Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
461 results about "Independent channels" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Channels TV is an independent News TV channel which produces featured news programs. It was founded in 1992. Its programming is mainly focusing on the Nigerian public. Part of the Channels TV mission, is to be a watch-dog of the government and its policies.
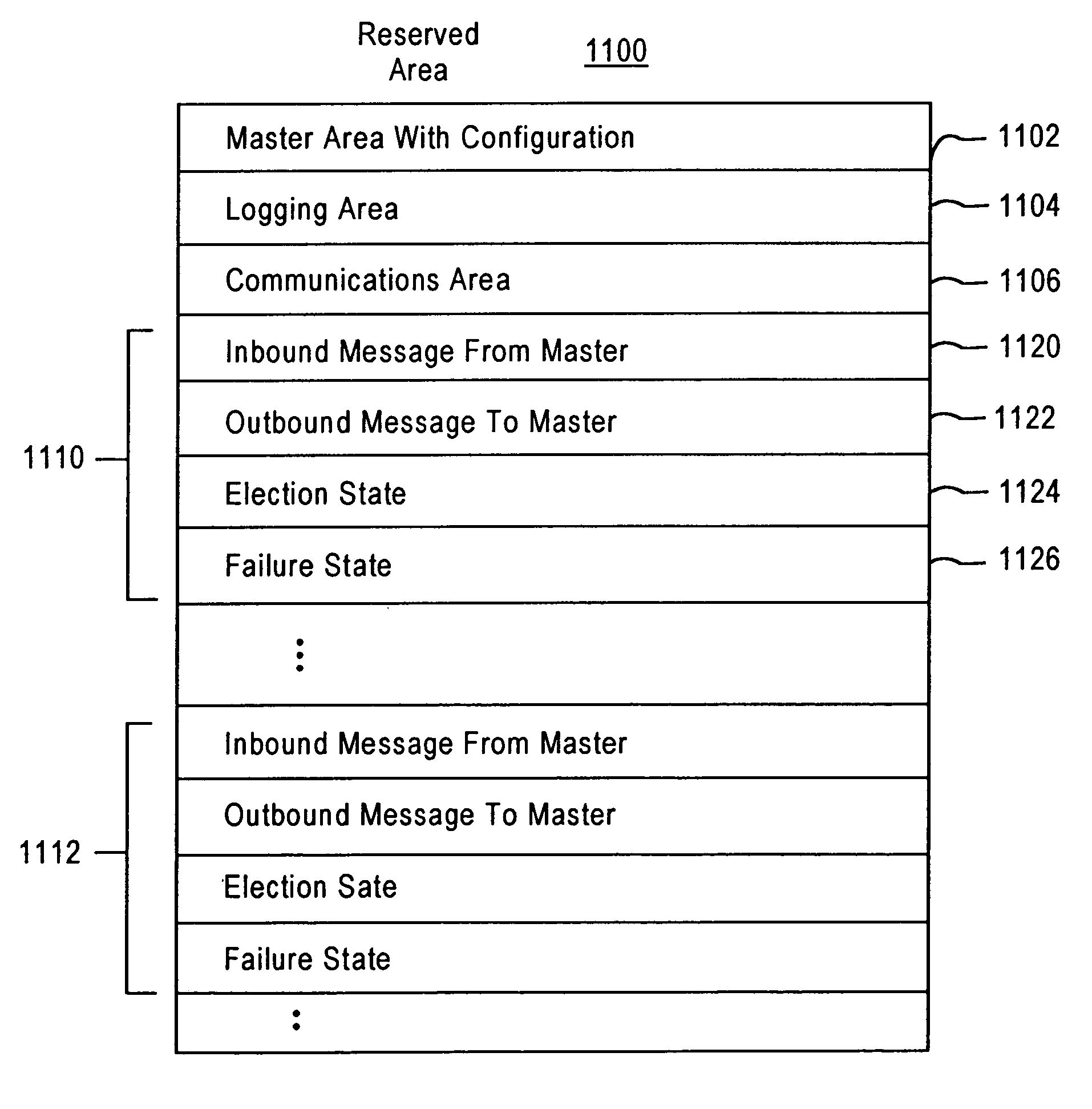
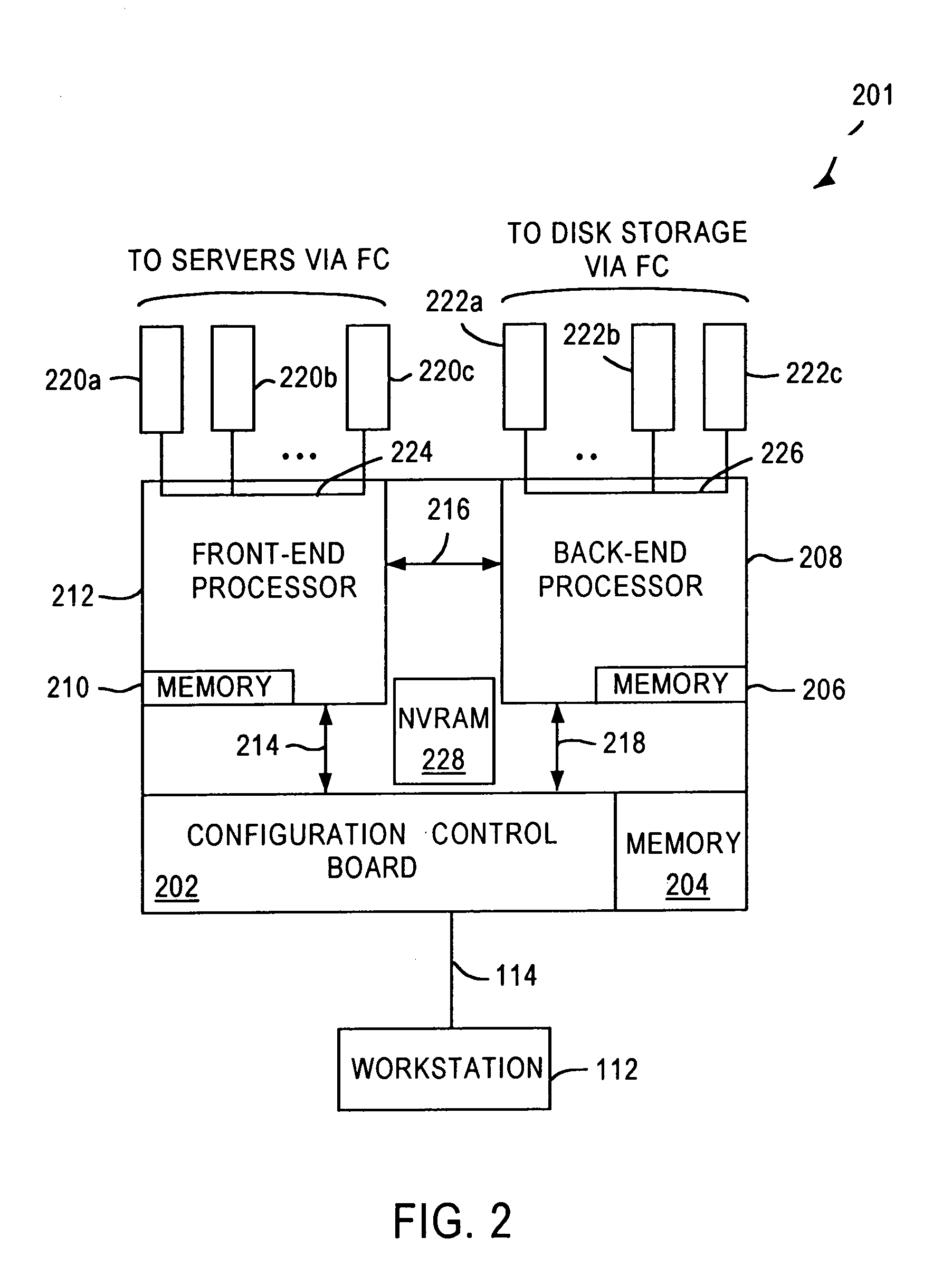
System and method for a reserved memory area shared by all redundant storage controllers
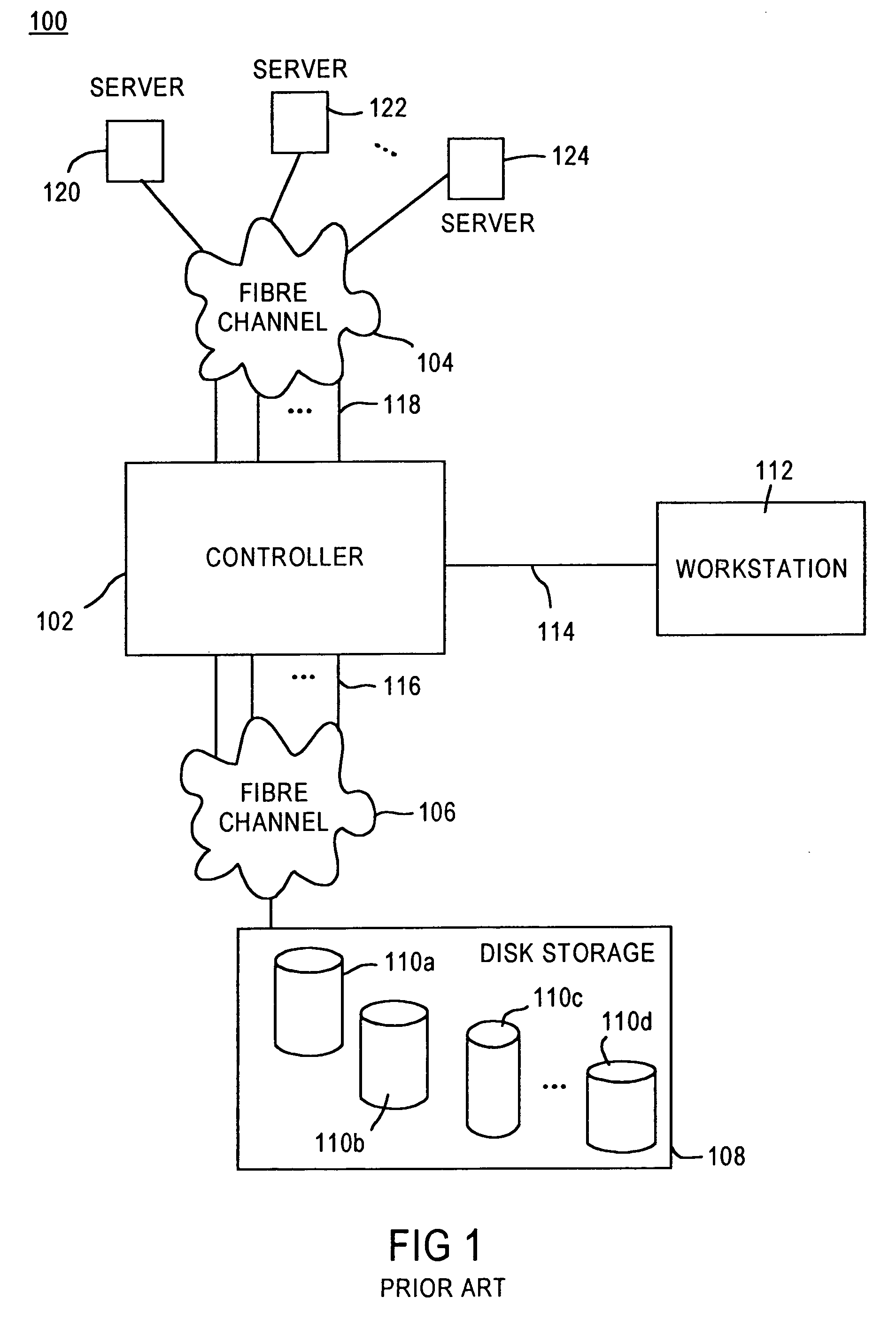
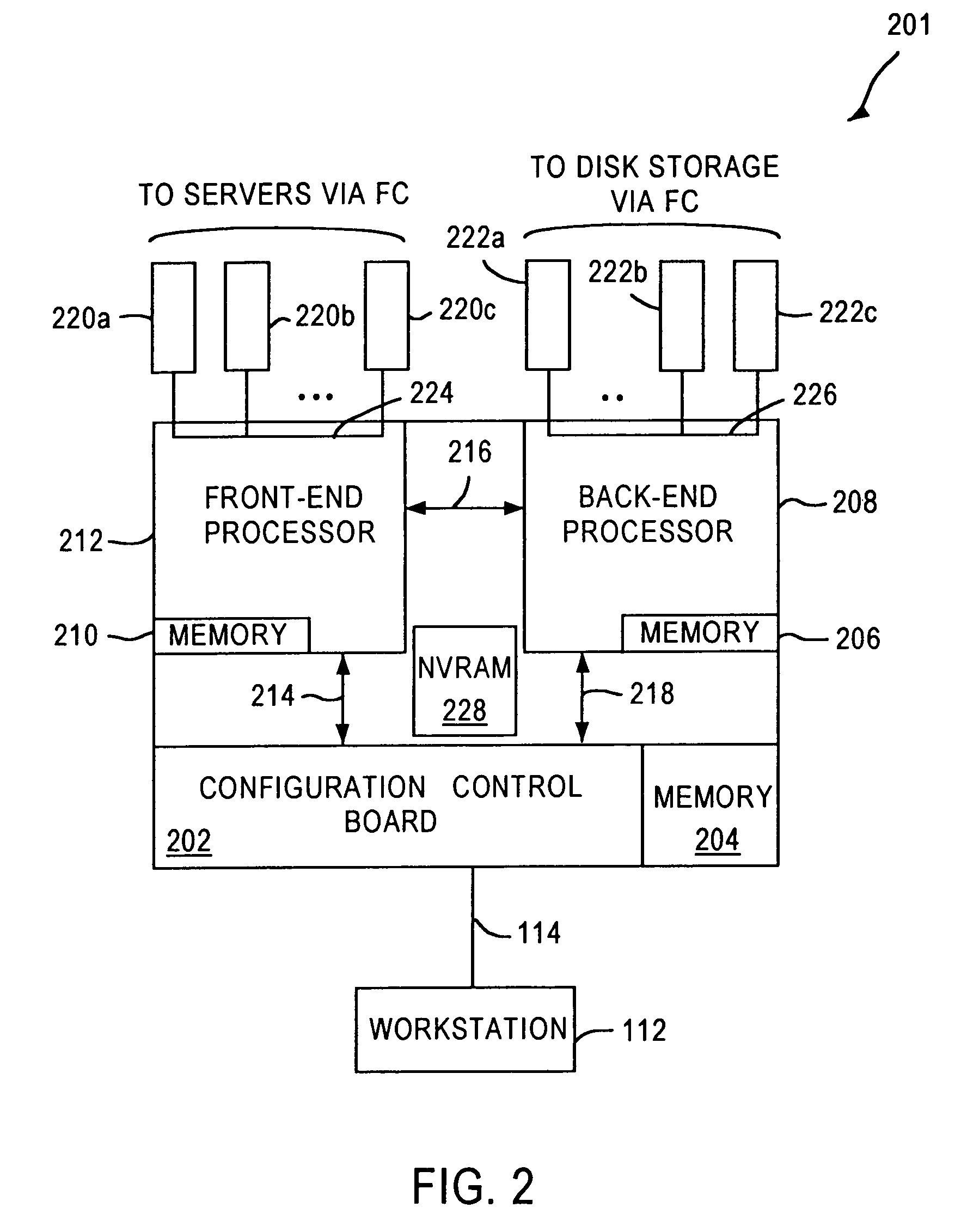
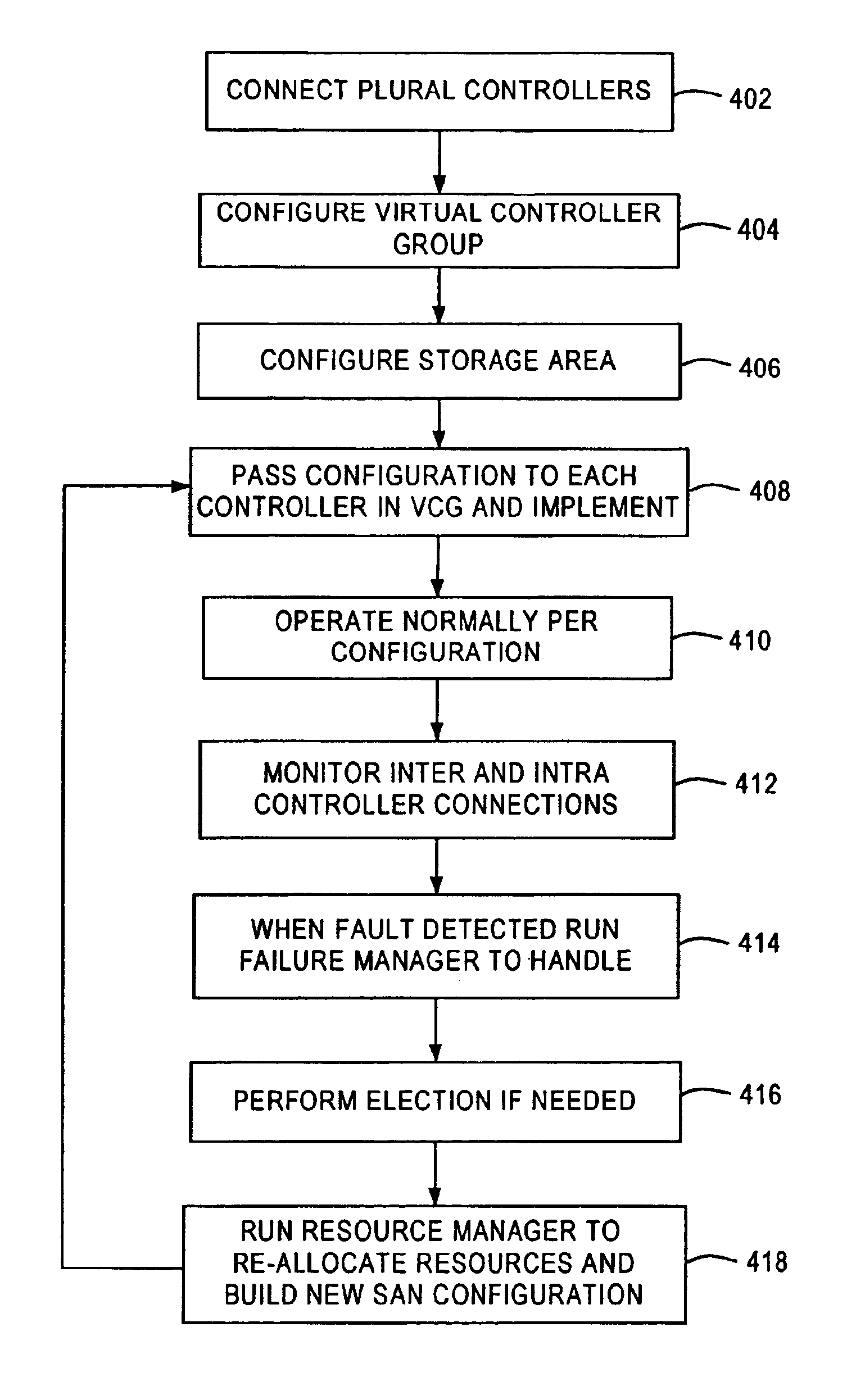
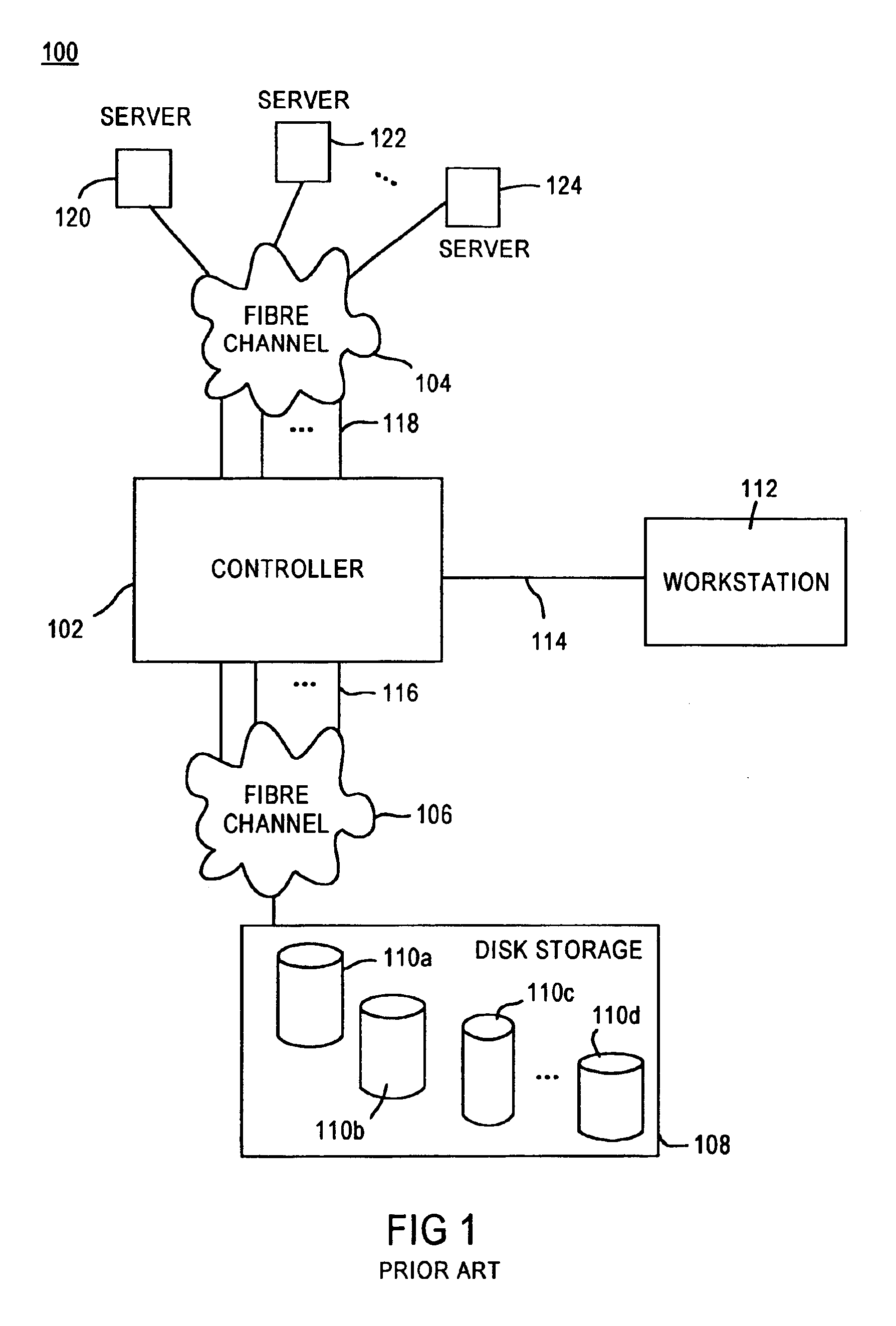
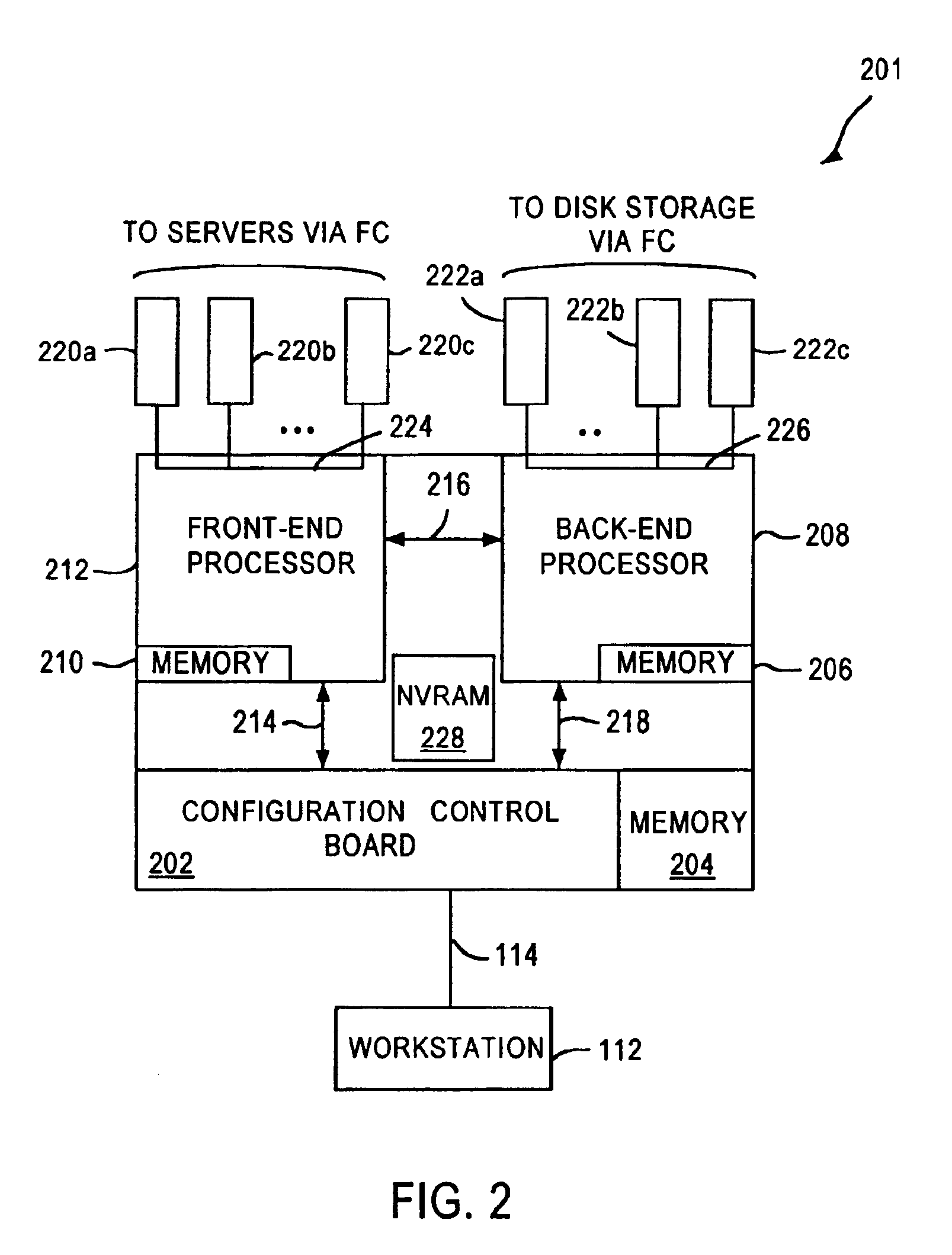
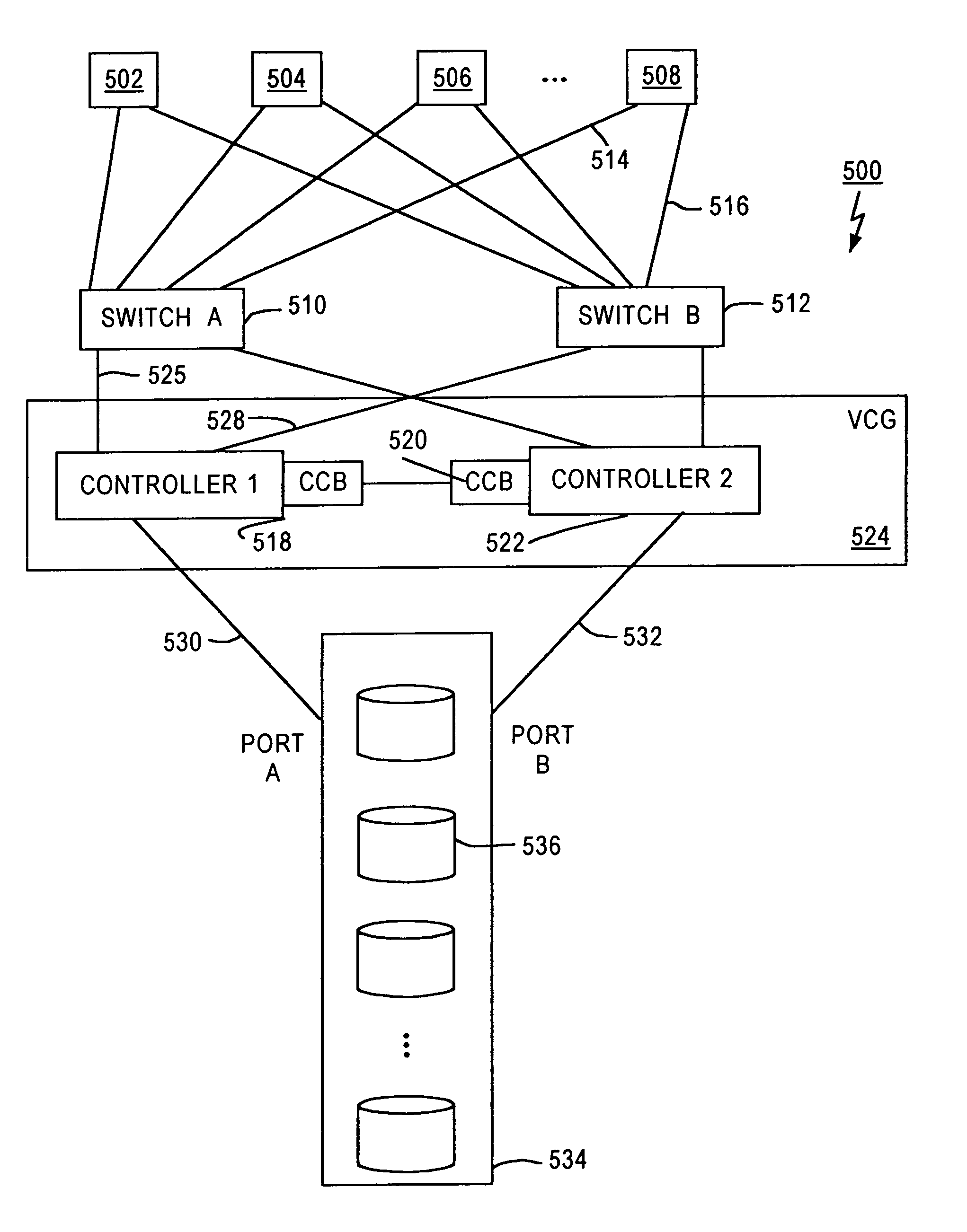
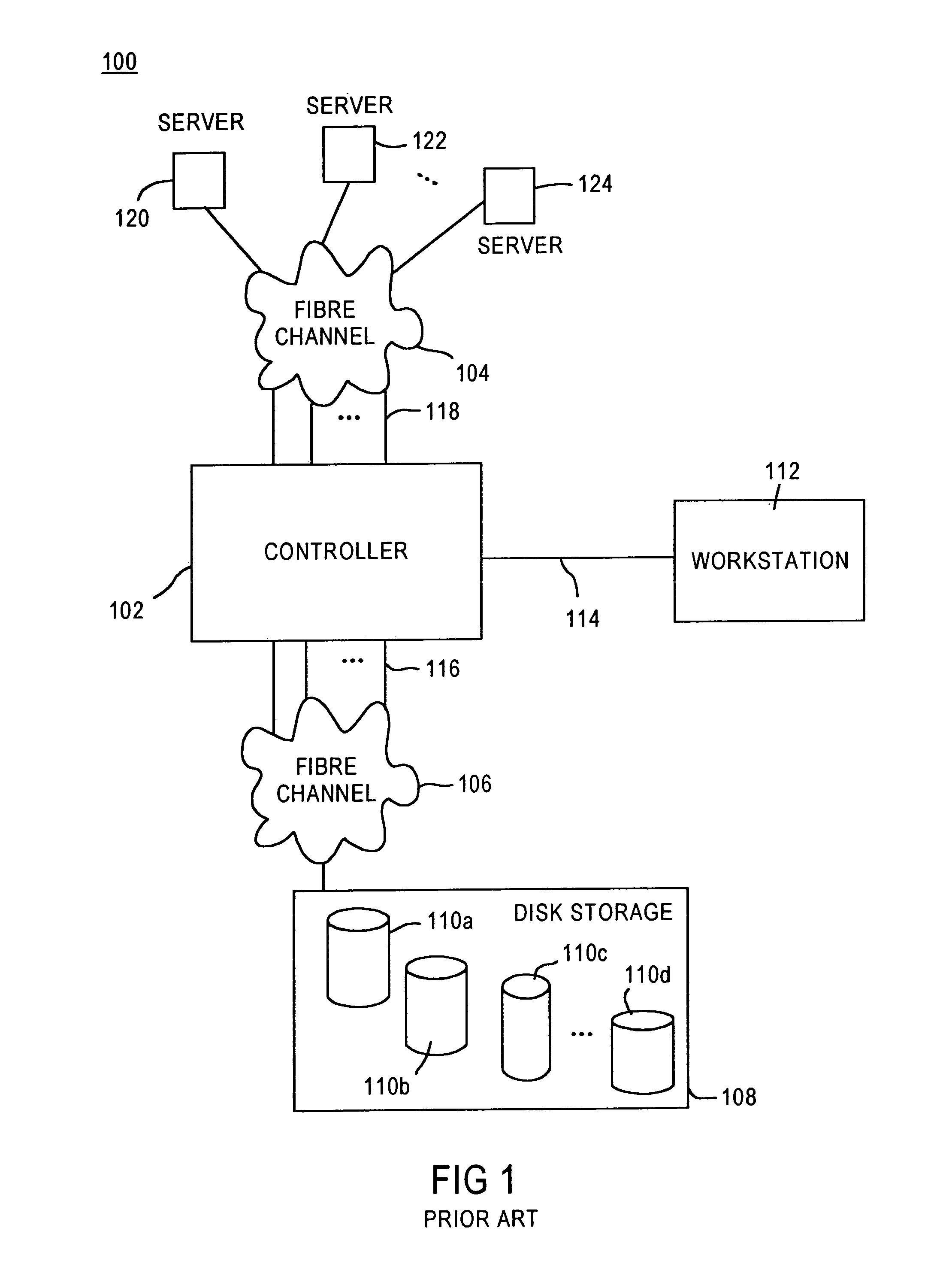
A fibre channel storage area network (SAN) provides virtualized storage space for a number of servers to a number of virtual disks implemented on various virtual redundant array of inexpensive disks (RAID) devices striped across a plurality of physical disk drives. The SAN includes plural controllers and communication paths to allow for fail-safe and fail-over operation. The plural controllers can be loosely-coupled to provide n-way redundancy and have more than one independent channel for communicating with one another. In the event of a failure involving a controller or controller interface, the virtual disks that are accessed via the affected interfaces are re-mapped to another interface in order to continue to provide high data availability. In particular, a common memory storage device is connected to the back-ends of every controller to provide a storage area. In this manner, the common memory storage device can be accessed via operations similar to those a controller already uses to presently access the physical disks which are connected to the back-end of the controllers.
