Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
307 results about "Intravenous catheter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
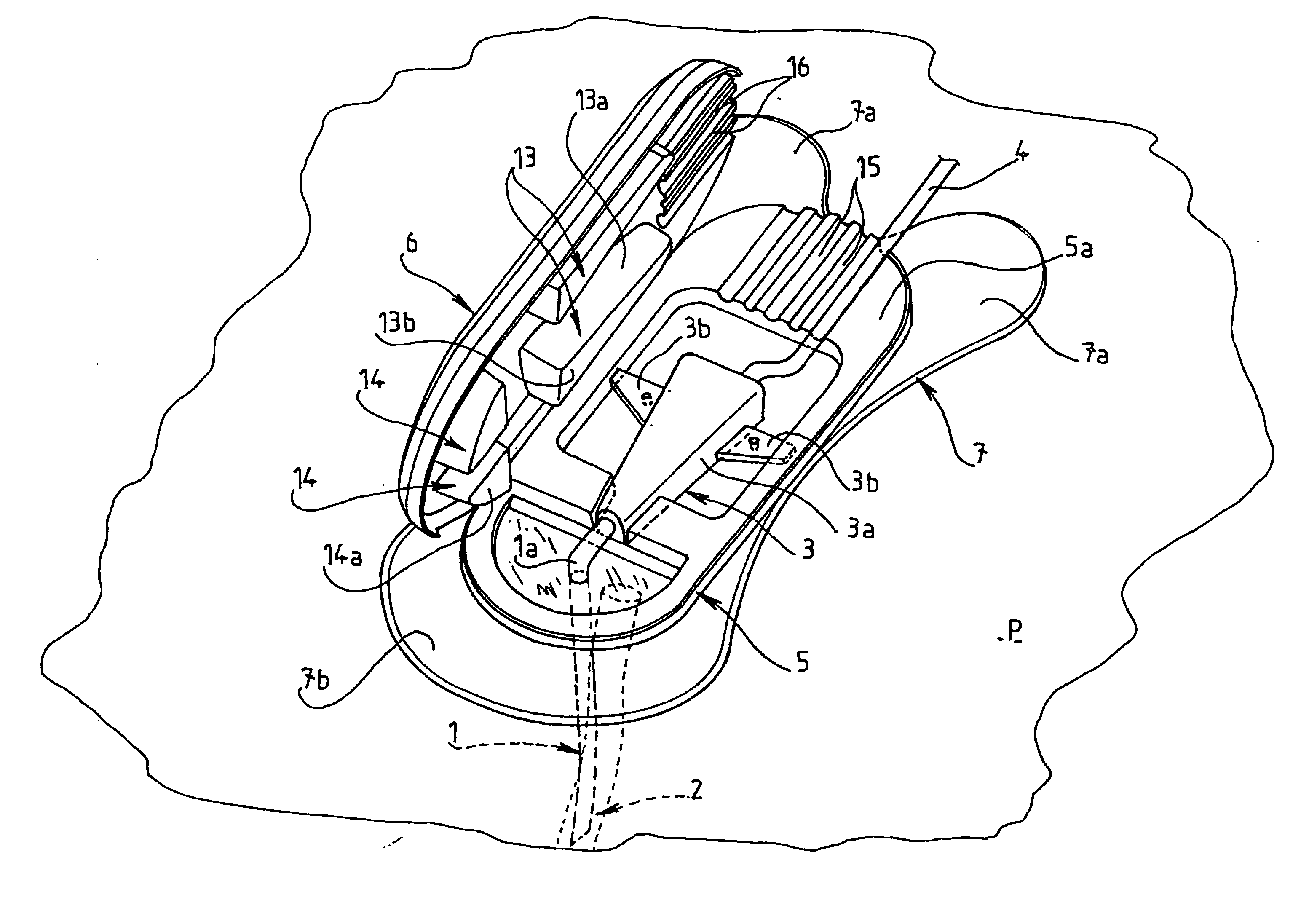
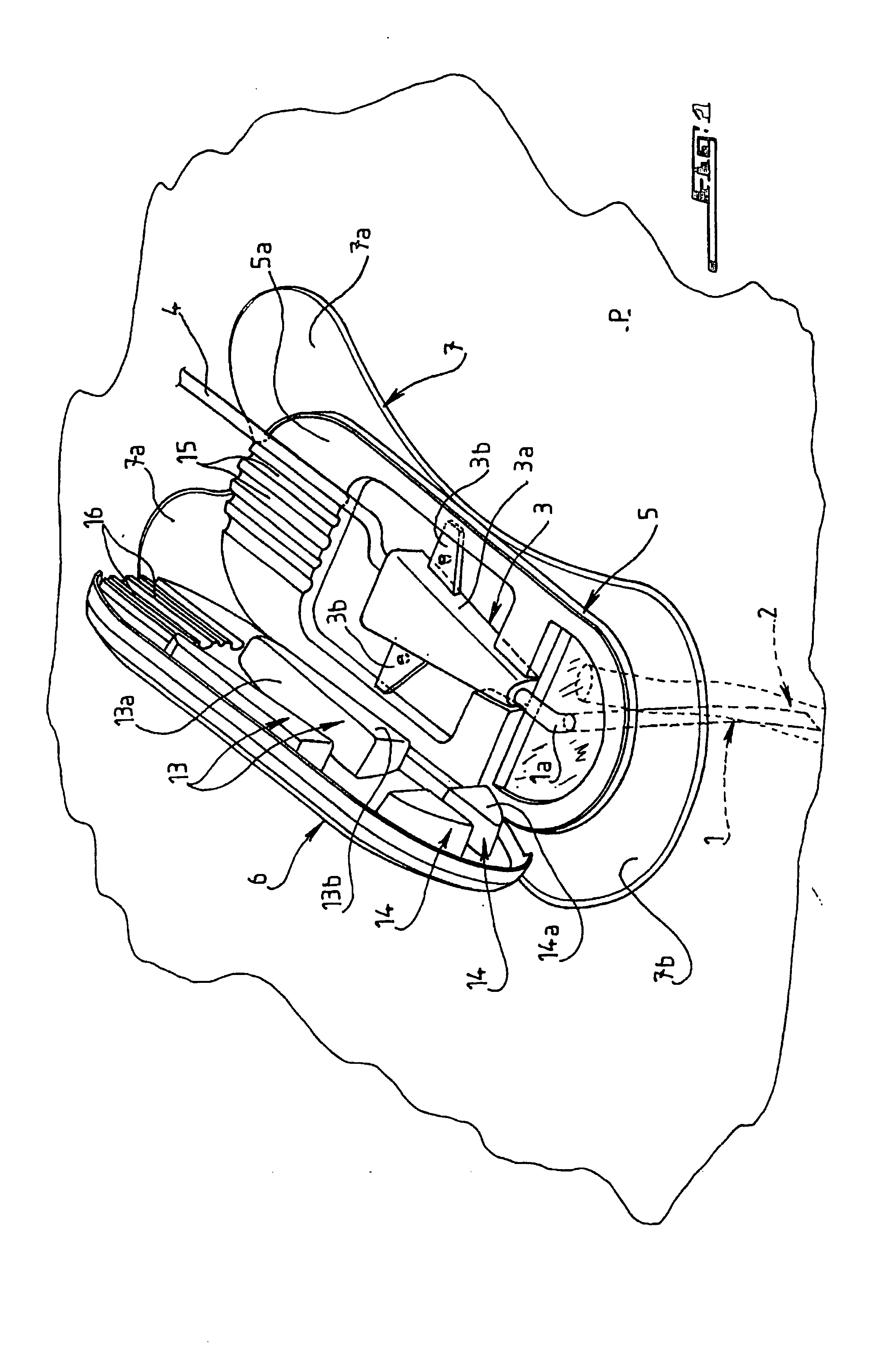
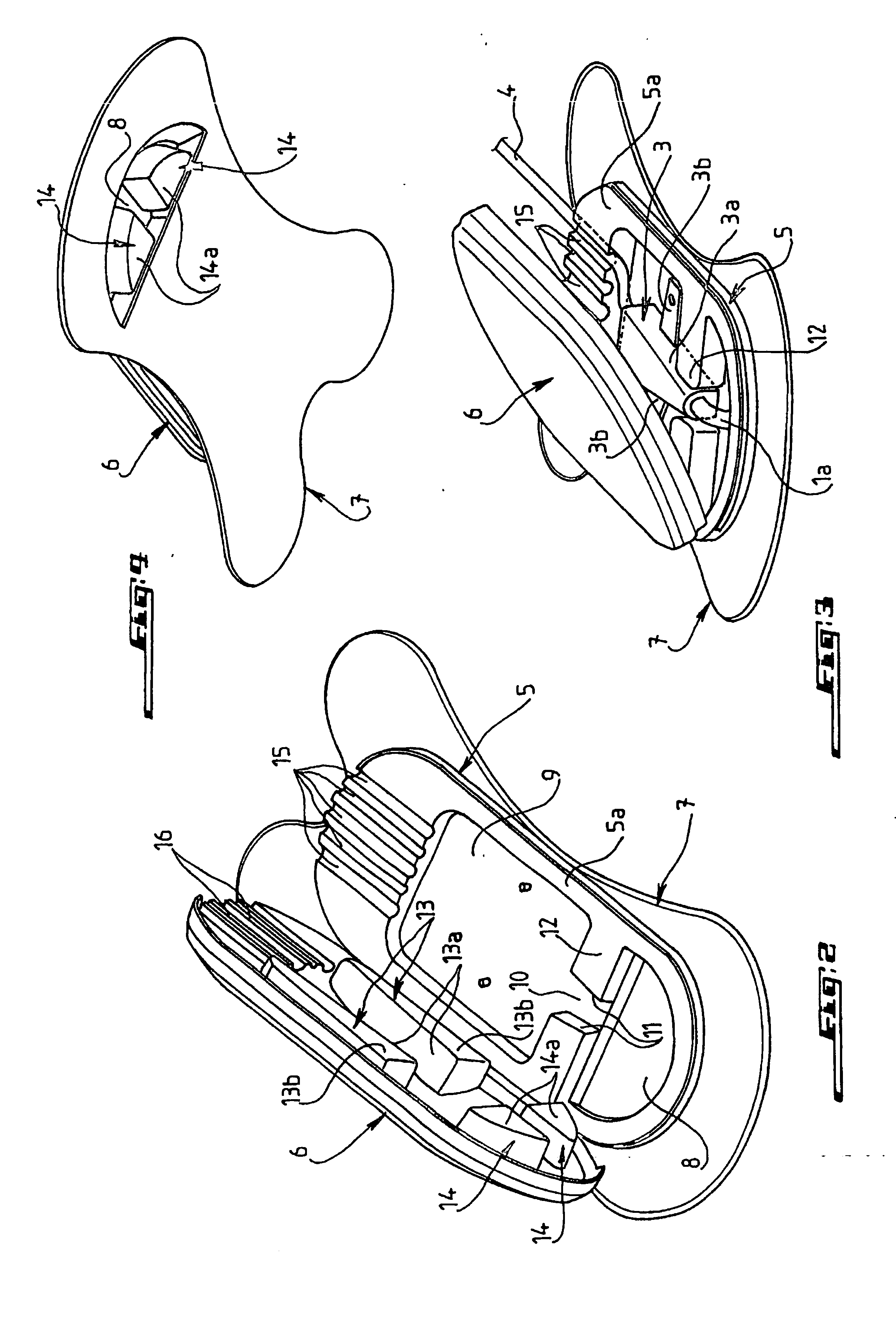
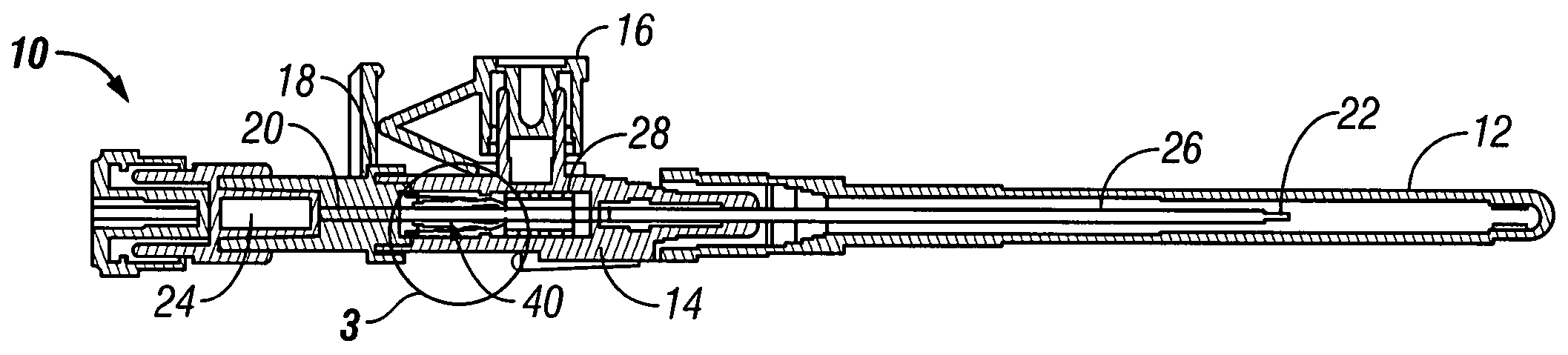
Intravenous Catheter (IV Cannula) What is an Intravenous Catheter or IV cannula? An Intravenous Catheter(IV cannula or peripheral venous catheter) is a catheter (small, flexible tube) placed into a peripheral vein(usually in a Patient’s arm or leg) in order to administer medication or fluids. Upon insertion, the line can be used to draw blood.
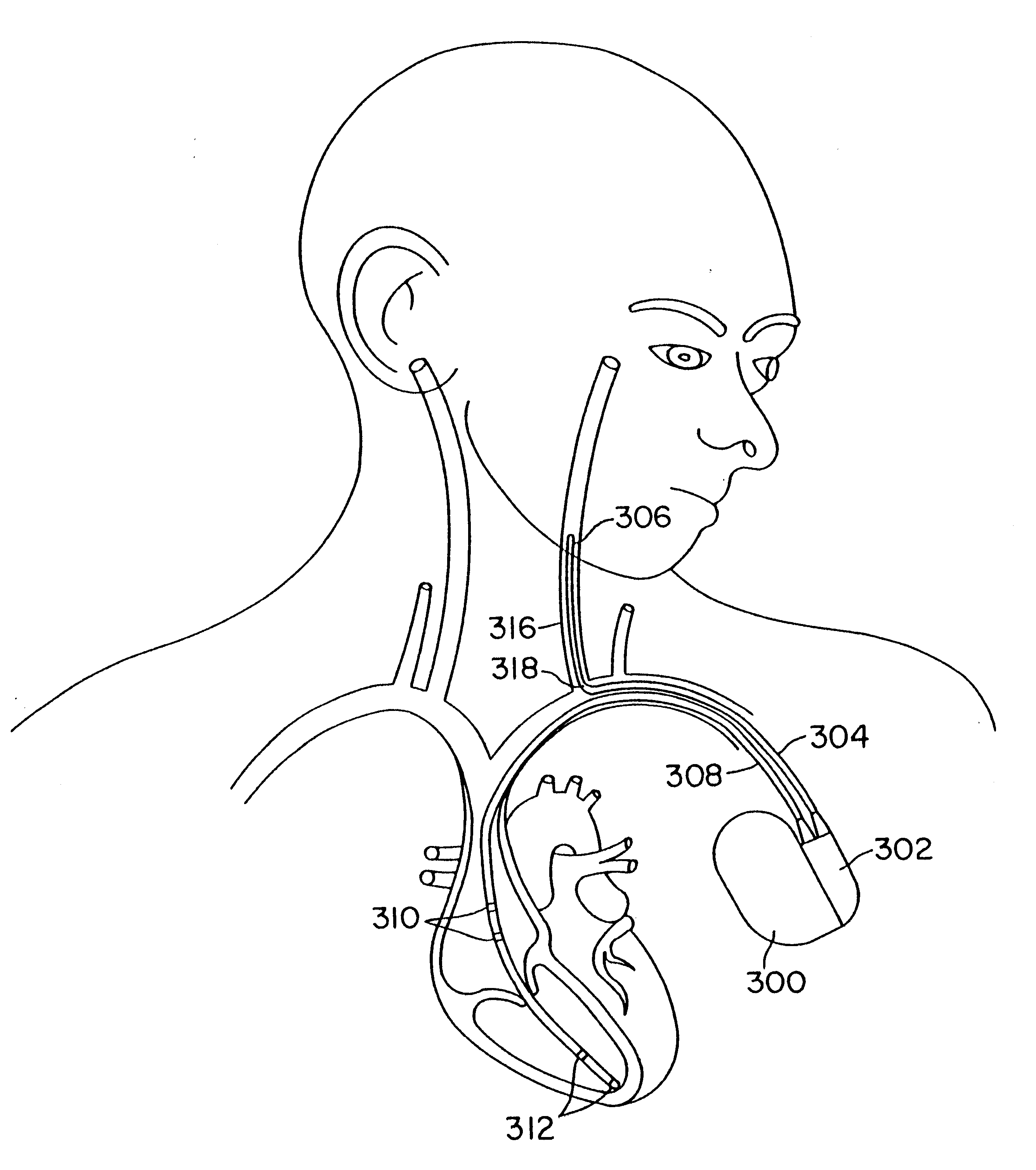
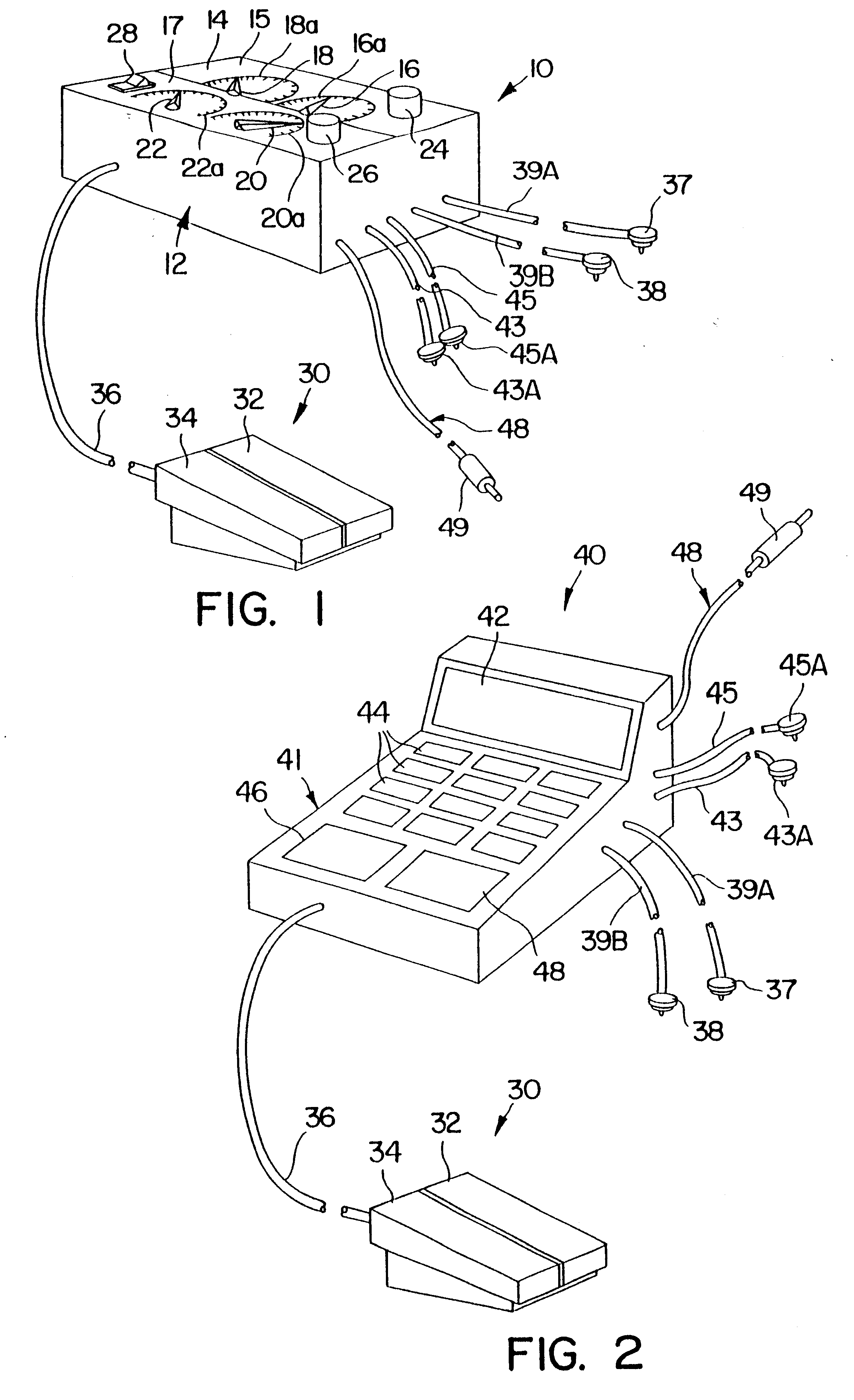
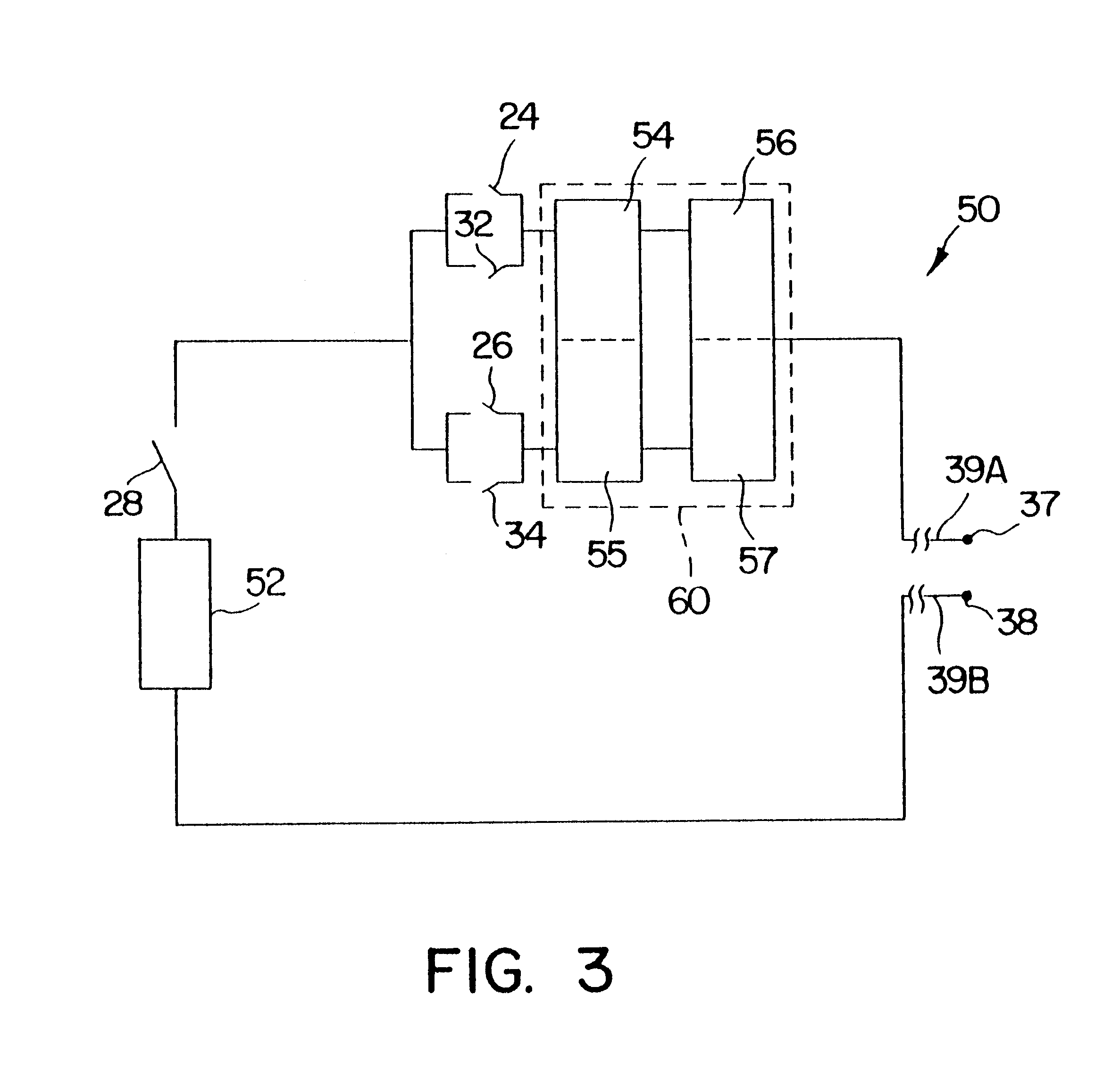
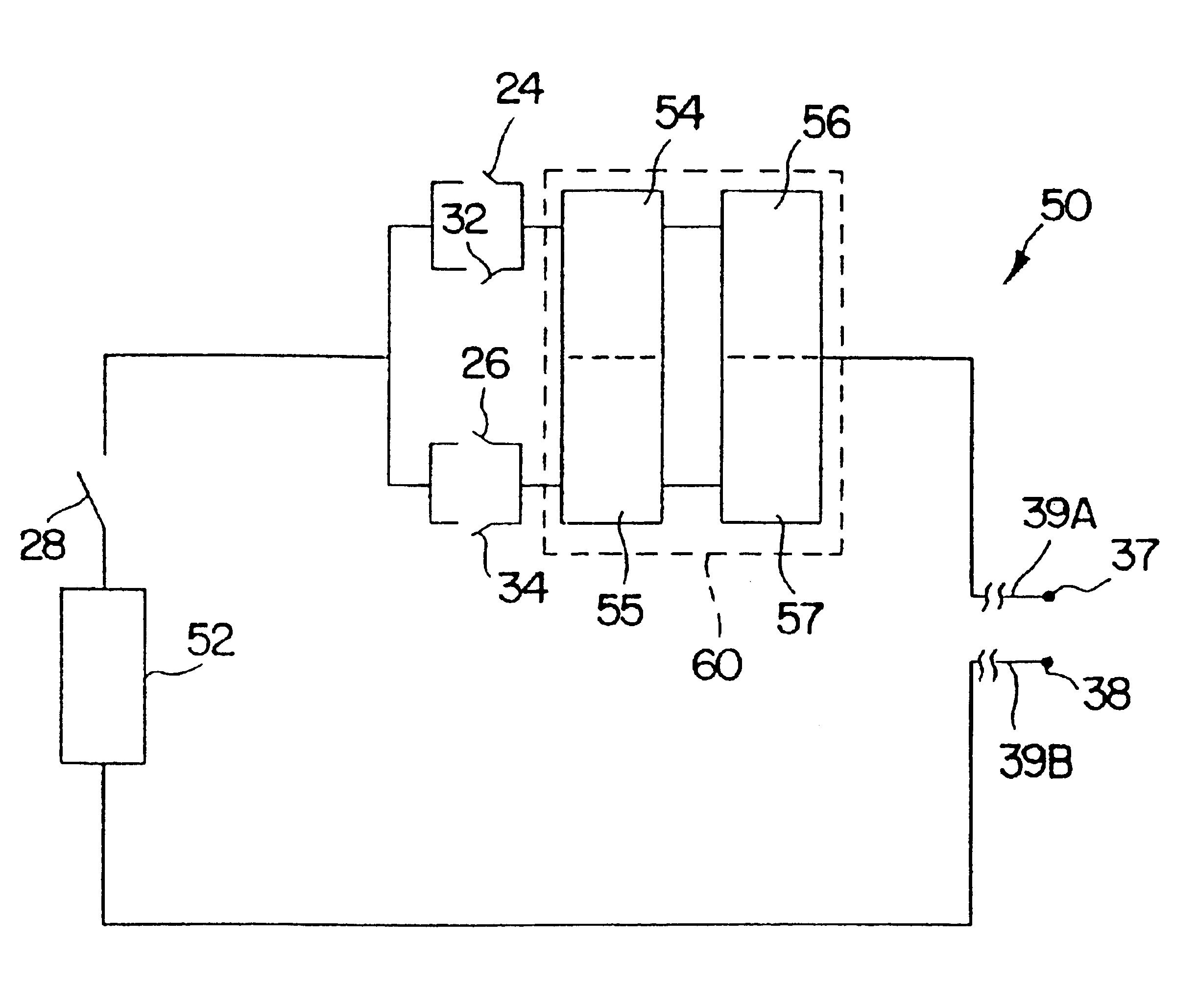
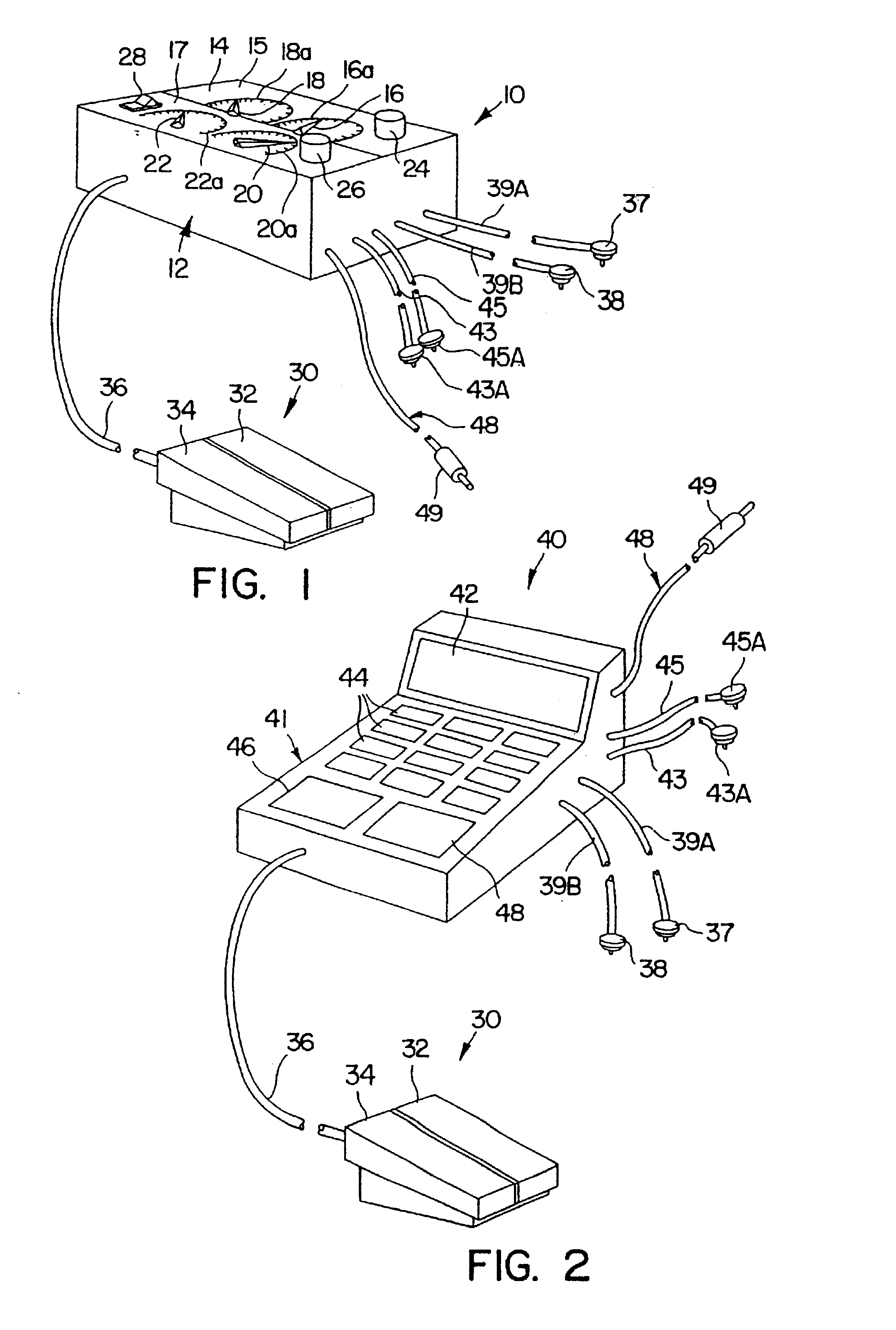
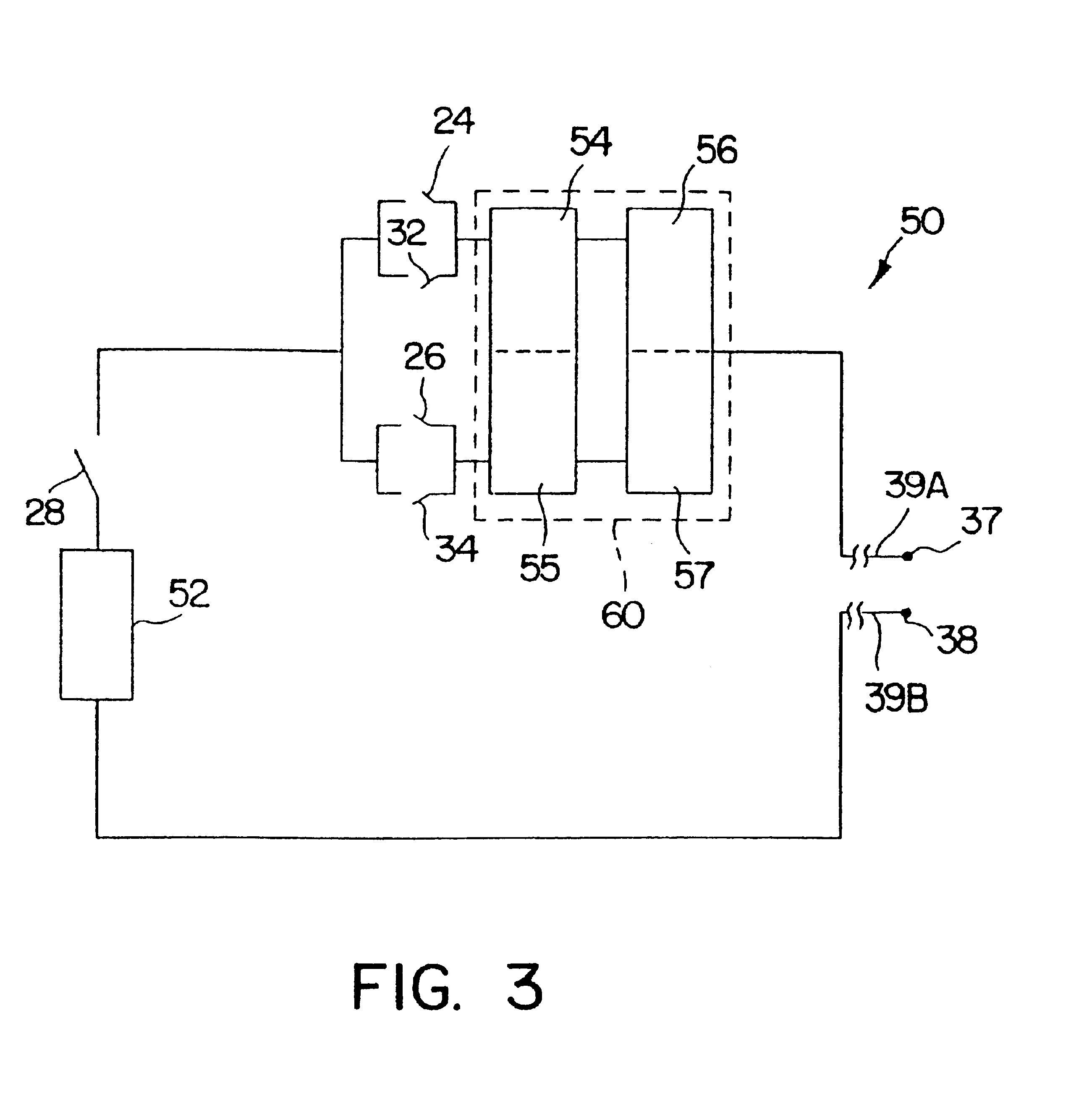
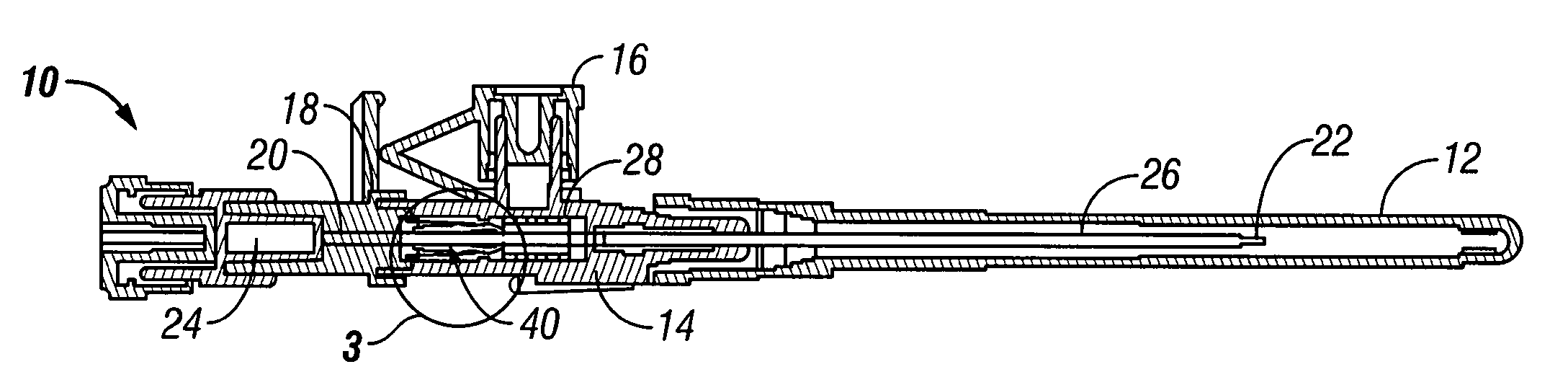
Method and device for electronically controlling the beating of a heart using venous electrical stimulation of nerve fibers
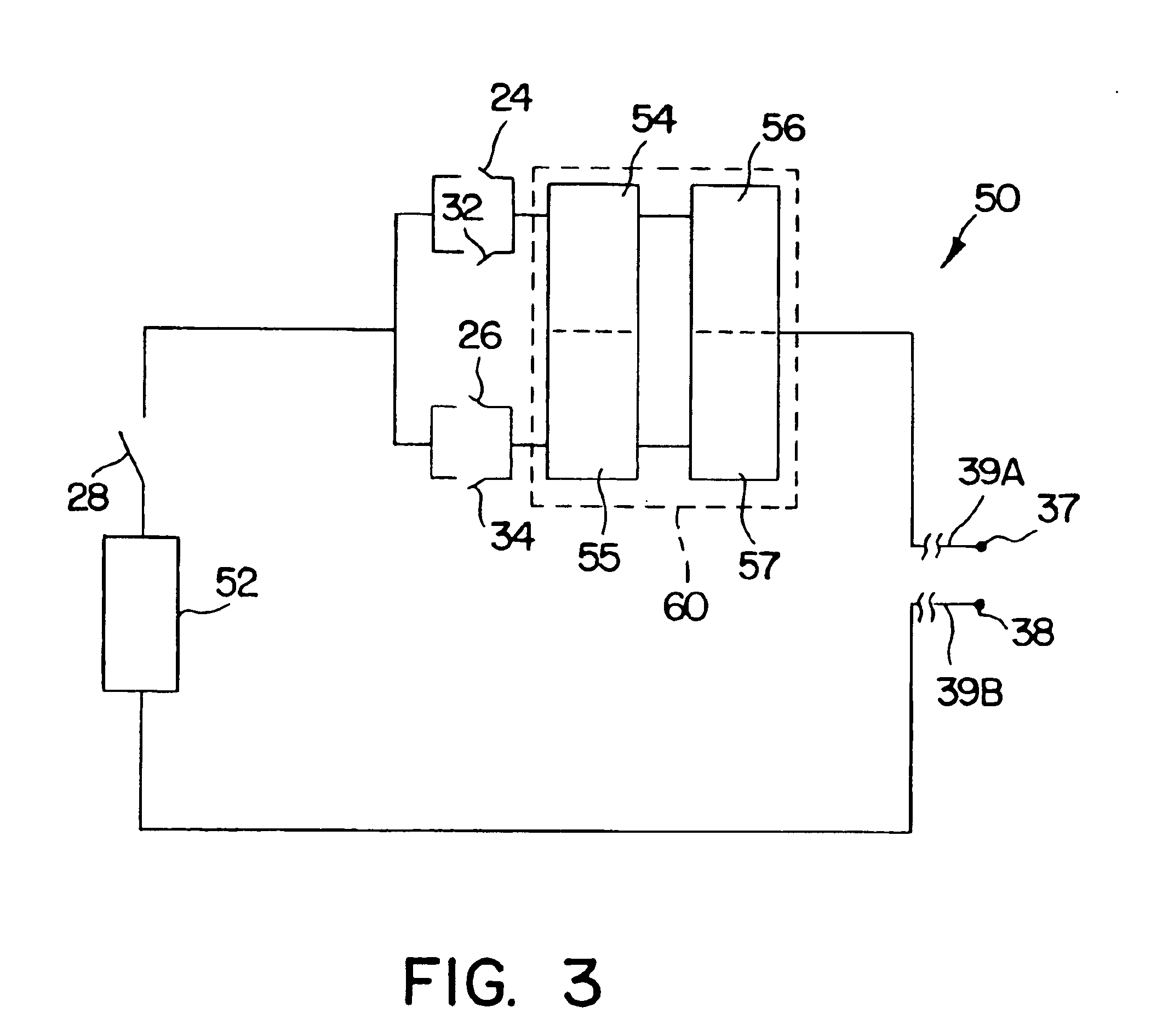
An electro-stimulation device includes a pair of electrodes for connection to at least one location in the body that affects or regulates the heartbeat. The electro-stimulation device both electrically arrests the heartbeat and stimulates the heartbeat. A pair of electrodes are provided for connection to at least one location in the body that affects or regulates the heartbeat. The pair of electrodes may be connected to an intravenous catheter for transvenous stimulation of the appropriate nerve. A first switch is connected between a power supply and the electrodes for selectively supplying current from the power supply to the electrodes to augment any natural stimuli to the heart and thereby stop the heart from beating. A second switch is connected between the power supply and the electrodes for selectively supplying current from the power supply to the electrodes to provide an artificial stimulus to initiate heartbeating. In another aspect, the invention is directed to a method for arresting the beat of a heart in a living body comprising the steps of connecting the pair of electrodes to at least one location in the body that affects or regulates the heartbeat and supplying an electrical current to the electrodes of sufficient amplitude and duration to arrest the heartbeat. The device may also serve to still the lungs by input to a respirator or by stimulation of the phrenic nerve during surgical procedures.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Valve for intravenous catheter
The present invention is directed to a valve assembly in an intravenous catheter that facilitates the administration of fluid to a patient through the intravenous catheter by a needleless device. The valve assembly of the present invention contains means for providing a positive displacement of fluid from the catheter at a time when a needleless device is removed from the valve assembly following its connection to the valve assembly.
