Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
188 results about "Arteriovenous fistula" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
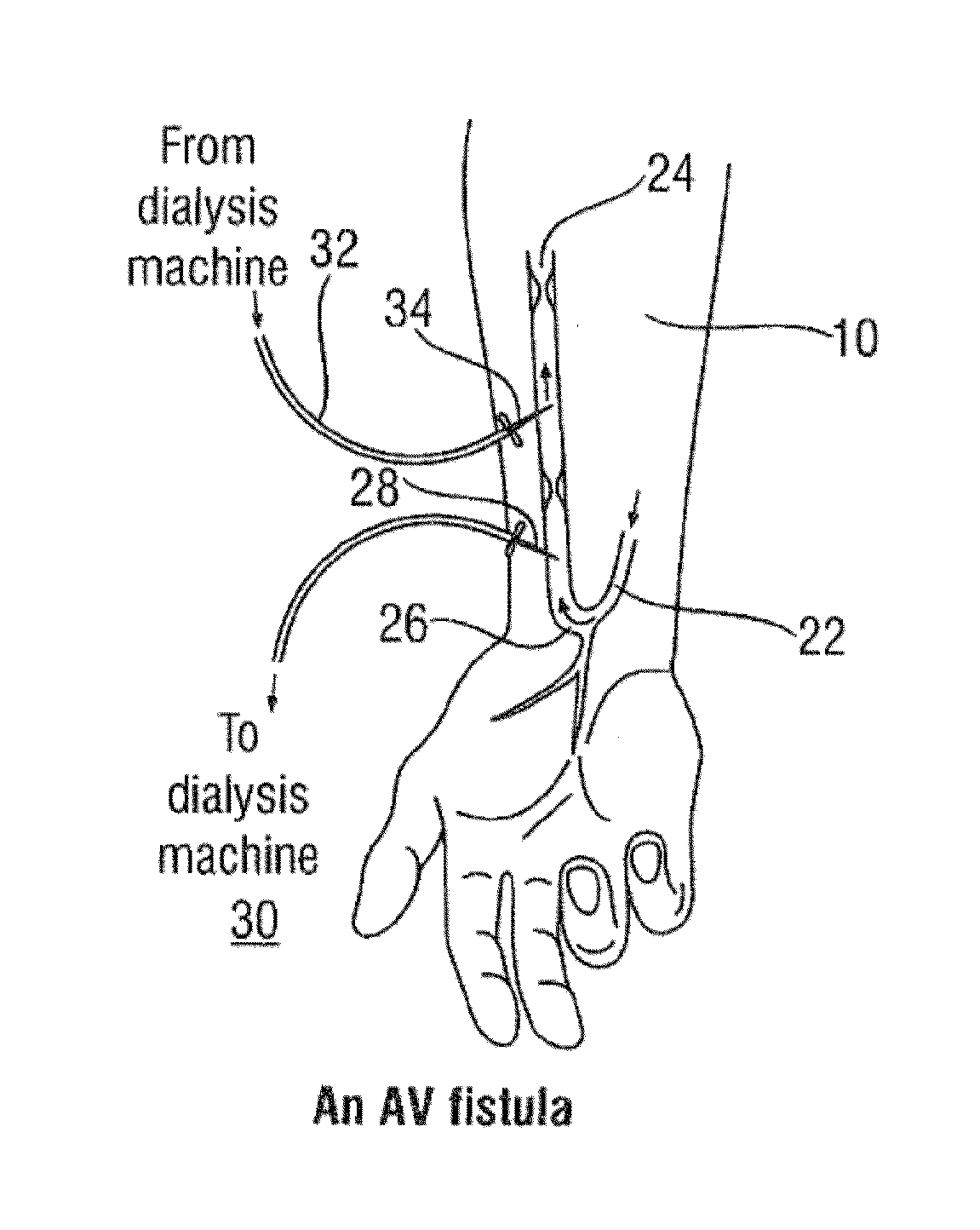
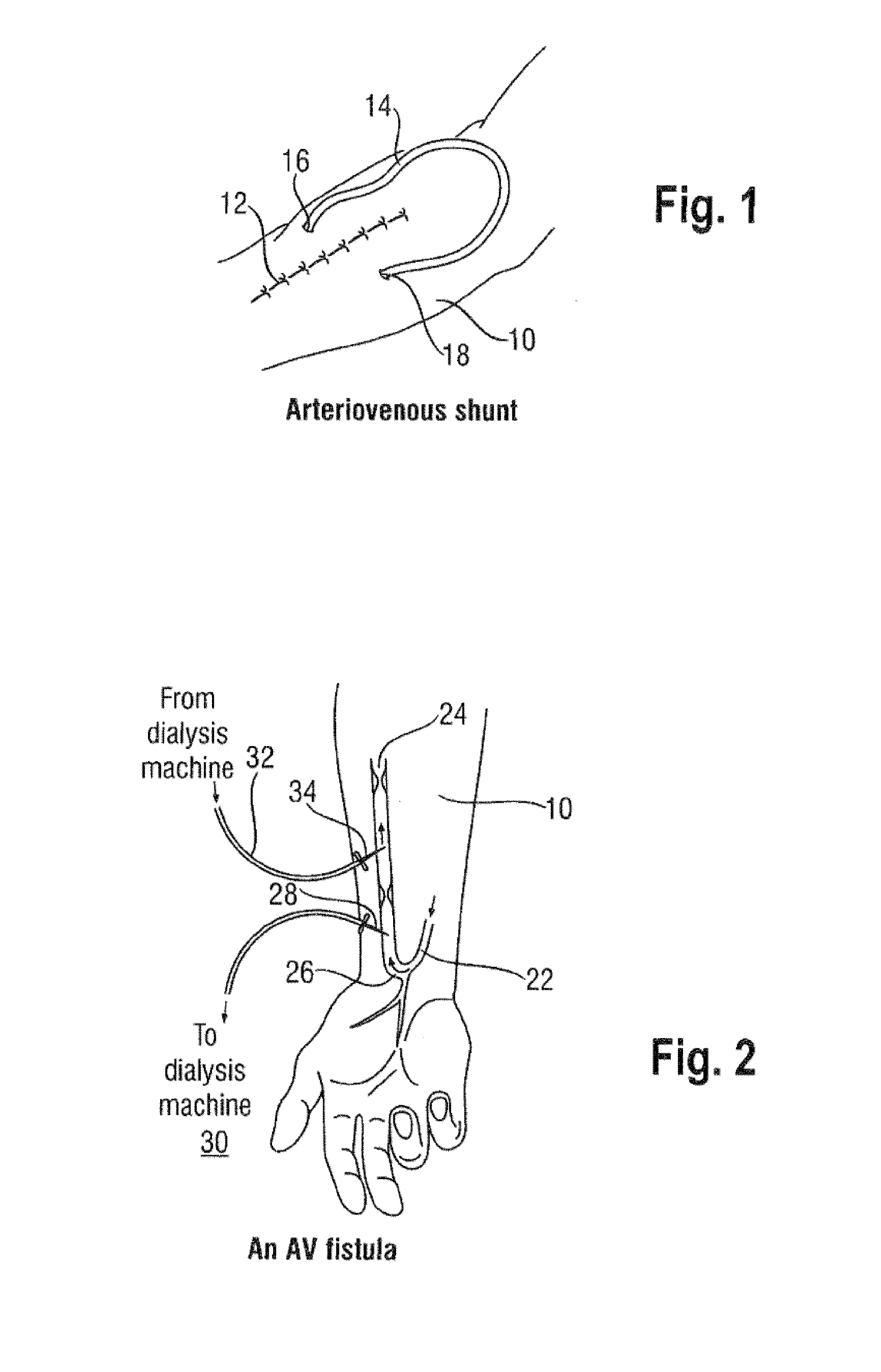
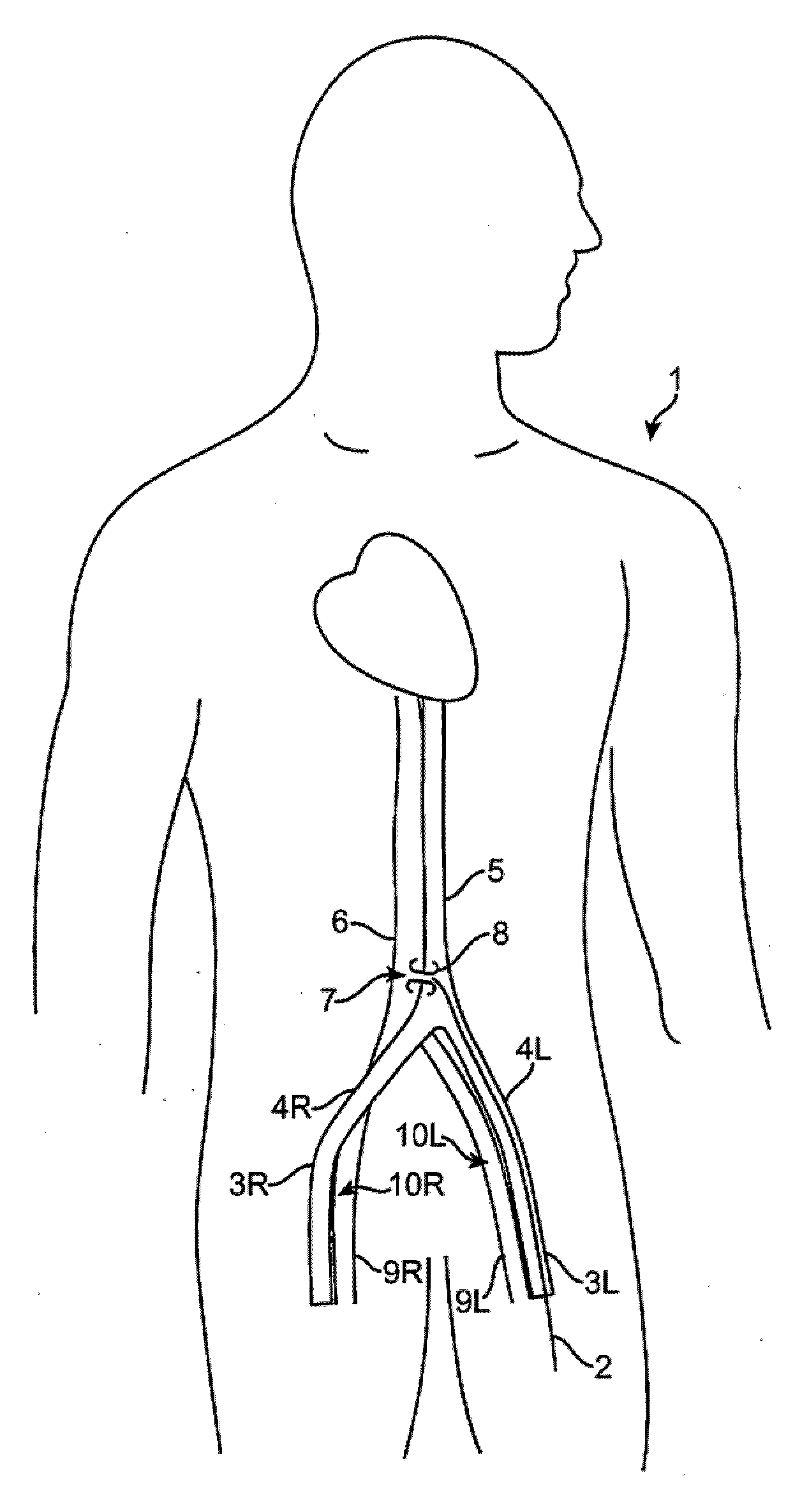
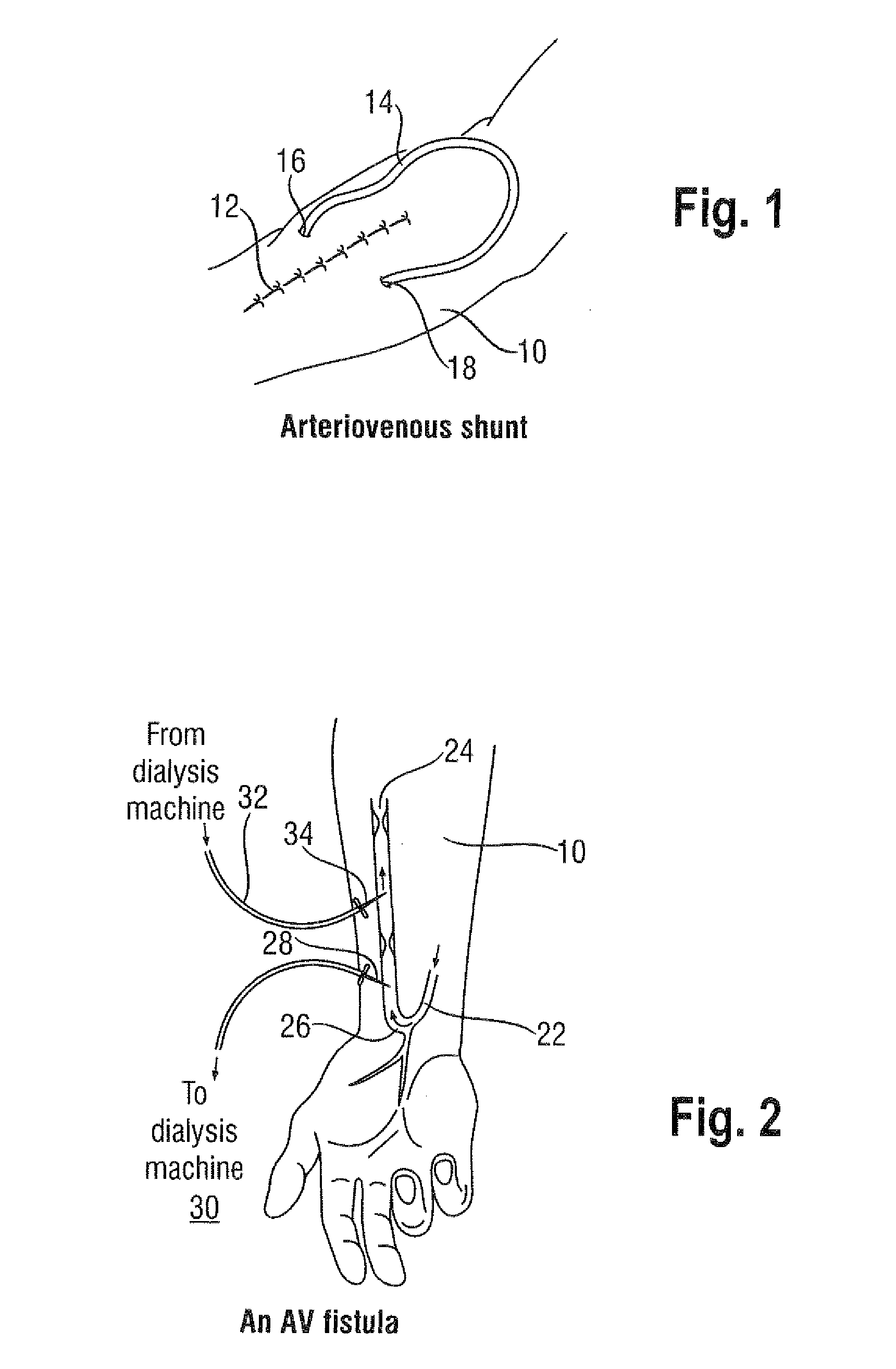
An abnormality in communication between an artery and a vein.
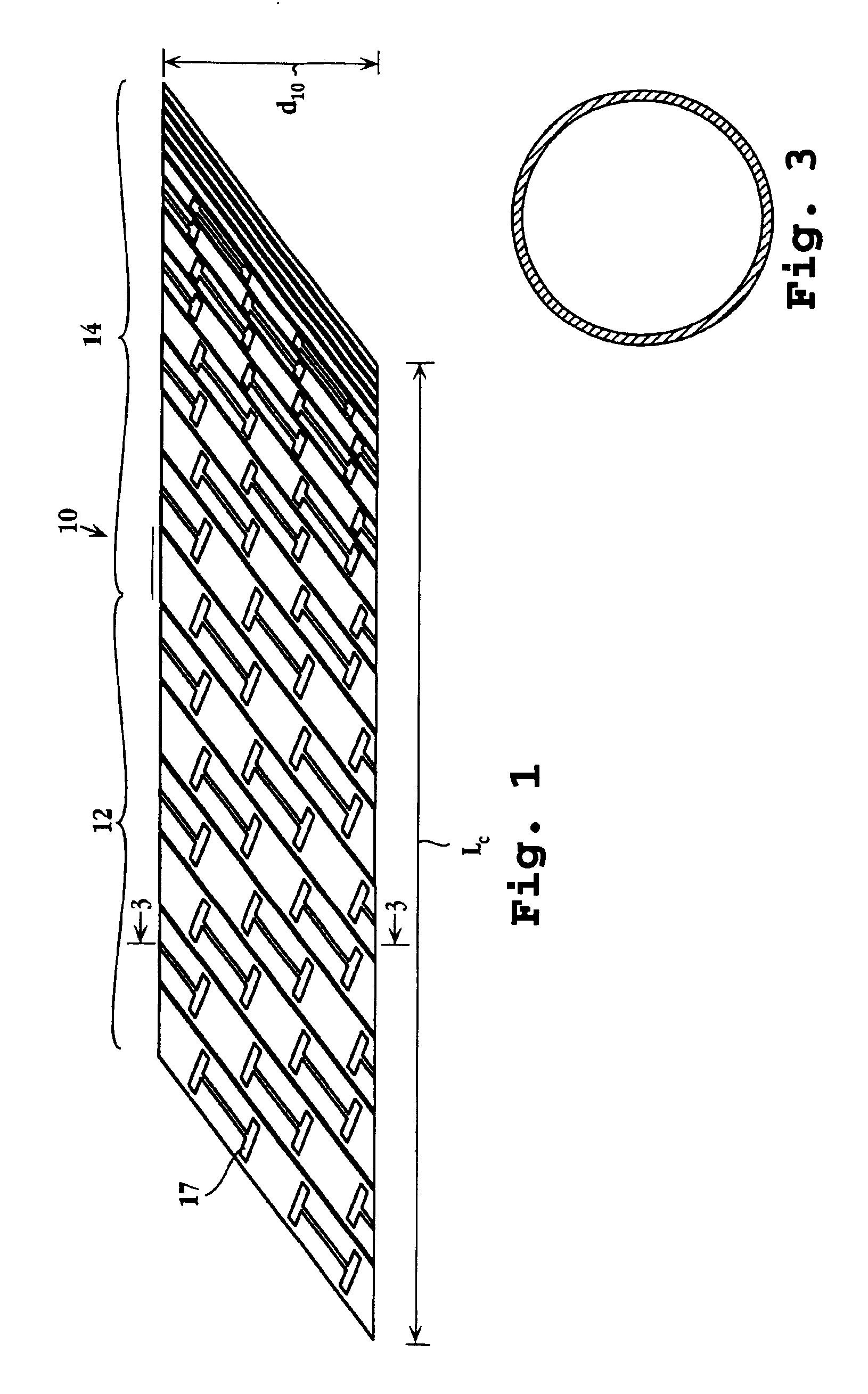
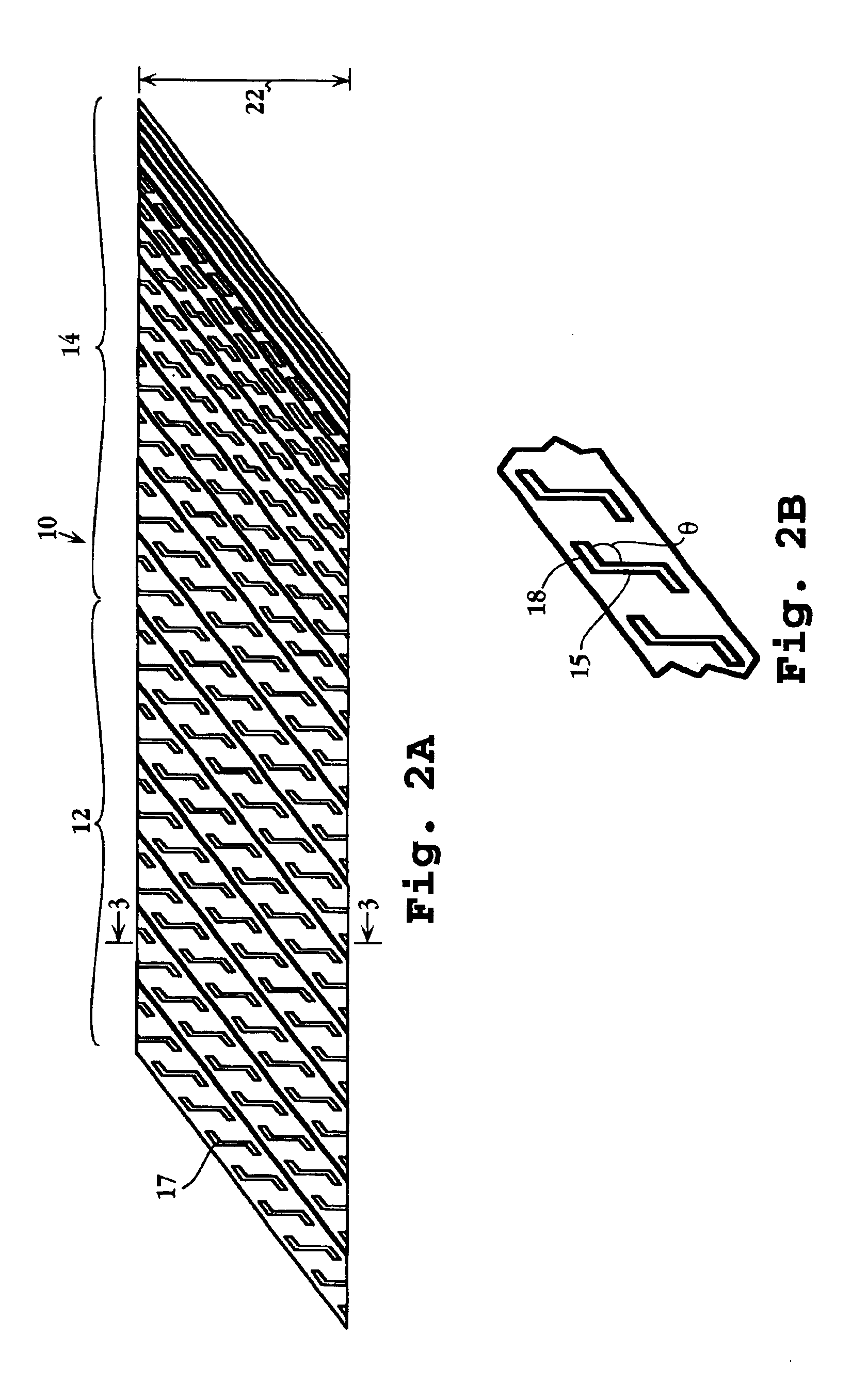
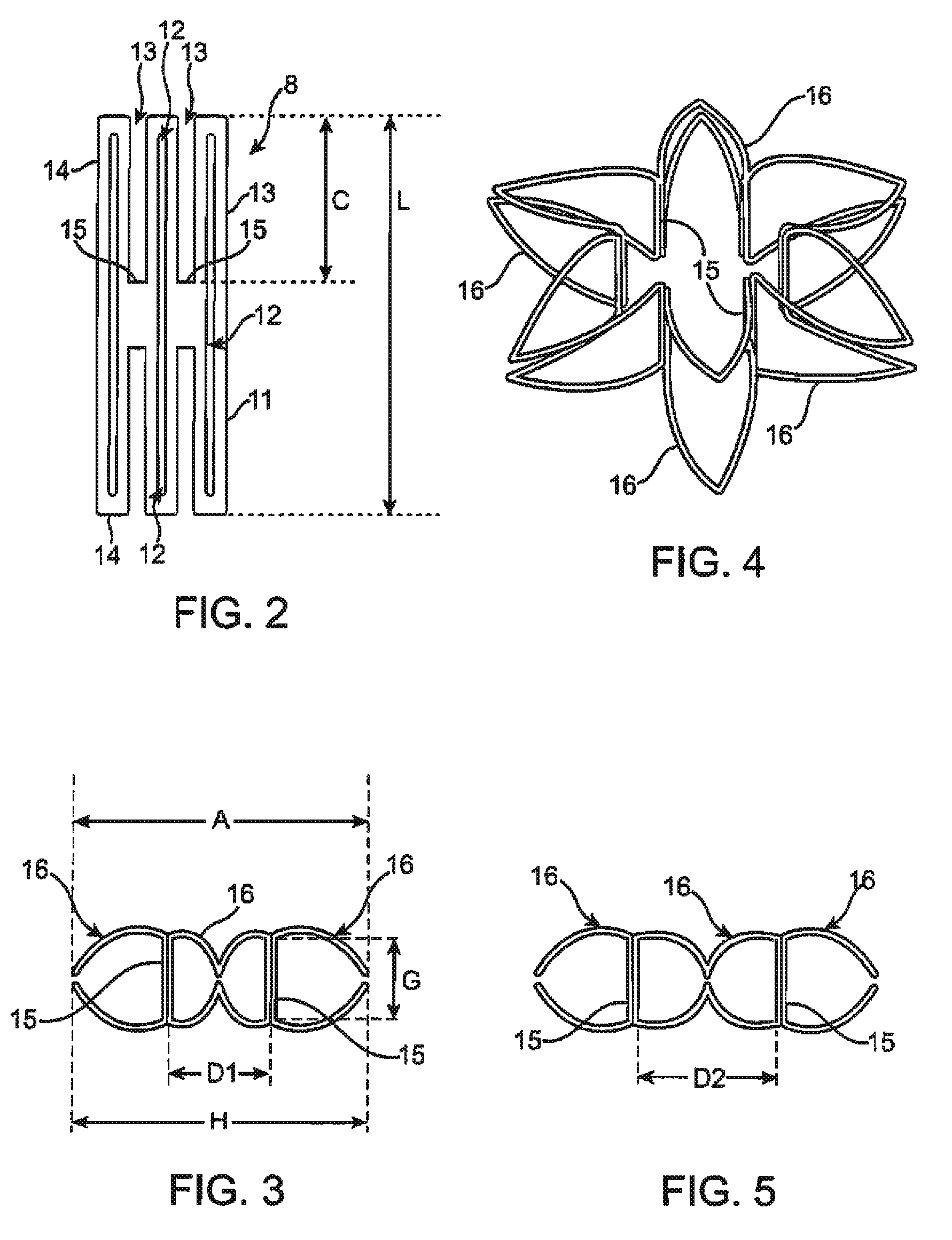
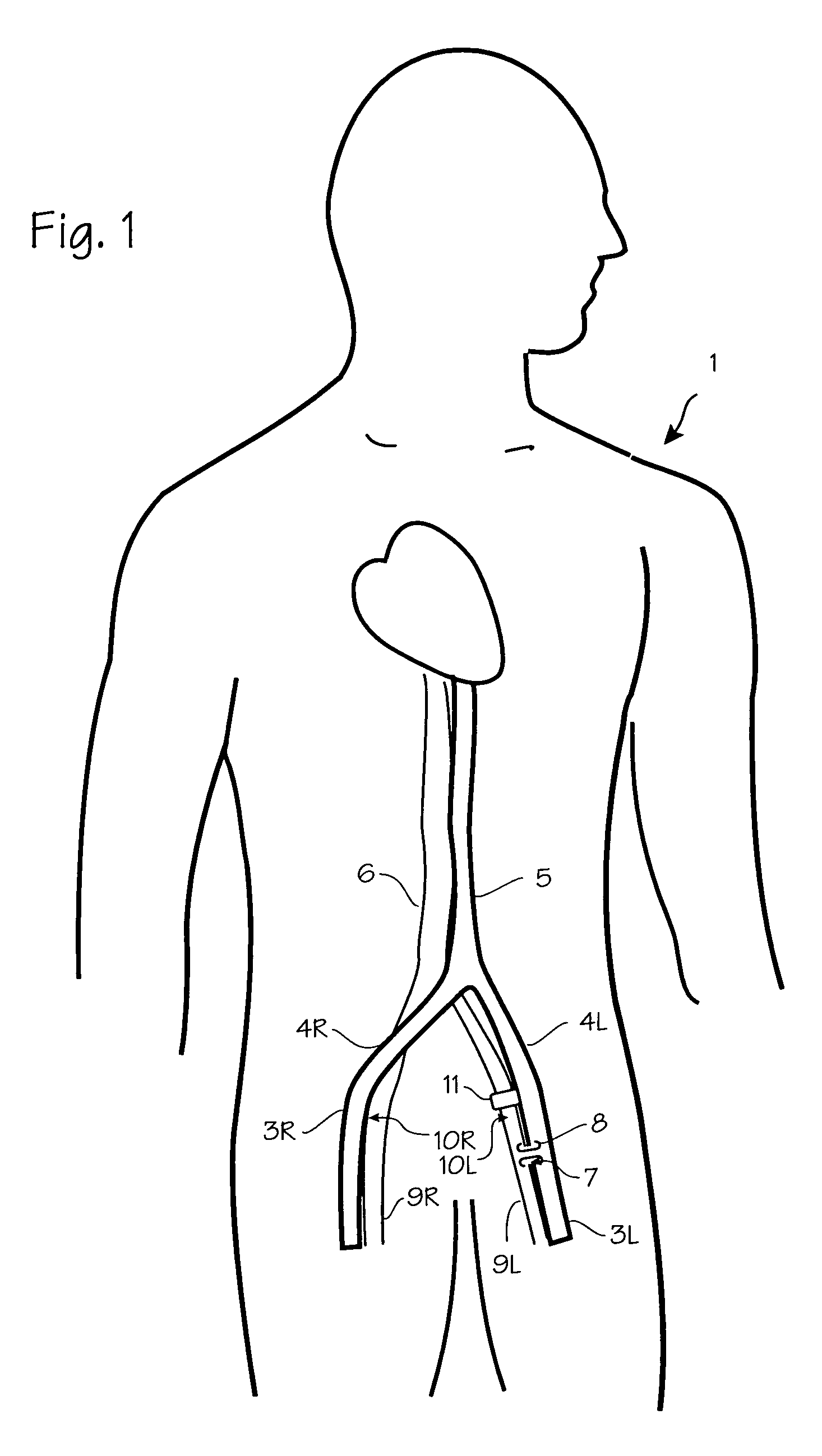
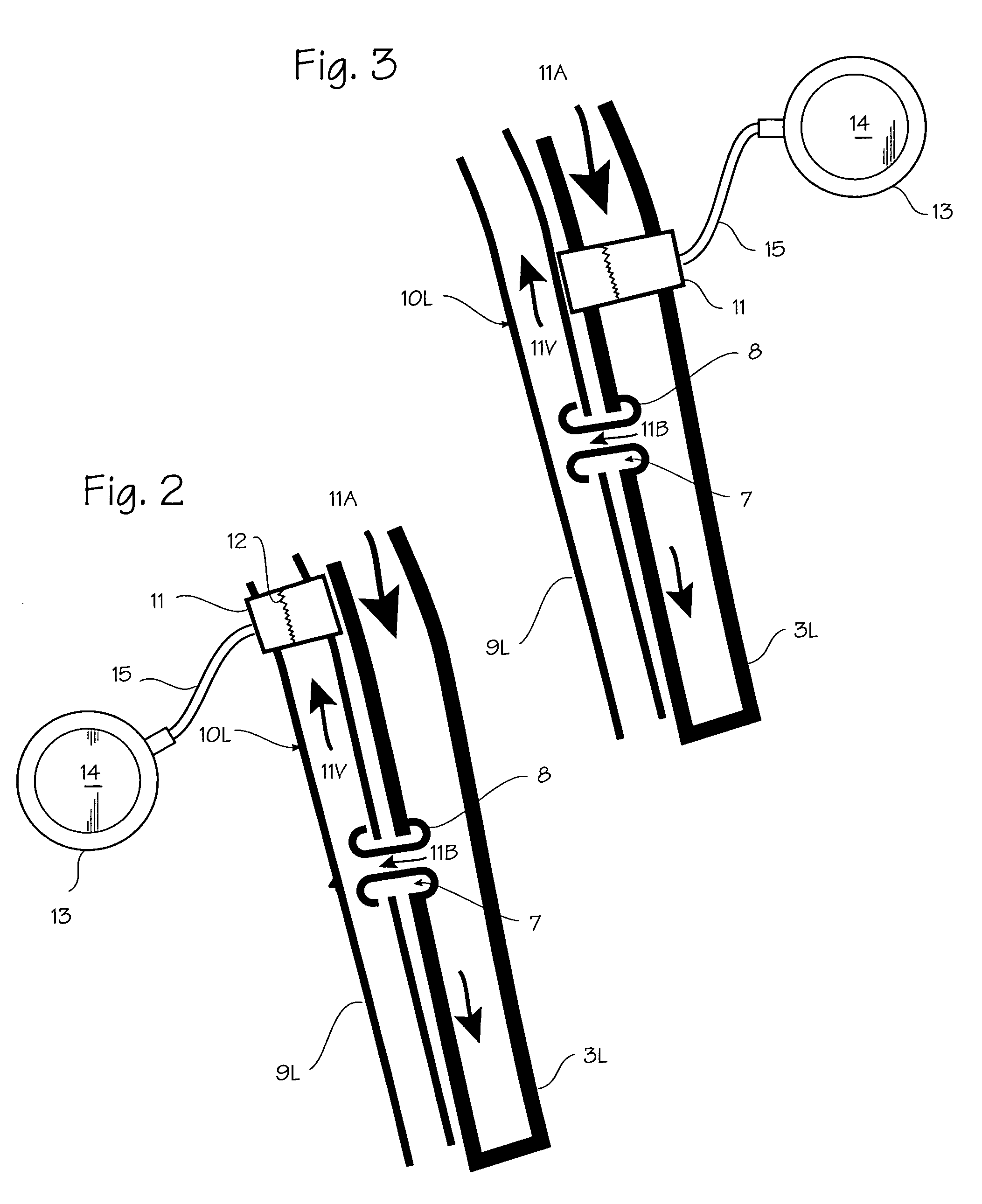
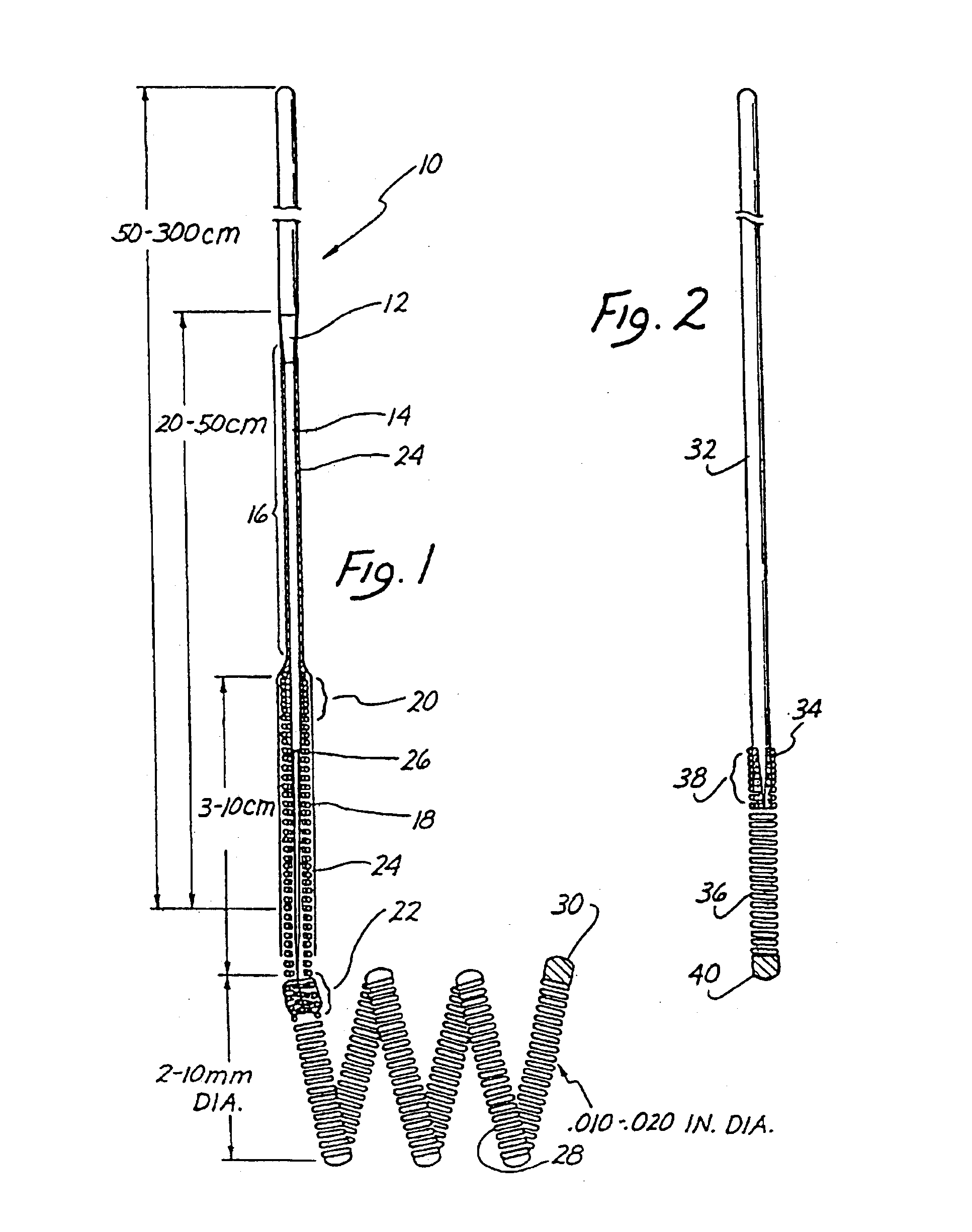
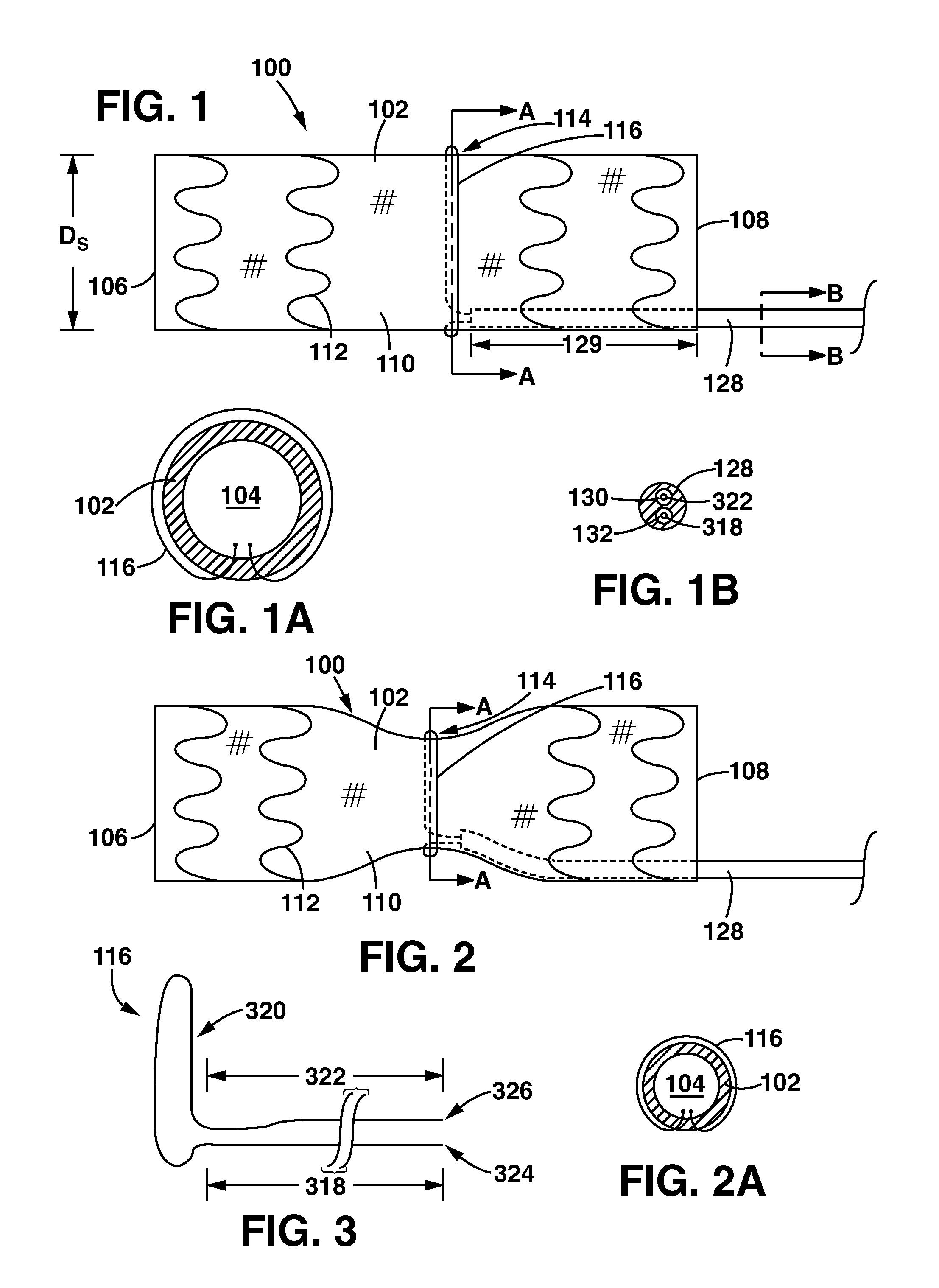
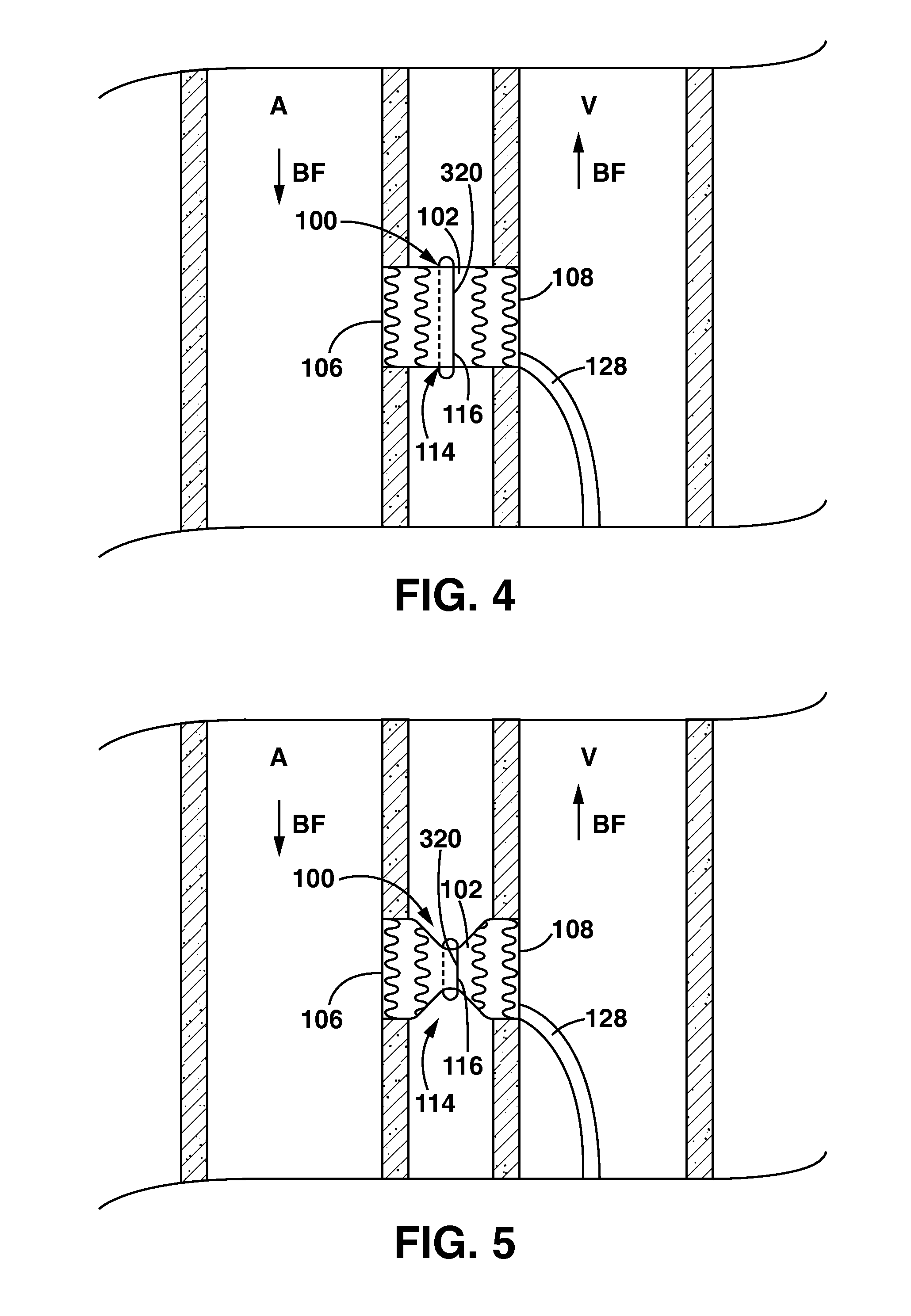
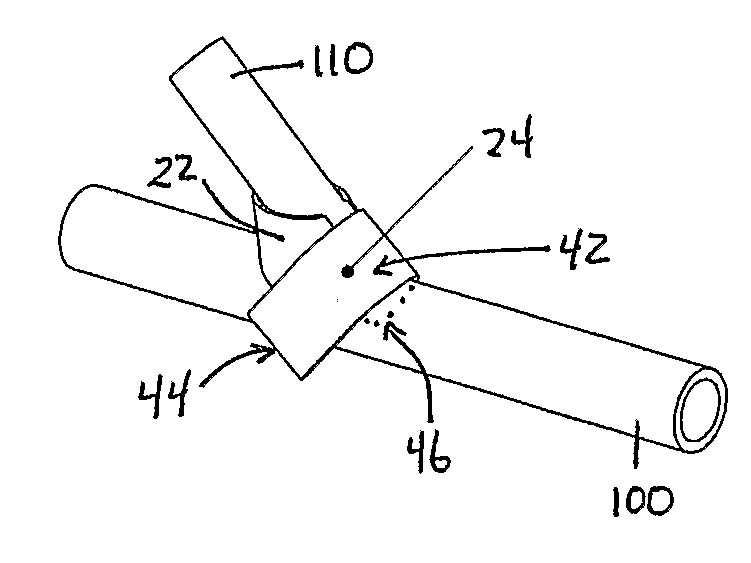
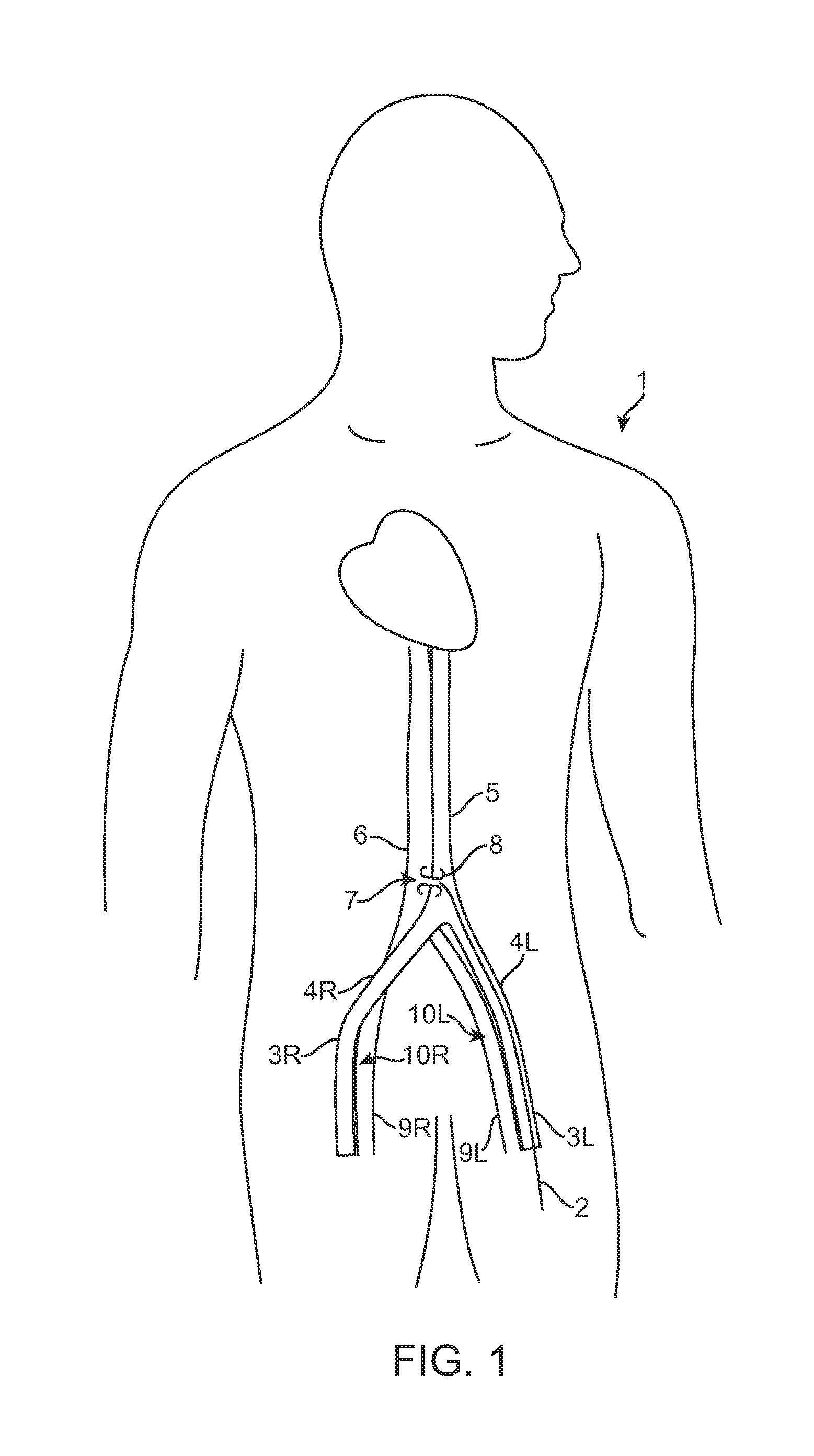
Catheter apparatus and methodology for generating a fistula on-demand between closely associated blood vessels at a pre-chosen anatomic site in-vivo
The present invention provides catheter apparatus and catheterization methodology for generating an arteriovenous fistula or a veno-venous fistula on-demand between closely associated blood vessels and at a chosen anatomic site in-vivo. The catheter apparatus is preferably employed in pairs, each catheter of the pair being suitable for percutaneous introduction into and extension through a blood vessel. The catheterization methodology employs the catheter apparatus preferably in conjunction with conventional radiological techniques in order to place, verify, and confirm a proper alignment, orientation, and positioning for the catheters in-vivo prior to activating the perforation means for generating a fistula. The invention permits the generation of arteriovenous fistulae and veno-venous fistulae anatomically anywhere in the vascular system of a patient; nevertheless, the invention is most desirably employed in the peripheral vascular system as exists in the extremities of the body to aid in the treatment of the patient under a variety of different medical ailments and pathologies.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Method for treating neurovascular aneurysms
InactiveUS6860899B1Reduce expansionIncrease the angleStentsOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsInsertion stentProsthesis
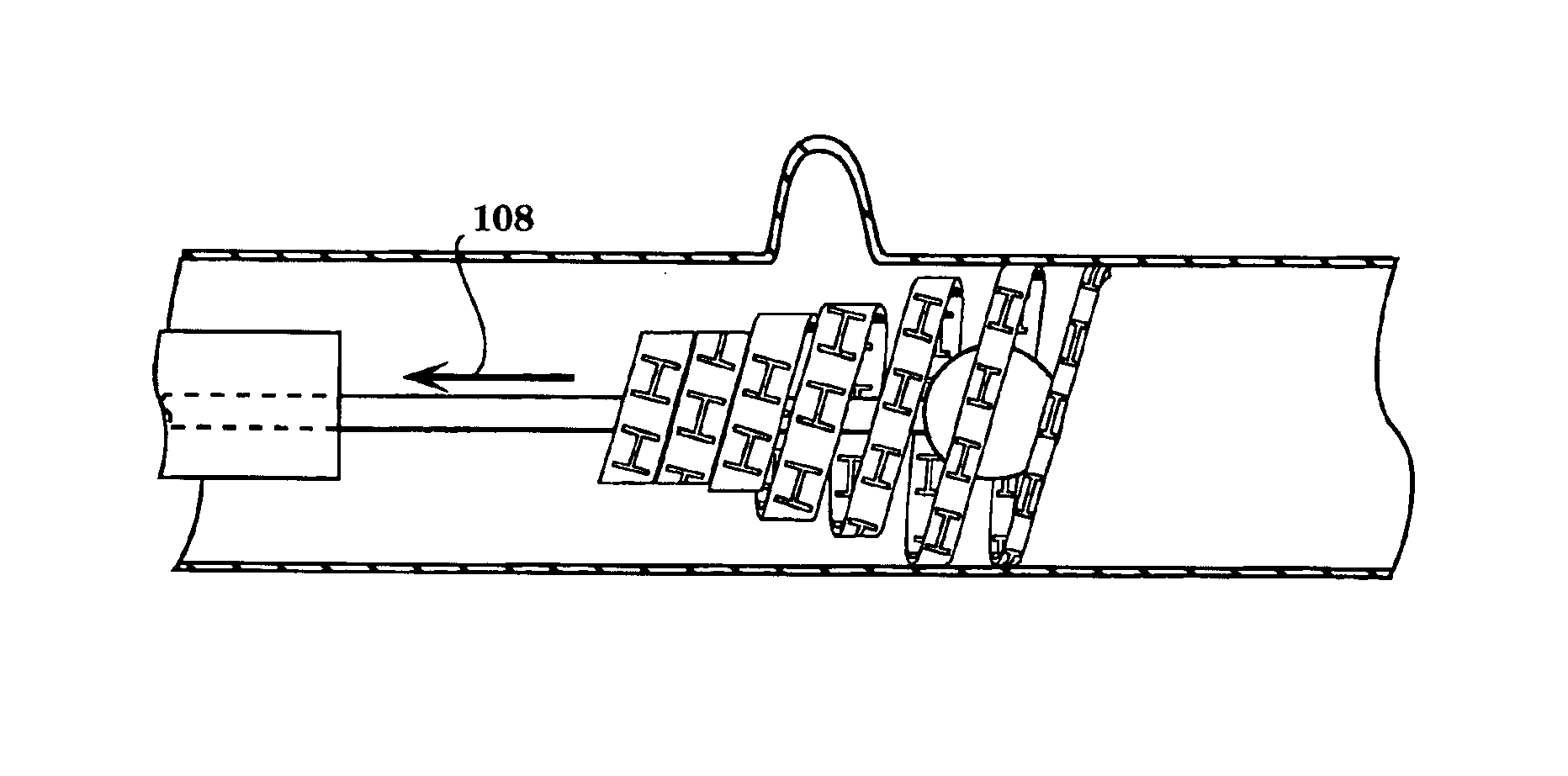
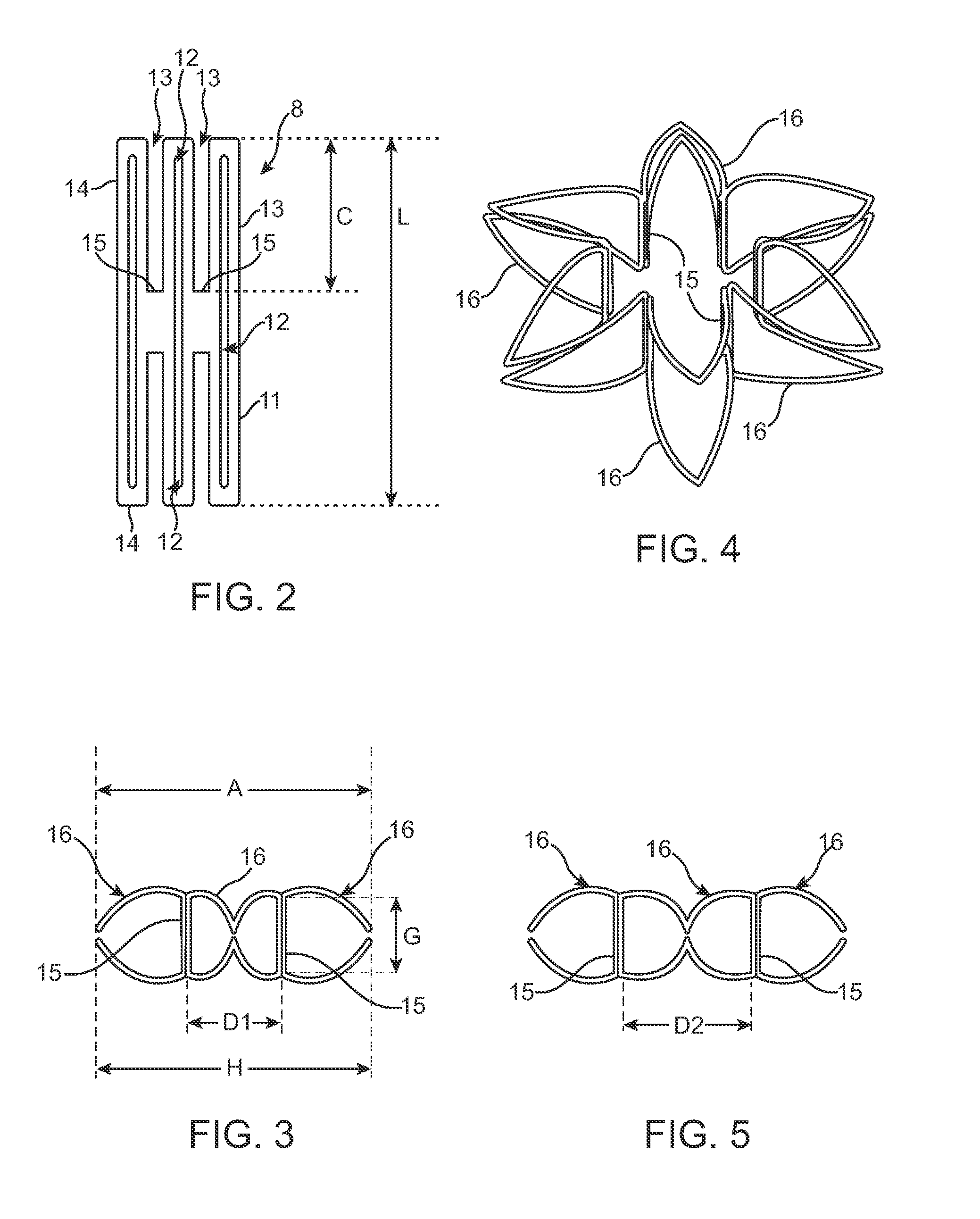
A graftless prosthetic stent for treatment of vascular lesions such as aneurysms and arterio-venous fistulas, especially in neurovascular vessels, comprises a continuous helical ribbon formed of a shape-retaining metal having a transition temperature at which the stent expands from its contracted condition to a radially expanded condition, the stent remaining substantially cylindrical in its contracted and expanded conditions. The helical windings have variable width, thickness, number or size of openings, or combinations of these features, which affect the stiffness, rate of expansion at the transition temperature, and the area of vessel wall covered by the stent. A catheter device which includes the stent, and a method of treatment using the stent are also provided.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC +1