Owner:VSIP HLDG LLC
System and method for a redundant communication channel via storage area network back-end
InactiveUS6883065B1Redundancy and robustness in systemInput/output to record carriersFault responseFailoverRAID
A fiber channel storage area network (SAN) provides virtualized storage space for a number of servers to a number of virtual disks implemented on various virtual redundant array of inexpensive disks (RAID) devices striped across a plurality of physical disk drives. The SAN includes plural controllers and communication paths to allow for fail-safe and fail-over operation. The plural controllers can be loosely-coupled to provide n-way redundancy and have more than one independent channel for communicating with one another. In particular, respective portions from each of the back-end physical disk drives within the SAN are used as one of these alternative communication channels to pass messages between controllers. Such an alternative communications channel provides even further redundancy and robustness in the system.
Owner:INNOVATIONS IN MEMORY LLC
System and method to monitor and isolate faults in a storage area network
A fiber channel storage area network (SAN) provides virtualized storage space for a number of servers to a number of virtual disks implemented on various virtual redundant array of inexpensive disks (RAID) devices striped across a plurality of physical disk drives. The SAN includes plural controllers and communication paths to allow for fail-safe and fail-over operation. The plural controllers can be loosely-coupled to provide n-way redundancy and have more than one independent channel for communicating with one another. In the event of a failure involving a controller or controller interface, the virtual disks that are accessed via the affected interfaces are re-mapped to another interface in order to continue to provide high data availability. In particular, deadman timers, heartbeat signals internal to each controller, and heartbeat signals between different controllers are used to detect controllers that are no longer communicating with other controllers in order to identify those controllers which are failing or have failed.
Owner:XIOTECH CORP
Ultrawide-band communication system and method
InactiveUS6847675B2Remove distortionUndesirable modulationAngle modulationCode division multiplexTime delaysRadio receiver
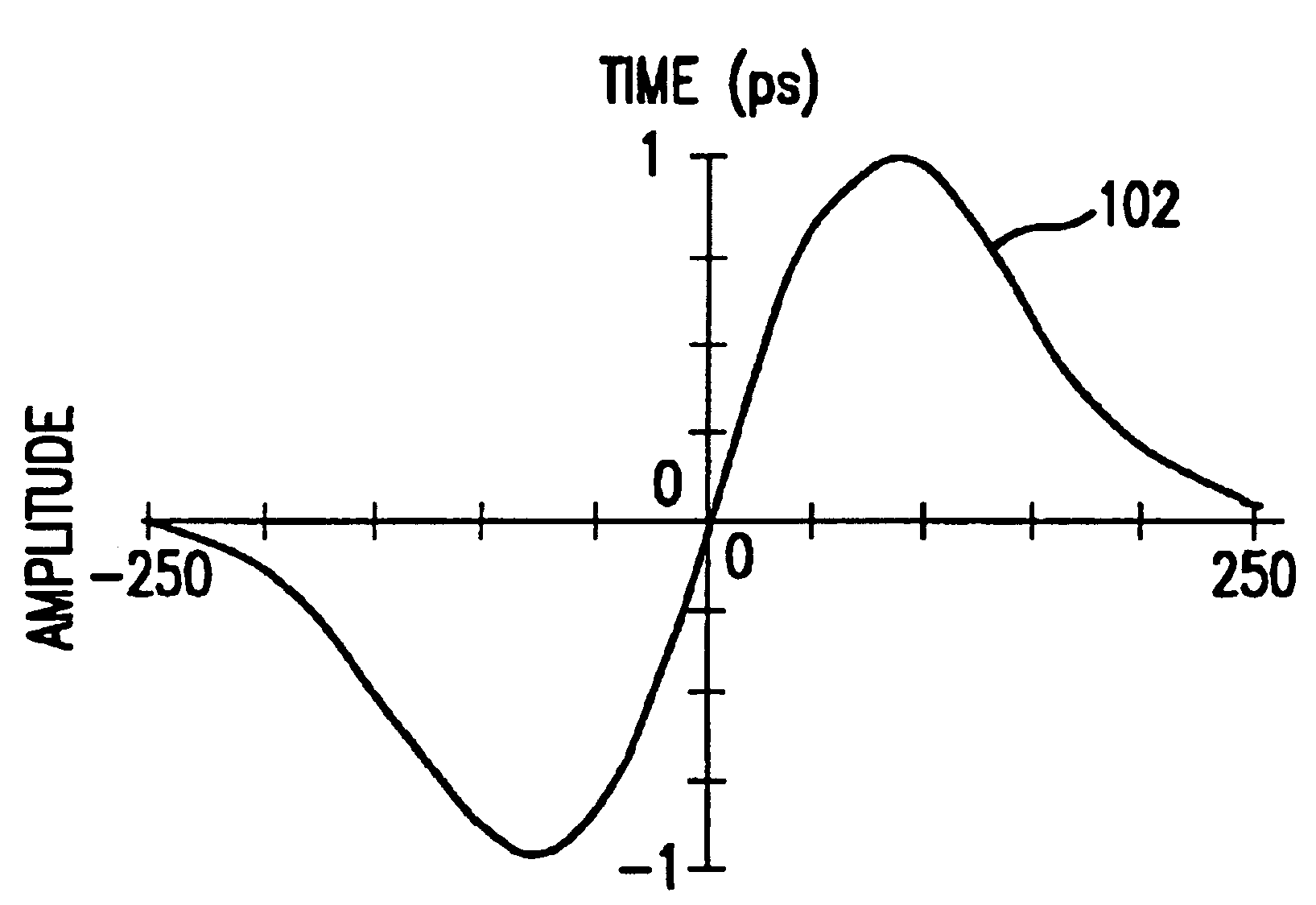
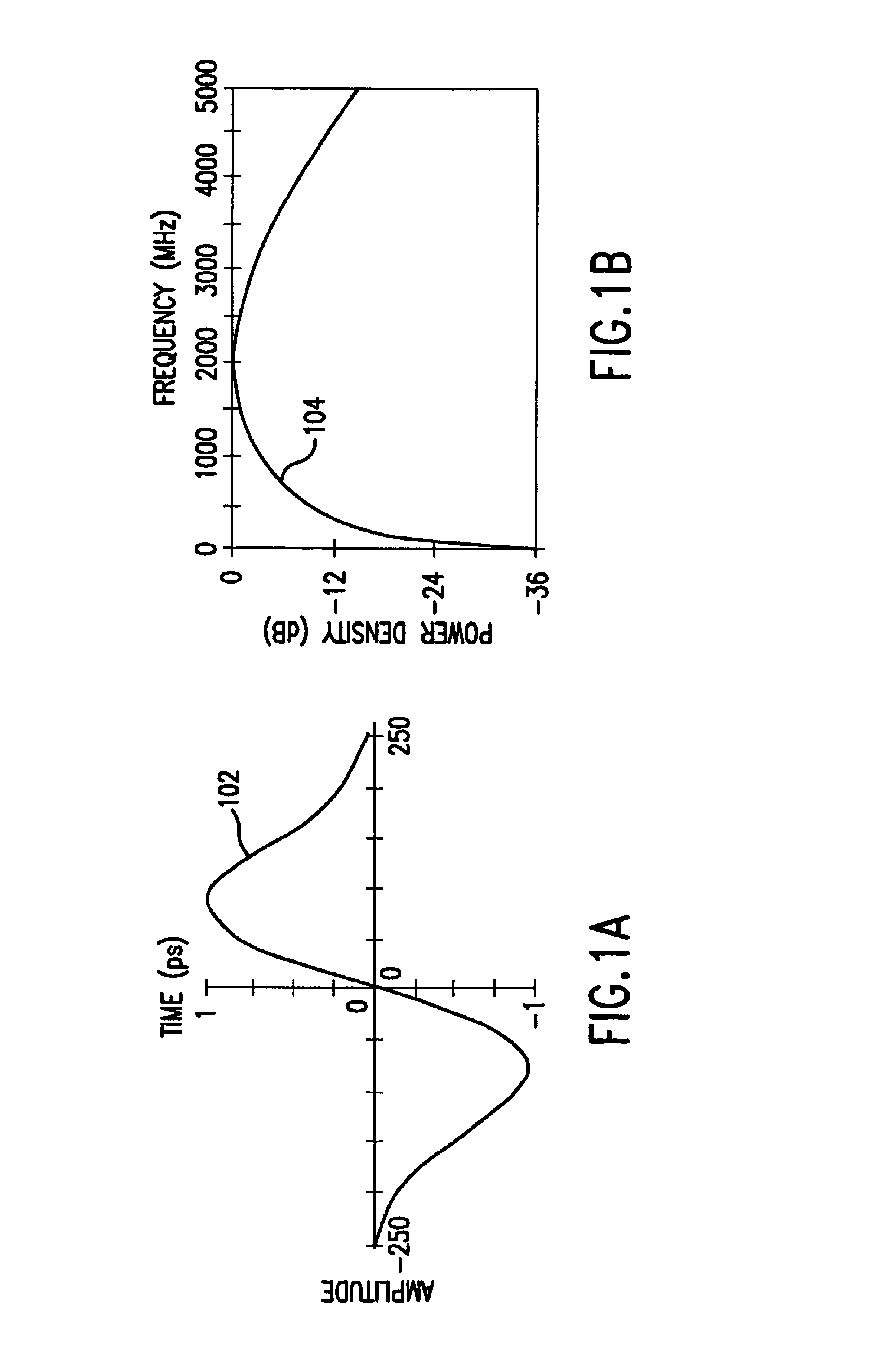
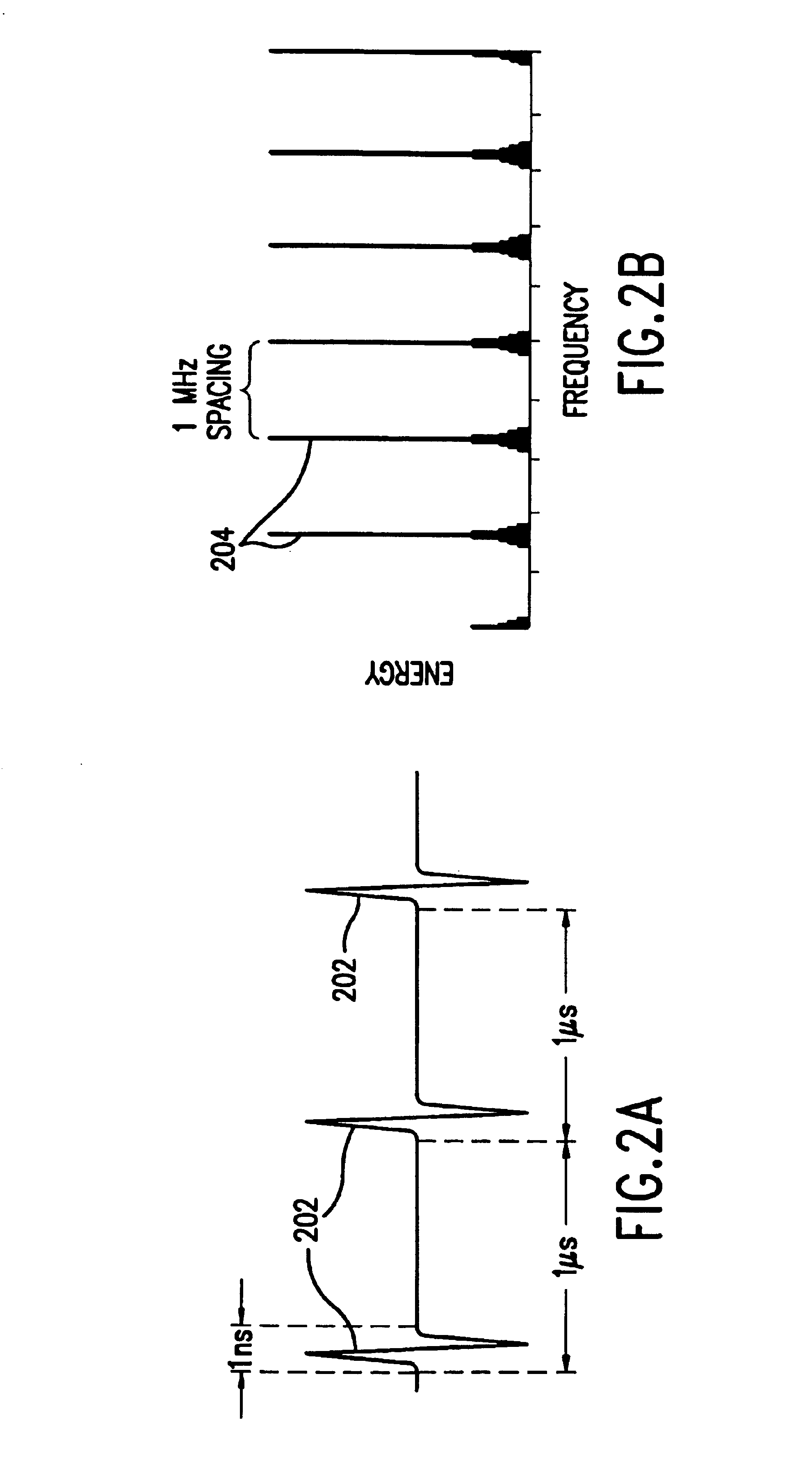
An impulse radio communications system using one or more subcarriers to communicate information from an impulse radio transmitter to an impulse radio receiver. The impulse radio communication system is an ultrawide-band time domain system. The use of subcarriers provides impulse radio transmissions added channelization, smoothing and fidelity. Subcarriers of different frequencies or waveforms can be used to add channelization of impulse radio signals. Thus, an impulse radio link can communicate many independent channels simultaneously by employing different subcarriers for each channel. The impulse radio uses modulated subcarrier(s) for time positioning a periodic timing signal or a coded timing signal. Alternatively, the coded timing signal can be summed or mixed with the modulated subcarrier(s) and the resultant signal is used to time modulate the periodic timing signal. Direct digital modulation of data is another form of subcarrier modulation for impulse radio signals. Direct digital modulation can be used alone to time modulate the periodic timing signal or the direct digitally modulated the periodic timing signal can be further modulated with one or more modulated subcarrier signals. Linearization of a time modulator permits the impulse radio transmitter and receiver to generate time delays having the necessary accuracy for impulse radio communications.
