Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
48 results about "Tissue welding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
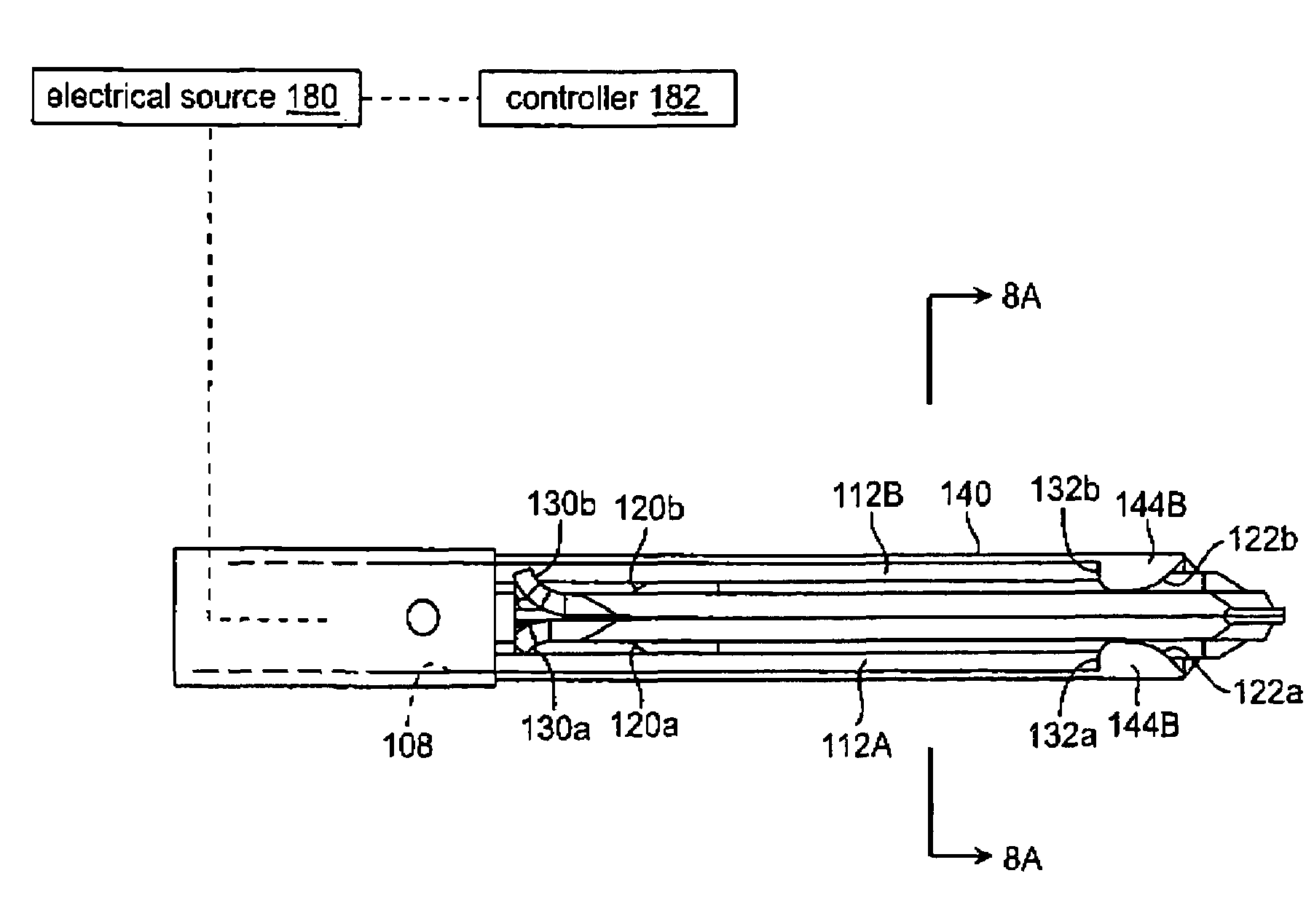
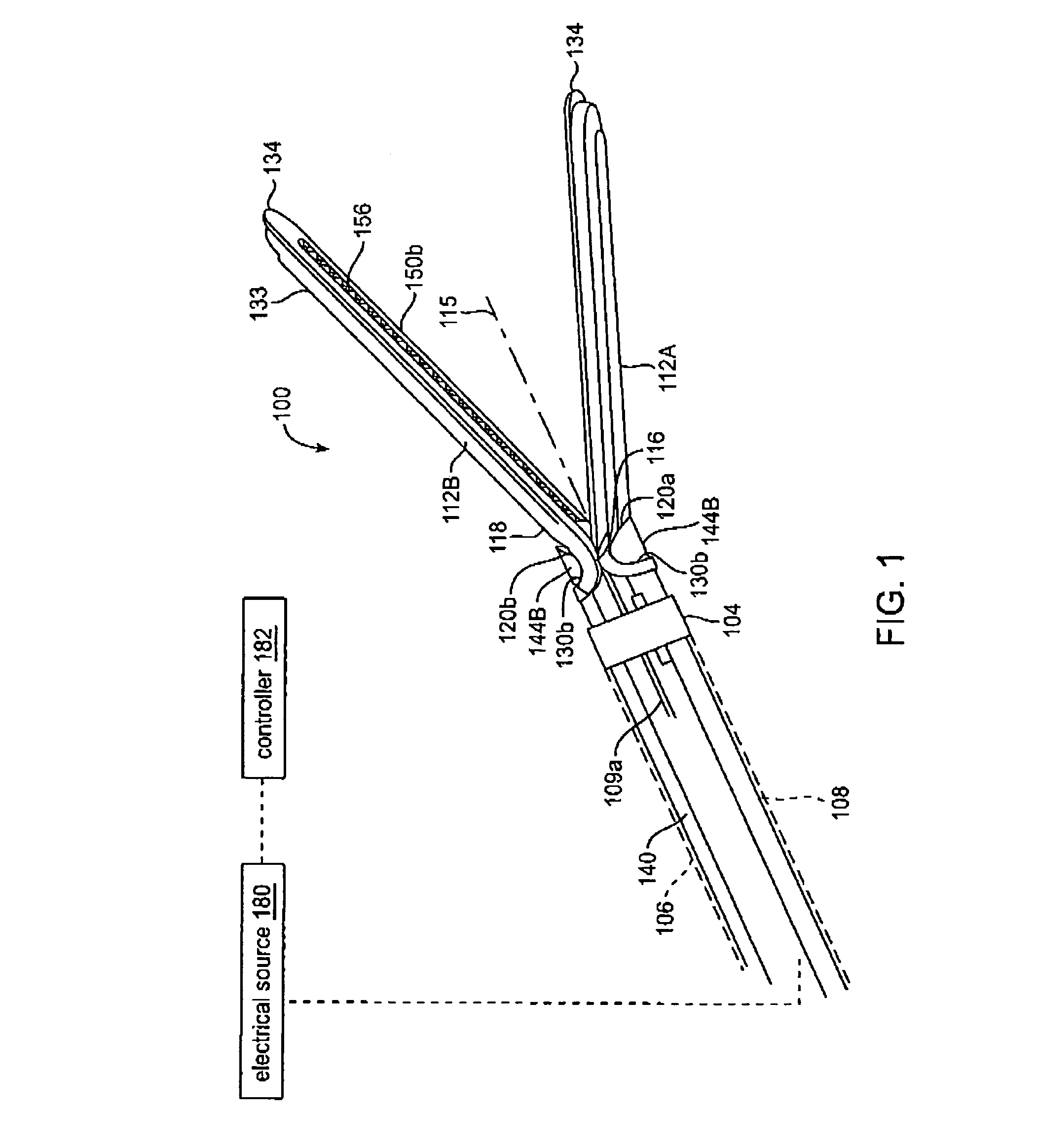
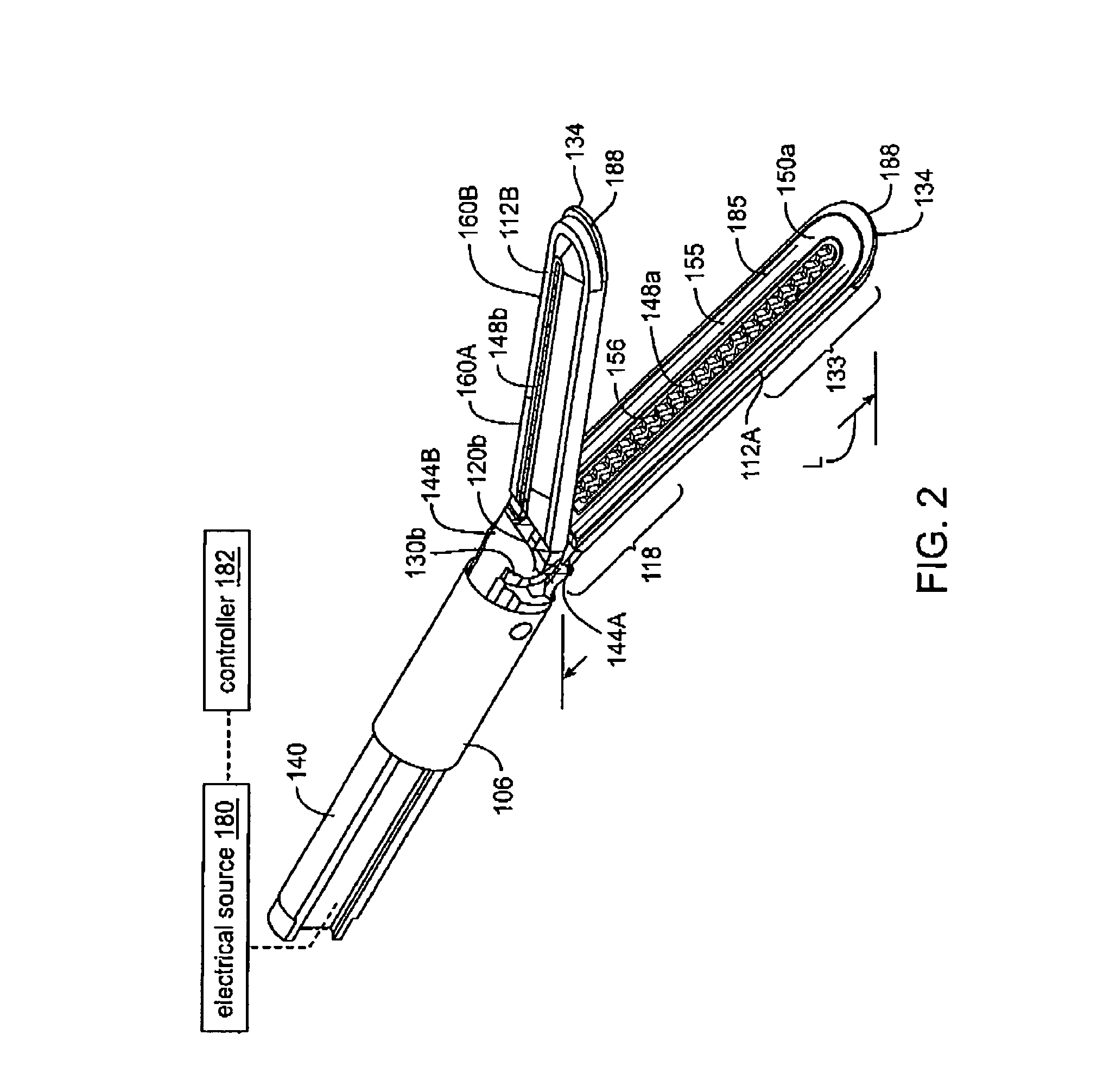
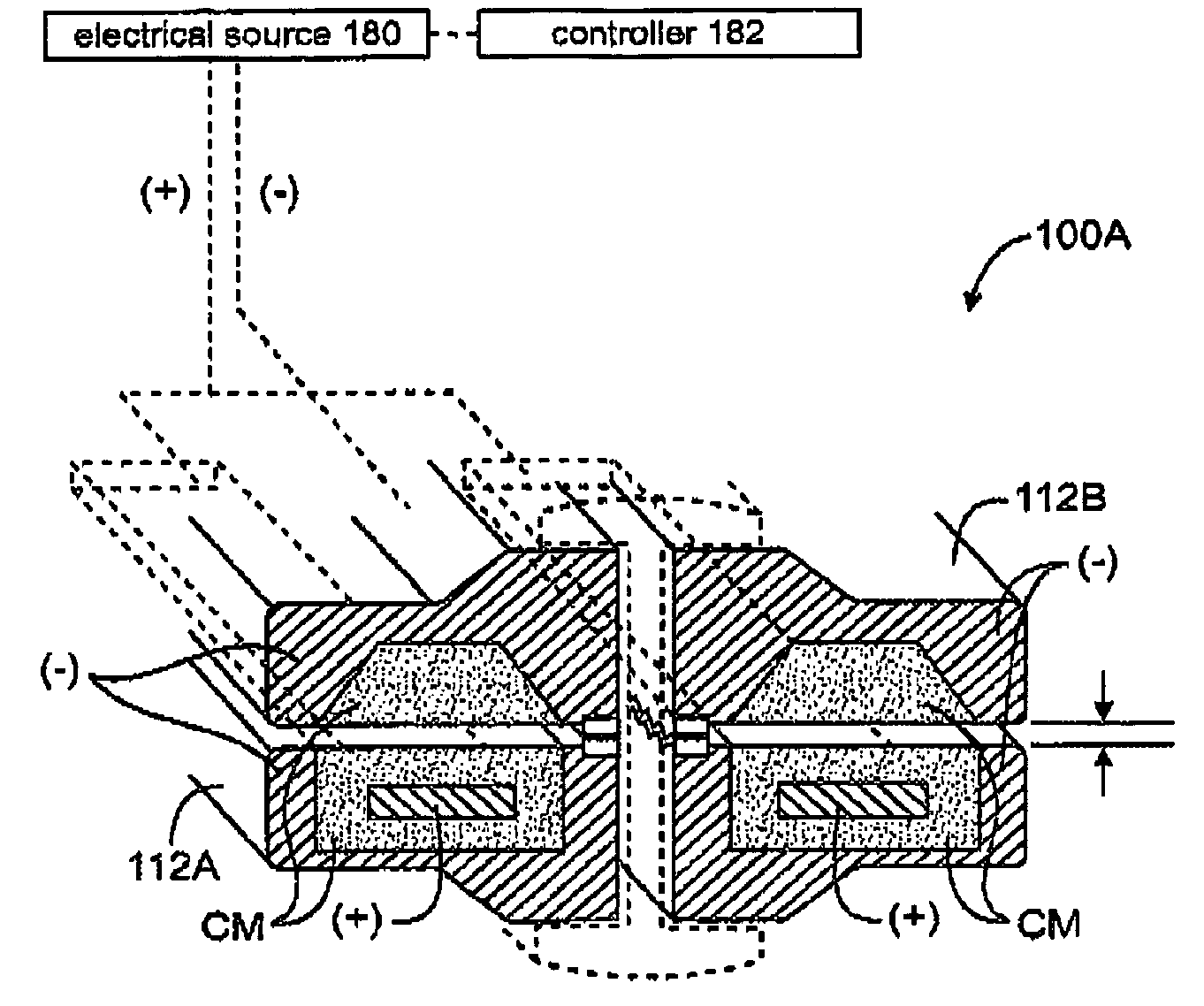
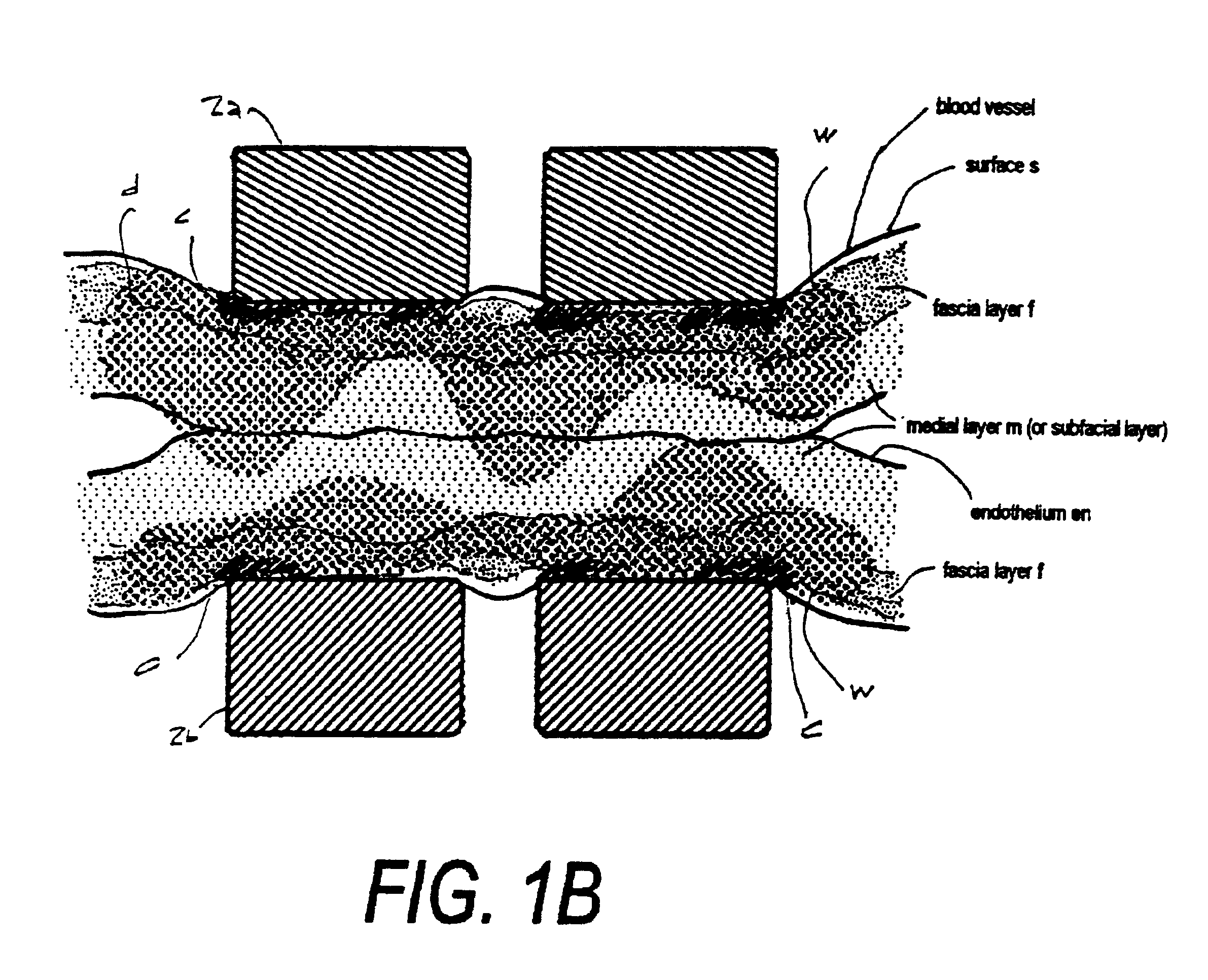
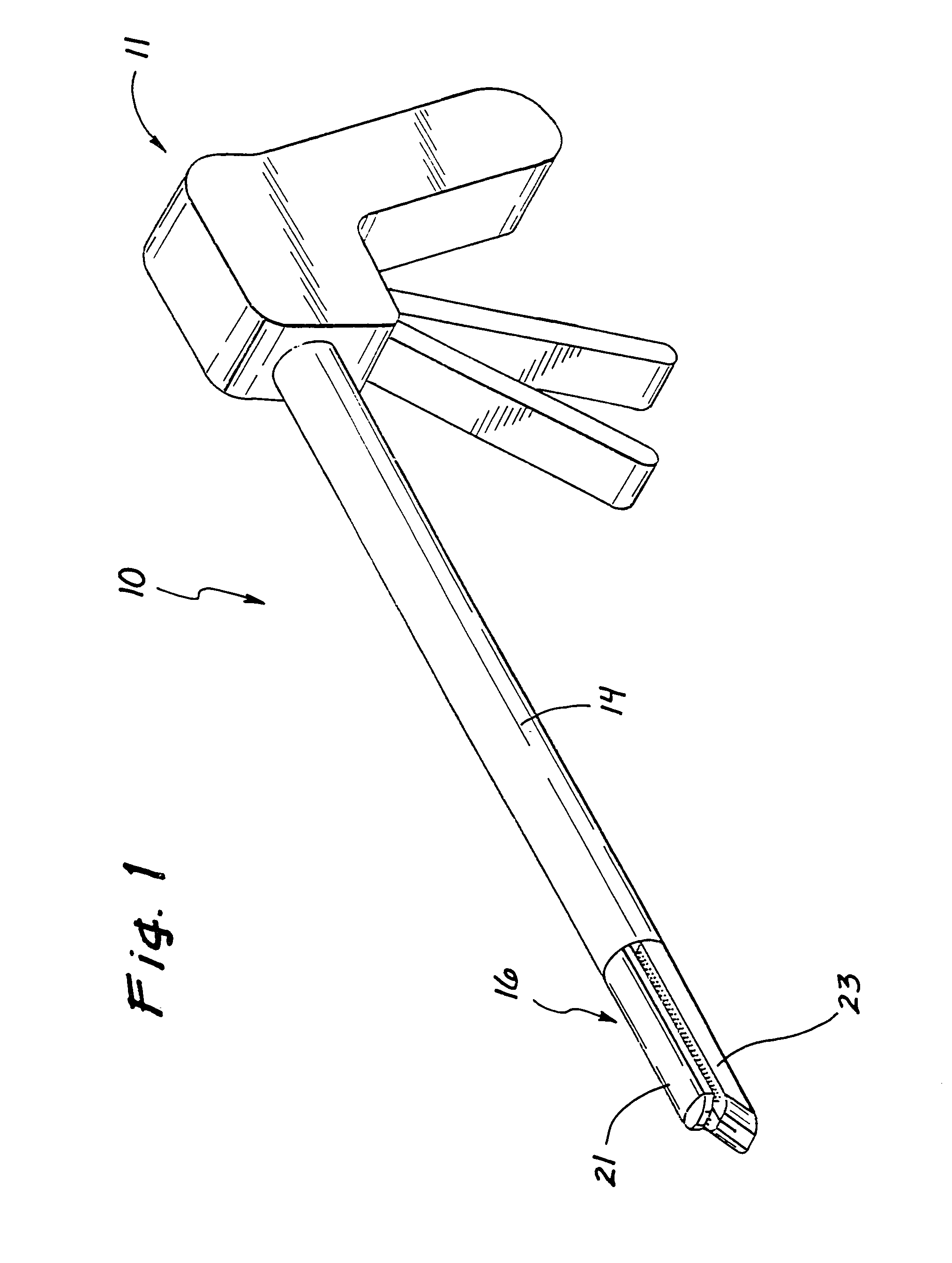
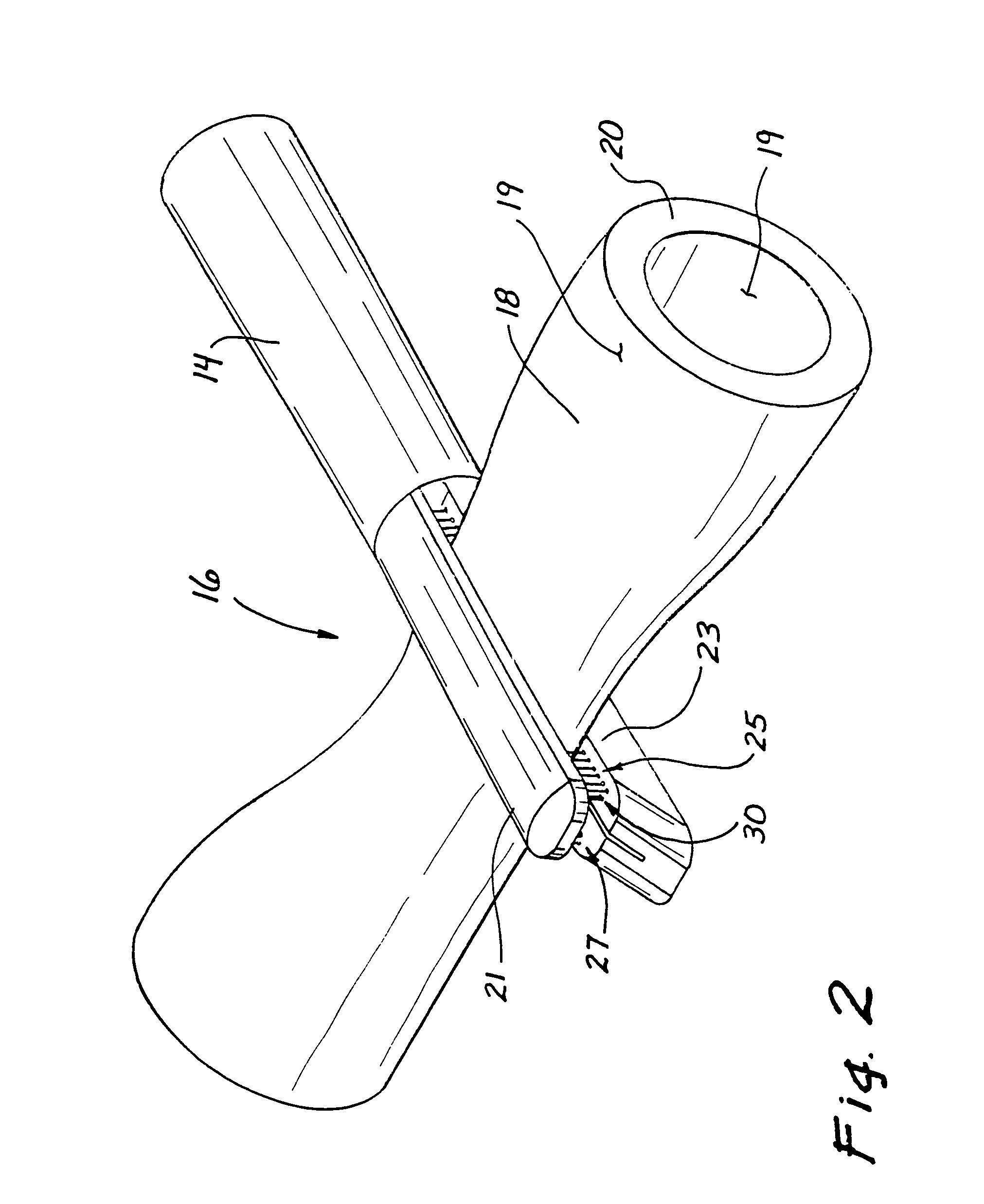
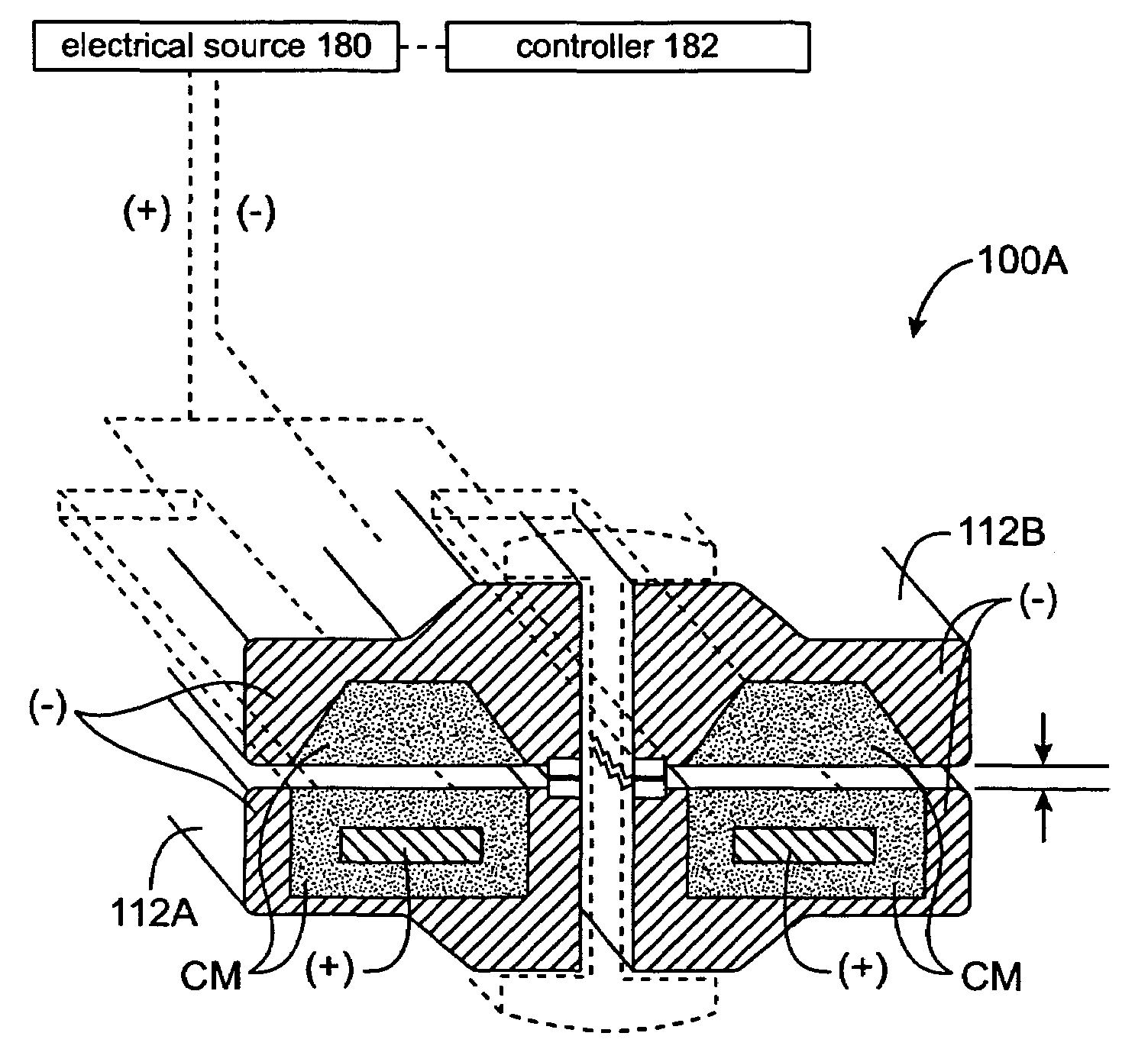
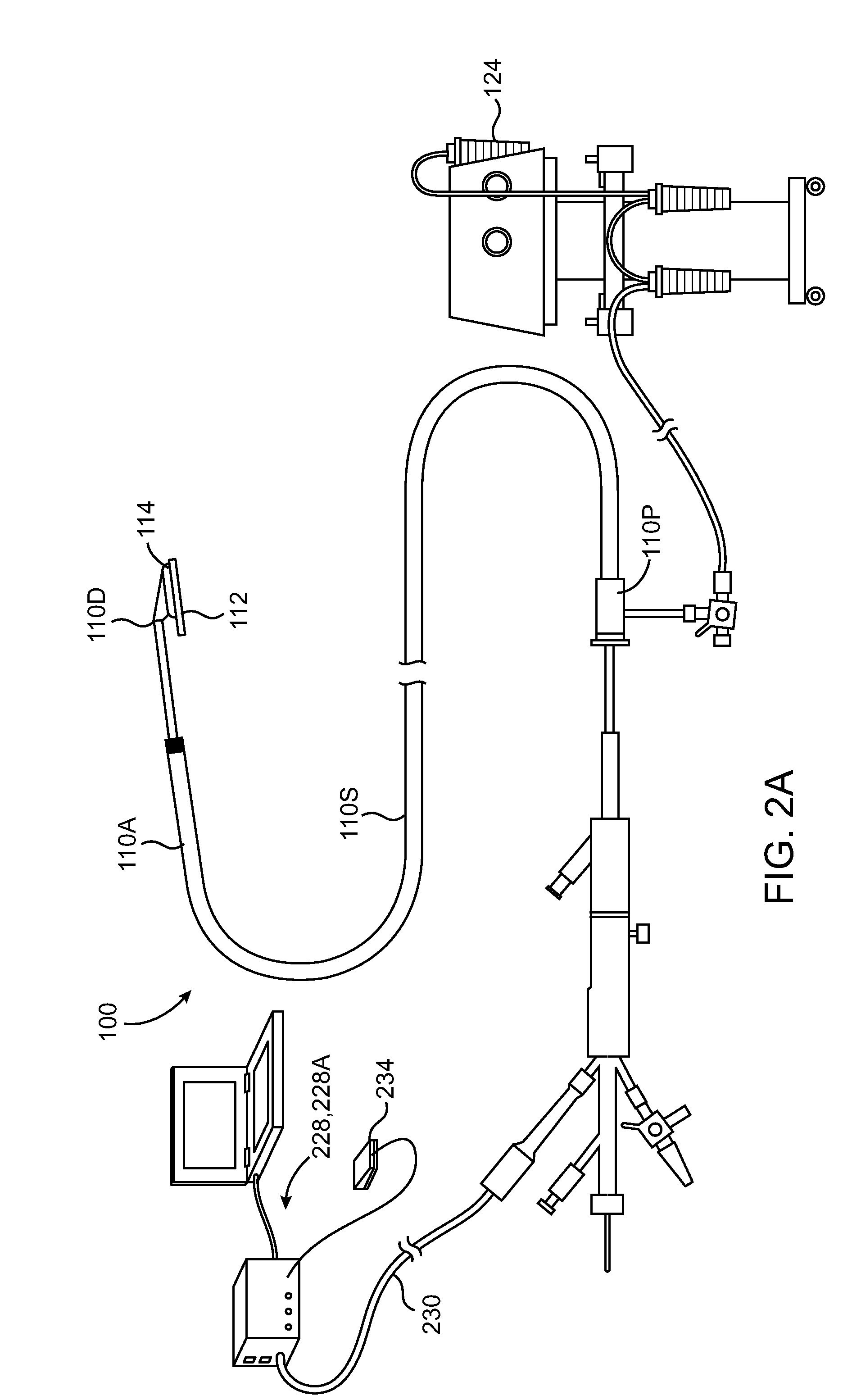
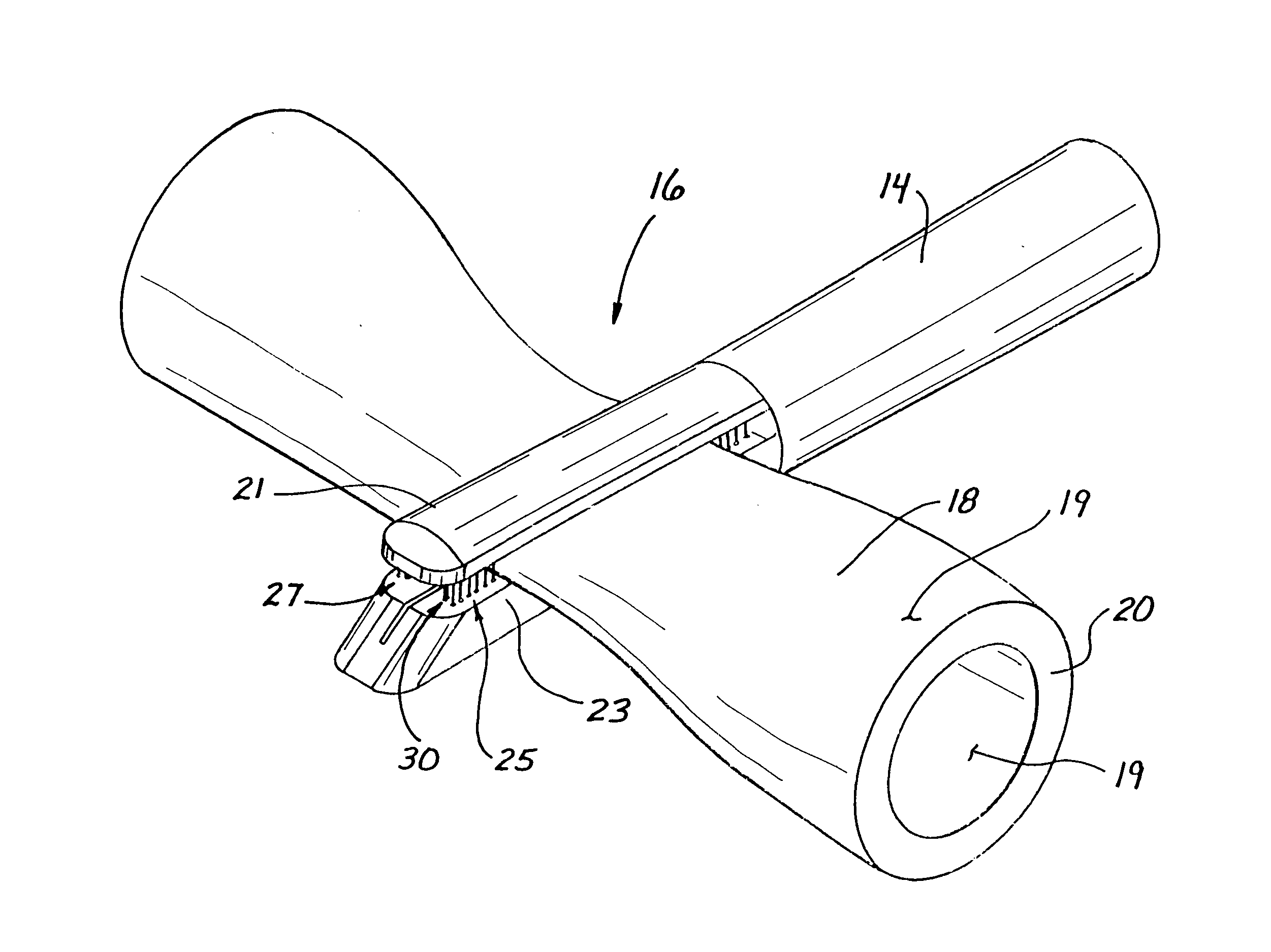
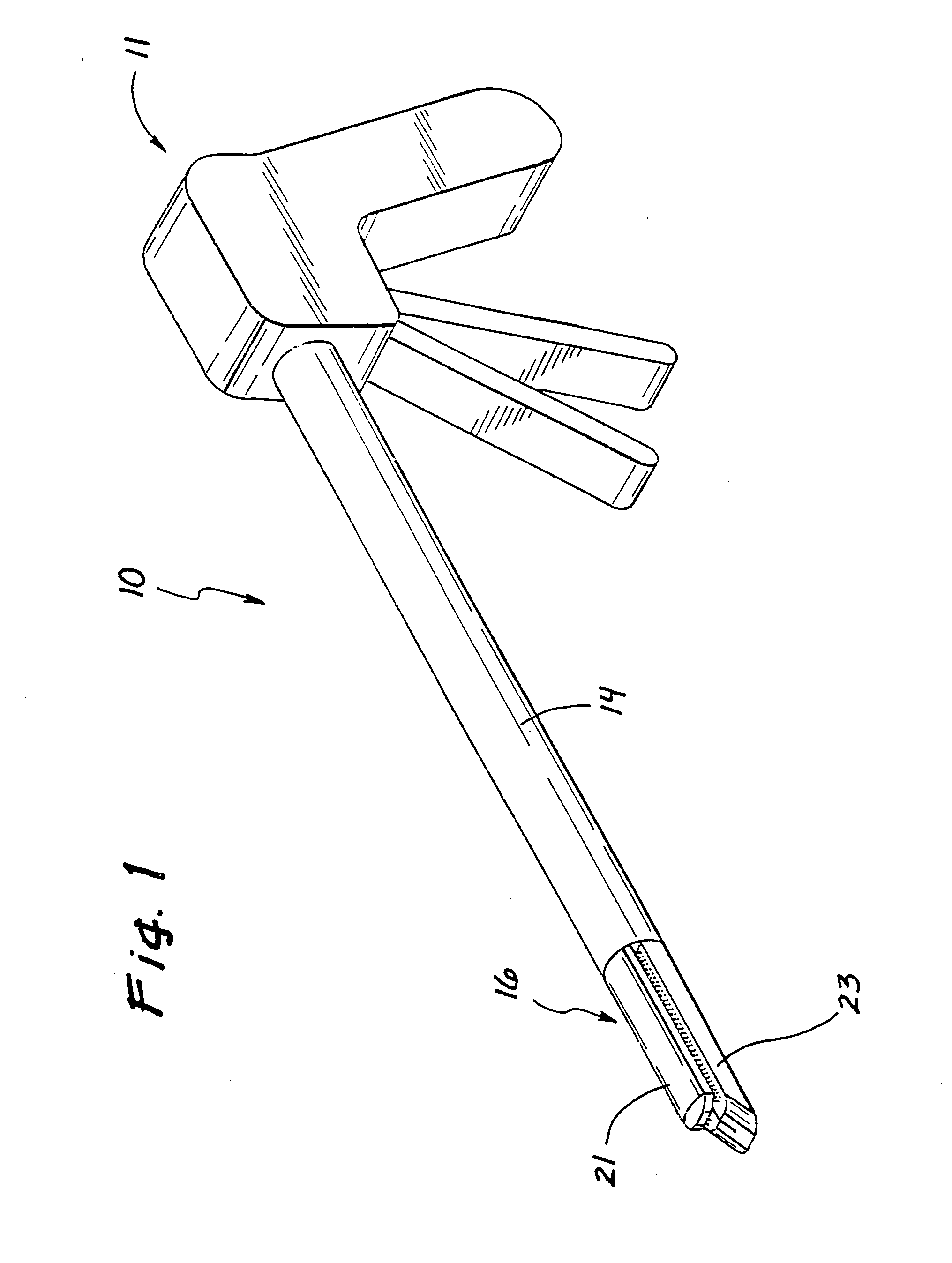
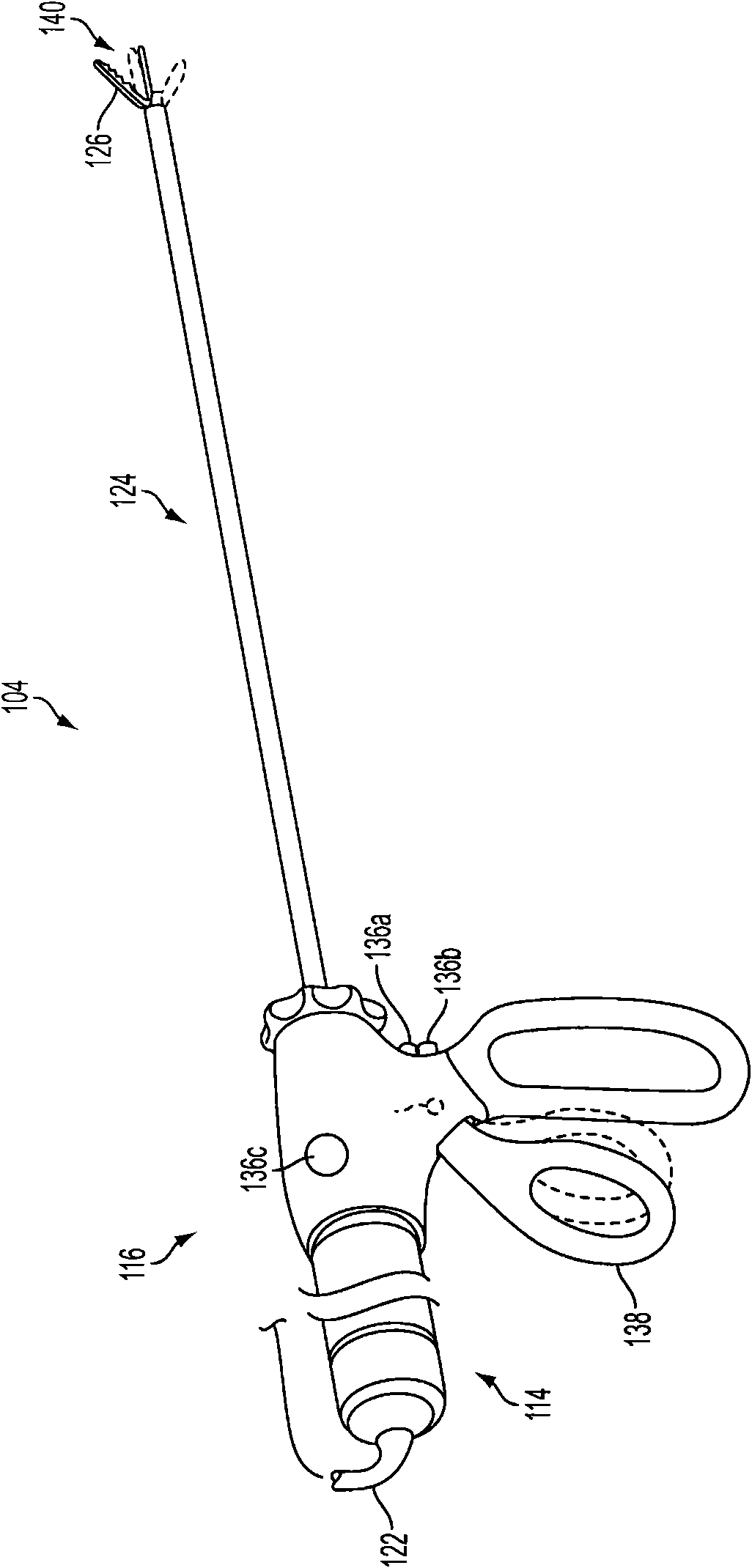
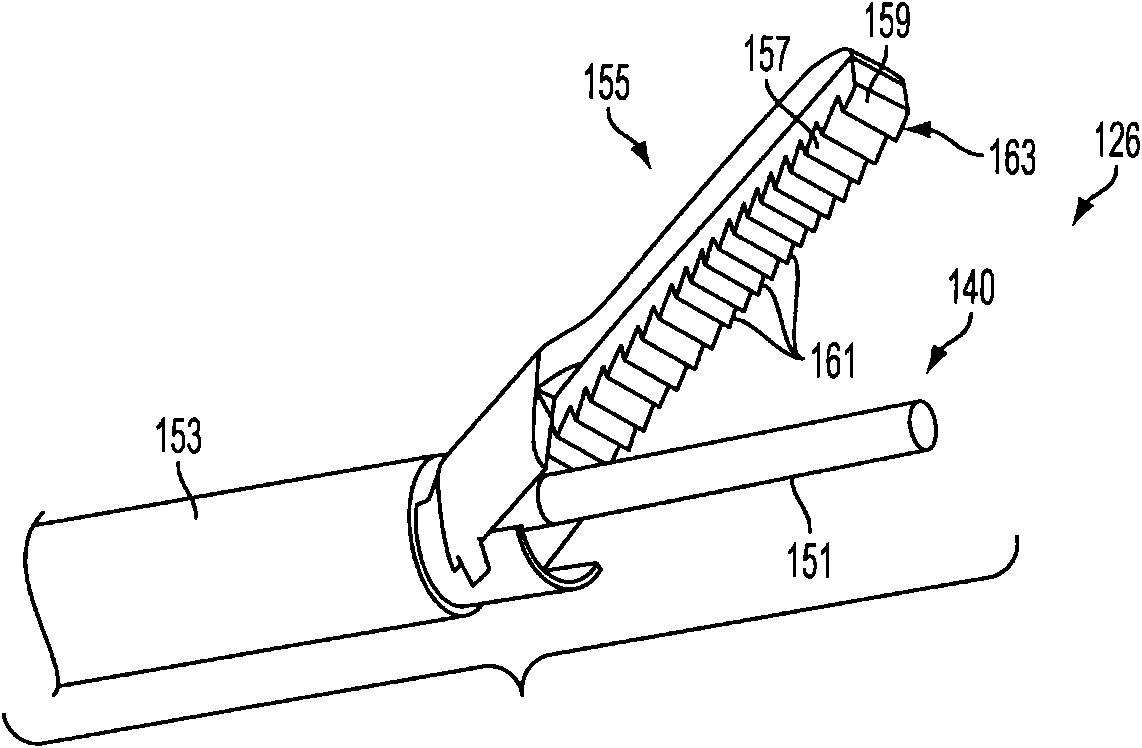
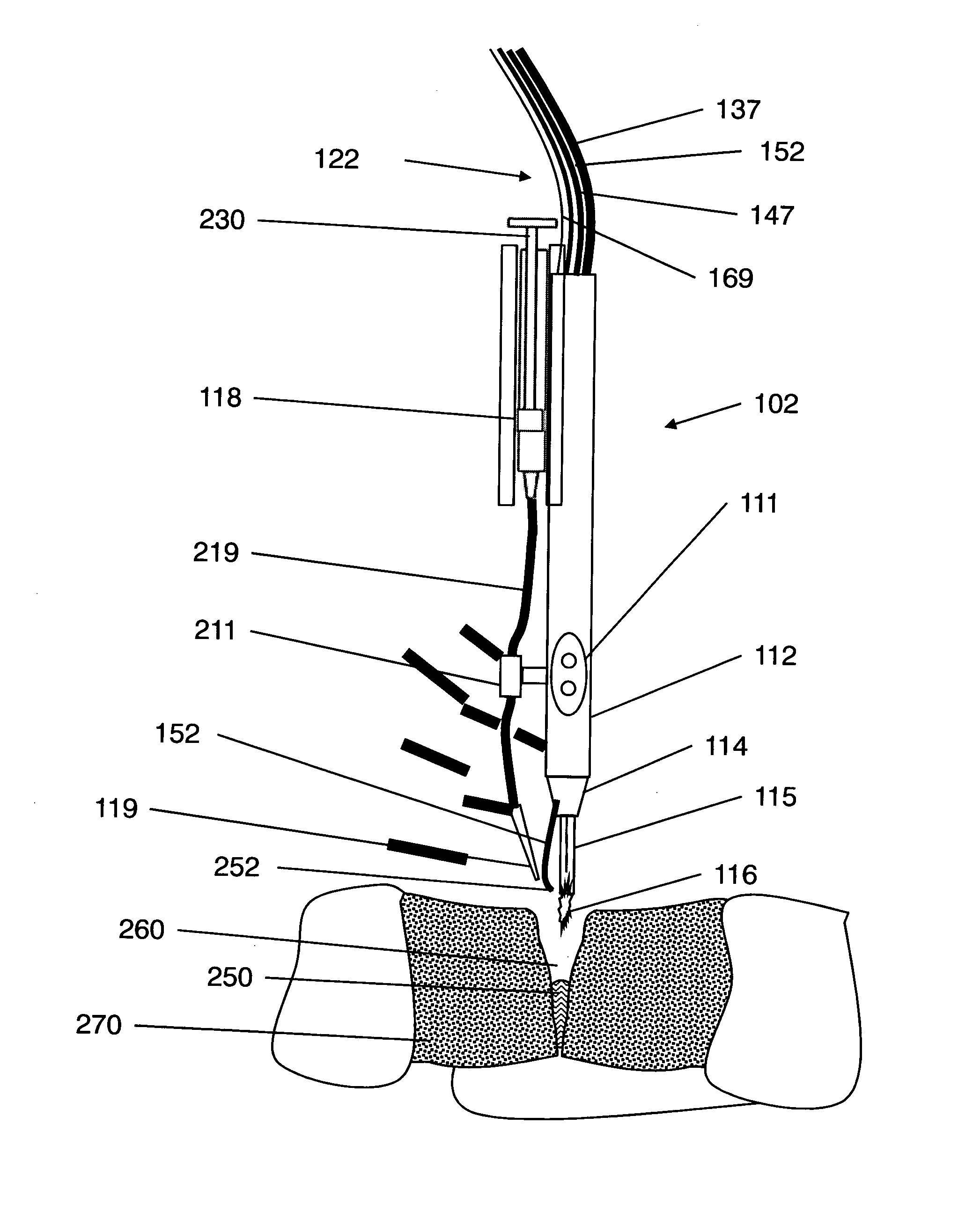
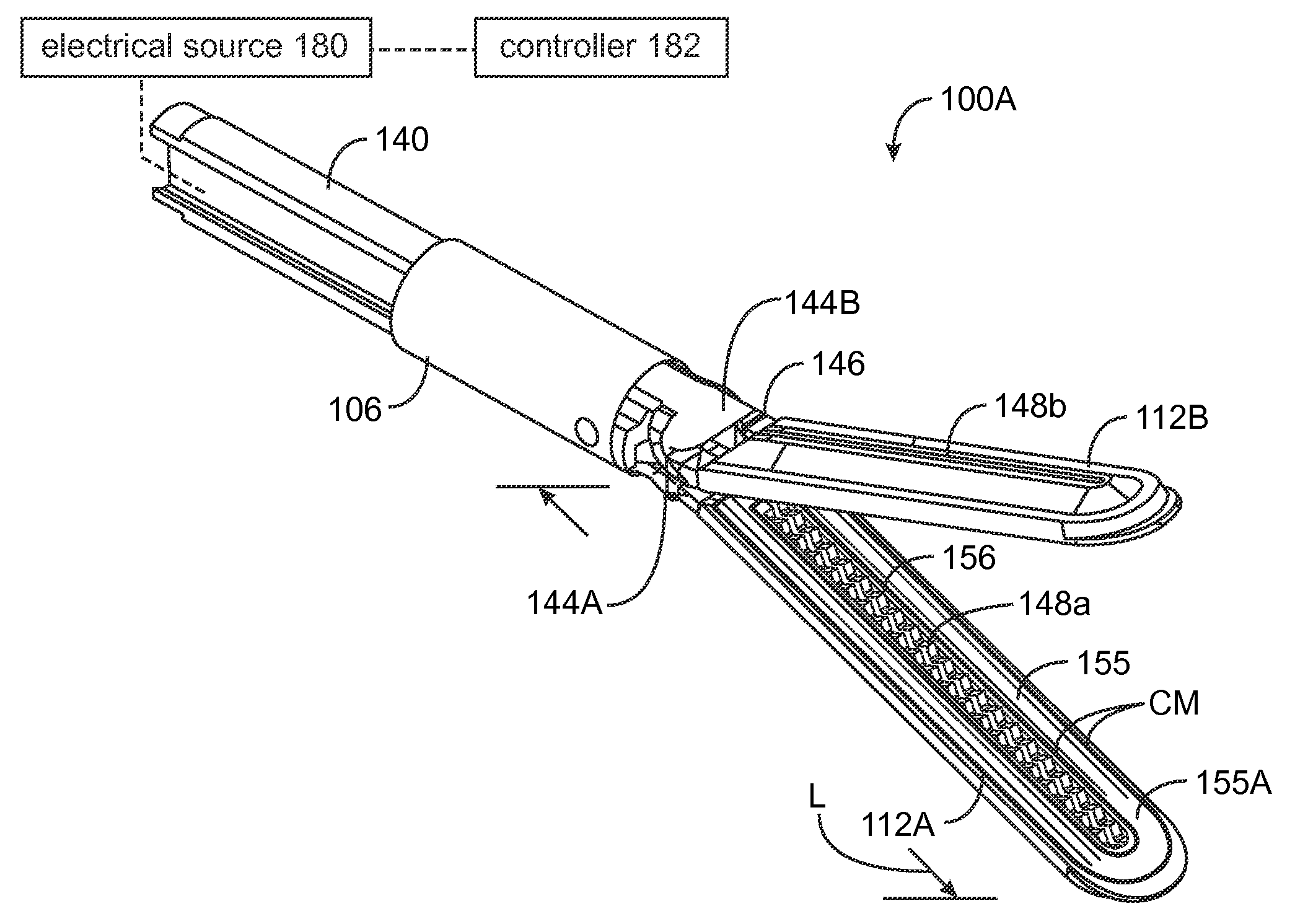
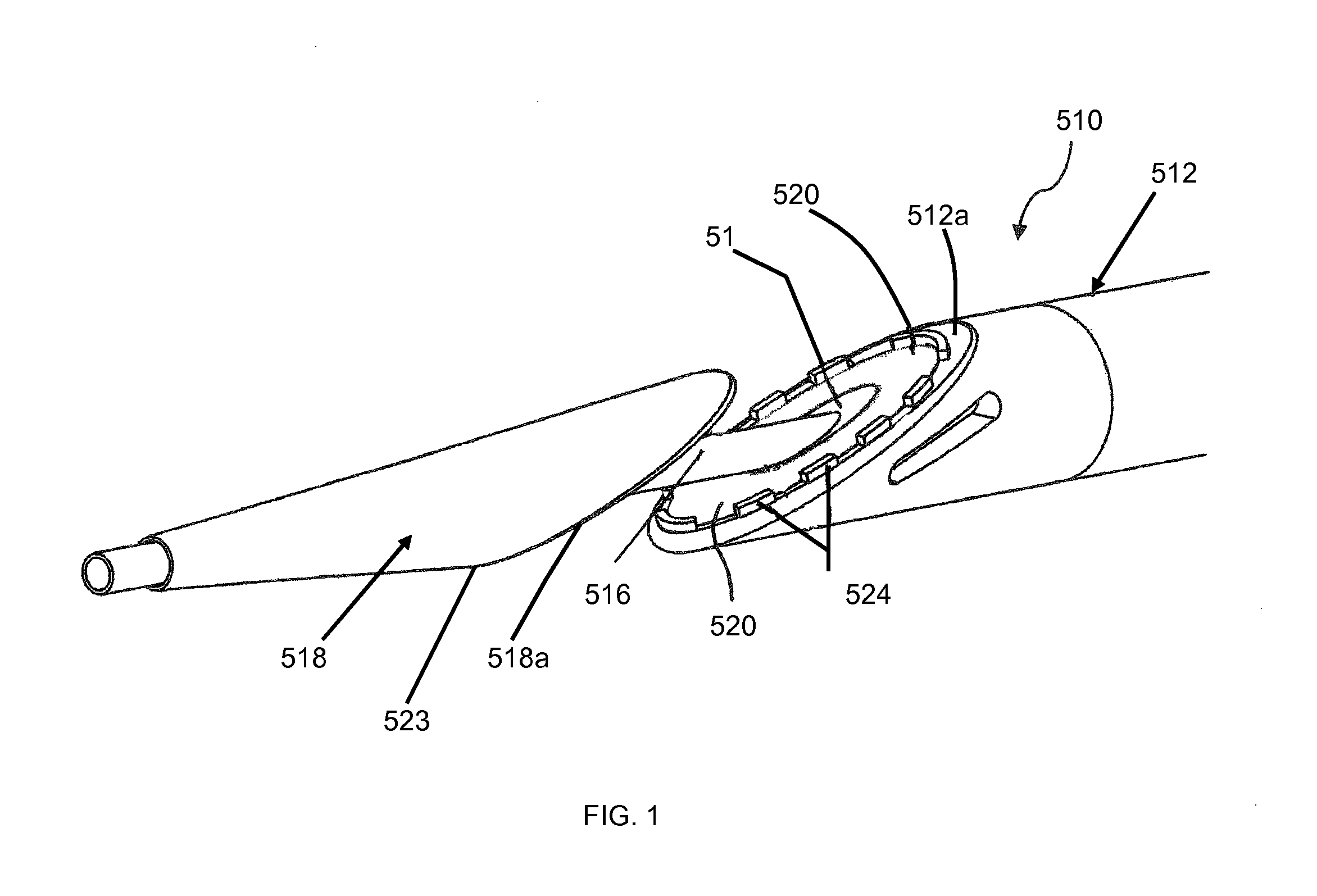
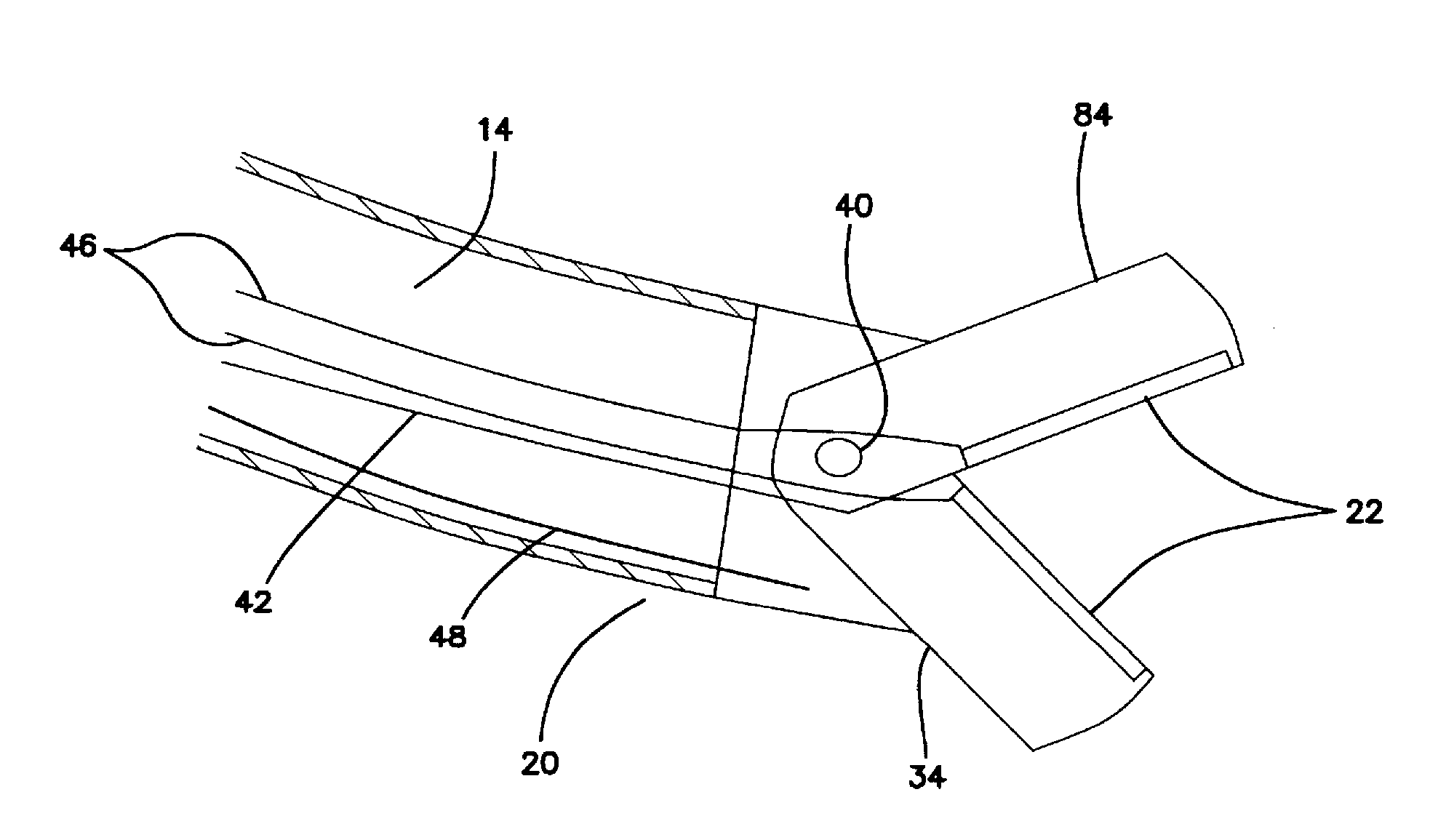
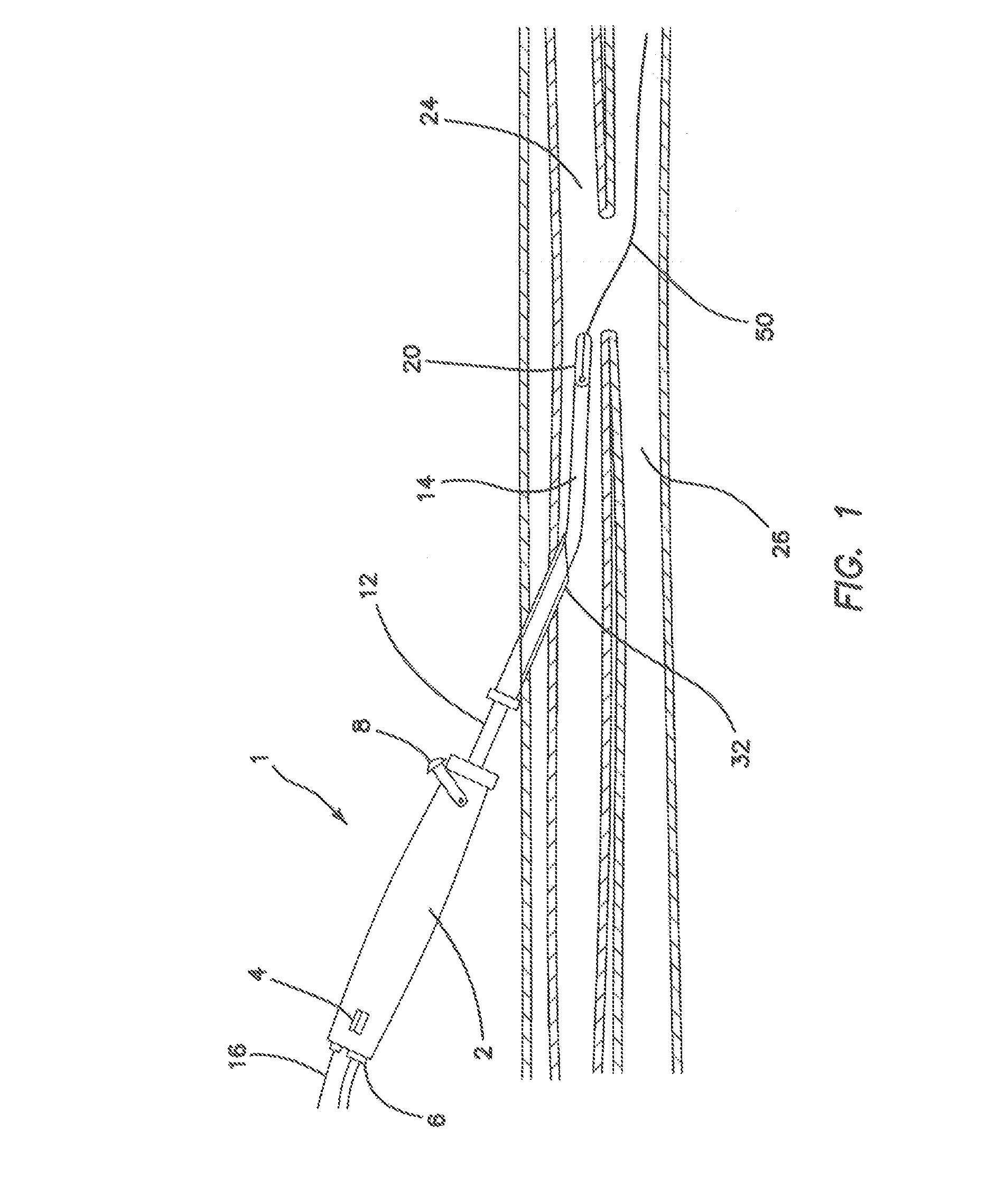
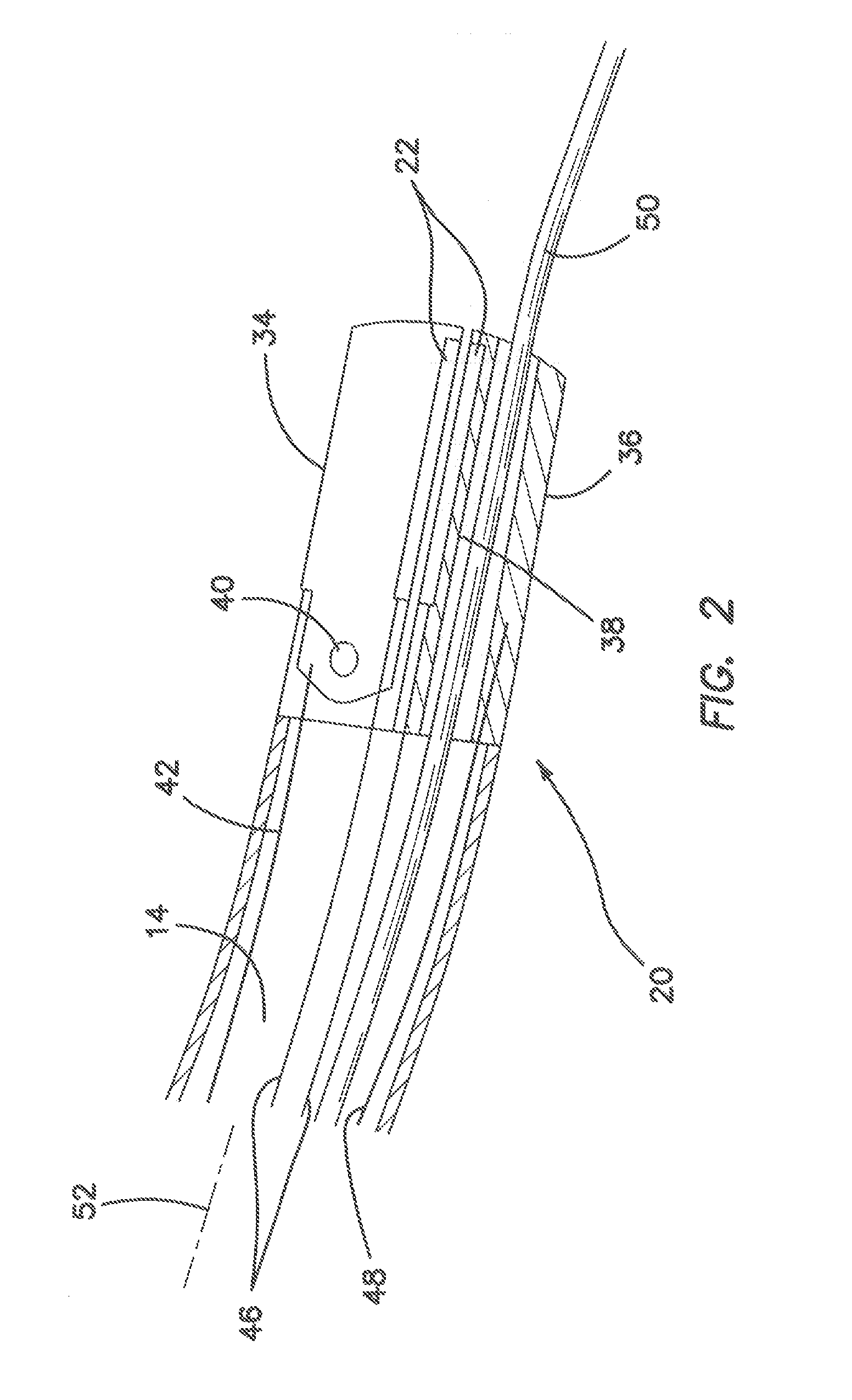
Jaw structure for electrosurgical instrument and method of use
InactiveUS7011657B2Improve the immunityEfficient weldingElectrotherapySurgical instruments for heatingTissue heatingVolumetric Mass Density
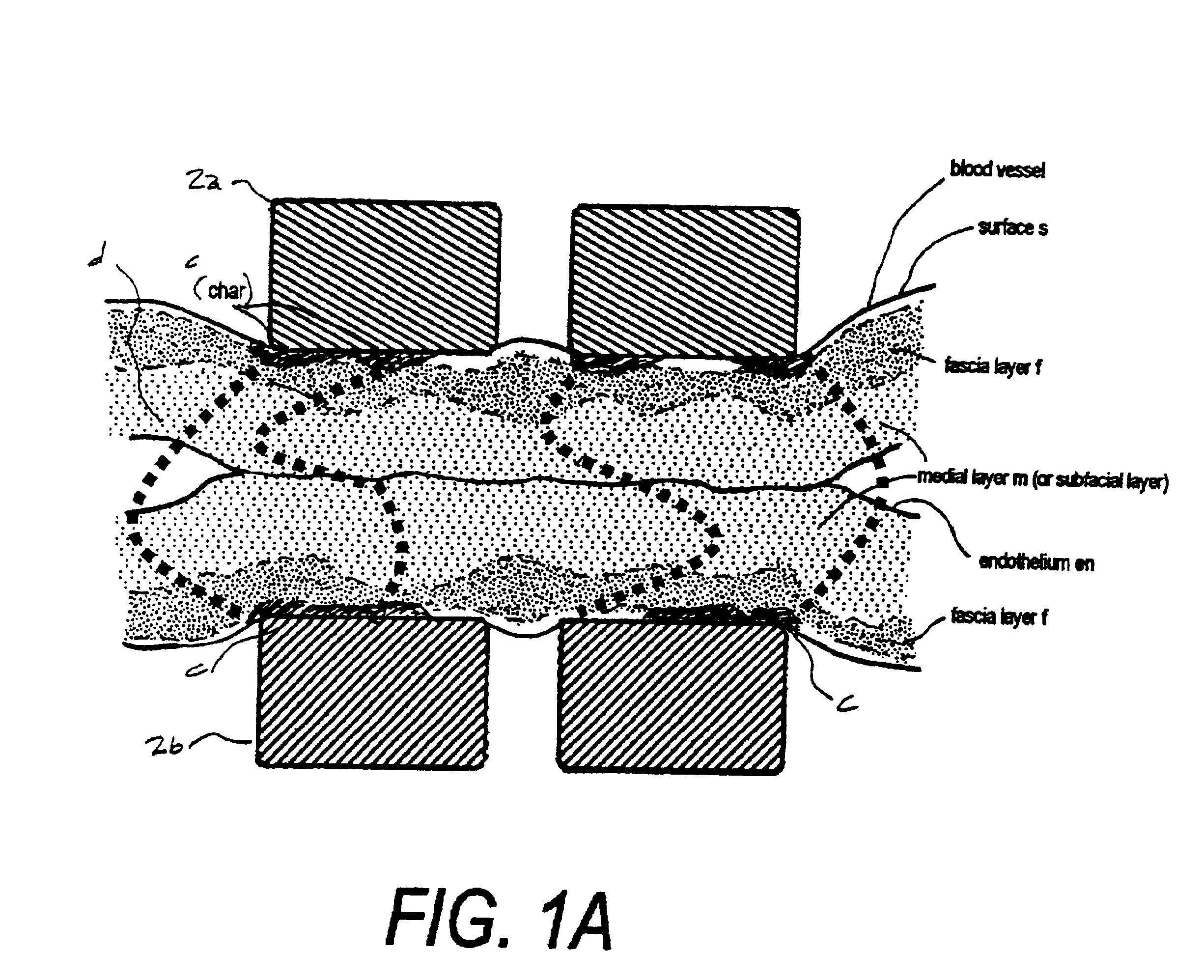
An electrosurgical medical device and technique for creating thermal welds in engaged tissue that provides very high compressive forces. In one exemplary embodiment, at least one jaw of the instrument defines a tissue engagement plane carrying first and second surface portions that comprise (i) an electrically conductive material and (ii) a positive temperature coefficient (PTC) material having a selected increased resistance that