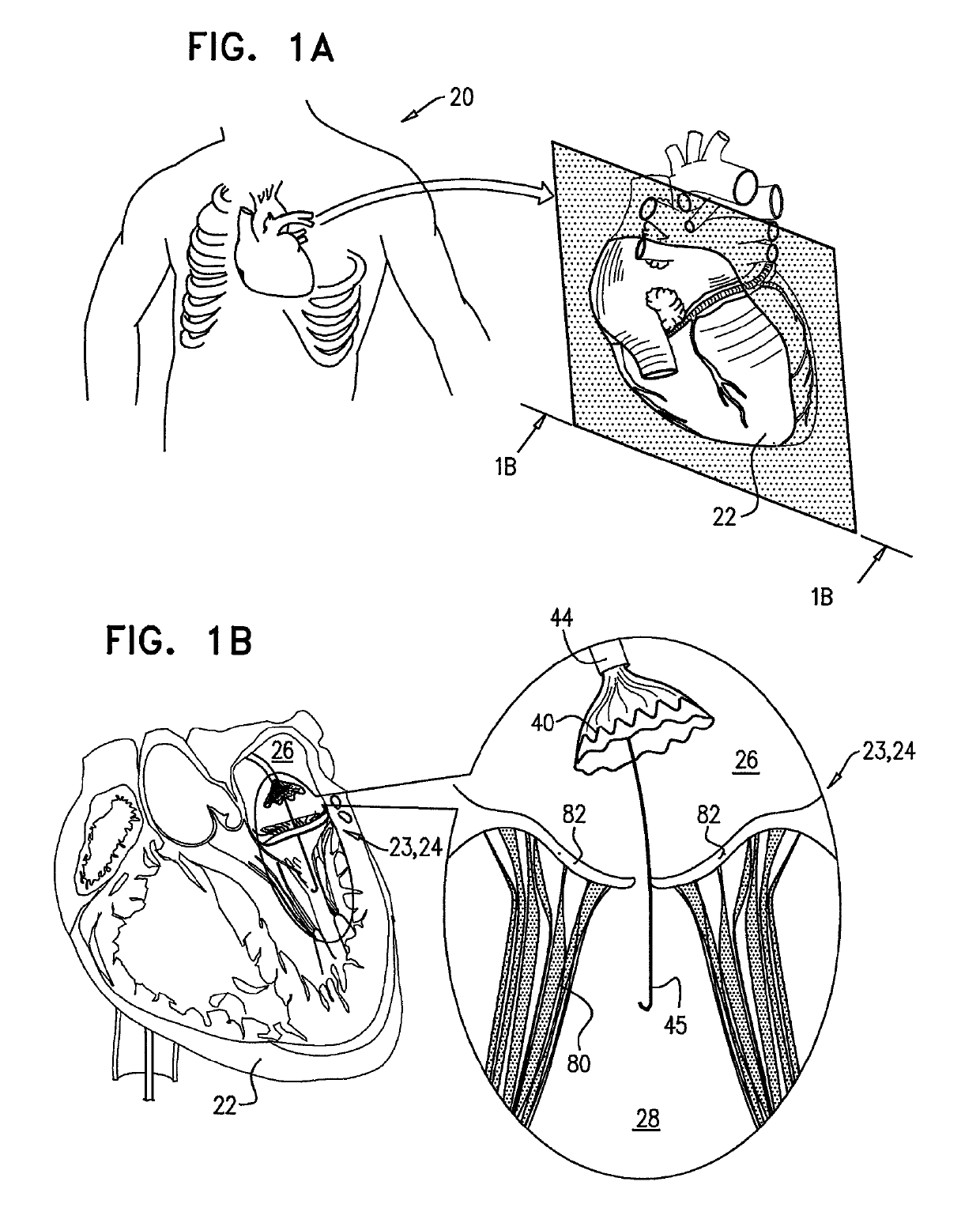
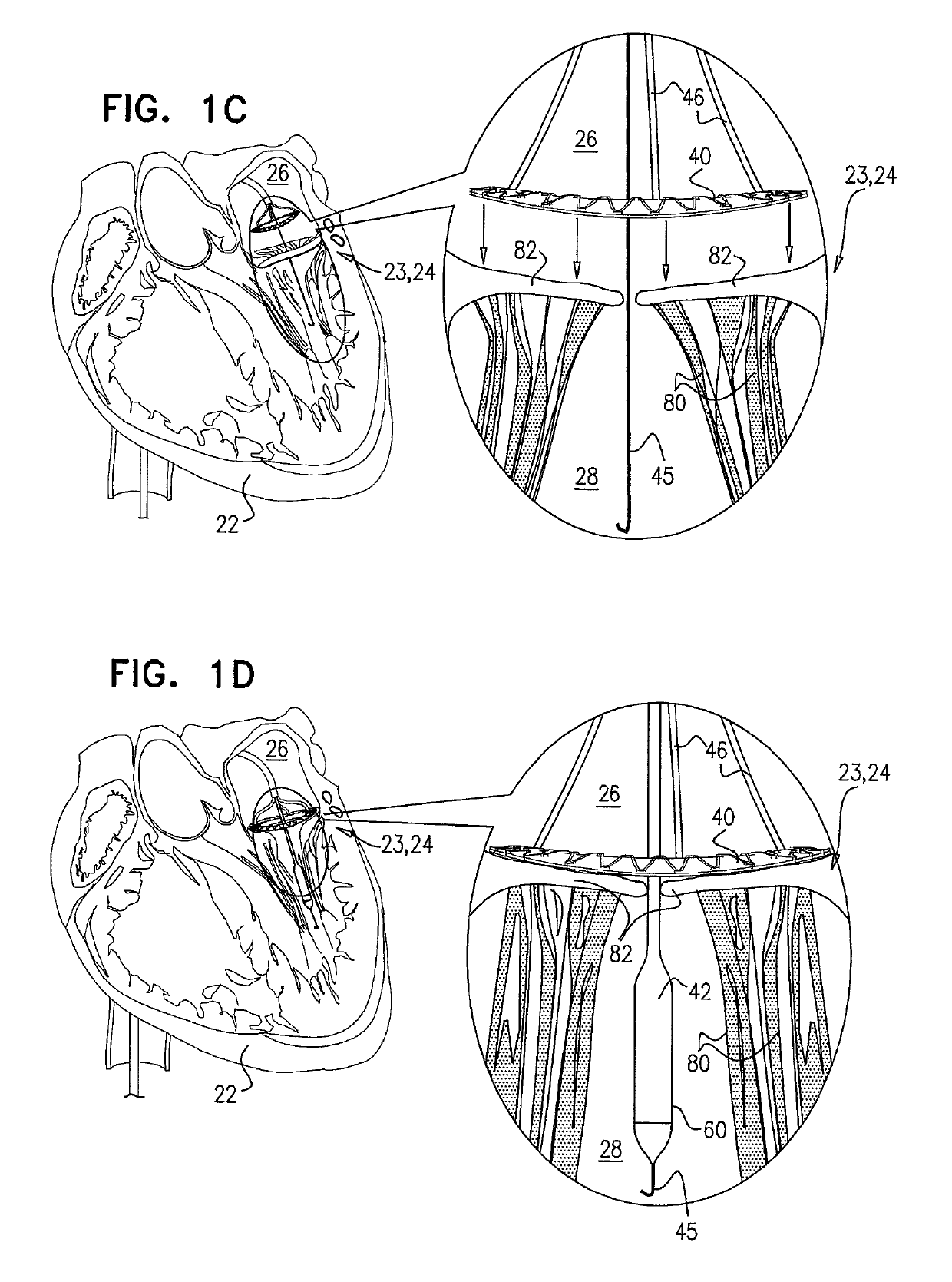
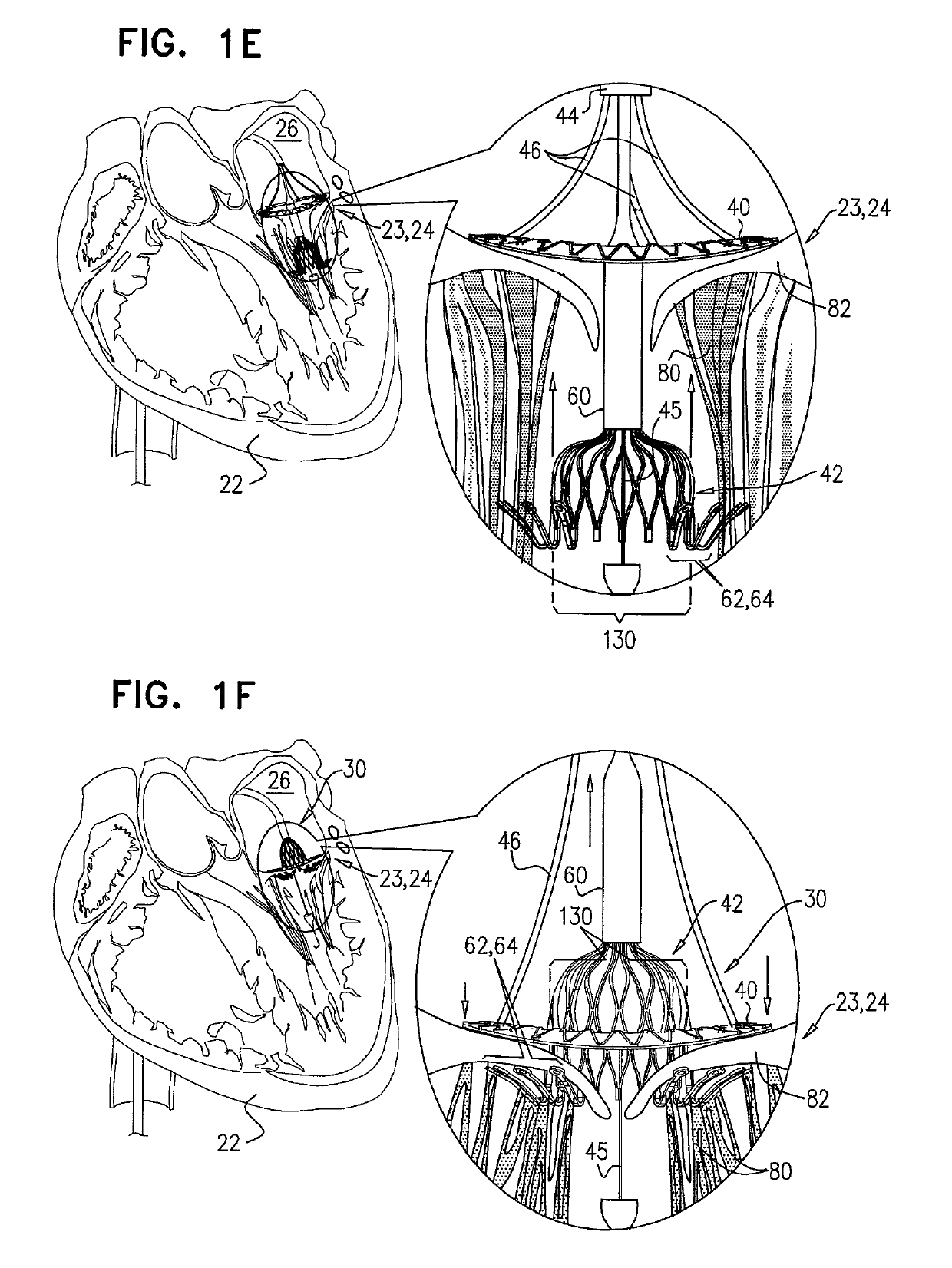
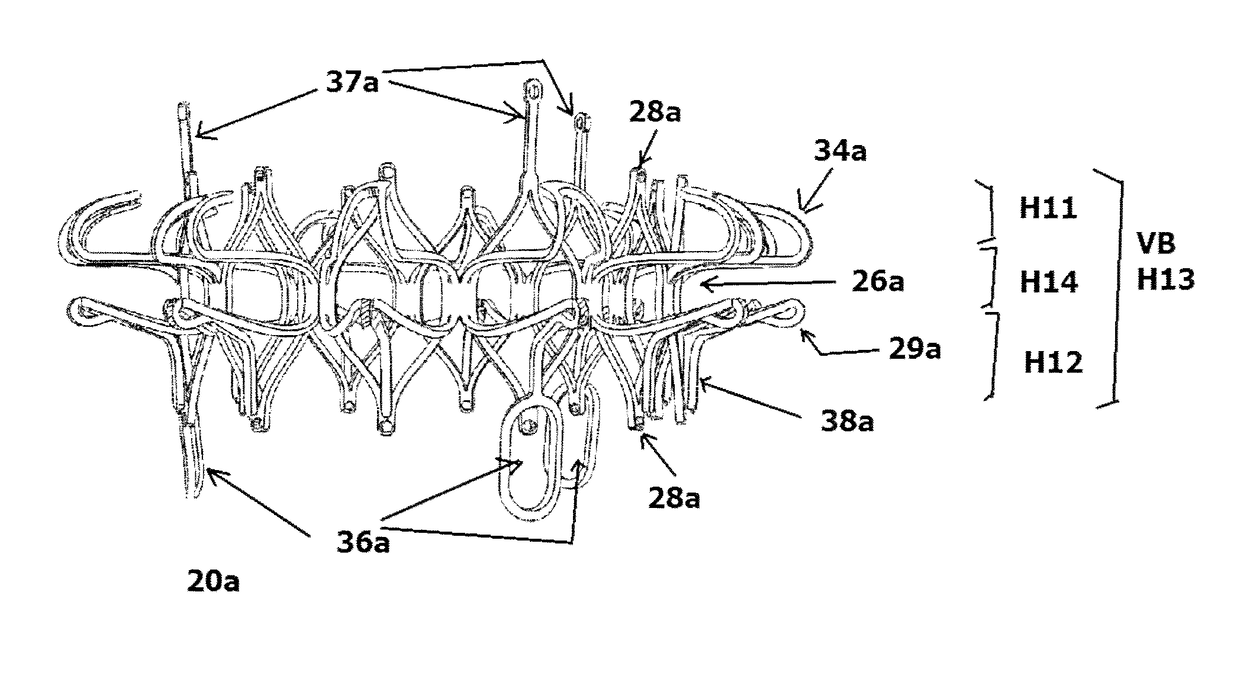
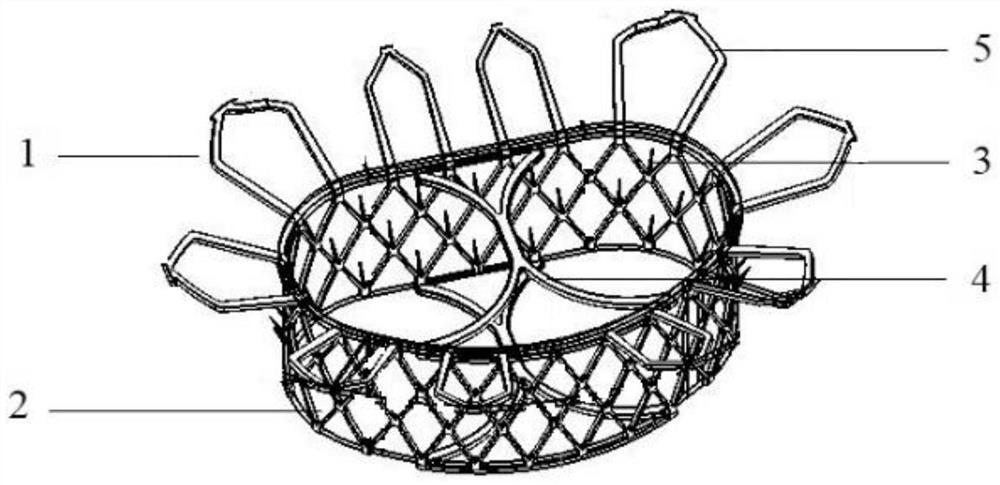
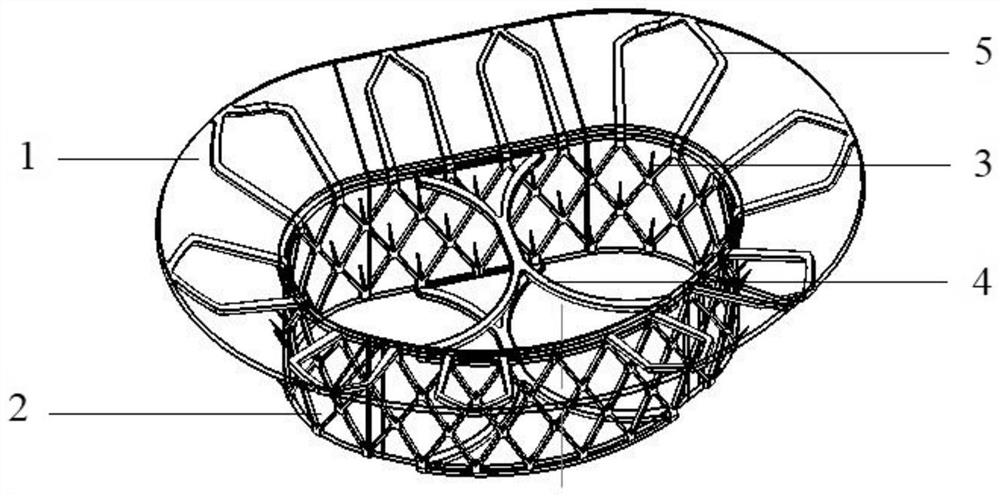
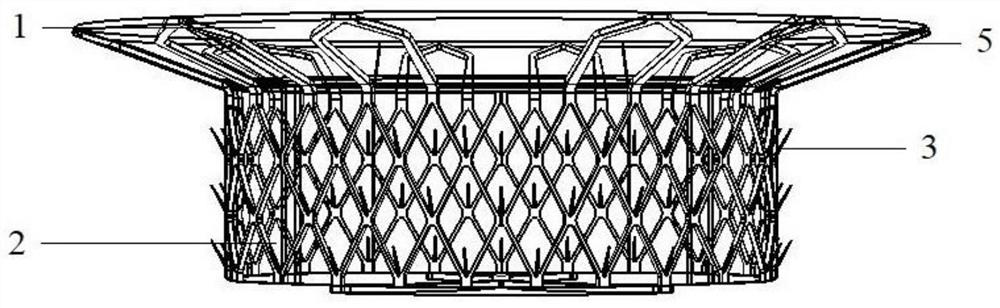
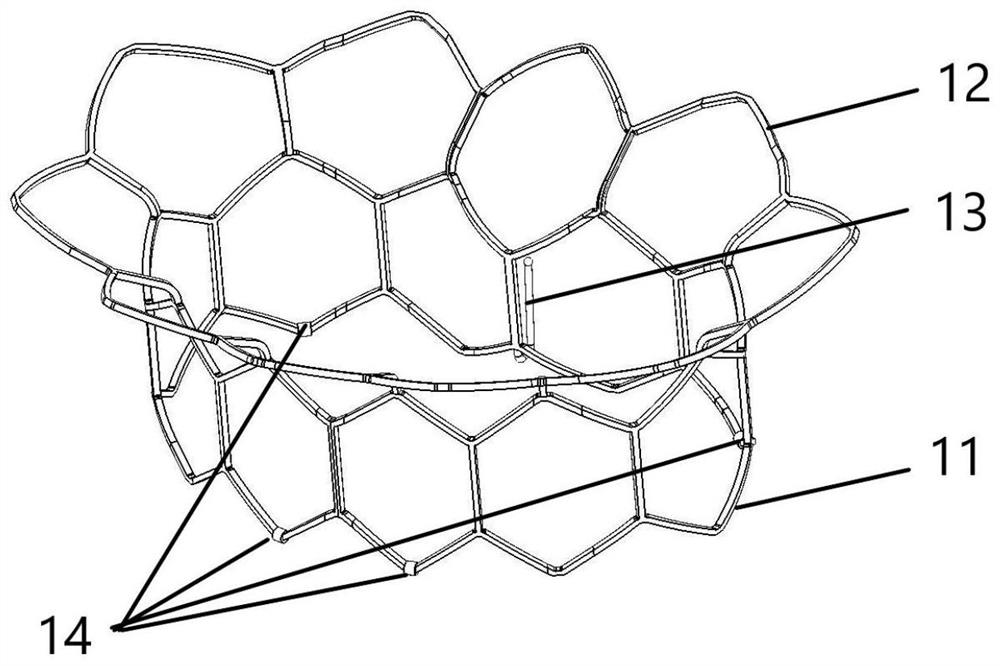
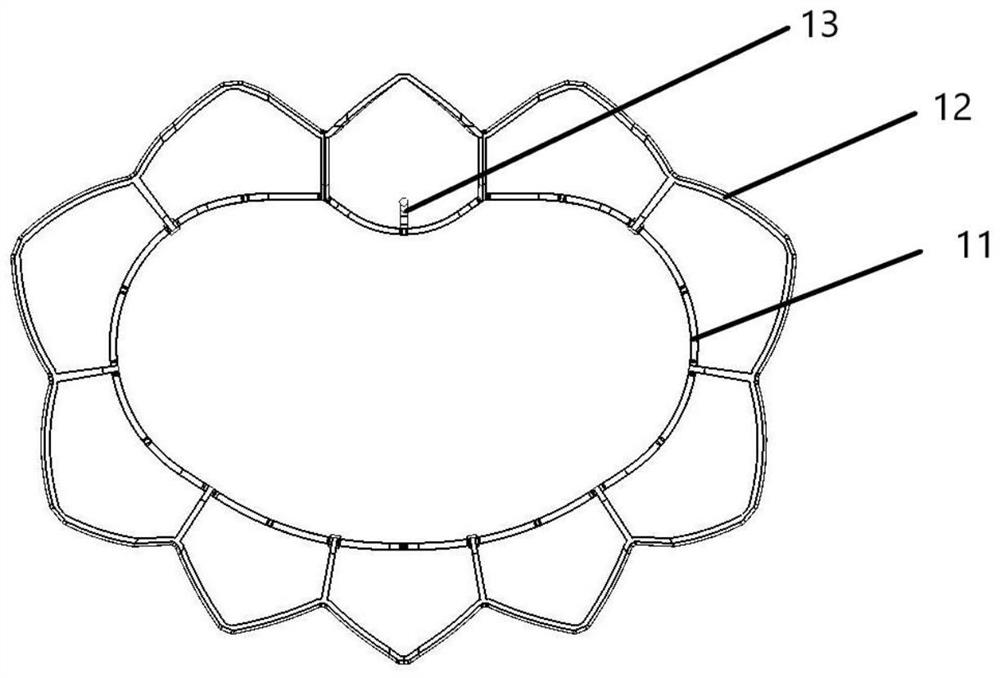
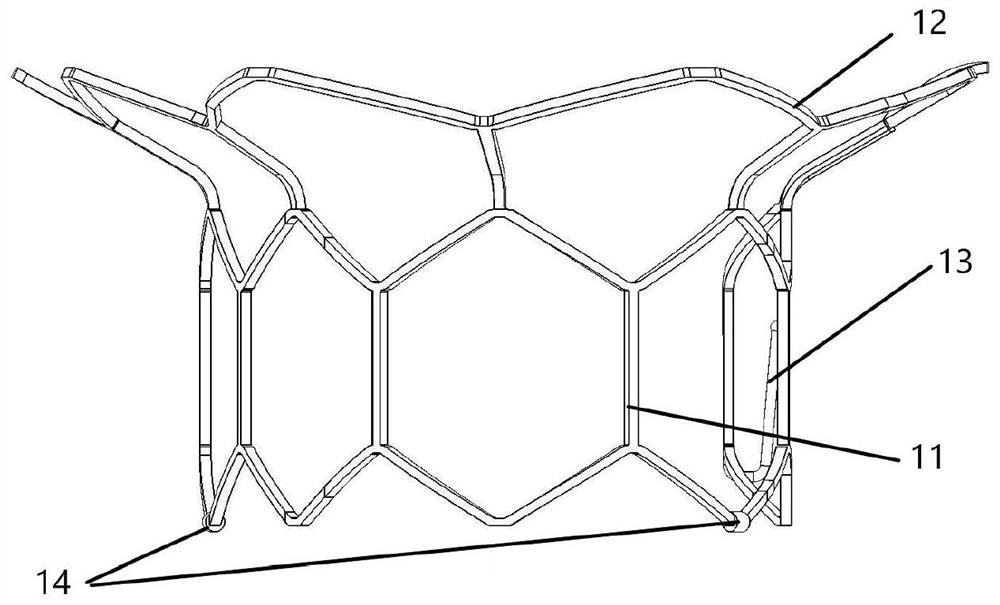
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
54 results about "Bioprosthetic mitral valve replacement" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
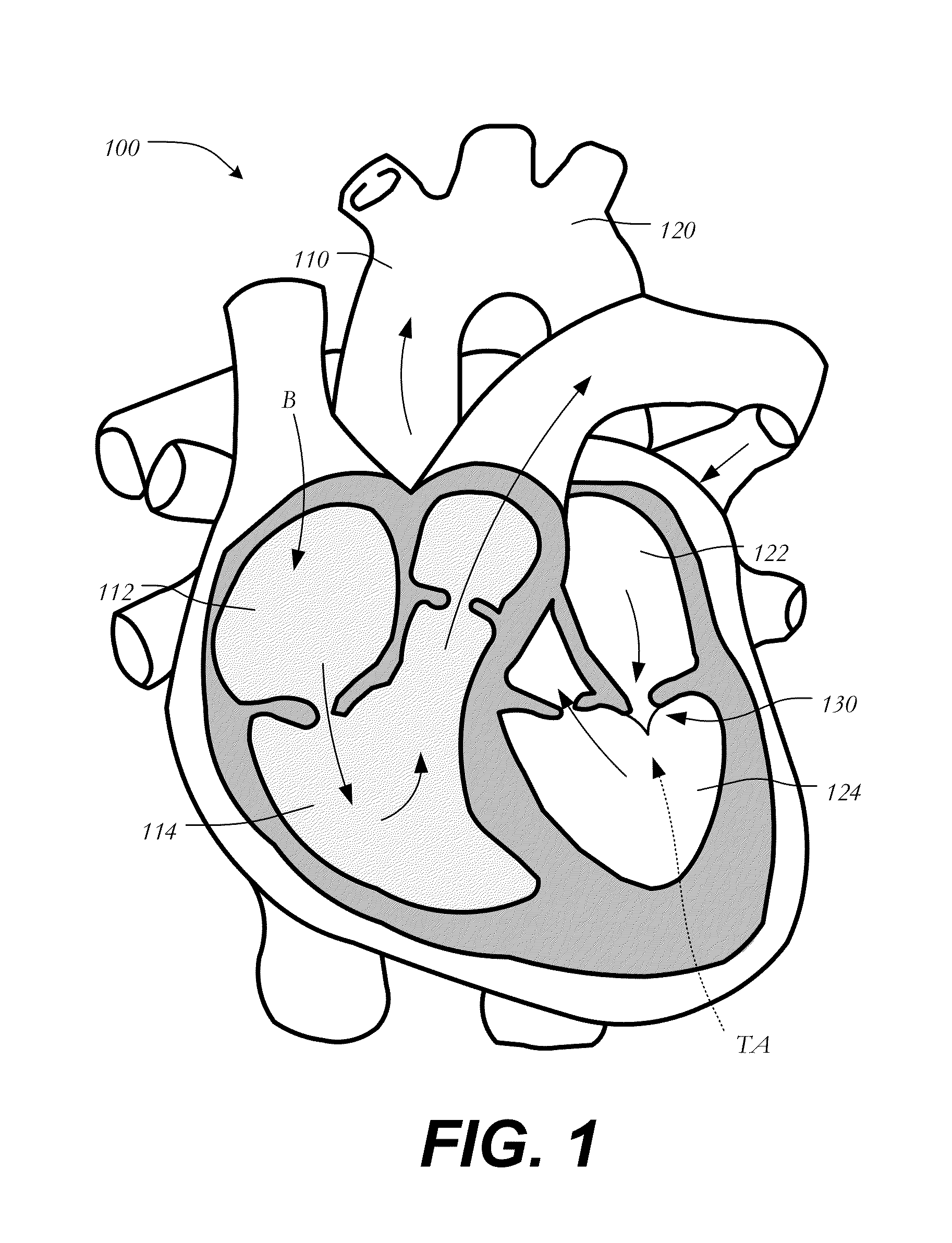
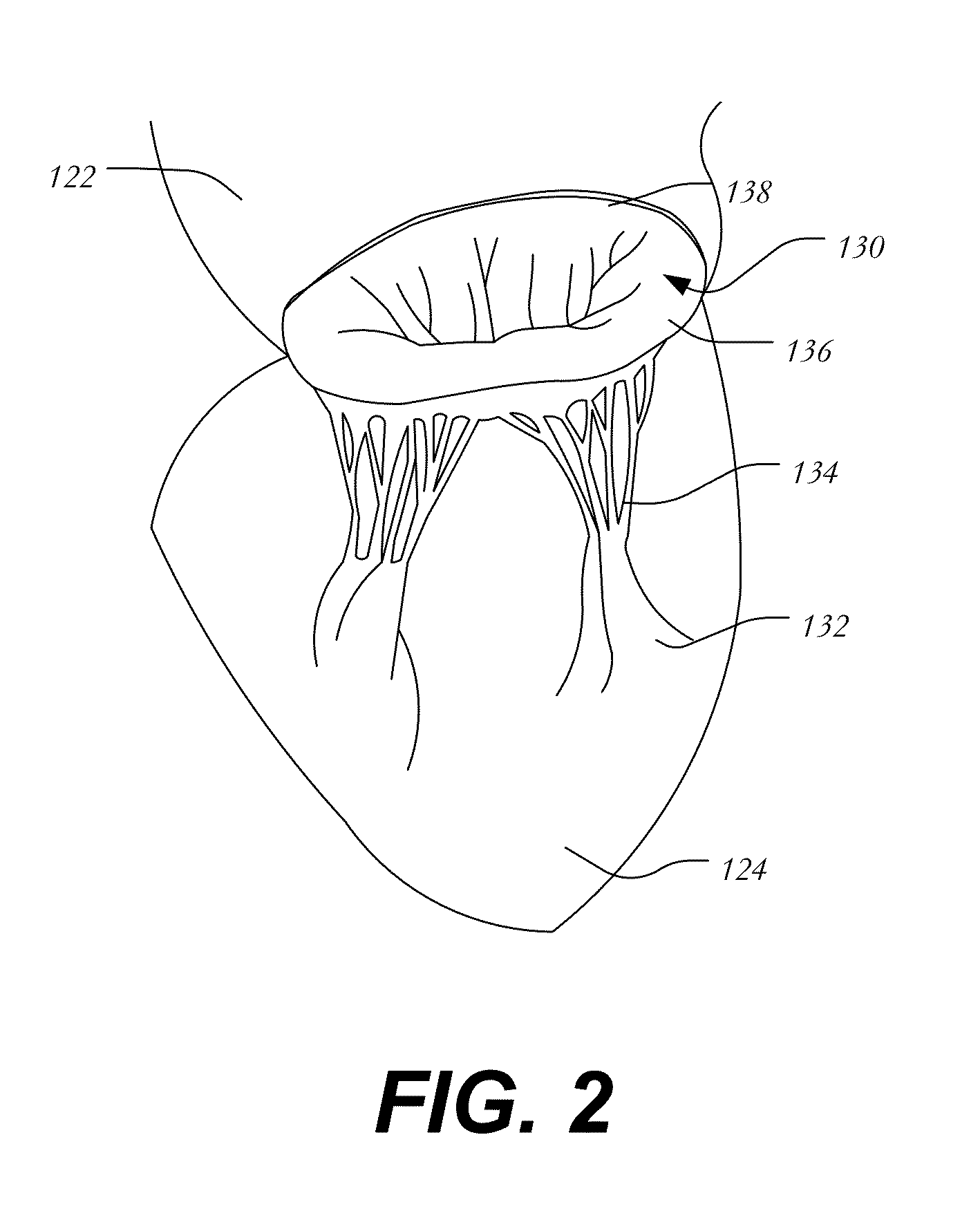
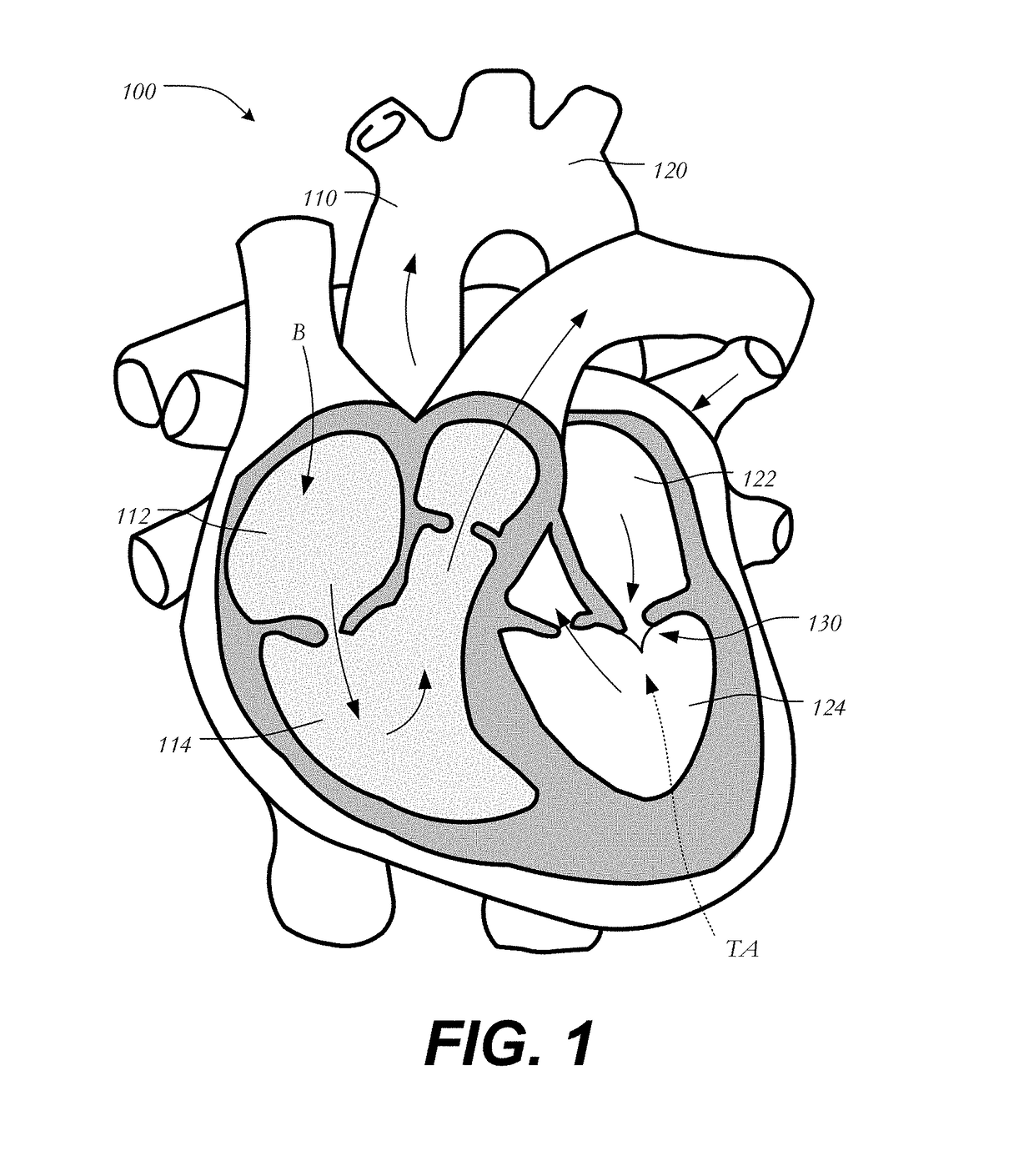
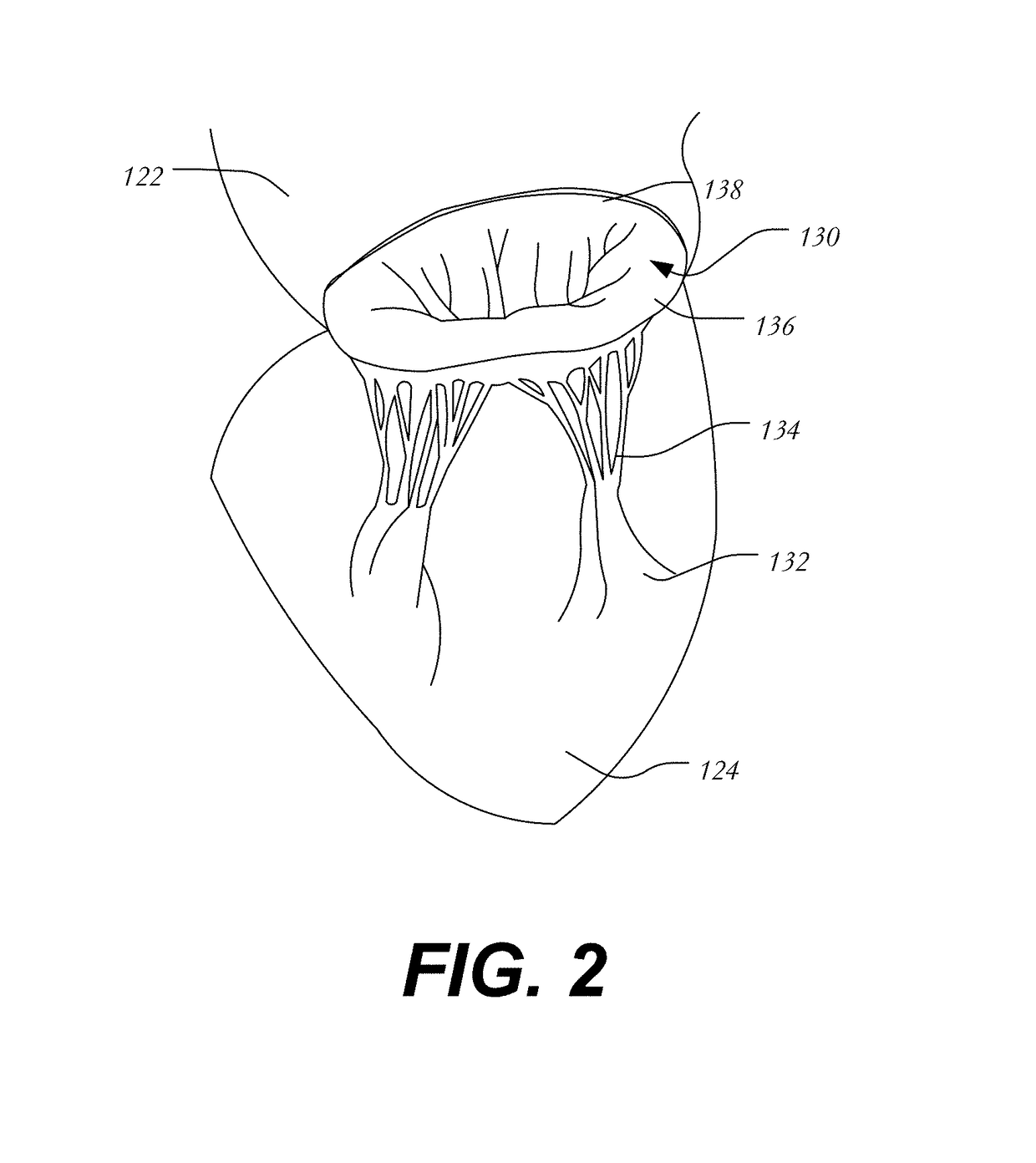
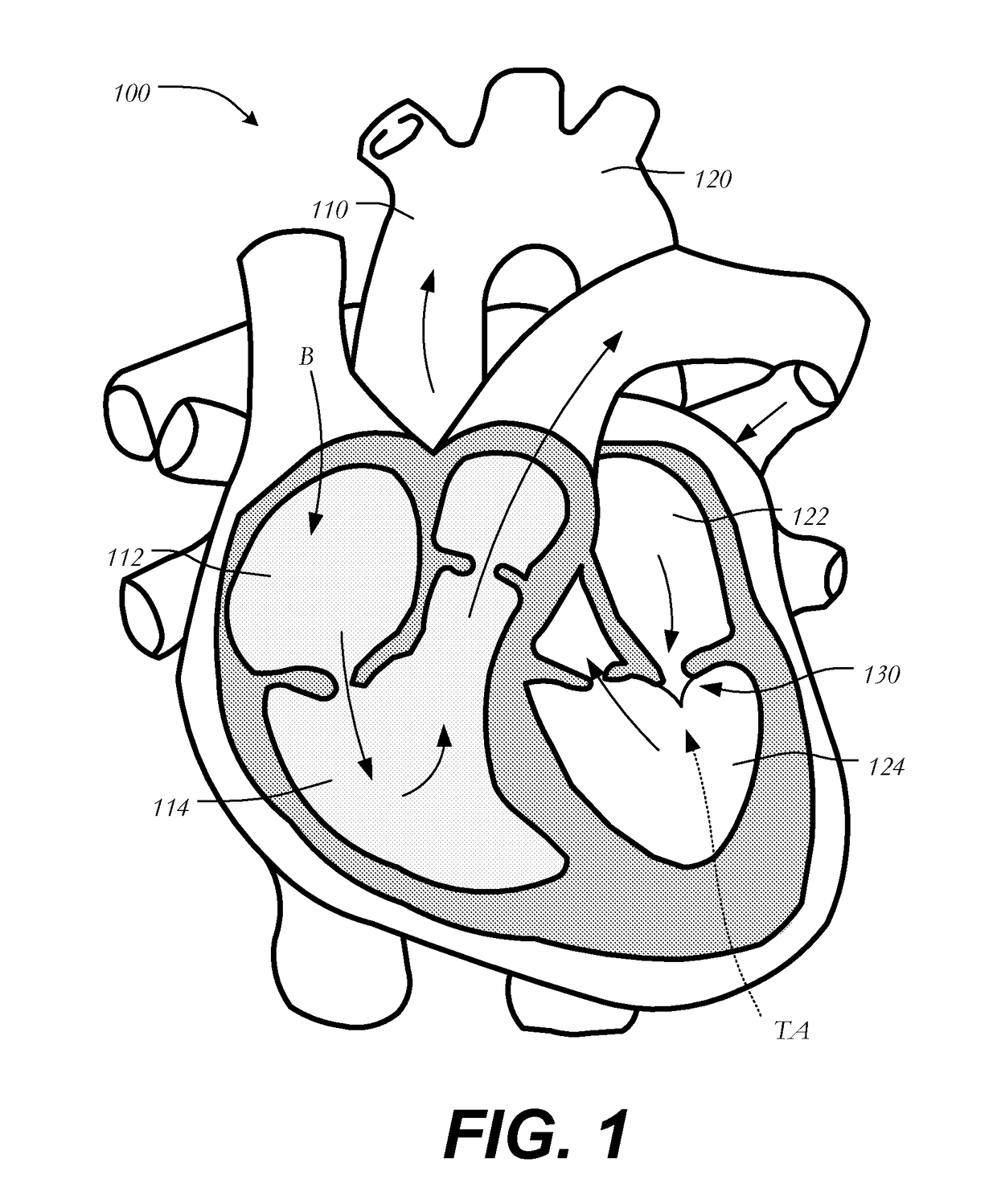
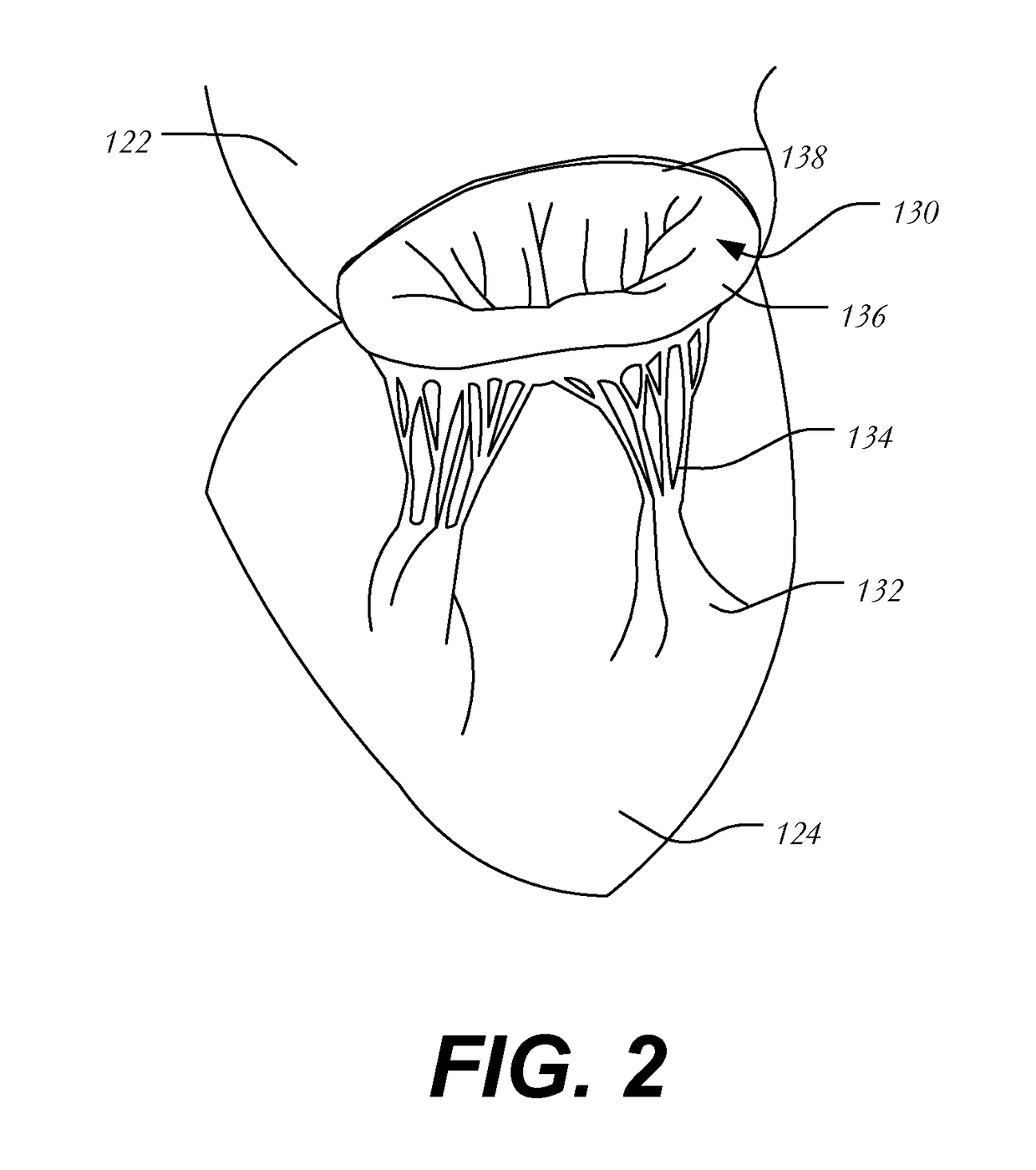
