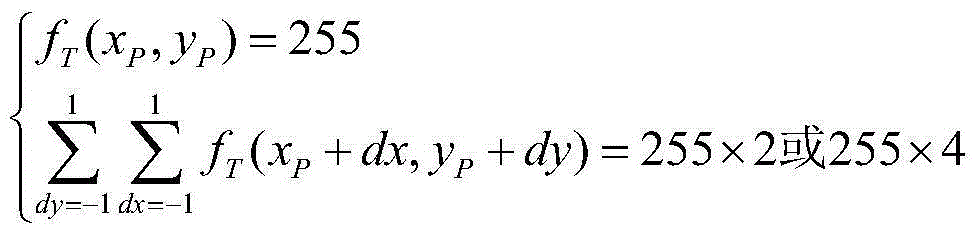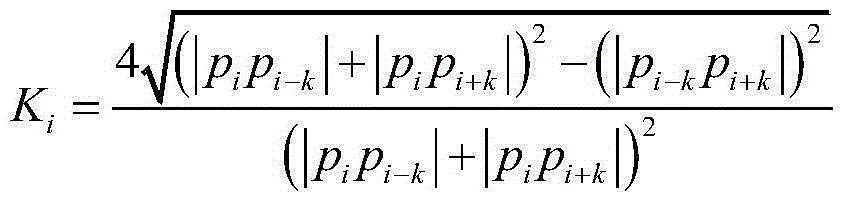Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
64 results about "Venous line" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
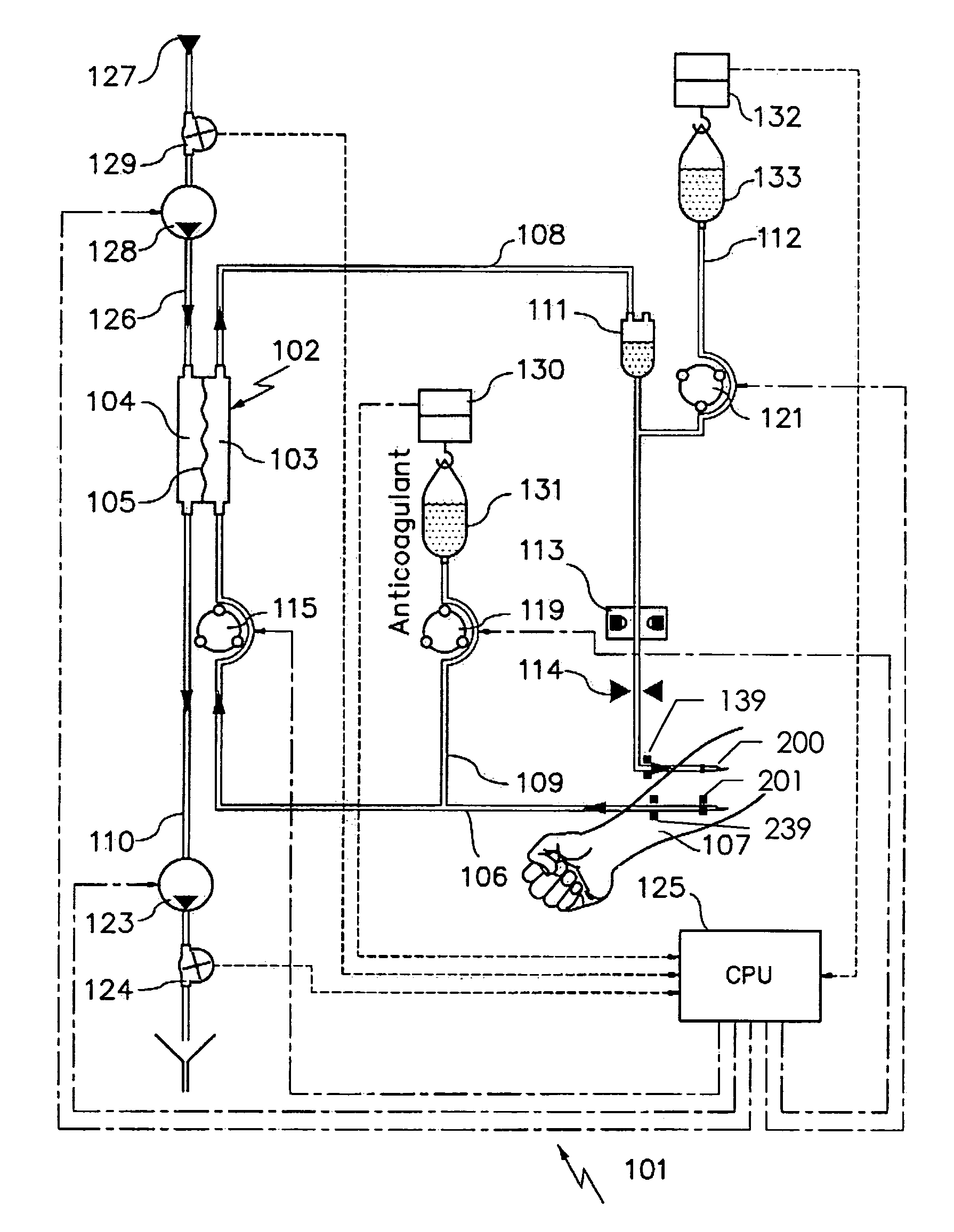
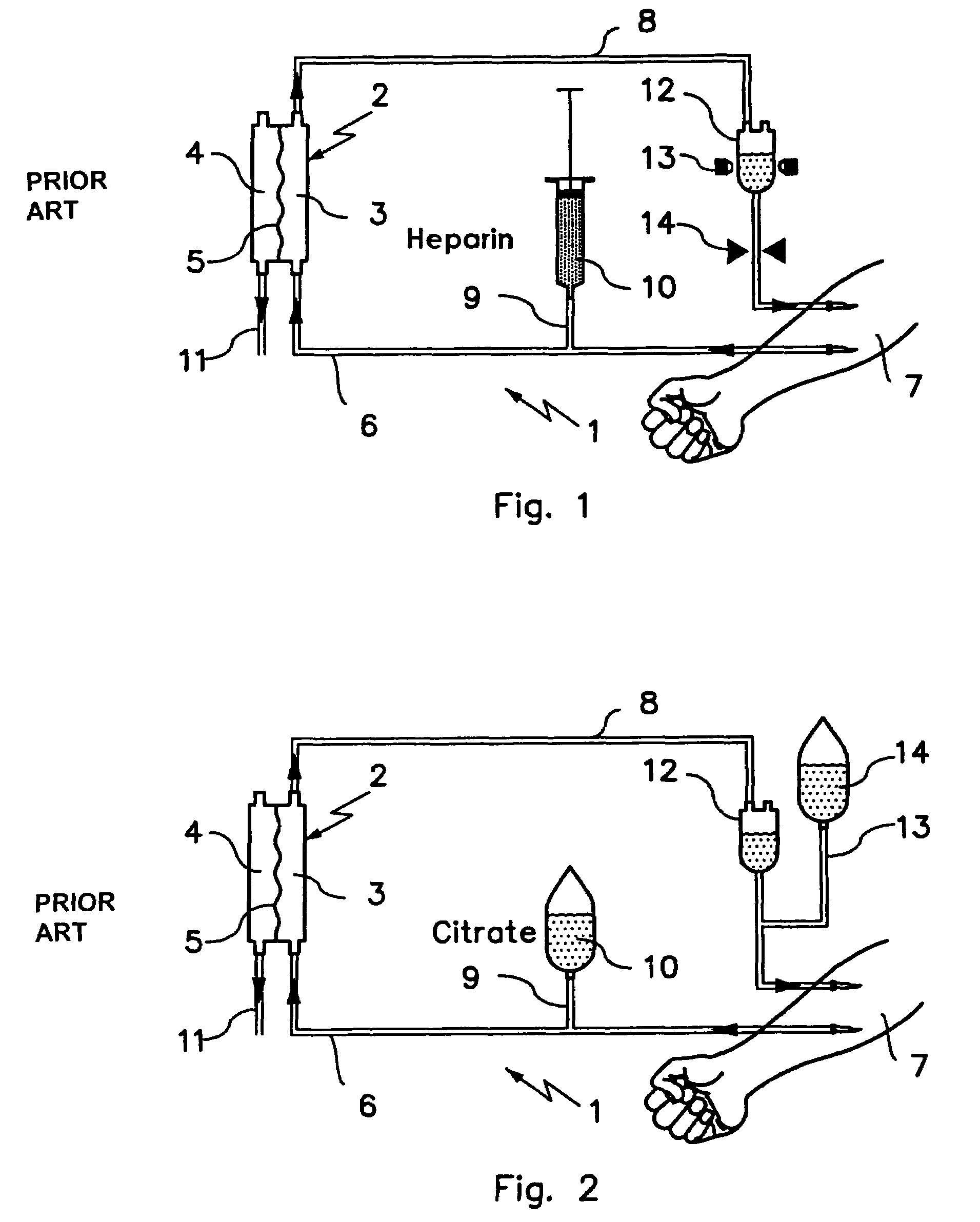
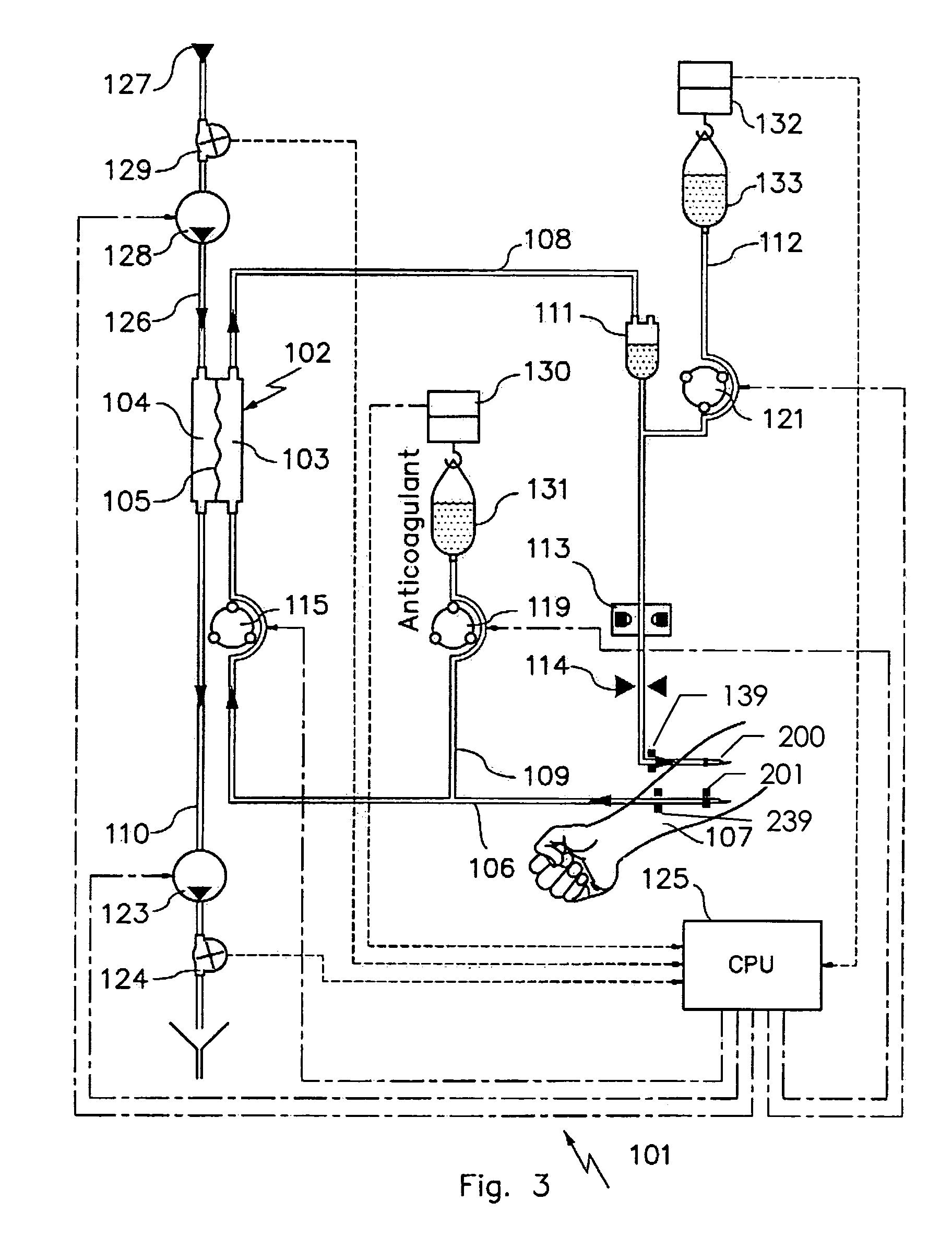
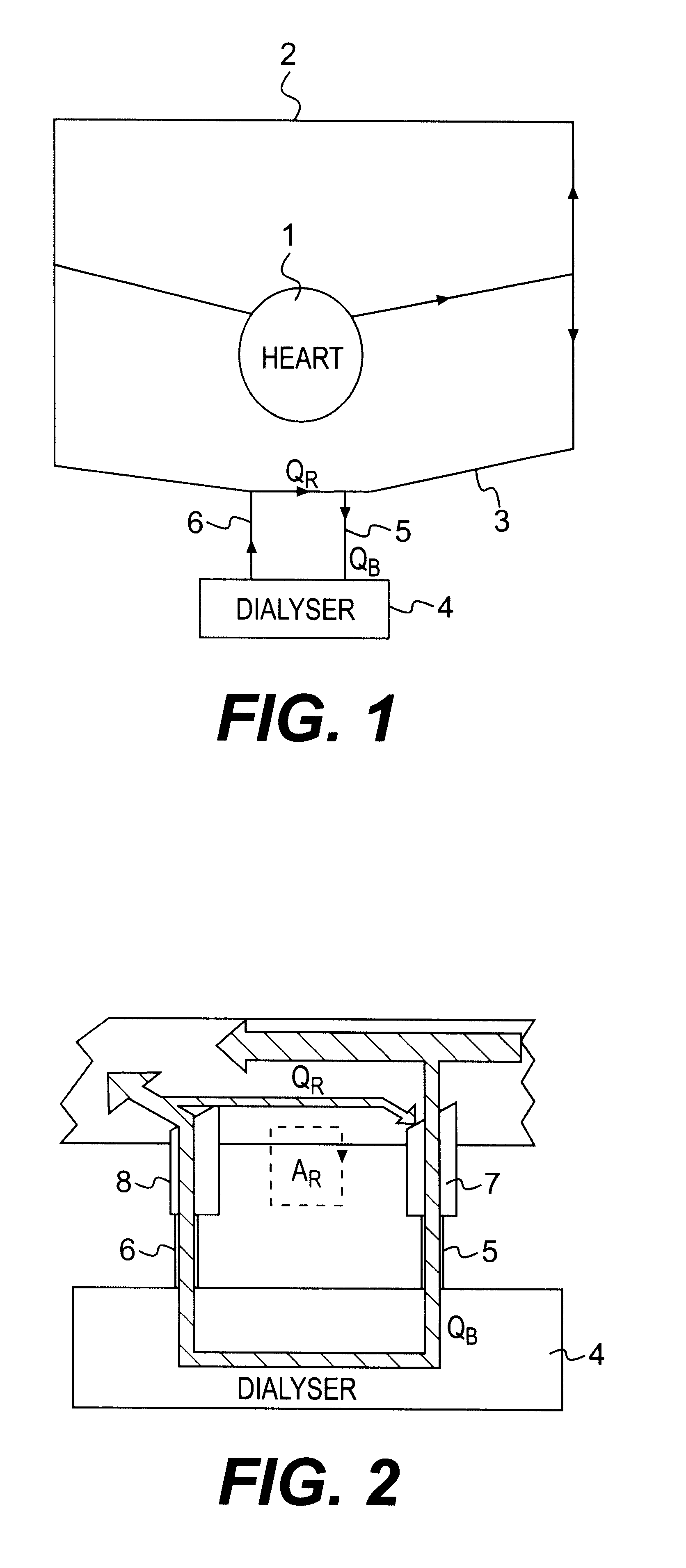
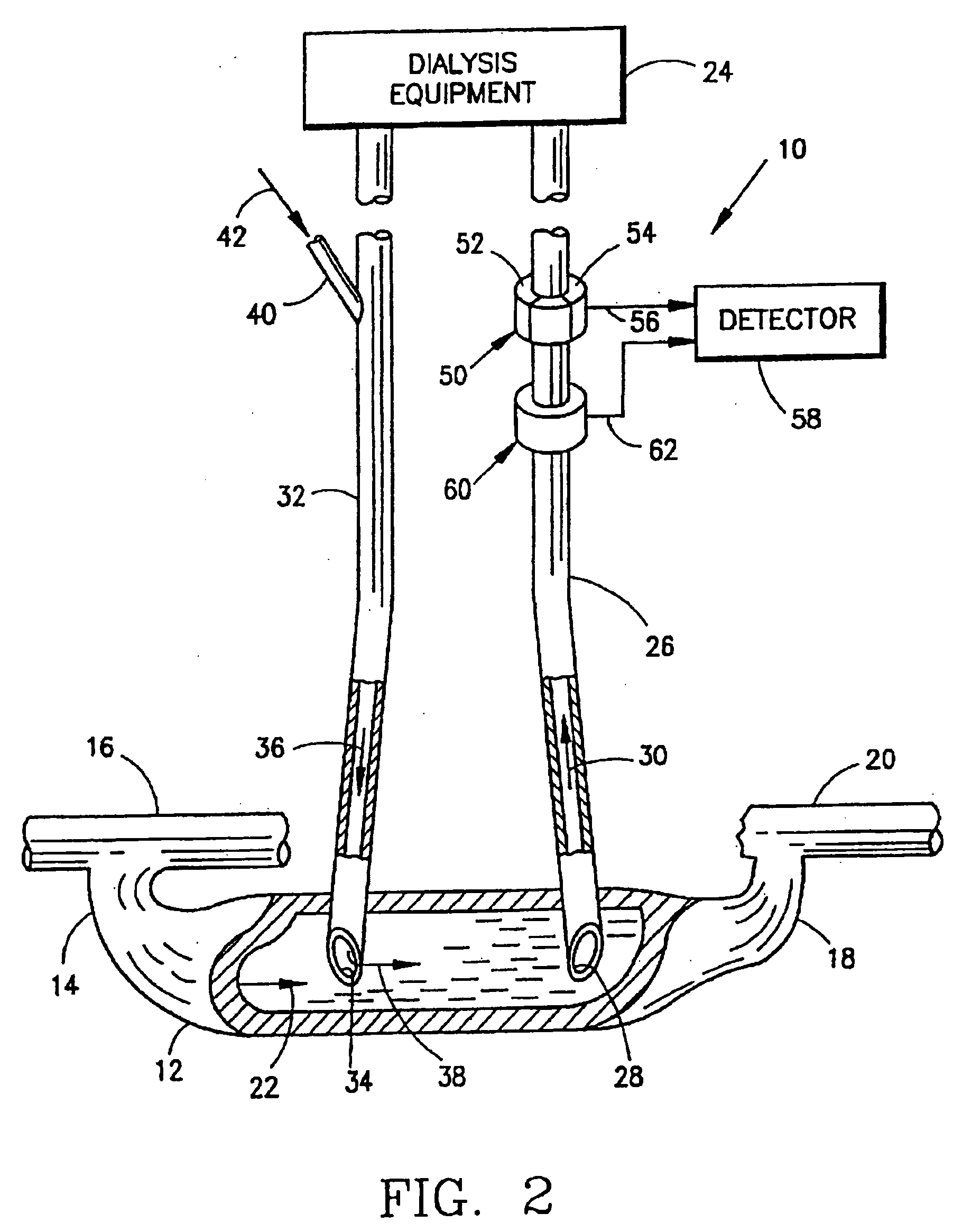
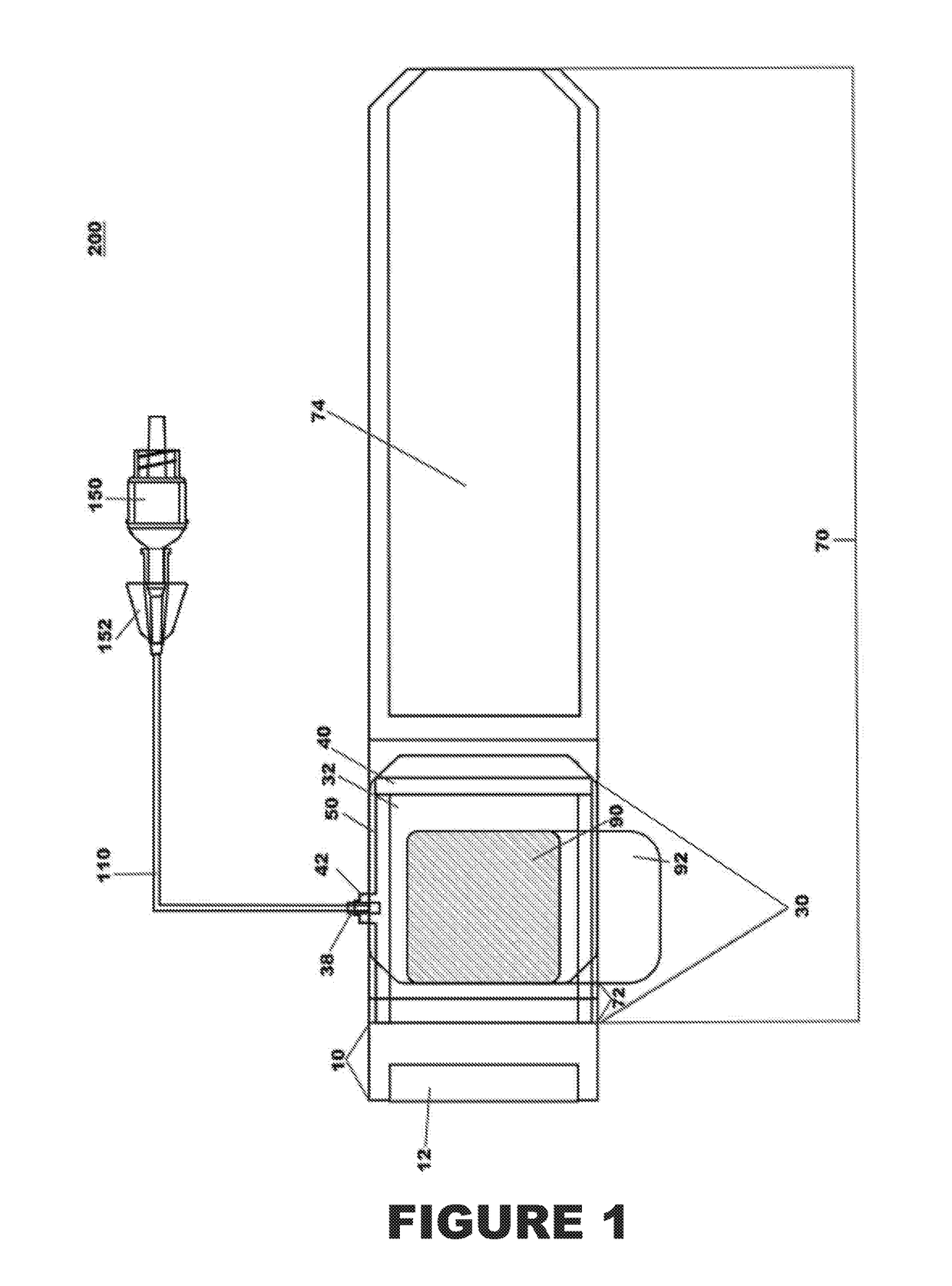
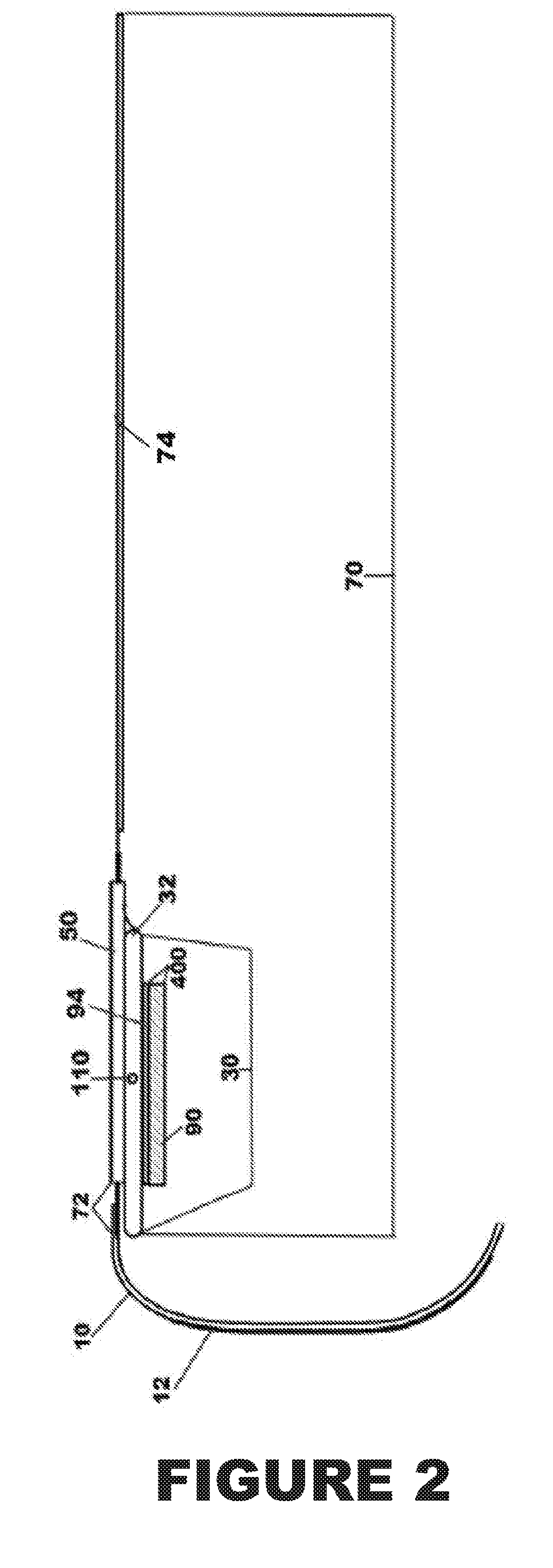
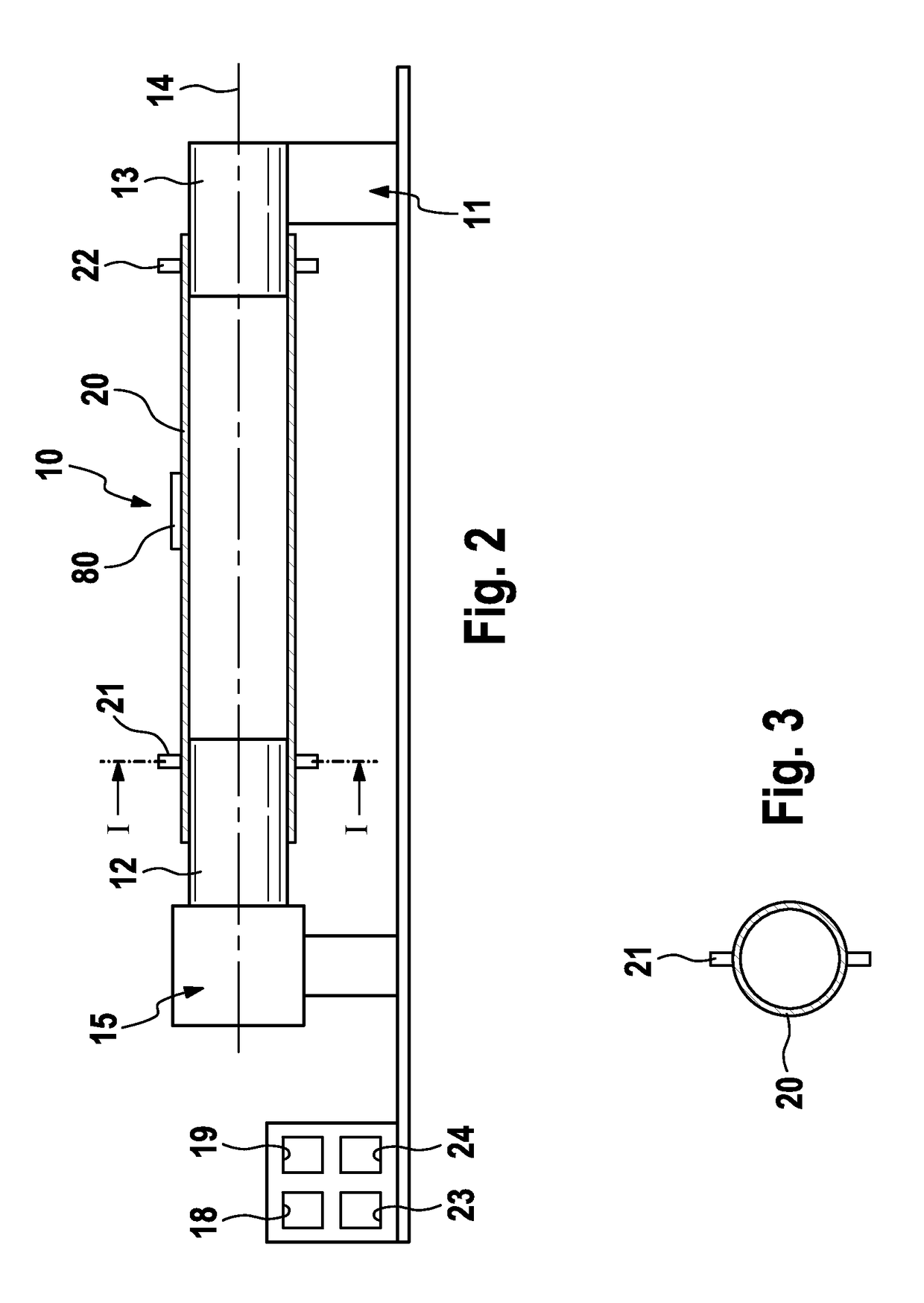
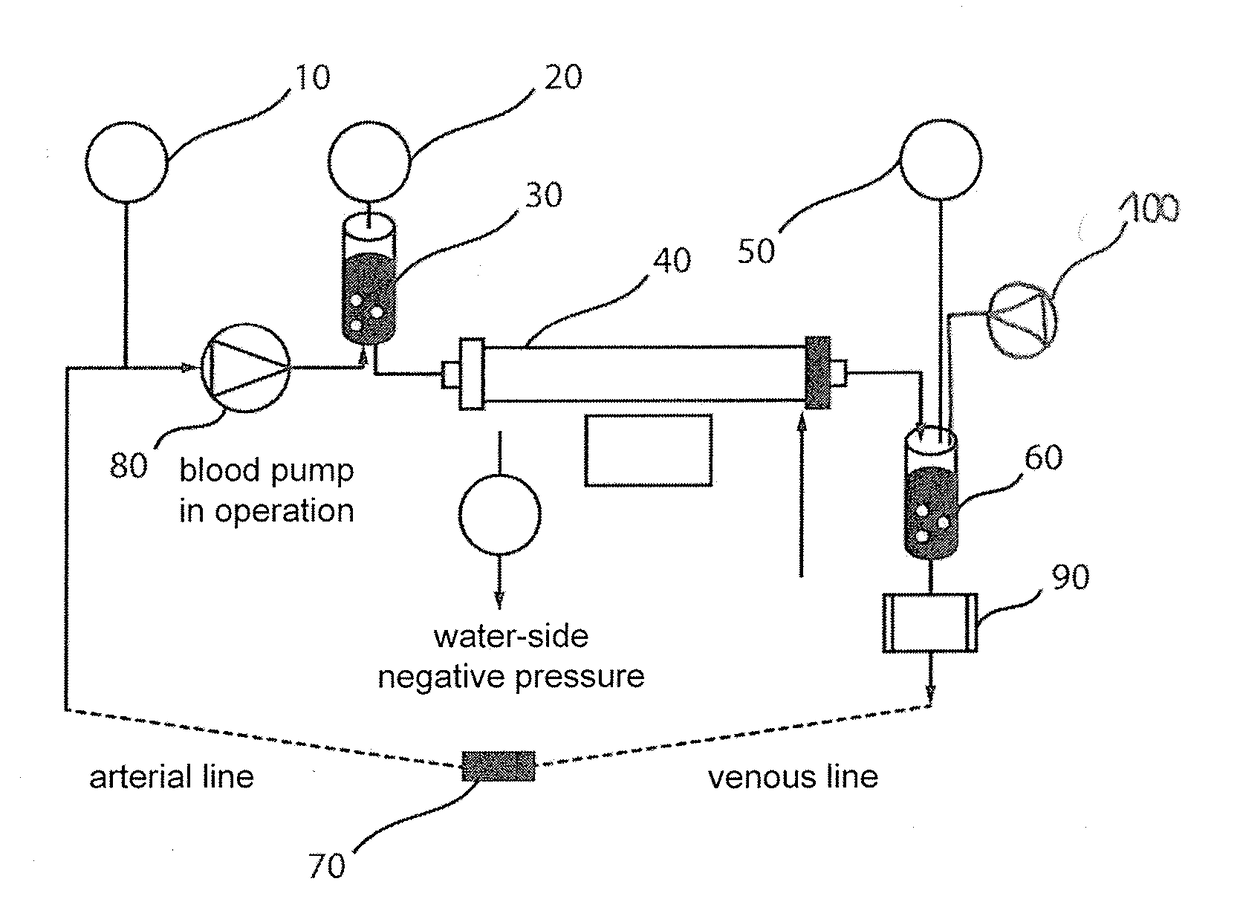
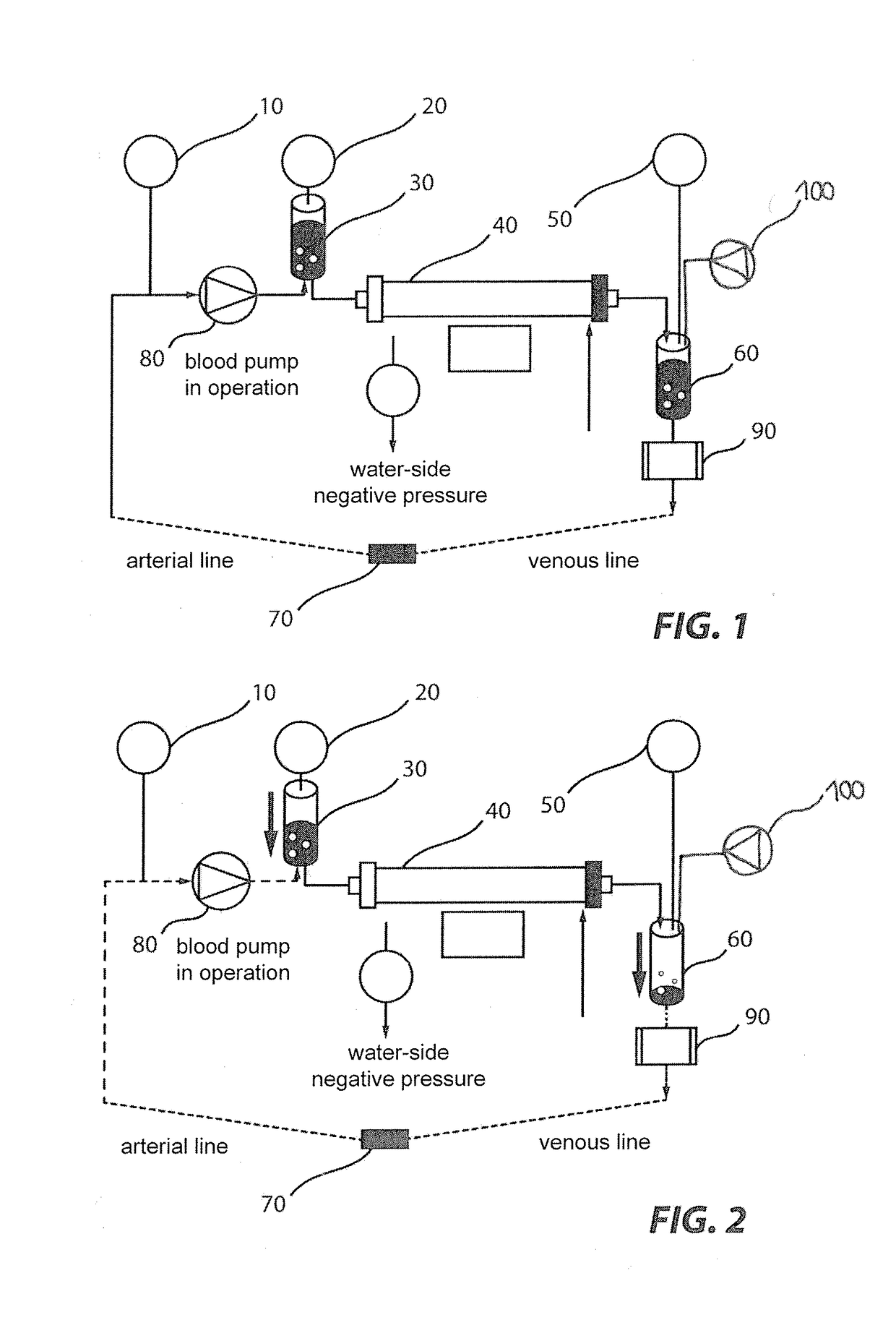
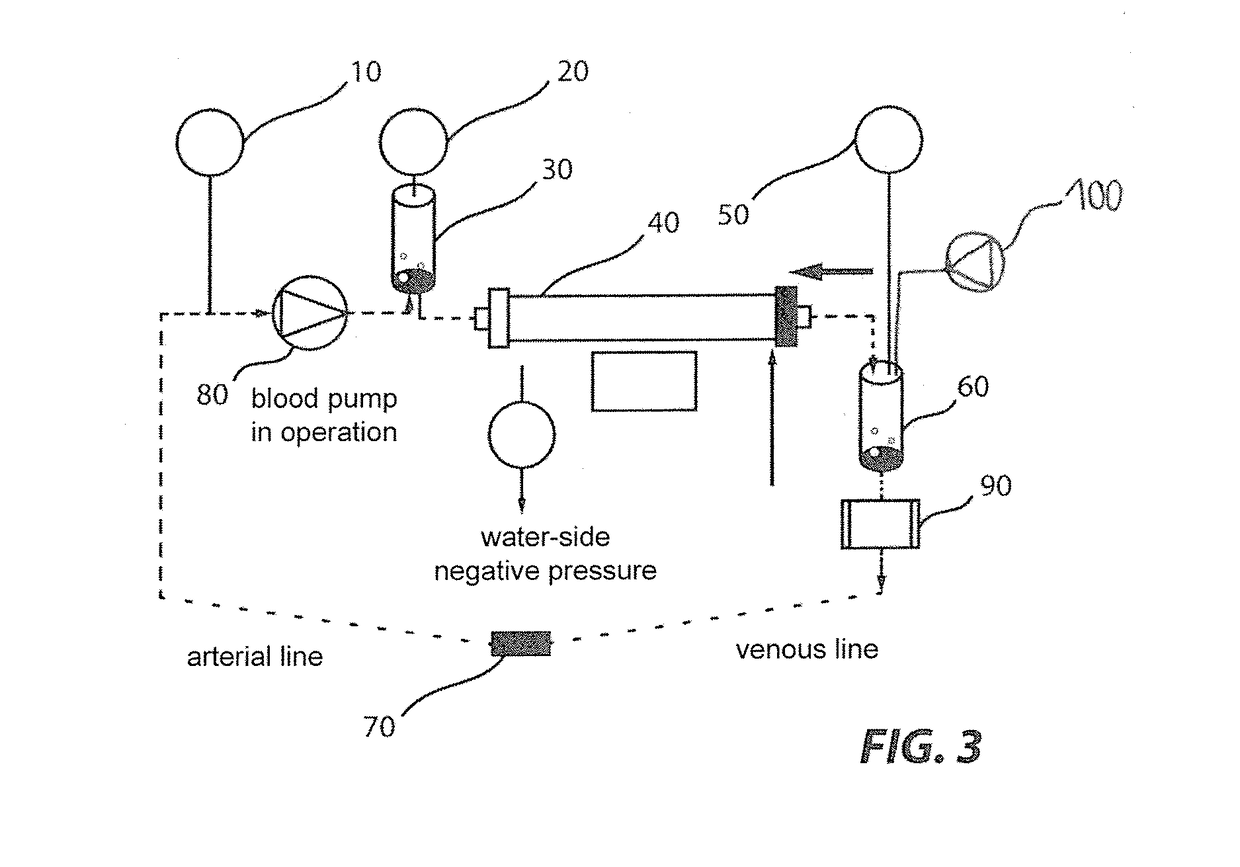
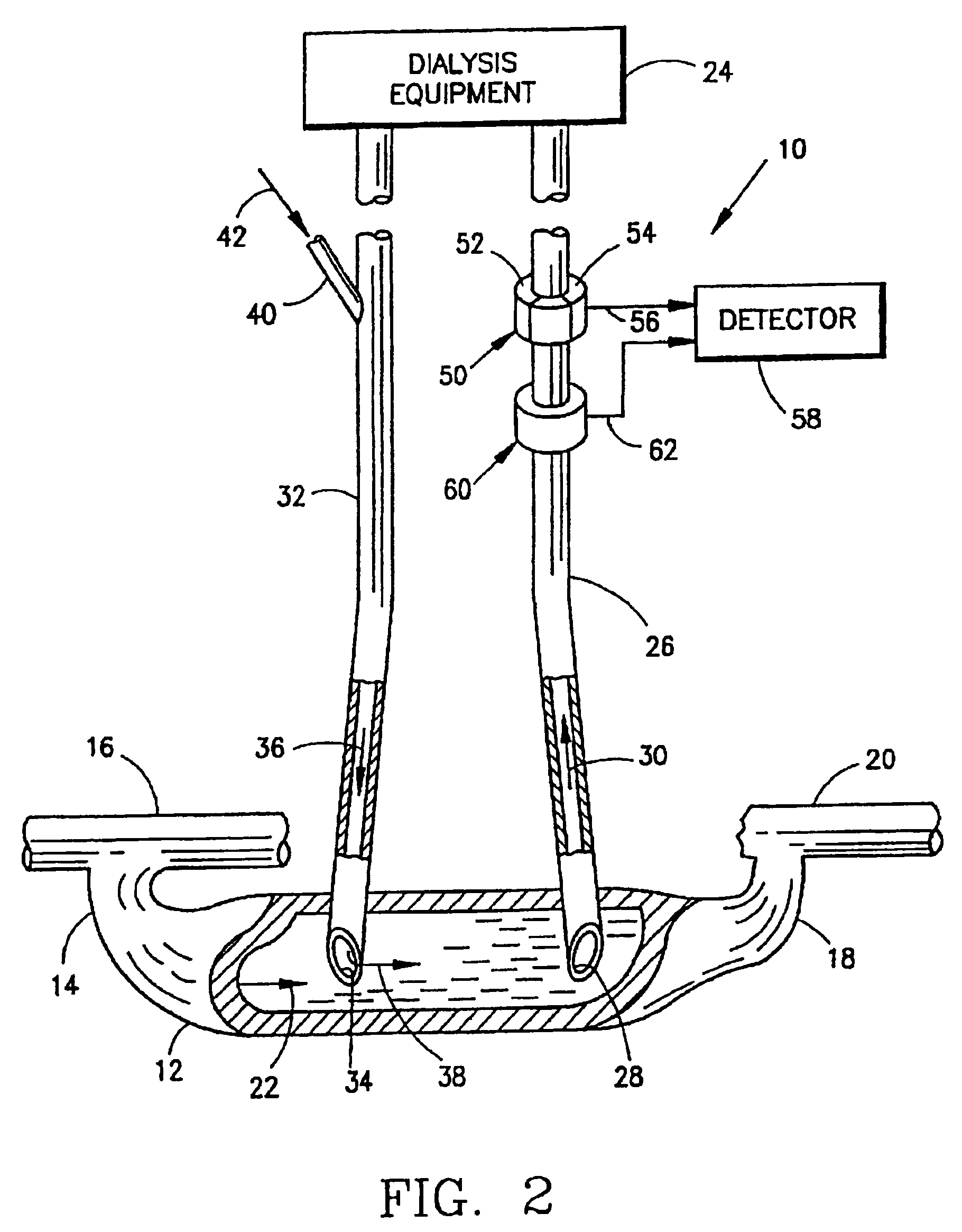
Device and process for extracorporeal treatment by citrate anticoagulant
ActiveUS7351218B2Inhibit blood coagulationSimple structureOther blood circulation devicesHaemofiltrationExtracorporeal circulationVein
