Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
223results about "Glass melting apparatus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
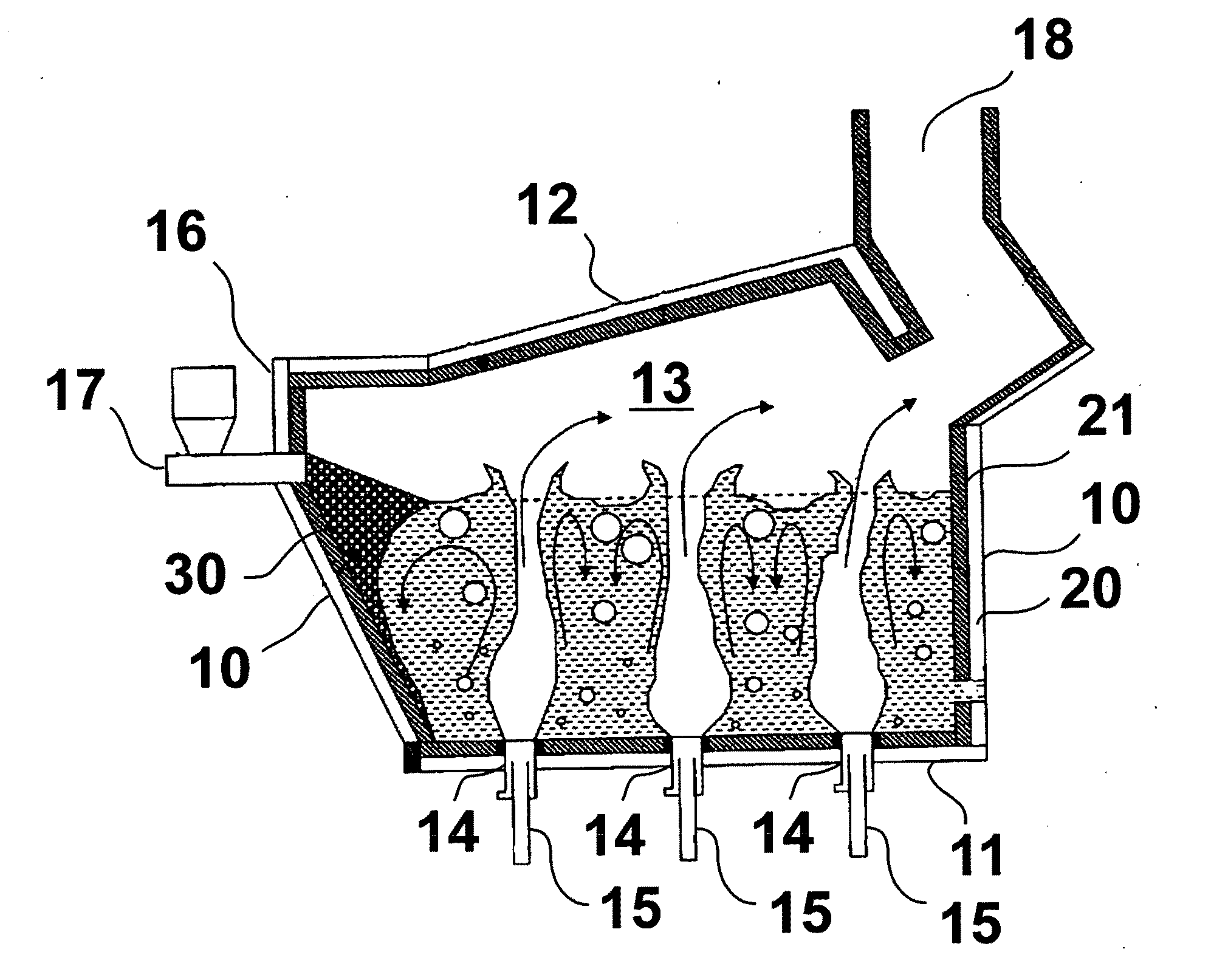
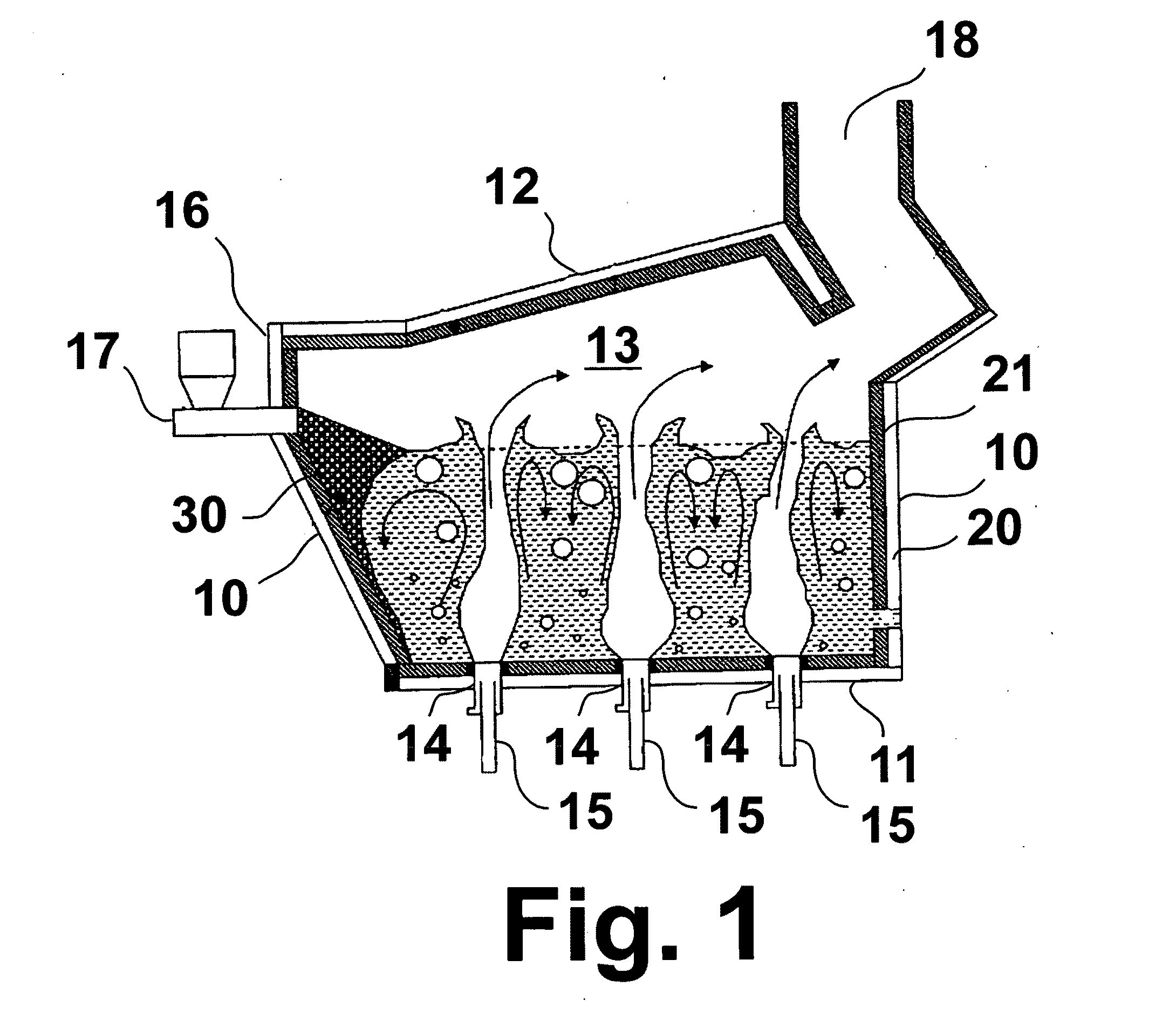
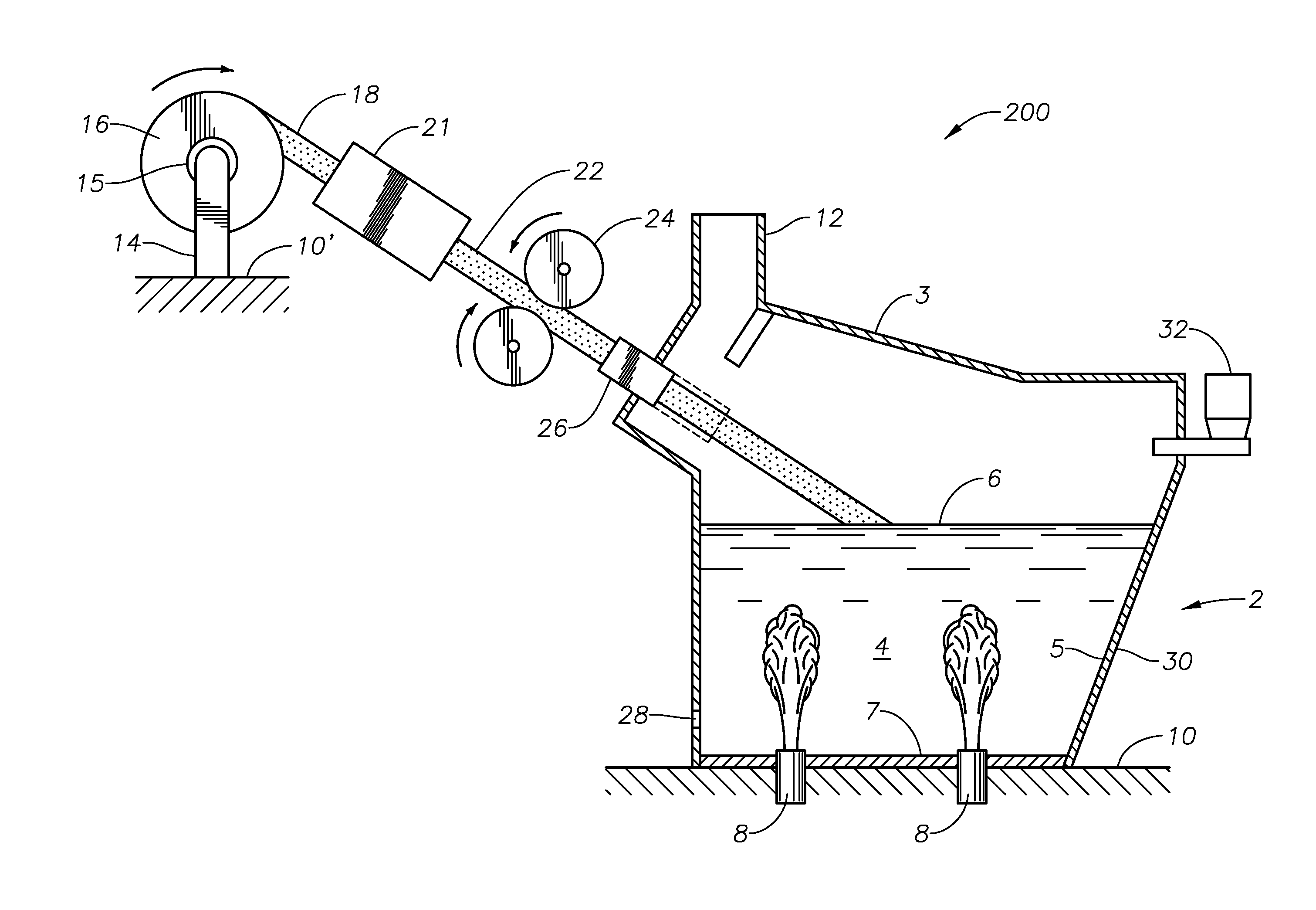
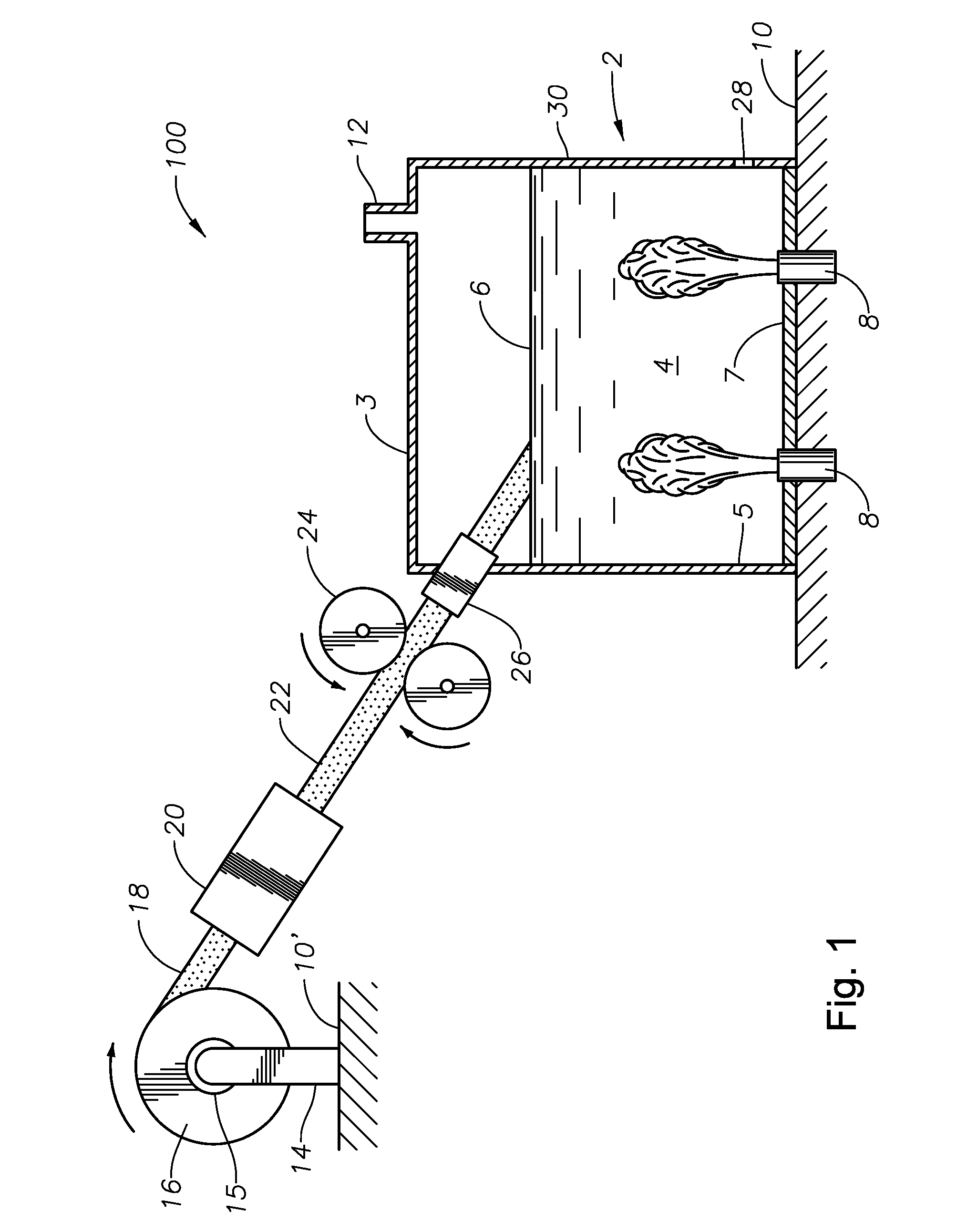
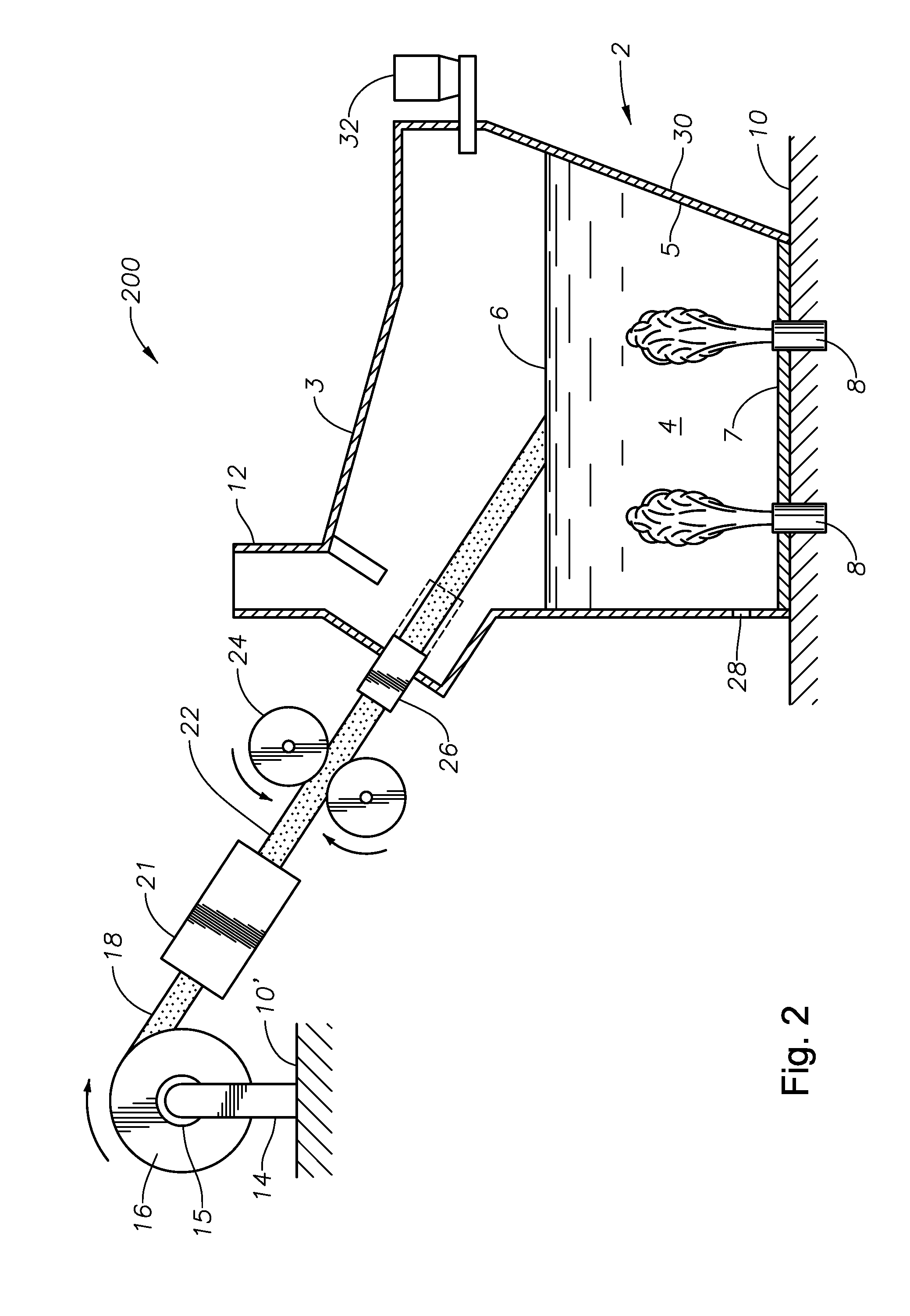
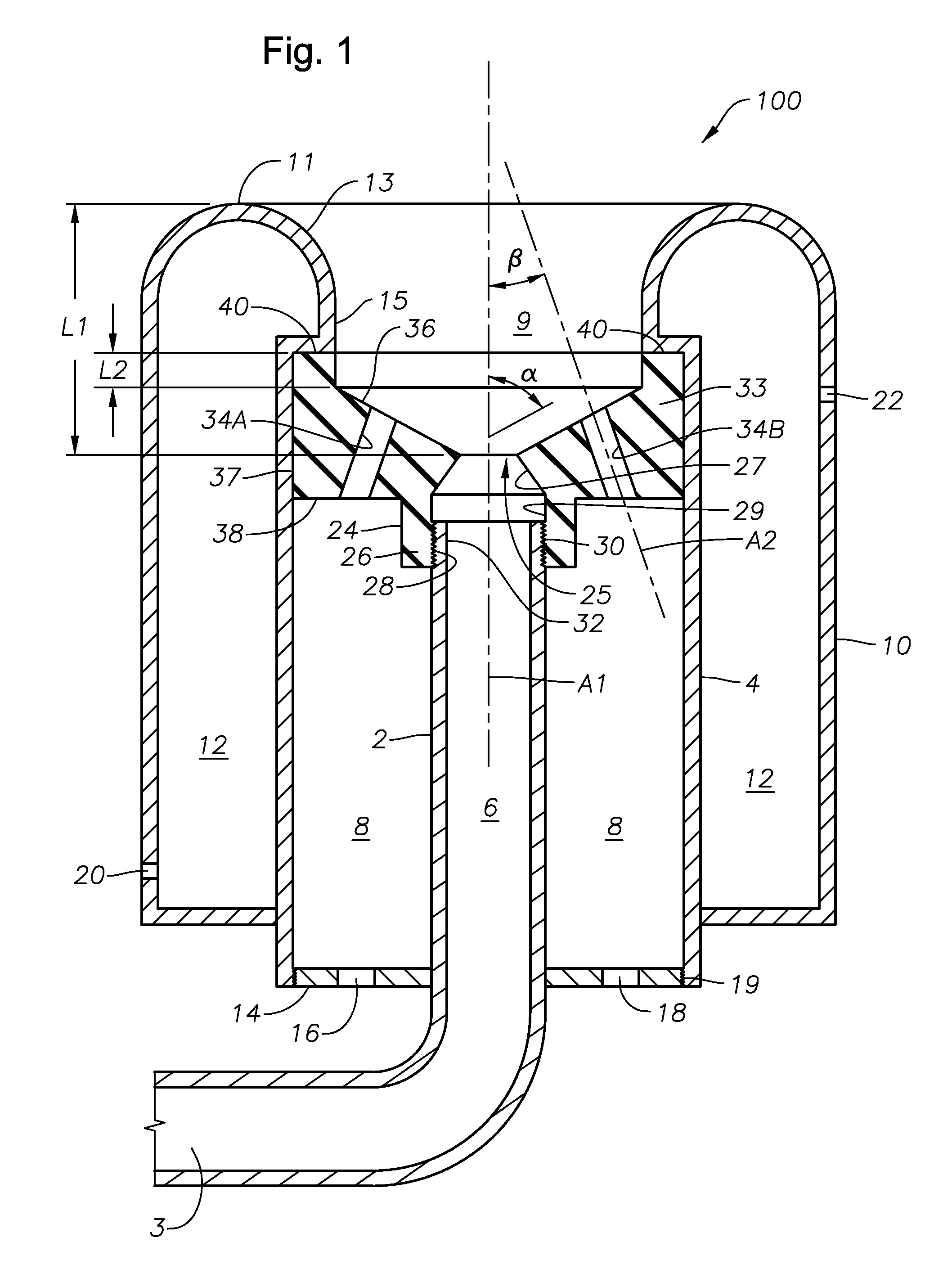
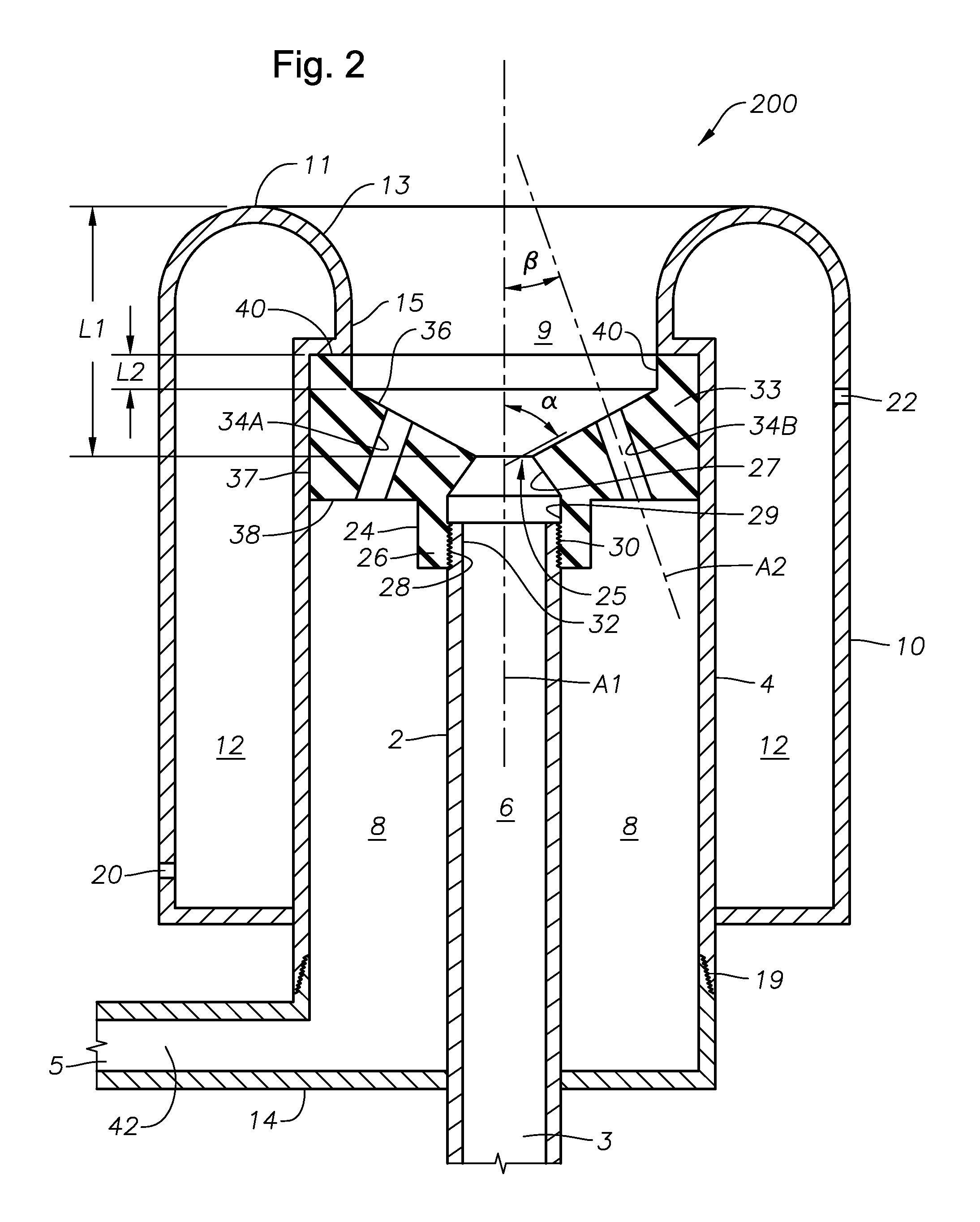
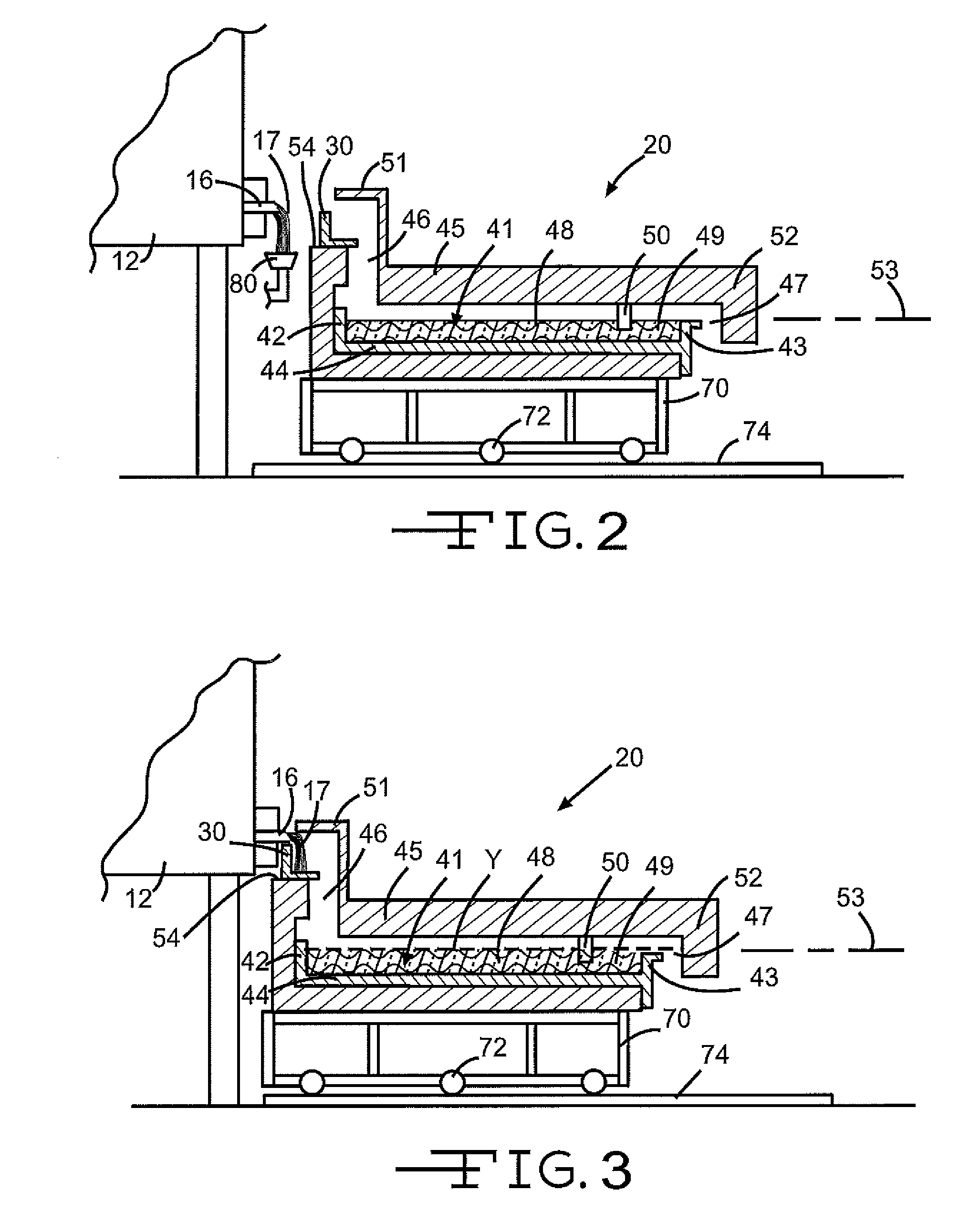
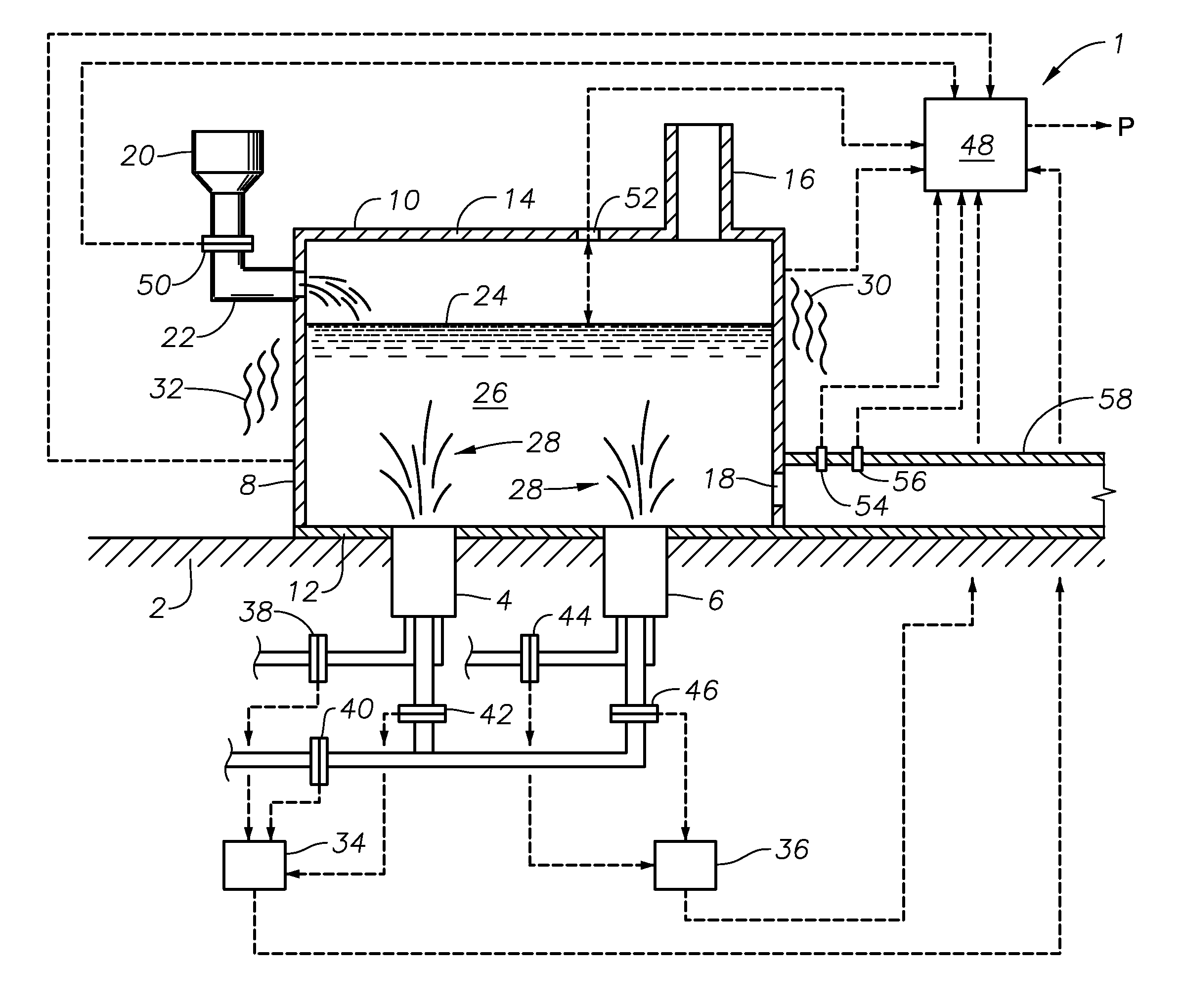
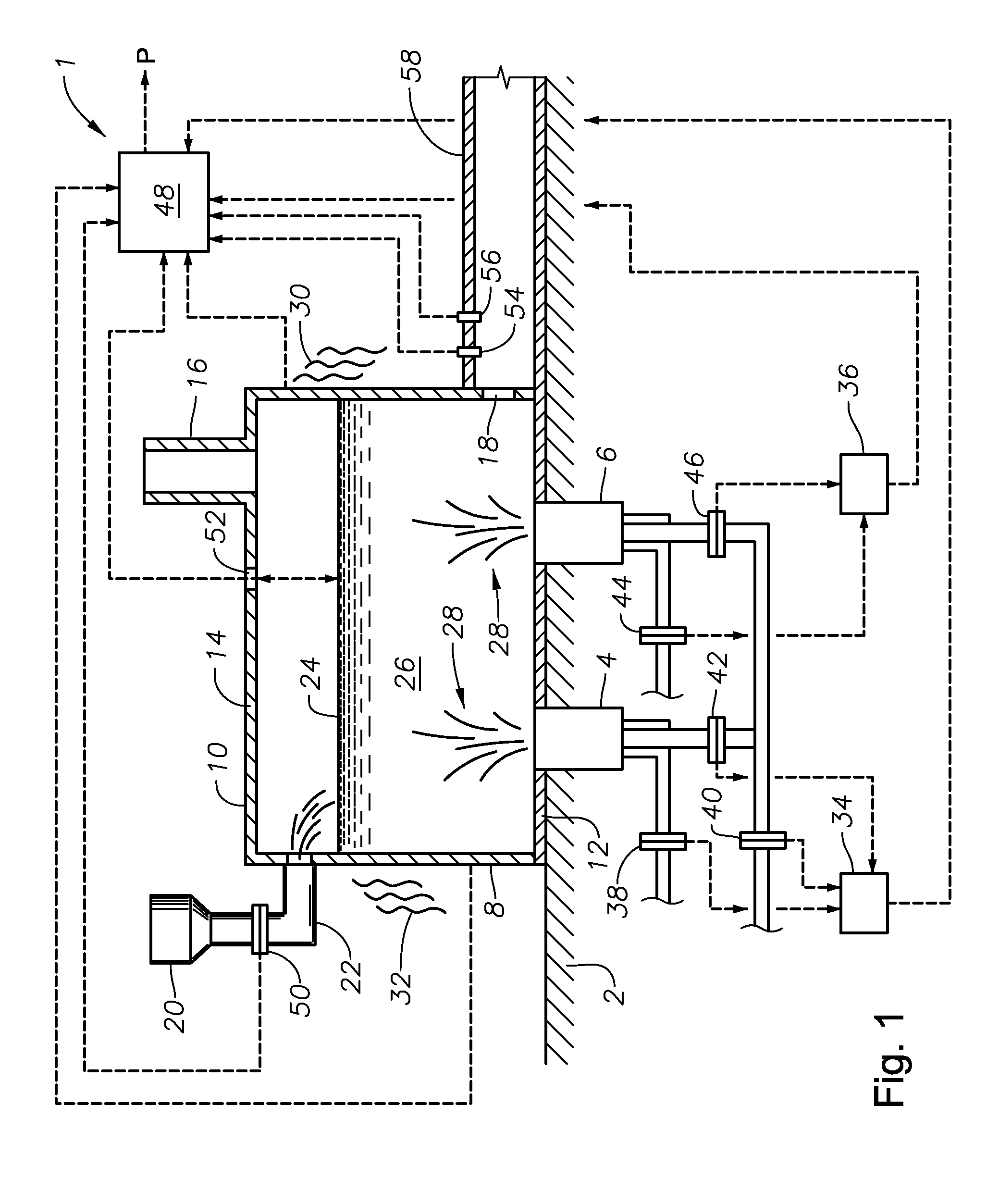
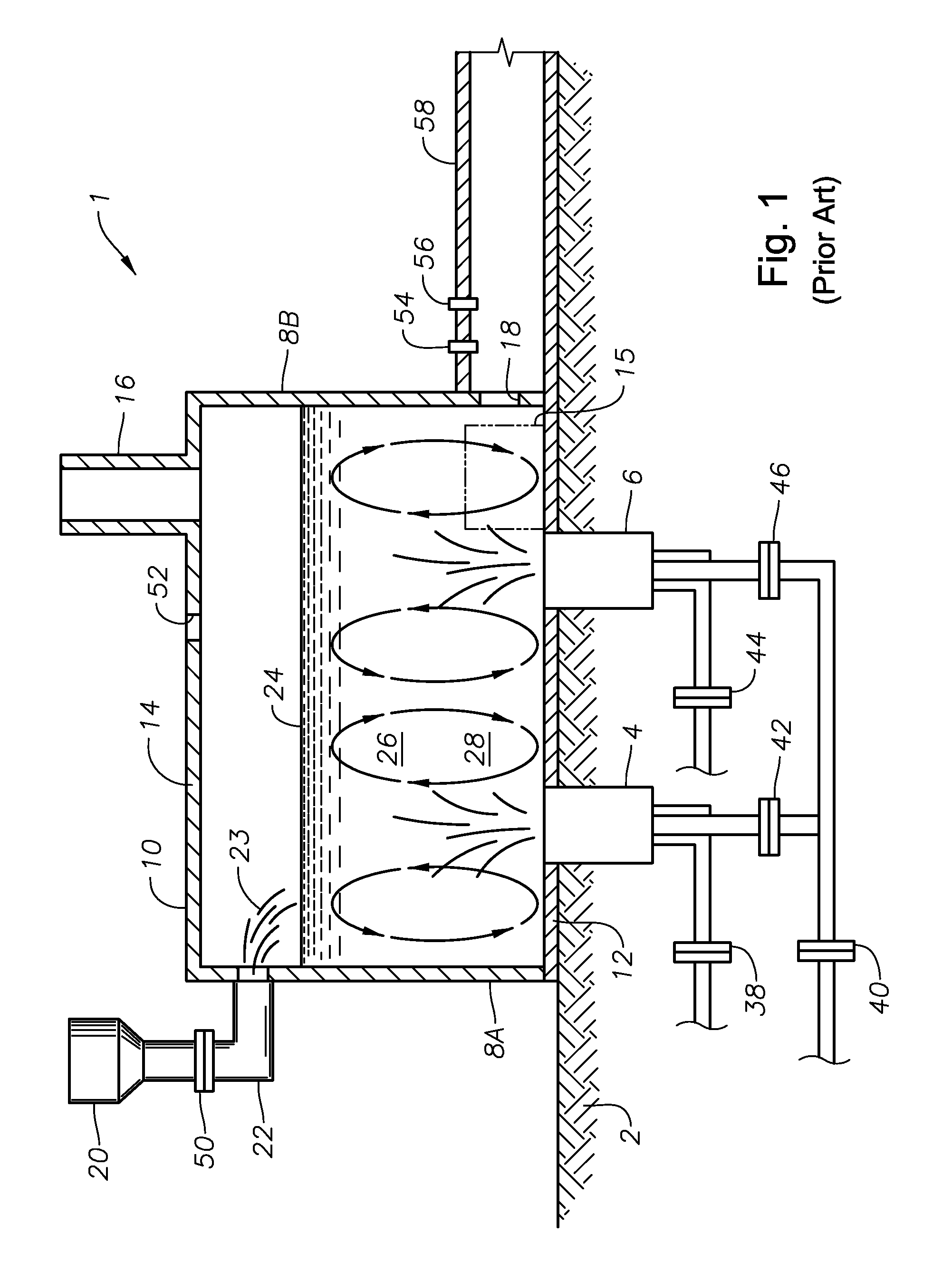
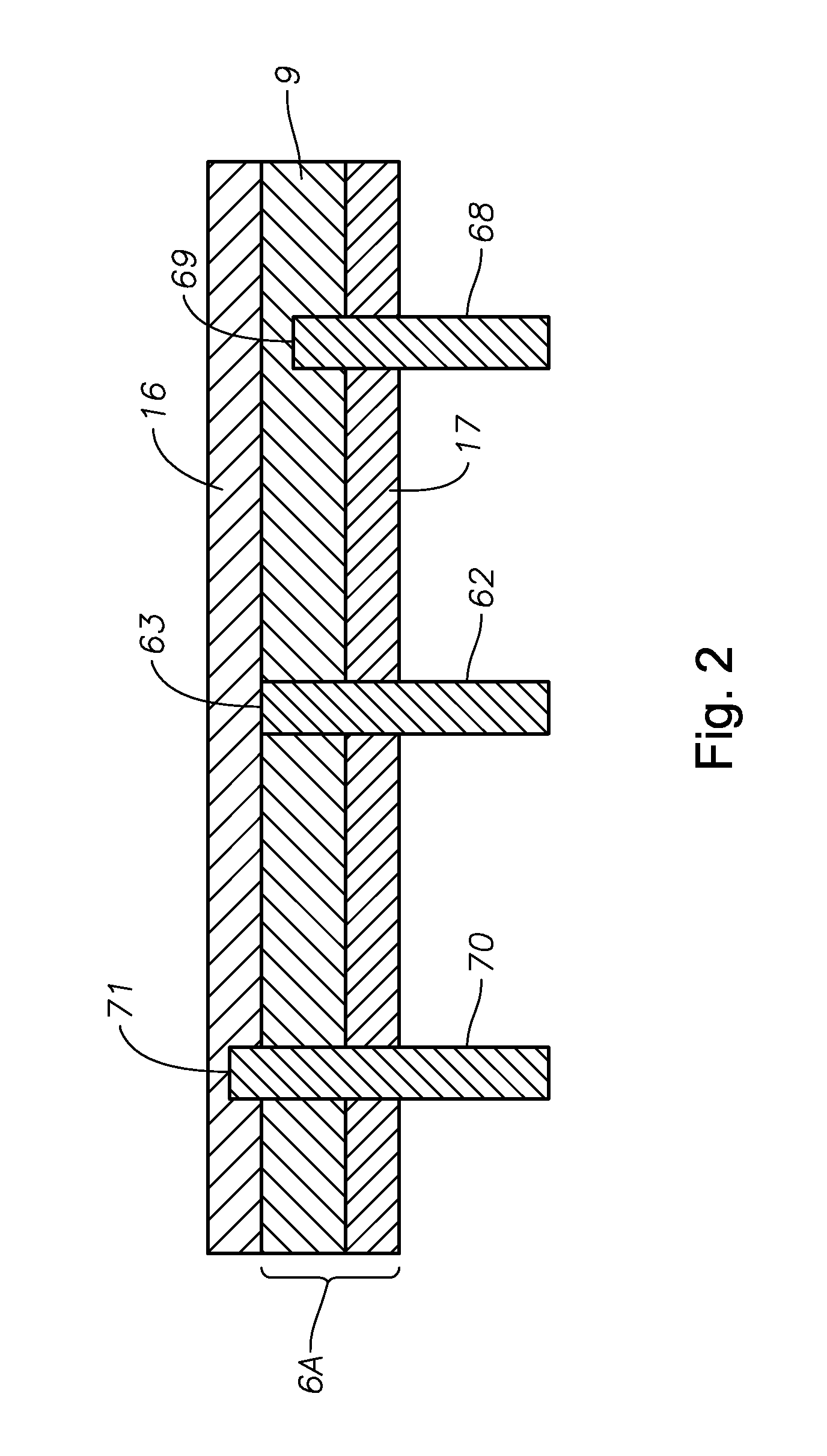
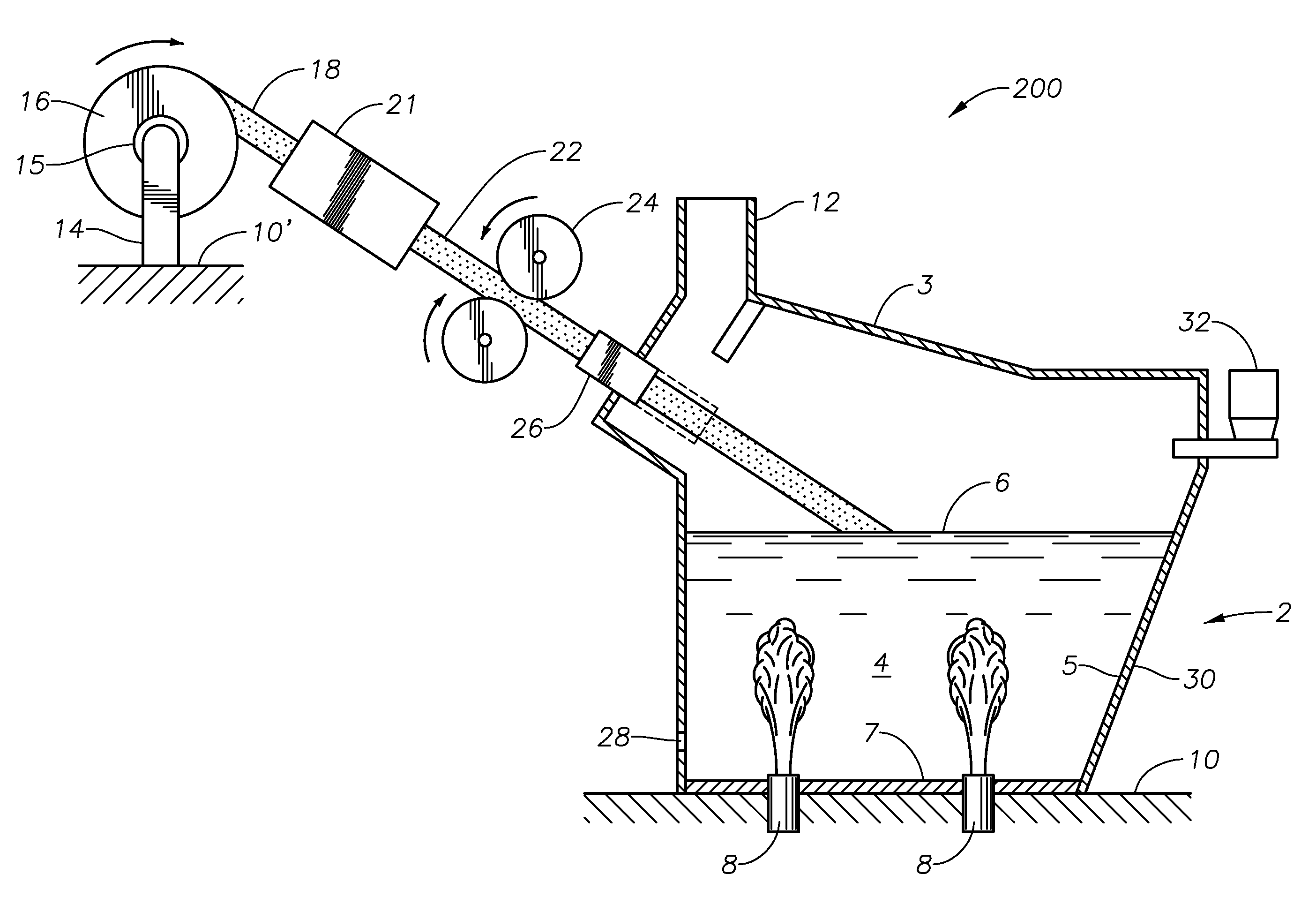
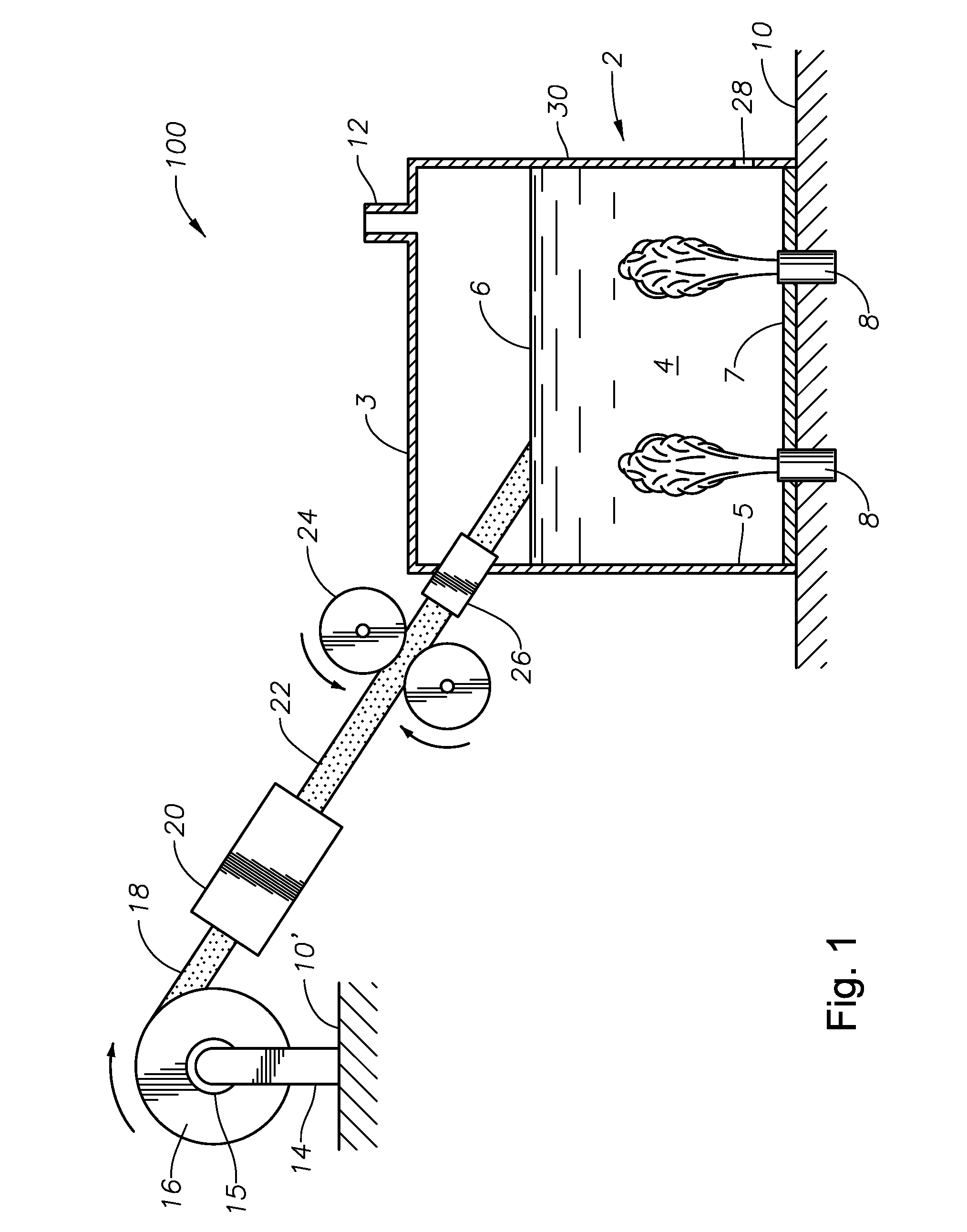
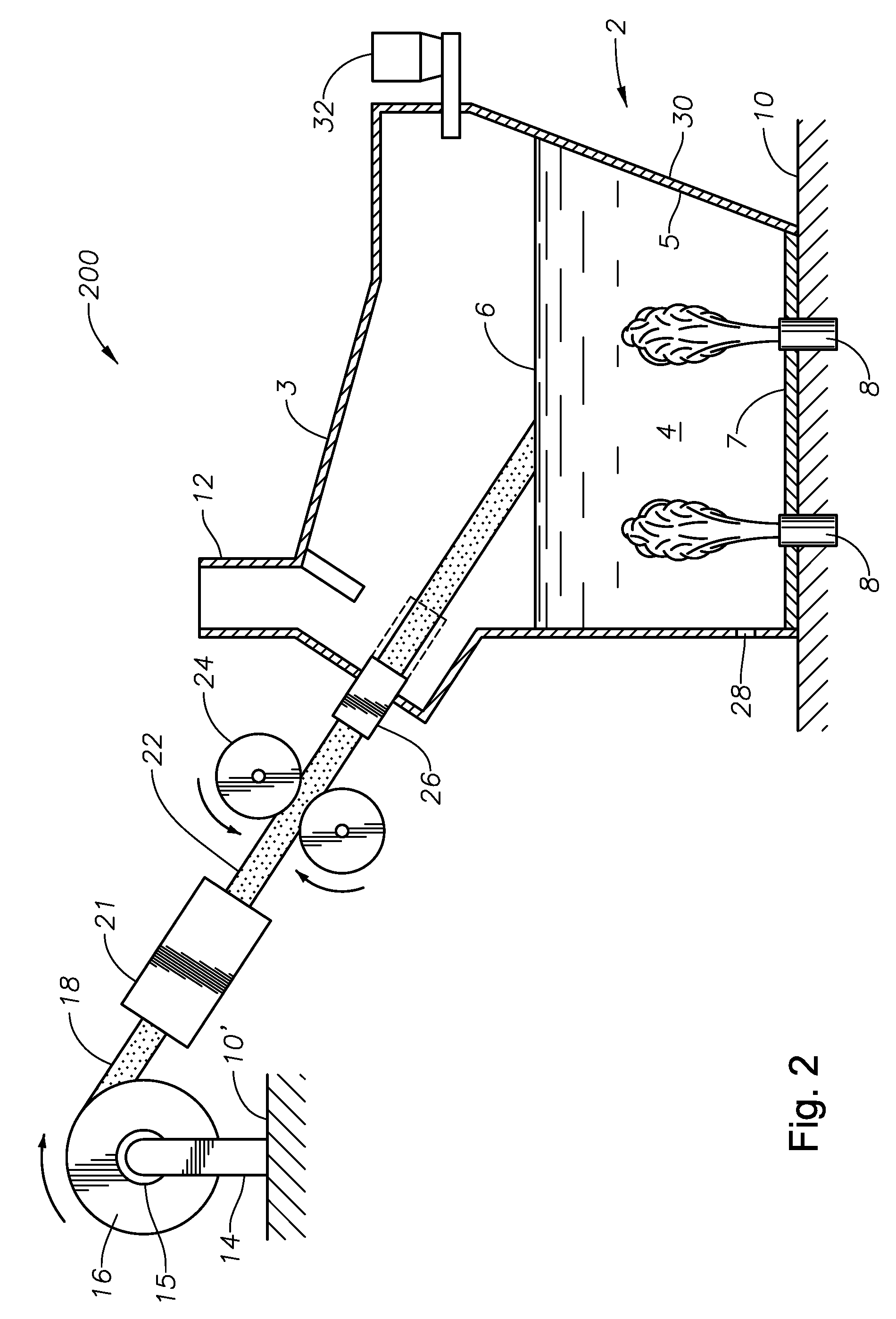
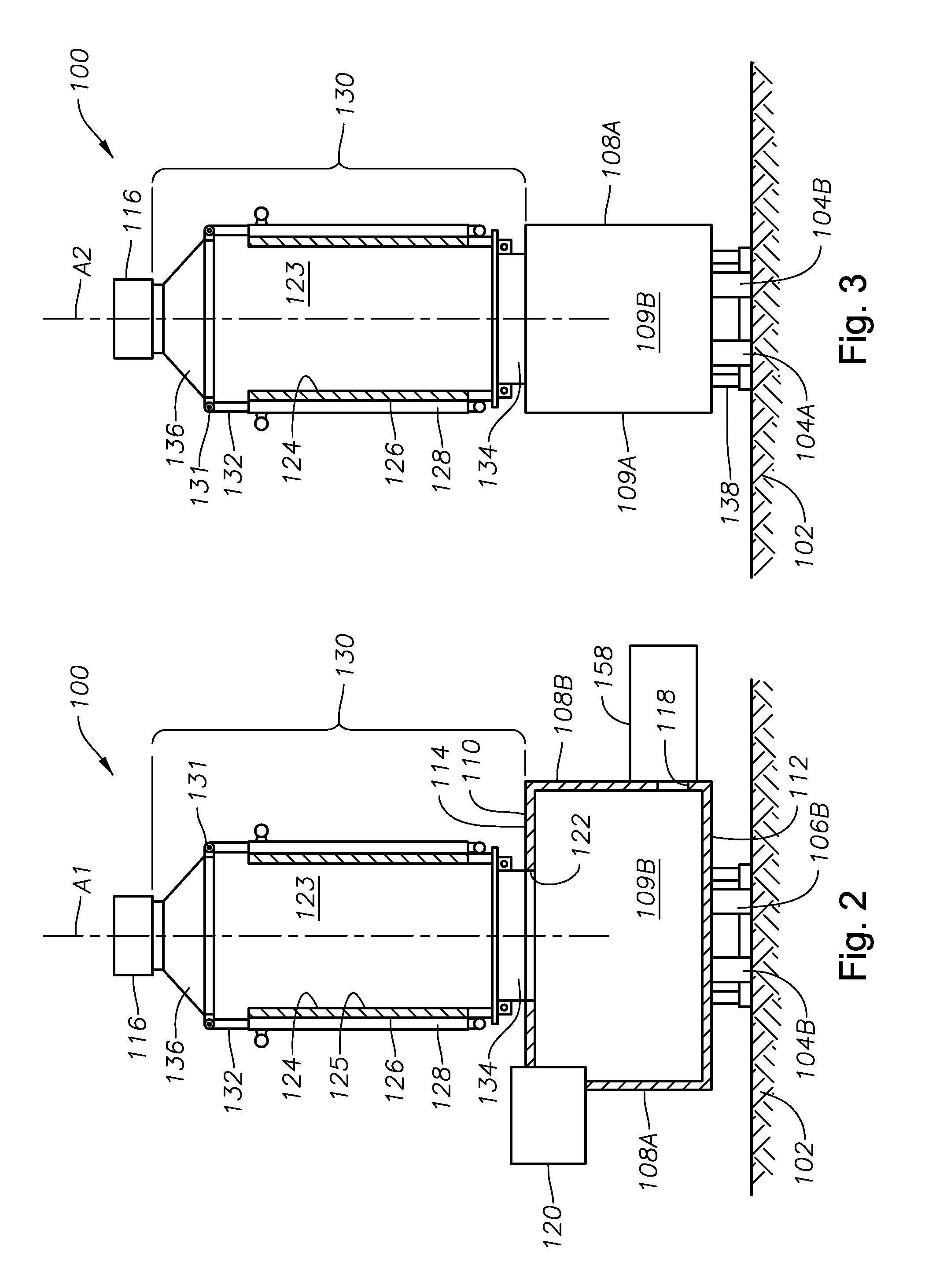
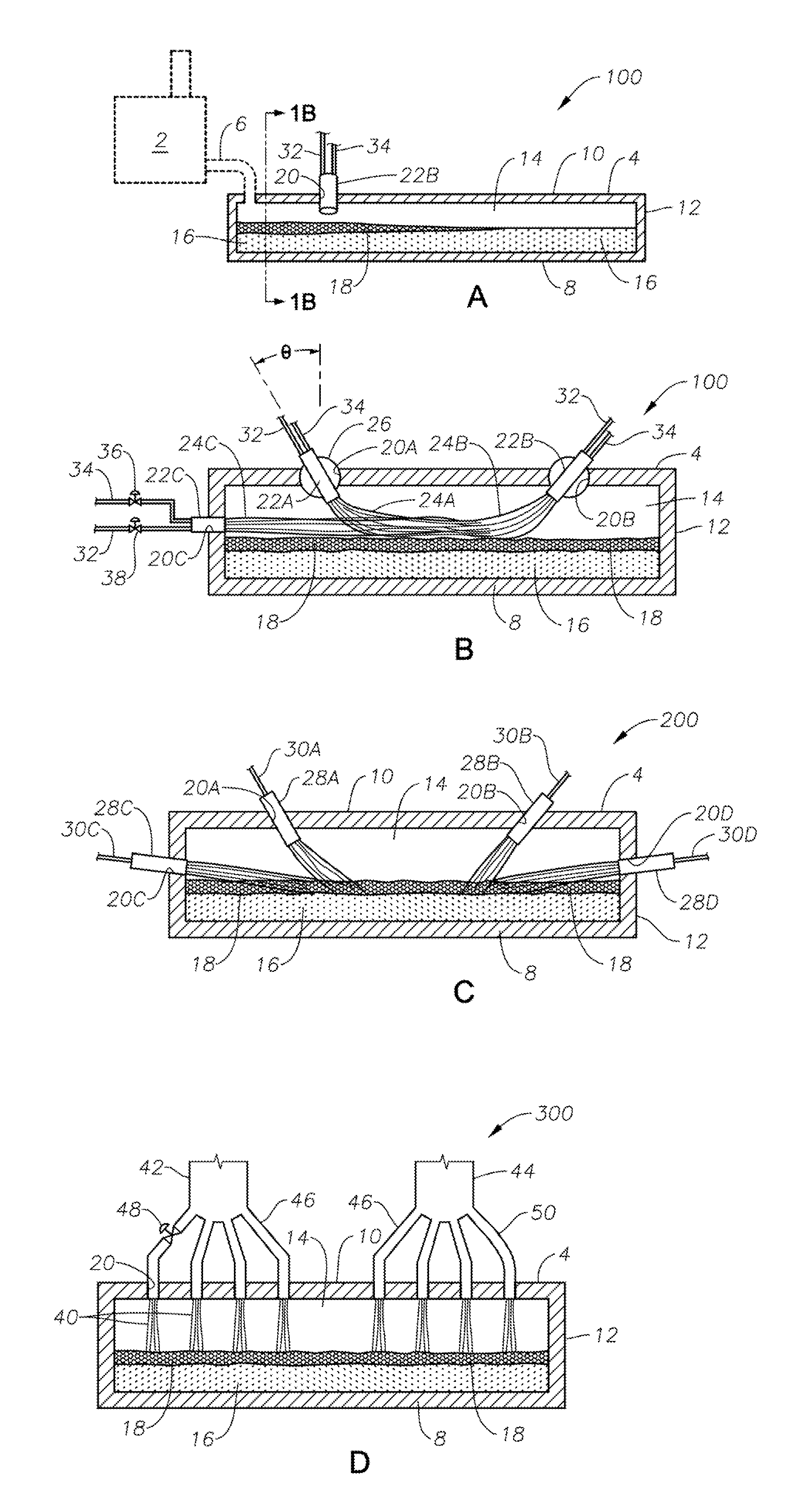
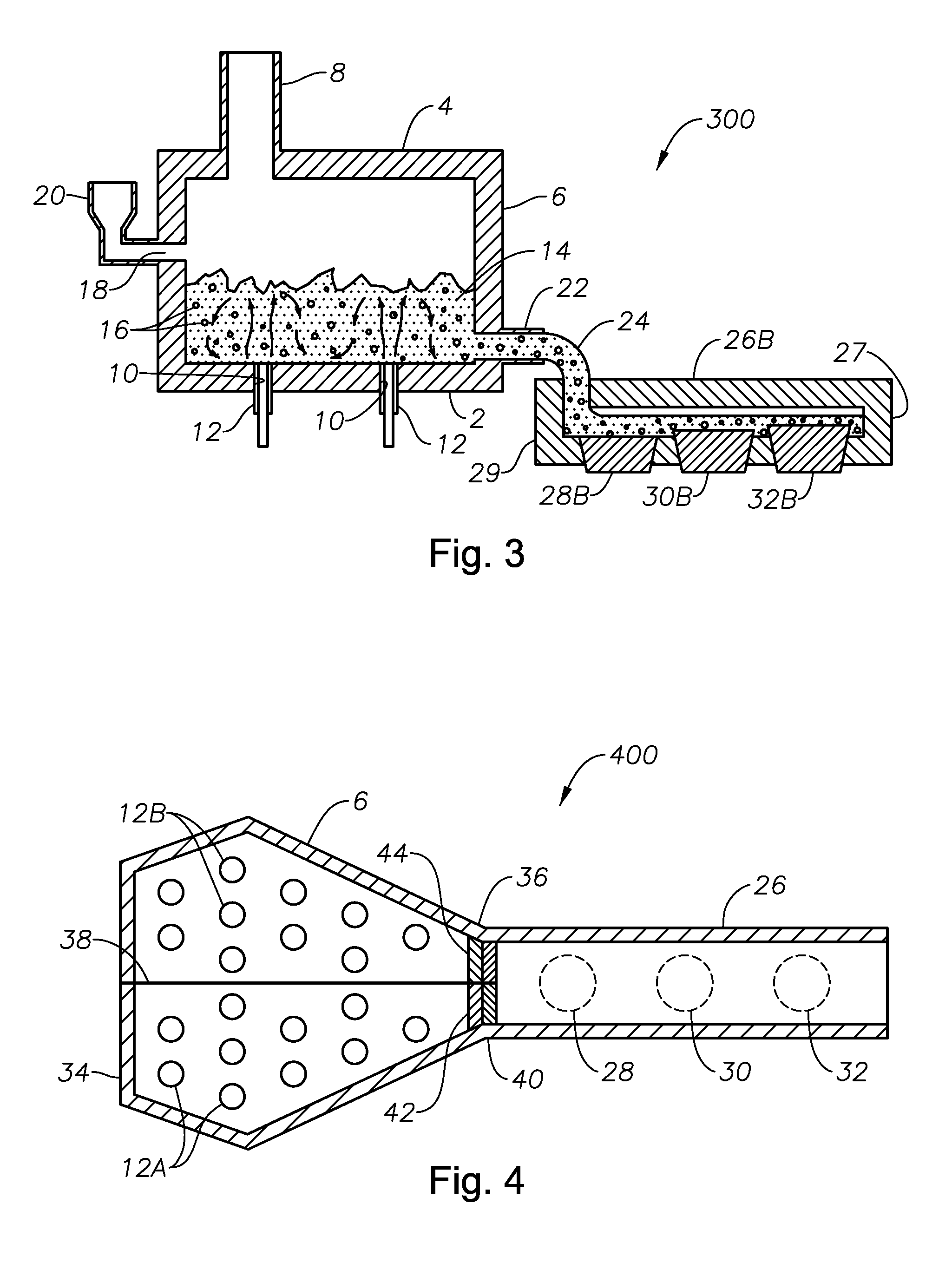
