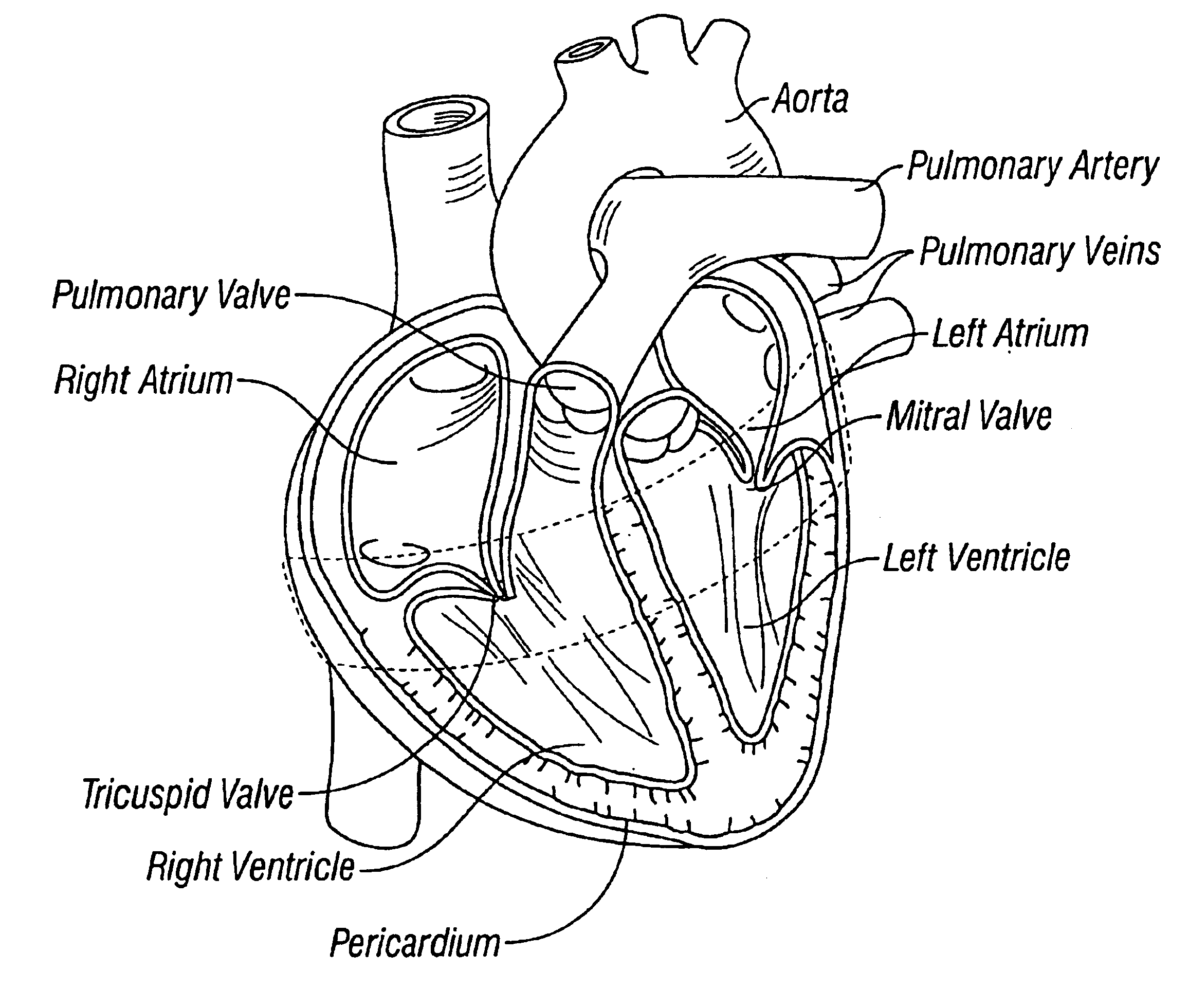
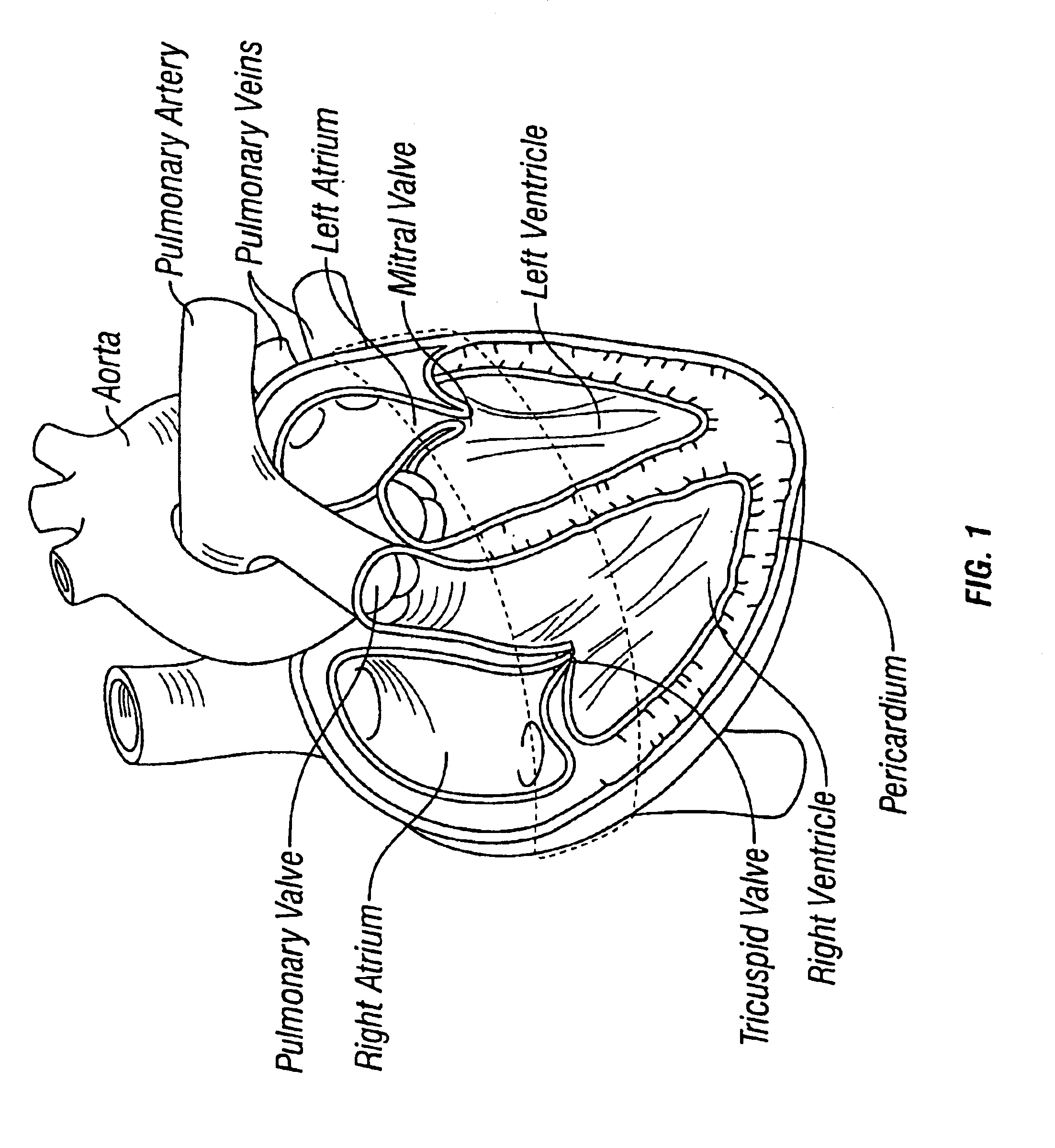
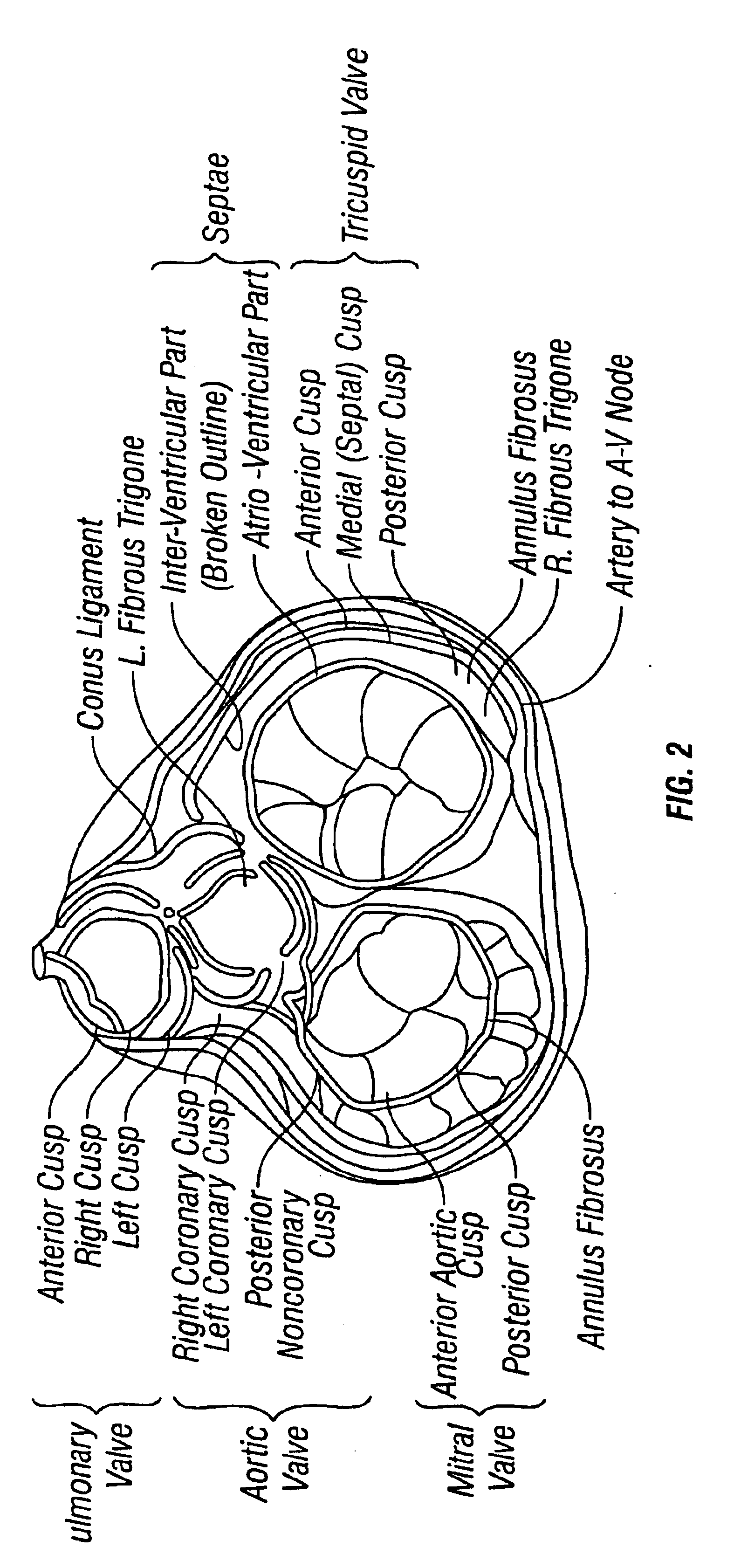
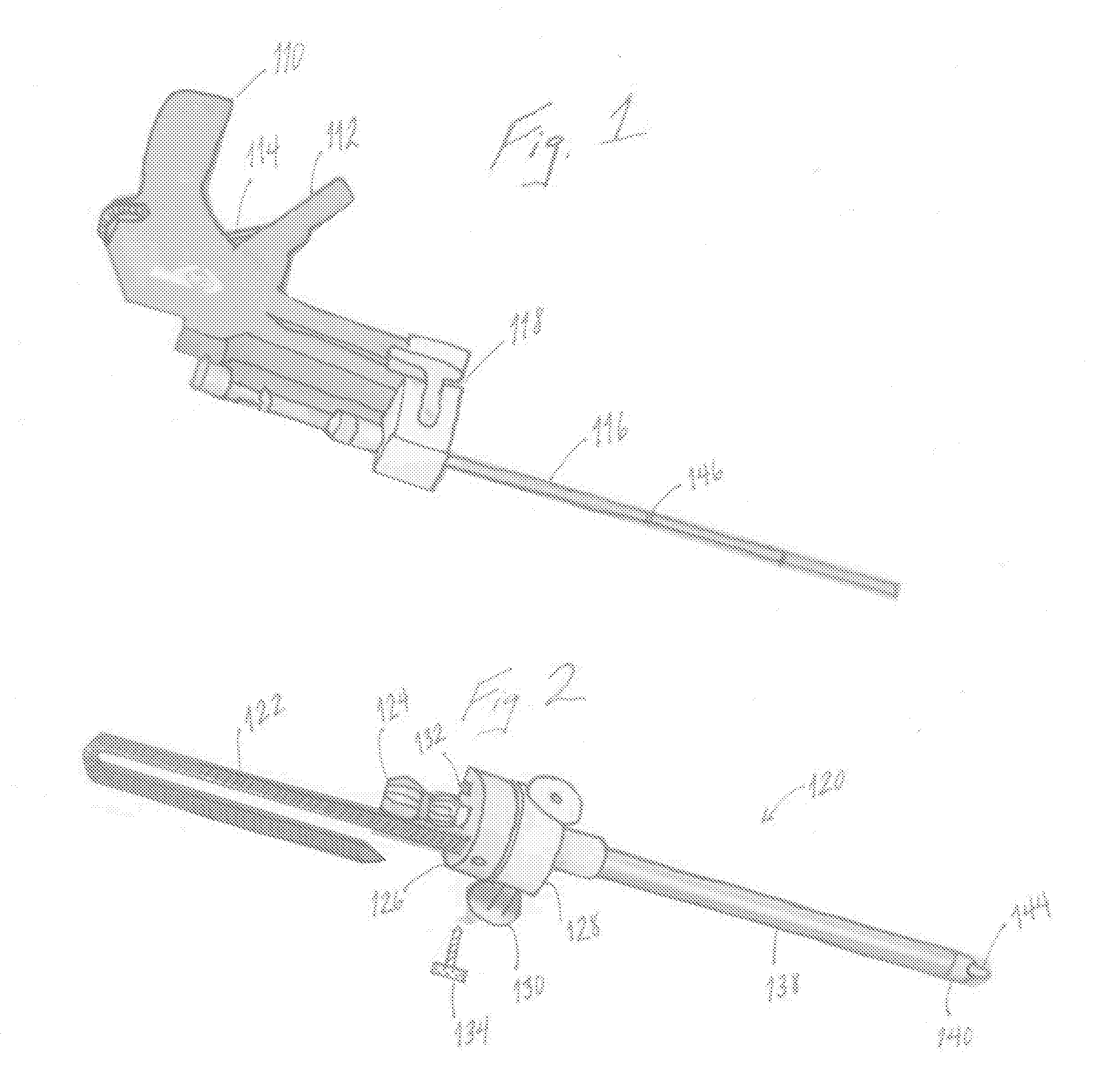Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
656 results about "Extracorporeal circulation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
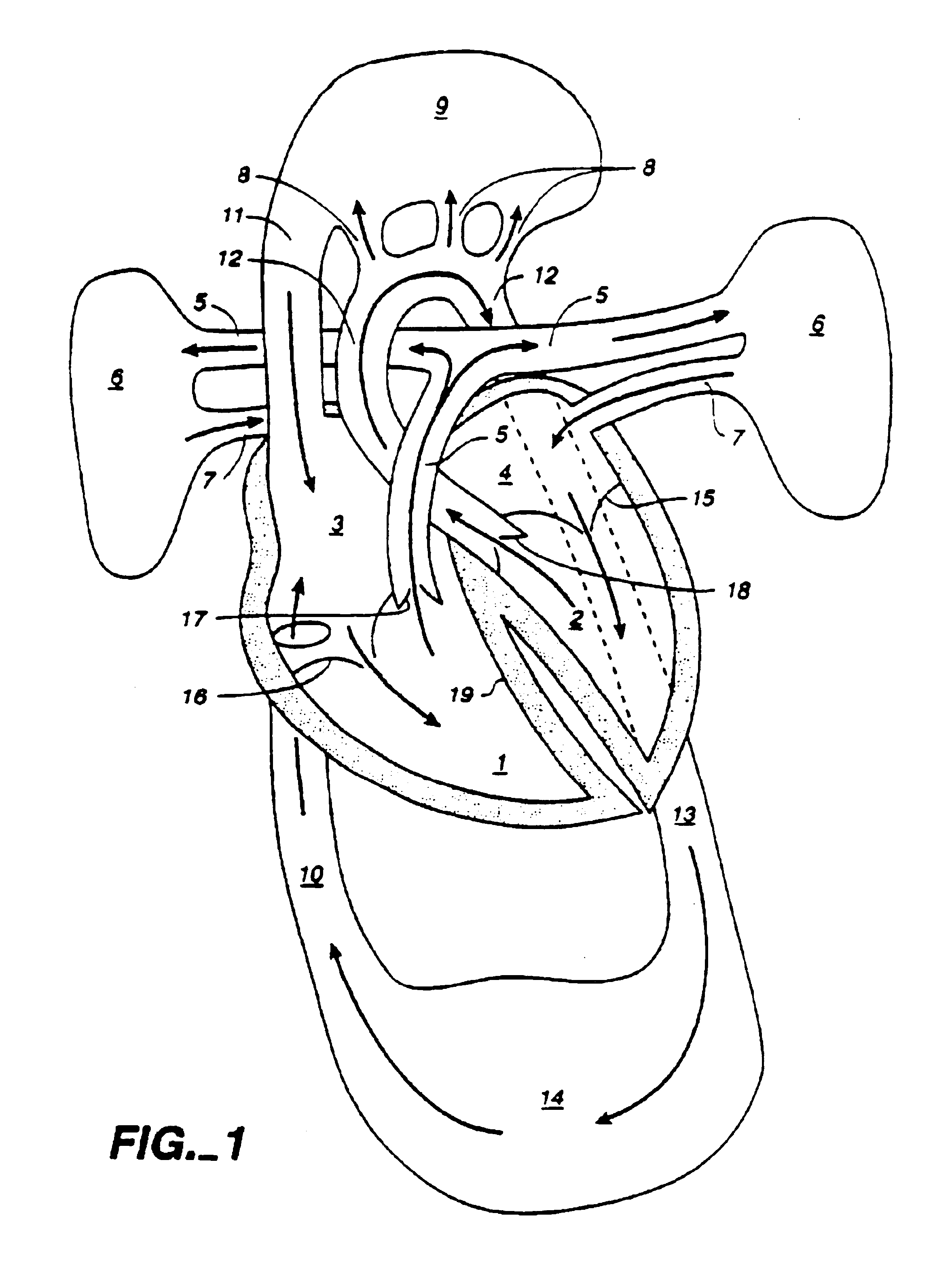
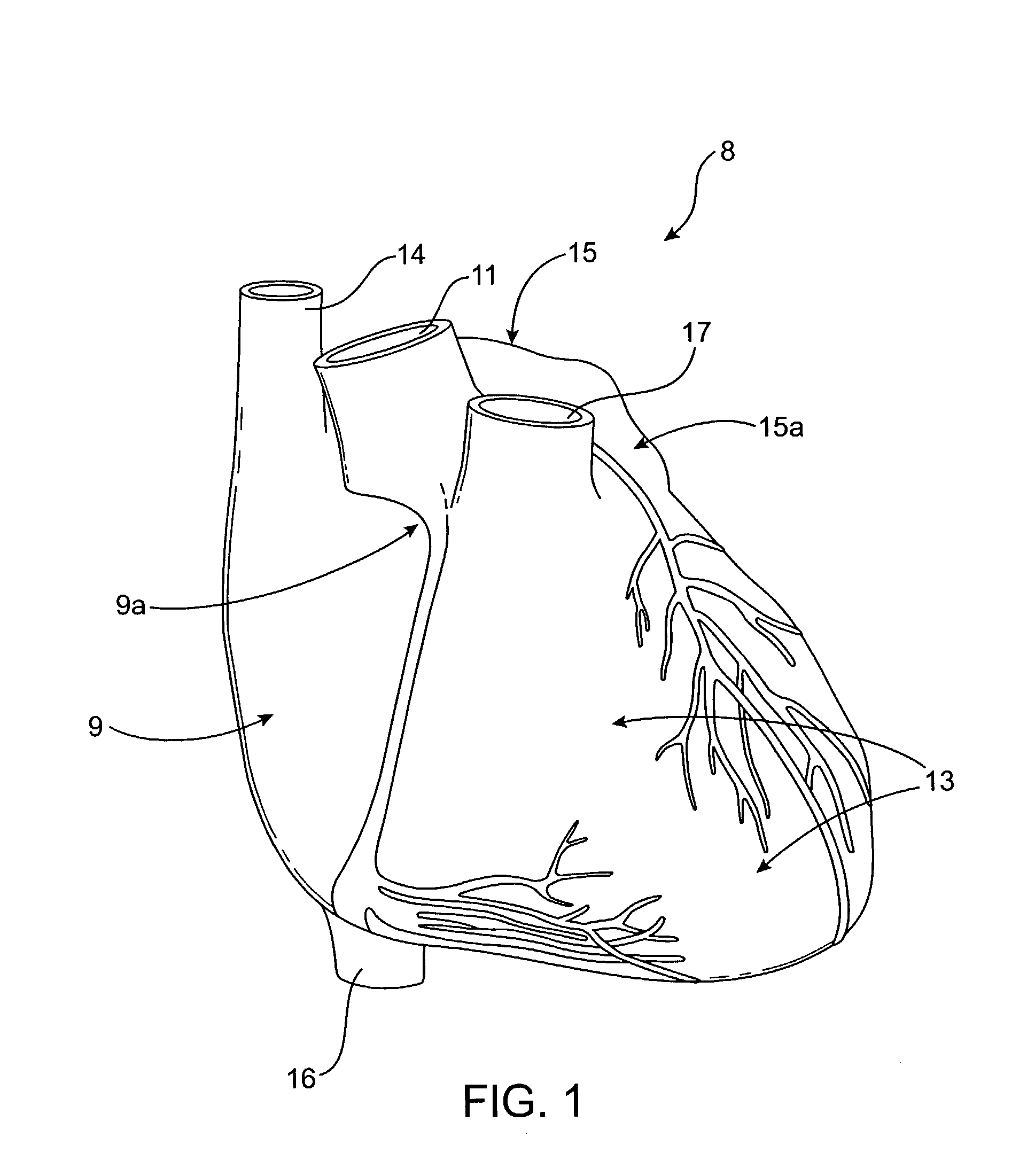
Extracorporeal circulation. the circulation of blood outside the body, as through a hemodialyzer for removal of substances usually excreted in the urine, or through an extracorporeal circulatory support unit for carbon dioxide-oxygen exchange (see below).
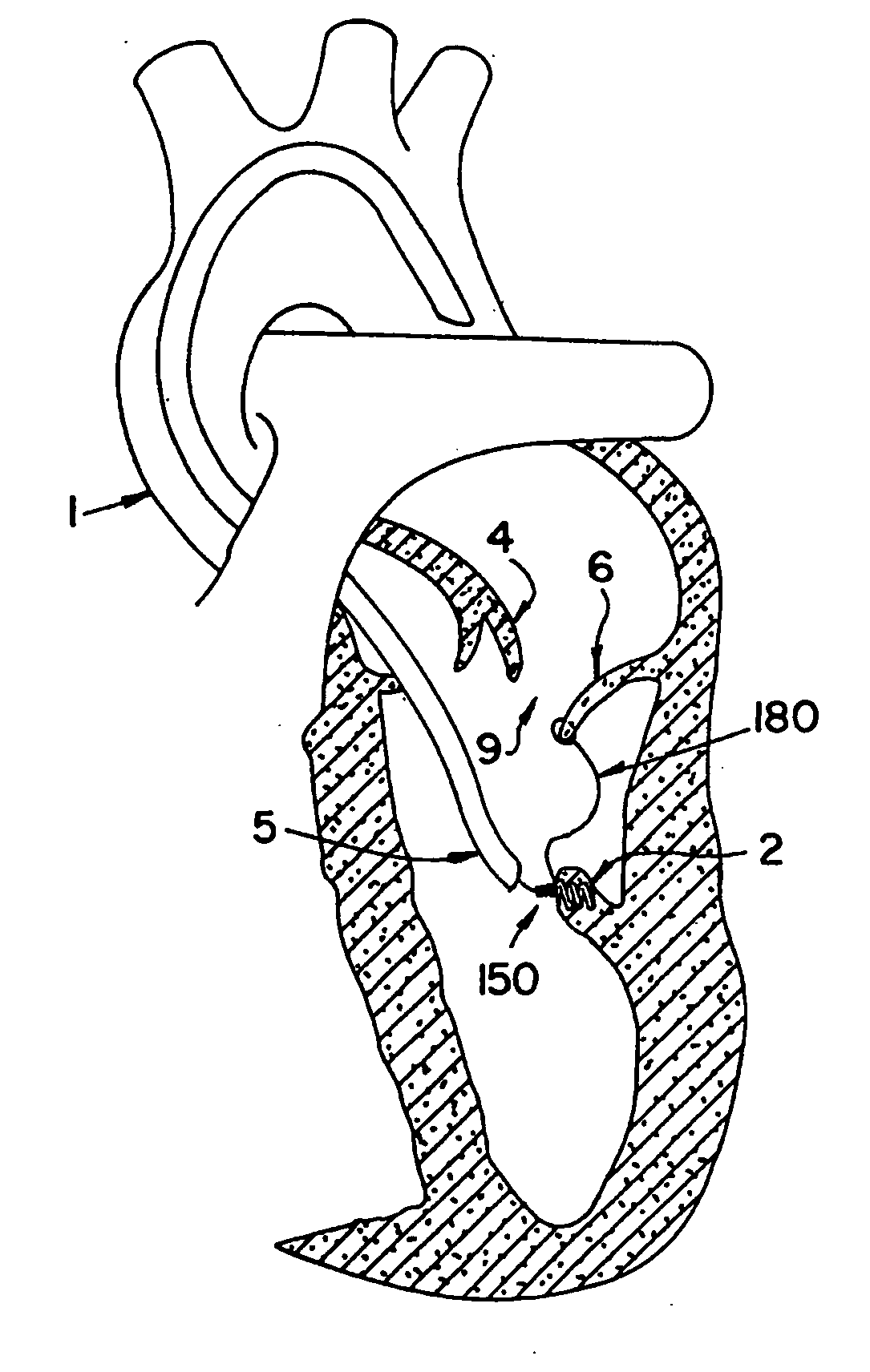
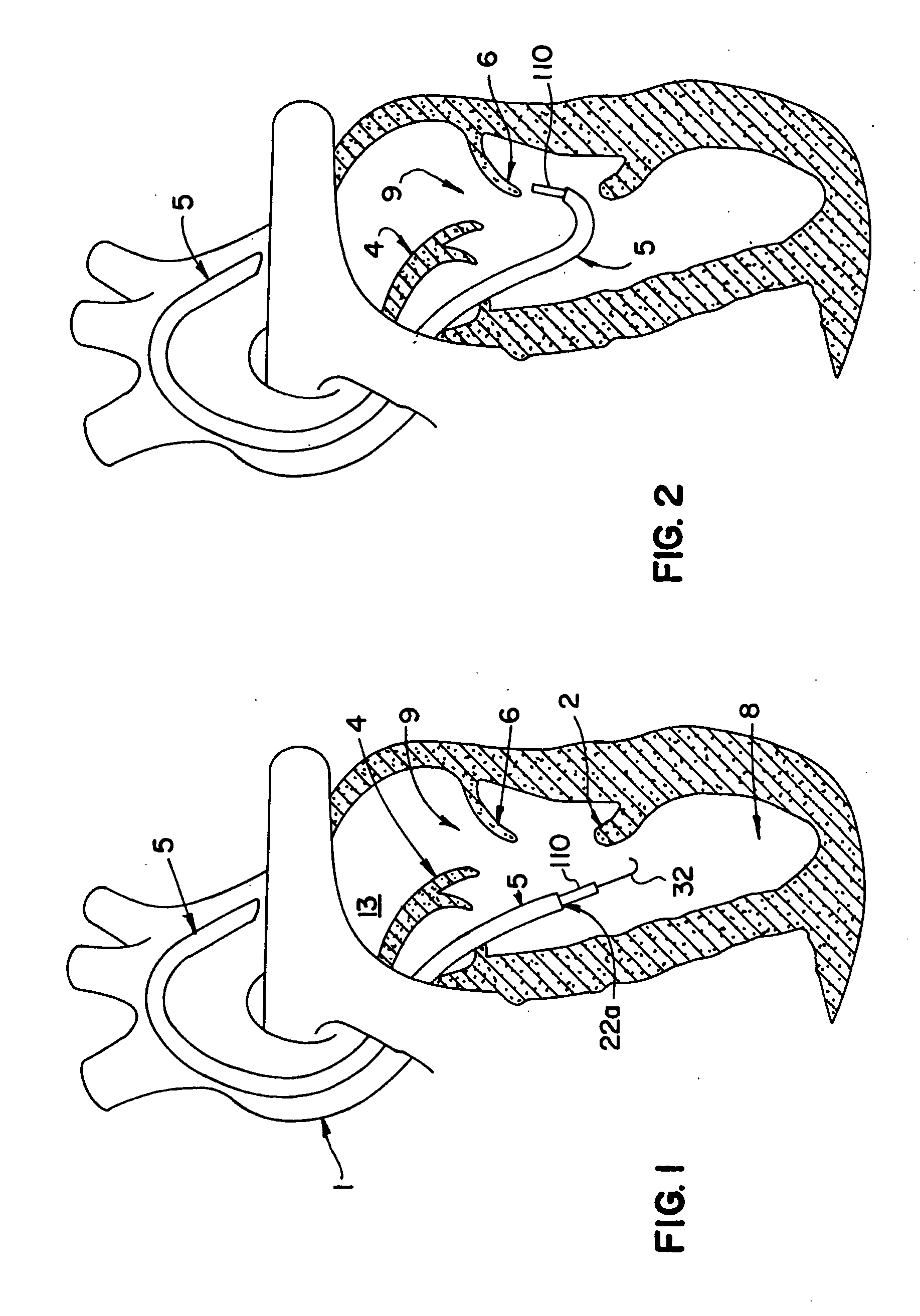
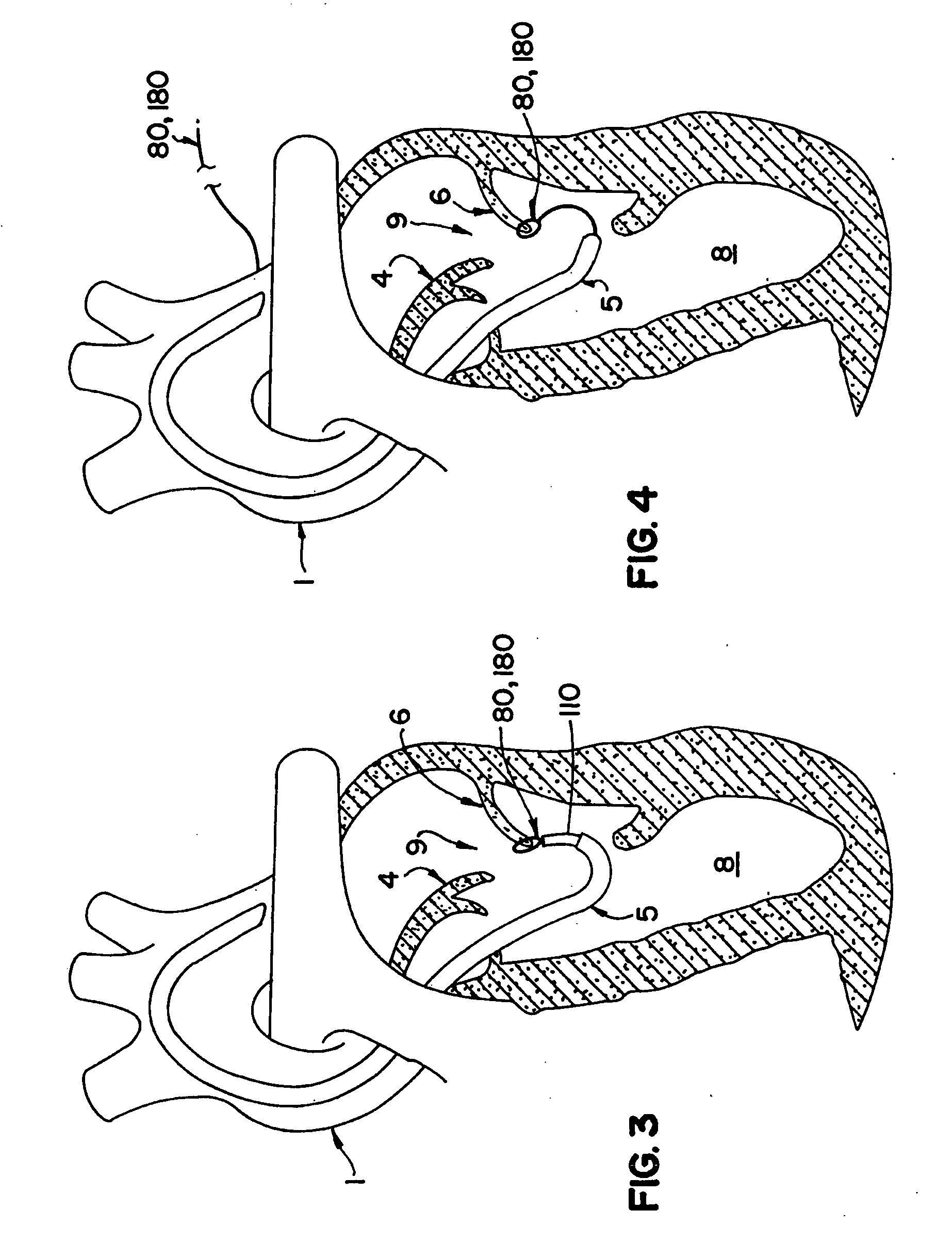
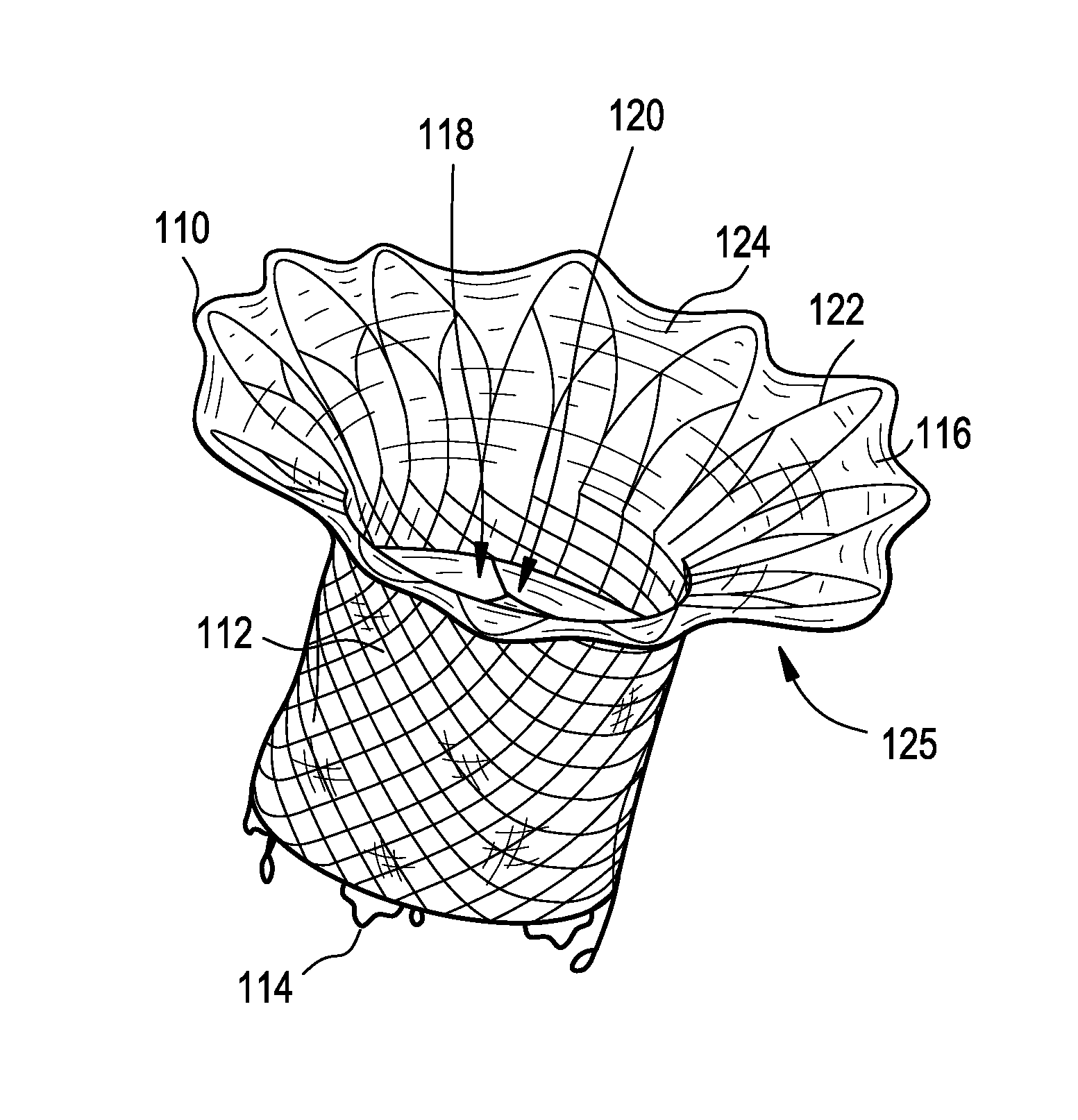
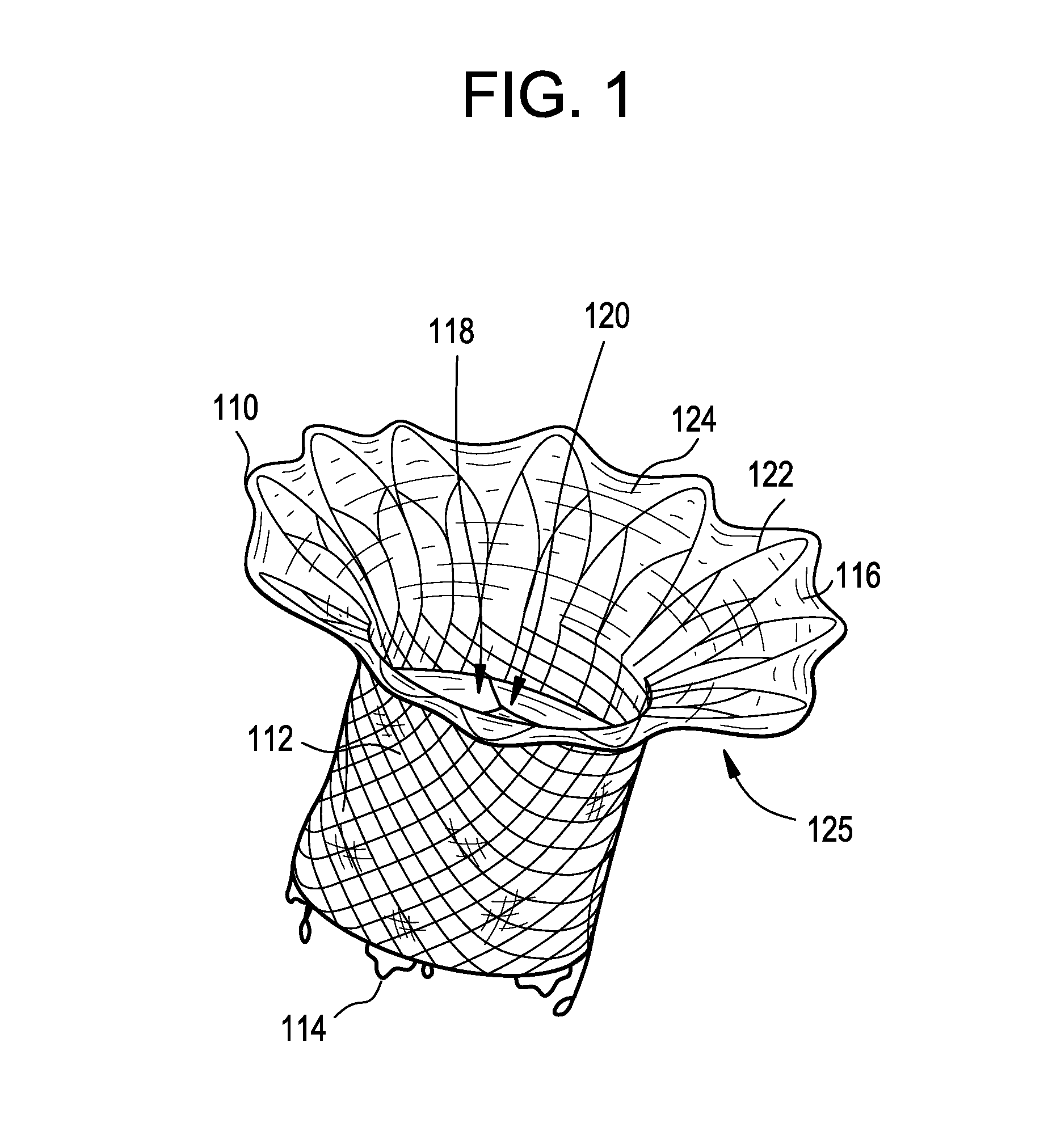
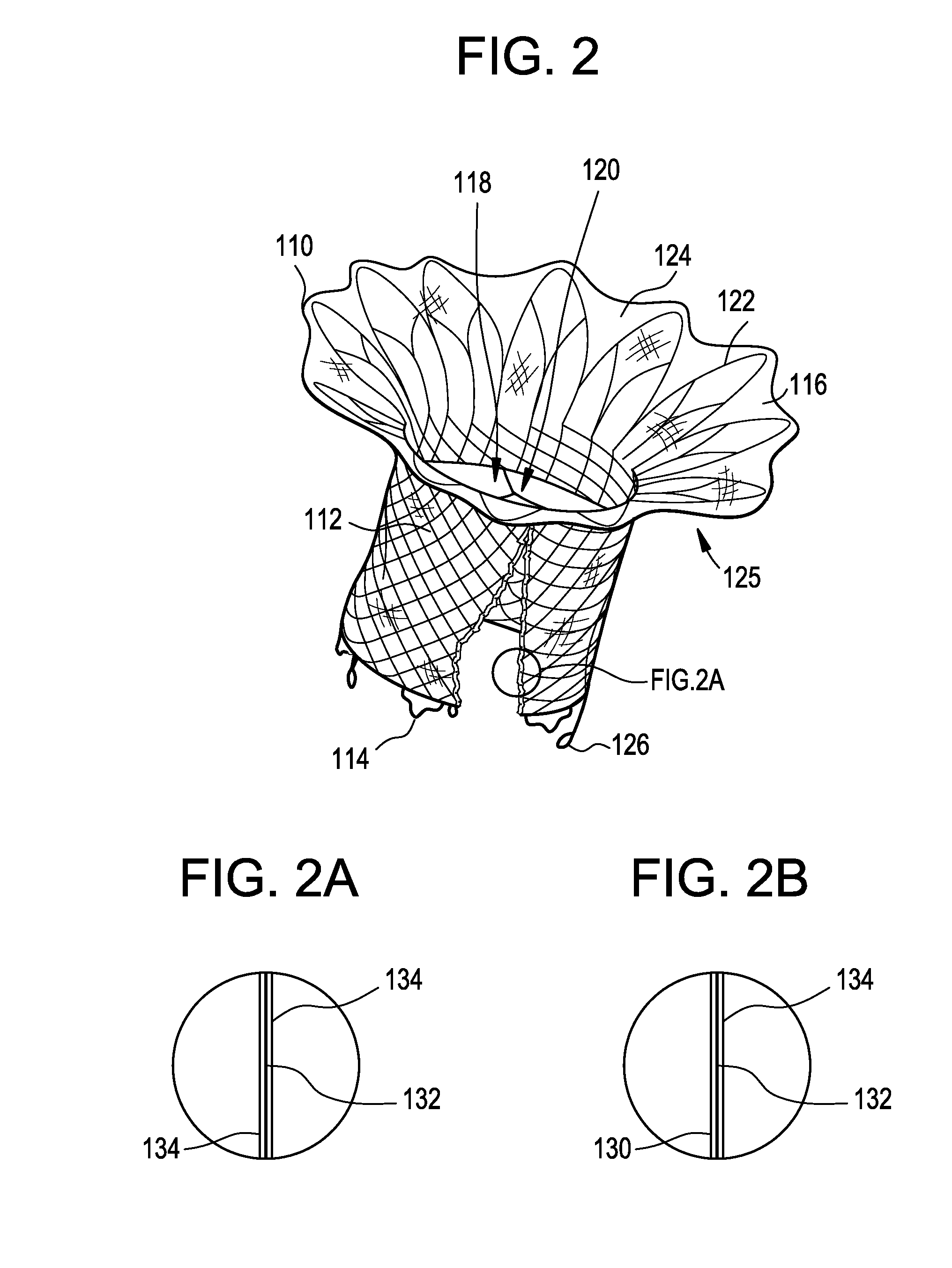
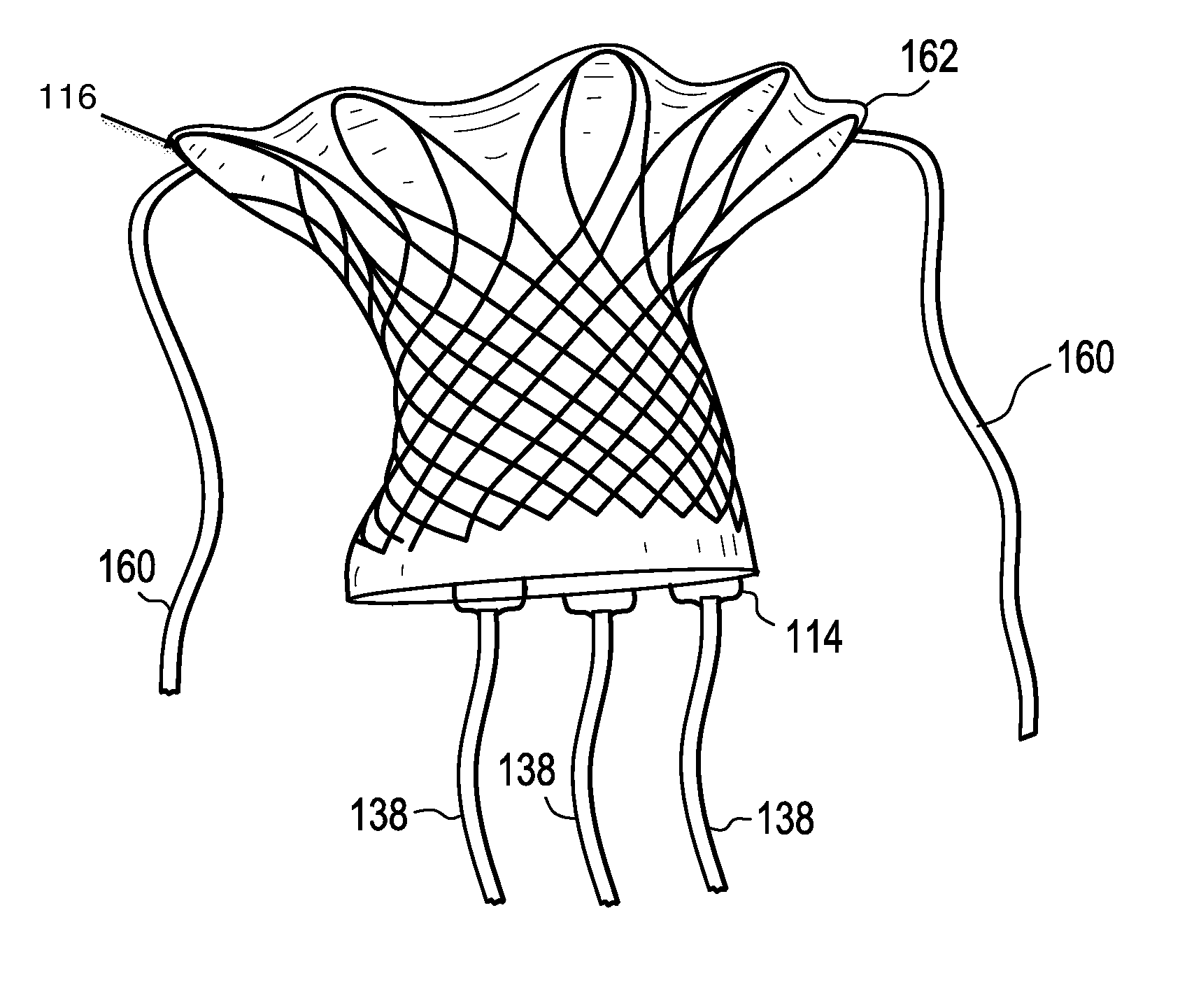
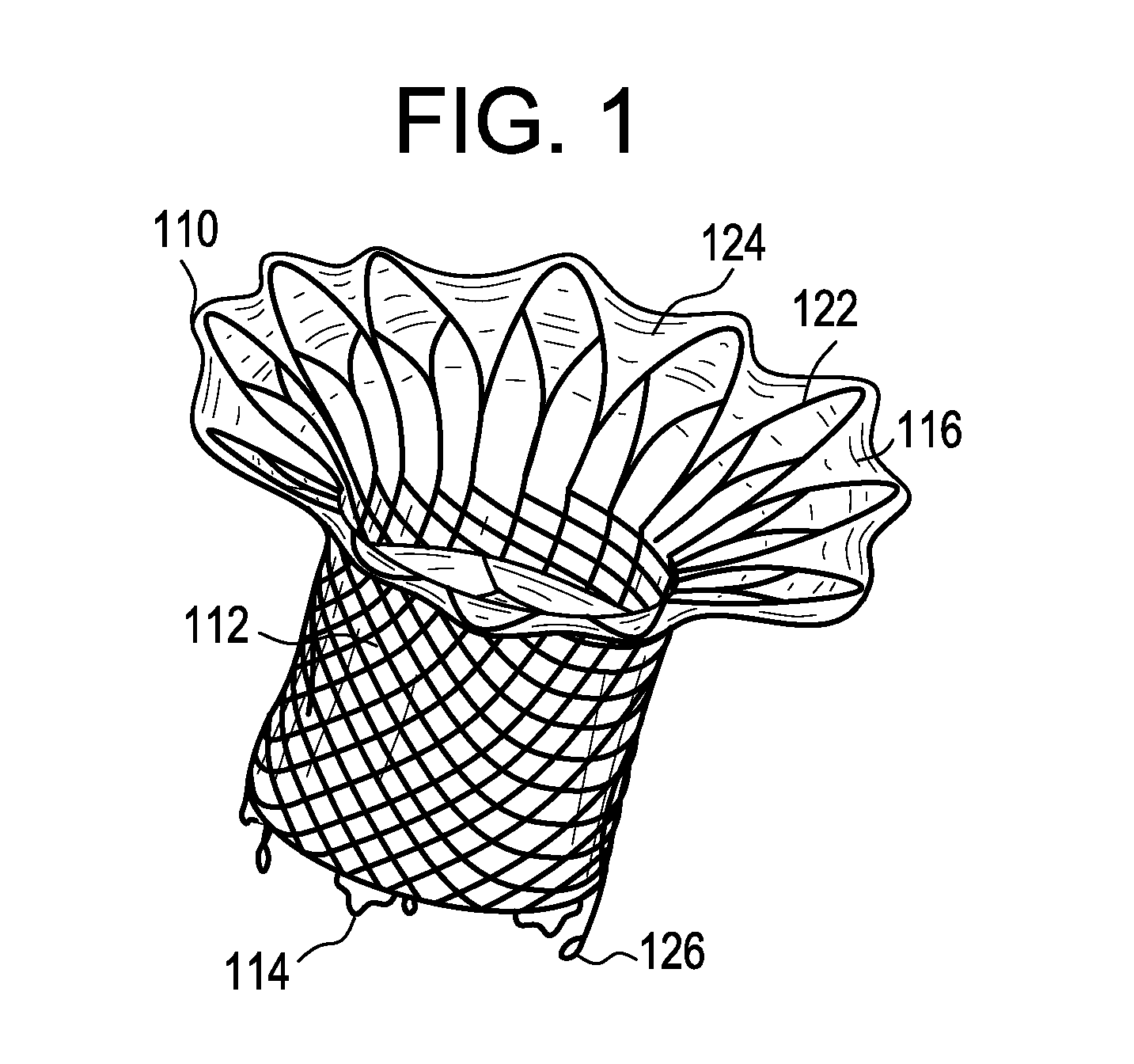
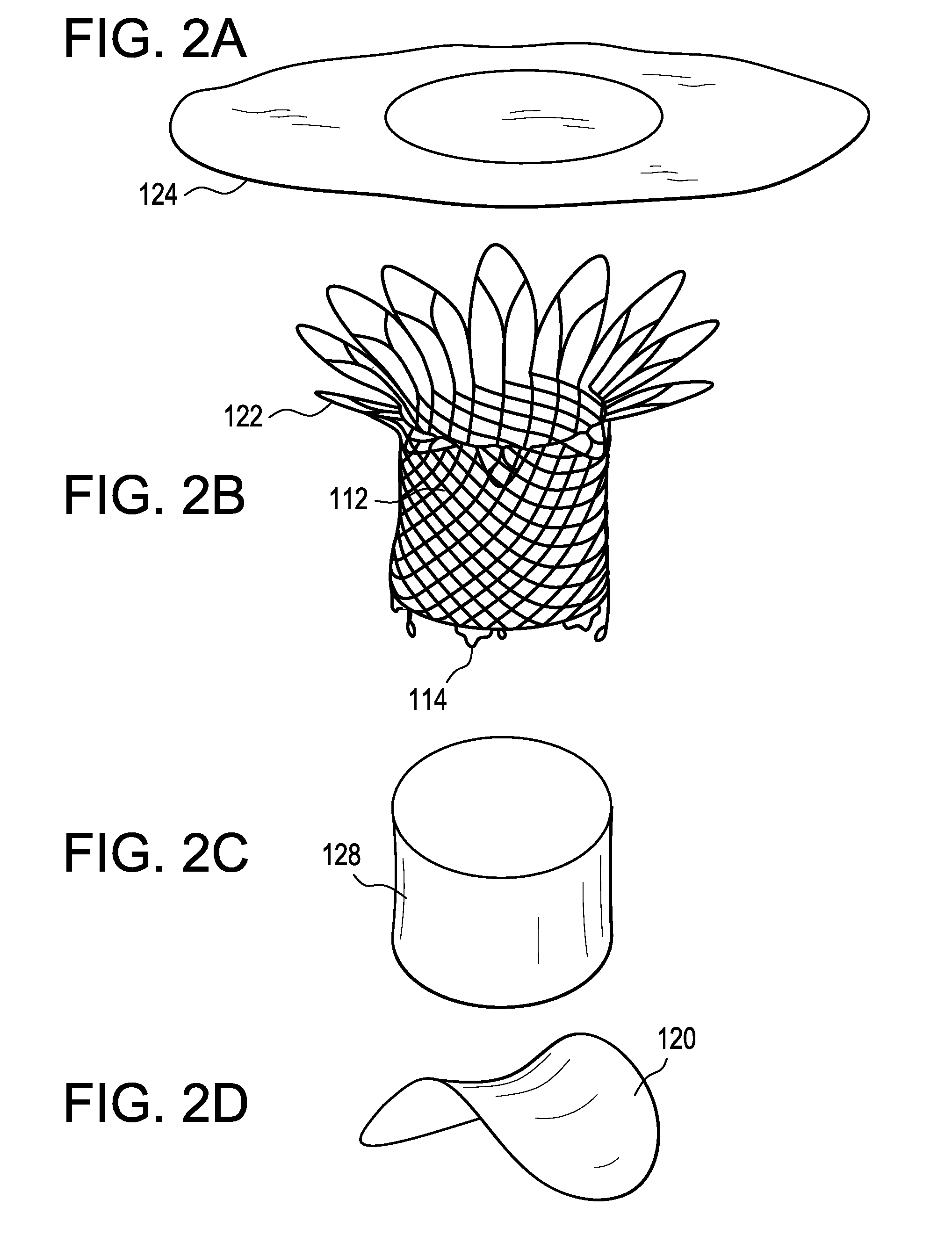
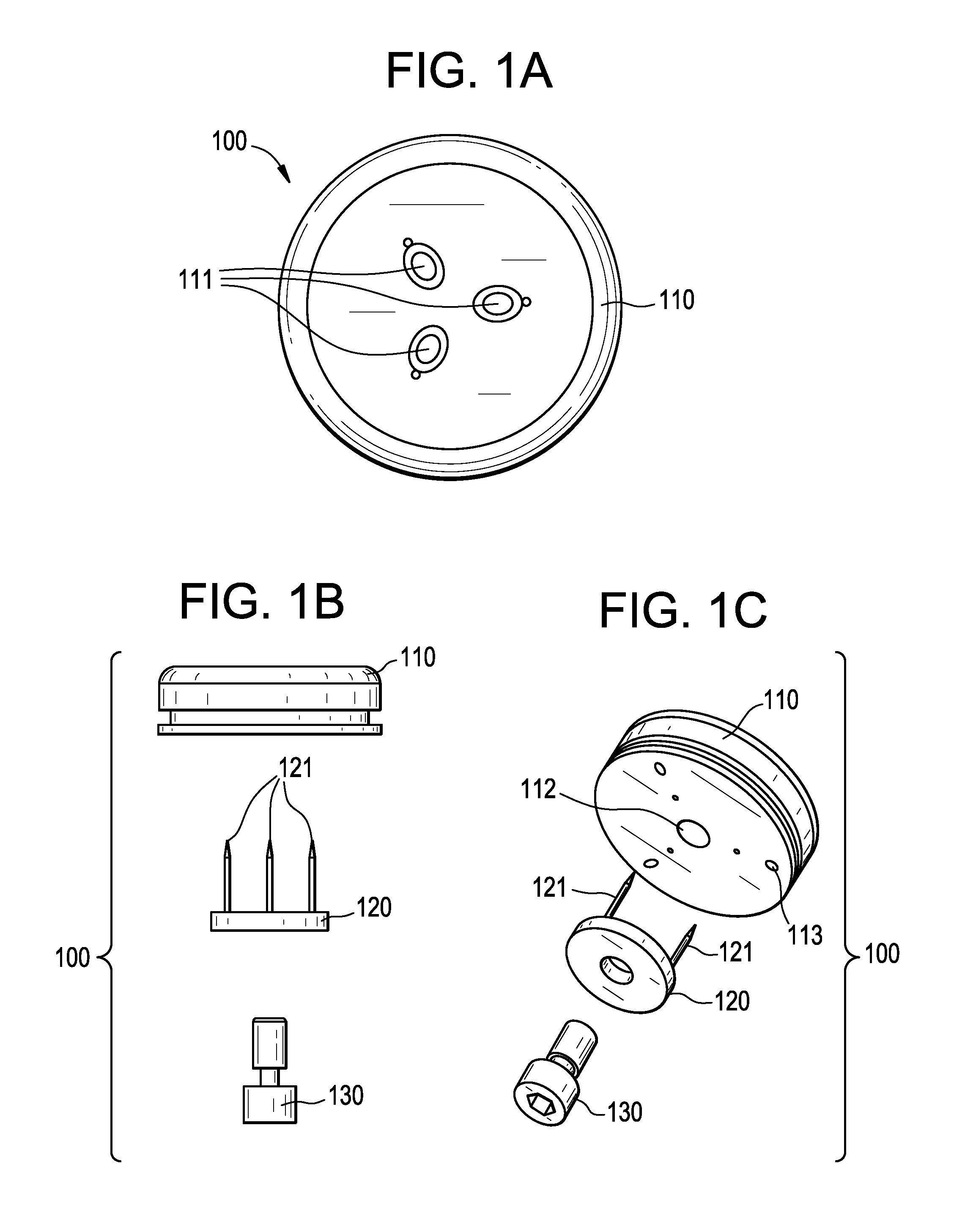
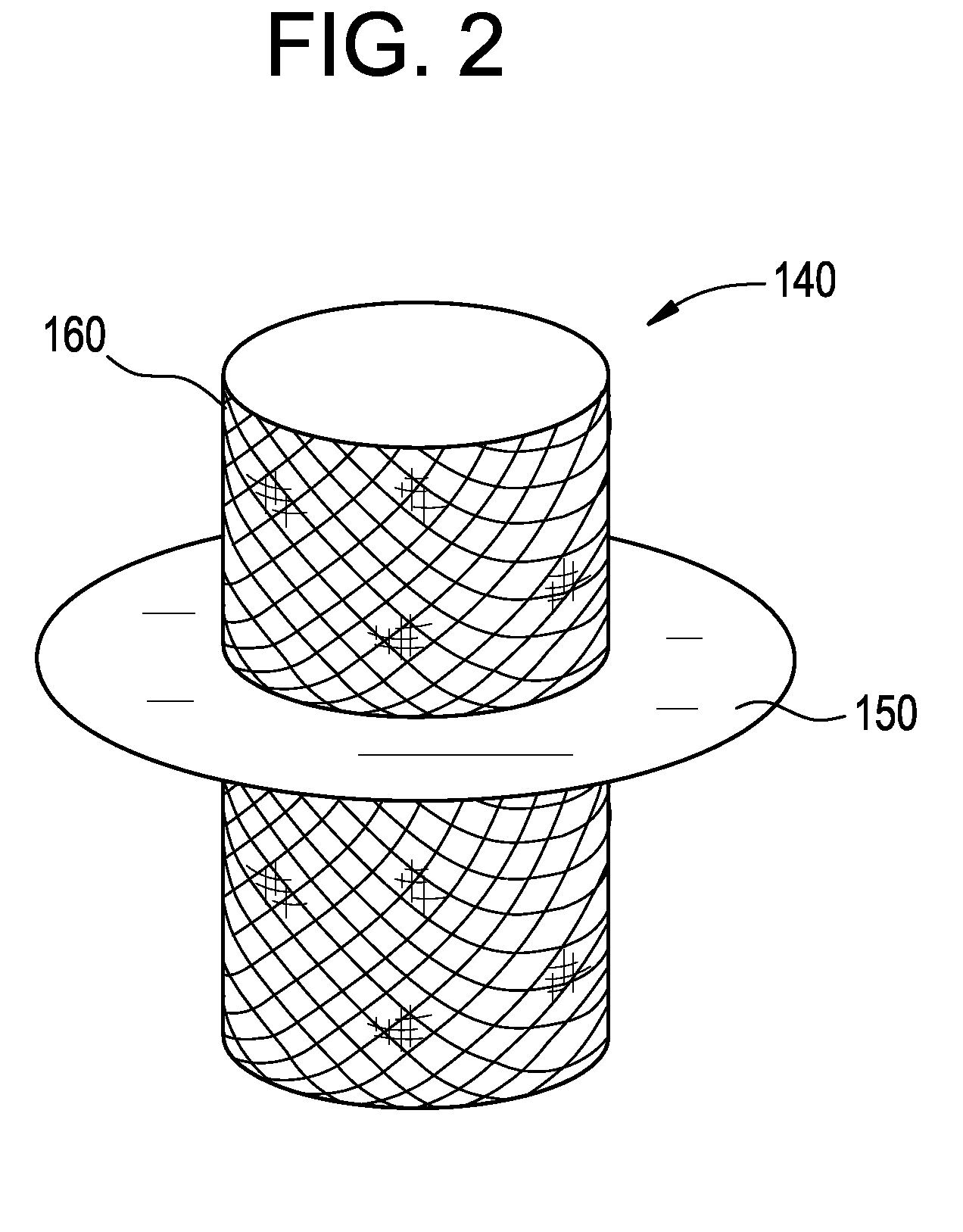
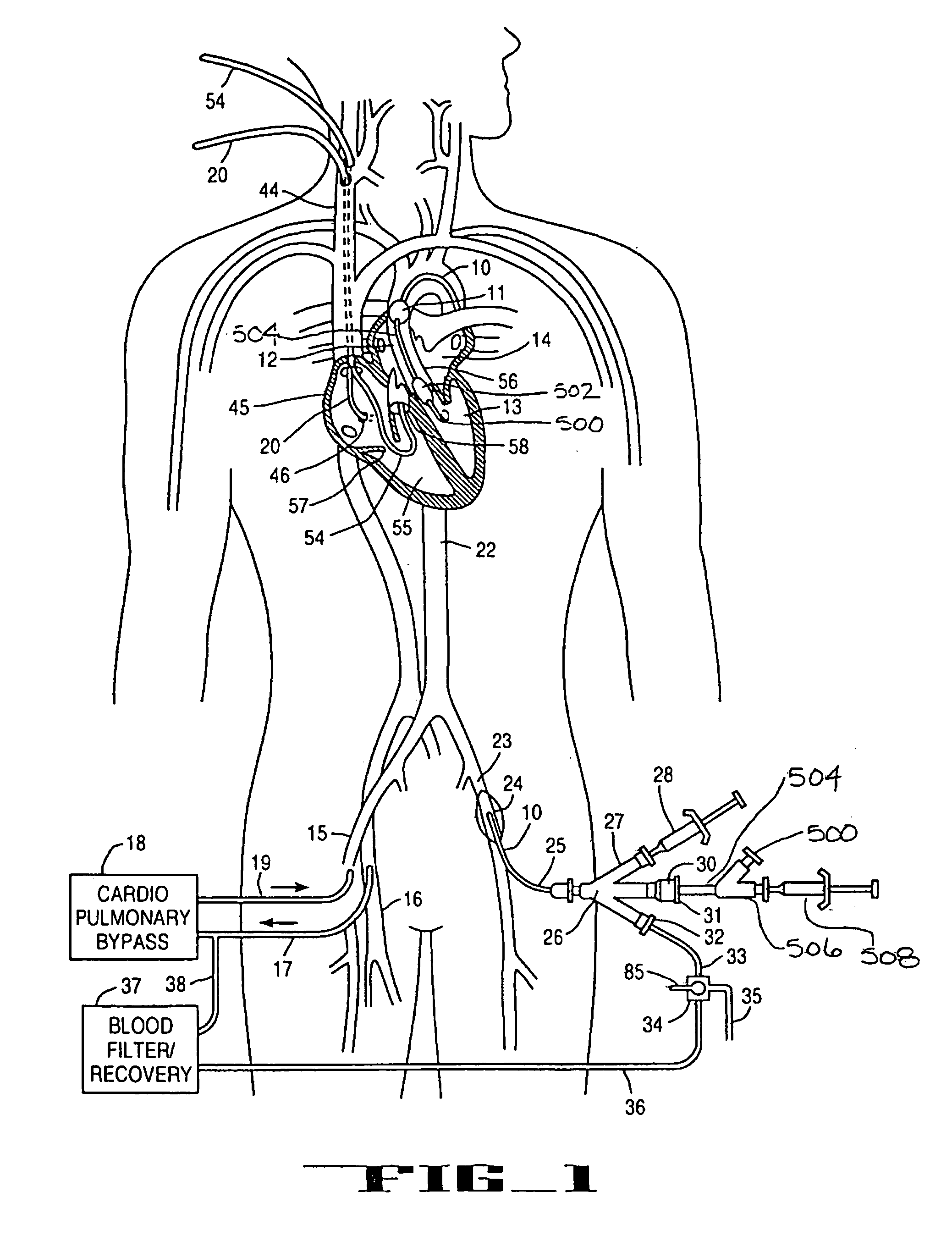
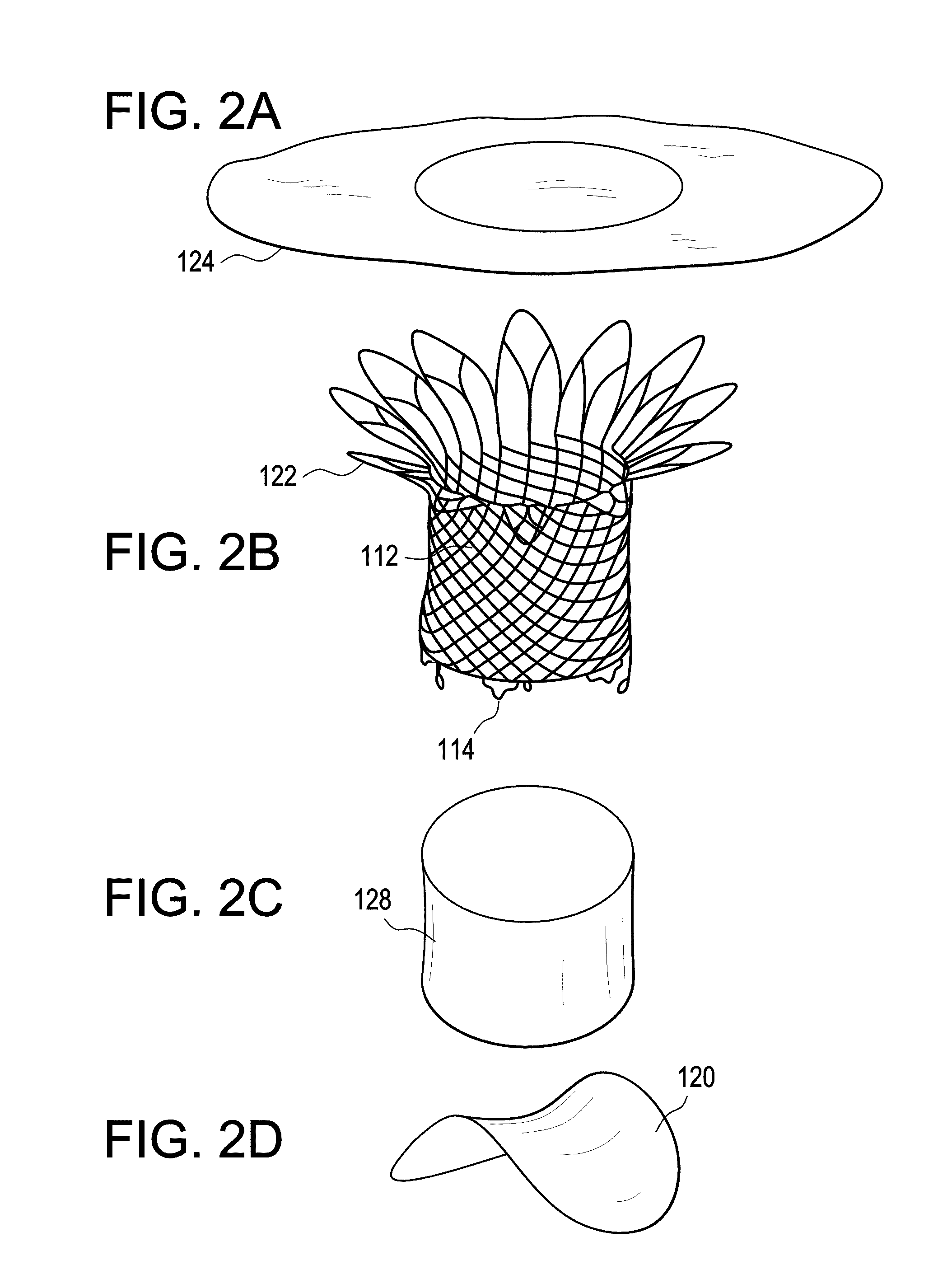
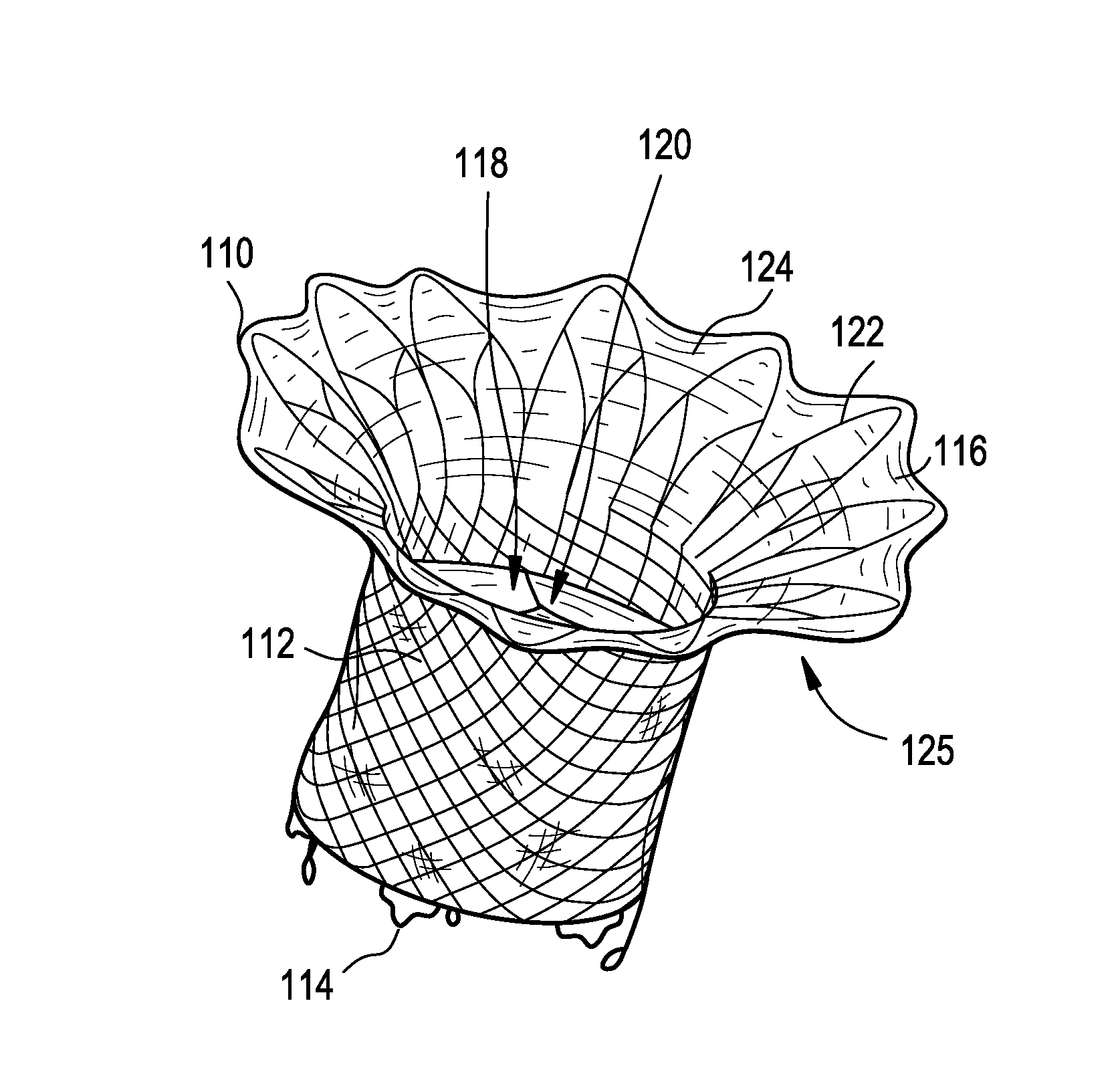
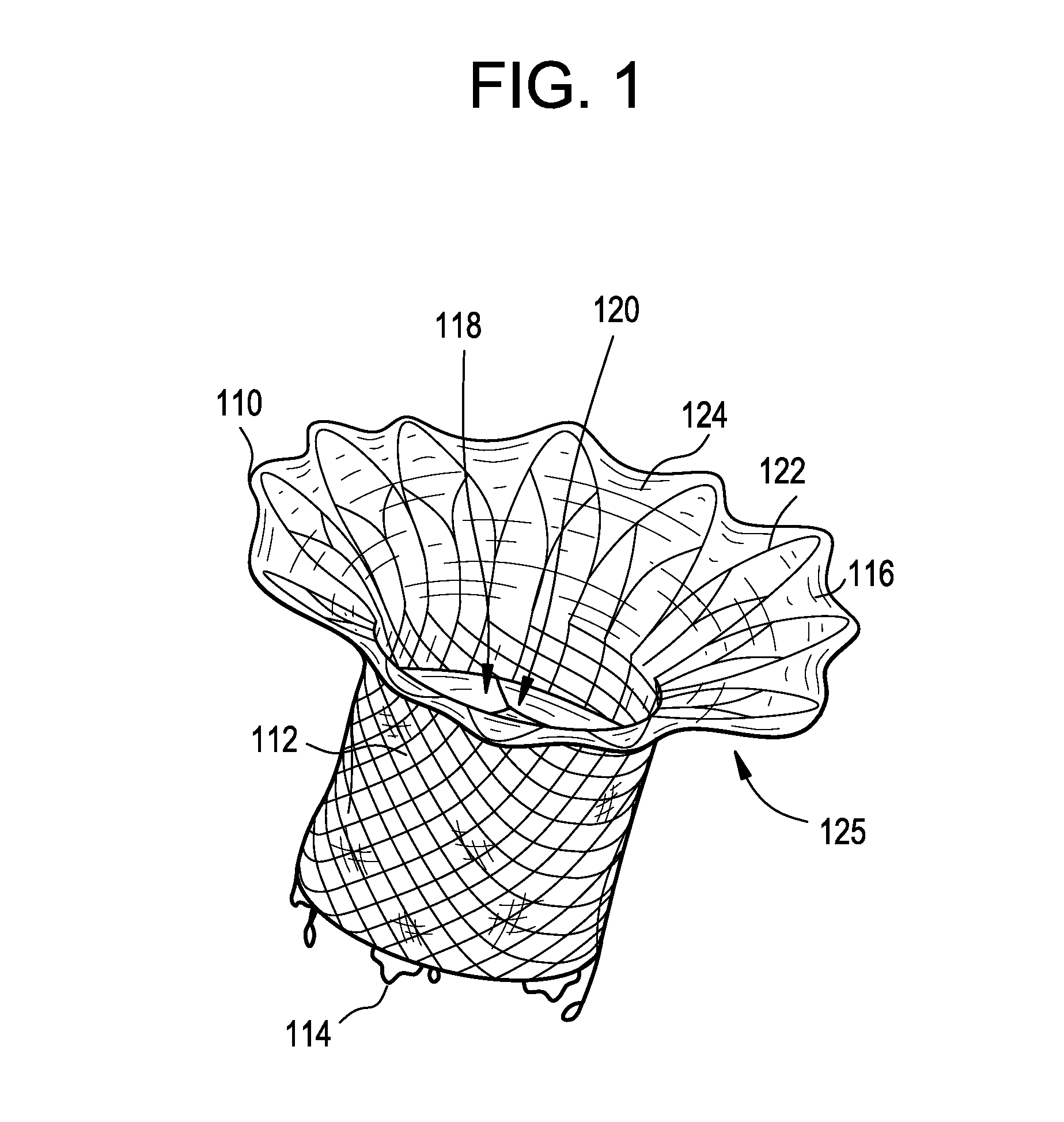
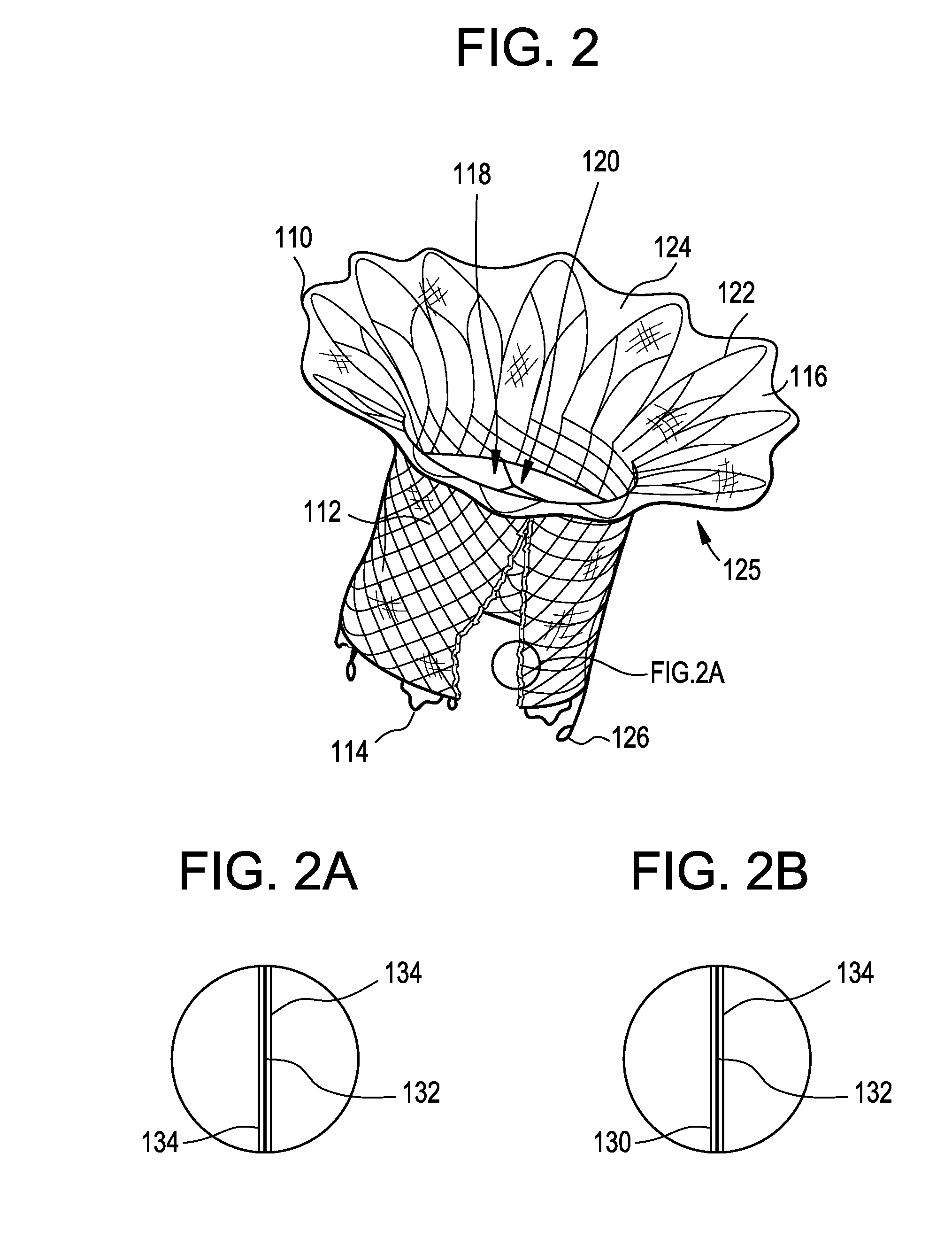
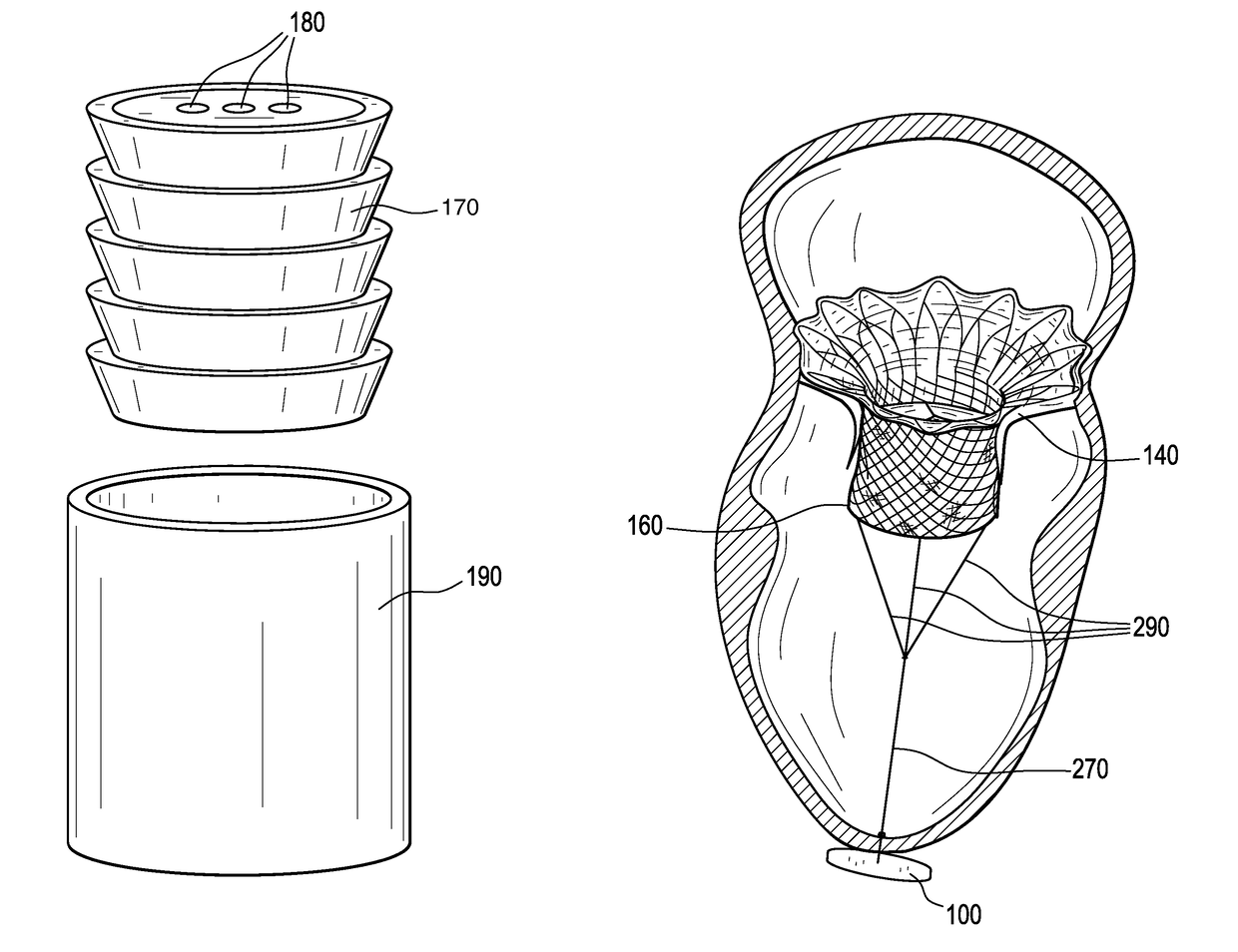
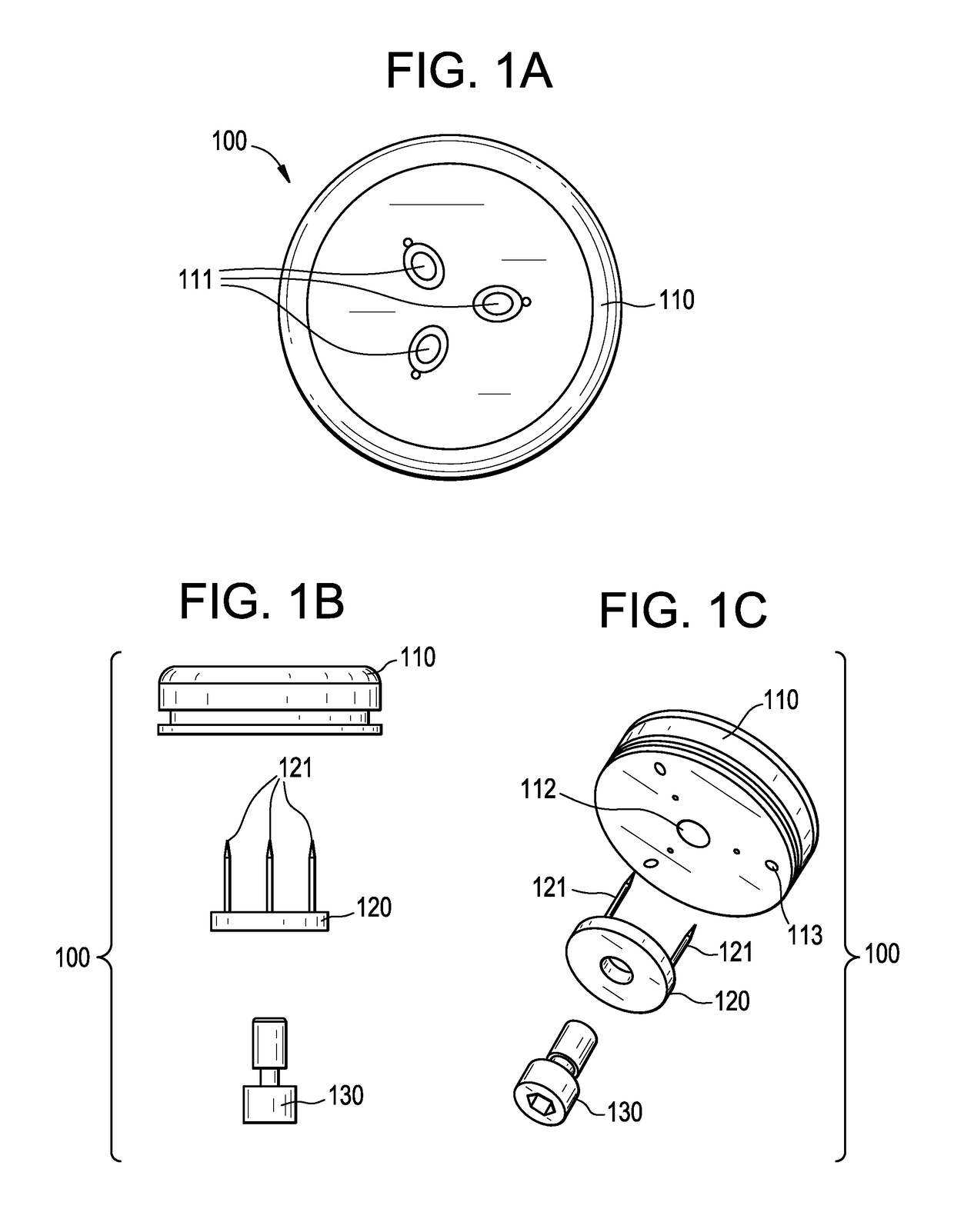
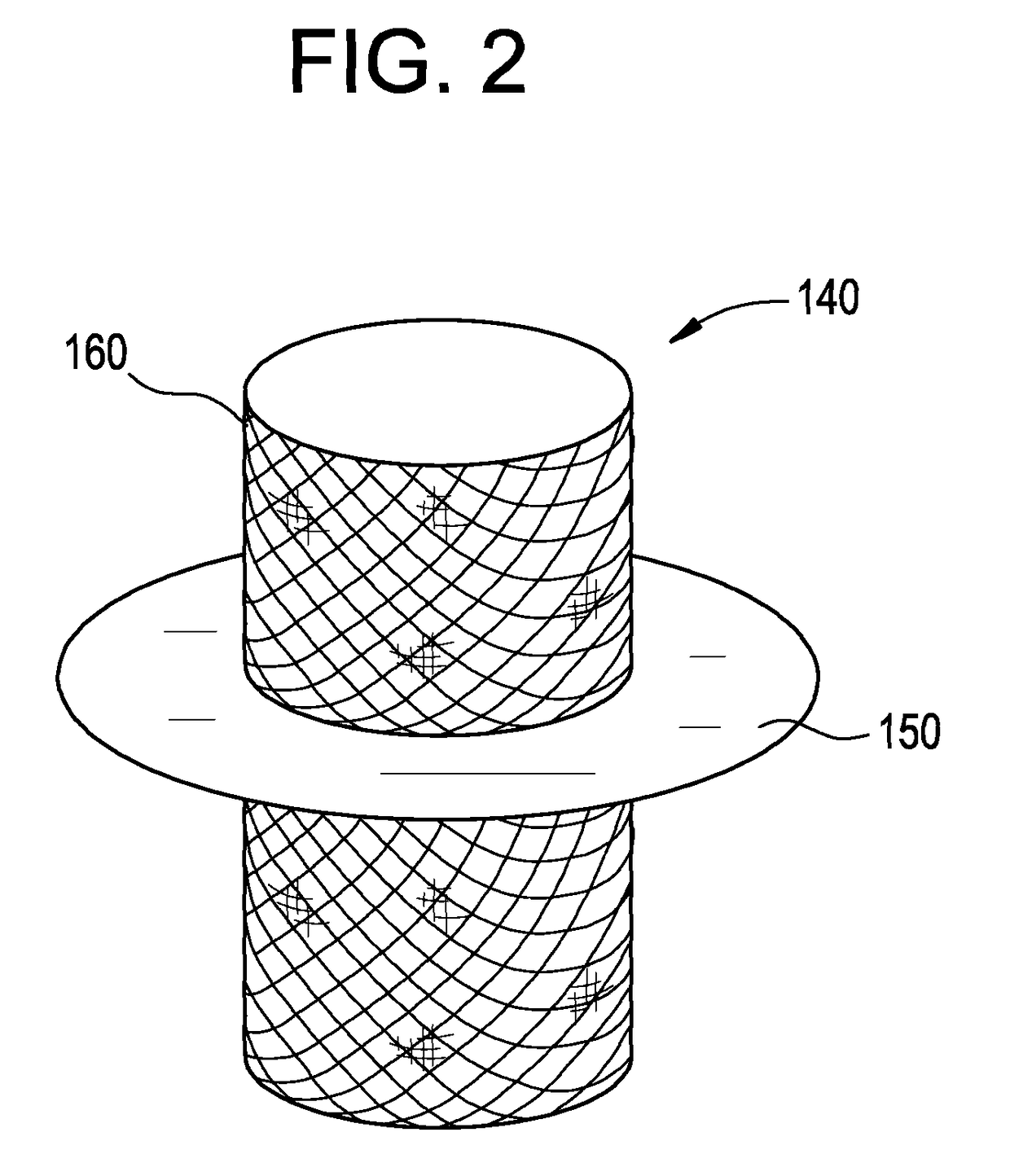
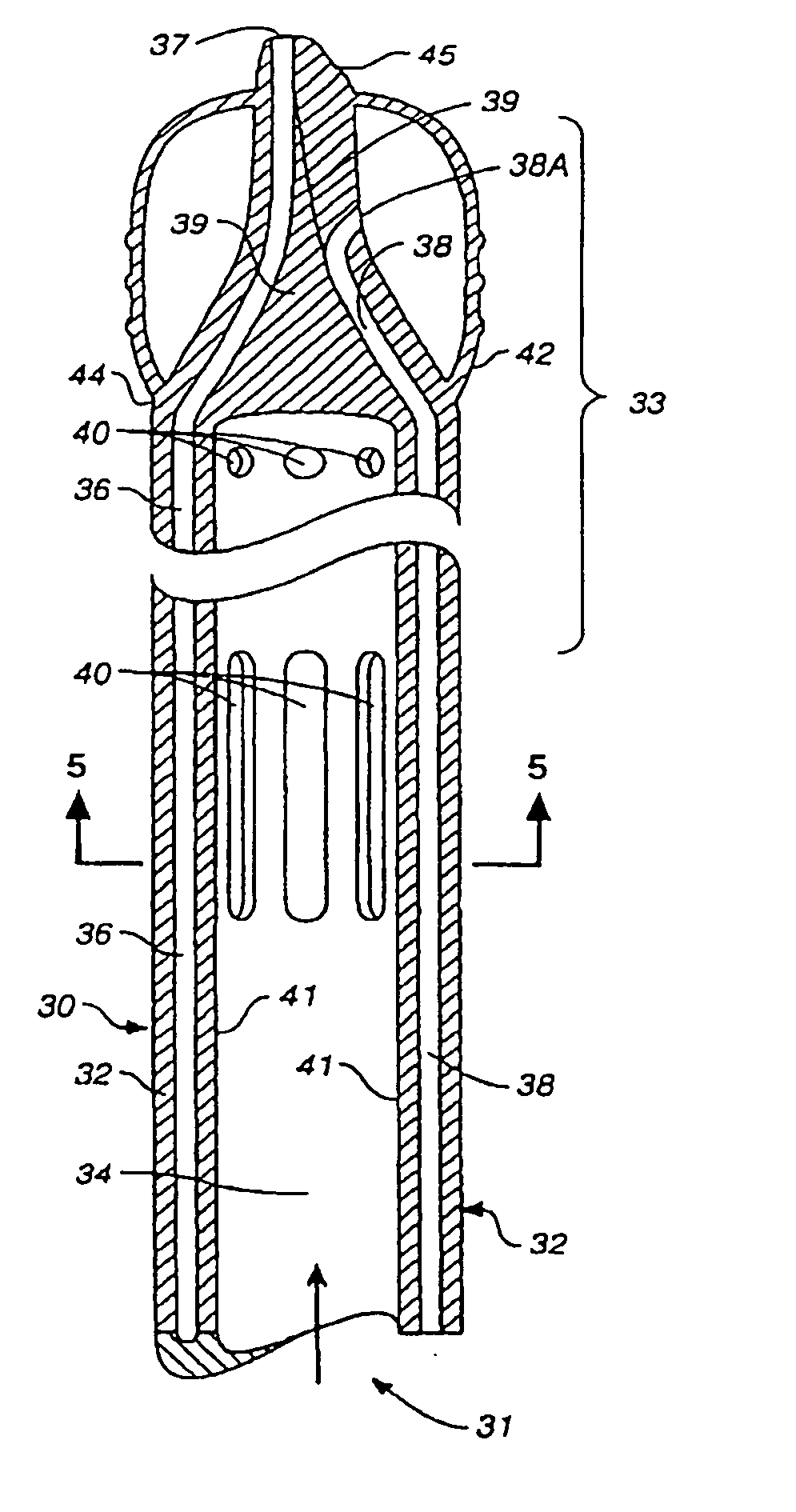
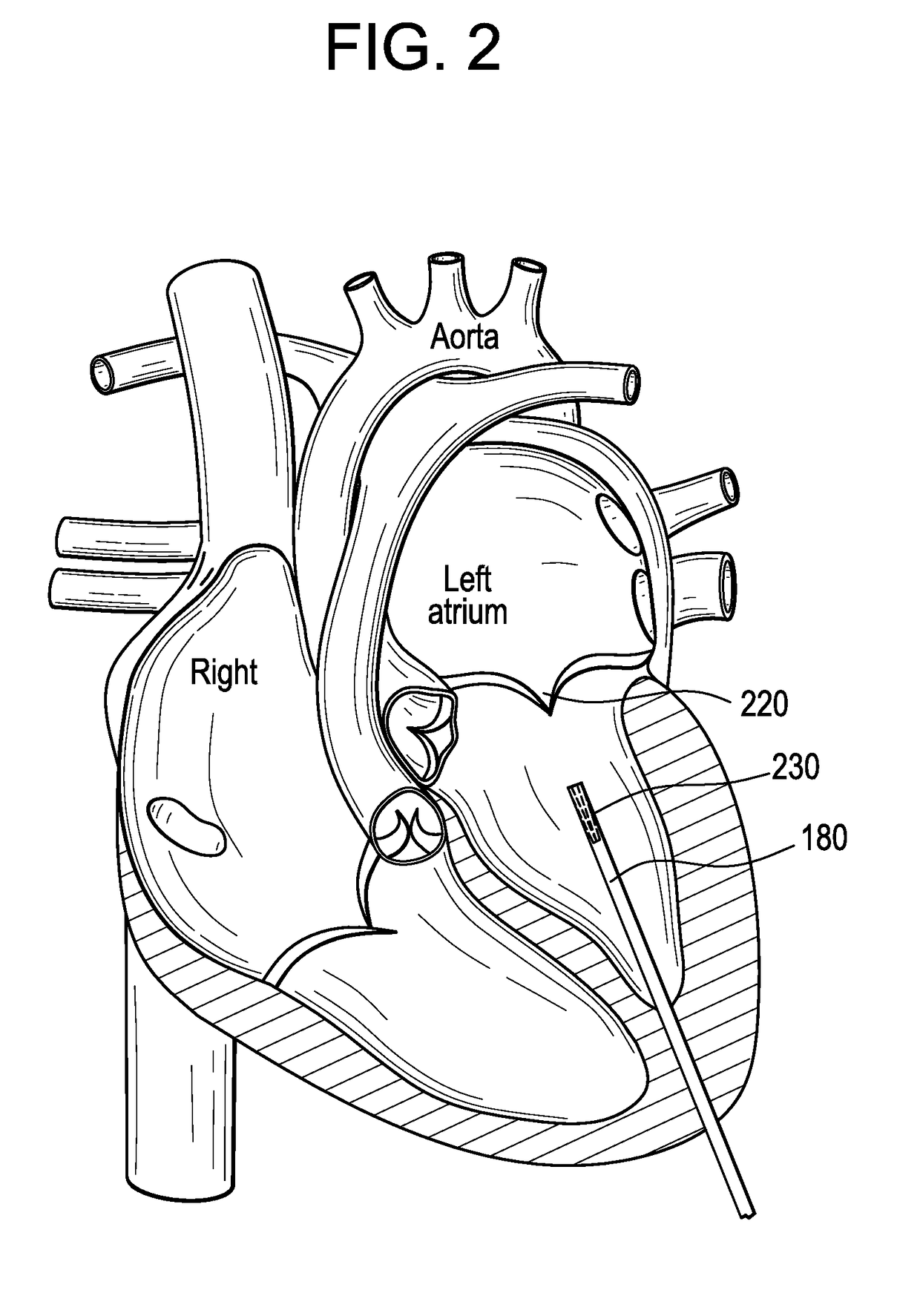
Percutaneous cardiac valve repair with adjustable artificial chordae
InactiveUS20070118151A1Reduction of mitral valve regurgitationEasy to operateSuture equipmentsHeart valvesExtracorporeal circulationCardiopulmonary bypass time
The invention includes a novel method and system to achieve leaflet coaptation in a cardiac valve percutaneously by creation of neochordae to prolapsing valve segments. This technique is especially useful in cases of ruptured chordae, but may be utilized in any segment of prolapsing leaflet. The technique described herein has the additional advantage of being adjustable in the beating heart. This allows tailoring of leaflet coaptation height under various loading conditions using image-guidance, such as echocardiography. This offers an additional distinct advantage over conventional open-surgery placement of artificial chordae. In traditional open surgical valve repair, chord length must be estimated in the arrested heart and may or may not be correct once the patient is weaned from cardiopulmonary bypass. The technique described below also allows for placement of multiple artificial chordae, as dictated by the patient's pathophysiology.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
Prosthetic valves and related inventions
ActiveUS20140214159A1Low height to width profilePrevent perivalvular leakSuture equipmentsHeart valvesExtracorporeal circulationProsthetic valve
This invention relates to the design and function of a compressible valve replacement prosthesis, collared or uncollared, which can be deployed into a beating heart without extracorporeal circulation using a transcatheter delivery system. The design as discussed focuses on the deployment of a device via a minimally invasive fashion and by way of example considers a minimally invasive surgical procedure preferably utilizing the intercostal or subxyphoid space for valve introduction. In order to accomplish this, the valve is formed in such a manner that it can be compressed to fit within a delivery system and secondarily ejected from the delivery system into the annulus of a target valve such as a mitral valve or tricuspid valve.
