Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
26479 results about "Heat treating" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Heat treating (or heat treatment) is a group of industrial and metalworking processes used to alter the physical, and sometimes chemical, properties of a material. The most common application is metallurgical. Heat treatments are also used in the manufacture of many other materials, such as glass. Heat treatment involves the use of heating or chilling, normally to extreme temperatures, to achieve the desired result such as hardening or softening of a material. Heat treatment techniques include annealing, case hardening, precipitation strengthening, tempering, carburizing, normalizing and quenching. It is noteworthy that while the term heat treatment applies only to processes where the heating and cooling are done for the specific purpose of altering properties intentionally, heating and cooling often occur incidentally during other manufacturing processes such as hot forming or welding.
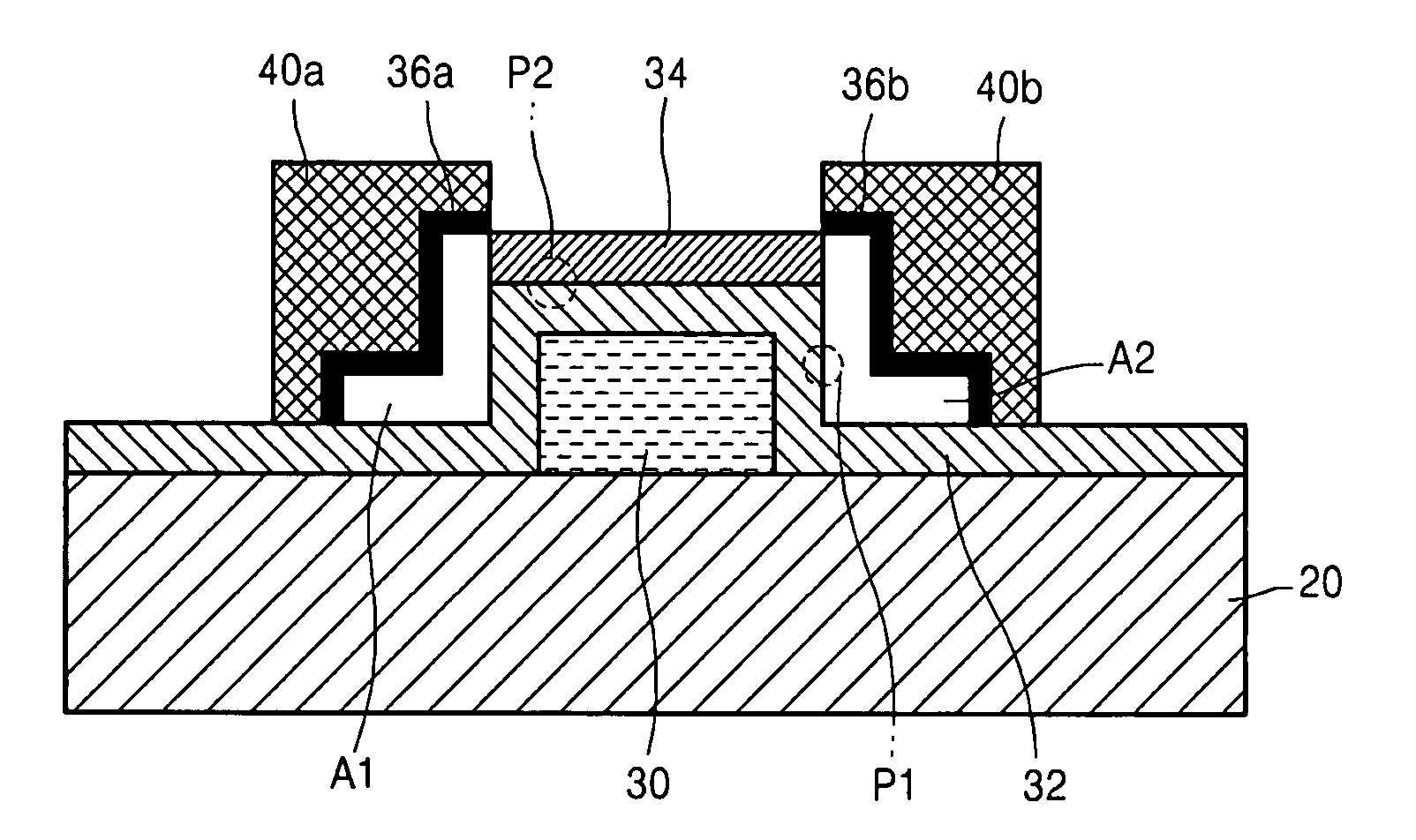
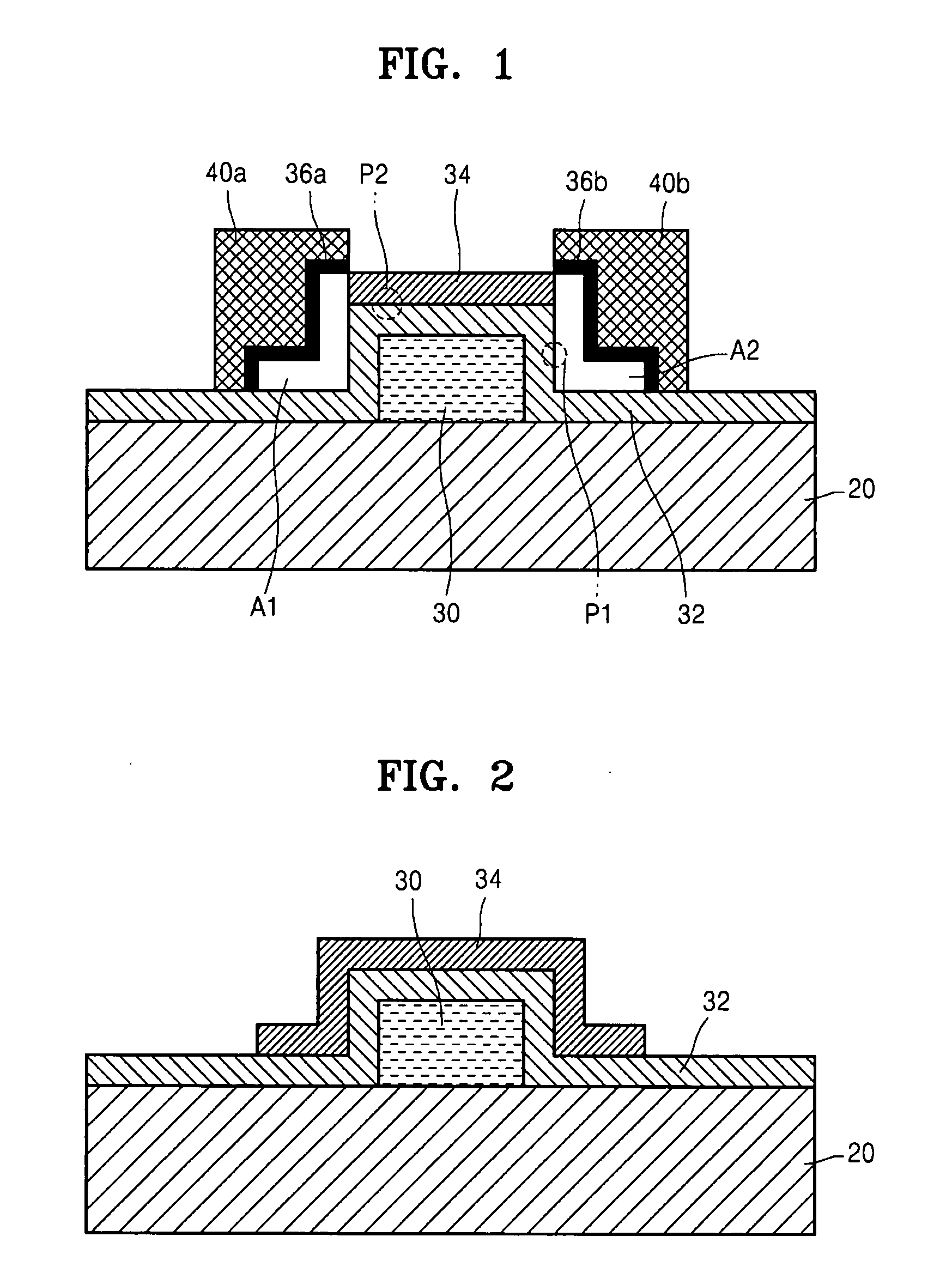
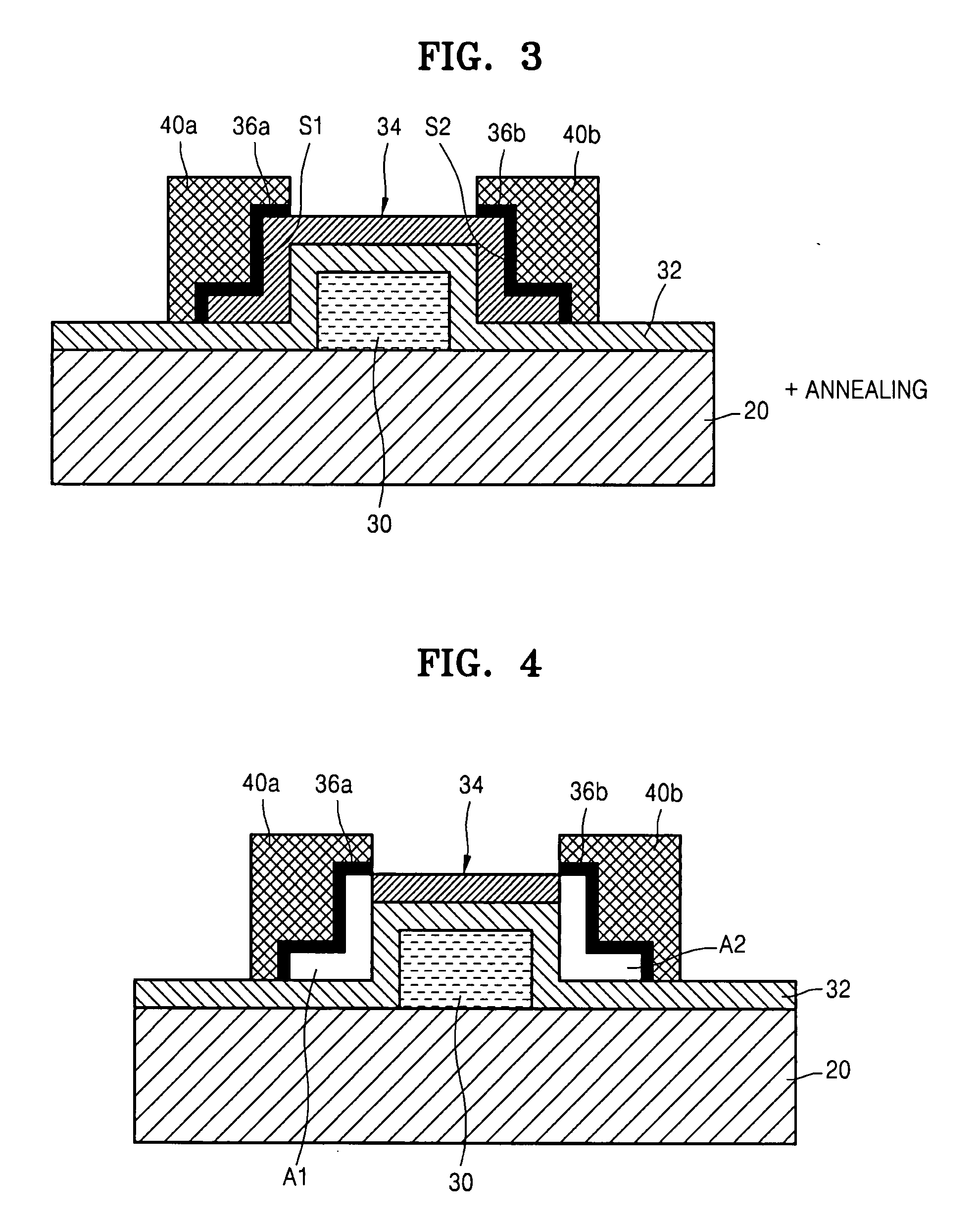
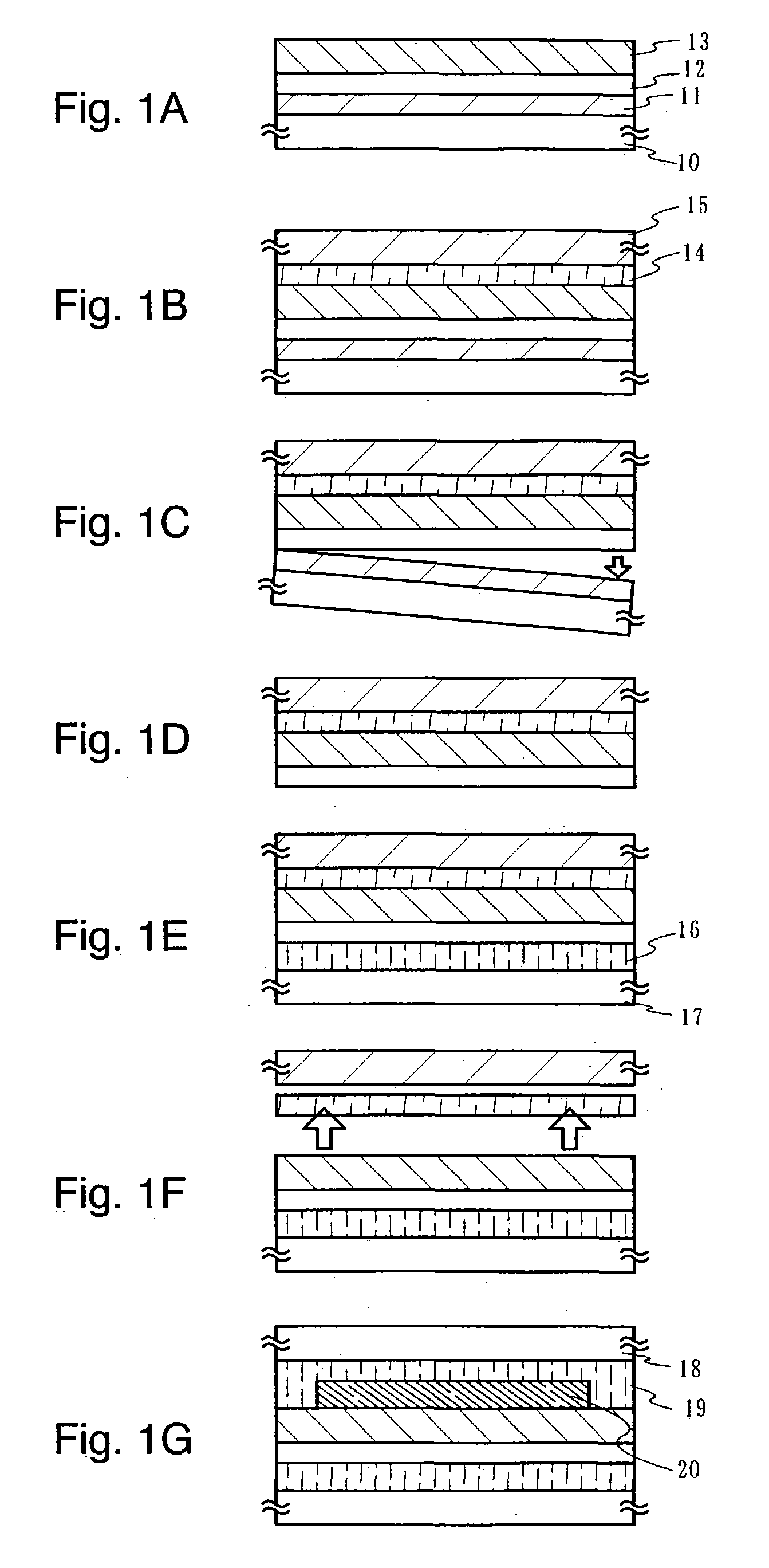
Thin film transistor including selectively crystallized channel layer and method of manufacturing the thin film transistor
ActiveUS20080258140A1Stable contact characteristicHigh carrier mobilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesEngineeringIon implantation
Provided are a thin film transistor (TFT) including a selectively crystallized channel layer, and a method of manufacturing the TFT. The TFT includes a gate, the channel layer, a source, and a drain. The channel layer is formed of an oxide semiconductor, and at least a portion of the channel layer contacting the source and the drain is crystallized. In the method of manufacturing the TFT, the channel layer is formed of an oxide semiconductor, and a metal component is injected into the channel layer so as to crystallize at least a portion of the channel layer contacting the source and the drain. The metal component can be injected into the channel layer by depositing and heat-treating a metal layer or by ion-implantation.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Electrosurgical instrument and method of use
InactiveUS7112201B2Reduce conductancePrevent any substantial dehydrationSurgical instruments for heatingCoatingsMicron scaleElastomer
An electrosurgical medical device and method for creating thermal welds in engaged tissue. In one embodiment, at least one jaw of the instrument defines a tissue engagement plane carrying a conductive-resistive matrix of a conductively-doped non-conductive elastomer. The engagement surface portions thus can be described as a positive temperature coefficient material that has a unique selected decreased electrical conductance at each selected increased temperature thereof over a targeted treatment range. The conductive-resistive matrix can be engineered to bracket a targeted thermal treatment range, for example about 60° C. to 80° C., at which tissue welding can be accomplished. In one mode of operation, the engagement plane will automatically modulate and spatially localize ohmic heating within the engaged tissue from Rf energy application—across micron-scale portions of the engagement surface. In another mode of operation, a conductive-resistive matrix can induce a “wave” of Rf energy density to sweep across the tissue to thereby weld tissue.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Fabrication of biocompatible polymeric composites
InactiveUS6147135ASure easyImprove performanceSuture equipmentsCosmetic preparationsFiberPolymer science
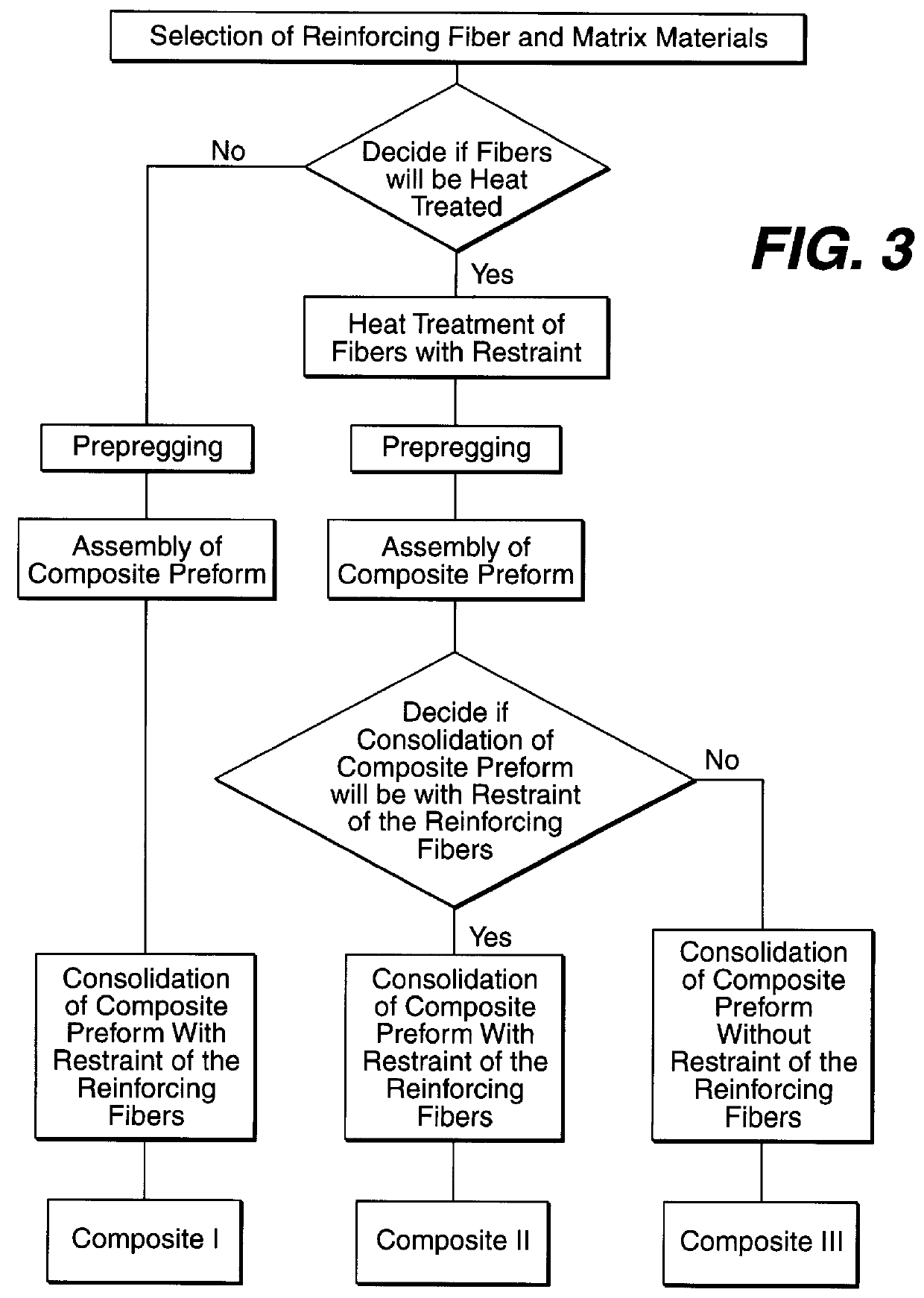
Composite materials formed from biocompatible polymer fibers and biodegradable polymers are disclosed. The heat treatment conditions for the reinforcing fibers are described so that the mechanical properties of the fibers can be retained during composite consolidation process. The processing conditions and set-ups to consolidations are constrained to the temperatures lower than fiber heat treatment temperatures. The reinforcing fibers are restrained under tension so that the minimum relaxation occurs during consolidation process.
