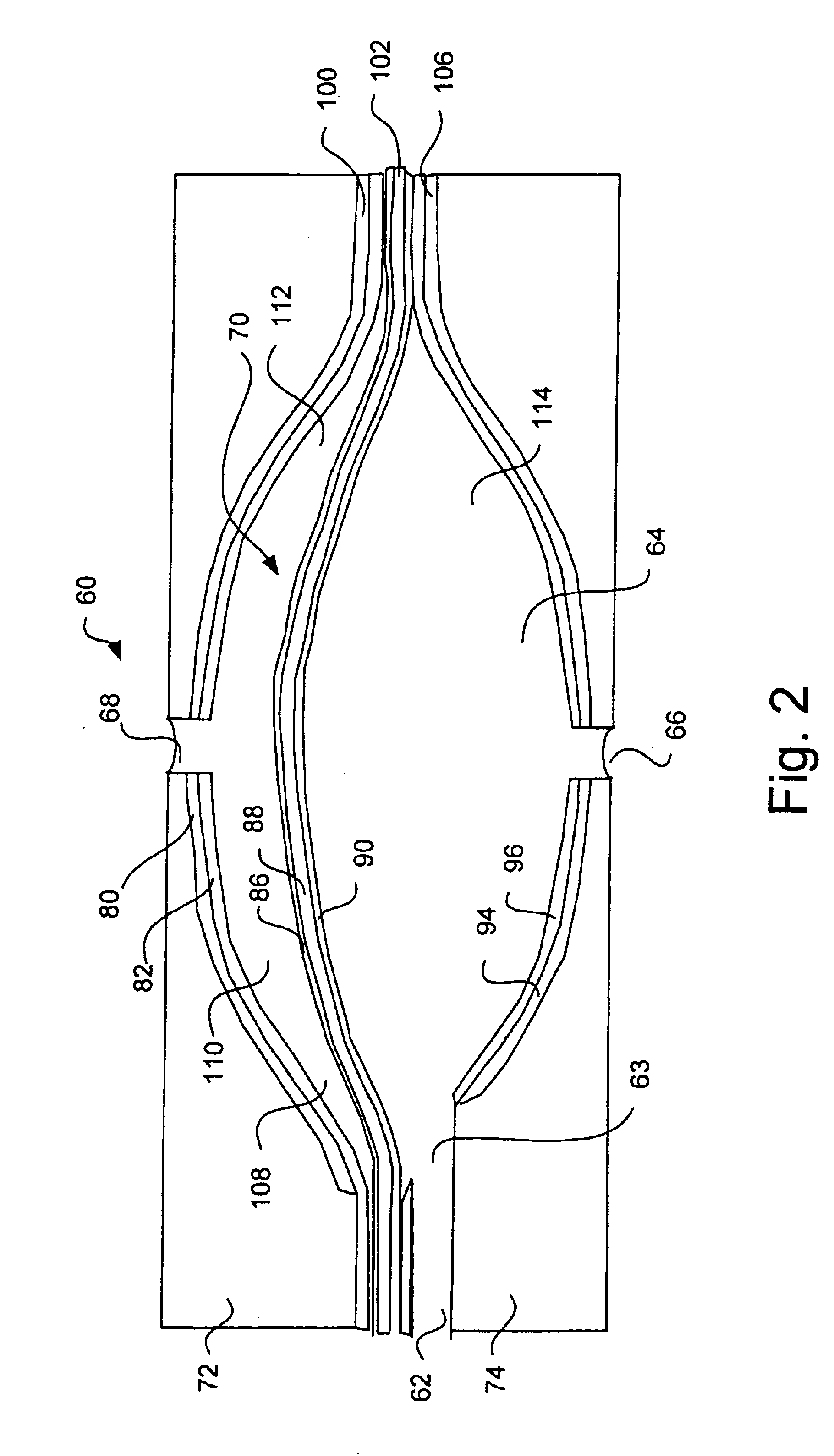
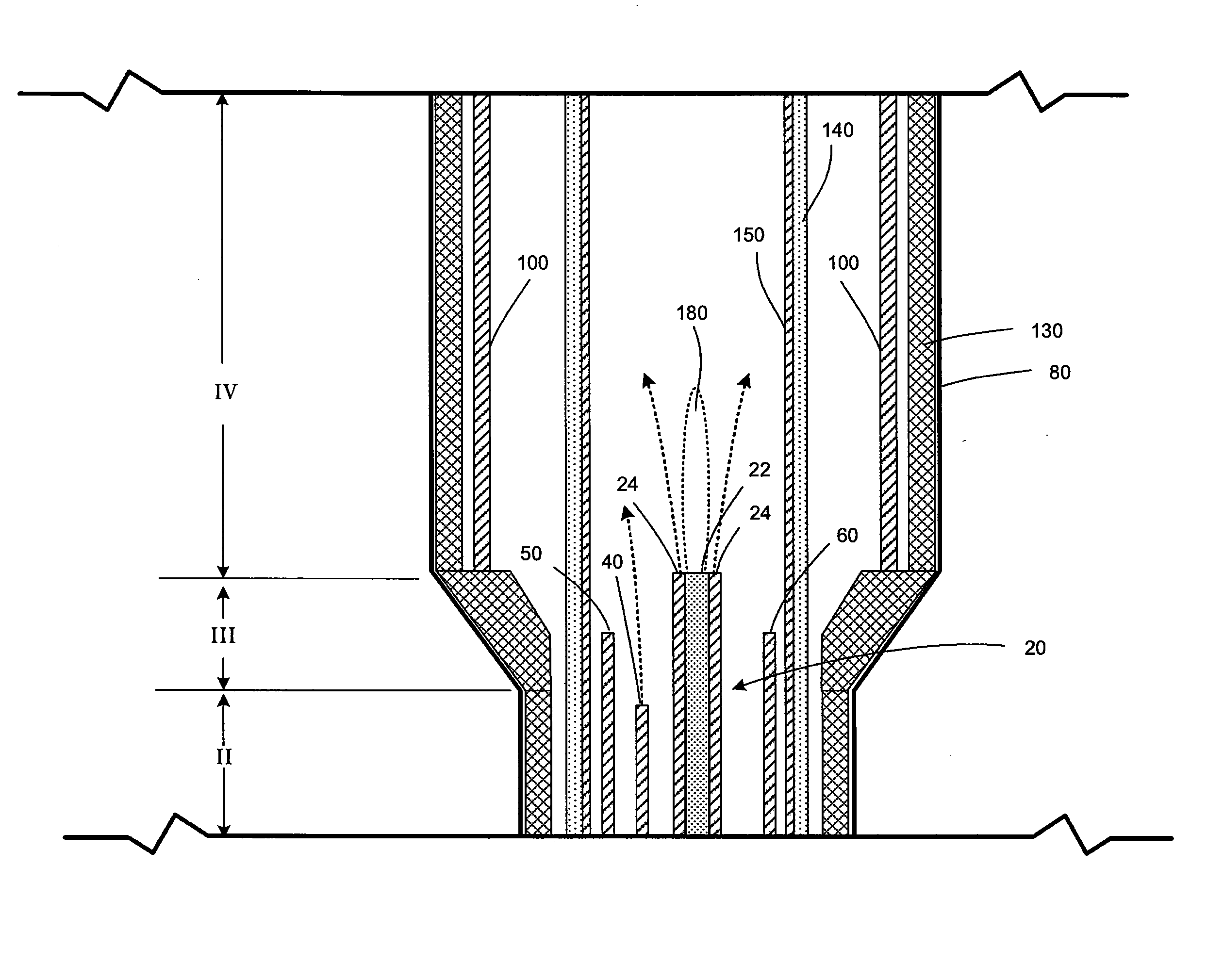
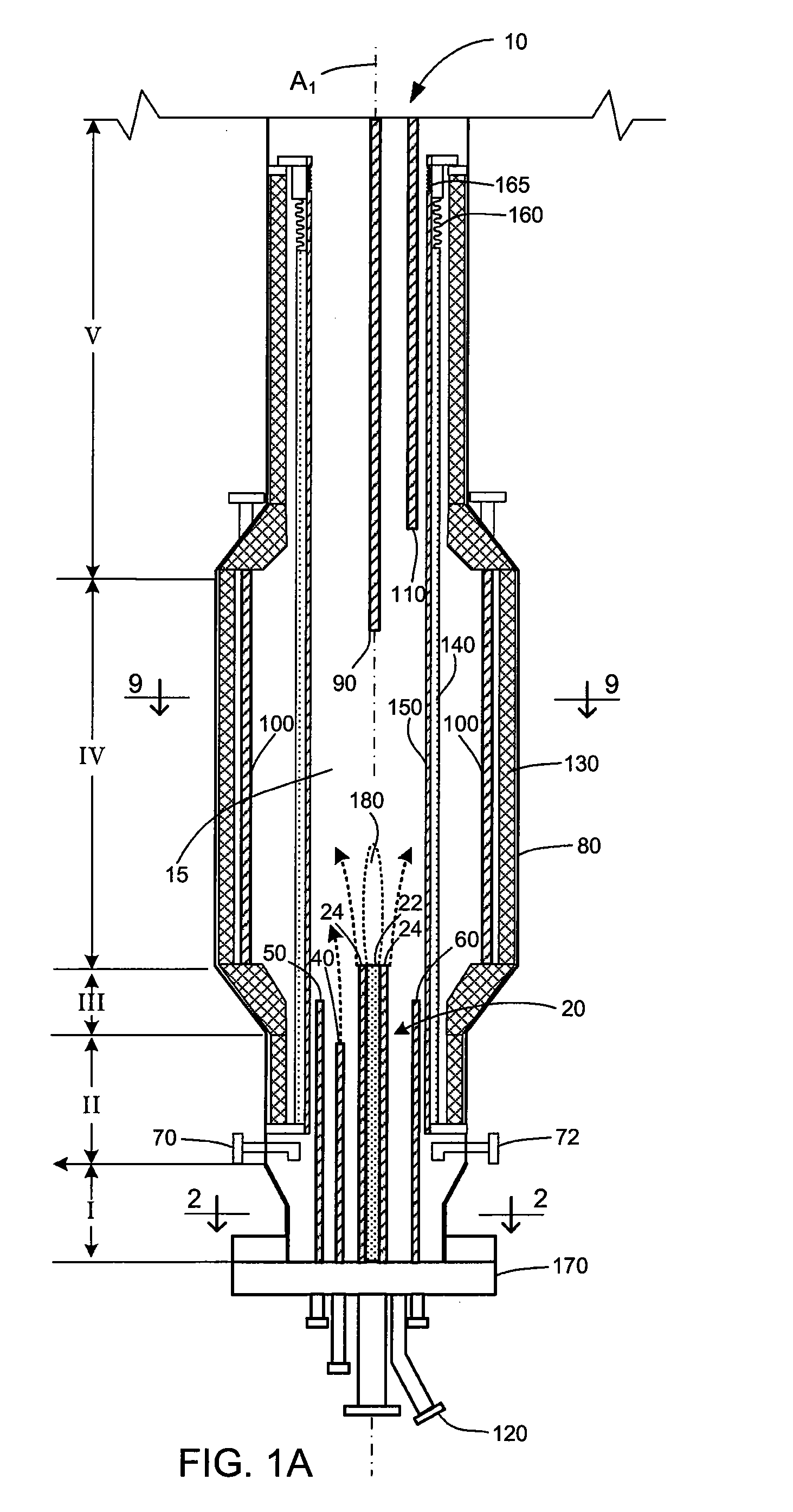
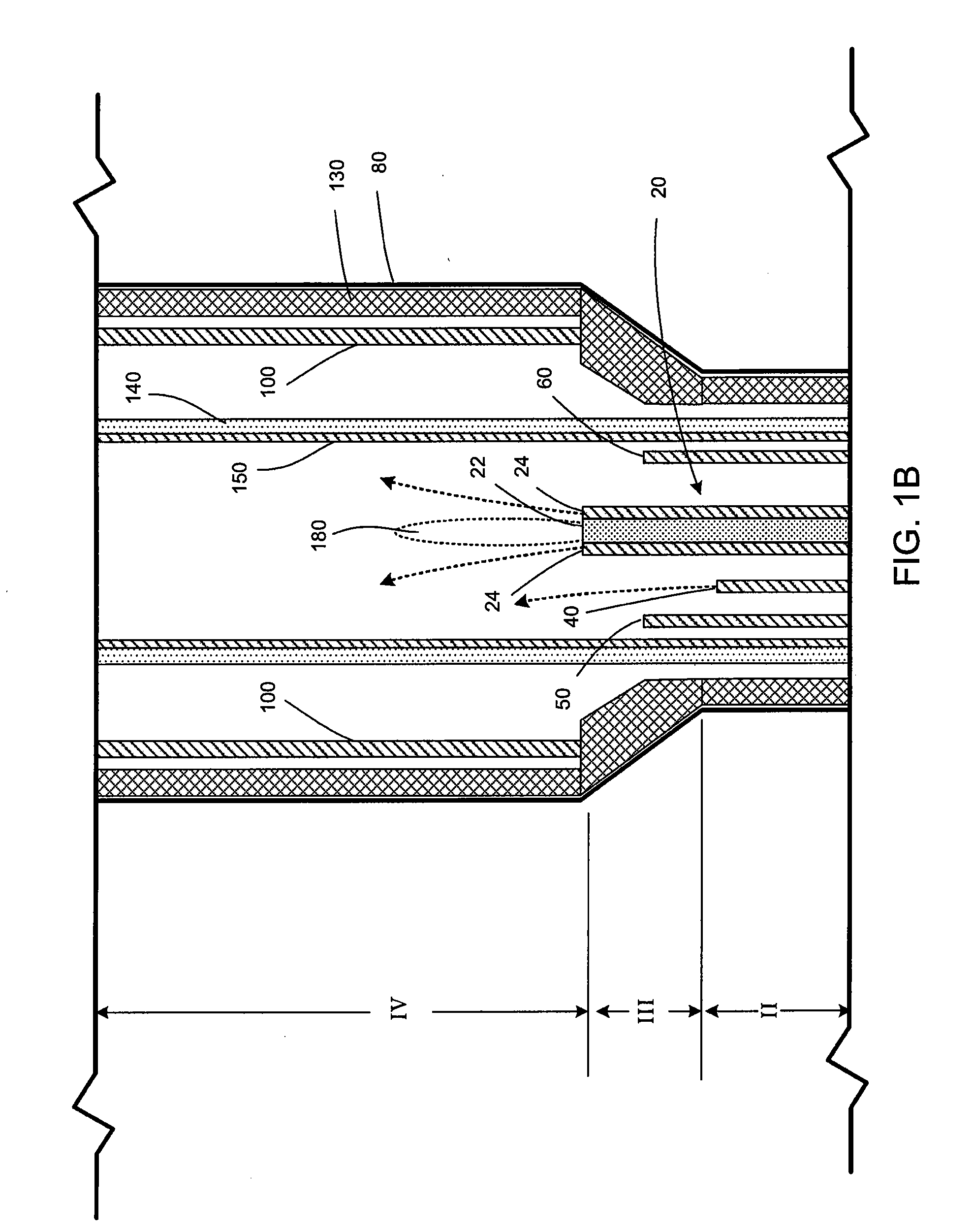
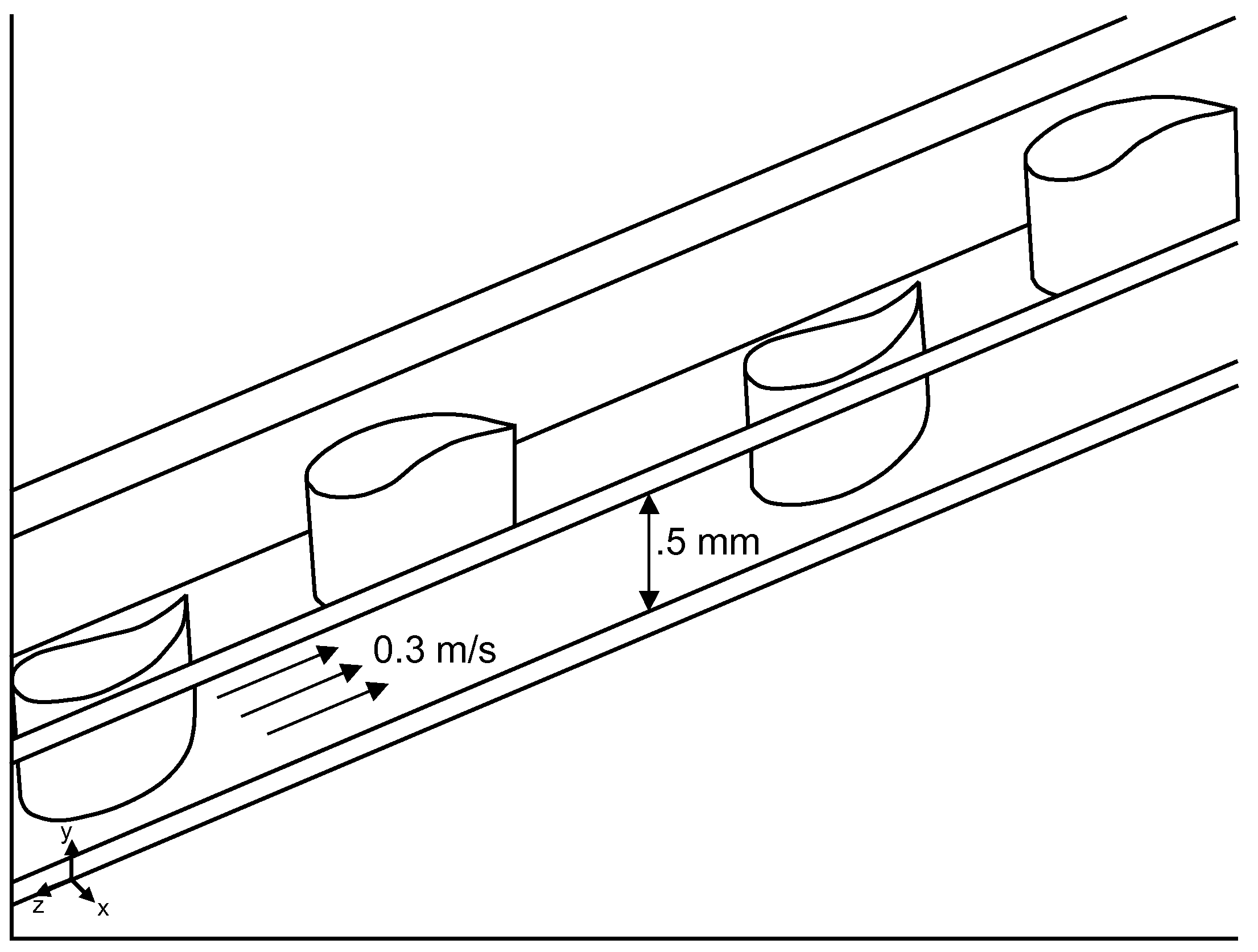
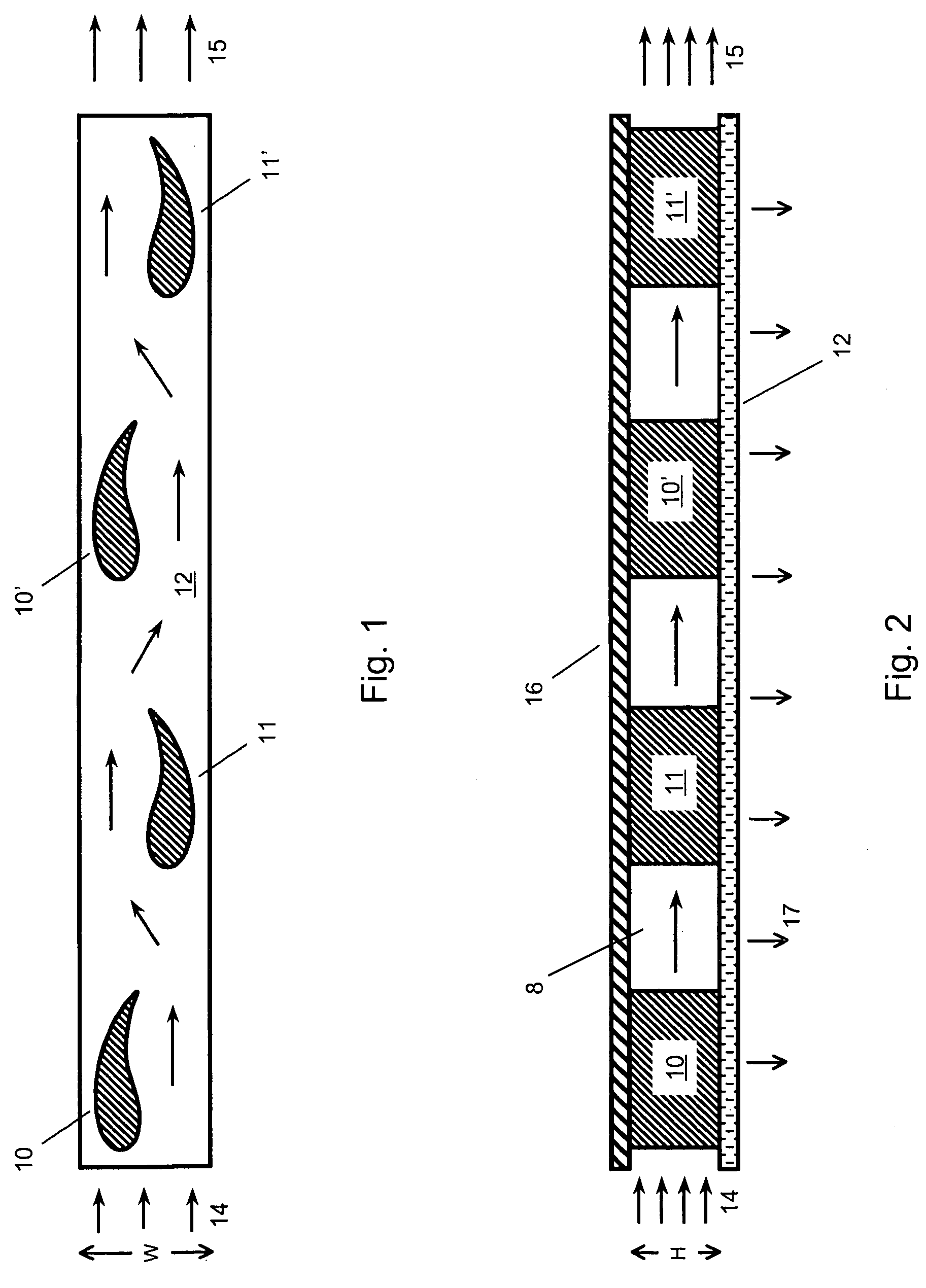
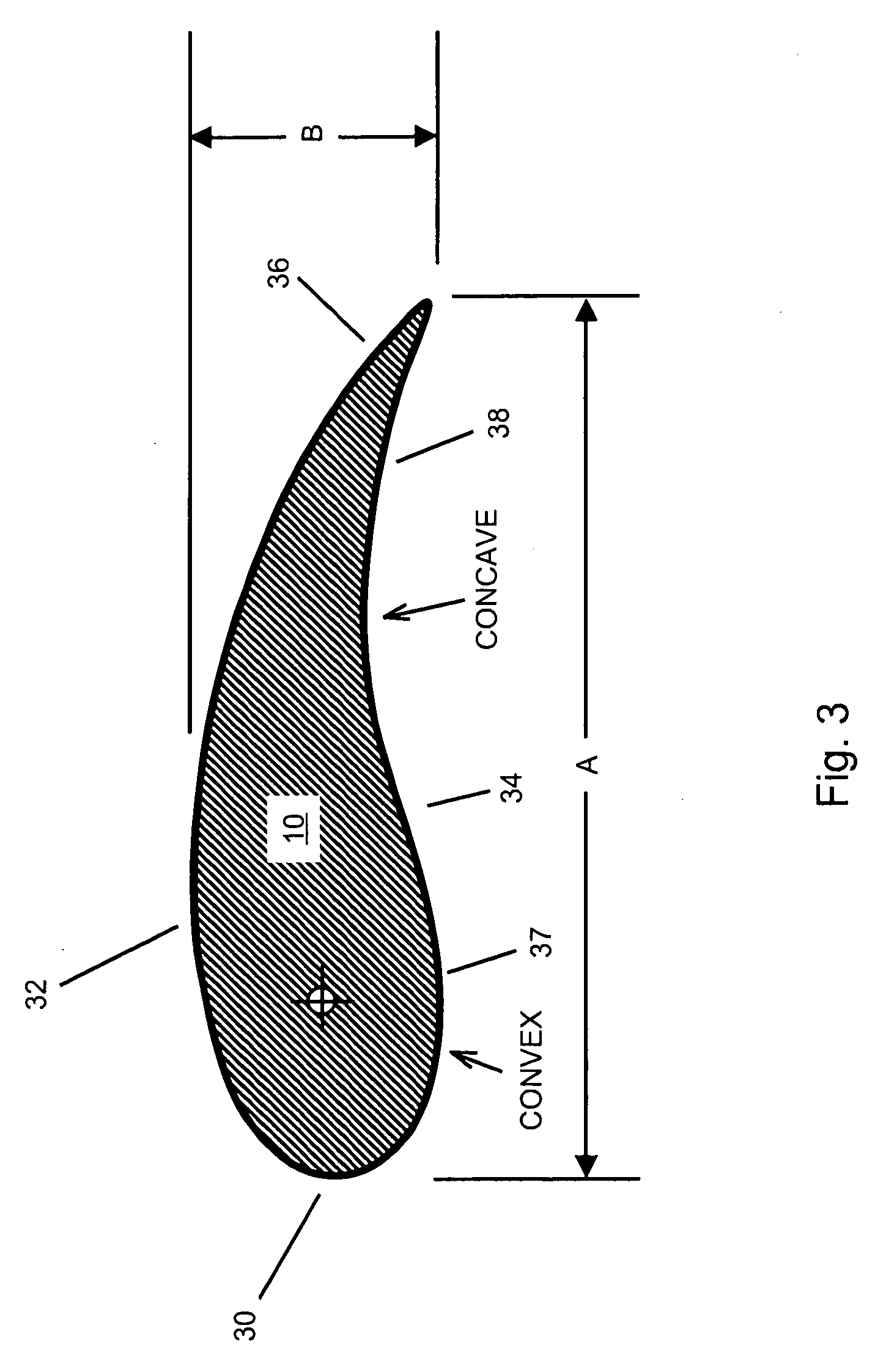
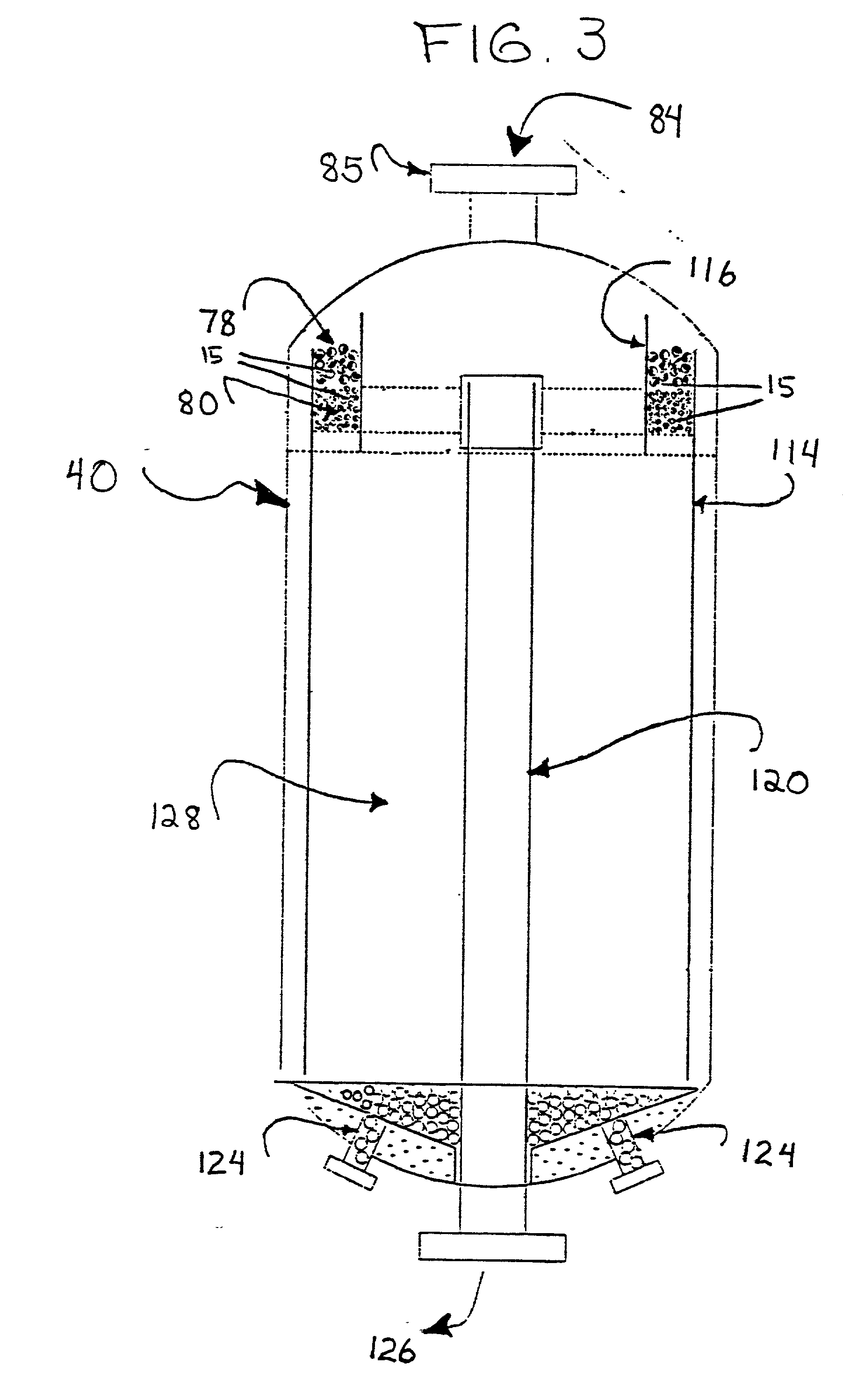
Vertical skein of hollow fiber membranes and method of maintaining clean fiber surfaces while filtering a substrate to withdraw a permeate
A vertical skein of "fibers", opposed terminal portions of which are held in headers unconfined in a modular shell, is aerated with a gas-distribution means which produces a mass of bubbles serving the function of a scrub-brash for the outer surfaces of the fibers. The membrane device is surprisingly effective with relatively little cleansing gas, the specific flux through the membranes reaching an essentially constant relatively high value because the vertical deployment of fibers allows bubbles to rise upwards along the outer surfaces of the fibers. Further, bubbles flowing along the outer surfaces of the fibers make the fibers surprisingly resistant to being fouled by build-up of deposits of inanimate particles or microorganisms in the substrate provided that the length of each fiber is only slightly greater than the direct center-to-center distance between opposed faces of the headers, preferably in the range from at least 0.1% to about 5% greater. For use in a large reservoir, a bank of skeins is used with a gas distributor means and each skein has fibers preferably >0.5 meter long, which together provide a surface area >10 m2. The terminal end portions of fibers in each header are kept free from fiber-to-fiber contact with a novel method of potting fibers.