Owner:TENDYNE HLDG
Device and System for Transcatheter Mitral Valve Replacement
InactiveUS20120179244A1Prevent perivalvular leakStentsHeart valvesExtracorporeal circulationBioprosthetic mitral valve replacement
This invention relates to the design and function of a compressible valve replacement prosthesis which can be deployed into a beating heart without extracorporeal circulation using a transcatheter delivery system. The design as discussed focuses on the deployment of a device via a minimally invasive fashion and by way of example considers a minimally invasive surgical procedure preferably utilizing the intercostal or subxyphoid space for valve introduction. In order to accomplish this, the valve is formed in such a manner that it can be compressed to fit within a delivery system and secondarily ejected from the delivery system into the annulus of a target valve such as a mitral valve or tricuspid valve.
Owner:COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY +1
Tethers for Prosthetic Mitral Valve
ActiveUS20130172978A1Improve the sealing levelSuture equipmentsHeart valvesExtracorporeal circulationInsertion stent
This invention relates to the design and function of a single-tether compressible valve replacement prosthesis which can be deployed into a beating heart without extracorporeal circulation using a transcatheter delivery system. The design as discussed combats the process of wear on anchoring tethers over time by using a plurality of stent-attached, centering tethers, which are themselves attached to a single anchoring tether, which extends through the ventricle and is anchored to a securing device located on the epicardium.
Owner:TENDYNE HLDG
Methods, systems, and kits for the extracorporeal processing of blood
InactiveUS7004924B1Easy to detectOther blood circulation devicesControl devicesExtracorporeal circulationLine tubing
Methods, systems, and kits for extracorporeally circulating and processing blood are described. The systems include a pump, a processing unit, and blood drawn return lines for accessing a patient's vasculature. Blood flow through the return line is measured and pump speed controlled to maintain a desired blood flow rate. Alarm conditions can be initiated when expected pump performance differs from that needed to maintain the control point flow rate. By using a ultrasonic flow detector, gas bubbles in the blood flow can be detected.
Owner:NXSTAGE MEDICAL
System and methods for performing endovascular procedures
InactiveUS20060058775A1Procedure is complicatedEasy to controlStentsGuide needlesExtracorporeal circulationAtherectomy
A system for inducing cardioplegic arrest and performing an endovascular procedure within the heart or blood vessels of a patient. An endoaortic partitioning catheter has an inflatable balloon which occludes the ascending aorta when inflated. Cardioplegic fluid may be infused through a lumen of the endoaortic partitioning catheter to stop the heart while the patient's circulatory system is supported on cardiopulmonary bypass. One or more endovascular devices are introduced through an internal lumen of the endoaortic partitioning catheter to perform a diagnostic or therapeutic endovascular procedure within the heart or blood vessels of the patient. Surgical procedures such as coronary artery bypass surgery or heart valve replacement may be performed in conjunction with the endovascular procedure while the heart is stopped. Embodiments of the system are