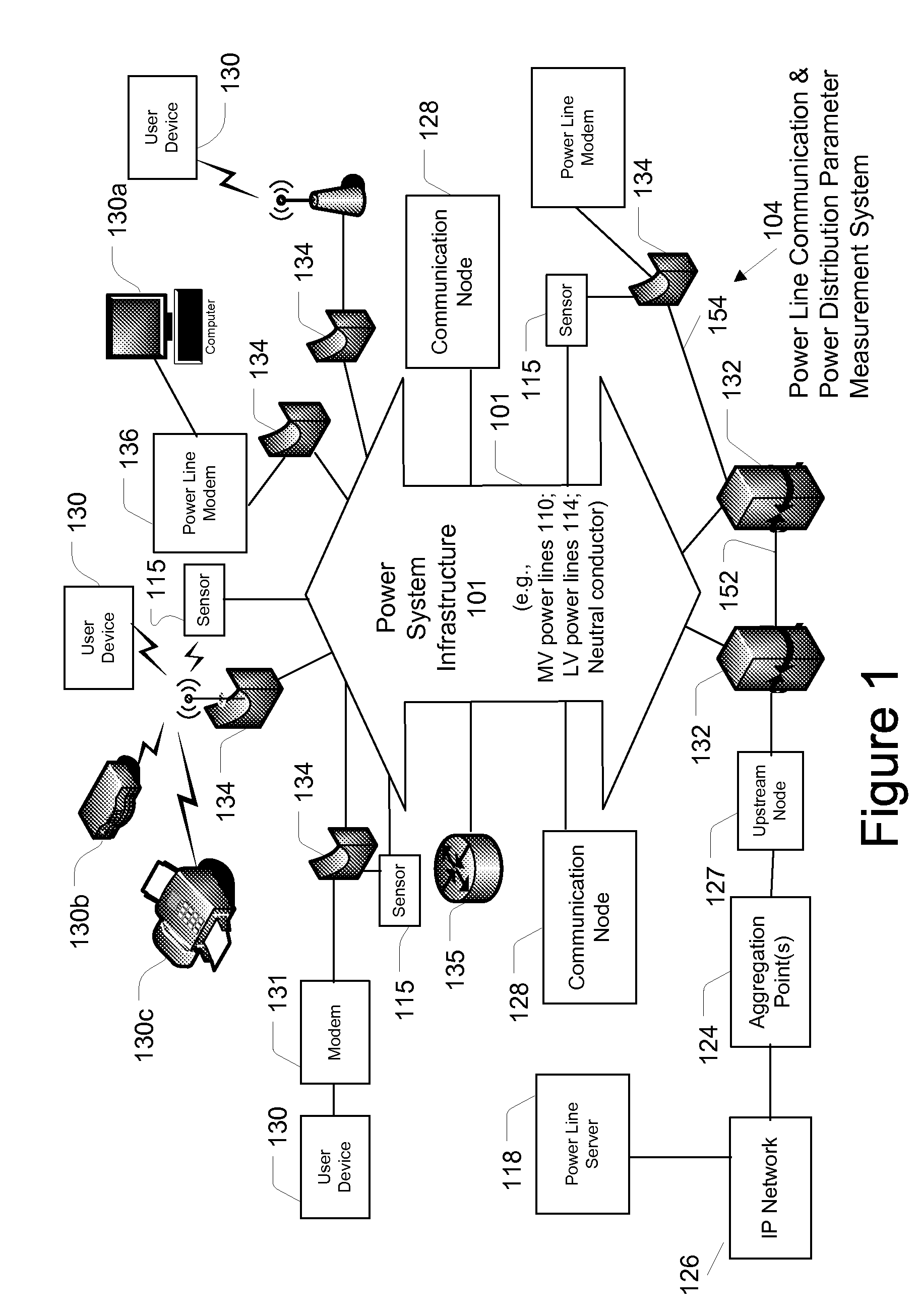
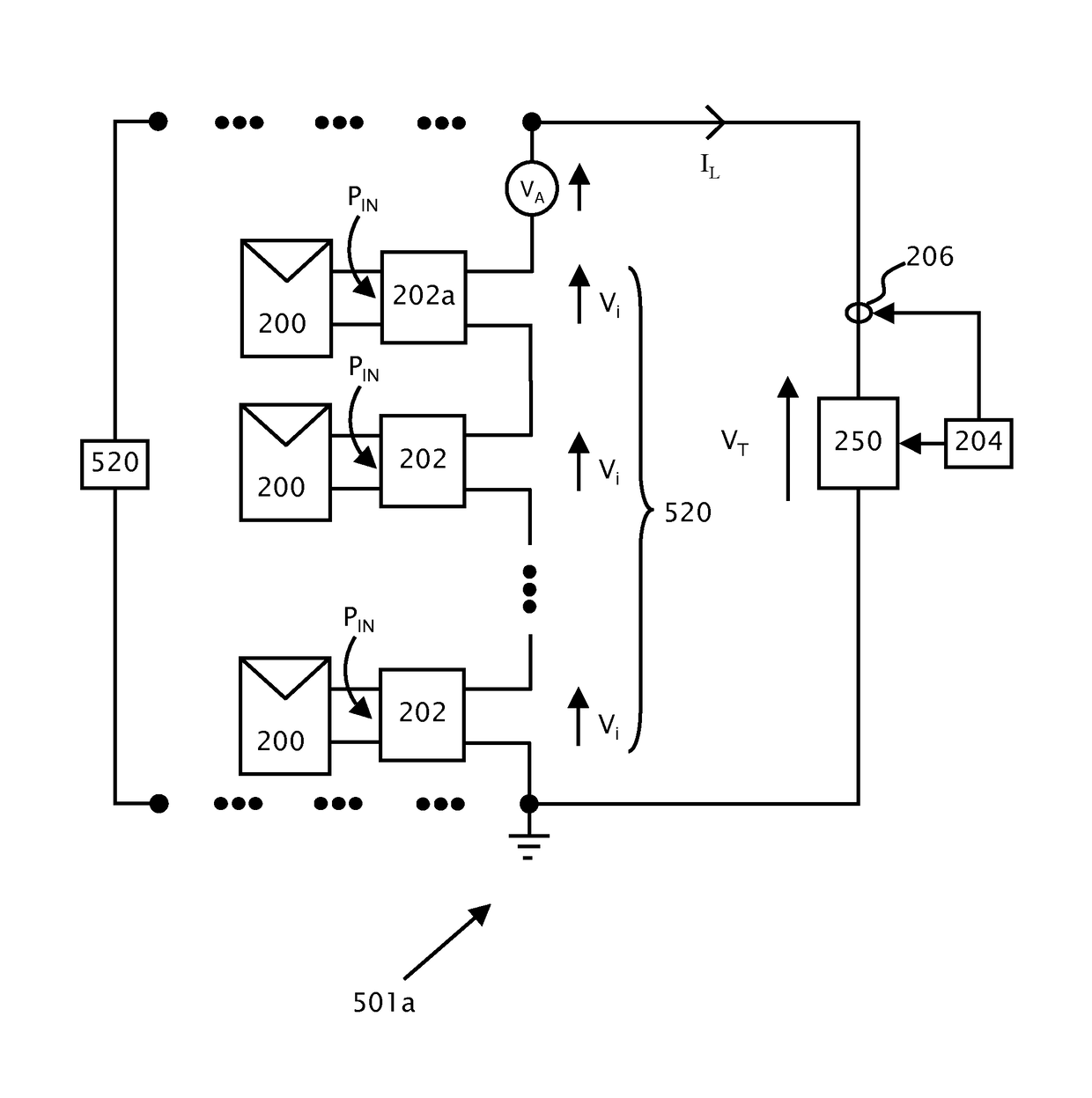
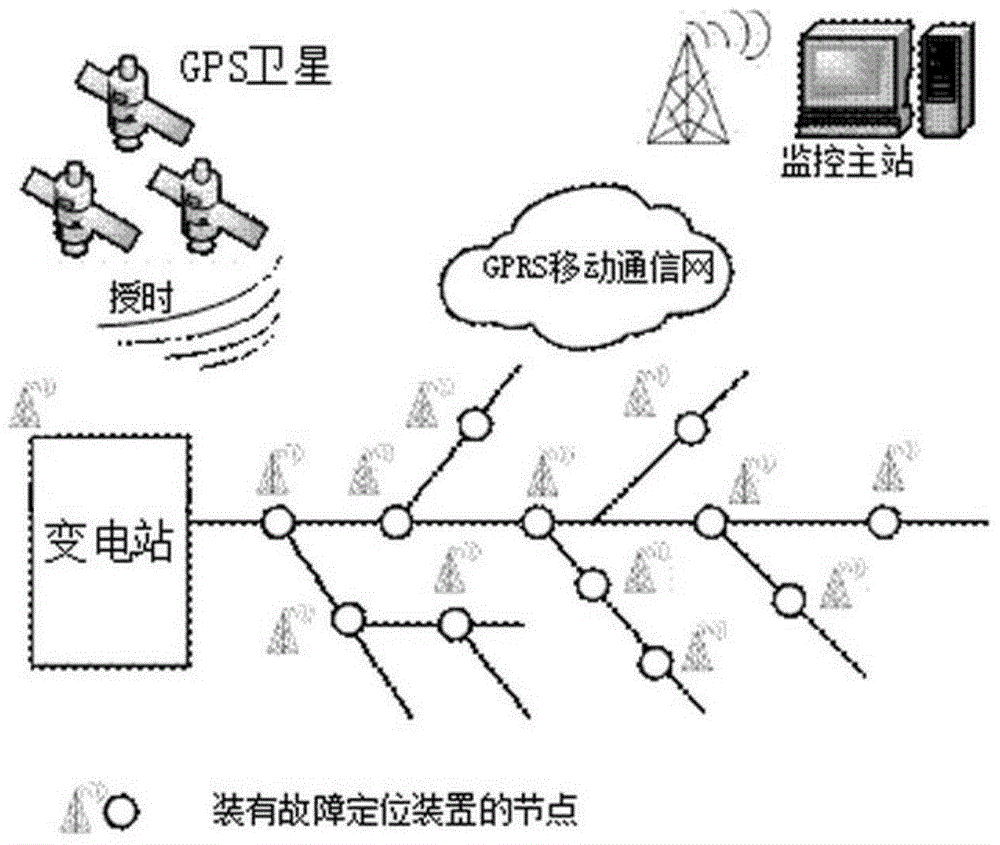
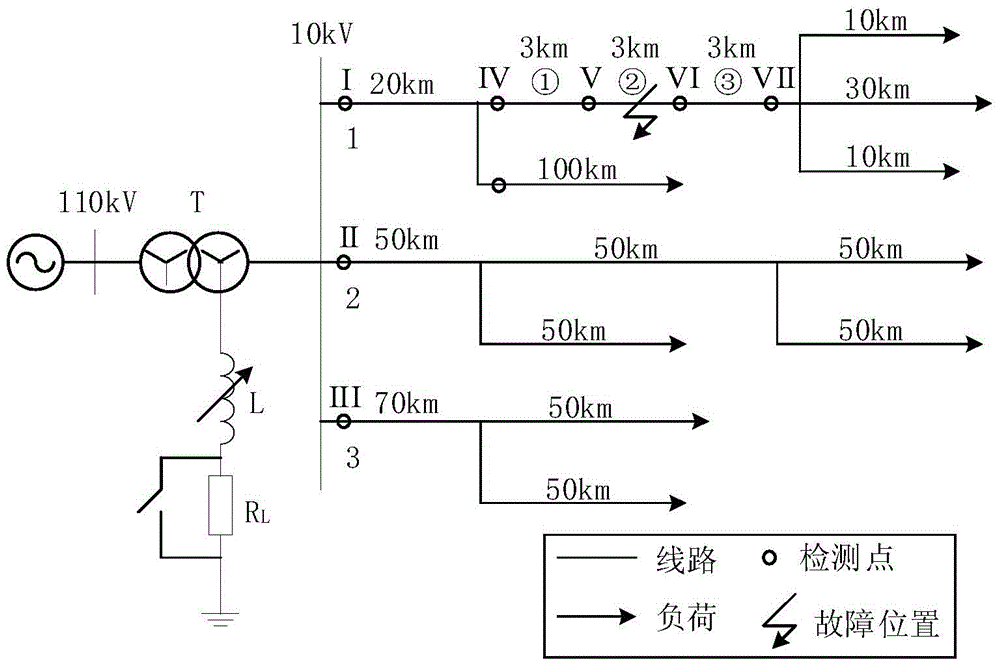
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
8352results about "Fault location by conductor types" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
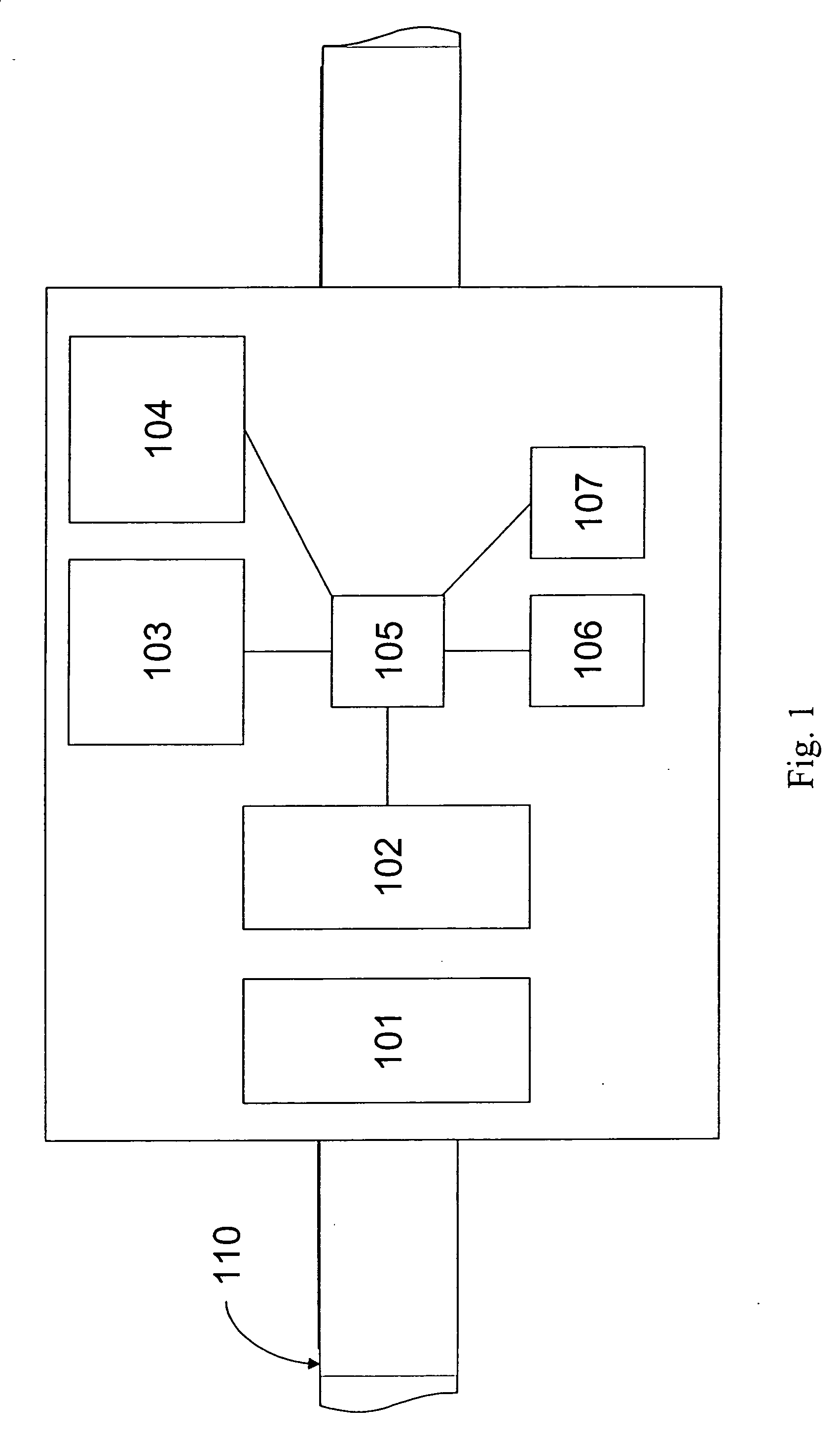
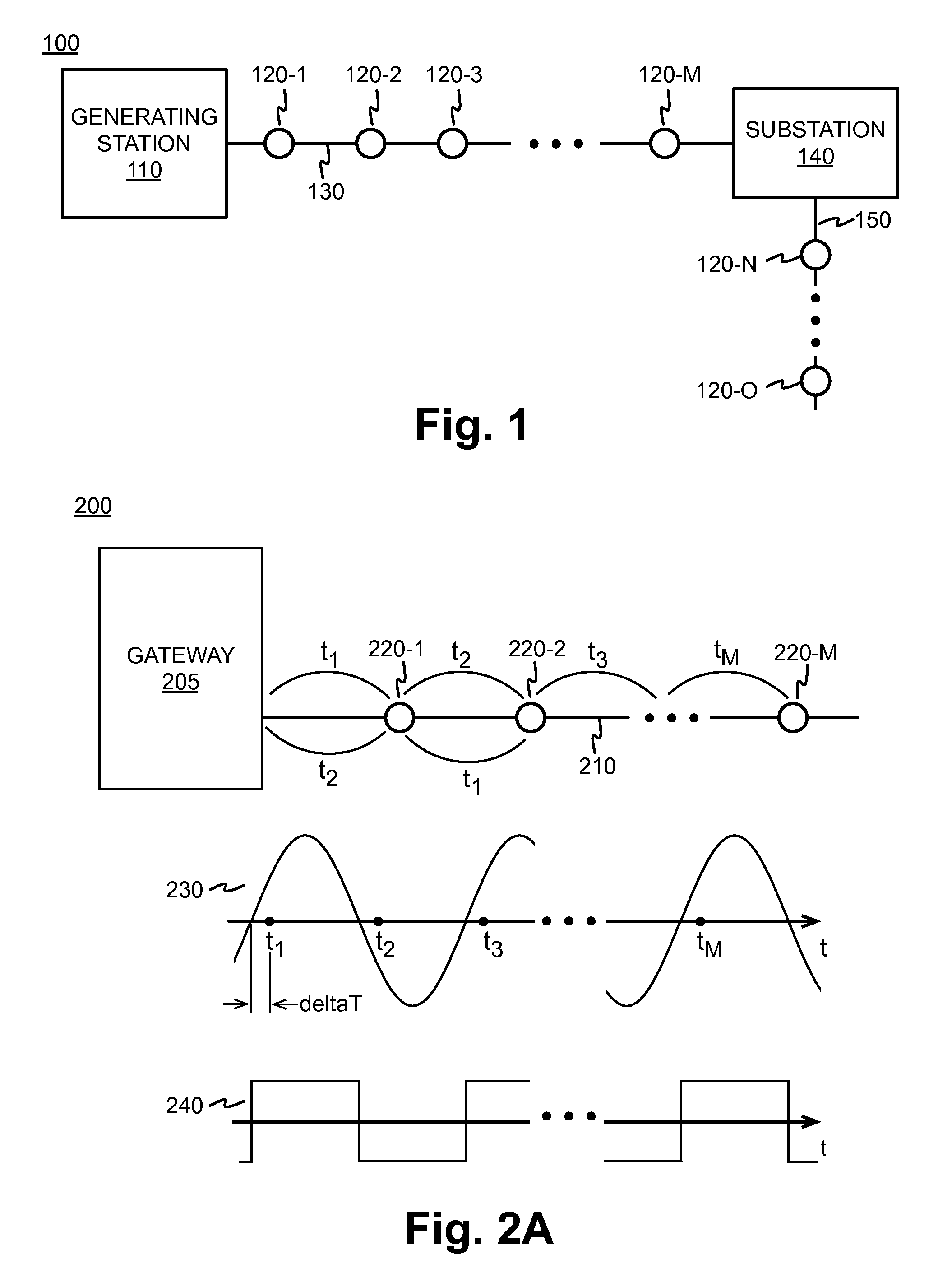
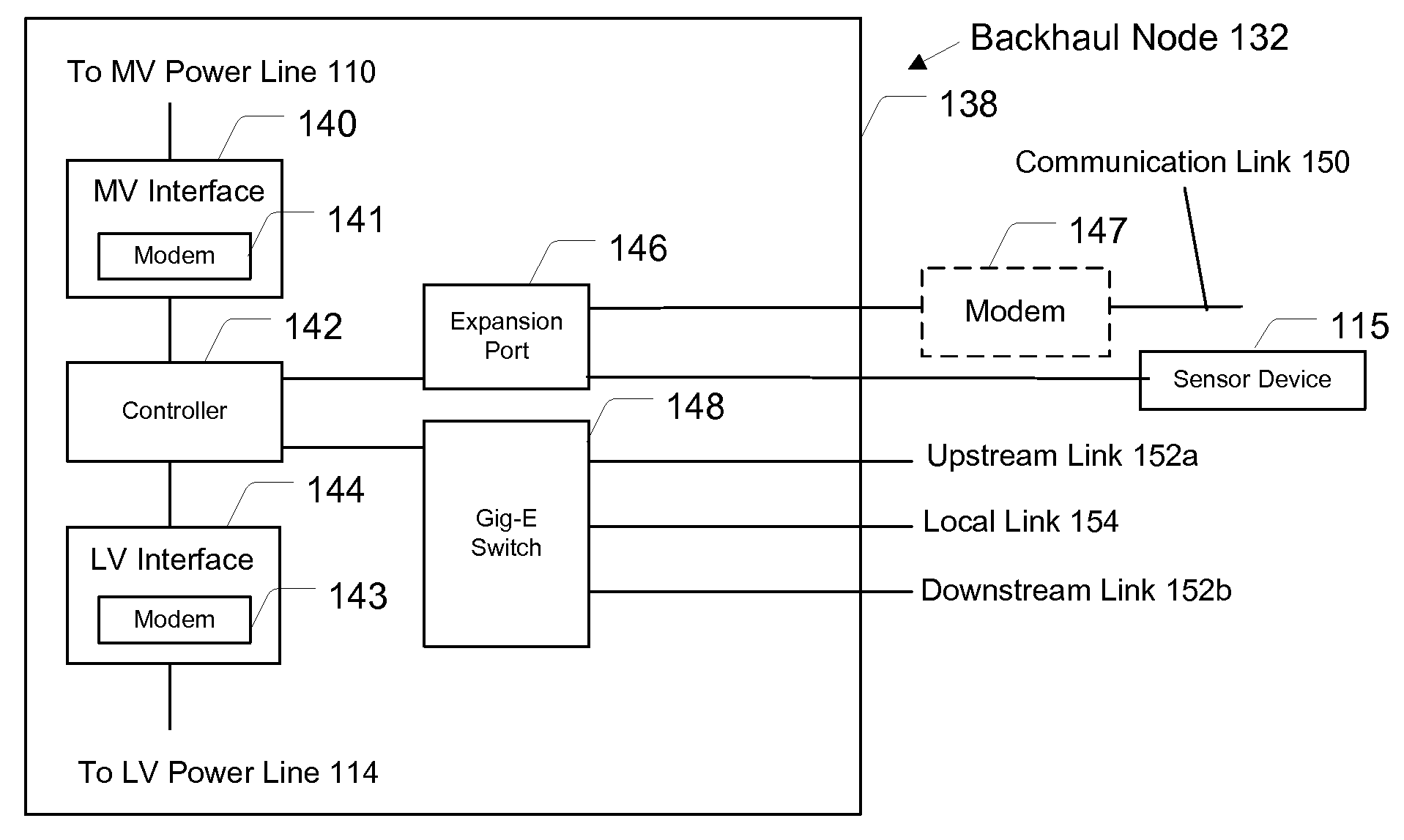
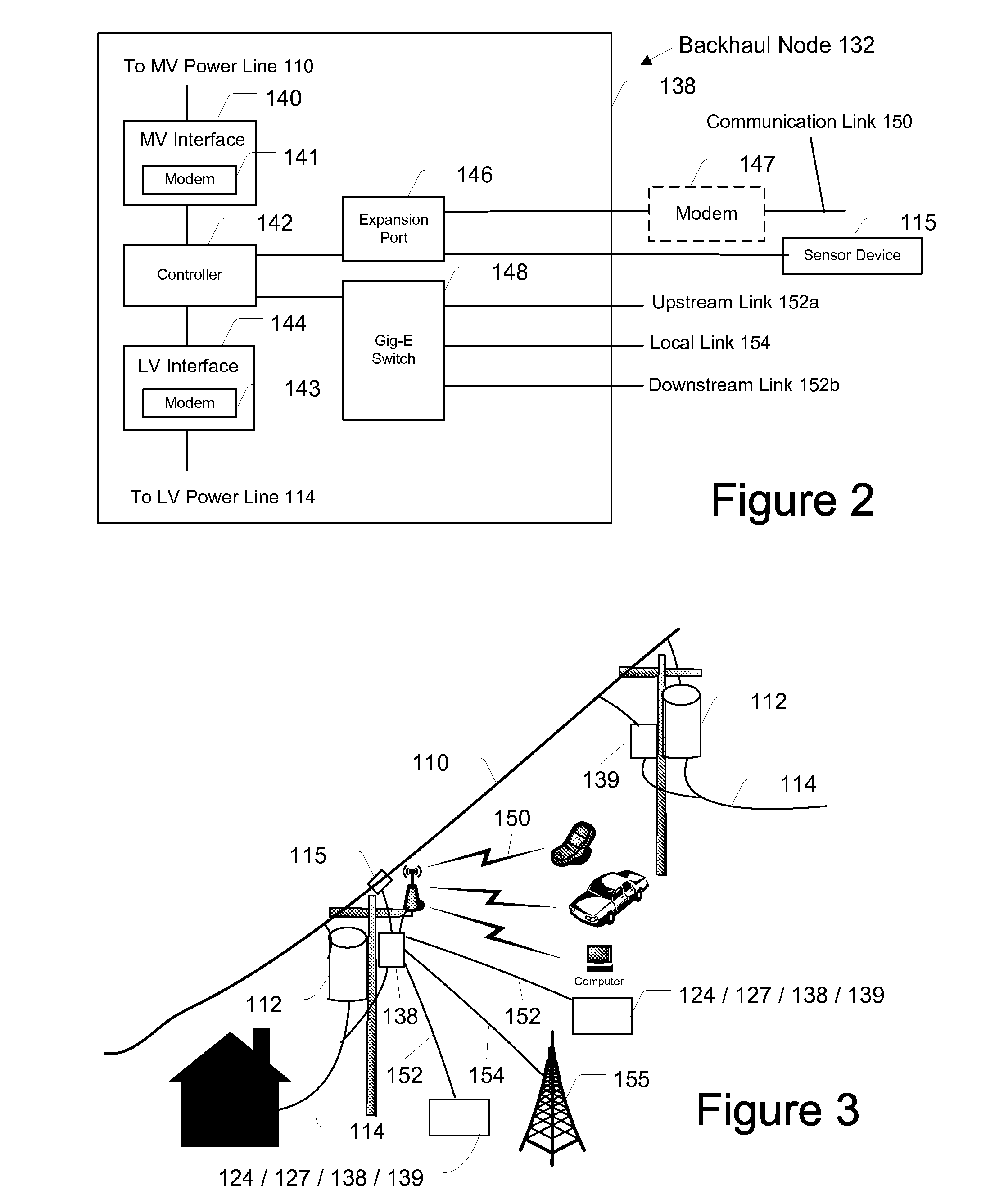
Transmission/distribution line fault indicator with remote polling and current sensing and reporting capability
