Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2597 results about "Flat glass" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Plate glass, flat glass or sheet glass is a type of glass, initially produced in plane form, commonly used for windows, glass doors, transparent walls, and windscreens. For modern architectural and automotive applications, the flat glass is sometimes bent after production of the plane sheet. Flat glass stands in contrast to container glass (used for bottles, jars, cups) and glass fibre (used for thermal insulation, in fibreglass composites, and optical communication).
Method for providing a grinding surface on glass implements used in personal care
ActiveUS8790749B2Increase variabilityEasy to manufacturePretreated surfacesManicure/pedicurePersonal careFlat glass
Manufacturing method of grinding surface on glass cosmetics, in particular the nail and skin file, from flat glass of FLOAT type, is carried out by marking at least one abrasive surface on one or two sides of a glass pane or intermediate product. This surface is then coated with fusing glue, powdered with clean quartz sand with grain size between 1 and 500 μm using a sieve, and the surplus sand is knocked-down. The intermediate product with fixed sand is inserted into the fusing furnace where it is baked at the temperature of up to 900° C. The abrasive surface may be roughened by sand blasting before the fusing glue application; the intermediate product coated with fusing glue can be decorated with glass fritte.
Owner:HACEK OVER SKUTCHANOVA ZUZANA
Method and apparatus for generation of electrical power from solar energy
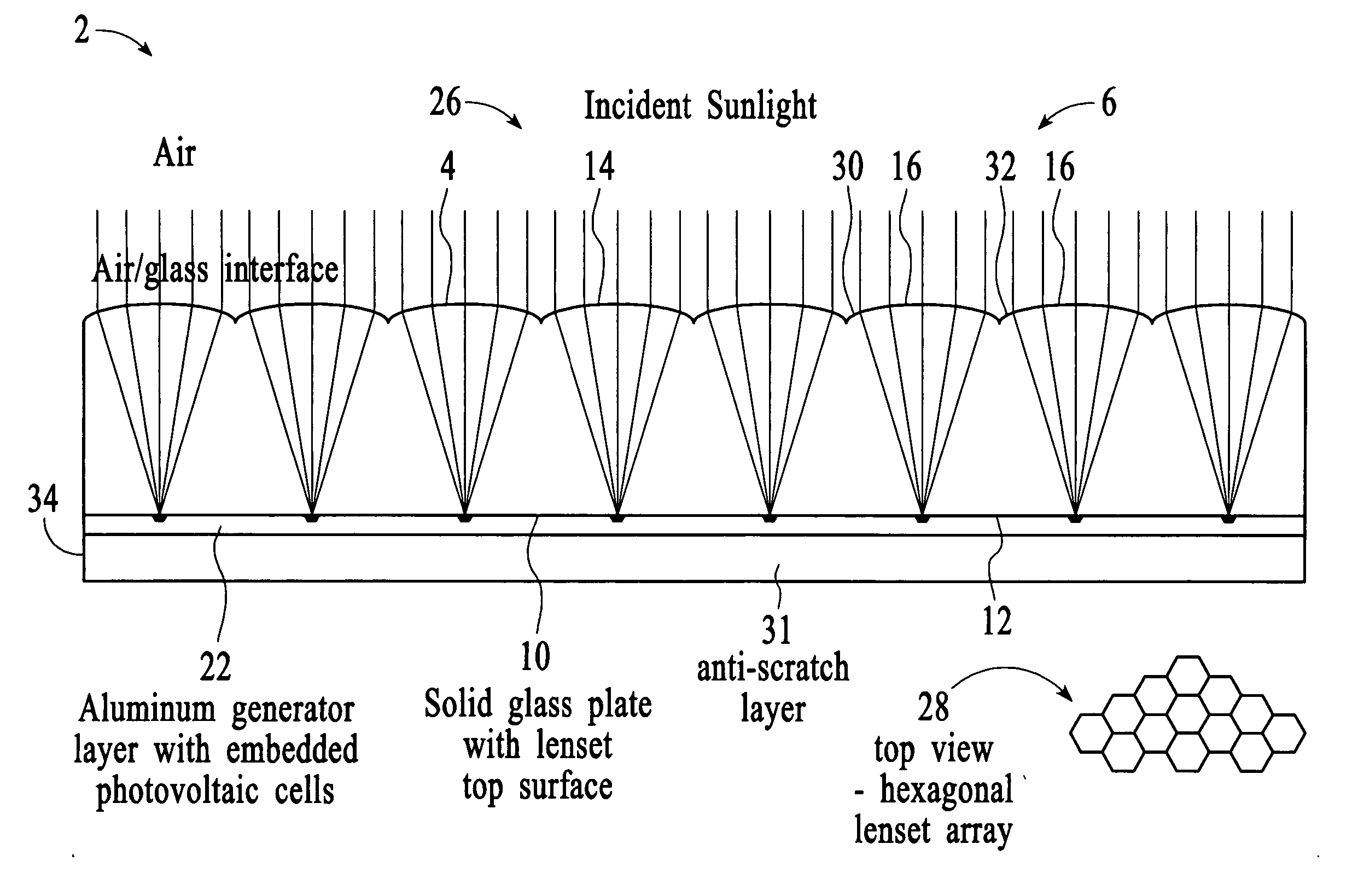
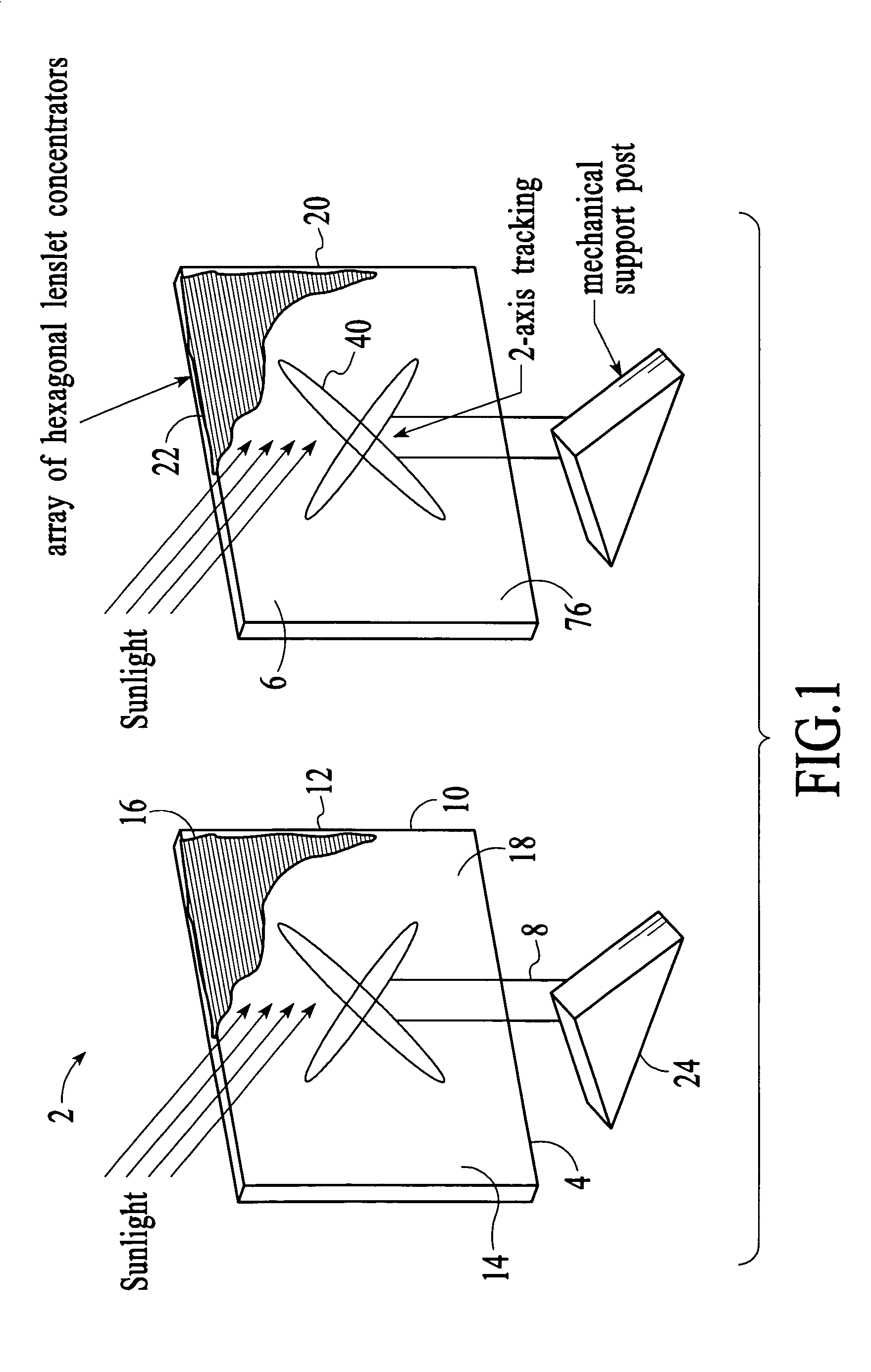
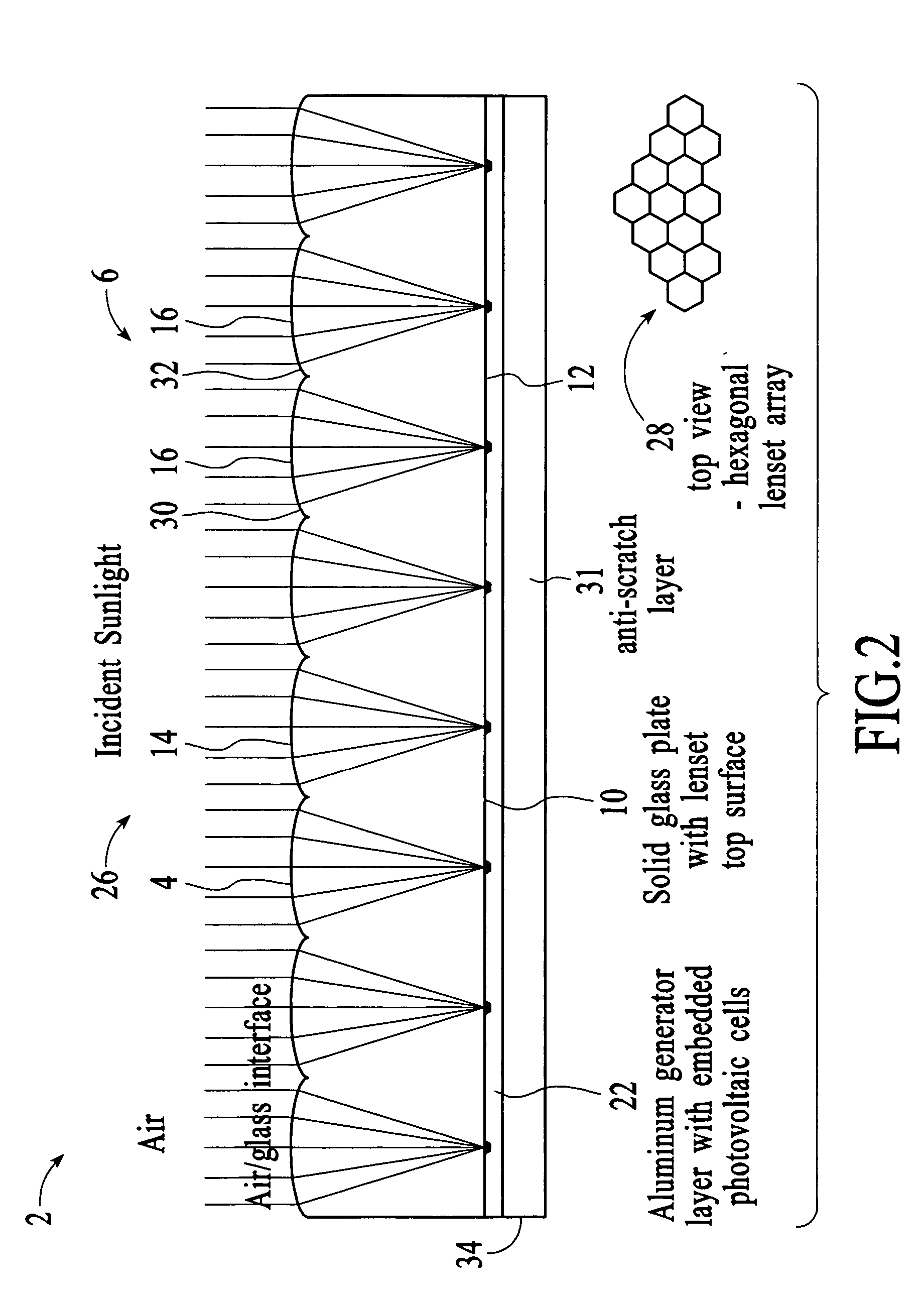
InactiveUS20050081908A1Reduce usageLow costFinal product manufacturePV power plantsFlat glassConcentration ratio
A method of providing an apparatus and system comprising a complete smart solar electrical power generator system integrated into the form of a thin flat glass plate. The novel elements include: a micro-scale optical array, a new type of miniaturized photovoltaic cell, an inside-the-lens concentrator design, integral heat sinking and mechanical support, a sealed solid-state design with no air gaps and a new process for building it, combined reflective / refractive light concentration around the photovoltaic cell, variable solar concentration ratios, and a new integrated structure for interconnecting the system together.
Owner:STEWART ROGER G
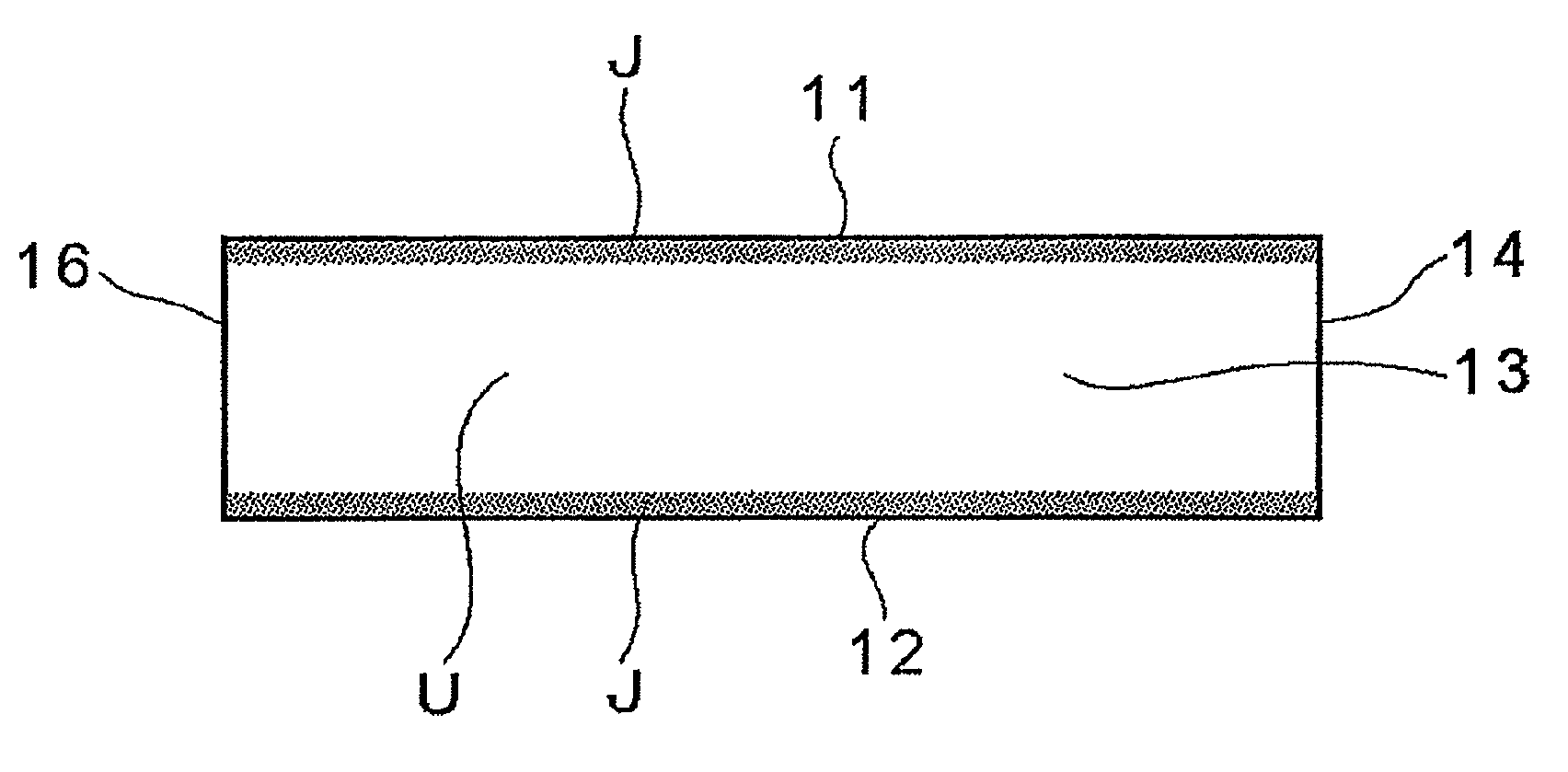
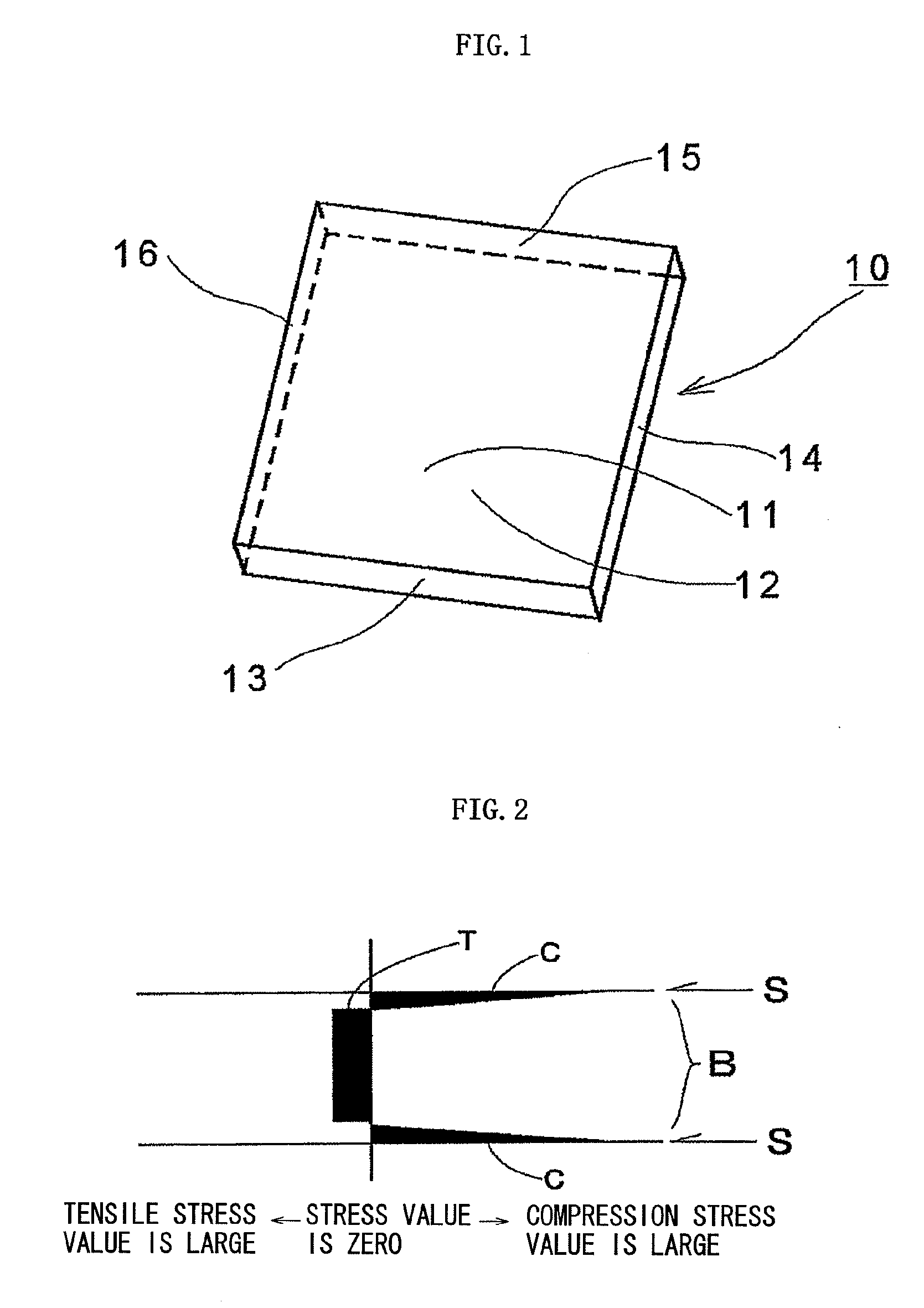
Reinforced plate glass and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20100119846A1Quality improvementStrength of plate glass surfaces opposed to each otherGlass/slag layered productsGlass severing apparatusFlat glassUltimate tensile strength
[Object] To provide a method of manufacturing a reinforced plate glass by which glass surface strength can be sufficiently increased, and a stable quality reinforced plate glass is manufactured at high production efficiency, and to provide a reinforced plate glass manufactured by the manufacturing method.[Solving Means] A reinforced plate glass (10) is formed of an inorganic oxide glass, and is provided with a compression stress layer by chemical reinforcement on plate surfaces (11, 12) opposed to each other in a plate thickness direction. Plate end faces (13, 14, 15, 16) have regions where a compression stress is formed and regions where no compression stress is formed.
