Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
475 results about "Bronchus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
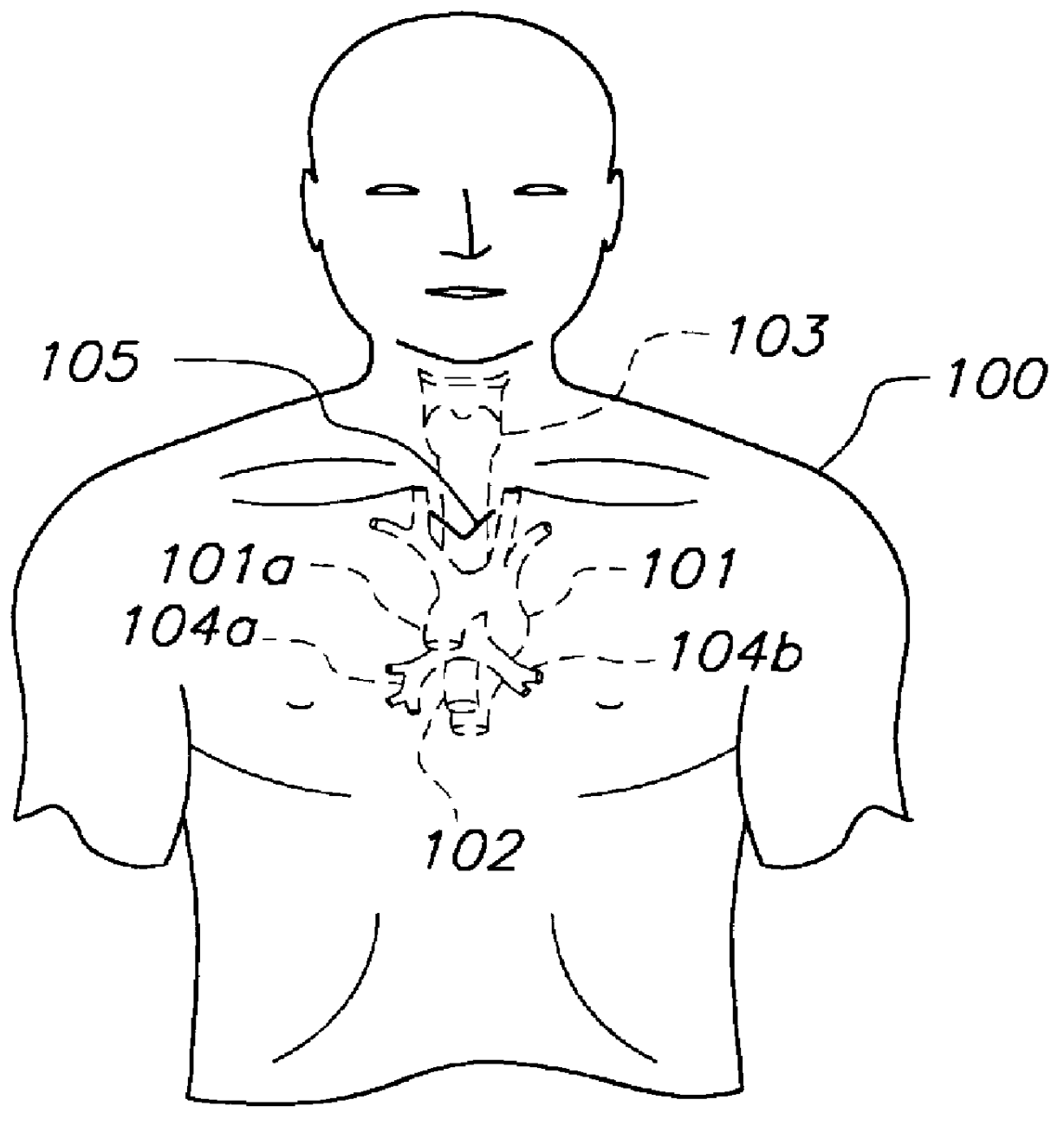
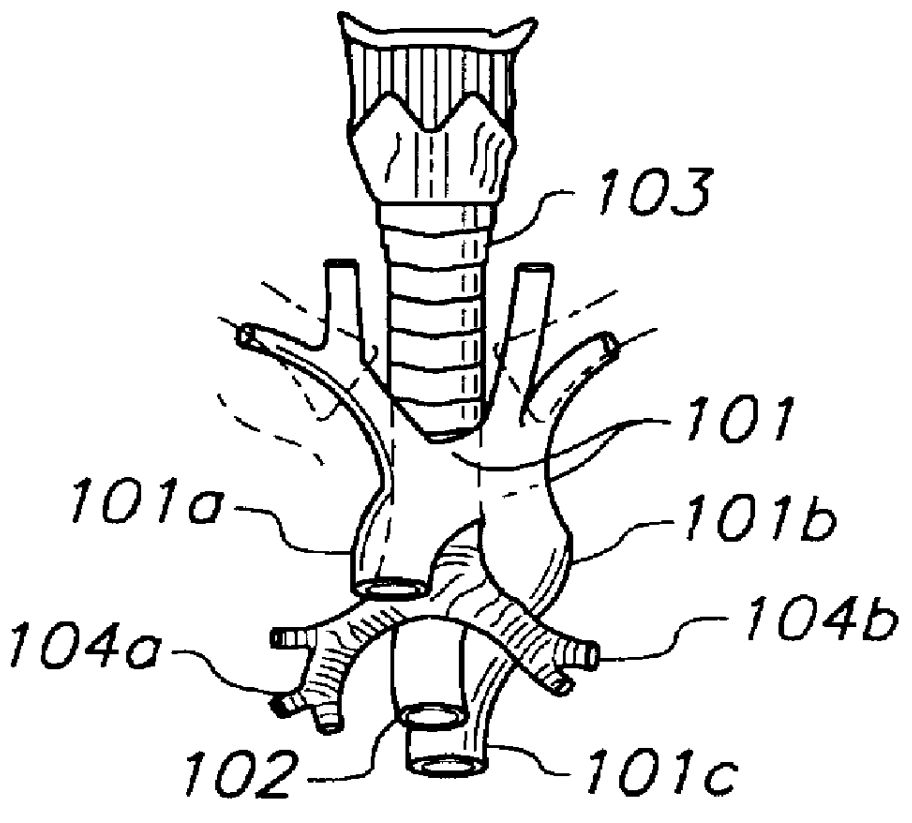
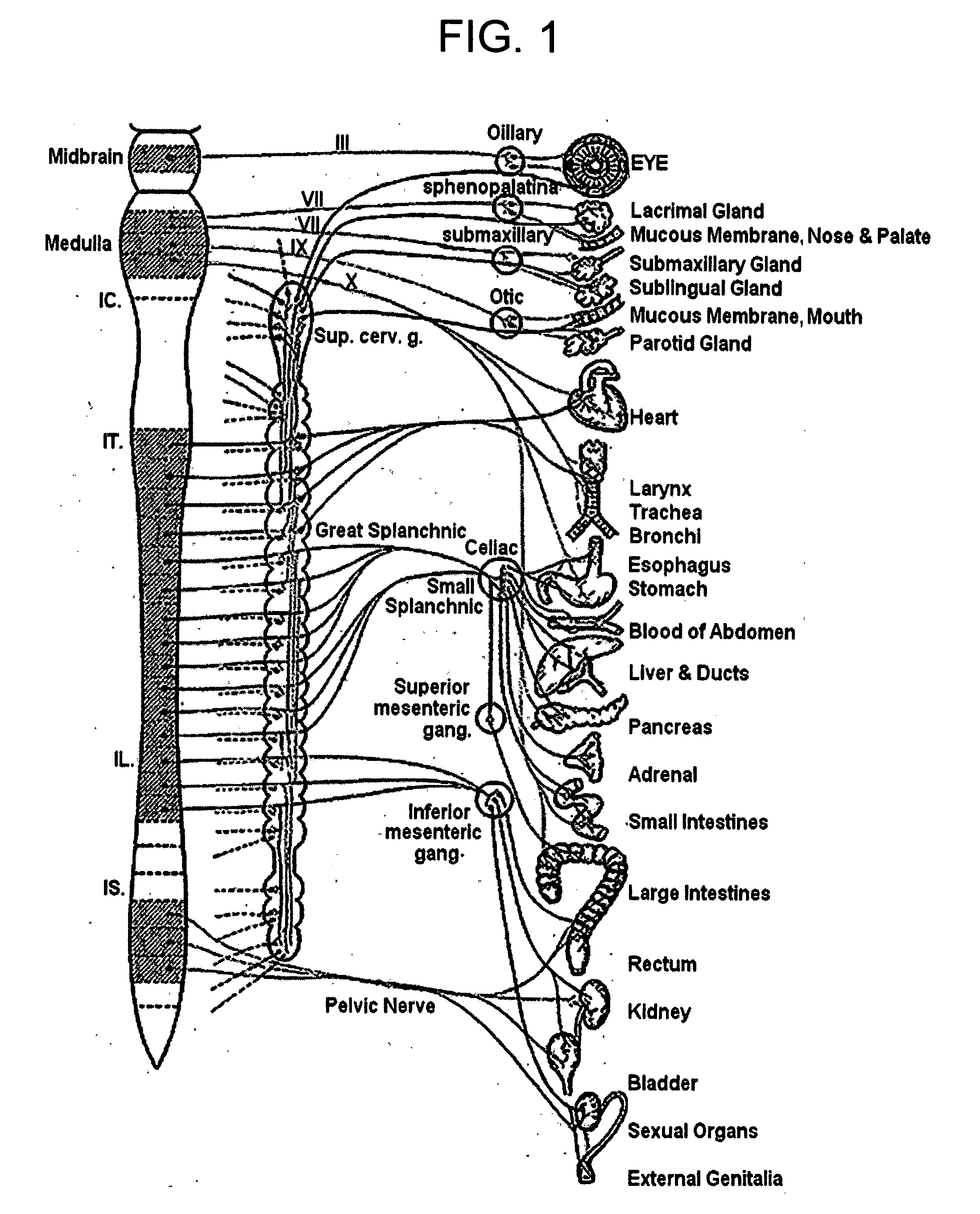
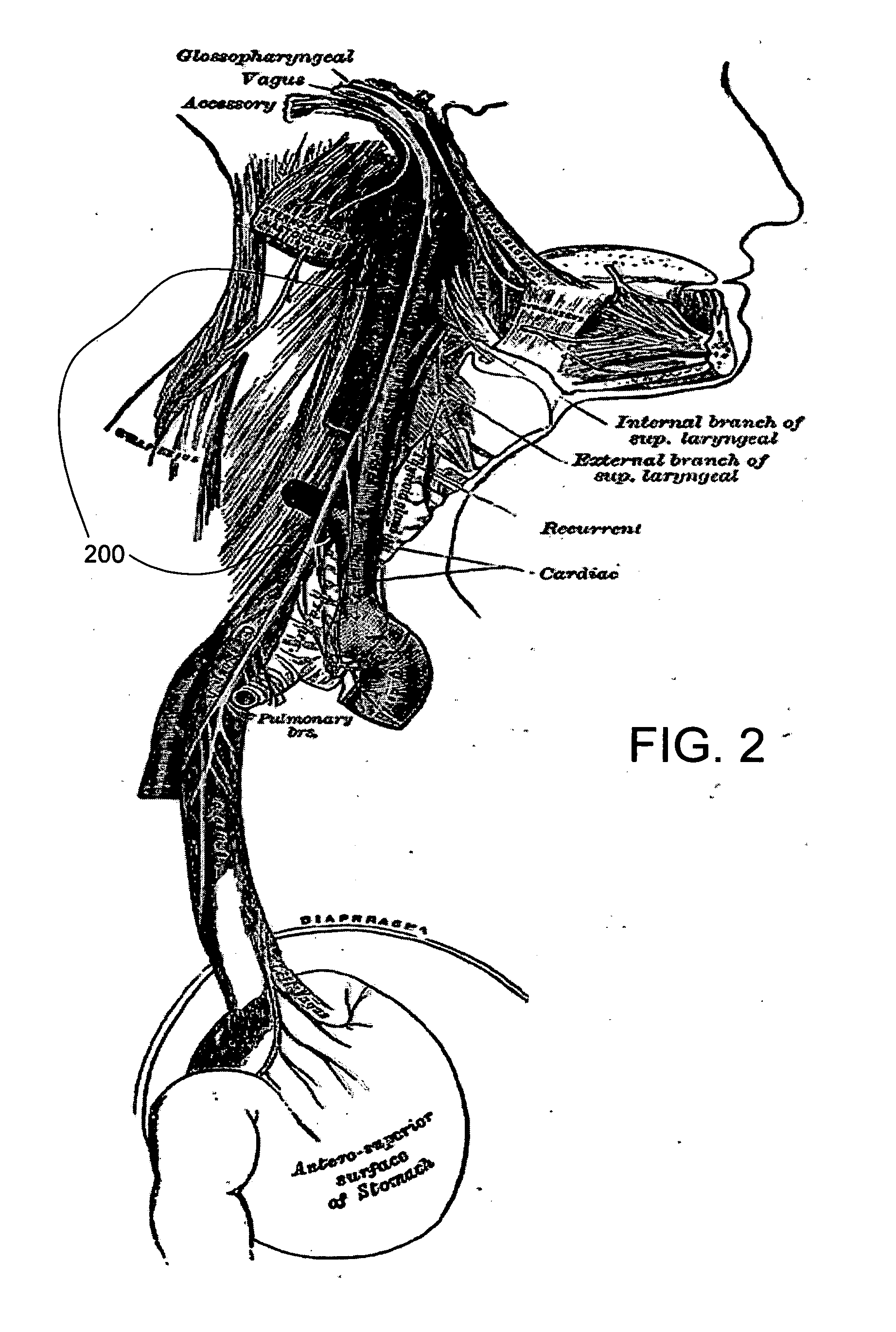
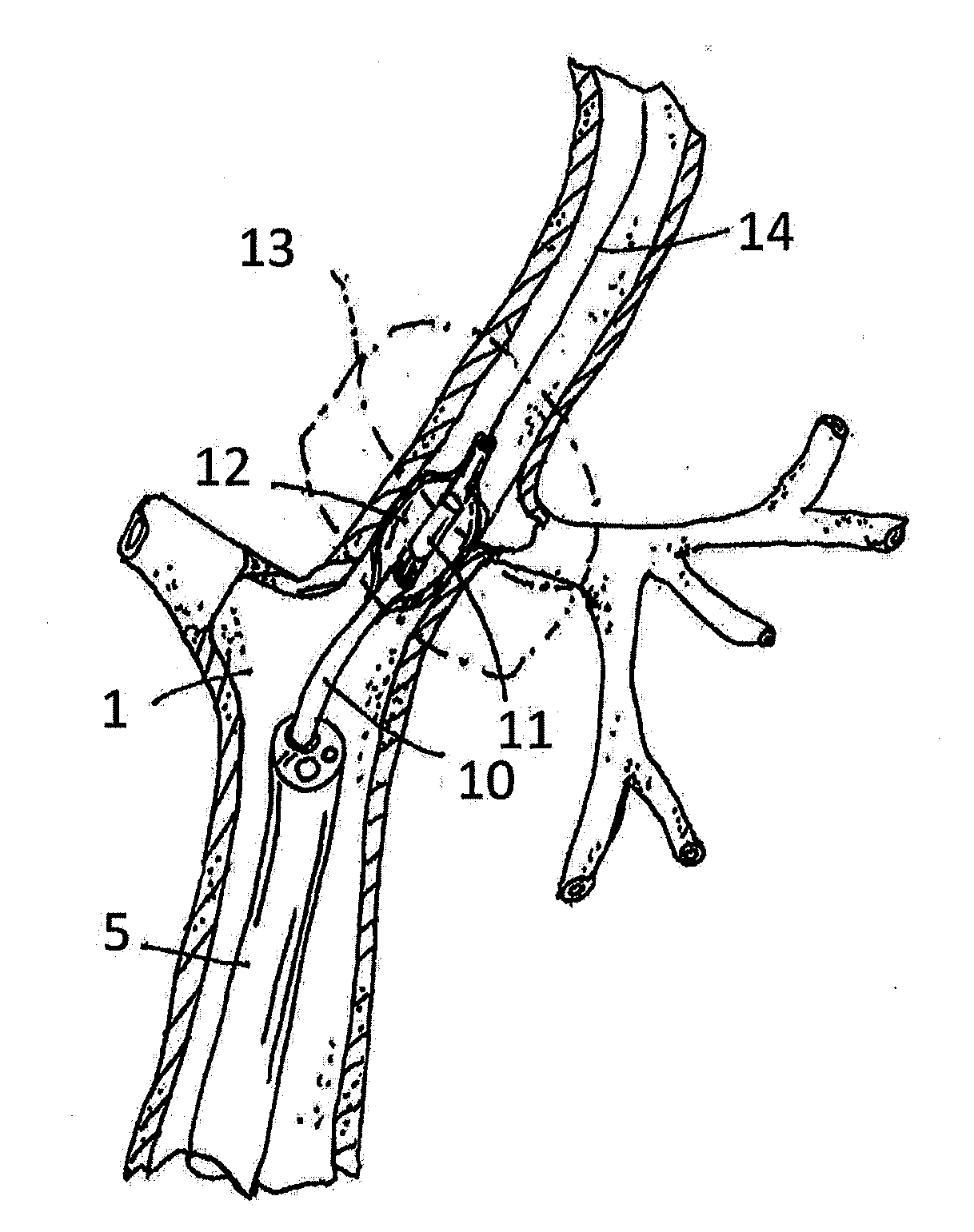
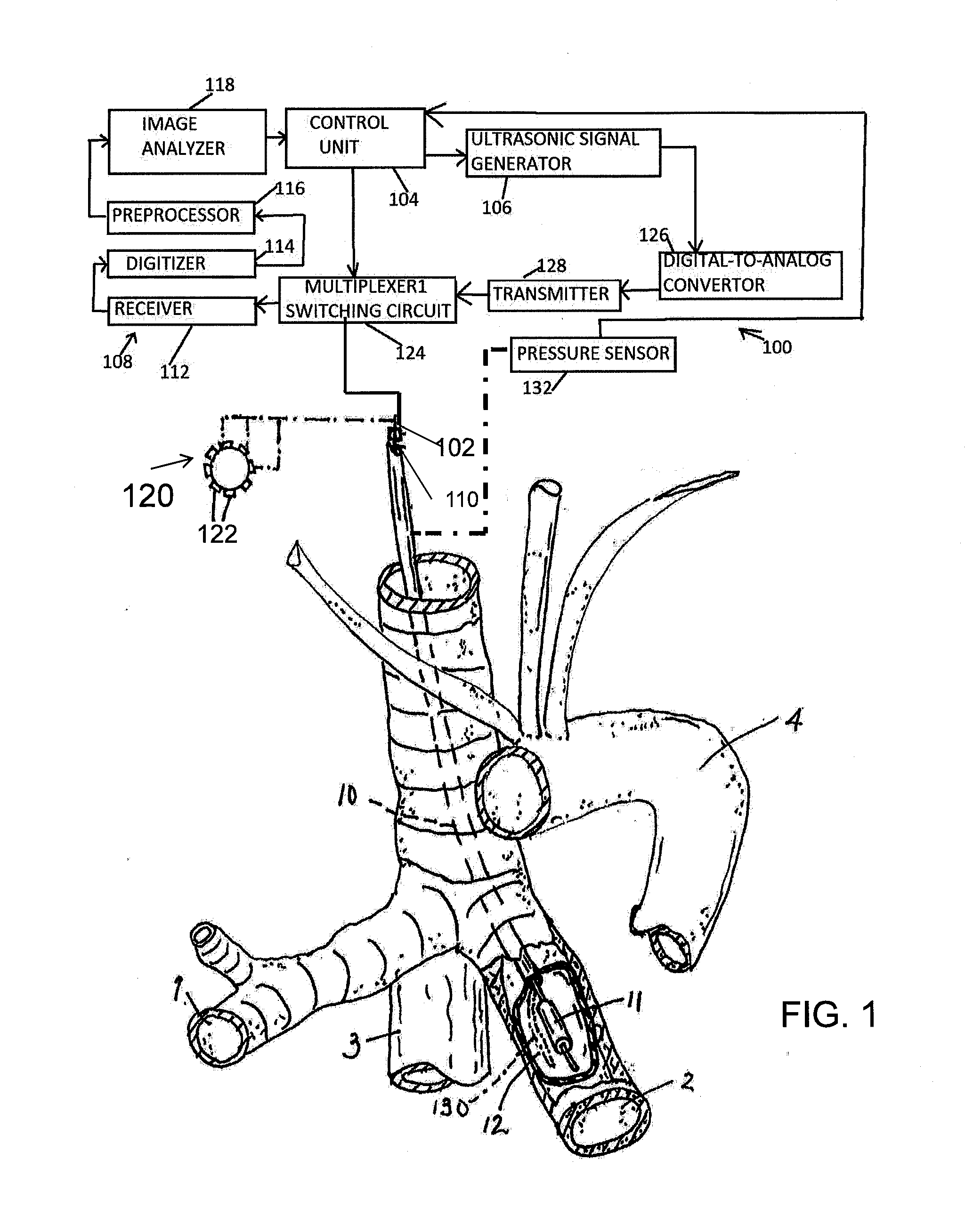
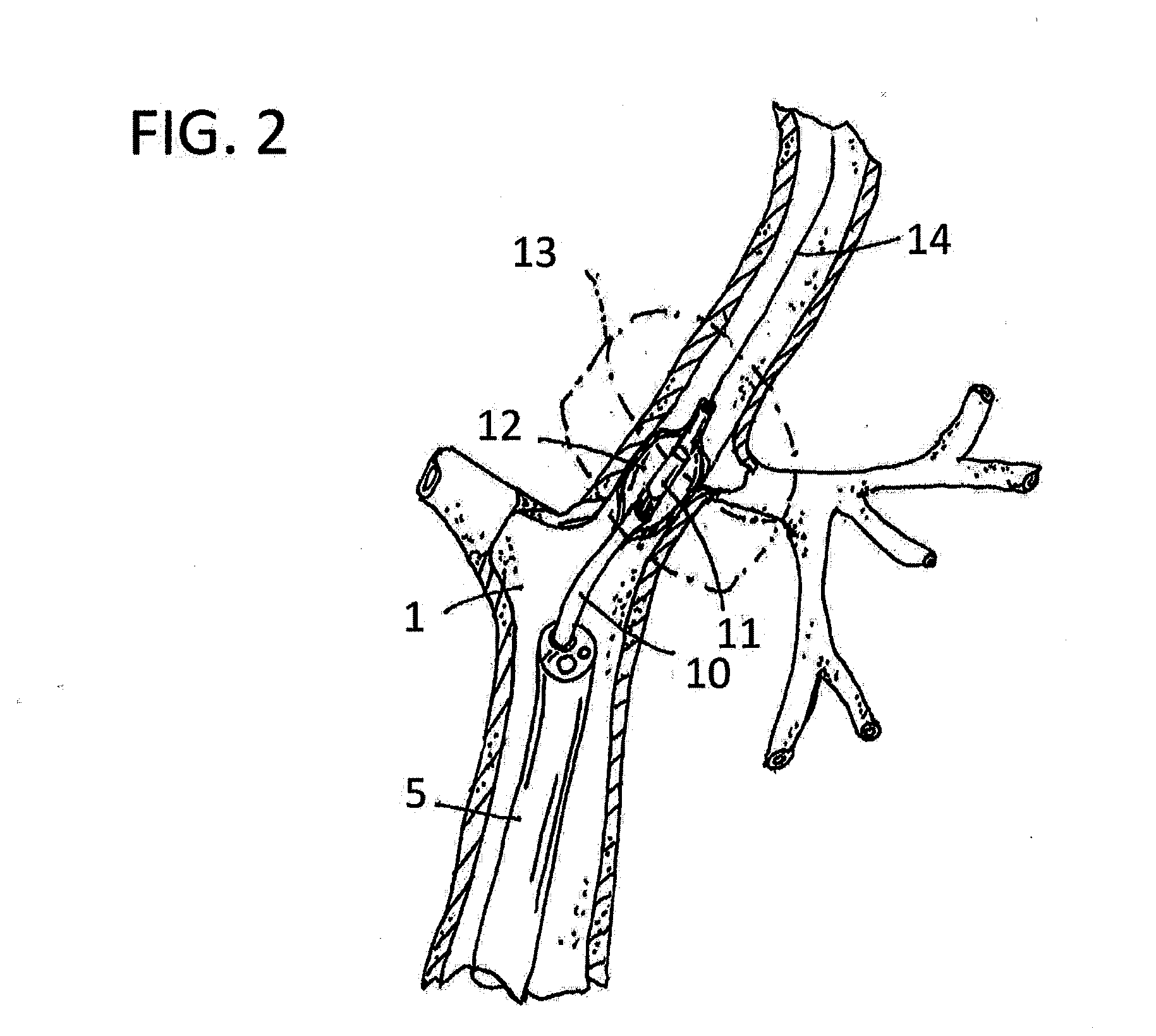
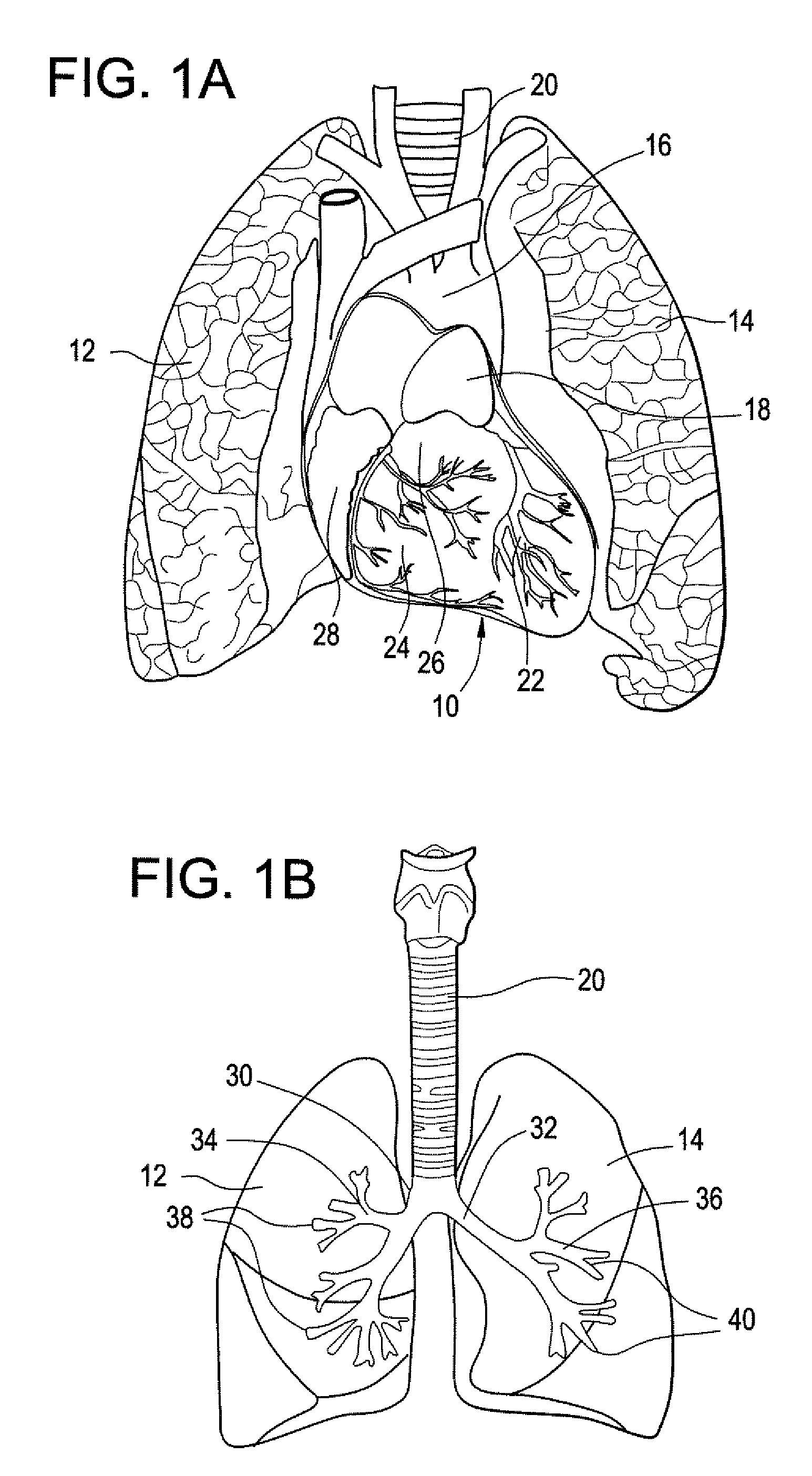
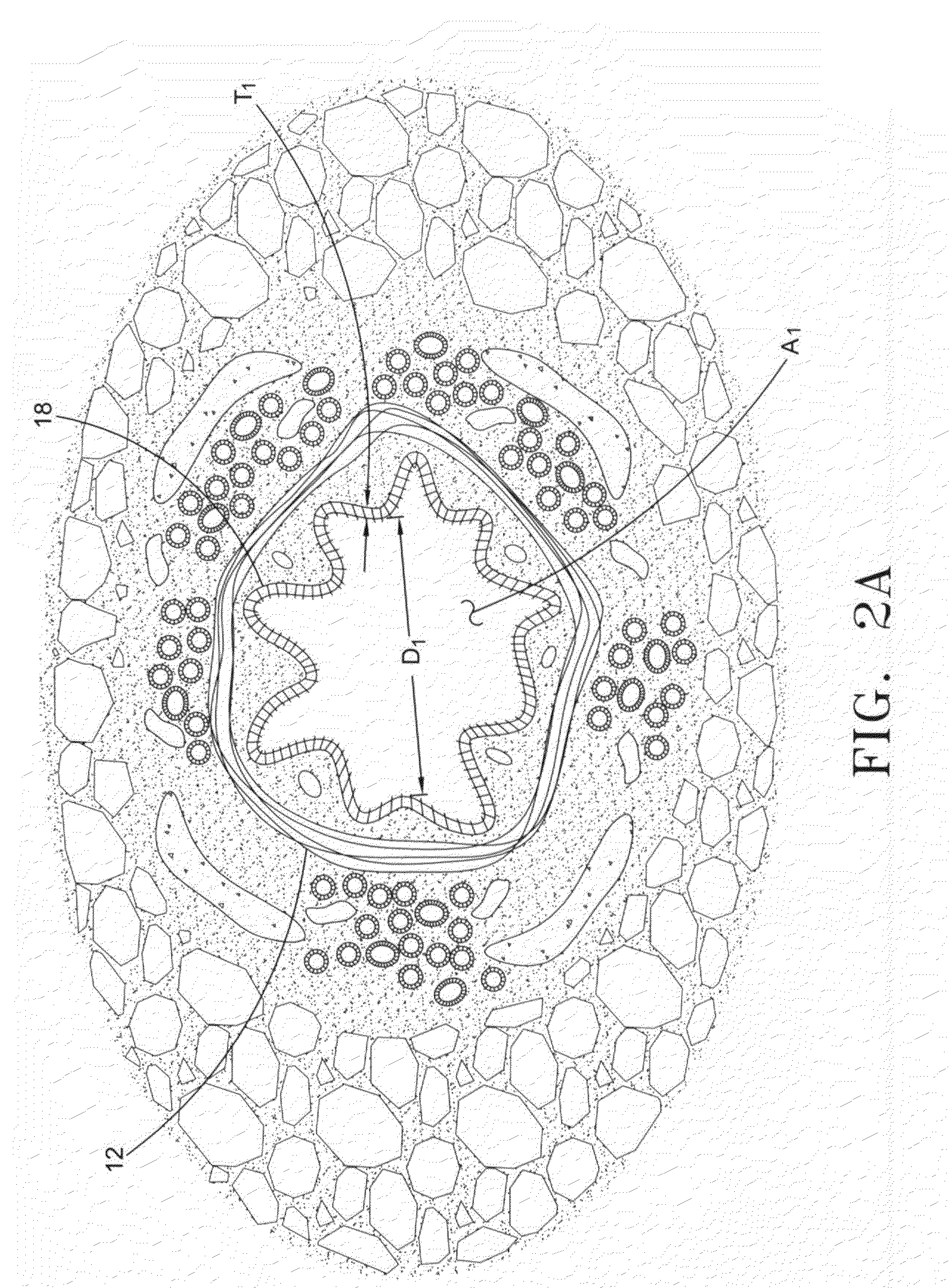
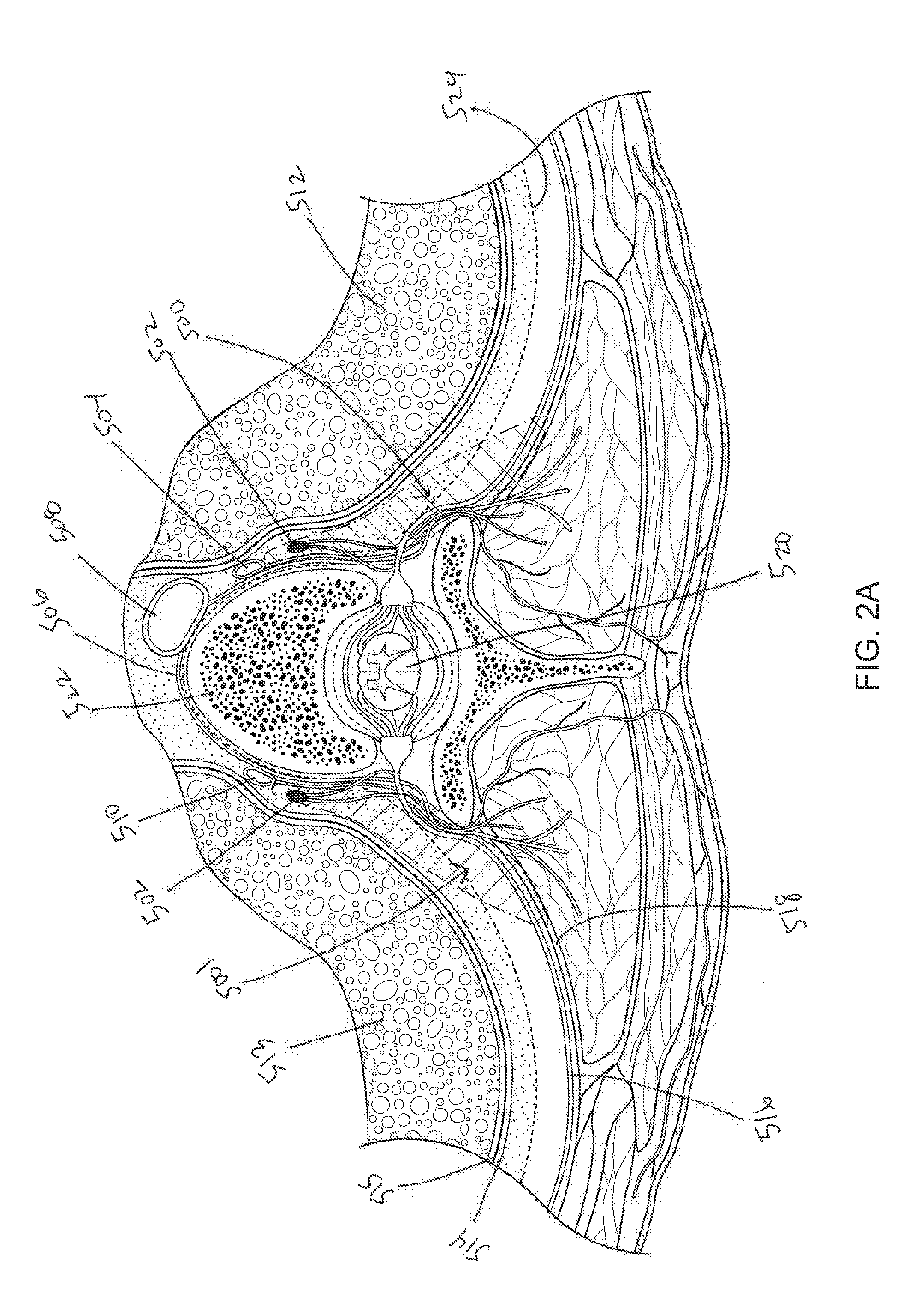
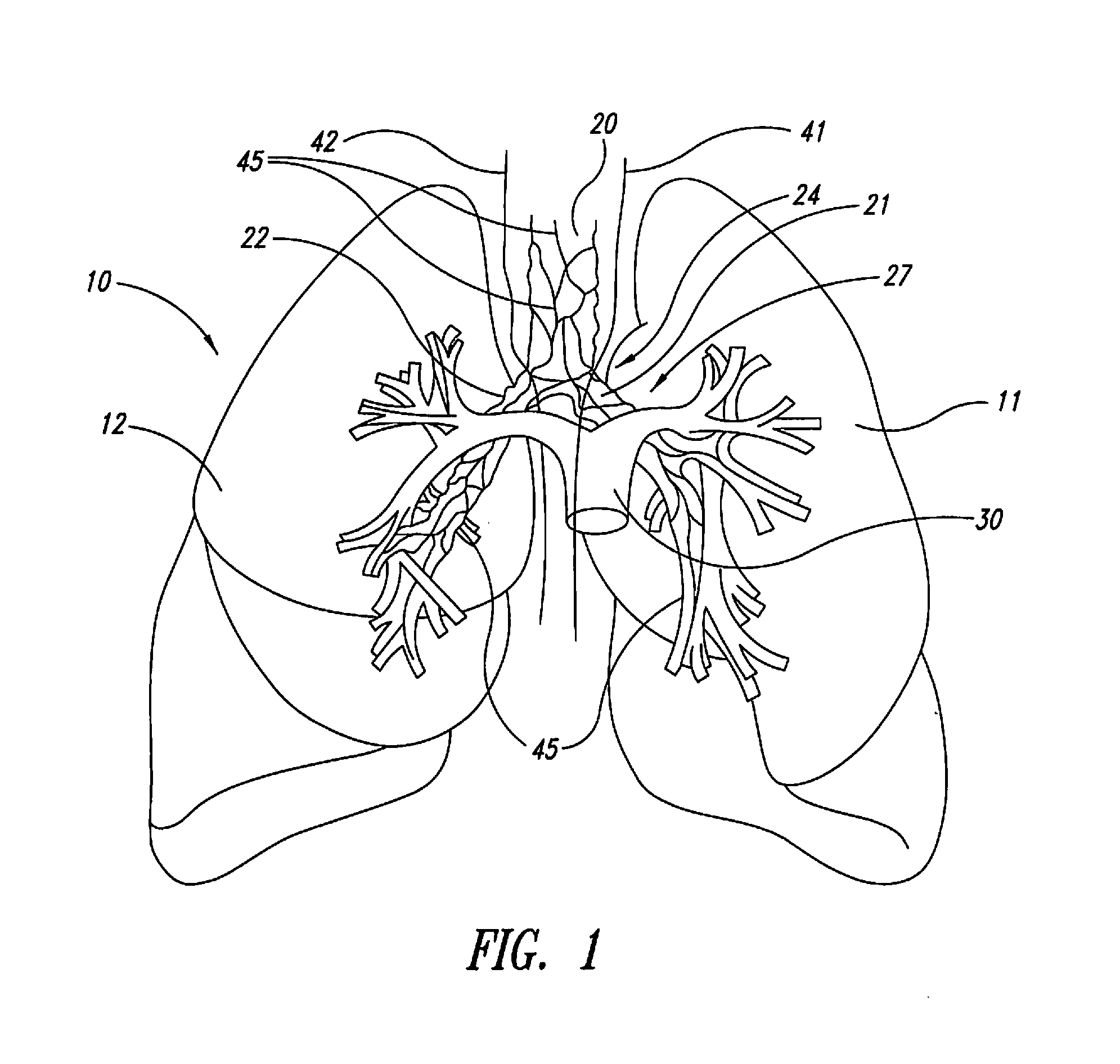
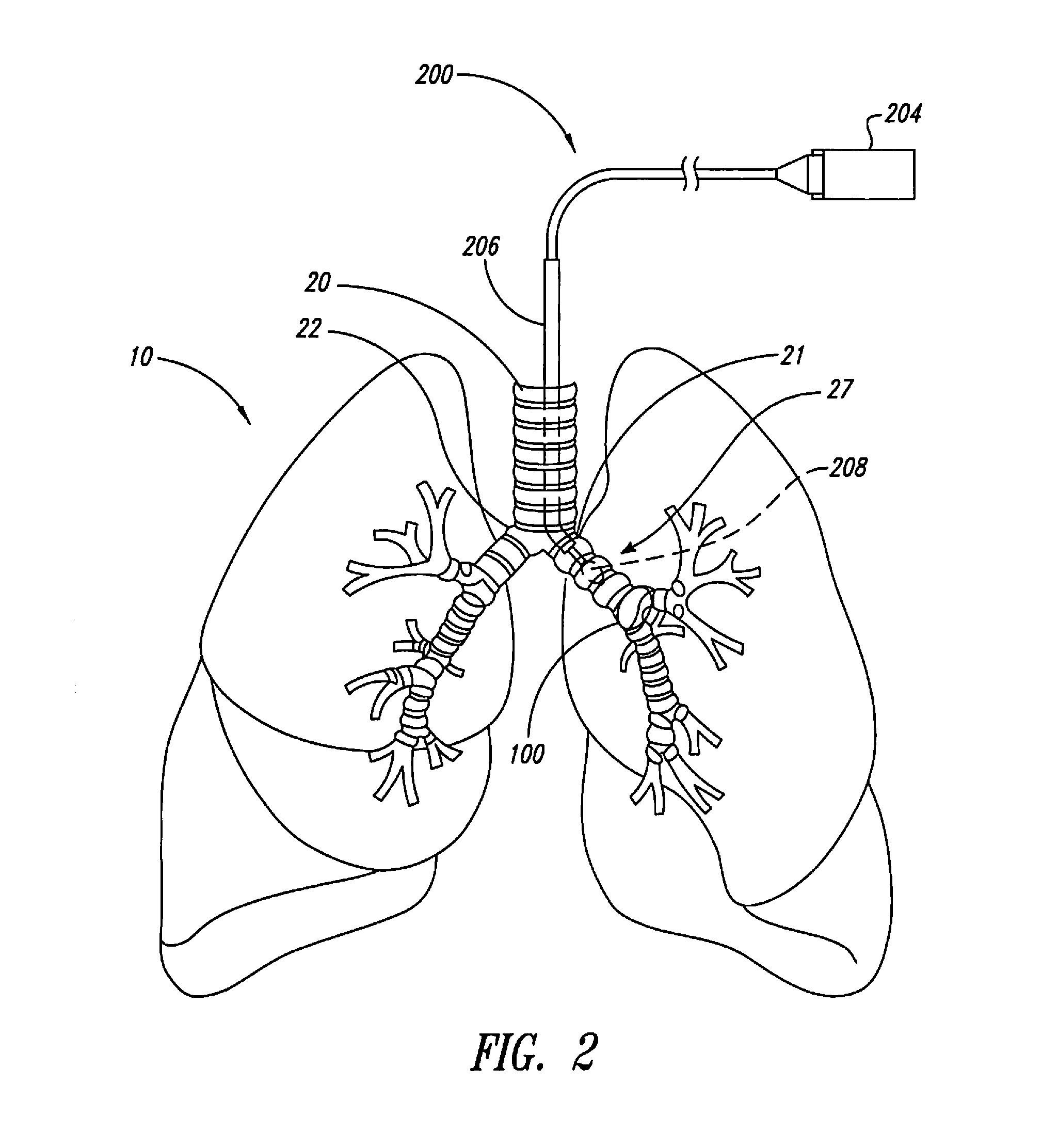
A bronchus is a passage or airway in the respiratory system that conducts air into the lungs. The first bronchi to branch from the trachea are the right main bronchus and the left main bronchus, also known as the primary bronchi. These are the widest and enter the lungs at each hilum, where they branch into narrower secondary bronchi or lobar bronchi, and these branch into narrower tertiary bronchi or segmental bronchi. Further divisions of the segmental bronchi are known as 4th order, 5th order, and 6th order segmental bronchi, or grouped together as subsegmental bronchi. The bronchi when too narrow to be supported by cartilage are known as bronchioles. No gas exchange takes place in the bronchi.
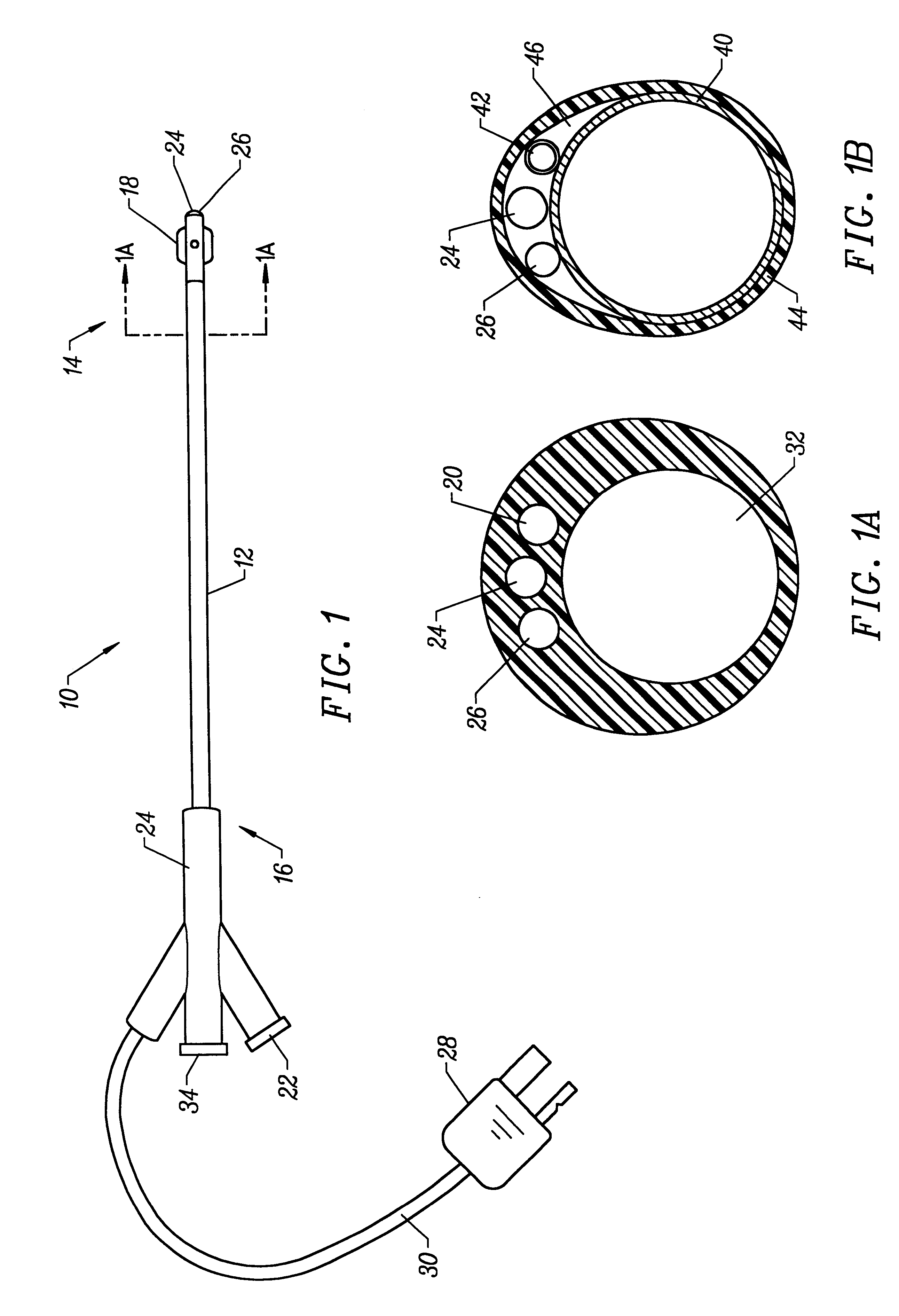