InactiveUS20050151659A1Overhead installationTransmission systemsCurrent loadElectric power transmission
The present invention includes a fault indicator for an electrical transmission line comprising: a fault indicator circuit; and a remote communicator operatively coupled to the fault indicator circuit to transmit condition data to a remote location, where such condition data includes current load data. The invention also includes a method of monitoring and responding to current faults and load variations across an electrical transmission network, the method comprising: installing two fault indicators in electrical communication with an electrical transmission network and including two-way communication capability; generating, by the two fault indicators, condition data specific to a respective location of each of the two fault indicators, where such condition data includes current load data; transmitting the condition data from the two fault indicators to a remote location; receiving, at the remote location, the condition data transmitted from the two fault indicators; and, monitoring and processing the condition data received.
Owner:DONOVAN DAVID L +2
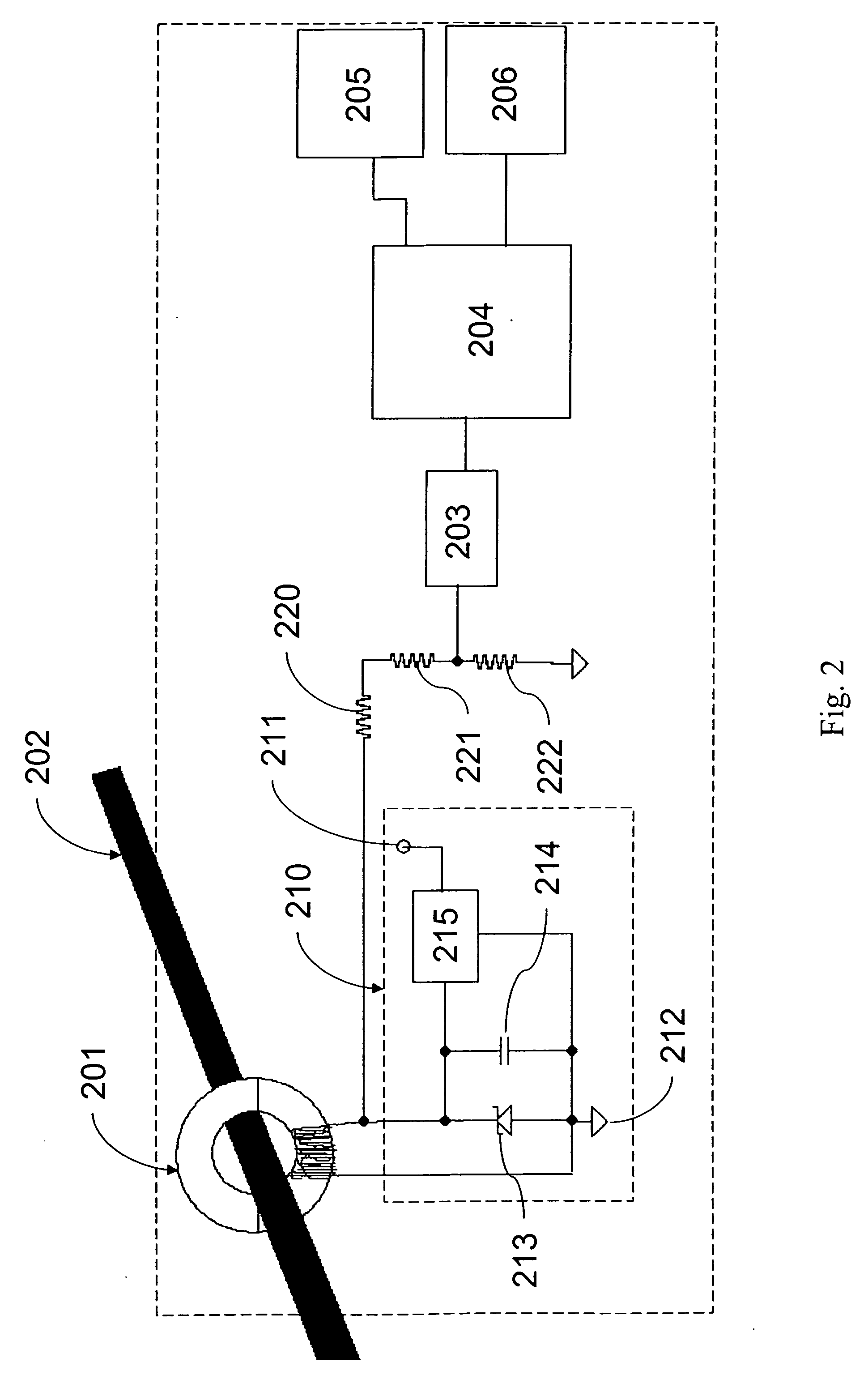
Energy Harvest Split Core Design Elements for Ease of Installation, High Performance, and Long Term Reliability
A power distribution monitoring system is provided that can include a number of features. The system can include a plurality of power line sensing devices configured to attach to individual conductors on a power grid distribution network. In some embodiments, the power line sensors can include a split-core transformer. In some embodiments, a power line sensing device is disposed on each conductor of a three-phase network. The sensing devices can be configured to measure and monitor, among other things, current and electric-field on the conductors. Methods of installing, sealing, and protecting the split-core transformers of the power line sensors are also discussed.