Owner:TDC ACQUISITION HLDG
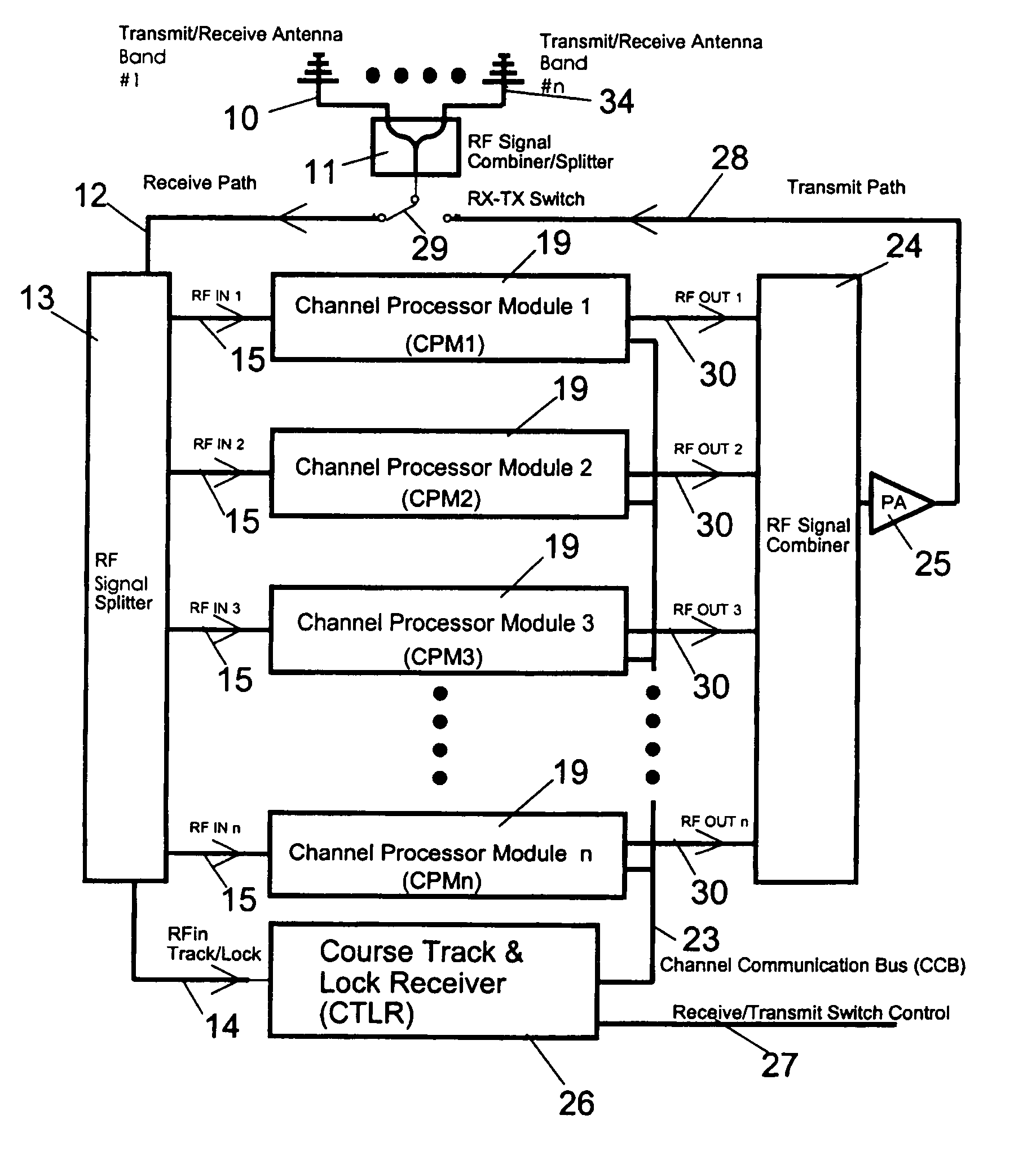
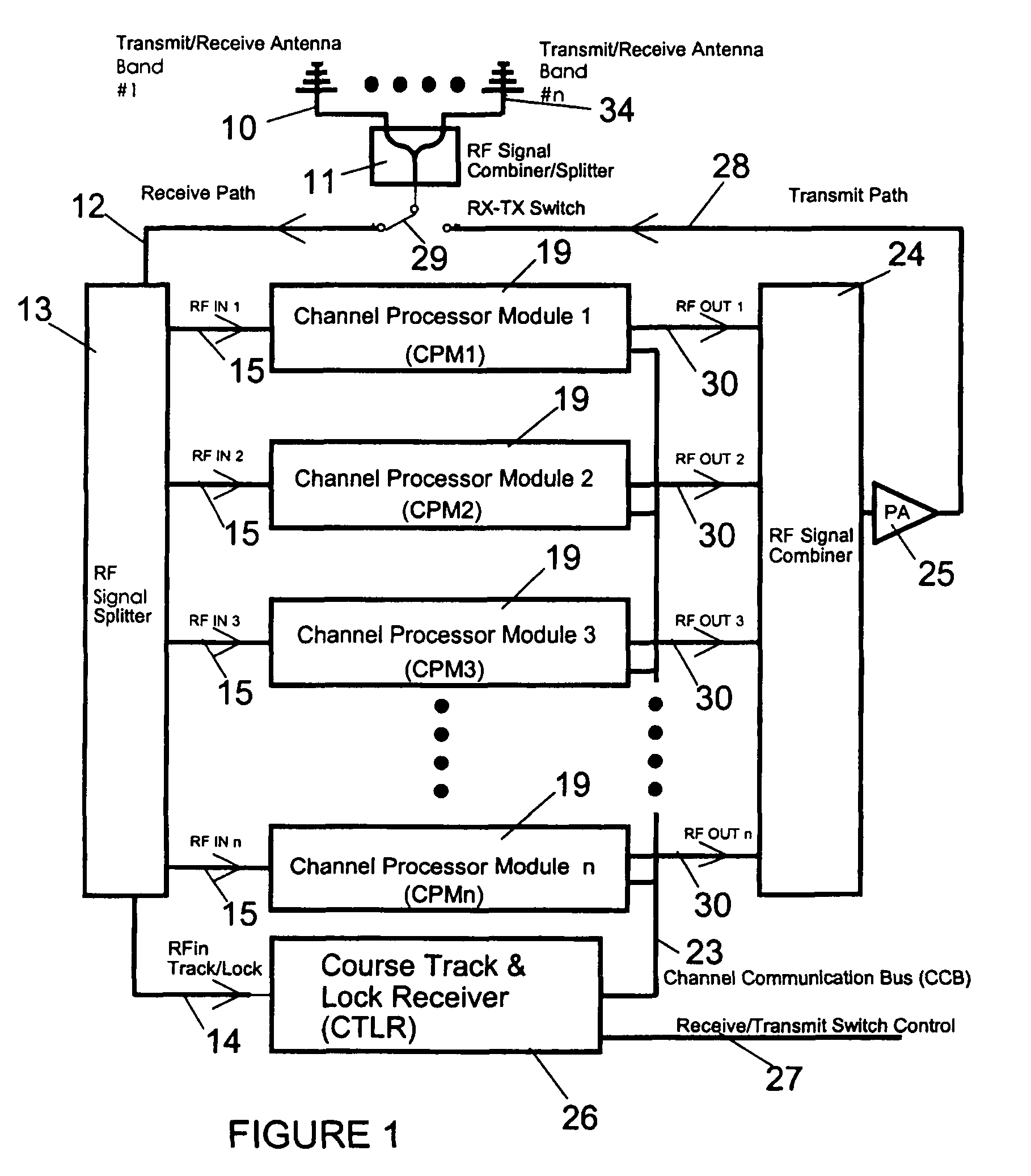
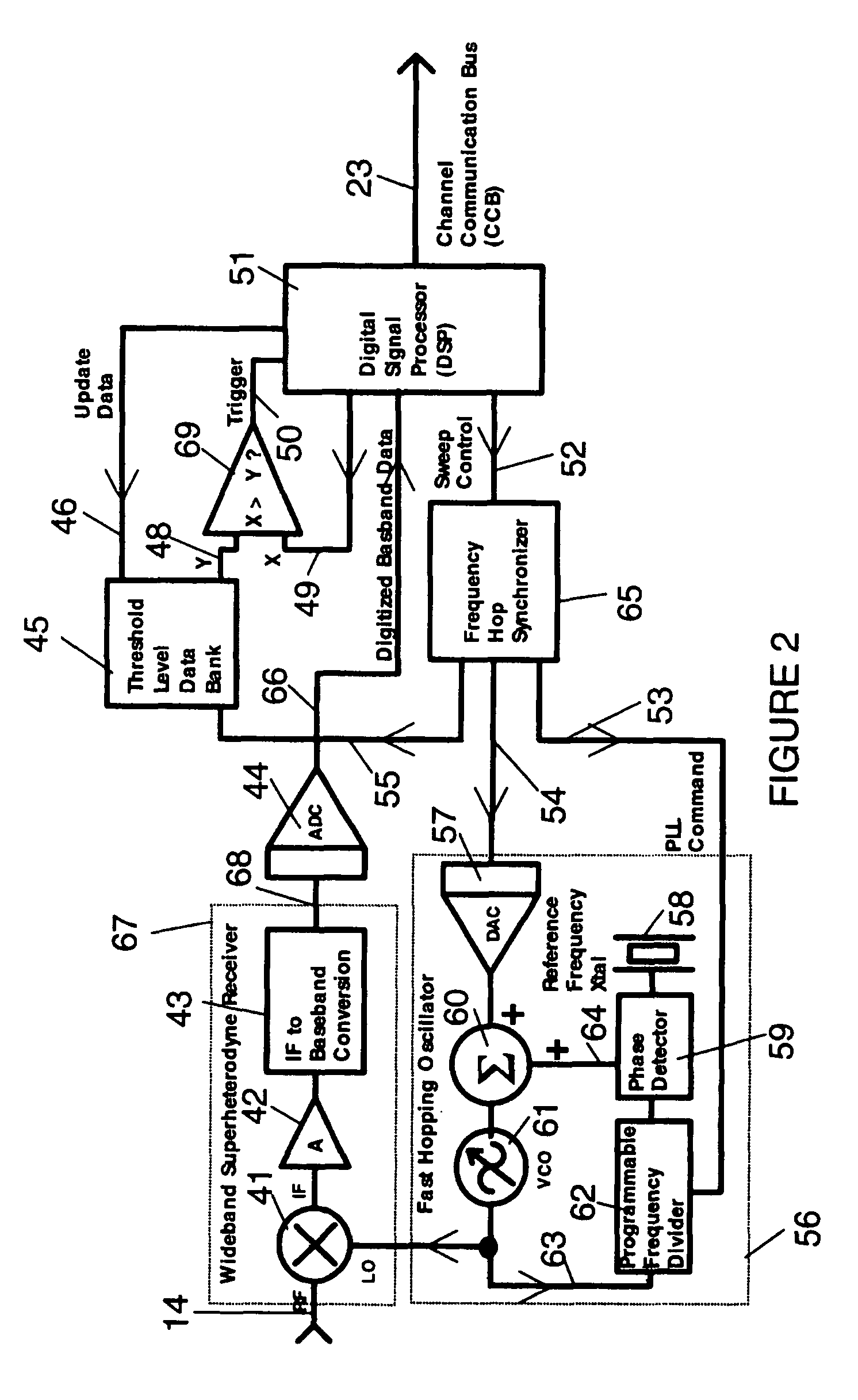
Reactive parallel processing jamming system
InactiveUS7728755B1Improve efficiencyRapidity and signal multiplicityCommunication jammingTransmissionBroadbandWide band
The system is a parallel processing jamming architecture that is designed to automatically attack and concurrently investigate multiple signals simultaneously in the radio environment. The system implements multiple wideband independent channels to allow simultaneous threat signals to be processed in parallel and jammed in real-time. The system automatically attacks a radio communication channel when the suspect radio signal surpasses a dynamic composite threshold which is internally updated using multi-channel data feedback, in real-time. The concurrent analysis with transmission allows the system to optimize the jam efficiency quickly to an unknown signal, and while determining the validity of the threat. The high throughput parallel architecture allows the intelligent jamming process to occur with rapidity and signal multiplicity.
Owner:JOCIC DAMJAN
Fluidic connectors and microfluidic systems
Fluidic connectors, methods, and devices for performing analyses (e.g., immunoassays) in microfluidic systems are provided. In some embodiments, a fluidic connector having a fluid path is used to connect two independent channels formed in a substrate so as to allow fluid communication between the two independent channels. One or both of the independent channels may be pre-filled with reagents (e.g., antibody solutions, washing buffers and amplification reagents), which can be used to perform the analysis. These reagents may be stored in the channels of the substrate for long periods amounts of time (e.g., 1 year) prior to use. Prior to connection of the fluid connector and the substrate, the fluid path may be filled with a sample (e.g., blood). The sample may be obtained, for example, by pricking a finger of a user until blood is drawn from the finger into the fluid path (e.g., by capillary forces). Upon connection of the fluidic connector and the channels of the substrate, the sample can pass through a reaction area within the first channel of the substrate. This process can allow components of the sample to interact with components disposed in the reaction area. Afterwards, reagents from the second channel can flow to the reaction area via the fluid path, allowing components in the reaction area to be processed (e.g., amplified to produce detectable signal). Components in the reaction area can then be determined using various methods of detection.
Owner:OPKO DIAGNOSTICS
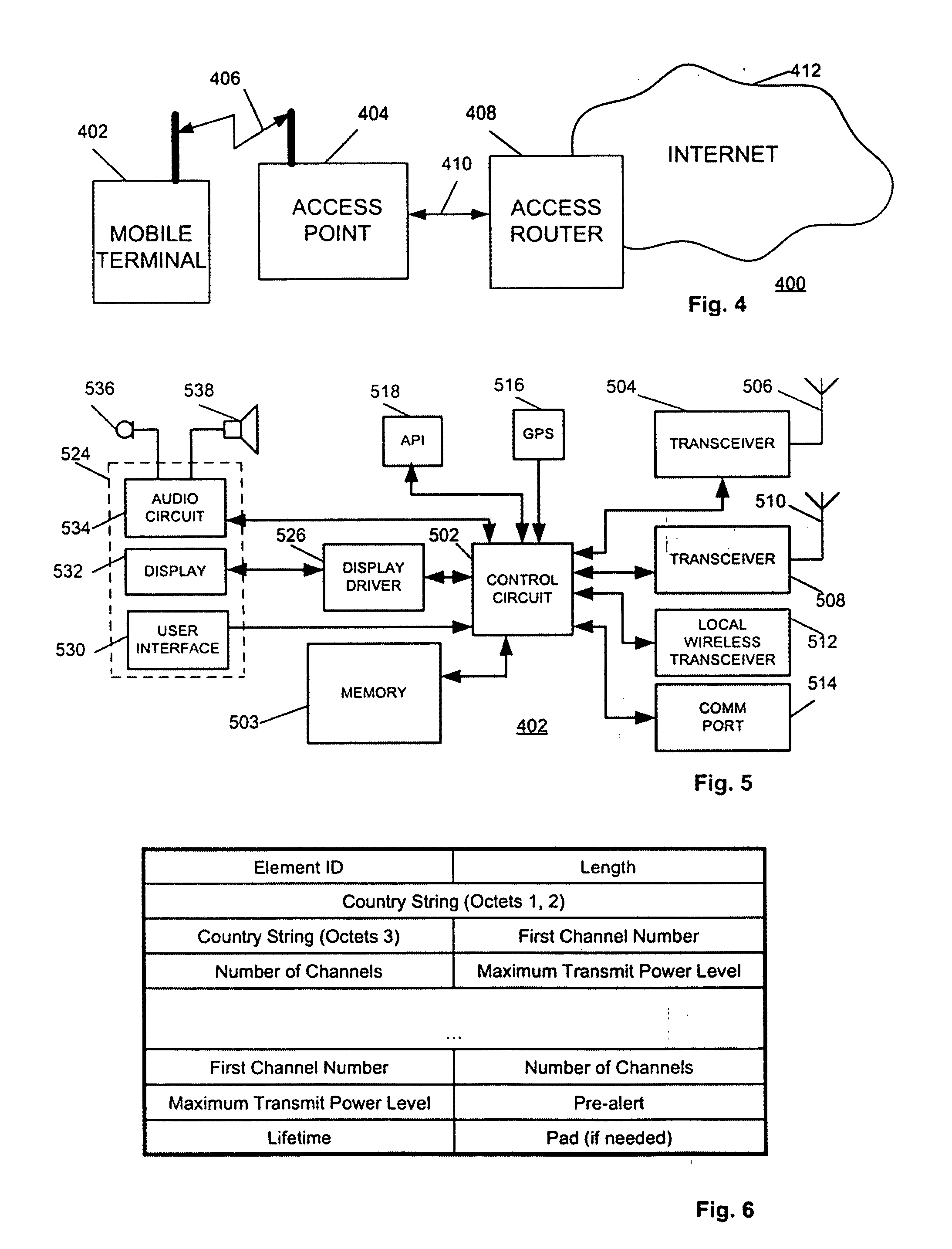
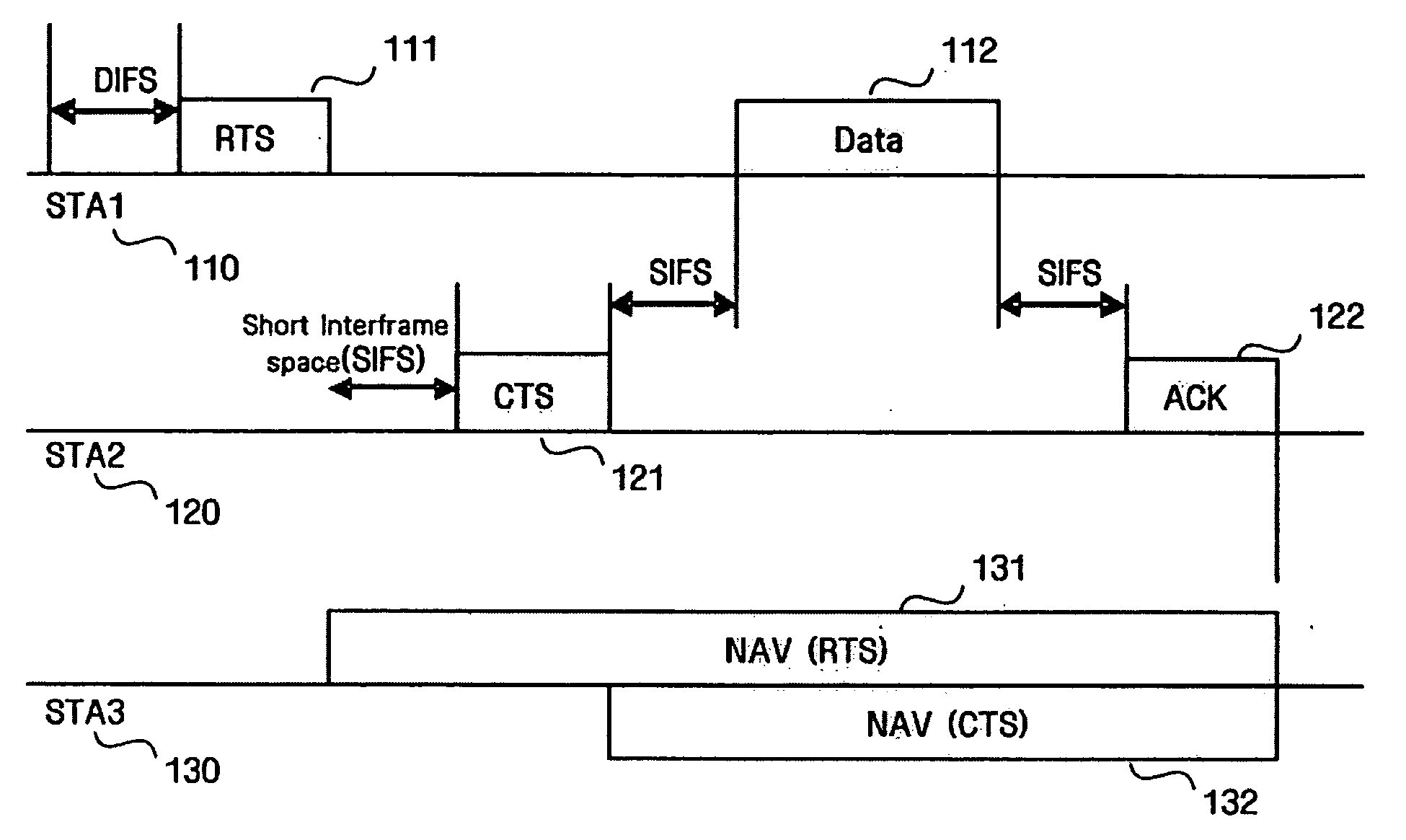
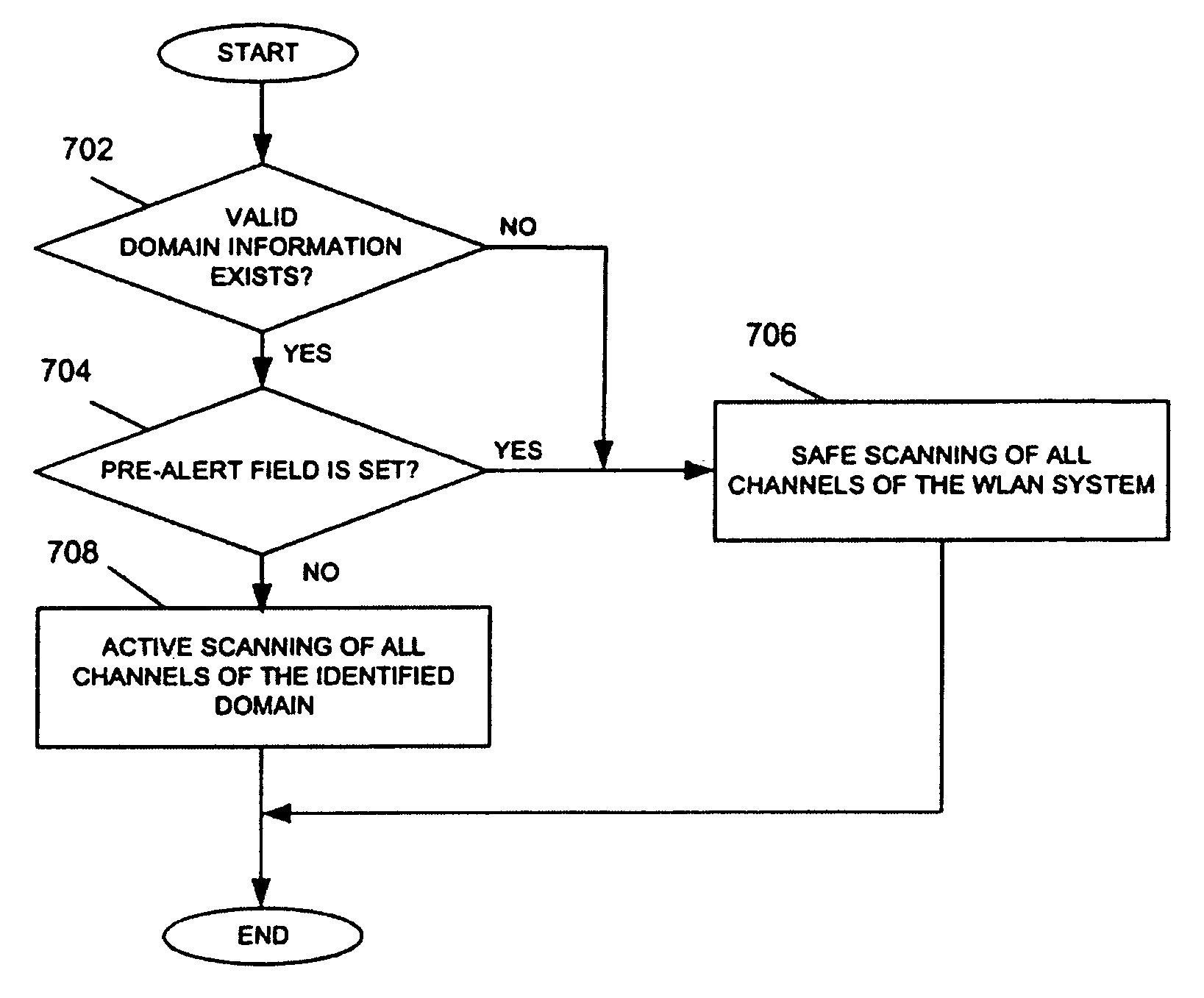
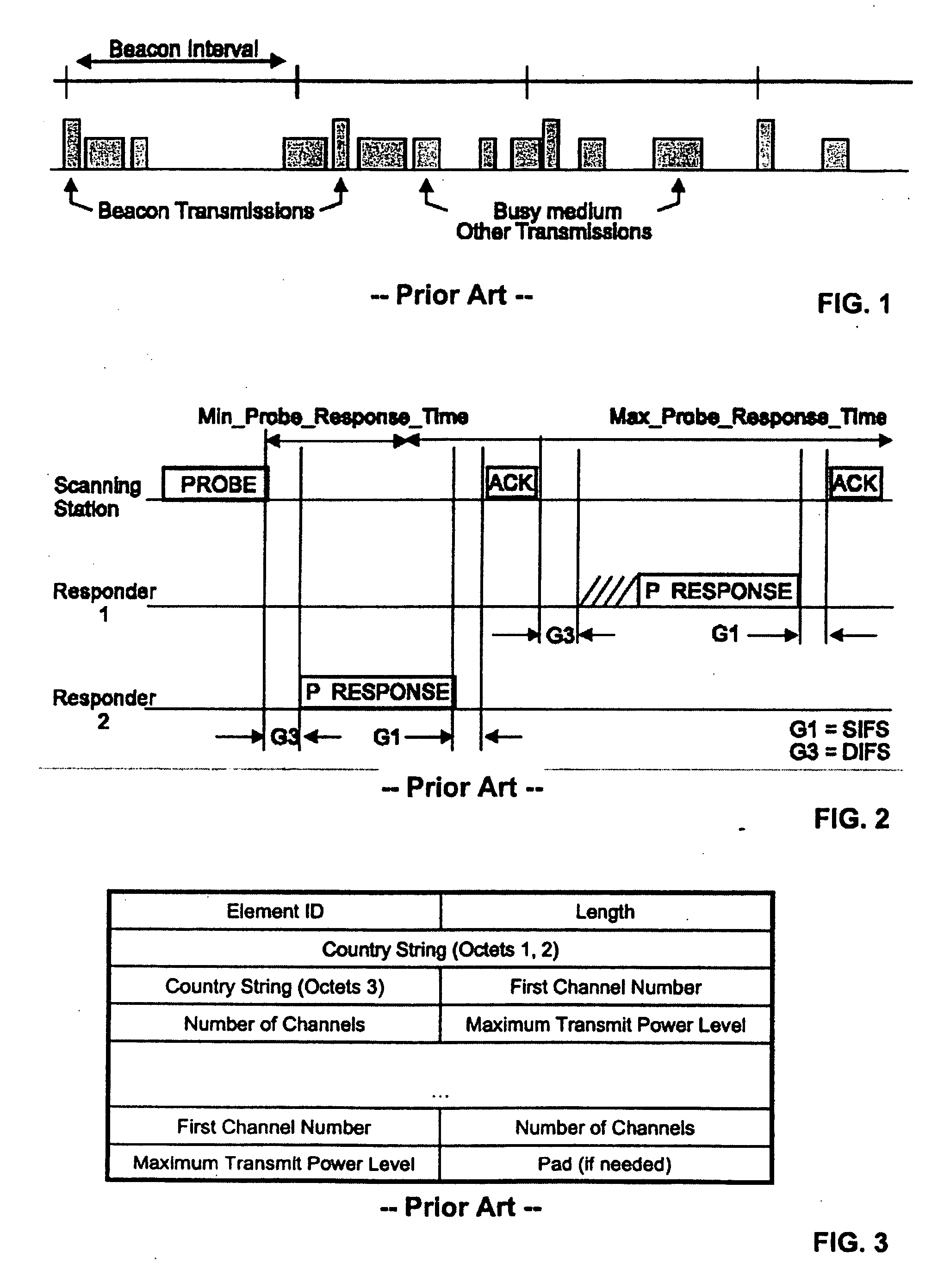
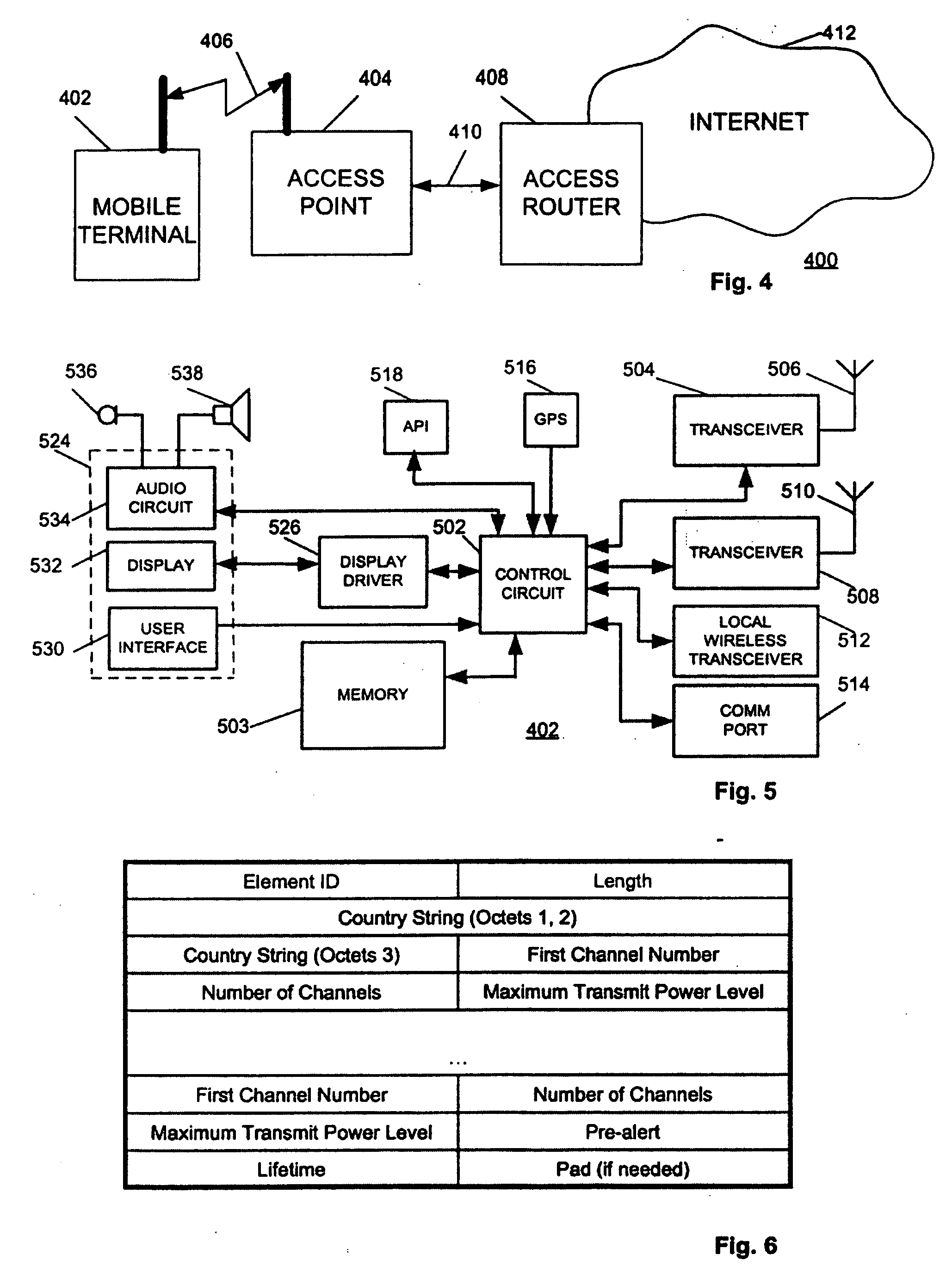
System and method for channel scanning in wireless networks
InactiveUS20040137905A1Assess restrictionData switching by path configurationWireless networkIndependent channels
Channel scanning for wireless networks, such as Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs), generally provides a wireless station with the information on the available WLAN resources, such as the frequency band and the maximum transmission power. The present invention provides safe and fast domain-aware channel scanning, enabling a wireless station to comply with applicable local regulations, in spite of the possibility of domain changes, with short channel-scanning time. Fast channel scanning is accomplished by active channel scanning if valid domain information is available and there is no possibility of domain change. Also, domain-independent channels, if any, are first scanned using active scan to get domain information faster.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Fluidic connectors and microfluidic systems
Fluidic connectors, methods, and devices for performing analyses (e.g., immunoassays) in microfluidic systems are provided. In some embodiments, a fluidic connector having a fluid path is used to connect two independent channels formed in a substrate so as to allow fluid communication between the two independent channels. One or both of the independent channels may be pre-filled with reagents (e.g., antibody solutions, washing buffers and amplification reagents), which can be used to perform the analysis. These reagents may be stored in the channels of the substrate for long periods amounts of time (e.g., 1 year) prior to use. Prior to connection of the fluid connector and the substrate, the fluid path may be filled with a sample (e.g., blood). The sample may be obtained, for example, by pricking a finger of a user until blood is drawn from the finger into the fluid path (e.g., by capillary forces). Upon connection of the fluidic connector and the channels of the substrate, the sample can pass through a reaction area within the first channel of the substrate. This process can allow components of the sample to interact with components disposed in the reaction area. Afterwards, reagents from the second channel can flow to the reaction area via the fluid path, allowing components in the reaction area to be processed (e.g., amplified to produce detectable signal). Components in the reaction area can then be determined using various methods of detection.