Owner:NIPPON ELECTRIC GLASS CO LTD
Non-contact porous air bearing and glass flattening device
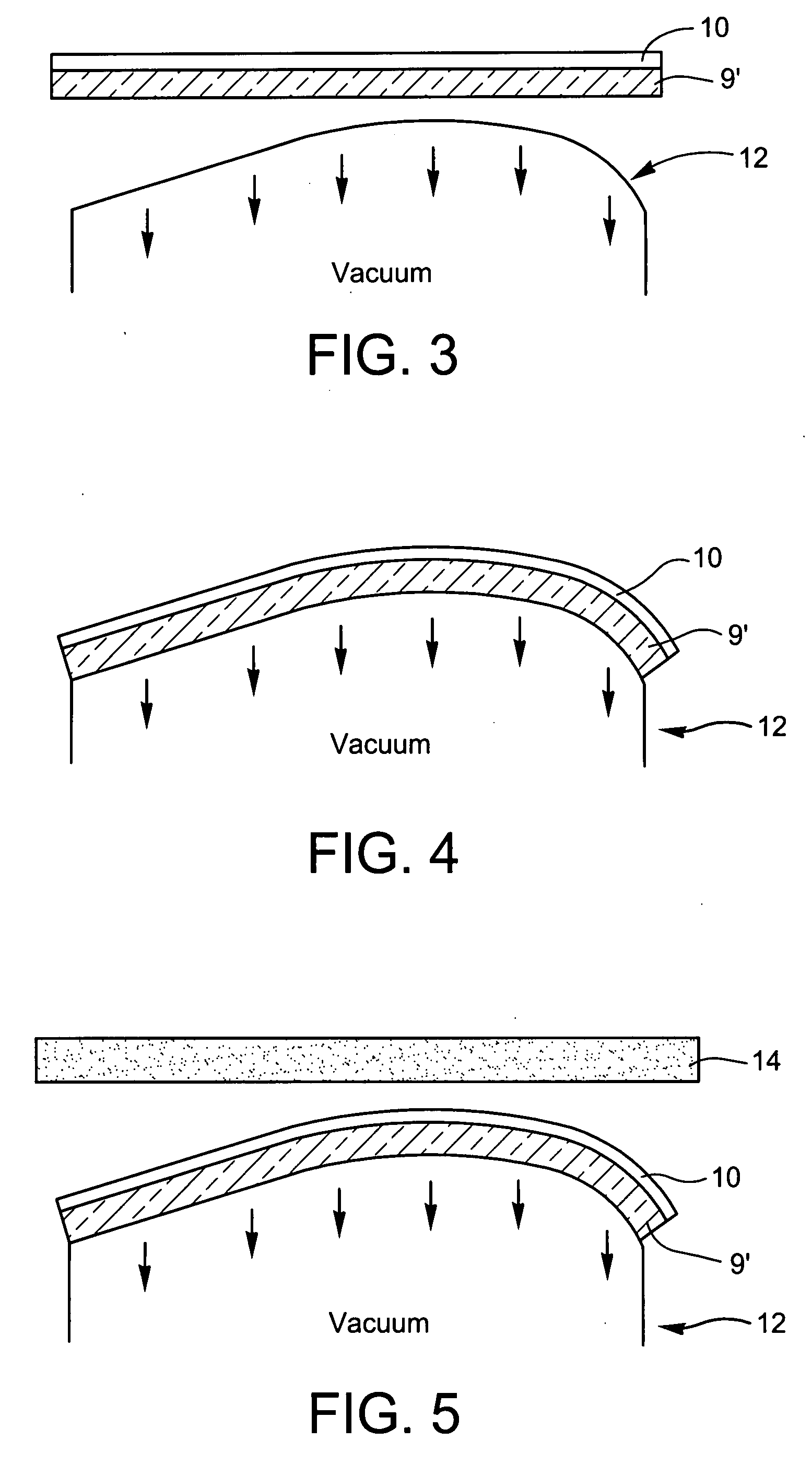
Thin substrates, such as flat glass panels, are levitated on a porous media air bearing creating a pressurized film of air and preloaded against the air film by negative pressure areas. The pressure can be distributed most uniformly across the pressure areas by defusing the pressure through a porous medium. Such a bearing can be used for glass flattening by holding the glass such that the unevenness is migrated to the side opposite the side to be worked on.
Owner:NEW WAY MACHINE COMPONENTS
Pulling rolls for use in manufacturing sheet glass
InactiveUS6896646B2Easy to useImprove the level ofShaft and bearingsMetal-working apparatusFlat glassRoom temperature
Owner:CORNING INC
Sag control of isopipes used in making sheet glass by the fusion process
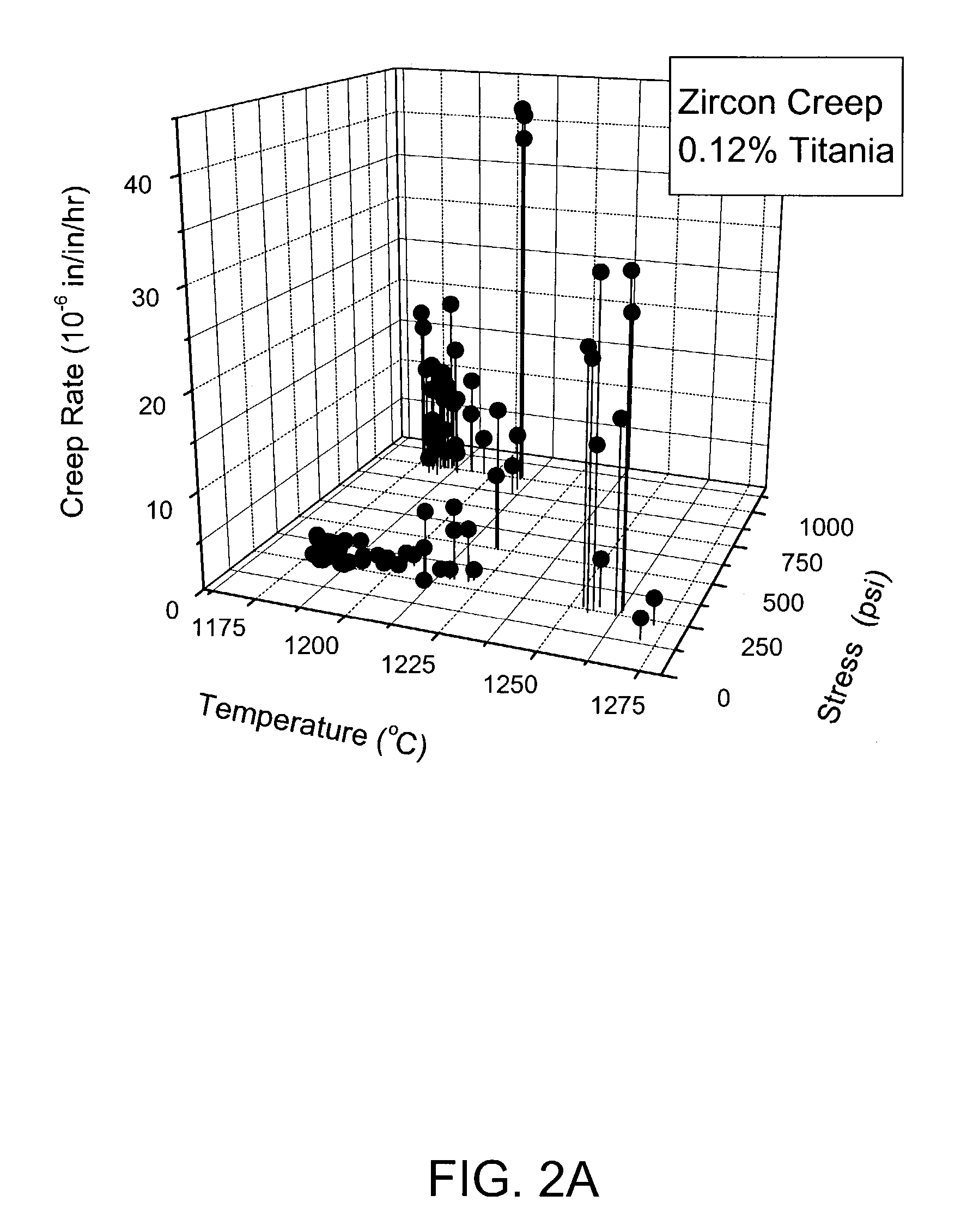
Isopipes for use in making sheet glass by a fusion process are provided which exhibit reduced sag. The isopipes are composed of a zircon refractory which has a mean creep rate (MCR) at 1180° C. and 250 psi and a 95 percent confidence band (CB) for said mean creep rate such that the CB to MCR ratio is less than 0.5, the MCR and the CB both being determined using a power law model. The zircon refractory can contain titania (TiO2) at a concentration greater than 0.2 wt. % and less than 0.4 wt. %. A concentration of titania in this range causes the zircon refractory to exhibit a lower mean creep rate than zircon refractories previously used to make isopipes. In addition, the variation in mean creep rate is also reduced which reduces the chances that the zircon refractory of a particular isopipe will have an abnormally high creep rate and thus exhibit unacceptable sag prematurely.
Owner:CORNING INC
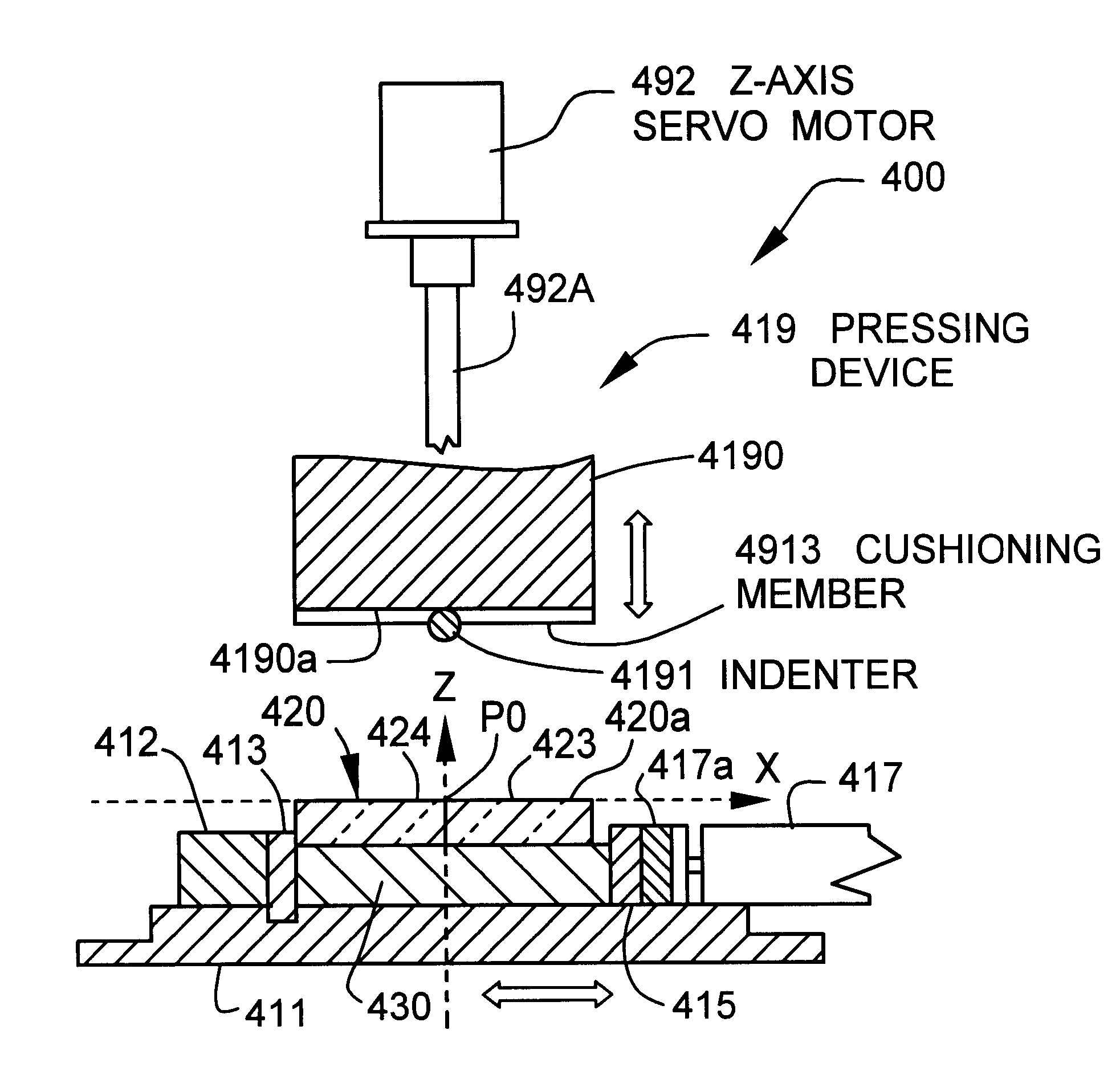
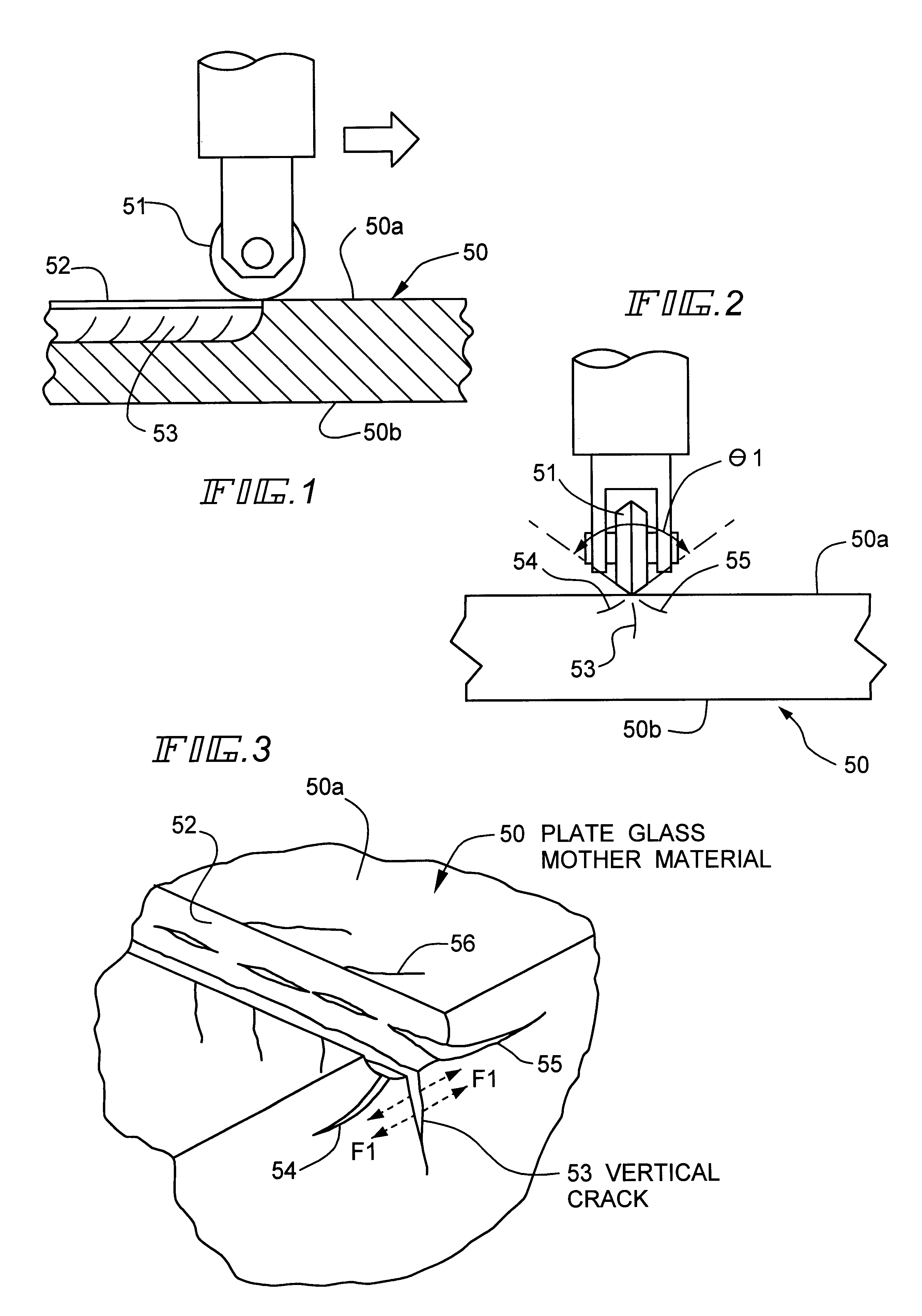
Cutting method for plate glass mother material
The present invention is directed to a method of cutting glass mother material involving preparing the plate glass mother material in which a plurality of grooves are scribed, disposing the plate glass mother material with the grooves turned inward; and pressing an outer surface of the plate glass mother material with a cushioning member having a thickness not to be protruded downward from a lowermost portion of an indenter, with the cushioning member being attached onto an under surface of an indenter base excluding the indenter, pressing a portion opposite to the groove on the outer surface with the indenter having a stretched shape, and cutting the plate glass mother material.