Owner:ETHICON INC
Nano-scaled graphene plates
A nano-scaled graphene plate material and a process for producing this material. The material comprises a sheet of graphite plane or a multiplicity of sheets of graphite plane. The graphite plane is composed of a two-dimensional hexagonal lattice of carbon atoms and the plate has a length and a width parallel to the graphite plane and a thickness orthogonal to the graphite plane with at least one of the length, width, and thickness values being 100 nanometers or smaller. The process for producing nano-scaled graphene plate material comprises the steps of: a). partially or fully carbonizing a precursor polymer or heat-treating petroleum or coal tar pitch to produce a polymeric carbon containing micron- and / or nanometer-scaled graphite crystallites with each crystallite comprising one sheet or a multiplicity of sheets of graphite plane; b). exfoliating the graphite crystallites in the polymeric carbon; and c). subjecting the polymeric carbon containing exfoliated graphite crystallites to a mechanical attrition treatment to produce the nano-scaled graphene plate material.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
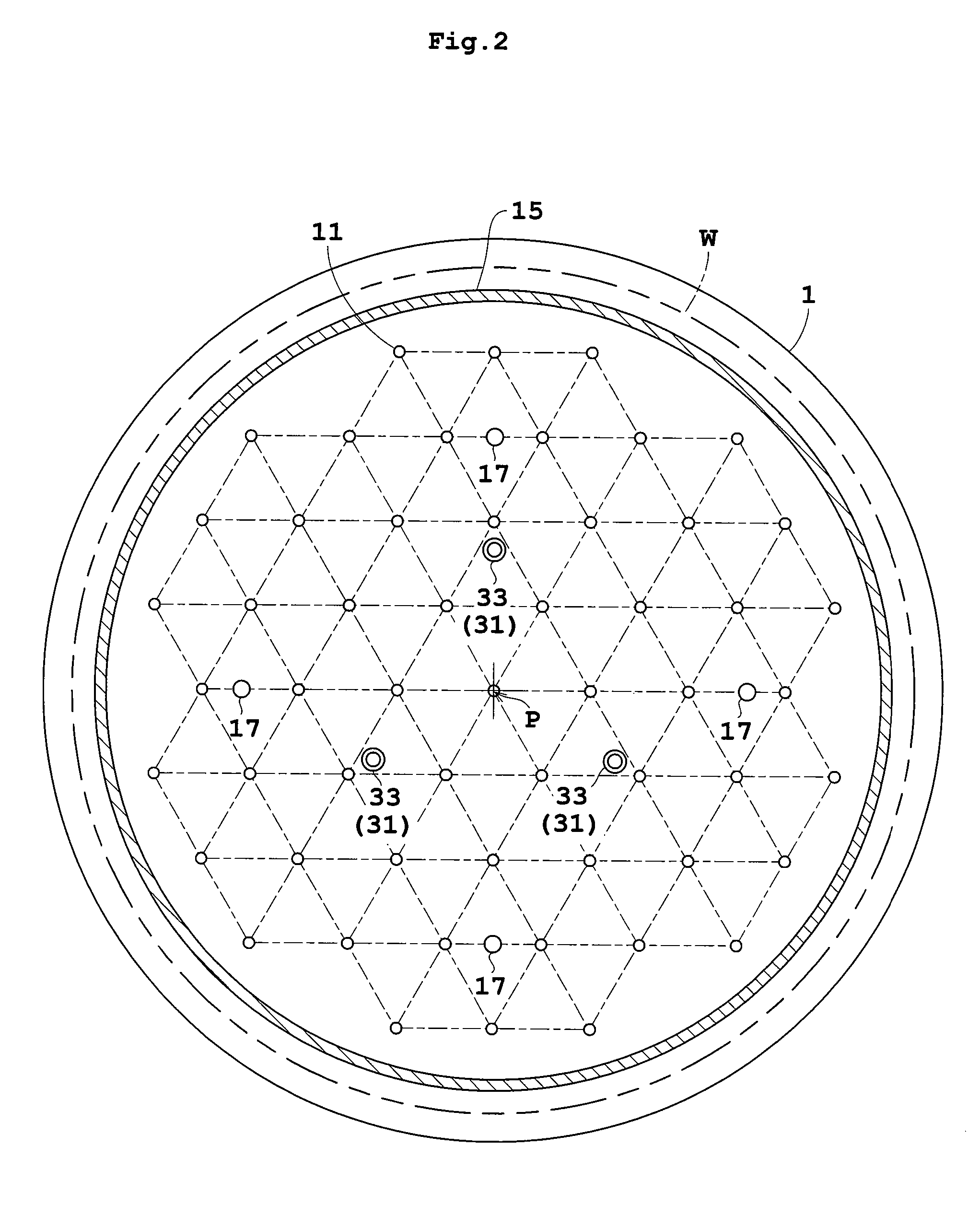
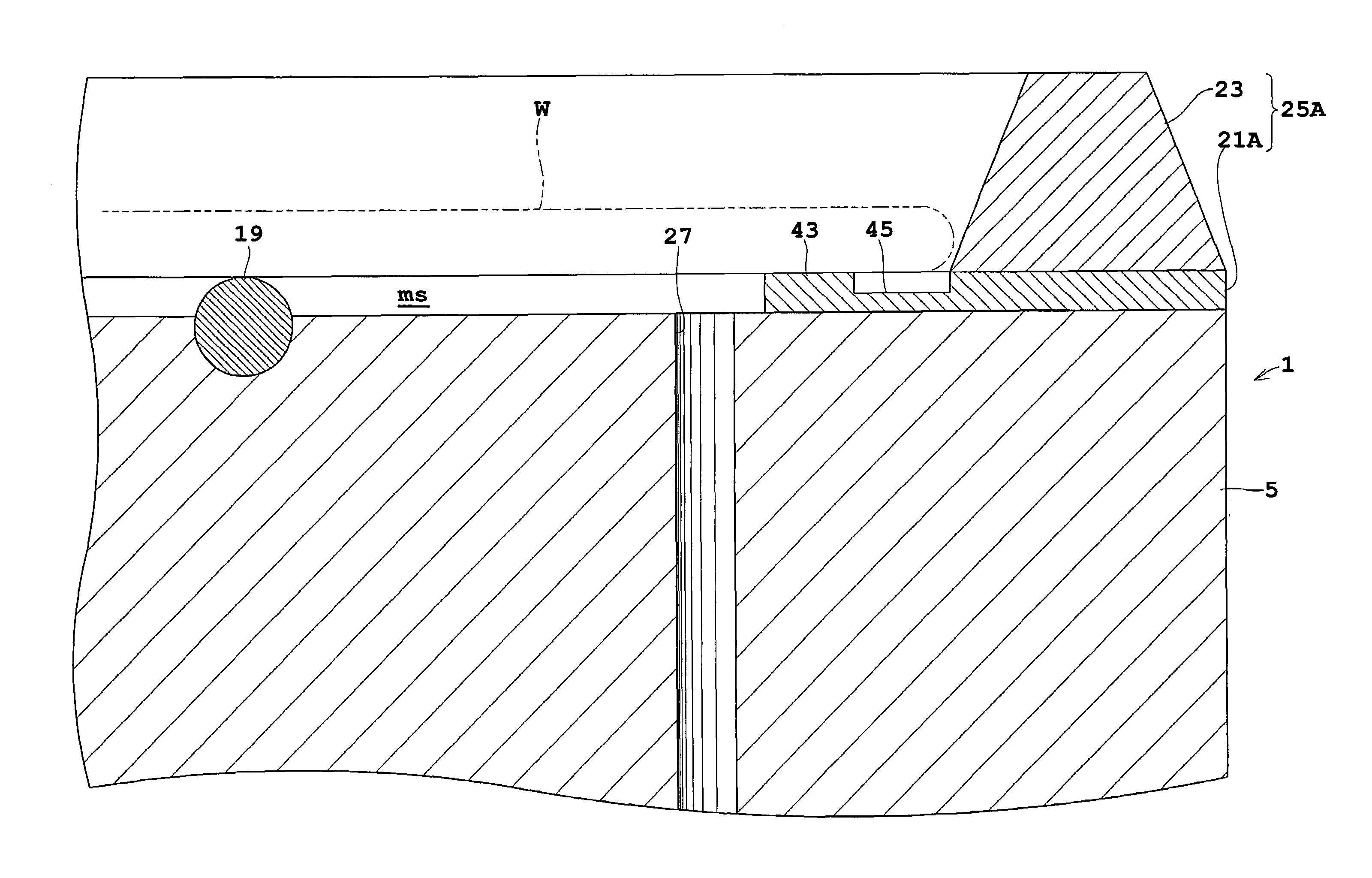
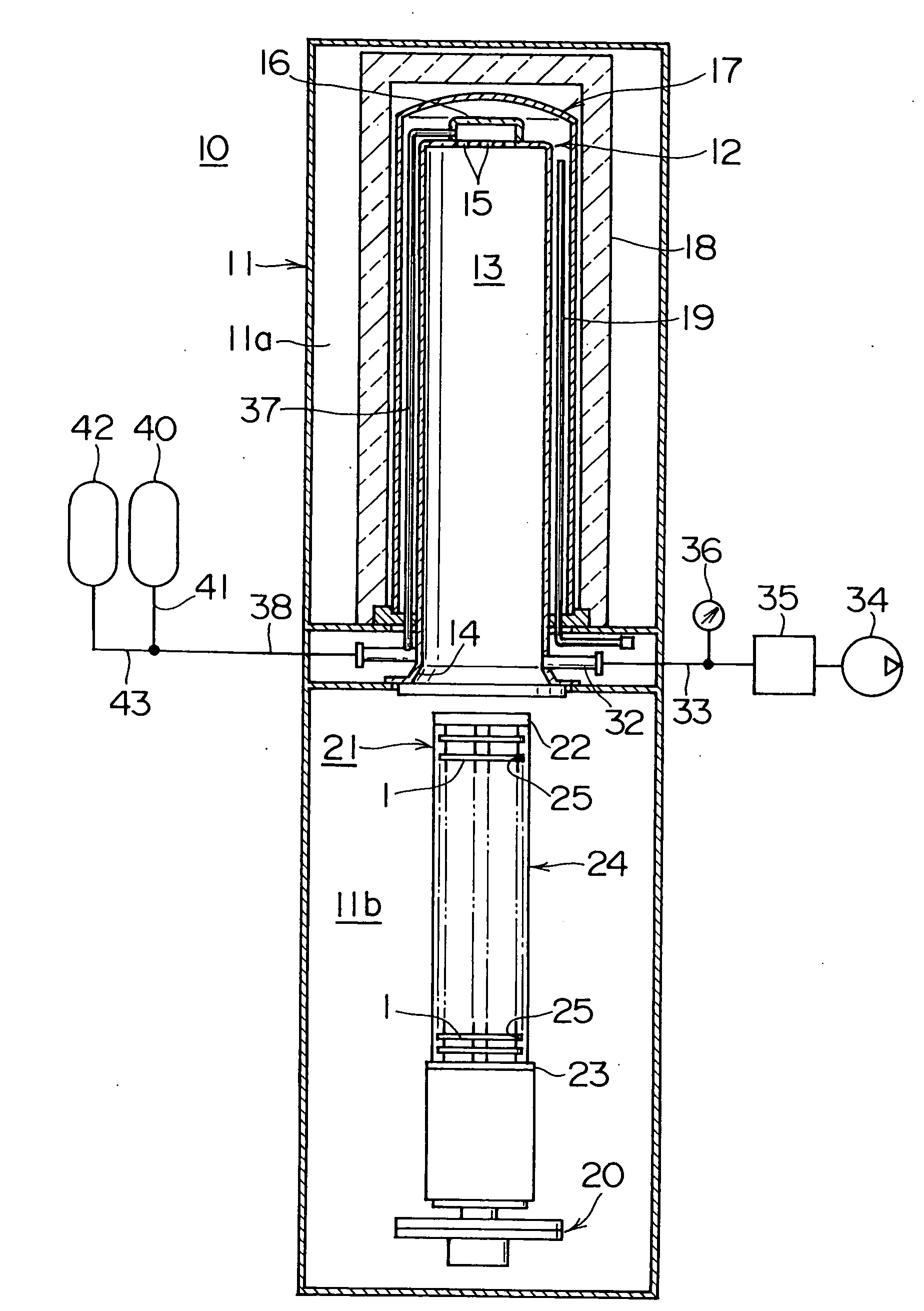
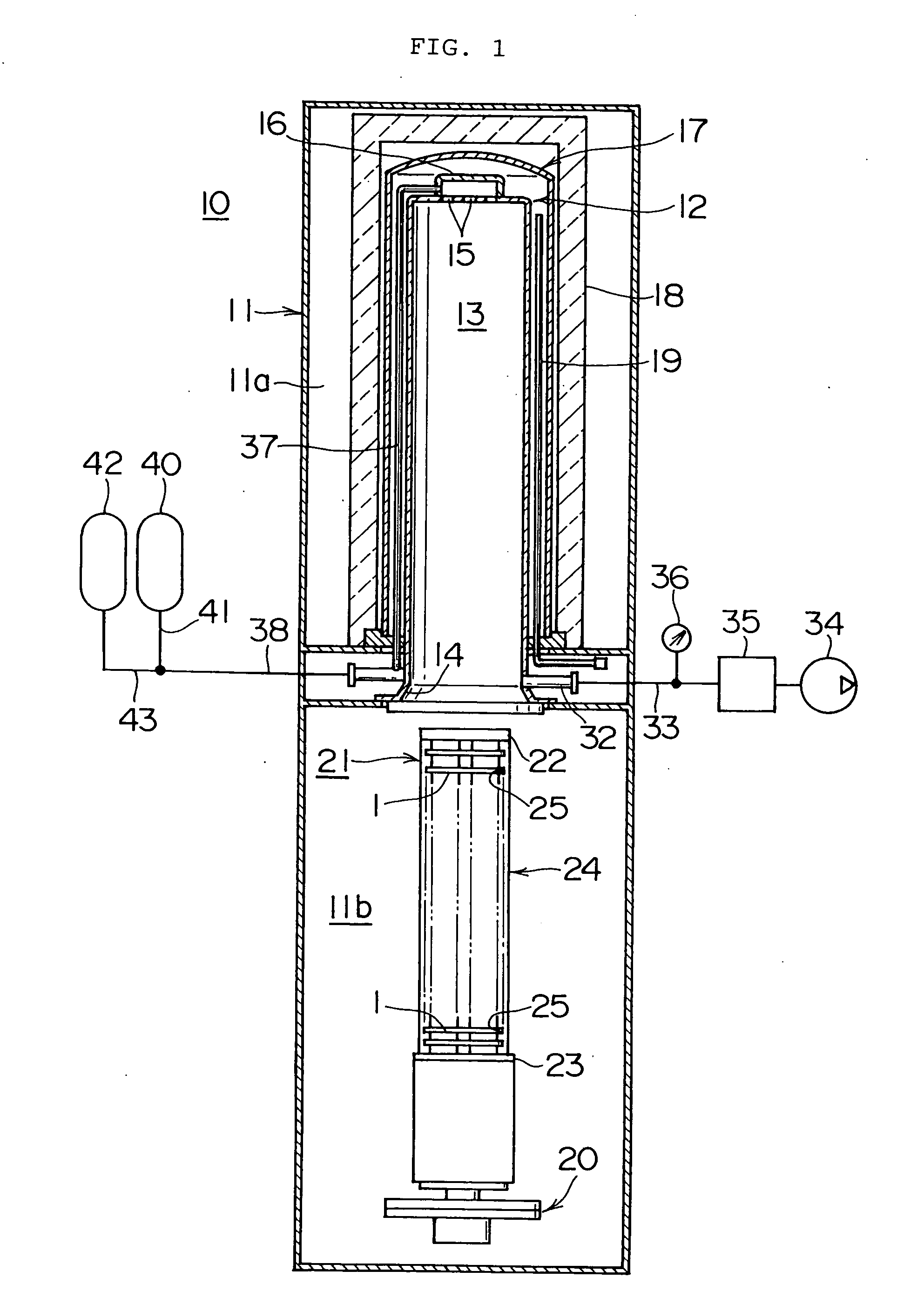
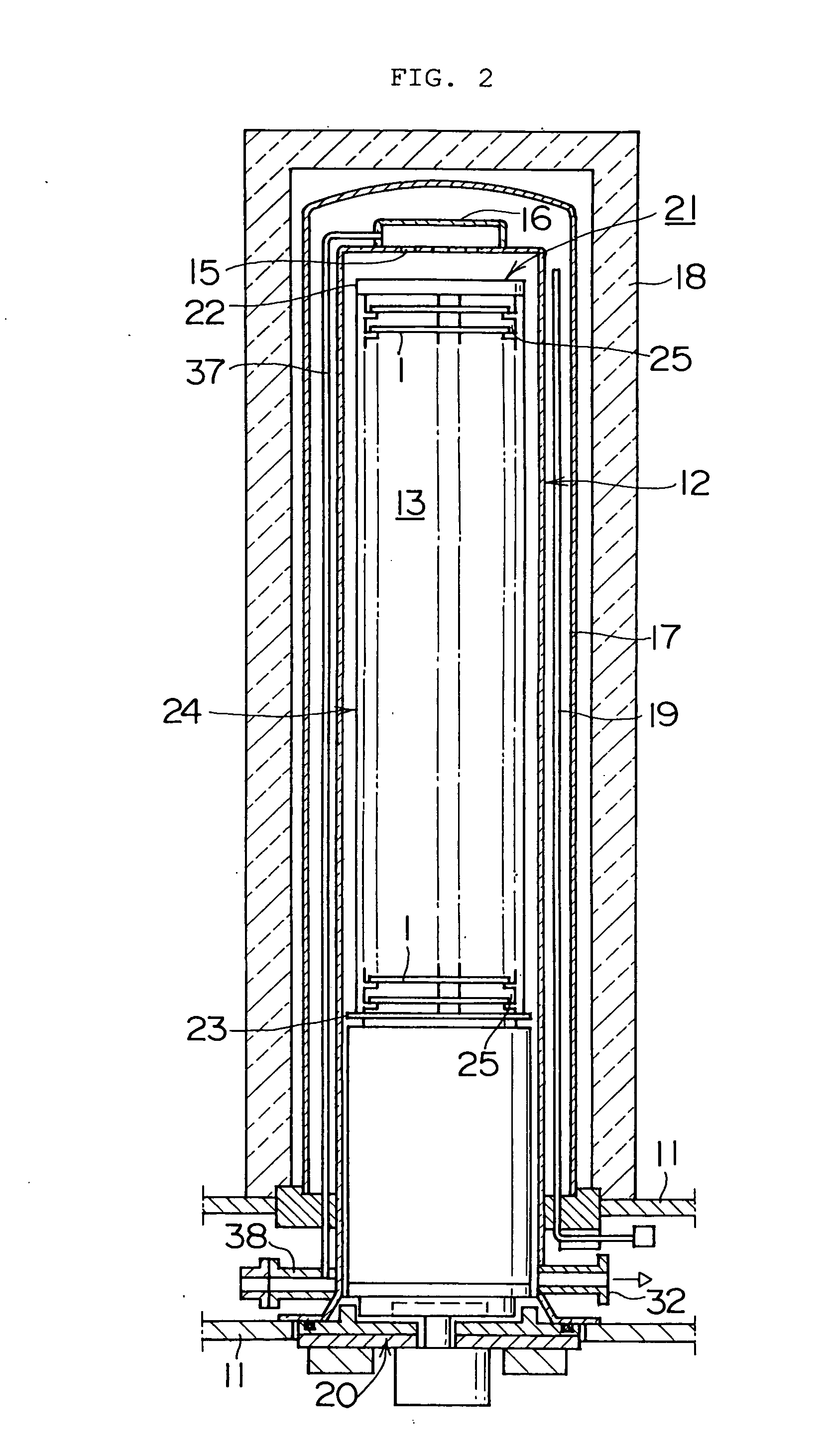
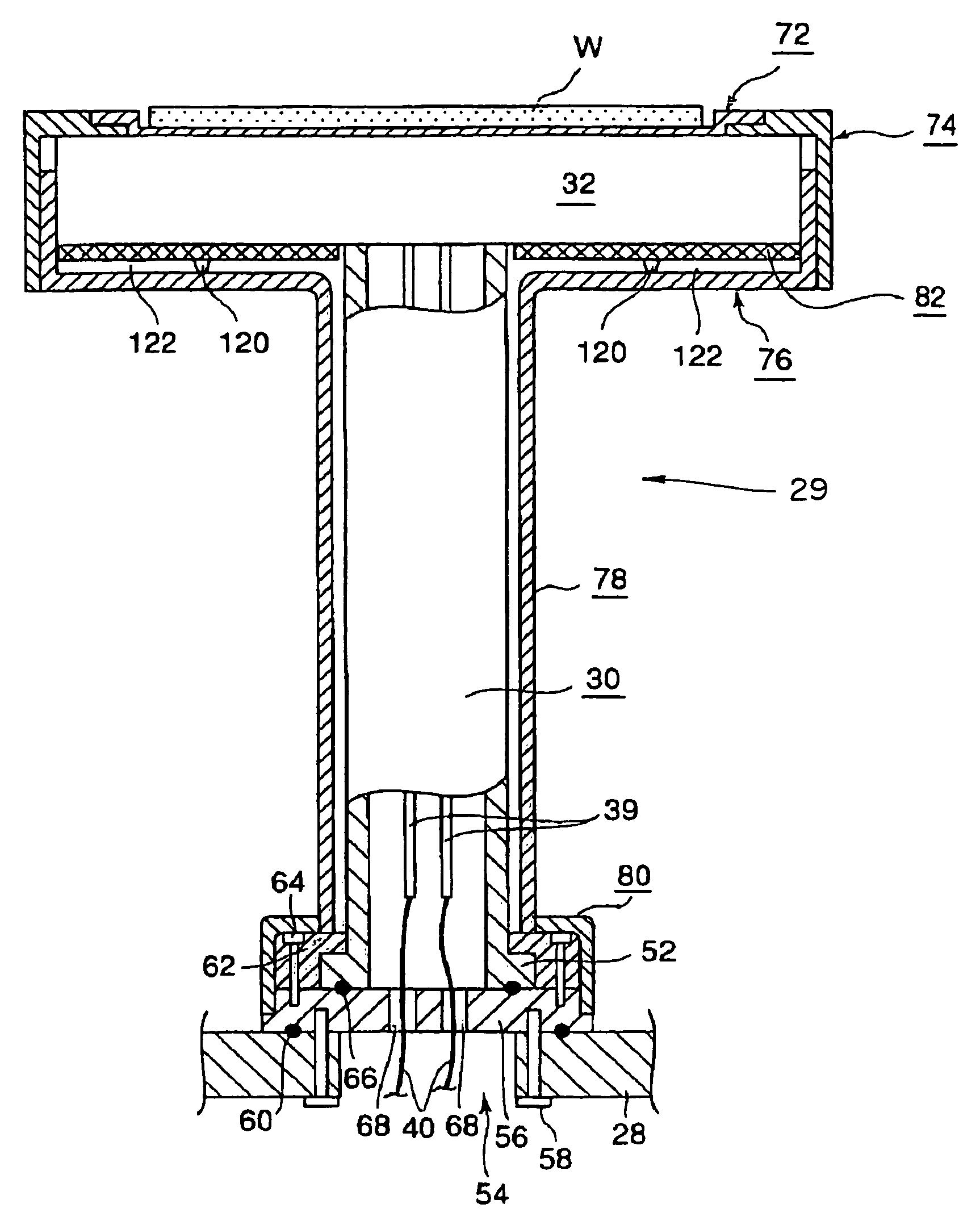
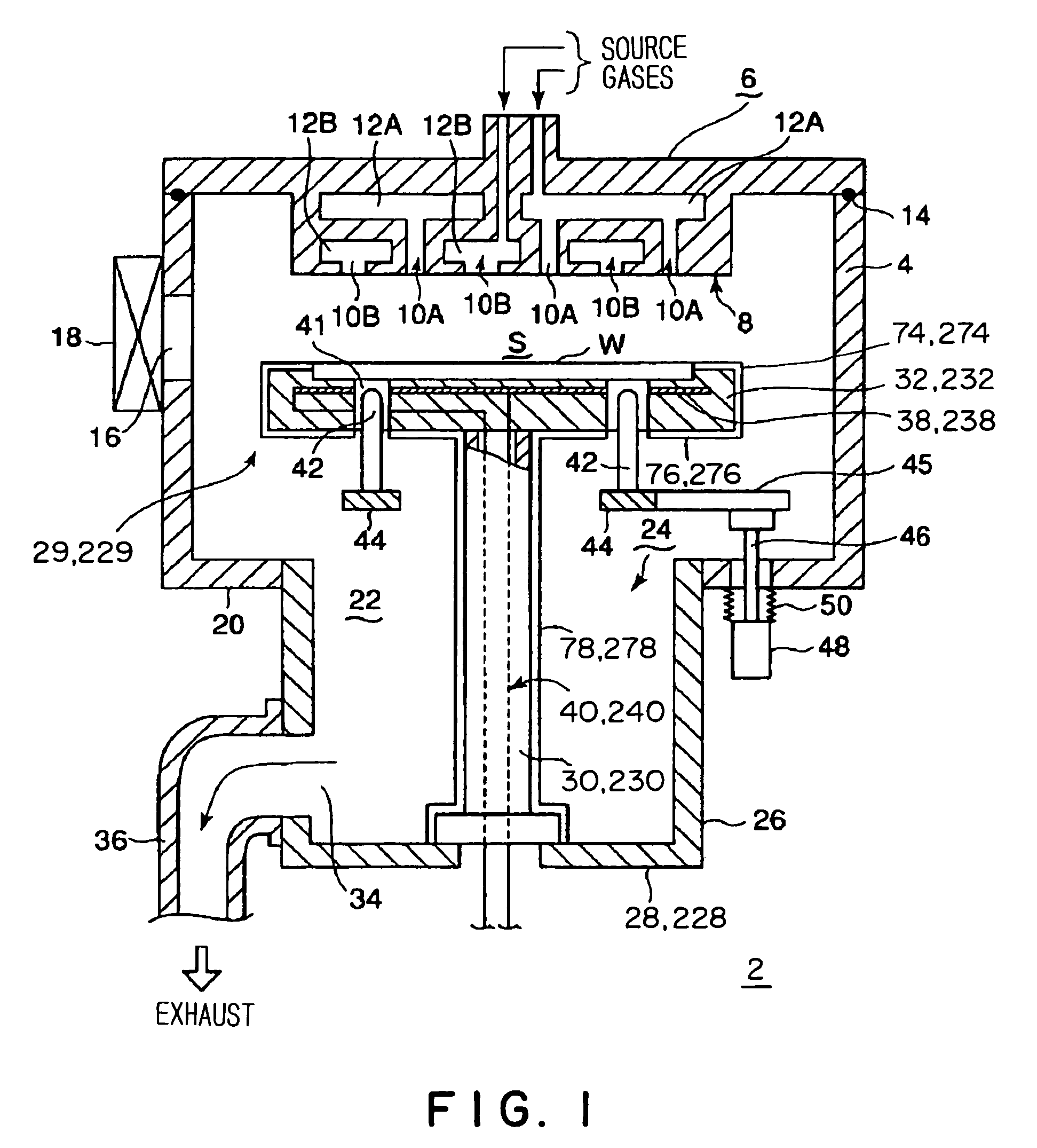
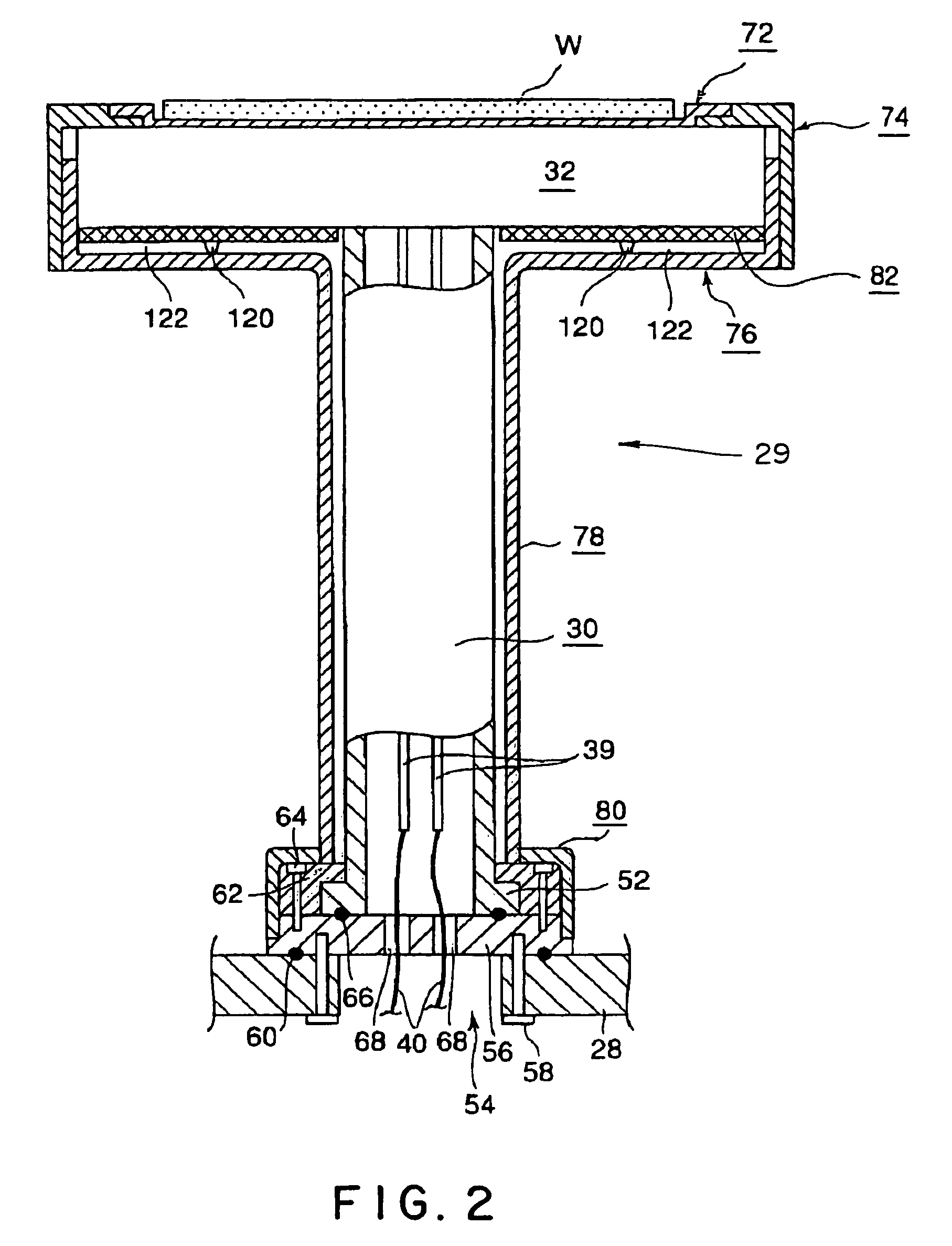
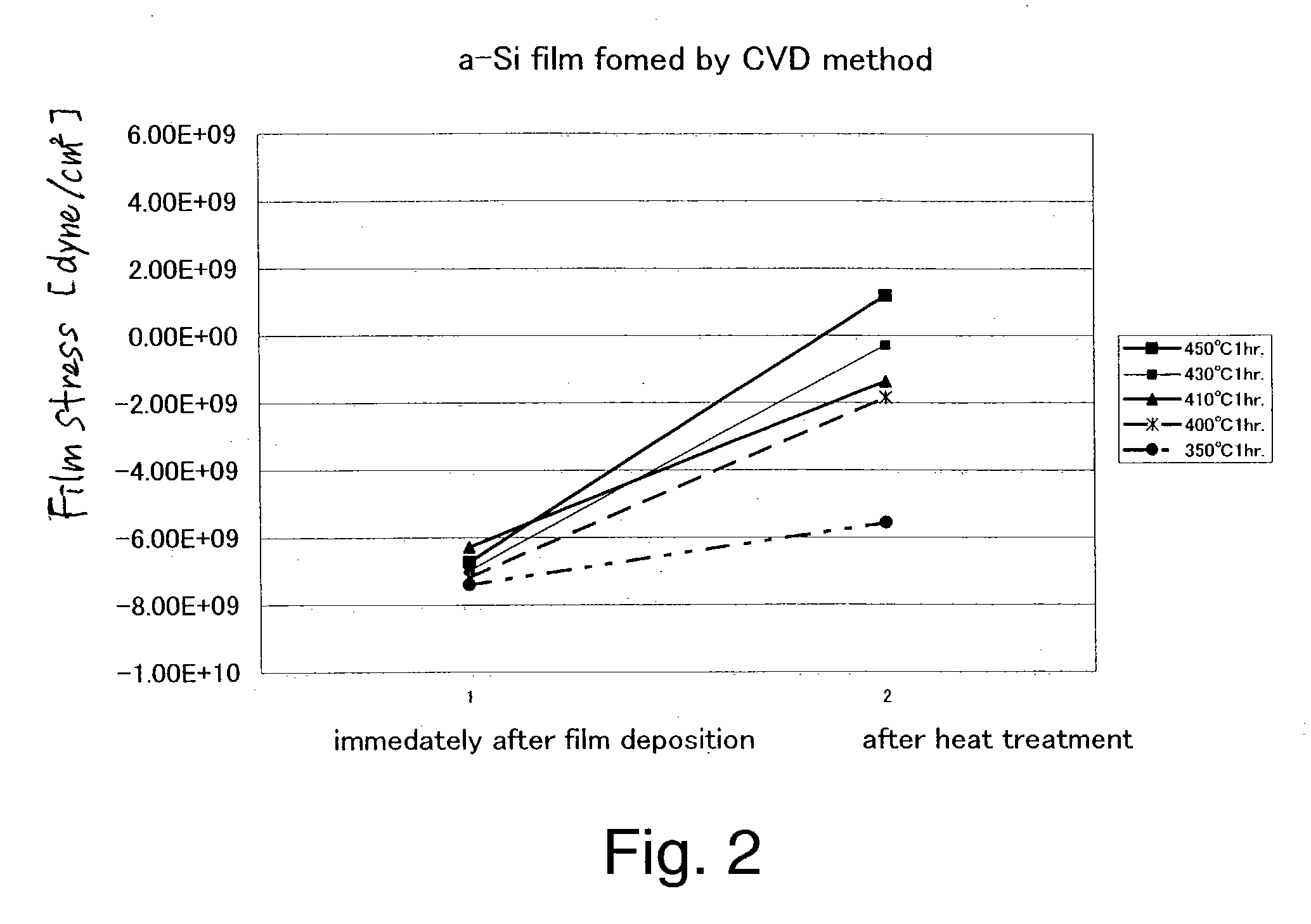
Substrate heat treatment apparatus
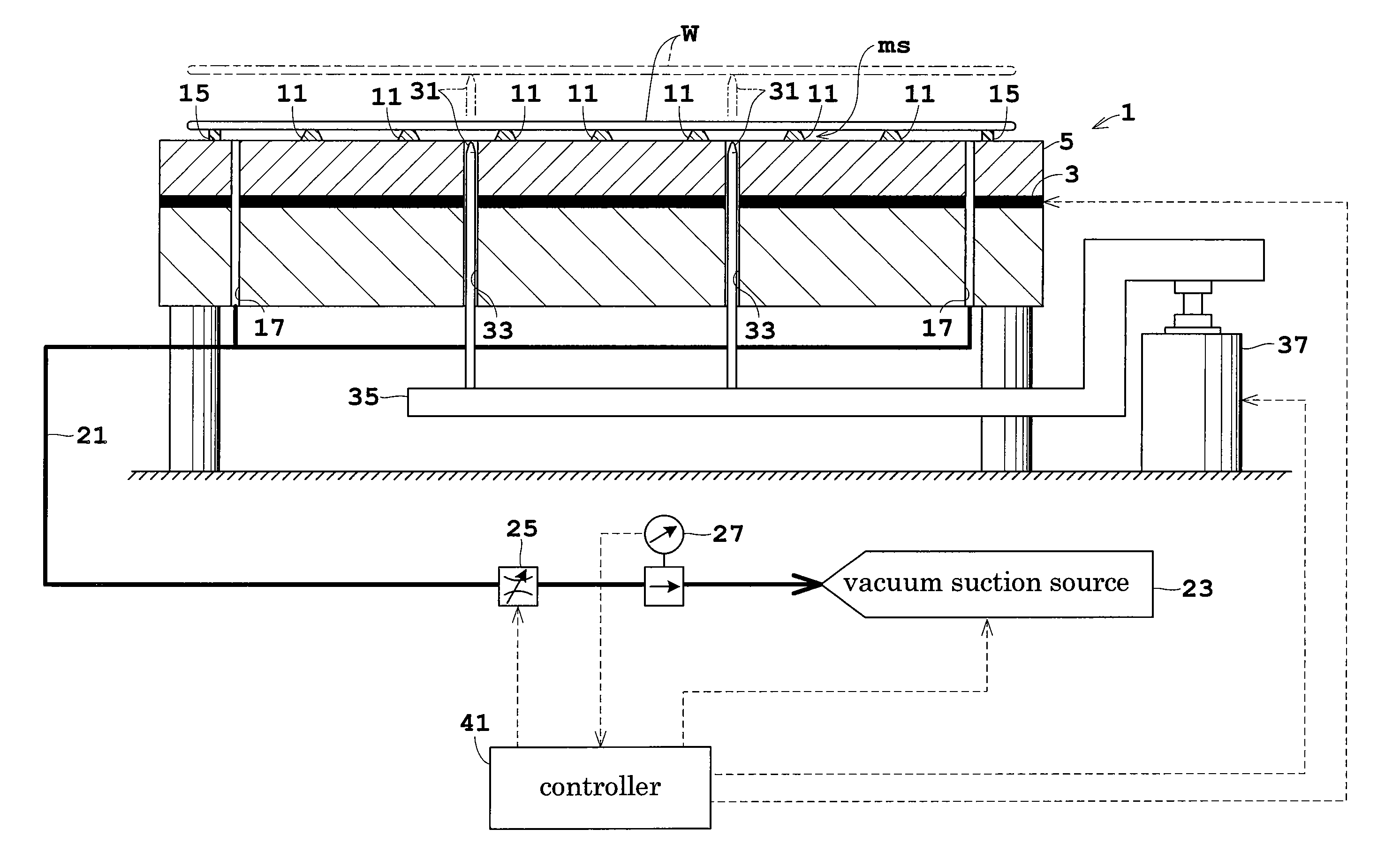
