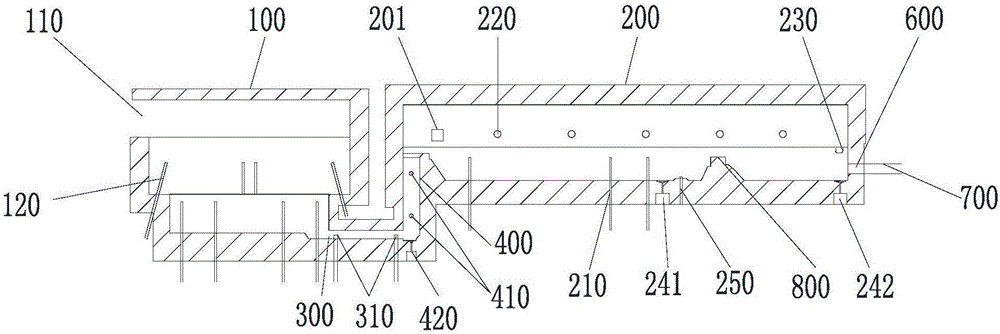
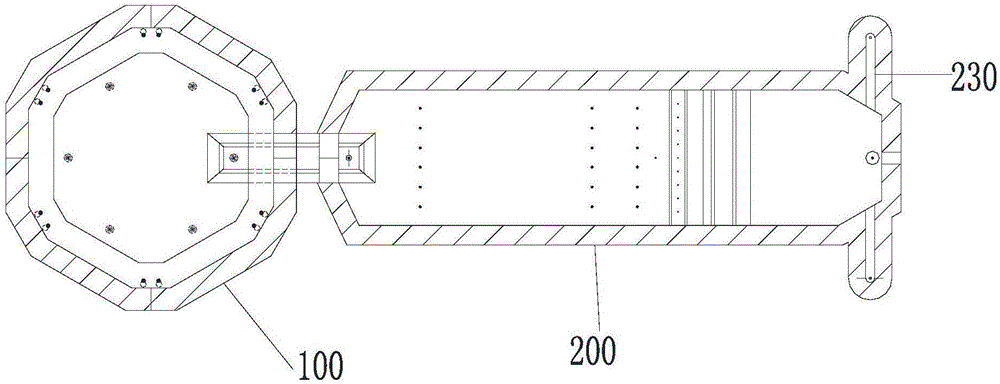
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
358results about "Tank furnaces" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
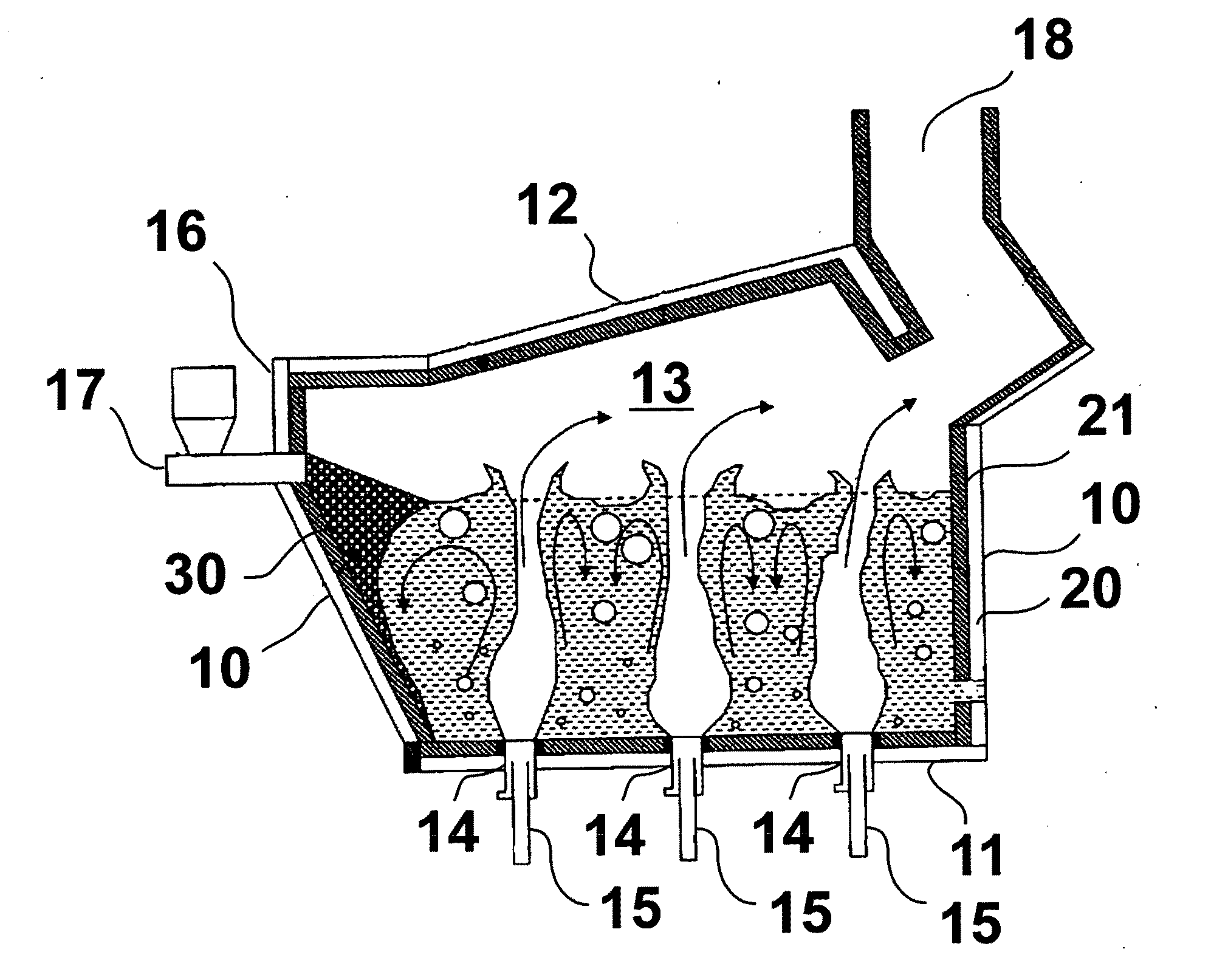
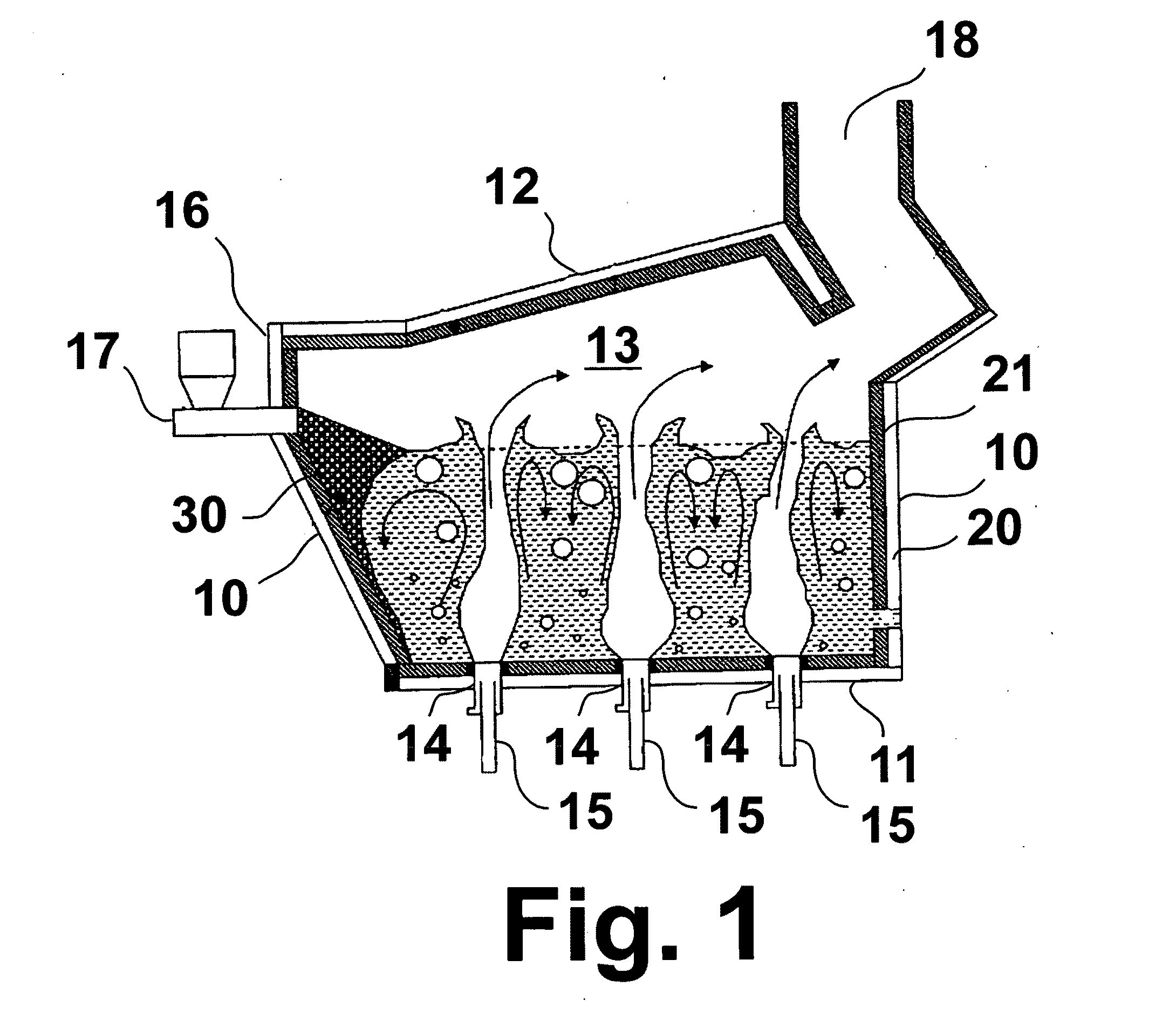
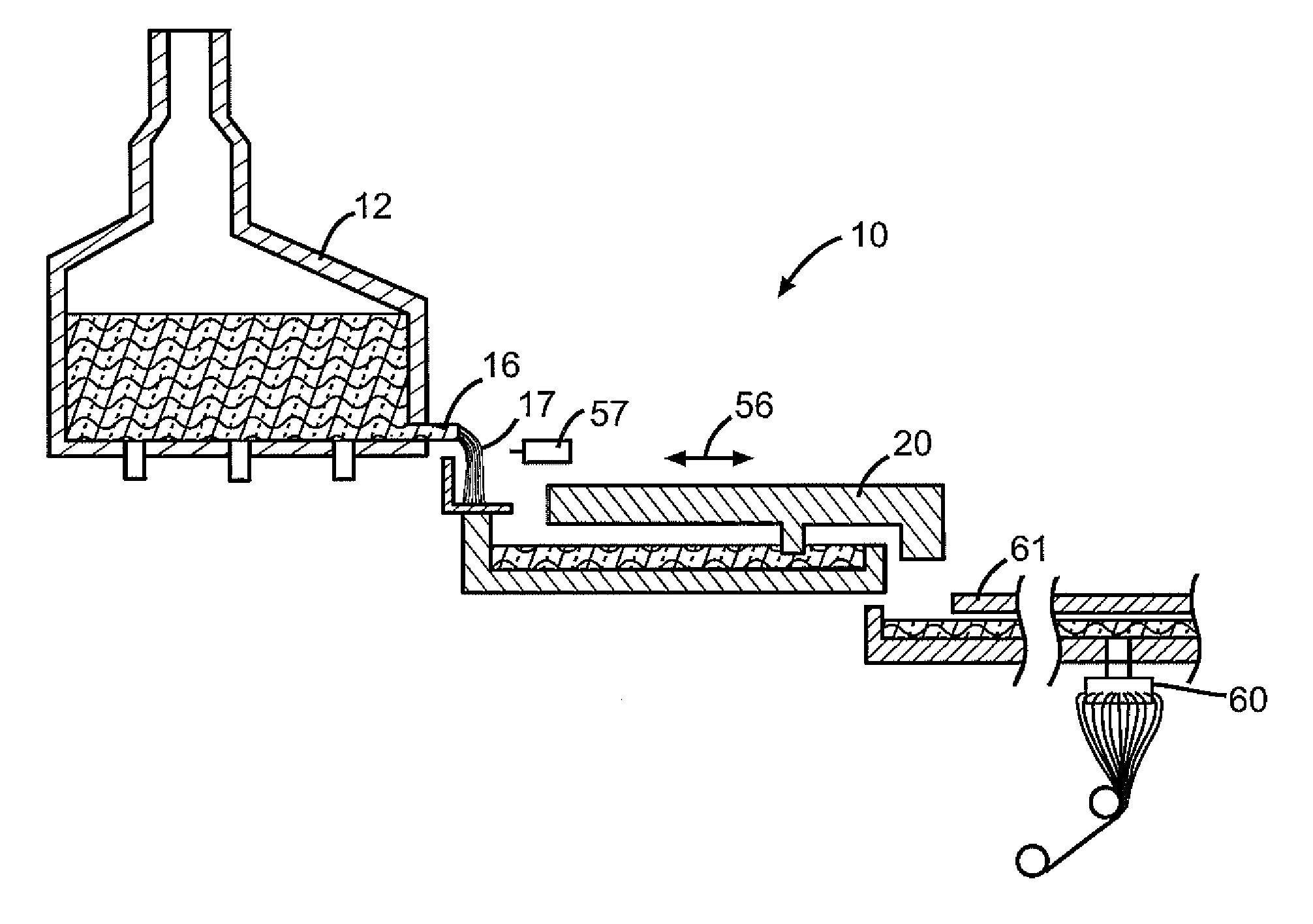
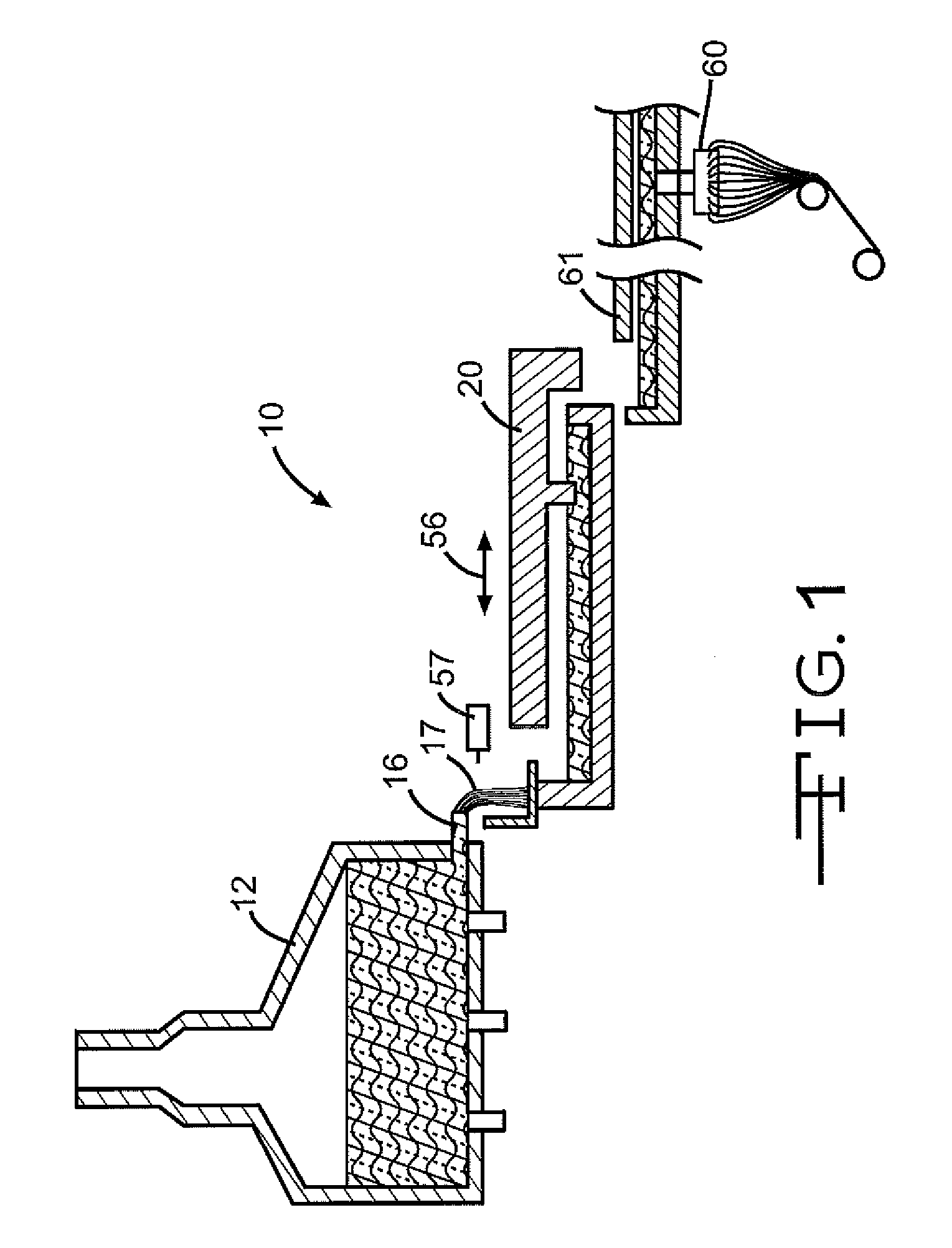
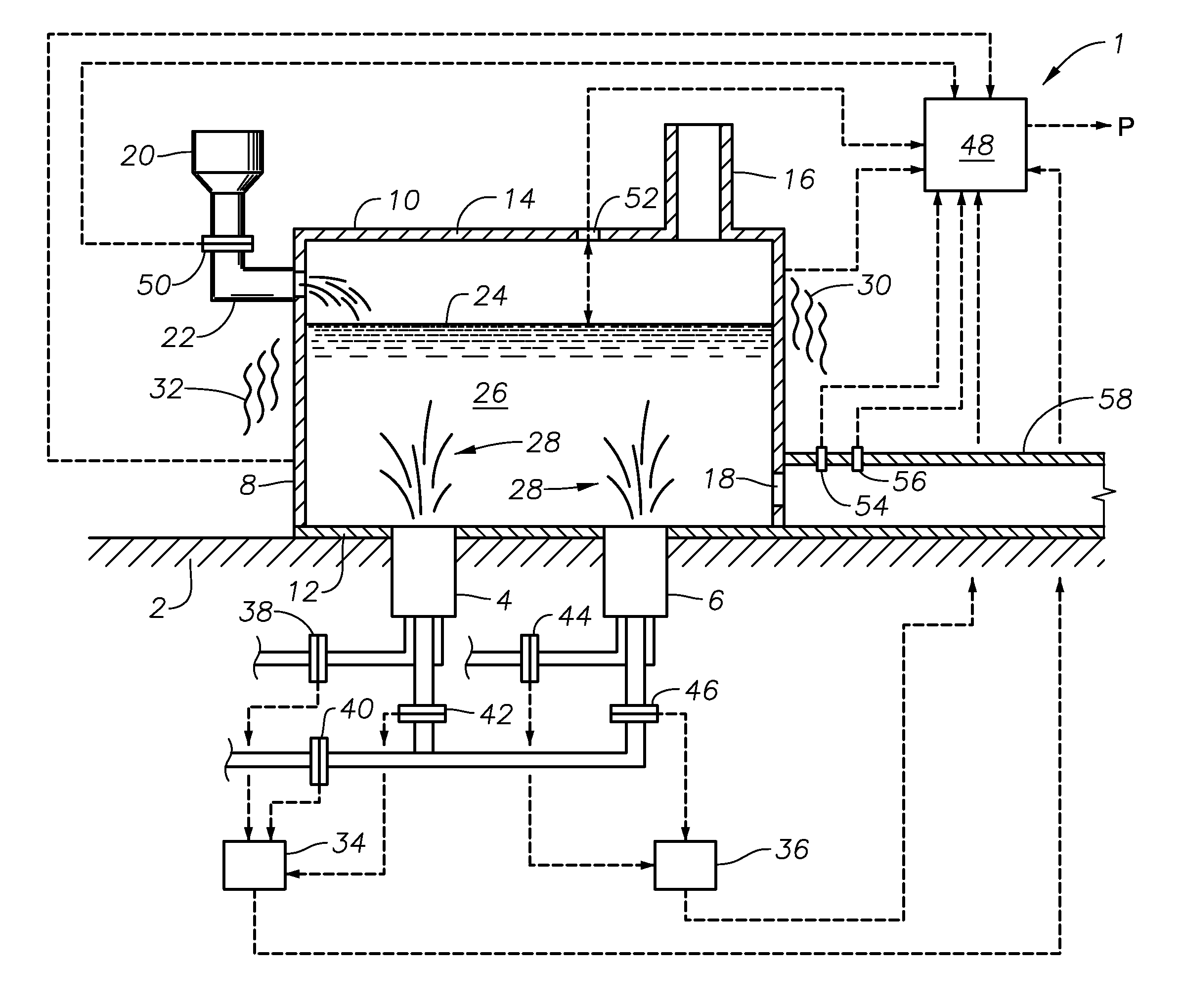
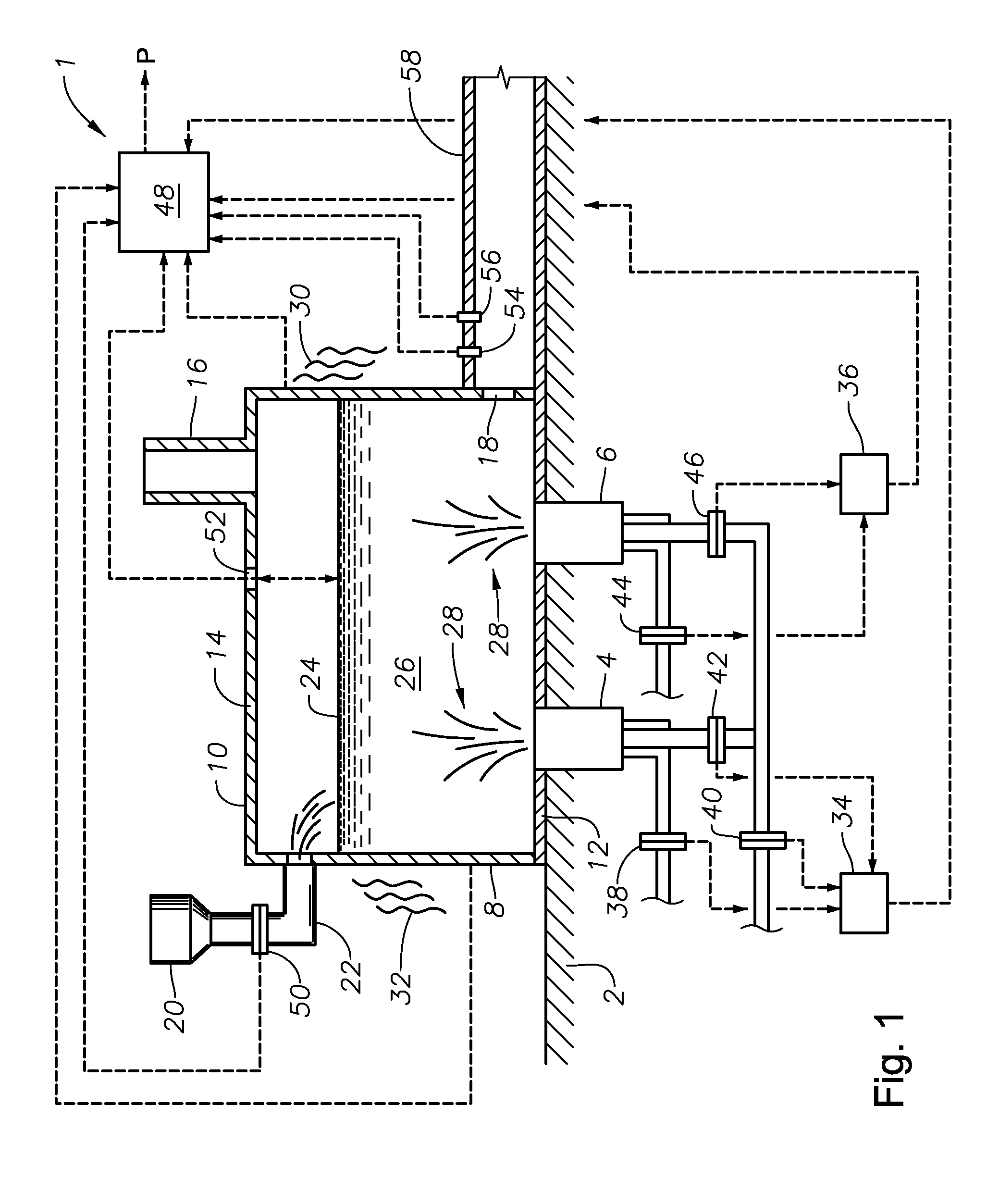
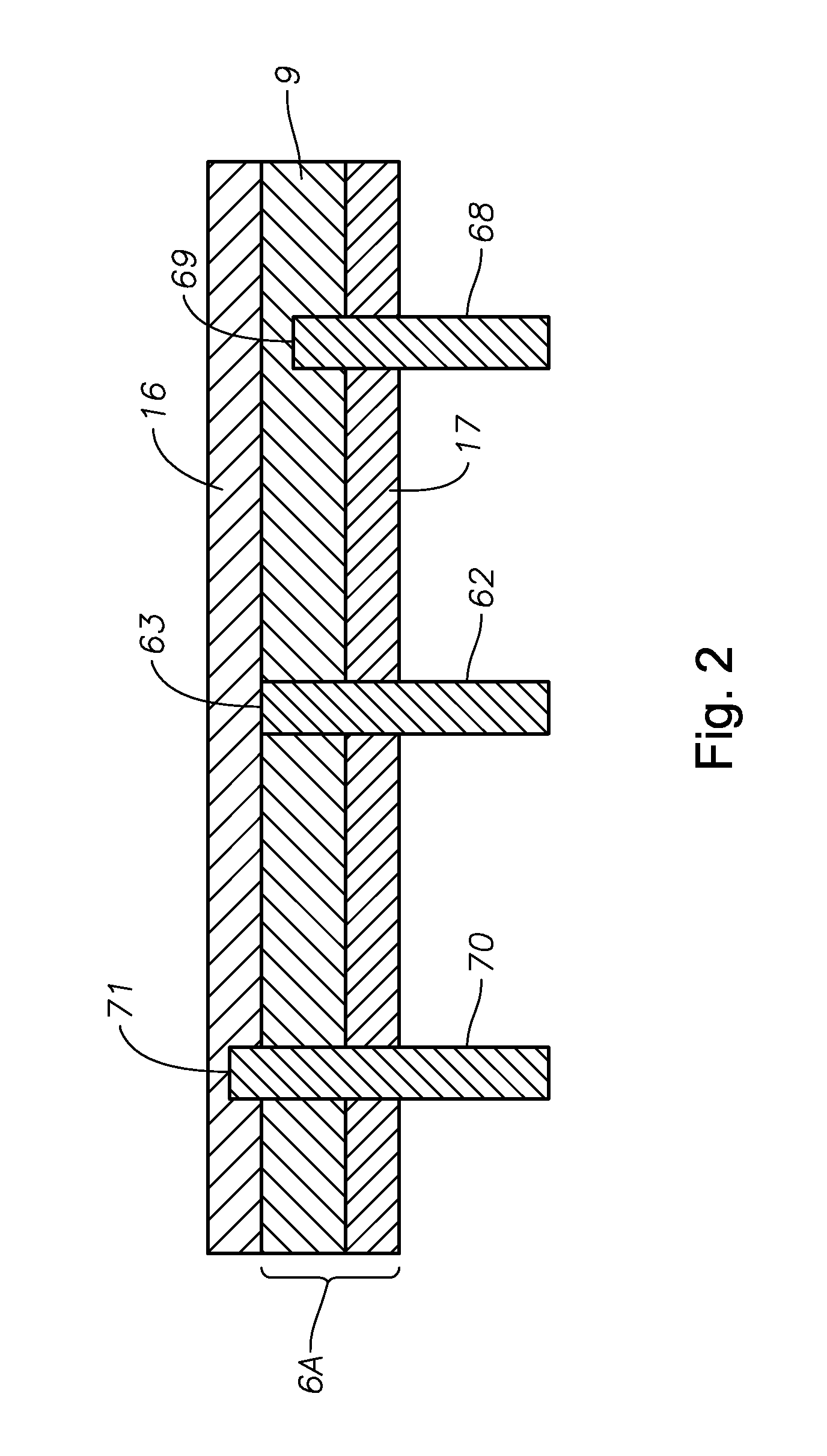
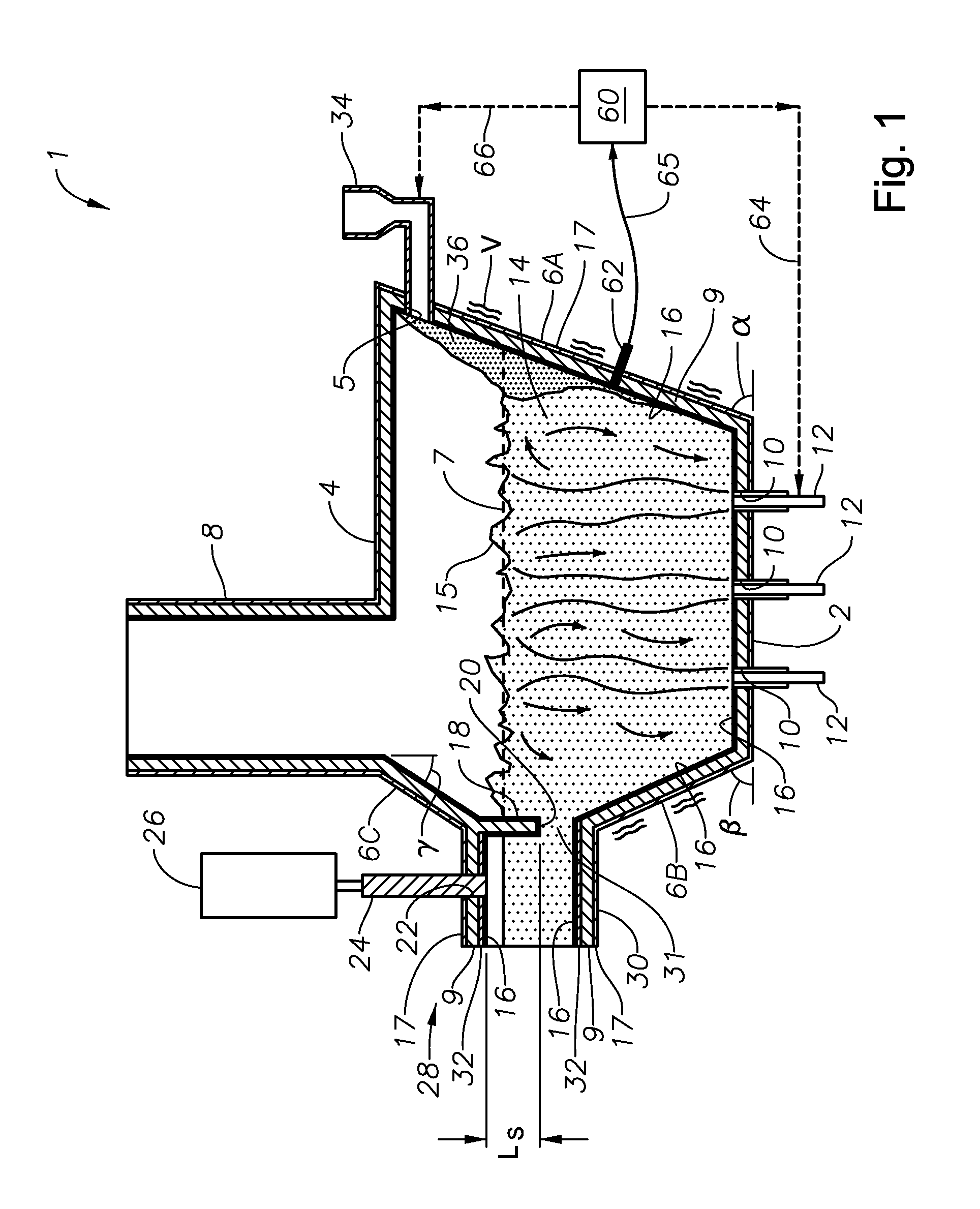
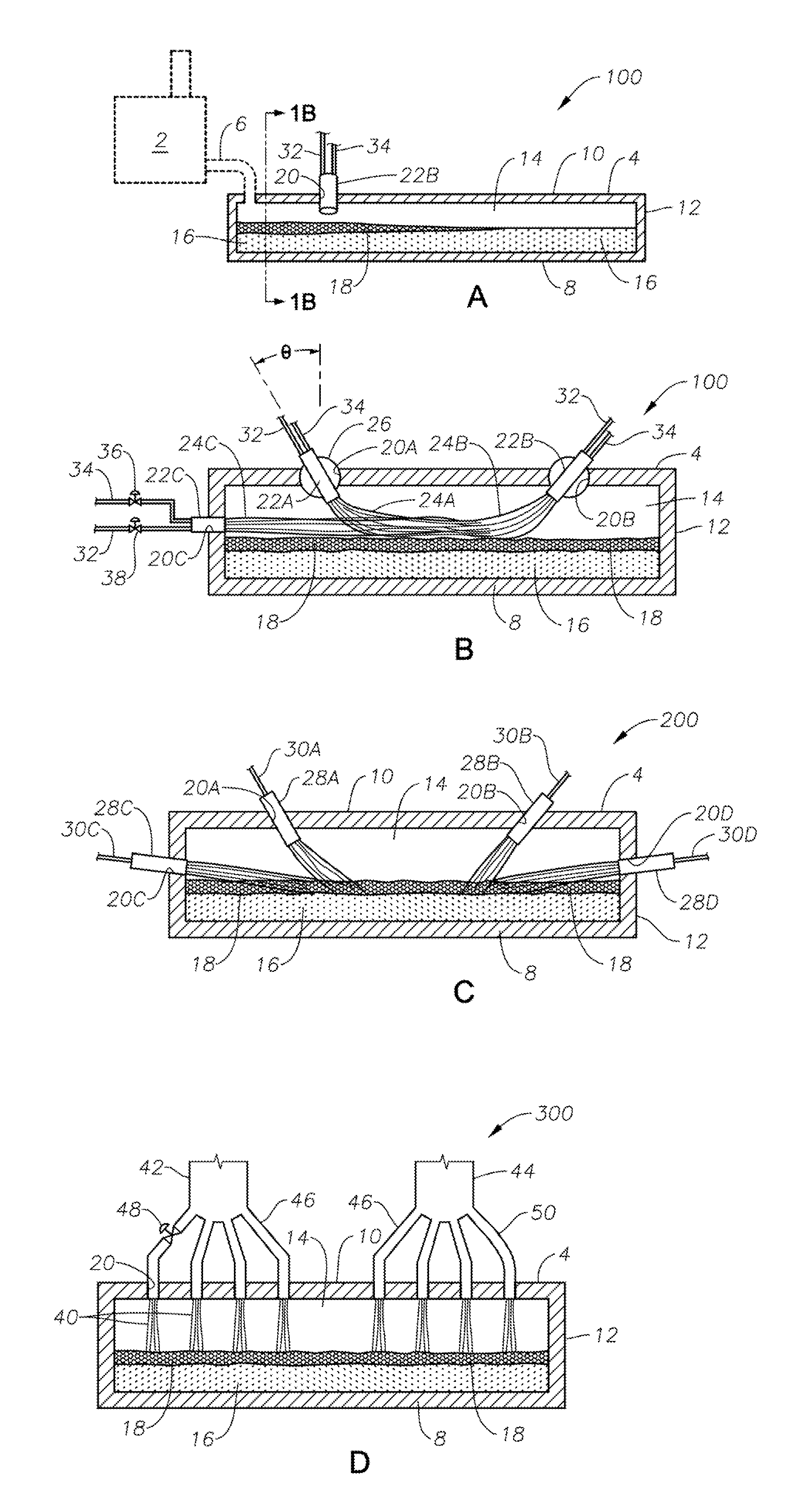
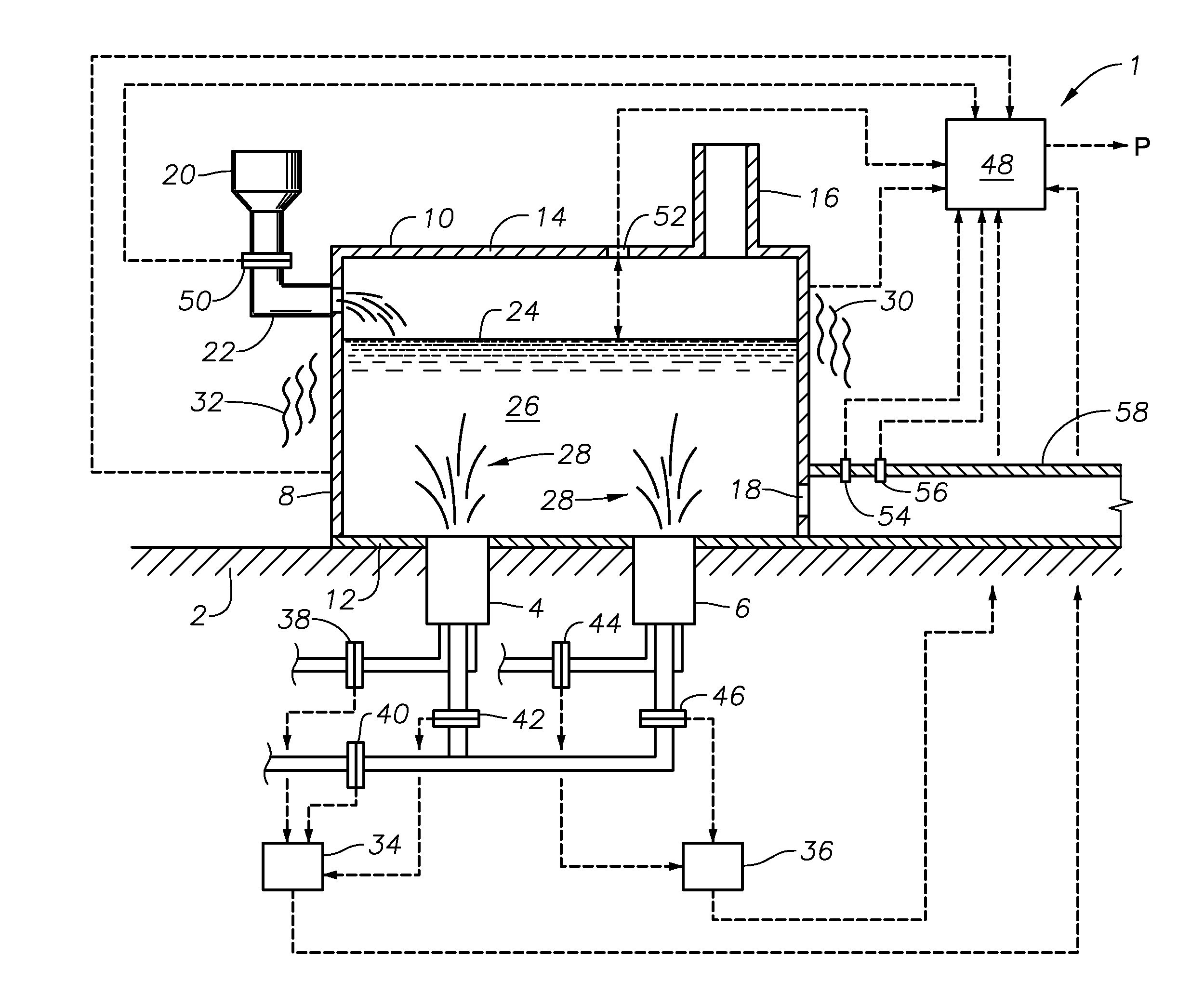
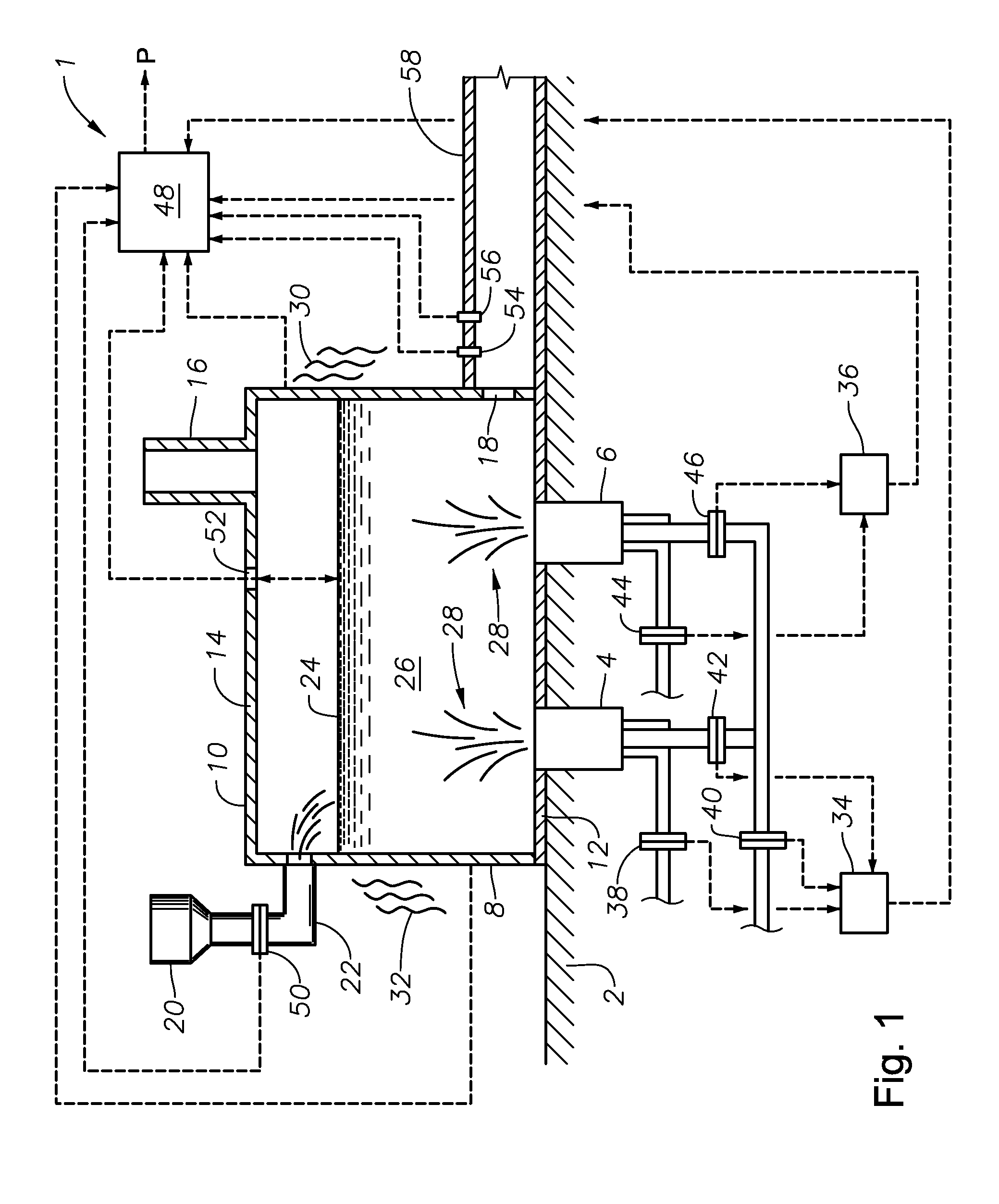
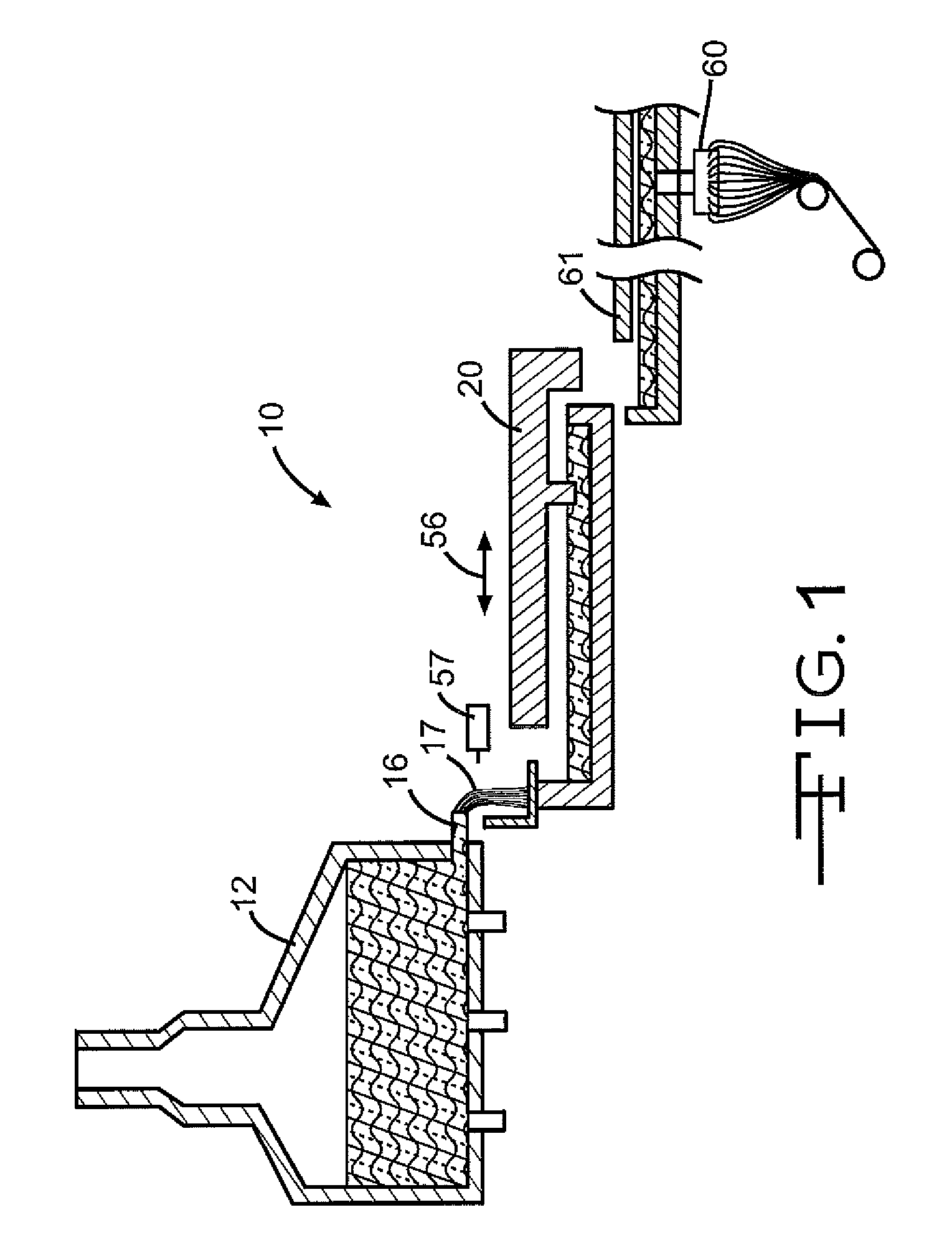
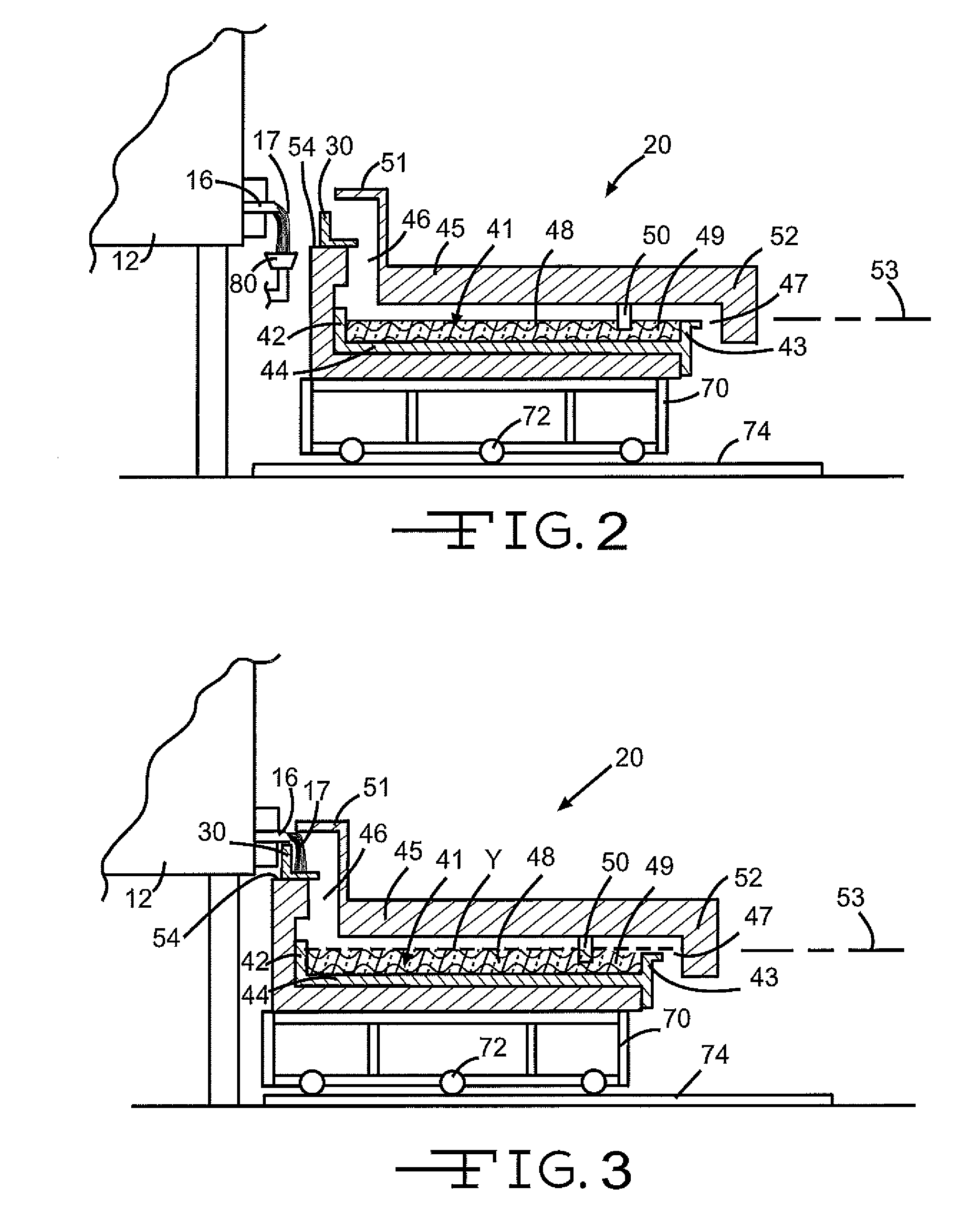
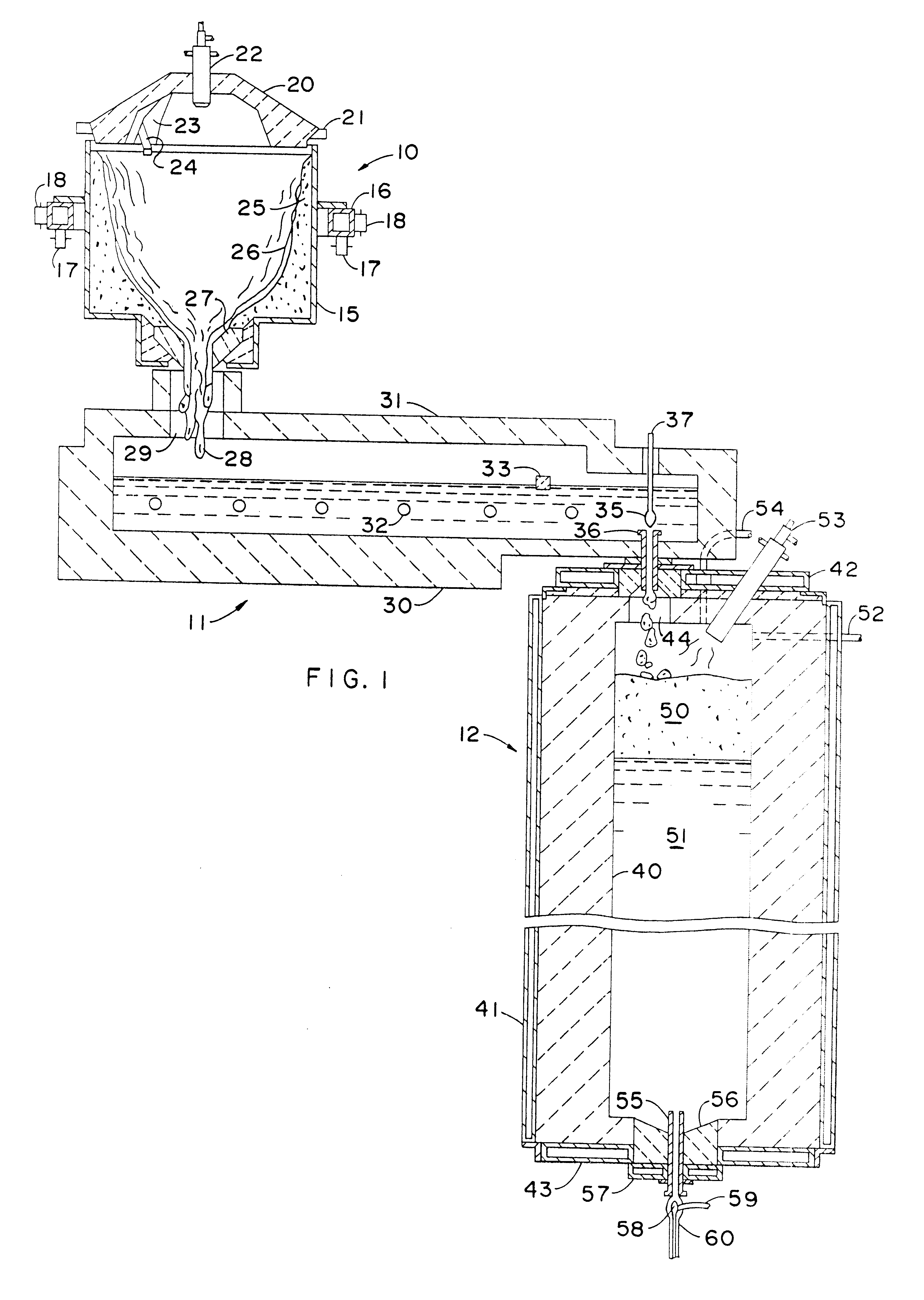