described for performing: fiberoptic angioscopy of structures within the heart and its blood vessels, valvuloplasty for correction of valvular stenosis in the aortic or mitral valve of the heart, angioplasty for therapeutic dilatation of coronary artery stenoses, coronary stenting for dilatation and stenting of coronary artery stenoses, atherectomy or endarterectomy for removal of atheromatous material from within coronary artery stenoses, intravascular ultrasonic imaging for observation of structures and diagnosis of disease conditions within the heart and its associated blood vessels, fiberoptic laser angioplasty for removal of atheromatous material from within coronary artery stenoses, transmyocardial revascularization using a side-firing fiberoptic laser catheter from within the chambers of the heart, and electrophysiological mapping and ablation for diagnosing and treating electrophysiological conditions of the heart.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES LLC
Device and System for Transcatheter Mitral Valve Replacement
InactiveUS20110319988A1Prevent perivalvular leakStentsHeart valvesExtracorporeal circulationBioprosthetic mitral valve replacement
This invention relates to the design and function of a compressible valve replacement prosthesis which can be deployed into a beating heart without extracorporeal circulation using a transcatheter delivery system. The design as discussed focuses on the deployment of a device via a minimally invasive fashion and by way of example considers a minimally invasive surgical procedure preferably utilizing the intercostal or subxyphoid space for valve introduction. In order to accomplish this, the valve is formed in such a manner that it can be compressed to fit within a delivery system and secondarily ejected from the delivery system into the annulus of a target valve such as a mitral valve or tricuspid valve.
Owner:AVALON MEDICAL +1
Prosthetic valves and related inventions
ActiveUS9480559B2Low height to width profilePrevent perivalvular leakSuture equipmentsHeart valvesExtracorporeal circulationProsthetic valve
This invention relates to the design and function of a compressible valve replacement prosthesis, collared or uncollared, which can be deployed into a beating heart without extracorporeal circulation using a transcatheter delivery system. The design as discussed focuses on the deployment of a device via a minimally invasive fashion and by way of example considers a minimally invasive surgical procedure preferably utilizing the intercostal or subxyphoid space for valve introduction. In order to accomplish this, the valve is formed in such a manner that it can be compressed to fit within a delivery system and secondarily ejected from the delivery system into the annulus of a target valve such as a mitral valve or tricuspid valve.
Owner:TENDYNE HLDG
Method and apparatus for external stabilization of the heart
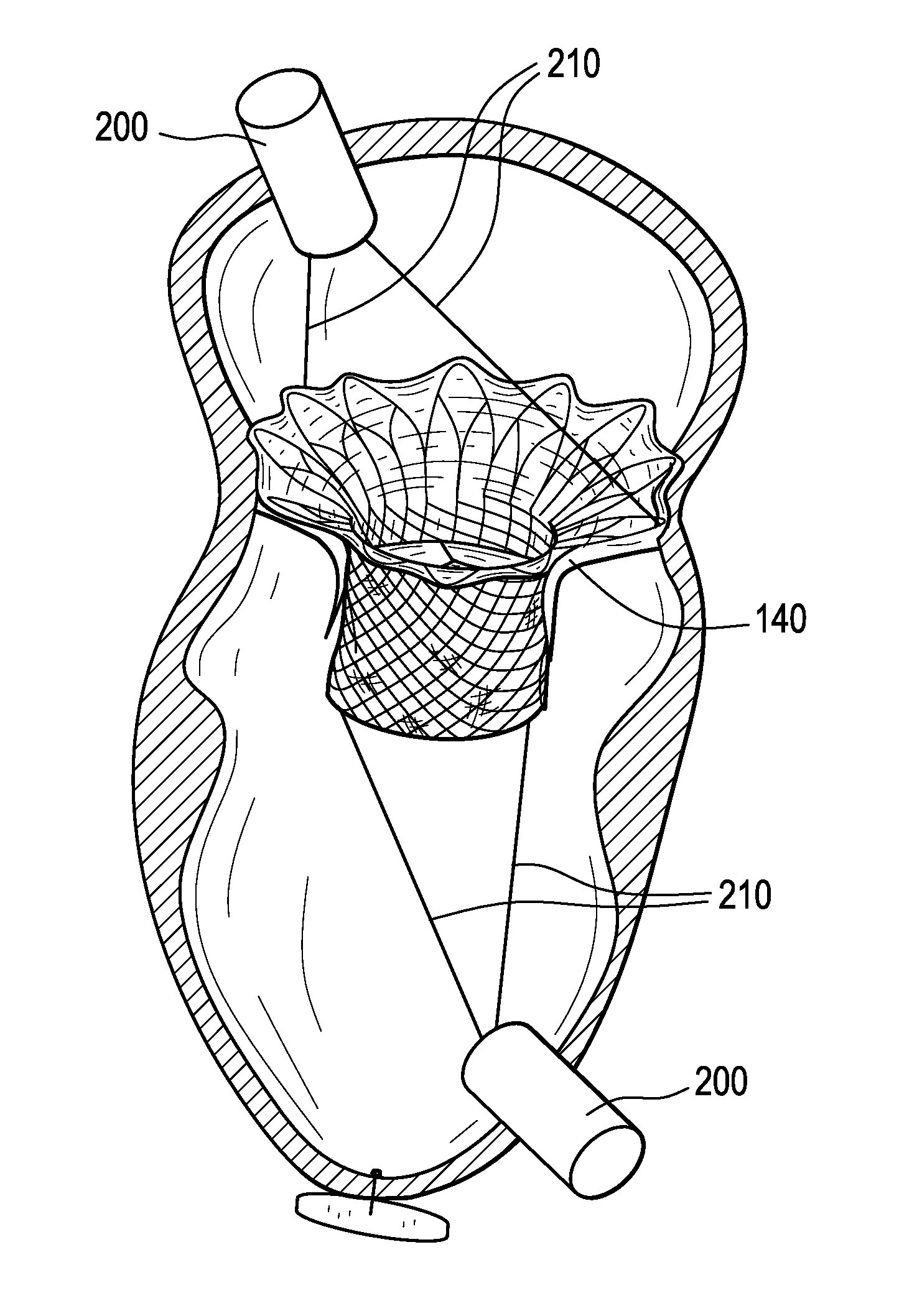
The present disclosure is directed to an external cardiac basal annuloplasty system (ECBAS or BACE-System: basal annuloplasty of the cardia externally) and methods for treatment of regurgitation of mitral and tricuspid valves. The BACE-System provides the ability to correct leakage of regurgitation of the valves with or without the use of cardiopulmonary bypass, particularly when the condition is related to dilation of the base of the heart. This ECBAS invention can be applied to the base of the heart epicardially, either to prevent further dilation or to actively reduce the size of the base of the heart.
