Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
706 results about "Positive correlation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A perfectly positive correlation means that 100% of the time, the variables in question move together by the exact same percentage and direction. A positive correlation can be seen between the demand for a product and the product's associated price.
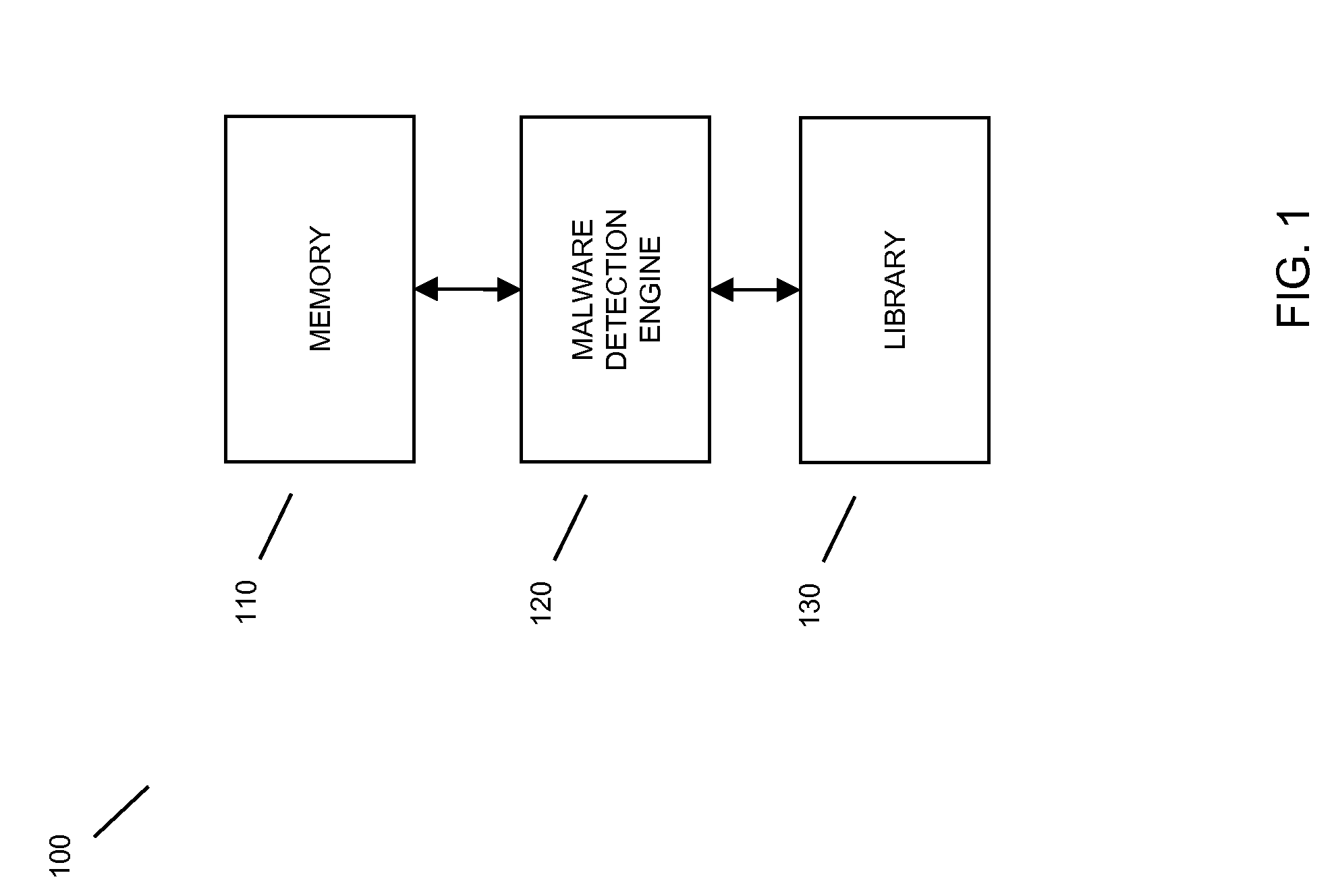
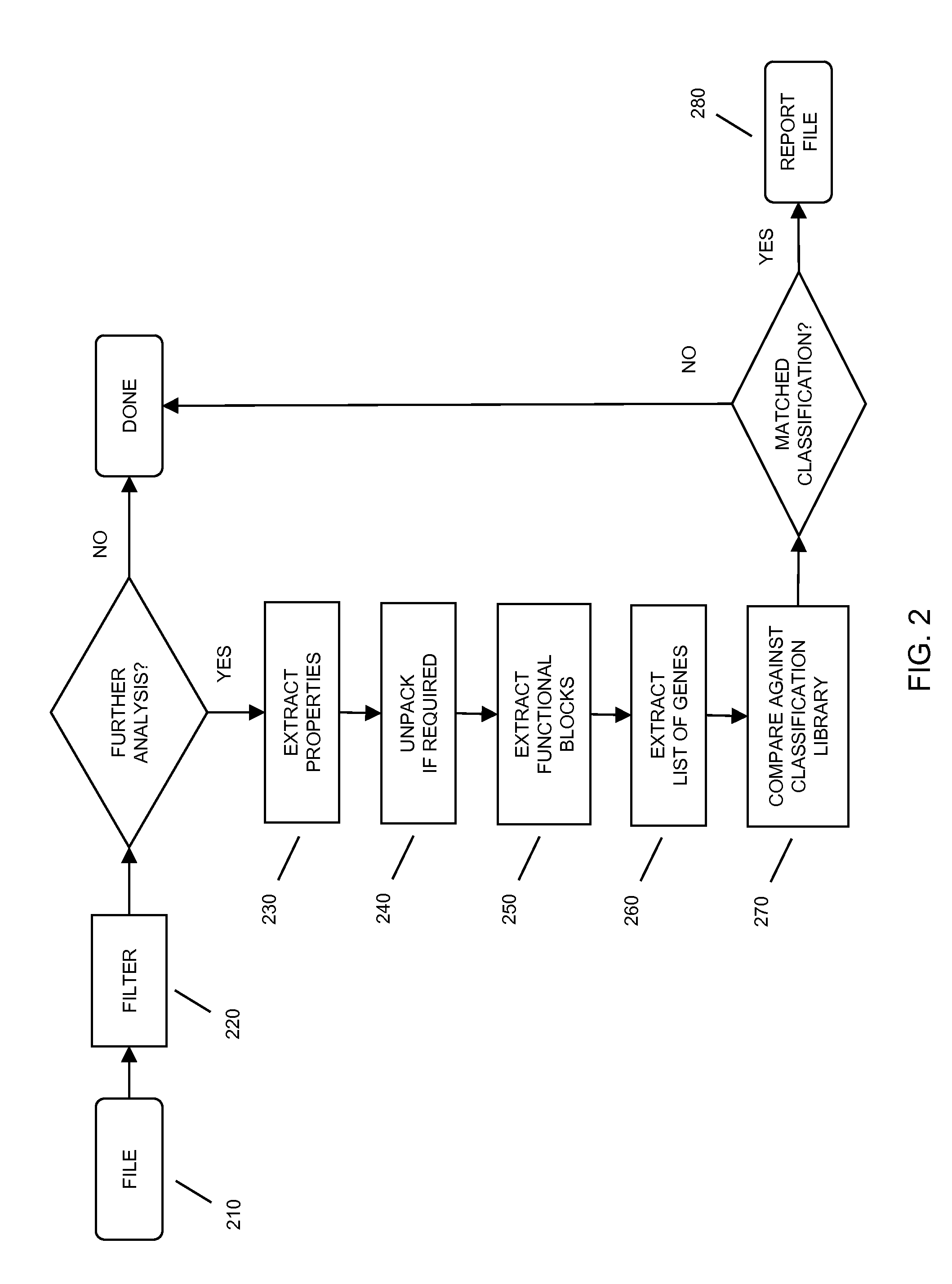
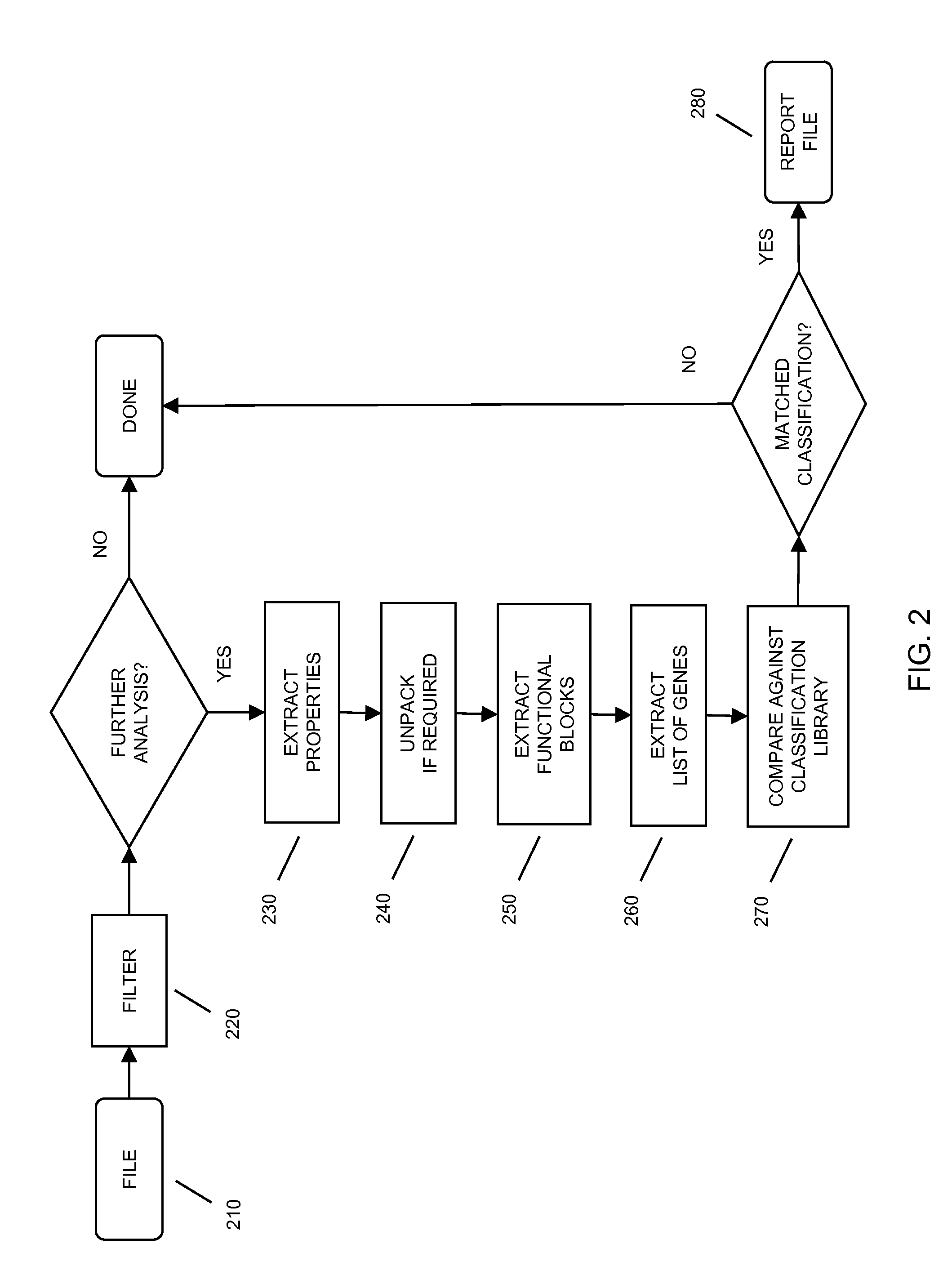
Method and system for classification of software using characteristics and combinations of such characteristics
In embodiments of the present invention improved capabilities are described for the steps of identifying a functional code block that performs a particular function within executable code; transforming the functional code block into a generic code representation of its functionality by tokenizing, refactoring, or the like, the functional code block; comparing the generic code representation with a previously characterized malicious code representation; and in response to a positive correlation from the comparison, identifying the executable code as containing malicious code.
Owner:SOPHOS
Method and system for classification of software using characteristics and combinations of such characteristics
ActiveUS20090187992A1Provide capabilityMemory loss protectionUnauthorized memory use protectionCoding blockSoftware
In embodiments of the present invention improved capabilities are described for the steps of identifying a functional code block that performs a particular function within executable code; transforming the functional code block into a generic code representation of its functionality by tokenizing, refactoring, or the like, the functional code block; comparing the generic code representation with a previously characterized malicious code representation; and in response to a positive correlation from the comparison, identifying the executable code as containing malicious code.
Owner:SOPHOS
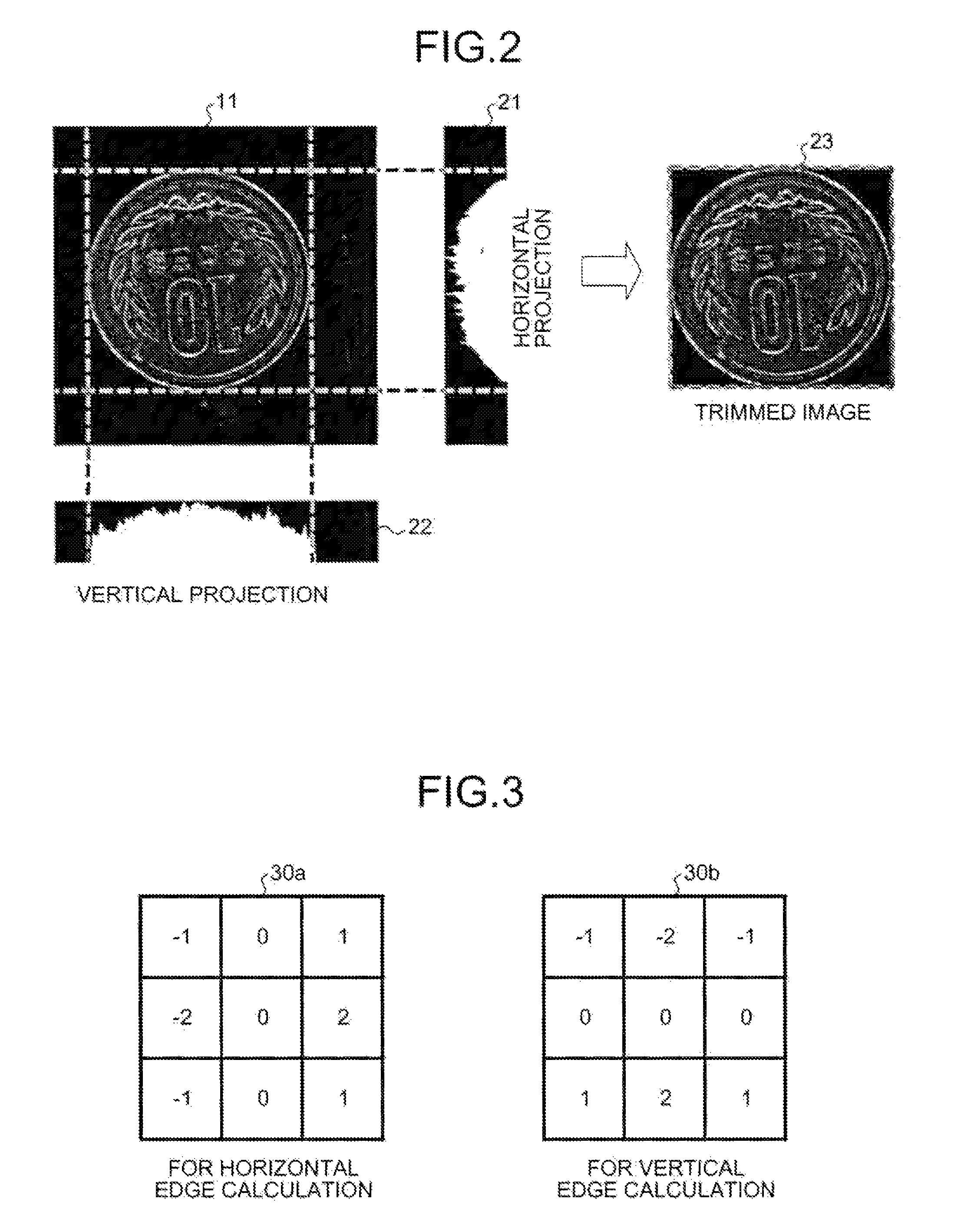
Image blurring method and image blurring device
ActiveCN104333700AAutomated virtualizationWeak degree of blurTelevision system detailsColor television detailsComputer visionFocus area
The invention discloses an image blurring method and an image blurring device. The image blurring method comprises the following steps: triggering a first camera and a second camera to synchronously collect images on a same plane along the same shooting direction so as to obtain a first image and a second image; obtaining depth information of the first image according to the first image and the second image, wherein the depth information of the first image includes the distance between a shot object corresponding to each pixel point on the first image and the plane; selecting an area on the first image as a focusing area; calculating a deviation value of each pixel point on the first image according to the focusing area; and performing blurring treatment on all of the pixel points according to absolute values of the deviation values of the pixel points, wherein positive correlation is formed between the blurring degrees of the pixel points and the absolute values of the deviation values of the pixel points. By adopting the technical scheme provided by the invention, automatic blurring of the images can be realized.