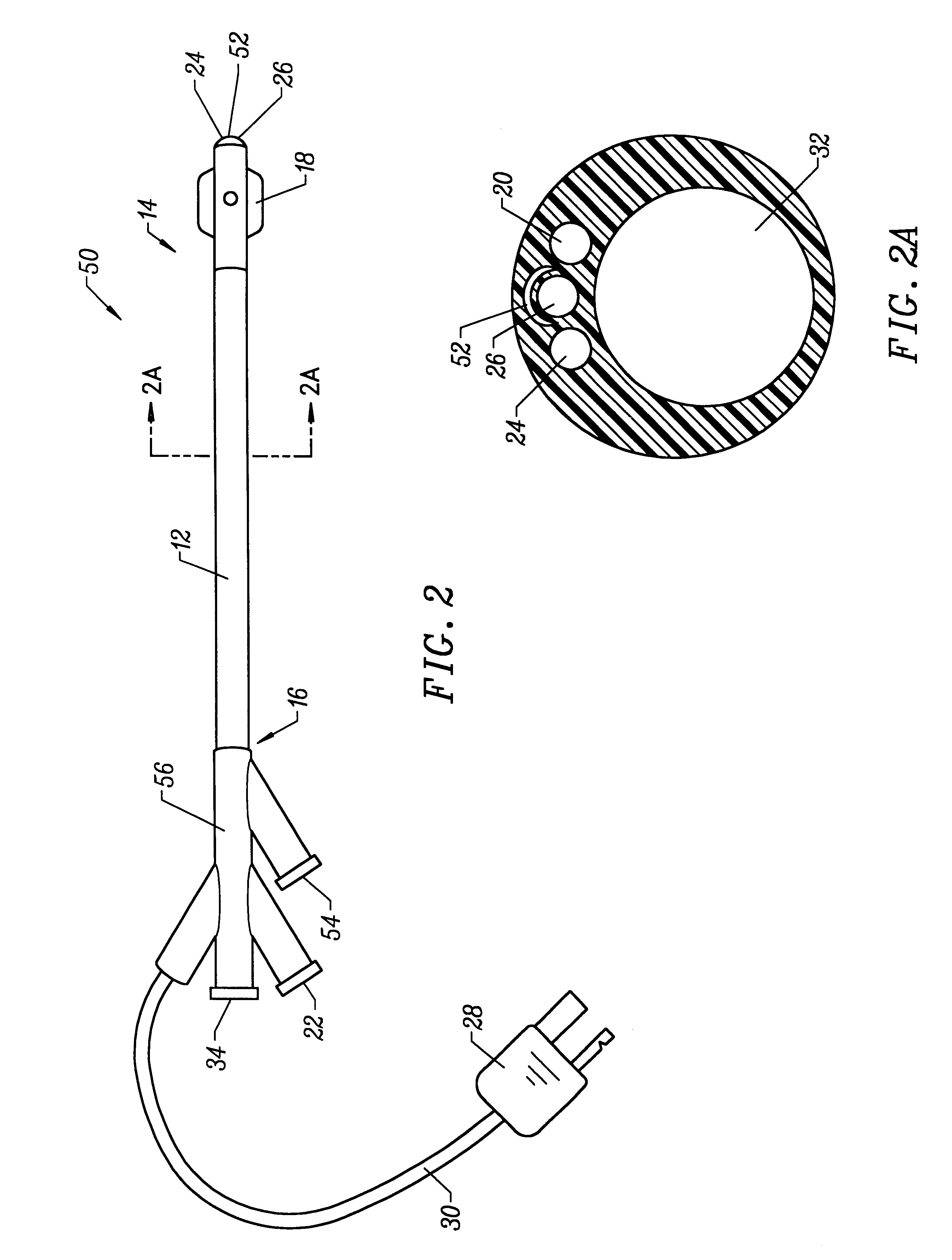
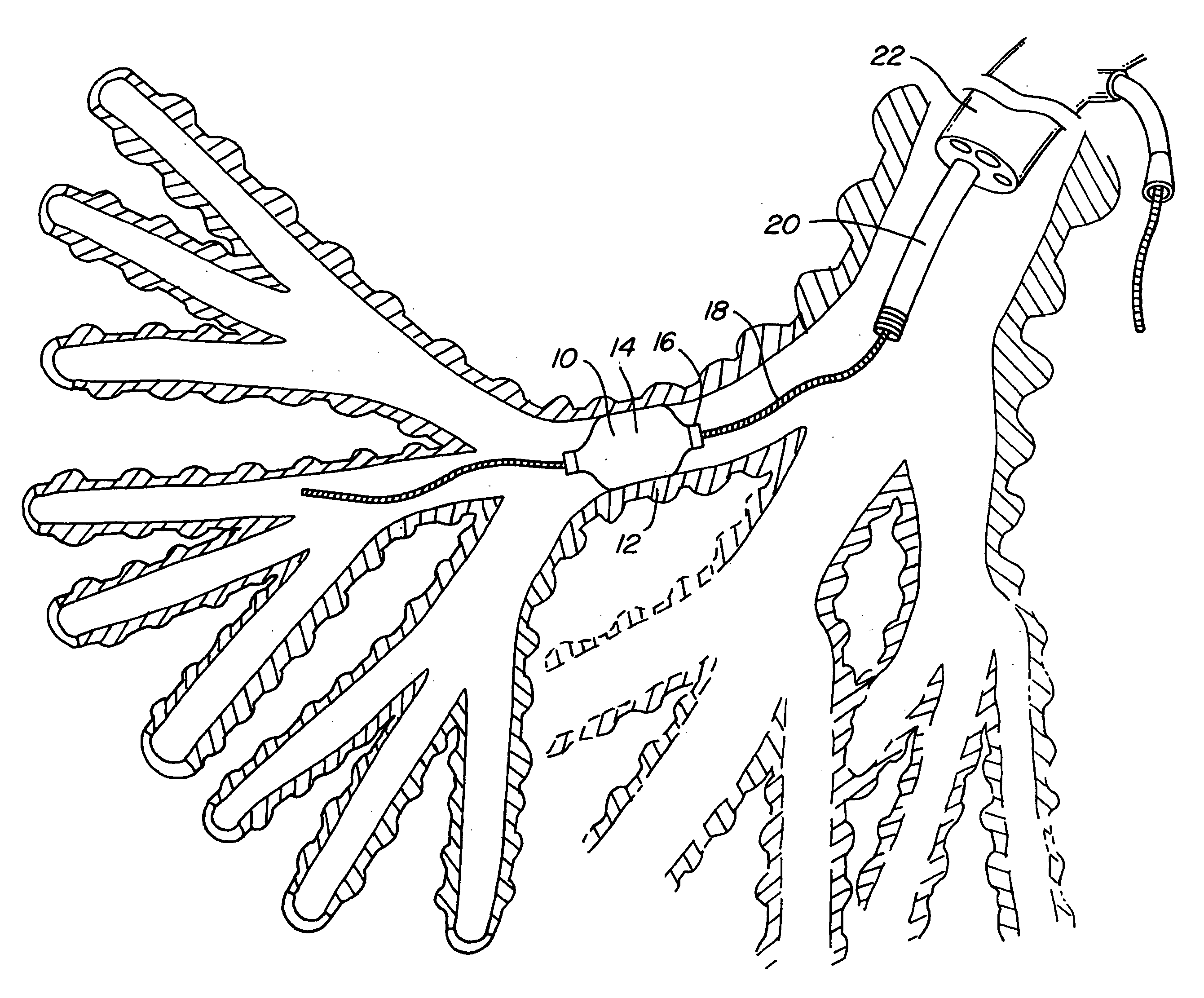
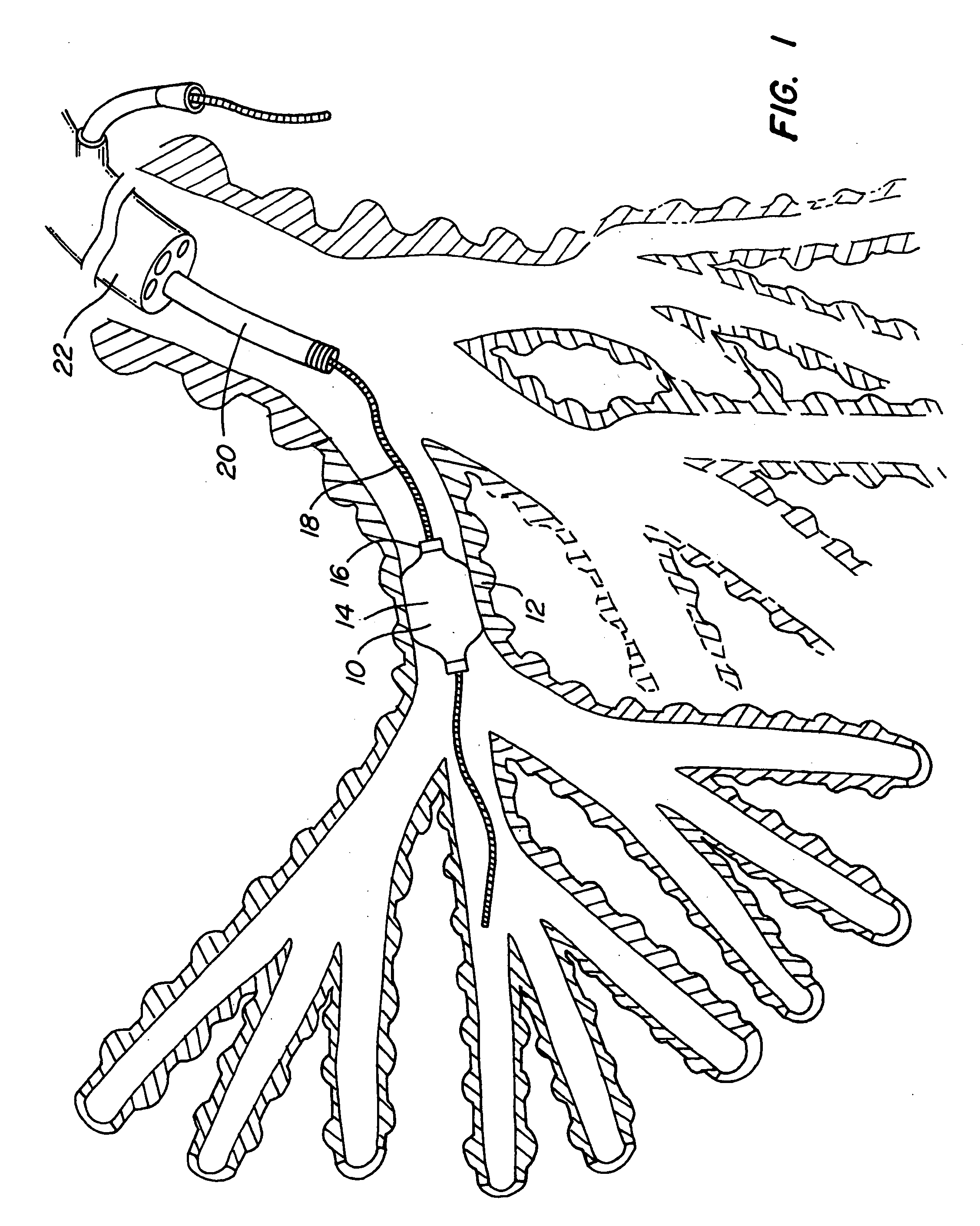
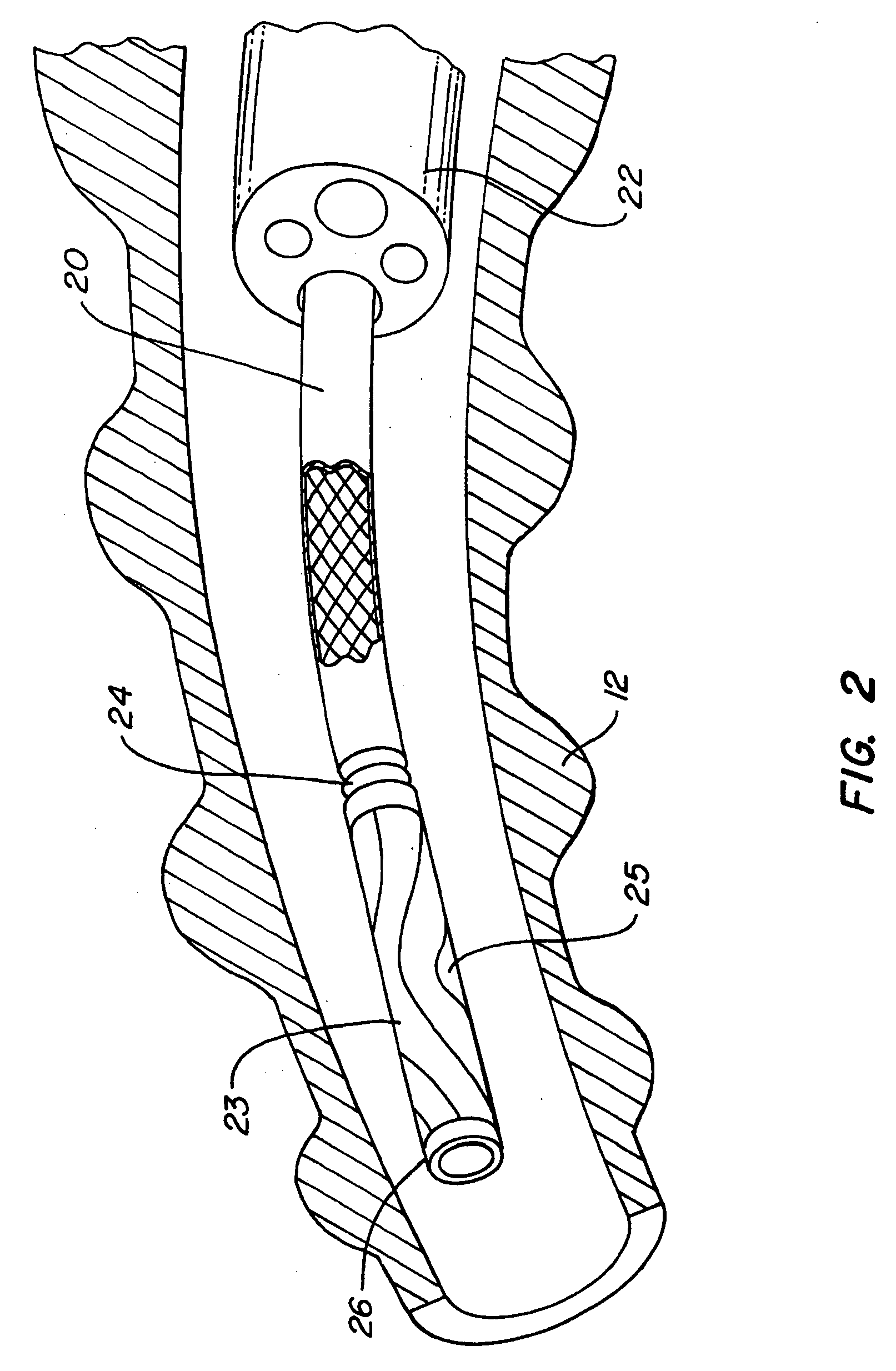
Apparatus and methods of bioelectrical impedance analysis of blood flow
InactiveUS6095987AAccurately and non-invasively and continuously measuring cardiac outputCatheterSensorsBioelectrical impedance analysisCardiac pacemaker electrode
Apparatus and methods are provided for monitoring cardiac output using bioelectrical impedance techniques in which first and second electrodes are placed in the trachea and / or bronchus in the vicinity of the ascending aorta, while an excitation current is injected into the thorax via first and second current electrodes, so that bioelectrical impedance measurements based on the voltage drop sensed by the first and second electrodes reflect voltage changes induced primarily by blood flow dynamics, rather than respiratory or non-cardiac related physiological effects. Additional sense electrodes may be provided, either internally, or externally, for which bioelectrical impedance values may be obtained. Methods are provided for computing cardiac output from bioelectrical impedance values. Apparatus and methods are also provided so that the measured cardiac output may be used to control administration of intravenous fluids to an organism or to optimize a heart rate controlled by a pacemaker.