A substrate heat treatment apparatus includes a heat-treating plate having a flat upper surface, support devices formed of a heat-resistant resin for contacting and supporting a substrate, a seal device disposed annularly for rendering gastight a space formed between the substrate and heat-treating plate, and exhaust bores for exhausting gas from the space. The support devices are formed of resin, and the upper surface of the heat-treating plate is made flat, whereby a reduced difference in the rate of heat transfer occurs between contact parts and non-contact parts on the surface of the substrate. Consequently, the substrate is heat-treated effectively while suppressing variations in heat history over the surface of the substrate.
Owner:DAINIPPON SCREEN MTG CO LTD
Substrate heat treatment apparatus
ActiveUS7432476B2Efficient actionEfficient use ofMuffle furnacesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMechanical engineeringHeat treated
Owner:DAINIPPON SCREEN MTG CO LTD
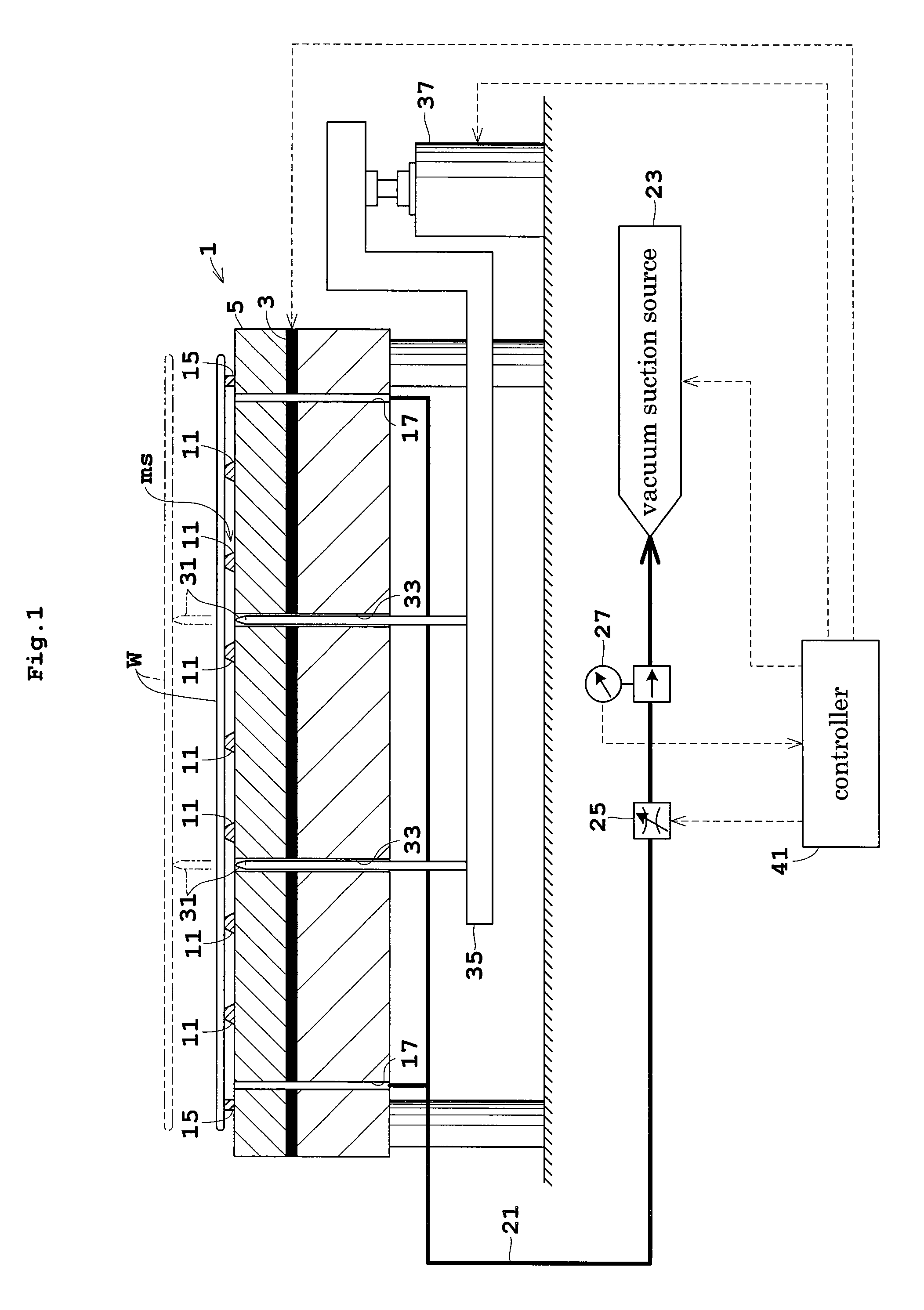
Heat treating apparatus
ActiveUS7865070B2Minimal amountReliably preventing both slipsRespiratorsDrying solid materials with heatSurface roughnessHeat treating
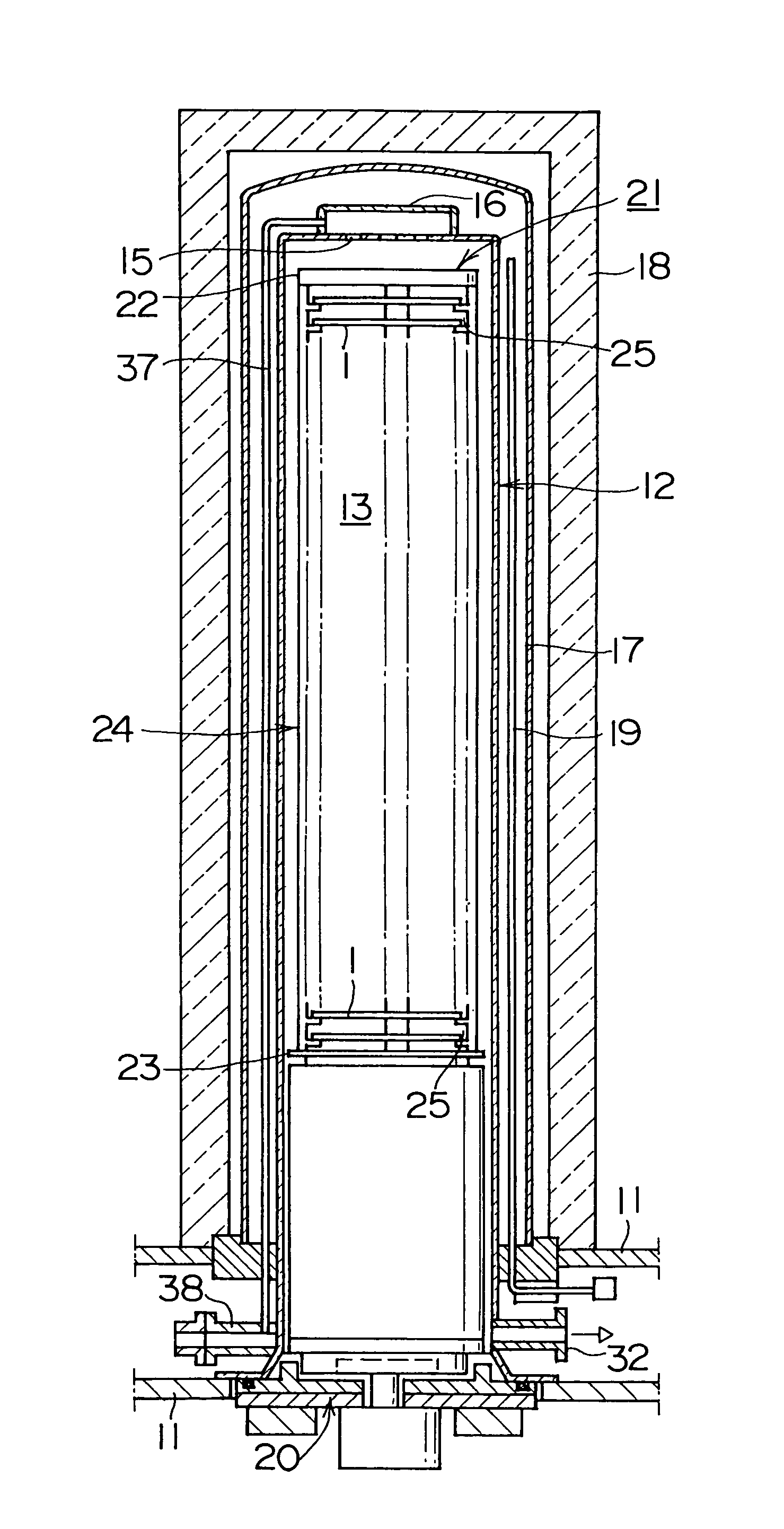
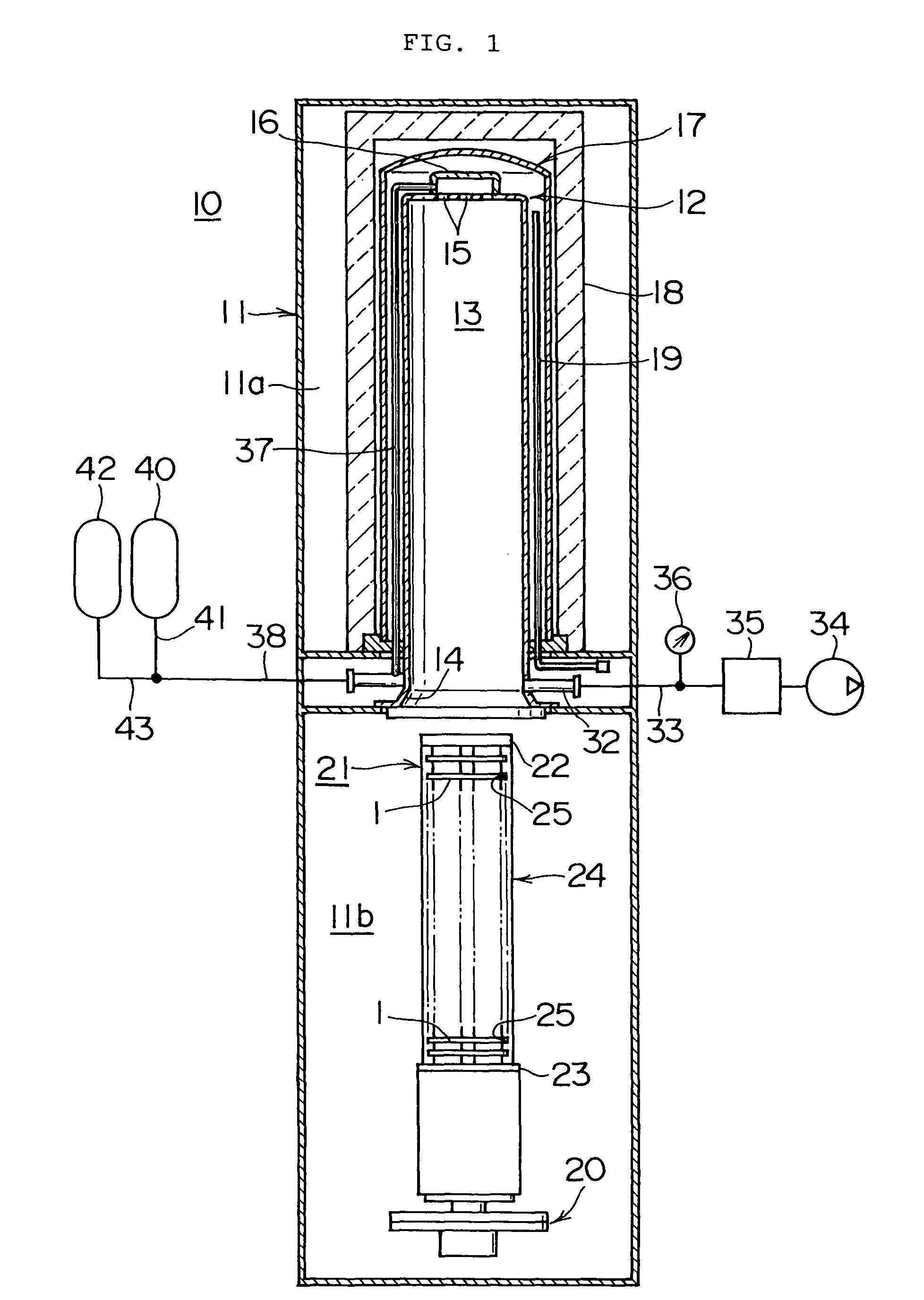
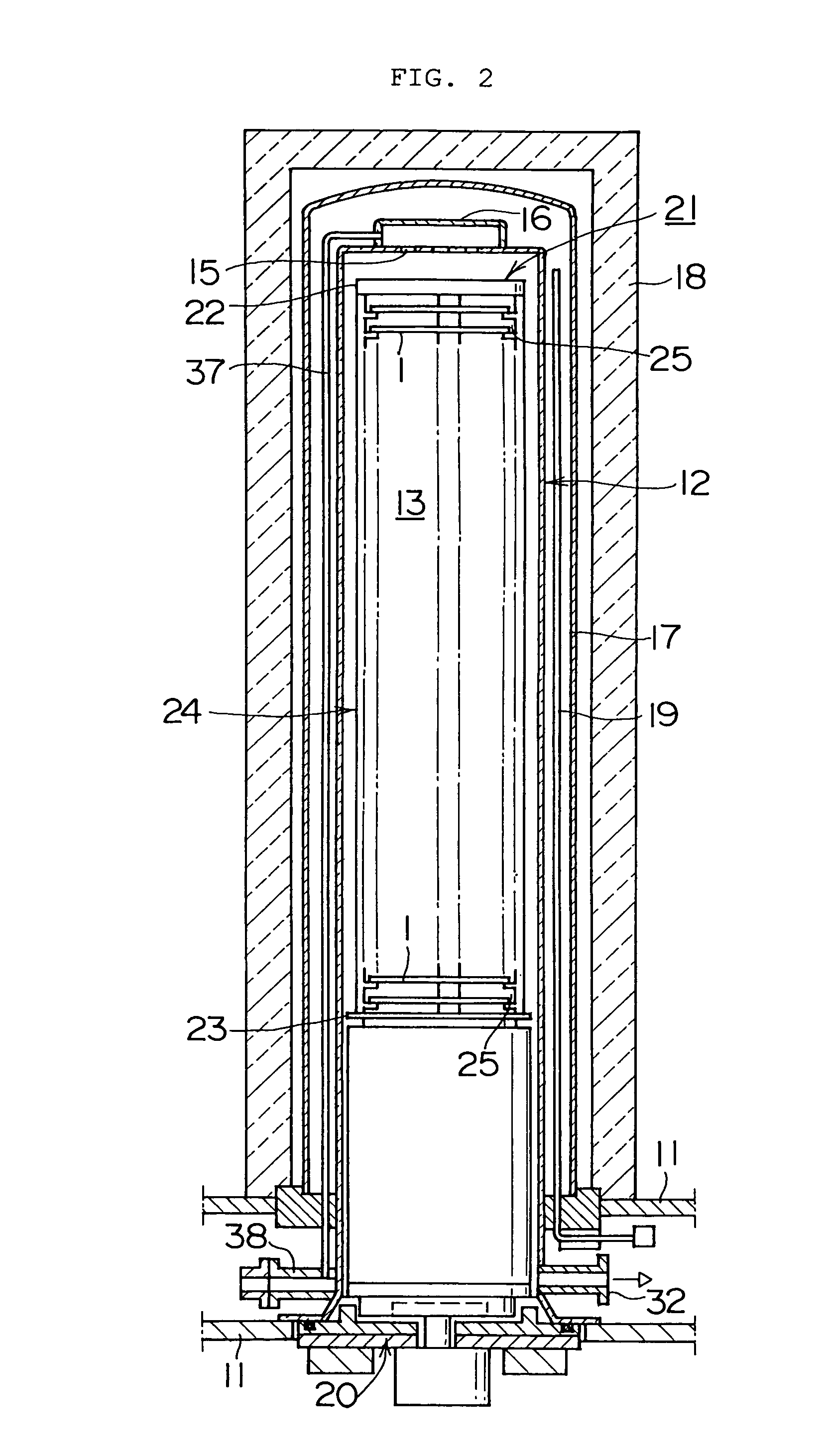
To prevent both slips caused by damage from projections, and slips caused by adhesive force occurring due to excessive smoothing.The heat treating apparatus includes a processing chamber for heat treating wafers and a boat for supporting the wafers in the processing chamber. The boat further includes a wafer holder in contact with the wafer and a main body for supporting the wafer holder. The wafer holder diameter is 63 to 73 percent of the wafer diameter, and the surface roughness Ra of the portion of the wafer holder in contact with the wafer is set from 1 μm to 1,000 μm. The wafer can be supported so that the amount of wafer displacement is minimal and both slips due to damage from projections on the wafer holder surface, and slips due to the adhesive force occurring because of excessive smoothing can be prevented in that state.