differs at each selected increased temperature over a targeted treatment range. One type of PTC material is a doped ceramic that can be engineered to exhibit a selected positively sloped temperature-resistance curve over about 37° C. to 100° C. The 70° C. to 100° C. range can bracket a targeted “thermal treatment range” at which tissue welded can be accomplished. The engineered resistance of the PTC matrix at the upper end of the temperature range will terminate current flow through the matrix. In one mode of operation, the engagement plane cause ohmic heating within tissue from Rf energy delivery tissue PTC matrix is heated to exceed the treatment range. Thereafter, energy density in the engaged tissue will be modulated as the conductivity of the second portion hovers within the targeted treatment range to thereby provide optical tissue heating for purposes of tissue welding.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
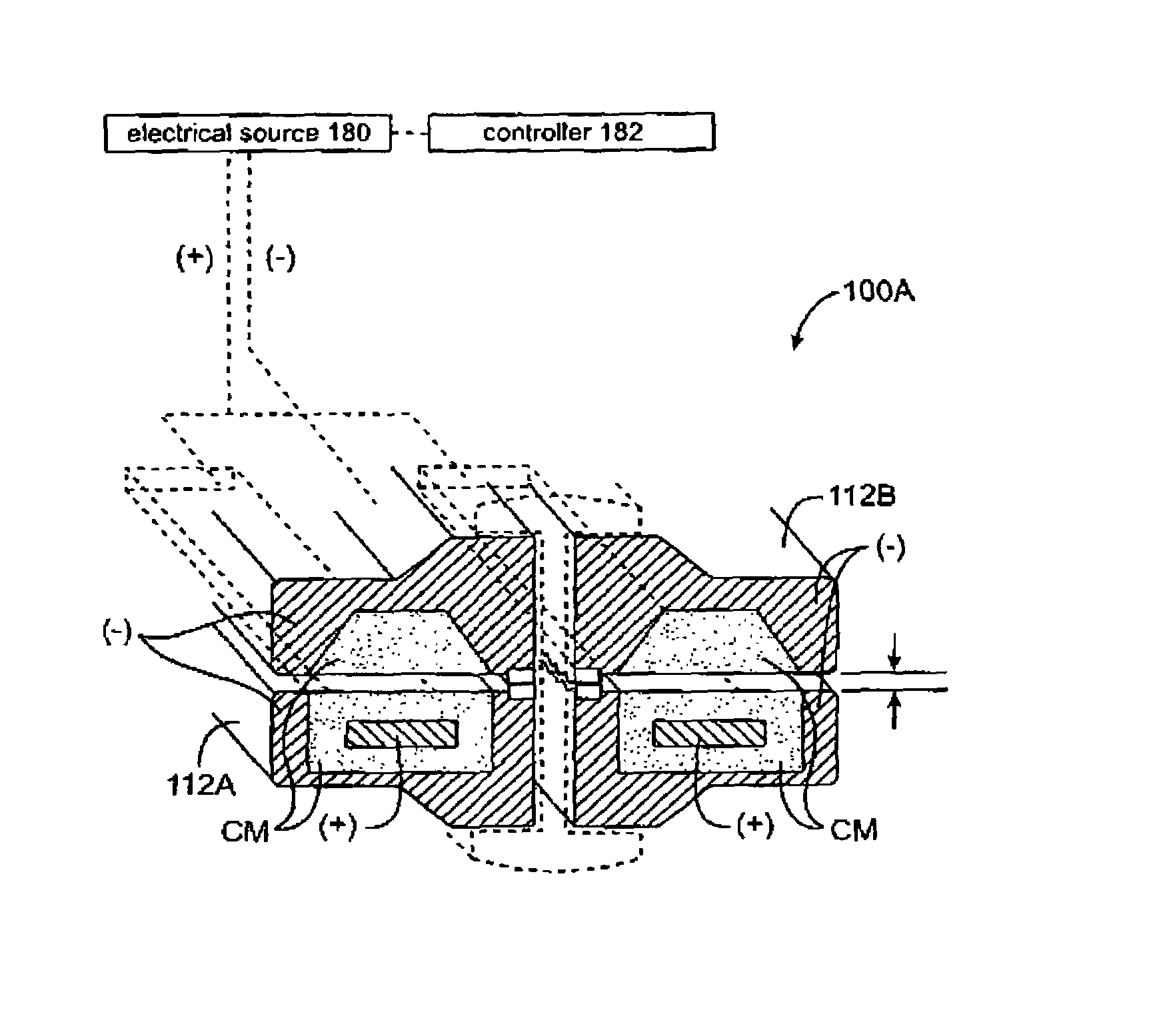
Electrosurgical instrument and method of use
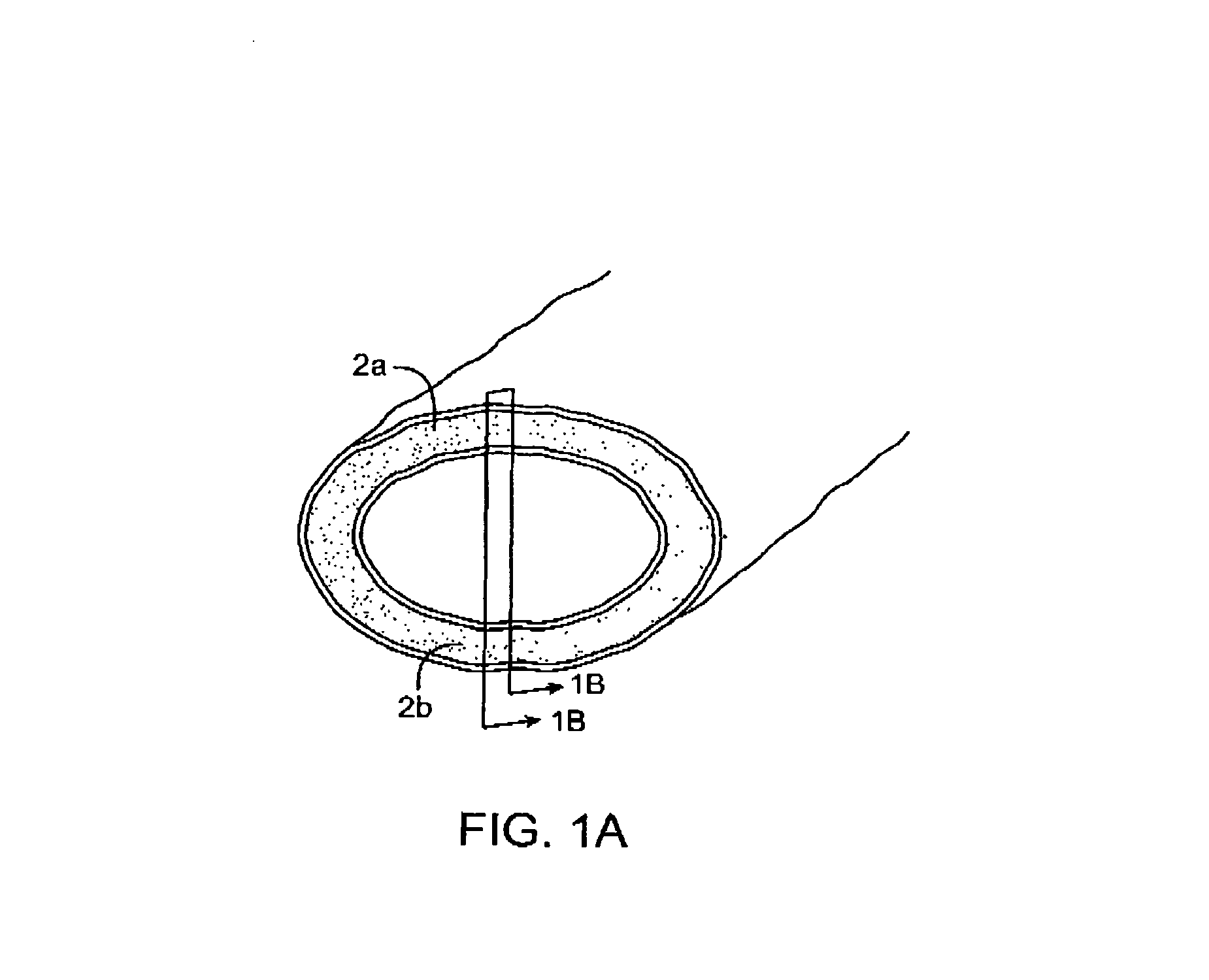
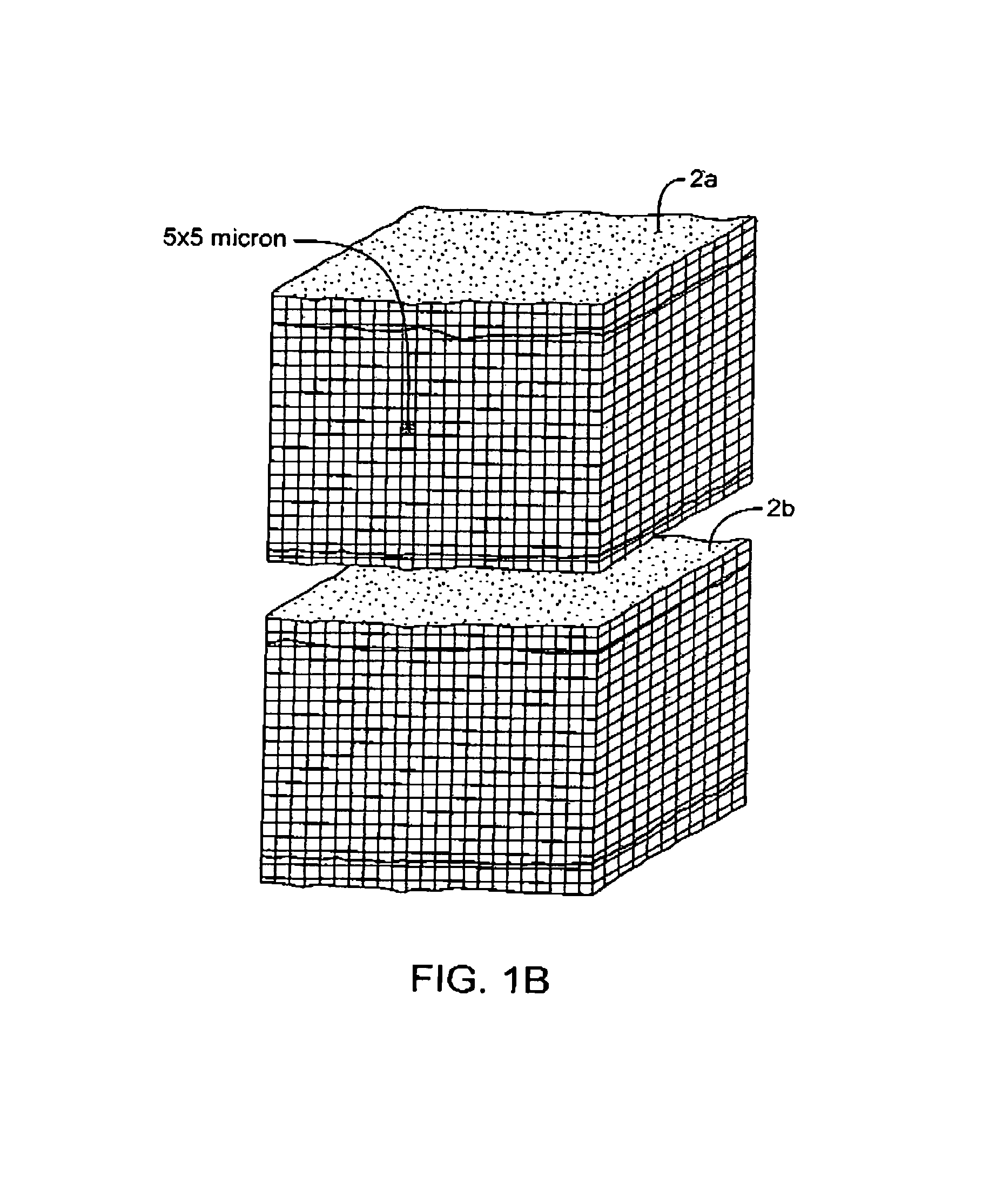
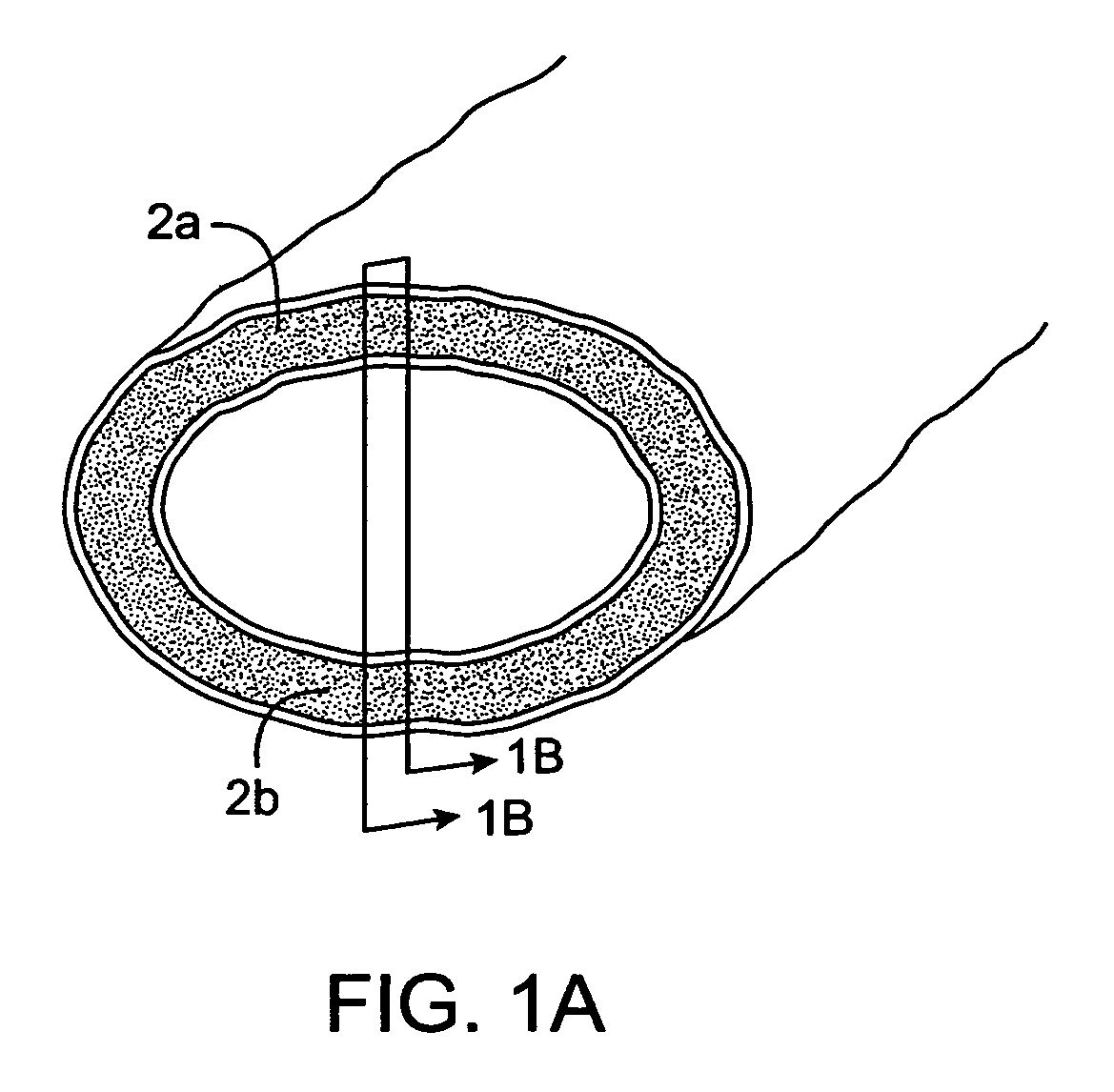
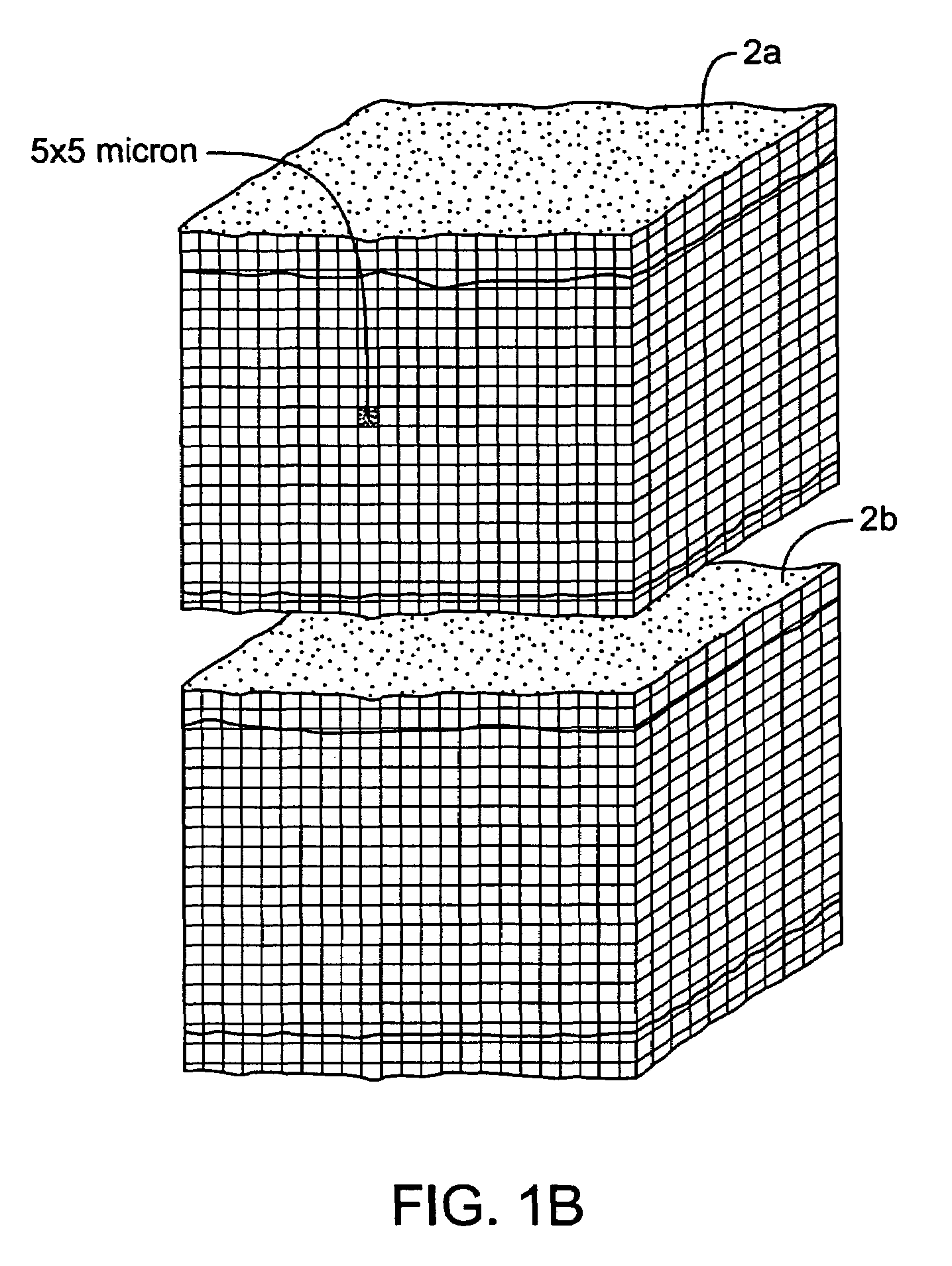
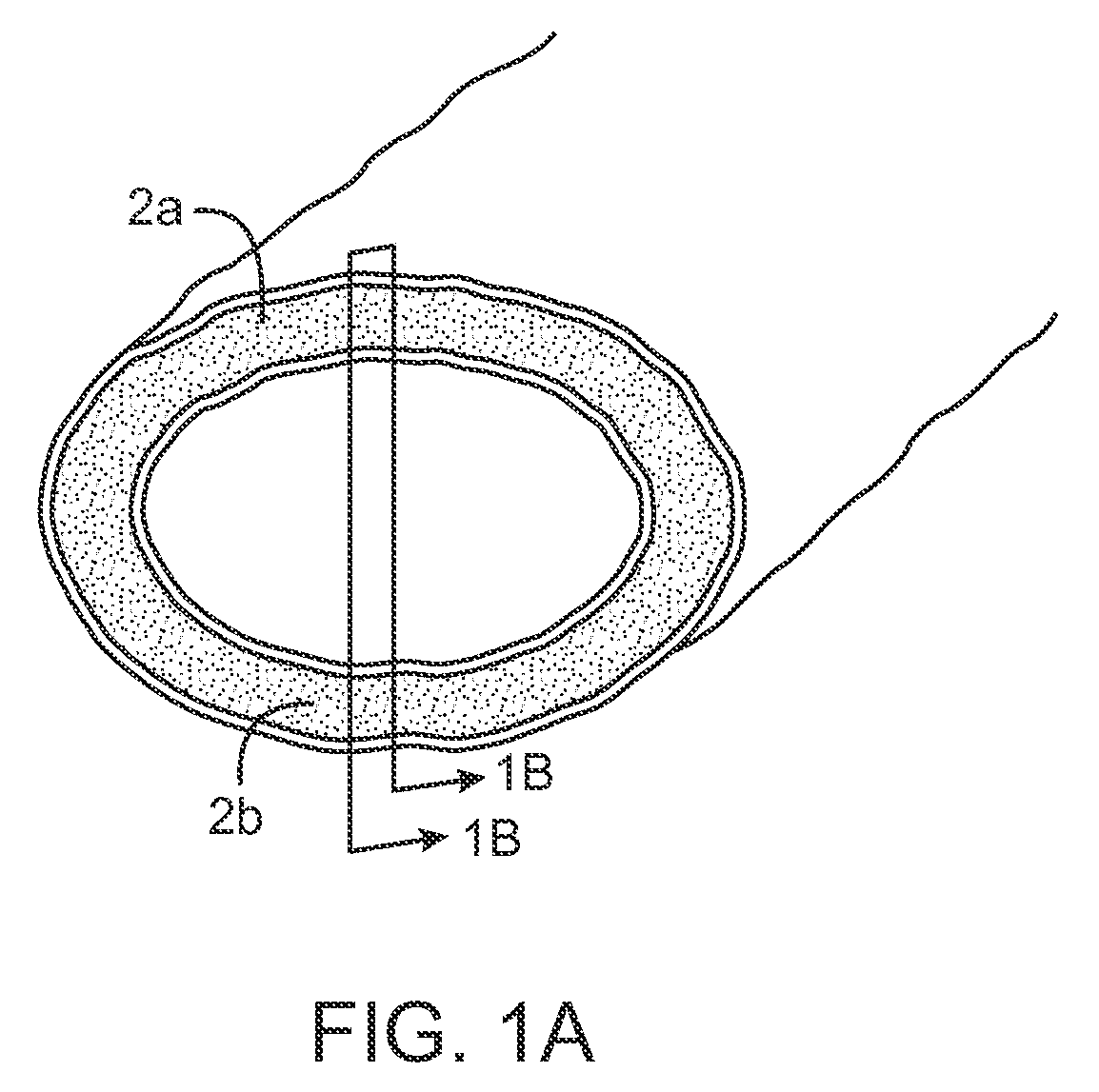
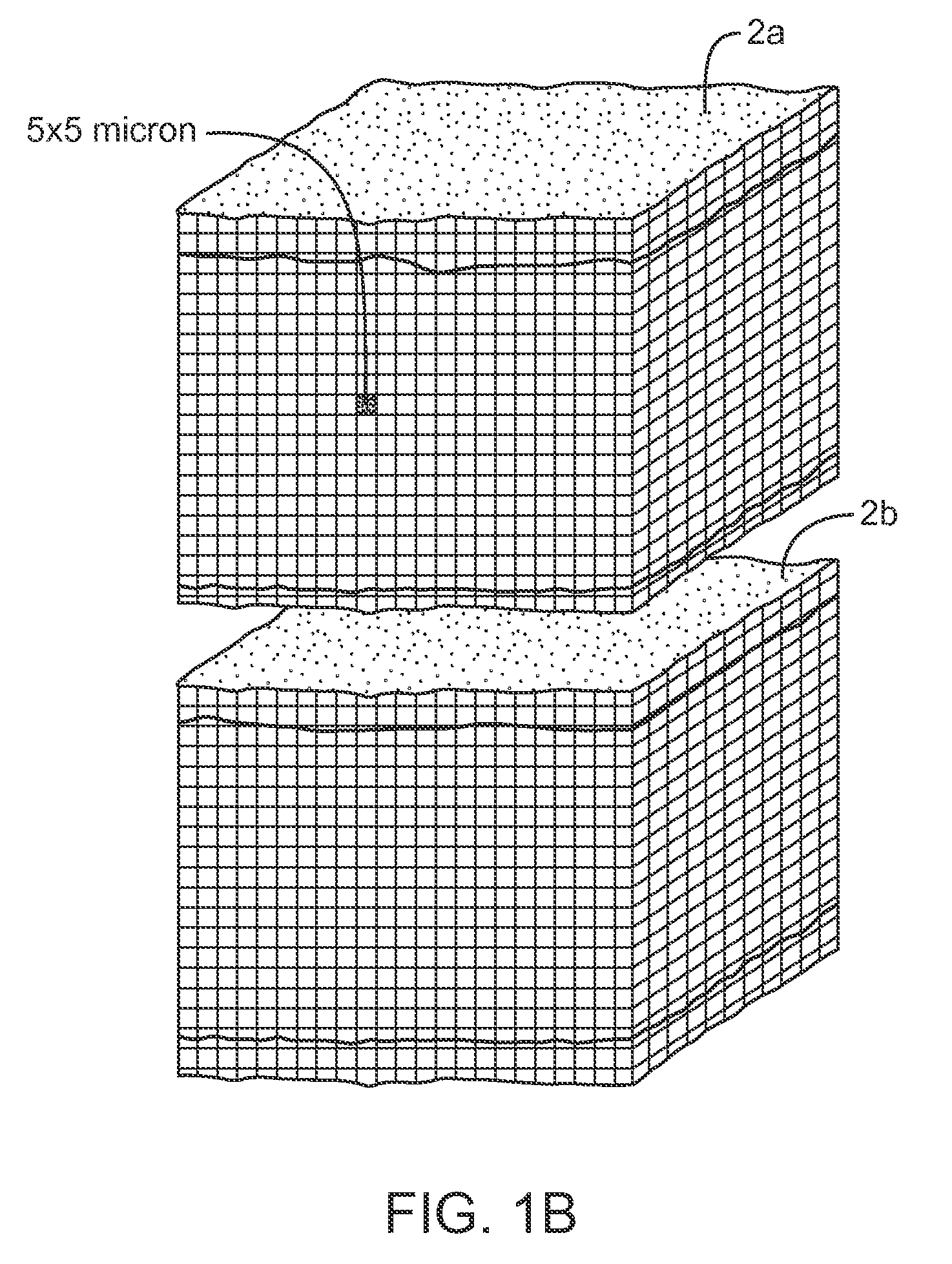
InactiveUS7083619B2Reduce conductancePrevent any substantial dehydrationSurgical instruments for heatingCoatingsMicron scaleElastomer
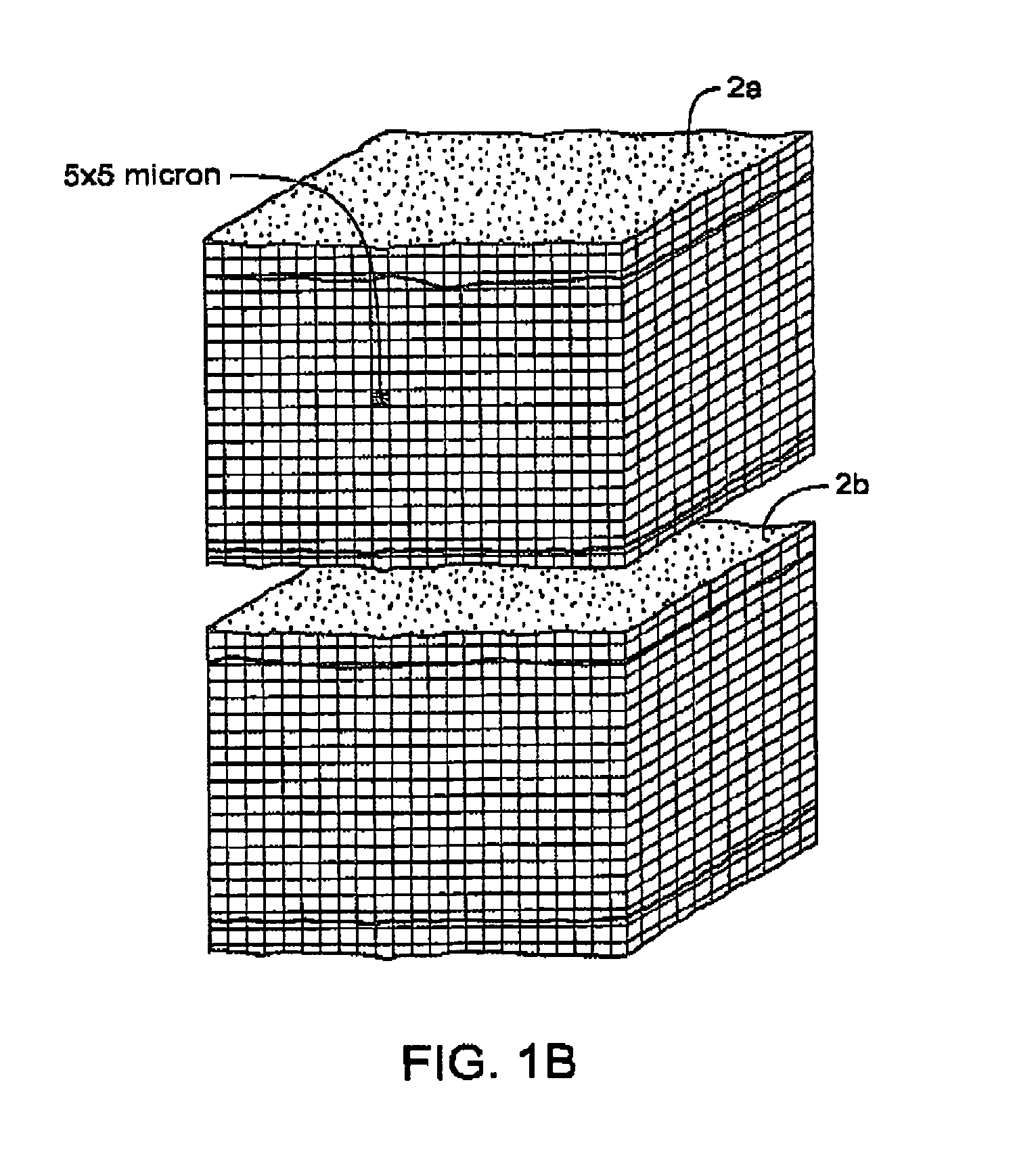