Owner:ZENON TECH PARTNERSHIP
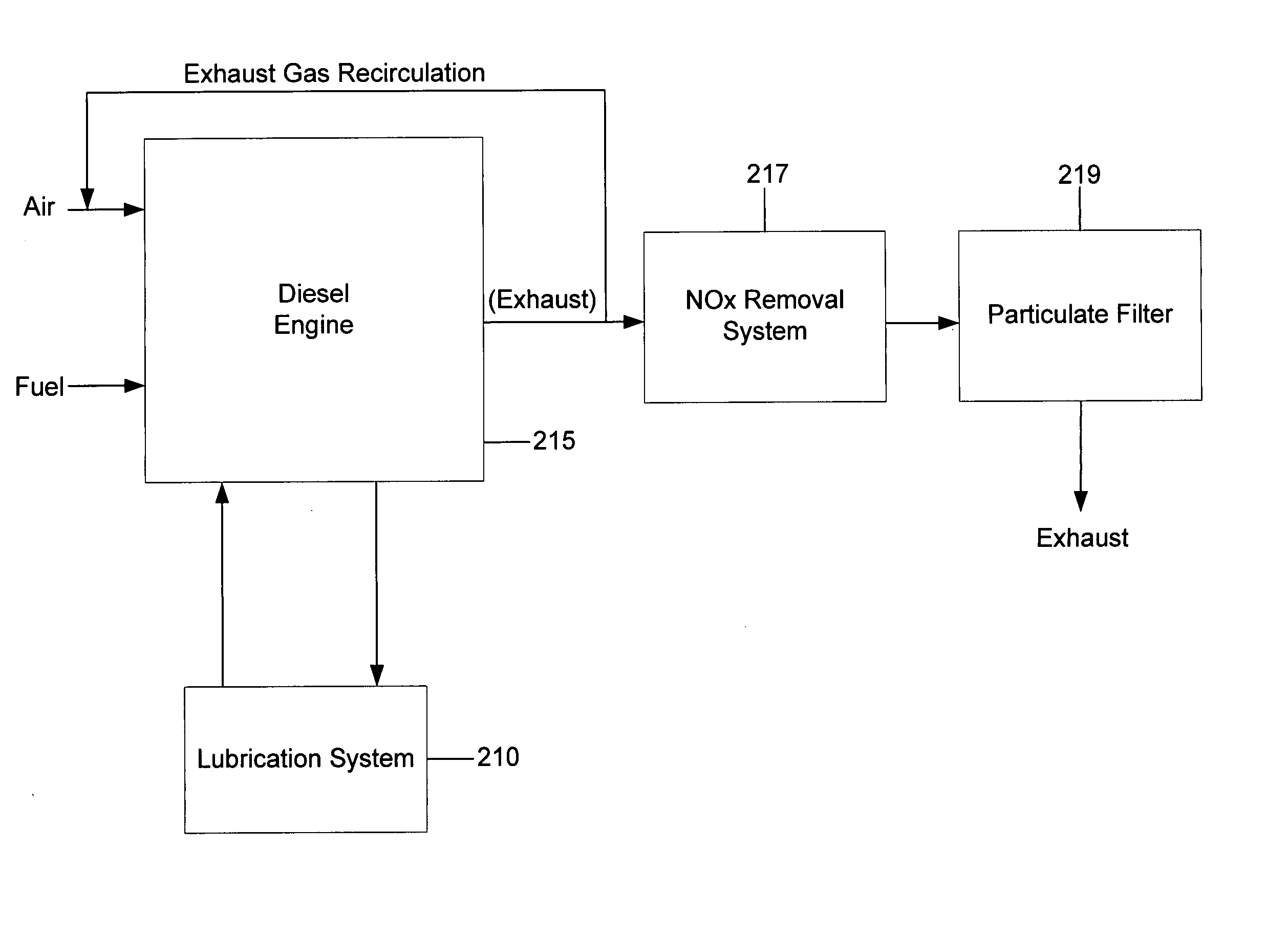
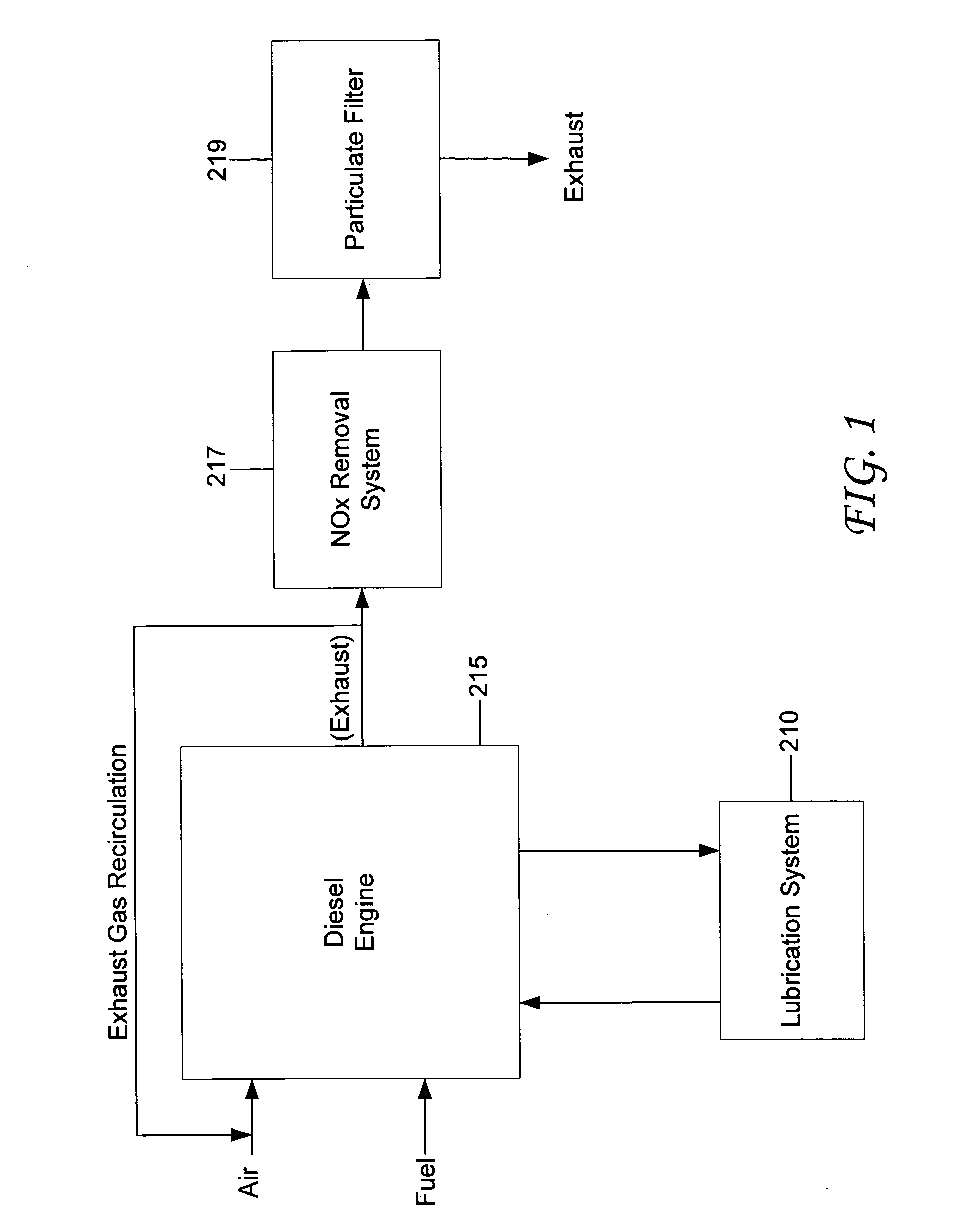
Fuel composition for a diesel engine
InactiveUS20040055209A1Meet quality requirementsImprove low temperature performanceSolid fuelsLiquid carbonaceous fuelsProcess engineeringDiesel engine
The invention is directed to a fuel composition for diesel engines. The fuel composition comprises 0.1-99% by weight of a component or a mixture of components produced from biological raw material originating from plants and / or animals and / or fish. The fuel composition comprises 0-20% of components containing oxygen. Both components are mixed with diesel components based on crude oil and / or fractions from Fischer-Tropsch process.
Owner:NESTE OIL OY
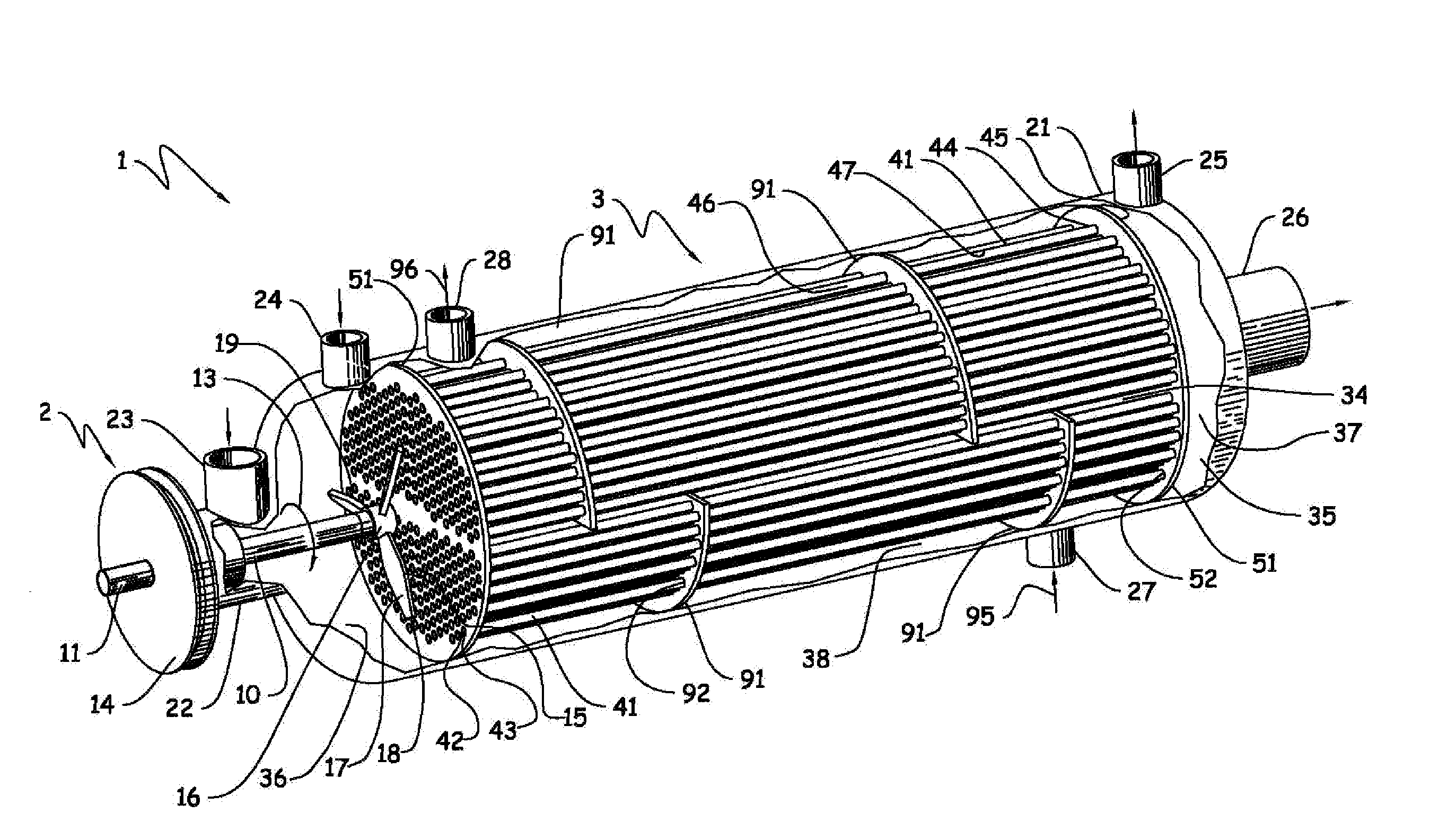
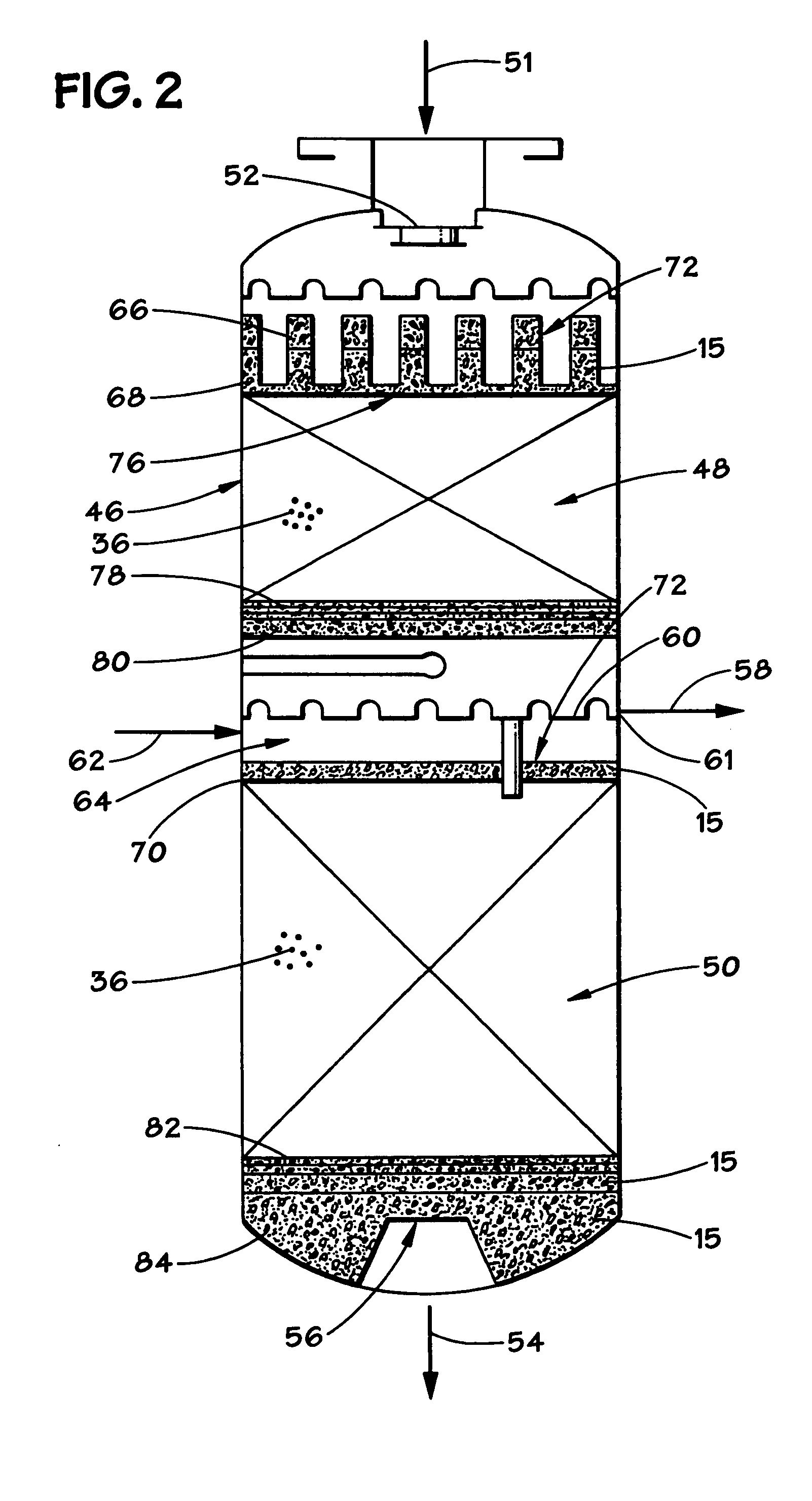
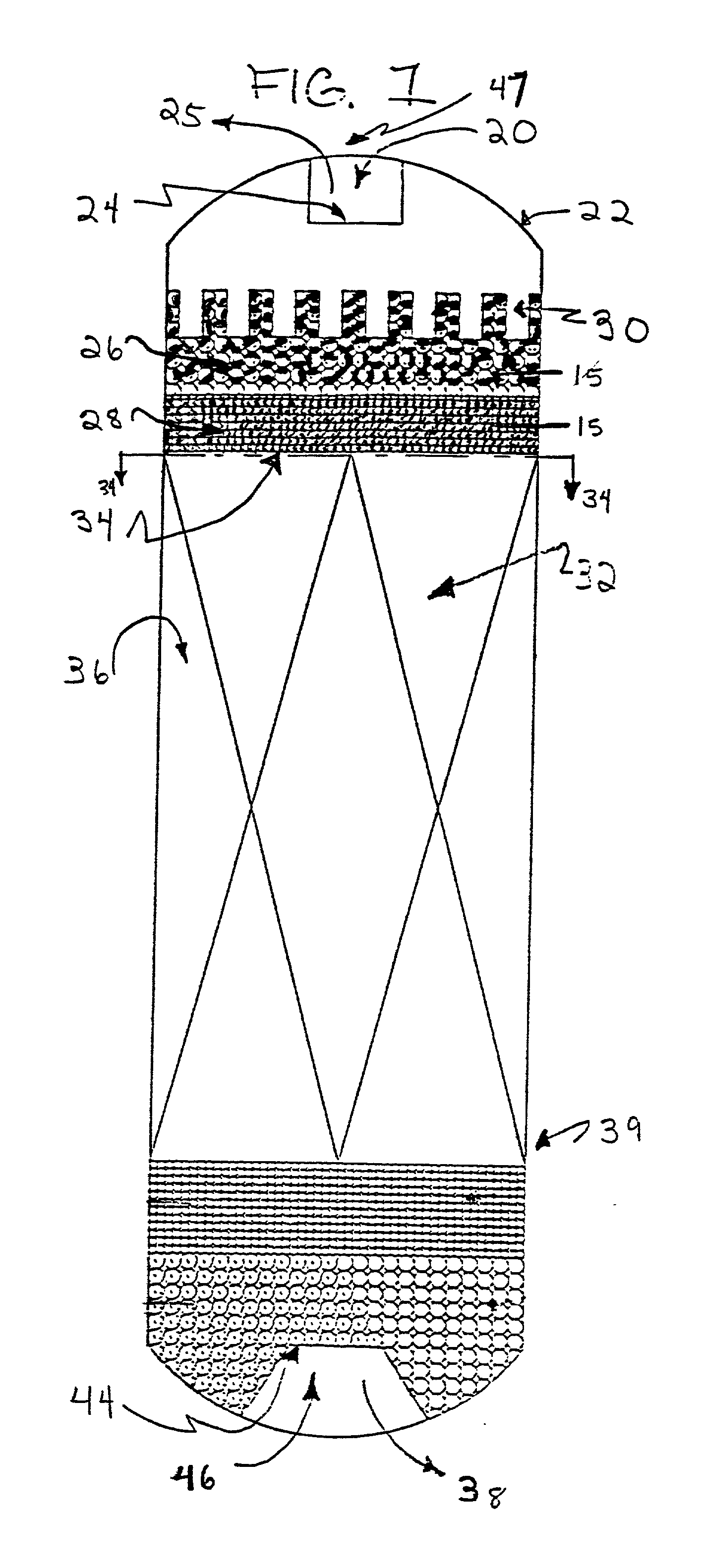
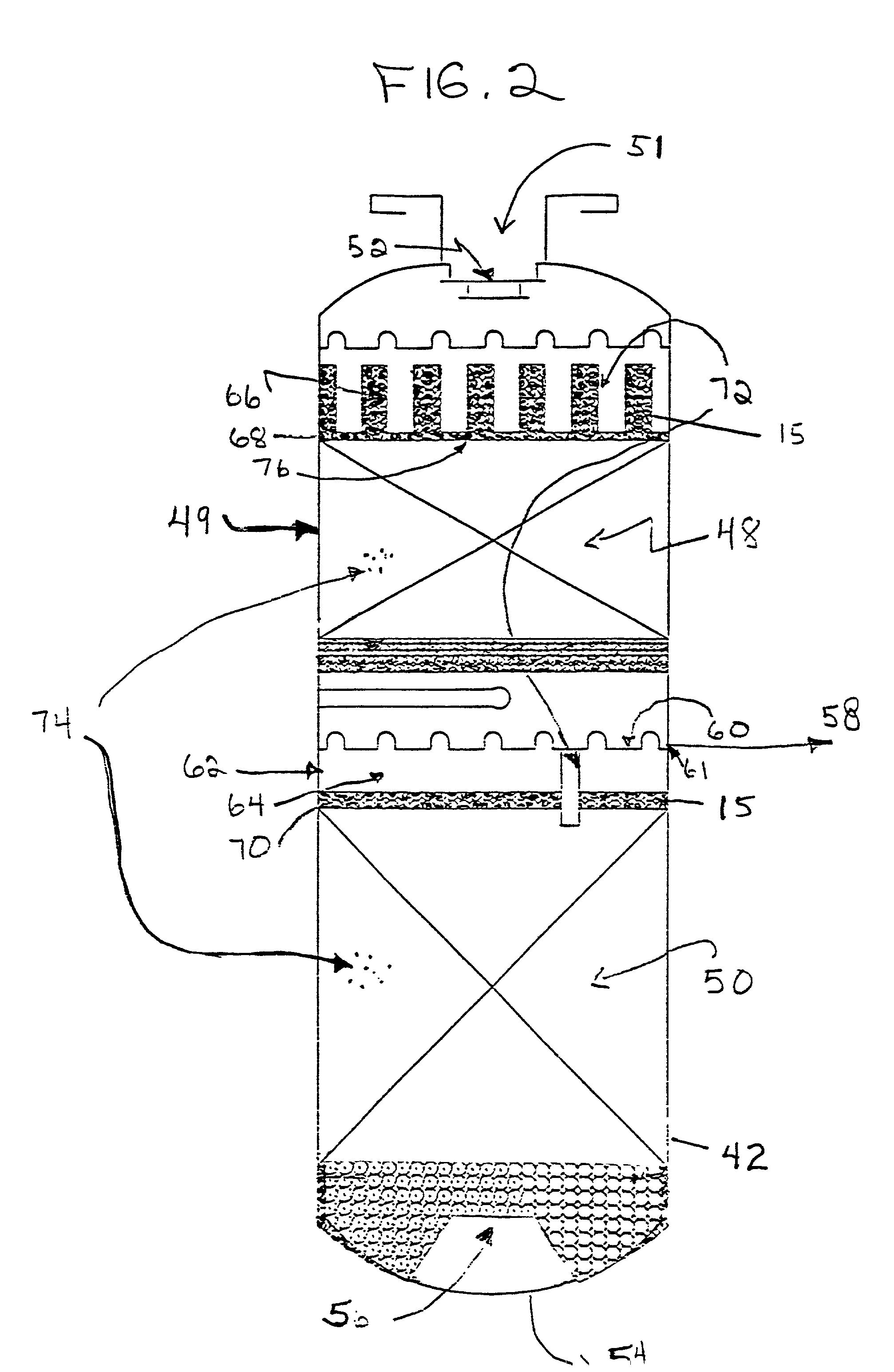
Method and apparatus for treatment of wastewater employing membrane bioreactors
InactiveUS6805806B2Accelerates the biodegradation processAvoid cloggingLiquid separation auxillary apparatusTreatment using aerobic processesAeration systemFiltration