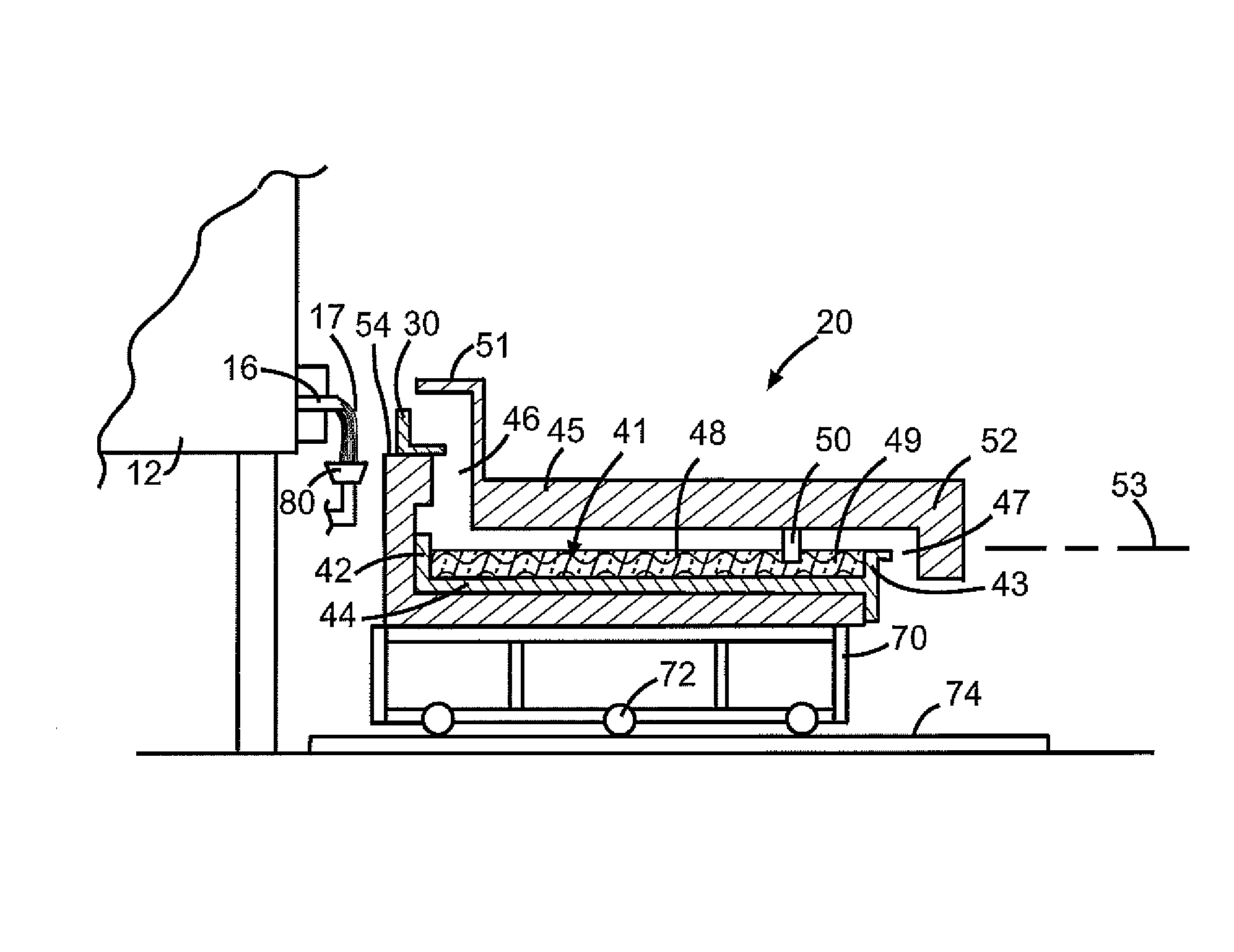
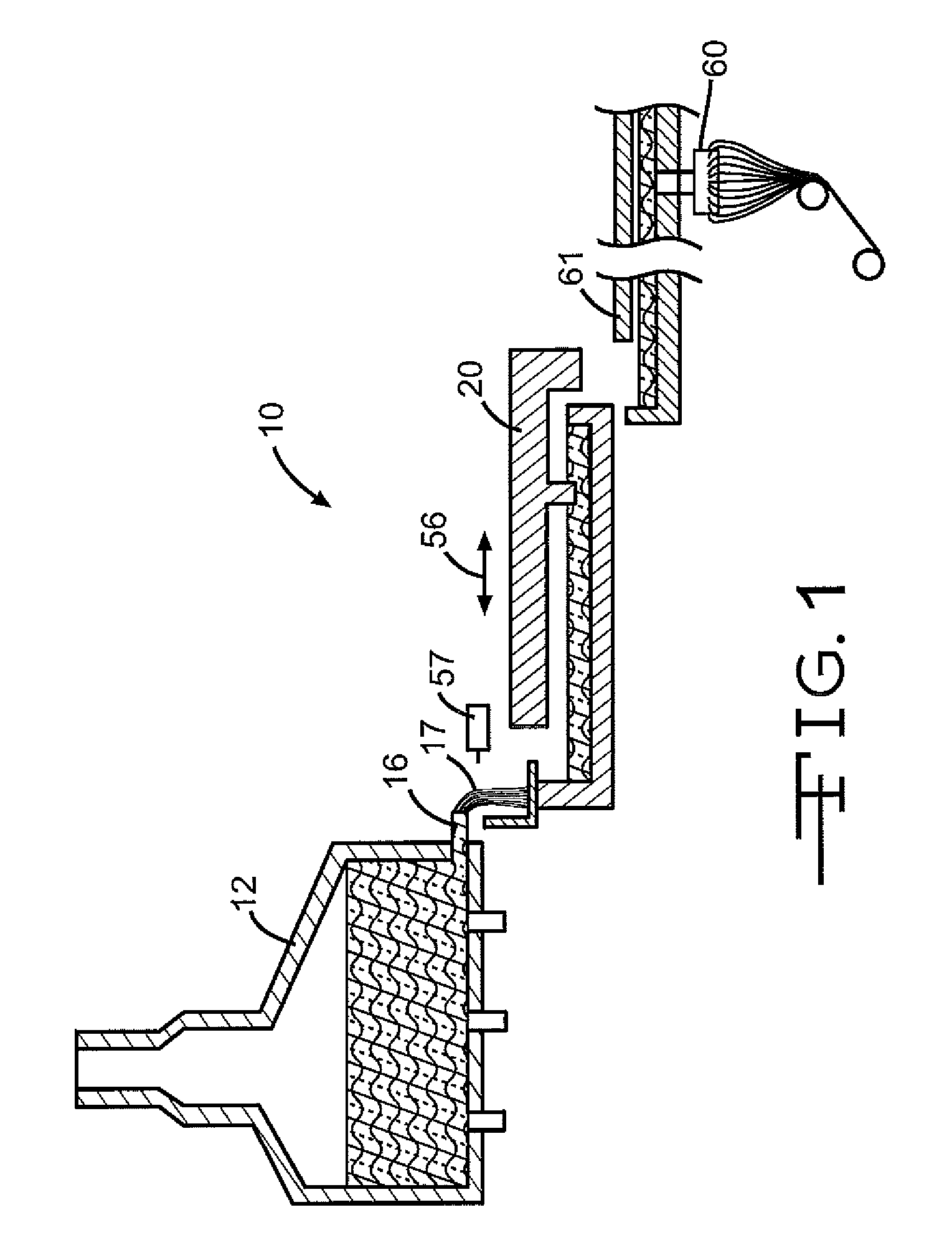
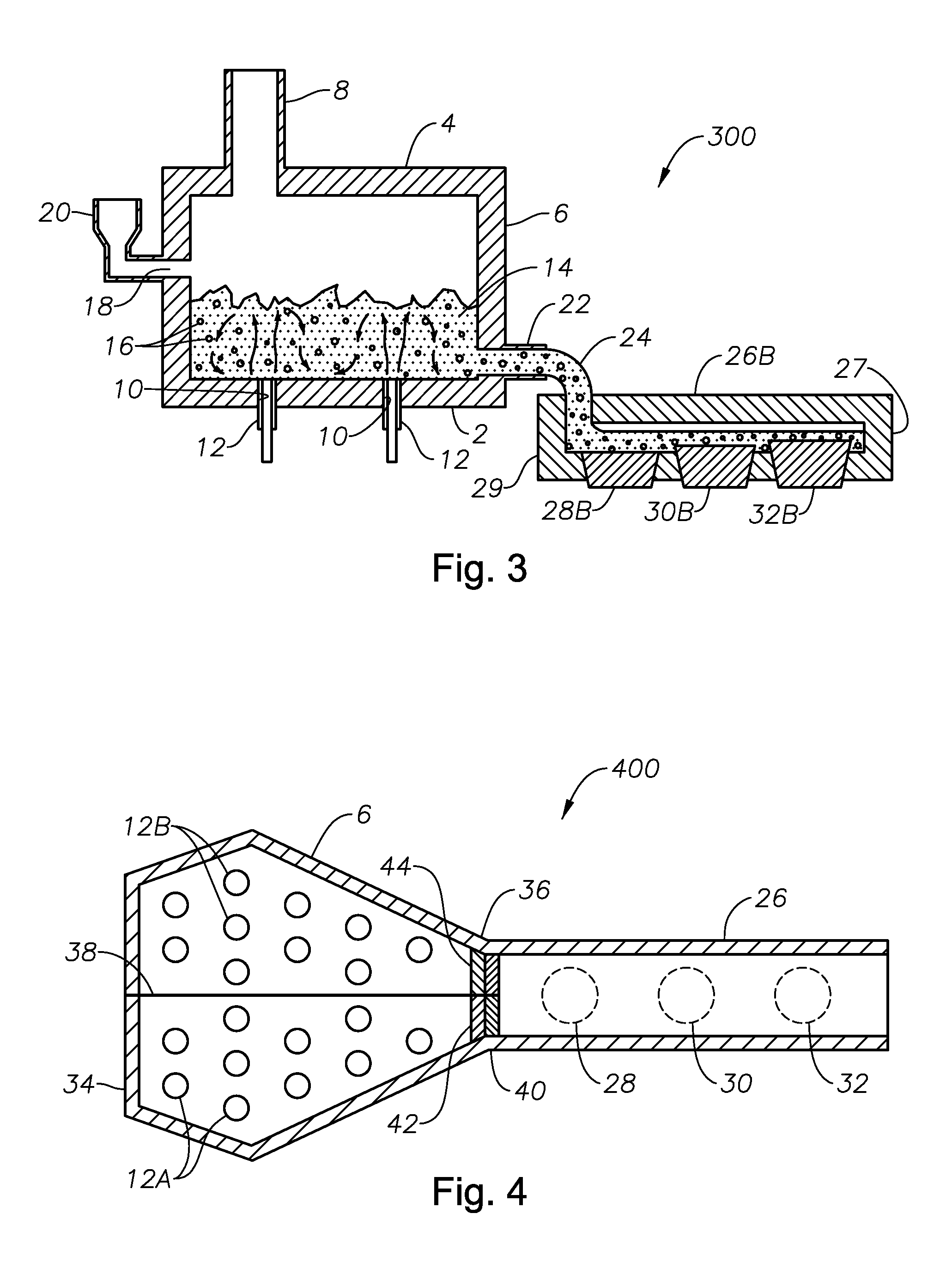
Submerged combustion melter
InactiveUS20110236846A1Increase melter efficiencyReduce bypassCharging furnaceGlass furnace apparatusCombustorEngineering
A submerged combustion melter having a plurality of side walls, a bottom wall adjacent the side walls, and a top wall adjacent the side walls, the walls collectively enclosing a melting chamber, and the bottom wall forming a plurality of openings, each of which is adapted to receive a submerged combustion burner. Each of the submerged combustion burners is positioned at least 4 inches from the side walls, at least twice as far apart from each other as the distance between the submerged combustion burners and the side walls, and less than or equal to about 20 inches apart.