An electrosurgical medical device and method for creating thermal welds in engaged tissue. In one embodiment, at least one jaw of the instrument defines a tissue engagement plane carrying a conductive-resistive matrix of a conductively-doped non-conductive elastomer. The engagement surface portions thus can be described as a positive temperature coefficient material that has a unique selected decreased electrical conductance at each selected increased temperature thereof over a targeted treatment range. The conductive-resistive matrix can be engineered to bracket a targeted thermal treatment range, for example about 60° C. to 80° C., at which tissue welding can be accomplished. In one mode of operation, the engagement plane will automatically modulate and spatially localize ohmic heating within the engaged tissue from Rf energy application—across micron-scale portions of the engagement surface.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
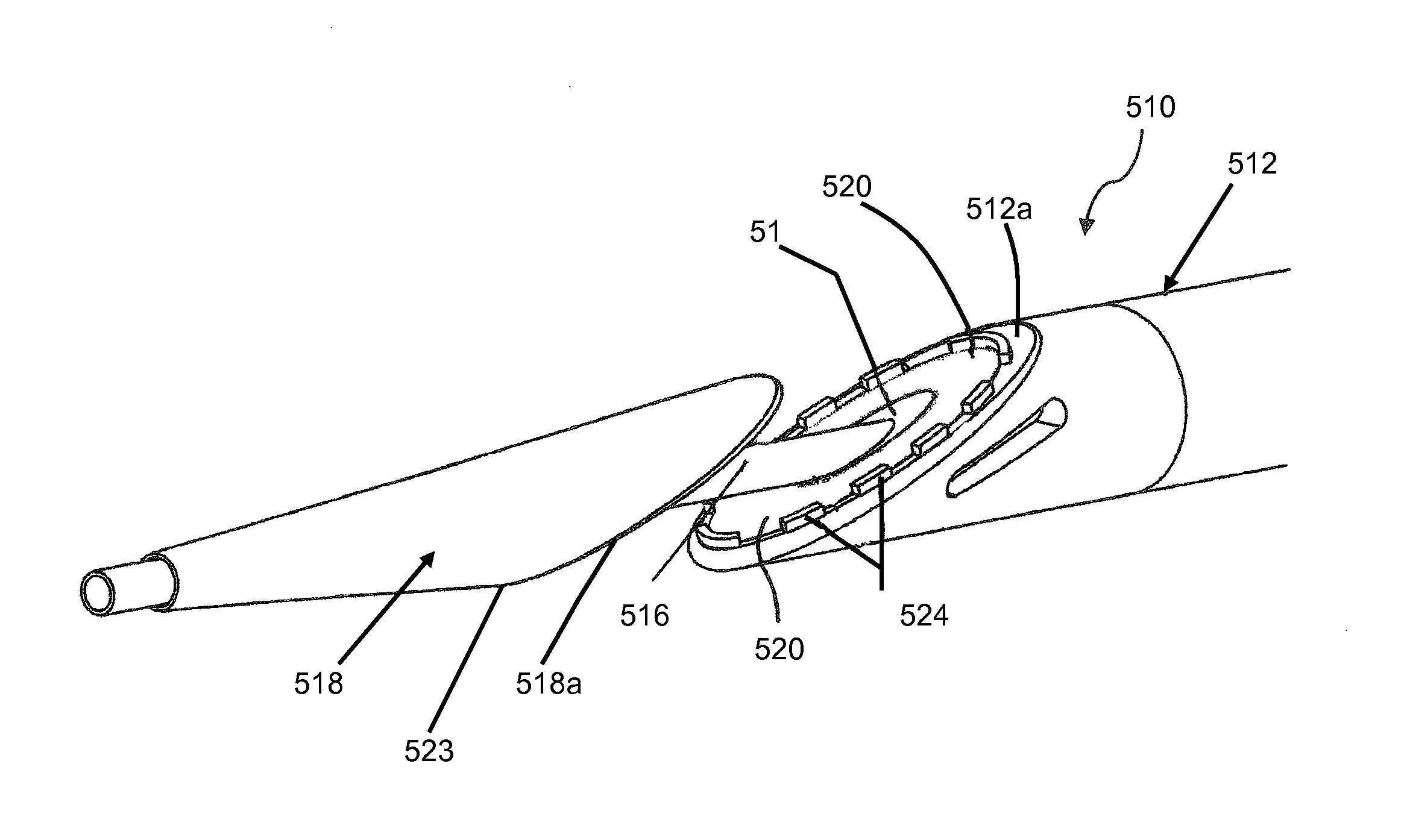
Electrosurgical working end and method for obtaining tissue samples for biopsy
InactiveUS6913579B2Speed up the flowHeating evenlyVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsSurgical instruments for heatingSurface layerTissue sample
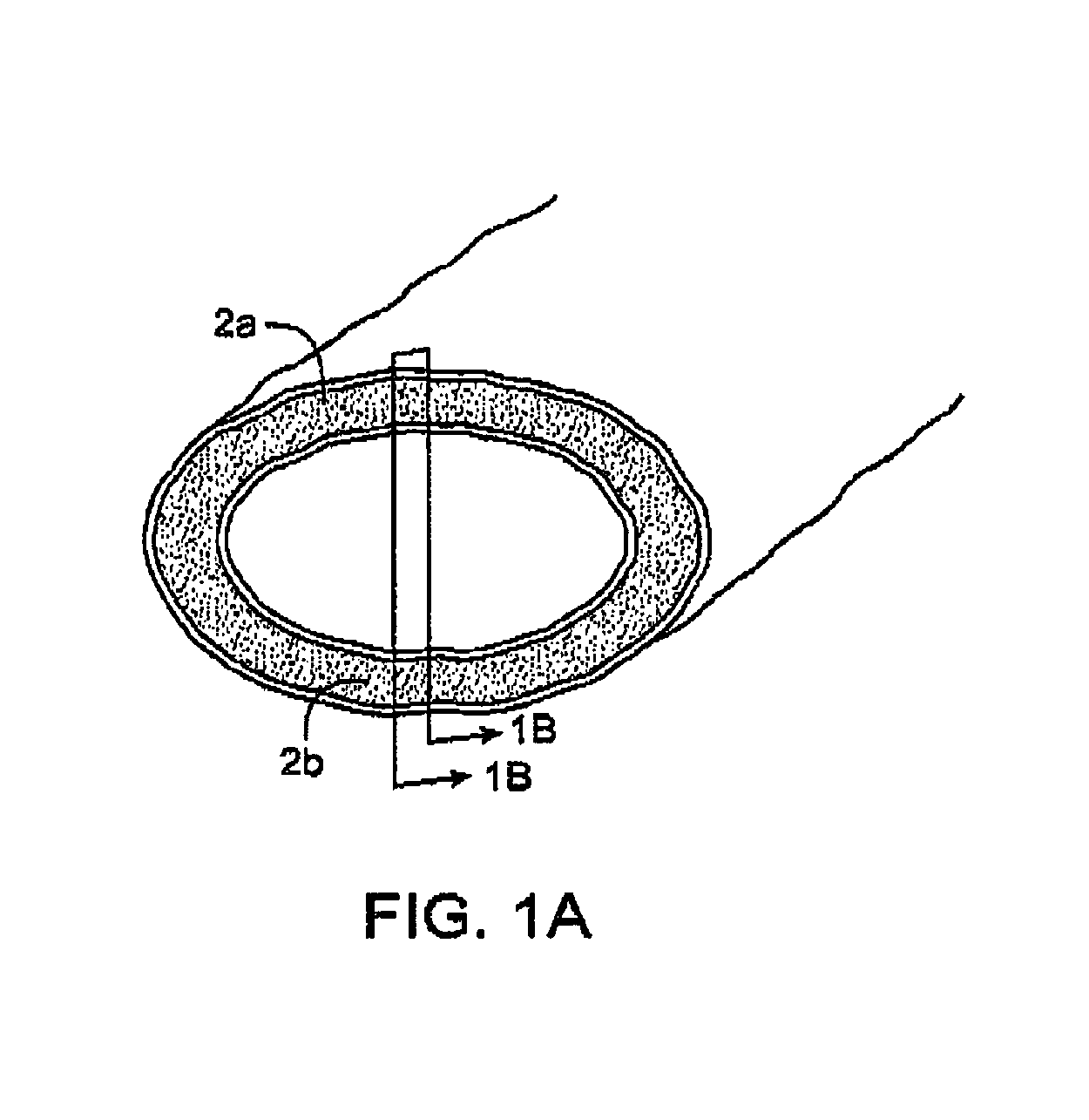
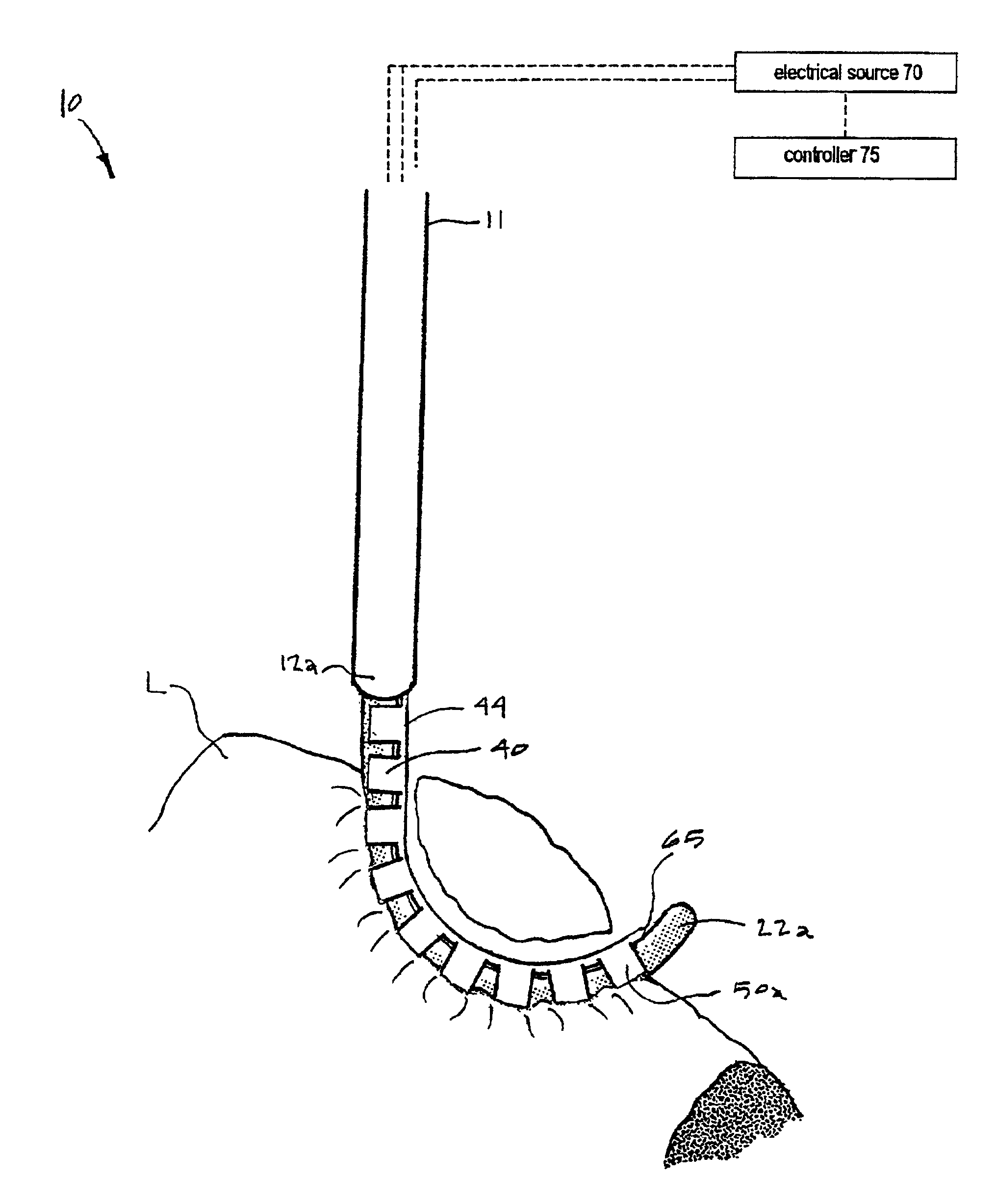
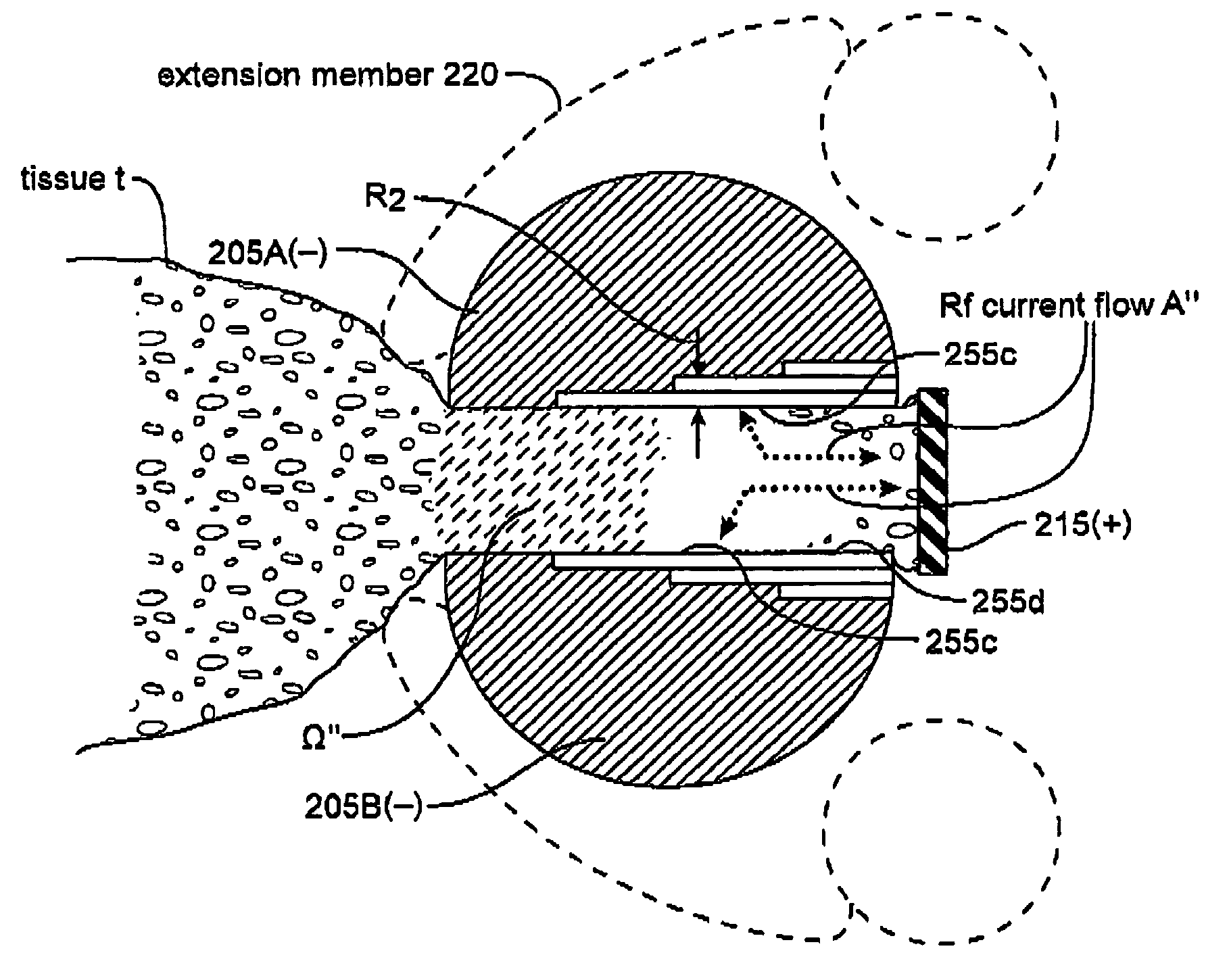
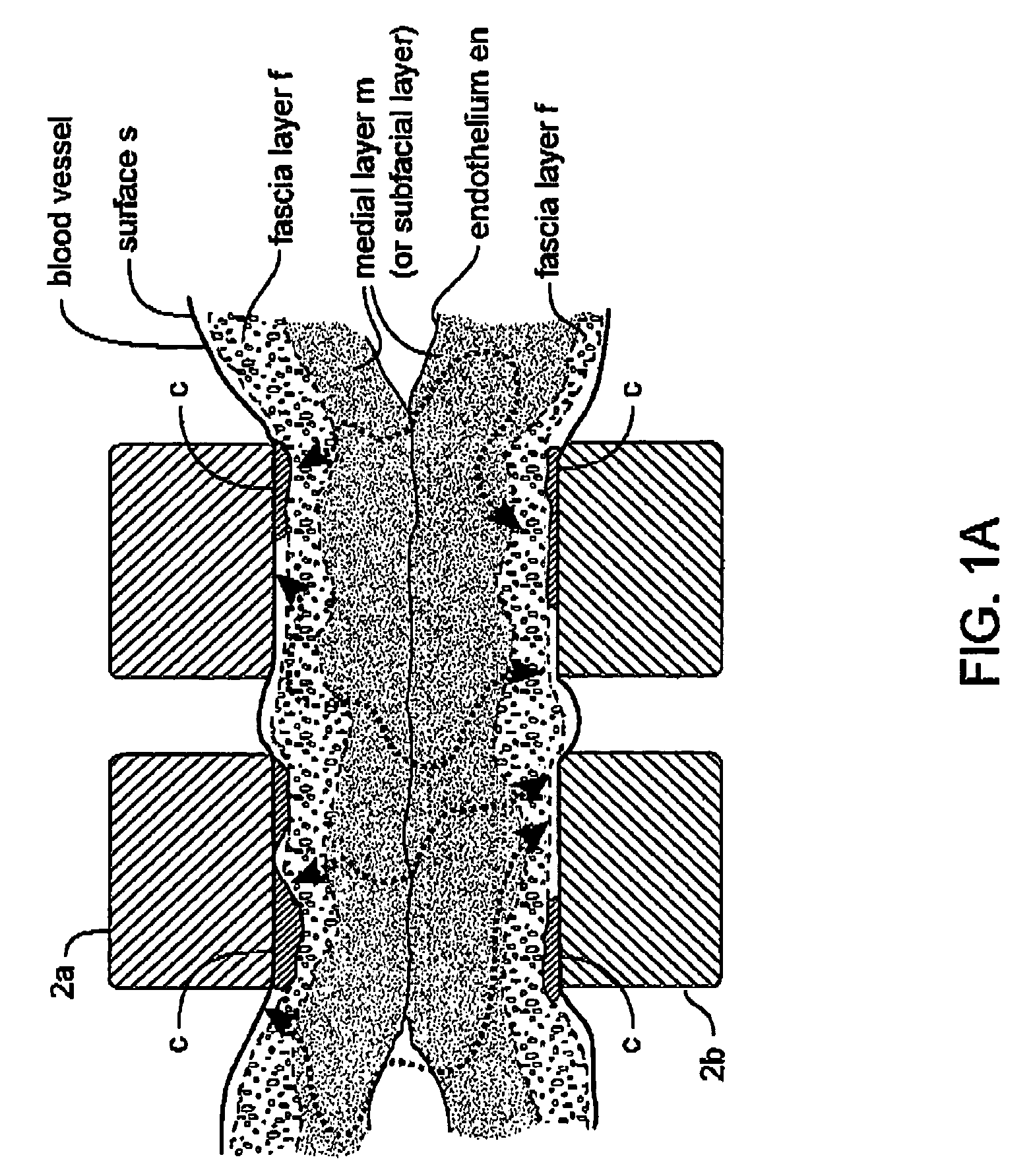
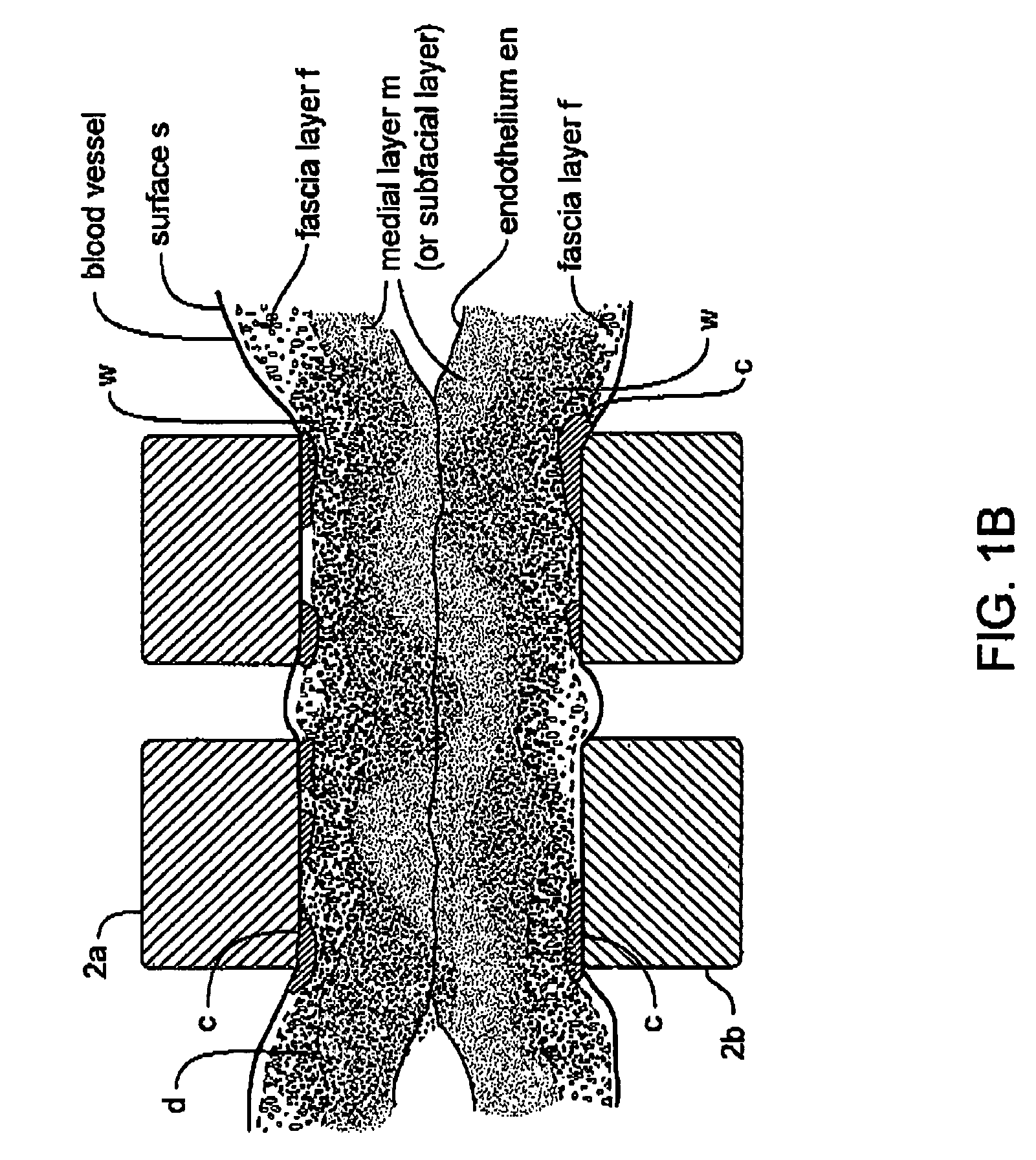
An electrosurgical working end and method for obtaining a tissue sample for biopsy purposes, for example, from a patient's lung or a liver. The working end provides curved jaw members that are positioned on opposing sides of the targeted anatomic structure. The working end carries a slidable extension