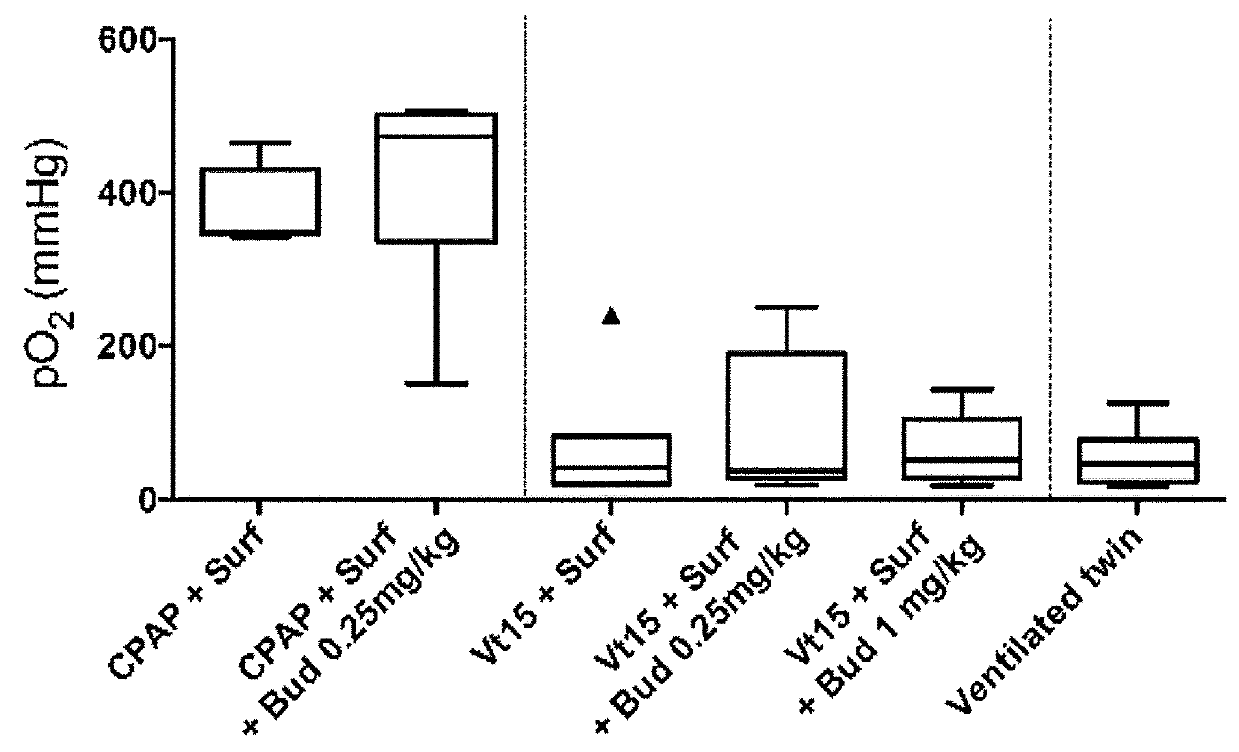
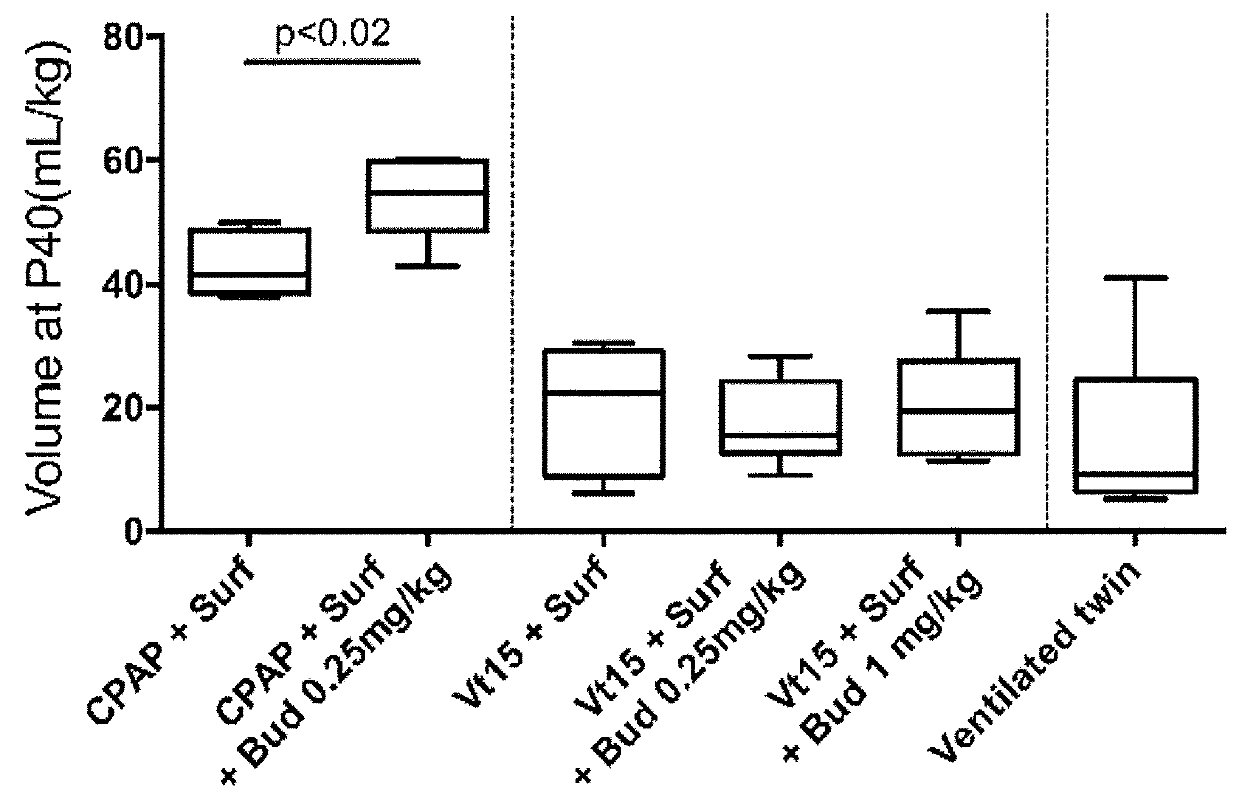
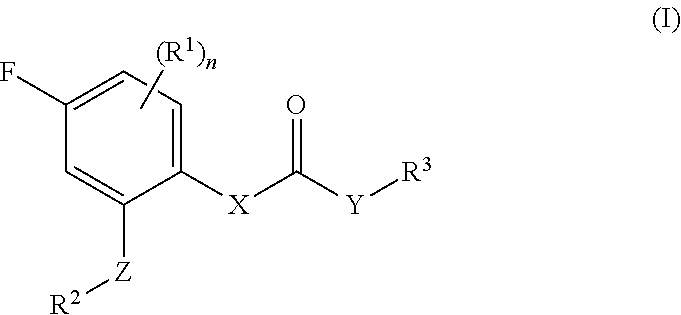
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
51 results about "Bronchopulmonary dysplasia" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
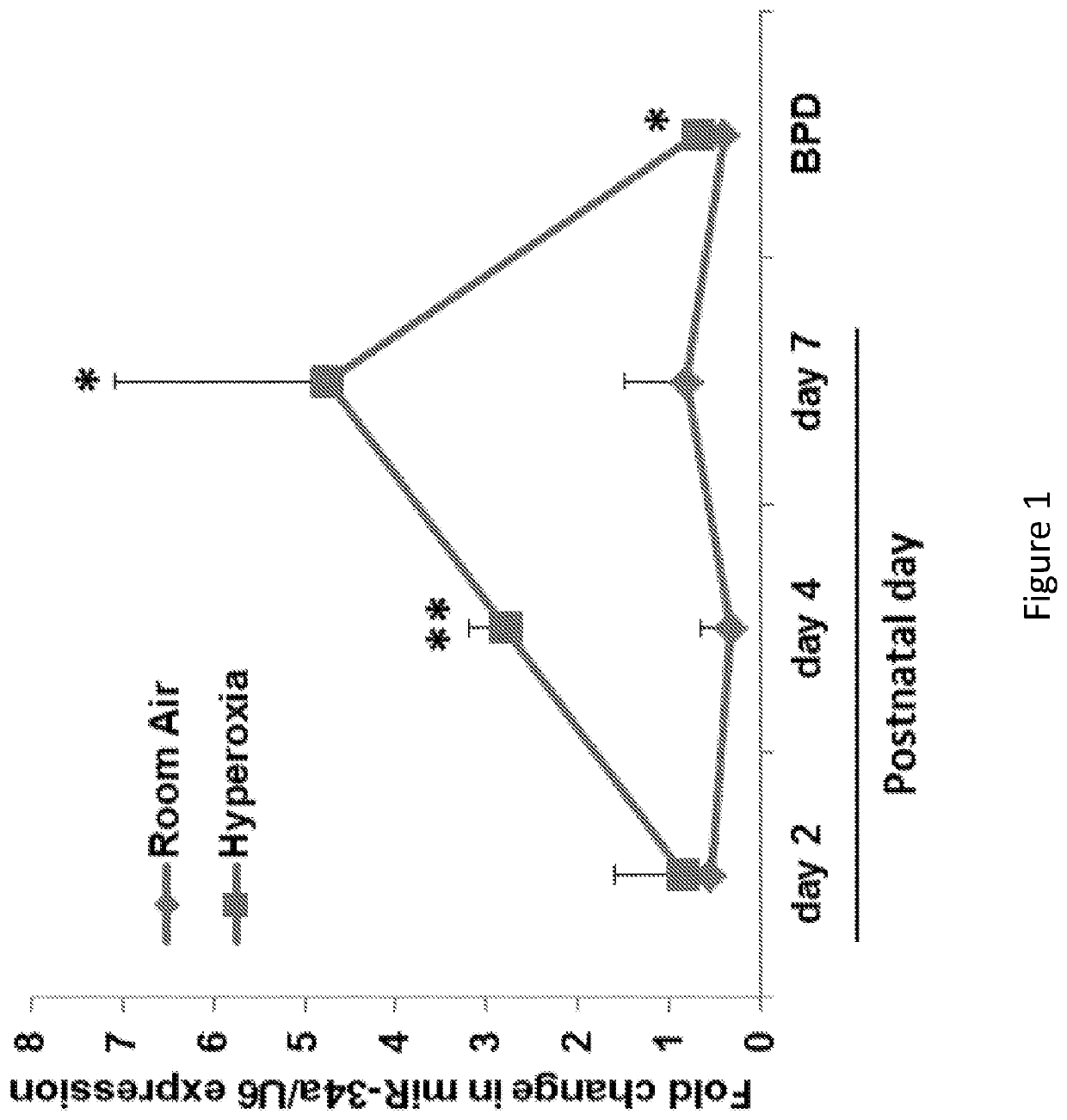
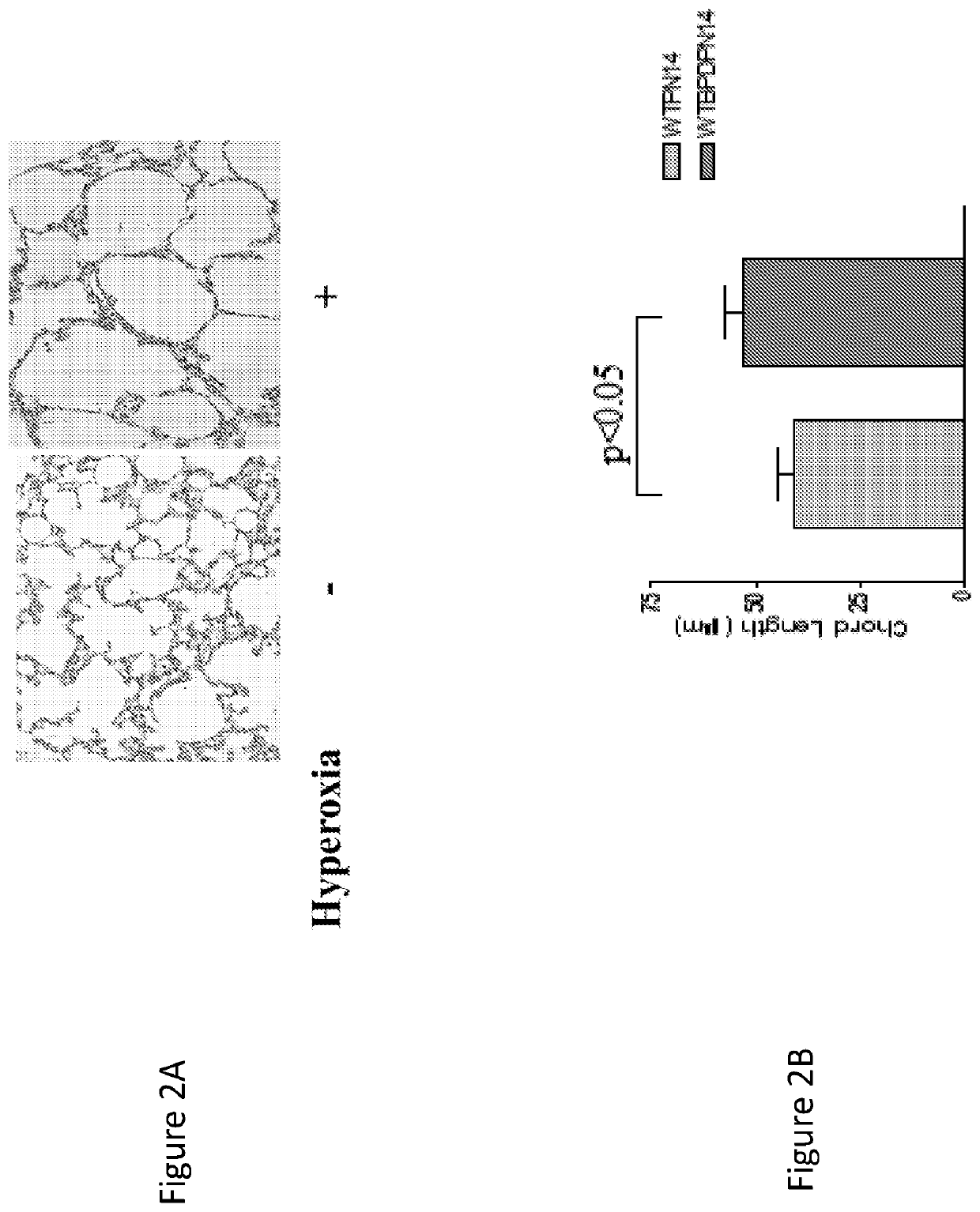
Bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD; formerly chronic lung disease of infancy) is a chronic lung disease in which premature infants, usually those who were treated with supplemental oxygen, require long-term oxygen. It is more common in infants with low birth weight (LBW) and those who receive prolonged mechanical ventilation to treat respiratory distress syndrome (RDS). It results in significant morbidity and mortality. The definition of BPD has continued to evolve primarily due to changes in the population, such as more survivors at earlier gestational ages, and improved neonatal management including surfactant, antenatal glucocorticoid therapy, and less aggressive mechanical ventilation.
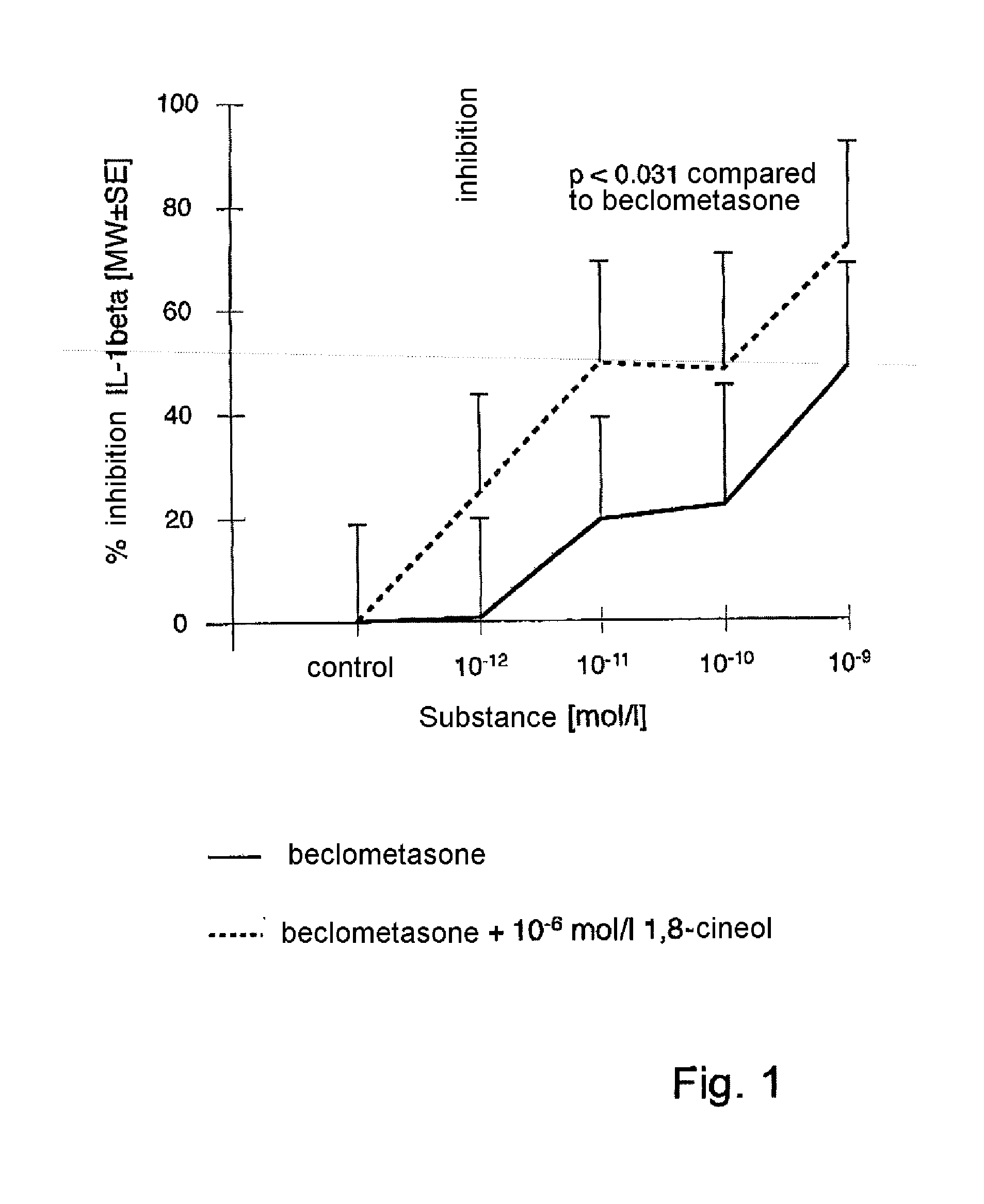
Treatment of Asthma and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease With Anti-proliferate and Anti-inflammatory Drugs
InactiveUS20080175887A1Promote absorptionOrganic active ingredientsPowdered material dispensingDiseaseObstructive Pulmonary Diseases
Embodiments of the present invention provide a method for treatment of respiratory disorders such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and chronic sinusitis, including cystic fibrosis, interstitial fibrosis, chronic bronchitis, emphysema, bronchopulmonary dysplasia and neoplasia. The method involves administration, preferably oral, nasal or pulmonary administration, of anti-inflammatory and anti-proliferative drugs (rapamycin or paclitaxel and their analogues).