Owner:SPAN-AMERICA MEDICAL SYSTEMS
Method and device for electronically controlling the beating of a heart
An electro-stimulation device includes a pair of electrodes for connection to at least one location in the body that affects or regulates the heartbeat. The electro-stimulation device both electrically arrests the heartbeat and stimulates the heartbeat. A pair of electrodes are provided for connection to at least one location in the body that affects or regulates the heartbeat. The pair of electrodes may be connected to an intravenous catheter for transvenous stimulation of the appropriate nerve. A first switch is connected between a power supply and the electrodes for selectively supplying current from the power supply to the electrodes to augment any natural stimuli to the heart and thereby stop the heart from beating. A second switch is connected between the power supply and the electrodes for selectively supplying current from the power supply to the electrodes to provide an artificial stimulus to initiate heartbeating. In another aspect, the invention is directed to a method for arresting the beat of a heart in a living body comprising the steps of connecting the pair of electrodes to at least one location in the body that affects or regulates the heartbeat and supplying an electrical current to the electrodes of sufficient amplitude and duration to arrest the heartbeat. The device may also serve to still the lungs by input to a respirator or by stimulation of the phrenic nerve during surgical procedures.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
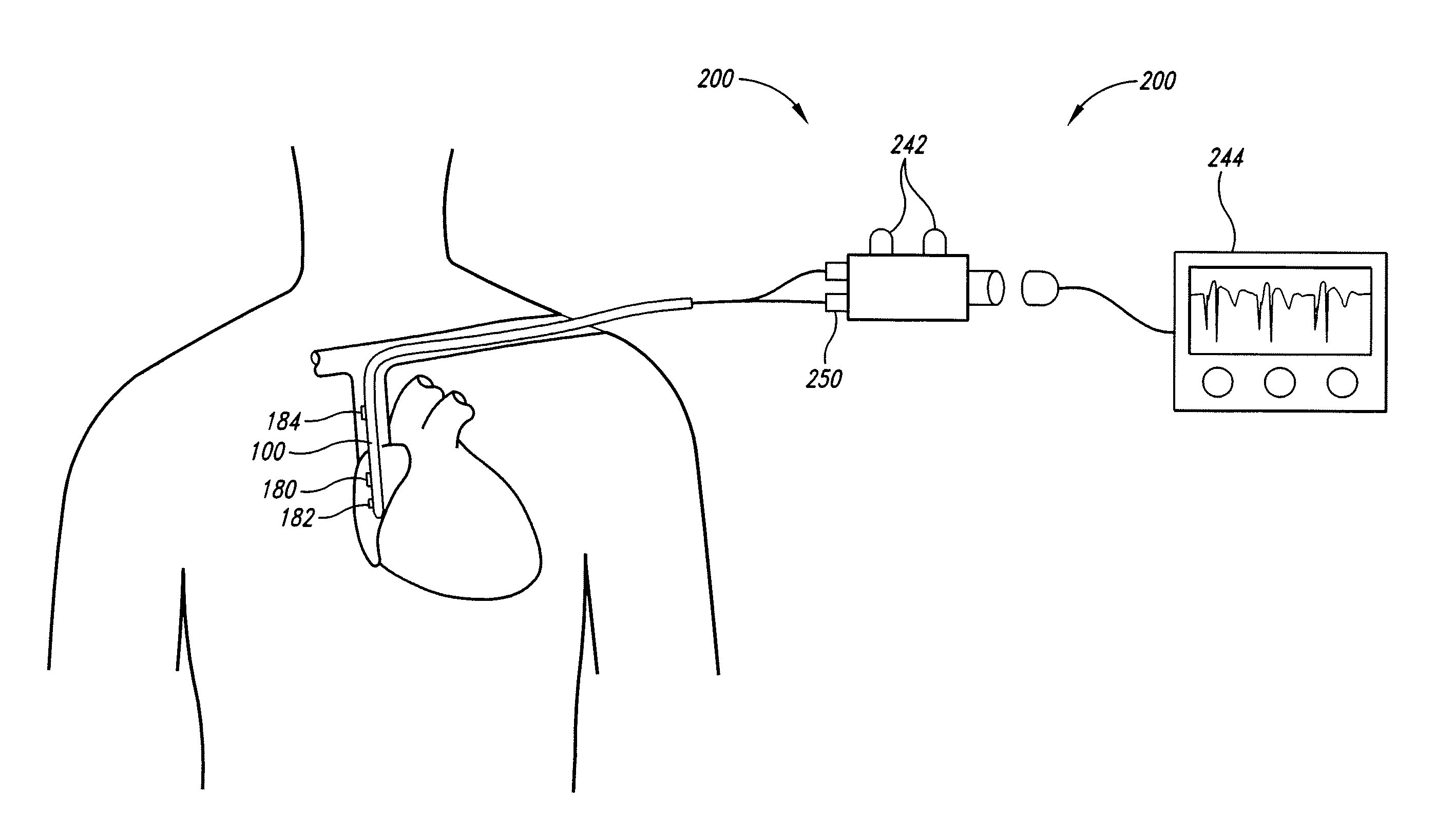
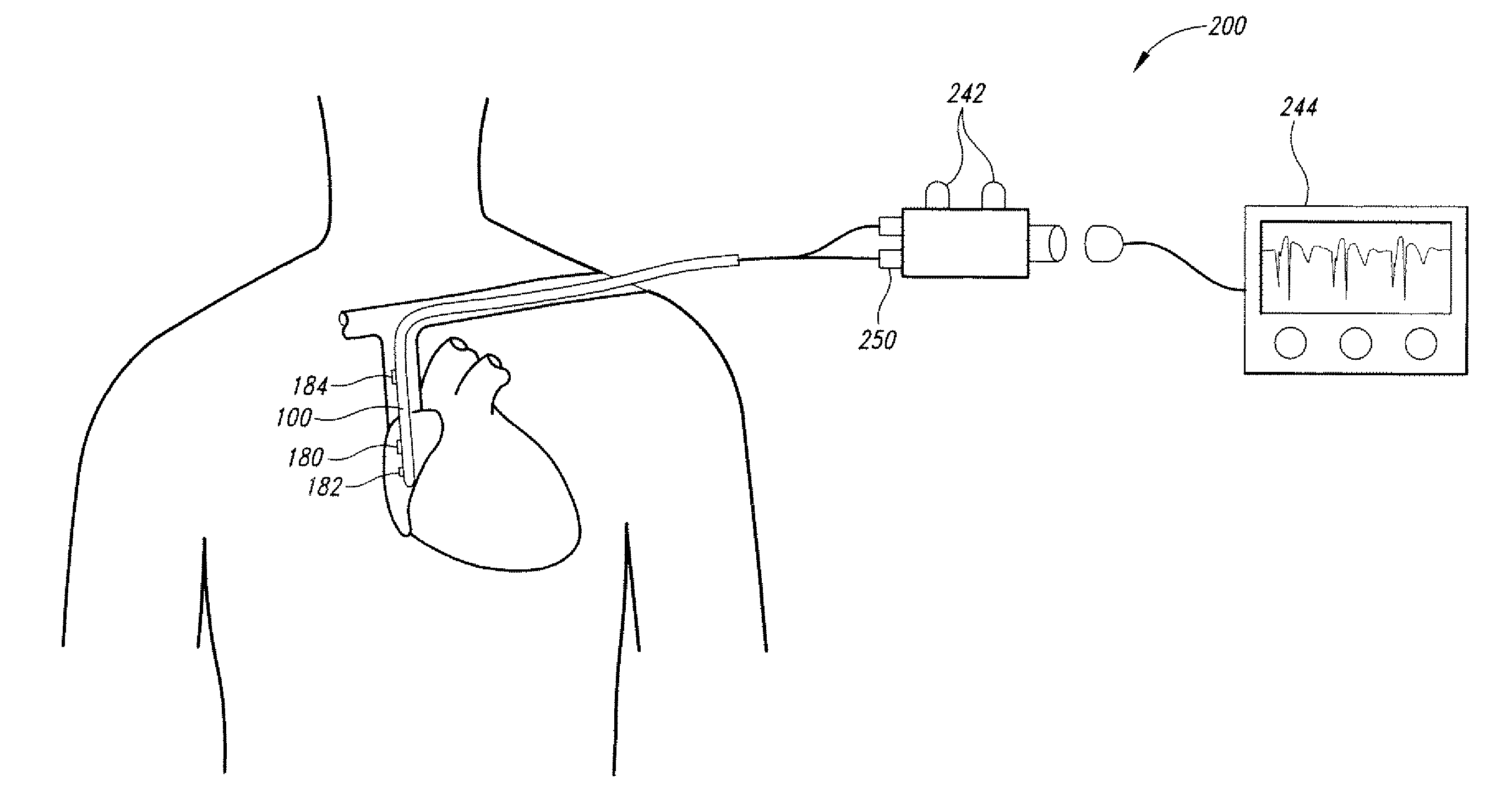
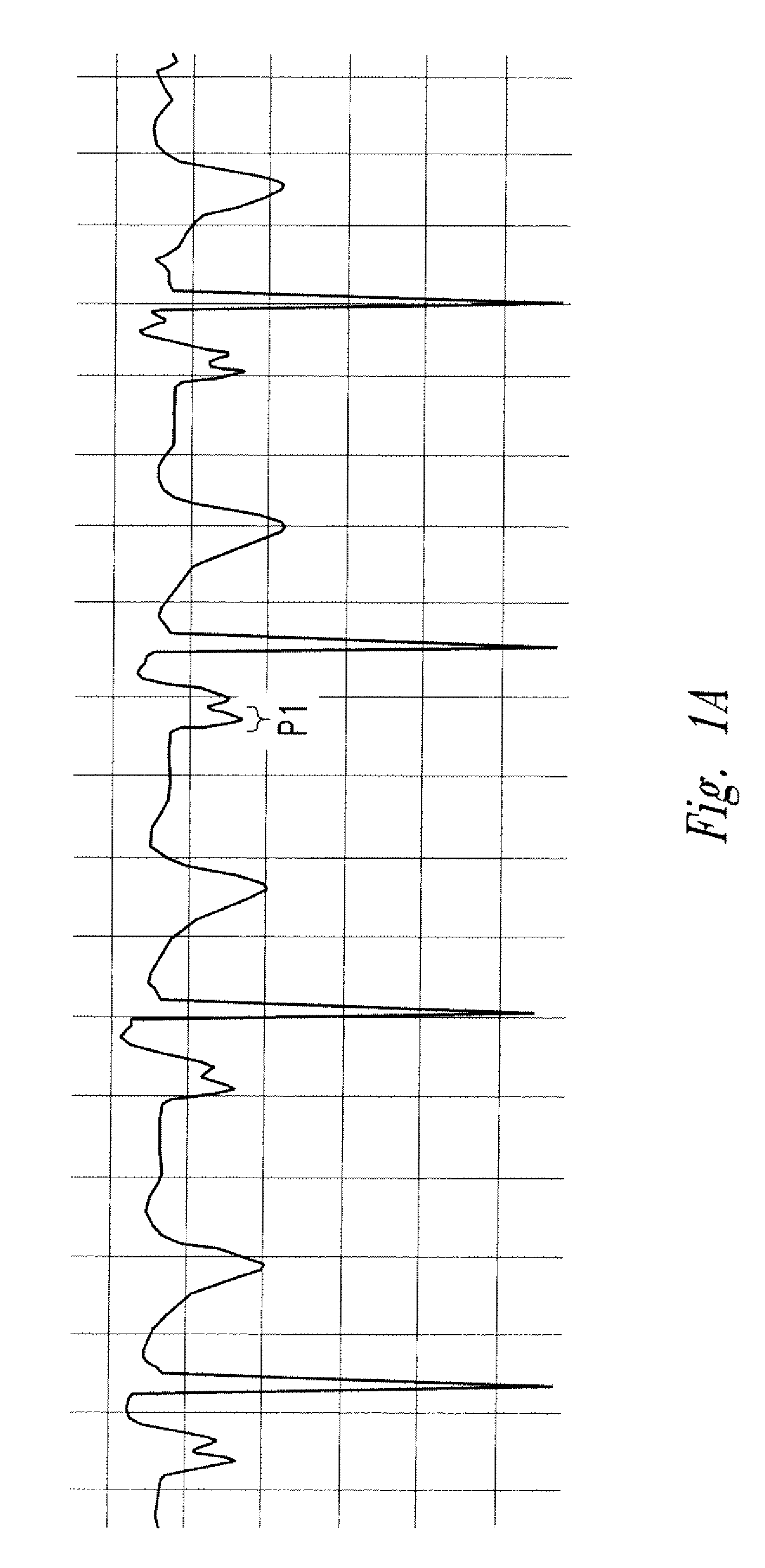
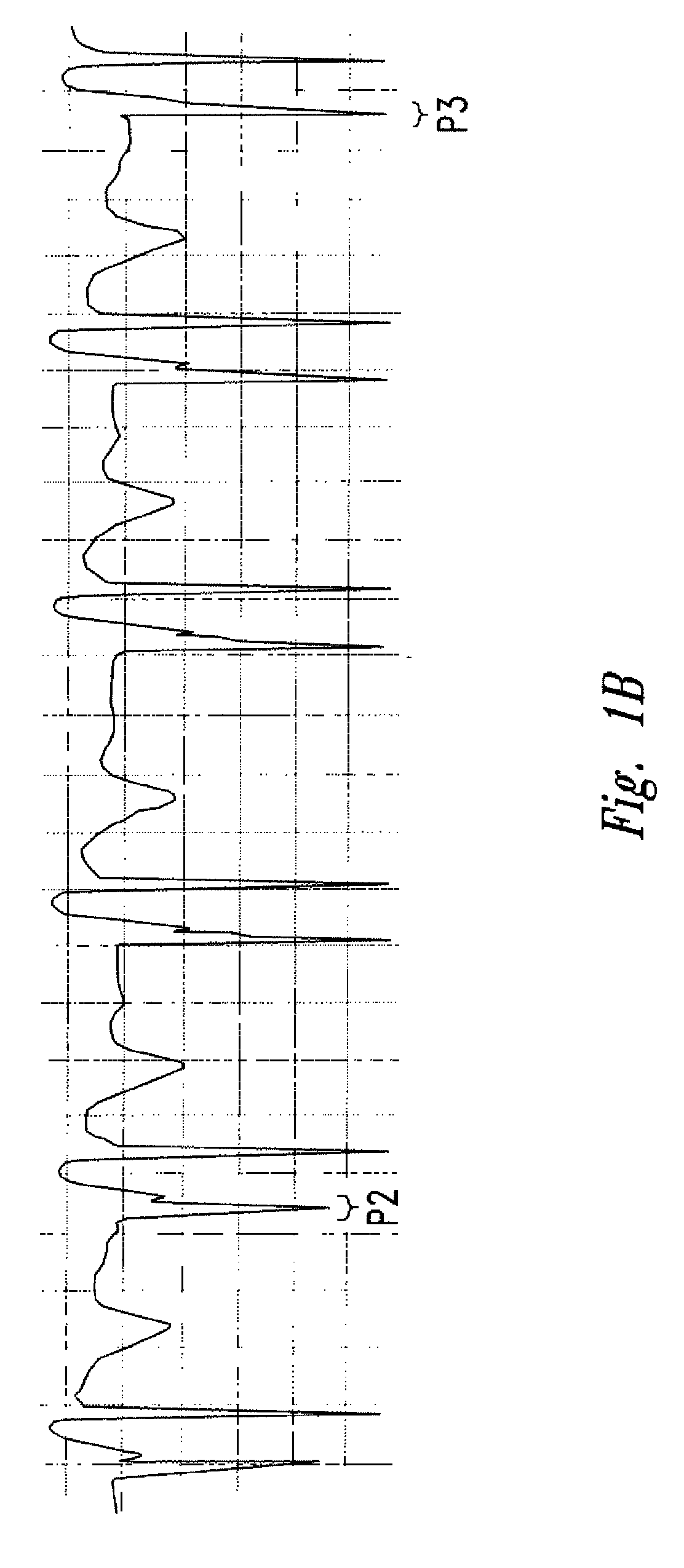
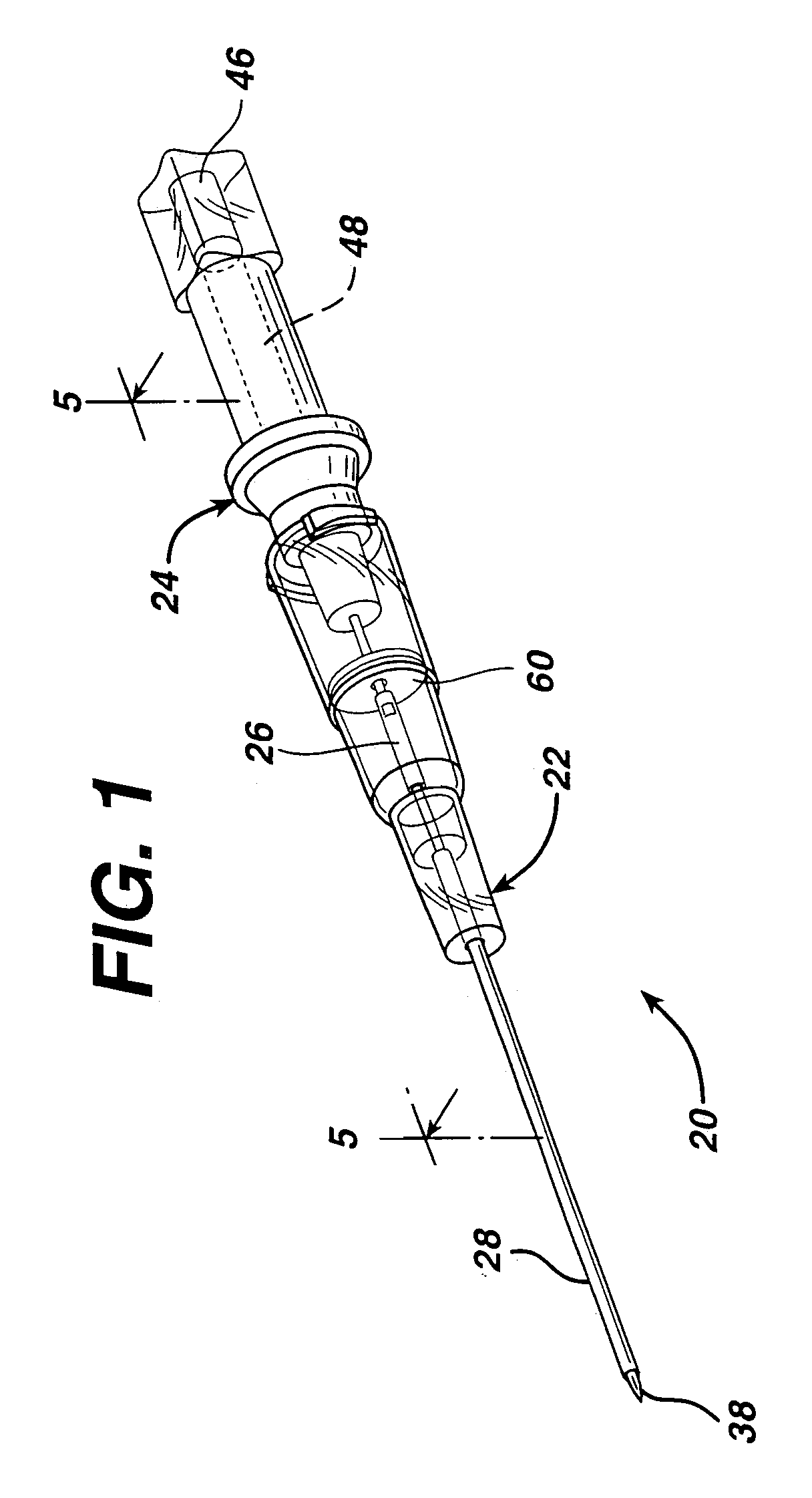
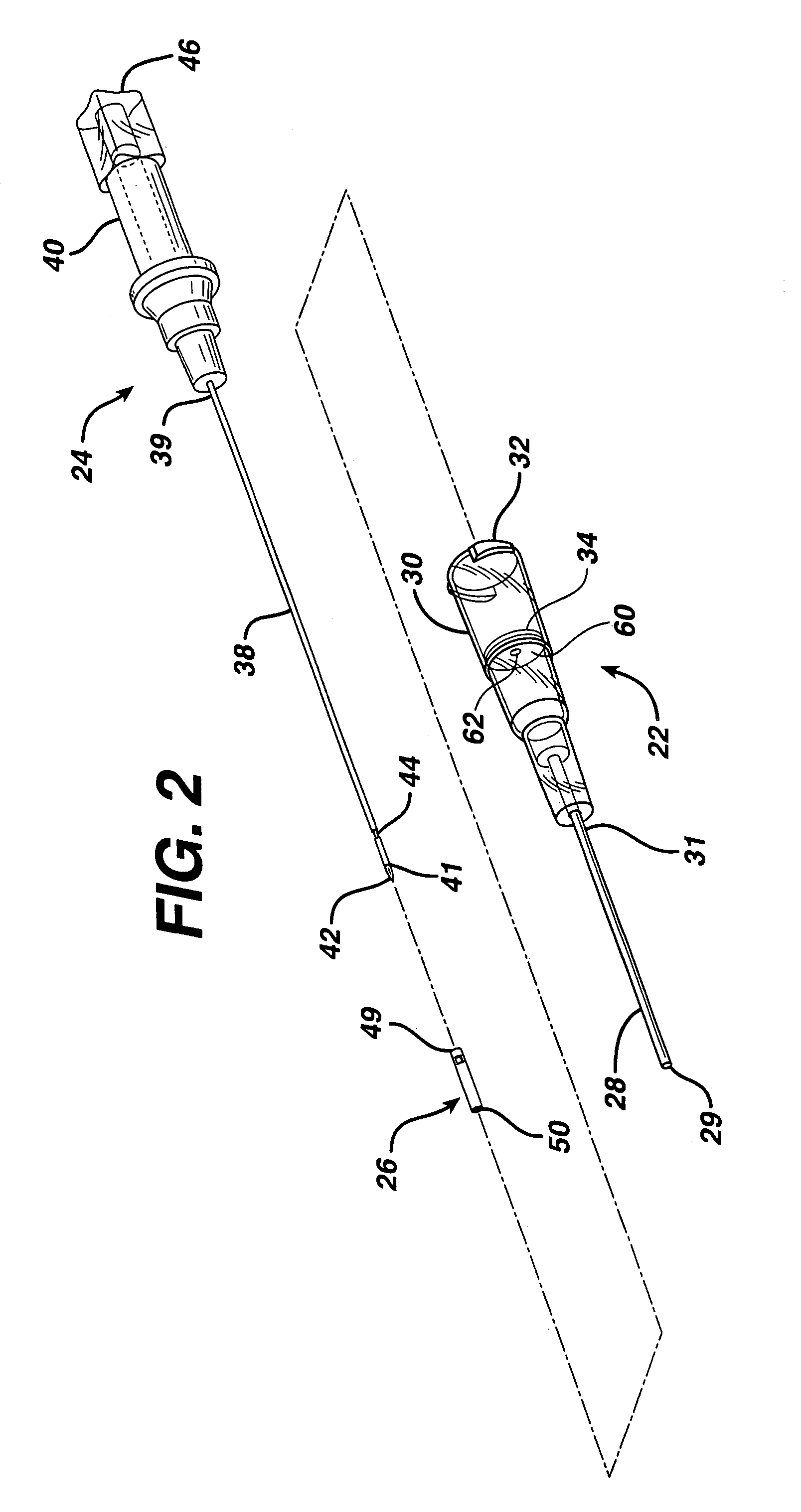
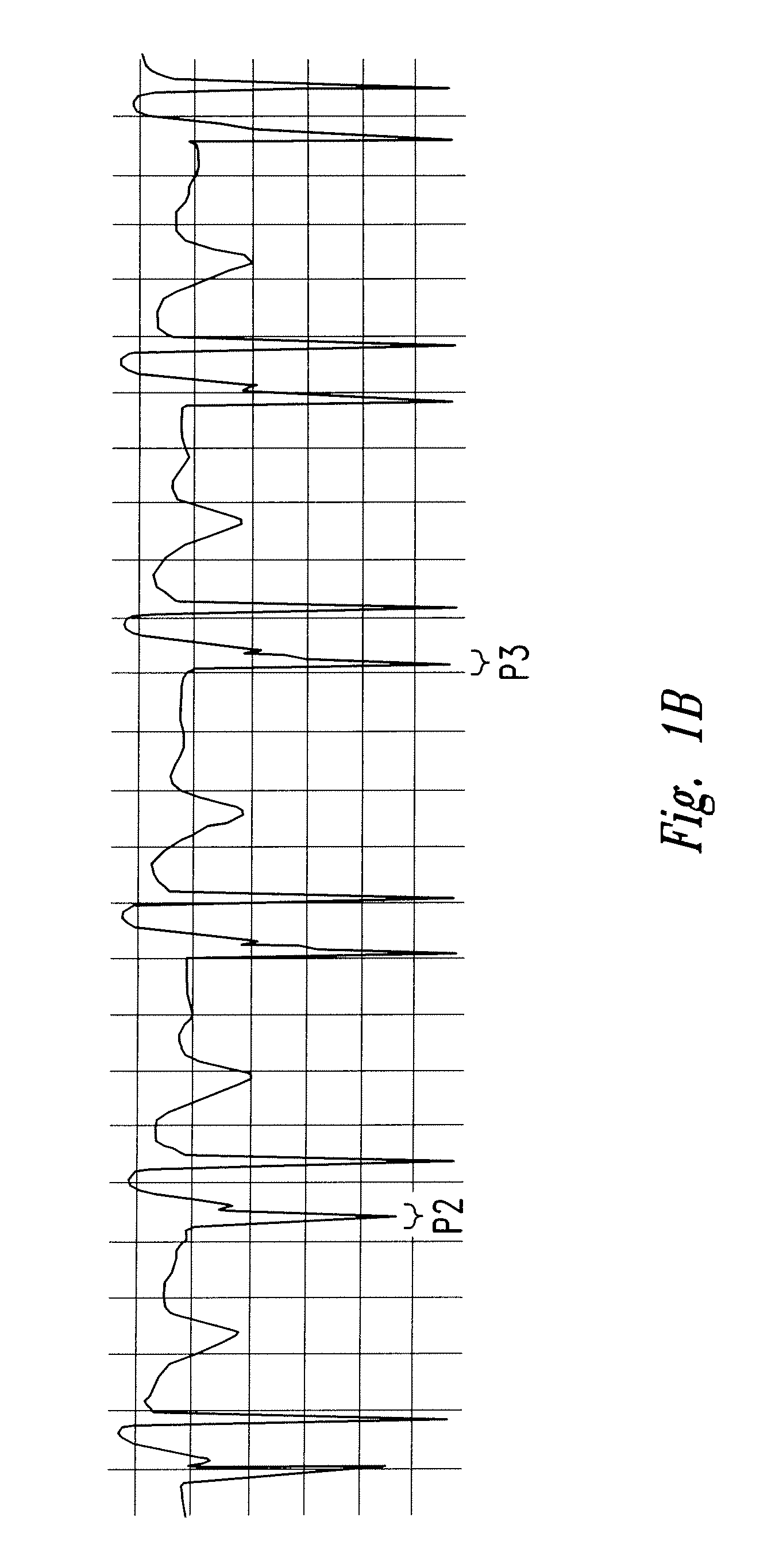
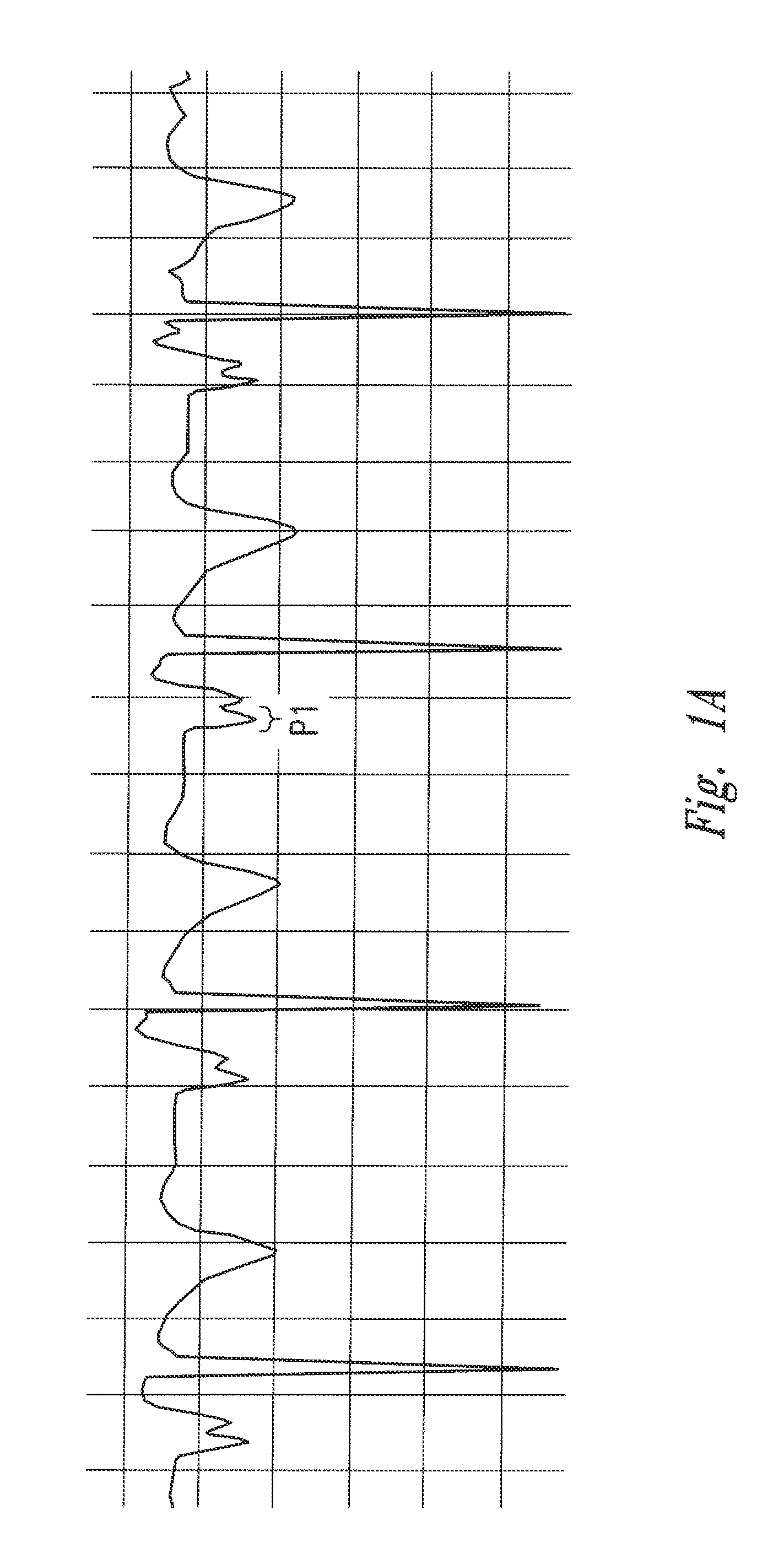
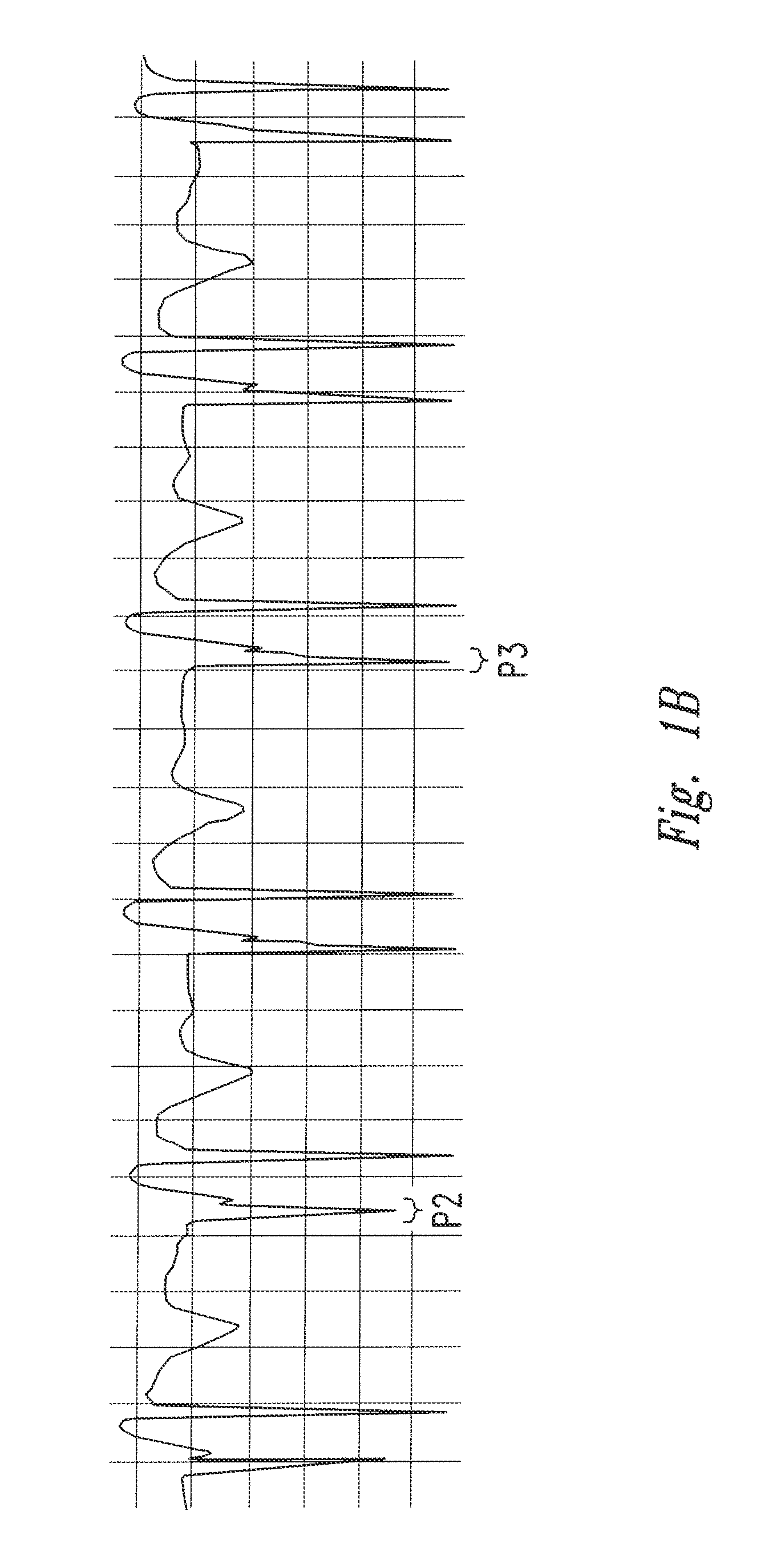
Method of locating the tip of a central venous catheter
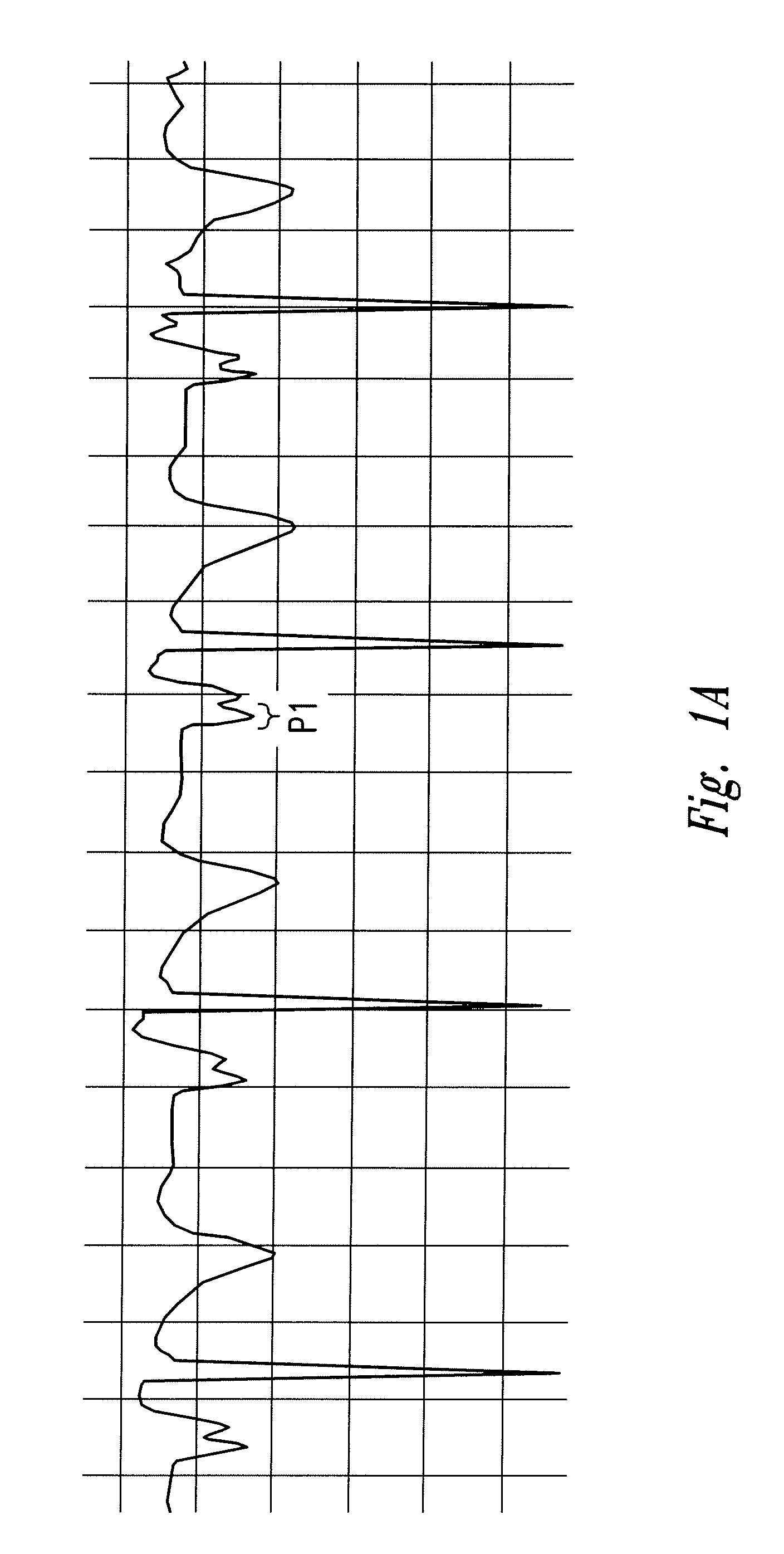
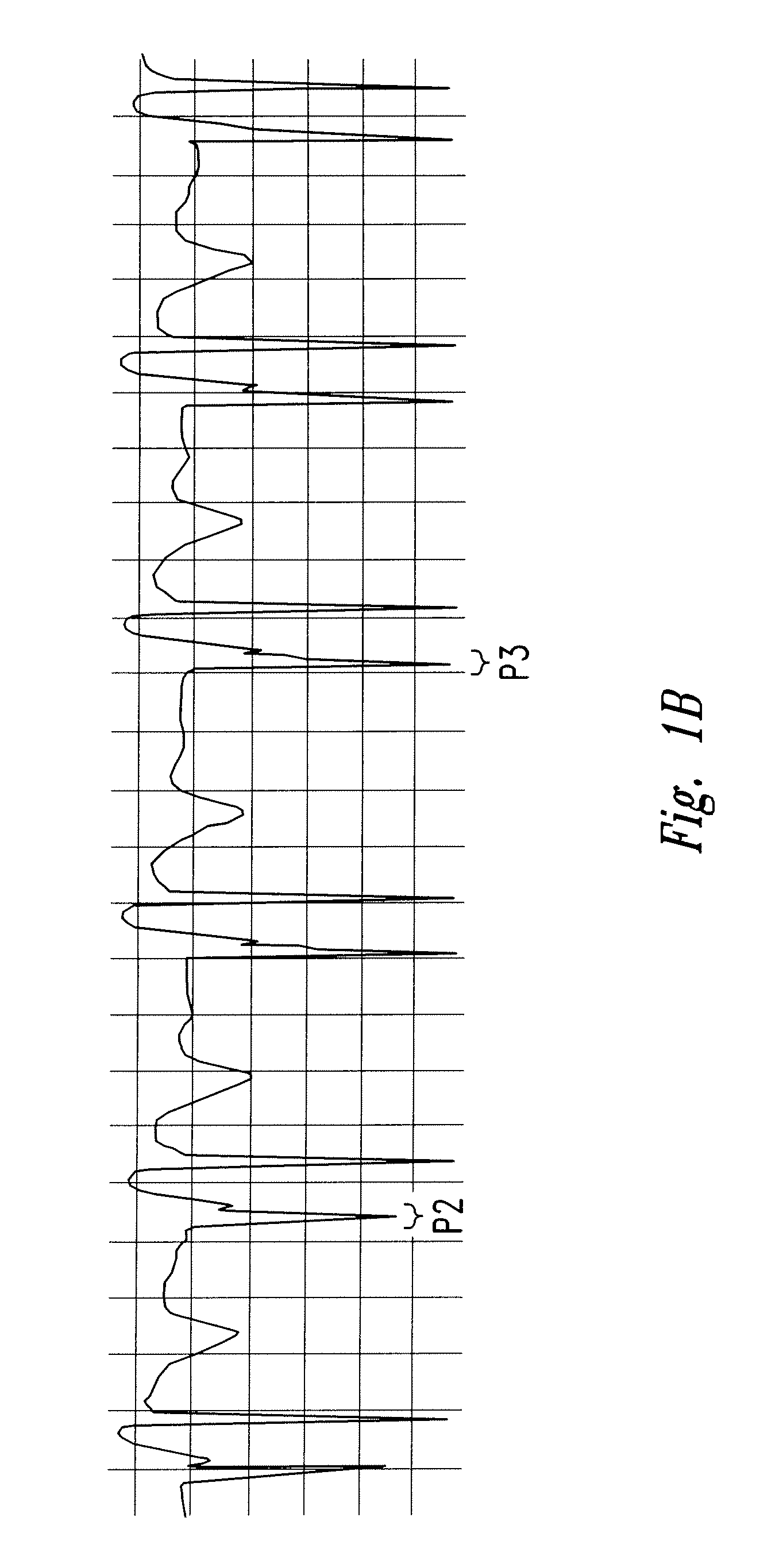
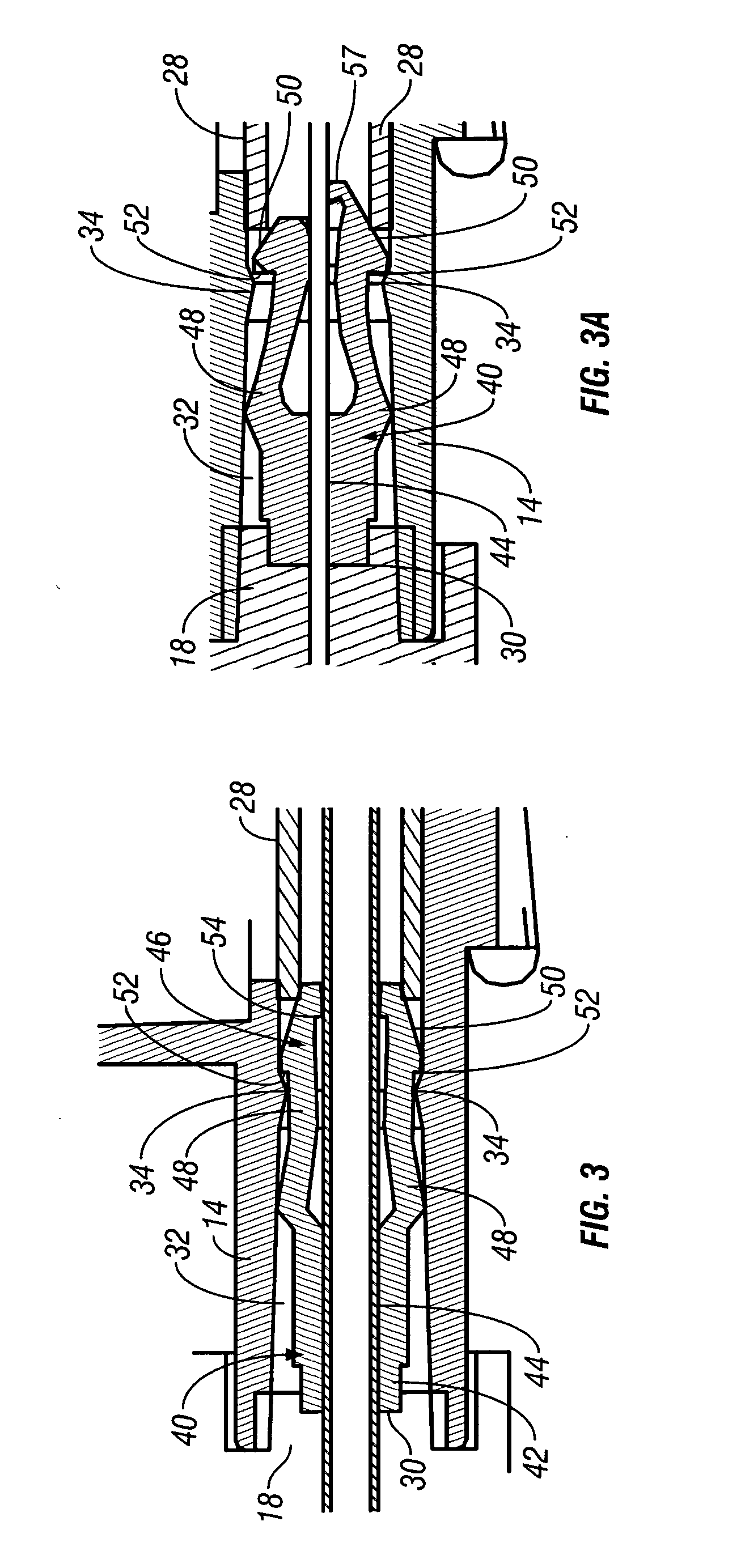
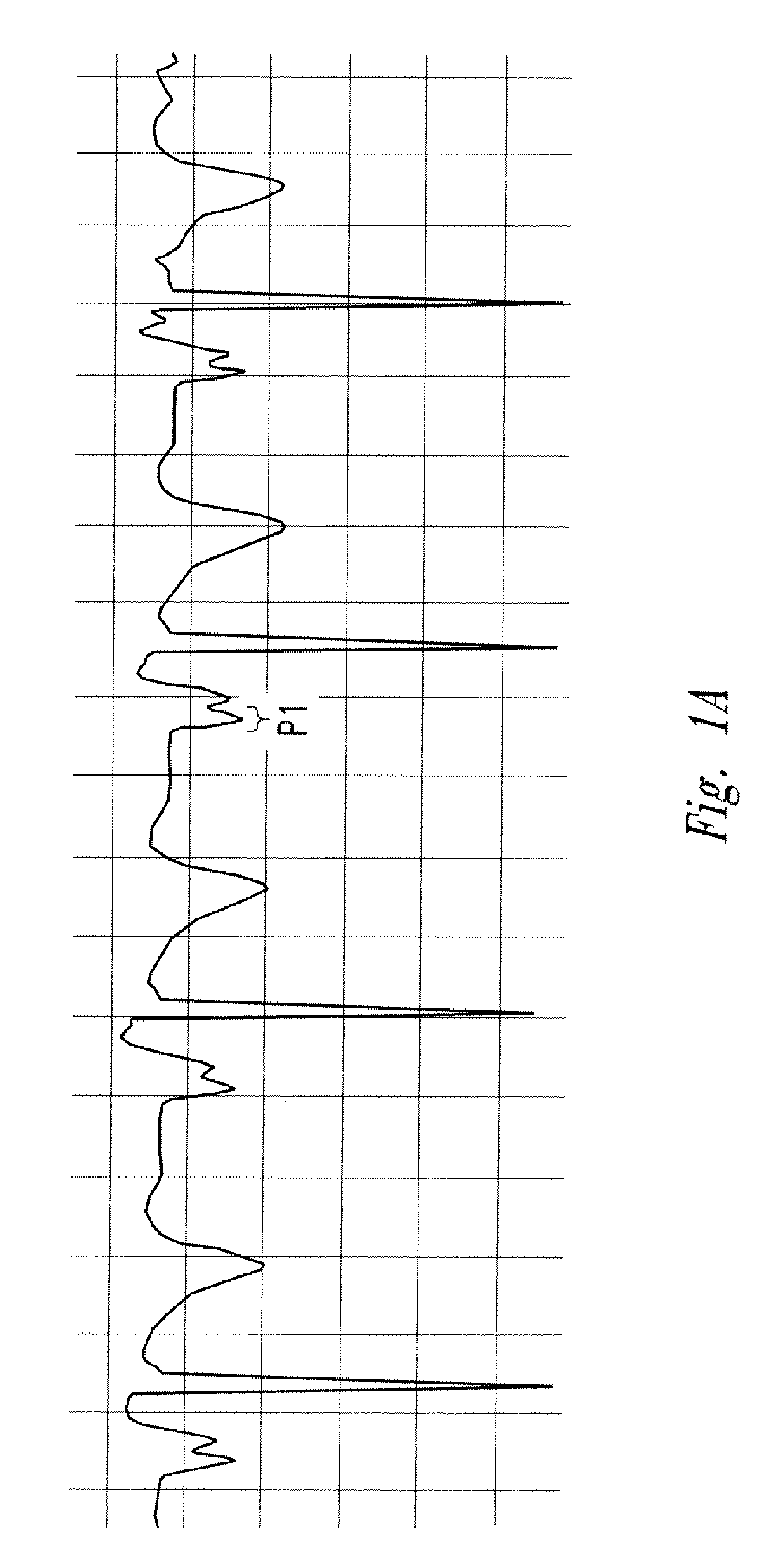
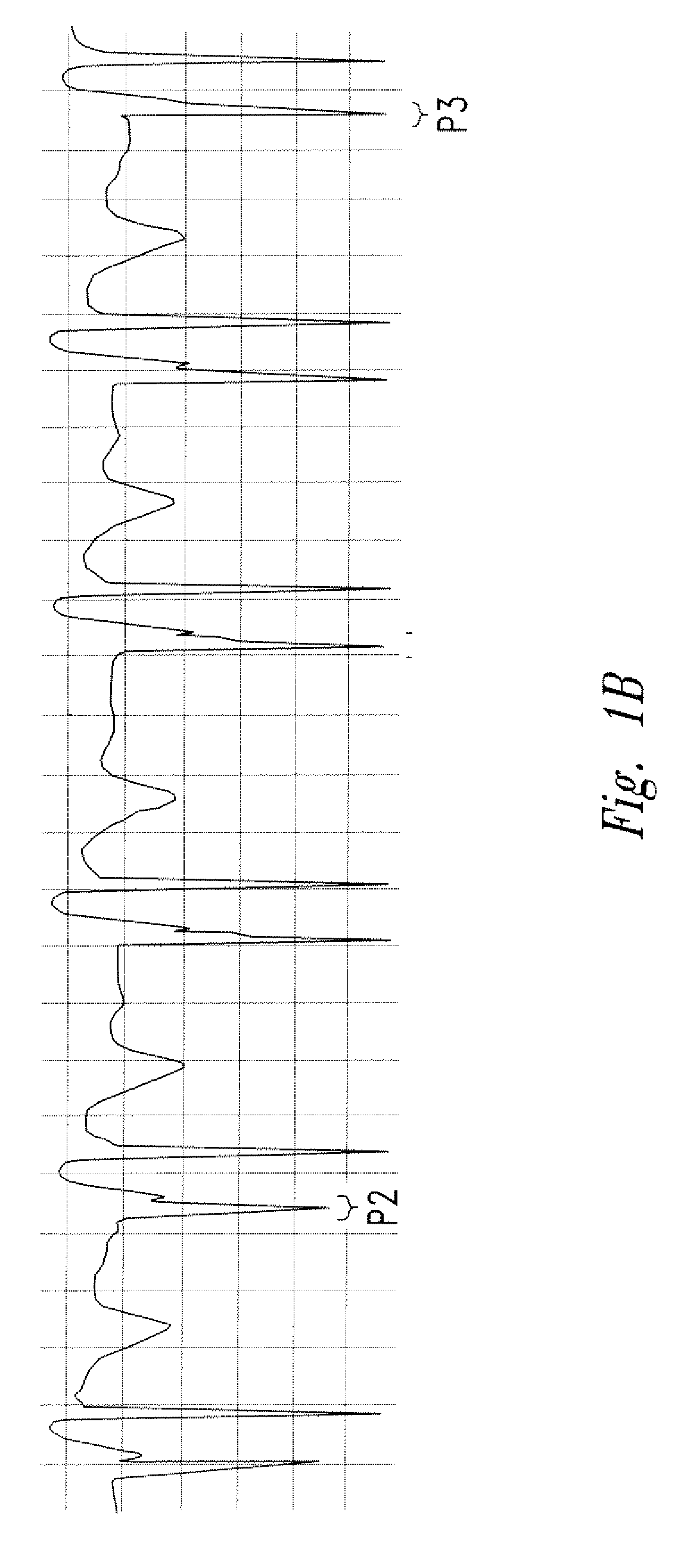
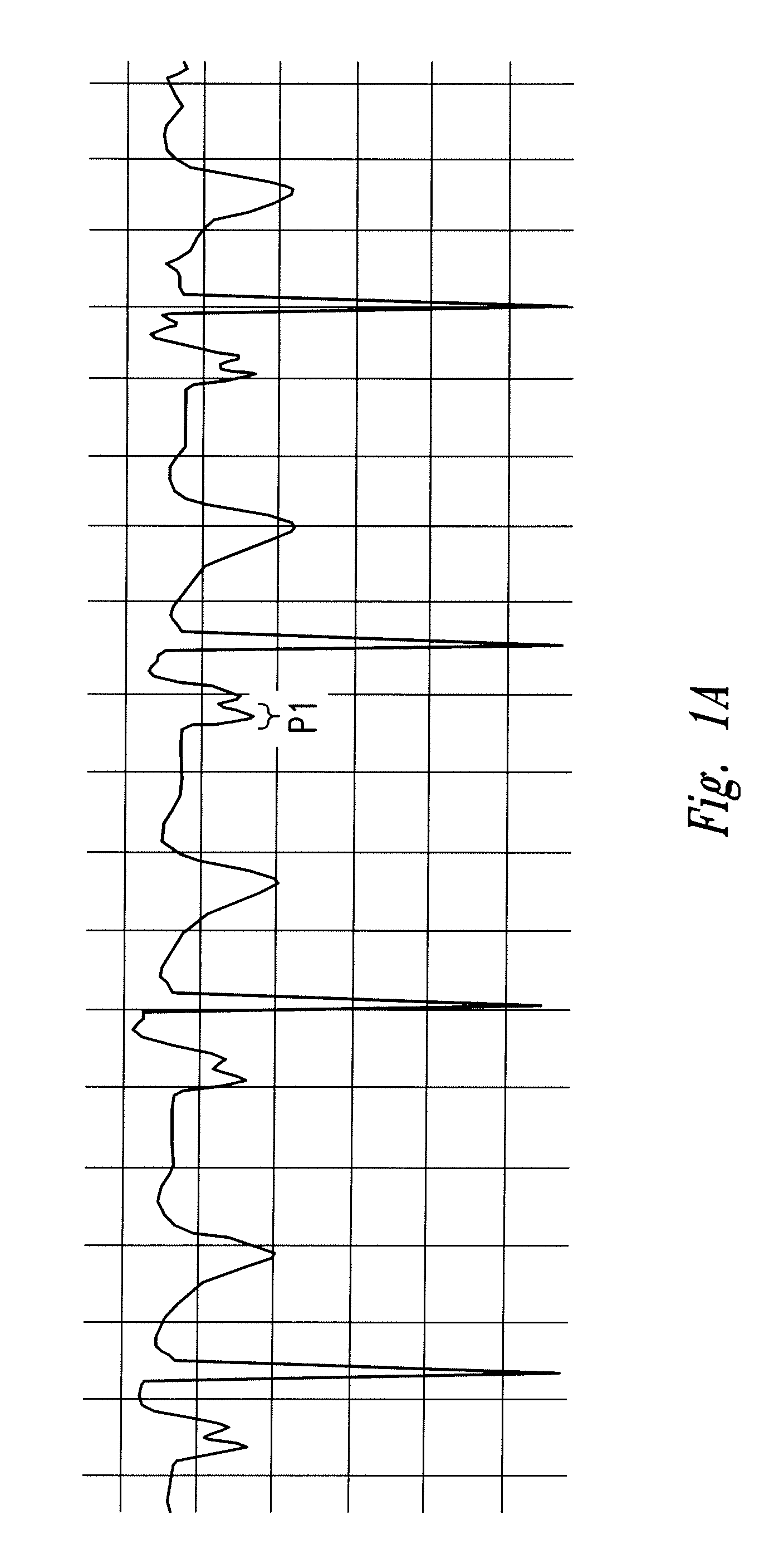
The invention includes a method of locating a tip of a central venous catheter (“CVC”) having a distal and proximal pair of electrodes disposed within the superior vena cava, right atrium, and / or right ventricle. The method includes obtaining a distal and proximal electrical signal from the distal and proximal pair and using those signals to generate a distal and proximal P wave, respectively. A deflection value is determined for each of the P waves. A ratio of the deflection values is then used to determine a location of the tip of the CVC. Optionally, the CVC may include a reference pair of electrodes disposed within the superior vena cava from which a reference deflection value may be obtained. A ratio of one of the other deflection values to the reference deflection value may be used to determine the location of the tip of the CVC.
