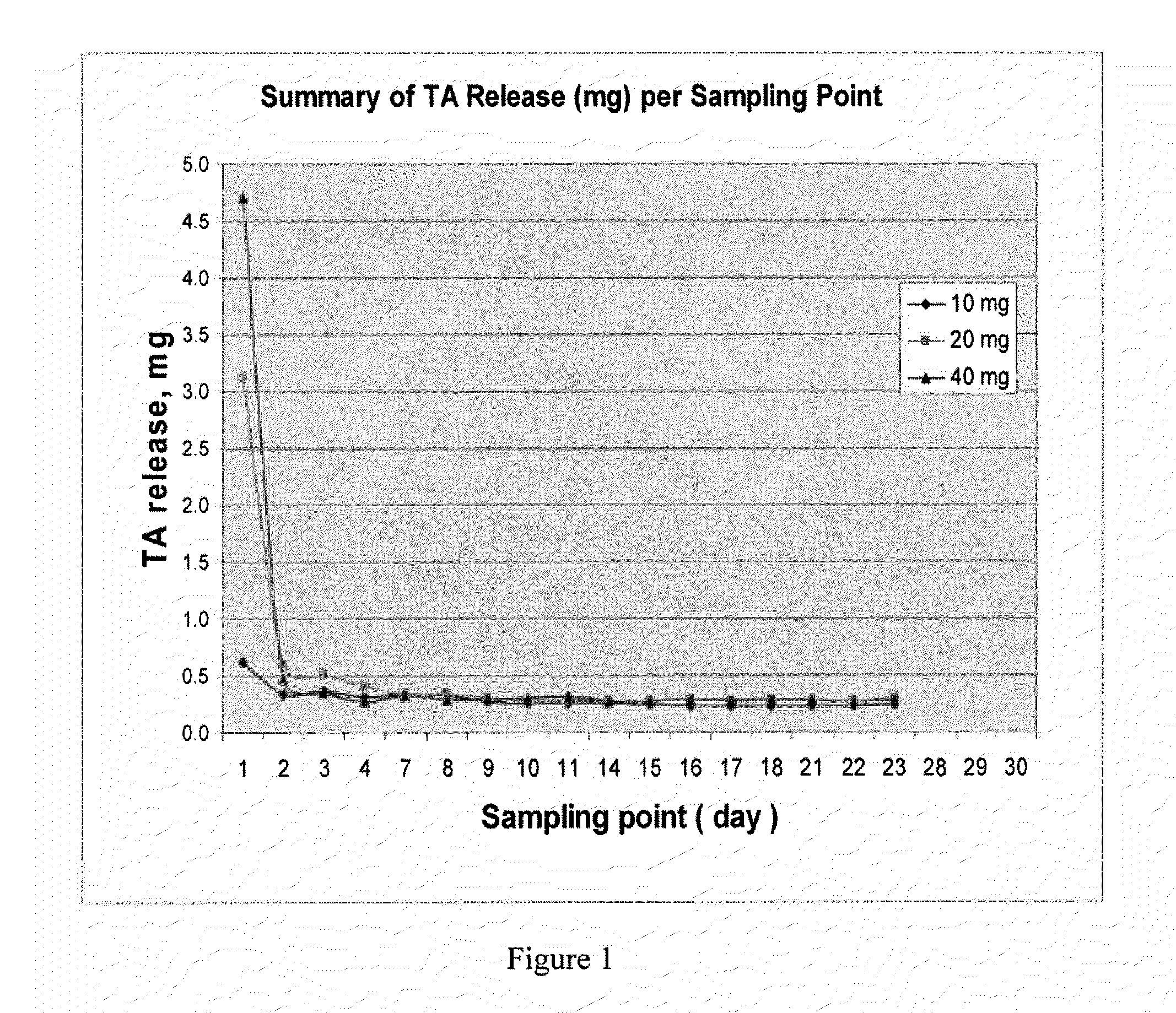
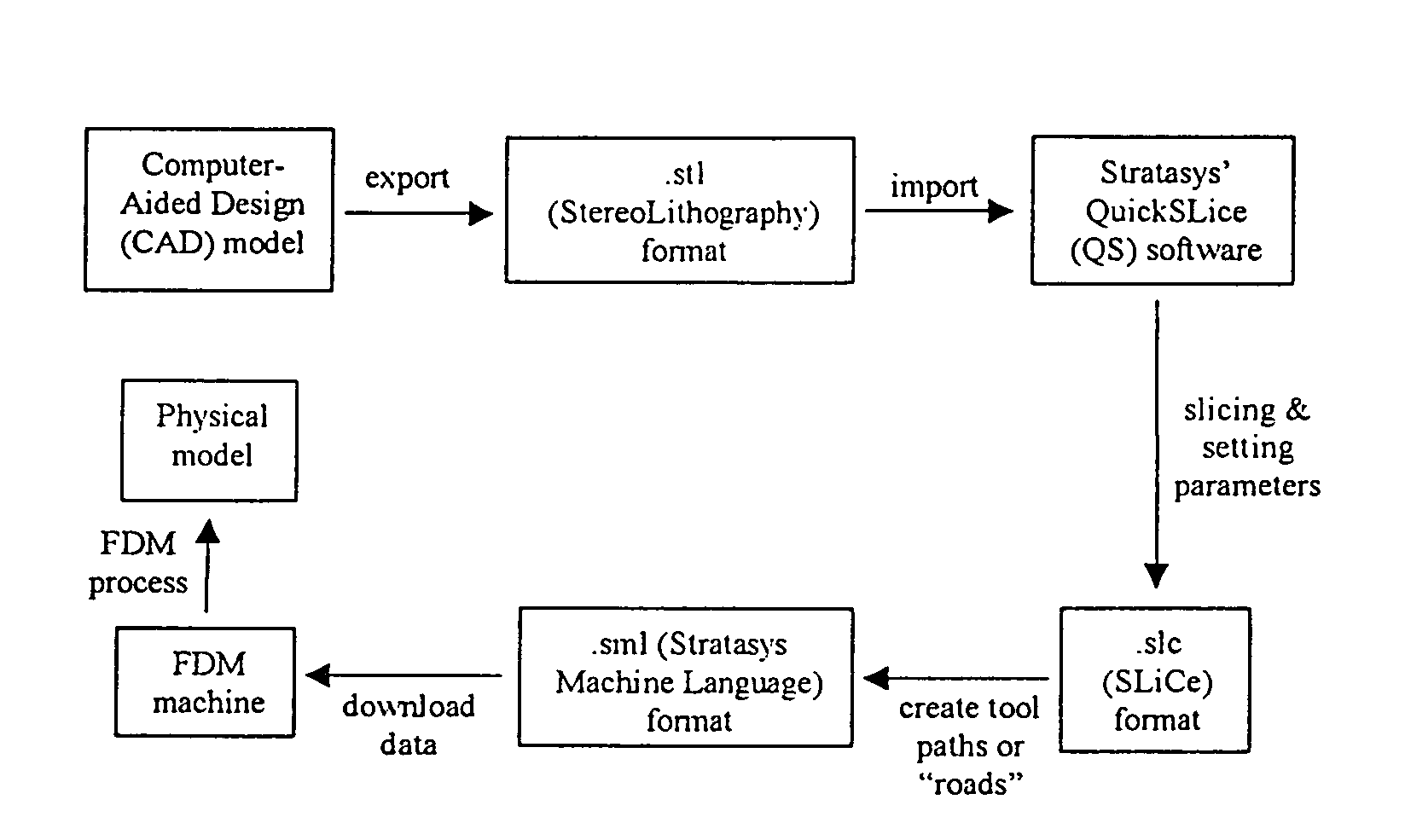
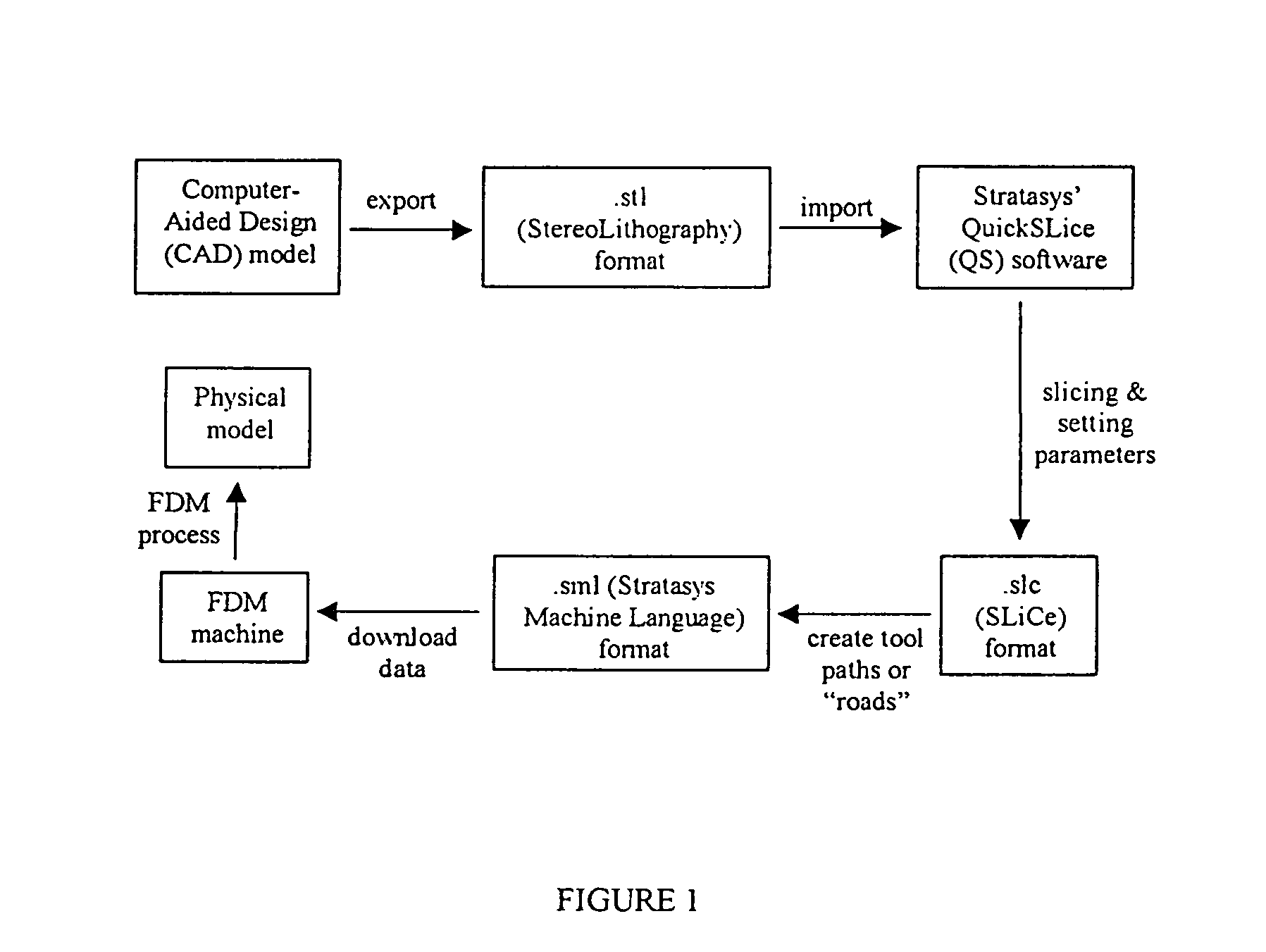
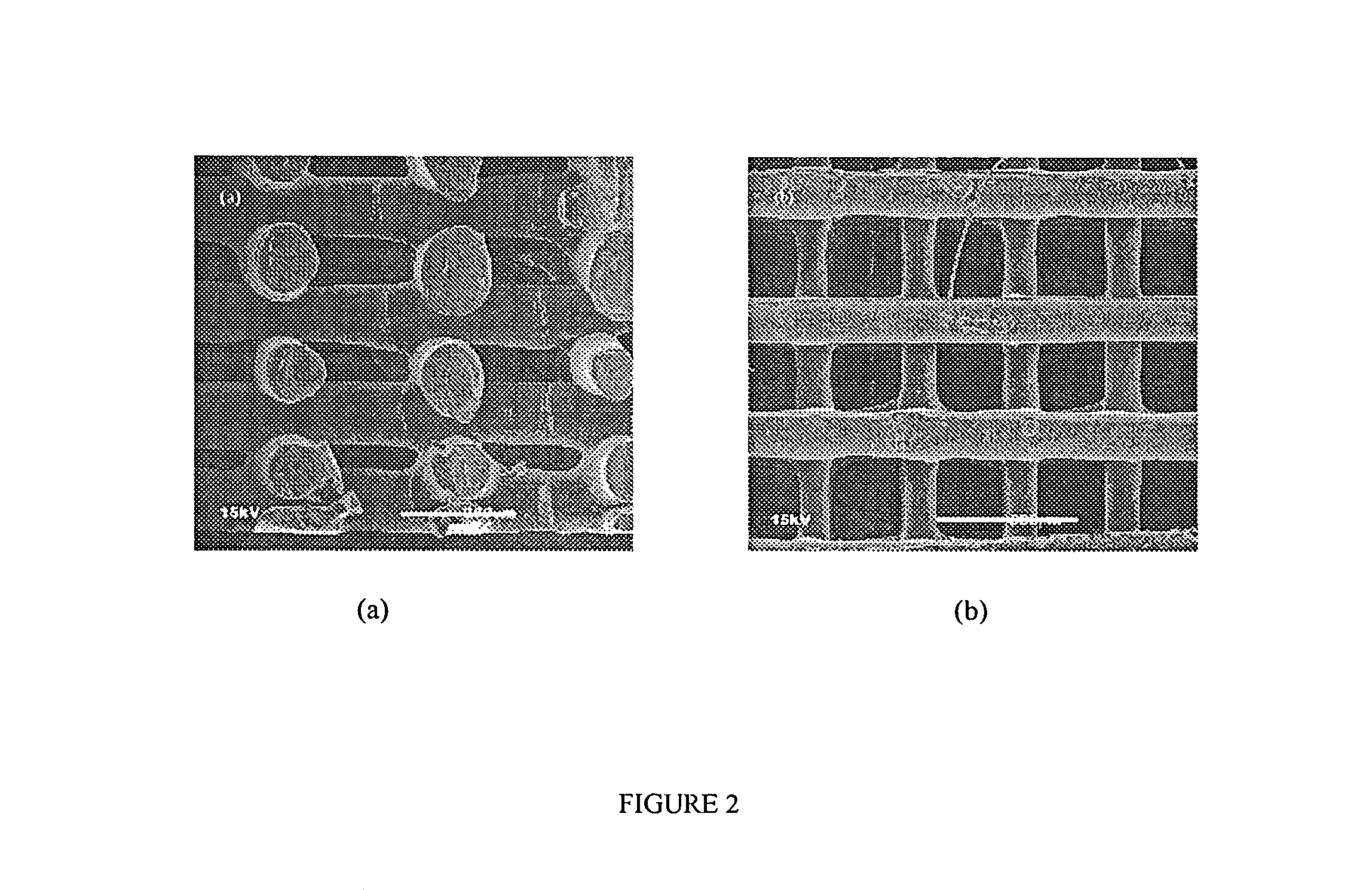
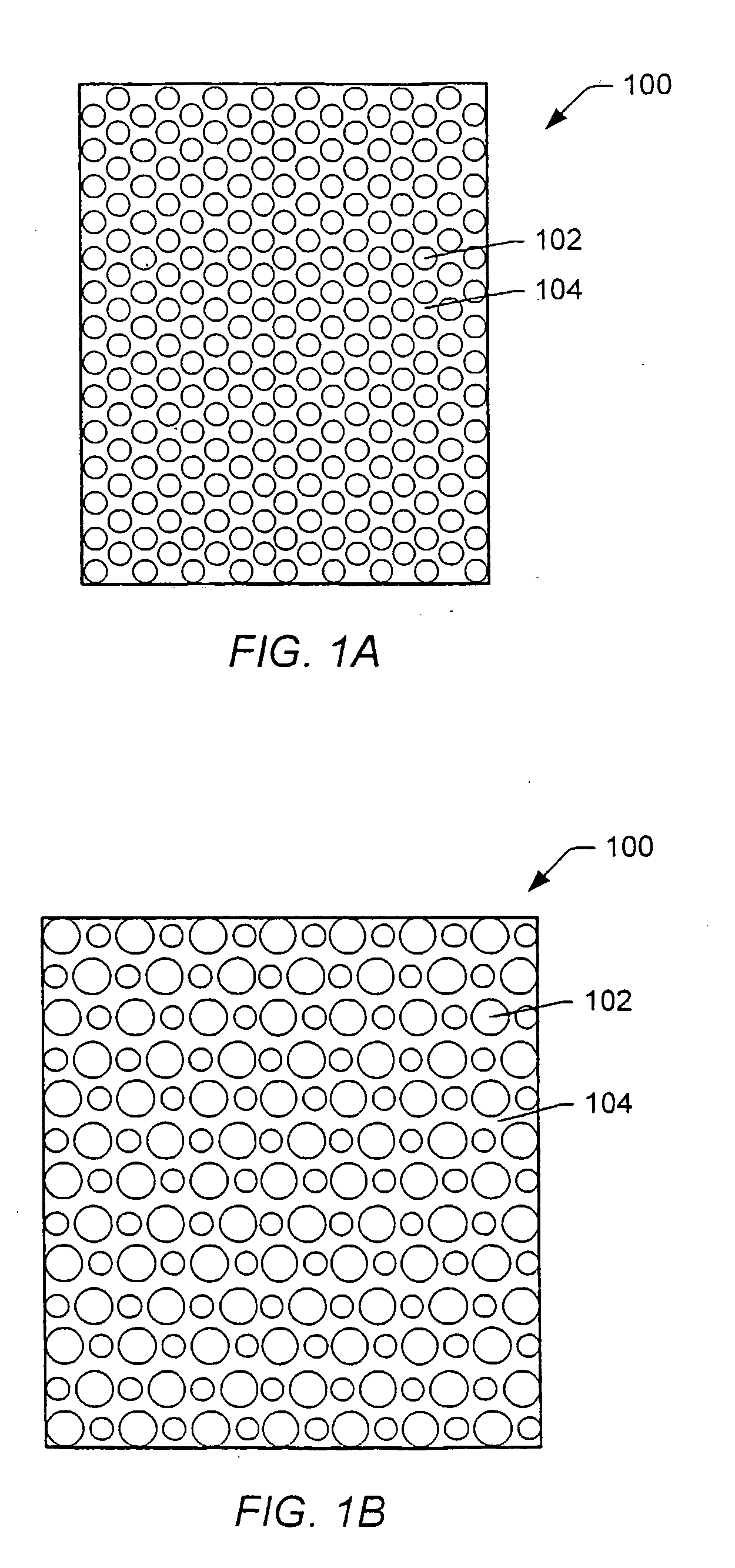
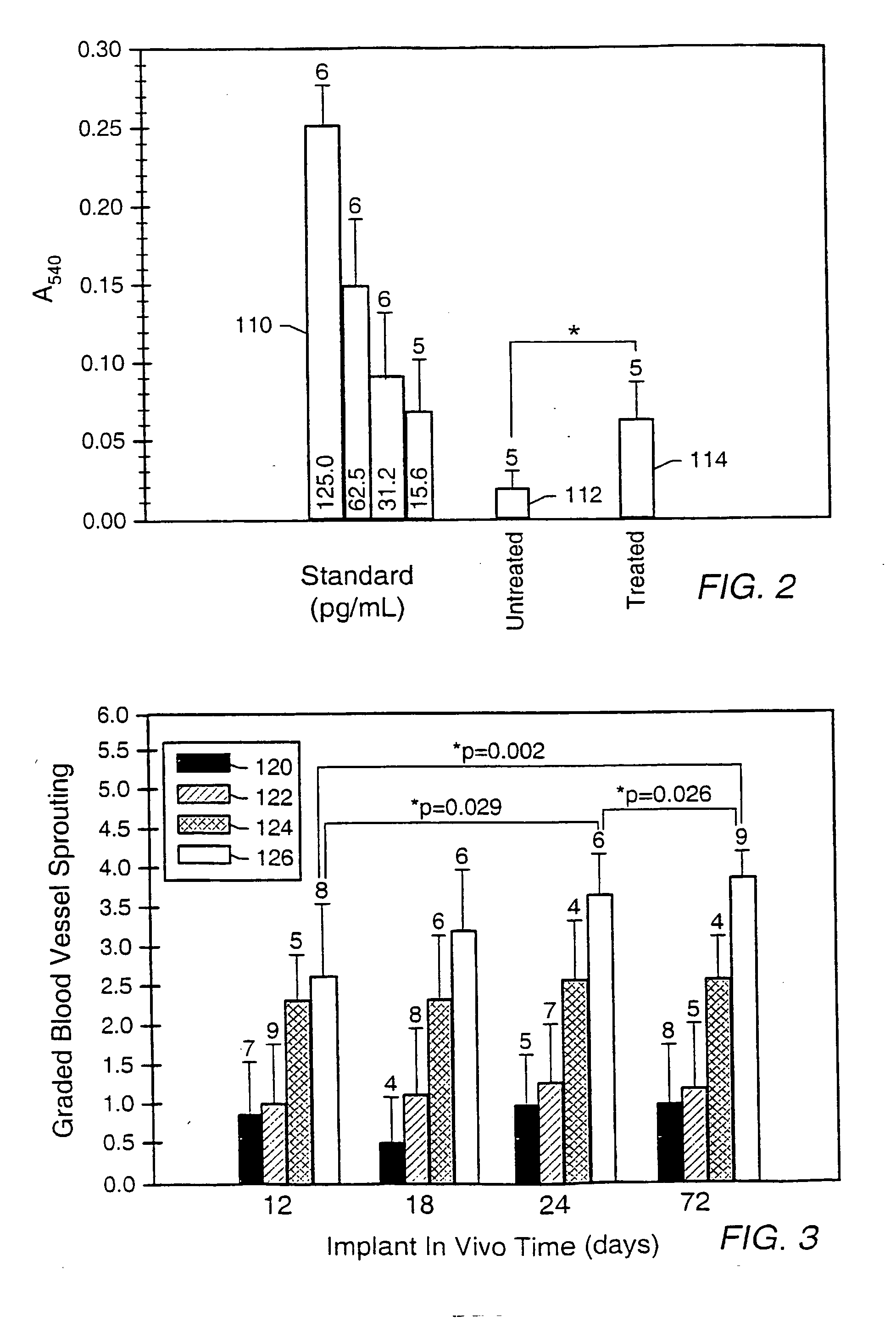
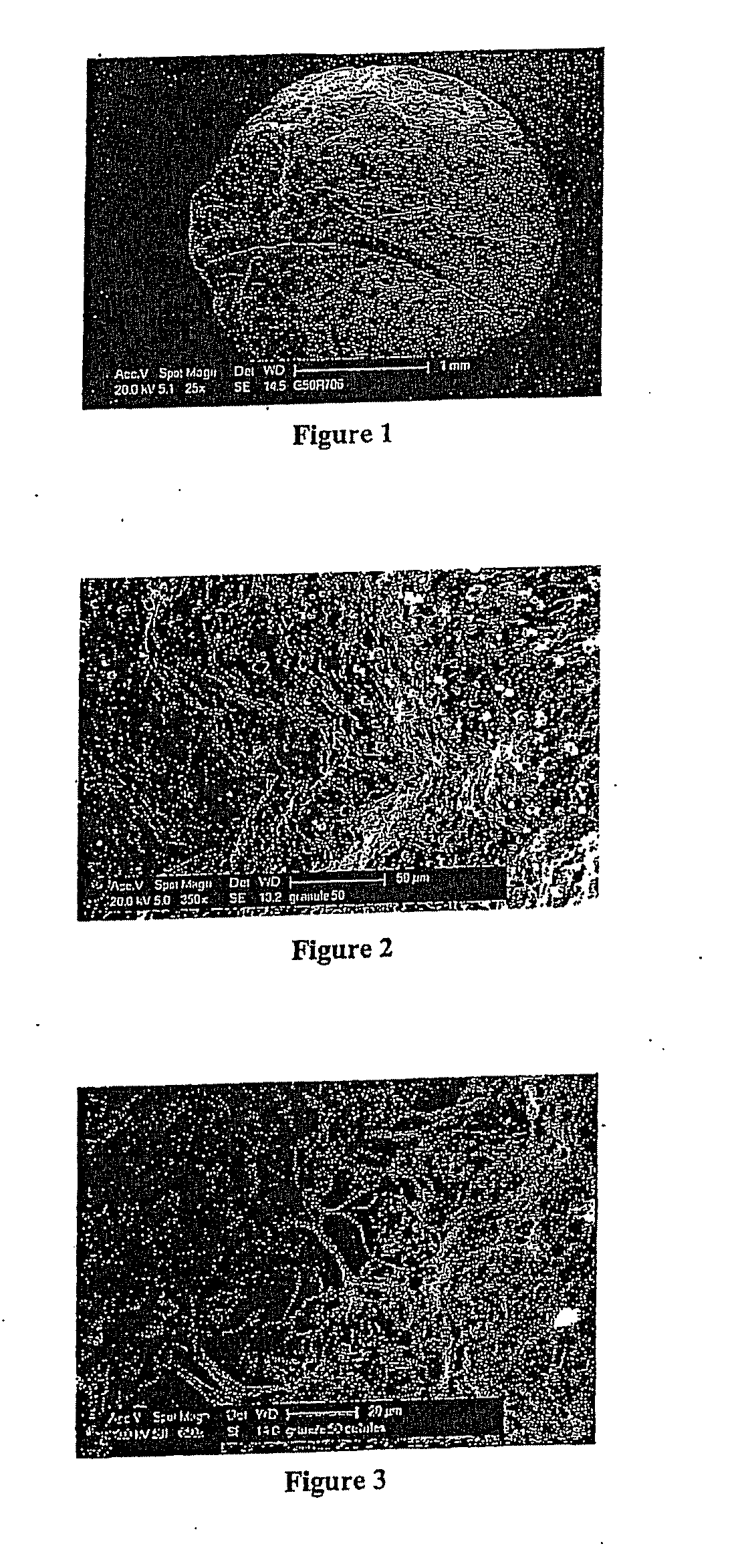
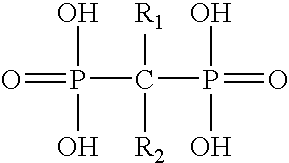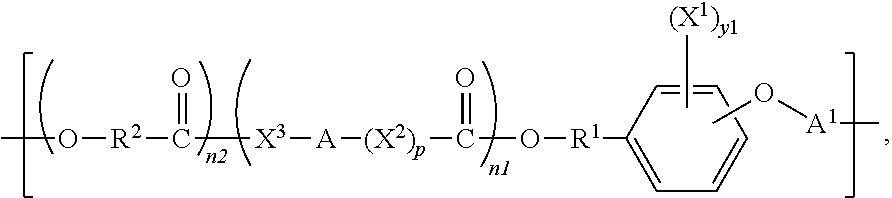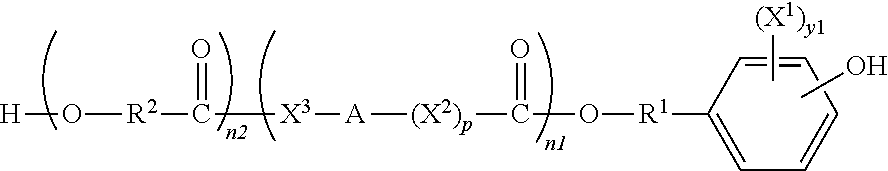Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
97 results about "Bioresorbable polymers" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Bioresorbable polymers are a class of materials frequently used for temporary implant applications. These materials degrade over time through hydrolysis.