Owner:OPKO DIAGNOSTICS
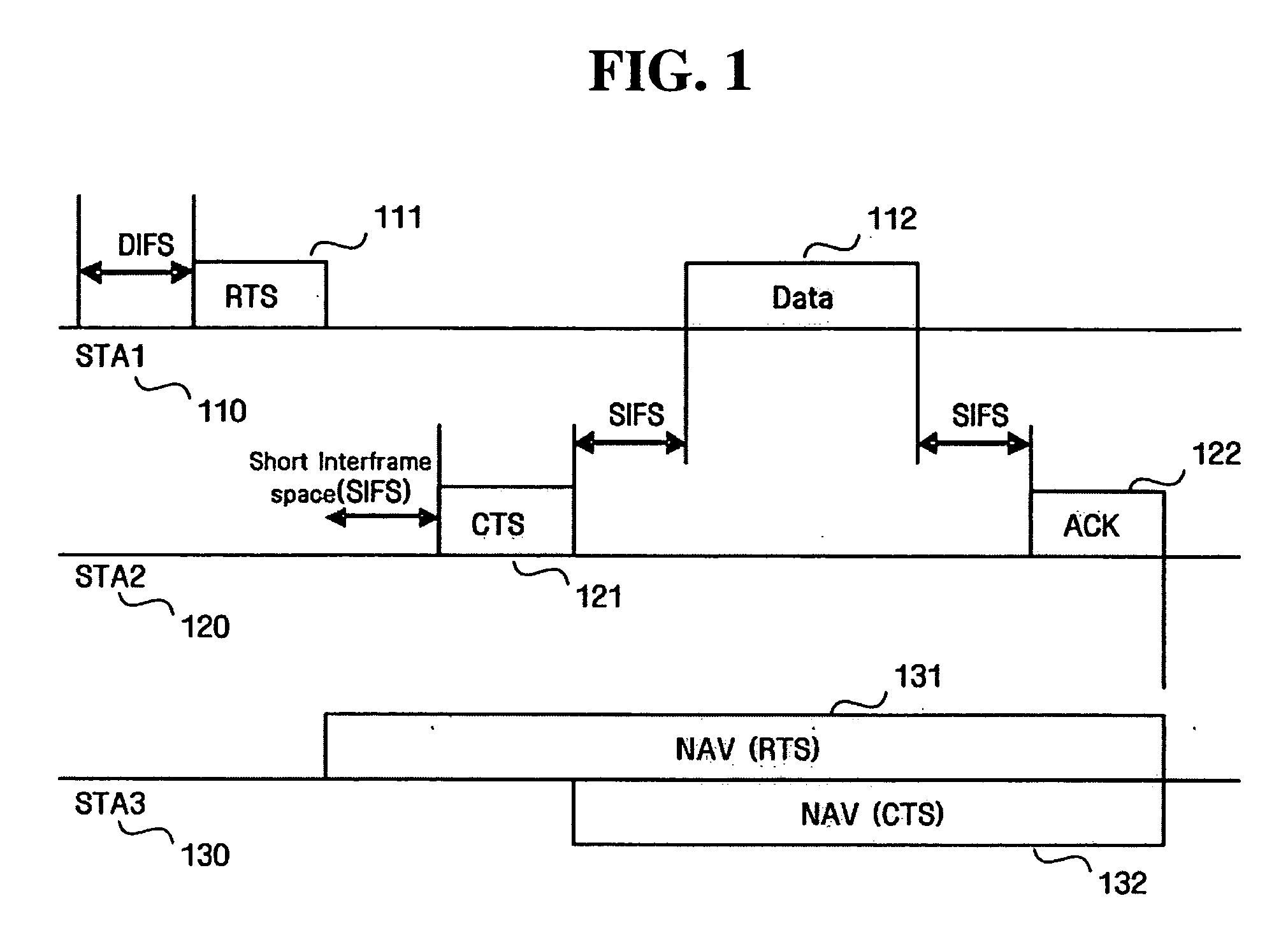
Method and apparatus for enhancing transfer rate using DLP and multi channels in wireless LAN using PCF and DCF
InactiveUS20050053015A1Reduce contentionData switching by path configurationWireless communicationWireless lanPrimary channel
A wireless network communication method and apparatus for enhancing a data transfer rate by using a direct link protocol (DLP) and multi channels during a point coordination function (PCF) period in wireless network communications in which an access point is employed in an infrastructure mode using both a contention-free period and a contention period. The wireless network communication method of the present invention including transmitting / receiving data among stations supporting a direct link, during a given duration, through the direct link using an independent channel; transmitting / receiving data among stations other than the stations supporting the direct link, during the duration, in a specific mode corresponding to the contention-free or contention period; switching the DLP stations to a primary channel after the given duration; and transmitting / receiving data among all stations including the DLP stations, during the remaining duration, in a specific mode corresponding to the contention-free or contention period.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
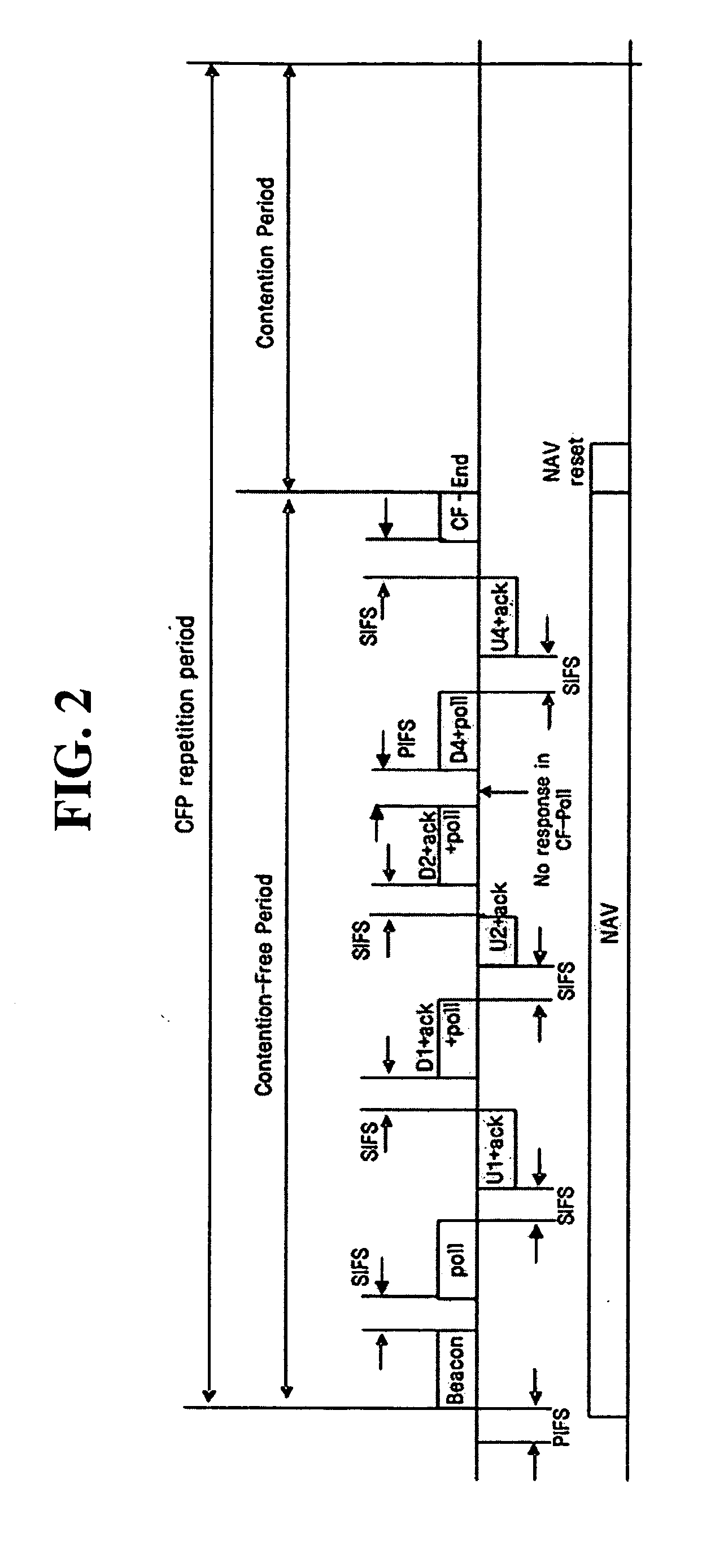
System and method for channel scanning in wireless networks
ActiveUS20060023686A1Speed maximizationAssess restrictionData switching by path configurationWireless lanWireless network
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
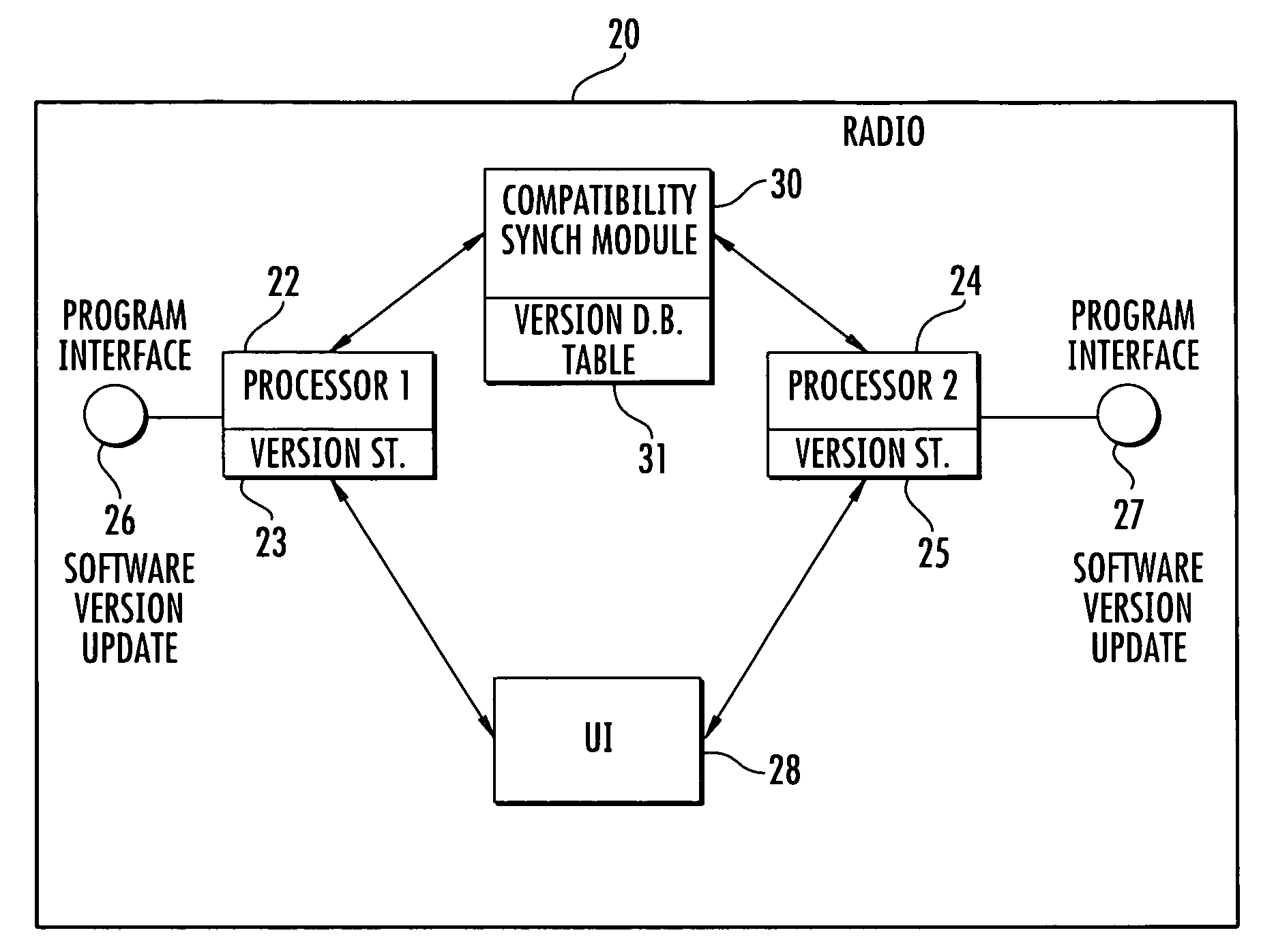
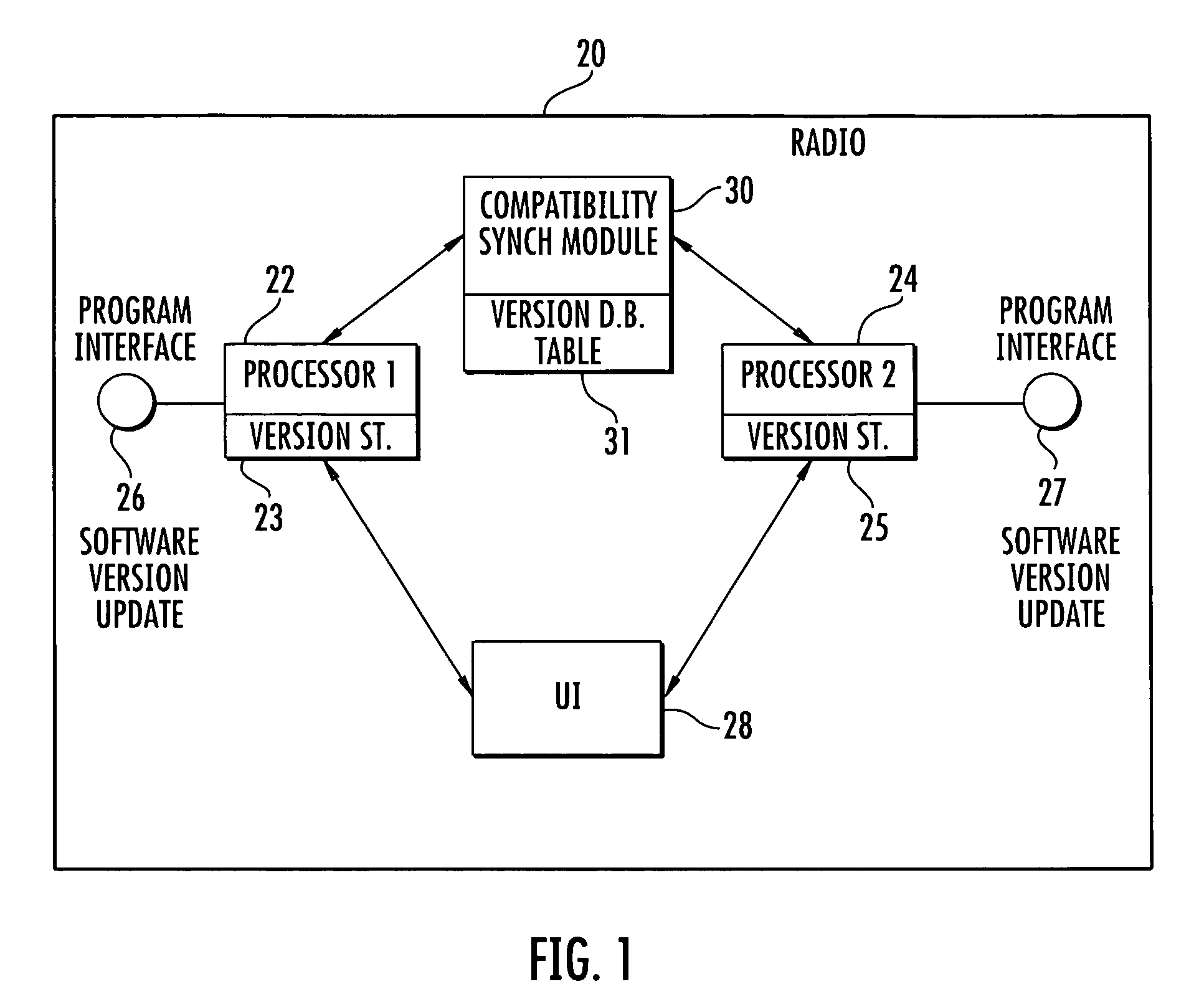
Communications device with a plurality of processors and compatibility synchronization module for processor upgrades and related method
InactiveUS20100146497A1Specific program execution arrangementsSpecial data processing applicationsSystem recoverySoftware update
A multiprocessor device includes a plurality of device subsystems each having a processor dependent on a respective other processor in another device subsystem for device operation. Each processor has at least one independent channel for updating a respective software version within the respective processor. A compatibility synchronization module has a database storing a table of compatible software versions for each processor. It is updated when a new software version for a processor is created. This table is independent of software images for the software versions. The compatibility synchronization module is operative for verifying if the software version for a processor is compatible with other software versions at other processors and instructs a respective device subsystem to revert back to a compatible software version within a respective processor or prevent any incompatible software updates within the processor.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
