Vertical skein of hollow fiber membranes and method of maintaining clean fiber surfaces while filtering a substrate to withdraw a permeate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
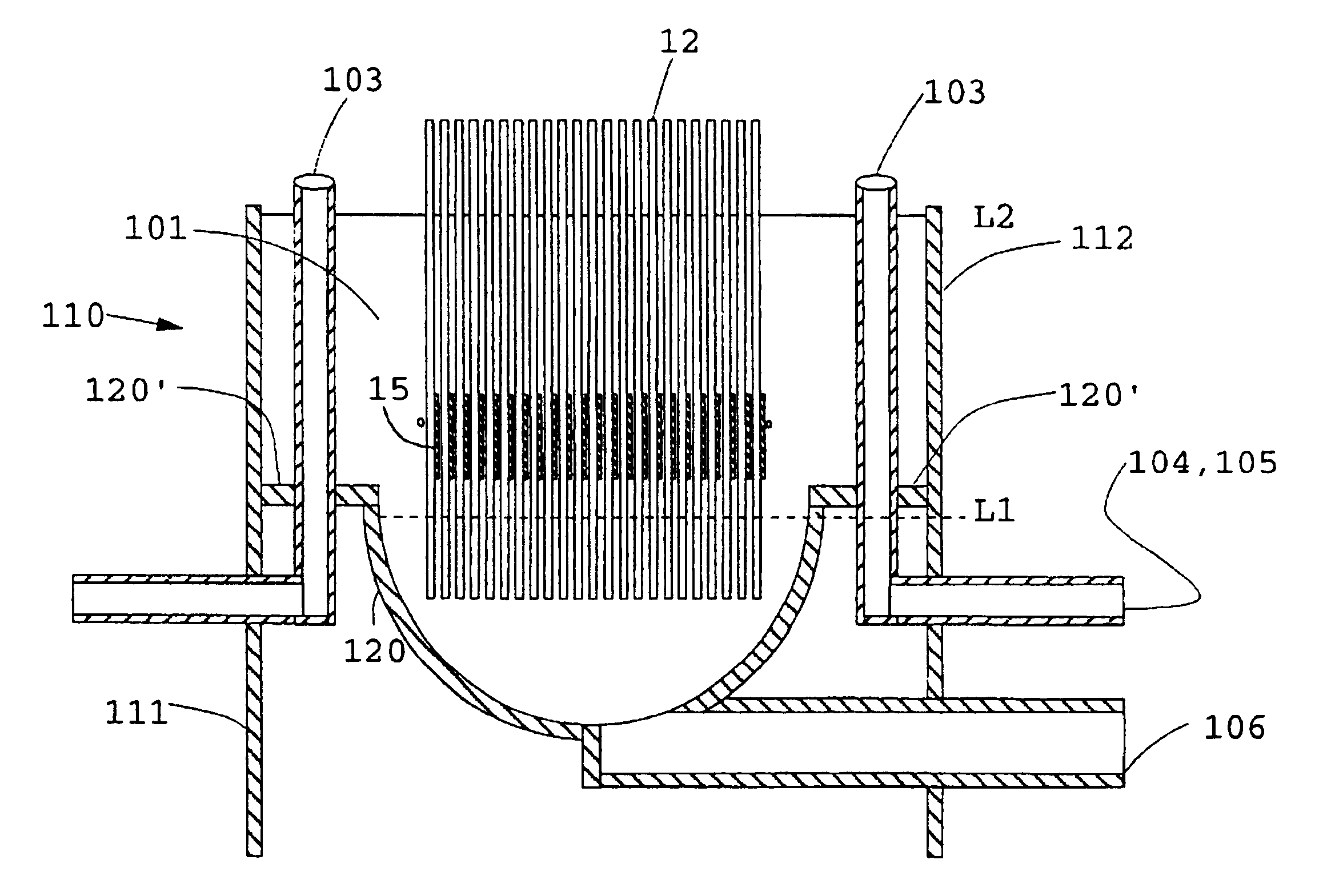
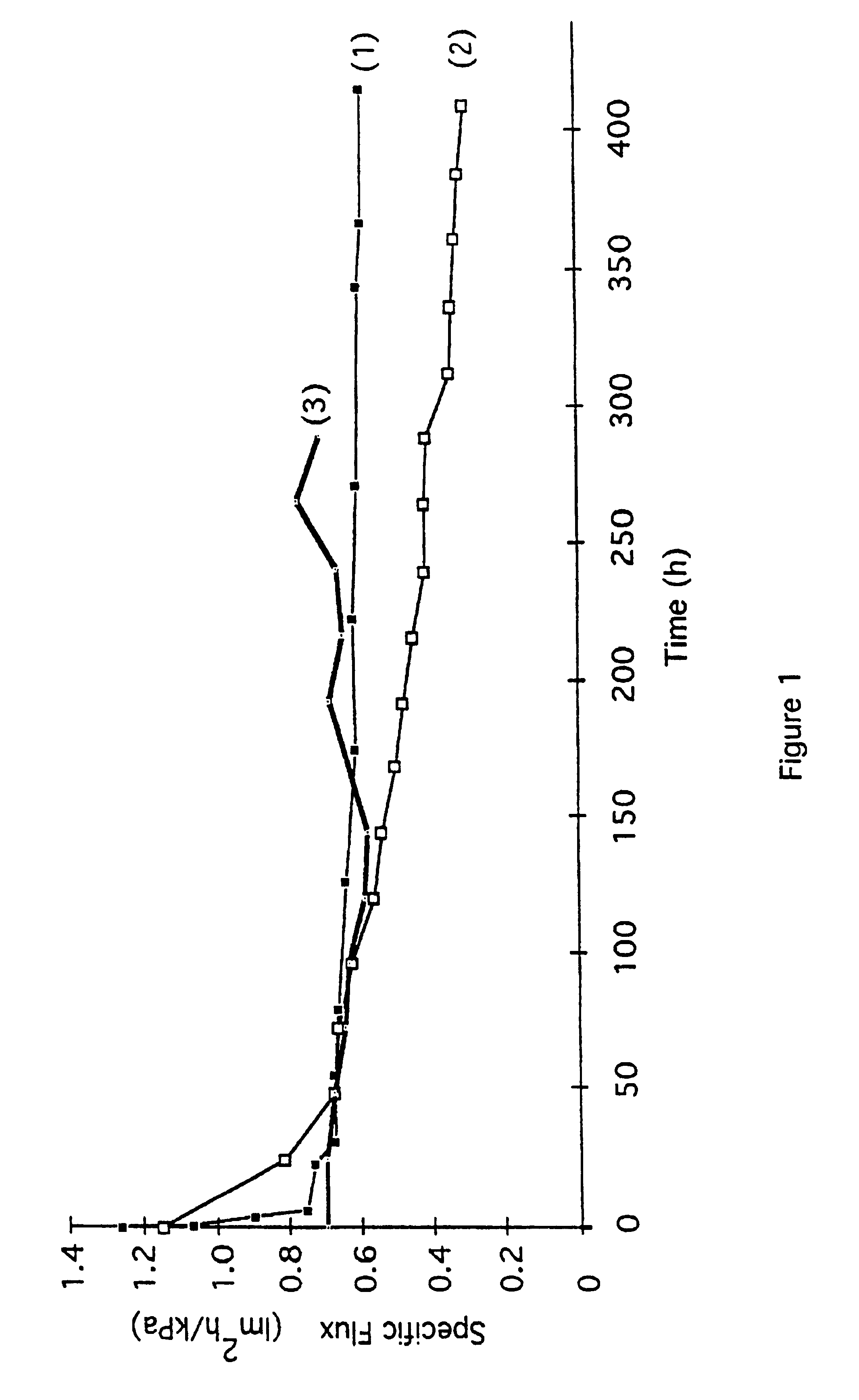
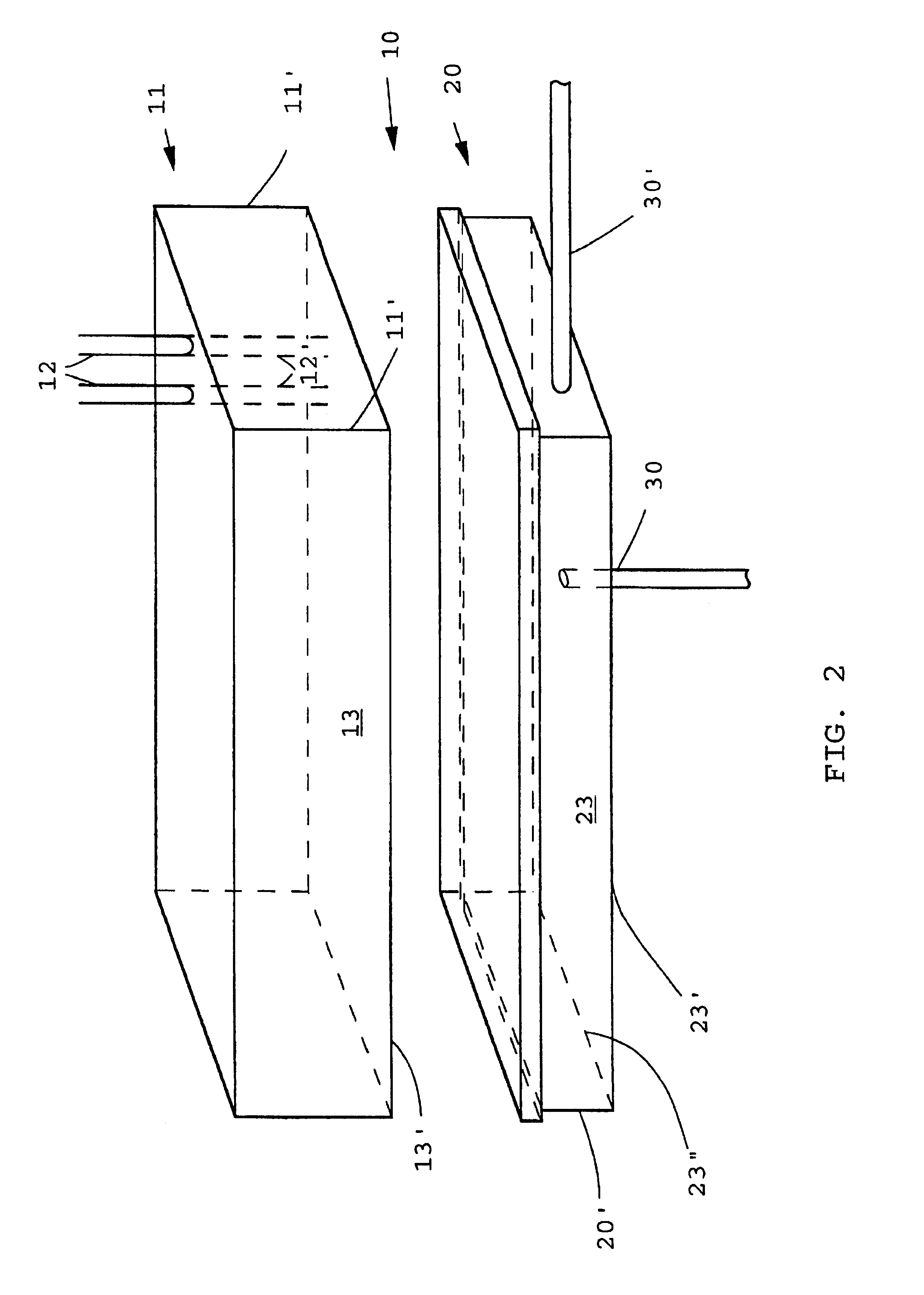
Microfiltration of an activated sludge at 30.degree. C. having a concentration of 25 g / L (2.5% TSS) is carried out with a skein of polysulfone fibers in a pilot plant tank. The fibers are "air scrubbed" at a flow rate of 12 CFM (0.34 m.sup.3 / min) with a coarse bubble diffuser generating bubbles in the range from about 5 mm to 25 mm, in nominal diameter. The air is sufficient not only for the oxidation requirements of the biomass but also for adequate scrubbing. The fibers have an outside diameter of 1.7 mm, a wall thickness of about 0.5 mm, and a surface porosity in the range from about 20% to 40% with pores about 0.2 .mu.m in diameter, both latter physical properties being determined by a molecular weight cut off at 200,000 Daltons. The skein which has 1440 fibers with a surface area of 12 m.sup.2, is wall-mounted in the tank, the vertical spaced apart distance of the headers being about 1% less than the length of a fiber in the skein. The opposed ends of the fibers are potted in ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com