Methods and apparatus employing membrane filtration in biodegradation processes for treatment of wastewater are described. A bioreactor system is described having an equalization system, a membrane bioreactor system, and a controller. Aeration systems for a membrane bioreactor, such as a mixer, and an ultrafilter subsystem are also described, as is a rotary membrane ultrafilter.
Owner:HYDROTREAT
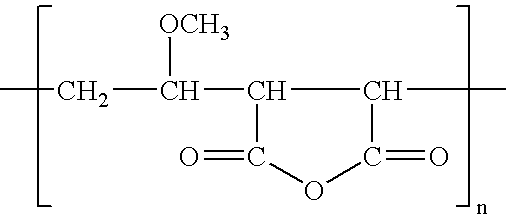
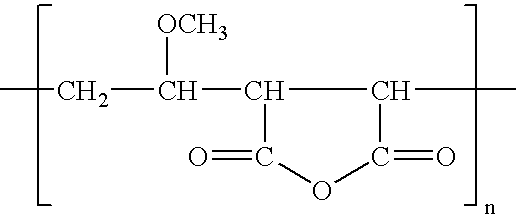
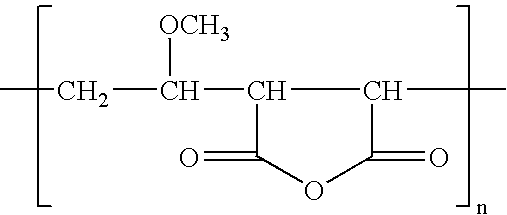
Modified membranes
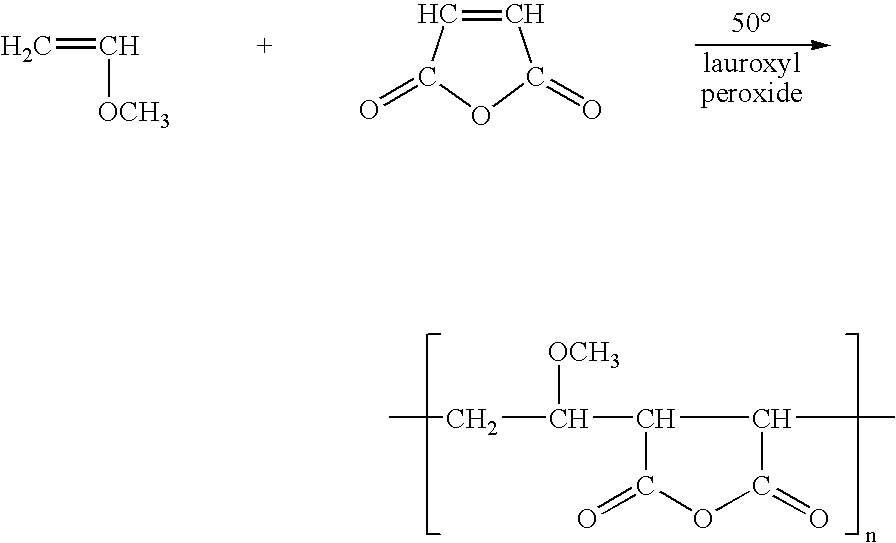
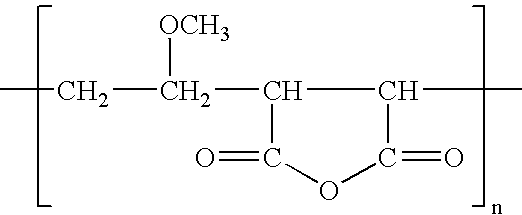
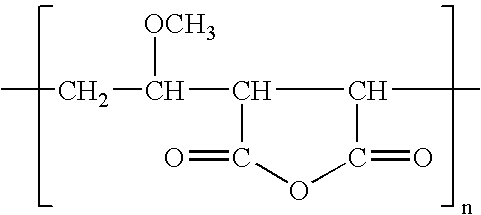
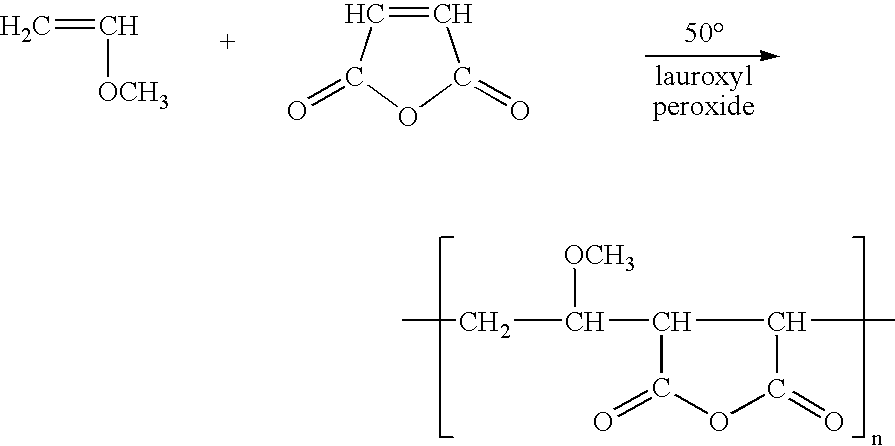
InactiveUS20050029186A1Reduce dirtEssential mechanical properties of the membranesSemi-permeable membranesMembranesVinyl etherReverse osmosis
A porous polymeric membrane formed from a blend of a polymeric membrane forming material, such as polyvinylidene fluoride or polysulfone and a polymeric reactivity modifying agent adapted to modify the surface active properties of the porous polymeric membrane. The reactivity modifying agent is preferably a linear polymeric anhydride, such as poly(alkyl vinyl ether / maleic anhydride). The surface activity modifications include modification of the hydrophilicity / hydrophobicity balance of the membrane, or hydrolysis followed by reaction with a polyamine to form a crosslinked polyamide layer. Such modified membranes have use as reverse osmosis membranes.