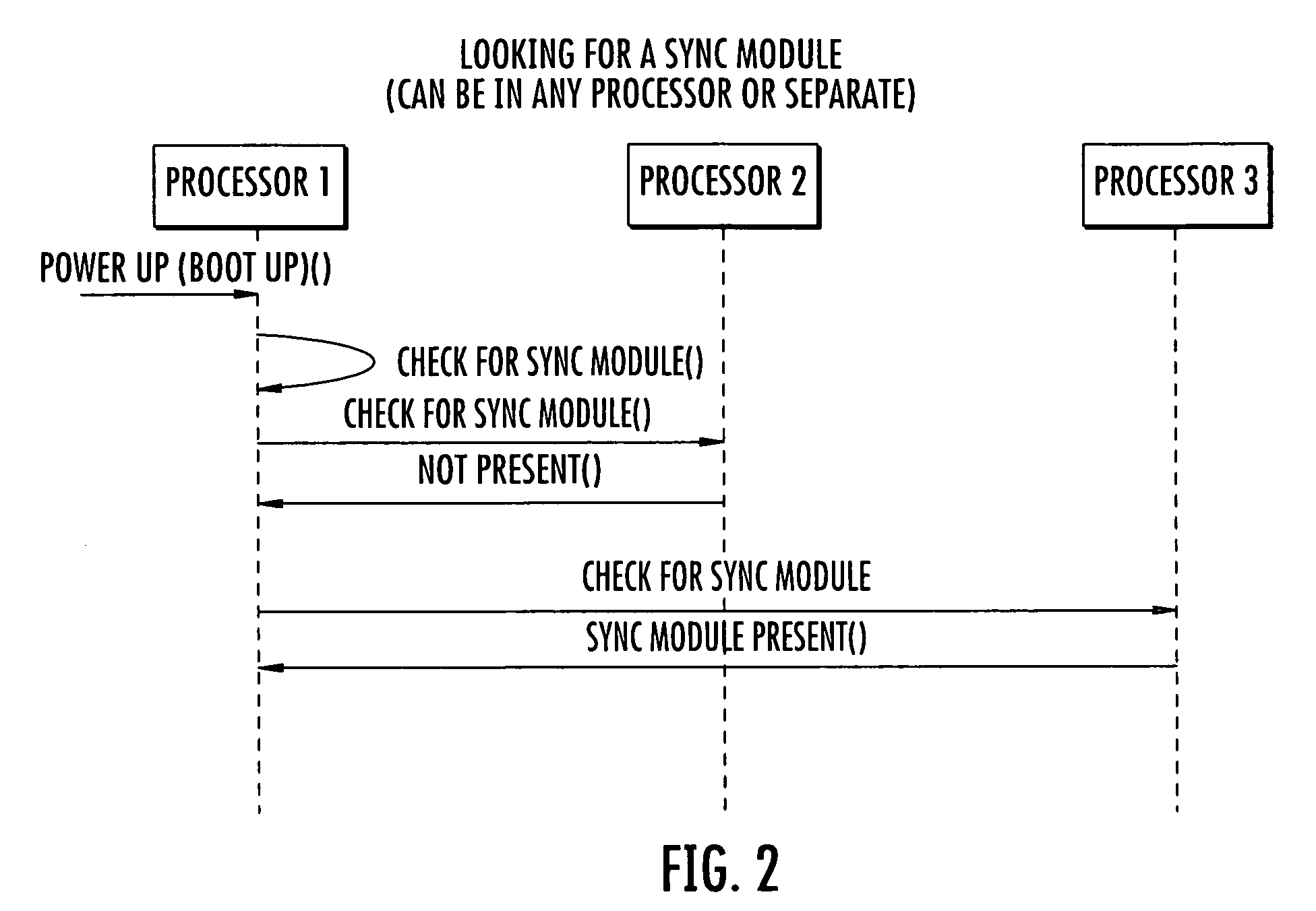
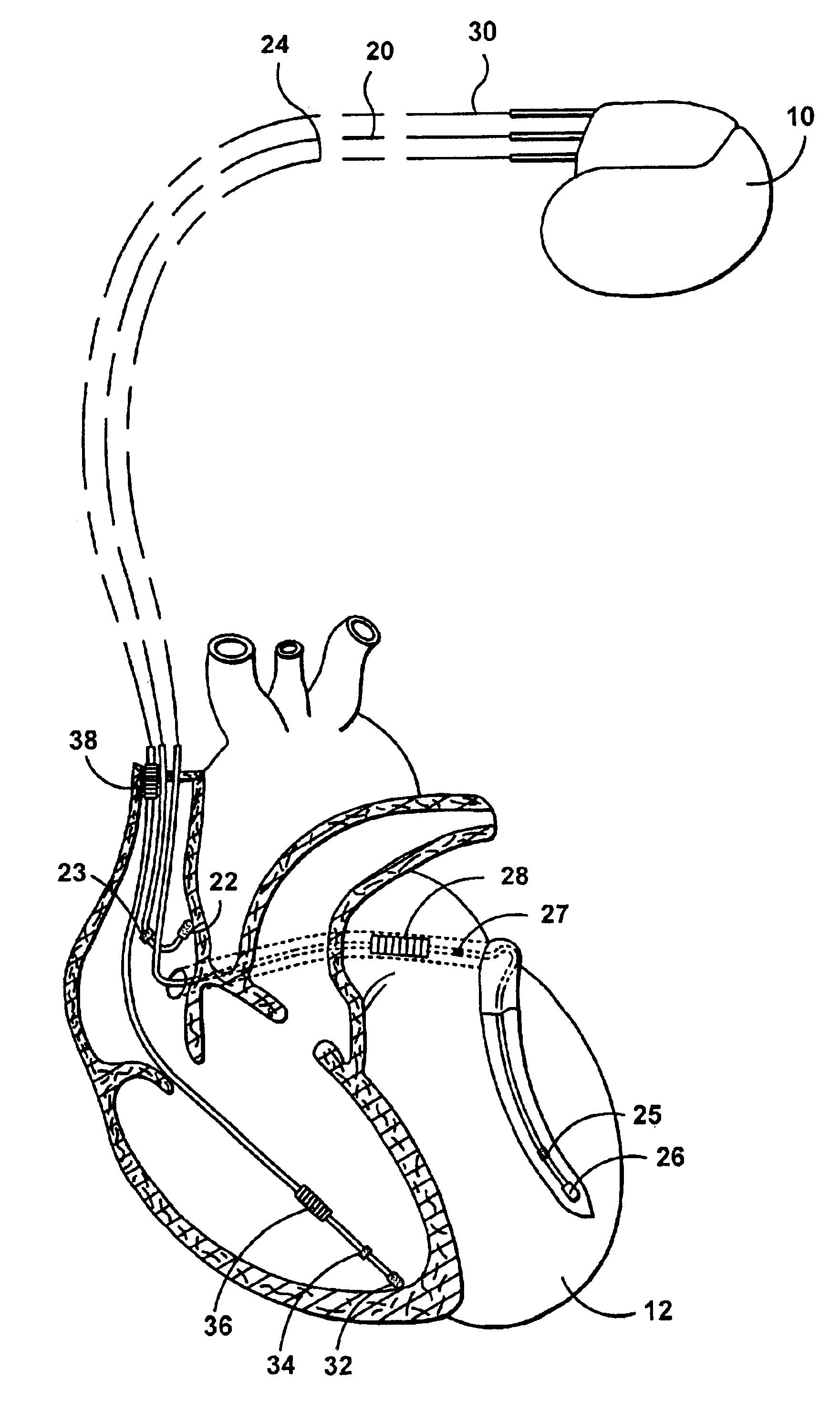
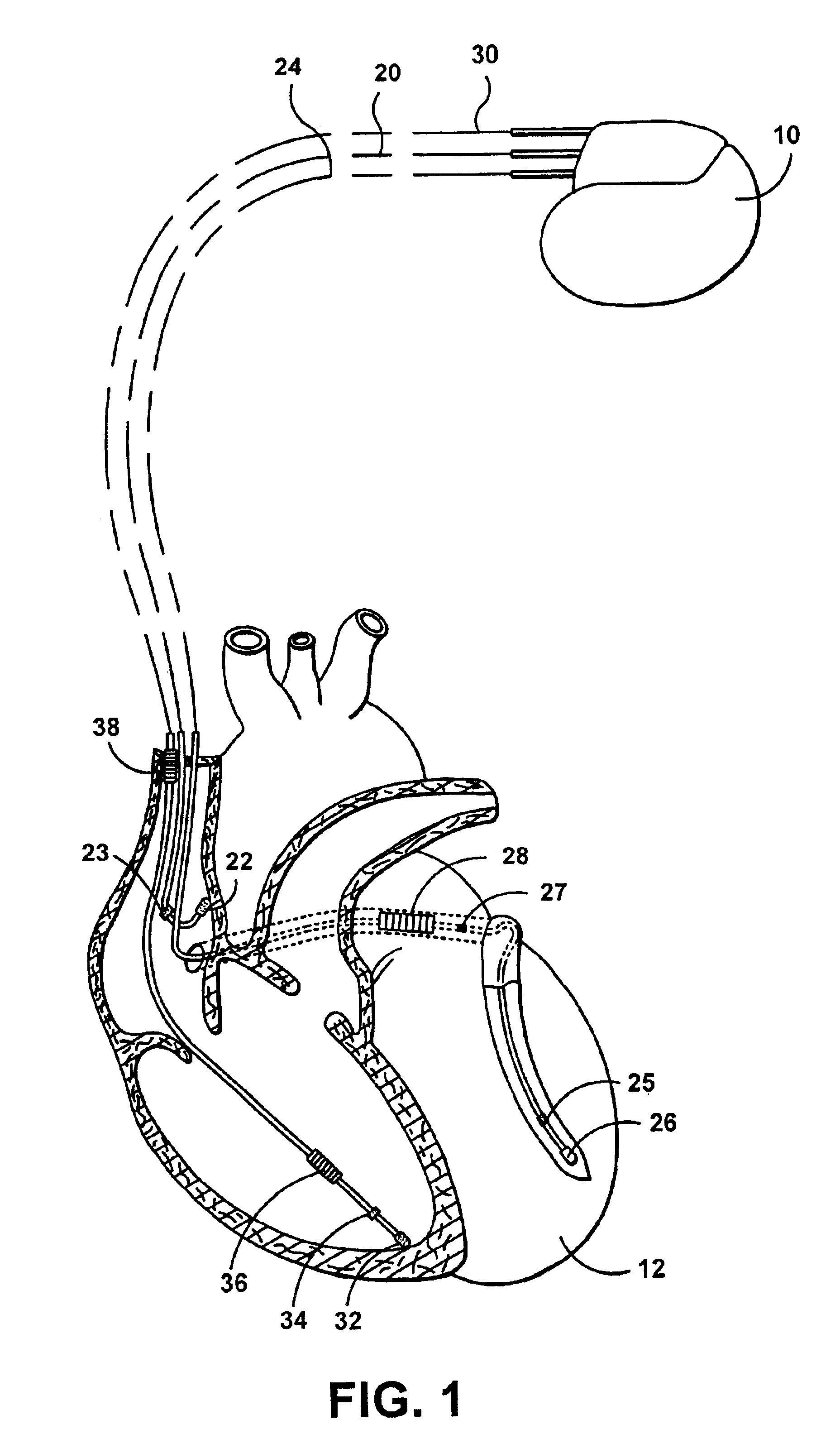
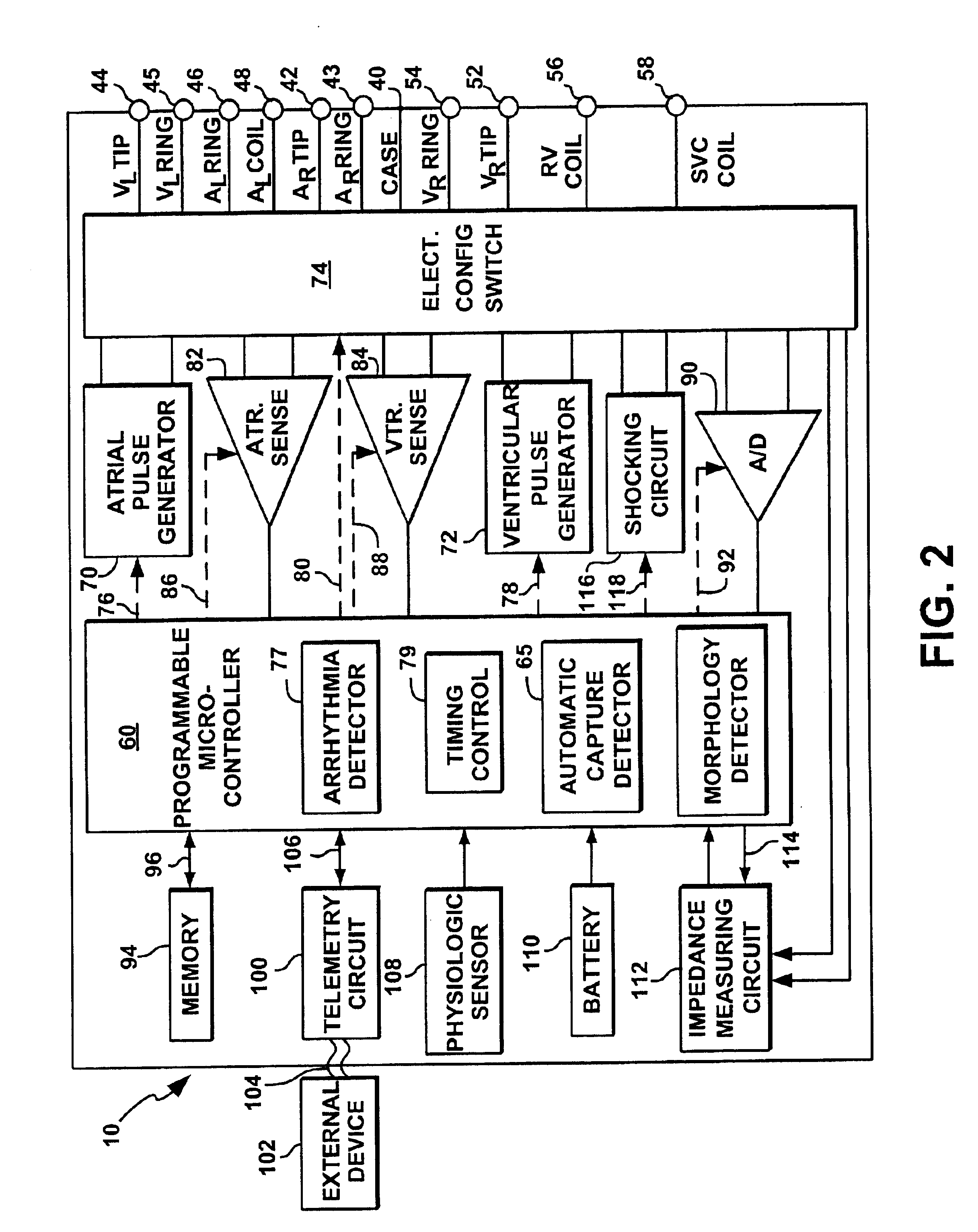
Automatic capture using independent channels in bi-chamber stimulation
InactiveUS6915164B2Extend battery lifeIncreased longevityHeart stimulatorsLeft cardiac chamberPulse energy
A cardiac stimulation device and method deliver independent stimulation pulses to right and left cardiac chambers, based on the capture thresholds of each chamber, and confirm capture in each chamber. A threshold test is performed in one chamber while stimulating the opposite chamber at increased pulse energy and adjusted interchamber delay.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
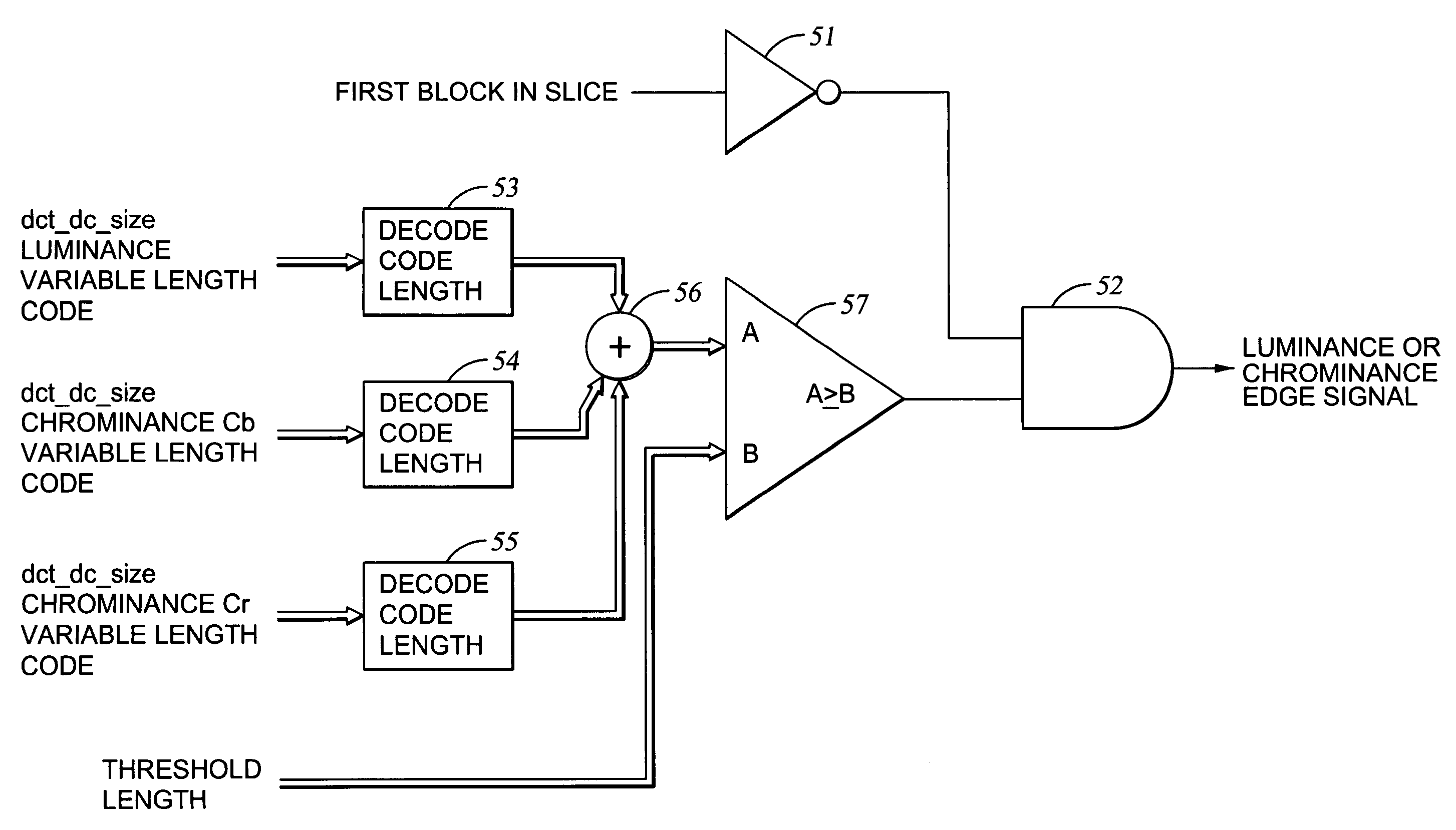
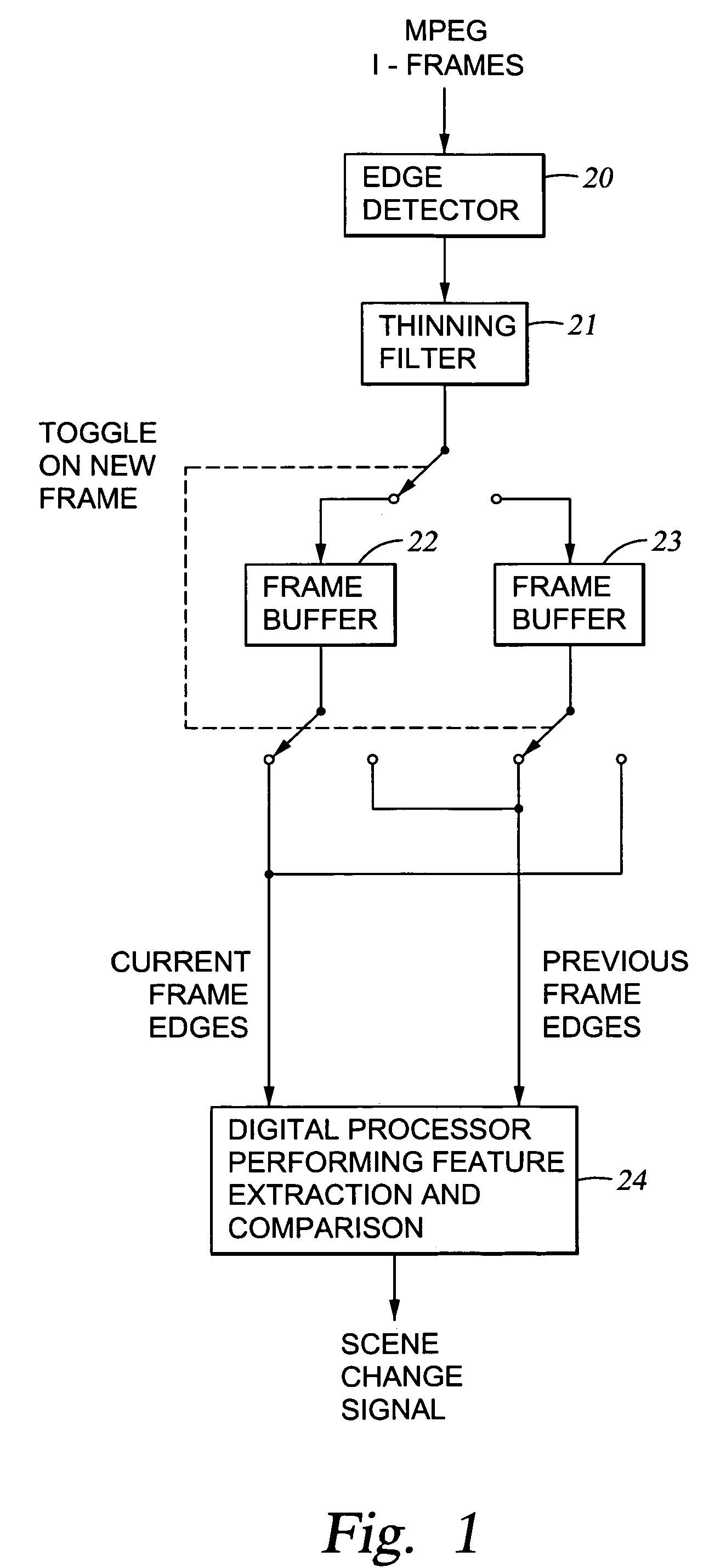
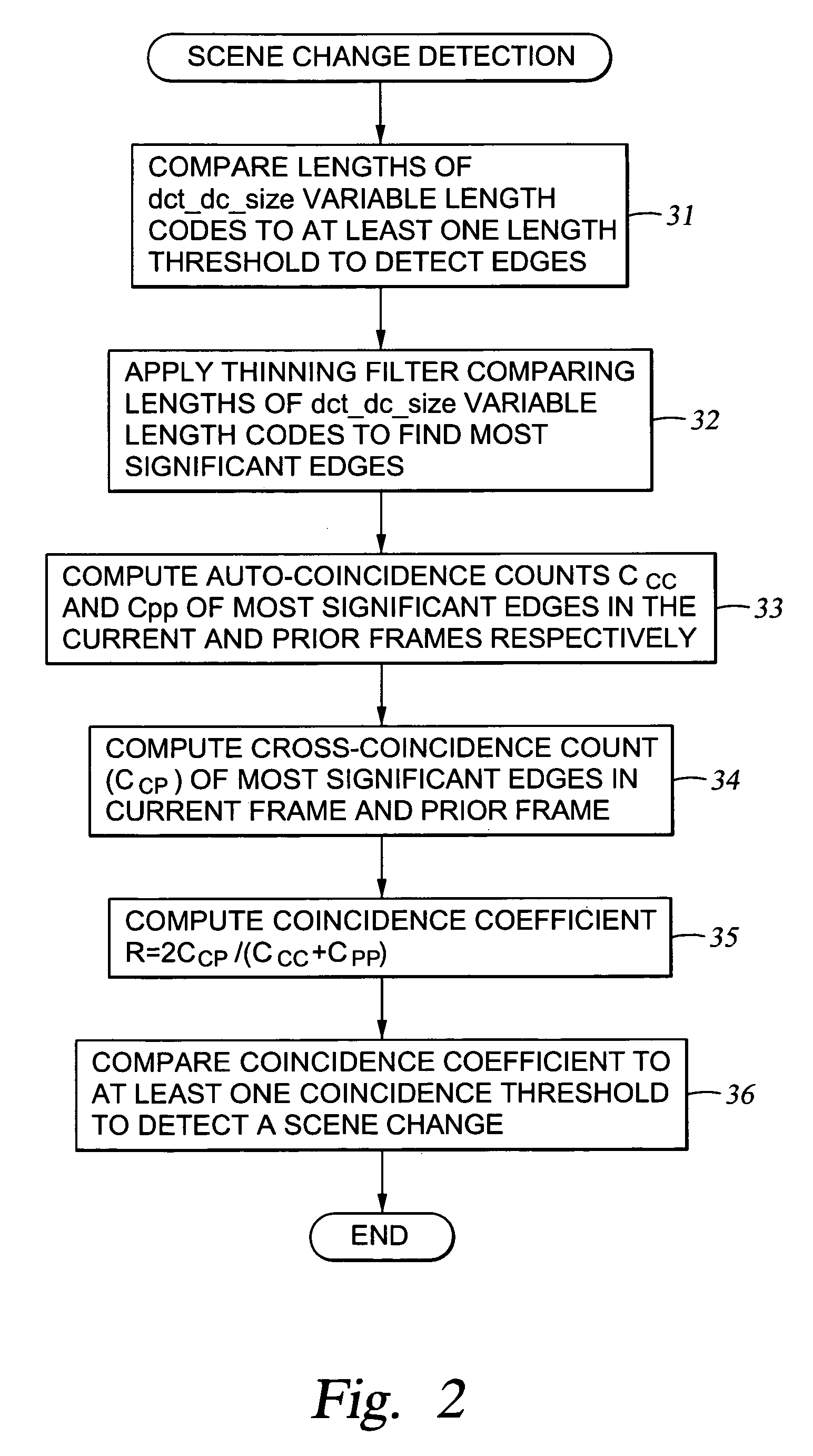
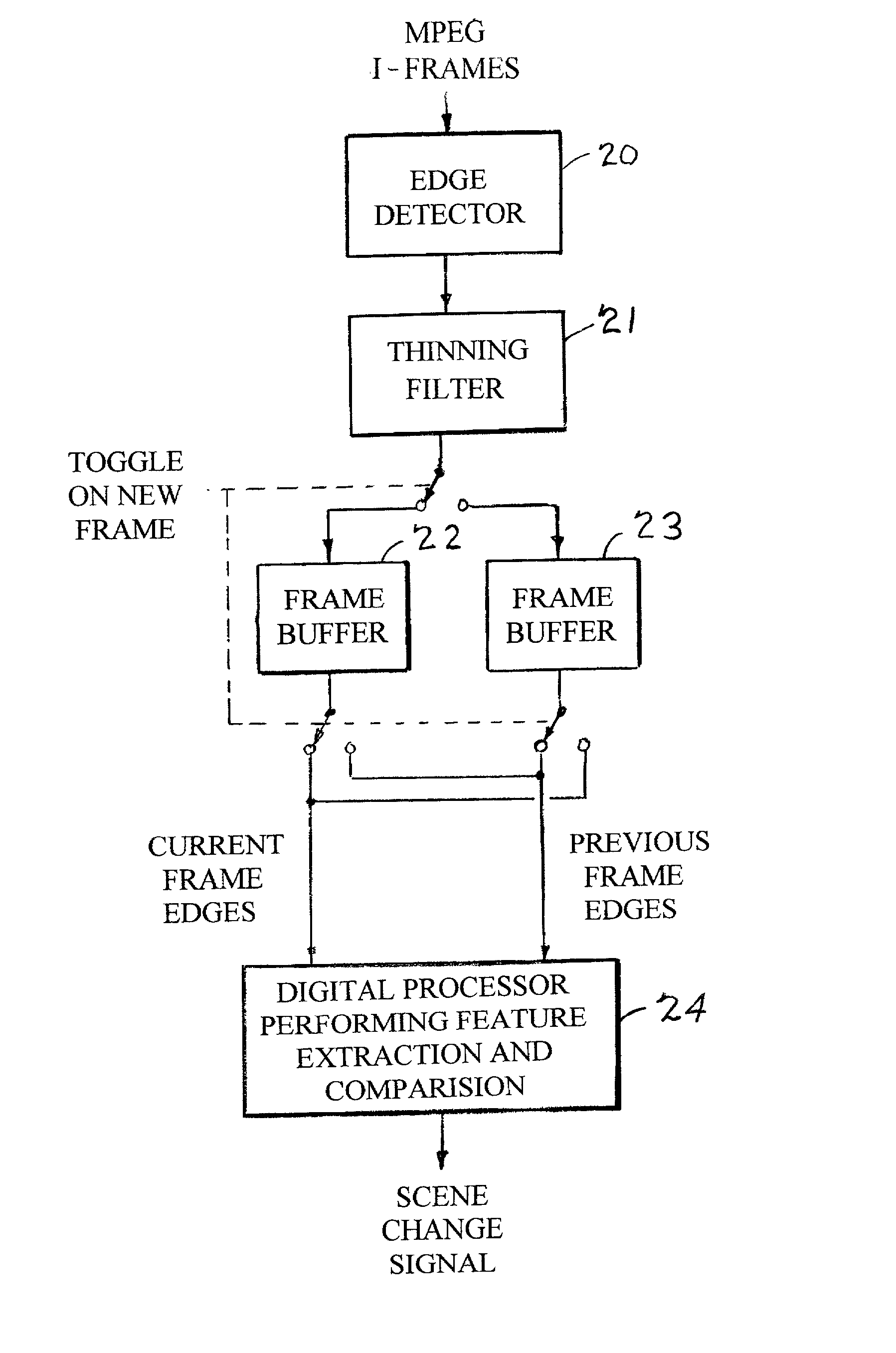
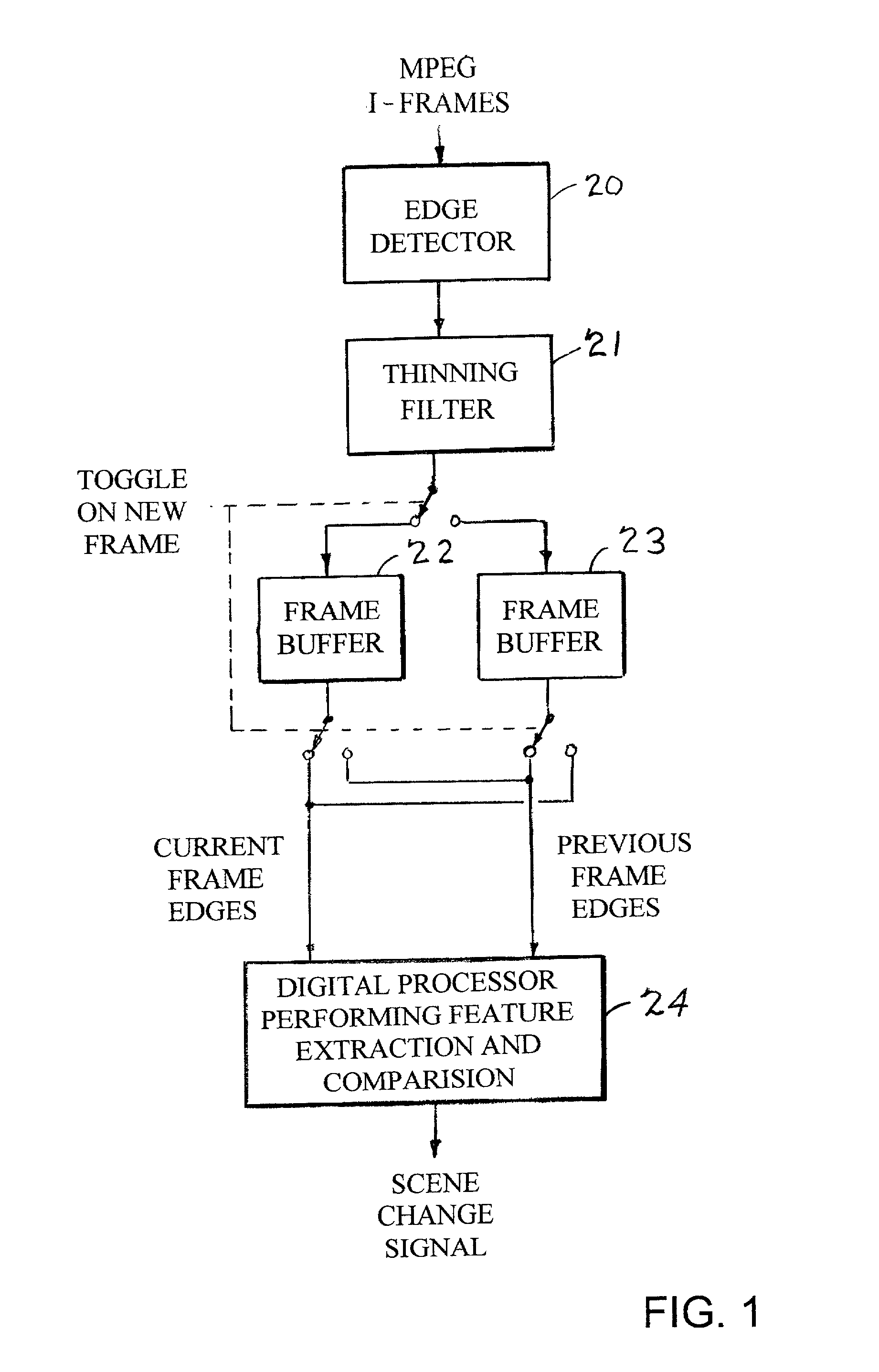
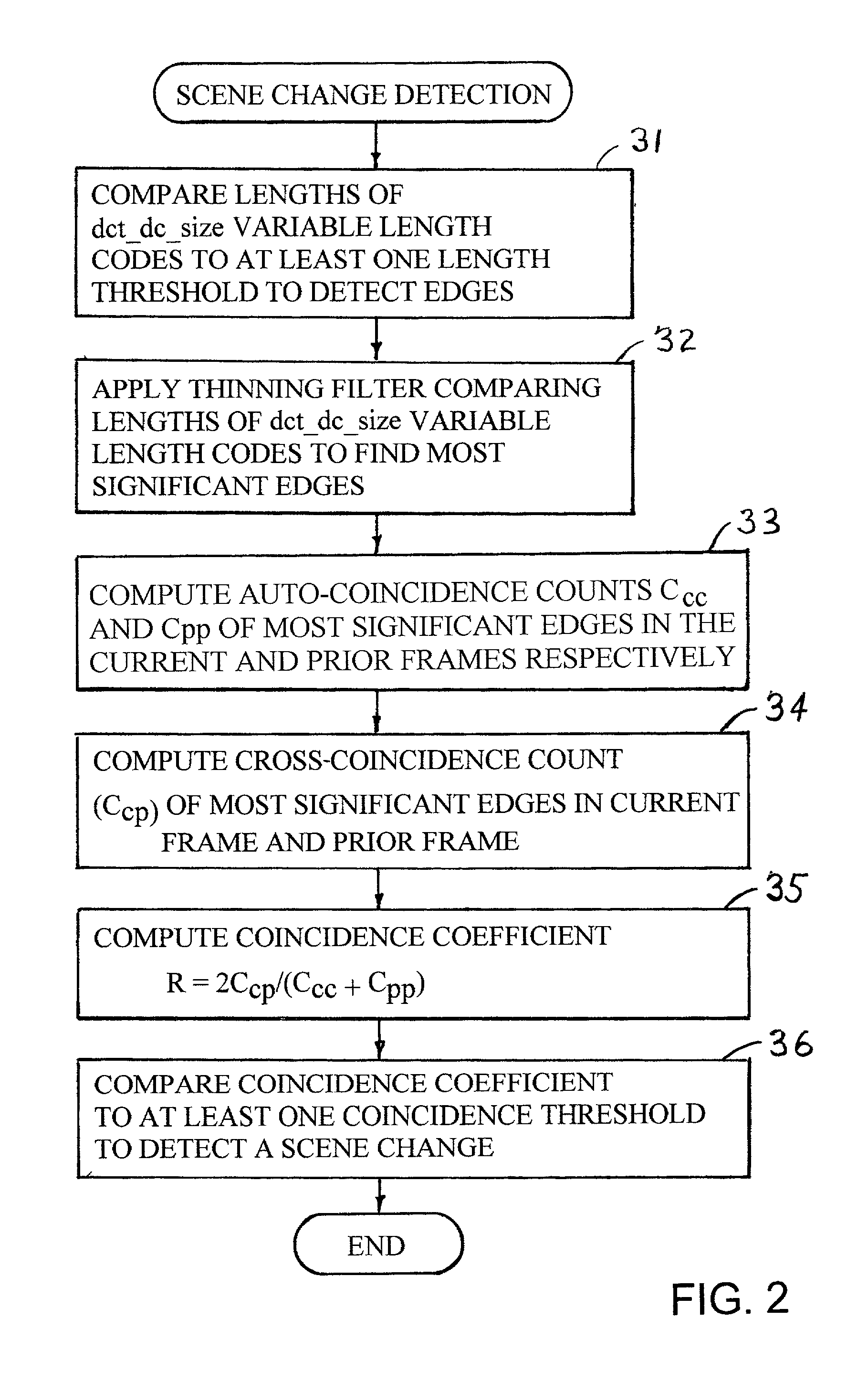
Edge detection based on variable-length codes of block coded video
ActiveUS7054367B2Television system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesVariable-length codePattern recognition
Edges are detected in block coded video by a threshold comparison upon the lengths of variable-length codes used for encoding the differential DC coefficients of the pixel blocks. A thinning filter compares the code lengths of the differential DC coefficients of adjacent blocks in order to retain the edge indications of more significant edges and to exclude the edge indications of less significant edges. The edge indications can be split into substantially independent channels for luminance or chrominance, for edges having positive or negative horizontal gradient components, and for edges having positive or negative vertical gradient components. The edge indications for successive frames in an MPEG sequence are compared to each other in various ways in order to detect scene changes.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Multi-antenna device channel access method and apparatus
ActiveCN106658751ASolve the technical problem of low spectral efficiencyReduce distractionsSpatial transmit diversityWireless communicationTelecommunicationsFrequency spectrum
The present invention discloses a multi-antenna device channel access method and apparatus. The method comprises the steps of acquiring a sending request of sending data by using a multi-antenna device; and performing independent channel access in each beam direction corresponding to the sending request. Through adoption of the multi-antenna device channel access method and apparatus, a technical problem of low spectrum efficiency of channel access of the multi-antenna device is solved.