Owner:BARD ACCESS SYST
Method and device for electronically controlling the beating of a heart
An electro-stimulation device includes a pair of electrodes for connection to at least one location in the body that affects or regulates the heartbeat. The electro-stimulation device both electrically arrests the heartbeat and stimulates the heartbeat. A pair of electrodes are provided for connection to at least one location in the body that affects or regulates the heartbeat. The pair of electrodes may be connected to an intravenous catheter for transvenous stimulation of the appropriate nerve. A first switch is connected between a power supply and the electrodes for selectively supplying current from the power supply to the electrodes to augment any natural stimuli to the heart and thereby stop the heart from beating. A second switch is connected between the power supply and the electrodes for selectively supplying current from the power supply to the electrodes to provide an artificial stimulus to initiate heartbeating. In another aspect, the invention is directed to a method for arresting the beat of a heart in a living body comprising the steps of connecting the pair of electrodes to at least one location in the body that affects or regulates the heartbeat and supplying an electrical current to the electrodes of sufficient amplitude and duration to arrest the heartbeat. The device may also serve to still the lungs by input to a respirator or by stimulation of the phrenic nerve during surgical procedures.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
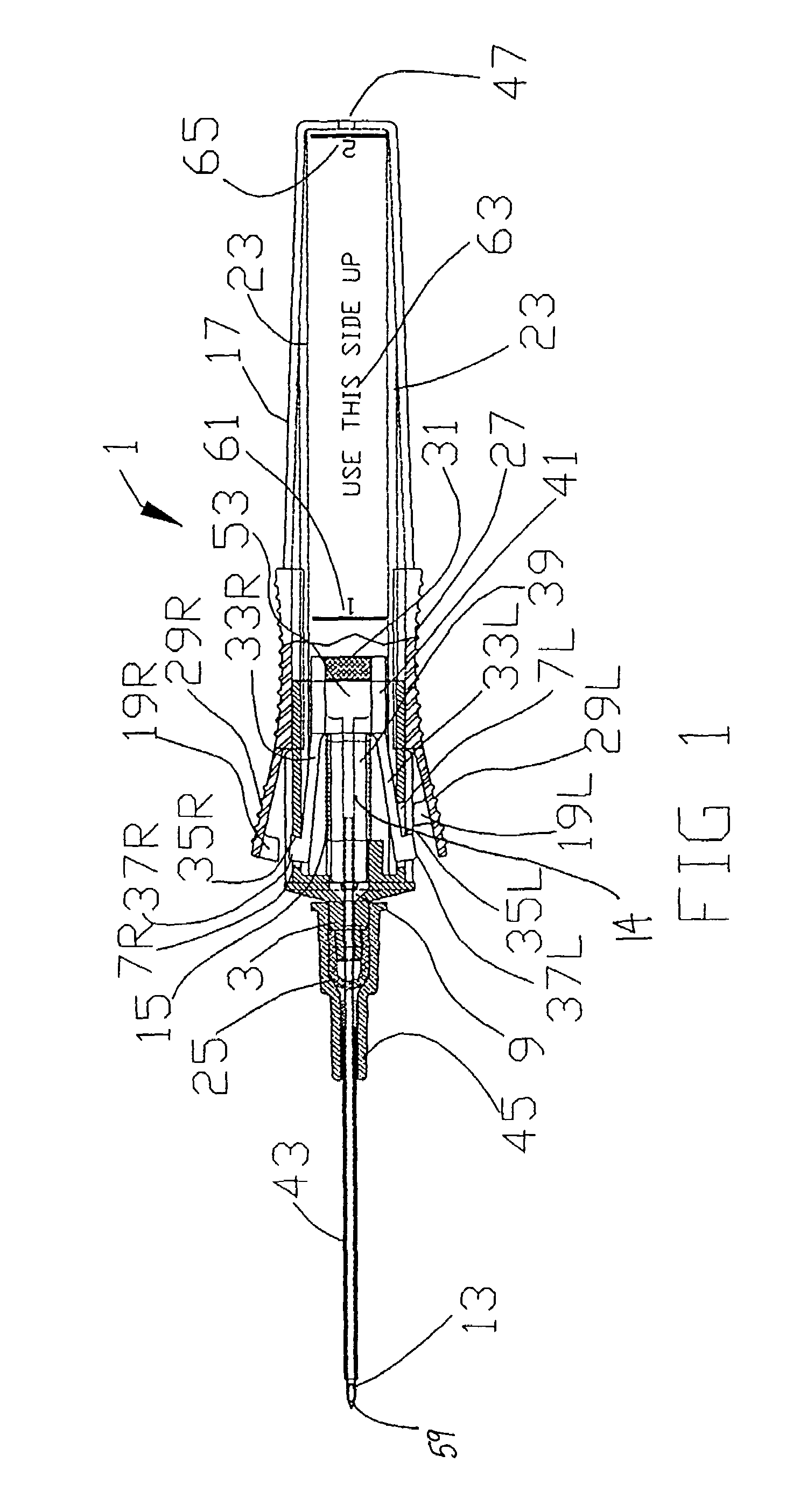
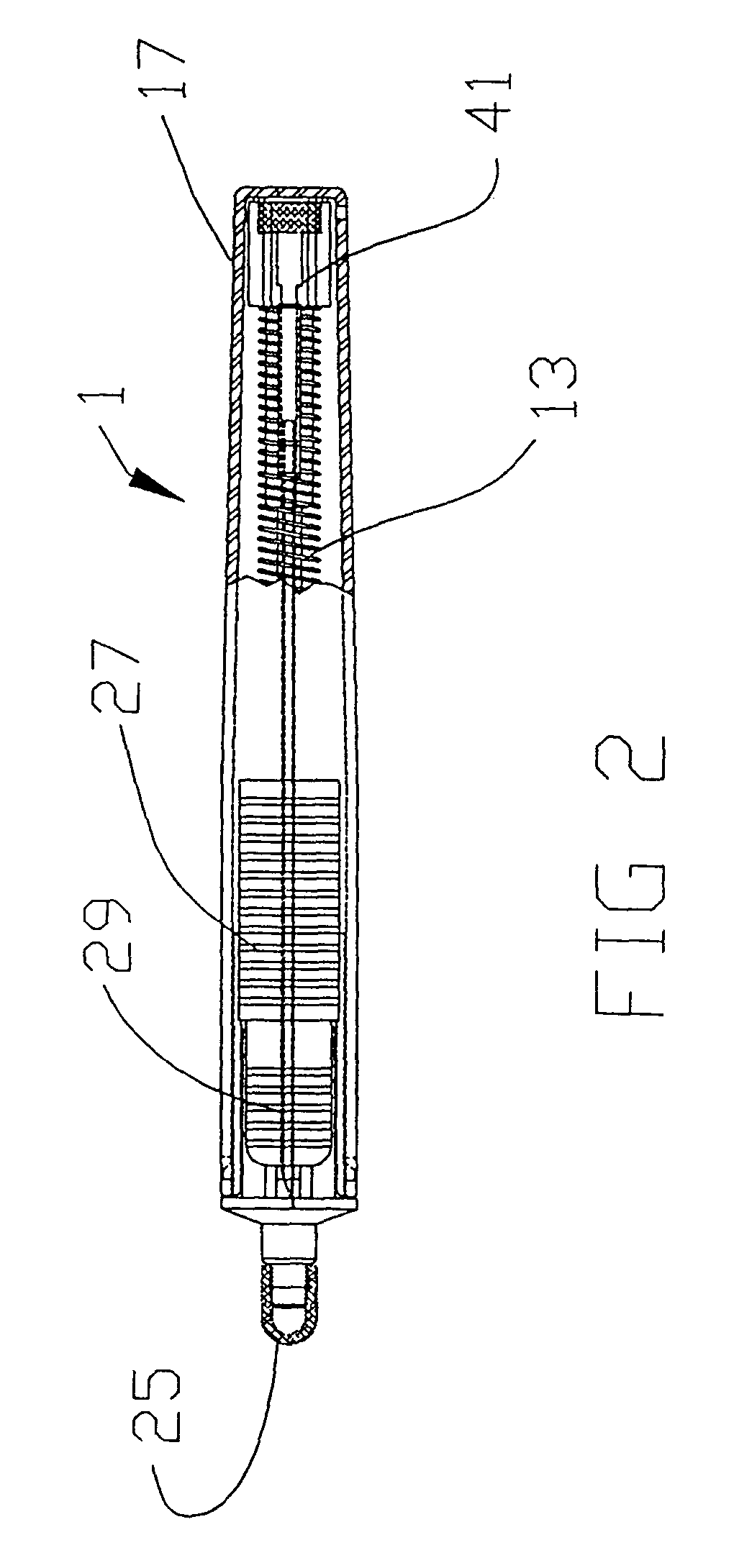
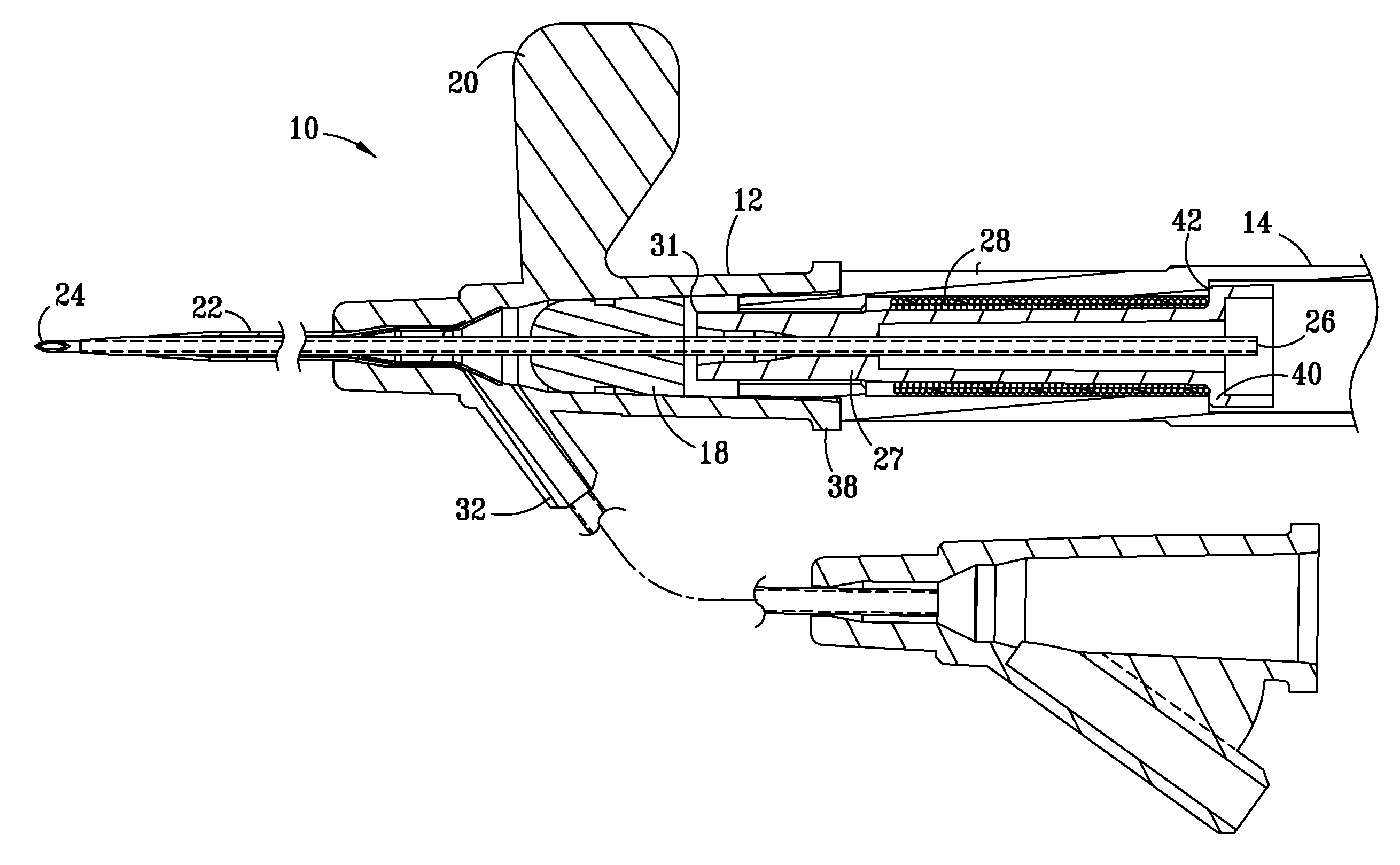
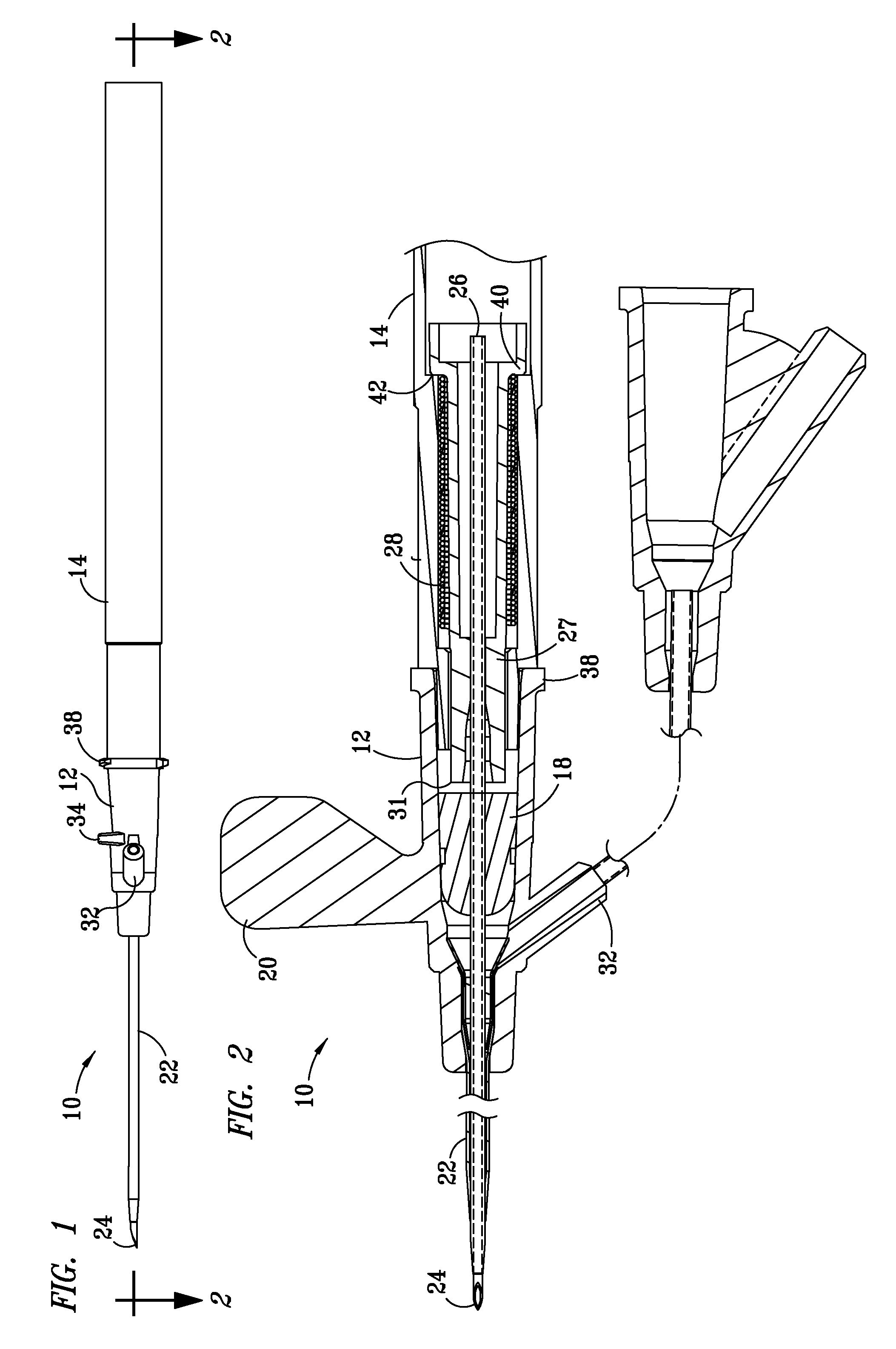
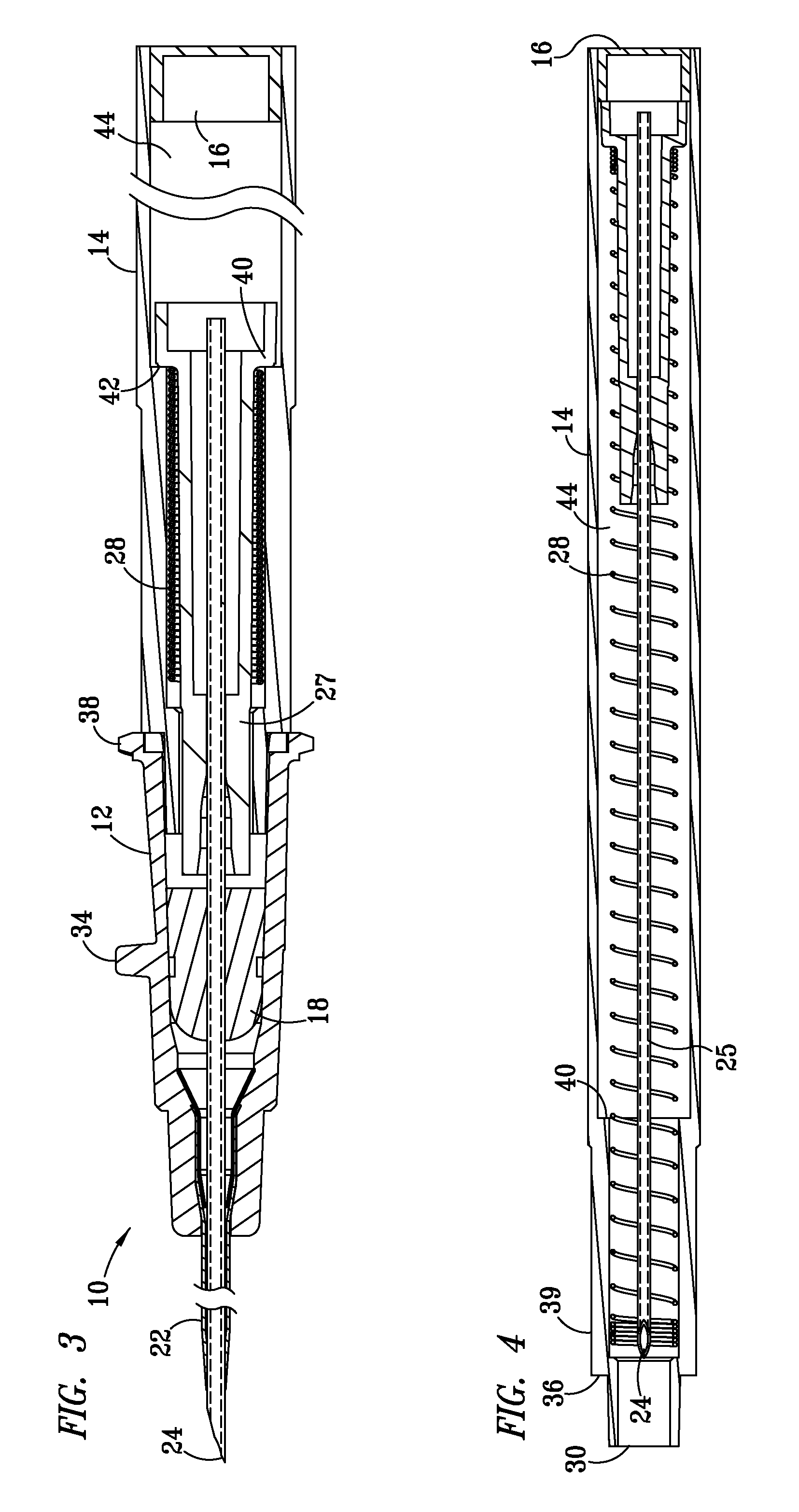
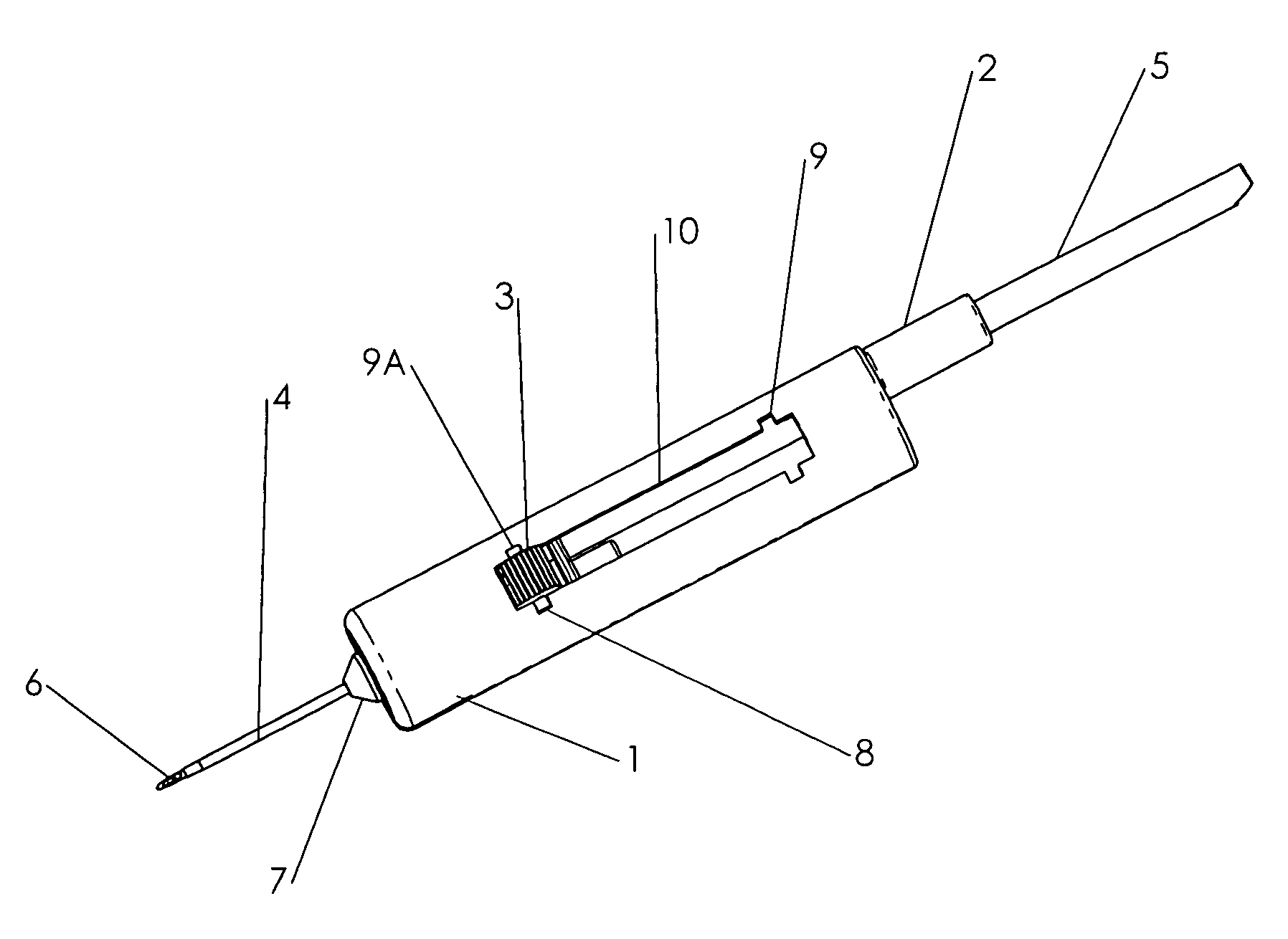
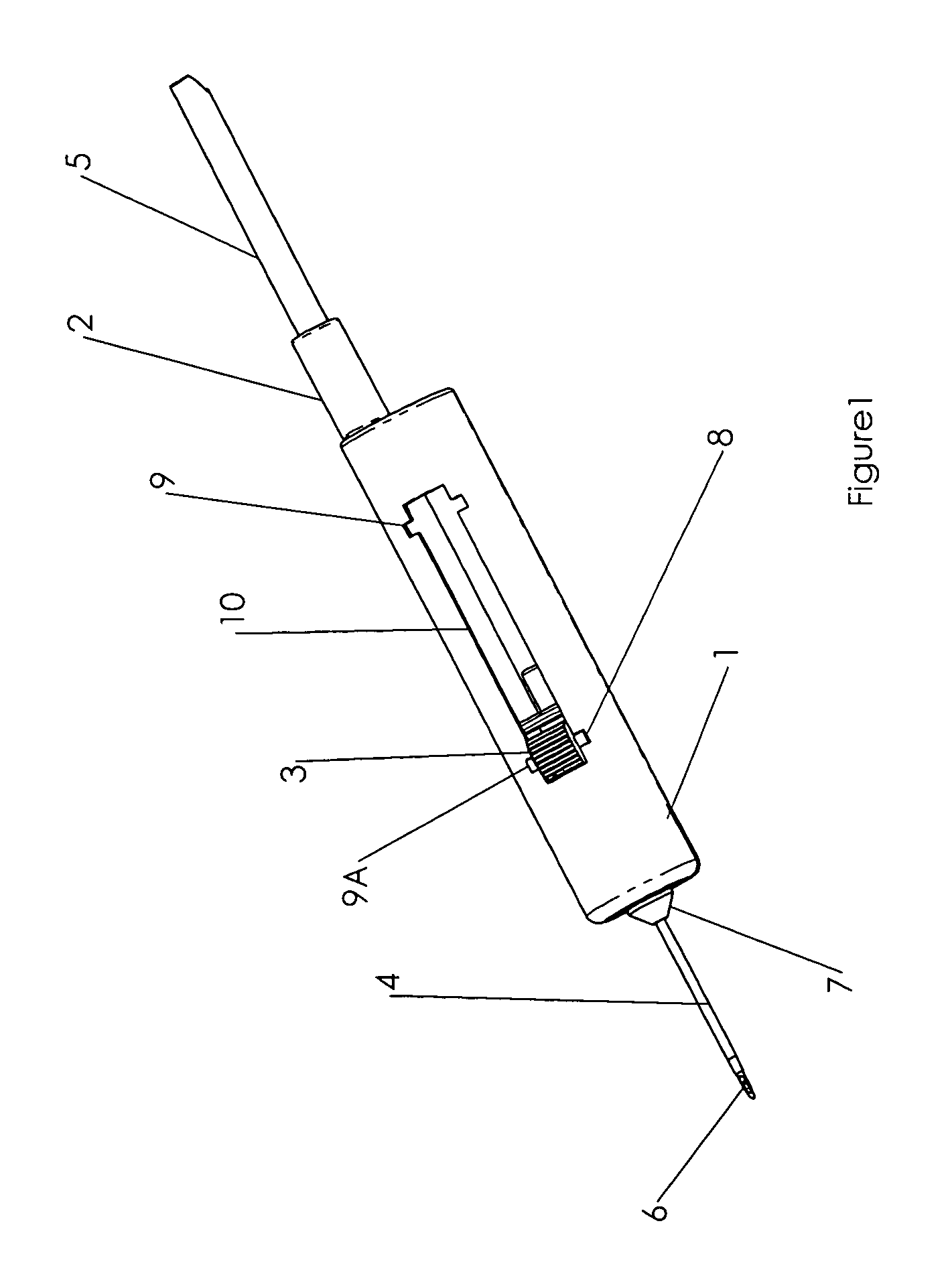
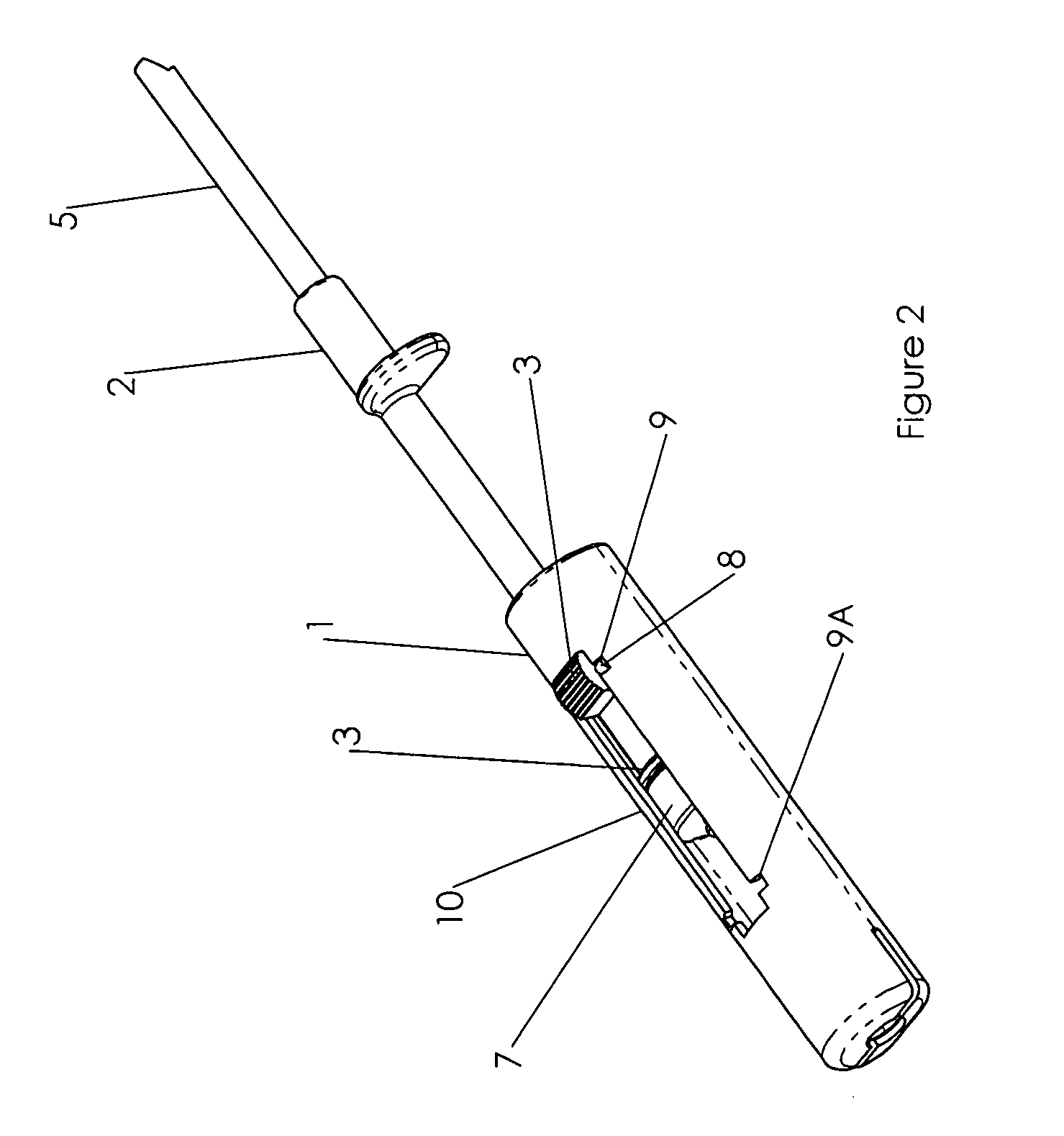
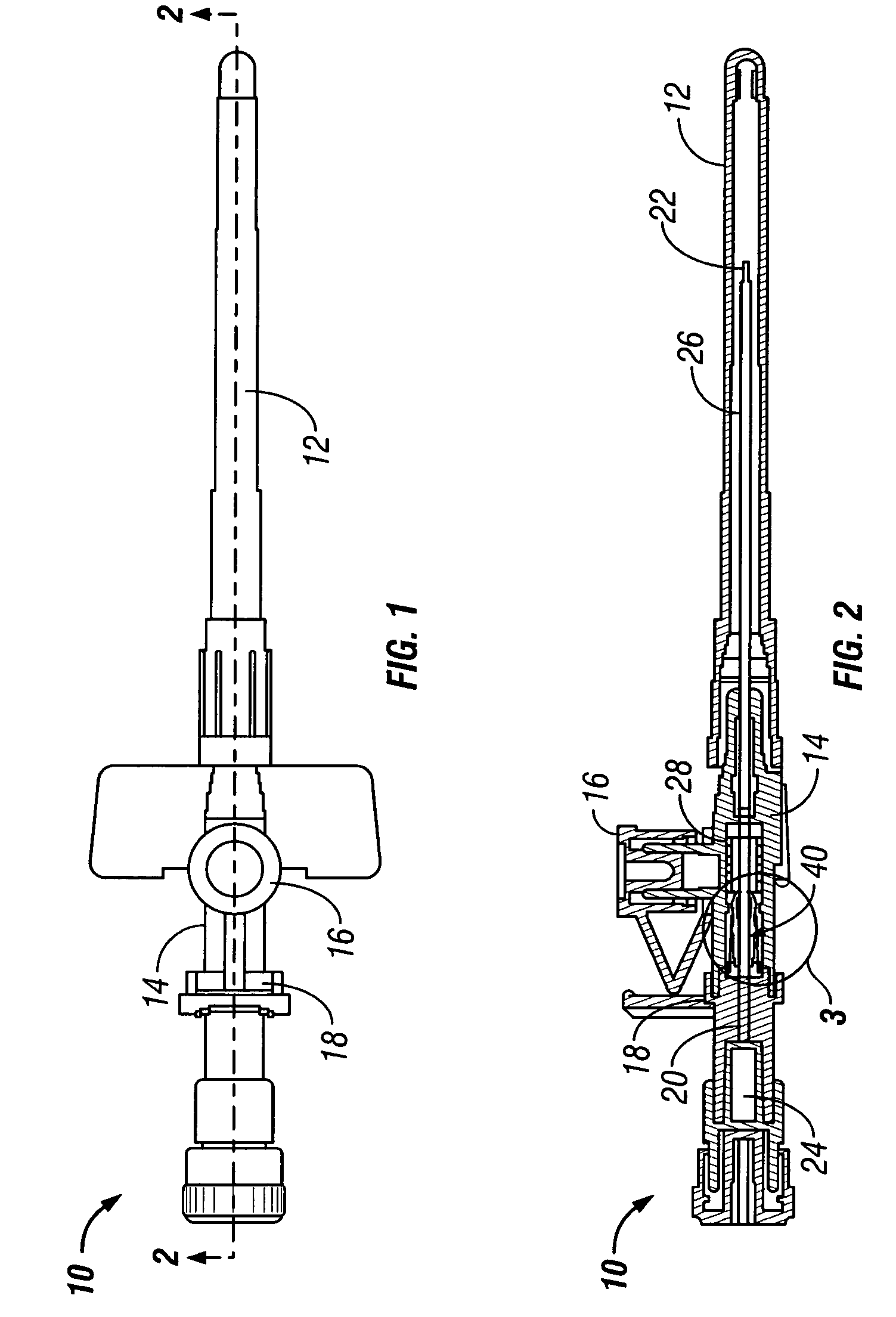
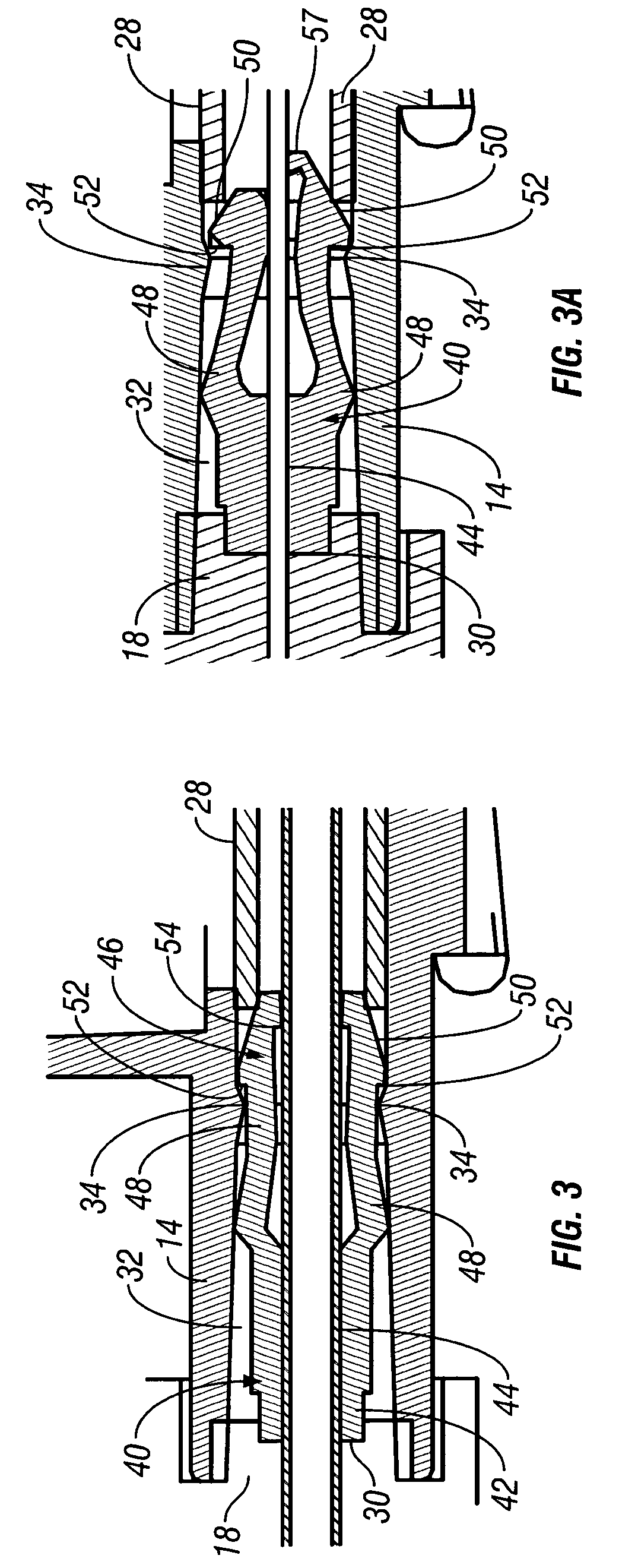
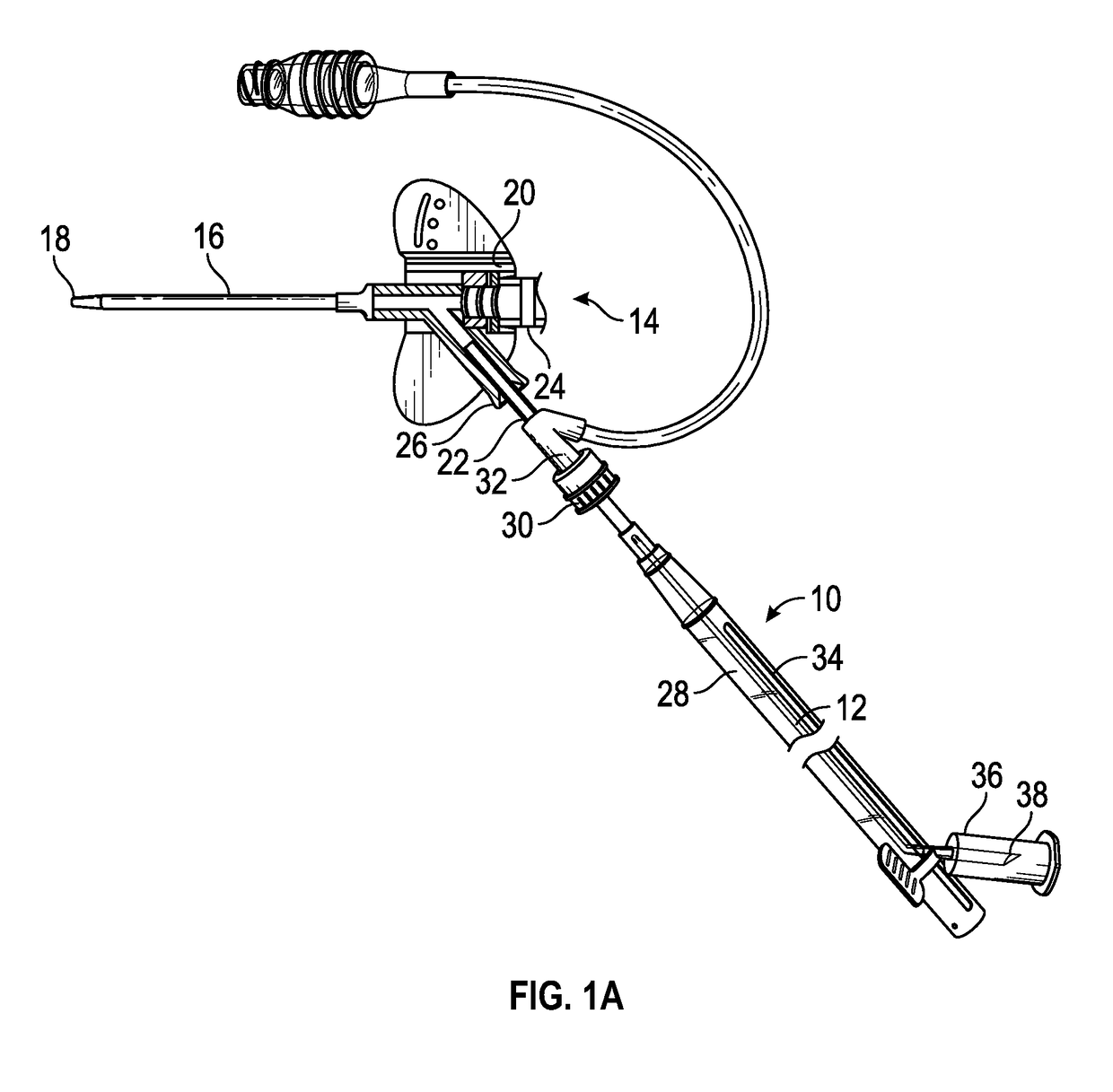
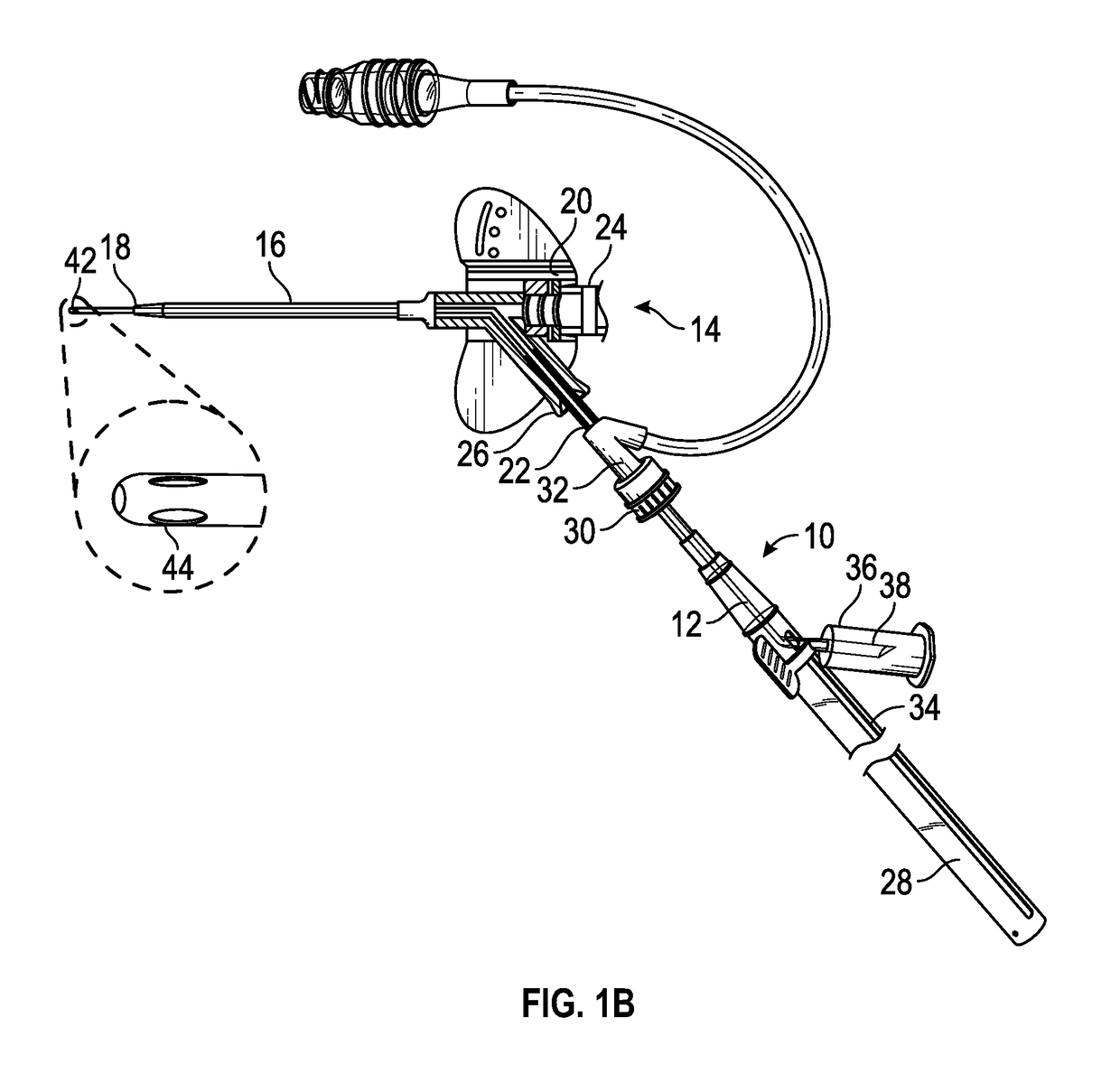
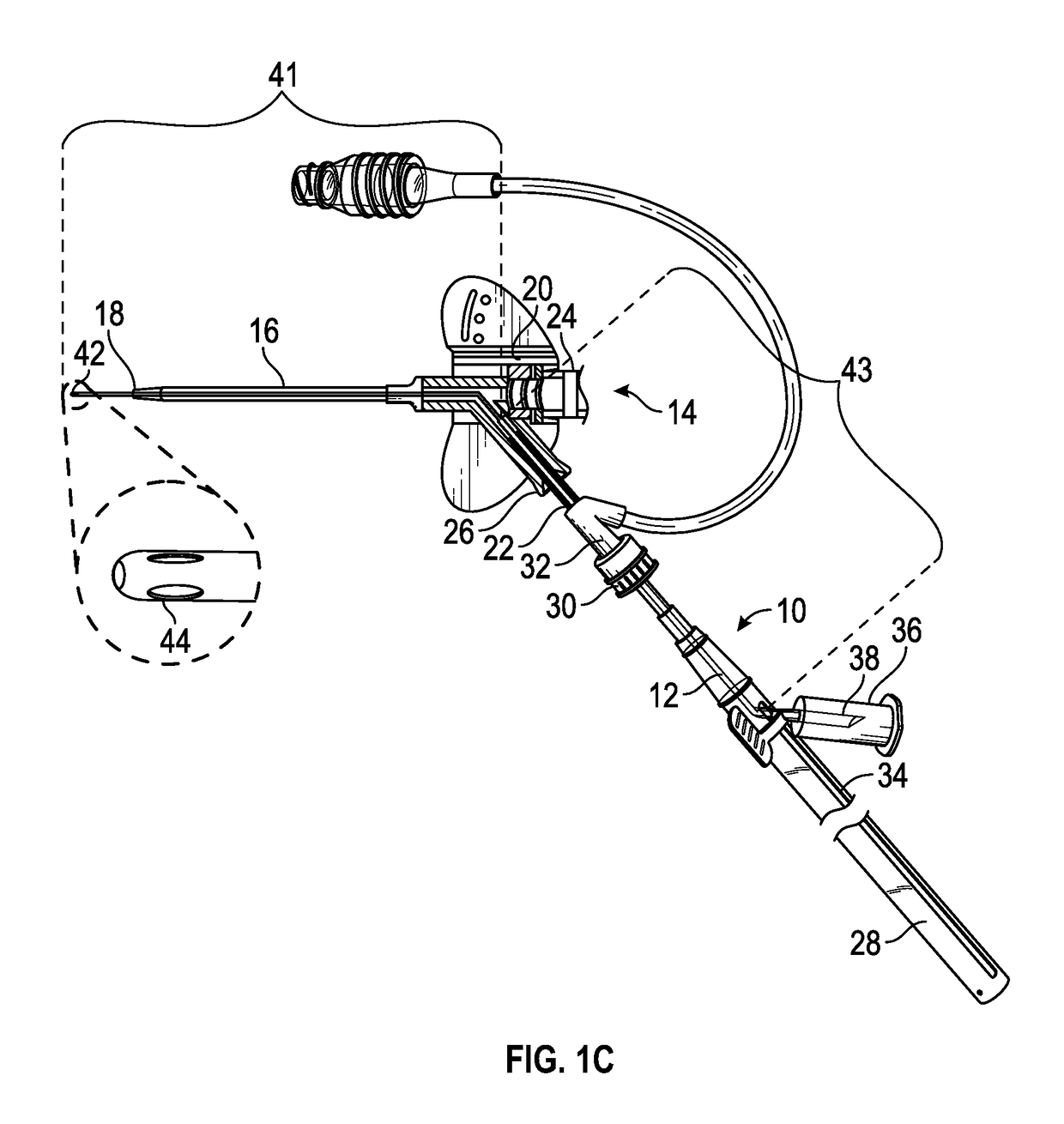
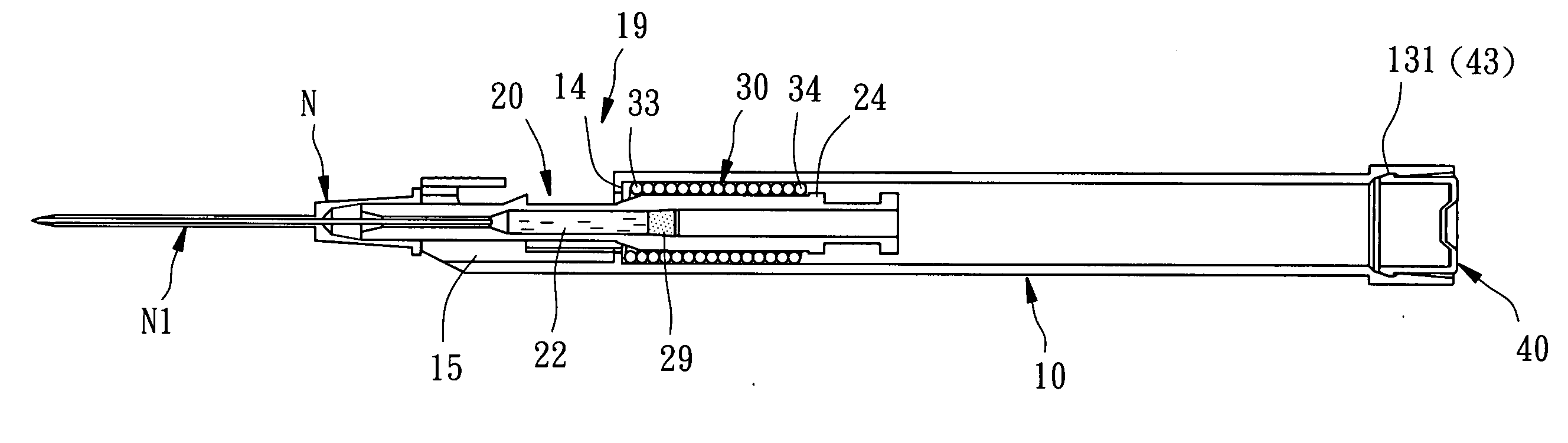
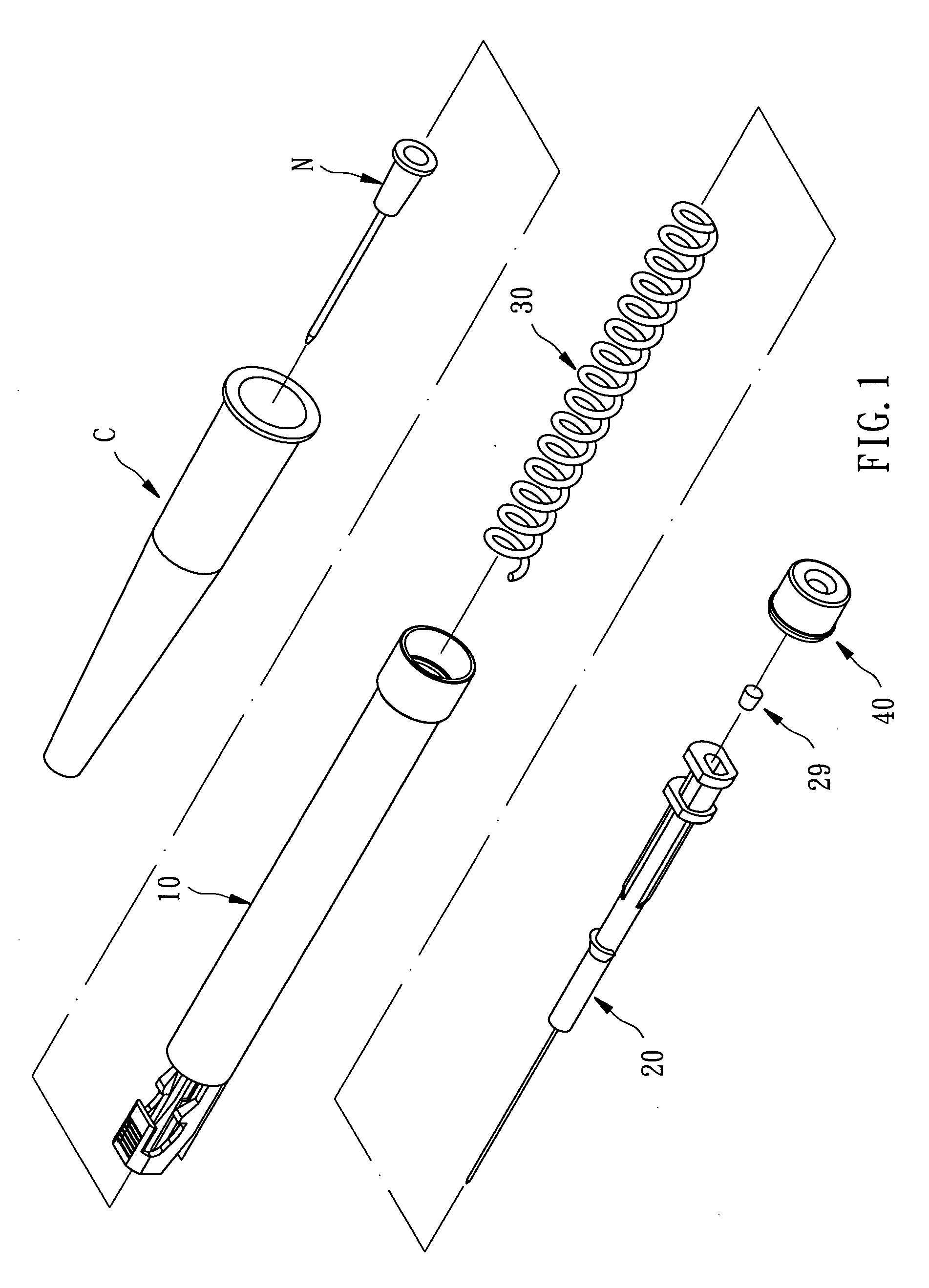
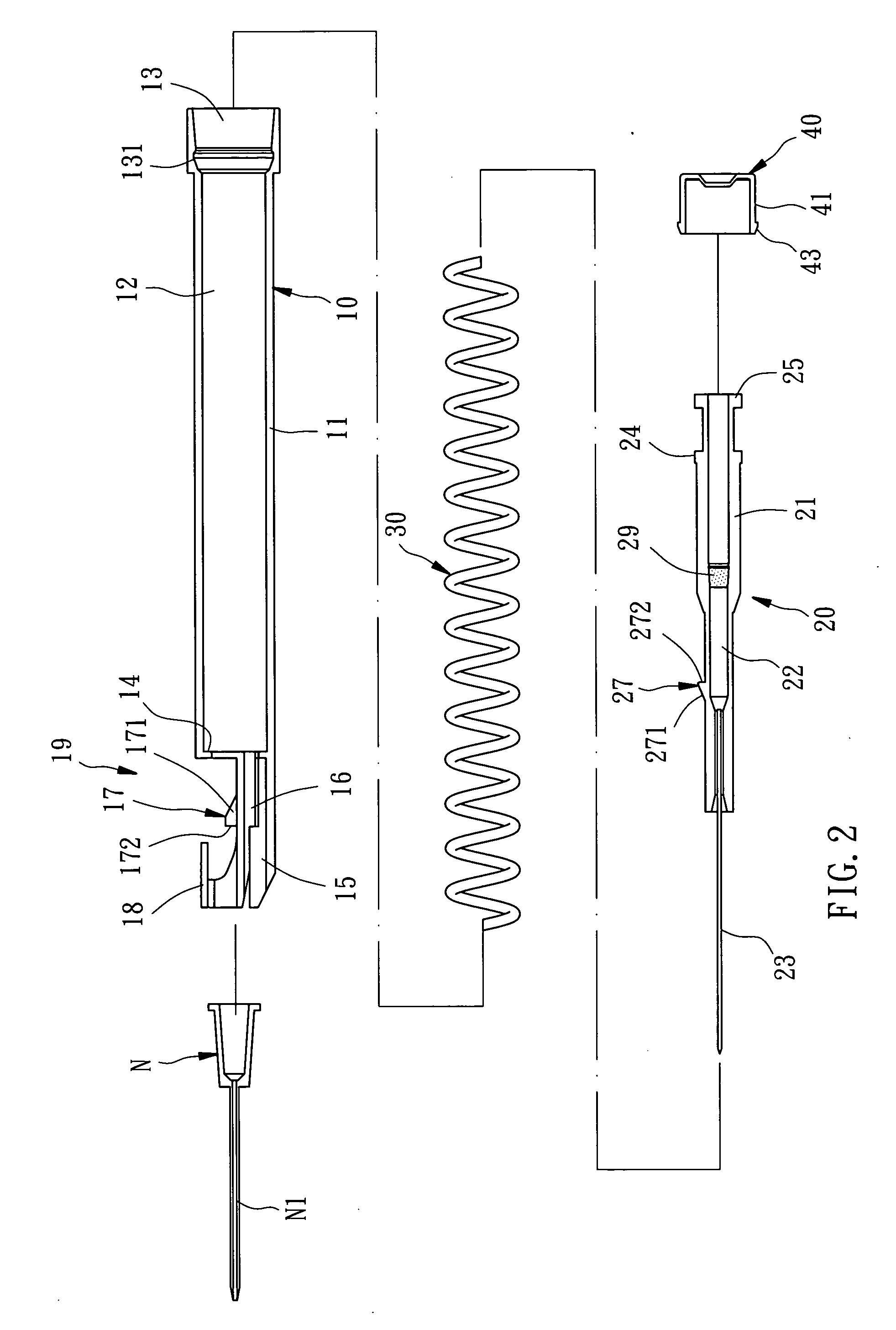
Needle safety device for an intravenous catheter apparatus and method of use
A needle safety device for an intravenous catheter apparatus that includes a base capable of receiving a needle into opposing jaws attached to the base and capable of being influenced by the needle. The jaws move between an expanded position which interact with an obstruction within a wing housing of the intravenous catheter apparatus. The jaws permit relative movement of the needle with the base when expanded, close around a needle tip as it passes the jaws, and prevent relative movement of the needle with the base when the jaws are collapsed. The needle of the intravenous catheter apparatus may then be safely disposed with the needle tip within the needle safety device.
Owner:RISHI BAID
Method of locating the tip of a central venous catheter
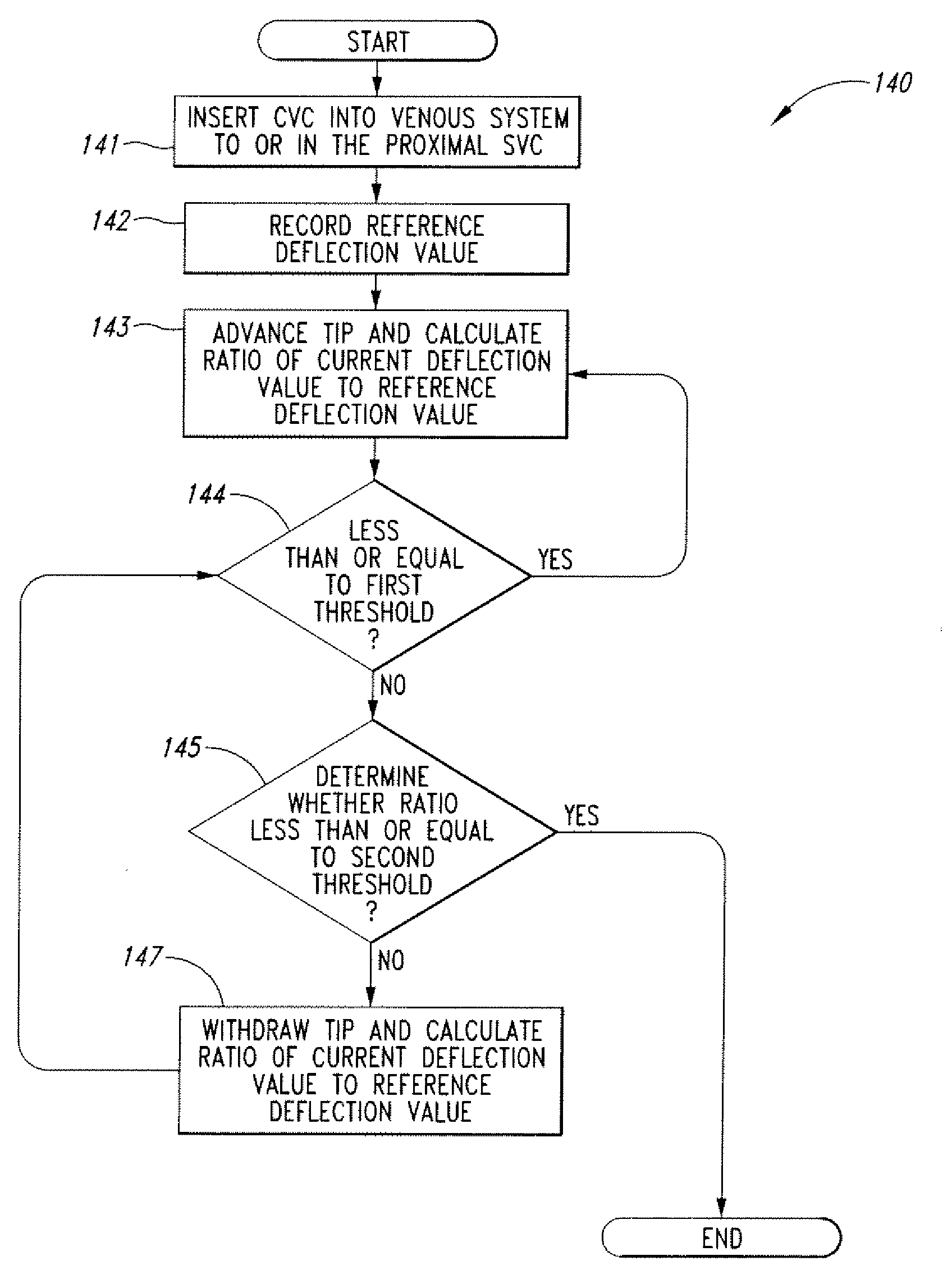
Methods of locating a tip of a central venous catheter (“CVC”) relative to the superior vena cava, sino-atrial node, right atrium, and / or right ventricle using electrocardiogram data. The CVC includes at least one electrode. In particular embodiments, the CVC includes two or three pairs of electrodes. Further, depending upon the embodiment implemented, one or more electrodes may be attached to the patient's skin. The voltage across the electrodes is used to generate a P wave. A reference deflection value is determined for the P wave detected when the tip is within the proximal superior vena cava. Then, the tip is advanced and a new deflection value determined. A ratio of the new and reference deflection values is used to determine a tip location. The ratio may be used to instruct a user to advance or withdraw the tip.
Owner:BARD ACCESS SYST
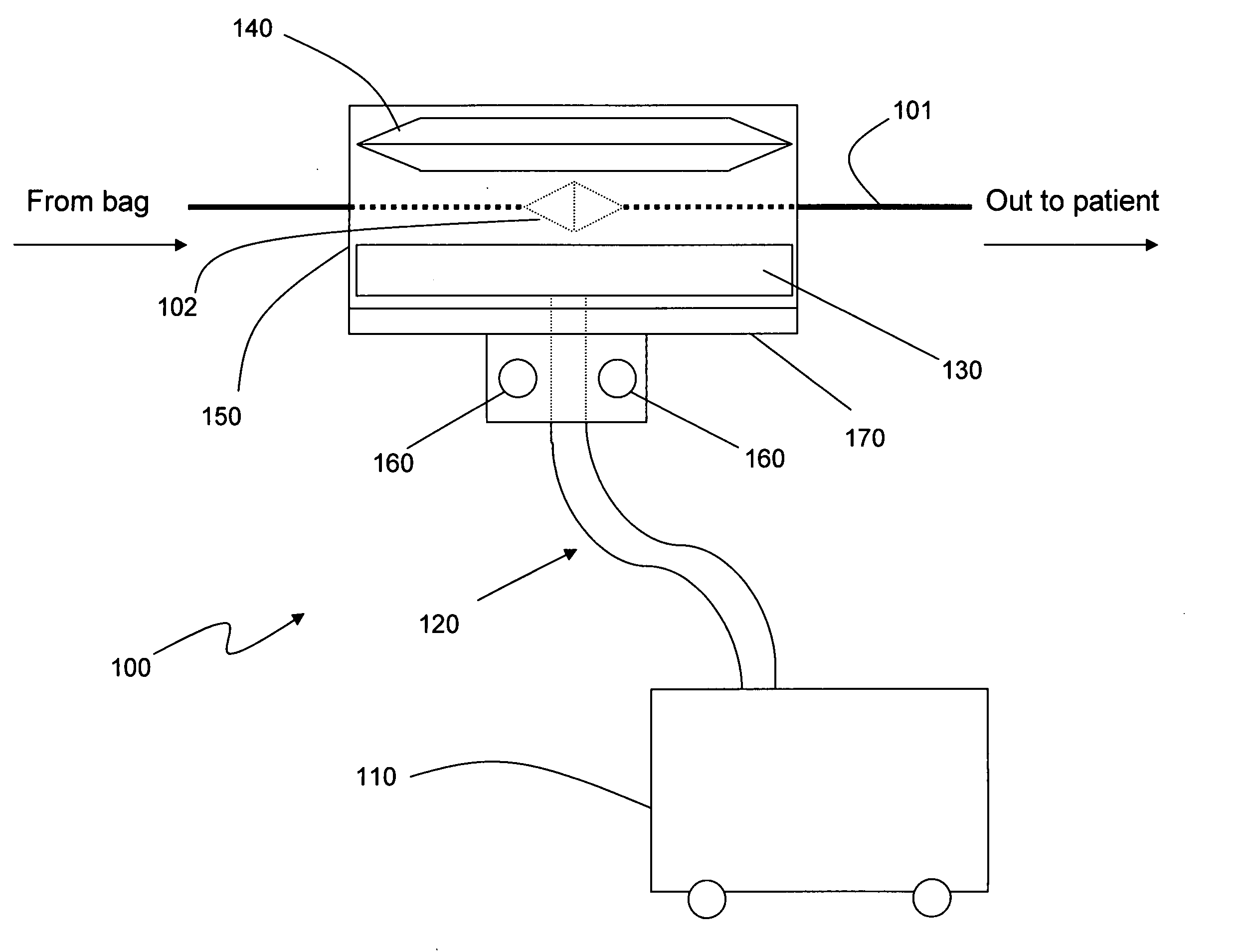
Medicament injection kit and medicament injection method