Owner:GUANGDONG OPPO MOBILE TELECOMM CORP LTD
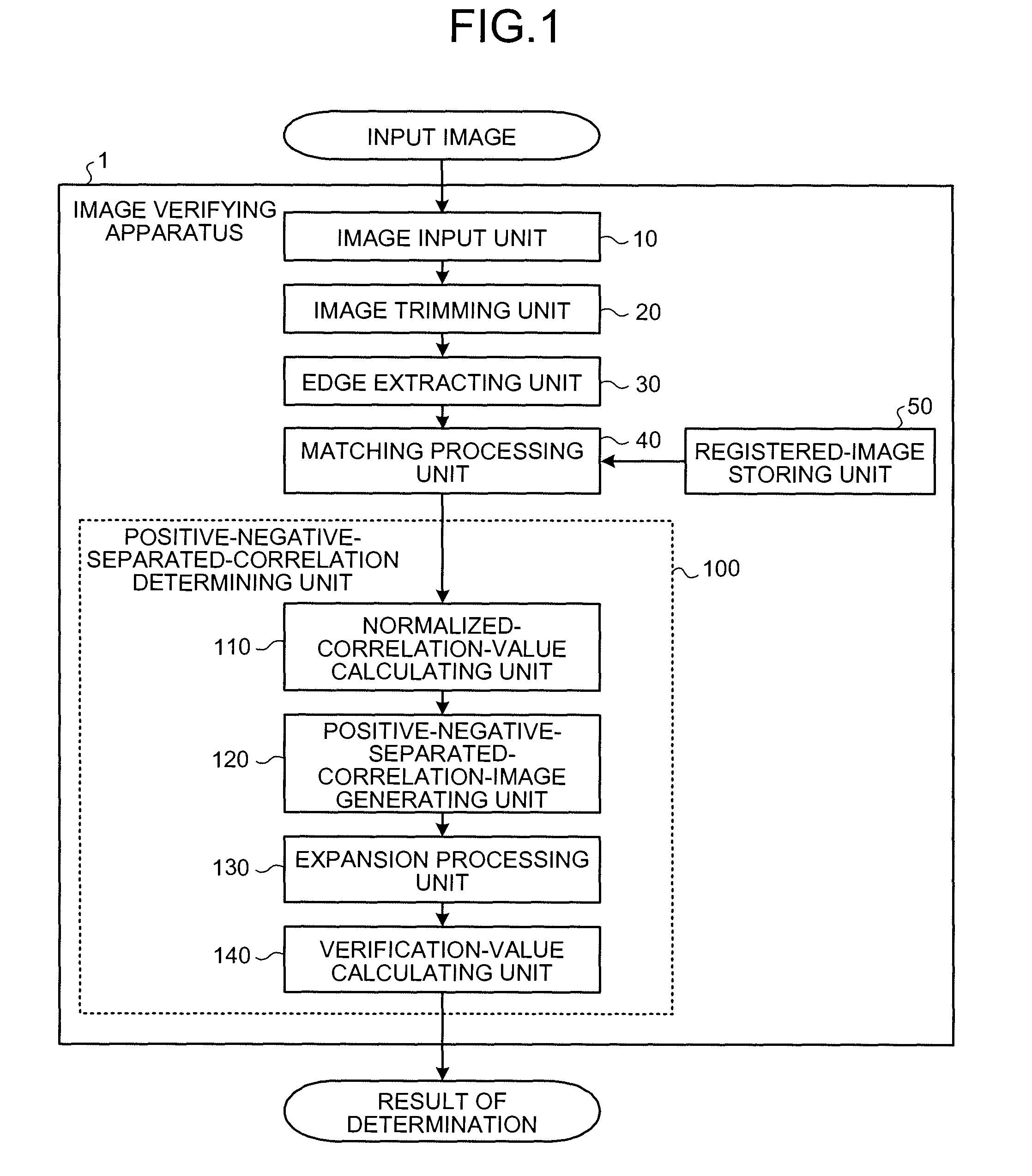
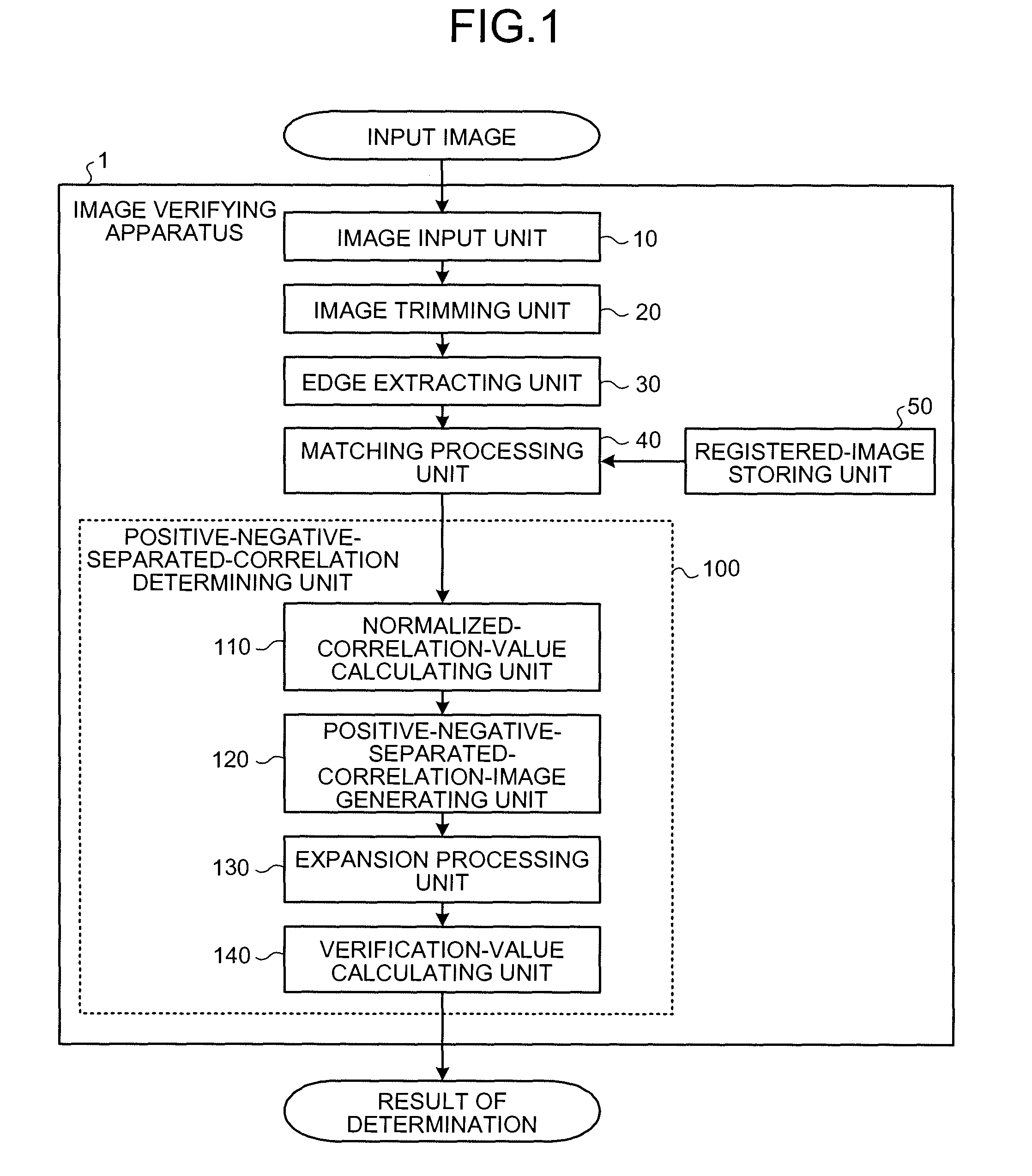
Apparatus and method for verifying image by comparison with template image
ActiveUS7856137B2High verification rateImprove accuracyCoin testingSpoof detectionPattern recognitionNegative correlation
A correlation value image is generated from an input image and a template image, and separated into a positive correlation value image and a negative correlation value image. The template image is separated into a positive template image and a negative template image. A plurality of positive-negative-separated correlation images are generated by combining the positive correlation value image and the negative correlation value image and the positive template image and the negative template image. A polar-coordinates-converted input image and a polar-coordinates-converted template image are employed as the input image and the template image, respectively.
Owner:GLORY KOGYO KK
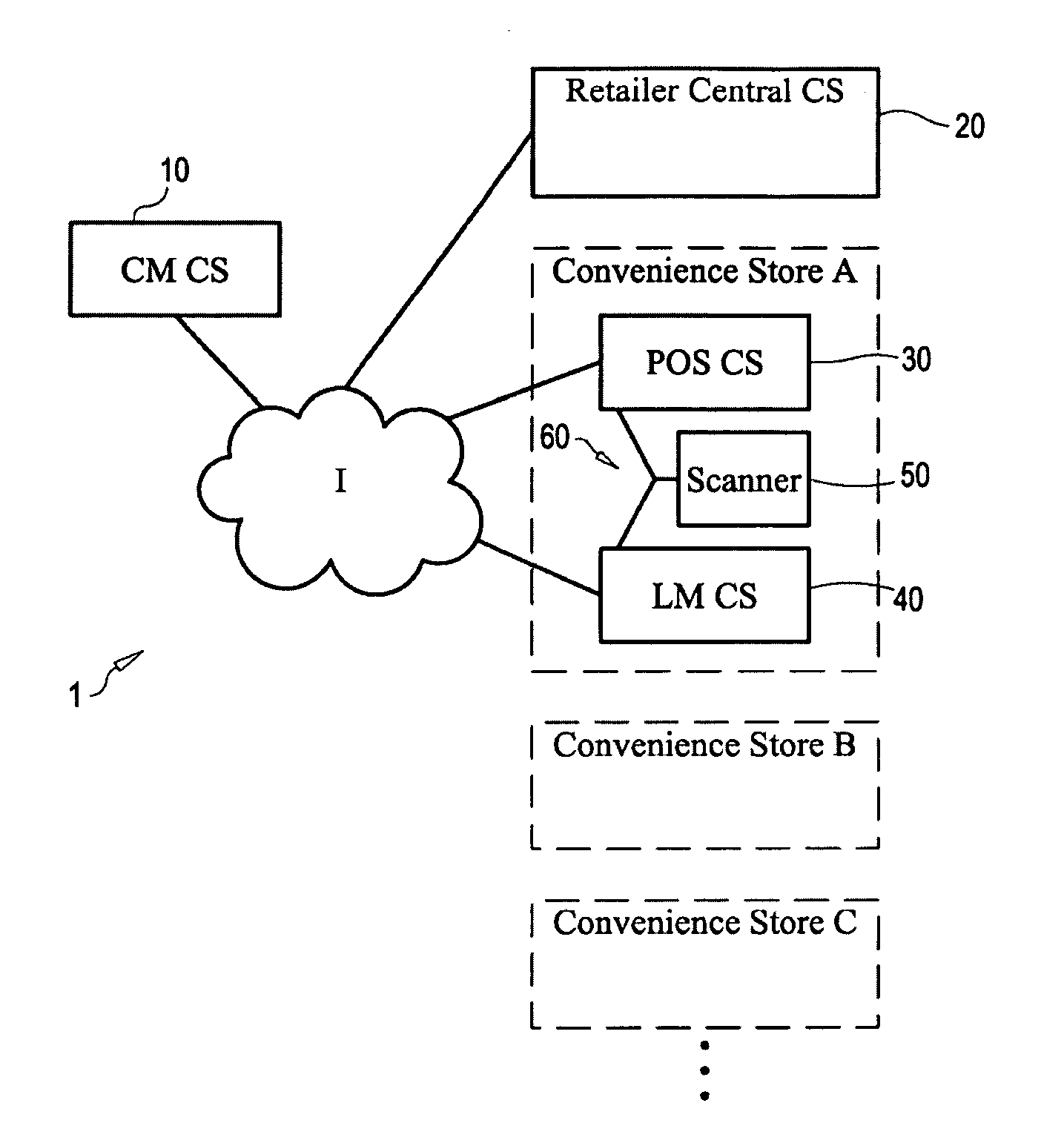
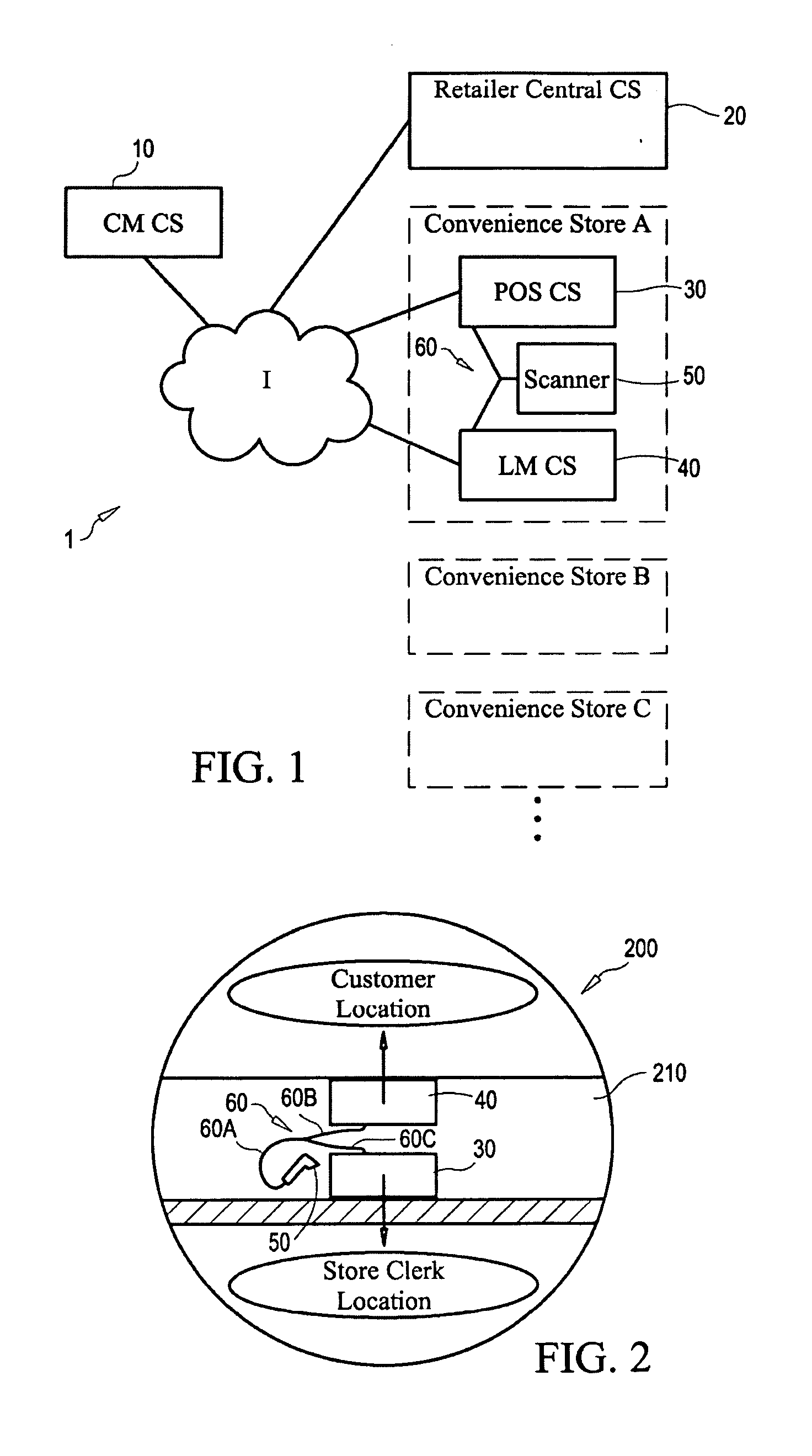
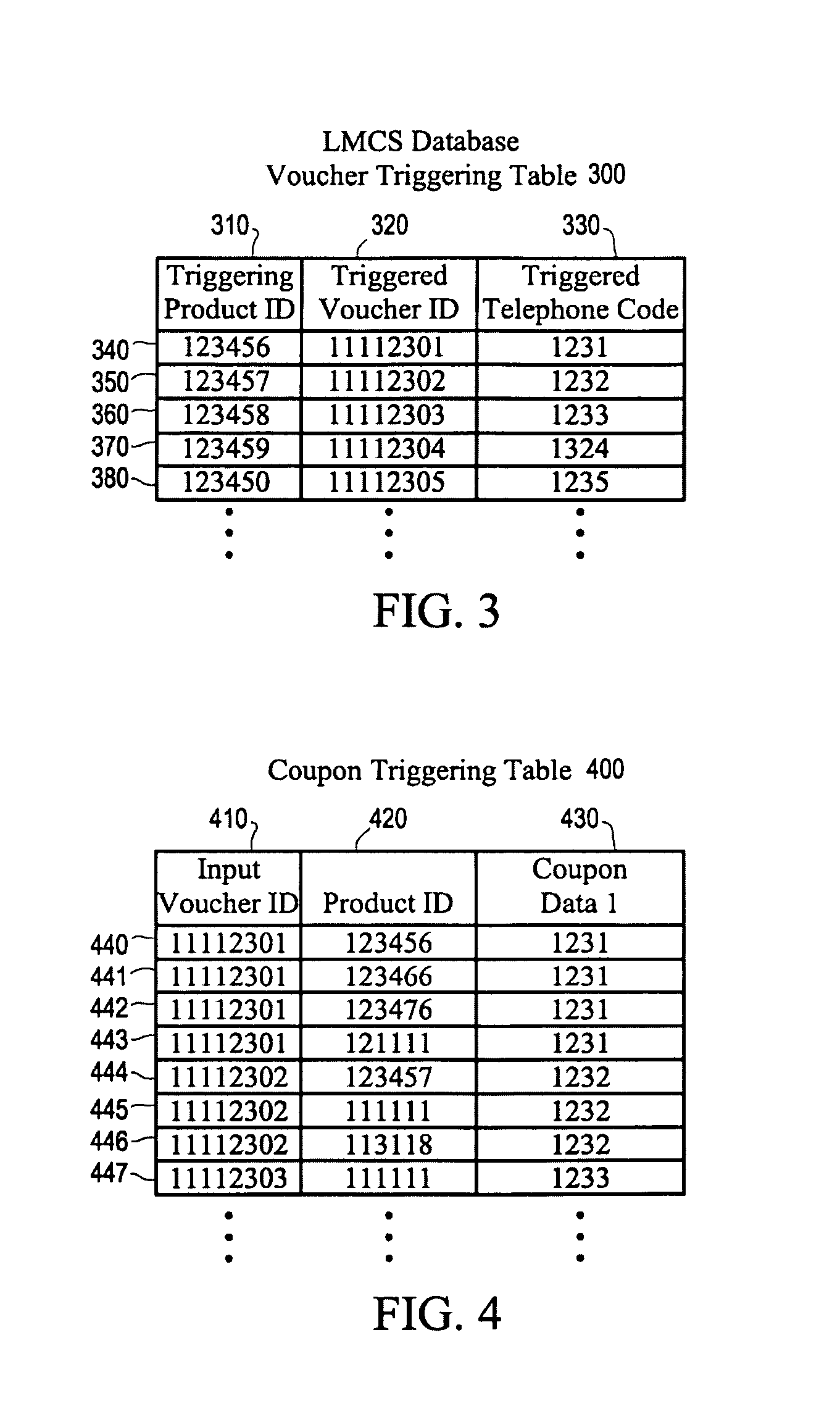
Store Solutions
ActiveUS20090026255A1Facilitate providing and redeemingDeterring fraudTicket-issuing apparatusDiscounts/incentivesTime correlationBarcode
Disclosed are systems and methods that time correlate input at a point of entry of consumer data of least two identifications for products, prescriptions, vouchers, or codes, uses positive correlation determinations for triggering output of predetermined information. The time correlation of identifications may be used to build a time correlation database, and thereafter use that database for targeted communications. Related inventions include an intelligent Y cable or the like to filter data transmitted from a scanner at a point of entry of consumer data, and a novel POS CS configured to receive bar codes that would otherwise cause the POS CS to enter an error condition.
Owner:CATALINA MARKETING CORP
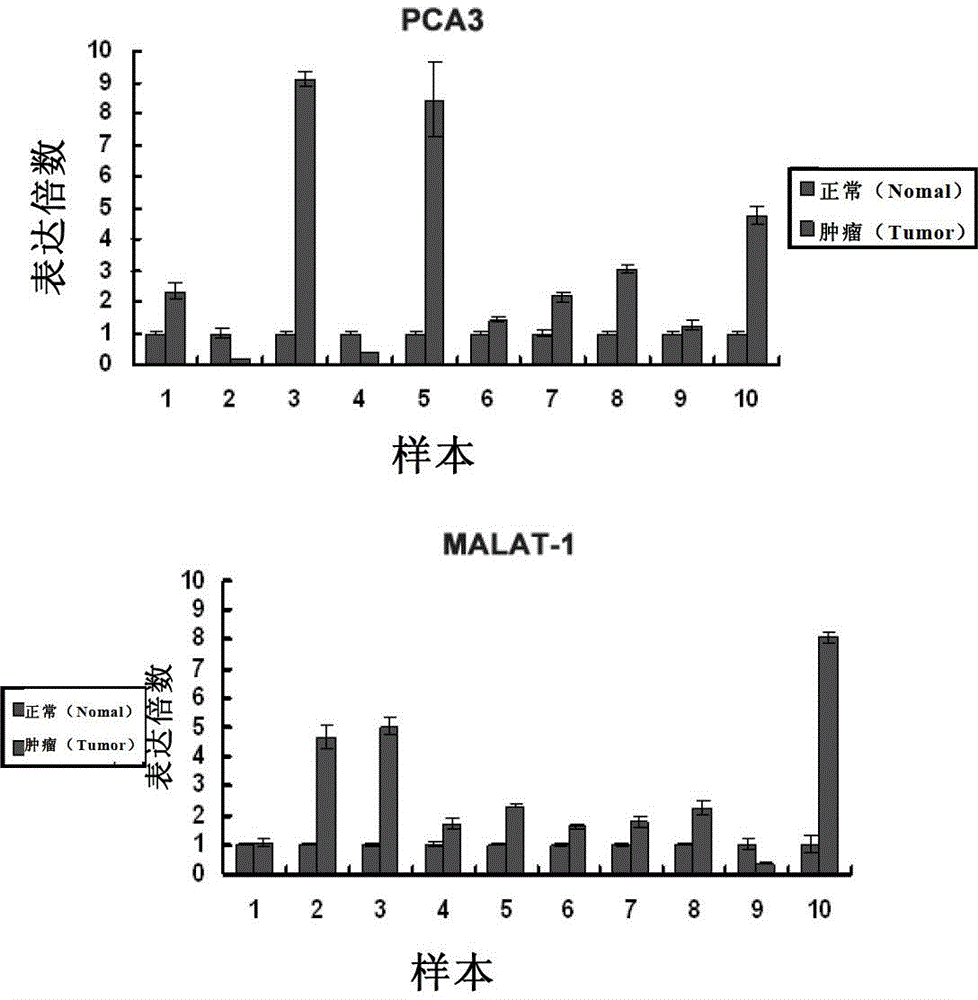
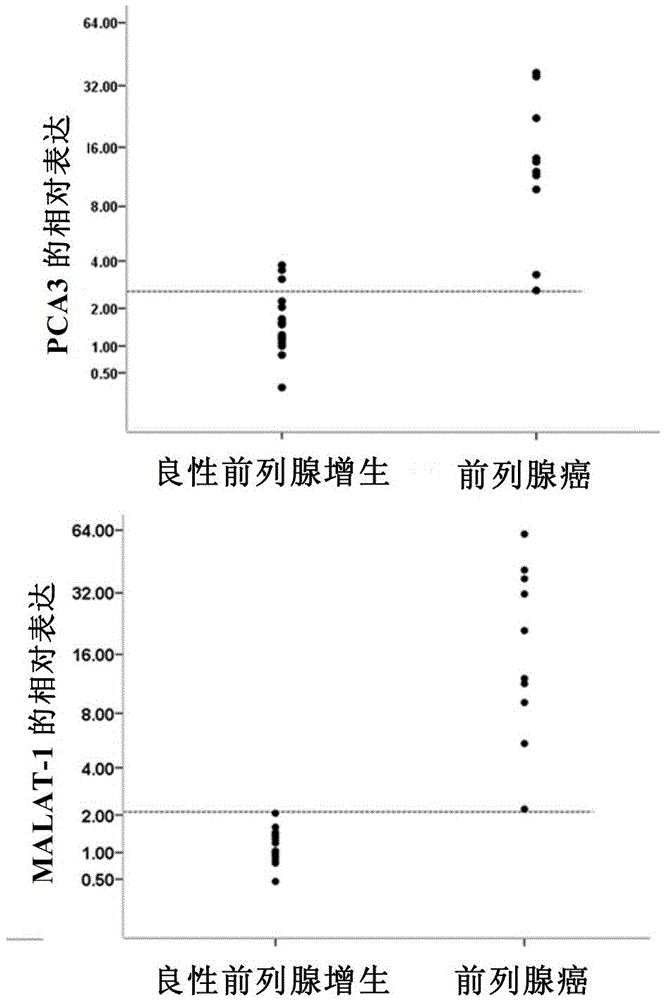
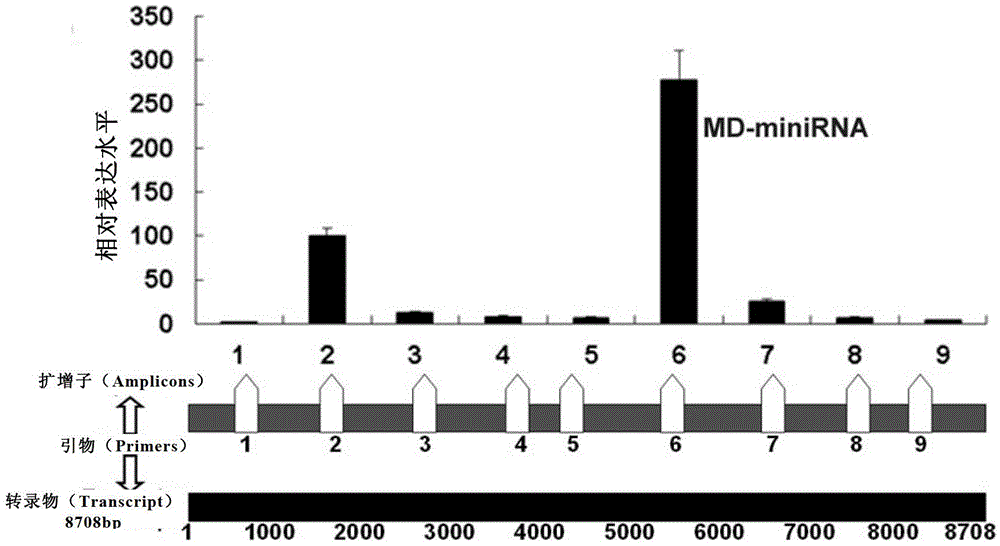
Application of long-chain non-coding RNA as blood molecular marker for disease diagnosis
The invention relates to application of a long-chain non-coding RNA as a blood molecular marker for disease diagnosis. Specifically, the inventor successfully isolates and detects a long-chain non-coding RNA (lncRNA) in blood of human or non-human mammal; the long-chain non-coding RNA in blood of human or non-human mammal stably exists in form of fragments with different expressive abundance; a short-chain RNA (named as MD miniRNA)from lncRNA MALAT-1 in blood is from prostate cancer (PCa) cells, and releases into blood; PCa cells cultured in vitro can secrete MD-miniRNA and release into a nutrient solution; and high expression of MD-miniRNA can be detected in transplanted tumor mice plasma. In addition, expression of MD-miniRNA is in positive correlation with morbidity of PCa, and the MD-miniRNA realizes sensitivity higher than 40% and specificity higher than 80% in distinguishing prostate puncture positive and negative patients. Therefore, the MD-miniRNA is a novel cancer (especially prostate cancer) blood molecular diagnostic marker, and can significantly improve the accuracy of diagnosis.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHANGHAI HOSPITAL