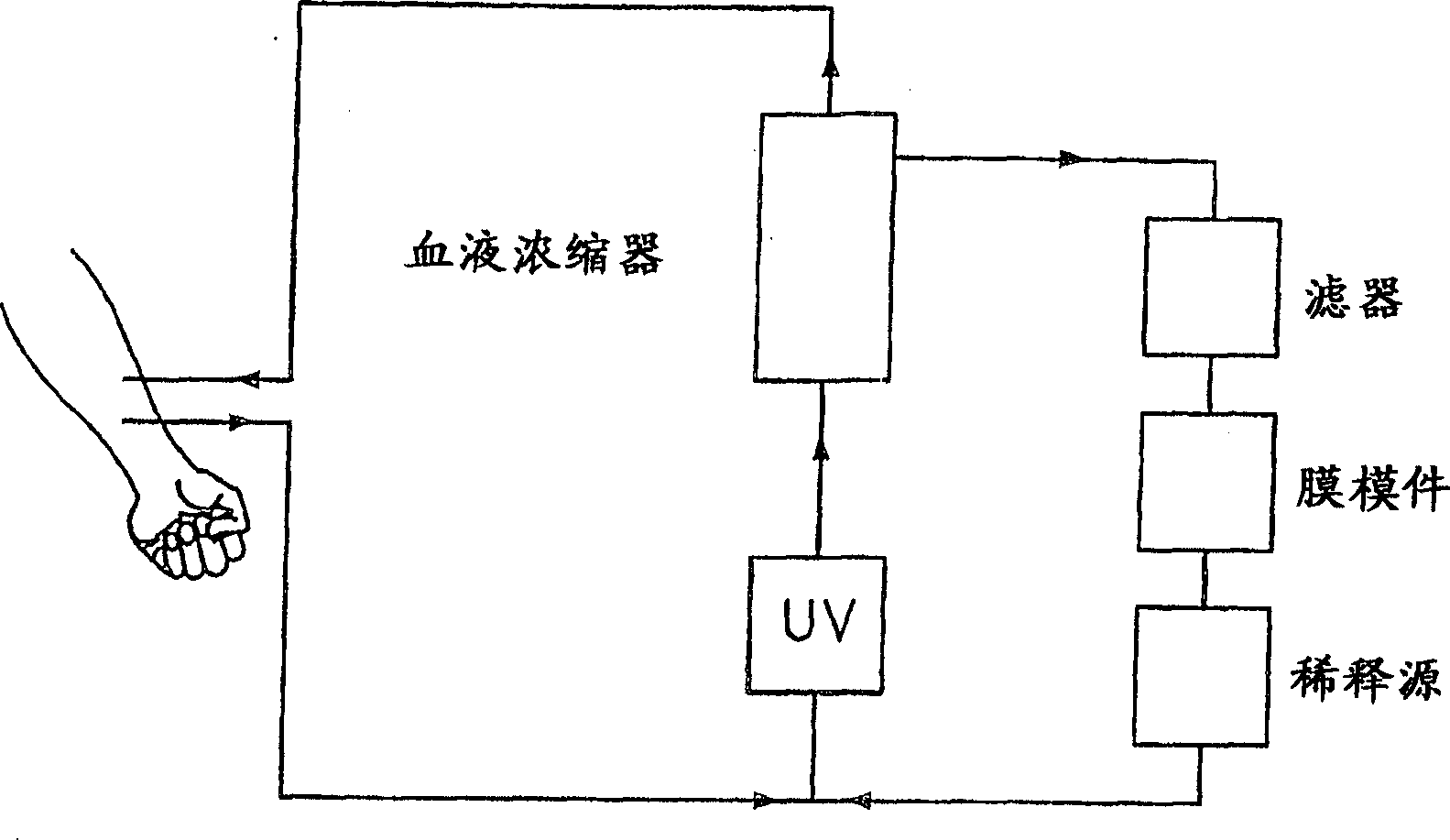
A device for treating blood by extracorporeal circulation comprising a filter having a first chamber and a second chamber separated by a semi-permeable membrane. The device has an arterial line connected to the first chamber of the filter, a venous line issuing from the first chamber of the filter, a channel used for pre-infusion of a substance for regional anticoagulation and linked to the arterial line, a purge channel issuing from the second chamber of the filter, and an air separator on the venous line. The device also includes a line for post-infusion of a solution at least partially re-establishing the ionic equilibrium of the blood downstream of the air separator, the post-infusion line being configured immediately upstream of an air detector.