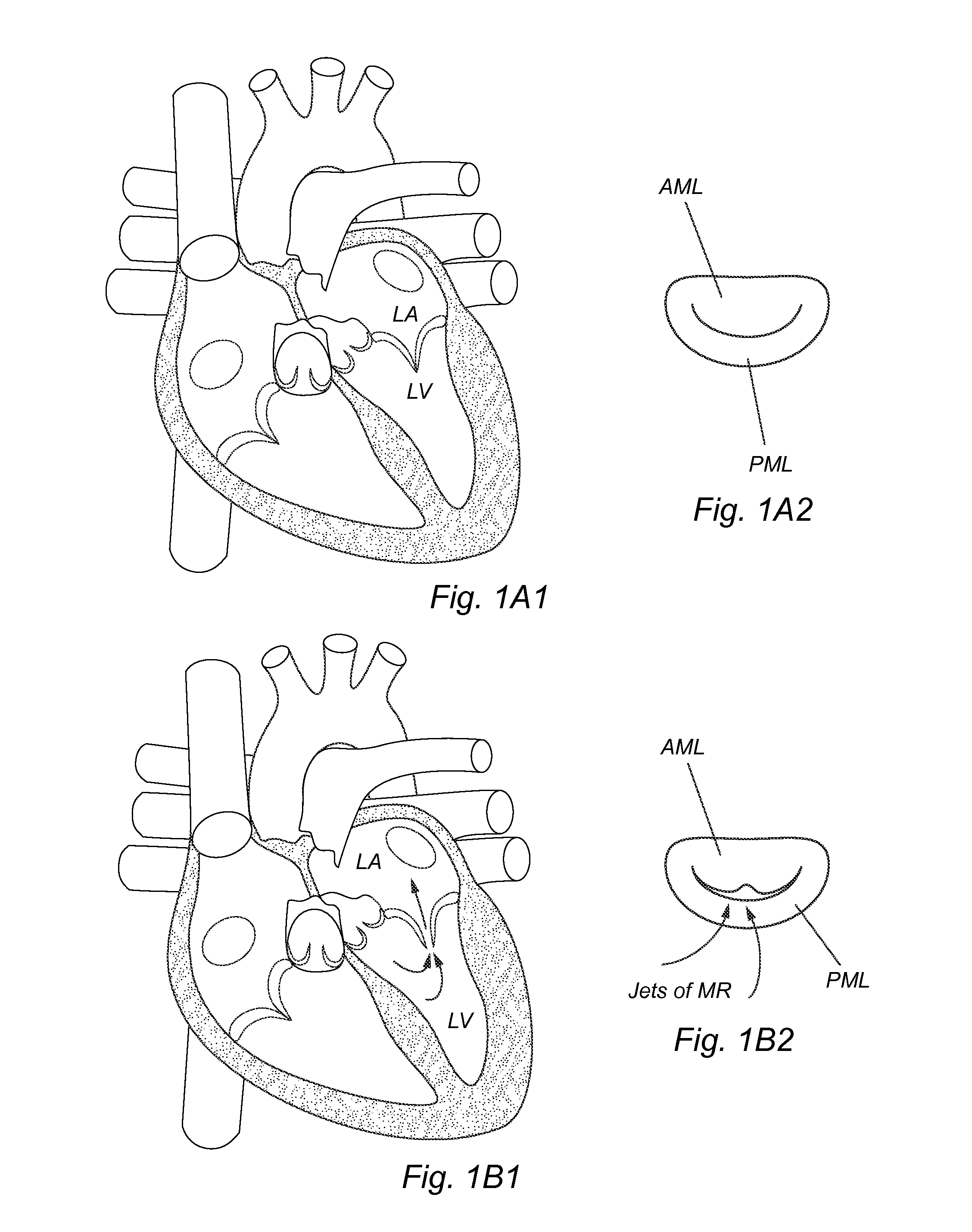
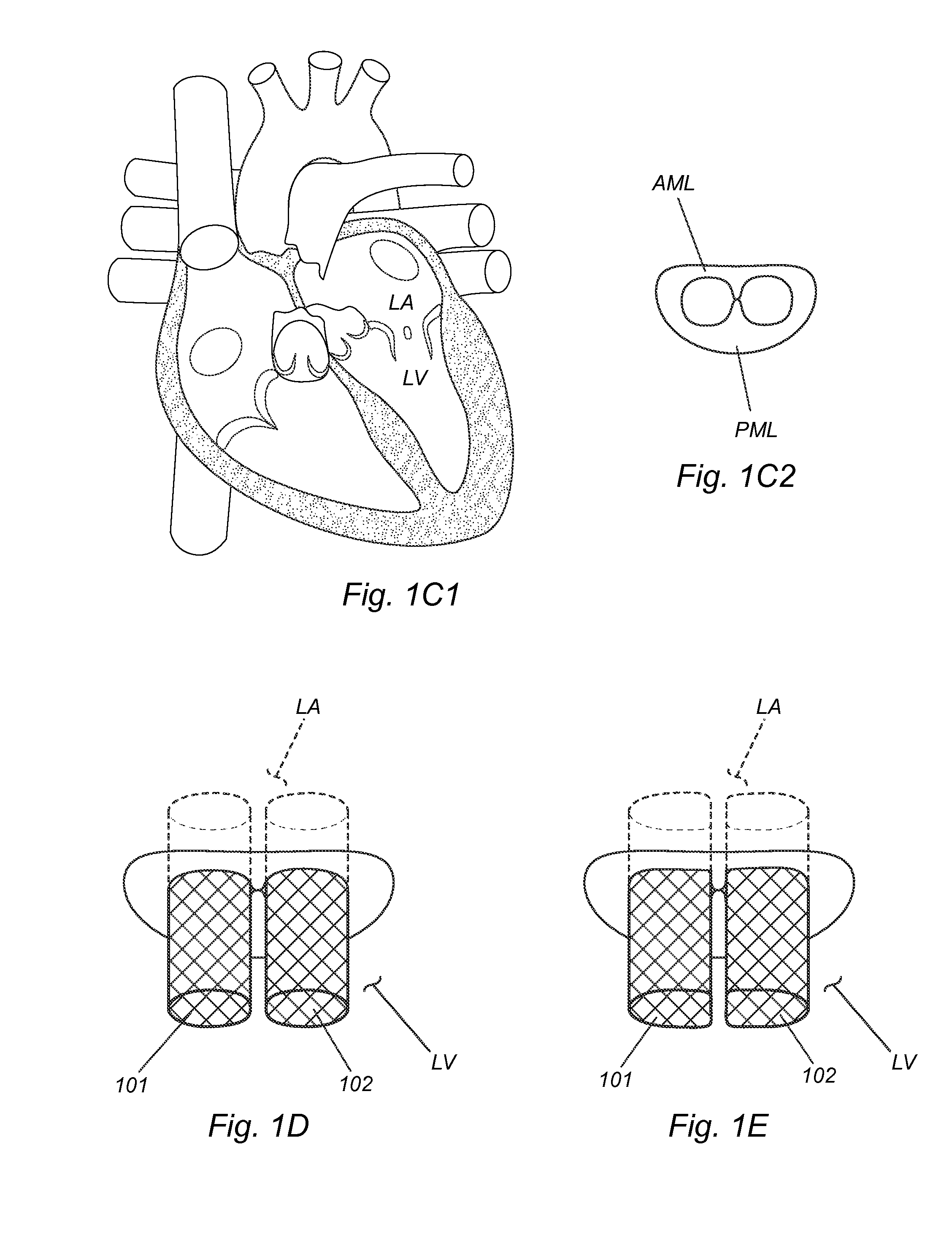
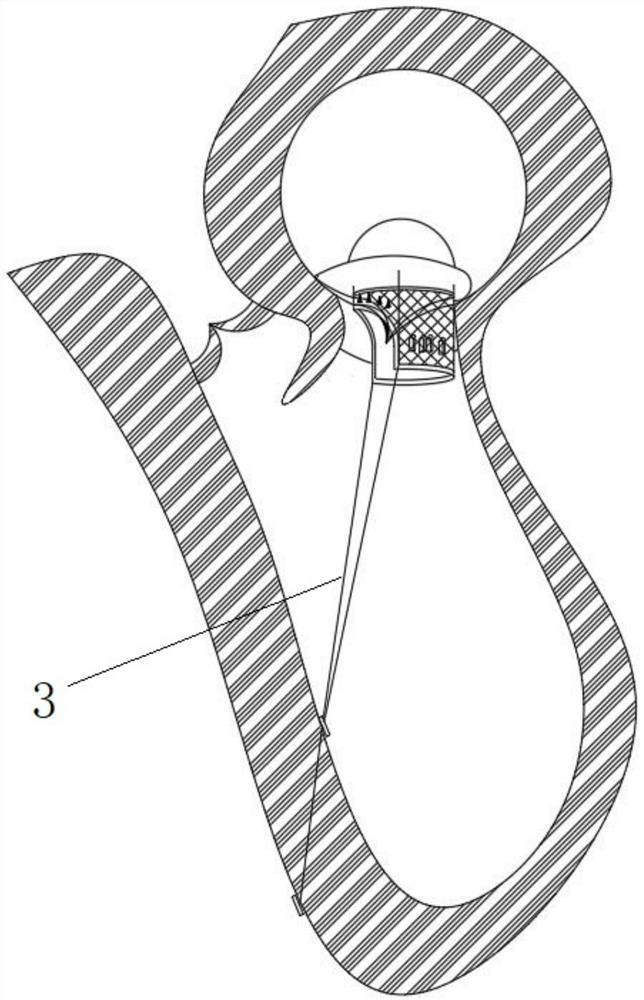
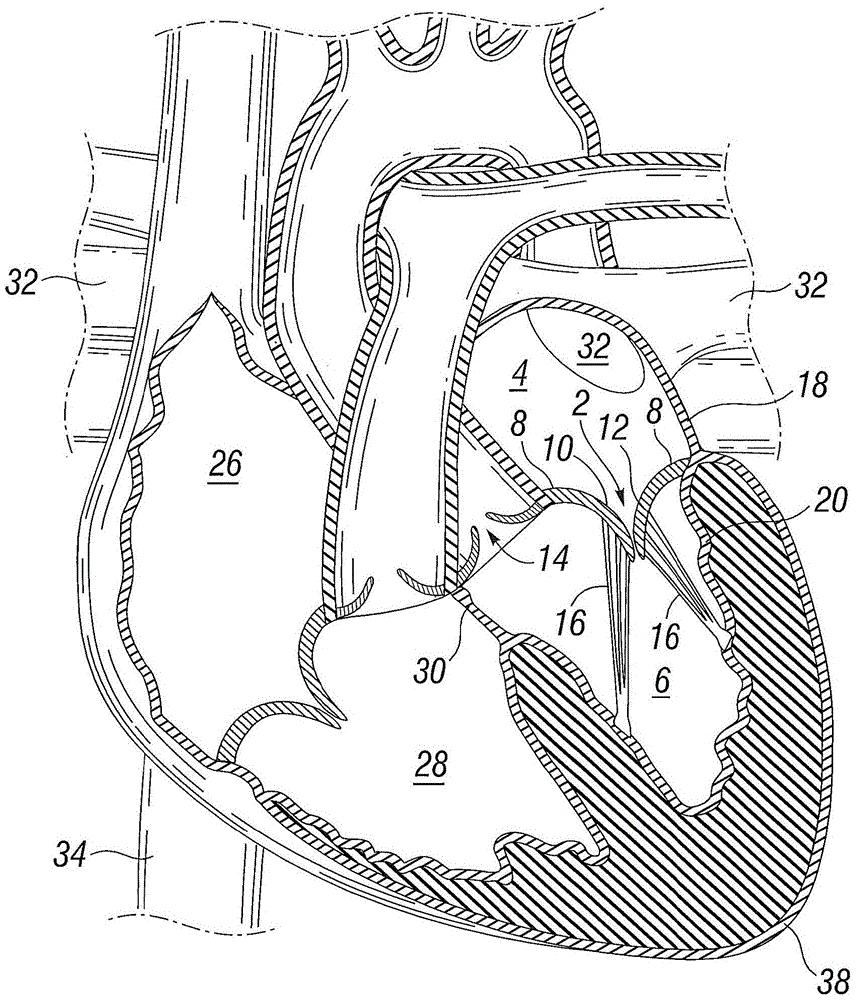
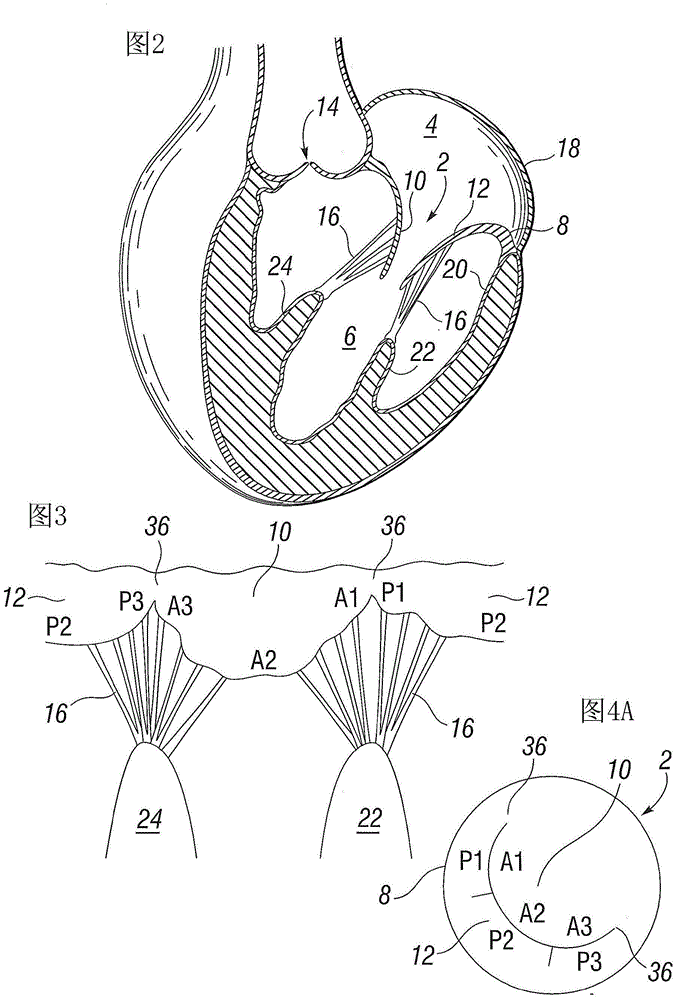
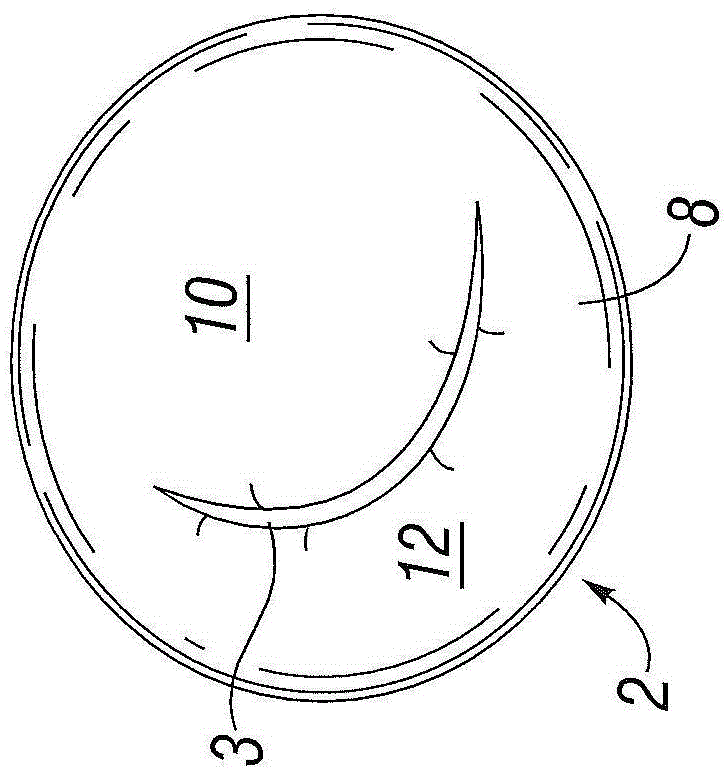
Mitral valve replacement is a cardiac surgical procedure in which a patient’s diseased mitral valve is replaced by either a mechanical or bioprosthetic valve.
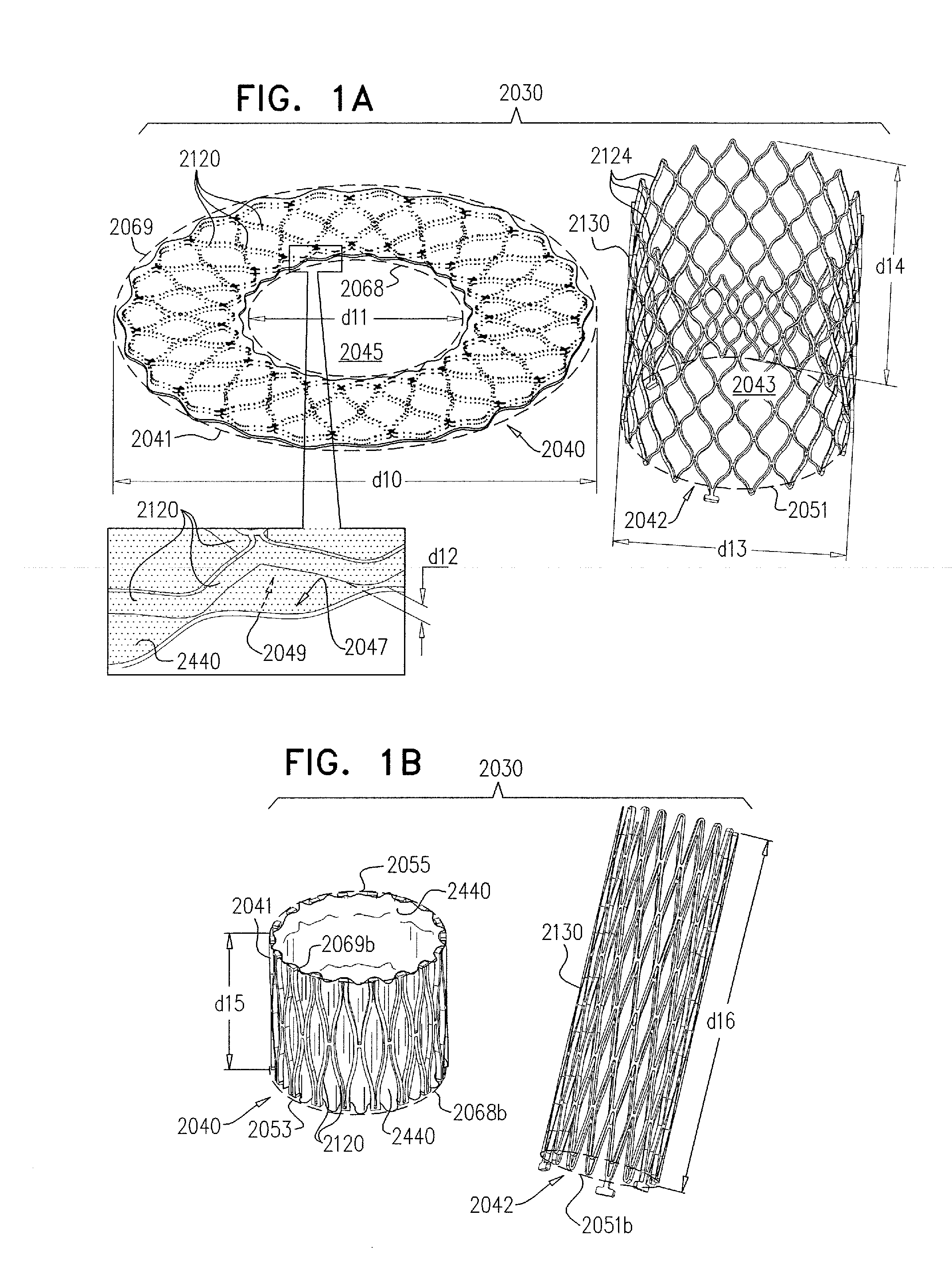
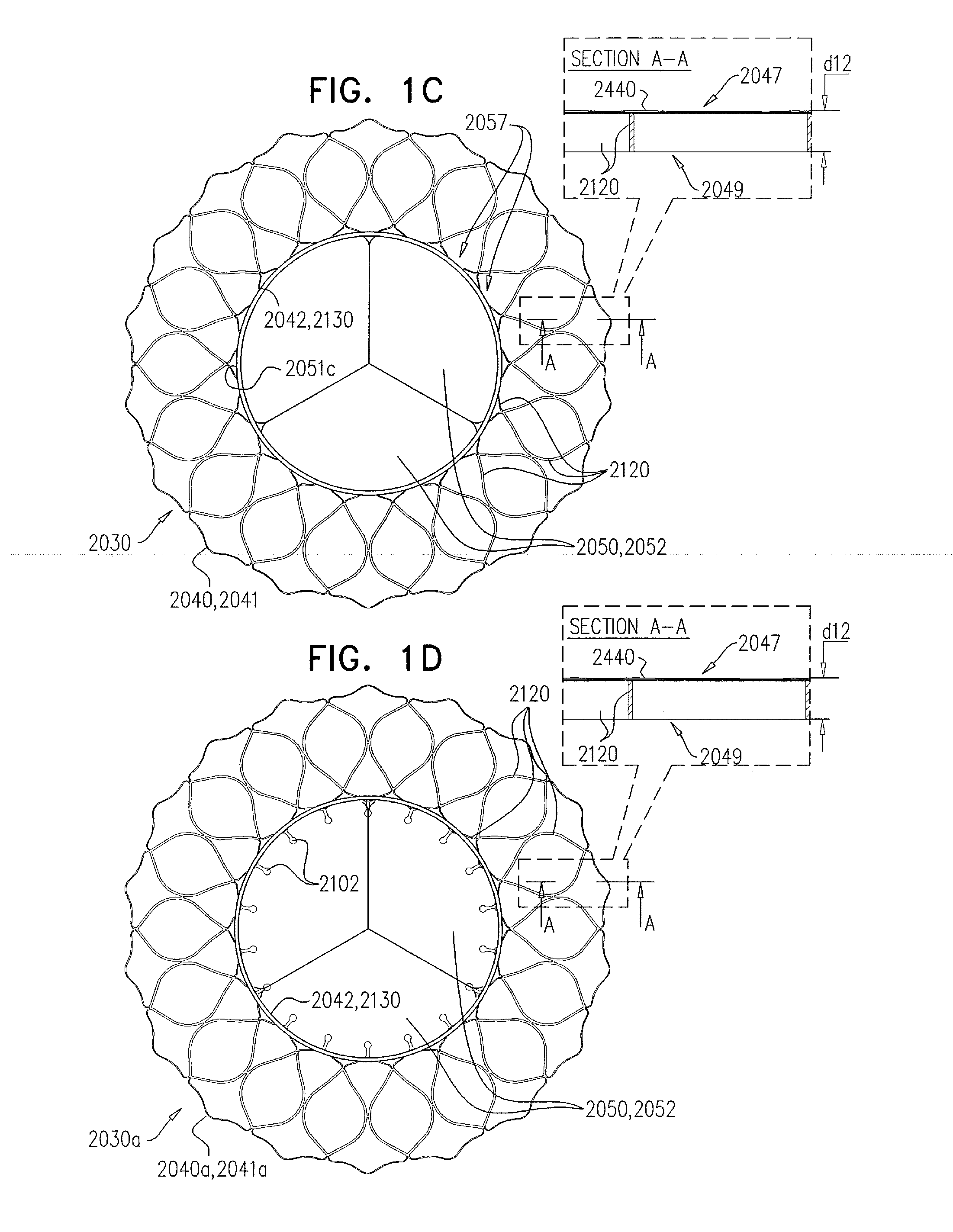
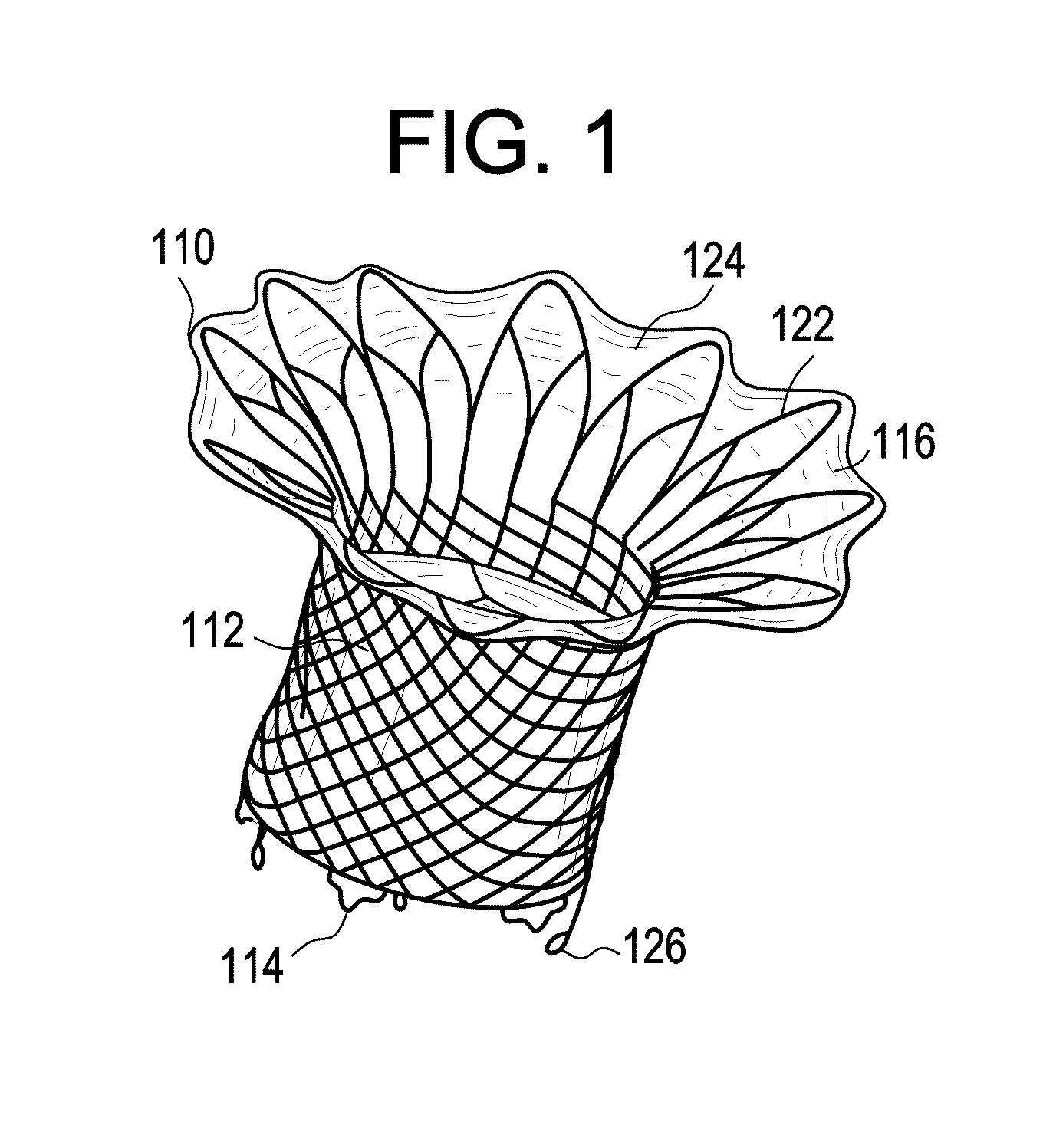
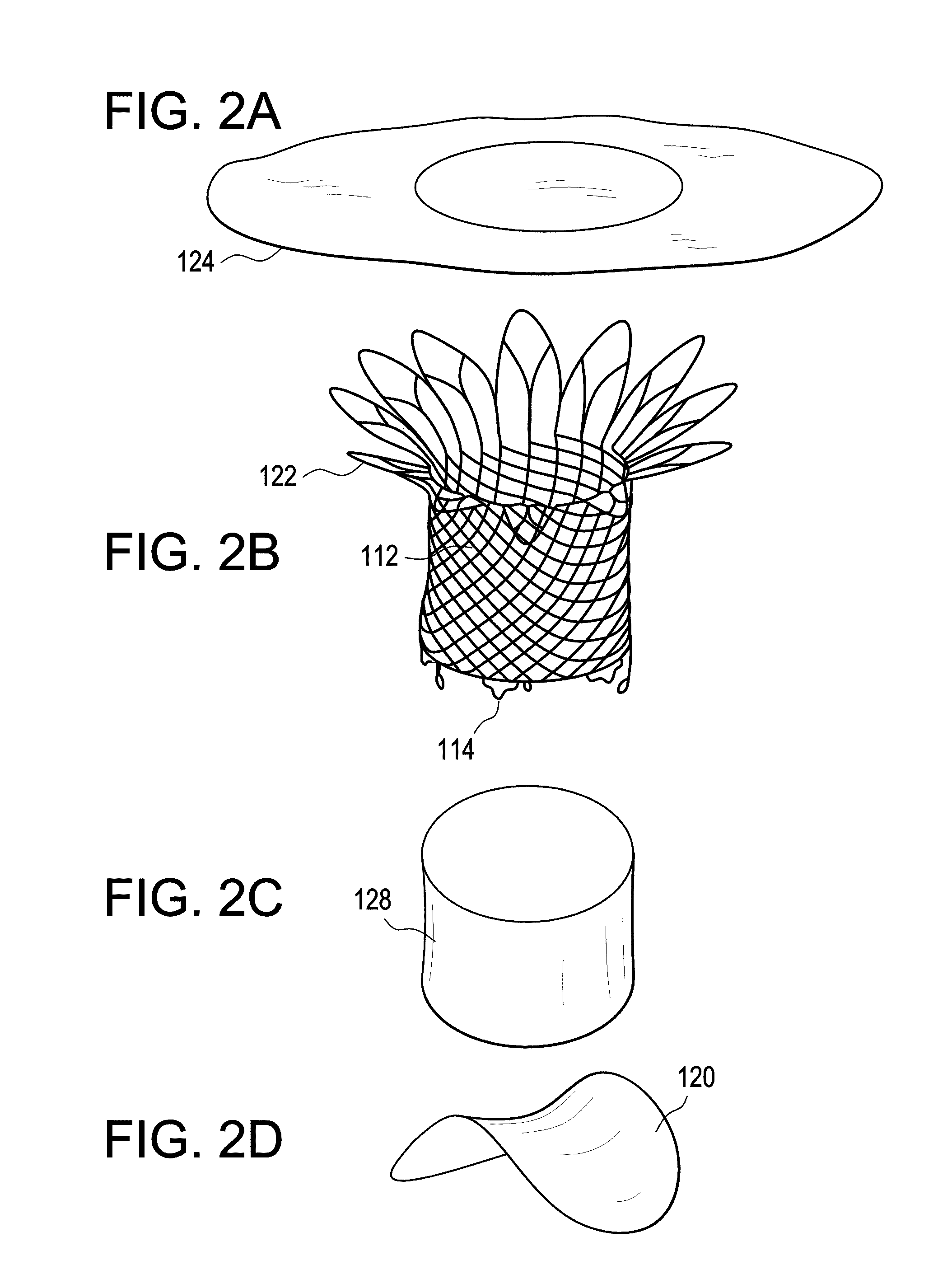
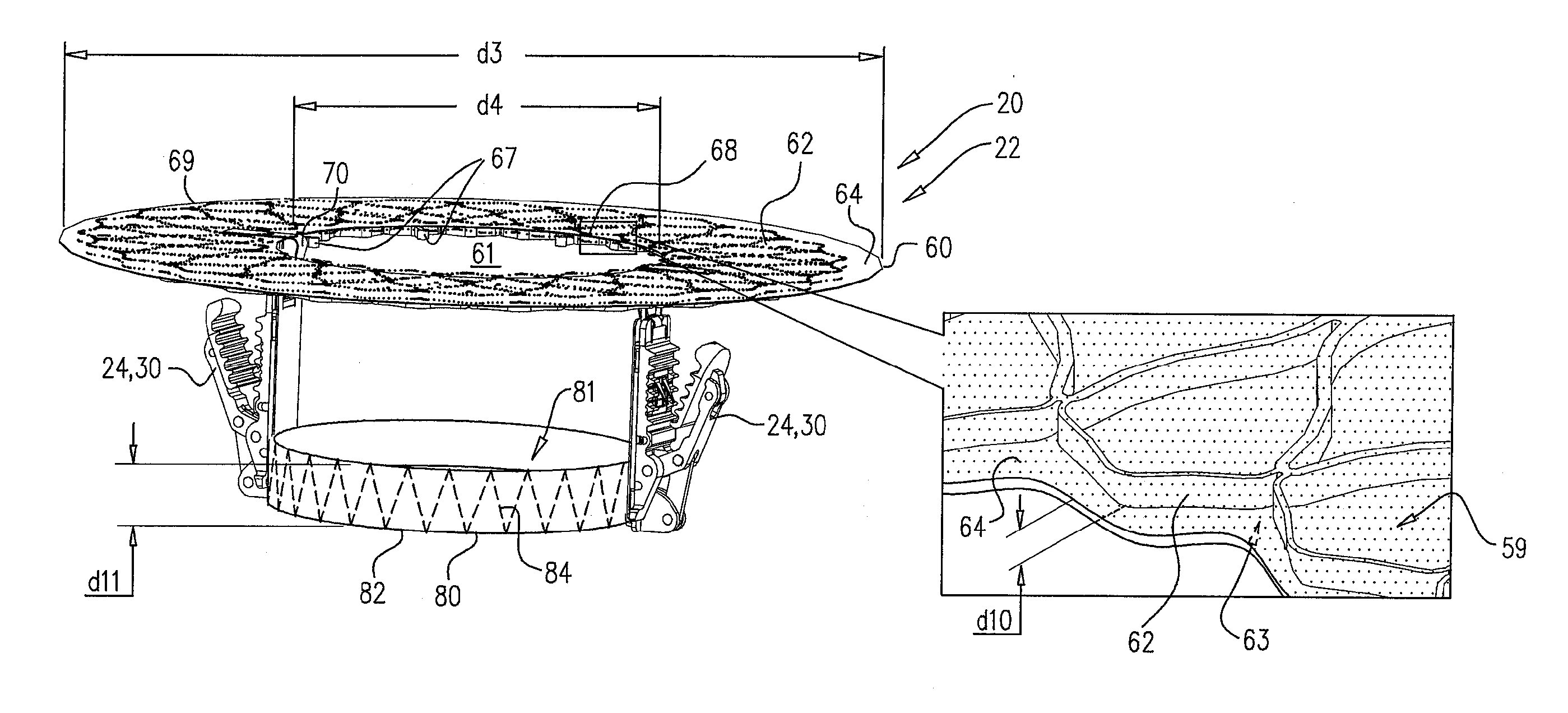
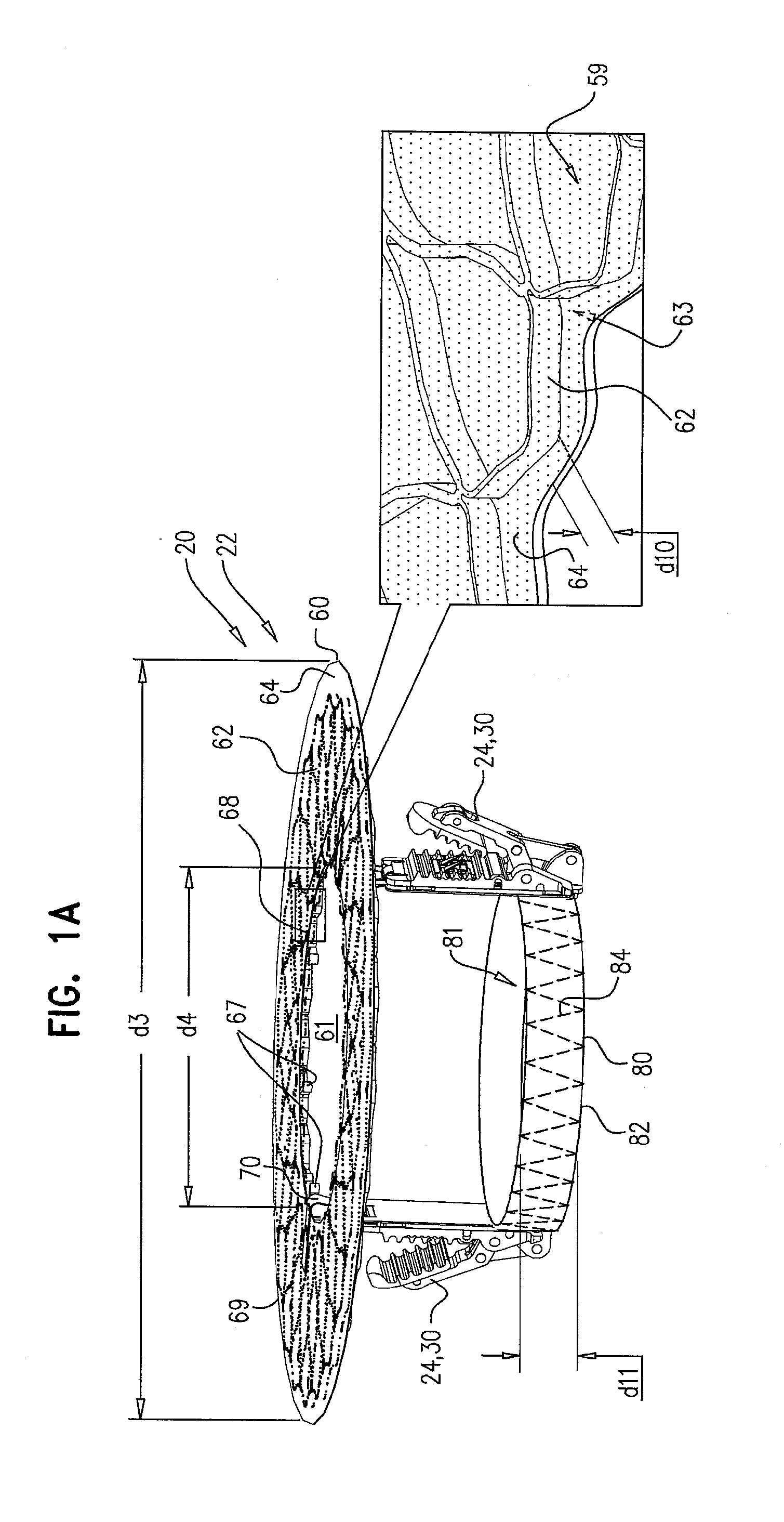
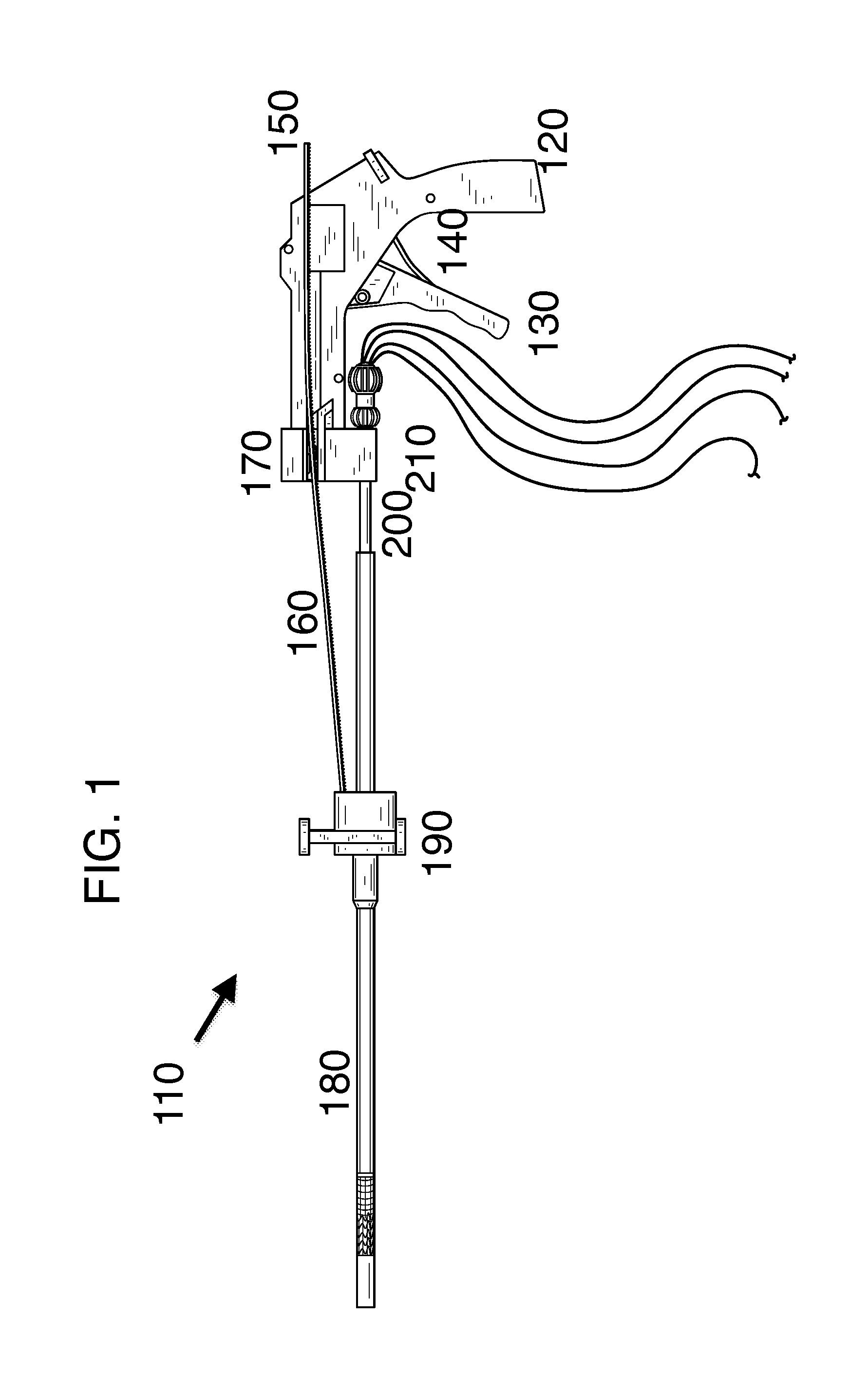
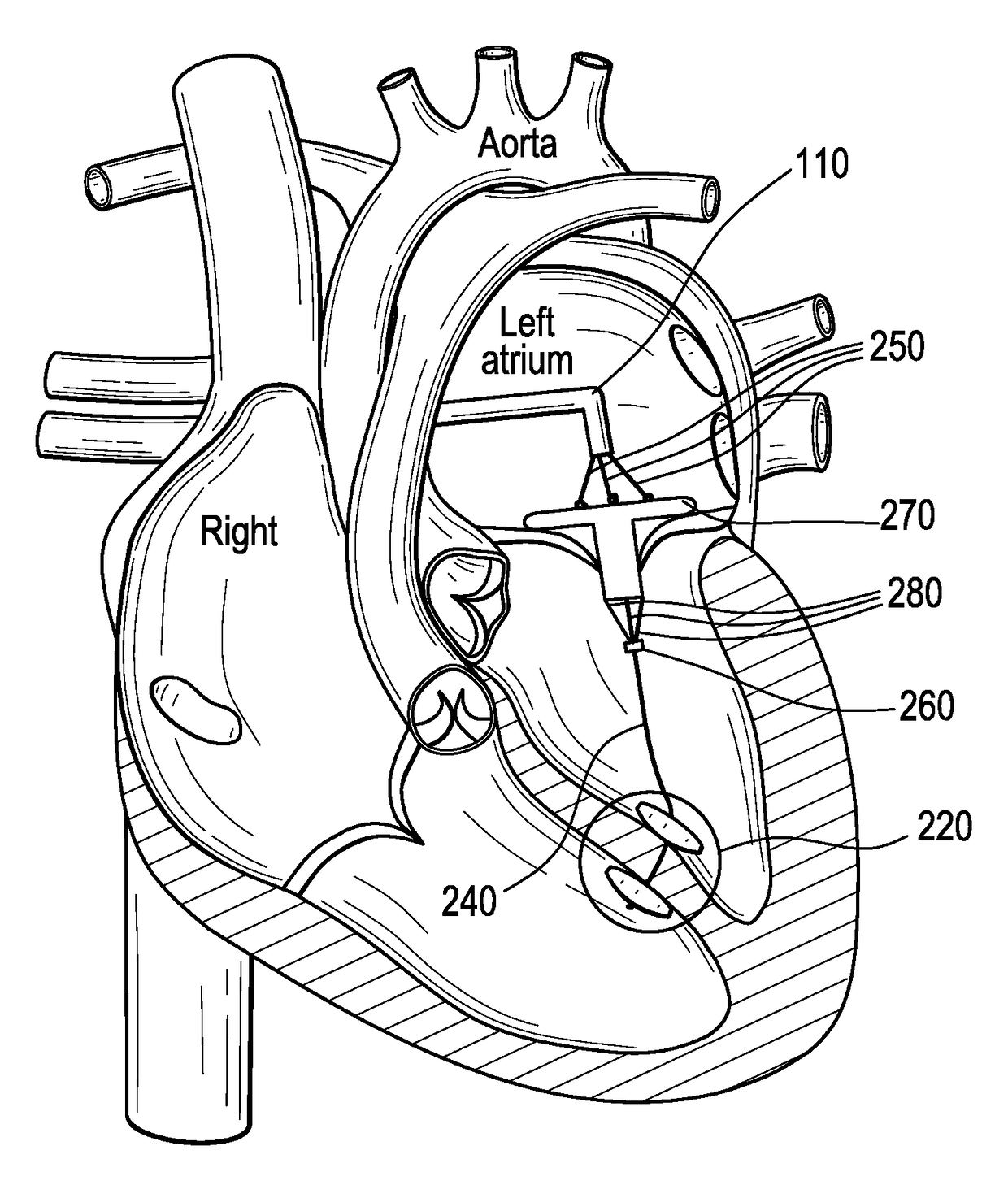
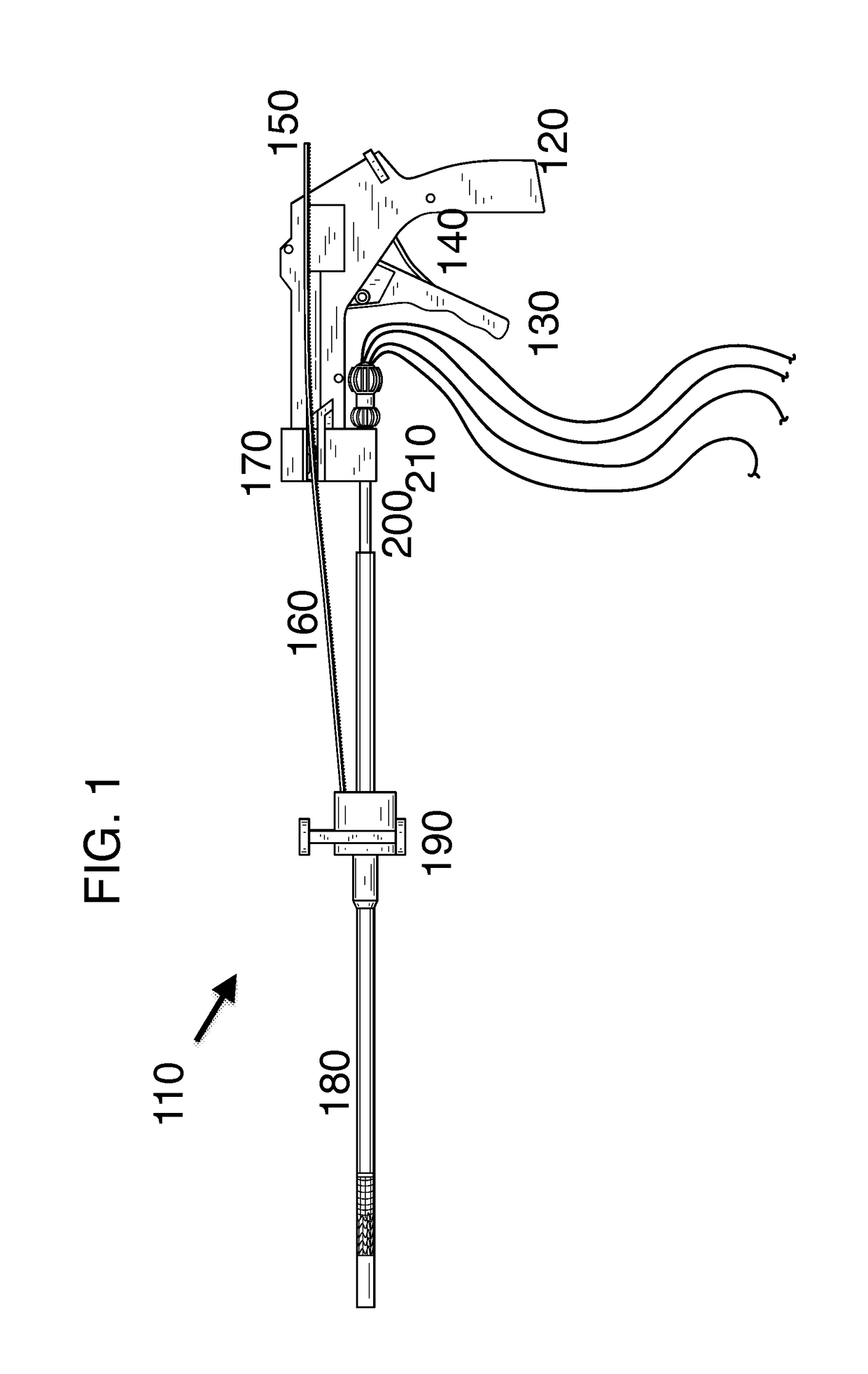
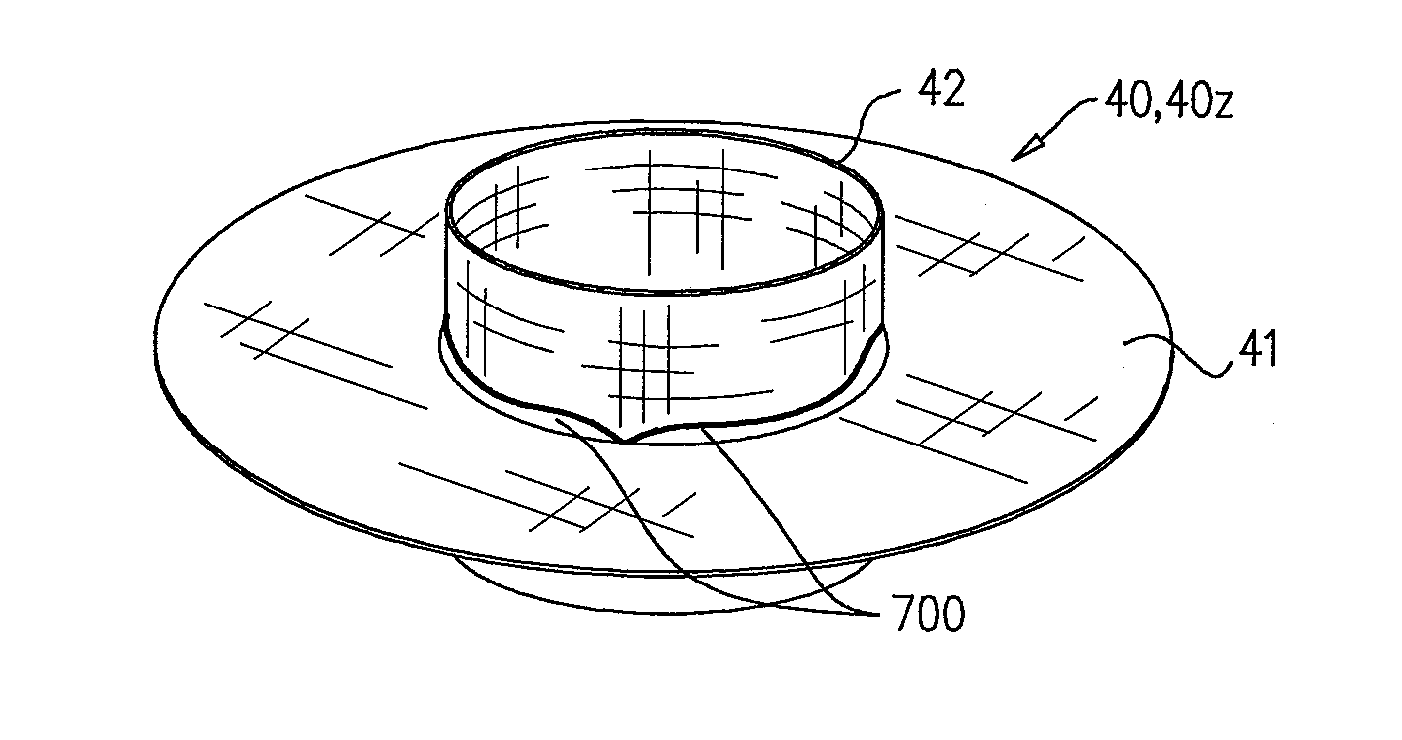