Owner:LUTONIX INC
Treatment of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease with Anti-proliferate and Anti-inflammatory drugs
ActiveUS20130261603A1Promote absorptionRespiratorsPowder deliveryDiseaseObstructive Pulmonary Diseases
Embodiments of the present invention provide a method for treatment of respiratory disorders such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and chronic sinusitis, including cystic fibrosis, interstitial fibrosis, chronic bronchitis, emphysema, bronchopulmonary dysplasia and neoplasia. The method involves administration, preferably oral, nasal or pulmonary administration, of anti-inflammatory and anti-proliferative drugs (rapamycin or paclitaxel and their analogues) and an additive.
Owner:LUTONIX INC
Methods and compositions for the reduction of neutrophil influx and for the treatment of bronchpulmonary dysplasia, respiratory distress syndrome, chronic lung disease, pulmonary fibrosis, asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
InactiveUS20060281681A1Suppress immune responseIncrease frequencyPeptide/protein ingredientsRespiratory disorderNeutrophil granulocyteObstructive Pulmonary Diseases
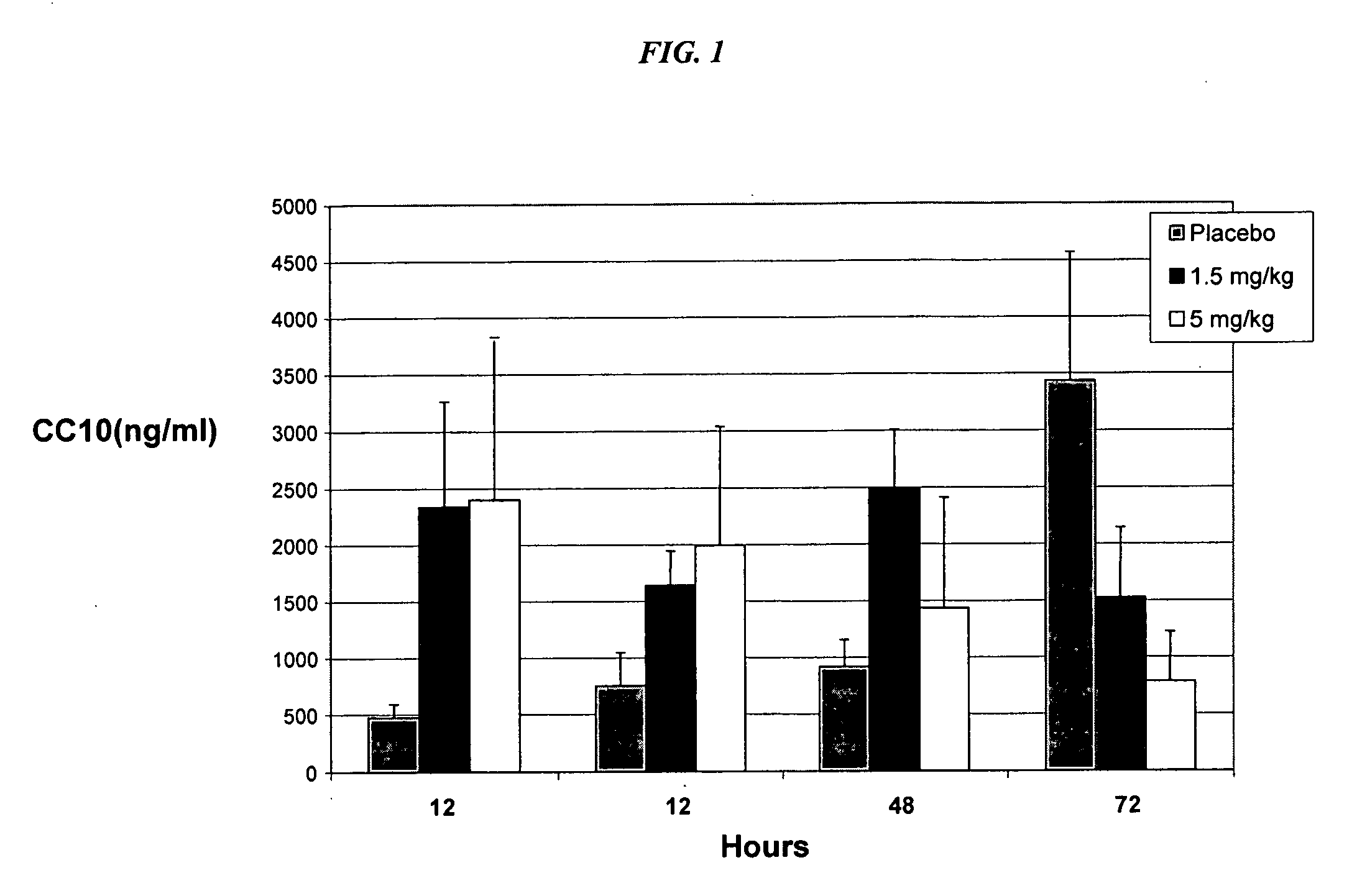
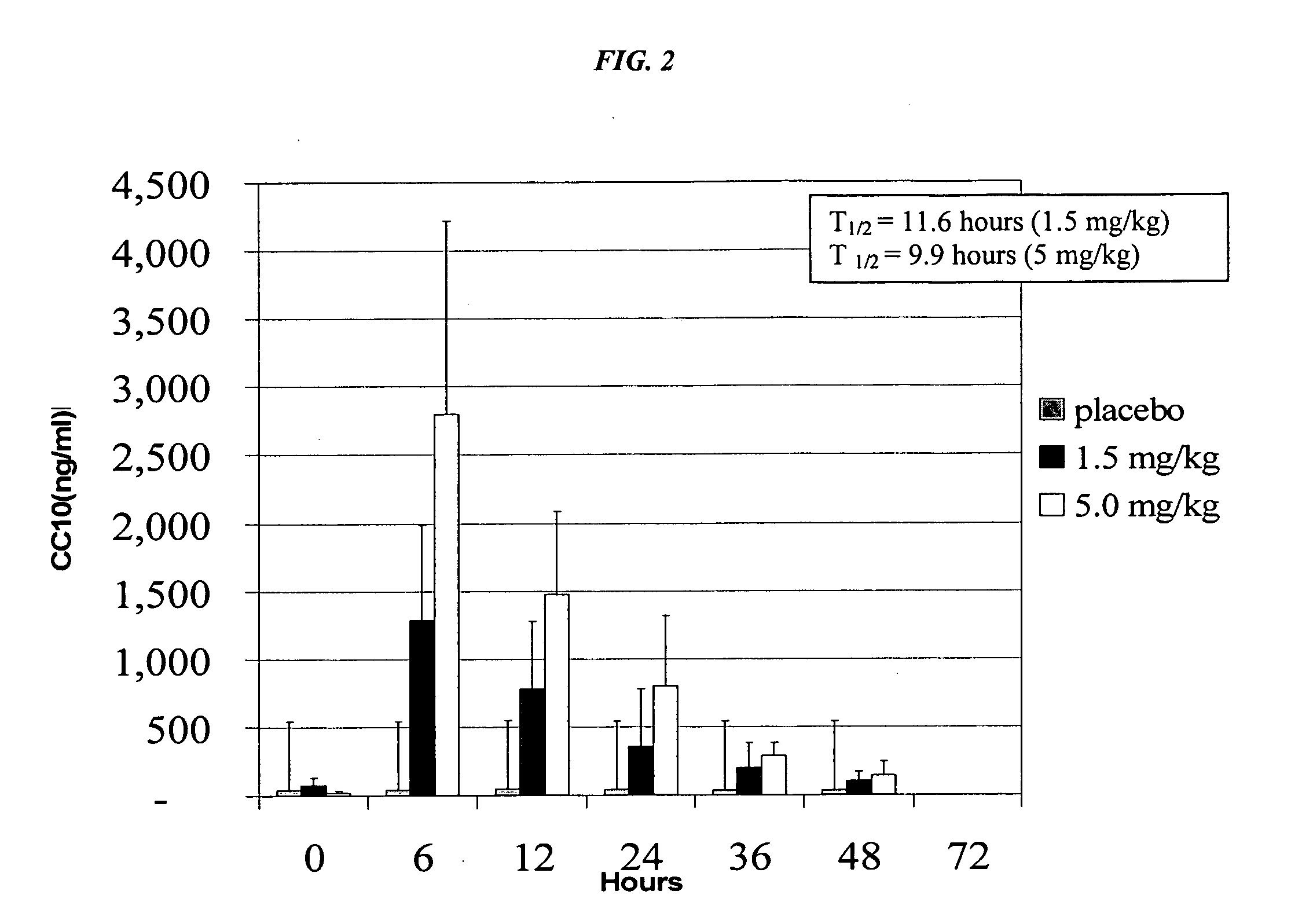
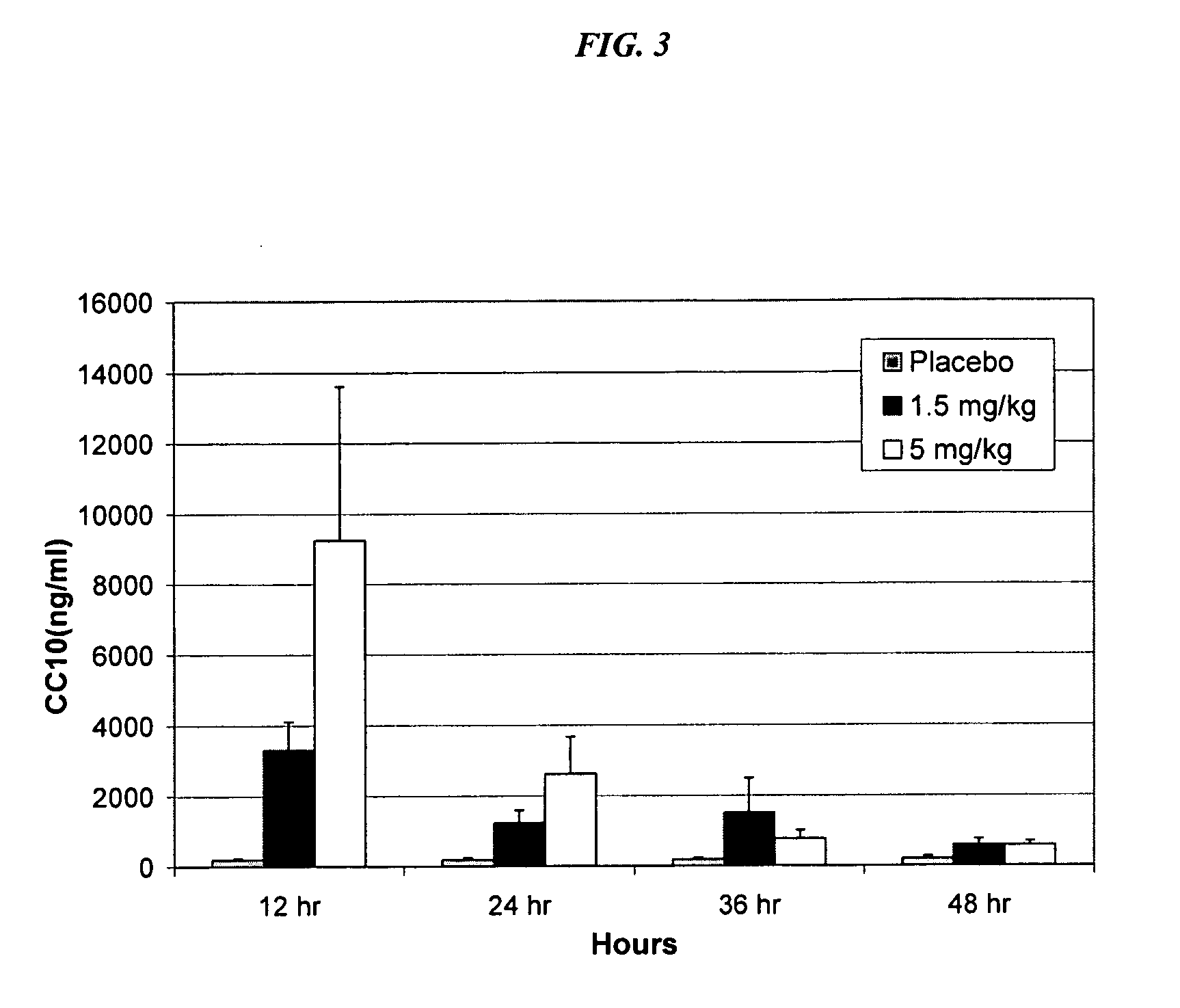
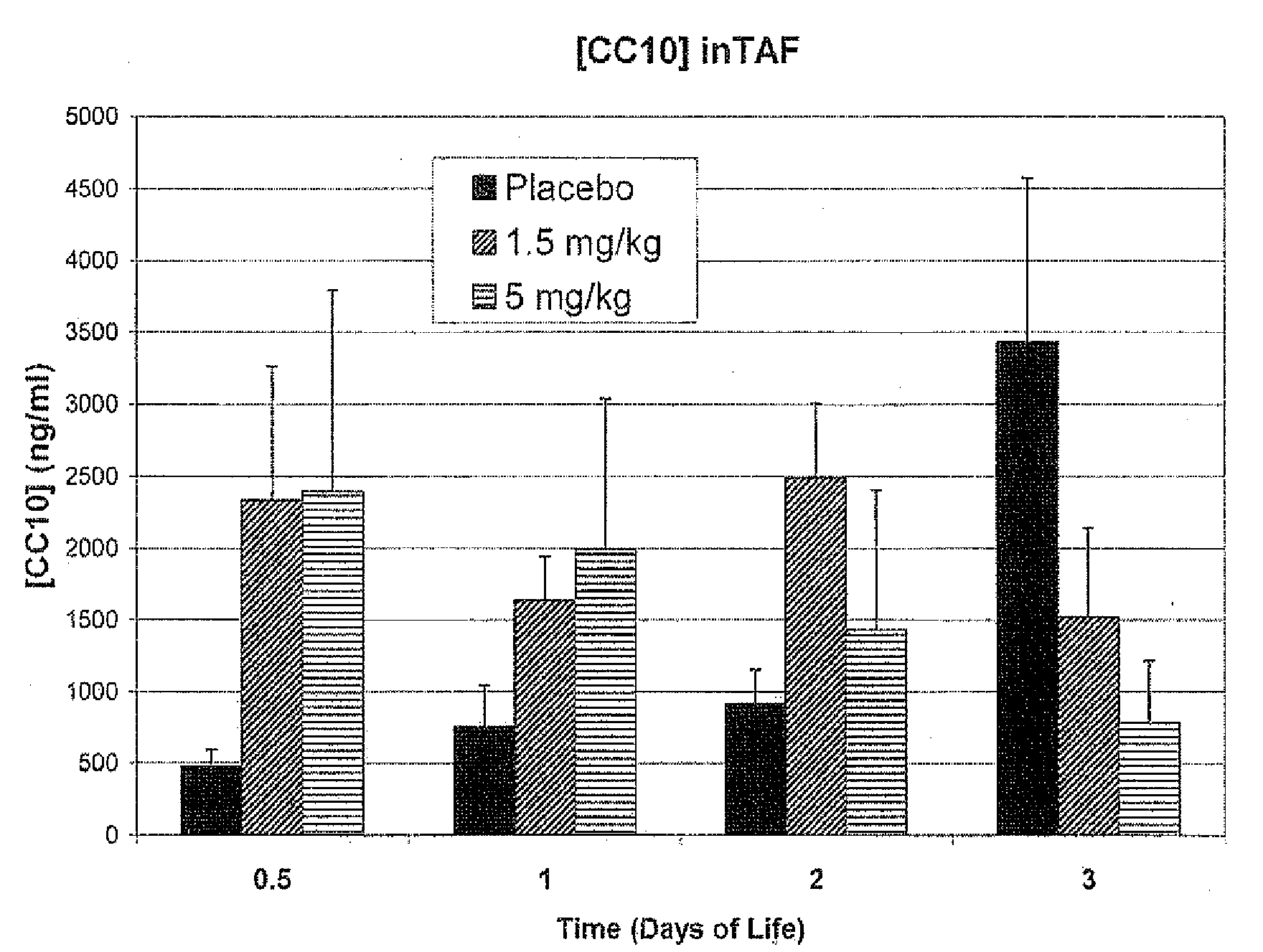
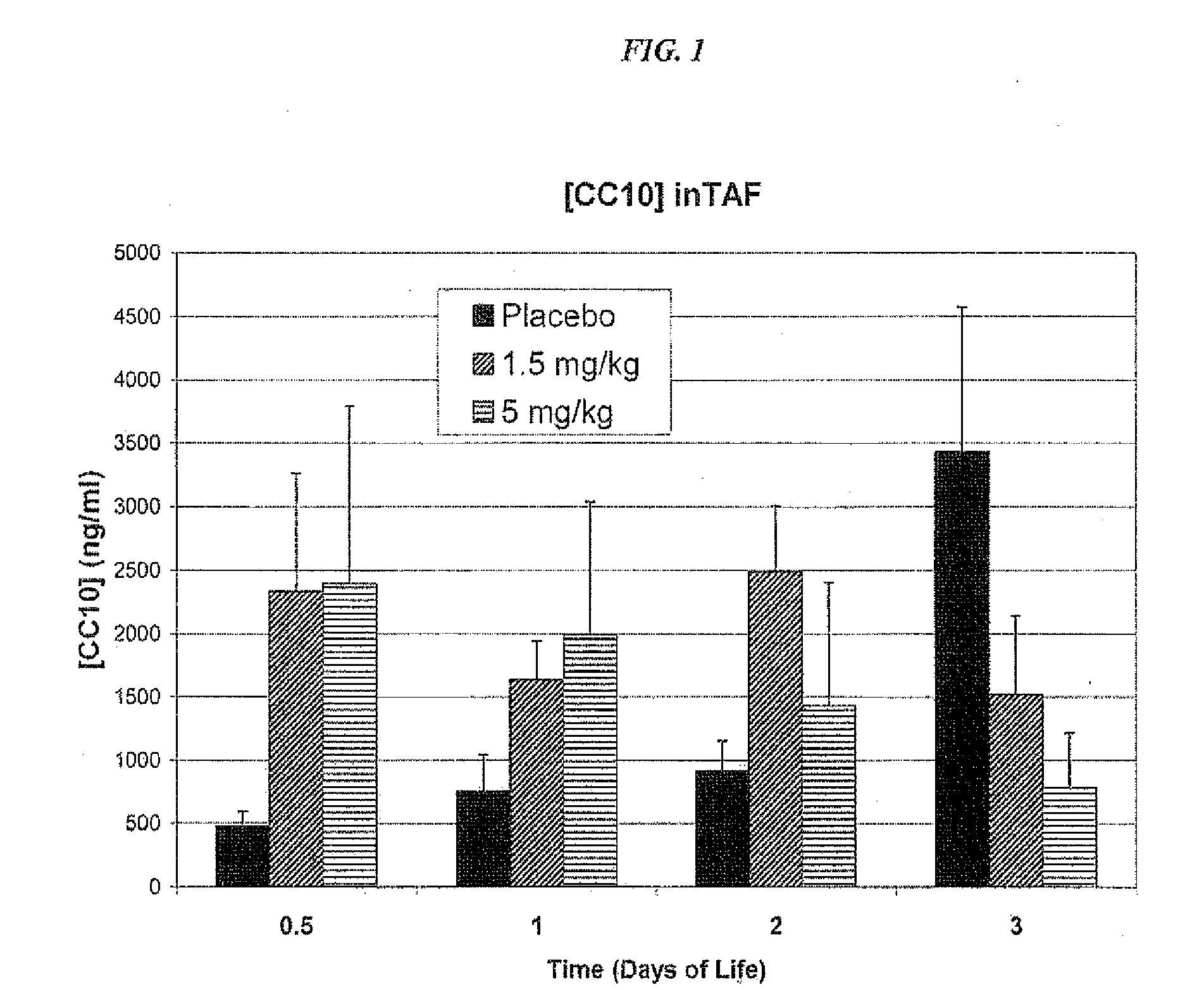
The present invention relates generally to the use of recombinant human CC10 (rhCC10), also known as recombinant human uteroglobin, for use as a therapeutic in the treatment of Respiratory Distress Syndrome (RDS), Bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD), chronic lung disease and / or pulmonary fibrosis, Asthma and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). More particularly, the invention provides methods, including broadly the critical dosage ranges of rhCC10, which may be administered to safely and effectively treat the aforementioned conditions. The invention further provides a composition useful in administering rhCC10 to humans.
