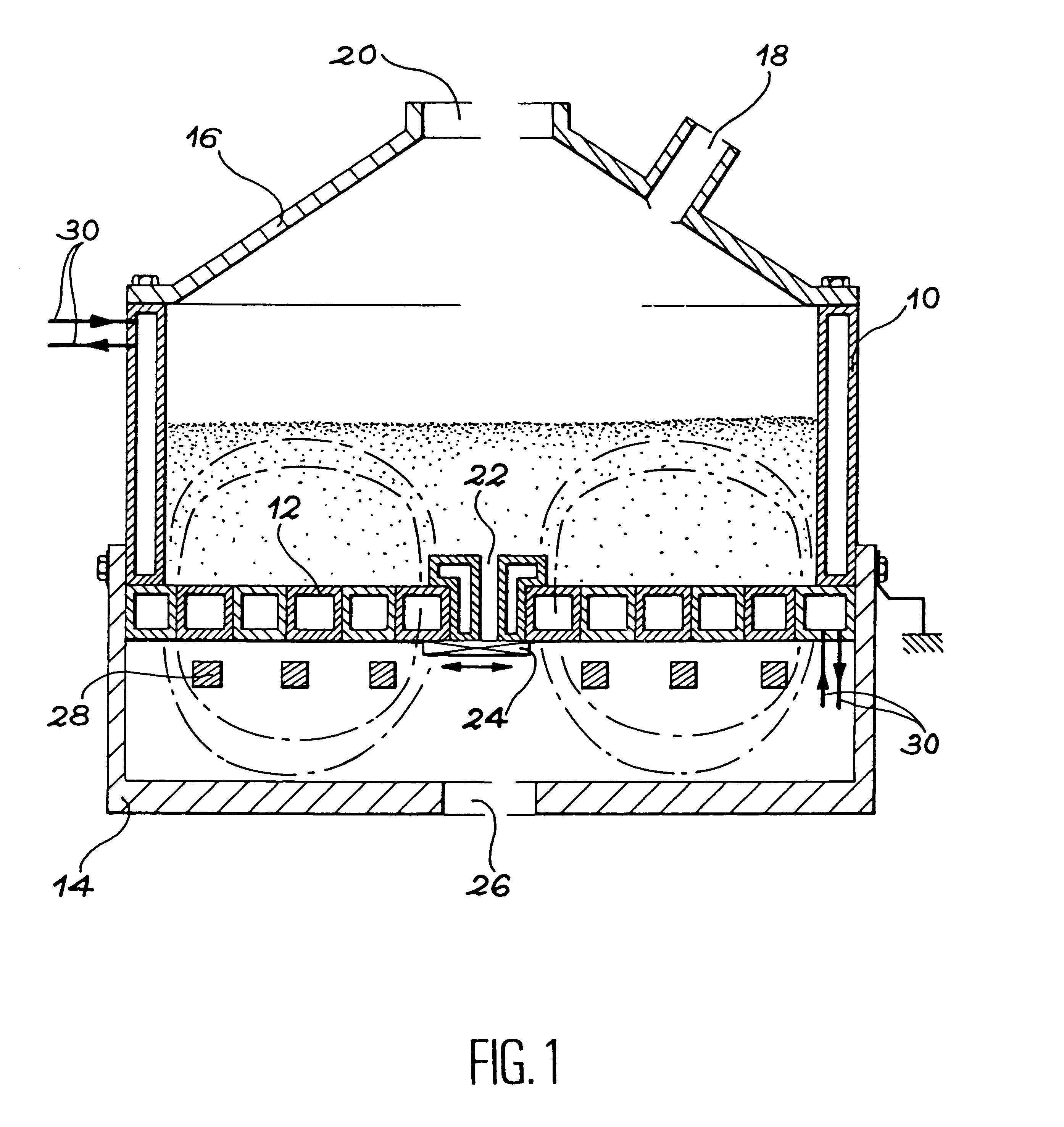
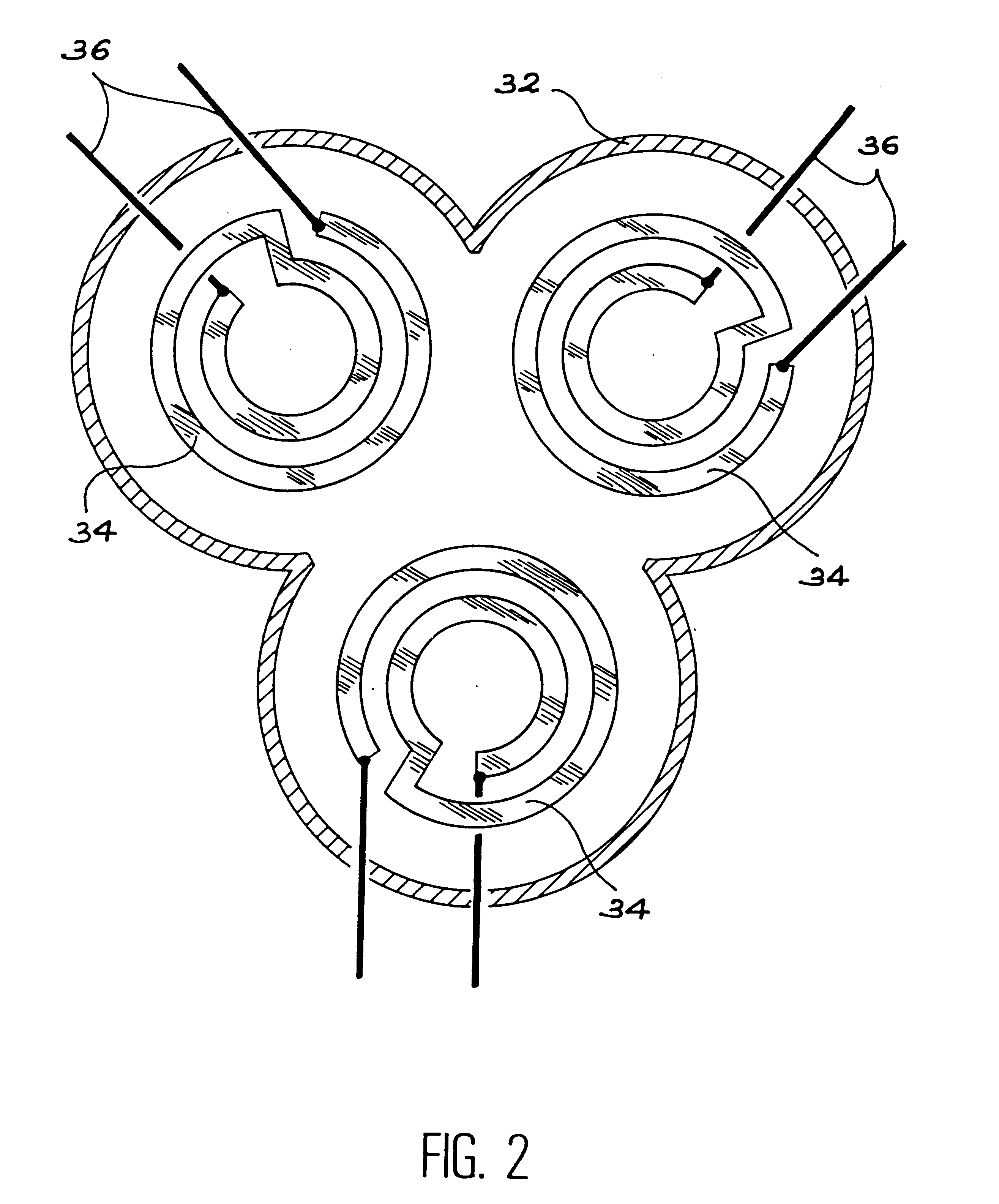
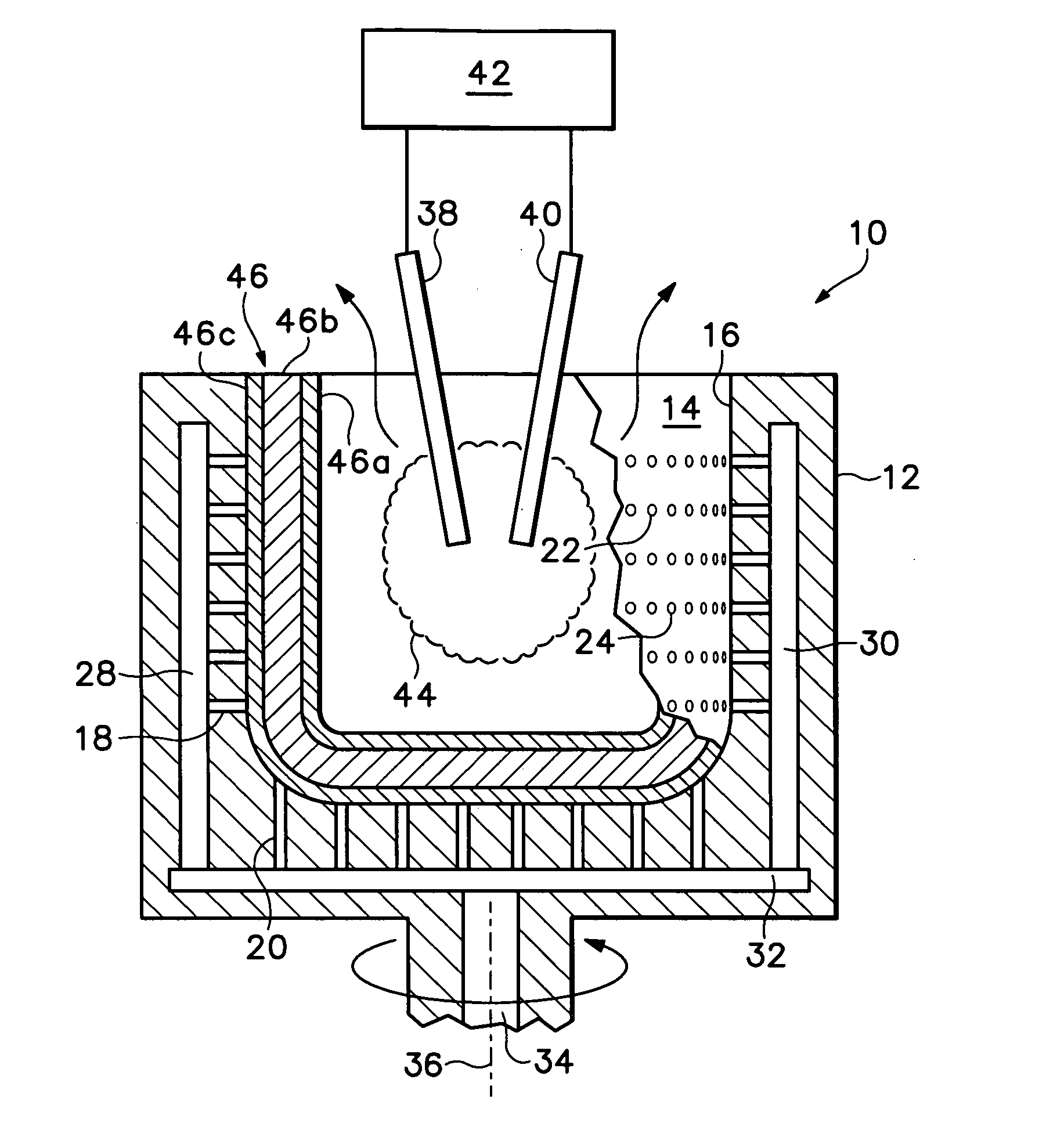
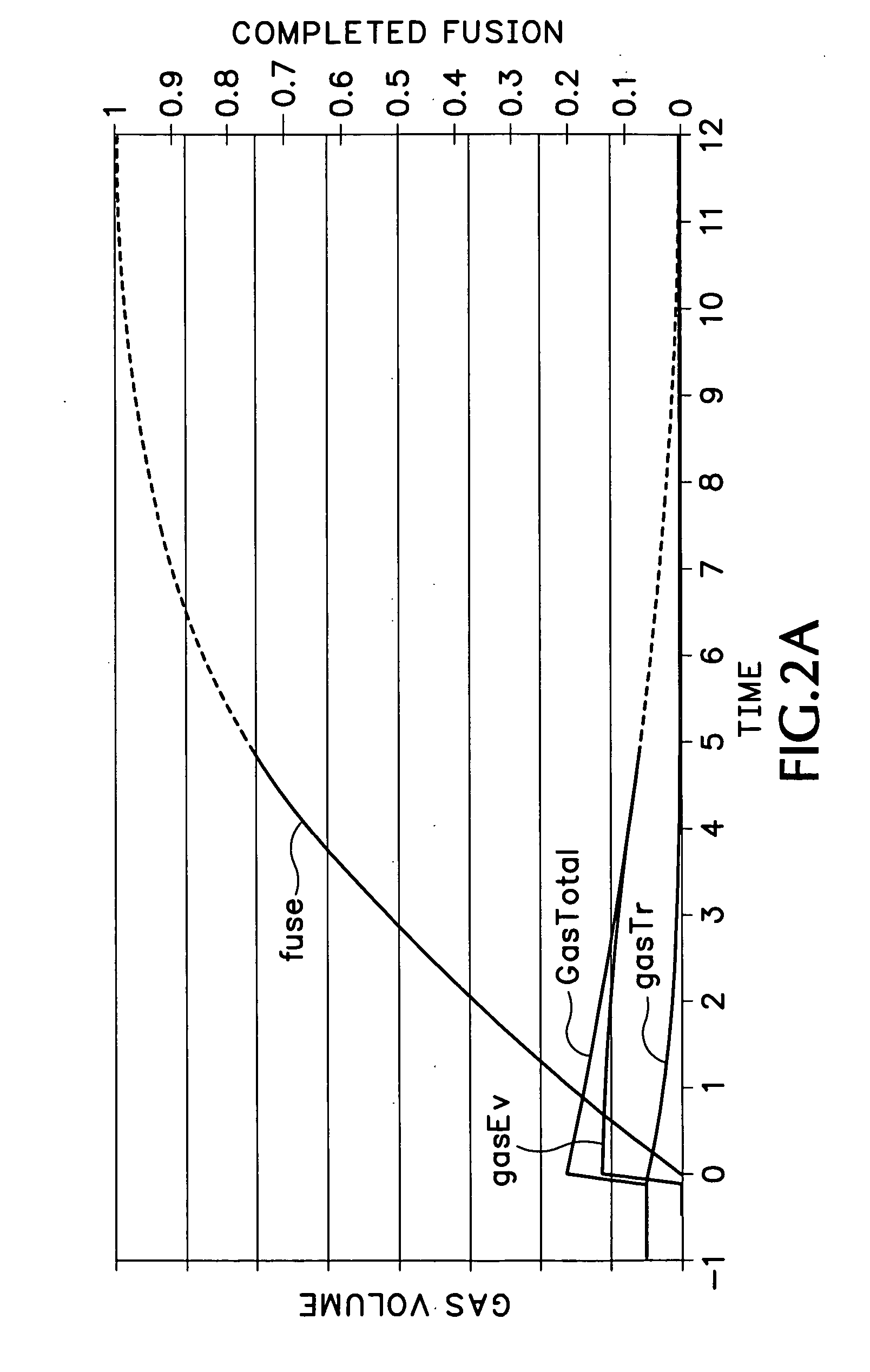
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
216results about "Pot furnaces" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
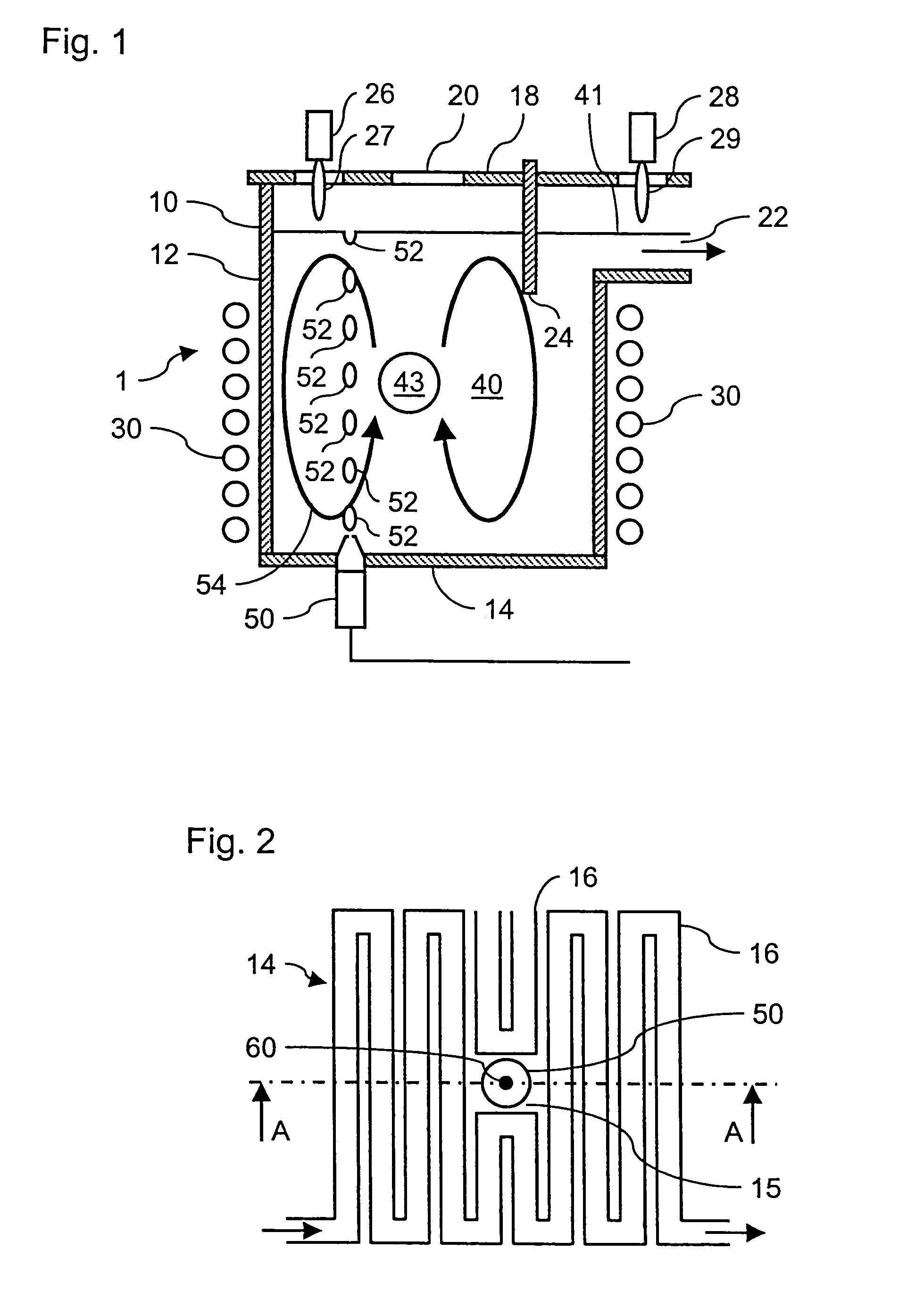
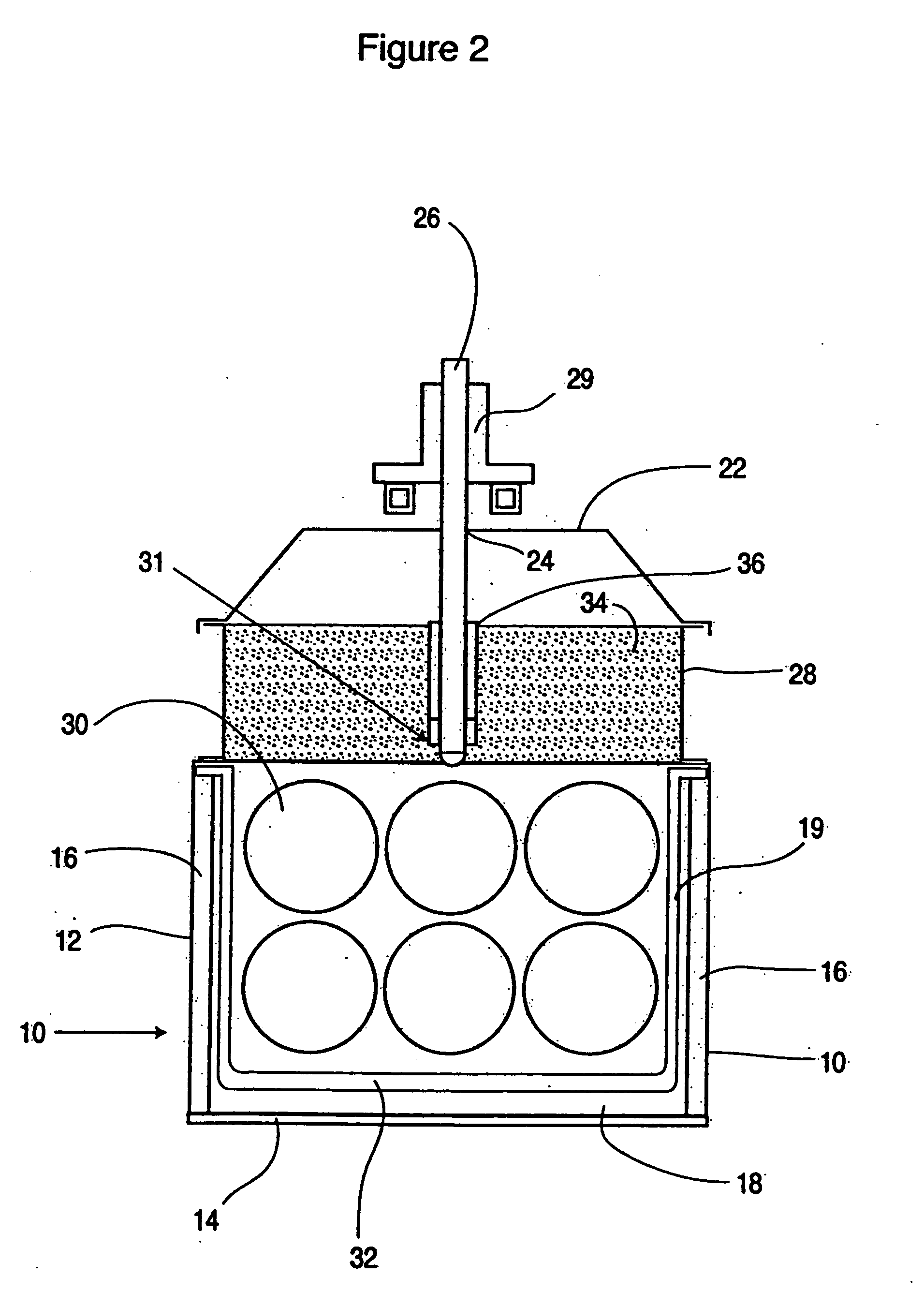
Fining of boroalumino silicate glasses
ActiveUS20060293162A1Pot furnacesGlass furnace apparatusActive-matrix liquid-crystal displaySilicate glass
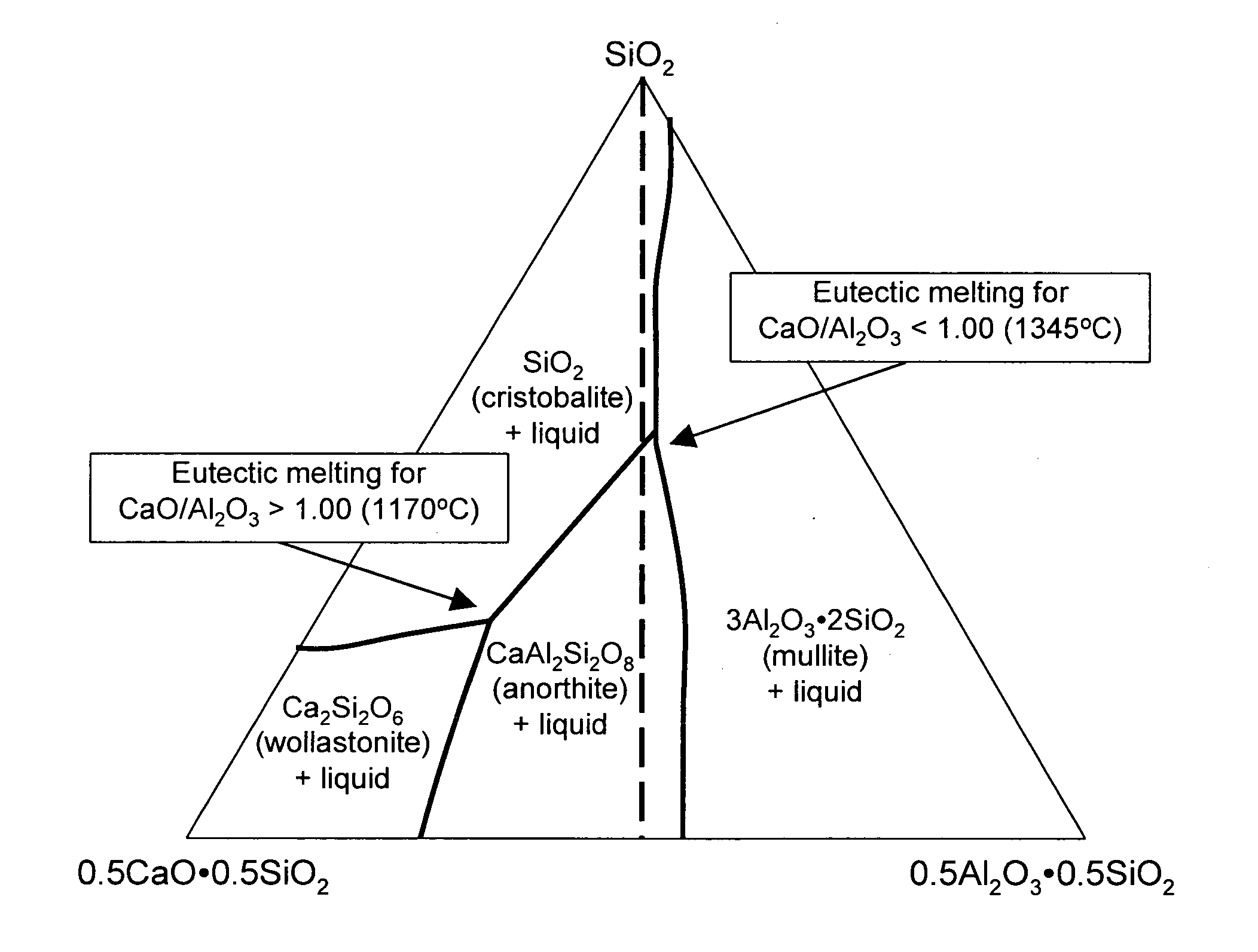