Cardiovascular pulse wave analysis method and system
InactiveUS20140249424A1Easy to useComputing time to provide the pulse analysis results is negligibleHealth-index calculationCatheterDiseaseFactor base
Factor retrieving is a major approach for pulse wave analysis. Stiffness index and cardiac output are widely used factors for cardiac risk detection. Research has been done on clinical pulse wave data which are collected by pulse oximeter. The result shows that collected factors have a positive correlation with certain cardiac risks. Some adjustments have been applied on the algorithms that increase the significance. In addition to the factor based analysis, other signal processing techniques for pulse waveforms are included such as bispectrum estimation, Wavelet transform, and weighted dynamic time warping. Bispectrum estimation and Wavelet transform have meaningful features of pulse waveforms with some special shapes. Weighted dynamic time warping compares the similarity of waveforms. It also includes medical significance into the calculation by adjusting the weight vector. This algorithm has higher accuracy when providing more samples to compare. The factor based analysis and waveform analysis compose an analytic model which can be used for risk evaluation, classification and disease detection.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF WINNIPEG
Method of Verifying or deriving Attribute Information of a Digital Transport Network Database Using Interpolation and Probe Traces
ActiveUS20120246192A1Beneficial attributeInstruments for road network navigationDigital data processing detailsAnalysis dataTransport network
A method of verifying or filling in attribution associated with segments of transportation networks that are digitally mapped from a digital transportation network database includes analyzing the database to identify at least one attribute of interest that is missing or whose accuracy is unreliable and associated with a segment of the network in; identifying first and second segments before and after segment in question which have associated attribution determined to be accurate; gathering a plurality of probe traces from users of probe-transmitting navigation devices that have traversed the segment(s) in question as well as traversed the first and second; and determining whether the probe-derived attribution information is reliable, and if so, comparing the trend of the probe-derived attribute information of the first and second segments with the trend of the database attributes of the first and second segments, and if there is a positive correlation, applying the probe-derived attribute information to the database for the segment(s) in question to fill in the missing or verify the unreliable database attribution for the segment(s) in question.