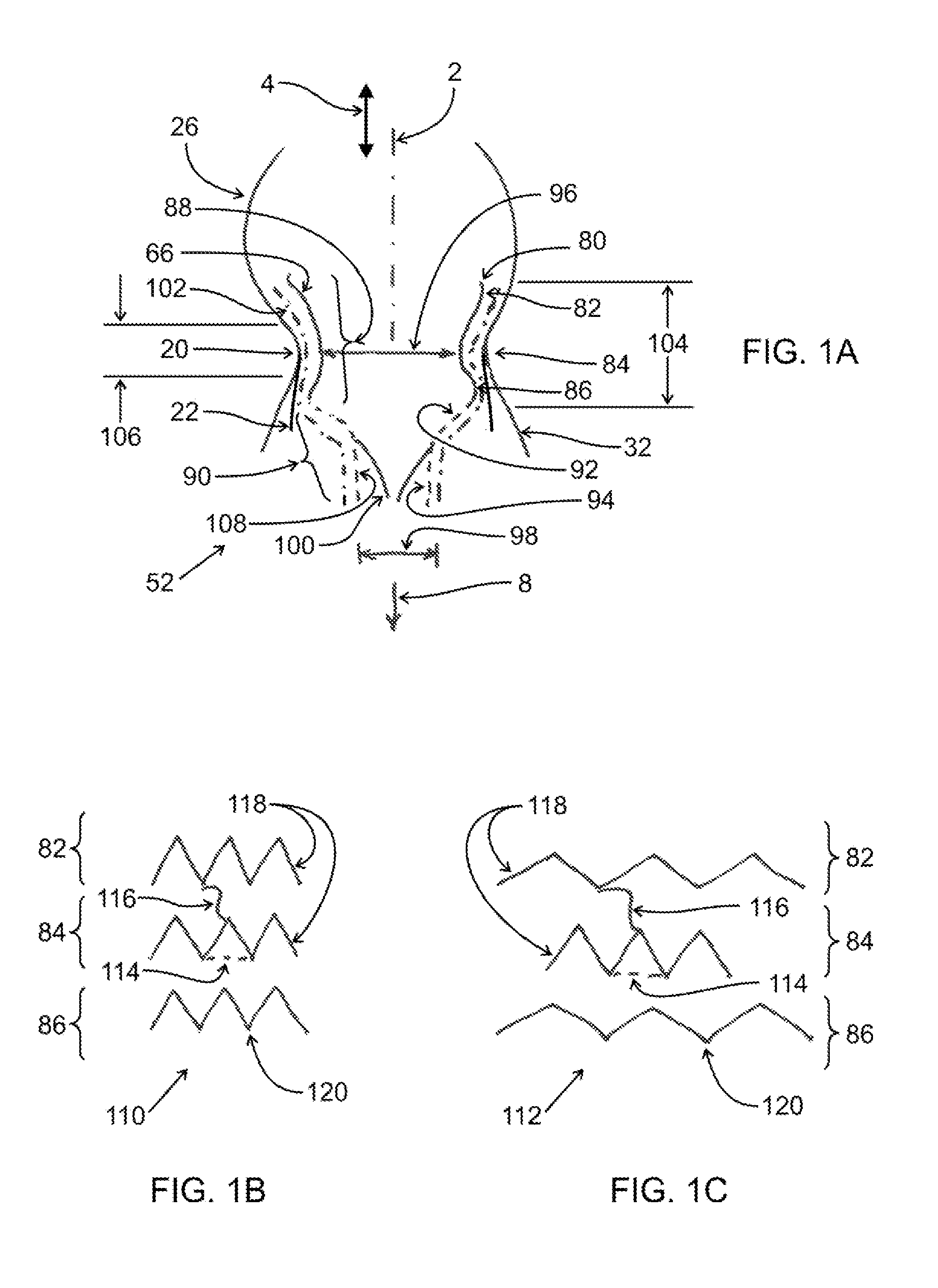
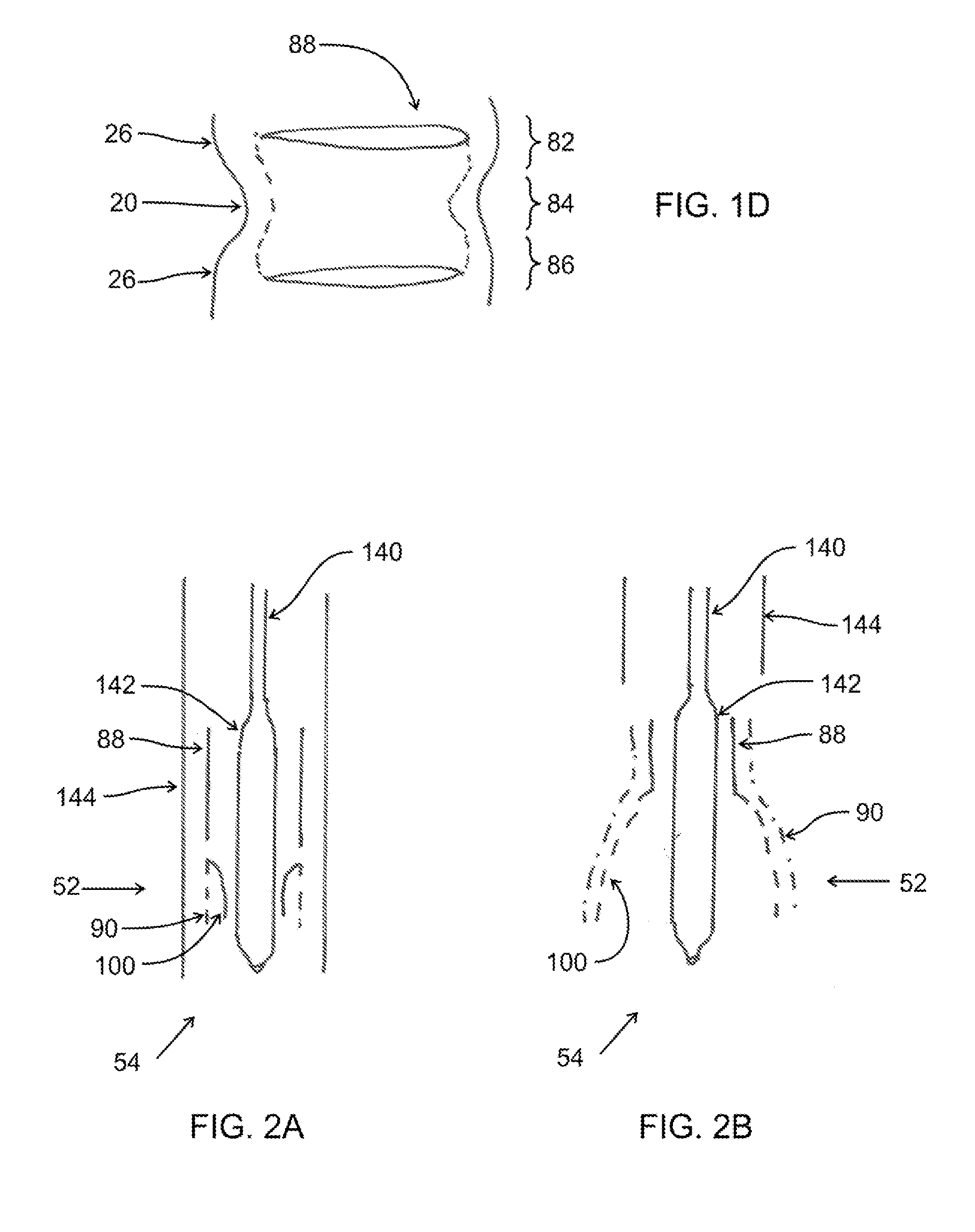
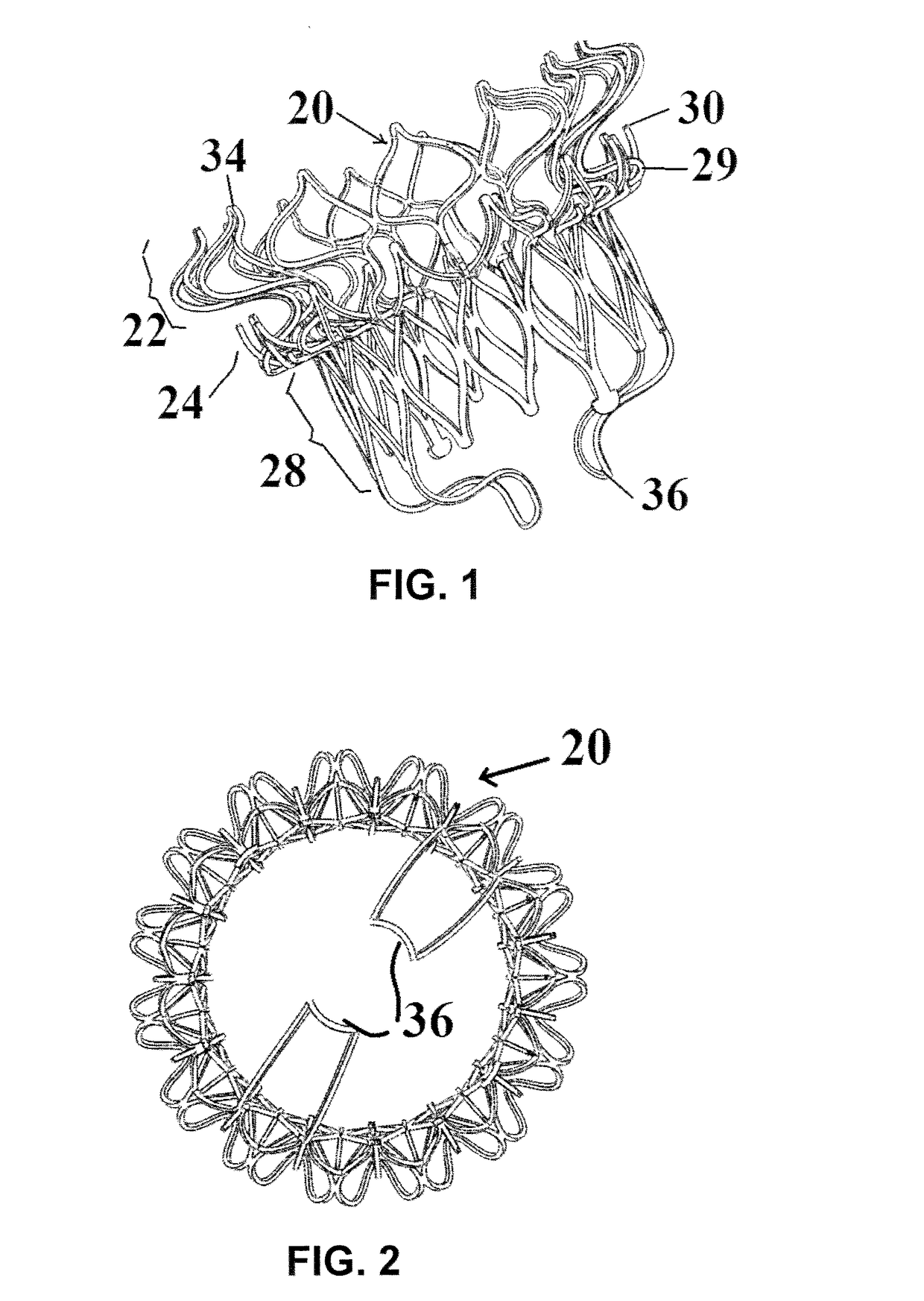
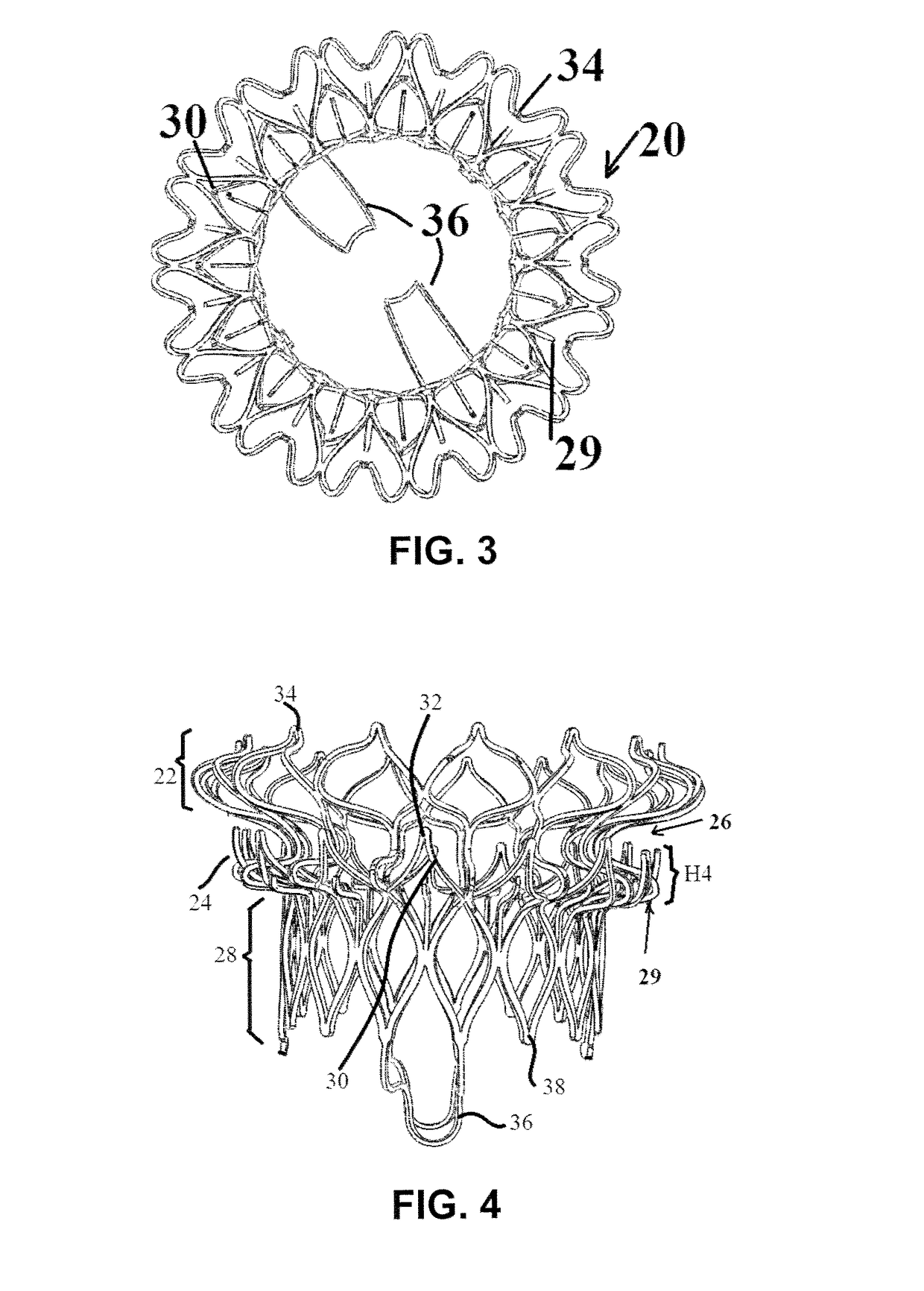
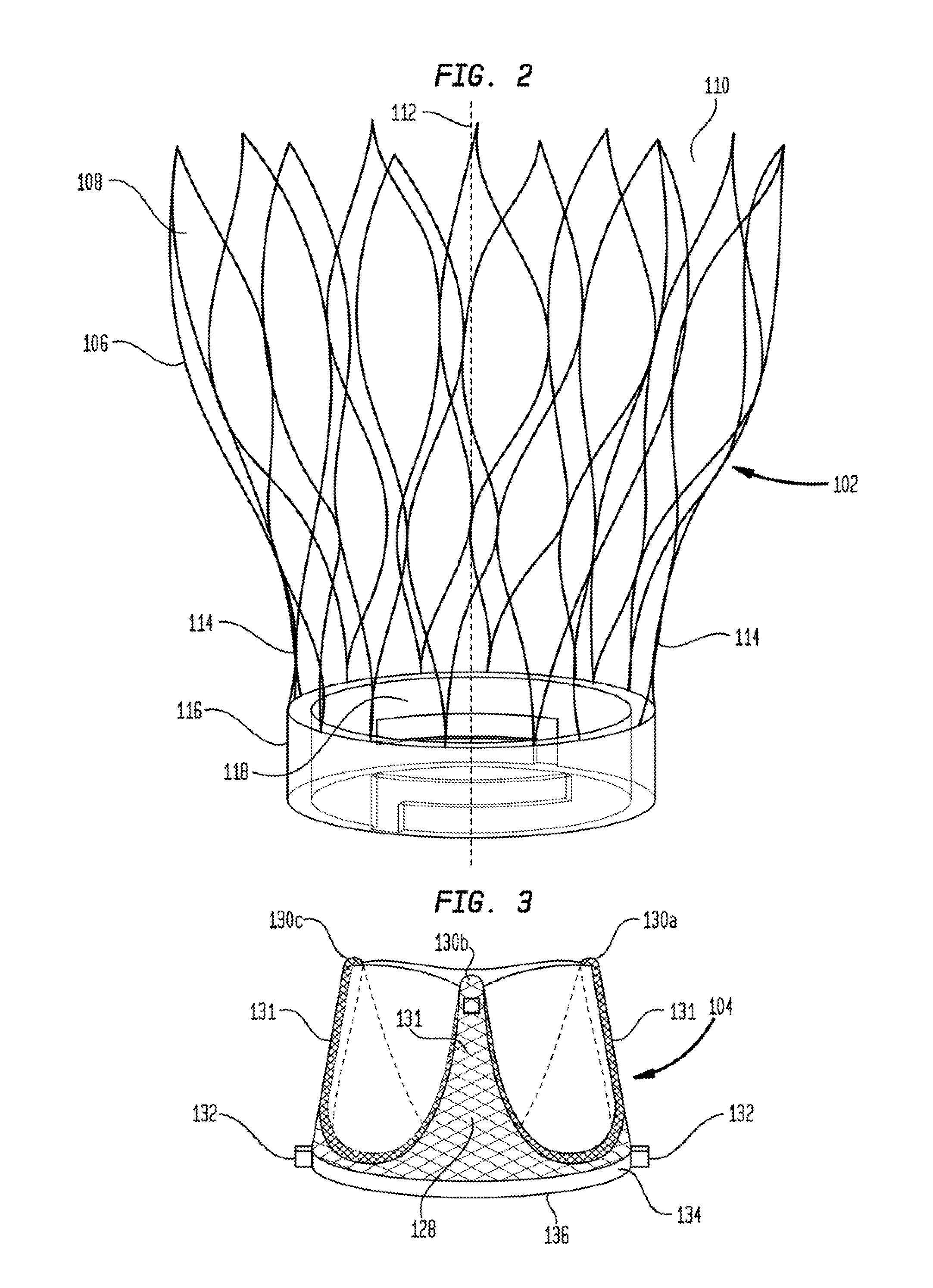
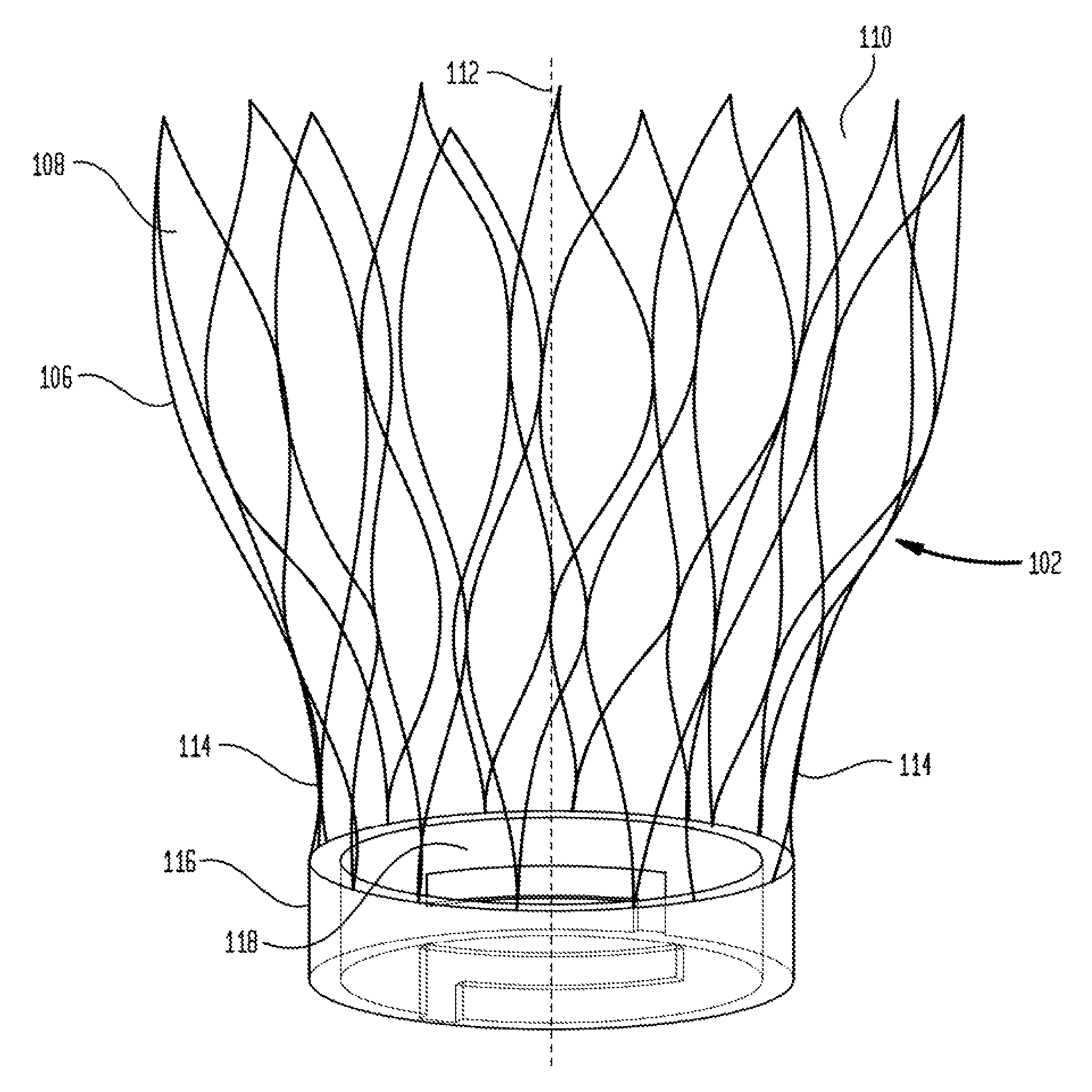
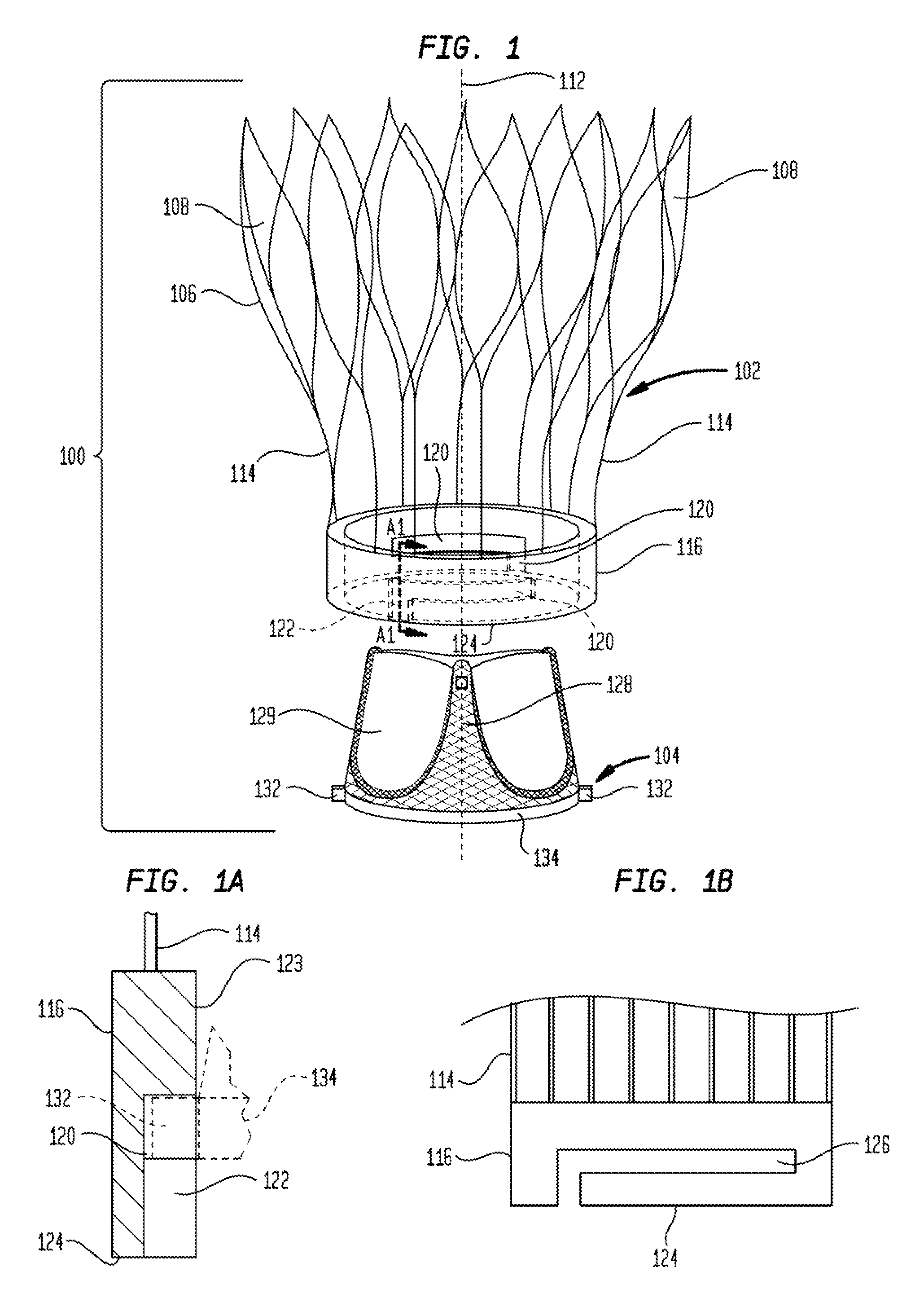
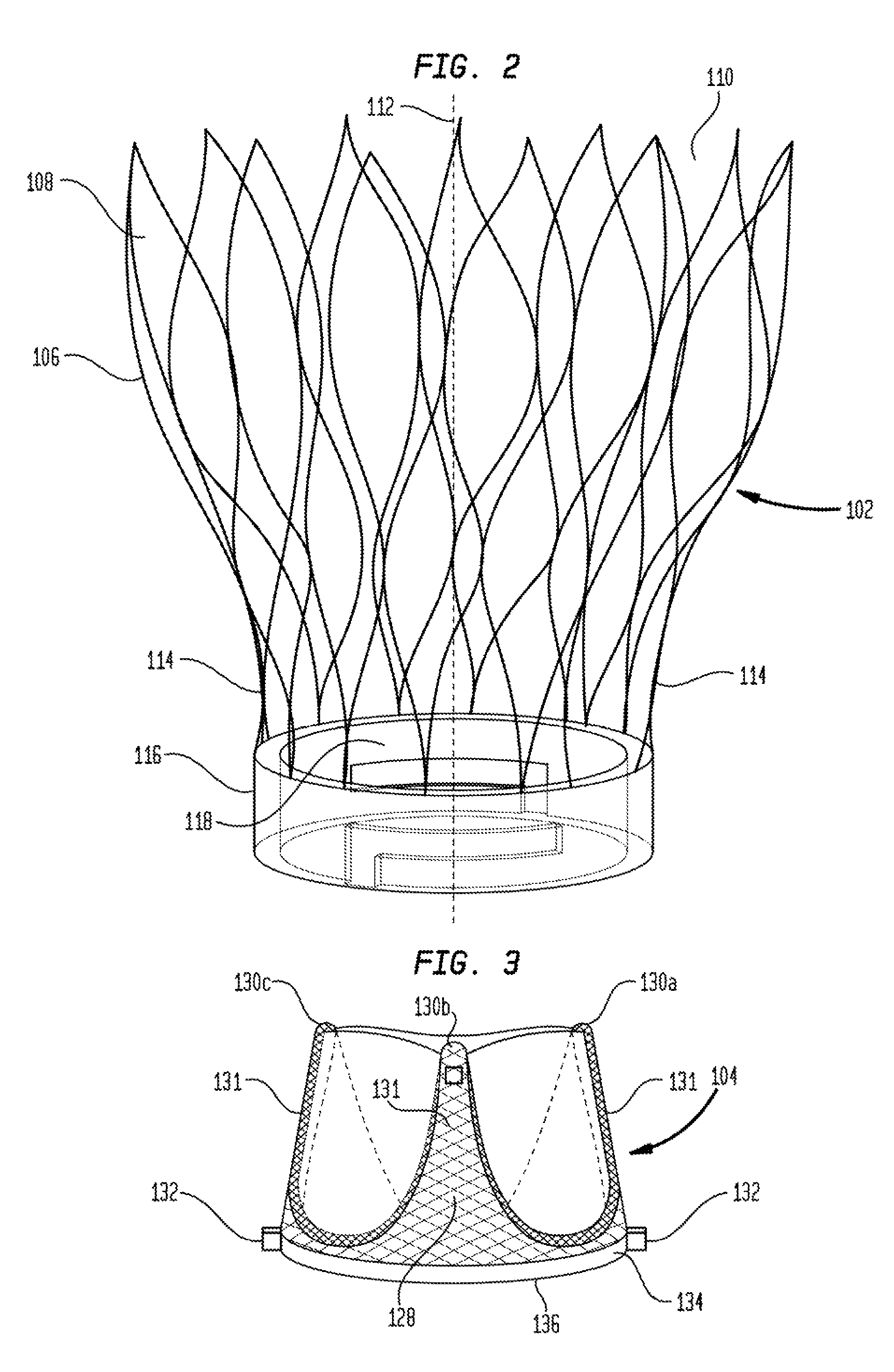
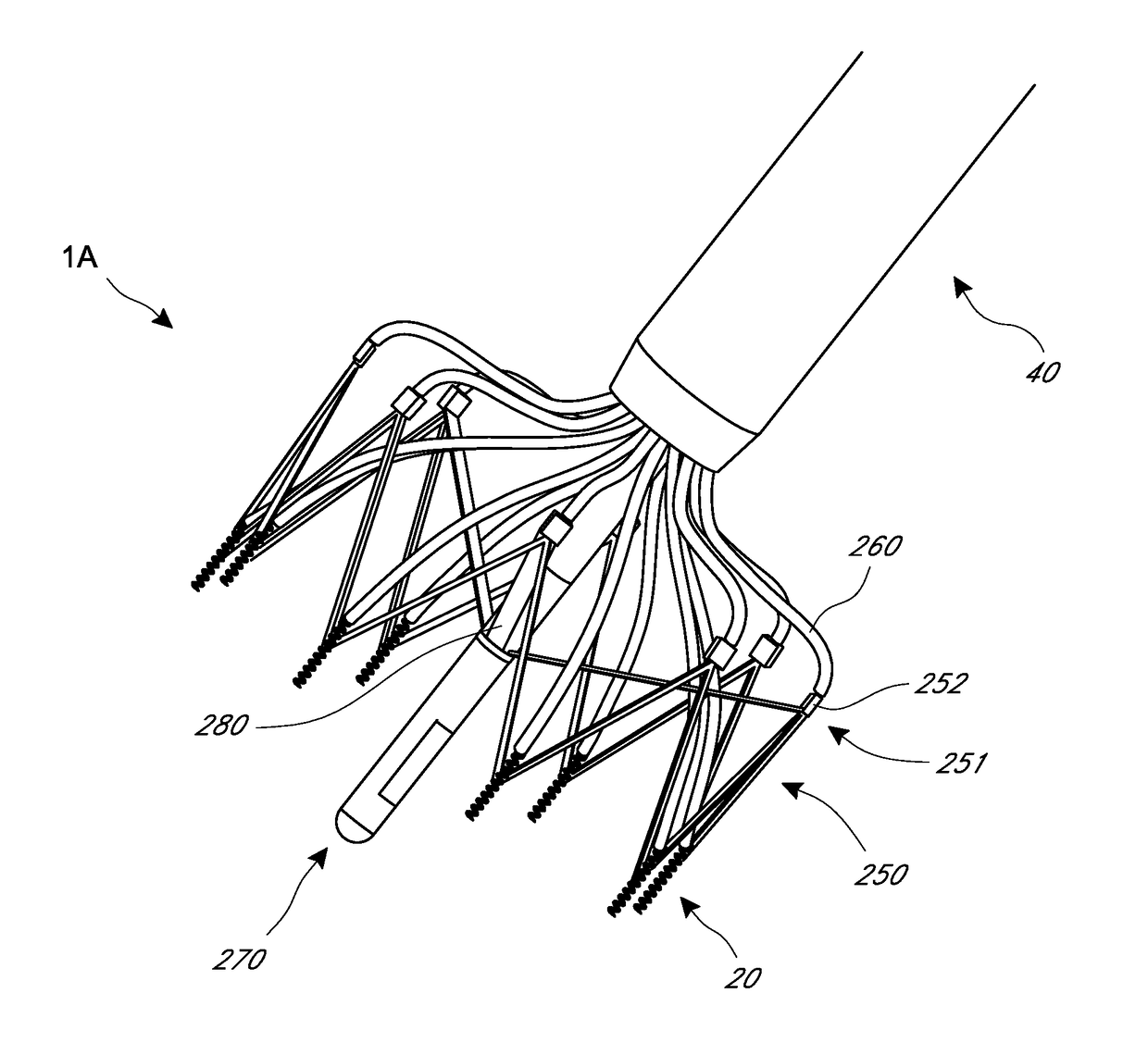
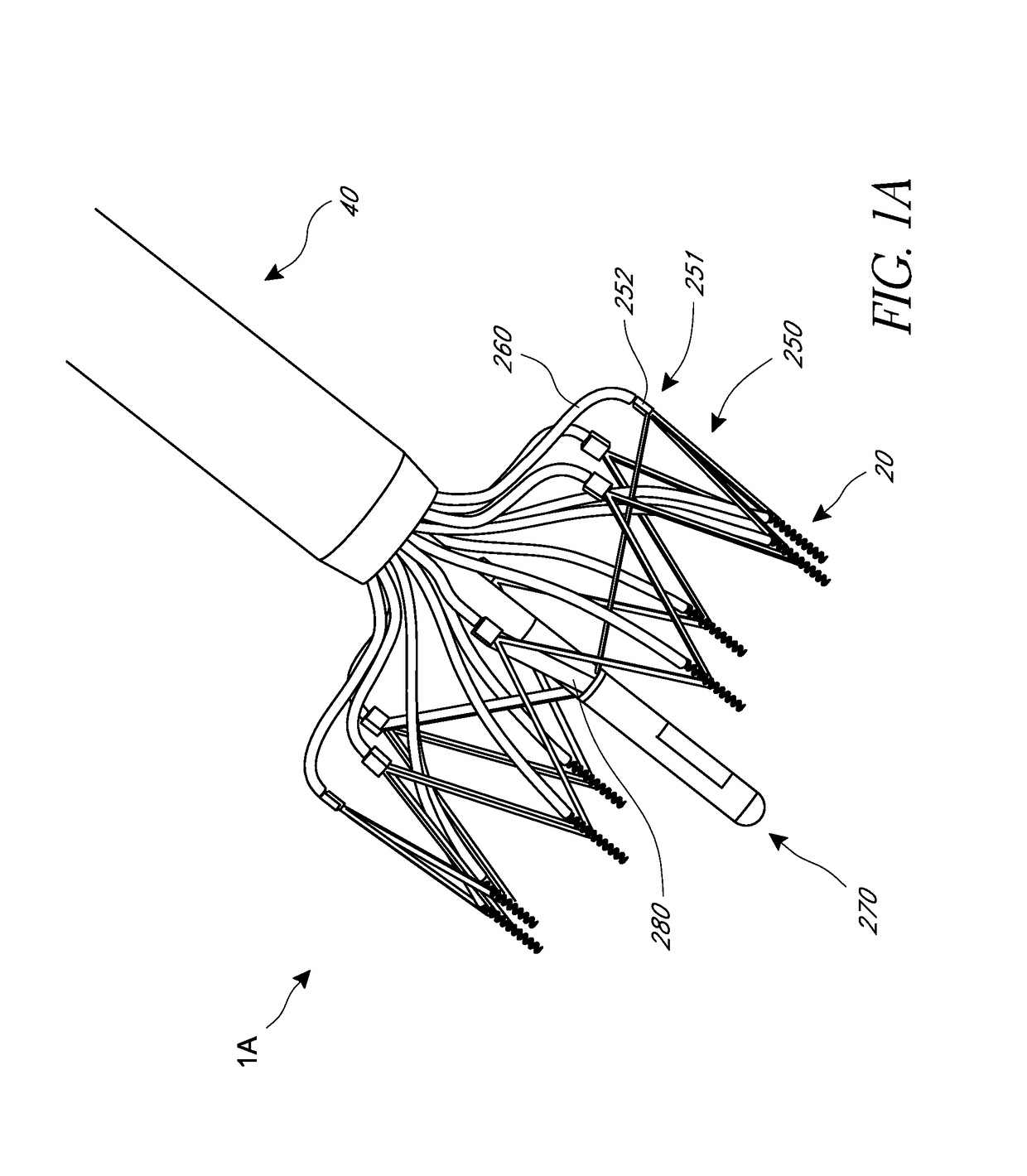
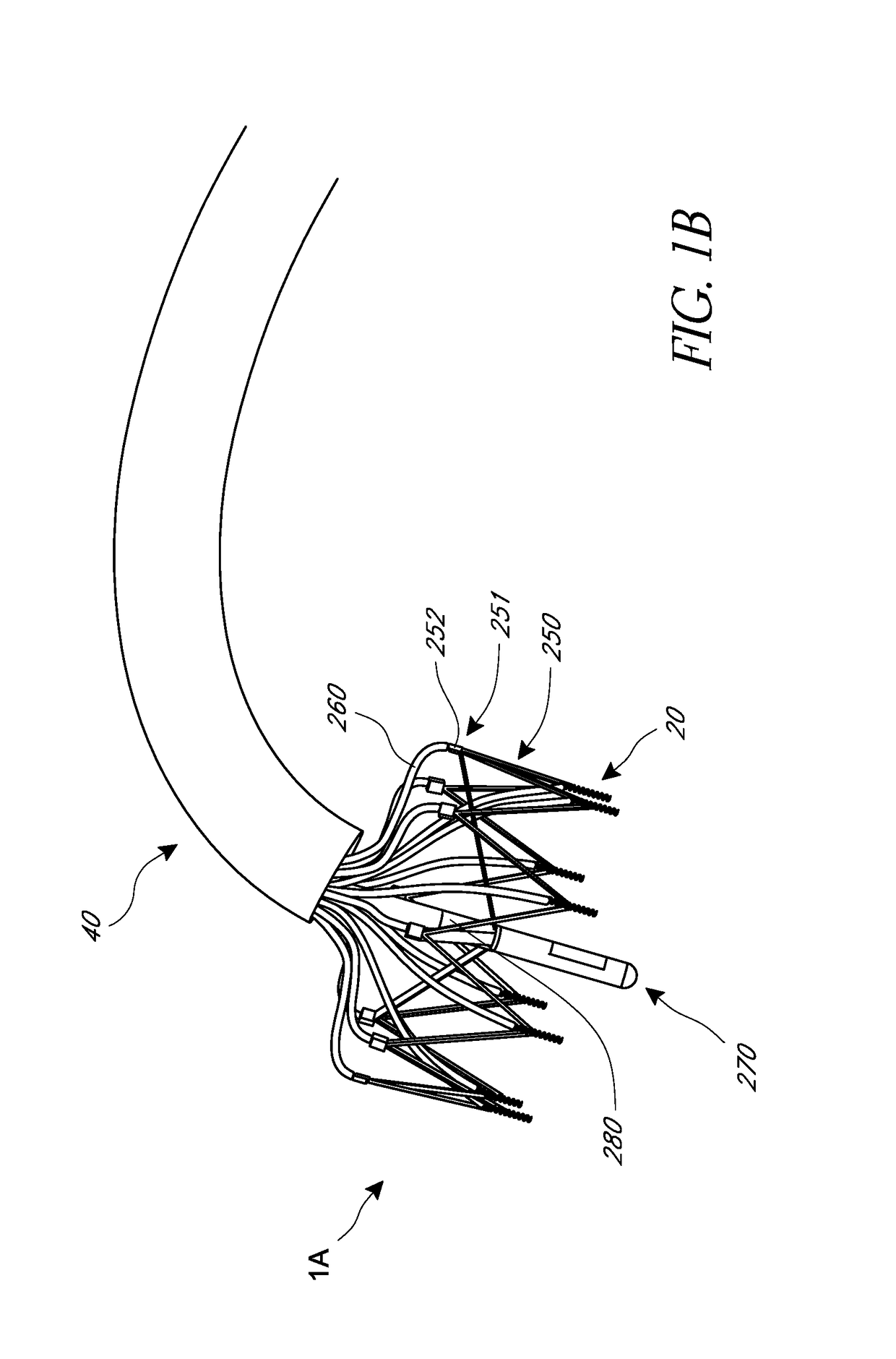
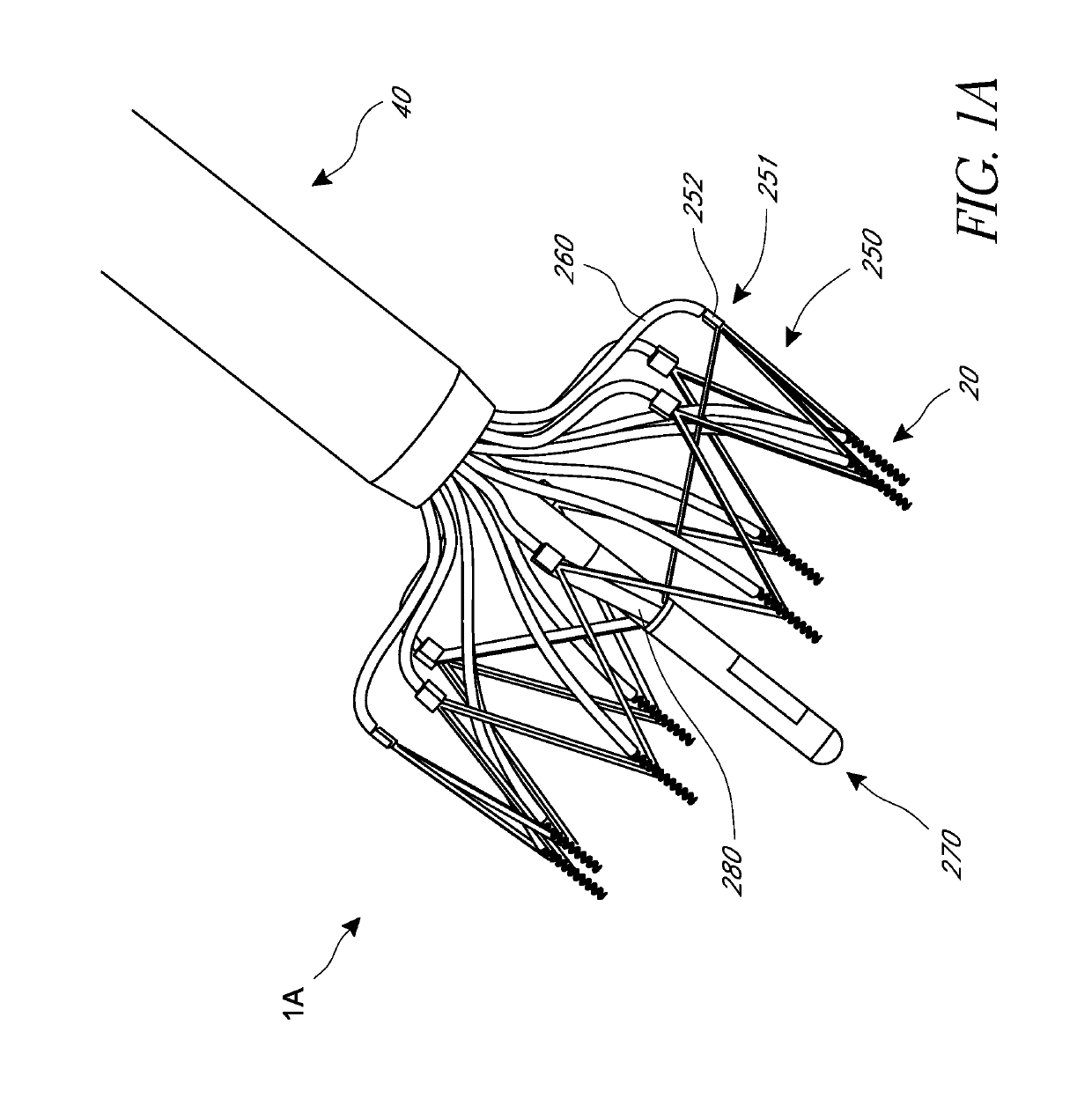
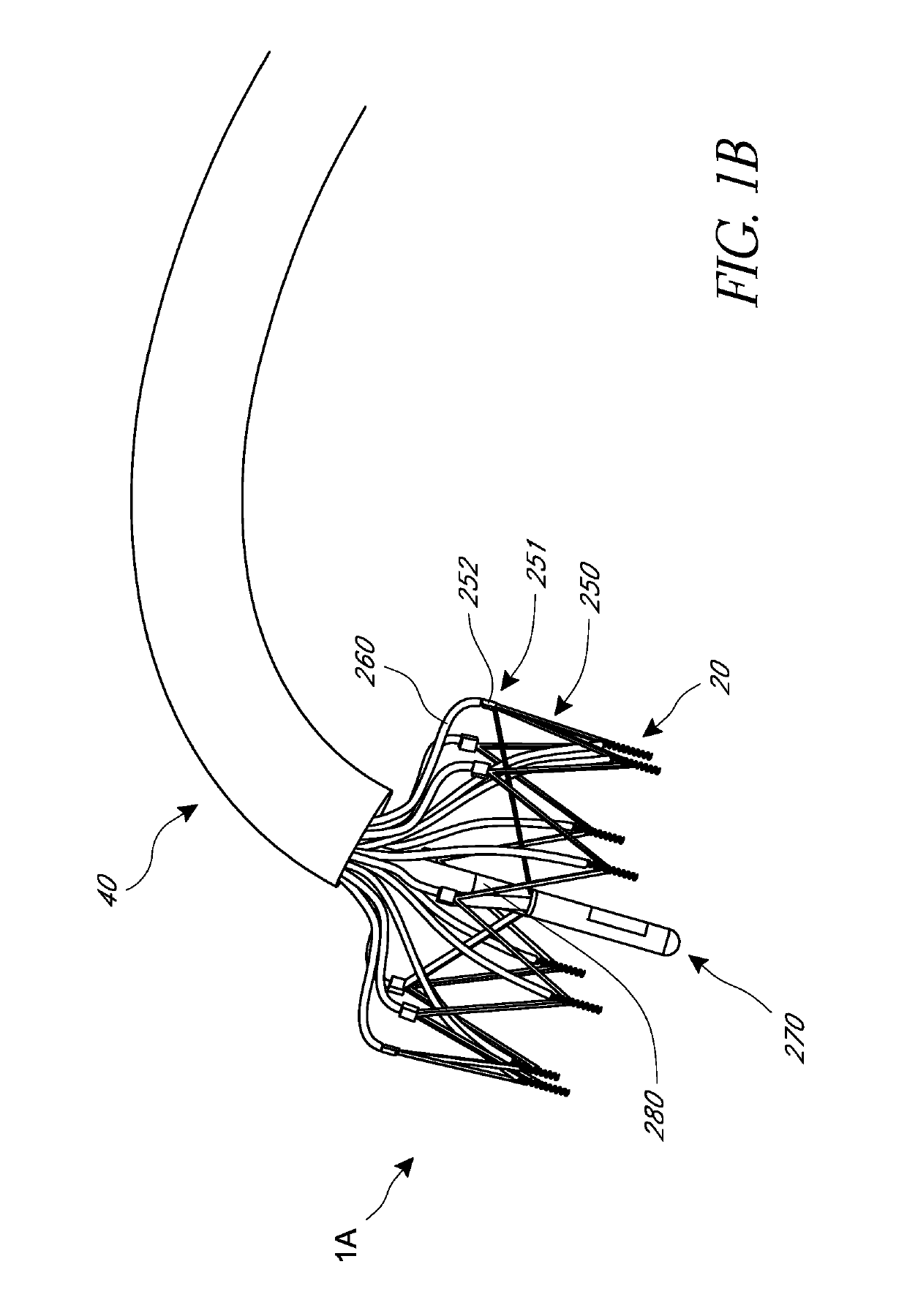
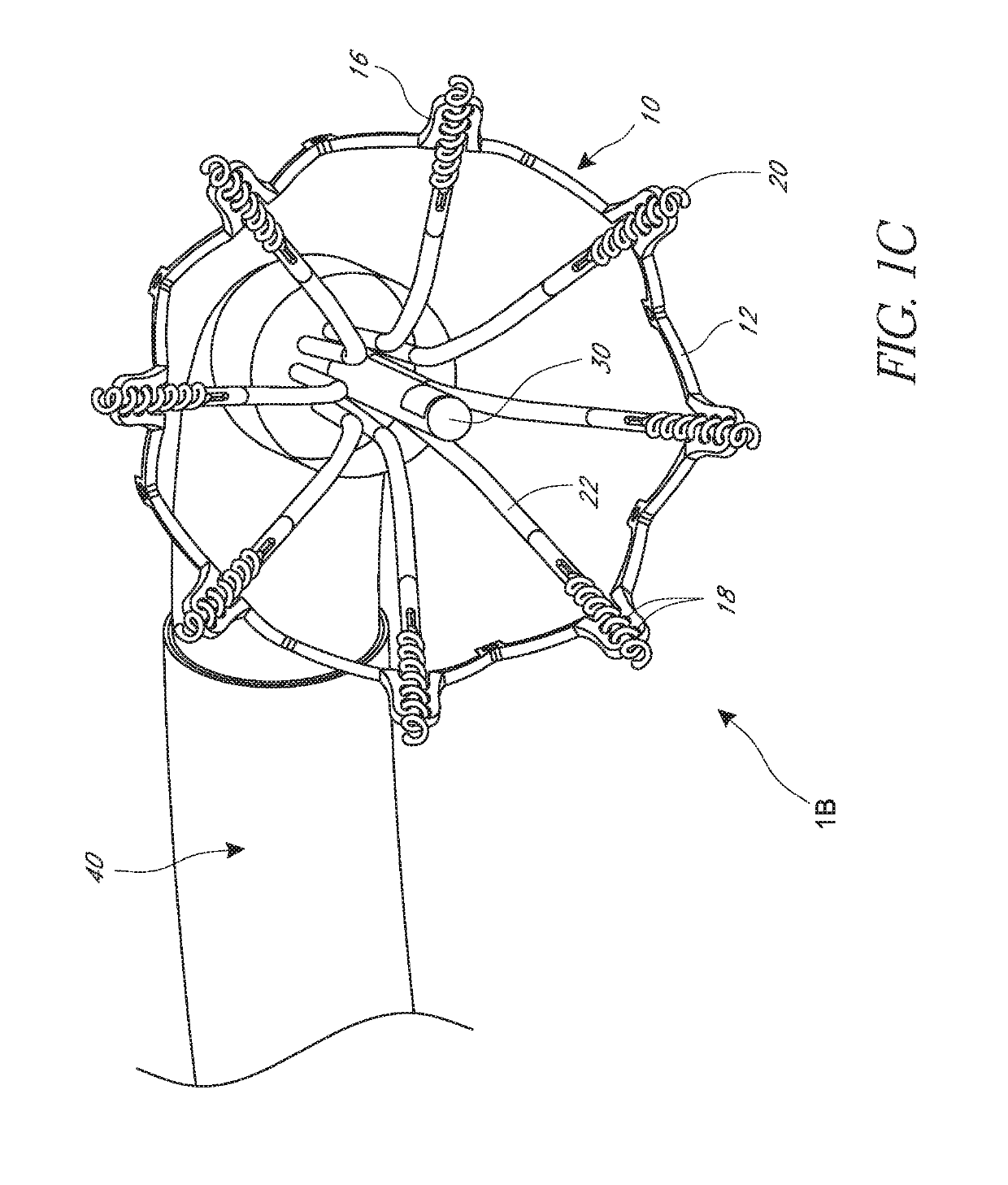
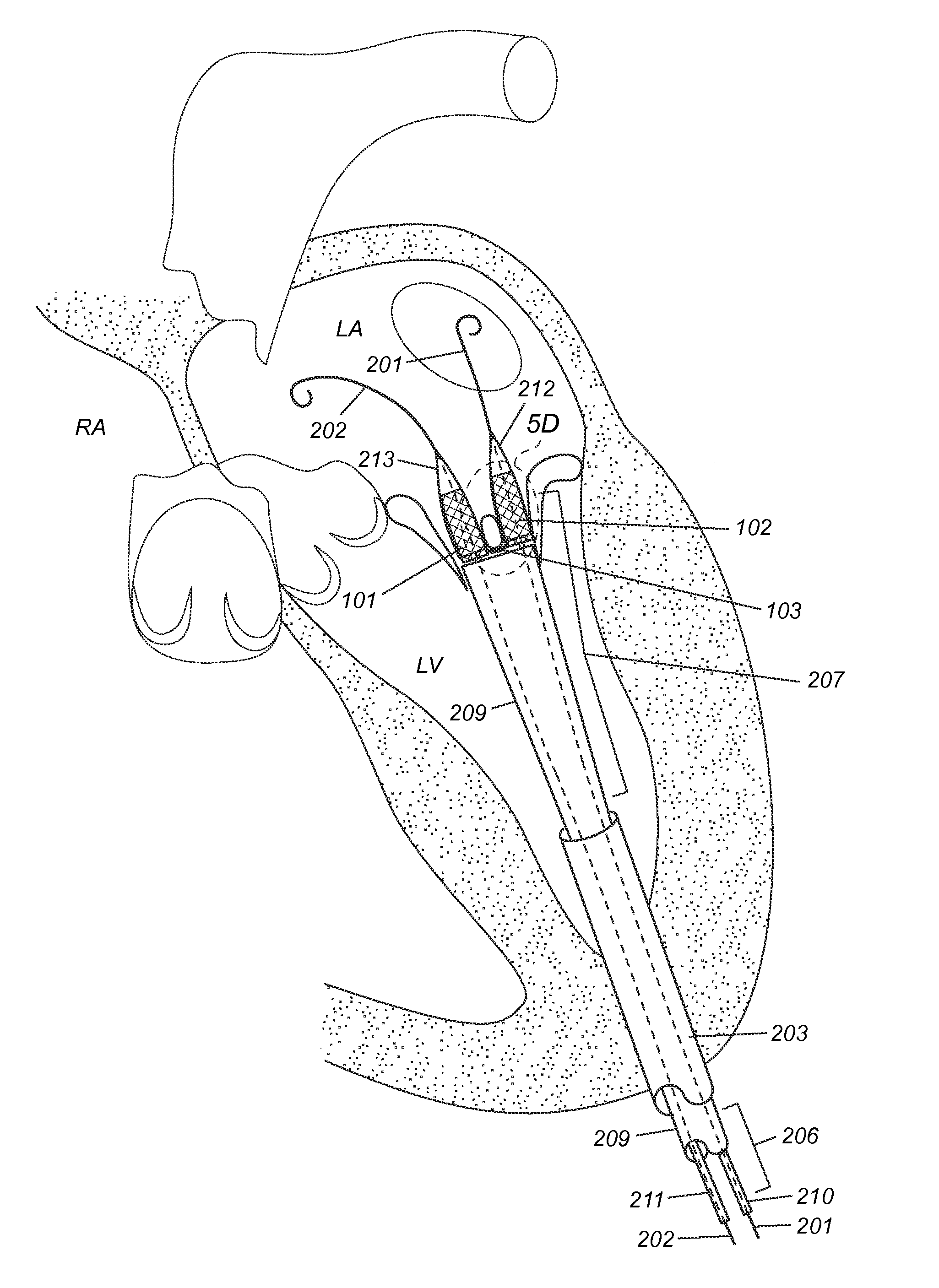
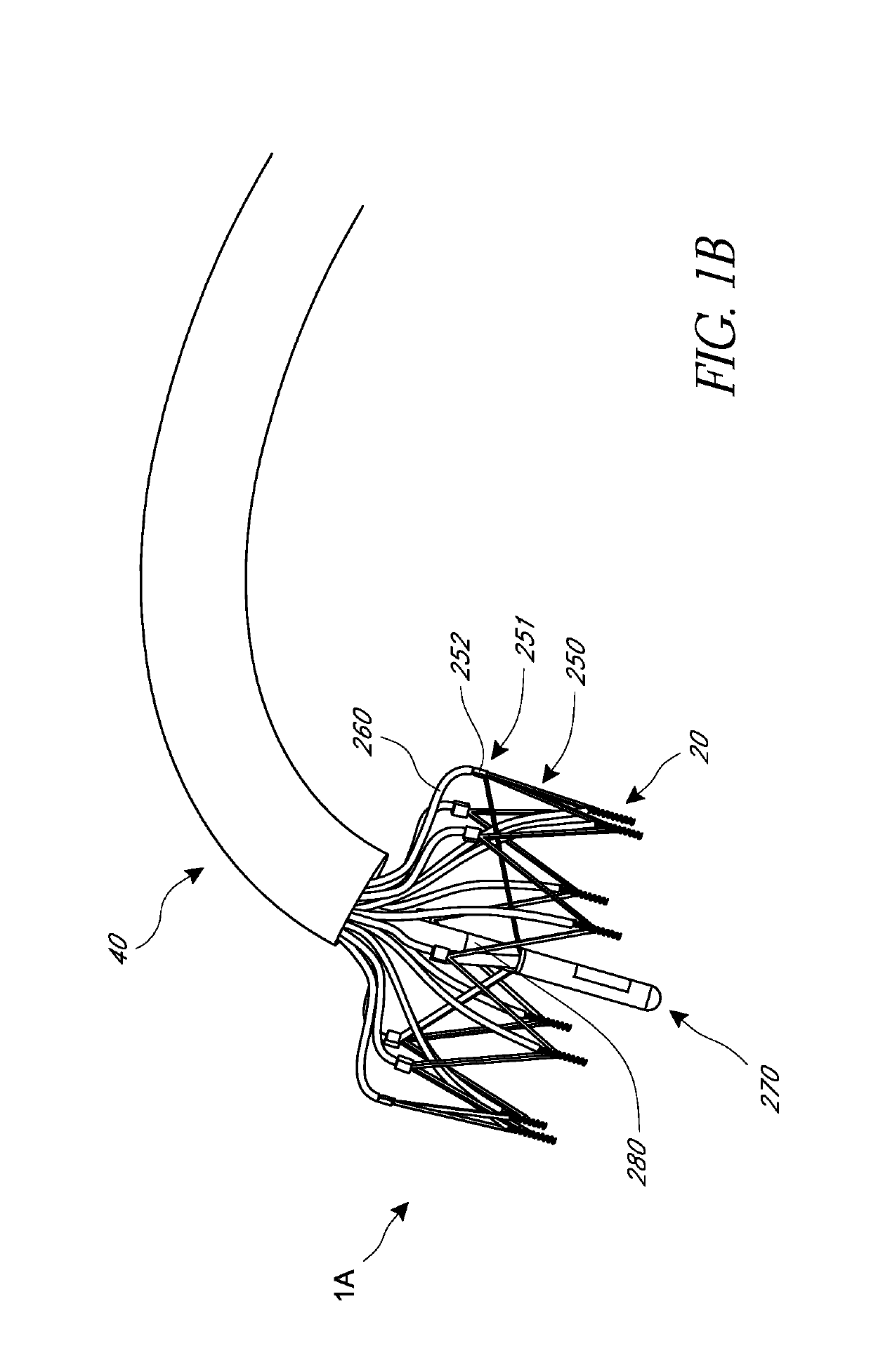
Device and System for Transcatheter Mitral Valve Replacement
InactiveUS20120179244A1Prevent perivalvular leakStentsHeart valvesExtracorporeal circulationBioprosthetic mitral valve replacement