Owner:HOYA CORP
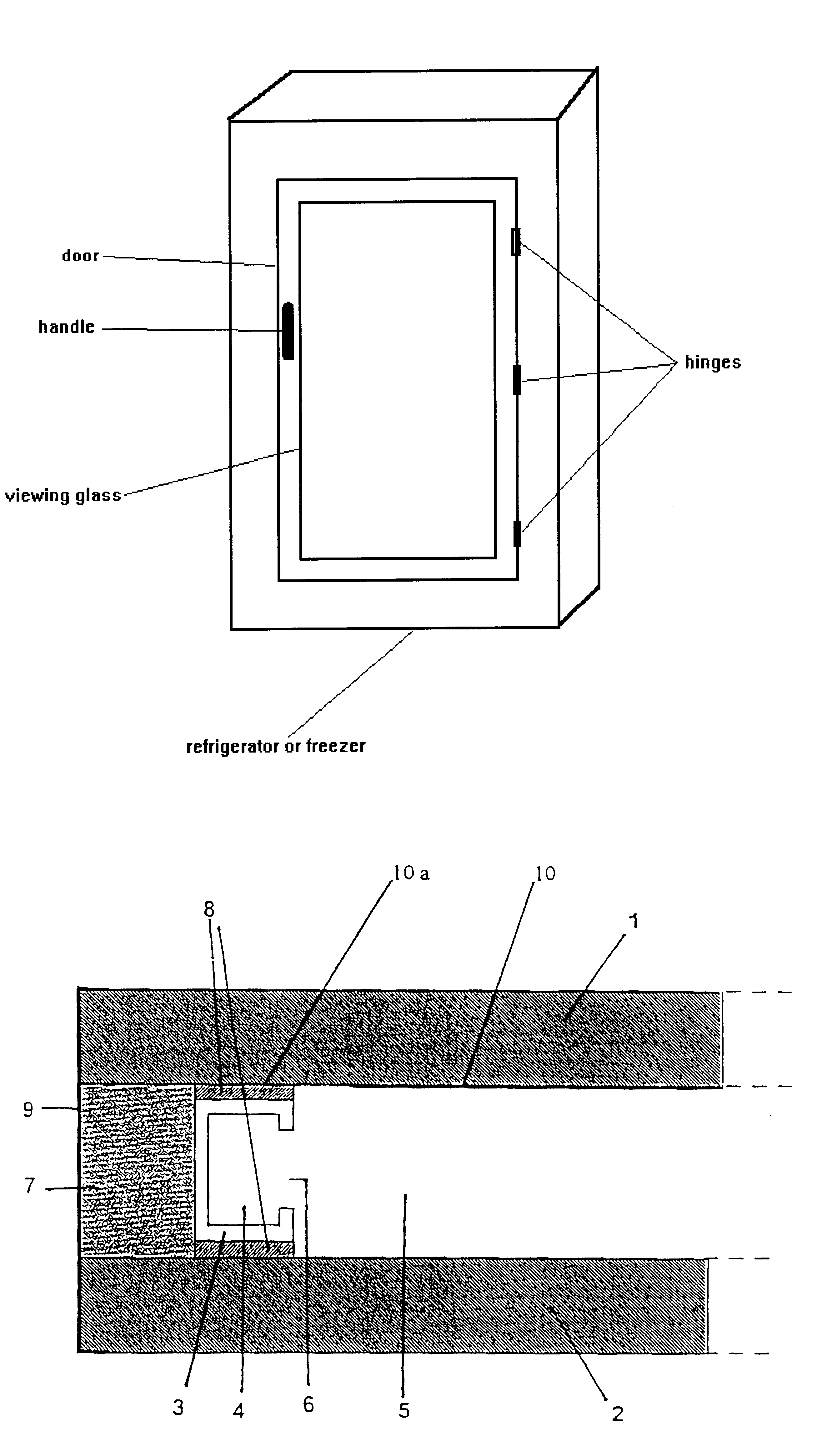
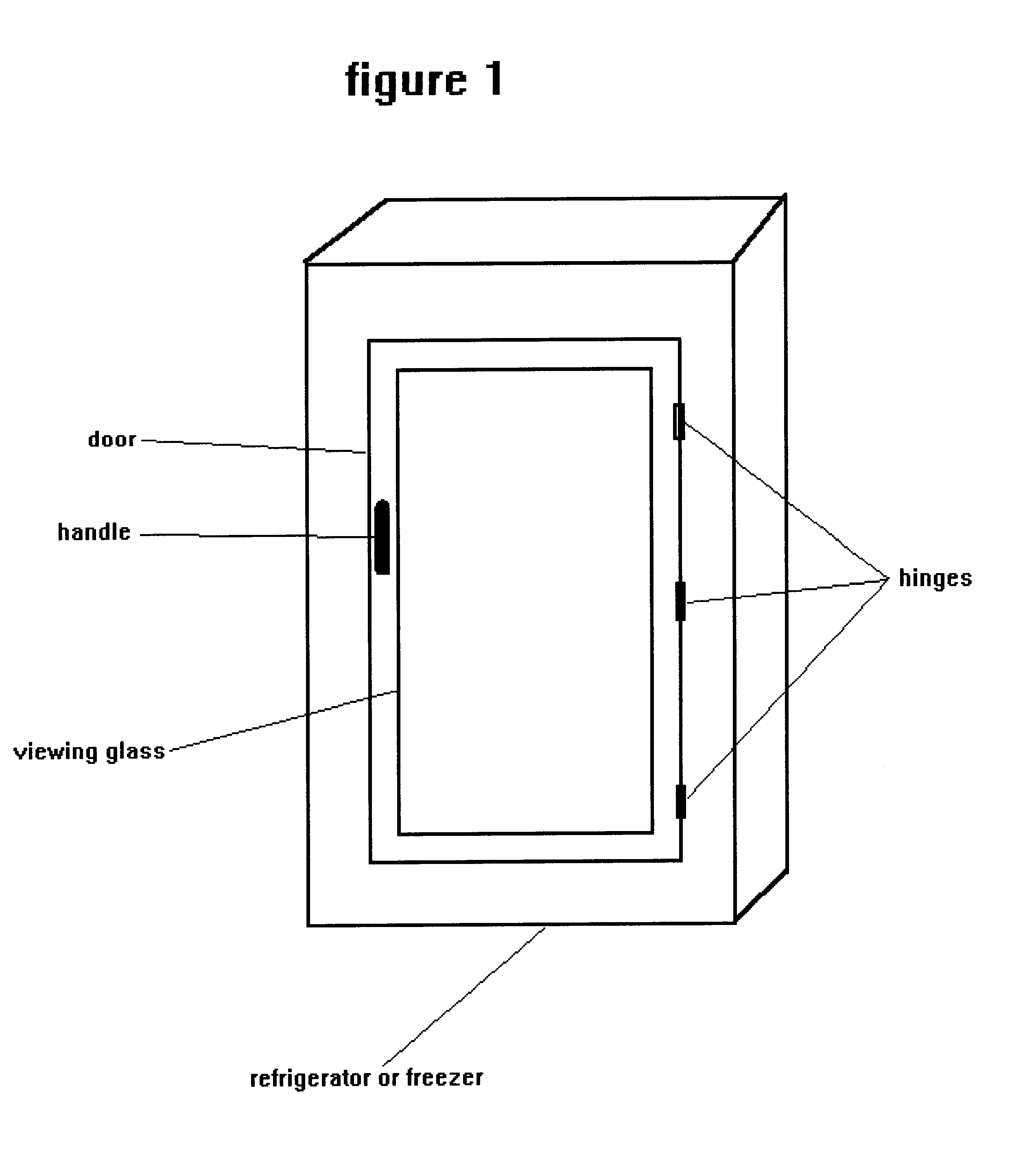
Appliance such as a refrigerator or freezer with a transparent viewing door and a method of manufacture of a refrigerator or freezer with a transparent viewing door
InactiveUS6268594B1Reduce formationLittle process outlayShow cabinetsConductive layers on insulating-supportsFlat glassInsulated glazing
A multipane insulating glass for appliances having an inner-chamber temperature which is lower than the ambient temperature, in particular for viewing doors of refrigerators and freezers comprises at least two panes which are of approximately equal size and are arranged at a distance from one another. The distance is maintained by a spacer which runs continuously around the vicinity of the edge. One of the two outer panes is provided with an electrically conductive, transparent coating on its side which faces towards the space between the panes. In this glass, the coating, which is applied to the entire surface, is deactivated in the peripheral area of the pane, containing the contact surface for the spacer. Also, a process for producing coated flat glass materials for such insulating glass materials, as described above.
Owner:GLAS SCHOTT +1
Single-use edging wheel for finishing glass
InactiveUS20090017736A1Uniform thicknessEdge grinding machinesPigmenting treatmentFlat glassMaterials science
A single-use grinding tool includes a wheel portion having a profiled recess (e.g., such as a U, V, or bowl shape) extending circumferentially along the wheel portion's periphery. A multi-layered bonded abrasive (e.g., 3-dimensional matrix of abrasive grains and bond material, or multiple layers of abrasive tape) is conformably coated or otherwise applied in a uniform thickness along the profiled recess. The bonded abrasive in one particular case includes a metal bond with diamonds. However, organic, resinous, vitrified, and hybrid bonds, as well as other abrasive grit types, can be used. The wheel portion is supported by an arbor portion which may be removably coupled to the wheel portion, or formed integrally with the wheel portion. The tool is useful, for example, in edge grinding a workpiece, such as sheet glass. Methods of tool use and tool manufacture are disclosed as well.
Owner:SAINT GOBAIN ABRASIFS INC +1
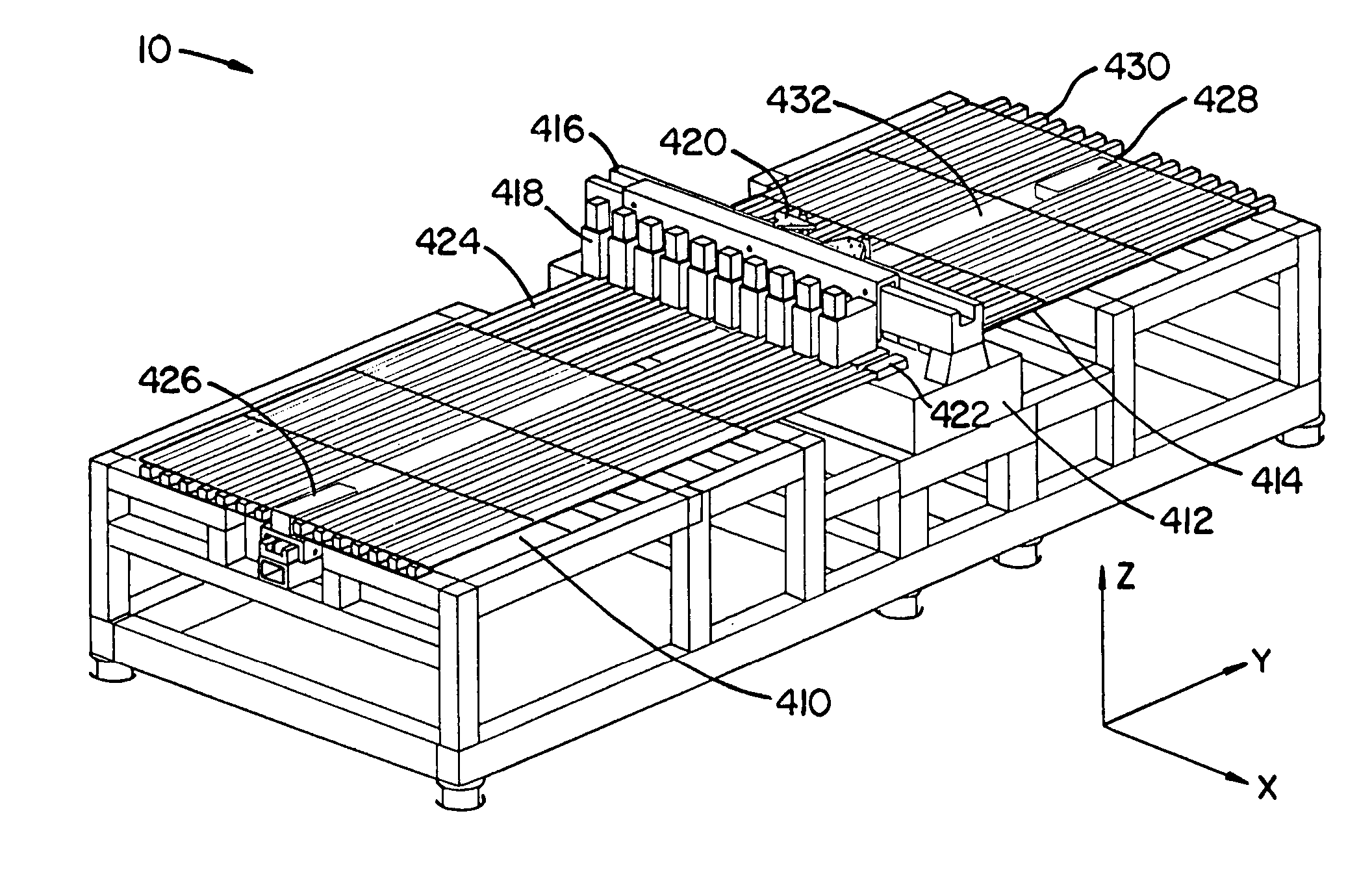
High precision gas bearing split-axis stage for transport and constraint of large flat flexible media during processing
ActiveUS20050040338A1Reduces system inspection tact timeTact time can be reducedConveyorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFlat glassPorous medium
A modular split-axis stage is used to inspect and / or repair large flat glass media suitable for LCD / TFT applications. Low-precision air table sections are detachably mounted to a centrally located, high-precision granite inspection / repair section. Glass media held by a vacuum contact is transported on air cushions from the up-web air table to the central inspection / repair section. Vacuum nozzles integrated with porous medium pads precisely control the height of the flexible media above the central section during inspection or repair. Embodiments includes structures in which the media is either stationary or moving during inspection / repair. A first media can be loaded / unloaded while a second media is undergoing inspection or repair in a pipelined operational mode.
Owner:ORBOTECH LTD
Parabolic trough or dish reflector for use in concentrating solar power apparatus and method of making same
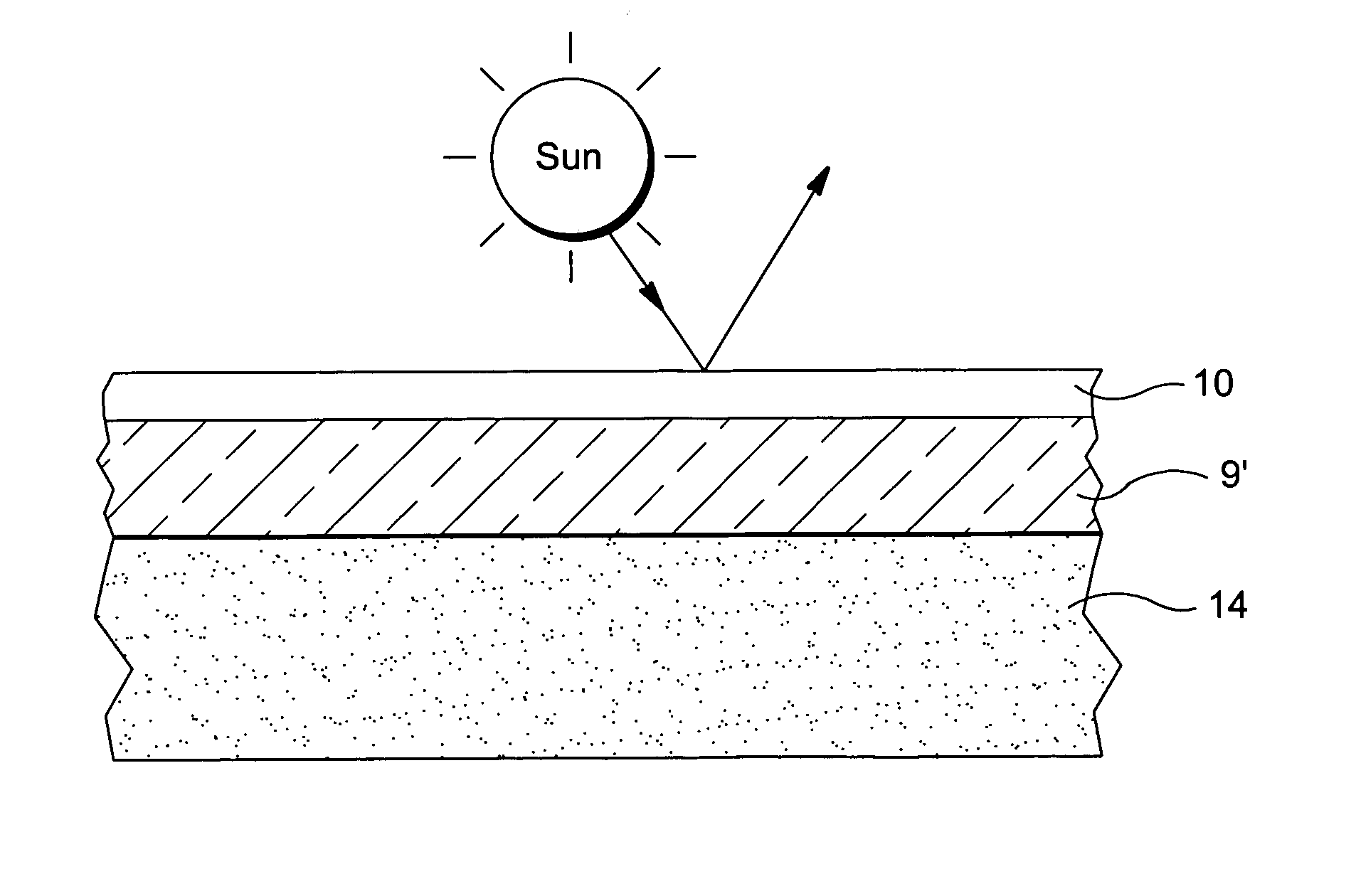
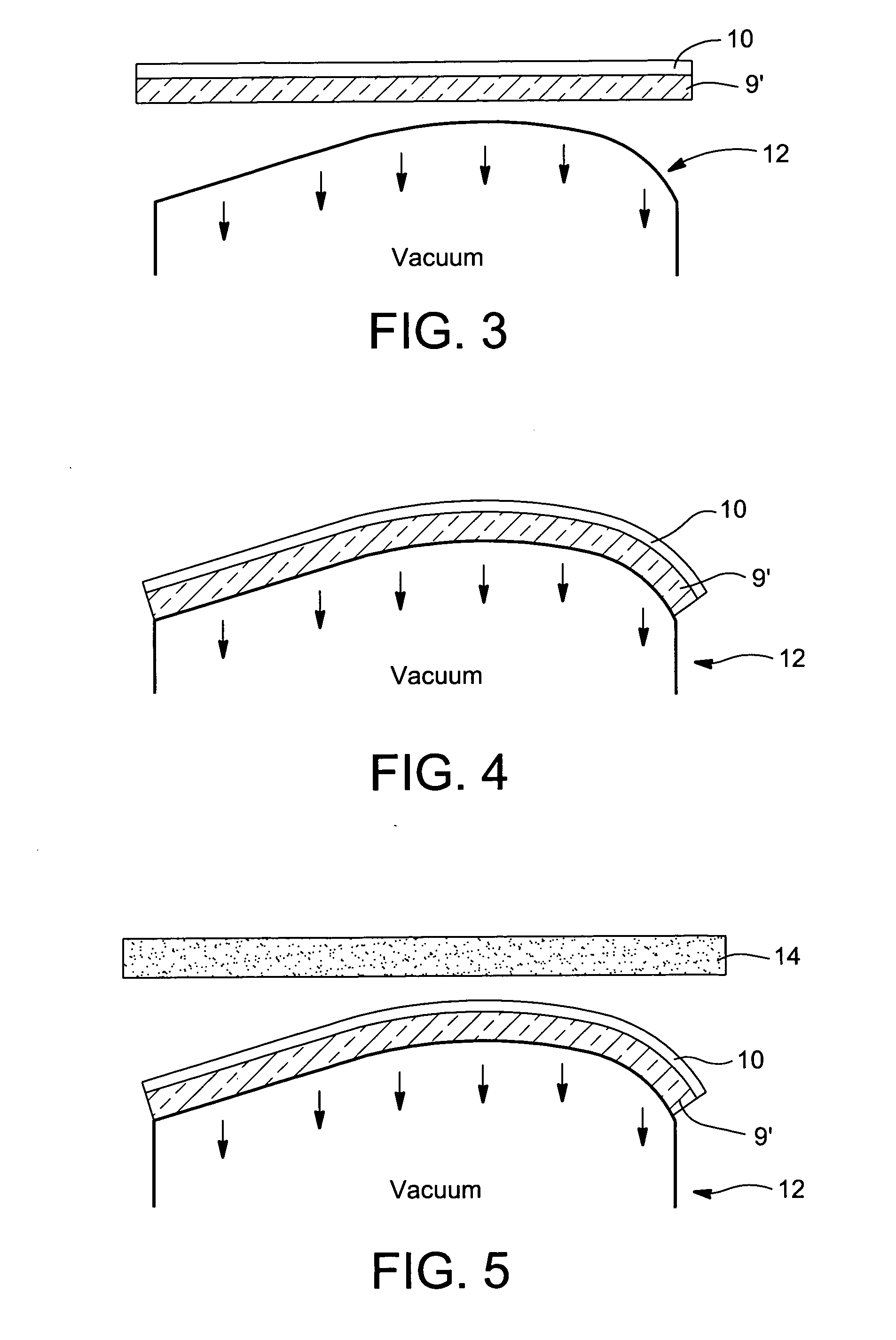
A reflector (e.g., mirror) for use in a solar collector or the like is provided. In certain example embodiments of this invention, a reflector is made by (a) forming a reflective coating on a thin substantially flat glass substrate (the thin glass substrate may or may not be pre-bent prior to the coating being applied thereto), (b) optionally, if the glass substrate in (a) was not prebent, then cold-bending the glass substrate with the reflective coating thereon; and (c) applying a plate or frame member to the thin bent glass substrate with the coating thereon from (a) and / or (b), the plate or frame member (which may be another thicker pre-bent glass sheet, for example) for maintaining the thin glass substrate and coating thereon in a desired bent orientation in a final product which may be used as parabolic trough or dish type reflector in a concentrating solar power apparatus or the like.