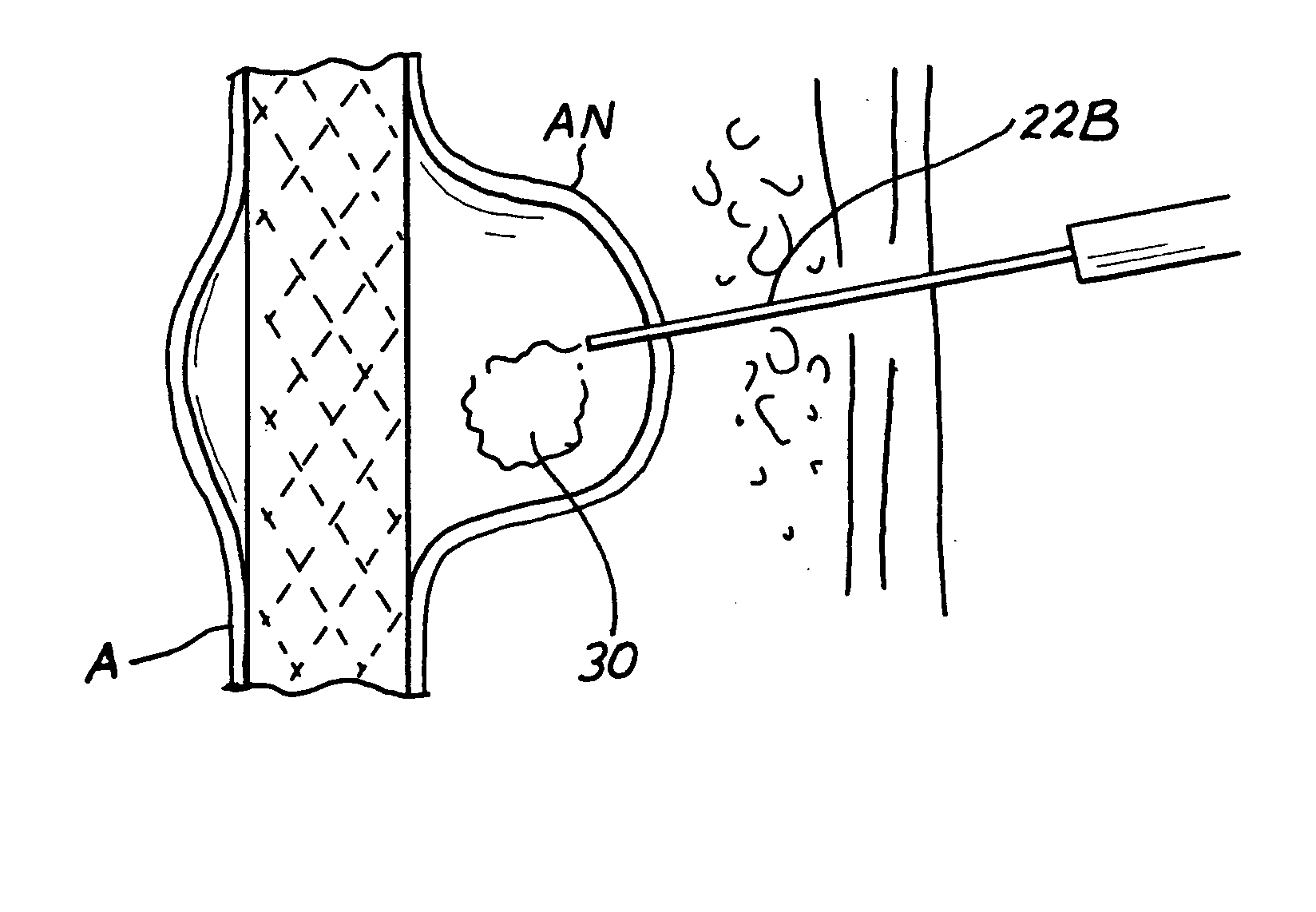
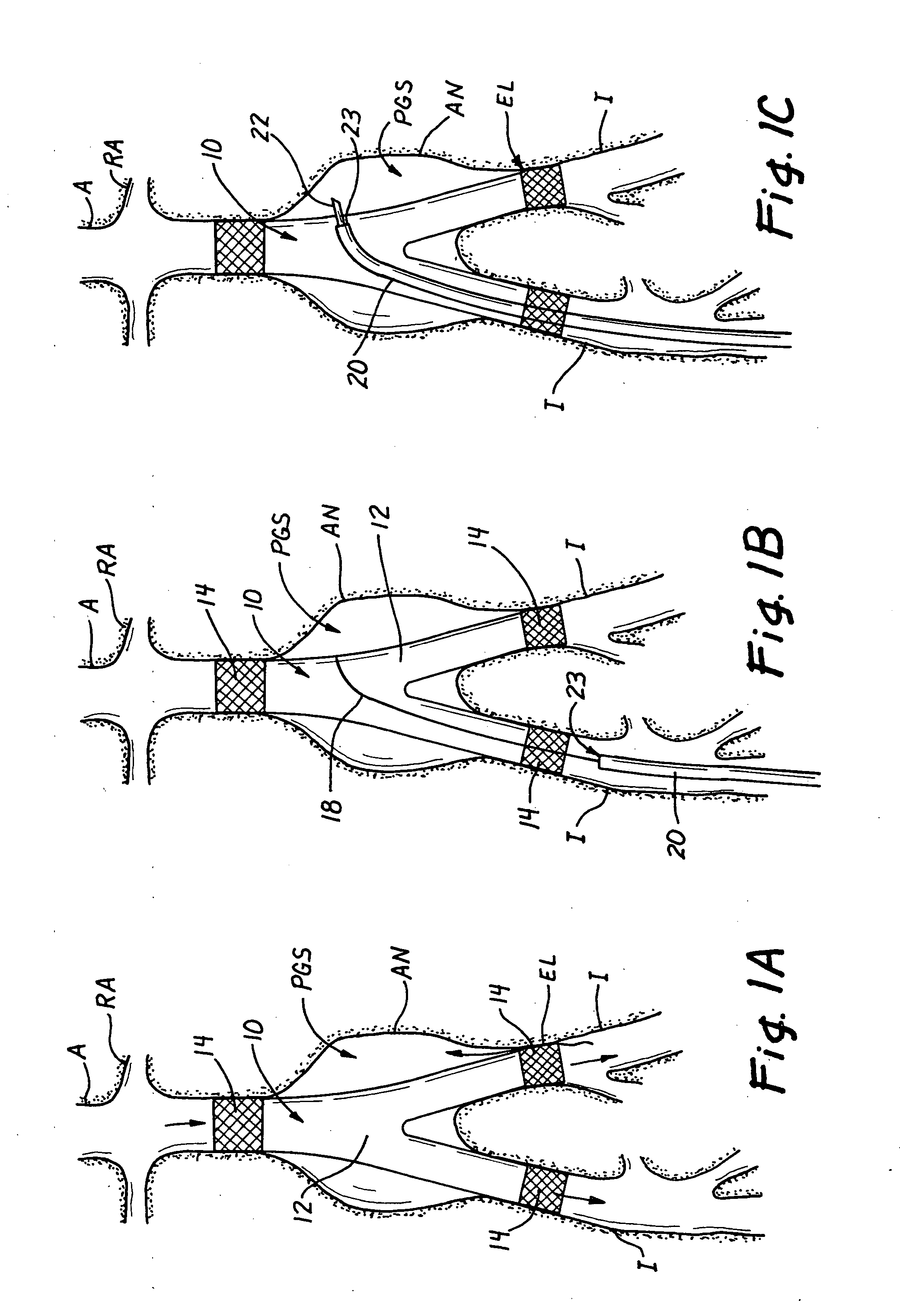
Device and method for establishing an artificial arterio-venous fistula
ActiveUS20100268316A1Avoid undesired alterationIncrease blood flowIntravenous devicesBlood vesselsObstructive Pulmonary DiseasesAnesthesia
A shunt rivet for implantation between a first body space and a second body space in a patient, such as to treat chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Methods, materials and apparatus for deterring or preventing endoleaks following endovascular graft implantation
Methods and apparatus for treating or preventing endoleaks after an endovascular graft (e.g., a stent, tubular graft, stent-graft, coated stent, covered stent, intravascular flow modifier or other endovascular implant that affects, limits or prevents blood flow into a vascular defect such as an aneurysm, arterio-venous fistula, arterio-venous malformation, vessel wall perforation, etc.) has been implanted in the vasculature of a human or veterinary patient. An expansile polymeric material, such as a swellable polymer (e.g., a hydrogel), a flexible or elastomeric polymer foam (e.g. silicone, polyurethane, etc.) or a carrier member (e.g, a coil, filament, wire, etc) that carries a quantity of such expansile polymer is delivered into a perigraft space (i.e., space between the endovascular graft and the surrounding blood vessel wall) such that the polymeric material expands in situ to substantially fill the perigraft space or a portion thereof. The expansile polymeric material is delivered into he perigraft space through a catheter and / or cannula that is placed prior to, during or after the implantation of the endovascular graft. The invention includes an injector apparatus that is useable to deliver the expansile polymeric material through the wall of a previously implanted graft. After delivery into the perigraft space, the expanded polymeric material expands so as to fill all or an intended portion of the perigraft space in a manner that substantially prevents additional blood from leaking or flowing into such perigraft space. One type of blood-absorbing, porous, expansile polymeric material useable in this invention is a super-expansile hydrogel.
Owner:MICROVENTION INC
Squitieri hemodialysis and vascular access systems
InactiveUS20070123811A1Increased longevityImprove performanceOther blood circulation devicesDialysis systemsVenous accessHaemodialysis machine