Owner:GAMBRO LUNDIA AB
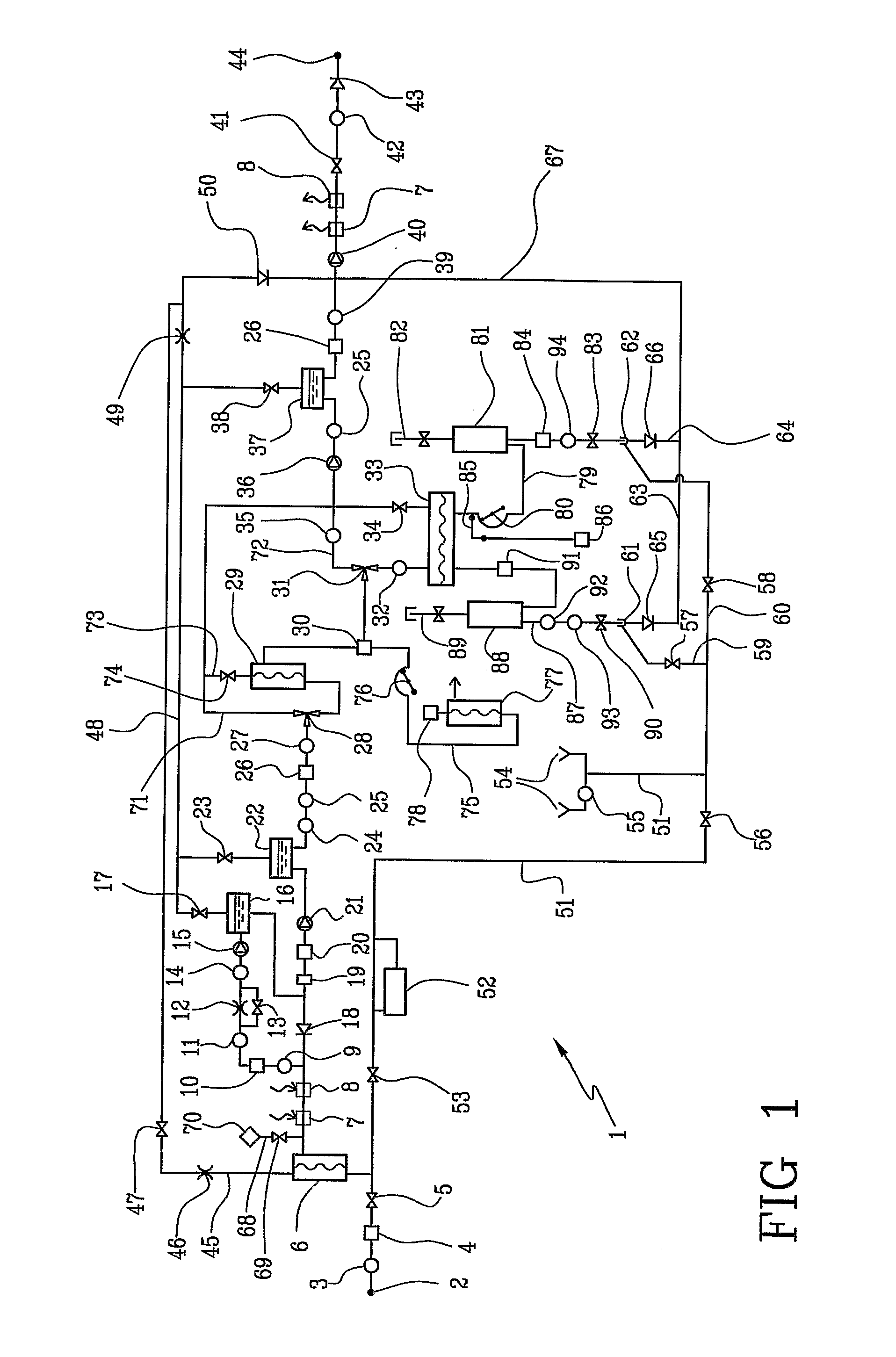
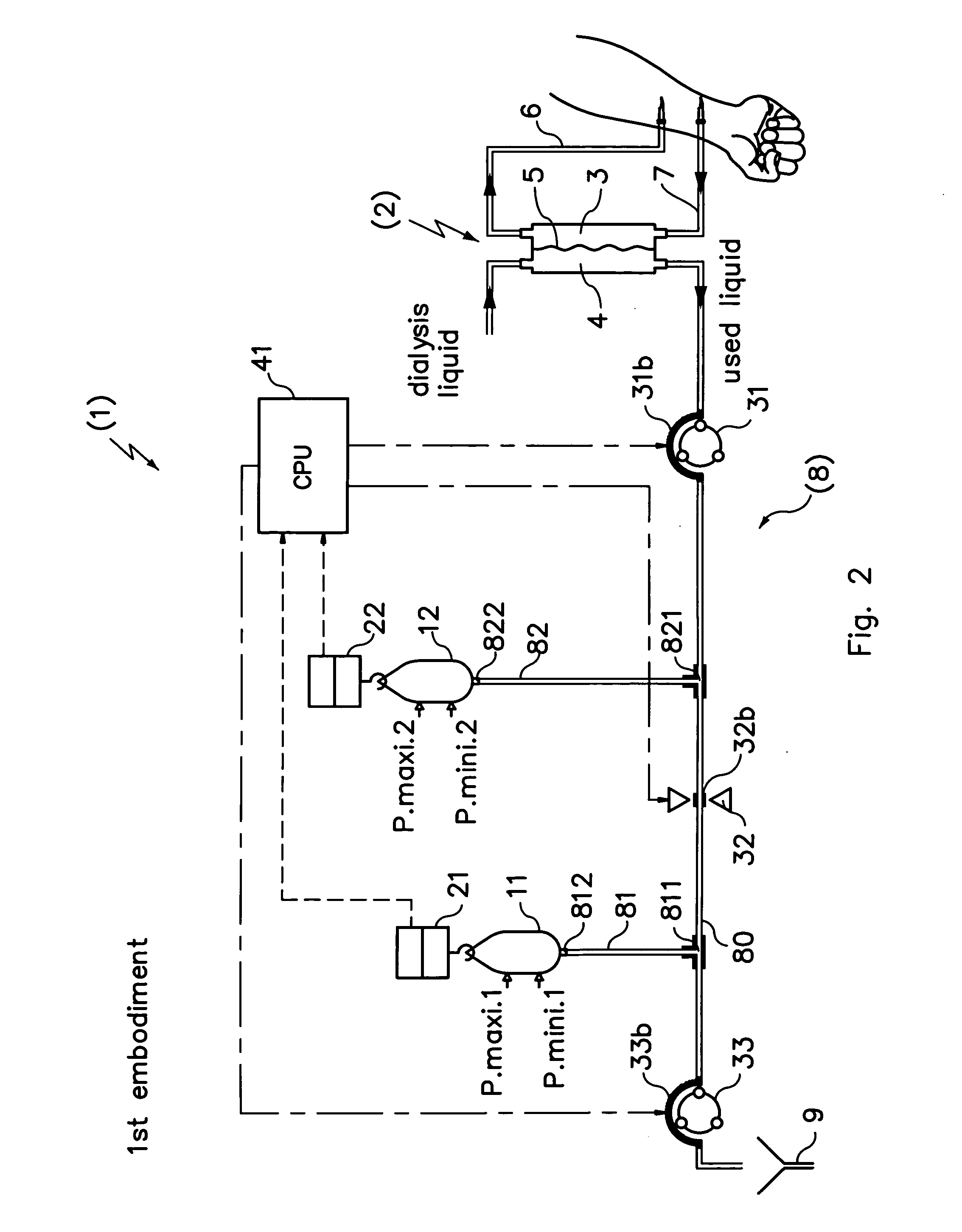
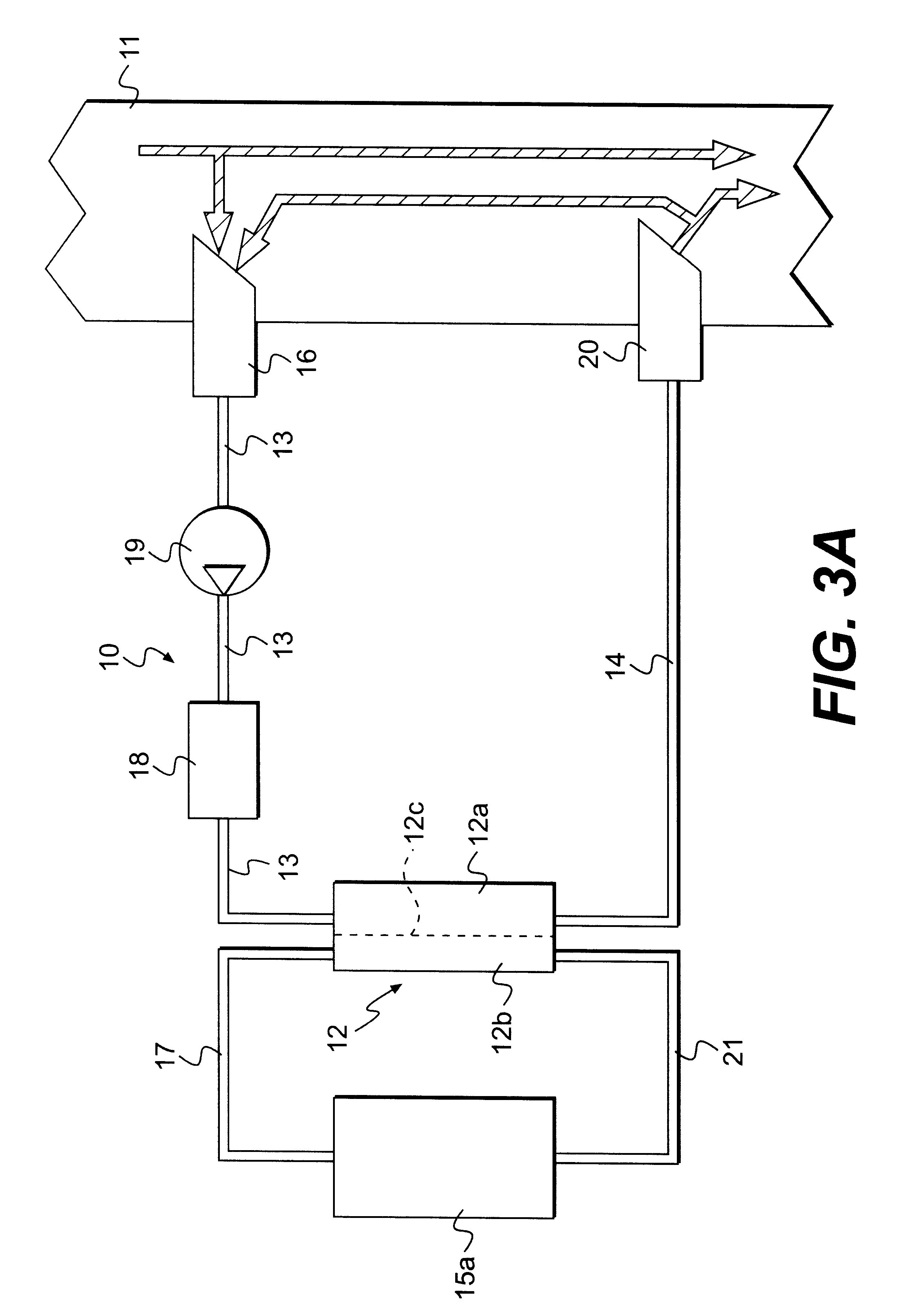
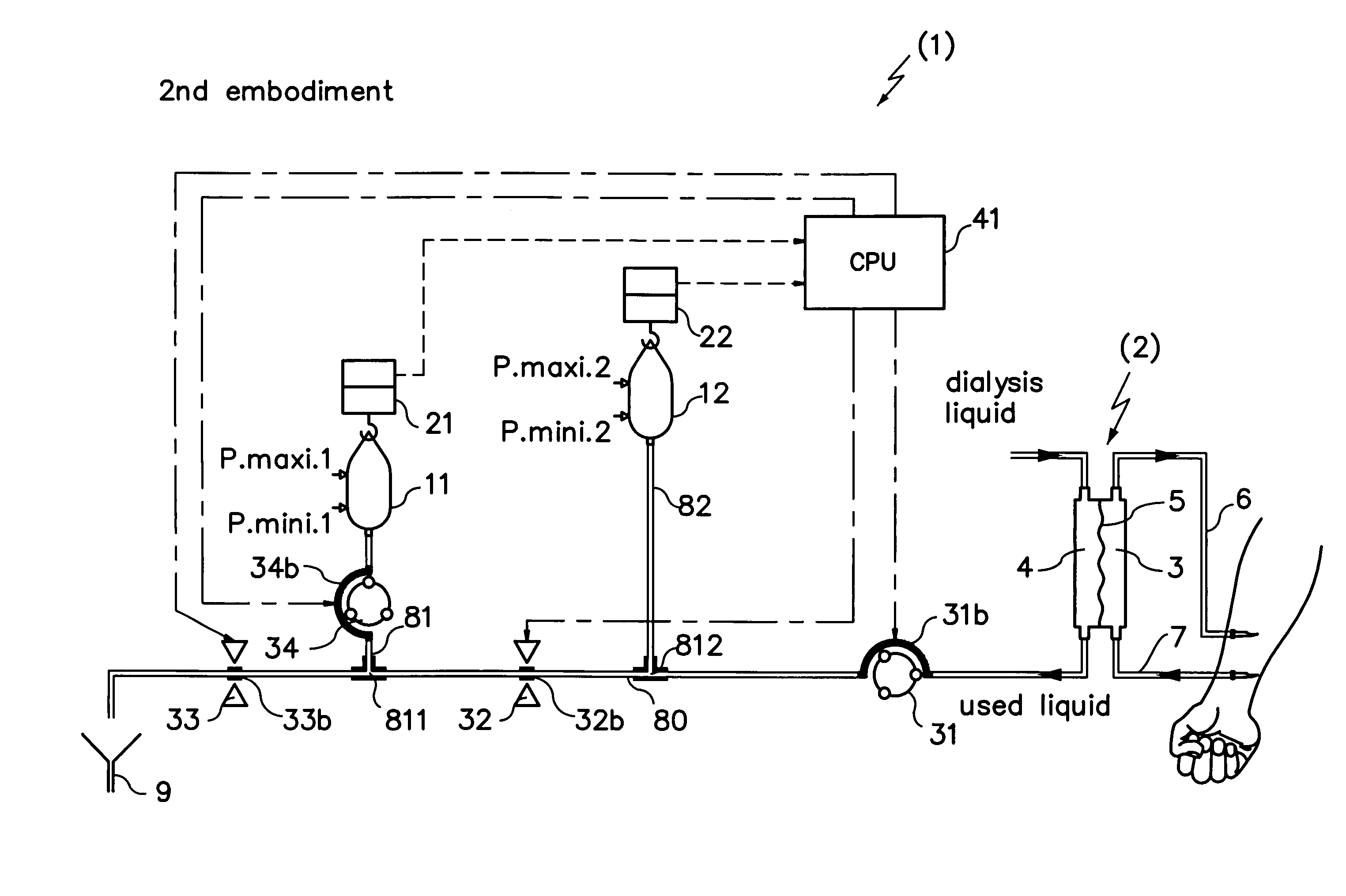
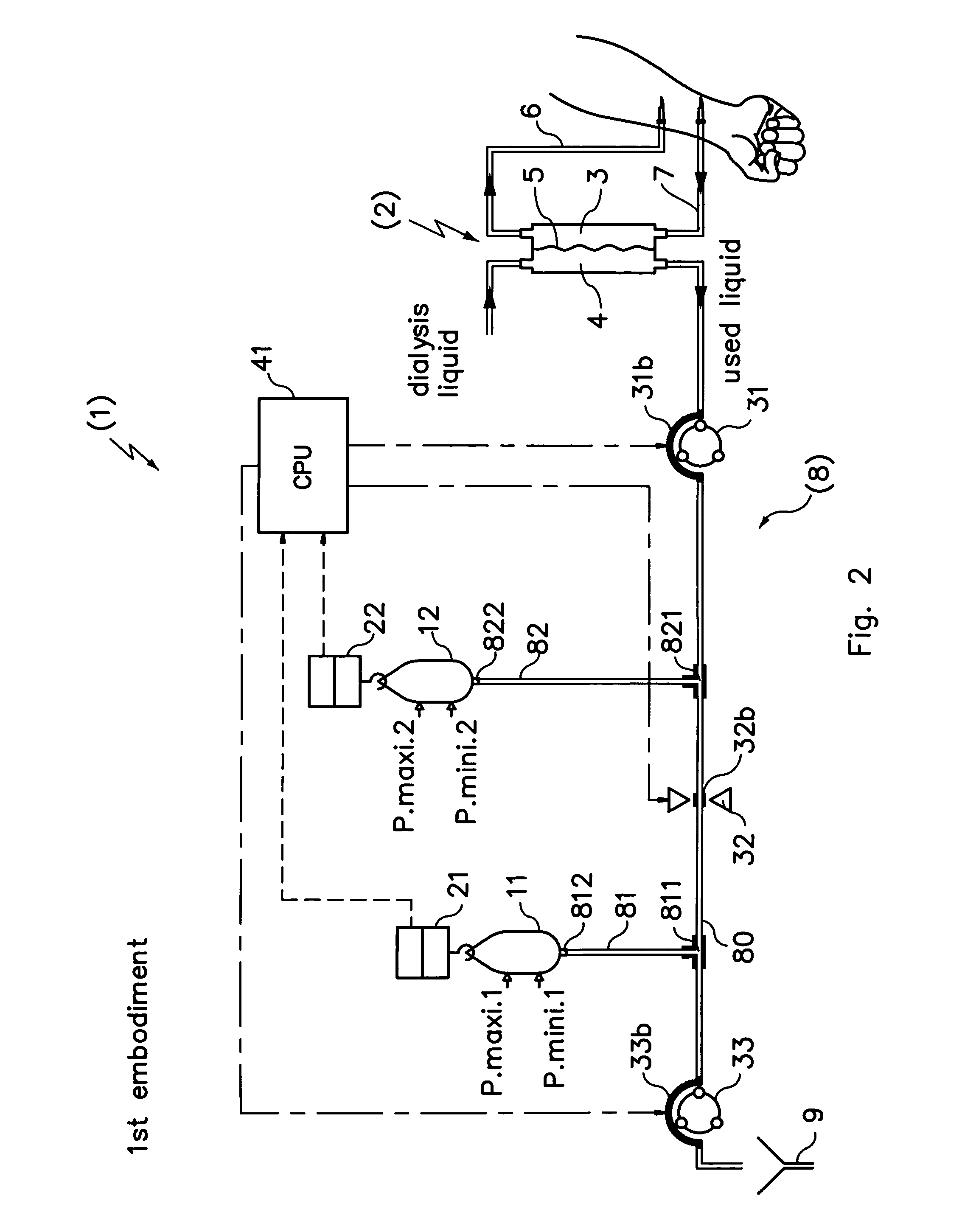
Dialysis machine, in particular for home use
The invention concerns a dialysis machine (10) comprising a dialyzer (20) having a first inlet (21) and a first outlet (22) for the bloodstream, dialysate supply mechanism (25), an arterial line (16) connected between the patent's arteriovenous fistula and the dialyzer, a venous line (17) connected between the arteriovenous fistula and the dialyzer, a pump (28) coupled with the arterial line, a dialysate supply line (31), connected between the dialysate supply mechanism and the dialyzer, a dialysate evacuation line (33) connected between a dialysate recuperating container (27) and the dialyzer. The sterile dialysate bags are arranged in a chamber (26) under a gas pressure.