Owner:EVOQUA WATER TECH LLC
Modified membranes
InactiveUS6884350B2Reduce dirtEssential mechanical properties of the membranesMembranesSemi-permeable membranesVinyl etherPolyamide
A porous polymeric membrane formed from a blend of a polymeric membrane forming material, such as polyvinylidene fluoride or polysulfone and a polymeric reactivity modifying agent adapted to modify the surface active properties of the porous polymeric membrane. The reactivity modifying agent is preferably a linear polymeric anhydride, such as poly(alkyl vinyl ether / maleic anhydride). The surface activity modifications include modification of the hydrophilicity / hydrophobicity balance of the membrane, or hydrolysis followed by reaction with a polyamine to form a crosslinked polyamide layer. Such modified membranes have use as reverse osmosis membranes.
Owner:EVOQUA WATER TECH LLC
Liquid filtration media, filter elements and methods
ActiveUS20110198280A1Permeability efficiencyPore size efficiencyLiquid carbonaceous fuelsMembrane filtersFiberFilter media
A filter and filter media configured and arranged for placement in a fuel stream is disclosed. The filter and filter media allow for filtering of liquid fuels, such as diesel fuel. In certain embodiments the filter media includes a media fiber (such as glass) and a binder fiber (such as bicomponent) that combine to create a media structure having low solidity and relatively low compressibility, and which contain a pore structure that avoids premature fouling of the filter by fuel degradation products.
Owner:DONALDSON CO INC
Modified membranes
InactiveUS20050032982A1Reduce dirtEssential mechanical properties of the membranesSemi-permeable membranesMembranesVinyl etherReverse osmosis
A porous polymeric membrane formed from a blend of a polymeric membrane forming material, such as polyvinylidene fluoride or polysulfone and a polymeric reactivity modifying agent adapted to modify the surface active properties of the porous polymeric membrane. The reactivity modifying agent is preferably a linear polymeric anhydride, such as poly(alkyl vinyl ether / maleic anhydride). The surface activity modifications include modification of the hydrophilicity / hydrophobicity balance of the membrane, or hydrolysis followed by reaction with a polyamine to form a crosslinked polyamide layer. Such modified membranes have use as reverse osmosis membranes.
Owner:MULLER HEINZ JOACHIM
Modified membranes
InactiveUS20050029185A1Reduce dirtEssential mechanical properties of the membranesSemi-permeable membranesMembranesVinyl etherReverse osmosis
A porous polymeric membrane formed from a blend of a polymeric membrane forming material, such as polyvinylidene fluoride or polysulfone and a polymeric reactivity modifying agent adapted to modify the surface active properties of the porous polymeric membrane. The reactivity modifying agent is preferably a linear polymeric anhydride, such as poly(alkyl vinyl ether / maleic anhydride). The surface activity modifications include modification of the hydrophilicity / hydrophobicity balance of the membrane, or hydrolysis followed by reaction with a polyamine to form a crosslinked polyamide layer. Such modified membranes have use as reverse osmosis membranes.
Owner:EVOQUA WATER TECH LLC
Muffler for exhaust gas
InactiveUS20060102420A1Easy constructionReduce weightSilencing apparatusMachines/enginesEngineeringMuffler
Owner:ANDREAS STIHL AG & CO KG
Filtration and flow distribution method for chemical reactors
InactiveUS6258900B1Reduce turbulenceHigh trafficCatalytic naphtha reformingMembrane filtersChemical reactorFiltration
Owner:CRYSTAPHASE PRODS
Reduction of fouling in heat exchangers
InactiveUS20080073063A1Reduce amountCost savingCorrosion preventionVibration cleaningCorrosionPetroleum
A method for reducing the formation of deposits on the inner walls of a tubular heat exchanger through which a petroleum-based liquid is flowing comprises applying one of fluid pressure pulsations to the liquid flowing through the tubes of the exchanger and vibration to the heat exchanger to effect a reduction of the viscous boundary layer adjacent the inner walls of the tubular heat exchange surfaces. Reduction of the viscous boundary layer at the tube walls not only reduces the incidence of fouling with its consequential beneficial effect on equipment life but it also has the desirable effect of promoting heat transfer from the tube wall to the liquid in the tubes. Fouling and corrosion are further reduced by the use of a coating on the inner wall surfaces of the exchanger tubes.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Filtration and flow distribution method for chemical reactors using reticulated ceramics with uniform pore distributions
InactiveUS6291603B1Reduce turbulenceEntrance losses may be reducedCatalytic naphtha reformingMembrane filtersPore distributionFiltration
Owner:CRYSTAPHASE PRODS
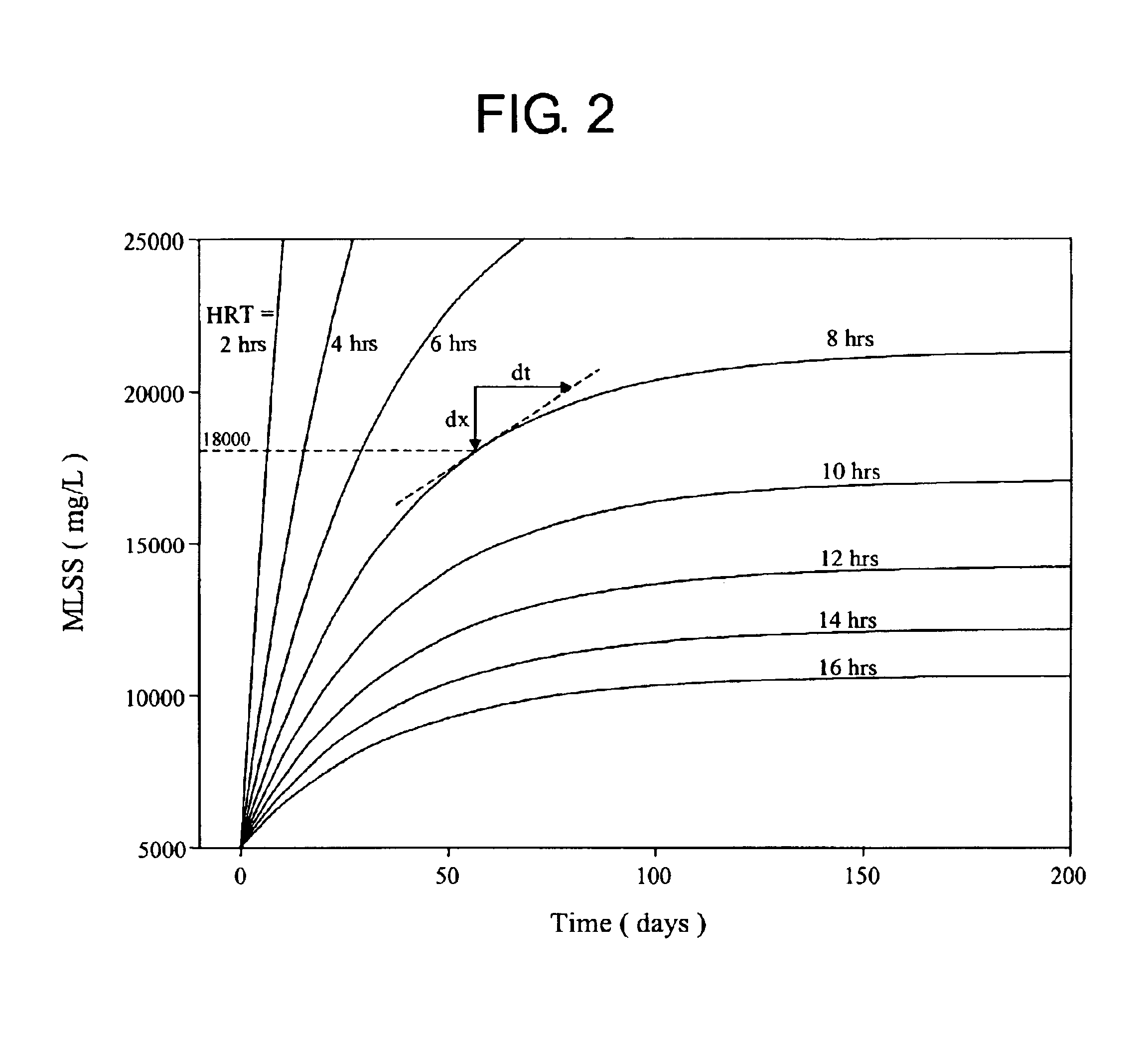
Method of using water soluble polymers in a membrane biological reactor
InactiveUS6926832B2Amount of timeLower cost of capitalMembranesTreatment using aerobic processesMembrane foulingWater soluble
A method of conditioning mixed liquor in a membrane biological reactor comprising adding to the mixed liquor an effective coagulating and flocculating amount of one or more water soluble cationic, amphoteric or zwitterionic polymers, or combination thereof and methods of reducing membrane fouling, enhancing membrane flux and reducing sludge production.
Owner:ECOLAB USA INC
Optical Communication Systems and Methods
InactiveUS20160121009A1Facilitate communicationReduce dirtElectromagnetic transmission optical aspectsCondensersCommunications systemEngineering
A system and method to reduce fouling of a surface subjected to an aquatic environment with a light source. According to one aspect, an antifouling system including an LED for emitting UV radiation, one or more mounts for directing emitted UV radiation toward the surface, and control circuitry for driving the LED disposed in a watertight housing. According to another aspect, an antifouling system which employs a fluorescent lamp disposed within a pressure vessel including a UV-transmissive material to allow UV light to pass through the pressure vessel and reduce bio-fouling of any surface.
Owner:WOODS HOLE OCEANOGRAPHIC INSTITUTION
Composite polyamide membrane with branched poly(alkylene oxide) modified surface
InactiveUS20090220690A1Improve stabilityImproved reduced fouling composite membranesMembranesGeneral water supply conservationHydrogenEnd-group
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Methods for making membranes based on anodic aluminum oxide structures
InactiveUS20100219079A1Reduce to practiceDecrease foulingAnodisationMembranesChemistryPorous anodic aluminum oxide
Membranes including anodic aluminum oxide structures that are adapted for separation, purification, filtration, analysis, reaction and sensing. The membranes can include a porous anodic aluminum oxide (AAO) structure having pore channels extending through the AAO structure. The membrane may also include an active layer, such as one including an active layer material and / or active layer pore channels. The active layer is intimately integrated within the AAO structure, thus enabling great robustness, reliability, resistance to mechanical stress and thermal cycling, and high selectivity. Methods for the fabrication of anodic aluminum oxide structures and membranes are also provided.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
Mitigation of in-tube fouling in heat exchangers using controlled mechanical vibration
Fouling of heat exchange surfaces is mitigated by a process in which a mechanical force is applied to a fixed heat exchanger to excite a vibration in the heat exchange surface and produce shear waves in the fluid adjacent the heat exchange surface. The mechanical force is applied by a dynamic actuator coupled to a controller to produce vibration at a controlled frequency and amplitude output that minimizes adverse effects to the heat exchange structure. The dynamic actuator may be coupled to the heat exchanger in place and operated while the heat exchanger is on line.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Tube-side sequentially pulsable-flow shell-and-tube heat exchanger appratus, system, and method
ActiveUS20100243208A1Increase heat exchange rateReduce dirtCorrosion preventionStationary tubular conduit assembliesChemical treatmentShell and tube heat exchanger
The present invention relates to a tube-side sequentially pulsable-flow, shell-and-tube heat exchanger apparatus and a chemical processing system comprising and methods of heat exchange employing the same.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
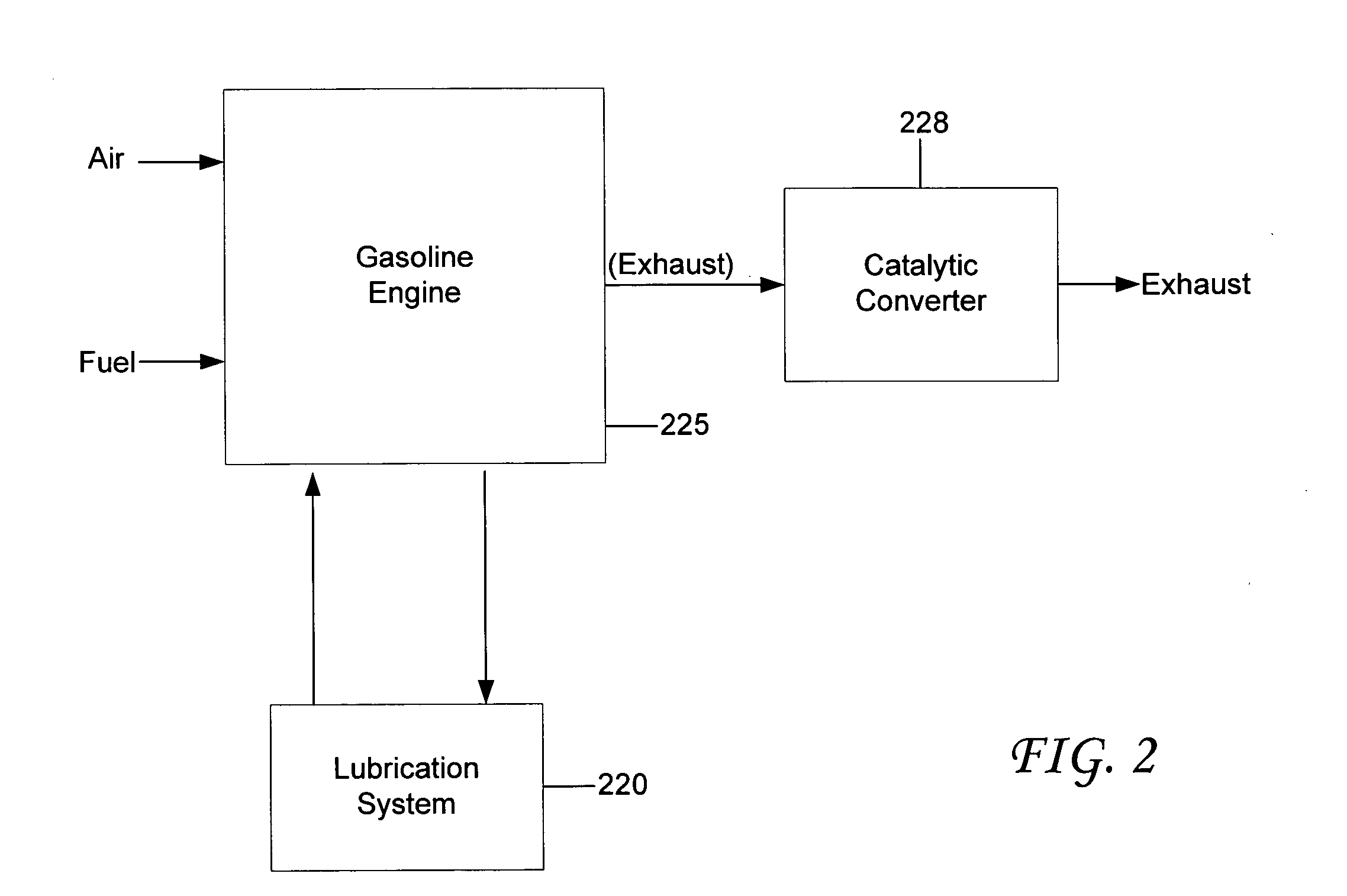
Internal combustion engine machine incorporating significant improvements in power, efficiency and emissions control
InactiveUS7104227B2Increase powerImprove efficiencyValve arrangementsLubrication of auxillariesExternal combustion engineFour-stroke engine
A two stroke cycle internal combustion engine machine that does not require lubricating oil to be mixed with its fuel, producing greater efficiency, higher power to weight ratio, cooler operating temperatures, a wider speed range, greater simplicity, and lower toxic emissions, many of the improvements also transferable to four stroke engines.