Owner:SENTIENT TECH HLDG LLC
System and method for island detection
A system and method is provided for detecting an island condition using active detection. The active detection involves biasing the voltage, frequency, current or phase of a distributed resource connected to a utility network. Biasing the distributed resource involves inducing a change of voltage, frequency, current or phases above or below the normal operating values. The impact of this biasing on the system operating parameters can then be measure to determine if an island condition exists. Once an island condition has been detected, the system can initiate an anti-islanding procedure to remove the distributed resource from the utility network such as opening a breaker connecting the distributed resource to the network. Additionally, the system and method can include a passive element for detecting frequency and voltage (or other parameters) shifts above certain points.
Owner:PRIMARY INTEGRATION - ENCORP
Monitoring electrical assets for fault and efficiency correction
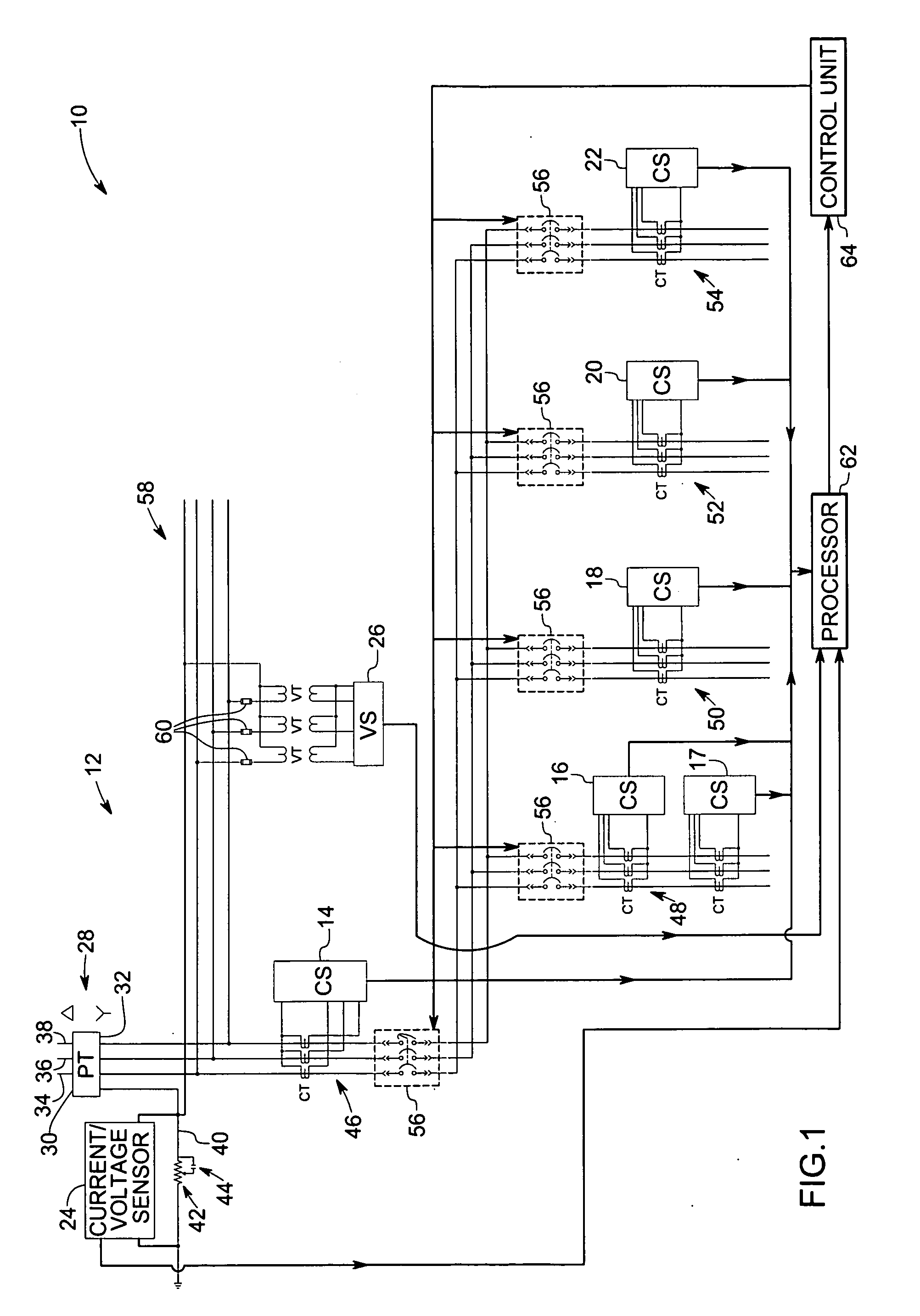
A system and method of monitoring a plurality of electrical assets comprise an electricity distribution infrastructure, including a plurality of electrical asset sensors coupled to the electrical assets for monitoring an operating condition of the electrical assets as well as any fault conditions. The sensors may include a current transformer for obtaining a current waveform, a GPS receiver for applying a synchronized time-stamp to the waveform data, and a mesh network radio for transmitting the time-stamped waveform data. Data from the plurality of sensors may be encrypted and transmitted over a mesh network to one or more gateways that are in communication with a central command processor. In response to an abnormal operating condition of any electrical asset, the central command processor may determine a probable fault location, a probable fault type, and a fault response.
Owner:ACLARA TECH LLC
Power line property measurement devices and power line fault location methods, devices and systems
InactiveUS20050040809A1Improve securityQuick and efficientMeasurement using dc-ac conversionElectric lighting sourcesMeasurement deviceDistribution power system
A device for use in locating a fault on a power line of a power distribution system includes: at least one sensor for measuring at least one property of the power line, and at least one output device in operative connection with the sensor to signal a state of the power line. The signaled state of the power line is determined from the measured property and indicates whether a fault has occurred in the power line. The output device can, for example, signal a current state or a previous state of the power line. The device can further include a controller in operative connection with the output device to control the operation of the output device based upon at least one of the current state or the past state of the power line. A device for use in measuring a property of power line of a power distribution system includes: a connector adapted to place the device in operative connection with the power line in the power distribution system without taking the power line out of operation; a sensor for measuring a property of the power line, and an output device in operative connection with the sensor to transmit a signal representative of the measured property.