Owner:ECOM MED
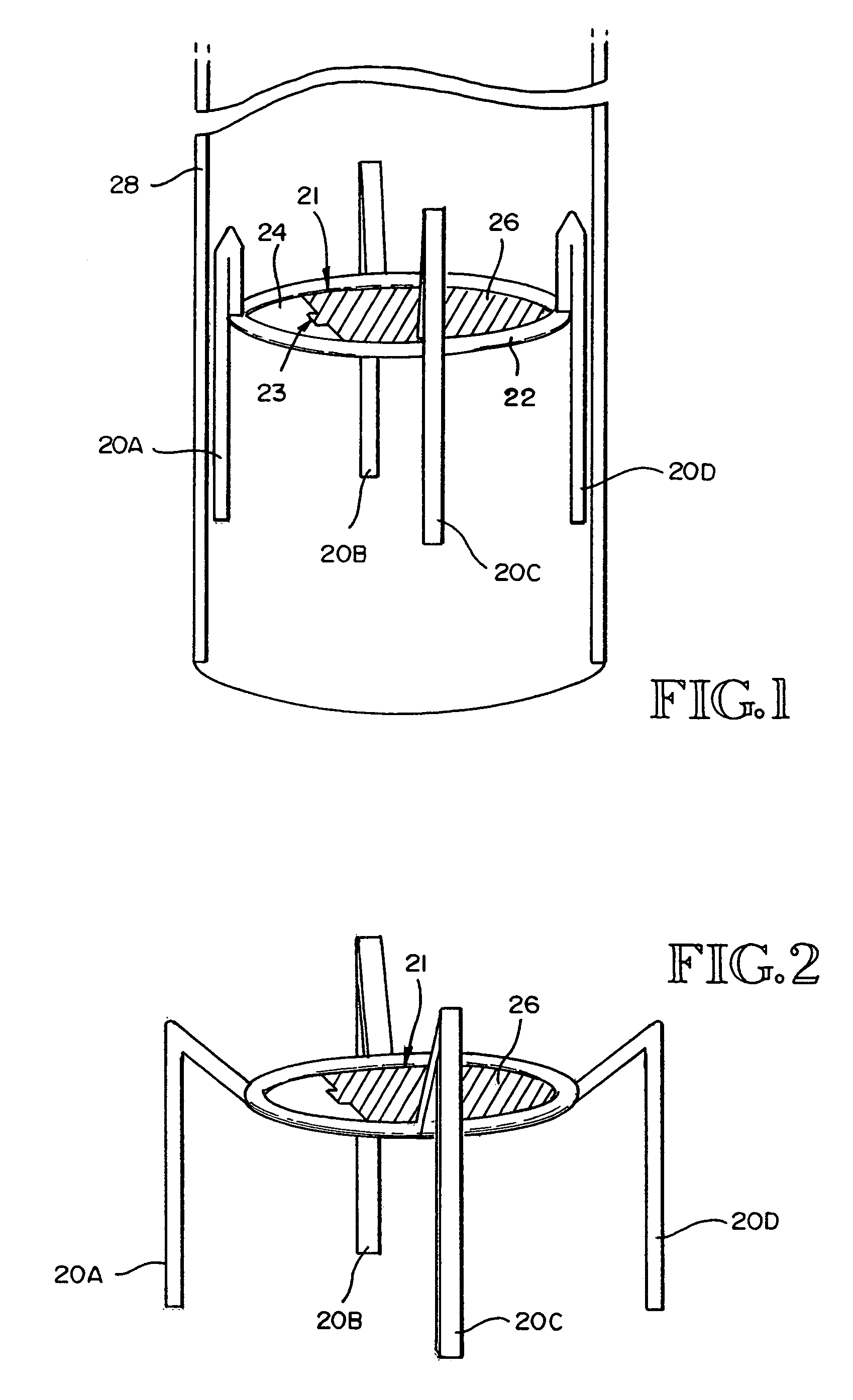
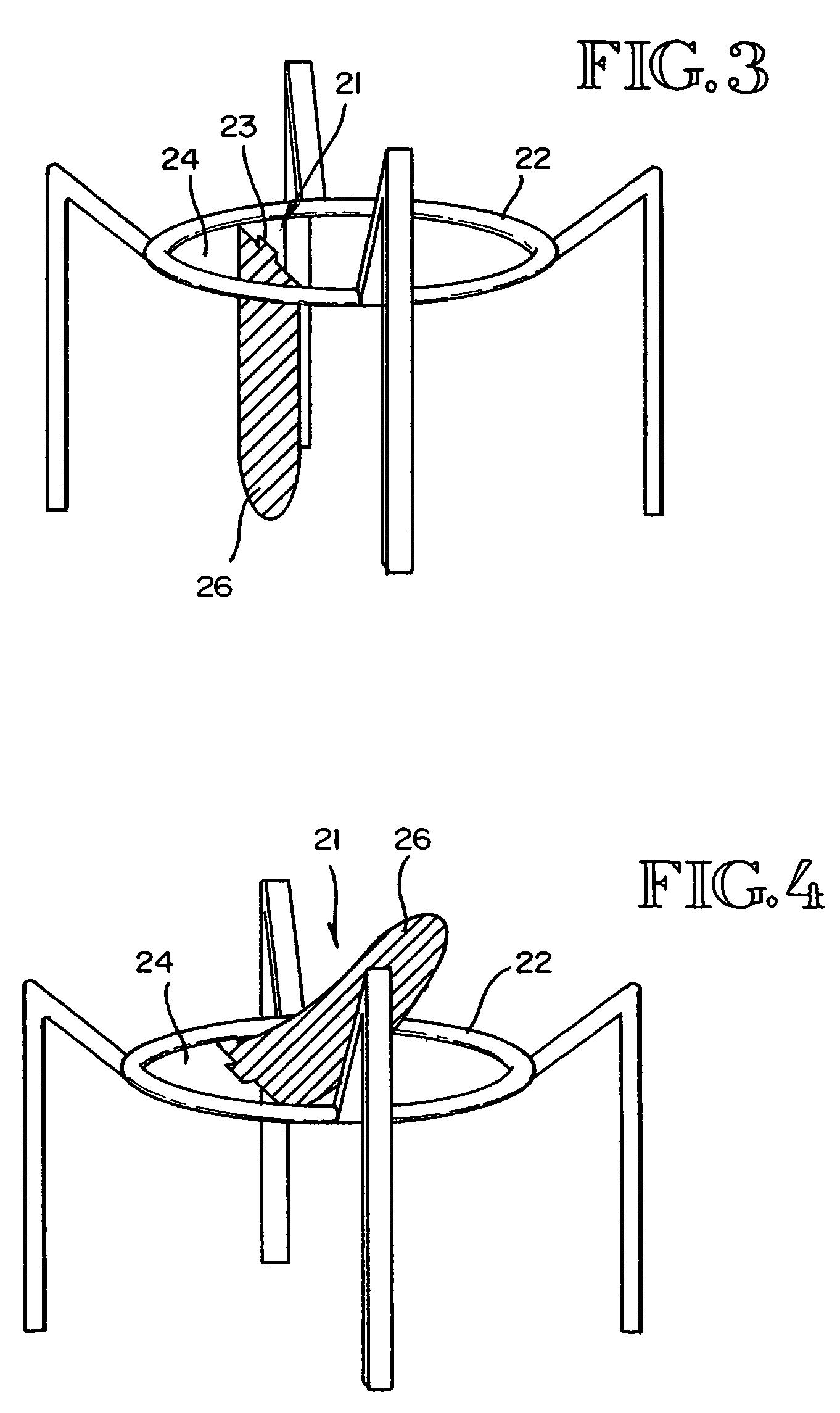
Apparatus and method for isolated lung access
Apparatus, systems, methods, and kits are provided for isolating a target lung segment and treating that segment, usually by drug delivery or lavage. The systems include at least a lobar or sub-lobar isolation catheter which is introduced beyond a second lung bifurcation (i.e., beyond the first bifurcation in a lobe of the lung) and which can occlude a bronchial passage at that point. An inner catheter is usually introduced through the isolation catheter and used in cooperation with the isolation catheter for delivering and / or removing drugs or washing liquids from the isolated lung region. Optionally, the inner catheter will also have an occluding member near its distal end for further isolation of a target region within the lung.
Owner:PULMONX
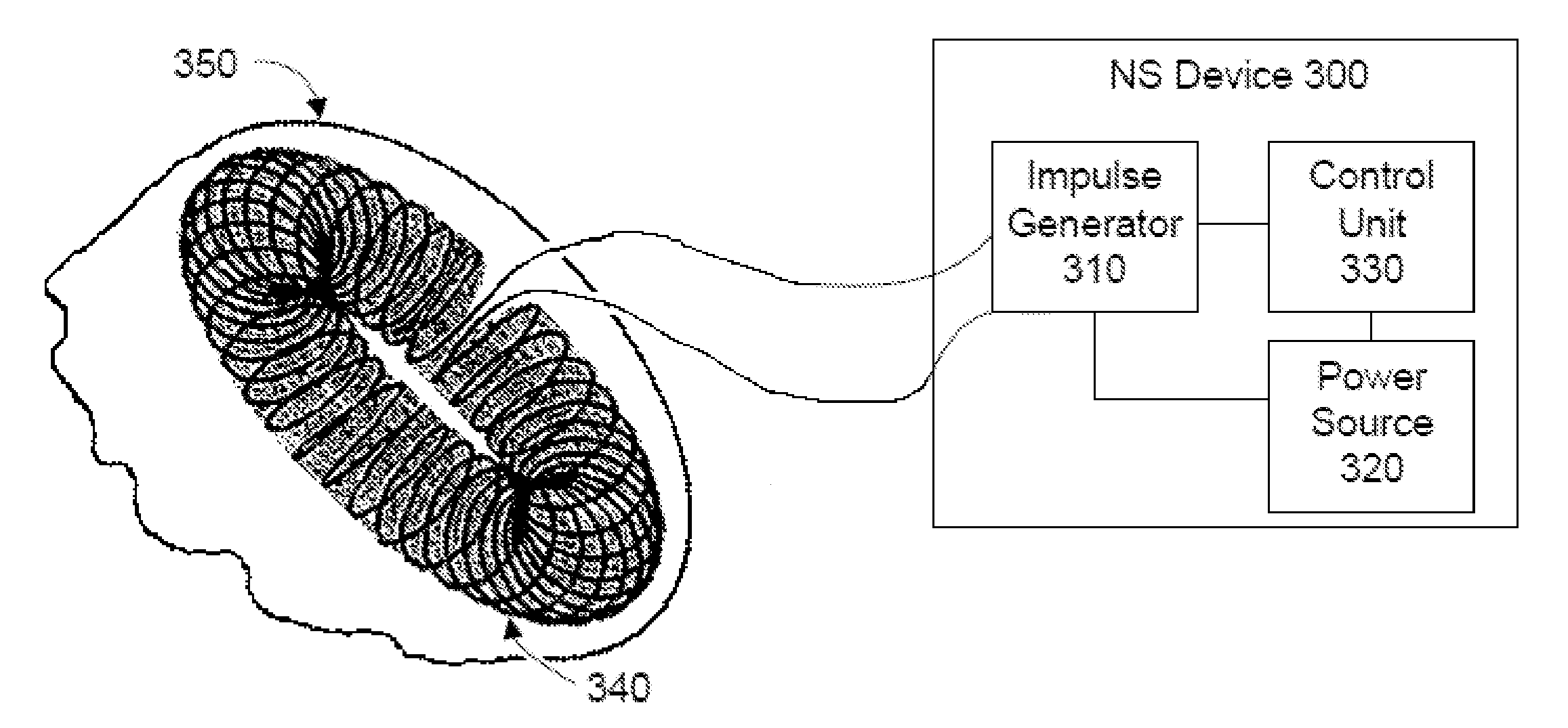
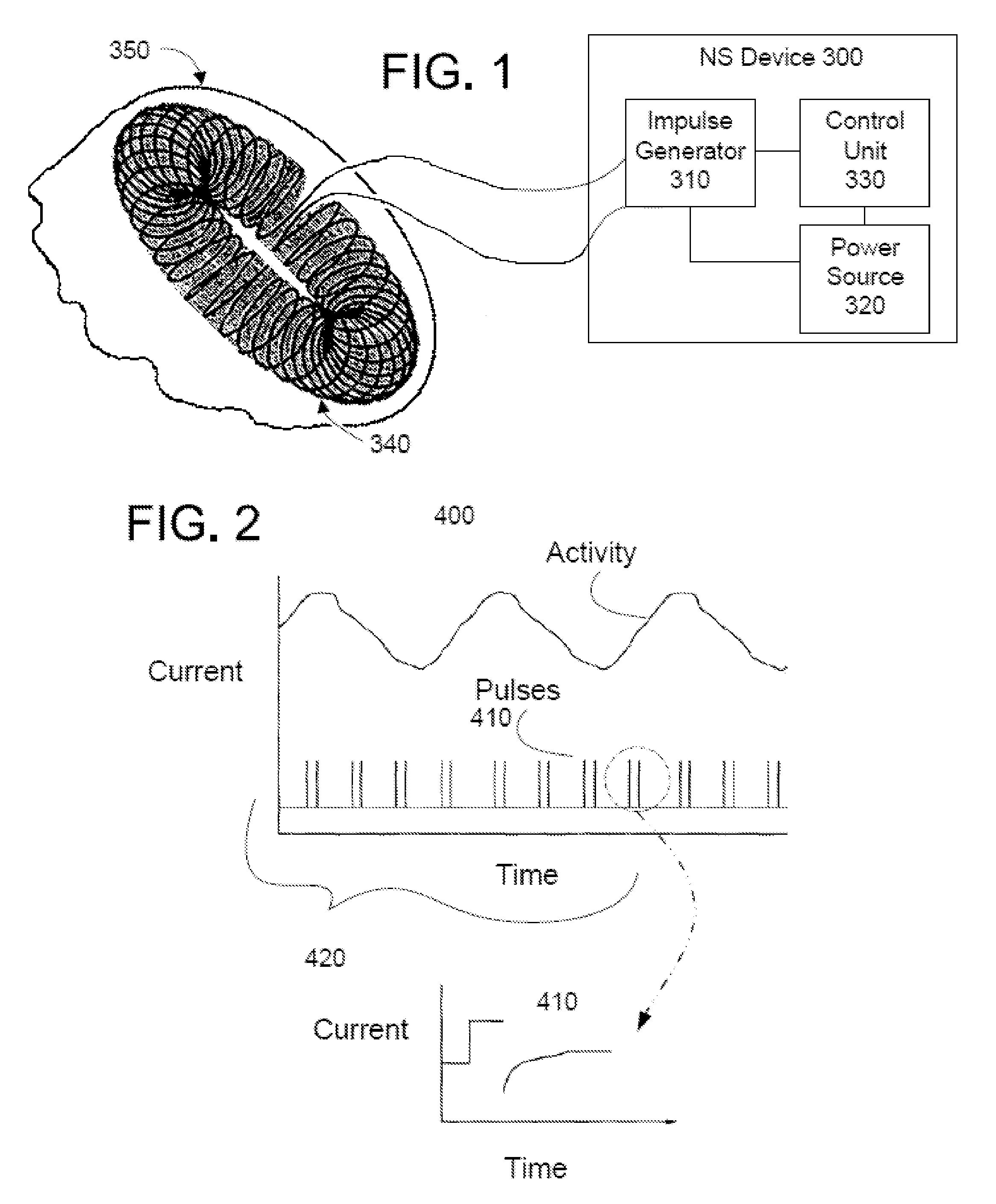
Non-invasive treatment of bronchial constriction
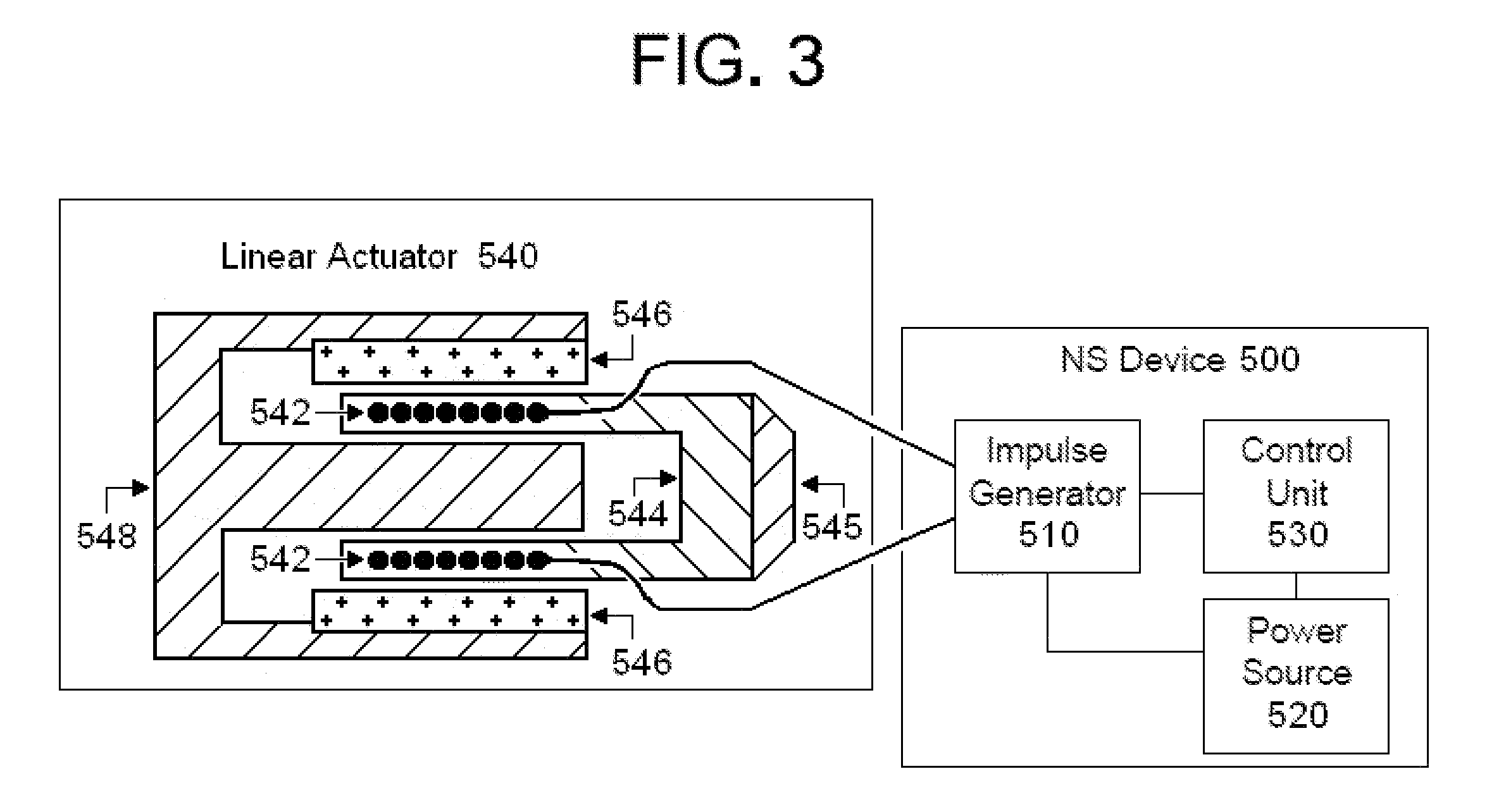
ActiveUS20110046432A1Relieve spasmsDilation increaseUltrasound therapyElectrotherapyNerve fiber bundleSmooth muscle
Devices, systems and methods are disclosed for treating bronchial constriction related to asthma, anaphylaxis or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. The treatment comprises transmitting impulses of energy non-invasively to selected nerve fibers that are responsible for smooth muscle dilation. The transmitted energy impulses, comprising magnetic and / or electrical, mechanical and / or acoustic, and optical and / or thermal energy, stimulate the selected nerve fibers.
Owner:ELECTROCORE
Bronchial flow control devices and methods of use
InactiveUS6941950B2Improved air flow dynamicSpeed up the flowBronchiEar treatmentRadiologyLung region
Disclosed are methods and devices for regulating fluid flow to and from a region of a patient's lung, such as to achieve a desired fluid flow dynamic to a lung region during respiration and / or to induce collapse in one or more lung regions. An identified region of the lung is targeted for treatment, such as to modify the flow to the targeted lung region or to achieve volume reduction or collapse of the targeted lung region. The targeted lung region is then bronchially isolated to regulate airflow into and / or out of the targeted lung region through one or more bronchial passageways that feed air to the targeted lung region. The bronchial isolation of the targeted lung region is accomplished by implanting a flow control device into a bronchial passageway that feeds air to a targeted lung region.
Owner:PULMONX
Methods, systems and devices for improving ventilation in a lung area
ActiveUS20050005936A1Facilitates of gas concentrationEasy pressure controlTracheal tubesOperating means/releasing devices for valvesDiseaseMechanical ventilation
Methods, systems and devices are described for new modes of ventilation in which specific lung areas are ventilated with an indwelling trans-tracheobronchial catheter for the purpose of improving ventilation and reducing hyperinflation in that specific lung area, and for redistributing inspired air to other healthier lung areas, for treating respiratory disorders such as COPD, ARDS, SARS, CF, and TB. Trans-Tracheobronchial Segmental Ventilation (TTSV) is performed on either a naturally breathing or a mechanical ventilated patient by placing a uniquely configured indwelling catheter into a bronchus of a poorly ventilated specific lung area and providing direct ventilation to that area. The catheter can be left in place for extended periods without clinician attendance or vigilance. Ventilation includes delivery of respiratory gases, therapuetic gases or agents and evacuation of stagnant gases, mixed gases or waste fluids. Typically the catheter's distal tip is anchored without occluding the bronchus but optionally may intermittently or continuously occlude the bronchus. TTSV is optionally performed by insufflation only of the area, or by application of vacuum to the area, can include elevating or reducing the pressure in the targeted area to facilitate stagnant gas removal, or can include blocking the area to divert inspired gas to better functioning areas.
Owner:BREATHE TECHNOLOGIES INC
Use of NSAIDs for prevention and treatment of cellular abnormalities of the lung or bronchial pathway
InactiveUS20030004142A1High concentrationMinimal exposureBiocideSalicyclic acid active ingredientsSurgeryNon steroidal anti inflammatory
Owner:PRIOR CHRISTOPHER P +2
Compositions, formulations and kit with anti-sense oligonucleotide and anti-inflammatory steroid and/or obiquinone for treatment of respiratory and lung disesase
InactiveUS20070021360A1Decreased airwayOrganic active ingredientsBiocideDiseaseAntiendomysial antibodies
A pharmaceutical composition and formulations comprise preventative, prophylactic or therapeutic amounts of an oligo(s) anti-sense to a specific gene(s) or its corresponding mRNA(s), and a glucocorticoid and / or non-glucocorticoid steroid or a ubiquinone or their salts. The agents, composition and formulations are used for treatment of ailments associated with impaired respiration, bronchoconstriction, lung allergy(ies) or inflammation, and abnormal levels of adenosine, adenosine receptors, sensitivity to adenosine, lung surfactant and ubiquinone, such as pulmonary fibrosis, vasoconstriction, inflammation, allergies, allergic rhinitis, asthma, impeded respiration, lung pain, cystic fibrosis, bronchoconstriction, COPD, RDS, ARDS, cancer, and others. The present treatment is effectively administered by itself for conditions without known therapies, as a substitute for therapies exhibiting undesirable side effects, or in combination with other treatments, e.g. before, during and after other respiratory system therapies, radiation, chemotherapy, antibody therapy and surgery, among others. Each of the agents of this invention may be administered directly into the respiratory system so that they gain direct access to the lungs, or by other effective routes of administration. A kit comprises a delivery device, the agents and instructions for its use.
Owner:EPIGENESIS PHARMA LLC
Methods, systems and devices for improving ventilation in a lung area
ActiveUS7588033B2Effective and direct cannulationIncrease hyperinflationTracheal tubesOperating means/releasing devices for valvesDiseasePrimary bronchus
Methods, systems and devices are described for new modes of ventilation in which specific lung areas are ventilated with an indwelling trans-tracheobronchial catheter for the purpose of improving ventilation and reducing hyperinflation in that specific lung area, and for redistributing inspired air to other healthier lung areas, for treating respiratory disorders such as COPD, ARDS, SARS, CF, and TB. Trans-Tracheobronchial Segmental Ventilation (TTSV) is performed on either a naturally breathing or a mechanical ventilated patient by placing a uniquely configured indwelling catheter into a bronchus of a poorly ventilated specific lung area and providing direct ventilation to that area. The catheter can be left in place for extended periods without clinician attendance or vigilance. Ventilation includes delivery of respiratory gases, therapeutic gases or agents and evacuation of stagnant gases, mixed gases or waste fluids. Typically the catheter's distal tip is anchored without occluding the bronchus but optionally may intermittently or continuously occlude the bronchus. TTSV is optionally performed by insufflation only of the area, or by application of vacuum to the area, can include elevating or reducing the pressure in the targeted area to facilitate stagnant gas removal, or can include blocking the area to divert inspired gas to better functioning areas.
Owner:BREATHE TECHNOLOGIES INC
Electrical stimulation treatment of bronchial constriction
ActiveUS20070106339A1Avoid hard activationElectrotherapyArtificial respirationRadiologyElectrical impulse
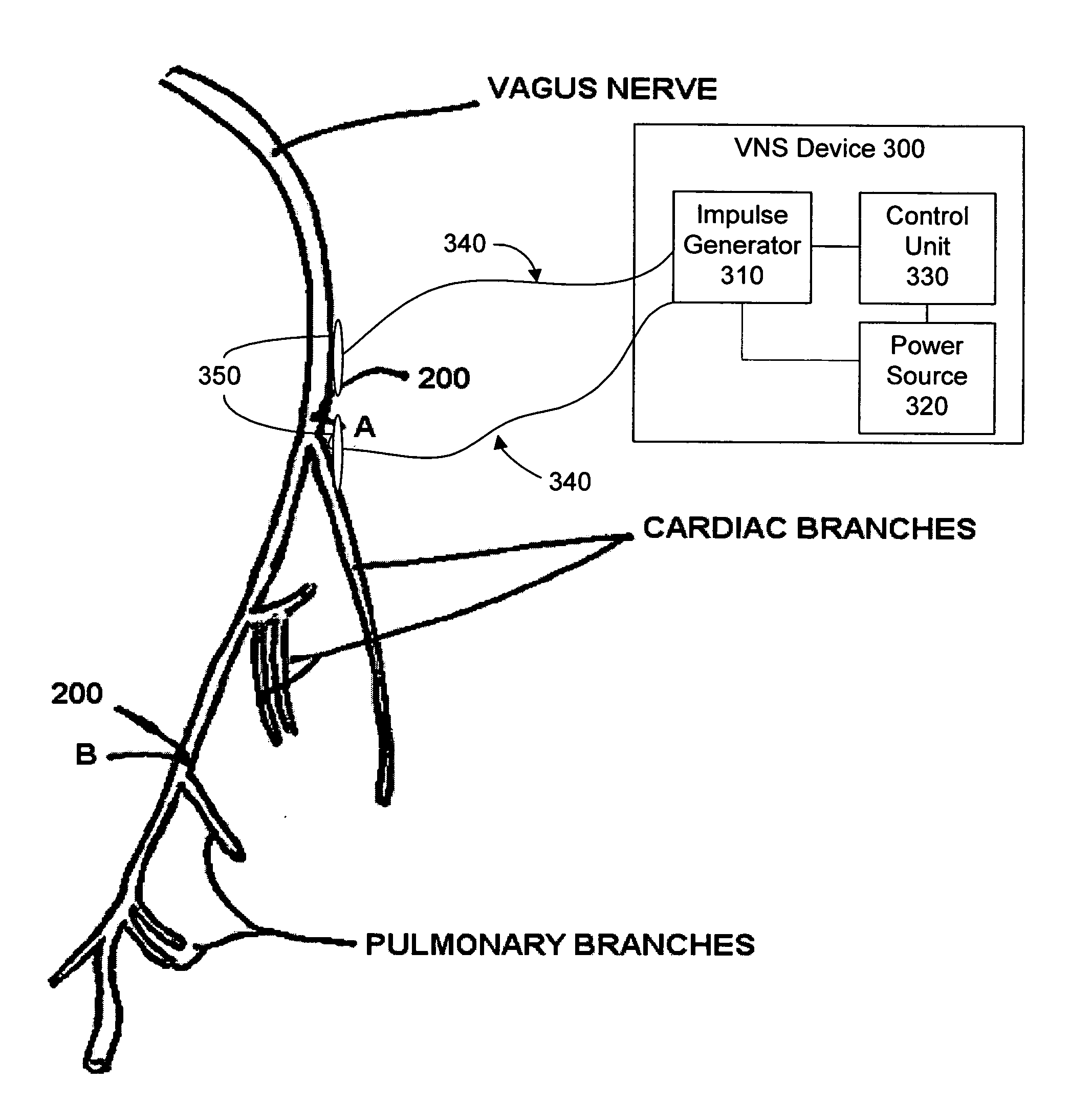
Methods and devices for treating bronchial constriction related to asthma and anaphylaxis wherein the treatment includes providing an electrical impulse to a selected region of the vagus nerve and / or the lungs of a patient suffering from bronchial constriction.
Owner:ELECTROCORE
Treatment of Asthma and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease With Anti-proliferate and Anti-inflammatory Drugs
InactiveUS20080175887A1Promote absorptionOrganic active ingredientsPowdered material dispensingDiseaseObstructive Pulmonary Diseases
Embodiments of the present invention provide a method for treatment of respiratory disorders such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and chronic sinusitis, including cystic fibrosis, interstitial fibrosis, chronic bronchitis, emphysema, bronchopulmonary dysplasia and neoplasia. The method involves administration, preferably oral, nasal or pulmonary administration, of anti-inflammatory and anti-proliferative drugs (rapamycin or paclitaxel and their analogues).
Owner:LUTONIX INC
Method and apparatus for performance of thermal bronchiplasty with unfocused ultrasound
InactiveUS20160287912A1Reduce the possibilityAvoid insufficient temperatureUltrasound therapyBronchoscopesSonificationLarge target
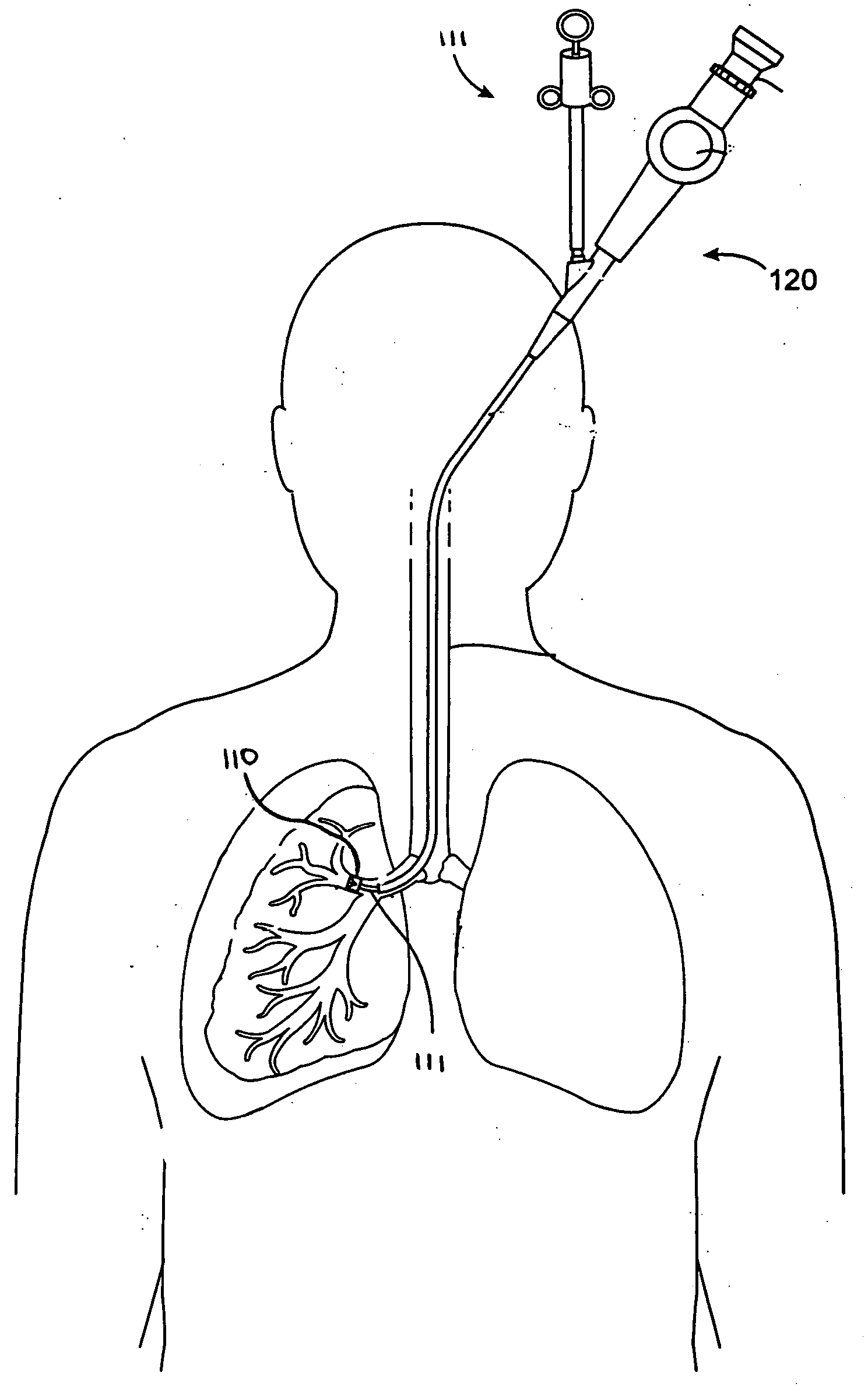
Apparatus and methods for deactivating bronchial nerves and smooth muscle extending along a bronchial branch of a mammalian subject to treat asthma and related conditions. An electromechanical transducer (11) is inserted into the bronchus as, for example, by advancing the distal end of a catheter (10) bearing the transducer into the bronchial section to be treated. The electromechanical transducer emits unfocused mechanical vibratory energy of one or more ultrasonic frequencies so as to heat tissues throughout a relatively large target region (13) as, for example, at least about 1 cm3 encompassing the bronchus to a temperature sufficient to inactivate nerves but insufficient to cause rapid ablation or necrosis of organic tissues. The treatment can be performed without locating or focusing on individual bronchial nerves.