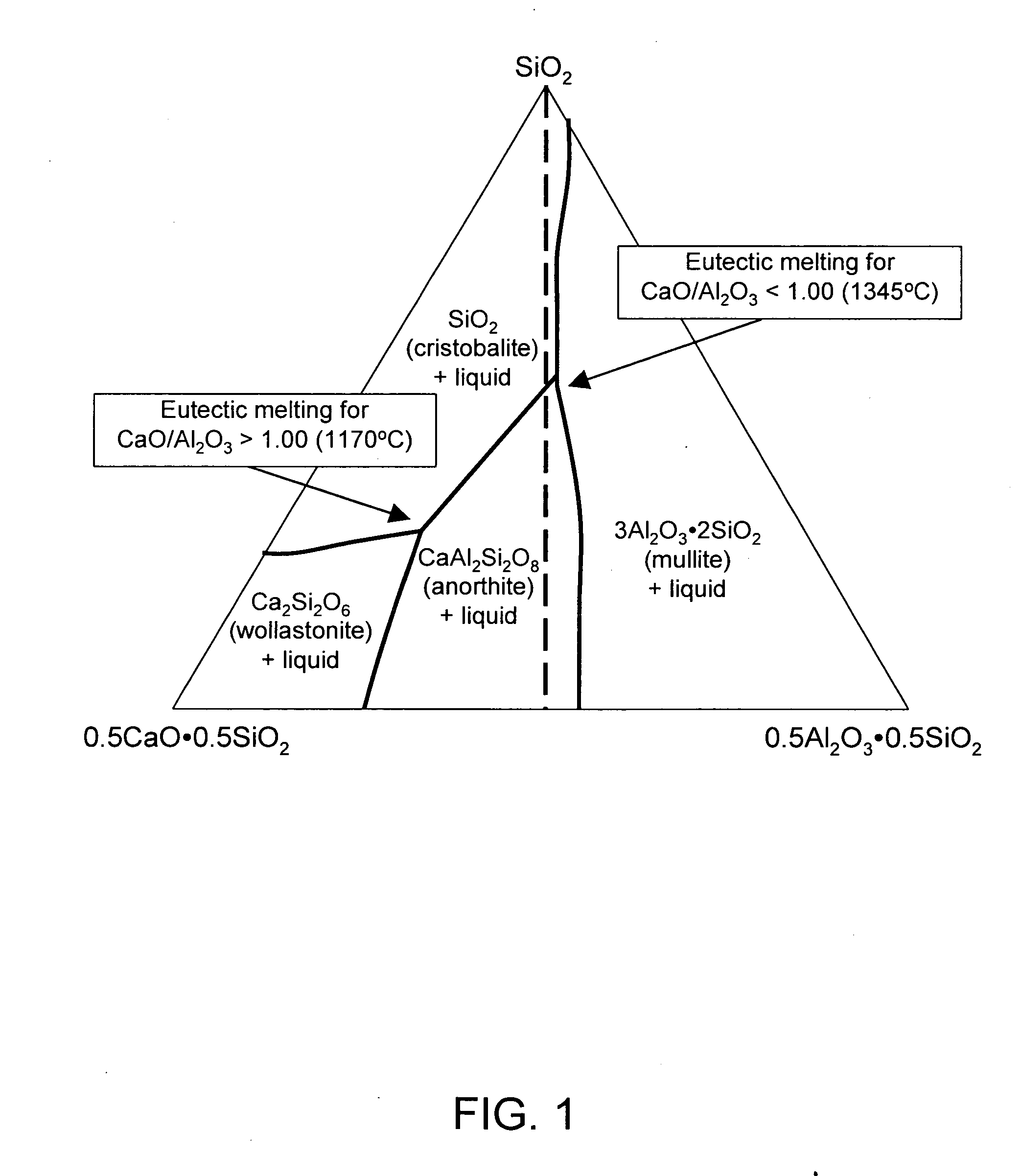
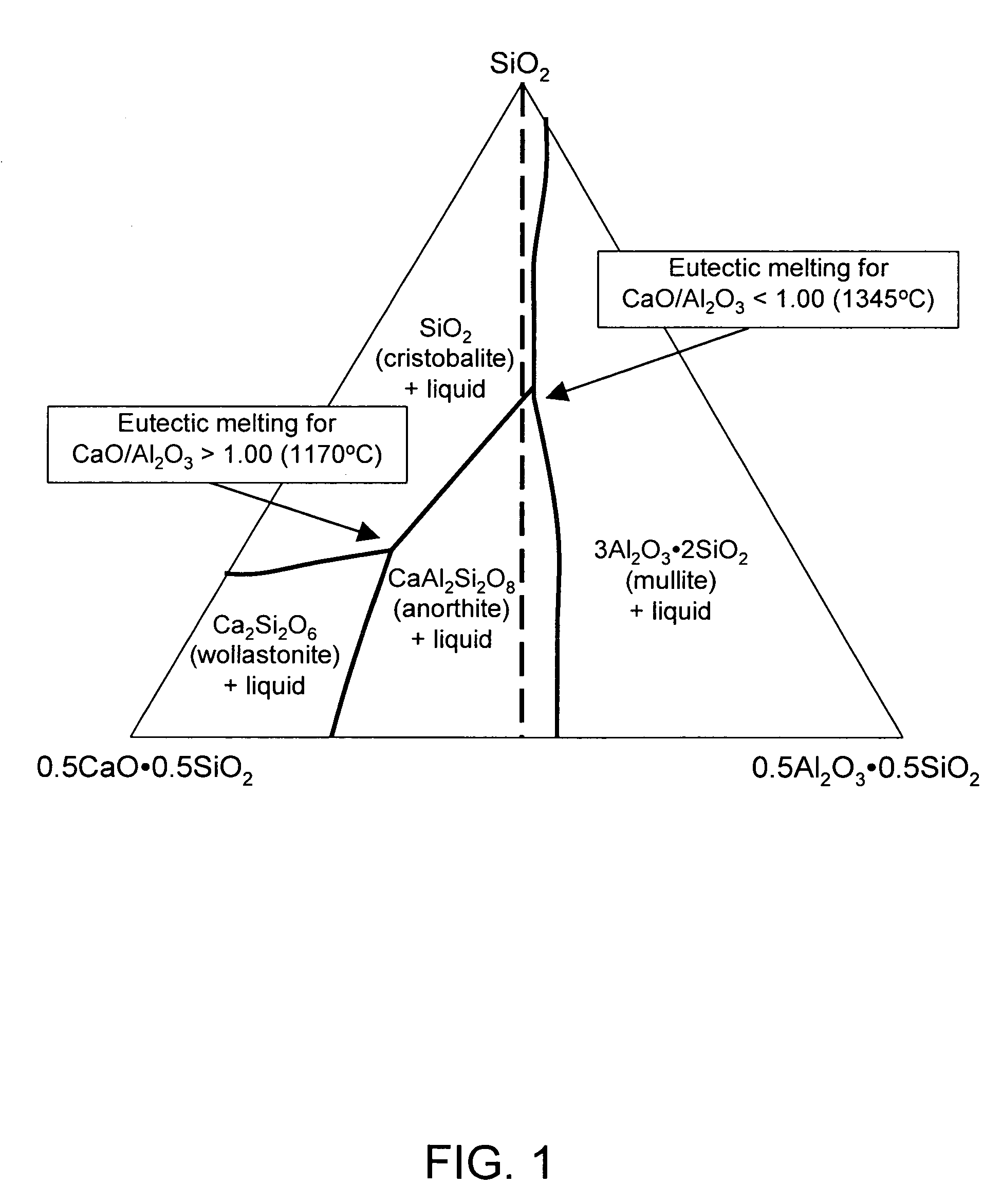
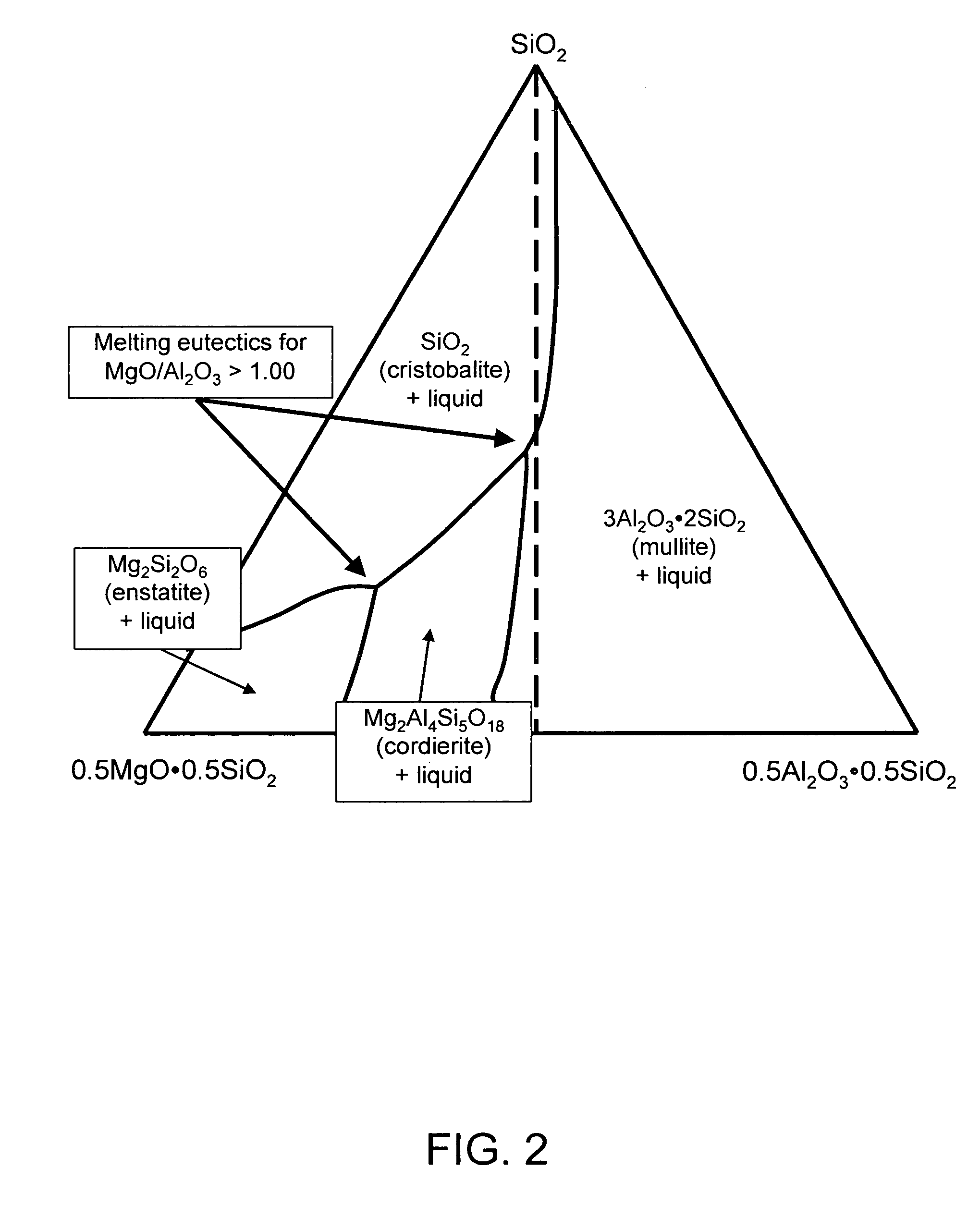
Glasses are disclosed which can be used to produce substrates for flat panel display devices, e.g., active matrix liquid crystal displays (AMLCDs). The glasses have MgO concentrations in the range from 1.0 mole percent to 3.0 mole percent and Σ[RO] / [Al2O3] ratios greater than or equal to 1.00, where [Al2O3] is the mole percent of Al2O3 and Σ[RO] equals the sum of the mole percents of MgO, CaO, SrO, and BaO. These compositional characteristics have been found to improve the melting properties of batch materials used to produce the glass, which, in turn, allows the glasses to be fined (refined) with more environmentally friendly fining agents, e.g., tin as opposed to arsenic and / or antimony.
Owner:CORNING INC
Fining of boroalumino silicate glasses
ActiveUS7851394B2Pot furnacesGlass forming apparatusActive-matrix liquid-crystal displayLiquid-crystal display
Glasses are disclosed which can be used to produce substrates for flat panel display devices, e.g., active matrix liquid crystal displays (AMLCDs). The glasses have MgO concentrations in the range from 1.0 mole percent to 3.0 mole percent and Σ[RO] / [Al2O3] ratios greater than or equal to 1.00, where [Al2O3] is the mole percent of Al2O3 and Σ[RO] equals the sum of the mole percents of MgO, CaO, SrO, and BaO. These compositional characteristics have been found to improve the melting properties of batch materials used to produce the glass, which, in turn, allows the glasses to be fined (refined) with more environmentally friendly fining agents, e.g., tin as opposed to arsenic and / or antimony.