Owner:CC10 SWEDEN
Methods and compositions for the reduction of neutrophil influx and for the treatment of bronchpulmonary dysplasia, respiratory distress syndrome, chronic lung disease, pulmonary fibrosis, asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
InactiveUS20090197808A1Inhibits platelet aggregationSuppress immune responsePeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementObstructive Pulmonary DiseasesNeutrophil granulocyte
The present invention relates generally to the use of recombinant human CC10 (rhCC10), also known as recombinant human uteroglobin, for use as a therapeutic in the treatment of Respiratory Distress Syndrome (RDS), Bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD), chronic lung disease and / or pulmonary fibrosis, Asthma and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). More particularly, the invention provides methods, including broadly the critical dosage ranges of rhCC10, which may be administered to safely and effectively treat the aforementioned conditions. The invention further provides a composition useful in administering rhCC10 to humans.
Owner:THERABRON THERAPEUTICS INC
Methods and compositions for promoting the respiratory development of an infant
The present invention relates to methods for promoting respiratory development, reducing the incidence of respiratory distress, bronchopulmonary dysplasia and / or hayfever in an infant by administration of fatty acids and compositions comprising same, wherein the fatty acids are enriched with respect to docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) content.
Owner:WOMENS & CHILDRENS HEALTH RES INST
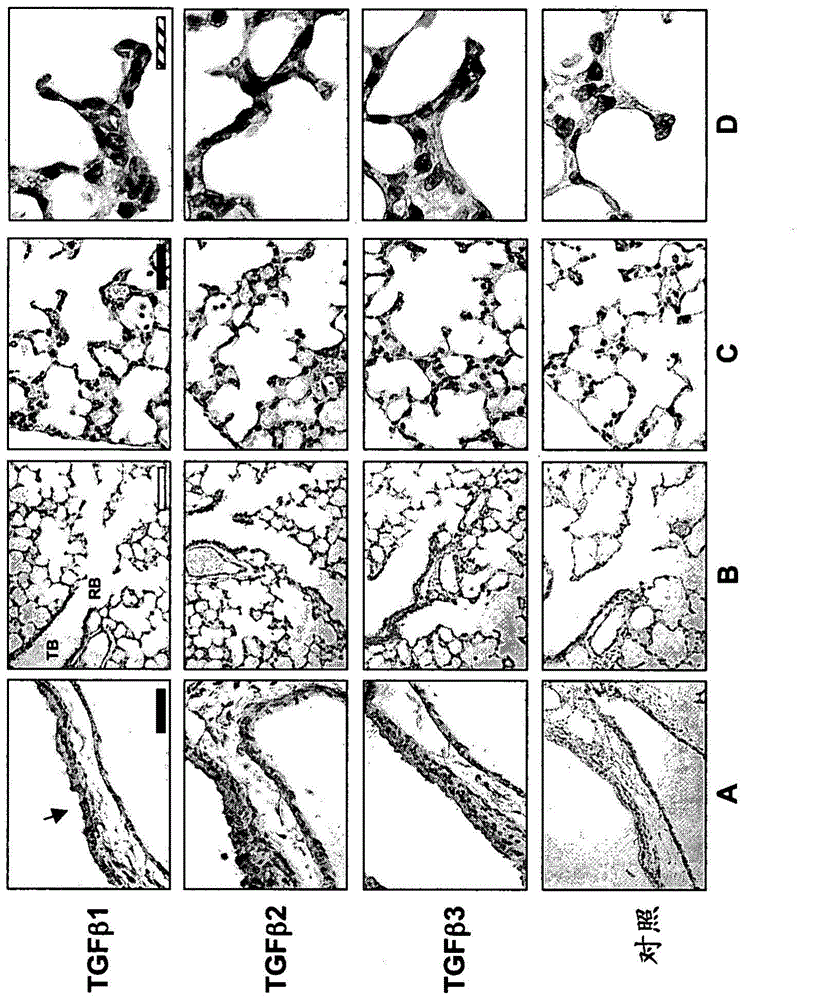
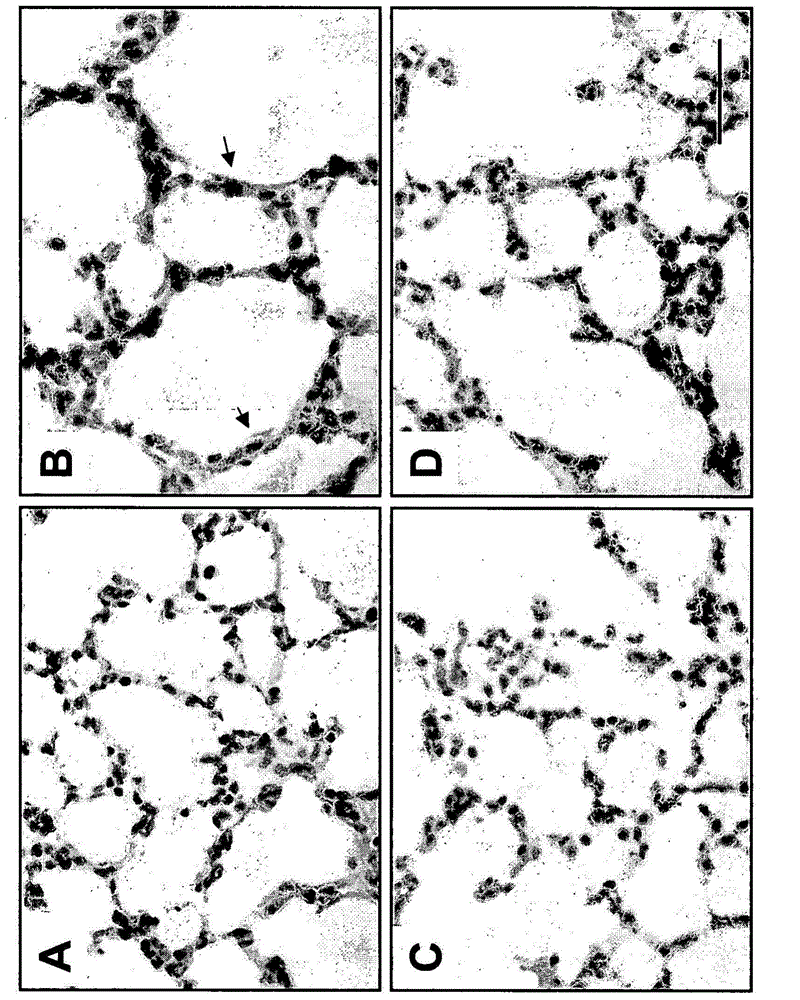
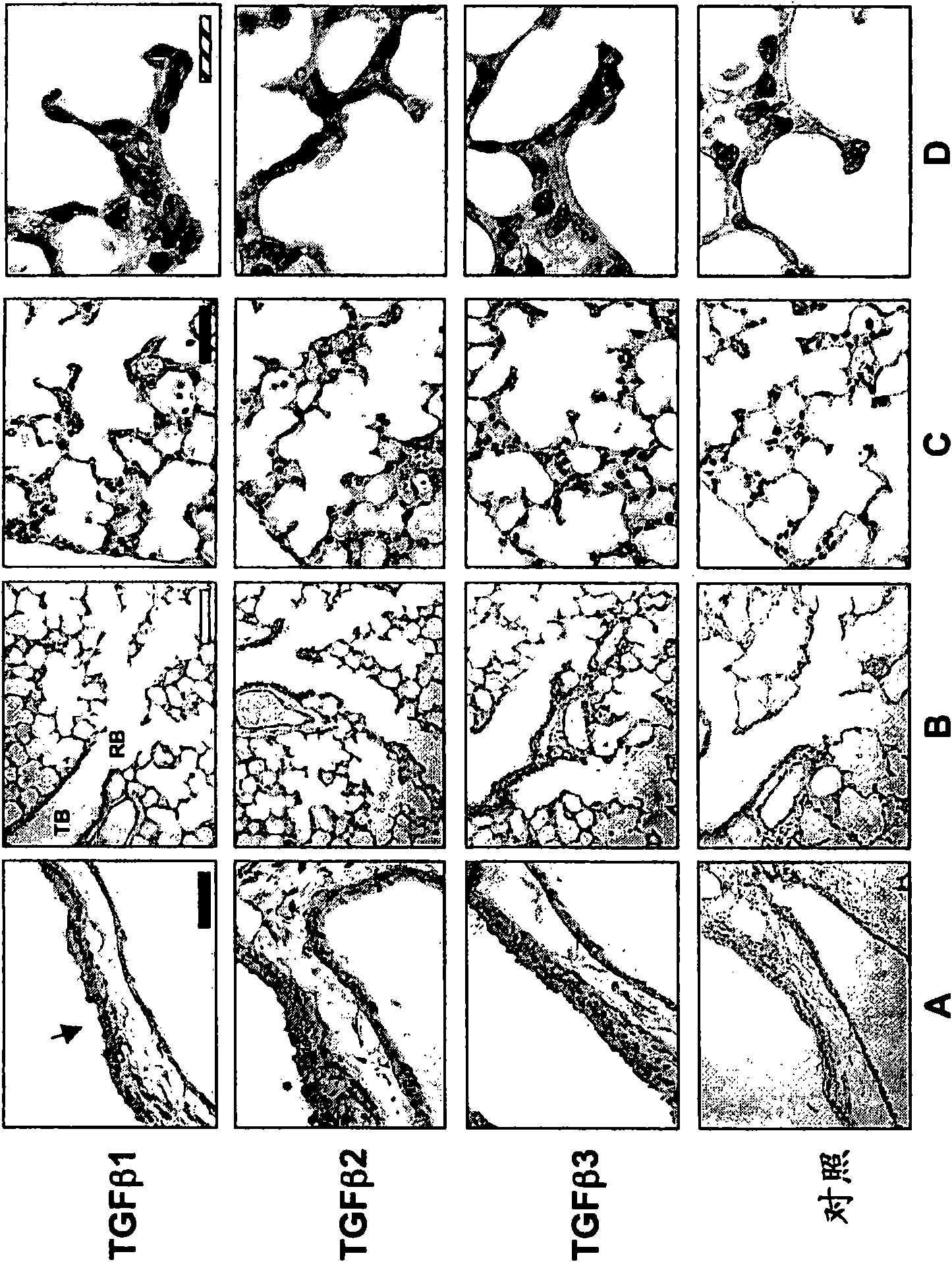
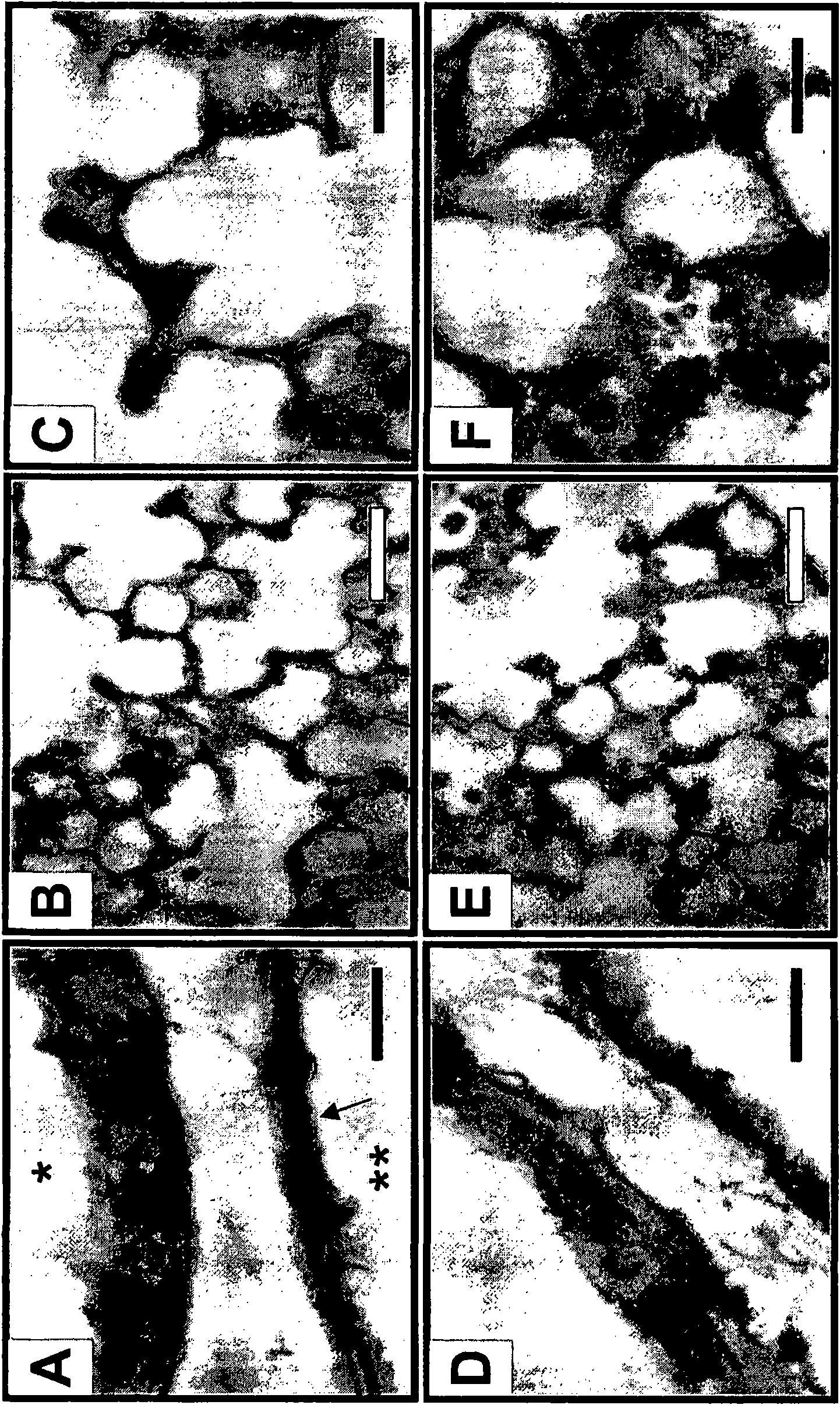
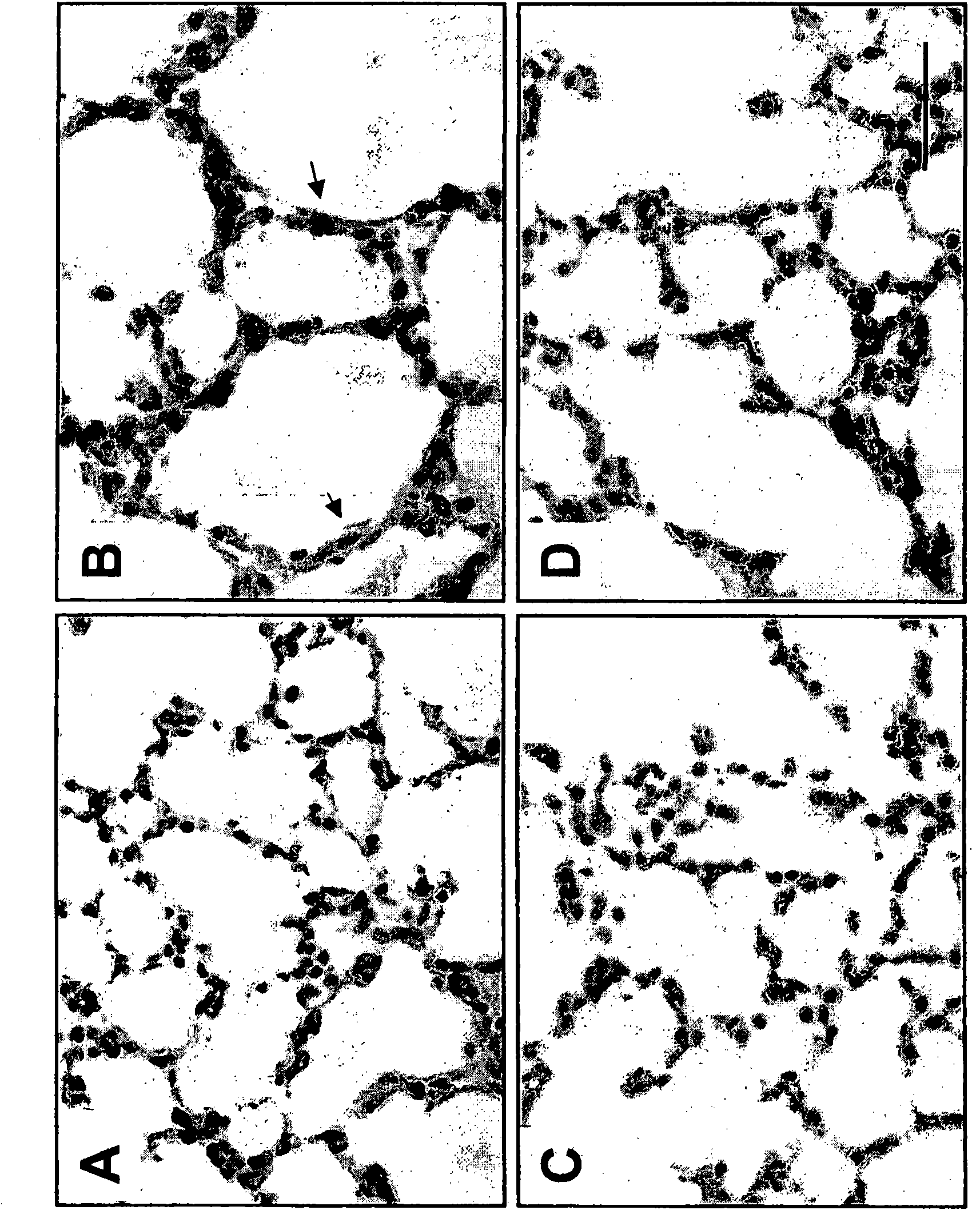