Owner:GUIDED INTERVENTIONS
Treatment planning with implantable bronchial isolation devices
Disclosed is a treatment planning method that can be used to maximize the effectiveness of minimally invasive treatment on a patient. Pursuant to the treatment planning method, the presence of lung disease, such as emphysema, is first identified, followed by a determination of the distribution and extent of damage of the disease, followed by a determination of whether the patient is suitable for treatment, and a determination of the appropriate strategy for treatment for a suitable patient.
Owner:PULMONX
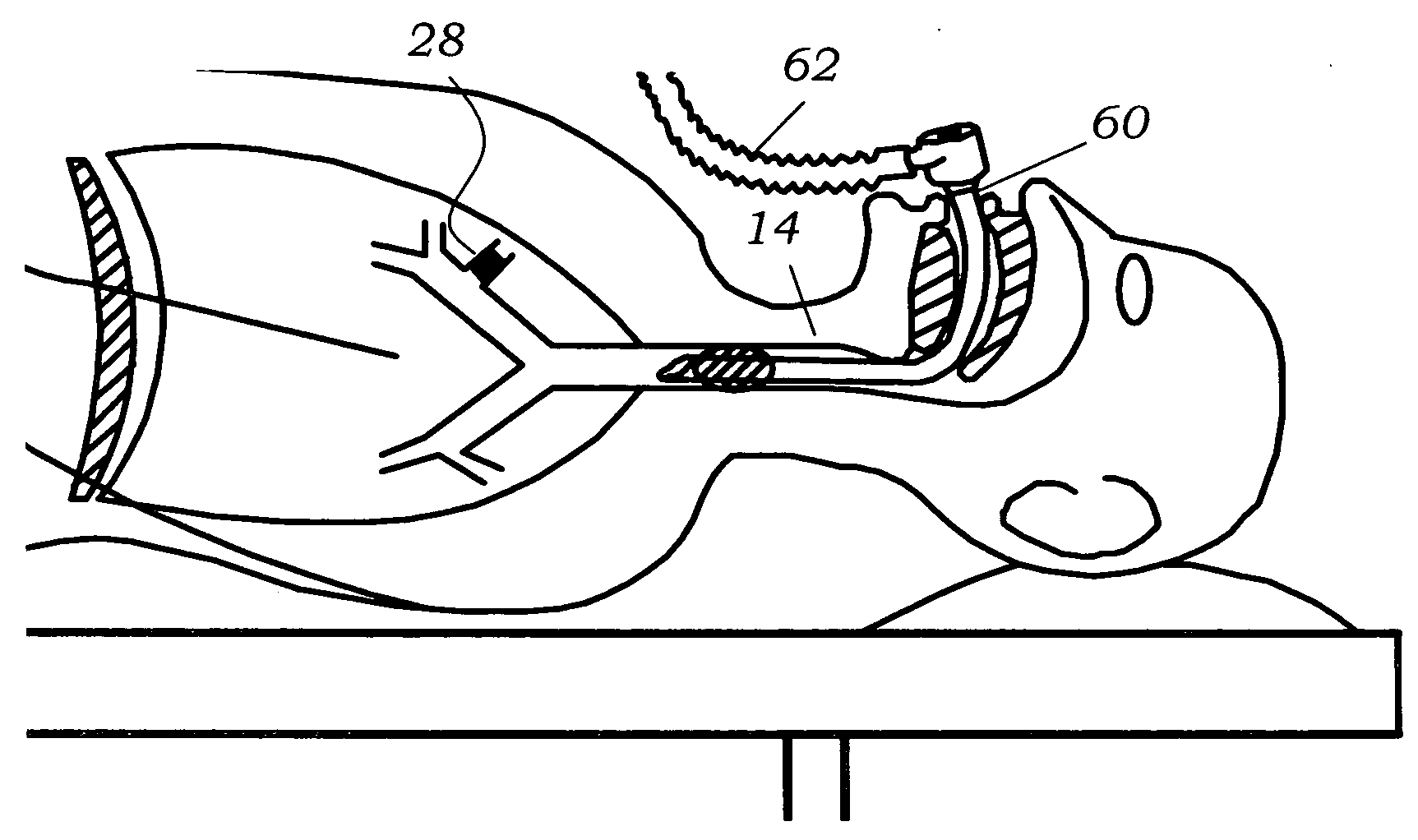
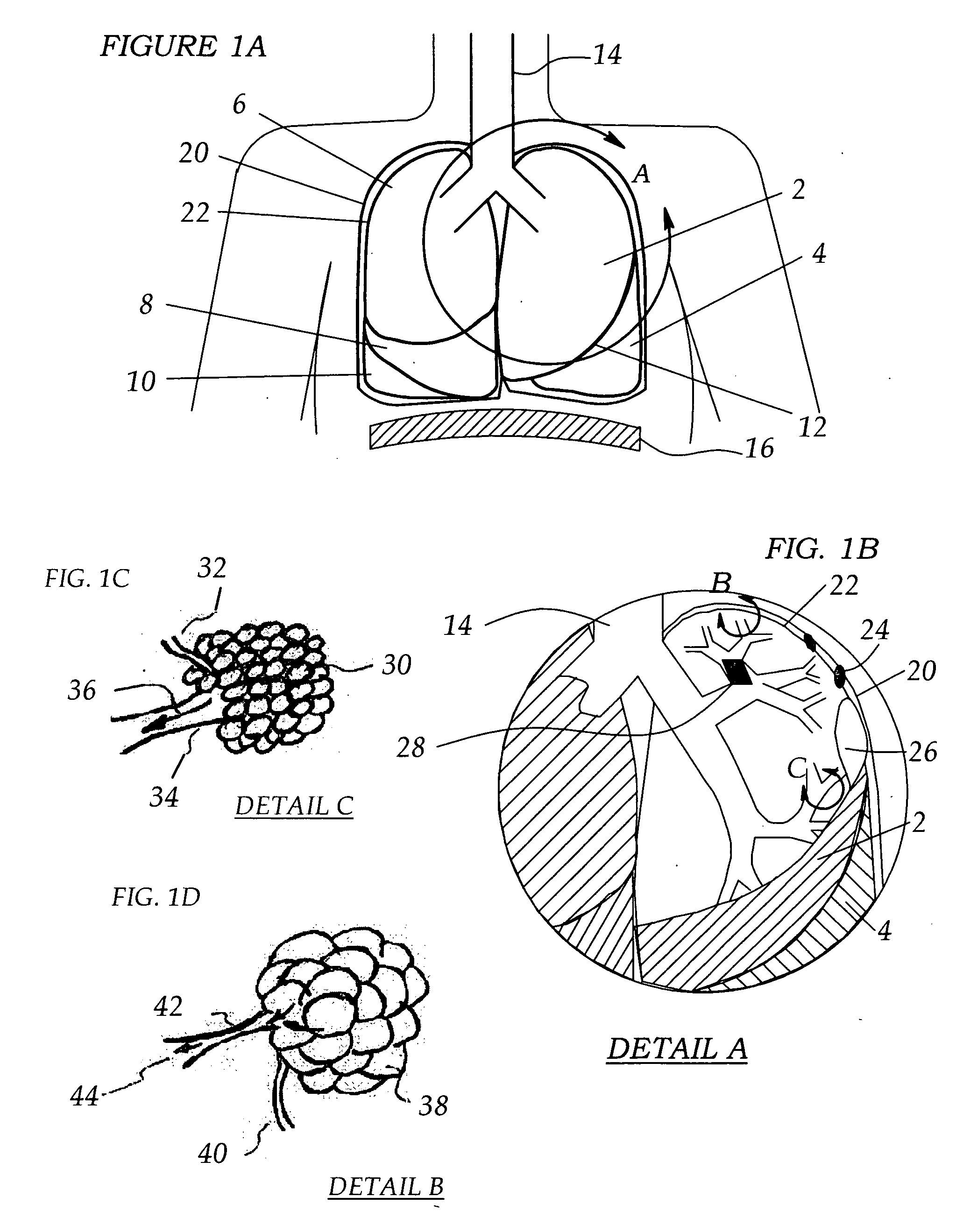
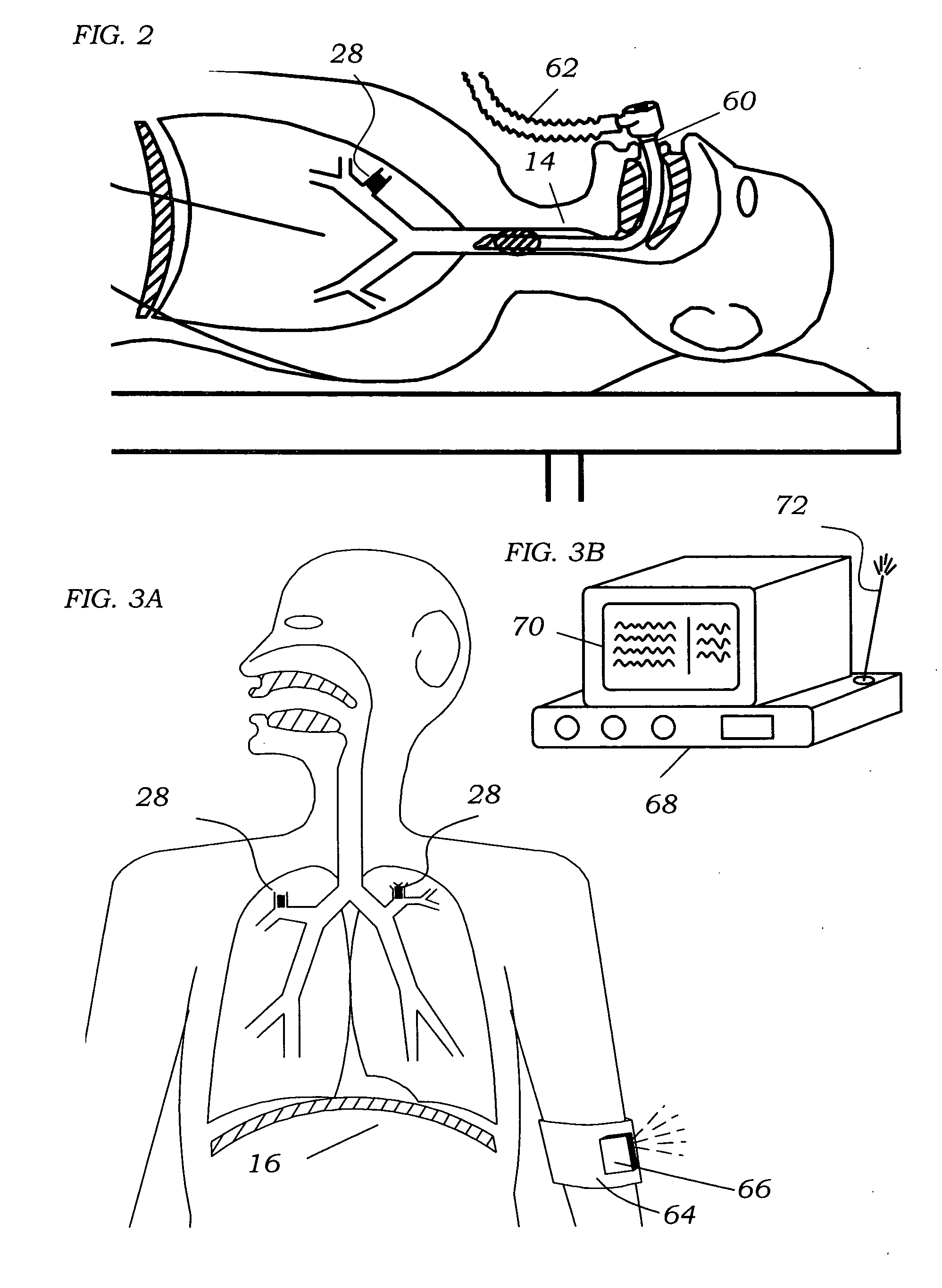
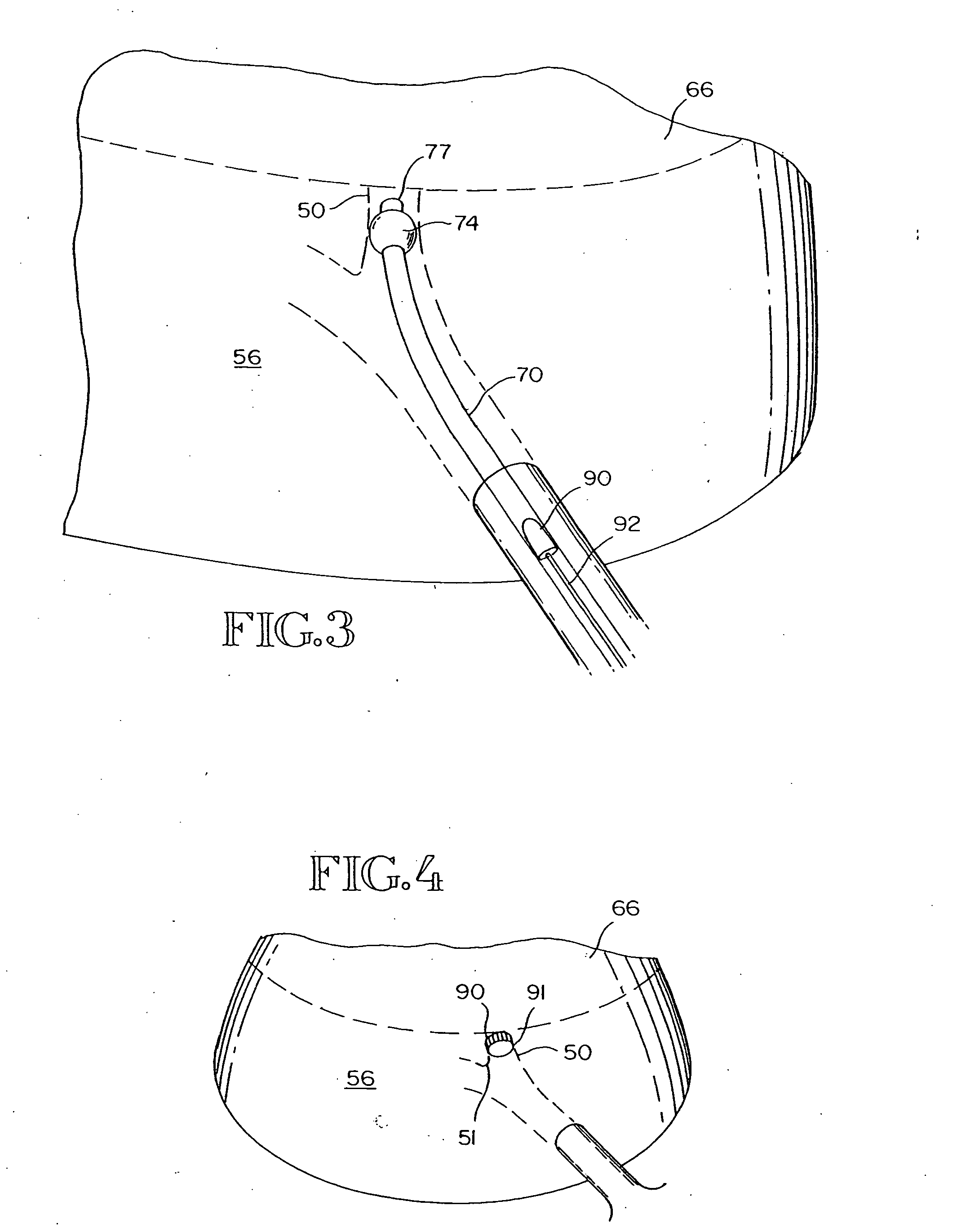
Implantable Devices And Methods For Stimulation Of Cardiac And Other Tissues
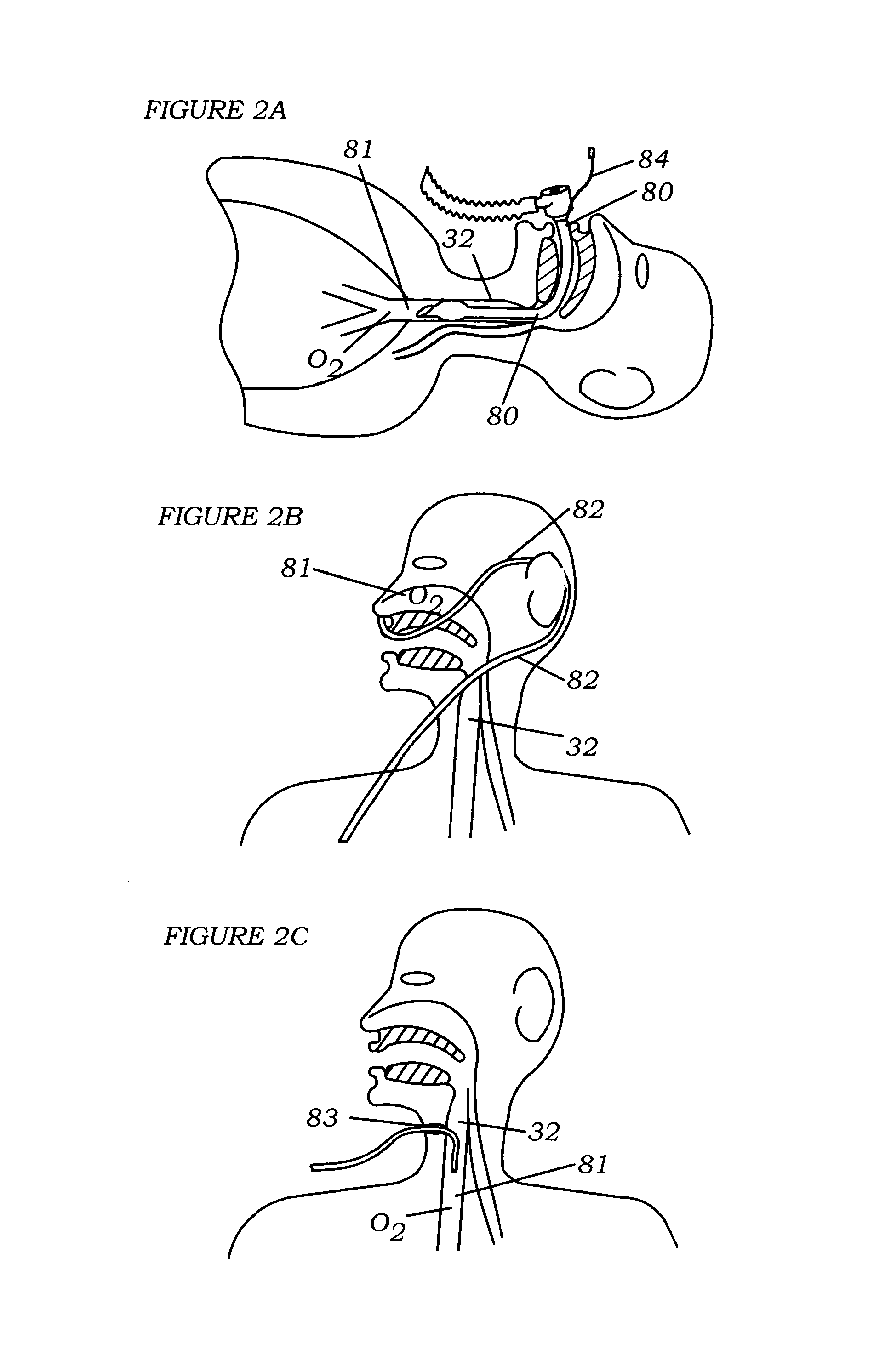
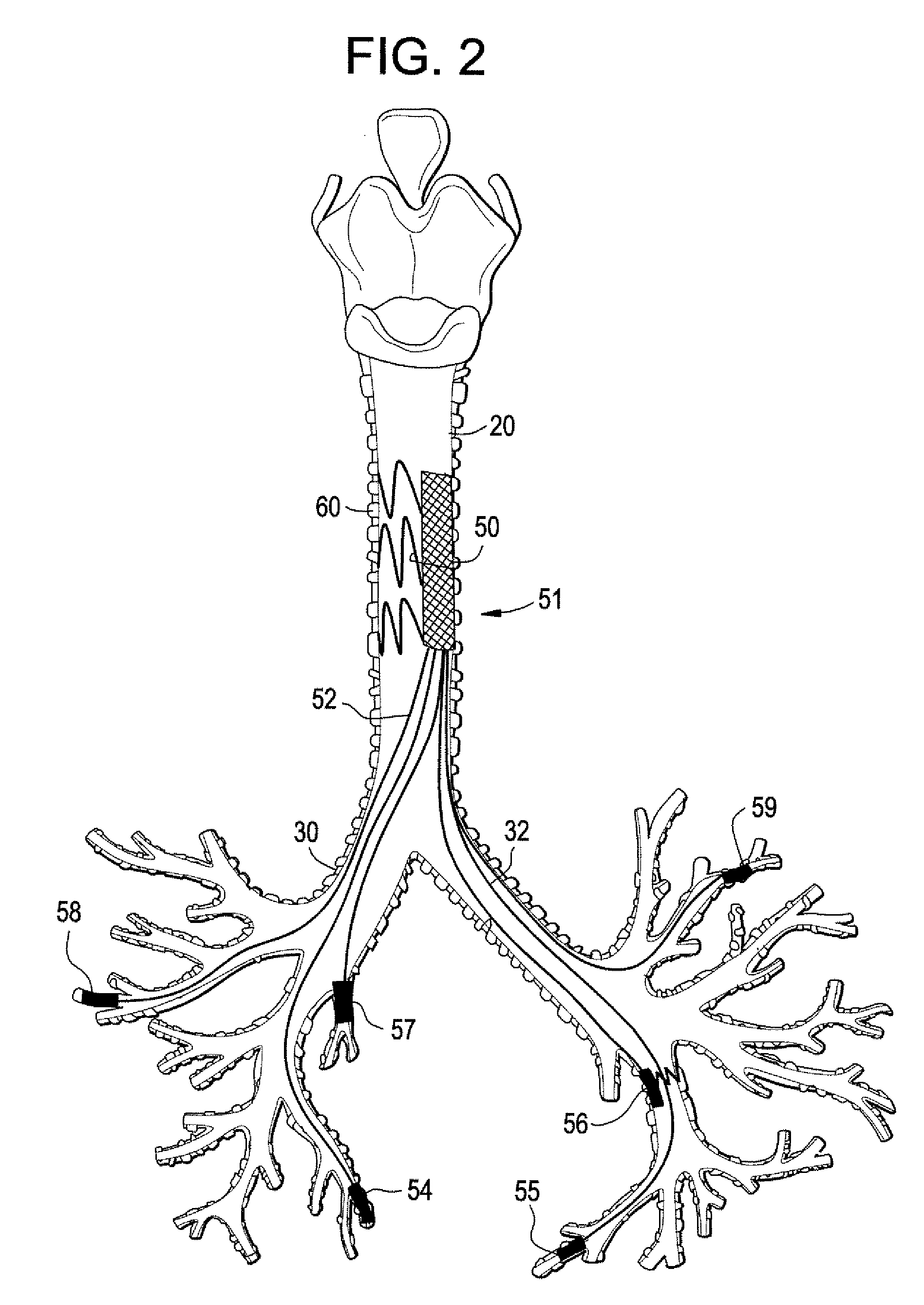
An implantable system is provided for stimulation of the heart, phrenic nerve, or other tissue structures accessible via a patient's airway. The stimulation system includes an implantable controller housing which includes a pulse generator; at least one electrical lead attachable to said pulse generator; and at least one electrode carried by the at least one electrical lead, wherein the at least one electrode is positionable and fixable at a selected position within an airway of a patient. The controller housing may be adaptable for implantation subcutaneous, or alternatively, at a selected position within the patient's trachea or bronchus, wherein the controller housing is proportioned to substantially permit airflow through the patient's airway about housing.