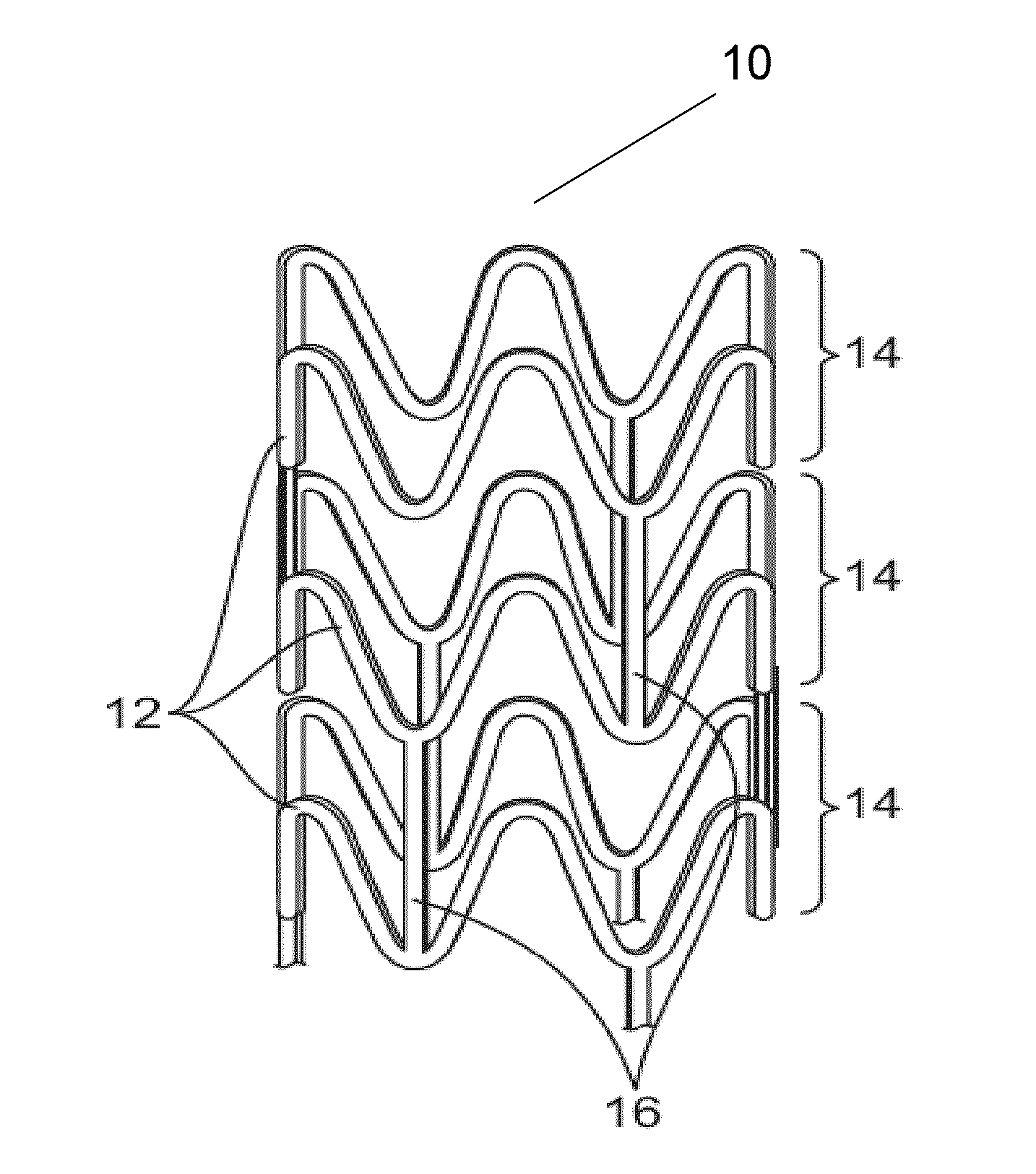
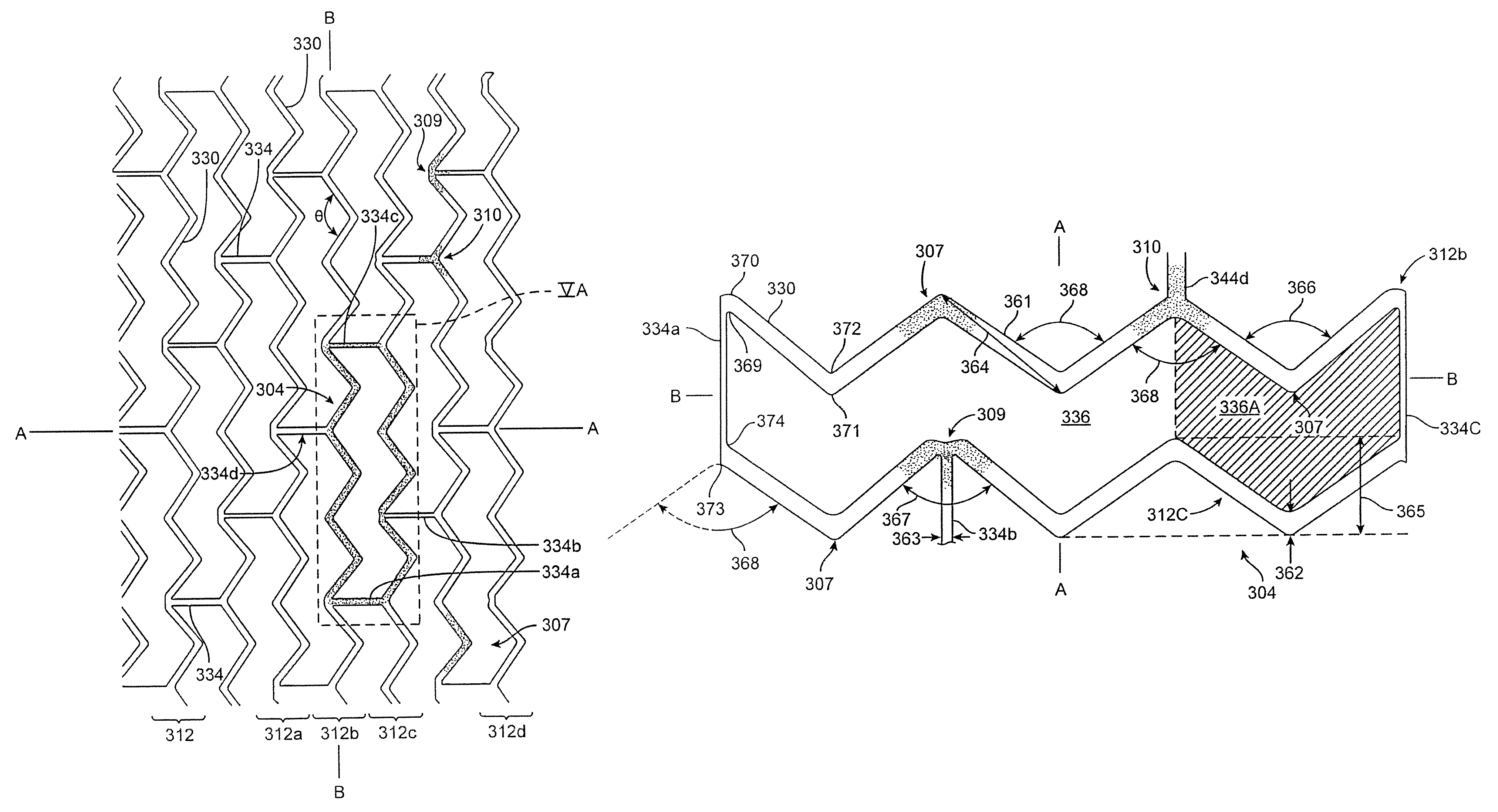
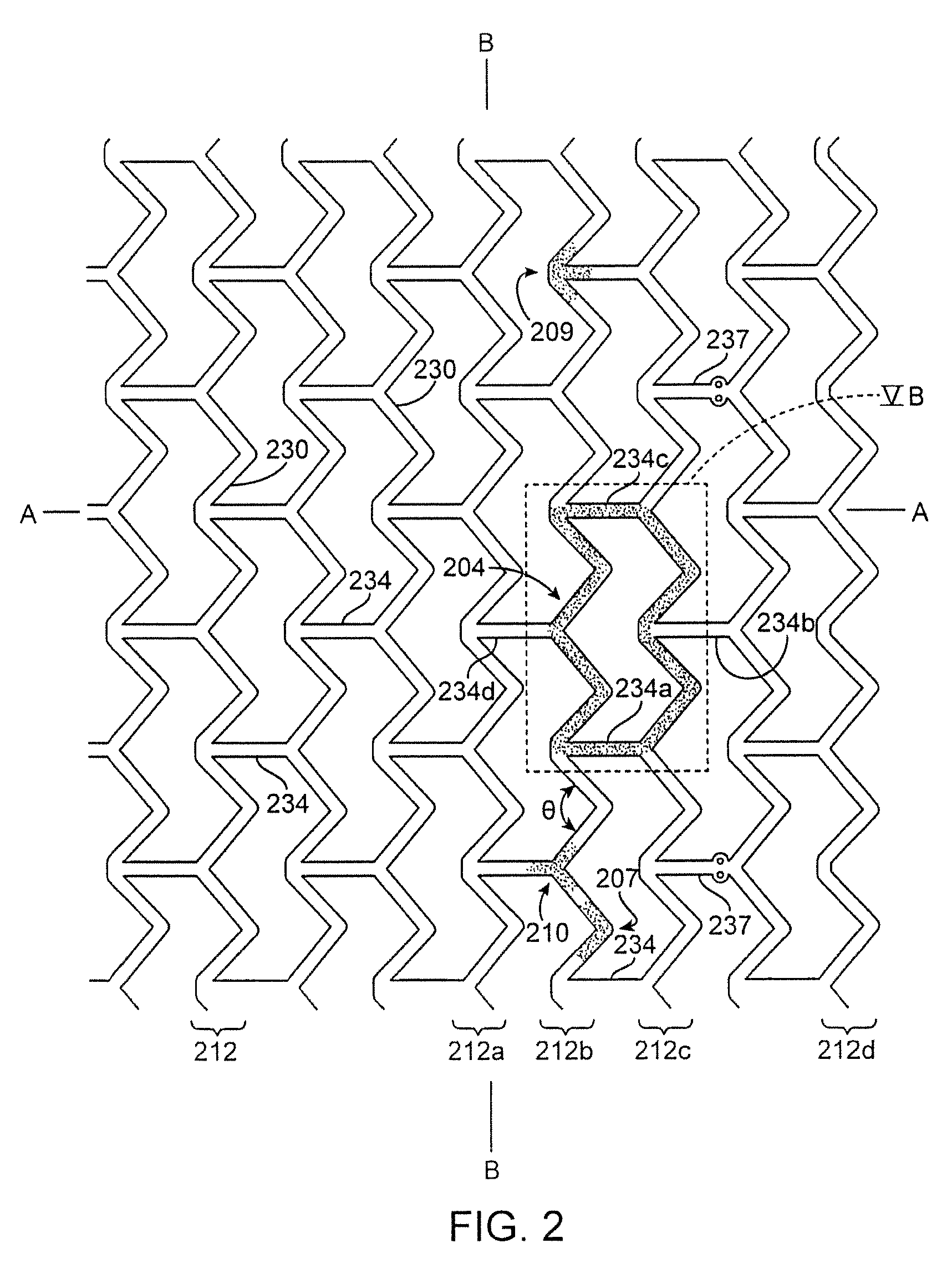
Inherently radiopaque bioresorbable polymers for multiple uses
Preferred embodiments of the present invention relate to polymeric medical devices, such as stents. More particularly, the compositions disclosed herein comprise halogen-containing phenol moeities, that may be used for medical devices and other uses whereby bioresorbable and radiopaque and physicomechanical properties are desired.