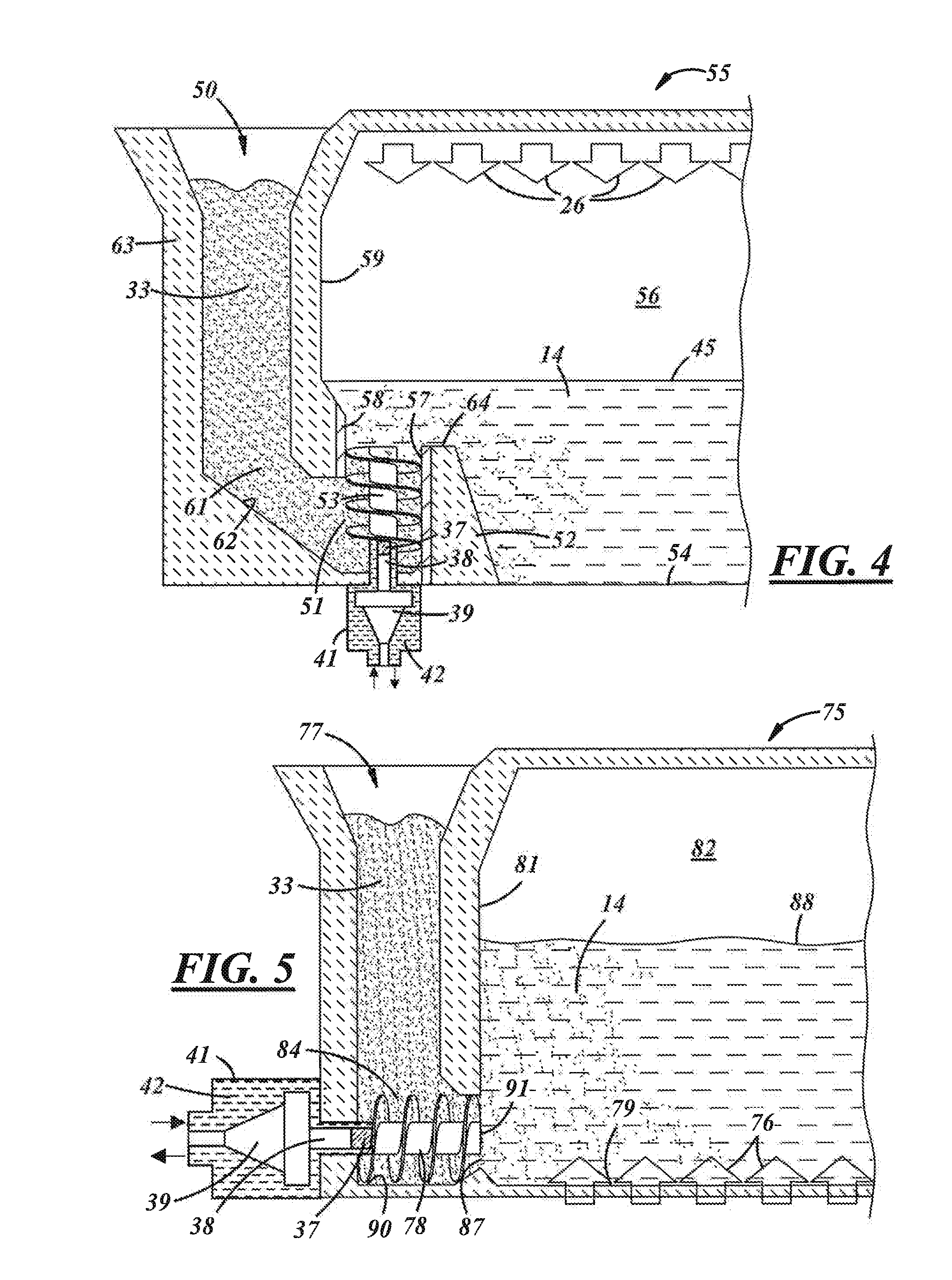
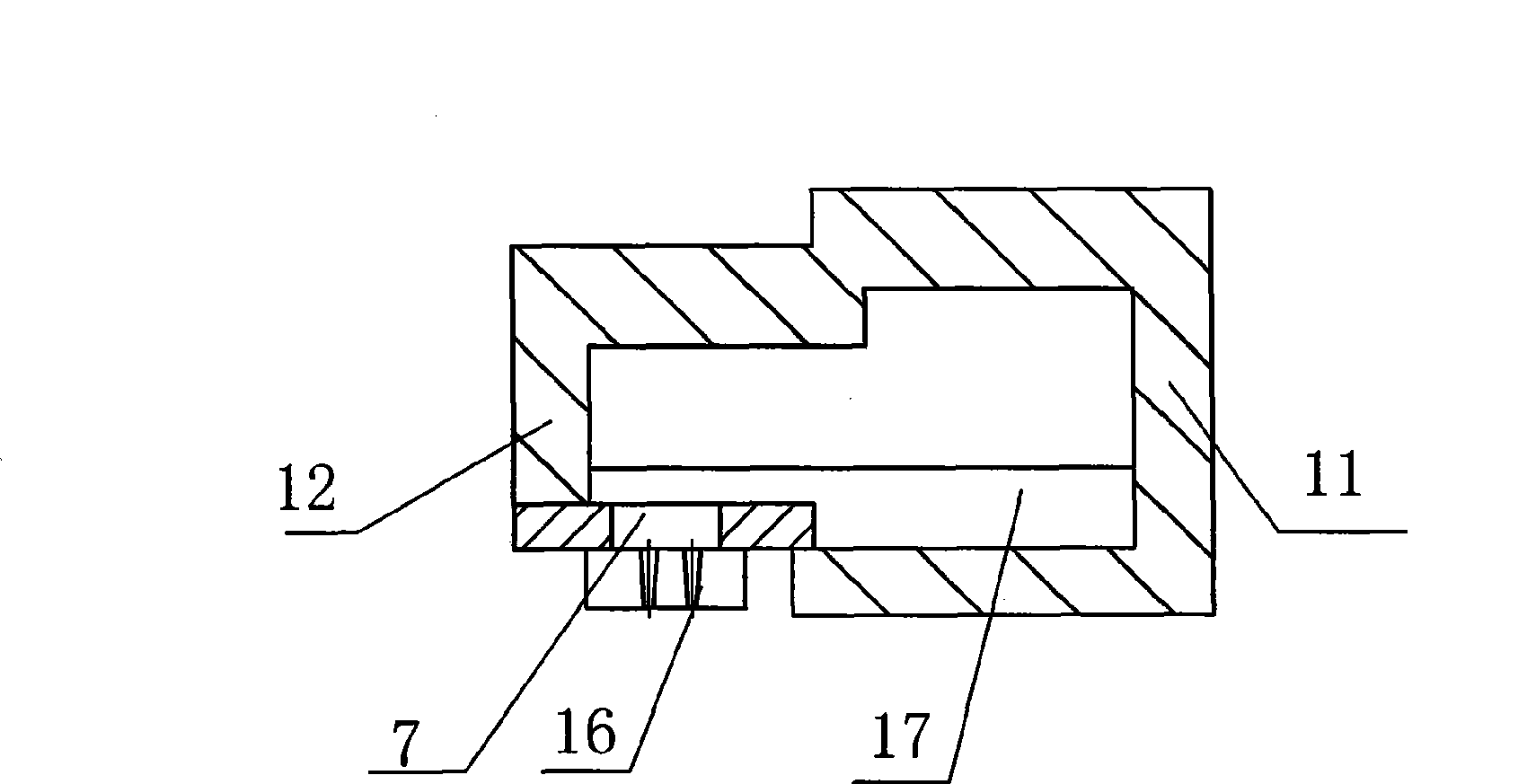
Submerged combustion melter
InactiveUS20110236846A1Increase melter efficiencyReduce bypassCharging furnaceGlass furnace apparatusCombustorEngineering
A submerged combustion melter having a plurality of side walls, a bottom wall adjacent the side walls, and a top wall adjacent the side walls, the walls collectively enclosing a melting chamber, and the bottom wall forming a plurality of openings, each of which is adapted to receive a submerged combustion burner. Each of the submerged combustion burners is positioned at least 4 inches from the side walls, at least twice as far apart from each other as the distance between the submerged combustion burners and the side walls, and less than or equal to about 20 inches apart.