Owner:E PACING
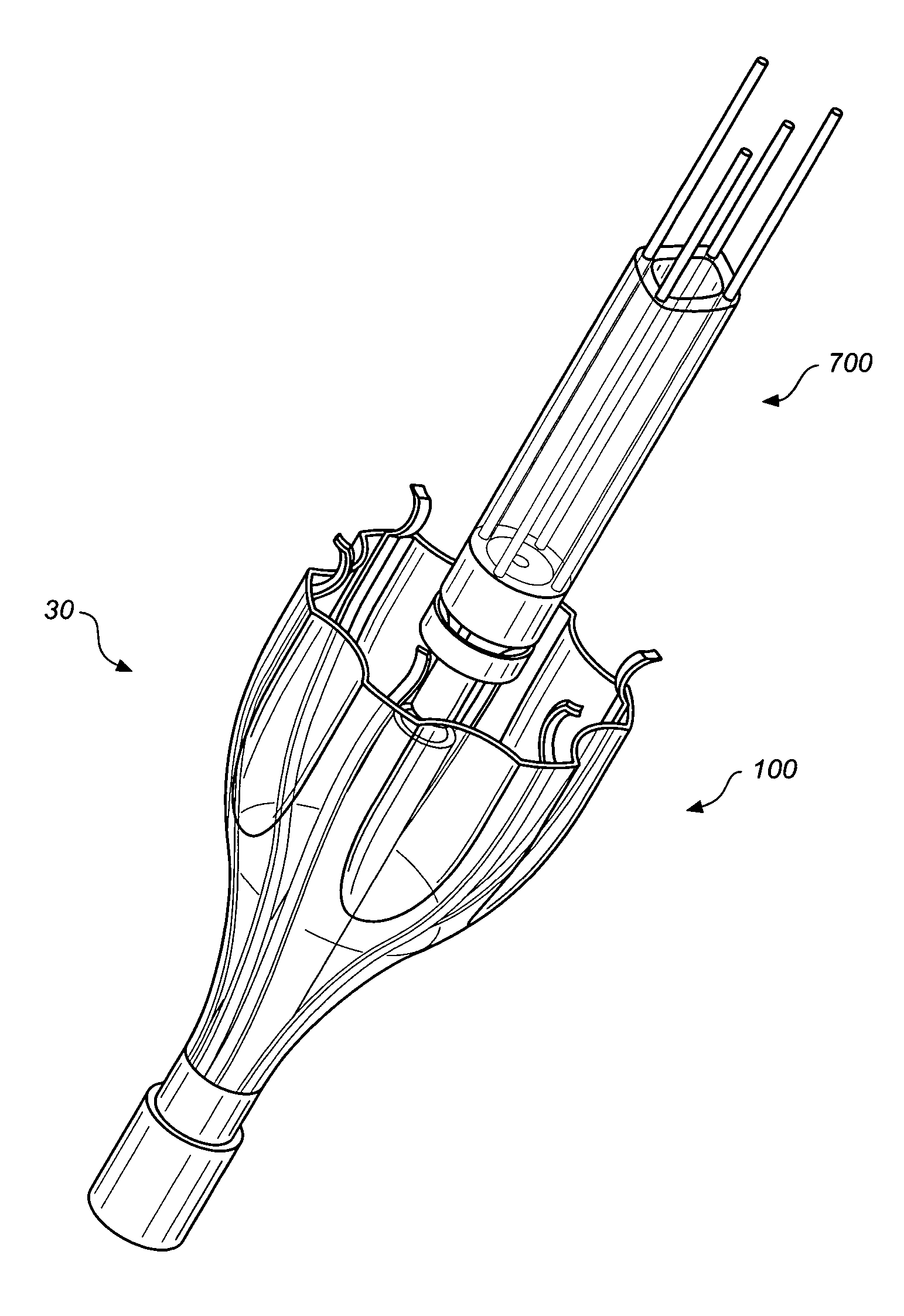
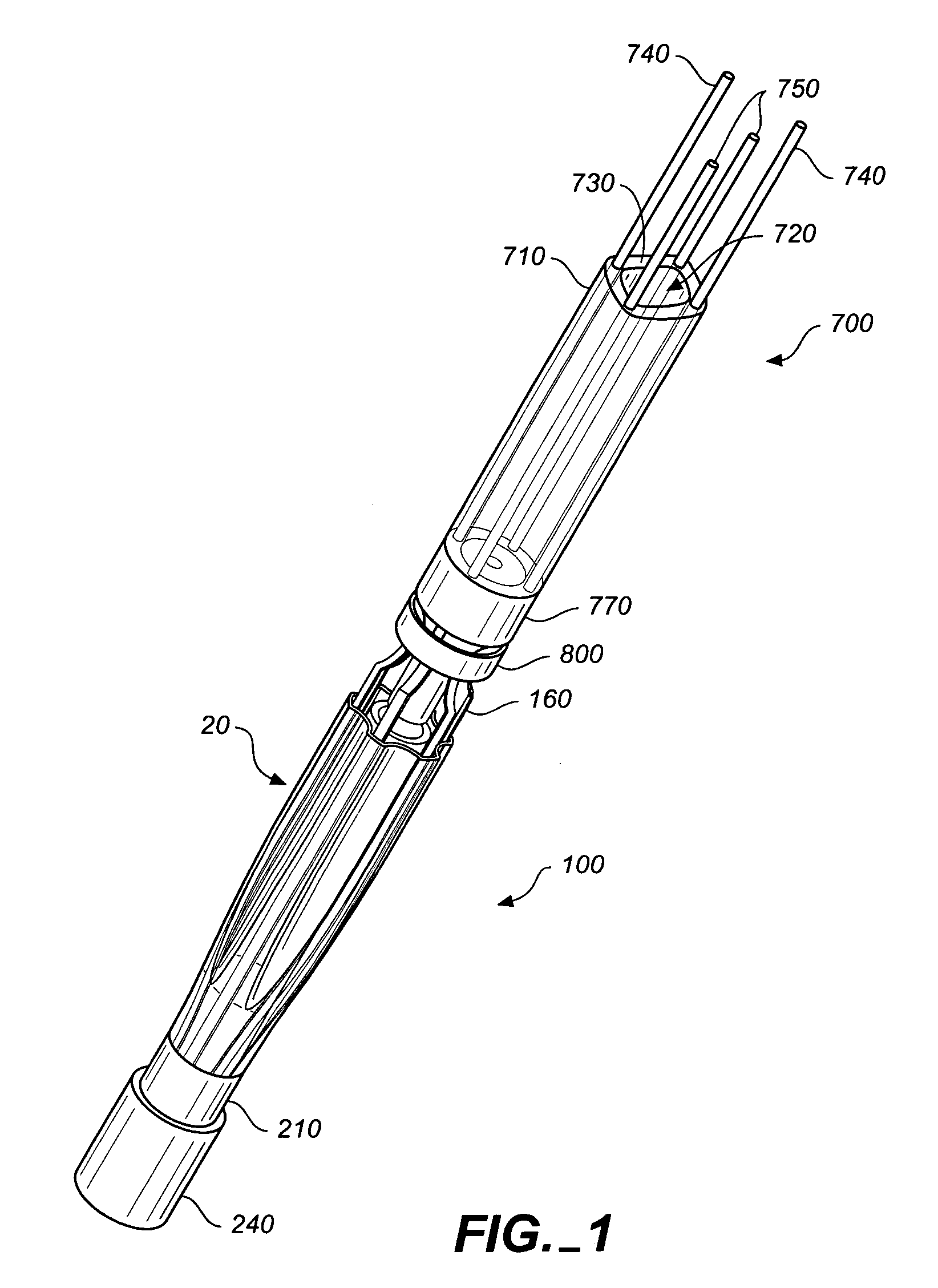
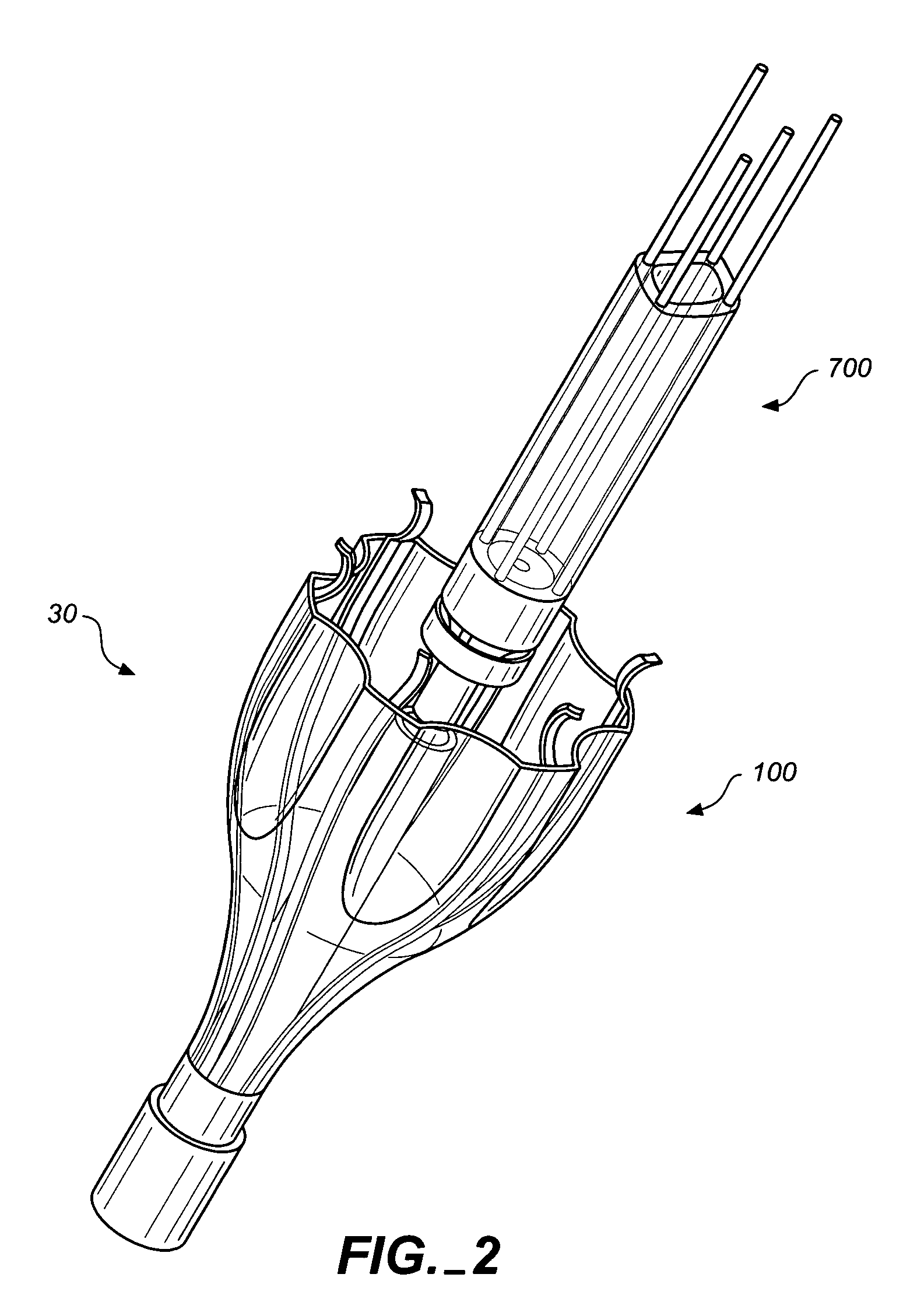
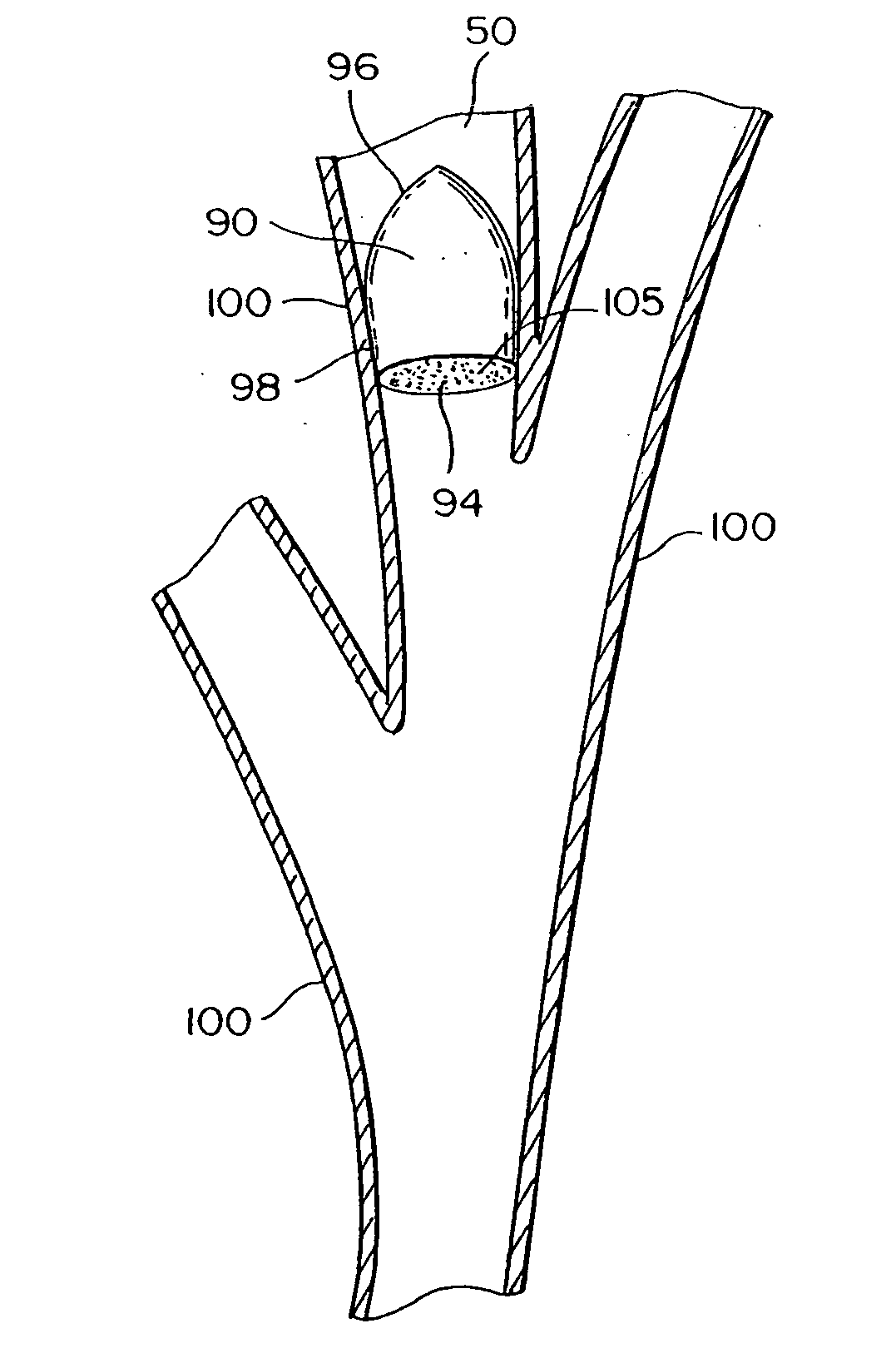
Intra-bronchial lung volume reduction system
InactiveUS20050288702A1Reducing collateral flowBalloon catheterMulti-lumen catheterLung volume reductionDelivery system
The invention provides devices and systems for treating lungs. One aspect of the invention provides a lung device with an expandable member having an open lumen formed therethrough, the expandable (e.g., inflatable and compliant) member having an expanded diameter adapted to contact a circumferential wall portion of a lung air passageway. The device may also include a plug adapted to close the open lumen and a coupler adapted to couple the plug and the expandable member. Another aspect of the invention provides a lung device and delivery system including: an expandable member having an open lumen formed therethrough, the expandable member having an expanded diameter adapted to fit within a lung air passageway; and a delivery catheter adapted to deliver the expandable member to a lung air passageway, the delivery catheter having a coupler adapted to couple the catheter to the expandable member.
Owner:PNEUMRX
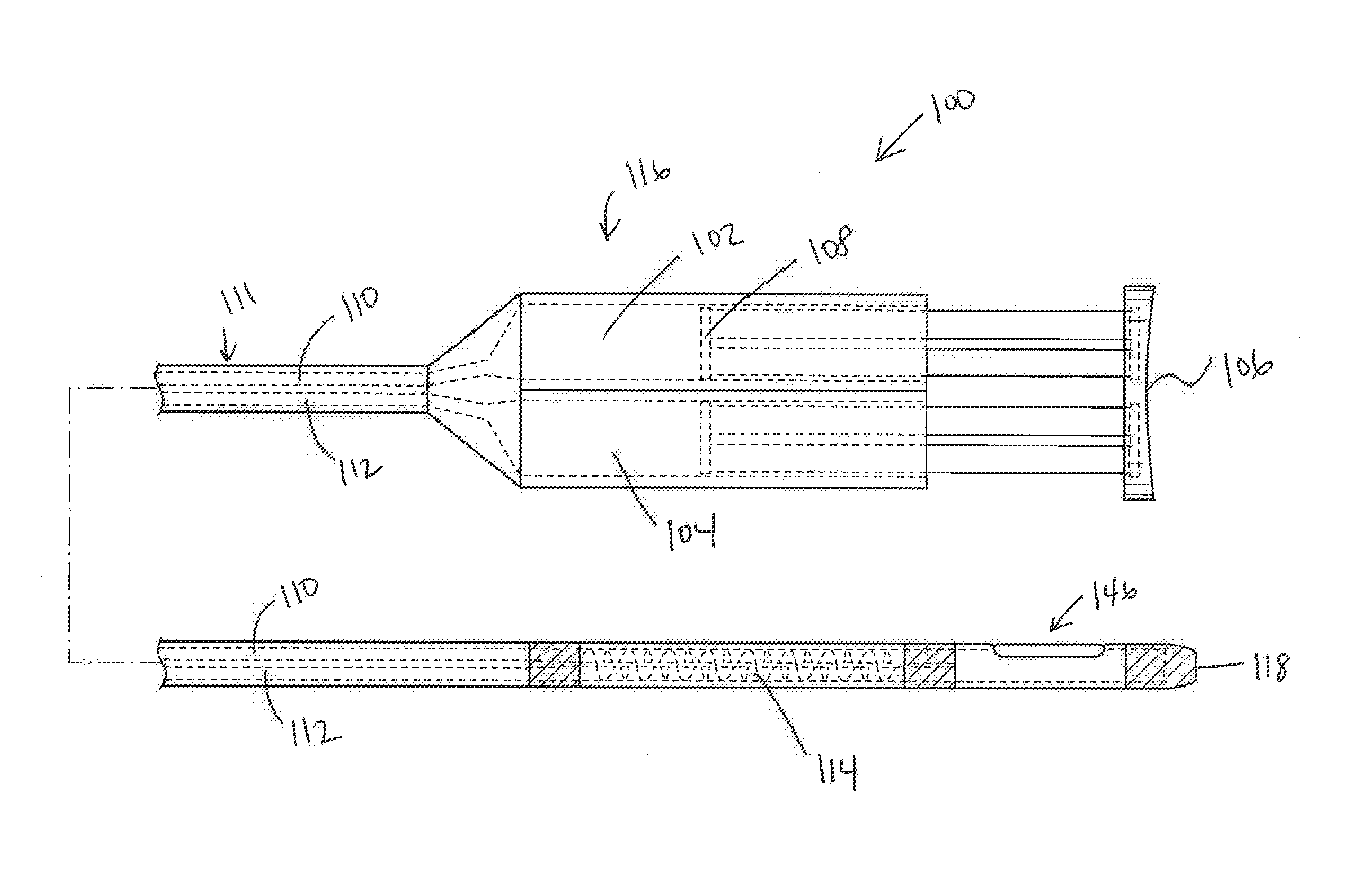
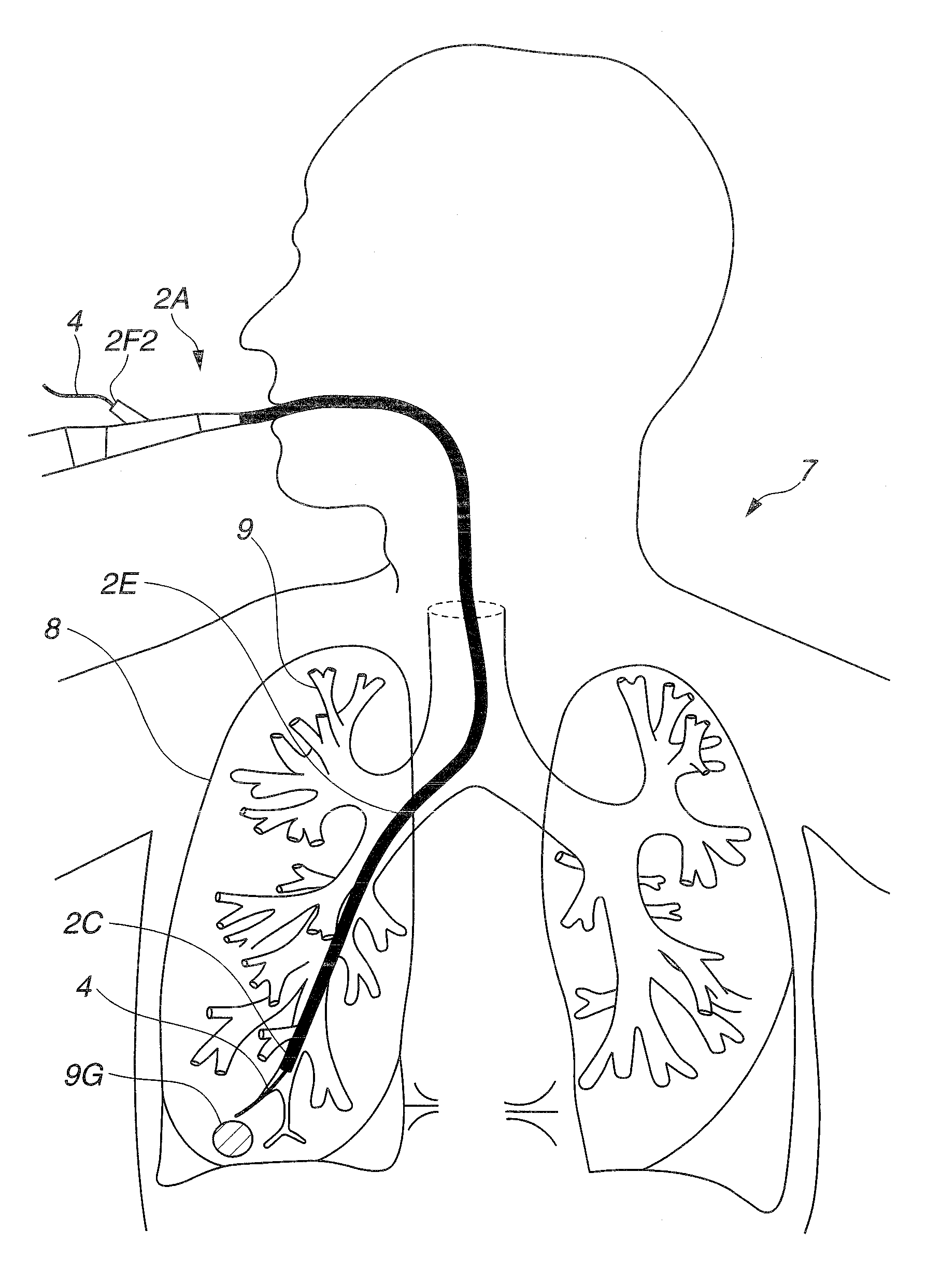
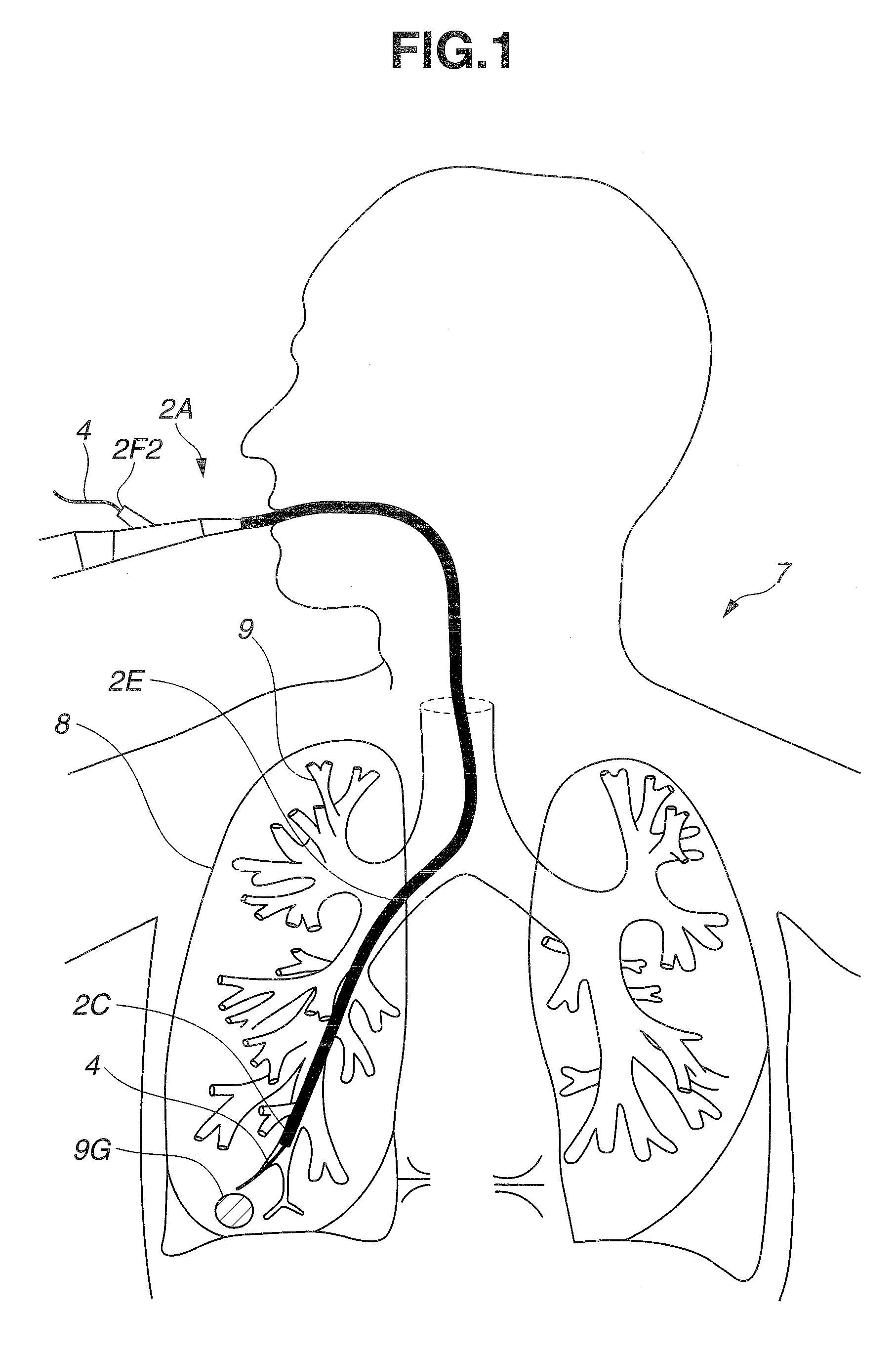
Intra-bronchial apparatus for aspiration and insufflation of lung regions distal to placement or cross communication and deployment and placement system therefor
InactiveUS7451765B2Reduce deliveryEasy to useTracheal tubesEar treatmentIntensive care medicineLung region
An anchored intra-bronchial apparatus for placement and deployment into selected airways and a method for using the same. When deployed, the apparatus creates a restriction of air flow to one or more targeted lung regions and achieves total lung volume reduction through a collapse or partial collapse of the targeted regions. The air flow valve of the apparatus includes a through lumen that permits drug delivery concurrent with lung volume reduction procedure.
Owner:ADLER MARK
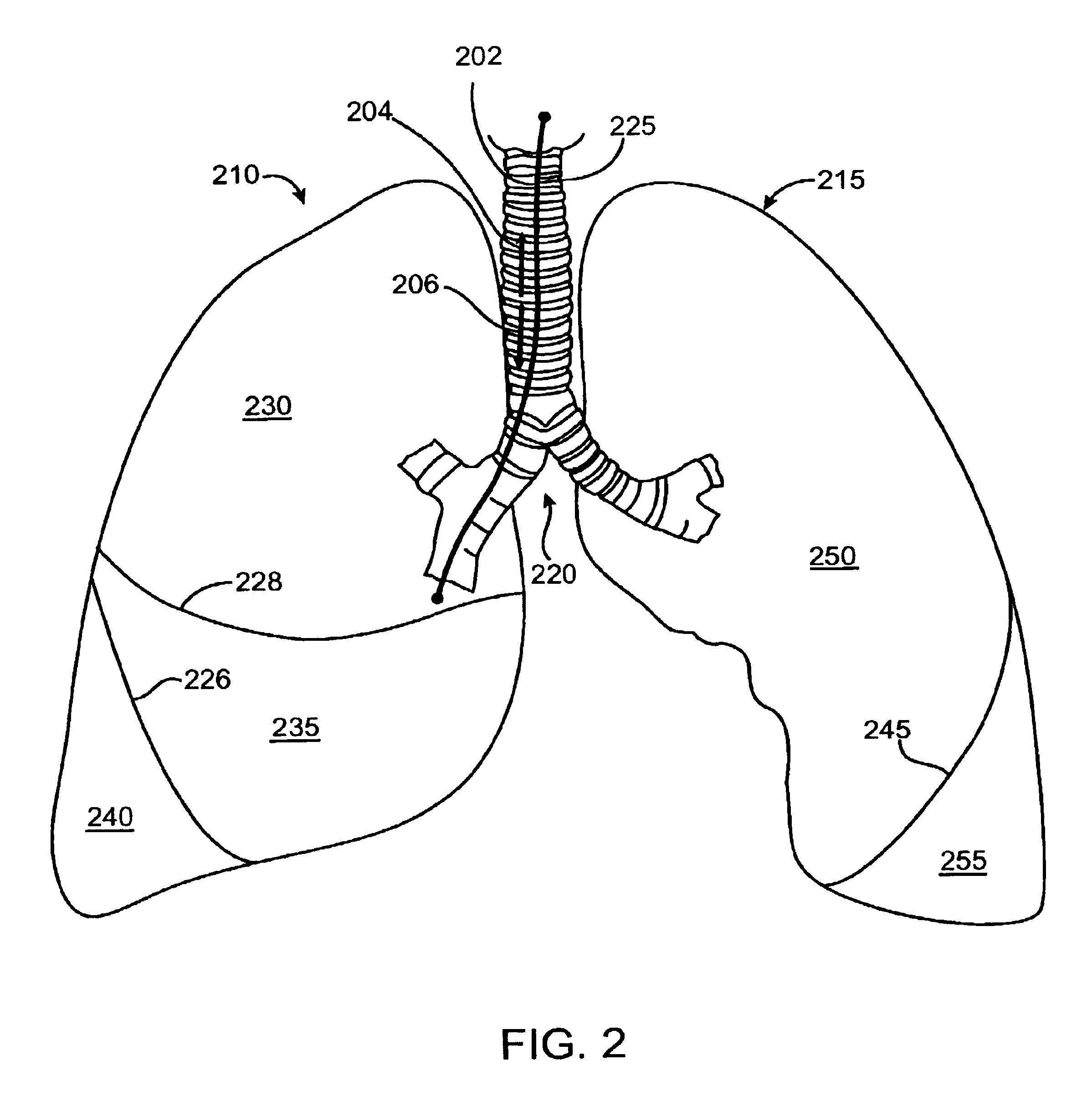
Methods, systems & devices for endobronchial ventilation and drug delivery
Methods, systems and devices are described for Endobronchial Ventilation using an endobronchially implanted ventilator for the purpose of treating COPD, emphysema and other lung diseases. Endobronchial drug delivery is also described using an endobronchially implanted drug pump, for therapeutic treatment of the lung or of other organs and tissues.
Owner:WONDKA ANTHONY DAVID
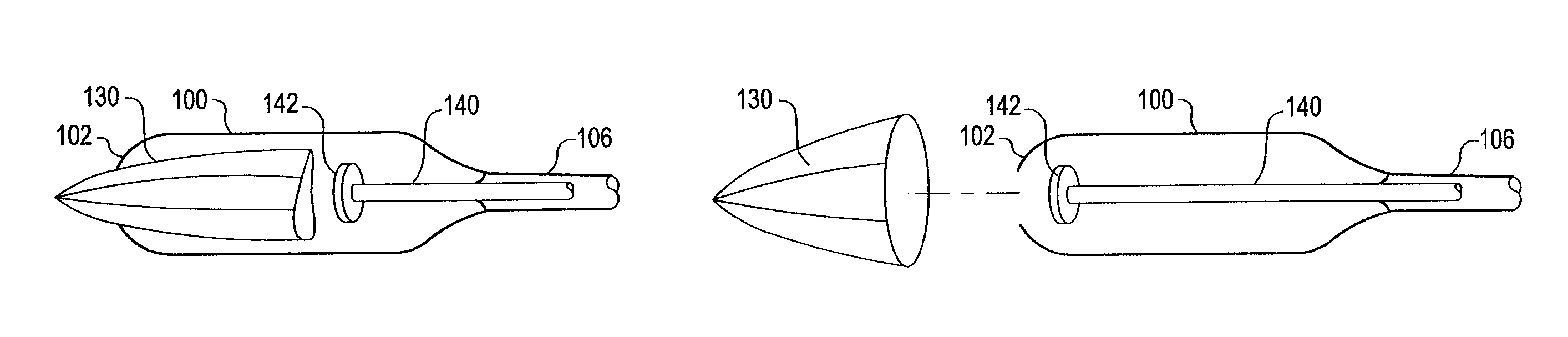
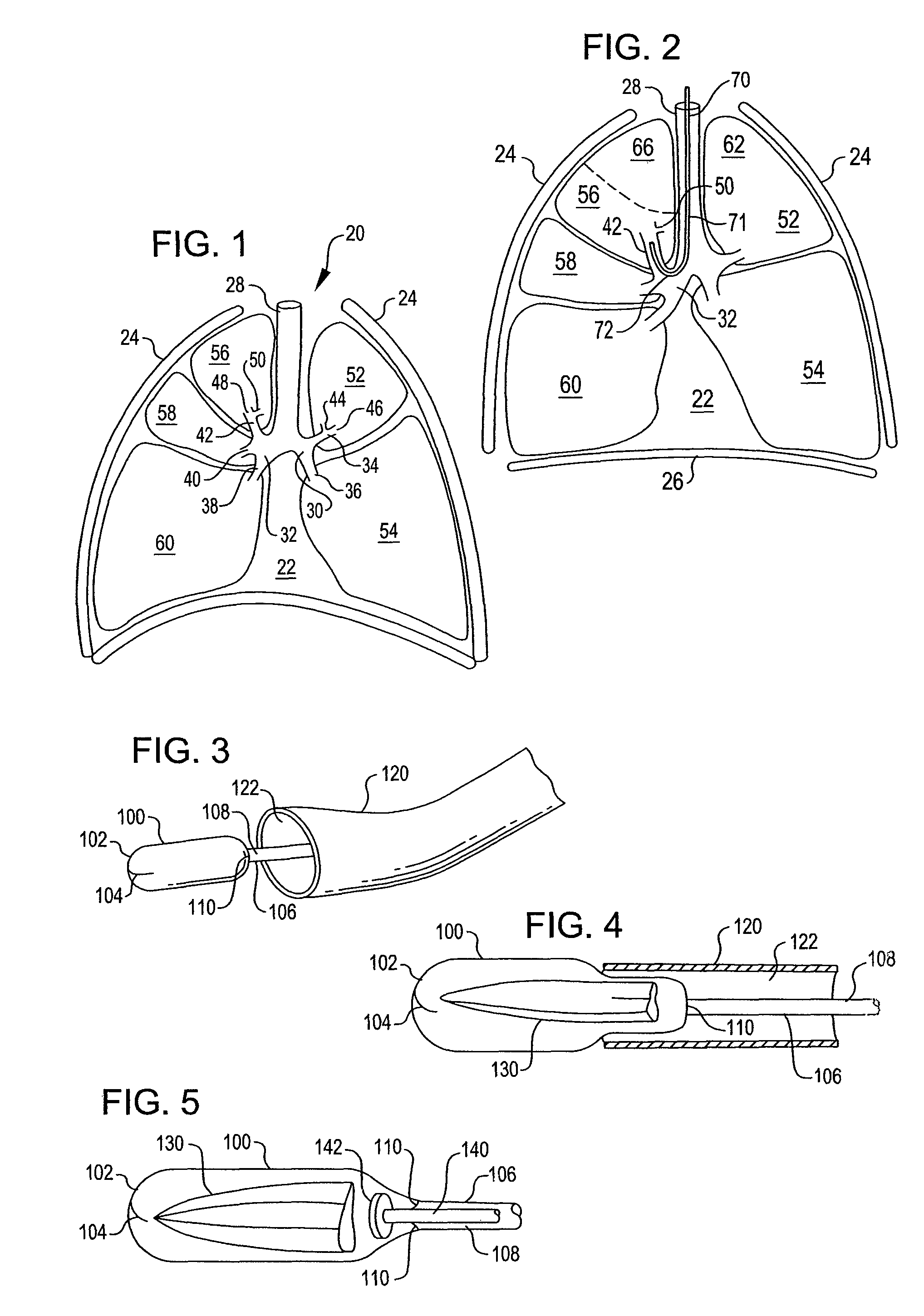
Apparatus and method for deployment of a bronchial obstruction device
An apparatus and method deploy a self-expandable bronchial obstruction device in an air passageway. The apparatus includes a catheter configured to be passed down the trachea. The apparatus further includes a capsule for housing the self-expandable bronchial obstruction device in a sterile environment. The capsule is configured to be advanced down the catheter. The capsule further includes a tubular extension. The capsule has a breakable seam so as to release the bronchial obstruction device in the air passageway upon a proximal force being exerted upon the bronchial obstruction device. The method includes guiding a conduit down a trachea into the air passageway. The method further includes advancing a capsule having a bronchial device therein down an internal lumen of the conduit into the air passageway. The method further includes releasing the bronchial device from the capsule. The method further includes deploying the bronchial device into the air passageway.