Owner:REVA MEDICAL LLC
Inherently radiopaque bioresorbable polymers for multiple uses
Preferred embodiments of the present invention relate to polymeric medical devices, such as stents. More particularly, the compositions disclosed herein comprise halogen-containing phenol moeities, that may be used for medical devices and other uses whereby bioresorbable and radiopaque and physicomechanical properties are desired.
Owner:REVA MEDICAL LLC
Spinal Stabilization Devices and Methods
InactiveUS20090248081A1More flexiblyEffective and stableInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsBioresorbable polymersSpinal locomotion
A device and method for stabilizing a spine utilizes one or more stabilization members made of, or including, a bioresorbable and / or biointegrable material such as natural tissue or a bioresorbable polymer. The stabilization member(s) may be elastic, and may secure one or more spinal motion segments in a manner effective to reduce the range of flexion and / or extension of the spinal motion segments. The stabilization member may include one or more elongate straps of nonosteogenic natural tissue, each of which may be secured to the spine using fasteners such as bone screws or tacks. The stabilization device may include a blocking member sized and configured to be effective for maintaining a medically desirable distance between adjacent spinous processes in the spine of a medical patient.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
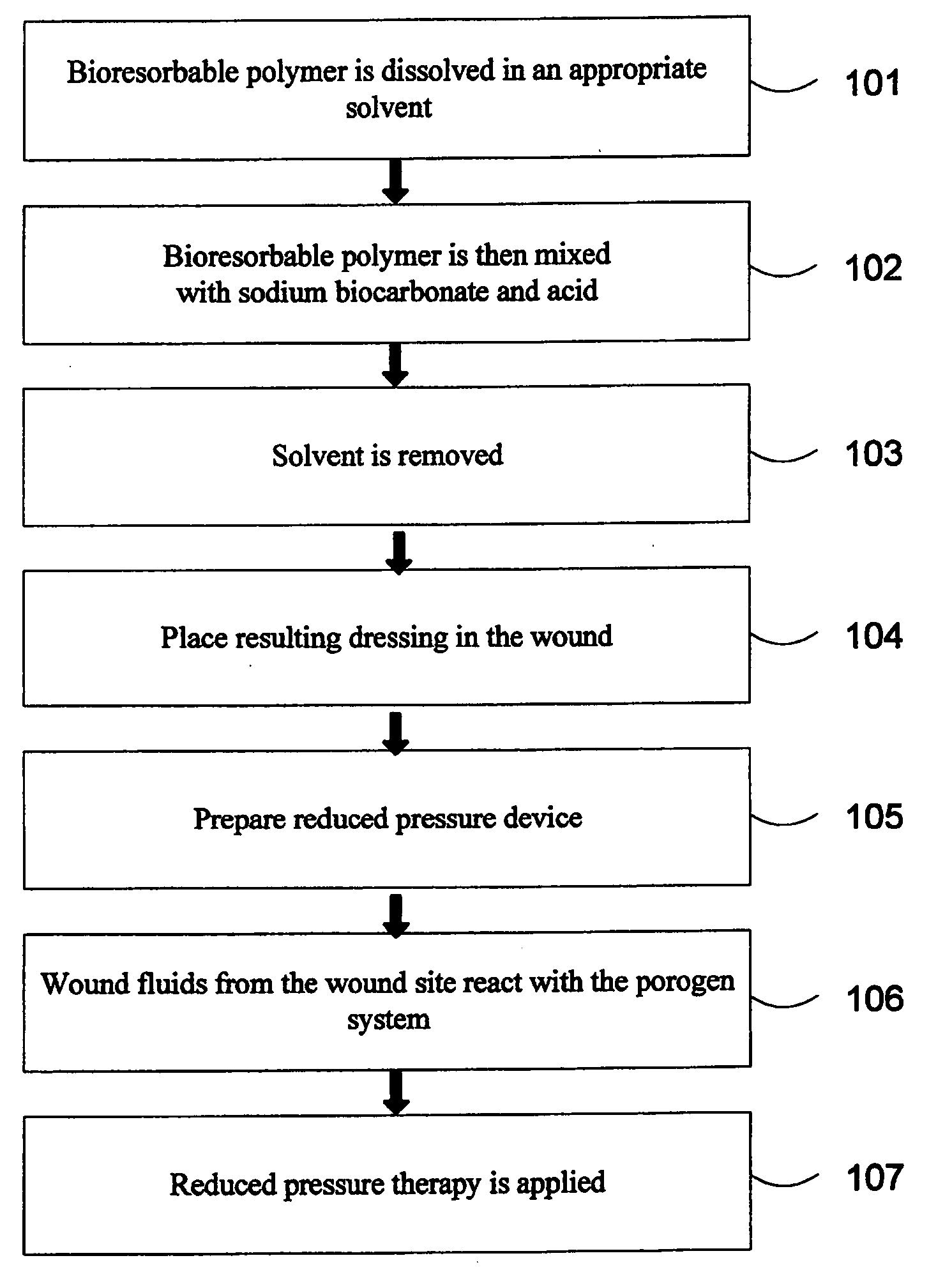
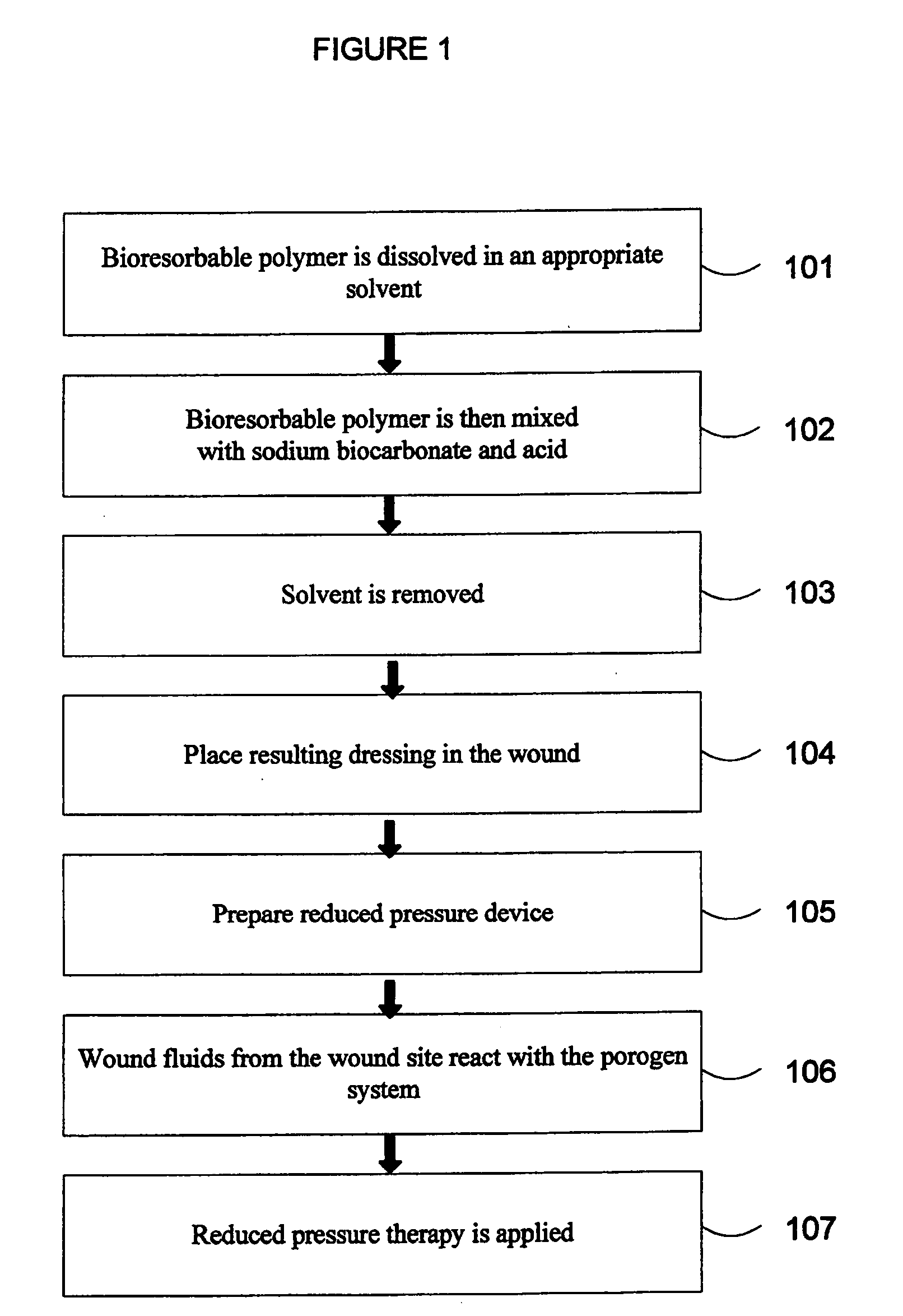
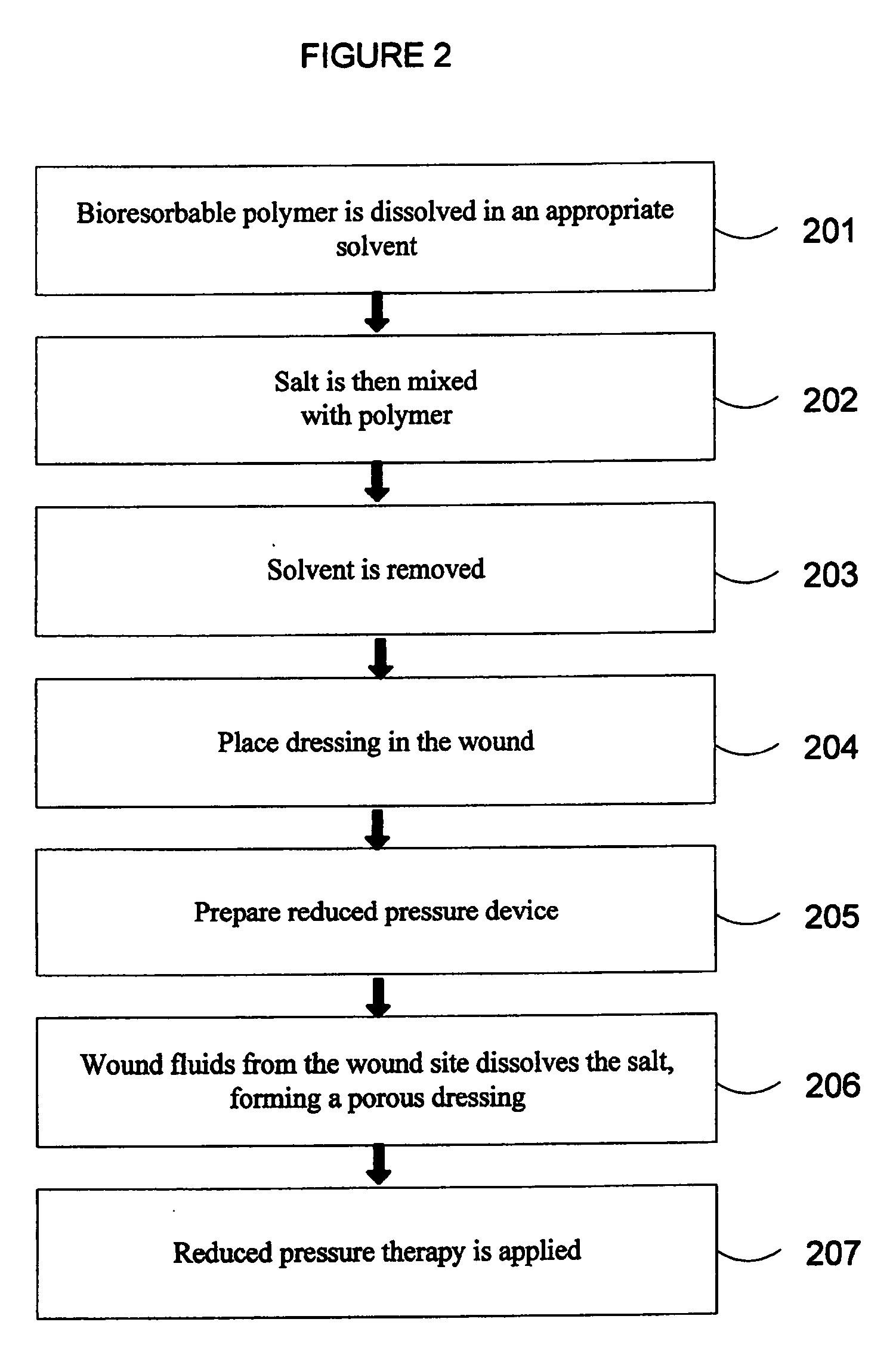
Porous bioresorbable dressing conformable to a wound and methods of making same
A method of making a porous bioresorbable dressing is provided for use in applying reduced pressure therapy to a wound site. The process includes manufacture of a dressing by use of one or more bioresorbable polymers and a porogen system. The malleability of the dressing allows the dressing to be placed into the wound site such that it fills the shape and size of the wound. Embodiments include use of hand molding and formation of a rope dressing. The porogen system may be activated external to the wound site or formed in situ within the wound site, thus creating a porous dressing. A reduced pressure delivery tube is fluidly connected to the wound site to delivery a reduced pressure to the wound site.