ActiveUS7297475B2Safely and efficiently in vivoSafely and efficiency in vivoBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsMedication injectionVein
A medicament injection kit, for use in occluding a renal artery and a renal vein in a kidney and injecting a therapeutic medicament into the kidney so as to pressurize the kidney, includes: an artery catheter which includes a first balloon capable of occluding the renal artery; a vein catheter which includes a second balloon capable of occluding the renal vein; a syringe for injecting the therapeutic medicament, the syringe being capable of being connected to at least one of the artery catheter and the vein catheter; and a syringe for pressurizing the inside of the kidney by injecting a liquid, the syringe being capable of being connected to at least one of the artery catheter and the vein catheter.
Owner:TERUMO KK
Method of locating the tip of a central venous catheter
Methods of locating a tip of a central venous catheter (“CVC”) relative to the superior vena cava, sino-atrial node, right atrium, and / or right ventricle using electrocardiogram data. The CVC includes at least one electrode. In particular embodiments, the CVC includes two or three pairs of electrodes. Further, depending upon the embodiment implemented, one or more electrodes may be attached to the patient's skin. The voltage across the electrodes is used to generate a P wave. A reference deflection value is determined for the P wave detected when the tip is within the proximal superior vena cava. Then, the tip is advanced and a new deflection value determined. A ratio of the new and reference deflection values is used to determine a tip location. The ratio may be used to instruct a user to advance or withdraw the tip.
Owner:BARD ACCESS SYST
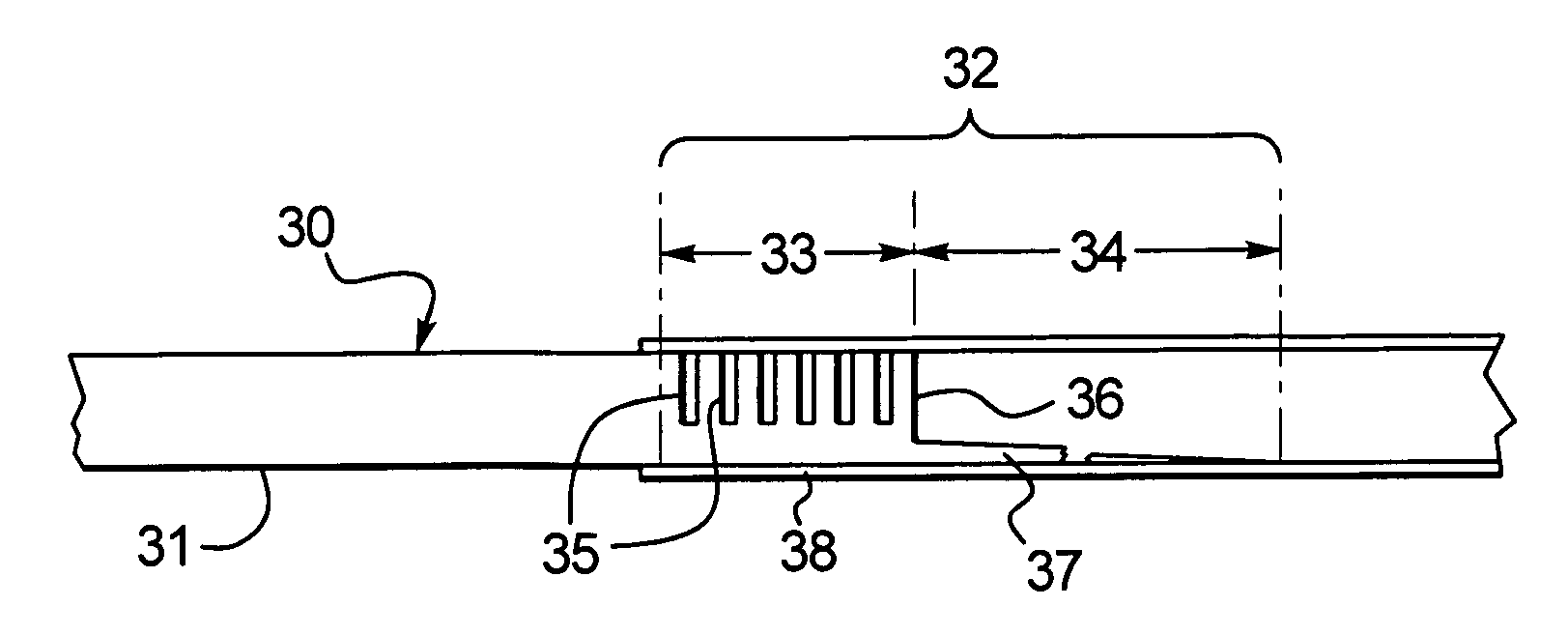
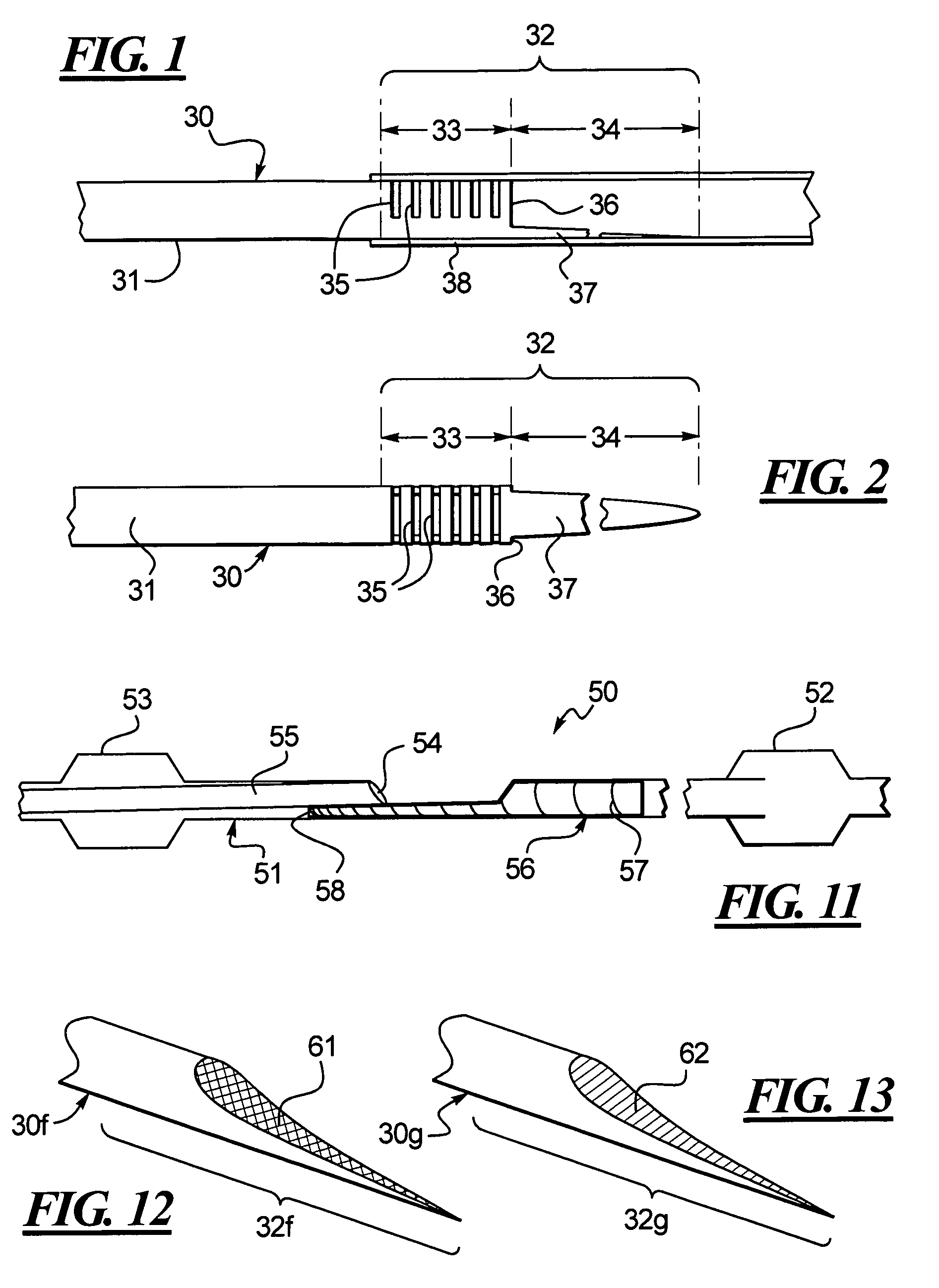
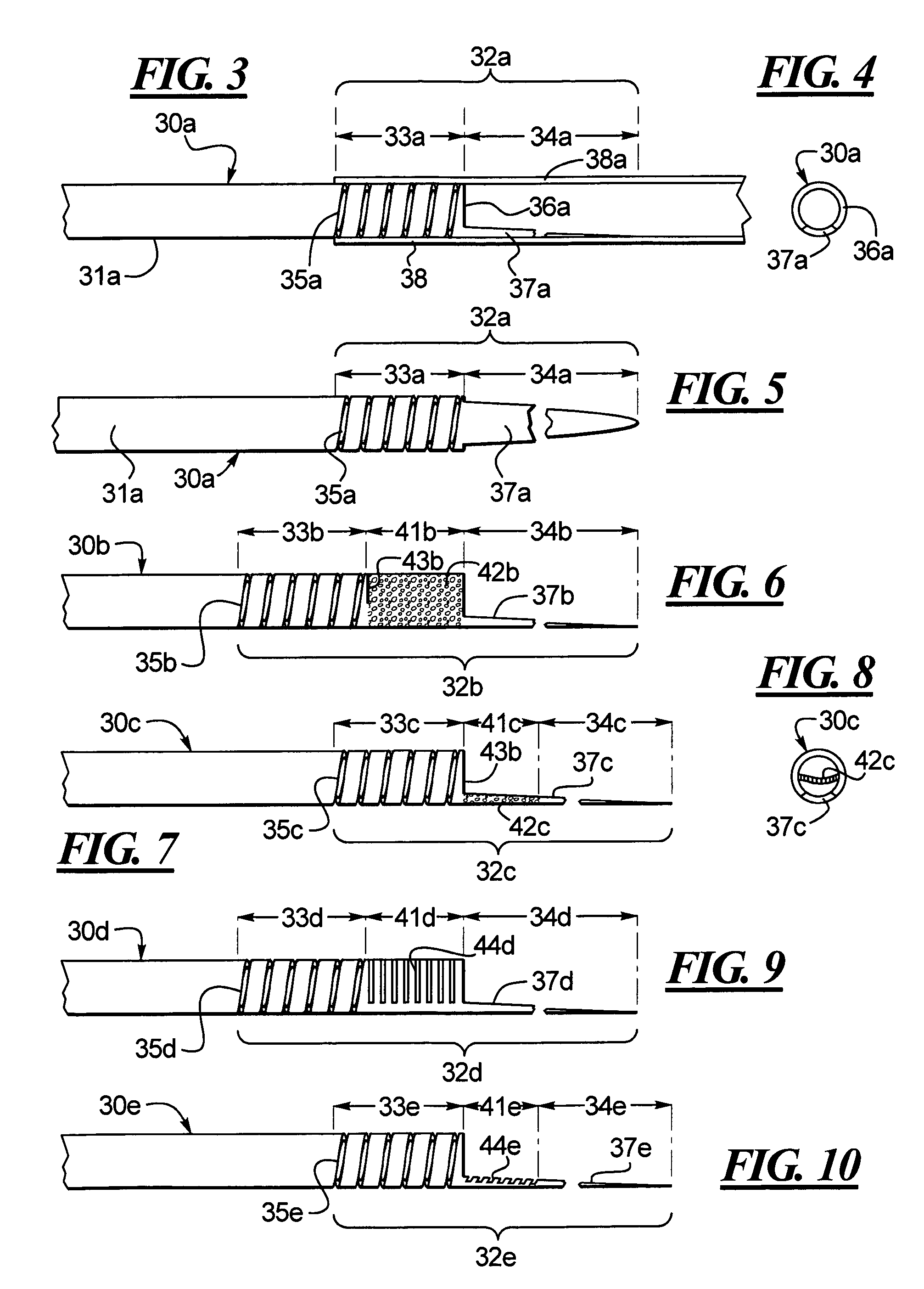
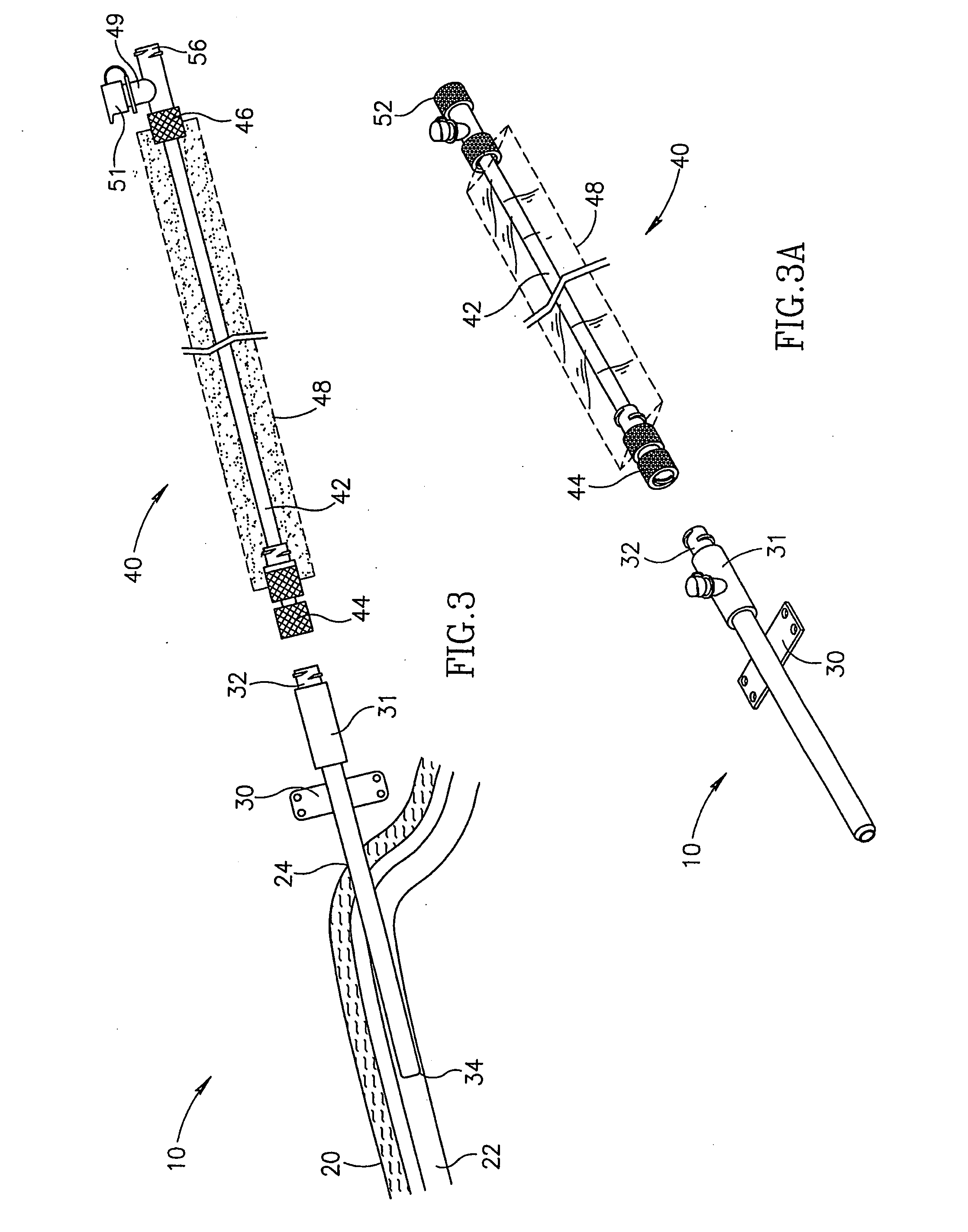
Hypotube with improved strain relief
InactiveUS7294124B2Increase flexibilityEasy transitionStentsGuide needlesIntravenous catheterAnimal sting
A hypotube for an intravenous catheter device is disclosed which includes a tubular shaft having a tubular wall defining a lumen. The shaft includes a main section integrally connected to a distal section. The distal section includes a first section connected to the second section and disposed between the second section and the main section. The second section includes an elongated stinger.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Catheter introducer assembly having safety shielded needle
InactiveUS7303548B2Prevent accidental needle stickGuide needlesInfusion syringesVeinIntravenous catheter
An intravenous catheter introducer assembly having a safety feature to prevent accidental needle sticks. The introducer assembly includes a needle assembly having a groove disposed on its outer surface. The introducer includes a protector made of a hollow member having an open distal end and an inwardly disposed resilient flange or a clip disposed thereon. The protector is coaxially slidably disposed around the needle with the flange abutting the outer surface of the needle and adapted to engage the groove when a catheter assembly is removed from the needle.
Owner:SMITHS MEDICAL ASD INC
Method of locating the tip of a central venous catheter
The invention includes a method of locating a tip of a central venous catheter (“CVC”) having a distal and proximal pair of electrodes disposed within the superior vena cava, right atrium, and / or right ventricle. The method includes obtaining a distal and proximal electrical signal from the distal and proximal pair and using those signals to generate a distal and proximal P wave, respectively. A deflection value is determined for each of the P waves. A ratio of the deflection values is then used to determine a location of the tip of the CVC. Optionally, the CVC may include a reference pair of electrodes disposed within the superior vena cava from which a reference deflection value may be obtained. A ratio of one of the other deflection values to the reference deflection value may be used to determine the location of the tip of the CVC.