Owner:GUARDIAN EURO S A R L +1
High precision gas bearing split-axis stage for transport and constraint of large flat flexible media during processing
InactiveUS20060096395A1Shorten the timeSmall sizeConveyorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFlat glassPorous medium
A modular split-axis stage is used to inspect and / or repair large flat glass media suitable for LCD / TFT applications. Low-precision air table sections are detachably mounted to a centrally located, high-precision granite inspection / repair section. Glass media held by a vacuum contact is transported on air cushions from the up-web air table to the central inspection / repair section. Vacuum nozzles integrated with porous medium pads precisely control the height of the flexible media above the central section during inspection or repair. Embodiments includes structures in which the media is either stationary or moving during inspection / repair. A first media can be loaded / unloaded while a second media is undergoing inspection or repair in a pipelined operational mode.
Owner:ORBOTECH LTD
Method and apparatus for making a glass sheet
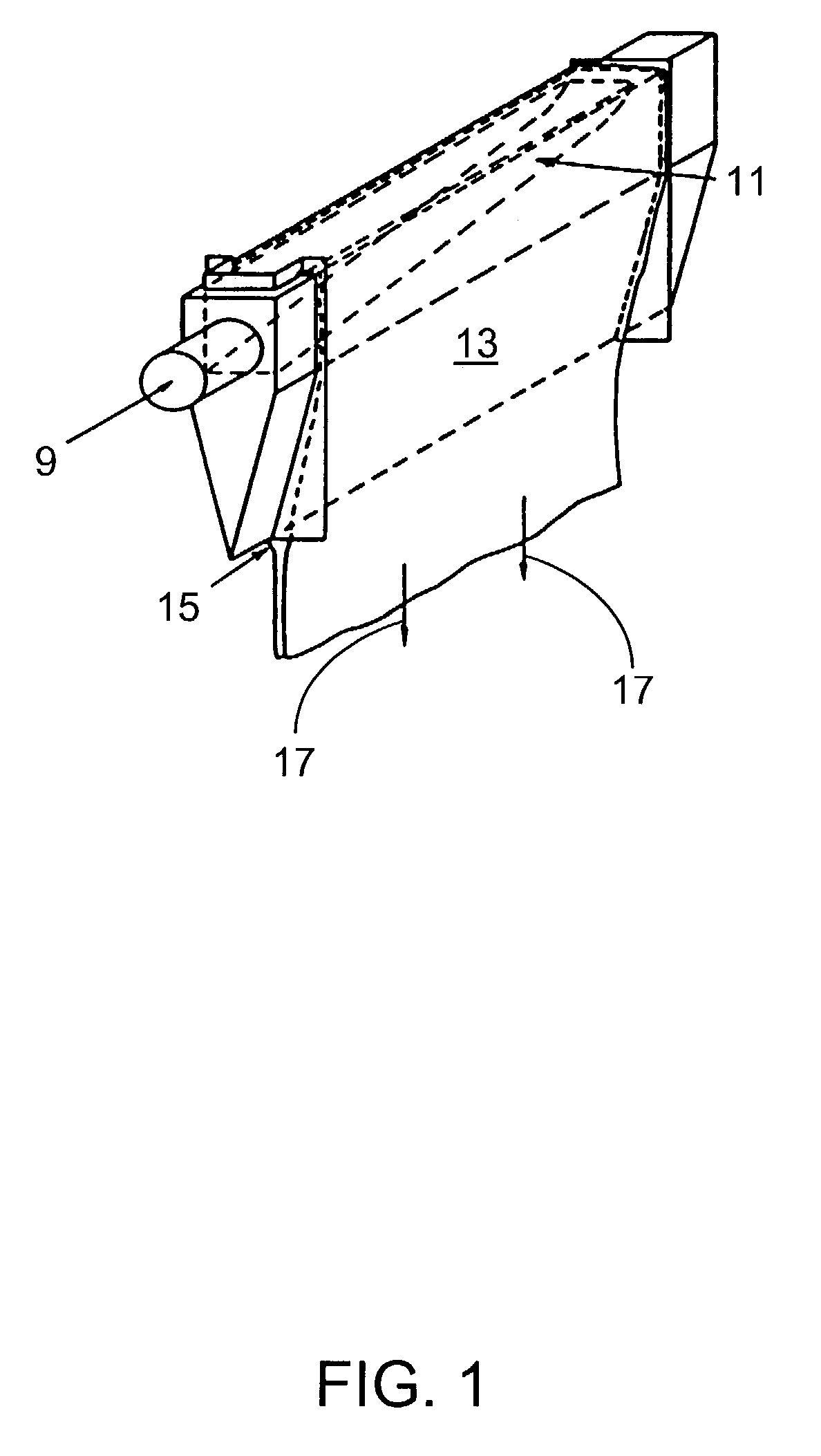
In the formation of sheet glass by the overflow downdraw process, the width of usable sheet glass is maximized by downwardly flowing edge portions of the sheet over web-like members and thereafter over extensions which intersect with and are downwardly inclined relative to the web-like members to thin edge portions of the glass flow and maintain sheet width. The extension members are preferably removably attached to the web-like members, greatly facilitating replacement of the more easily damaged extension members.
Owner:CORNING INC
Melting of glass
InactiveUS6715319B2Reduce the presence of air bubblesGlass furnace apparatusGlass rolling apparatusFlat glassMaterials science
A method of producing flat glass in which foam which appears on the surface of molten glass melted using oxy-fuel burners is dispersed by directing a diffuse, luminescent flame onto the surface of the glass carrying the foam.
Owner:PILKINGTON PLC
Strengthening flat glass by edge coating
InactiveUS6120908AMaximumHigh strengthCeramic layered productsGlass/slag layered productsFlat glassOptoelectronics
A method is described for strengthening or restoring strength to a flat brittle oxide substrate which includes the steps of coating the edges of the brittle oxide substrate with a strengthening composition without coating a significate portion of the flat surfaces. The strengthen brittle oxide substrate such as glass and a window containing as the window pane the edge strengthen glass are also provided.
Owner:ARKEMA INC
Devices and processes for nucleic acid extraction
ActiveUS20090215125A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFlat glassBinding site
Devices, processes, and kits for the extraction of nucleic acids from biological samples are disclosed. The devices comprise a first port, a second port, and a binding chamber intermediate and in fluid communication with the first port and the second port. The binding chamber comprises an unmodified flat glass surface effective for binding a heterogeneous population of nucleic acids. The first port, second port, and binding chamber define a continuous fluid pathway that is essentially free of nucleic acid-specific binding sites.
Owner:BLOOD CELL STORAGE
High strength aluminosilicate glass and chemically toughening process thereof
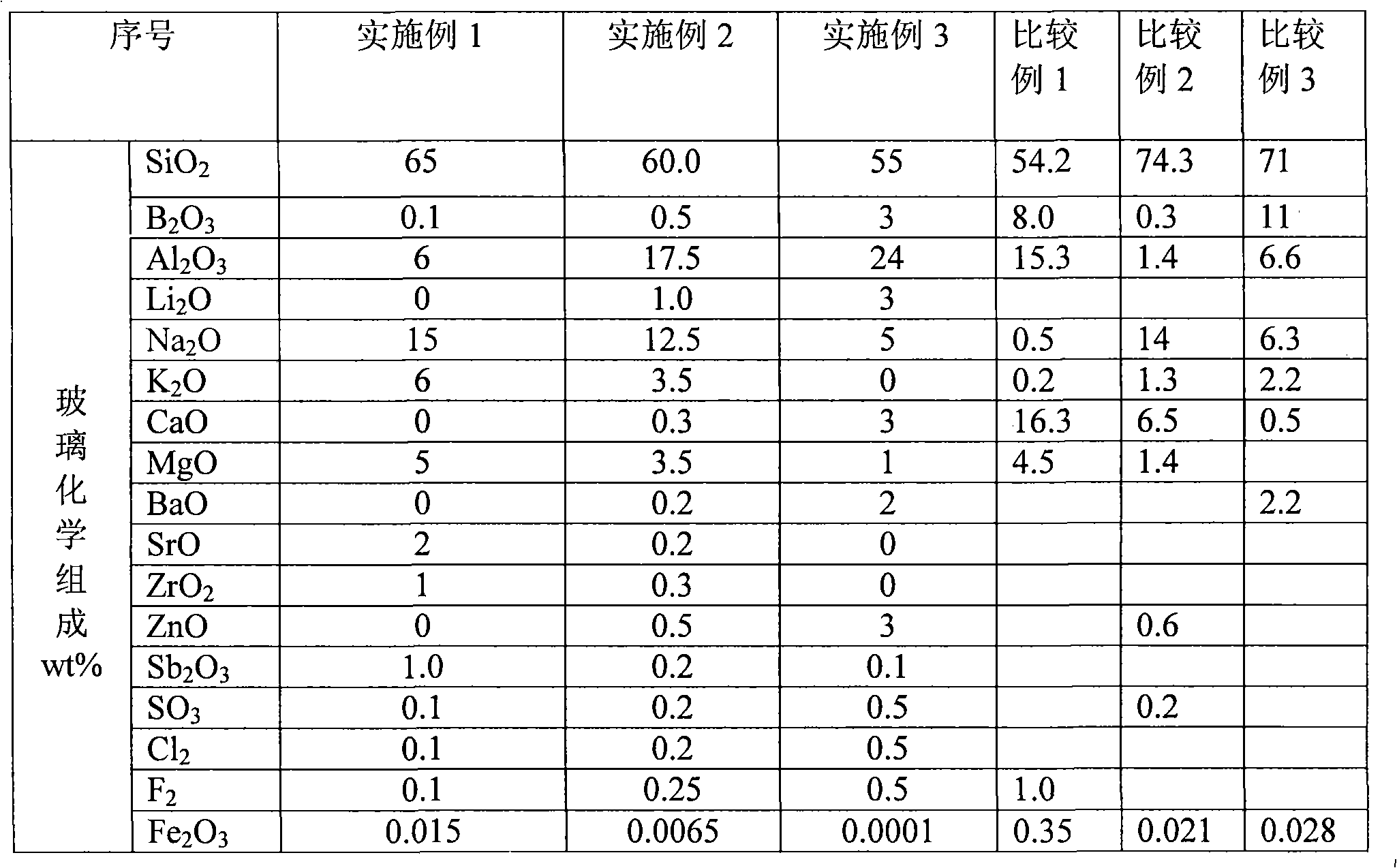
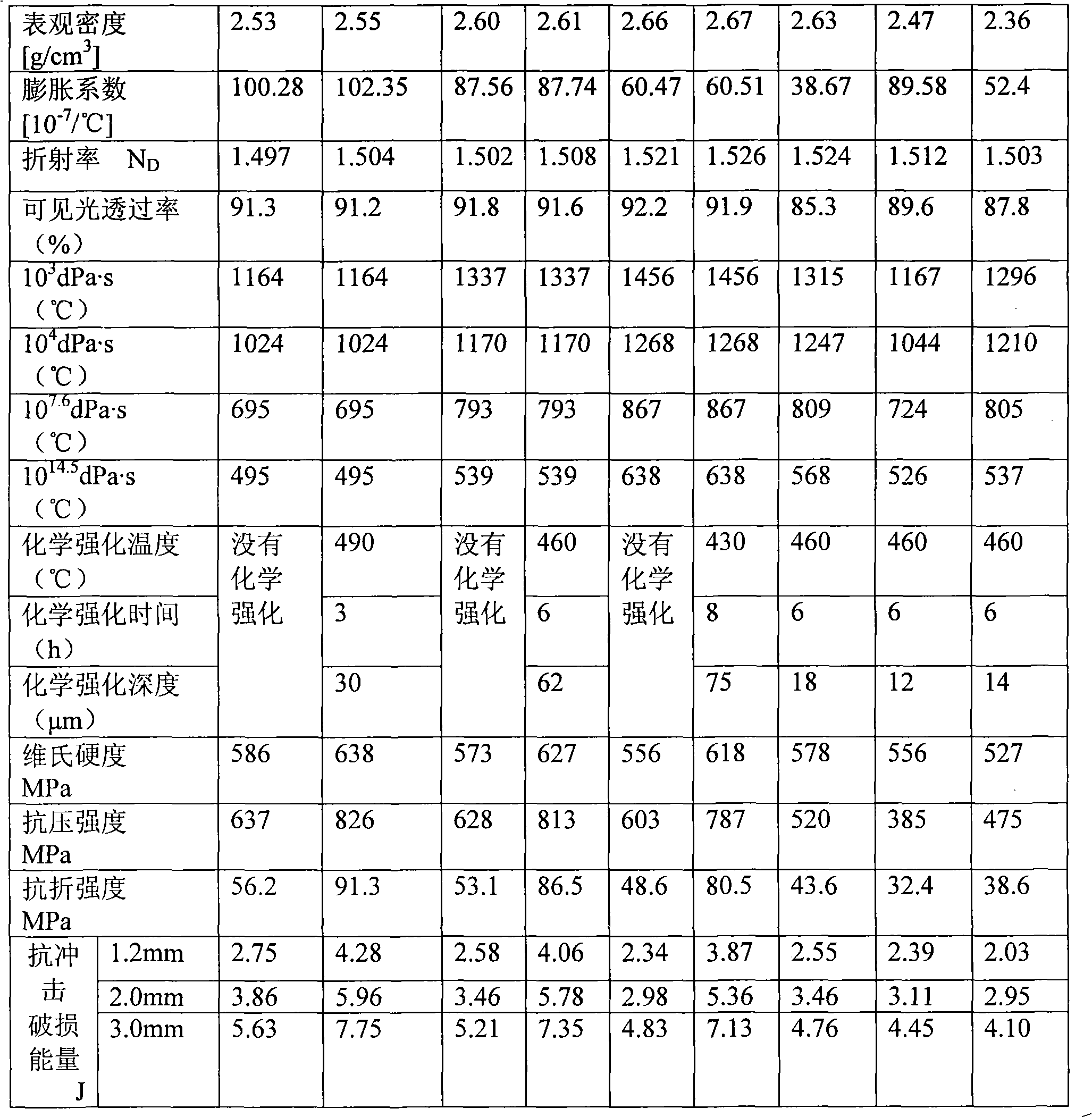
ActiveCN101337770AMeet the screen saver functionProtective functionGlass tempering apparatusAlkali freeShock resistance
The invention relates to a high-strength aluminate silicate glass and a chemical toughening method thereof, and belongs to the silicate glass field. The glass comprises the following chemical components (weight percent): 55 to 65 weight percent of SiO2, 0.1 to 3 weight percent of B2O3, 6 to 24 weight percent of Al2O3, 3 to 9 weight percent of MgO plus CaO plus BaO plus SrO, 0 to 1 weight percent of ZrO2, 0 to 2 weight percent of ZnO, 0.1 to 0.5 weight percent of Cl2, 0.1 to 1.0 weight percent of Sb2O3, 0.1 to 0.5 weight percent of SO3 and 0.1 to 0.5 weight percent of F2, and belongs to a aluminate silicate glass system. The high-strength aluminate silicate glass is prepared through a known plate glass production method, and then is subjected to the strengthening treatment by adopting the chemical toughening method. The glass has high permeability of visible light, and relatively common soda lime glass, neutral medicine glass and alkali-free high-aluminum glass have good shock resistance property, high scratch resistance property and high durability. The high-strength aluminate silicate glass is applied to the screen surface protection of plasma display products and liquid crystal display products, the protection of touch screens, the screen protection of automated teller machines, and the screen protection of other electronic products (Mobile phones, PDAs and media machines, etc.), thereby effectively preventing the impact and the scratch damage to the glass surface of display products. The high-strength aluminate silicate glass contains no harmful elements.
Owner:SUZHOU SHINWU OPTRONICS TECH
High-temperature polyamide molding compounds reinforced with flat glass fibers
ActiveUS20090062452A1Advantage in mechanical propertyAdvantage in in processingRotary stirring mixersSpecial tyresFlat glassGlass fiber
The present invention relates to reinforced polyamide molding compounds containing high-melting partially aromatic polyamides and flat glass fibers, in particular with a rectangular cross section, i.e., glass fibers with a noncircular cross-sectional area and a dimension ratio of the main cross-sectional axis to the secondary cross-sectional axis of 2 to 6, in particular 3 to 6, most especially preferably from 3.5 to 5.0. The present invention also relates to a method for manufacturing polyamide molding compounds and molded articles manufactured therefrom, i.e., in particular injection-molded parts. The inventive molded parts have a high transverse stiffness and transverse strength.