Owner:GYRUS ACMI INC (D B A OLYMPUS SURGICAL TECH AMERICA)
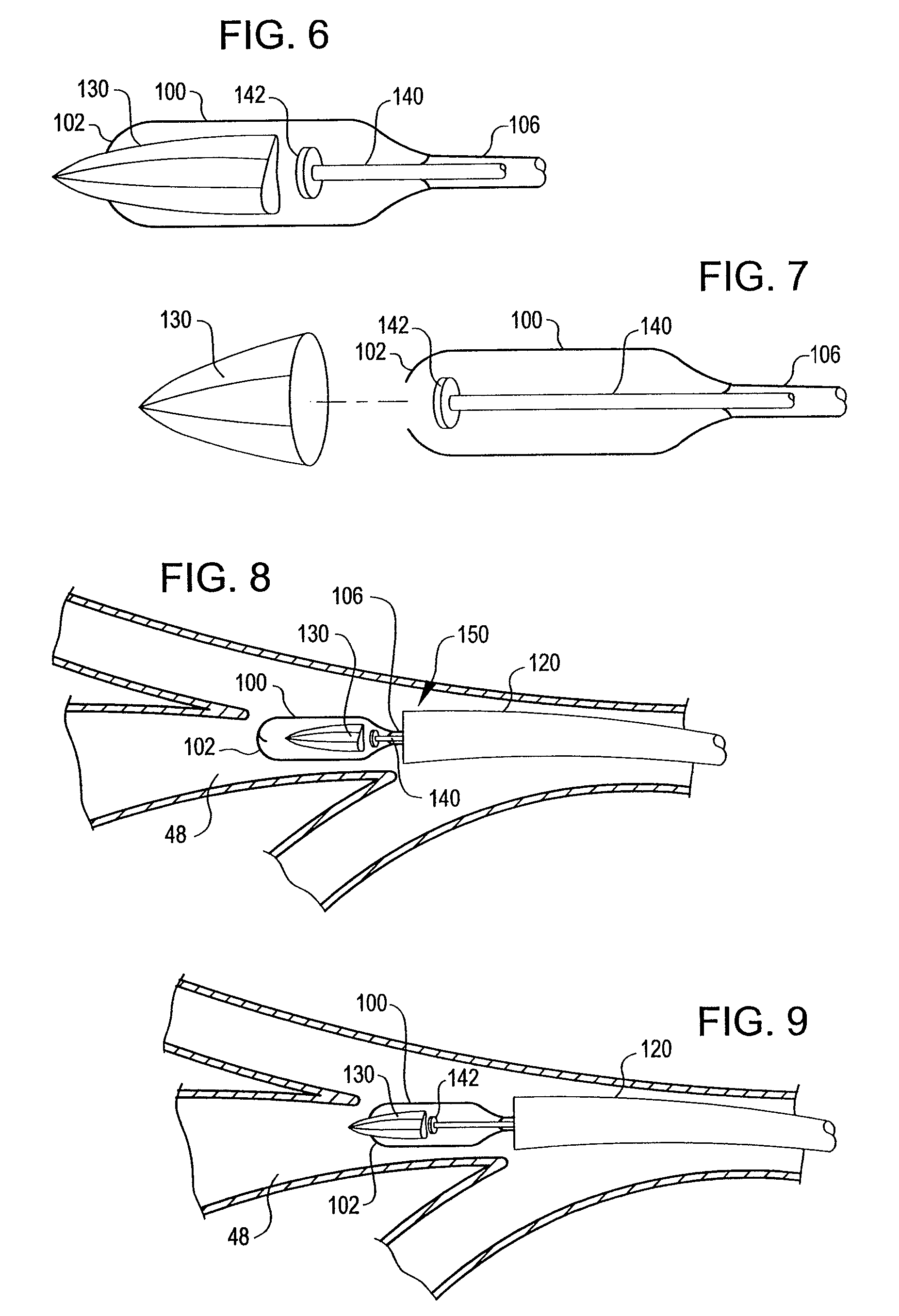
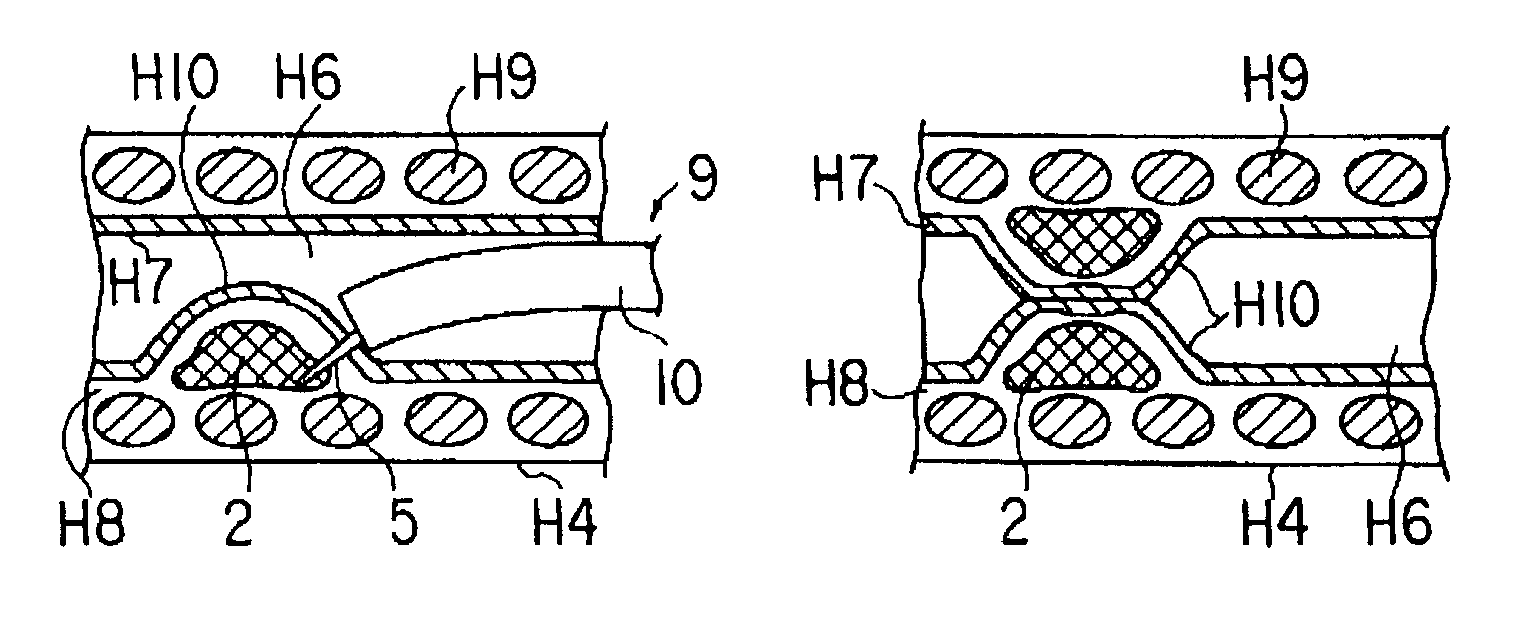
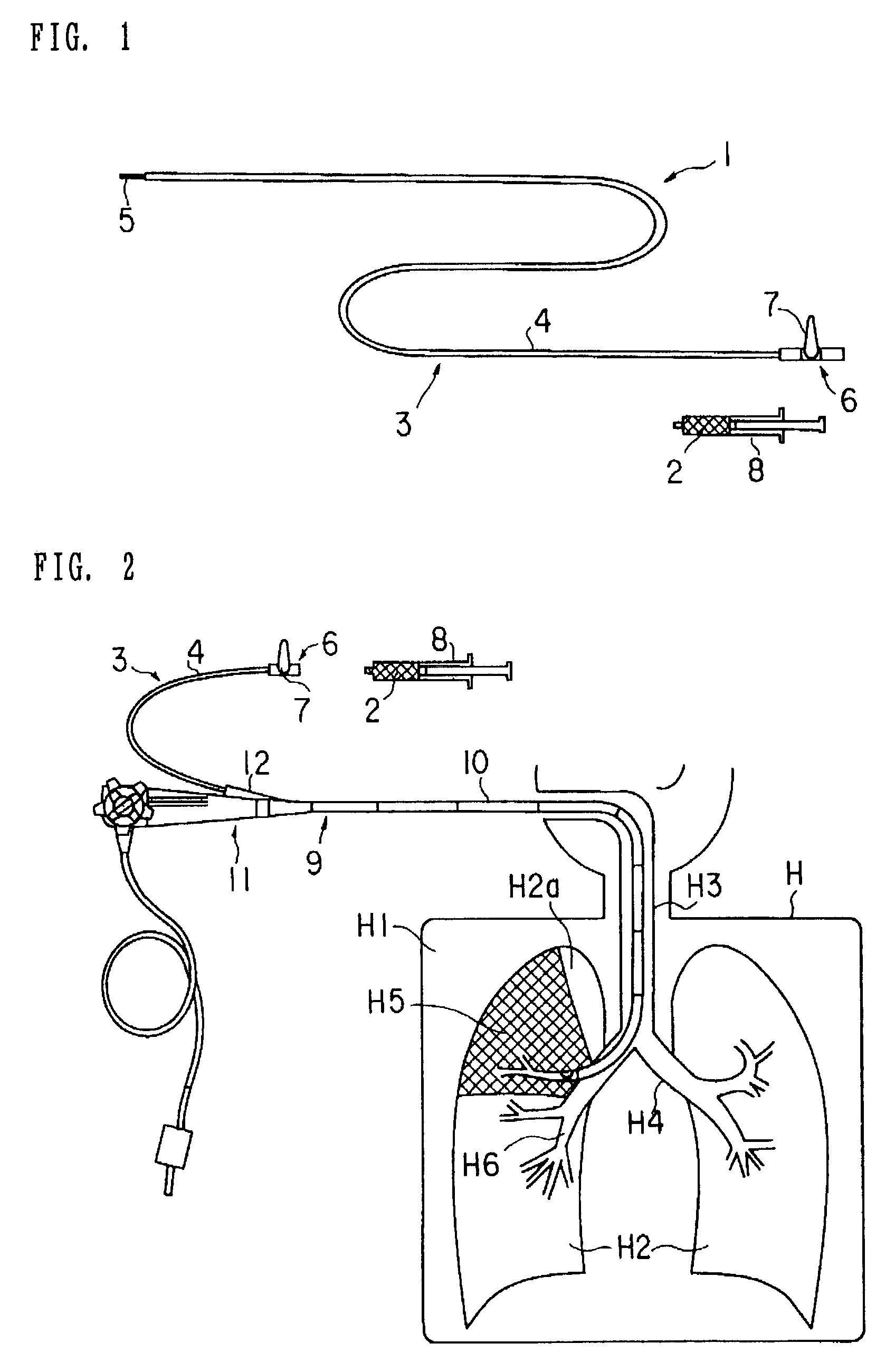
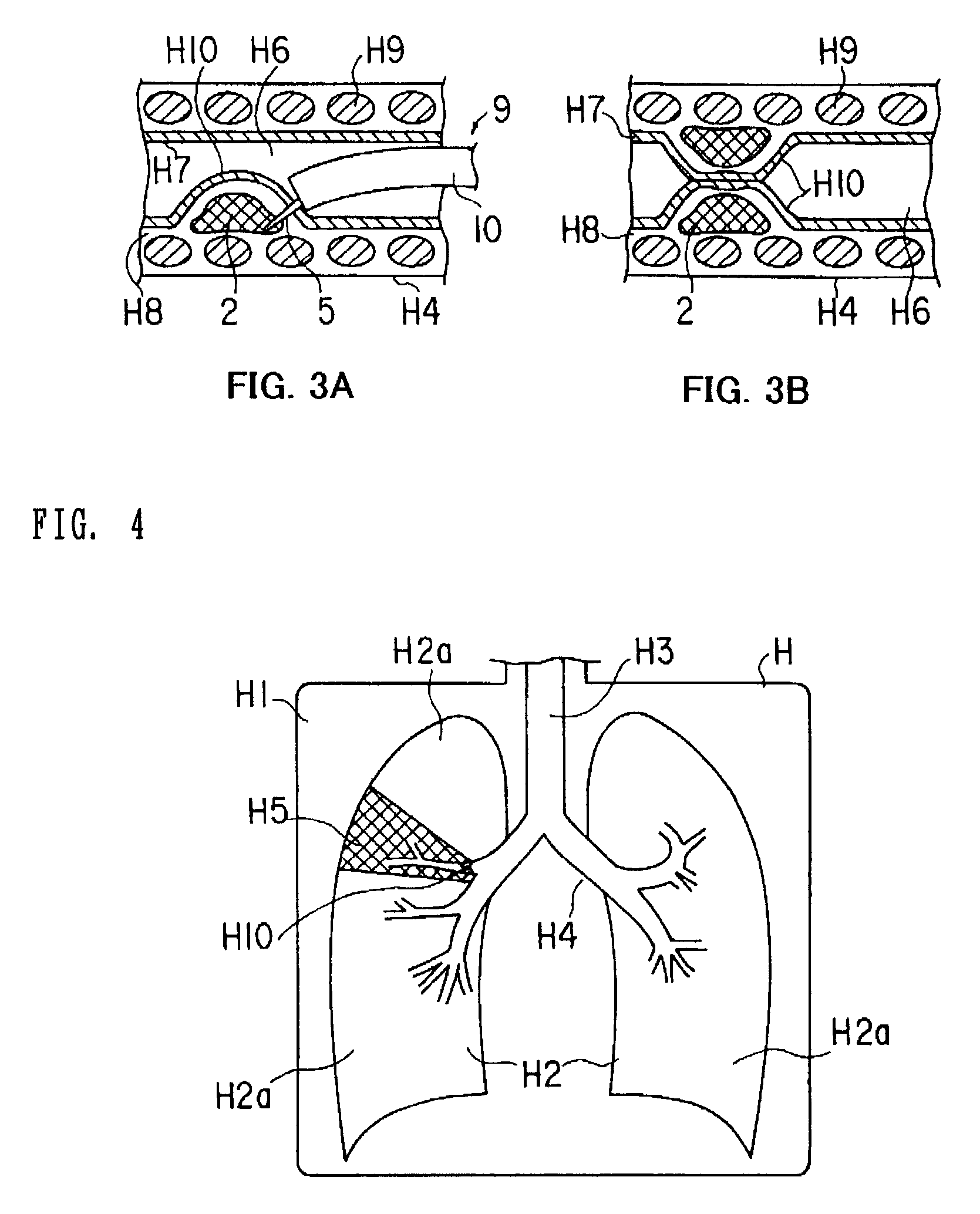
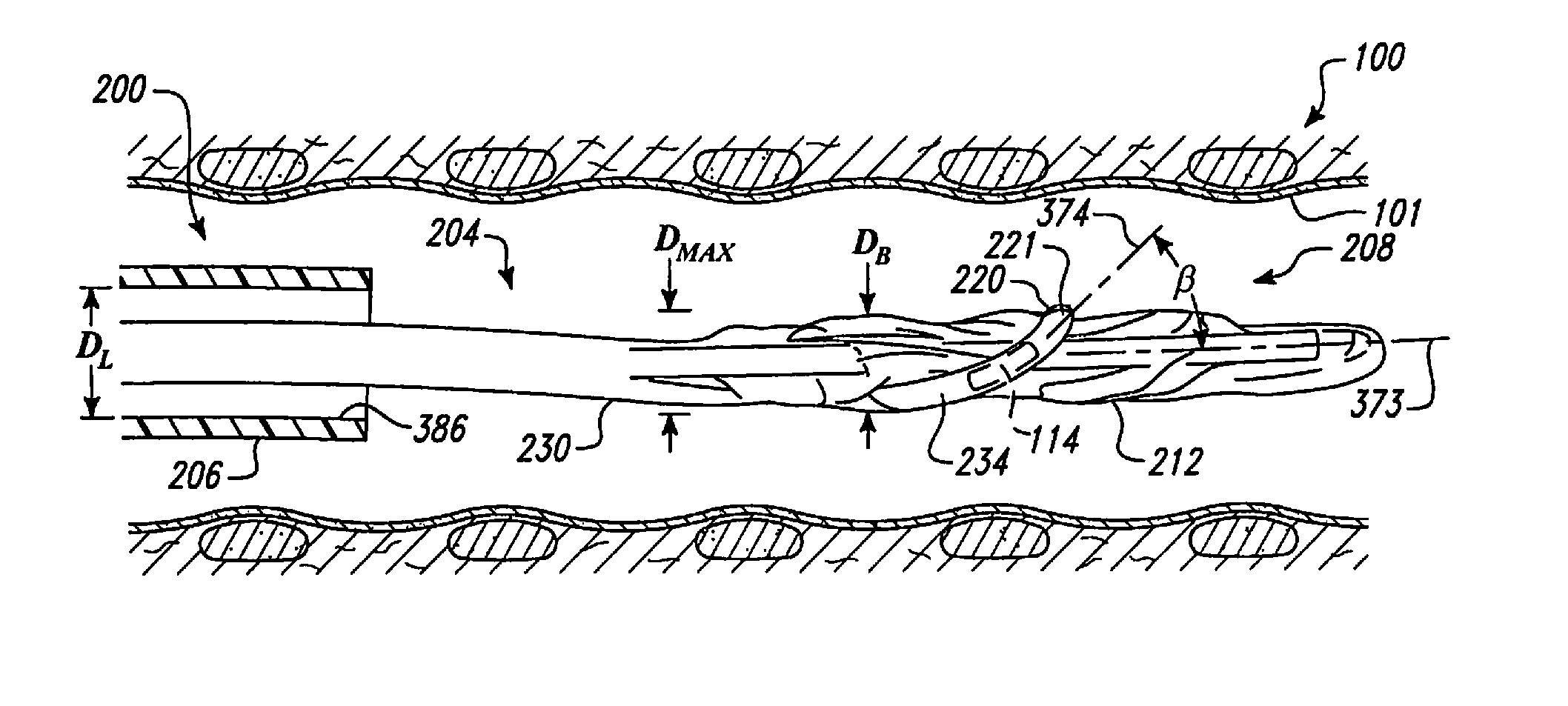
Medical device and method of embolizing bronchus or bronchiole
ActiveUS7357795B2Maintaining swellingGood biocompatibilityDiagnosticsDilatorsSurgical treatmentBronchial submucosa
To provide a medical device and a method both of which can suitably embolize a bronchus in a target part by embolizing the bronchus with (at least a part of) a living tissue during surgical treatment of lung emphysema. For example, an injection material is injected into a submucosa by the use of a syringe, and in the injected part, a swelling swollen into the internal cavity of the bronchus is formed to tightly seal the living tissue of the bronchus or a bronchiole, thereby embolizing a target bronchus.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
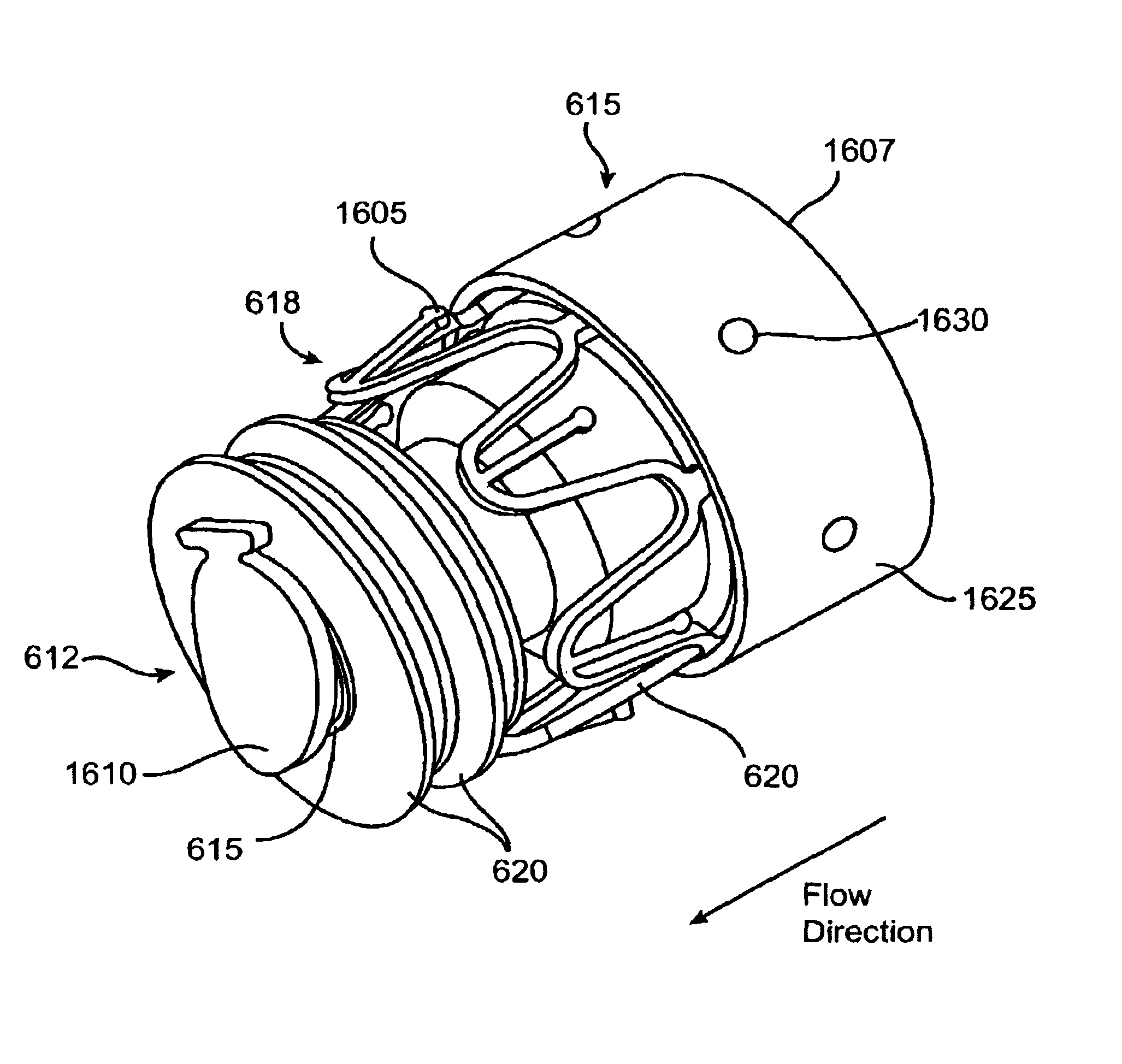
Bronchoscopic lung volume reduction valve
ActiveUS20070096048A1Permit flowAvoid flowStentsBronchiPorous coatingBronchoscopic lung volume reduction
A valve to perform lung volume reduction procedures is described. The valve is formed of a braided structure that is adapted for endoscopic insertion in a bronchial passage of a patient's lung. The braided structure has a proximal end and a distal end and is covered with a non porous coating adapted to prevent flow of air into the. A constricted portion of the braided structure is used to prevent flow of air through a central lumen of the structure, and to define at least one funnel shaped portion. The funnel shaped portion blocks the flow of air towards the constriction, i.e. towards the core of the lung. At least one hole is formed in the braided structure to permit flow of mucus from the distal end to the proximal end, to be expelled out of the lungs.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Medical device with endoscope and insertable instrument
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Irreversible electroporation (IRE) for congestive obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
A method for treating Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) or chronic bronchitis to alleviate the discomforts of breathing by using non-thermal electroporation energy to ablate diseased portions of the lung including the bronchus, airways and alveoli which, in effect, opens the restrictive diseased portions thereby maximizing the overall surface area thereof causing improved airflow and uninhibited breathing.
Owner:ANGIODYNAMICS INC
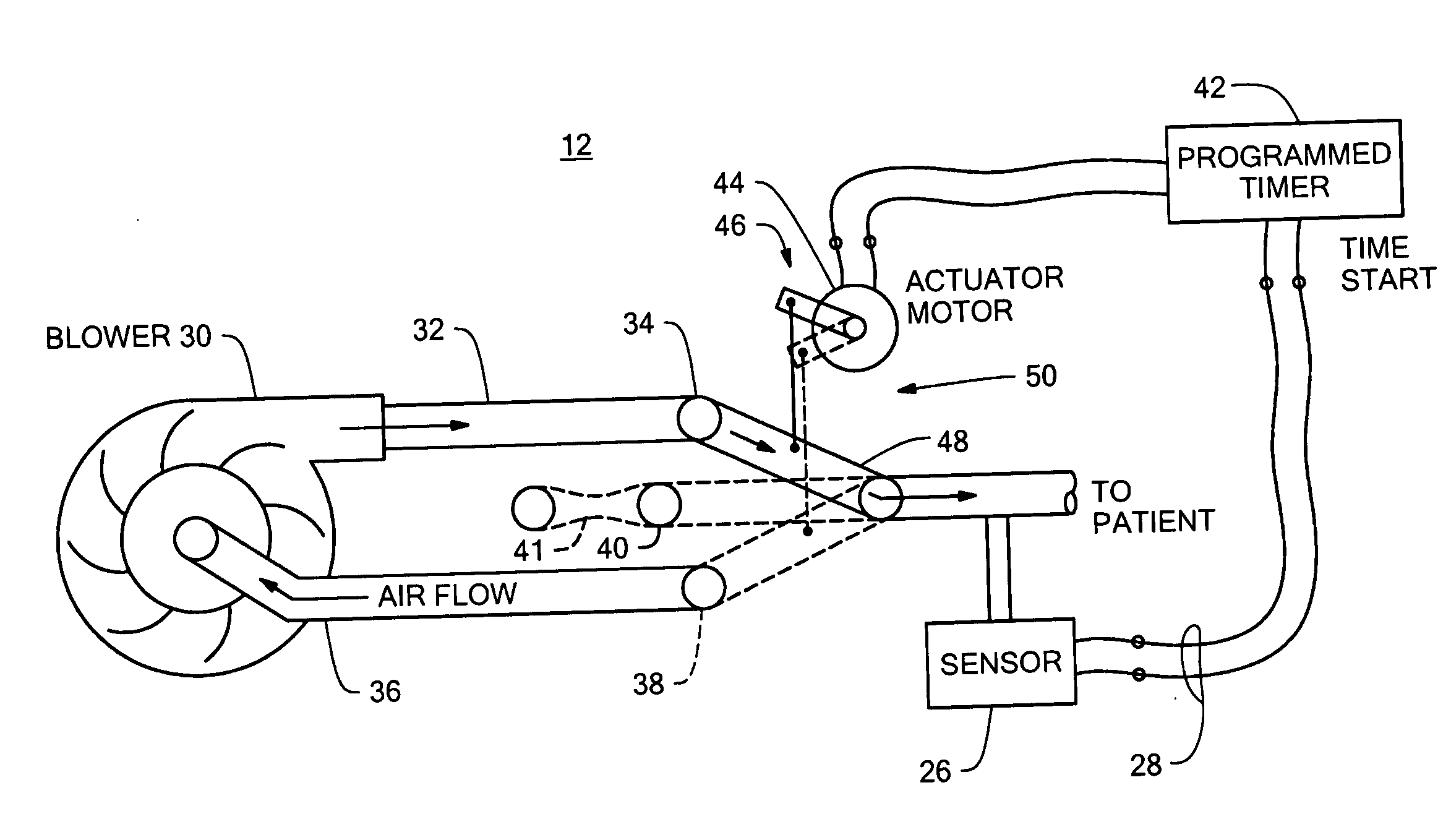
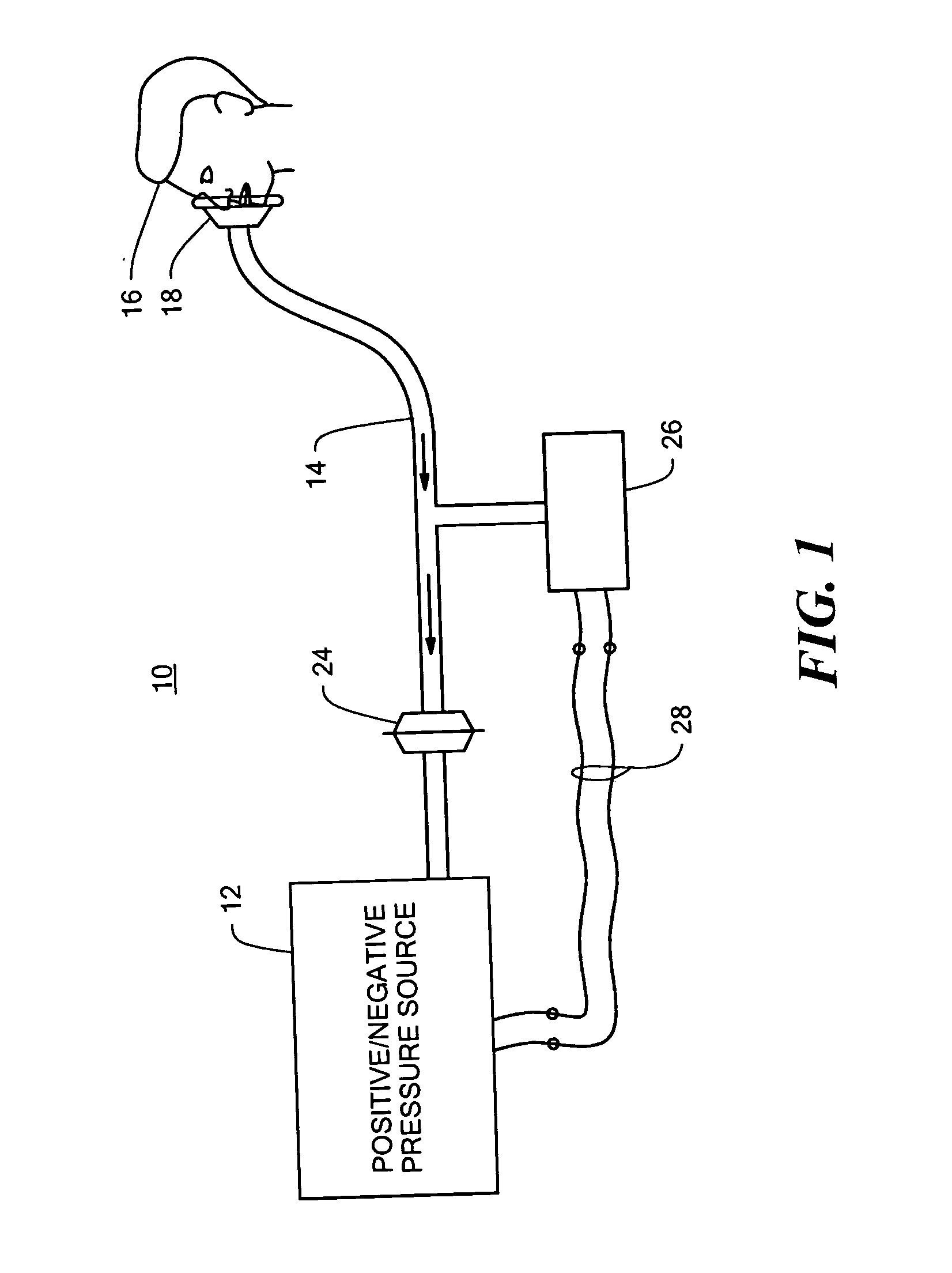
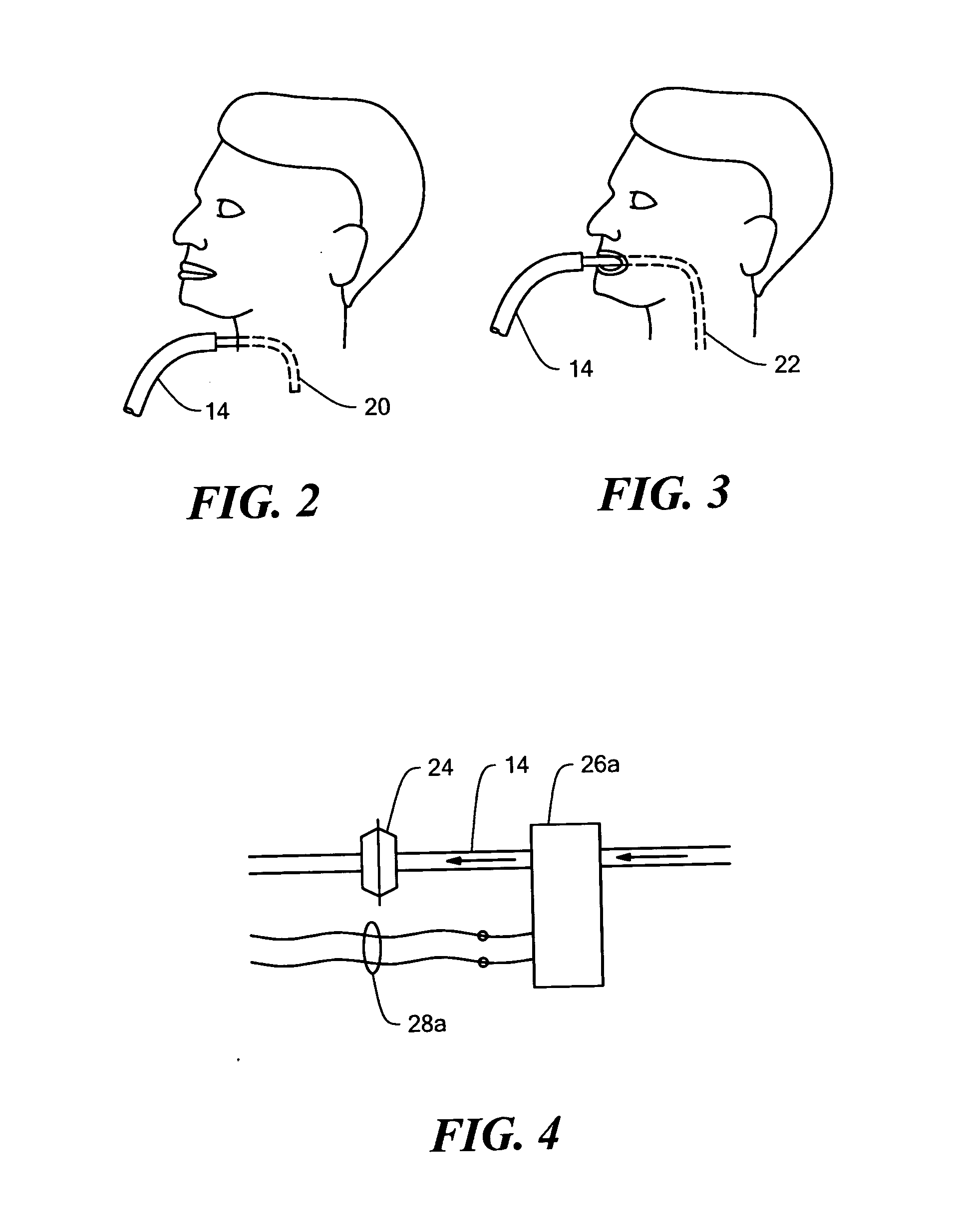
Insufflation-exsufflation system for removal of broncho-pulmonary secretions with automatic triggering of inhalation phase
ActiveUS20050039749A1Synchronization is simpleIncrease inhalationRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesBroncho-pulmonaryPositive pressure
An improved insufflation-exsufflation system for removal of broncho-pulmonary secretions with automatic triggering of inhalation phase includes a conduit for connection to a patient's airway; a pressure source with a positive pressure port and a negative pressure port; a switching device selectively connecting the conduit to the positive pressure port, the negative pressure port and the dwell port; the sensor system for sensing an inhalation by the patient; and a controller system for driving the switching device to connect the conduits sequentially to the positive port, the negative port and the dwell port and to return again to the positive port in response to the sensor system sensing an inhalation by the patient while the conduit is connected to the dwell port.