A hemodialysis and vascular access system comprises a subcutaneous composite PTFE silastic arteriovenous fistula having an indwelling silastic venous end which is inserted percutaneously into a vein and a PTFE arterial end which is anastomosed to an artery. Access to a blood stream within the system is gained by direct puncture of needle(s) into a needle receiving site having a tubular passage within a metal or plastic frame and a silicone upper surface through which needle(s) are inserted. In an alternate embodiment of the invention, percutaneous access to a blood stream may be gained by placing needles directly into the system (i.e. into the PTFE arterial end). The invention also proposes an additional embodiment having an arterialized indwelling venous catheter where blood flows from an artery through a tube and a port into an arterial reservoir and is returned to a vein via a port and a venous outlet tube distinct and distant from the area where the blood from the artery enters the arterial reservoir. The site where blood is returned to the vein is not directly fixed to the venous wall but is free floating within the vein. This system provides a hemodialysis and venous access graft which has superior longevity and performance, is easier to implant and is much more user friendly.
Owner:HEMOSPHERE
Device and method for establishing an artificial arterio-venous fistula
A shunt rivet for implantation in the aorta and inferior vena cava to treat chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and a method of treating chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
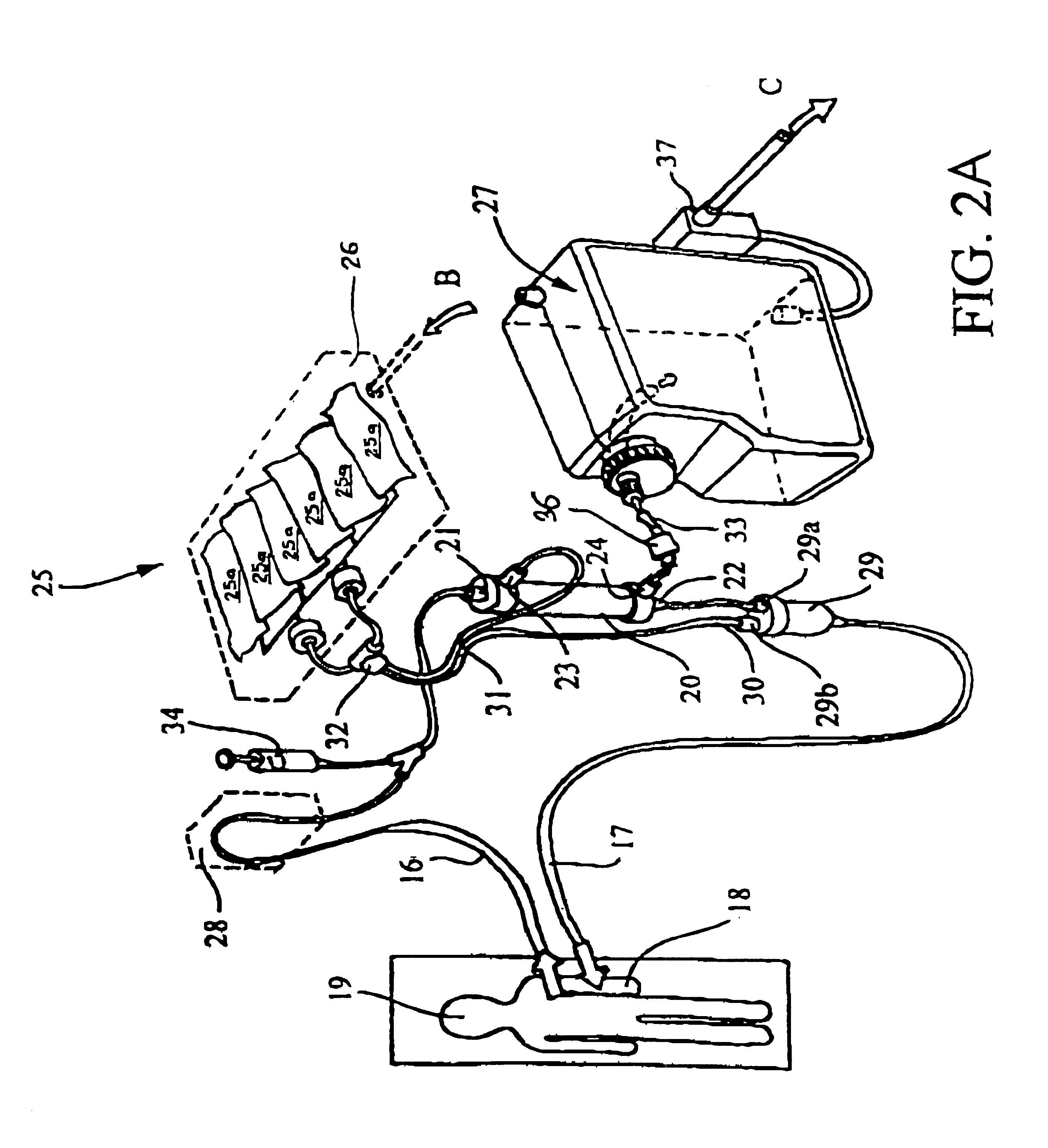
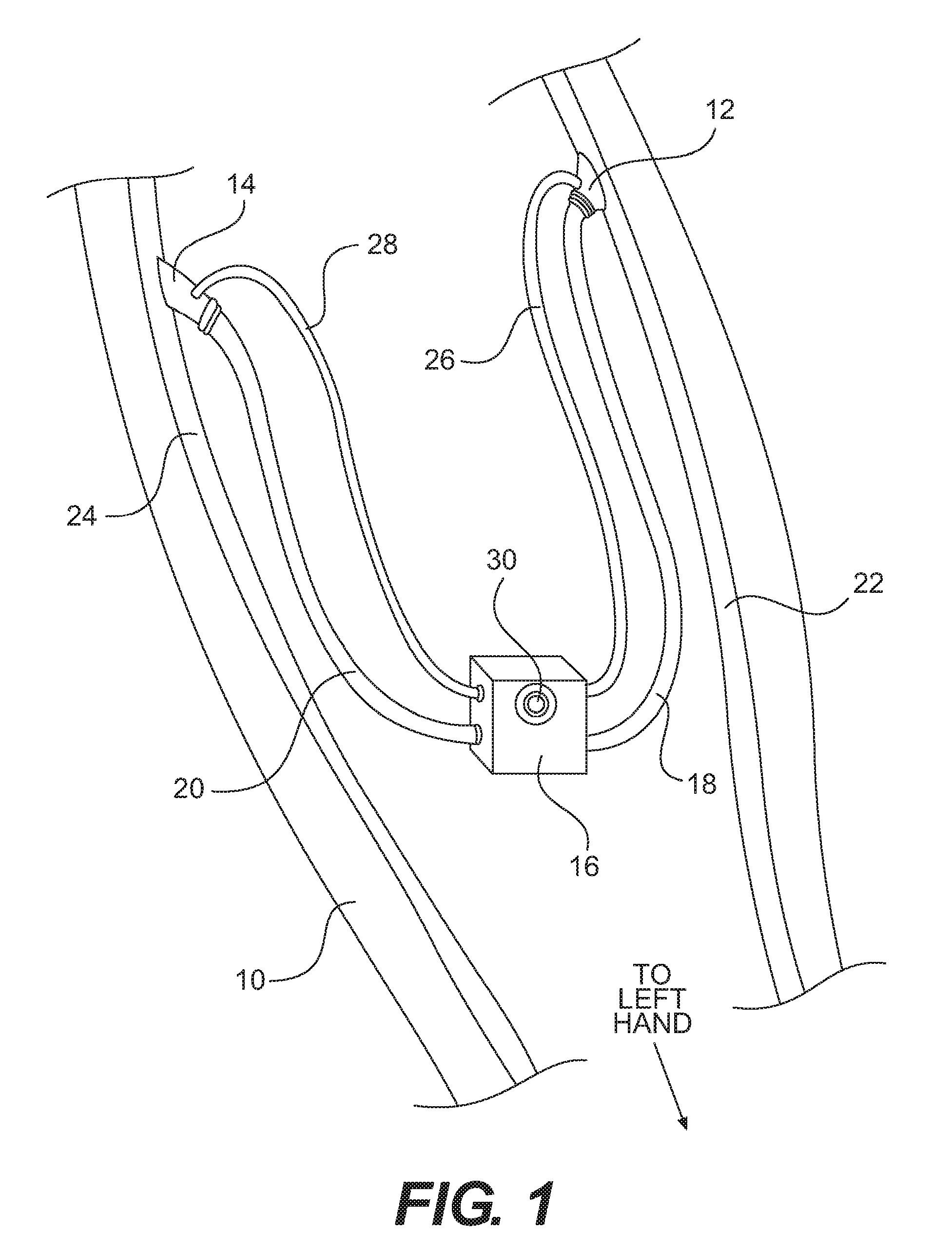
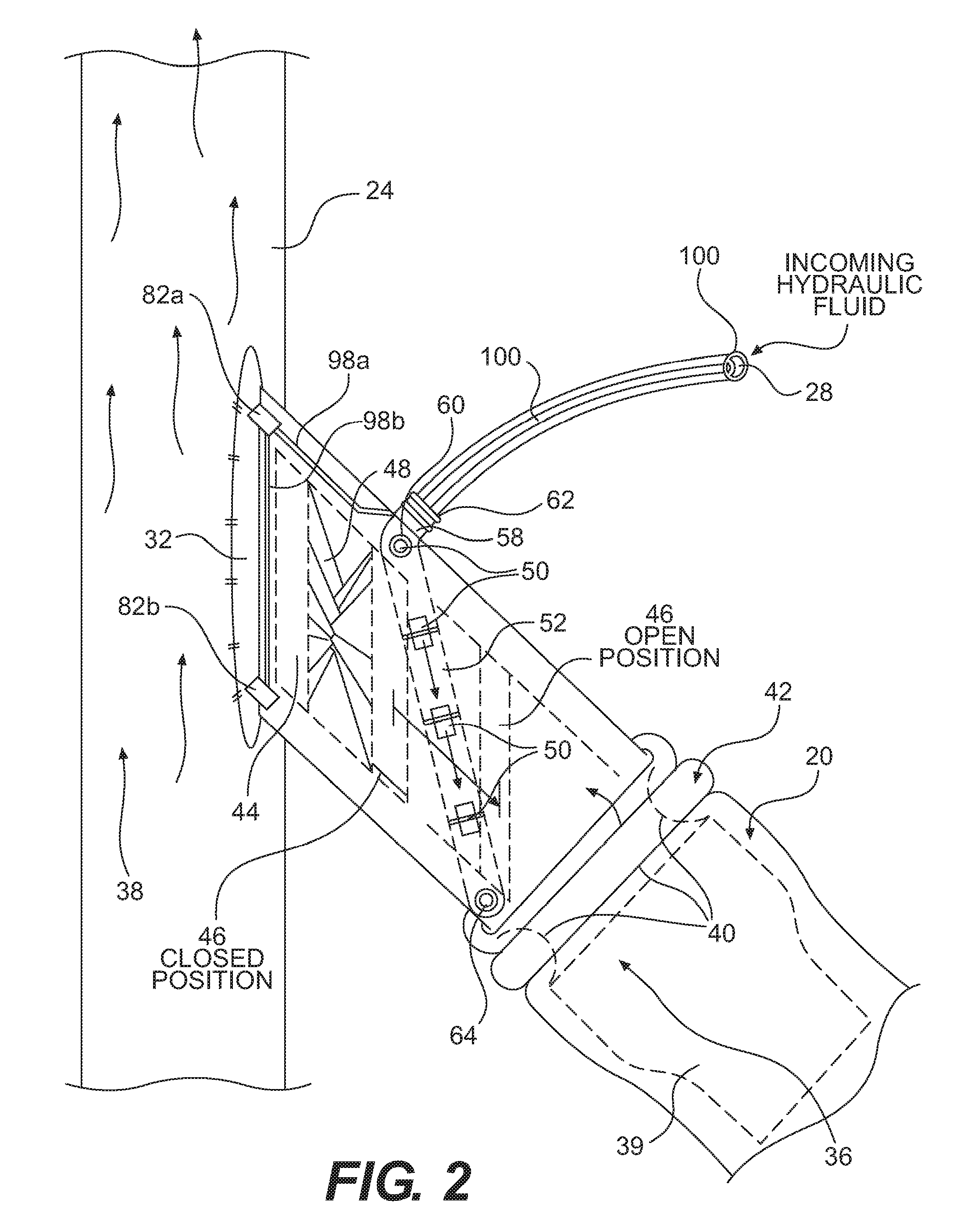
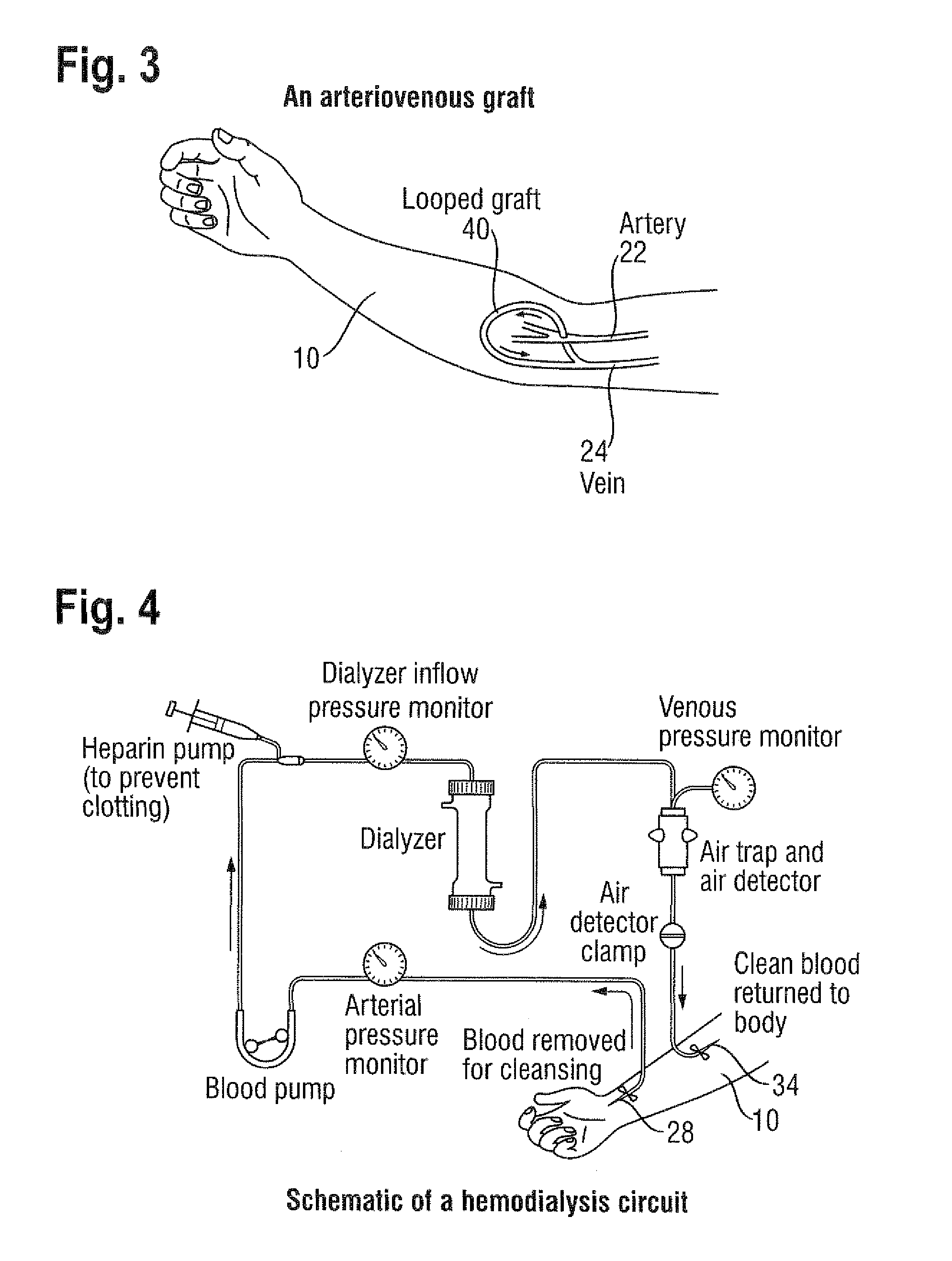
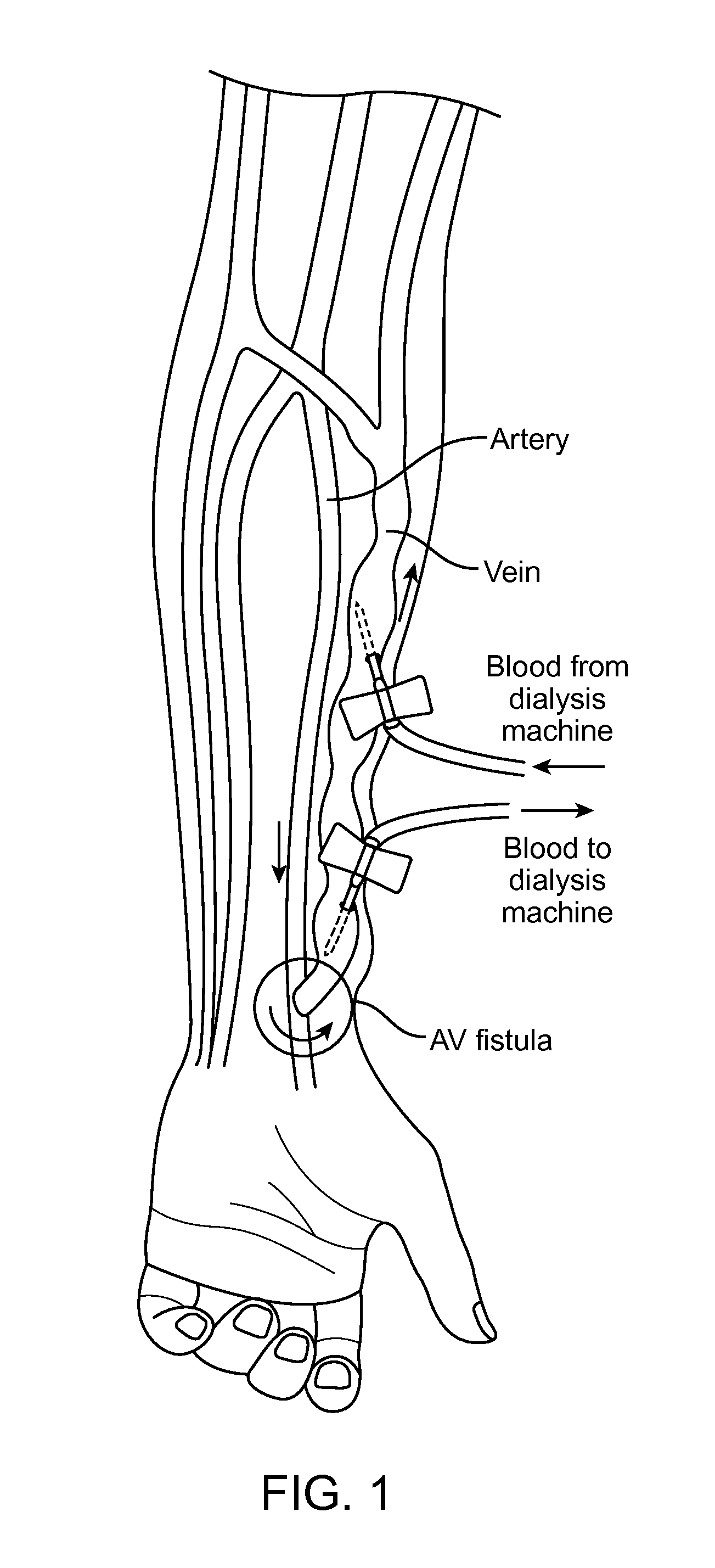
Dialysis machine, in particular for home use
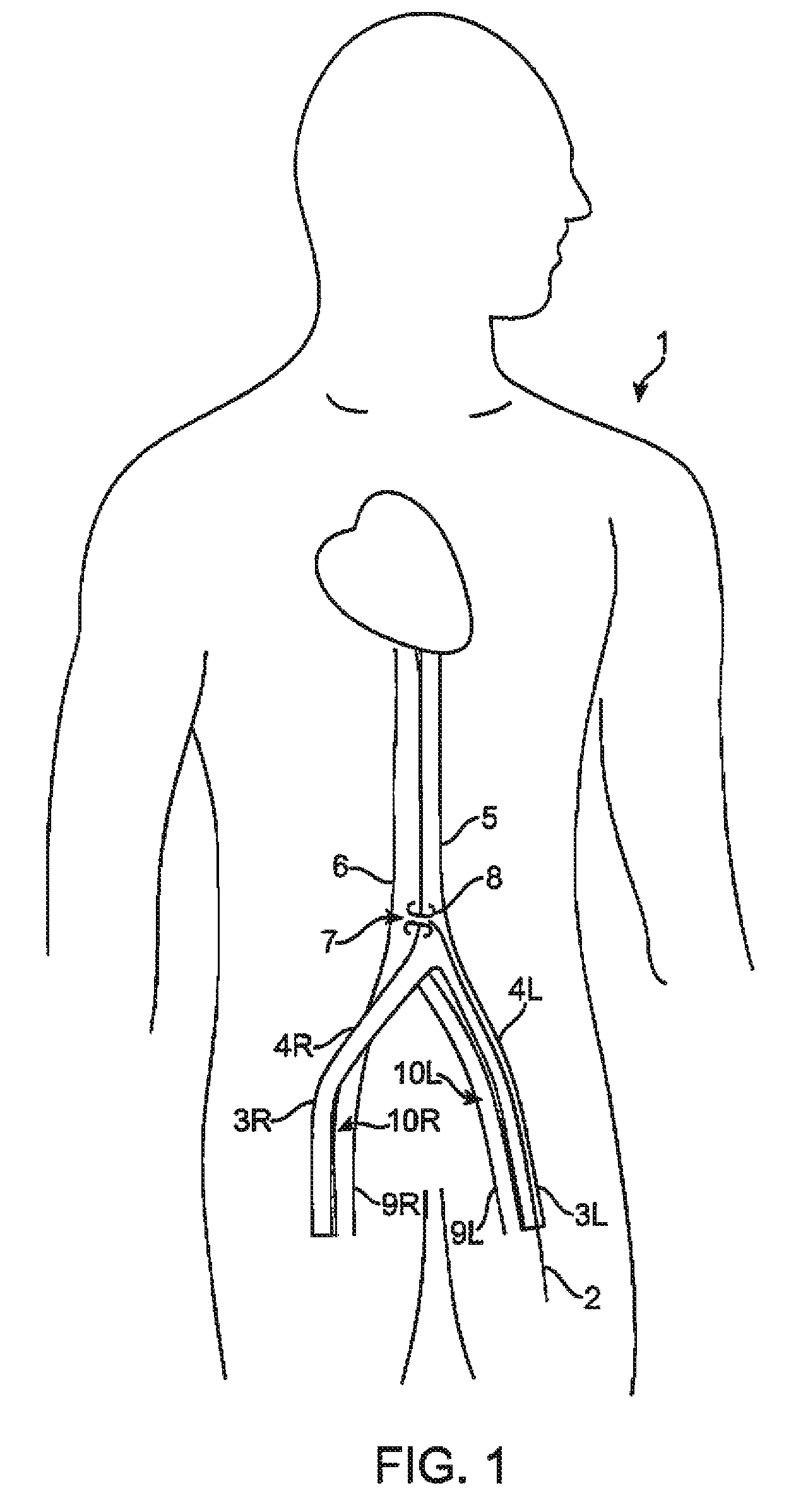
The invention concerns a dialysis machine (10) comprising a dialyzer (20) having a first inlet (21) and a first outlet (22) for the bloodstream, dialysate supply mechanism (25), an arterial line (16) connected between the patent's arteriovenous fistula and the dialyzer, a venous line (17) connected between the arteriovenous fistula and the dialyzer, a pump (28) coupled with the arterial line, a dialysate supply line (31), connected between the dialysate supply mechanism and the dialyzer, a dialysate evacuation line (33) connected between a dialysate recuperating container (27) and the dialyzer. The sterile dialysate bags are arranged in a chamber (26) under a gas pressure.
Owner:PHYSIDIA
Method of treating COPD with artificial arterio-venous fistula and flow mediating systems
A method for treatment of COPD, hypertension, and left ventricular hypertrophy, and chronic hypoxia including creation of an artificial arterio-venous fistula and installation of a flow mediating device proximate the fistula. The flow mediating device is operated to limit flow as medically indicated to provide the optimum amount of bypass flow.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Coiled sheet graft for single and bifurcated lumens and methods of making and use