Owner:GAS TECH INST
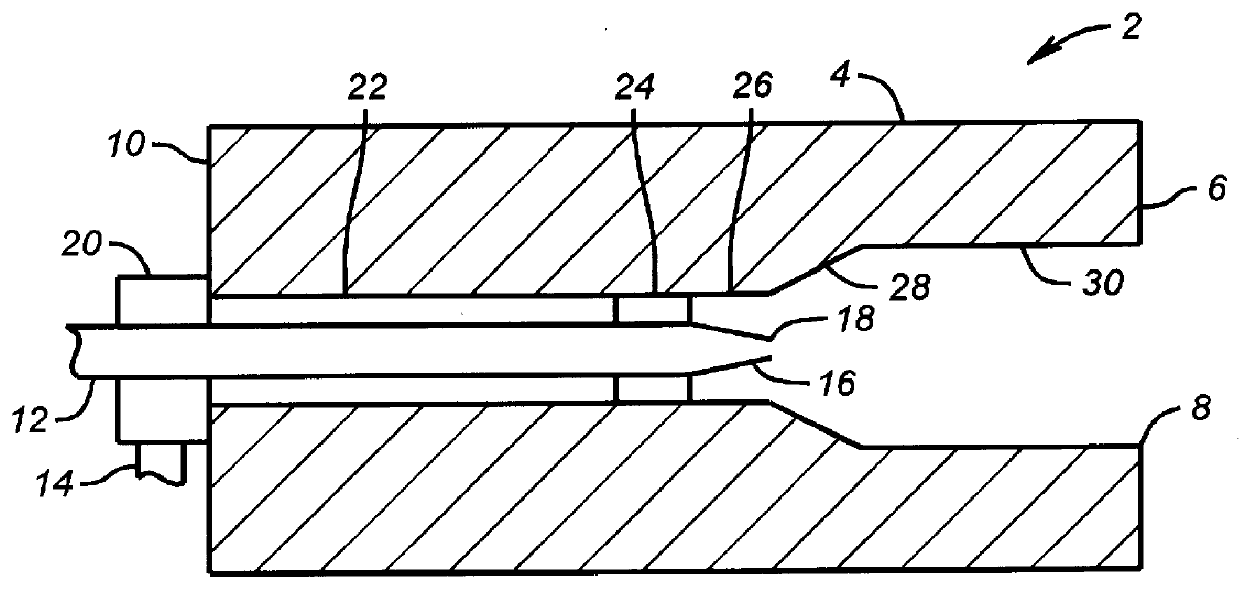
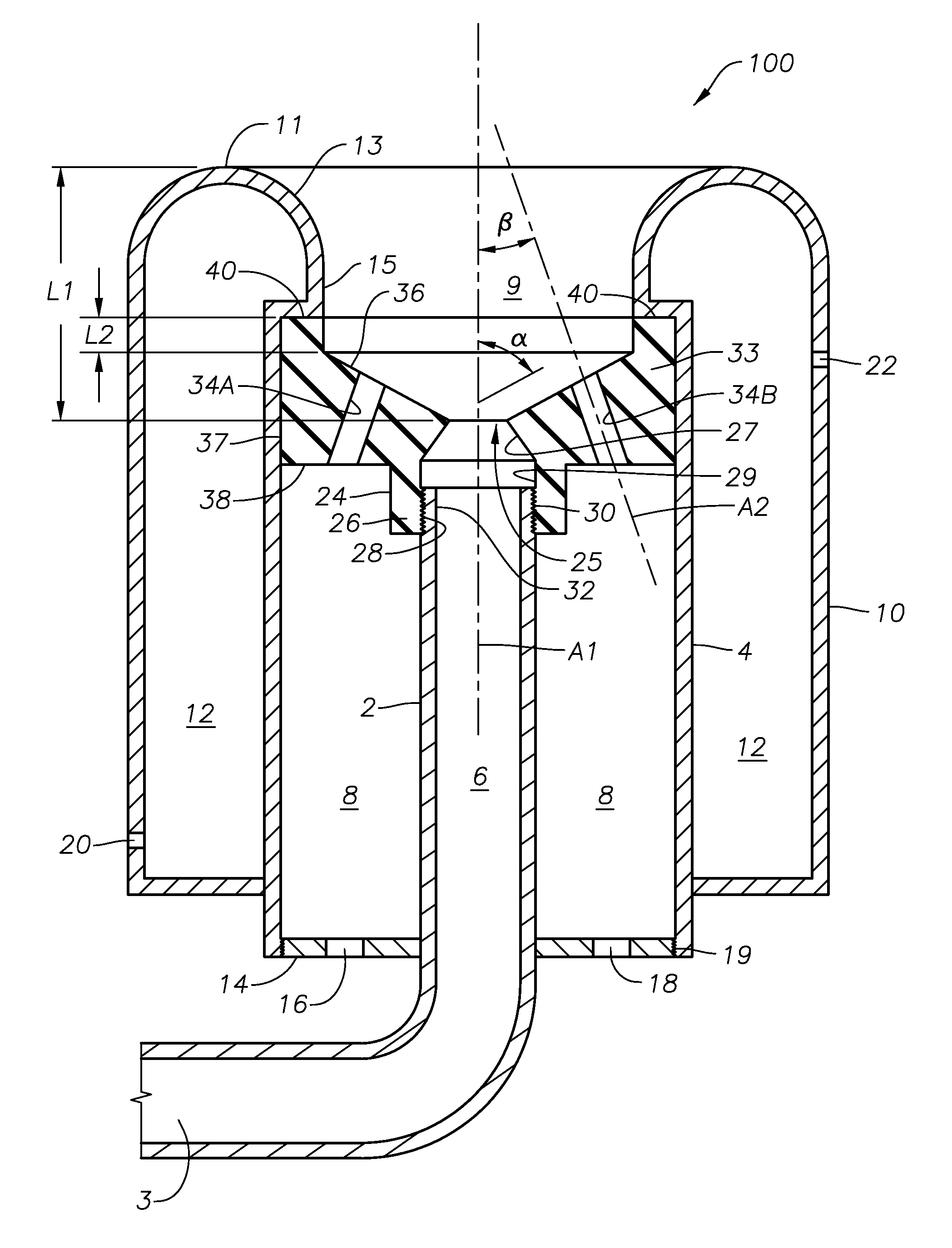
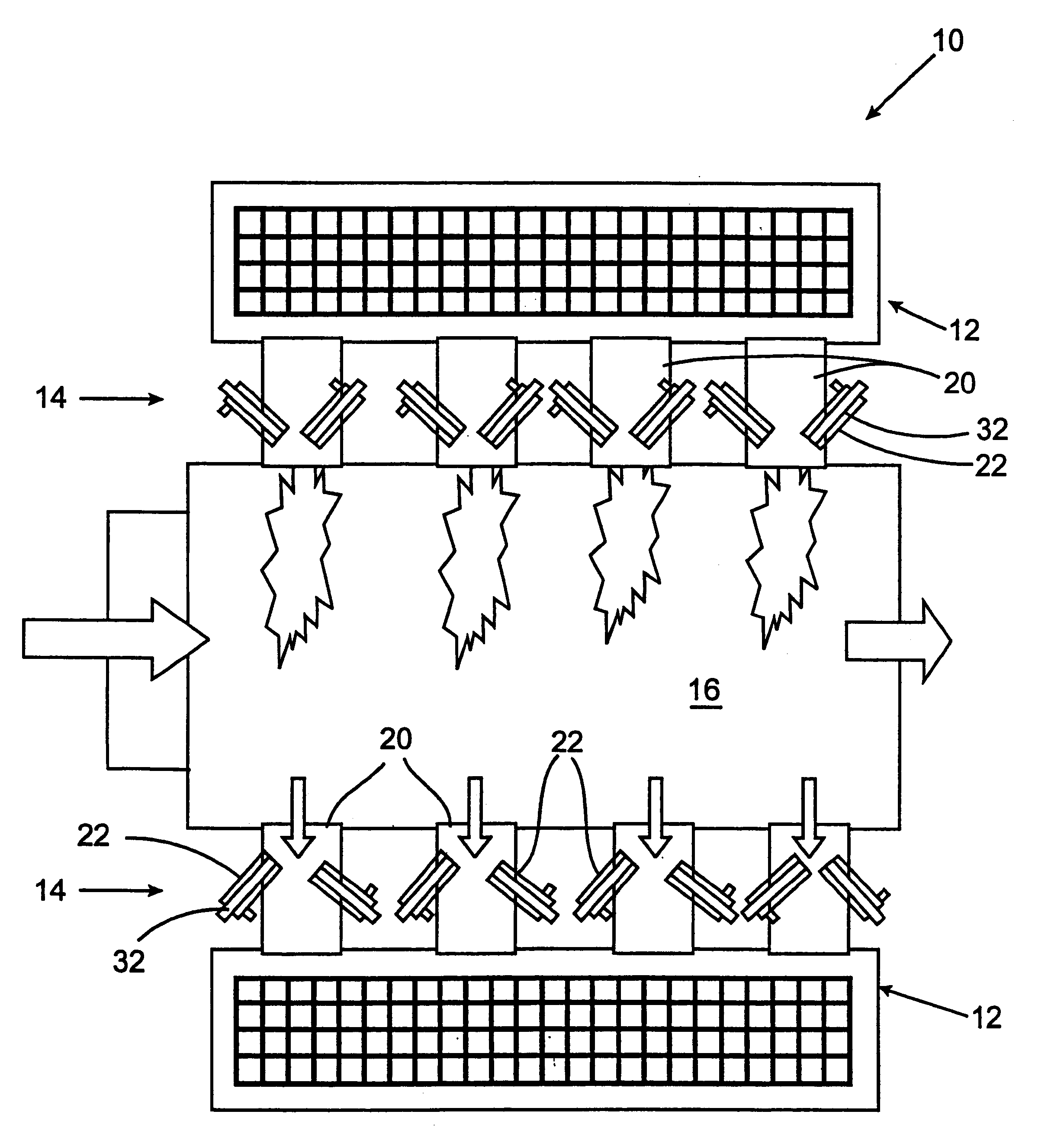
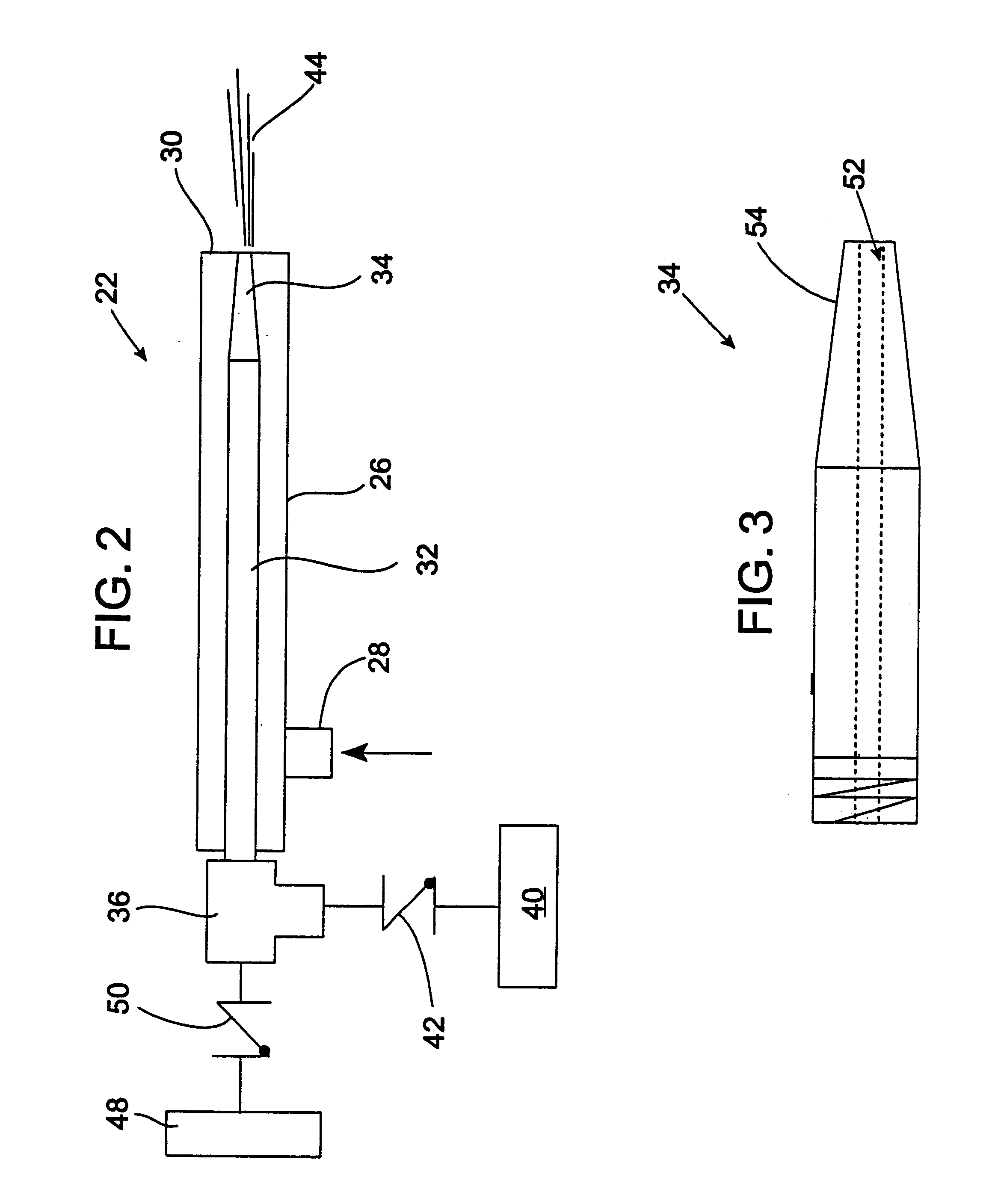
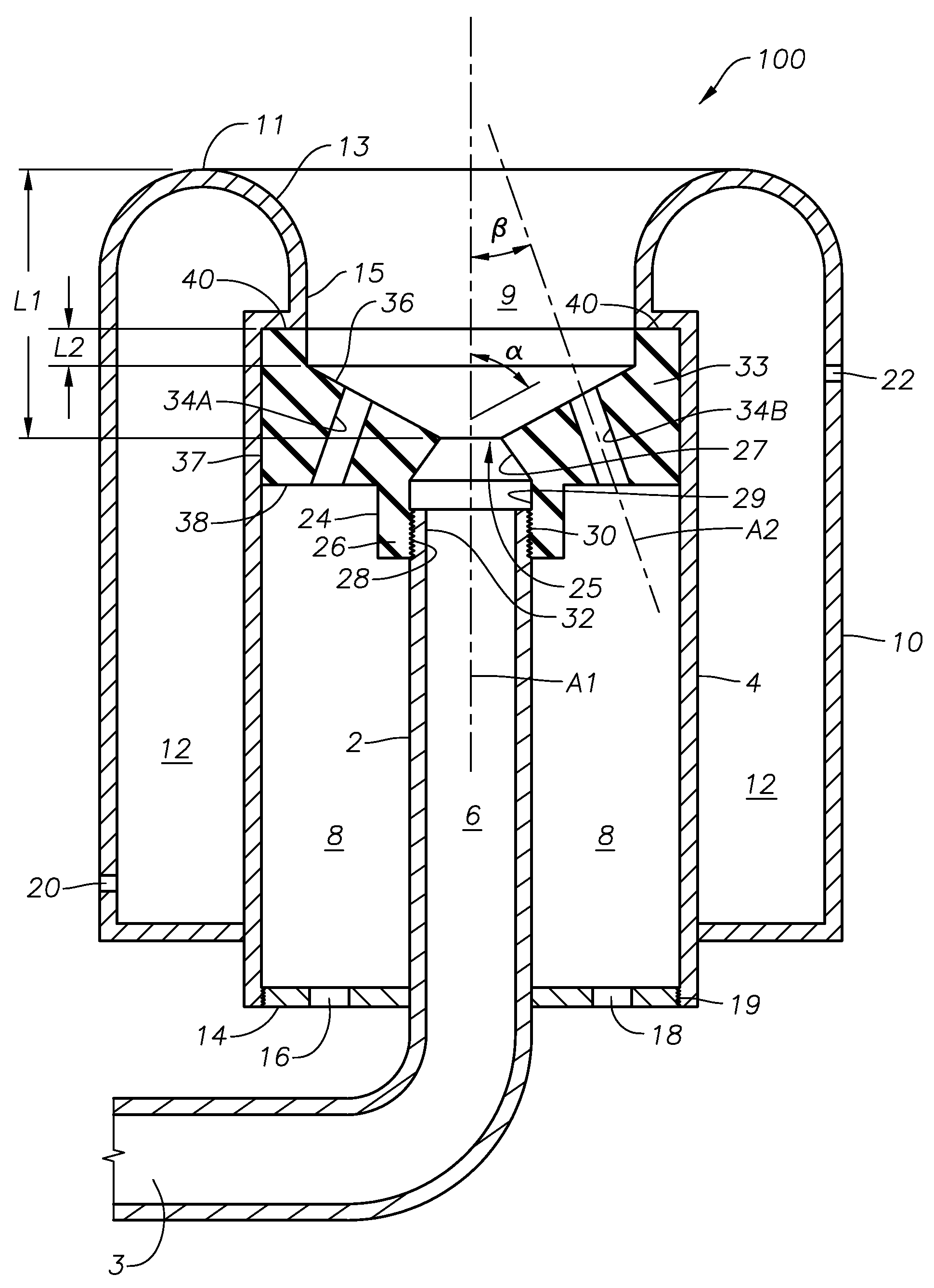
Self-cooled oxygen-fuel burner for use in high-temperature and high-particulate furnaces
InactiveUS6123542AAvoiding particulate inspiration.TheControl expansionGlass furnace apparatusGlass melting apparatusParticulatesCombustor
A self-cooled oxidant-fuel burner consisting novel fuel and oxidant nozzles and three compartment refractory burner block design is proposed. The new oxidant-fuel burner can fire in high-temperature (2200 DEG F. to 3000 DEG F.) and high-particulate (or high process volatiles / condensates) furnaces without over-heating or causing chemical corrosion damage to it's metallic burner nozzle and refractory burner block interior. Using various embodiments of nozzle and block shape, the burner can offer a traditional cylindrical flame or flat flame depending on the heating load requirements. The new features of this burner include unique fuel nozzle design for the streamline mixing of fuel and oxidant streams, a controlled swirl input to the oxidant flow for desired flame characteristics, a controlled expansion of flame envelope in the radial and axial dimensions, and efficient sweeping of burner block interior surface using oxidant to provide convective cooling and prevent any build up of process particulates. In addition, a relatively thick wall metallic nozzle construction with heat conduction fins enable efficient heat dissipation from the nozzle tip and providing a maintenance free burner operation.