Owner:KCI LICENSING INC
Luminal stent, holding structure therefor and device for attaching luminal stent
A luminal stent is a tubular body formed by knitting a sole yarn of a bioresorbable polymer fiber, such as fiber of polylactic acid, polyglycol acid or a polylactic acid—polyglycol acid copolymer. When introduced into and attached to the inside of the vessel by a catheter fitted with a balloon, the tubular member may retain its shape for several weeks to several months after attachment and subsequently disappears by being absorbed into the living tissue. In this manner, the luminal stent is not left as a foreign matter semi-permanently in the living body without producing inflammation or hypertrophy in the vessel. There is also provided a method for attaching the luminal stent in the vessel.
Owner:IGAKI IRYO SEKKEI
Polymer formulations for delivery of bioactive agents
InactiveUS20110033540A1Enhance and stabilize compositionEasy to preparePowder deliveryBiocideActive agentMedicine
Disclosed in the present application are compositions comprising a bioresorbable polymer matrix and a bio active agent, wherein the bioactive agent is dispersed within polymer matrix as a solid. Also provided herein are methods for preparing a bioactive agent formulation, wherein the agent is present in a solid form and, wherein the agent is occluded into a polymeric matrix by polymerization of polymer matrix precursors or by self assembly of the polymer.
Owner:CARBYLAN THERAPEUTICS
Three-dimensional bioresorbable scaffolds for tissue engineering applications
InactiveUS8071007B1Biocompatibility hardHard integrationAdditive manufacturing apparatusCeramic shaping apparatusBiocompatibility TestingHard tissue
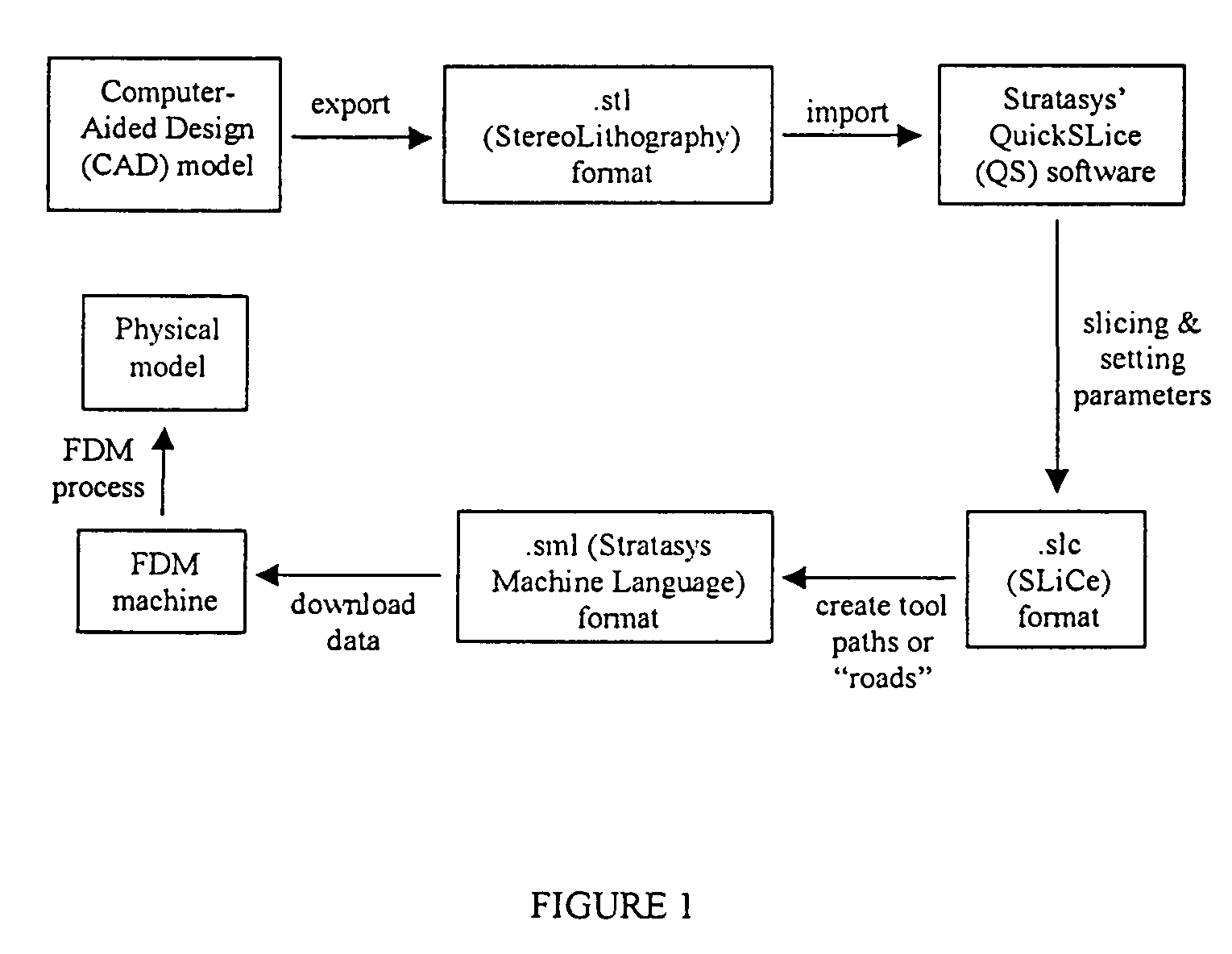
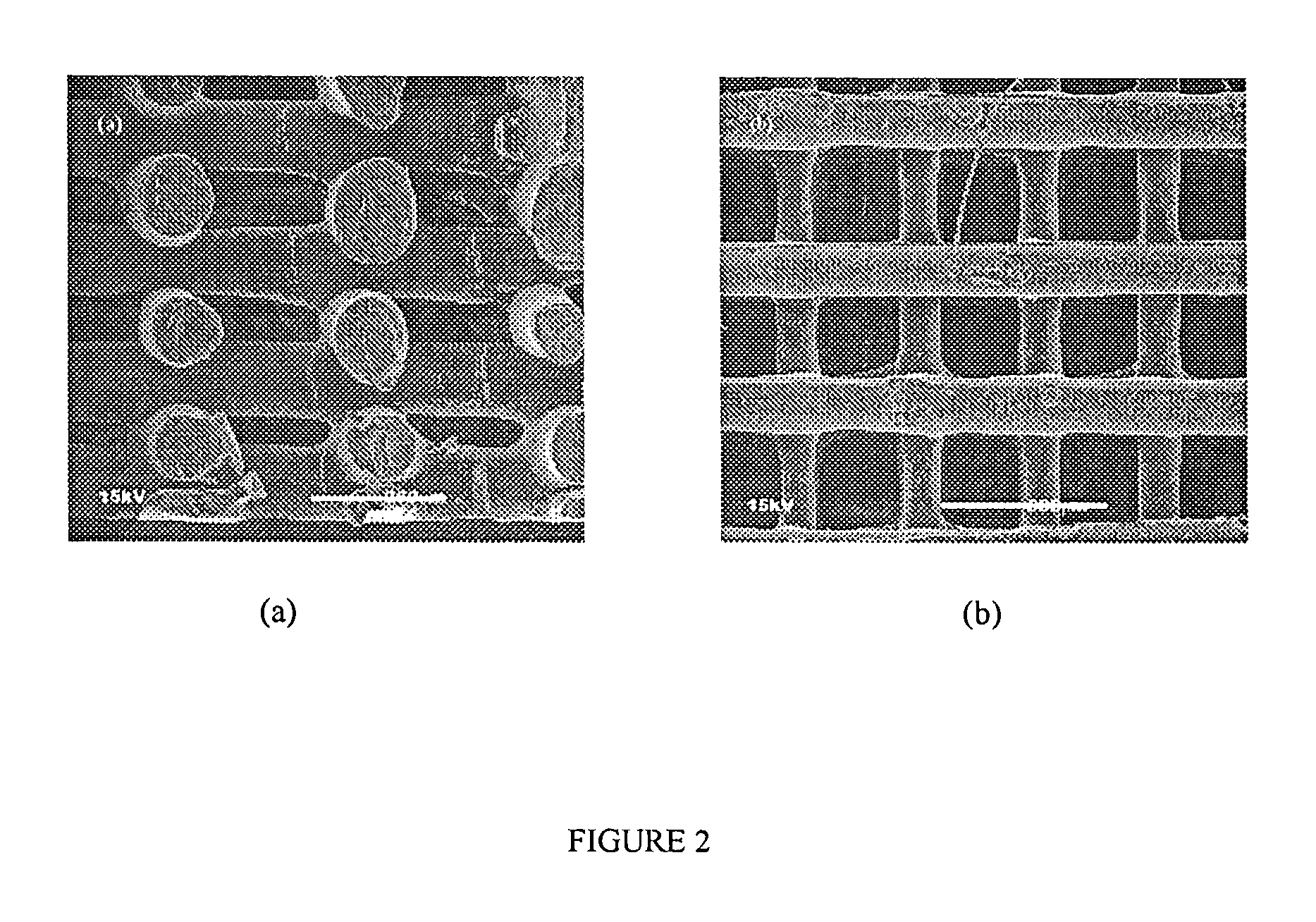
The invention relates to the use of Fused Deposition Modeling to construct three-dimensional (3D) bioresorbable scaffolds from bioresorbable polymers such as polycaprolactone (PCL), or from composites of bioresorbable polymers and ceramics, such as polycaprolactone / hydroxyapatite (PCL / HA). Incorporation of a bioresorbable ceramic to produce a hybrid / composite material support provides the desired degradation and resorption kinetics. Such a composite material improves the biocompatibility and hard tissue integration and allows for increased initial flash spread of serum proteins. The basic resorption products of the composite also avoids the formation of an unfavorable environment for hard tissue cells due to a decreased pH. The scaffolds have applications in tissue engineering, e.g., in tissue engineering bone and cartilage.
Owner:OSTEOPORE INT PTE
Bio-active construct created between fixation device and suture fixed in bone
Methods and constructs including a fixation device and a suture for fixation of soft tissue to bone, or of soft tissue to soft tissue, which amplifies the body's healing response created by the introduction of the suture material and the material properties of the fixation device. Fixation of soft tissue to bone (or of soft tissue to soft tissue) is conducted using a suture (for example, a suture strand, braid, a suture tape, or a combination thereof) and a fixation device (for example, a bone anchor, implant or screw). The suture and fixation device are manufactured from materials that have properties to amplify the body's healing response. Materials such as synthetic bioresorbable polymers (for example, poly-lactic acid) are utilized in the fabrication of orthopedic fixation devices. Once these materials are introduced into the body and are exposed to in vivo conditions, the devices manufactured with these materials undergo hydrolysis and degrade while maintaining specific mechanical properties over time.