Owner:COMPASS CONSULTING INT CORP
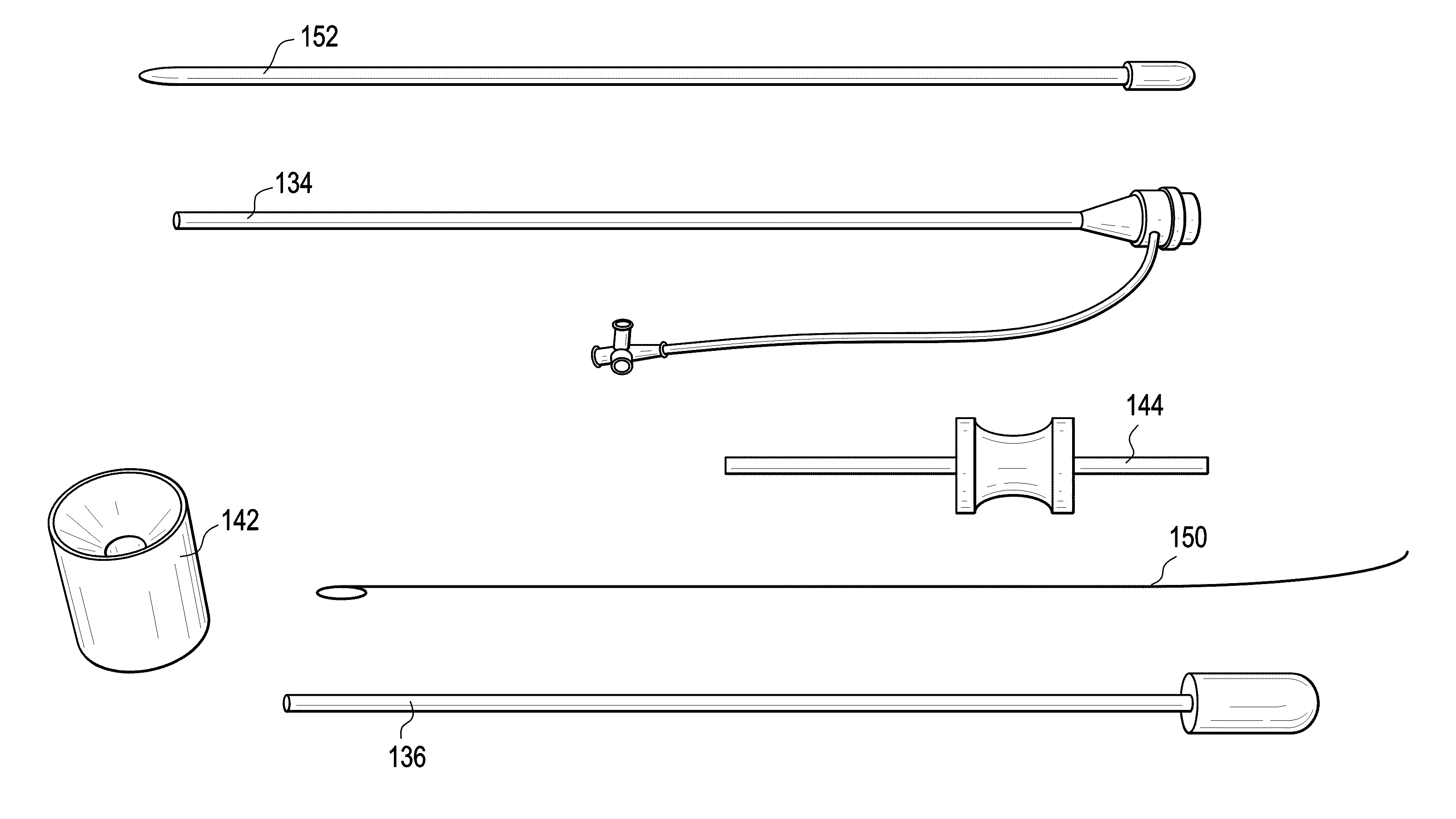
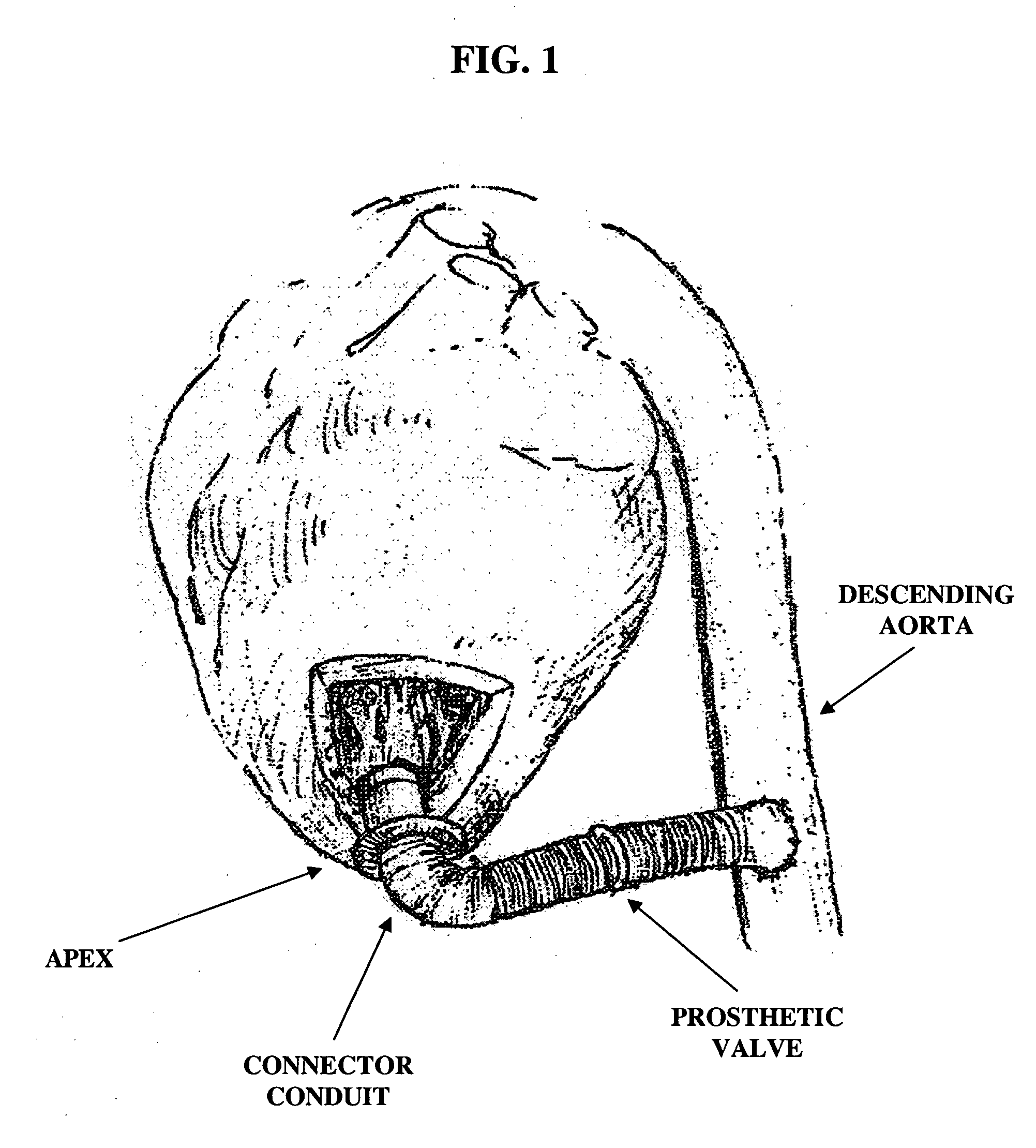
Apparatus and method for connecting a conduit to a hollow organ
InactiveUS20050251187A1Easy to optimizeReduce the possibilitySurgical instrument detailsExcision instrumentsExtracorporeal circulationProsthetic valve
An apparatus and method for connecting a first conduit to the heart without the need for cardiopulmonary bypass. The first conduit may then be attached to a second conduit that has a prosthetic device interposed. The second conduit may be connected to the aorta prior to the first conduit being attached to the heart. The prosthetic device may be a prosthetic valve or a pump, for example. The apparatus of the present invention includes an implantable connector with first conduit component, a retractor expansion component, a coring component, and a pushing component. The retractor expansion component is slide-ably coupled to the coring component. The retractor expansion component serves to seat against and separate the inside apical wall of the left ventricle so that the coring component may cut cleanly through the myocardium to form a tissue plug without leaving any hanging attachments to the inside walls. By remaining seated against the inside wall, the retractor expansion component follows the tissue plug into the coring component. The surgeon applies force and rotary motion to the pushing component sufficient to cut the tissue plug and implant the prosthetic component.
Owner:CORREX
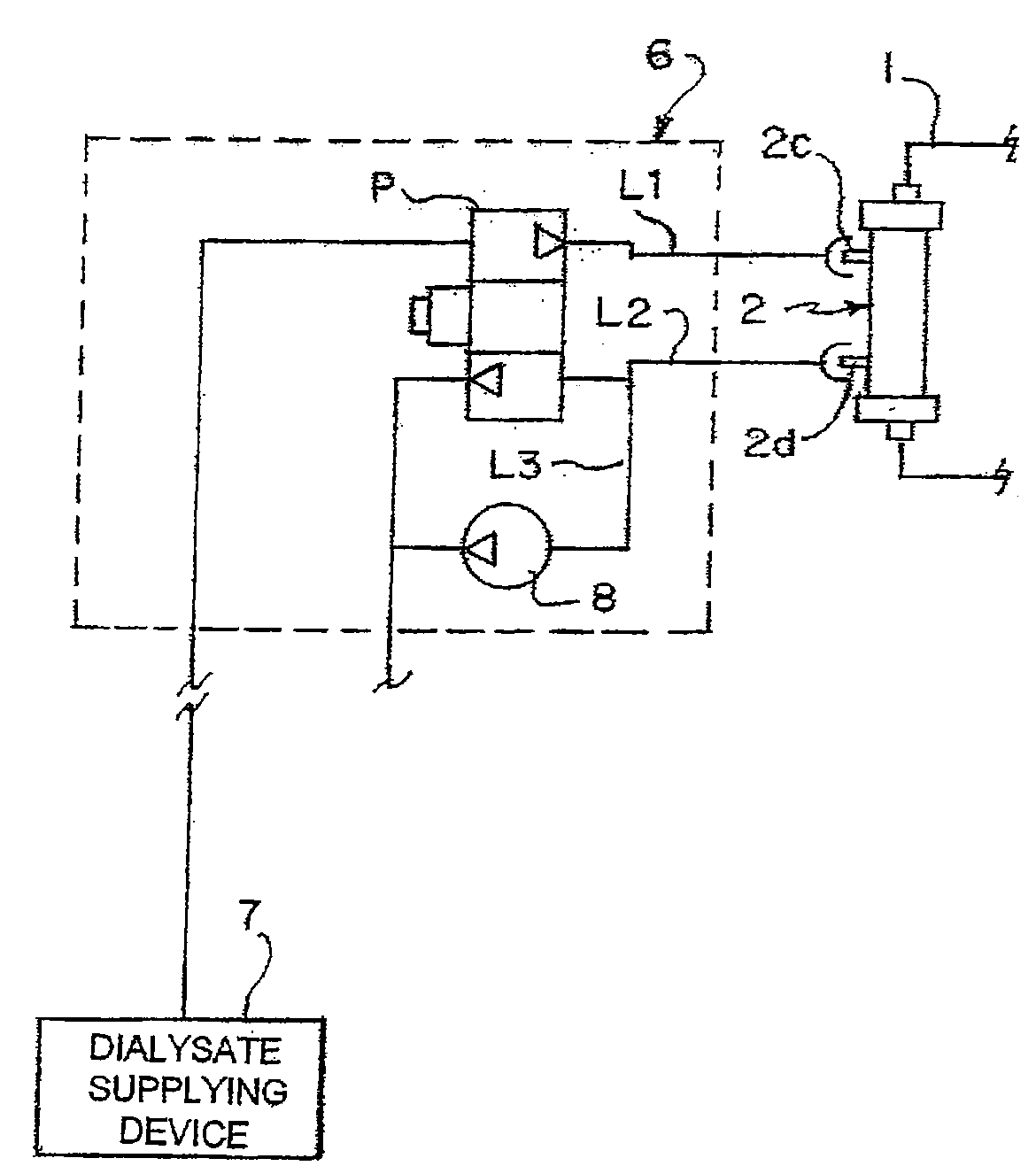
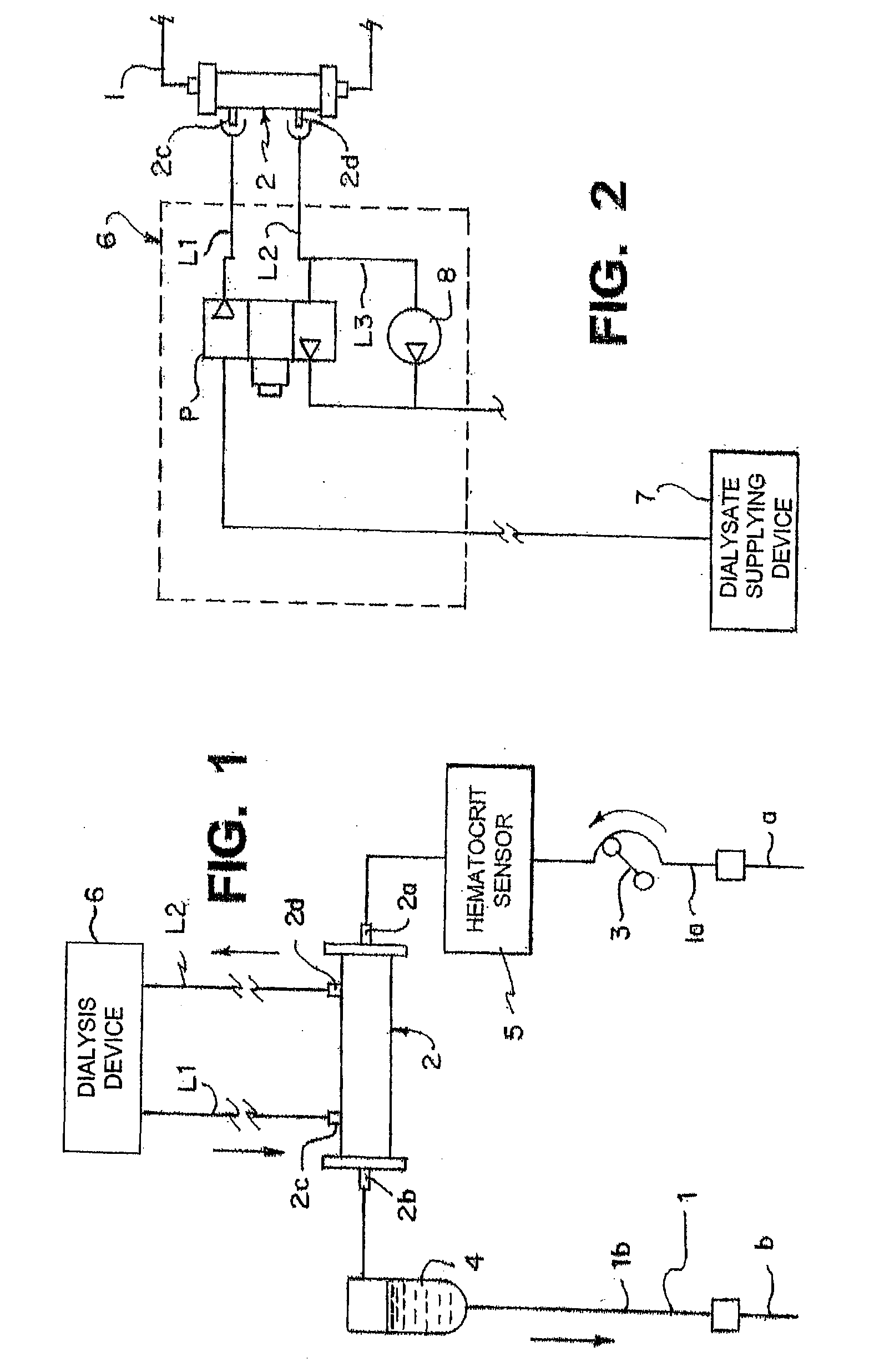
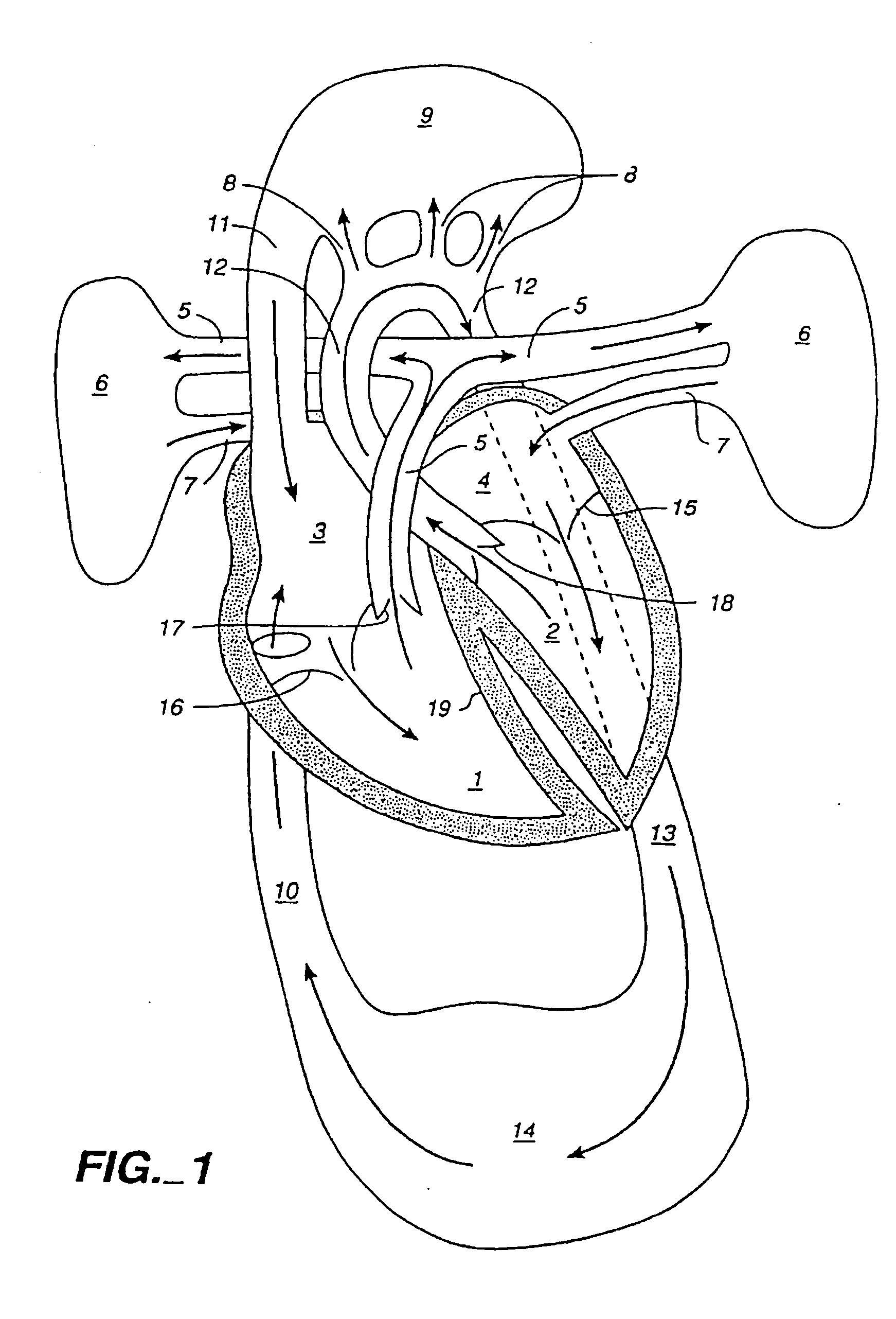
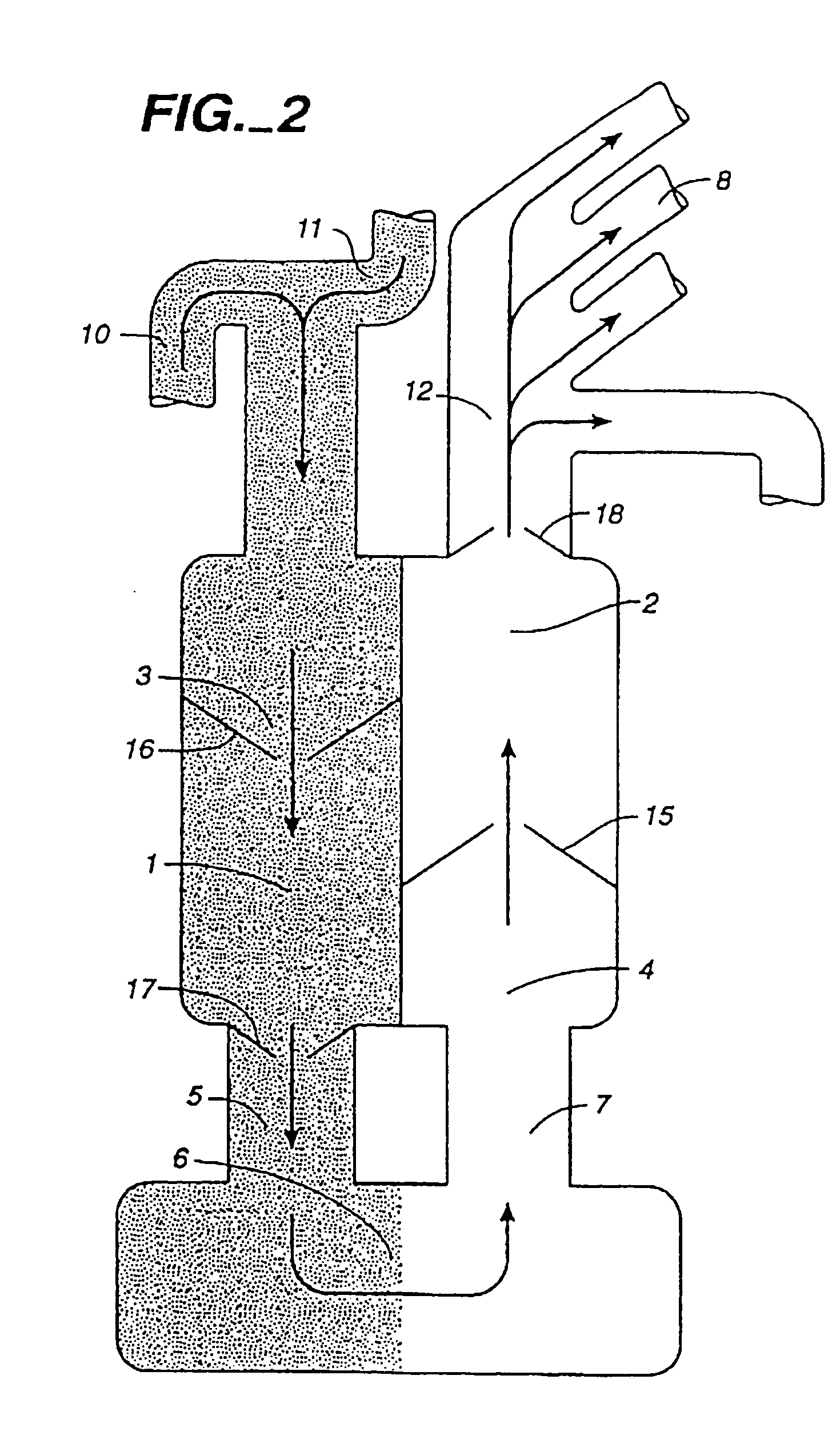
Hemodialysis apparatus and method for hemodialysis
InactiveUS20060226079A1Increase volumeEfficient sharingSemi-permeable membranesSolvent extractionExtracorporeal circulationHemodialysis
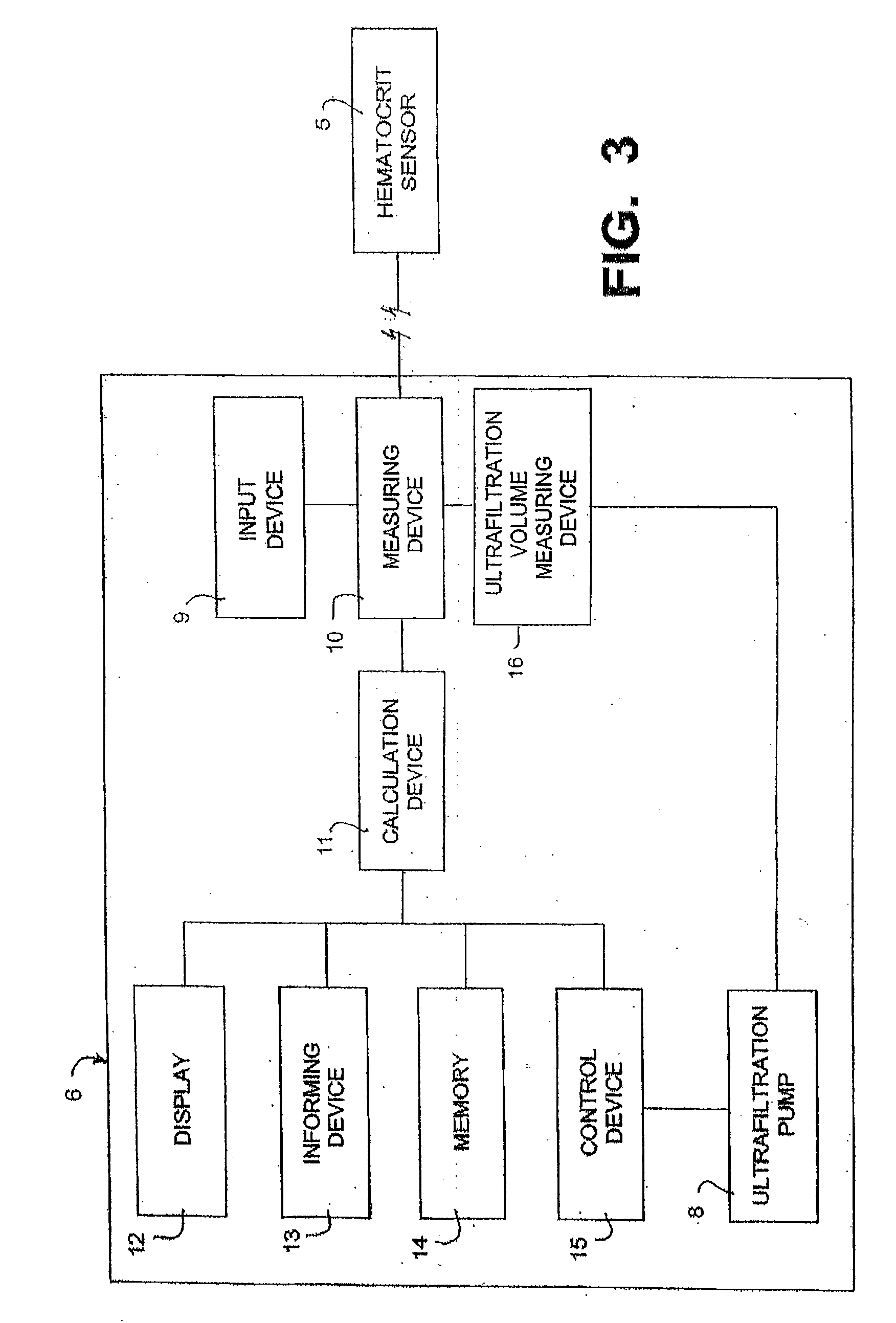
A hemodialysis apparatus includes a dialyzing device, a measuring device and a calculation device. The dialyzing device dialyzes and ultrafiltrates blood of a patient circulating extracorporeally to perform hemodialysis treatment. The measuring device measures a variation rate of a body weight of the patient and a variation rate of a predetermined blood benchmark during the hemodialysis treatment using the dialyzing device. The calculation device calculates, during the hemodialysis treatment, a parameter relating the variation rate of the body weight and the variation rate of the predetermined blood benchmark to each other, and correlating to a dry weight of the patient.