A prosthesis is provided for treating aneurysms, occlusive disease of vessels and body organs, and arterio-venous fistulas, occurring in single and bifurcated lumens. The prosthesis comprises an expandable coiled sheet portion having a biocompatible graft, either a sheet or tube, affixed thereto along part or all of the circumference of the coiled sheet portion. The prosthesis has a small delivery profile, making it suitable for use in a variety of body vessels. Methods of making and deploying the prosthesis in single and bifurcated lumens are also provided.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Catheter-stent device
A graftless prosthetic stent for treatment of vascular lesions such as aneurysms and arterio-venous fistulas, especially in neurovascular vessels, comprises a continuous helical ribbon formed of a shape-retaining metal having a transition temperature at which the stent expands from its contracted condition to a radially expanded condition, the stent remaining substantially cylindrical in its contracted and expanded conditions. The helical windings have variable width, thickness, number or size of openings, or combinations of these features, which affect the stiffness, rate of expansion at the transition temperature, and the area of vessel wall covered by the stent. A catheter device which includes the stent, and a method of treatment using the stent are also provided.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC +1
Aspiration and delivery safety system
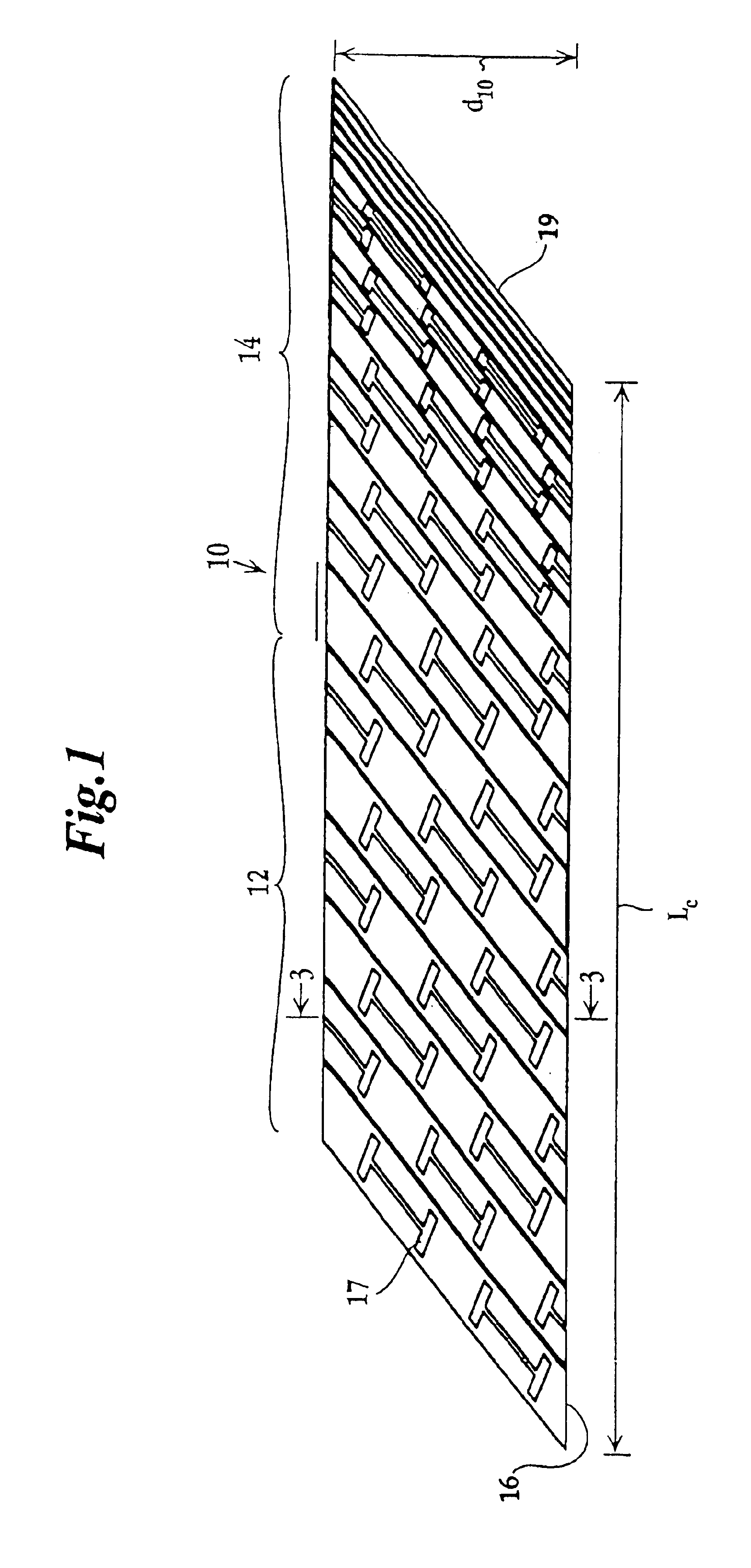
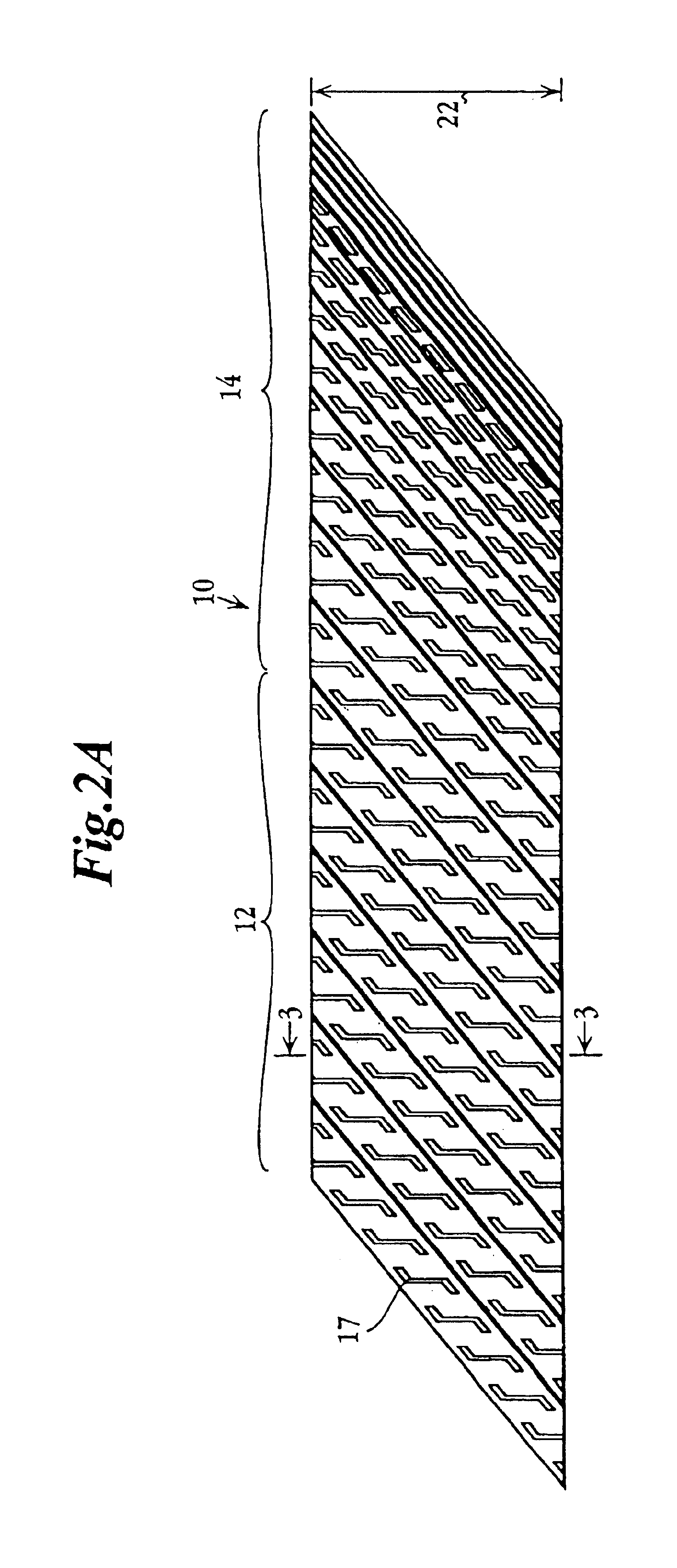
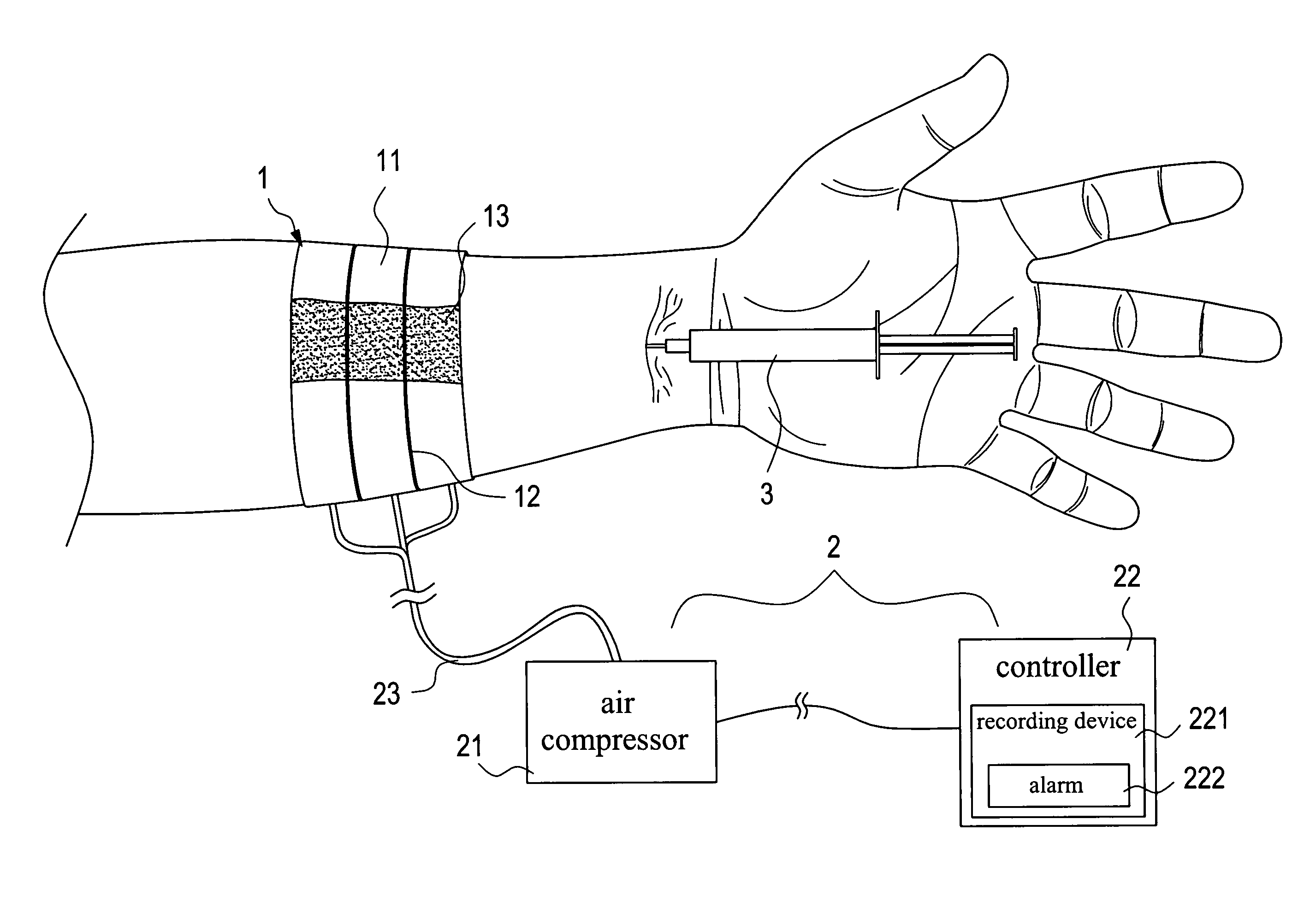
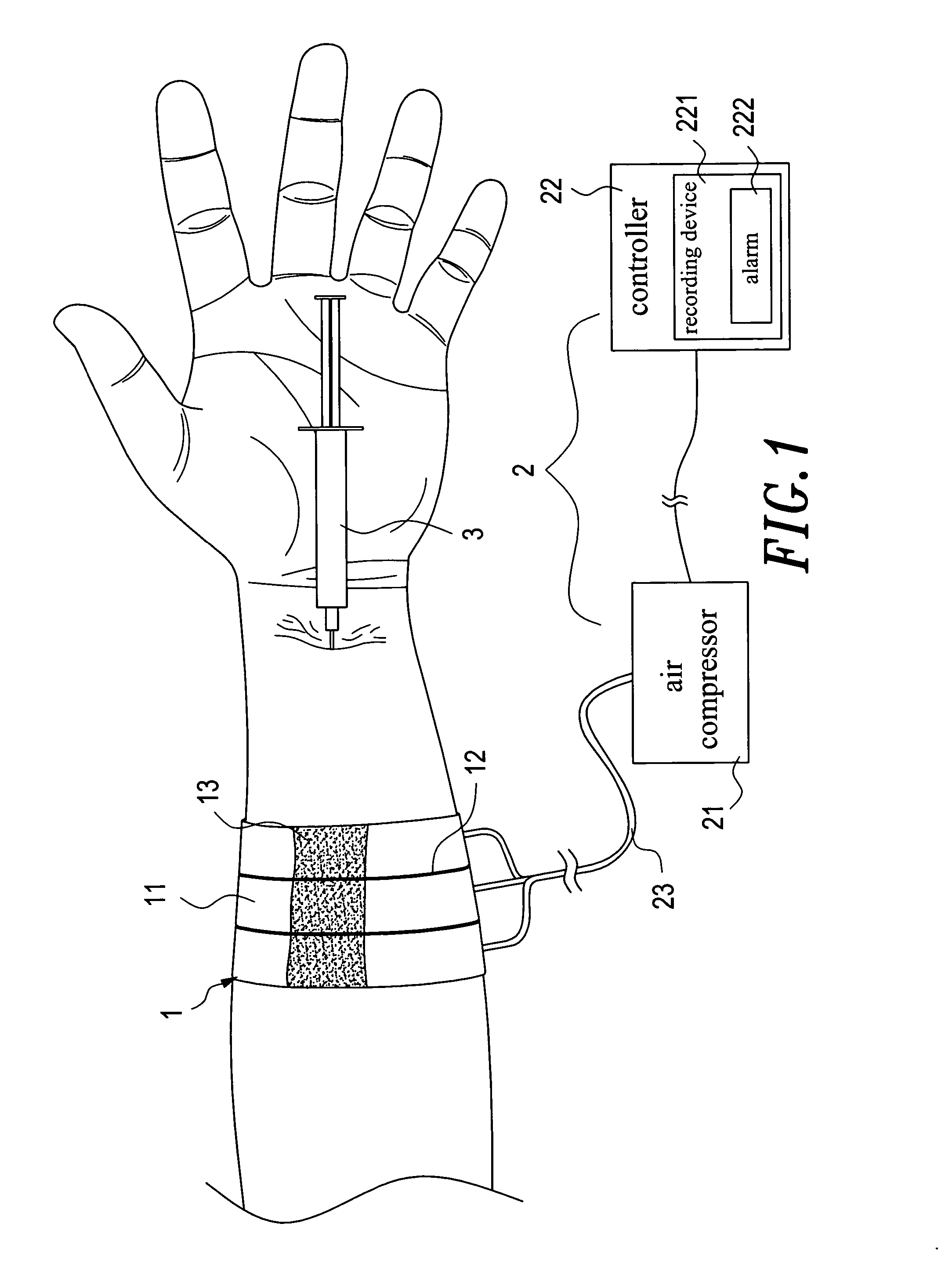
InactiveUS20060200195A1Adjustable widthDetect changeInfusion syringesEvaluation of blood vesselsVeinMedicine
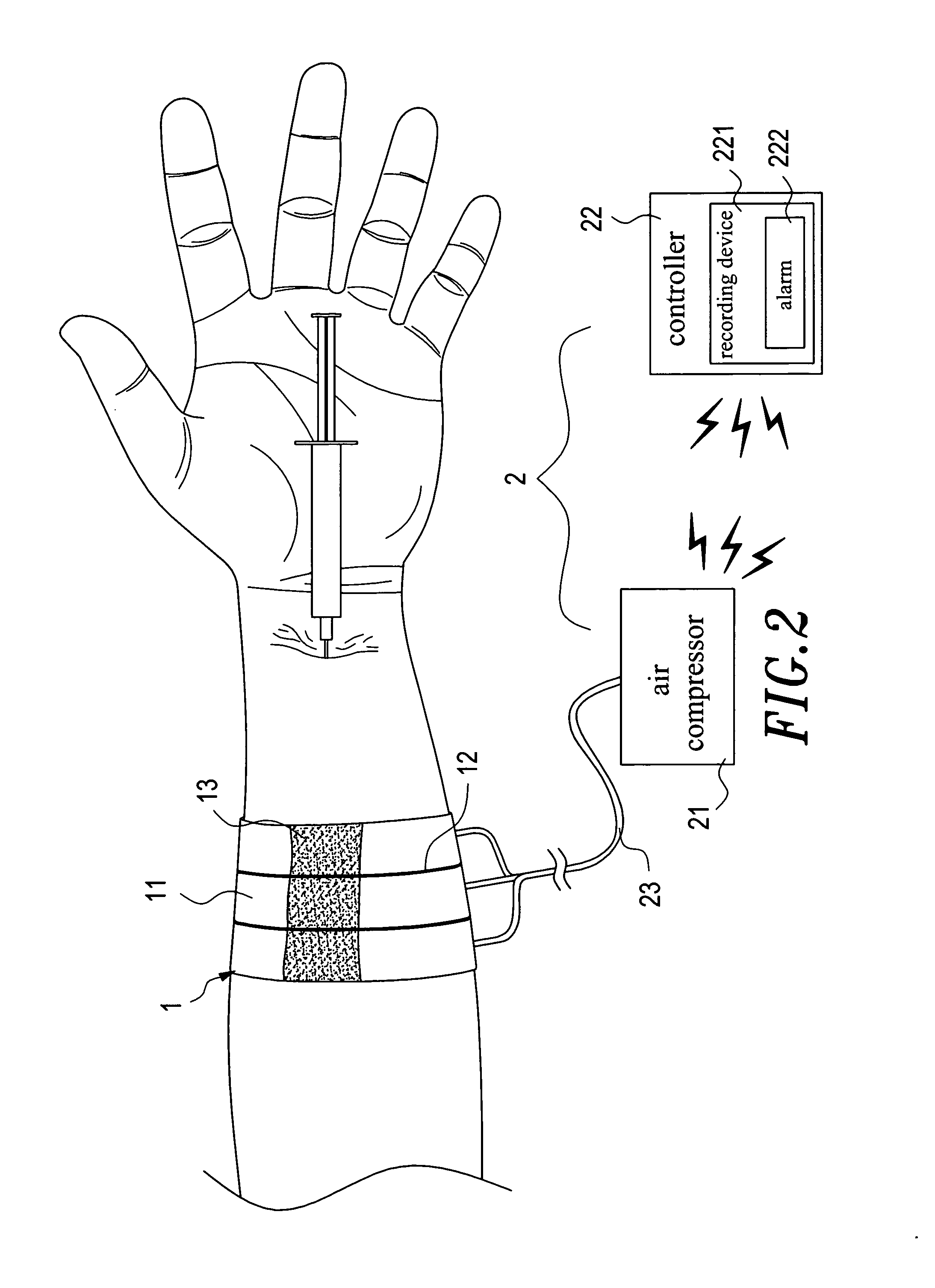
An aspiration and delivery safety system that includes a blood restriction unit, an inflating unit, a needle unit, and a puncture site press unit. The blood restriction unit is constituted by a plurality of air bands. The needle unit is a syringe or butterfly needle or blood collector or intravenous catheter or arteriovenous fistula needle. The inflating unit has a controller that monitors a patient's blood pressure and heart rate, and records these data by means of a recording device into which a medical person can also input other medical data. The puncture site press unit has disposed at the bottom thereof a haemostatic element. When applying an intravenous therapy, a needle and a soft catheter are inserted into a patient's body together. The puncture site press device holds the soft catheter during the withdrawal of the needle.