Owner:GAS TECH INST
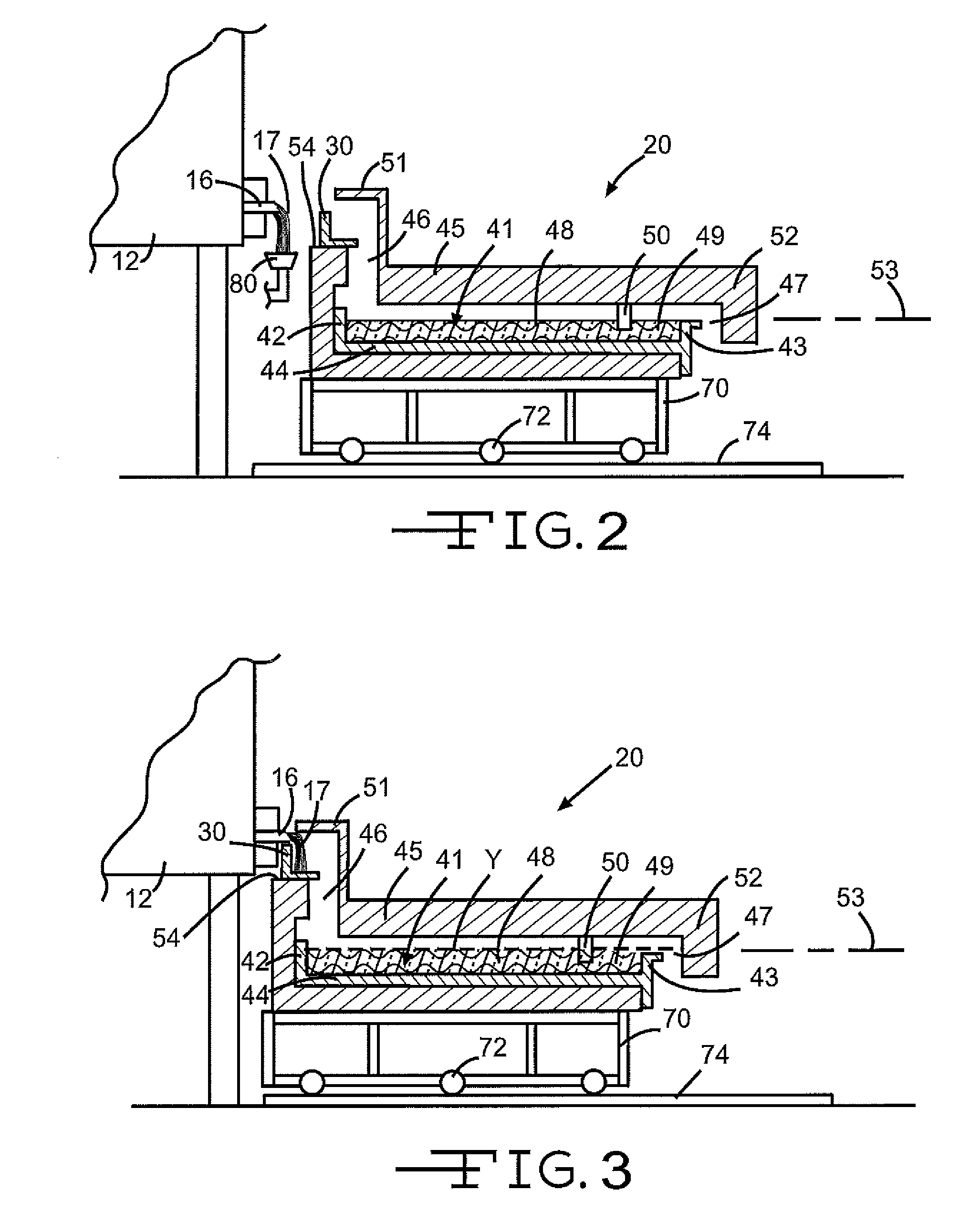
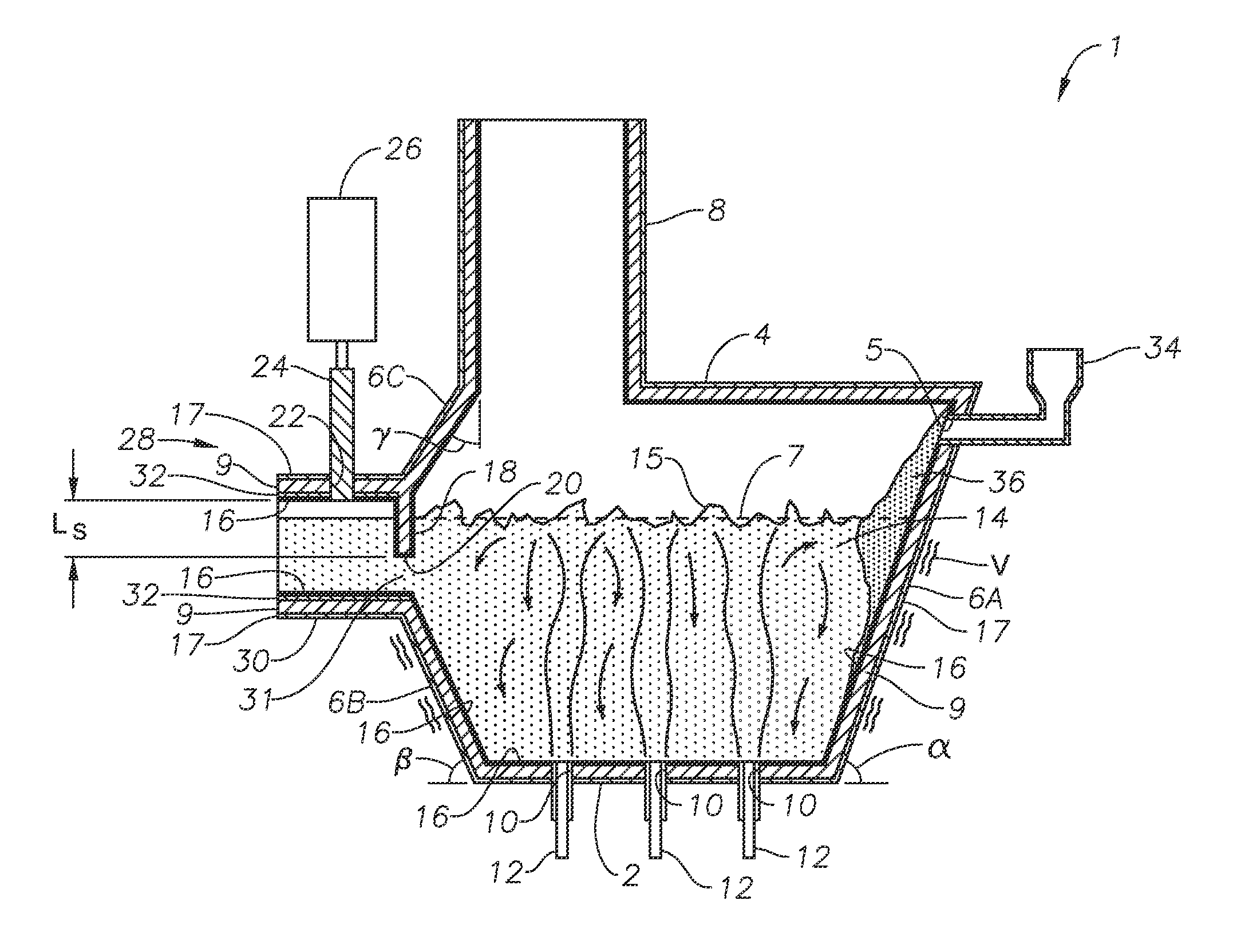
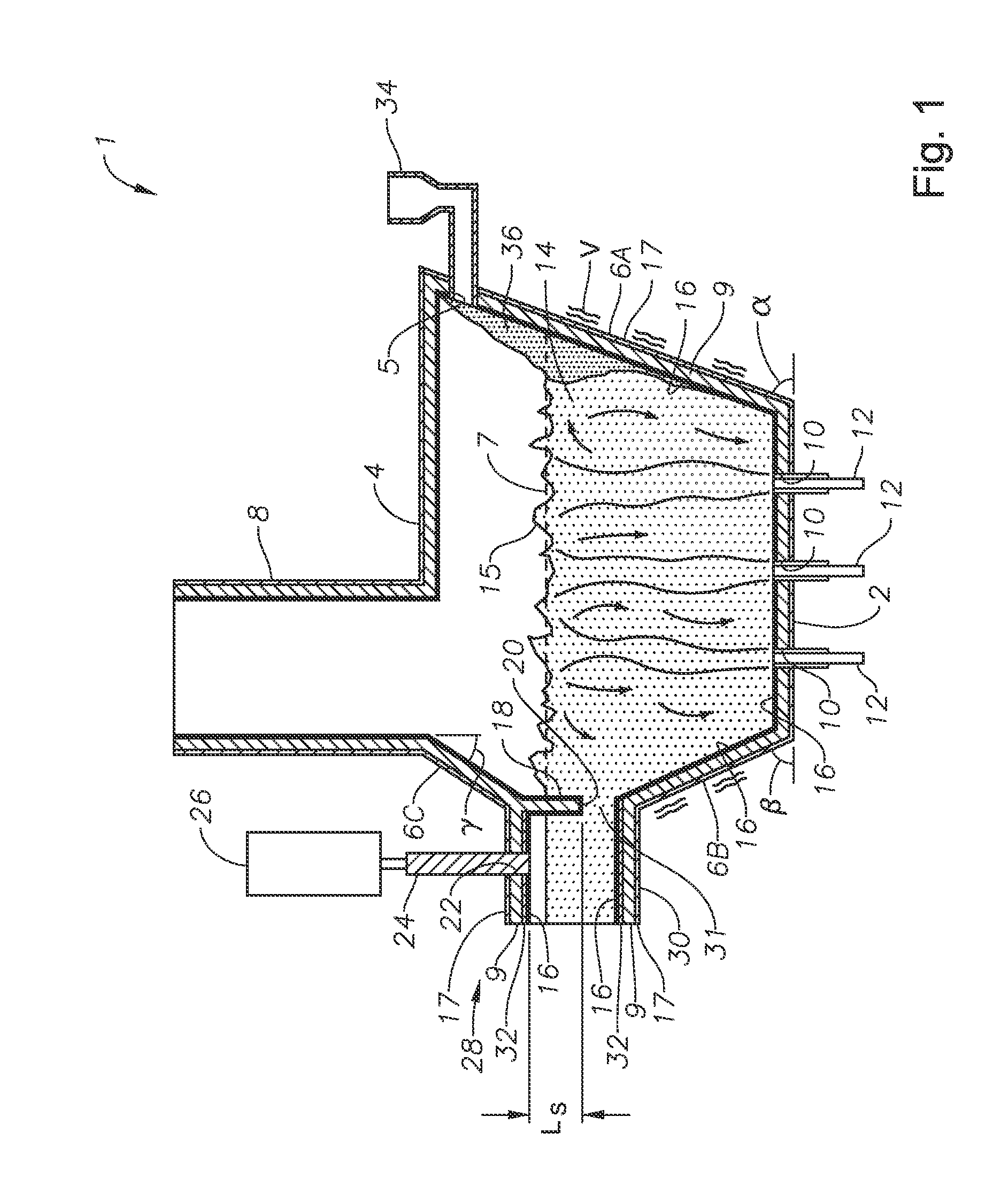
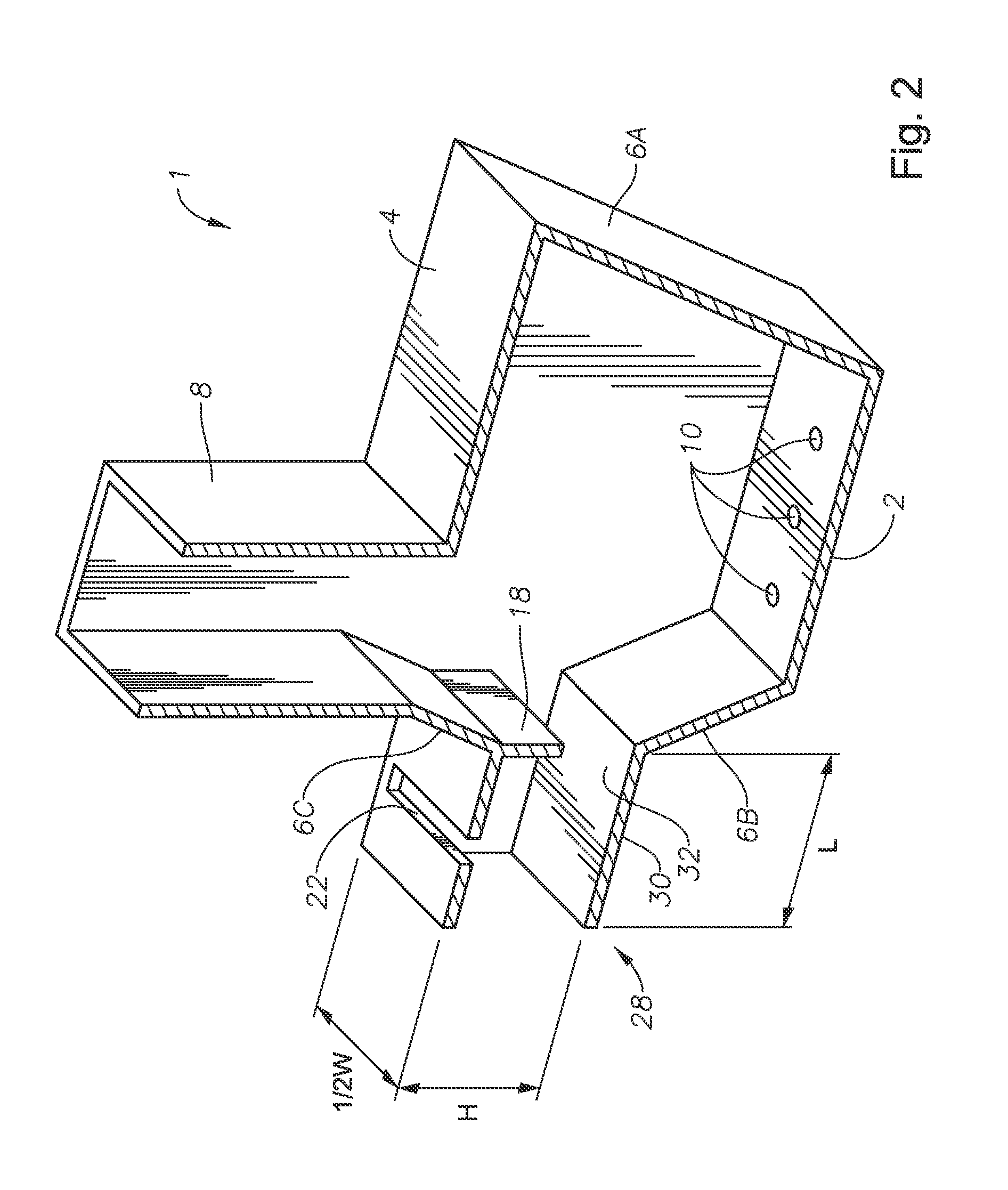
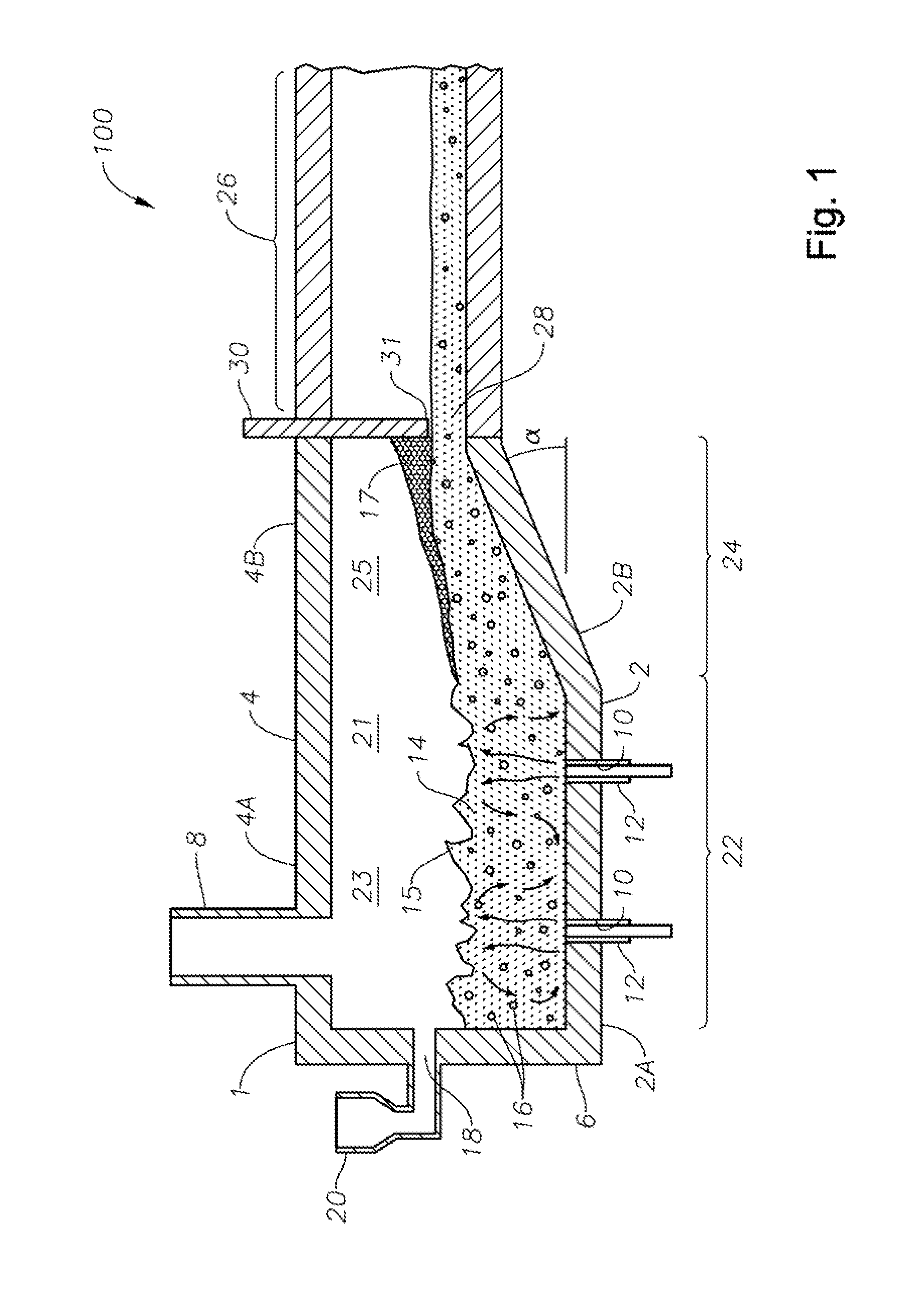
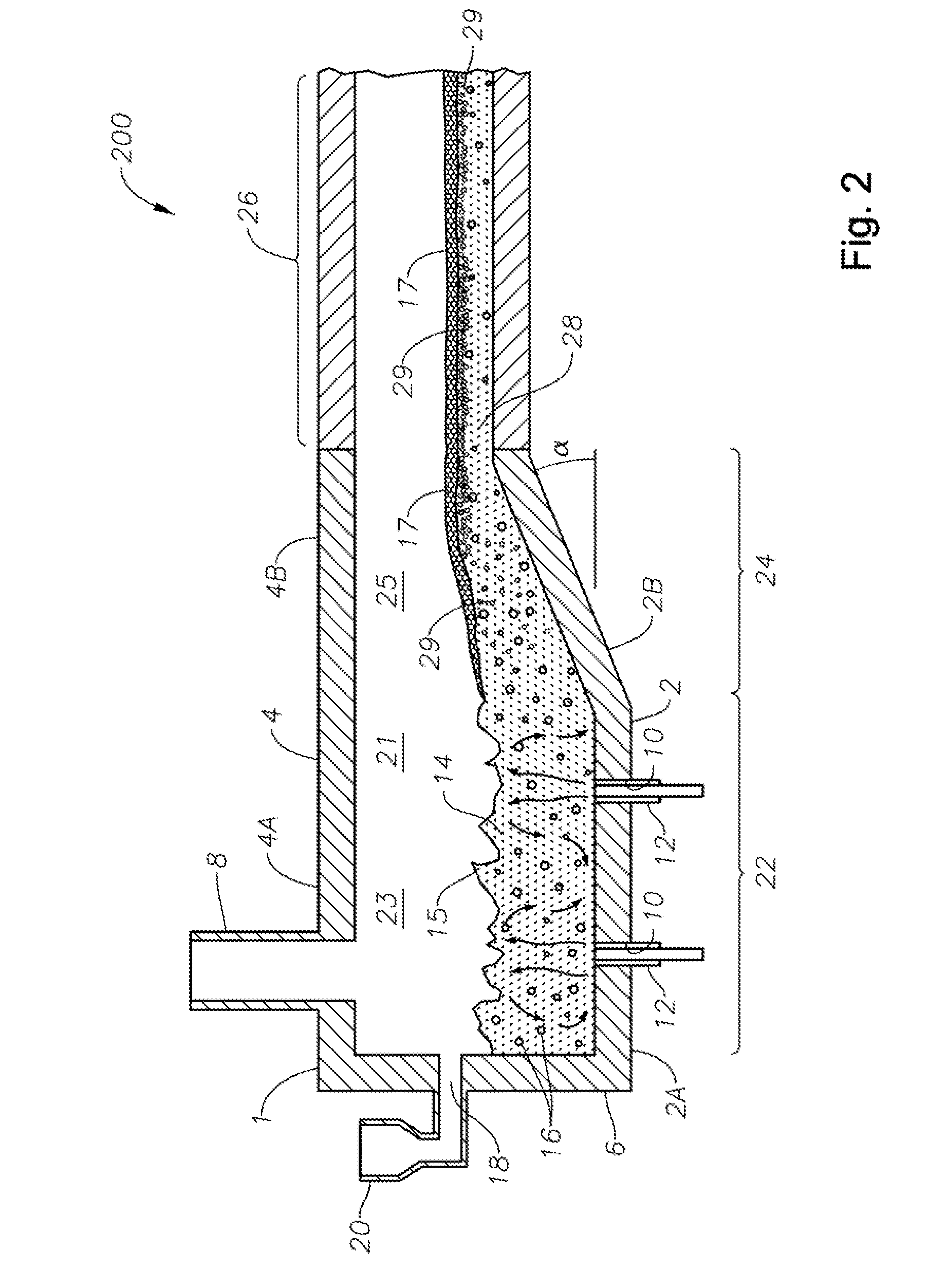
Panel-cooled submerged combustion melter geometry and methods of making molten glass
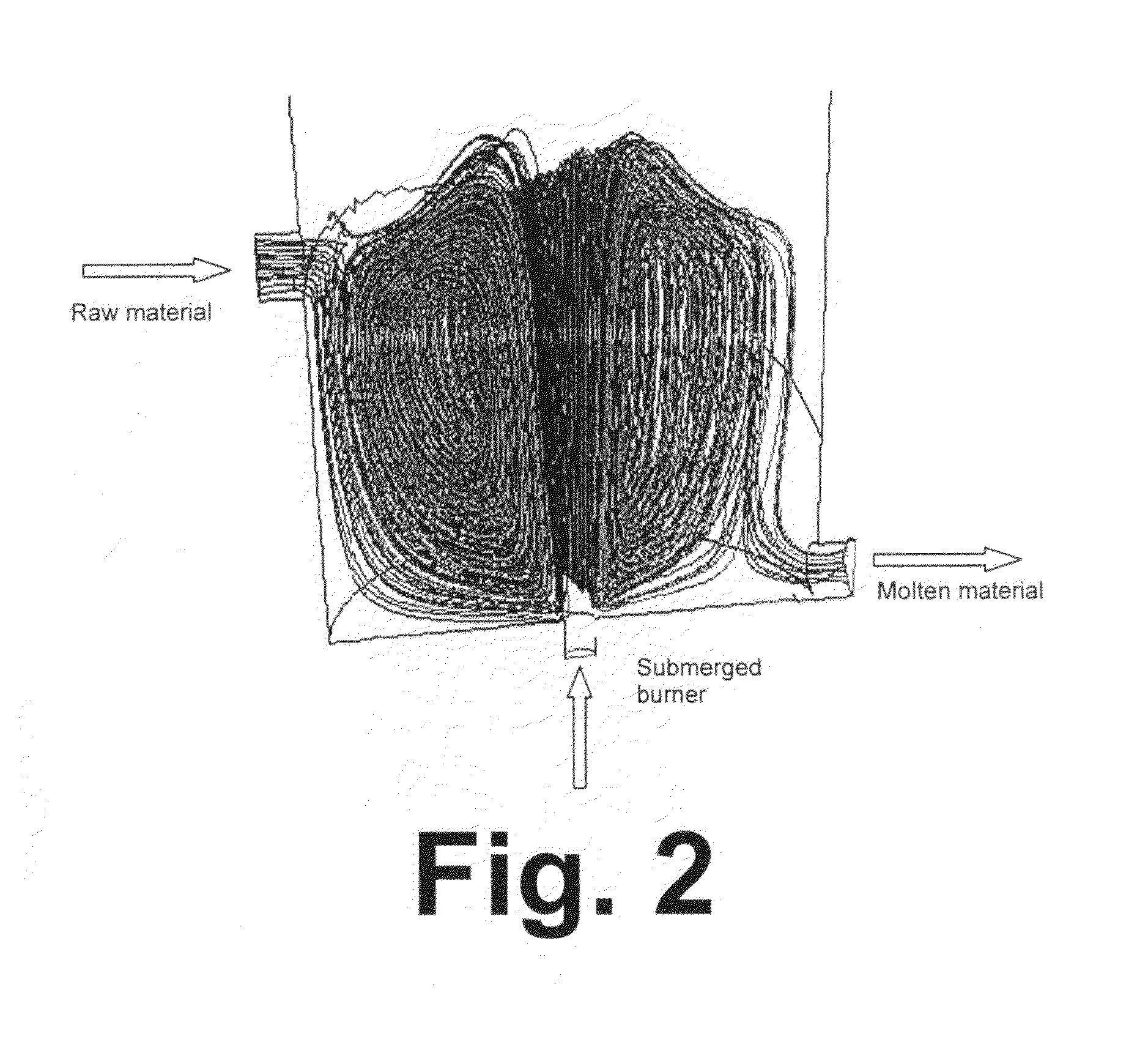
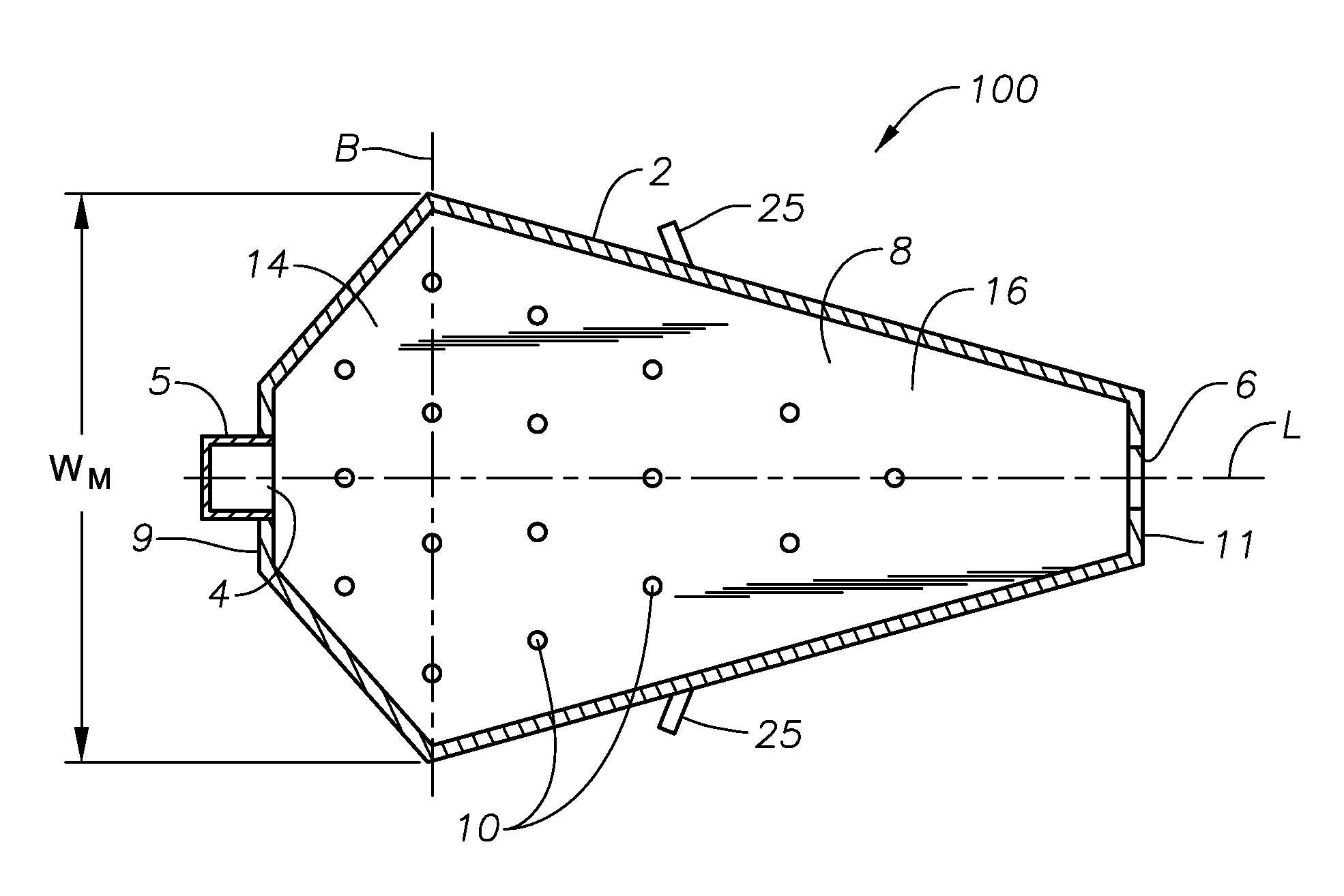
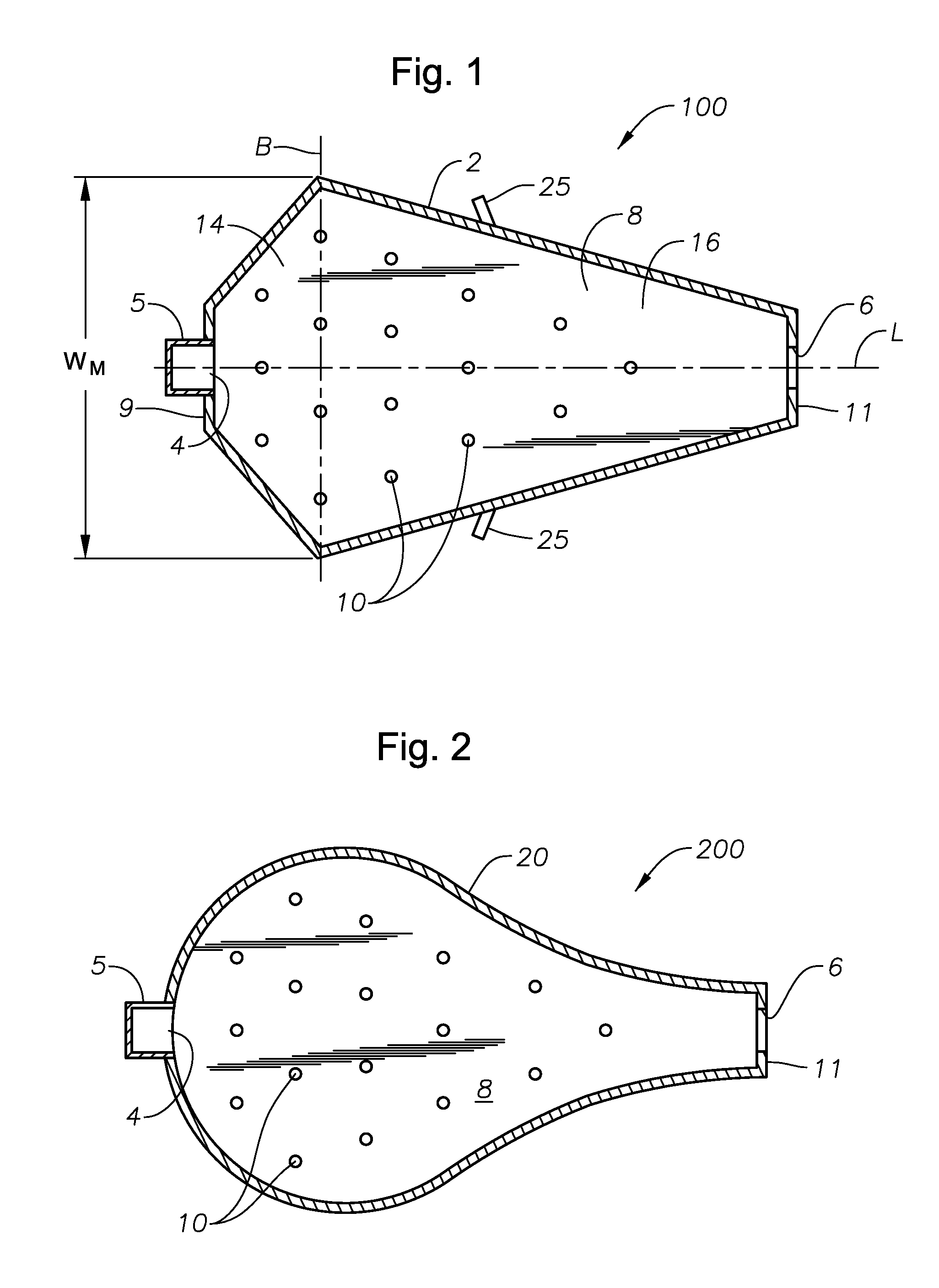
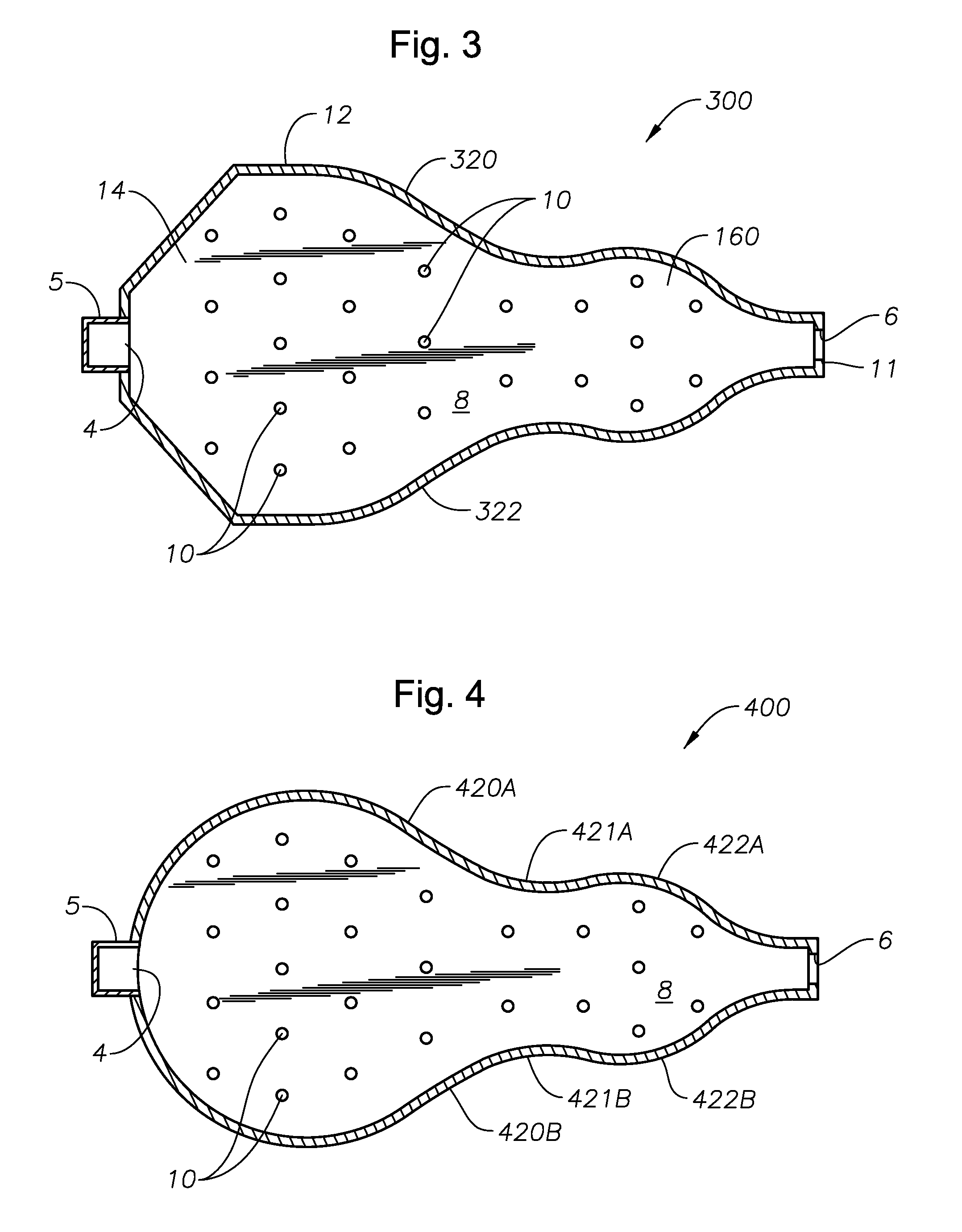
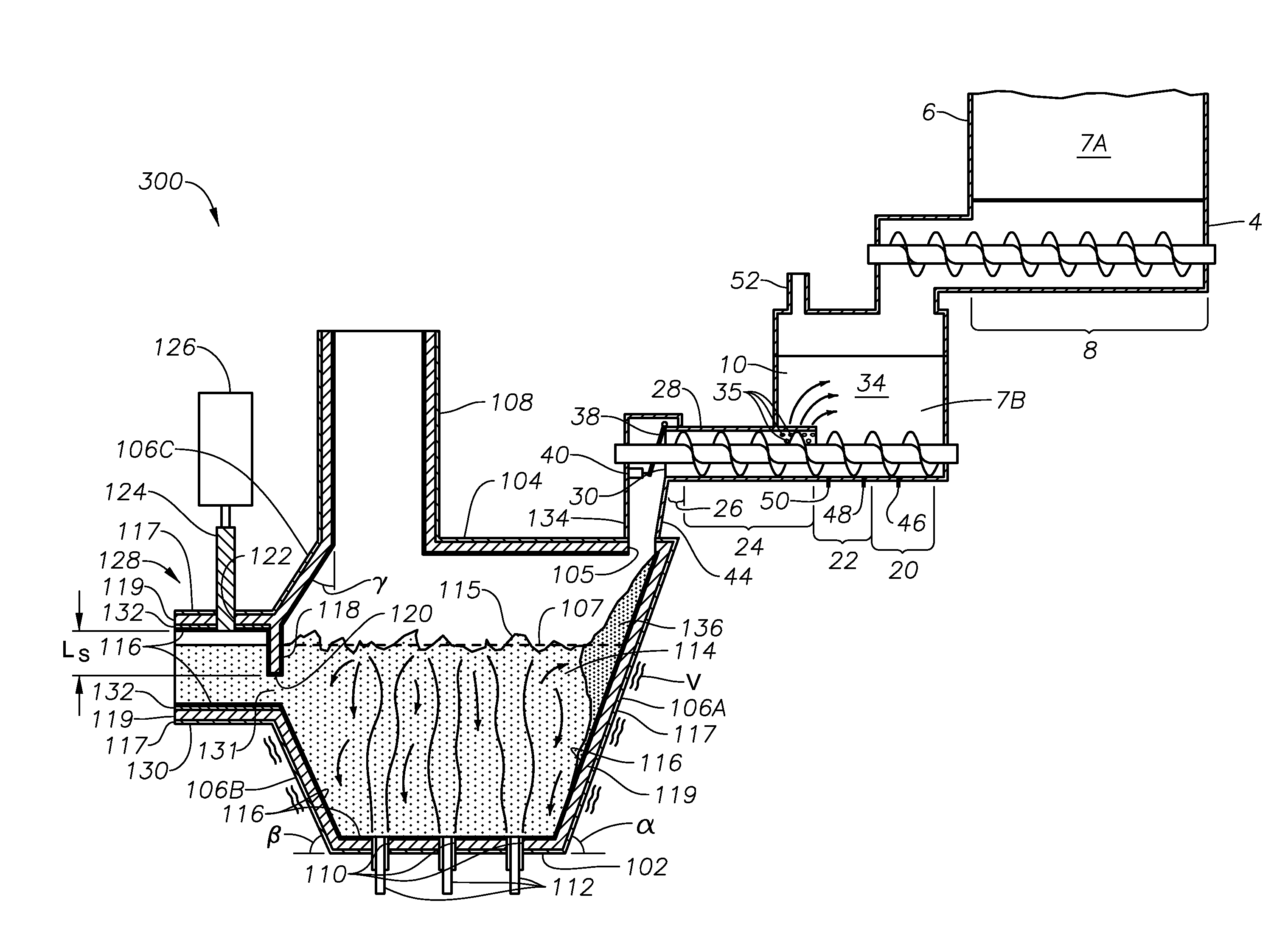
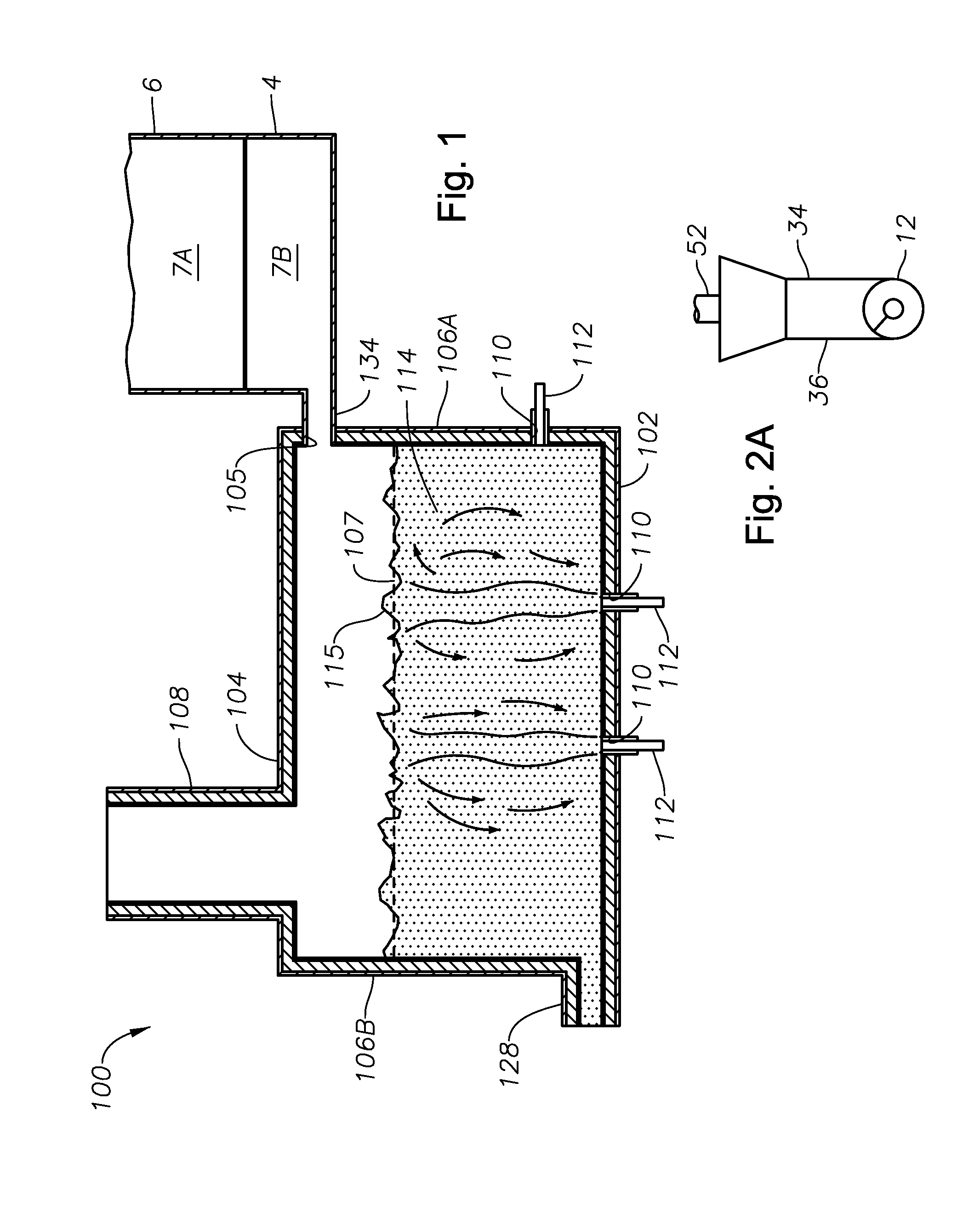
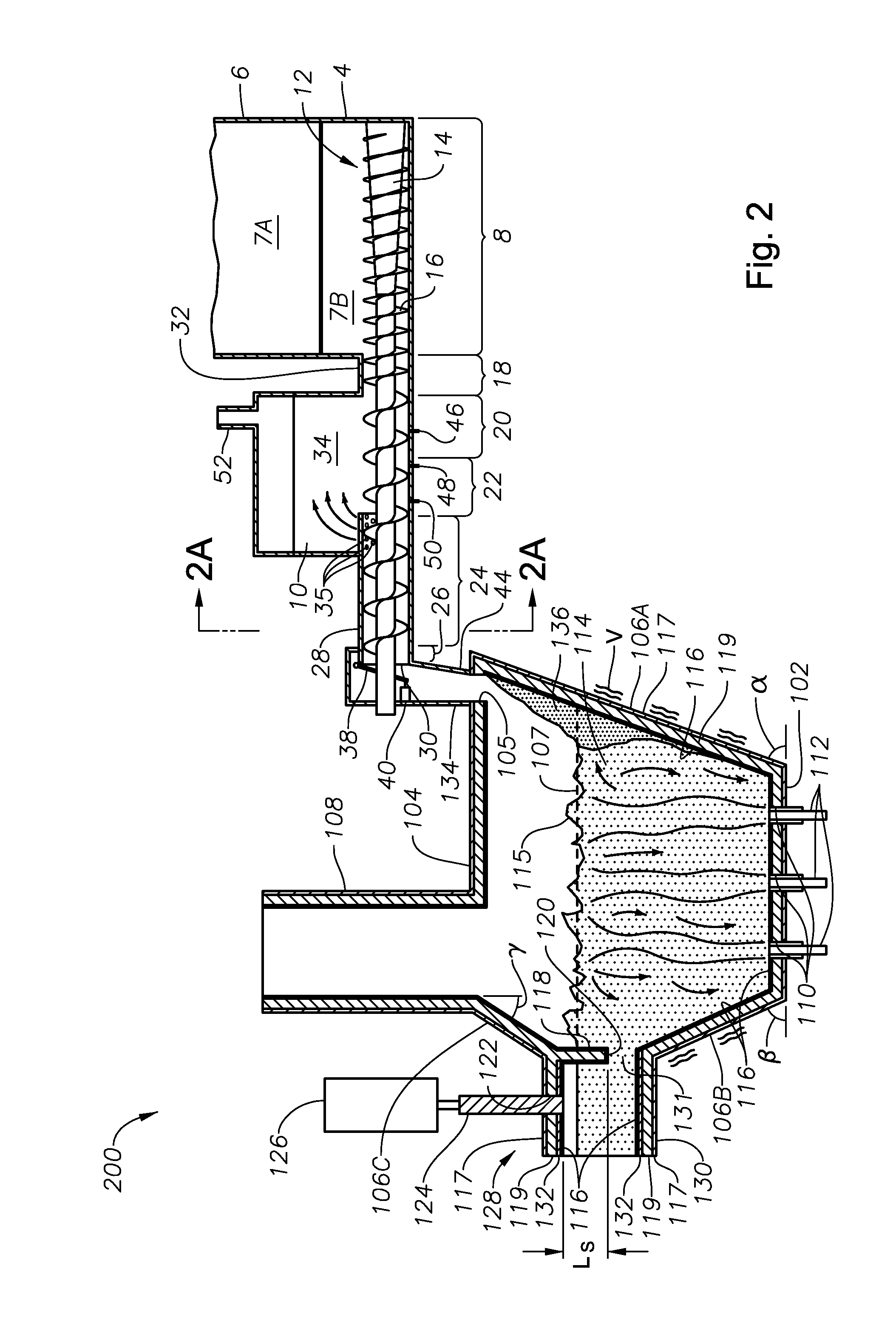
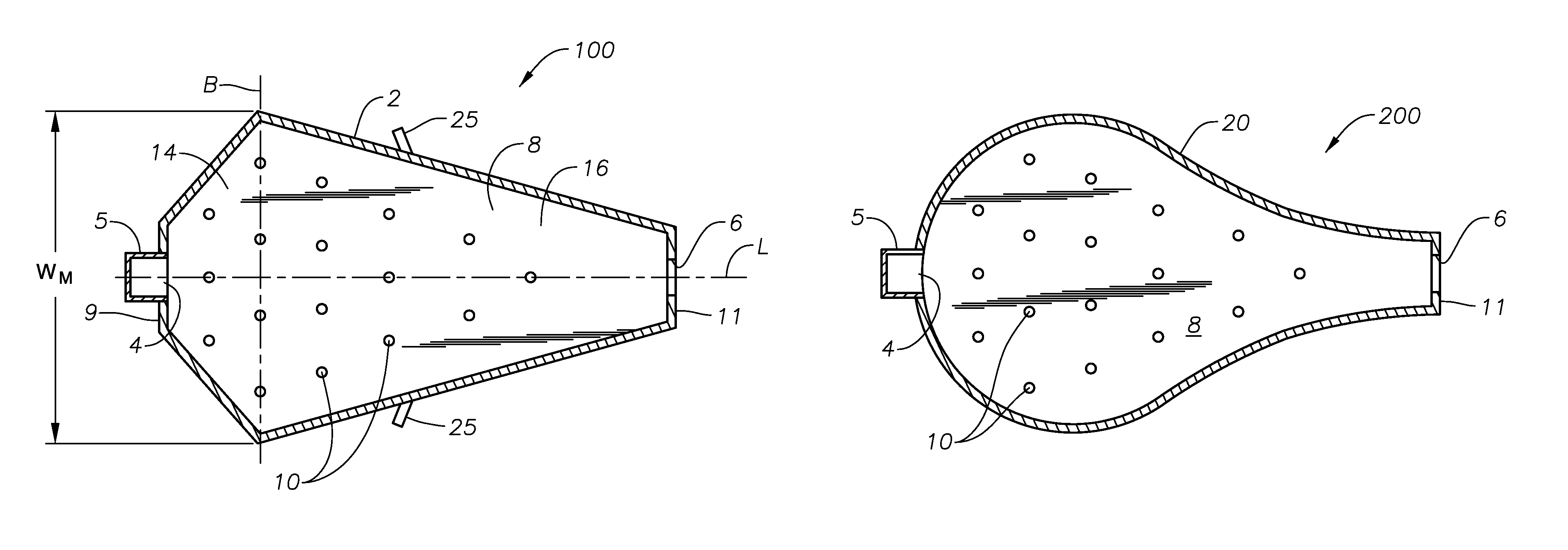
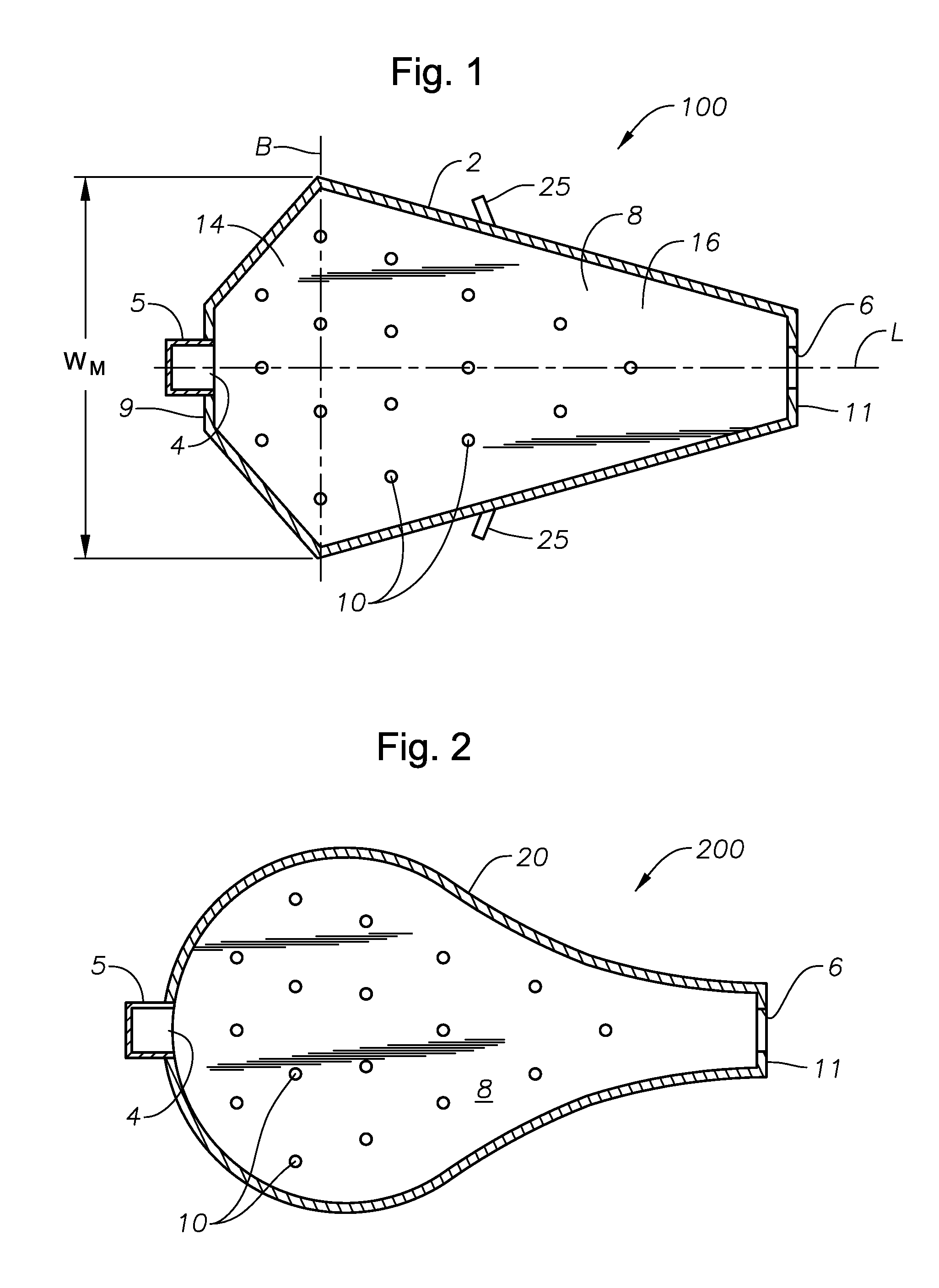
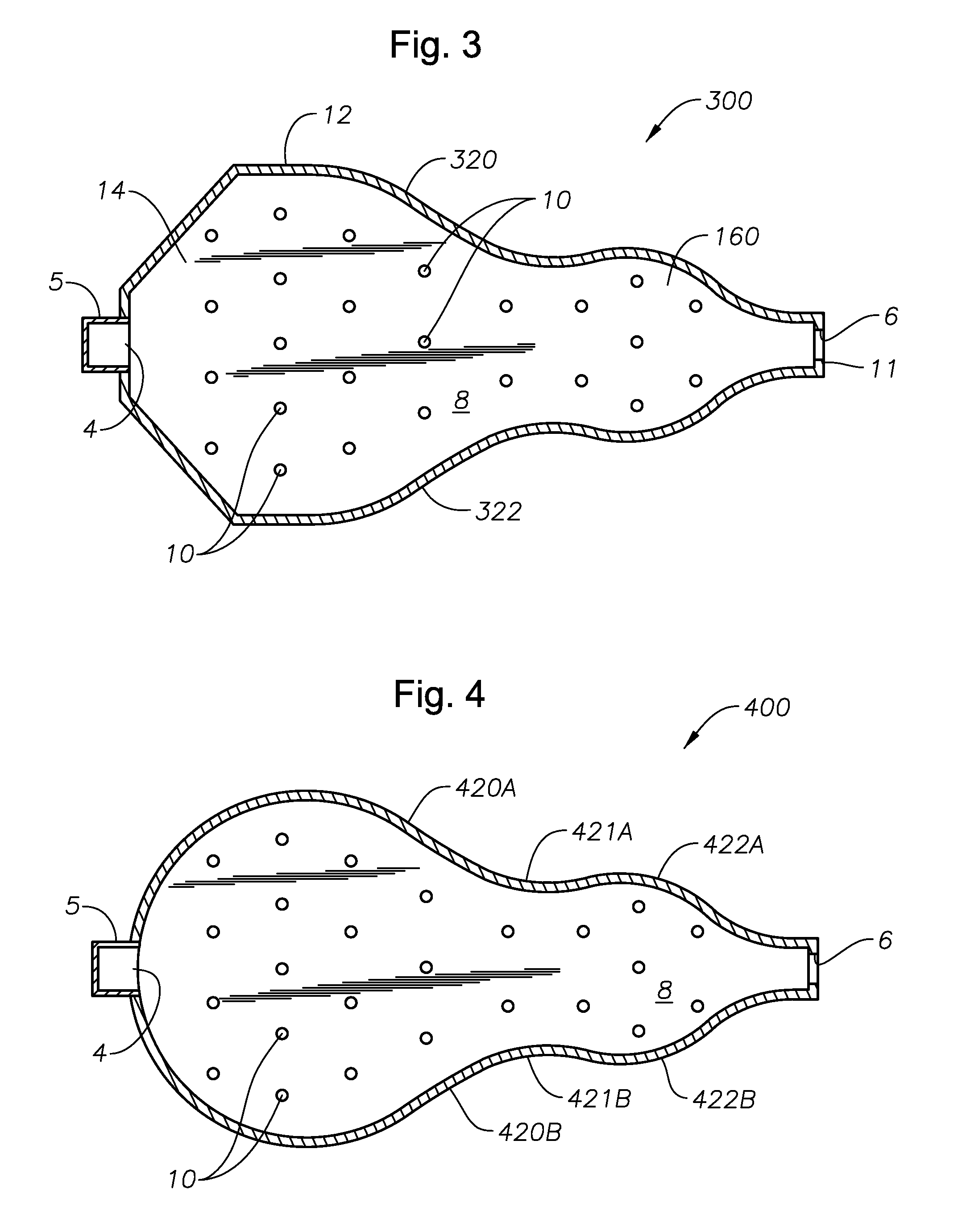
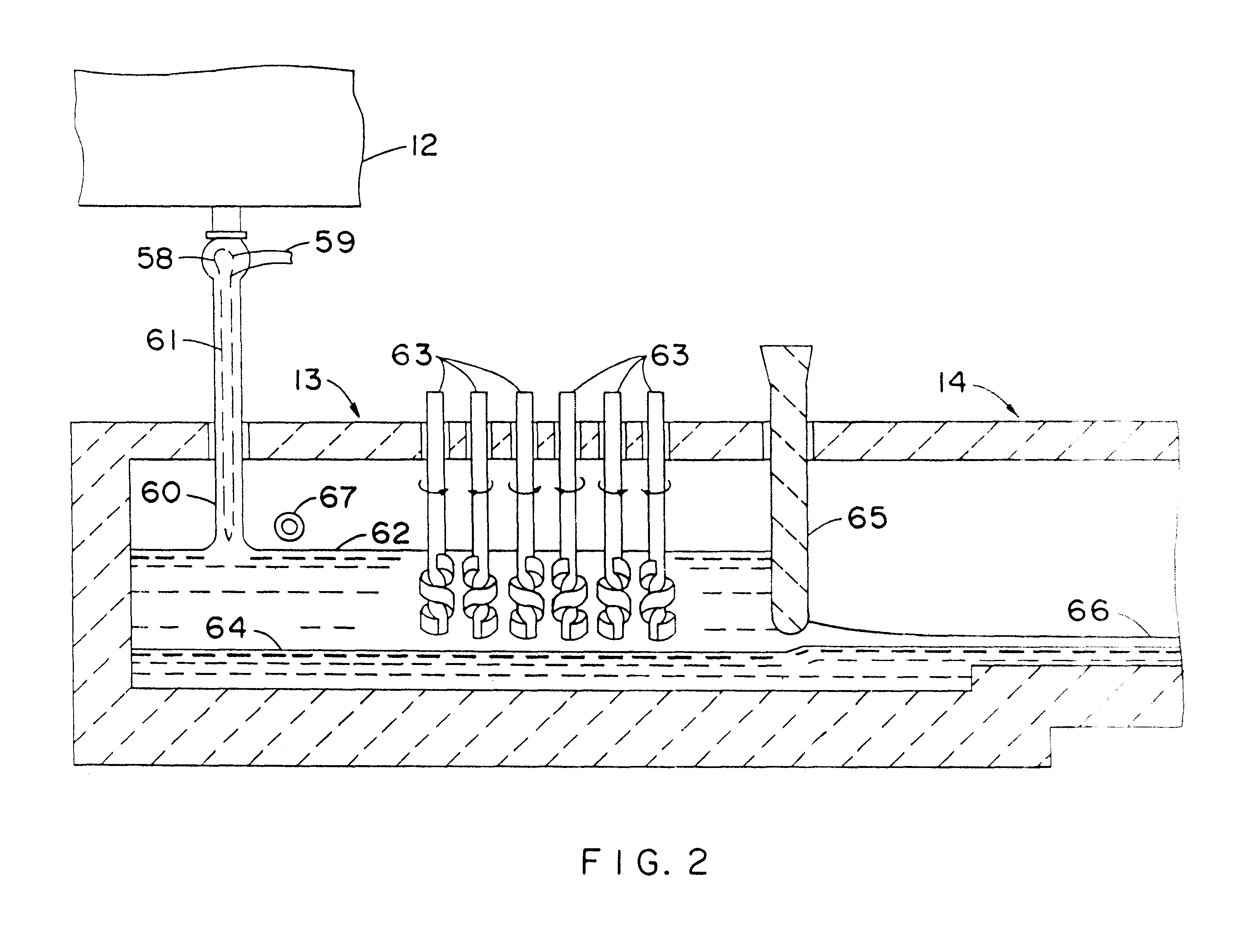
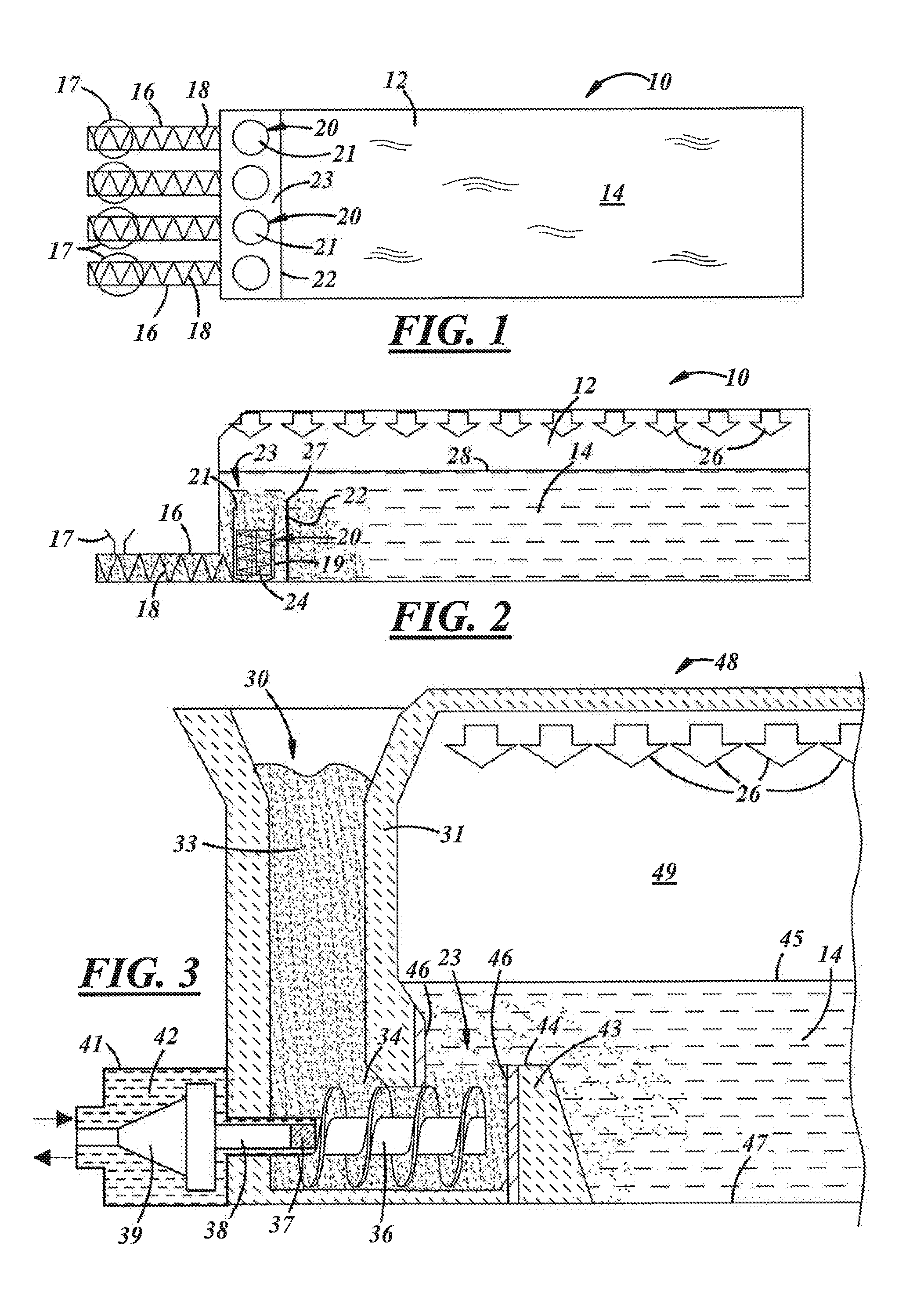
ActiveUS20110308280A1Reduce dead flow (stagnant) regionSmall sizePulsating combustionTank furnacesCombustorDirect combustion
A melter apparatus includes a floor, a ceiling, and a substantially vertical wall connecting the floor and ceiling at a perimeter of the floor and ceiling, a melting zone being defined by the floor, ceiling and wall, the melting zone having a feed inlet and a molten glass outlet positioned at opposing ends of the melting zone. The melting zone includes an expanding zone beginning at the inlet and extending to an intermediate location relative to the opposing ends, and a narrowing zone extending from the intermediate location to the outlet. One or more burners, at least some of which are positioned to direct combustion products into the melting zone under a level of molten glass in the zone, are also provided.