Owner:UBER ARTHUR E III +1
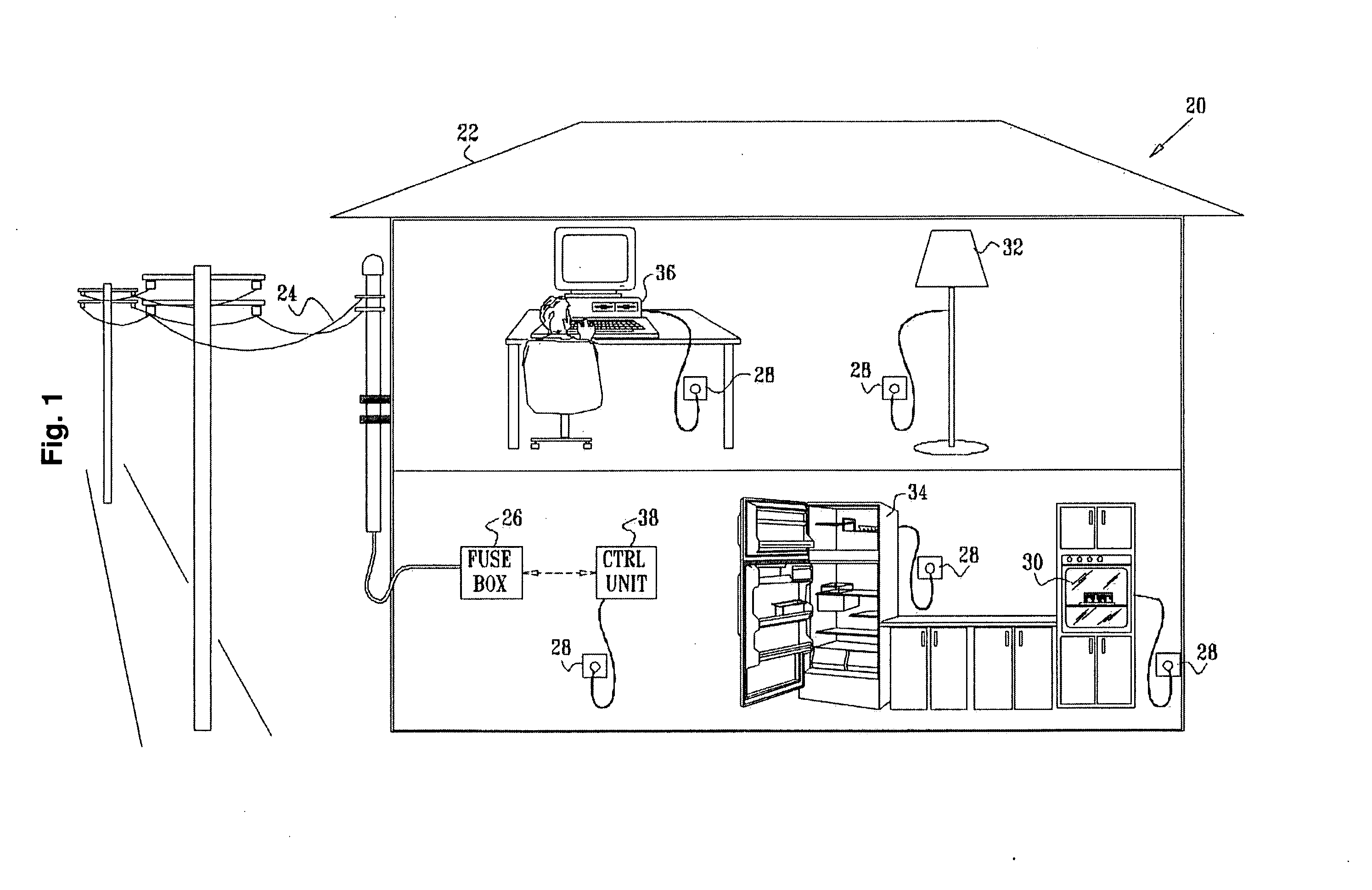
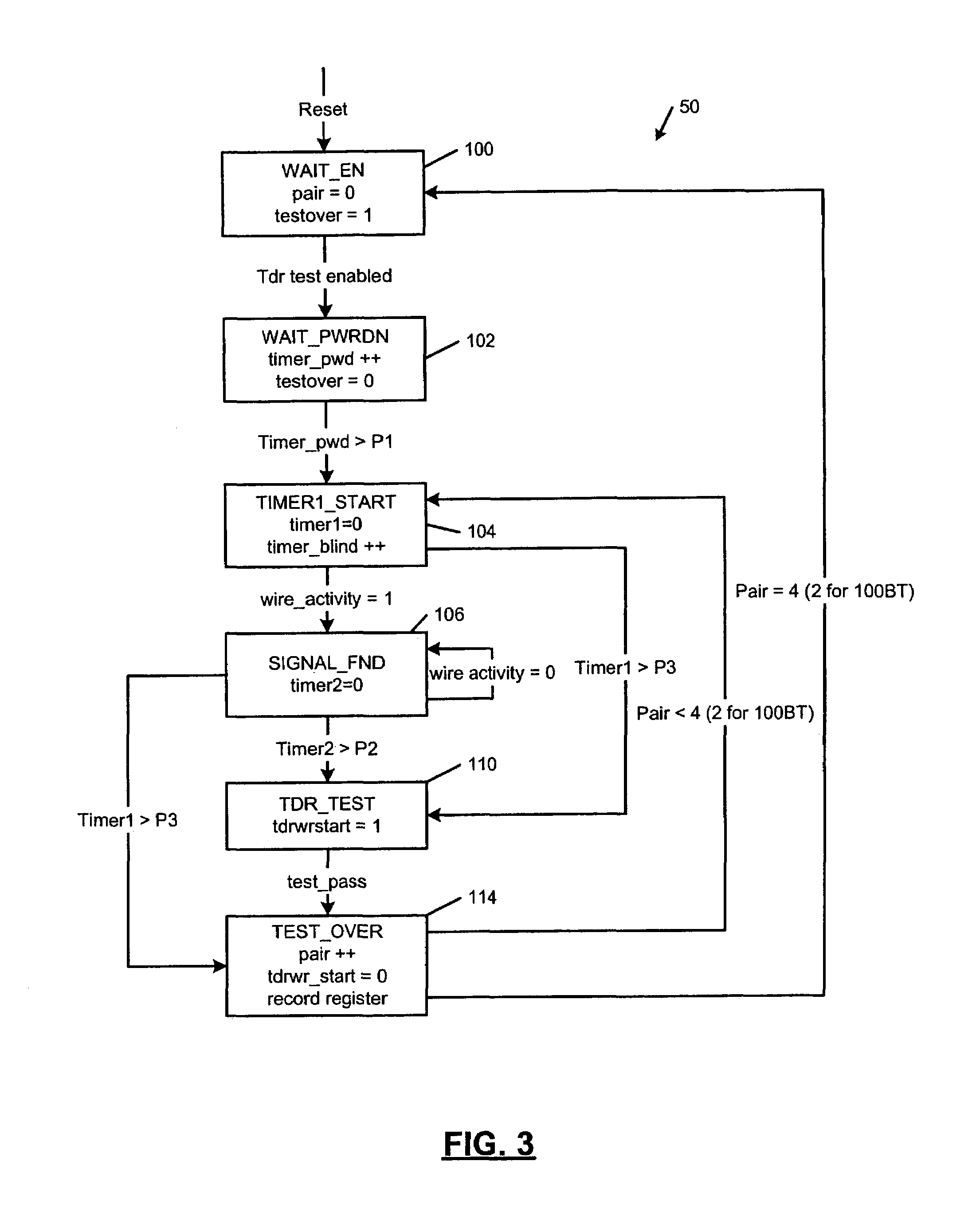
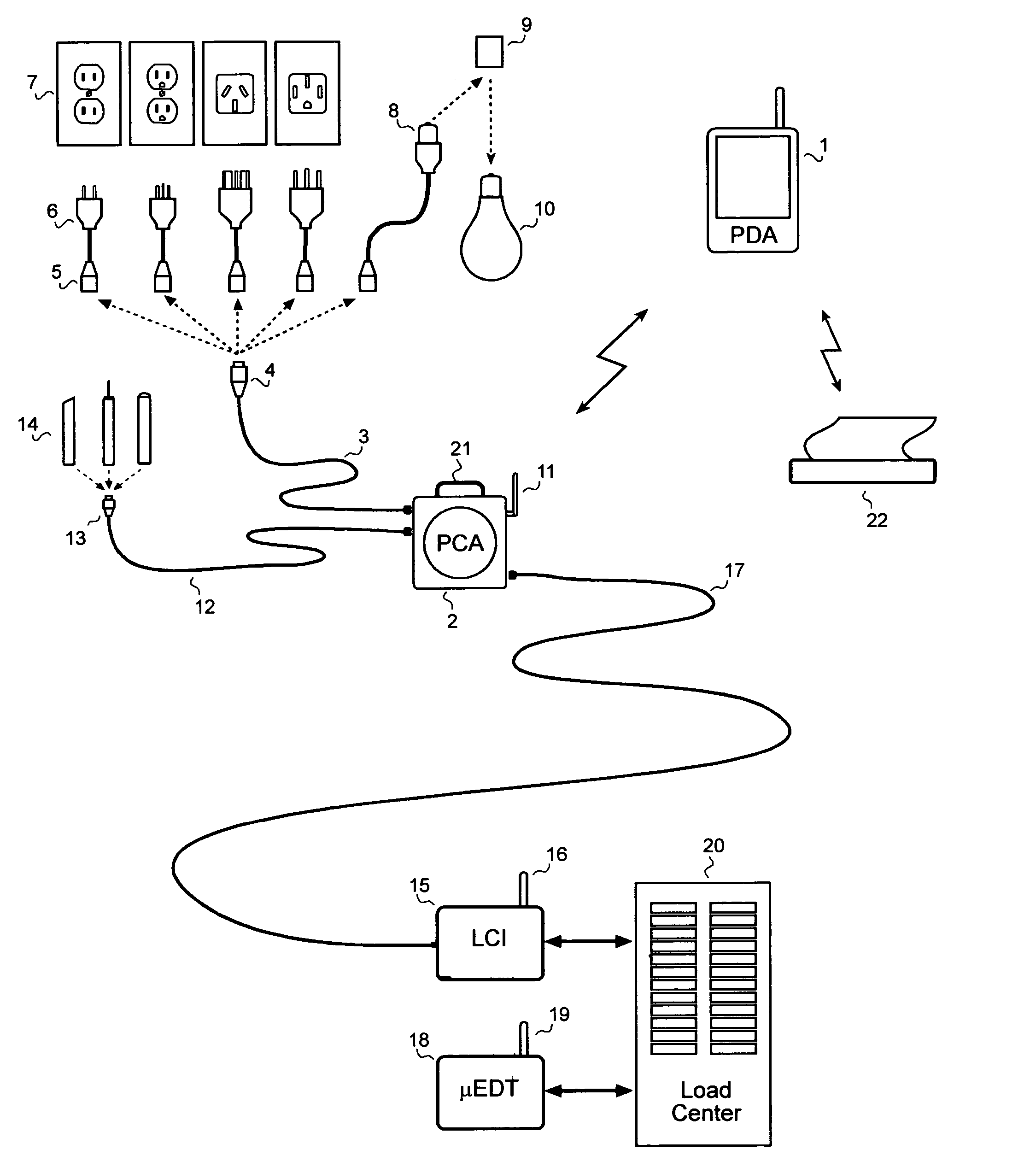