Owner:LAIR LIQUIDE SA POUR L ETUD ET LEXPLOITATION DES PROCEDES GEORGES CLAUDE +1
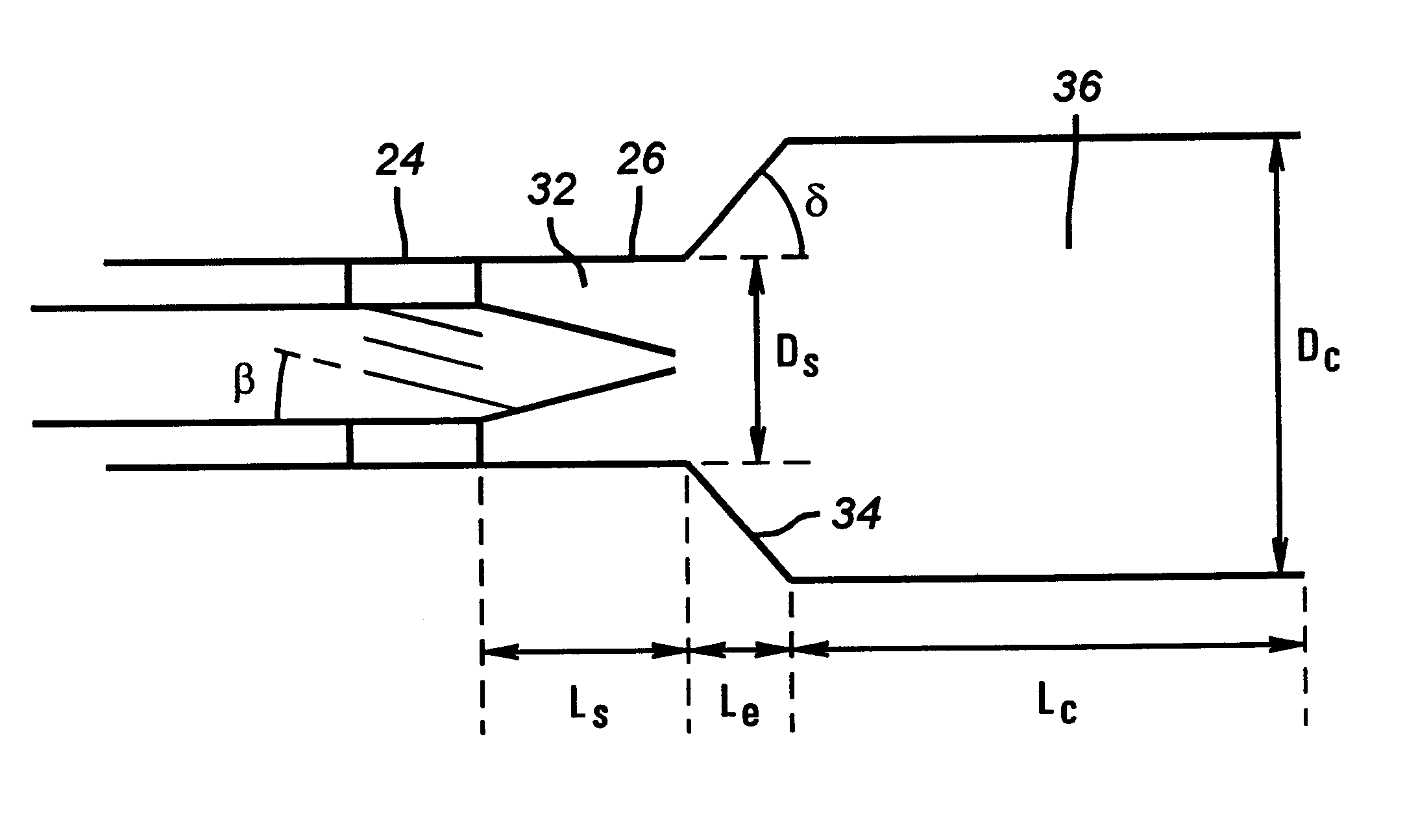
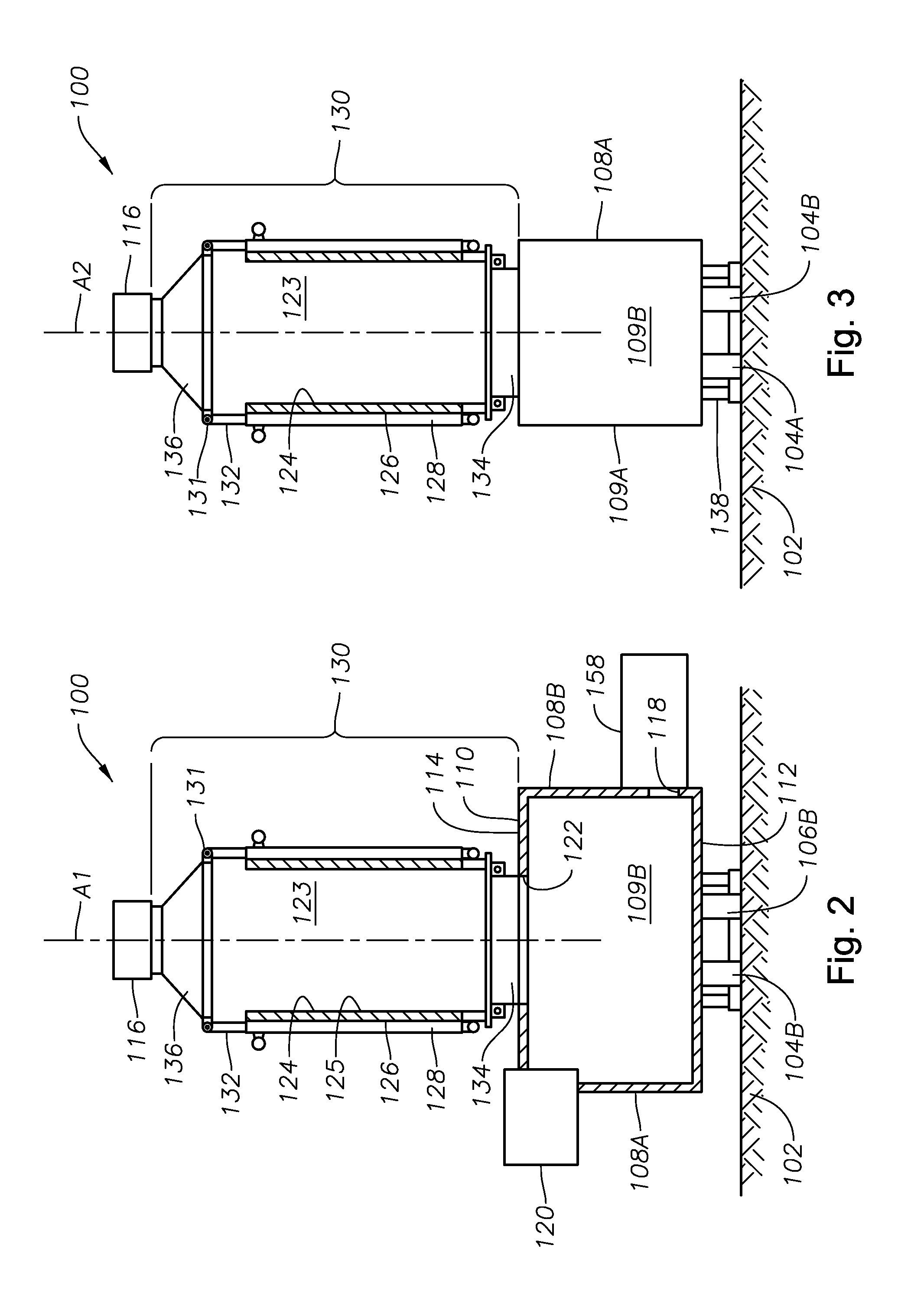
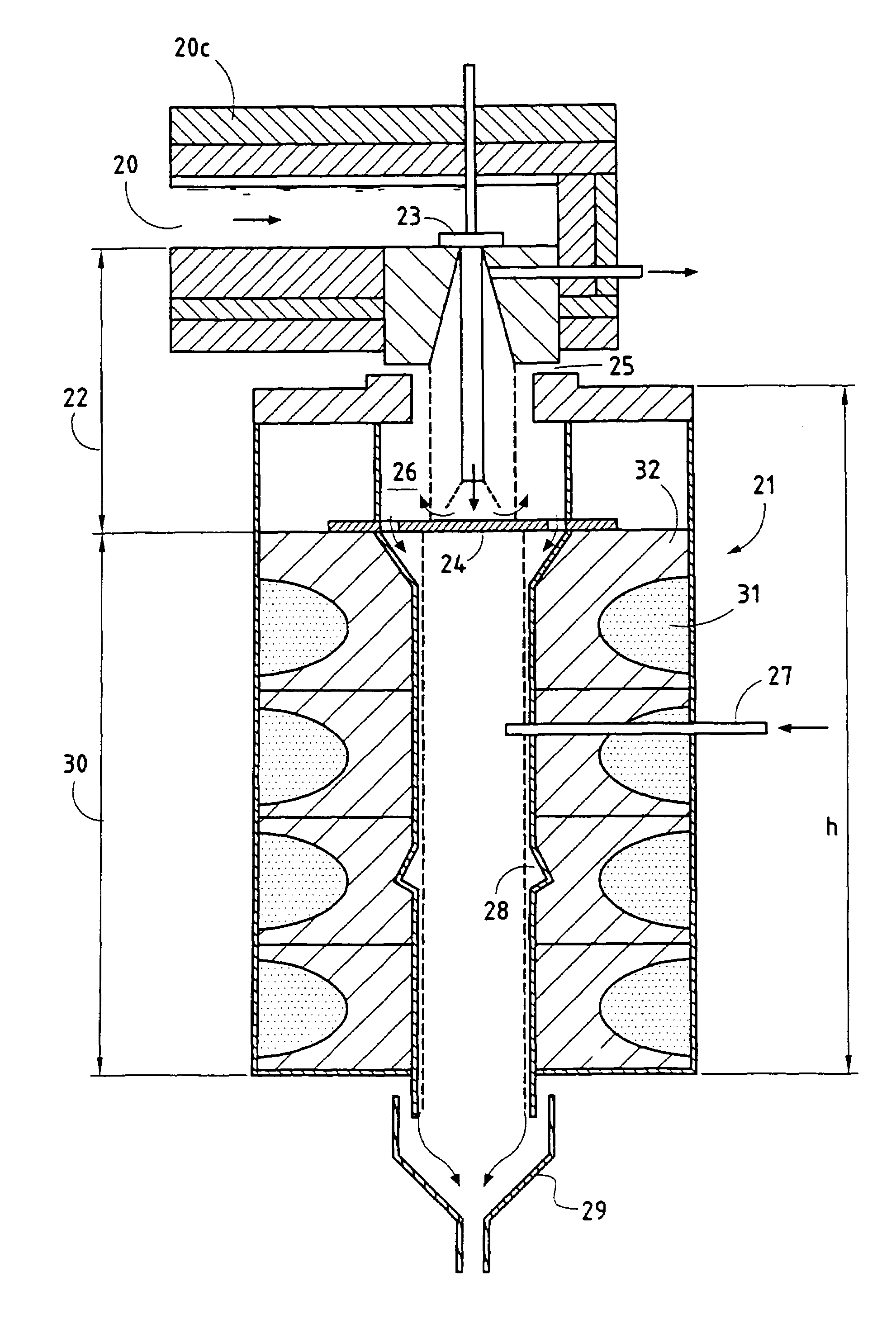
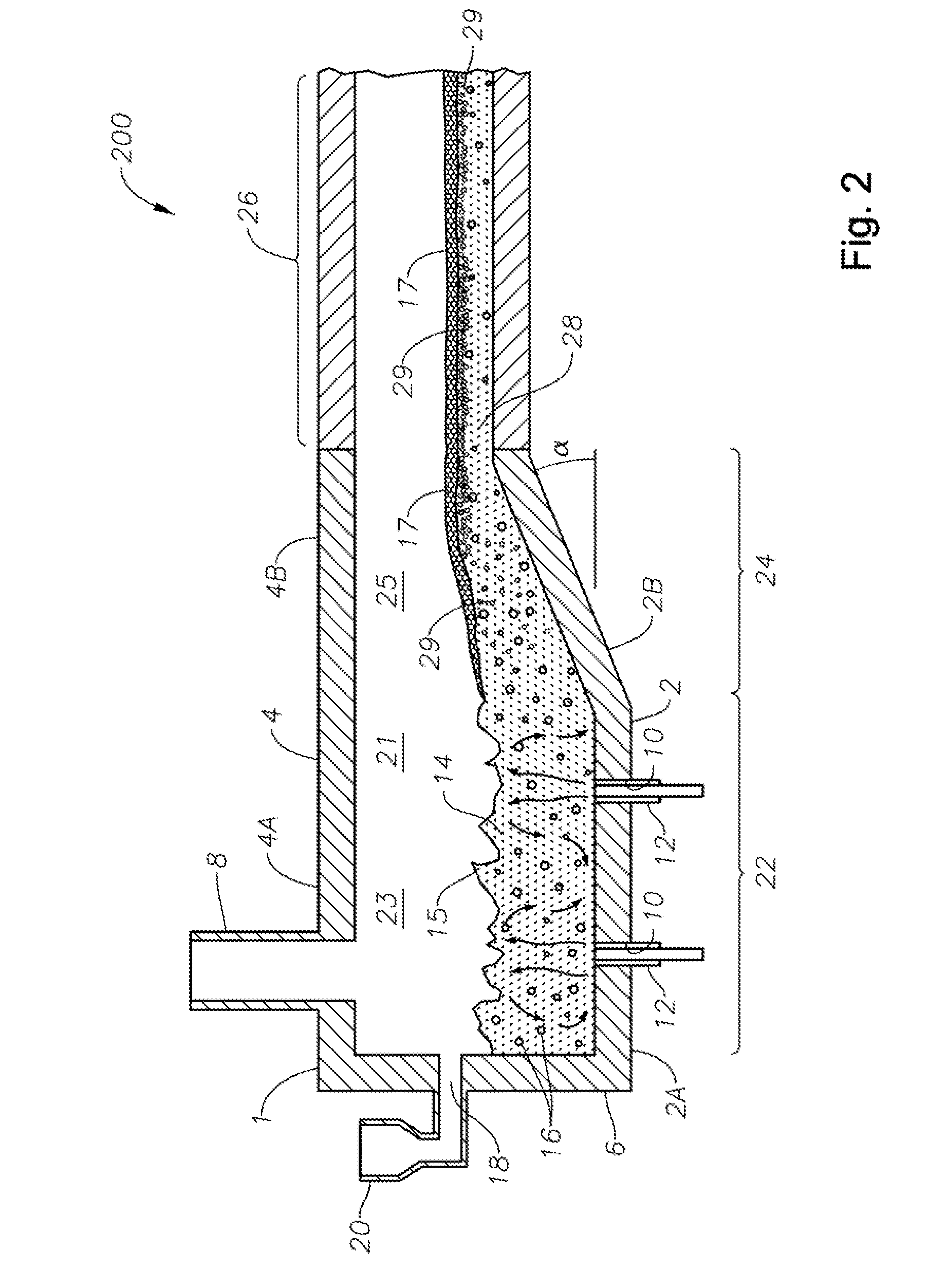
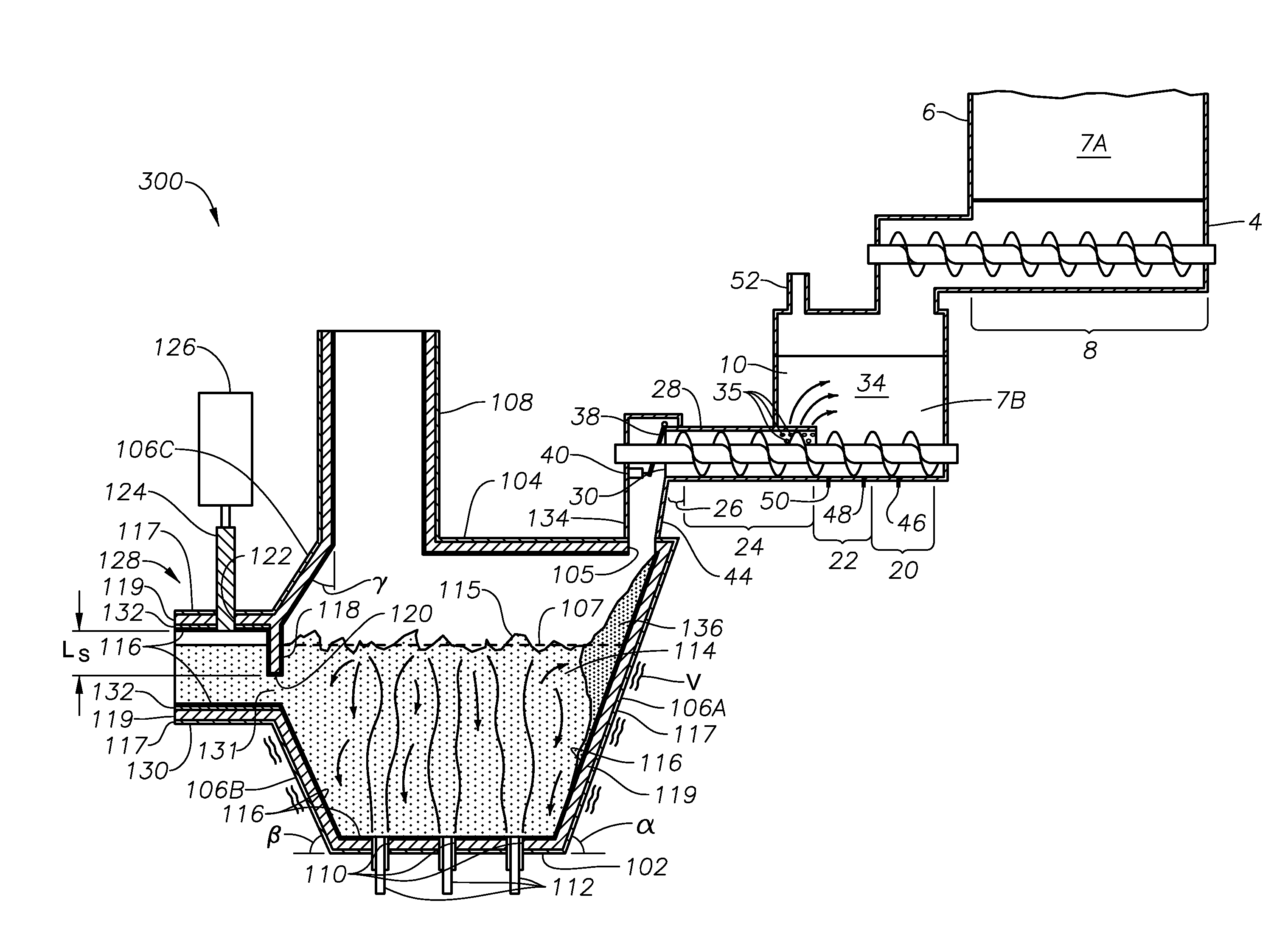
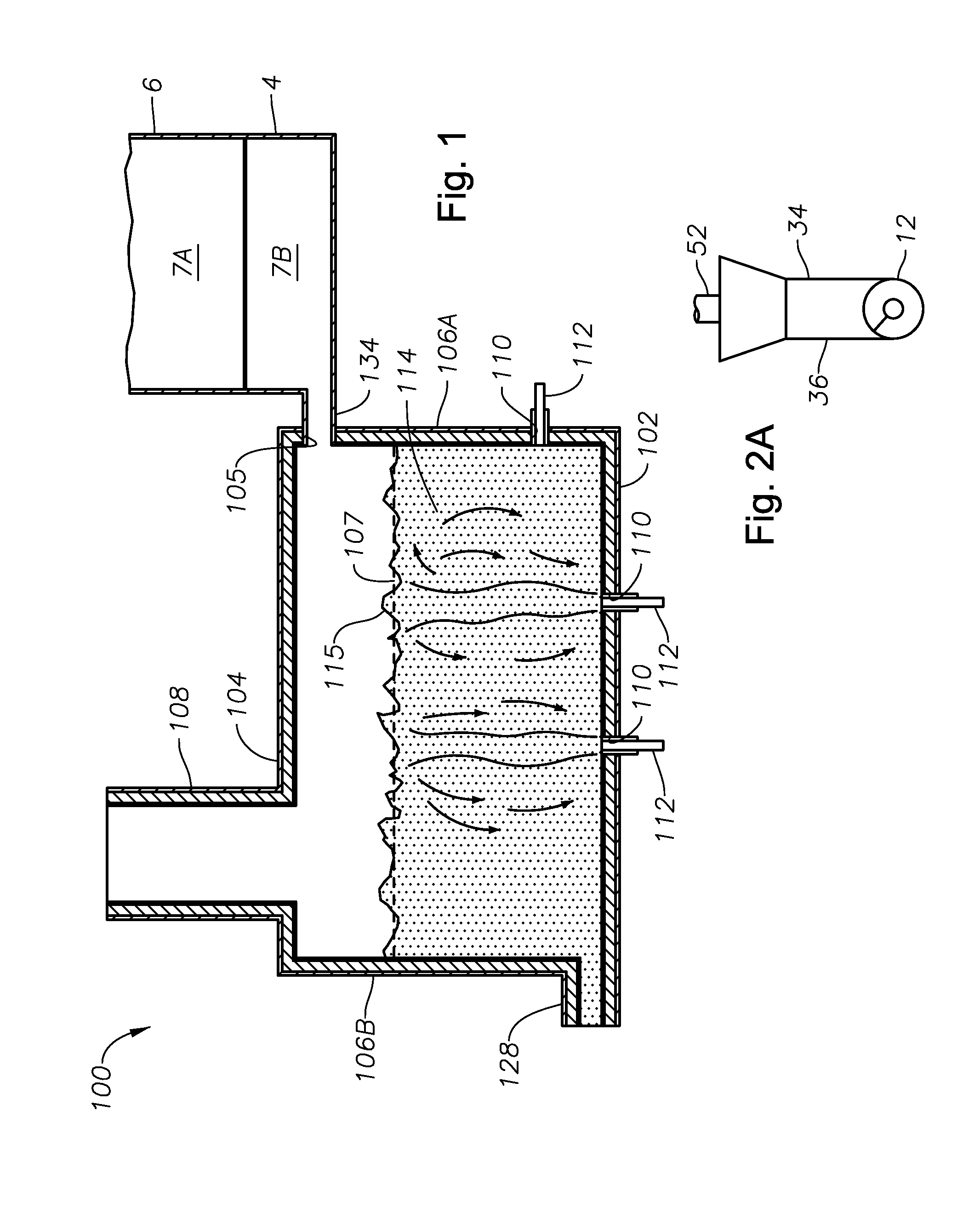
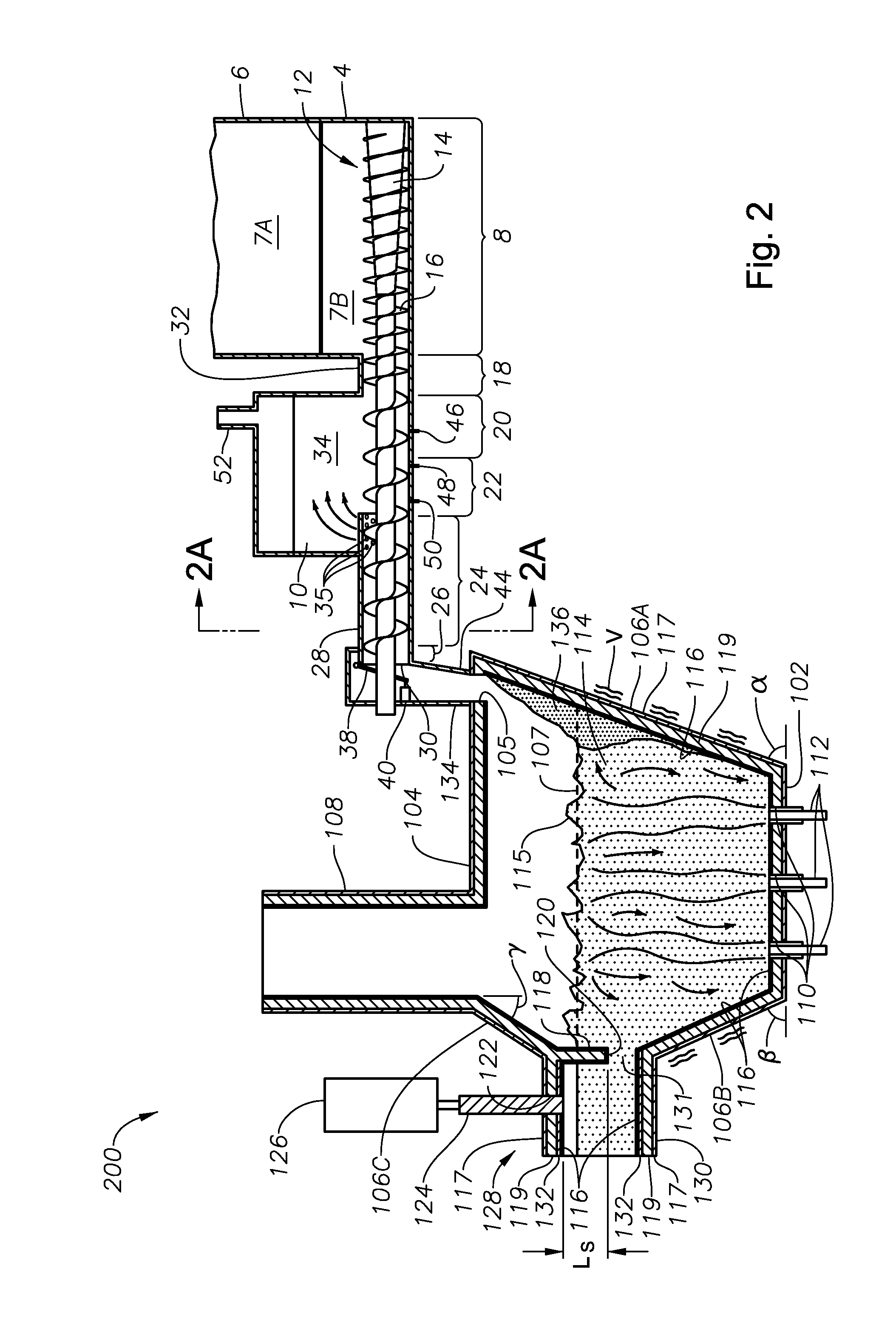
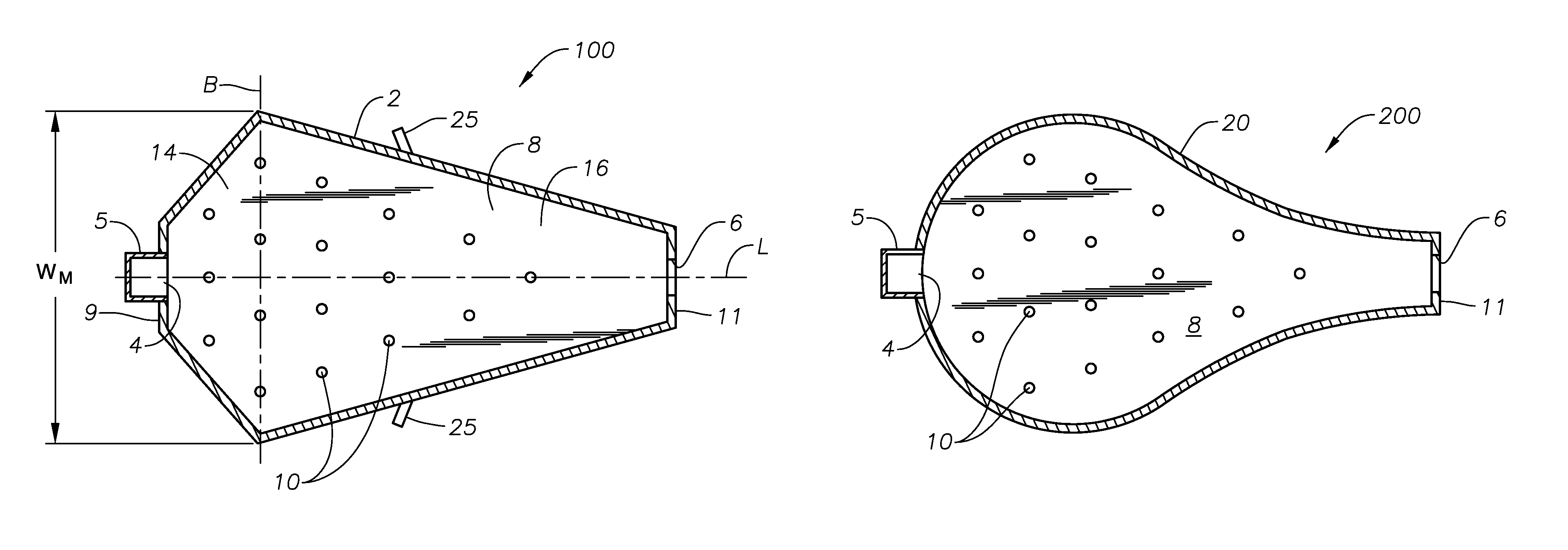
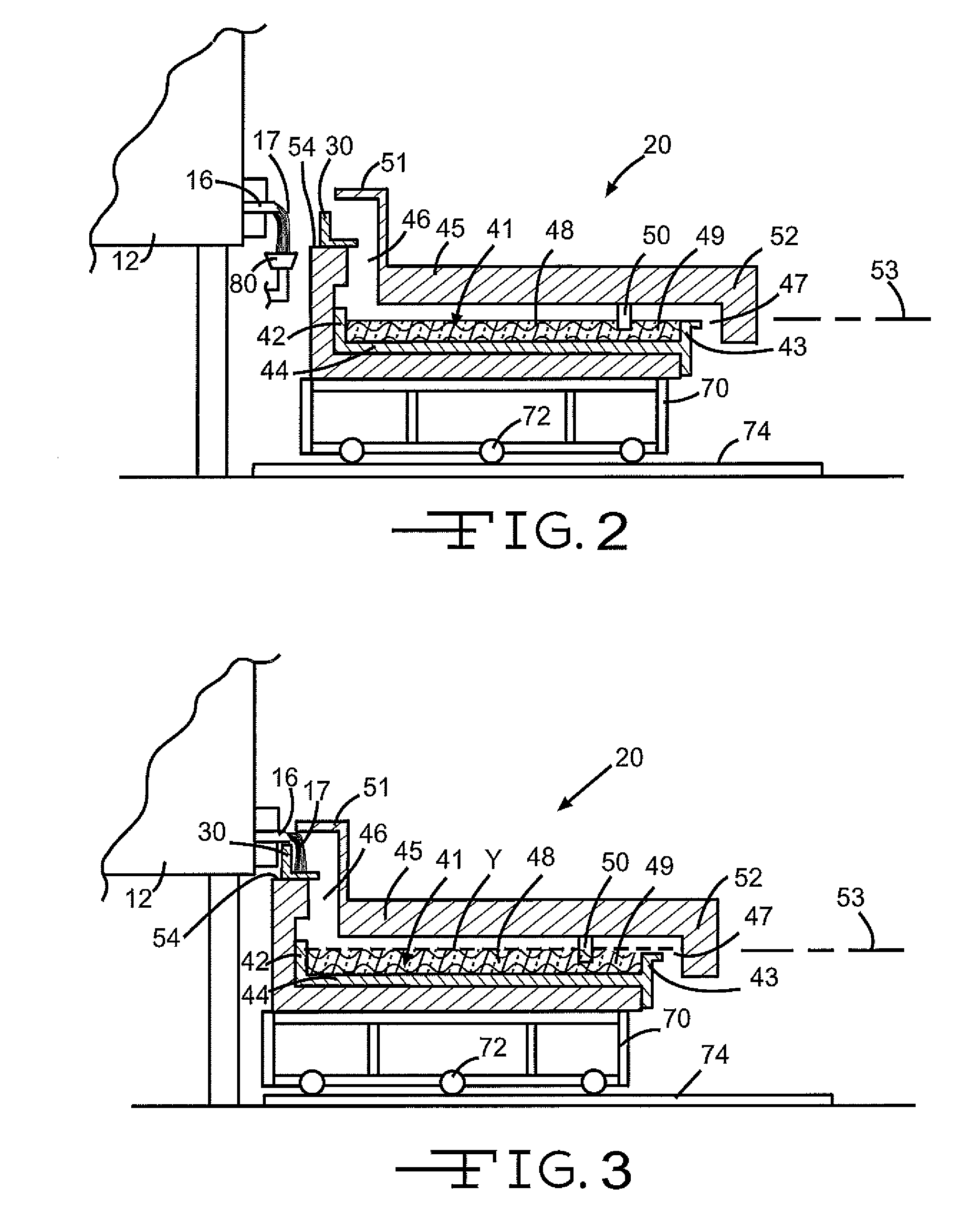
Panel-cooled submerged combustion melter geometry and methods of making molten glass
ActiveUS20110308280A1Reduce dead flow (stagnant) regionSmall sizePulsating combustionTank furnacesCombustorDirect combustion
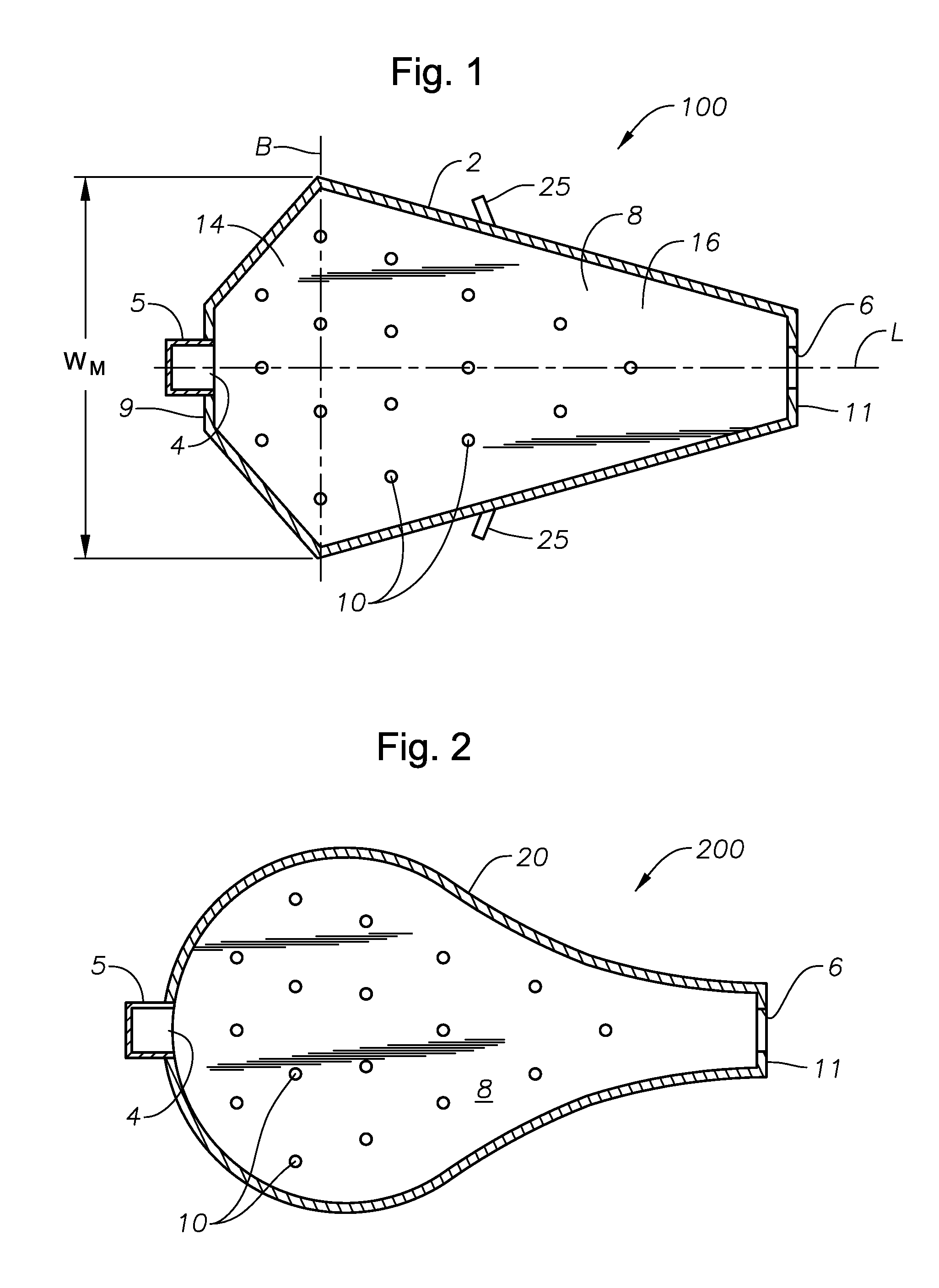
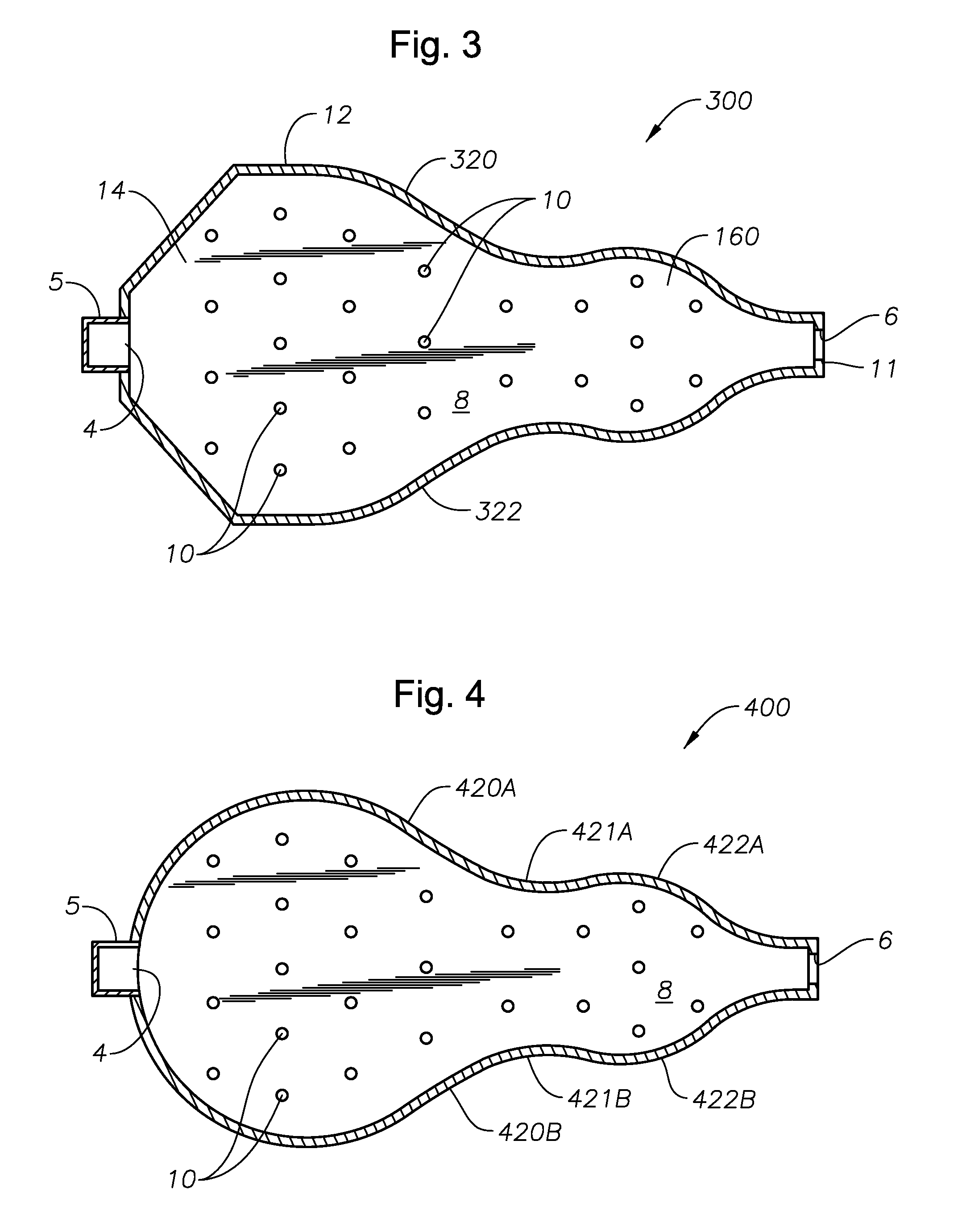
A melter apparatus includes a floor, a ceiling, and a substantially vertical wall connecting the floor and ceiling at a perimeter of the floor and ceiling, a melting zone being defined by the floor, ceiling and wall, the melting zone having a feed inlet and a molten glass outlet positioned at opposing ends of the melting zone. The melting zone includes an expanding zone beginning at the inlet and extending to an intermediate location relative to the opposing ends, and a narrowing zone extending from the intermediate location to the outlet. One or more burners, at least some of which are positioned to direct combustion products into the melting zone under a level of molten glass in the zone, are also provided.
Owner:MANVILLE JOHNS
Self-cooled oxygen-fuel burner for use in high-temperature and high-particulate furnaces
InactiveUS6210151B1Avoiding particulate inspiration.TheControl expansionIndirect carbon-dioxide mitigationGaseous fuel burnerParticulatesVolatiles
A self-cooled oxidant-fuel burner consisting novel fuel and oxidant nozzles and three compartment refractory burner block design is proposed. The new oxidant-fuel burner can fire in high-temperature (2200° F. to 3000° F.) and high-particulate (or high process volatiles / condensates) furnaces without over-heating or causing chemical corrosion damage to it's metallic burner nozzle and refractory burner block interior. Using various embodiments of nozzle and block shape, the burner can offer a traditional cylindrical flame or flat flame depending on the heating load requirements. The new features of this burner include unique fuel nozzle design for the streamline mixing of fuel and oxidant streams, a controlled swirl input to the oxidant flow for desired flame characteristics, a controlled expansion of flame envelope in the radial and axial dimensions, and efficient sweeping of burner block interior surface using oxidant to provide convective cooling and prevent any build up of process particulates. In addition, a relatively thick wall metallic nozzle construction with heat conduction fins enable efficient heat dissipation from the nozzle tip and providing a maintenance free burner operation.
Owner:AIR LIQUIDE AMERICA INC +1
Methods and apparatus for recycling glass products using submerged combustion
ActiveUS20120077135A1Reduce eliminate needCharging furnaceGlass furnace apparatusCombustionEngineering
A method for recycling glass mat waste, wound rovings, and other products includes providing a source of glass mat, or a plurality of rovings, for example on a roll, and routing the glass mat or rovings into a submerged combustion melter. An unwind system and a pair of powered nip rolls, powered conveyors, or other arrangement may work in combination to provide a substantially consistent rate of material into the melter. The melter may operate under less than atmospheric pressure to avoid fumes escaping the melter. A slot in the melter allows ingress of the glass mat or rovings into the melter, and a glass mat former such as a folder may be used to ensure that the mat fits through the slot. Alternatively, the glass mat may be cut by a slitter prior to entering the slot.