Owner:MANVILLE JOHNS
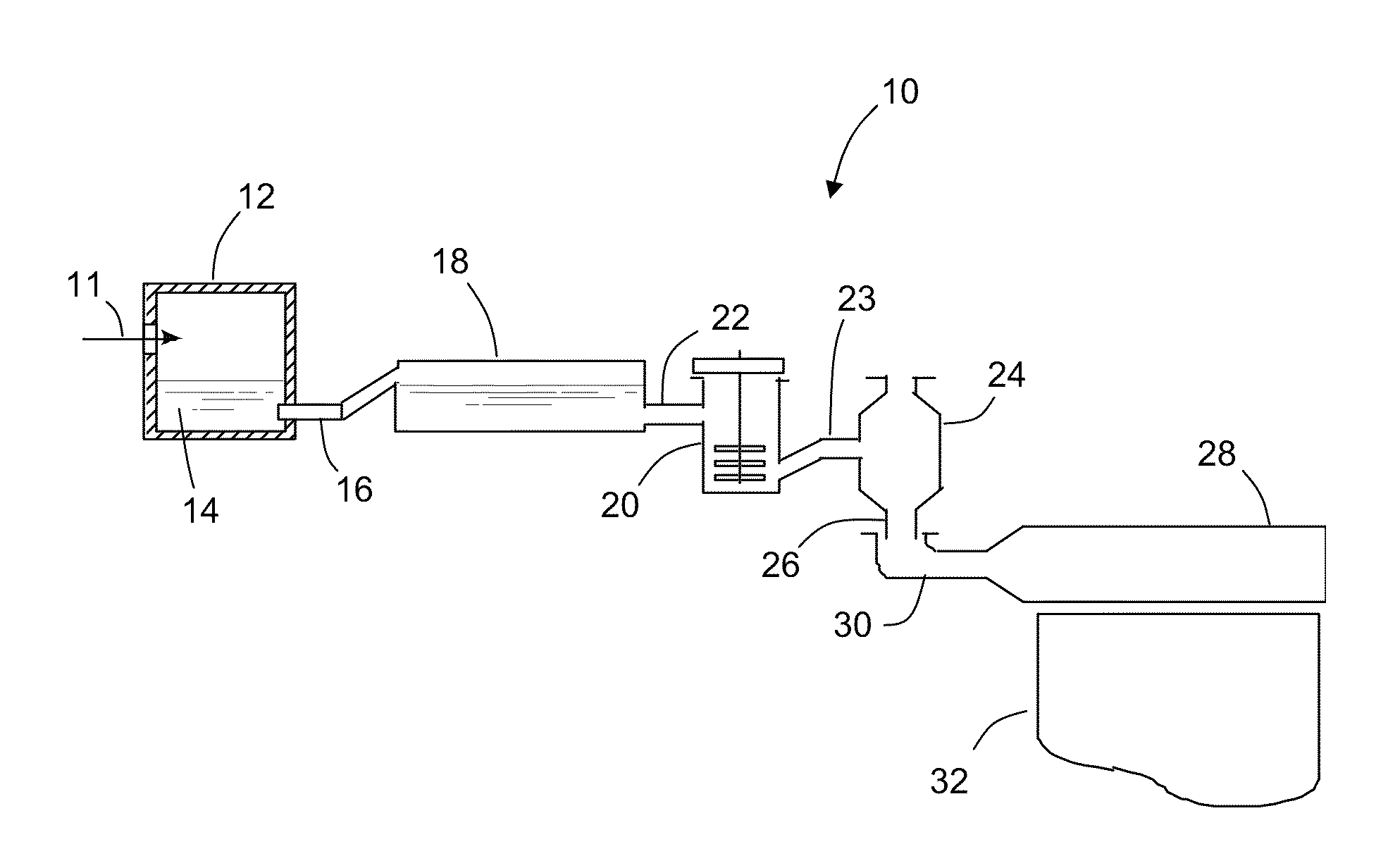
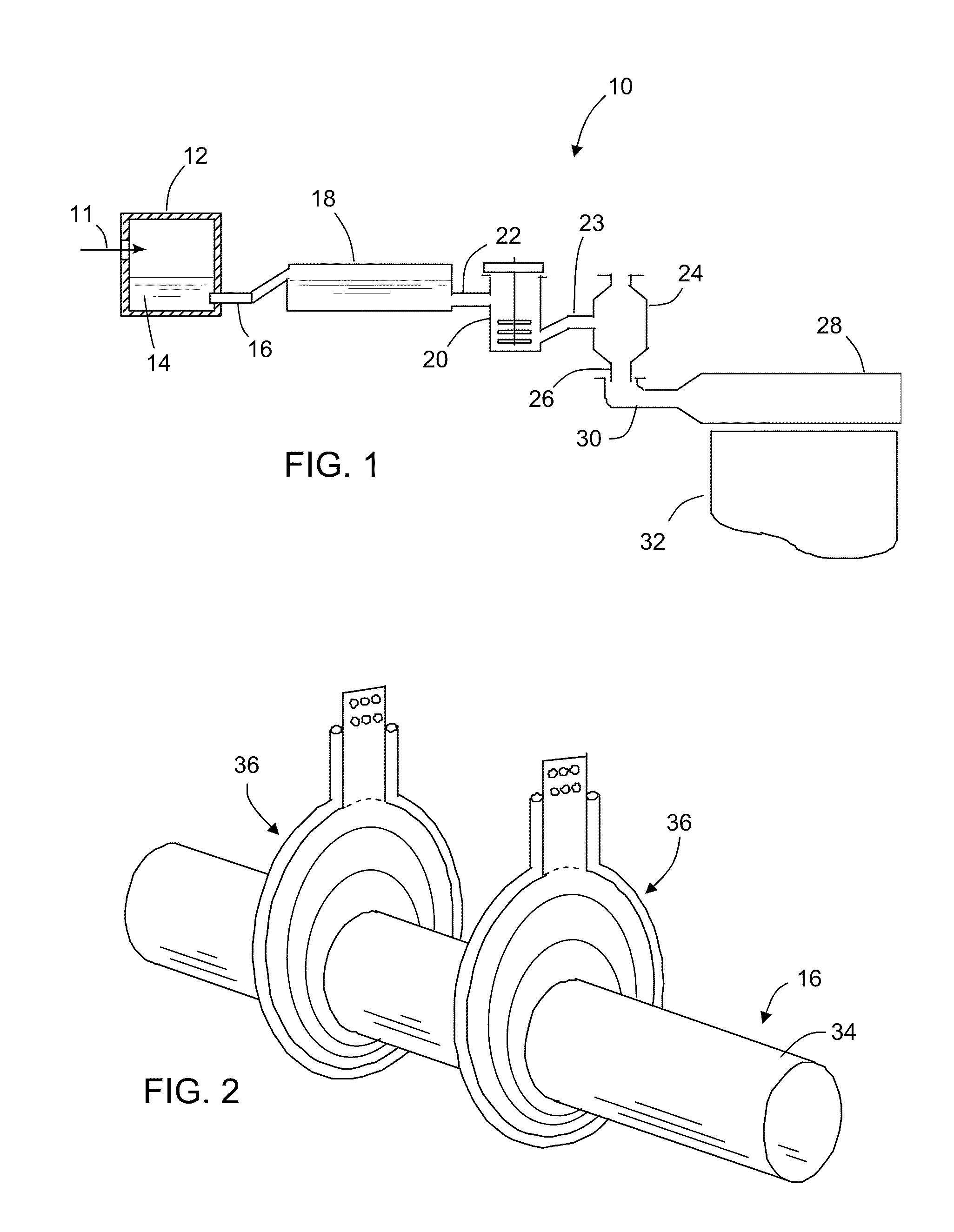
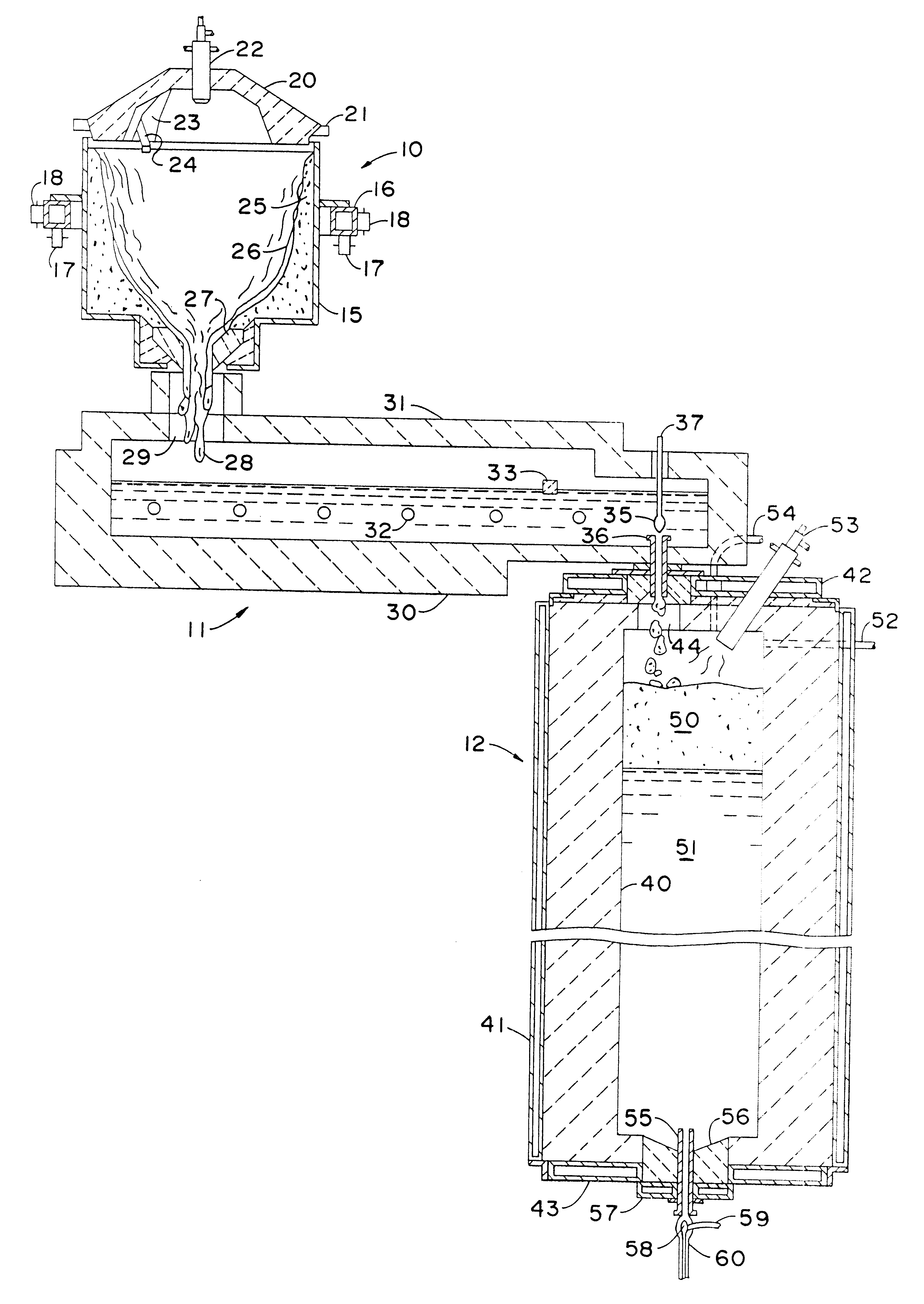
Method of forming a glass melt
ActiveUS7454925B2Promote vigorous boilingReduce partial pressureCharging furnaceGlass furnace apparatusMolten glassExcessive Cooling
A method of forming a glass melt including heating a glass feed material in a first melting furnace to form a glass melt, flowing the glass melt into a second melting furnace through a refractory metal connecting tube, and further heating the glass melt in the second melting furnace. The refractory metal connecting tube is heated to prevent the molten glass from excessive cooling, and to ensure that the glass melt entering the second melting furnace is equal to or greater than the temperature of the glass melt in the second melting furnace. An apparatus for performing the method is also disclosed.
Owner:CORNING INC
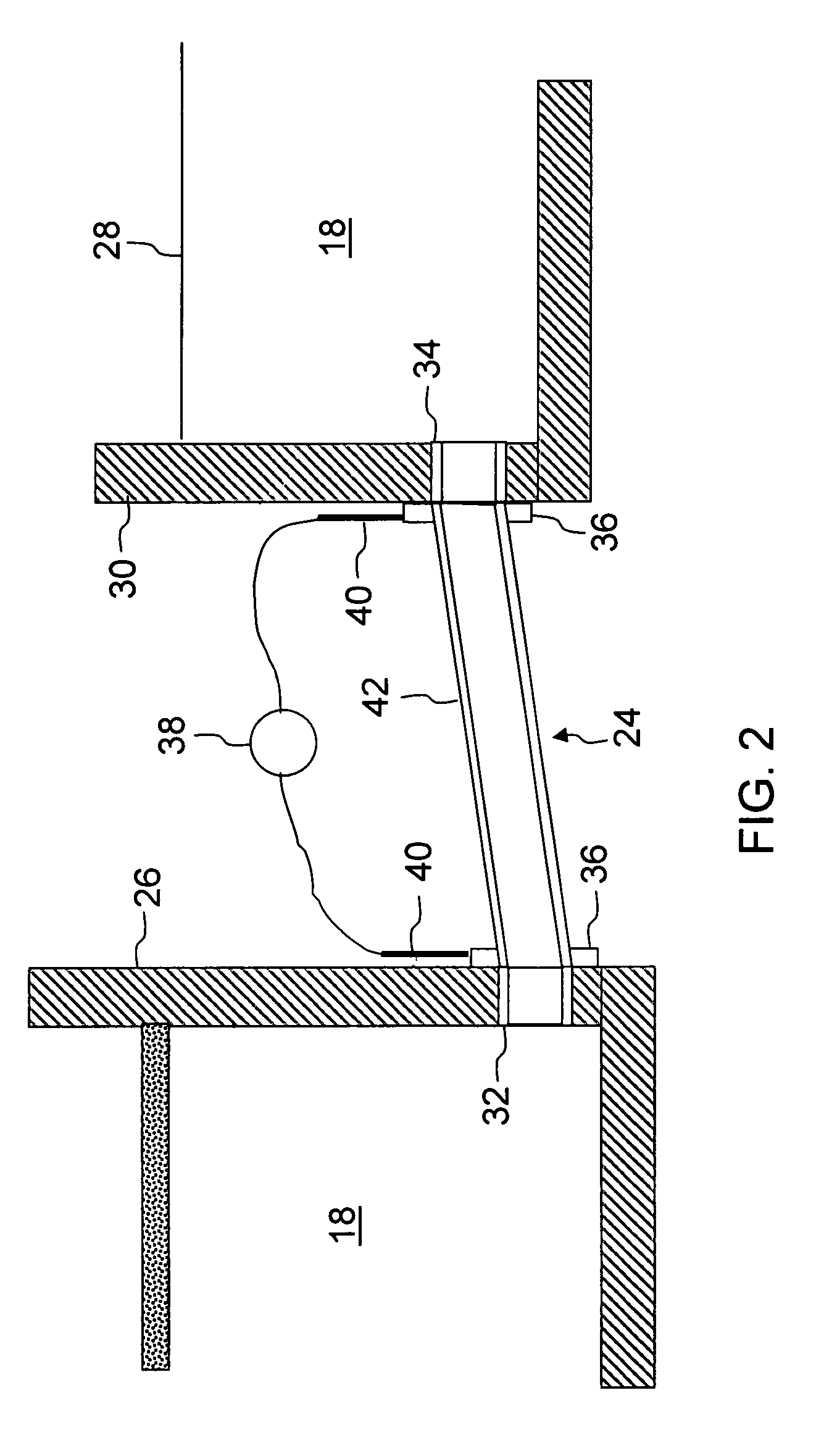
Molten glass delivery and refining system
Methods and apparatus for refining and delivering a supply of molten glass include melting a supply of glass in a melter and discharging a stream of molten glass. A refining section is provided to refine the molten glass discharged by the melter and to deliver the molten glass downstream to a glass forming apparatus. The refining section is mounted for movement into and out of contact with the stream of molten glass to connect and disconnect the glass forming apparatus with the stream of molten glass.
Owner:OWENS CORNING INTELLECTUAL CAPITAL LLC
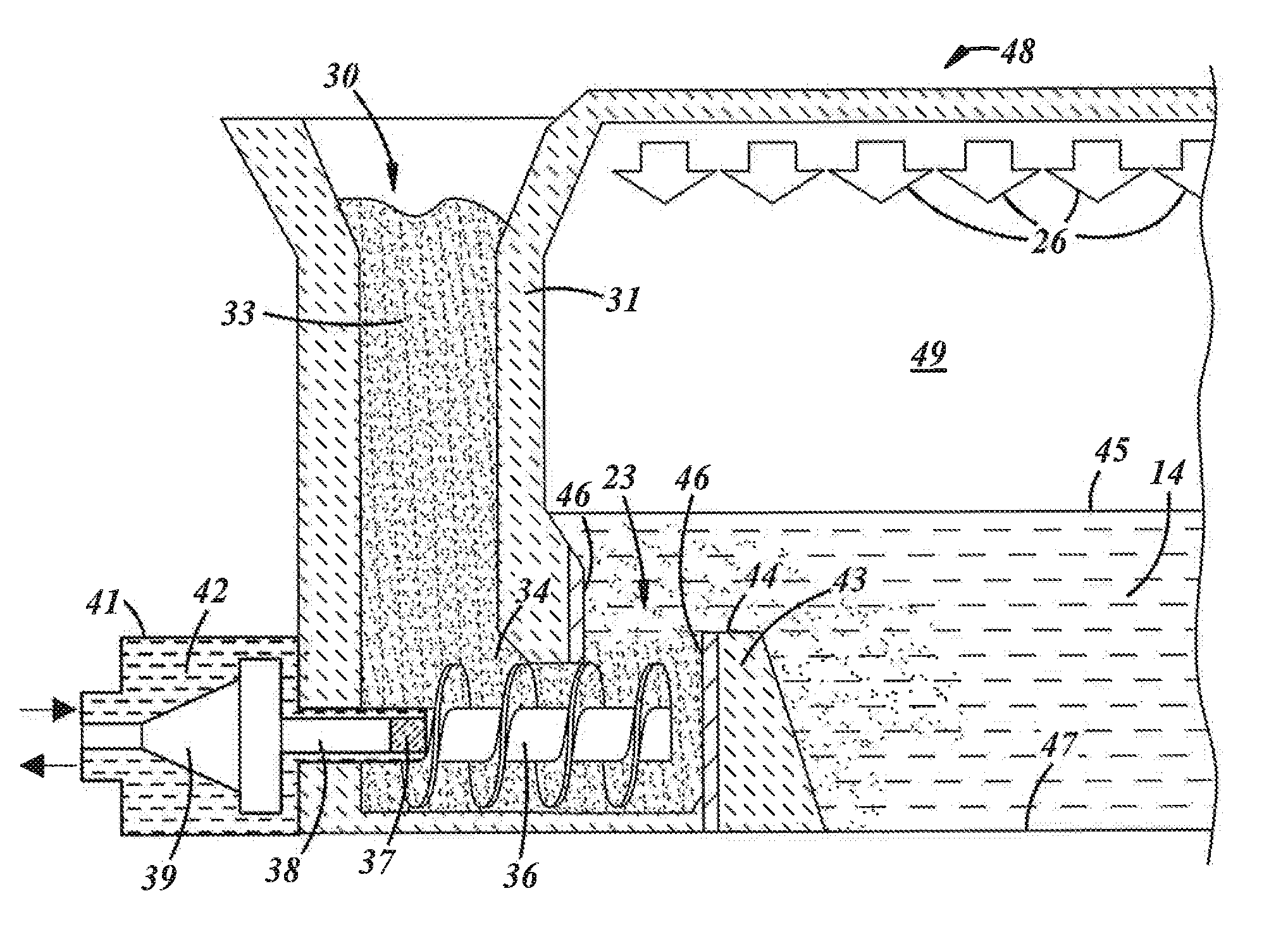
Submerged combustion melter comprising a melt exit structure designed to minimize impact of mechanical energy, and methods of making molten glass
A melter apparatus includes a floor, a ceiling, and a wall connecting the floor and ceiling at a perimeter of the floor and ceiling, a melting zone being defined by the floor, ceiling and wall, the melting zone having a feed inlet and a molten glass outlet positioned at opposing ends of the melting zone. Melter apparatus include an exit end having a melter exit structure for discharging turbulent molten glass formed by one or more submerged combustion burners, the melter exit structure fluidly and mechanically connecting the melter vessel to a molten glass conditioning channel. The melter exit structure includes a fluid-cooled transition channel configured to form a frozen glass layer or highly viscous glass layer, or combination thereof, on inner surfaces of the fluid-cooled transition channel and thus protect the melter exit structure from mechanical energy imparted from the melter vessel to the melter exit structure.