Owner:YANG CHANG MING
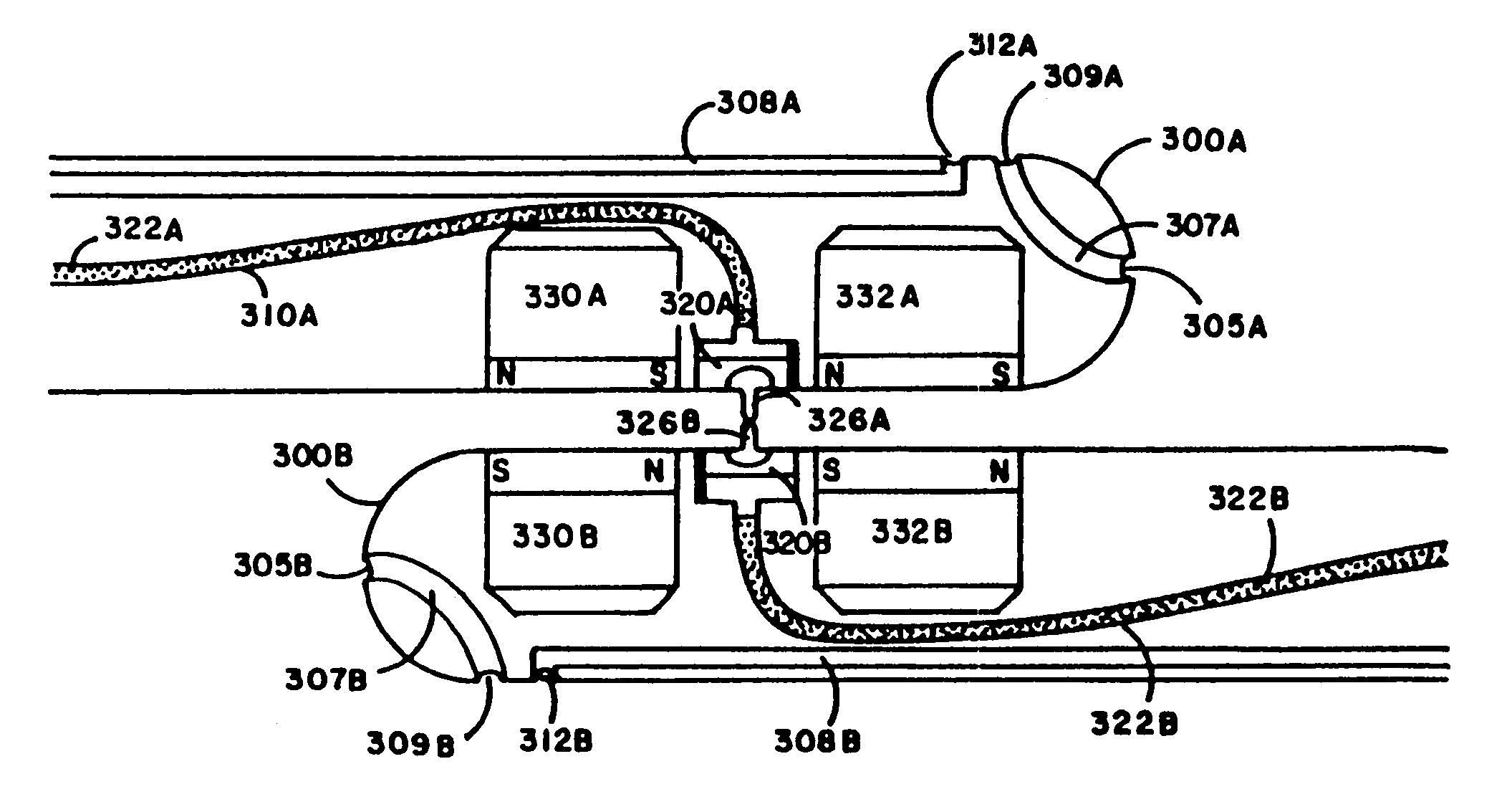
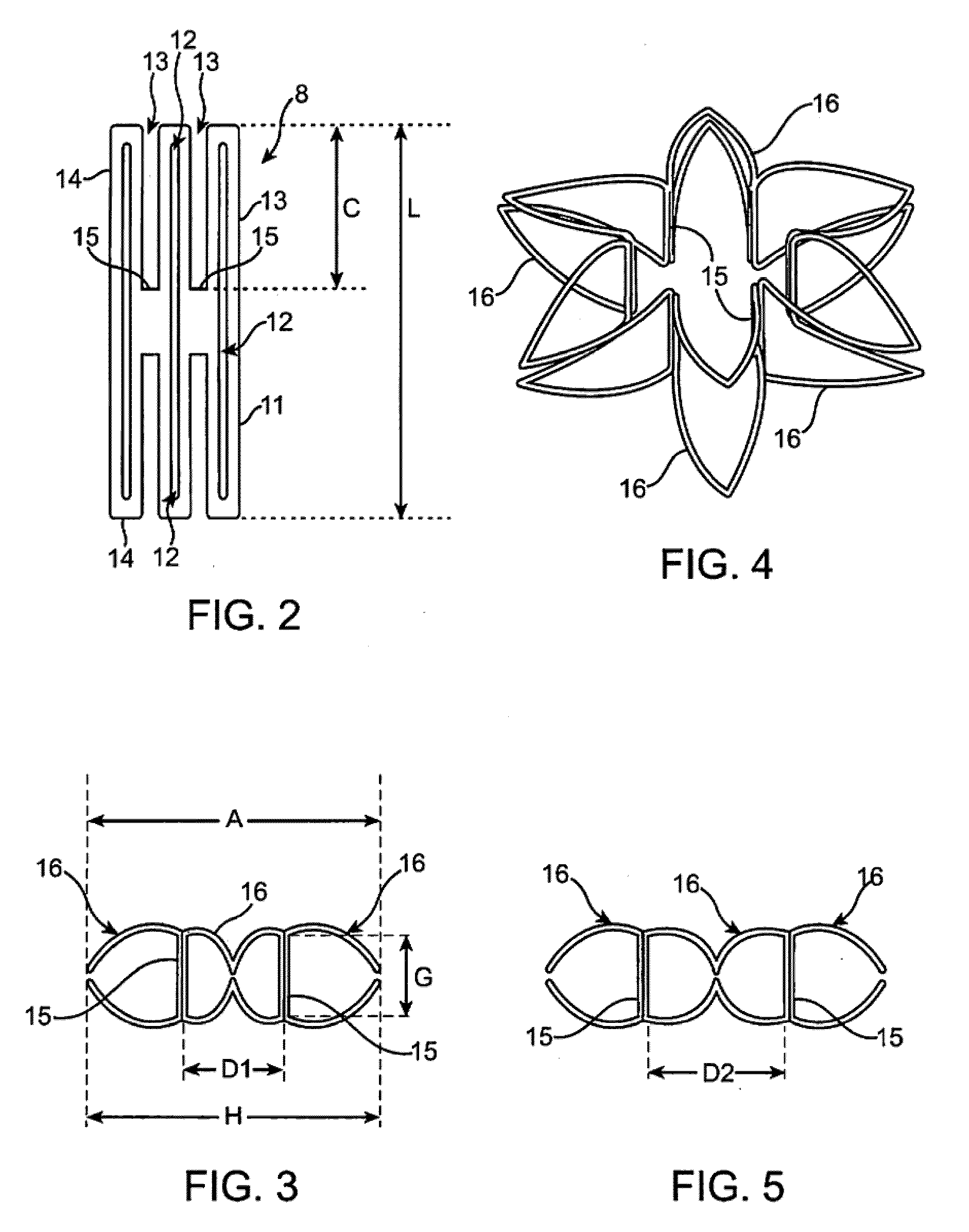
Arteriovenous Shunt Having Eccentric Anchor Stent
An arteriovenous shunt includes a self-expanding stent graft having a self-expanding anchor stent mounted eccentrically and externally about at least one end segment of the stent graft. A fluid passageway extends between open first and second ends of the shunt. The anchor stent has an expanded diameter greater than an expanded diameter of the stent graft. The expanded diameter of the stent graft is smaller than the artery or vein into which it is deployed. Methods of deploying the arteriovenous shunt are also disclosed,
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
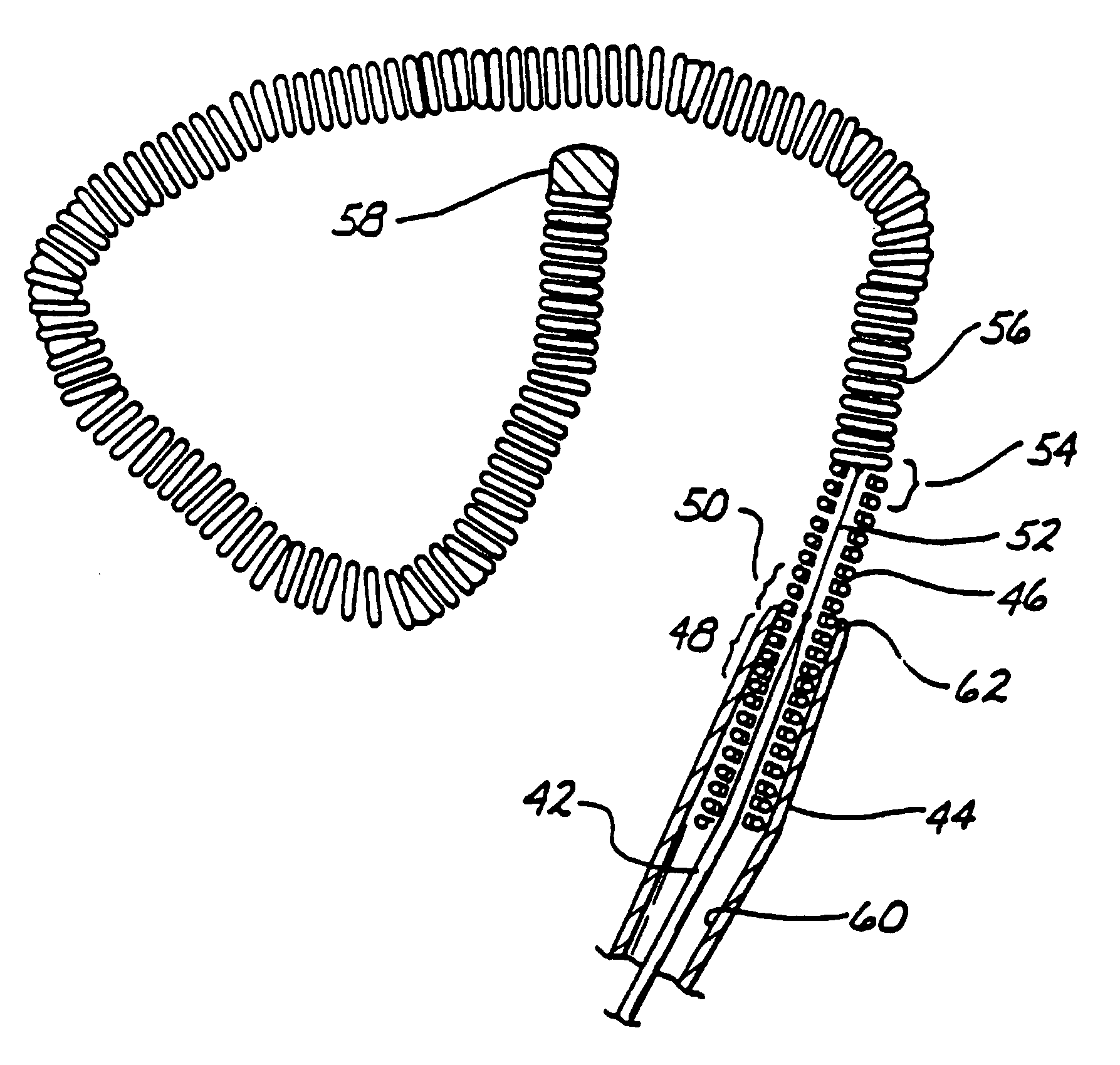
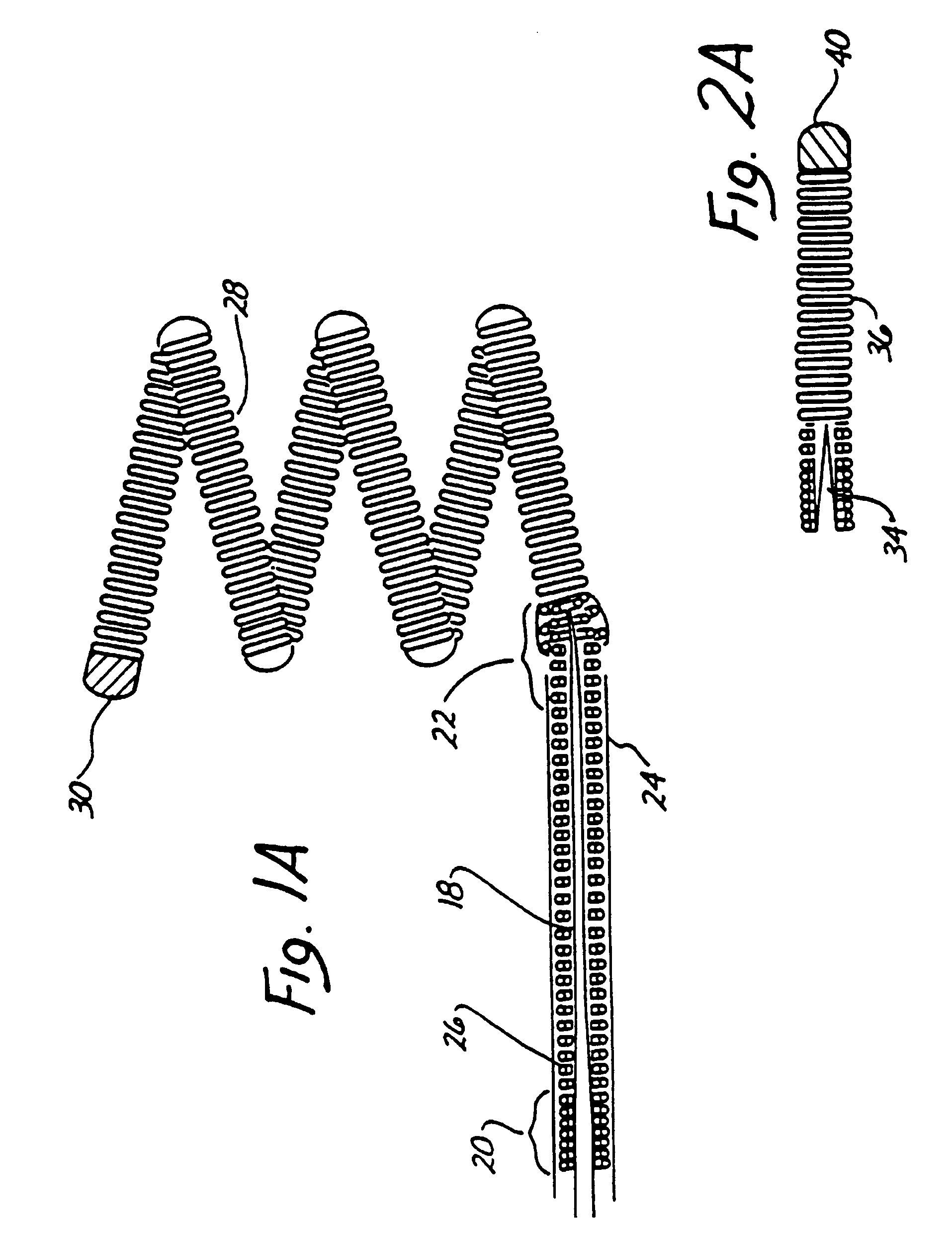
Endovascular electrolytically detachable wire and tip for the formation of thrombus in arteries, veins, aneurysms, vascular malformations and arteriovenous fistulas
An artery, vein, aneurysms vascular malformation or arterial fistula is occluded through endovascular occlusion by the endovascular insertion of a platinum wire and / or tip into the vascular cavity. The vascular cavity is packed with the tip to obstruct blood flow or access of blood in the cavity such that the blood clots in the cavity and an occlusion if formed. The tip may be elongate and flexible so that it packs the cavity by being folded upon itself a multiple number of times, or may pack the cavity by virtue of a filamentary or fuzzy structure of the tip. The tip is then separated from the wire mechanically or by electrolytic separation of the tip from the wire. The wire and the microcatheter are thereafter removed leaving the tip embedded in the thrombus formed within the vascular cavity. Movement of wire in the microcatheter is more easily tracked by providing a radioopaque proximal marker on the microcatheter and a corresponding indicator marker on the wire. Electrothrombosis is facilitate by placing the ground electrode on the distal end of the microcatheter and flowing current between the microcatheter electrode and the tip.REEAXMINATION RESULTS The questions raised in reexamination request 90 / 007,231, filed Oct. 4, 2004 have been considered and the results thereof are reflected in this reissue patent which constitutes the reexamination certificate required by 35 U.S.C. 307 as provided in 37 CFR 1.570(e), for ex parte reexaminations, or the reexamination certificate required by 35 U.S.C. 316 as provided in 37 CFR 1.99(e) for inter partes reexaminations.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
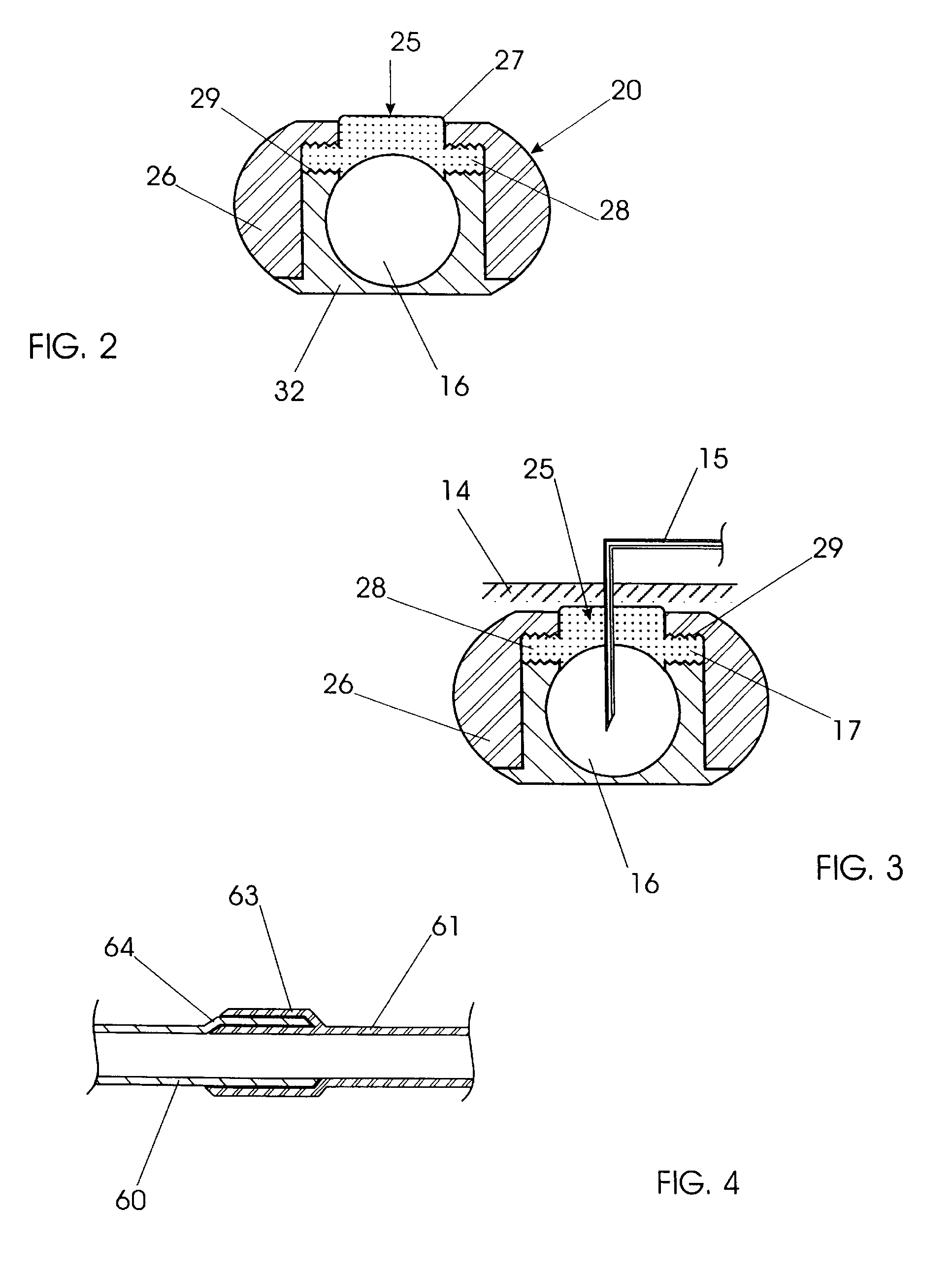
Hemodialysis and vascular access system
InactiveUSRE44639E1Encourage self sealing and tissue ingrowthAvoid the needOther blood circulation devicesDiagnosticsVenous accessHaemodialysis machine
A hemodialysis and vascular access system comprises a subcutaneous composite PTFE silastic arteriovenous fistula having an indwelling silastic venous end which is inserted percutaneously into a vein and a PTFE arterial end which is anastomosed to an artery. Access to a blood stream within the system is gained by direct puncture of needle(s) into a needle receiving site having a tubular passage within a metal or plastic frame and a silicone upper surface through which needle(s) are inserted. In an alternate embodiment of the invention, percutaneous access to a blood stream may be gained by placing needles directly into the system (i.e. into the PTFE arterial end). The invention also proposes an additional embodiment having an arterialized indwelling venous catheter where blood flows from an artery through a tube and a port into an arterial reservoir and is returned to a vein via a port and a venous outlet tube distinct and distant from the area where the blood from the artery enters the arterial reservoir. The site where blood is returned to the vein is not directly fixed to the venous wall but is free floating within the vein. This system provides a hemodialysis and venous access graft which has superior longevity and performance, is easier to implant and is much more user friendly.