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE CORP
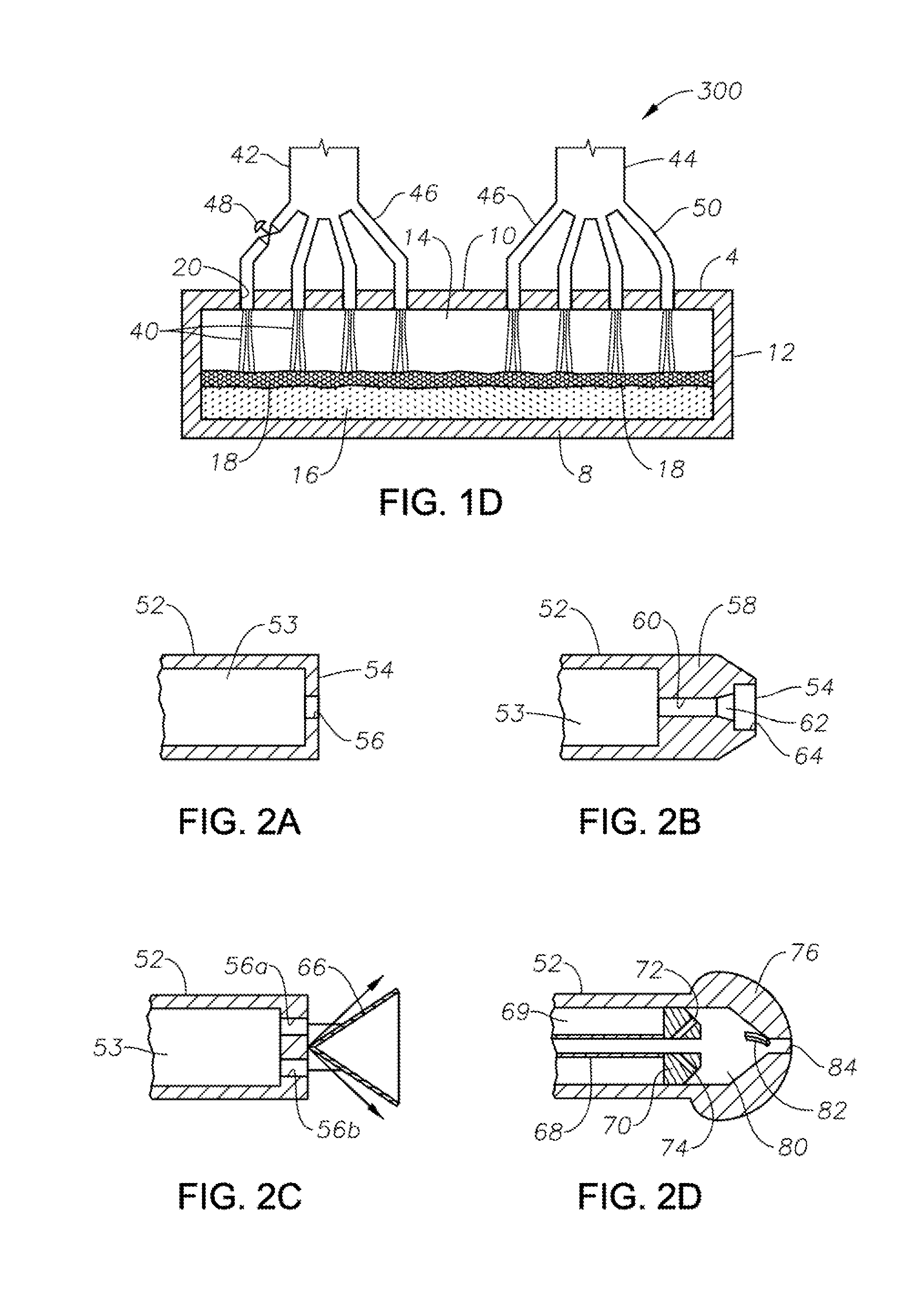
Burner apparatus, submerged combustion melters including the burner, and methods of use
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE CORP
Method of retrofitting a furnace to provide oxygen enrichment
An oxygen enrichment system is provided which uses the existing air / fuel burners of a regenerative furnace to distribute additional oxygen to the burners for increased efficiency, and reduced nitrous oxide emissions. The centrally positioned cooling air lances in the burners of a regenerative furnace are modified to deliver oxygen when the burners are firing for oxygen enrichment. During the burmer firing cycle, oxygen is delivered from an oxygen supply through the oxygen lance to provide a central oxygen jet. The fuel is delivered concentrically around the oxygen jet. During the non-firing cycle of the burner, cooling air or other cooling fluid is delivered from the cooling air supply through the oxygen jet for cooling the offside of the furnace.
Owner:AIR LIQUIDE AMERICA INC
Self-cooled oxygen-fuel for use in high-temperature and high-particulate furnaces
InactiveUS6276924B1Avoiding particulate inspiration.TheControl expansionGlass furnace apparatusGlass melting apparatusParticulatesCombustor
A self-cooled oxidant-fuel burner consisting novel fuel and oxidant nozzles and three compartment refractory burner block design is proposed. The new oxidant-fuel burner can fire in high-temperature (2200° F. to 3000° F.) and high-particulate (or high process volatiles / condensates) furnaces without over-heating or causing chemical corrosion damage to it's metallic burner nozzle and refractory burner block interior. Using various embodiments of nozzle and block shape, the burner can offer a traditional cylindrical flame or flat flame depending on the heating load requirements. The new features of this burner include unique fuel nozzle design for the streamline mixing of fuel and oxidant streams, a controlled swirl input to the oxidant flow for desired flame characteristics, a controlled expansion of flame envelope in the radial and axial dimensions, and efficient sweeping of burner block interior surface using oxidant to provide convective cooling and prevent any build up of process particulates. In addition, a relatively thick wall metallic nozzle construction with heat conduction fins enable efficient heat dissipation from the nozzle tip and providing a maintenance free burner operation.
Owner:AIR LIQUIDE AMERICA INC +1
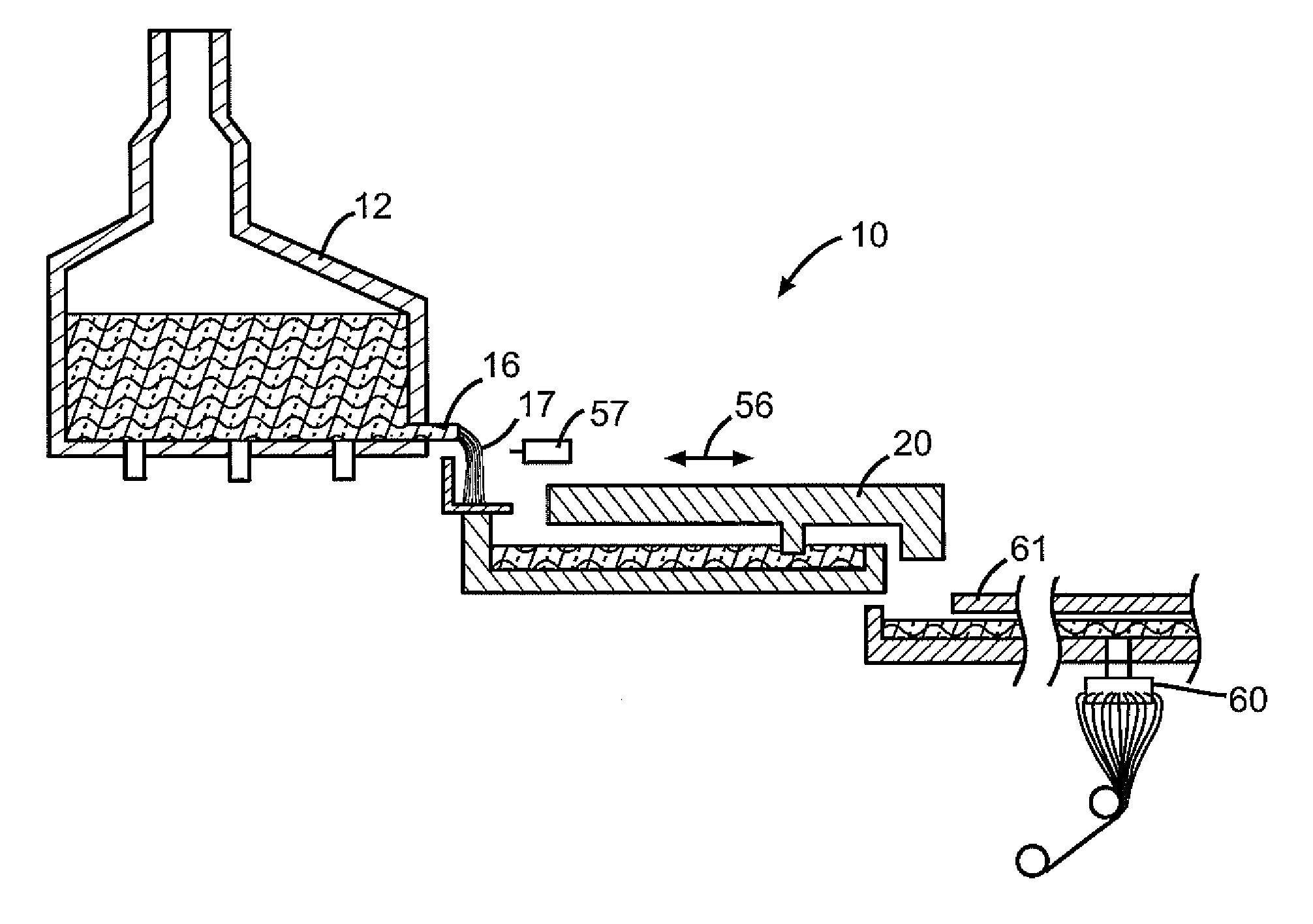
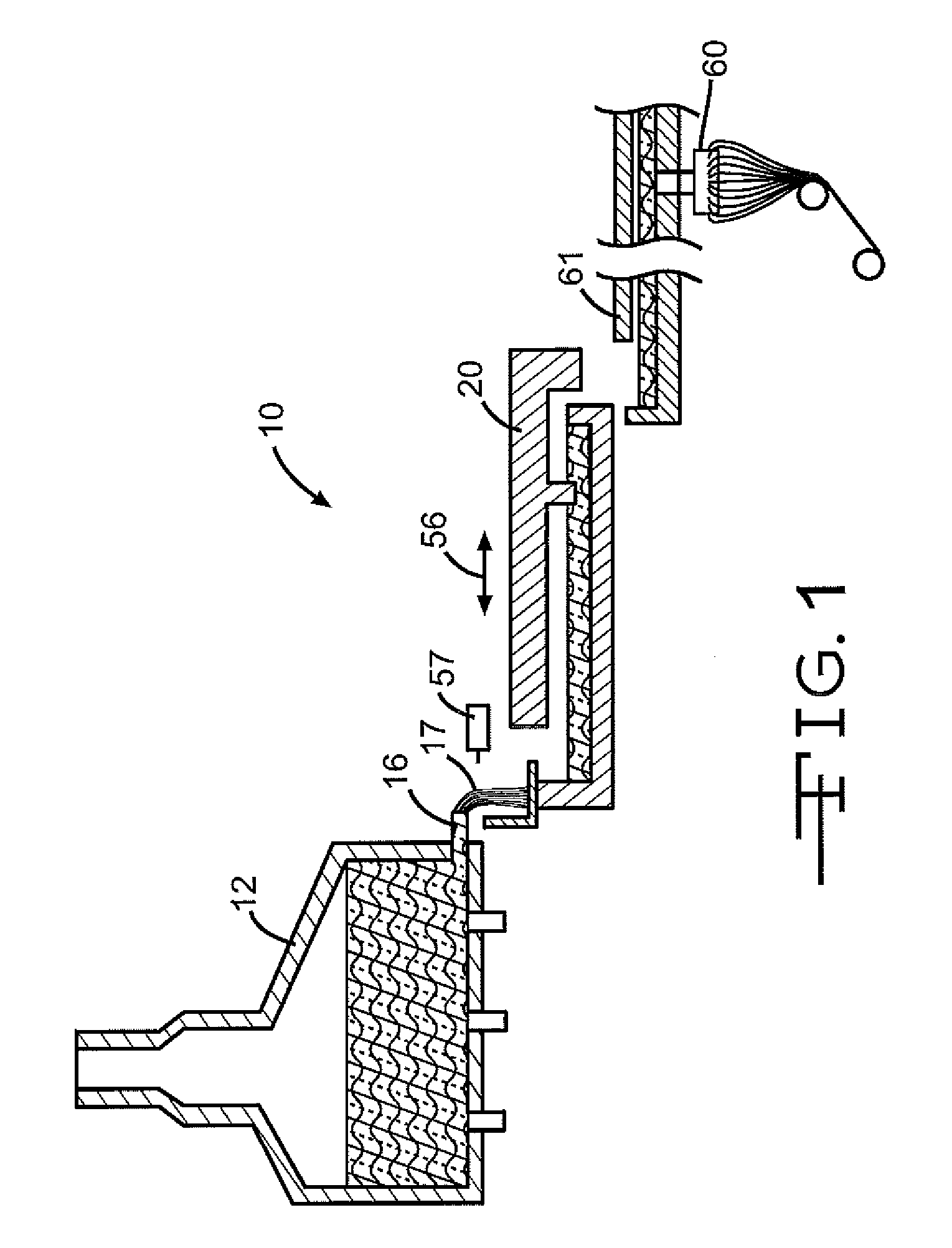
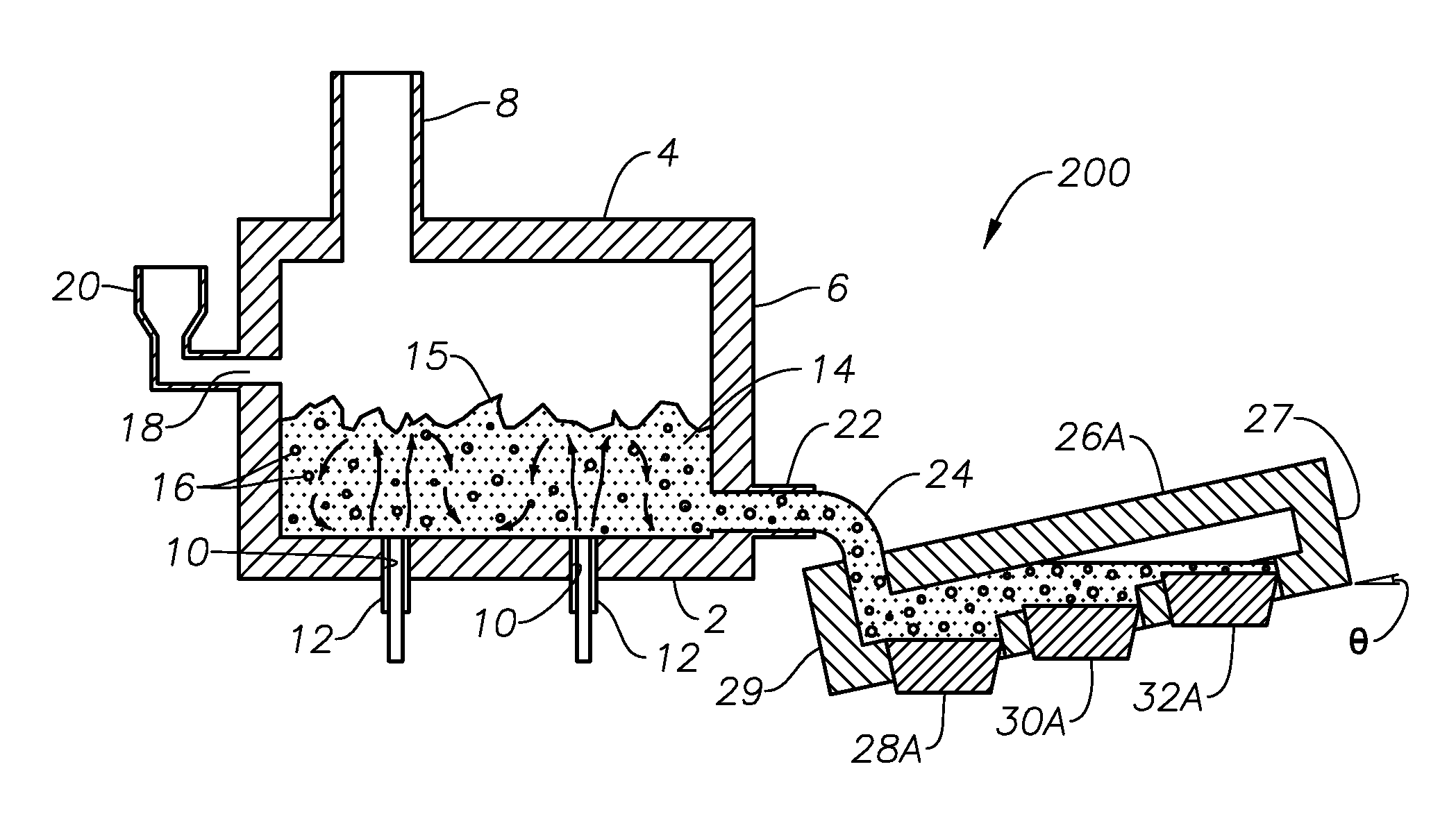
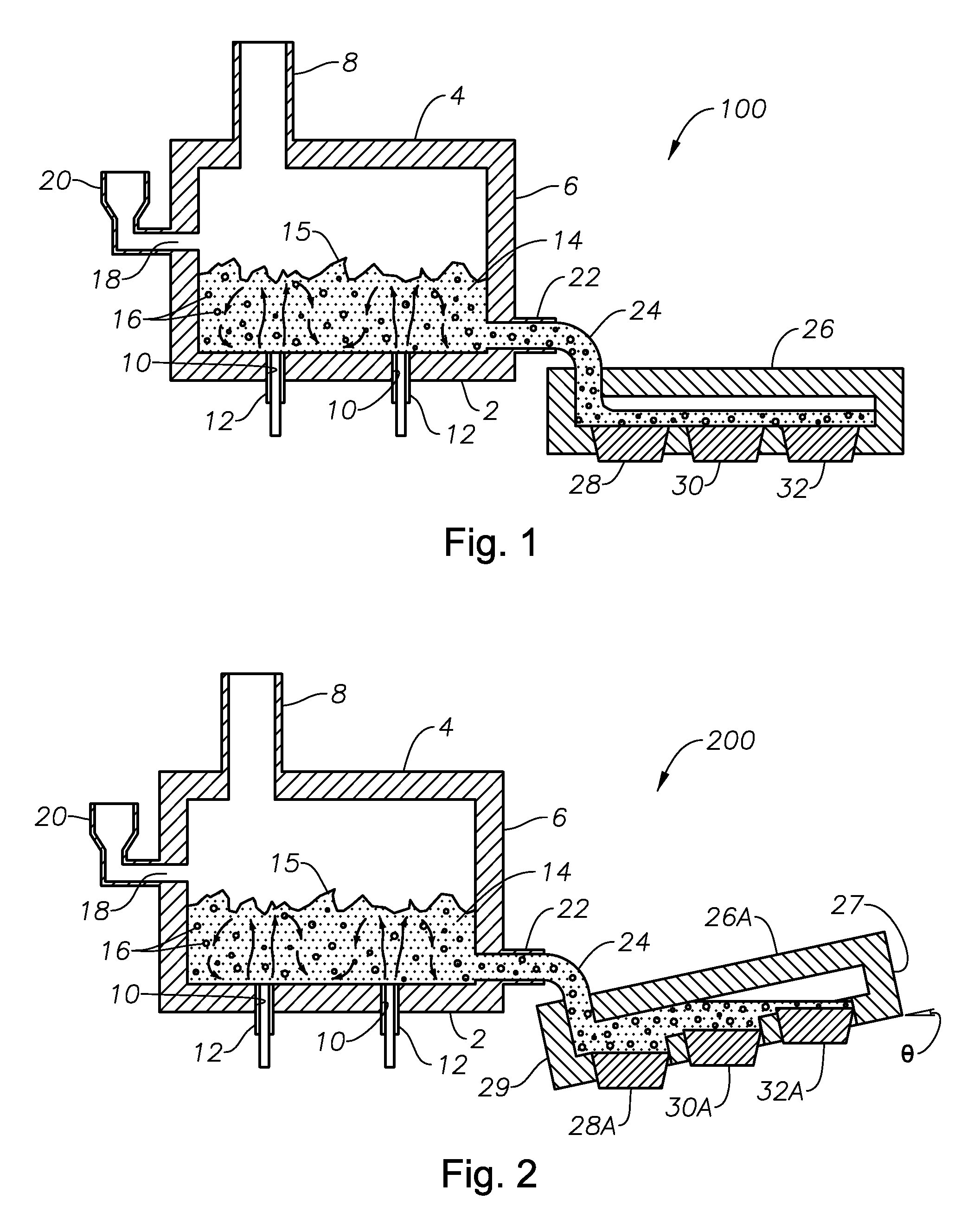
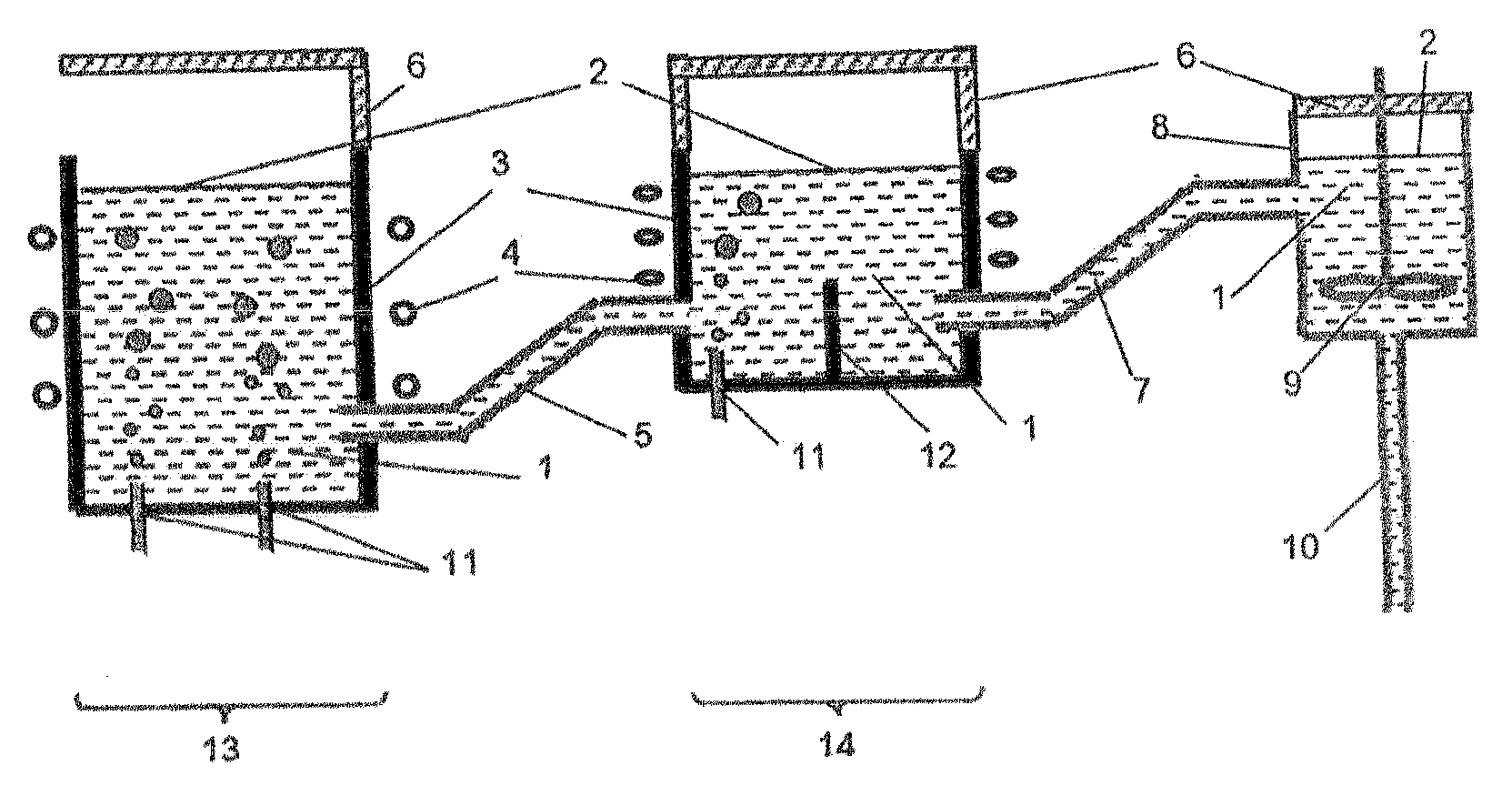
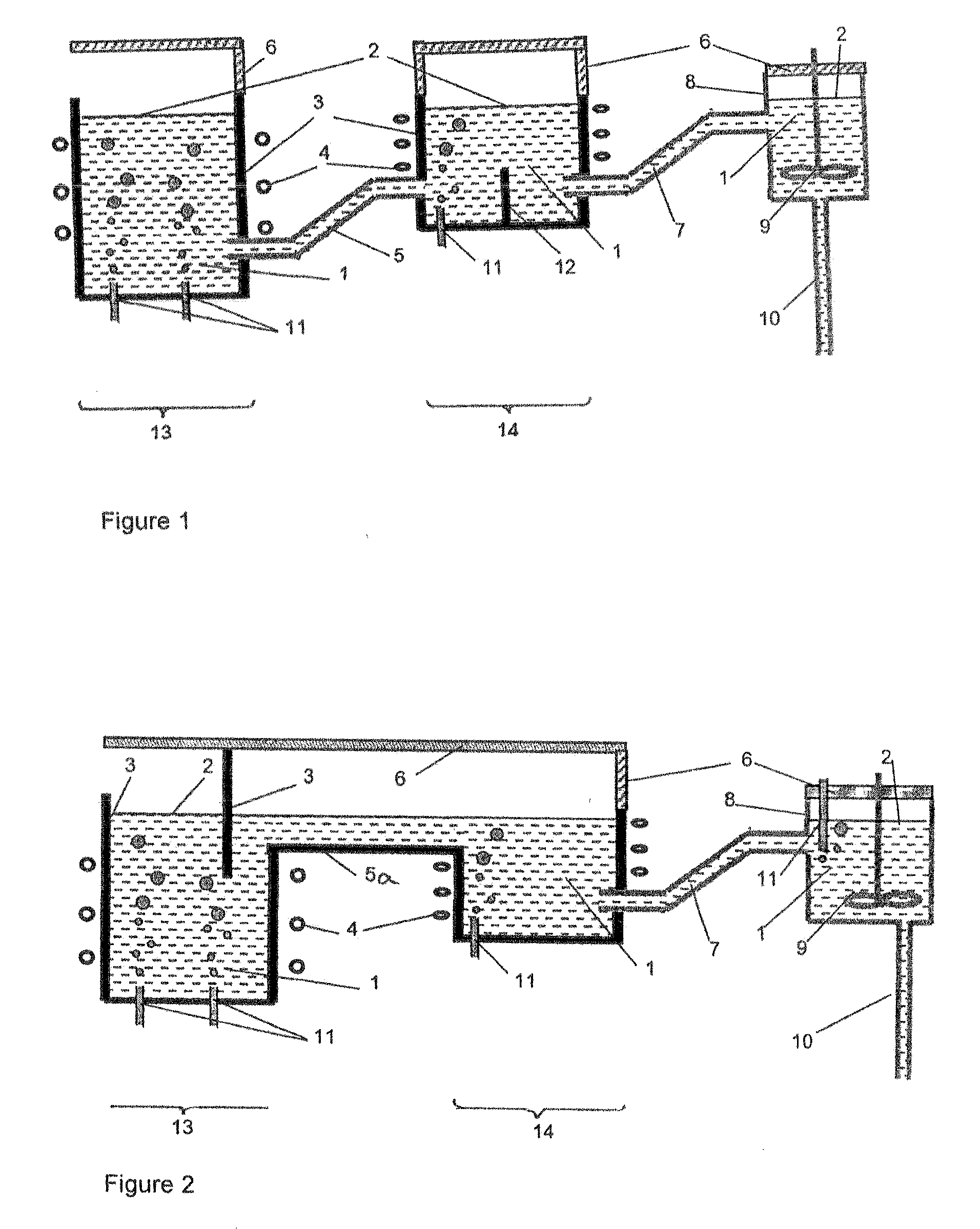
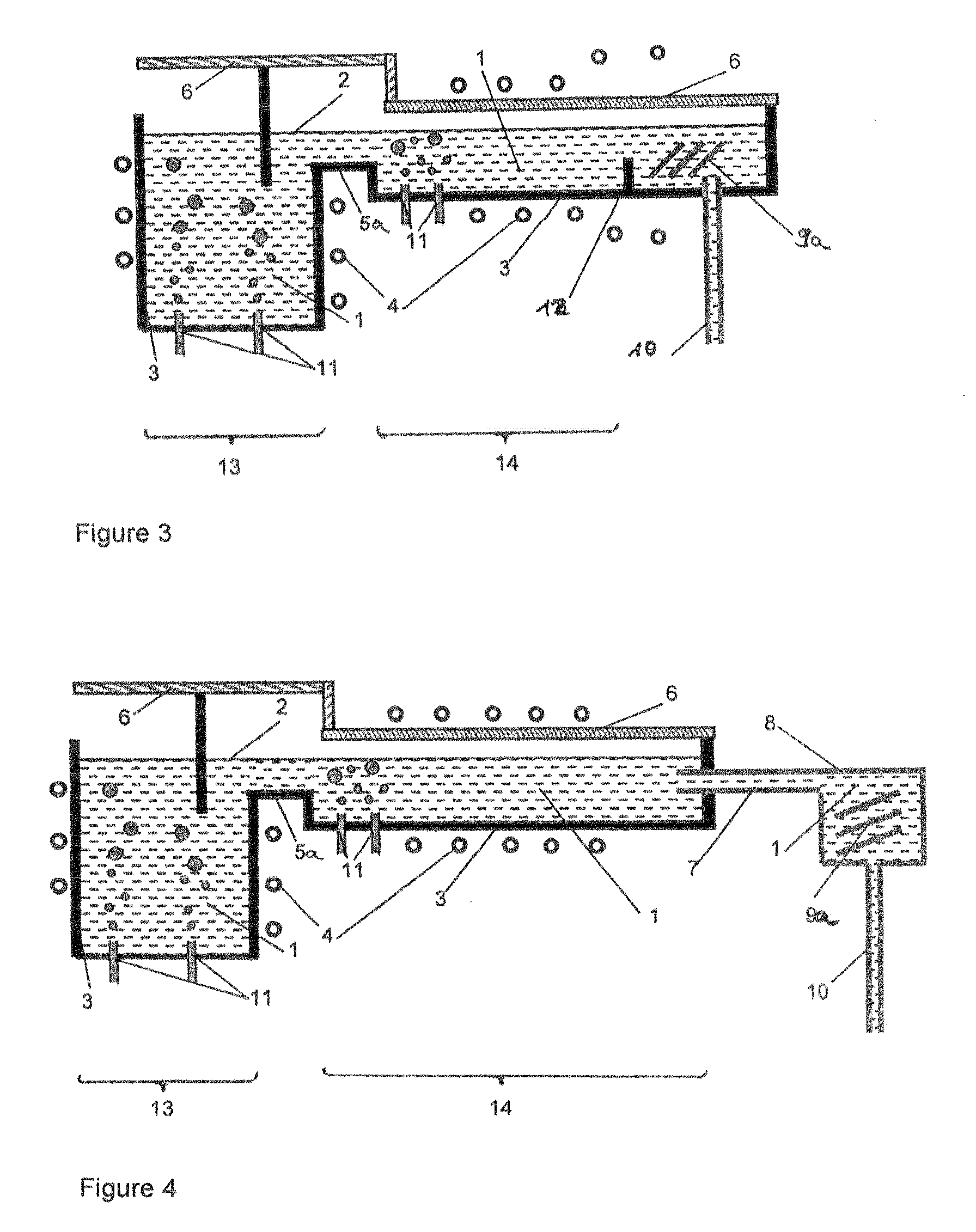
Molten glass delivery and refining system
Methods and apparatus for refining and delivering a supply of molten glass include melting a supply of glass in a melter and discharging a stream of molten glass. A refining section is provided to refine the molten glass discharged by the melter and to deliver the molten glass downstream to a glass forming apparatus. The refining section is mounted for movement into and out of contact with the stream of molten glass to connect and disconnect the glass forming apparatus with the stream of molten glass.
Owner:OWENS CORNING INTELLECTUAL CAPITAL LLC
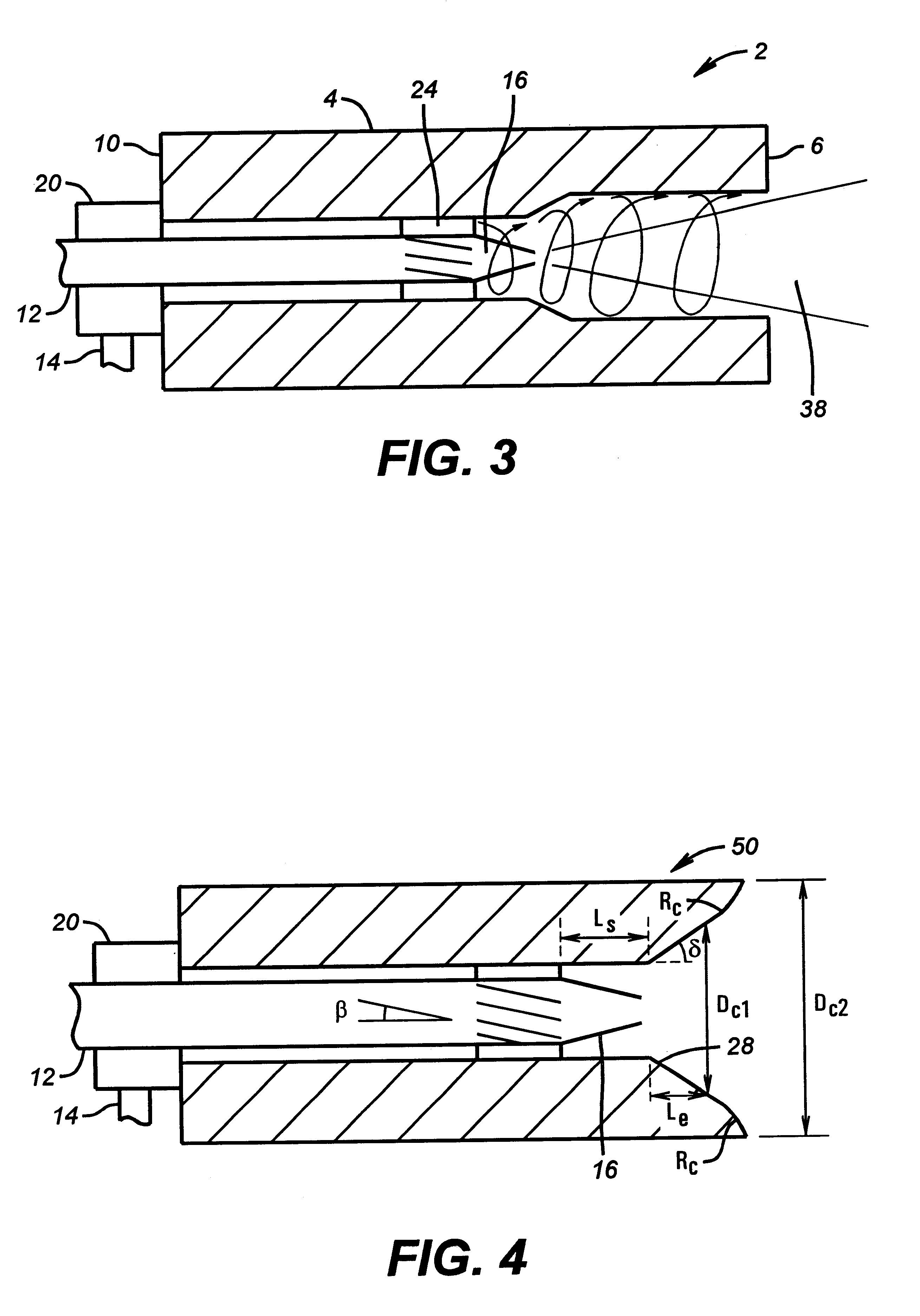
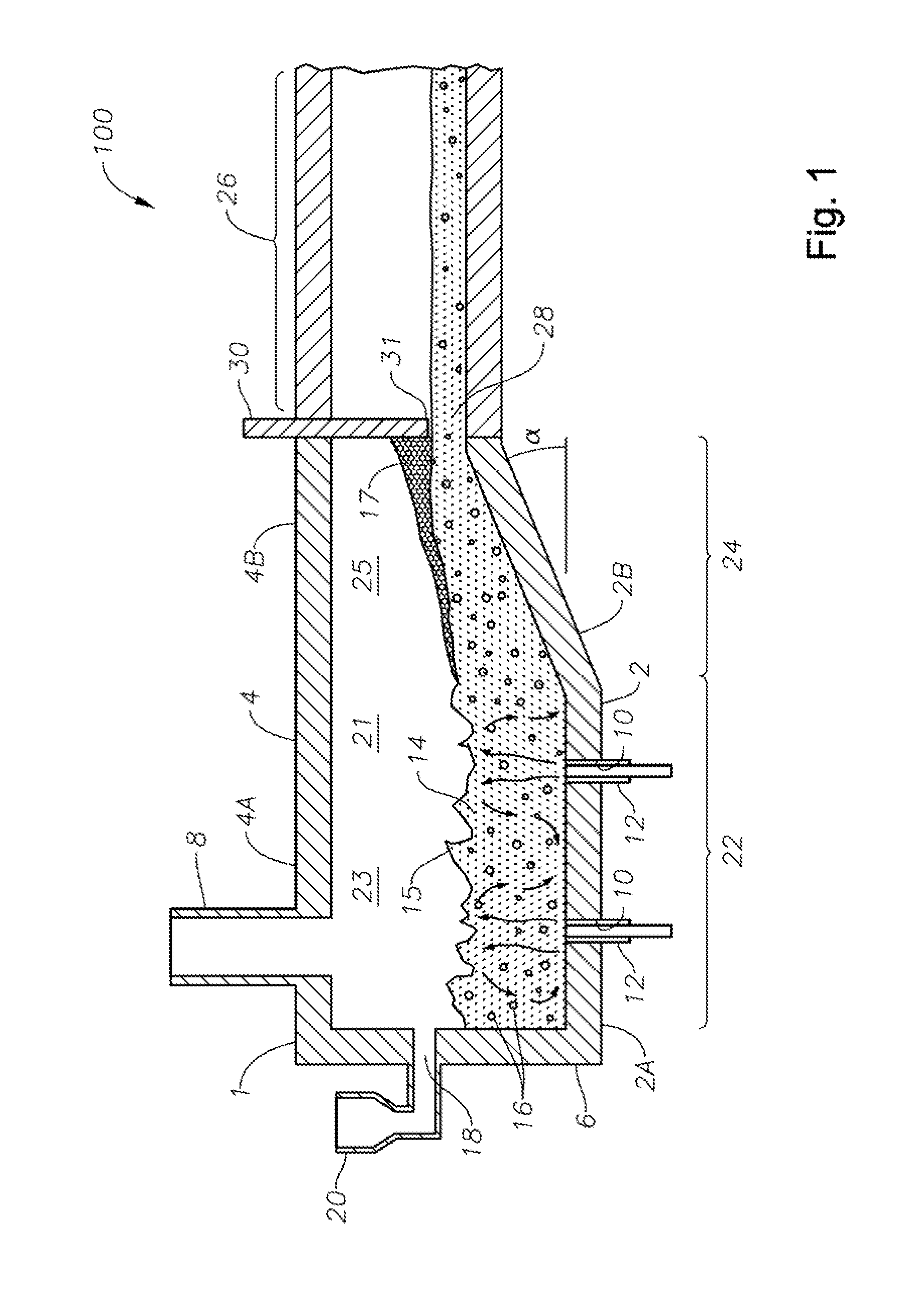
Submerged combustion melter comprising a melt exit structure designed to minimize impact of mechanical energy, and methods of making molten glass
A melter apparatus includes a floor, a ceiling, and a wall connecting the floor and ceiling at a perimeter of the floor and ceiling, a melting zone being defined by the floor, ceiling and wall, the melting zone having a feed inlet and a molten glass outlet positioned at opposing ends of the melting zone. Melter apparatus include an exit end having a melter exit structure for discharging turbulent molten glass formed by one or more submerged combustion burners, the melter exit structure fluidly and mechanically connecting the melter vessel to a molten glass conditioning channel. The melter exit structure includes a fluid-cooled transition channel configured to form a frozen glass layer or highly viscous glass layer, or combination thereof, on inner surfaces of the fluid-cooled transition channel and thus protect the melter exit structure from mechanical energy imparted from the melter vessel to the melter exit structure.