Owner:WARREN III C MADISON
Double bond hydroisomerization of butenes
ActiveUS7888541B2High selectivityIncrease productionHydrocarbon by isomerisationChemical industryHydrogenFractionation
A process is disclosed for the preferential conversion to 2-butene of a C4 stream containing 1-butene and 2-butene. The process involves mixing the C4 stream with a first hydrogen stream to form a feed stream, hydroisomerizing the feed stream in the presence of a first hydroisomerization catalyst in order to convert at least a portion of the 1-butene to 2-butene, thereby producing a hydroisomerization effluent, separating the hydroisomerization effluent in a fractionation column having an upper end and a lower end to form a 1-butene mixture at the upper end, a top effluent stream containing isobutane and isobutylene and a bottoms stream containing 2-butene, and hydroisomerizing the 1-butene mixture at the upper end of the column using a second hydroisomerization catalyst. A corresponding apparatus also is disclosed.
Owner:CHEM RES & LICENSING CO
Materials and processes for reducing combustion by-products in a lubrication system for an internal combustion engine
InactiveUS20060260874A1Minimizes engine depositEfficient emissionsMachines/enginesLubricant mounting/connectionSolubilityExternal combustion engine
A lubrication system having an oil filter modified to replace or supplement the performance of lubricant additives that may be used within an internal combustion engine to increase the performance of a lubricant. The formulation of the lubricant is changed in accordance with the chemicals placed in the oil filter. For example, when the oil filter contains a strong base, the lubricant concentration of detergent will decrease, in some cases to zero, while the dispersant concentration in the lubricant will increase. The dispersant is the ideal weak base to neutralize combustion acid at the piston ring zone, carry the resultant weak base-combustion acid complex to the strong base in the oil filter, undergo ion exchange with the strong base, immobilize the acid in the oil filter and recycle back to the piston ring zone for reuse as an acid neutralization agent. The reduction or elimination of detergent from the lubricant will reduce the fouling of the emission filter and of deposit formation on engine parts such as the piston. The oil filter may also contain an additive which is slowly released into the lubricant. For example, a ZnDDP anti-wear additive may be slowly released from the oil filter to the lubricant. Because the ZnDDP has low molecular weight alkyl groups it has limited solubility in the lubricant. The rate of release is limited by the equilibrium concentration of the additive in the lubricant. As a result, a relatively constant concentration of the additive may be maintained in the lubricant. The resultant closed system allows the oil drain intervals to be significantly extended.
Owner:LUTEK
Filtration, flow distribution and catalytic method for process streams
ActiveUS20040192862A1Increased operating lifeExtended run timeDispersed particle filtrationMembrane filtersProcess equipmentCatalytic method
A method for removing contaminants from an process stream that includes the use of reticulated material to filter the process stream. The reticulated material also facilitate process stream flow distribution in process units. The reticulated material can be packed with a void space between a substantial number of the reticulated material that can be varied to enhance filtration and flow distribution. The method of filtering also provides a method of removing contaminants leaving process equipment. The methods can be used on a variety of process streams and process equipment. The reticulated material can include ceramics, metallic materials, and chemical vapor deposition elements. The reticulated material can be of various shapes and sizes, and can also be catalytically active.
Owner:CRYSTAPHASE PRODS
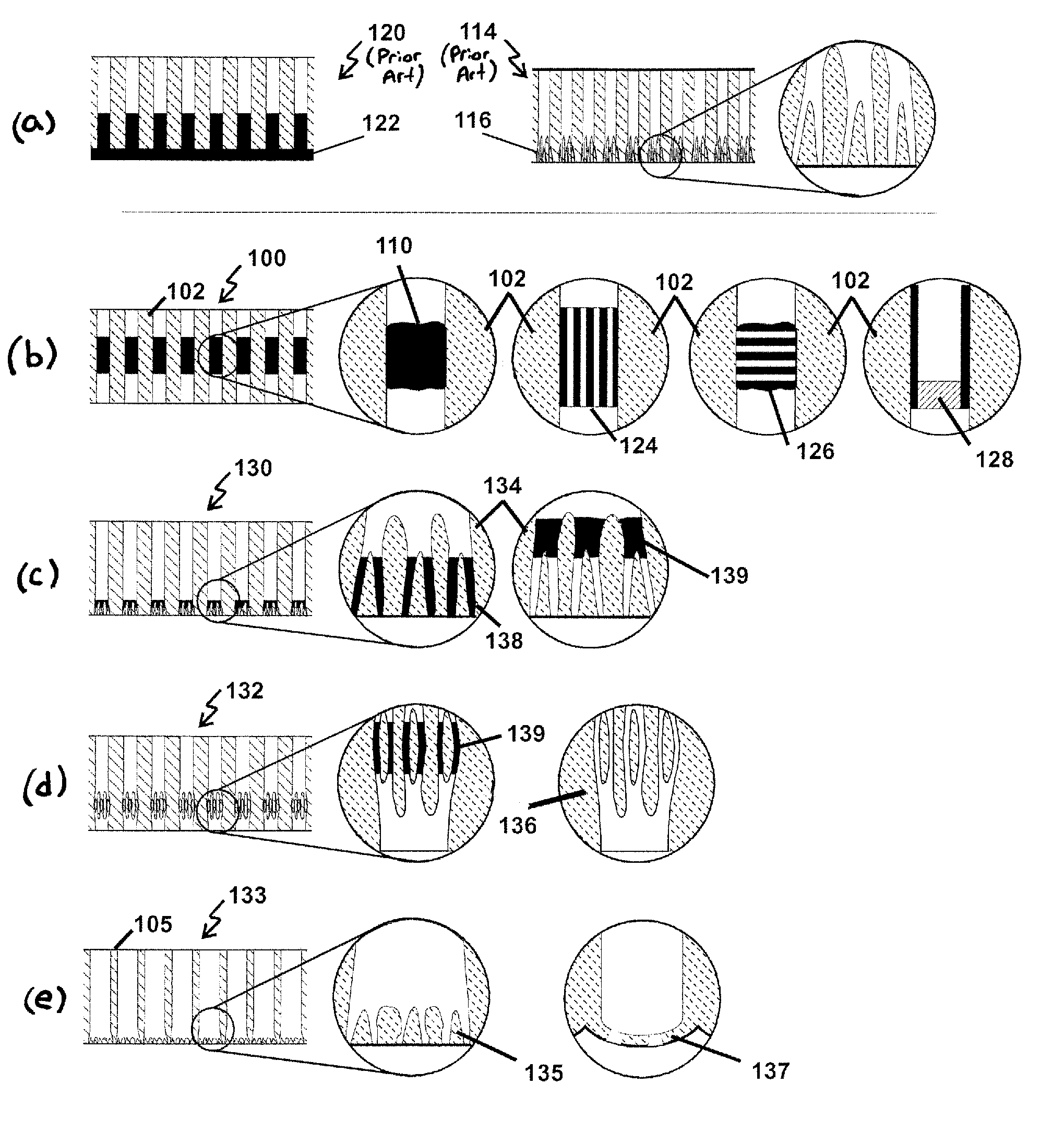
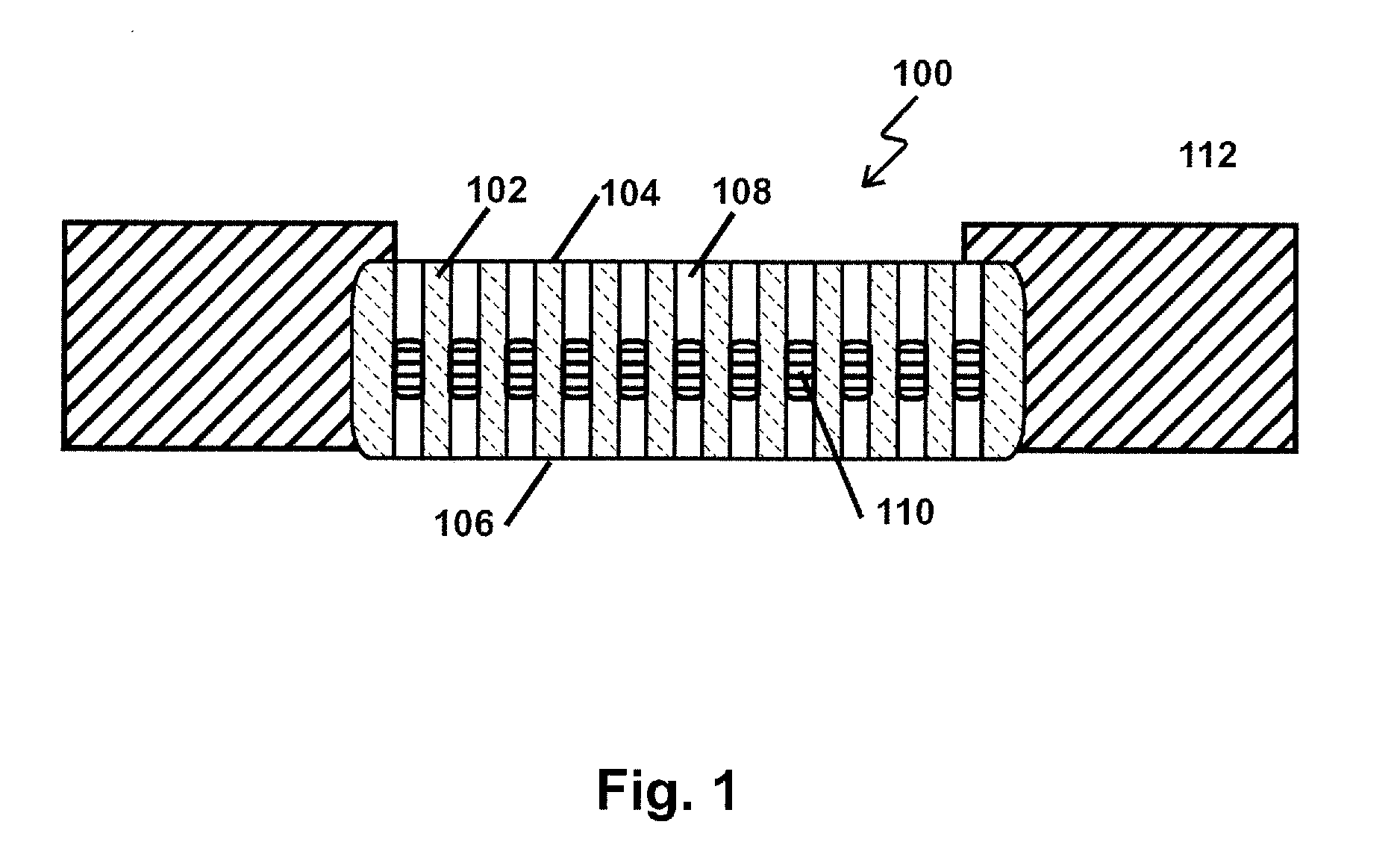
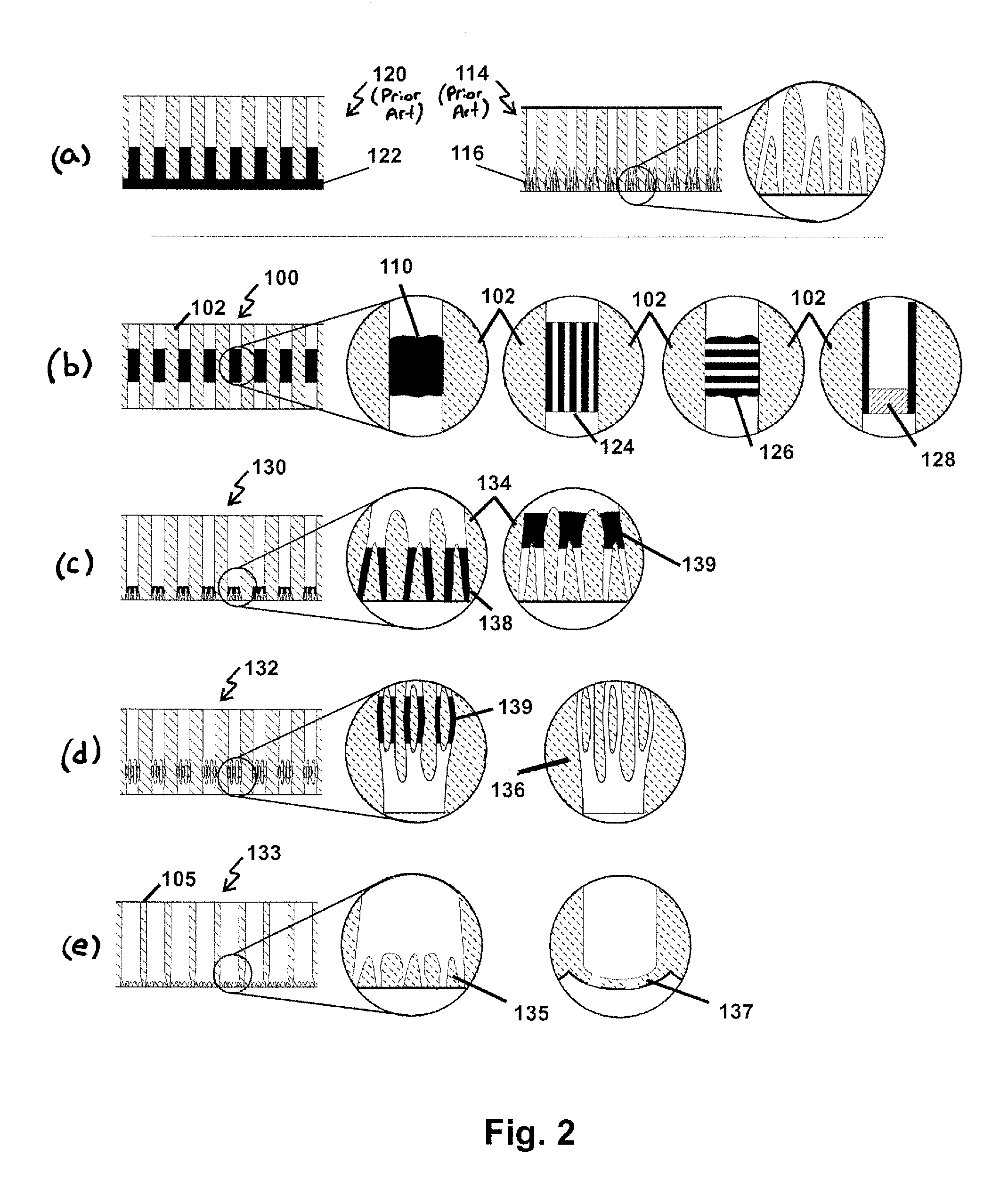
3D array integrated cells for the sampling and detection of air bound chemical and biological species
InactiveUS6889567B2Easy to mass produceEasy to detectWeather/light/corrosion resistanceWithdrawing sample devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceAnalyte
An integrated mesopump-sensor suitable for disposition in two- and three-dimensional arrays having small dimensions is disclosed. One mesopump is formed of an electrostatically attractable flexible diaphragm disposed through cavities or pumping chambers formed between two opposing electrostatically chargeable material layers. Fluid is pumped through the chambers by sequentially moving the diaphragm toward the first chargeable layer, then towards the second chargeable layer, which can pull and push the fluid through a series of chambers, and past the sensor. One group of sensors utilizes multiple and varied chemoresistive sensors which can vary in resistance differently in response to the presence of various analytes. Another group of sensors utilizes chemo-fluorescent sensors that fluoresce in the presence of particular analytes. Some mesopump-sensor systems can be manufactured using MEMS technology and can be coupled to controllers for sequencing the pumps and analyzing sensor outputs using methods including Principle Component Analysis.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
UV-oxide hybrid drying type engraving intaglio printing ink
ActiveCN101250354AAchieve dryingWell mixedInksOther printing apparatusPulp and paper industryPrinting ink
The invention relates to UV-oxidation mixing drying type incising gravure printing ink, which is prepared through firstly producing by rolling UV drying components and oxidation drying components assisting volatilization drying, penetration drying and complex drying effect, and evenly mixing according to 1%-99% proportion of UV drying component and 99%-1% oxidation drying components assisting volatilization drying, penetration drying and complex drying effect. The printing ink of the invention conducts UV drying in the process of printing, instantly realizes partial drying of printing ink to form a drying ink film, can finish oxidation drying and assisting volatilization drying, penetration drying and complex drying effect to achieve the complete drying of printing ink. The printing ink solves the technical problems that thick ink film existing in current UV drying incising gravure printing ink is incomplete, complete drying can not be realized in the natural storage process, and has the advantages of economical, energy-saving and environment-friendly.