Use of TGF-beta antagonists to treat infants at risk of developing bronchopulmonary dysplasia
The disclosure relates to methods of treating an infant at risk of developing bronchopulmonary dysplasia, including premature infants, by administering a TGF-beta antagonist during the perinatal period, including the prenatal period and / or the postnatal period. For administration during the prenatal period, the TGF-beta antagonist can be administered either directly to the infant in utero, or indirectly by administration to the mother.
Owner:GENZYME CORP +1
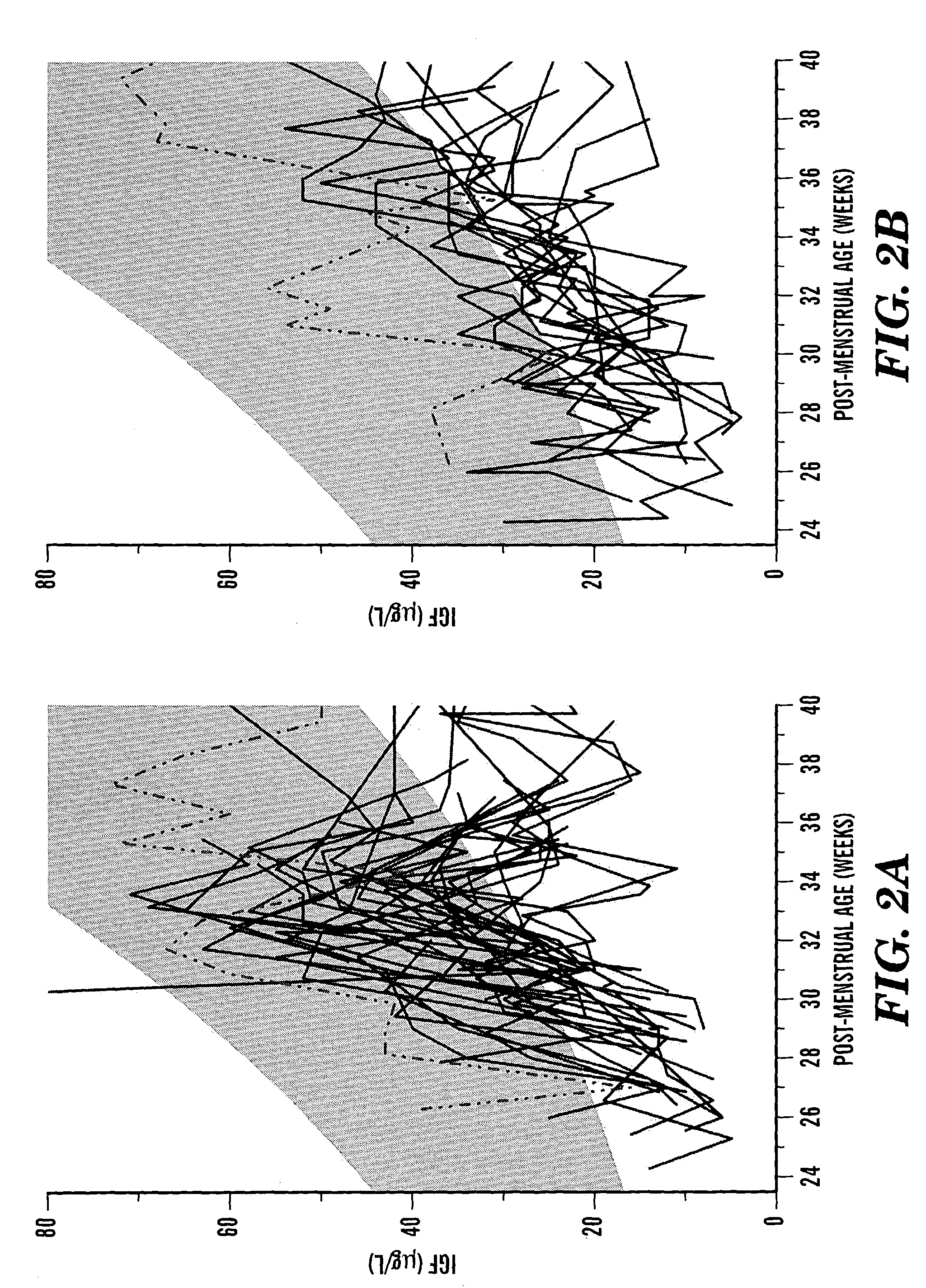
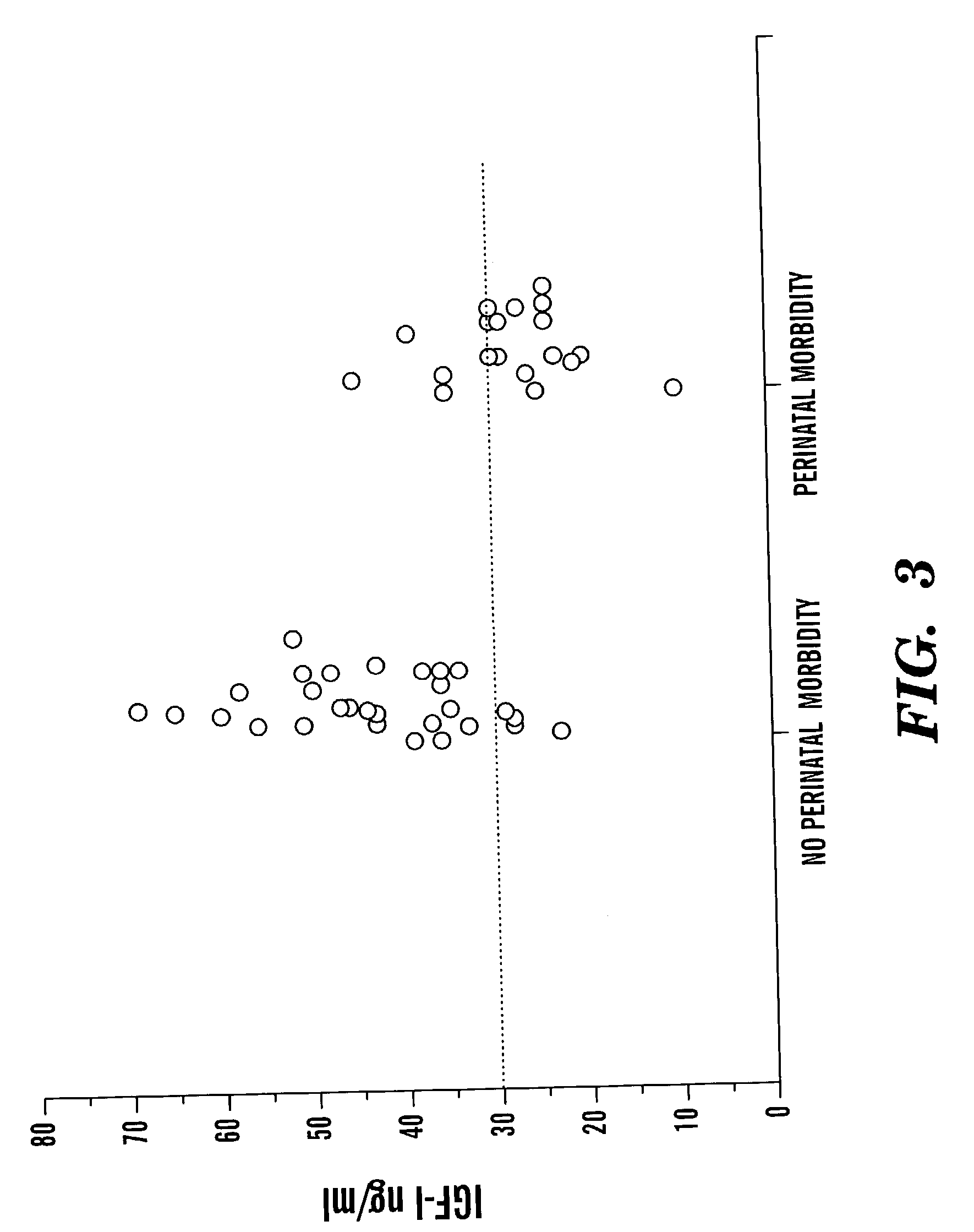
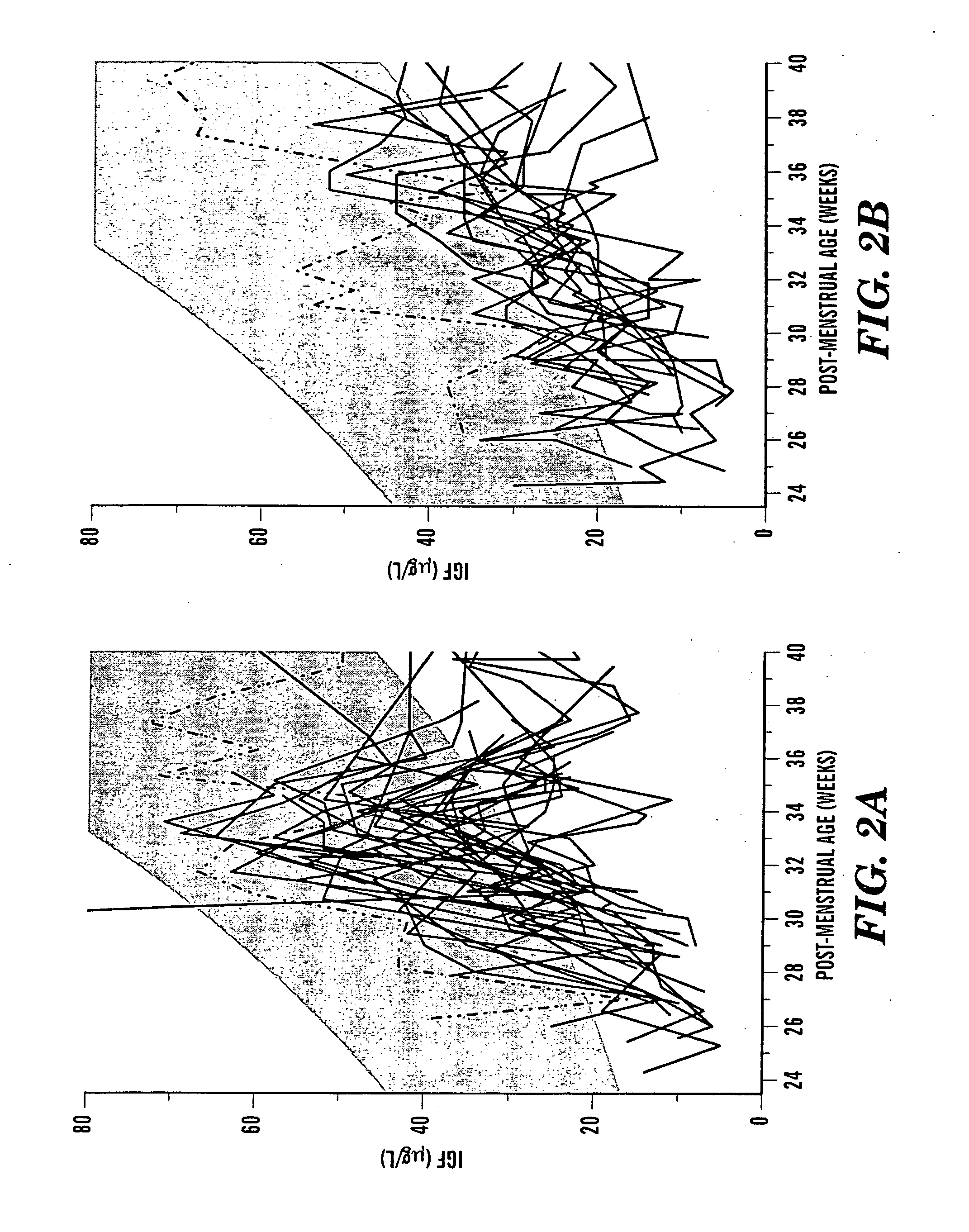
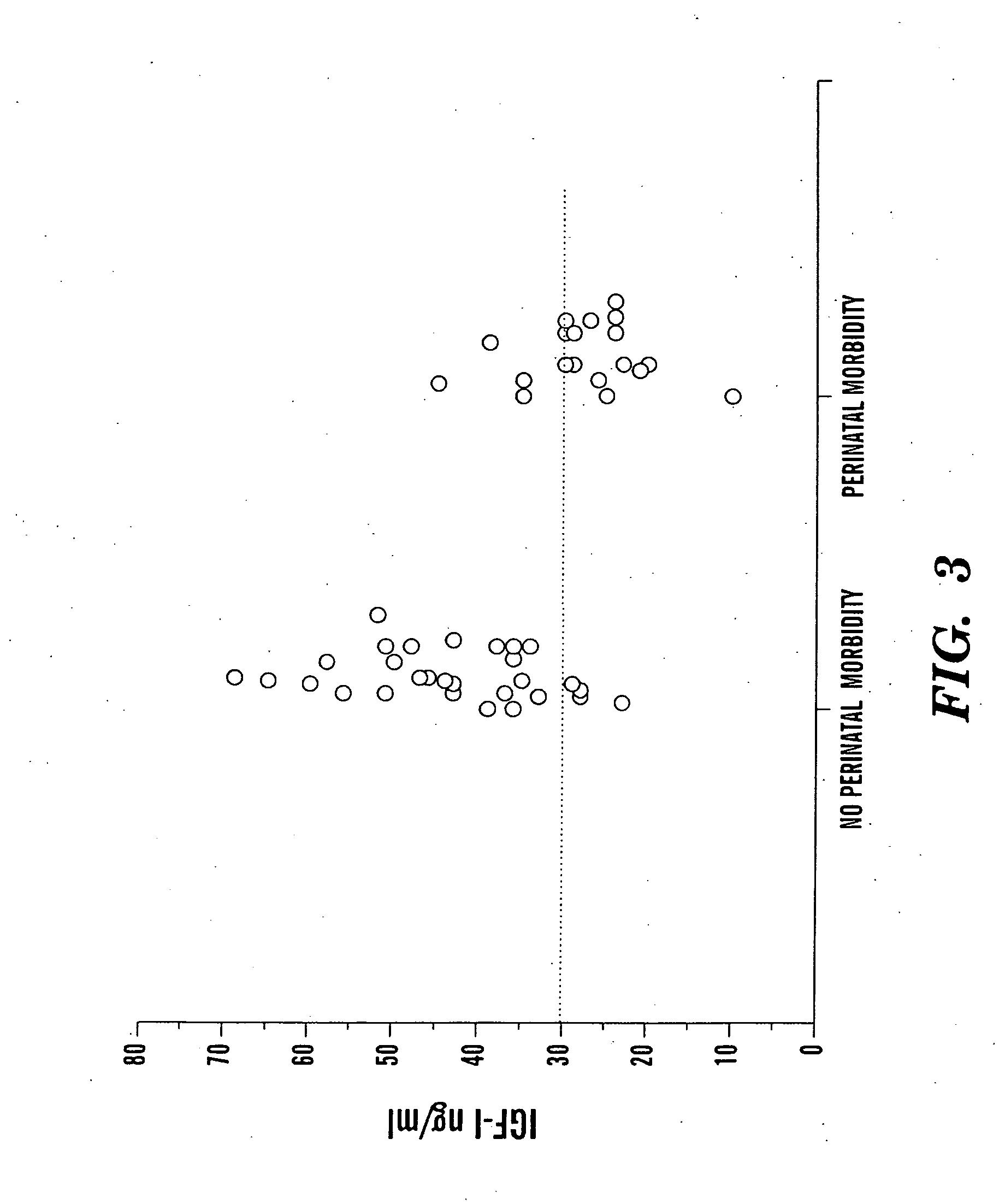
Determination of risk and treatment of complications of prematurity
In one aspect of the present invention there is provided a method for determining the risk of developing a complication of preterm birth in a patient born before 40 weeks of gestation or weighing 10% less than the average for the patient's gestational age. The method involves measuring serum IGF-I and / or IGF-I binding protein levels after birth of the patient to obtain an IGF-I or IGF-I binding protein level; and correlating said IGF-I or IGF-I binding protein level with an in utero baseline level of IGF-I or IGF-I binding protein based on gestational age matched mean levels in utero, wherein an IGF-I or IGF-I binding protein level below the mean gestational age in utero level indicates the patient is at an increased risk of developing a complication of preterm birth. The complications of preterm birth include retinopathy of prematurity, developmental delay, mental retardation, bronchopulmonary dysplasia, and intraventricular hemorrhage. Methods for treating / preventing complications of preterm birth are also provided.