Owner:NIKKISO COMPANY
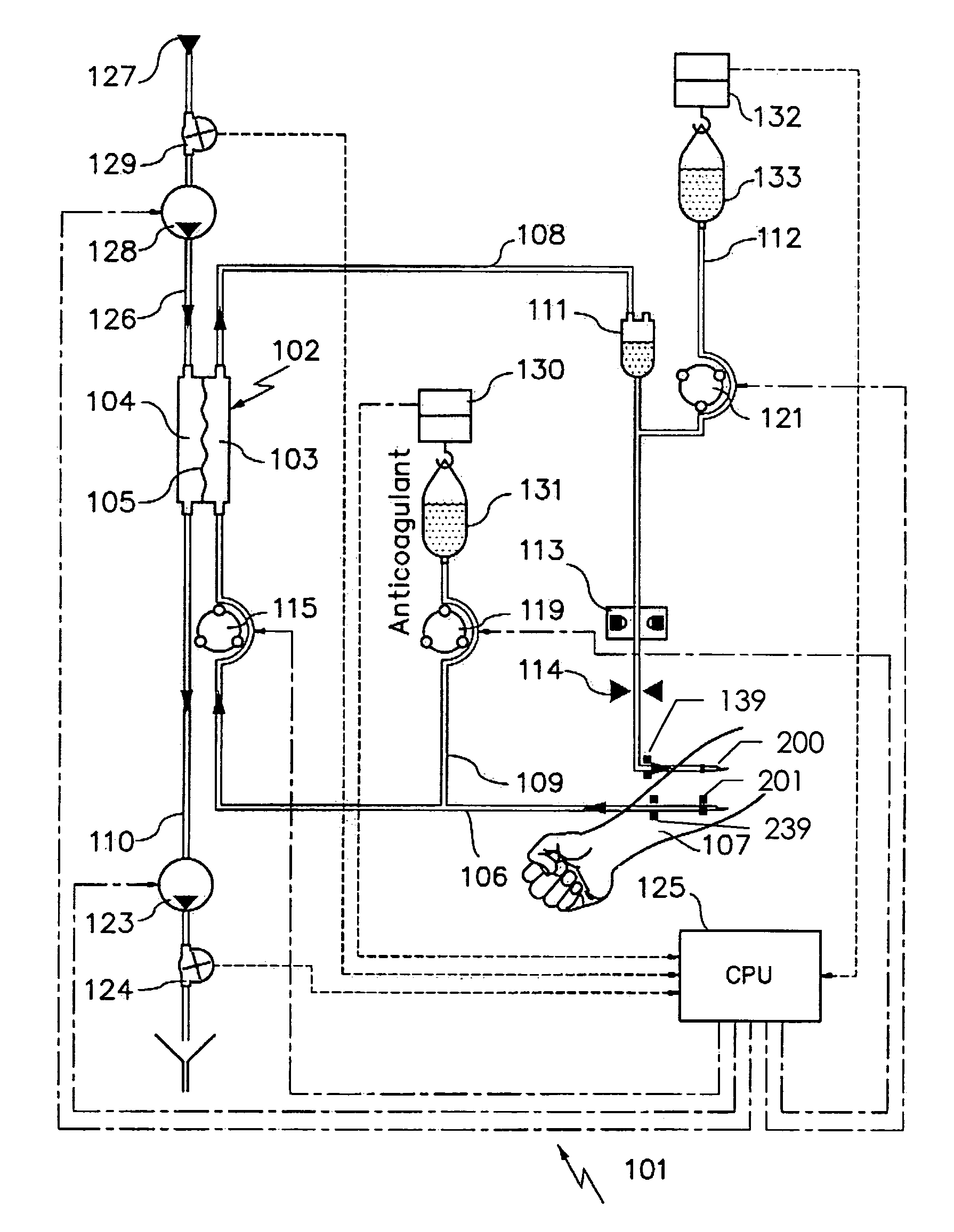
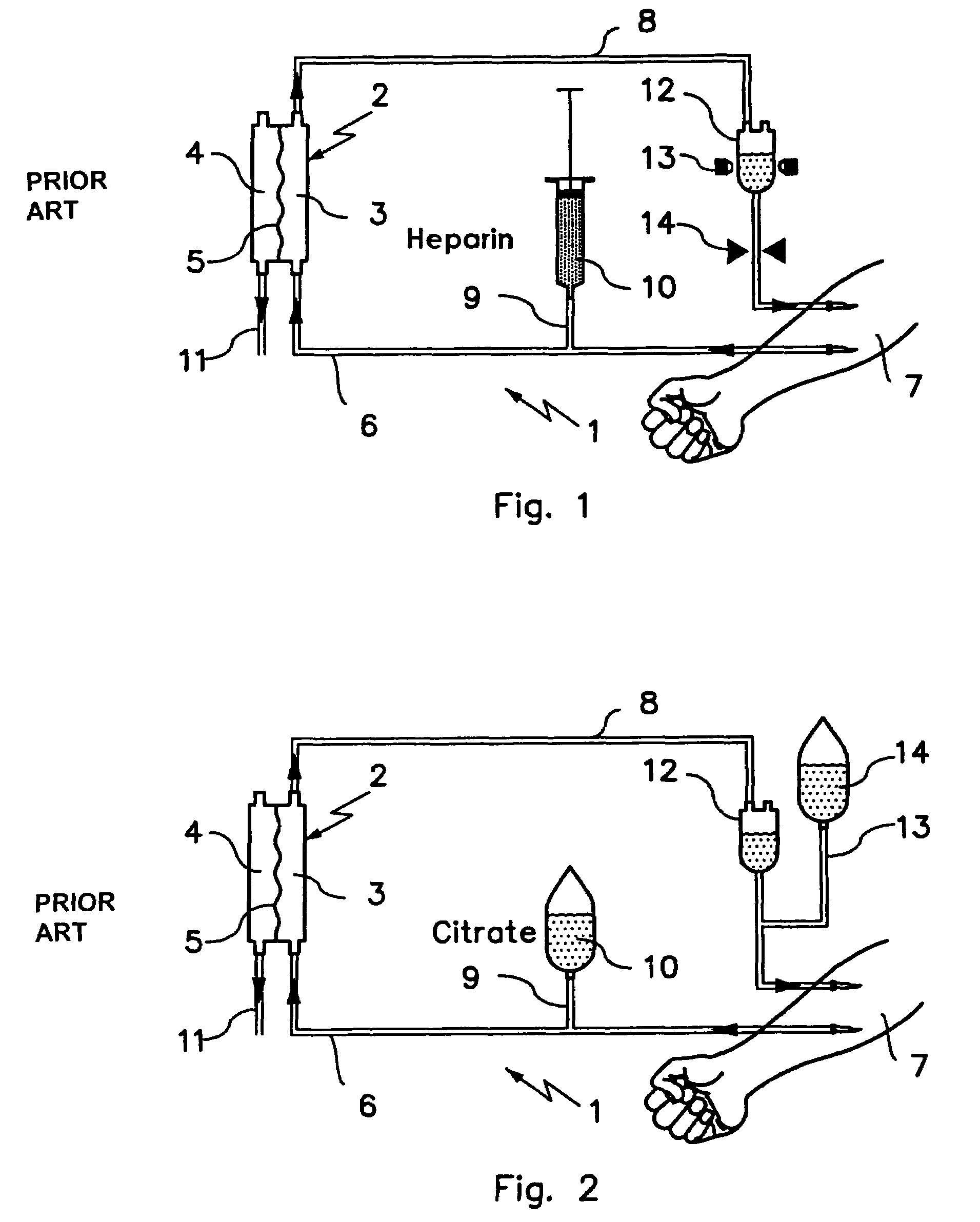
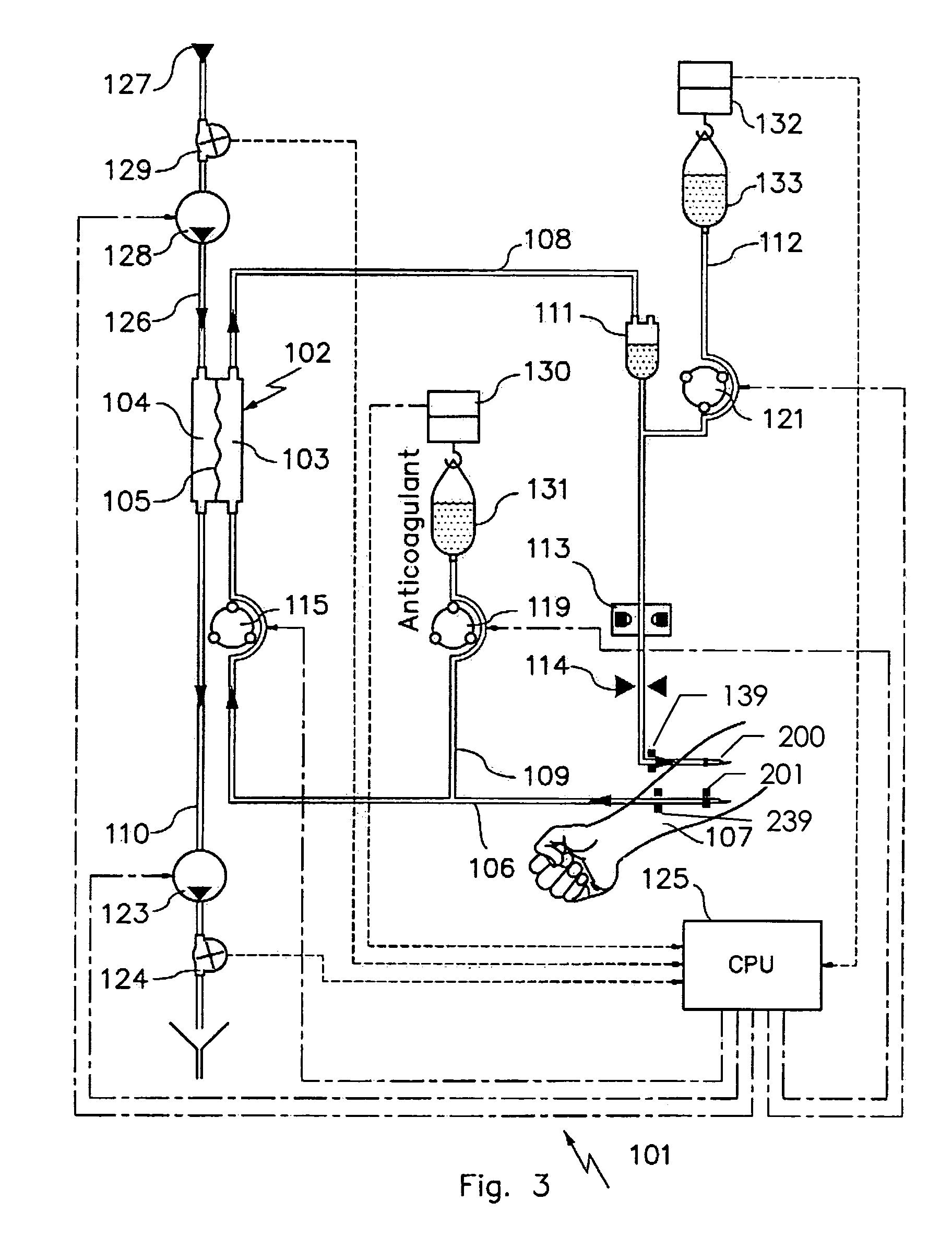
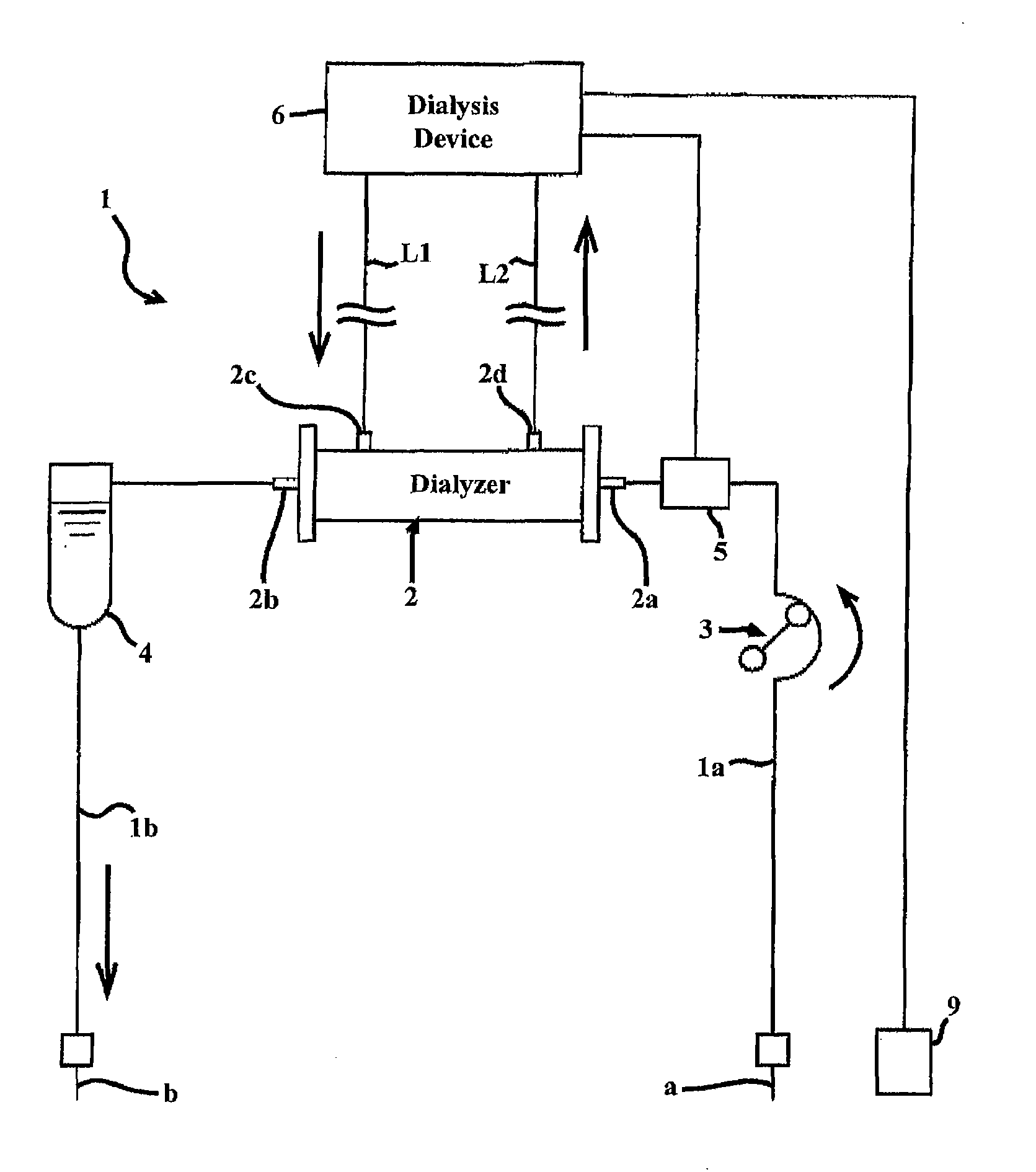
Device and process for extracorporeal treatment by citrate anticoagulant
ActiveUS7351218B2Inhibit blood coagulationSimple structureOther blood circulation devicesHaemofiltrationExtracorporeal circulationVein
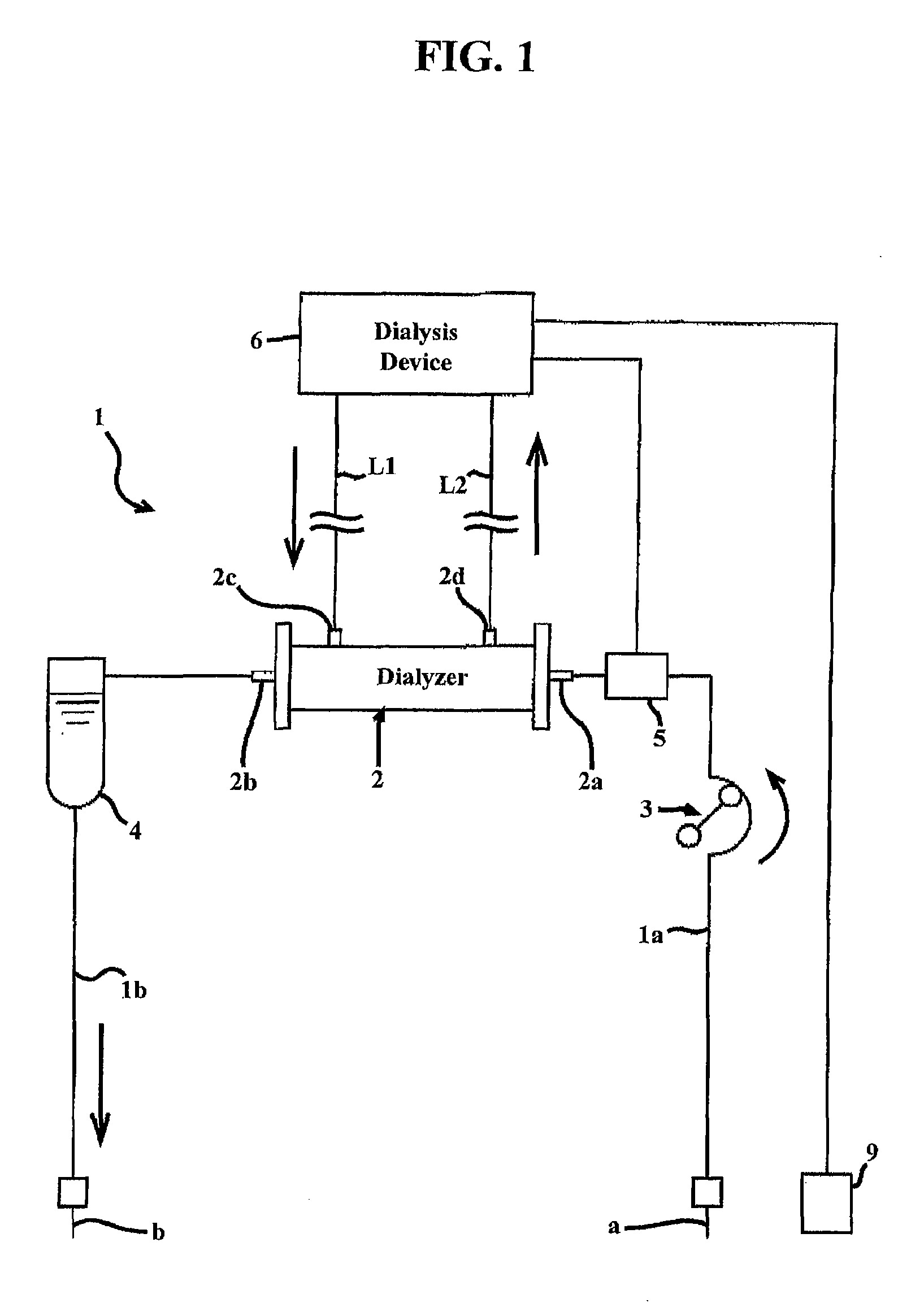
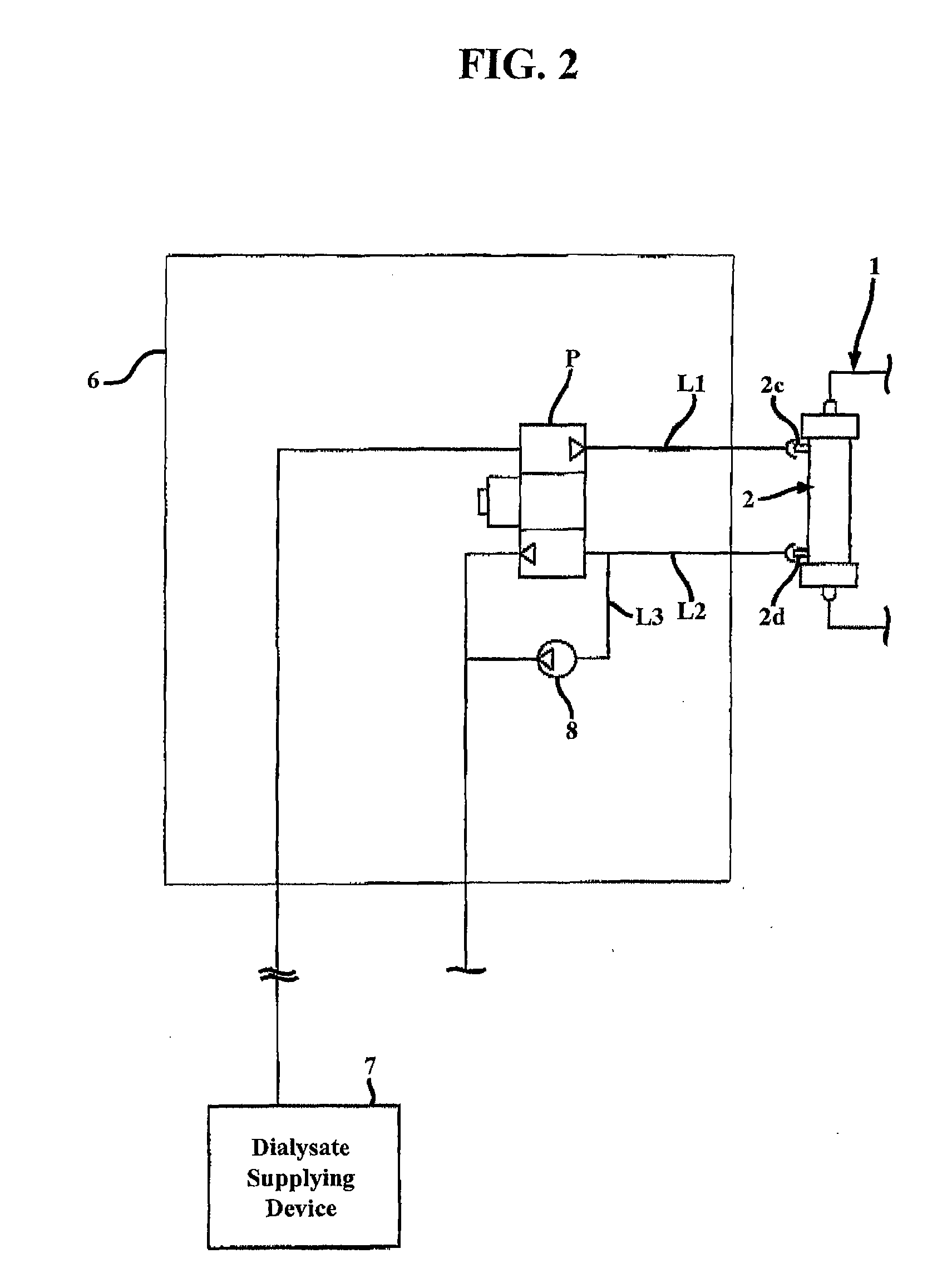
A device for treating blood by extracorporeal circulation comprising a filter having a first chamber and a second chamber separated by a semi-permeable membrane. The device has an arterial line connected to the first chamber of the filter, a venous line issuing from the first chamber of the filter, a channel used for pre-infusion of a substance for regional anticoagulation and linked to the arterial line, a purge channel issuing from the second chamber of the filter, and an air separator on the venous line. The device also includes a line for post-infusion of a solution at least partially re-establishing the ionic equilibrium of the blood downstream of the air separator, the post-infusion line being configured immediately upstream of an air detector.
Owner:GAMBRO LUNDIA AB
Tethers for prosthetic mitral valve
ActiveUS9827092B2Improve the sealing levelSuture equipmentsHeart valvesExtracorporeal circulationInsertion stent
This invention relates to the design and function of a single-tether compressible valve replacement prosthesis which can be deployed into a beating heart without extracorporeal circulation using a transcatheter delivery system. The design as discussed combats the process of wear on anchoring tethers over time by using a plurality of stent-attached, centering tethers, which are themselves attached to a single anchoring tether, which extends through the ventricle and is anchored to a securing device located on the epicardium.
Owner:TENDYNE HLDG
Retrieval and repositioning system for prosthetic heart valve
This invention relates to the design and function of a retrieval device for a prosthetic heart valve for re-positioning or removal of a previously implanted valve prosthesis from a beating heart without extracorporeal circulation using a transcatheter retrieval system.
Owner:TENDYNE HLDG
Retrieval and repositioning system for prosthetic heart valve
This invention relates to the design and function of a retrieval device for a prosthetic heart valve for re-positioning or removal of a previously implanted valve prosthesis from a beating heart without extracorporeal circulation using a transcatheter retrieval system.
Owner:TENDYNE HLDG
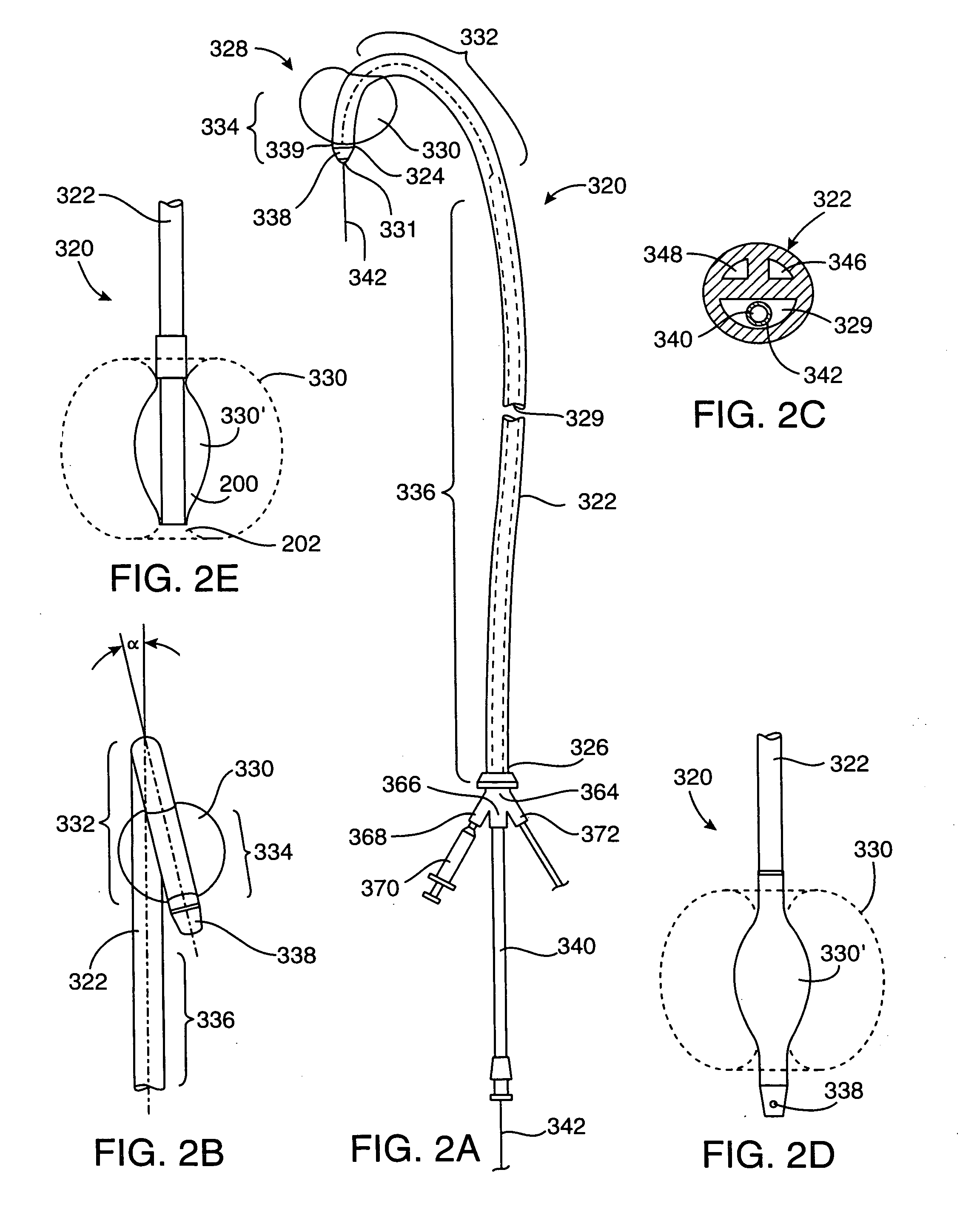
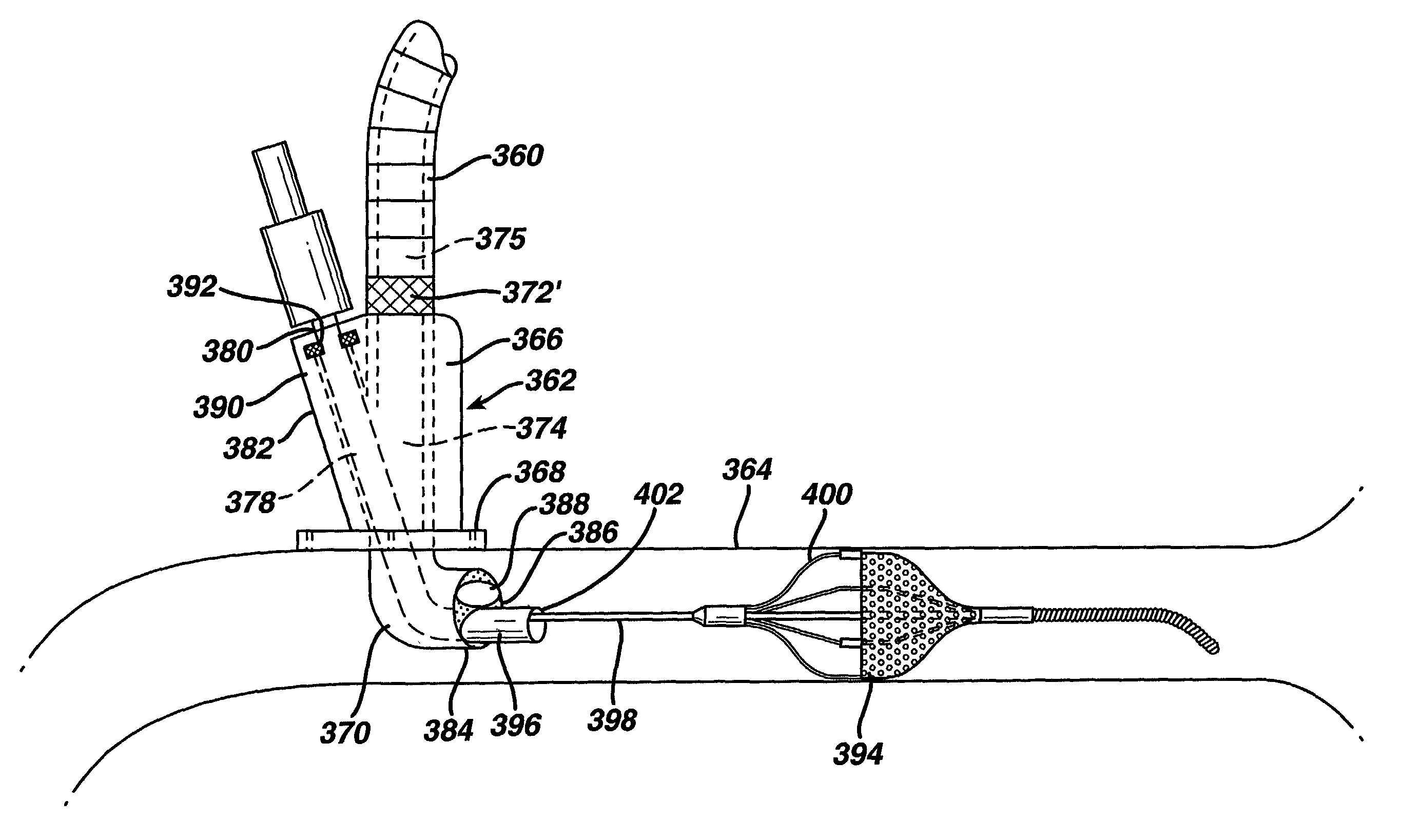
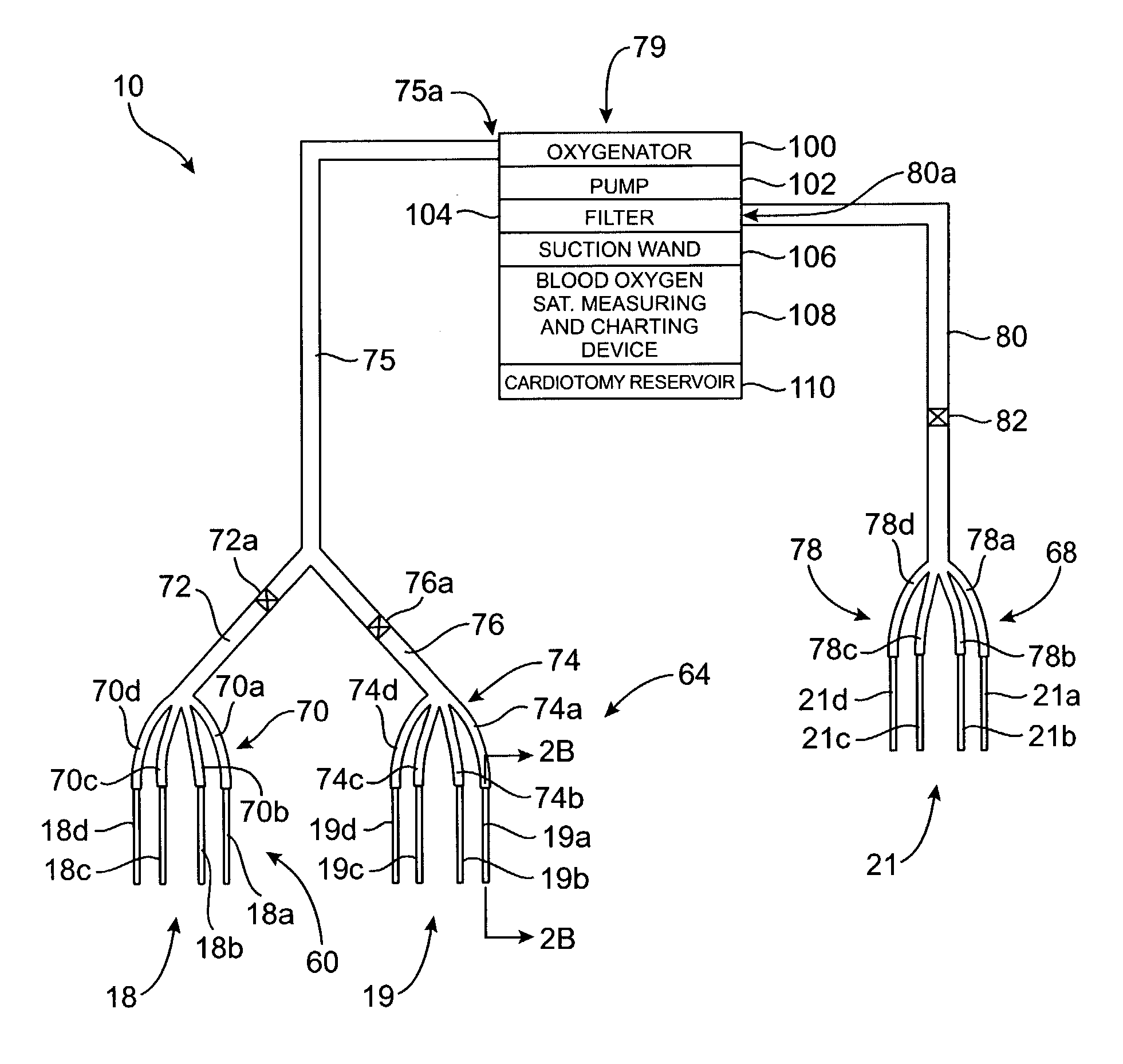
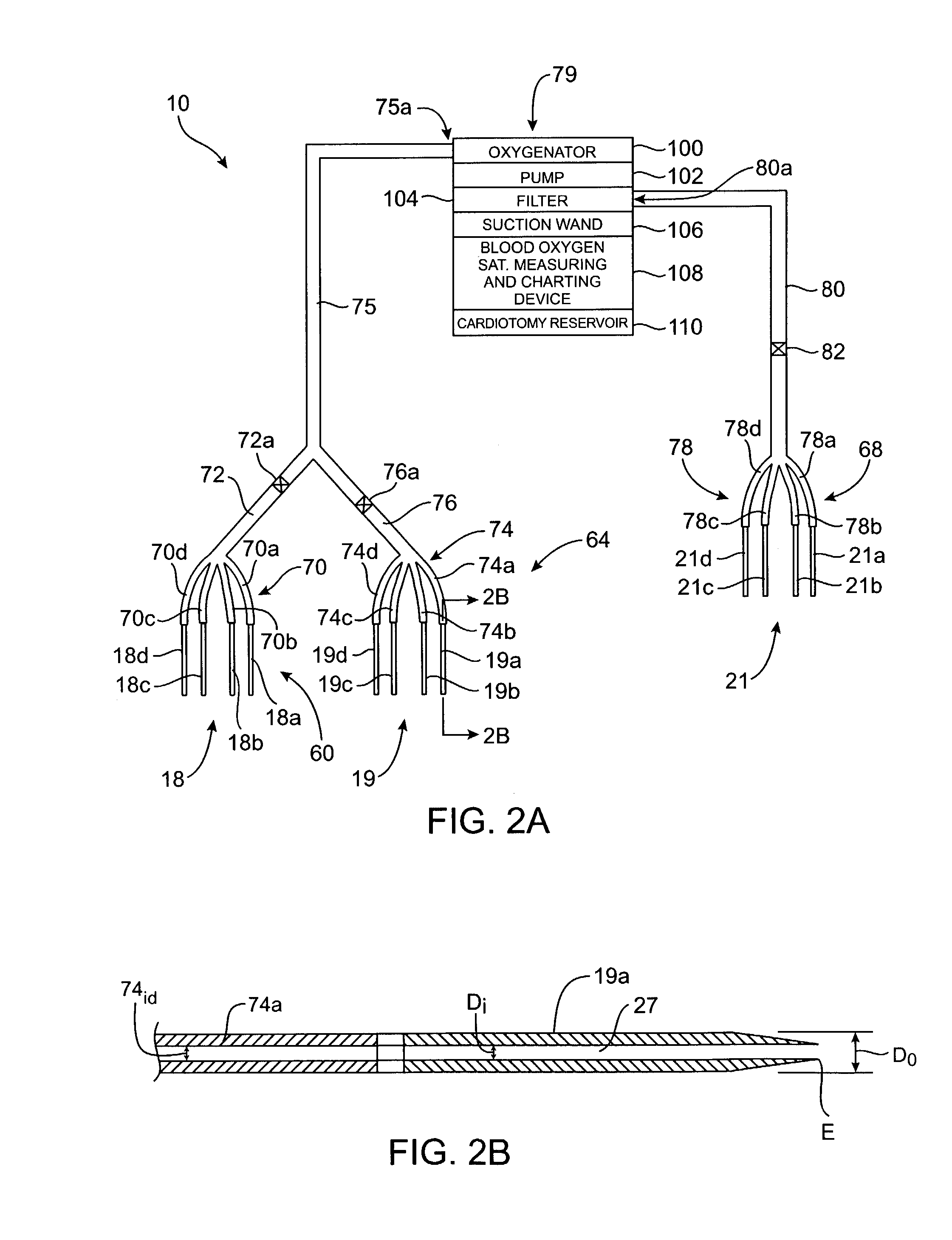
Venous cannula and cardiopulmonary bypass system
InactiveUS20050222532A1Improve efficiencyEasy to useStentsBalloon catheterExtracorporeal circulationVenous blood
This invention relates to a venous cannula for use in conjunction with cardiovascular examinations, treatments and surgery. The venous cannula is configured for two-stage drainage of oxygen-depleted venous blood from a central venous location via a peripheral venous insertion site, such as a femoral vein. The venous cannula is optimized for use in a cardiopulmonary bypass system that includes a multichannel arterial perfusion catheter. The cardiopulmonary bypass system is advantageous for use in performing standard open chest or least invasive cardiac surgical procedures.
Owner:SORIN GRP USA INC
Hemodialysis treatment apparatus and method for hemodialysis treatment
ActiveUS20060289342A1Efficient and effectiveEfficient and effective in determiningSemi-permeable membranesSolvent extractionExtracorporeal circulationHemodialysis
A hemodialysis treatment apparatus includes a circulating blood volume variation rate detecting device, a vital sign detecting device and a display. The circulating blood volume variation rate detecting device detects a circulating blood volume variation rate of a patient in a time-course of a hemodialysis treatment. The vital sign detecting device detects a vital sign value of the patient in the time-course of the hemodialysis treatment. The display has a screen and displays both the circulating blood volume variation rate and the vital sign value on the screen along a time scale. The hemodialysis treatment apparatus dialyzes and ultrafiltrates extracorporeally circulating blood of the patient to perform the hemodialysis treatment.
Owner:NIKKISO COMPANY
Method and device for monitoring vessel access during extracorporeal blood treatment
InactiveUS6663585B1Improve reliabilitySimple technical meanSemi-permeable membranesSolvent extractionExtracorporeal circulationBlood treatments
A method and device for monitoring vascular access is described. A field coil is placed at a location on an extracorporeal circulation loop connected to the vascular system of a patient, and an induction coil is placed at another different location. A voltage is supplied to the field coil, inducing an electric current in the blood. The current induces a voltage in the induction coil. Monitoring the voltage in the induction coil reveals if vascular access is defective.