member that is laterally flexible with inner surfaced that slide over the jaw members to clamp tissue therebetween. As the extension member advances, the jaws compress the tissue just ahead of the advancing extension member to allow the laterally-outward portion of the extension member to ramp over the tissue while a cutting element contemporaneously cuts the tissue. By this means, the transected tissue margin is captured under high compression. The working end carries a bi-polar electrode arrangement that engages the just-transected medial tissue layers as well as surface layers to provides Rf current flow for tissue welding purposes that is described as a medial-to-surface bi-polar approach.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
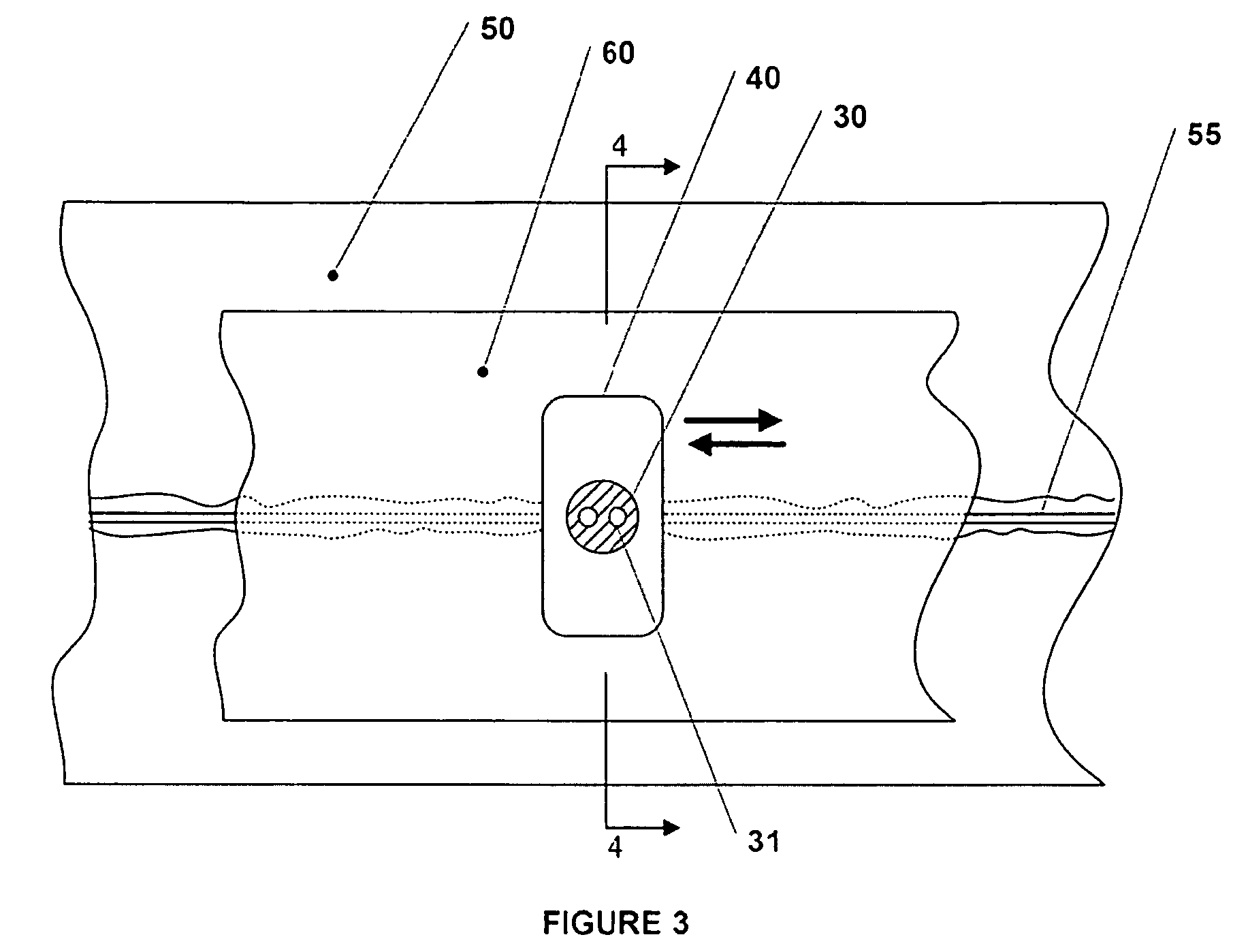
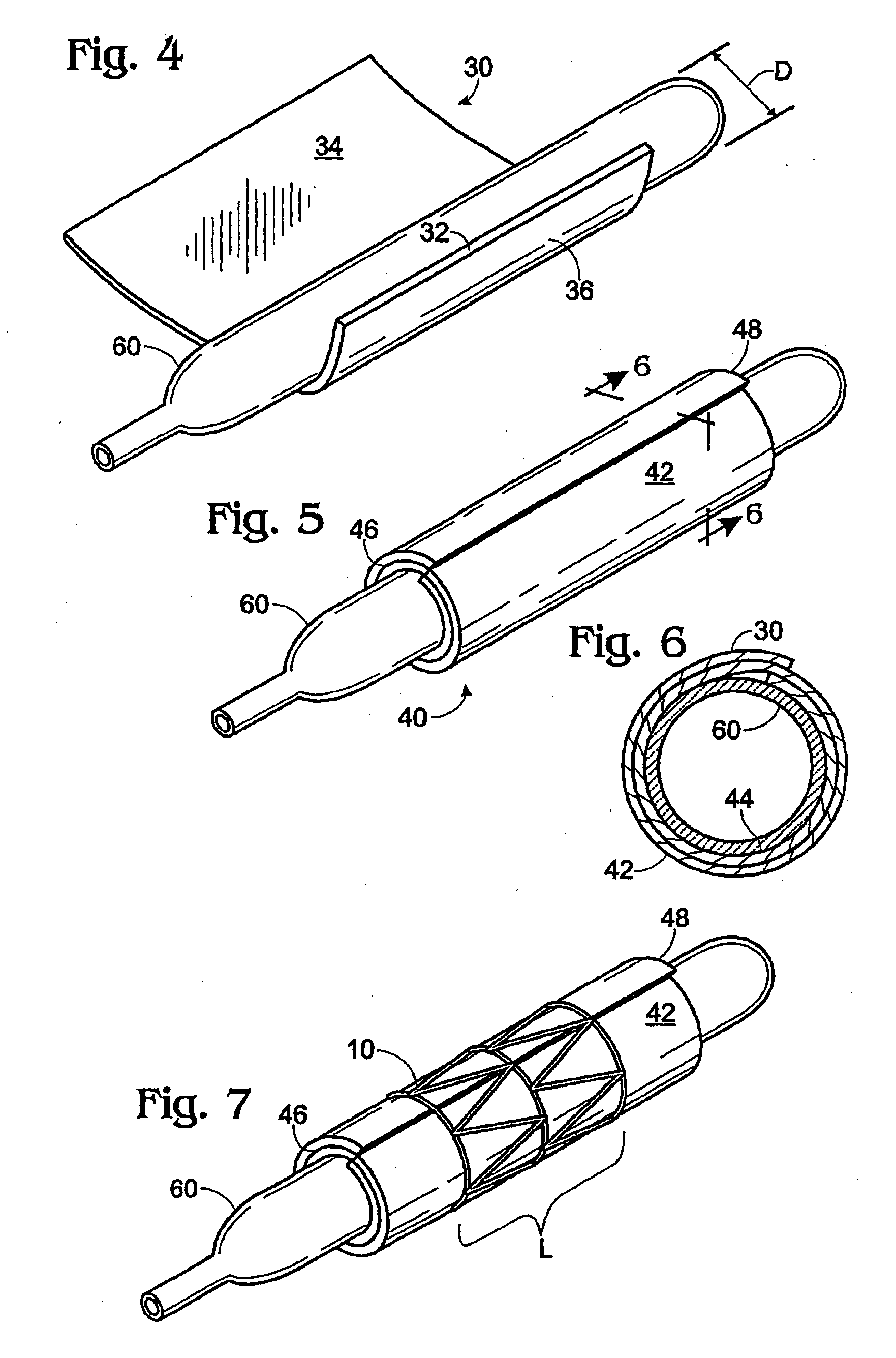
Tissue fusion/welder apparatus and method
A tissue welding apparatus is adapted to fuse a first piece of tissue to a second piece of tissue which are disposed in a surface proximate relationship. An elongate shaft carries a first jaw, and a second opposing jaw moveable relative to the first jaw. At least one penetrating member is carried by the first jaw and moveable relative to the second jaw to create a channel through the first piece of material and the second piece of material. A source of heat is coupled to the penetrating member for denaturing the tissue defining the channel. This denatured tissue forms a column binding the first piece of tissue to the second piece of tissue. A chemical agent can be carried to the tissue with the penetrating member.