Owner:CHINA BANKNOTE PRINTING & MINTING
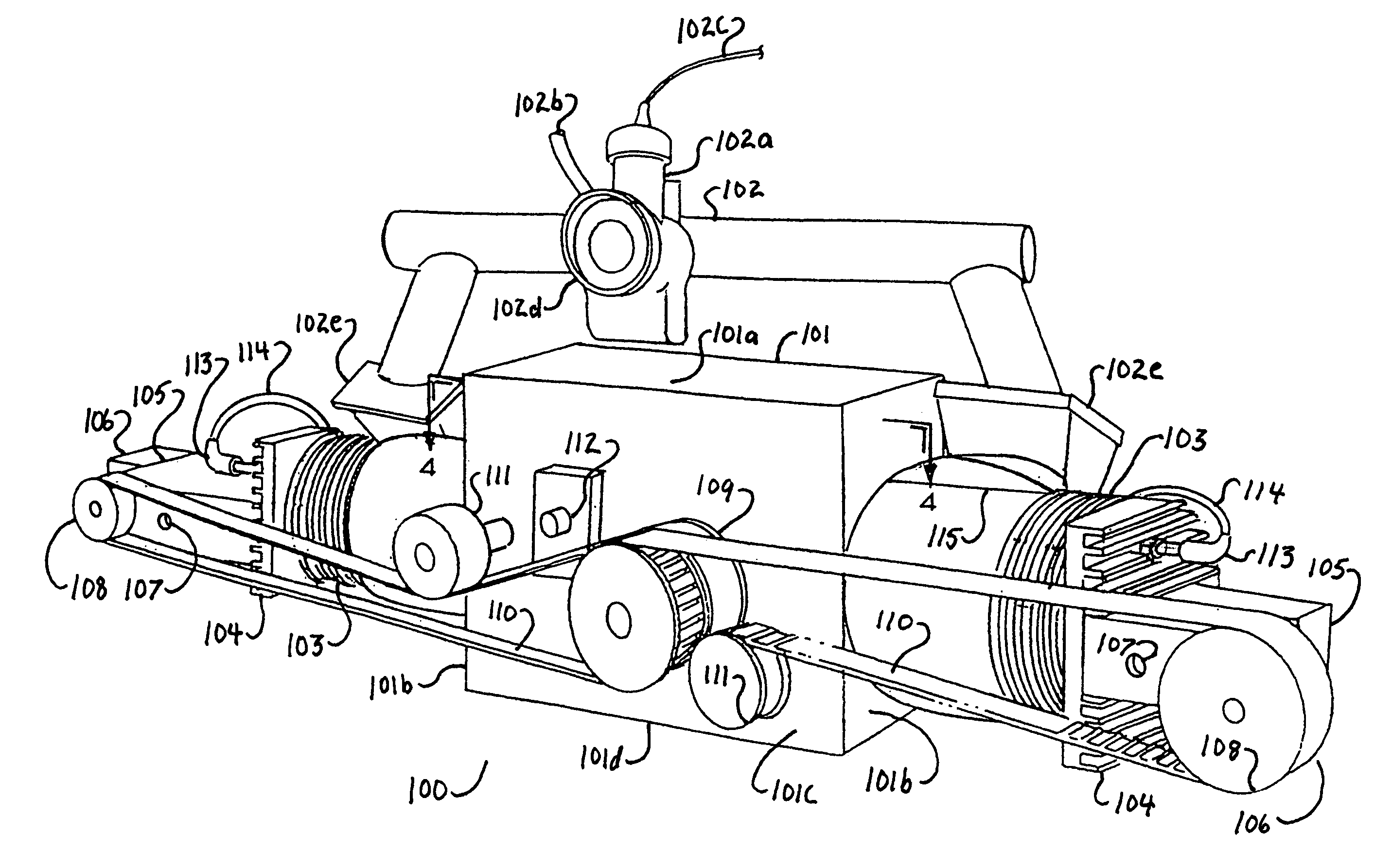
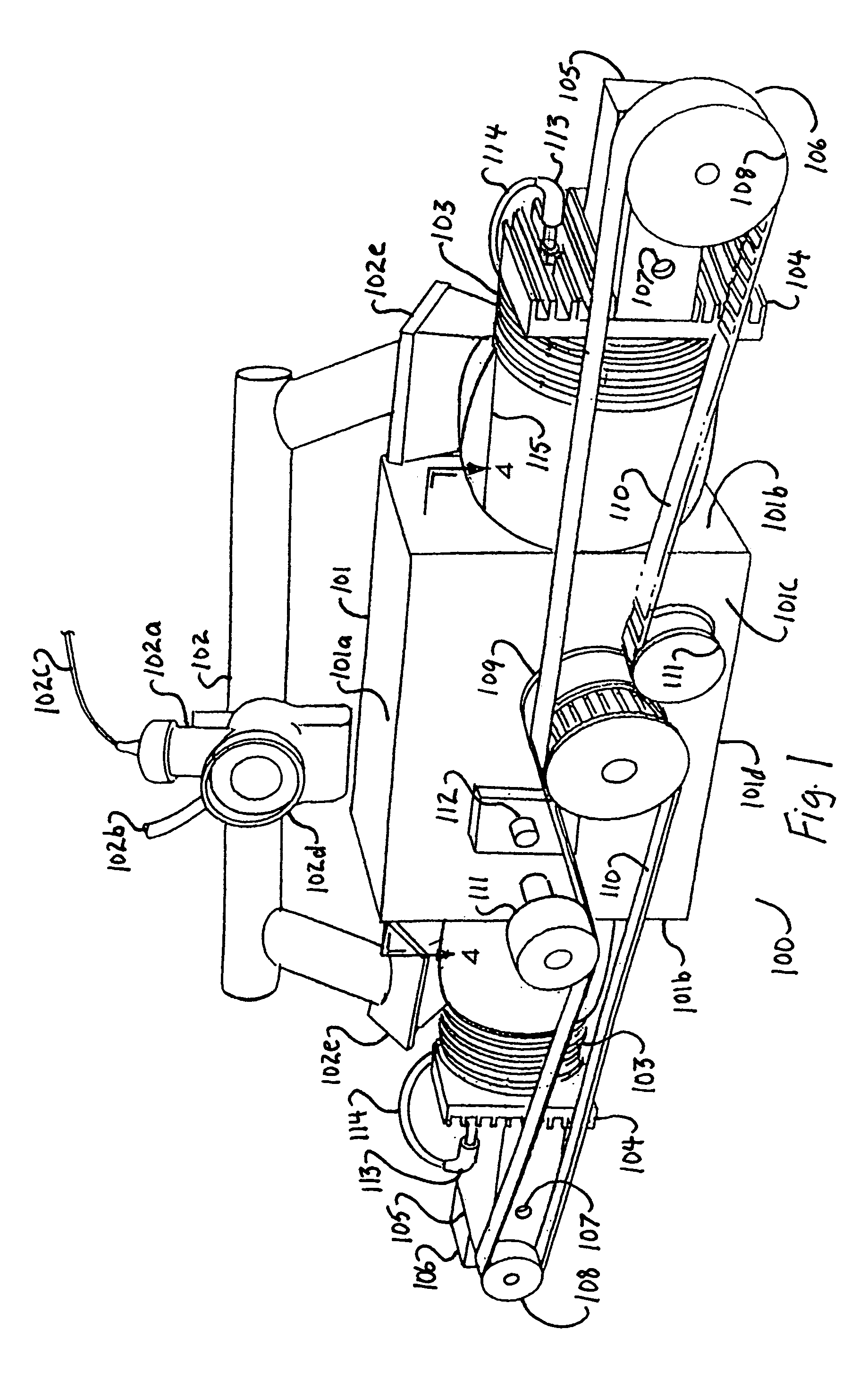
Ink jet head unit and ink jet printing apparatus incorporating the same
There are provided an ink jet head unit which is capable of incorporating a large number of ink jet heads with ease and precision, and an ink jet printing apparatus incorporating the ink jet head unit. The ink jet head unit performs printing color printing by using a plurality of ink nozzle arrays each for use in printing one line, the plurality of ink nozzle arrays corresponding to a plurality of basic colors. A plurality of head groups are each formed by a plurality of ink jet heads, and have the plurality of ink nozzle arrays arranged therein such that the plurality of ink nozzle arrays are divided among the plurality of head groups. A plurality of sub-carriages have respective ones of the plurality of head groups mounted thereon. A unitizing carriage has the plurality of sub-carriages mounted thereon.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
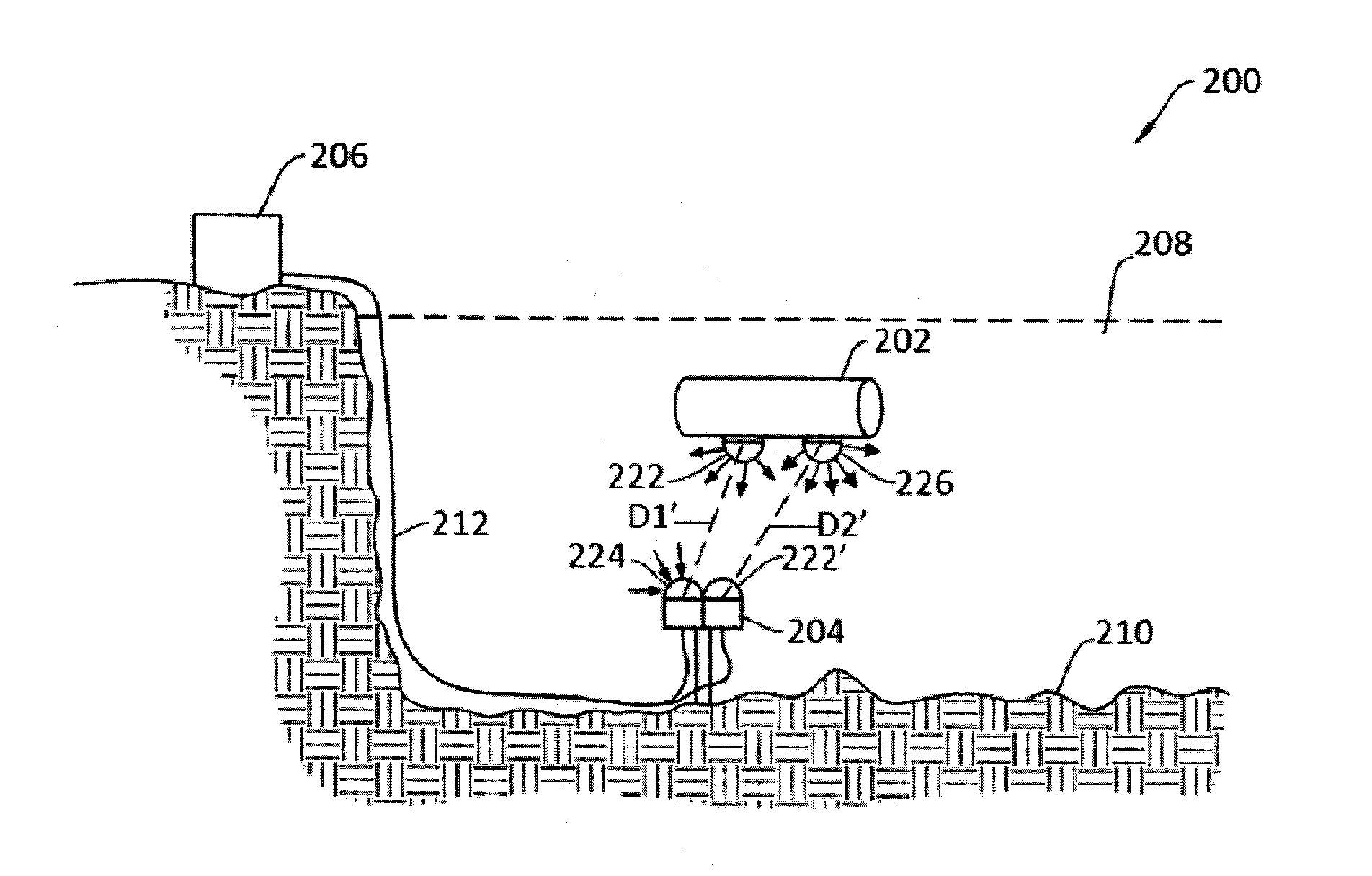
Fluid bed reactor
ActiveUS20110117729A1Reduce foulReduce contaminationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingNuclear engineeringInsulation layer
Fluidized bed reactor systems for producing high purity silicon-coated particles are disclosed. A vessel has an outer wall, an insulation layer inwardly of the outer wall, at least one heater positioned inwardly of the insulation layer, a removable concentric liner inwardly of the heater, a central inlet nozzle, a plurality of fluidization nozzles, at least one cooling gas nozzle, and at least one product outlet. The system may include a removable concentric sleeve inwardly of the liner. In particular systems the central inlet nozzle is configured to produce a primary gas vertical plume centrally in the reactor chamber to minimize silicon deposition on reactor surfaces.