Owner:PHYSIDIA
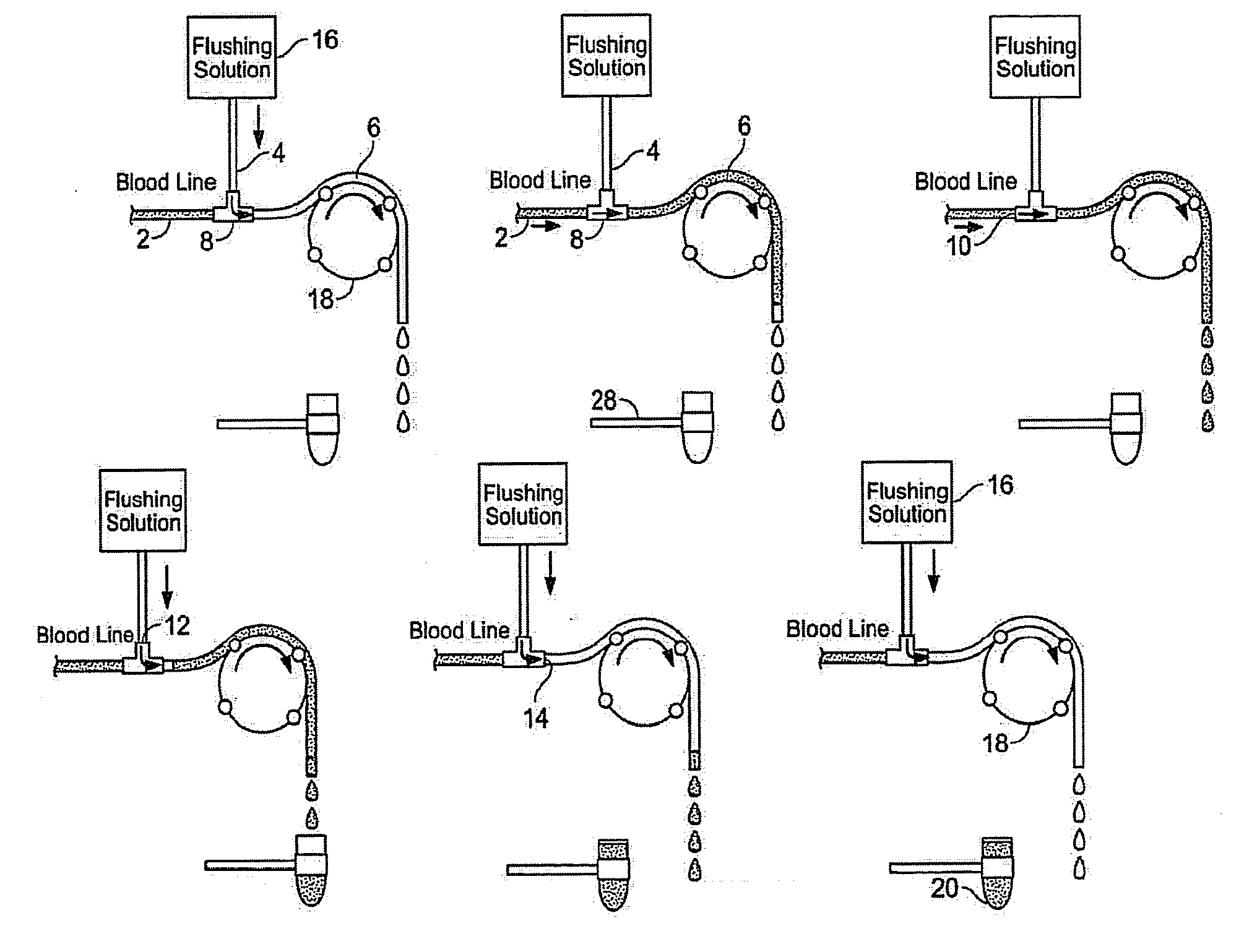
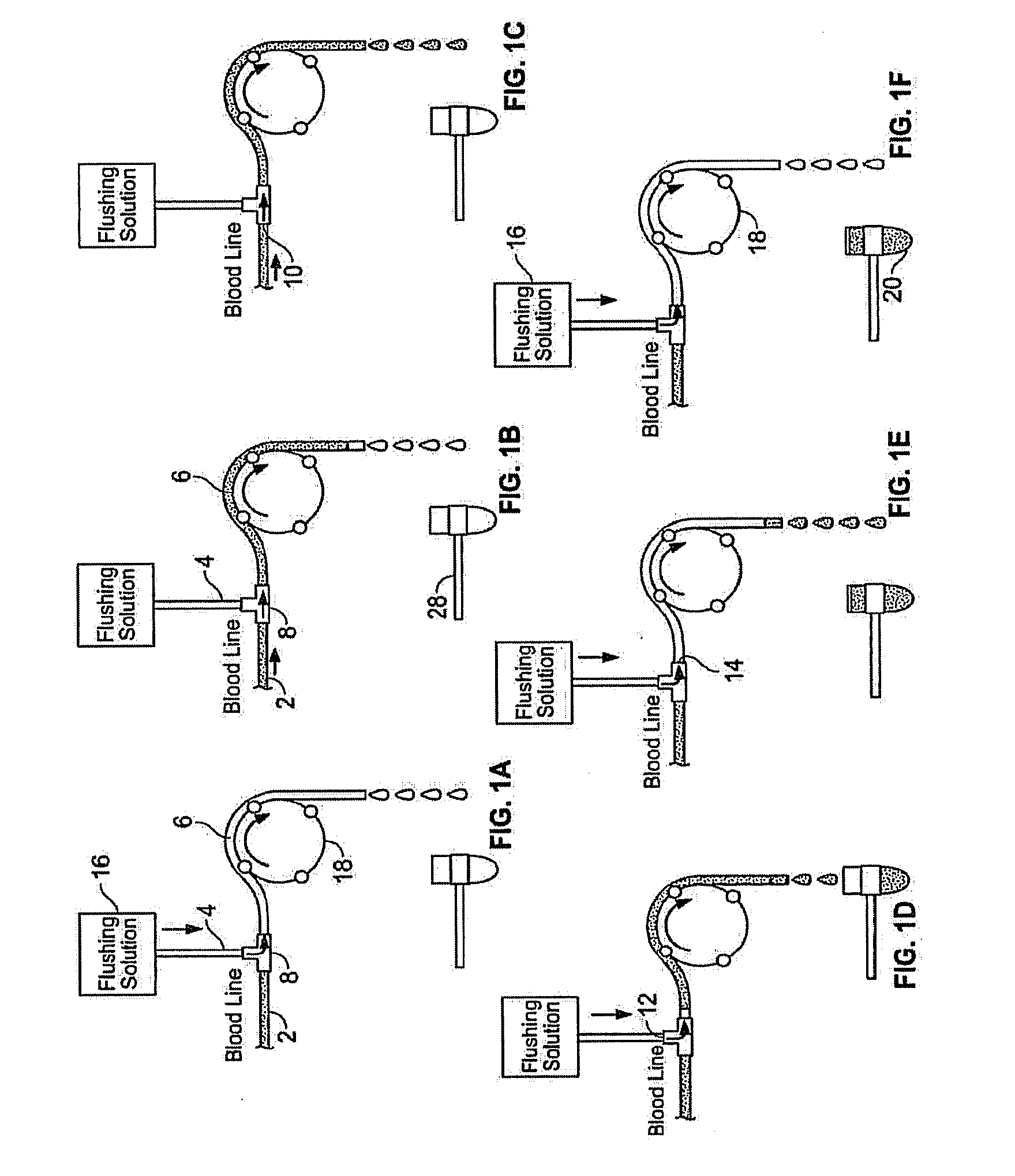
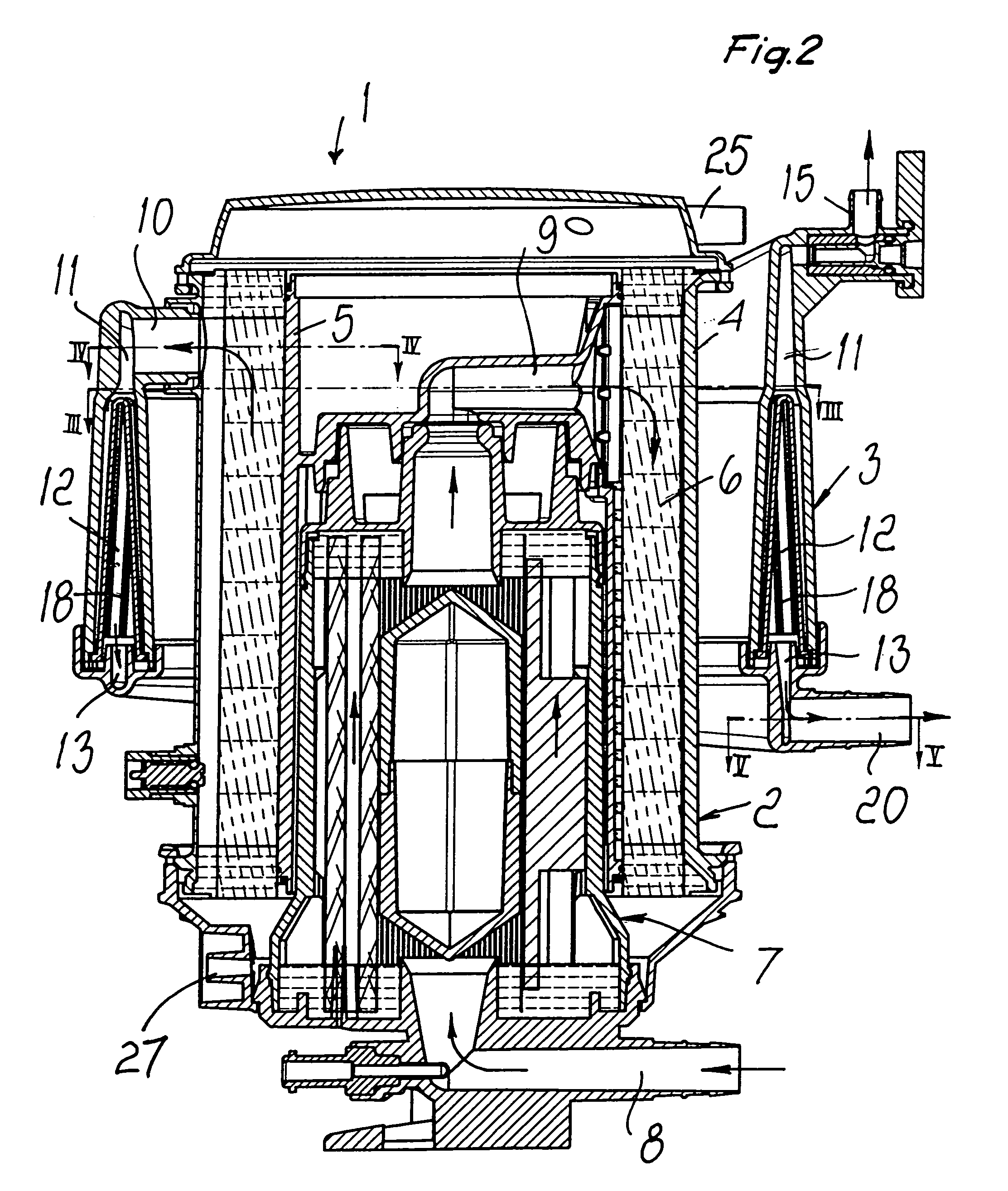
Method and apparatus for priming an extracorporeal blood circuit
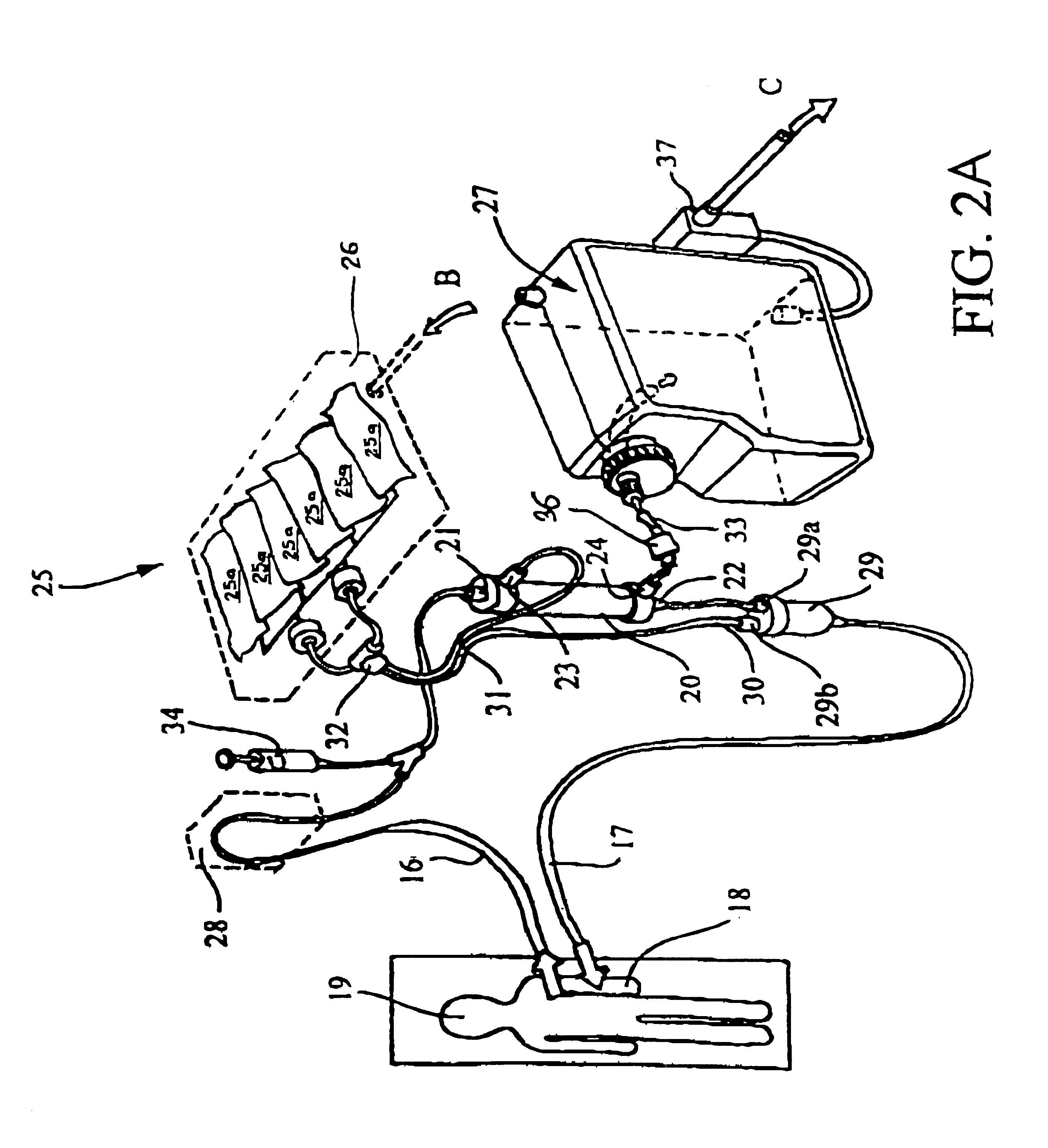
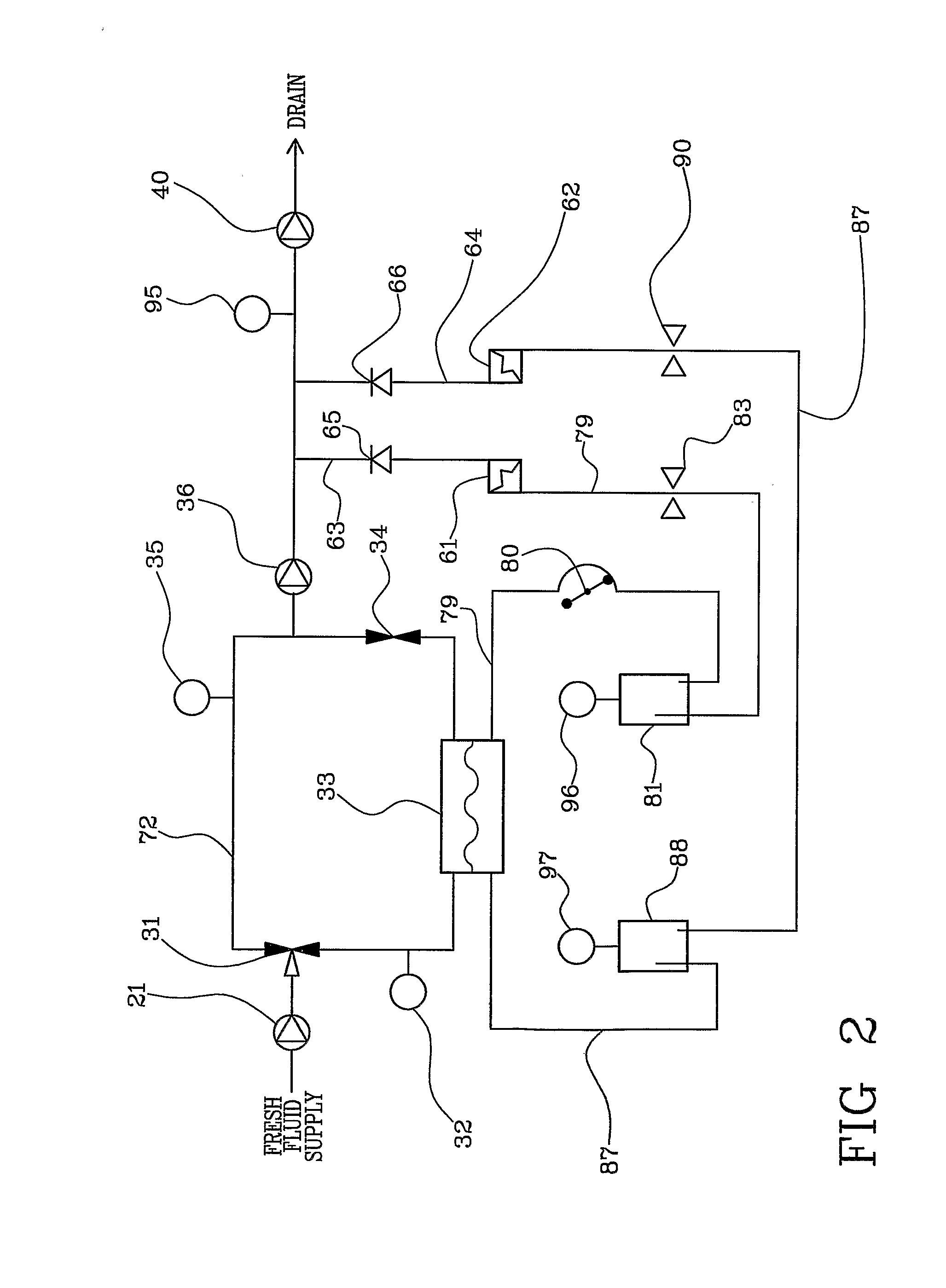
ActiveUS20120265117A1Facilitates taskShorten working timeMedical devicesReciprocating systemExtracorporeal circulationVein
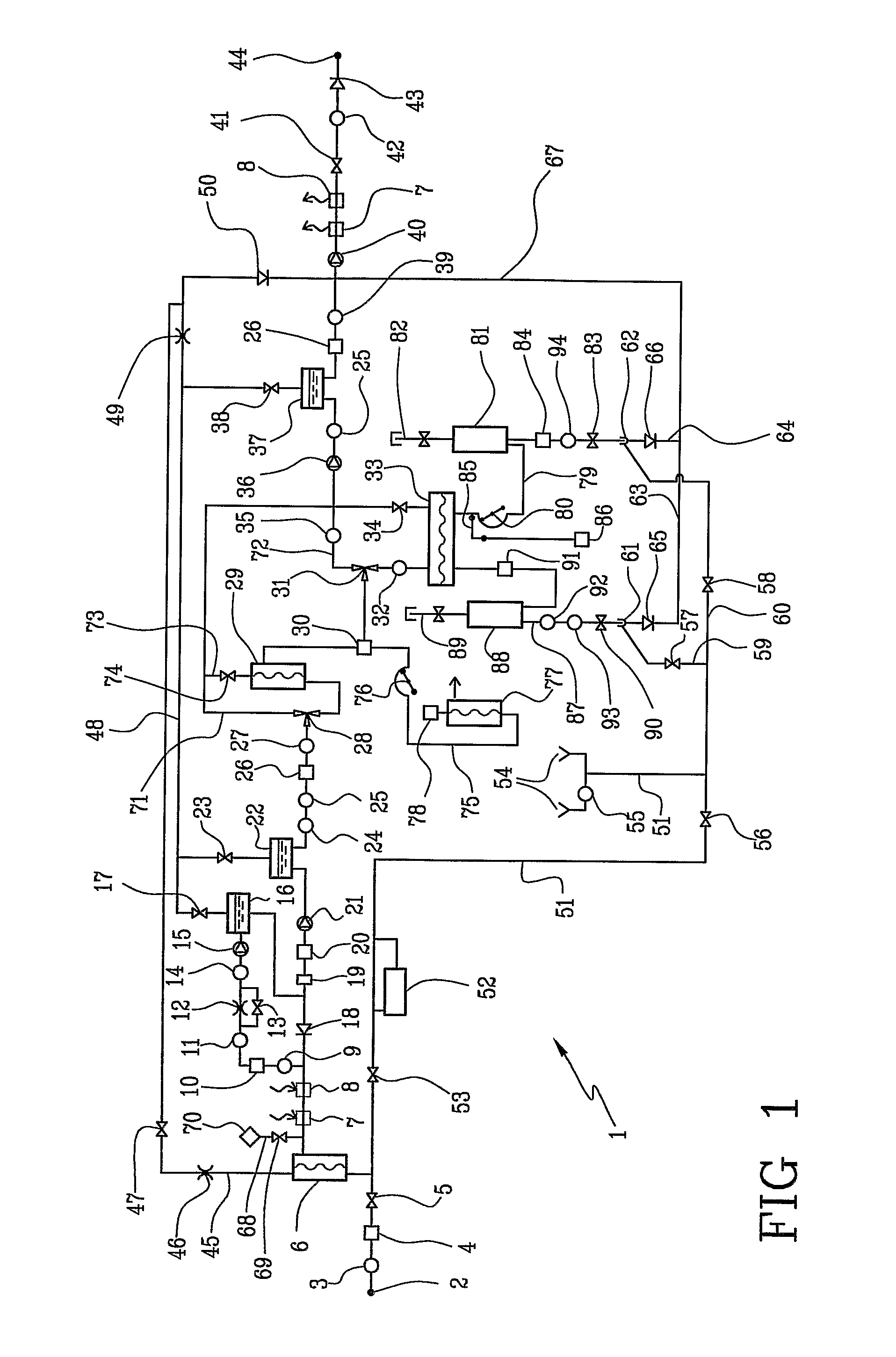
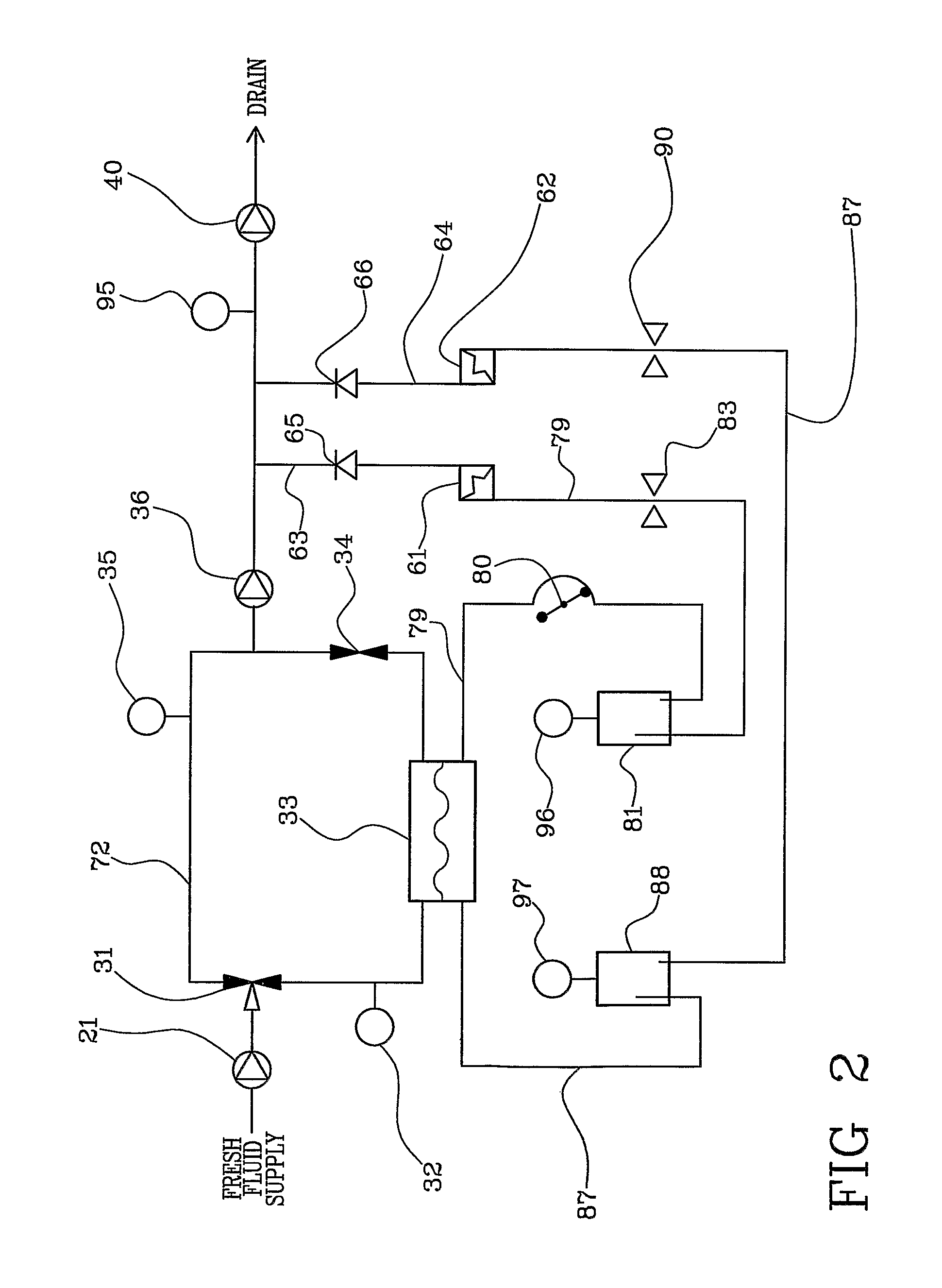
A method and apparatus for priming an extracorporeal blood circuit, in which the patient end of an arterial line (79) is connected to a first discharge port (61), and the patient end of a venous line (87) is connected to a second discharge port (62). The two discharge ports are connected to a used dialysate line which connects a dialyser (33) to a drain. The arterial and venous lines are filled with a priming fluid, while the air contained in the arterial and venous lines is evacuated partly through the first discharge port and partly through the second discharge port. Two check valves (65, 66) prevent flow from the used dialysate line towards the two discharge ports. The invention reduces the risk of errors on the part of an operator readying the priming configuration, as well as the risk of contamination of the extracorporeal circuit during the priming phase.
Owner:GAMBRO LUNDIA AB
Extracorporeal treatment device with automatic emptying of waste bag
ActiveUS20040267183A1Semi-permeable membranesSolvent extractionExtracorporeal circulationBlood treatments
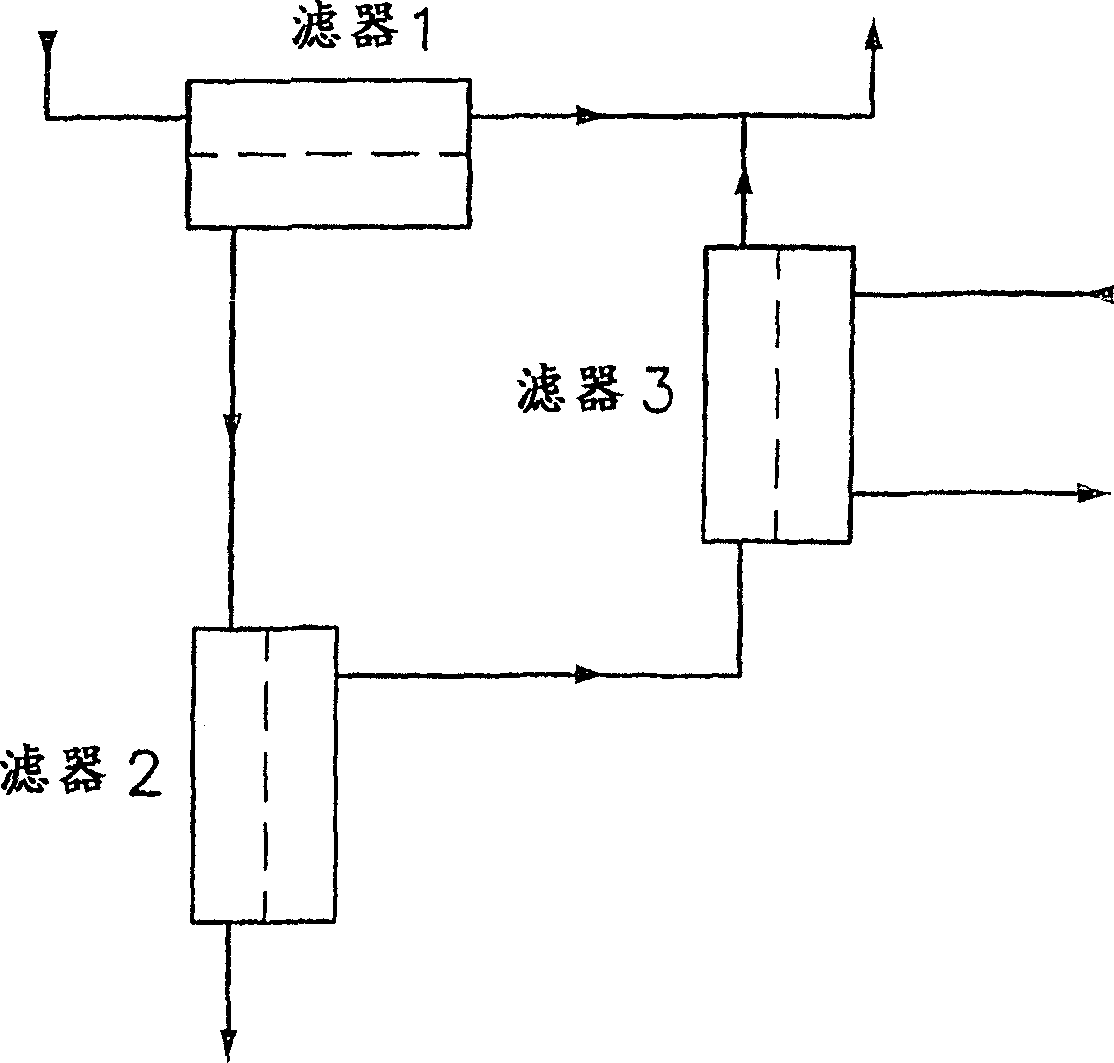
The invention relates to a blood treatment device by extracorporeal circulation comprising a filter having a primary chamber and a secondary chamber separated by a semi-permeable membrane; a blood circuit comprising an arterial line intended to come from the patient, the filter's primary chamber and the venous line intended to return to the patient; a dialysate circuit comprising the filter's secondary chamber and at least a drain line for circulating the waste intended to come from the filter and intended to go to a drain; a first bag in fluid communication with the drain line; at least a first gravimetric weighing means linked to the first bag, fluid flow rate adjustment means acting on the drain line; a control unit linked to the first gravimetric weighing means and with the fluid flow rate adjustment means; a second bag in fluid communication with the drain line, the control unit being capable of receiving weight signals from the first gravimetric weighing means and of controlling the fluid flow rate adjustment means to load one of the bags with liquid while the other bag unloads liquid, and vice-versa. The invention also relates to a single-use drain line for use in a treatment device according to the invention.