Owner:KOKUSA ELECTRIC CO LTD +1
Heat Treating Apparatus
ActiveUS20080267598A1Minimal amountPrevent slipping or slippingRespiratorsDrying solid materials with heatSurface roughnessHeat treating
[Problems] To prevent both slips caused by damage from projections, and slips caused by adhesive force occurring due to excessive smoothing.[Means for Solving the Problems] The heat treating apparatus includes a processing chamber for heat treating wafers and a boat for supporting the wafers in the processing chamber. The boat further includes a wafer holder in contact with the wafer and a main body for supporting the wafer holder. The wafer holder diameter is 63 to 73 percent of the wafer diameter, and the surface roughness Ra of the portion of the wafer holder in contact with the wafer is set from 1 μm to 1,000 μm. The wafer can be supported so that the amount of wafer displacement is minimal and both slips due to damage from projections on the wafer holder surface, and slips due to the adhesive force occurring because of excessive smoothing can be prevented in that state.
Owner:KOKUSA ELECTRIC CO LTD +1
Substrate heat treatment apparatus
ActiveUS8003919B2Efficient heat treatmentEfficiently inhibiting sagging of a substrateMuffle furnacesCharge supportsIsoetes triquetraEngineering
Owner:DAINIPPON SCREEN MTG CO LTD
Graphene sheet and method of preparing the same
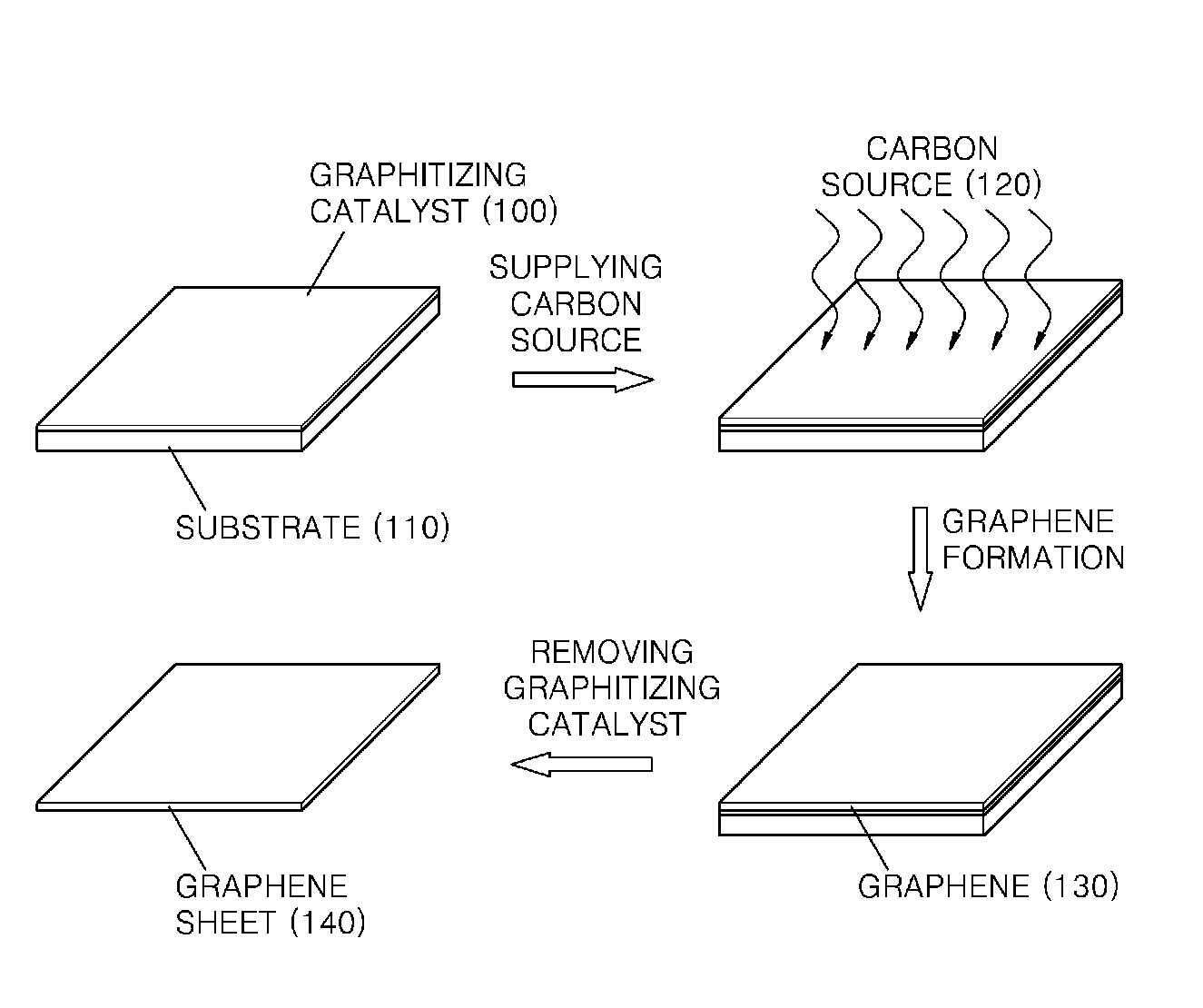
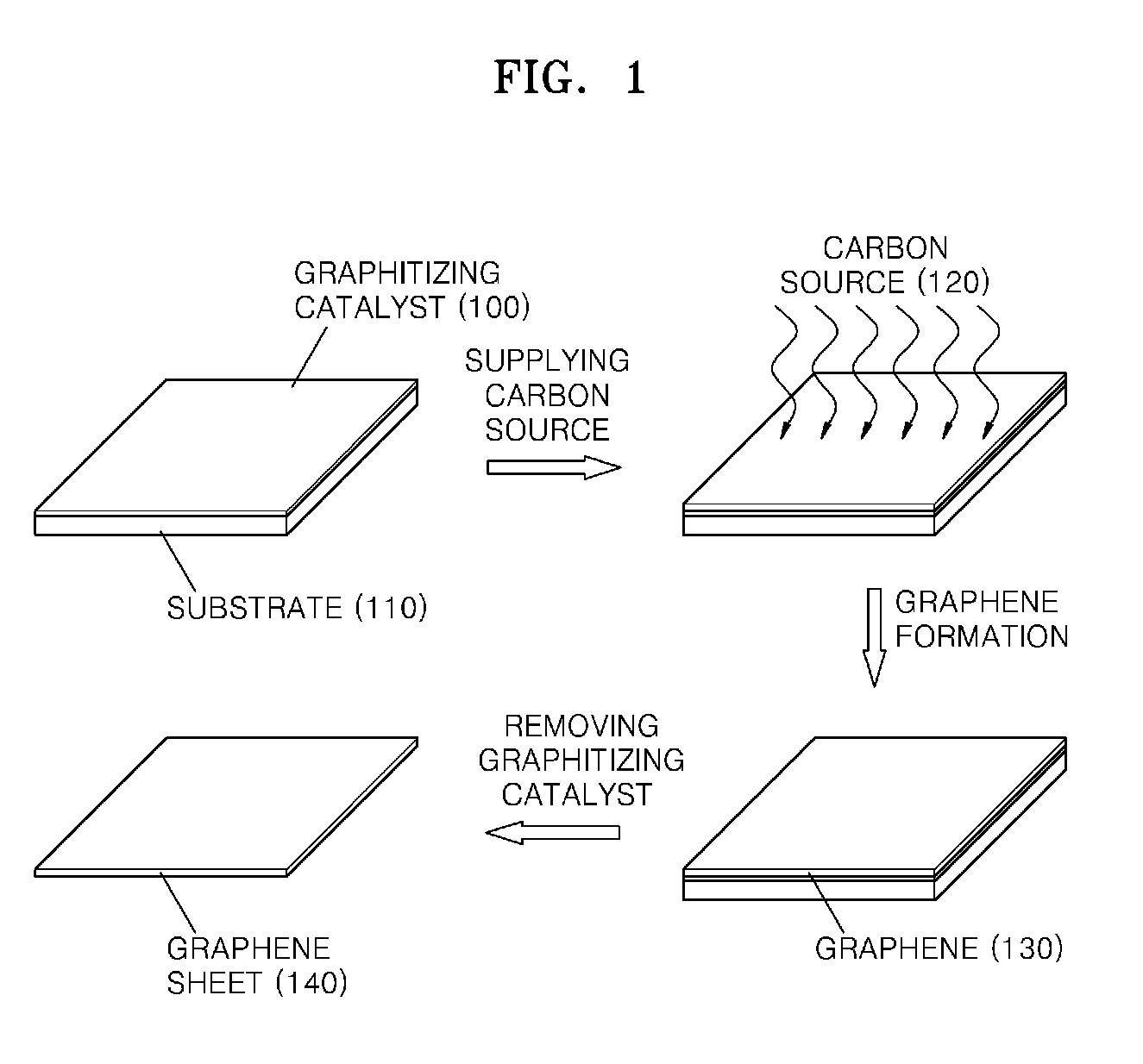
An economical method of preparing a large-sized graphene sheet having a desired thickness includes forming a film, the film comprising a graphitizing catalyst; heat-treating a gaseous carbon source in the presence of the graphitizing catalyst to form graphene; and cooling the graphene to form a graphene sheet. A graphene sheet prepared according to the disclosed method is also described.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Heat treatment equipment
InactiveUS7850449B2Growth inhibitionReduce processing stepsMuffle furnacesBaking ovenProcess engineeringPressure controlled ventilation
In an embodiment, heat treatment equipment comprises a process tube, an exhaust duct connected to the process tube, and, during operation, exhausting gases present within the process tube. The heat treatment equipment also comprises a hollow pressure control member interposed between the process tube and the exhaust duct, the pressure control member being operatively connected to the process tube and the exhaust duct respectively, and including one or a number of openings. Negative pressure is avoided in the process tube during heat treatment processes so that unwanted gas and impurities cannot enter the process tube from outside.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
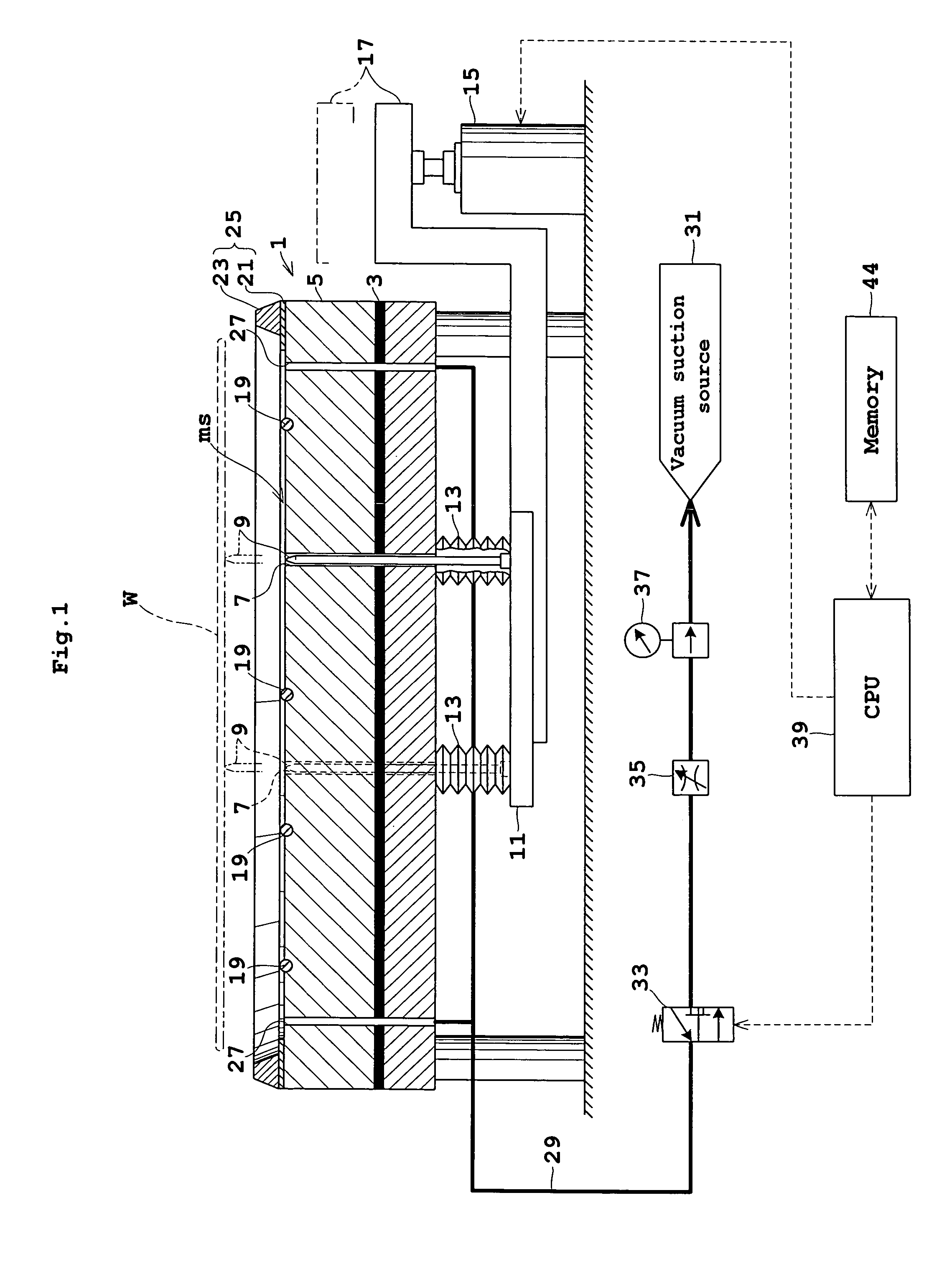
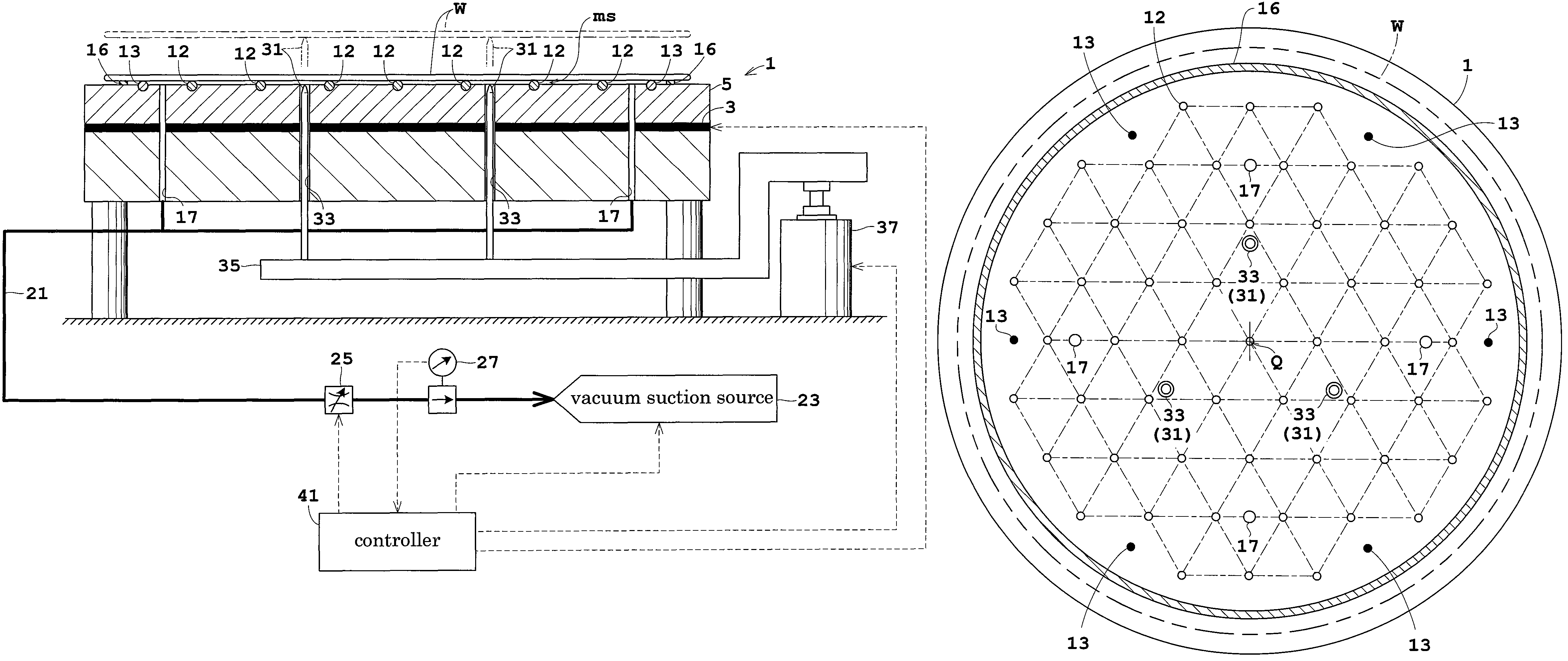
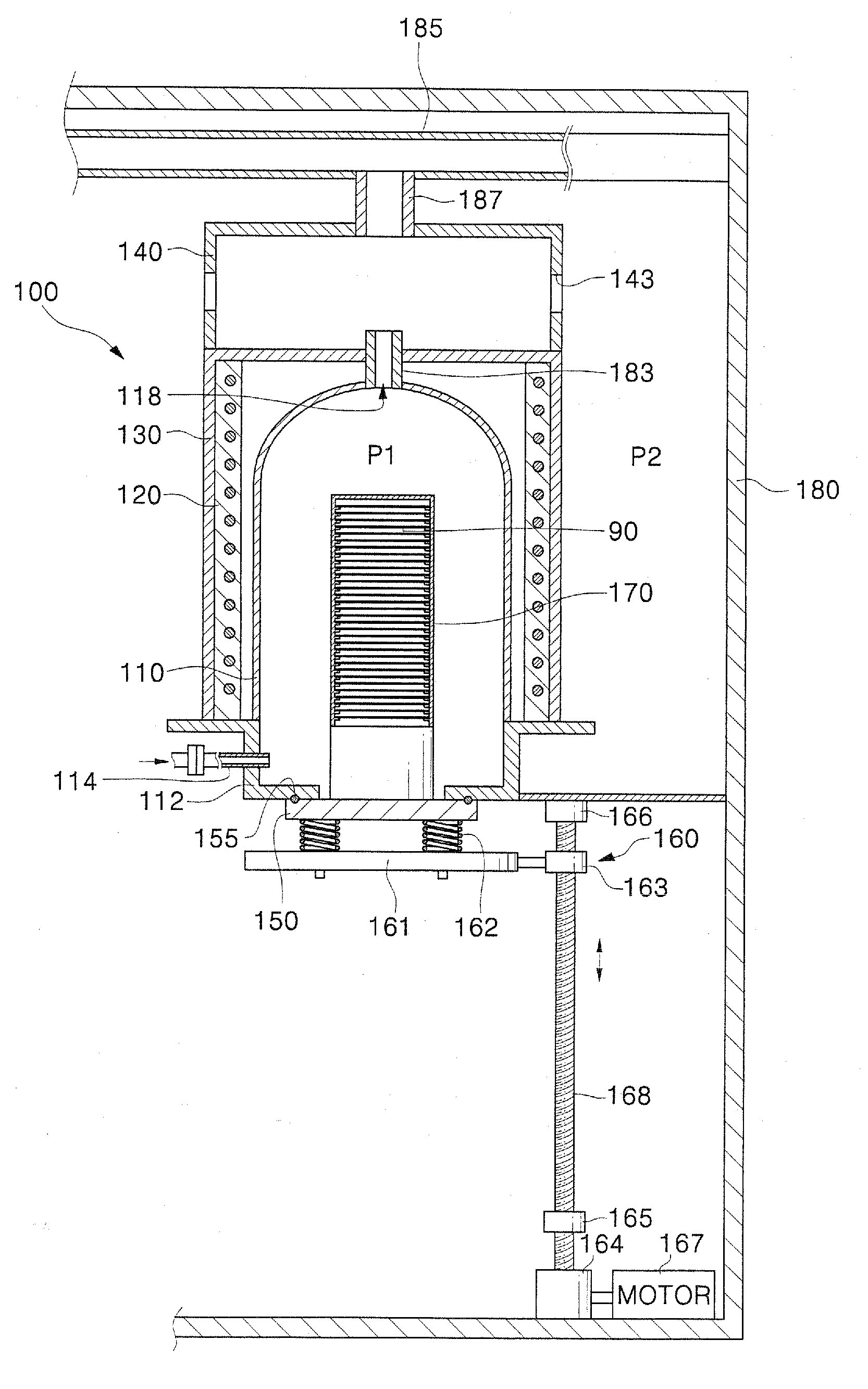
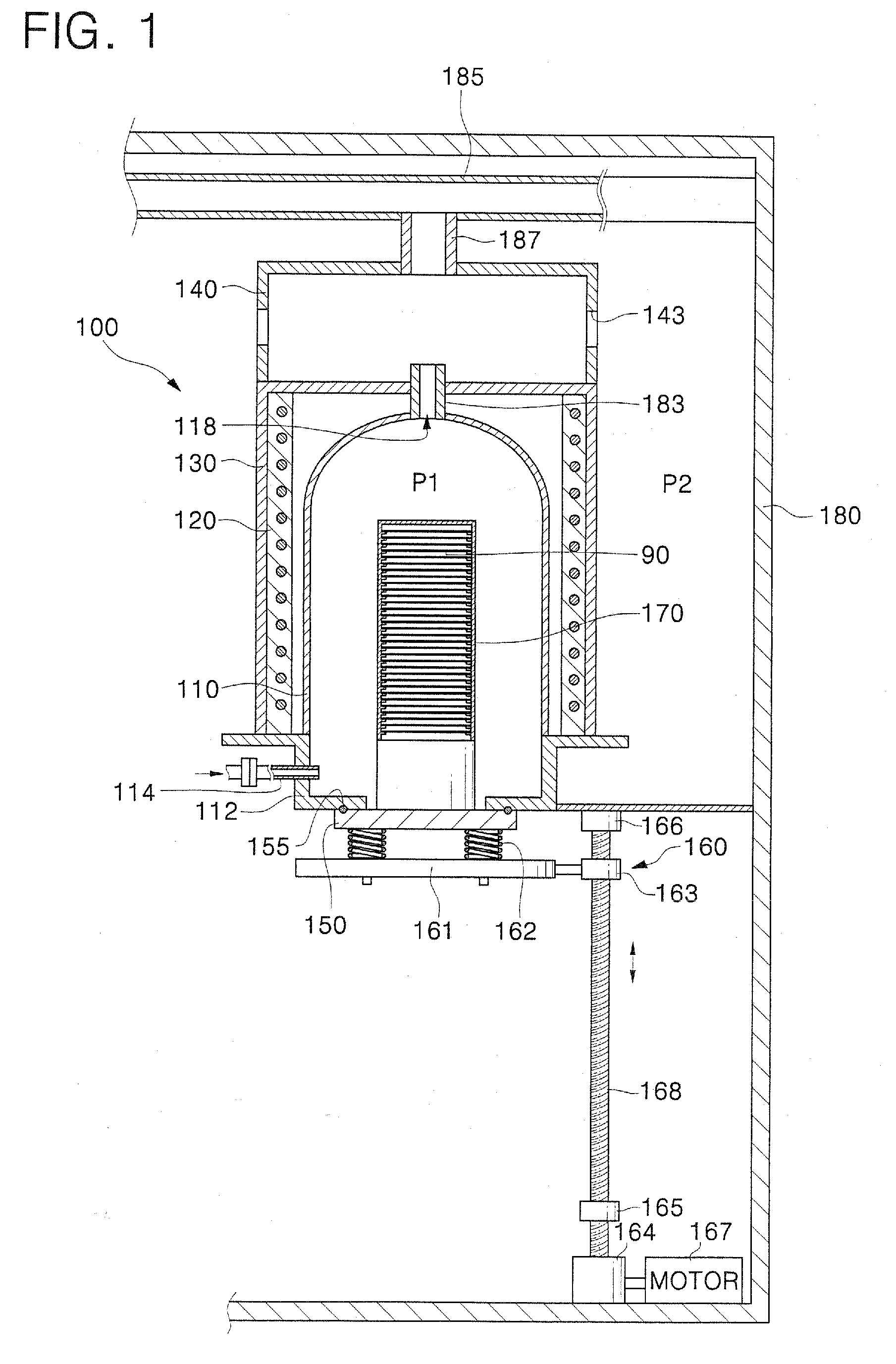
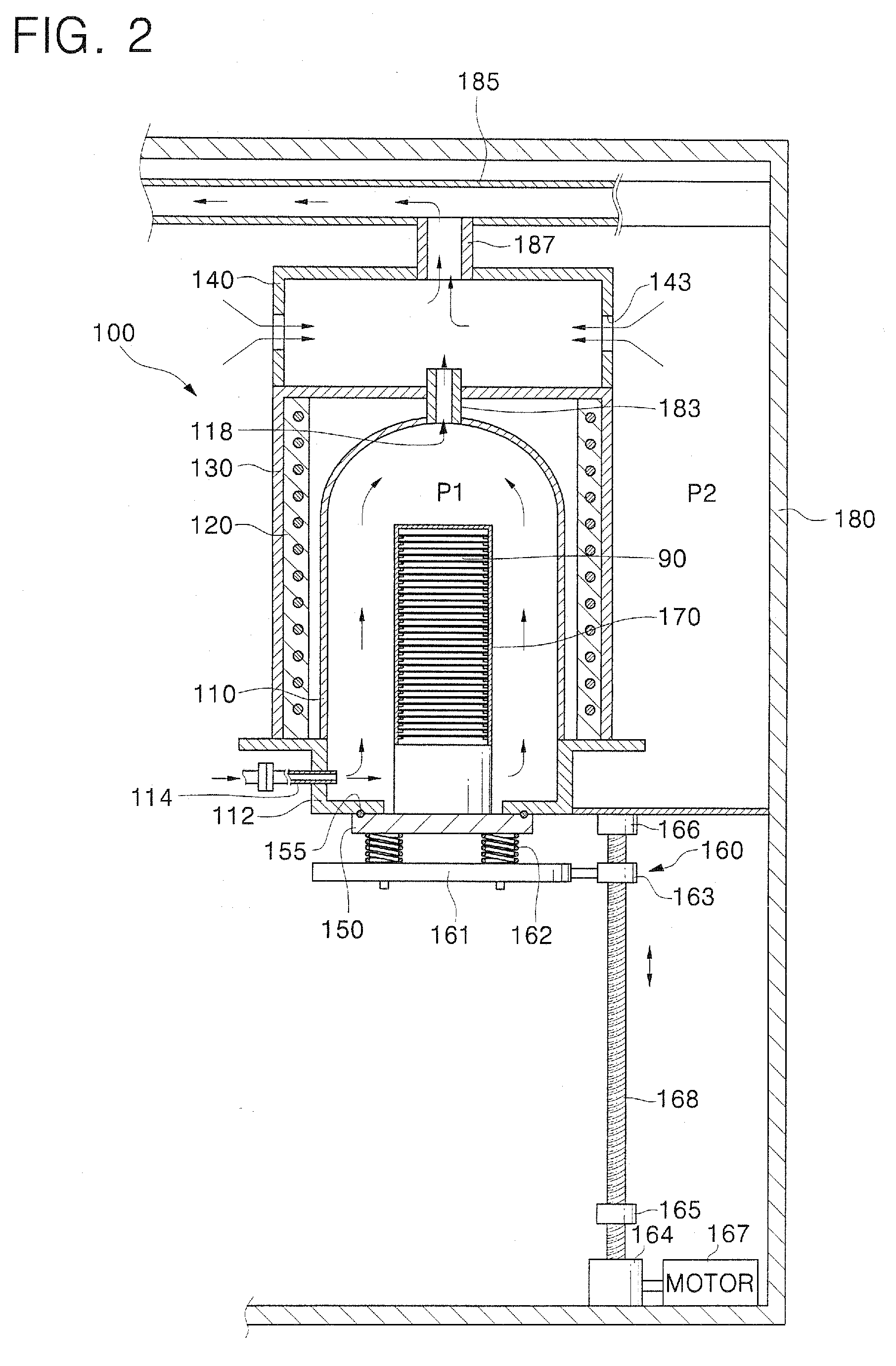