Owner:BARD ACCESS SYST
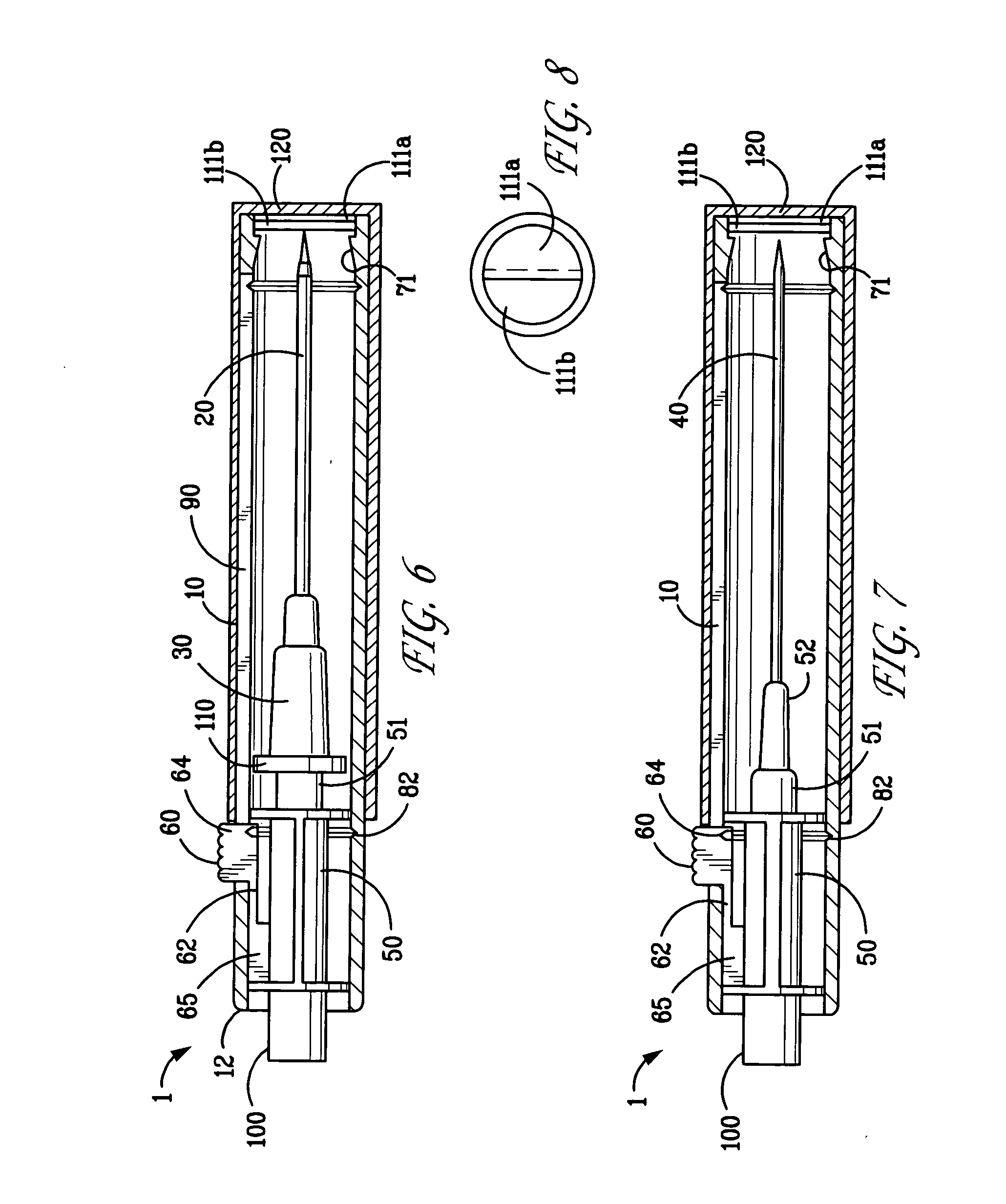
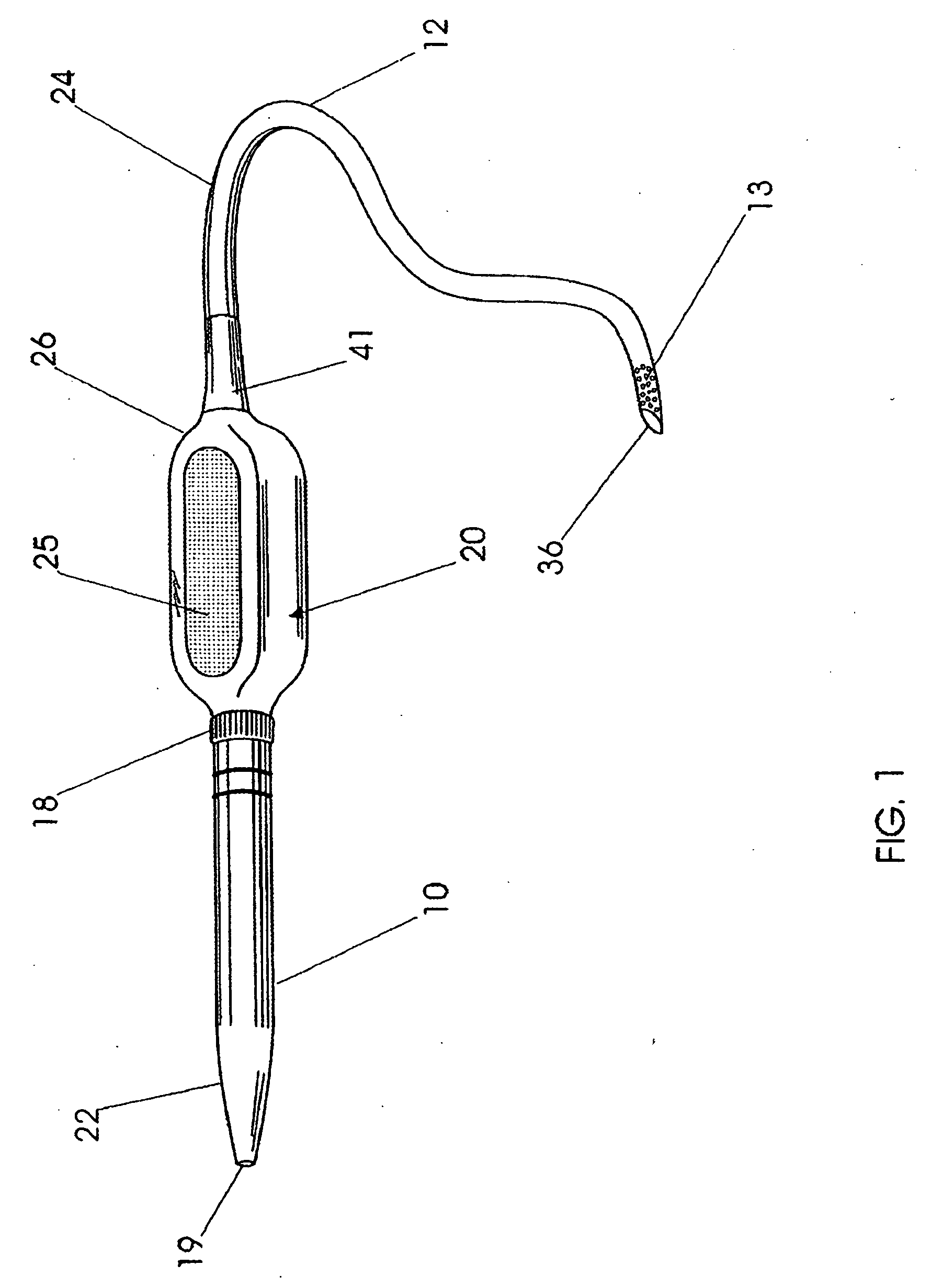
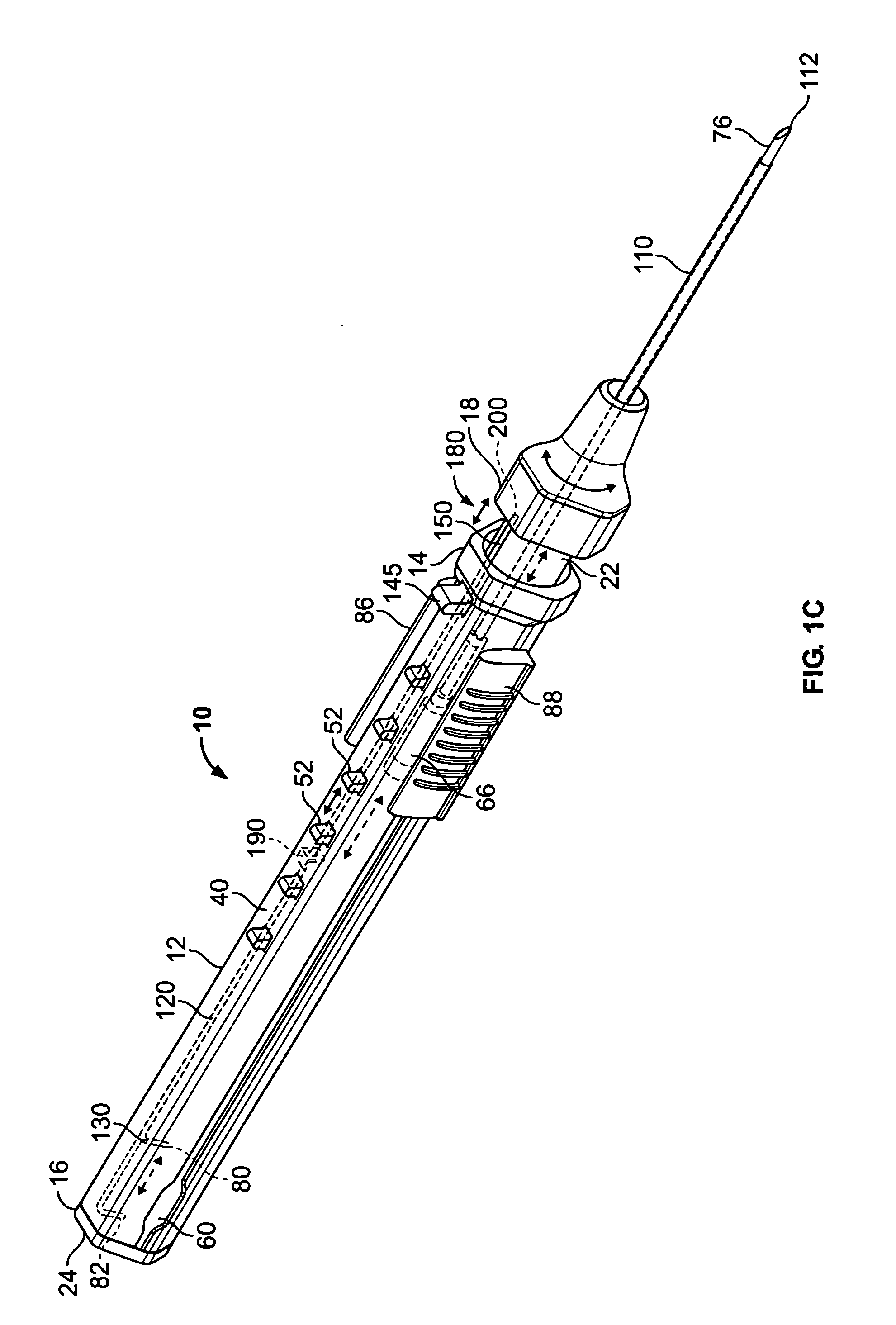
Intravenous catheter device
A catheter device is disclosed which the hypodermic needle used for insertion is retracted into a protective sheath and left in place during use. An IV fluid flow path is provided that is blocked by the hypodermic needle prior to retraction but is opened by the retraction of the needle from the catheter. The insertion hypodermic needle is not discarded separately but only after the use of the whole catheter device to inject fluids.
Owner:SMITH P ROWAN
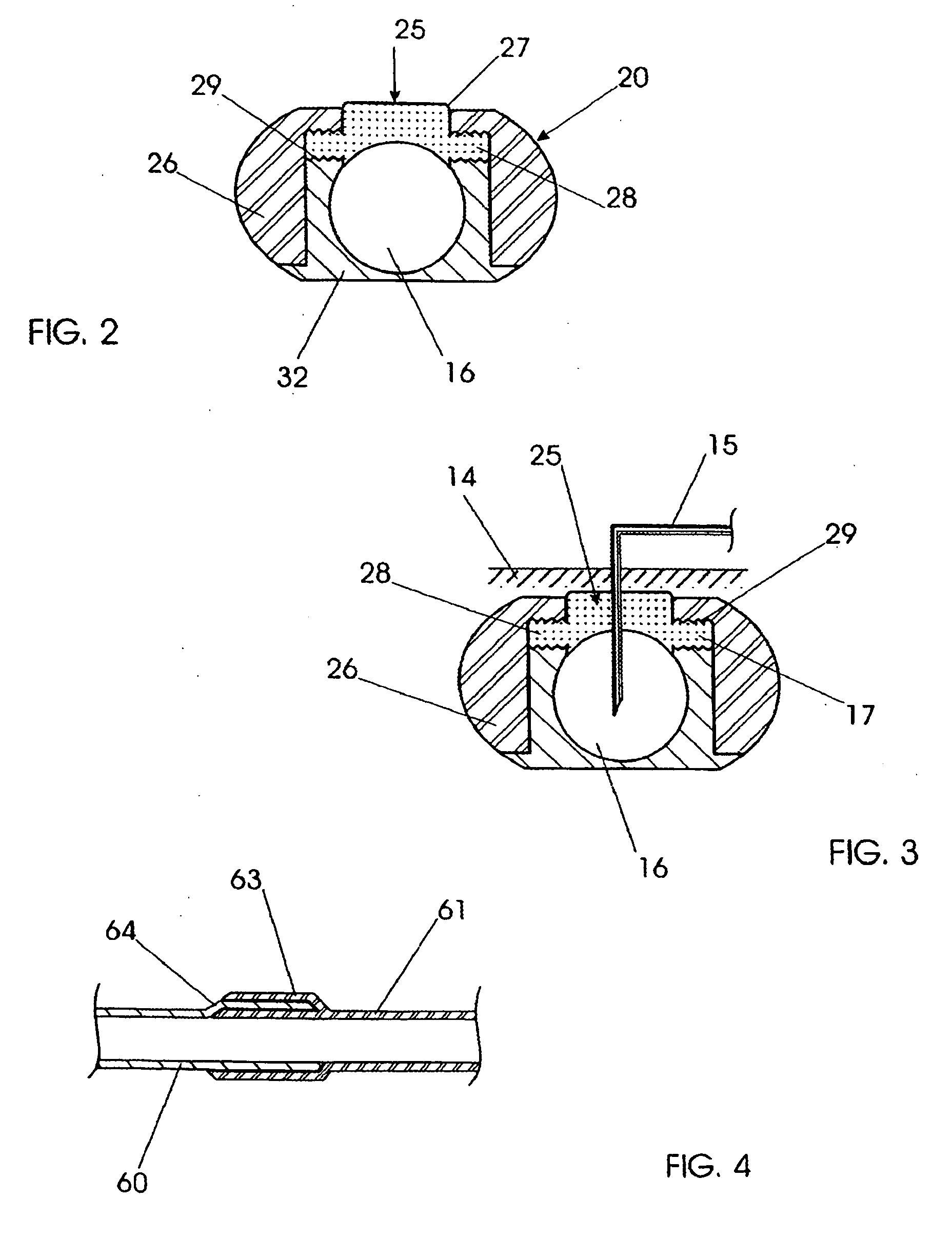
Retractable I-V catheter placement device
InactiveUS6942652B1Improve securityMinimize the possibilityGuide needlesInfusion syringesVeinIntravenous catheter
An intravenous catheter placement device having a hollow body and a nose on one end of the hollow body. A needle hub fits within the nose and contains a needle embedded therein. A catheter is free to slide along the needle and substantially covers the shaft of the needle. Winged beams on the needle hub include catches and release tabs that cooperate with slots in the nose to retain the needle hub in the nose. A magnified transparent verification cavity in the needle hub provides for viewing blood flash in the cavity to verify that the intravenous catheter is inserted into the correct location. An energy storage device in contact with the needle hub releasably retains the needle hub to prevent premature projection of the needle hub into the hollow body. Upon insertion of the intravenous catheter and introducer needle into a patient, depressing the release tabs triggers the needle hub and blunts the needle within the catheter and projects the needle hub and embedded needle into the hollow body.
Owner:MEDSAFE TECH
Intravenous catheter and insertion device
to protect against accidental needle prick a catheter and insertion device are provided wherein the needle is retractable within the device after insertion of the catheter. The device comprises a hollow barrel or tube of semi-rigid plastic material into which the needle can be retracted after use. The barrel includes a resealable closure at the insertion that opens to allow passage of the needle and catheter and closes to reseal the barrel when the needle is retracted. A cap is provided that covers the barrel to further seal the device after use.
Owner:HAINING MICHAEL L
Method of locating the tip of a central venous catheter
Owner:BARD ACCESS SYST
Intravenous Catheter Introducer with Needle Retraction Controlled by Catheter Hub Seal
A passive intravenous (“IV”) catheter introducer having a spring-biased needle retraction system that is triggered when the needle is manually withdrawn through a catheter hub seal. The catheter hub seal constricts to block the rearward flow of bodily fluid and wipe potentially infectious fluids off the outer surface of the needle as the needle is manually withdrawn through the catheter sheath and seal following insertion of the catheter into a patient's vein. No additional steps are needed to activate the needle retraction mechanism beyond manual removal of the needle from the catheter hub seal.
Owner:RETRACTABLE TECH INC
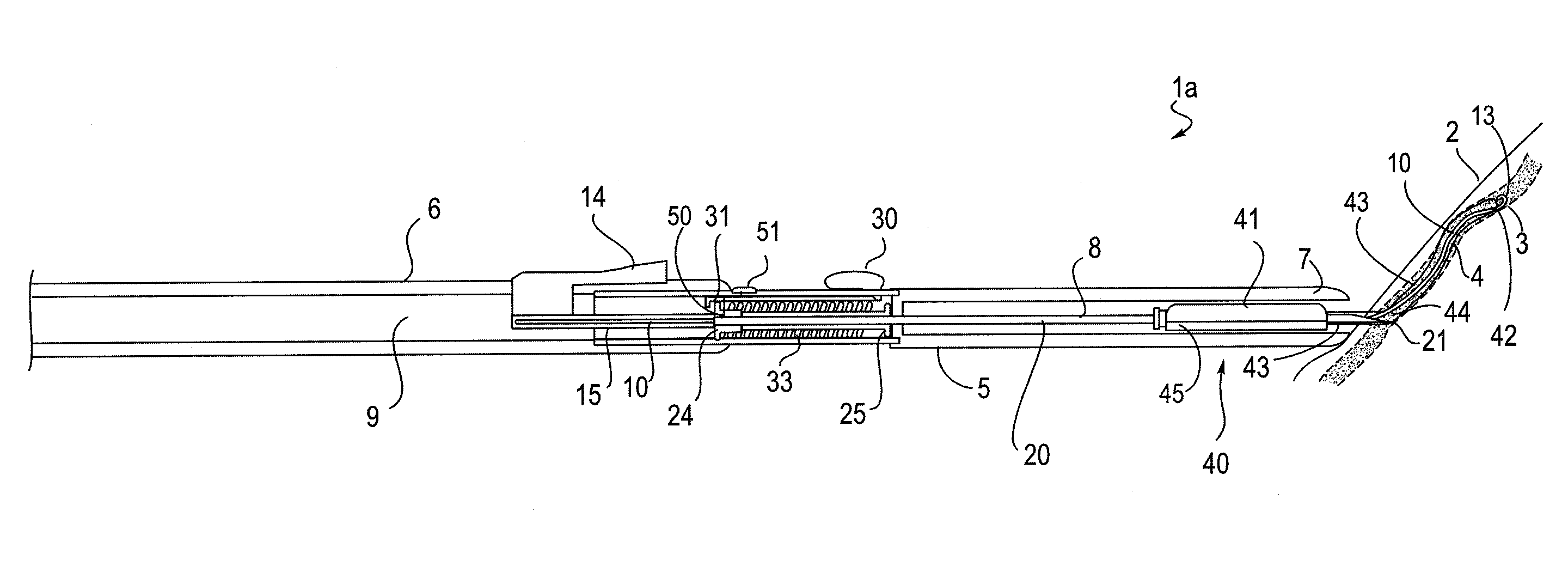
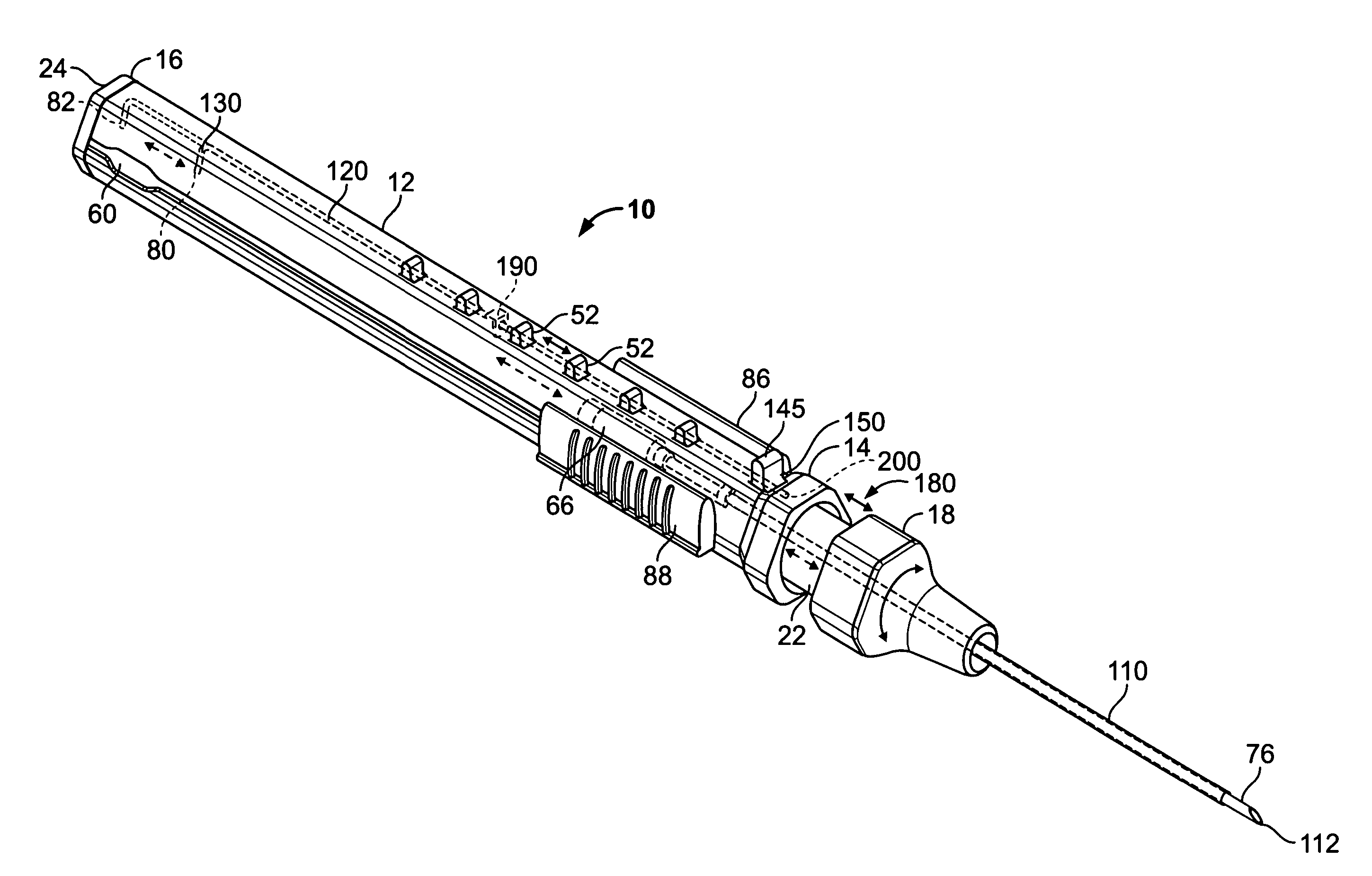
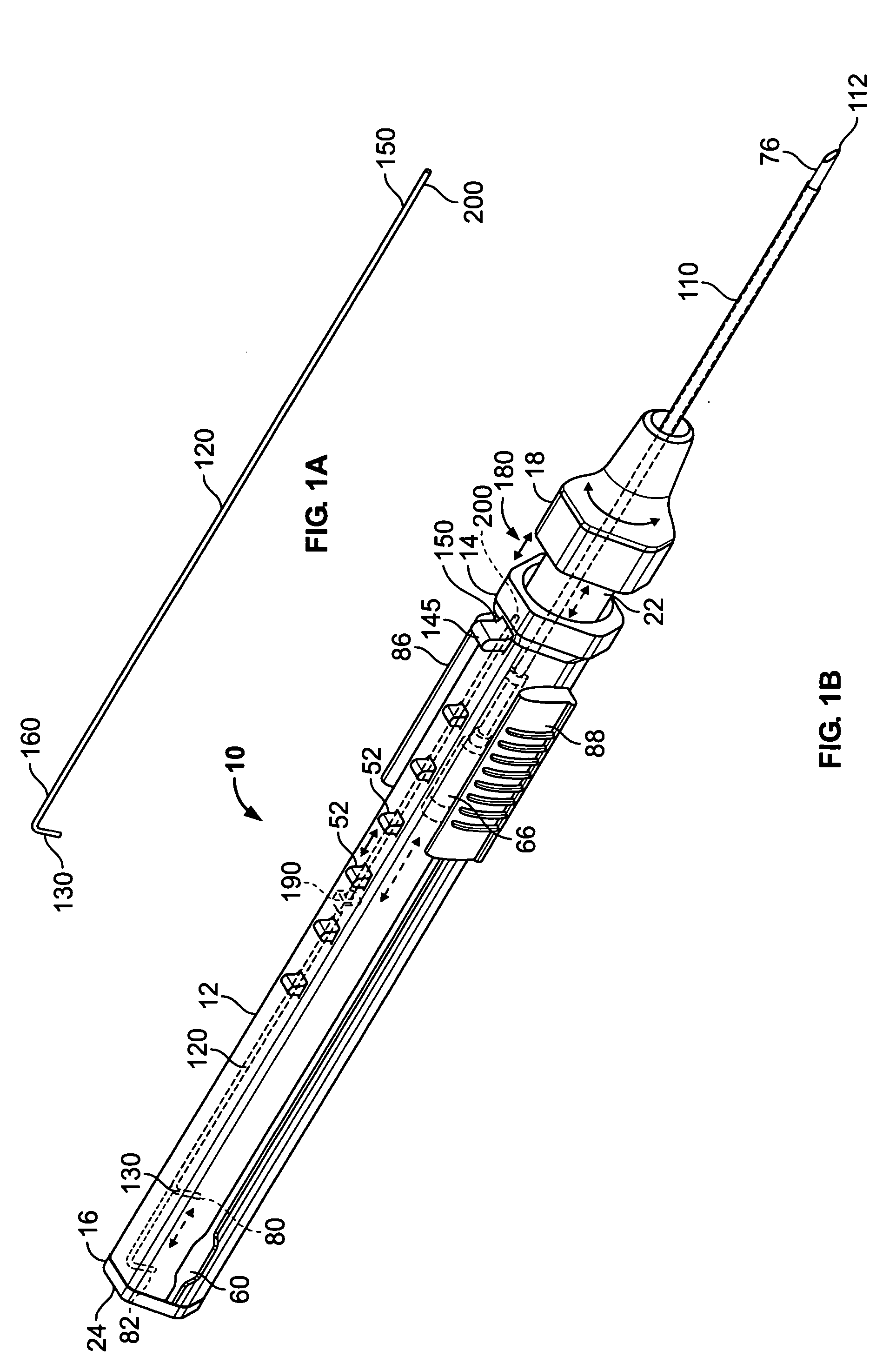
Intravenous catheter insertion and blood sample devices and method of use
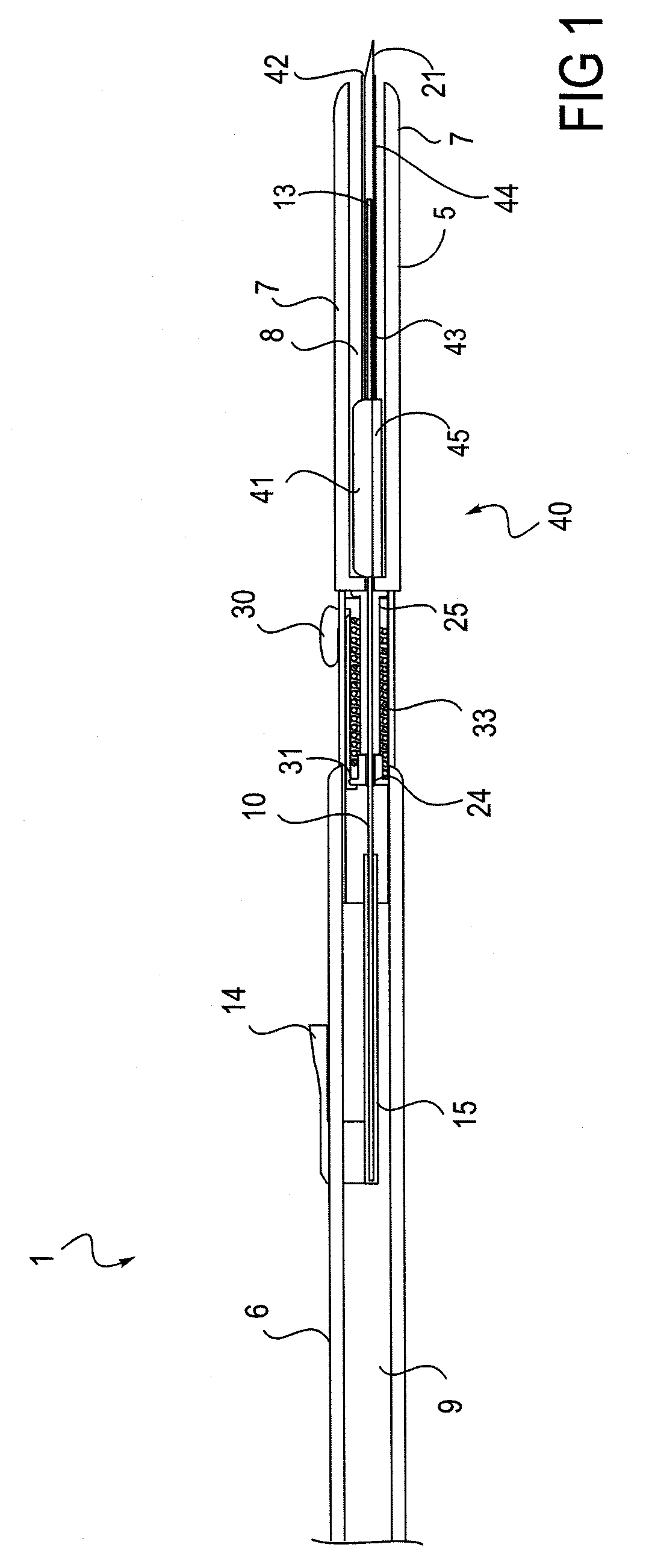
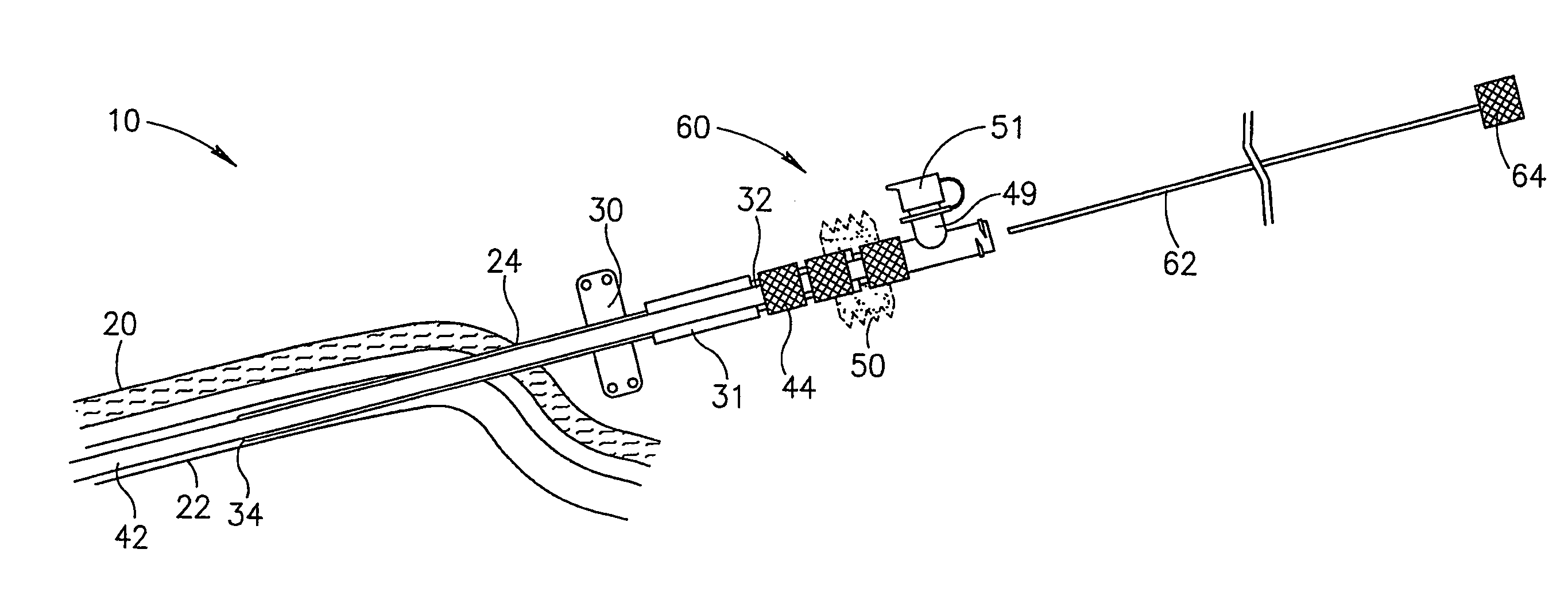
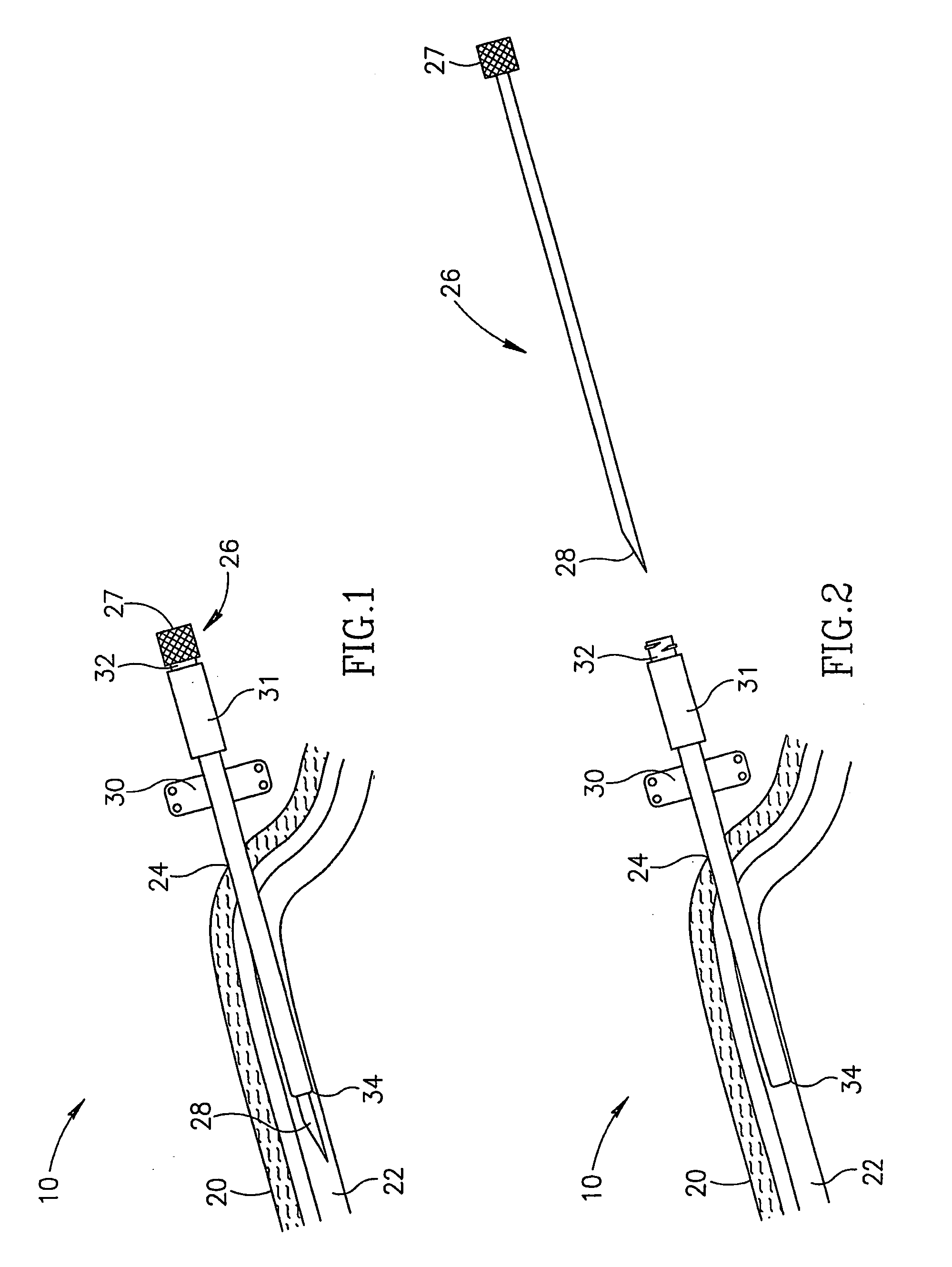
Devices and methods for guidewire assisted placement of catheters into blood vessels are described. Some of the devices and methods relate to automated or partially automated or assisted insertion and placement of an intravenous catheter into a vein or artery of a patient. Other of the devices are blood draw devices and methods for insertion and placement of an intravenous device into a vein or artery of a patient or to withdraw a blood sample from the patient. The devices also provide for guide wire tip inspection after use.