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP
Methods of preventing and treating bronchopulmonary dysplasia using high fat human milk products
InactiveUS20170367364A1Shorten the durationReduce severityMilk preparationRespiratory disorderMedicineHigh fat
The disclosure features a human milk cream composition, standardized high fat human milk formulations as well as methods of making and using such compositions. In particular, the disclosure features a method of using a human milk cream composition and / or standardized high fat human milk formulations to treat infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) or at risk of developing BPD.
Owner:PROLACTA BIOSCI
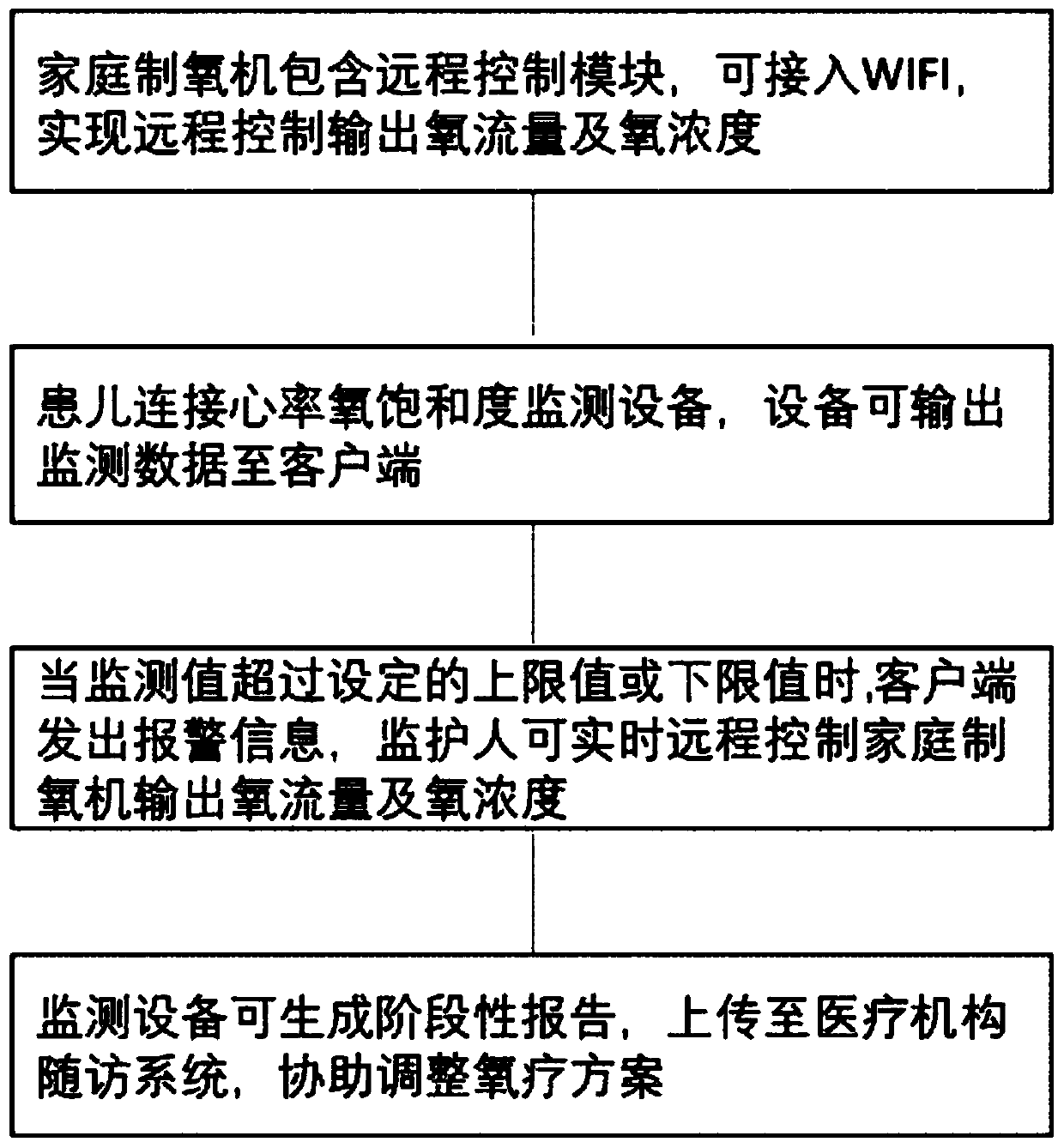
Household oxygen therapy intelligent management system and method for child patient with bronchopulmonary dysplasia
PendingCN110152146ARealize regulationRealize intelligent managementRespiratorsMedical devicesNostrilOxygen monitoring
The invention relates to an intelligent management system and method in the technical field of household oxygen therapy. The system comprises a household oxygen generator and heart rate and blood oxygen saturation degree monitoring equipment; the household oxygen generator is connected into the nostrils of a child patient through a nasal catheter, the heart rate and blood oxygen saturation degreemonitoring equipment comprises a finger vein oxygen monitoring probe connected with the child patient, a control valve of the household oxygen generator is provided with a control module, and a remoteclient side is connected with the control module through a network so that the oxygen flow rate or / and inspired oxygen concentration of the household oxygen generator can be remotely adjusted; the heart rate and blood oxygen saturation degree monitoring equipment comprises a data acquisition module, the data acquisition module is connected with the remote client side through the network, and real-time monitoring data is displayed on the remote client side. The system is reasonable in design, the monitoring data can be timely fed back to the remote client side of an oxygen supply system through the network, real-time control can be achieved, the fine adjustment and intelligent management of the household oxygen therapy are achieved accordingly, and the oxygen saturation degree is maintained within a reasonable range.
Owner:XIN HUA HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
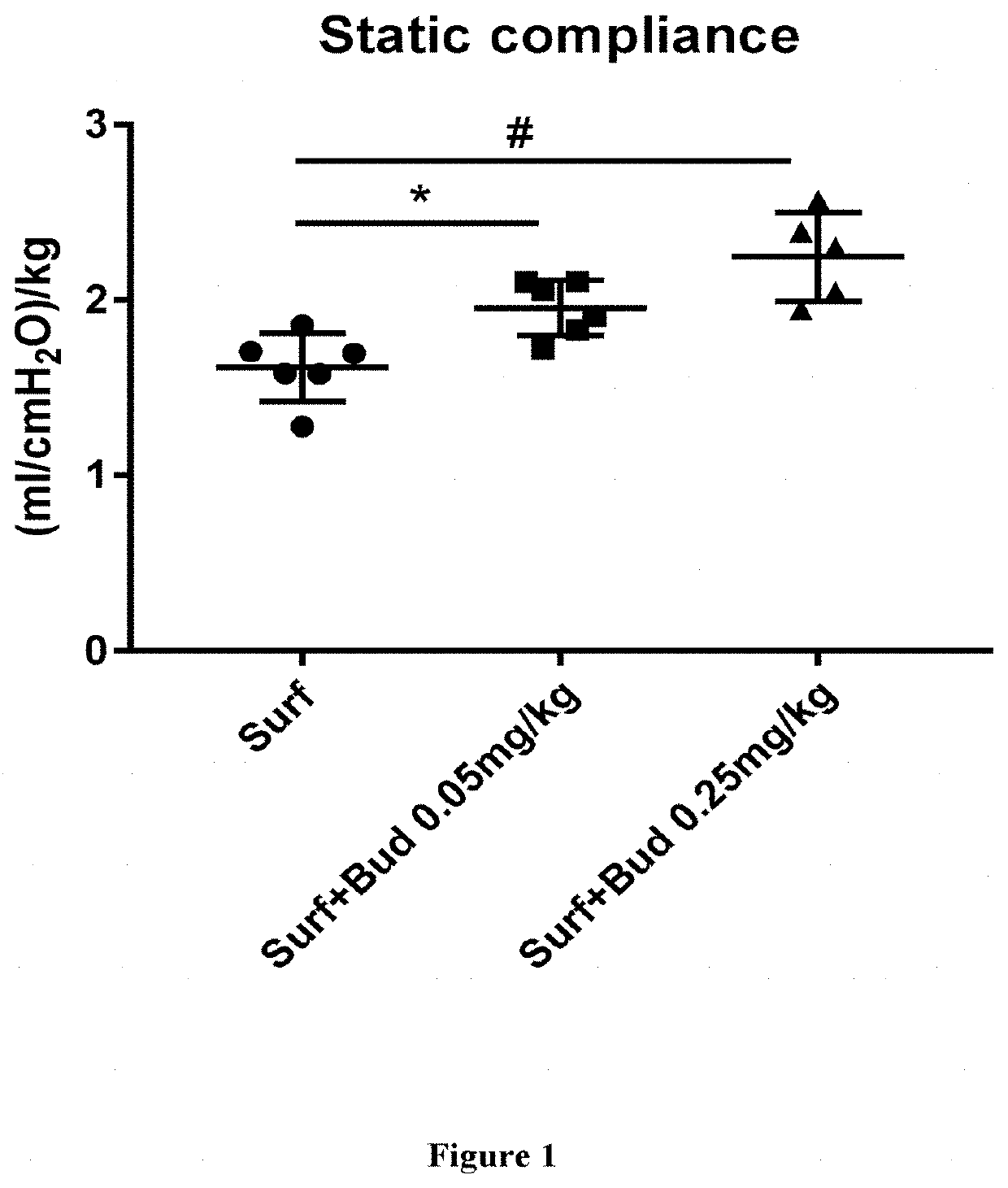
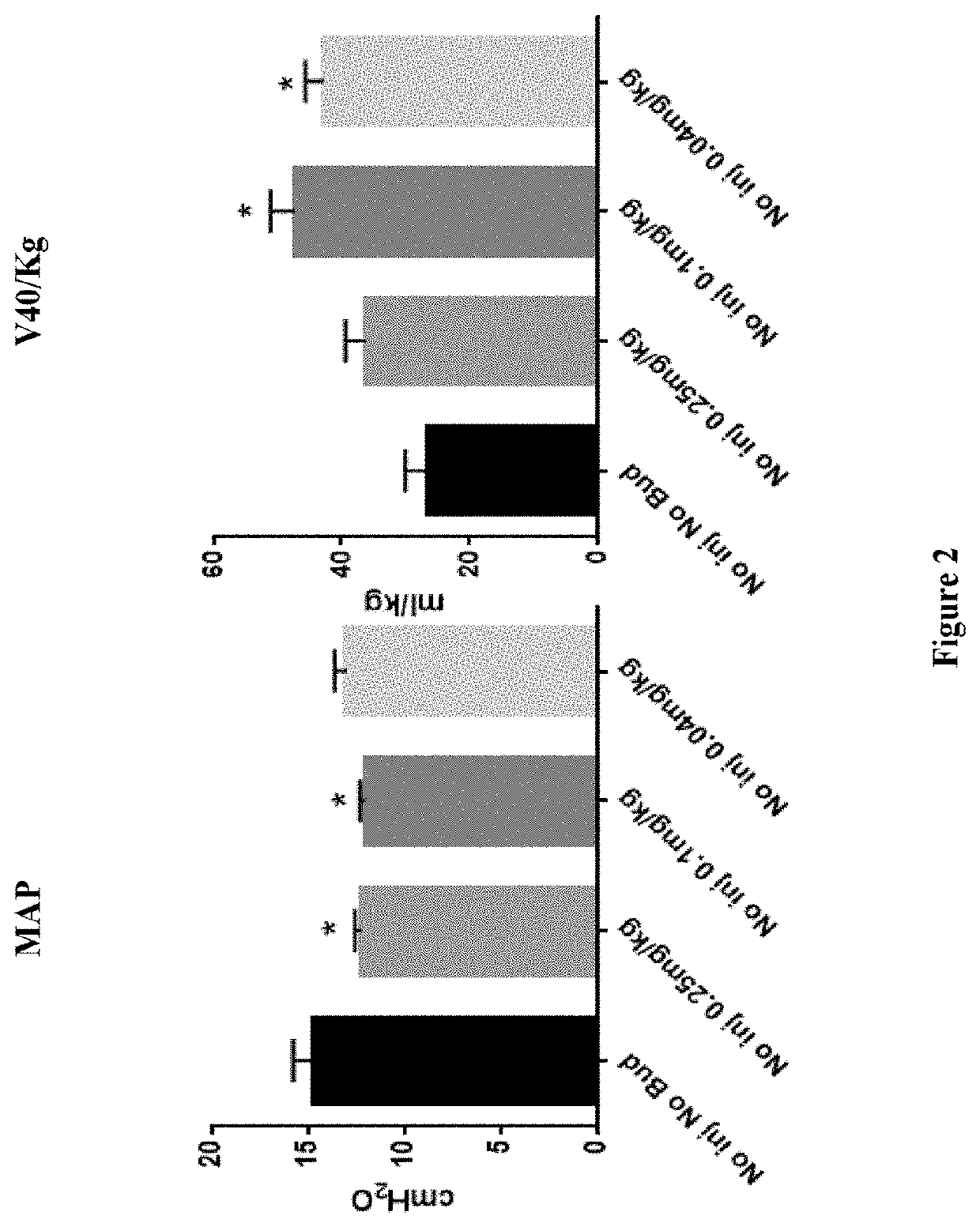
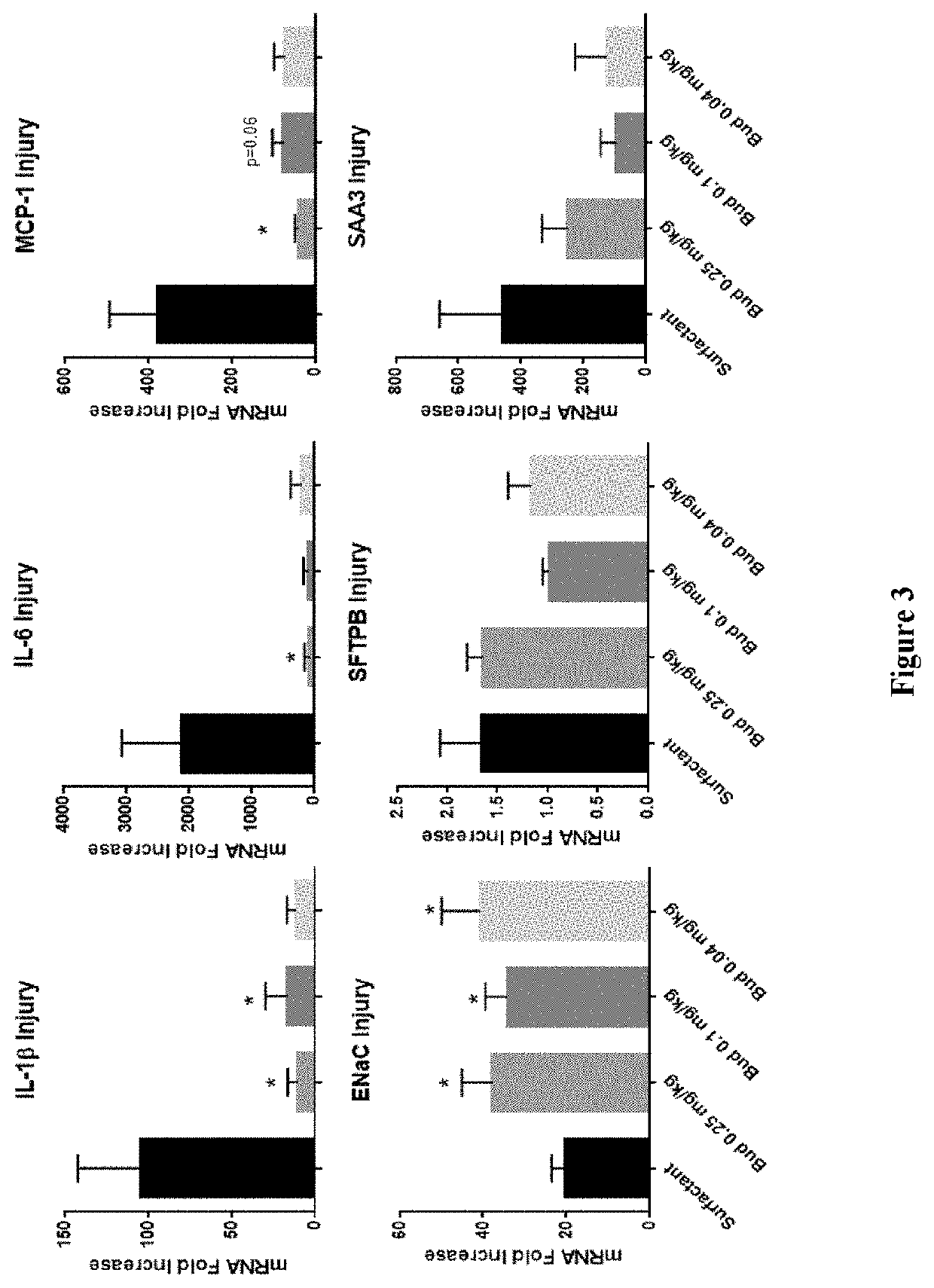
Therapeutic combination comprising a pulmonary surfactant and a steroid for the treatment of evolving BPD
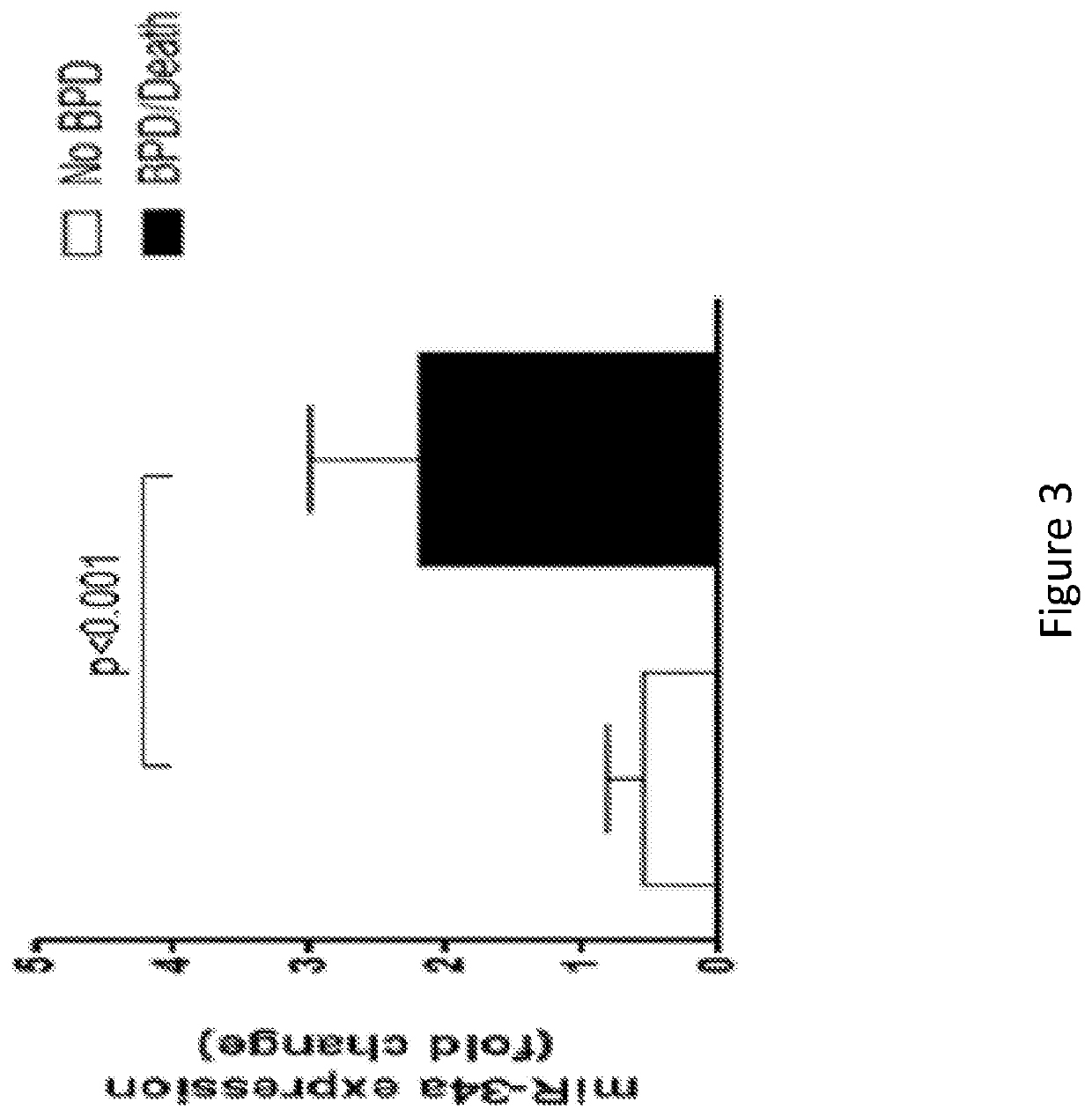
ActiveUS10668110B2Increase mRNA expressionOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismActive agentDecreased surfactant
Administering a pulmonary surfactant and a corticosteroid is effective for the treatment of evolving bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) in preterm neonates.
Owner:CHIESI FARM SPA
Methods and compositions for the treatment and prevention of lung disease
InactiveUS20060116425A1Reduce probabilityPromote growthBiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsGas exchangePneumatocele
Methods and compositions for the treatment of lung disease such as emphysema and / or bronchopulmonary dysplasia in a mammal. Also disclosed are methods and compositions promoting the formation of alveolar septa and increasing the gas-exchange surface area of a mammalian lung, and for the prevention and / or treatment of alveolar destruction.