Owner:EMS PATENT AG
Non-contact porous air bearing and glass flattening device
Owner:NEW WAY MACHINE COMPONENTS
Sheet width control for overflow downdraw sheet glass forming apparatus
InactiveUS20050183455A1Minimize distortionKeep widthBlowing machine gearingsGlass furnace apparatusFlat glassManufactured apparatus
Owner:CORNING INC
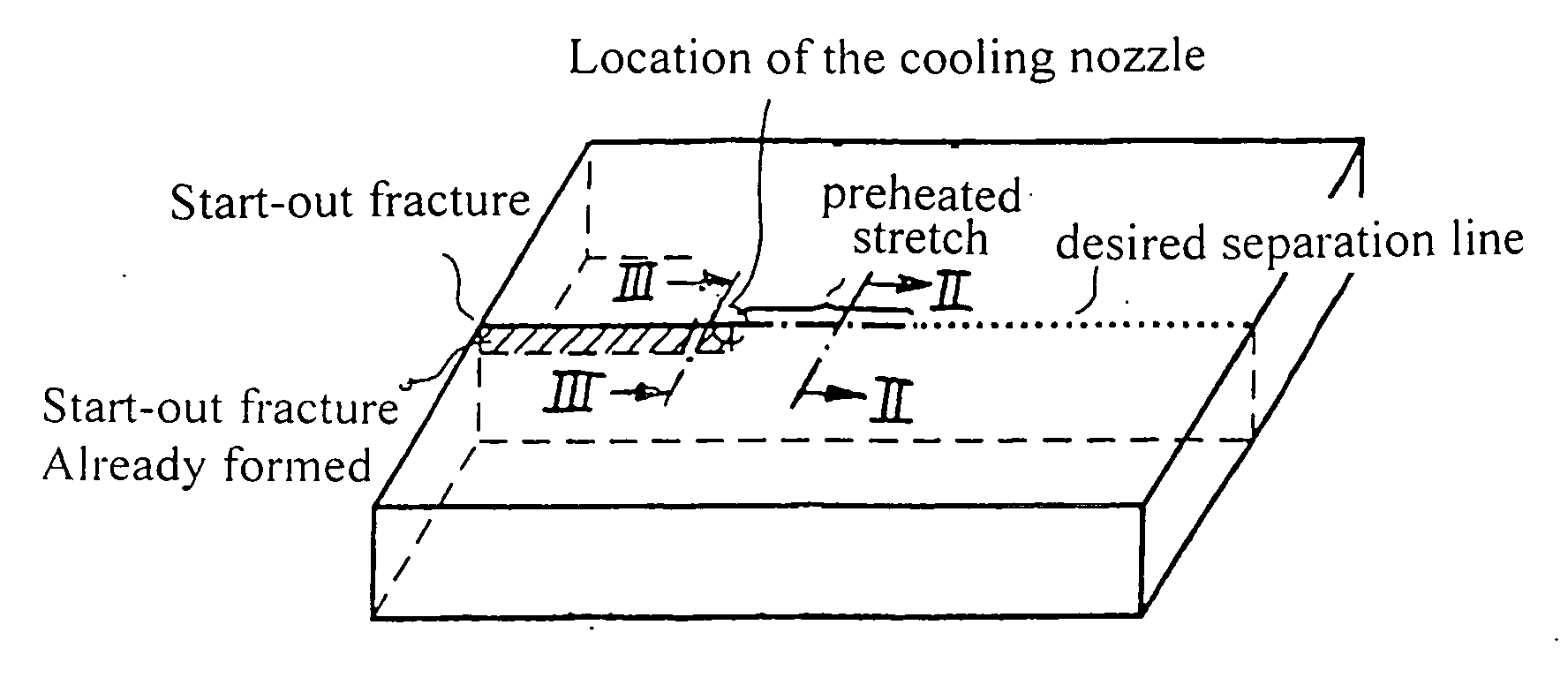
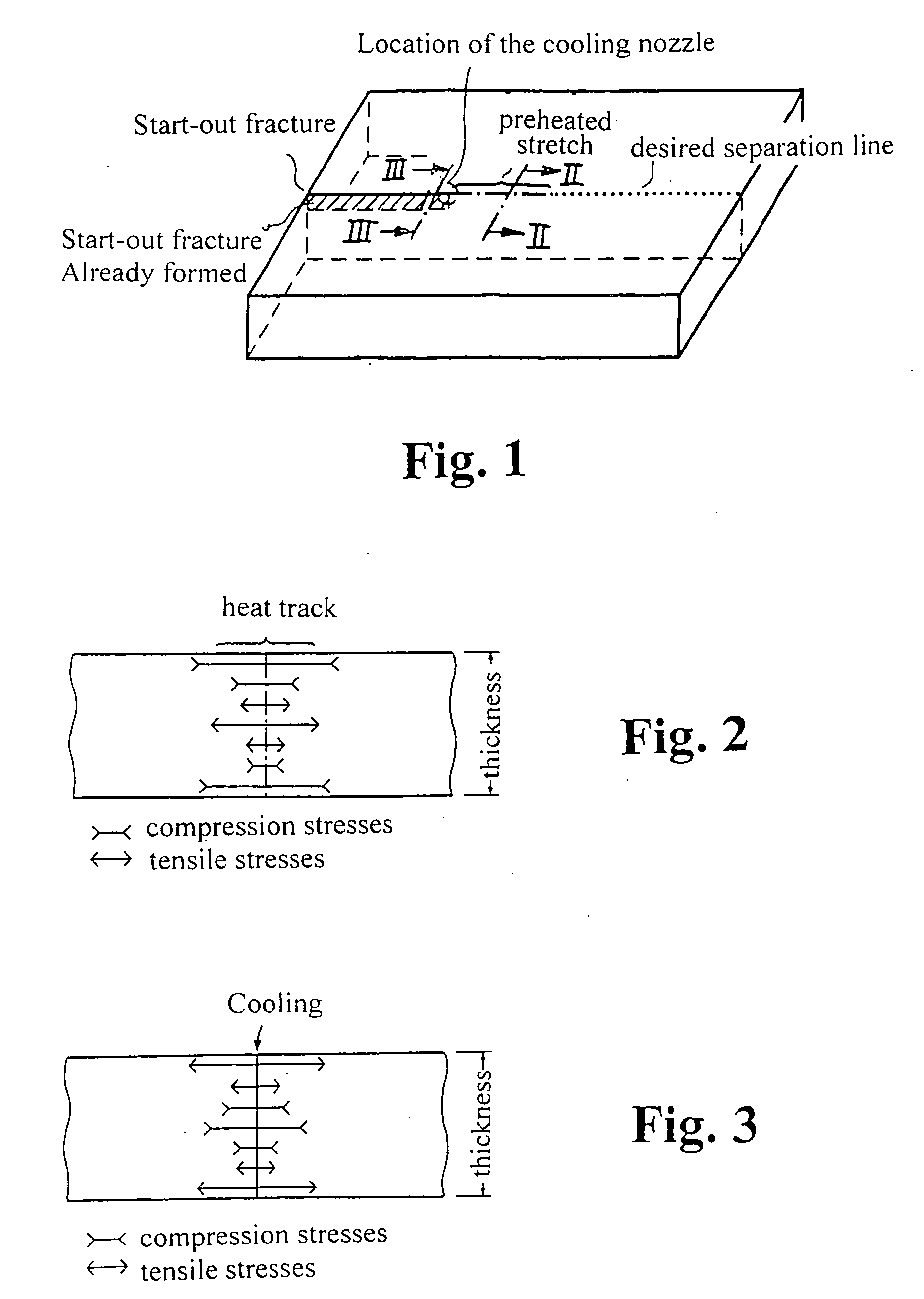
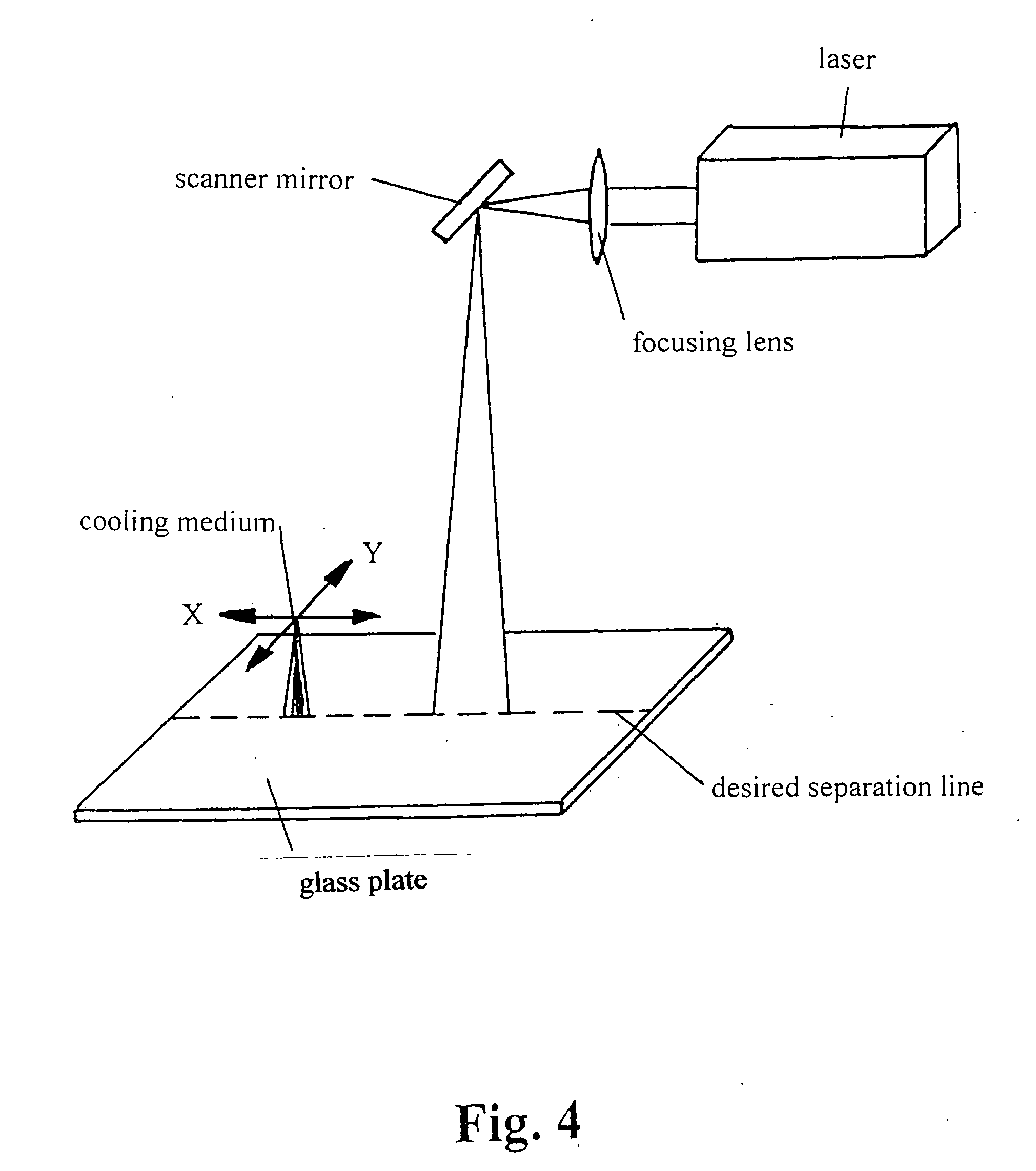
Method for laser-induced thermal separation of plate glass
InactiveUS20070151962A1Reduce surface temperatureFast cutting speedGlass severing apparatusWelding/soldering/cutting articlesFlat glassLaser heating
In a method for a laser-induced thermal separation of plate glass by thermal scoring using a laser beam heating the glass along a desired separation line with subsequent cooling of the laser-heated line, wherein the heat is applied by the laser beam in a number of repetitive passes at intensities based on glass thickness and desired cutting speeds.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV +1
Near Infrared Ray Reflective Substrate And Near Infrared Ray Reflective Laminated Glass Employing That Substrate, Near Infrared Ray Reflective Double Layer Glass
InactiveUS20090237782A1High visible lightImprove insulation effectMirrorsOptical filtersInfraredRefractive index
In a near-infrared reflective substrate prepared by forming on a transparent substrate a near-infrared reflective film prepared by alternate deposition of low-refractive-index dielectric films and high-refractive-index dielectric films, there is provided a near-infrared reflective substrate characterized in that the transparent substrate is a plate glass or polymer resin sheet, that it is 70% or greater in visible light transmittance defined in JIS R3106-1998, and that it has a maximum value of reflection that exceeds 50% in a wavelength region of 900 nm to 1400 nm.
Owner:CENT GLASS CO LTD
Overflow Downdraw Glass Forming Method and Apparatus
InactiveUS20070068197A1Reduce unevennessEfficient degradationBlowing machine gearingsGlass furnace apparatusFlat glassThermal creep
The present invention discloses improved methods and apparatus for forming sheet glass. In one embodiment, the invention introduces a counteracting force to the stresses on the forming structure in a manner such that the thermal creep which inevitably occurs has a minimum impact on the glass flow characteristics of the forming structure.
Owner:CORNING INC
Illuminated glass deck light panel and method of installation