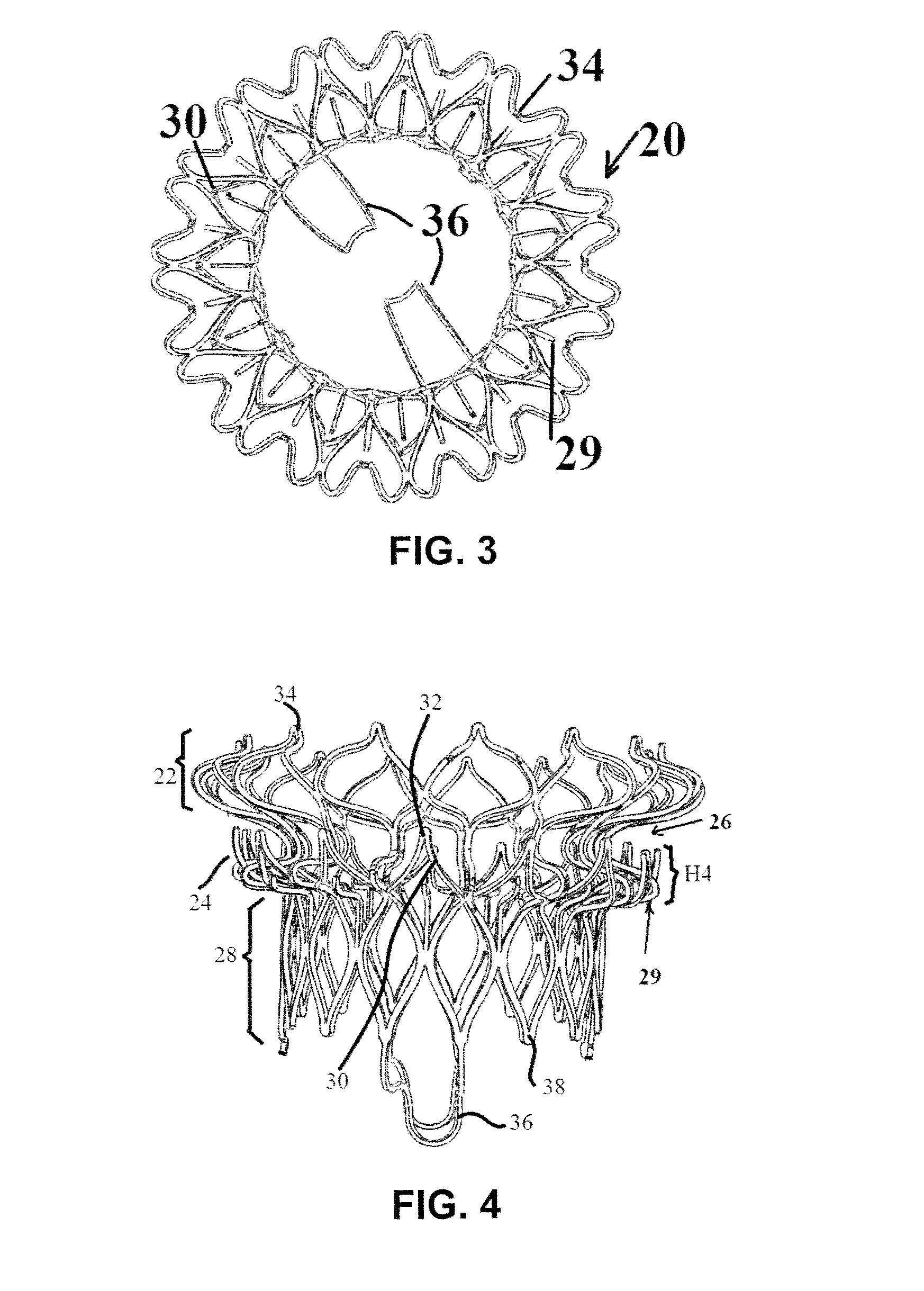
This invention relates to the design and function of a compressible valve replacement prosthesis which can be deployed into a beating heart without extracorporeal circulation using a transcatheter delivery system. The design as discussed focuses on the deployment of a device via a minimally invasive fashion and by way of example considers a minimally invasive surgical procedure preferably utilizing the intercostal or subxyphoid space for valve introduction. In order to accomplish this, the valve is formed in such a manner that it can be compressed to fit within a delivery system and secondarily ejected from the delivery system into the annulus of a target valve such as a mitral valve or tricuspid valve.