Owner:VASCULAR PATHWAYS
Intravenous catheter assembly
A self-contained sterile catheter apparatus for use with an intravenous cannula element. The cannula element has first and second ends and a bore formed therebetween, and is configured for transcutaneous positioning such that the first end is adapted to protrude from a limb of a subject and the second end is brought into communication with an interior of a body organ of a subject. The self-contained sterile catheter apparatus includes first and second ends and a flexible catheter tube therebetween, the catheter tube having a predetermined length and a diameter adapted for slidable insertion through the bore of the intravenous cannula element into the subject, and an integral sterile environment containment element thereby to allow insertion of the catheter tube through the cannula element into the subject in a generally non-sterile environment.
Owner:AMISAR SHAI +2
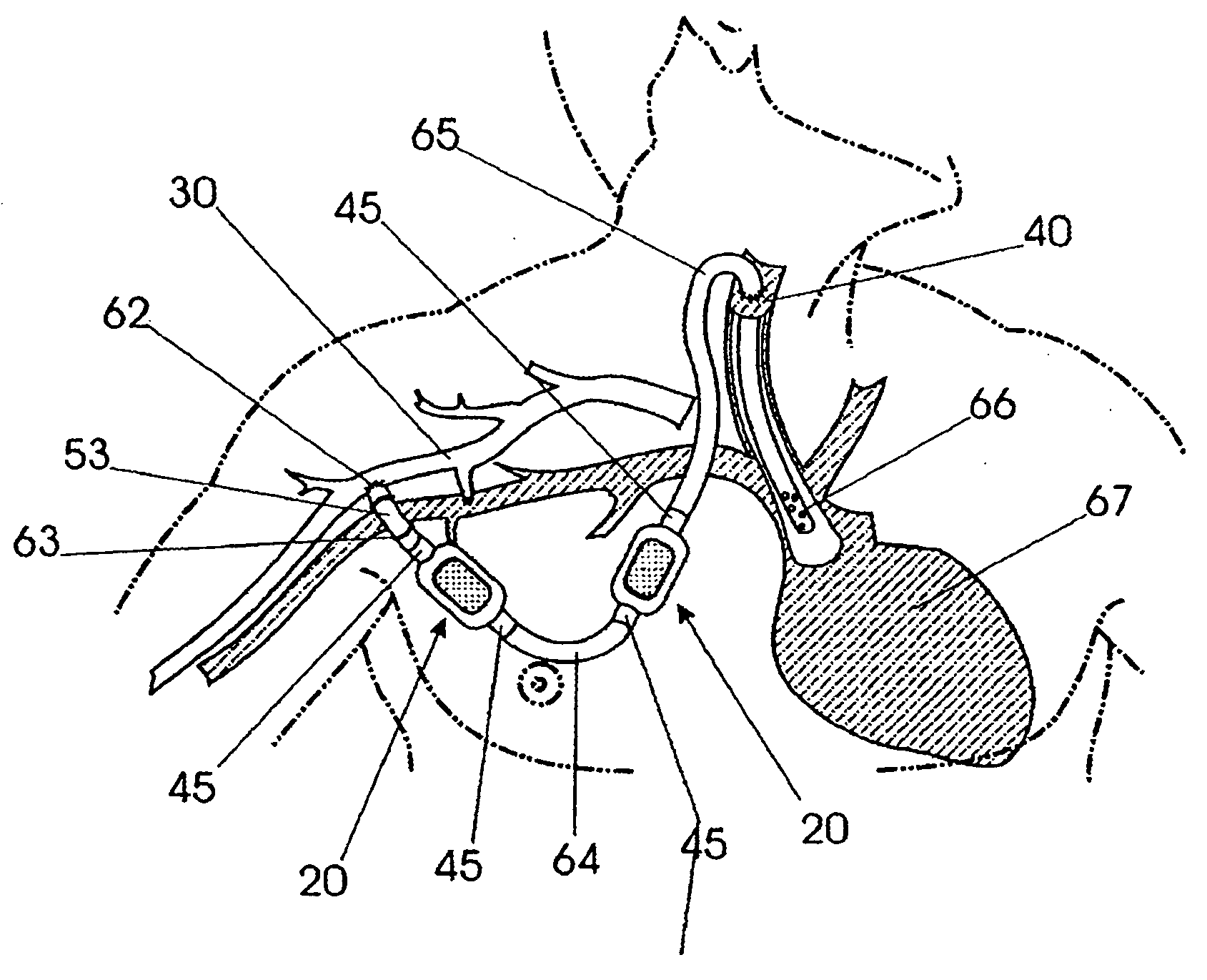
Squitieri hemodialysis and vascular access systems
InactiveUS20070123811A1Increased longevityImprove performanceOther blood circulation devicesDialysis systemsVenous accessHaemodialysis machine
A hemodialysis and vascular access system comprises a subcutaneous composite PTFE silastic arteriovenous fistula having an indwelling silastic venous end which is inserted percutaneously into a vein and a PTFE arterial end which is anastomosed to an artery. Access to a blood stream within the system is gained by direct puncture of needle(s) into a needle receiving site having a tubular passage within a metal or plastic frame and a silicone upper surface through which needle(s) are inserted. In an alternate embodiment of the invention, percutaneous access to a blood stream may be gained by placing needles directly into the system (i.e. into the PTFE arterial end). The invention also proposes an additional embodiment having an arterialized indwelling venous catheter where blood flows from an artery through a tube and a port into an arterial reservoir and is returned to a vein via a port and a venous outlet tube distinct and distant from the area where the blood from the artery enters the arterial reservoir. The site where blood is returned to the vein is not directly fixed to the venous wall but is free floating within the vein. This system provides a hemodialysis and venous access graft which has superior longevity and performance, is easier to implant and is much more user friendly.
Owner:HEMOSPHERE
Intravenous catheter device
A catheter device is disclosed which the hypodermic needle used for insertion is retracted into a protective sheath and left in place during use. An IV fluid flow path is provided that is blocked by the hypodermic needle prior to retraction but is opened by the retraction of the needle from the catheter. The insertion hypodermic needle is not discarded separately but only after the use of the whole catheter device to inject fluids.
Owner:SMITH P ROWAN
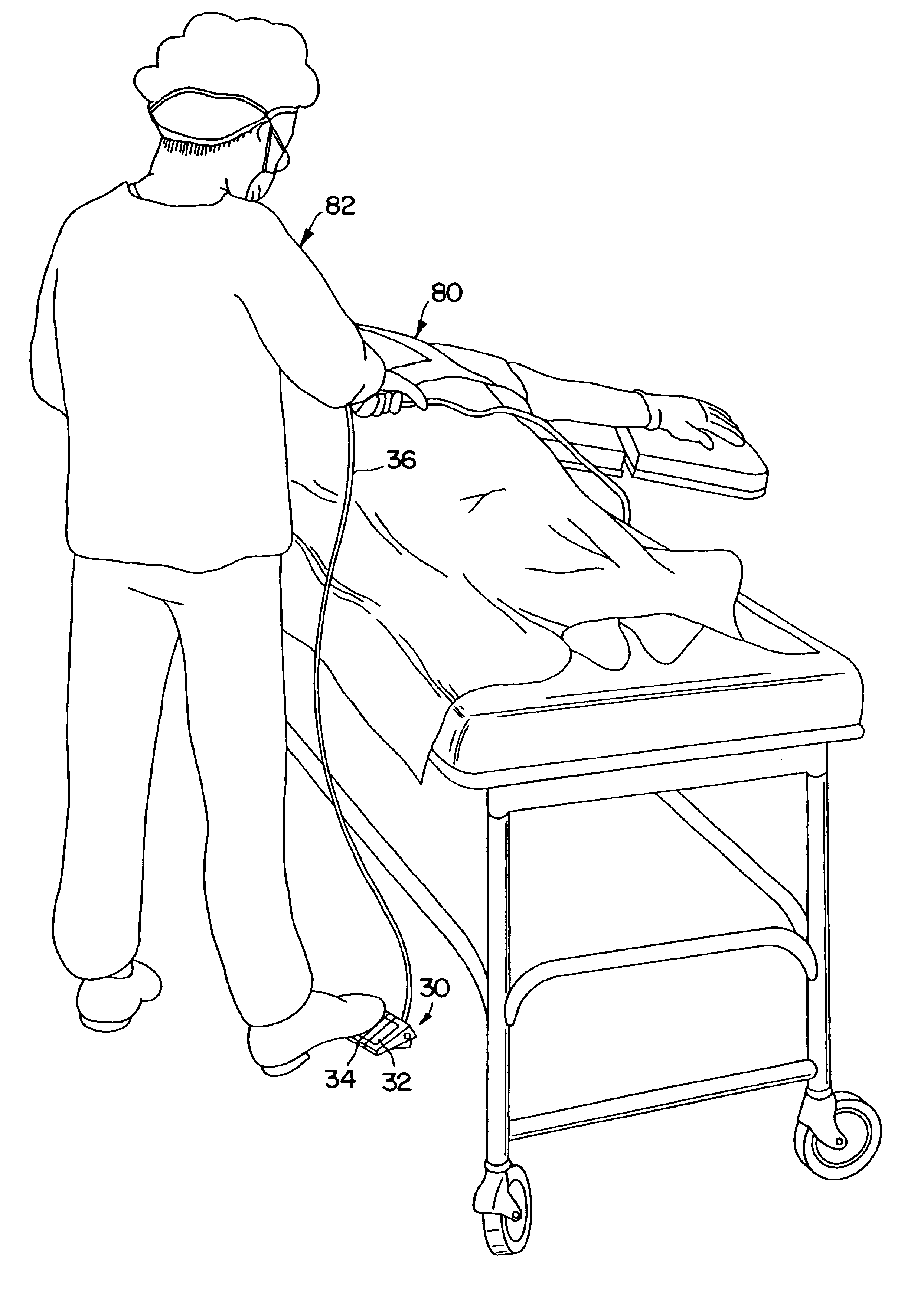
Intravenous catheter connection point disinfection
InactiveUS20090257910A1Prevent leakageMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesFiberLight delivery
A system for disinfecting an intravenous catheter and / or other fluidic tubing includes attaching a device around the catheter and delivering a high dose of ultraviolet or other type of radiation to the catheter connection point and adjacent tubing. The device may include a UV radiation source connected to a catheter attachment assembly via fiber optic cable, allowing transmission of UV radiation from the source to an internal reflector unit. The UV source may be built into the catheter connection assembly. The device may be a handheld device that fits over a catheter connection point, with single or multiple integrated UV sources to deliver 360 degree radiation around the catheter, with mirrors to increase light delivery. The method involves controlled exterior irradiation of a catheter connection point to disinfect the lumen via transmitted light through the catheter wall. Commercially available catheters or those specially designed for passage of radiation may be used.
Owner:SEGAL JEREMY P
Passive needle-stick protector
The present invention relates to a needle-stick protector for an intravenous catheter having a body, a needle hub, a needle, and means for ensuring that the needle-stick protector is not removed from a catheter hub before the needle is fully retracted and locked in the body of the needle-stick protector.
Owner:SPAN-AMERICA MEDICAL SYSTEMS
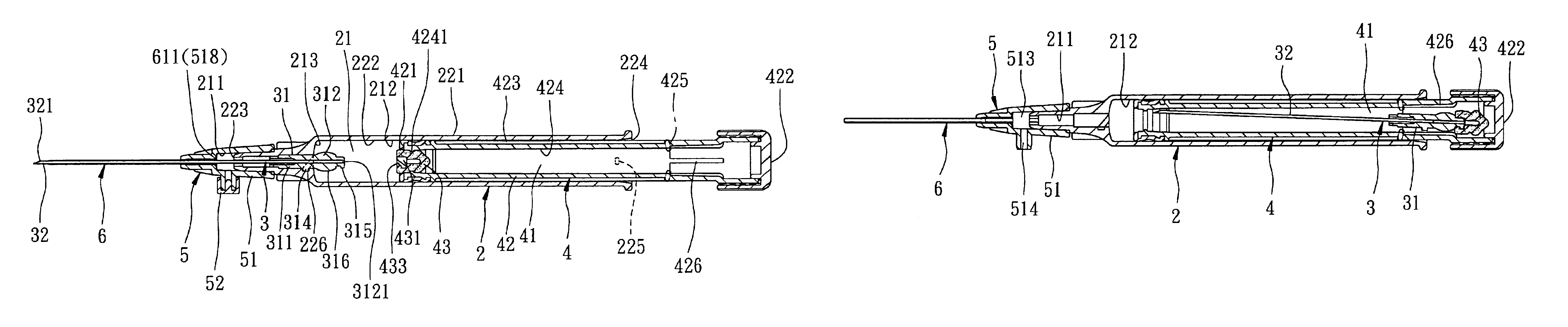
Intravenous catheter inserting device
An intravenous catheter inserting device includes a catheter hub engaging an open forward end of a barrel and having a duct that communicates with a passage of the barrel. A tubular catheter is disposed to communicate with the duct, and permits a needle cannula to pass therethrough. A plunger is received in the passage and extends rearwardly of the barrel so as to be manually operable. The plunger has a cavity containing fluid at a reduced pressure, and is coupled with the needle cannula within the passage such that the needle cannula can be retracted into the cavity due to a pressure difference between the ambient air and the reduced pressure.
Owner:SHUE MING JENG +2
Device for fixing a catheter to the body of a patient