Owner:MERIT MEDICAL SYST INC
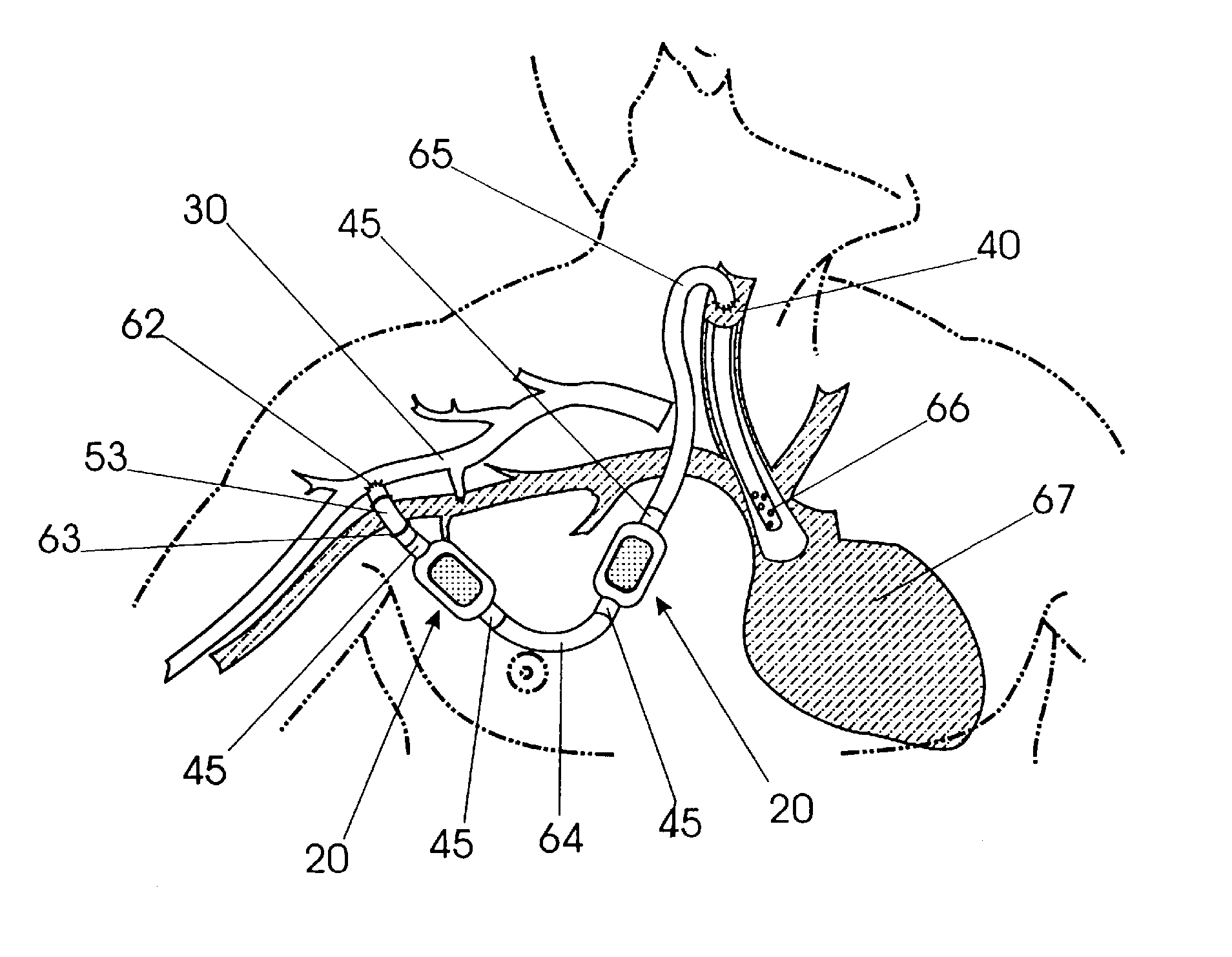
Arteriovenous shunt with integrated surveillance system
Owner:INDIANA UNIV RES & TECH CORP
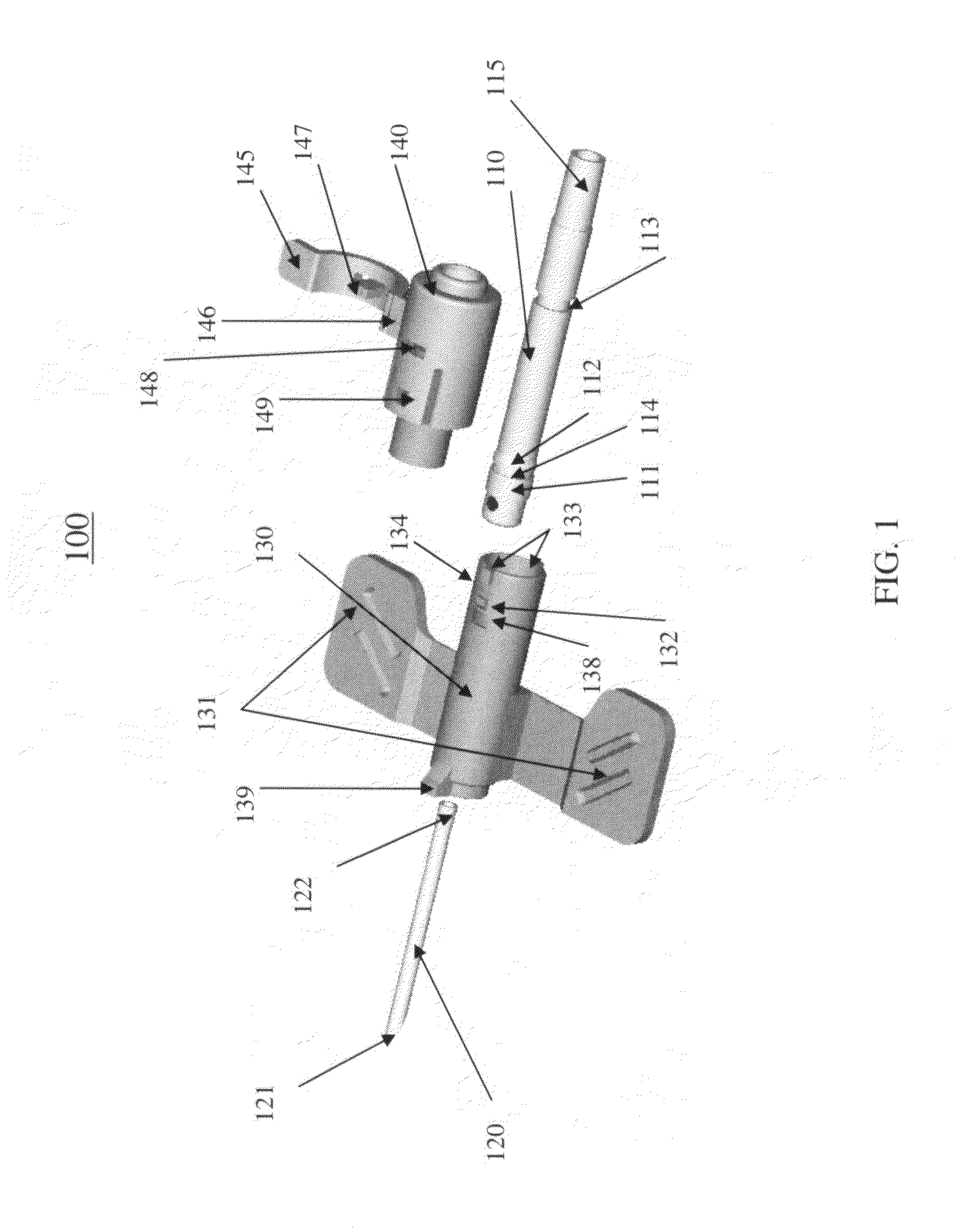
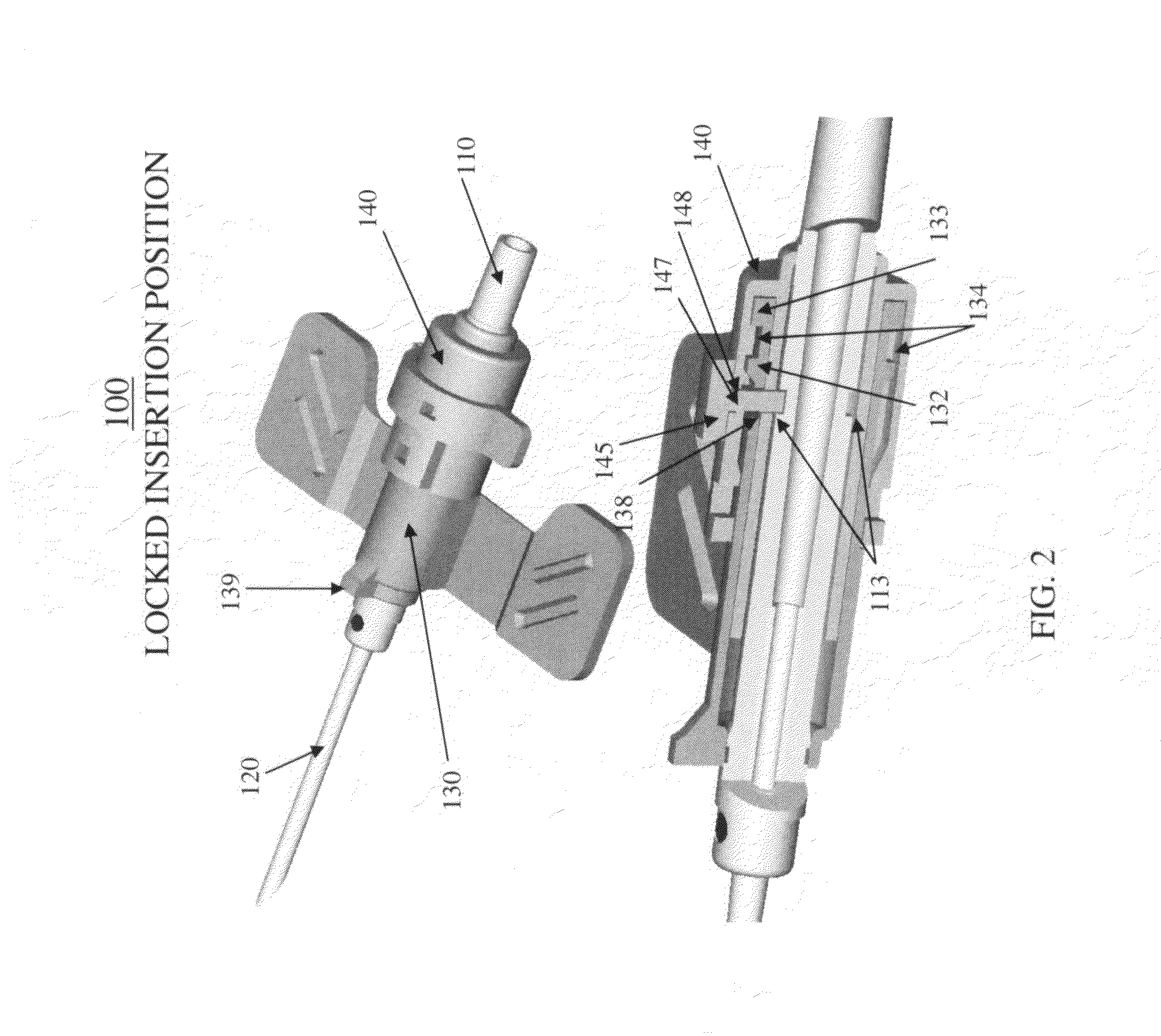
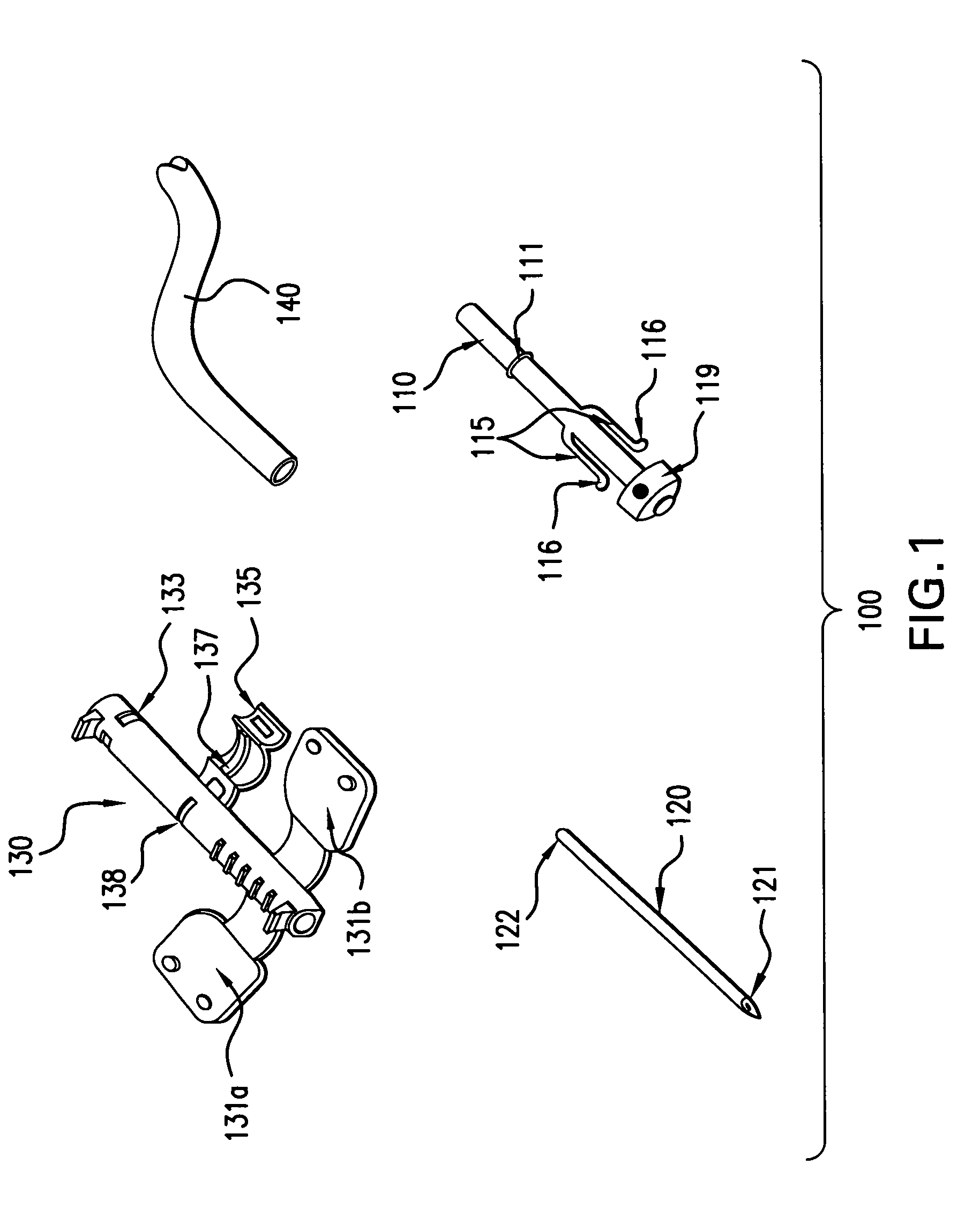
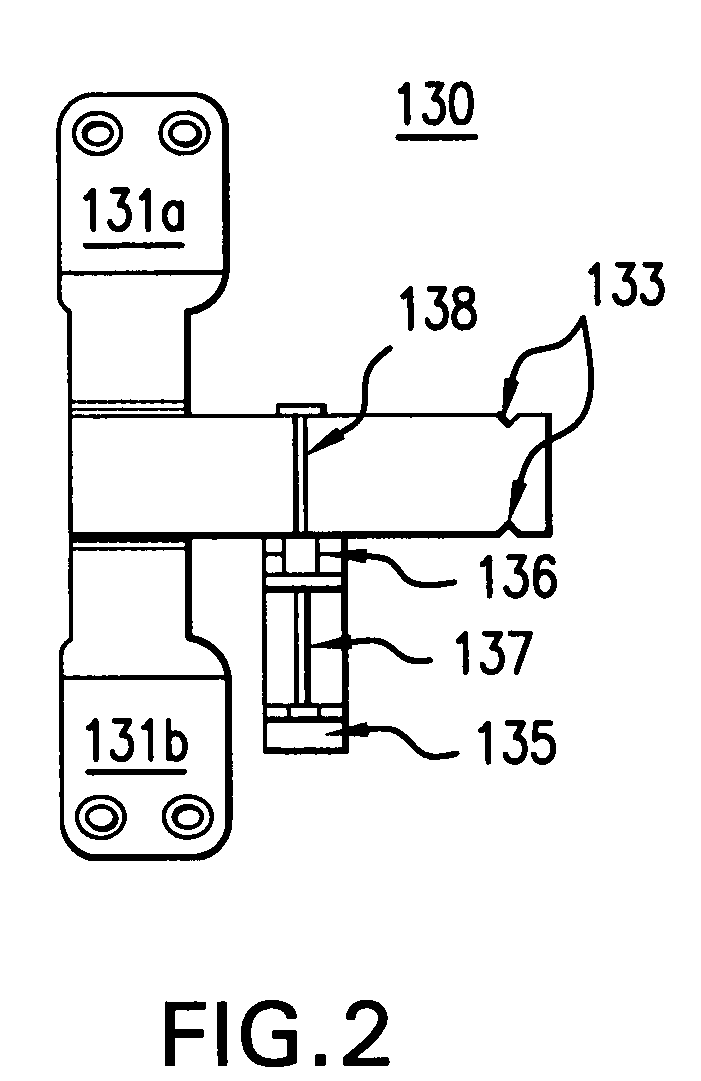
Telescopic safety arteriovenous fistula needle
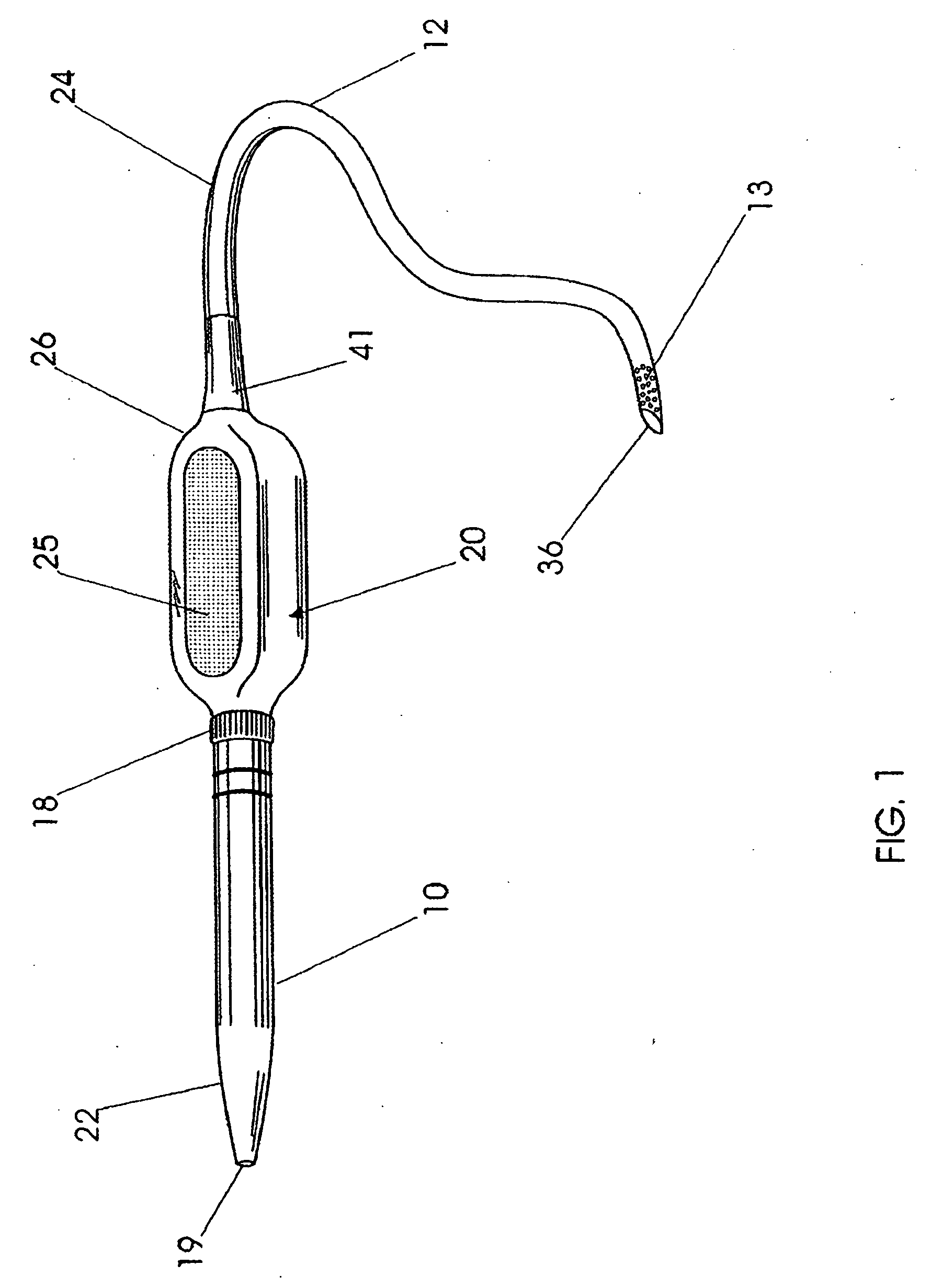
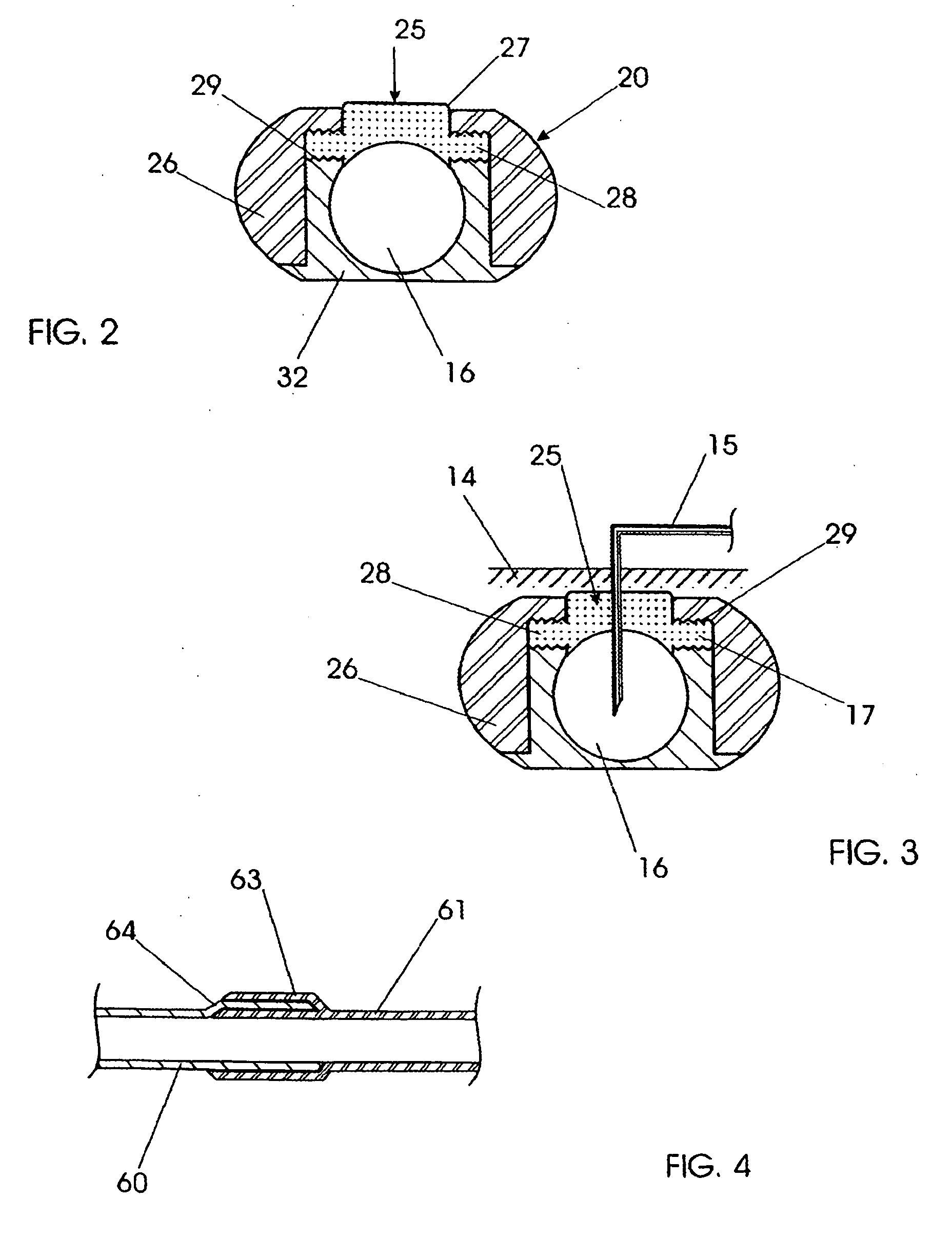
A telescopic intravenous infusion set and / or blood collection assembly is provided with a safety feature for covering the used needle. The safety feature is a telescopic device including a shield with handling wings, which when placed in cooperating relationship, allows accommodation of a conventional unmodified blood collection needle affixed to a hub, and a sleeve with a locking cap. After use, the hub with the needle are pulled rearwardly into positive locking position which prevent the hub and needle from moving out of the shield thereafter. The telescopic nature of the device then allows the locked needle / hub to move rearward in relation to the shield until the shield is unreleasably locked to the sleeve. The shield provides for passage of the needle and hub from a releasable locked use position to a shielded and unreleasable locked protected position.