Owner:COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY +1
Techniques for percutaneous mitral valve replacement and sealing
Apparatus is described for use with a native heart valve of a subject, the apparatus including (1) a prosthetic valve support, comprising an upstream support portion, the upstream support portion having (a) a compressed configuration and an uncompressed configuration in which the upstream support portion has an inner perimeter that defines an opening; and (2) a prosthetic valve, advanceable into the opening defined by the upstream support portion, and intracorporeally couplable to the upstream support portion by being expanded within the opening defined by the upstream support portion, the apparatus being configured such that, when the prosthetic valve is expanded within the opening defined by the upstream support portion, the expansion of the prosthetic valve is restricted by the inner perimeter of the upstream support portion, without causing the prosthetic valve support to apply a radially-expansive force to the native annulus. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:CARDIOVALVE LTD
Device and Method for Mitral Valve Regurgitation Treatment
ActiveUS20150196390A1Effective protectionAdjustable positionHeart valvesBioprosthetic mitral valve replacementMitral valve leaflet
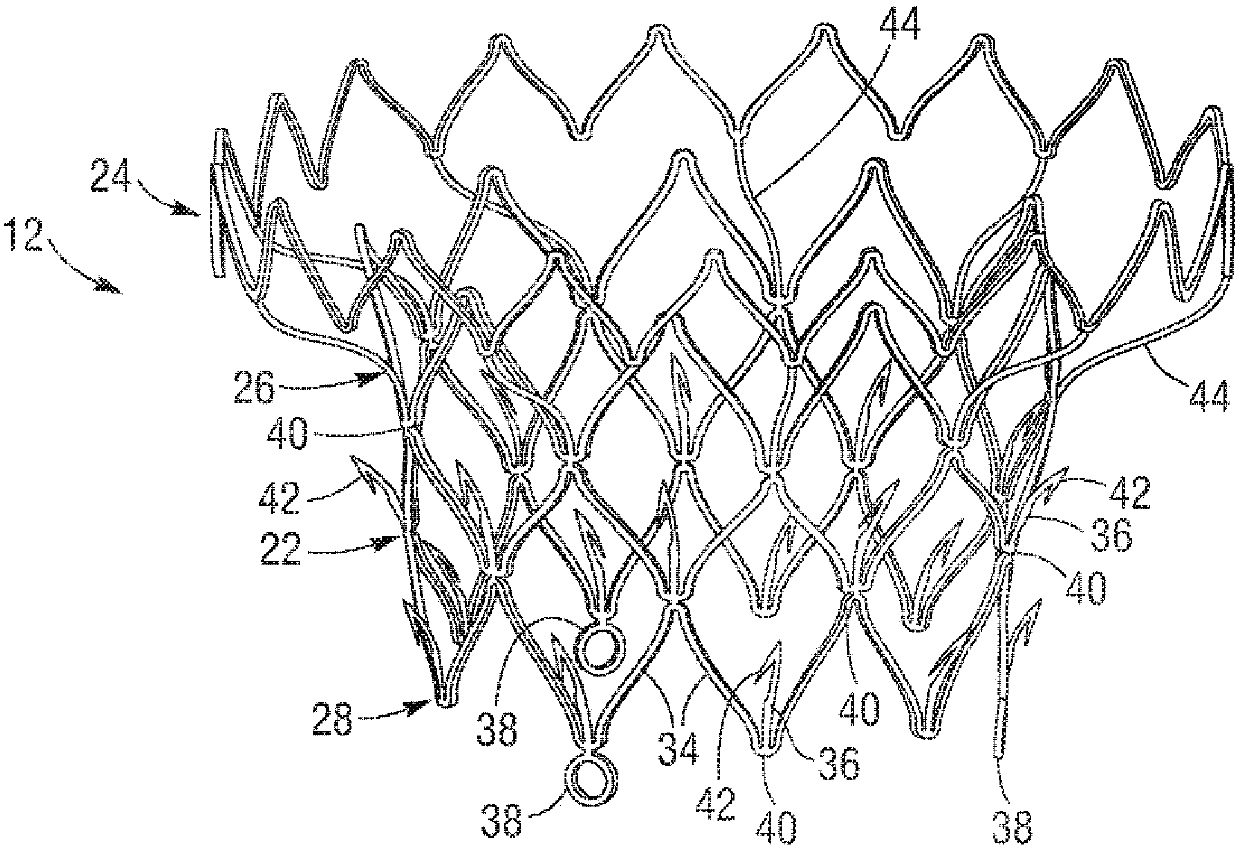
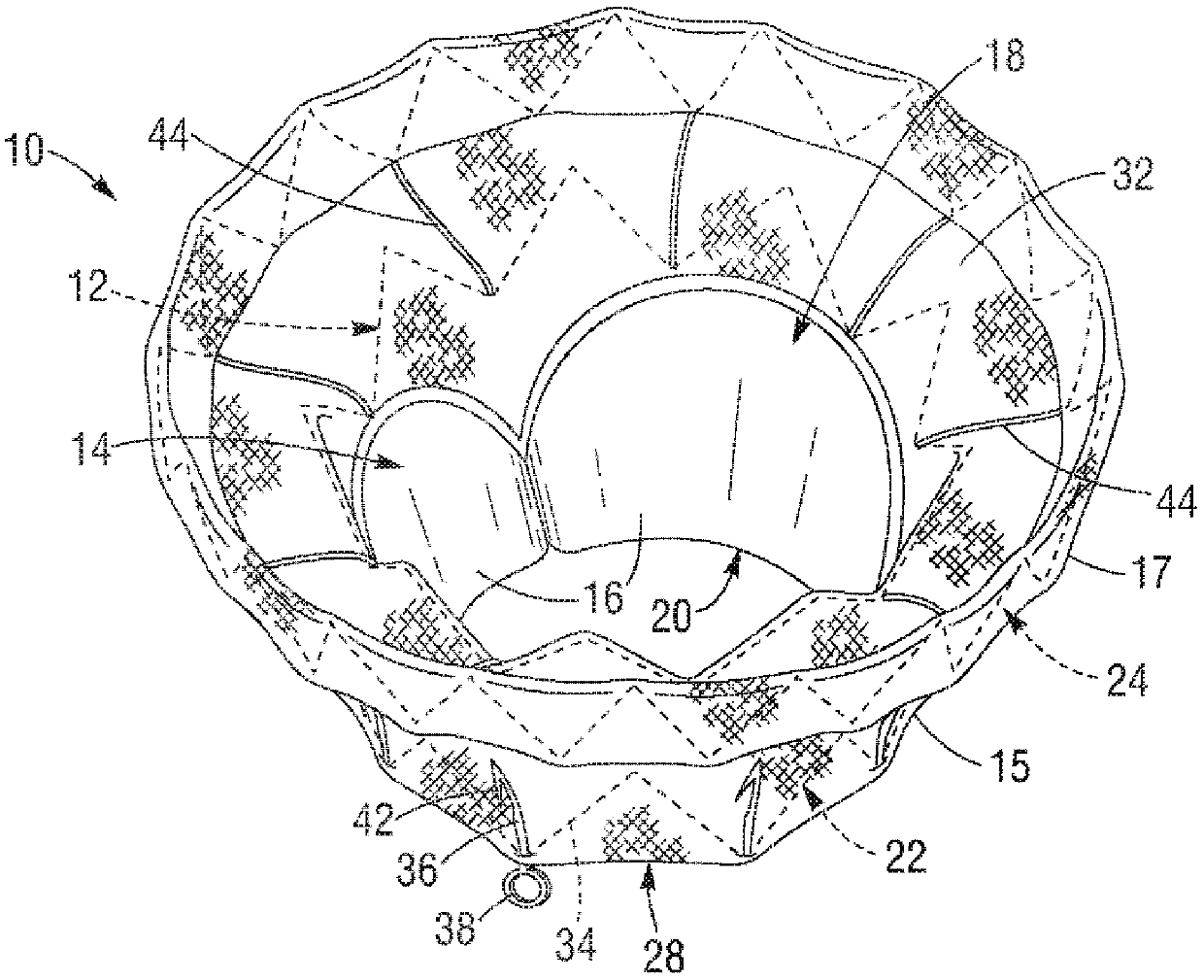
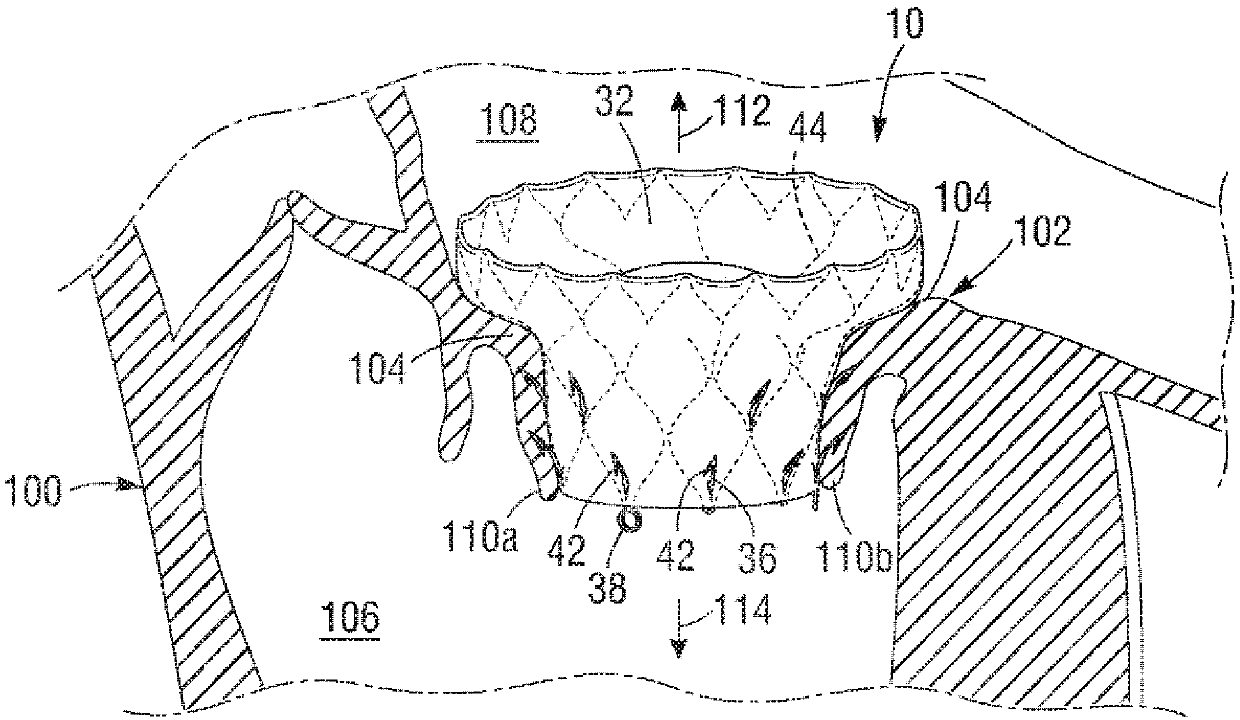
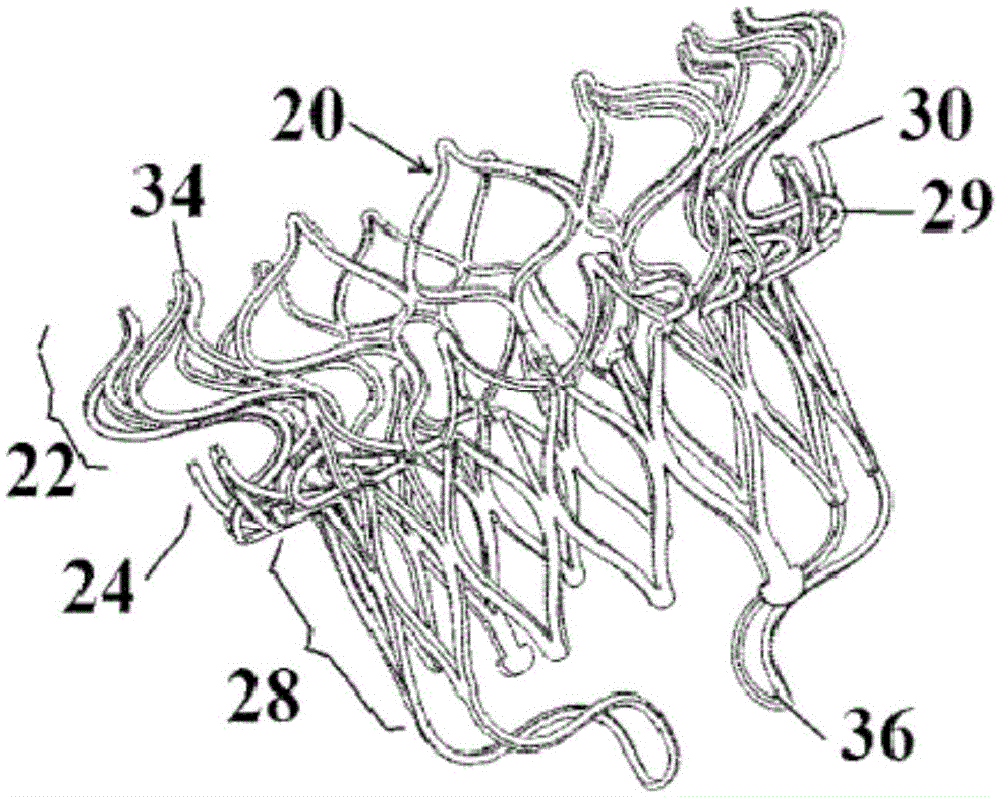
A mitral valve replacement device is adapted to be deployed at a mitral valve position in a human heart. The device has an atrial flange defining an atrial end of the device, a valve body defining a ventricular end of the device, and an annulus support that connects the atrial flange and the valve body, the annulus support including a ring of tabs extending radially therefrom and adapted to engage the native mitral annulus and / or the native leaflet(s) of the human heart. The atrial flange can be seated in the atrium above the native mitral valve annulus in a human heart, and the ring of tabs can engage the native mitral annulus in a manner where the atrial flange and tabs provide a clipping effect to secure the mitral valve replacement device at the native mitral valve position
Owner:SINOMED CARDIOVITA TECH INC
Device and System for Transcatheter Mitral Valve Replacement
InactiveUS20110319988A1Prevent perivalvular leakStentsHeart valvesExtracorporeal circulationBioprosthetic mitral valve replacement
This invention relates to the design and function of a compressible valve replacement prosthesis which can be deployed into a beating heart without extracorporeal circulation using a transcatheter delivery system. The design as discussed focuses on the deployment of a device via a minimally invasive fashion and by way of example considers a minimally invasive surgical procedure preferably utilizing the intercostal or subxyphoid space for valve introduction. In order to accomplish this, the valve is formed in such a manner that it can be compressed to fit within a delivery system and secondarily ejected from the delivery system into the annulus of a target valve such as a mitral valve or tricuspid valve.
Owner:AVALON MEDICAL +1
Percutaneous mitral valve replacement and sealing
ActiveUS20140257475A1Enhanced couplingStentsAnnuloplasty ringsBioprosthetic mitral valve replacementBiomedical engineering
Apparatus is provided for use with a prosthetic valve for implantation at a native valve of a subject, the native valve including at least one native leaflet, the apparatus including (1) a prosthetic valve support, including (a) an upstream support portion, being configured to be placed against an upstream side of the native valve, and having an inner perimeter that defines an opening that is configured to receive the prosthetic valve, and (b) at least one clip (i) comprising at least two clip arms and a clip-controller interface, the clip-controller interface being coupled to at least one of the clip arms, and (ii) being configured to be coupled to a native leaflet of the native valve; and (2) at least one clip controller, reversibly couplable to the clip-controller interface, and configured to facilitate opening and closing of the clip. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:CARDIOVALVE LTD
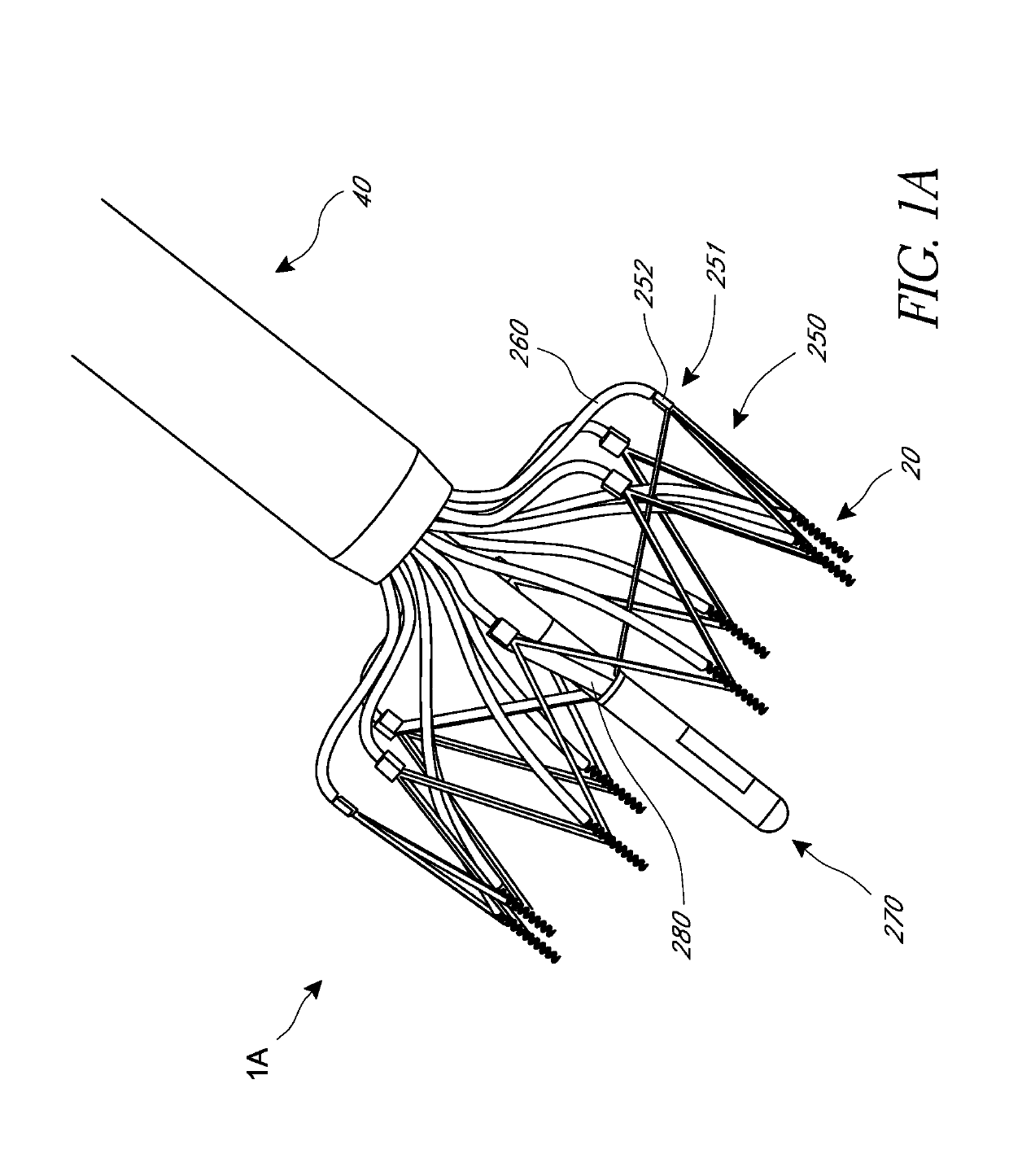
Delivery systems and methods for transcatheter prosthetic valves
ActiveUS20150196393A1Easy to deployHeart valvesProsthetic valveBioprosthetic mitral valve replacement
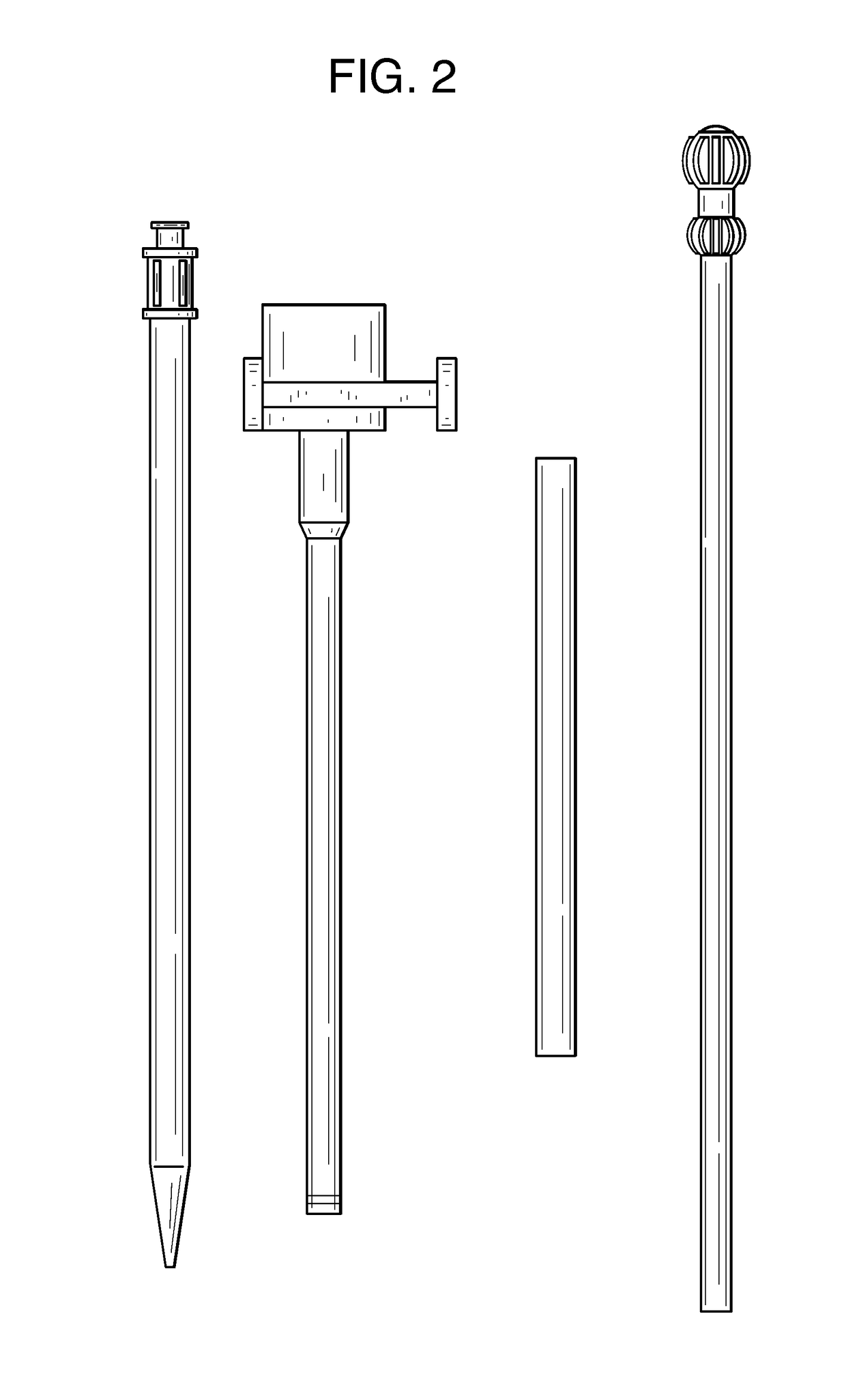
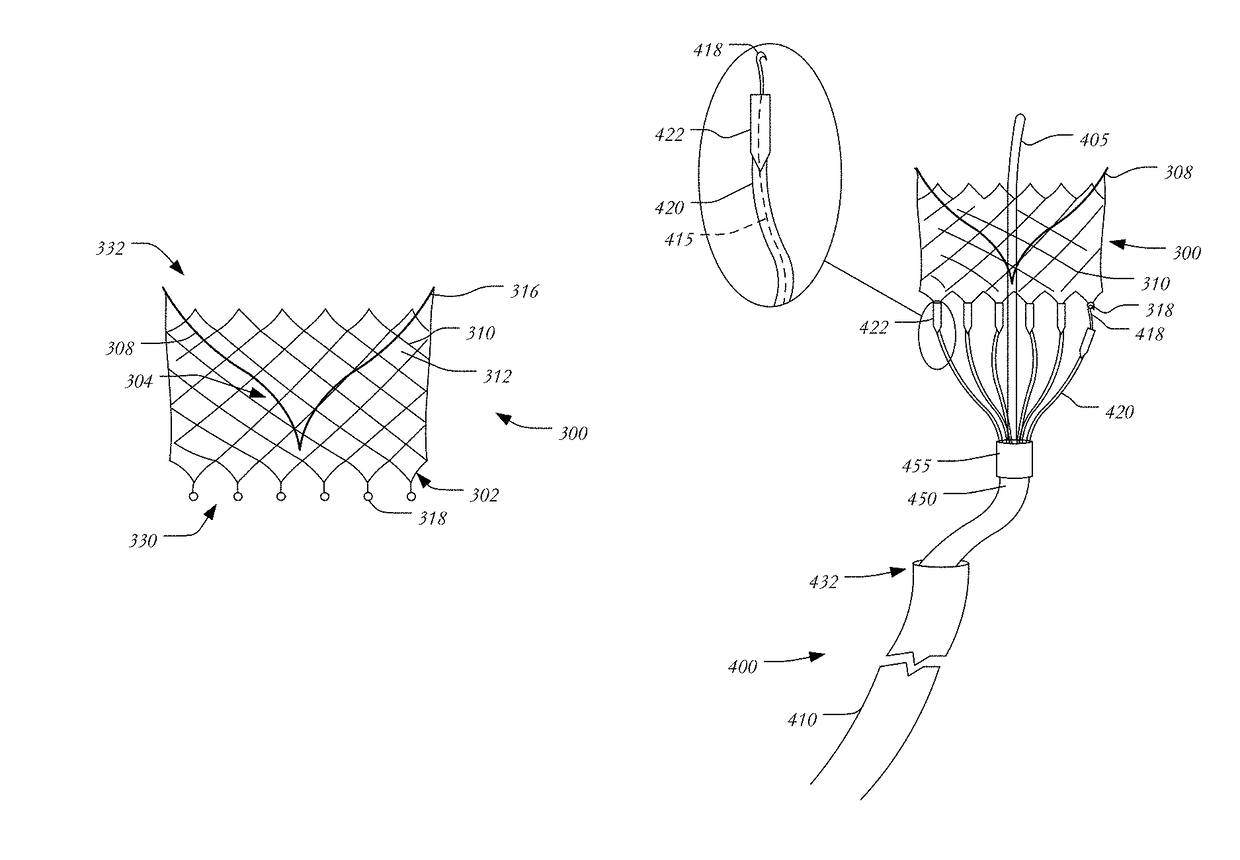
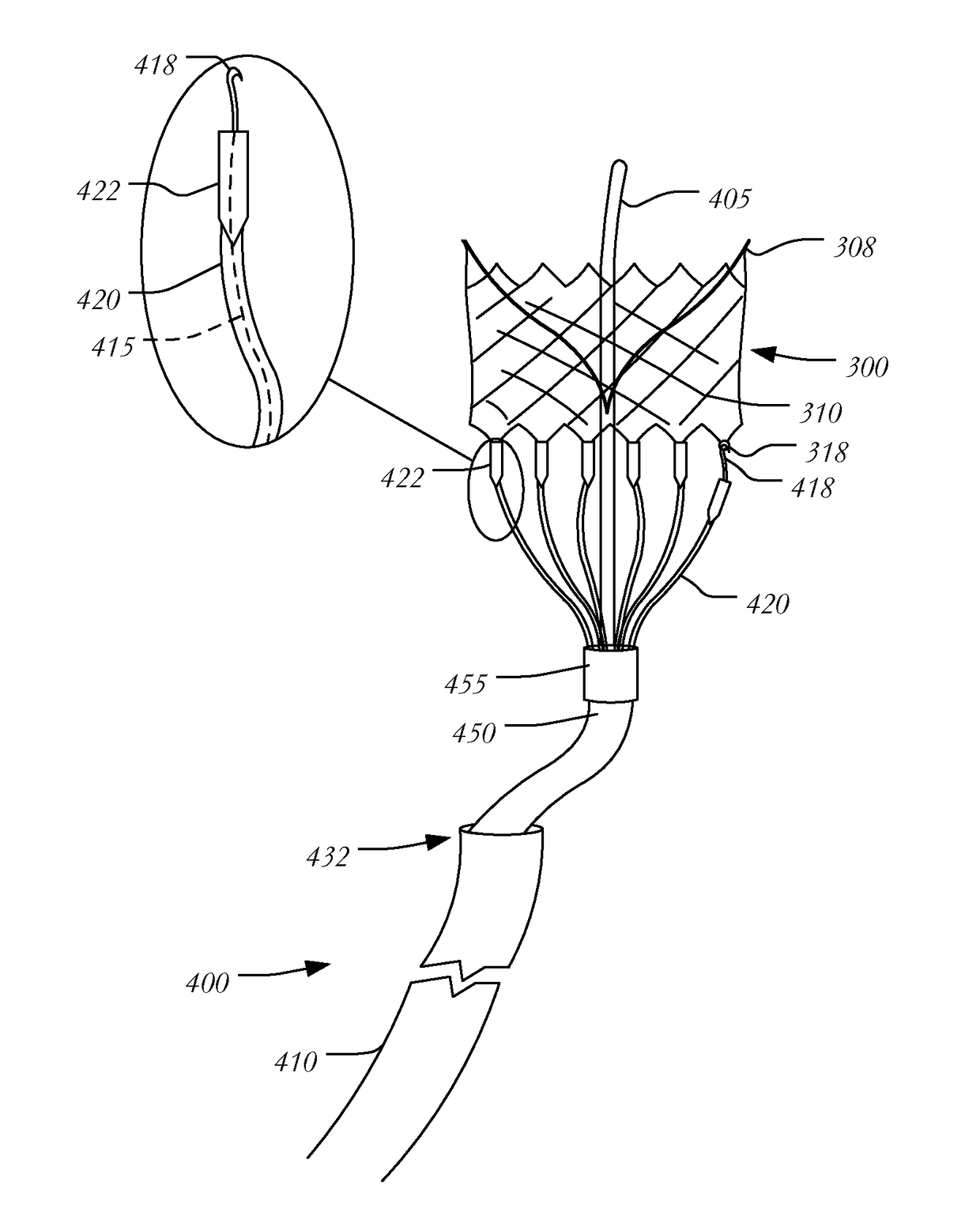
This invention relates to a delivery apparatus and method for deployment of a mitral valve replacement.