Owner:TOMTOM GLOBAL CONTENT
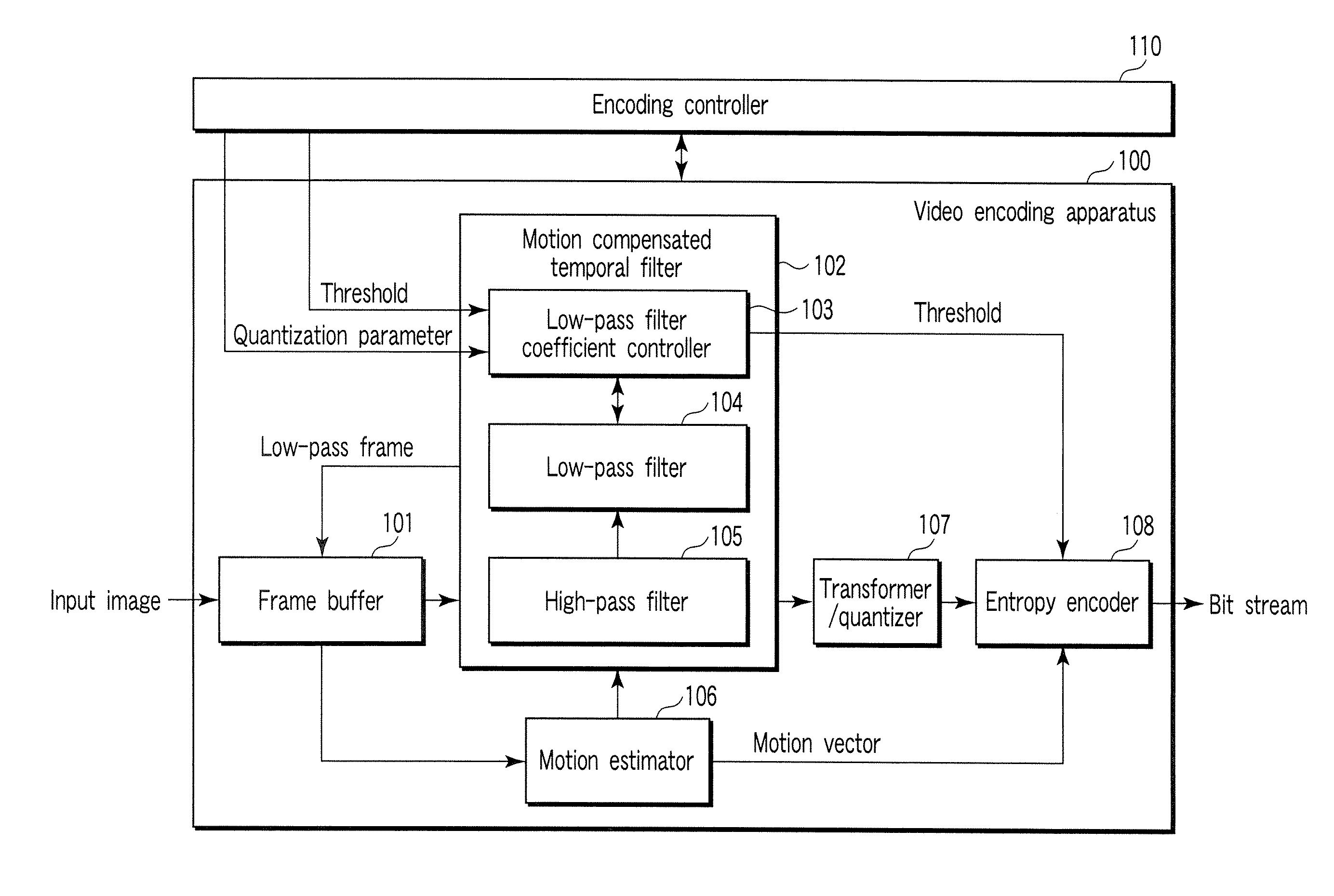
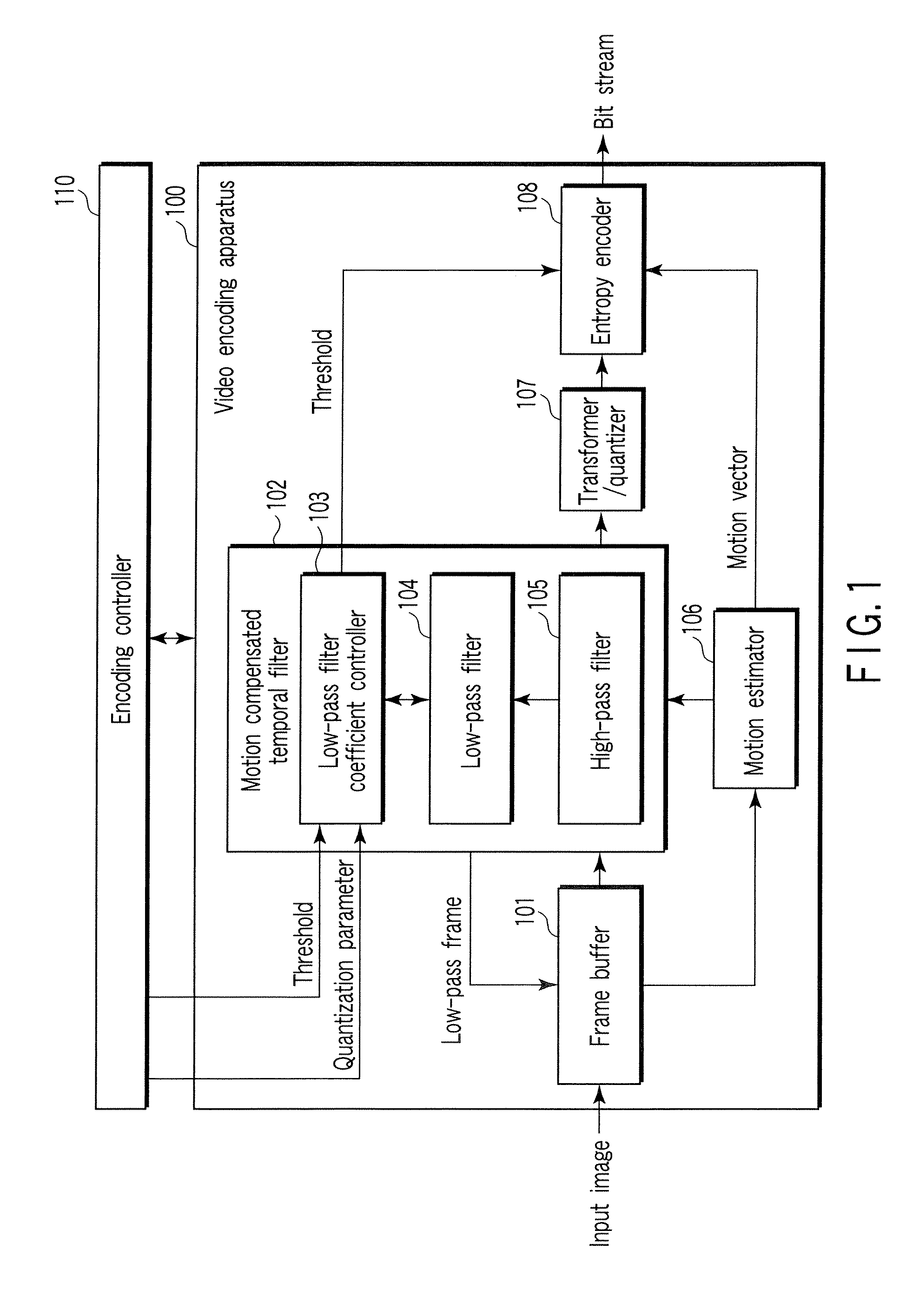
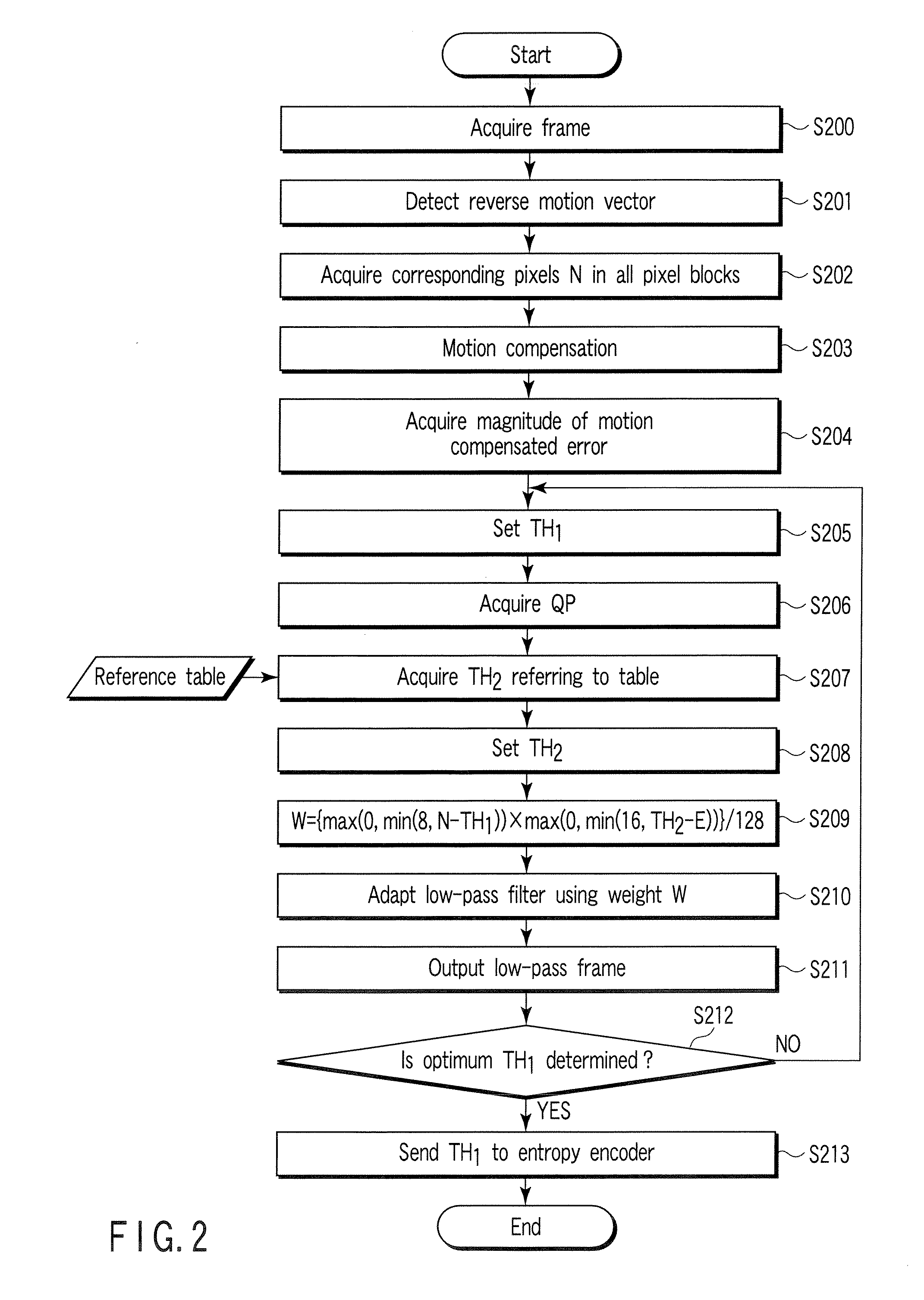
Video encoding/decoding method and apparatus
InactiveUS20070116125A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionVideo encodingLow-pass filter
A video encoding method includes subjecting an input video image to motion compensated temporal filtering using a motion compensated temporal filter to produce a low-pass filtered image, quantizing a transform coefficient of the low-pass filtered image, encoding a quantized transform coefficient, calculating a weight to be given to a low-pass filter coefficient of a low-pass filter of the motion compensated temporal filter according to coarseness of quantization and a magnitude of a motion compensated error, and controlling a high band stopping characteristic of the low-pass filter according to the low-pass filter coefficient weighted by the weight, wherein the controlling controls the high band stopping characteristic of the low-pass filter to provide a positive correlation with respect to the quantization parameter and provide a negative correlation with respect to the magnitude of the motion compensated error.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
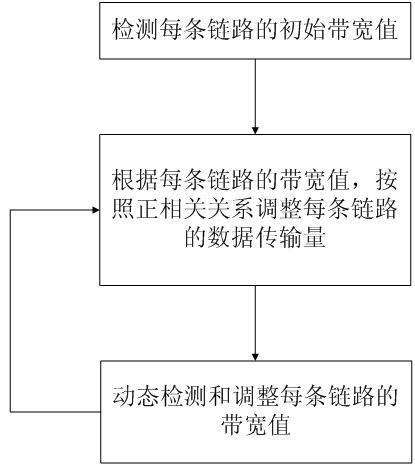
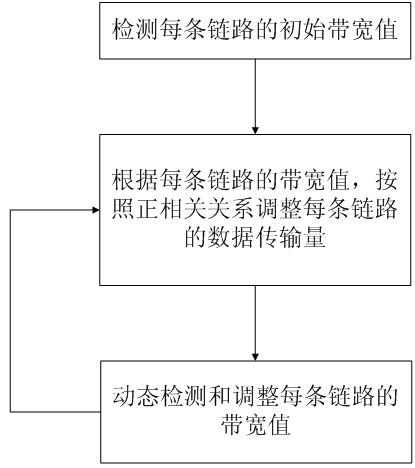
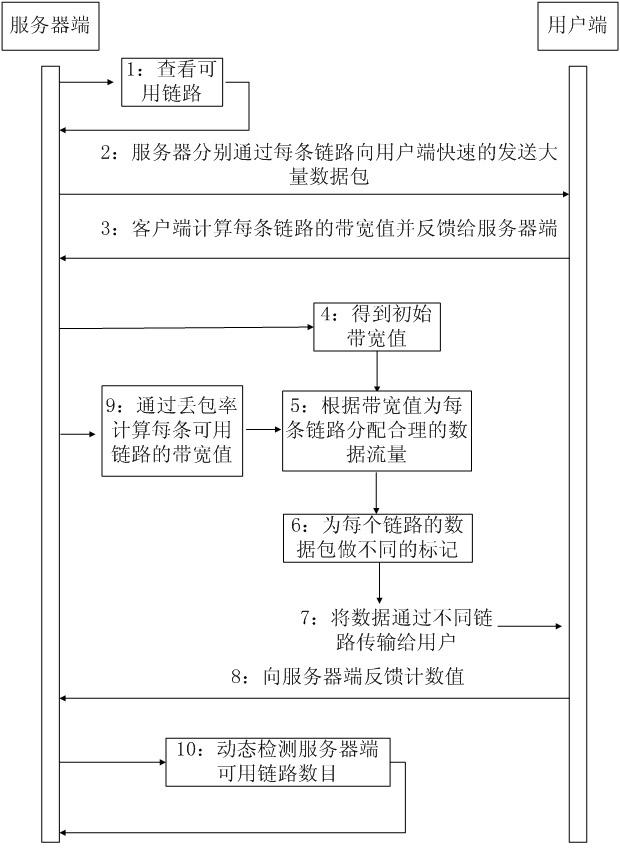
Multilink self-adaptation data transmission method and system
InactiveCN102098301AIncrease profitRaise the upper limitData switching networksTransmission qualityReal time transmission
The invention belongs to the technical field of network transmission and particularly relates to a multilink self-adaptation data transmission method and system. The method comprises the steps of: initially detecting the bandwidth value of each link, and dynamically detecting and regulating the bandwidth of each link by using 90% of a theoretical bandwidth value as the actual data transmission rate of each link. The system comprises a network transmission quality detecting module, a link transmission bandwidth regulating module and a data shunting module, wherein the network transmission quality detecting module is used for dynamically detecting the states of a network; the link transmission bandwidth regulating module is used for regulating the real-time transmission bandwidth value of each link according to positive correlation and network transmission quality; and the data shunting module is used for determining packet transmission links to a client side according to information in different packets. By means of the method and the system provided by the invention, the link resources of a user can be sufficiently utilized to provide higher bandwidth for the user, meanwhile, the detection and the regulation of the bandwidth of each link ensure that higher bandwidth utilization rate can be achieved. The invention truly realizes multilink bandwidth fusion.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Adaptive stream media playing method, apparatus, system and mobile terminal
InactiveCN101499918AGood online viewing experienceGuaranteed viewingSpecial service provision for substationError prevention/detection by using return channelVideo qualityMedia server
The invention discloses a playing method, a playing device, a playing system and a mobile terminal for self-adaptive stream media, and the method comprises the following steps: a media server dynamically detects network transmission quality; the media server adjusts video quality of a stream media through a positive correlation relation according to the network transmission quality; and the media server issues the adjusted stream media to a client end for playing. The self-adaptive stream media playing device comprises the media server which comprises the following modules: a network transmission quality detecting module, which is used for dynamically detecting the network transmission quality; a stream media quality adjusting module, which is used for adjusting the video quality of the stream media through the positive correlation relation according to the network transmission quality; and a stream media issuing module, which is used for issuing the adjusted stream media to the client end for playing. The self-adaptive stream media playing method, device, system and mobile terminal can ensure the quality of videos for users to watch as better as possible, simultaneously can ensure the playing fluency by reducing transmission data amount when the network is congested, thus bringing good online watching experience to users.