Owner:FRESENIUS MEDICAL CARE DEUTSCHLAND GMBH
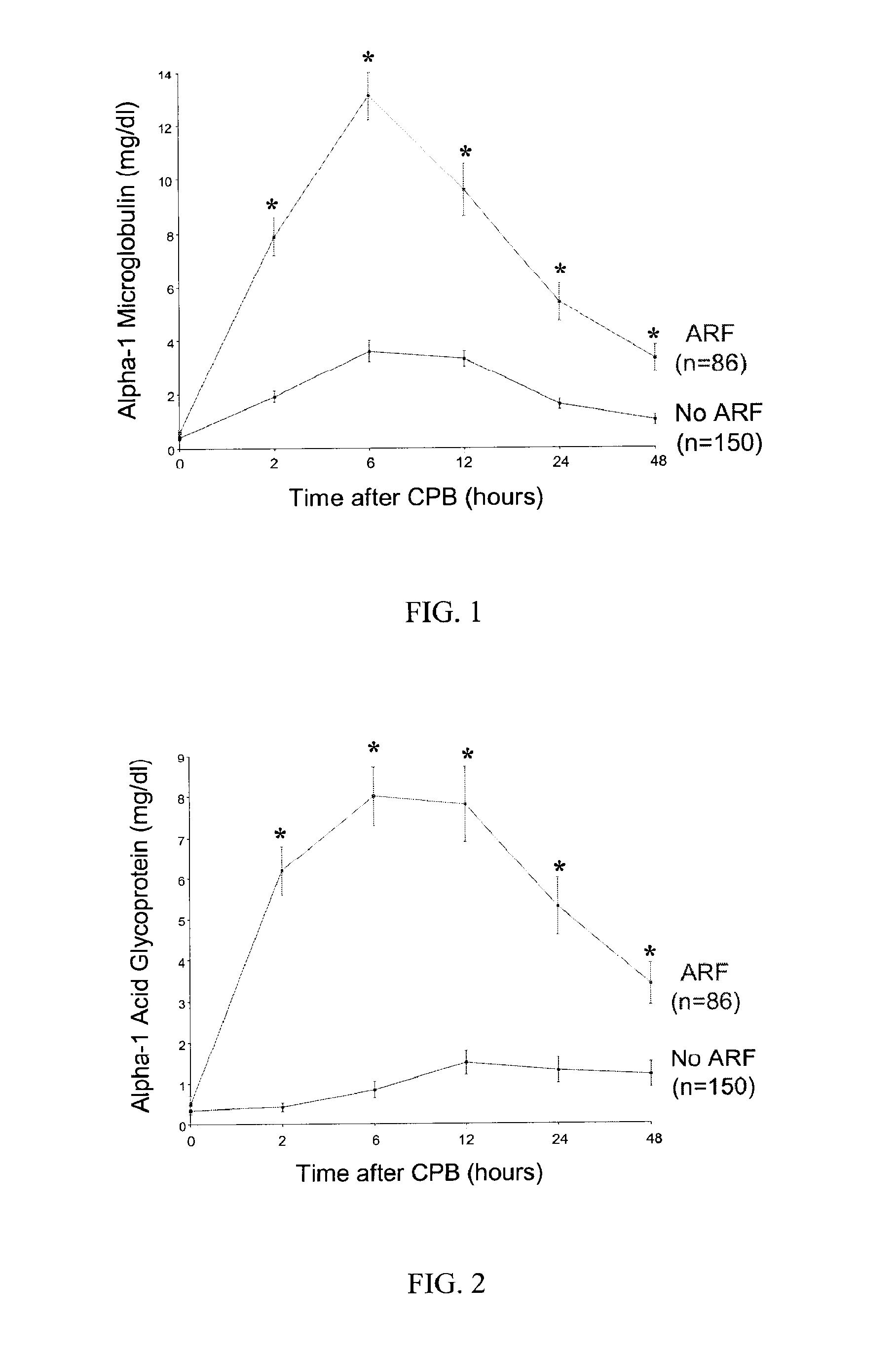
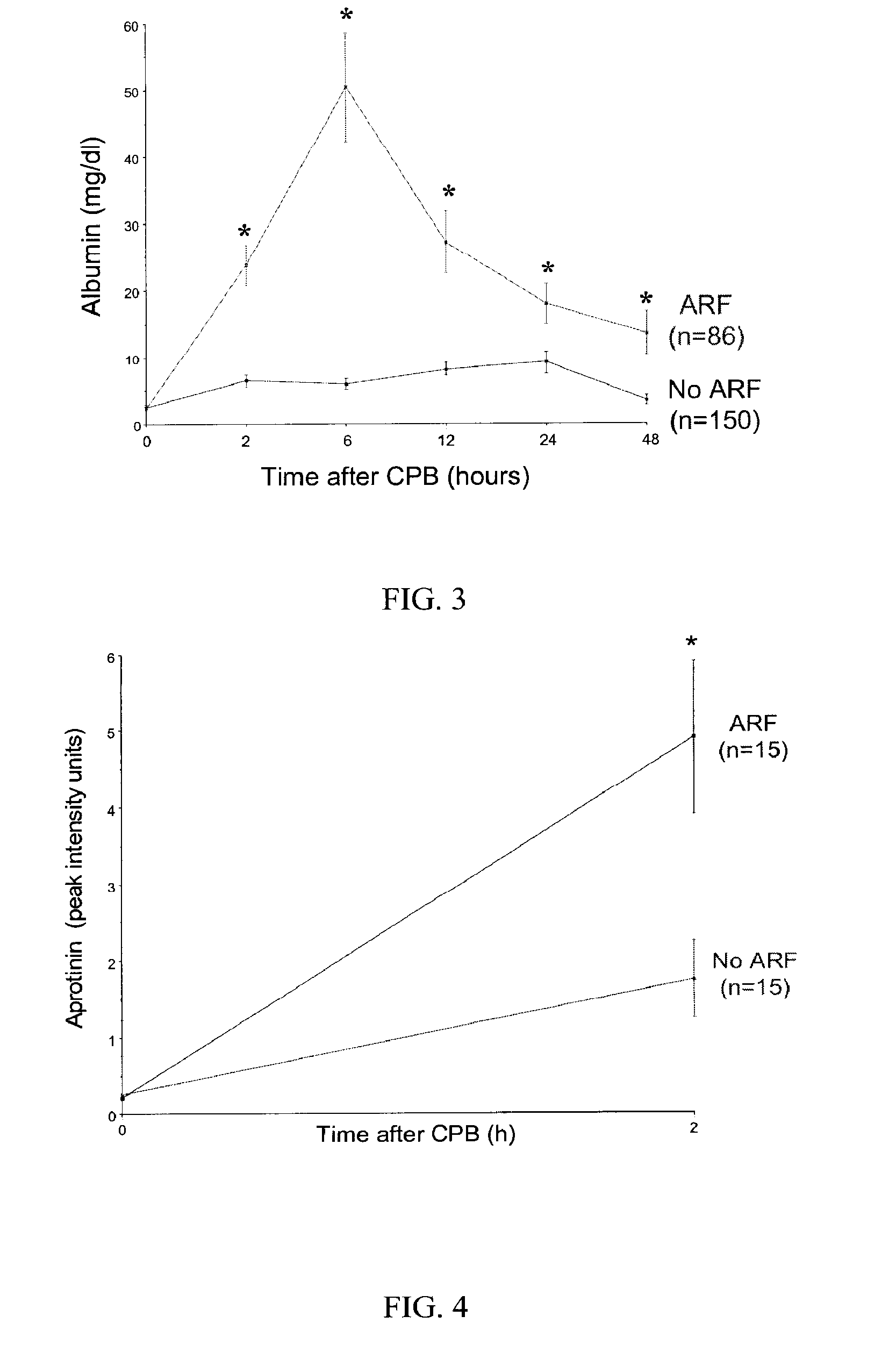
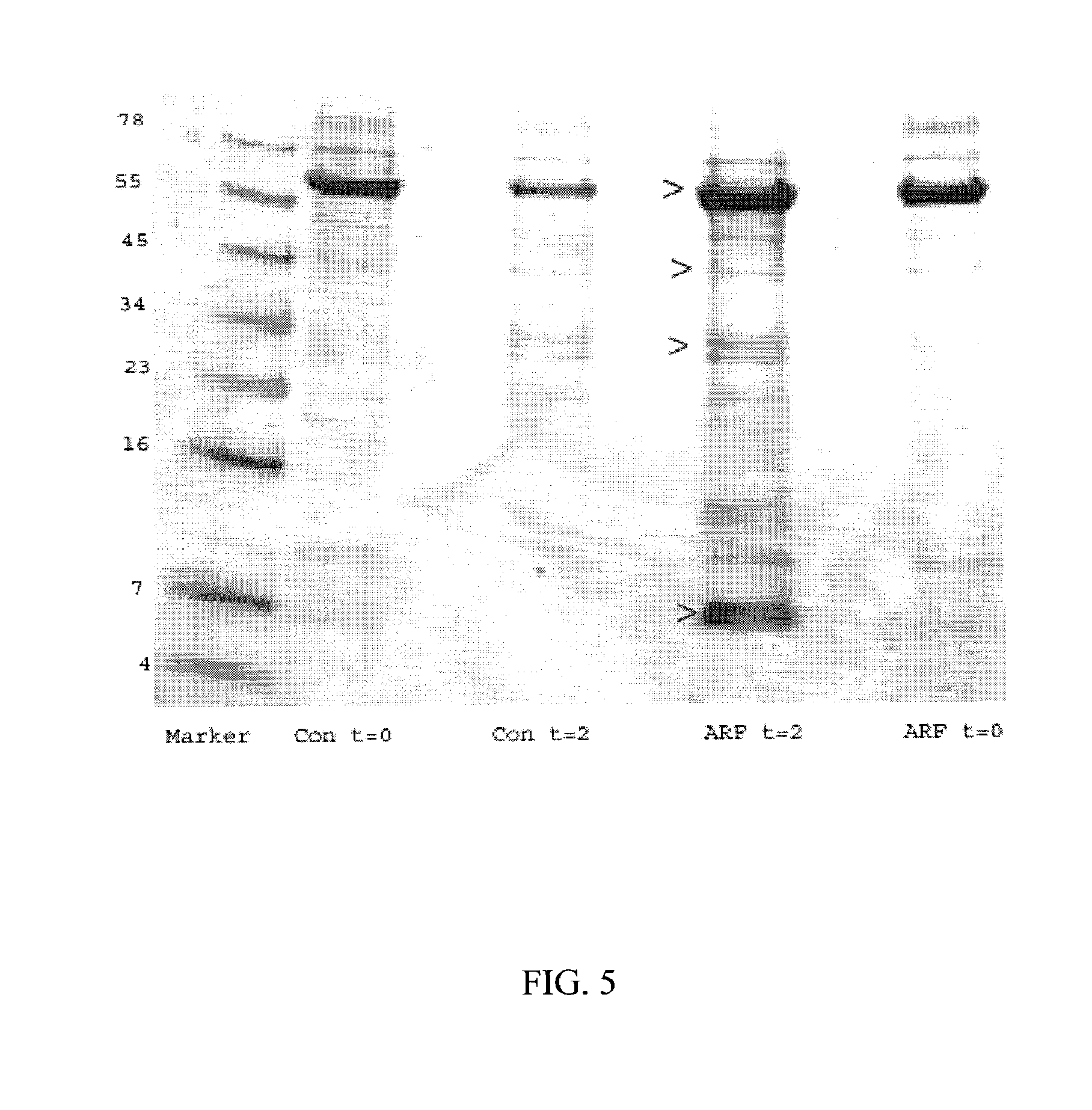
Method and Kit for the Early Detection of Impaired Renal Status
InactiveUS20070248989A1Pharmaceutical containersMedical packagingPoint of careExtracorporeal circulation
A method and kit for identifying the presence of an early biomarker of impaired renal status following a renal event in a mammalian subject. The method typically comprises (a) providing a body fluid sample obtained from a mammalian subject following a renal event; and (b) detecting in the provided sample the presence of a protein selected from the group consisting of aprotinin, alpha-1-microglobulin (A1M), alpha-1-acid-glycoprotein (A1AG), microalbumin, and combinations thereof, the presence thereof serving as an early biomarker of a change in renal status. The method can include a kit for point-of-care detection of the early biomarker of impaired renal status. Identification of the presence or absence of the early biomarker typically directs a caregiver's therapeutic decision regarding managing treatment of the subject for impaired renal status The invention also includes a method of assessing the administration of aprotinin during cardiopulmonary bypass surgery and provides for methods where the level of aprotinin in the subject's urine directs a caregiver's therapeutic decision regarding the intra-operative administration of aprotinin.
Owner:NIH
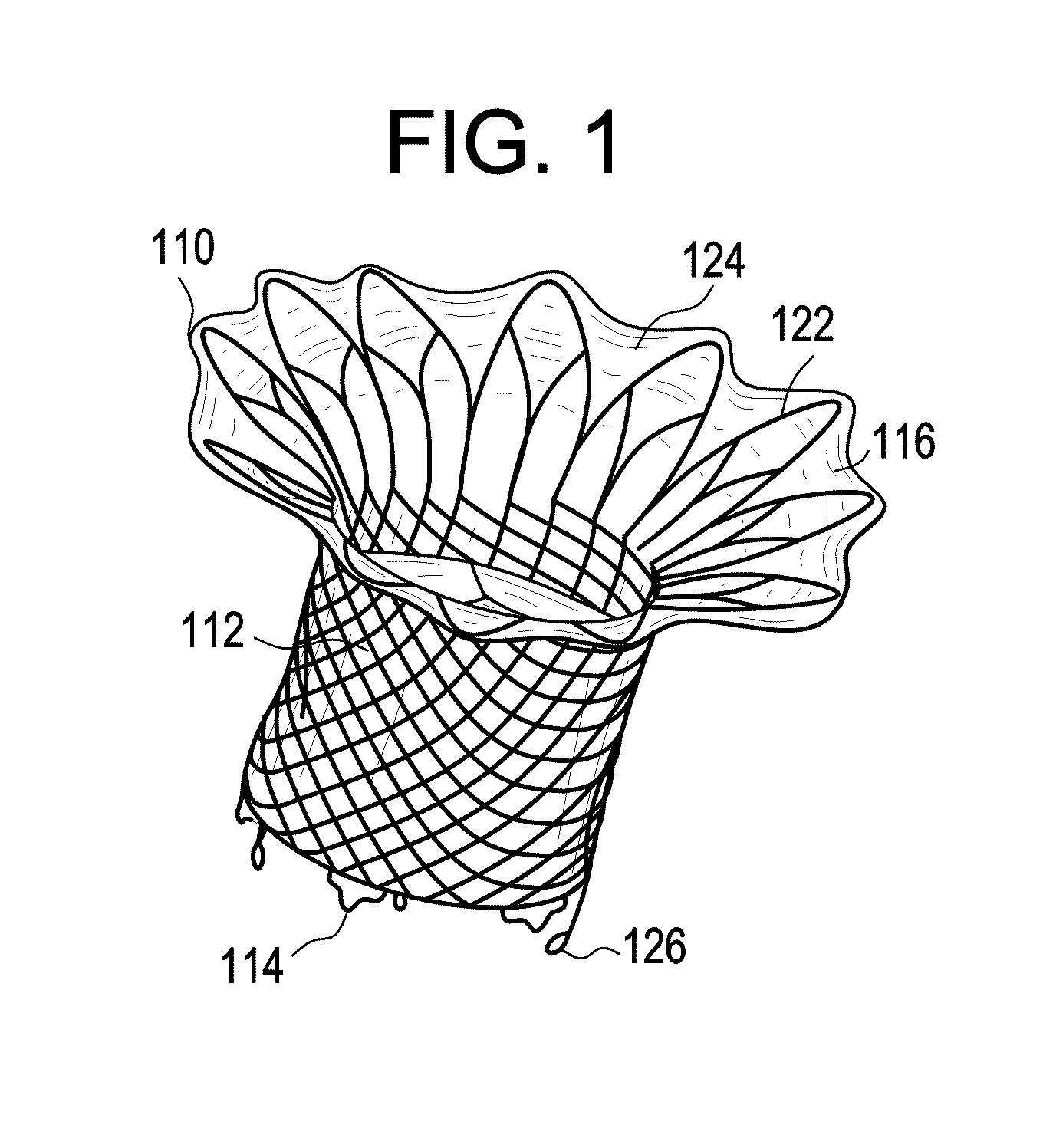
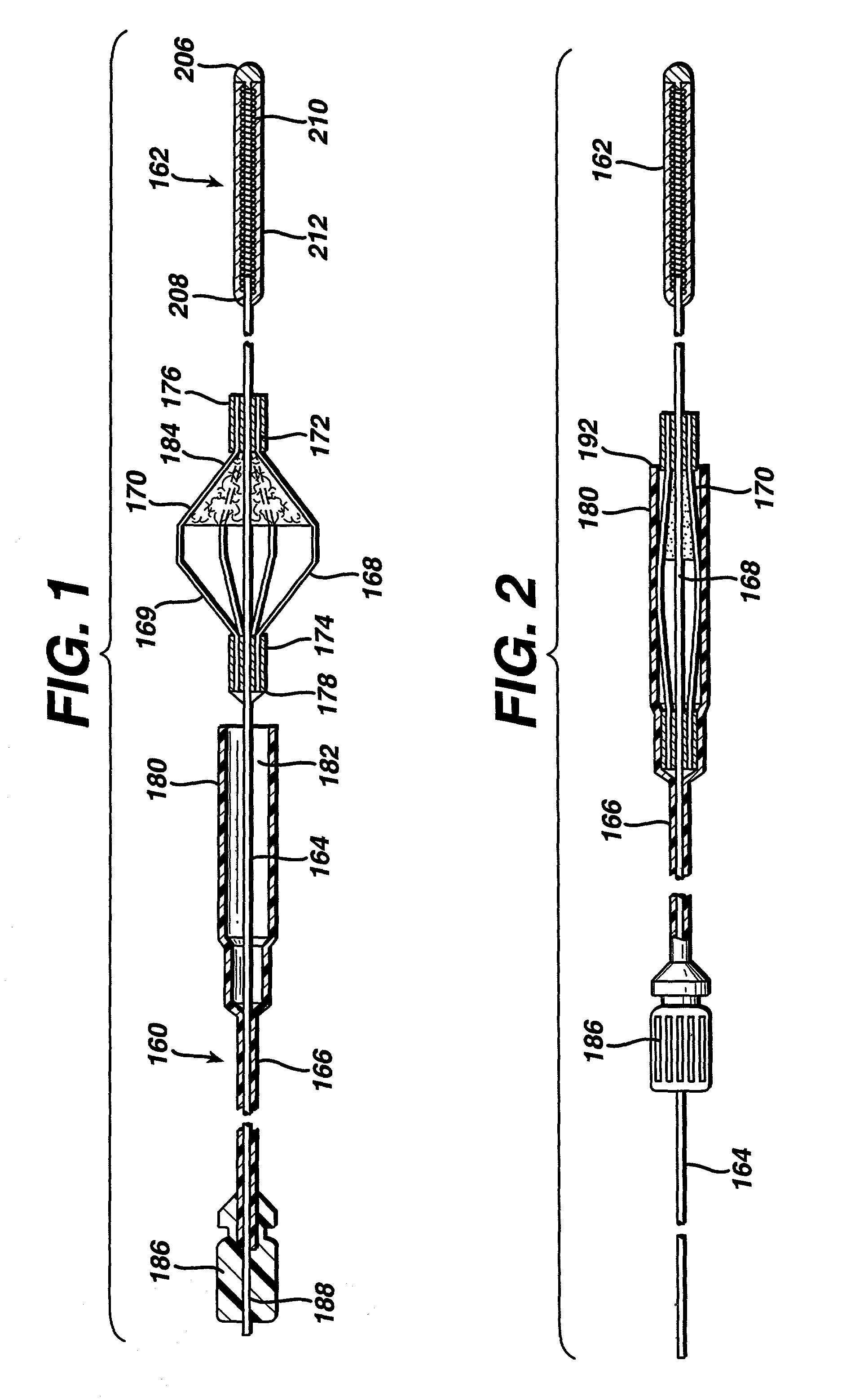
Multi-component designs for heart valve retrieval device, sealing structures and stent assembly
ActiveUS9895221B2Easy to take backPrevent perivalvular leakStentsHeart valvesExtracorporeal circulationVALVE PORT
This invention relates to the design and function of a device which allows for retrieval of a previously implanted valve prosthesis from a beating heart without extracorporeal circulation using a transcatheter retrieval system, including a guide component to facilitate the compression of the valve and retraction into a retrieval catheter, as well as an improved prosthetic transcatheter heart valve having one or more of: a series of radially extending tines having a loop terminus to improve sealing a deployed prosthetic mitral valve against hemodynamic leaking, a pre-compressible stent-in-stent design, or an articulating cuff attached to a covered stent-valve and a commissural sealing skirt structure attached to the underside of the articulating cuff.
Owner:TENDYNE HLDG
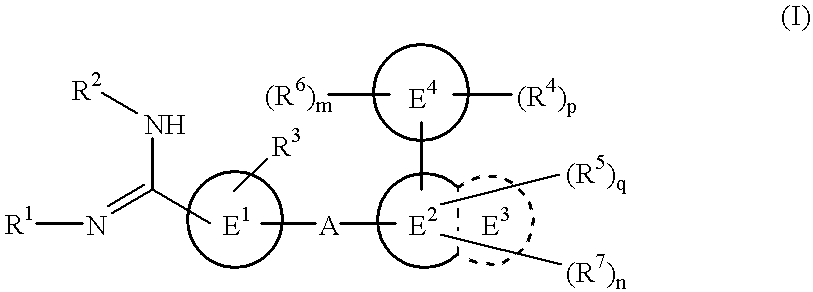
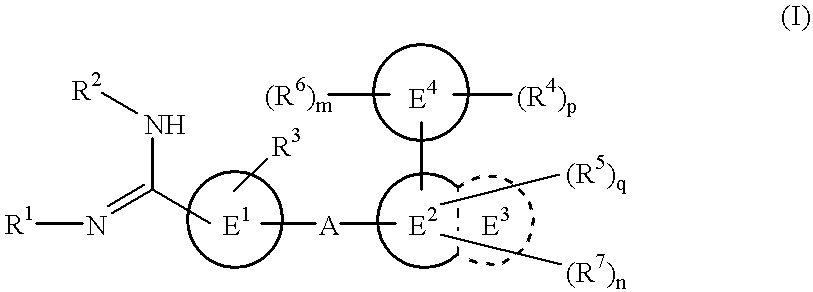
Amidino derivatives and drugs containing the same as the active ingredient
InactiveUS6358960B1BiocideGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsExtracorporeal circulationDisseminated coagulopathy
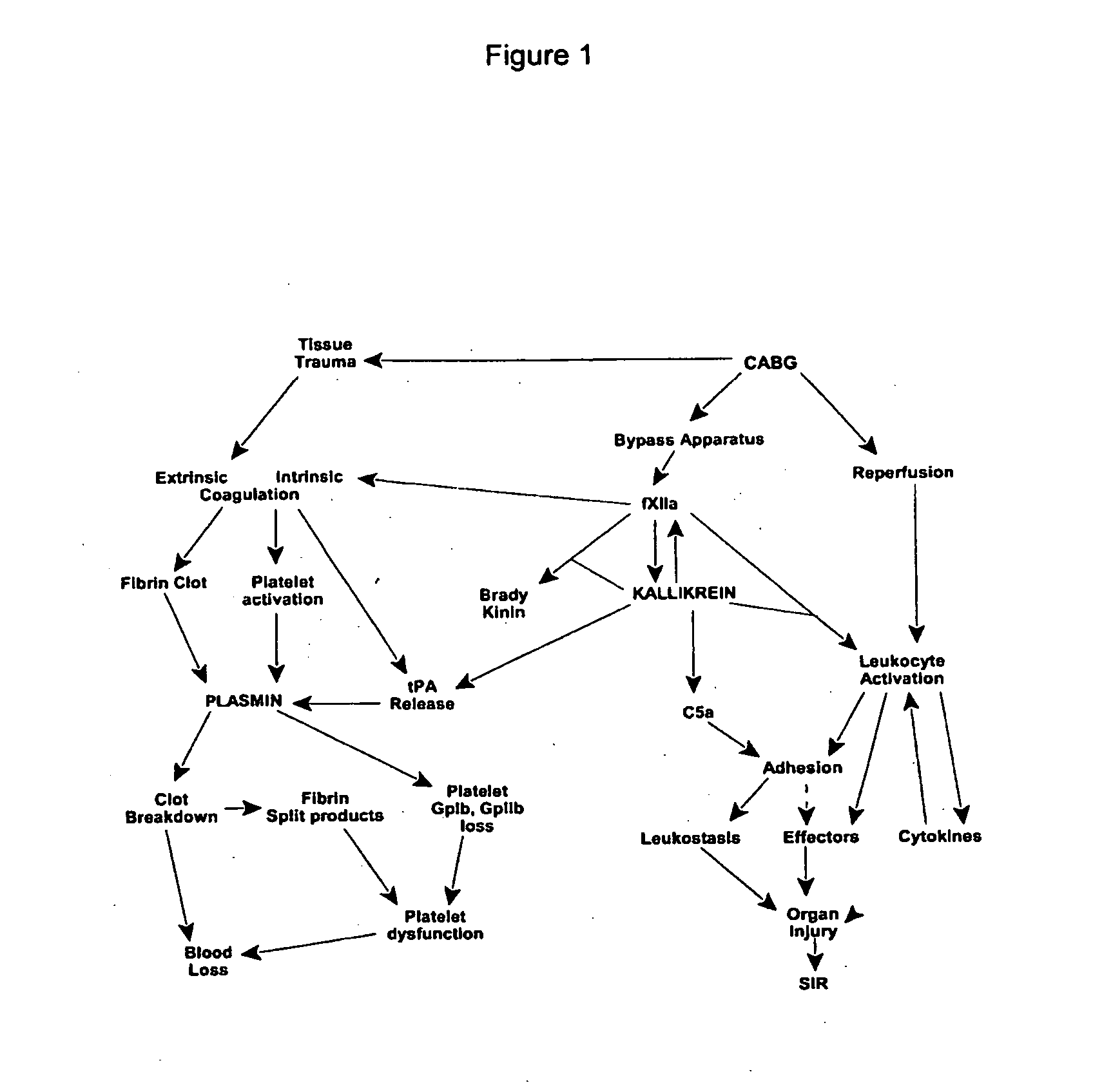
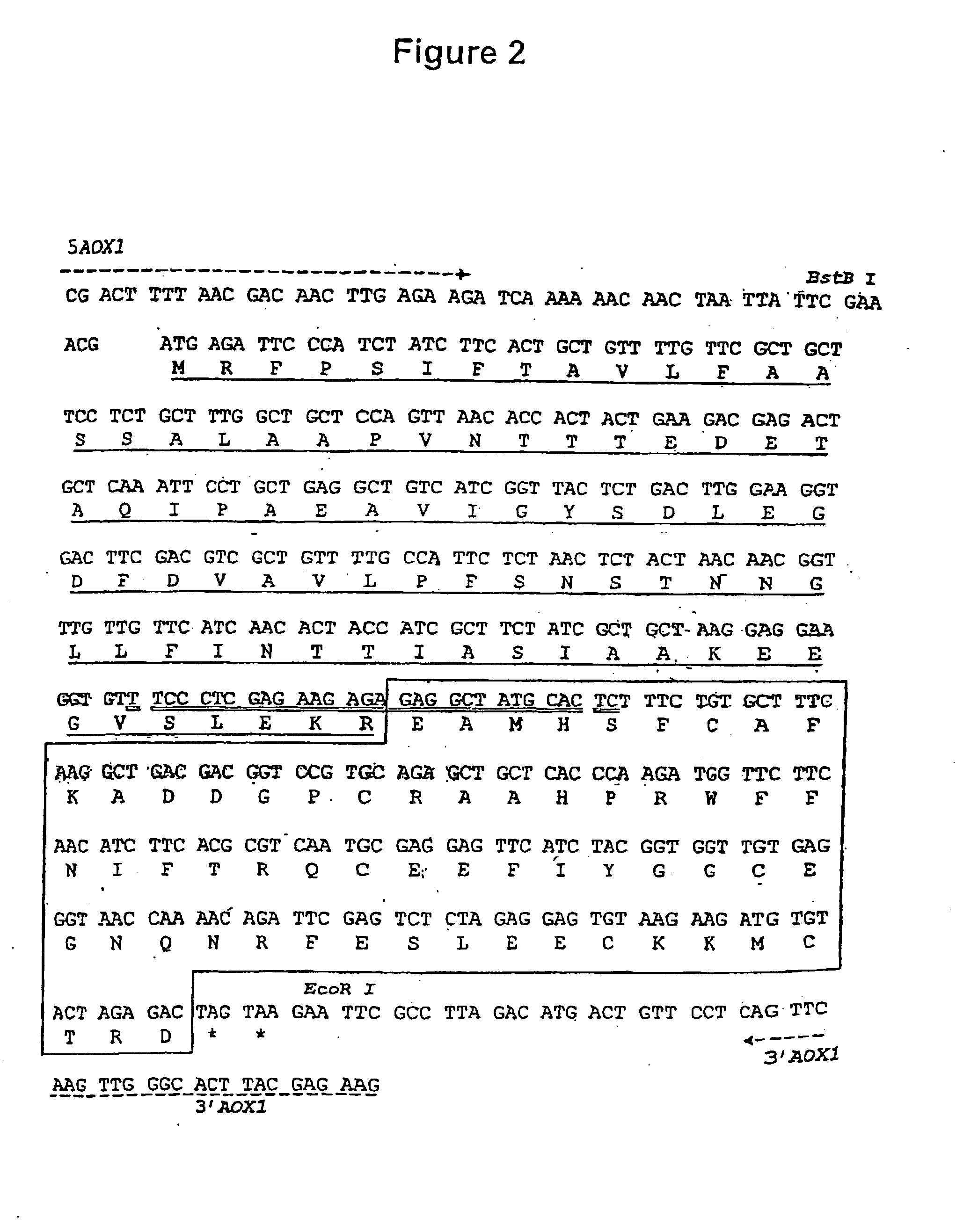
The novel amidino derivatives of the formula (I):wherein all the symbols are as in specification defined;have an inhibitory activity of a blood coagulation factor VIIa and are useful for treatment and / or prevention of several angiopathy caused by enhancing a coagulation activity, such as disseminated intravascular coagulation, coronary thrombosis, cerebral infarction, cerebral embolism, transient ischemic attack, cerebrovascular disorders, pulmonary vascular diseases, deep venous thrombosis, peripheral arterial obstruction, thrombosis after artificial vascular transplantation and artificial valve transplantation, post-operative thrombosis, reobstruction and restenosis after coronary artery bypass operation, reobstruction and restenosis after PTCA or PTCR, thrombosis by extracorporeal circulation and procoagulative diseases such as glomerlonephriitis.