In a preferred embodiment, an illuminated glass deck light panel, including: a plurality of glass pavers, structural plank glass elements, or other structural lenses; a longitudinally extending support pan for embedding in a supporting substrate; the plurality of glass pavers, structural plank glass elements, or other structural lenses resting on ledges formed in the support pan; a sealing material disposed between the glass pavers, structural plank glass elements, or other structural lenses and the support pan; a plurality of illumination sources disposed in the support pan underneath the plurality of glass pavers, structural plank glass elements, or other structural lenses; and the plurality of illumination sources being at all times illuminated whenever one of the plurality of illumination sources is illuminated. The plurality of illumination sources may also be selected from the group consisting of: pulsed illumination sources, blinking illumination sources, and progressive illumination sources to direct persons in a certain direction.
Owner:SANDOR FREDERICK J SR
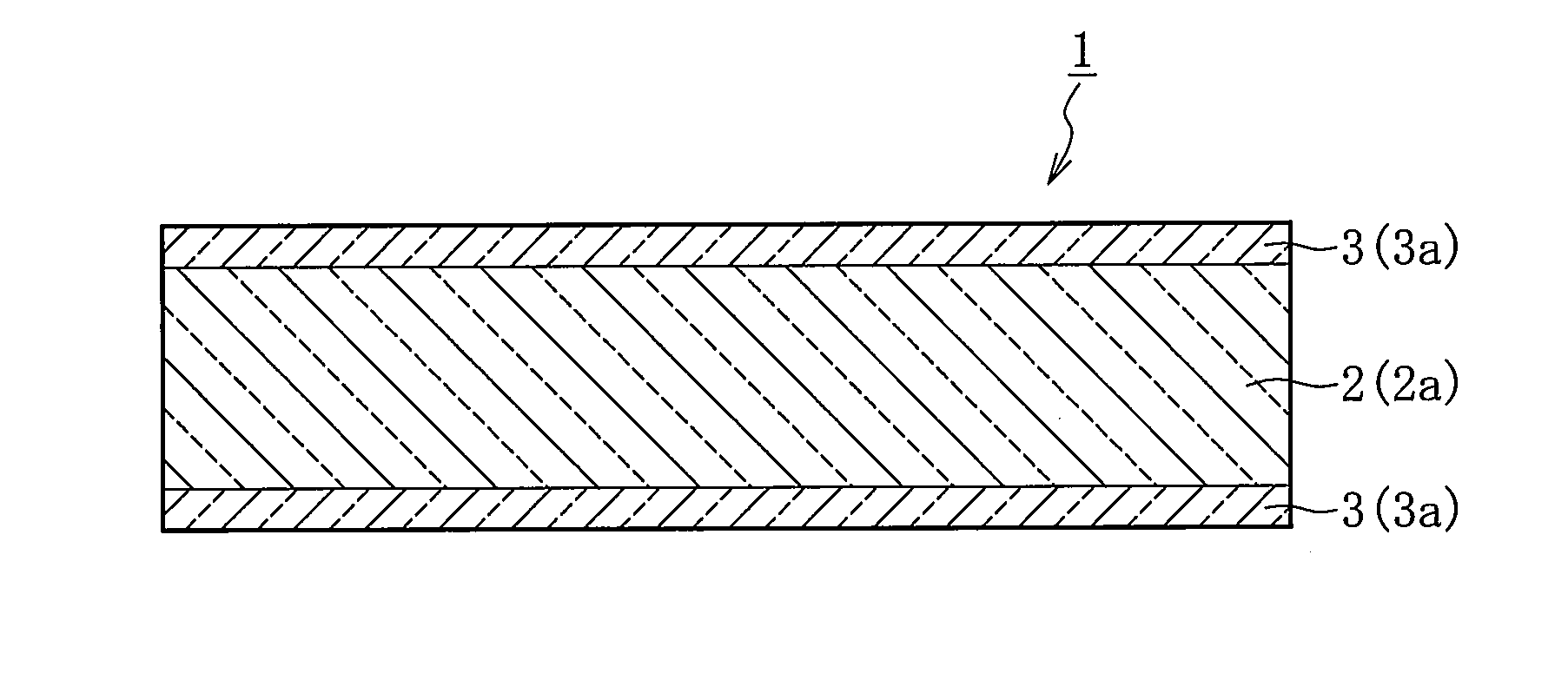
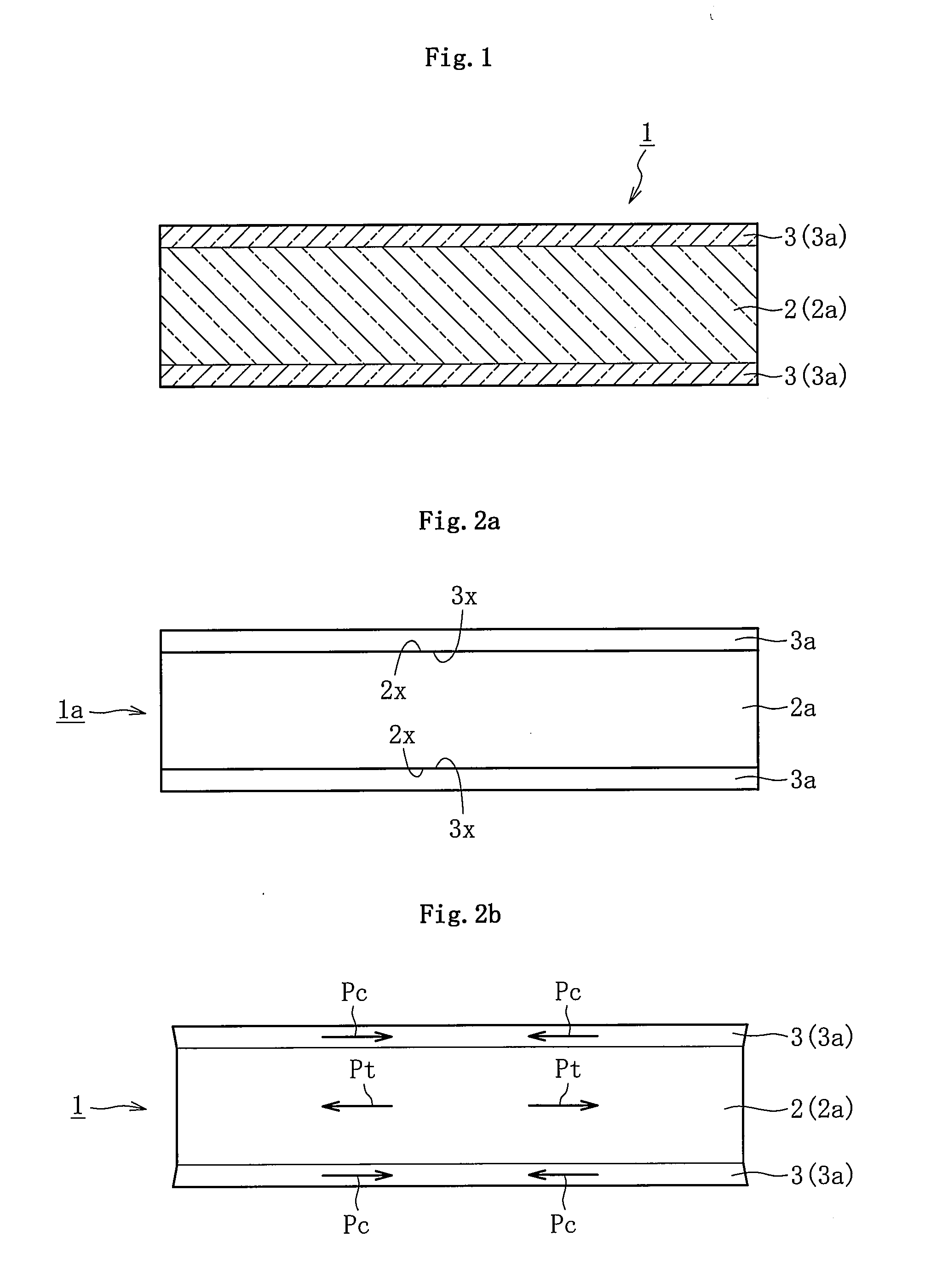
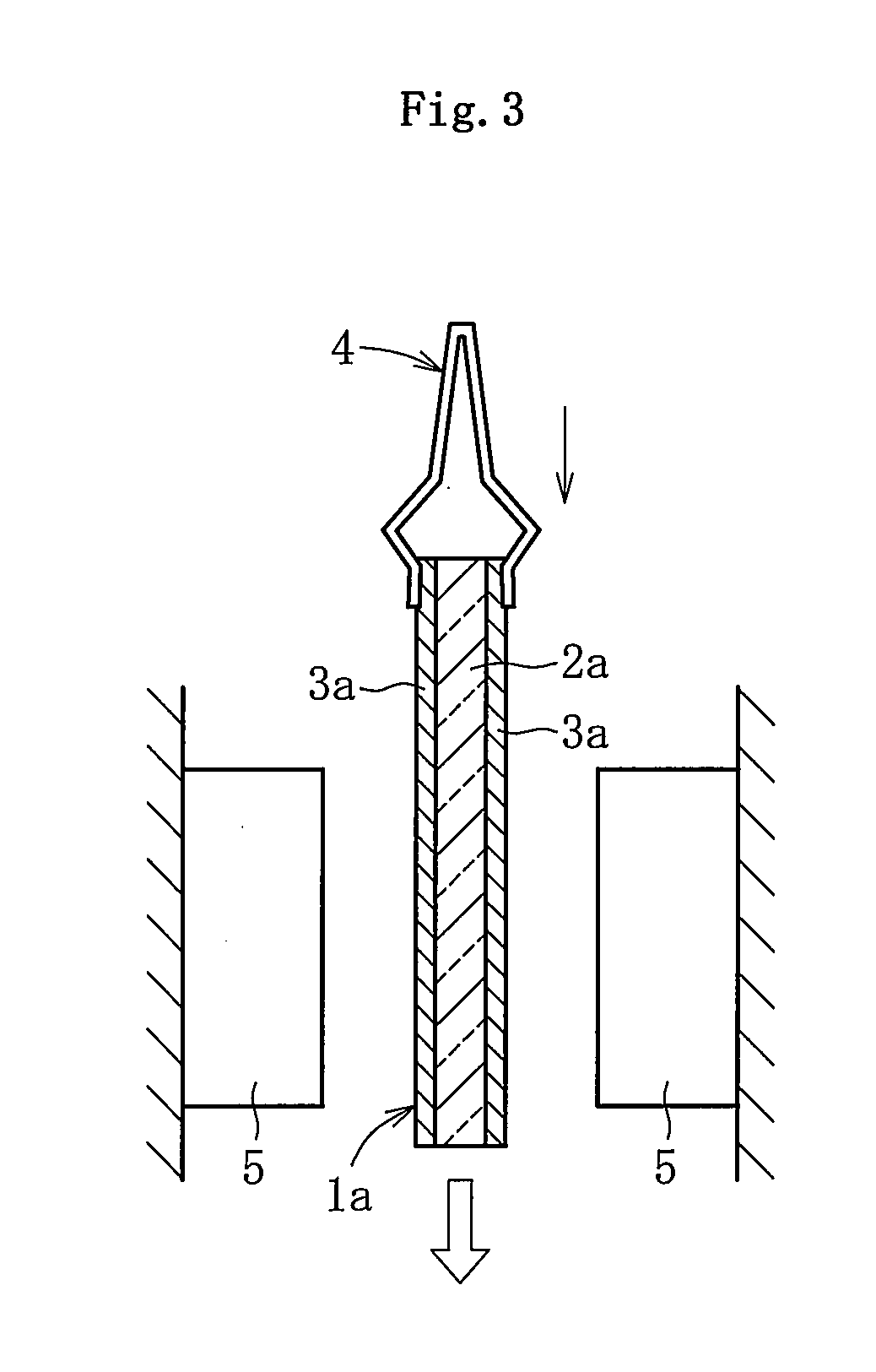
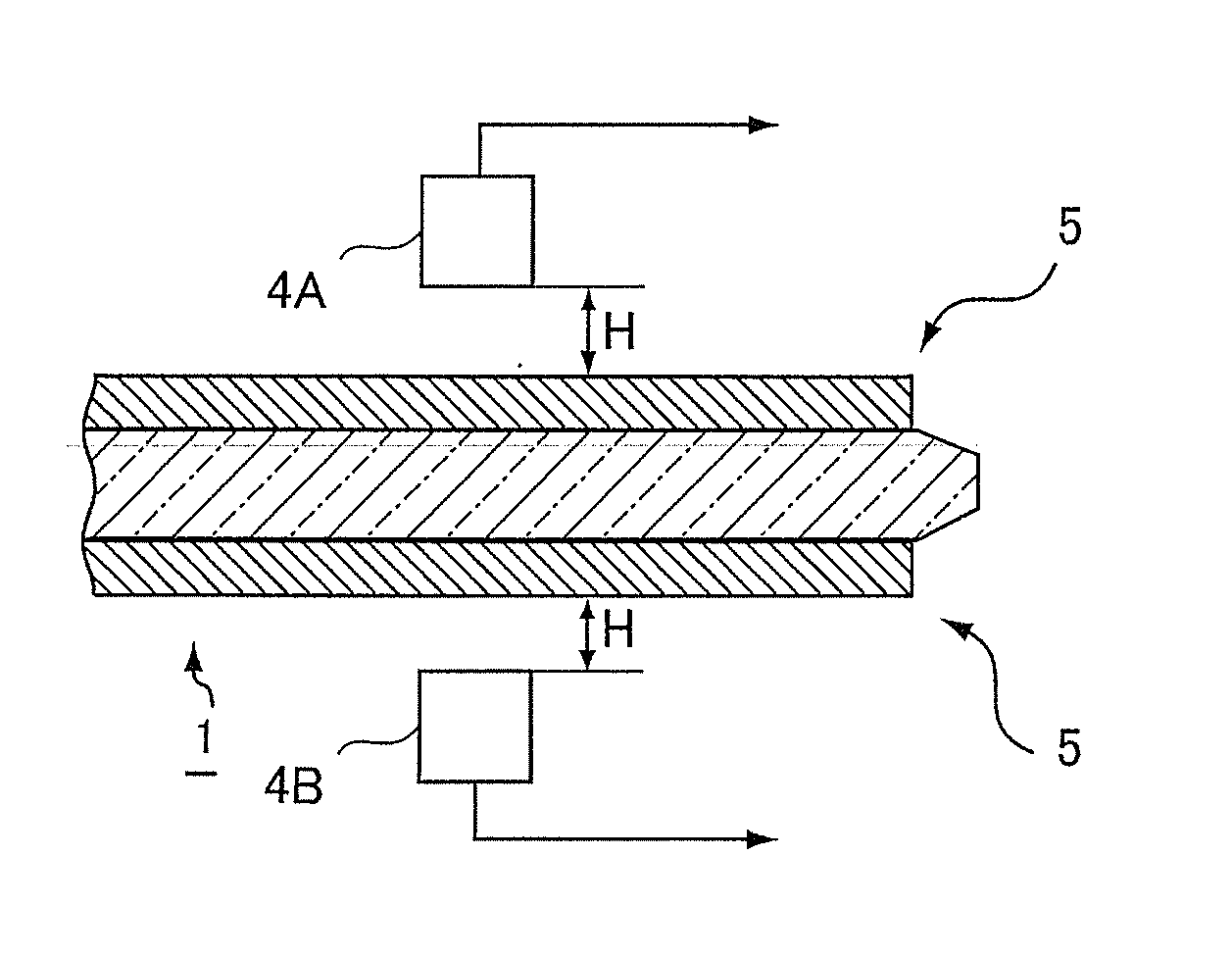
Reinforced plate glass and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20110200805A1Simple processReduce work costsGlass/slag layered productsGlass reforming apparatusFlat glassSurface layer
Provided is a method, including: performing heat treatment, under a state in which a thick core plate glass (2a) having a higher thermal expansion coefficient and a thin surface-layer plate glass (3a) having a lower thermal expansion coefficient are laminated together, so that the laminated portion has a temperature equal to or higher than the lower softening point out of the softening points of the core plate glass (2a) and the surface-layer plate glass (3a), thereby melt-bonding the core plate glass (2a) and the surface-layer plate glass (3a); and then performing cooling so as to attain a temperature less than the lower strain point out of strain points of the core plate glass (2a) and the surface-layer plate glass (3a), to thereby form a compression stress in a surface layer portion (3) corresponding to the surface-layer plate glass (3a) and form a tensile stress in a core portion (2) corresponding to the core plate glass (2a).
Owner:NIPPON ELECTRIC GLASS CO LTD
Glass substrate for magnetic disk and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20110159321A1Good surface irregularity accuracyImprove impact resistanceMagnetic materials for record carriersRecord information storageFlat glassSurface roughness