Owner:BAICELLS TECH CO LTD
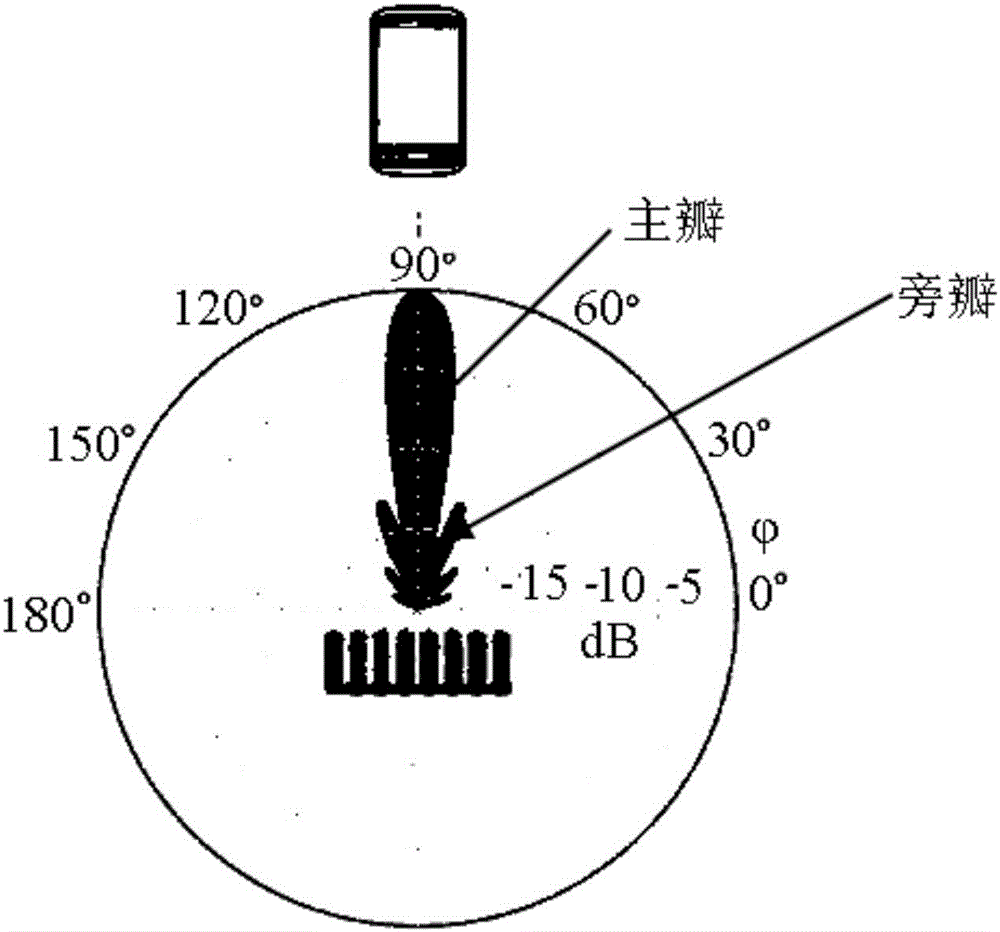
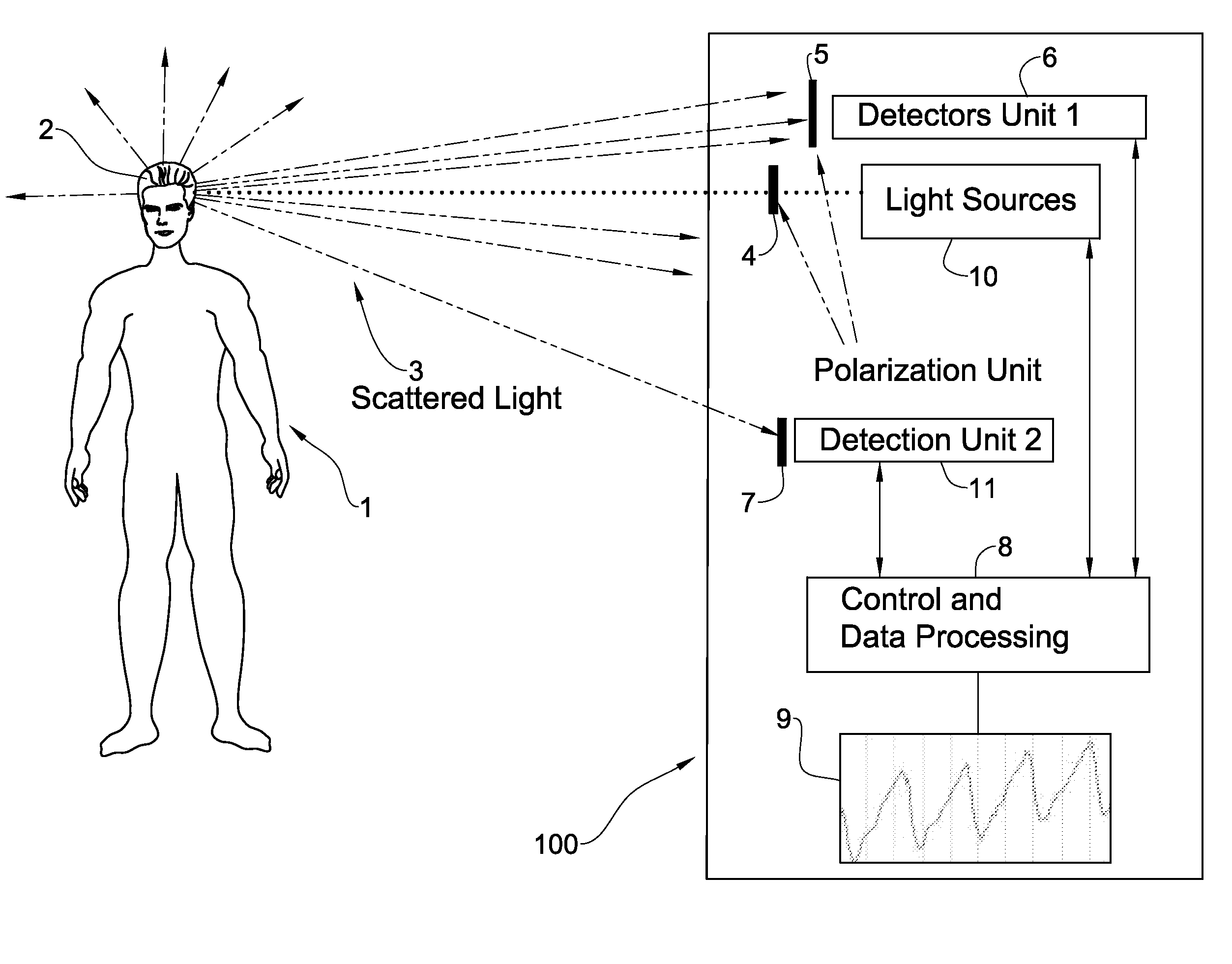
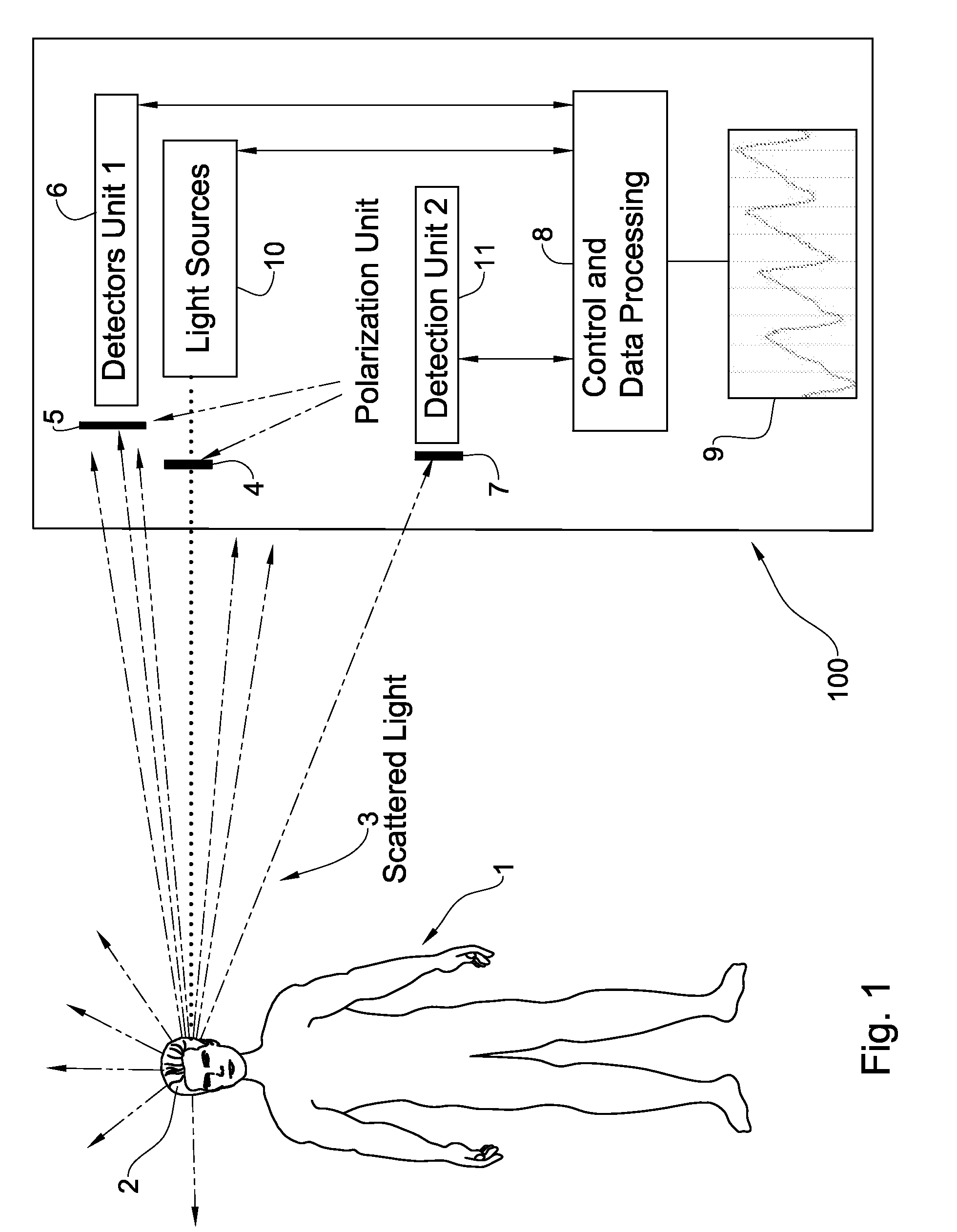
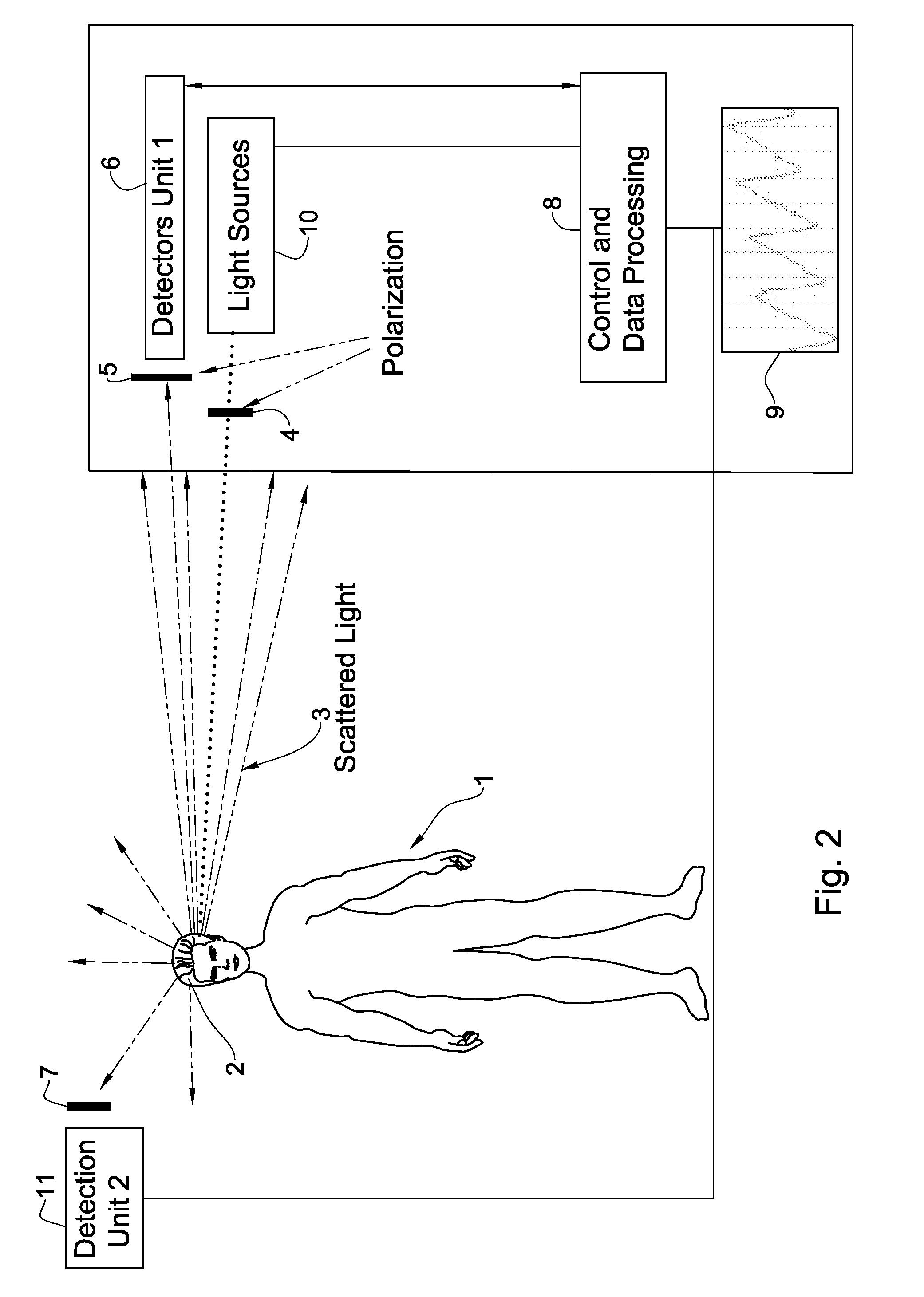
System and method for measurement of biological parameters of a subject
InactiveUS20090082642A1Minimize contactContinuous monitoringDiagnostics using lightSensorsPhysicsIndependent channels
Disclosed is a system and method for use in monitoring of biological parameters of a subject. The system includes an illumination unit including at least one light source of at least one pre-selected wavelength band, to be applied to a selected region in the subject; and a detection system configured for measuring reflections of the light at different angles and different spatial locations with respect to the illuminated region. The detection system is configured and operable to detect spatially separated light components corresponding to the specular dependent component of the signal and the pulsatile-related diffused component of the signal coming from the subject in different directions respectively, thereby defining at least two independent channels of information, enabling identification of the reflected signal part dependent on motion effects.
Owner:ELFI TECH
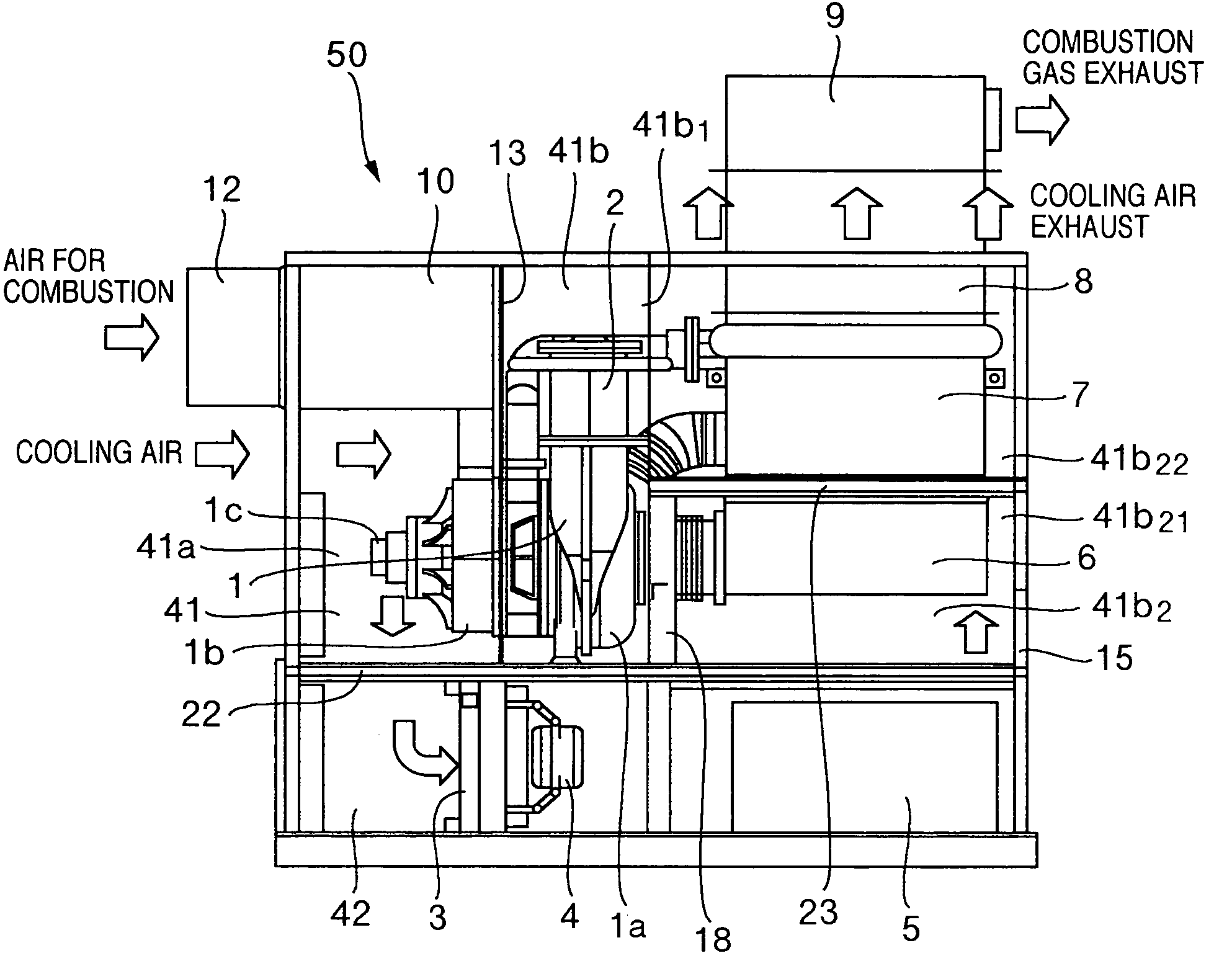
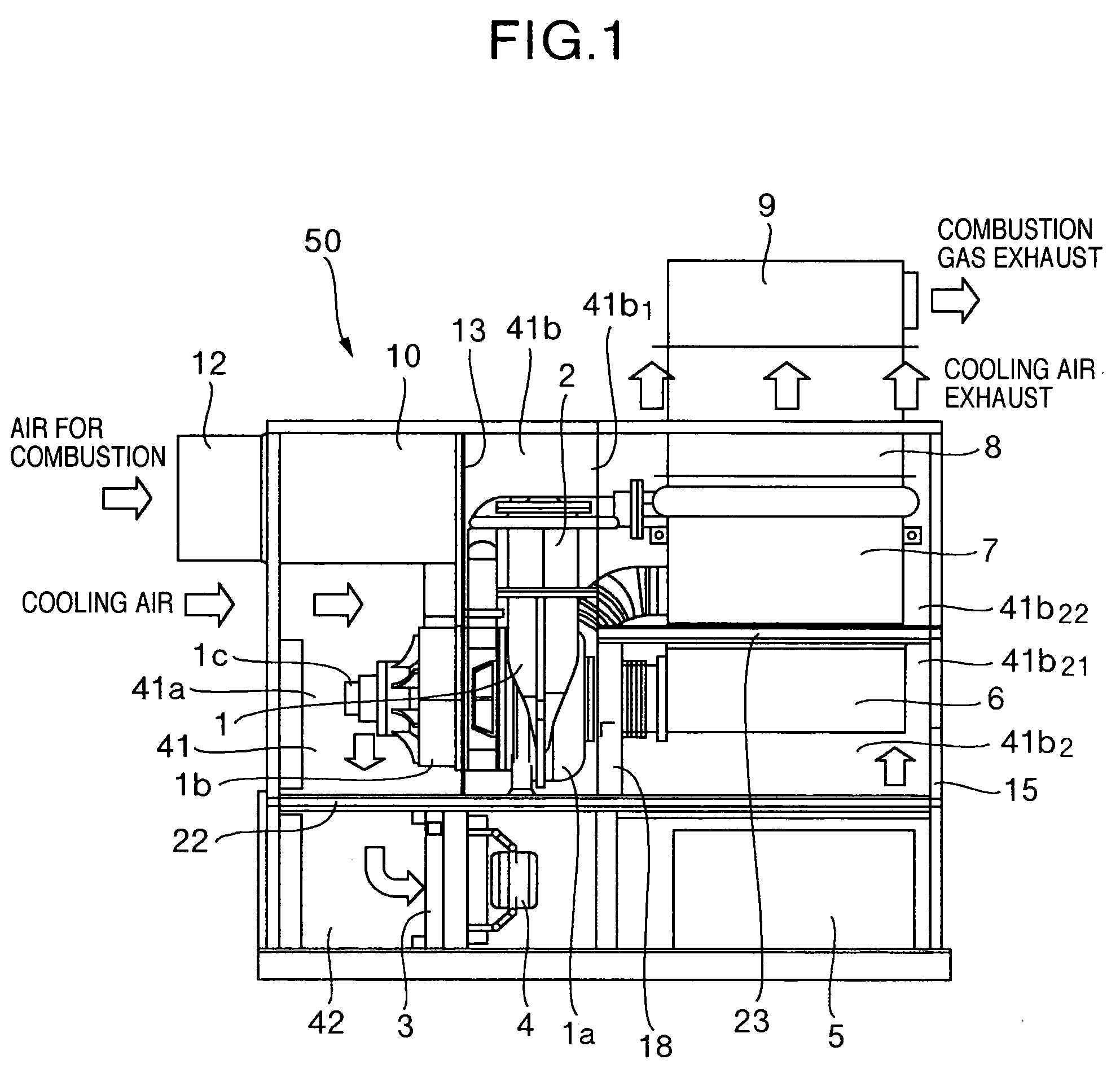
Gas turbine power generator plant and silencer for the same
InactiveUS20050160740A1Reduce noiseEngine fuctionsTurbine/propulsion engine coolingCombustion chamberEngineering
A gas turbine power generator plant, intended to reduce its noise by making small the intake and exhaust outlets of the cooing air channel of a case, comprises an engine core in which a turbine, a compressor and a generator are installed on the same axis, a combustor for burning air for combustion compressed by the compressor and supplying the air to the turbine, a radiator for cooling a coolant or a lubricant, a cooling fan for ventilating the radiator with cooling air, an electric power converter for converting electric power generated by the generator, and the case for housing these constituent elements. And, a combustion air channel passing the compressor, the combustor and the turbine and a cooling air channel passing the radiator, the cooling fan and the electric power converter are formed as mutually independent channels from intake to exhaust.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Foot-operated controller
InactiveUS7186270B2Eliminate needProgramme controlComputer controlIndependent functionRadiotransmitter
A practical control device having up to eight independent channels of communication for simultaneously operating a plurality of electromechanical devices or for simultaneously performing a plurality of independent functions on an electromechanical device, such as a prosthetic hand, includes a foot-operated controller and a microprocessor. The foot-controller includes a plurality of pressure sensors mounted at selected locations on a substrate. The microprocessor converts sensor inputs from the foot-operated controller into commands for a controllable electromechanical device such as a prosthetic hand. Commands may be communicated via a radio transmitter or via hard-wiring.
Owner:JEFFREY ELKINS 2002 TRUST
Broadband wireless sensor network transmission scheme based on collaborative communication of amplification forward single node
InactiveCN101237306AReduce processing complexityEffective expansionDiversity/multi-antenna systemsMulti-frequency code systemsLine sensorCyclic prefix
The invention discloses a broadband wireless sensor network transmission scheme based on amplify-and-forward single-node cooperation communication. The scheme is as follows: a source node is firstly used to make an orthogonal space-frequency coding to an original signal, two time slots are respectively used to transmit orthogonal signal frames, then a pilot frequency is inserted and coded signals are subject to IFFT operation to fight against the multi-path attenuation, the coded signals are converted onto a time domain, and the serial data flow is broadcast and sent after the insertion of a cyclic prefix and a training sequence. A first time slot relay node receives signals of the source node, makes frequency deviation and phase compensation, then adopts an amplify-and-forward protocol to synchronously send the processed signals to an information sink node at a second time slot and the source node; an information sink receiver receives a mixed signal from two independent channels, firstly detects a frame head of the signal of the second time slot, then synchronizes with the frame head, then carries out FFT operation to the signal part, converts the signal back to the frequency domain, and performs space-frequency decoding to obtain an original sending symbol. The scheme is simple and easy to operate, can effectively improve the error code rate performance of the system, has strong practicability, and is convenient for the realization of the hardware.