Owner:REC SILICON
Reducing environmental pollution and fouling when burning coal
InactiveUS20140299028A1Lower Level RequirementsEmission reductionEmission preventionSolid fuel pretreatmentAlkalinityHalogen
Powder components containing calcium, alumina, silica, iron, magnesium, and a halogen sorbent are used in combination during coal combustion to produce environmental benefits. Sorbents are added to the coal ahead of combustion and / or are added into the flame or downstream of the flame. The alkalinity and chlorine of the powder is minimized in order to mitigate unwanted fouling, especially when used with sub-bituminous and lignite coals.
Owner:NOX II LTD
Airfoil-Shaped Micro-Mixers for Reducing Fouling on Membrane Surfaces
ActiveUS20100118642A1Enhance fluid mixingMinimized pressure dropSemi-permeable membranesMembranesFiltrationMembrane channel
An array of airfoil-shaped micro-mixers that enhances fluid mixing within permeable membrane channels, such as used in reverse-osmosis filtration units, while minimizing additional pressure drop. The enhanced mixing reduces fouling of the membrane surfaces. The airfoil-shaped micro-mixer can also be coated with or comprised of biofouling-resistant (biocidal / germicidal) ingredients.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Filtering medium and method for contacting solids-containing feeds for chemical reactors
InactiveUS20010015336A1Increase particulate trappingShorten speedSemi-permeable membranesSolvent extractionOrganic baseChemical reactor
A filtering medium and method for removing contaminants from an organic-based feed stream which includes the use of a layer of ceramic filter units having a plurality of elliptical or trisoidal openings extending therethrough to filter organic-based feed streams and to provide liquid distribution upstream of the catalyst beds.
Owner:CRYSTAPHASE PRODS
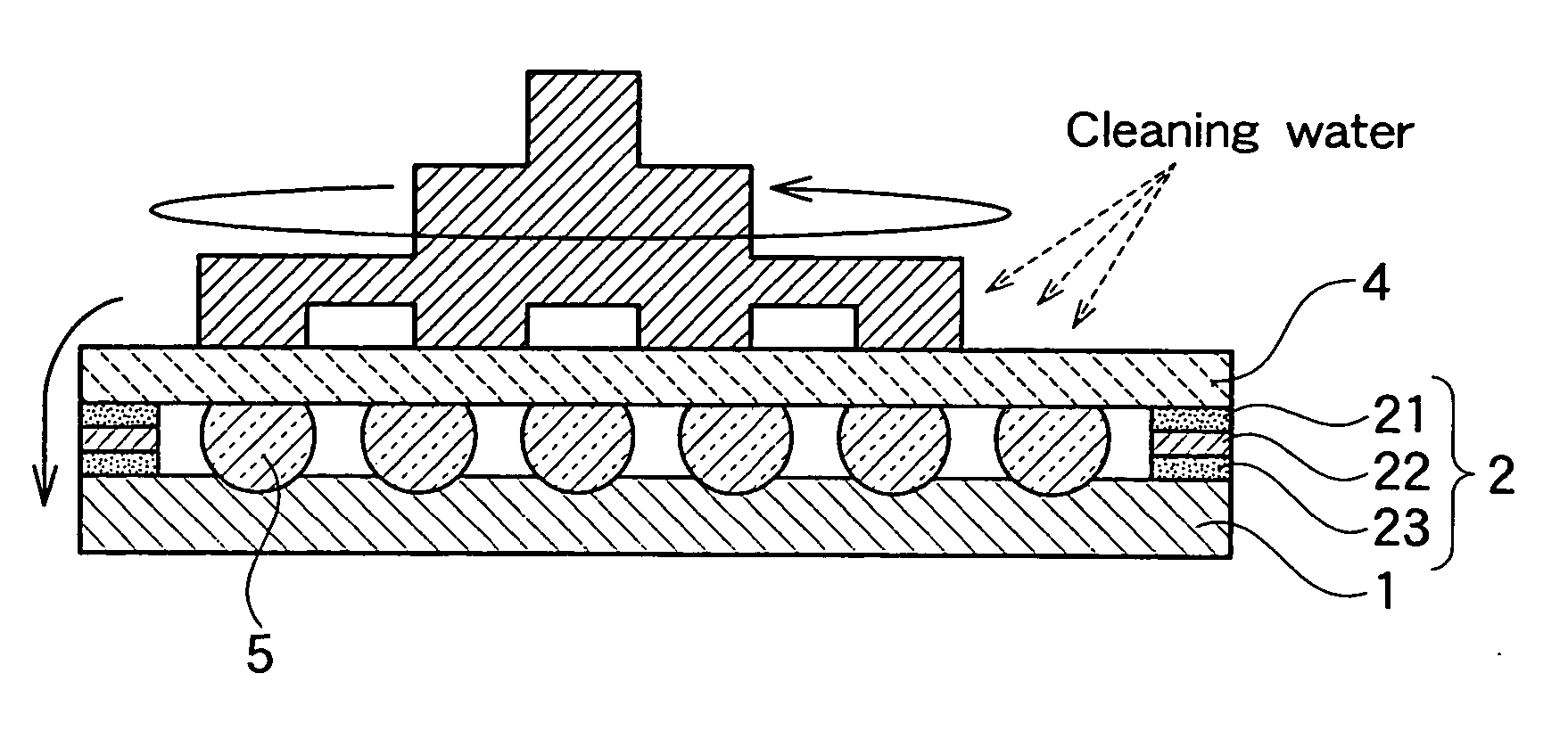
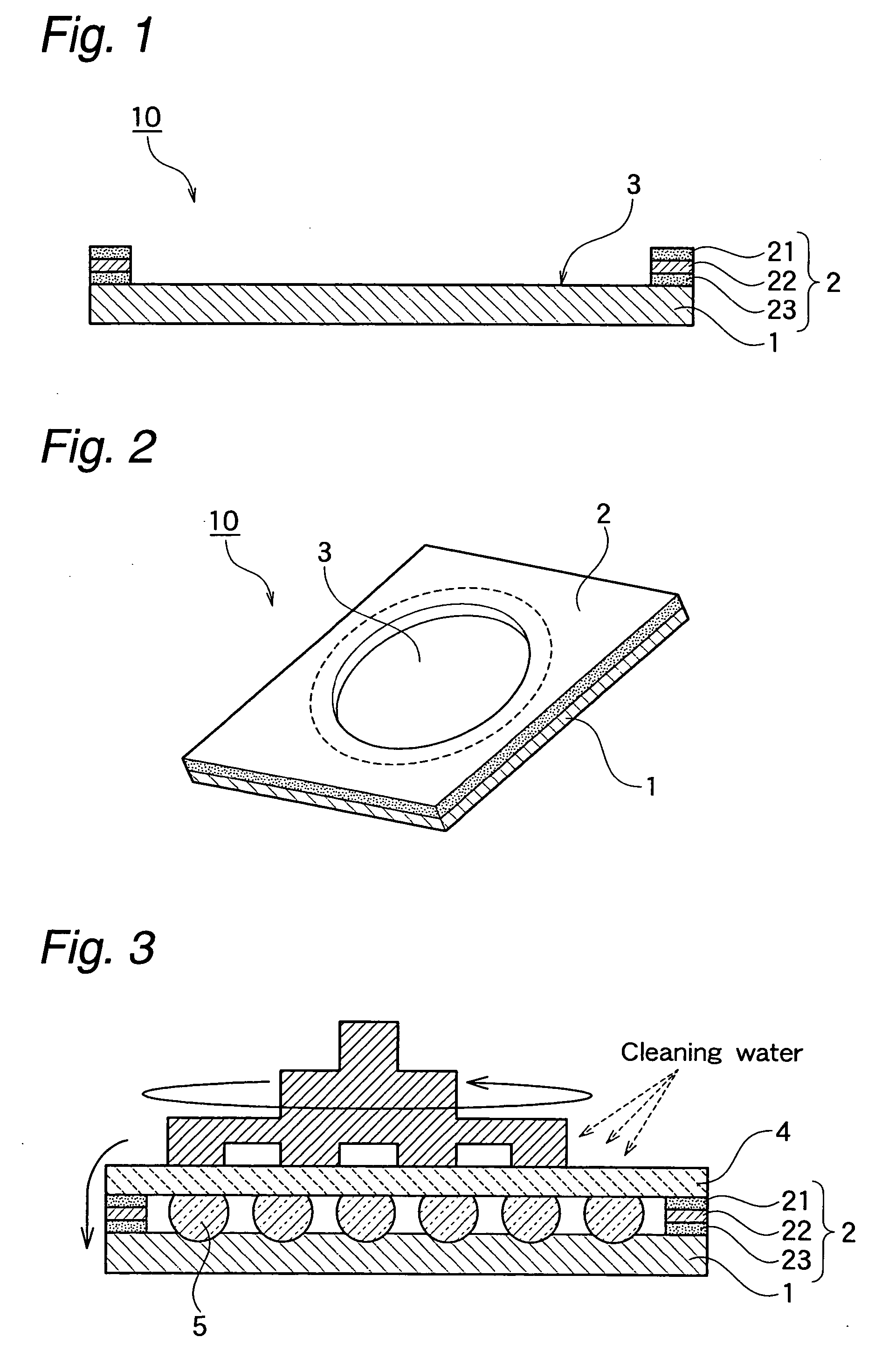
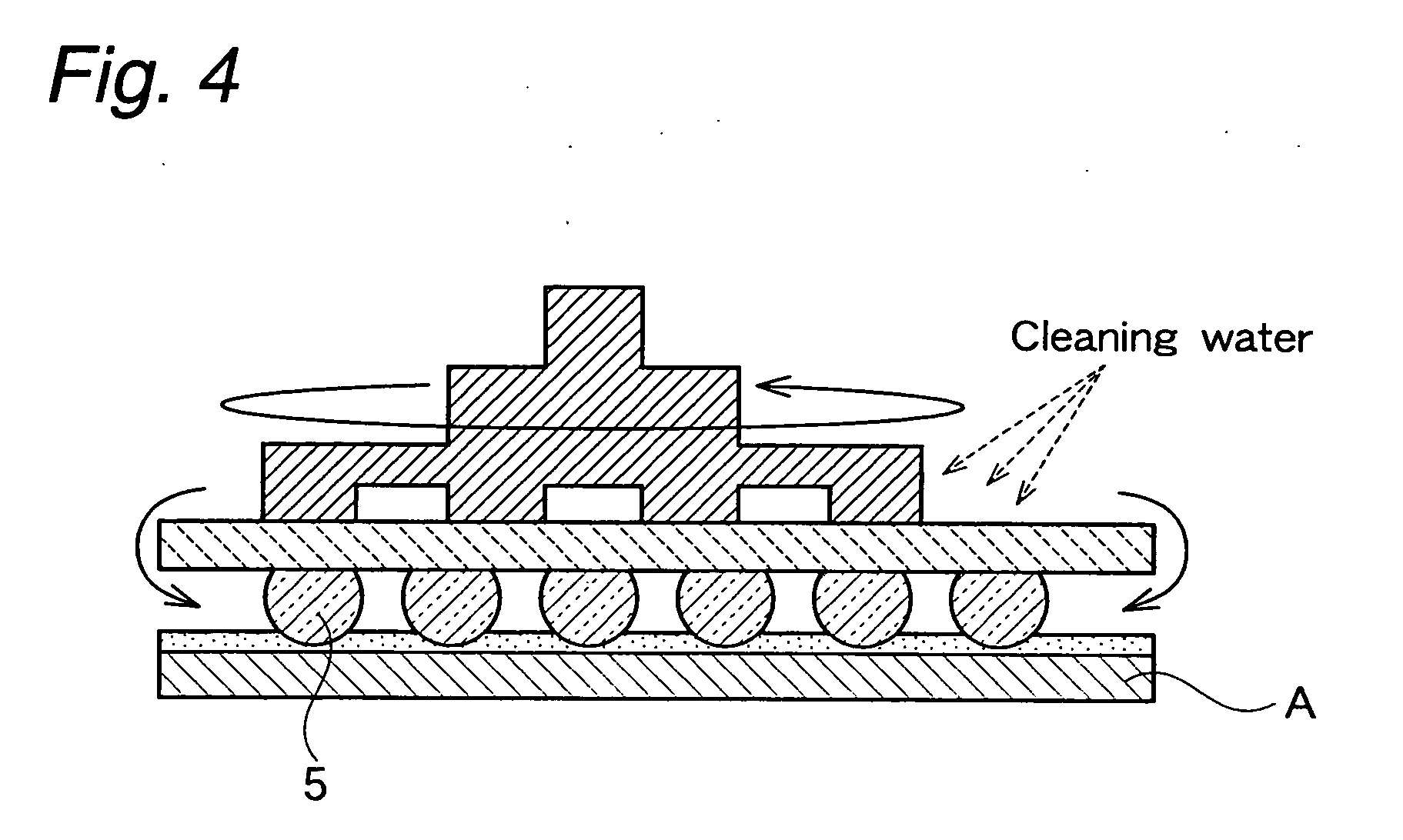
Surface-protecting sheet and semiconductor wafer lapping method
ActiveUS20070066184A1Reduce foulFouling of the wafer can be reducedFilm/foil adhesivesSolid-state devicesCHEEK DIMPLESEngineering
It is an object of the present invention to provide a surface protective sheet and a method for grinding a semiconductor wafer, by the use of which any dimple is not formed, nor occurs breakage and fouling of a wafer even when a wafer having high bumps which are highly densely arranged is ground to an extremely small thickness, and besides, no adhesive is left at the roots of the bumps after the surface protective sheet is peeled. The surface protective sheet of the invention is used for grinding a back surface of a semiconductor wafer, and in the surface protective sheet, one surface of a base sheet is provided with an opening portion having a diameter smaller than an outer diameter of a semiconductor wafer to be stuck, on said opening portion no adhesive layer being formed, and a portion which is provided around the opening portion and on which an adhesive layer is formed.
Owner:LINTEC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com