Owner:CORNING INC
Sulfide-based lithium-ion-conducting solid electrolyte glass, all-solid lithium secondary battery, and method for manufacturing all-solid lithium secondary battery
ActiveUS20090142669A1Promote crystallizationReduce processing timePot furnacesFinal product manufactureLithiumOptoelectronics
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
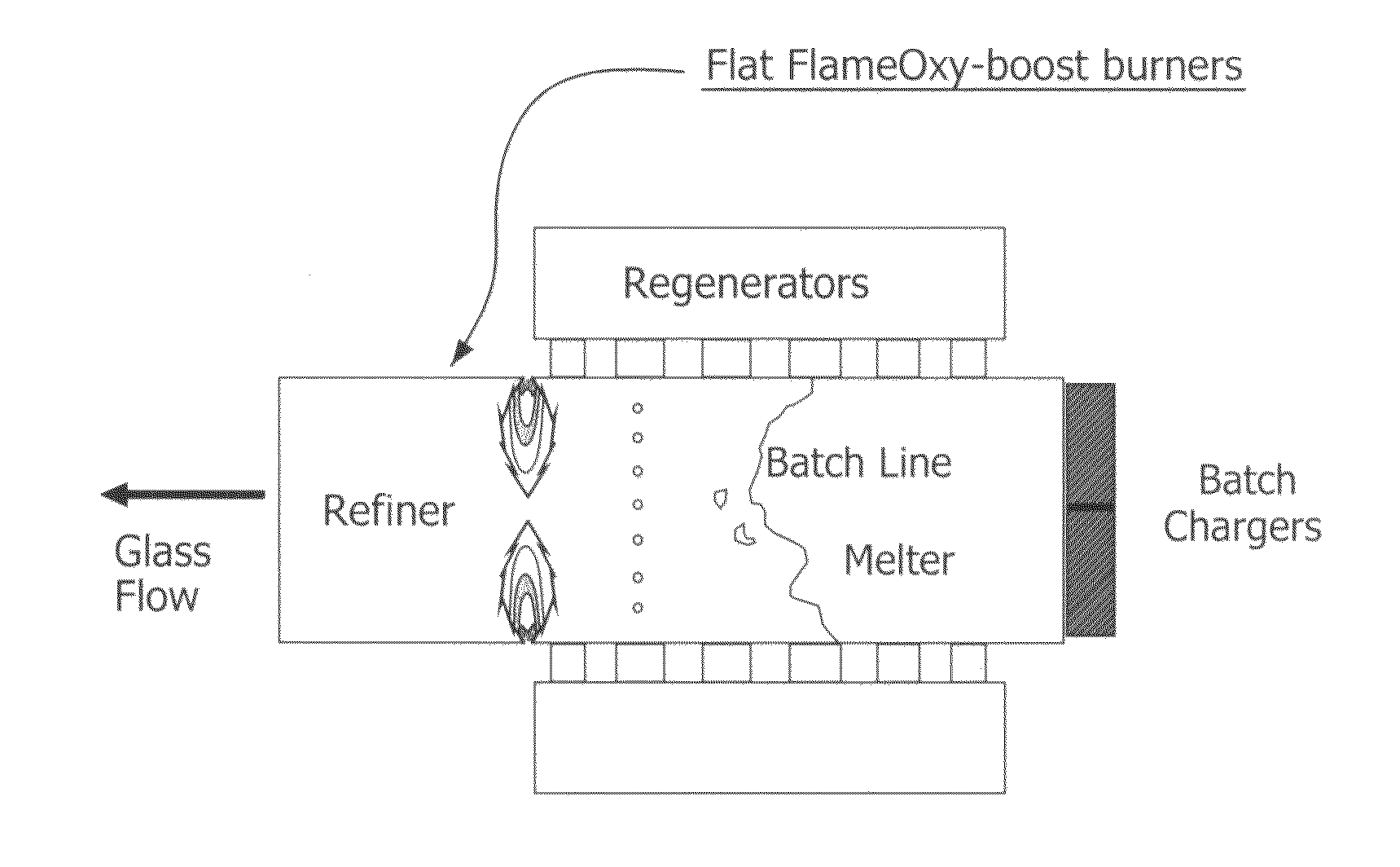
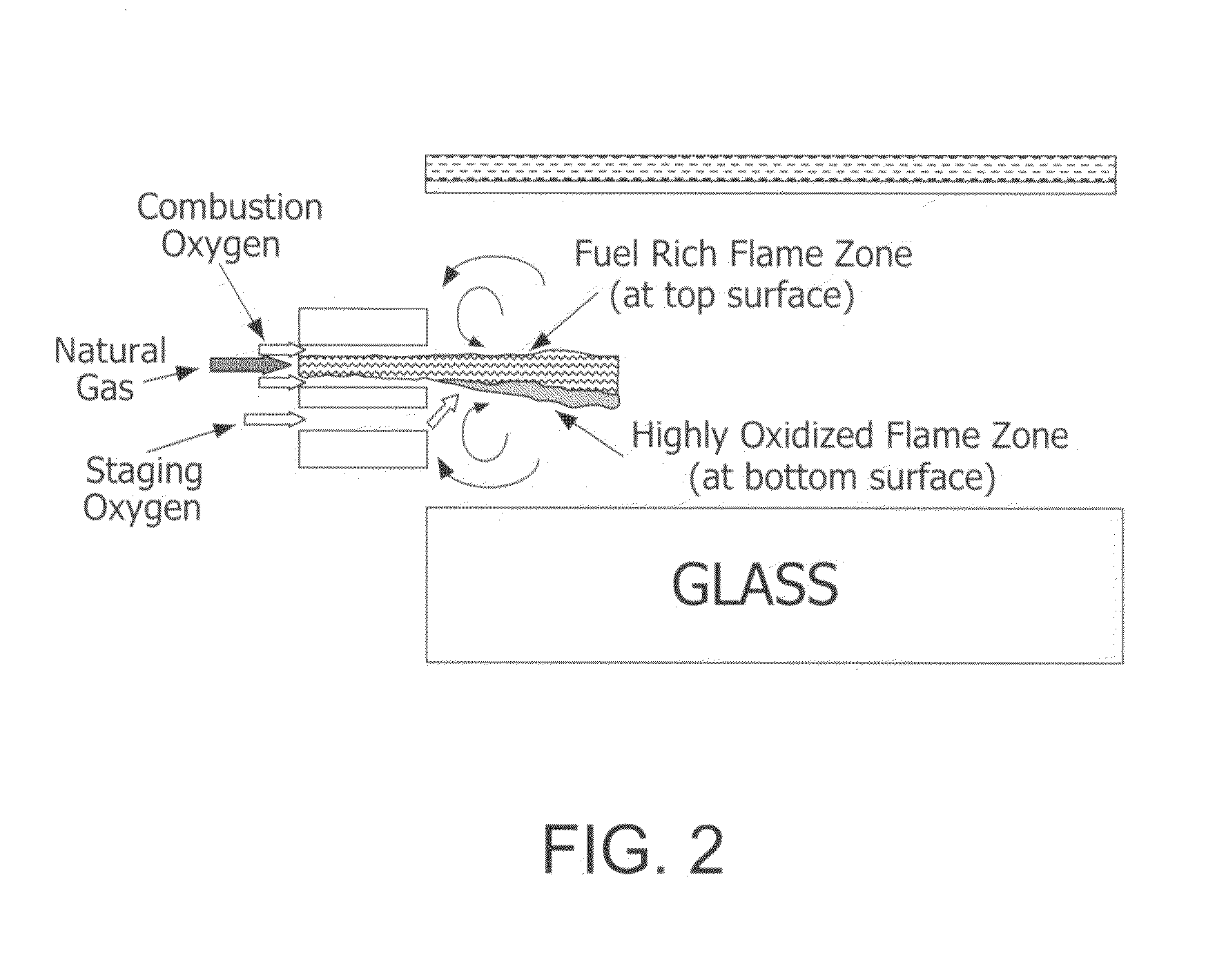
Furnace and Process for Controlling the Oxidative State of Molten Materials
ActiveUS20100313604A1Quality improvementImprove clarityPot furnacesGlass furnace apparatusChemical measurementAtmosphere
A method useful with oxy-fuel combustion and in a furnace which contains molten material, wherein either substoichiometric or superstoichiometric combustion and low velocity injection of fuel and primary and secondary oxidant in an oxy-fuel burner are carried out in an orientation which forms either a reducing or oxidizing atmosphere proximate the molten surface.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Glass scaffolds with controlled resorption rates and methods for making same
InactiveUS7005135B2Promote bone growthEconomical and simple methodPot furnacesGlass furnace apparatusFiberDissolution
The present invention relates to resorbable glass scaffolds for use in biological applications and methods for making same. Specifically, these scaffolds are composed of phosphate glass fibers, where the rate of dissolution into biological fluids is controlled by the length of time the glass is held above its melt temperature prior to spinning the fiber.