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE CORP
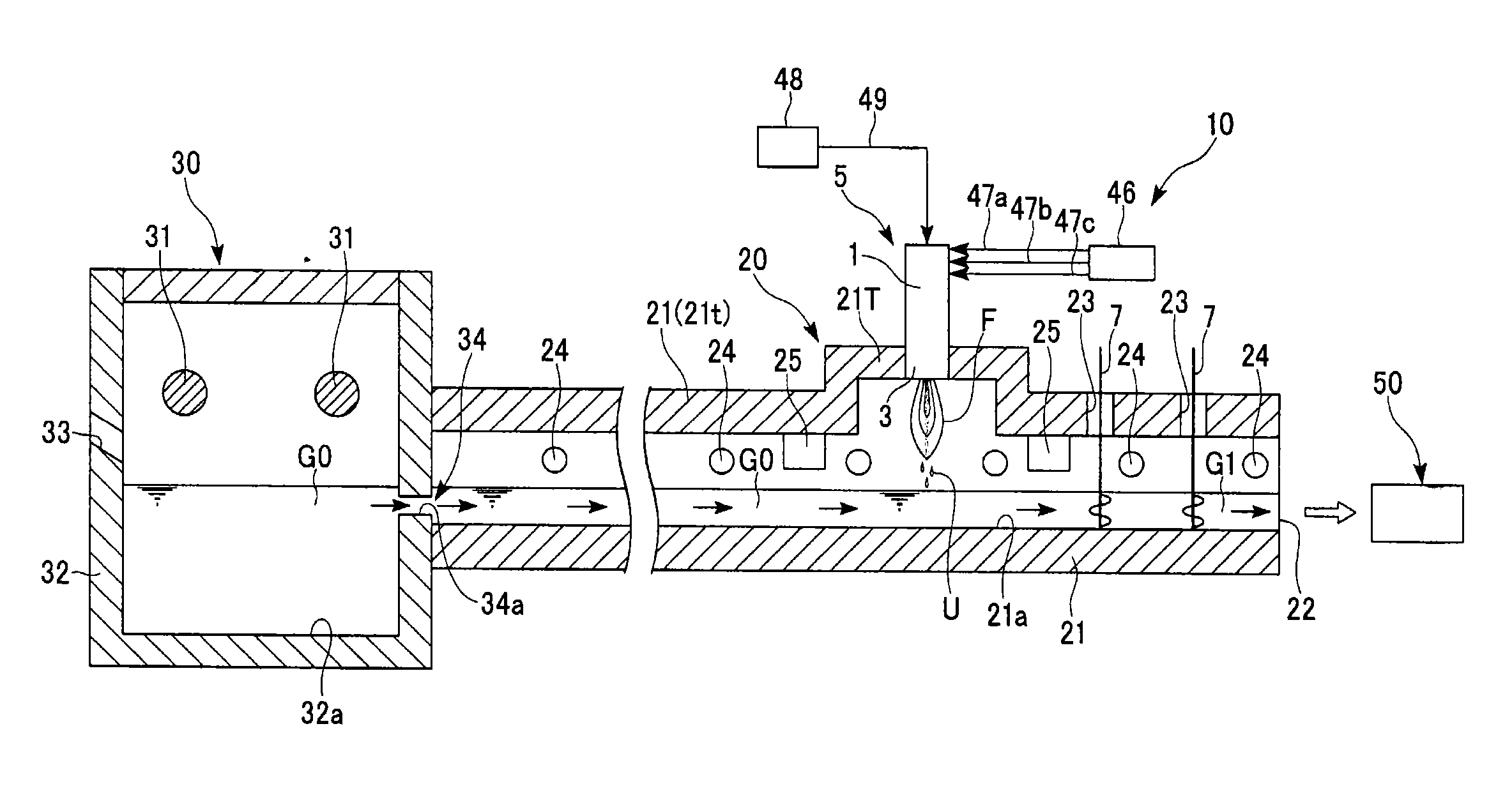
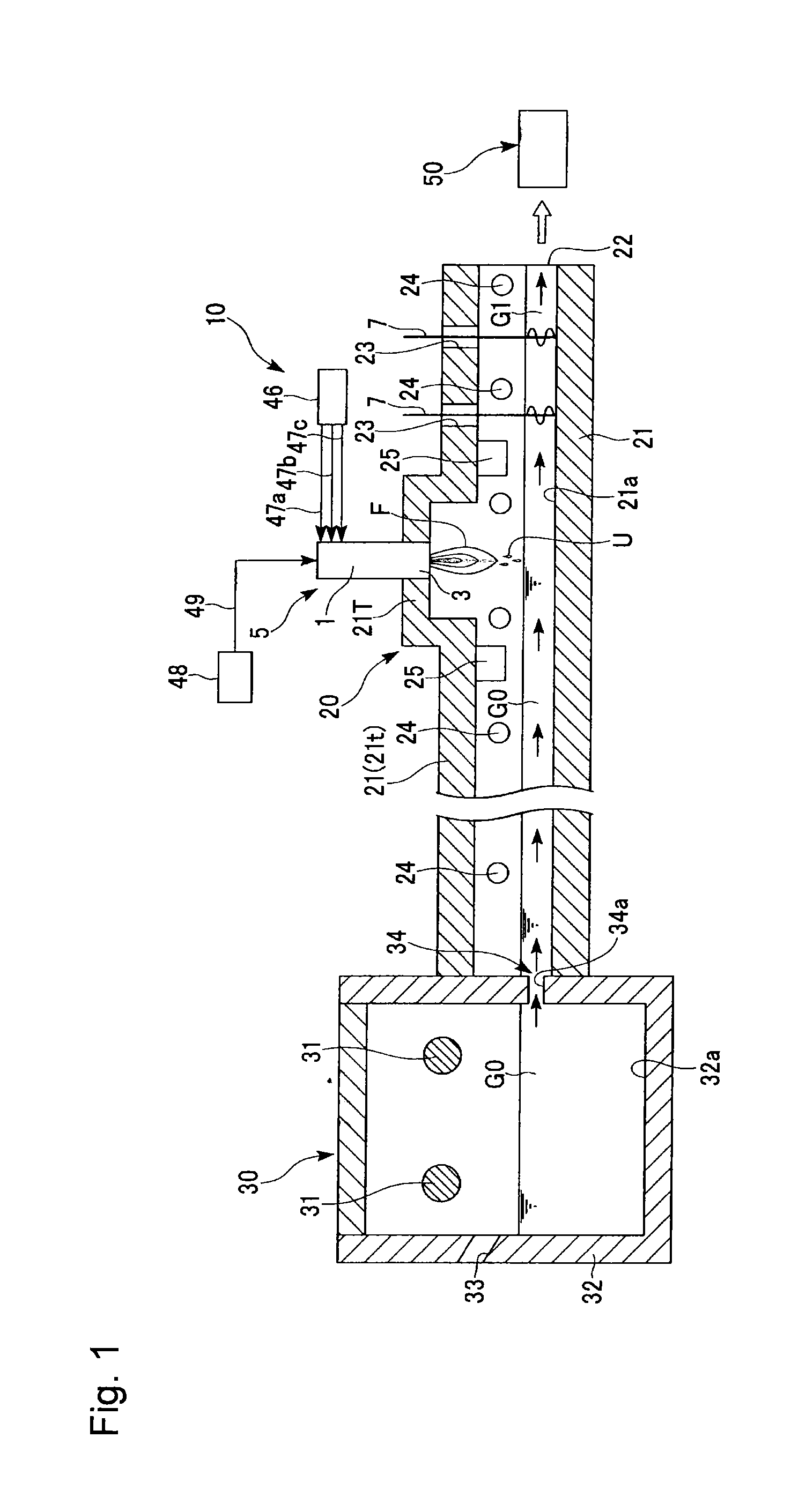
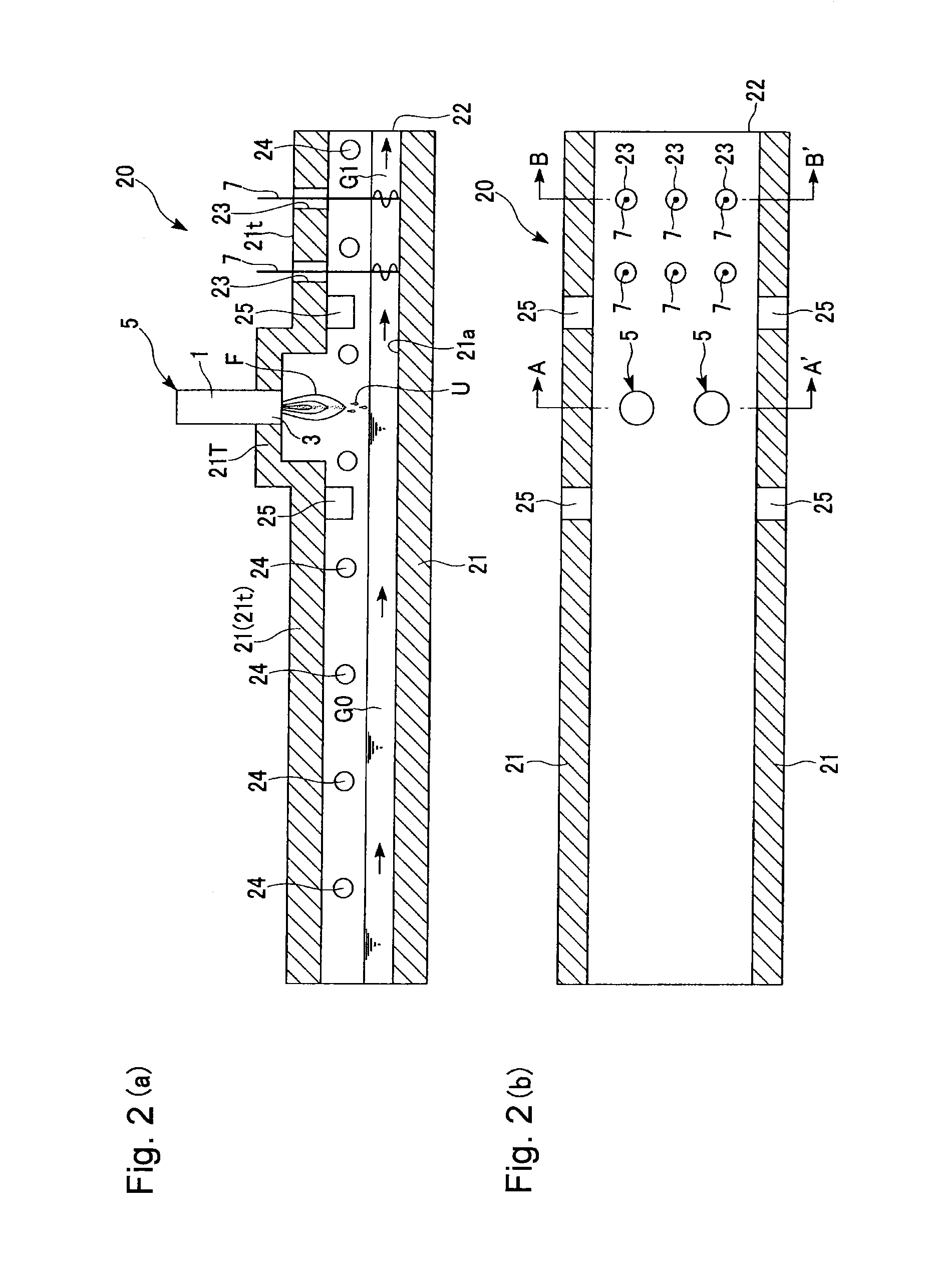
Methods of using a submerged combustion melter to produce glass products
A method comprises flowing an oxidant and a fuel into a submerged combustion burner in a glass tank furnace, the glass tank furnace receiving a feed of glass forming material and producing molten glass, the burner and furnace comprising a melting system. The melting system has a variable system vibration and / or oscillation due to the nature of submerged combustion. One method includes predicting a value of at least one property, such as viscosity, of the molten glass using the variable system vibration and / or oscillation.
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE CORP
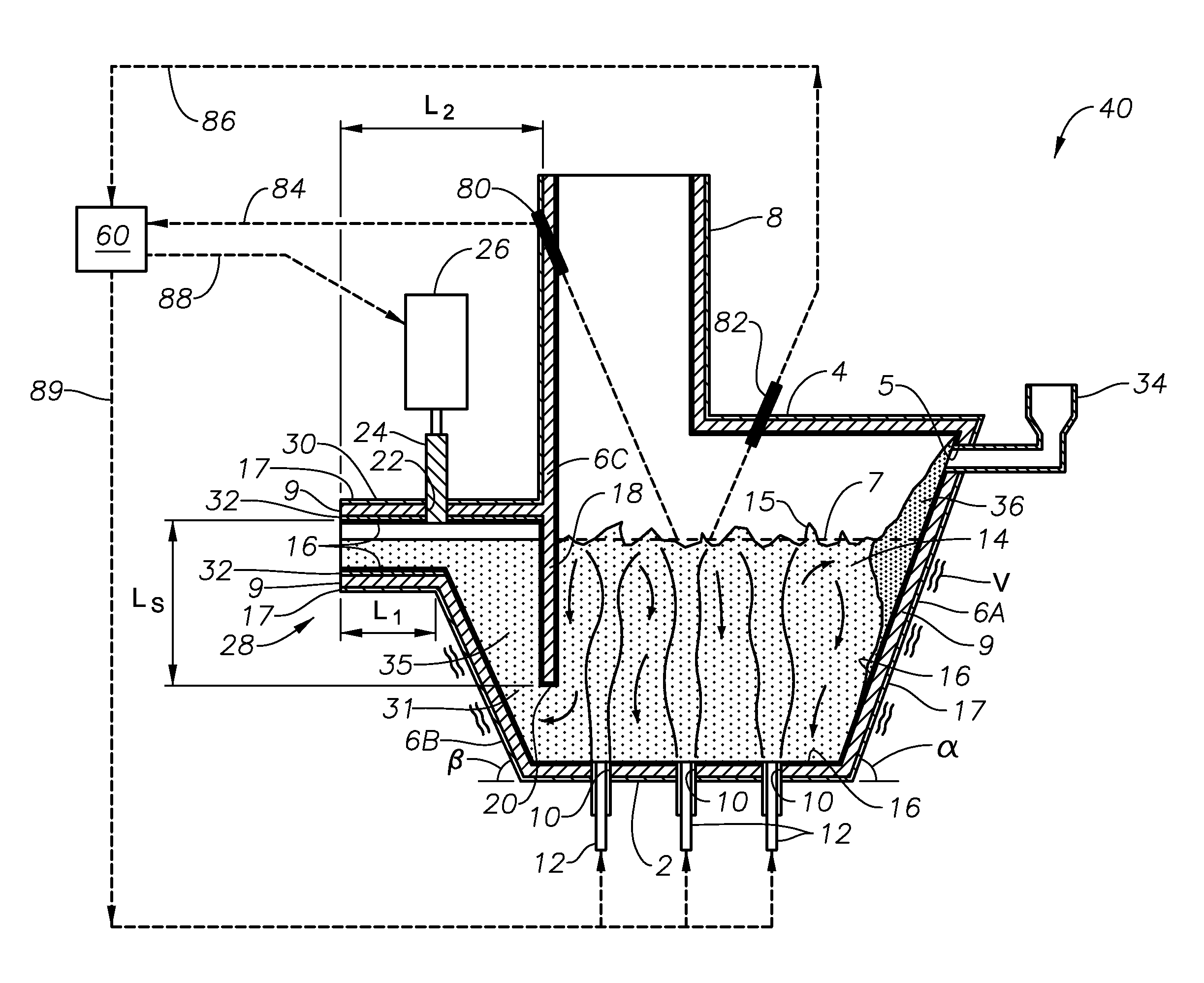
Submerged combustion melting processes for producing glass and similar materials, and systems for carrying out such processes
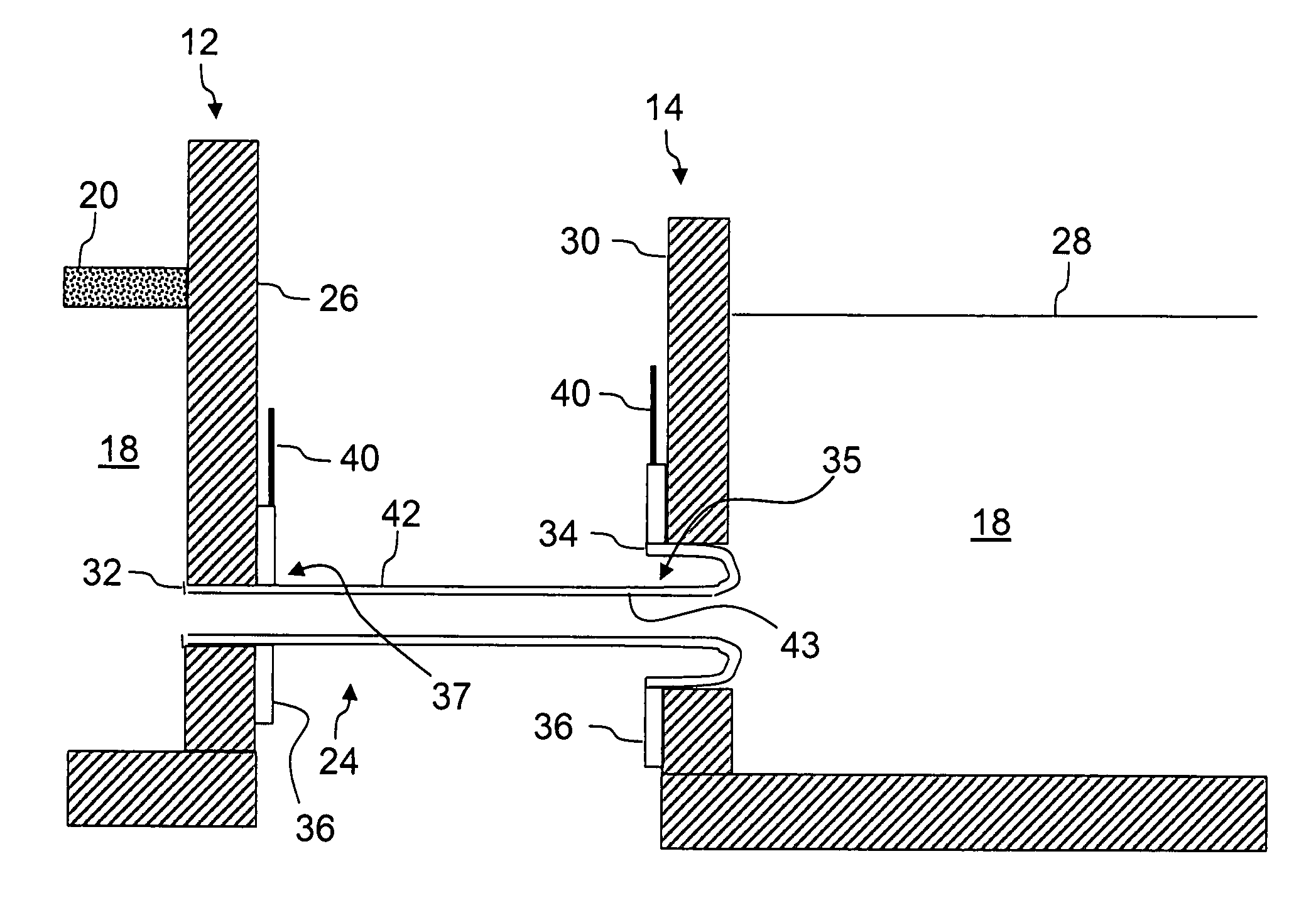
Processes of controlling submerged combustion melters, and systems for carrying out the methods. One process includes feeding vitrifiable material into a melter vessel, the melter vessel including a fluid-cooled refractory panel in its floor, ceiling, and / or sidewall, and heating the vitrifiable material with a burner directing combustion products into the melting zone under a level of the molten material in the zone. Burners impart turbulence to the molten material in the melting zone. The fluid-cooled refractory panel is cooled, forming a modified panel having a frozen or highly viscous material layer on a surface of the panel facing the molten material, and a sensor senses temperature of the modified panel using a protected thermocouple positioned in the modified panel shielded from direct contact with turbulent molten material. Processes include controlling the melter using the temperature of the modified panel. Other processes and systems are presented.
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE CORP
Submerged combustion melters having an extended treatment zone and methods of producing molten glass
A submerged combustion melter includes a floor, a roof, and a sidewall structure connecting the floor and roof defining an internal space. A first portion of the internal space defines a melting zone, and a second portion defines a fining zone immediately downstream of the melting zone. One or more combustion burners in either the floor, roof, the sidewall structure, or any combination of these, are configured to emit the combustion gases from a position under a level of, and positioned to transfer heat to and produce, a turbulent molten mass of glass containing bubbles in the melting zone. The fining zone is devoid of combustion burners or other apparatus or components that would increase turbulence above that in the melting zone. The melter may include a treating zone that stabilizes or destabilizes bubbles and / or foam. Processes of using the melters are a feature of the disclosure.
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE CORP
Submerged combustion melting processes for producing glass and similar materials, and systems for carrying out such processes
Processes of controlling submerged combustion melters, and systems for carrying out the methods. One process includes feeding vitrifiable material into a melter vessel, the melter vessel including a fluid-cooled refractory panel in its floor, ceiling, and / or sidewall, and heating the vitrifiable material with a burner directing combustion products into the melting zone under a level of the molten material in the zone. Burners impart turbulence to the molten material in the melting zone. The fluid-cooled refractory panel is cooled, forming a modified panel having a frozen or highly viscous material layer on a surface of the panel facing the molten material, and a sensor senses temperature of the modified panel using a protected thermocouple positioned in the modified panel shielded from direct contact with turbulent molten material. Processes include controlling the melter using the temperature of the modified panel. Other processes and systems are presented.
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE CORP
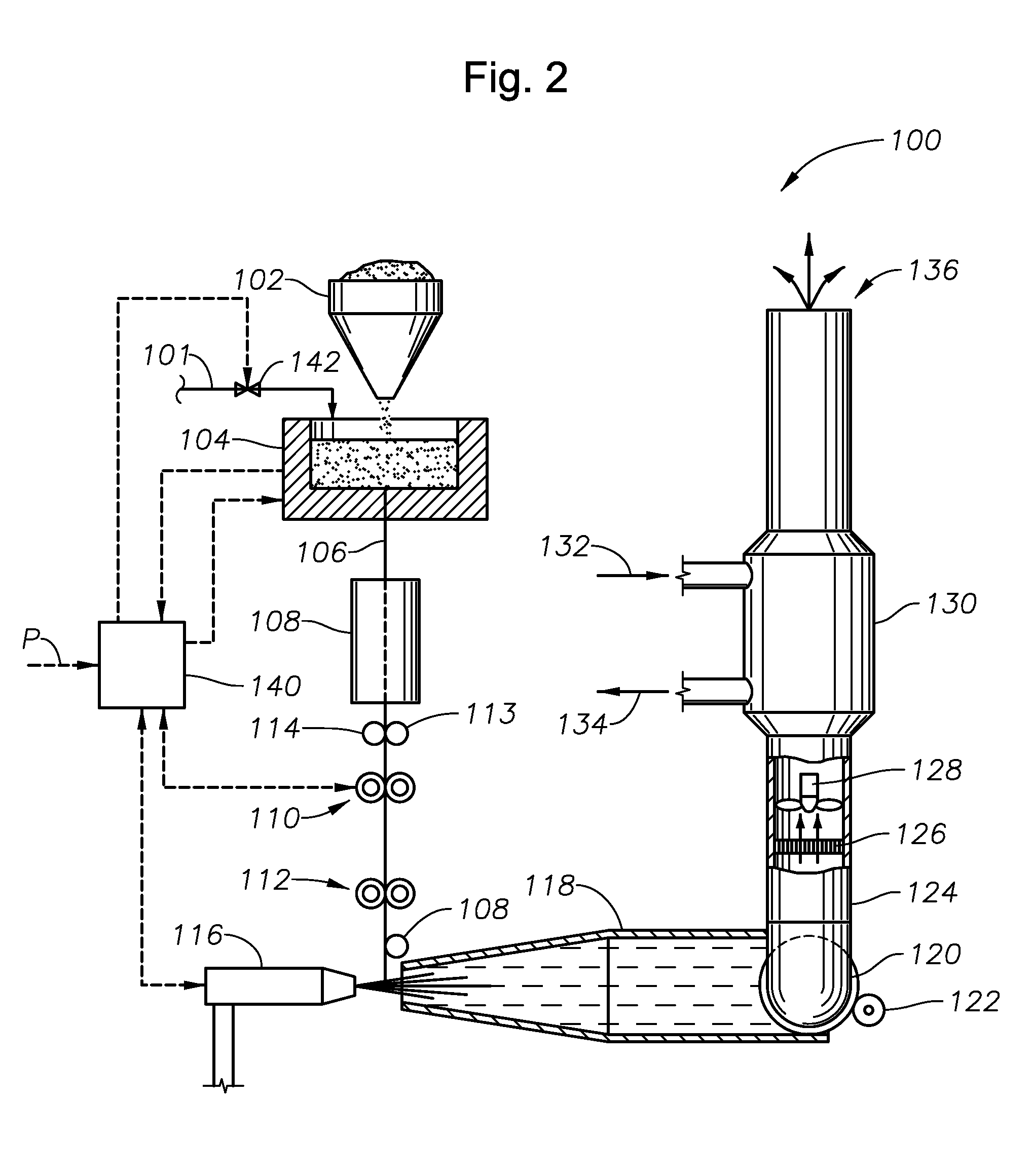
Processes for producing molten glasses from glass batches using turbulent submerged combustion melting, and systems for carrying out such processes
ActiveUS20140007622A1Reduce and eliminate batch lossCharging furnaceTank furnacesParticulatesCombustor
Processes and systems for producing molten glass using submerged combustion melters, including densifying an initial composition comprising vitrifiable particulate solids and interstitial gas to form a densified composition comprising the solids by removing a portion of the interstitial gas from the composition. The initial composition is passed from an initial environment having a first pressure through a second environment having a second pressure higher than the first pressure to form a composition being densified. Any fugitive particulate solids escaping from the composition being densified are captured and recombined with the composition being densified to form the densified composition. The densified composition is fed into a feed inlet of a turbulent melting zone of a melter vessel and converted into turbulent molten material using at least one submerged combustion burner in the turbulent melting zone.
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE CORP
Panel-cooled submerged combustion melter geometry and methods of making molten glass
ActiveUS8769992B2Small sizeAllows more flexibility in the shape of the melterPulsating combustionGlass furnace apparatusThermodynamicsCombustor
A melter apparatus includes a floor, a ceiling, and a substantially vertical wall connecting the floor and ceiling at a perimeter of the floor and ceiling, a melting zone being defined by the floor, ceiling and wall, the melting zone having a feed inlet and a molten glass outlet positioned at opposing ends of the melting zone. The melting zone includes an expanding zone beginning at the inlet and extending to an intermediate location relative to the opposing ends, and a narrowing zone extending from the intermediate location to the outlet. One or more burners, at least some of which are positioned to direct combustion products into the melting zone under a level of molten glass in the zone, are also provided.
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE CORP
Methods and systems for destabilizing foam in equipment downstream of a submerged combustion melter
Methods and systems for de-stabilizing foam produced in submerged combustion melters. A molten mass of glass and bubbles is flowed into an apparatus downstream of a submerged combustion melter. The downstream apparatus includes a floor, a roof and a wall connecting the floor and roof, but is devoid of submerged combustion burners and other components that would increase turbulence of the molten mass. The molten mass has foam on at least a portion of a top surface of the molten mass. One method includes directly impinging an impinging composition onto at least a portion of the foam in the downstream apparatus. Systems for carrying out the methods are described.
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE CORP
Oxidant injection method
A method of combustion in a furnace comprising a firing zone and an exhaust zone, three oxidants and fuel comprising the steps of: introducing fuel into said firing zone; introducing a first oxidant into the firing zone; introducing a second oxidant into the firing zone; and introducing a third oxidant into the exhaust zone; wherein during said step of introducing a first oxidant, the step of introducing a second oxidant, and the step of introducing a third oxidant occur.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Methods of using a submerged combustion melter to produce glass products
A method comprises flowing an oxidant and a fuel into a submerged combustion burner in a glass tank furnace, the glass tank furnace receiving a feed of glass forming material and producing molten glass, the burner and furnace comprising a melting system. The melting system has a variable system vibration and / or oscillation due to the nature of submerged combustion. One method includes predicting a value of at least one property, such as viscosity, of the molten glass using the variable system vibration and / or oscillation.
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE CORP
Molten glass delivery and refining system
Methods and apparatus for refining and delivering a supply of molten glass include melting a supply of glass in a melter and discharging a stream of molten glass. A refining section is provided to refine the molten glass discharged by the melter and to deliver the molten glass downstream to a glass forming apparatus. The refining section is mounted for movement into and out of contact with the stream of molten glass to connect and disconnect the glass forming apparatus with the stream of molten glass.
Owner:OWENS CORNING INTELLECTUAL CAPITAL LLC
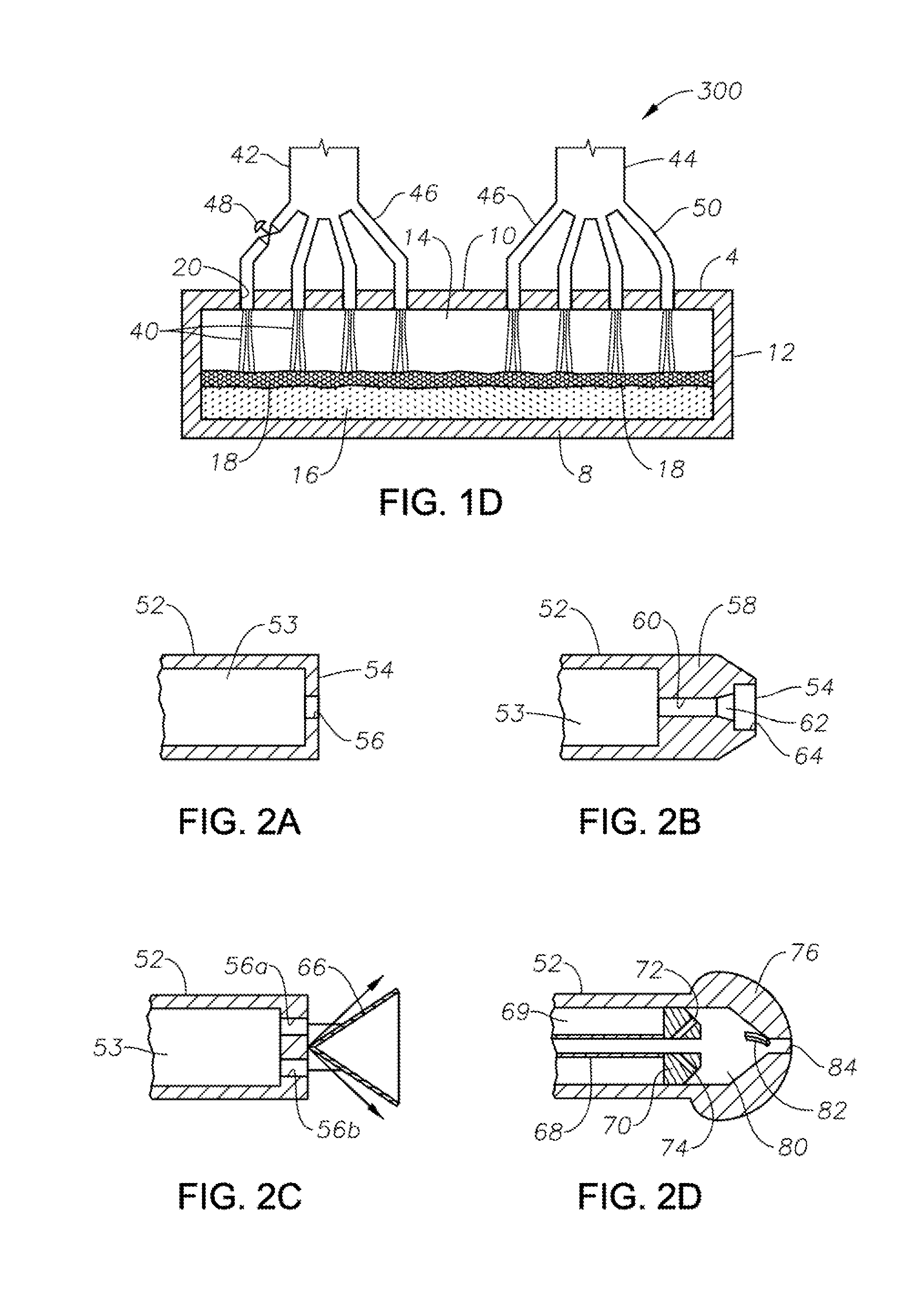
Apparatus for use in direct resistance heating of platinum-containing vessels
InactiveUS20110204039A1Improve uniformityEqually distributedForehearthsTank furnacesPlatinumElectrical resistance and conductance
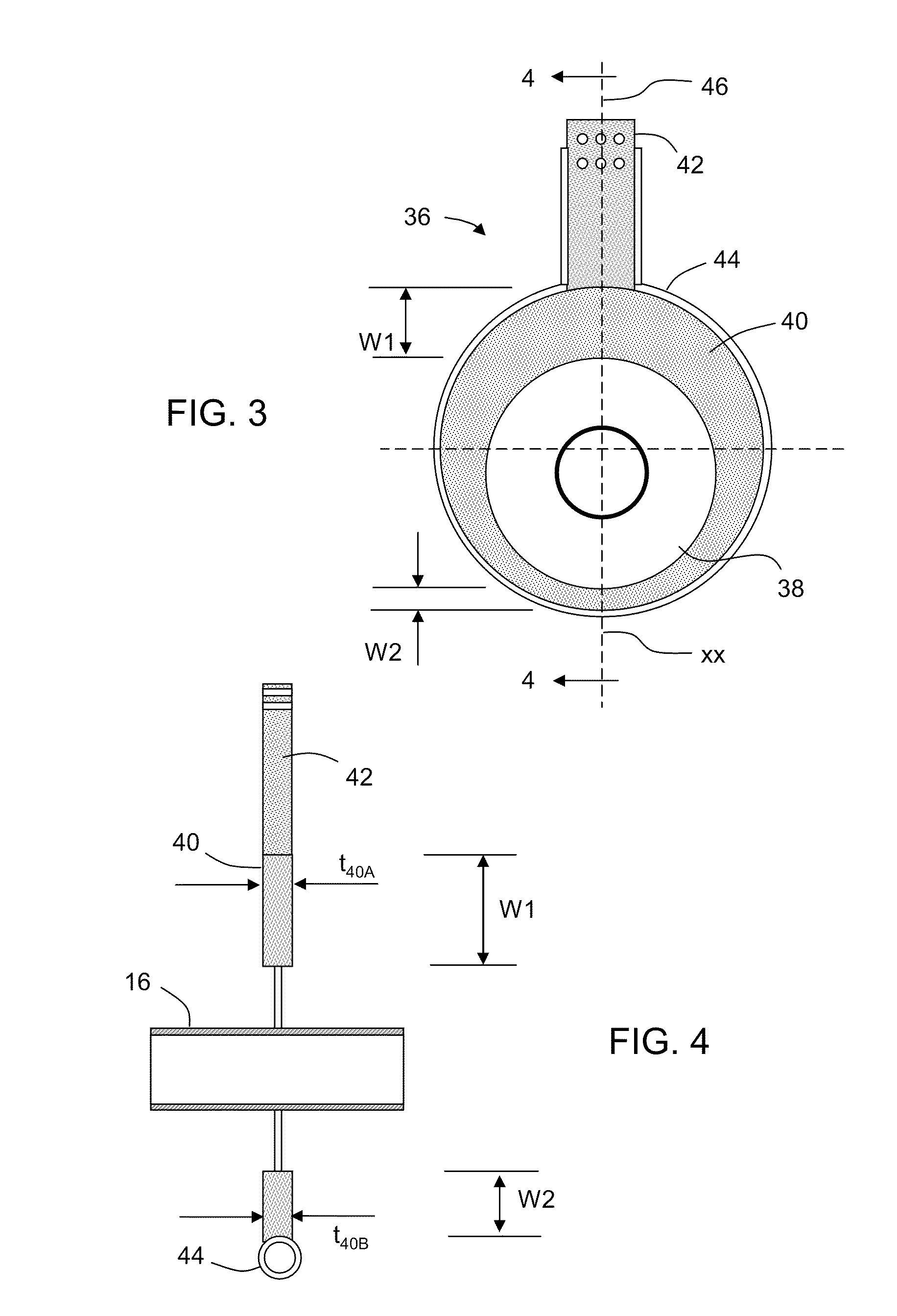
An apparatus for use in direct resistance heating of a molten glass-carrying vessel, such as a finer or connecting pipe, is provided. The apparatus comprises a flange comprises a plurality of electrically-conductive rings that include an inner ring joined to the vessel's exterior wall during use of the flange and an outer ring that receives electric current during use of the flange. The innermost ring comprises a high-temperature resistant metal preferably comprising at least 80% platinum, and the outermost ring preferably comprising at least 99.0% nickel. This combination of materials both increases the reliability of the flange and reduces its cost. Either one or both of the width or thickness of one or both of the inner or outer rings varies as a function of angular position relative to the vessel. The width and / or thickness of the inner and the outer rings with relation to each other produces a uniform current distribution in the flange and the vessel.