Owner:JMS SINGAPORE PTE
Safety arteriovenous fistula needle
A Safety Arteriovenous Fistula (AVF) winged safety needle device provides a safety feature including a protective shield with handling wings, which when placed in cooperating relationship, allows accommodation of a blood collection needle and a hub. The Safety AVF provides a reliable and user friendly first releasable locking mechanism in an insertion position and a second unreleaseable locking mechanism in a protected position. The Safety AVF also allows for rotation of the needle after cannulation in order to maximize blood or fluid flow to or from a vessel.
Owner:JMS NORTH AMERICA
Method for treating neurovascular aneurysms
InactiveUS20050149164A1Reduce expansionIncrease the angleStentsGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsInsertion stentProsthesis
A graftless prosthetic stent for treatment of vascular lesions such as aneurysms and arterio-venous fistulas, especially in neurovascular vessels, comprises a continuous helical ribbon formed of a shape-retaining metal having a transition temperature at which the stent expands from its contracted condition to a radially expanded condition, the stent remaining substantially cylindrical in its contracted and expanded conditions. The helical windings have variable width, thickness, number or size of openings, or combinations of these features, which affect the stiffness, rate of expansion at the transition temperature, and the area of vessel wall covered by the stent. A catheter device which includes the stent, and a method of treatment using the stent are also provided.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC +1
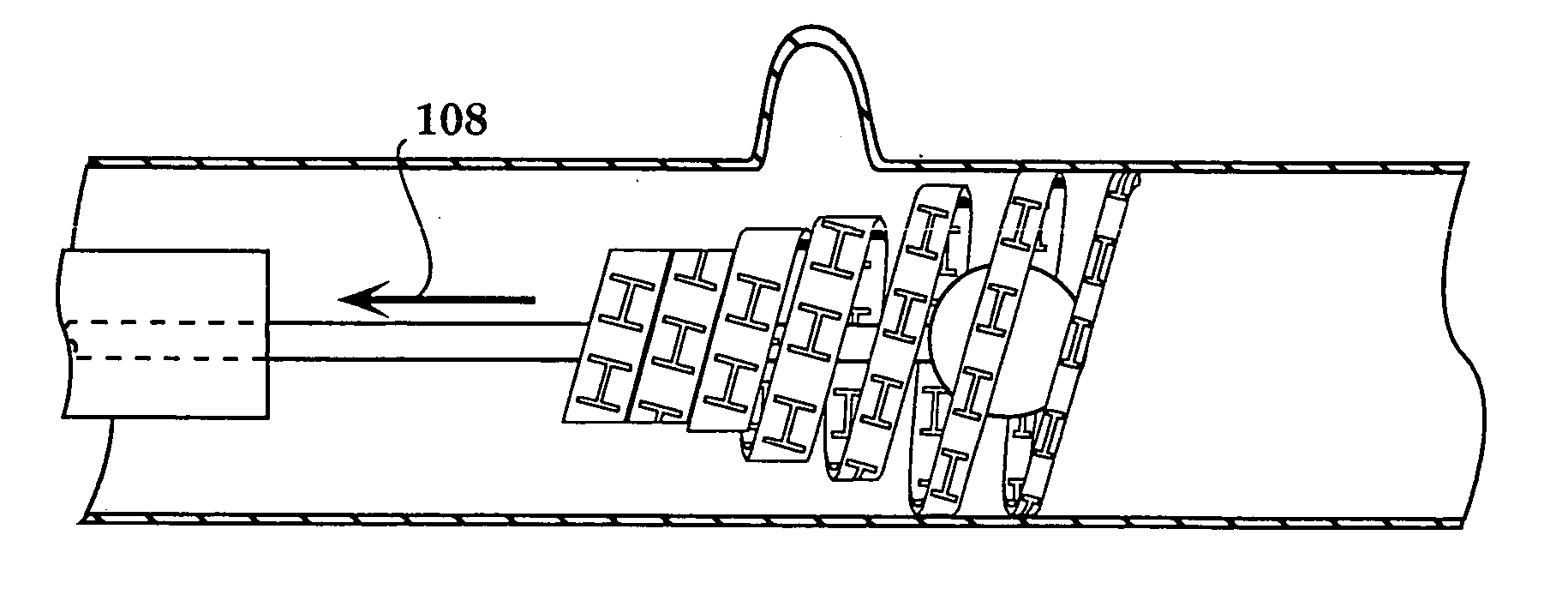
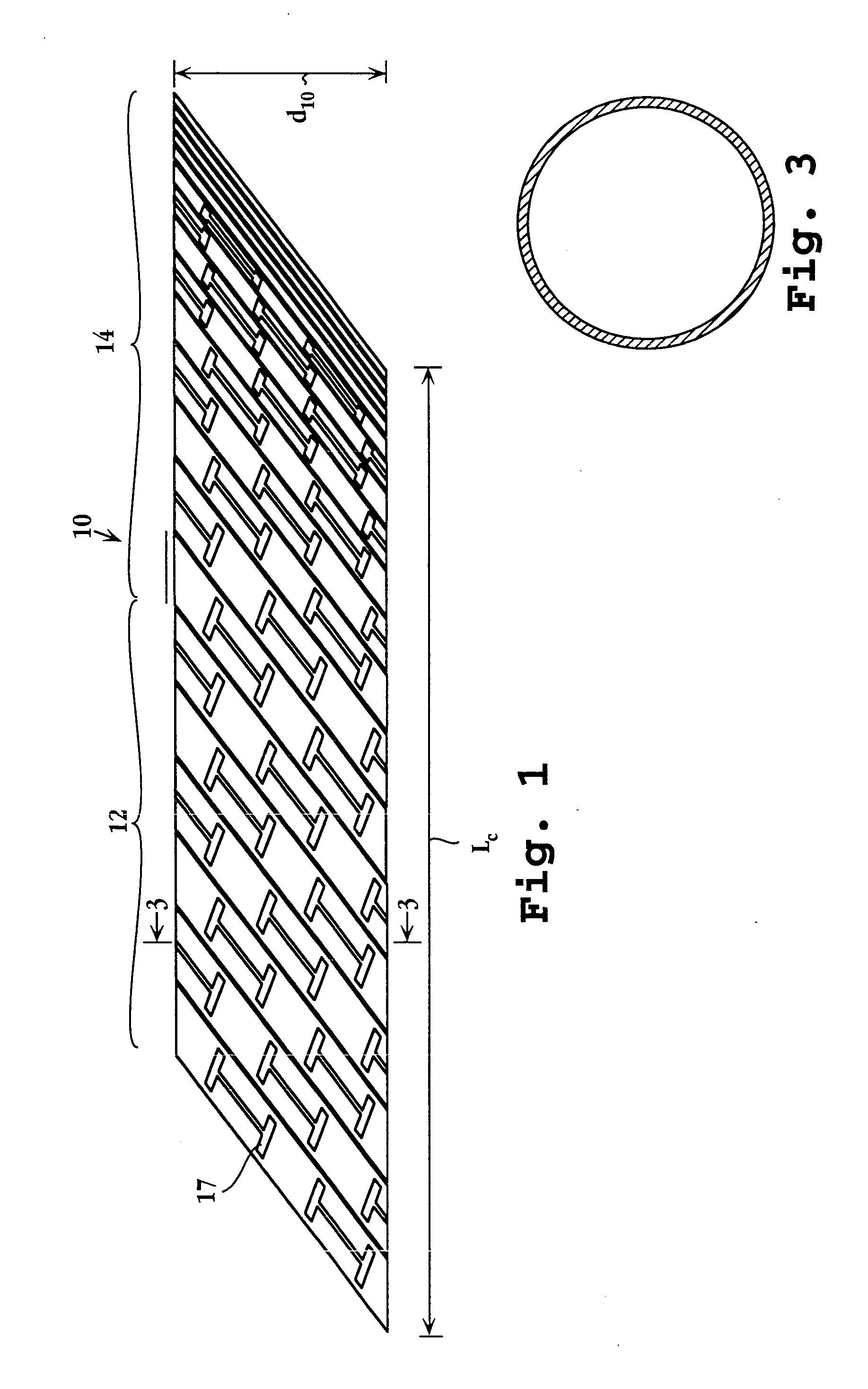
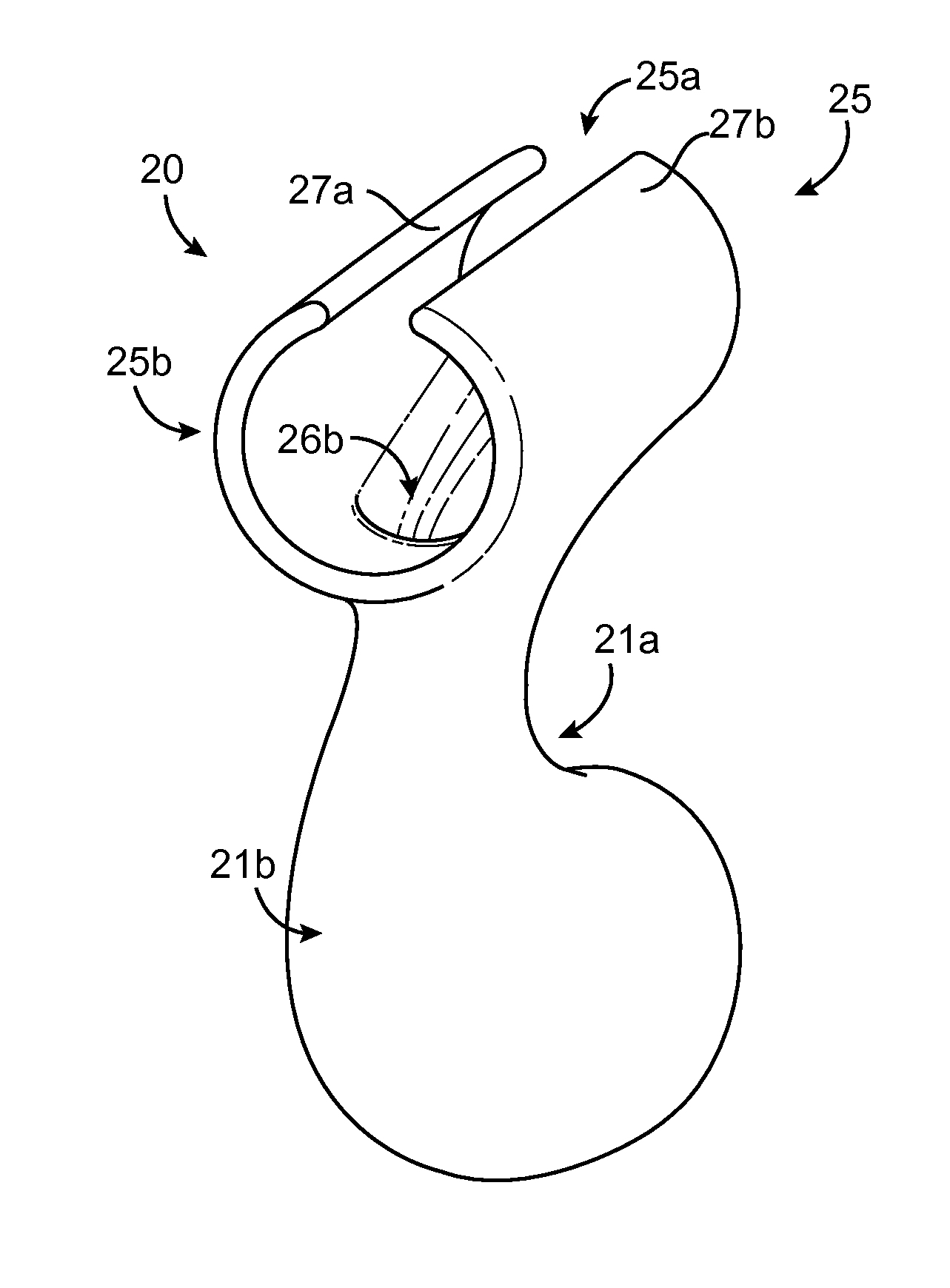
Arteriovenous fistula
InactiveUS20140358064A1Improve sealingEasy to useStentsOther blood circulation devicesCoelomArteriovenous fistula
A covered radially-expansible stent, capable of being advanced along a bodily lumen, and capable of performing as an arteriovenous shunt, and with a covering that stops short of one end of the stent at a line that slants to the longitudinal axis of the stent at an angle intermediate between 0° and 90°.
Owner:CR BARD INC
Arteriovenous Shunt Having a Moveable Valve
An arteriovenous shunt assembly including a shunt having a hollow bore between open first and second ends thereof and a valve slidably disposed through the hollow bore. The valve includes means for retaining the valve in a closed position or in any of various selected open positions that provide corresponding different rates of blood flow through the shunt assembly. In some embodiments, the AV shunt assembly is self-expandable from a collapsed tow-profile configuration employed during transluminal delivery. The valve position in the hollow bore may be adjusted in vivo by inflating a catheter balloon in a blood vessel to bear against an end of the valve. Methods for using the shunt assembly are also disclosed.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Body-associated fluid transport structure evaluation devices
Implantable devices for evaluating body-associated fluid transport structures and methods for using the same are provided. In some instances, the implantable devices include an elongated structure with at least one hermetically sealed integrated circuit sensor stably associated therewith and a transmitter. The devices find use in a variety of different applications, including monitoring the function of various types of body-associated fluid transport structures, such as arteriovenous fistulae, vascular grafts, catheters, cerebrospinal fluid shunts, and implantable central venous access devices.
Owner:PROTEUS DIGITAL HEALTH INC
Arteriovenous shunt having a flow control mechanism
An arteriovenous shunt assembly including a shunt and a pull wire operated flow control mechanism. The shunt has a tubular body that defines a fluid passageway between a first end and a second end thereof The pull wire mechanism includes a portion disposed around the tubular shunt in at least one loop. The at least one loop may be selectively tightened or loosened remotely from the shunt to regulate the rate of blood flow through the tubular shunt.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Methods And Compositions For Enhacing Vascular Access