Owner:MASSARO DONALD +2
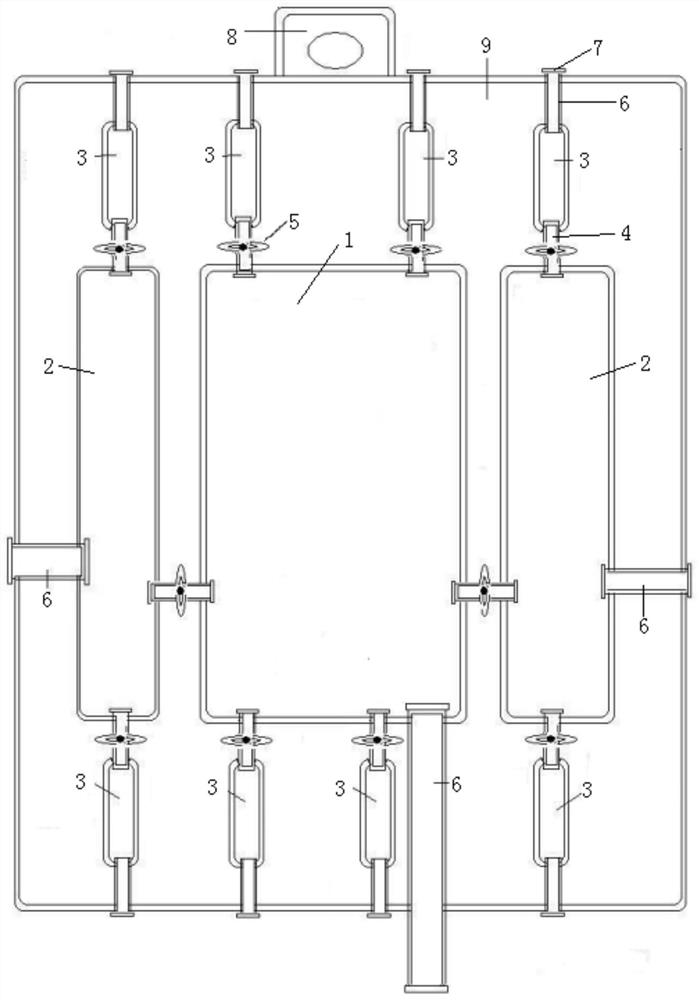
Artificial airway management devices, systems and methods
Systems and methods for cleaning and maintaining artificial airways sized for insertion within pediatric or neonatal patients (e.g., external diameters of less than 5 mm) are disclosed. The system includes a multi-port ventilator manifold configured to couple to a ventilation source, thereby forming a ventilator circuit with the patient. The manifold includes an occluder configured to advantageously reduce an amount of dead space in the manifold so as to prevent loss of positive end expiratory pressure of the ventilator circuit and reduce the likelihood of broncho-pulmonary dysplasia of the patient, or even premature death.
Owner:ENDOCLEAR
Use of TGF-BETA antagonists to treat infants at risk of developing bronchopulmonary dysplasia
The disclosure relates to methods of treating an infant at risk of developing bronchopulmonary dysplasia, including premature infants, by administering a TGF-β antagonist during the perinatal period, including the prenatal period and / or the postnatal period. For administration during the prenatal period, the TGF-β antagonist can be administered either directly to the infant in utero, or indirectly by administration to the mother.
Owner:GENZYME CORP +1
Attenuation of hyperoxia-induced cell death with mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase
InactiveUS20080058278A1Reducing and eliminating generationPrevent and reduce incidenceGenetic material ingredientsGenetically modified cellsExtracellular signalPhosphorylation
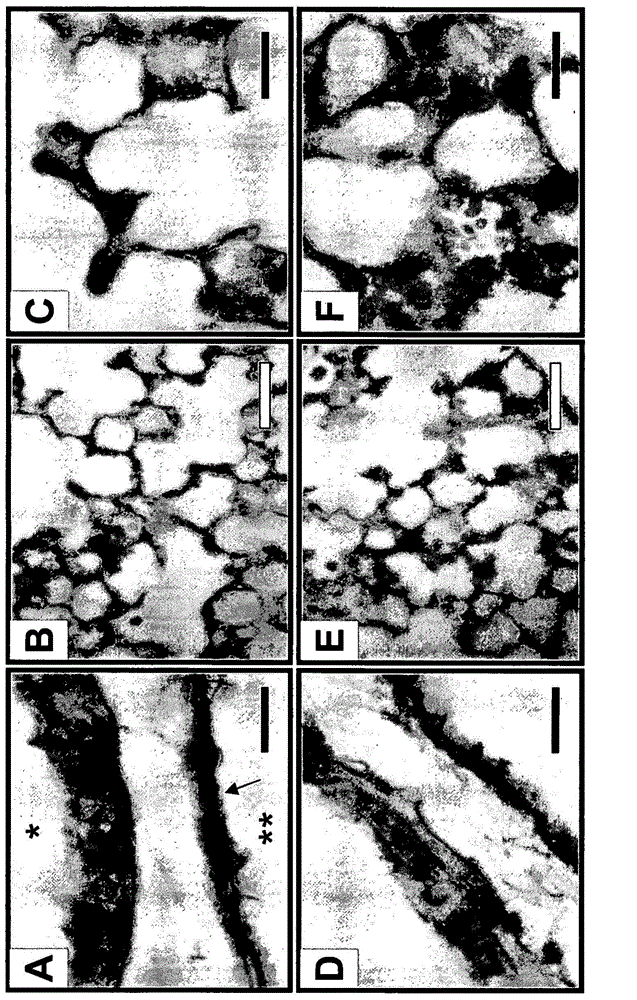
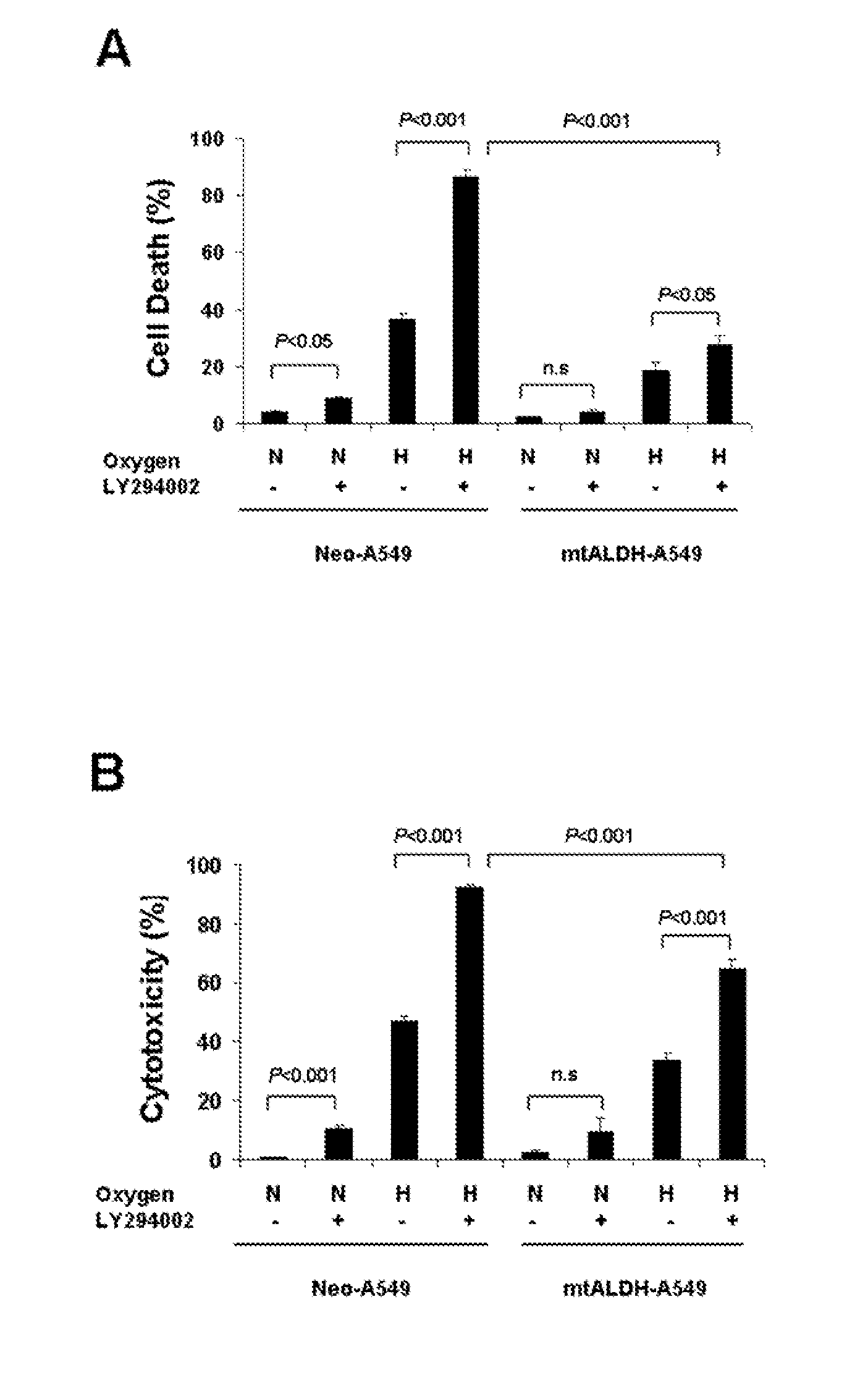
Oxygen toxicity is one of the major risk factors in the development of the chronic lung disease or bronchopulmonary dysplasia in premature infants. Using proteomic analysis, we discovered mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase (mtALDH or ALDH2) was down-regulated in neonatal rat lung after hyperoxic exposure. To study the role of mtALDH in hyperoxic lung injury, we overexpressed mtALDH in human lung epithelial cells (A549) and found that mtALDH significantly reduced hyperoxia-induced cell death. Compared to control cells (Neo-A549), the necrotic cell death in mtALDH overexpressing cells (mtALDH-A549) decreased from 25.3% to 6.5%, 50.5% to 9.1% and 52.4% to 15.06% after 24-, 48- and 72-hour hyperoxic exposure, respectively. The levels of intracellular and mitochondria-derived reactive oxygen species (ROS) in mtALDH-A549 cells after hyperoxic exposure were significantly lowered compared to Neo-A549 cells. mtALDH overexpression significantly stimulated extracellular signal regulated kinase (ERK) phosphorylation under normoxic and hyperoxic conditions. Inhibition of ERK phosphorylation partially eliminated the protective effect of mtALDH in hyperoxia-induced cell death, suggesting ERK activation by mtALDH conferred cellular resistance to hyperoxia. mtALDH overexpression augmented Akt phosphorylation and maintained the total Akt level in mtALDH-A549 cells under normoxic and hyperoxic conditions. Inhibition of PI3K activation by LY294002 in mtALDH-A549 cells significantly increased necrotic cell death after hyperoxic exposure, indicating that PI3K / Akt activation by mtALDH played an important role in cell survival after hyperoxia. Taken together, these data demonstrate that mtALDH overexpression attenuates hyperoxia-induced cell death in lung epithelial cells through reduction of ROS, activation of ERK / MAPK and PI3K / Akt cell survival signaling pathways.