Owner:ARTHREX
Complex braided scaffolds for improved tissue regeneration
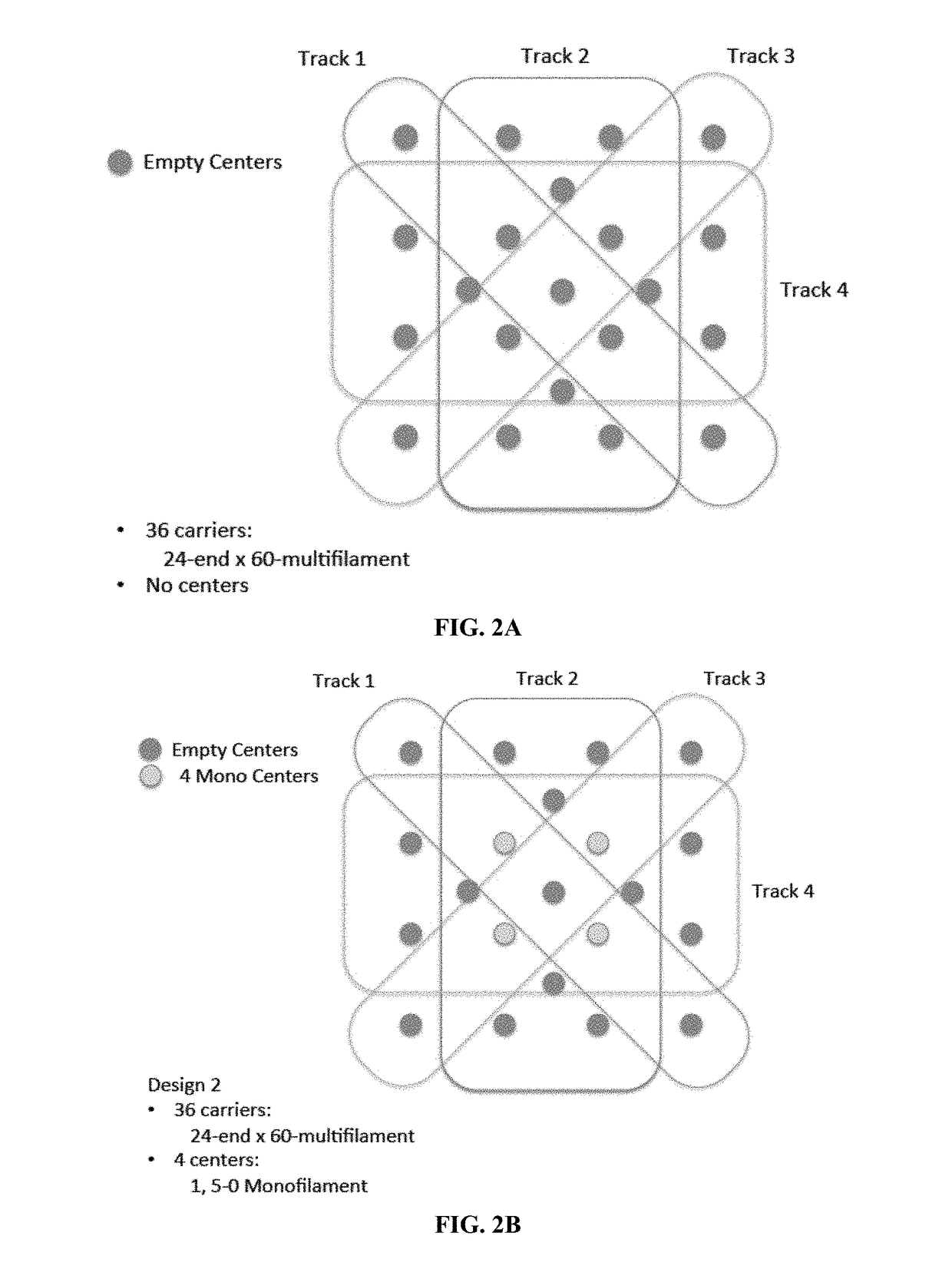
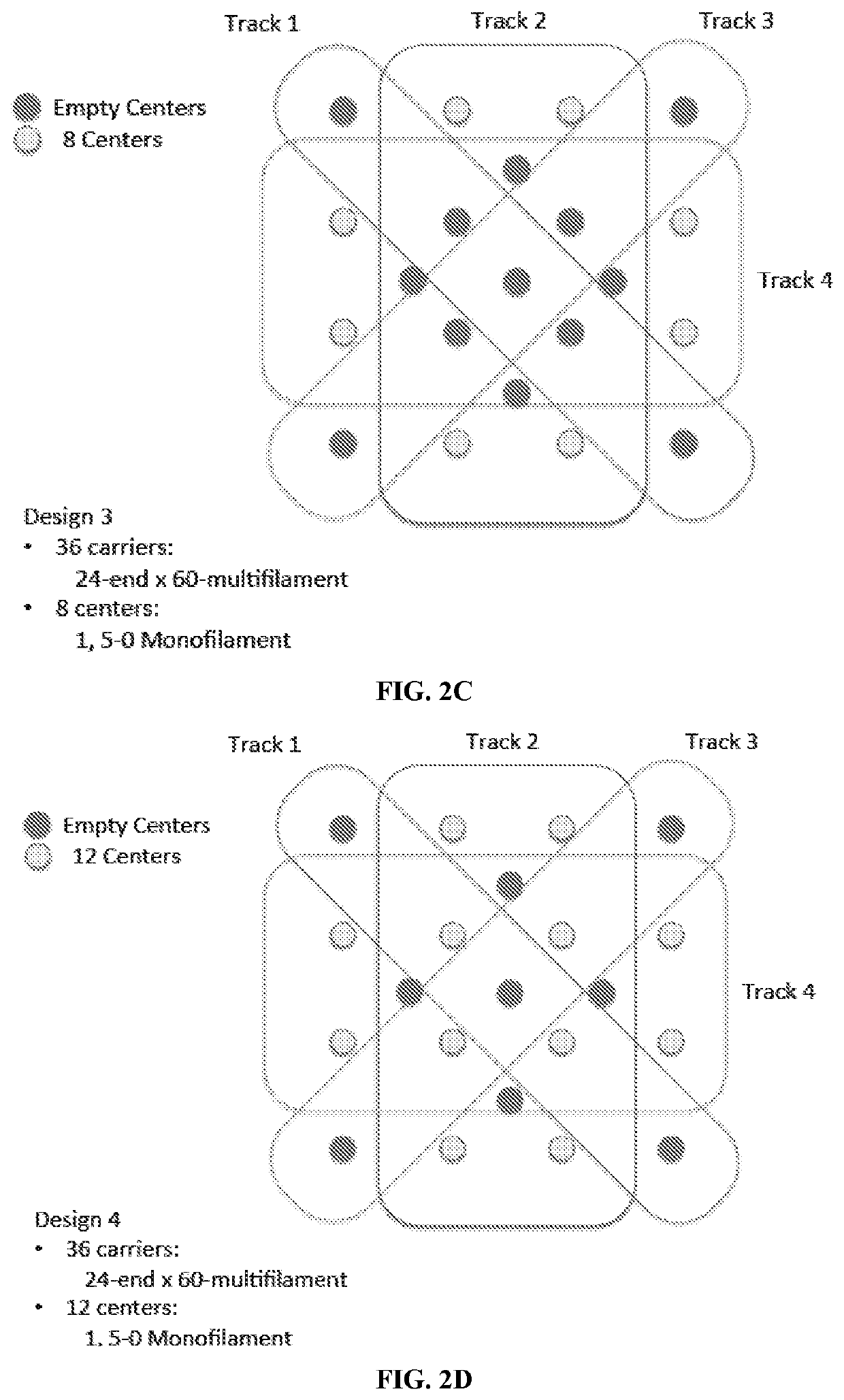
Implantable medical devices and prosthesis for rapid regeneration and replacement of tissues, and methods of making and using the devices, are described. The medical devices include a complex three-dimensional braided scaffold with a polymer composition and structure tailored to desired degradation profiles and mechanical properties. The composite three-dimensional braided scaffolds are braided from yarn bundles of biodegradable and bioresorbable polymeric fibers and / or filaments. Monofilament fibers and / or multifilament fibers can be twisted / plied in different combinations to form multifilament yarns, composite multifilament yarns, or composite yarns. The medical devices are useful as both structural prosthetics taking on the function of the tissue as it regenerates and as in vivo scaffolds for cell attachment and ingrowth.
Owner:BIOREZ INC
Multifunctional implant device
InactiveUS20070191851A1Mechanical strengthAchieve mechanical strengthInternal osteosythesisBone implantSelf reinforcedBioactive glass
Bone fixation or augmentation in a mammalian body to enhance the mechanical strength of a fracture is provided by reinforcement fixing bone ends together using the implant device. A resorbable device can be rendered anti-osteolytic by incorporating materials such as bisphosphonates. It can also be rendered osteoconductive by the incorporation of an osteoconductive material such as bioactive glass or TCP. The implant device has a matrix as one phase, where the matrix is made of a bioresorbable polymer. One phase of the implant is made from self-reinforcing elements and the matrix contains an antiosteolytic agent component. The implant contains further osteoconductive and / or osteoconductive material.
Owner:ASHAMMAKHI NUREDDIN
Three-dimensional bioresorbable scaffolds for tissue engineering applications
ActiveUS7968026B1Good biocompatibilityImproves hard tissue integrationAdditive manufacturing apparatusMouldsBiocompatibility TestingHard tissue
The invention relates to the use of Fused Deposition Modeling to construct three-dimensional (3D) bioresorbable scaffolds from bioresorbable polymers such as polycaprolactone (PCL), or from composites of bioresorbable polymers and ceramics, such as polycaprolactone / hydroxyapatite (PCL / HA). Incorporation of a bioresorbable ceramic to produce a hybrid / composite material support provides the desired degradation and resorption kinetics. Such a composite material improves the biocompatibility and hard tissue integration and allows for increased initial flash spread of serum proteins. The basic resorption products of the composite also avoids the formation of an unfavorable environment for hard tissue cells due to a decreased pH. The scaffolds have applications in tissue engineering, e.g., in tissue engineering bone and cartilage.
Owner:OSTEOPORE INT PTE
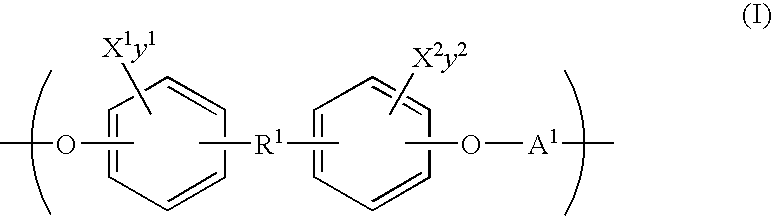
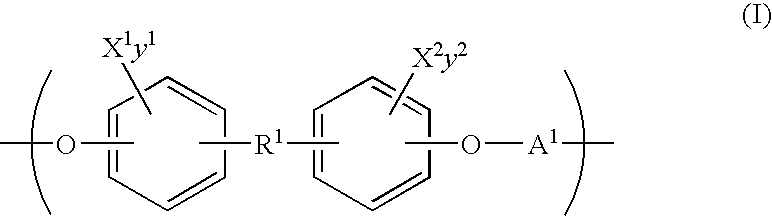
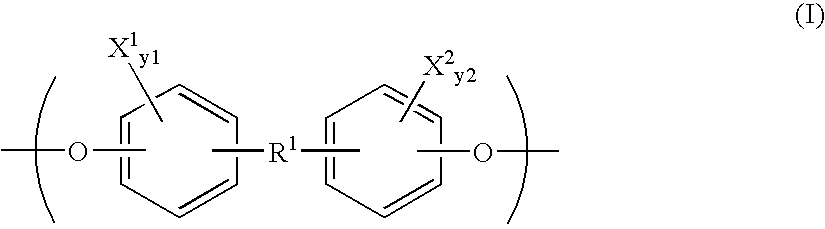
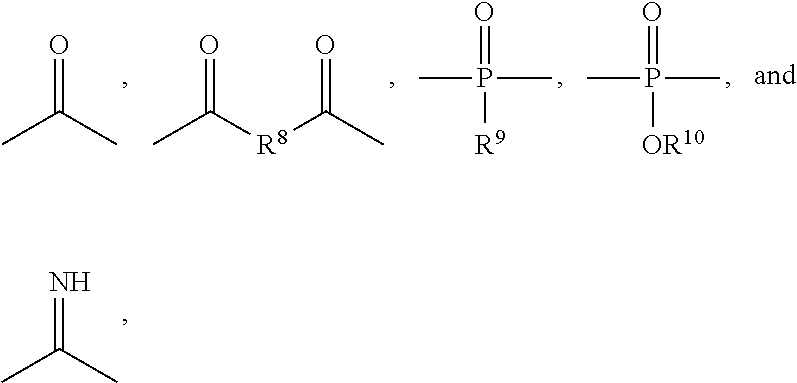
Polymeric biomaterials derived from phenolic monomers and their medical uses
ActiveUS20130203713A1Increasing resorption rateLower Level RequirementsOrganic active ingredientsBiocideTyrosolControlled release