Owner:CORNING INC
Energy efficient high-temperature refining
ActiveUS20130279532A1Reduce heat emissionsReduce financial costsPot furnacesElectrical apparatusCrucibleElectric current flow
An energy-efficient device for refining a glass melt to produce a glass and / or a glass ceramic is provided. The device includes a refining crucible defined at least by lateral walls with a metallic lining as a melt contact surface, so that a melt refining volume is defined by a base surface, a top surface and a circumferential surface; at least one heating device that conductively heats the lining by an electric current in the lining, so that the melt is heated through the lining, the heating device and the lining are connected to one another by a feeding device. The feeding device establishes contact with the lining so that an electric current runs from the top surface to the base surface or from the base surface to the top surface, at least in sections of the lining.
Owner:SCHOTT AG
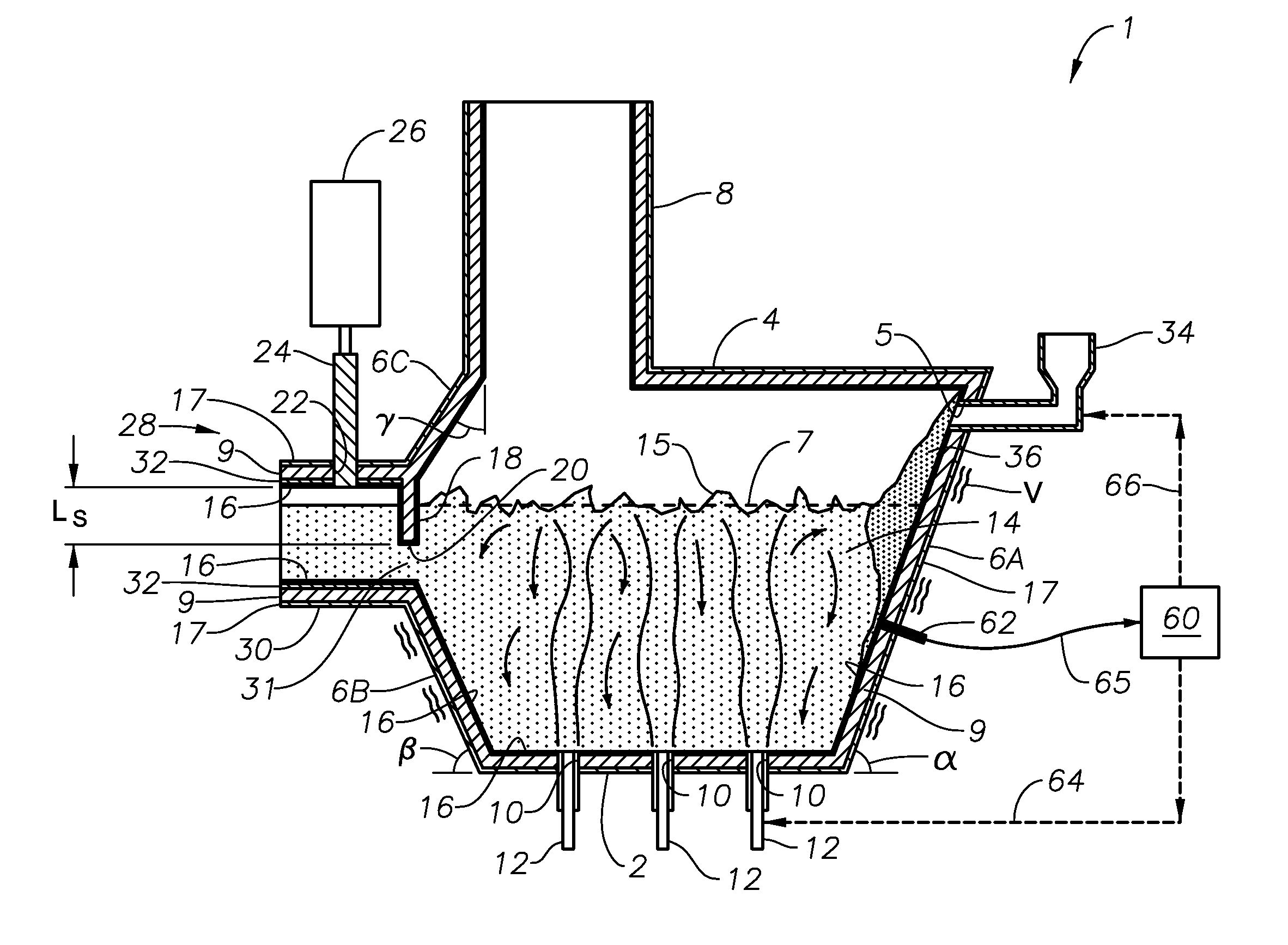
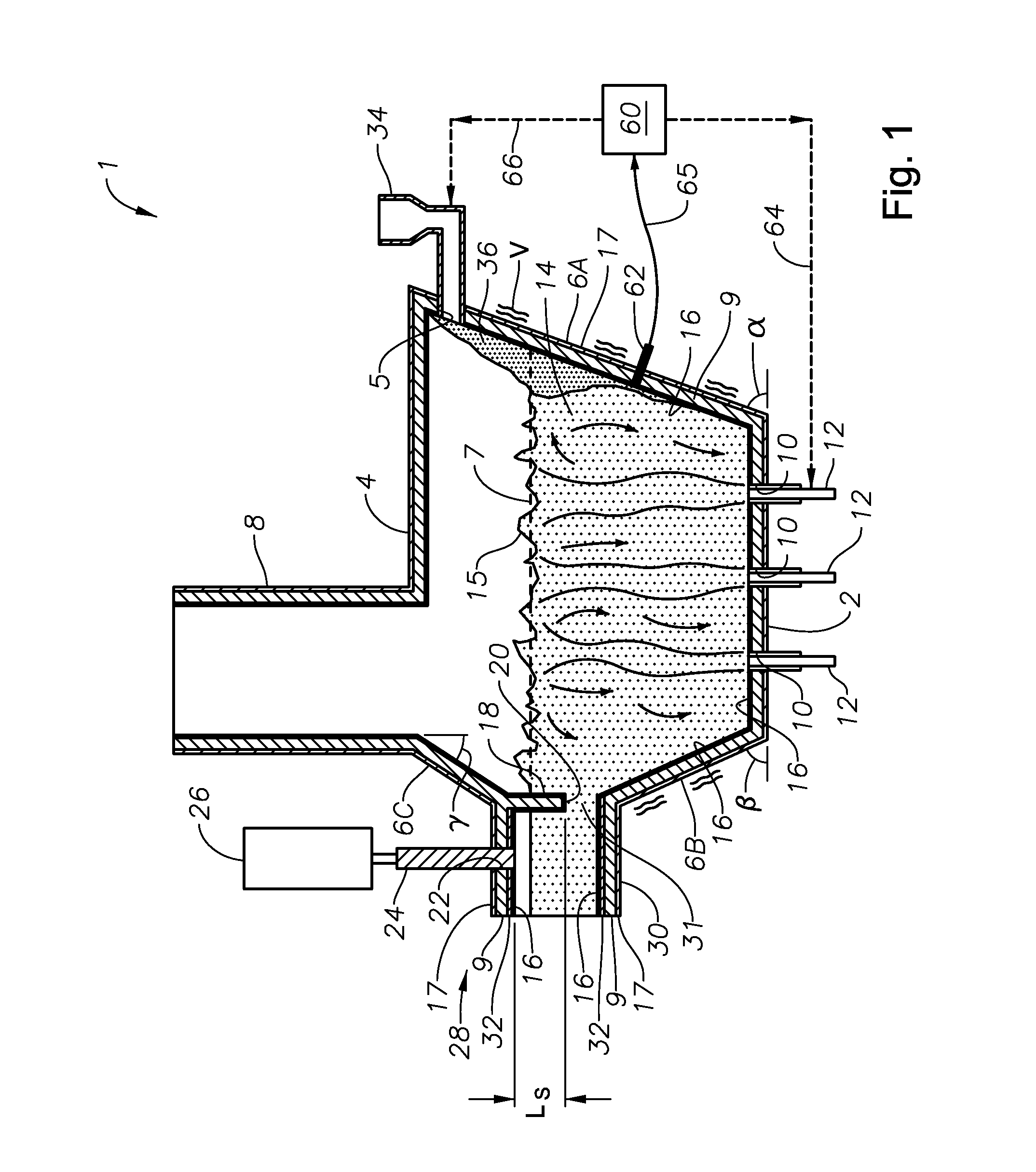
Melting and refining in tanks with cooled walls
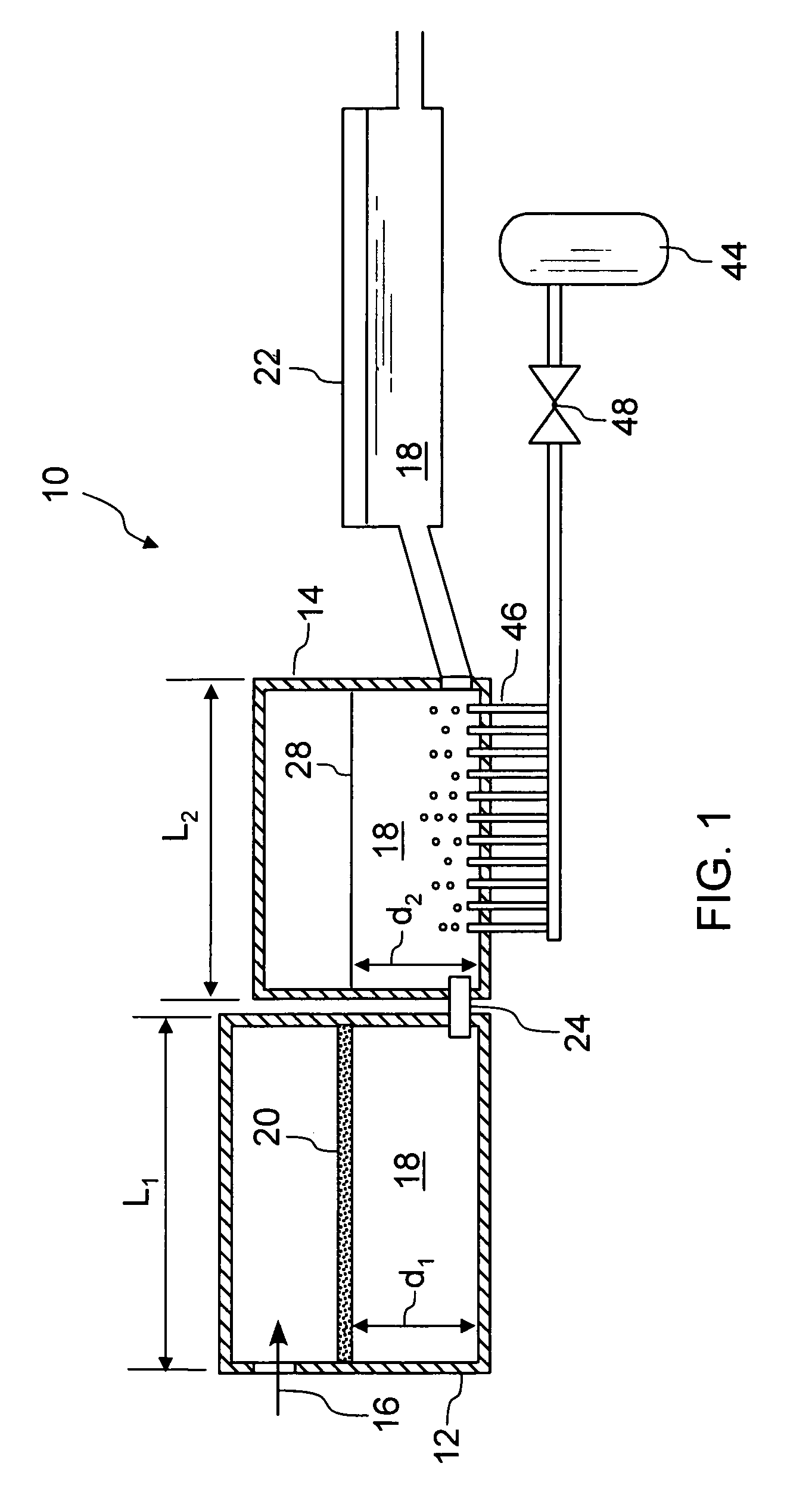
InactiveUS8424342B2Reduce energy demand per unit weightCharging furnaceTank furnacesResidence timeGlass-ceramic
A method for melting inorganic materials, preferably glasses and glass-ceramics, in a melting unit with cooled walls is provided. The method includes selecting the temperature of at least one region of the melt is selected in such a way as to be in a range from Teff−20% to Teff+20%, where the temperature Teff is given by the temperature at which the energy consumption per unit weight of the material to be melted is at a minimum, with the throughput having been selected in such a way as to be suitably adapted to the required residence time.
Owner:SCHOTT AG
Method and device for the homogenous heating of glass and/or glass-ceramic articles using infrared radiation
InactiveUS7017370B1Quality improvementImprove overall utilizationElectric discharge heatingTank furnacesGlass-ceramicHeat treating
A method for the homogeneous heating of semitransparent and / or transparent glass and / or glass-ceramic articles using infrared radiation so that the glass and / or glass-ceramic articles undergo heat treatment at between 20 and 3000° C., notably at between 20 and 1705° C. Heating is achieved by a component of infrared radiation which acts directly on the glass and / or glass-ceramic articles and by a component of infrared radiation which acts indirectly on said glass and / or glass-ceramic articles. The radiation component indirectly acting on the glass and / or glass-ceramic articles accounts for more than 50% of total radiation output.
Owner:SCHOTT AG
Method of forming a glass melt
ActiveUS20070151297A1Reduce partial pressurePromote vigorous boilingCharging furnaceTank furnacesMolten glassExcessive Cooling
A method of forming a glass melt including heating a glass feed material in a first melting furnace to form a glass melt, flowing the glass melt into a second melting furnace through a refractory metal connecting tube, and further heating the glass melt in the second melting furnace. The refractory metal connecting tube is heated to prevent the molten glass from excessive cooling, and to ensure that the glass melt entering the second melting furnace is equal to or greater than the temperature of the glass melt in the second melting furnace. An apparatus for performing the method is also disclosed.
Owner:CORNING INC
Method for temperature manipulation of a melt
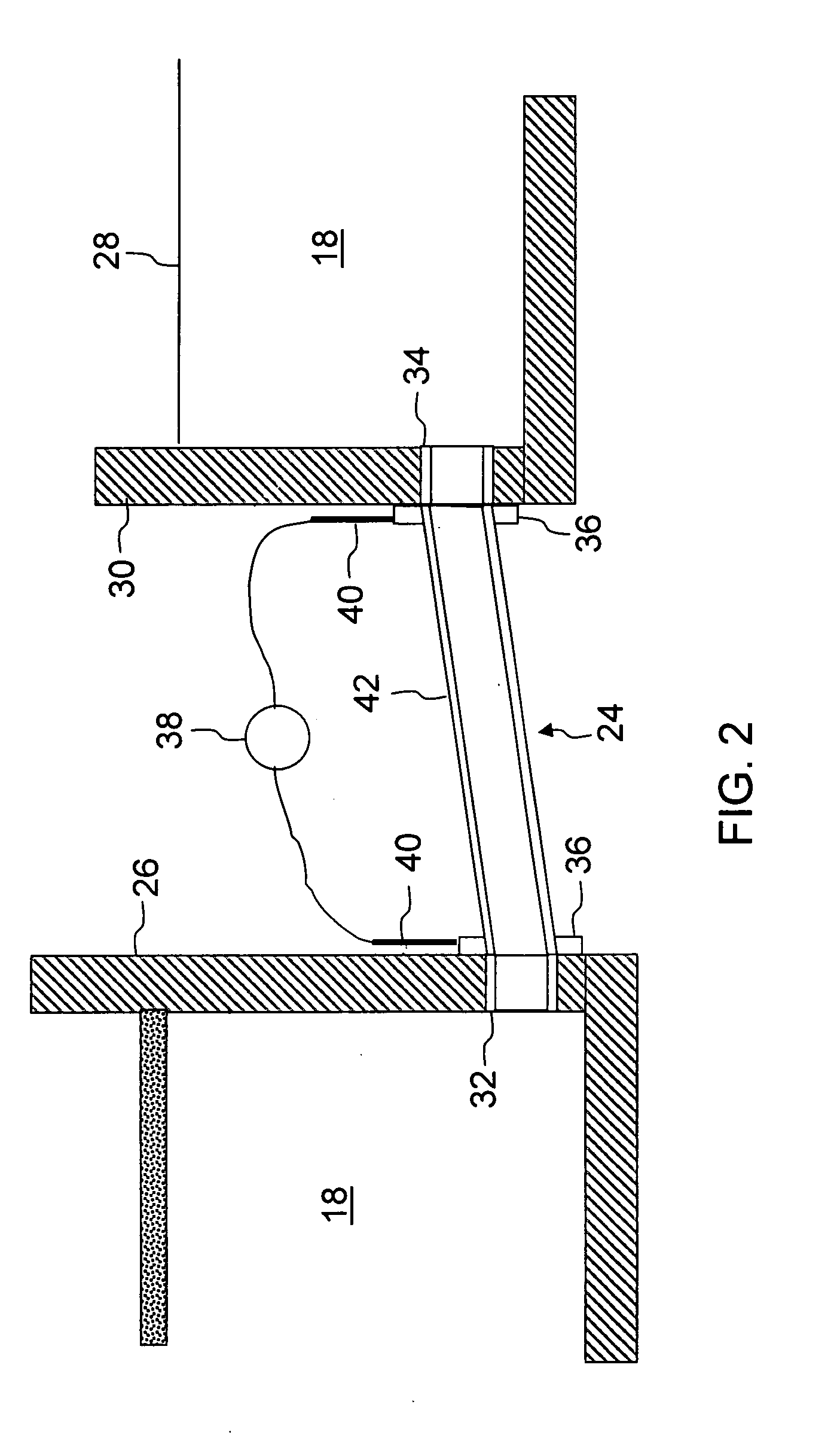
InactiveCN101405231AIncrease temperatureReduce the temperatureOhmic-resistance electrodesTank furnacesElectrical resistance and conductanceElectrical resistivity and conductivity
A method and device are disclosed for temperature manipulation of a melt even with conductivity below 10<-1> O <-1>cm<-1>, thus permitting refining of the melt at temperatures above 1700 DEG C. According to the method for temperature manipulation of a melt (16), in particular, in a refiner unit, the melt (16) is heated at least by ohmic resistance heating, at least two electrodes (4) are arranged in the melt (16) and at least a part of the melt (16) is cooled. The device (1) for temperature manipulation and / or refining and / or purification and / or homogenisation of a melt (16) comprises at least one arrangement for accommodating melt material (36, 16), defining an inner chamber and at least two electrodes (4) for ohmic resistance heating of the melt (16), wherein the electrodes (4) project into the inner chamber of the arrangement in particular of the vessel (2).
Owner:SCHOTT AG
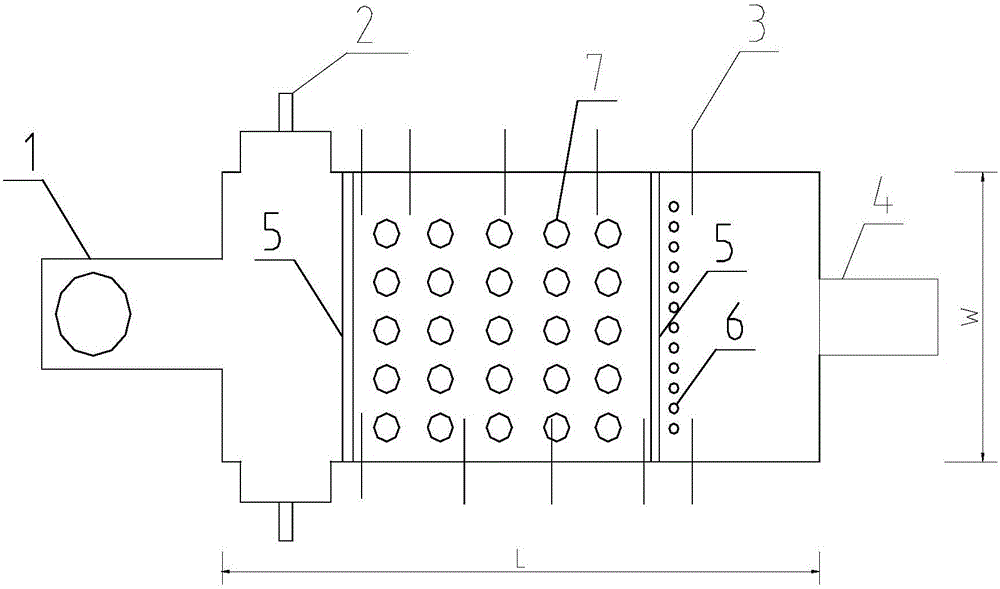
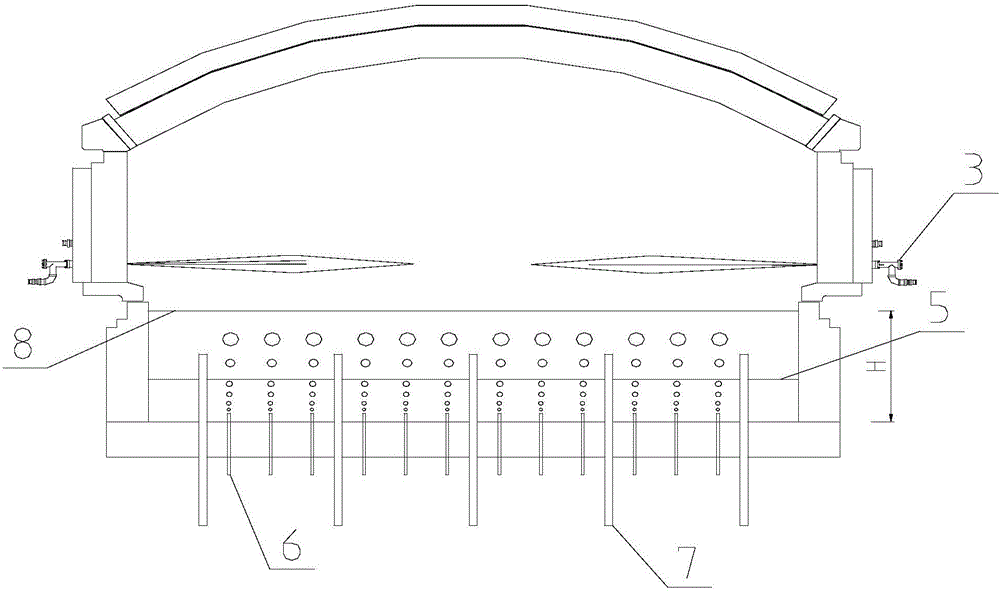
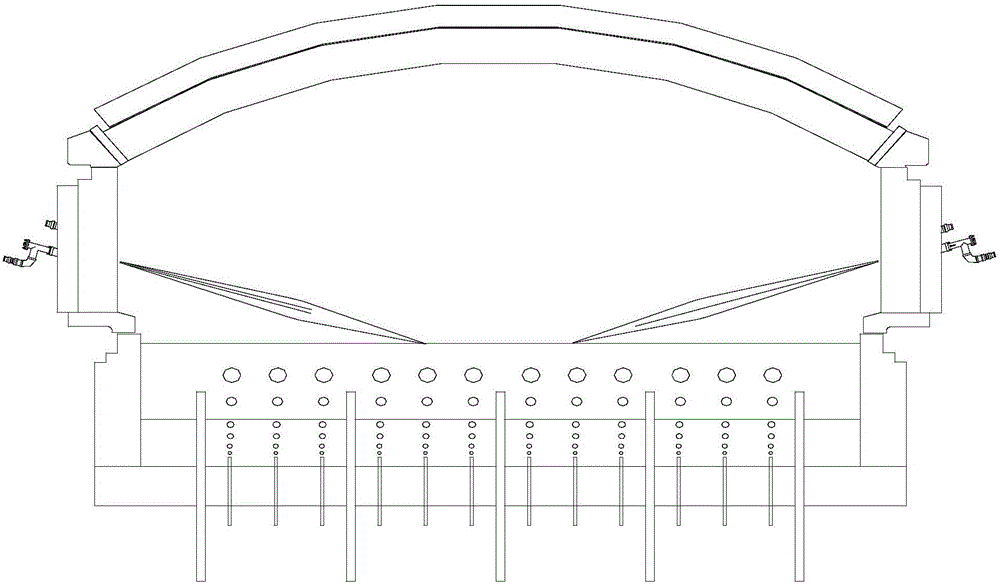
Glass tank furnace with high melting rate
ActiveCN105776819AHigh aspect ratioReduce lossTank furnacesGlass furnace apparatusHeat lossesEngineering
The invention discloses a glass tank furnace with high melting rate. The ratio of the length of the glass tank furnace to the width of the glass tank furnace is 2.3-2.8. The glass tank furnace has the advantages that the area of the tank furnace is reduced and the length-width ratio of the tank furnace is optimized so as to reduce heat loss; reasonable liquid glass tank depth is designed to improve the bottom temperature of the tank furnace and guarantee the quality of liquid glass; a pure-oxygen burner and an auxiliary capacitor provides sufficient energy to increase the melting ability and heating efficiency of the tank furnace, and the energy consumption and the discharge amount of carbon dioxide are lowered greatly; furnace ridges at the bottom of the tank furnace increase the outlet temperature of the liquid glass, lower energy consumption, lower the furnace bottom temperature of an electrode area, prolong the service life of the furnace bottom and guarantee the increasing of auxiliary electric energy proportion; bubbling at the bottom of the tank furnace increases the return strength of the liquid glass and increases the melting ability and the quality of the liquid glass; to sum up, the melting rate of the tank furnace can be increased effectively, and the energy consumption can be lowered.
Owner:JUSHI GRP CO
Transparent infrared absorbing glass and method of making
InactiveUSRE37328E1Minimized total iron contentHighly reduced glassCharging furnaceWindowsFlat glassTransmittance
Owner:PPG IND OHIO INC
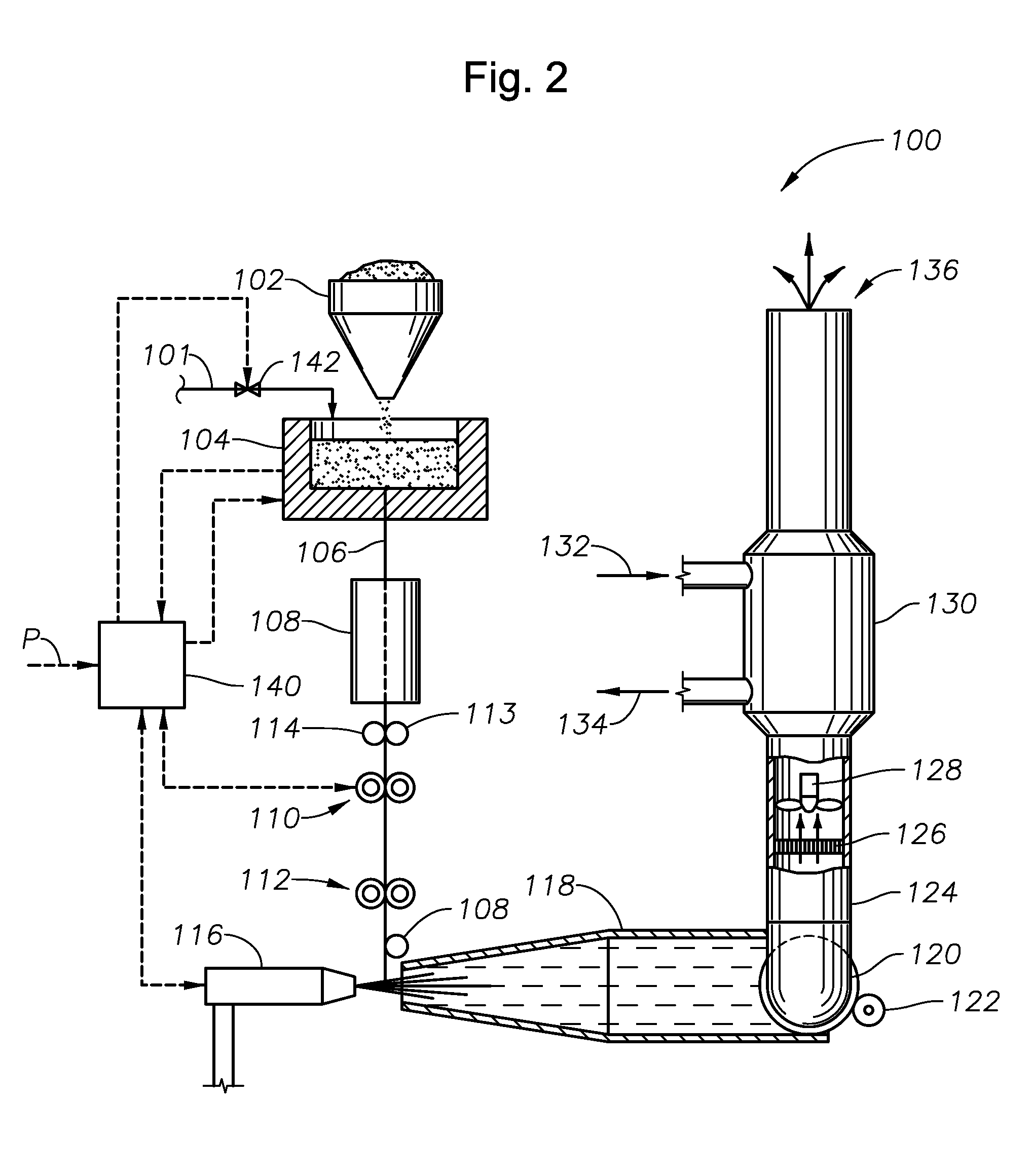
Glass Furnace with Bottom Material Feed
ActiveUS20150307382A1Eliminate the problemCharging furnaceGlass furnace apparatusGlass furnaceScrew conveyor
A glass furnace includes a furnace chamber for containing glass melt and a screw conveyor for receiving glass batch material and feeding the glass batch material to the furnace chamber. A dam wall is disposed with respect to the screw conveyor such that batch material from the screw conveyor must flow upward over the dam wall before entering the furnace chamber. The top of the dam wall may be below the level of the melt pool in the furnace chamber.
Owner:OWENS-BROCKWAY GLASS CONTAINER INC
Medicinal glass pipe prepared by full electric melting wilo method and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN101033115ASolve the problem of small expansion coefficient and acid resistanceSolve the problem of weak alkali resistanceTank furnacesGlass furnace apparatusPotassiumBoron trioxide
This invention relate to a medical glass tube drawn by the Wieluo method and its preparation method, in which, the weight percentage includes: SiO2 71-77.1, Al2O3 5.2-7.1, B2O3 8.2-11.6, BaO 0.6-2.6, CaO 1.2-2.4, Li2O 4.6-7.7, K2O 5.0-7.4 and Na2O 5.1-7.6, and the preparation method includes: preparing raw materials, smelting the materials, drawing the tube to molding and cutting the gouge accurately, checking and packaging.