The present invention provides a method for efficiently manufacturing a glass substrate for magnetic disk having good accuracy of a surface irregularity and an impact resistance. The method includes the steps of: performing press forming to molten glass to prepare a sheet glass material, the sheet glass material having a roughness of the principal surface of 0.01 μm or less and target flatness of a glass substrate for magnetic disk; chemically strengthening the sheet glass material by dipping the sheet glass material in a chemically strengthening salt, thereby preparing a disk substrate; polishing the principal surfaces of the disk substrate. A thickness of the sheet glass material prepared in the press forming step is larger than a target thickness of the glass substrate for magnetic disk by a polishing quantity of the principal surface polishing step.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Methods of fabricating flat glass with low levels of warp
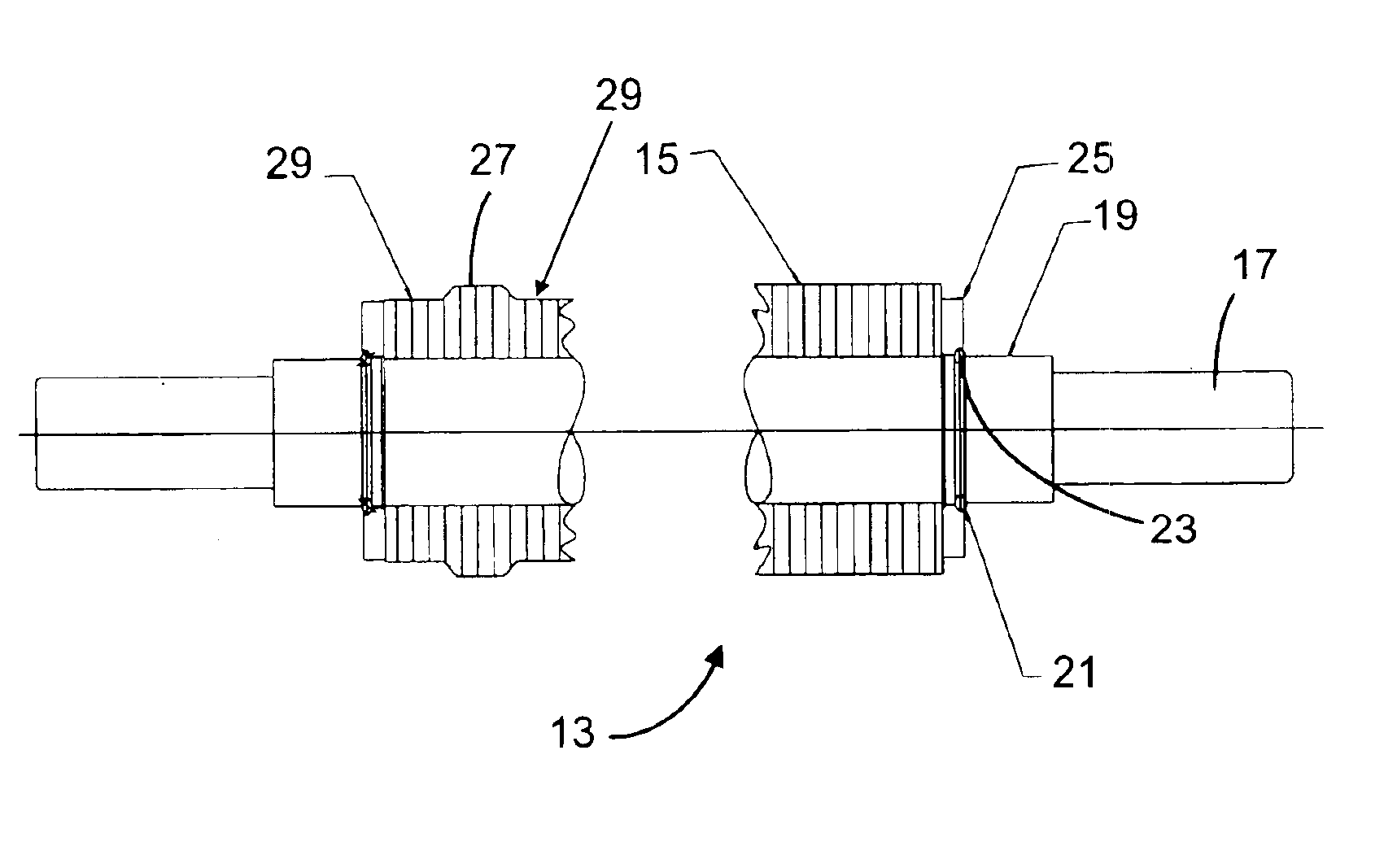
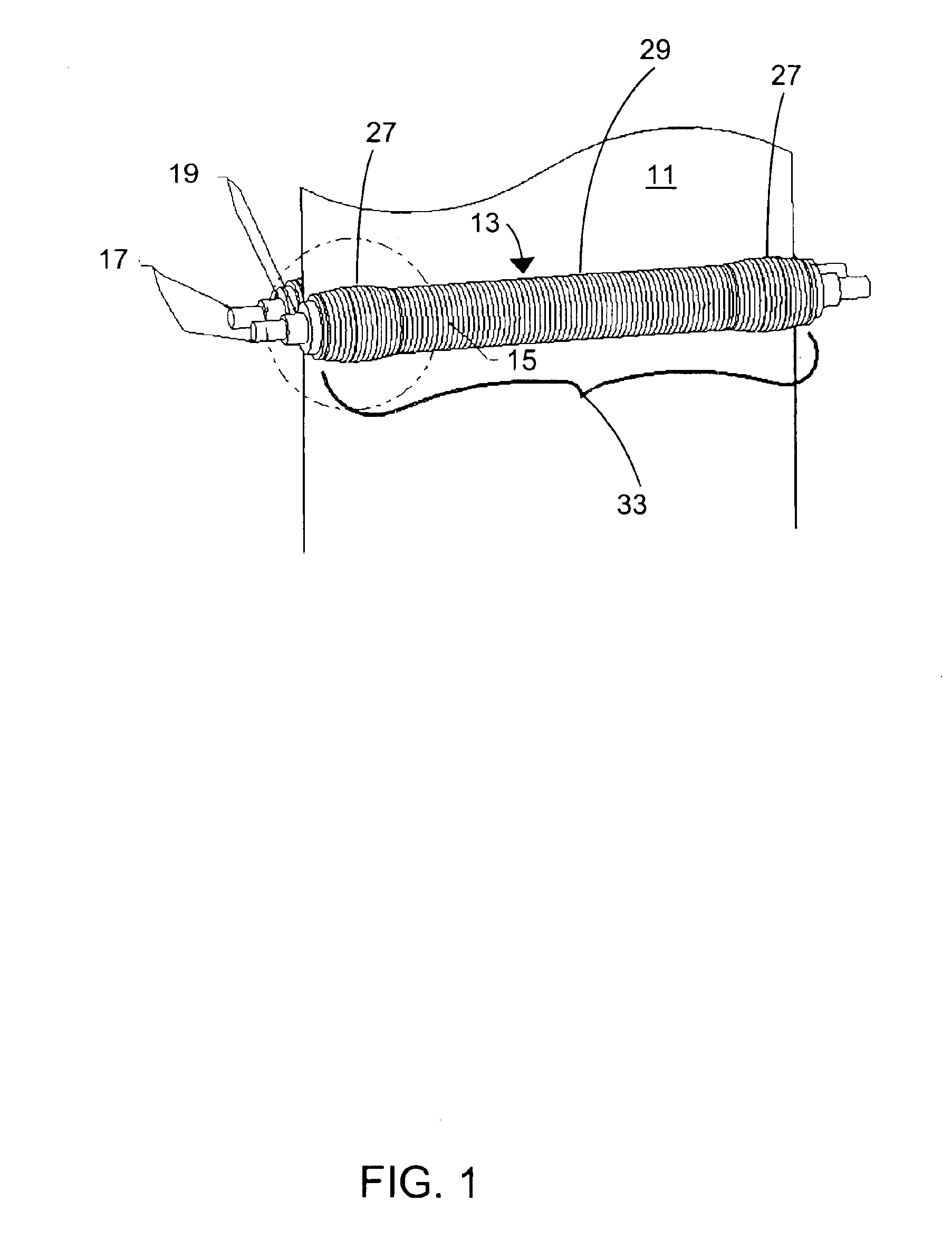
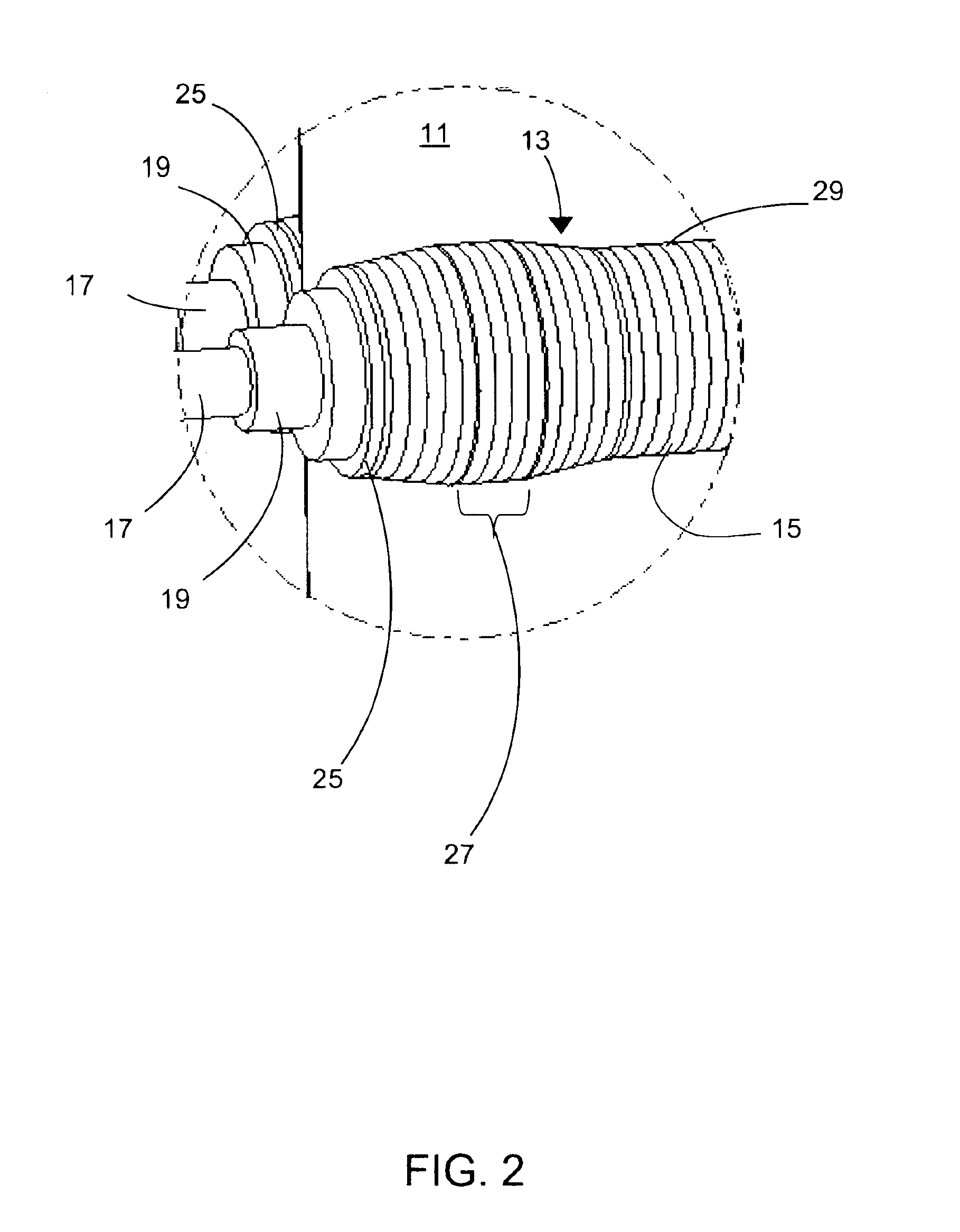
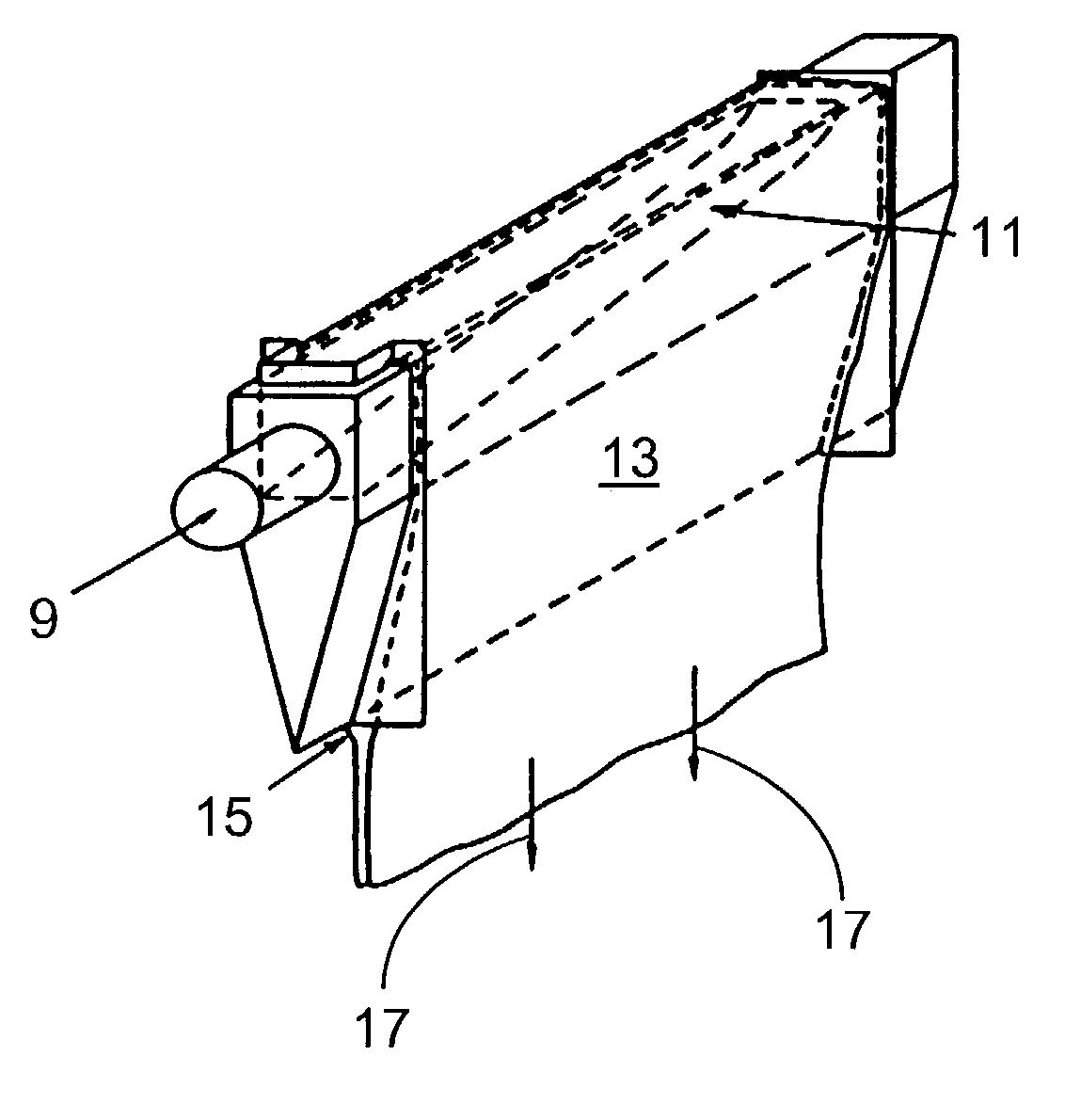
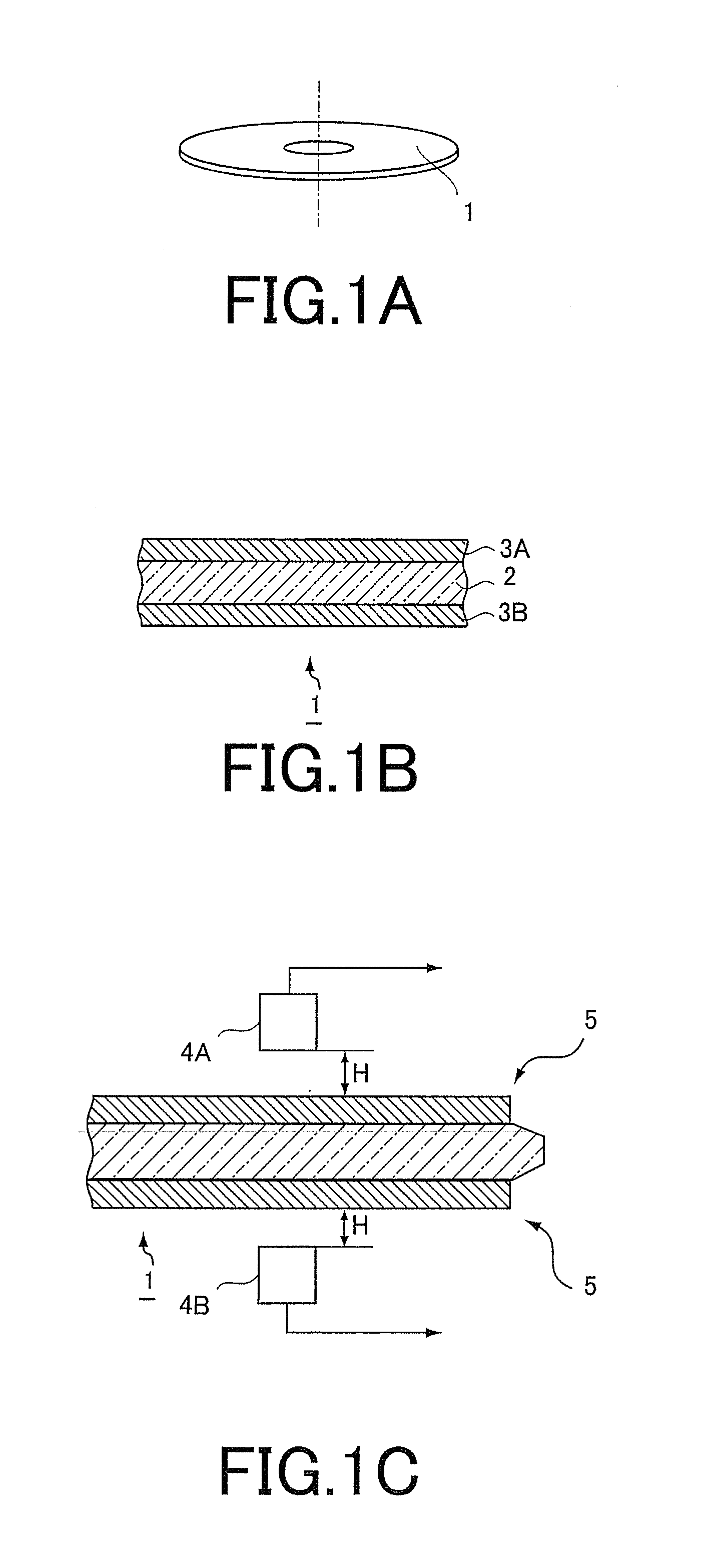
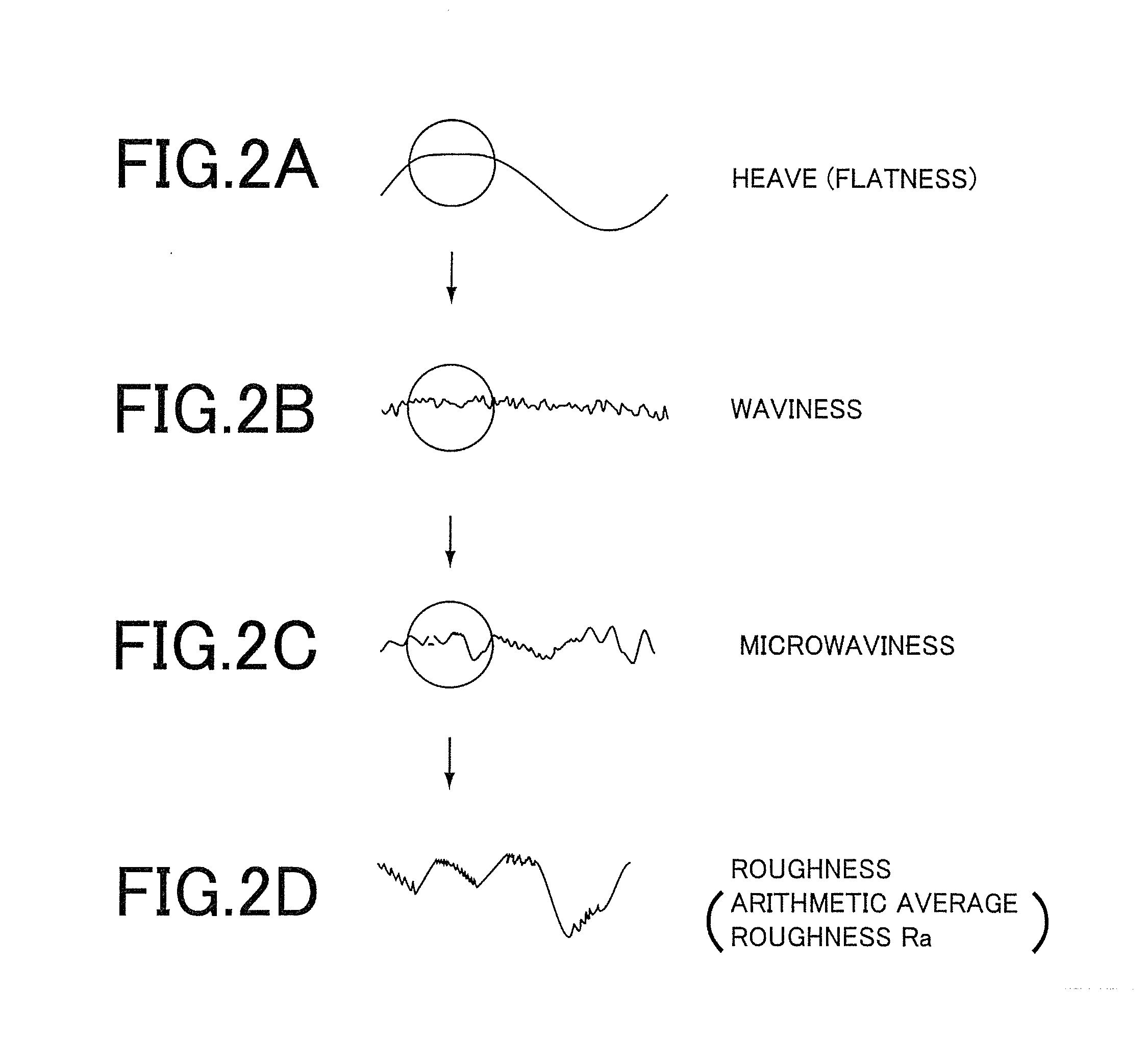
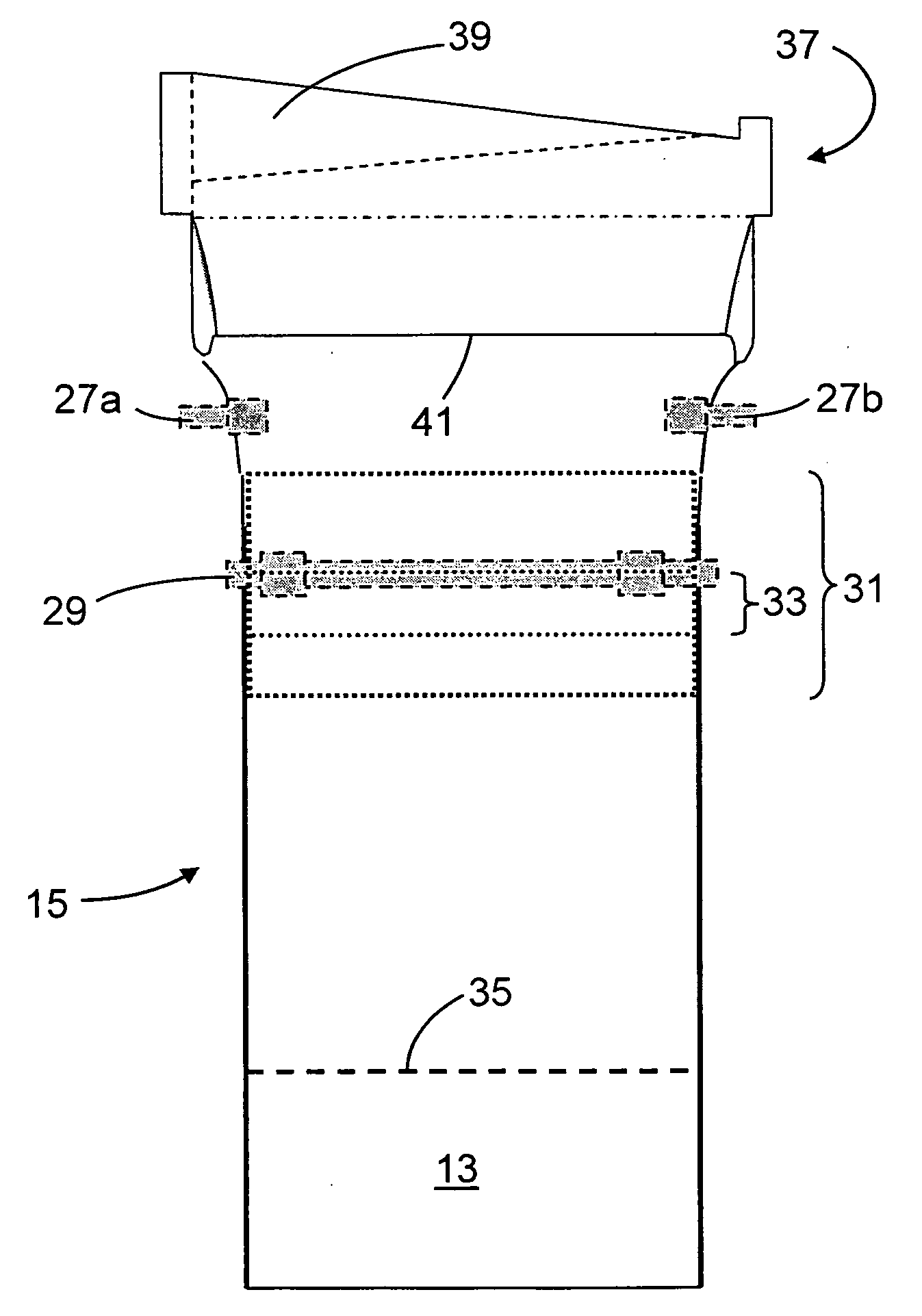
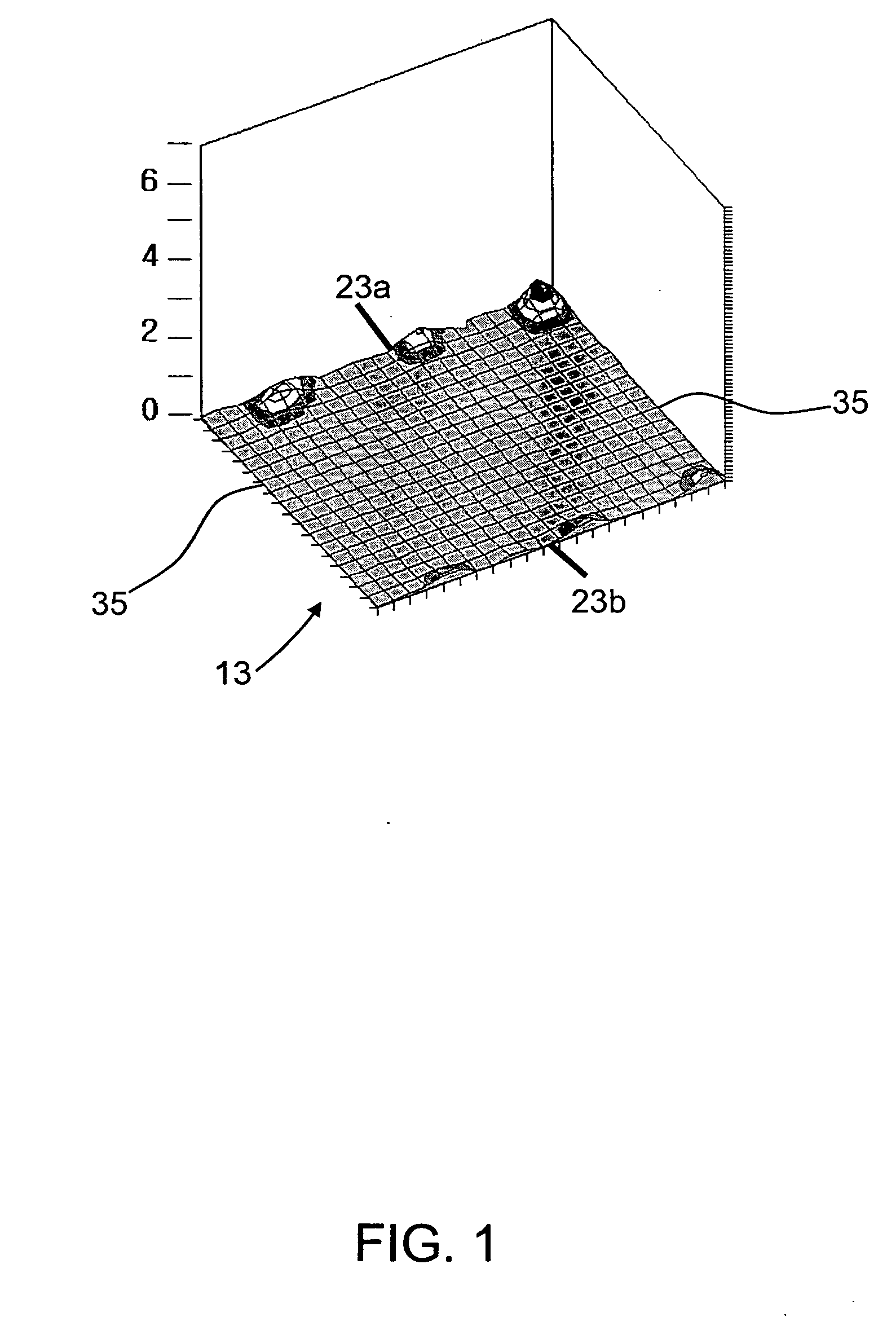
InactiveUS20070062219A1Reduces temperature of glassReduce widthGlass drawing apparatusGlass forming apparatusFlat glassVitrification
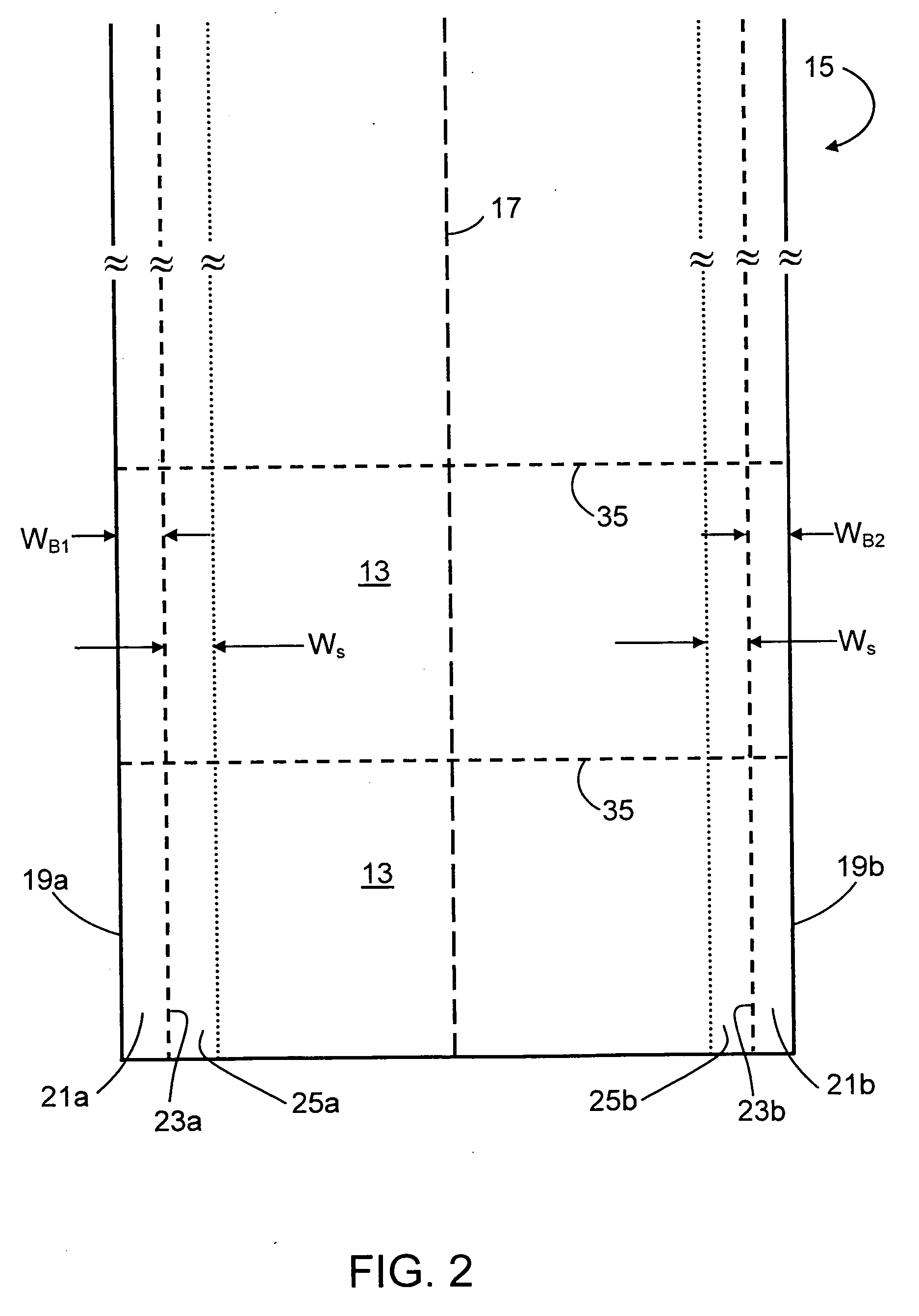
A method of fabricating glass sheets (13) is provided in which the sheets are cut from a glass ribbon (15) composed of a glass having a glass transition temperature range (GTTR). The ribbon (15) is formed by a drawing process in which edge rollers (27a,27b) contact the glass ribbon (15) at a location along the length of the ribbon where the temperature along the center line (17) of the ribbon (15) is above the GTTR. The edge rollers (27a,27b) locally cool the ribbon (15), and the cooling produces a sine wave type buckling (S-warp) along the edges of the glass sheets (13). The S-warp is reduced or eliminated by heating the bead portions (21a, 21b) of the ribbon (15) and / or portions of the ribbon (the S-warp portions 25a and 25b) which are located next to the bead portions (21a, 21b) and / or by cooling the center portion of the ribbon (15) at least one location along the length of the ribbon (15) where the temperature at the ribbon's center line (17) is within the GTTR.
Owner:CORNING INC
Method of making reflector for solar collector or the like and corresponding product