Loading table and heat treating apparatus having the loading table
ActiveUS7718930B2Thermal diffusionPrevent heat from spreadingDrying solid materials with heatMuffle furnacesEngineeringContamination
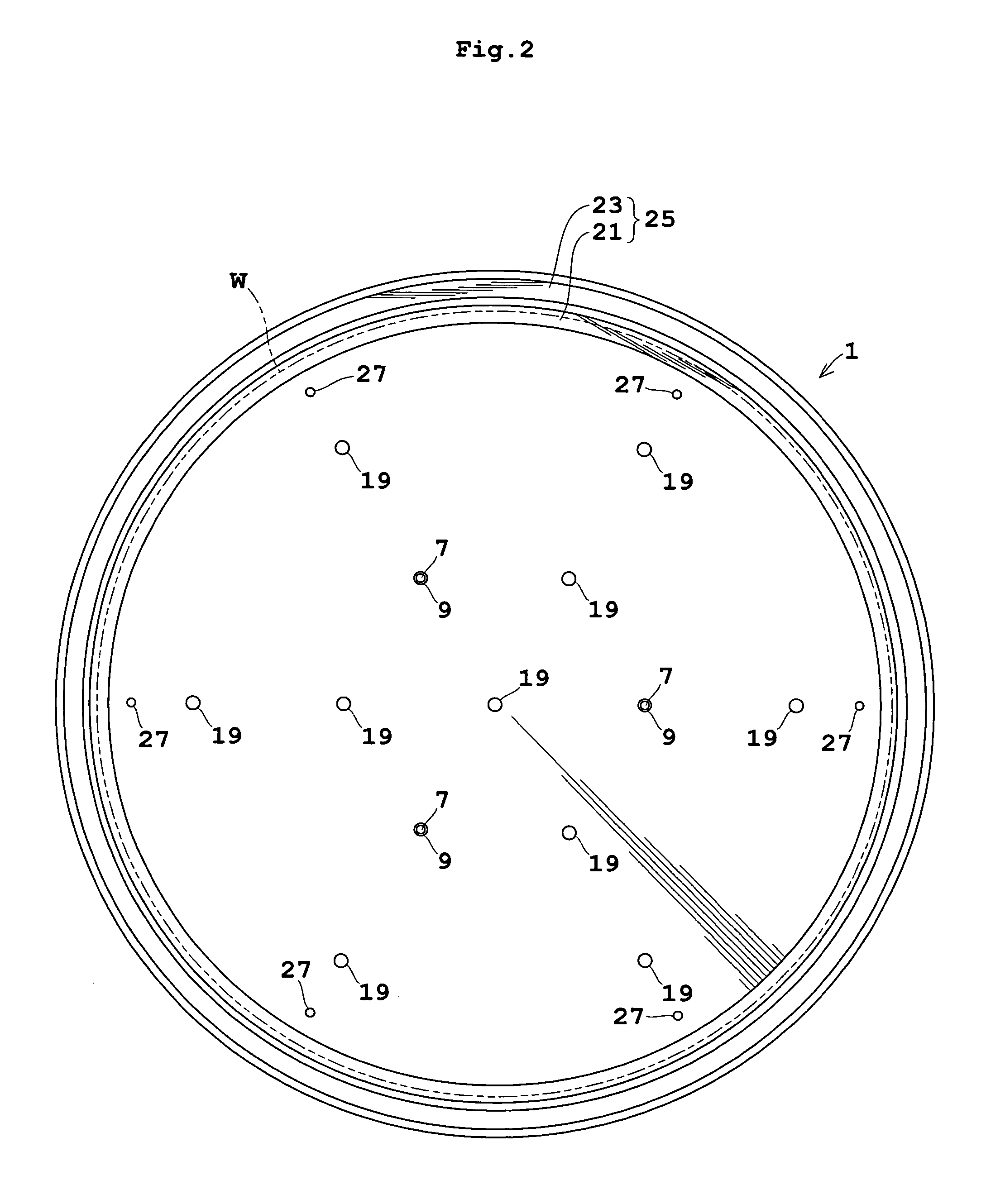
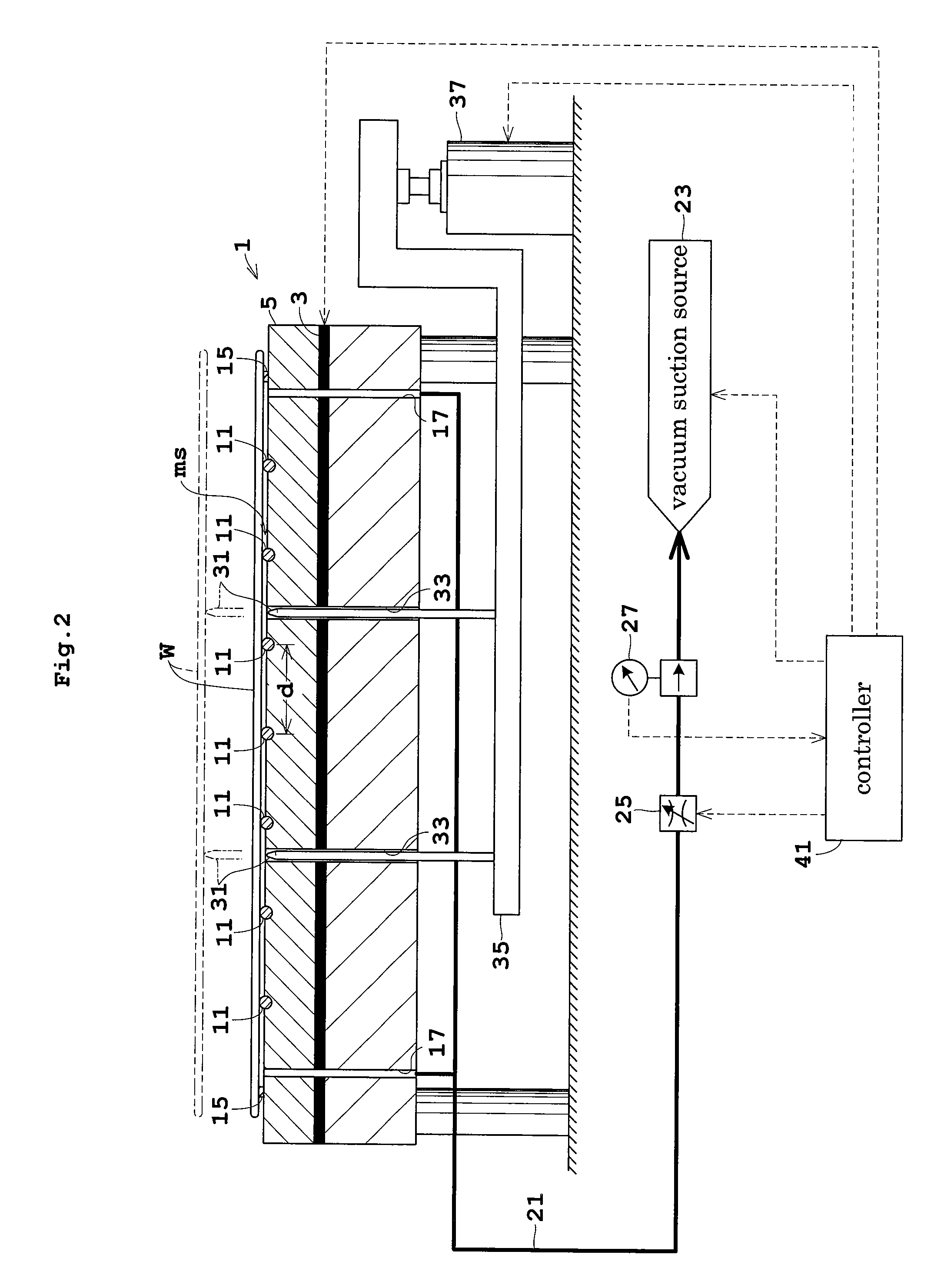
A thermal processing system has a processing vessel 4, a support post 30 stood on the bottom wall of the processing vessel 4, and a support table 32 internally provided with a heating means 38 and supported on the support post 30. A workpiece W is placed on the upper surface of the support table 32 and is subjected to a predetermined thermal process. The upper, the side and the lower surface of the support table 32 are covered with heat-resistant covering members 72, 74 and 76 to prevent the thermal diffusion of metal atoms causative of contamination from the support table 32. thus, various types of contamination, such as metal and organic contamination, can be prevented.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
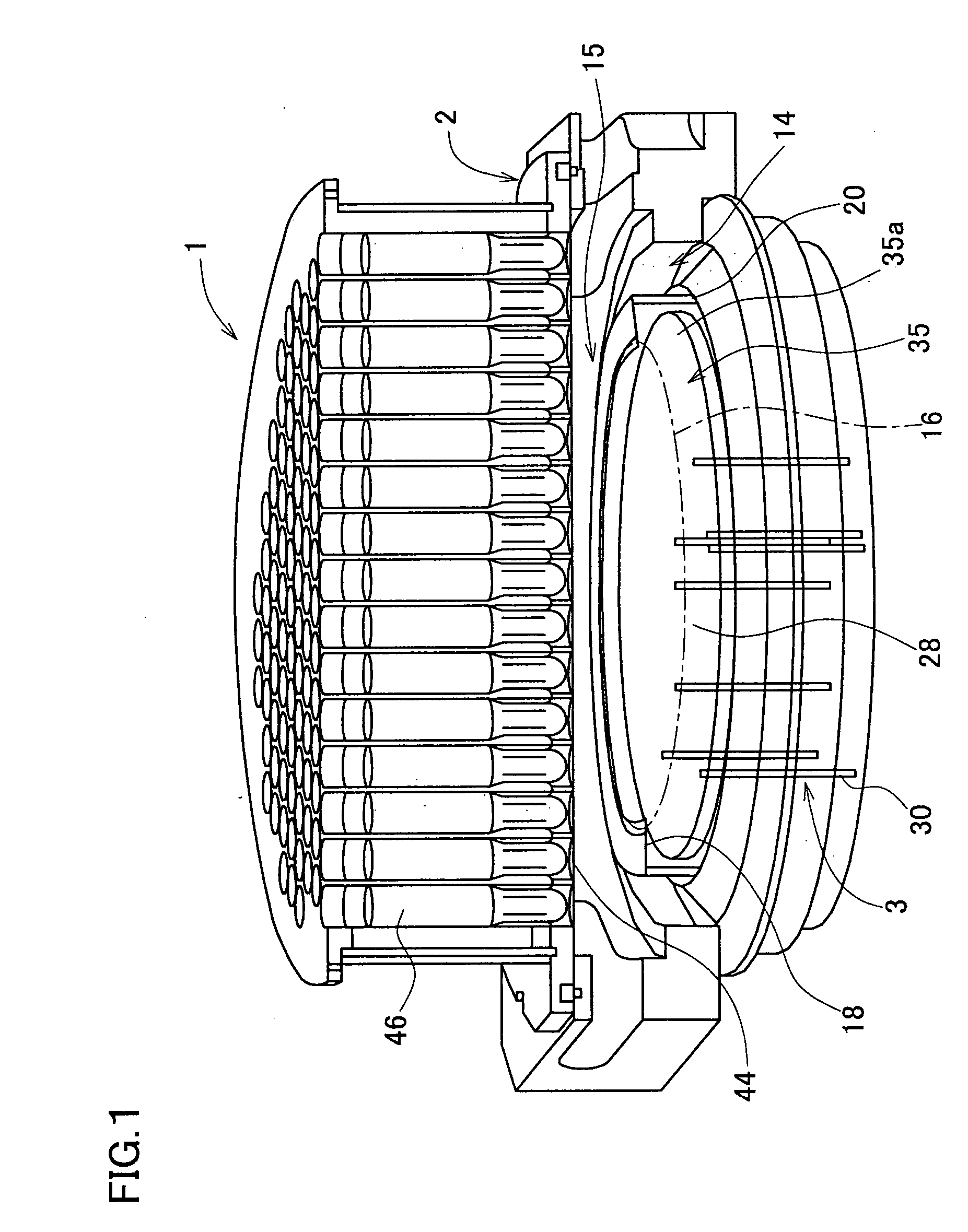
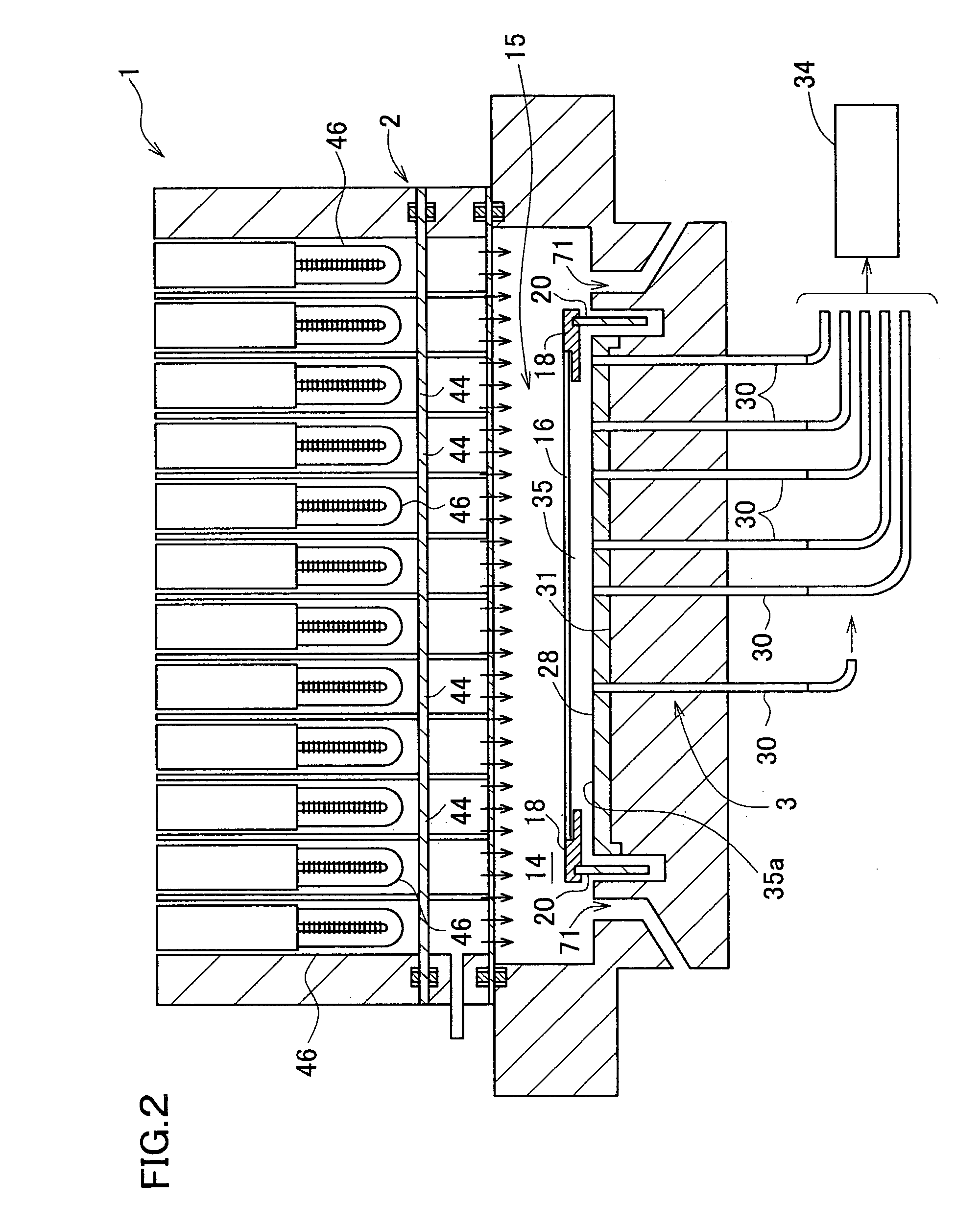
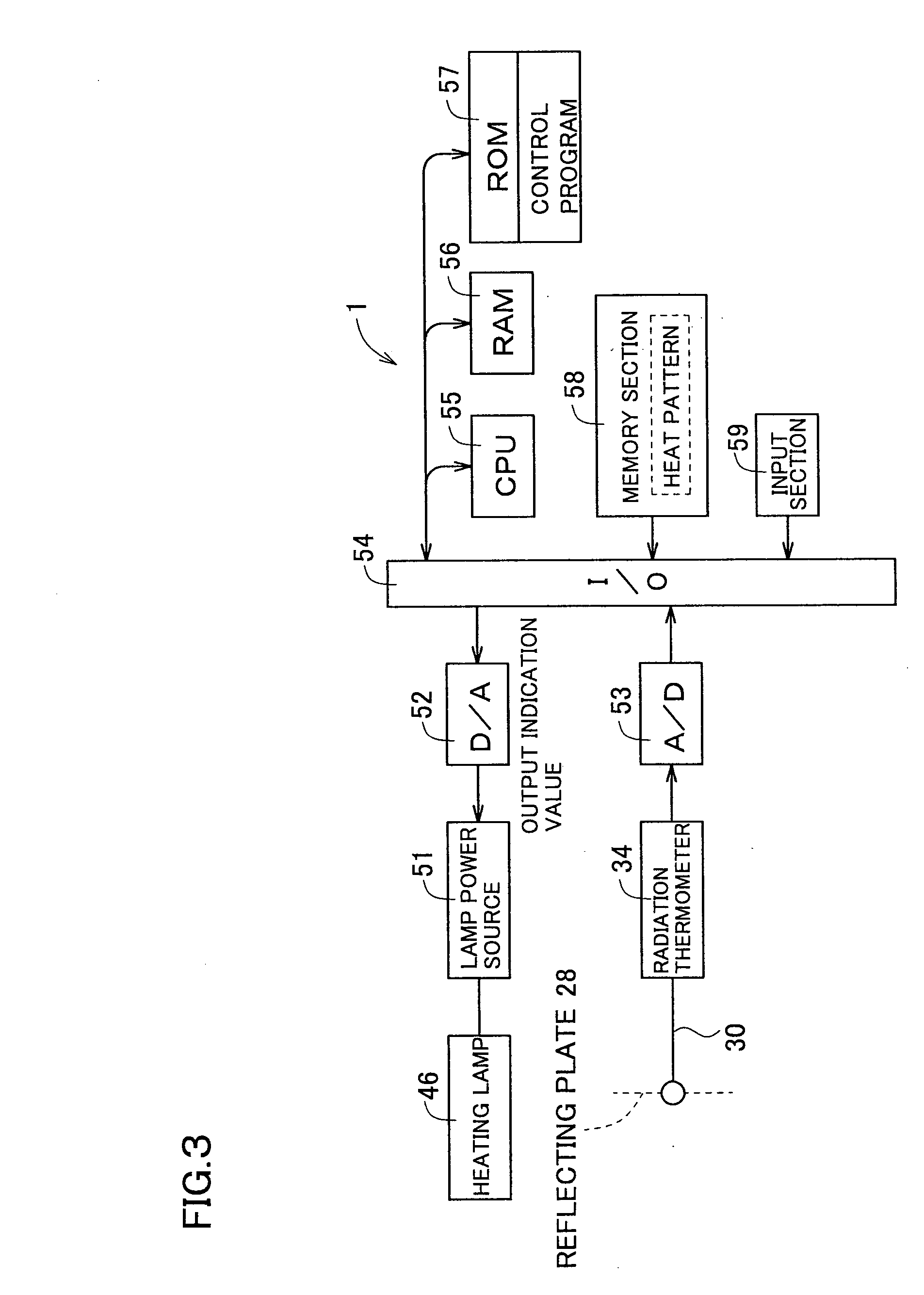
Temperature measuring system, heating device using it and production method for semiconductor wafer, heat ray insulating translucent member, visible light reflection membner, exposure system-use reflection mirror and exposure system, and semiconductor device produced by using them and vetical heat treating device
InactiveUS20050063451A1Necessary numberGood choiceRadiation pyrometryDoor/window protective devicesDevice materialRadiation thermometer
Oppositely of a temperature measuring surface of an object-to-be-measured 16, a reflecting member 28 is disposed while being spaced by a reflection gap 35 from the temperature measuring surface. The reflecting member 28 is composed of a heat ray reflecting material capable of reflecting heat ray in a specific wavelength band, in a portion including a reflection surface 35a. A heat ray extraction pathway section 30 is disposed through the reflecting member 28 so that one end thereof faces the temperature measuring surface. Heat ray extracted through the heat ray extraction pathway section from the reflection gap is detected by a temperature detection section 34. The heat ray reflecting material is configured in a form of a stack comprising a plurality of element reflecting layers composed of a material having transparent properties to the heat ray, in which every adjacent two element reflecting layers are composed of a combination of materials having refractive indices which differ from each other by 1.1 or more. This makes the measurement be hardly affected by radiation ratio of the object-to-be-measured when temperature of the object-to-be-measured is measured by a radiation thermometer, enables to measure its temperature more correctly irrespective of the surface state thereof, and can simplify configuration of a measurement system.