Owner:TENDYNE HLDG
Delivery systems and methods for transcatheter prosthetic valves
This invention relates to a delivery apparatus and method for deployment of a mitral valve replacement.
Owner:TENDYNE HLDG
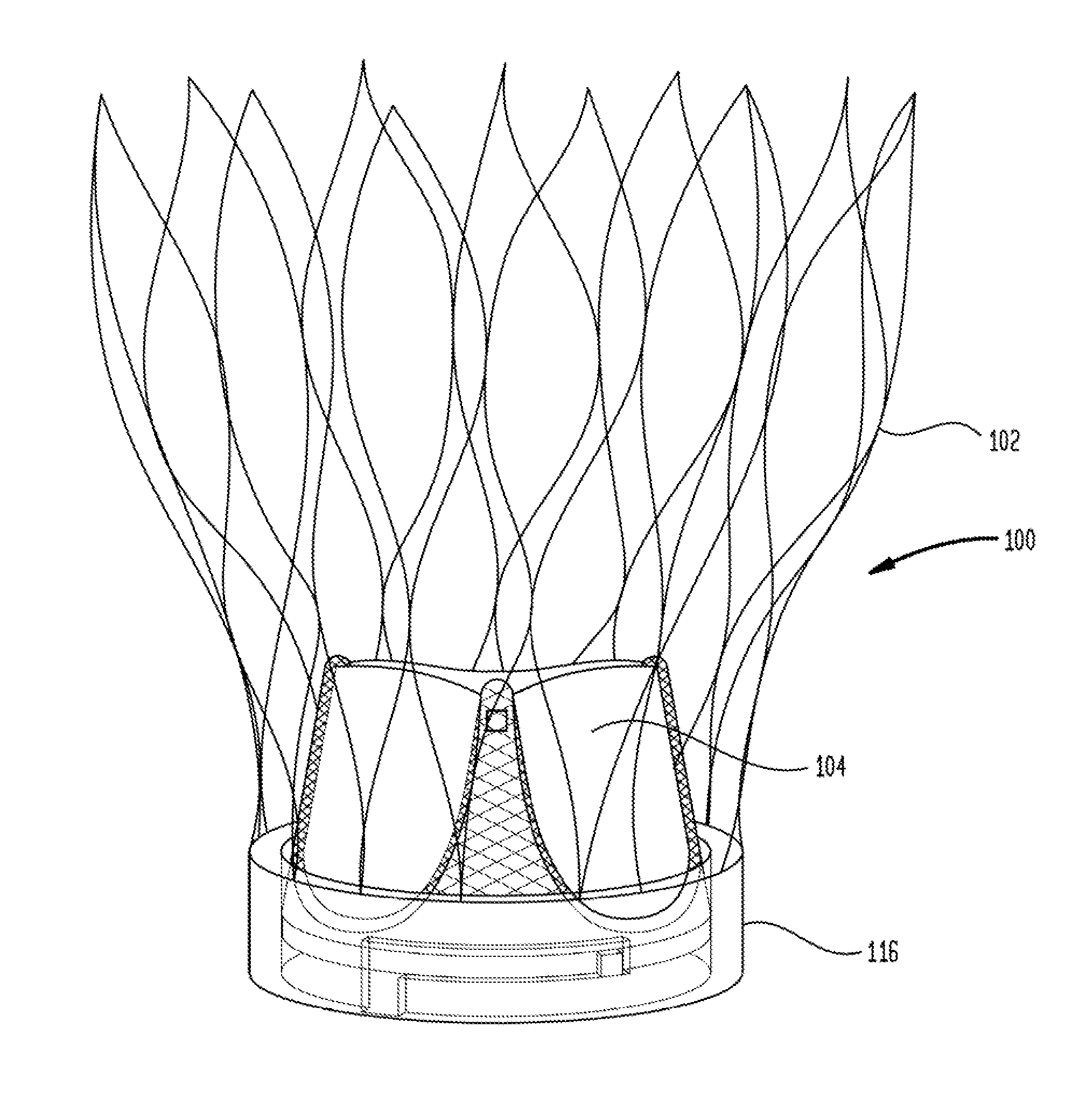
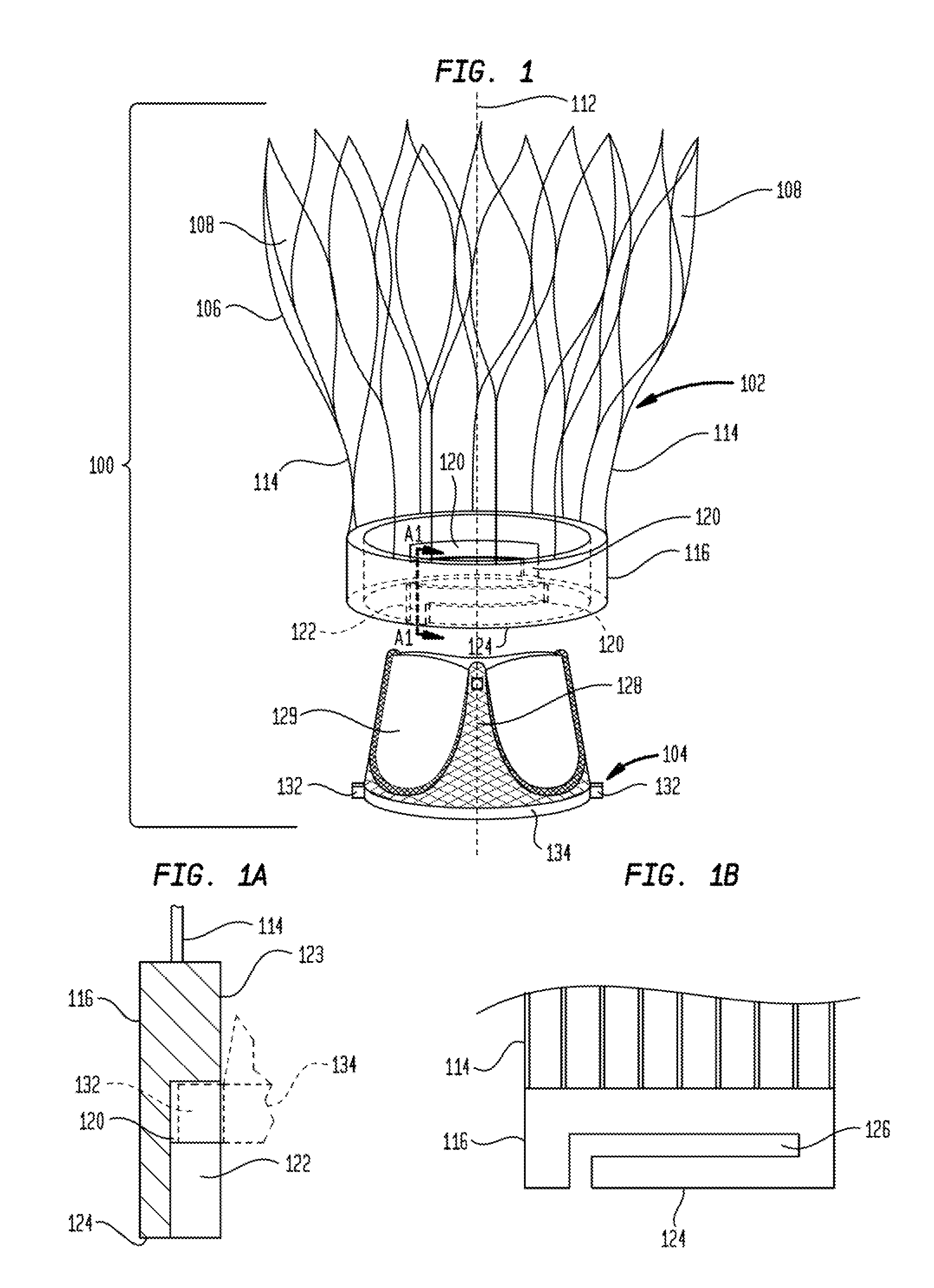
Transapical Mitral Valve Replacement
A prosthetic heart valve includes a collapsible and expandable stent having an outflow end and an inflow end, a plurality of commissure features attached to the stent, a plurality of anchoring features disposed on legs of the stent, the plurality of anchoring features being coupleable to a delivery device for repositioning, and a valve assembly disposed within the stent. The anchoring features may be configured to attach to heart tissue to help secure the prosthetic heart valve in an operating position.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
Techniques for percutaneous mitral valve replacement and sealing
ActiveUS20160324633A1Improve scalabilityEasy to compressStentsBalloon catheterBioprosthetic mitral valve replacementRat heart
Apparatus for use at a native heart valve of a subject is described. For some applications, the apparatus comprises a prosthetic valve support, configured (a) to be implanted at the native valve, (b) to facilitate, at a first period, implantation at the native valve of a first prosthetic valve, and (c) to facilitate, at a second period, implantation at the native valve of a second prosthetic valve. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:CARDIOVALVE LTD
Transcatheter Mitral Valve Replacement Apparatus
InactiveUS20150173898A1Reduced delivery profileIncrease blood flowBalloon catheterAnnuloplasty ringsBioprosthetic mitral valve replacementInsertion stent
Owner:DRASLER WILLIAM JOSEPH +3
Device and Method for Mitral Valve Regurgitation Treatment
ActiveUS20160235529A1Effective protectionHeart valvesBioprosthetic mitral valve replacementMitral valve leaflet
A mitral valve replacement device is adapted to be deployed at a mitral valve position in a human heart. The device has an atrial flange defining an atrial end of the device, a ventricular portion defining a ventricular end of the device, the ventricular portion having a height ranging between 2 mm to 15 mm, and an annulus support that is positioned between the atrial flange and the ventricular portion. The annulus support includes a ring of anchors extending radially therefrom, with an annular clipping space defined between the atrial flange and the ring of anchors. A plurality of leaflet holders positioned at the atrial end of the atrial flange, and a plurality of valve leaflets secured to the leaflet holders, and positioned inside the atrial flange at a location above the native annulus.
Owner:SINOMED CARDIOVITA TECH INC
Techniques for percutaneous mitral valve replacement and sealing
ActiveUS10376361B2Improve scalabilityEasy to compressStentsBalloon catheterPolyesterBioprosthetic mitral valve replacement
Apparatus is provided for use with a native valve of a heart of a subject. The apparatus includes: (1) an annular upstream support portion, comprising an expandable first frame, the upstream support portion configured to be placed against an upstream surface of the native valve; (2) a flexible polyester connector; and (3) an anchoring element, flexibly coupled to the upstream support portion by the connector, and configured to anchor the upstream support portion to the native valve by engaging tissue of the native valve.
Owner:CARDIOVALVE LTD
Techniques for percutaneous mitral valve replacement and sealing
ActiveUS10245143B2Improve scalabilityEasy to compressStentsBalloon catheterBioprosthetic mitral valve replacementProsthesis
Owner:CARDIOVALVE LTD
Device and method for mitral valve regurgitation treatment
ActiveUS9839511B2Effective protectionHeart valvesBioprosthetic mitral valve replacementMitral valve leaflet
A mitral valve replacement device is adapted to be deployed at a mitral valve position in a human heart. The device has an atrial flange defining an atrial end of the device, a ventricular portion defining a ventricular end of the device, the ventricular portion having a height ranging between 2 mm to 15 mm, and an annulus support that is positioned between the atrial flange and the ventricular portion. The annulus support includes a ring of anchors extending radially therefrom, with an annular clipping space defined between the atrial flange and the ring of anchors. A plurality of leaflet holders positioned at the atrial end of the atrial flange, and a plurality of valve leaflets secured to the leaflet holders, and positioned inside the atrial flange at a location above the native annulus.
Owner:SINOMED CARDIOVITA TECH INC
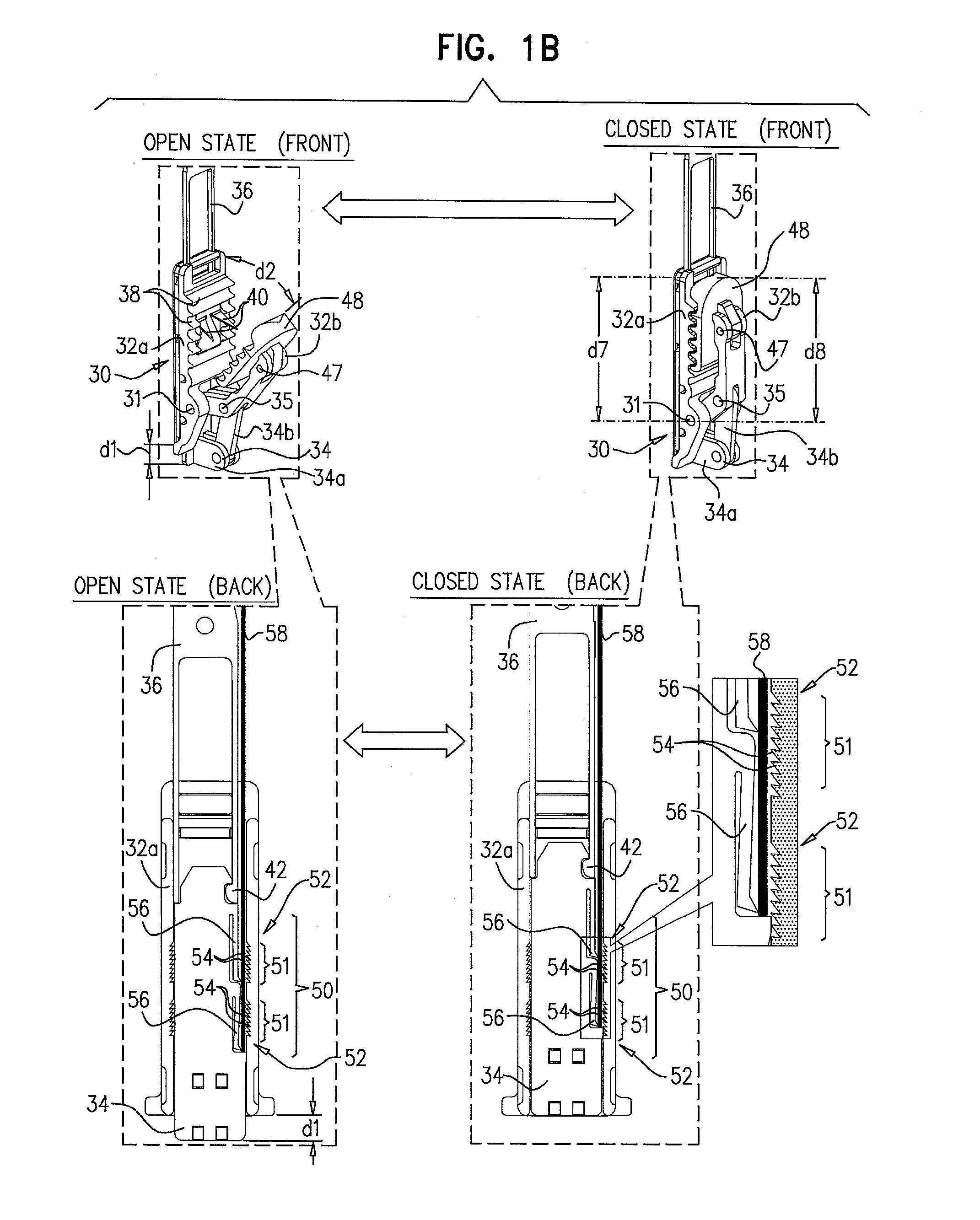
Sutureless prosthetic device
InactiveUS20140243964A1Minimize cardiopulmonary bypass timeMinimize timeHeart valvesProsthetic valveBioprosthetic mitral valve replacement
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
Sutureless prosthetic device
InactiveUS9326850B2Minimize timeHeart valvesBlood vesselsProsthetic valveBioprosthetic mitral valve replacement
A prosthetic device for use in an anatomical orifice or lumen of a patient includes an expandable first stent structure coupled to a valve support structure having at least one leaflet. The stent structure includes a collar provided with at least one groove or opening adapted to engage a tab extending from the valve support structure. Rotation of the stent structure and valve support structure relative to one another assembles the prosthetic valve device. The prosthetic valve device may be used for sutureless treatment of various valvular conditions such as aorta stenosis and mitral valve replacement.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
Transapical mitral valve replacement
A prosthetic heart valve includes a collapsible and expandable stent having an outflow end and an inflow end, a plurality of commissure features attached to the stent, a plurality of anchoring features disposed on legs of the stent, the plurality of anchoring features being coupleable to a delivery device for repositioning, and a valve assembly disposed within the stent. The anchoring features may be configured to attach to heart tissue to help secure the prosthetic heart valve in an operating position.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