Owner:CHILDRENS MERCY HOSPITAL
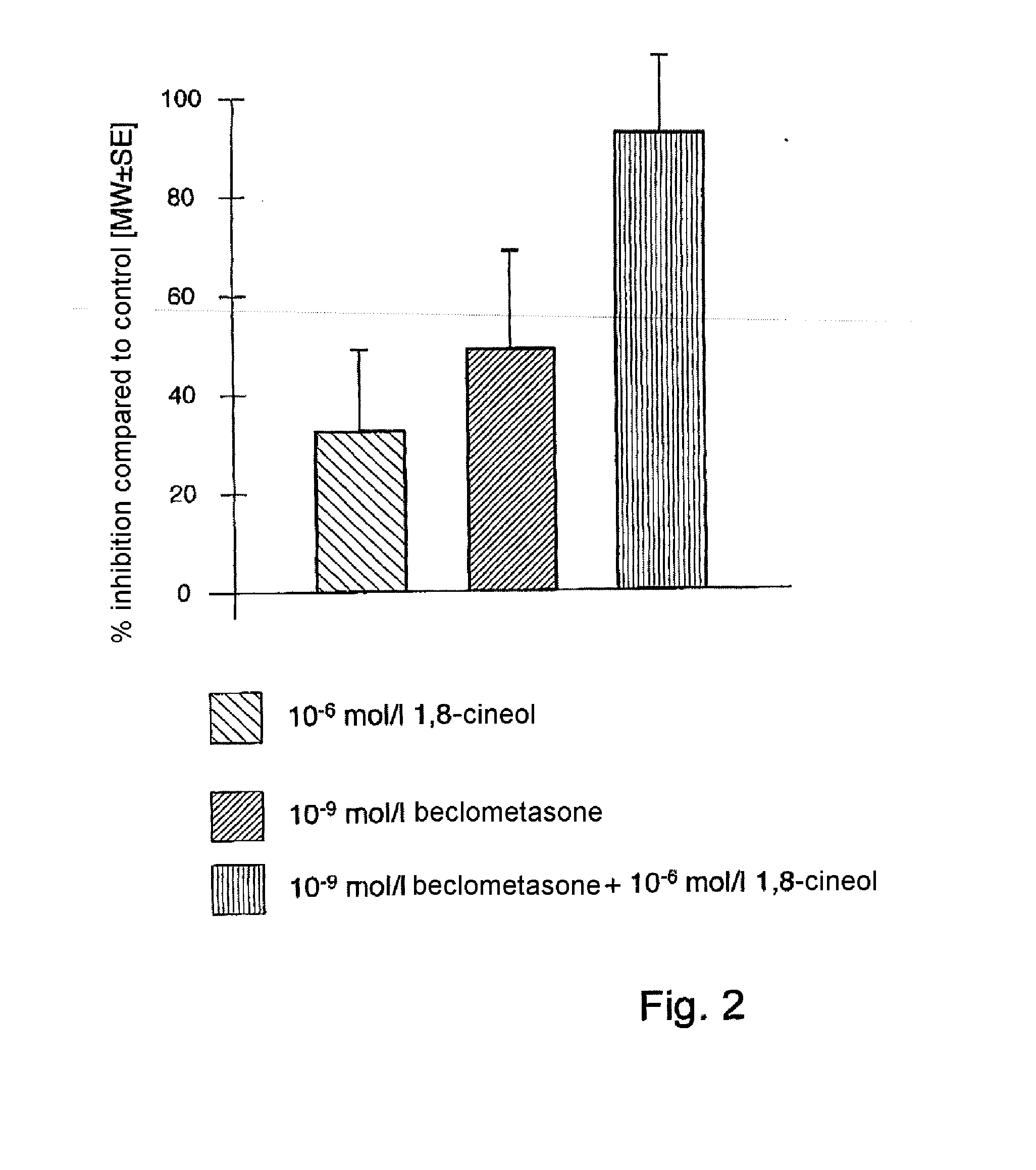
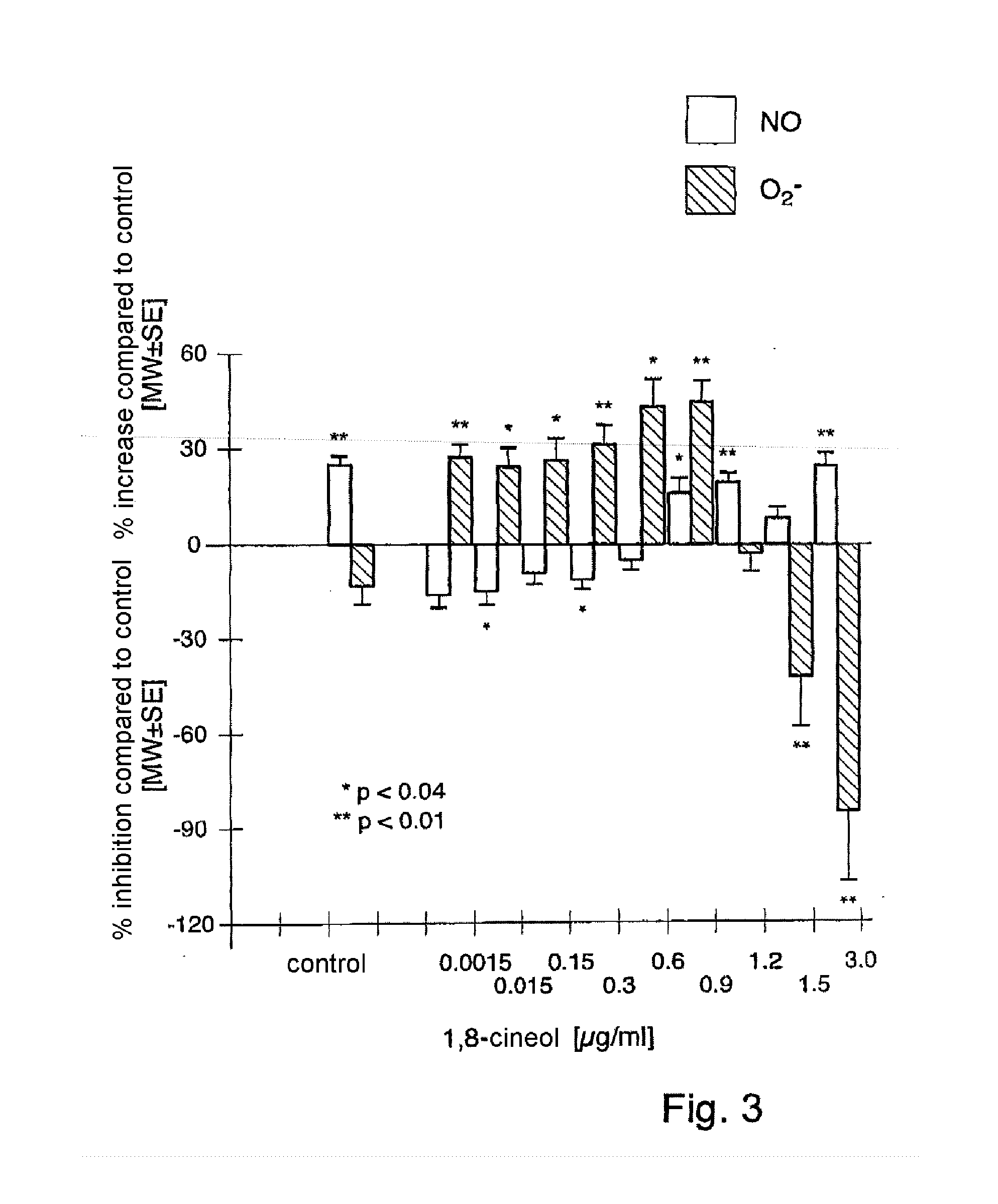
Monoterpenes for treating respiratory tract diseases, in particular bronchopulmonary diseases
InactiveUS20110257138A1Avoid disadvantagesReduce disadvantagesBiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsDiseaseSide effect
The invention relates to the combined use of at least one monoterpene which can be applied systemically, in particular perorally, and at least one respiratory tract therapeutic agent which can be applied topically, in particular through inhalation, for the prophylactic and / or therapeutic treatment, in particular combination therapy and / or co-medication, of respiratory tract diseases, in particular bronchopulmonary diseases. Through the combined use of the systemic monoterpene with the topical, in particular inhaled respiratory tract therapeutic agent, the effect or efficiency of the topical or inhaled respiratory disease therapeutic agent can be increased significantly, in particular in a synergistic manner, on the one hand, and the required dosage thereof can be reduced significantly on the other hand, combined with the resulting advantages (e.g., avoidance or reduction of side effects).
Owner:MARIA CLEMENTINE MARTIN KLOSTERFRAU VERTRIEBS GMBH
Determination of risk and treatment of complications of prematurity
In one aspect of the present invention there is provided a method for determining the risk of developing a complication of preterm birth in a patient born before 40 weeks of gestation or weighing 10% less than the average for the patient's gestational age. The method involves measuring serum IGF-I and / or IGF-I binding protein levels after birth of the patient to obtain an IGF-I or IGF-I binding protein level; and correlating said IGF-I or IGF-I binding protein level with an in utero baseline level of IGF-I or IGF-I binding protein based on gestational age matched mean levels in utero, wherein an IGF-I or IGF-I binding protein level below the mean gestational age in utero level indicates the patient is at an increased risk of developing a complication of preterm birth. The complications of preterm birth include retinopathy of prematurity, developmental delay, mental retardation, bronchopulmonary dysplasia, and intraventricular hemorrhage. Methods for treating / preventing complications of preterm birth are also provided.
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP
Methods and compositions for the treatment and prevention of lung disease
InactiveUS20080125489A1Reduce probabilityPromote growthBiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsGas exchangePneumatocele
Methods and compositions for the treatment of lung disease such as emphysema and / or bronchopulmonary dysplasia in a mammal. Also disclosed are methods and compositions promoting the formation of alveolar septa and increasing the gas-exchange surface area of a mammalian lung, and for the prevention and / or treatment of alveolar destruction.
Owner:MASSARO DONALD +2
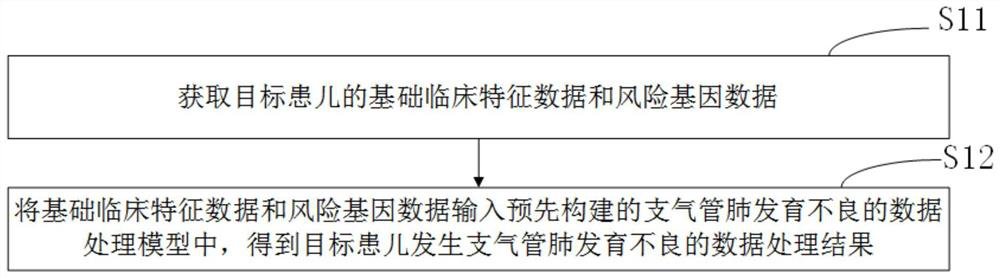
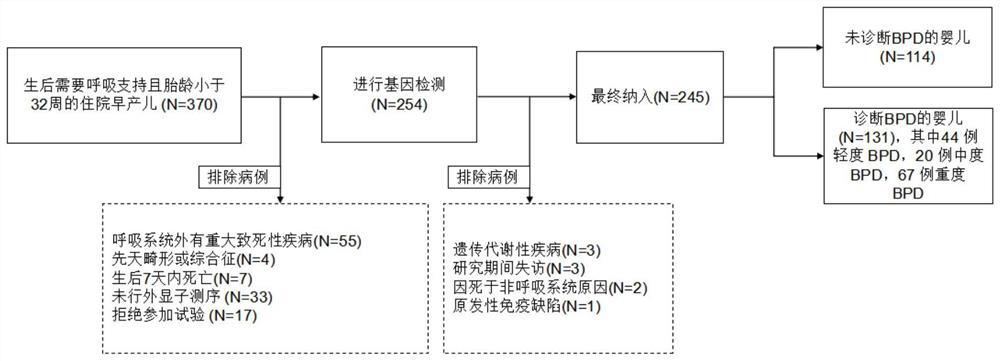
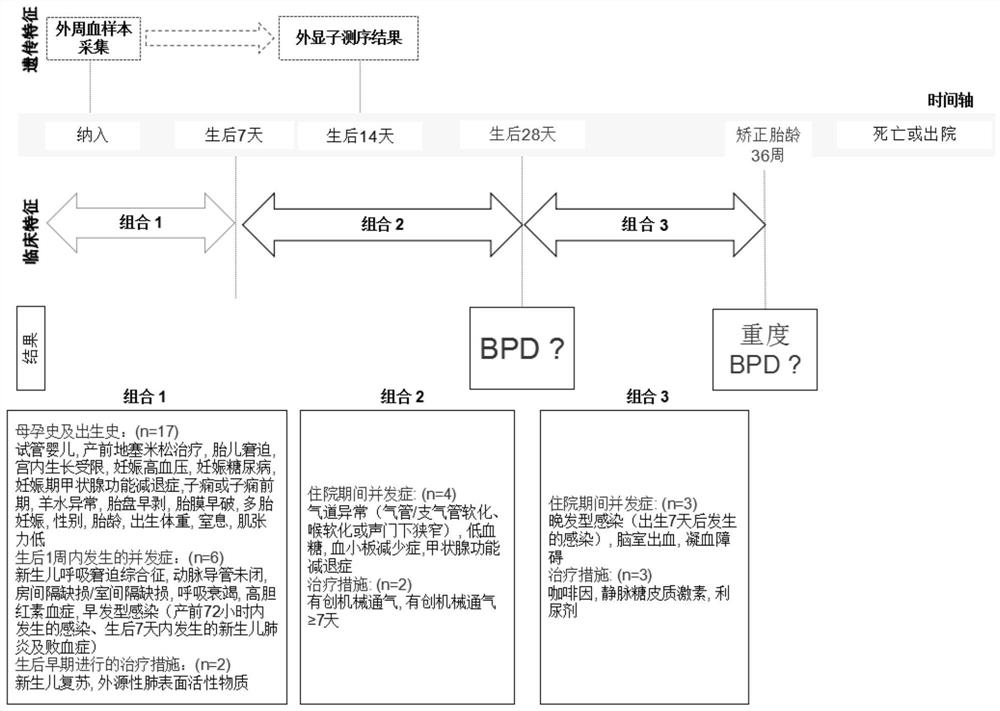
Bronchial pulmonary dysplasia data processing method and device and related equipment
ActiveCN113270146AMeet the accuracyShorten the timeMedical data miningBiostatisticsBronchial epitheliumIntensive care medicine
The invention relates to a data processing method and device for bronchial pulmonary dysplasia and related equipment, and belongs to the technical field of medicines. The method comprises the steps that when bronchial pulmonary dysplasia data processing is carried out on a target child patient, basic clinical feature data and risk gene data are input into a pre-constructed bronchial pulmonary dysplasia data processing model, and a data processing result of bronchial pulmonary dysplasia of the target child patient is obtained. According to the embodiment of the invention, after the data processing result that the target child patient suffers from the bronchial pulmonary dysplasia is obtained, medical staff can judge the possibility that the target child patient suffers from the bronchial pulmonary dysplasia according to the data processing result, so that the bronchial pulmonary dysplasia is predicted. According to the invention, the combination of the risk gene data and the basic clinical feature data is utilized for the first time to obtain the data processing result of the bronchial pulmonary dysplasia of the target child patient, the accuracy is met, the time is saved, and the popularization is promoted.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL OF FUDAN UNIV
Therapeutic combination comprising a pulmonary surfactant and a steroid
ActiveUS8357657B2Useful in treatmentReduce riskOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsNaturally occurring surfactantsOxidative stress
Administration of a modified natural surfactant in combination with a corticosteroid is effective for the prevention of bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) and lowers the markers of pulmonary oxidative stress.