Owner:SHIN-ETSU HANDOTAI CO LTD
Method and apparatus for photothermal treatment of tissue at depth
ActiveUS7351252B2Effective protectionFast resultsUltrasound therapyElectrotherapyOptical radiationElectricity
The present invention provides method and apparatus for treating tissue in a region at depth by applying optical radiation thereto of a wavelength able to reach the depth of the region and of a selected relatively low power for a duration sufficient for the radiation to effect the desired treatment while concurrently cooling tissue above the selected region to protect such tissue. Treatment may be enhanced by applying mechanical, acoustic or electrical stimulation to the region.
Owner:PALOMAR MEDICAL TECH +1
Optical system and apparatus for laser heat treatment and method for producing semiconductor devices by using the same
InactiveUS6437284B1High crystallinityReduced lattice defectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMetal working apparatusLight beamOptoelectronics
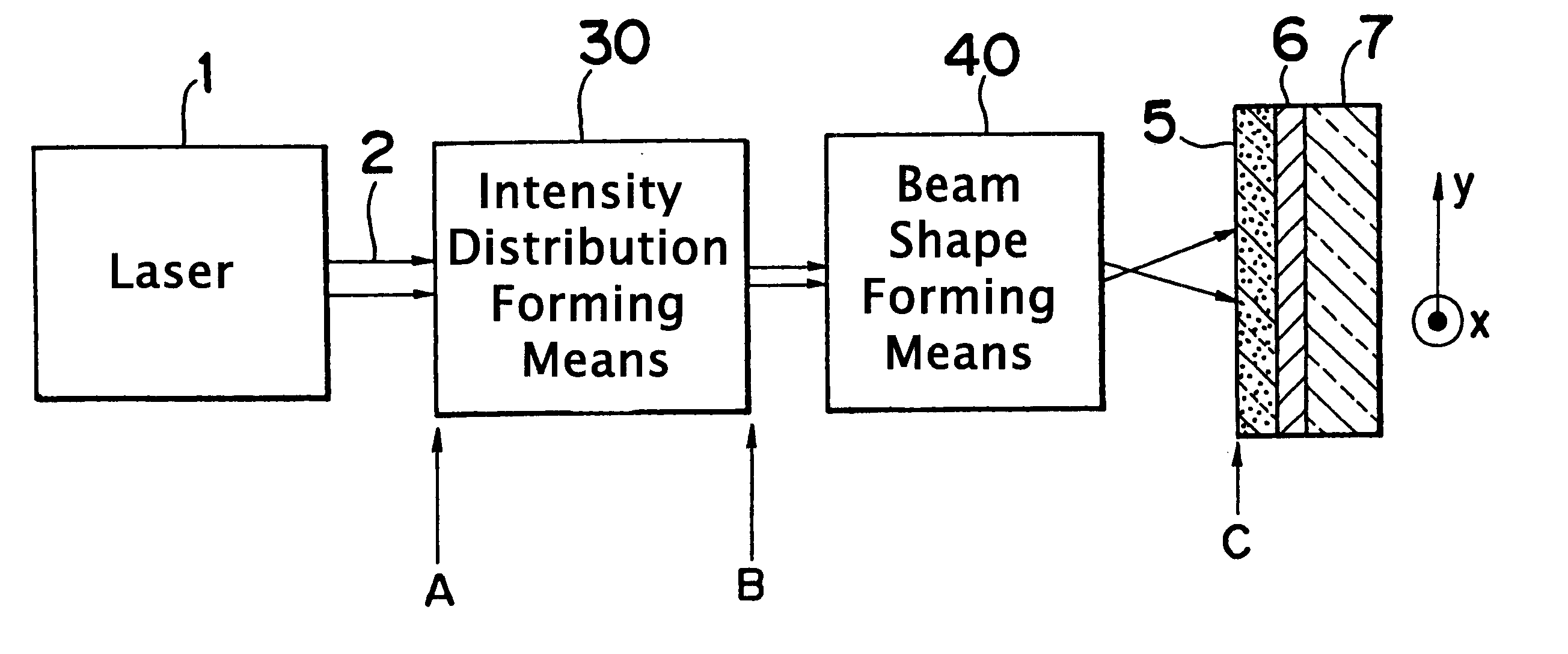
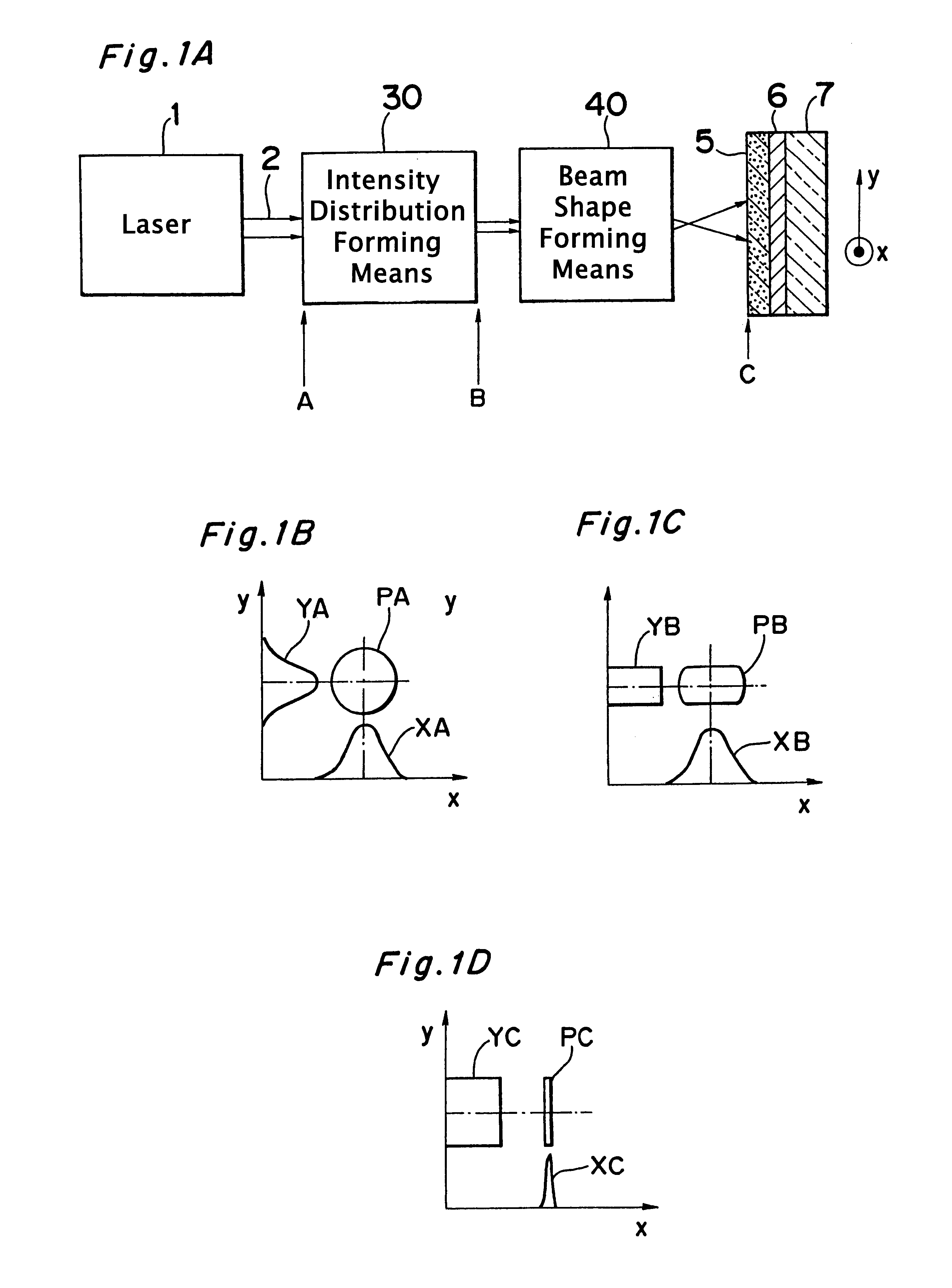
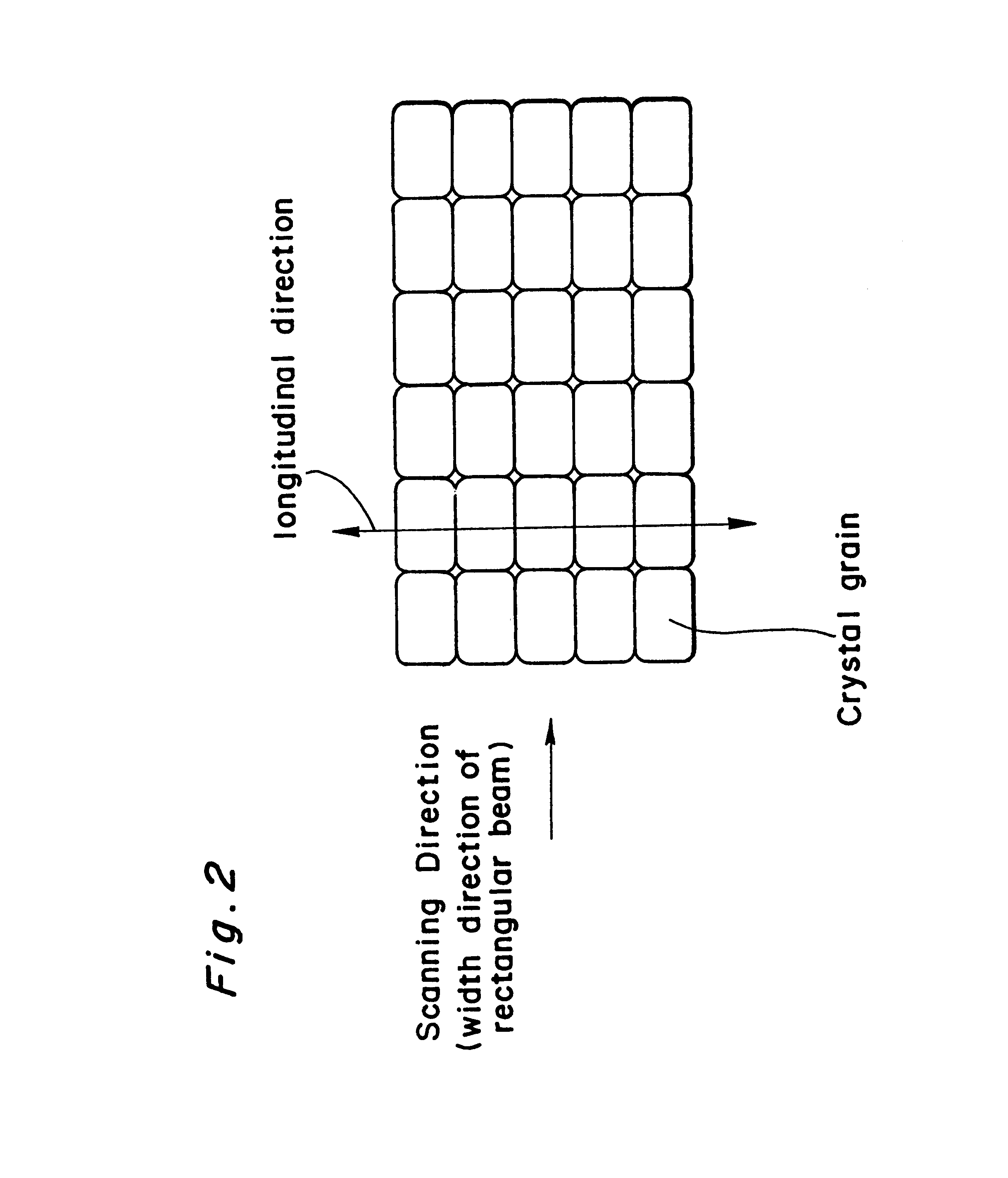
An optical system that controls laser beam spot profile for forming a high performance thin film by a laser heat treatment process is provided. In the optical system that irradiates a rectangular laser beam on a film formed on a substrate, intensity distribution forming, apparatus makes the intensity distribution uniform in the longitudinal direction while maintaining the properties of the laser beam 2 such as directivity in the direction of shorter side, making it possible to concentrate the light to a limit permitted by the nature of the laser beam and achieve the maximum intensity gradient on the film disposed on the substrate. Thus a steep temperature distribution can be generated on the film disposed on the substrate and, as a result, high performance thin film can be formed.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Method for fabricating a semiconductor device
InactiveUS6180439B1Promote crystallizationReduce concentrationTransistorSolid-state devicesAtmospheric airLaser light
Concentration of metal element which promotes crystallization of silicon and which exists within a crystalline silicon film obtained by utilizing the metal element is reduced. A first heat treatment for crystallization is performed after introducing nickel to an amorphous silicon film 103. Then, laser light is irradiated to diffuse nickel element which is concentrated locally. After that, another heat treatment is performed within an oxidizing atmosphere at a temperature higher than that of the previous heat treatment. At this time, HCl or the like is added to the atmosphere. A thermal oxide film 106 is formed in this step. At this time, gettering of the nickel element into the thermal oxide film 106 takes place. Then, the thermal oxide film 106 is removed. Thereby, a crystalline silicon film 107 having low concentration of the metal element and a high crystallinity can be obtained.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Method of making a product with improved material properties by moderate heat-treatment of a metal incorporating a dilute additive
InactiveUS6150186AStable mechanical propertiesImprove conductivitySemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementFinal product manufactureUltimate tensile strengthMechanical property
Deposition of metal in a preferred shape, including coatings on parts, or stand-alone materials, and subsequent heat treatment to provide improved mechanical properties. In particular, the method gives products with relatively high yield strength. The products often have relatively high elastic modulus, and are thermally stable, maintaining the high yield strength at temperatures considerably above 25 DEG C. This technique involves depositing a material in the presence of a selected additive, and then subjecting the deposited material to a moderate heat treatment. This moderate heat treatment differs from other commonly employed "stress relief" heat treatments in using lower temperatures and / or shorter times, preferably just enough to reorganize the material to the new, desired form. Coating a shape and heat treating provides a shaped deposit with improved material properties. Coating a shape with a portion connected to a base and a portion detached therefrom can provide a resilient, conductive contact useful for electronic applications.
Owner:FORMFACTOR INC
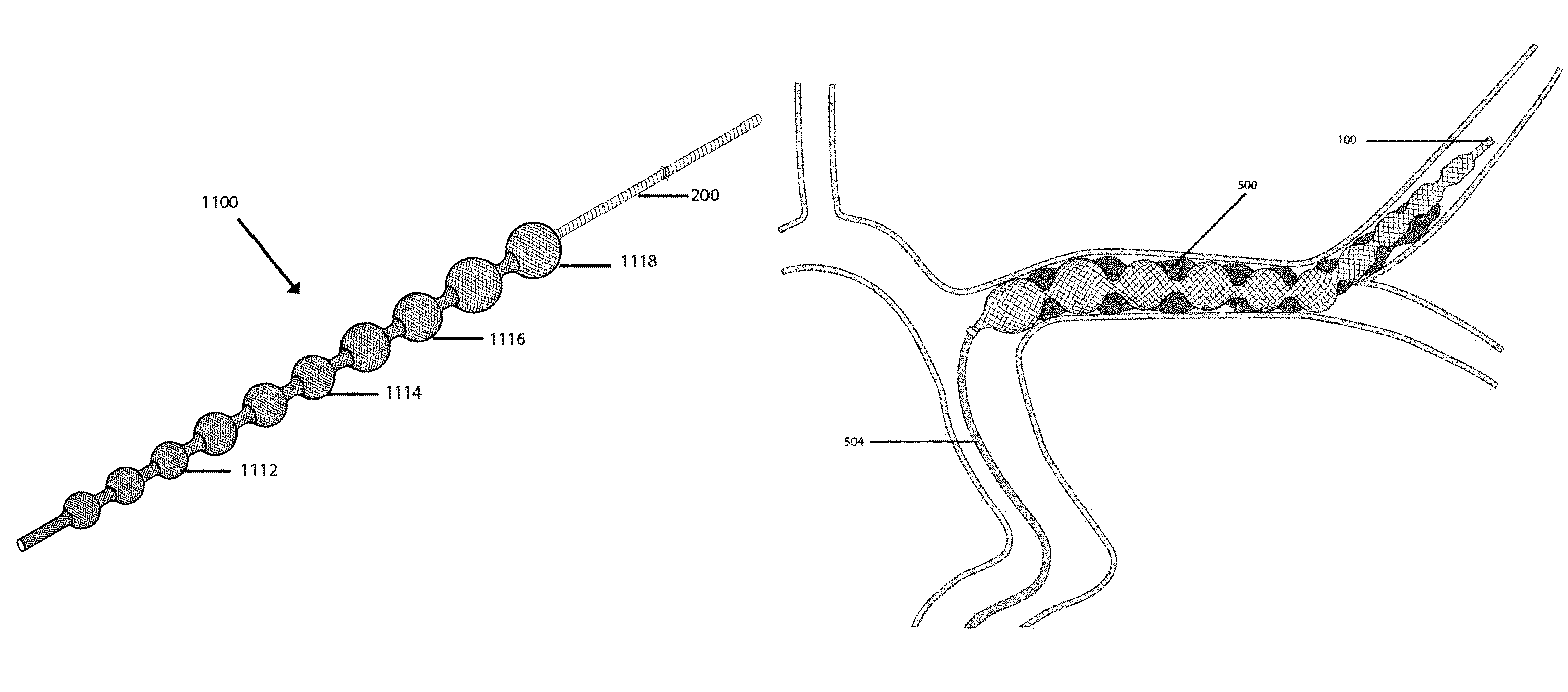
Vascular treatment methods
ActiveUS8690907B1Effectively and efficiently capturingIncrease awarenessStentsDiagnosticsX-rayCatheter
Vascular treatment and methods include a plurality of self-expanding bulbs and a hypotube including interspersed patterns of longitudinally spaced rows of kerfs. Joints between woven structures and hypotubes include solder. Woven structures include patterns of radiopaque filaments measurable under x-ray. Structures are heat treated to include at least shapes at different temperatures. A catheter includes a hypotube including interspersed patterns of longitudinally spaced rows of kerfs. Heat treating systems include a detachable flange. Laser cutting systems include a fluid flow system.
Owner:INSERA THERAPEUTICS
Synthesis-reactivation technique for preparing inorganic coagulation material
InactiveCN1990413ASimple processImprove adjustabilitySolid waste managementSlagBiological activation
The invention relates to a process of preparing inorganic cementing material. It comprises following steps: mixing industrial slag, silicon-containing material, lime, plaster, addictive and water according to a certain proportion; pressing mixed material or compressing it into briquetting, maintaining naturally for thorough reaction, heat treating for activation under 450-850 Deg. C, adding addictive and grinding until sifting leaves is less than 15% with screen of 80 um, and getting inorganic cementing material, which is used as special cement or expansive agent. The invention is characterized by good physical property, stable volume, long durability and workability, low energy consumption and cost and environmental friendly.