Owner:GAMBRO LUNDIA AB
Automated blood draw system
An automated blood draw system operates in conjunction with an arterial or venous line. The aspiration mechanism allows the rate of aspiration, volume of aspirate, and the time interval of aspiration to be predetermined. Blood can be collected in sequential collection vials for subsequent analysis of a given laboratory parameter, or delivered directly to integrated analysis devices. While a predetermined volume of aspirate can be wasted, excessive aspiration is prevented by monitoring waste obtained in a collection receptacle. A flush system maintains the patency of the line without contamination of the specimen.
Owner:CATHOLIC HEALTHCARE WEST ST JOSEPHS HOSPITAL
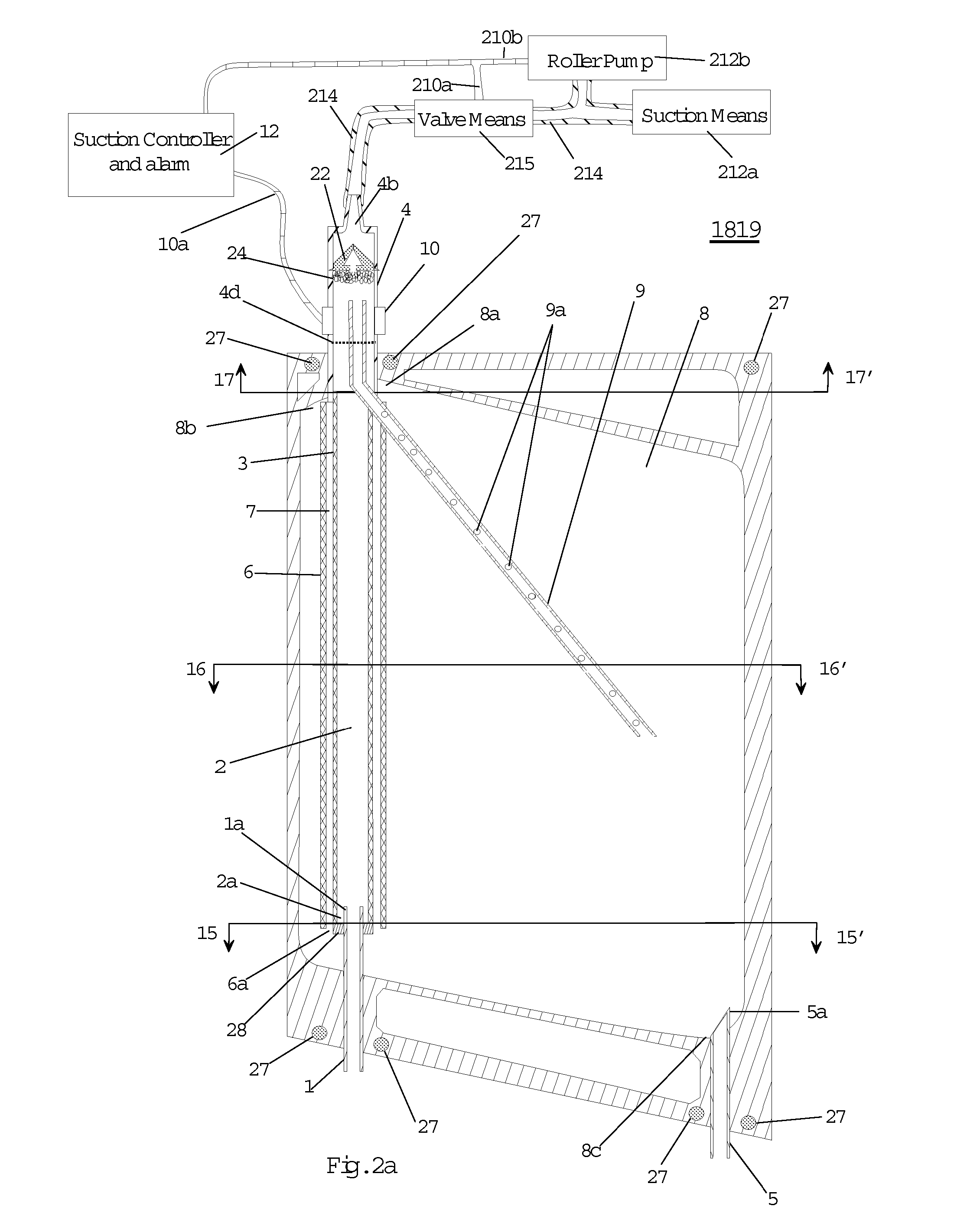
Automated means to remove air from venous blood during CPB
InactiveUS7131966B1Enhanced advantageImprove uniquenessOther blood circulation devicesDiagnosticsVacuum assistedVenous blood
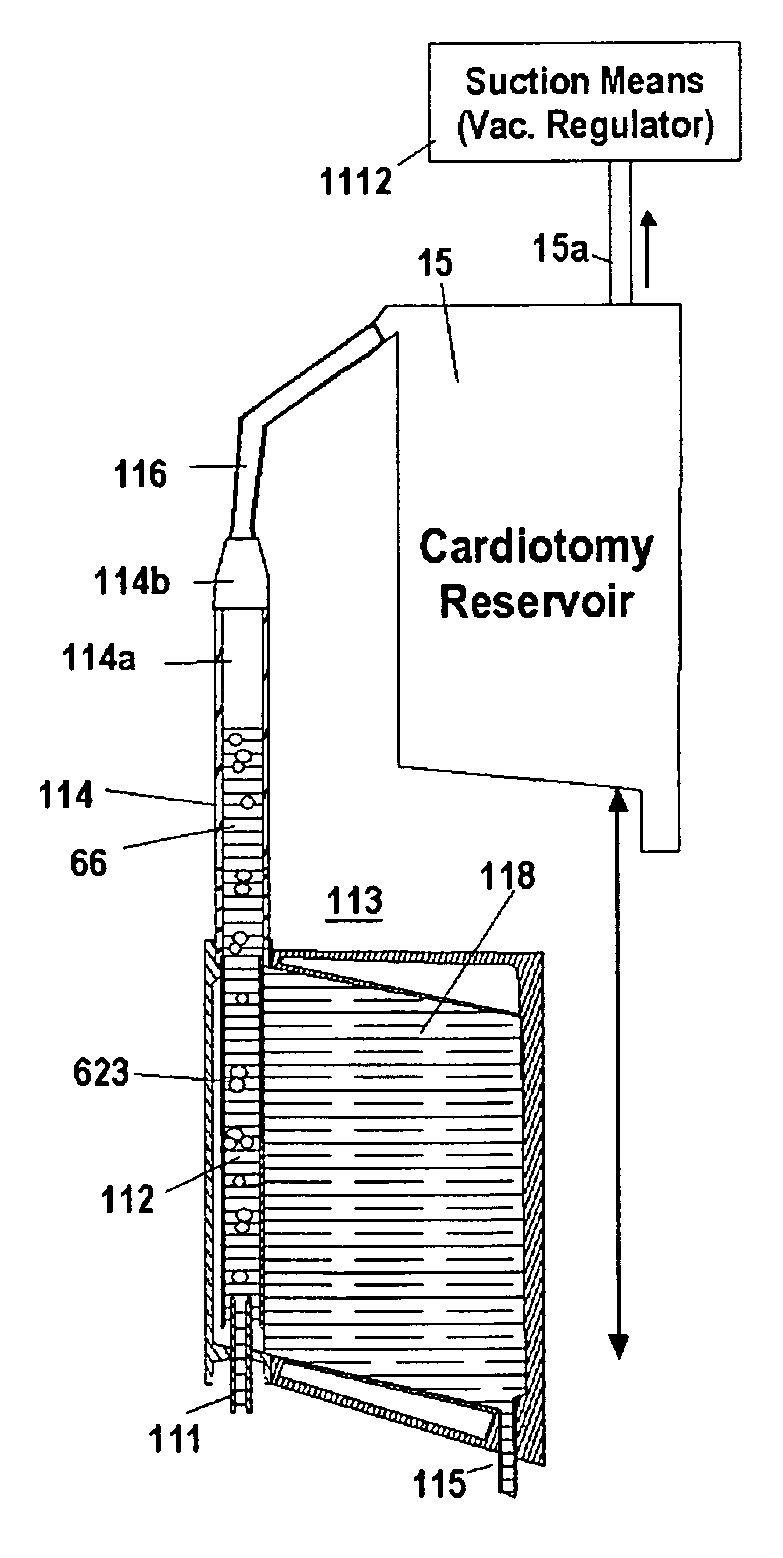
Venous reservoirs are interposed between the patient and the arterial pump and serve to remove air bubbles and provide compliance that accommodates variations in the volume of blood circulating in the extracorporeal circuit during cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB). The invention is a reservoir that incorporates automated means to remove air bubbles from the venous line prior to the blood entering the arterial blood pump. In another form, the reservoir includes means that handles foam prior to the blood entering the blood pump. In yet another form, the invention is means that improve air removal in a soft shell venous reservoir. These features are applicable to CPB circuits using gravity drainage or vacuum assisted venous drainage.
Owner:TAMARI YEHUDA
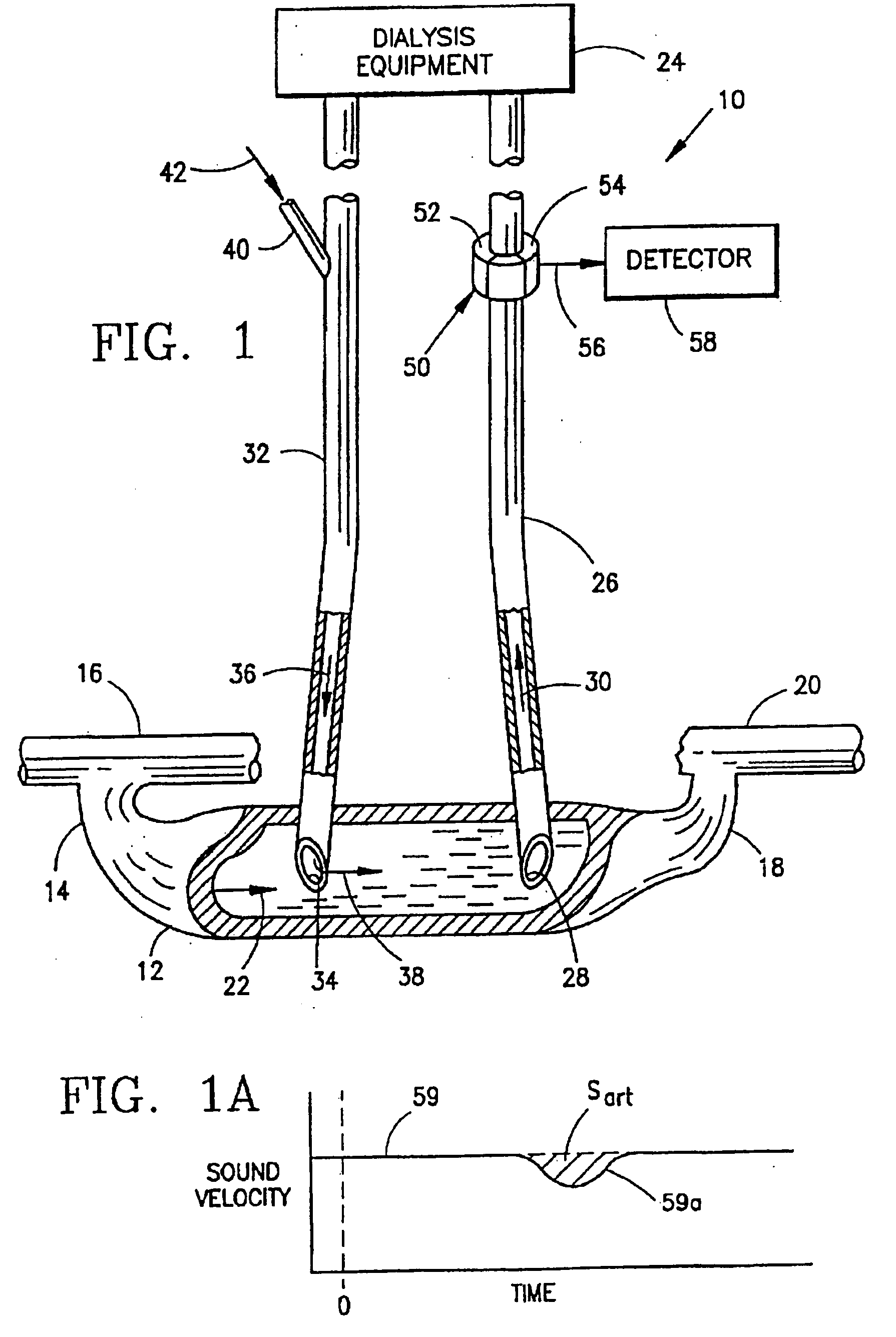
Method and apparatus for determining hemodialysis parameters
InactiveUS7097630B2Accurately and reliably and inexpensively determiningSimple and cheap equipmentSemi-permeable membranesOther blood circulation devicesVeinPresent method
This invention provides a method and apparatus for calculating a hemodialysis parameter, especially blood access flow rate, using multiple dialysance values. The dialysance values may be calculated based upon either sodium or urea concentrations. One dialysance value can be determined for conditions in which a patient's arterial line withdraws blood from an upstream location in a patient's fistula and treated blood is returned by a venous line to a downstream location in a patient's fistula. The second dialysance value can be determined when the lines have been reconfigured so that the arterial line withdraws blood from a downstream portion of a patient's fistula and the venous line returns treated blood to an upstream portion of a patient's fistula. Since it is possible to determine the dialysance values solely from concentration measurements made on the dialysate side of the dialysis apparatus, the present method and apparatus provide a non-invasive means for determining hemodialysis parameters such as blood access flow rate and recirculation.
Owner:FRESENIUS MEDICAL CARE HLDG INC +1
Method and apparatus for determining access flow
InactiveUS20050082226A1High precisionEasy to implementSolvent extractionOther blood circulation devicesLine tubingMembrane configuration
A method and apparatus for determining a fluid flow rate blood access having an upstream position and a downstream position using a dialysis system. The dialysis system includes a dialyzer having a semi permeable membrane delimiting a first chamber through which blood removed from said blood access passes, and a second chamber through which dialysis liquid passes. In addition, an arterial line and a venous line are connected to an inlet and an outlet of the first chamber, respectively.
Owner:GAMBRO LUNDIA AB
Method for determining the recirculation of blood in a vascular access and a system for implementing same
In an extracorporeal blood treatment system, non-treated blood may be withdrawn from a patient through an arterial line connected to a first compartment of a blood treatment apparatus. The blood treatment apparatus also includes a second compartment separated from the first component by a semi-permeable membrane. Treated blood may be returned to the patient through a venous line connected to the second compartment. In order to determine blood recirculation, i.e., a mixture of treated blood and non-treated blood in the arterial line, the ultrafiltration rate of plasma water through the semi permeable membrane of the treatment apparatus may be temporarily increased or decreased, and the resulting variation of the blood concentration, i.e., of the ratio of the volume of the plasma volume to the blood volume, is determined. The extent of the mixture of the treated blood and the non-treated blood in the arterial line may then be calculated as a function of the blood flow rate in the treatment apparatus, of the amplitude of the variation of the ultrafiltration rate, and of at least two values of the blood concentration, determined before and during the variation of the ultrafiltration flow rate, respectively.
Owner:BAXTER HEALTHCARE SA
Venous reservoir
InactiveUS20070078369A1Enhanced advantageImprove uniquenessOther blood circulation devicesSurgeryExtracorporeal circulationVacuum assisted
Venous reservoirs are interposed between the patient and the arterial pump and serve to remove air bubbles and provide compliance that accommodates variations in the volume of blood circulating in the extracorporeal circuit during cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB). The invention is a reservoir that incorporates automated means to remove air bubbles from the venous line prior to the blood entering the arterial blood pump. In another form, the reservoir includes means that handles foam prior to the blood entering the blood pump. In yet another form, the invention is means that improve air removal in a soft shell venous reservoir. These features are applicable to CPB circuits using gravity drainage or vacuum assisted venous drainage.