The present invention provides new classes of phenol compounds, including those derived from tyrosol and analogues, useful as monomers for preparation of biocompatible polymers, and biocompatible polymers prepared from these monomeric phenol compounds, including novel biodegradable and / or bioresorbable polymers. These biocompatible polymers or polymer compositions with enhanced bioresorbabilty and processibility are useful in a variety of medical applications, such as in medical devices and controlled-release therapeutic formulations. The invention also provides methods for preparing these monomeric phenol compounds and biocompatible polymers.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
N-substituted monomers and polymers
InactiveUS20080187567A1Improve solubilityReduce melt viscosityAdditive manufacturing apparatusOrganic chemistryBioresorbable polymersViscosity
Biocompatible, bioresorbable polymers comprising a plurality of monomeric repeating units containing an amide group, wherein said amide groups are N-substituted and the N-substituent and degree of N-substitution are effective to lower the melt viscosity, the solution viscosity, or both, compared to the same polymer without N-substitution.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
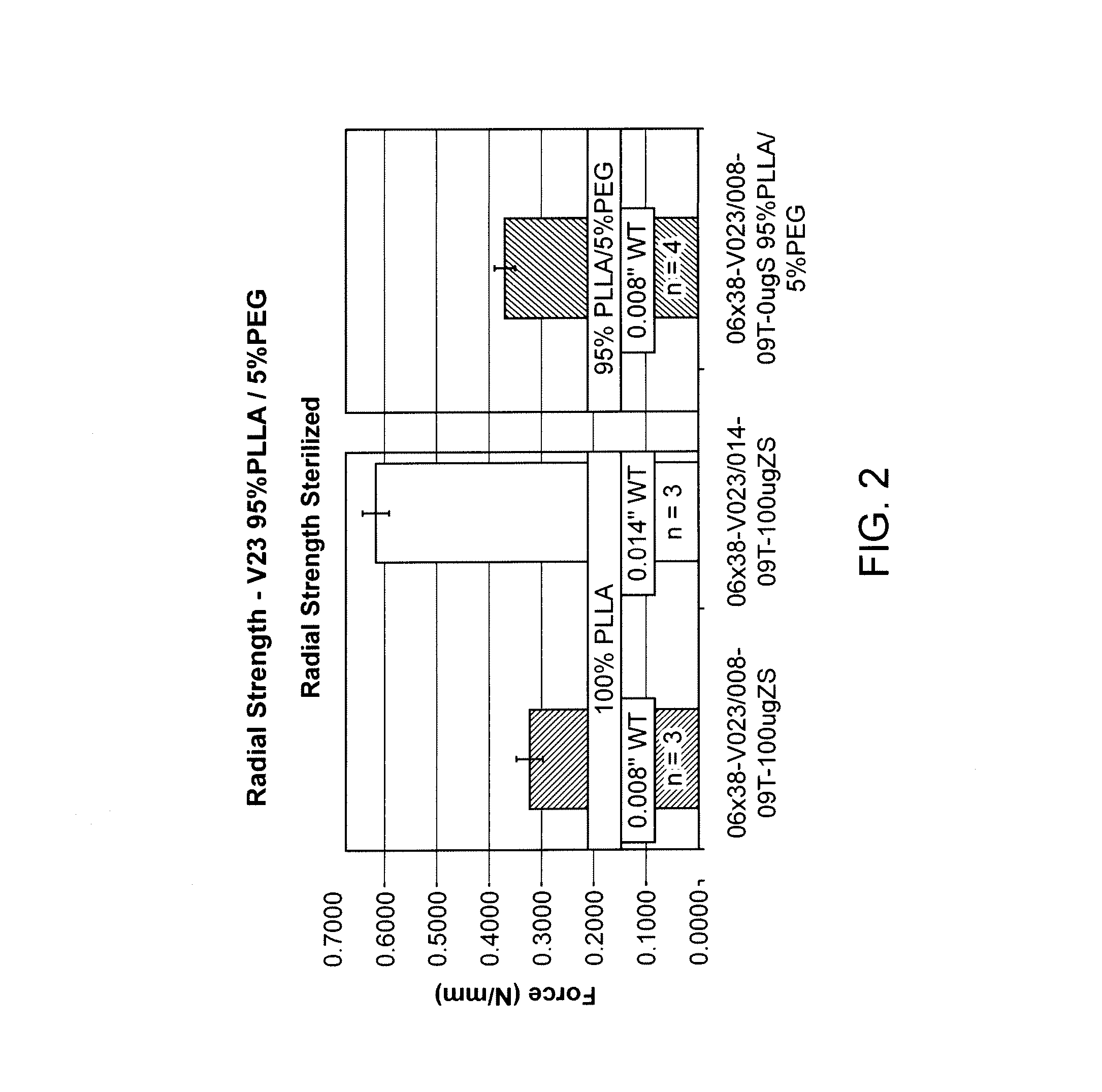
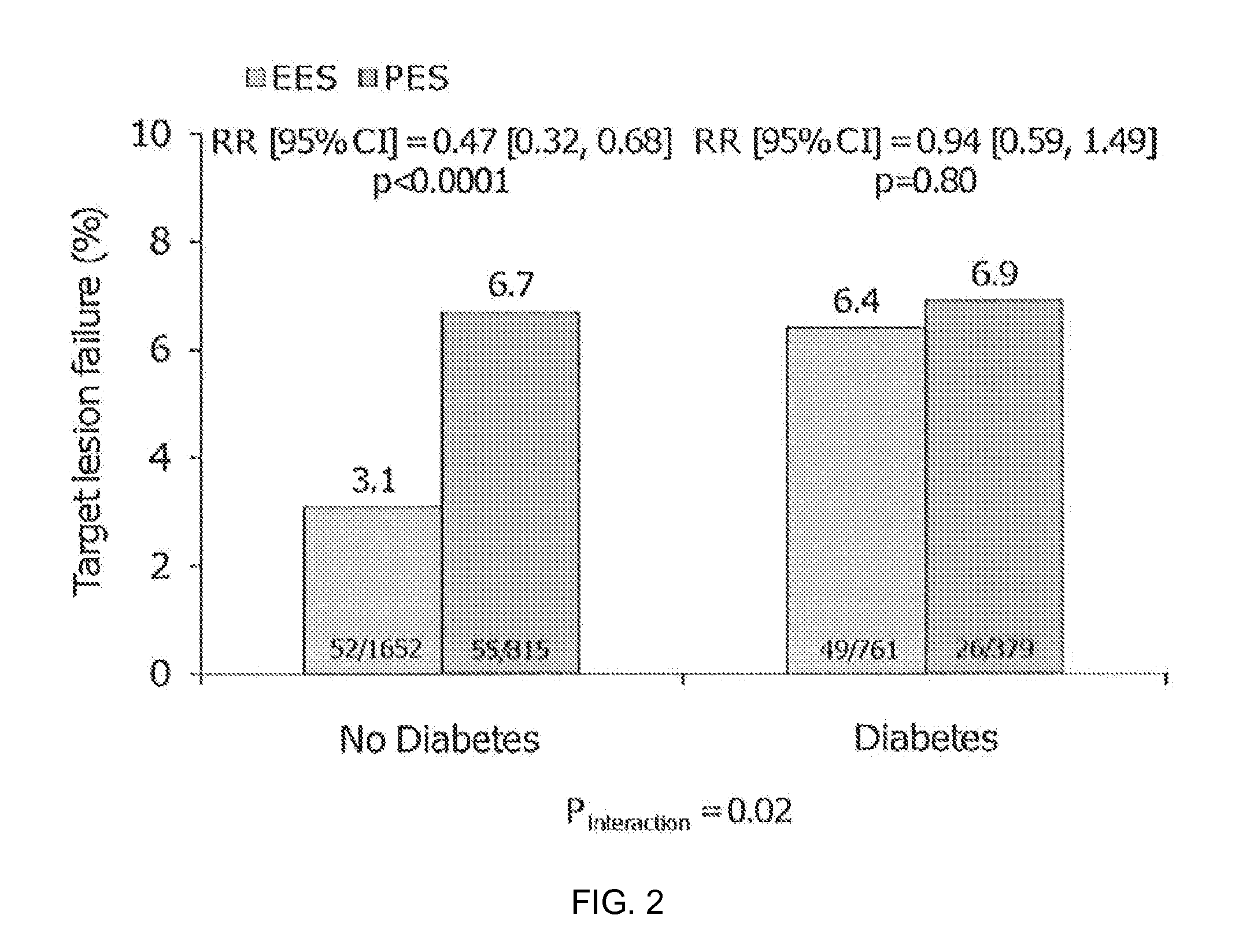
Bioresorbable Polymer Scaffold Treatment of Coronary and Peripheral Artery Disease in Diabetic Patients
Methods of treating coronary and peripheral artery disease in diabetic patients with bioresorbable polymer stents are described. The stents may include everolimus.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Compositions and Methods for Preventing Sternal Wound Infections
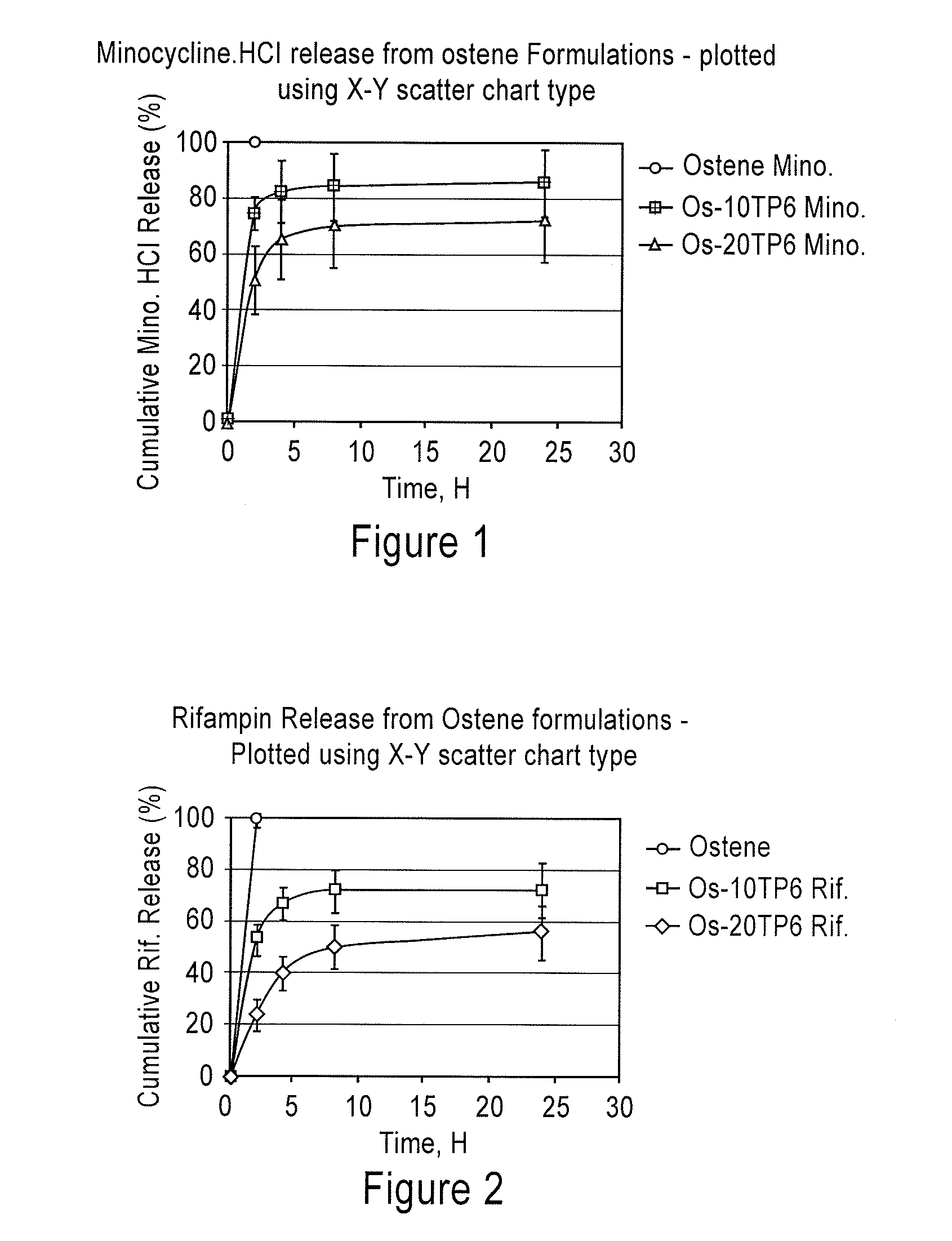
ActiveUS20110294760A1Reduce infectionAvoid developmentBiocideTetracycline active ingredientsIncision SiteMedicine
The invention generally relates to compositions and methods for preventing sternal wound infections, such as mediastinitis. In certain embodiments, the invention provides an antimicrobial composition including at least one bioresorbable polymer, such as a tyrosine-derived polyesteramide, and at least one antimicrobial agent, in which the composition is adapted to be topically applied to an esophageal perforation in a subject or a median sternotomy incision site in the subject, and in which the at least one antimicrobial agent is present in an amount effective to inhibit development of mediastinitis in the subject.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
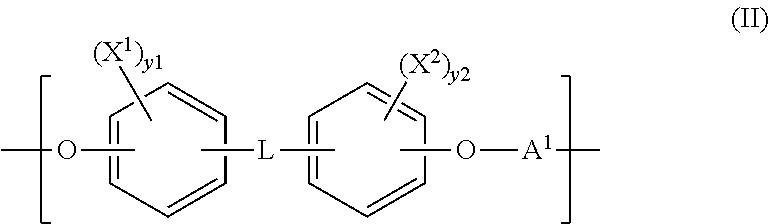
Polymeric biomaterials derived from monomers comprising hydroxyacids and phenol compounds and their medical uses
ActiveUS20150045451A1Provide mechanical strengthProvide rigidity strengthSurgeryPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsTyrosolControlled release
The present invention provides new classes of phenolic compounds derived from hydroxyacids and tyrosol or tyrosol analogues, useful as monomers for preparation of biocompatible polymers, and the biocompatible polymers prepared from these monomeric hydroxyacid-phenolic compounds, including novel biodegradable and / or bioresorbable polymers. These biocompatible polymers or polymer compositions with enhanced bioresorbabilty and processibility are useful in a variety of medical applications, such as in medical devices and controlled-release therapeutic formulations. The invention also provides methods for preparing these monomeric hydroxyacid-phenolic compounds and biocompatible polymers.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV +1
Bioabsorbable polymeric medical device
In embodiments there is described a cardiovascular tube-shaped lockable and expandable bioabsorbable scaffold having a low immunogenicity manufactured from a crystallizable bioabsorbable polymer composition or blend.