Owner:ADVANCED TECH & REGENERATIVE MEDICINE
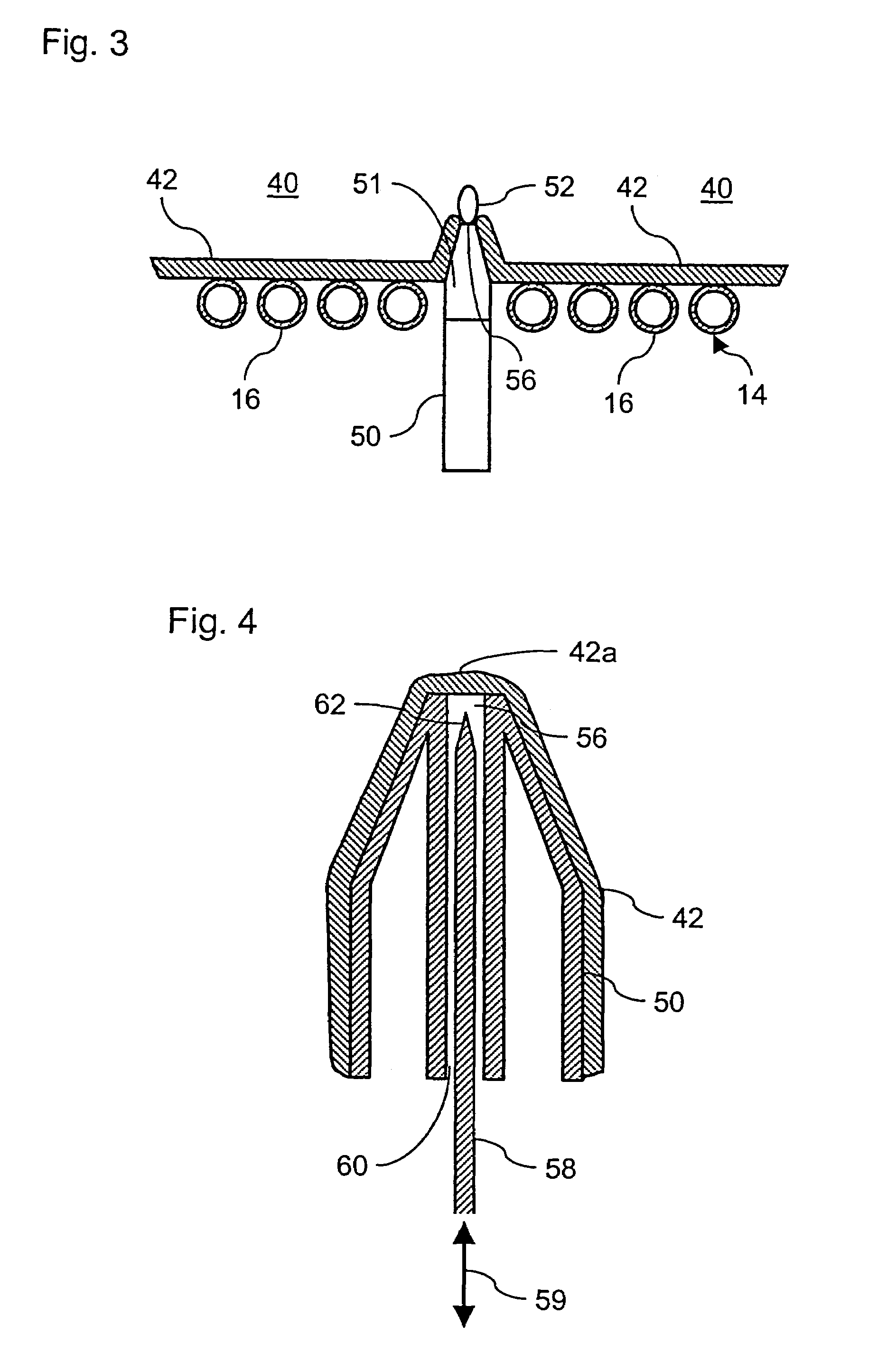
Device and method for the production of high-melting glass materials or glass ceramic materials or glass material or glass ceramic material
InactiveUS20050109062A1Maintain good propertiesQuality improvementPot furnacesGlass drawing apparatusIridiumSpectral transmission
The invention relates to a device for the production of high-melting glass materials or high-melting glass ceramic materials, comprising a vessel for accommodating molten glass and a container that accommodates the vessel, whereby the vessel has a tubular outlet. According to the invention, the device is characterised by the fact that the vessel and a first section of the tubular outlet if formed of iridium or a material with a high iridium content, whereby the container is designed to accommodate the vessel and the first section of the tubular outlet under a protective gas atmosphere. The invention also relates to a corresponding method. The molten glass is shaped into a formed part in a discontinuous operation. The choice of the material for the vessel used as the crucible allows the attainment of high temperatures according to the invention which enables glass materials or glass ceramic materials with a much higher spectral transmission in the visible wavelength range. The use of an inert protective gas enables the prevention of unwanted oxide formation on the vessel and the tubular outlet. According to the invention, the glass can be used as a transitional glass between types of glass with very different coefficients of thermal expansion.
Owner:SCHOTT AG
Glass scaffolds with controlled resorption rates and methods for making same
The present invention relates to resorbable glass scaffolds for use in biological applications and methods for making same. Specifically, these scaffolds are composed of phosphate glass fibers, where the rate of dissolution into biological fluids is controlled by the length of time the glass is held above its melt temperature prior to spinning the fiber.
Owner:ADVANCED TECH & REGENERATIVE MEDICINE
Energy efficient high-temperature refining
ActiveUS20130279532A1Reduce heat emissionsReduce financial costsPot furnacesElectrical apparatusCrucibleElectric current flow
An energy-efficient device for refining a glass melt to produce a glass and / or a glass ceramic is provided. The device includes a refining crucible defined at least by lateral walls with a metallic lining as a melt contact surface, so that a melt refining volume is defined by a base surface, a top surface and a circumferential surface; at least one heating device that conductively heats the lining by an electric current in the lining, so that the melt is heated through the lining, the heating device and the lining are connected to one another by a feeding device. The feeding device establishes contact with the lining so that an electric current runs from the top surface to the base surface or from the base surface to the top surface, at least in sections of the lining.
Owner:SCHOTT AG
Glass induction melting furnace using a cold crucible
InactiveUS6185243B1Reduce inductanceLess expensiveFurnaces without endless corePot furnacesCrucibleMetal
A melting furnace for insulating materials is provided with a cooled crucible (10) having continuous metal side malls, a partitioned and cooled bottom (12) and at least one induction coil (28) placed under the bottom which serves as the sole heating means. The depth of the melting bath contained in the crucible and the excitation frequency of the induction coil are selected so that the depth and half of the inside radius of the crucible are less than the skin thickness of the bath.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Silica glass crucible with bubble-free and reduced bubble growth wall
A silica glass crucible includes a stable, bubble-free inner layer and an opaque outer layer, both layers demonstrating reduced bubble growth during a Czochralski process. When used in the CZ process, little volume change is observed in the crucible wall, and the crucible has little influence on melt level. The present crucible is especially suited for slow silicon ingot pulling with reduced crystalline defects. The fusion process of the present invention controls the dynamic gas balance at the fusion front where formed grain is melted to dense fused silica.
Owner:SHIN ETABU QUARTZ PRODS
Apparatus and method for producing high-purity sulphur glass
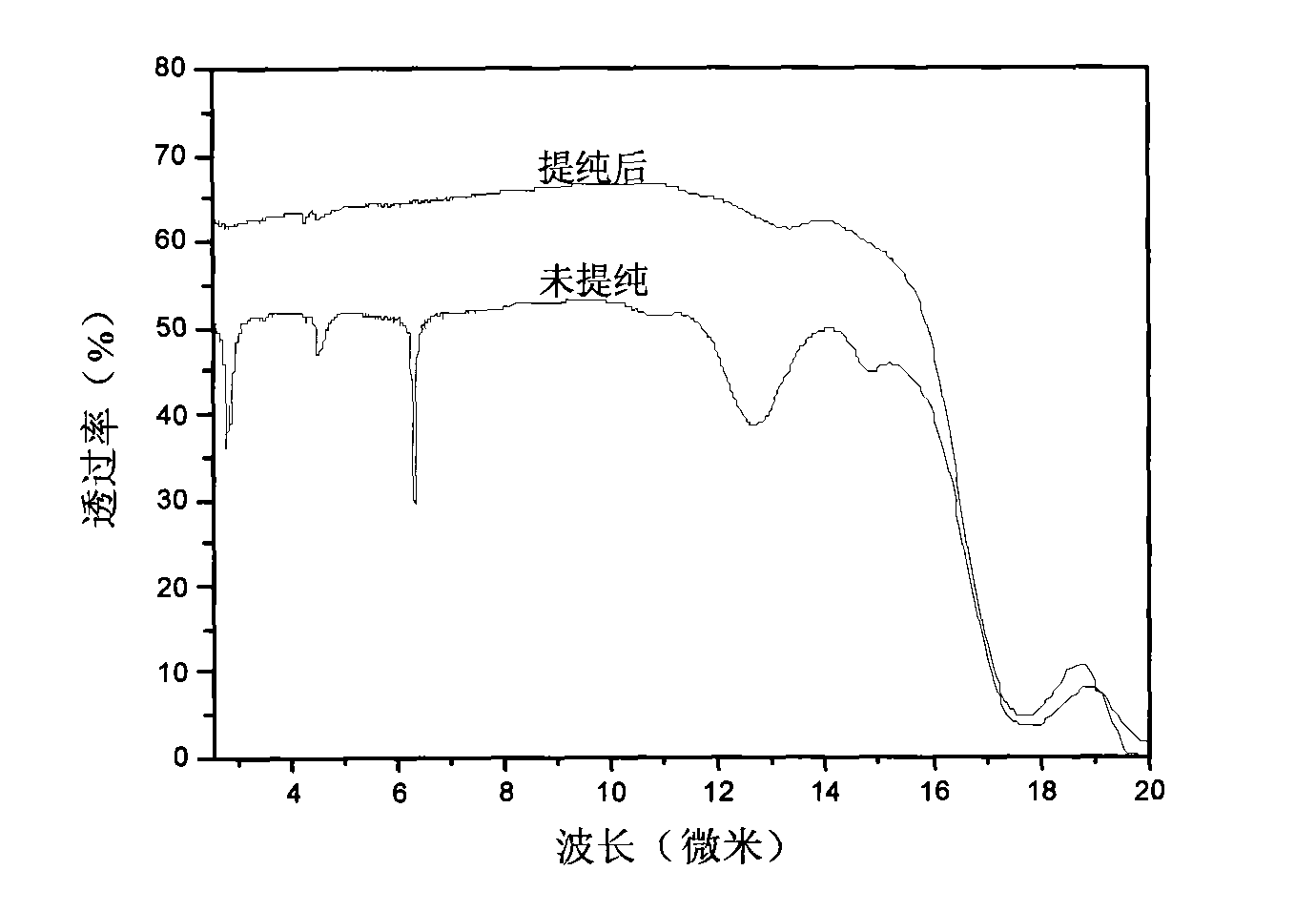
ActiveCN101492235AUniform optical qualityGood infrared transmittancePot furnacesGlass furnace apparatusTemperature controlChalcogenide glass
The invention discloses a device for preparing high-purity chalcogenide glass, which is characterized by comprising a swaying furnace body with the function of swaying backwards and forwards and a quartz ampoule, wherein the swaying furnace body is provided with a first hearth and a second hearth which are provided with an independent temperature control and heating system respectively and are communicated with each other through a transition area; the quartz ampoule comprises a glass raw material tube and a purification glass tube which are communicated with each other through a connecting tube; the glass raw material tube is arranged in the first hearth; the purification glass tube is arranged in the second hearth; and the connecting tube is positioned in the transition area. The device has the advantages that one quartz ampoule provided with the glass raw material tube and the purification glass tube is arranged on the device, the glass raw material tube and the purification glass tube are placed in two hearths with different temperatures respectively, the temperature difference between the two hearths is controlled to realize the purification of glass so that the high-purity chalcogenide glass with even optical quality and good infrared light transmittance can be obtained.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV +1
Bismuth containing fluorophosphate glass and method for making thereof
ActiveUS20070010390A1Increased durabilityImprove efficiencyPot furnacesCharging furnaceRare-earth elementRefractive index
New and improved compositions of doped and co-doped bismuth fluorophosphate glasses for lasers is disclosed that have a high refractive index (nD) of approximately 1.6 and higher, high transmission in the near infrared part of the spectrum, and a wide glass forming domain. The disclosed glass systems Al(PO3)3-Ba(PO3)2-Bi(PO3)3-BaF2+RFx+dopands use dopants from the group of oxides and or fluorides of rare earth elements Nd, Er, Yb, Tm, Tb, Ho, Sm, Eu and Pr as well as MnO and mixtures thereof over 100 percent (wt %) of the glass-base composition. These glasses have high chemical durability, radiation resistance, efficiency of laser use in the infrared and blue spectrum, and improved duration of luminescence.