Owner:APPL MEDICAL RESOURCES CORP
Electrosurgical instrument and method of use
InactiveUS7311709B2Reduce conductancePrevent any substantial dehydrationSurgical instruments for heatingCoatingsMicron scaleSpatial positioning
An electrosurgical medical device and method for creating thermal welds in engaged tissue. In one embodiment, at least one jaw of the instrument defines a tissue engagement plane carrying a variable resistive body of a positive temperature coefficient material that has a selected decreased electrical conductance at each selected increased temperature thereof over a targeted treatment range. The variable resistive body can be engineered to bracket a targeted thermal treatment range, for example about 60° C. to 80° C., at which tissue welding can be accomplished. In one mode of operation, the engagement plane will automatically modulate and spatially localize ohmic heating within the engaged tissue from Rf energy application across micron-scale portions of the engagement surface. In another mode of operation, a variable resistive body will focus conductive heating in a selected portion of the engagement surface.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Electrosurgical instrument and method of use
InactiveUS7112201B2Reduce conductancePrevent any substantial dehydrationSurgical instruments for heatingCoatingsMicron scaleElastomer
An electrosurgical medical device and method for creating thermal welds in engaged tissue. In one embodiment, at least one jaw of the instrument defines a tissue engagement plane carrying a conductive-resistive matrix of a conductively-doped non-conductive elastomer. The engagement surface portions thus can be described as a positive temperature coefficient material that has a unique selected decreased electrical conductance at each selected increased temperature thereof over a targeted treatment range. The conductive-resistive matrix can be engineered to bracket a targeted thermal treatment range, for example about 60° C. to 80° C., at which tissue welding can be accomplished. In one mode of operation, the engagement plane will automatically modulate and spatially localize ohmic heating within the engaged tissue from Rf energy application—across micron-scale portions of the engagement surface. In another mode of operation, a conductive-resistive matrix can induce a “wave” of Rf energy density to sweep across the tissue to thereby weld tissue.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
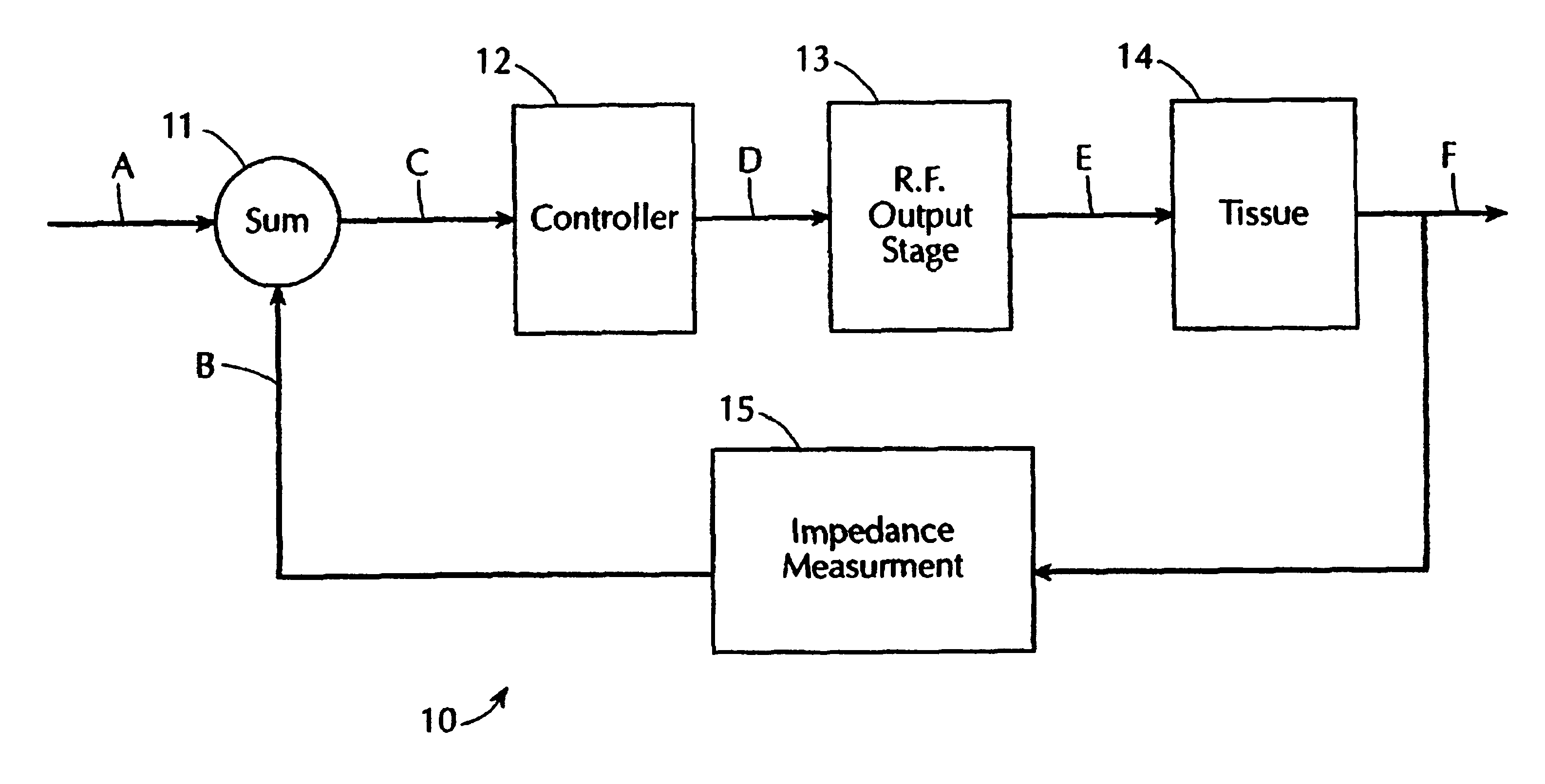
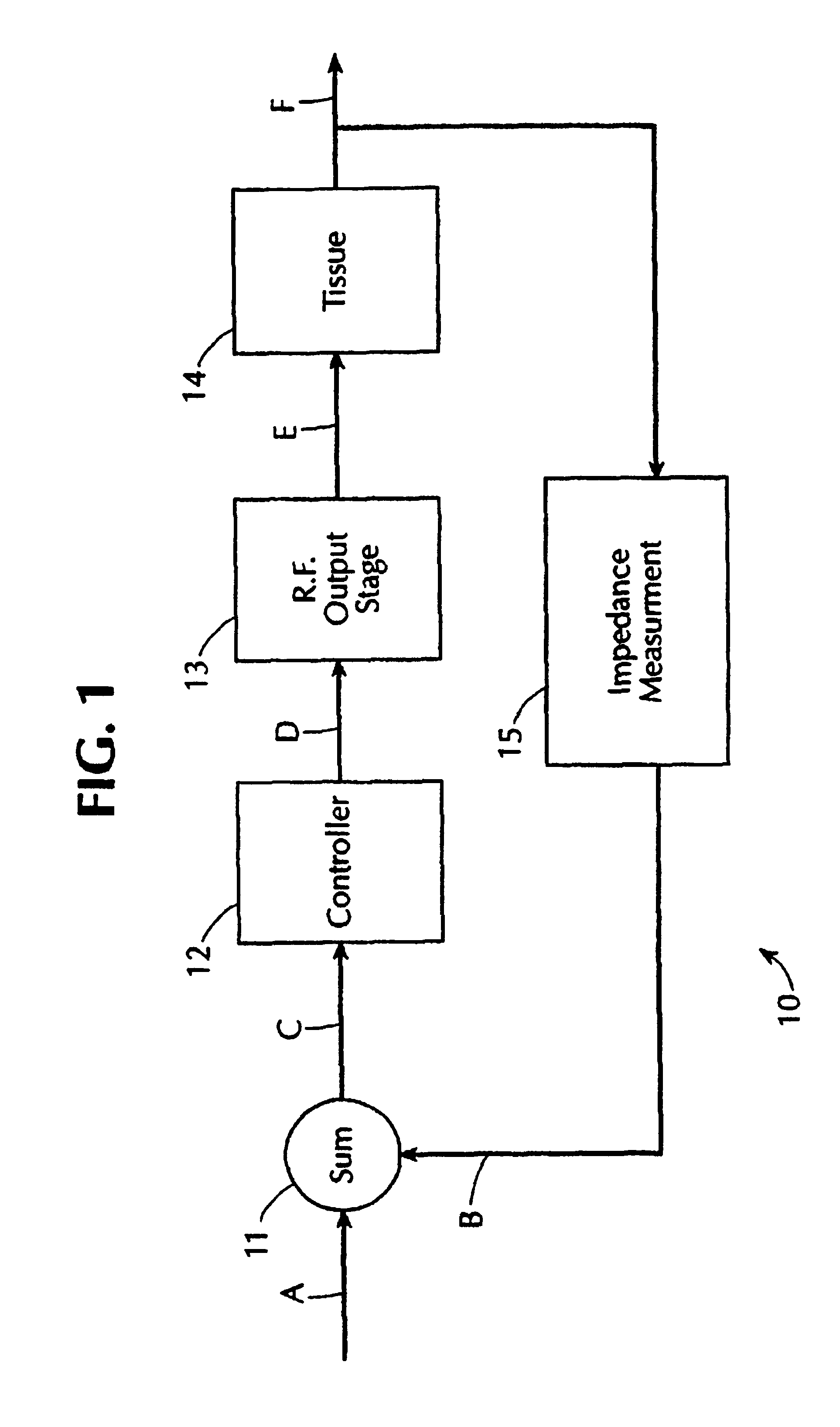
Electrosurgical generator with adaptive power control
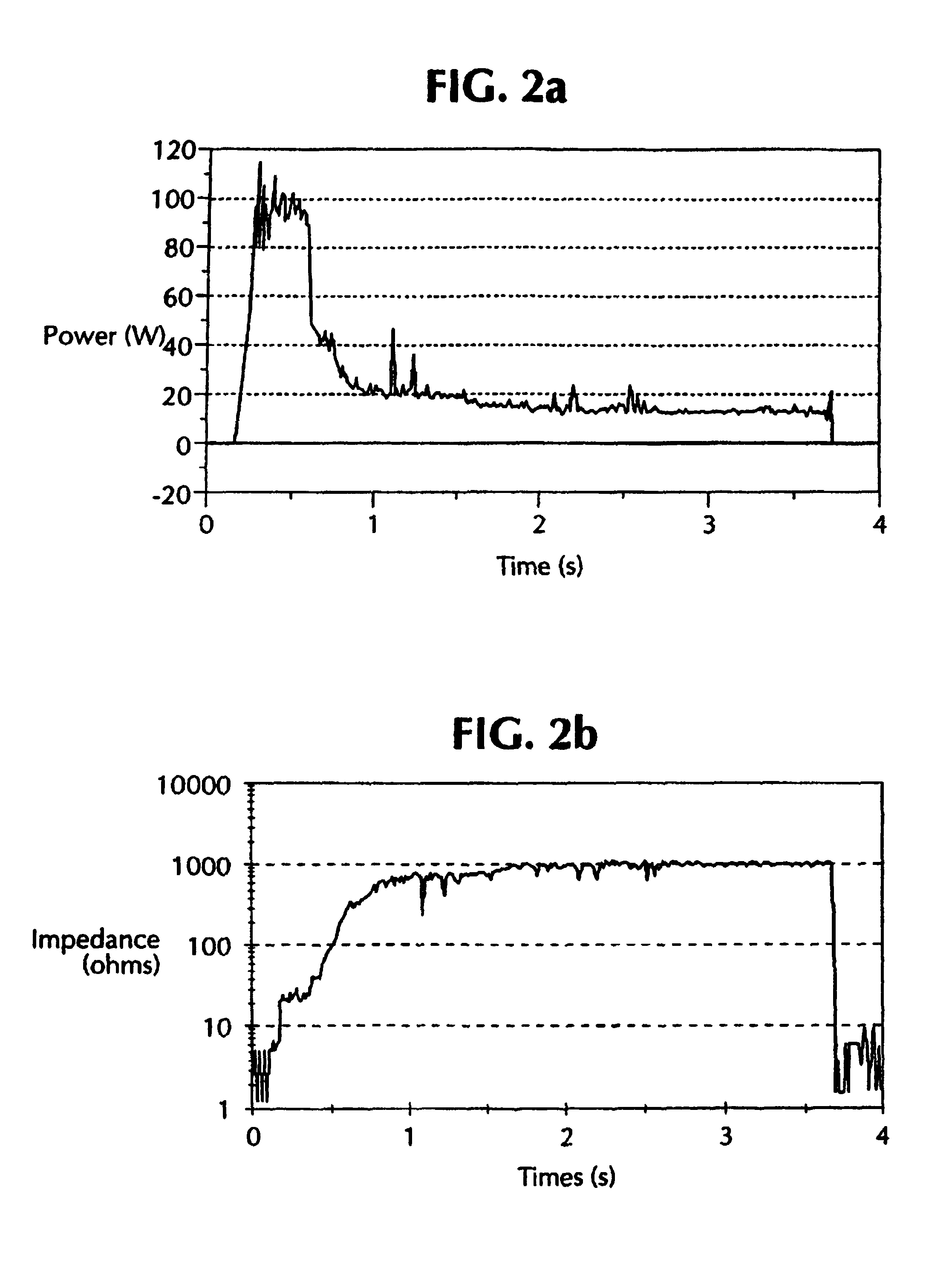
InactiveUSRE40388E1Lower Level RequirementsImproved tissue sealing characteristicPulse automatic controlSurgical instruments for heatingThermal energyVessel sealing
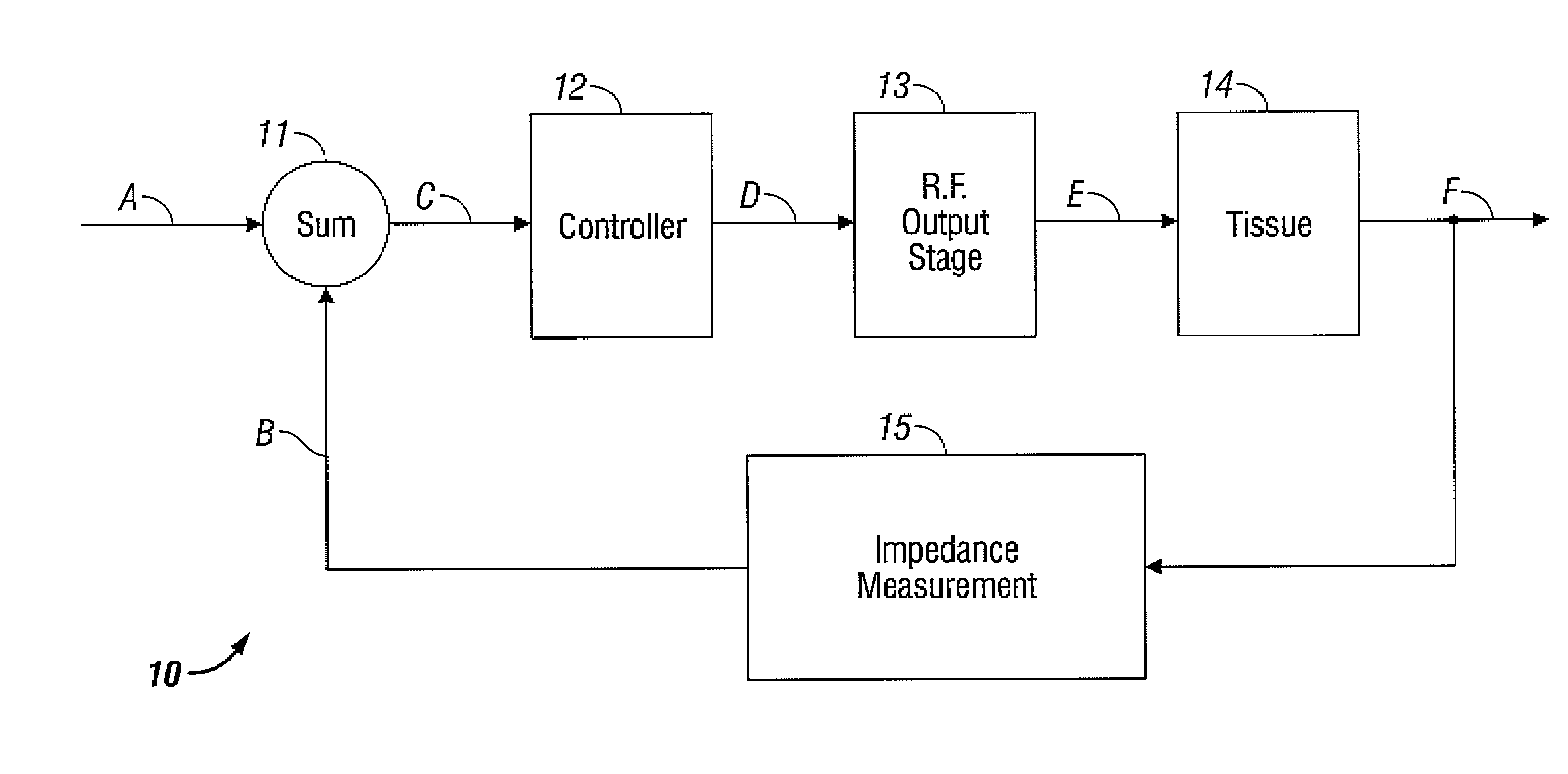
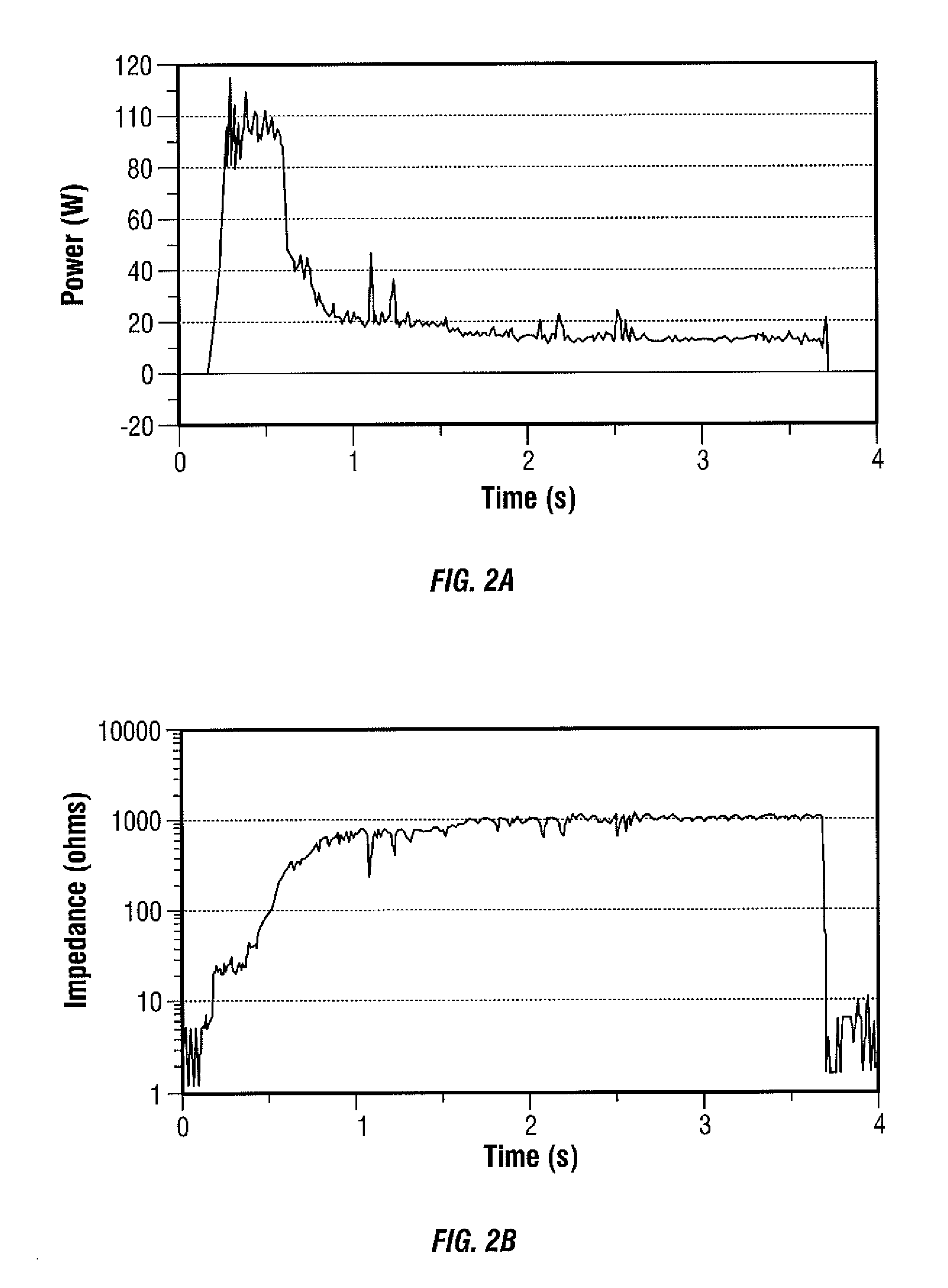
An electrosurgical generator has an output power control system that causes the impedance of tissue to rise and fall in a cyclic pattern until the tissue is desiccated. The advantage of the power control system is that thermal spread and charring are reduced. In addition, the power control system offers improved performance for electrosurgical vessel sealing and tissue welding. The output power is applied cyclically by a control system with tissue impedance feedback. The impedance of the tissue follows the cyclic pattern of the output power several times, depending on the state of the tissue, until the tissue becomes fully desiccated. High power is applied to cause the tissue to reach a high impedance, and then the power is reduced to allow the impedance to fall. Thermal energy is allowed to dissipate during the low power cycle. The control system is adaptive to tissue in the sense that output power is modulated in response to the impedance of the tissue.
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
Electrosurgical Generator With Adaptive Power Control
InactiveUS20080281315A1Pulse automatic controlSurgical instruments for heatingThermal energyVessel sealing
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
Electrosurgical instrument and method of use
InactiveUS20050267464A1Efficient weldingSpeed up the flowSurgical instruments for heatingSurgical forcepsElectrical resistance and conductanceEngineering
An embodiment of a method of the invention provides a method for welding tissue comprising providing a tissue welding device having first and second tissue engaging surfaces with at least one surface including an electrode surface that defines a plurality of surface portions having different resistances to electrical current flow therethrough. A target tissue volume is engaged with the tissue engaging surfaces. Rf energy is delivered to the target volume to create a substantially even temperature distribution across at least a portion of the target tissue volume to substantially uniformly weld at least a portion of the target tissue volume.
Owner:SURGRX
Multi-electrode apparatus for tissue welding and ablation
InactiveUS20080140069A1Promote crashSurgical instruments for heatingSurgical instruments using microwavesTissue weldingBiomedical engineering
Owner:TERUMO KK
Tissue fusion/welder apparatus corporation
A tissue welding apparatus is adapted to fuse a first piece of tissue to a second piece of tissue which are disposed in a surface proximate relationship. An elongate shaft carries a first jaw, and a second opposing jaw moveable relative to the first jaw. At least one penetrating member is carried by the first jaw and moveable relative to the second jaw to create a channel through the first piece of material and the second piece of material. A source of heat is coupled to the penetrating member for denaturing the tissue defining the channel. This denatured tissue forms a column binding the first piece of tissue to the second piece of tissue. A chemical agent can be carried to the tissue with the penetrating member.
Owner:APPL MEDICAL RESOURCES CORP
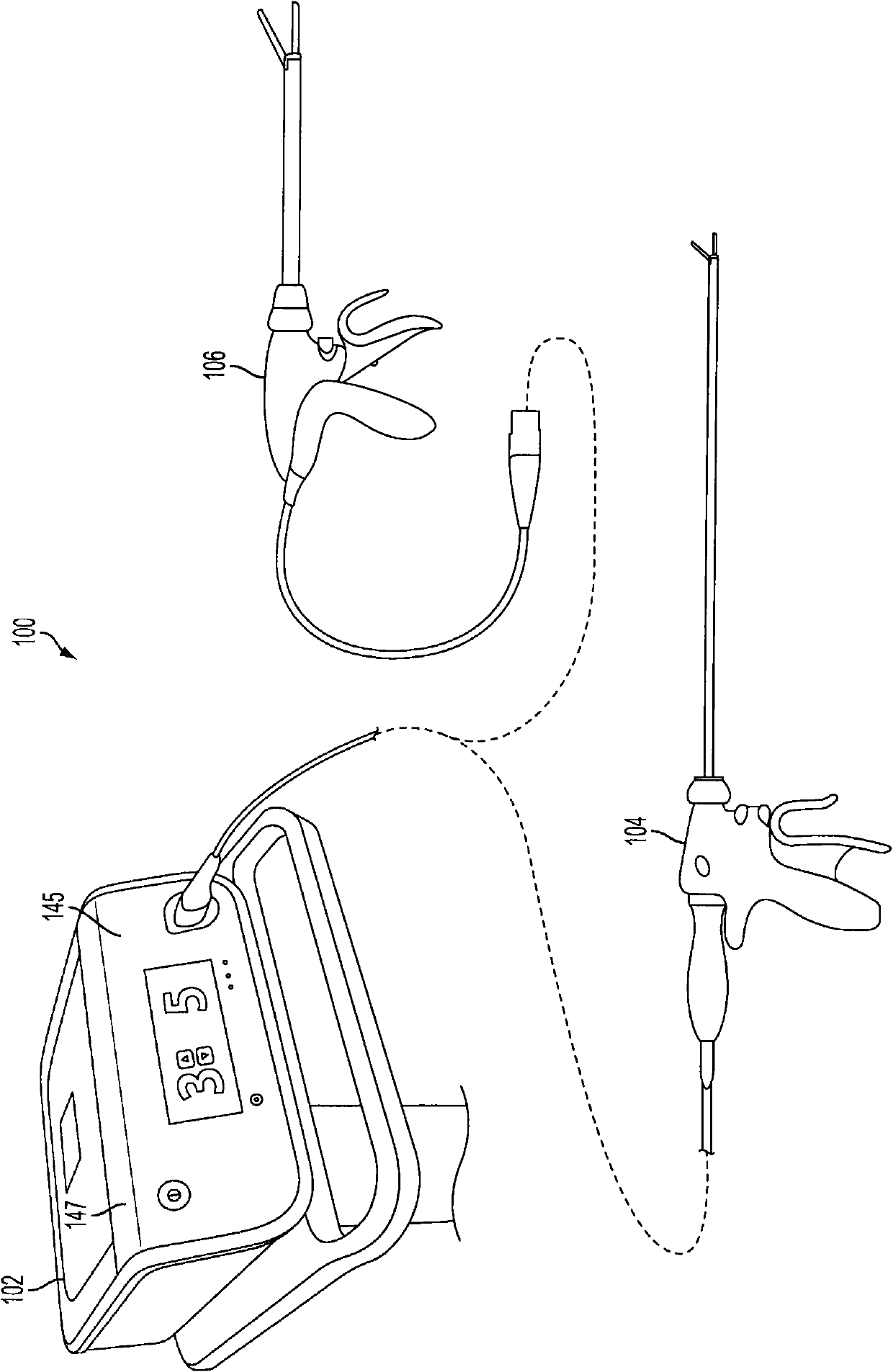
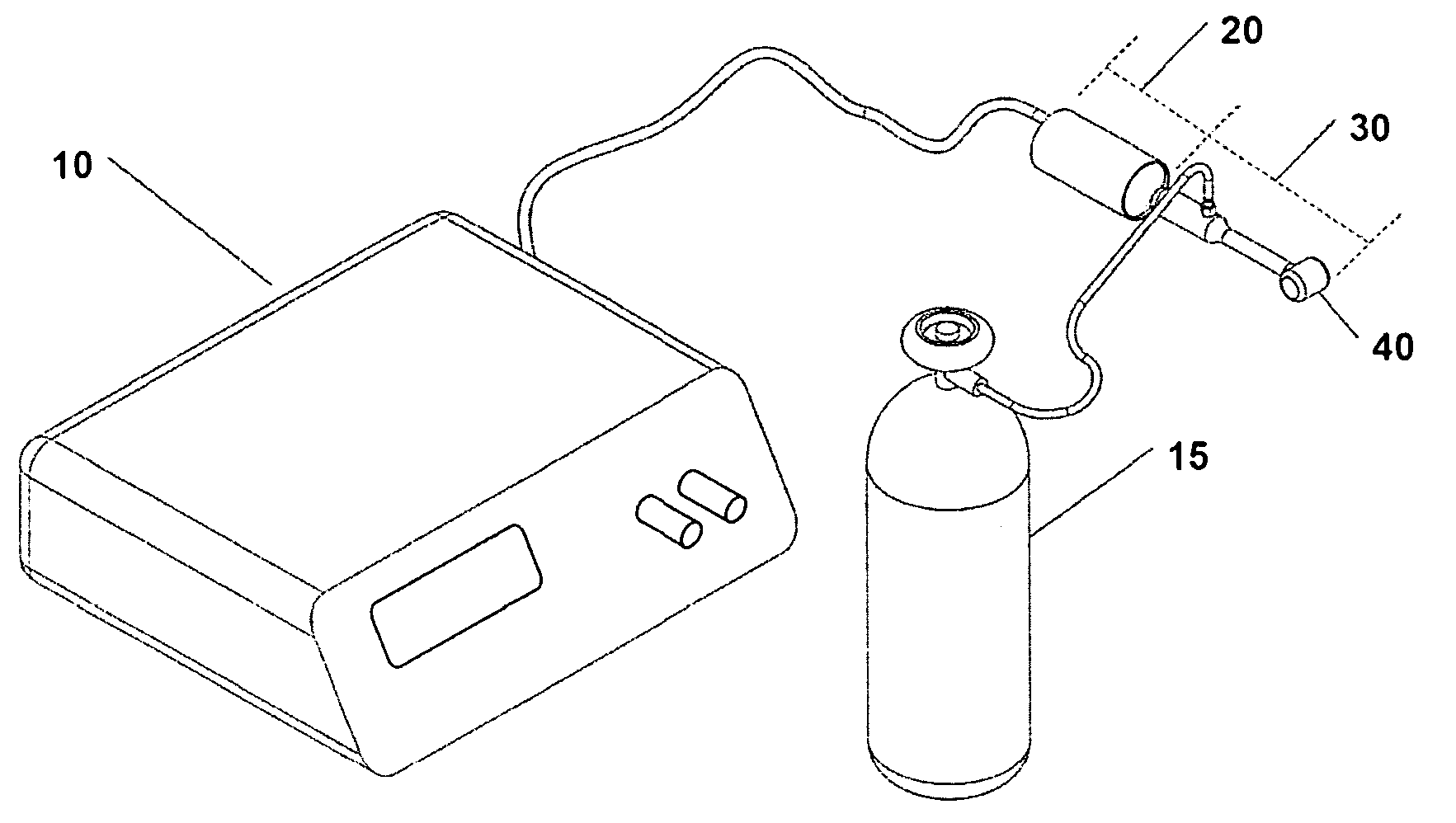
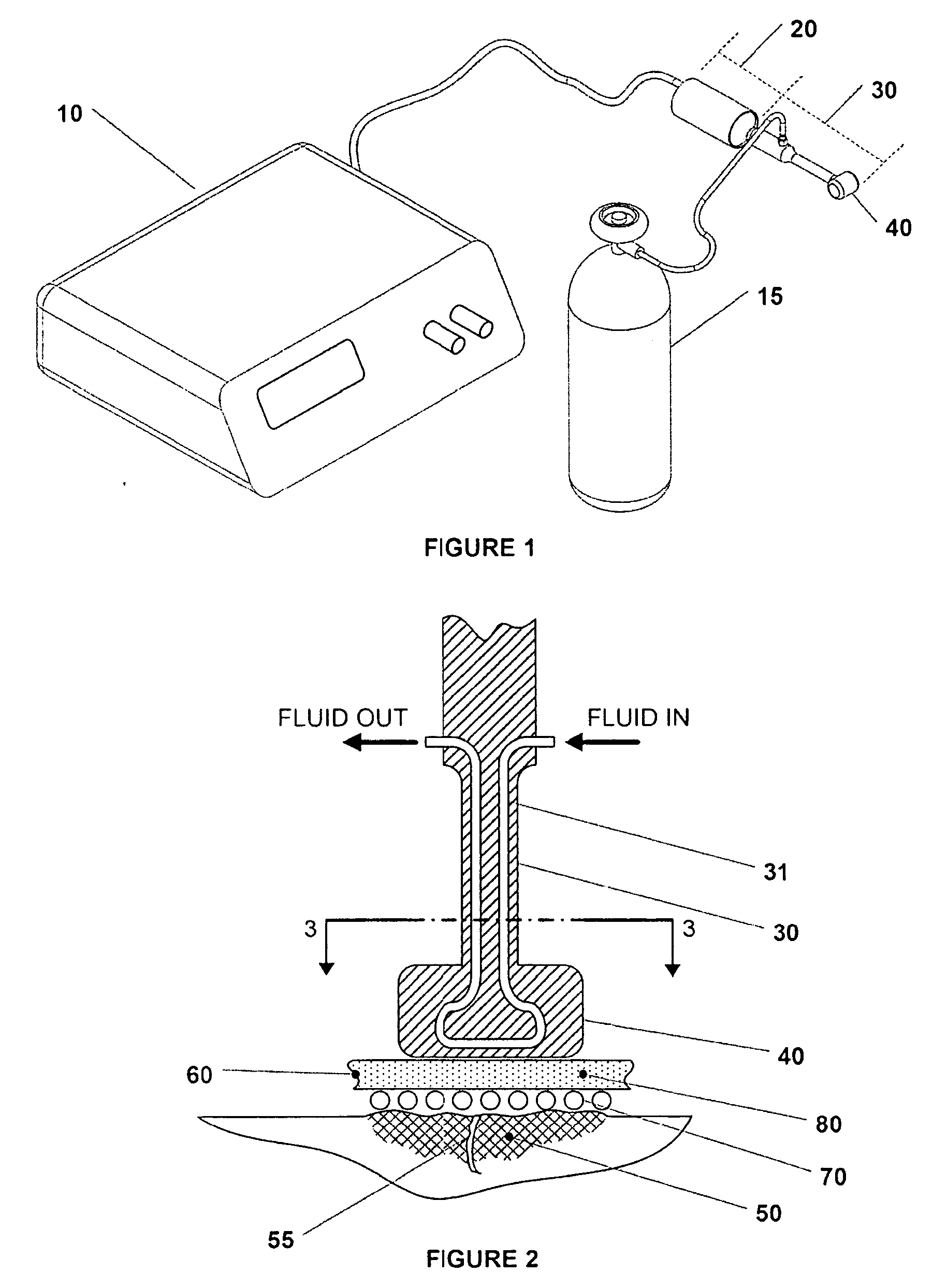
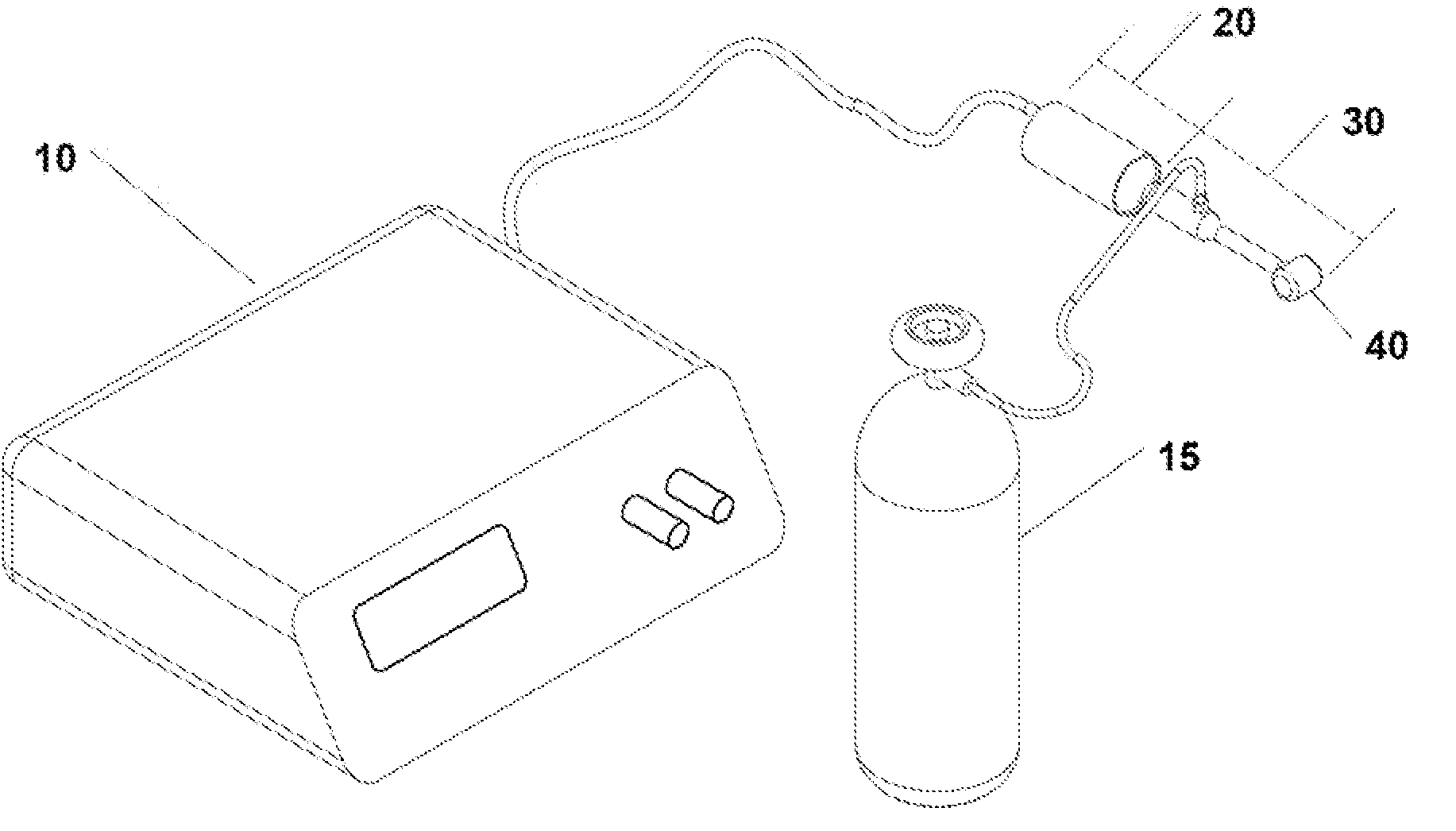
Surgical generator for ultrasonic and electrosurgical devices
ActiveCN102665585AUltrasound therapyMechanical vibrations separationSurgical operationUltrasonic sensor
A surgical generator that may produce a drive signal or signals of particular voltages, currents, and frequencies, e.g. 55,500 cycles per second (Hz). The drive signal or signals may be provided to an ultrasonic surgical device, and specifically to a transducer. In one embodiment, the generator may be configured to produce a drive signal of a particular voltage, current, and / or frequency output signal that can be stepped with high resolution, accuracy, and repeatability. Additionally, the surgical generator may generate a drive signal or signals with output power sufficient to perform bipolar electrosurgery using radio frequency (RF) energy. The drive signal may be provided, for example, to electrodes of the electrosurgical device.; Accordingly, the generator may be configured for therapeutic purposes by applying electrical signals to an ultrasonic transducer or electrical energy to the tissue sufficient for treating the tissue (e.g., cutting, coagulation, cauterization, tissue welding, etc.).