Owner:TAMARI YEHUDA
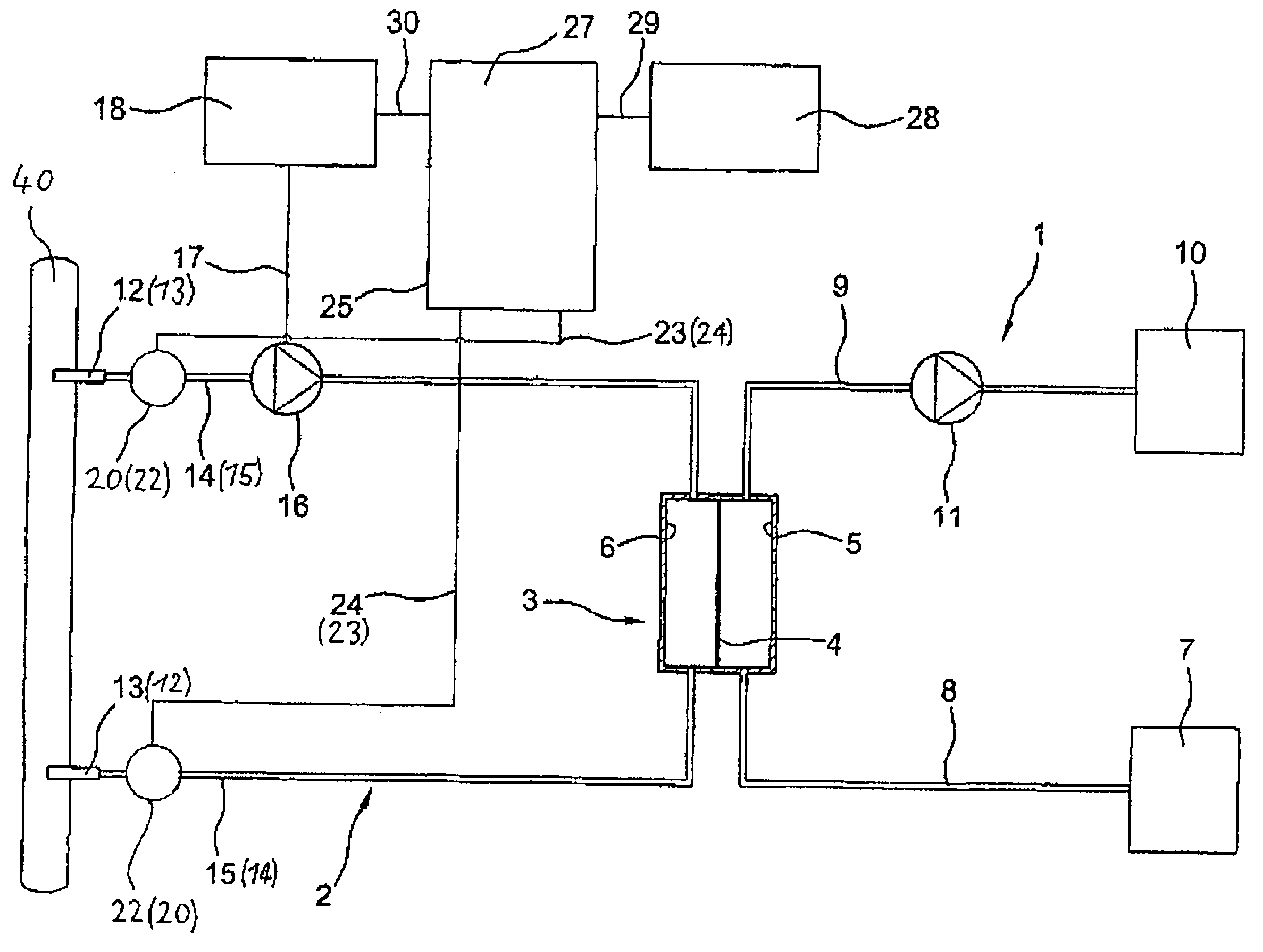
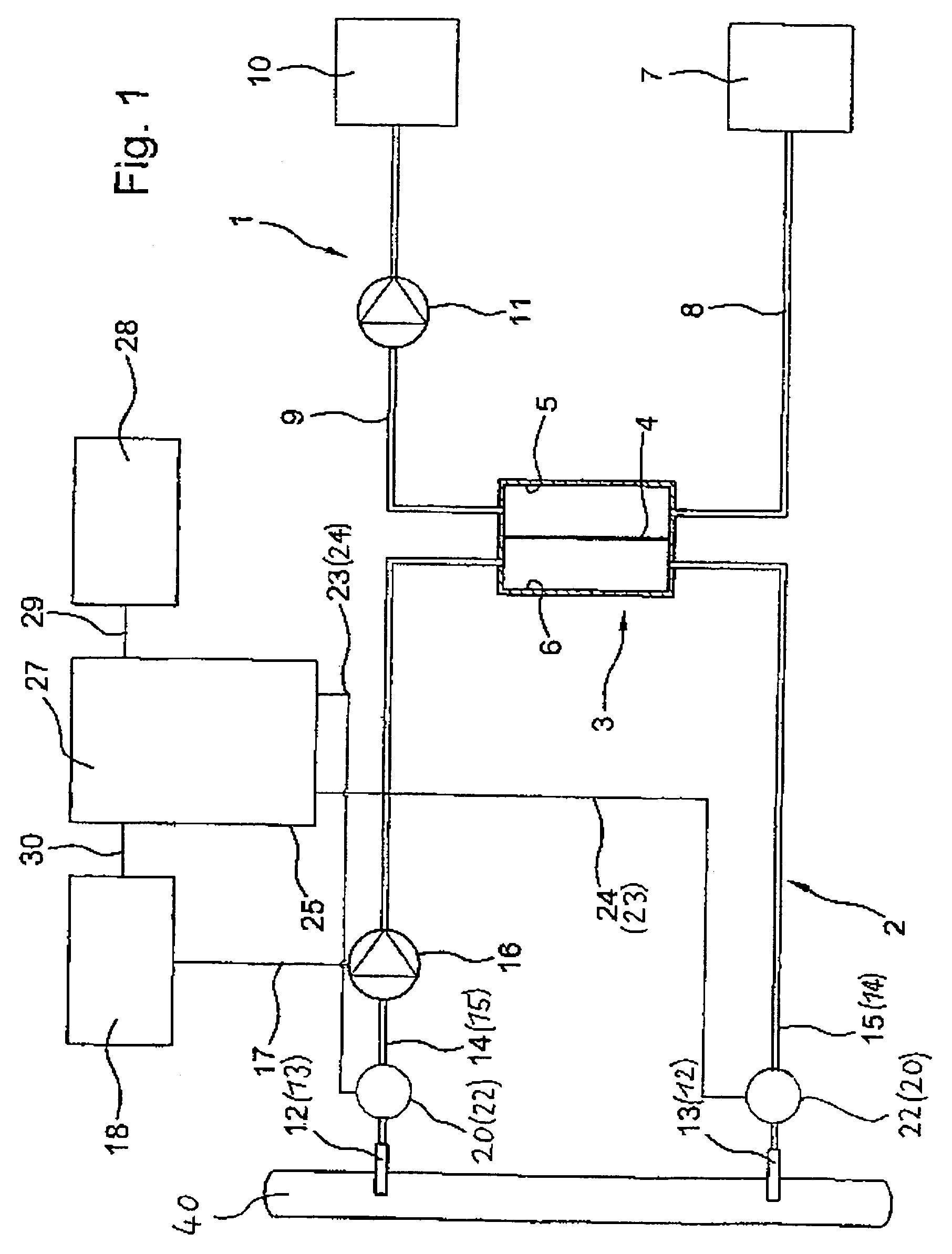
Blood treatment device and method with selective solute extraction
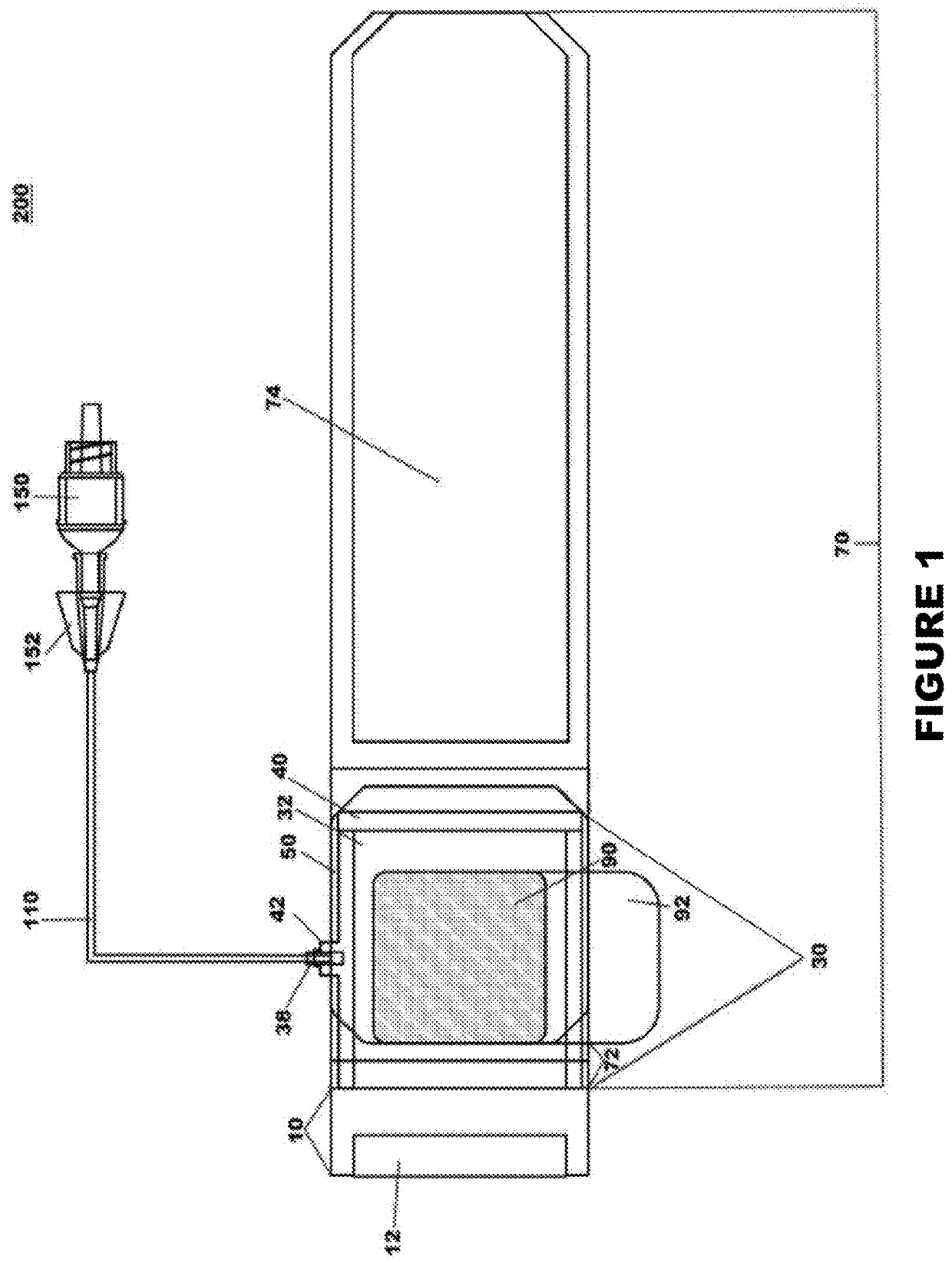
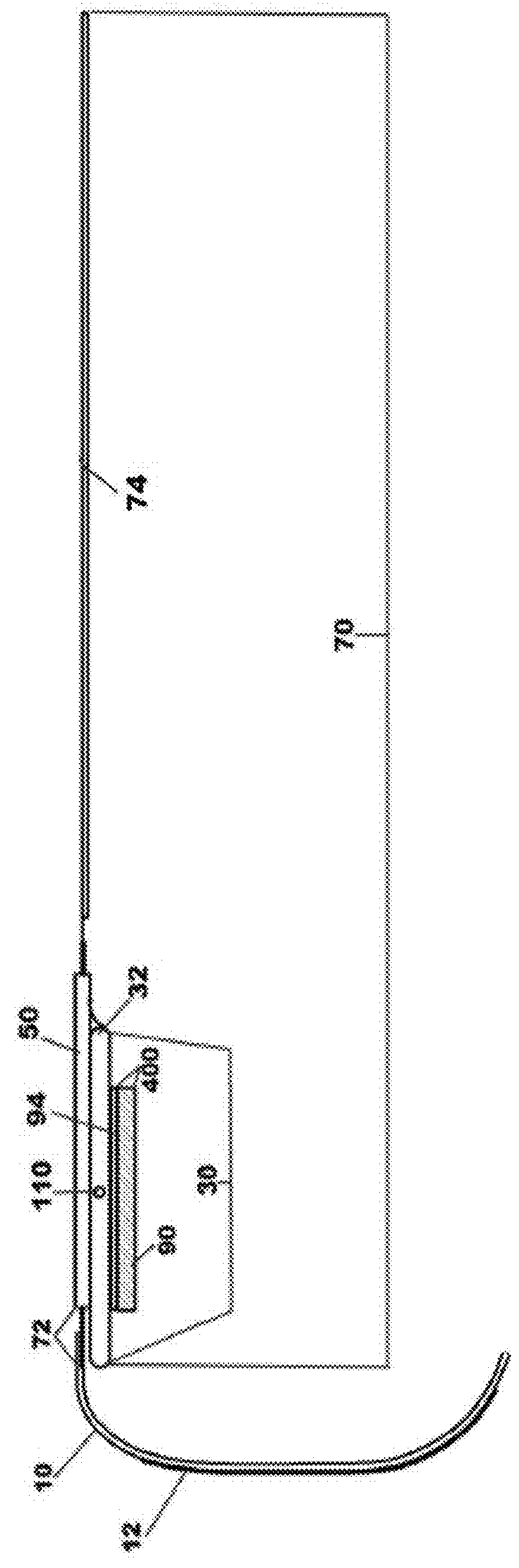
The object of the present invention is the filtration of blood in order to selectively separate and extract molecules of a given size via extracorporeal systems for separating substances. The invention thus concerns an extracorporeal blood treatment device including: one or more exchangers (1) comprising a first inlet (2) for the blood to be treated, a first fluid outlet (4) and a second fluid outlet (5), an inlet line (10) for the blood to be treated, connected to the first inlet (2) of the exchanger (1), a blood outlet line (or venous line) (11) coupled to the first outlet (4) of the exchanger (1), one or more treatment units (21) comprising at least a first fluid inlet (22) and at least a first fluid outlet (24), wherein the second outlet (5) of the exchanger (1) is in fluid communication with the first inlet (22) of the treatment unit (21), the invention being characterised in that the first outlet (24) of the treatment unit (21) is in fluid communication with the inlet line (10).
Owner:GAMBRO LUNDIA AB
Method of measuring transcutaneous access blood flow
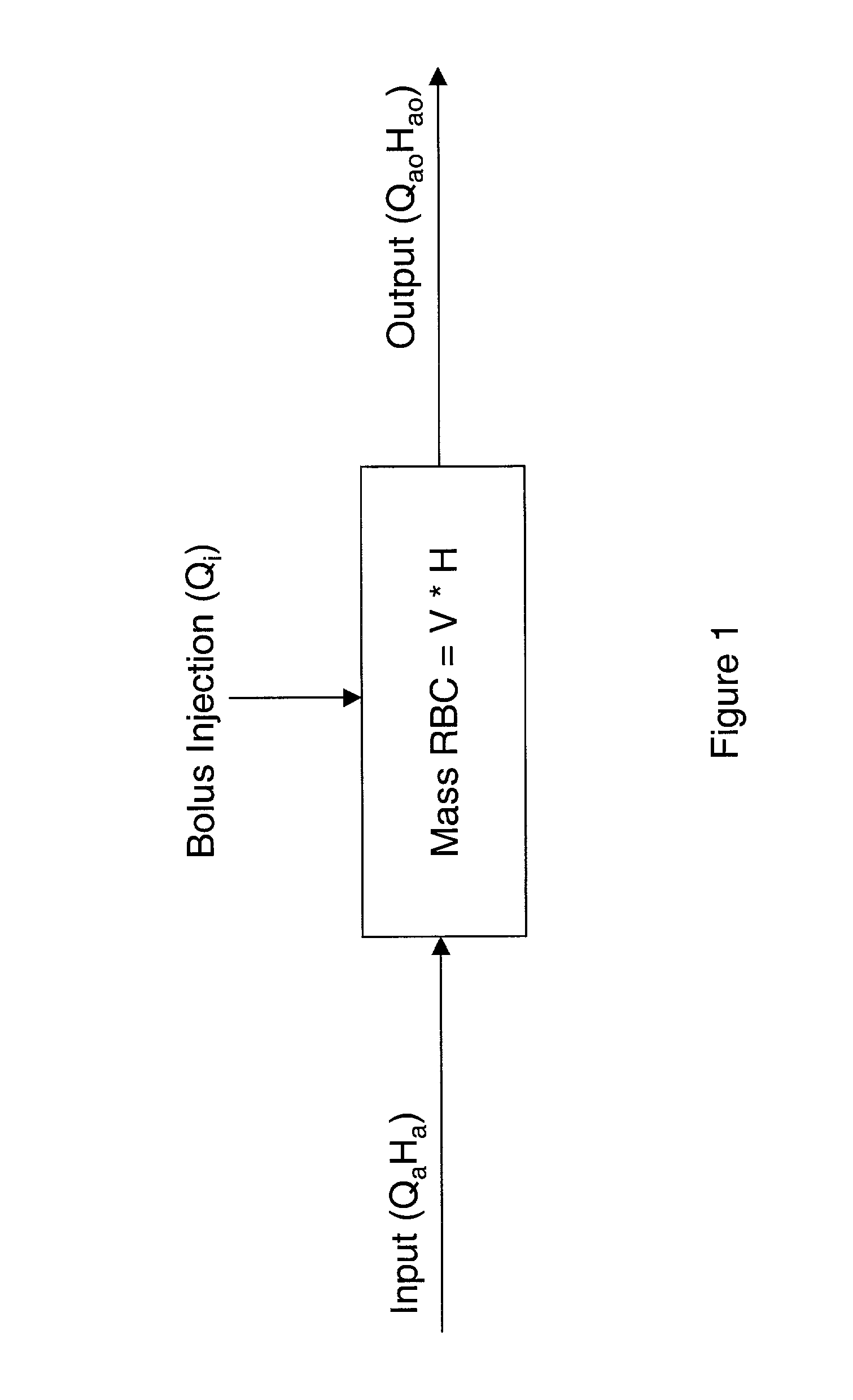
InactiveUS20020128545A1Other blood circulation devicesVolume/mass flow measurementIndicator dilutionInjection site
Indicator dilution techniques are used to measure vascular access flow rates during routine hemodialysis. A bolus injection port is used to infuse a specific volume (V.sub.i) of an indicator diluent, such as saline or dye, into the patient cardiovascular circuit by one of the following: 1. Needle injection of a known volume (bolus) of indicator diluent directly into the access site in the presence or absence of the hemodialysis circuit. 2. Infusion of an indicator diluent into the arterial, venous line upstream of the venous needle. 3. Turning the ultrafiltration of the dialysis delivery system from OFF to ON and OFF again over a predetermined time period. 4. In a hemodialysis circuit, turning on the hemodialysis pump and using the priming saline volume as a single saline bolus. A transdermal sensor is used to measure the percent change in a blood parameter. The sensor is positioned directly over the vascular access site a prescribed distance downstream of the injection site and upstream of the access-vein connection. The sensor employs emitter and detector elements at multiple spacings (d.sub.1, d.sub.2) for the purpose of measuring the bulk absorptivity (.alpha.) of the area immediately surrounding and including the access site, and the absorptivity (.alpha..sub.0) of the tissue itself.
Owner:IN LINE DIAGNOSTICS CORP +1
Apparatus and process for extracorporeal treatment of blood with selective extraction of solutes
ActiveUS7291269B2Satisfactory eliminationSolvent extractionOther blood circulation devicesBlood treatmentsBiomedical engineering
A device and method for an extracorporeal blood treatment is described. The device comprising at least one exchanger equipped with at least one first inlet for the blood to be treated, a first fluid outlet and a second fluid outlet, an input line for blood to be treated connected to the first inlet of the exchanger, a blood output line (or venous line) connected to the first outlet of the exchanger, at least one treatment unit comprising at least one first fluid inlet and at least one first fluid outlet, the second outlet of the exchanger being in fluid communication with the first inlet of the treatment unit, where the first outlet from the treatment unit is in fluid communication with the input line and the second outlet of the treatment unit is in fluid communication with a first waste liquid discharge line.
Owner:GAMBRO LUNDIA AB
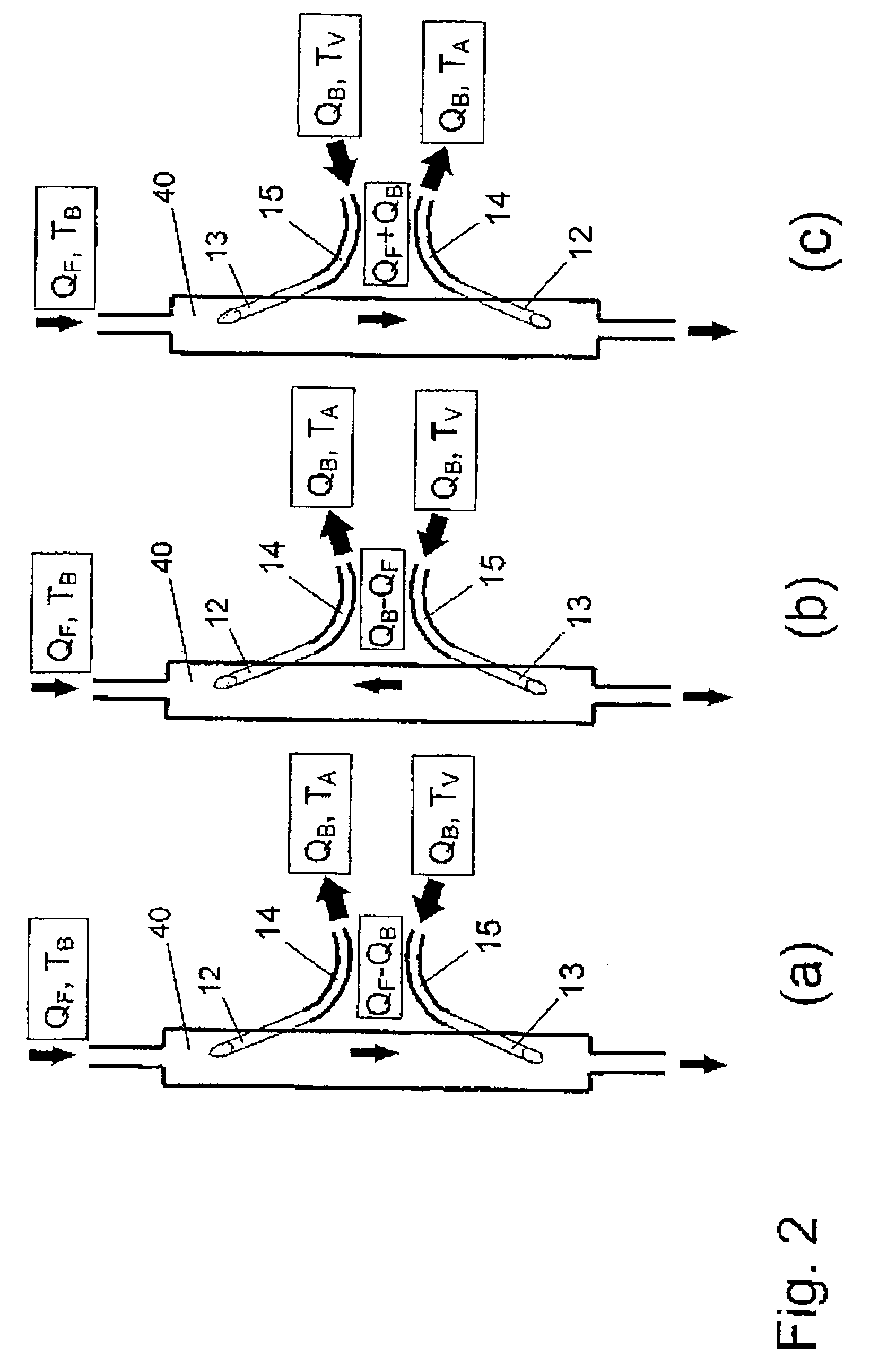
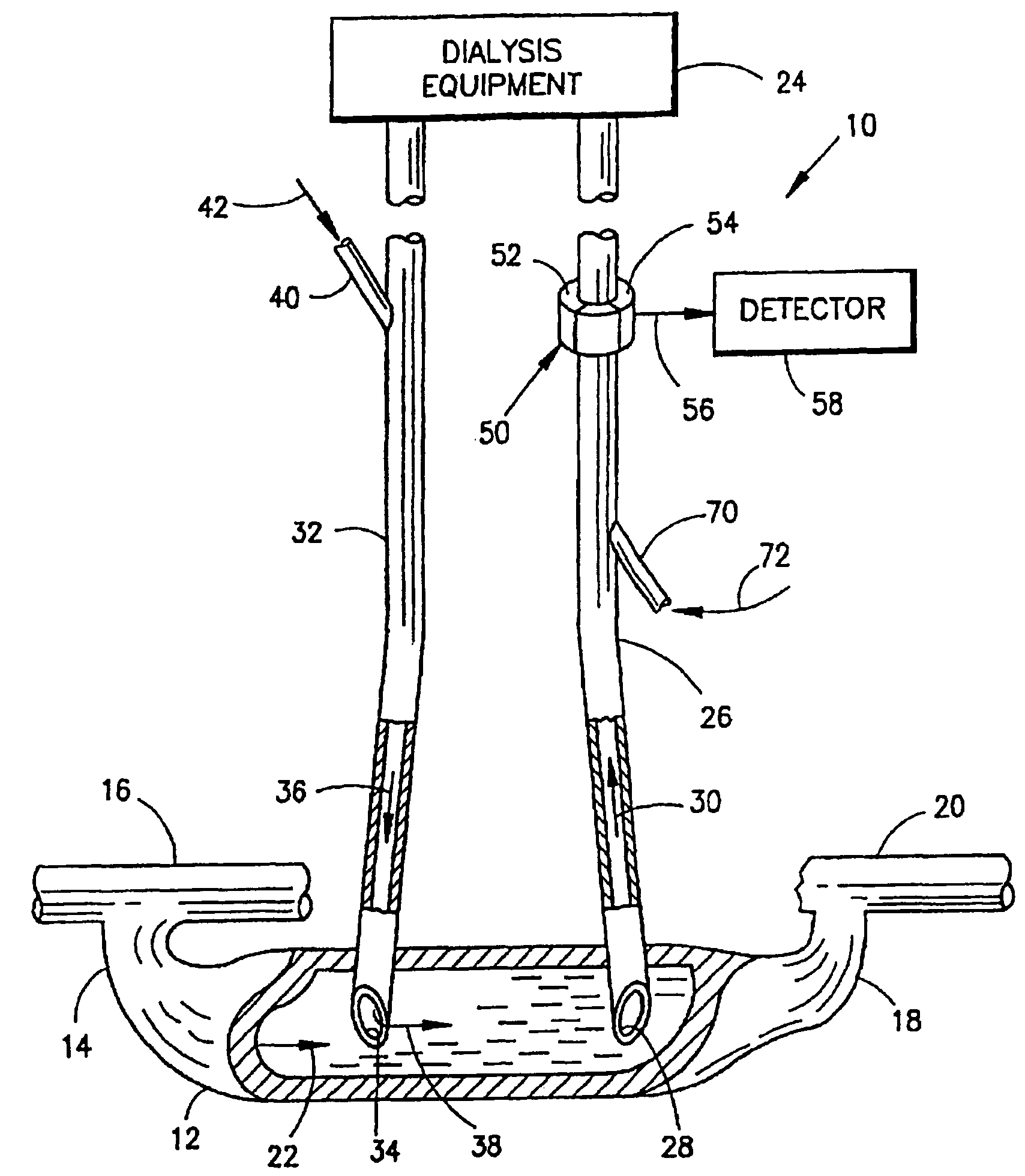
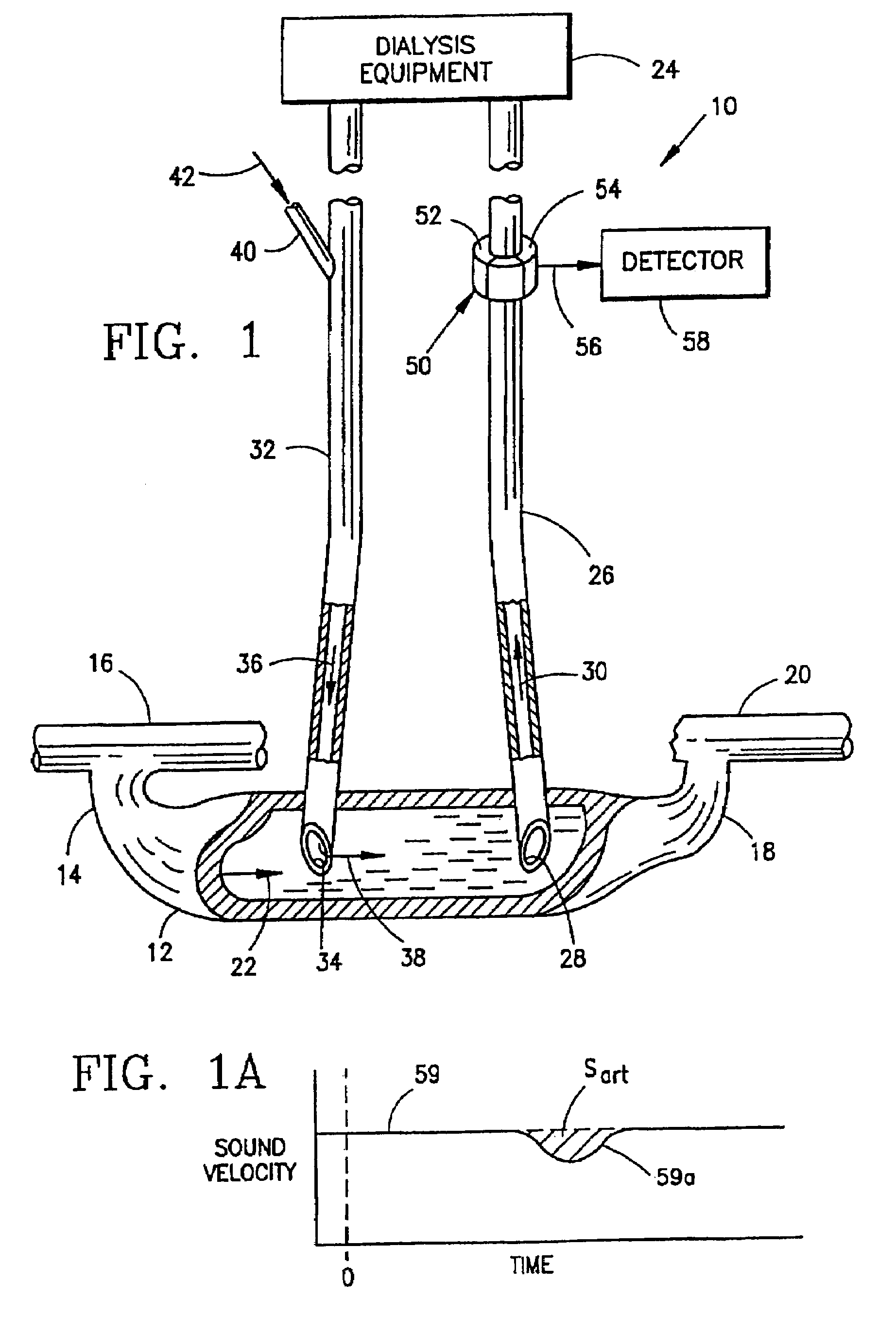
Measurement of a blood flow rate in hemodialysis shunts
InactiveUS20050178732A1Accurate measurementLow costOther blood circulation devicesVolume/mass flow measurementVeinLine tubing
The measurement of blood flow in a dialysis shunt is obtained by injection of an indicator material into a venous line leading from dialysis equipment to the shunt. The blood flow in an arterial line leading from the shunt at a location downstream of the venous line to the dialysis equipment is monitored by an arterial line sensor for the presence of the indicator material. A detector connected to the sensor provides a dilution curve in response to the presence of the indicator material and the blood flow in the shunt is calculated from the area under the dilution curve. The locations of the arterial and venous lines in the shunt can be reversed to obtain a measurement of blood recirculation from the venous line into the arterial line.