Owner:YULONG COMPUTER TELECOMM SCI (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
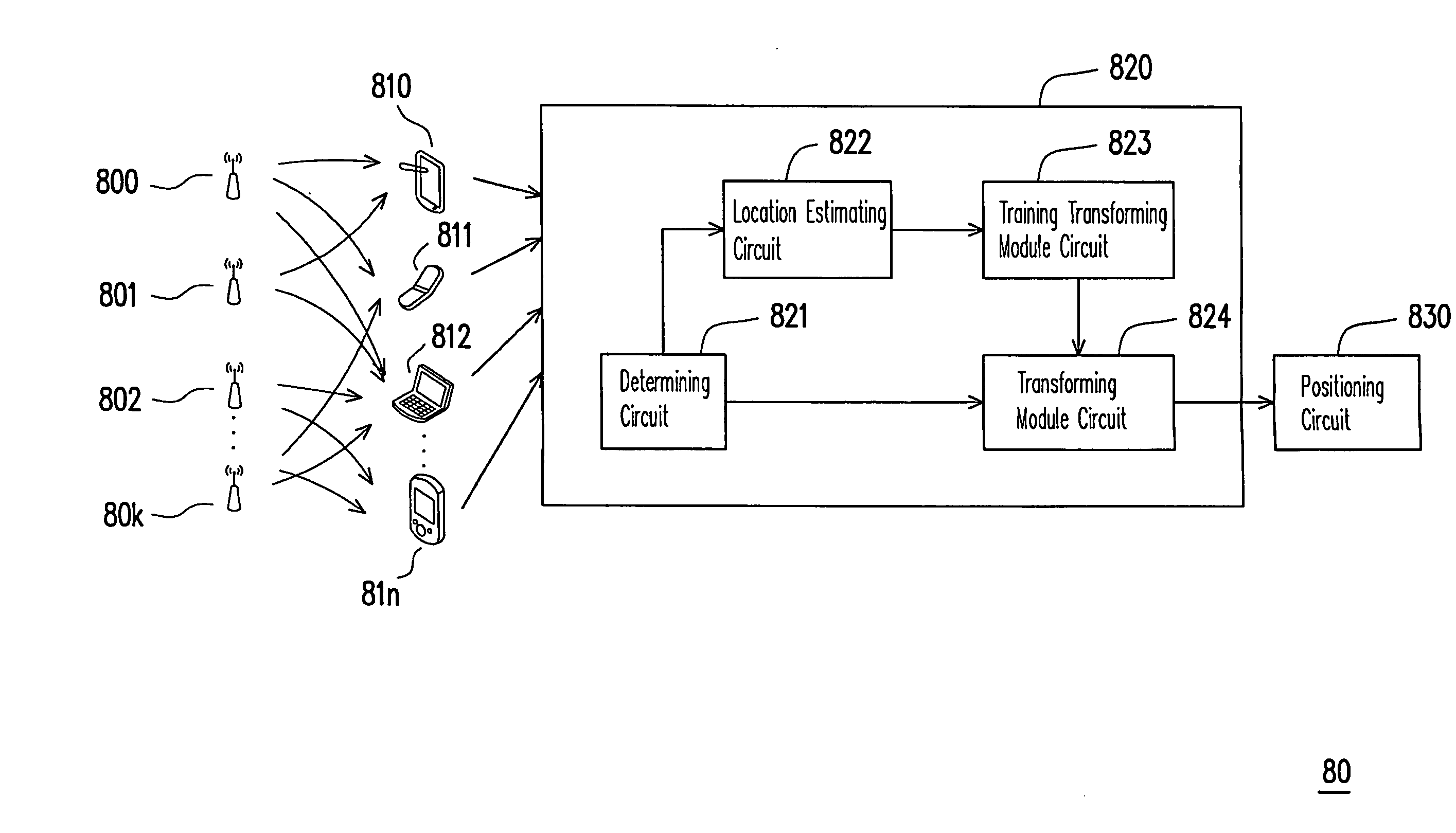
Apparatus and method for transforming signal strength of wireless positioning system
ActiveUS20090221316A1Receivers monitoringDirection finders using radio wavesApproximation algorithmComputer science
An apparatus for transforming a signal strength of a wireless positioning system is provided. The apparatus is adapted for eliminating the difference of signal strengths between different mobile communication apparatuses or different environments. The apparatus includes a location estimation circuit. The location estimation circuit is adapted to obtain a possible coordinate by calculating a first signal strength distribution received by a mobile communication apparatus. The possible coordinate and the first signal strength distribution are taken as training data for training a transforming module with an approximation algorithm. Accordingly, the present invention adopts a positive correlation index and the approximation algorithm for automatically training a transforming module for the mobile communication apparatus without using the information of chip model and location of mobile communication apparatus.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
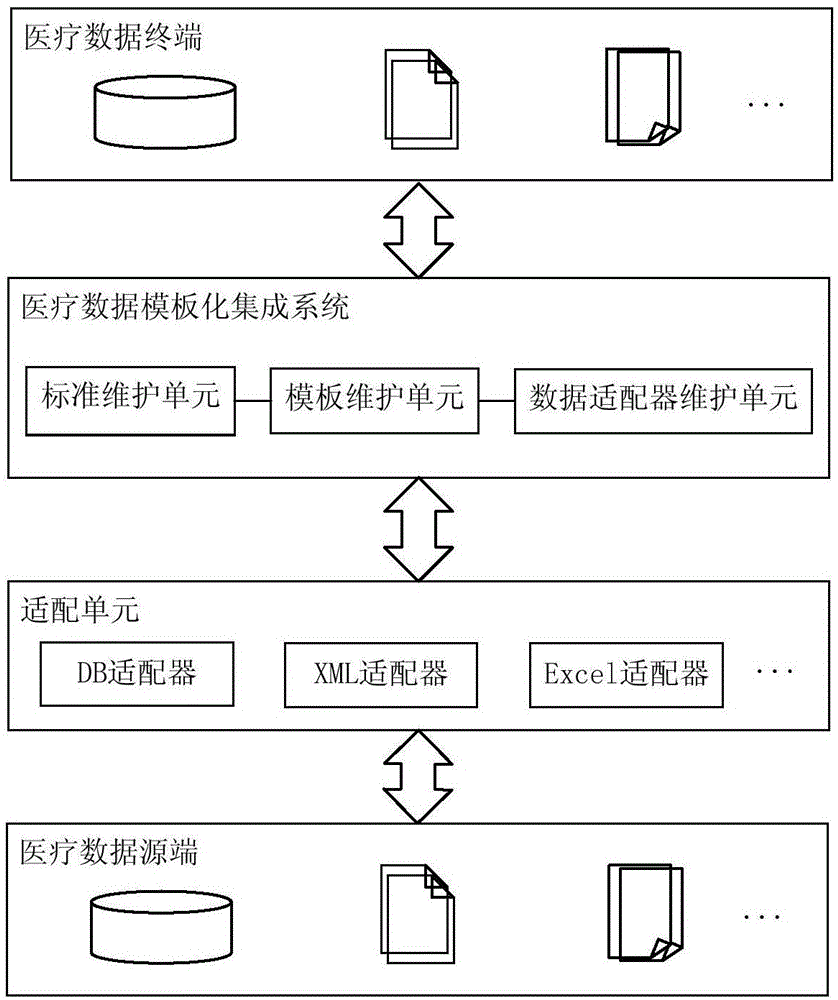
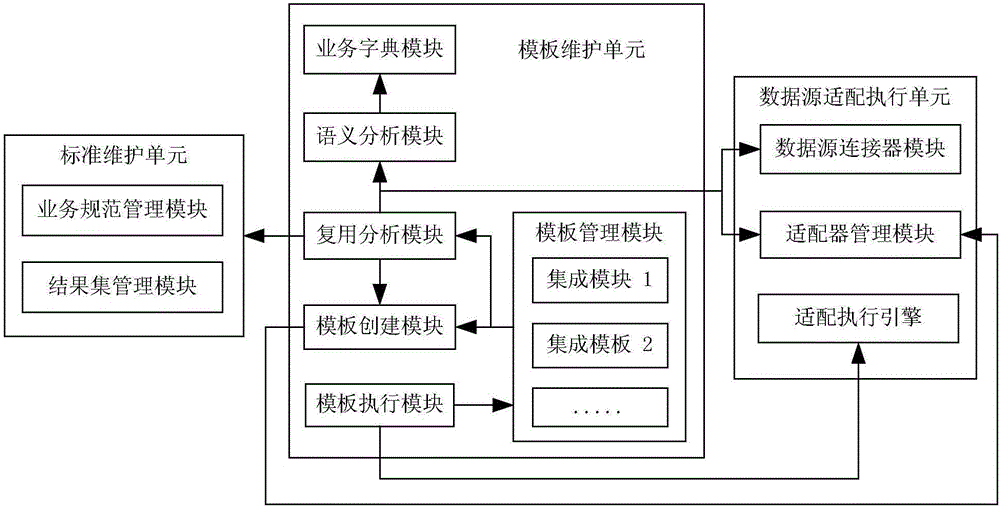
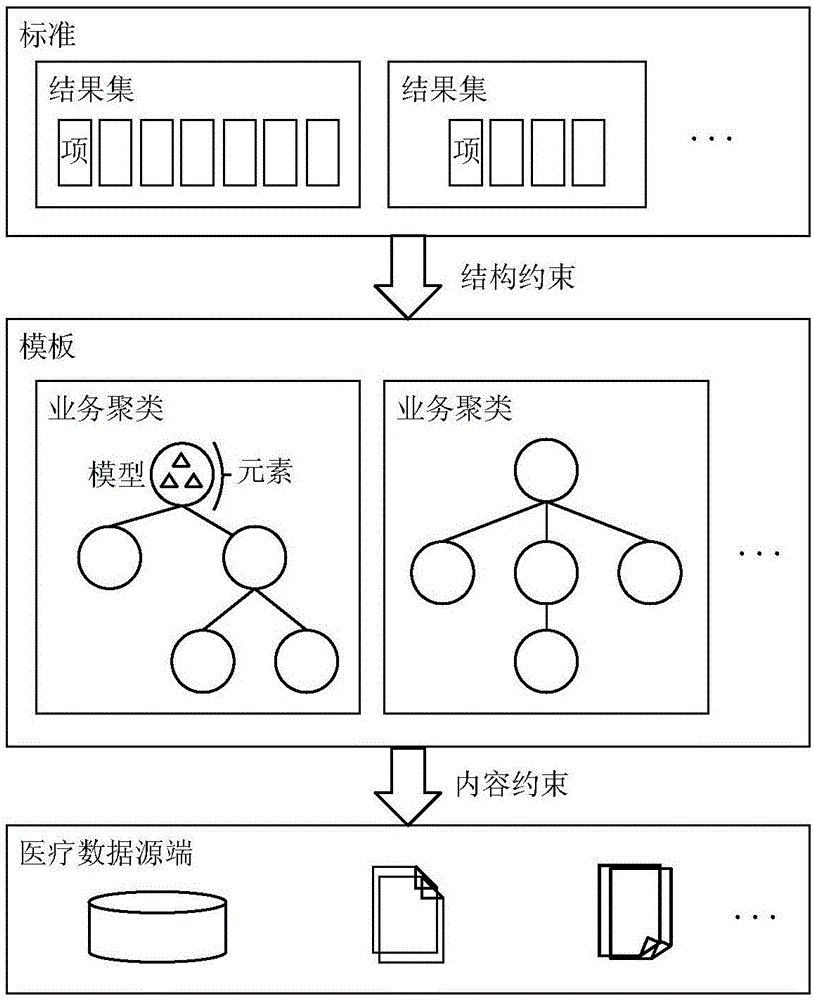
Templated integration system and method for medical information system data
InactiveCN106777970AEfficient integrationStrong industry attributesMedical data managementSpecial data processing applicationsData setMedical treatment
The invention provides a templated integration system and method for medical information system data and relates to the technical field of medical industry data integration. During the process of medical information system data integration, combined with target data standards and aimed at medical information system features (including manufacturers and versions, etc.), a reusable medical information system data integration template is established so as to realize data integration of different medical information systems (such as HIS, LIS, RIS, EMR,PEIS, etc.) Through solidification of special data set and the data conversion rules thereof, a reusable template for a certain medical information system during the process of multiple medical institution data integration is formed; at the same time, the different system templated integration process will enhance the adaptability of the template; a positive correlation between the reuse rate and completeness of the template is established; depending on the continuously improved and optimized template library resource, the implementation difficulty can be effectively reduced, the data integration efficiency can be increased, and the efficient and high quality development of medical information system integration programs is guaranteed.