Owner:ONO PHARMA CO LTD
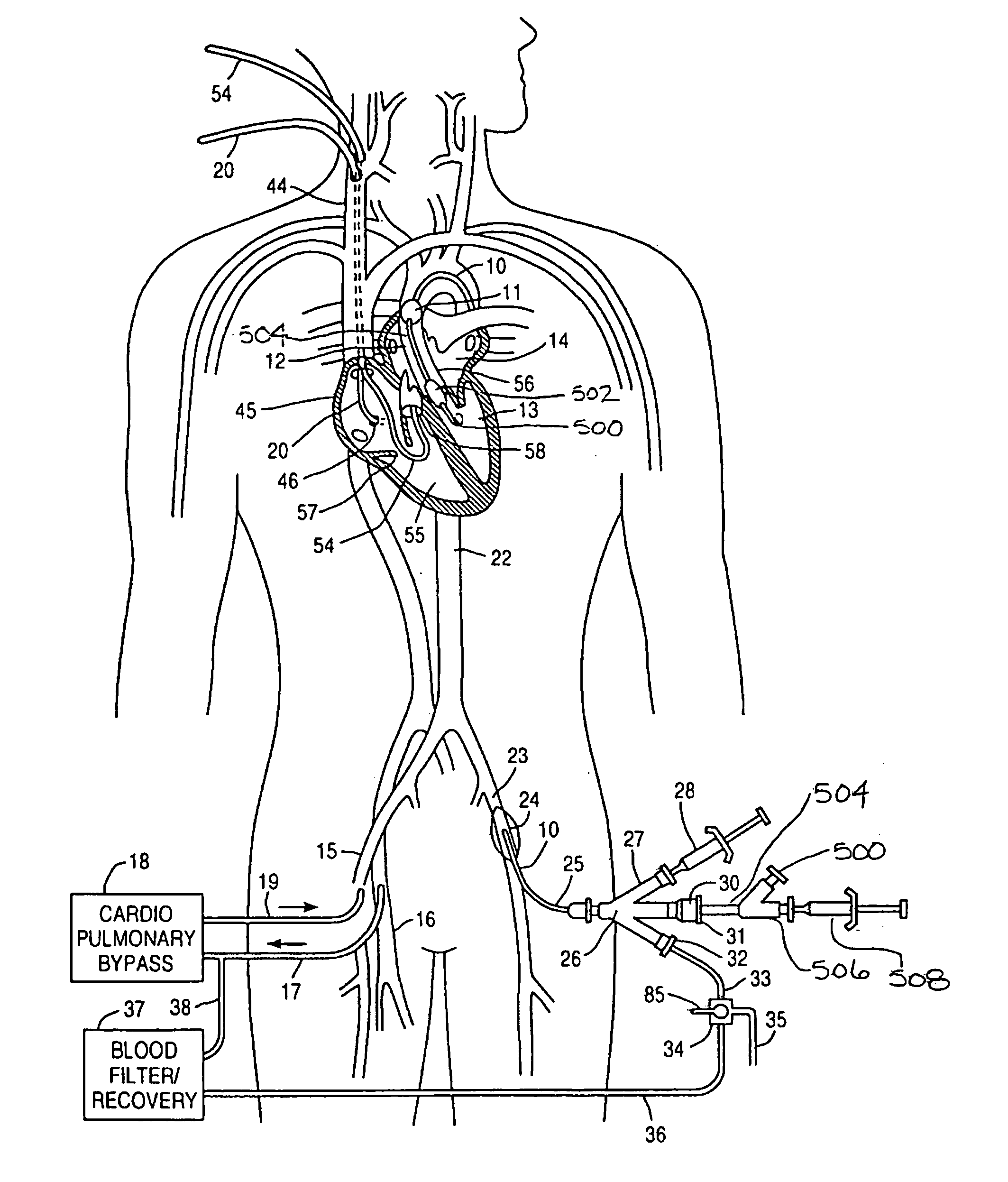
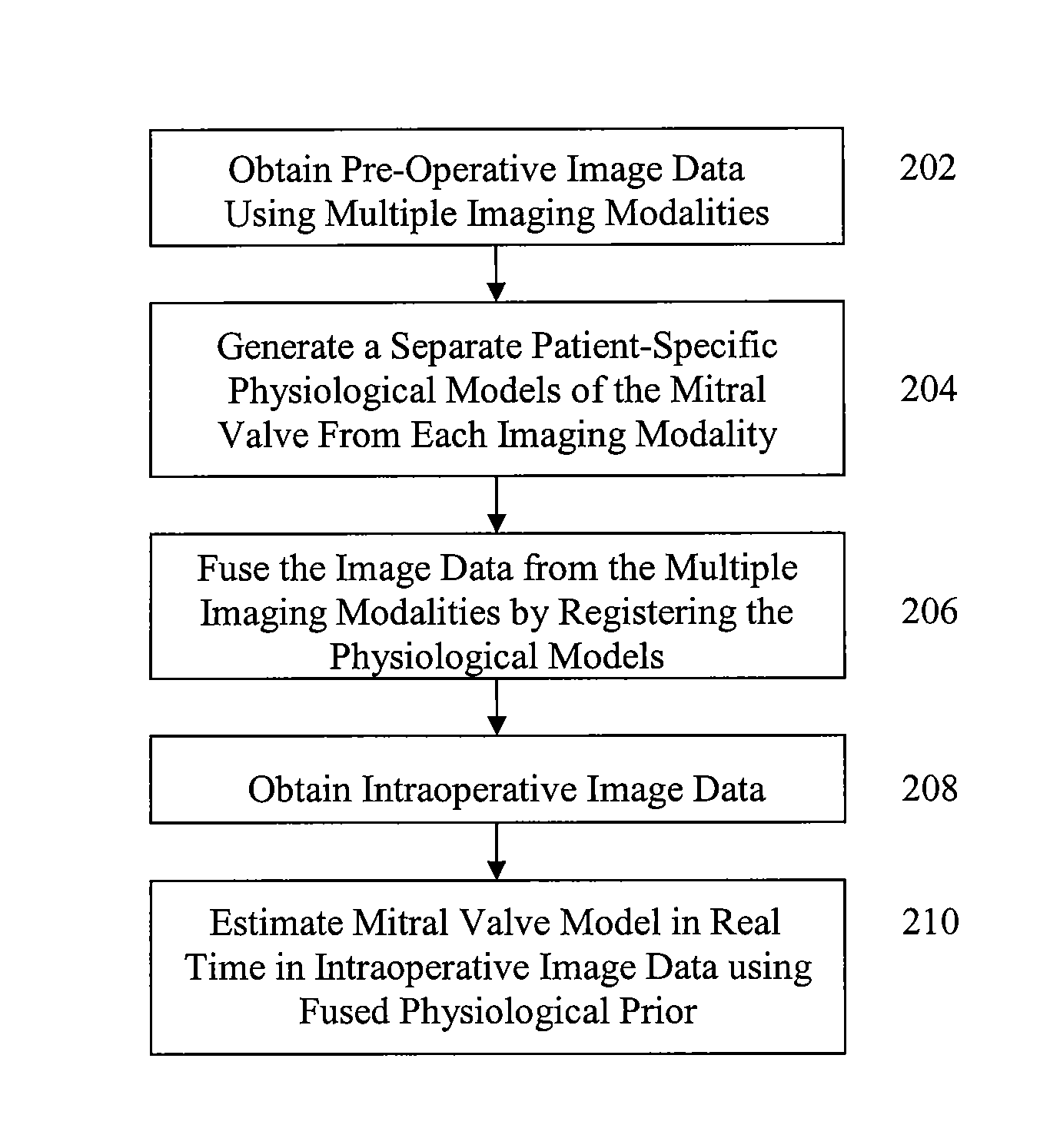
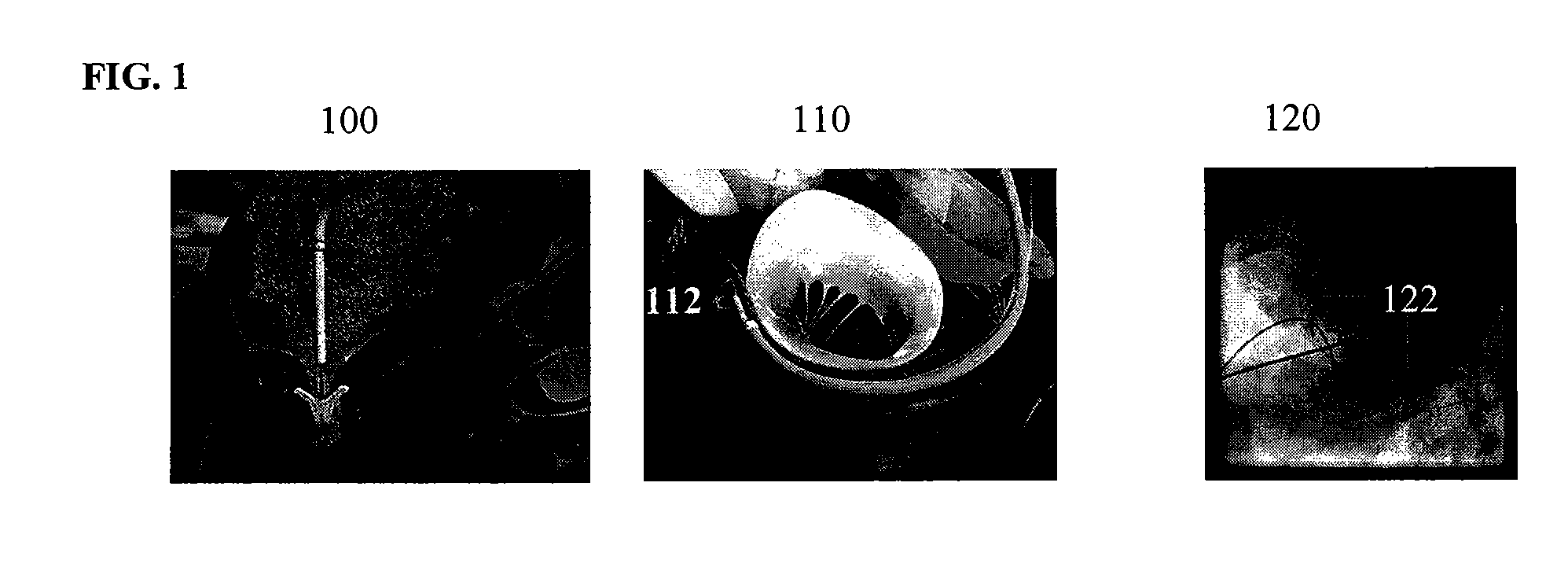
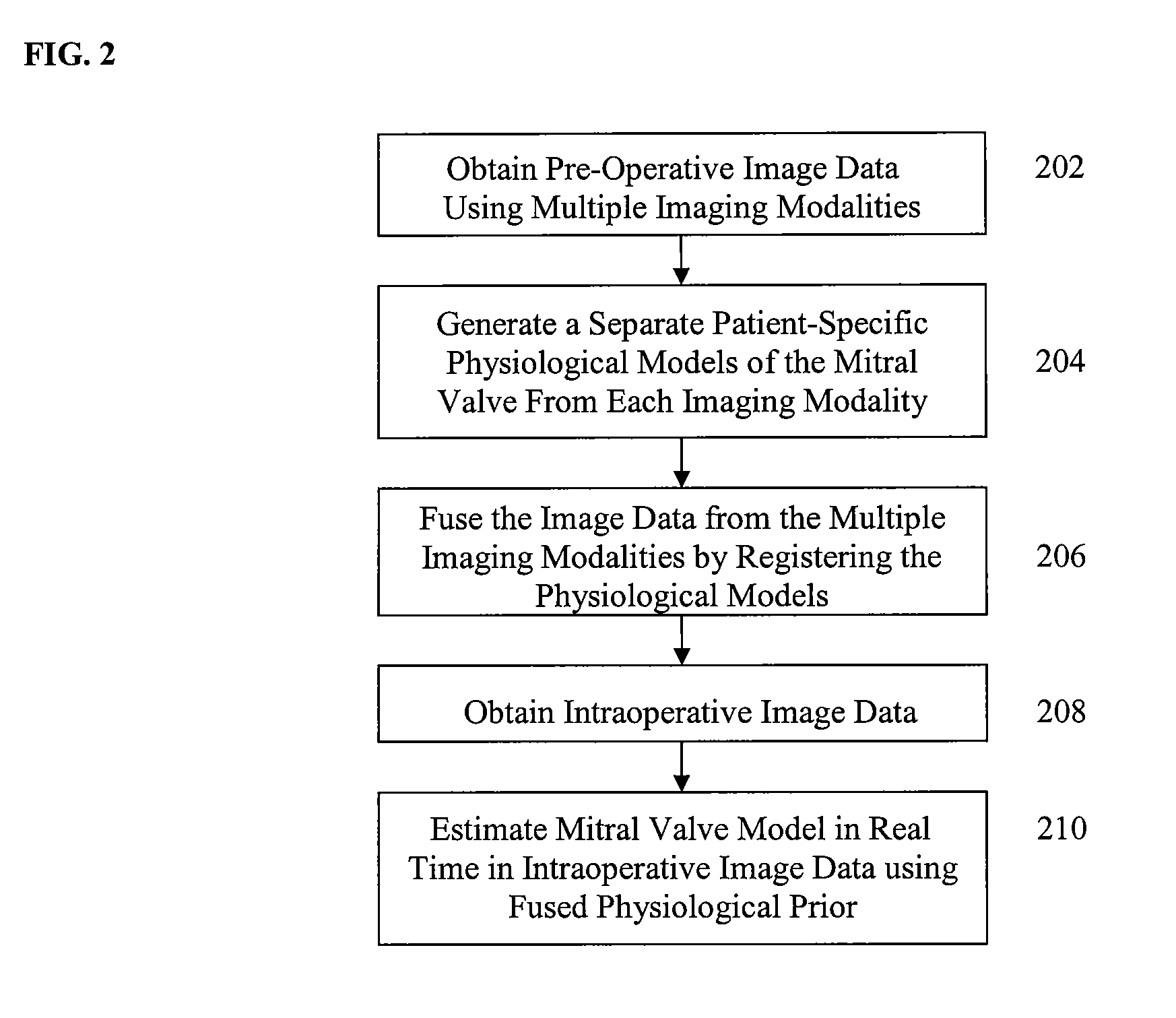
Method and system for intraoperative guidance using physiological image fusion
ActiveUS8532352B2Improve accuracyReduce riskMedical simulationImage enhancementDiagnostic Radiology ModalityExtracorporeal circulation
A method and system for intraoperative guidance in an off-pump mitral valve repair procedure is disclosed. A plurality of patient-specific models of the mitral valve are generated, each from pre-operative image data obtained using a separate imaging modality. The pre-operative image data from the separate imaging modalities are fused into a common coordinate system by registering the plurality of patient-specific models. A model of the mitral valve is estimated in real-time in intraoperative image data using a fused physiological prior resulting from the registering of the plurality of patient-specific models.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
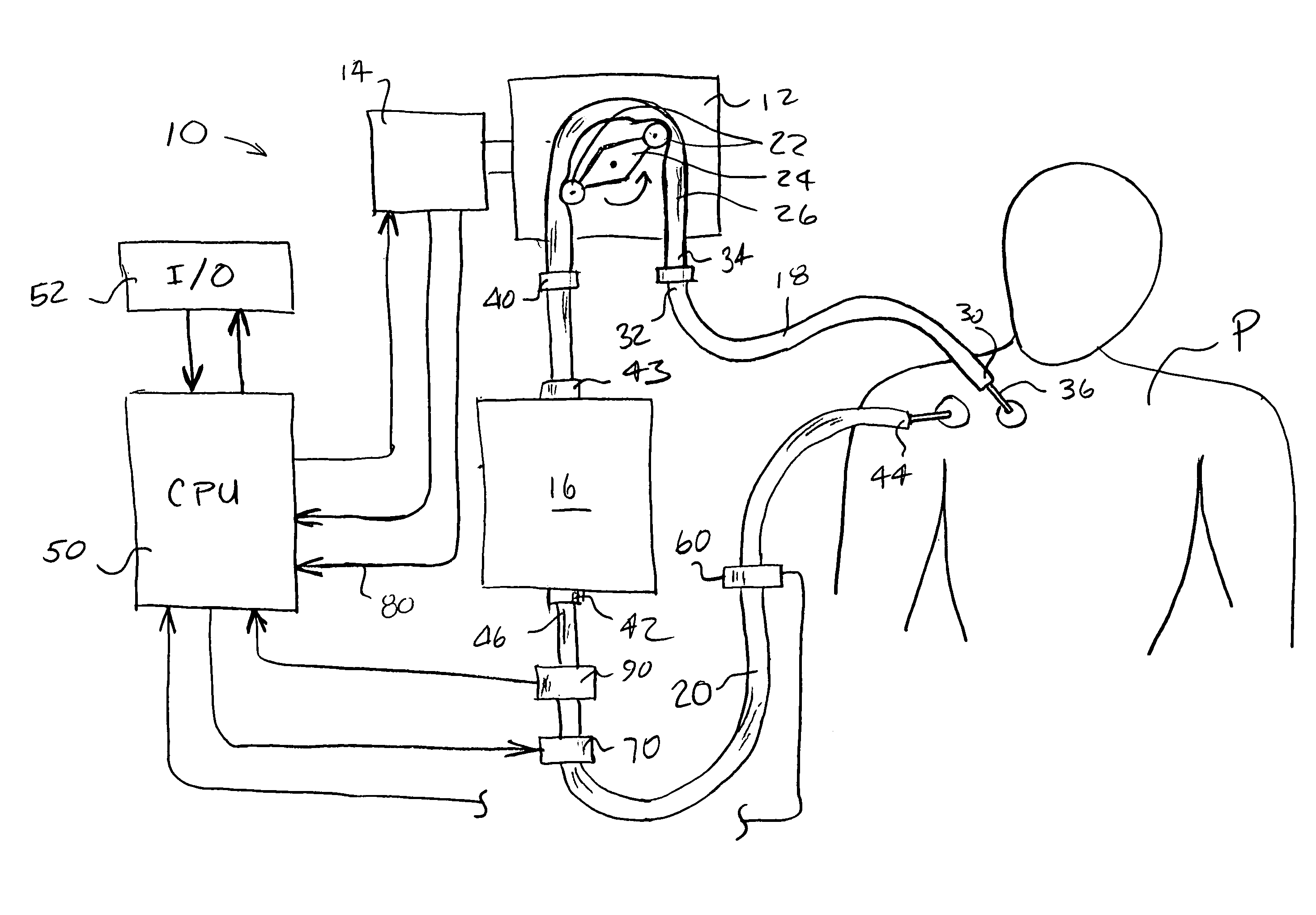
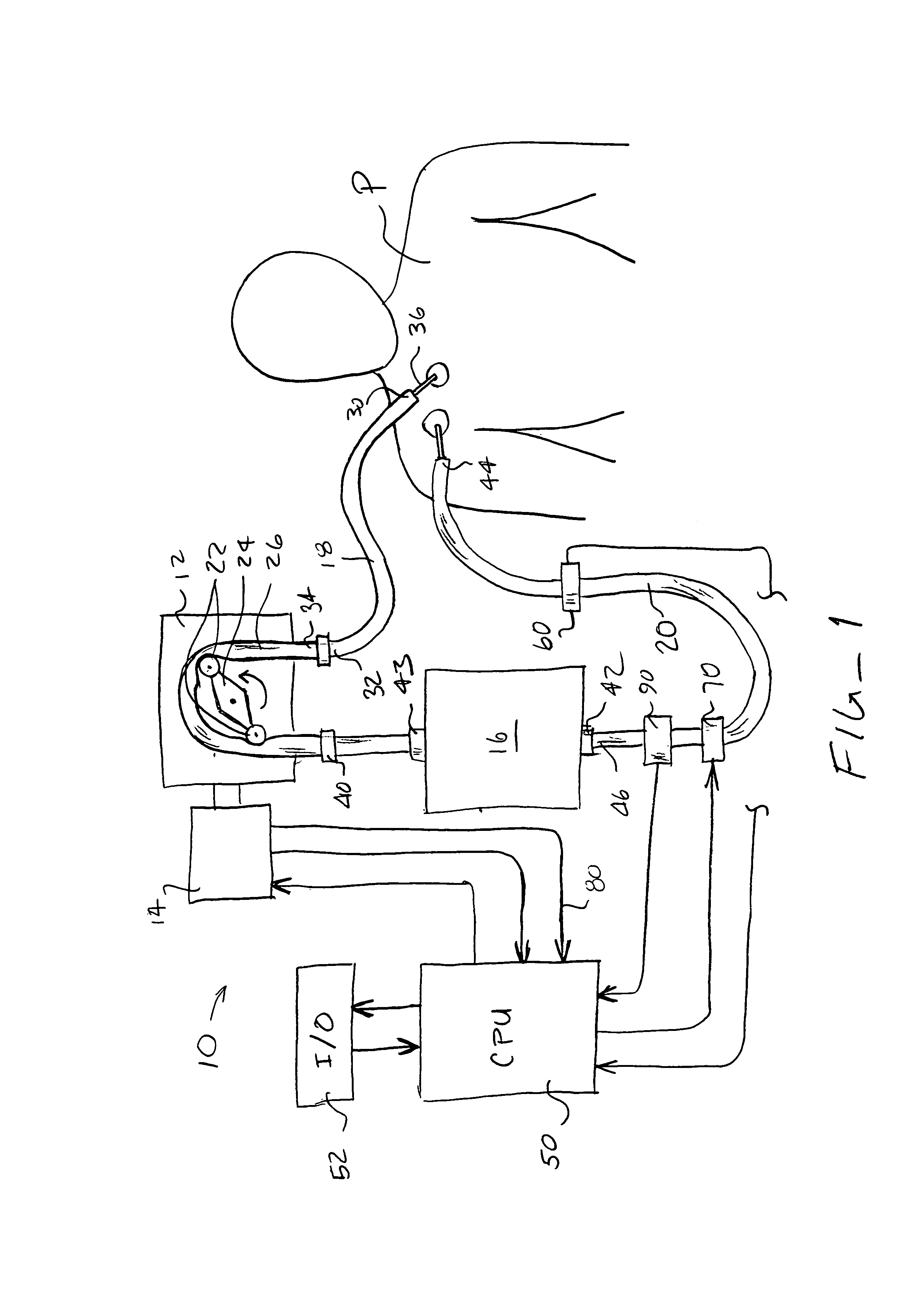
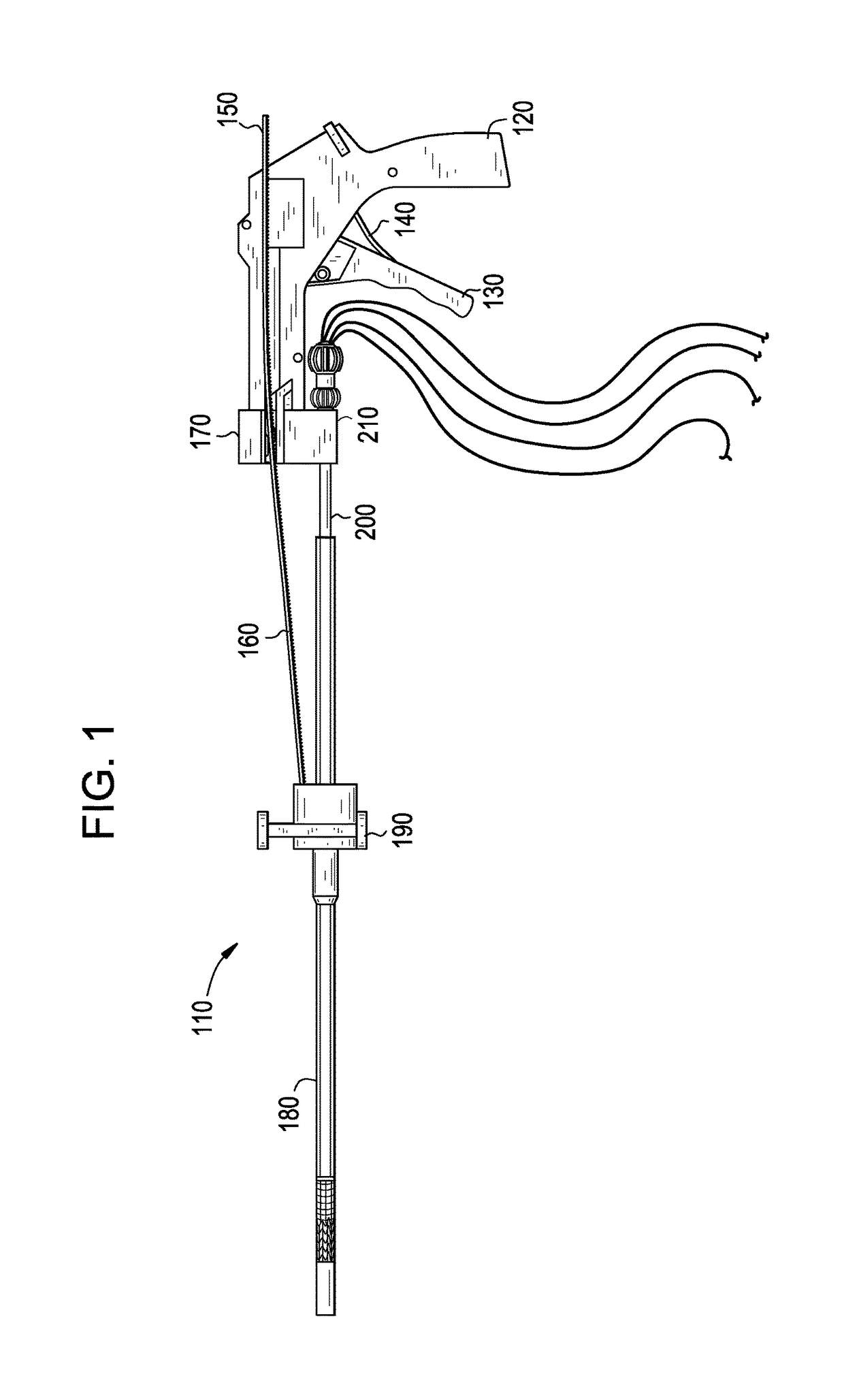
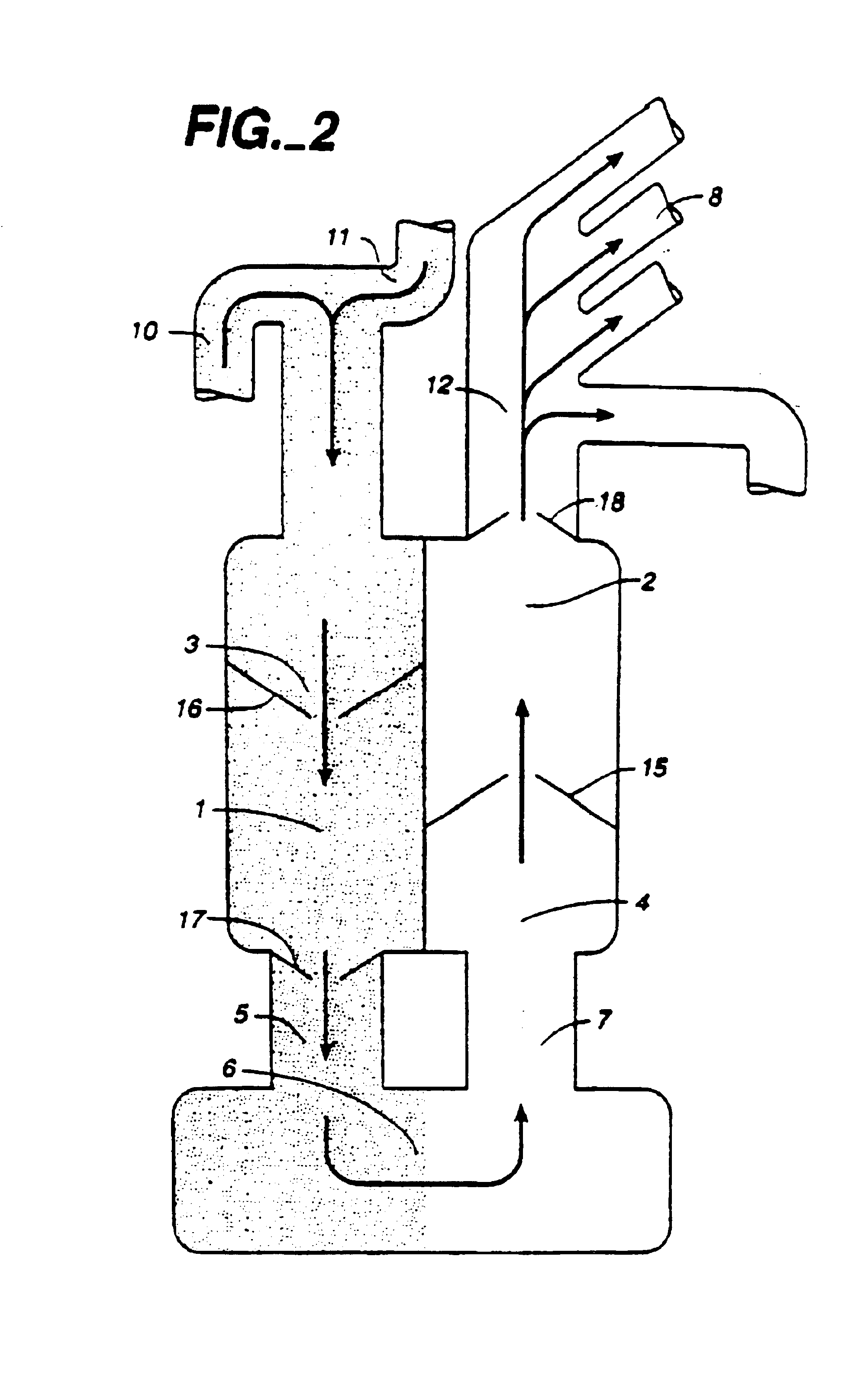
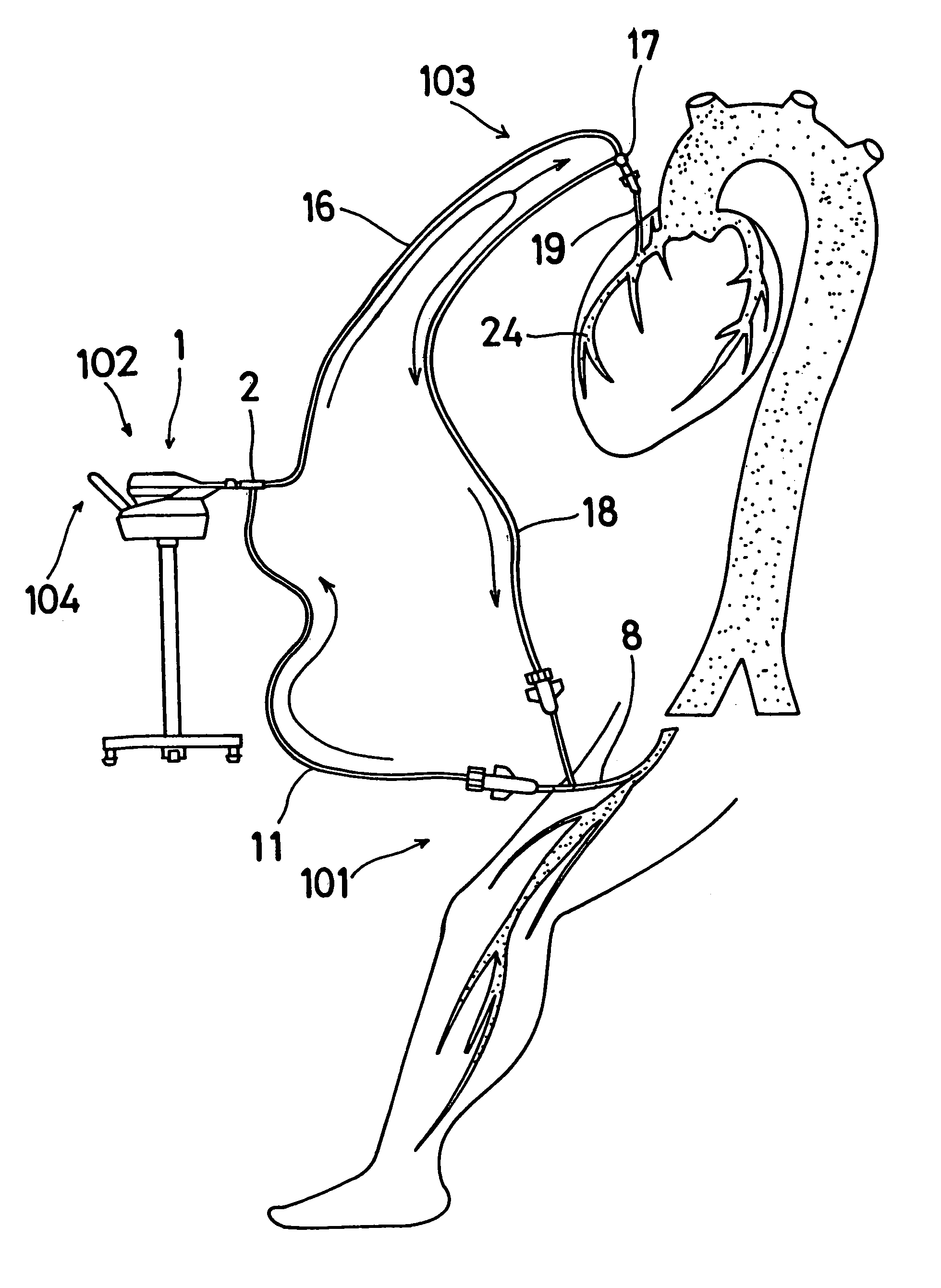
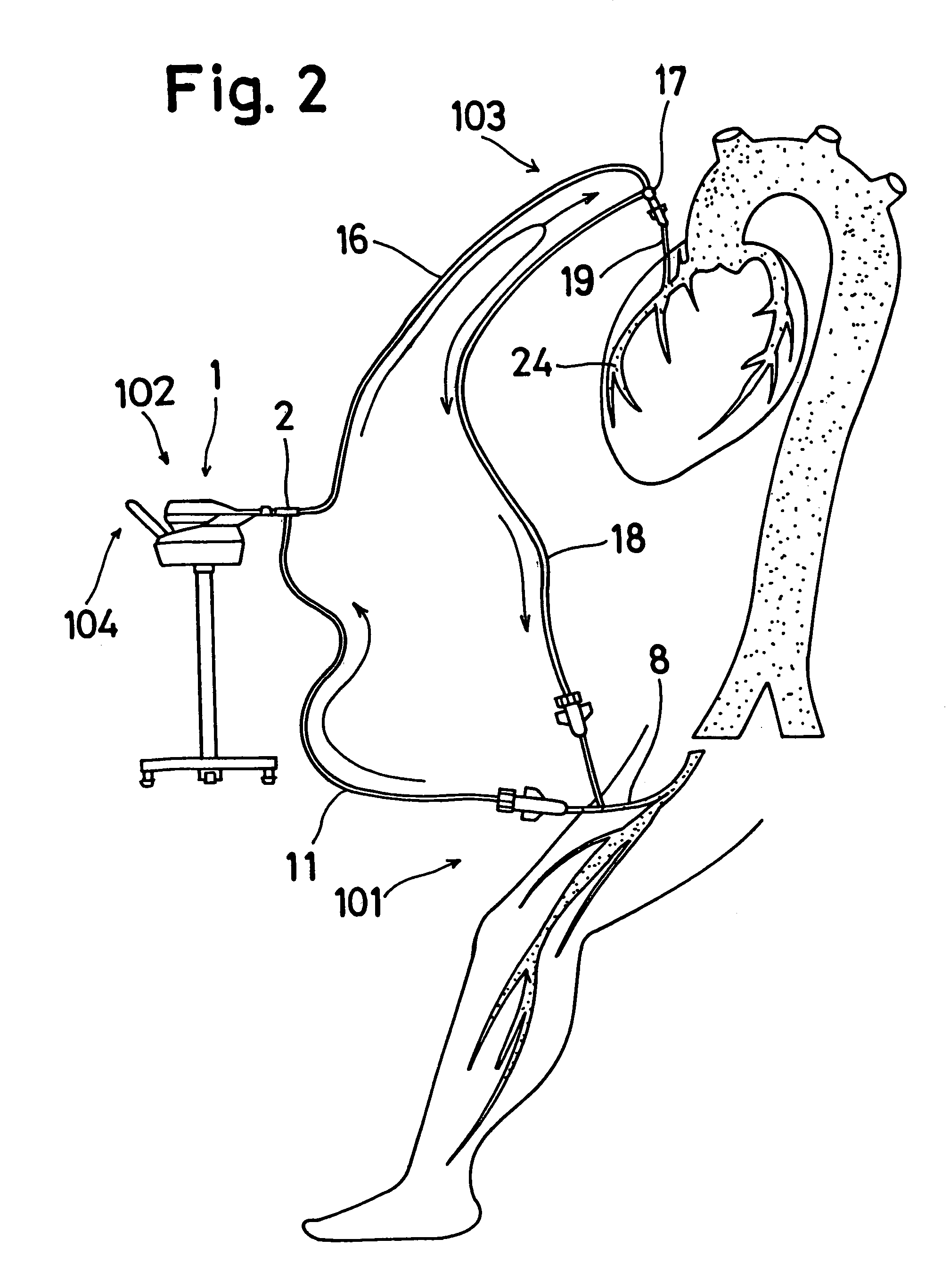
Multichannel catheter with obturator
This invention is a multichannel catheter for extracorporeal circulation of blood to a patient undergoing cardiovascular treatments or surgery. The catheter has three independent channels, an obturator and an expandable balloon at one end of the catheter. The first channel is the largest and is of a size that allows for delivery of blood through outlet parts in the wall of the first channel to a patient in an amount sufficient to maintain the patient's metabolism and perfusion throughout the treatment or surgery. The obturator is longitudinally insertable into the first channel. A second channel, smaller than the first, is integrated into the wall of the first channel, and is suitable for delivering a biologically active fluid (e.g., for cardioplegia) to the heart and / or venting the left heart. A third channel, also smaller than the first, is integrated into the wall of the first channel, and suitable for delivering a fluid to the balloon for its expansion when positioned in the ascending aorta to occlude the flow of blood to the heart. The catheter provides an improved means of preparing for or performing cardiovascular surgery on a patient using a cardiopulmonary machine for extracorporeal circulation of blood. The catheter is particularly useful for cardiac surgery.
Owner:SORIN GRP USA INC
Vascular filter system for cardiopulmonary bypass
InactiveUS7229463B2Other blood circulation devicesSurgeryExtracorporeal circulationCardiopulmonary bypass
A removable vascular filter system for capture and retrieval of emboli while allowing continuous perfusion of blood during a cardiopulmonary bypass procedure, comprising a porous filter membrane with variable diameter holes, and a filter membrane support structure. The system may minimize the incidence of stroke, myocardial infarction or other clinical complications that may be associated with cardiopulmonary bypass procedures.
Owner:CARDINAL HEALTH SWITZERLAND 515 GMBH
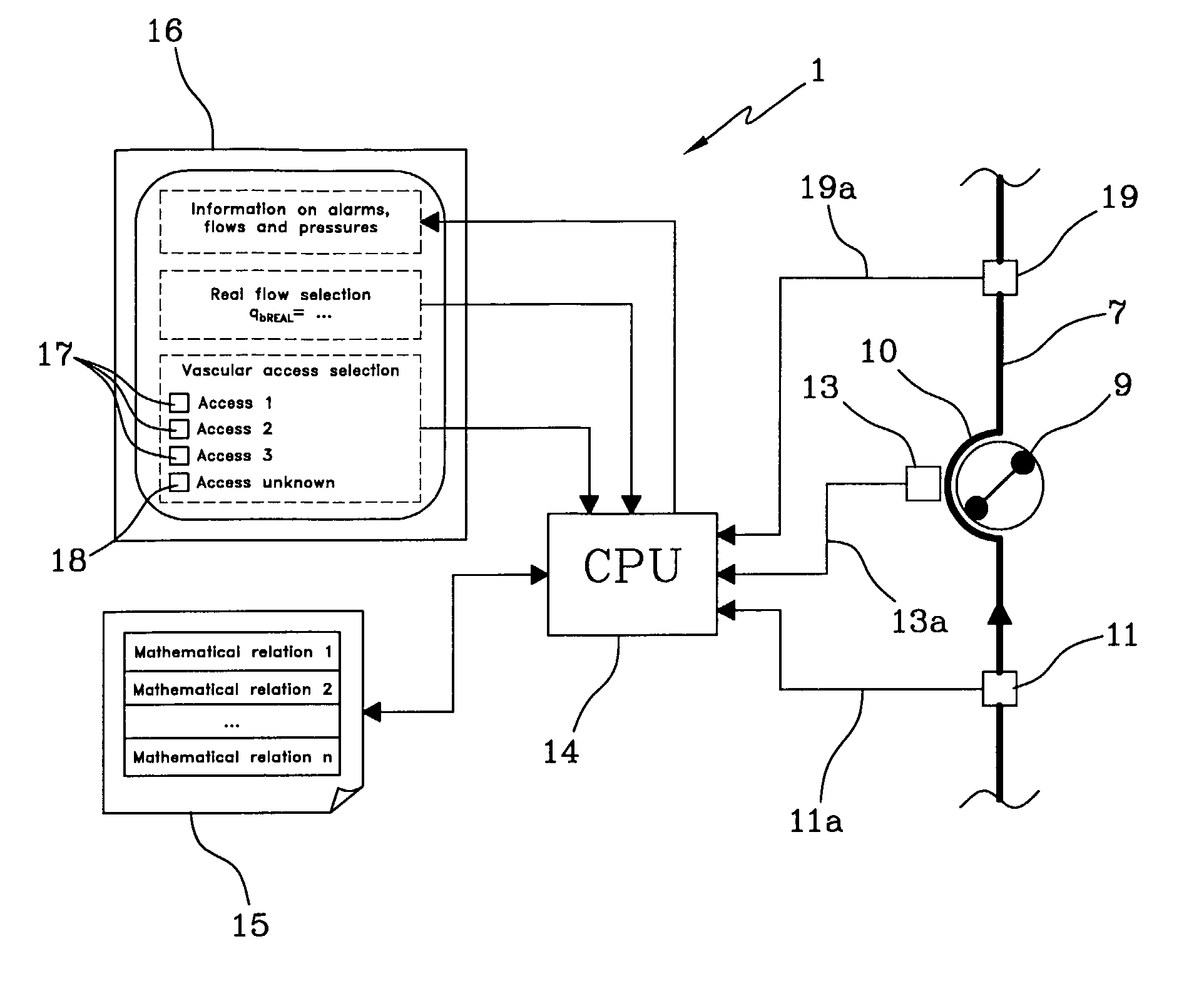
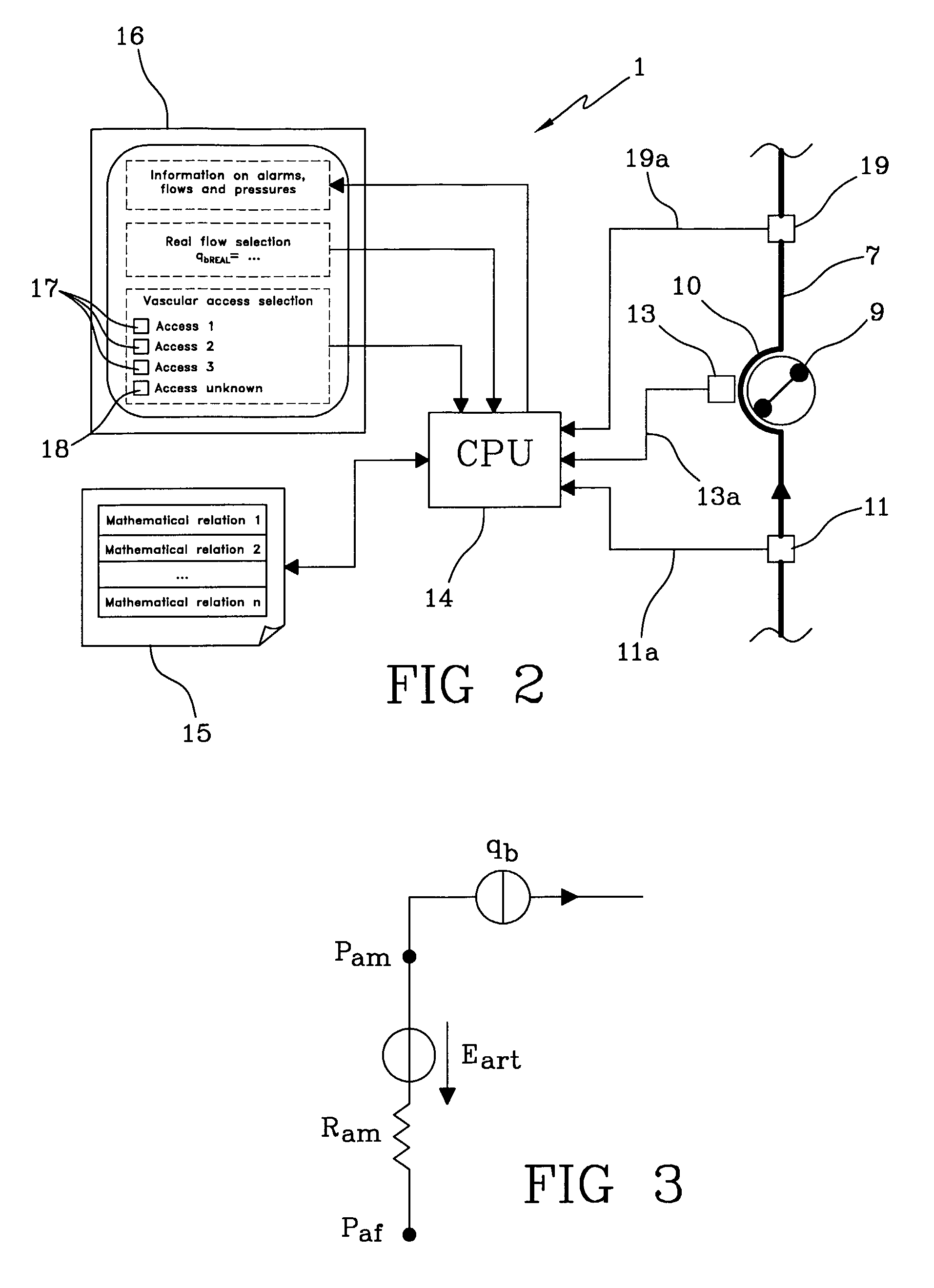
Apparatus for controlling blood flow in an extracorporeal circuit
ActiveUS7794419B2Semi-permeable membranesSolvent extractionExtracorporeal circulationAngular velocity
The apparatus for blood flow control in an extracorporeal circuit comprises: a user interface for setting a desired blood flow value (qbREAL) and a datum relating to the vascular access, a memory for recording a plurality of mathematical relations having mathematical expressions relating to the vascular access organ to be used, and a control unit. The control unit identifies the vascular access, selects, from among the plurality of mathematical relations present in the memory, a relation which corresponds to the vascular access identified, and calculates, as a mathematical function of the set value for the desired flow (qbREAL), a value at which to set the angular velocity of the pump associated to the extracorporeal circuit and / or a theoretical value of the arterial pressure upstream of the pump.