Disclosed is an implantable material comprising a biocompatible matrix and cells which, when provided to a vascular access structure, can promote functionality generally. For example, implantable material of the present invention can enhance maturation of an arteriovenous native fistula as well as prolong the fistula in a mature, functional state suitable for dialysis. Additionally, the present invention can promote formation of a functional arteriovenous graft suitable for dialysis as well as promote formation of a functional peripheral bypass graft. Implantable material can be configured as a flexible planar form or a flowable composition with shape retaining properties suitable for implantation at, adjacent or in the vicinity of an anastomoses or arteriovenous graft. According to the methods disclosed herein, the implantable material is provided to an exterior surface of a blood vessel. Certain embodiments of the flexible planar form define a slot. The materials and methods of the present invention comprise cells, preferably endothelial cells or cells having an endothelial-like phenotype.
Owner:SHIRE REGENERATIVE MEDICINE INC
Device and method for establishing an artificial arterio-venous fistula
A shunt rivet for implantation in the aorta and inferior vena cava to treat chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and a method of treating chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Arteriovenous fistula
A covered radially-expansible stent (50), capable of being advanced along a bodily lumen, and capable of performing as an arteriovenous shunt, and with a covering that stops short of one end of the stent at a line that slants to the longitudinal axis of the stent at an angle intermediate between 0° and 90°.
Owner:CR BARD INC
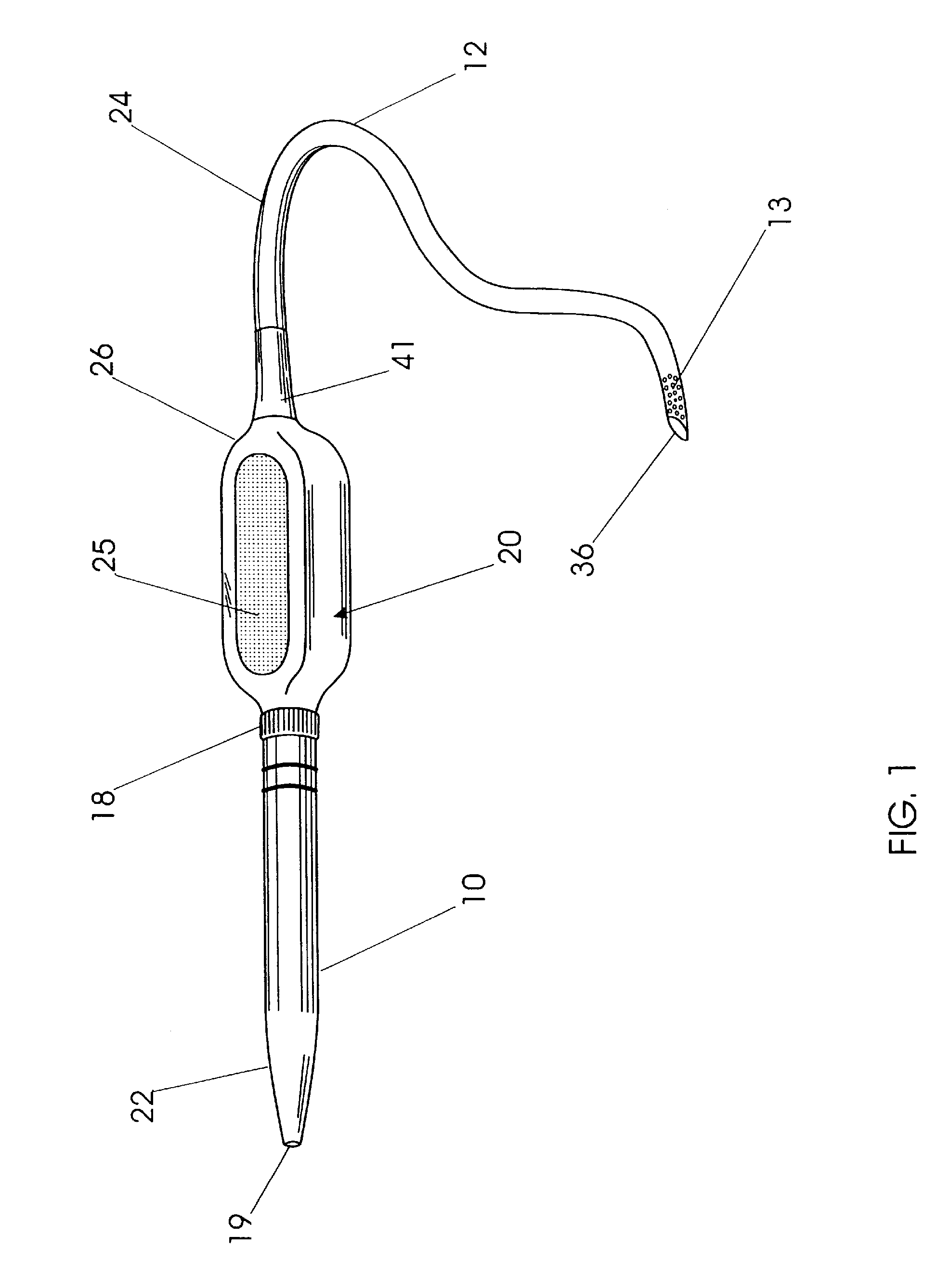
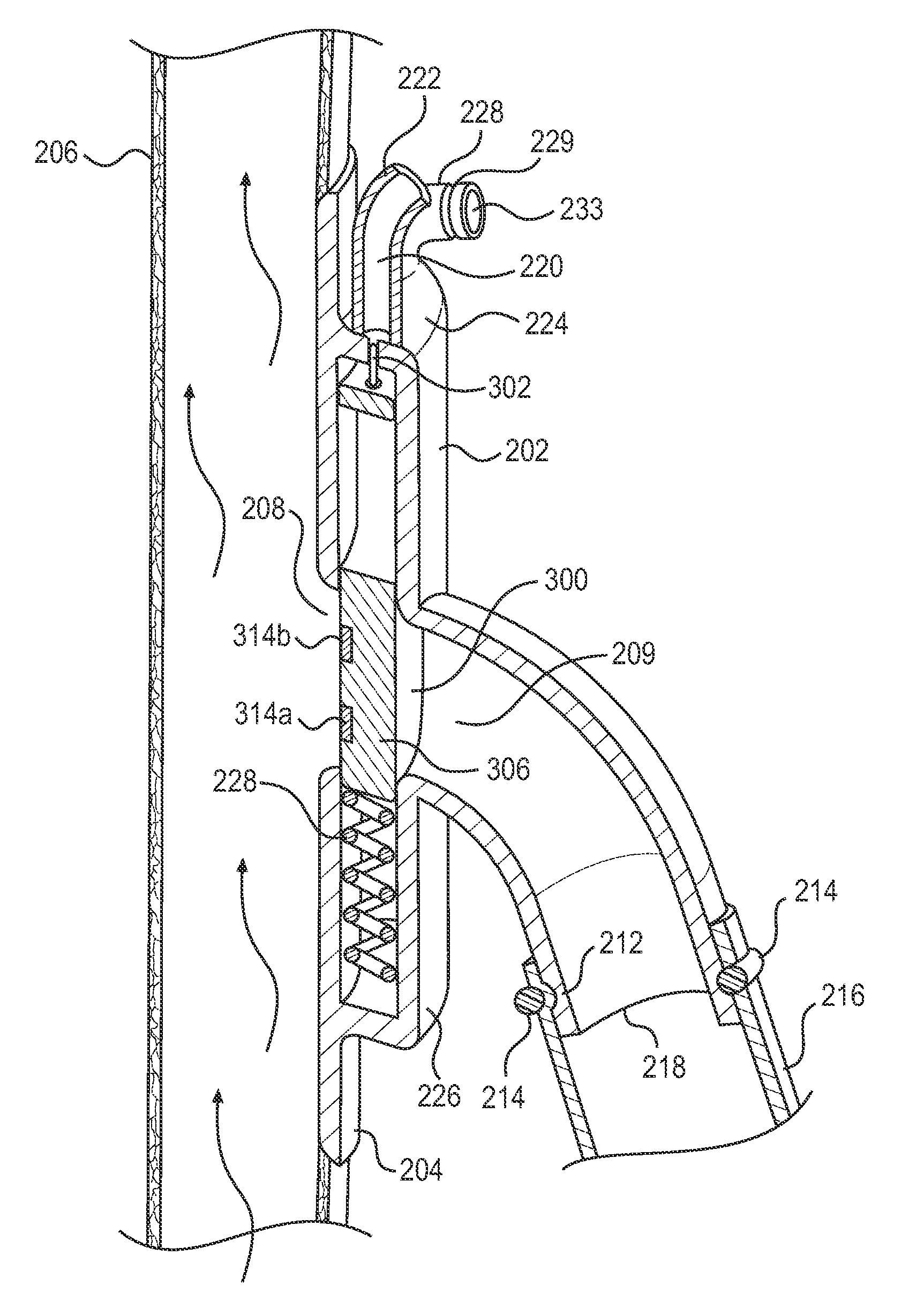
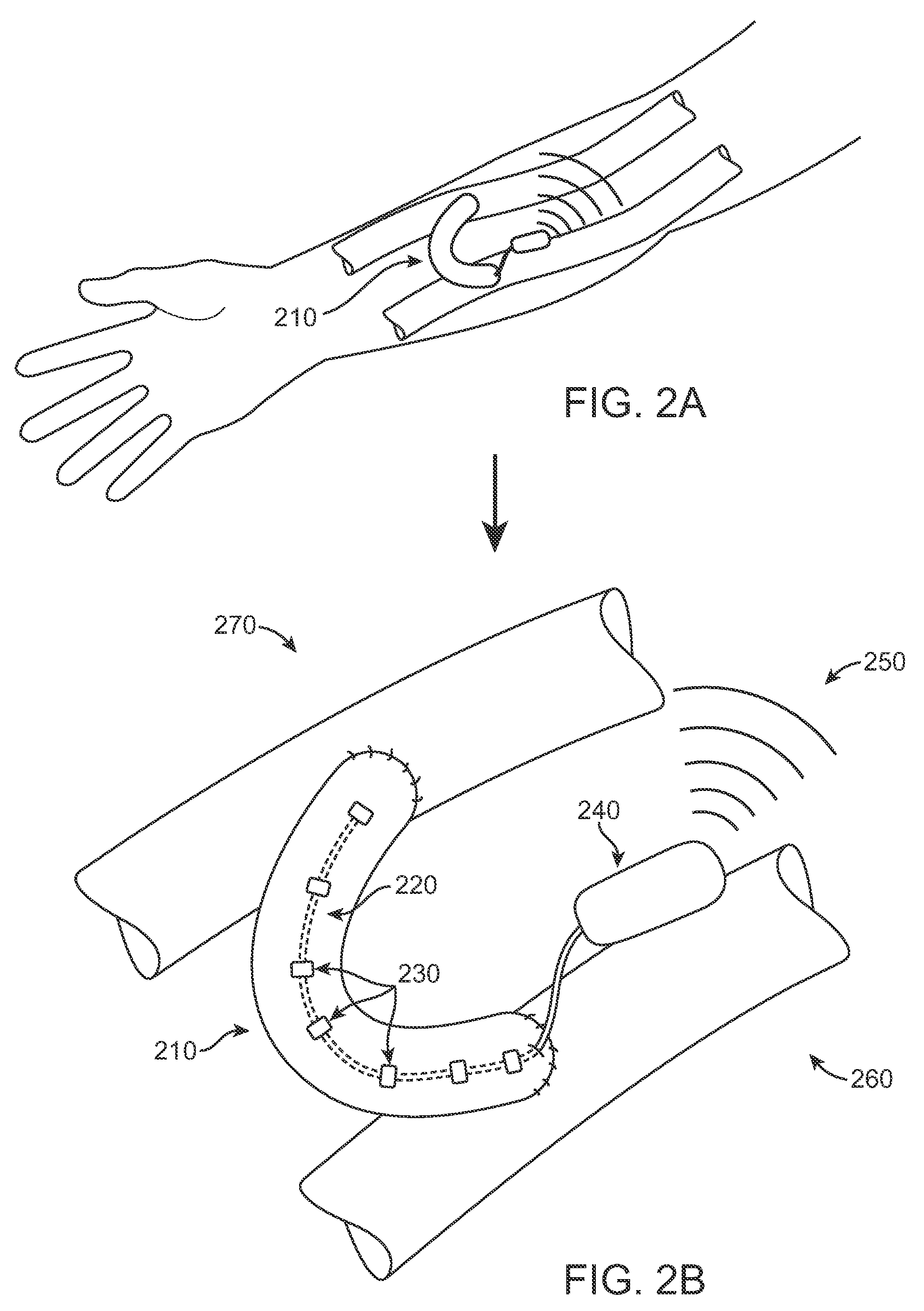
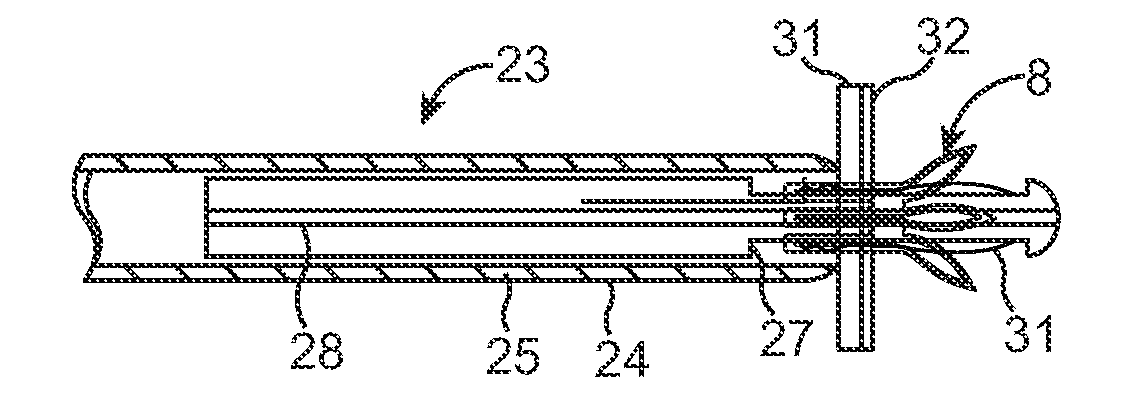
Extravascular devices supporting an arteriovenous fistula
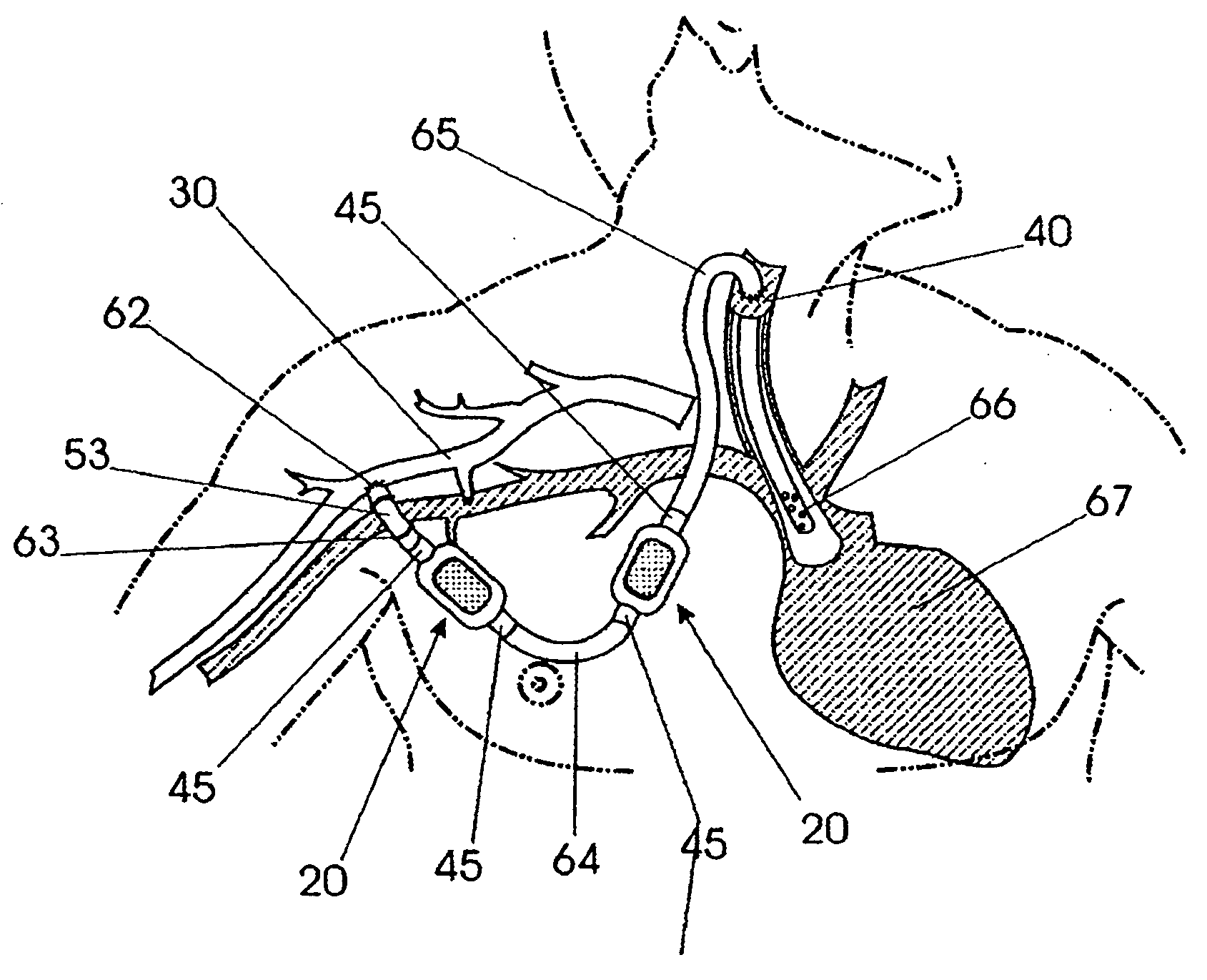
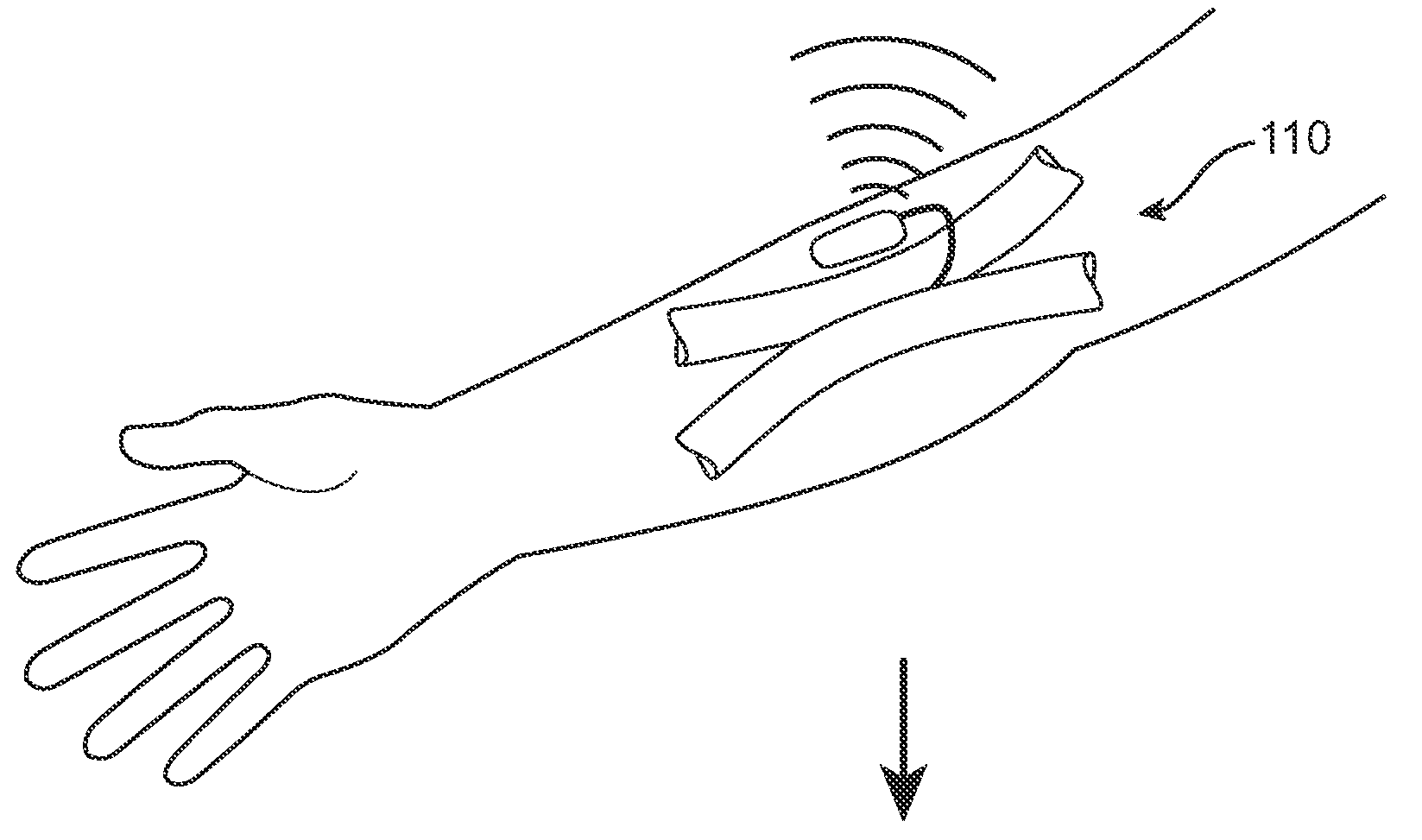
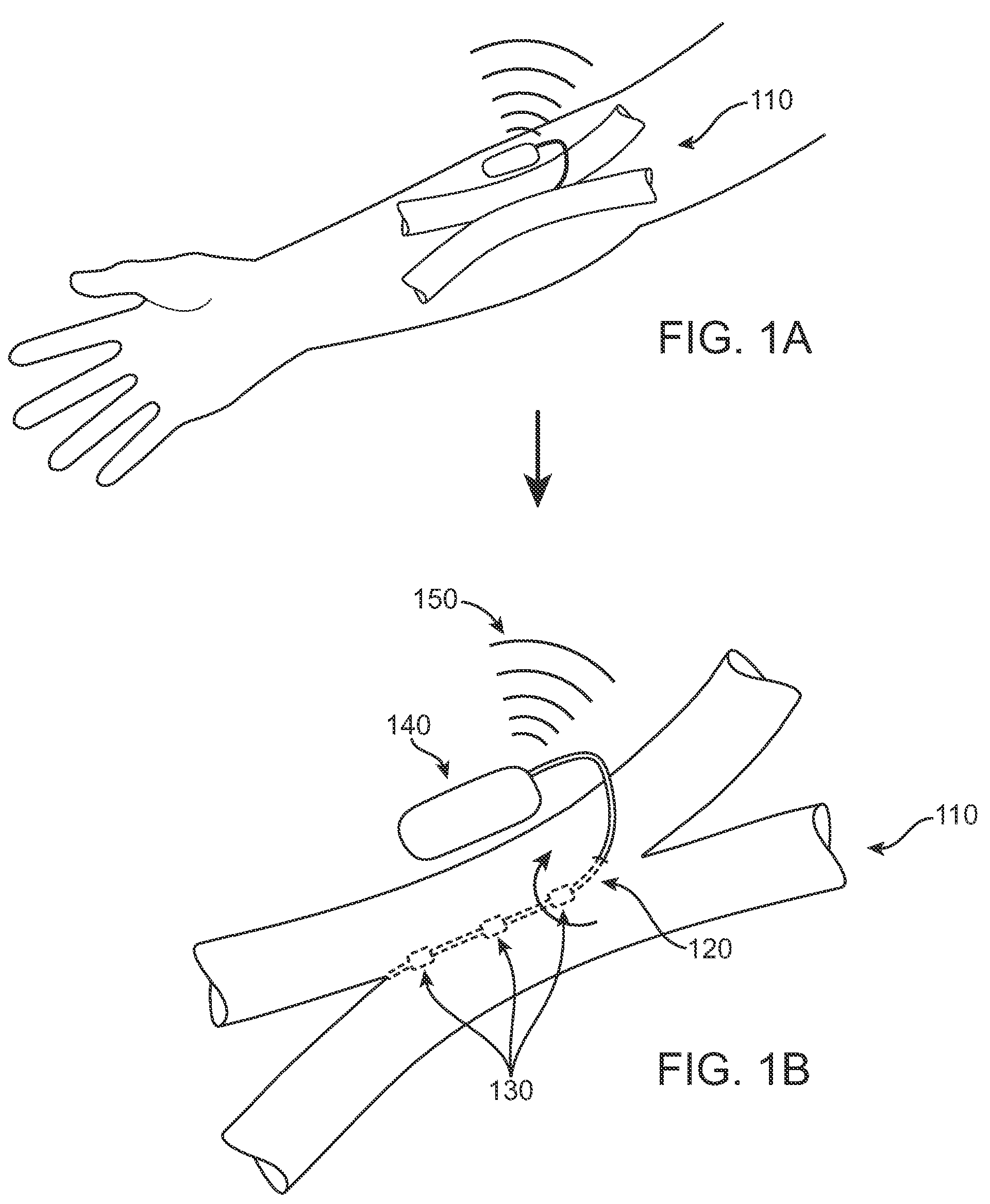
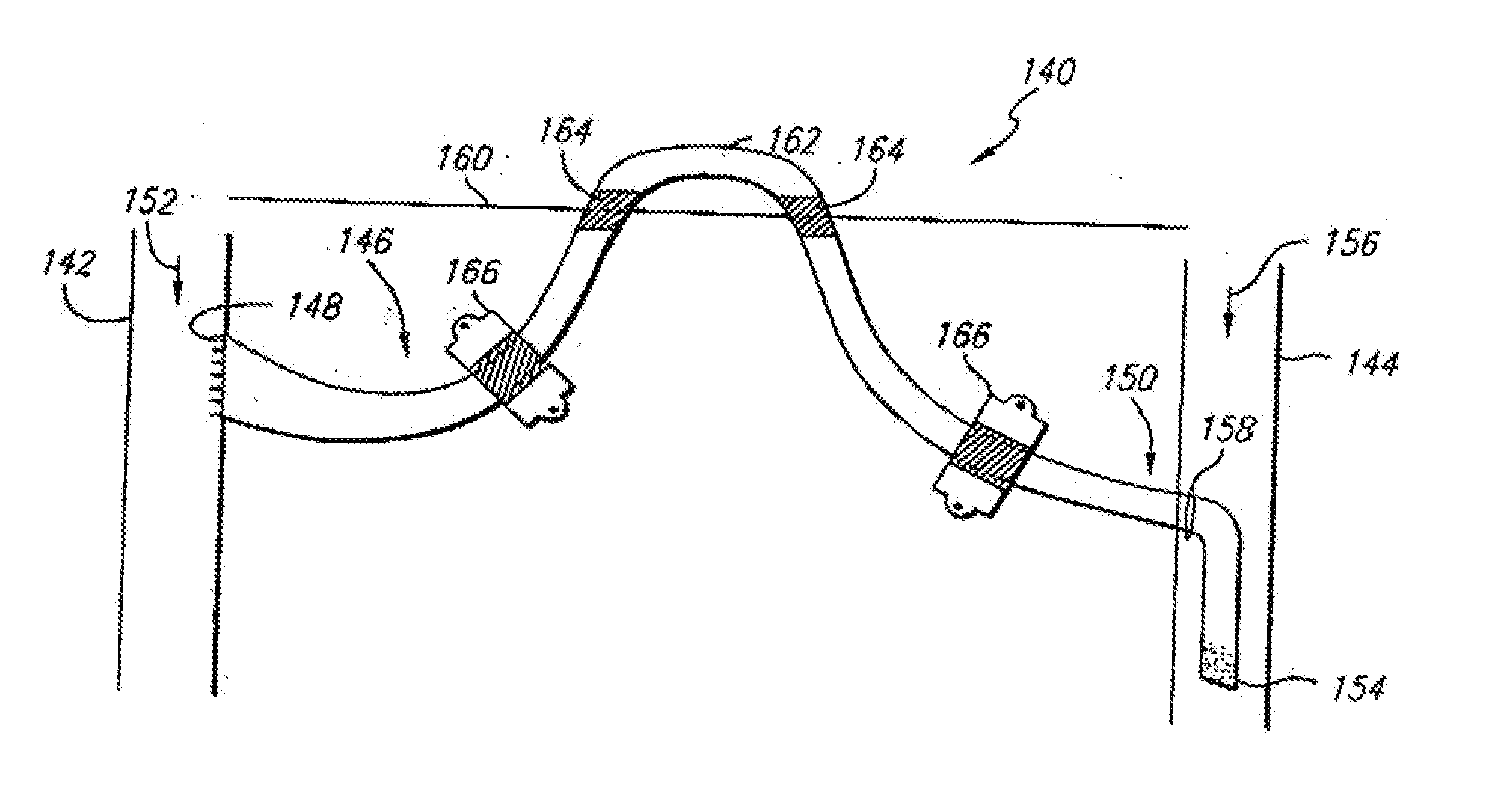
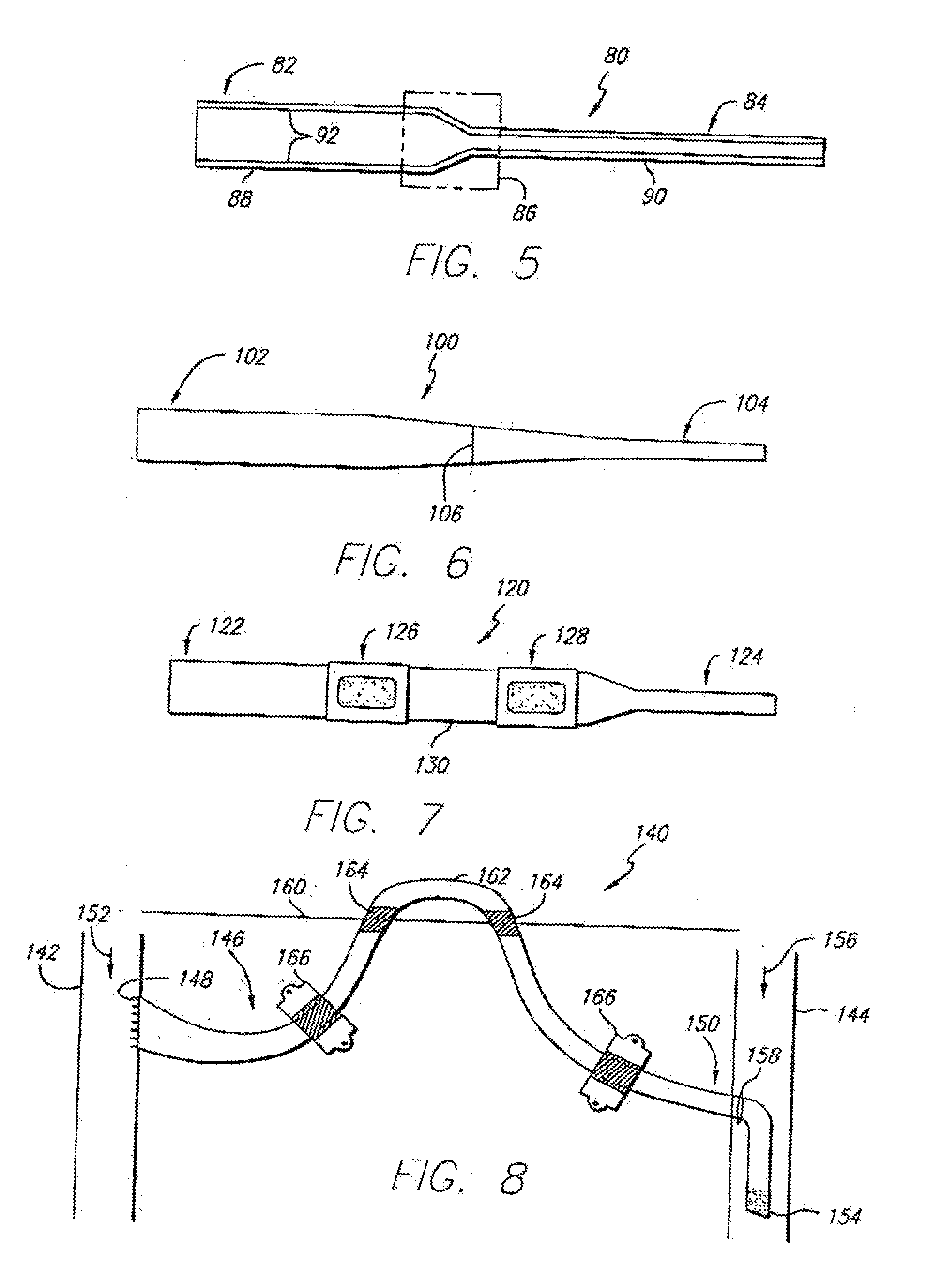
InactiveUS20150119908A1Less acceleratedConvenient and smoothSuction devicesWound clampsEntrance angleVein
A medical device includes a curved tubular body configured for being used as an extravascular device to support vein maturation following the formation of an arteriovenous fistula. The tubular body is curved. The tubular body has an entrance angle of less than about 40 degrees to improve blood flow from the artery into the vein. And the tubular body includes a cuff or edge at the proximal end to stabilize the tubular body at the fistula.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Coating film capable of adhering or directly adhering on blood vessel
ActiveCN102824198AWith thermal shrinkage and cold expansionEasy to operateSurgeryCoatingsCarotid-cavernous fistulaEmbolization material
The invention provides a coating film capable of adhering or directly adhering on blood vessel. Surface of the inventive artificial blood vessel coating film is coated with a nano-gel coating layer made from mixture of adhesive embolic material and poly(N-isopropylacrylamide). After release of the adhesive embolic material in the nano-gel coating layer, the artificial blood vessel coating film is tightly bonded with blood vessel intima, and simultaneously blocks aneurysm to isolate aneurysm from blood flow. The inventive coating film has the advantages of simple operation during surgery, low cost, and high safety and reliability; is suitable for pathology such as intracranial aneurysms, carotid cavernous fistula (CCF), arteriovenous fistula, thoracic aortic aneurysm and abdominal aortic aneurysm; and has wide application in medical field.
Owner:SHANGHAI SIXTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL
Device and method for establishing an artificial arterio-venous fistula
A shunt rivet for implantation in the aorta and inferior vena cava to treat chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and a method of treating chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Endovascular electrolytically detachable wire and tip for the formation of thrombus in arteries, veins, aneurysms, vascular malformations and arteriovenous fistulas
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
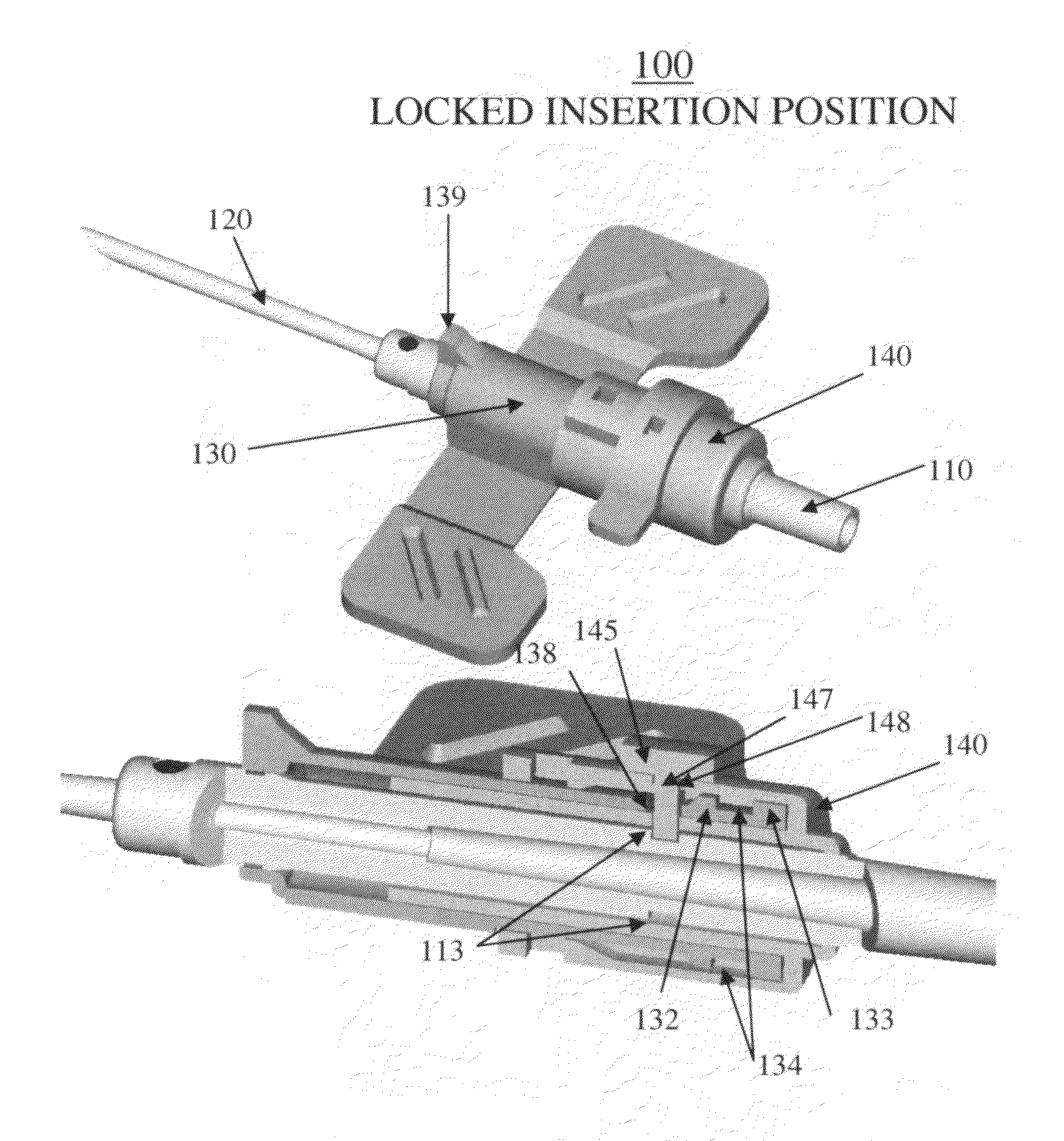
Graft-Catheter Vascular Access System
InactiveUS20130102950A1Prevent thrombosisEasy to optimizeOther blood circulation devicesSurgeryVeinVascular Access Devices
A vascular access device, for implantation at least partially below the skin of a patient to provide an arteriovenous fistula, includes a graft portion coupled to a catheter portion. The graft portion is sutured to an opening in an artery while the catheter portion is inserted into a vein so that its end lies within the vein downstream from the point of entry into the vein. The device may be comprised of ePTFE with an outer polyurethane coating or the graft portion may comprise ePTFE with an outer polyurethane coating and the catheter portion may comprise polyurethane. There may also be an inner polyurethane coating. Alternatively, the device may be comprised entirely of polyurethane.
Owner:CR BARD INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com