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
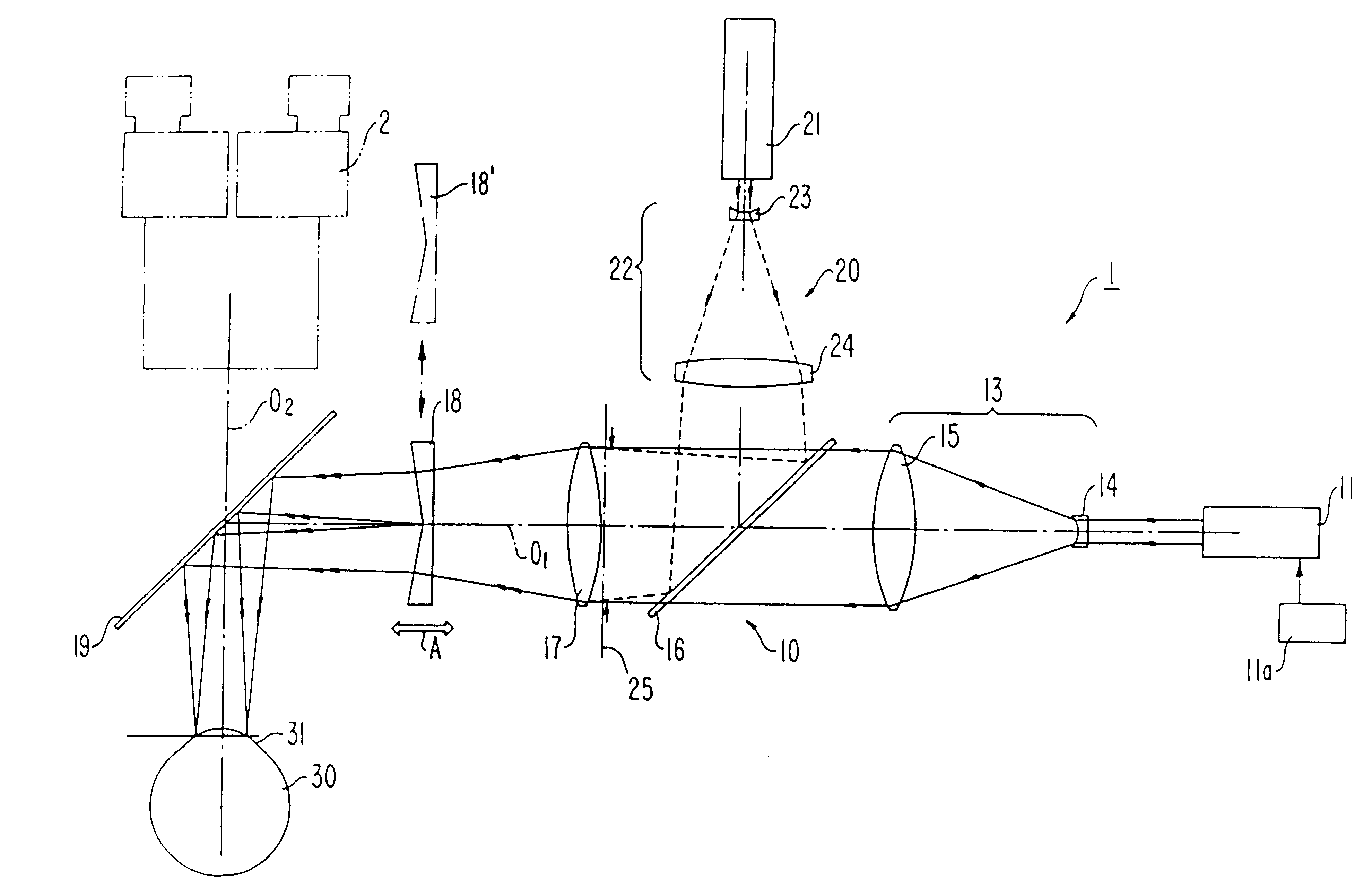
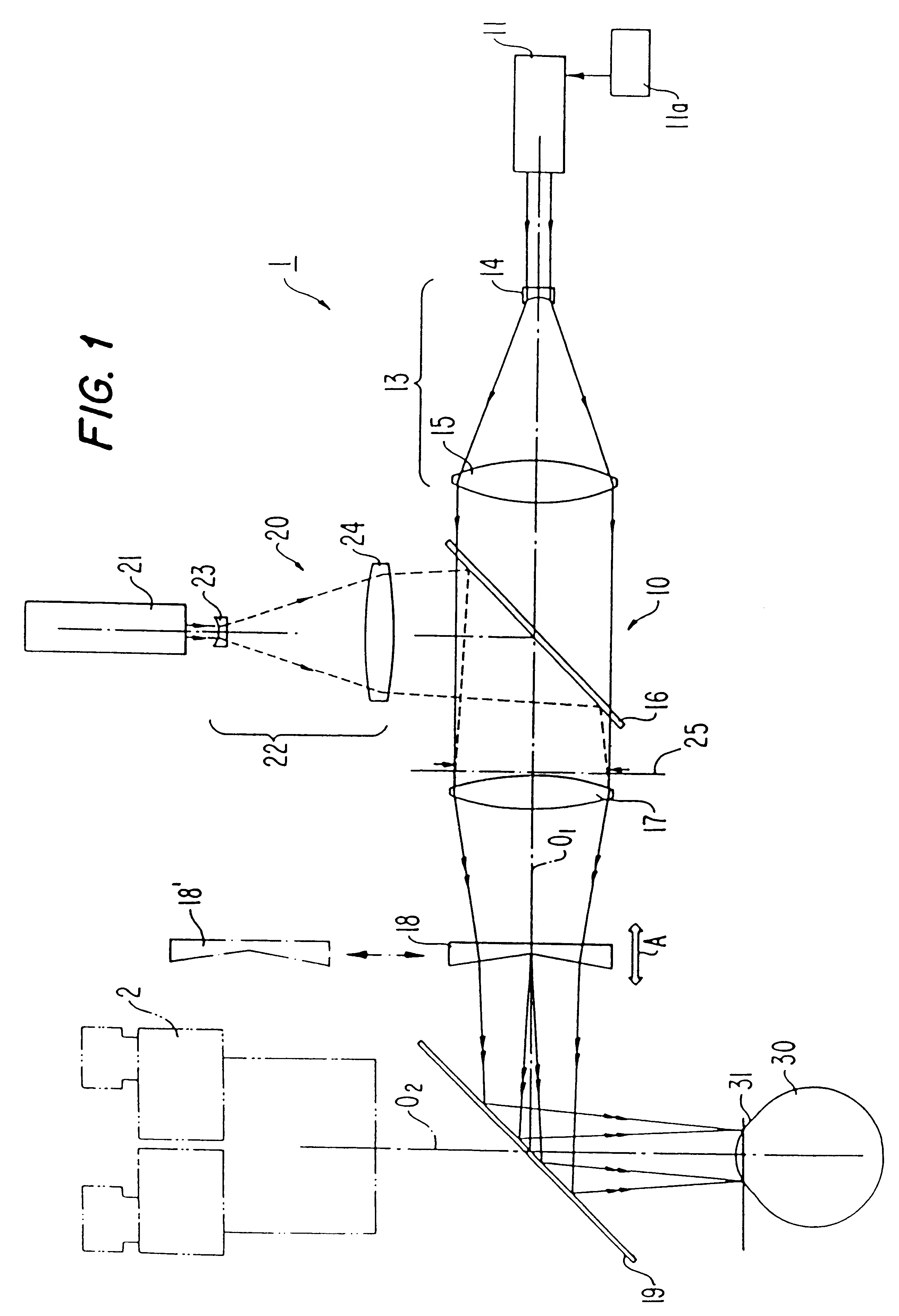
Noncontact laser microsurgical method
InactiveUS6210399B1Reduce astigmatismAlleviate corneal refractive errorLaser surgeryDiagnosticsGonioplastyEpikeratoplasty
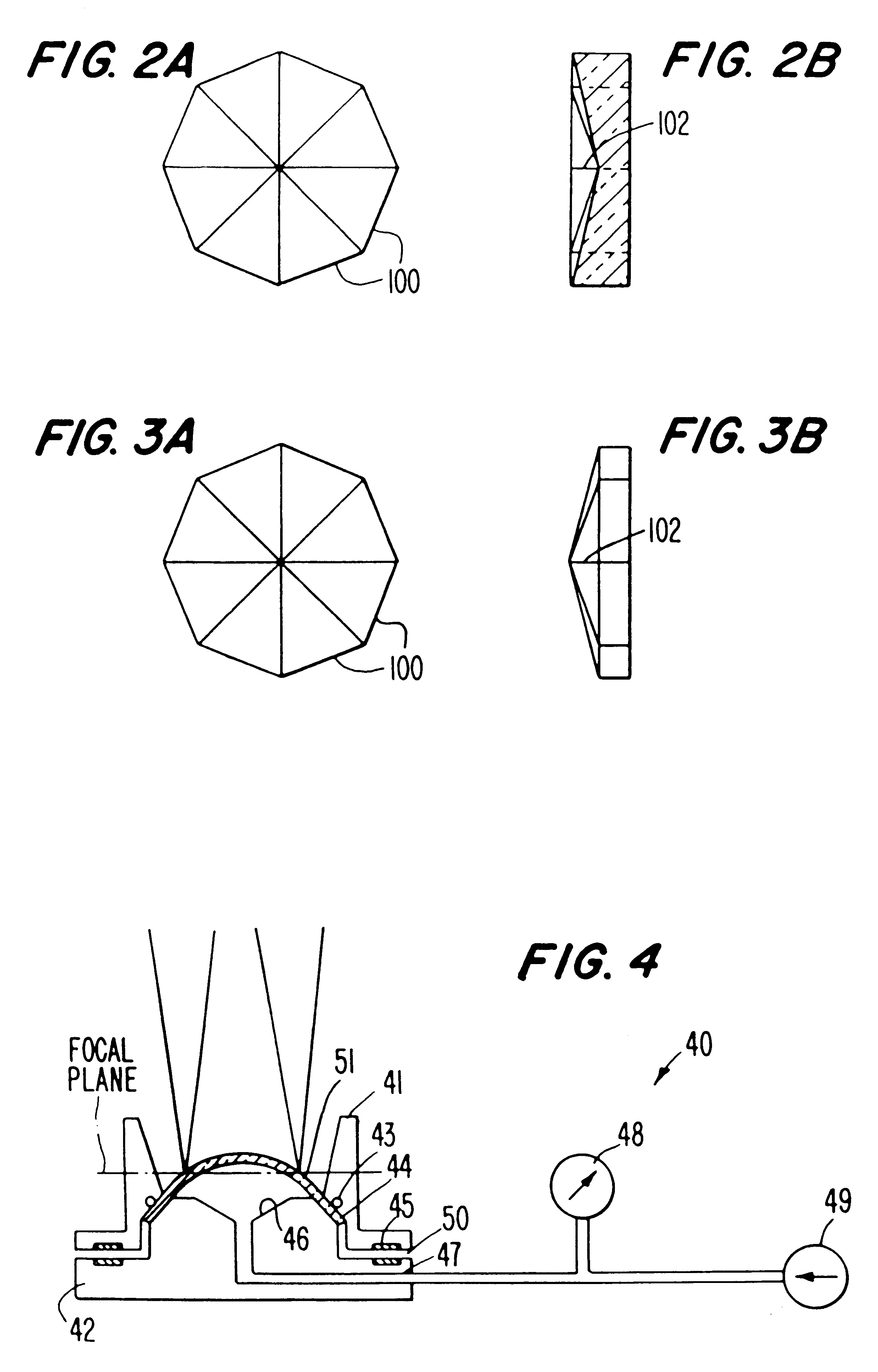
A noncontact laser microsurgical apparatus and method for marking a cornea of a patient's or donor's eye in transplanting surgery or keratoplasty, and in incising or excising the corneal tissue in keratotomy, and for tissue welding and for thermokeratoplasty. The noncontact laser microsurgical apparatus comprises a laser source and a projection optical system for converting laser beams emitted from the laser source into coaxially distributed beam spots on the cornea. The apparatus further includes a multiple-facet prismatic axicon lens system movably mounted for varying the distribution of the beam spots on the cornea. In a further embodiment of the method of the present invention, an adjustable mask pattern is inserted in the optical path of the laser source to selectively block certain portions of the laser beams to thereby impinge only selected areas of the cornea.
Owner:UNIV OF MIAMI
Gelatin based on Power-gel(TM) as solders for Cr4+laser tissue welding and sealing of lung air leak and fistulas in organs
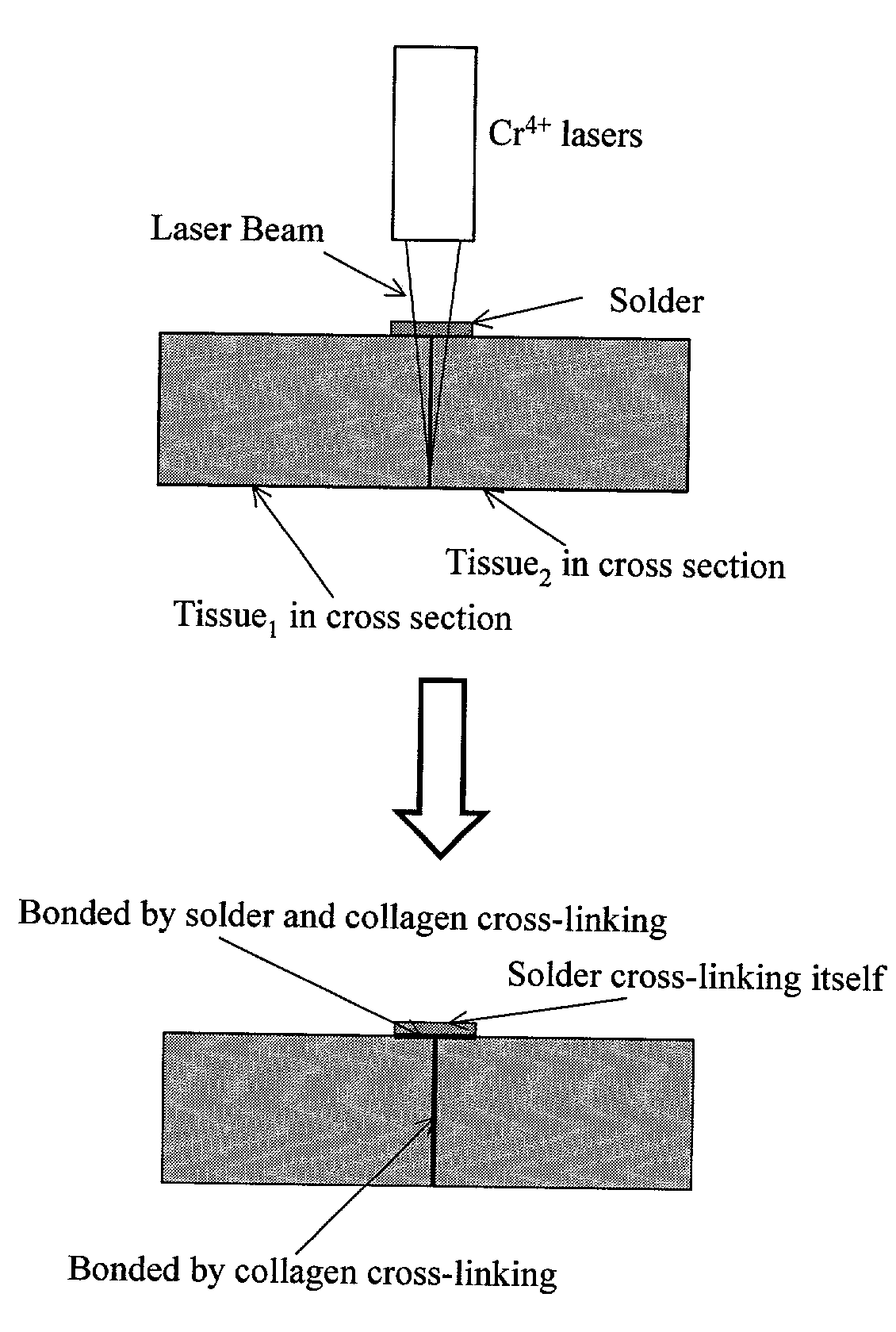
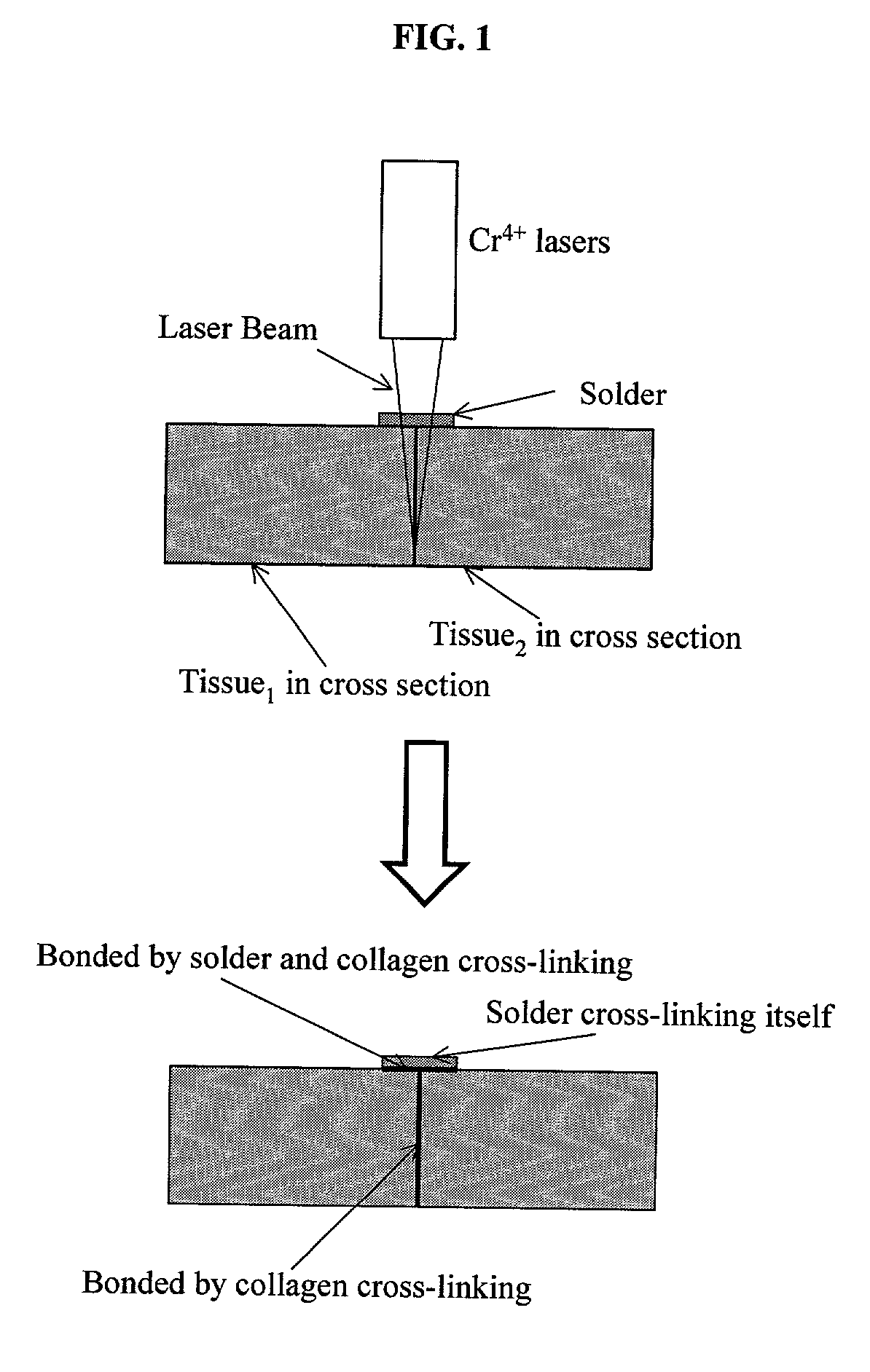
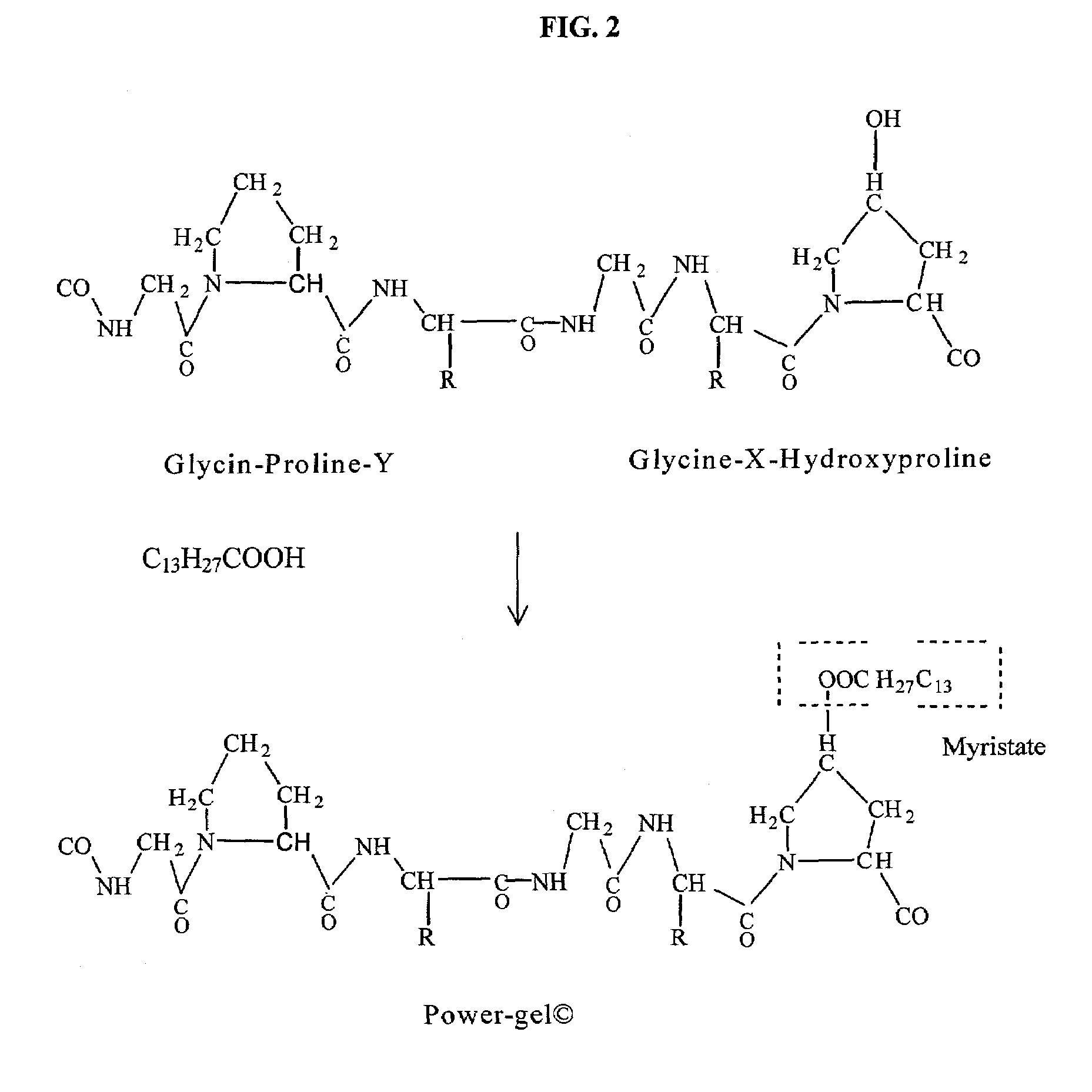
InactiveUS7033348B2Enhancement in post-procedure effectivenessImprove welding strengthDiagnosticsSurgical instrument detailsEngineeringWeld strength
Laser tissue welding can be achieved using tunable Cr4+ lasers, semiconductor lasers and fiber lasers, where the weld strength follows the absorption spectrum of water. The use of gelatin and esterified gelatin as solders in conjunction with laser inducted tissue welding impart much stronger tensile and torque strengths than albumin solders. Selected NIR wavelength from the above lasers can improve welding and avoid thermal injury to tissue when used alone or with gelatin and esterified gelatin solders. These discoveries can be used to enhance laser tissue welding of tissues such as skin, mucous, bone, blood vessel, nerve, brain, liver, pancreas, spleen, kidney, lung, bronchus, respiratory track, urinary tract, gastrointestinal tract, or gynecologic tract and as a sealant for pulmonary air leaks and fistulas such as intestinal, rectal and urinary fistulas.