A reflector (e.g., mirror) for use in a solar collector or the like is provided. In certain example embodiments of this invention, a reflector is made performing at least the following steps: (a) forming a reflective coating on a flat glass substrate, (b) cold-bending the glass substrate with the reflective coating thereon; and (c) applying a plate member (e.g., thermoplastic or glass based) to the cold-bent glass substrate, the plate member for maintaining the coated glass substrate in a desired bent orientation. In certain example embodiments, the glass substrate supporting the reflective coating may be maintained in desired bent form by using another glass substrate and a glue layer provided between the another glass substrate and the glass substrate supporting the coating. The bent reflector (e.g., mirror) may be used in a solar collector, or in any other suitable application.
Owner:GUARDIAN EURO S A R L
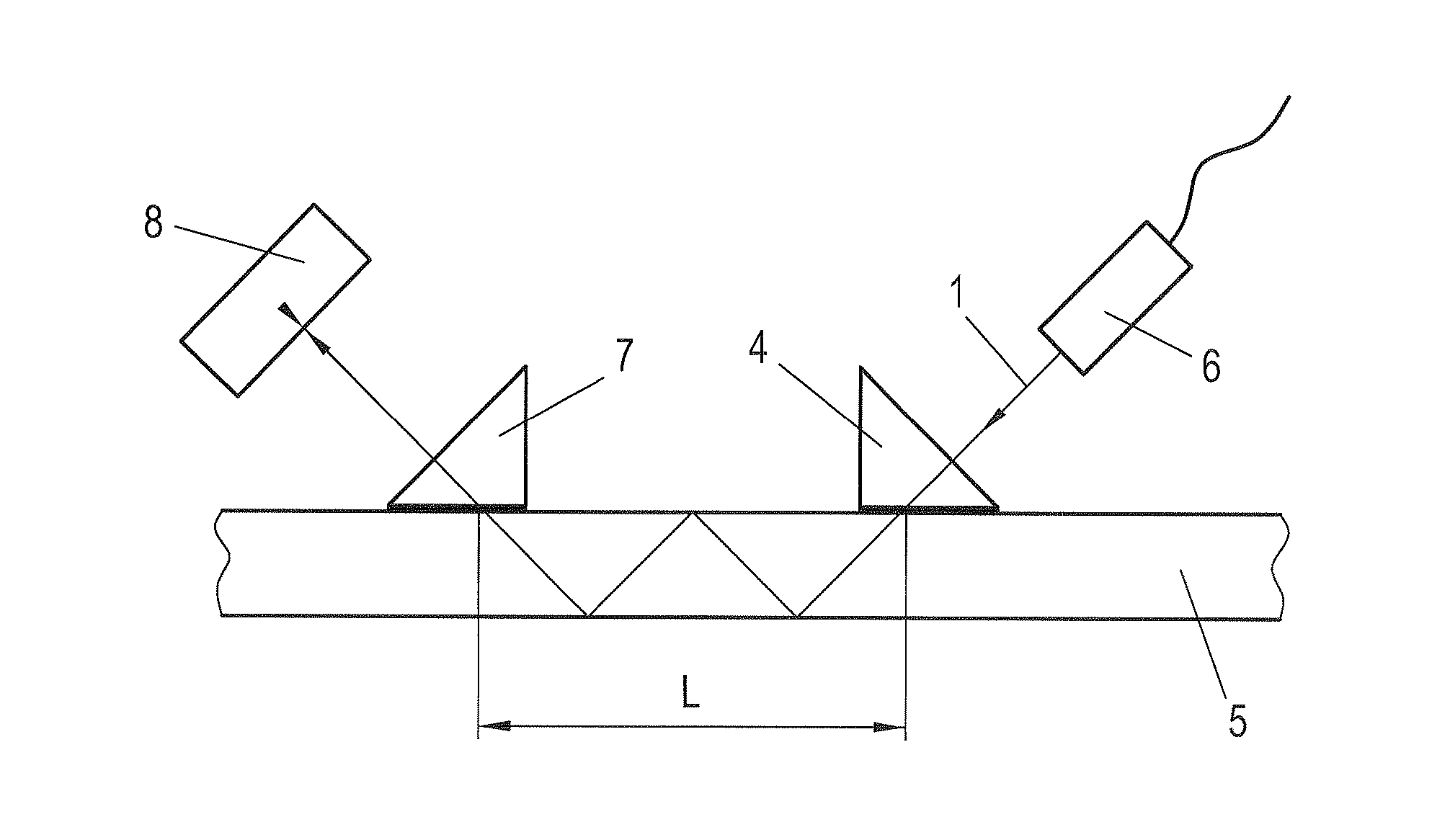
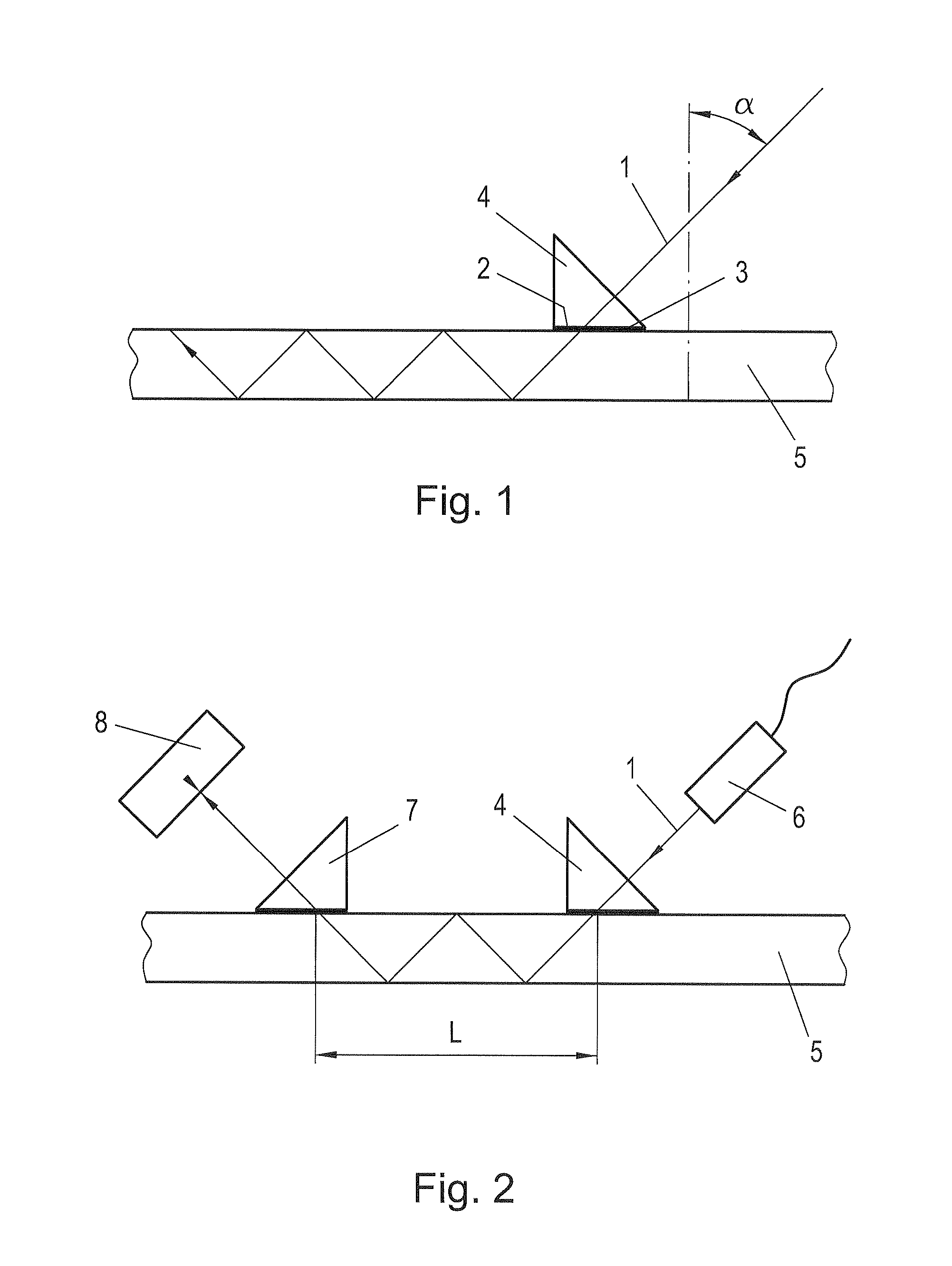
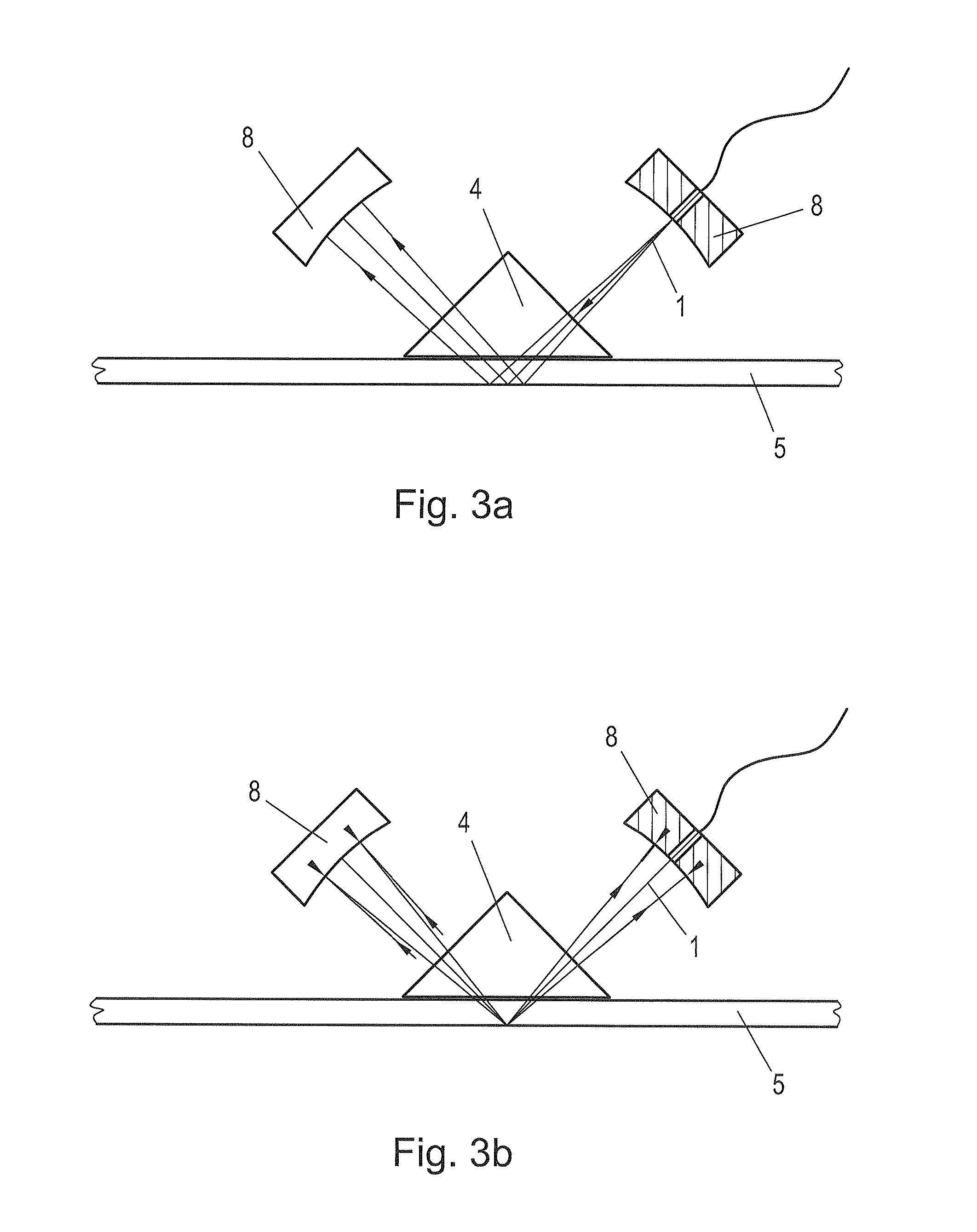
Method and arrangement for creating bevels on the edges of flat glass
When dividing glass using laser radiation into blanks (5) made of glass, a bundled laser beam (1) is directed onto the glass to be divided, and while forming at least two blanks (5), the glass is divided with sides (15) lying in the area of the cut. After the glass is divided, a laser beam (1) is directed onto at least one edge (16) of a side (15) of the formed blank (5) in order to separate glass from the edge (16) while forming a bevel (17) that lies on the side (15). For forming the bevel (17), at least one laser source (6) and a reflector (19) assigned to the latter are moved along the side (15) so that the laser beam (1)—which with the plane of the blank (5) encompasses an acute angle—is effective for forming the bevel (17).
Owner:LISEC AUSTRIA
Touch Force Detecting Apparatus For Infrared Touch Screen
InactiveUS20090015564A1Reducing and even eliminating false touchImprove touch accuracyInput/output processes for data processingFlat glassSignal processing circuits
An apparatus for detecting touch force of an infrared touch screen comprises a plate glass, a sensor, an infrared transmit and receive array, a signal processing circuit, and a micro-controller for controlling the touch screen. Said sensor is a mechanical force sensor, and its signal output port is connected with a input port of the signal processing circuit. An output port of the signal processing circuit is connected with an I / O interface of the micro-controller for control the touch screen.
Owner:BEIJING UNITOP NEW TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com