Owner:JIAXING WIRELESS SENSOR NETWORKS CENT CAS
Edge detection based on variable-length codes of block coded video
ActiveUS20030142750A1Television system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesVariable-length codePattern recognition
Edges are detected in block coded video by a threshold comparison upon the lengths of variable-length codes used for encoding the differential DC coefficients of the pixel blocks. A thinning filter compares the code lengths of the differential DC coefficients of adjacent blocks in order to retain the edge indications of more significant edges and to exclude the edge indications of less significant edges. The edge indications can be split into substantially independent channels for luminance or chrominance, for edges having positive or negative horizontal gradient components, and for edges having positive or negative vertical gradient components. The edge indications for successive frames in an MPEG sequence are compared to each other in various ways in order to detect scene changes.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
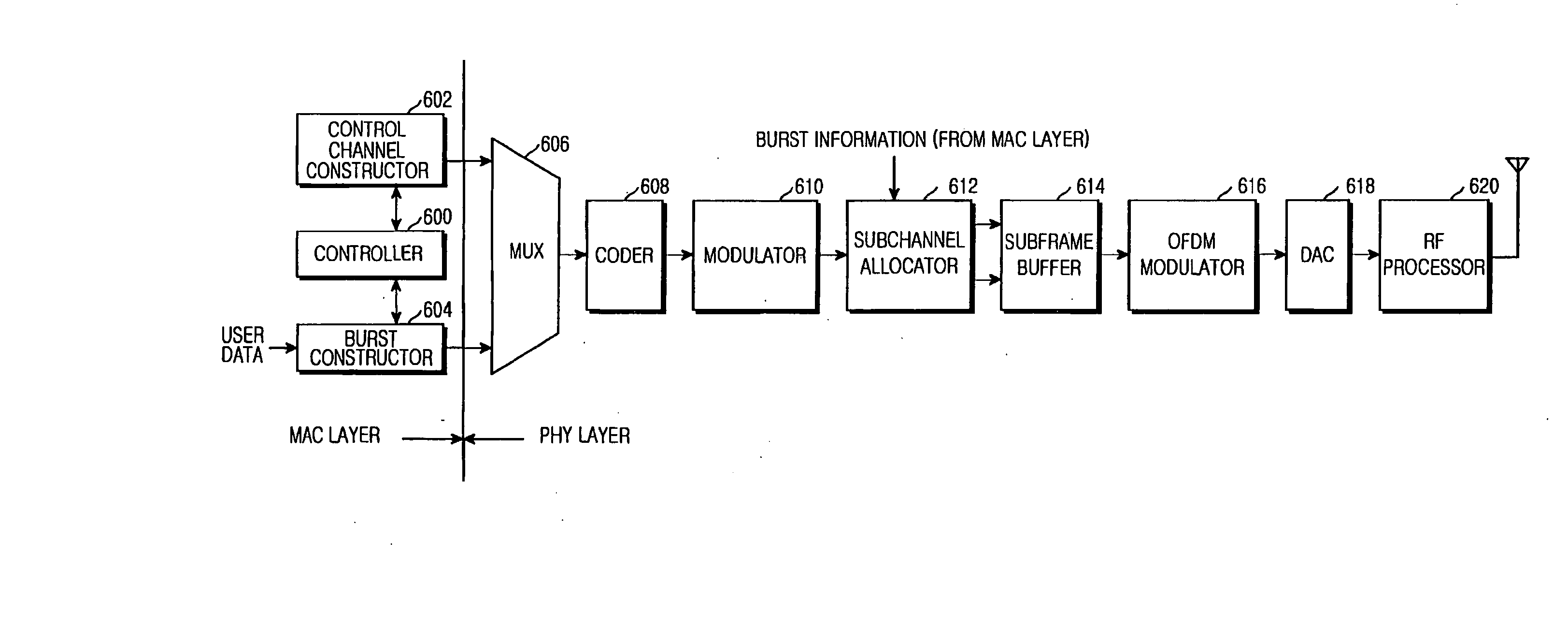
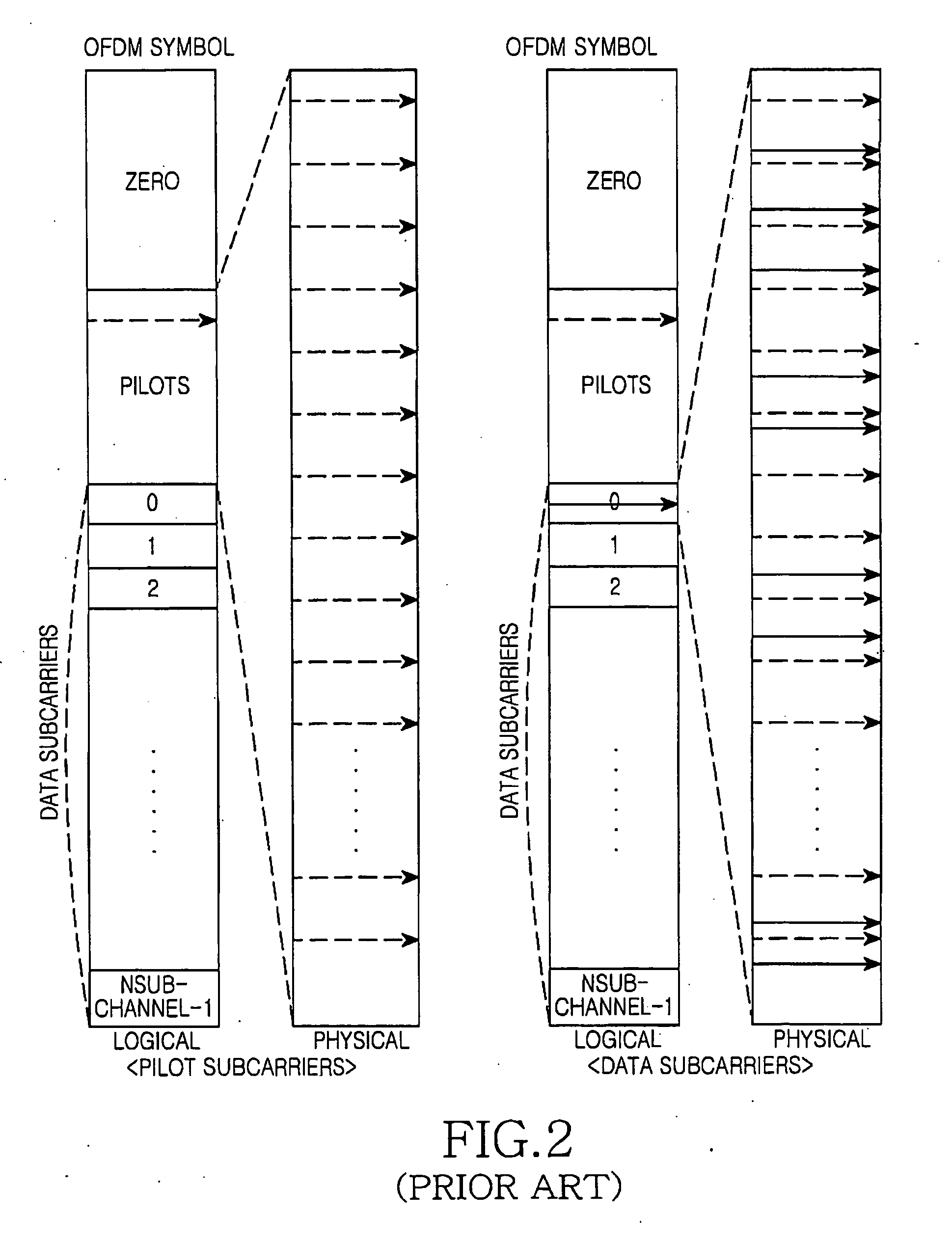
Apparatus and method of providing relay service in broadband wireless access (BWA) communication system
InactiveUS20080025251A1Reduce pilot overheadCriteria allocationNetwork topologiesCommunications systemMulti hop relay
An apparatus and method of providing relay service in a broadband wireless access (BWA) communication are provided. The communication method includes dividing an entire frequency band into a plurality of bands to support a plurality of links; determining subcarrier allocation schemes for the divided bands independently from one another; and communicating using the determined subcarrier allocation schemes by the plurality of the links. When the direct link and the relay link are distinguished through the frequency multiplexing in the multihop relay BWA communication system, the present invention enables the independent channel estimation from the relay link by adopting the dedicated pilot based permutation scheme for the relay link.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
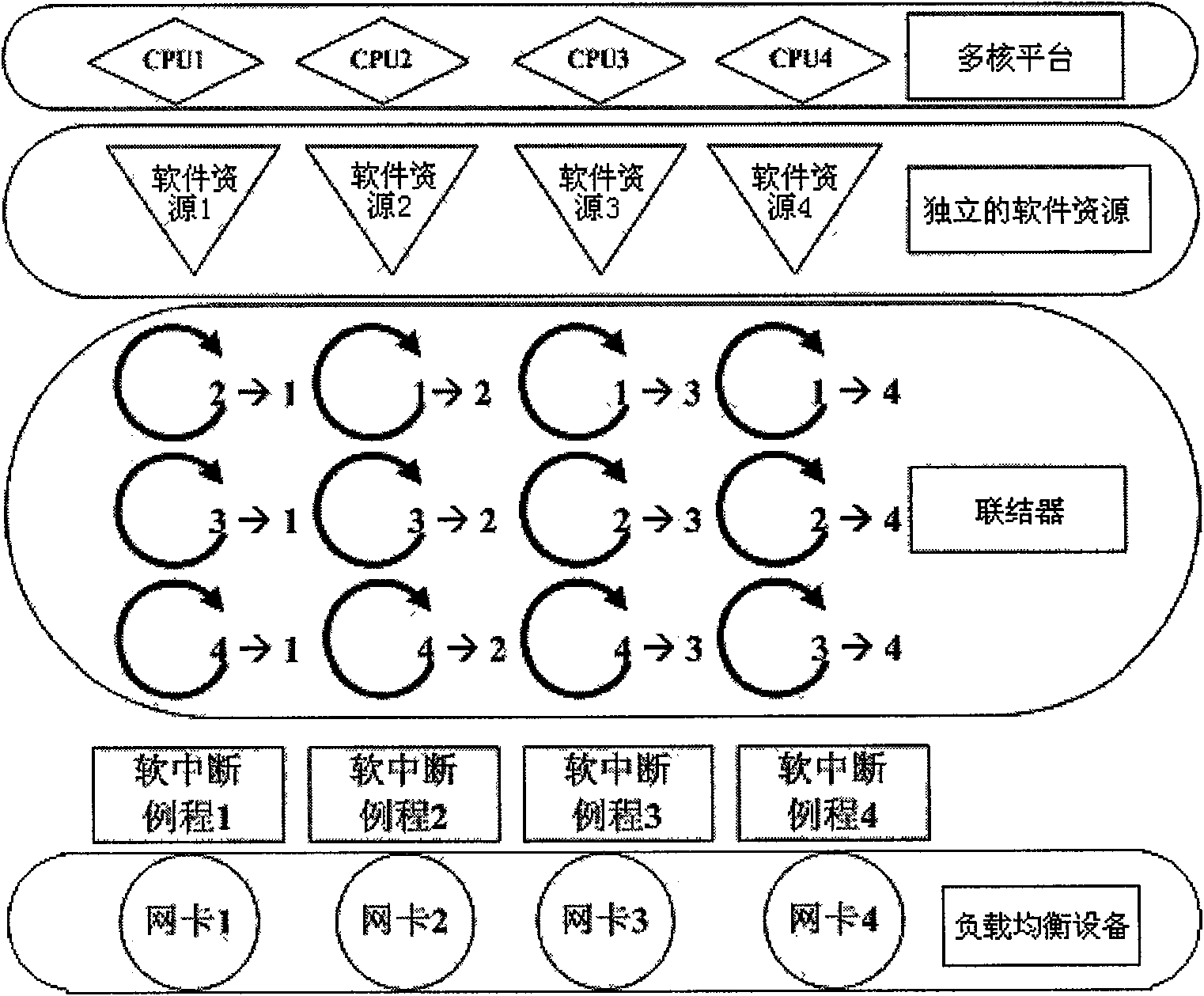
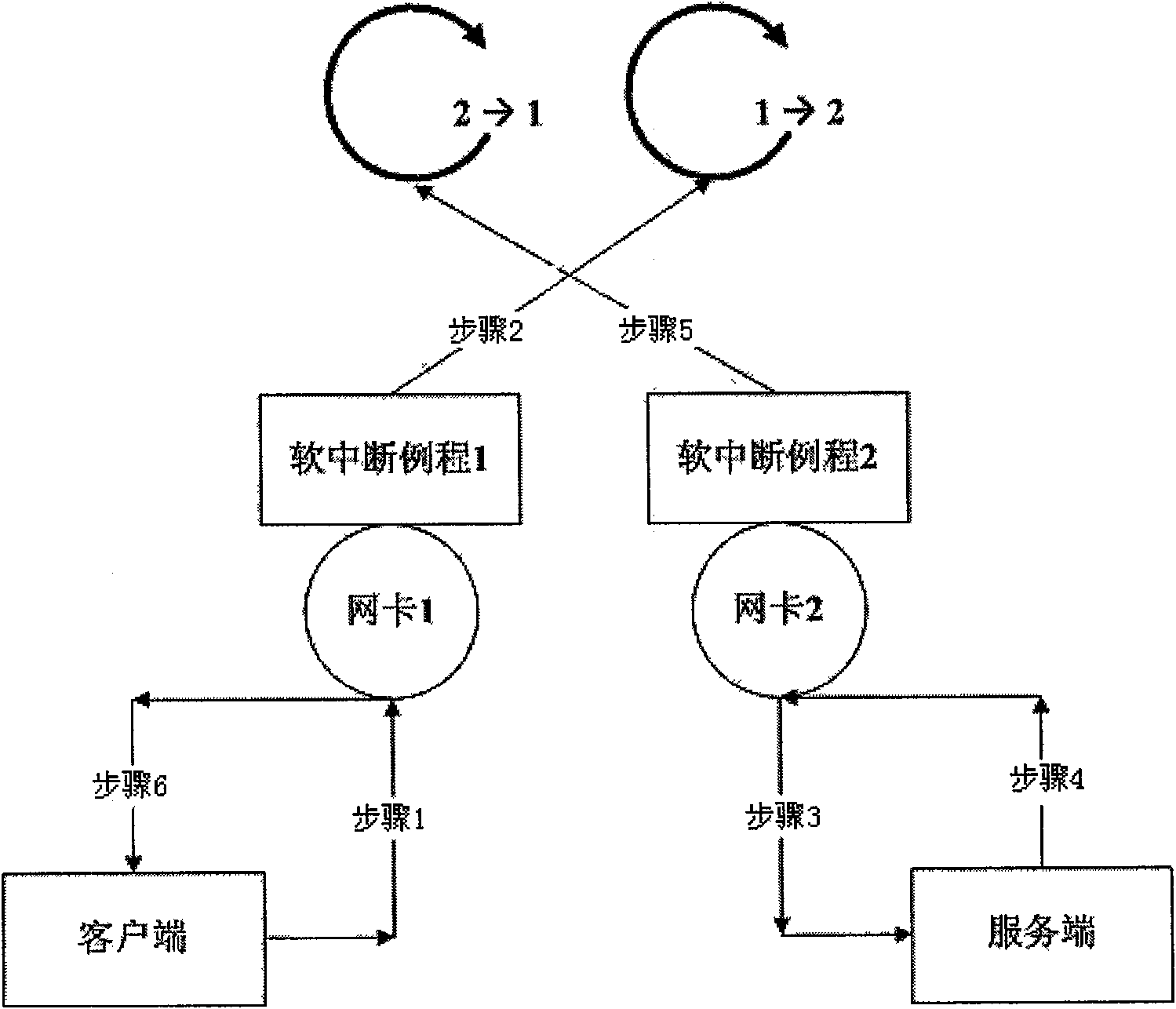
Load balancing software architecture based on multi-core platform and method therefor
ActiveCN101631139AAchieve independenceFlexible configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionSoftware architectureParallel computing
The invention relates to a load balancing software architecture based on a multi-core platform and a method therefor, comprising the following content: 1) the multi-core platform and load balancing equipment are taken as framework elements, and a kernel thread is initialized for every network card on the load balancing equipment to be taken as the soft interruption routine of the network card; the kernel threads respectively process input and output of the corresponding network cards, and the kernel threads are independent; 2) an independent channel is set up for the information exchange between every two network card threads, and a group of bidirectional ring-shaped arrays can be set up in each channel and taken as a coupler between the multi-core platform and load balancing equipment; the ring-shaped arrays can maintain a writing point and a reading point and are respectively operated by two threads, so that the information exchange between the threads is not needed to be locked; 3) routing policy of balanced load of a server can be realized in the soft interruption routine of the input of the network card, and all work of an application layer is executed in a link layer. The multithreading lockless software architecture is adopted to realize the balanced load of the server; furthermore, the practice proves that the invention can remarkably improve the performance of the load balancing equipment.
Owner:ARRAY NETWORKS BEIJING
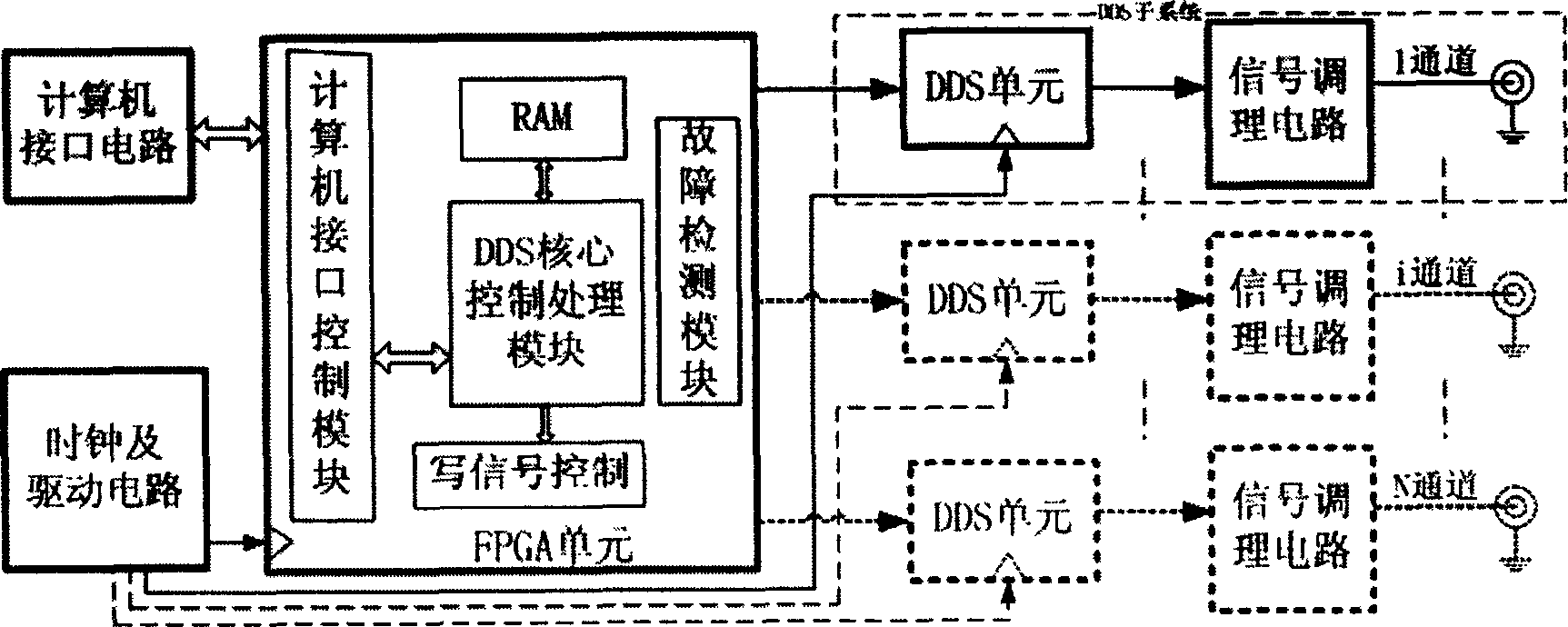
Multiple carrier-frequency digital frequency source
InactiveCN1832350AImprove adaptabilityEnsure consistencyPulse automatic controlAnalog signalEngineering
This invention discloses a multi-carrier frequency digital frequency source including a computer interface circuit, a clock and drive circuit, a field programmable gate array FPGA unit, a direct digital synthesizing DDS sub-system, in which, said clock and drive circuit provides clock signals with strong driving ability to FPGA and DDS units in the system, said FPGA unit controls multiple same DDS sub-systems, each of which forms an independent channel output to generate different signal kinds, signals of different modulations, different frequencies and phases according to the time sequence sent by the FPGA unit and generates echo analog signals by simulating actual signals, especially the LFMICW signals.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
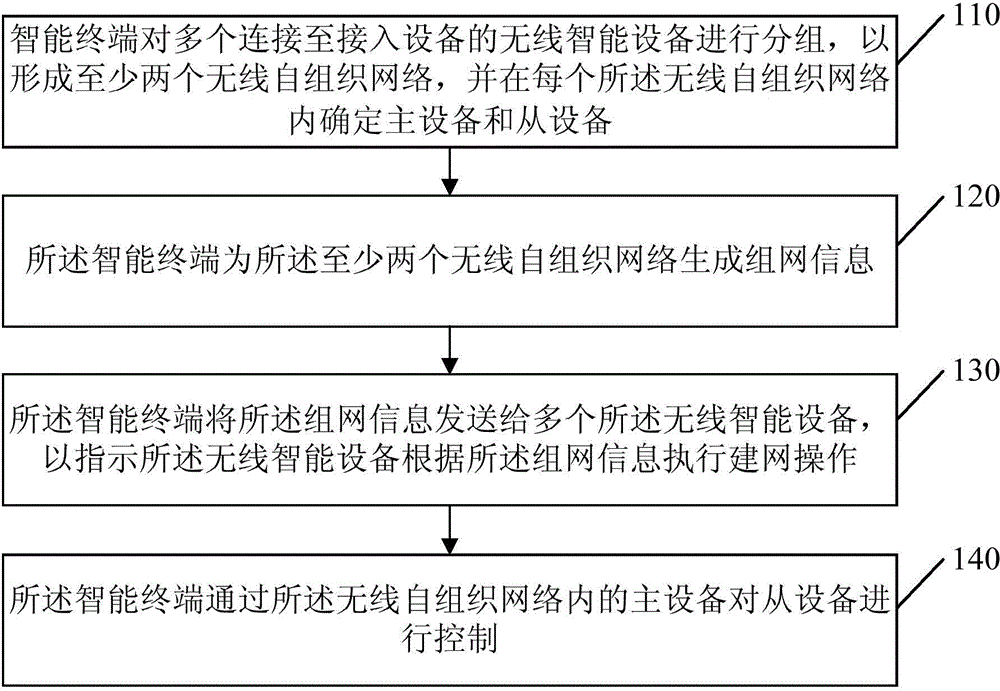
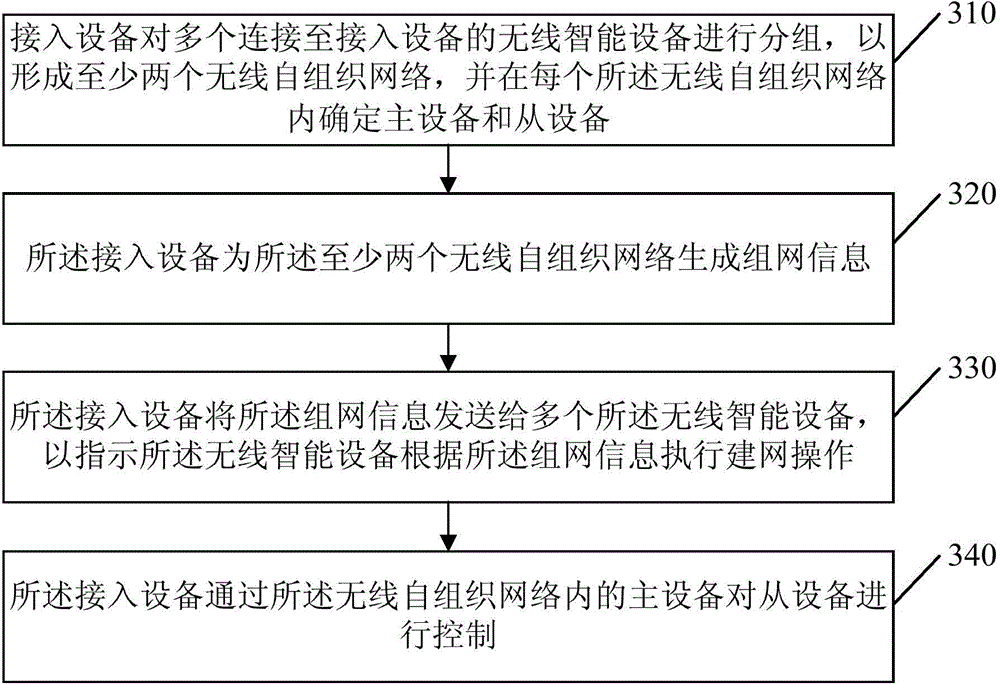
Control method, device and system for wireless intelligent equipment
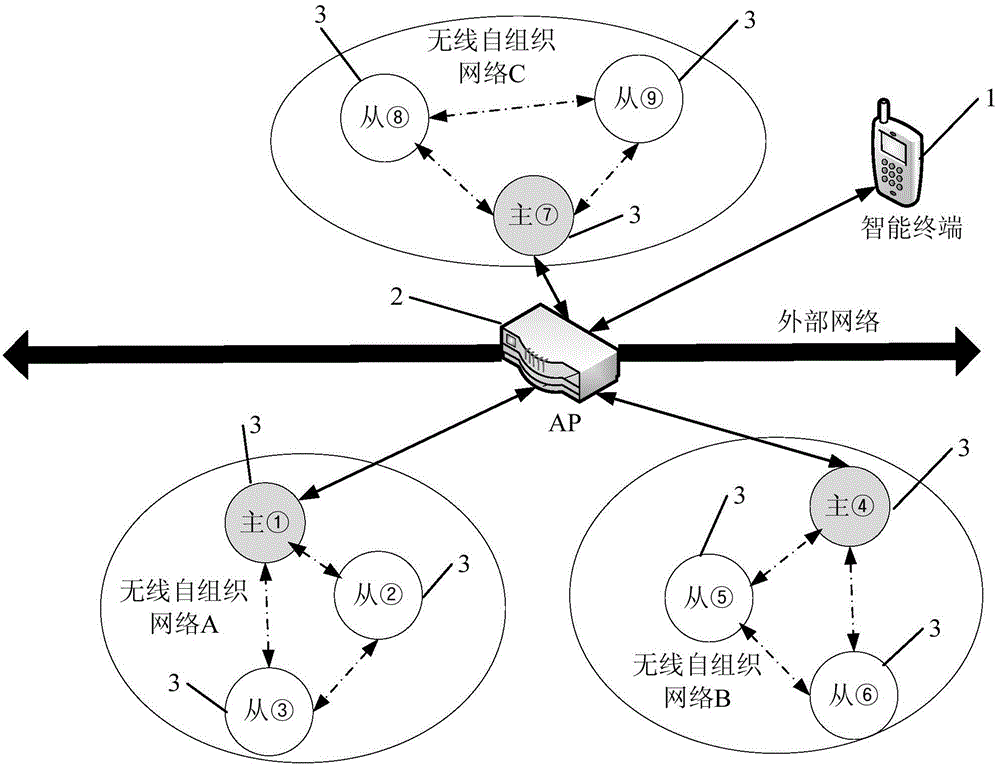
ActiveCN104902424ASolve the problem of complex control operationFlexible controlPublic address systemsWireless transmissionSelf-organizing network
The invention discloses a control method, device and system for wireless intelligent equipment. The method comprises the following steps: grouping a plurality of pieces of wireless intelligent equipment connected to access equipment to form at least two wireless self-organization networks, and determining master equipment and slave equipment in each wireless self-organization network; generating grouping information for the at least two wireless self-organization networks; transmitting the grouping information to the plurality of pieces of wireless intelligent equipment in order to instruct the wireless intelligent equipment to execute networking operation according to the grouping information; and controlling the slave equipment through the master equipment in the wireless self-organization networks. Through adoption of the control method, device and system, the problem of complex control operation of the wireless intelligent equipment in the prior art is solved, and the effect of controlling flexibly and conveniently is achieved. Independent channels are allocated to each wireless self-organization network, so that the wireless transmission bandwidths in groups are increased.