Owner:RES FOUND OF THE CITY UNIV OF NY THE
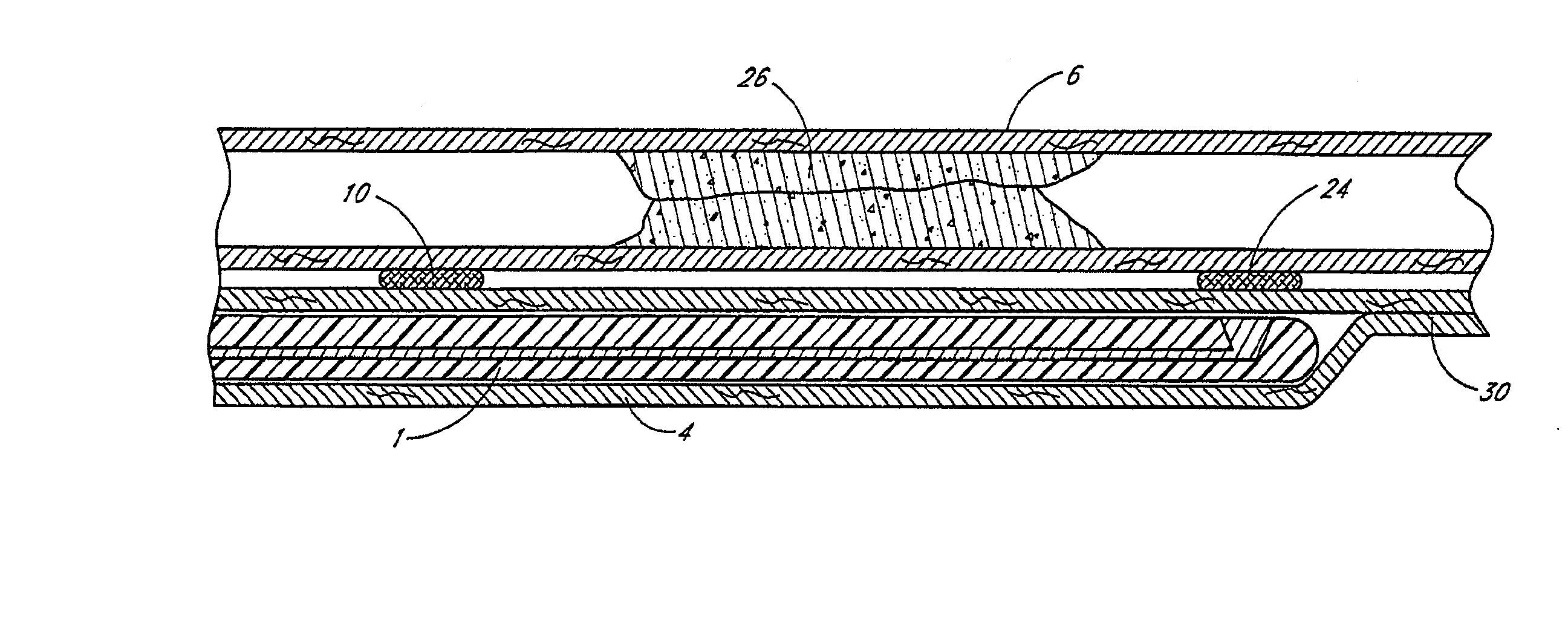
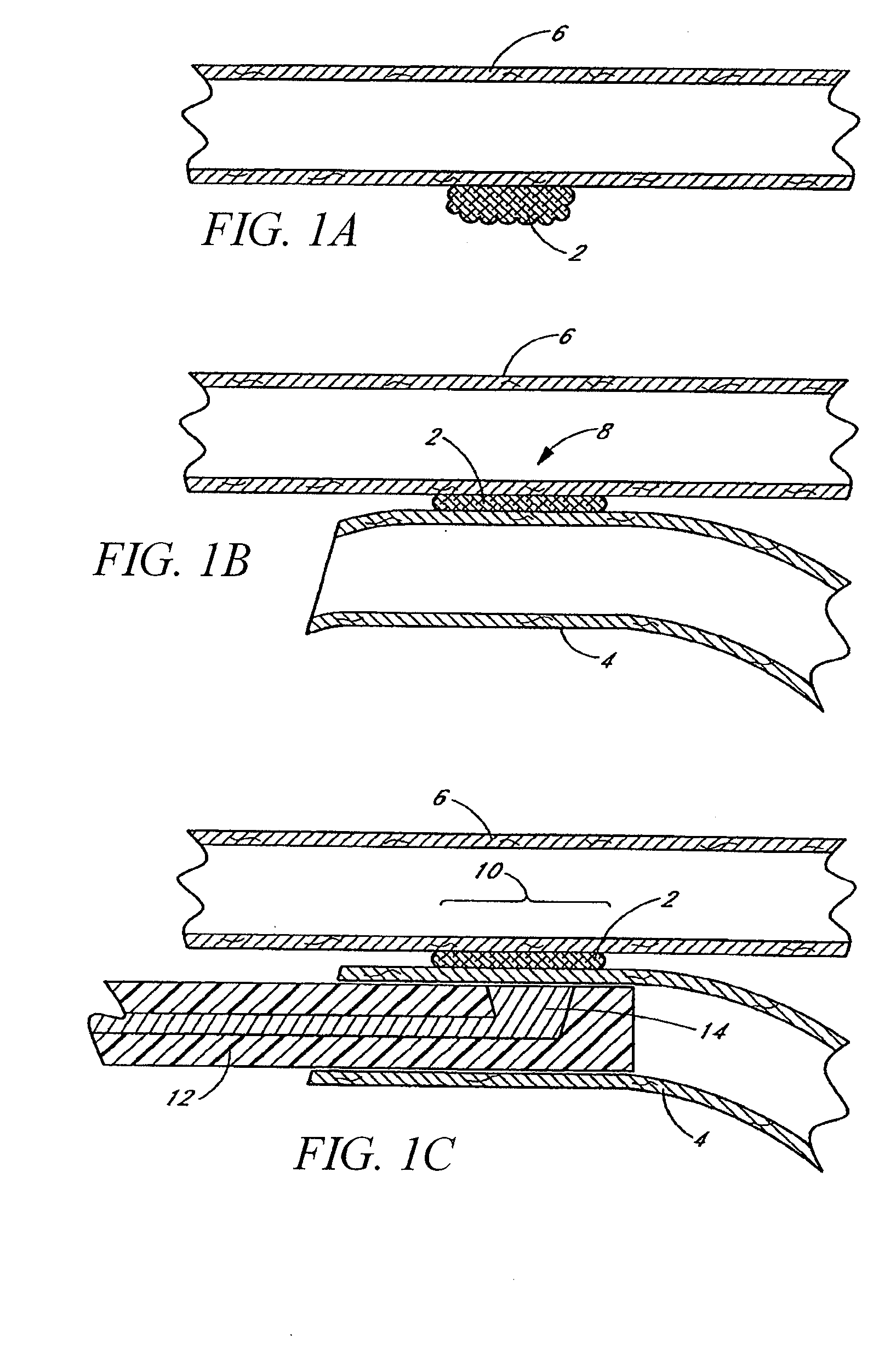
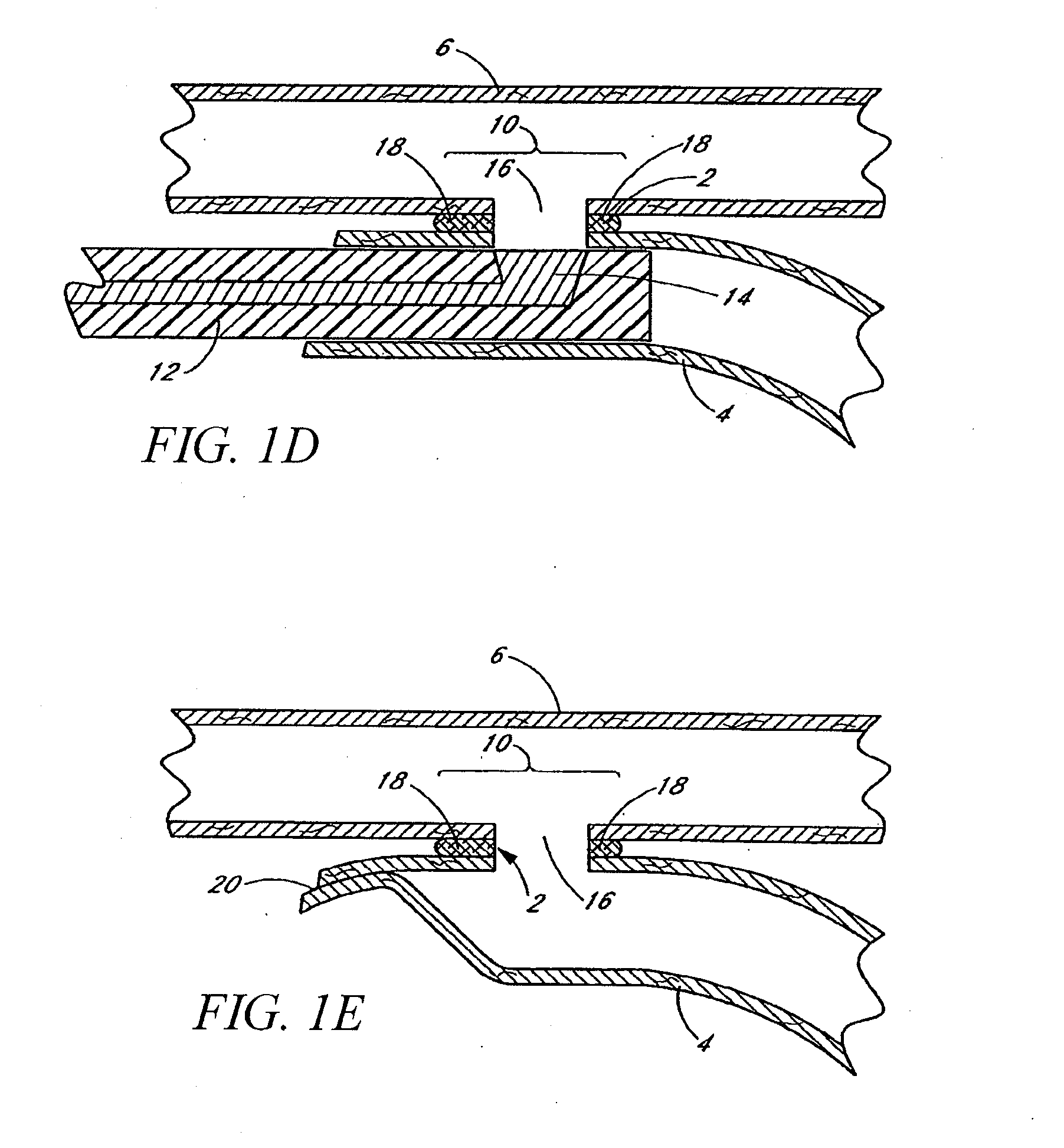
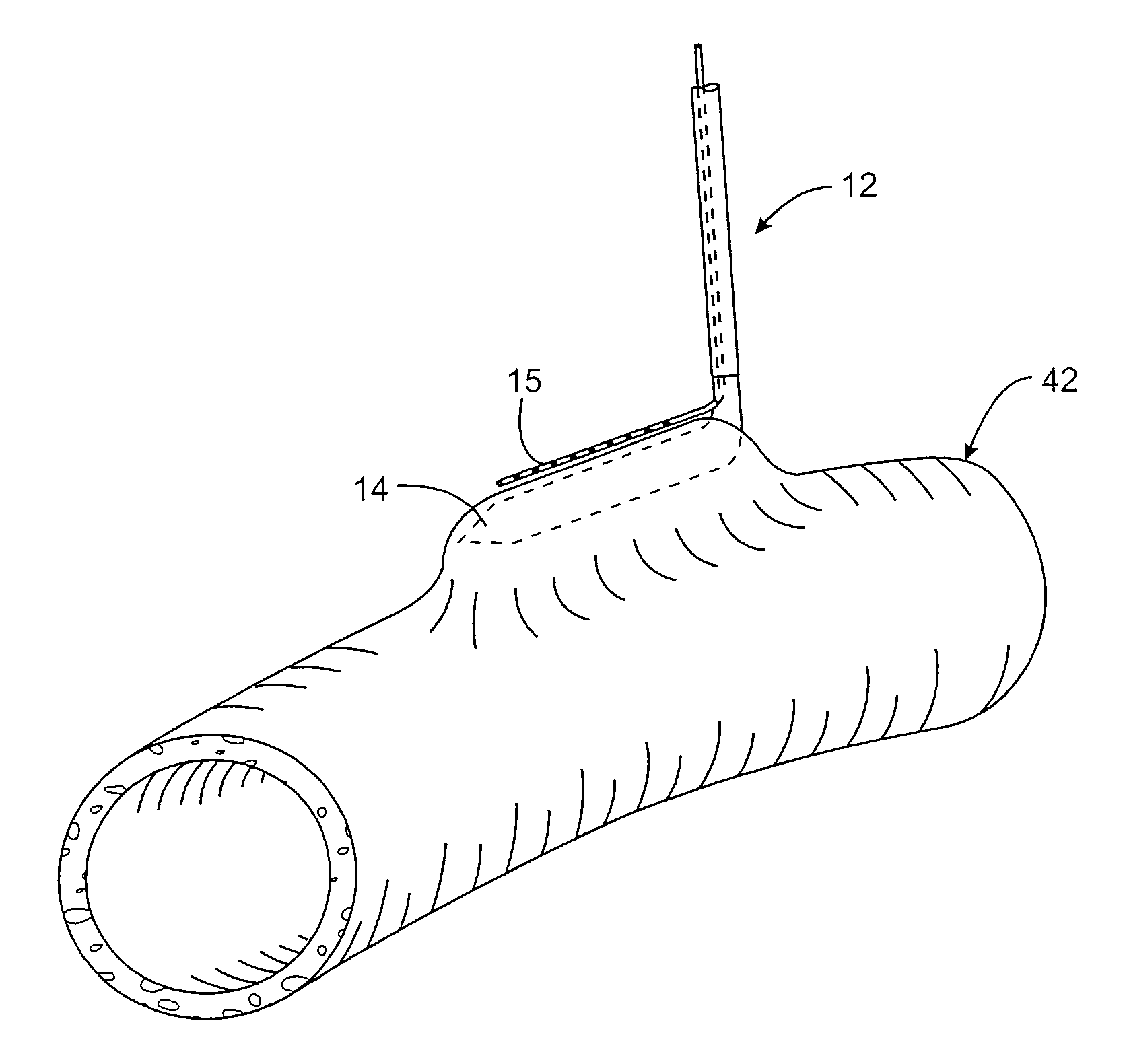
Devices and methods for tissue welding
InactiveUS20070239260A1Avoiding overheating adjacent tissueStentsSurgical instruments for heatingTissue weldingBiological tissue
Tissue implants configured to adhere to biological tissues when activated by electrical energy may include an electrically conductive structure, a connector releasably connected to the electrically conductive structure, and a thermally crosslinkable coating covering at least the exposed portion of the electrically conductive structure. These tissue implants may be used for welding tissues to other tissues, or for welding tissue to the implant, and thus may be used to attach implants within a body, or for therapeutic uses. These implants may be used for wound closure or to create occlusions. Thermal damage to the tissue may be minimized by use of the thermally-crosslinkable material having a resistivity higher than that of the adjacent tissue.
Owner:PEAK SURGICAL
Tissue welding using plasma
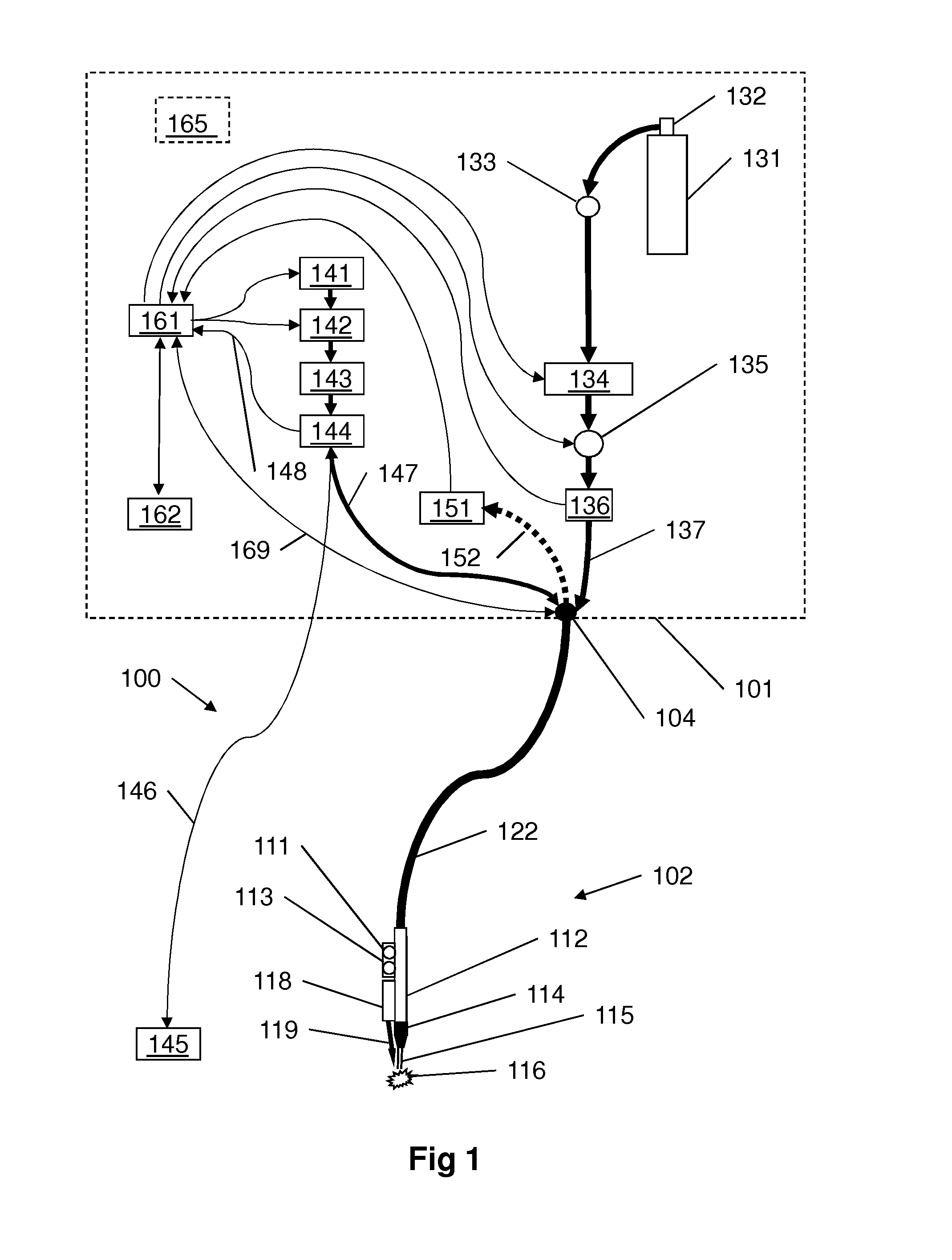
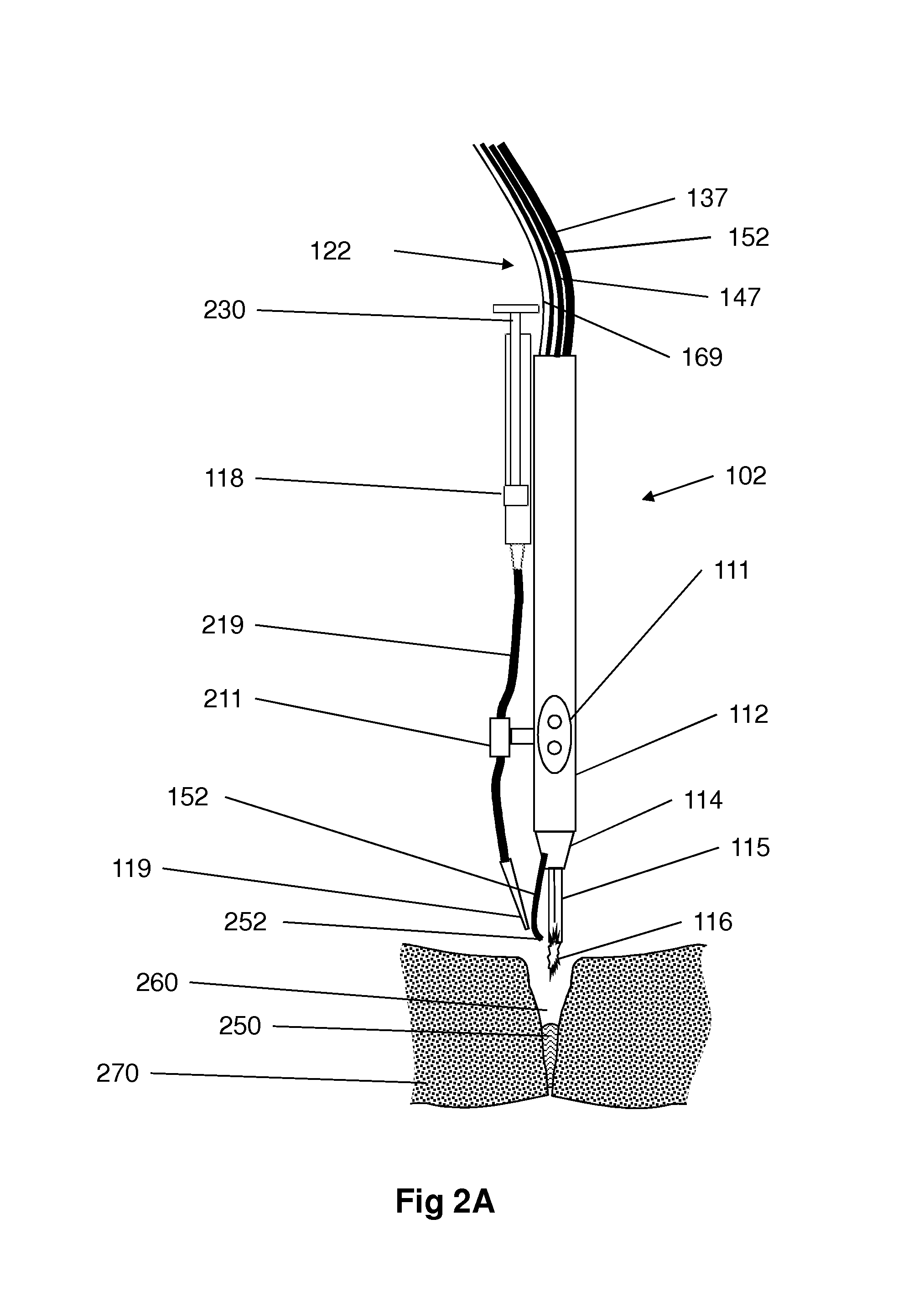
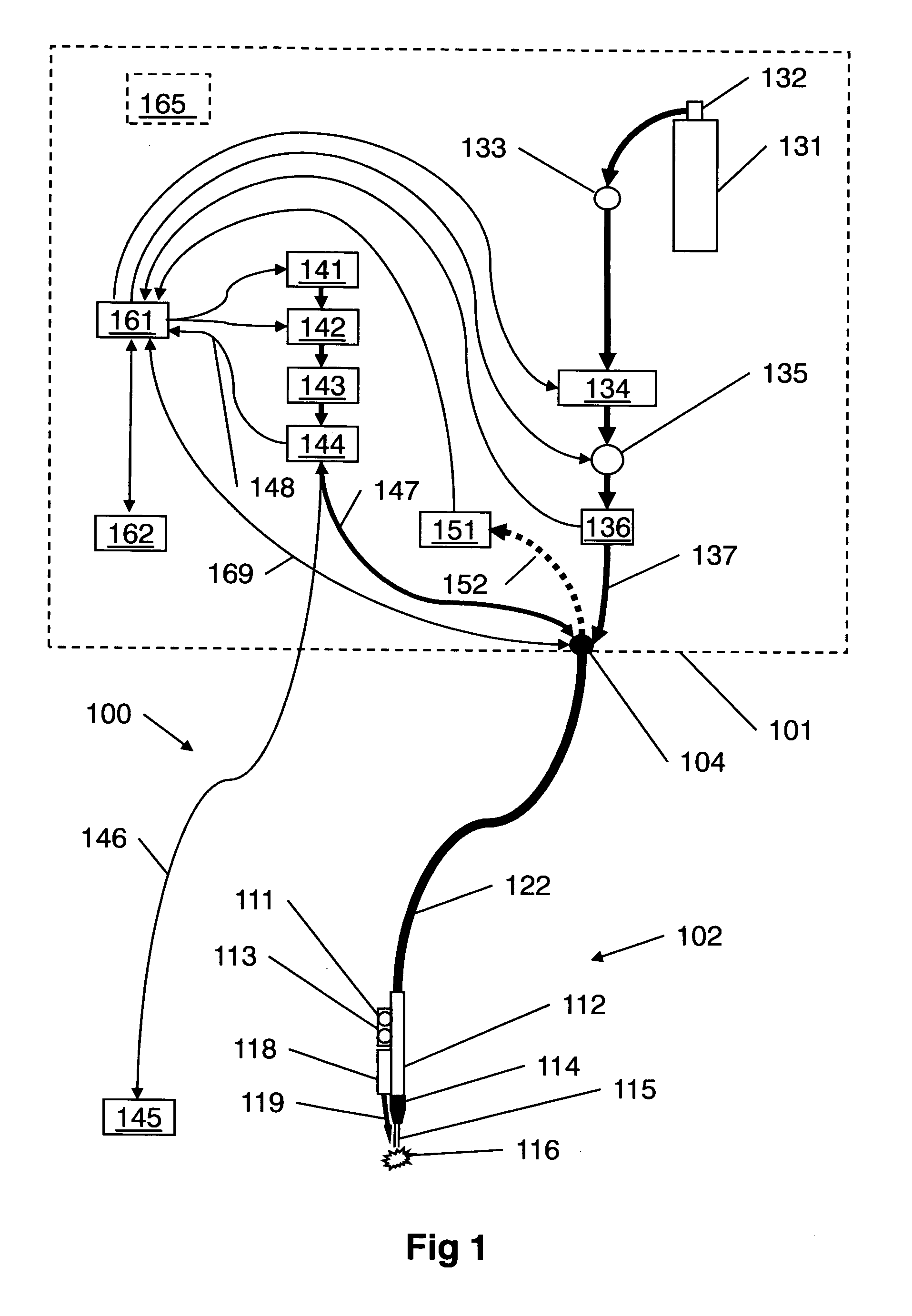
A medical device (100) for tissue welding is provided that comprises at least one processor (161) configured to regulate cold plasma production in a plasma head (102) by controlling an RF power source (141) to supply RF plasma-producing power to the plasma head.
Owner:IONMED
Methods for tissue welding using laser-activated protein solders
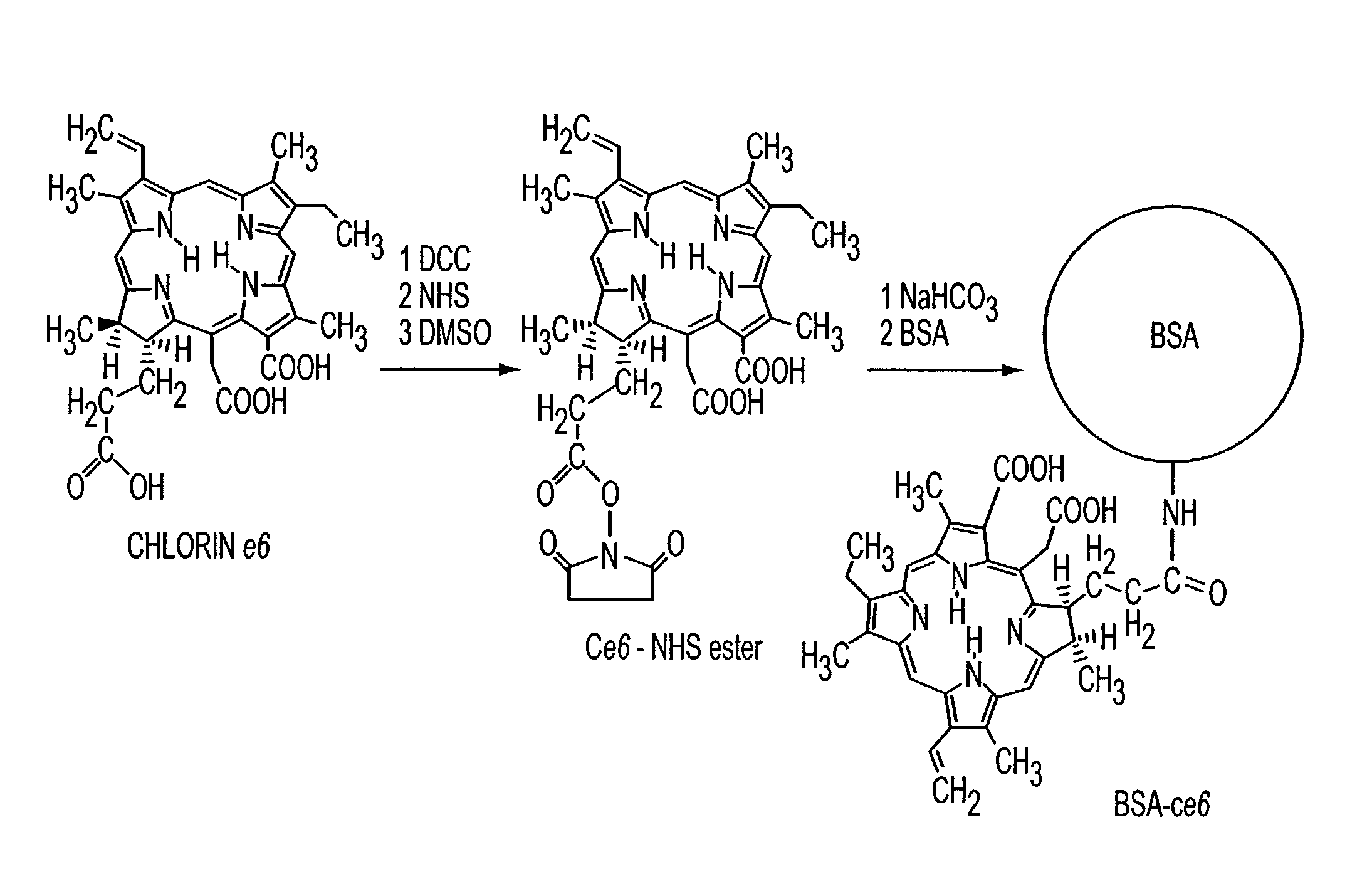
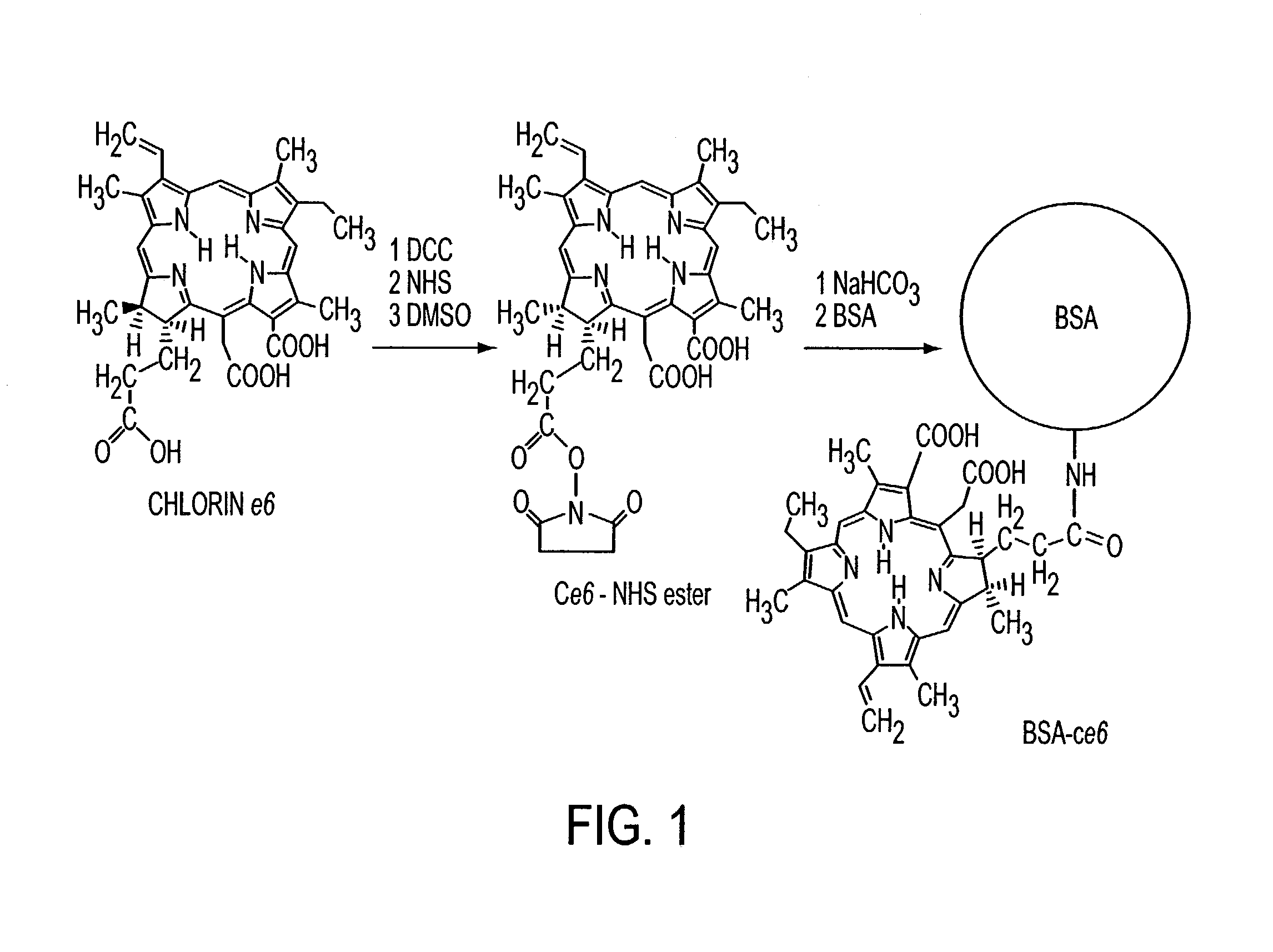
Various tissue glues have drawback such as toxicity, causing inflammatory reactions or insufficient bonding strength. The present invention is directed to methods of form tissue adhesion by administering to tissues compositions comprising proteins conjugated to one or more novel photosensitizers and irradiating the composition. The composition may further comprise one or more proteins not conjugated to the photosensitizer. Additionally, the present invention relates to compositions and methods wherein increased ratios of protein to photosensitizer enhance weld strength.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Multi-electrode apparatus for tissue welding and ablation
InactiveUS20080140074A1Promote crashInternal electrodesSurgical instrument detailsTissue weldingBiomedical engineering
An apparatus for delivering energy to tissue, comprising an elongate flexible shaft having a proximal end and a distal end; an first electrode operably connected to the elongate flexible shaft; and an second electrode operably connected to the elongate flexible shaft and electrically independent from the first electrode, said second electrode at least partially surrounding and spaced apart from the first electrode.