Owner:沧州四星玻璃股份有限公司
Melting and refining in baths with cooled walls
InactiveUS20060291528A1Increase ratingsHigh chemical reaction rateCharging furnaceGlass furnace apparatusEnergy expenditureInorganic materials
A method for melting inorganic materials, preferably glasses and glass-ceramics, in a melting unit with cooled walls is provided. The method includes selecting the temperature of at least one region of the melt is selected in such a way as to be in a range from Teff−20% to Teff+20%, where the temperature Teff is given by the temperature at which the energy consumption per unit weight of the material to be melted is at a minimum, with the throughput having been selected in such a way as to be suitably adapted to the required residence time.
Owner:SCHOTT AG
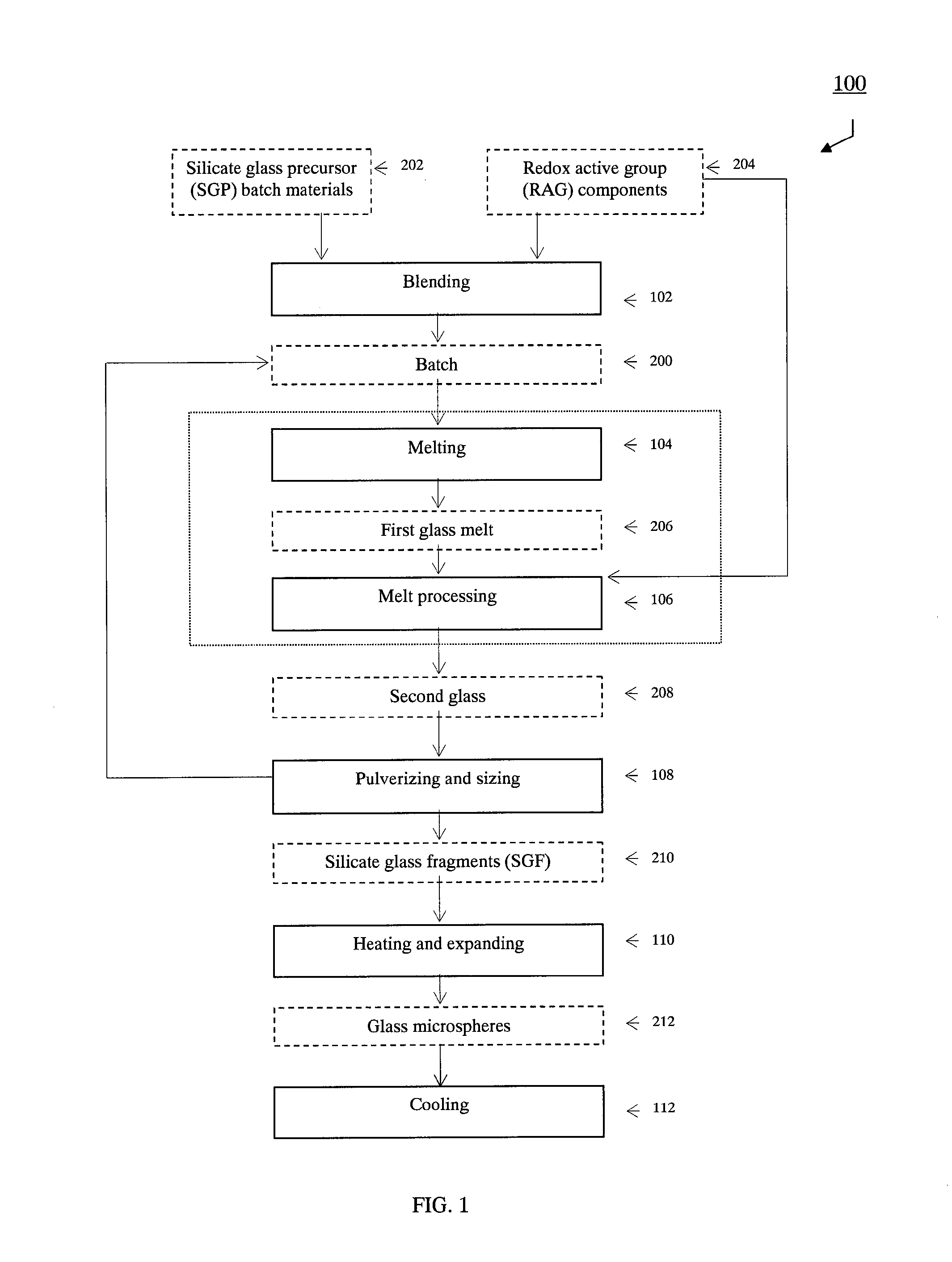
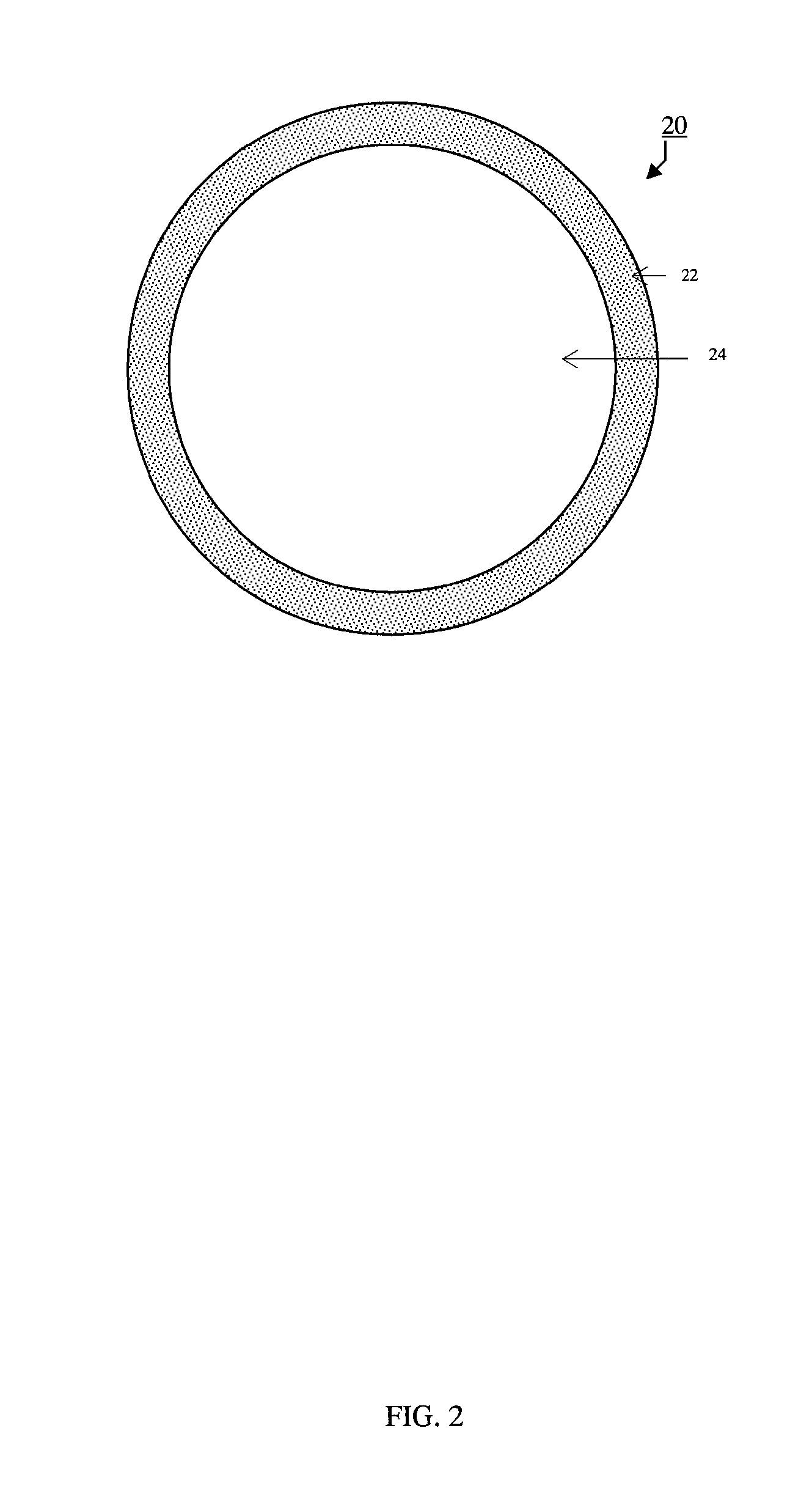
Fluid permeable and vacuumed insulating microspheres and methods of producing the same
ActiveUS20160207817A1Lowering firing temperature requirementImprove fuel efficiencyTank furnacesGlass blowing apparatusMicrosphereMaterials science
Microsphere comprising an outer shell enclosing a substantially hollow inner space, the outer shell comprising a fluid permeable porous structure, the fluid permeable porous structure comprising interconnected pores, the microsphere being capable of maintaining a vacuum in its substantially hollow inner space when its outer shell is sealed.
Owner:HOJAJI HAMID +1
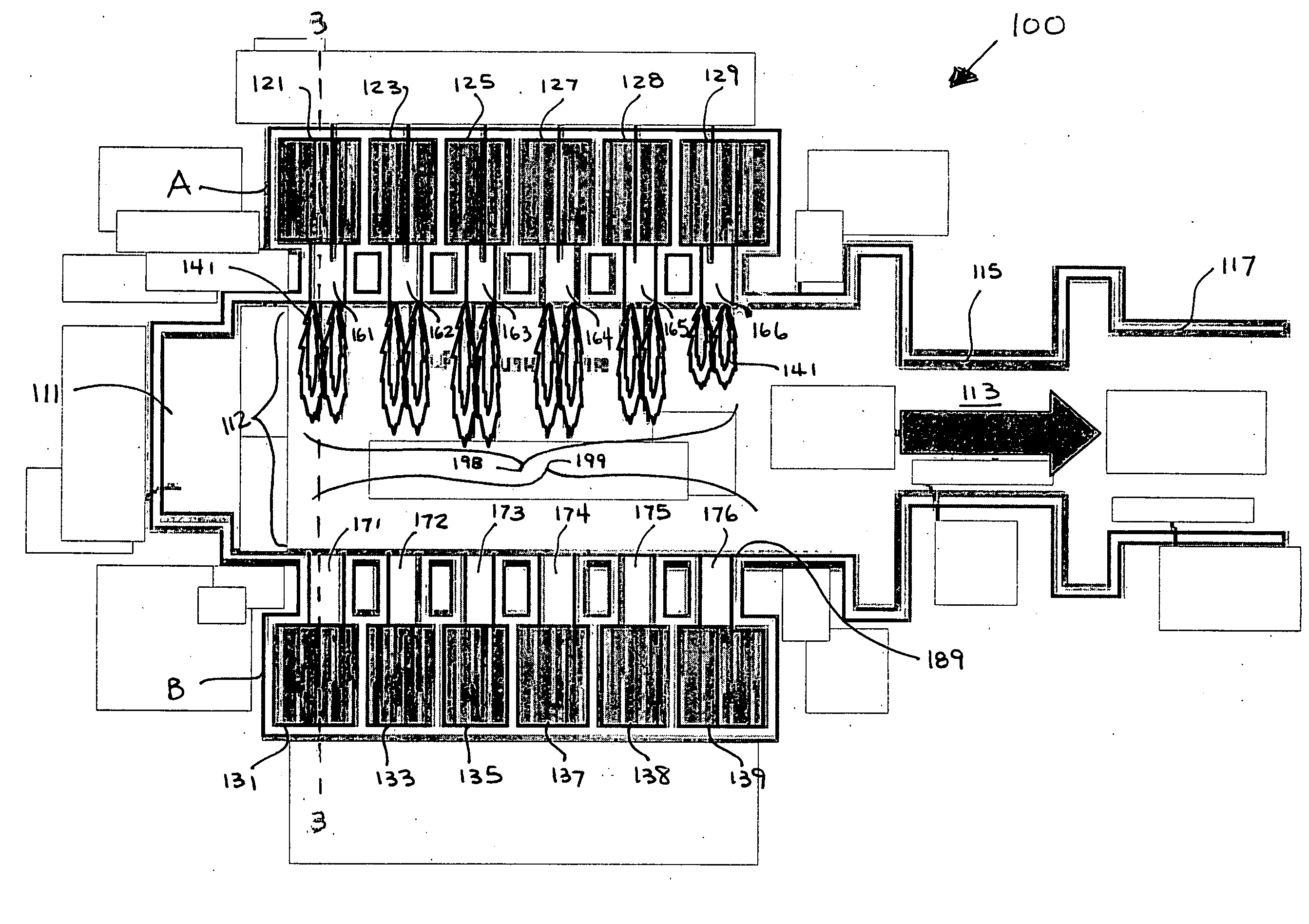
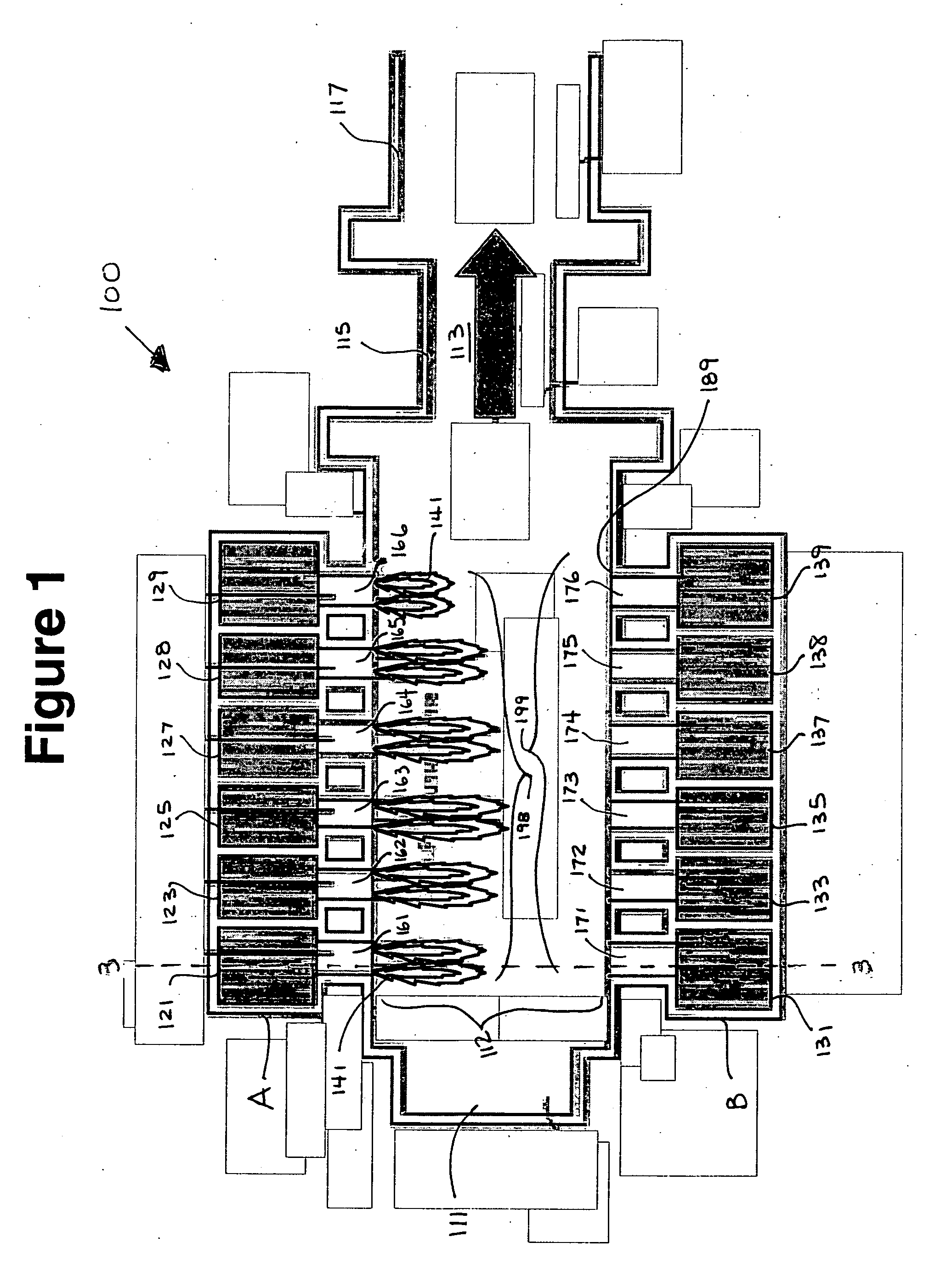
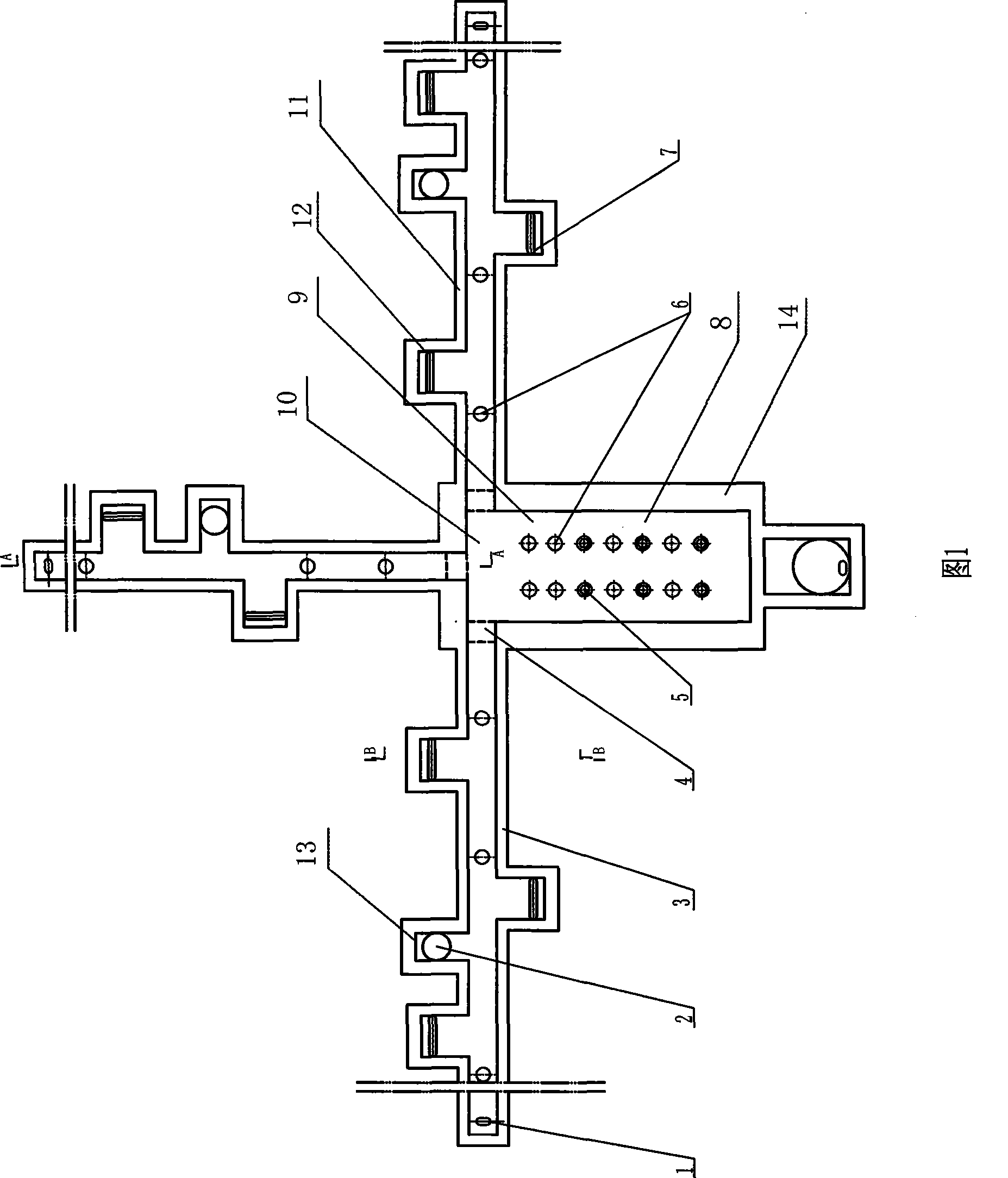
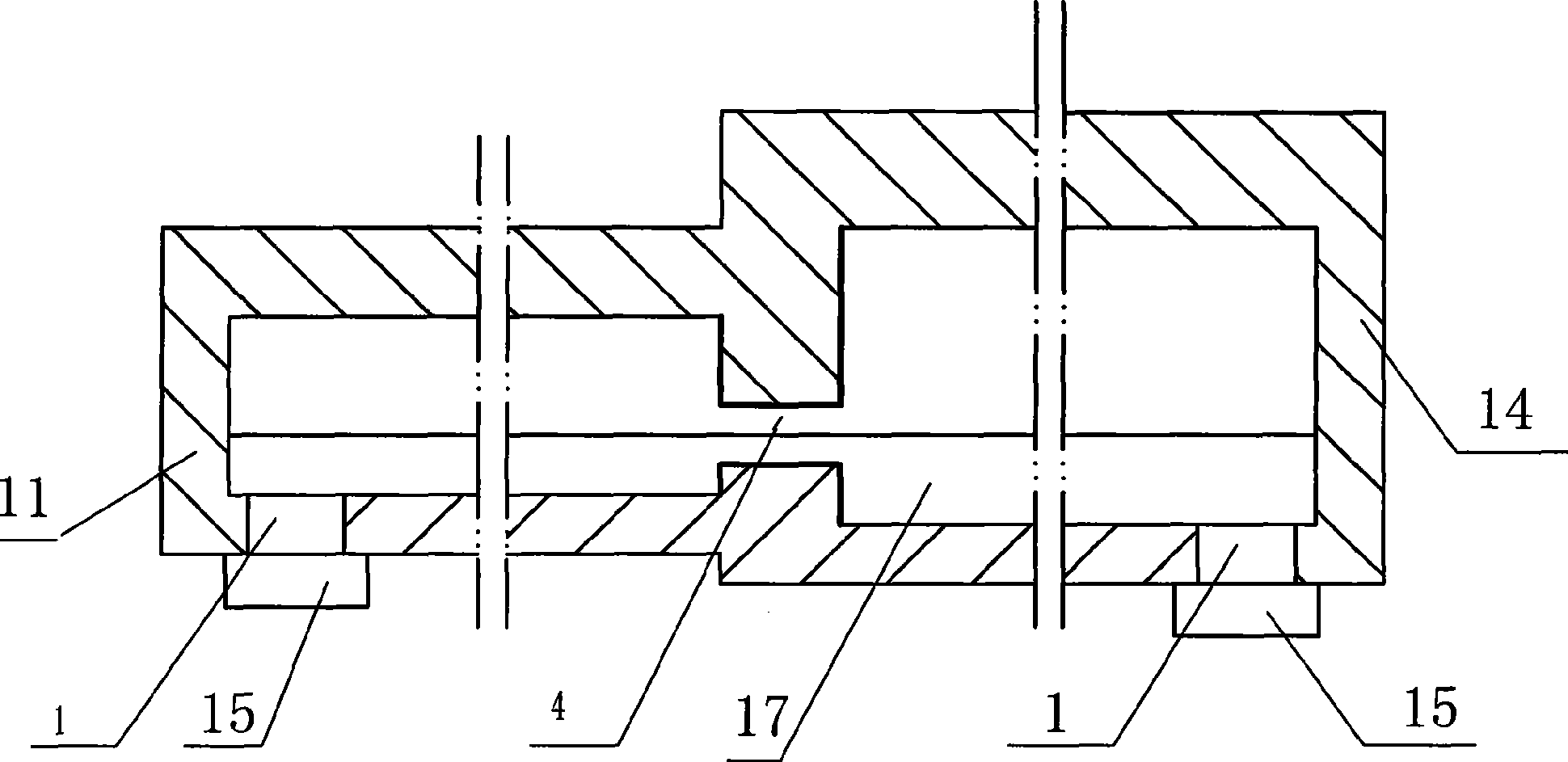
Tank furnace for producing basalt continuous fiber
ActiveCN101397182AHigh melting temperatureGuaranteed temperatureForehearthsTank furnacesMelting tankFiber
The invention relates to a tank furnace for producing basalt continuous filament and pertains to the technical field of novel inorganic non-metallic material processing equipment, the main characteristics are that the furnace body consists of a melting tank and material channels, the melting tank and the material channels are connected by non-submerged dog-holes, the melting tank is divided into a melting area and a homogenization area, a burner is arranged at the top of the furnace vertically, the burner guns of melting area and the feeding pipes are arranged in intervals, and the strong melting area of even feeding and even heating is formed. The material channels are arranged in three directions in the homogenization area of the melting tank, burner guns are arranged in the material channel in sections, the temperature of the fused mass in the material channels is guaranteed, more than 12 wiredrawing shaping areas are evenly arranged in each material channel so as to supply basalt melt mass for the wiredrawing bushing well, emptying devices are arranged at the tail part of the melting tank and the tail parts of all material channels, during the operation, the operation of discharging the meltwater can be carried out when impurities are stored in the meltwater for a long time or the varieties of raw materials are changed. The invention is in favor of improving the quality and industrialized production of the basalt continuous filament.
Owner:江苏天龙玄武岩连续纤维股份有限公司
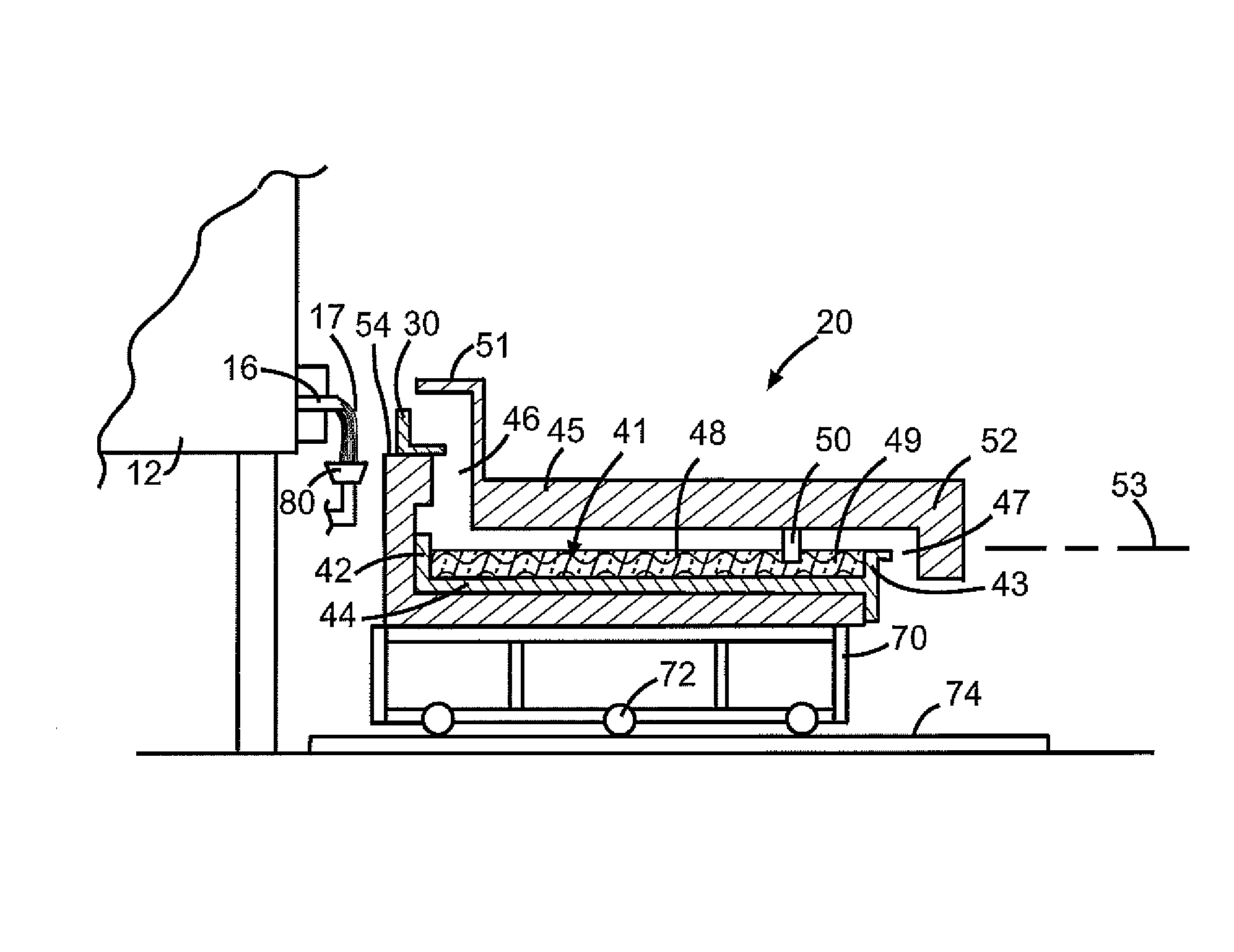
Glass melting furnace, process for modifying glass melt, process for producing glass melt, process for producing glass product, and apparatus for producing glass product
InactiveUS20130239618A1Easy to installSuitable for productionCharging furnaceForehearthsHigh concentrationMolten state
Objective of the present invention is to provide a glass melting furnace, a process for modifying a glass melt and a process for producing glass melt, whereby composition-modified glass melt containing an additive component at a high concentration can be produced with an excellent quality. The glass melting furnace 10 of the present invention is a glass melting furnace 10 for adding an additive to a molten state glass to form composition-modified glass melt, discharging the composition-modified glass melt, and a forehearth 20, said forehearth comprising a feed portion to feed an additive, and a heating means to form a heating gas phase portion above the liquid surface of the glass melt to convert the additive from the feed portion into melted particles of additive below the feed portion.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
Melting furnace for TFT (thin film transistor) glass
InactiveCN107522387AReduce high volatilityReduce the defectsTank furnacesGlass furnace apparatusBrickBoron
The invention provides a melting furnace for TFT (thin film transistor) glass. The melting furnace comprises a cold-top all-electric melting furnace body and a settling pond which are arranged in sequence; a liquid flow hole is arranged in the bottom of the cold-top all-electric melting furnace body, an outlet end of the liquid flow hole is communicated with an ascending channel, and the ascending channel is communicated with a feed inlet of the settling pond; a feed inlet for feeding TFT glass matching materials is arranged in the upper portion of the cold-top all-electric melting furnace body, and multiple furnace electrodes are arranged in the cold-top all-electric melting furnace body; multiple in-pond electrodes and multiple flame-heating spray guns are arranged in the settling pond, and a smoke vent for discharging smoke is arranged in the settling pond; a bubbling device and a furnace ridge are sequentially arranged on a bottom brick of the bottom of the settling pond, and the bubbling device is arranged in the rear of all the in-pond electrodes. By the arrangement that melting is separated from processes of high-temperature settling and homogenizing, high volatilization of boron and defects produced thereby in melting of the TFT glass matching material can be effectively reduced, effective settling and homogenizing of molten glass of the TFT glass are achieved, defects that lines and the like occur to the product are avoided, and quality of the product is remarkably improved.
Owner:CHINA TRIUMPH INT ENG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com