A device for fixing a catheter, such as a peripheral veinous catheter, a central veinous catheter or a central arterial catheter, to the body of a patient. The device includes a housing, which can be closed by a lid, and a base coupled to the housing, surrounding the housing and enabling the housing to be fixed to the skin of the patient. The housing includes a first chamber through which the outer part of the catheter, which is placed in the vein, passes and a second chamber for accommodating and maintaining the catheter.
Owner:NAVARRO +1
Needle safety device for an intravenous catheter apparatus and method of use
ActiveUS7112191B2Prevent movementCooperate effectivelyGuide needlesInfusion syringesVeinIntravenous catheter
A needle safety device for an intravenous catheter apparatus that includes a base capable of receiving a needle into opposing jaws attached to the base and capable of being influenced by the needle. The jaws move between an expanded position which interact with an obstruction within a wing housing of the intravenous catheter apparatus. The jaws permit relative movement of the needle with the base when expanded, close around a needle tip as it passes the jaws, and prevent relative movement of the needle with the base when the jaws are collapsed. The needle of the intravenous catheter apparatus may then be safely disposed with the needle tip within the needle safety device.
Owner:RISHI BAID
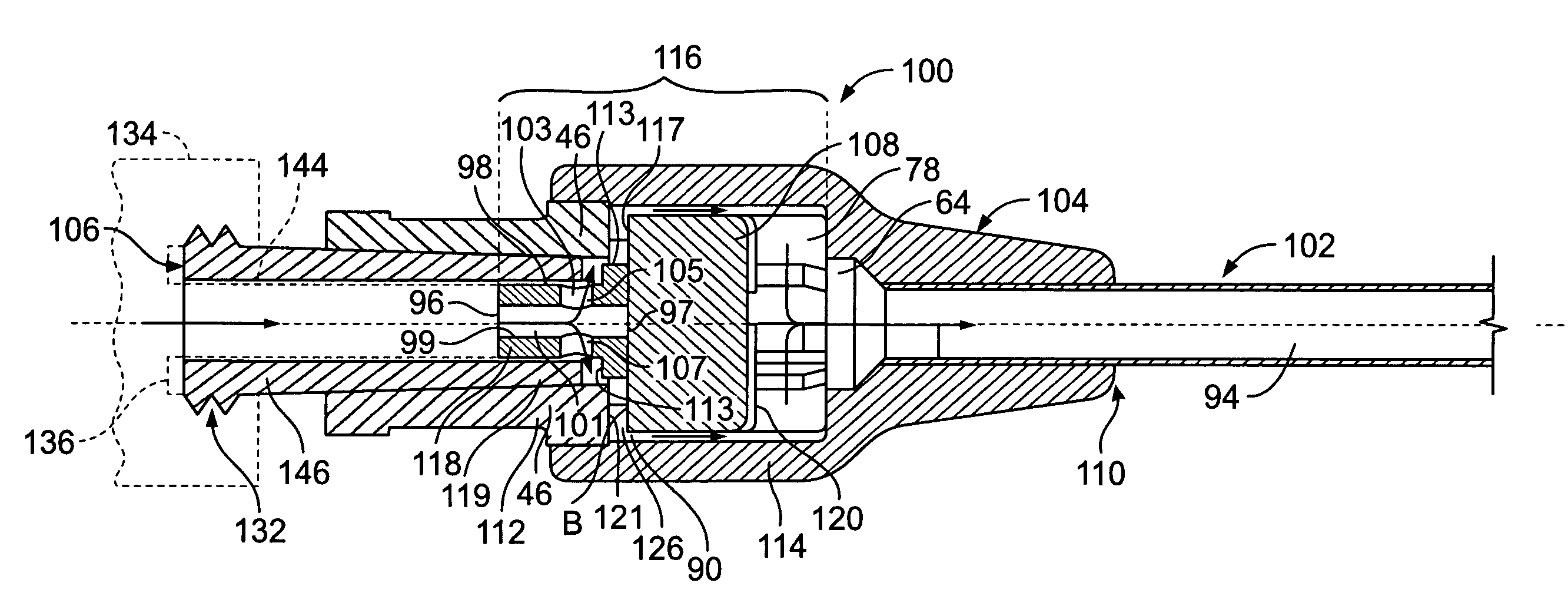
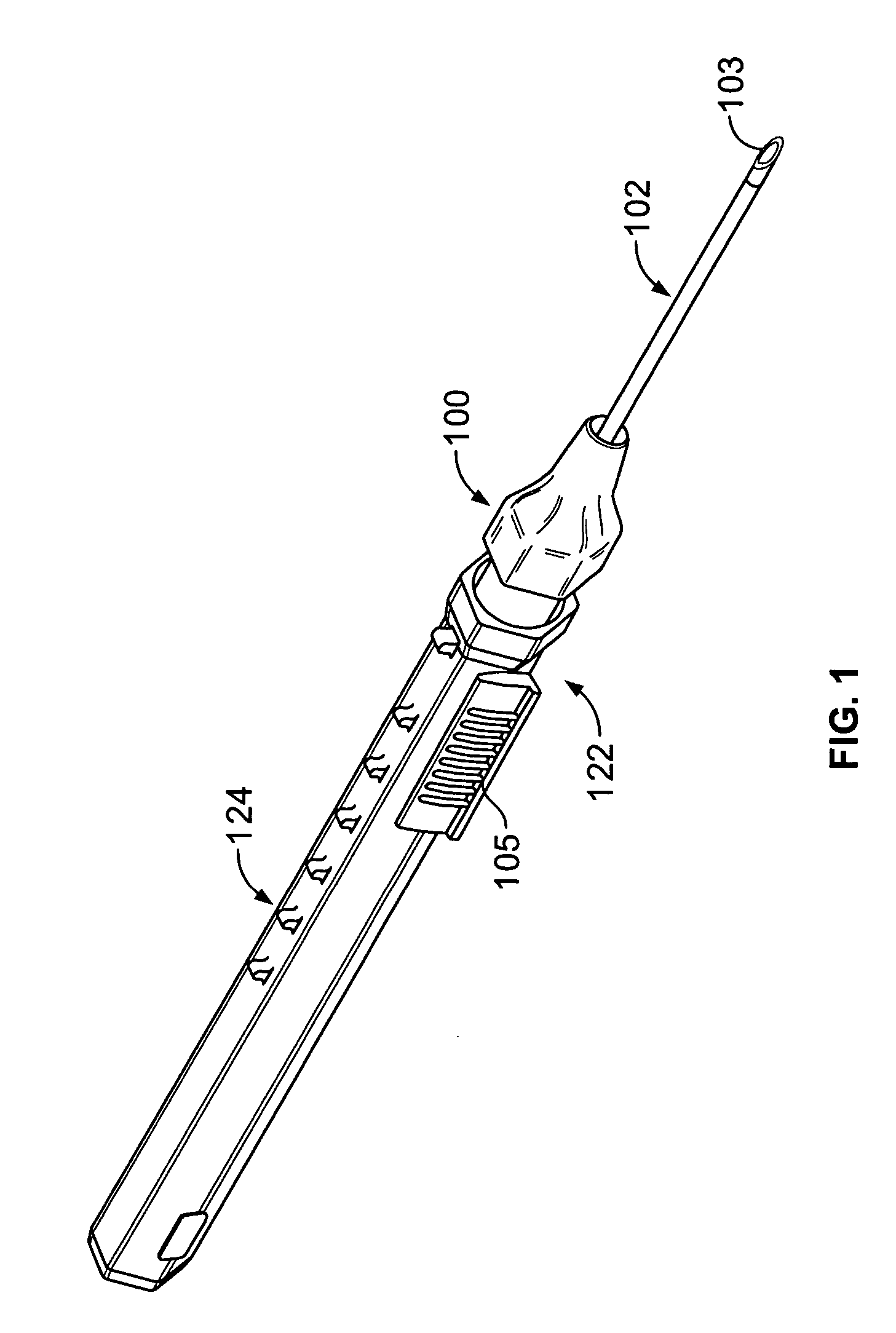
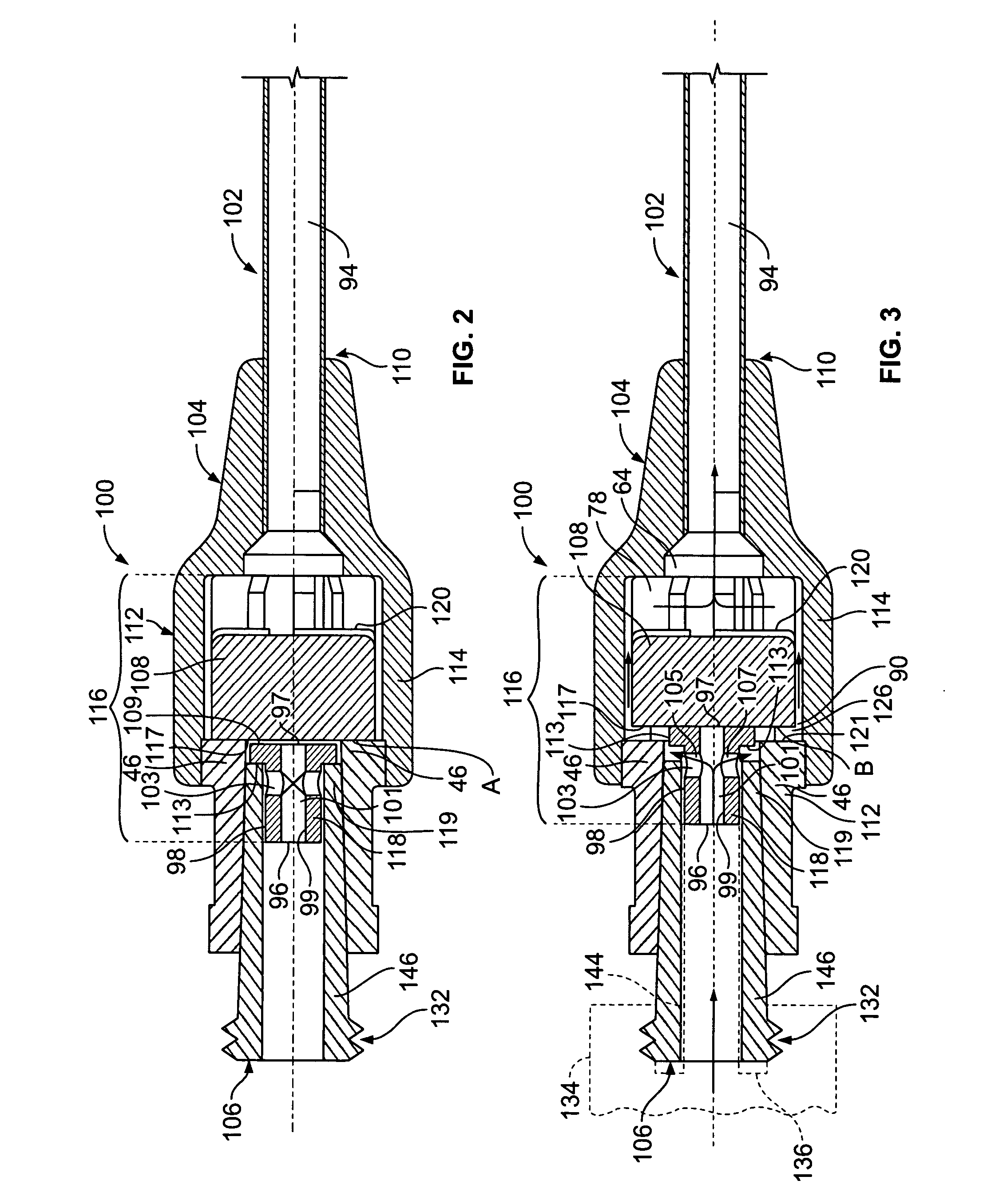
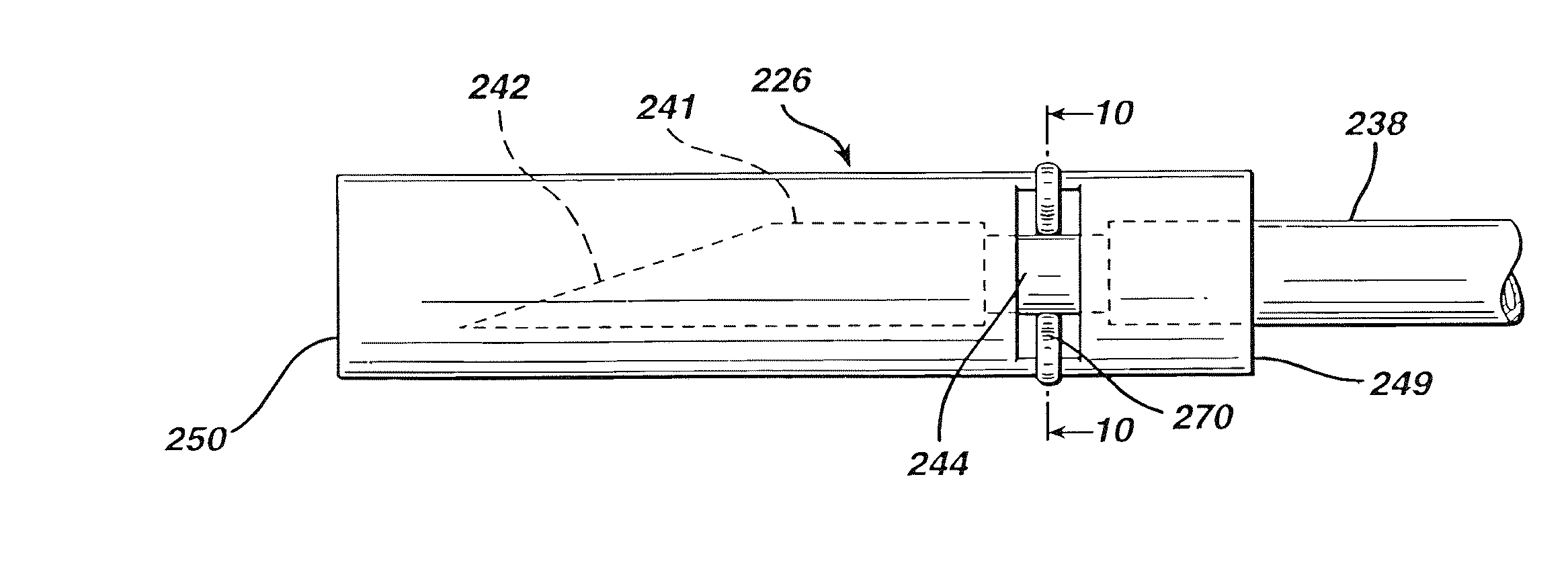
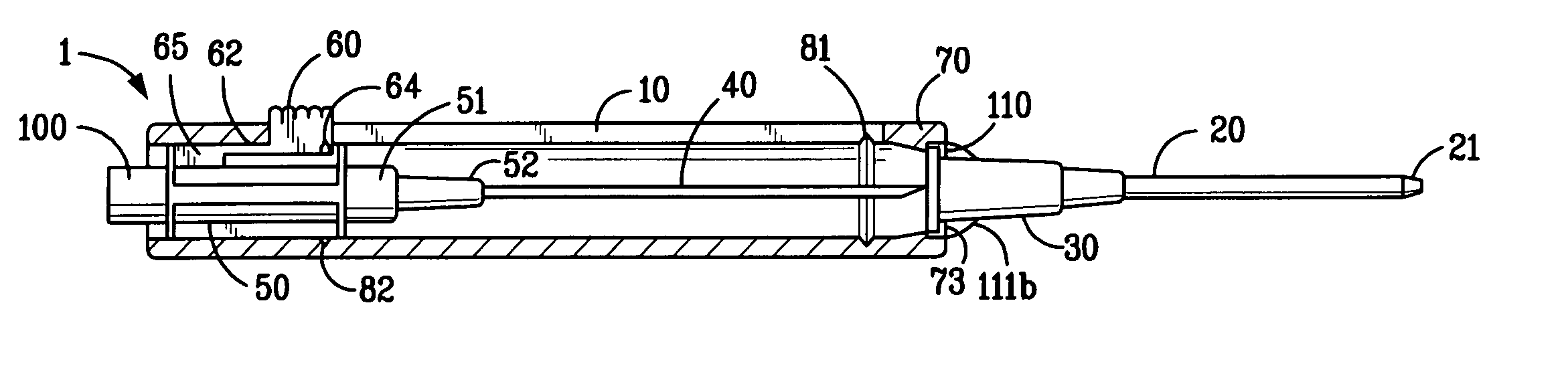
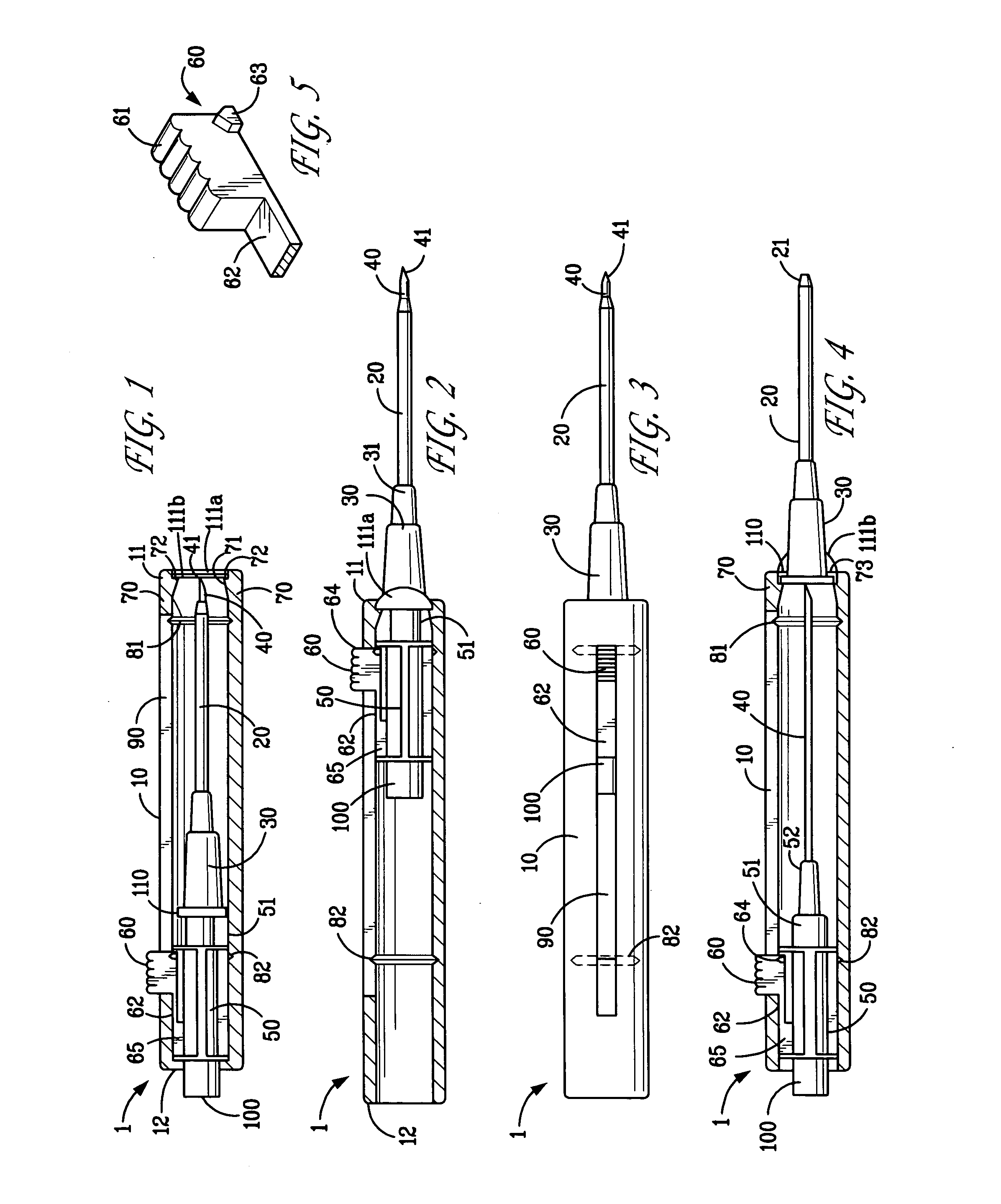
Extension housing a probe or intravenous catheter
PendingUS20190021640A1Reducing dislodgementReduce disturbanceInfusion syringesCatheterVeinVascular Access Devices
A vascular access device may include a housing, which may include a proximal end, a distal end, and a slot. The distal end of the housing may be configured to be coupled to a catheter assembly. The vascular access device may also include an instrument disposed within the housing. The instrument may include a catheter or a probe. The instrument may include a proximal end and a distal tip. The proximal end of the instrument may extend through the slot and may be configured to move along the slot to move the instrument from a proximal position to a distal position. In response to movement of the proximal end of the instrument from the proximal position to the distal position, the catheter may be advanced beyond the distal end of the housing into the catheter assembly and / or vasculature of a patient.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
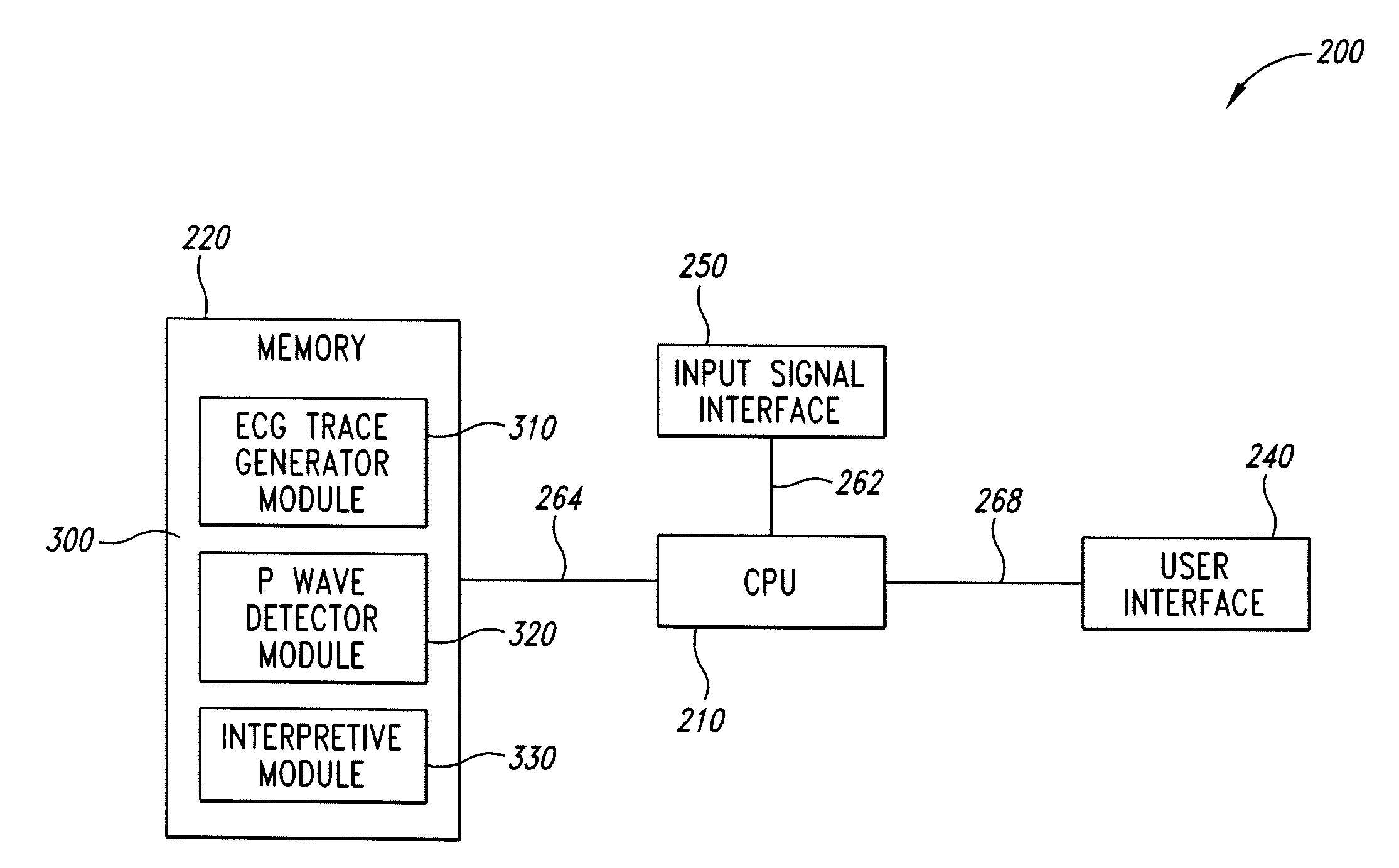
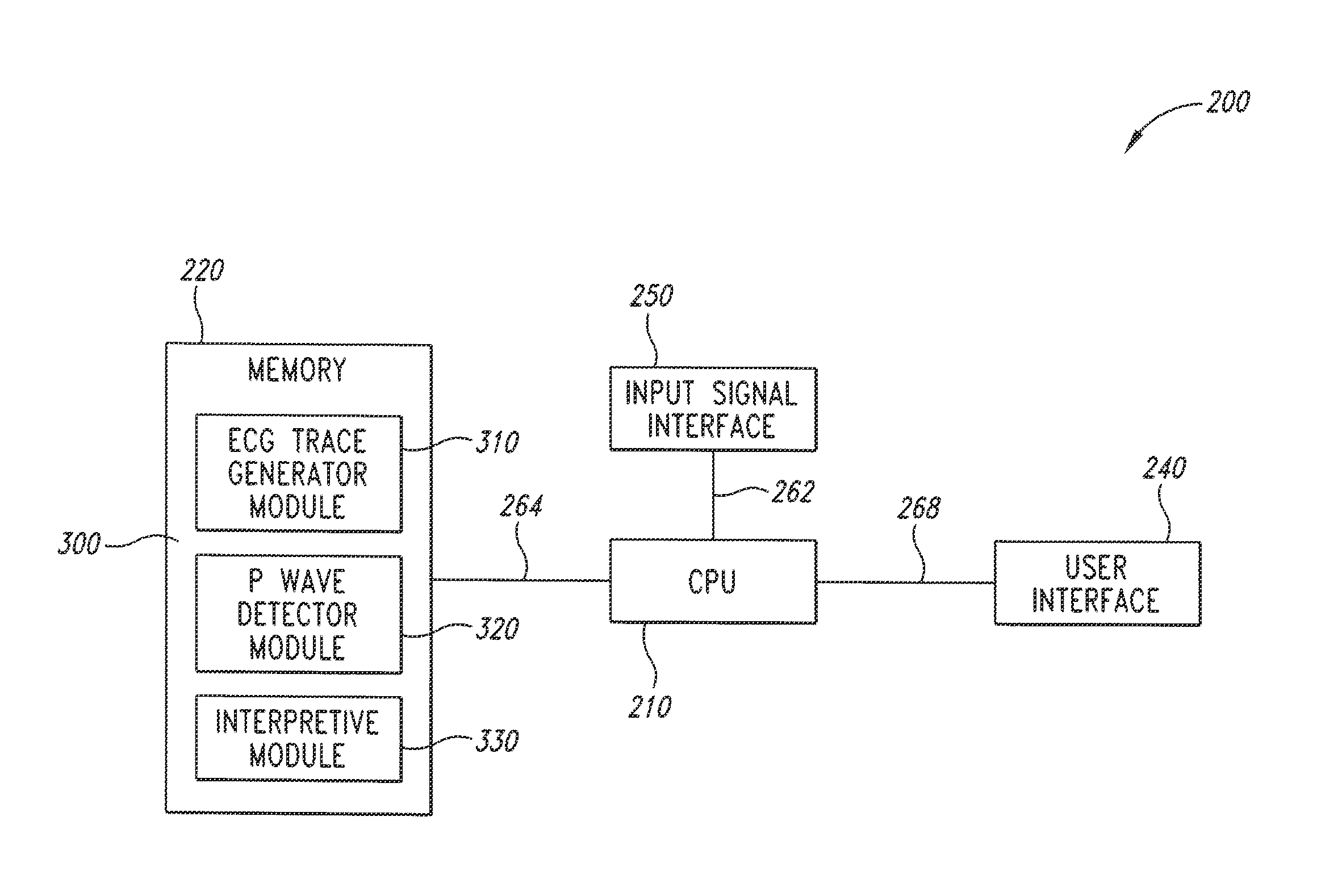
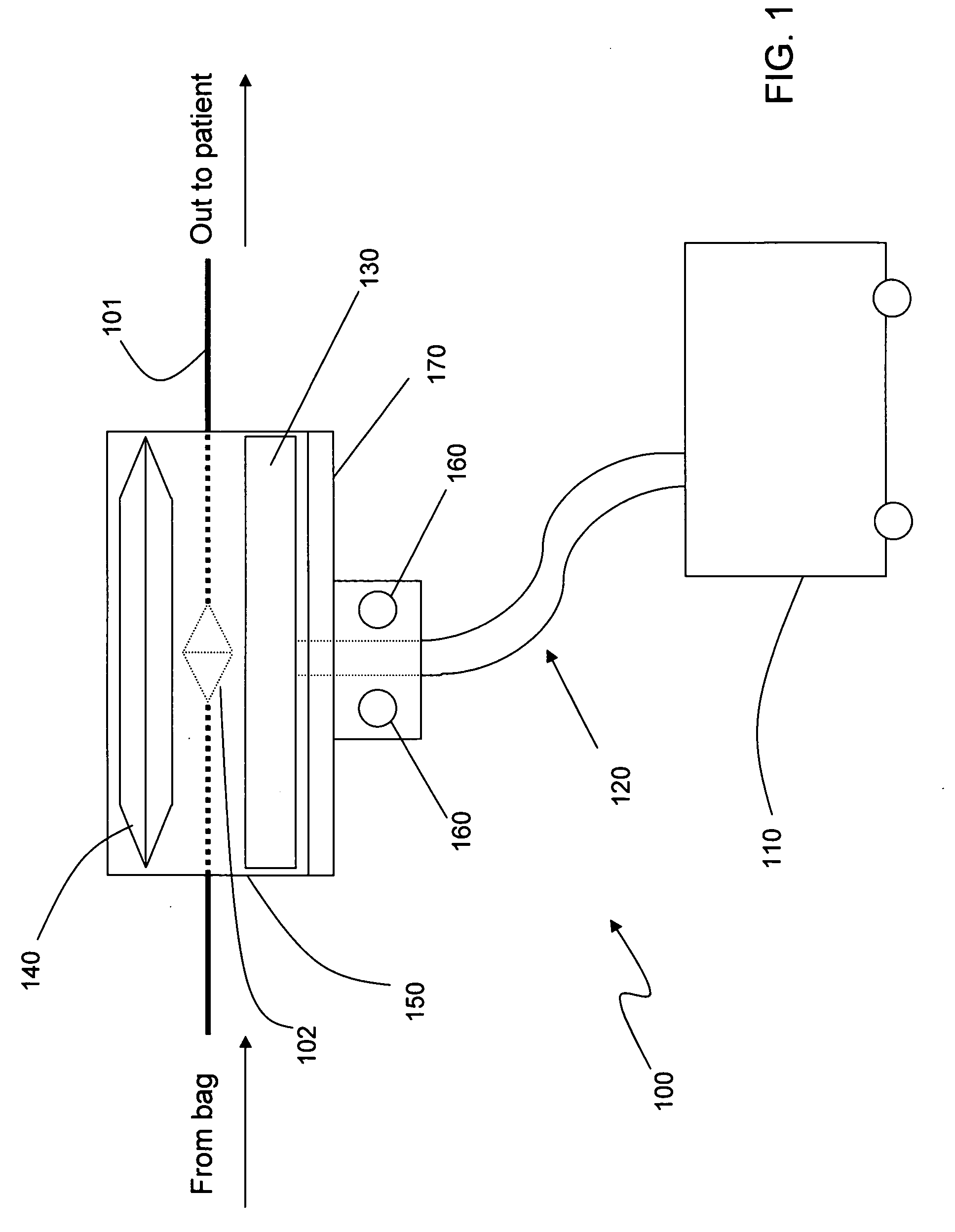
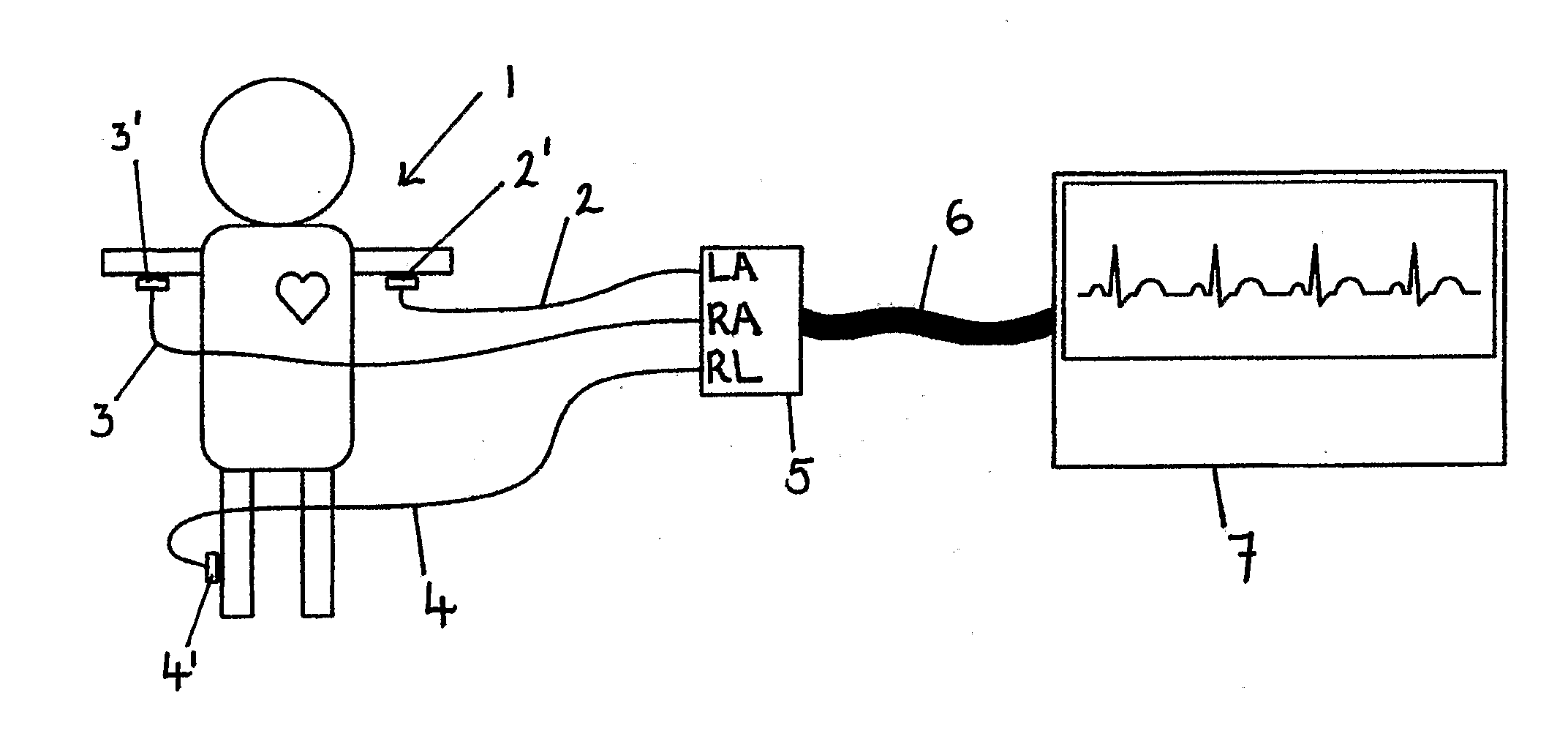
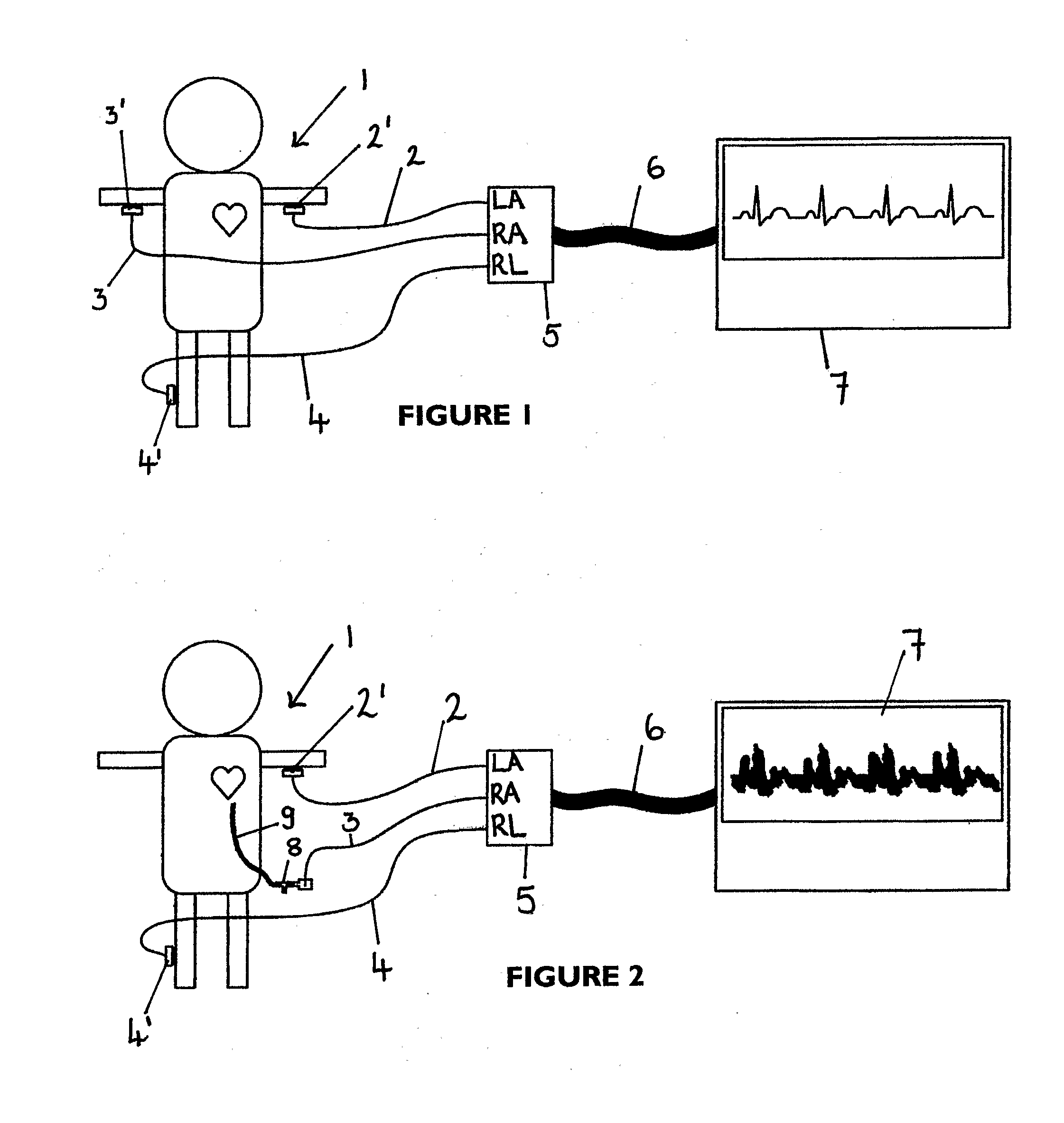
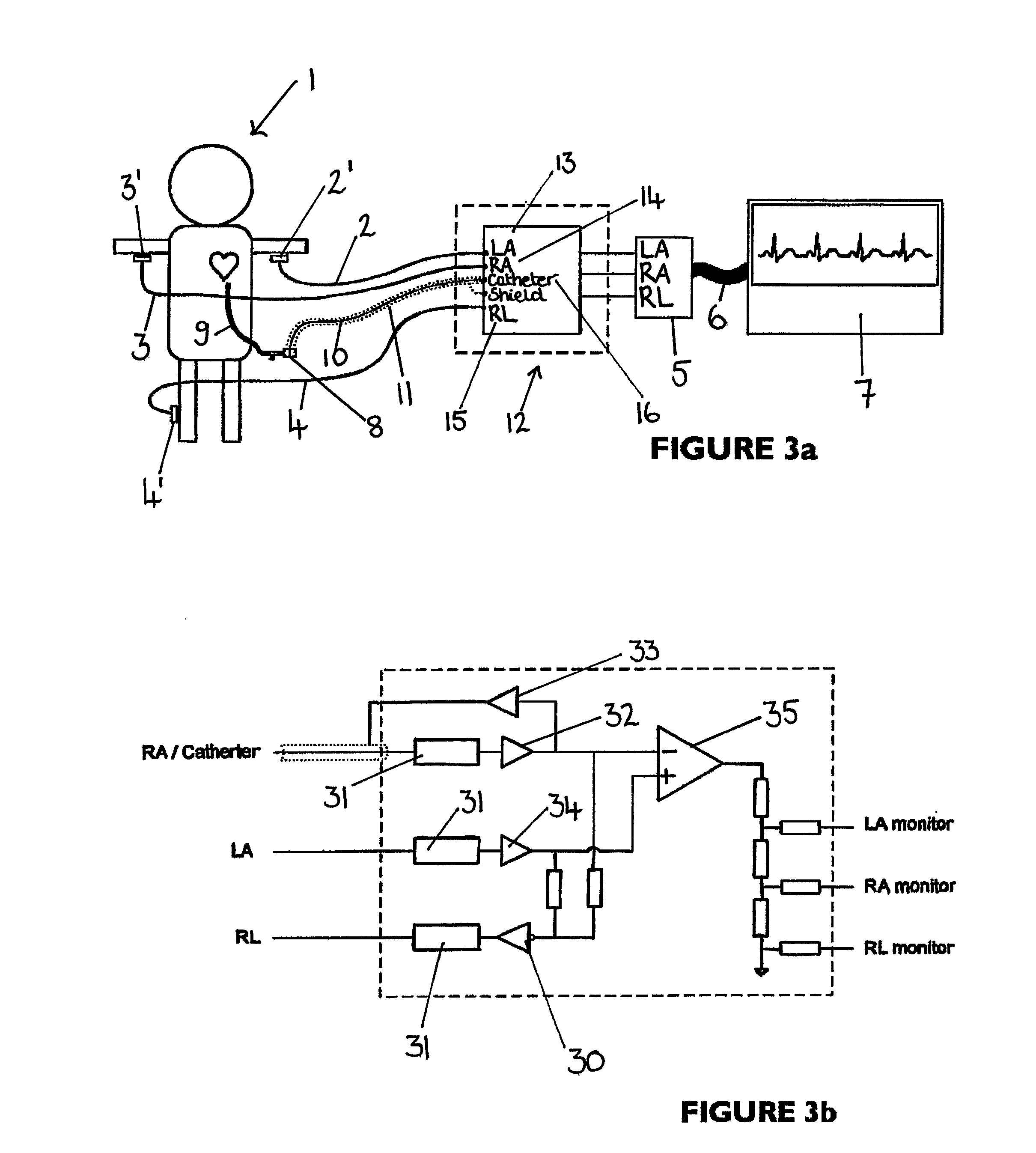
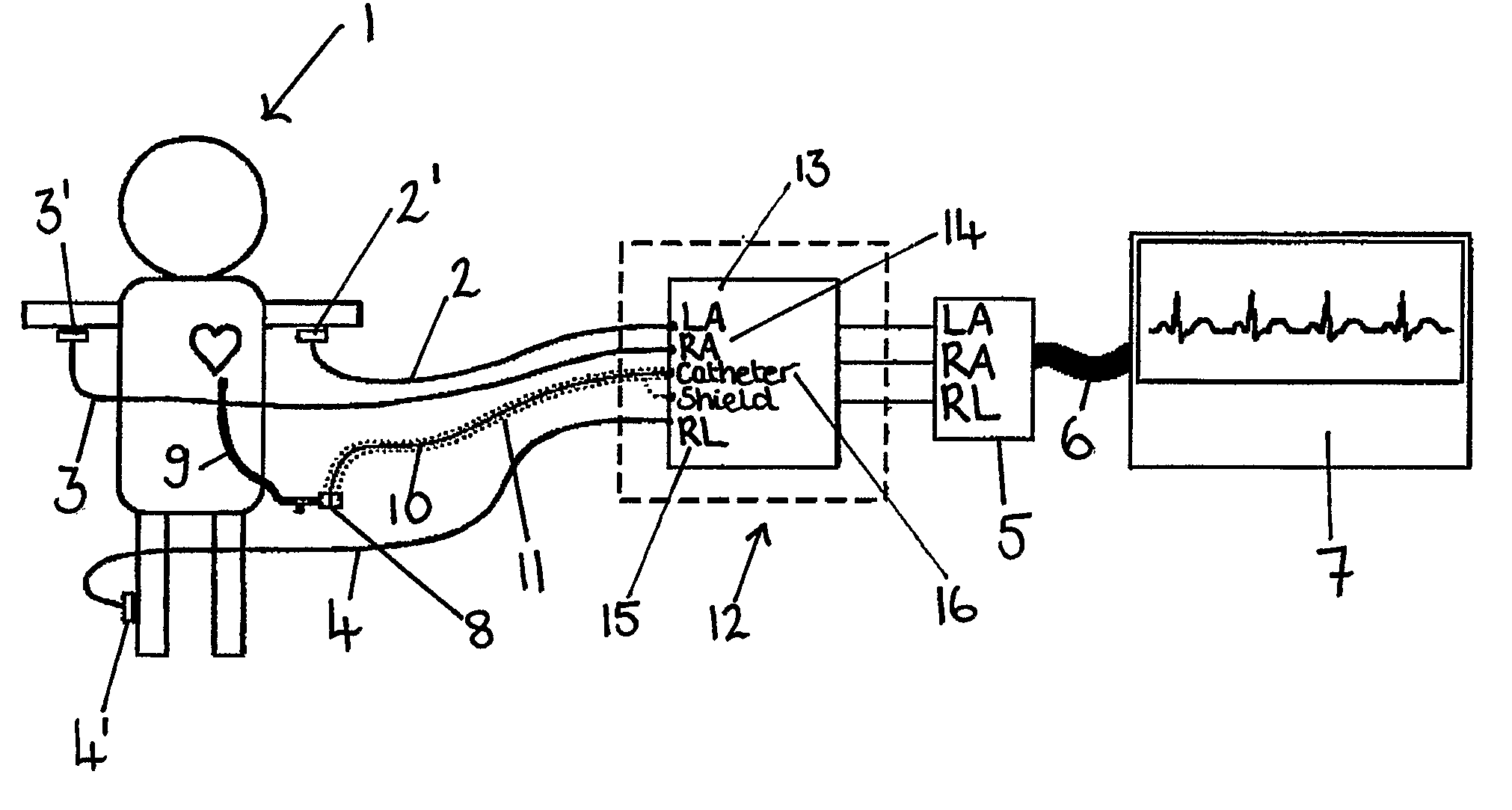
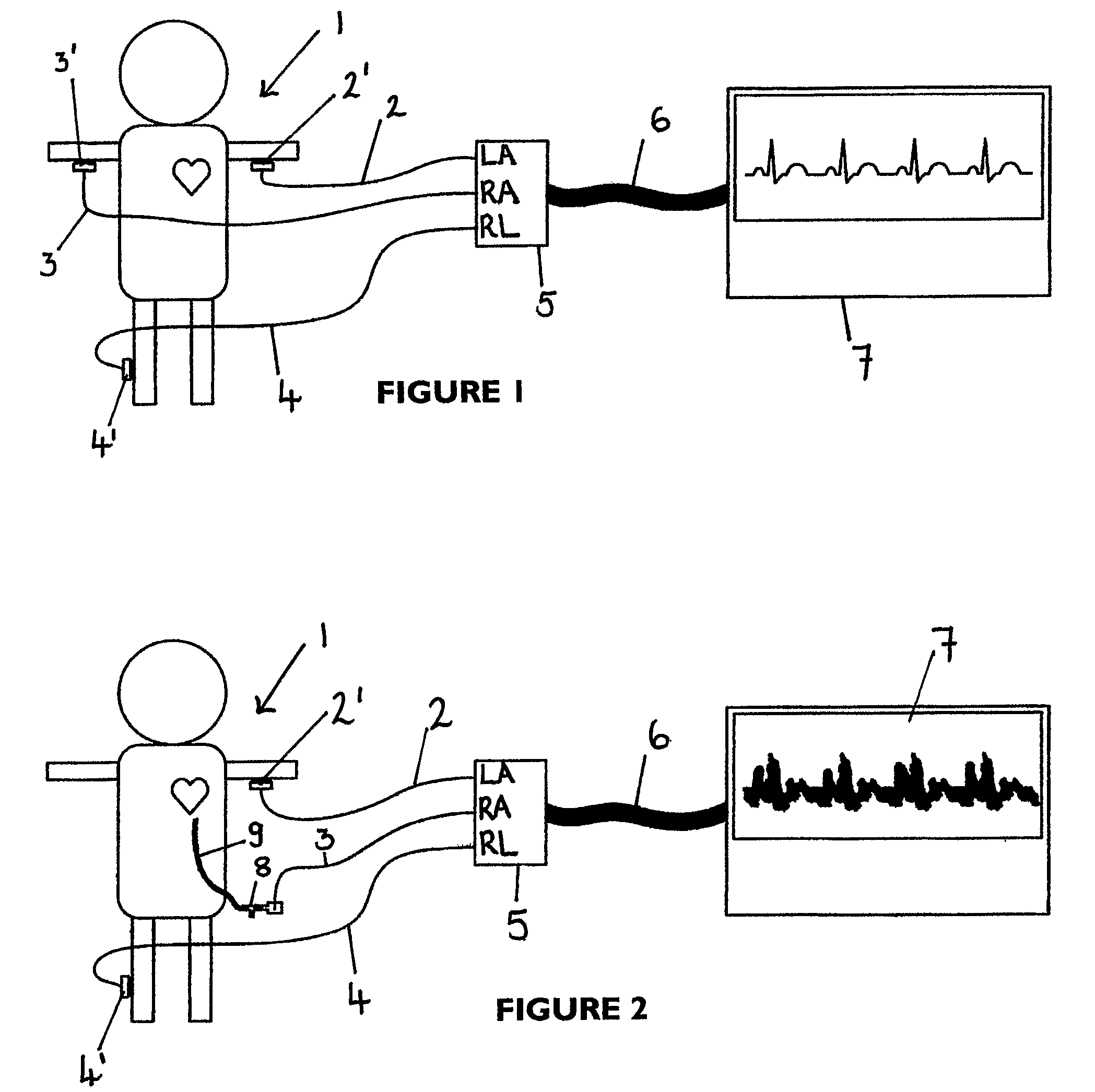
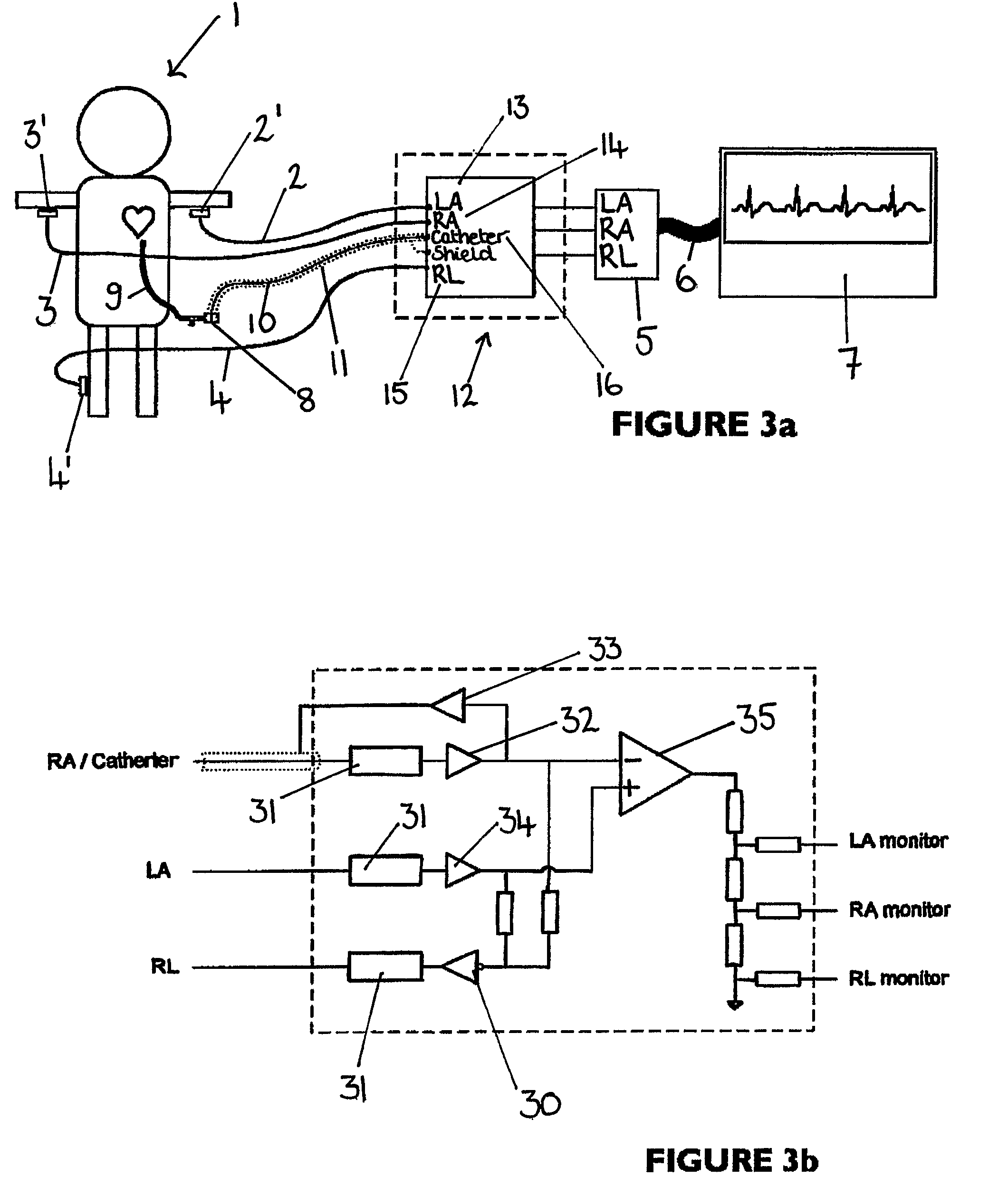
Apparatus for detecting the position of a percutaneously-inserted intravenous catheter
Apparatus for Detecting the Position of a Catheter Apparatus for detecting the position of a catheter comprising a catheter, electrically conductive means associated with the catheter, a connector for establishing an electrical connection between the electrically conductive means associated with the catheter and an output of the connector and a controller having at least one output connectable to an ECG patient connector, wherein the controller includes at least one input and the said at least one input includes an electrical connection from the controller to the output of the connector and wherein the controller includes means for generating a low impedance output signal.
Owner:NEWCASTLE UPON TYNE HOSPITALS NAT HEALTH SERVICE TRUST
Intravenous catheter insertion device with retractable needle
InactiveUS20060173413A1Simple and steady structureEasy to useAutomatic syringesCatheterVeinIntravenous catheter
An intravenous catheter insertion device is disclosed to include a barrel, which has a body and a stop wall, a deformable portion extending from the body, a retainer connected with the deformable portion, and a press portion for pressing by the user to deform the deformable portion. A needle set, which has a cylindrical needle holder, a needle fastened to the needle holder at the front side, a springy stop portion extending from the needle holder, and a retainer connected with the needle holder near the front end of the needle holder. And a spring member, which is mounted around the needle set inside the barrel, and has a first end stopped against the stop wall of the barrel and a rear end stopped against the springy stop portion of the needle set.
Owner:TAIJECT MEDICAL DEVICE CO LTD
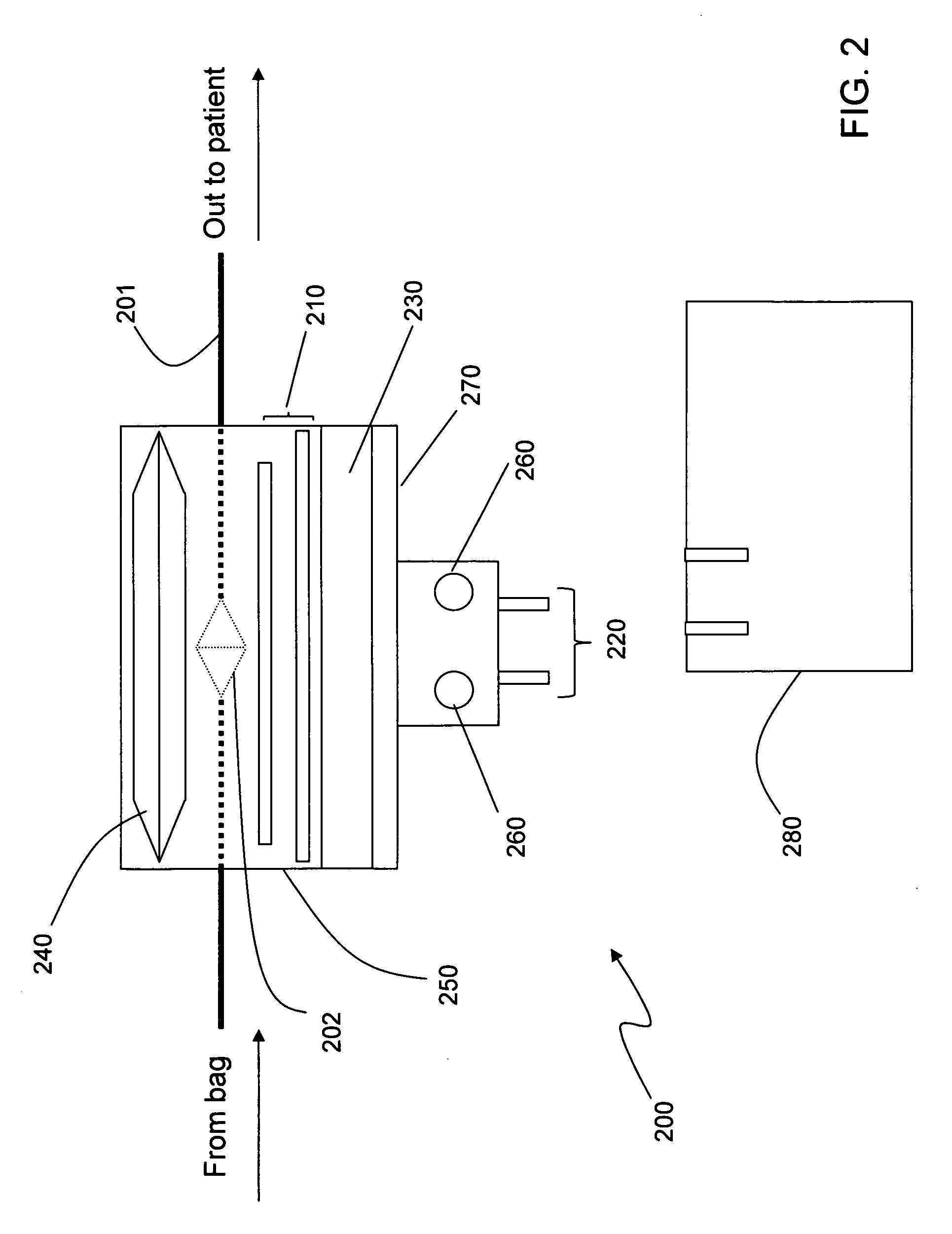
Apparatus for detecting the position of a percutaneously-inserted intravenous catheter
An apparatus that is able to detect the position of a catheter. The apparatus utilizes a catheter filled with electrically-conductive physiological saline and a connector for establishing an electrical connection between the saline of the catheter and an input of a controller. The controller includes at least one output connectable to a standard ECG lead connector, wherein the controller includes circuitry for generating a low impedance output signal. The controller provides an output which replicates the input a standard ECG patient lead connector is configured to receive. The apparatus provides a more convenient and cost effective solution for providing specialized ECG functions without having to replace a hospital's existing ECG beside monitoring equipment.
Owner:NEWCASTLE UPON TYNE HOSPITALS NAT HEALTH SERVICE TRUST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com