Owner:GAMBRO LUNDIA AB
Cardiopulmonary bypass device and method
InactiveUS6979423B2Other blood circulation devicesSurgeryExtracorporeal circulationCardiopulmonary bypass
A method and system for performing a cardiopulmonary bypass procedure are provided. The method includes accessing a source of blood in a patient body from which source the blood is to be passed through a cardiopulmonary bypass machine, drawing blood from the source through the cardiopulmonary bypass machine and introducing the blood into an aortic artery of the patient body through a plurality of separate passages, after the blood has been passed through the cardiopulmonary bypass machine. The system includes a cardiopulmonary bypass machine, a tubular member coupled to an outlet port of the cardiopulmonary bypass machine and a plurality of separate needle members connected in fluid flow communication with the tubular member, the needle members being arranged to be connected in fluid flow communication with an aortic artery, during a cardiopulmonary bypass procedure.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
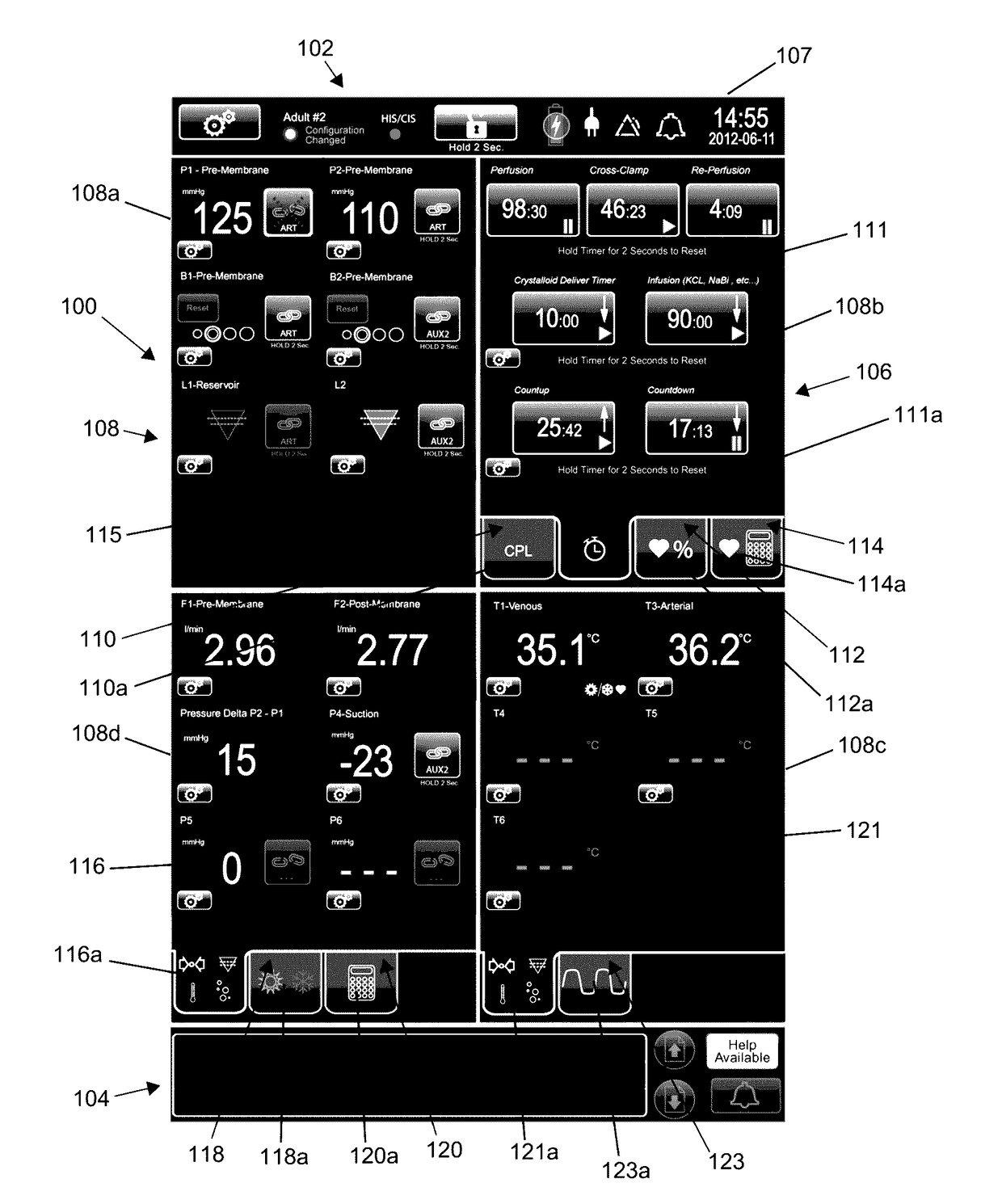
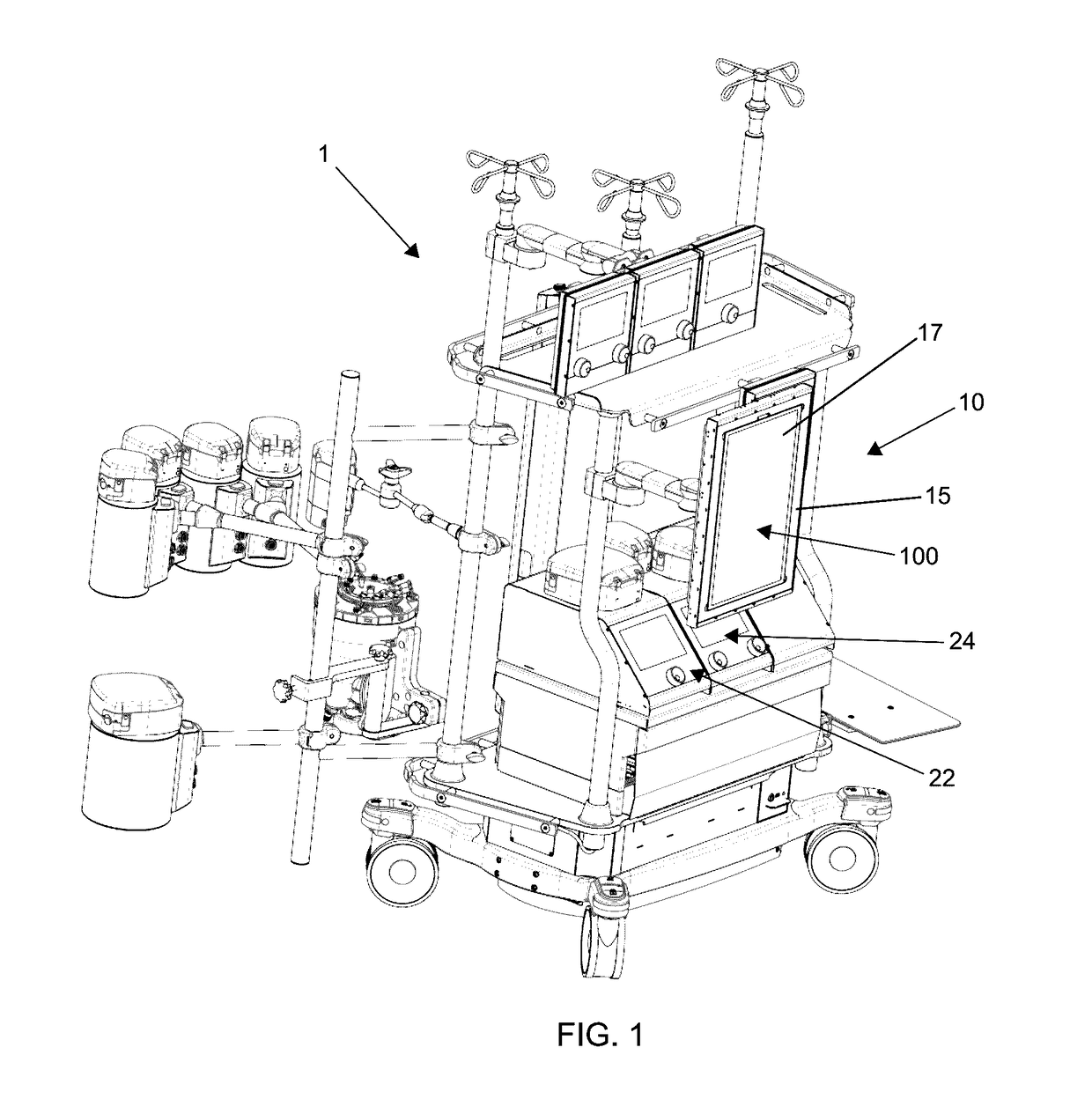
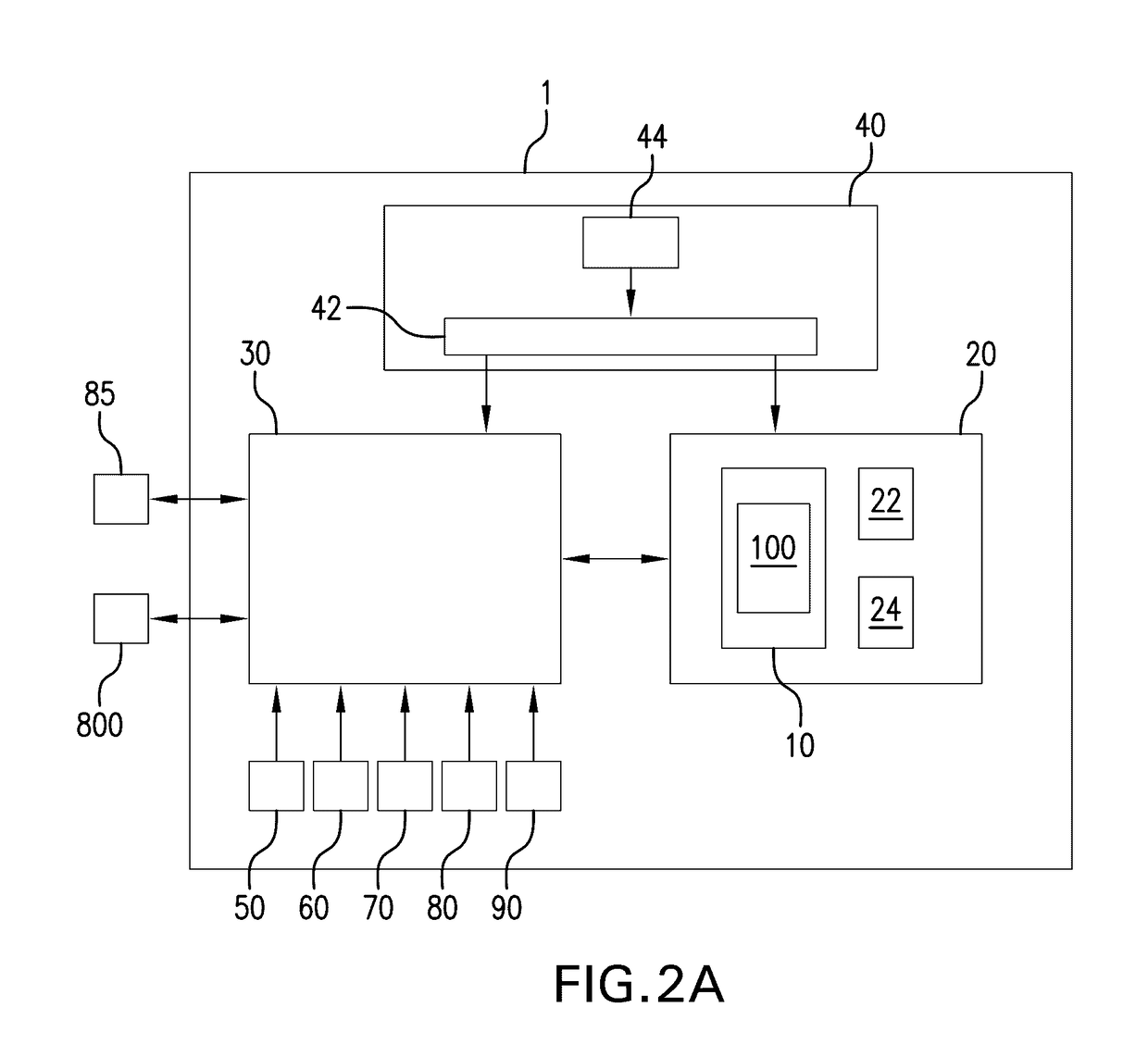
User interface system for a medical device
PendingUS20170102846A1Easy to modularizeEasy to useMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesOther blood circulation devicesCardiopulmonary bypassExtracorporeal circulation
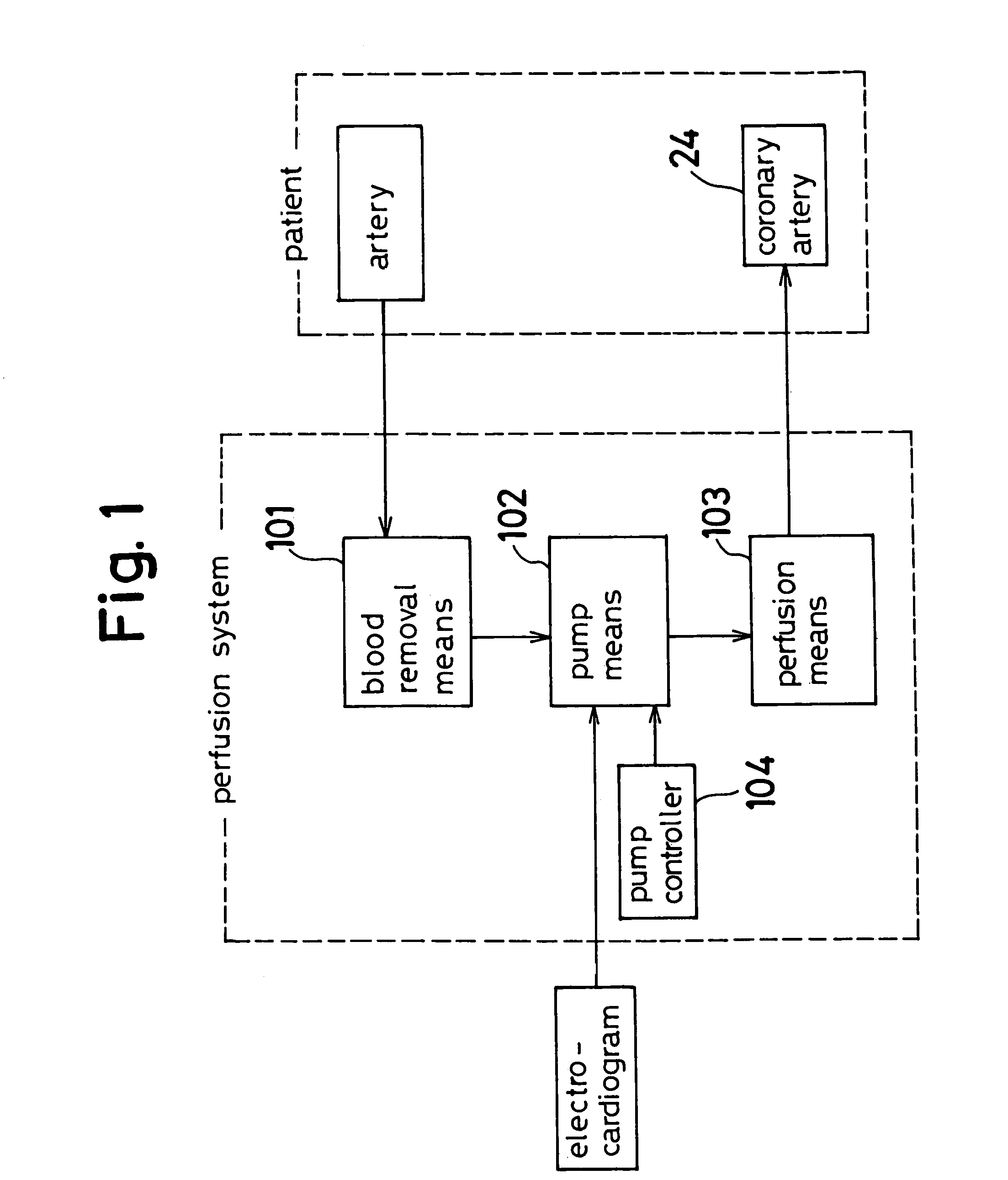
A customizable and intuitive user interface for medical systems and devices, such as cardiopulmonary bypass systems, perfusion systems, extracorporeal circulation apparatuses, and heart-lung machines, is provided, which allows for ease of access to critical patient data to facilitate blood perfusion and to monitor and regulate various physiological parameters of a patient and an extracorporeal blood flow circuit during surgical procedures, such as cardiopulmonary bypass and extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO).
Owner:MAQUET CARDIOPULMONARY GMBH
Prevention and reduction of blood loss
InactiveUS20070249807A1Peptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticExtracorporeal circulationCardiopulmonary bypass time
Methods are described for preventing or reducing ischemia and / or systemic inflammatory response in a patient such as perioperative blood loss and / or systemic inflammatory response in a patient subjected to cardiothoracic surgery, e.g. coronary artery bypass grafting and other surgical procedures, especially when such procedures involve extra-corporeal circulation, such as cardiopulmonary bypass.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Perfusion system for off-pump coronary artery bypass
InactiveUS7001354B2Advanced technologyRestrict bleeding amountOther blood circulation devicesControl devicesExtracorporeal circulationOff-pump coronary artery bypass
Owner:NEMOTO KYORINDO KK +1
Apparatus and method for monitoring a vascular access of a patient subjected to an extracorporeal blood treatment
InactiveUS7172570B2Possible to selectSemi-permeable membranesSolvent extractionExtracorporeal circulationHaemodialysis machine
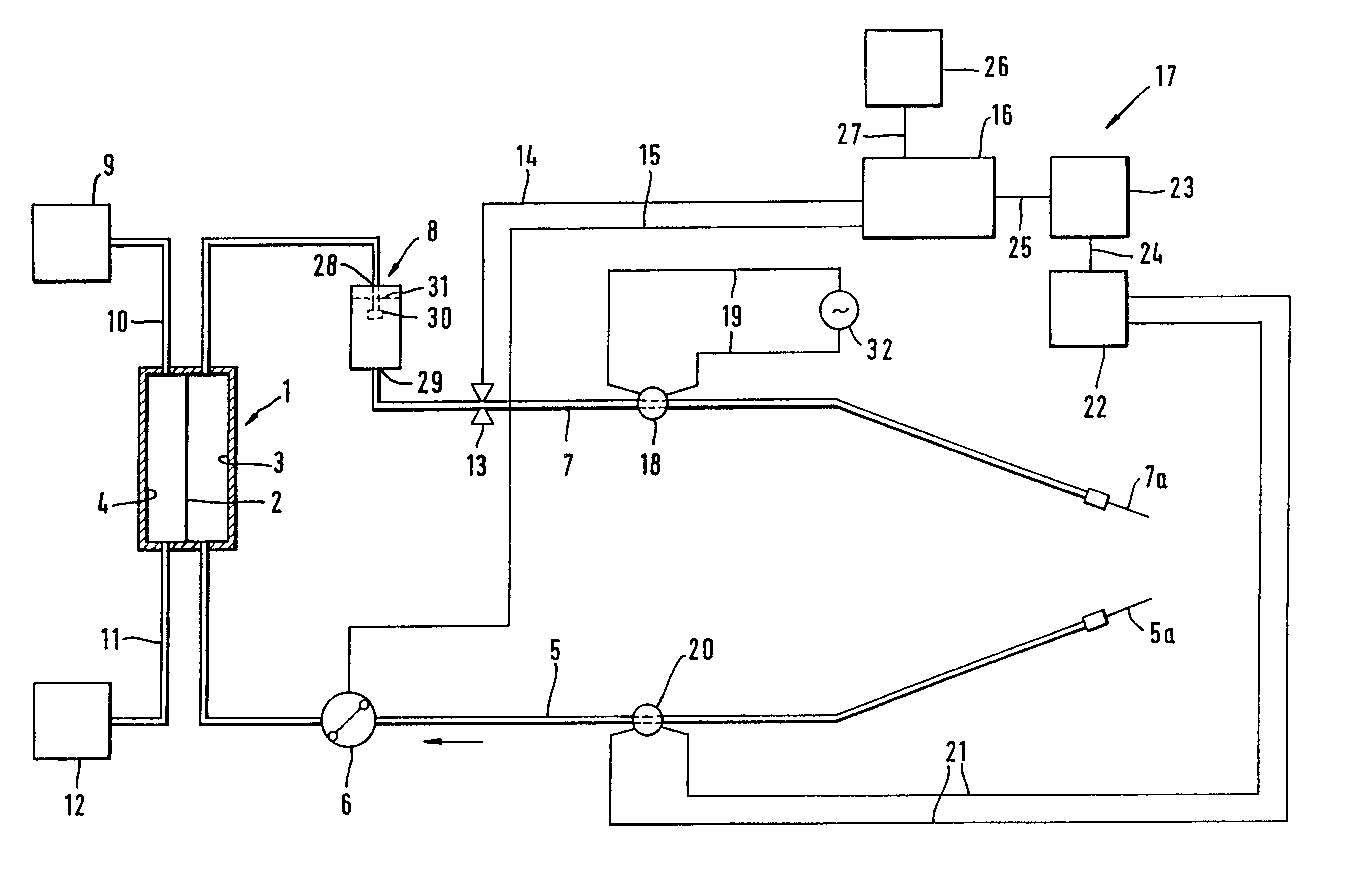
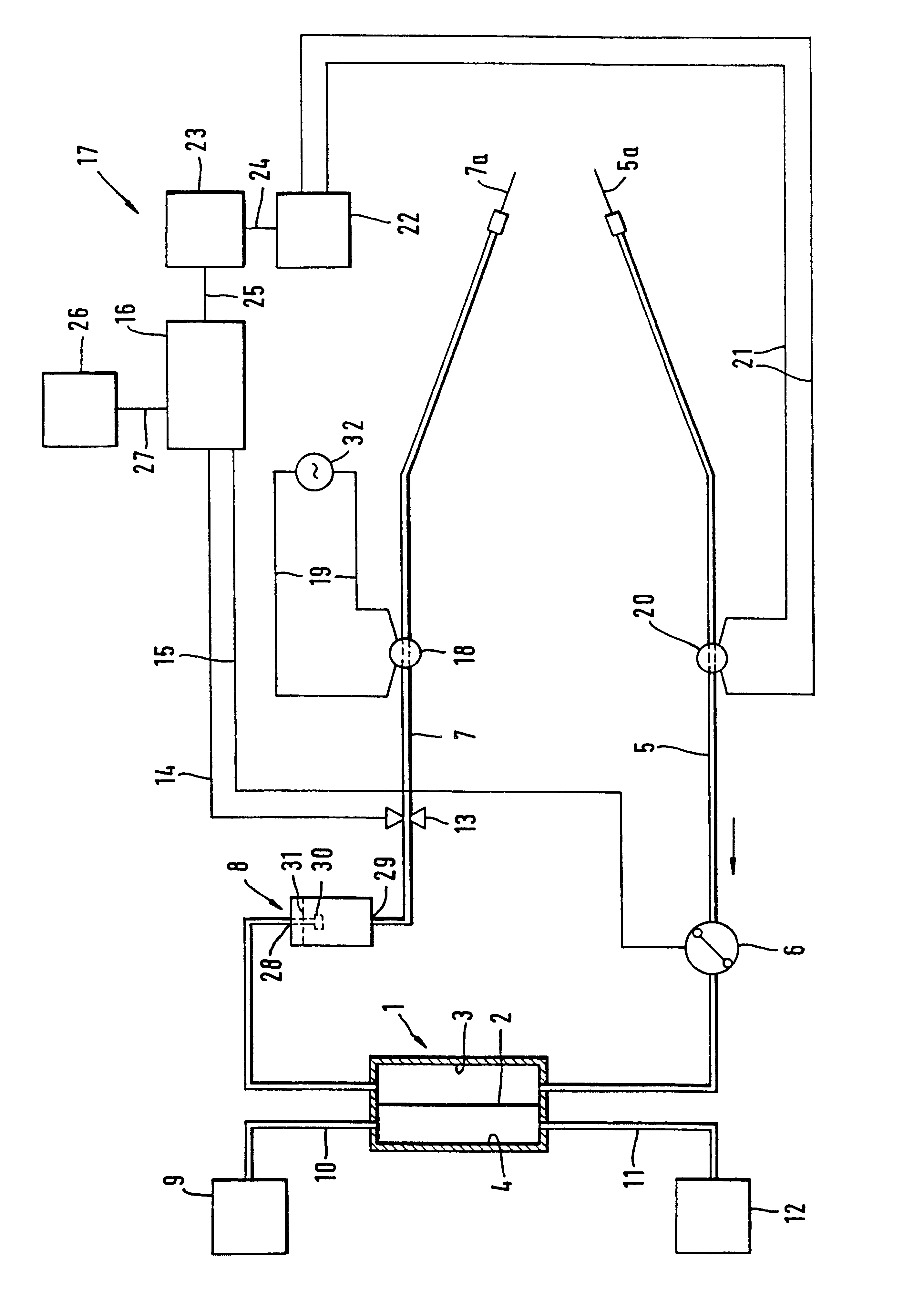
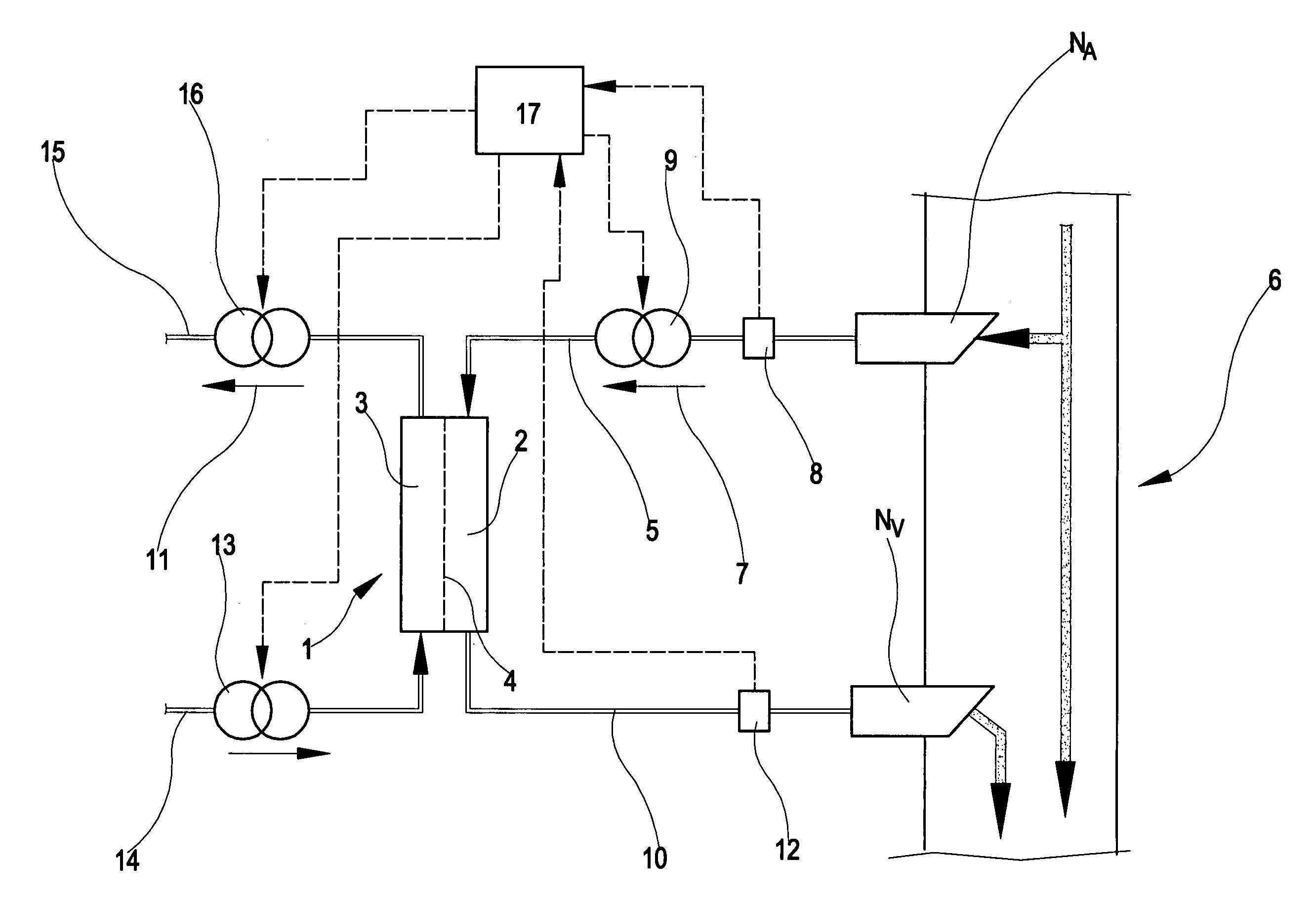
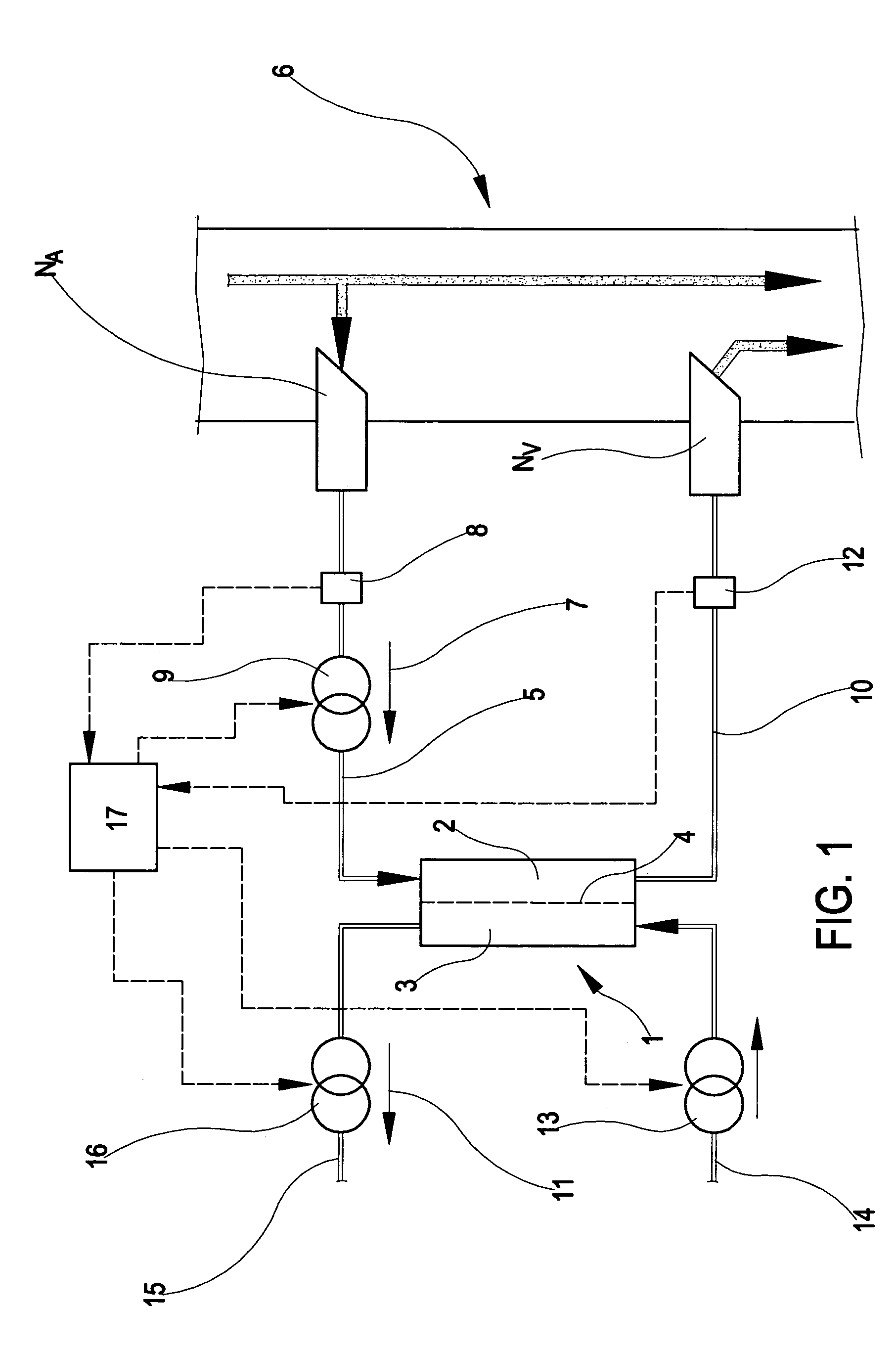
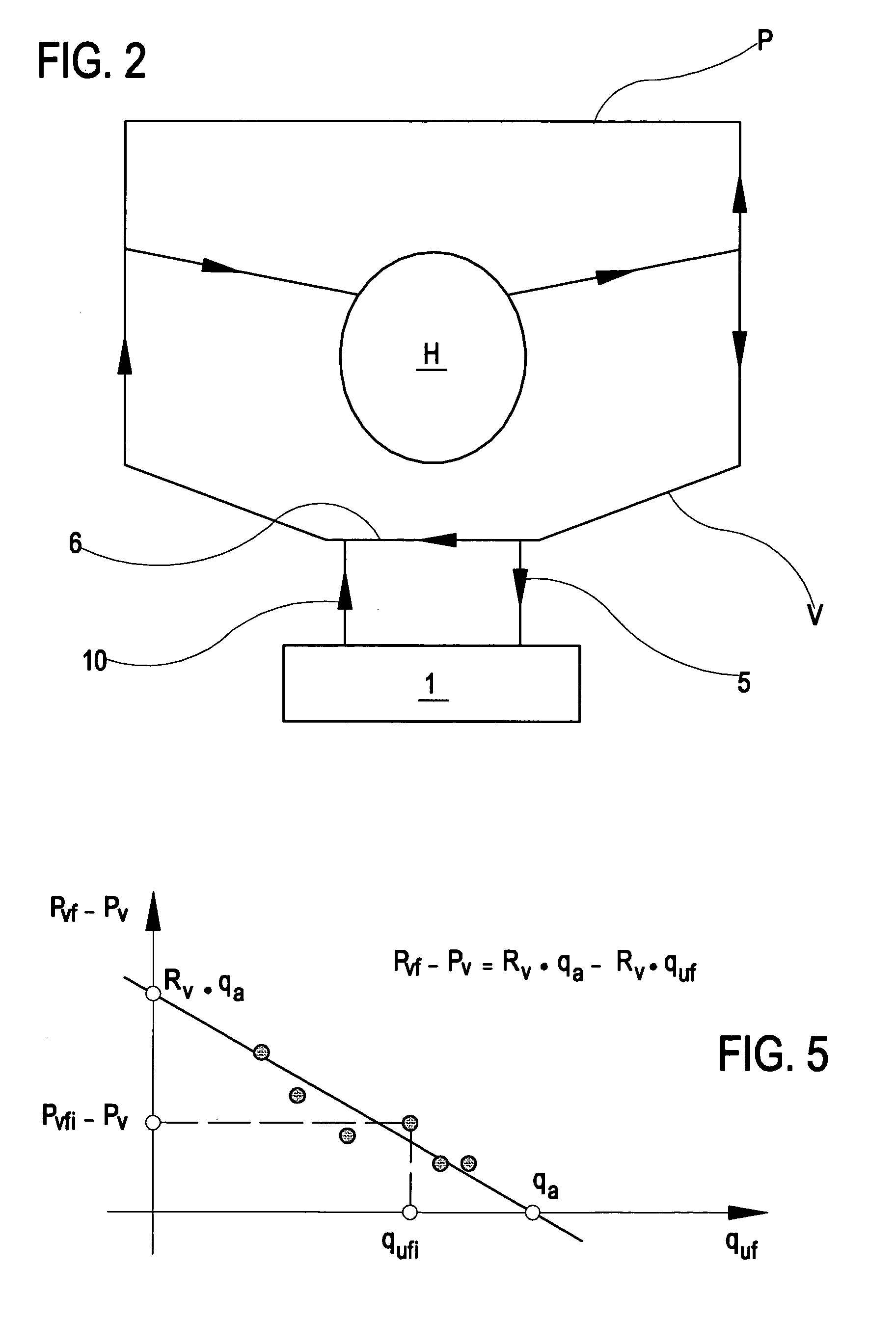
In the apparatus and method for monitoring a vascular access (6) of an extracorporeal circuit (5; 10) of a patient, a control and calculation unit (17) varies a flow rate of a blood pump (9) predisposed to cause blood to circulate in the extracorporeal circuit. The control and calculation unit receives the pressure values in the blood withdrawal line (5) and the blood return line (10) from two pressure sensors (8, 12); the pressure values are a series of different values of the blood flow rate. The control and calculation unit processes the data gathered by means of a mathematical model which describes the variation of pressure in the vascular access as a function of the flow rate, in order to determine the blood flow rate in the vascular access. The invention detects the presence and location of a stenosis at the vascular access of a patient subjected to a hemodialysis treatment.
Owner:GAMBRO LUNDIA AB
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com