Owner:AFO RES INC
Process for waste confinement by vitrification in metal cans
ActiveUS20110144408A1Increase resistancePossible to usePot furnacesGlass furnace apparatusVitrificationChemical species
Process for confinement of waste containing at least one chemical species to be confined, by in-can vitrification in a hot metal can into which waste and a vitrification additive are added, the waste and the vitrification additive are melted to obtain a glass melt which is then cooled, characterised in that at least one oxidising agent is also added into the metal can and in that the concentration of oxidising agent(s) expressed as oxide(s) in the glass melt is between 0.1 and 20% by mass, preferably 4 and 20% by mass, even more preferably 5 and 15% by mass, and even more preferably 10 and 13% by mass of the glass melt mass.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Method of producing large diameter transparent quartz glass tube for semiconductor technology by continuous melting method
InactiveCN101054260AIncrease pressureImprove melting conditionsPot furnacesGlass furnace apparatusFused quartzMelting furnace
A continuous method of manufacturing large aperture transparent quartz glass tube for semiconductor technology, which is characterized in that high pure quartz sand of quartz glass material is added in a continuous melting furnace, through electric heating and fusing, fused quartz glass liquid is drew as large aperture transparent quartz glass tubes through a former, a material stage and a tube drawing machine; the high pure quartz sand added in the continuous melting furnace, before heating and fusing, preheating the high pure quartz sand 200-280 minutes to 750-850 DEG C, then heating and fusing; the upper part of the continuous melting furnace tungsten-molybdenum crucible is a preheating section, the lower part is a fusing section, the preheating treatment is processed in the preheating section; the diameter of the tungsten-molybdenum crucible is 340-360 mm, height is 1400-1600 mm; the fusing temperature in the continuous melting furnace is 2150-2250 DEG C; the diameter of the former is 244-264 mm; the current passing through the continuous melting furnace for electric heating molybdenum electrode is 215-225 A, the voltage is 19-20 V. The obtained quartz tube has wide gauge, good quality, can be fully suitable for semiconductor technical requirement.
Owner:徐胜利
Methods for melting of materials to be treated
Owner:GEOSAFE CORP
Preparation of quartz glass bodies from silicon dioxide powder
InactiveUS20190152827A1Reduce contentLower refractive indexPot furnacesSilicaSilica particleLight guide
One aspect relates to a process for the preparation of a quartz glass body, including providing a silicon dioxide granulate, making a glass melt out of silicon dioxide granulate and making a quartz glass body out of at least part of the glass melt. The silicon dioxide granulate is obtained by providing and processing a silicon dioxide powder. One aspect also relates to silicon dioxide granulate, which is obtained by providing a silicon dioxide powder and processing it. One aspect further relates to a quartz glass body which is obtainable by this process. One aspect further relates to a light guide, an illuminant and a formed body, which are each obtainable by further processing of the quartz glass body.
Owner:HERAEUS QUARZGLAS
Silica glass crucible with bubble-free and reduced bubble growth wall
A silica glass crucible includes a stable, bubble-free inner layer and an opaque outer layer, both layers demonstrating reduced bubble growth during a Czochralski process. When used in the CZ process, little volume change is observed in the crucible wall, and the crucible has little influence on melt level. The present crucible is especially suited for slow silicon ingot pulling with reduced crystalline defects. The fusion process of the present invention controls the dynamic gas balance at the fusion front where formed grain is melted to dense fused silica.
Owner:SHIN ETABU QUARTZ PRODS
Device and method for melting a substance with the occurrence of a low level of contamination
InactiveUS7296441B2Improve homogeneityImprove smelting effectPot furnacesGlass drawing apparatusOxidation-Reduction AgentOxygen
The invention relates to an apparatus and a method for low-contamination melting of high-purity, aggressive and / or high-melting glass or glass-ceramic. According to the invention, for this purpose a melt is heated in a crucible or melting skull crucible by means of high-frequency radiation and is mixed or homogenized in the melting crucible. It is preferable for a gas nozzle, from which gas bubbles, e.g. oxygen bubbles (known as O2 bubbling), escape into the melt, to be provided at the base of the crucible. This alone makes it possible to achieve surprising multiple benefits in the melting skull crucible. Firstly, unmelted batch which drops into the melt in solid form, for example from above, is melted down more quickly as a result of more intensive mixing with the liquid fraction of the melt, secondly the temperature distribution in the melt is made more even, thirdly a uniform distribution or mixing of different glass constituents is achieved, and fourthly the redox state of the glass can be adjusted.
Owner:SCHOTT AG
Gas flushing for melting ovens and process for preparation of quartz glass
One aspect is an oven including a melting crucible with a crucible wall, a solids feed with an outlet, a gas inlet and a gas outlet, wherein in the melting crucible the gas inlet is arranged below the solids feed outlet and the gas outlet is arranged at the same height as or above the solids feed outlet. One aspect further relates to a process for making a quartz glass body, including providing and introducing a bulk material selected from silicon dioxide granulate and quartz glass grain into the oven and providing a gas, making a glass melt from the bulk material, and making a quartz glass body from at least a part of the glass melt. One aspect relates to a quartz glass body obtainable by this process and a light guide, an illuminant and a formed body which are each obtainable by processing the quartz glass body further.
Owner:HERAEUS QUARZGLAS
Preparation of a quartz glass body in a melting crucible of refractory metal
ActiveUS20190071344A1Reduce contentIncrease pointsPot furnacesMaterial analysis by optical meansSilica particleLight guide
The invention relates to a process for preparing a quartz glass body comprising the process steps i.) Providing a silicon dioxide granulate, ii.) Making a glass melt from the silicon dioxide granulate in a melting crucible, and iii.) Making a quartz glass body from at least a part of the glass melt, wherein the melting crucible is comprised in an oven and is made of at least one material comprising tungsten or molybdenum or a combination thereof. The invention further relates to a quartz glass body which can be obtained by this process. Further, the invention relates to a light guide, an illuminant and a formed body, each of which can be obtained by processing the quartz glass body further.
Owner:HERAEUS QUARZGLAS
Bismuth containing fluorophosphate glass and method for making thereof
ActiveUS20090255297A1Increased durabilityImprove efficiencyPot furnacesGlass furnace apparatusRare-earth elementRefractive index
New and improved compositions of doped and co-doped bismuth fluorophosphate glasses for lasers is disclosed that have a high refractive index (nD) of approximately 1.6 and higher, high transmission in the near infrared part of the spectrum, and a wide glass forming domain. The disclosed glass systems Al(PO3)3−BA (PO3)2−Bi(PO3)3−BaF2+RFx+dopands use dopants from the group of oxides and or fluorides of rare earth elements Nd, Er, Yb, Tm, Tb, Ho, Sm, Eu and Pr as well as MnO and mixtures thereof over 100 percent (wt %) of the glass-base composition. These glasses have high chemical durability, radiation resistance, efficiency of laser use in the infrared and blue spectrum, and improved duration of luminescence.
Owner:AFO RES INC
Preparation of a quartz glass body in a standing sinter crucible
The invention relates to a process for the preparation of a quartz glass body comprising the process steps i.) Providing a silicon dioxide granulate, ii.) Making a glass melt out of silicon dioxide granulate in an oven and iii.) Making a quartz glass body out of at least part of the glass melt, wherein the oven comprises a standing sinter crucible. The invention further relates to a quartz glass body which is obtainable by this process. The invention further relates to a light guide, an illuminant and a formed body, which are each obtainable by further processing of the quartz glass body.