Owner:BEIJING RUISOFT TECH CO LTD
Virtual prop recommendation method and client
InactiveCN106779933AAccurate recommendationAvoid repeated referralsBuying/selling/leasing transactionsVideo gamesClient-sideHuman–computer interaction
Embodiments of the invention disclose a virtual prop recommendation method and a client, which can accurately recommend proper virtual props to a user. The method comprises the steps of obtaining a target object which is being operated currently in a target application, wherein the target application is installed in user equipment; creating a first prop recommendation list according to the target object, wherein the first prop recommendation list comprises at least two virtual props, the virtual props has different recommendation priorities, and the recommendation priority of each virtual prop is in positive correlation with a matching degree of the virtual prop and the target object; and if it is determined that a target virtual prop in the first prop recommendation list meets a preset recommendation rule, sending the target virtual prop to the user equipment according to the recommendation priority of the target virtual prop.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
High-speed aircraft lifting surface aerodynamic heating structure multidisciplinary optimization design platform
InactiveCN101916314AImprove efficiencySimple planSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringModelling analysis
The invention relates to a high-speed aircraft lifting surface aerodynamic heating structure multidisciplinary optimization design platform belonging to the technical field of modern high-speed aircraft designs. In the invention, by aiming at the demands of lifting surface heat vibration analysis in an aerodynamic heating environment when a high-speed aircraft lifting surface is designed and considering the positive correlation among aerodynamic heating structures, an aerodynamic heating structure integrated analysis method including aerodynamic heating calculation, transient heat conduction analysis, structural heat model analysis and non-constant aerodynamic force and heat vibration analysis is researched, and the aerodynamic heating structure multidisciplinary optimization design taking the most dangerous heat vibration speed as the constraint and taking the lifting surface structural quality as a target function is researched to achieve the goal of the optimization design on the high-speed aircraft lifting surface. The invention breaks through the problem that the multidisciplinary design optimization is carried out without combining with the influence of three aspects of aerodynamic heating on the structure in the traditional high-speed aircraft design, provides a set of high-speed aircraft lifting surface aerodynamic heating structure optimization design methods and waysand has the advantages of simple scheme and high efficiency.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Multi-service scheduling method, apparatus and system
ActiveCN101510164AReasonable Scheduling OpportunitiesImprove quality assuranceProgram initiation/switchingClosed circuit television systemsDistributed computingService quality
The invention discloses a multi-service dispatching method, a device and a system. The service receiving queues storing the service requests according to the service types are scanned in the current dispatching scanning cycle so as to determine the service receiving queues storing the service requests; the current weight corresponding to each service receiving queue is respectively determined among the service receiving queues storing the service requests; the current weight is in positive correlation with a preset priority value of the corresponding service receiving queue and increases as the increase of the dispatching times of the corresponding service receiving queue; the bigger the priority value is, the lower the priority of the corresponding service receiving queue is; the corresponding number of service receive queues are selected according to both the smaller-to-bigger sequence of the current weight and the number of the task executing queues; and a service request is acquired respectively from the selected service receiving queues as a task to be dispatched to different task executing queues. With the invention, the guarantee of the multi-service quality can be realized.
Owner:GUANGDONG VIMICRO
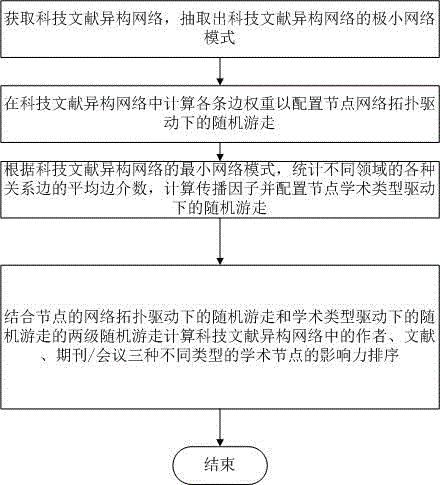
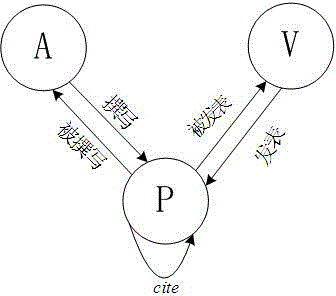
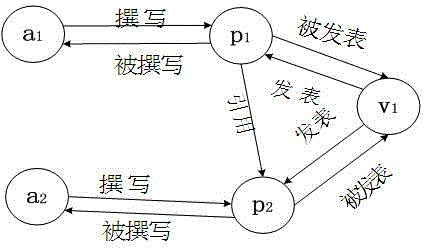
Academic influence cooperative sequencing method of nodes in scientific and technical literature heterogeneous network
InactiveCN104133843AAvoid Node InfluenceAvoid the phenomenon of positive in-degree correlationWeb data indexingSpecial data processing applicationsNODALTechnical literature
The invention discloses an academic influence cooperative sequencing method of nodes (papers, authors and periodicals / conference) in a scientific and technical literature heterogeneous network. By aiming at the heterogeneity of the scientific and technical literature network, according to the method provided by the invention, two stages of random walk are adopted for calculating and sequencing the academic influence of the nodes in the scientific and technical literature, wherein the two stages of the random walk are respectively the random walk driven by the node network topology on the scientific and technical literature heterogeneous network and the random walk driven by the academic type in a minimum network mode of the scientific and technical literature network; the weight of each edge is calculated in the scientific and technical literature heterogeneous network for configuring the random walk driven by the node network topology; and according to the minimum network mode of the scientific and technical literature heterogeneous network, an average edge betweenness of various relation edges in different fields is counted, a propagation factor is calculated, and the rand walk driven by the node academic type is configured. The method provided by the invention solves the problems caused by the heterogeneity of the heterogeneous network and avoids phenomena of node influence and in-degree positive correlation, so that the sequencing result is relatively accurate.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
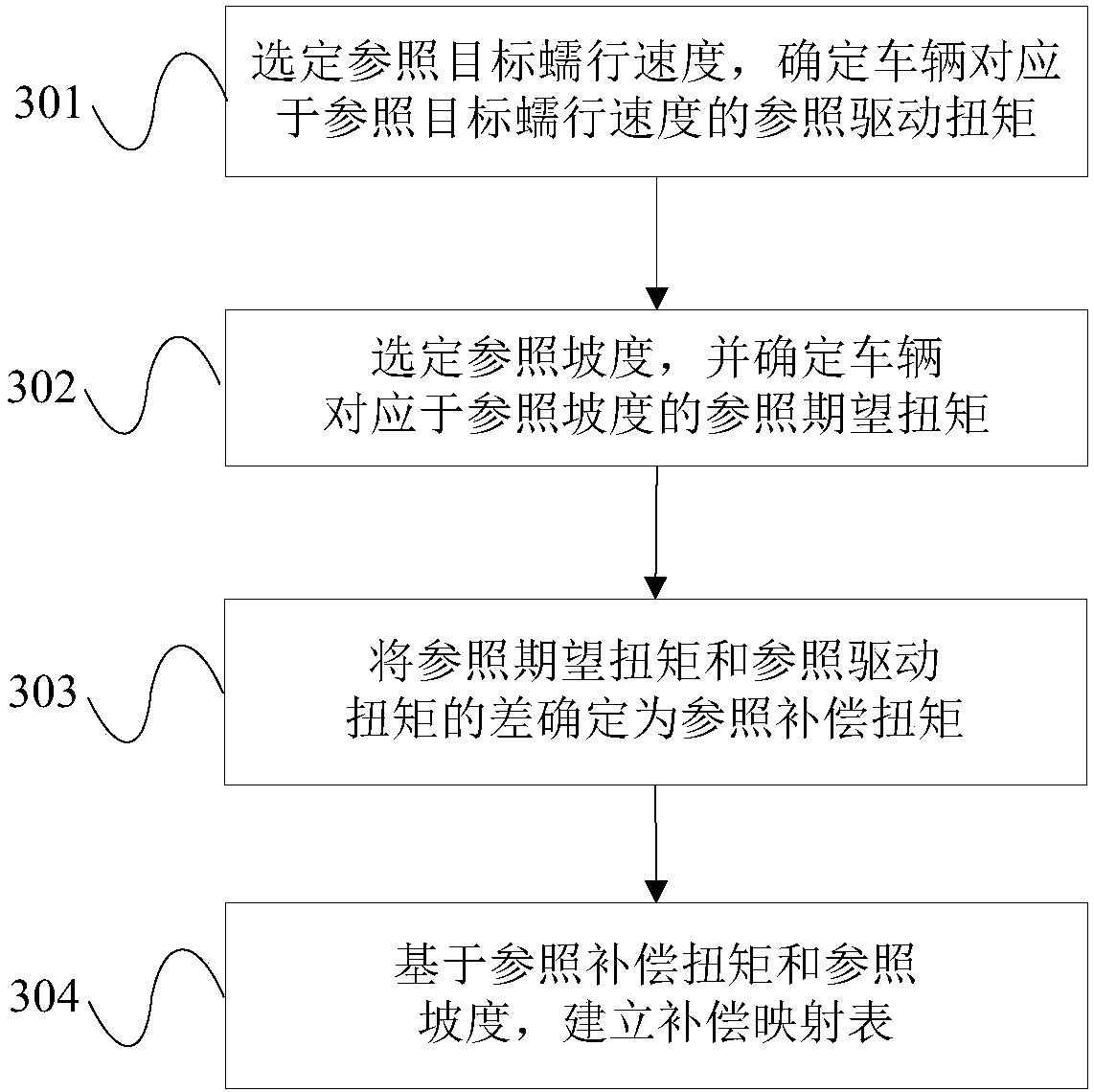
A vehicle ramp crawling control method and a vehicle
InactiveCN109720214AAdvantages of creep control methodAvoid getting off to a hard startSpeed controllerElectric energy managementRoad surfaceVehicle control
The invention relates to the technical field of vehicle control, and provides a vehicle ramp crawling control method and a vehicle. The vehicle ramp crawling control method comprises the steps of determining the gradient of a ramp on which the vehicle is driving; determining a compensation torque corresponding to the gradient, wherein the compensation torque and the gradient are in a positive correlation relationship; and outputting the compensation torque to compensate the driving torque to the expected torque, and wherein under the action of the expected torque, the vehicle can travel on ramp with the gradient according to the target creeping speed. Therefore, by means of the vehicle ramp crawling control method, the crawling function of the vehicle can be well achieved on the road surfaces with various gradients, and the crawling driving safety and driving comfort of the vehicle are improved.