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE CORP
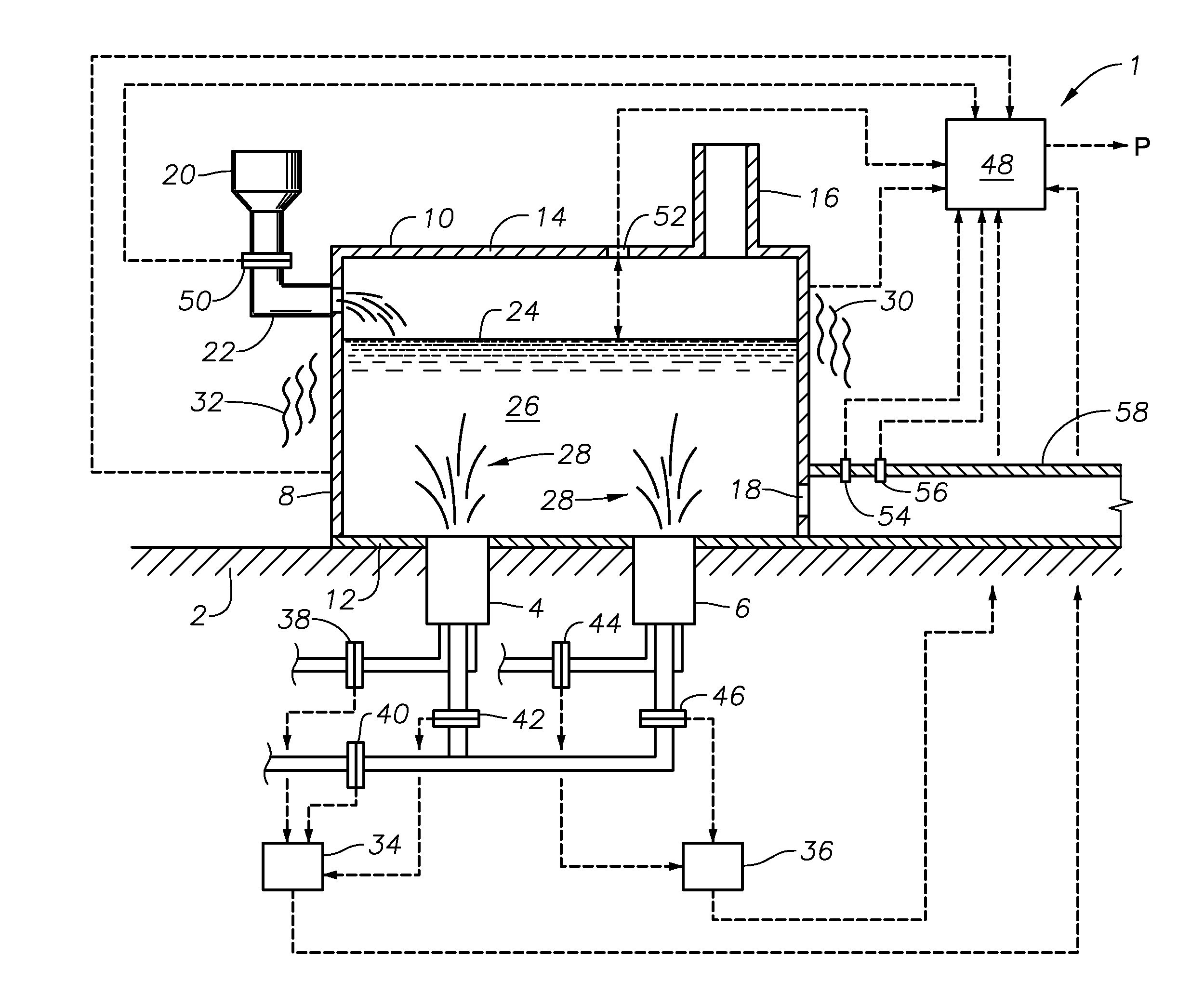
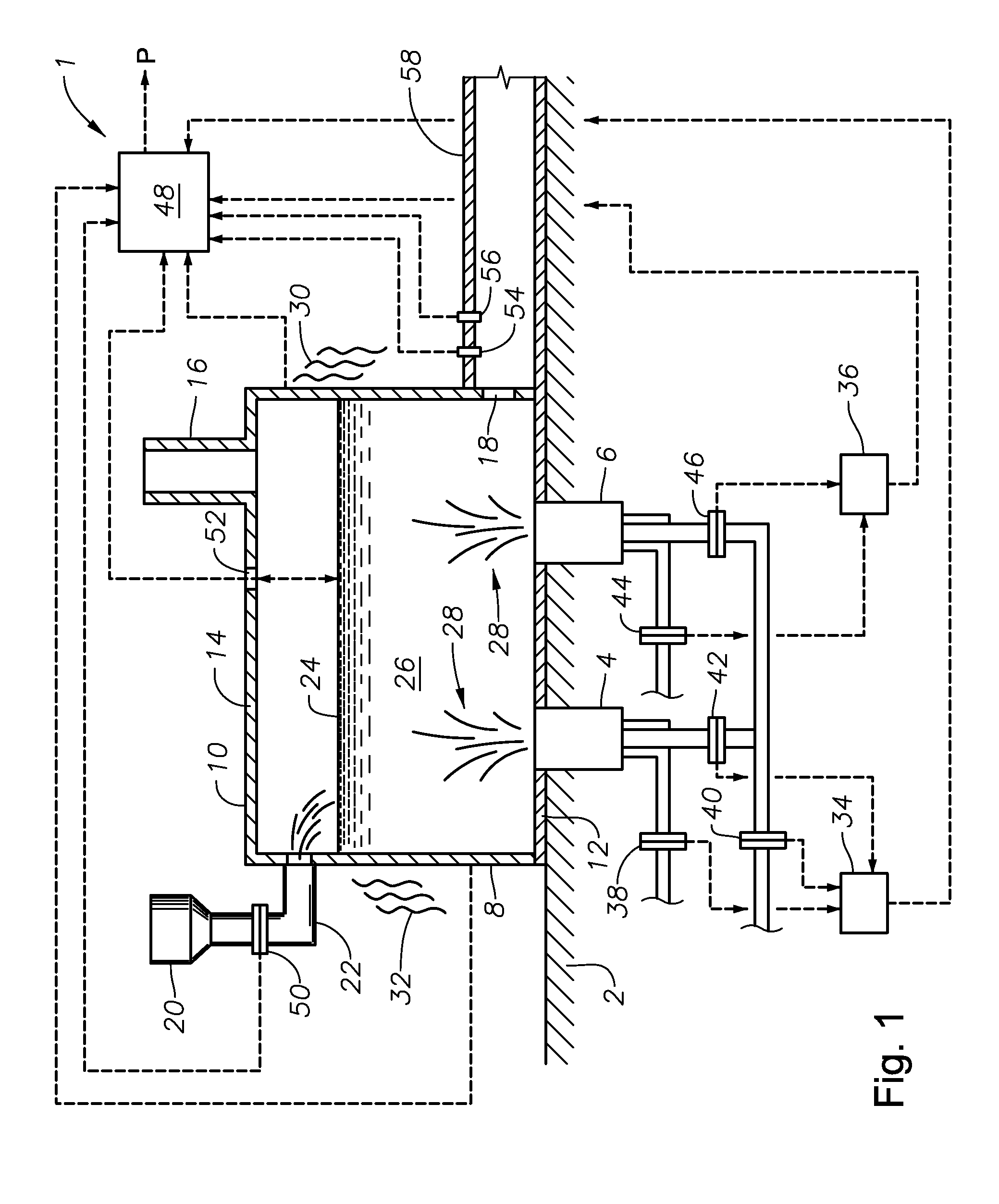
Methods of using a submerged combustion melter to produce glass products
A method comprises flowing an oxidant and a fuel into a submerged combustion burner in a glass tank furnace, the glass tank furnace receiving a feed of glass forming material and producing molten glass, the burner and furnace comprising a melting system. The melting system has a variable system vibration and / or oscillation due to the nature of submerged combustion. One method includes predicting a value of at least one property, such as viscosity, of the molten glass using the variable system vibration and / or oscillation.
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE CORP
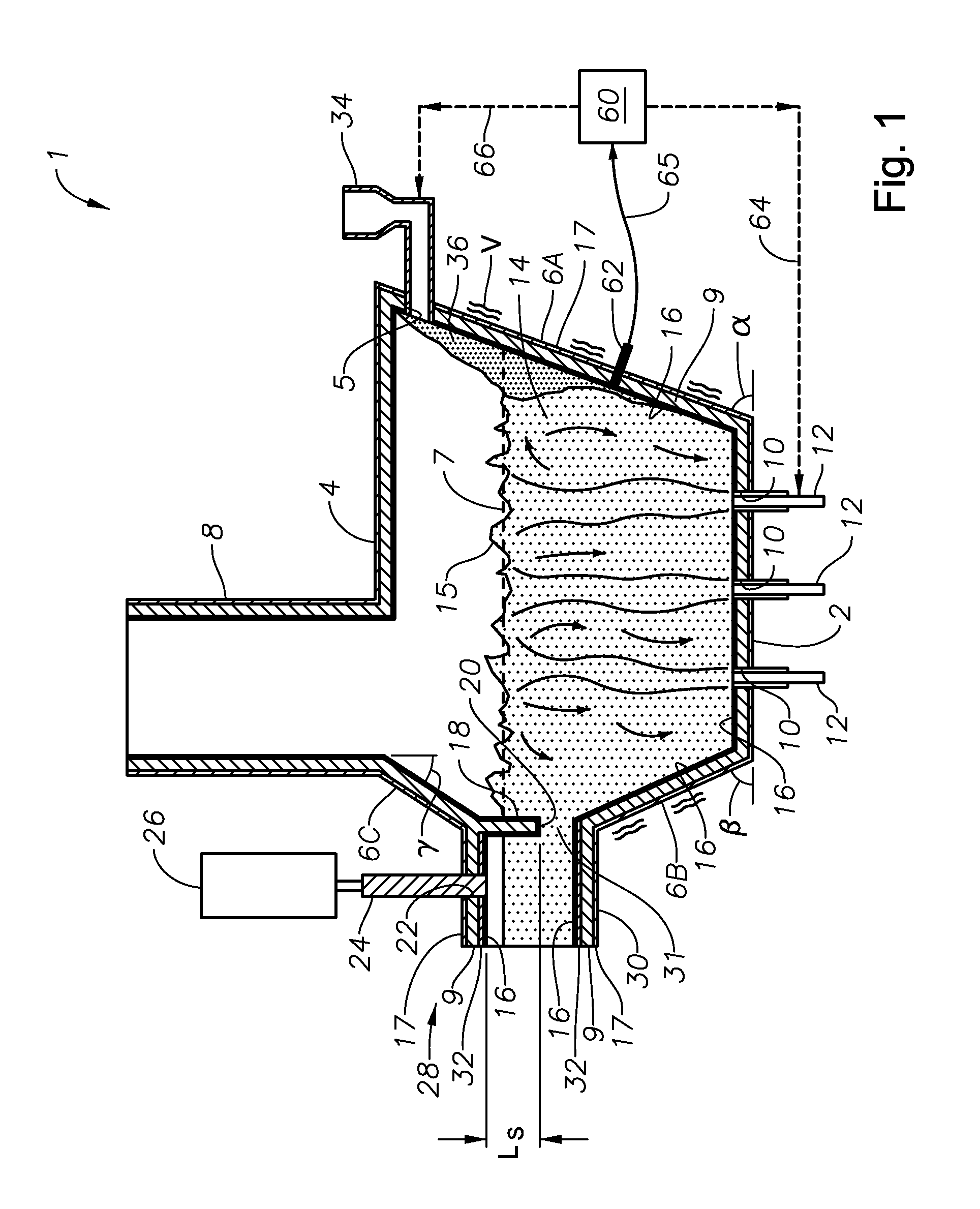
Submerged combustion glass manufacturing systems and methods
ActiveUS20130086950A1Reduction of melter pressure fluctuationReduce carryoverGlass furnace apparatusGlass melting apparatusGlass manufacturingTemperature and pressure
Submerged combustion glass manufacturing systems include a melter having a floor, a roof, a wall structure connecting the floor and roof, and an exhaust passage through the roof. One or more submerged combustion burners are mounted in the floor and / or wall structure discharging combustion products under a level of material being melted in the melter and create turbulent conditions in the material. The melter exhausts through an exhaust structure connecting the exhaust passage with an exhaust stack. The exhaust structure includes a barrier defining an exhaust chamber having an interior surface, the exhaust chamber having a cross-sectional area greater than that of the exhaust stack but less than the melter. The barrier maintains temperature and pressure in the exhaust structure at values sufficient to substantially prevent condensation of exhaust material on the interior surface.
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE CORP
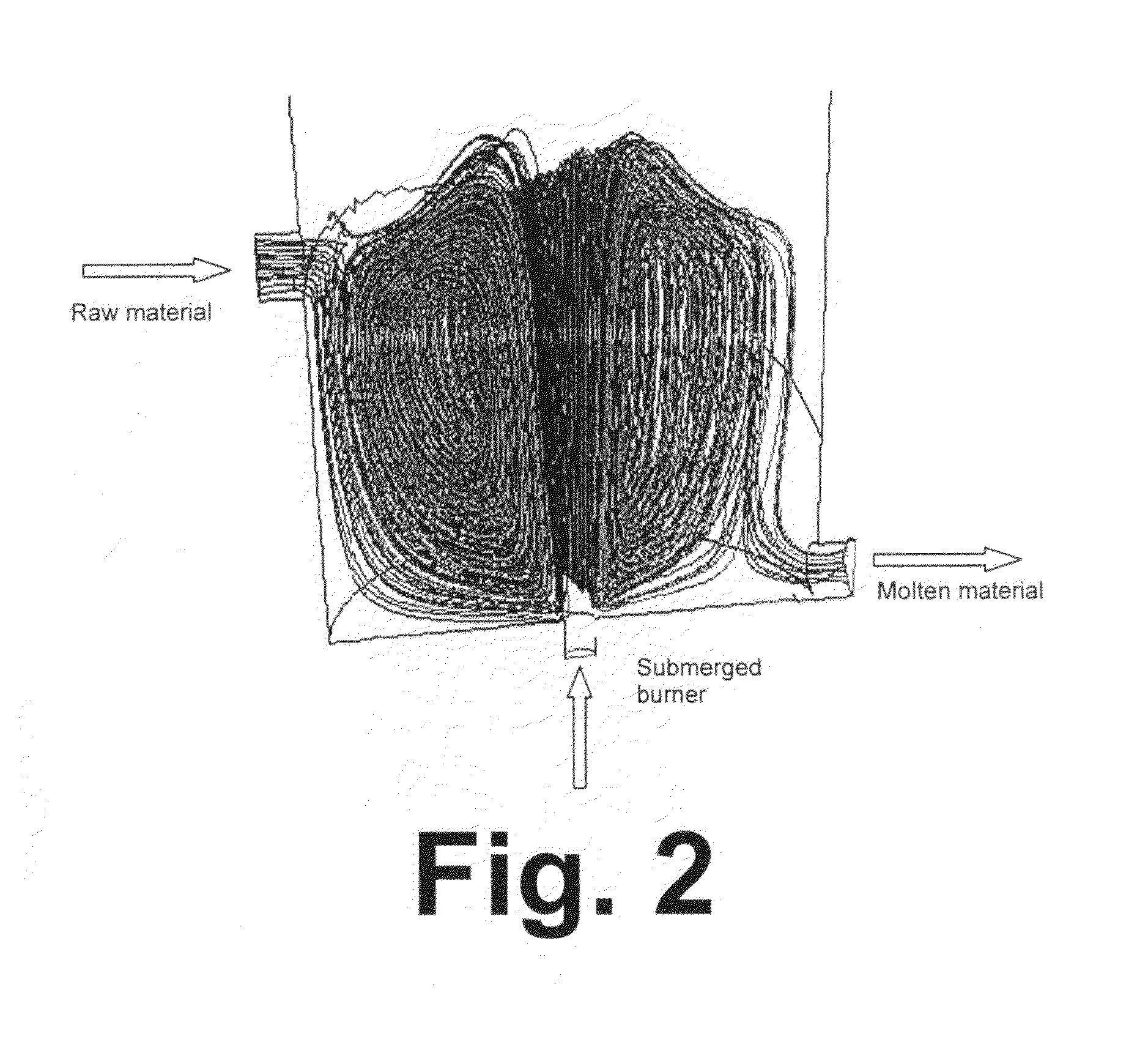
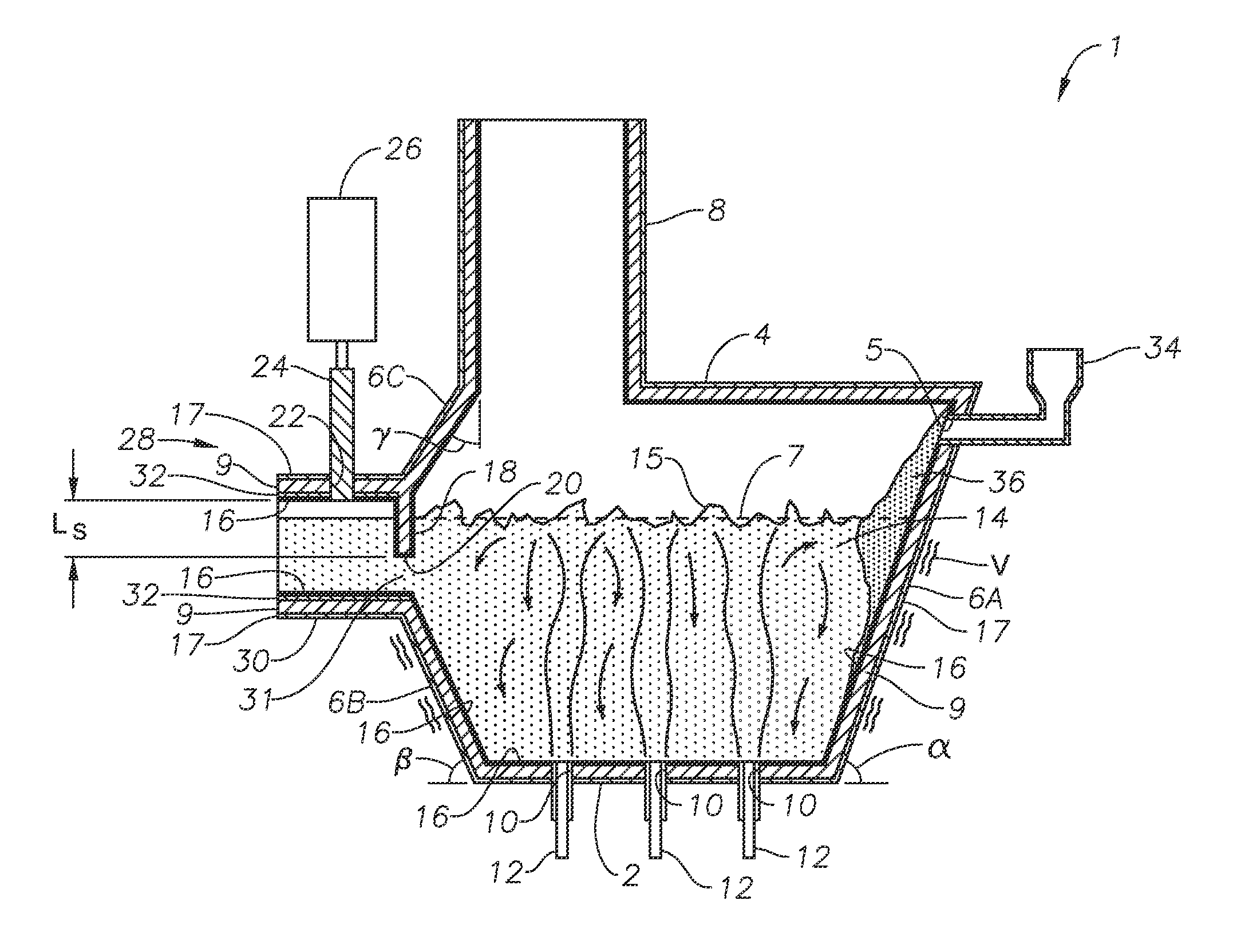
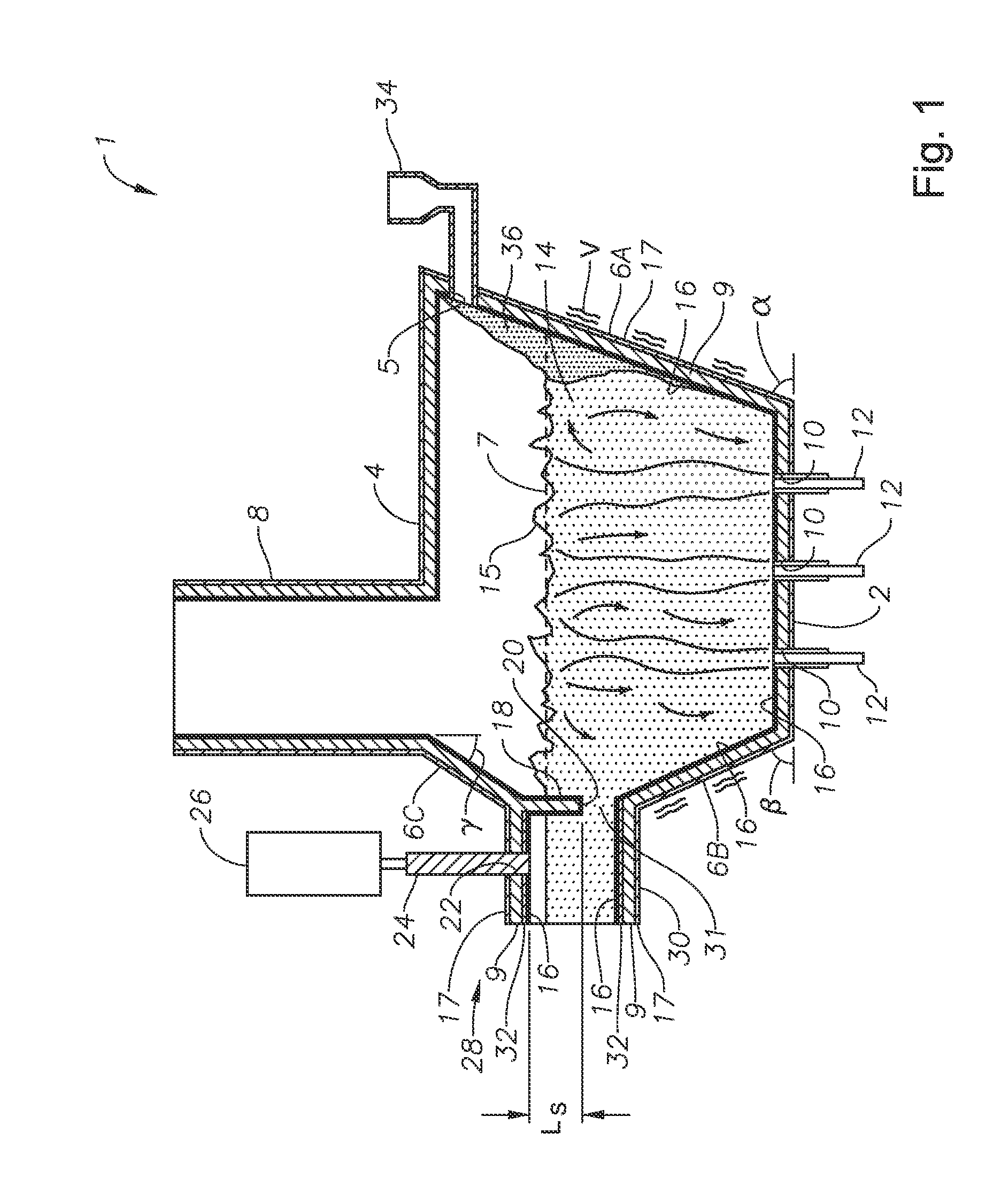
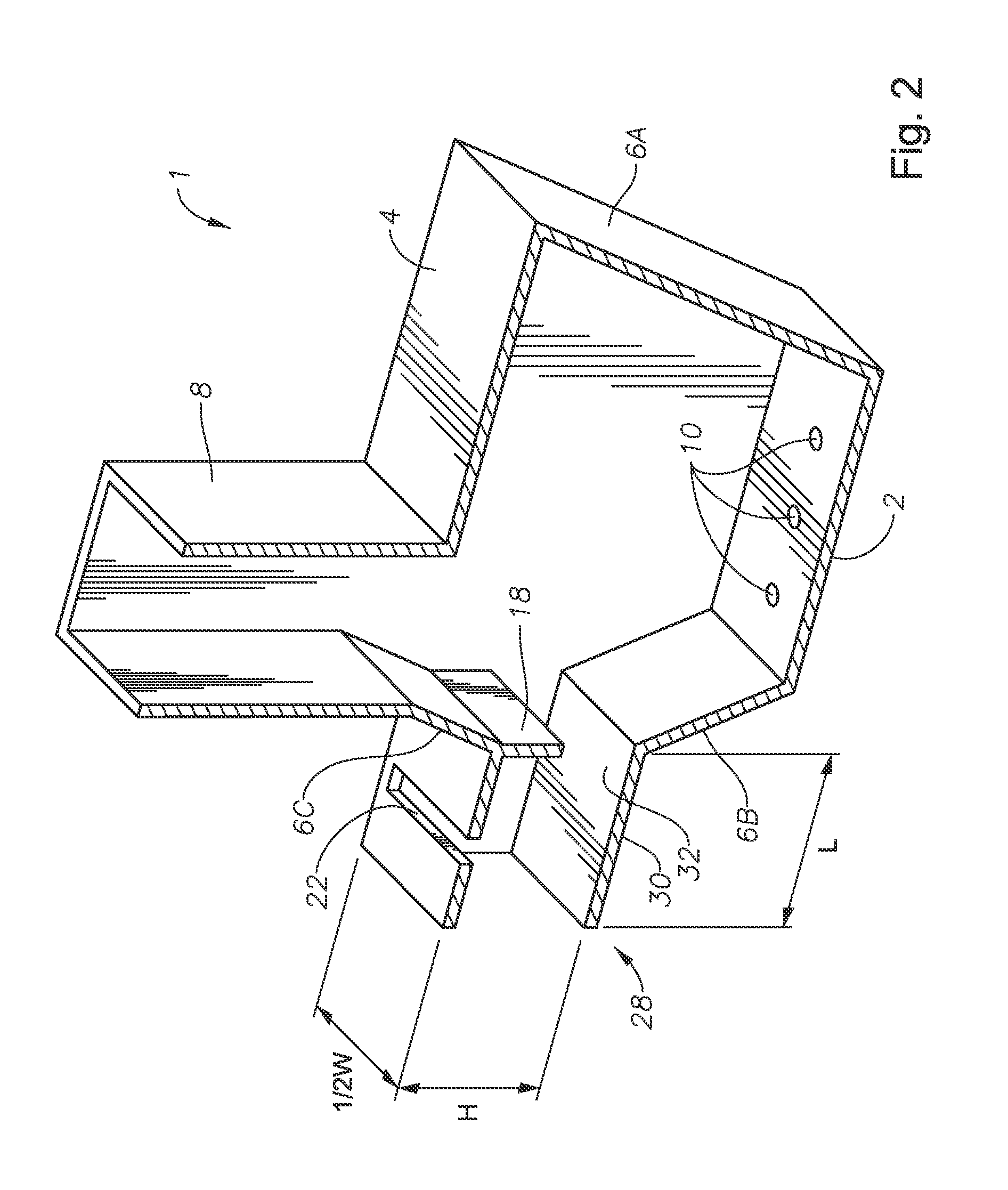
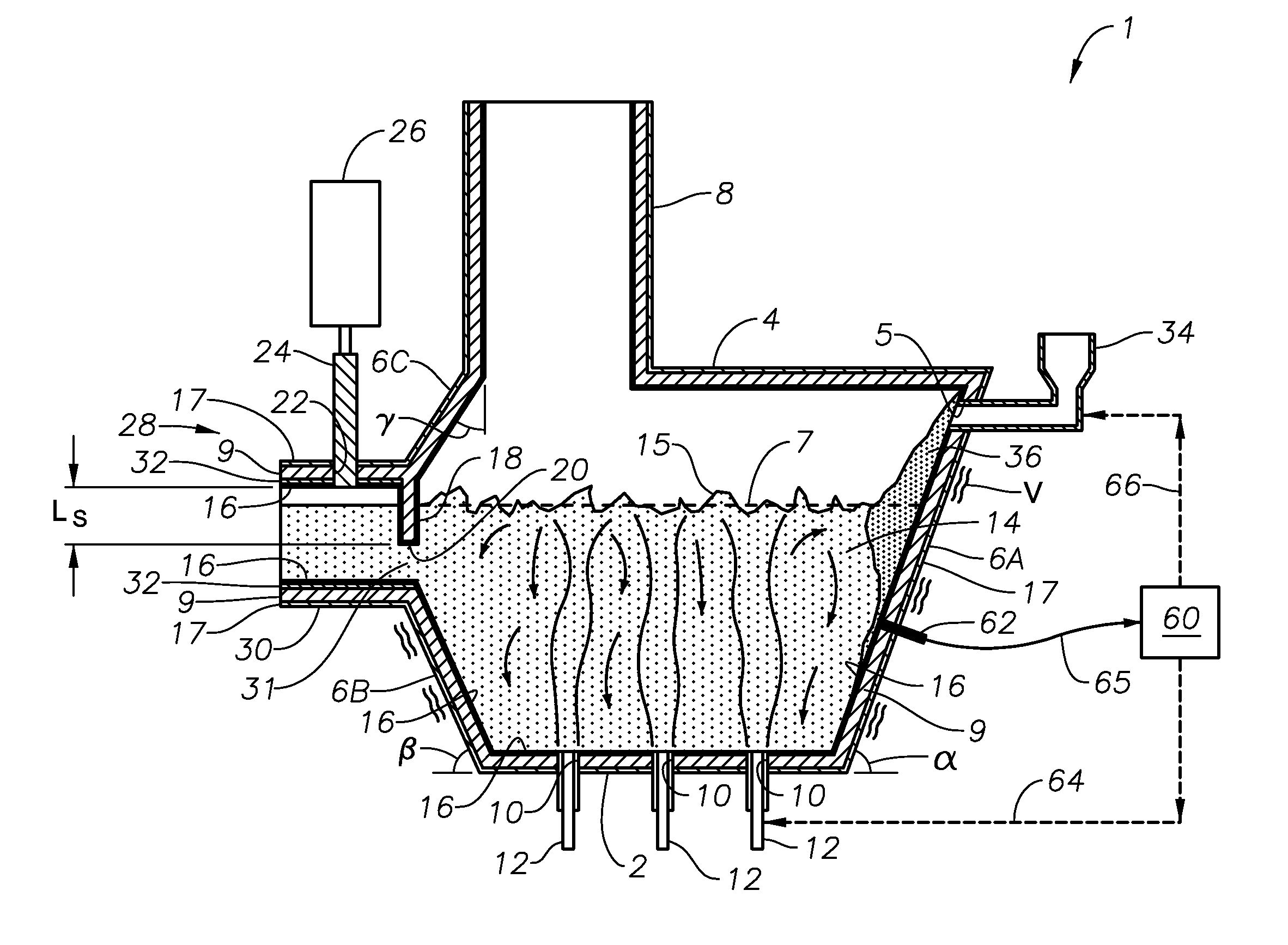
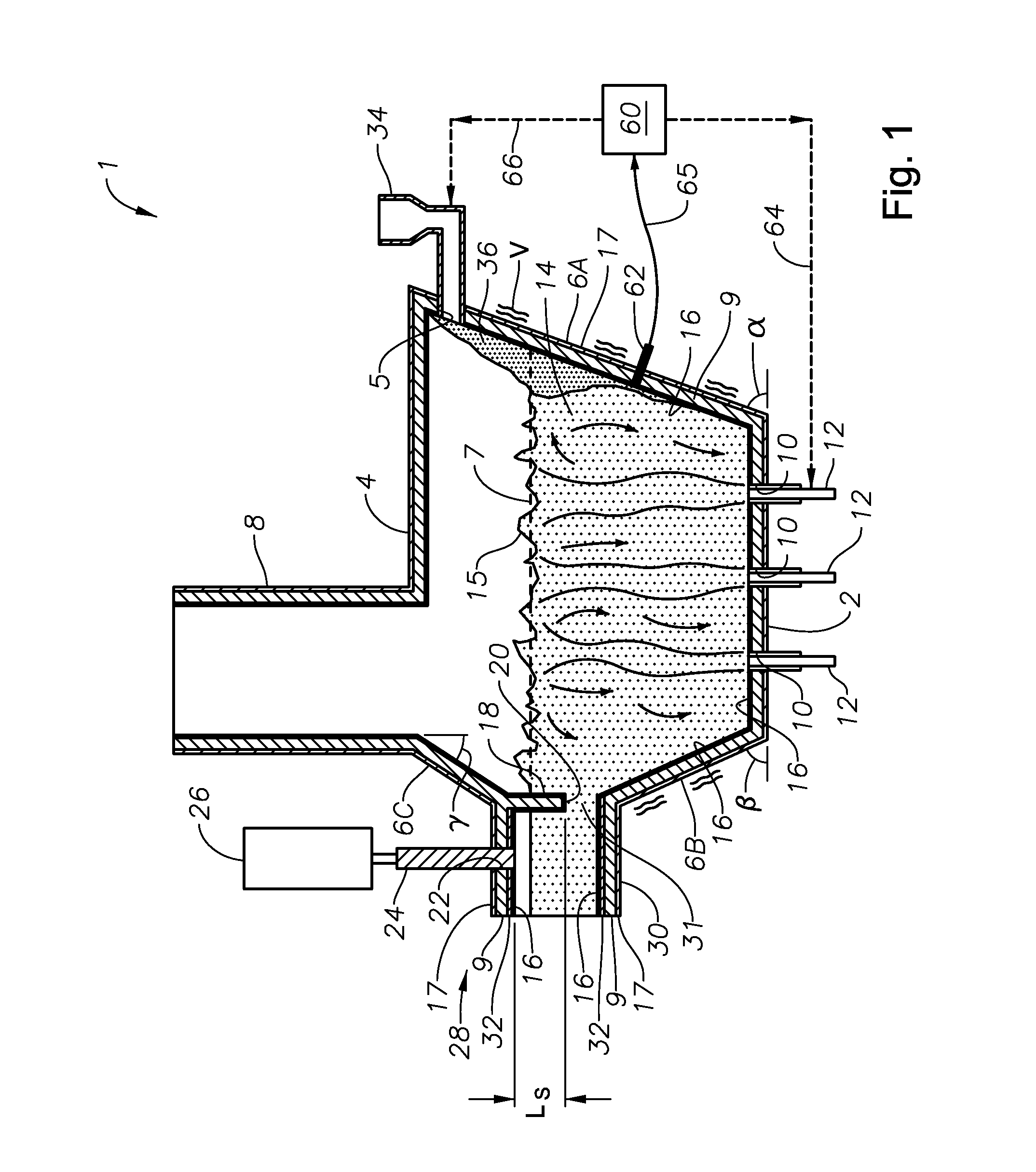
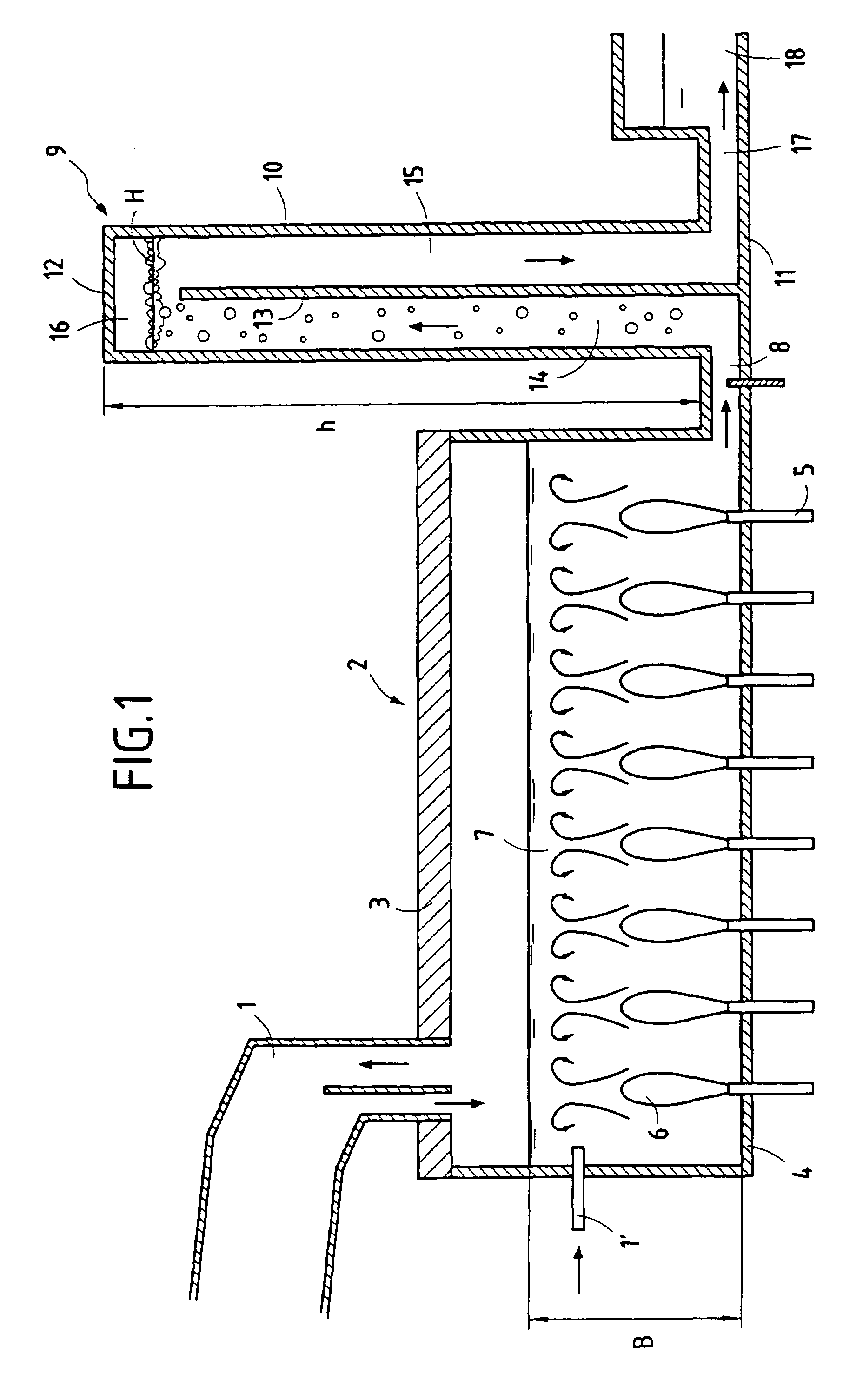
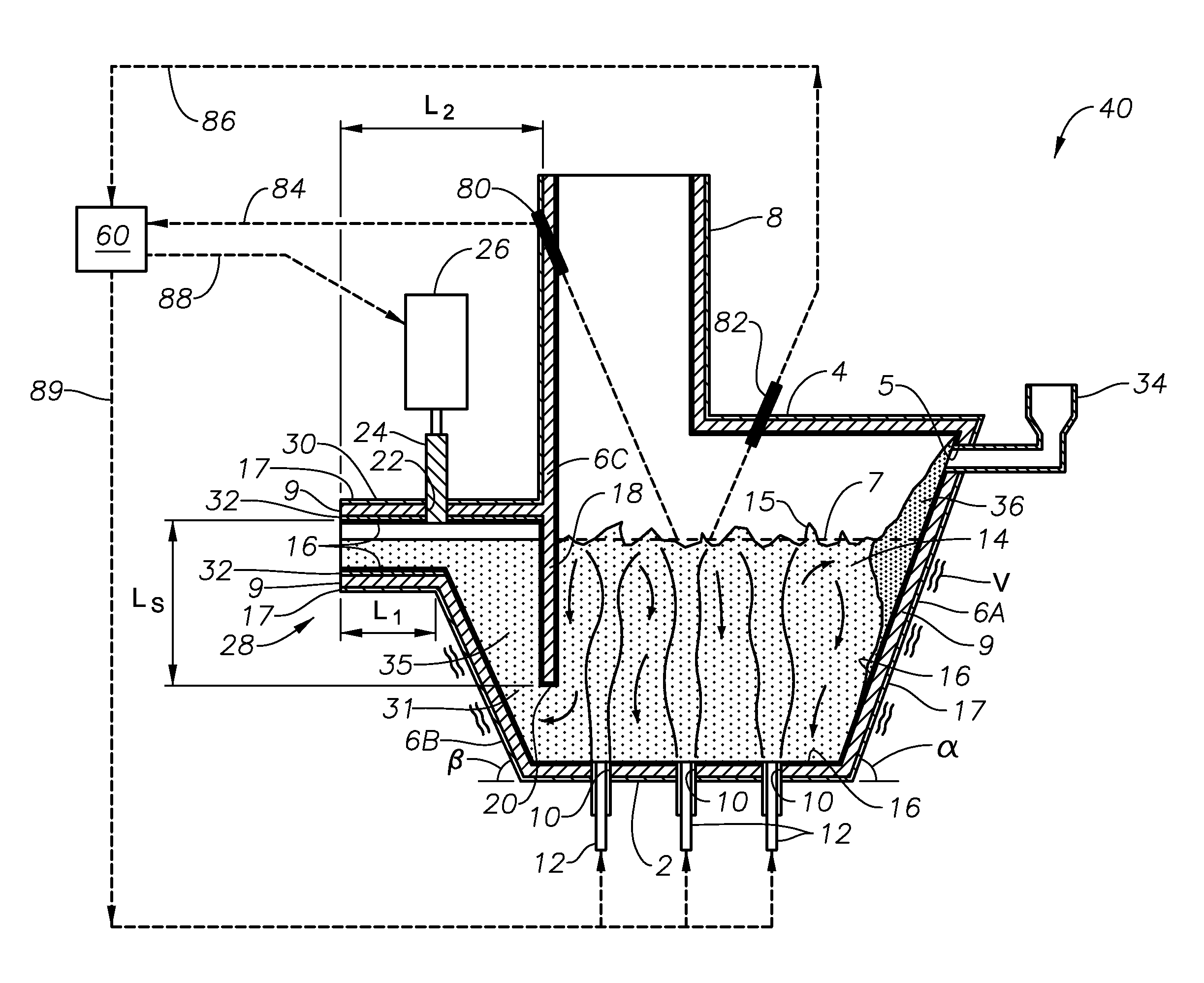
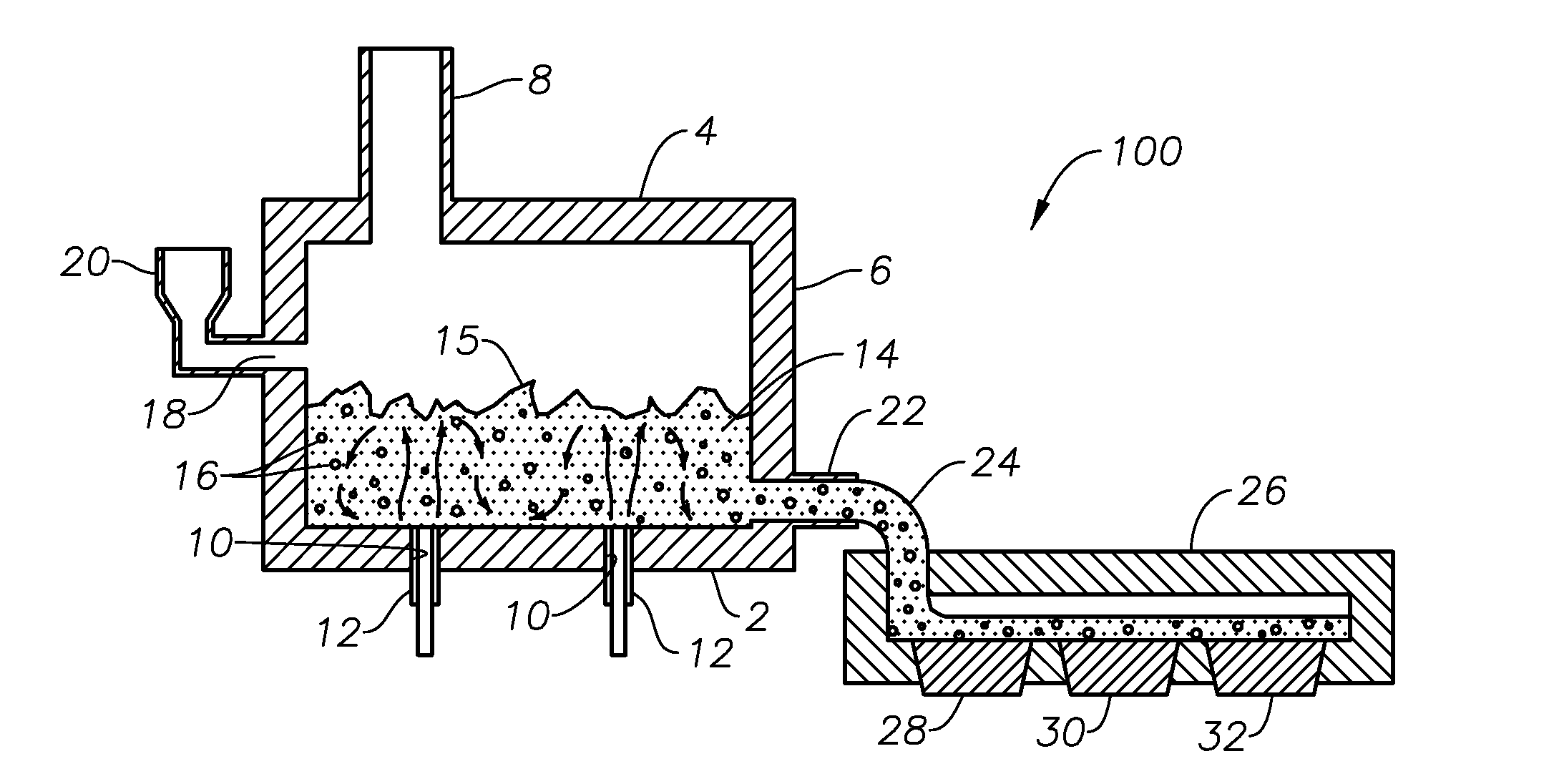
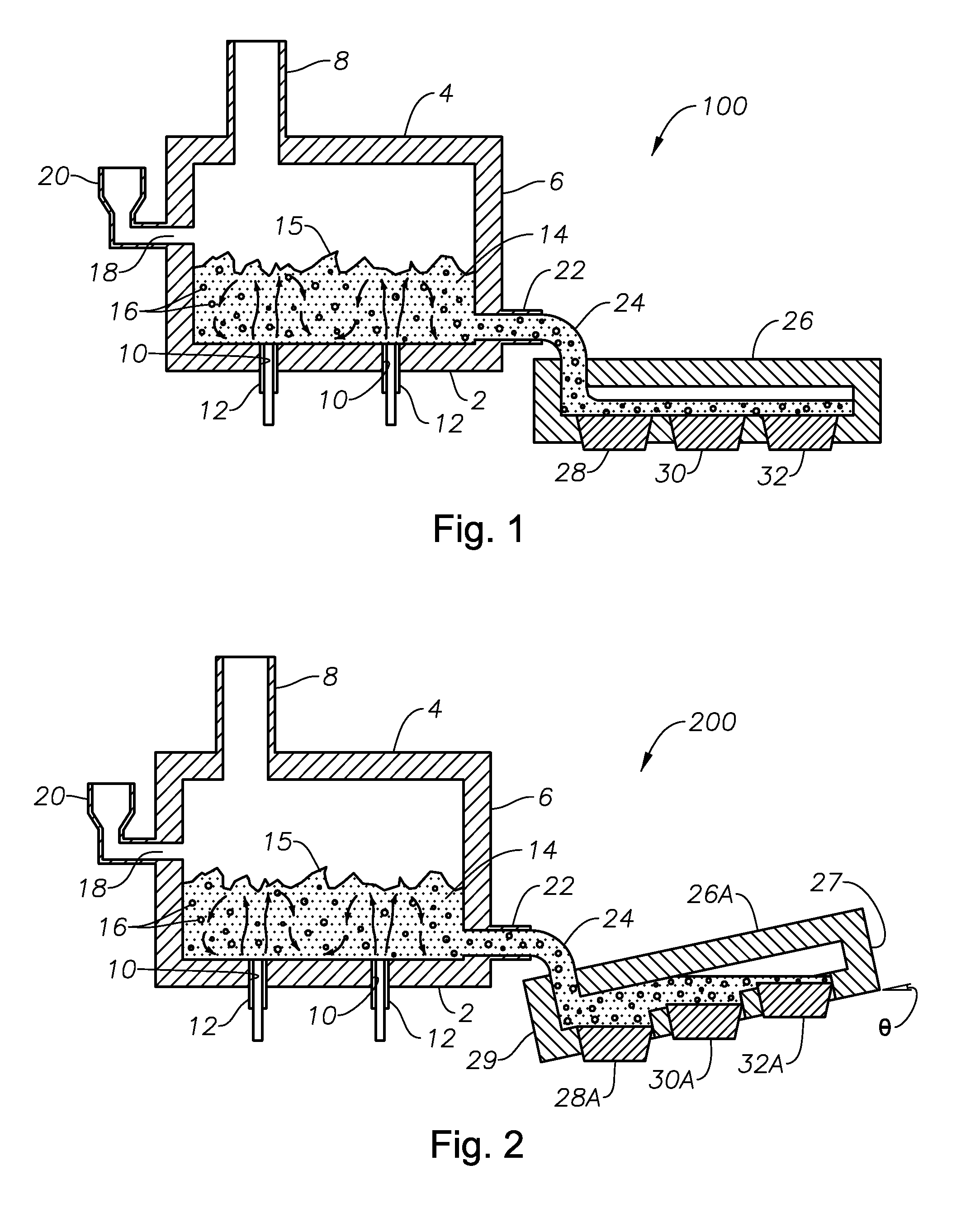
Submerged combustion melting processes for producing glass and similar materials, and systems for carrying out such processes
Processes of controlling submerged combustion melters, and systems for carrying out the methods. One process includes feeding vitrifiable material into a melter vessel, the melter vessel including a fluid-cooled refractory panel in its floor, ceiling, and / or sidewall, and heating the vitrifiable material with a burner directing combustion products into the melting zone under a level of the molten material in the zone. Burners impart turbulence to the molten material in the melting zone. The fluid-cooled refractory panel is cooled, forming a modified panel having a frozen or highly viscous material layer on a surface of the panel facing the molten material, and a sensor senses temperature of the modified panel using a protected thermocouple positioned in the modified panel shielded from direct contact with turbulent molten material. Processes include controlling the melter using the temperature of the modified panel. Other processes and systems are presented.
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE CORP
Method and device for melting and refining materials capable of being vitrified
InactiveUS7624595B2Speed up the processGreat operating flexibilityCharging furnaceGlass furnace apparatusVitrificationThermal energy
A process for melting and refining vitrifiable materials, such that all or part of the thermal energy necessary for melting the said vitrifiable materials is supplied by the combustion of fossil fuel(s) with at least one oxidizer gas, the fuel(s) / gas or the gaseous products resulting from the combustion being injected below the level of the mass of vitrifiable materials (7). The refining of the vitrifiable materials after melting comprises at least one step of subjecting them to subatmospheric pressure while centrifuging.
Owner:SAINT-GOBAIN GLASS FRANCE
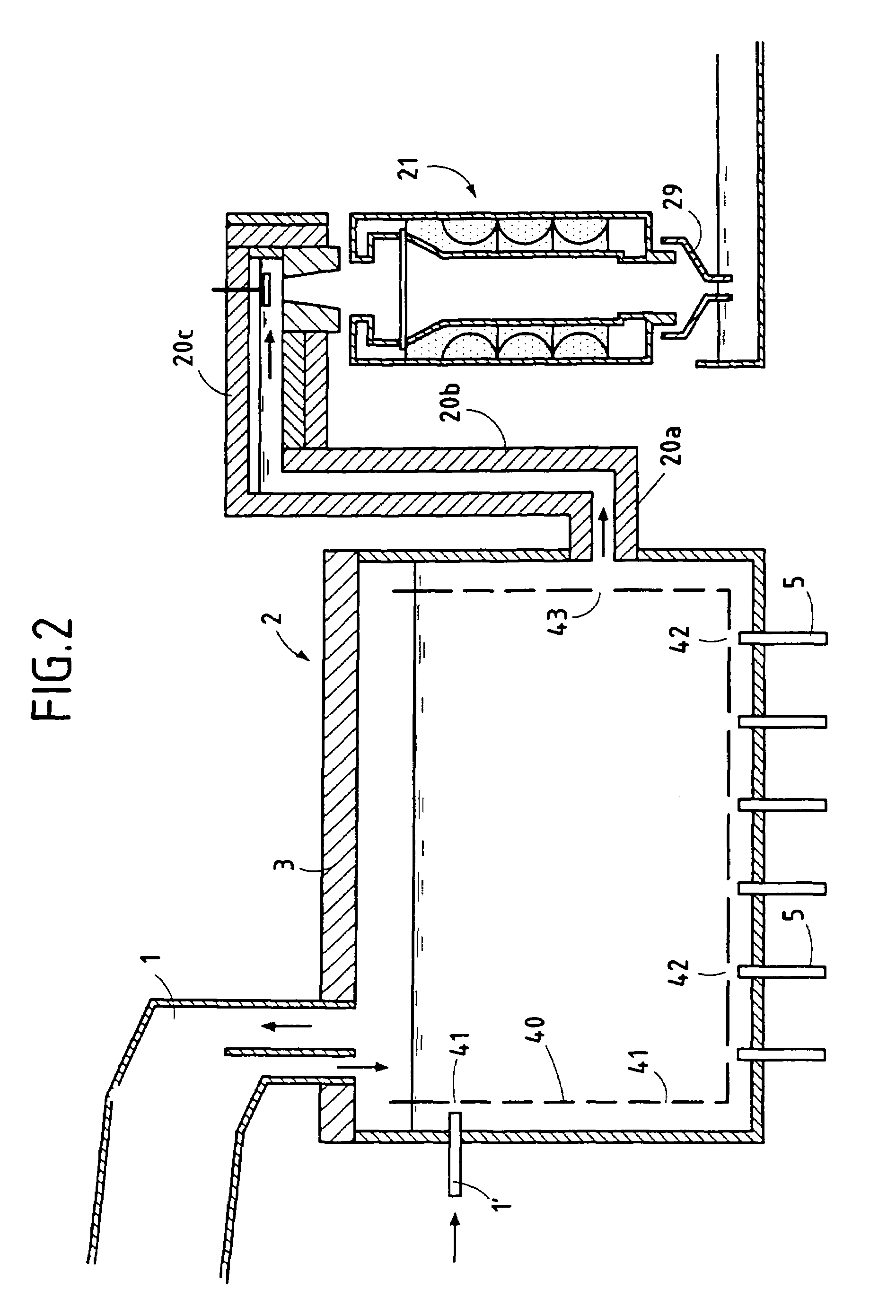
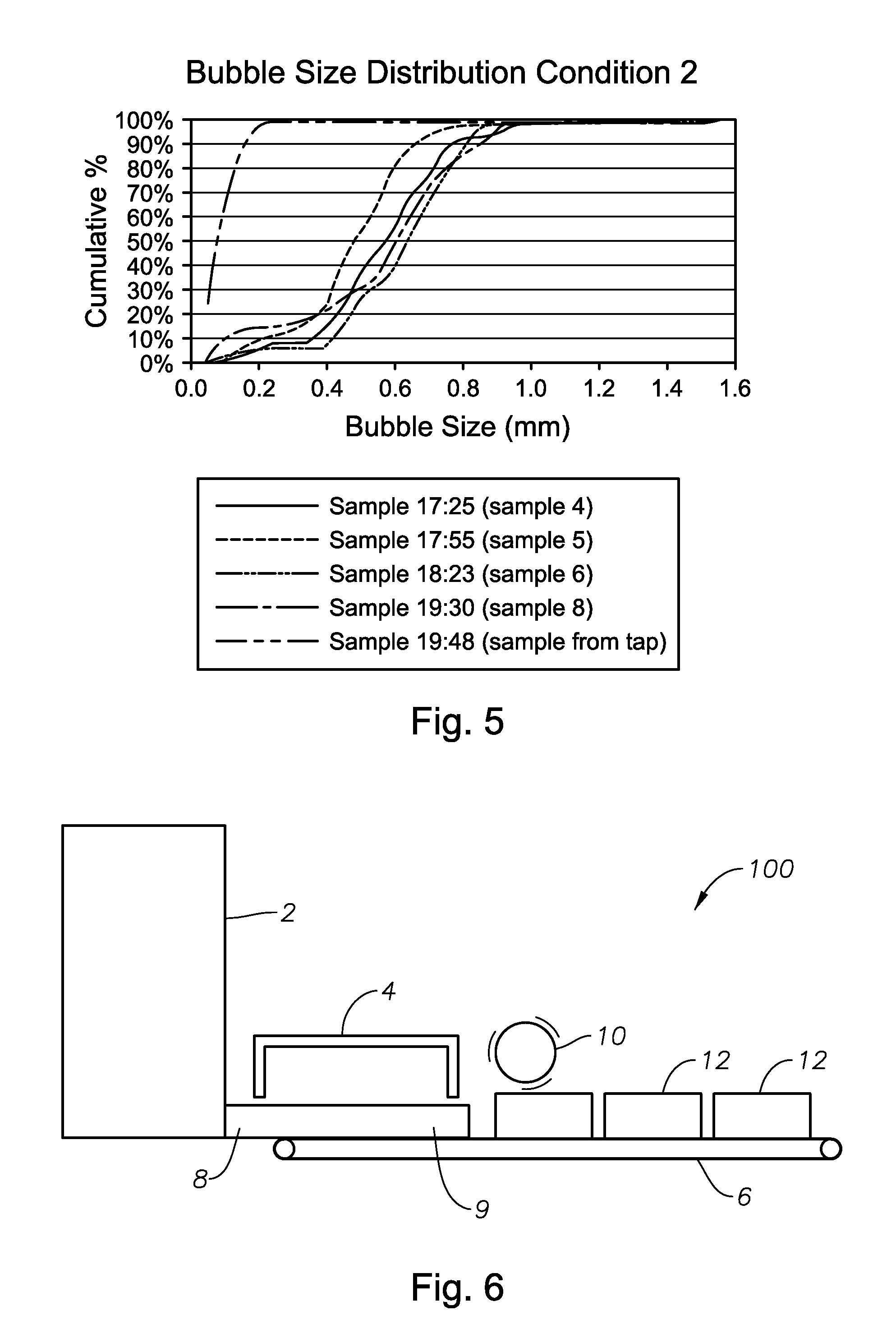
Systems and methods for making foamed glass using submerged combustion
ActiveUS20130086944A1High densityLow densityRibbon machinesGlass furnace apparatusCombustion systemDownstream processing