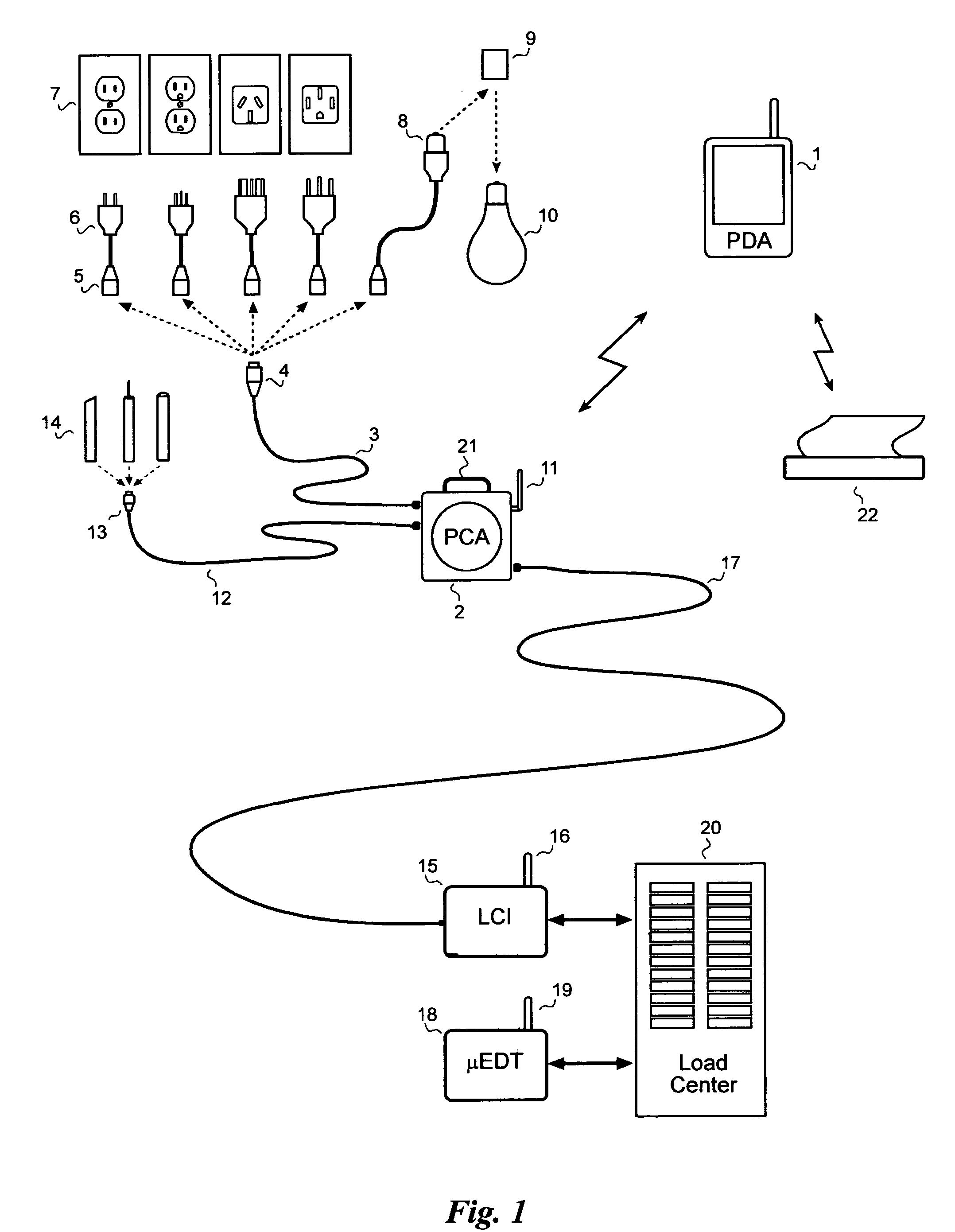
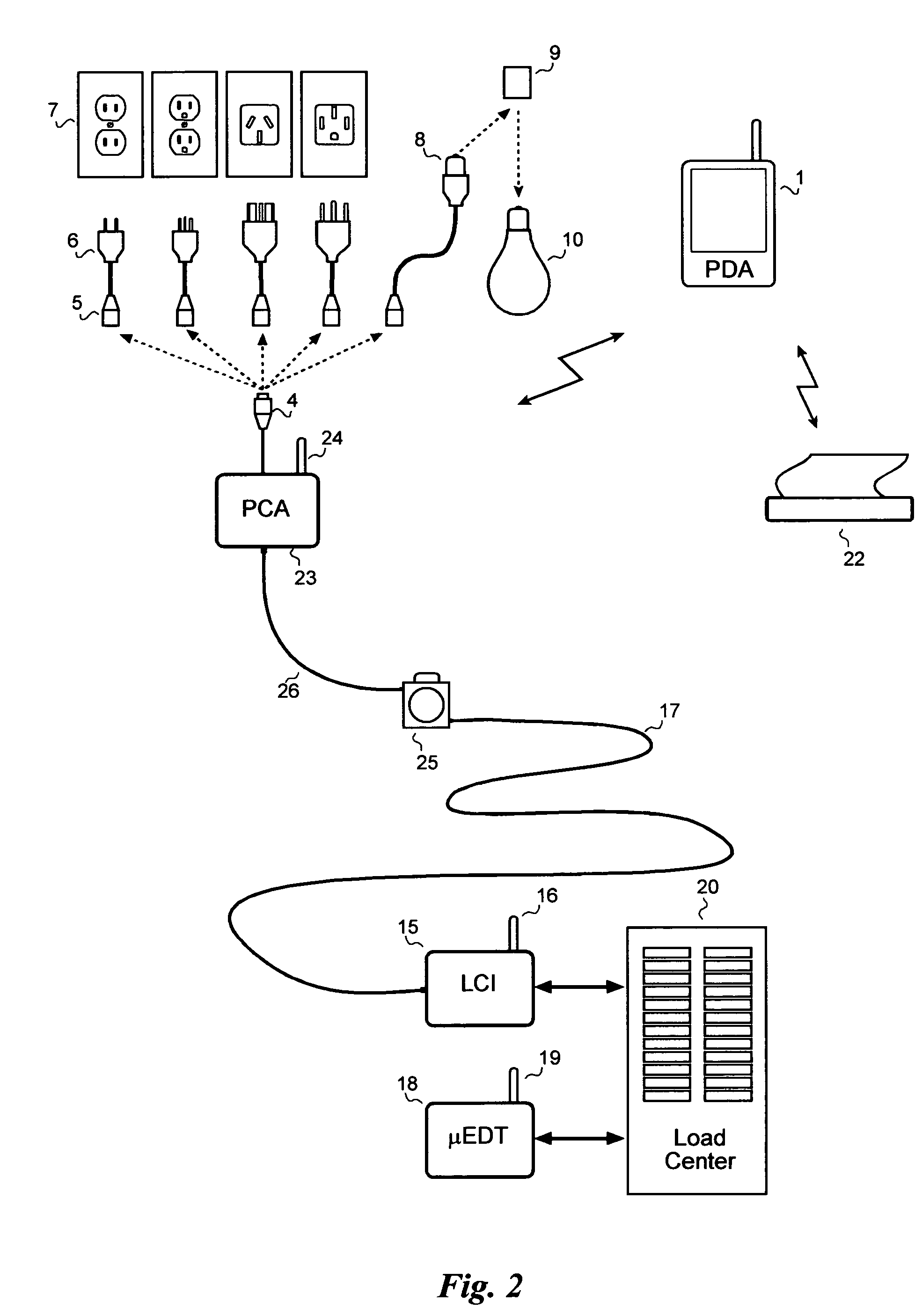
Electrical wiring inspection system
InactiveUS20050212526A1Electrical