Owner:RIC INVESTMENTS LLC
Intra-bronchial obstruction device that provides a medicant intra-bronchially to the patient
An intra-bronchial device provides a medicant intra-bronchially. The medicant may be used for controlling biological interaction of an intra-bronchial obstruction device with the patient, to treat a disease or condition of the lungs such as pneumonia or lung cancer, or to treat a systemic disease or condition. The medicant is provided by associating a medicant with the intra-bronchial device, either before, at the time of placement, or after placement. The medicant may overlie at least a portion of the intra-bronchial device, be absorbed into at least a portion of the intra-bronchial device, or be carried in a chamber. The intra-bronchial device may further include an absorptive member, and the medicant is absorbed by the absorptive member.
Owner:GYRUS ACMI INC (D B A OLYMPUS SURGICAL TECH AMERICA)
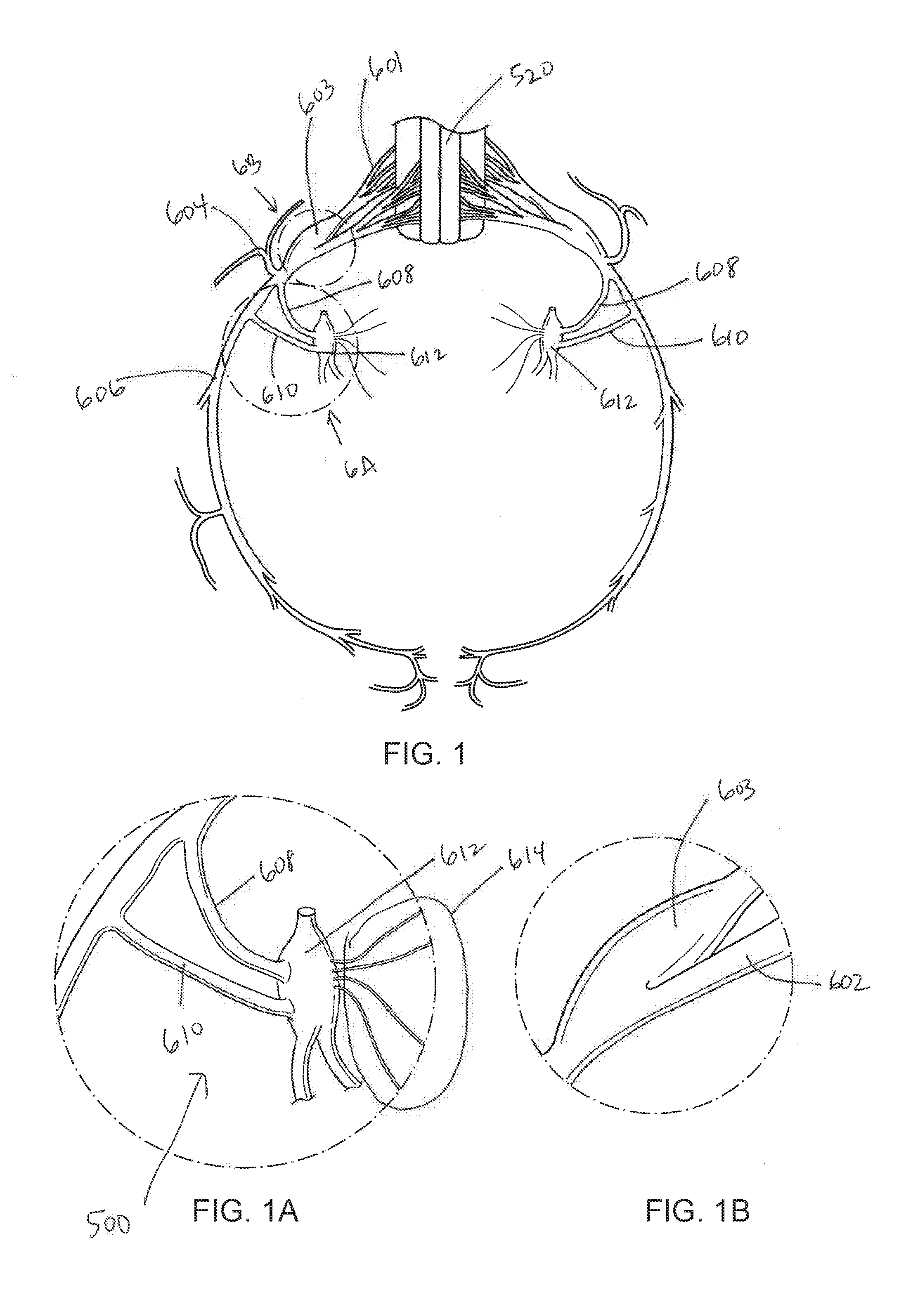
Systems and methods for sympathetic cardiopulmonary neuromodulation
ActiveUS20160317621A1Prevents and blocks releaseUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsNervous disorderDiseaseNeurolysis
Methods, devices and systems are described for decreasing the activity of the sympathetic nervous innervation to and from the lungs and the vessels supplying the lungs to treat pulmonary medical conditions such as asthma. In one embodiment, the method may involve advancing an intravascular instrument to a target location in a blood vessel within the intercostal vasculature to ablate either or both the sympathetic afferent and efferent nerves lying within the paravertebral gutter including the visceral fibers that travel to the cardiothoracic cavity and abdominopelvic viscera and the T1 to T4 / 5 sympathetic chain. In another embodiment, an intravascular instrument may be advanced to the bronchial vessels to ablate either or both the sympathetic afferent and efferent nerves in and around the posterior pulmonary plexus. In one embodiment the ablative agent is a neurolytic agent delivered in a gel. This approach may be utilized to treat other cardiac and pulmonary diseases.
Owner:TULAVI THERAPEUTICS INC
Visualizing different types of airway wall abnormalities
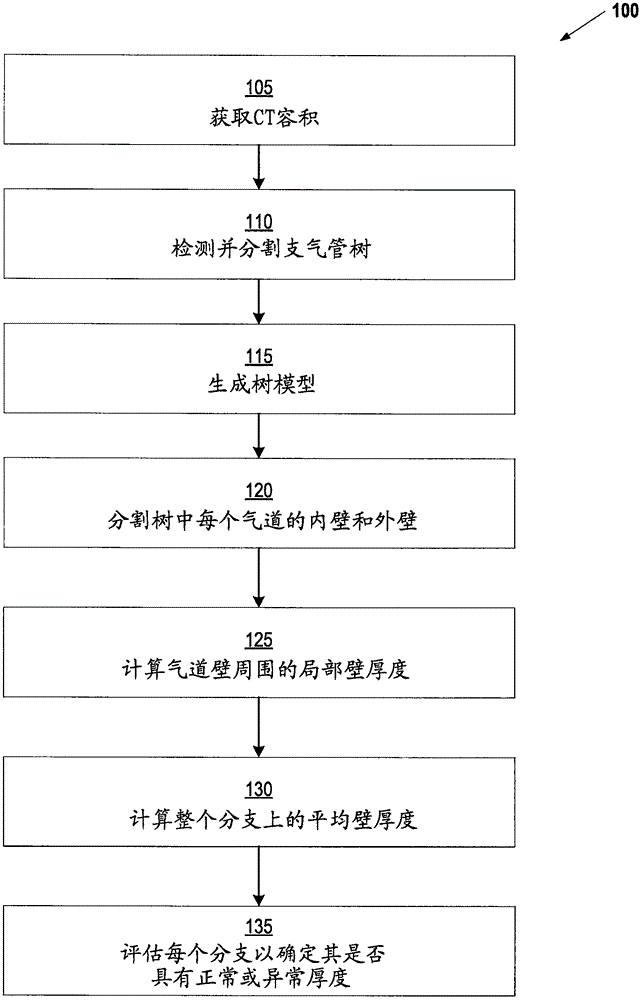
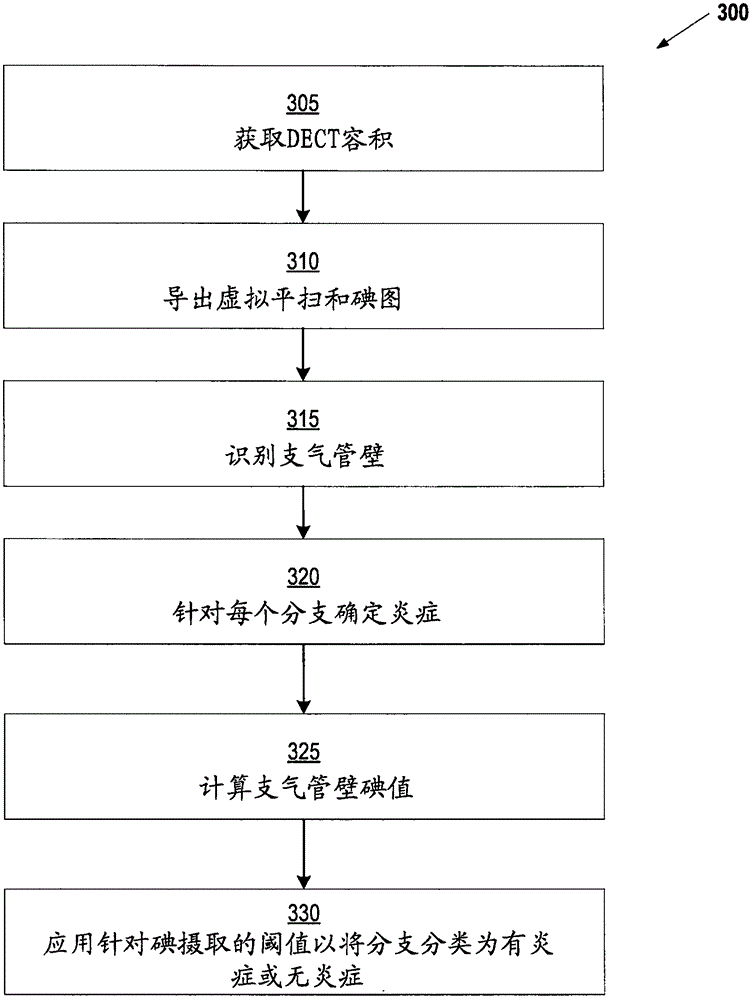
The invention relates to visualizing different types of airway wall abnormalities. A method for visualizing airway wall abnormalities includes acquiring Dual Energy Computed Tomography (DECT) imaging data comprising one or more image volumes representative of a bronchial tree. An iodine map is derived using the DECT imaging data and the bronchial tree is segmented from the image volume(s). A tree model representative of the bronchial tree is generated. Then, for each branch, this tree model is used to determine an indicator of normal or abnormal thickness. Locations corresponding to bronchial walls in the bronchial tree using the tree model are identified. Next, for each branch, the locations corresponding to bronchial walls in the bronchial tree and the iodine map are used to determine an indicator of normal or abnormal inflammation. A visualization of the bronchial tree may be presented with visual indicators at each of the locations corresponding to bronchial walls indicating whether a bronchial wall is thickened and / or inflamed.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Methods and devices for improving breathing in patients with pulmonary disease
Methods, apparatus, and kits for enhancing breathing in patients suffering from chronic pulmonary obstructive disease are described. The methods and apparatus rely on increasing flow resistance to expiration in a manner which mimics “pursed lip” breathing which has been found to benefit patients suffering from this disease. In a first example, a device is implanted in a trachea or bronchial passage to increase flow resistance, preferably selectively increase resistance to expiration relative to inspiration. In a second embodiment, a mouthpiece is provided, again to increase resistance to expiration, preferably with a lesser increase in flow resistance to inspiration. In a third embodiment, the patient's trachea or bronchial passage is modified by the application of energy in order to partially close the lumen therethrough.