Owner:ORBUSNEICH MEDICAL INC
Gas-plasma treatment of implants
An implant for use in biological / biomedical applications may be prepared by subjecting a substrate to a gas-plasma treatment. The substrate may be a biocompatible material, including metals, ceramics, and polymers. More specifically, the substrate may be a bioresorbable polymer. The gas-plasma treatment may include subjecting the substrate to a plasma formed by a reactive gas. The gas-plasma treatment may be performed for a chosen duration at a radio frequency within a temperature range, a pressure range, and a supplied energy range. The substrate may be exposed to living cells, such that some of the living cells become coupled to the substrate. Gas-plasma treatment parameters may be chosen such that the living cells coupled to the treated substrate produce more of a cellular product than living cells coupled to an untreated substrate.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Macroporous and highly resorbable apatitic calcium-phosphate cement
ActiveUS20100068243A1Improve toleranceHigh compressive strengthBiocidePowder deliveryCalcium biphosphateApatite
The present invention is directed to a novel cement powder comprising an organic component consisting of one or more biocompatible and bioresorbable polymers and an inorganic component consisting of one or more calcium phosphate compounds. The invention also relates to the apatitic CPC resulting from the mixing of said cement powder with a liquid phase and setting.
Owner:GRAFTYS +1
Bio-degradable/ absorbable polymer having reduced metal catalyst content, and process for production thereof
InactiveUS20090171064A1Small molecular weightSuitable for useSuture equipmentsProsthesisAbsorbable polymersAcetic acid
The present invention provides a safe biodegradable and bioabsorbable polymer having an extremely low metal catalyst content, while retaining the properties desired for a medical implant or the like; and a process for producing the same. The present invention further provides a method for reducing the content of a metal catalyst in a biodegradable and absorbable polymer that can be applied on an industrial scale. A method for producing a biodegradable and bioabsorbable polymer having a metal catalyst content of less than 1 ppm in terms of a metal comprising the steps of (1) copolymerizing lactide and ε-caprolactone at a molar ratio ranging from 40 / 60 to 60 / 40 in the presence of the metal catalyst to produce a copolymer; and (2) washing the copolymer with a mixed solvent comprising acetic acid and isopropanol at a volume ratio ranging from 25 / 75 to 45 / 55 at less than 40° C., and drying the copolymer. 13. A method for producing a biodegradable and bioabsorbable polymer having a metal catalyst content of less than 1 ppm in terms of a metal comprising the steps of (1) copolymerizing lactide and ε-caprolactone at a molar ratio ranging from 65 / 35 to 85 / 15 in the presence of the metal catalyst to produce a copolymer; and (2) washing the copolymer with a mixed solvent comprising acetic acid and isopropanol at a volume ratio ranging from 45 / 55 to 55 / 45 at less than 40° C., and drying the copolymer.
Owner:GUNZE LTD
Neural restoration sleeve and preparing method and application thereof
InactiveCN105412992AHigh strengthImprove stabilityElectro-spinningTissue regenerationBioresorbable polymersBiocompatibility Testing
The invention provides a neural restoration sleeve and a preparing method and application thereof. The neural restoration sleeve is a double-layer fiber sleeve, the inner layer of the sleeve is an orientation polymer fiber layer, the outer layer of the sleeve is a non-orientation polymer fiber layer, bioresorbable polymers are adopted, and the nerve growth promoting factors are embedded in the inner layer. The neural restoration sleeve prepared through the preparing method can induce nerve cells to grow in the fiber orientation, meanwhile, the nerve growth promoting factors are embedded in the inner layer to promote growth of nerve axon and accelerate nerve tissue restoration, the non-woven non-orientation polymer fiber layer on the outer layer plays a role in supporting and endows the neural restoration sleeve with high strength and stability, and the polymers on the inner layer and the outer layer are the bioresorbable polymers, have high biocompatibility, will not cause chronic inflammation reaction and are high in safety; the preparing method is simple, and industrial production can be realized.
Owner:WUXI ZHONGKE GUANGYUAN BIOMATERIALS
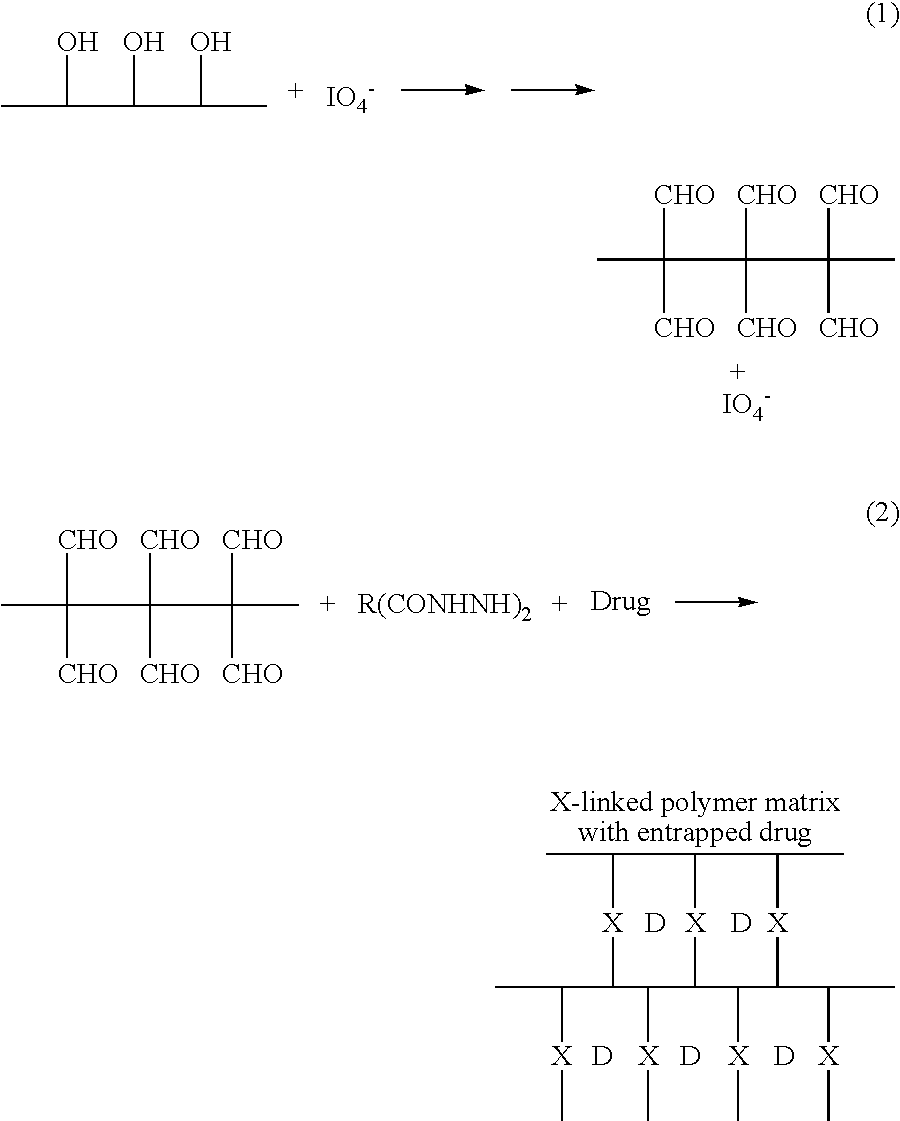
Bioresorbable polymer matrices and methods of making and using the same
InactiveUS20080069894A1Promote migrationAvoid reactionPowder deliveryAntipyreticControl releaseActive agent
A bioerodible composition for delivery of a bioactive agent is the reaction product of a reaction mixture which includes an oxidized dextran solution, and a mixture of solids containing a dihydrazide, a bioactive agent, and optionally a pH adjusting agent in an amount sufficient to achieve a pH of the reaction mixture of 6 or less. The composition may include a release agent for the controlled release of the bioactive agent from the composition. A bioactive agent may therefore be administered to a body site in need of the same by providing a first aliquot portion of a reaction mixture comprising an oxidized dextran solution, and a second aliquot portion of a reaction mixture comprising a mixture of solids comprised of a dihydrazide, a bioactive agent, and a solid acid which is present in an amount sufficient to achieve a pH of the reaction mixture of 6 or less, mixing the first and second aliquot portions to form the reaction mixture thereof, and thereafter installing the reaction mixture at the body site and allowing a solidified bioerodible drug delivery composition to be formed thereby in situ. The present invention may be provided in the form of a kit comprised of a double syringe which respectively contains the first and second aliquot portions of the reaction mixture so that the same may be mixed just prior to use.
Owner:ROYER BIOMEDICAL INC
Polymer formulations for delivery of bioactive agents
Disclosed in the present application are compositions comprising a bioresorbable polymer matrix and a bio active agent, wherein the bioactive agent is dispersed within polymer matrix as a solid. Also provided herein are methods for preparing a bioactive agent formulation, wherein the agent is present in a solid form and, wherein the agent is occluded into a polymeric matrix by polymerization of polymer matrix precursors or by self assembly of the polymer.
Owner:CARBYLAN THERAPEUTICS
Short pulse laser machining of polymers enhanced with light absorbers for fabricating medical devices
ActiveUS20140263217A1Promote absorptionStentsDomestic articlesLaser processingBioresorbable polymers
A method of laser machining a polymer construct to form a stent that includes a bioresorbable polymer and an absorber that increases absorption of laser energy during laser machining. The laser cuts the tubing at least in part by a multiphoton absorption mechanism and the polymer and absorber have a very low absorbance or are transparent to light at the laser wavelength.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Shape memory bioresorbable polymer peripheral scaffolds
Bioabsorbable scaffolds having high crush recoverability, high fracture resistance, and reduced or no recoil due to self expanding properties at physiological conditions are disclosed. The scaffolds are made from a random copolymer of PLLA and a rubbery polymer such as polycaprolactone.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Neural restoration sleeve tube and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN105455923AHigh strengthImprove stabilitySurgeryProsthesisBioresorbable polymersBiocompatibility Testing
The invention provides a neural restoration sleeve tube and a preparation method and application thereof. The neural restoration sleeve tube is a double-layer fiber sleeve tube, the inner layer of the sleeve tube is an orientated polymer fiber layer, the outer layer of the sleeve tube is a non-woven non-orientated polymer fiber layer, and the polymer is a bioresorbable polymer. According to the neural restoration sleeve tube prepared through the preparation method, nerve cells can grow along the fiber orientation, then nervous tissue is restored, the non-woven non-non-orientated polymer fiber layer on the outer layer achieves a supporting function, and the neural restoration sleeve tube achieves good strength and stability. Meanwhile, due to the fact that the polymer on the inner layer and the outer layer is the bioresorbable polymer, good biocompatibility is achieved, no chronic inflammation reaction is caused, high safety is achieved, the preparation method is simple, and industrial production can be achieved.
Owner:WUXI ZHONGKE GUANGYUAN BIOMATERIALS
Method for preparing a composite material, resulting material and use thereof
InactiveUS20100094418A1Increase contentPromoting osseo-integrationImpression capsWood working apparatusSolventAqueous solution
The invention relates to a method for preparing a composite material having a homogeneous composition, containing at least one bioactive ceramic phase and at least one bioresorbable polymer. The inventive method is characterised in that it comprises the following steps: a) a bioactive ceramic phase in powder form is obtained, b) the bioactive ceramic powder is suspended in a solvent, c) a bioresorbable polymer is added to the suspension obtained in (b) and mixed to produce a viscous homogeneous dispersion of said bioactive ceramic powder in a solution formed by the solvent and the polymer, and d) the dispersion obtained in (c) is precipitated in an aqueous solution in order to obtain a homogeneous composite material. The invention also relates to the resulting composite material and to the use thereof in the production of implantable medical devices.
Owner:NORAKER
Absorbable luminal stent and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104644295AAvoid damageIncreased radial support durationStentsSurgeryBioresorbable polymersInsertion stent
The invention provides an absorbable luminal stent and a preparation method thereof. The absorbable luminal stent comprises a stent body, a plurality of through holes prepared on the stent body and bioresorbable polymer materials full filled in the through holes. When the stent is transplanted into a blood vessel, by compounding of the materials in the through holes and the material of the stent body, damage caused in the pressure holding and opening process of the stent is reduced, duration time of a radial supporting force of the stent is prolonged and mechanical performance of the transplanted stent is ensured.
Owner:SHANGHAI BIO HEART BIOLOGICAL TECHNOLOGY CO LTD +1
Complex braided scaffolds for improved tissue regeneration
PendingUS20200306029A1Maximize number of cellIncrease surface areaLigamentsMusclesBraided stentBioresorbable polymers
Implantable medical devices and prosthesis for rapid regeneration and replacement of tissues, and methods of making and using the devices, are described. The medical devices include a complex three-dimensional braided scaffold with a polymer composition and structure tailored to desired degradation profiles and mechanical properties. The composite three-dimensional braided scaffolds are braided from yarn bundles of biodegradable and bioresorbable polymeric fibers and / or filaments. Monofilament fibers and / or multifilament fibers can be twisted / plied in different combinations to form multifilament yarns, composite multifilament yarns, or composite yarns. The medical devices are useful as both structural prosthetics taking on the function of the tissue as it regenerates and as in vivo scaffolds for cell attachment and ingrowth.
Owner:BIOREZ INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com