Owner:TRANSONIC SYST
Extracorporeal treatment device with automatic emptying of waste bag
The invention relates to a blood treatment device by extracorporeal circulation comprising a filter having a primary chamber and a secondary chamber separated by a semi-permeable membrane; a blood circuit comprising an arterial line intended to come from the patient, the filter's primary chamber and the venous line intended to return to the patient; a dialysate circuit comprising the filter's secondary chamber and at least a drain line for circulating the waste intended to come from the filter and intended to go to a drain; a first bag in fluid communication with the drain line; at least a first gravimetric weighing means linked to the first bag, fluid flow rate adjustment means acting on the drain line; a control unit linked to the first gravimetric weighing means and with the fluid flow rate adjustment means; a second bag in fluid communication with the drain line, the control unit being capable of receiving weight signals from the first gravimetric weighing means and of controlling the fluid flow rate adjustment means to load one of the bags with liquid while the other bag unloads liquid, and vice-versa.The invention also relates to a single-use drain line for use in a treatment device according to the invention.
Owner:GAMBRO LUNDIA AB
Percutaneous vascular injury treatment systems and methods
InactiveUS20180214160A1Fast, effective, non-occlusive bleeding controlReduce morbidityTourniquetsTibiaHaemodialysis machine
The present invention relates to a compressive band and hemostatic dressing system and related methods of use to provide rapid, non-occlusive bleeding control, arterial injury treatment, and injury protection comfortably and reliably after vascular access procedures. The present invention may comprise some or all of the following elements: a positioner assembly, a compressive cushion component, a compression plate, a strap with a flexible hinge assembly, and a hemostatic dressing. In a preferred embodiment, the systems and methods are applied to treat and ameliorate vascular injury in a transradial percutaneous access procedure and protect against underlying vascular injury; however, the systems and methods described herein may be applied to any vascular access procedure including arm or leg vascular approaches such as the femoral, brachial, dorsalis pedis or tibial blood vessels in arterial or venous line or sheath removal or trocar removal, and in hemodialysis.
Owner:TRICOL BIOMEDICAL INC
Device for oxygenating blood in an extracorporeal circuit
InactiveUS7238320B2Maximum safetyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsOther blood circulation devicesBlood collectionExtracorporeal circulation
A device for oxygenating blood in an extracorporeal circuit includes a first structure suitable to delimit a portion of space-containing capillaries made of microporous membrane. The capillaries convey oxygen and are wet externally by blood flowing through a portion of space between an intake connector, which is connected to a venous line of the extracorporeal circuit, and a delivery connector. The device includes a second structure monolithically connected and contiguous to the first structure. The second structure is suitable to contain blood filtration means that divide the portion of space delimited thereby into a blood distribution chamber, provided with an air vent and connected to the delivery connector of the first structure, and a blood collection chamber provided with a delivery connector connected to the arterial line of the extracorporeal circuit.
Owner:SORIN GRP ITAL SRL
Method for removing blood from an extracorporeal blood circuit as well as apparatuses
ActiveUS20130030346A1Reduce the risk of contaminationReduce riskElectrotherapyDialysis systemsBlood treatmentsVein
The present invention relates to a method for removing blood from an extracorporeal blood circuit and / or a functional device, each connectable or connected with a blood treatment apparatus for the purpose of blood treatment of a patient. The blood treatment apparatus of the method comprises or is connected with at least one extracorporeal blood circuit with a line having interior portions, the extracorporeal blood circuit comprising at least one arterial line section and at least one venous line section, wherein a first section of the arterial line section is configured to be connected with a second section of the venous line section, and further comprises at least one blood pump for conveying blood within the line interior portions. The method includes the step of operating the blood pump in a second conveying direction which is opposite to a first customary conveying direction. It further relates to corresponding apparatuses.
Owner:FRESENIUS MEDICAL CARE DEUTSCHLAND GMBH
Method and apparatus for priming an extracorporeal blood circuit
ActiveUS8529487B2Facilitates taskRisk of errorOther blood circulation devicesMedical devicesVeinExtracorporeal circulation
A method and apparatus for priming an extracorporeal blood circuit, in which the patient end of an arterial line (79) is connected to a first discharge port (61), and the patient end of a venous line (87) is connected to a second discharge port (62). The two discharge ports are connected to a used dialysate line which connects a dialyser (33) to a drain. The arterial and venous lines are filled with a priming fluid, while the air contained in the arterial and venous lines is evacuated partly through the first discharge port and partly through the second discharge port. Two check valves (65, 66) prevent flow from the used dialysate line towards the two discharge ports. The invention reduces the risk of errors on the part of an operator readying the priming configuration, as well as the risk of contamination of the extracorporeal circuit during the priming phase.
Owner:GAMBRO LUNDIA AB
Vascular access device for hemodialysis
Single needle vascular access systems, devices and methods for use in hemodialysis and apheresis procedures. A single needle vascular access device includes a body having an upper and lower passage with both in fluid communication with a vascular dilator. A cannulation needle is guided through the lower passage and vascular dilator to cannulate a graft or fistula. Following cannulation, the dilator is gently introduced into the vessel. The cannulation needle is removed, and a venous tube is introduced through the upper passageway through the vascular dilator and into the fistula or graft. Blood is then removed from the body through the vascular dilator side orifices and returned through the venous line. Depending on the clinical situation, the vascular dilator can be used with one or both needles of a conventional two needle system. In the later case, the vascular dilator may be connected to the dialysis tubes using conventional standard connectors.
Owner:TSYRULNYKOV EDUARD +1
Device and a method for determining blood recirculation in a vascular access
InactiveUS7001353B2Overcome limitationsSemi-permeable membranesSolvent extractionUltrafiltrationBlood vessel
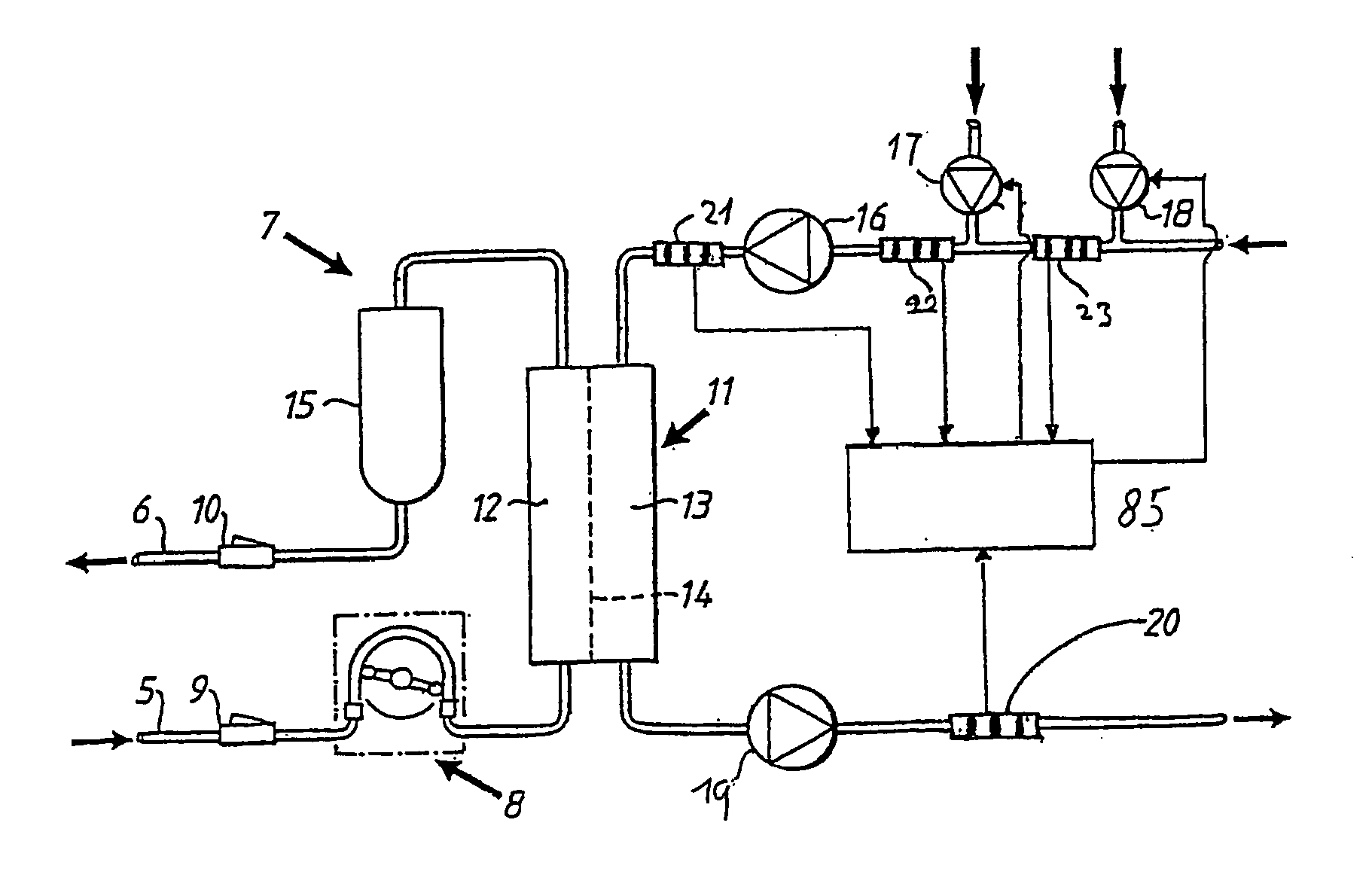
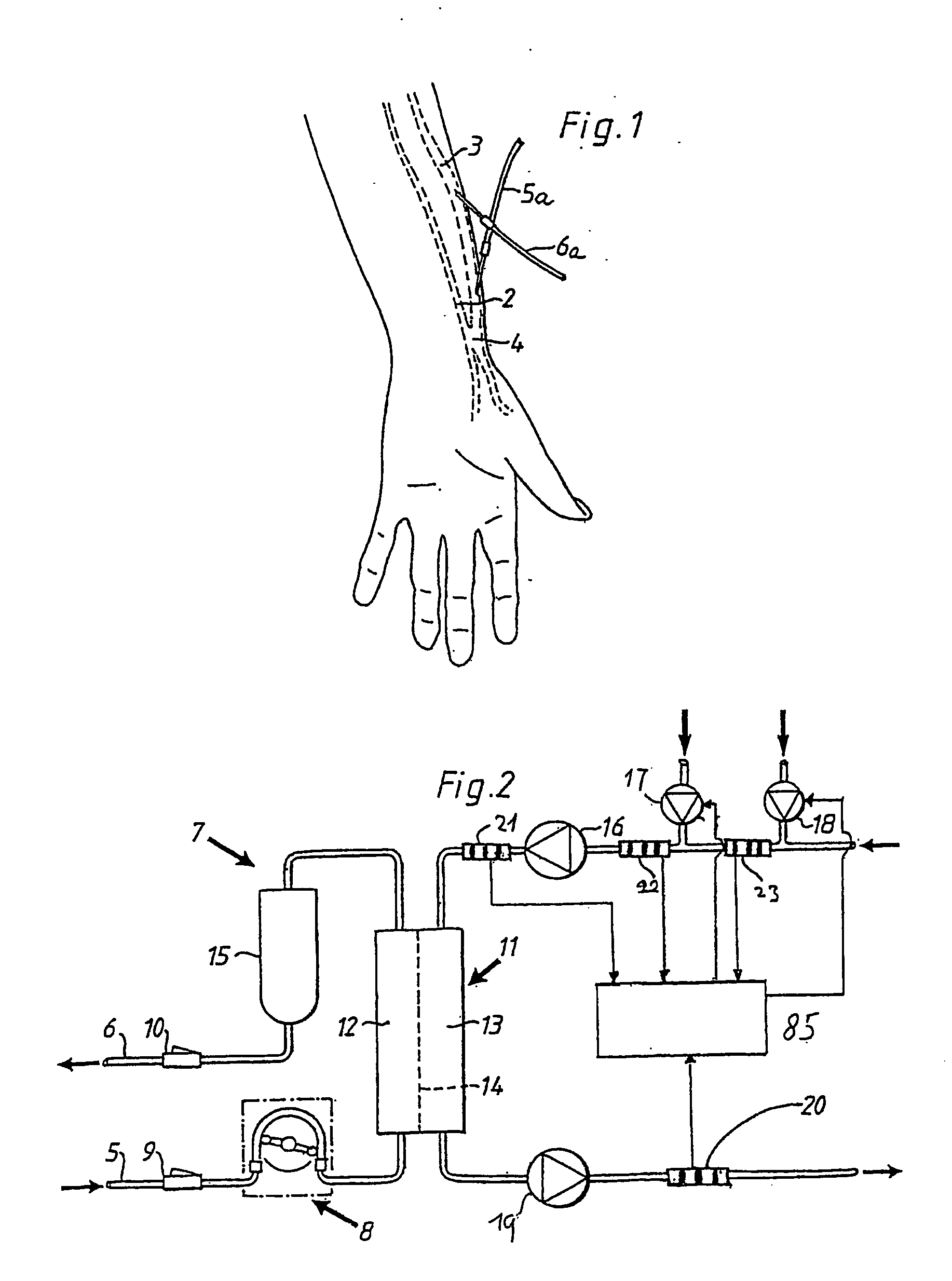
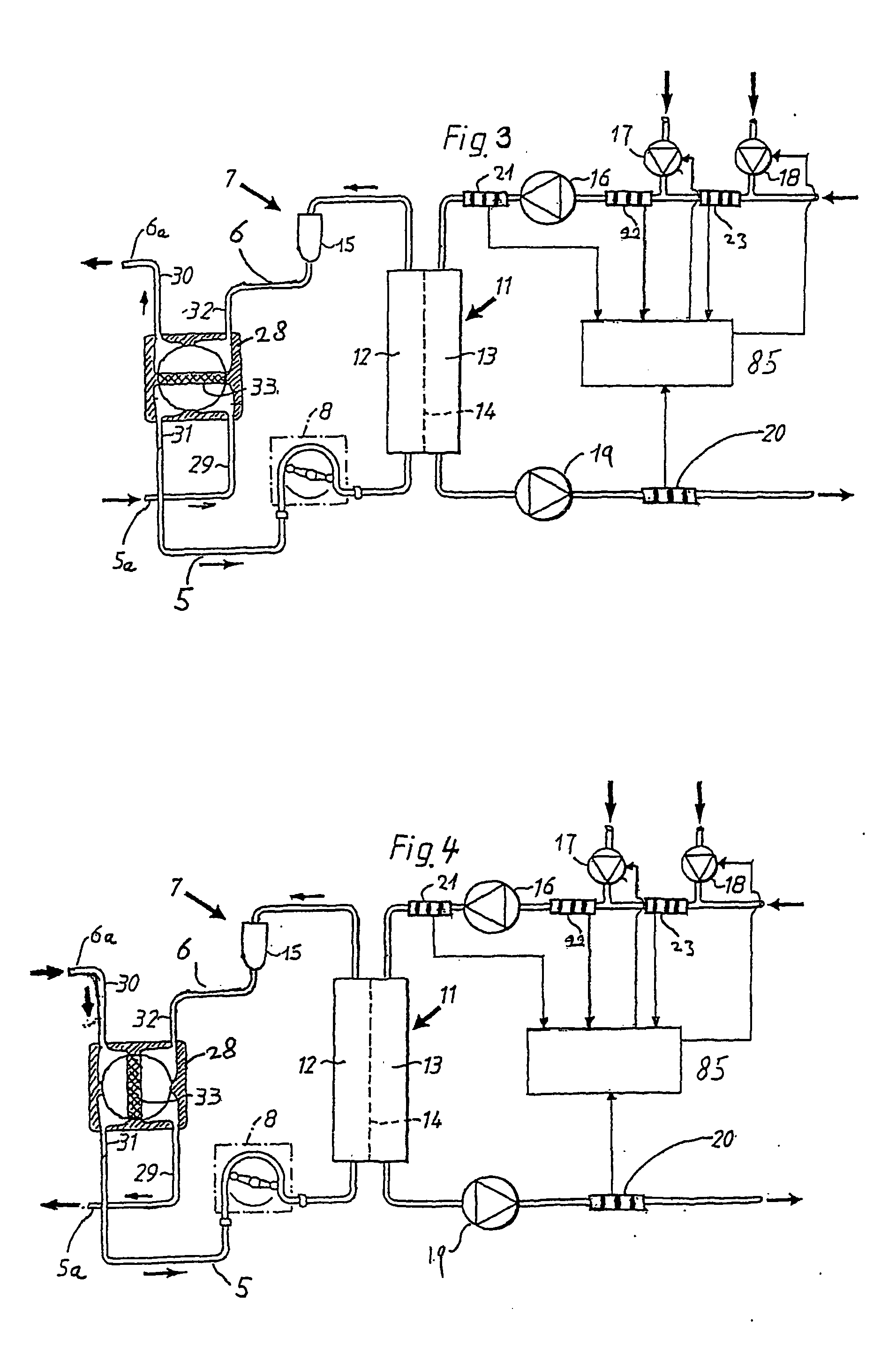
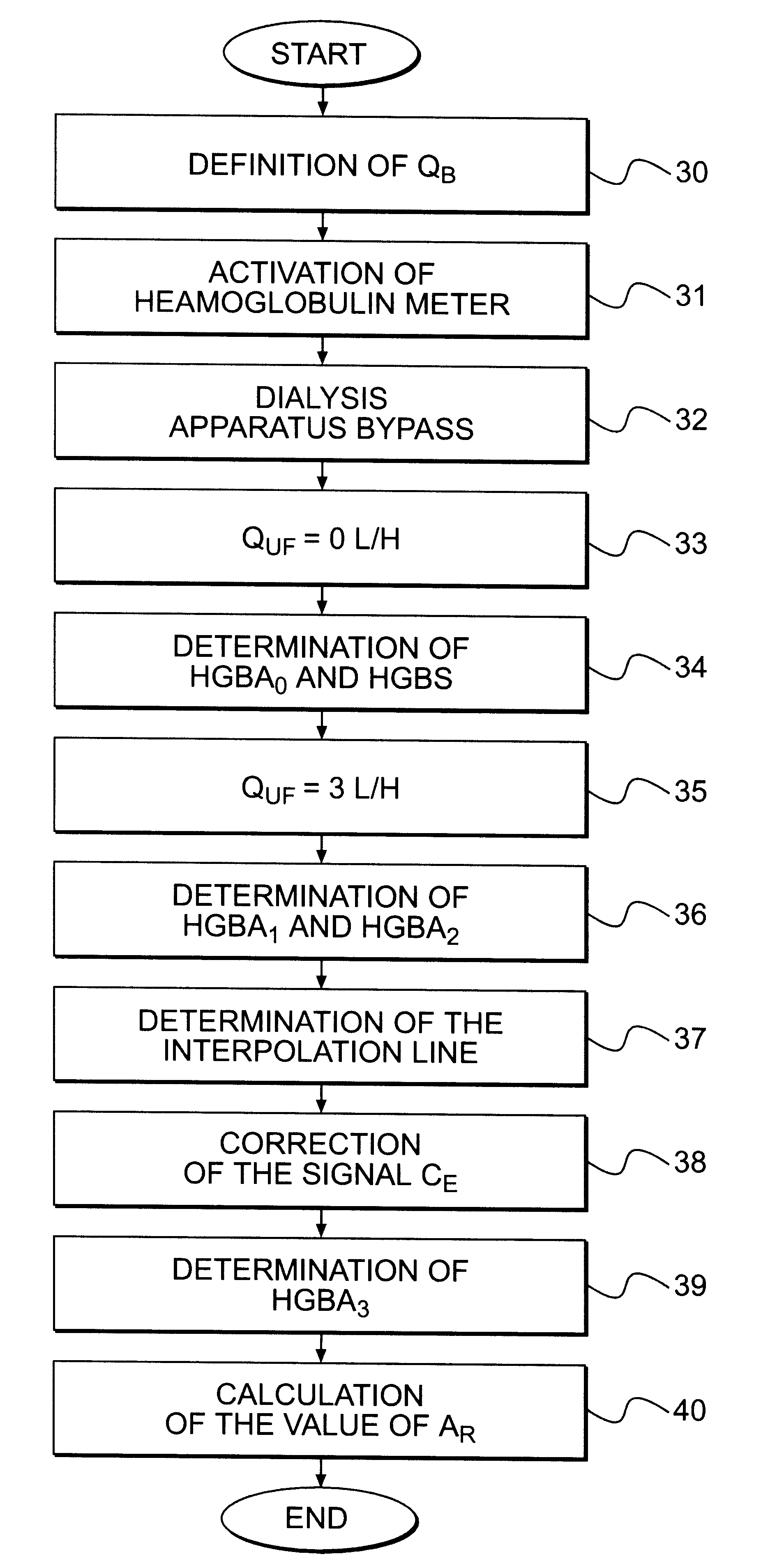
A method is described for determining recirculation of blood in a vascular access of a patient undergoing dialysis treatment using a dialysis machine with an arterial line for withdrawing blood from the patient's body, a dialysis filter, and a venous line for returning blood to the patient's body. The method induces a disturbance in the blood flowing in the venous line. The disturbance is of a magnitude capable of bringing the system into a transient state and determining blood recirculation in the vascular access during the transient state as a function of the magnitude of the disturbance induced in the arterial line. In particular, the disturbance relates to the variation of the hemoglobin concentration in the blood flowing in the venous line. The variation is caused by controlling a change in the ultrafiltration flow in the dialysis filter.