Owner:CHIESI FARM SPA
Therapeutic treatment for lung conditions
InactiveCN101969974AOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsCitrullineTherapeutic treatment
Methods and compositions for treating lung conditions such as bronchopulmonary dysplasia or hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension in a subject, including administering to the subject an effective amount of a nitric oxide precursor such as citrulline.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Intratracheal administration of lysozyme with other therapeutic agents in the prevention and treatment of respiratory disorders
The subject invention is directed to the prevention and treatment of respiratory disorders by intratracheal administration of an effective amount of lysozyme, either alone or in combination with other therapeutic agents. Applicable respiratory disorders include, but are not limited to, pulmonary emphysema, asthma, bronchitis, pneumonia, respiratory distress syndrome, bronchopulmonary dysplasia, interstitial fibrosis, cystic fibrosis, and neoplasia. The method is intended for a variety of mammals, including humans ranging from premature neonates to adults.
Owner:CANTOR JEROME OWEN +1
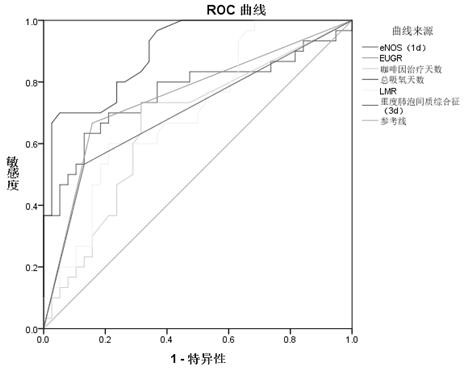
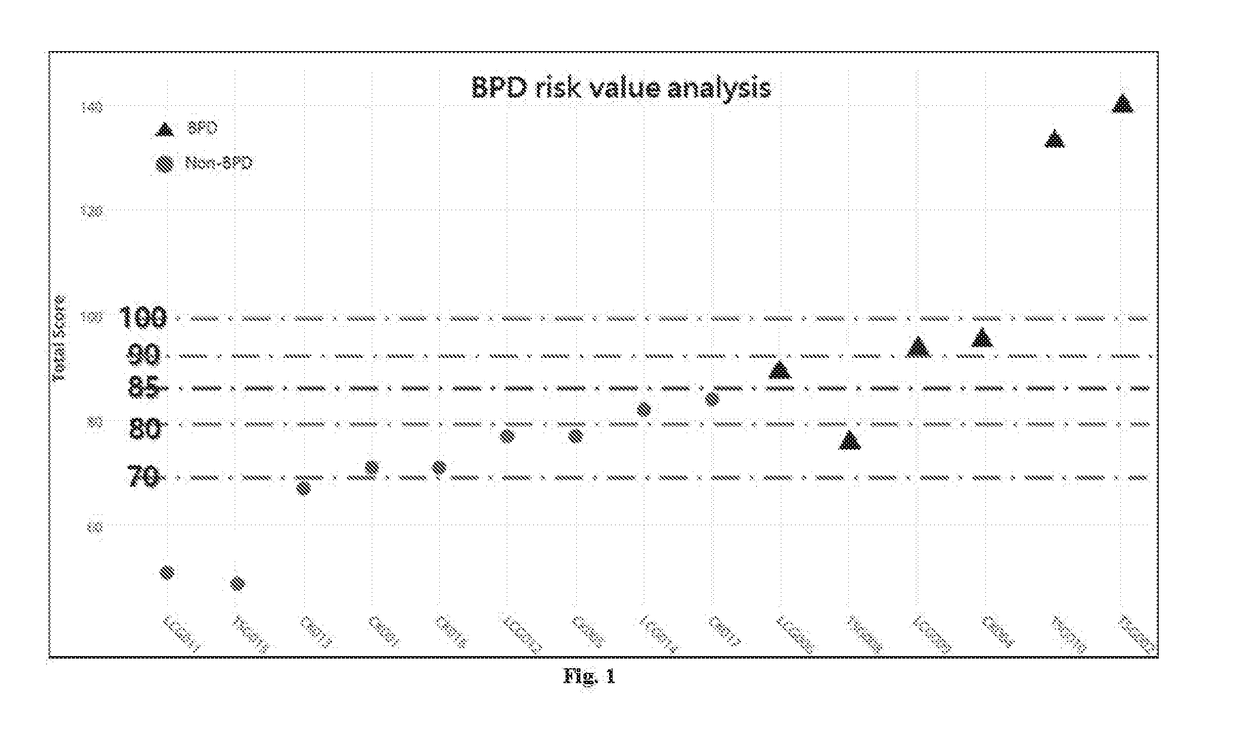
Prediction marker, prediction model and prediction system for premature infant bronchopulmonary dysplasia
The invention discloses a predictive marker, a predictive model and a predictive system for bronchial lung dysplasia of a premature infant. EUGR, caffeine treatment days, total oxygen uptake days and LMR are independent risk factors of BPD occurrence of the premature infant. The lung ultrasound prompts the occurrence rate of the severe alveolar interstitial syndrome on the third day after the premature infant is born, the lung ultrasound prompts the pleural line change on the 28th day after the premature infant is born, and the occurrence rate of the alveolar interstitial syndrome, the pulmonary metaplasia or the fragment symptom has a prediction effect on the occurrence of the BPD. The serum eNOS level of a child patient in a BPD group on the first day after birth is remarkably higher than that of a child patient in a non-BPD group and is in positive correlation with the severity of BPD, and when the serum eNOS level of the child patient on the first day after birth is larger than 6.48 ng / ml, the risk that a premature infant suffers from BPD is obviously increased. The BPD occurrence of the premature infant can be well predicted by constructing a regression model through combination of six indexes, namely the serum eNOS (1d) level, the severe alveolar interstitial syndrome (3d), EUGR, caffeine treatment days, the total oxygen uptake days and LMR6 indexes.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Therapeutic combination comprising a pulmonary surfactant and a steroid for the treatment of evolving bpd
ActiveUS20180177832A1Increase mRNA expressionOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismDecreased surfactantIntensive care medicine
Administering a pulmonary surfactant and a corticosteroid is effective for the treatment of evolving bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) in preterm neonates.
Owner:CHIESI FARM SPA
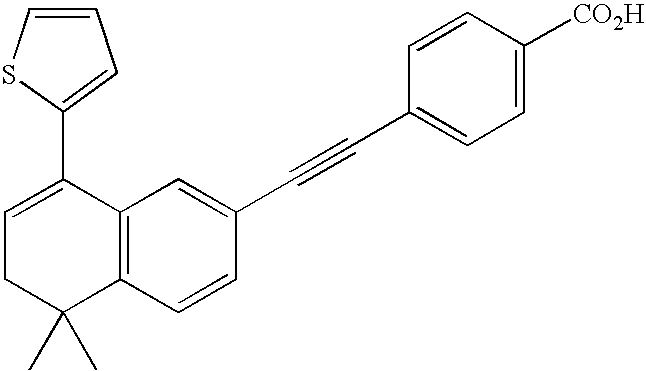
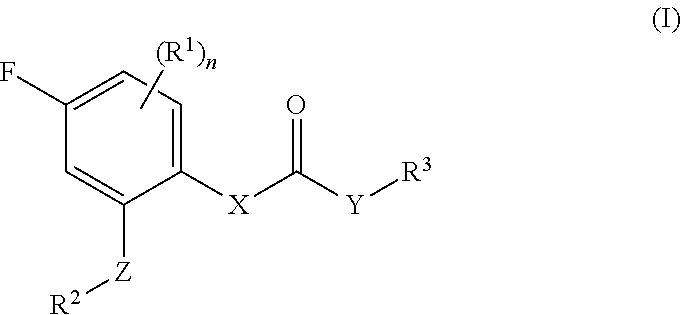
Fluorophenyl substituted muscarinic receptor ligands with selectivity for m3 over m2
The present invention relates to fluorophenyl substituted muscarinic receptor ligands with selectivity for M3 over M2 and to the use of these compounds in the treatment of various diseases such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) and urinary incontinence.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +2
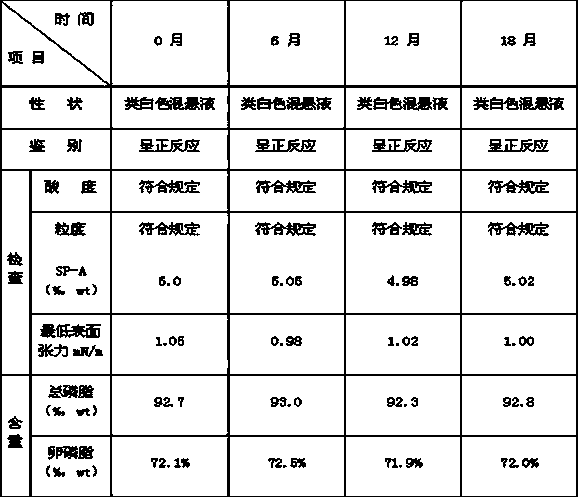
Composition of pulmonary surfactant extract and pulmonary surfactant-associated protein A, preparation method and pharmaceutical application thereof
ActiveCN102552879BHigh purityEasy to industrializePowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsExtracorporeal circulationDisease
The invention relates to a composition of pulmonary surfactant extract and pulmonary surfactant-associated protein A (SP-A), a pharmaceutical preparation and a preparation method thereof. The pulmonary surfactant extract is prepared by the methods of ceramic filtering pipe concentration and filtration, organic solvent extraction, purification and the like; at the same time, high-purity SP-A is prepared from the waste in the production process of the pulmonary surfactant extract; and the pulmonary surfactant extract and the SP-A are combined to obtain the pulmonary phospholipid SP-A composition. The composition has an antipathogenic activity inhibition effect; and the curative effect is better than that of the PS preparation without SP-A in treating the pulmonary surfactant deficiency or dysfunction diseases such as acute respiratory distress syndrome and chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases caused by pneumonia, meconium aspiration syndrome, bronchopulmonary dysplasia, infant extracorporeal circulation, lung injury and the like.
Owner:BEIJING SHUANGHE RUNCHUANG TECH CO LTD
Therapeutic combination comprising a pulmonary surfactant and a steroid for the prophylaxis of bpd
Administering a pulmonary surfactant and a corticosteroid in a low dose is effective for the prophylaxis of bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) in preterm neonates.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL MEDICAL CENT CINCINNATI
Compositions and methods of inhibiting gene expression in a lung
The present invention provides compositions and methods for delivery to a lung tissue comprising a small interfering RNA (siRNA) capable of inhibiting expression of a gene, and a surfactant. In one aspect, a non-polymeric methods composition comprising a small interfering RNA (siRNA) capable of inhibiting expression of a gene, and a surfactant is disclosed. In other aspects, a method of inhibiting gene expression in a lung of a subject in need thereof and treating bronchopulmonary dysplasia in a lung of a subject also disclosed. The methods comprise administering a therapeutically effective amount of a non-polymeric composition to the lung of the subject, wherein the non-polymeric composition comprises a small interfering RNA (siRNA) capable of inhibiting expression of a gene, and a surfactant.
Owner:BHANDARI VINEET
Method for identifying a greater risk for developing bronchopulmonary dysplasia
Disclosed is a method of identifying a greater risk for developing bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) in a preterm infant. The method comprises obtaining a genomic DNA sample from the preterm infant's mother, identifying the nucleotide of rs2280789 SNP in the RANTES gene and the nucleotide of rs1800566 SNP in the NQO1 gene, and determining the preterm infant as being at risk of developing BPD when the genotype of rs2280789 SNP carries C nucleotide and the genotype of rs1800566 SNP carries T nucleotide.
Owner:MERIBANK BIOTECH CO LTD
Therapeutic combination comprising a pulmonary surfactant and a steroid
ActiveUS20110130333A1Useful in treatmentReduce riskOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsNaturally occurring surfactantsOxidative stress
Administration of a modified natural surfactant in combination with a corticosteroid is effective for the prevention of bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) and lowers the markers of pulmonary oxidative stress.
Owner:CHIESI FARM SPA
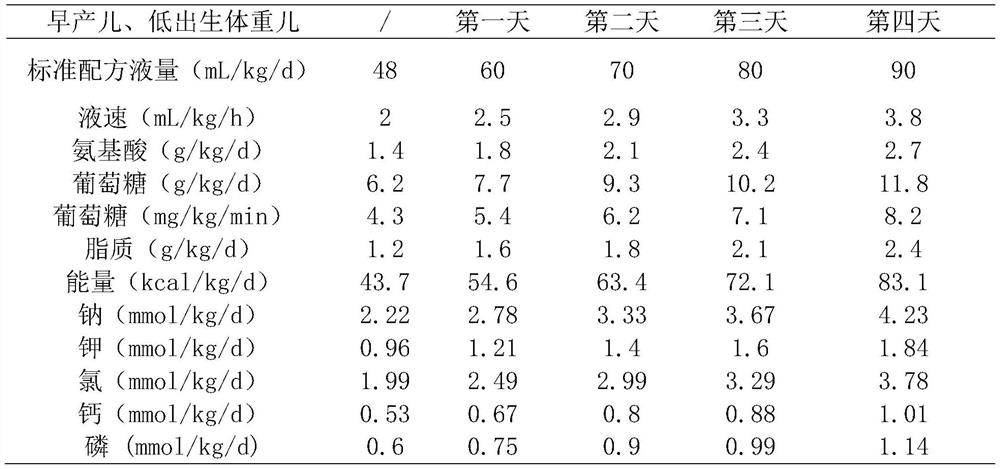
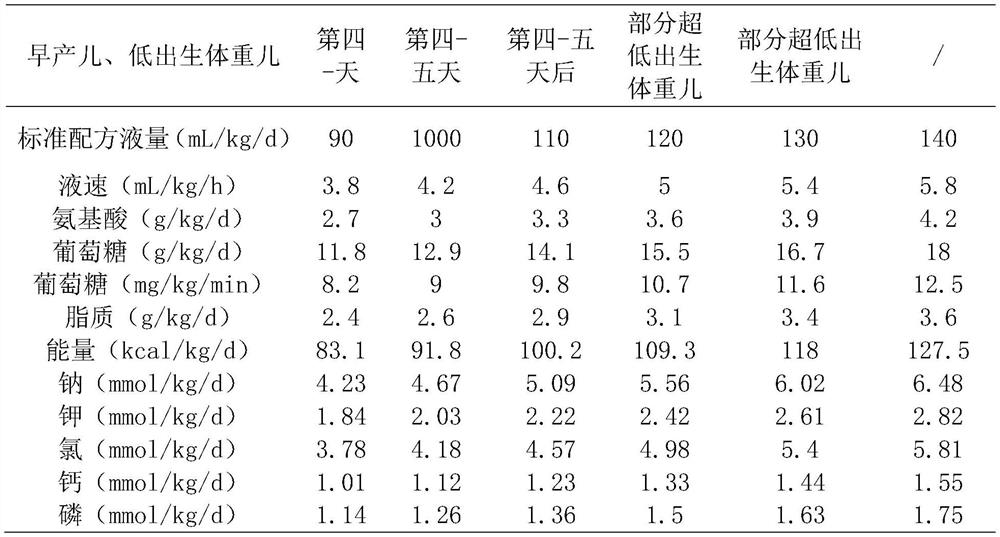
Standardized vein nutrient solution formula for newborns with low birth weight and preparation device
PendingCN114028424AReduce exceptionsPromotes weight gainHydroxy compound active ingredientsMetabolism disorderSodium phosphatesIntracranial Hemorrhages
The invention relates to a standardized vein nutrient solution formula for a newborn with low birth weight and a preparation device. The nutrient solution is prepared from the following components: vitamins, electrolyte, sodium glycerophosphate, fat emulsion, amino acid, glucose, compound trace elements, calcium salt and levocarnitine. The vitamins comprise water-soluble vitamins and fat-soluble vitamins, the electrolyte is any one or more of sodium chloride, potassium chloride and magnesium sulfate, and the compound trace elements comprise zinc, copper, manganese, selenium and iodine. The nutrient solution provided by the invention provides liquid, calorie, mineral substances and vitamins required by individual metabolism, growth and development for newborns with low birth weight, promotes the growth of body mass of the newborns, reduces abnormal conditions of electrolyte, blood sugar, blood fat and serum albumin, reduces abnormal conditions such as cholestasis, bronchial lung dysplasia, intracranial hemorrhage and retinopathy of premature infants. The effect is quick and no side effect appears. the preparation device is easy to operate, preparation is simple and quick, and sterile operation can be achieved.
Owner:BEIJING SHIJITAN HOSPITAL CAPITAL MEDICAL UNIVERSTY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com