Submerged combustion systems and methods of use to produce foamed glass. One system includes a submerged combustion melter having an outlet, the melter configured to produce an initial foamy molten glass having a density and comprising bubbles filled primarily with combustion product gases. The initial foamy molten glass is deposited directly onto or into a transport apparatus that transports the initial foamy molten glass to a downstream processing apparatus. An intermediate stage may be included between the melter and the transport apparatus. One intermediate stage is a channel that includes gas injectors. Another intermediate stage is a channel that produces an upper flow of a less dense glass and a relatively more dense glass lower flow. The upper flow may be processed into foamed glass products, while the more dense flow may be processed into dense glass products.
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE CORP
Submerged combustion melters having an extended treatment zone and methods of producing molten glass
A submerged combustion melter includes a floor, a roof, and a sidewall structure connecting the floor and roof defining an internal space. A first portion of the internal space defines a melting zone, and a second portion defines a fining zone immediately downstream of the melting zone. One or more combustion burners in either the floor, roof, the sidewall structure, or any combination of these, are configured to emit the combustion gases from a position under a level of, and positioned to transfer heat to and produce, a turbulent molten mass of glass containing bubbles in the melting zone. The fining zone is devoid of combustion burners or other apparatus or components that would increase turbulence above that in the melting zone. The melter may include a treating zone that stabilizes or destabilizes bubbles and / or foam. Processes of using the melters are a feature of the disclosure.
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE CORP
Submerged combustion melting processes for producing glass and similar materials, and systems for carrying out such processes
Processes of controlling submerged combustion melters, and systems for carrying out the methods. One process includes feeding vitrifiable material into a melter vessel, the melter vessel including a fluid-cooled refractory panel in its floor, ceiling, and / or sidewall, and heating the vitrifiable material with a burner directing combustion products into the melting zone under a level of the molten material in the zone. Burners impart turbulence to the molten material in the melting zone. The fluid-cooled refractory panel is cooled, forming a modified panel having a frozen or highly viscous material layer on a surface of the panel facing the molten material, and a sensor senses temperature of the modified panel using a protected thermocouple positioned in the modified panel shielded from direct contact with turbulent molten material. Processes include controlling the melter using the temperature of the modified panel. Other processes and systems are presented.
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE CORP
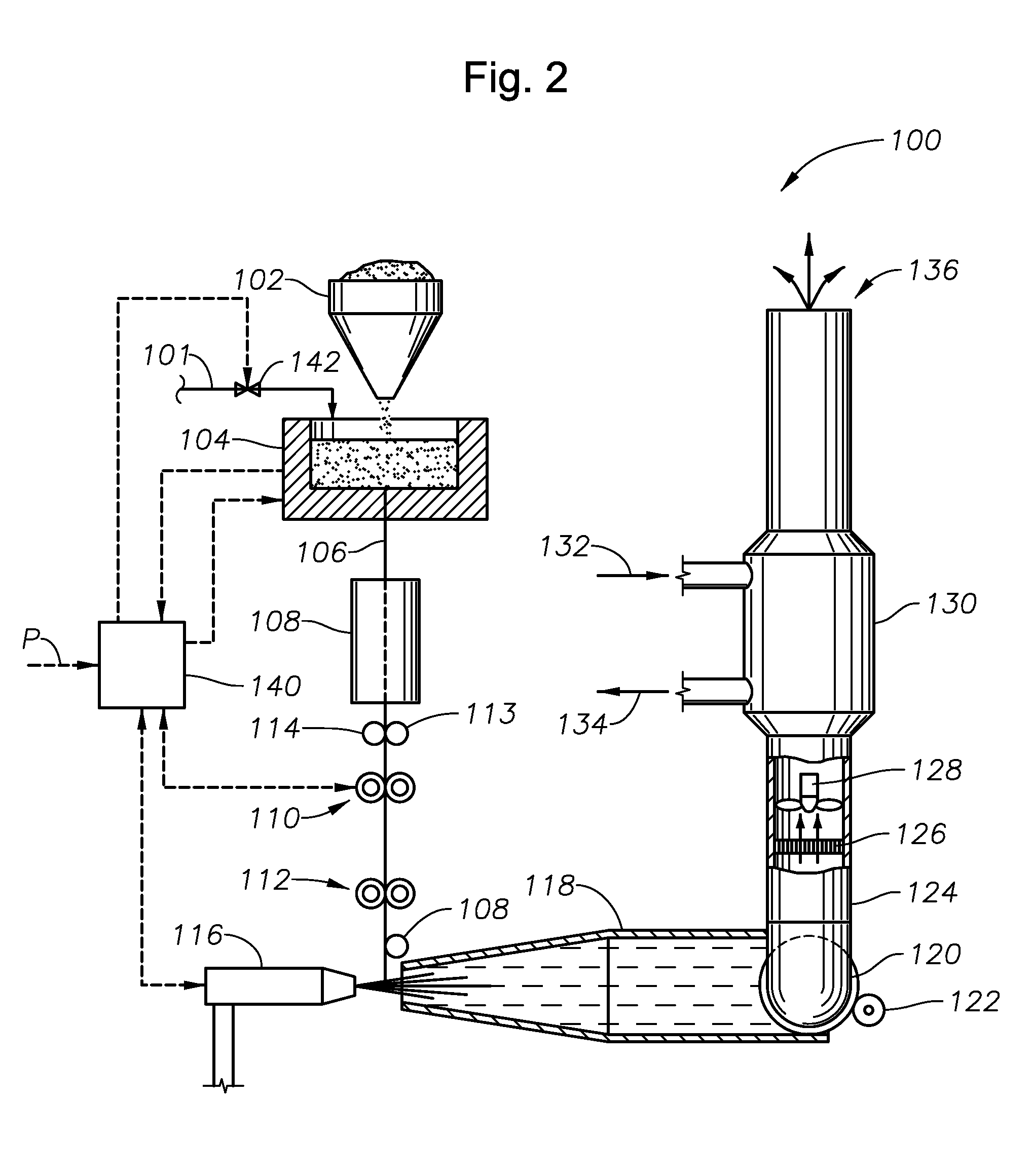
Processes for producing molten glasses from glass batches using turbulent submerged combustion melting, and systems for carrying out such processes
ActiveUS20140007622A1Reduce and eliminate batch lossCharging furnaceTank furnacesParticulatesCombustor
Processes and systems for producing molten glass using submerged combustion melters, including densifying an initial composition comprising vitrifiable particulate solids and interstitial gas to form a densified composition comprising the solids by removing a portion of the interstitial gas from the composition. The initial composition is passed from an initial environment having a first pressure through a second environment having a second pressure higher than the first pressure to form a composition being densified. Any fugitive particulate solids escaping from the composition being densified are captured and recombined with the composition being densified to form the densified composition. The densified composition is fed into a feed inlet of a turbulent melting zone of a melter vessel and converted into turbulent molten material using at least one submerged combustion burner in the turbulent melting zone.
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE CORP
Panel-cooled submerged combustion melter geometry and methods of making molten glass
ActiveUS8769992B2Small sizeAllows more flexibility in the shape of the melterPulsating combustionGlass furnace apparatusThermodynamicsCombustor
A melter apparatus includes a floor, a ceiling, and a substantially vertical wall connecting the floor and ceiling at a perimeter of the floor and ceiling, a melting zone being defined by the floor, ceiling and wall, the melting zone having a feed inlet and a molten glass outlet positioned at opposing ends of the melting zone. The melting zone includes an expanding zone beginning at the inlet and extending to an intermediate location relative to the opposing ends, and a narrowing zone extending from the intermediate location to the outlet. One or more burners, at least some of which are positioned to direct combustion products into the melting zone under a level of molten glass in the zone, are also provided.