Owner:GREAT WALL MOTOR CO LTD
A wafer defect detecting method
ActiveCN103646893AAccurate detectionEfficient detectionSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementImage resolutionEngineering
The invention relates to a wafer defect detecting method comprising following steps: gradually moving a wafer in order to perform first defect detection on various chip regions of the wafer with a first scanning resolution; dividing the surface of the wafer into multiple detecting regions according to defect distribution information obtained from the first defect detection and setting a defect amount threshold value for each detecting region, wherein the defect amount threshold value is in positive correlation relation to the defect amount of a corresponding detecting region; gradually moving the wafer in order to perform second defect detection on various chip regions of the wafer with a second scanning resolution, wherein the second scanning resolution is less than the first scanning resolution; performing defect correction technology on the wafer if the defect amount of any detecting region exceeds a corresponding defect amount threshold value. The wafer defect detecting method increases the applicability of the wafer defect detecting method in actual technology, substantially increases defect recognition rate and technology efficiency. The wafer defect detecting method has high precision and low cost and is beneficial to popularization in industry field.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUALI MICROELECTRONICS CORP
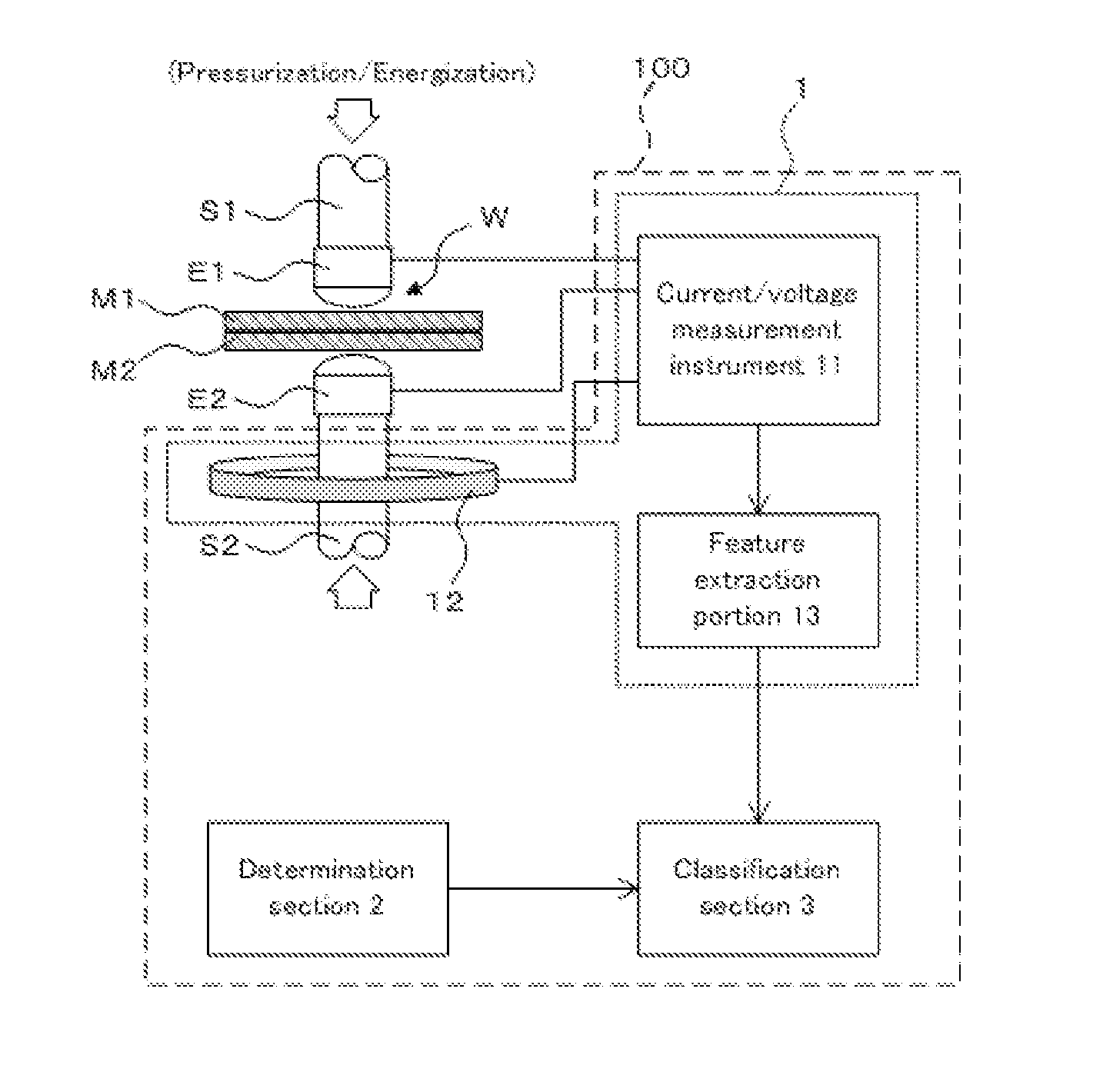
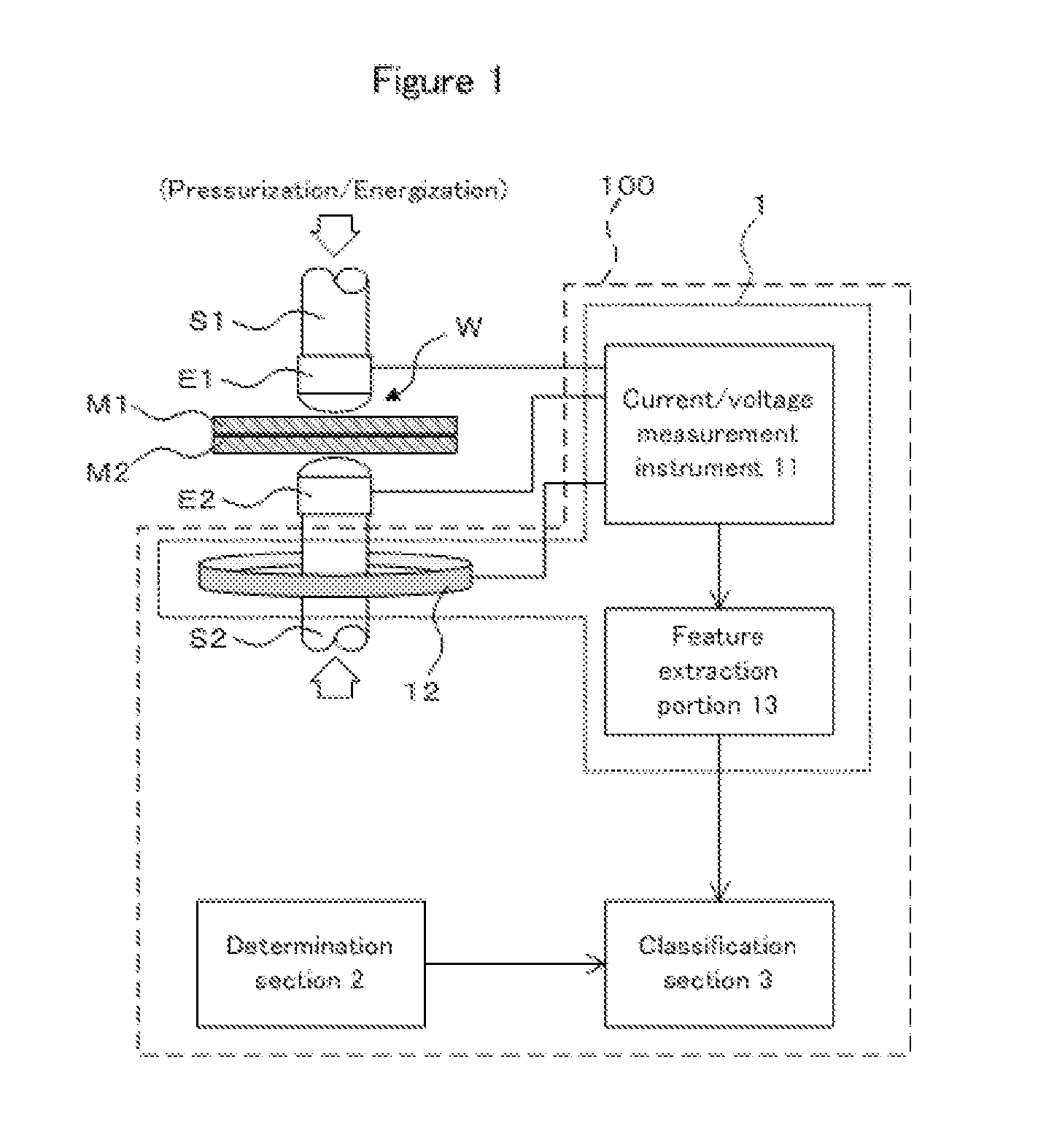
Welding quality classification apparatus
InactiveUS20130248505A1Avoid welding qualityImprove accuracyArc welding apparatusResistance welding apparatusDecision boundaryData set
The welding quality classification apparatus relating to the present invention is an apparatus, wherein a data point indicating feature information of a welded joint to be classified whose welding quality is unknown is mapped to a point in a mapping space which has a dimensional number higher than the number of the features constituting the feature information, and the welding quality of a welded joint to be classified is classified based on which of regions of two welding qualities, which are formed by separating the mapping space with a decision boundary, contains the mapped point, and wherein a discriminant function is determined by adopting a weight which minimizes the sum of the classification error corresponding to classification accuracy of a training dataset and a regularization term having a positive correlation with the dimensional number of the discriminant function as weight for each feature constituting the discriminant function indicating the decision boundary.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL & SUMITOMO METAL CORP
Distribution network single-phase grounding section positioning method based on fault phase voltage and current abrupt change
The invention provides a distribution network single-phase grounding section positioning method based on fault phase voltage and current abrupt change. Fault phase voltage and current of each line section are measured, the phase with lower phase voltage is determined to be the fault phase, and the higher phase voltage is determined to be the sound phase. Under a certain frequency band, the fault phase current abrupt change of the downstream of the fault point of a fault wire and a sound wire is in positive correlation to the derivative of the phase voltage abrupt change, with the correlation coefficient greater than zero. The fault phase current abrupt change of the upstream of the fault point of the fault wire is in negative correlation to the derivative of the phase voltage abrupt change, with the correlation coefficient smaller than zero. The section positioning can be realized by determining the correlation coefficient between the phase current abrupt change and the derivative of the phase voltage abrupt change of each section. The method overcomes the defect that a conventional distribution network single-phase grounding section can be positioned through communication. No communication is needed, and the method is of a bootstrapping method and can solve the problem of positioning single-phase grounding section of a power distribution network.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV +2
Car-door-opening collision preventing method and device
InactiveCN105857172AAvoid hittingReduce processing burdenSignalling/lighting devicesInverse correlationEngineering
The invention relates to the technical field of automobiles, and provides a car-door-opening collision preventing method and device. When it is detected that obstacles exist within a first preset range around a car door, an alarming signal of the highest level is sent, and safety and timeliness are good; meanwhile, when it is detected that obstacles do not exist in the first preset range around the car door and obstacles exist in a second preset range around the car door, the moving speed and the relative distance of the obstacles in the second preset range relative to the car door start to be detected, and alarming signals of corresponding levels are determined according to the moving speed and the relative distance; the level of the alarming signals is in positive correlation with the moving speed and in inverse correlation with the relative distance. By means of the method and device, whether obstacles exist around or behind the car door is actively detected, corresponding alarming prompts are sent, and the situation that the car door collides with obstacles is avoided to the maximum extent; meanwhile, on the basis of guaranteeing safety, the processing burden of a control module is reduced, and operation efficiency is improved.
Owner:LETV HLDG BEIJING CO LTD +1
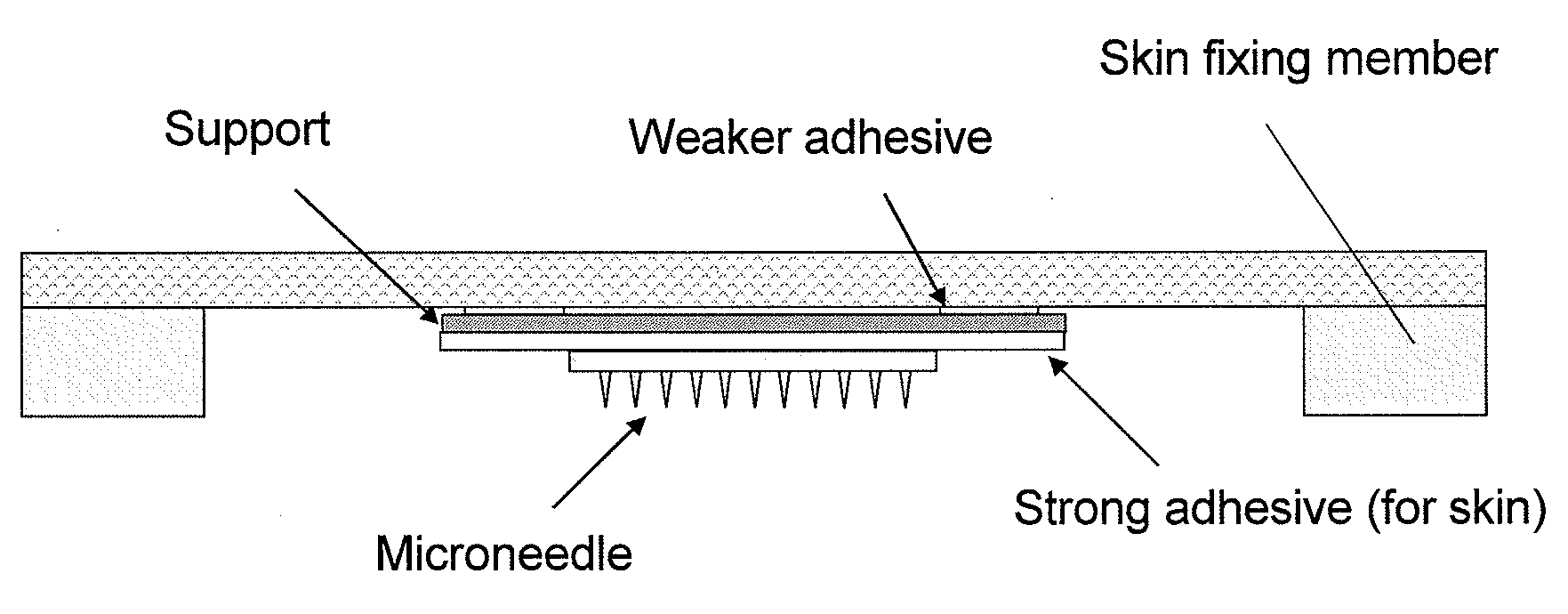
Applicator device of pinholder type microneedle
InactiveUS20120184916A1Easy to carryAvoid breakingMicroneedlesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismDrug administrationSkin puncture
Provided is a microneedle device which protects a microneedle, has an easily portable shape, is free from such problems as breakage of small needles in the step of puncturing the skin with the microneedle, and ensures appropriate skin puncture to administer a drug. By studying the relationship between the device to be pressed to the skin and the height of the elevation of the skin surface during the pressing, it is found that there is a positive correlation between the placement and interval of skin fixing members and the height of the elevation of the skin. It is furthermore found that the elevated skin surface is always parallel to the flat plate of the device. This reveals that since the microneedle installed in the device can be inserted at right angle to the skin surface, the skin can reliably be punctuated avoiding the breakage etc. of the small needles of the microneedle. Thus, a microneedle patch which is easily portable and ensures convenient drug administration to the skin can be produced.
Owner:MEDRX CO LTD
High-accuracy geomagnetic vector measurement method and device
InactiveCN103389517ASimplify preparationImprove measurement efficiencyDrill bitsSeismologyObservational errorMeasurement device
A high-accuracy geomagnetic vector measurement method is characterized in that a vertical additional magnetic field and a horizontal additional magnetic field which have the same intensity but different directions are added to the position of a probe of a high-accuracy total-field magnetometer; a geomagnetic field without additional magnetic fields and a resultant magnetic field with an additional forward magnetic field and an additional reversed magnetic field are measured respectively; and then, each component, including a vertical component Z, a horizontal component H, a geomagnetic inclination I and a declination D, of a geomagnetic vector can be computed, and the method is suitable for fast and high-accuracy geomagnetic vector measurement outdoors or in a fixed station. According to the method, the geomagnetic vector measuring accuracy is in positive correlation with the accuracy of the matched magnetometer, and the high-accuracy total-field magnetometer is superior to a fluxgate three-component magnetometer with 10 nT of measuring errors. A high-accuracy geomagnetic vector field measurement device comprises one group or two groups of field coils and a tripod, the field coils are added to the outside of the high-accuracy total-field magnetometer probe, and the field measurement device is matched with the high-accuracy total-field magnetometer and used for rapidly measuring each component of the geomagnetic vector outdoors or in the fixed station.