Owner:尹小林
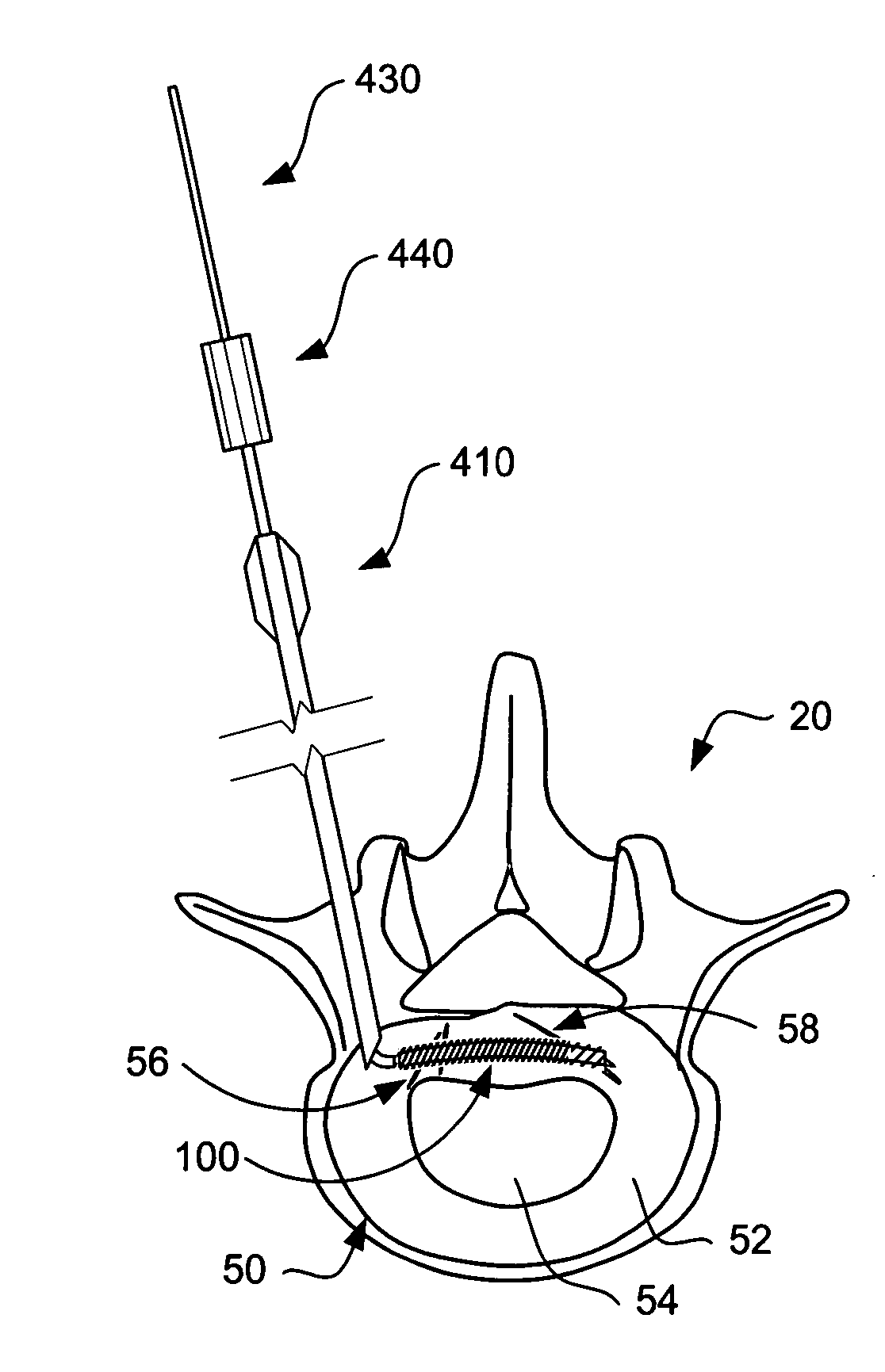
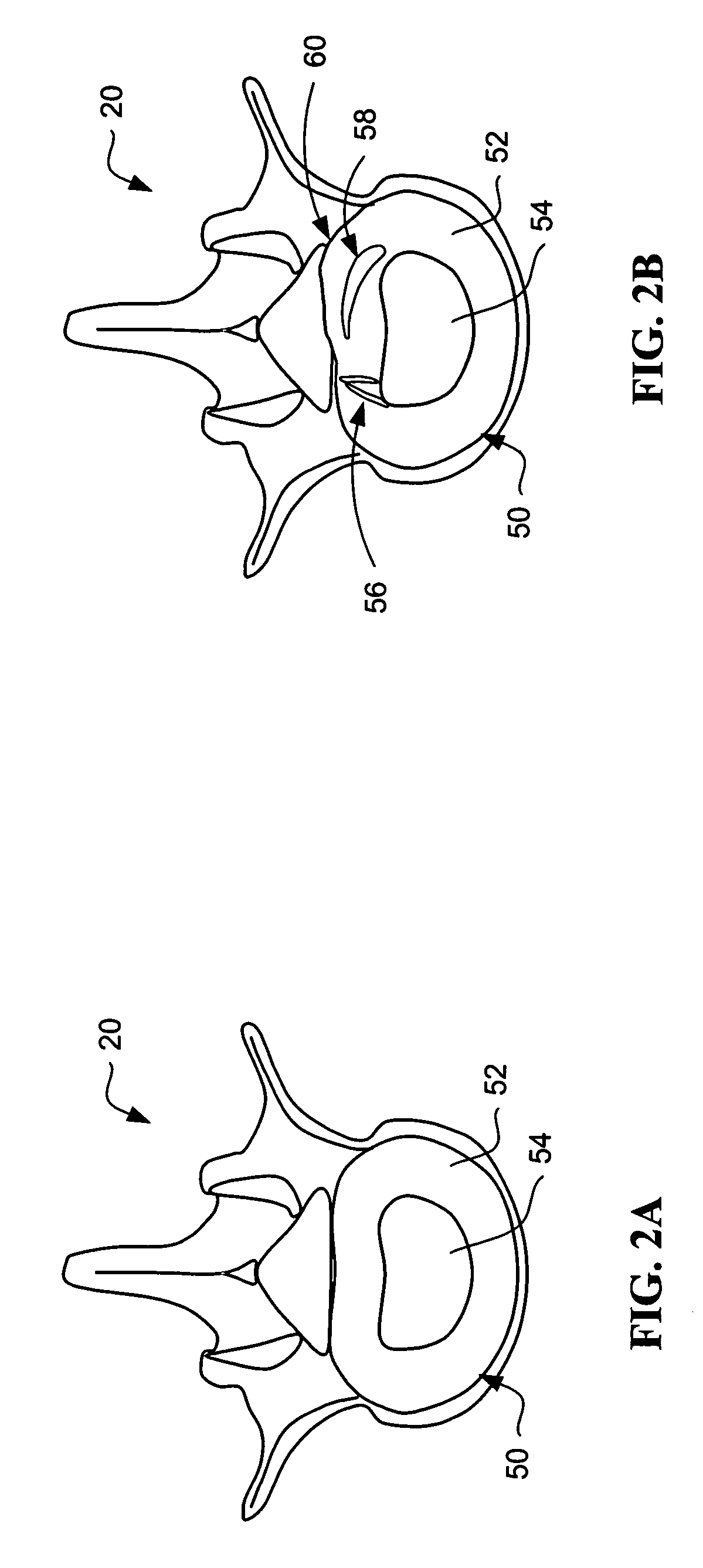
Devices and methods for annular repair of intervertebral discs
InactiveUS20050049592A1Eliminate back painPermit some movementSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisIntervertebral discBACK DISCOMFORT
Devices and methods for treating a damaged intervertebral disc to reduce or eliminate associated back pain. The present invention provides disc reinforcement therapy (DRT) which involves implanting one or more reinforcement members in and preferably around the annulus of the disc. The reinforcement members may be used to stabilize the annulus and / or compresses a portion of the annulus so as to reduce a bulge and / or close a fissure. The implantable devices and associated delivery tools may incorporate heating capabilities to thermally treat the annular tissue. Alternatively or in combination, other devices may be specifically employed for such thermal treatment.
Owner:KRT INVESTORS
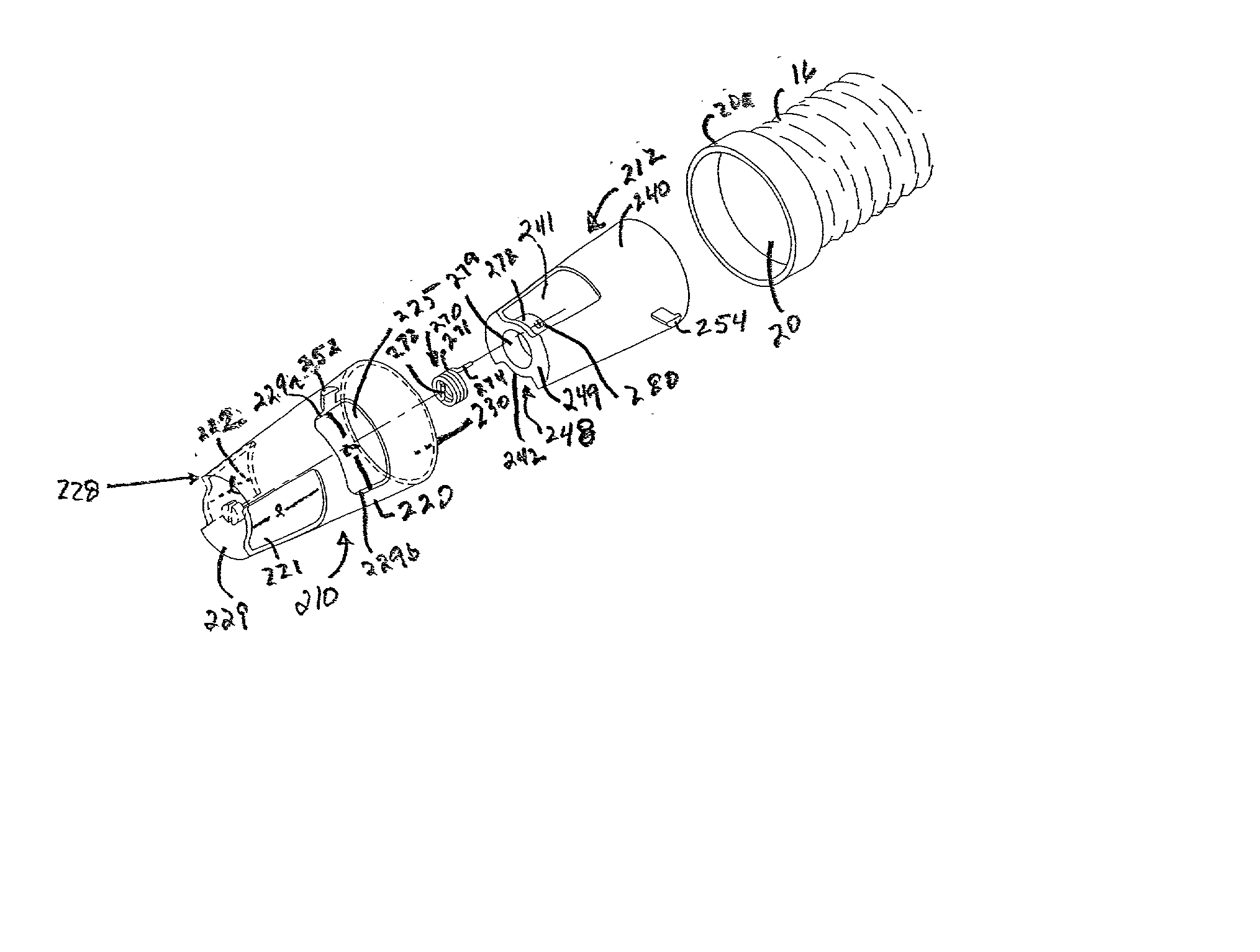
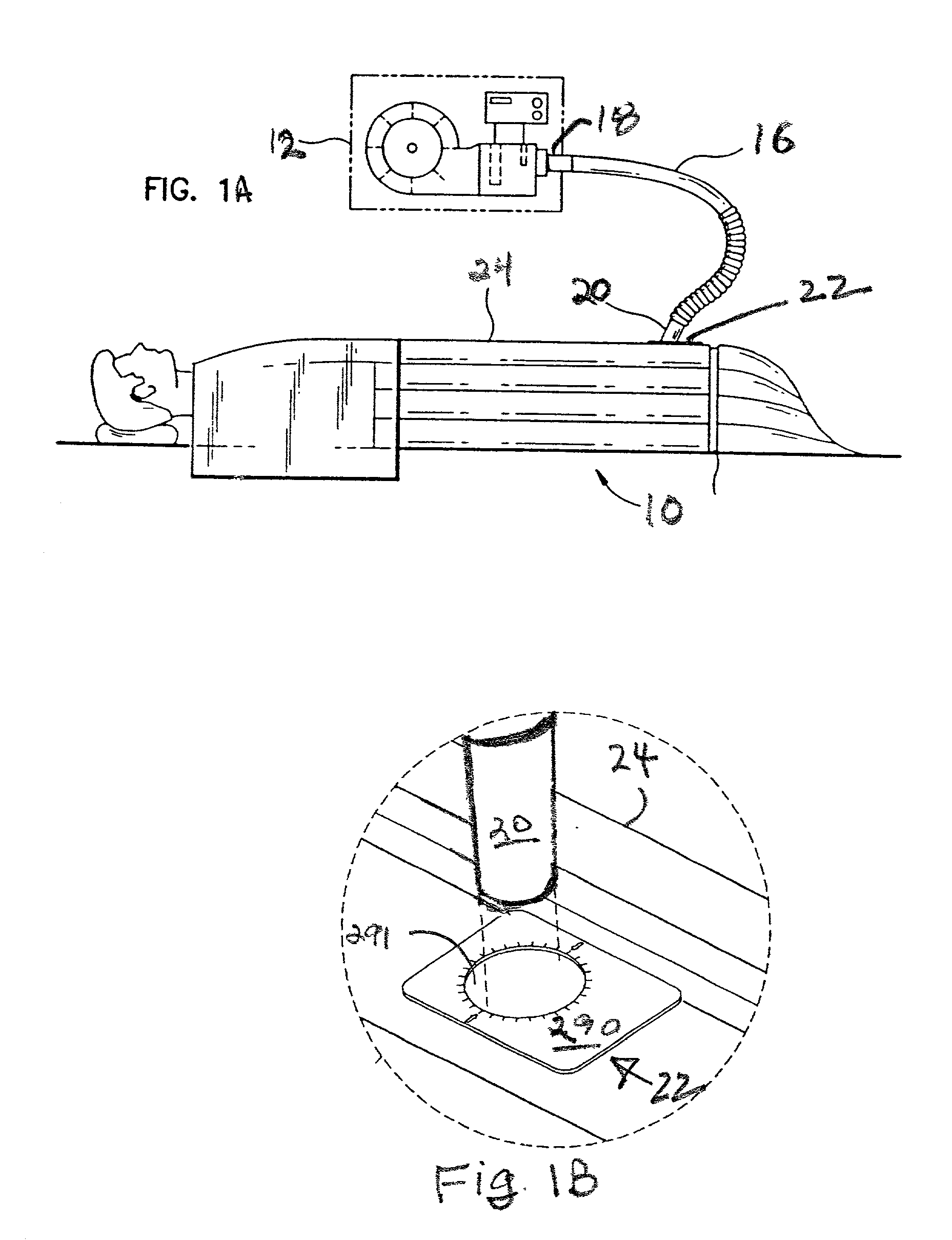
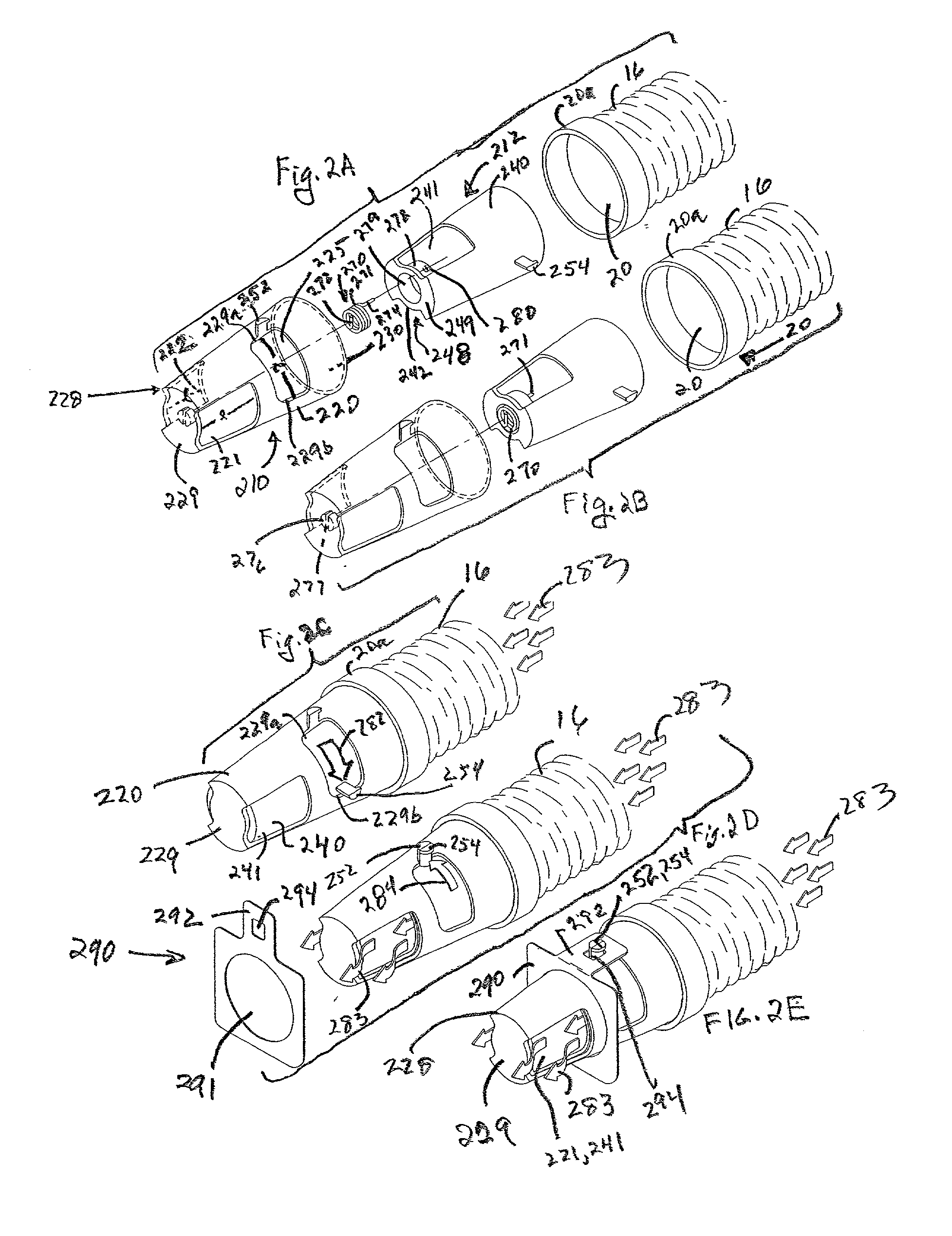
System, combination and method for controlling airflow in convective treatment
InactiveUS20030036786A1Accurate conditionSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsLighting and heating apparatusEngineeringHeat treating
In a convective system that includes a blower to thermally treat and pressurize air, a convective device to receive and convect the thermally-treated pressurized air, and an air hose to conduct a flow of thermally-treated pressurized air from the blower to an inlet port in the convective device, an interface device is provided to control the flow of air at the interface where the inlet port and an end of the air hose operate to conduct the flow of air out of the air hose into the convective device. The interface device is received at the end of the air hose and operates to support the flow of air out of the end when the end and the inlet port are brought together. The interface device operates to stop, inhibit, or restrict the flow of air out of the end when the end and the inlet port are separated.
Owner:GEN ELECTRIC CAPITAL +1
Process for the production of ultrafine powders of metal oxides
InactiveUS6503475B1Low costHigh yield rateAlkaline earth titanatesMaterial nanotechnologyDiluentBiological activation
A process for the production of ultrafine powders that includes subjecting a mixture of precursor metal compound and a non-reactant diluent phase to mechanical milling whereby the process of mechanical activation reduces the microstructure of the mixture to the form of nano-sized grains of the metal compound uniformly dispersed in the diluent phase. The process also includes heat treating the mixture of nano-sized grains of the metal compound uniformly dispersed in the diluent phase to convert the nano-sized grains of the metal compound into a metal oxide phase. The process further includes removing the diluent phase such that the nano-sized grains of the metal oxide phase are left behind in the form of an ultrafine powder.