Transapical mitral valve replacement
A prosthetic heart valve includes a collapsible and expandable stent having an outflow end and an inflow end, a plurality of commissure features attached to the stent, a plurality of anchoring features disposed on legs of the stent, the plurality of anchoring features being coupleable to a delivery device for repositioning, and a valve assembly disposed within the stent. The anchoring features may be configured to attach to heart tissue to help secure the prosthetic heart valve in an operating position.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
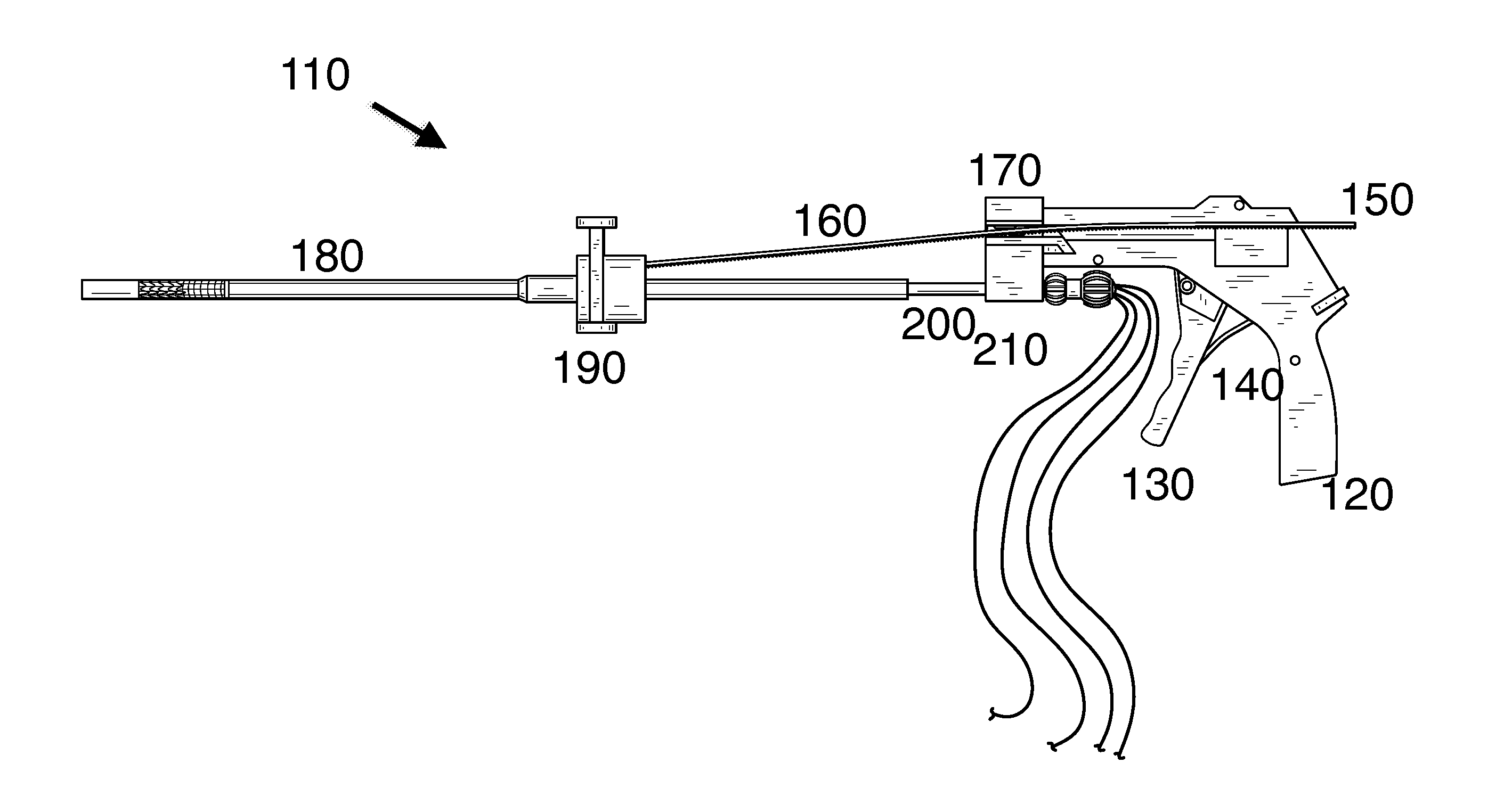
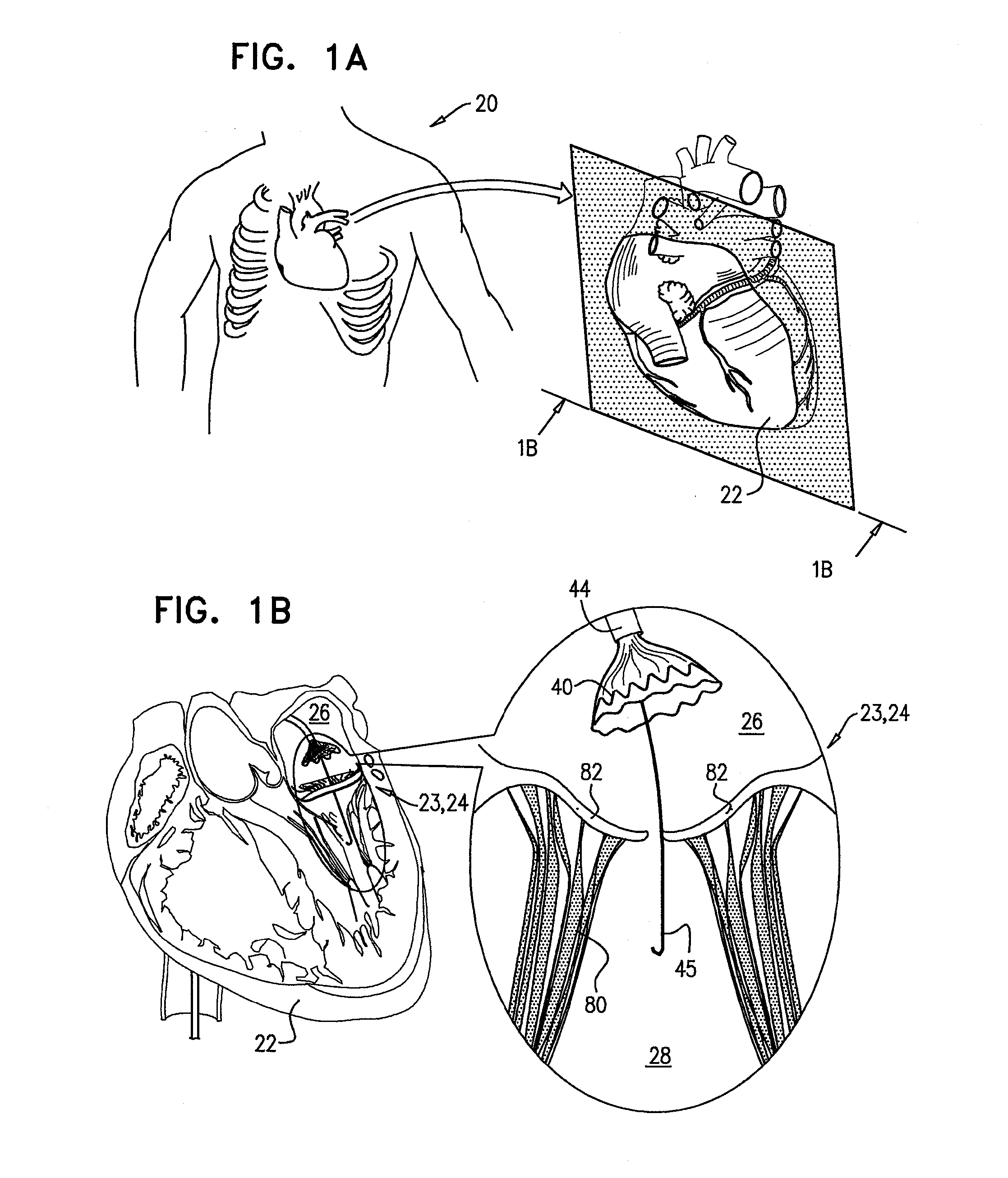
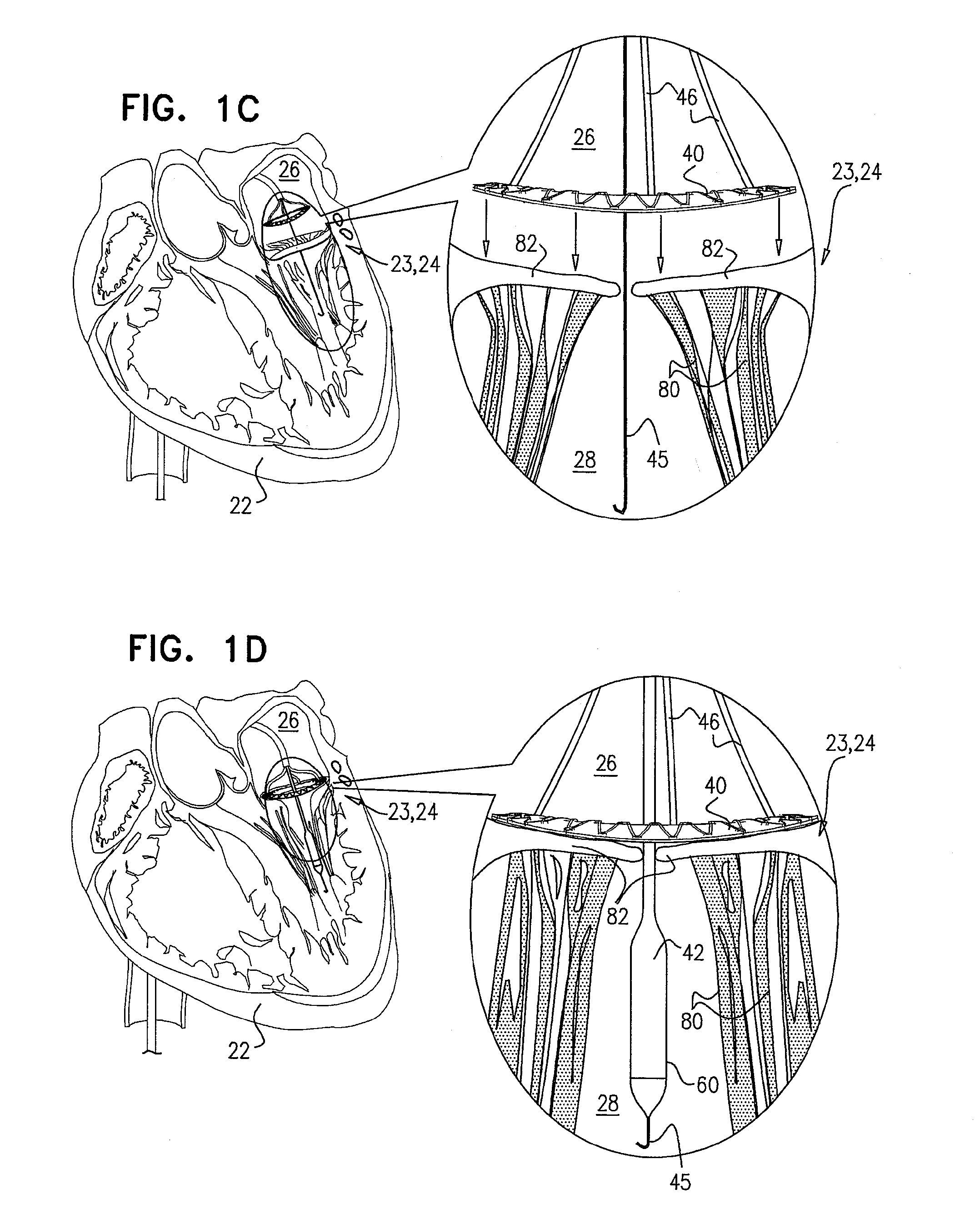
Methods for delivery of heart valve devices using intravascular ultrasound imaging
ActiveUS20170086974A1Shorten the construction periodReduce eliminateOrgan movement/changes detectionHeart valvesAnatomical landmarkBioprosthetic mitral valve replacement
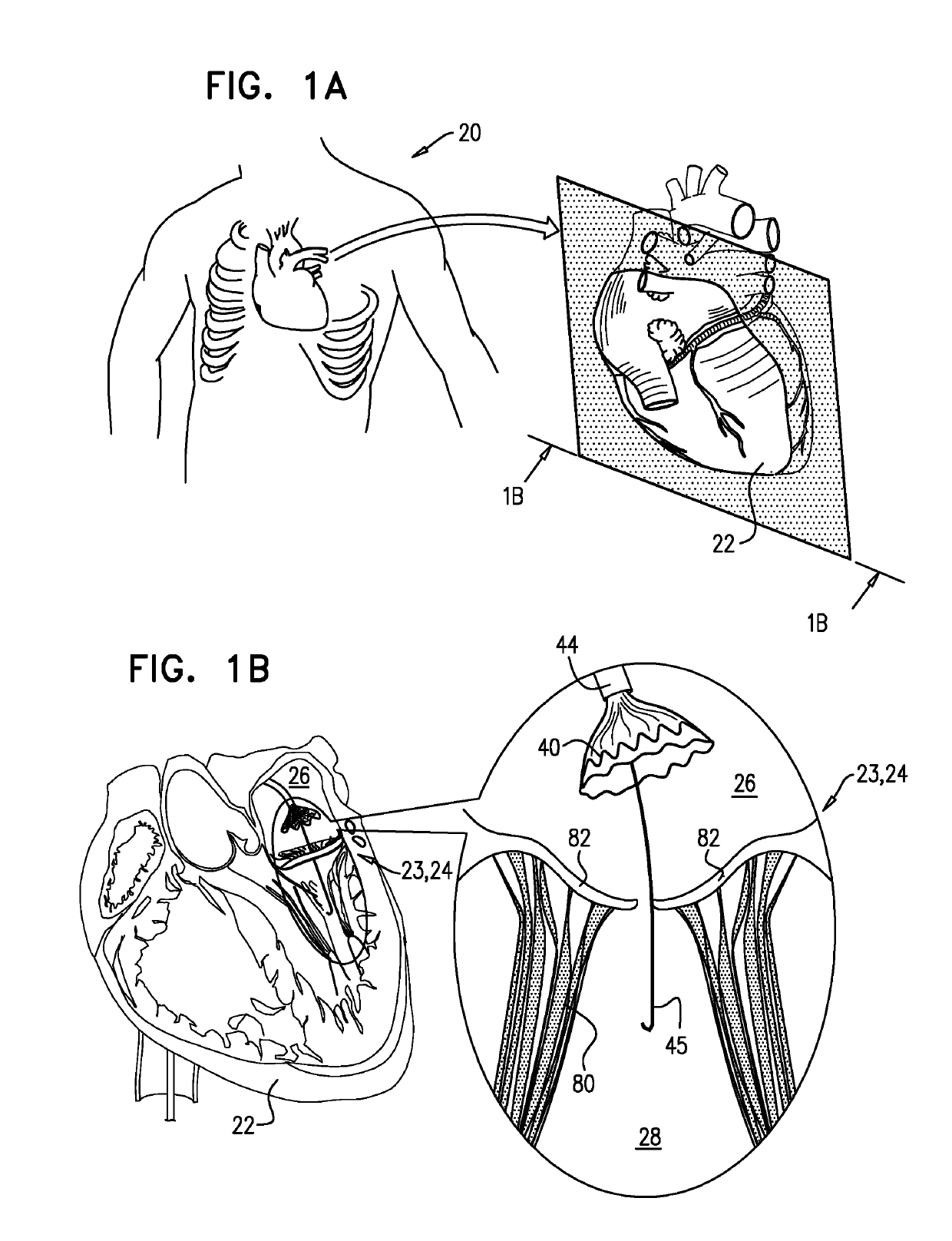
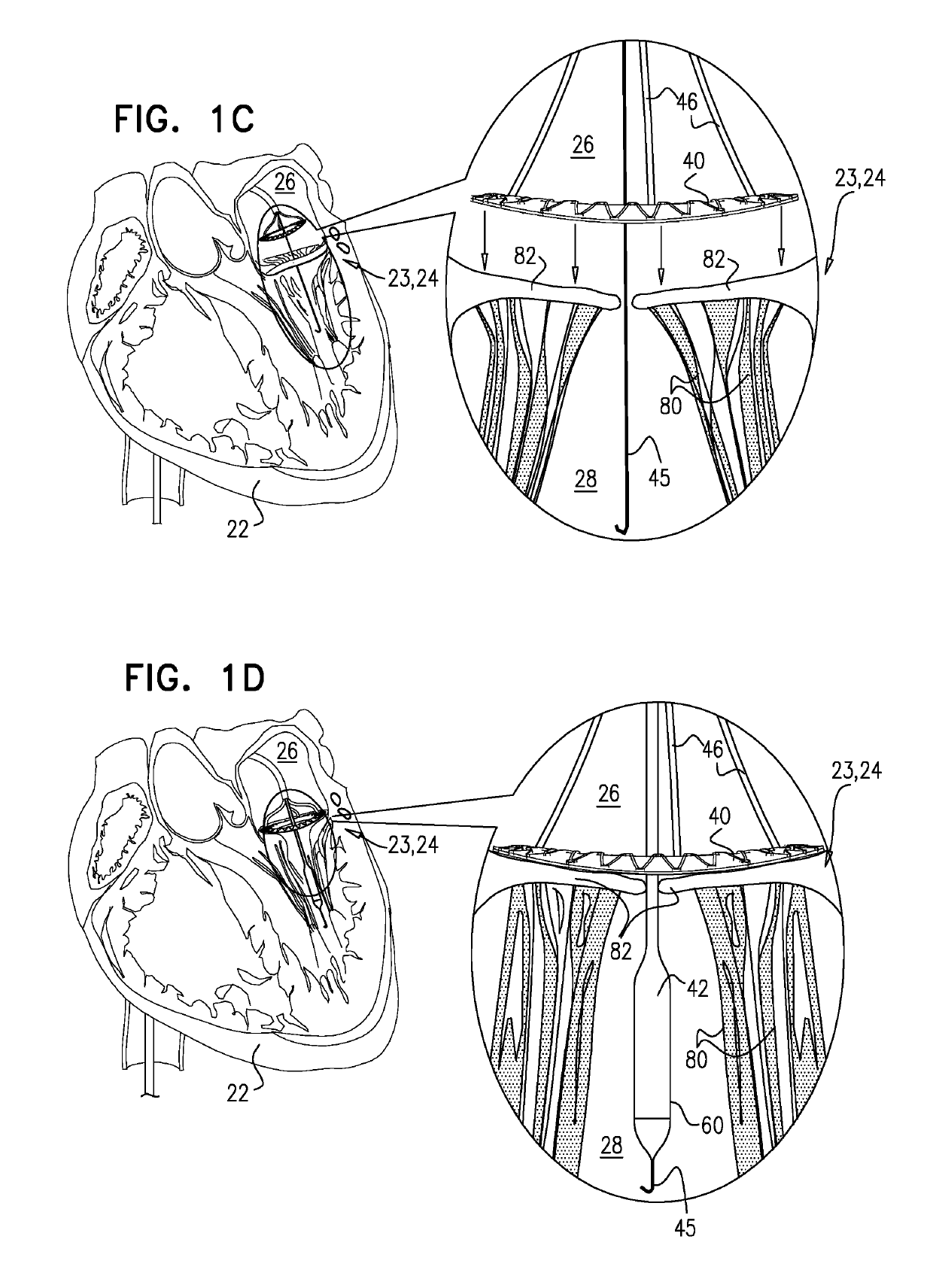
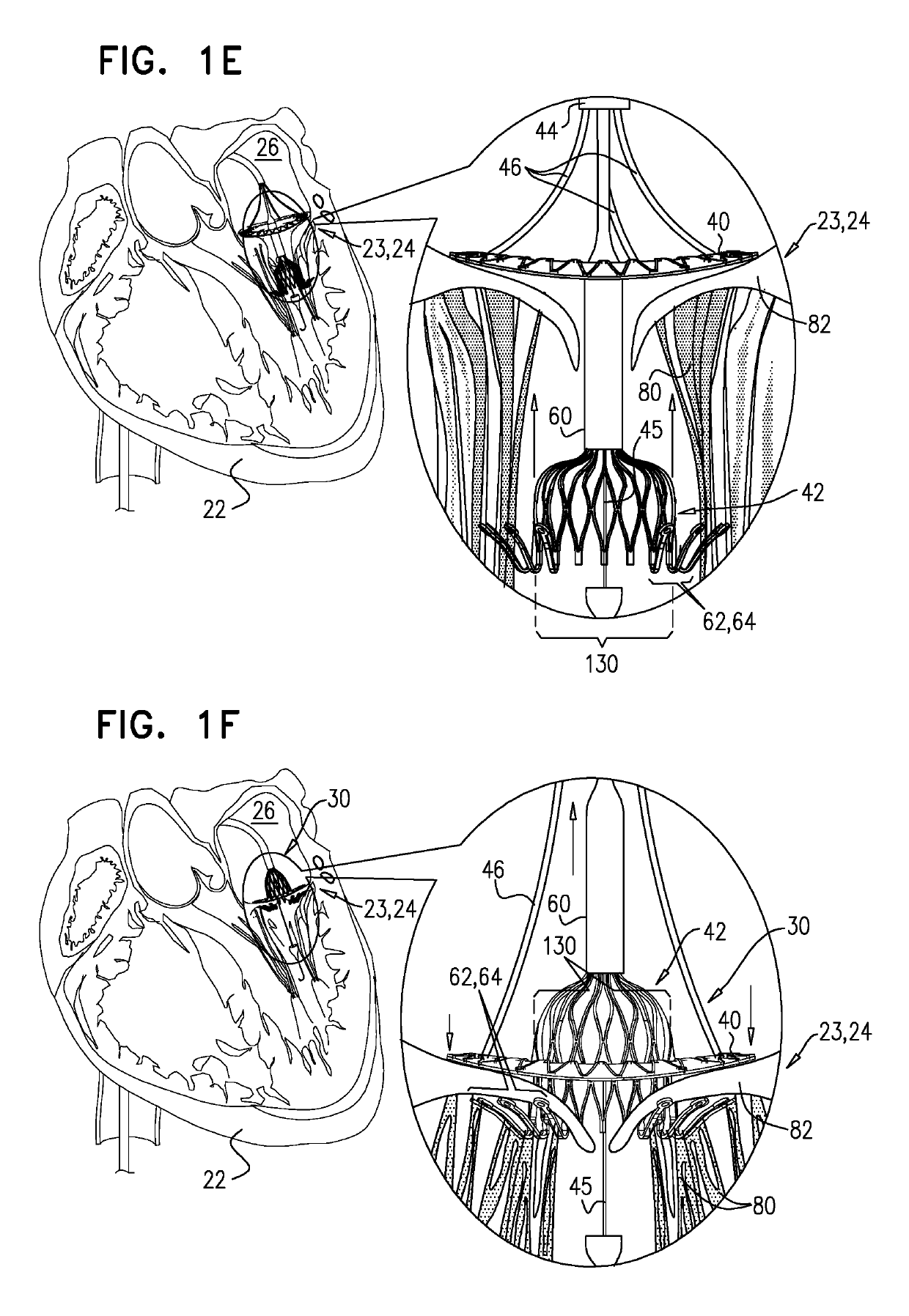
Methods related to delivery of various heart valve implants are described. The implant may be delivered using an ultrasound imaging delivery system. The ultrasound imaging delivery system may be used to deliver a variety of different devices, including mitral valve reshaping devices, mitral valve replacement valves, and others. A deployment catheter carrying an implant having a tissue anchor is advanced to a deployment site in a heart. An imaging element is positioned adjacent the implant and a relationship between the tissue anchor and an anatomical landmark in the heart is visualized. The implant is then attached by driving the tissue anchor into tissue in the heart.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Methods for delivery of heart valve devices using intravascular ultrasound imaging
ActiveUS10335275B2Reduce eliminateSmall diameterOrgan movement/changes detectionHeart valvesAnatomical landmarkBioprosthetic mitral valve replacement
Methods related to delivery of various heart valve implants are described. The implant may be delivered using an ultrasound imaging delivery system. The ultrasound imaging delivery system may be used to deliver a variety of different devices, including mitral valve reshaping devices, mitral valve replacement valves, and others. A deployment catheter carrying an implant having a tissue anchor is advanced to a deployment site in a heart. An imaging element is positioned adjacent the implant and a relationship between the tissue anchor and an anatomical landmark in the heart is visualized. The implant is then attached by driving the tissue anchor into tissue in the heart.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Methods, devices and systems for transcatheter mitral valve replacement in a double-orifice mitral valve
ActiveUS20160302920A1Balloon catheterHeart valvesBioprosthetic mitral valve replacementMitral valve leaflet
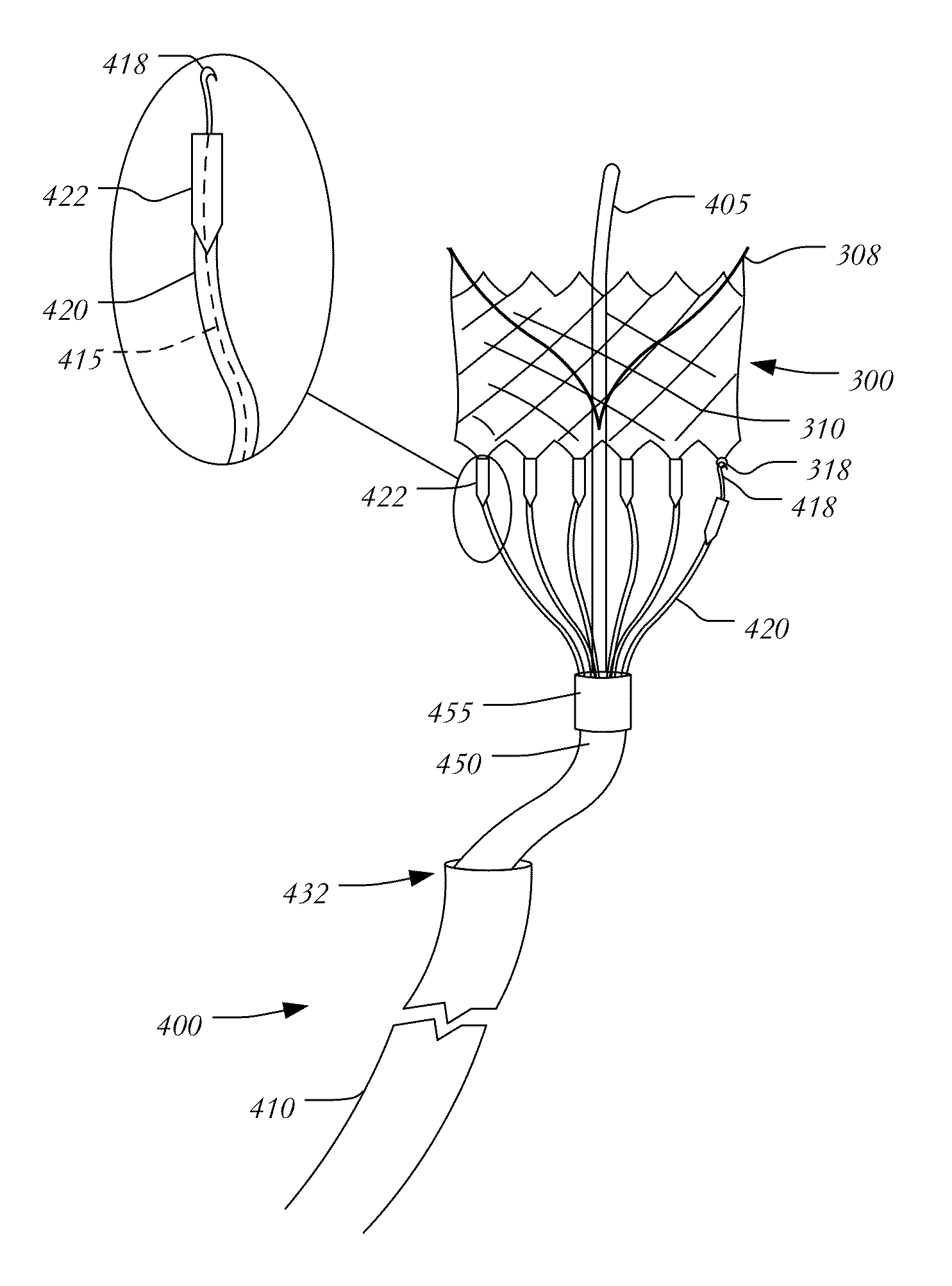
In various embodiments, provided herein are methods, devices and systems for transcatheter mitral valve replacement in a double-orifice mitral valve. These methods, devices and systems are used to treat patients with mitral valve disease, particularly those who have had failed edge-to-edge leaflet repair, or patients presently considered anatomically unsuitable for edge-to-edge leaflet repair alone.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
Methods for delivery of heart valve devices using intravascular ultrasound imaging
ActiveUS20190321176A1Reduce eliminateSmall diameterOrgan movement/changes detectionHeart valvesAnatomical landmarkUltrasound imaging
Methods related to delivery of various heart valve implants are described. The implant may be delivered using an ultrasound imaging delivery system. The ultrasound imaging delivery system may be used to deliver a variety of different devices, including mitral valve reshaping devices, mitral valve replacement valves, and others. A deployment catheter carrying an implant having a tissue anchor is advanced to a deployment site in a heart. An imaging element is positioned adjacent the implant and a relationship between the tissue anchor and an anatomical landmark in the heart is visualized. The implant is then attached by driving the tissue anchor into tissue in the heart.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Mitral valve replacement system for percutaneous transcatheter
PendingCN112137764APrevention of Weekly LeakagePeripheral leakage reducedHeart valvesHeart apexBioprosthetic mitral valve replacement
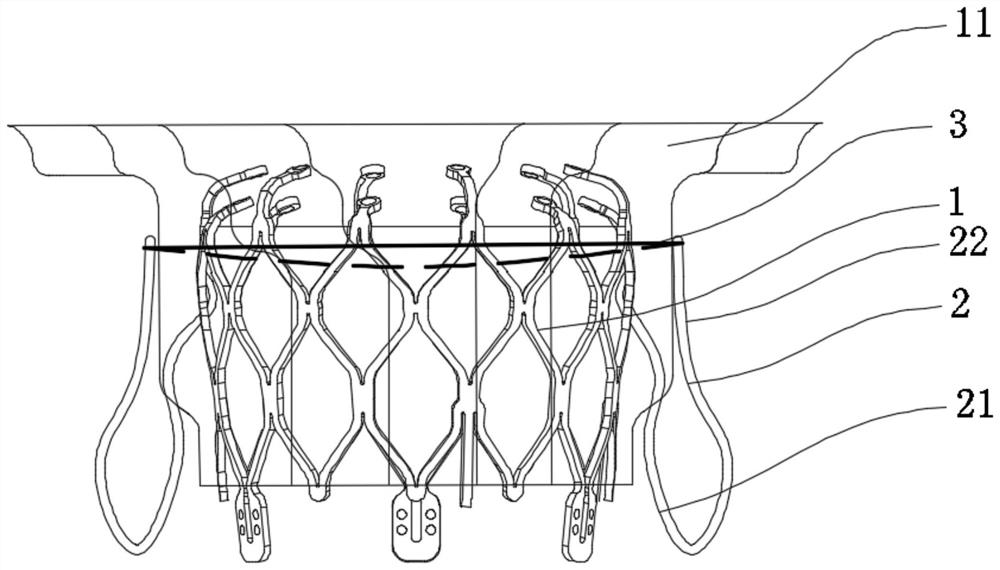
The invention relates to a mitral valve replacement system for a percutaneous transcatheter, and belongs to the technical field of medical instruments. The mitral valve replacement system comprises avalve frame supporting body, an artificial valve leaflet and a ventricular septum anchoring structure. The valve frame supporting body is arranged between an atrium and a ventricle and provided with ahollow cavity with the two ends open. The artificial valve leaflet is arranged on the inner wall of the cavity of the valve frame supporting body. The ventricular septum anchoring structure is arranged between the valve frame supporting body and a ventricular septum. The invention provides the mitral valve replacement device intervened through a catheter via a femoral vein admission passage and aims to solve the problems that an existing interventional mitral valve system is generally large in valve stent, has the left ventricular outflow passage obstruction risk, has potential complicationsin transapical admission passage and anchoring and the like, and the mitral valve replacement device provided by the invention is more minimally invasive and firmer in anchoring, and the technical scheme of mitral valve replacement suffering from left ventricular outflow tract obstruction can be effectively avoided.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN HOSPITAL FUDAN UNIV +1
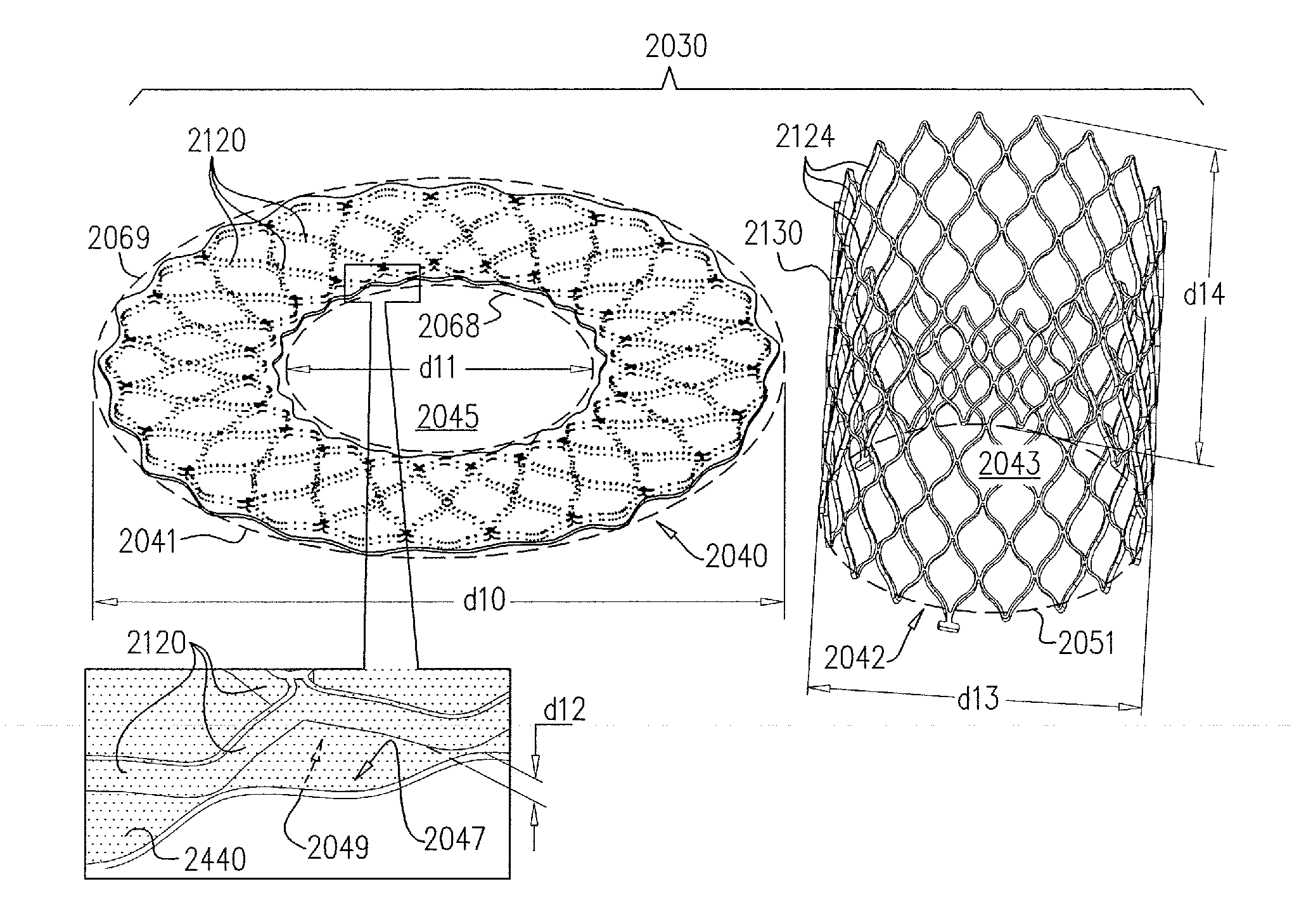
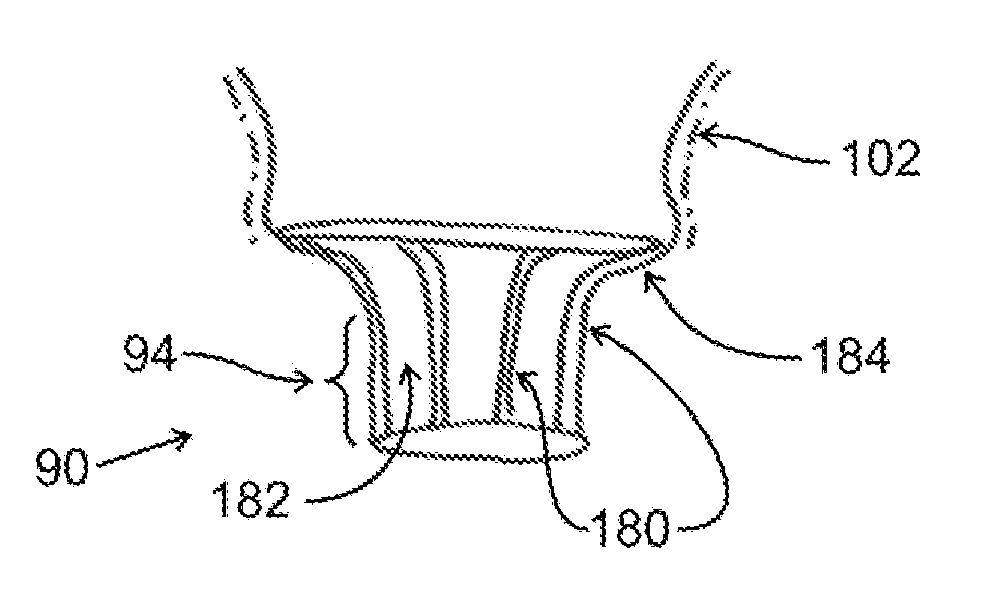
Prosthetic valve for mitral valve replacement
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Percutaneous mitral valve replacement device