Owner:高建东
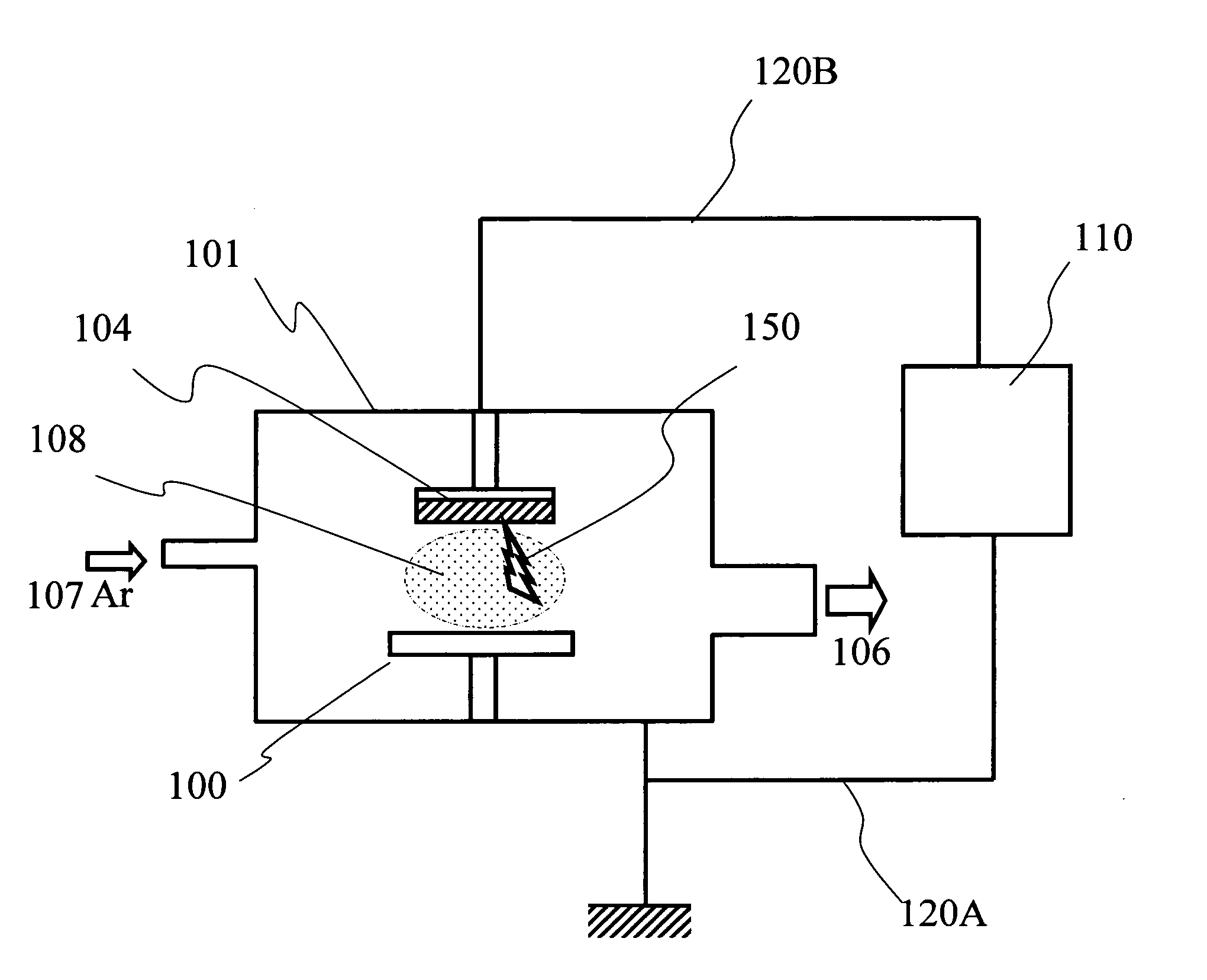
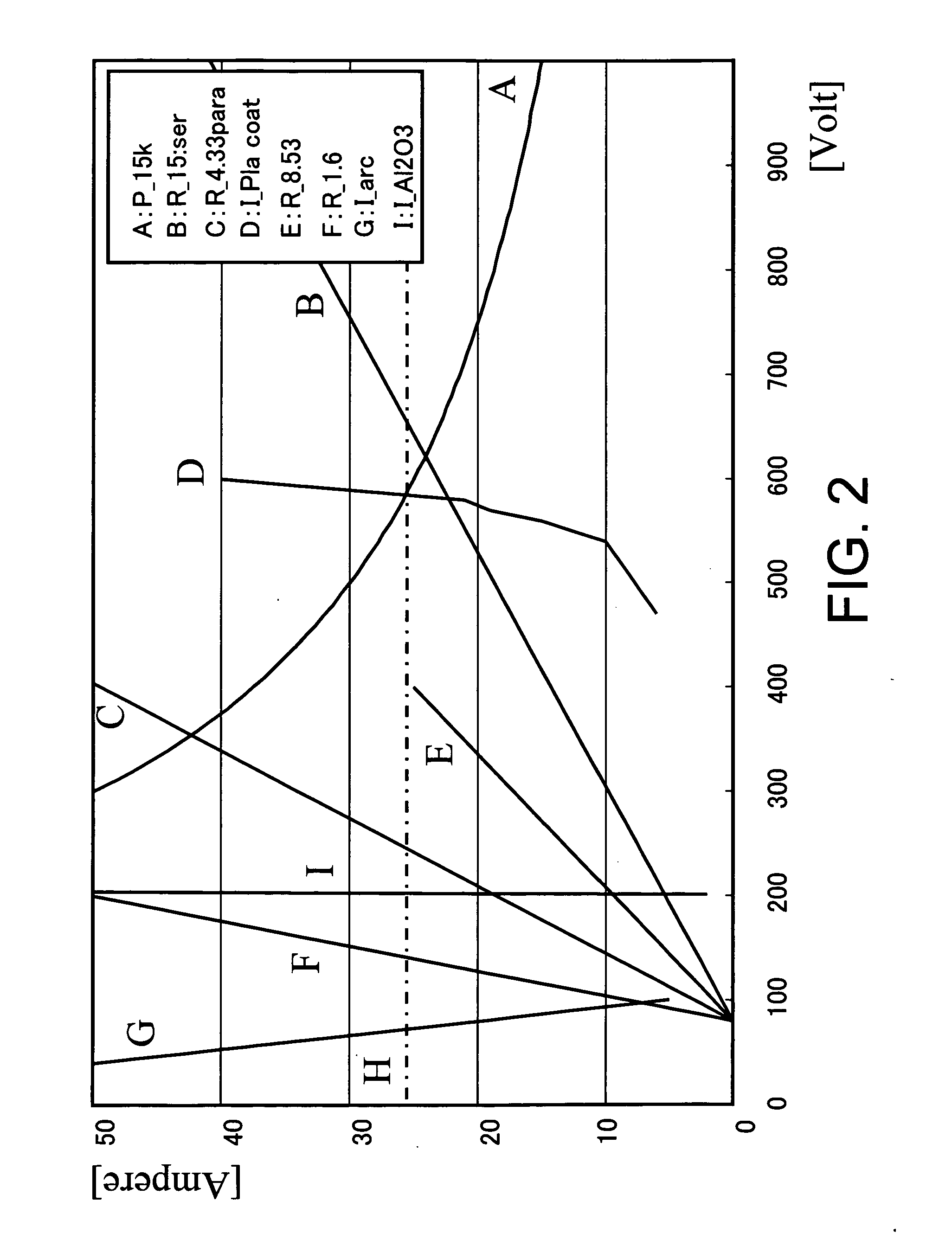
Discharging power source, sputtering power source, and sputtering device
InactiveUS20060011473A1Large amplitudeImprove reliabilityCellsElectric discharge tubesCapacitanceVoltage range
A discharging power supply according to the invention comprises: a direct current power supply unit; a control unit for controlling an output of the direct current power supply unit; and a vibrating current generation unit having a capacitance connected in parallel with a pair of outputs from the direct current power supply unit and an inductance connected to at least one of the pair of outputs, wherein the discharging power supply outputs discharging power via the vibrating current generation unit, the control unit controls the direct current power supply unit so that current outputted from the direct current power supply unit does not exceed a limit current value in at least a portion of a range of voltage that can be outputted from the direct current power supply unit, and the limit current value has a positive correlation with the absolute value of the voltage in the at least a portion of the range of voltage. According to this discharging power supply, regardless of whether the discharge power is set to be high or low, discharge current exceeding the limit characteristic line can be prevented from flowing. Even if arc discharge occurs, the amplitude of the vibrating current can be kept always larger than the discharge current. Thus the vibrating current definitely falls below zero ampere, and thereby arc can be definitely quenched.
Owner:SHIBAURA MECHATRONICS CORP
Method and electronic equipment for adjusting brightness of display
InactiveCN103390395AImprove the display effectCathode-ray tube indicatorsDisplay deviceComputer science
The invention provides a method and electric equipment for adjusting brightness of a display. The display comprises pixels, each pixel is provided with a corresponding light source which has a Gamma value, and the Gamma values are in positive correlation with the brightness of the light sources. The method includes the steps that a standard Gamma curve for adjusting the brightness of the display is obtained; all application scenes of the display are obtained; in each application scene, the display is used for processing pictures needing displaying by the application scene, an application Gamma curve is set up for at least one application scene, and the application Gamma curve deviates from the standard Gamma curve. The gray scale brightness output by the display is adjusted by adjusting the Gamma curves according to the needs for processing pictures, input picture data can be analyzed without depending on a hardware circuit, the brightness output by the display can be matched with display content, and the better display effect is achieved.
Owner:摩托罗拉移动互联科技(厦门)有限公司
Safety risk evaluation method and device, computer equipment and storage medium
ActiveCN108959934AImprove accuracyStability accurately reflectsPlatform integrity maintainanceComputer scienceRisk evaluation
The application relates to a safety risk evaluation method and device, computer equipment and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps of: acquiring a target risk evaluation parameter set corresponding to a to-be-evaluated object, wherein the target risk evaluation parameter set comprises at least two target risk evaluation parameters; acquiring risk influence degrees corresponding to current target risk evaluation parameters; calculating parameter difference values of the current target risk evaluation parameters relative to corresponding historical risk evaluation parameters; according to the risk influence degree of each target risk evaluation parameter and the corresponding parameter difference value, obtaining a first weight corresponding to each target risk evaluation parameter, wherein the risk influence degree and the first weight are in positive correlation relationship, and the parameter difference value and the first weight are in positive correlation relationship; and according to a risk score corresponding to each target risk evaluation parameter and the corresponding first weight, obtaining a target risk evaluation value corresponding to the to-be-evaluated object. By adopting the method, safety risk evaluation accuracy can be improved.
Owner:PING AN TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Method and device for refreshing data by dragging
ActiveCN103699313AImprove the efficiency of the amplification effectImprove the success rate of interactionInput/output processes for data processingComputer terminalComputer science
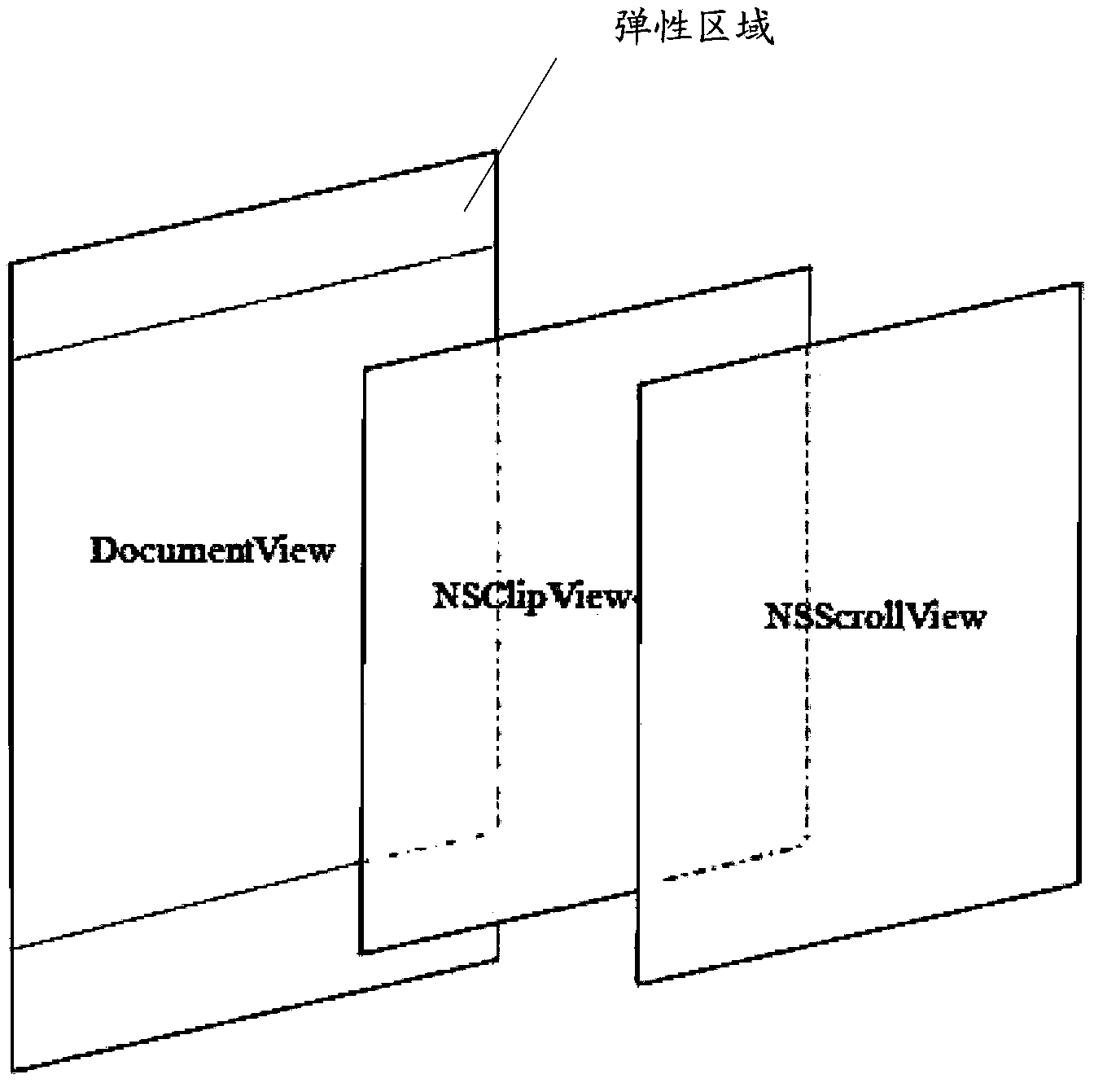
The embodiment of the invention provides a method and a device for refreshing data by dragging. The method comprises the following steps of arranging a header in an elastic region of a scroll bar, wherein the header comprises a dragging prompt message; detecting a dragging displacement event on the scroll bar; judging whether a dragging displacement value of the dragging displacement event exceeds a preset threshold value or not, and if yes, refreshing the data and representing the elastic region in the loading process of data refreshment, wherein a representing mode of the header in the elastic region has positive correlation with the dragging displacement value. According to the embodiment of the invention, an amplification effect between an interface and operation is expanded and the interaction success rate is improved. The method and the device which are disclosed by the embodiment of the invention can also be applied to various terminals, can be used in a cross-platform and cross-terminal manner and have a very wide application range.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Image checking device, image checking method, and image checking program
ActiveUS20070165936A1High verification rateImprove accuracyCoin testingSpoof detectionPattern recognitionImage Inspection
A correlation value image is generated from an input image and a template image, and separated into a positive correlation value image and a negative correlation value image. The template image is separated into a positive template image and a negative template image. A plurality of positive-negative-separated correlation images are generated by combining the positive correlation value image and the negative correlation value image and the positive template image and the negative template image. A polar-coordinates-converted input image and a polar-coordinates-converted template image are employed as the input image and the template image, respectively.
Owner:GLORY KOGYO KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com