Owner:SAMSUNG CORNING PRECISION MATERIALS CO LTD +1
Peeling method
InactiveUS7122445B2Slow performanceImprove suppression propertiesTransistorSolid-state devicesHydrogenEngineering
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Interstitial microwave system and method for thermal treatment of diseases
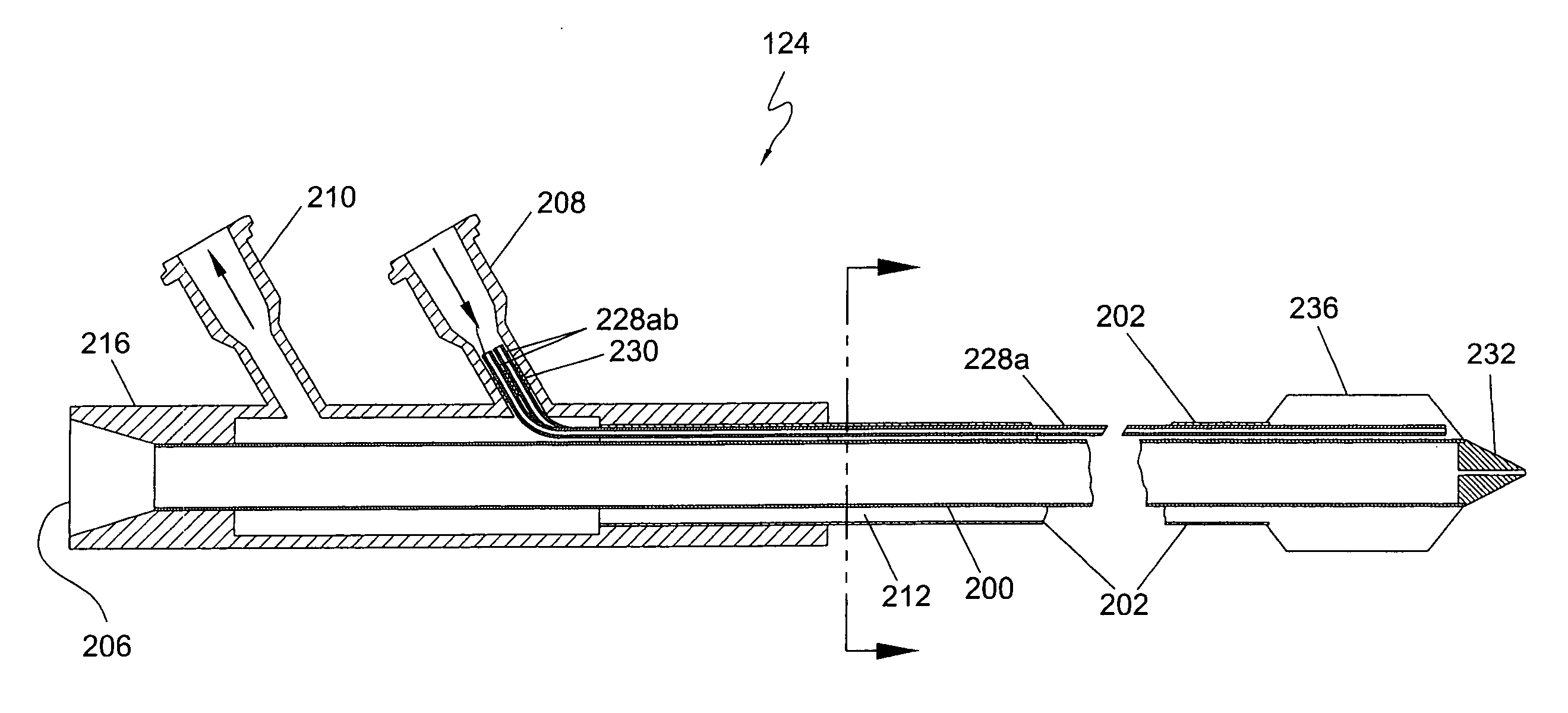
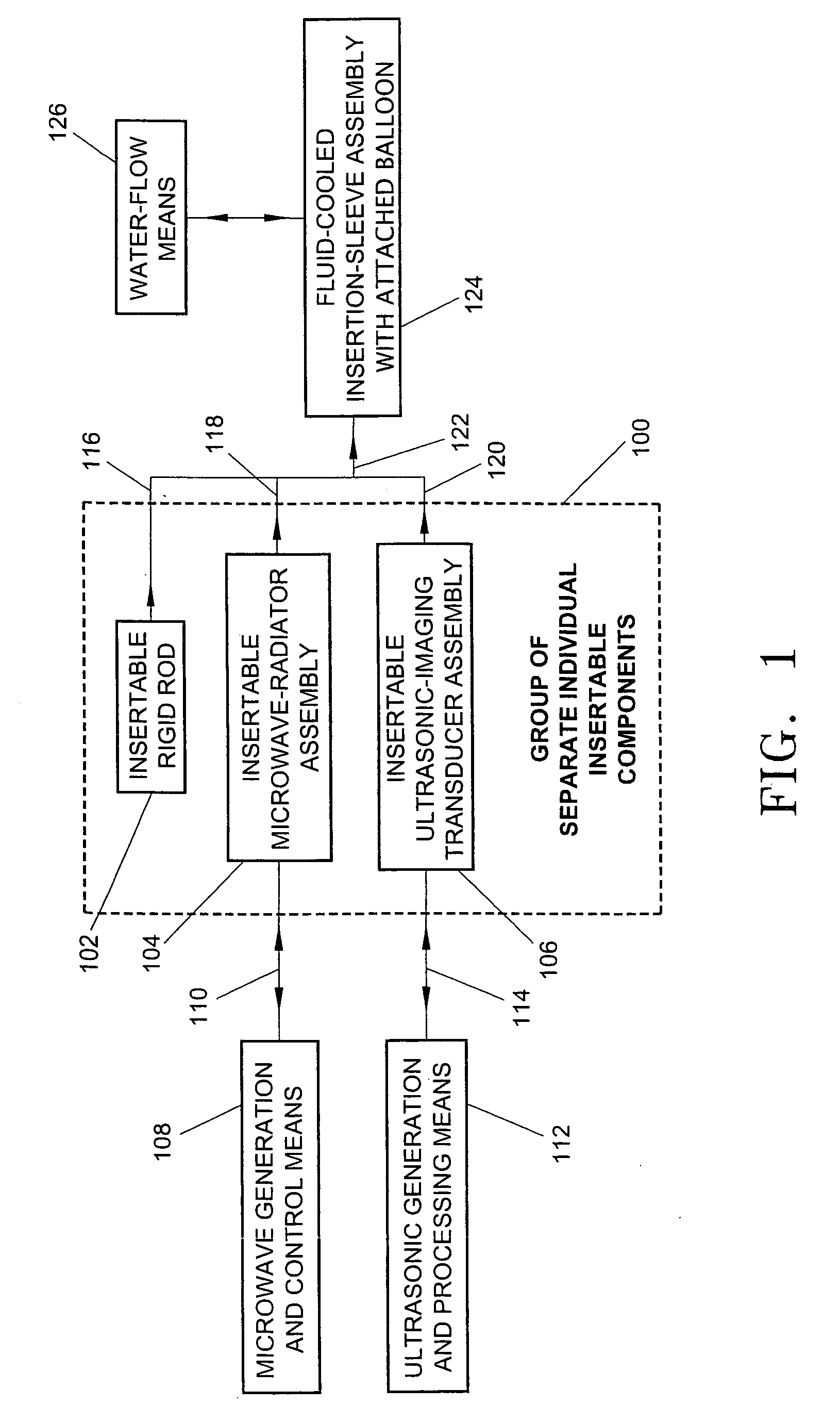
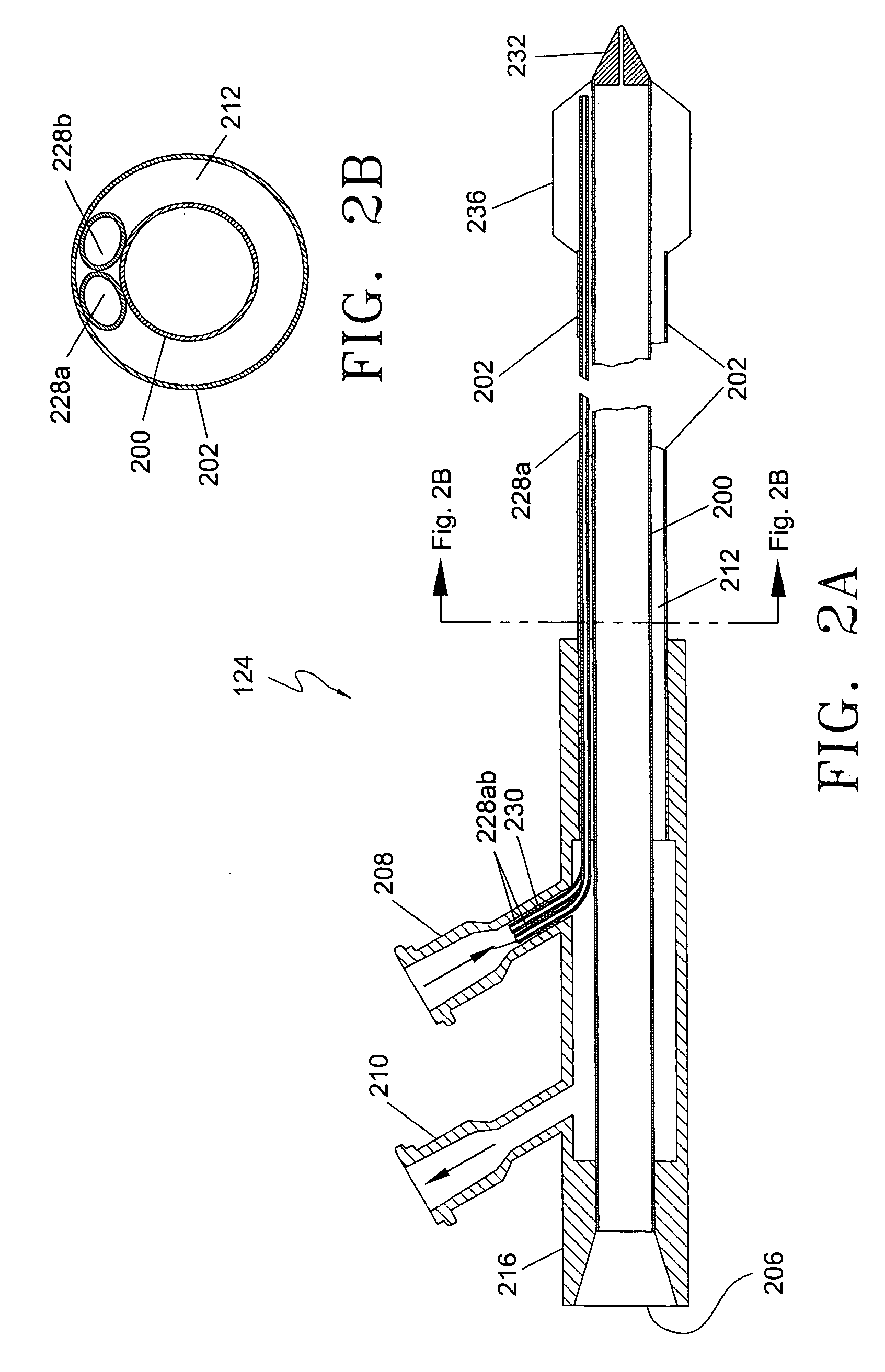
A minimally-invasive fluid-cooled insertion sleeve assembly, with an attached balloon and distally-located penetrating tip, into which sleeve any of a group comprising a rigid rod, a microwave-radiator assembly and an ultrasonic-imaging transducer assembly may be inserted, constitutes a probe of the system. The sleeve assembly comprises spaced inner and outer plastic tubes with two fluid channels situated within the coaxial lumen between the inner and outer tubes. The fluid coolant input flows through the fluid channels into the balloon, thereby inflating the balloon, and then exits through that coaxial lumen. An alternative embodiment has no balloon. The method employs the probe for piercing sub-cutaneous tissue and then ablating deep-seated tumor tissue with microwave-radiation generated heat.
Owner:MMTC LTD +1
Peeling method
InactiveUS20040087110A1Slow performanceAdhesive propertyTransistorSolid-state devicesHydrogenEngineering
A peeling method is provided which does not cause damage to a layer to be peeled, and the method enables not only peeling of the layer to be peeled having a small area but also peeling of the entire layer to be peeled having a large area at a high yield. Further, there are provided a semiconductor device, which is reduced in weight through adhesion of the layer to be peeled to various base materials, and a manufacturing method thereof. In particular, there are provided a semiconductor device, which is reduced in weight through adhesion of various elements, typically a TFT, to a flexible film, and a manufacturing method thereof. A metal layer or nitride layer is provided on a substrate; an oxide layer is provided contacting with the metal layer or nitride layer; then, a base insulating film and a layer to be peeled containing hydrogen are formed; and heat treatment for diffusing hydrogen is performed thereto at 410° C. or more. As a result, complete peeling can be attained in the oxide layer or at an interface thereof by using physical means.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Anti-sulfur well mouth valve body welding repair method
ActiveCN107520526AImprove carrying capacityAvoid softening problemsArc welding apparatusWelding/cutting media/materialsCarbon alloyTungsten
The invention belongs to the welding industry, and particularly relates to an anti-sulfur well mouth valve body welding repair method, and in particular to a welding repair method of 4130 medium-carbon alloy steel in an anti-sulfur valve body with the hardness being 197 HBW -237 HBW. The anti-sulfur well mouth valve body welding repair method is characterized by comprising the following steps that a product to be repaired is cleaned to determine a damage position; a pit badly eroded needs to be polished; a workpiece is totally preheated to 130 DEG C before welding; filling of the pit is firstly achieved by adopting the argon tungsten-arc welding; then, the machined surface is subject to repair welding; the local or total heat treatment insulation is performed for 3 hours at 640 DEG C; in the welding repair method, preheating is performed to reach 130 DEG C before welding; the local or total heat treatment insulation is performed for 3 hours at 640 DEG C after welding; and the Ar+CO2 mixed gas arc welding is adopted in the method, and the method greatly increases the product utilization rate and improves the comprehensive efficiency.
Owner:YANTAI JEREH PETROLEUM EQUIP & TECH
Flow diverting devices
ActiveUS8715317B1Effectively and efficiently capturingIncrease awarenessLathesOrnamental textile articlesLaser cuttingBlood vessel
Vascular treatment and methods include a plurality of self-expanding bulbs and a hypotube including interspersed patterns of longitudinally spaced rows of kerfs. Joints between woven structures and hypotubes include solder. Woven structures include patterns of radiopaque filaments measureable under x-ray. Structures are heat treated to include at least shapes at different temperatures. A catheter includes a hypotube including interspersed patterns of longitudinally spaced rows of kerfs. Heat treating systems include a detachable flange. Laser cutting systems include a fluid flow system.
Owner:INSERA THERAPEUTICS
Method for preparing medical porous tantalum implant material
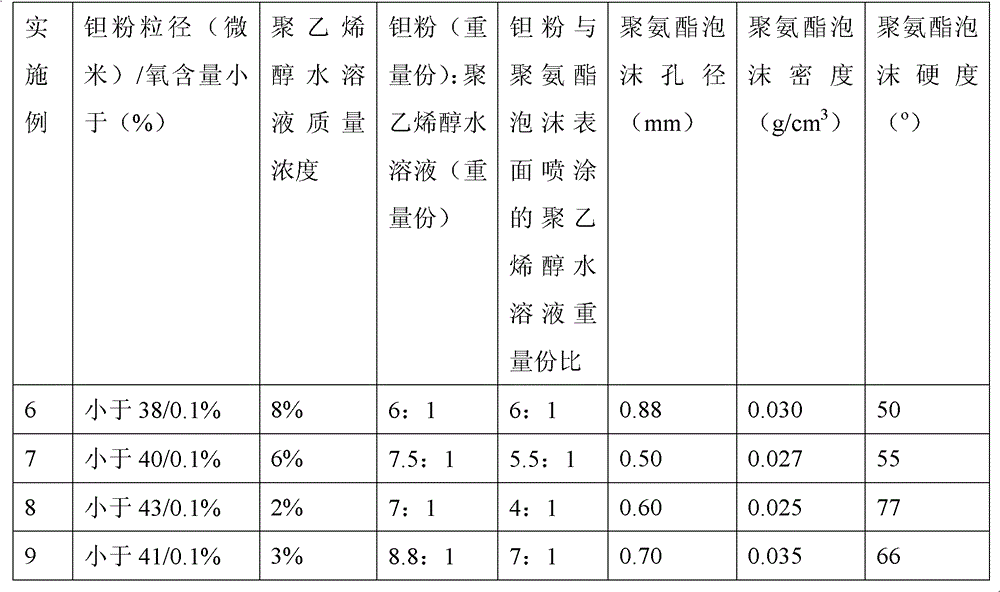
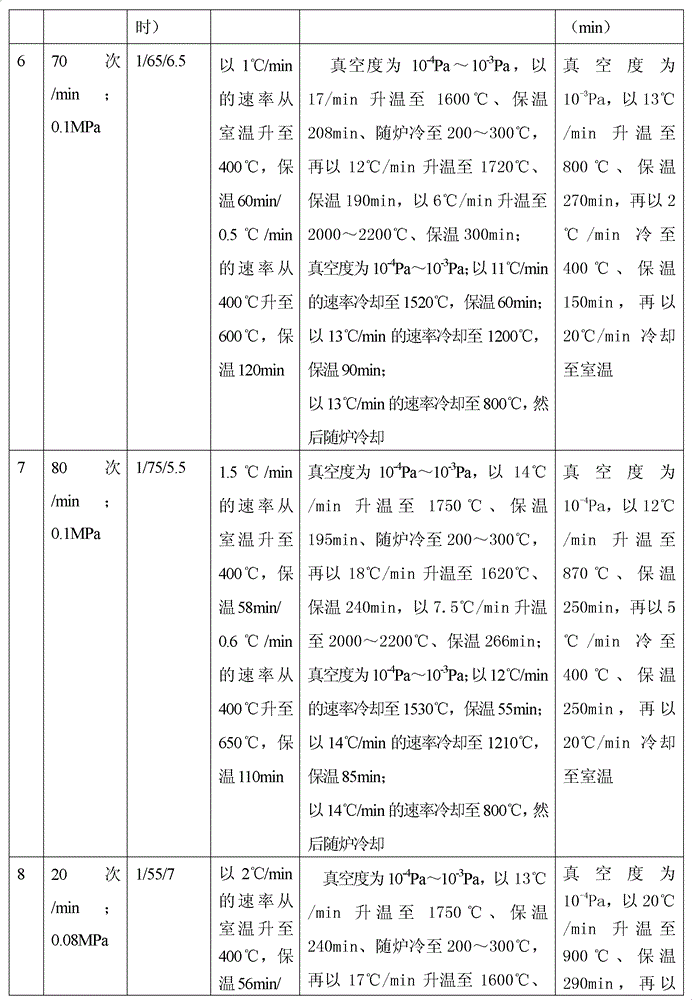
ActiveCN102796894AReduce contentImprove mechanical propertiesProsthesisPolyvinyl alcoholBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses a method for preparing a medical porous tantalum material. The method comprises the following steps of: mixing a poly ethanol aqueous solution and tantalum powder to obtain slurry, wherein the mass concentration of the poly ethanol aqueous solution is 2 to 8 percent; injecting the slurry into an organic foam by vibrating and pressurizing, wherein the vibrating frequency is 20 to 80 times / min; drying; degreasing; sintering, namely raising temperature to 1,500 to 1,800 DEG C at the speed of 10 to 20 DEG C / min under the vacuum degree of 10<-4> to 10<-3>Pa, preserving heat for 120 to 240 minutes, cooling to 200 to 300 DEG C along with a furnace, raising temperature to 1,500 to 1,800 DEG C at the speed of 10 to 20 DEG C / min again, preserving heat for 180 to 240 minutes, raising temperature to 2,000 to 2,200 DEG C at the speed of 5 to 10 DEG C / min, and preserving heat for 120 to 360 minutes; cooling; and performing thermal treatment, namely raising temperature to 800 to 900 DEG C at the speed of 10 to 20 DEG C / min under the vacuum degree of 10<-4> to 10<-3> Pa, preserving heat for 240 to 480 minutes, cooling to 400 DGE C at the speed of 2 to 5 DGE C / min, preserving heat for 120 to 300 minutes, and cooling to room temperature along with the furnace. The porous tantalum prepared by the method is very suitable to be used for the medical implant material for replacing bearing bone tissues, and biocompatibility and the mechanical property can be guaranteed simultaneously.
Owner:CHONGQING RUNZE PHARM CO LTD
Method and Apparatus for Micro-Needle Array Electrode Treatment of Tissue
InactiveUS20070142885A1Avoid overall overheatingMaintain temperatureSurgical needlesMicroneedlesAging skinsMicro-needle
The invention describes a system and method for revitalizing aging skin using electromagnetic energy that is delivered using a plurality of needles that are capable of penetrating the skin to desired depths. A particular aspect of the invention is the capability to spare zones of tissue from thermal exposure. This sparing of tissue allows new tissue to be regenerated while the heat treatment can shrink the collagen and tighten the underlying structures. Additionally, the system is capable of delivering therapeutically beneficial substances either through the penetrating needles or through channels that have been created by the penetration of the needles.
Owner:RELIANT TECH INC
Method for manufacturing bonded substrate having an insulator layer in part of bonded substrate
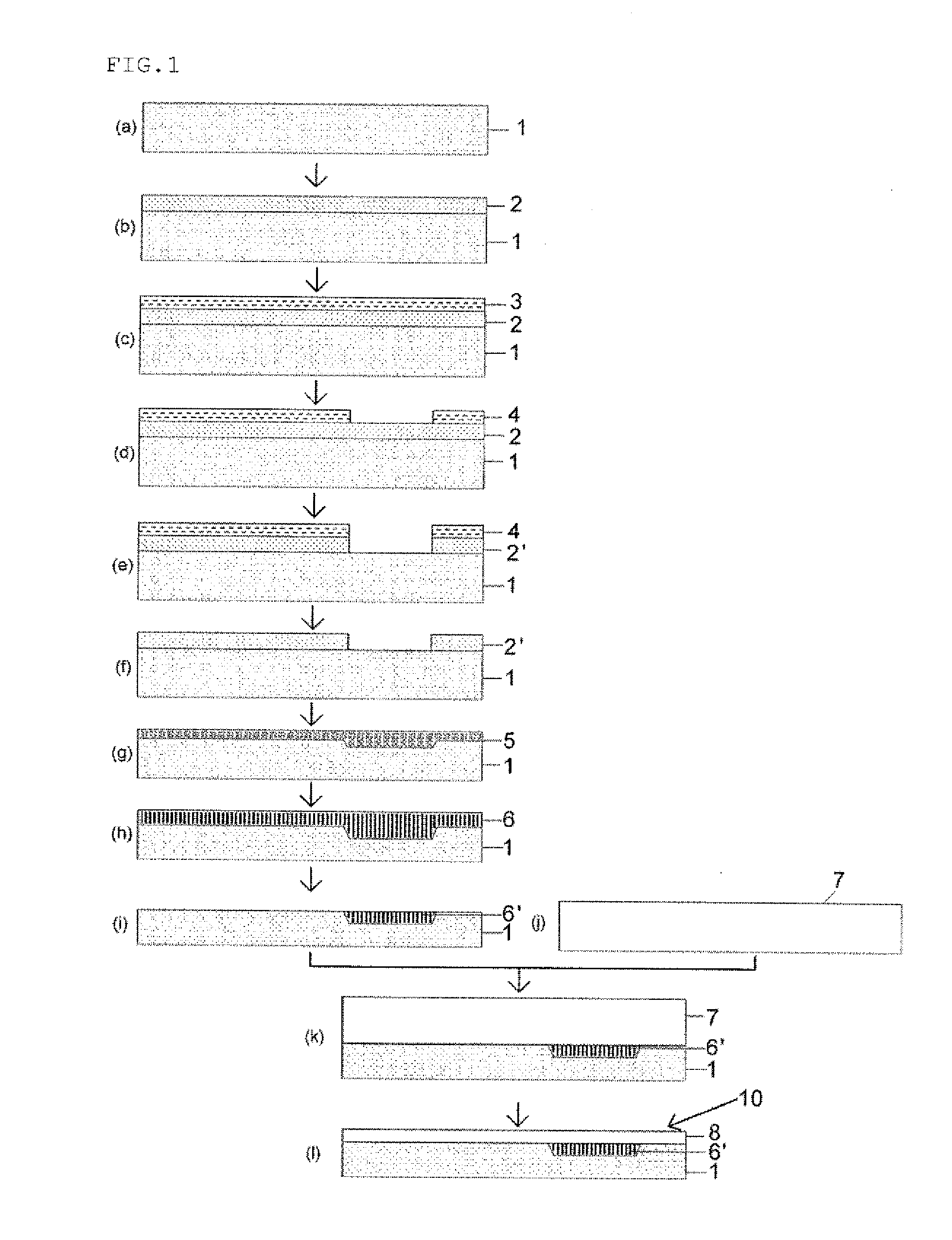
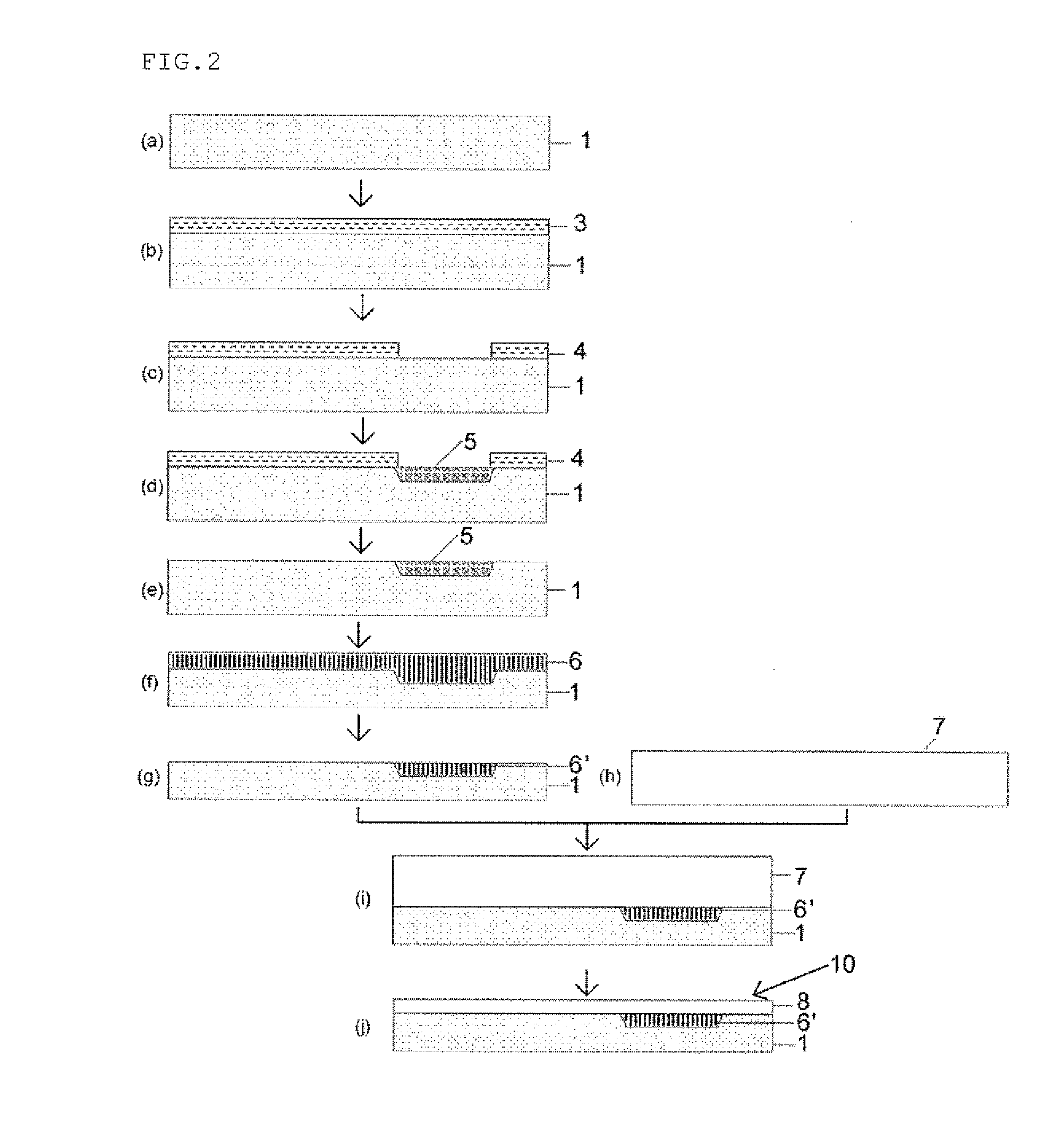
ActiveUS20140120695A1Low costIncreasing the thicknessSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPorous layerThin membrane
A method for manufacturing a bonded substrate that has an insulator layer in part of the bonded substrate includes: partially forming a porous layer or forming a porous layer whose thickness partially varies on a bonding surface of the base substrate; performing a heat treatment to the base substrate having the porous layer formed thereon to change the porous layer into the insulator layer, and thereby forming the insulator layer whose thickness partially varies on the bonding surface of the base substrate; removing the insulator layer whose thickness varies by an amount corresponding to a thickness of a small-thickness portion by etching; bonding the bonding surface of the base substrate on which an unetched remaining insulator layer is exposed to a bond substrate; and reducing a thickness of the bonded bond substrate and thereby forming a thin film layer.
Owner:SHIN-ETSU HANDOTAI CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com