ActiveCN107787209ABalloon catheterHeart valvesProsthetic valveBioprosthetic mitral valve replacement
In one representative embodiment, a prosthetic valve assembly for replacing a native heart valve comprises a radially expandable and compressible support structure, the support structure comprising anannular frame having a lumen extending from an inflow end to an outflow end, the support structure further comprising an annular sealing member extending radially inwardly into the lumen of the frameand having an inner peripheral portion defining an orifice, and a radially expandable and compressible valve component, the valve component comprising an annular frame and a valve structure supportedinside of the frame for permitting the flow blood through the valve component in one direction and blocking the flow of blood in the opposite direction, wherein the valve component is configured to expand within the orifice of the sealing member and engage the inner peripheral portion of the sealing member when radially expanded.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Device and method for mitral valve regurgitation method
A mitral valve replacement device is adapted to be deployed at a mitral valve position in a human heart. The device has an atrial flange defining an atrial end of the device, a ventricular portion defining a ventricular end of the device, the ventricular portion having a height ranging between 2 mm to 15 mm, and an annulus support that is positioned between the atrial flange and the ventricular portion. The annulus support includes a ring of anchors extending radially therefrom, with an annular clipping space defined between the atrial flange and the ring of anchors. A plurality of leaflet holders positioned at the atrial end of the atrial flange, and a plurality of valve leaflets secured to the leaflet holders, and positioned inside the atrial flange at a location above the native annulus.
Owner:赛诺心畅医疗科技有限公司
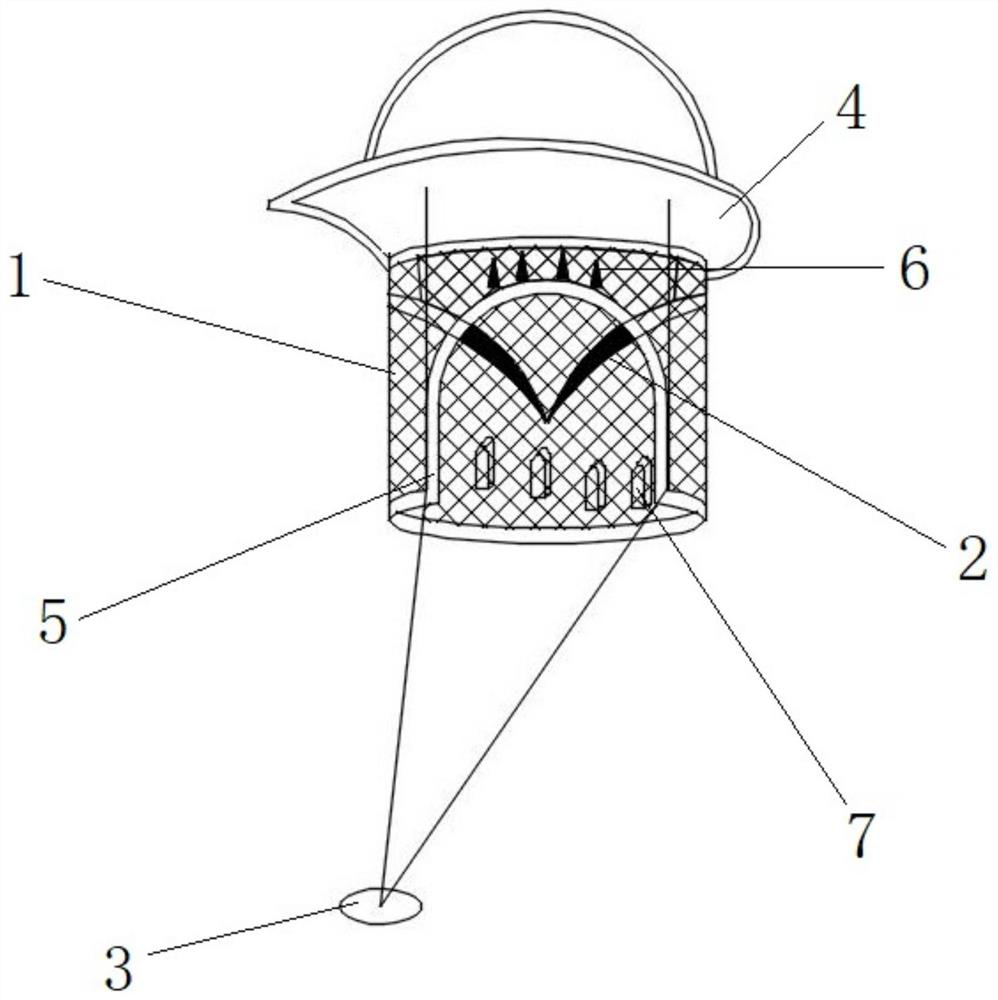
Heart valve prosthesis capable of being anchored with autologous valve leaflets
InactiveCN113730036AAvoid influenceReduce the impactAnnuloplasty ringsHeart valvesBioprosthetic mitral valve replacementRat heart
The invention relates to the field of medical instruments, in particular to a heart valve prosthesis capable of being anchored with autologous valve leaflets. The heart valve prosthesis comprises: a valve stent with a preset form; a clamping mechanism which has a preset form, wherein the near end of the clamping mechanism is connected with the valve stent, and at least part of the clamping mechanism is attached to the outer side of the valve stent; and an anchoring ring which is connected with the far end of the clamping mechanism in a matched mode, wherein when the clamping mechanism is released, the clamping mechanism is located on the periphery of the autologous valve leaflet, the anchoring ring surrounds the autologous valve leaflet, and when the valve stent is released, the clamping mechanism is attached to the valve stent, and the valve stent supports the anchoring ring in the radial direction. In addition, the anchoring ring in the scheme can curl part of the autologous valve leaflet, the influence of original valve leaflet tissue on blood flow after replacement is reduced, the two technical pain points about mitral valve replacement therapy in the prior art are solved, and good clinical significance is achieved.
Owner:NINGBO JENSCARE BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
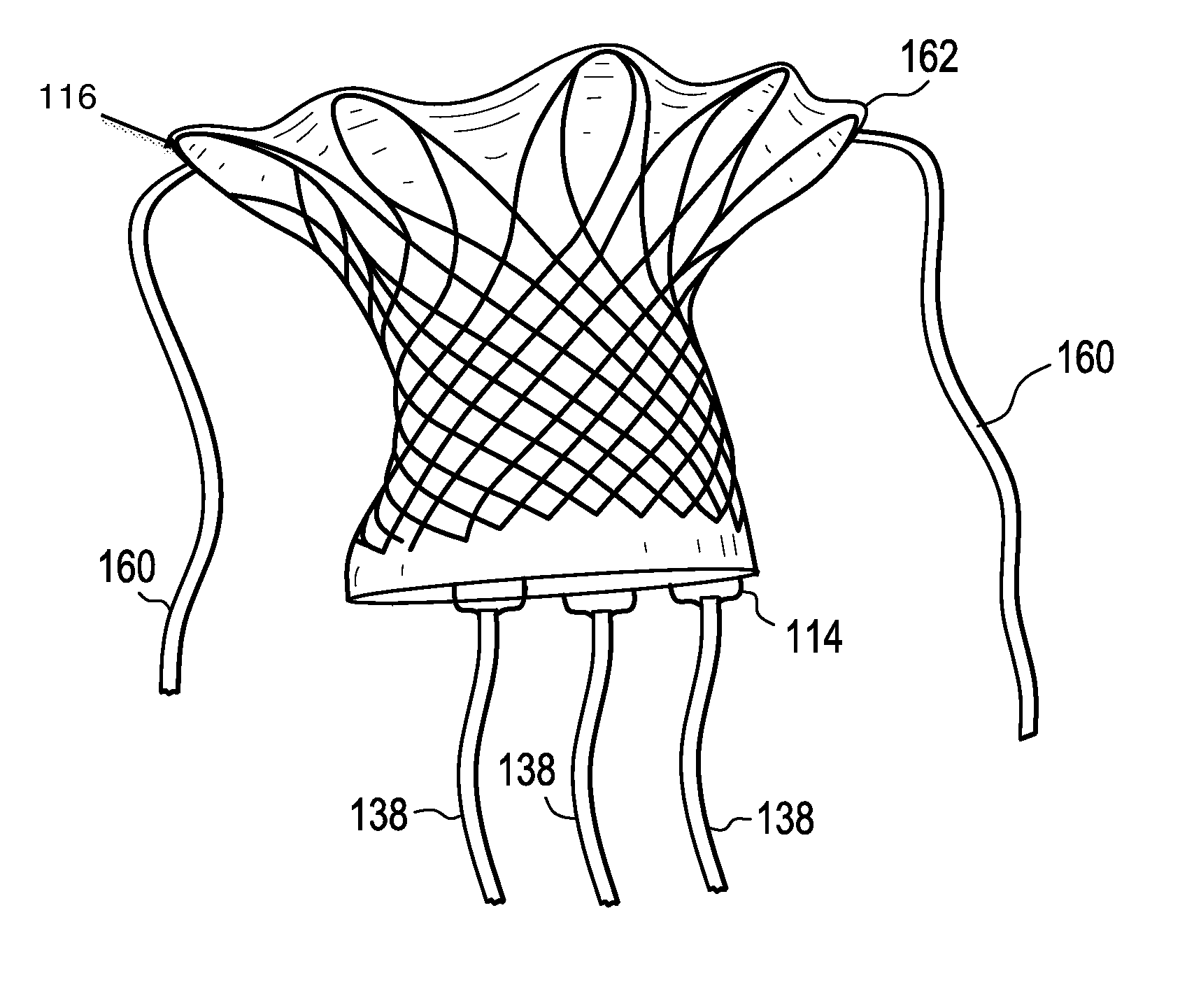
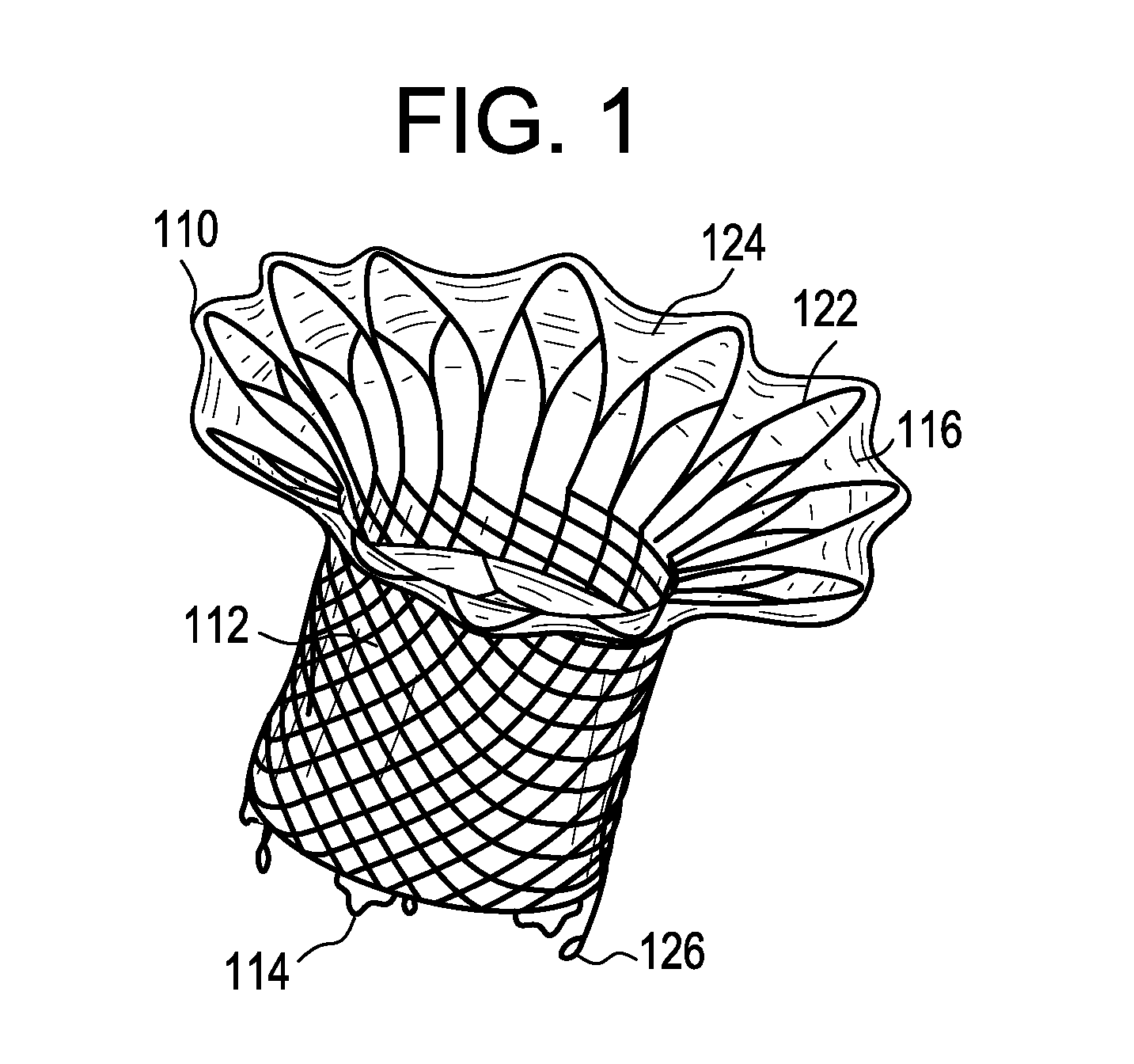
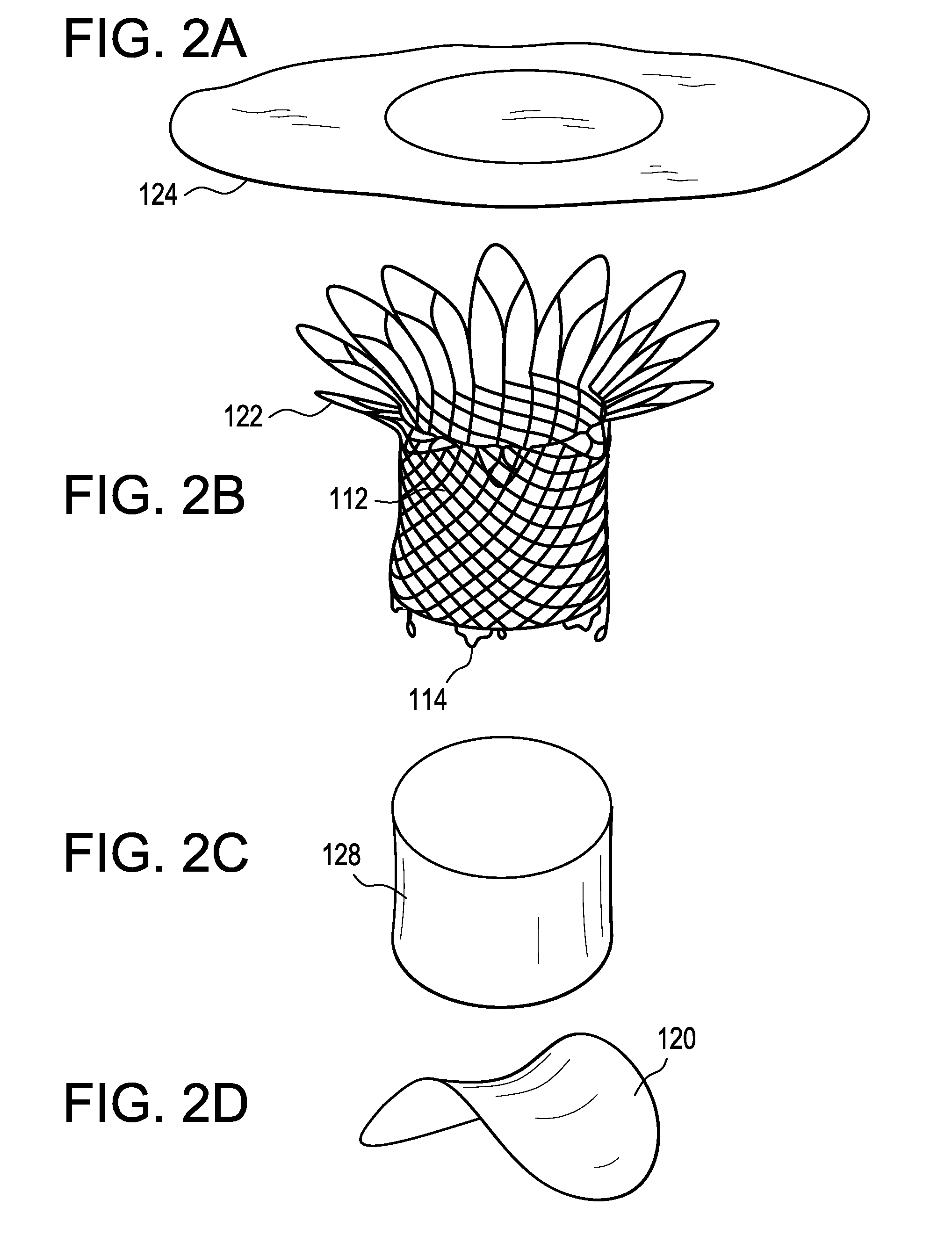
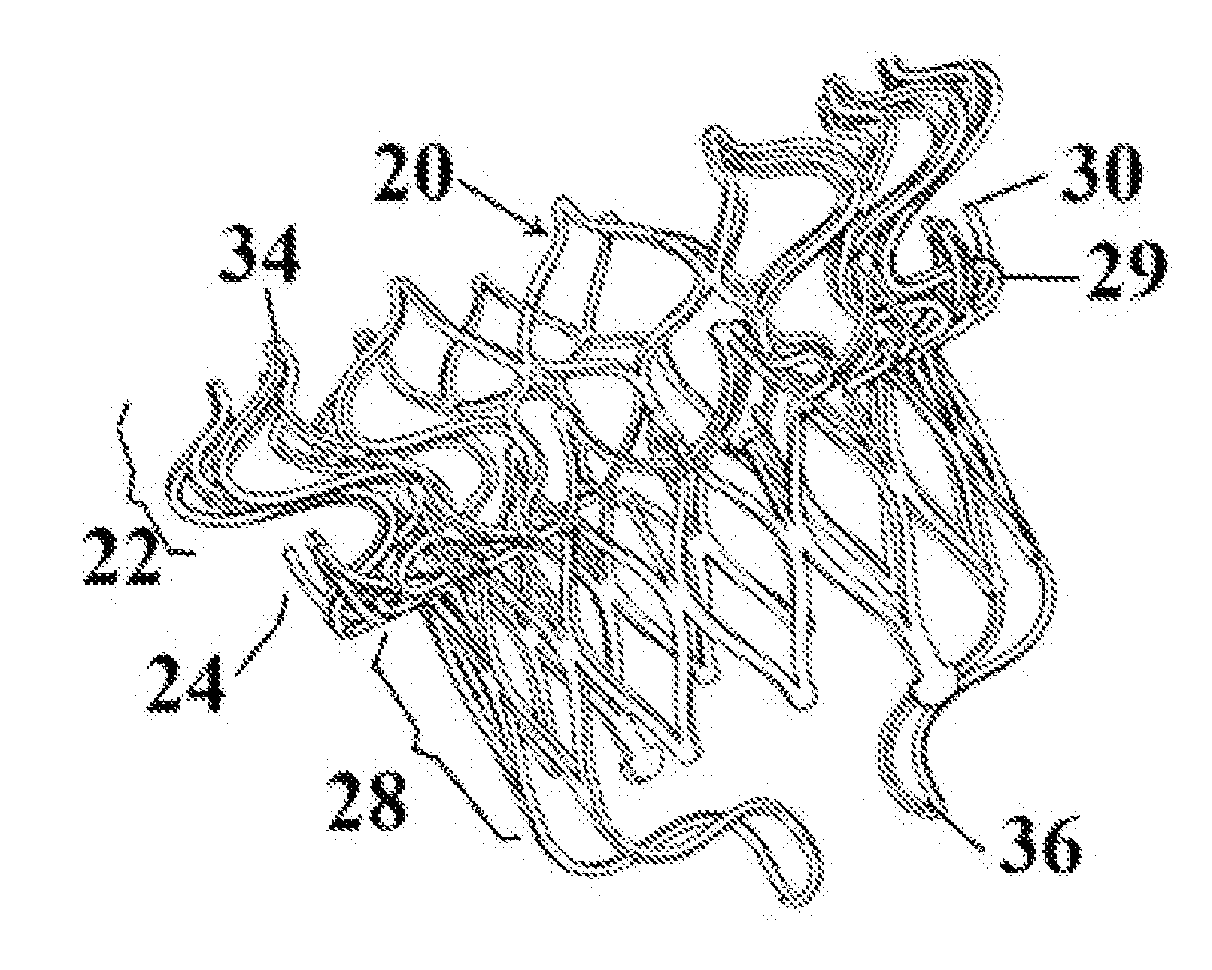
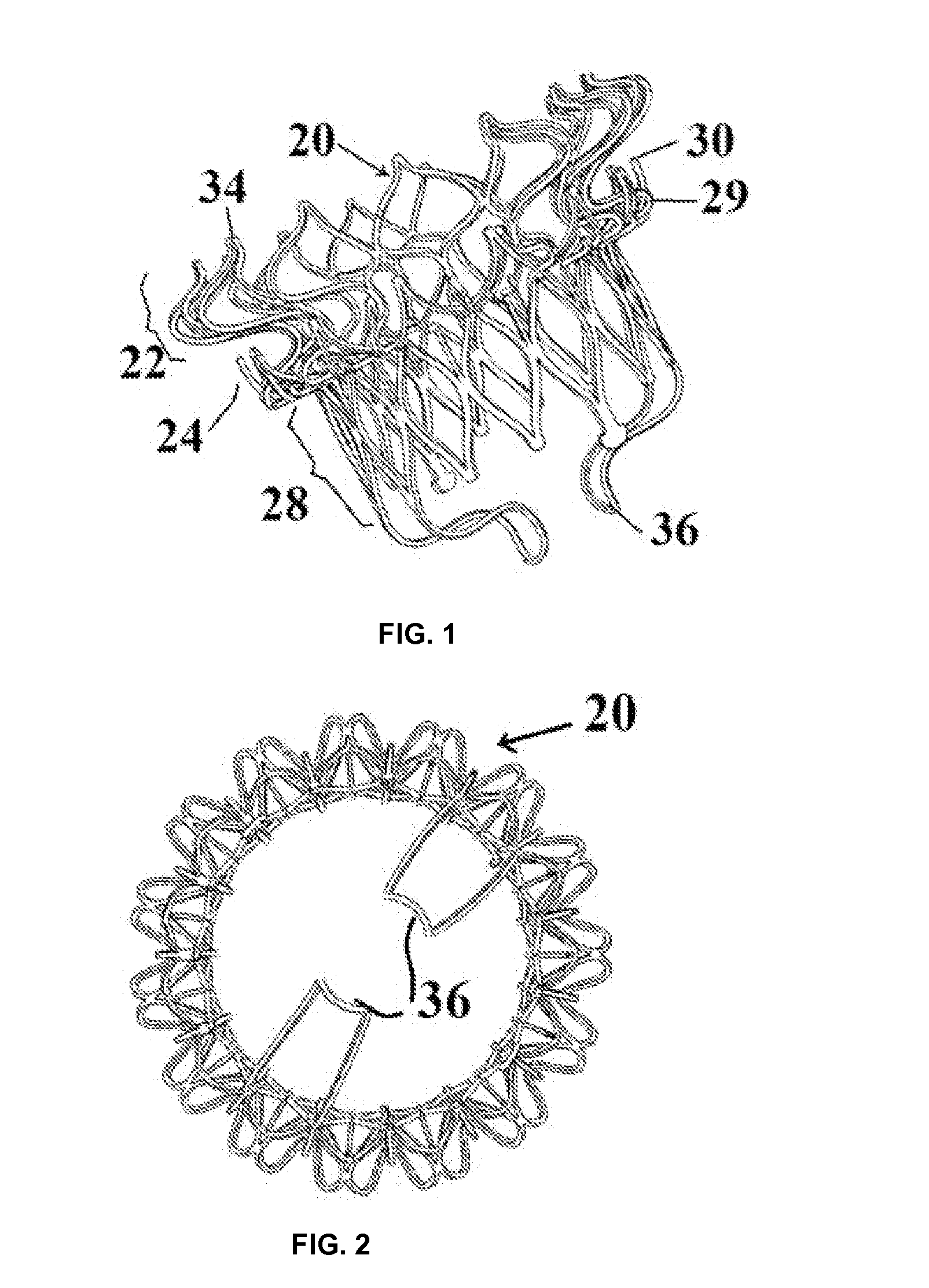
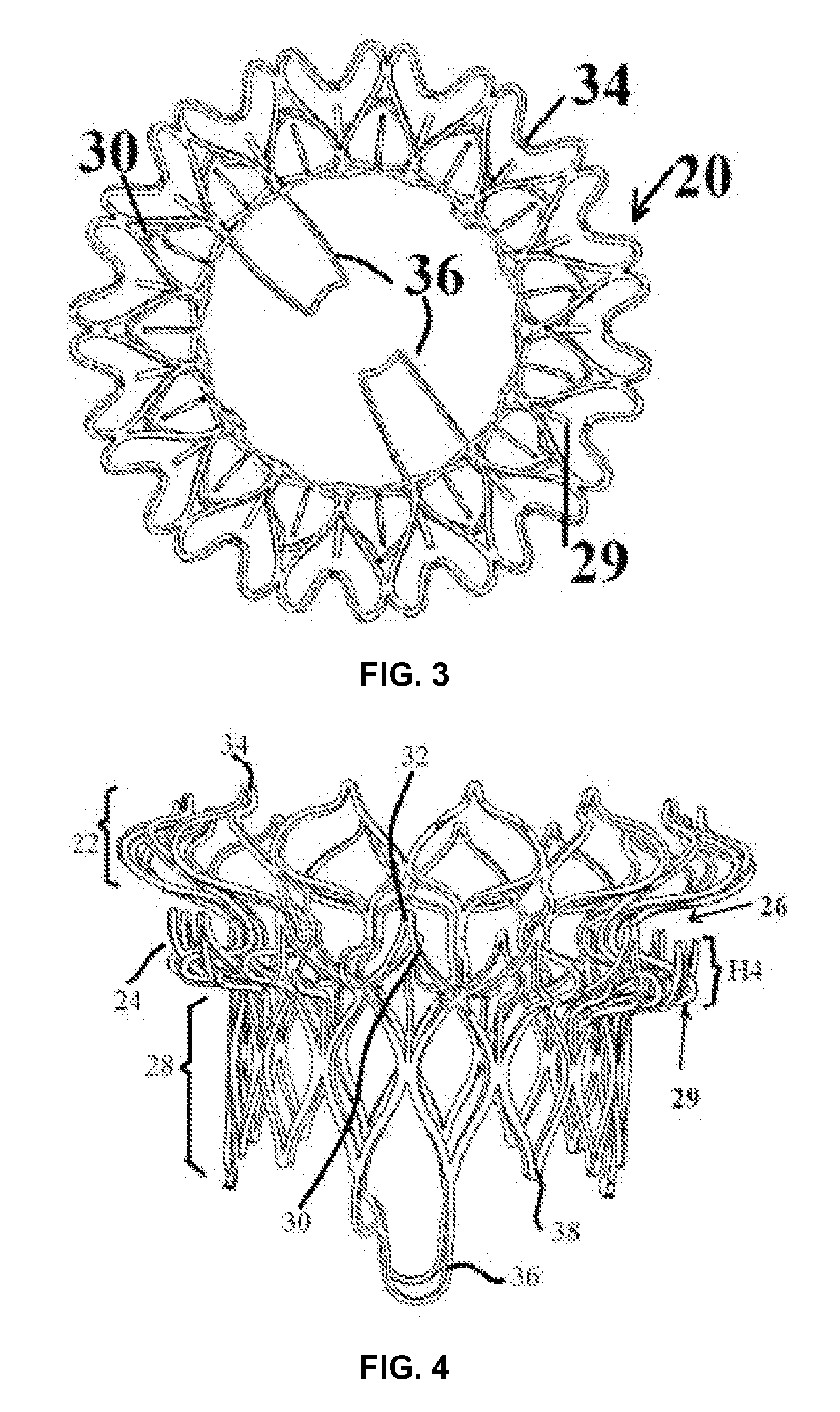
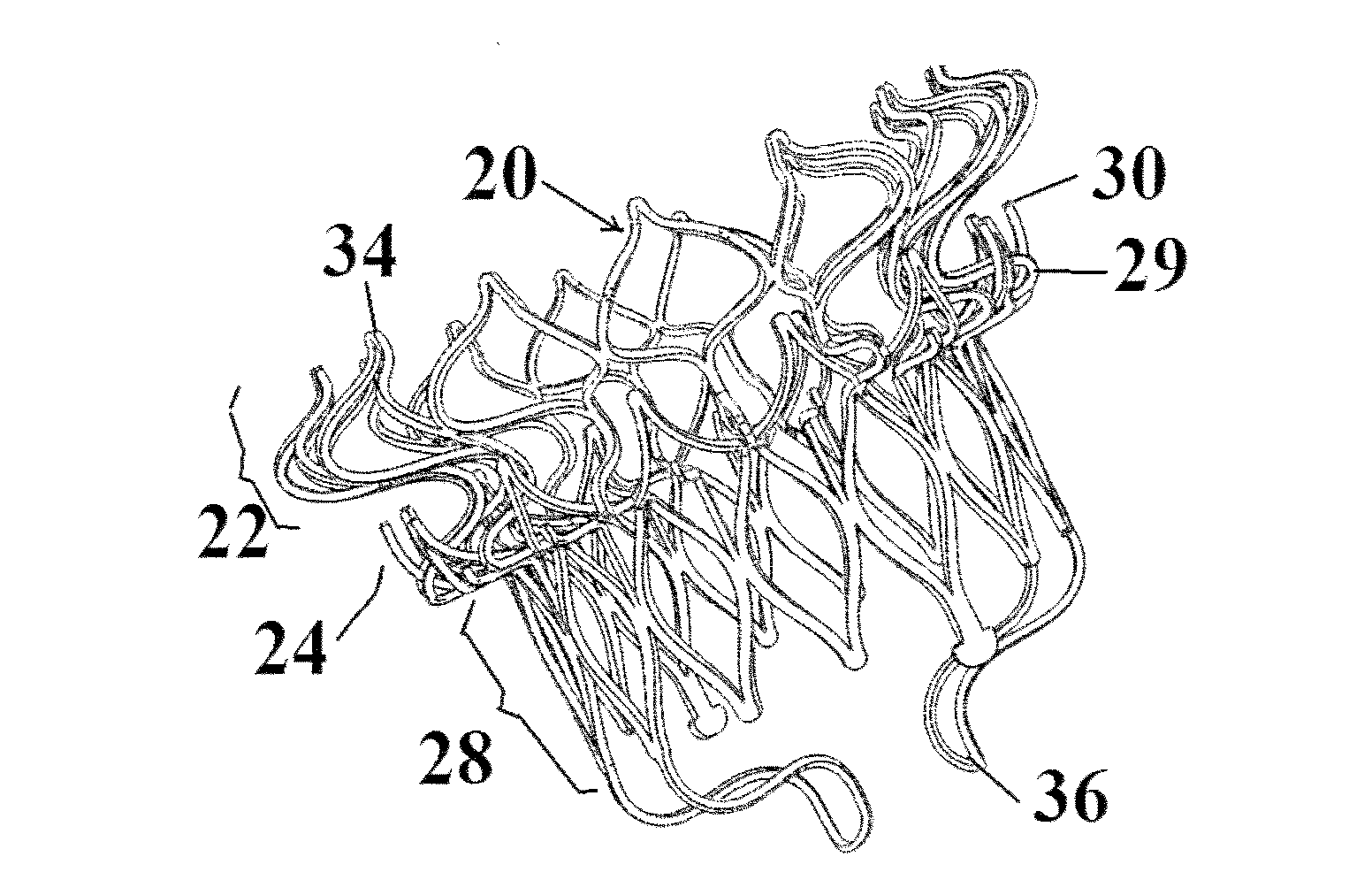
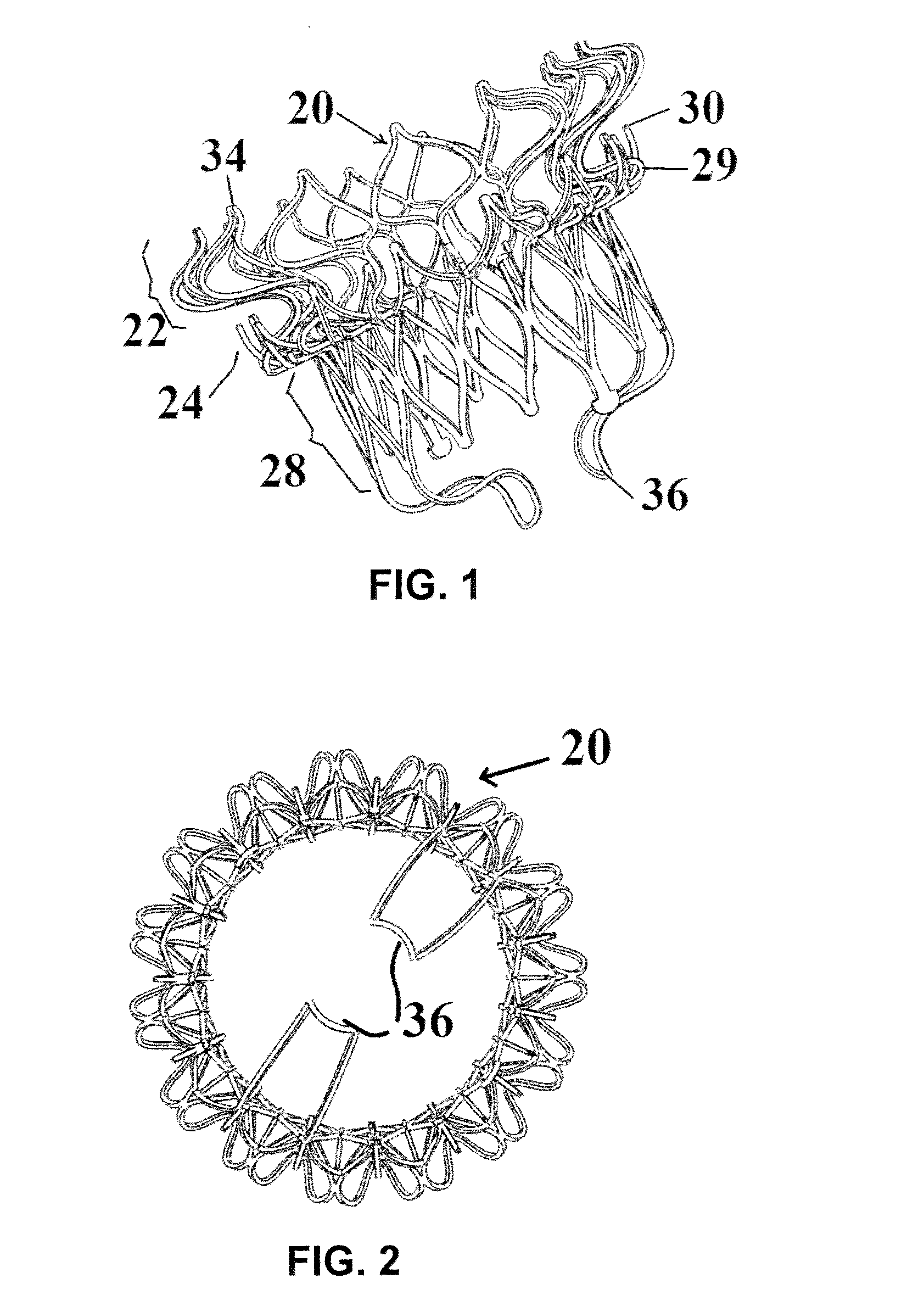
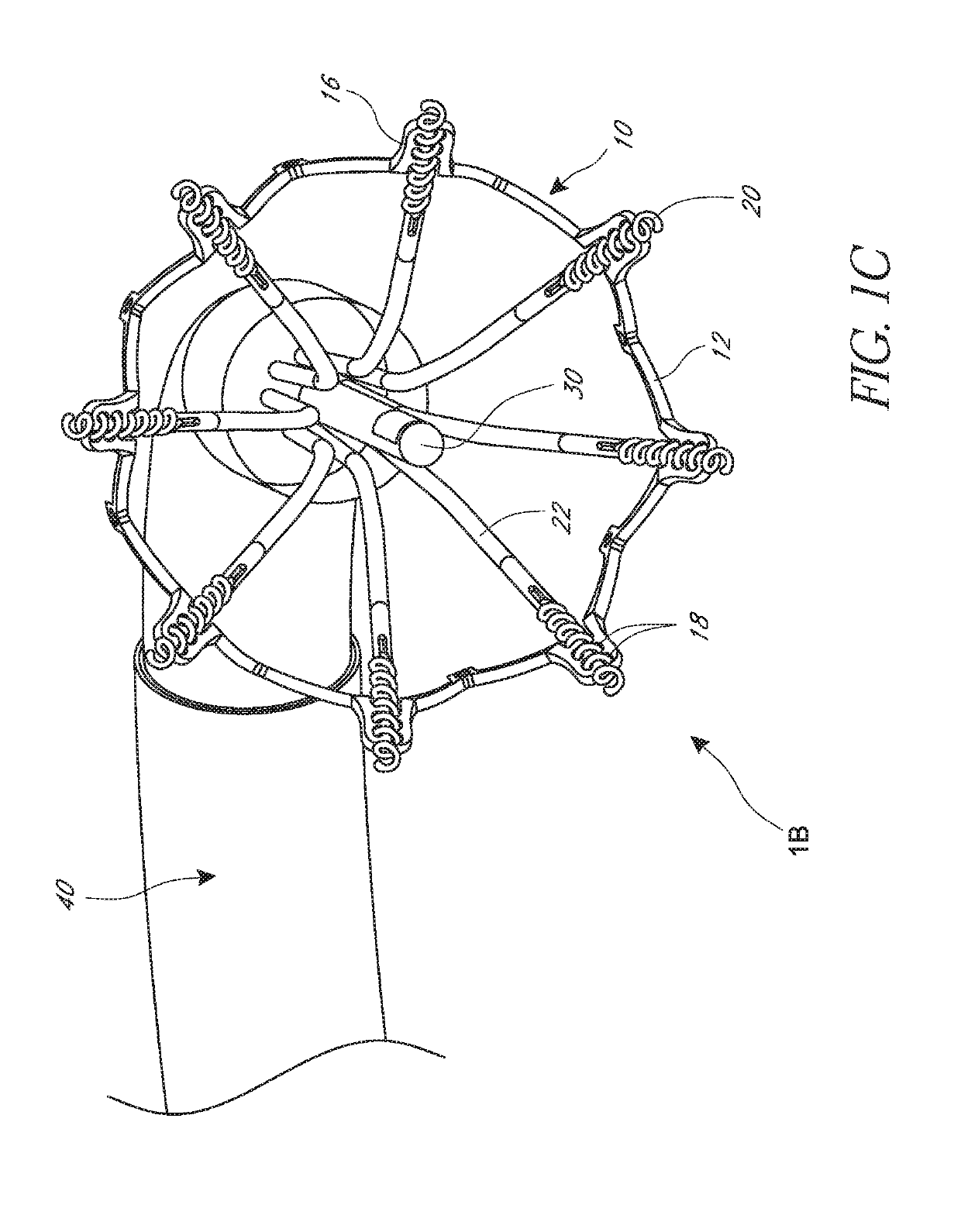
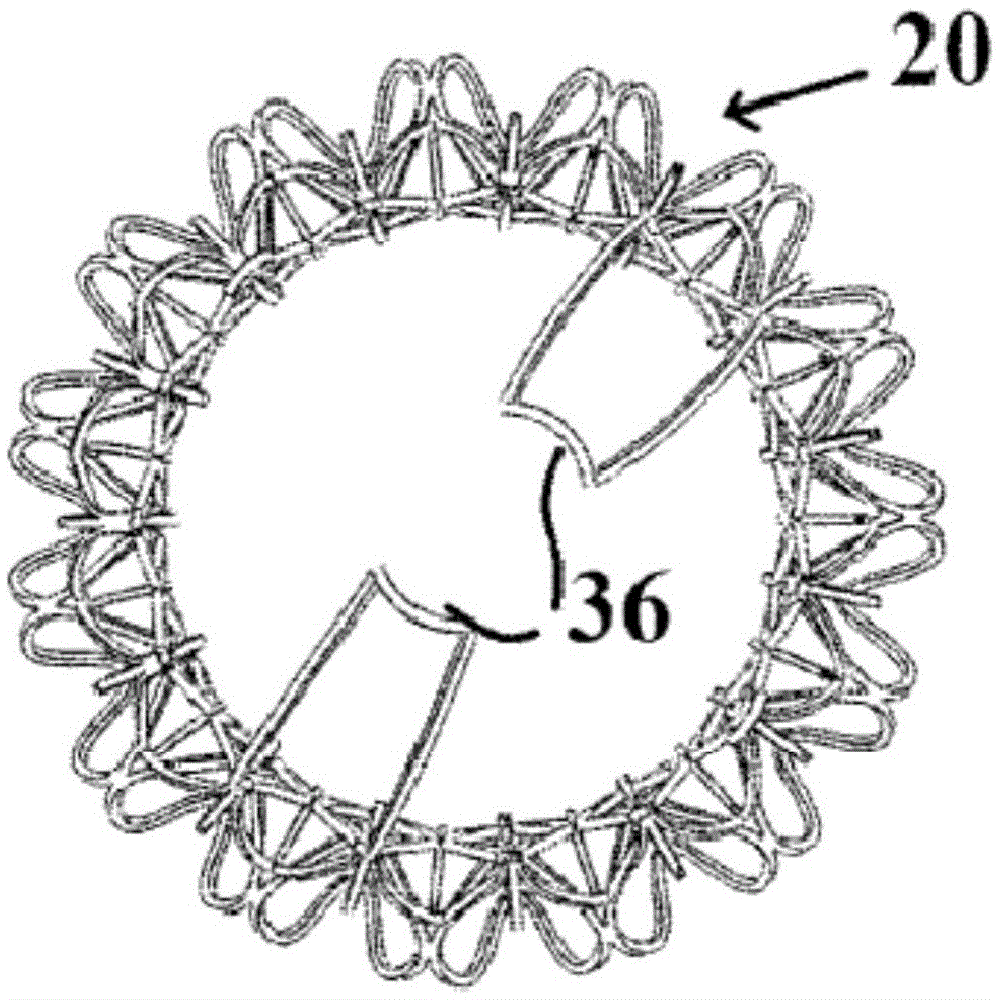
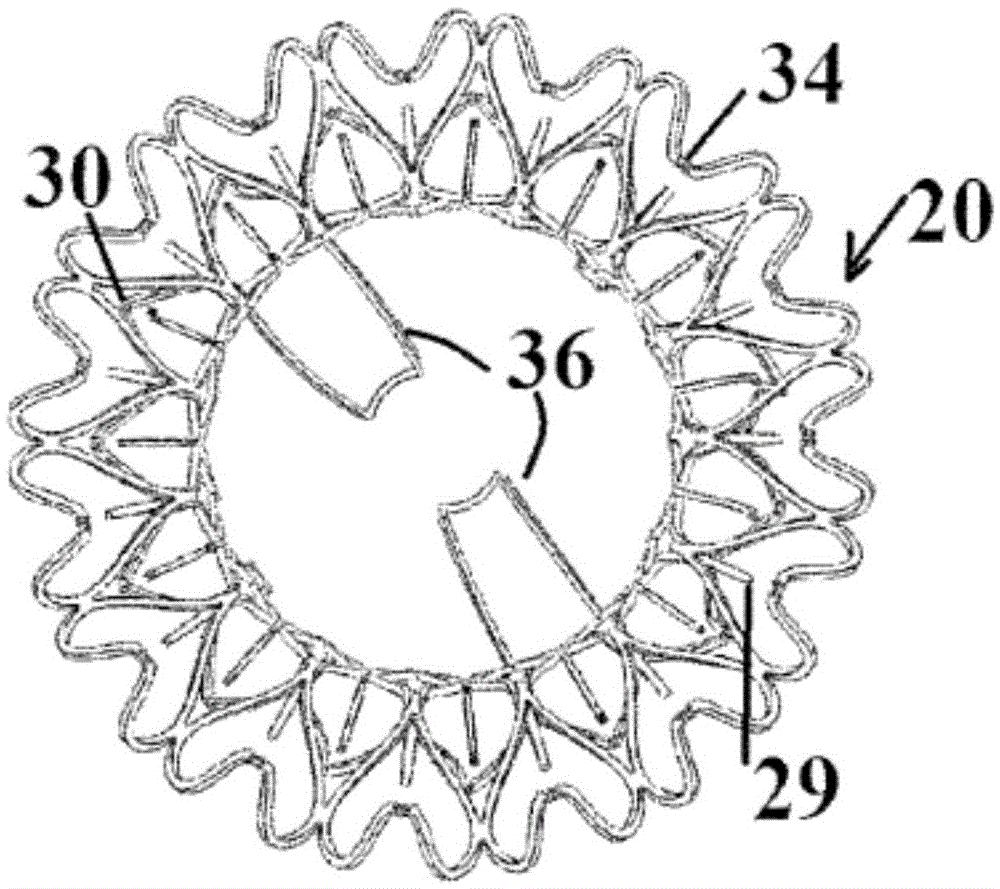
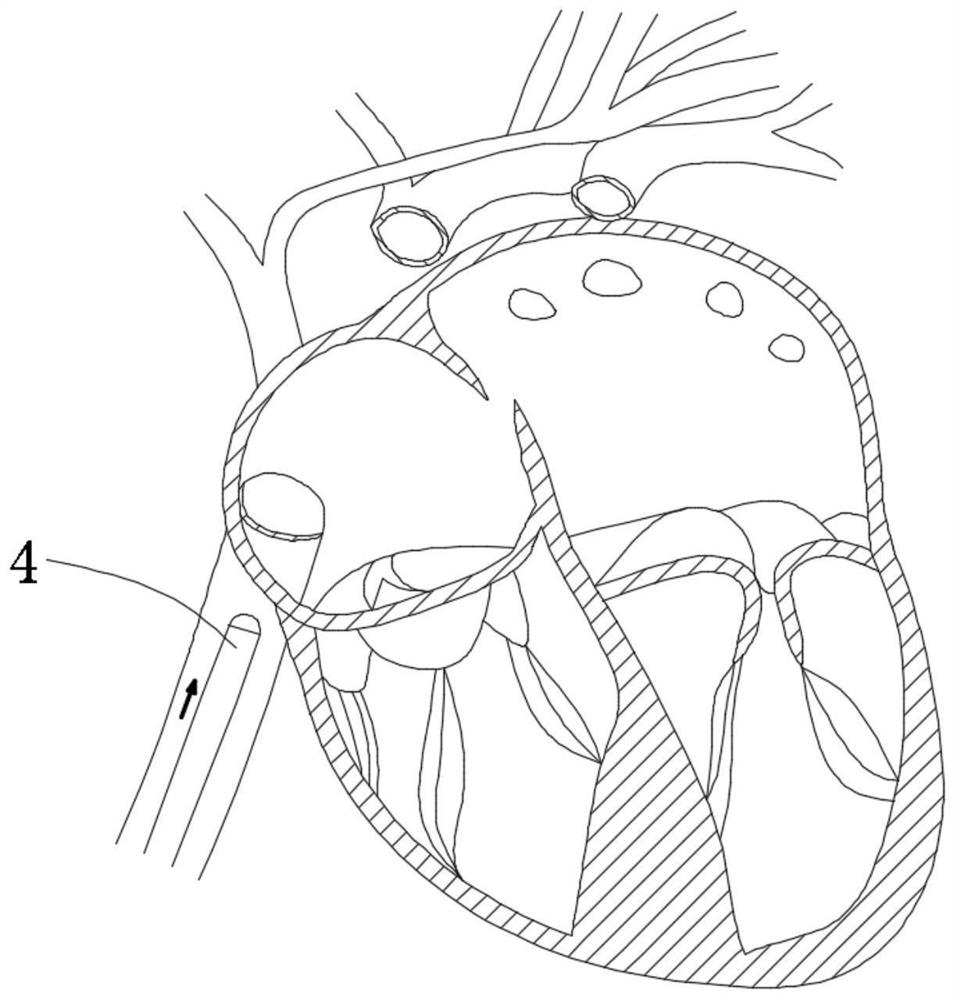
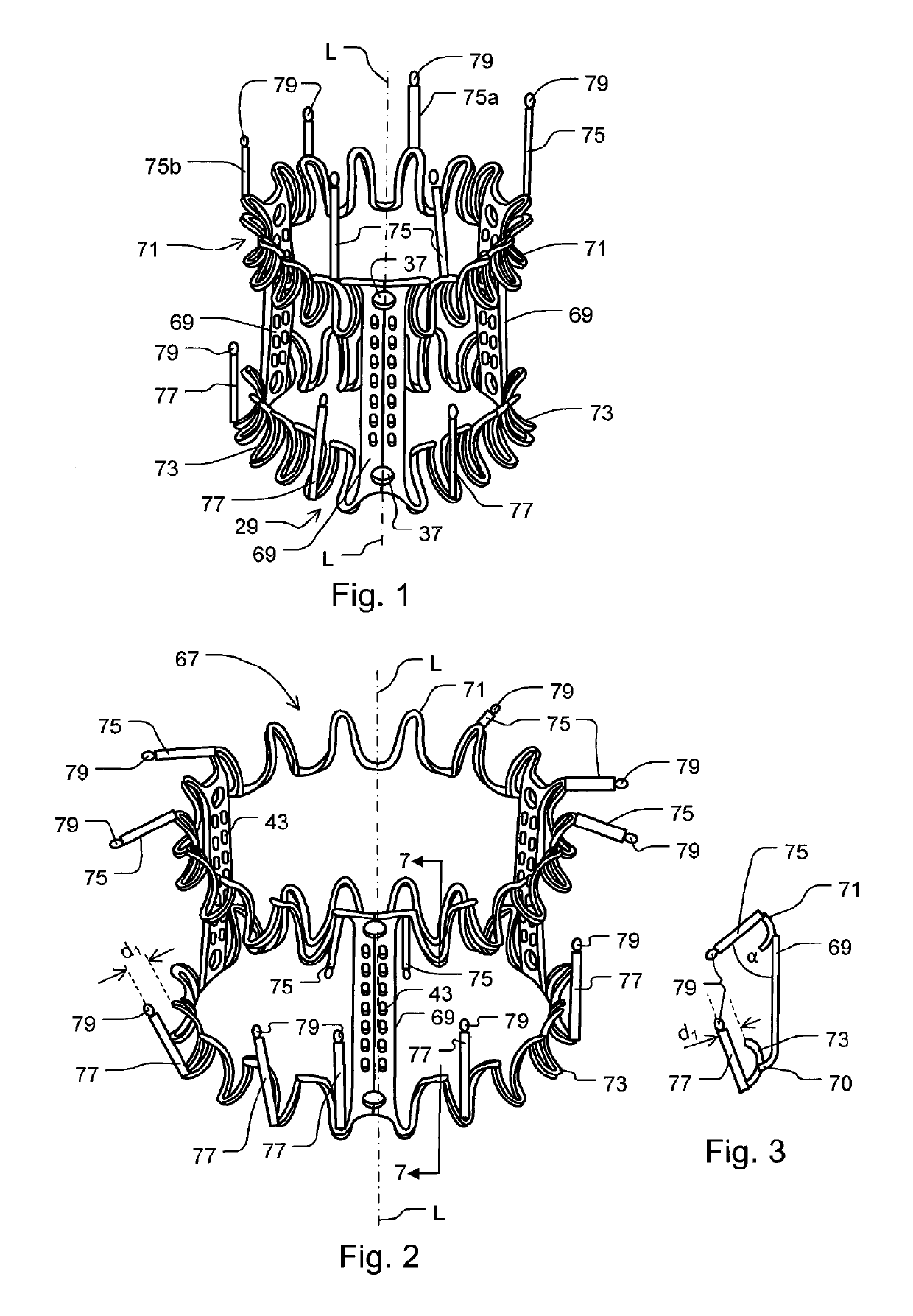
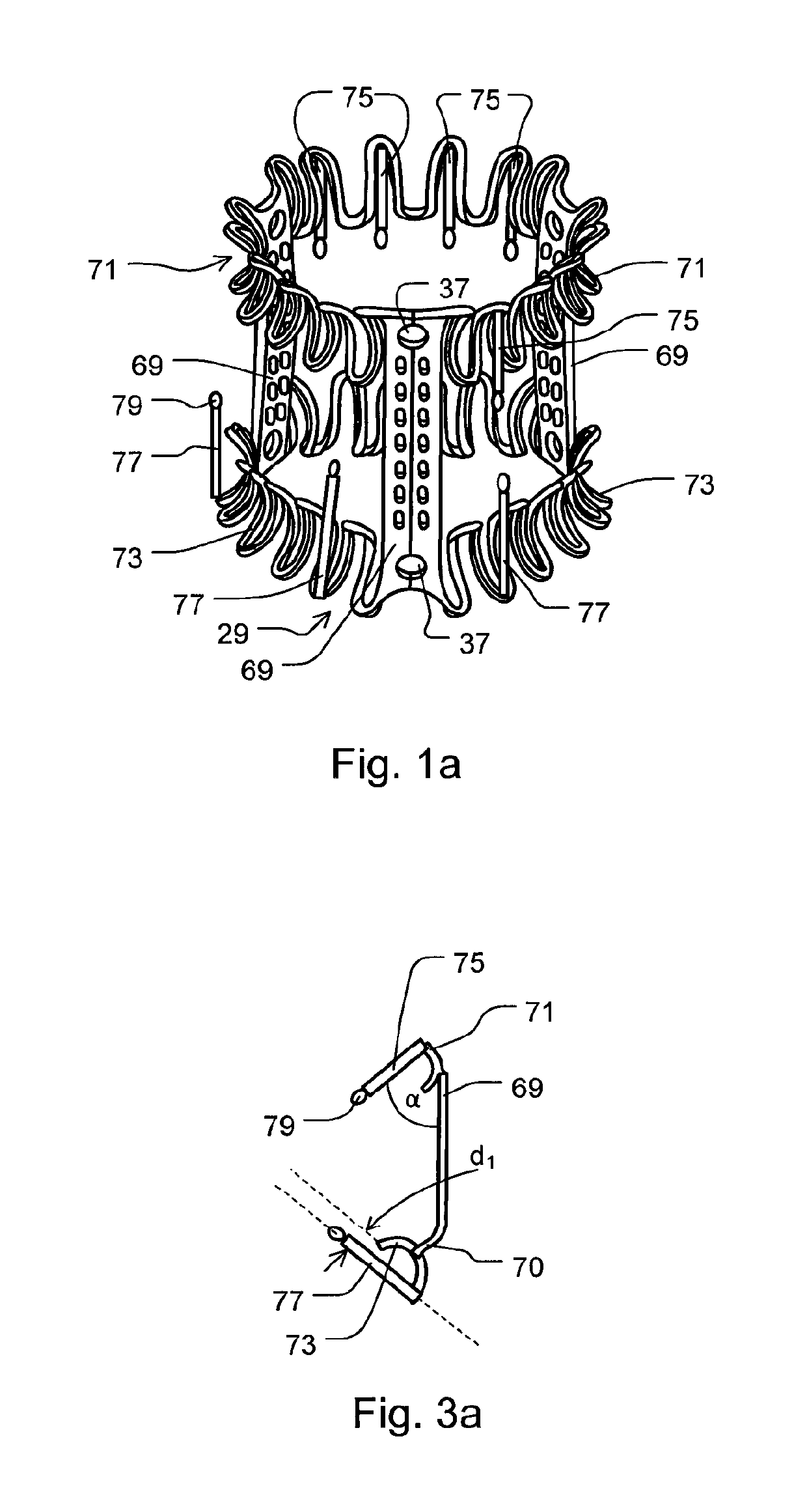
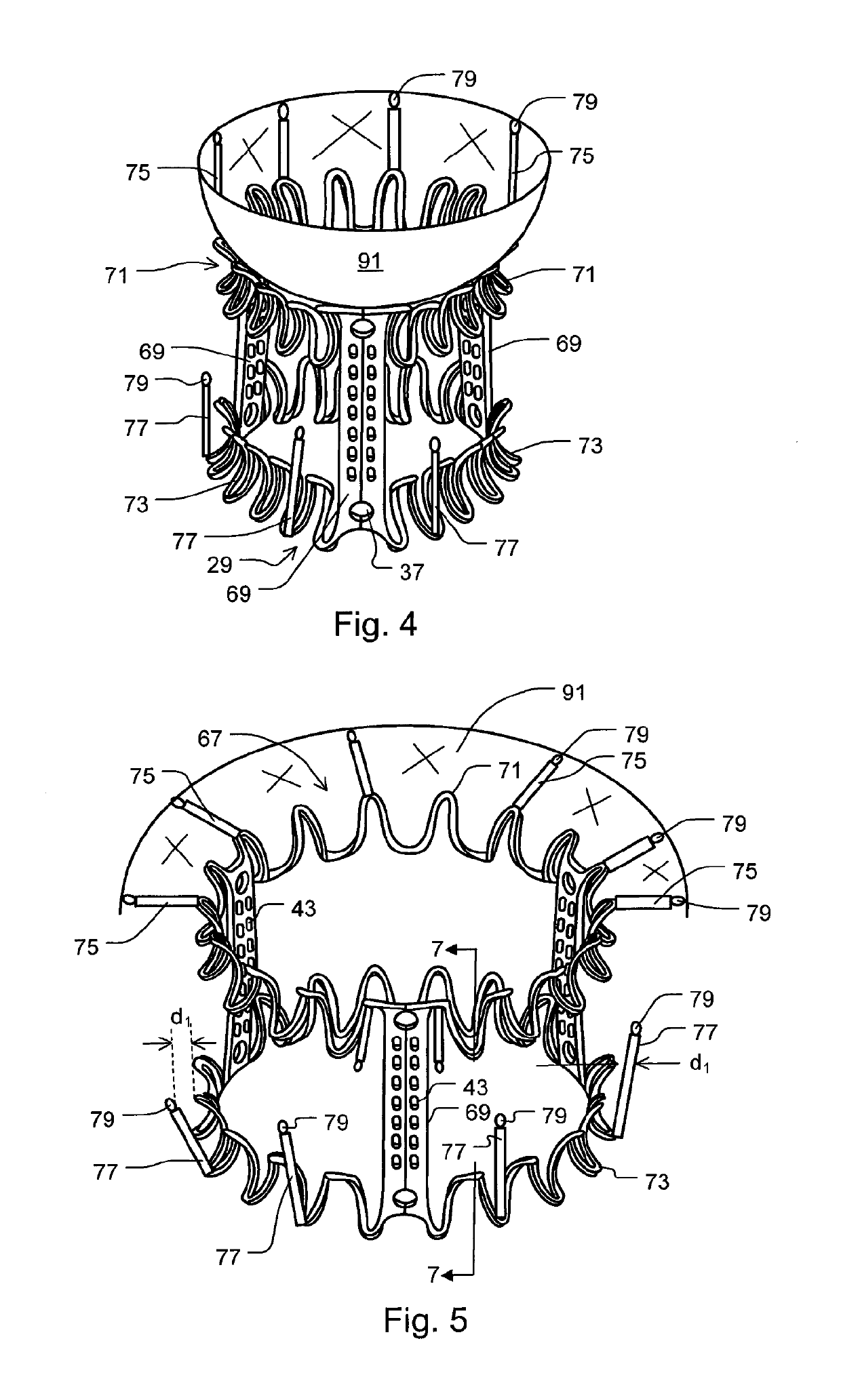
Minimally invasive mitral valve replacement with brim
A collapsible-expandable tubular stent (29) constructed of shape-memory material which is implantable into a human heart, which comprises proximal and distal rings (71, 73) and at least two spaced apart posts (69) that extend axially between said rings (71, 73), said distal ring (73) comprising a plurality of distal arms (77) which are connected to the distal ring (73) at only one end and which have a free opposite end; said proximal ring (71) comprising a plurality of, which are connected at only one end to the proximal ring (71) and which have a free opposite end, which proximal arms (75) are constructed to swing radially outward at their free ends.
Owner:VENUS MEDTECH (HANGZHOU) INC
Valve stent and interventional mitral valve replacement system comprising same
InactiveCN113855324AAvoid oppressionAvoid Weekly LeakageAnnuloplasty ringsBioprosthetic mitral valve replacementMetal framework
The invention provides a valve stent and an interventional mitral valve replacement system comprising the same. The valve stent comprises a metal frame, and a supporting ring is arranged at the edge of one end of the metal frame along the outer edge in the circumferential direction; the metal frame is formed in a surrounding mode by a curved surface straight wall and a plane straight wall so as to form a D-shaped straight cylindrical structure; two strands of connecting wires are respectively arranged at the two ends of the metal frame; the two strands of connecting wires are respectively used for connecting the edge of the curved surface straight wall and the edge of the plane straight wall at the two ends of the metal frame; and the two strands of connecting wires at each end intersect in an X shape to cut interfaces at the two ends of the metal frame into an 8 shape. The valve stent is used for supporting, fixing and sealing a subsequent interventional mitral valve.
Owner:SHANGHAI CINGULAR BIOTECH
Split valve stent and interventional mitral valve replacement system comprising same
PendingCN113855333ALow flap heightPrecise positioningAnnuloplasty ringsBioprosthetic mitral valve replacementMetal framework
Owner:SHANGHAI CINGULAR BIOTECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com