Owner:TERUMO KK
Multi-electrode apparatus for tissue welding and ablation
InactiveUS20080140070A1Promote crashSurgical instruments using microwavesTissue weldingBiomedical engineering
An apparatus for delivering energy to tissue, comprising: an elongate flexible shaft having a proximal end and a distal end; a sheath disposed over at least a portion of the flexible shaft; a housing provided on the distal end of the flexible shaft; a plurality of electrodes mounted on the housing, the electrodes having a tissue apposition surface having a non-coplanar shape that conforms to the anatomy of a patient.
Owner:TERUMO KK
Plasma head for tissue welding
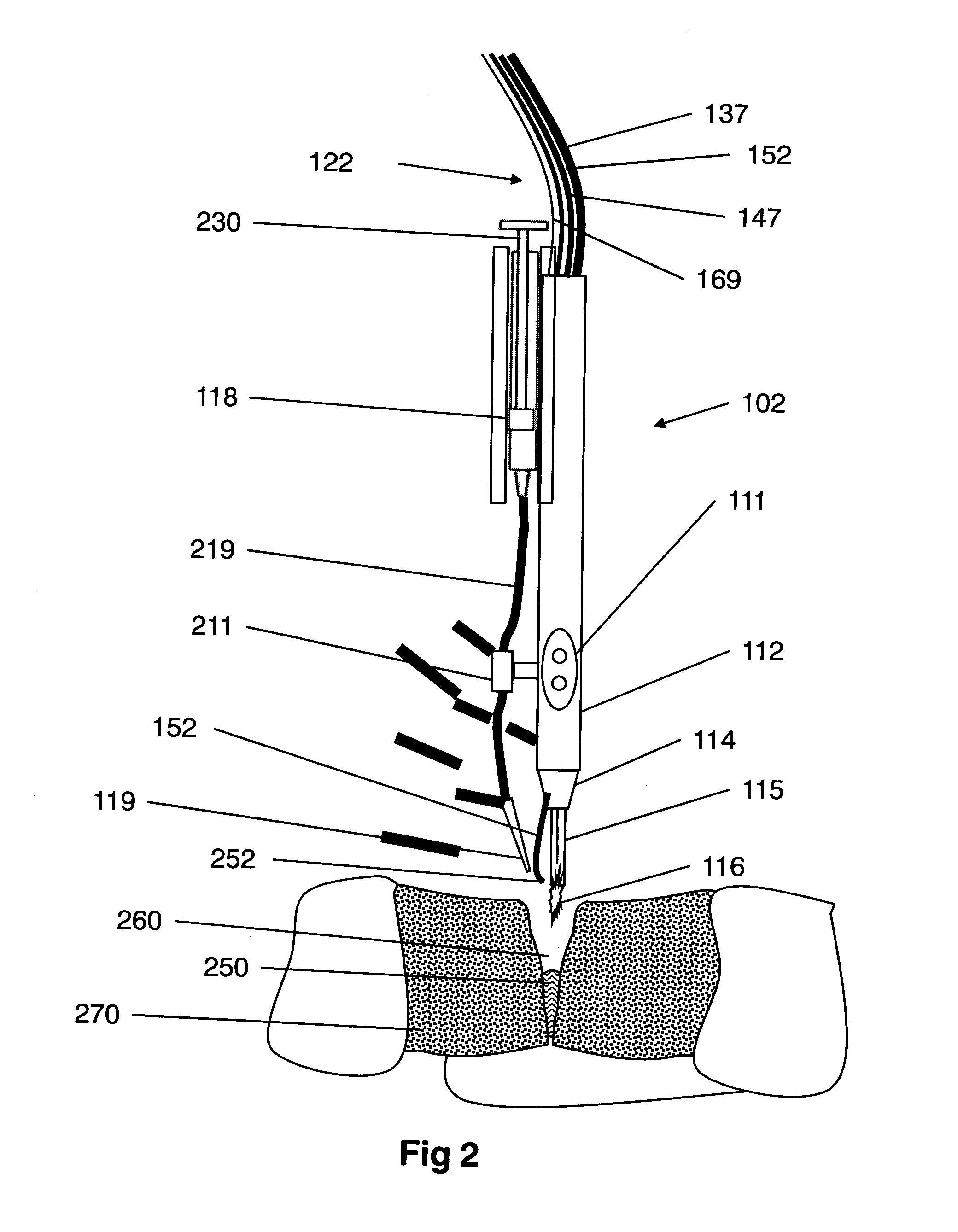
InactiveUS9060750B2Easy to adjustIncreasing RF power/frequencyDiagnosticsSurgical instruments for heatingAlbumin solutionHand held
A compact medical device for tissue welding is provided. The hand-held plasma heads are configured for deep cuts and long cuts. A bio-compatible liquid capable of solidifying in response to application of plasma, such as an albumin solution, is applied to the wound. Plasma created from a gas such as helium is then applied to said bio-compatible liquid to solidify it and seal the wound. An additional polymerizing gas may also be applied. A feedback mechanism may maintain the temperature of said plasma. A wiper fort removal of excess liquid may also be provided.
Owner:IONMED
Multi-electrode apparatus for tissue welding and ablation
An apparatus for delivering energy to tissue, including: an elongate flexible member having a proximal end and a distal end; a sheath disposed over the elongate flexible member; a plurality of resilient members disposed attached to the elongate member and predisposed to assume a first predefined shape, wherein the resilient members are adapted to be housed in a collapsed state within the sheath prior to deployment; and at least one energy delivery device formed on each said resilient member.
Owner:TERUMO KK
Apparatus and method for performing laser-assisted vascular anastomoses using bioglue
Methods and devices for creating vascular anastomoses are disclosed. In a preferred embodiment, a vein is tissue welded to an artery at a desired anastomosis site. A laser is then used to vaporize tissue within the anastomosis site to form an access pathway between the vein and artery. Single-fiber or multi-fiber lasers devices may be used, and are preferably configured to emit the laser light at an angle from the longitudinal axis of the laser device to permit intravascular access to the anastomosis site. The tissue welding may be performed using a mussel or frog-derived bioglue.
Owner:KWON KIHONG
Electrosurgical instrument and method of use
InactiveUS20080045942A1Improve pressure resistanceFacilitate cross-linkingSurgical instruments for heatingCoatingsMicron scalePositive temperature
An electrosurgical medical device and method for creating thermal welds in engaged tissue. In one embodiment, at least one jaw of the instrument defines a tissue engagement plane carrying a variable resistive body of a positive temperature coefficient material that has a selected decreased electrical conductance at each selected increased temperature thereof over a targeted treatment range. The variable resistive body can be engineered to bracket a targeted thermal treatment range, for example about 60° C. to 80° C., at which tissue welding can be accomplished. In one mode of operation, the engagement plane will automatically modulate and spatially localize ohmic heating within the engaged tissue from Rf energy application across micron-scale portions of the engagement surface. In another mode of operation, a variable resistive body will focus conductive heating in a selected portion of the engagement surface.
Owner:SURGRX
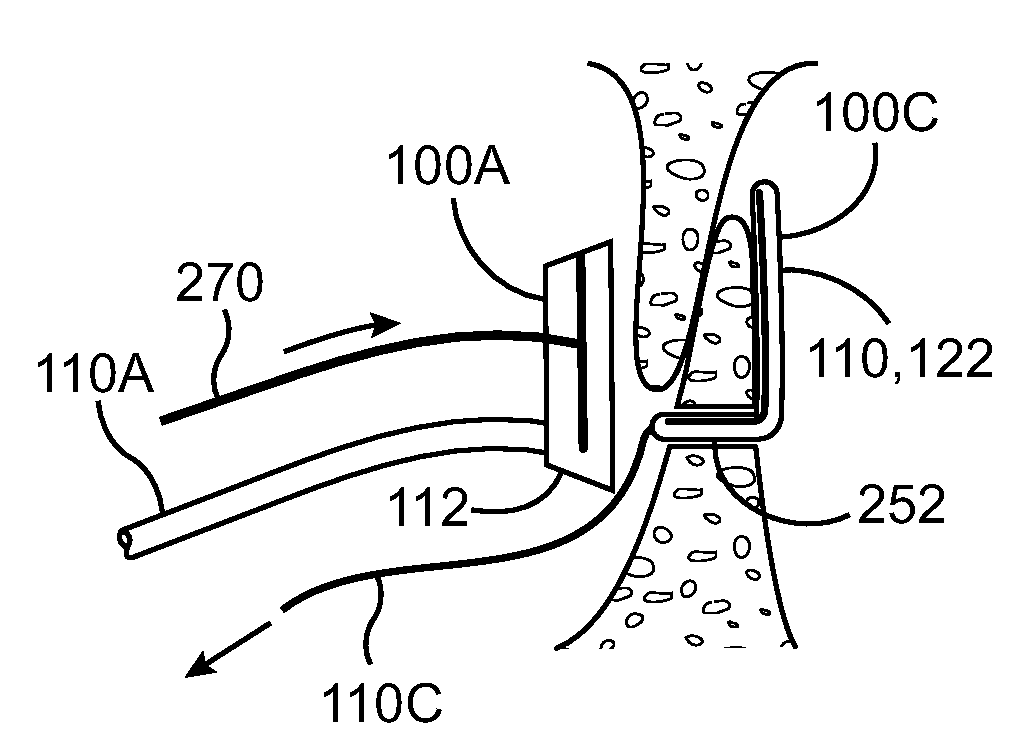
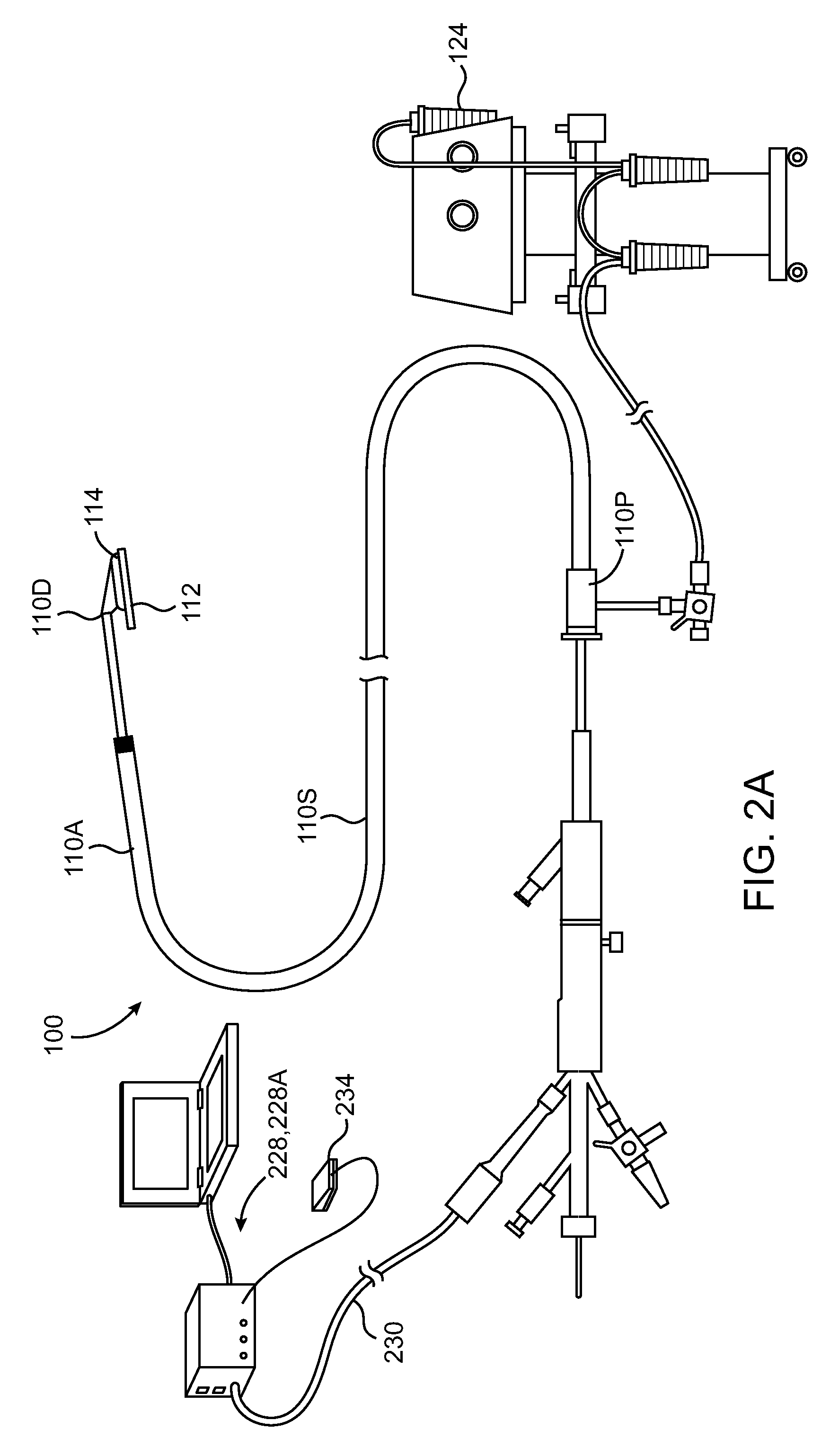
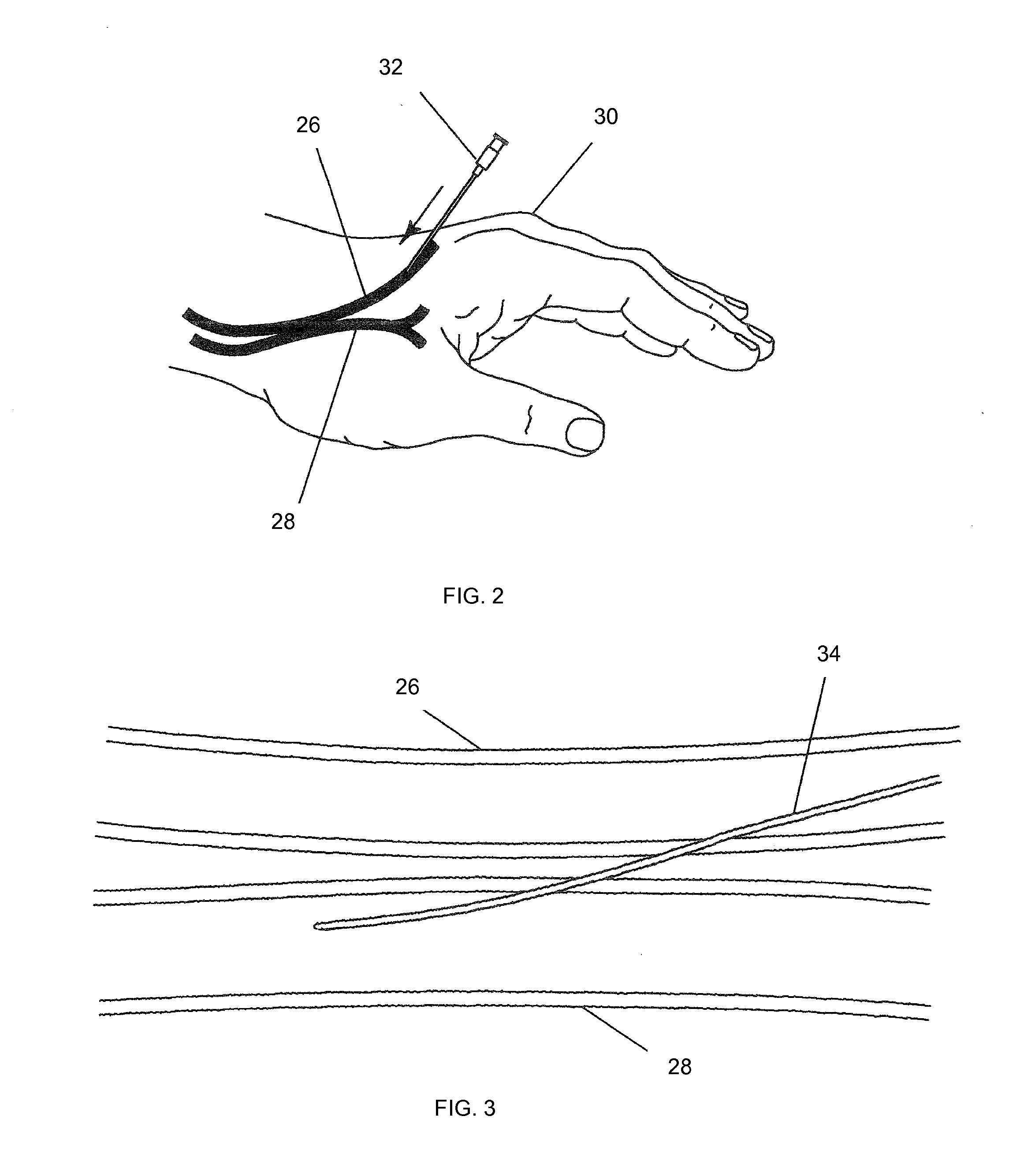
Intravascular arterial to venous anastomosis and tissue welding catheter
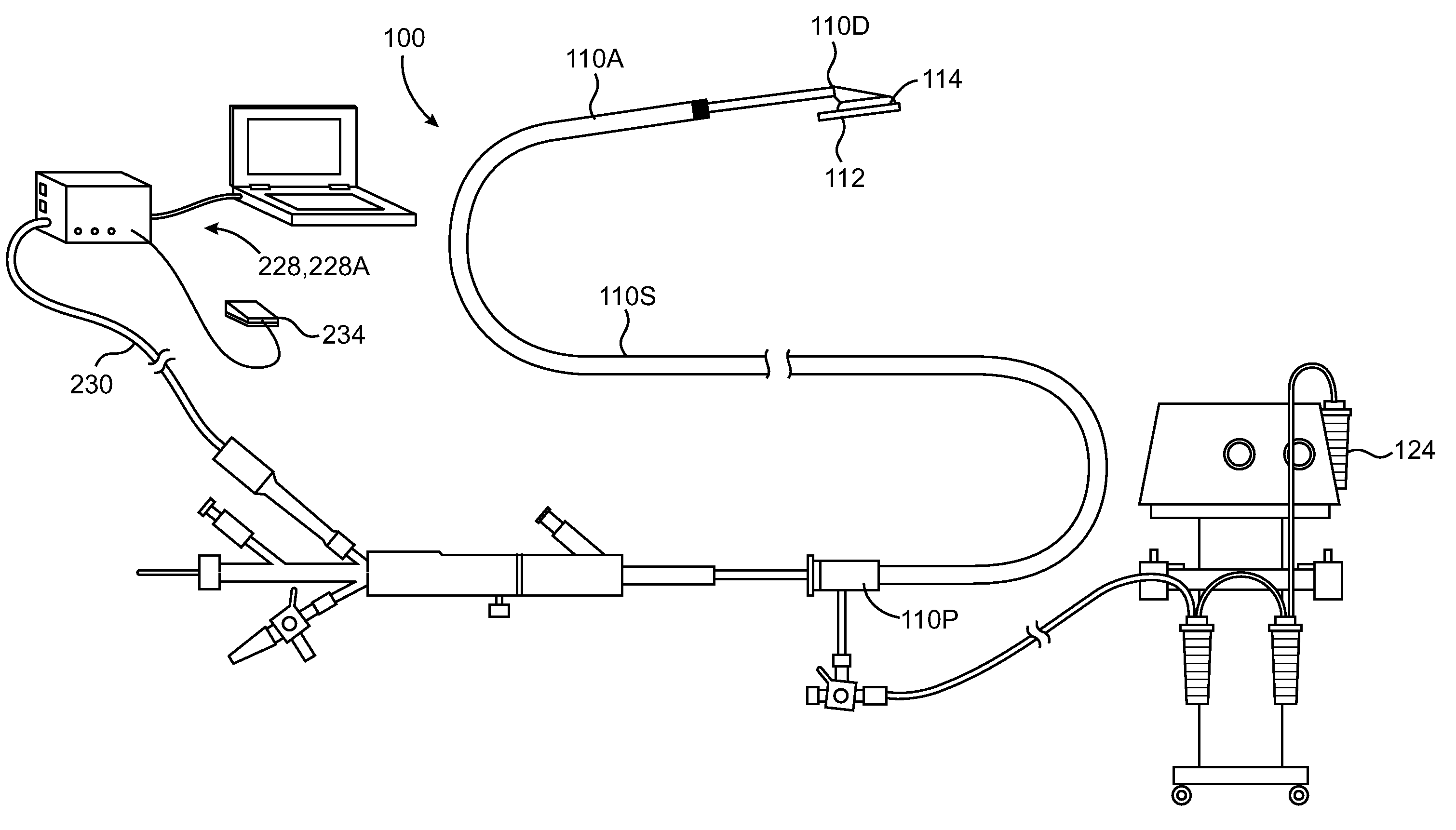
ActiveUS9474562B2Shorten operation timeAdvance easilySurgical instruments for heatingCoatingsProximal pointFistula
A catheter-based device tracks over a guidewire which has been placed from a first blood vessel into a second blood vessel. The distal tip of the catheter is advanced into the second vessel while a proximal member remains in the first vessel. Matching blunt tapered surfaces on each of the distal tip and the proximal member are clamped together, with adjacent walls of each vessel between them, after which a known, controlled pressure is applied between the two surfaces. Heat energy is then applied to the blunt surfaces for approximately 1-30 seconds to weld the walls of the two vessels together. After coaptation of the vessel walls, the heat is increased to then cut through the vessel walls to create a fistula of the desired size.
Owner:AVENU MEDICAL
Ultrasound assisted tissue welding method
The present invention relates to ultrasound assisted tissue welding, more particularly, to a method and device utilizing ultrasound energy for effective closure and sealing of surgical incisions or other wounds. The device of the present invention comprises an ultrasound generator, an ultrasound transducer, a transducer tip at the distal end of the ultrasound transducer, and a radiation surface. A web such as gauze is placed over the incision. In an embodiment, the device may be used to bring the edges of the tissue to be sealed together as the device applies energy to the tissues. Ultrasonic waves emanating from the radiation surface pass through the web and seal the incision creating a continuous seam. The device may be used with or without additional adhesive materials or therapeutic agents.
Owner:BABAEV EILAZ
Solder formulation and use in tissue welding
PendingUS20110172704A1High bonding strengthSurgical adhesivesPeptide/protein ingredientsTissue repairUterus
Supersaturated gel formulations including a solution of chitosan, albumin, and a laser specific chromophore. Laser tissue welding methods using the gel formulations of the present invention are also described. In the methods, the gel formulation of the present invention is provided to a site for tissue repair and the laser specific chromophore within the gel is excited with a laser in order to fuse tissue by inducing protein denaturation. The gel formulations and laser tissue welding methods may be used, for example, to enable skull base repairs, aerodigestive endoscopic repairs, endoscopic endonasal surgical repairs, iatrogenic esophageal perforation repairs, laparoscopic abdominal surgical repairs, lung repairs, colon repairs, anastomosis of vessels, urologic / gynecologic endoscopic pelvic repairs, orofacial surgical repairs, dental replacement, skin closure, uterine closure and repairs after fibroidectomies and bladder surgery.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
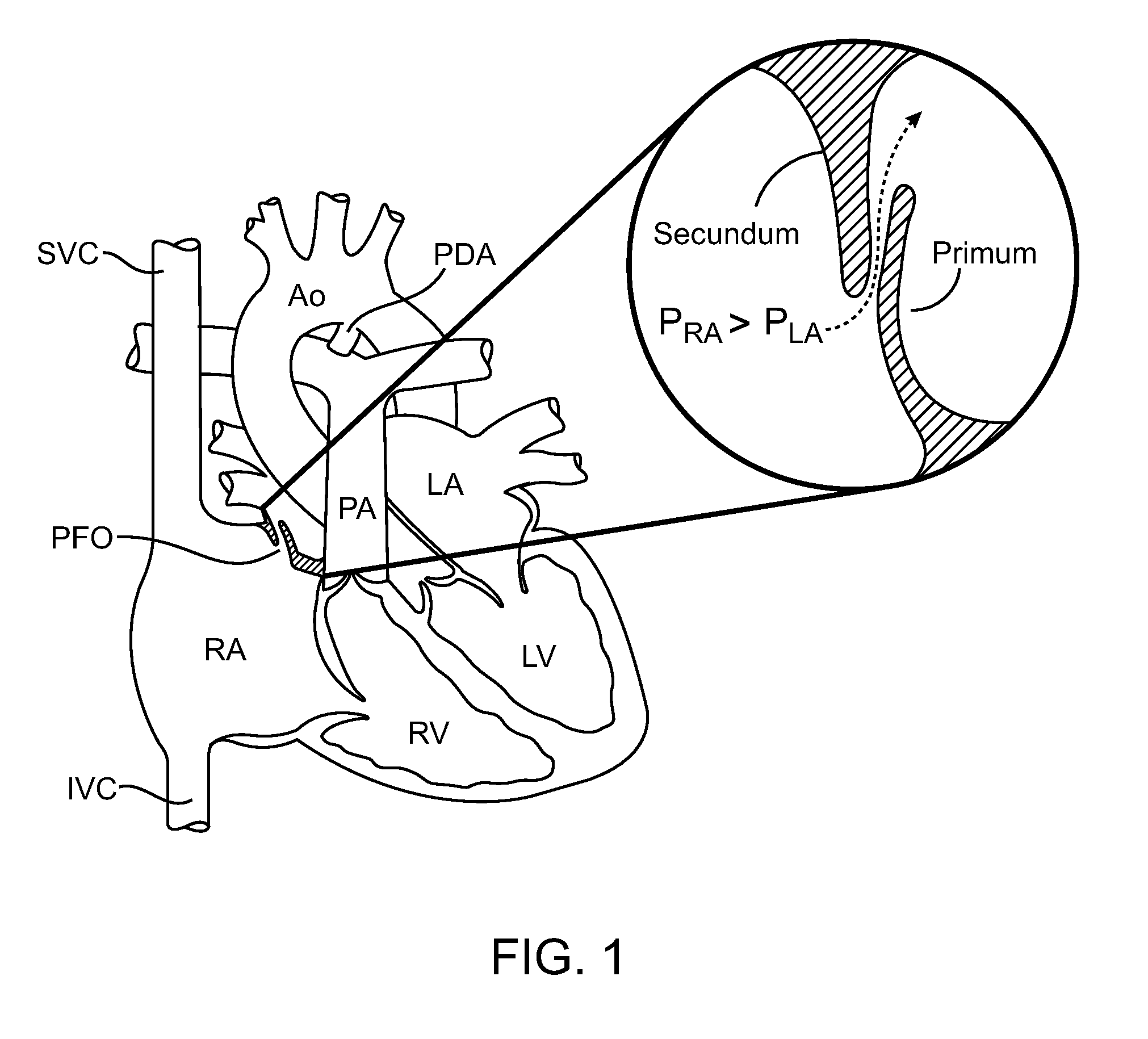
Systems and methods for percutaneous intravascular access for arteriovenous fistula
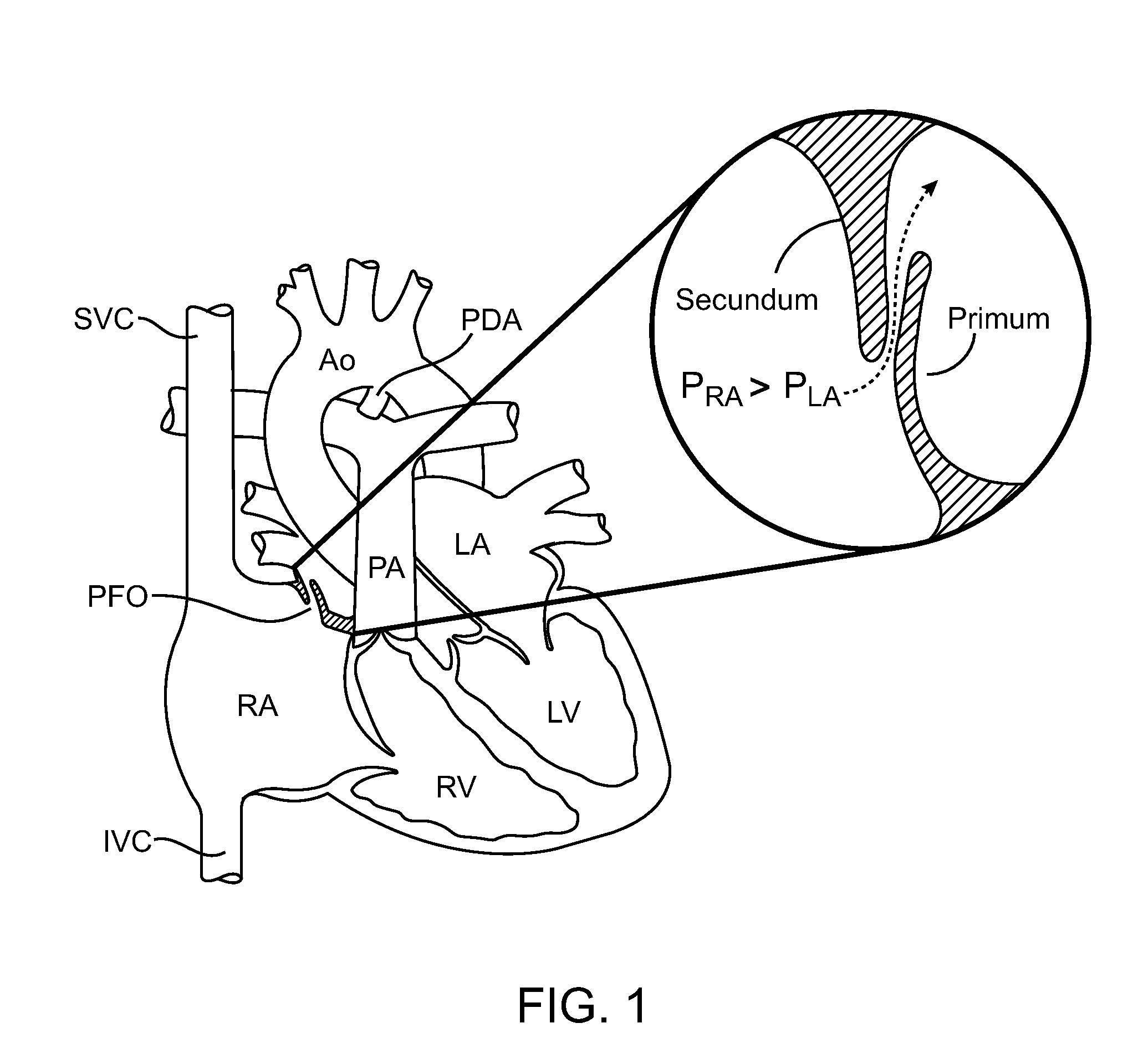
A device for extending, elongating, or repairing a previously created arteriovenous fistula between a first blood vessel and an adjacent second blood vessel includes a main body having a primary lumen and an articulating jaw member disposed at the distal end of the main body. The jaw member is configured with two elements to allow rotation of one element about a pivot point to grasp tissue while being rotated. The jaw member is also configured to allow thermal energy delivery to one or both elements of the jaw member that allow tissue welding and cutting with DC, RF, Laser or Ultrasonic energy. A second lumen located within one element of the jaw member is configured to allow advancement over a guidewire into the second vessel while the other element of the jaw member remains within the first blood vessel at the position where the arteriovenous fistula, or aperture, exists between the first and second blood vessel.
Owner:AVENU MEDICAL
Ultrasound assisted tissue welding device
The present invention relates to ultrasound assisted tissue welding, more particularly, to a method and device utilizing ultrasound energy for effective closure and sealing of surgical incisions or other wounds. The device of the present invention comprises an ultrasound generator, an ultrasound transducer, a transducer tip at the distal end of the ultrasound transducer, and a radiation surface. A web such as gauze is placed over the incision. In an embodiment, the device may be used to bring the edges of the tissue to be sealed together as the device applies energy to the tissues. Ultrasonic waves emanating from the radiation surface pass through the web and seal the incision creating a continuous seam. The device may be used with or without additional adhesive materials or therapeutic agents.
Owner:BABAEV EILAZ
Automated manufacturing device and method for biomaterial fusion
An apparatus for making a bioprosthetic stent graft is disclosed, the stent having a stent frame and a biomaterial sheath suturelessly bonded to the stent frame. An automated energy irradiator guidance system is disclosed which reduces the potential for human error and improves the consistency and repeatability of tissue welding techniques. The system includes a mapper, a patternizer, an energy director and can additionally include an energy regulator. An interface is included, allowing pattern creation, selection and editing by a user. The system further provides control of energy irradiator parameters for use in tissue welding.
Owner:PROVIDENCE HEALTH SYST OREGON +1
Tissue bonding system and method for controlling a tissue site during anastomosis
A method and system for performing anastomosis uses an anvil to control and support a tissue site during an anastomosis procedure involving tissue bonding techniques such as tissue welding and adhesive tissue bonding. The anvil is particularly useful for supporting a wall of a coronary artery during attachment of a graft vessel in a coronary artery bypass graft procedure. The anvil is inserted into a pressurized or unpressurized target vessel and is pulled against an inner wall of the target vessel causing tenting of the thin tissue of the vessel wall. A graft vessel is then advanced to the anastomosis site and an end of the graft vessel is positioned adjacent an exterior of the target vessel. When tissue welding is used, a graft vessel fixture is positioned over the tissue surfaces to be welded in order to clamp the graft and target vessel tissue together. The tissue contacting surfaces of the anvil and / or graft vessel fixture are provided with one or more energy applying surfaces. Energy in the form of RF power, laser energy or ultrasonic energy is then applied to the compressed graft and target vessel tissue to weld the vessels together. When adhesive bonding is used, the adhesive may be applied to mating surfaces of the graft and / or target vessels either before or after the vessels are brought into contact. After tissue bonding is complete, an incision is formed in the wall of the target vessel to allow blood flow between the target vessel and the graft vessel. The incision may be made with an electro-cautery cutting device.
Owner:AESCULAP AG +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com