Owner:BAXTER HEALTHCARE SA
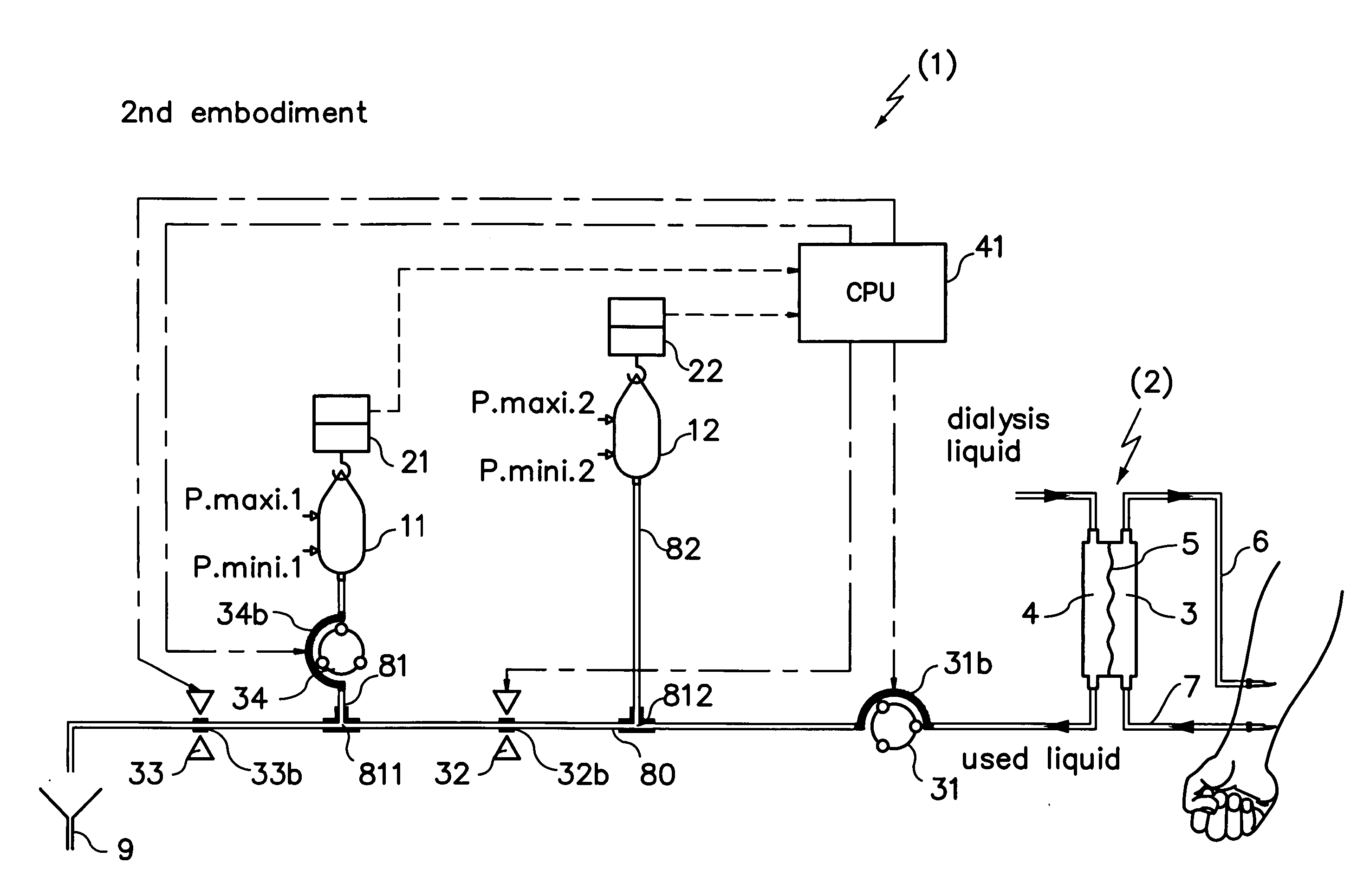
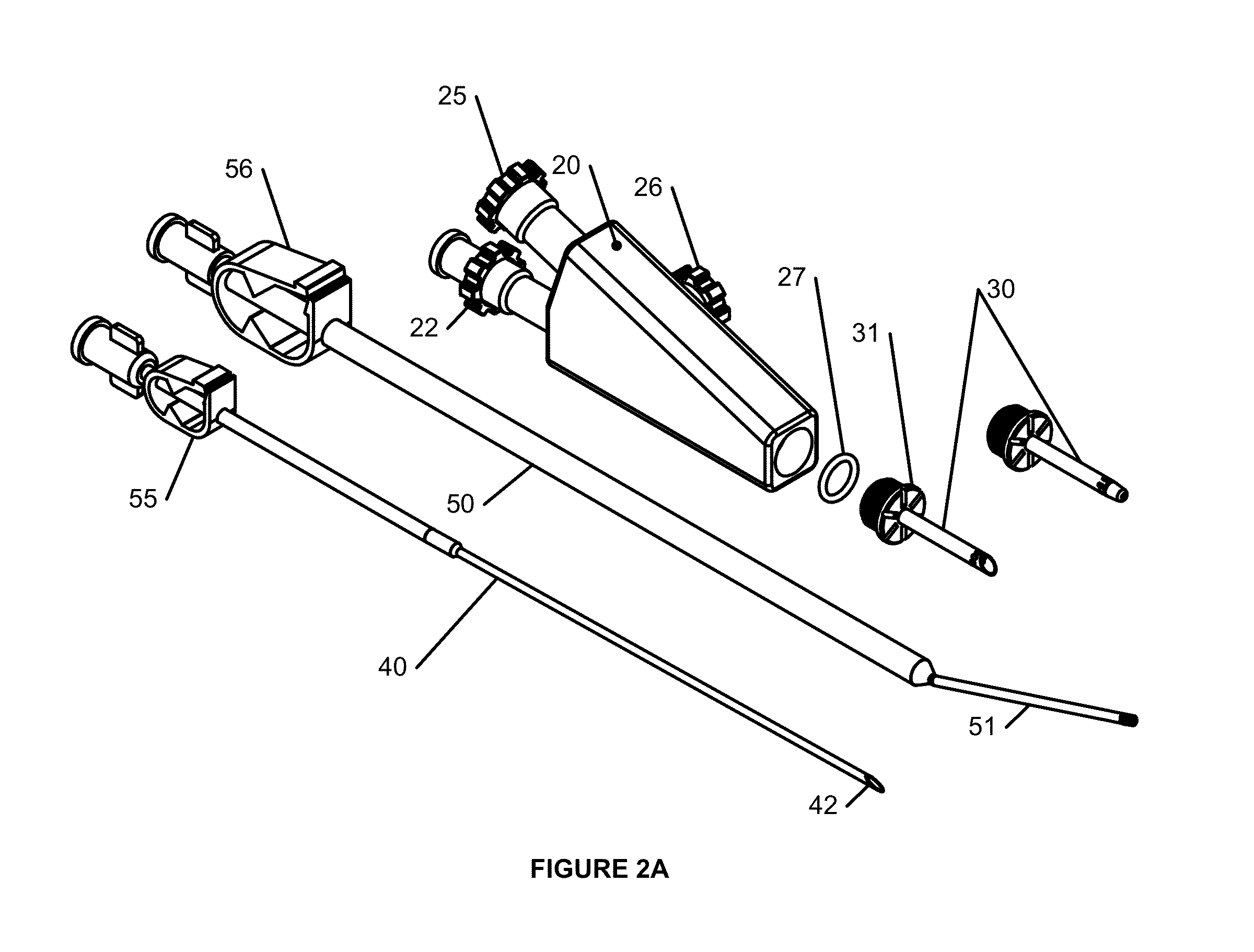
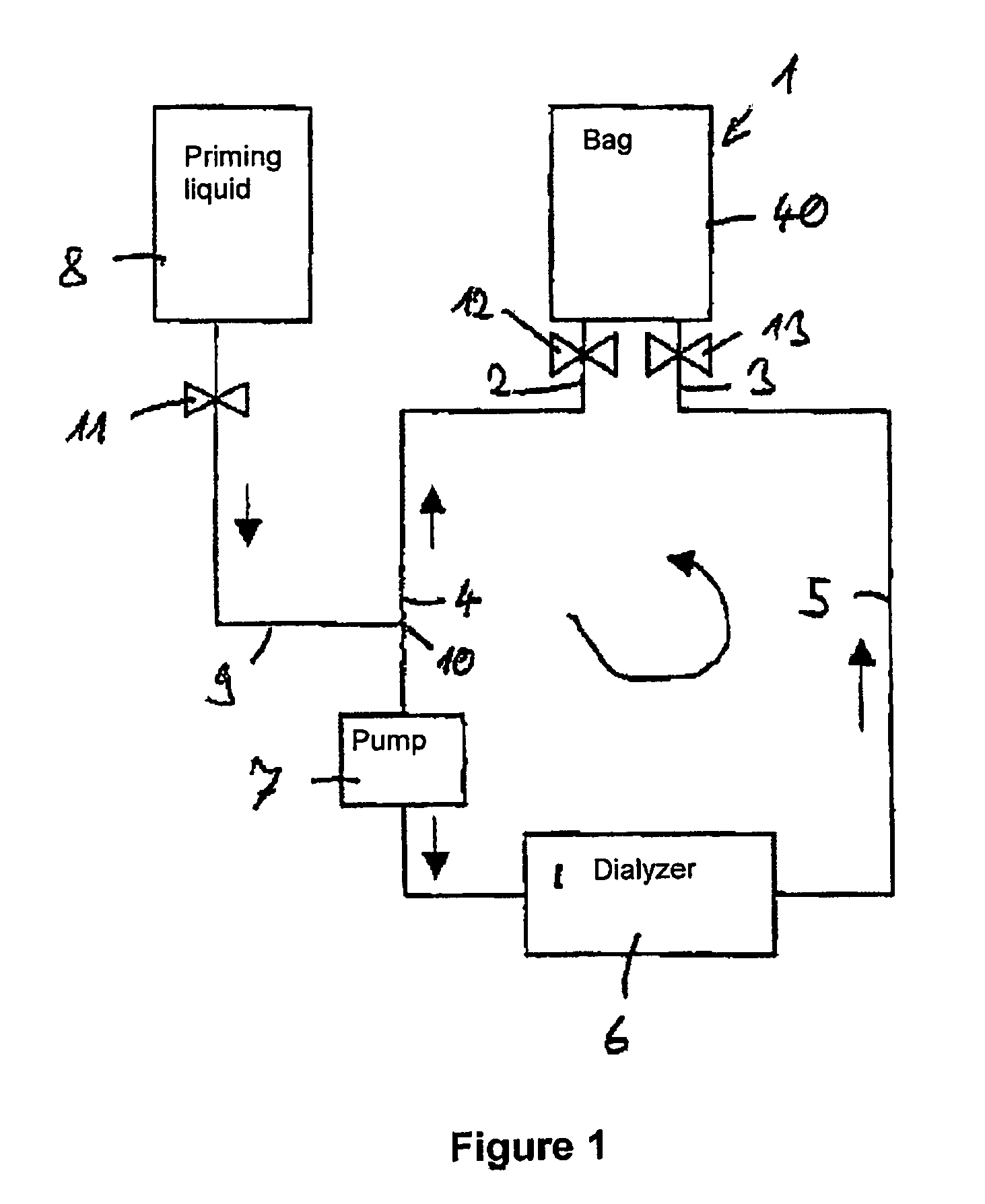
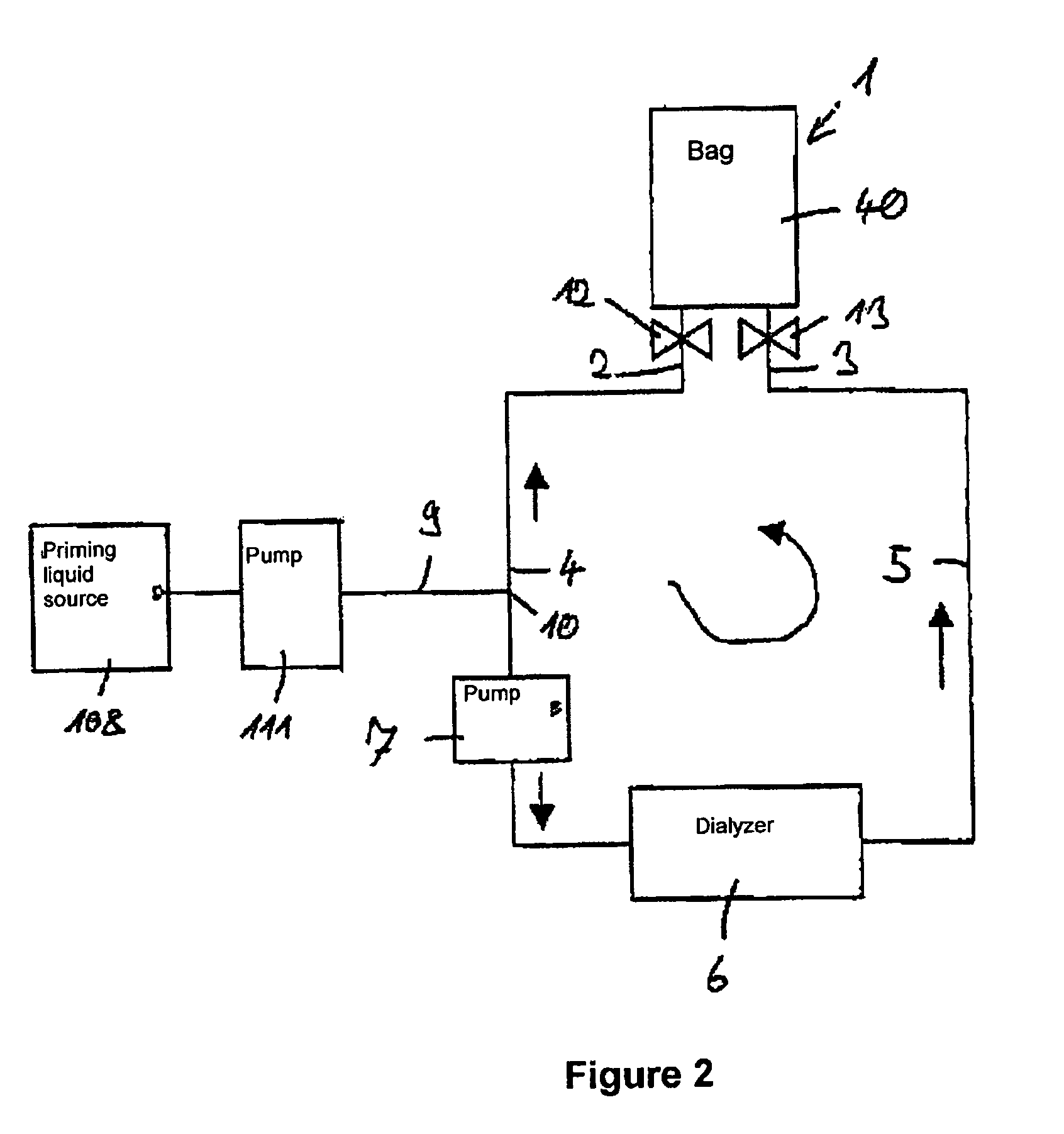
Method for priming a blood line set
ActiveUS8523799B2Simple and cost-effective sterilizationSimple and cost-effectiveDiagnosticsSurgeryLine tubingFeed line
A method for priming a blood tubing set having a venous line and an arterial line whose connections at the patient side are in communication with two separate inlets of a chamber of, in particular, a bag and whose connections at the machine side are in communication with a dialyzer. The method includes the steps of parallel filling of both the venous and the arterial lines via a feed line so that priming liquid flows through both inlets into the chamber; and circulation of the priming liquid in the circuit of the lines, the dialyzer and the chamber via a pump so that one of the inlets of the chamber acts as an inlet and the other as an outlet.
Owner:FRESENIUS MEDICAL CARE DEUTSCHLAND GMBH
Percutaneous vascular injury treatment systems and methods
InactiveUS20180263634A1Fast, effective, non-occlusive bleeding controlReduce morbidityTourniquetsTibiaHaemodialysis machine
The present invention relates to a compressive band and hemostatic dressing system and related methods of use to provide rapid, non-occlusive bleeding control, arterial injury treatment, and injury protection comfortably and reliably after vascular access procedures. The present invention may comprise some or all of the following elements: a positioner assembly, a compressive cushion component, a compression plate, a strap with a flexible hinge assembly, and a hemostatic dressing. In a preferred embodiment, the systems and methods are applied to treat and ameliorate vascular injury in a transradial percutaneous access procedure and protect against underlying vascular injury; however, the systems and methods described herein may be applied to any vascular access procedure including arm or leg vascular approaches such as the femoral, brachial, dorsalis pedis or tibial blood vessels in arterial or venous line or sheath removal or trocar removal, and in hemodialysis.
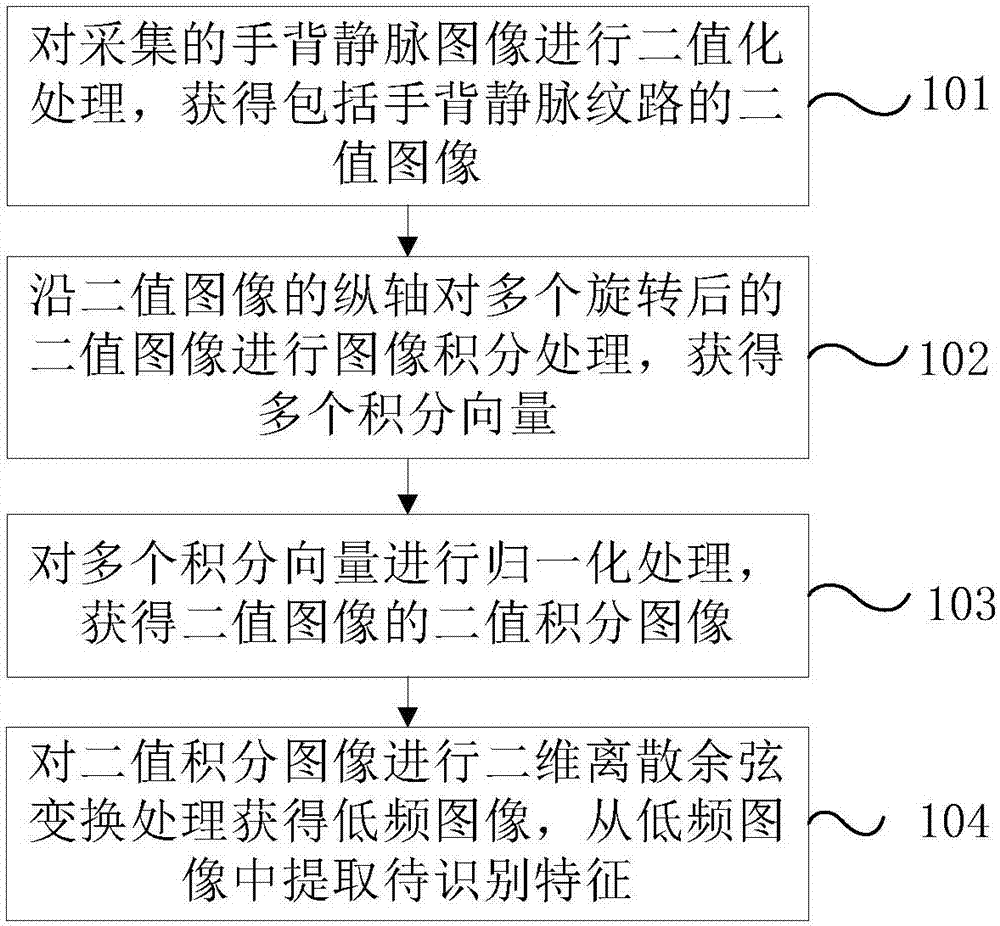
Owner:TRICOL BIOMEDICAL INC
Hand vein recognition method based on curve matching
ActiveCN105184272AImprove vein recognition performanceImprove feature matching speedSubcutaneous biometric featuresBlood vessel patternsVeinSample rotation
The present invention provides a hand vein recognition method based on curve matching. The method comprises the steps of firstly scanning the vein branch curves according to the venous line endpoints and the intersection points, then extracting the characteristics of each curve, such as the curvature, the length, etc., and finally, realizing the reliable recognition of the hand veins by combining the coarse screening and the curve matching. Under the premise of enhancing the anti-interference ability of the characteristics, the inter-cluster distinguishing ability of the characteristics is improved, and the reliable recognition of the hand veins is realized. The hand vein recognition method based on curve matching of the present invention solves the problems that the sample rotation and translation influences the recognition, the algorithm matching speed is accelerated, etc., and the efficiency of the method accords with the requirements of a mode recognition system. The hand vein recognition method based on curve matching of the present invention enables the hand vein recognition performance to be improved effectively, and is widely used in an intelligent access control system.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Method and device for testing sensors to be applied on a patient's skin for the detection of fluid or moisture
ActiveUS9645218B2Reliable quality controlLarge movementDetection of fluid at leakage pointOther blood circulation devicesVeinBlood treatments
A method and device for testing sensors to be applied on a patient's skin for detection of liquid or moisture are described, in particular for monitoring vascular access in an extracorporeal blood treatment, in which a patient's blood is carried away from the patient via an arterial line and is fed to the patient via a venous line. A method for producing sensors to be applied on a patient's skin for detection of liquid or moisture is also described. The method and device according to the present invention are based on the testing of one or more moisture sensors which are taken from current production. The method includes providing a large number of twists of the moisture sensor applied onto a torsion body, the mechanical stresses thus recreating the stresses that can occur in practice when the moisture sensor is applied or stuck onto the patient's skin or forearm.
Owner:FRESENIUS MEDICAL CARE DEUTSCHLAND GMBH
Method and device for determining the blood flow in a blood-conducting tube
InactiveUS7704213B2Eliminate the effects ofOther blood circulation devicesVolume/mass flow measurementExtracorporeal circulationVein
A measurement method for determining the blood flow rate QF in blood carrying lines is provided. It may be used in particular to determine the blood flow in a patient's vessel, which is connected to the extracorporeal circulation of a blood treatment machine by an arterial line and a venous line. According to the method, the net rate dX / dt of a variable X is determined, with X being derived from a physicochemical variable Y of the blood with the help of values YA and YV which are adequately constant over time and which respectively characterize the physicochemical property in the arterial line and the venous line during the measurement interval. The net rate dX / dt is then used to determine the blood flow rate QF. The targeted use of indicators is not necessary.
Owner:FRESENIUS MEDICAL CARE DEUTSCHLAND GMBH
Hand dorsum vein image identification processing method and hand dorsum vein image identification processing device
ActiveCN107153827AHigh feature accuracyStrong feature stabilitySubcutaneous biometric featuresBlood vessel patternsVeinPattern recognition
The invention provides a hand dorsum vein image identification processing method and a hand dorsum vein image identification processing device. Binarization processing of acquired hand dorsum vein images is carried out to acquire binary images including hand dorsum venous lines. The image integration processing of a plurality of rotated binary images is carried out along the vertical axes of the binary images, and a plurality of integral vectors are acquired. The normalization processing of the plurality of integral vectors is carried out to acquire the binary integral images of the binary images. The two-dimensional discrete cosine transform processing of the binary integral images is carried out to acquire low-frequency images, and to-be-identified characteristics are extracted from the low-frequency images. The binary images are rotated a plurality of times, and the image integration processing of the binary images is carried out after each time of rotation, and therefore the characteristic accuracy of the finally-acquired to-be-identified characteristics is higher, the characteristic stability thereof is stronger, and therefore the robustness of identification results of identity identification adopting the to-be-identified characteristics is higher.
Owner:NORTH CHINA UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Method of draining a device for extracorporeal blood treatment
ActiveUS20170296733A1Simple and safe operationRisk minimizationOther blood circulation devicesDialysis systemsBlood treatmentsVein
A method of draining a device for extracorporeal blood treatment, wherein the device comprises a dialyzer which is divided by means of a membrane into a first chamber and a second chamber, an arterial line connected to a blood inlet of the first chamber, a venous line connected to a blood outlet of the first chamber, a dialysis fluid line for fresh dialysis fluid connected to a dialysis fluid inlet of the second chamber and a dialysis fluid line for used dialysis fluid connected to a dialysis fluid outlet of the second chamber, a blood pump disposed in the arterial line, a venous expansion chamber disposed in the venous line and an air detector unit downstream of the venous expansion chamber, and wherein the method comprises the following steps of: connecting a patient-side port of the arterial line to a patient-side port of the venous line; generating a negative pressure in the second chamber; operating the blood pump in a first direction and draining the arterial and venous lines in the first direction via the membrane and the second chamber; and stopping the blood pump and draining the arterial and venous lines in a second direction opposed to the first direction via the membrane and the second chamber.
Owner:B BRAUN AVITUM
Measurement of a blood flow rate in hemodialysis shunts
InactiveUS7473371B2Simplifies withdrawalIncrease blood flowOther blood circulation devicesBlood flow measurement devicesVeinBlood flow
The measurement of blood flow in a dialysis shunt is obtained by injection of an indicator material into a venous line leading from dialysis equipment to the shunt. The blood flow in an arterial line leading from the shunt at a location downstream of the venous line to the dialysis equipment is monitored by an arterial line sensor for the presence of the indicator material. A detector connected to the sensor provides a dilution curve in response to the presence of the indicator material and the blood flow in the shunt is calculated from the area under the dilution curve. The locations of the arterial and venous lines in the shunt can be reversed to obtain a measurement of blood recirculation from the venous line into the arterial line.
Owner:TRANSONIC SYST
Puncturing practice device for nurses
The invention relates to a puncture practice device for nurses. A separate water tank with multiple interfaces, a storage battery, a vibration module and a power supply interface with switches are installed in the chest and abdominal cavity of the human body model frame device. Magnetic induction switches are installed on the corresponding positions of the sacral plexus, lumbar plexus, sciatic nerve, femoral nerve, etc., and two booster pumps are installed in the separated water tank and hold liquids of different colors, which are respectively connected to the corresponding silicone arterial tube and silicone venous tube. When you need to practice injection puncture, turn on the switch, the booster pump works, and the water in the separated water tank flows into the silicone arterial tube and the silicone venous tube connected to it. The color of the blood returns to distinguish the arteries and veins. When the corresponding nerve or nerve plexus is pierced, the vibration module starts to vibrate. To achieve the purpose of improving the operation skills by practicing puncture by the simulated person.
Owner:崔金兰
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com