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE CORP
Furnace and Process for Controlling the Oxidative State of Molten Materials
ActiveUS20100313604A1Quality improvementImprove clarityPot furnacesGlass furnace apparatusChemical measurementAtmosphere
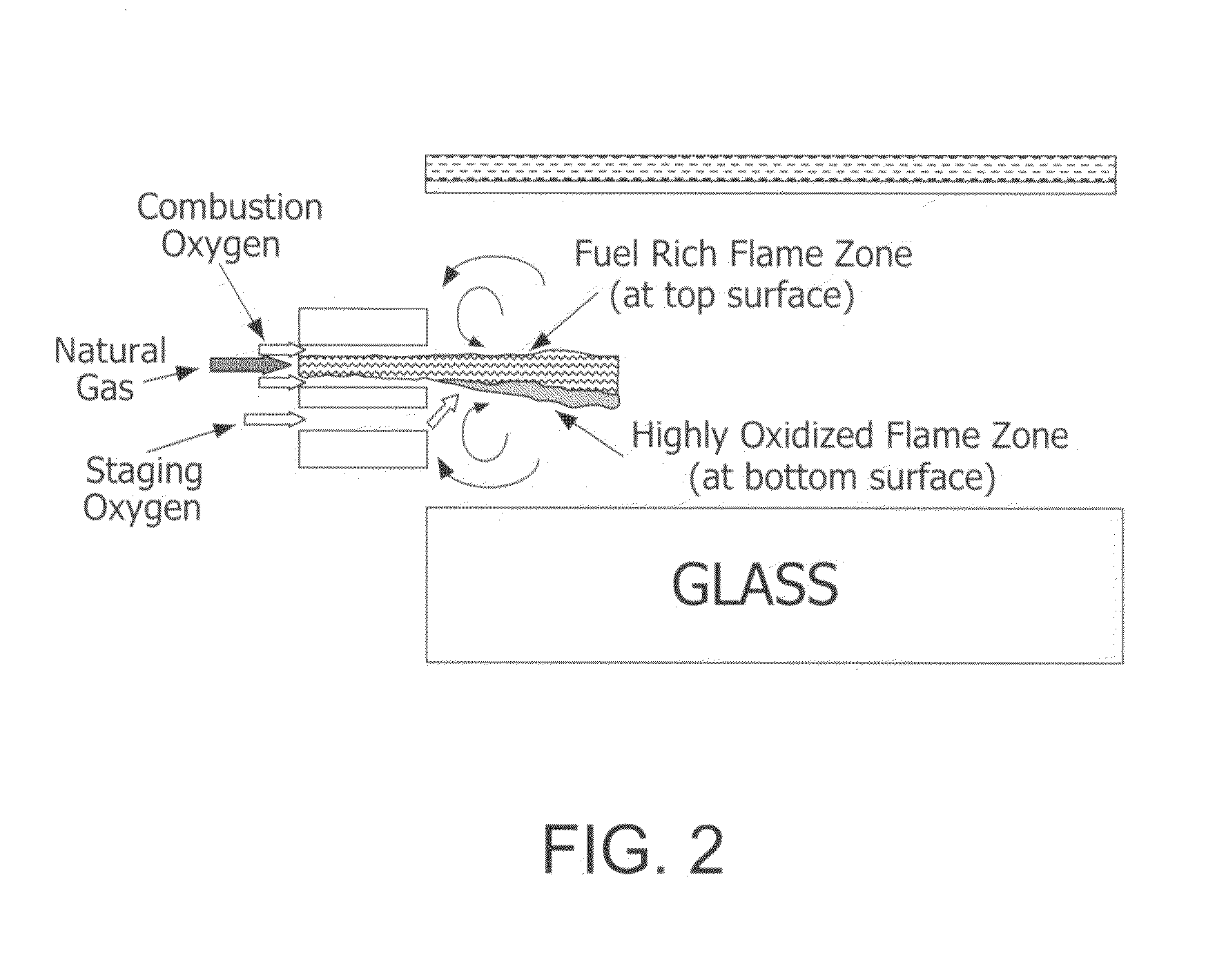
A method useful with oxy-fuel combustion and in a furnace which contains molten material, wherein either substoichiometric or superstoichiometric combustion and low velocity injection of fuel and primary and secondary oxidant in an oxy-fuel burner are carried out in an orientation which forms either a reducing or oxidizing atmosphere proximate the molten surface.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Methods and apparatus for recycling glass products using submerged combustion
A method for recycling glass mat waste, wound rovings, and other products includes providing a source of glass mat, or a plurality of rovings, for example on a roll, and routing the glass mat or rovings into a submerged combustion melter. An unwind system and a pair of powered nip rolls, powered conveyors, or other arrangement may work in combination to provide a substantially consistent rate of material into the melter. The melter may operate under less than atmospheric pressure to avoid fumes escaping the melter. A slot in the melter allows ingress of the glass mat or rovings into the melter, and a glass mat former such as a folder may be used to ensure that the mat fits through the slot. Alternatively, the glass mat may be cut by a slitter prior to entering the slot.
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE CORP
Burner apparatus, submerged combustion melters including the burner, and methods of use
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE CORP
Submerged combustion glass manufacturing systems and methods
ActiveUS8707740B2Suppress pressure fluctuationsAvoid condensationGlass furnace apparatusGlass melting apparatusGlass manufacturingTemperature and pressure
Submerged combustion glass manufacturing systems include a melter having a floor, a roof, a wall structure connecting the floor and roof, and an exhaust passage through the roof. One or more submerged combustion burners are mounted in the floor and / or wall structure discharging combustion products under a level of material being melted in the melter and create turbulent conditions in the material. The melter exhausts through an exhaust structure connecting the exhaust passage with an exhaust stack. The exhaust structure includes a barrier defining an exhaust chamber having an interior surface, the exhaust chamber having a cross-sectional area greater than that of the exhaust stack but less than the melter. The barrier maintains temperature and pressure in the exhaust structure at values sufficient to substantially prevent condensation of exhaust material on the interior surface.
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE CORP
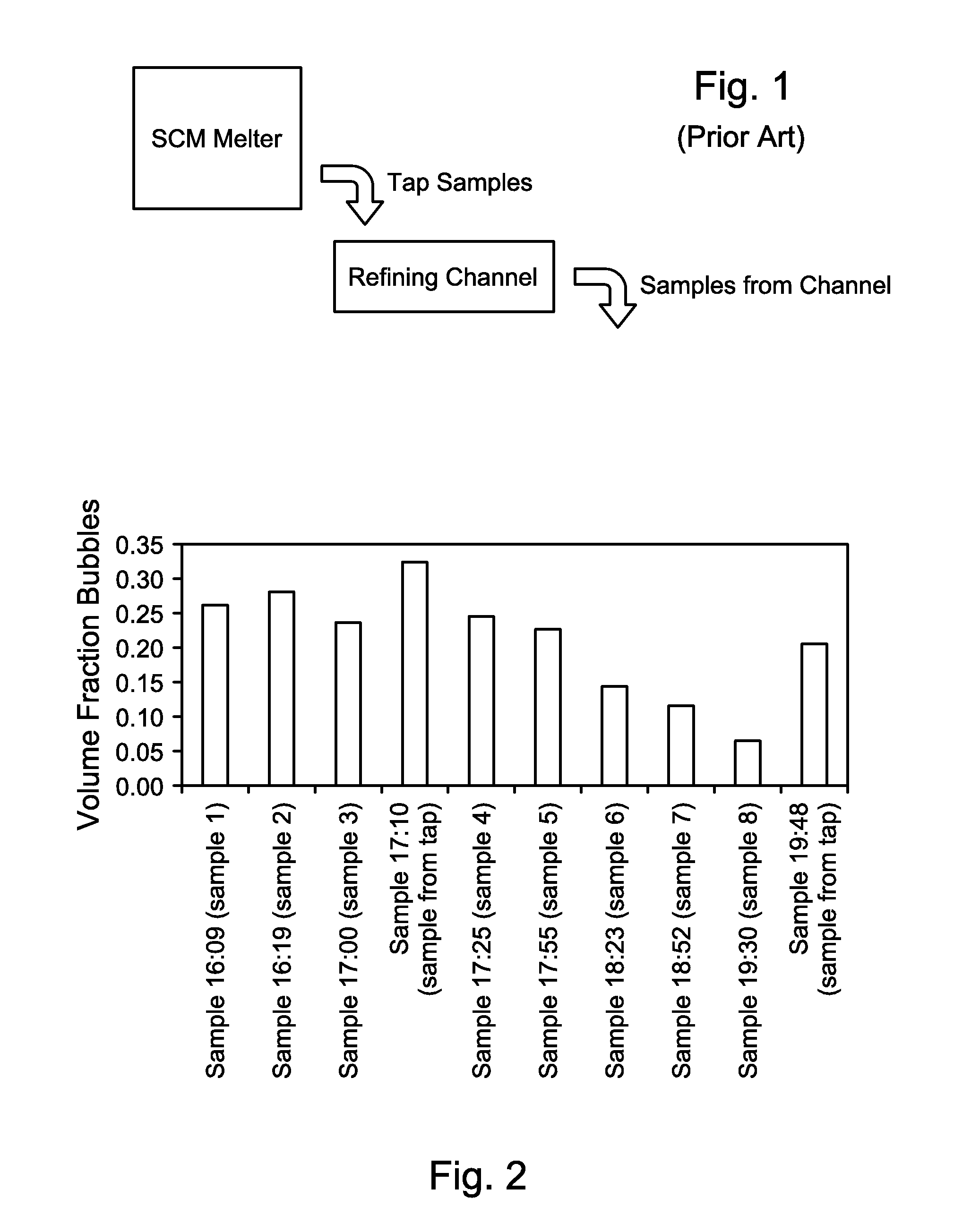
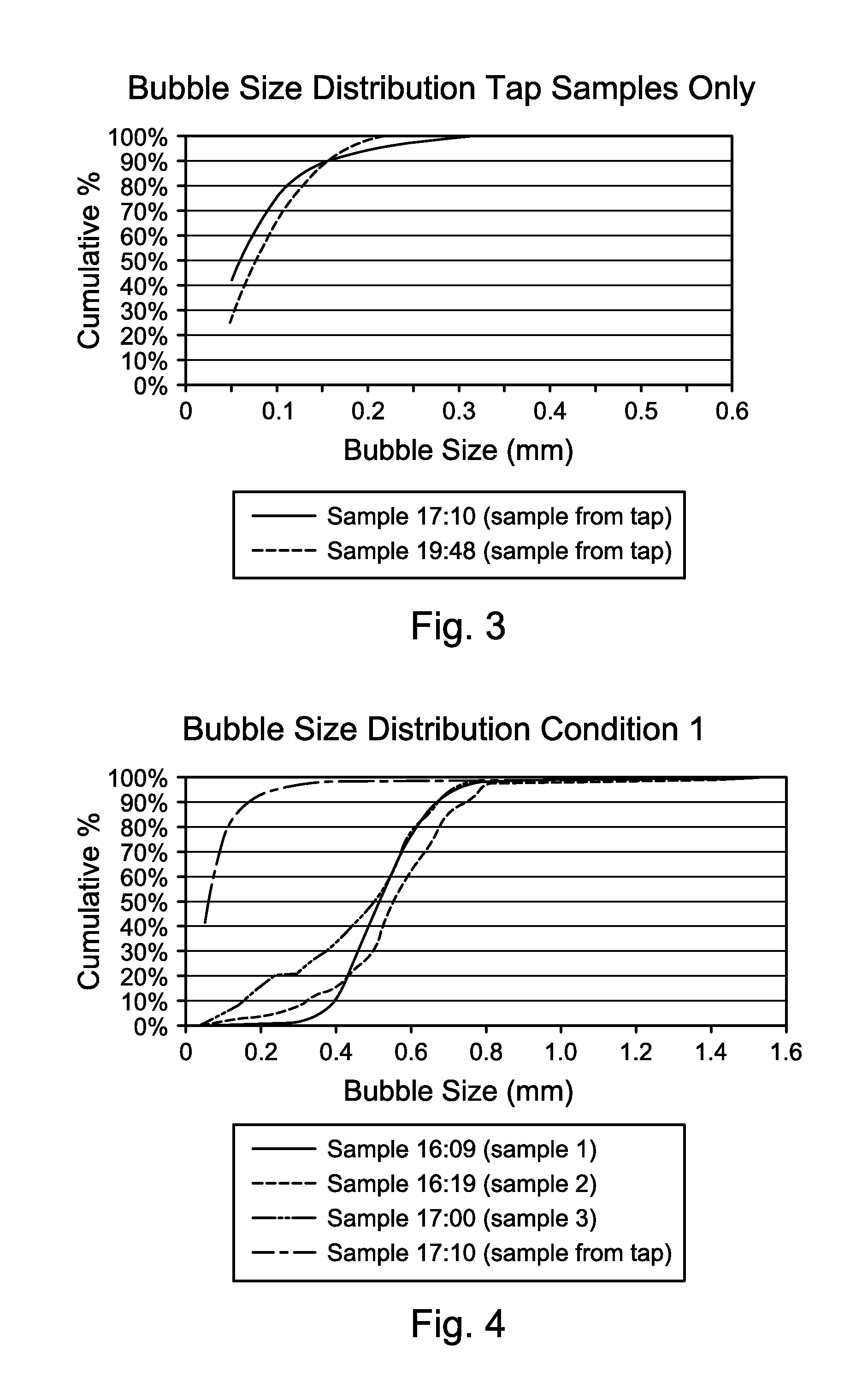
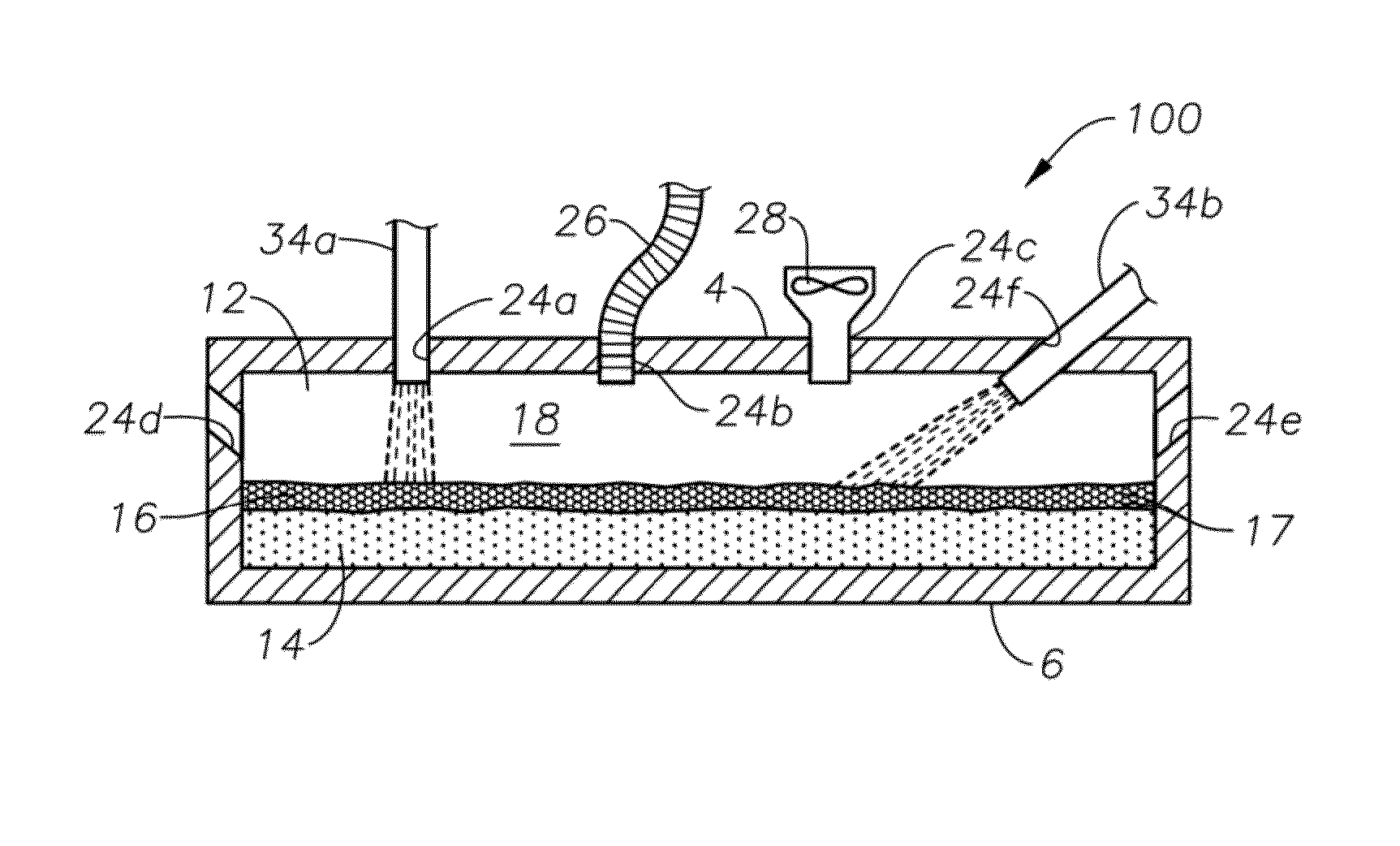
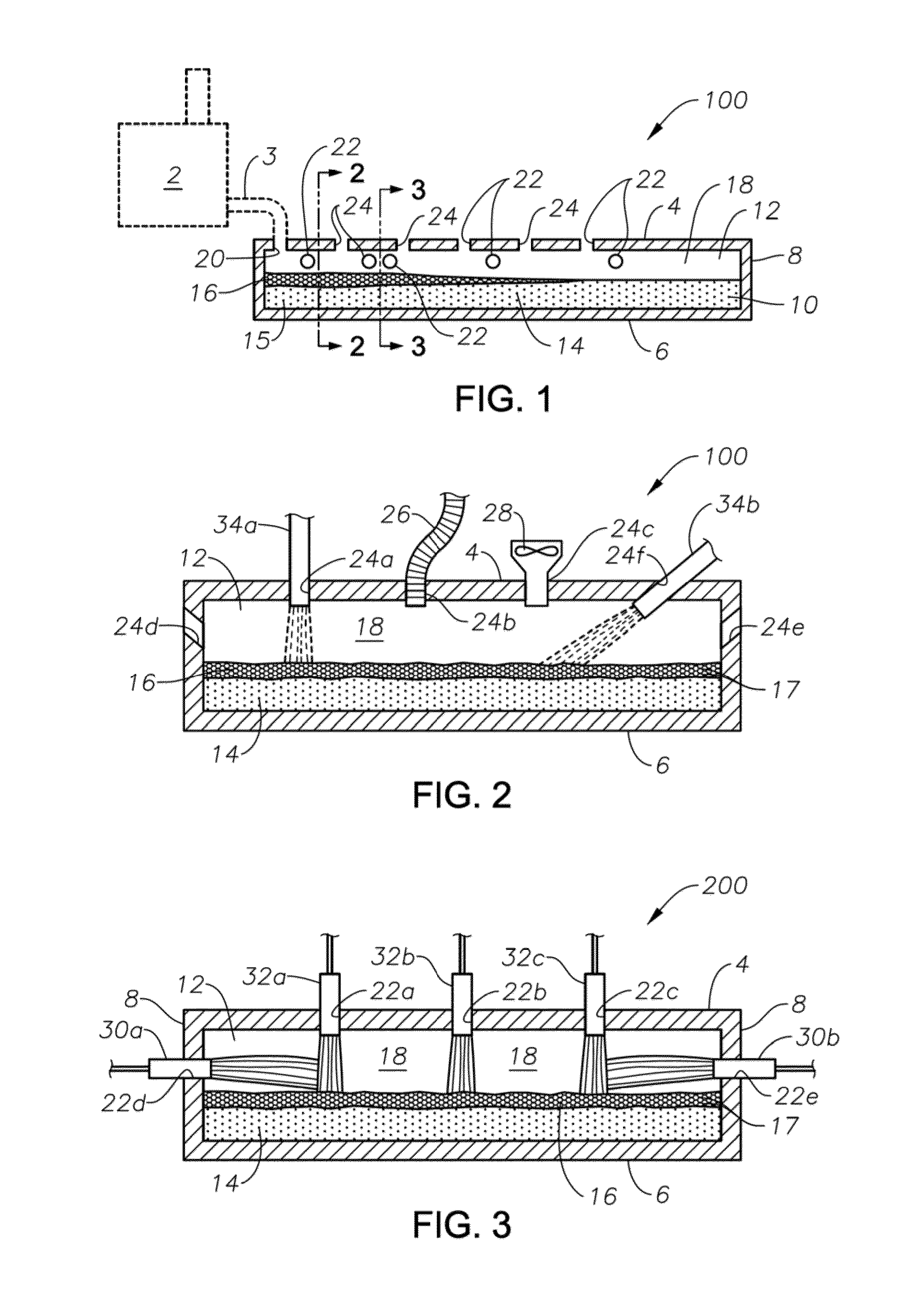
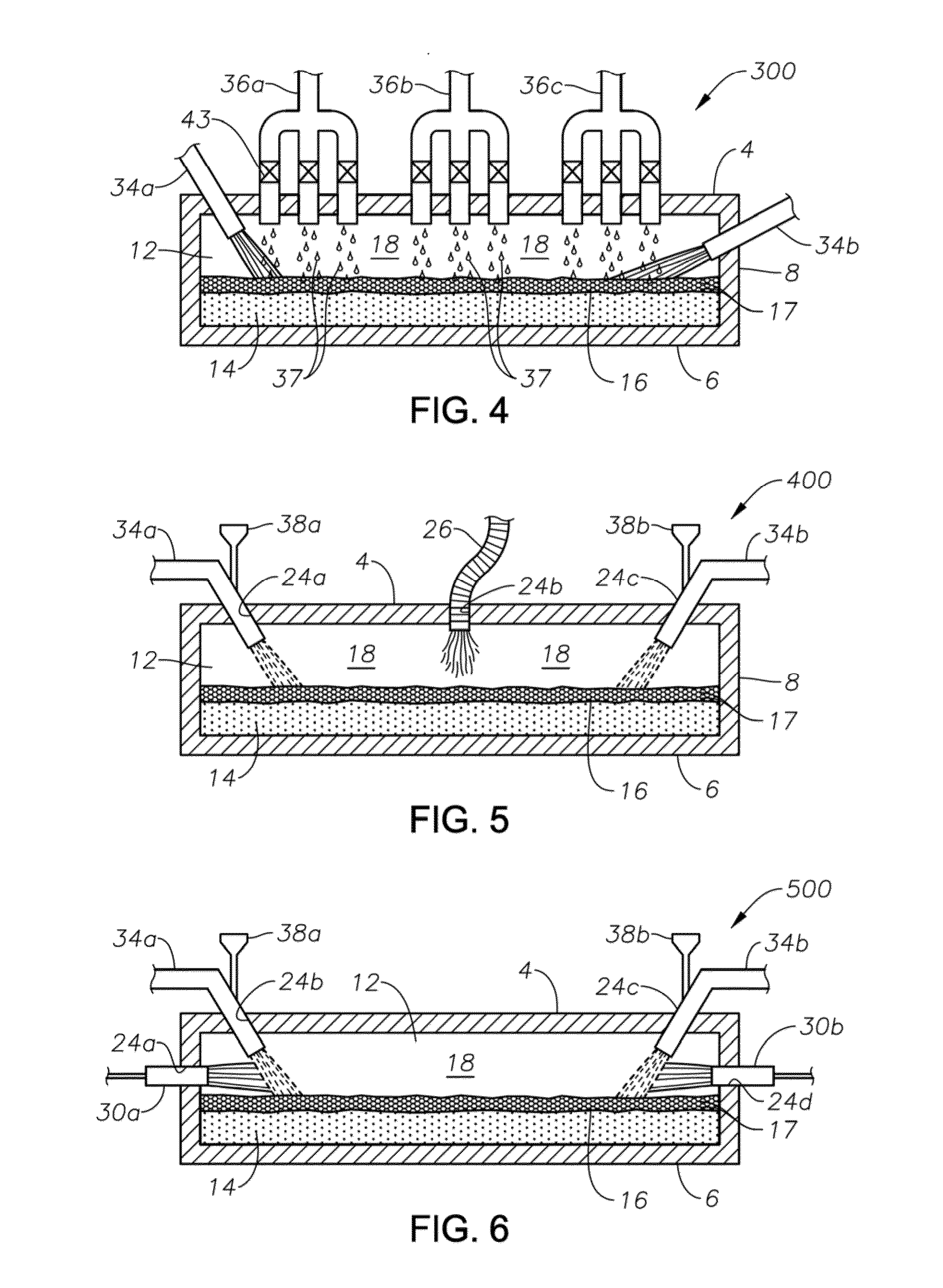
Methods and systems for controlling bubble size and bubble decay rate in foamed glass produced by a submerged combustion melter
ActiveUS20140090421A1Increase reduction rateGlass furnace apparatusGlass melting apparatusCombustionGaseous atmosphere
Methods and systems for controlling bubble size and bubble decay rate of glass foams formed during submerged combustion melting. Flowing a molten mass of foamed glass comprising molten glass and bubbles entrained therein into an apparatus downstream of a submerged combustion melter. The downstream apparatus has a floor, a roof, and a sidewall structure connecting the floor and roof. The foamed glass has glass foam of glass foam bubbles on its top surface, and the downstream apparatus defines a space for a gaseous atmosphere above and in contact with the glass foam. The downstream apparatus includes heating components to heat or maintain temperature of the foamed glass. Adjusting composition of the atmosphere above the glass foam, and / or contacting the foam with a liquid or solid composition controls bubble size of the glass foam bubbles, and / or foam decay rate.
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE CORP
Methods and systems for destabilizing foam in equipment downstream of a submerged combustion melter
Methods and systems for de-stabilizing foam produced in submerged combustion melters. A molten mass of glass and bubbles is flowed into an apparatus downstream of a submerged combustion melter. The downstream apparatus includes a floor, a roof and a wall connecting the floor and roof, but is devoid of submerged combustion burners and other components that would increase turbulence of the molten mass. The molten mass has foam on at least a portion of a top surface of the molten mass. One method includes directly impinging an impinging composition onto at least a portion of the foam in the downstream apparatus. Systems for carrying out the methods are described.
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE CORP
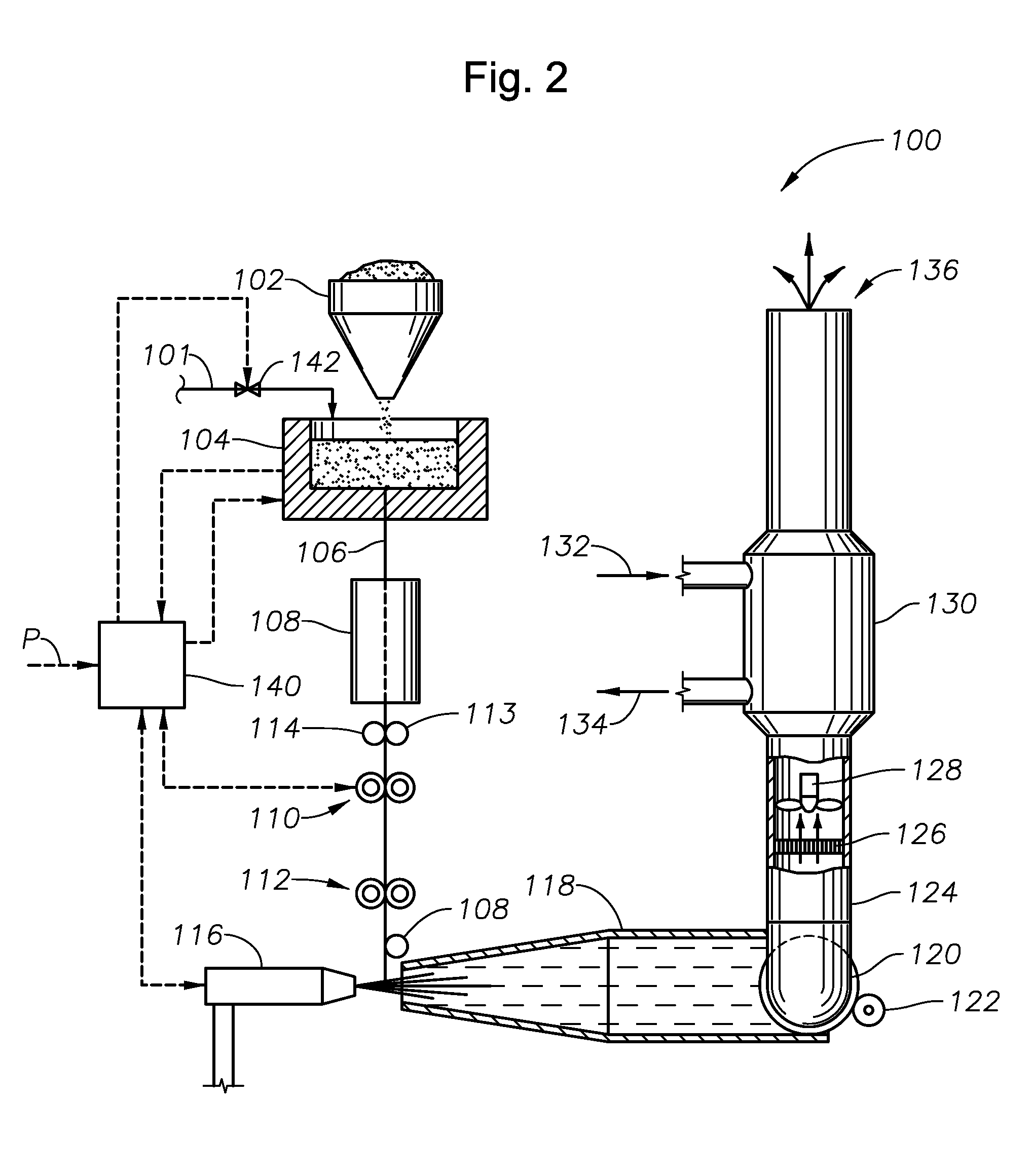
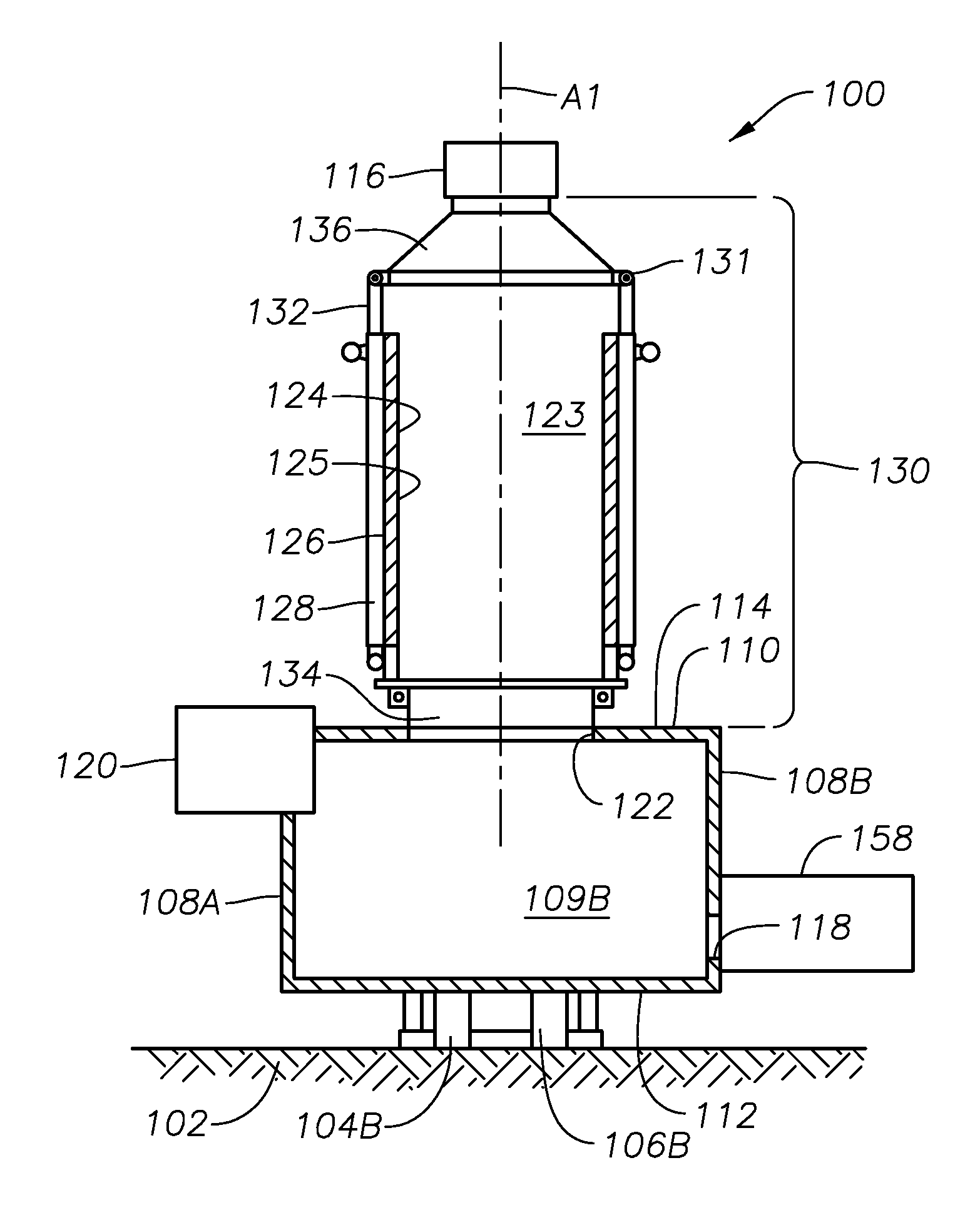
Process of using a submerged combustion melter to produce hollow glass fiber or solid glass fiber having entrained bubbles, and burners and systems to make such fibers
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE CORP
Methods of using a submerged combustion melter to produce glass products
A method comprises flowing an oxidant and a fuel into a submerged combustion burner in a glass tank furnace, the glass tank furnace receiving a feed of glass forming material and producing molten glass, the burner and furnace comprising a melting system. The melting system has a variable system vibration and / or oscillation due to the nature of submerged combustion. One method includes predicting a value of at least one property, such as viscosity, of the molten glass using the variable system vibration and / or oscillation.
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE CORP
Method and system for producing glass, in which chemical reduction of glass components is avoided
InactiveUS20100242543A1High refractive indexReduce componentsGlass furnace apparatusGlass drawing apparatusOxygenOxidizing agent
In the apparatus for producing glass reduction of reduction-sensitive components in the glass melt is reduced or preferably is prevented during the melting and / or fining processes by introducing an oxidizing agent into the glass melt. The apparatus has a melt crucible, a fining vessel, and a device for conducting oxygen and / or ozone into the glass melt in the melt crucible and / or fining vessel, in order to suppress reduction of reduction-sensitive components of the glass melt. A preferred embodiment of the apparatus has a metallic skull crucible, which includes the melt crucible and / or the fining vessel. The apparatus preferably includes a homogenization unit connected to the fining vessel to receive glass melt from the fining vessel in order to further process the glass melt after refining.
Owner:SCHOTT AG
Molten glass delivery and refining system
Methods and apparatus for refining and delivering a supply of molten glass include melting a supply of glass in a melter and discharging a stream of molten glass. A refining section is provided to refine the molten glass discharged by the melter and to deliver the molten glass downstream to a glass forming apparatus. The refining section is mounted for movement into and out of contact with the stream of molten glass to connect and disconnect the glass forming apparatus with the stream of molten glass.
Owner:OWENS CORNING INTELLECTUAL CAPITAL LLC
Process of using a submerged combustion melter to produce hollow glass fiber or solid glass fiber having entrained bubbles, and burners and systems to make such fibers
Processes and systems for producing glass fibers having regions devoid of glass using submerged combustion melters, including feeding a vitrifiable feed material into a feed inlet of a melting zone of a melter vessel, and heating the vitrifiable material with at least one burner directing combustion products of an oxidant and a first fuel into the melting zone under a level of the molten material in the zone. One or more of the burners is configured to impart heat and turbulence to the molten material, producing a turbulent molten material comprising a plurality of bubbles suspended in the molten material, the bubbles comprising at least some of the combustion products, and optionally other gas species introduced by the burners. The molten material and bubbles are drawn through a bushing fluidly connected to a forehearth to produce a glass fiber comprising a plurality of interior regions substantially devoid of glass.
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com