Owner:GUANGDONG OPPO MOBILE TELECOMM CORP LTD
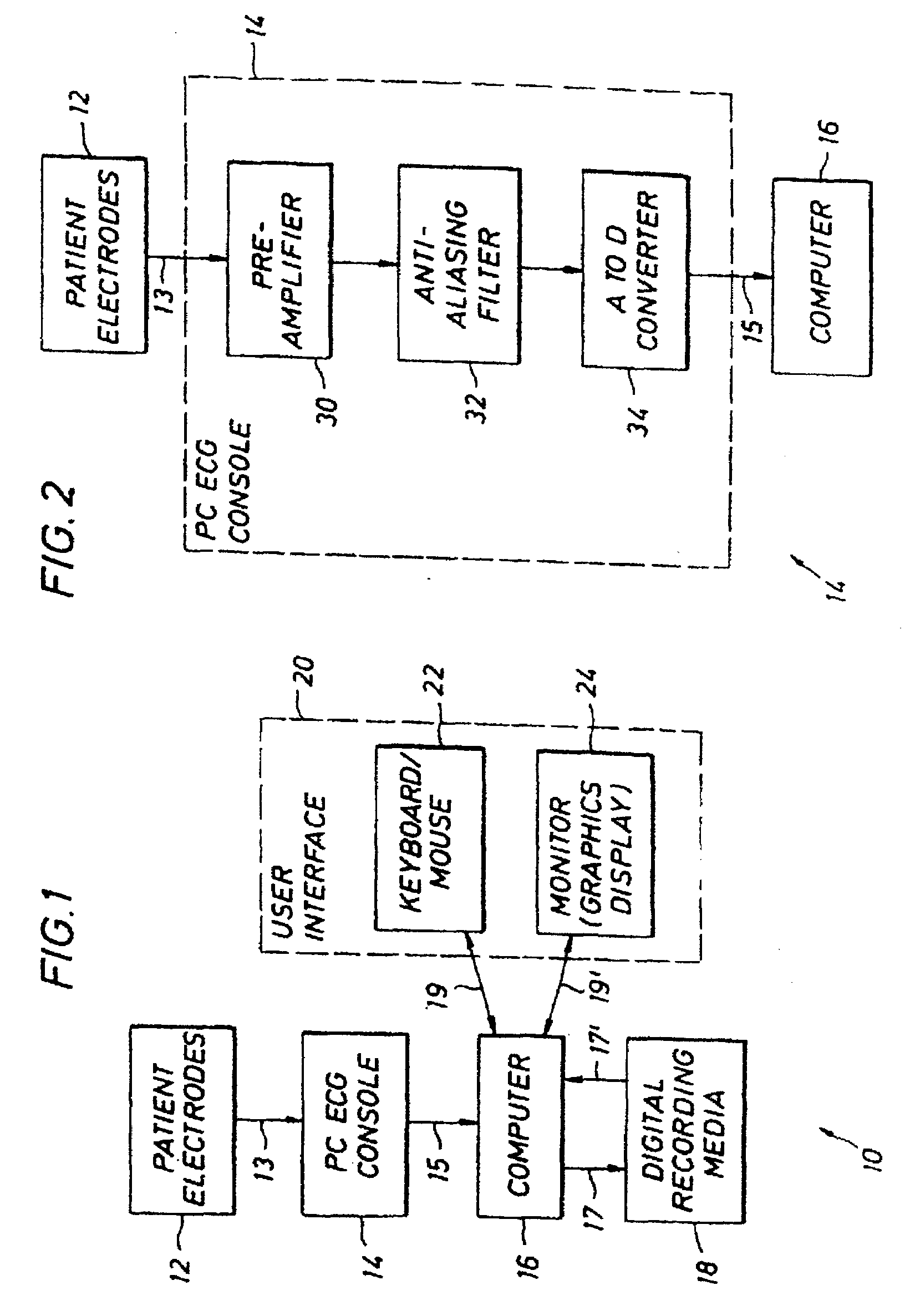
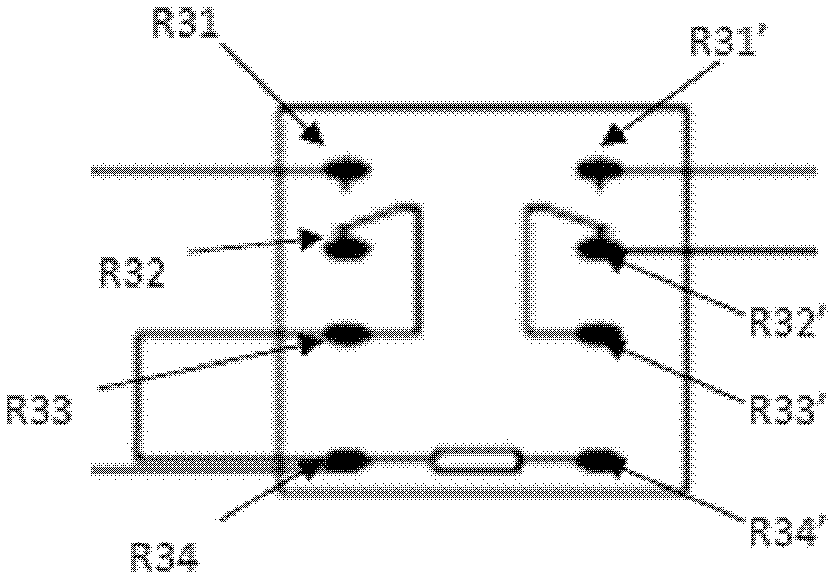
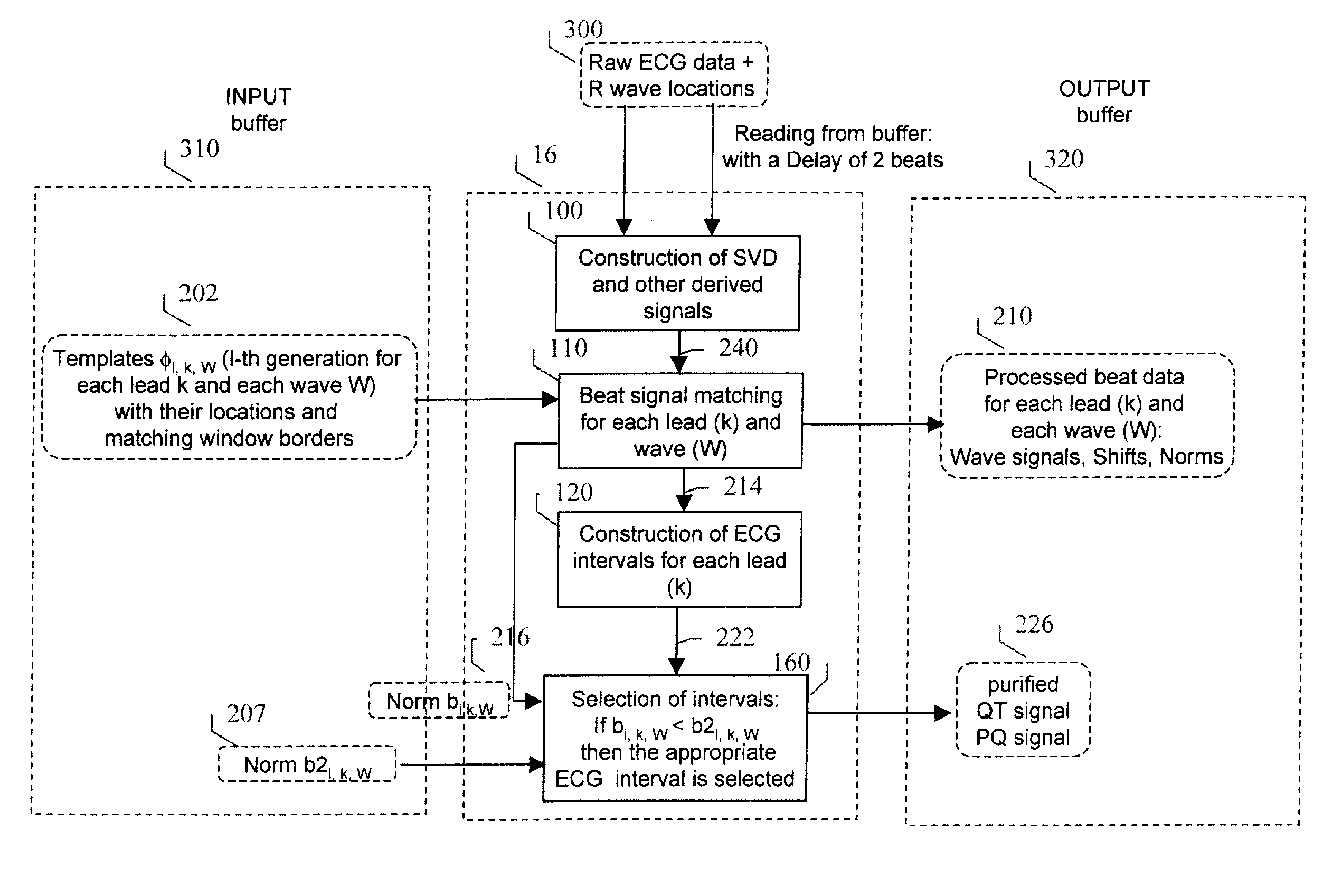
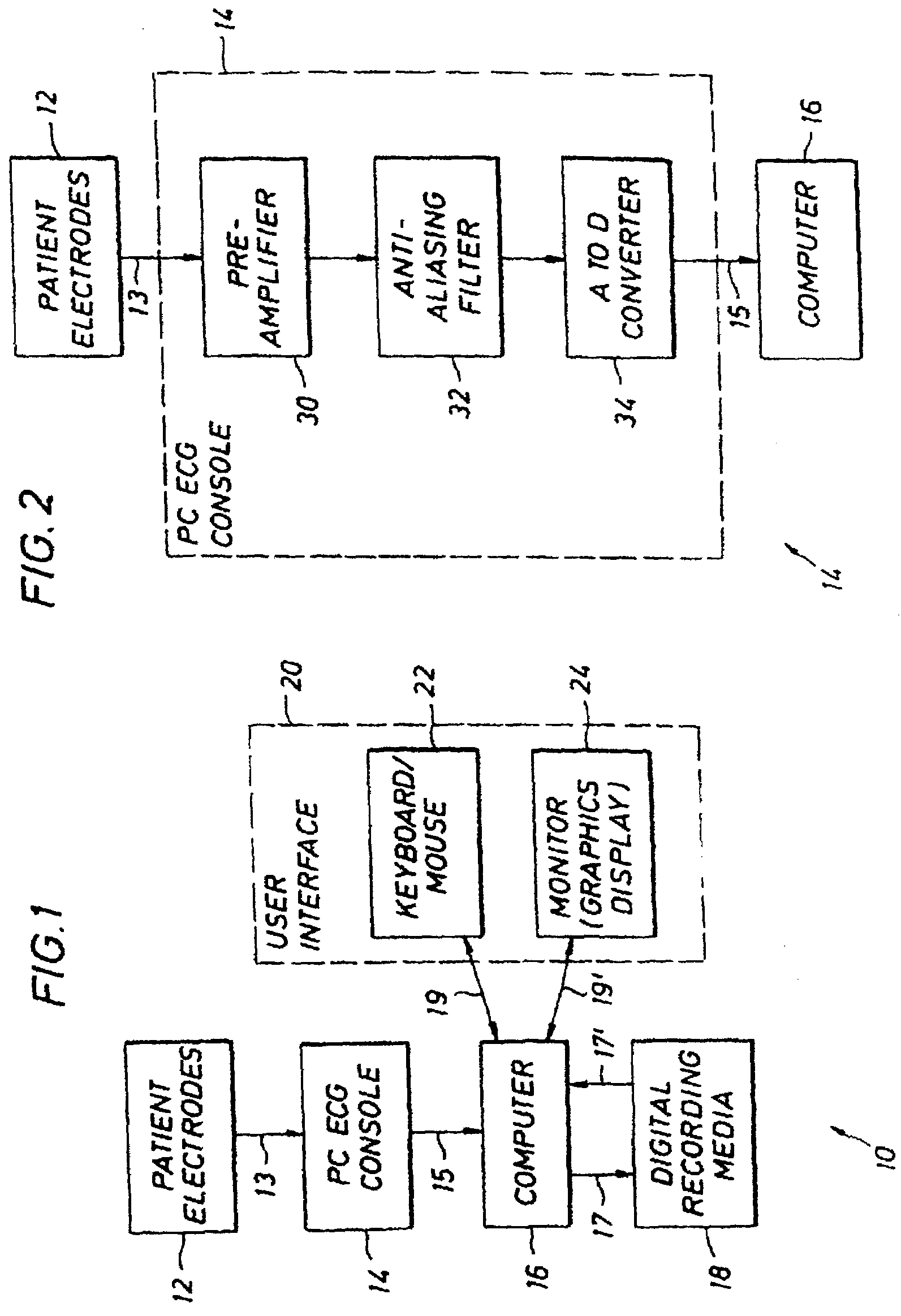
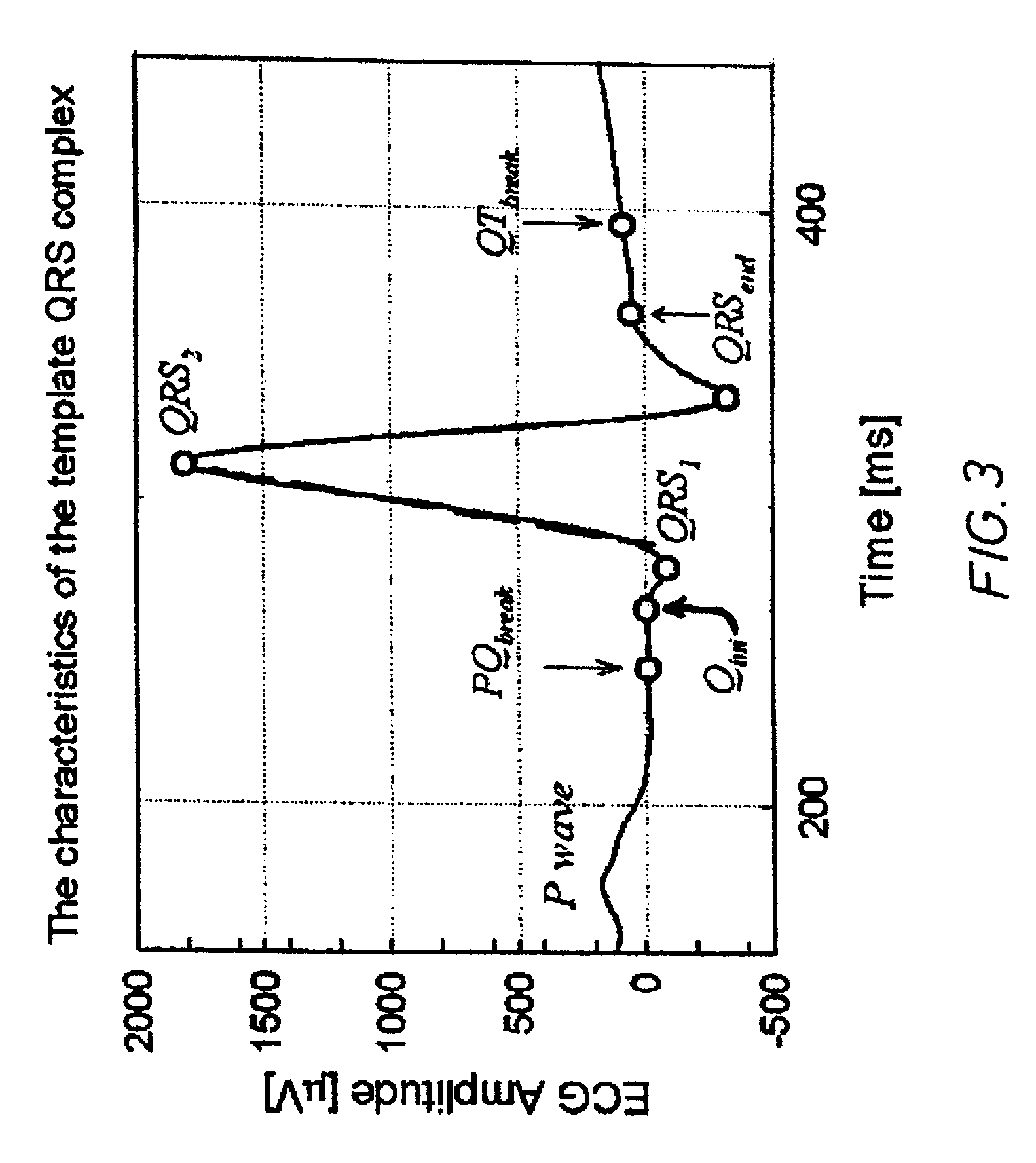
Multi-Channel System for Beat to Beat QT Interval Variability
InactiveUS20070203418A1Reduce the impact of noiseRapid and regular updatingElectroencephalographyElectrocardiographySingular value decompositionT wave
The measurement of beat-to-beat QT interval variability (QTV) shows clinical promise for identifying several types of cardiac pathology. However, until now, there has been no device capable of displaying, in real time on a beat-to-beat basis, changes in QTV in all 12 conventional leads in a continuously monitored patient. While several software programs have been designed to analyze QTV, heretofore, such programs have all involved only a few channels (at most) and / or have required laborious user interaction or off-line calculations and post-processing, limiting their clinical utility. This invention discloses a PC-based ECG software program that in real time, acquires, analyzes and displays QTV and PQ interval variability (PQV) in each of the independent channels that constitute the 12-lead conventional and / or Frank X, Y, Z lead ECG. The system also analyzes and displays the QTV and PQV from QT and PQ interval signals that are derived from multiple channels and from singular value decomposition such that the effect of noise and other artifacts on the QTV and PQV results are substantially reduced compared to existing single-channel methods. Moreover, this invention also discloses certain new parameters of T-wave (and QRS and P-wave) morphology, that in initial studies have improved clinical diagnostic utility and / or reproducibility and reliability compared to known existing parameters of T-wave morphology. Finally, it also discloses a method for determining the beat-to-beat variability these T, QRS and P-wave morphologic parameters.
Owner:CARDIOSOFT
W-waveband dual polarized slot antenna working in TM210 resonant mode and feed network
InactiveCN108550981AImprove efficiencyHigh Q valueSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsCouplingWaveguide
The invention discloses a W-waveband dual polarized slot antenna working in a TM210 resonant mode and a feed network. A radiating part and a feed part are respectively composed of a radiation chamberand a substrate integrated waveguide. Characteristics of high Q-value and low loss of a metal radiating chamber and characteristics of easy machining and easy integration are combined. A metal chamberis used as a radiator which has high radiation efficiency and improves integral efficiency of the antenna. The substrate integrated waveguide is used as a feed structure and has advantages of easy machining, relatively simple realization of a multilayer structure, and can remarkably reduce cost when compared with a metal waveguide slot feed network. The upper surface of the metal radiator is provided with four independent radiating channels, and the lower surface is provided with a resonant chamber for coupling signals of a horizontal polarized feed structure and a vertical polarized feed structure into four independent channels, thereby realizing one-to-four same-phase feeding from a single coupling slot to four radiating channels, simplifying the feed structure and reducing complexity of the feed network.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Detecting and eliminating spurious energy in communications systems via multi-channel processing
The present invention allows multi-channel communications equipment to detect and eliminate a false interpretation of interference as a valid signal. The solution is based on the observation that the simultaneous arrival of energy on two independent channels is an impossible event. So, when such an event happens, it is a reliable signature of confusing out-of-band energy for a valid signal.
Owner:EDGEWATER WIRELESS SYST
Simulation device and simulation method of on-site driving apparatus of nuclear power station
ActiveCN102360571AHigh working reliabilityWill not affect normal operationNuclear energy generationNuclear power plant controlControl systemNuclear power
The invention discloses a simulation device and simulation method of an on-site driving apparatus of a nuclear power station. Simulation of the on-site driving apparatus of the nuclear power station is realized in a function test of a DCS (Digital Control System) of the nuclear power station. The simulation device of the on-site driving apparatus of the nuclear power station comprises a simulator and an interface cable; and the simulator is seamlessly terminated with the digital control system through the interface cable. The simulator comprises at least a channel circuit; and each channel circuit enables the simulator to respectively simulate corresponding apparatuses by switching states of interconnected first switching component and second switching component so as to make a corresponding response to a command signal sent from the digital control system, so that a user has no need to build a model and organize states in the function test of the DCS control system of the nuclear power station. However, a plurality of independent channel circuits enables the simulation device of the on-site driving apparatus of the nuclear power station disclosed by the invention to have high operational reliability and discover and remove fault points conveniently.
Owner:中广核工程有限公司 +1
Multi-channel system for beat to beat QT interval variability
InactiveUS7983742B2Reduce the impact of noiseRapid and regular updatingElectroencephalographyElectrotherapySingular value decompositionT wave
A PC-based ECG software program that in real time, acquires, analyzes and displays QTV and PQ interval variability (PQV) in each of the independent channels that constitute the 12-lead conventional and / or Frank X, Y, Z lead ECG. The system also analyzes and displays the QTV and PQV from QT and PQ interval signals that are derived from multiple channels and from singular value decomposition such that the effect of noise and other artifacts on the QTV and PQV results are substantially reduced compared to existing single-channel methods. Moreover, this invention also provides certain new parameters of T-wave (and QRS and P-wave) morphology, that in initial studies have improved clinical diagnostic utility and / or reproducibility and reliability compared to known existing parameters of T-wave morphology. Finally, it also provides a method for determining the beat-to-beat variability these T, QRS and P-wave morphologic parameters.
Owner:CARDIOSOFT
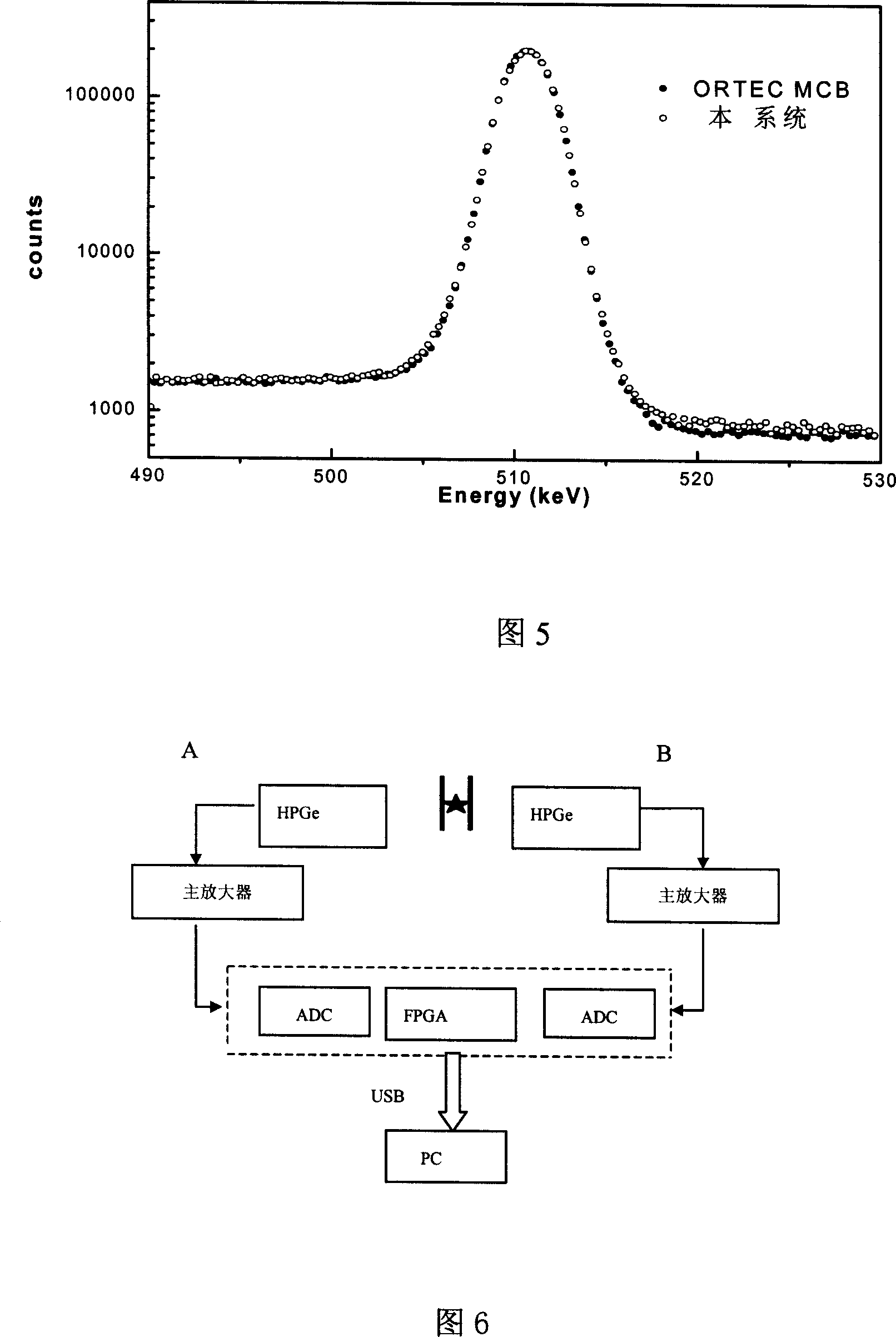
High-speed parallel multi-path multi-path-data system for mulclear spectroscope and nuclear electronics
InactiveCN1979220ASimplified measurement setupSimplify usabilityX-ray spectral distribution measurementRadiation intensity measurementData systemDistributor
The invention relates to high speed parallel multichannel data system for nucleus spectrum and nuclear electronics. It is made up of 4 independent channels, and includes analog circuit, 14 bits ADC, and a 4 channel timer distributor. The analog signal would be transformed to digital quantity and input into large capacity FPGA chip to take online analysis of time, amplitude, sampling points information and relativity, taking effective data selection and inputting into host computer through network or USB2.0 interface.
Owner:INST OF HIGH ENERGY PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Segmentation polarization code coding and decoding method and system based on LSC-CRC decoding
ActiveCN106888026AReduce space complexityEasy to operateError correction/detection using linear codesError detection onlyCoding decodingChannel code
The invention discloses a segmentation polarization code coding and decoding method and system based on LSC-CRC decoding. The method comprises steps of combining and separating a plurality of independent channels to obtain bit channels as many as the independent channels, obtaining the capacity of each bit channel, and obtaining the number of the fully polarized bit channels; dividing the free information bit sequence to be transmitted into the corresponding number of sub-sequences according to the number of fully polarized bit channels, subjecting each sub-sequence to polarization code decoding, and transmitting the encoded information to the corresponding bit channel; and after a receiving end receives the encoded information, performing segmentation decoding according to the LSC-CRC decoding algorithm, and finally connecting the obtained decoded sub-sequences in an end-to-end manner to obtain the decoding sequence. The channel coding and decoding method is simple to operate, the coding and decoding space complexity is reduced, and the decoding accuracy is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com