Owner:THERAVENT
Medical device
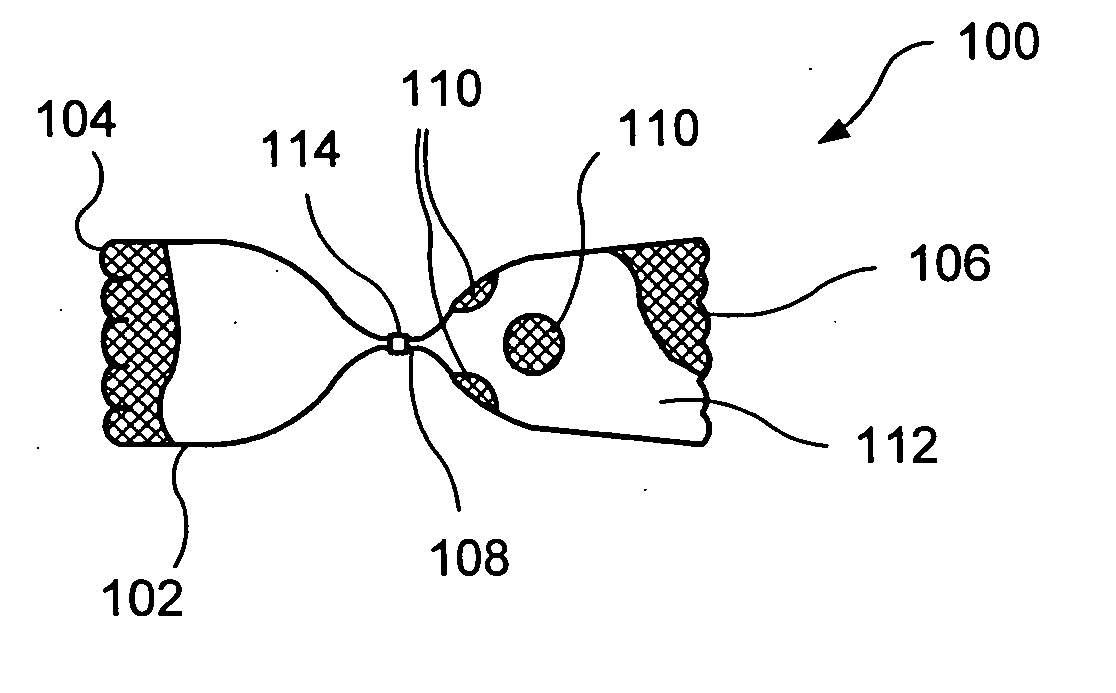
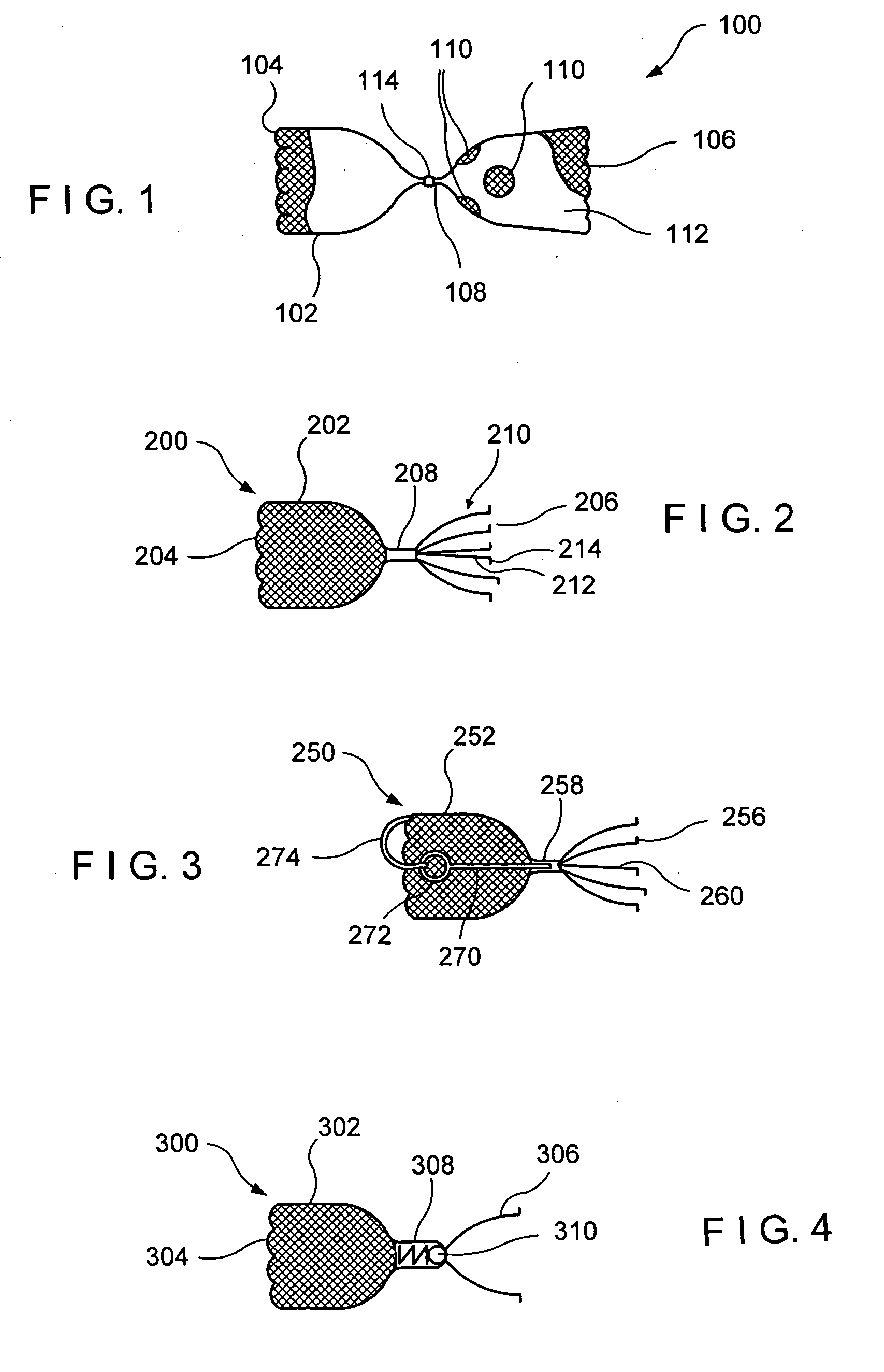
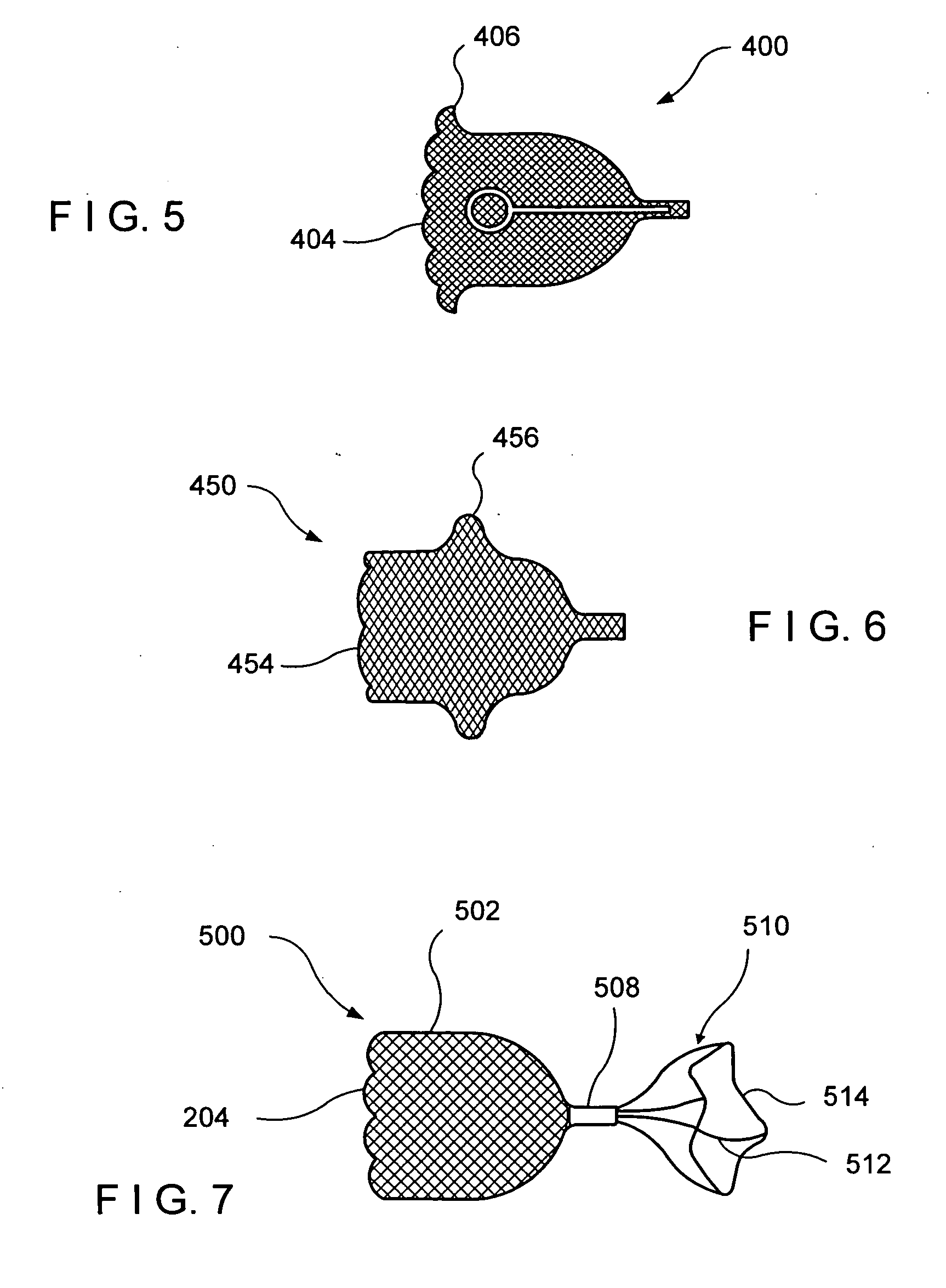
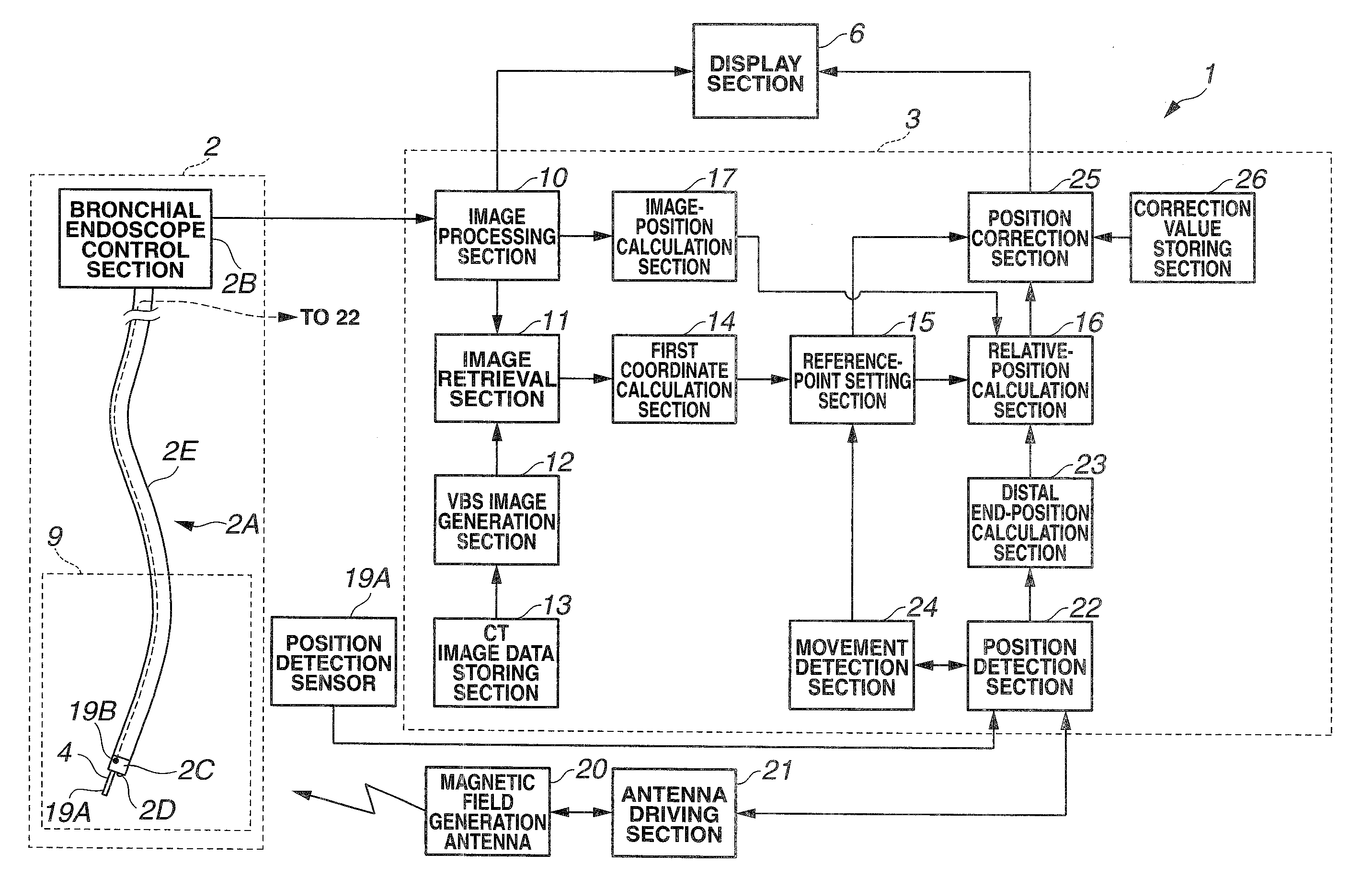
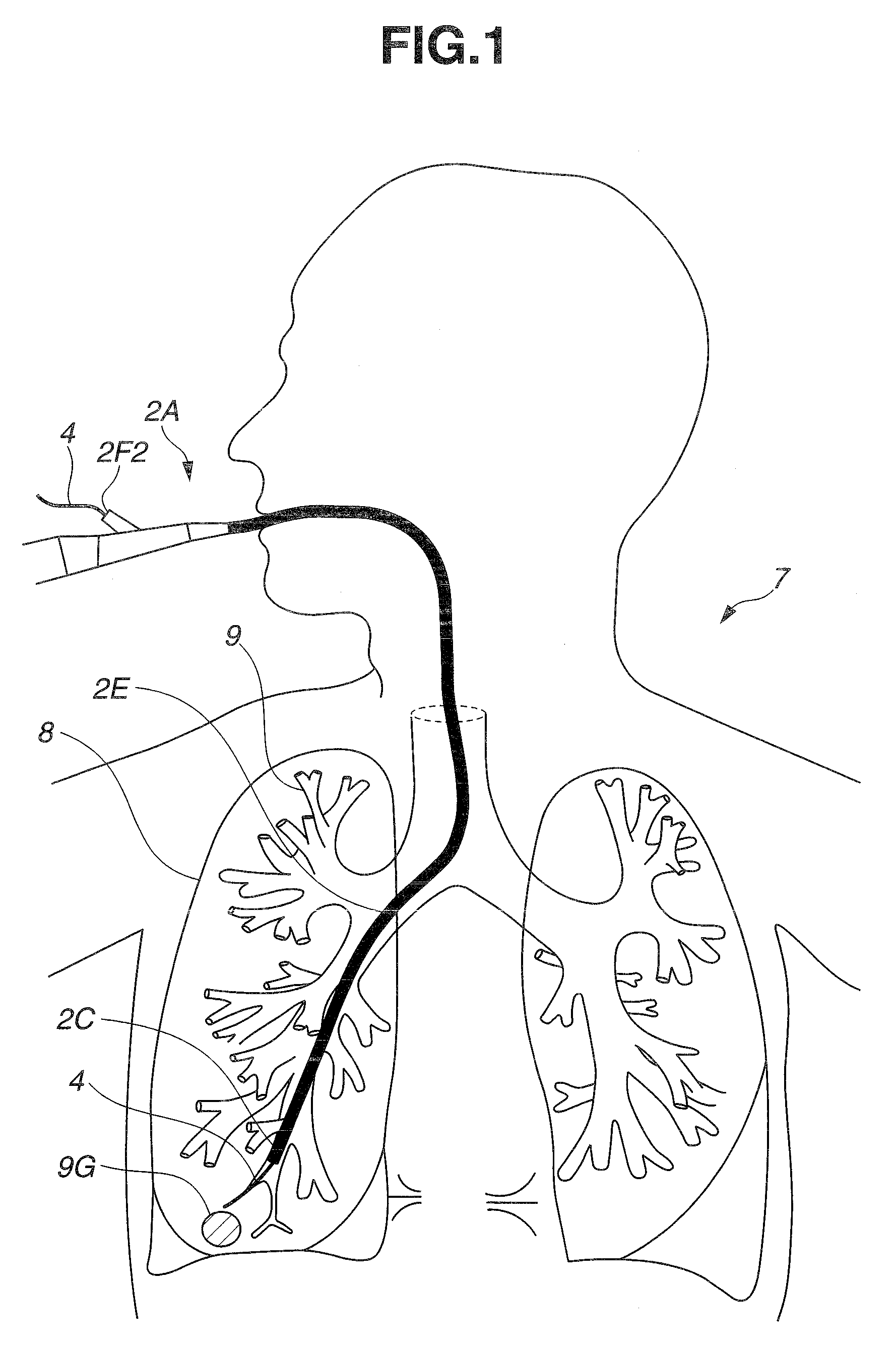
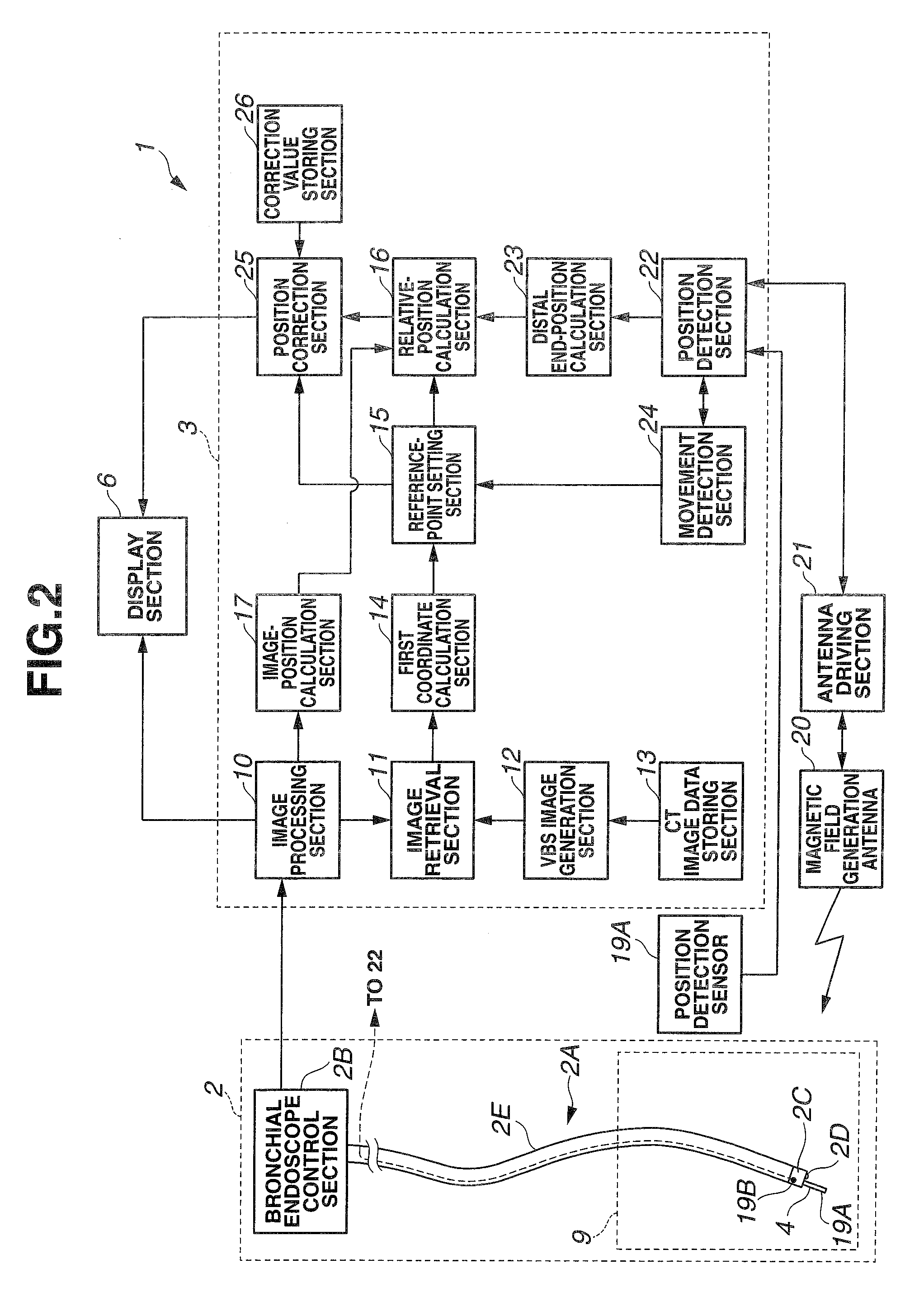
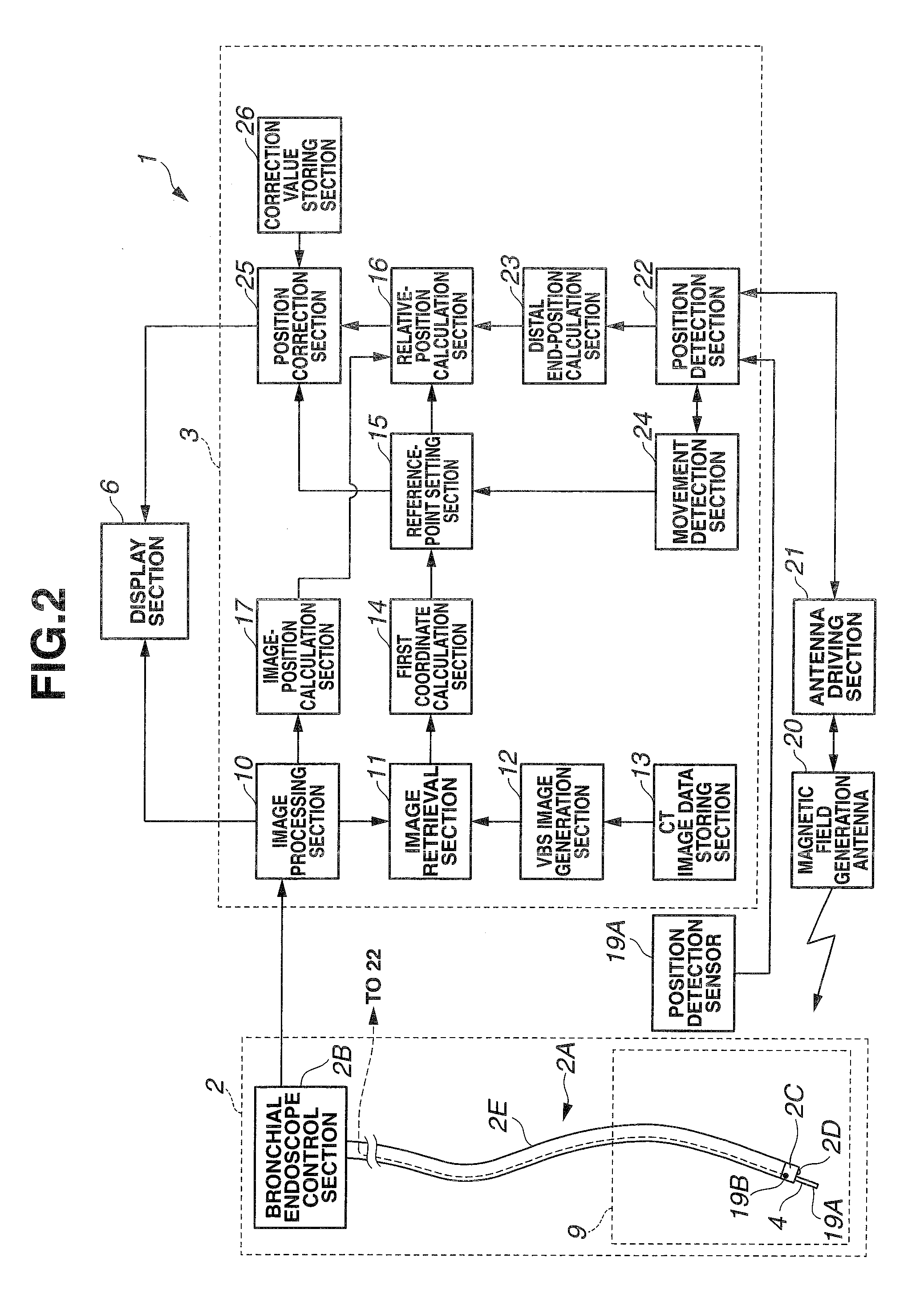
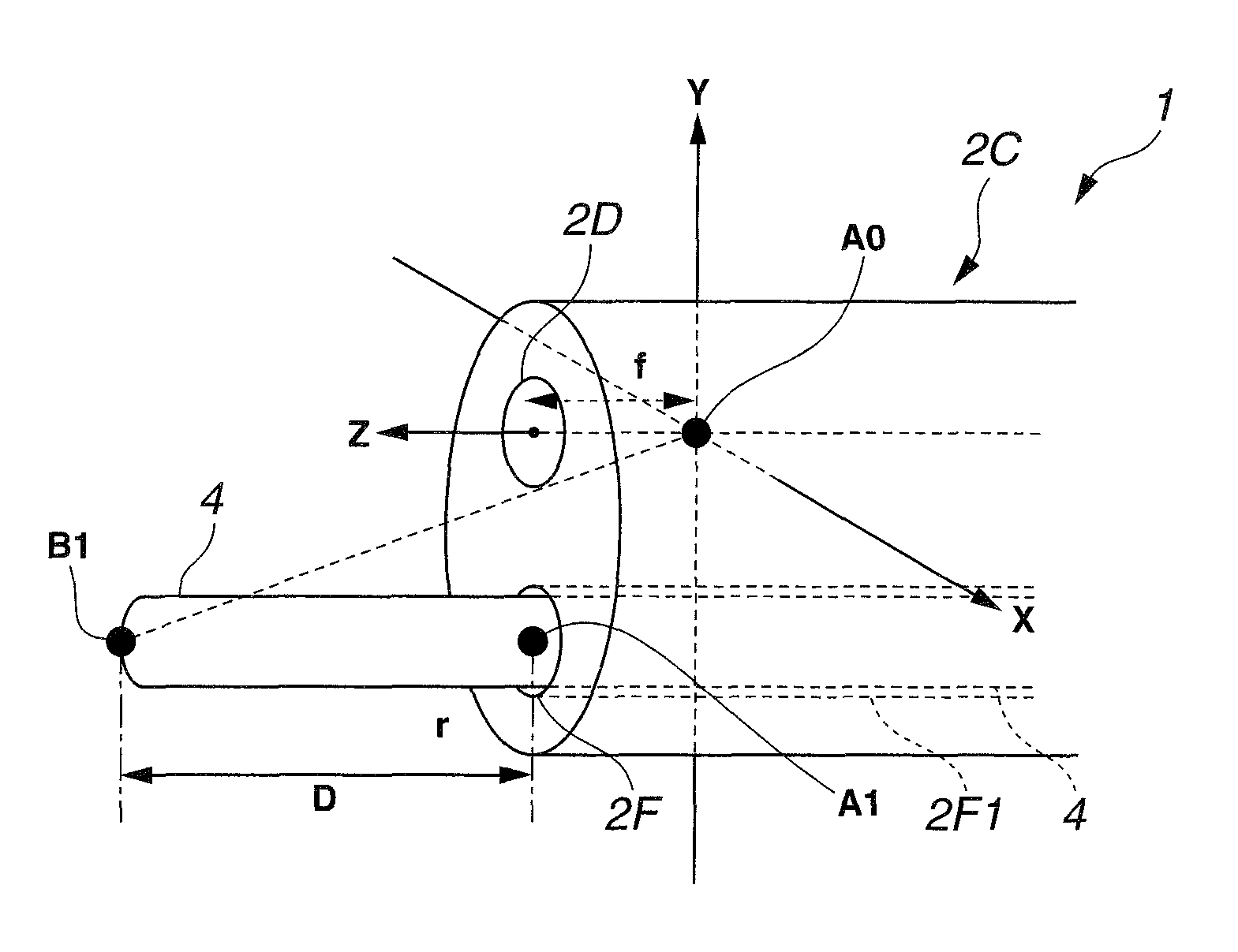
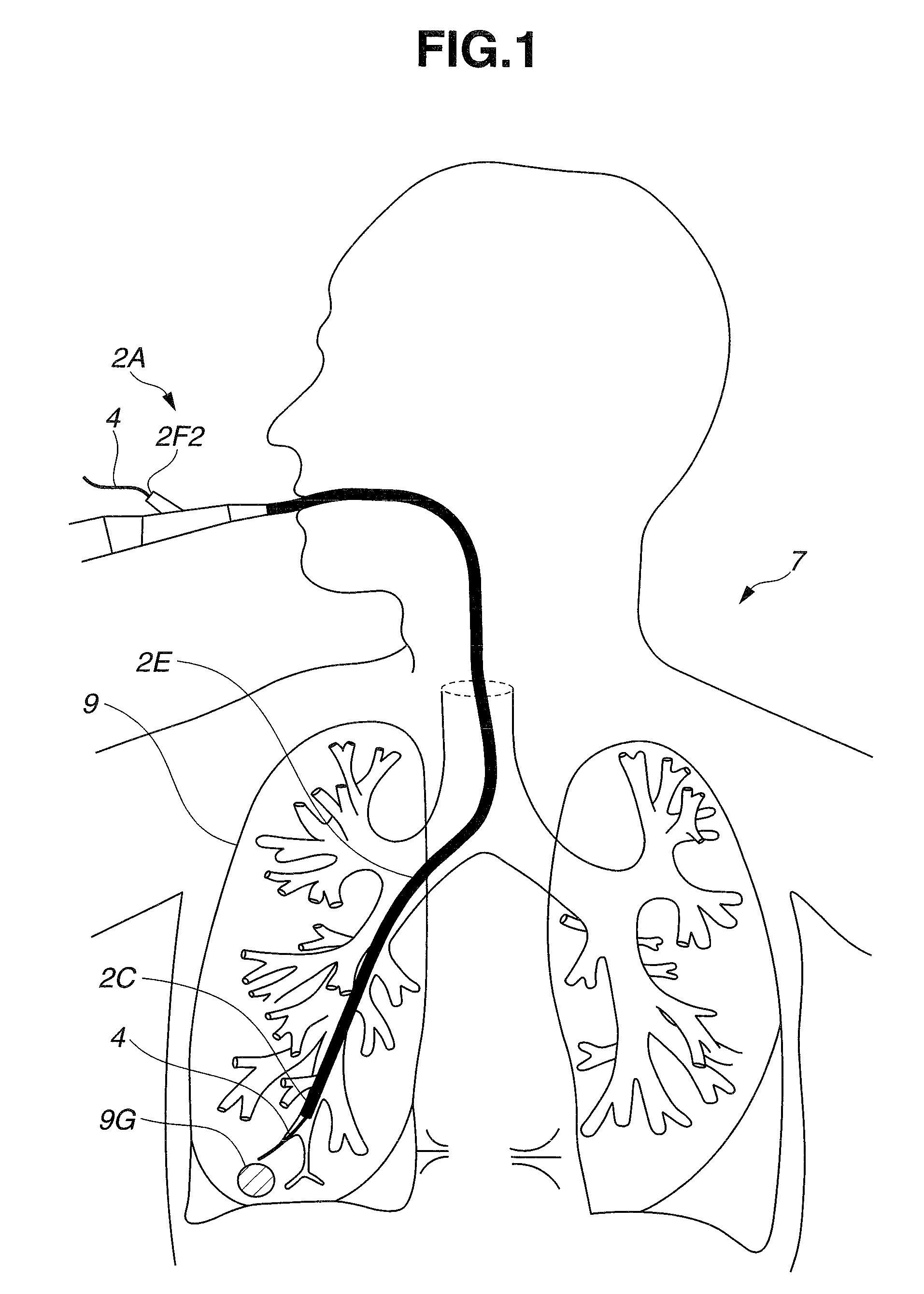
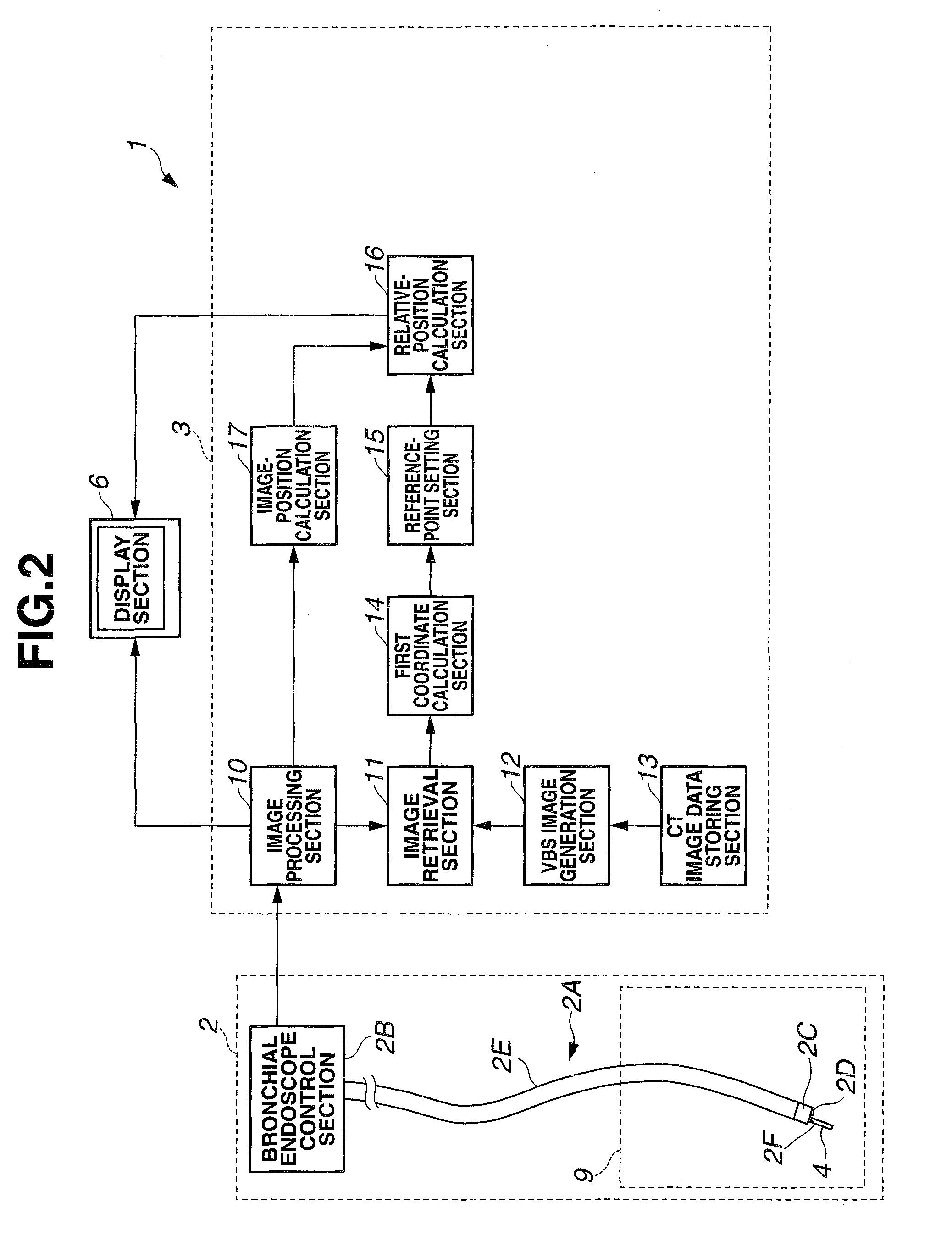
A medical device for examination or treatment based on a reference point A1, including: a virtual endoscopic image generation section configured to generate a virtual endoscopic image from a plurality of different sight line positions using three-dimensional image data of a bronchus that is obtained in advance; an image retrieving section configured to retrieve a virtual endoscopic image highly similar to a real image; a reference-point setting section configured to set the reference point A1 based on a line-of-sight position A0 of the highly similar virtual endoscopic image; a relative-position calculation section configured to calculate a relative position of a treatment instrument to the reference point A1; a movement detection section configured to detect a movement of the reference point A1 or the bronchus; and a position correction section configured to correct the relative position in response to the movement of the reference point A1 or the bronchus.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
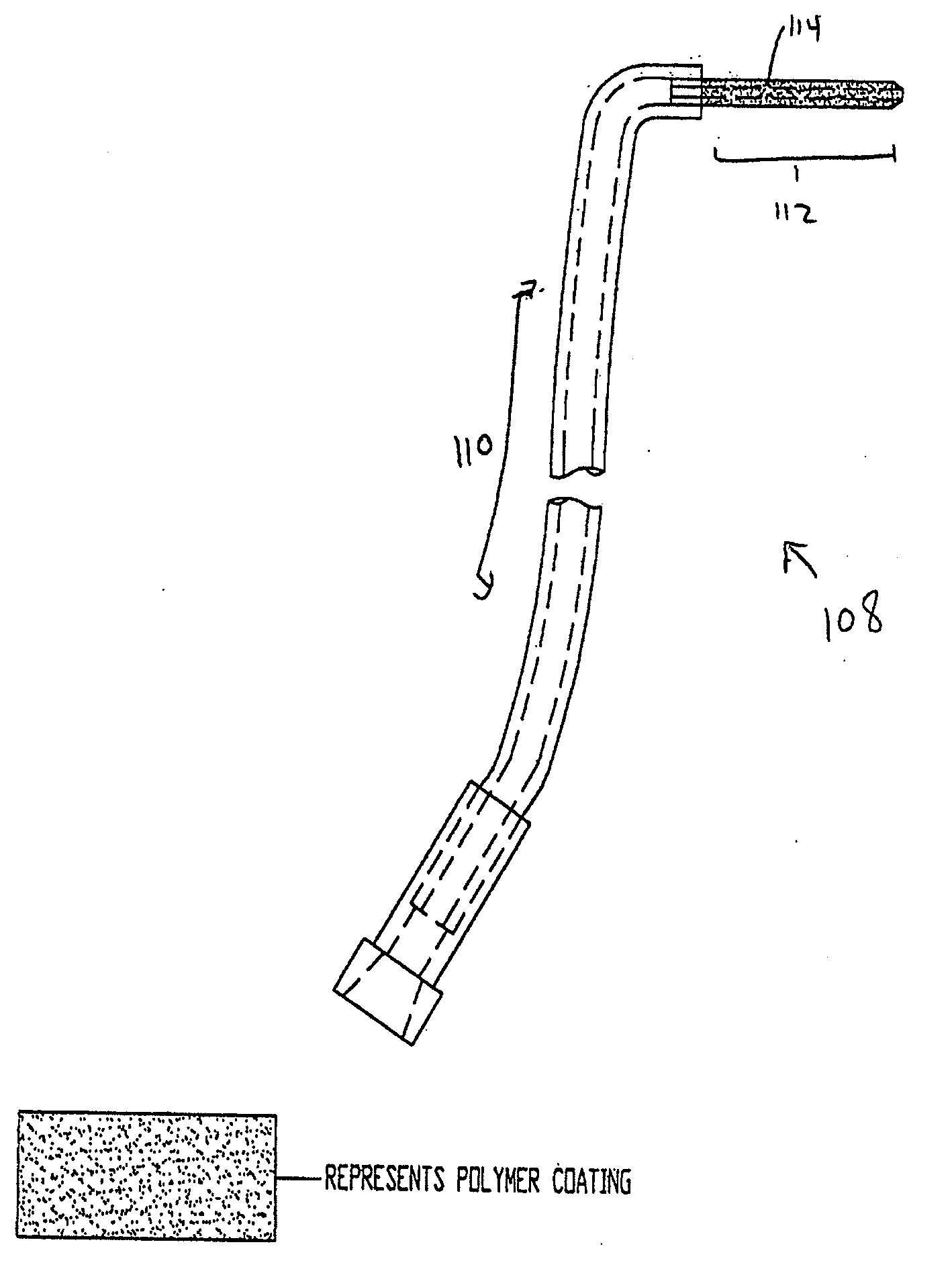
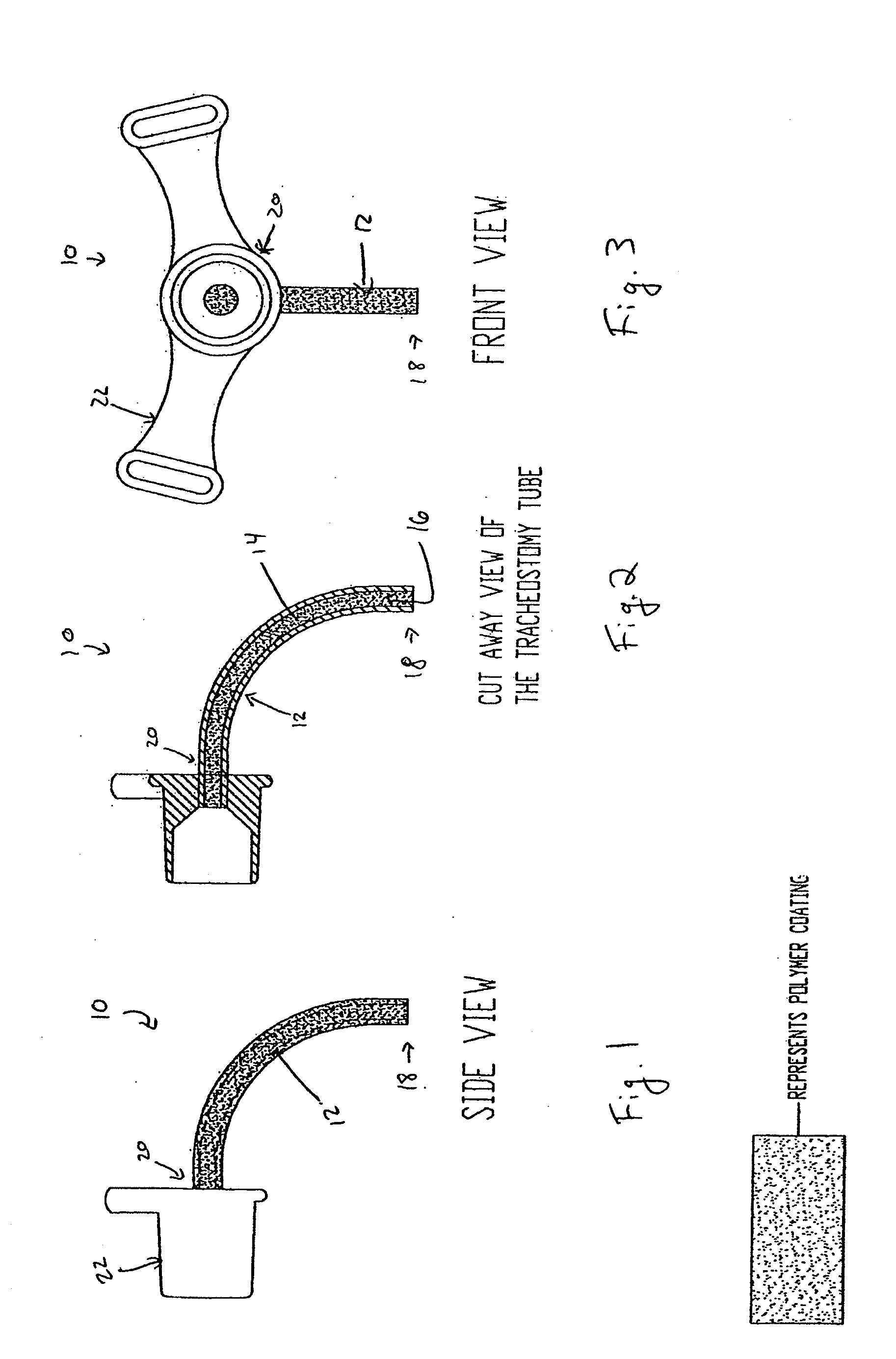
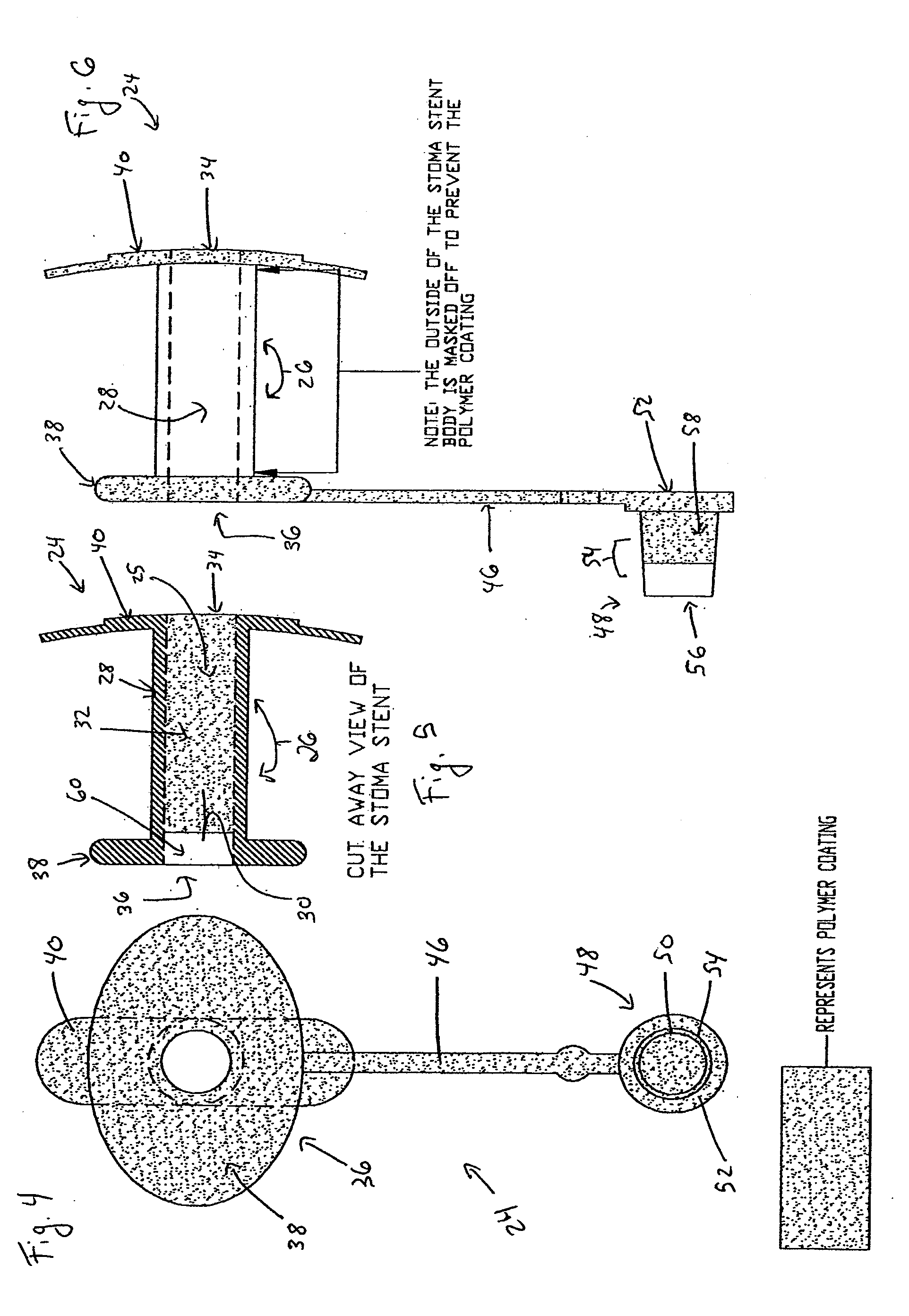
Coated Tracheostomy Tube and Stoma Stent or Cannula
The present invention relates to devices used in the management of bodily airways including tracheostomy tubes, laryngectomy tubes, bronchial stents, bronchial Y-tubes, bronchial TY-tubes, and nasal stents. The devices may comprise a protective coating to prevent the accumulation of mucus, crusting and granulation on or around airway management devices, as well as prevent adhesion to tissues which can cause bleeding upon removal, and prevent build-up of blood, or blood clots, to the stent.
Owner:E BENSON HOOD LAB
Medical device
A medical device for examination or treatment based on a reference point, includes: a virtual endoscopic image generation section configured to generate a virtual endoscopic image of a bronchus from a plurality of different line-of-sight positions using three-dimensional image data of the bronchus of a subject that is obtained in advance; an image retrieval section configured to retrieve a virtual endoscopic image highly similar to an endoscopic image of the bronchus picked up by an image pickup section arranged at a distal end portion of an insertion section; a reference-point setting section configured to set a reference point based on a line-of-sight position of the highly similar virtual endoscopic image; and a relative-position calculation section configured to calculate a relative position of a treatment instrument to the reference point.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Methods for improving drug efficacy
ActiveUS20140186341A1Reduce airway obstructionImprove efficacyBiocideElectrotherapyNervous systemObstructive Pulmonary Diseases
The present disclosure provides methods for improving drug efficacy in a patient having an obstructed airway in a lung. Such methods modulate nerve activity in the autonomic nervous system of a patient to reduce obstruction of an airway in a lung of the patient prior to administering a drug to the patient. These methods are especially useful in improving efficacies of bronchodilators in treating obstructive lung diseases, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Owner:NUVAIRA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com