Owner:HERAEUS QUARZGLAS
Detachable optical glass successive melting furnace
ActiveCN102206032AAvoid deformationAvoid tearingPot furnacesGlass productionHeating furnaceOptical glass
The invention, which relates to a detachable optical glass successive melting furnace and belongs to the technical field of optical glass melting devices, mainly solves the problem that the present melting furnaces highly lead to the aging of platinum vessels which further results in the damage of the platinum vessels, the blowing out of furnaces and long maintenance time. The detachable optical glass successive melting furnace is characterized by comprising successively connected parts of a fusing-section smelting furnace, a heating-section smelting furnace, a clarification-section smelting furnace, a cooling-section pipeline and a working-section smelting furnace, wherein the fusing-section smelting furnace, the heating-section smelting furnace and the clarification-section smelting furnace are connected by connecting pipes; the fusing-section smelting furnace, the heating-section smelting furnace, the clarification-section smelting furnace and the working-section smelting furnace are all equipped with an independent heating device; and the connection pipelines connecting the fusing-section smelting furnace, the heating-section smelting furnace and the clarification-section smelting furnace and the cooling-section pipeline are all provided with a flow control device. The detachable optical glass successive melting furnace provided by the invention has the summing effect of minimizing the container expansion, reduces the crucible damage, is convenient for maintenance, raises the smelting furnace production efficiency, and is mainly used in optical glass successive melting furnaces which can be split and assembled.
Owner:HUBEI NEW HUAGUANG NEW INFORMATION MATERIALS CO LTD
Apparatus and method for melting of materials to be treated
A process for melting material to be treated includes placing material to be treated in a container that may include an insulating lining, heating the material to be treated and melting the material to be treated, preferably allowing the melted material to cool to form a vitrified and / or crystalline mass, and disposing of the mass. The mass is either disposed while contained in container or removed from container after cooling and disposed. Insulating lining may comprise one or more layers of a thermal insulating material, one or more layers of refractory material, or a combination thereof. The material to be treated may be heated by placing at least two electrodes in the material to be treated and passing a current between the electrodes, or alternatively, by placing at least one heating element in the material to be treated and passing heat into the material to be treated.
Owner:GEOSAFE CORP
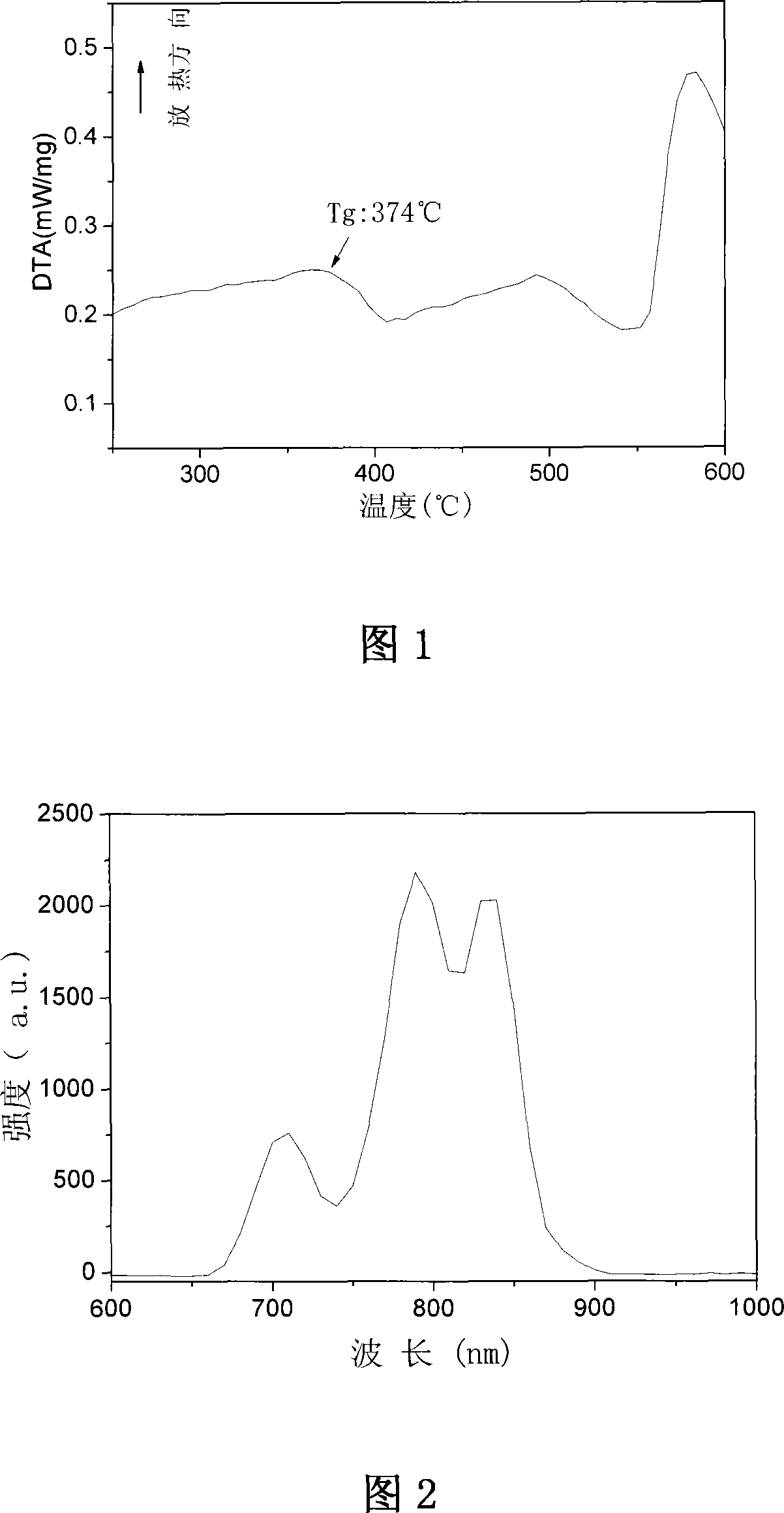
Tellurate glass and method for producing the same
InactiveCN101219857AHigh densityHigh refractive indexPot furnacesGlass furnace apparatusFiberMetallurgy
The invention tellurate glass and a preparation method is disclosed, among which the basic compositions of the glass are 65-85 mol percent of TeO2, 0-20 mol percent PbO, 2-8 mol percent of PbF2, 0-10 mol percent of Bi2O3, 0-15 mol percent Nb2O5. , Being prepared through a common melting method. In the melting process, preparation technologies like stirring, putting into dry nitrogen and clarification are adopted to ensure that [OH-] mass in the glass compositions can be effectively removed. The glass material is characterized by good materialization stability, favorable fiber-forming, high third-order nonlinear susceptibility, small dispersion slope and so on; the preparation process has simple and easy operation and low cost. The invention is applicable to use optical fiber matrix material in super short pulser source of optical communication.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation of a quartz glass body in a hanging metal sheet crucible
One aspect relates to a process for the provision of a quartz glass body, including providing a silicon dioxide granulate, making a glass melt from the silicon dioxide granulate in an oven and making a quartz glass body from at least part of the glass melt. The oven includes a hanging metal sheet crucible. One aspect also relates to a quartz glass body which is obtainable by this process. One aspect further relates to a light guide, an illuminant and a formed body which are obtainable by processing the quartz glass body further.
Owner:HERAEUS QUARZGLAS
Continuous melting furnace for producing quartz glass bar and manufacture technology
The invention discloses a continuous melting furnace for producing a quartz glass bar and a manufacture technology. The continuous melting furnace comprises a furnace body and a furnace cover which are matched to each other, wherein a tungsten crucible is arranged in the furnace body; a heating net and heat insulating sand are arranged outside the tungsten crucible, and the heating net is connected with an electrode; high-temperature bricks, a water sleeve and a dust removing device are arranged at a port of the furnace; and the upper end of the tungsten crucible is communicated with a feeding device and a heat insulating device, and the lower end of the tungsten crucible is connected with a forming device. According to the continuous melting furnace disclosed by the invention, a mandril device in the tungsten crucible is removed; the forming device at the lower part of the tungsten crucible is used or stretching to form under a certain temperature; because the mandril device is removed, no bubble, air line and black core are generated; and moreover, the manufactured quartz glass bar has large diameter, and can be widely applied to industries such as a semiconductor industry, a solar energy industry and an optical fiber industry.
Owner:JIANGSU PACIFIC QUARTZ
Method and device for continuous melting or refining of melt
The invention relates to a method and a device for continuous melting or refining of a melt. The invention particularly relates to a method for continuously producing a product from the melt, wherein the melt is heated to a predetermined temperature in a shell crucible, and the bottom of the shell crucible is made of nonconductive heat-conducting material.
Owner:SCHOTT AG
Preparation of a quartz glass body in a hanging sinter crucible
InactiveUS20190092676A1Reduce contentEasy to buildPot furnacesMaterial analysis by optical meansSilica particleLight guide
The invention relates to a process for the preparation of a quartz glass body comprising the process steps i.) Providing a silicon dioxide granulate, ii.) Making a glass melt from the silicon dioxide granulate in an oven, and iii.) Making a quartz glass body from at least a part of the glass melt, wherein the oven comprises a hanging sinter crucible. The invention also relates to a quartz glass body which is obtainable by this process. The invention further relates to a light guide, an illuminant and a formed body which are each obtainable by further processing the quartz glass body.
Owner:HERAEUS QUARZGLAS
Increase in silicon content in the preparation of quartz glass
PendingUS20190119141A1Reduce contentPot furnacesMaterial analysis by optical meansSilica particleLight guide
A quartz glass body and a process for the preparation of a quartz glass body is disclosed. In one aspect, the process includes providing a silicon dioxide granulate from a pyrogenic silicon dioxide powder, making a glass melt out of the silicon dioxide granulate and making a quartz glass body out of at least part of the glass melt. In at least one process a silicon component different from silicon dioxide is added. One aspect further relates to a quartz glass body which is obtainable by this process. A light guide, an illuminant and a formed body, are each obtainable by further processing of the quartz glass body.
Owner:HERAEUS QUARZGLAS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com