measurement instrument detailsElectric connection testingElectrical resistance and conductanceOperating energy
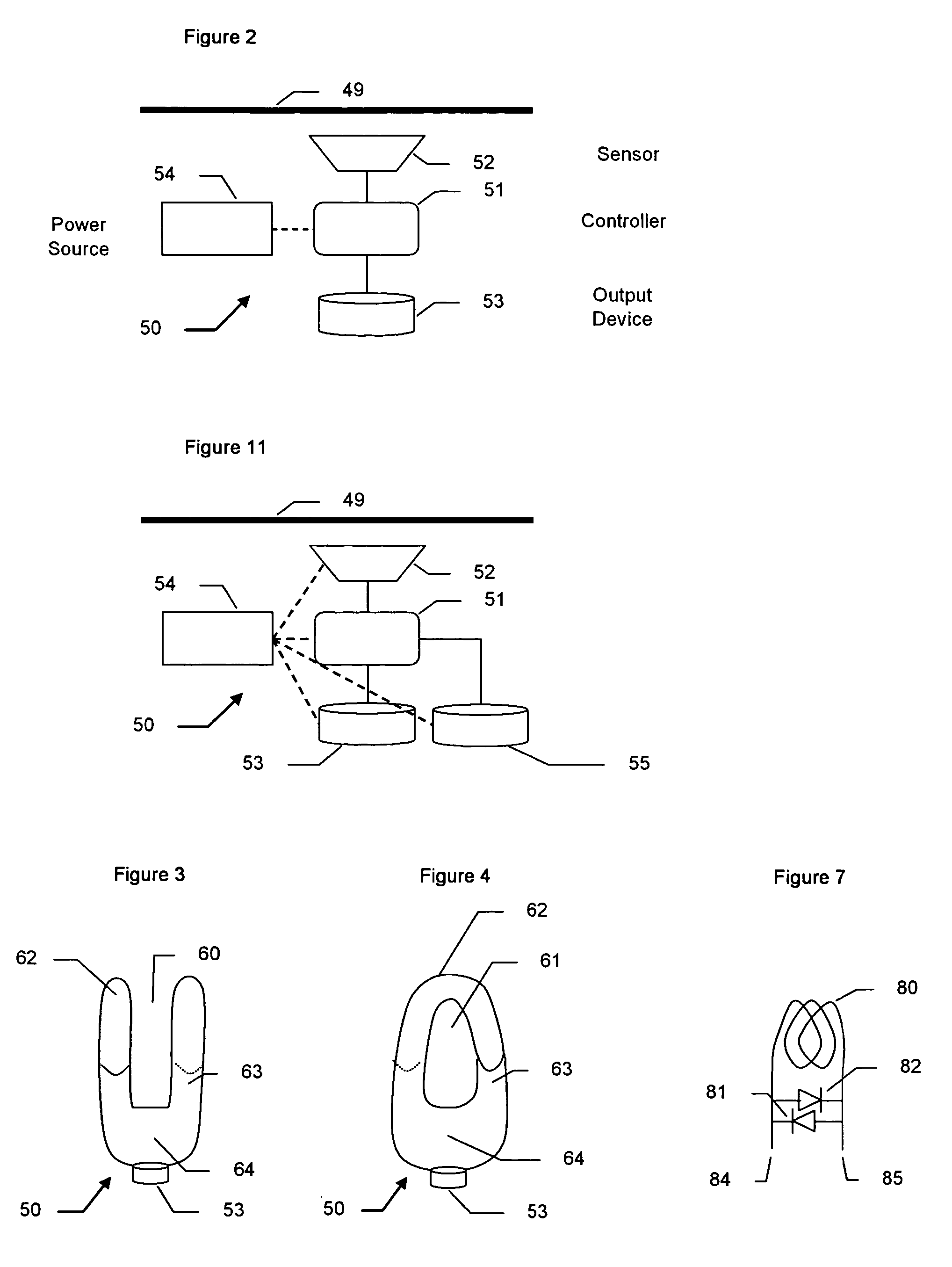
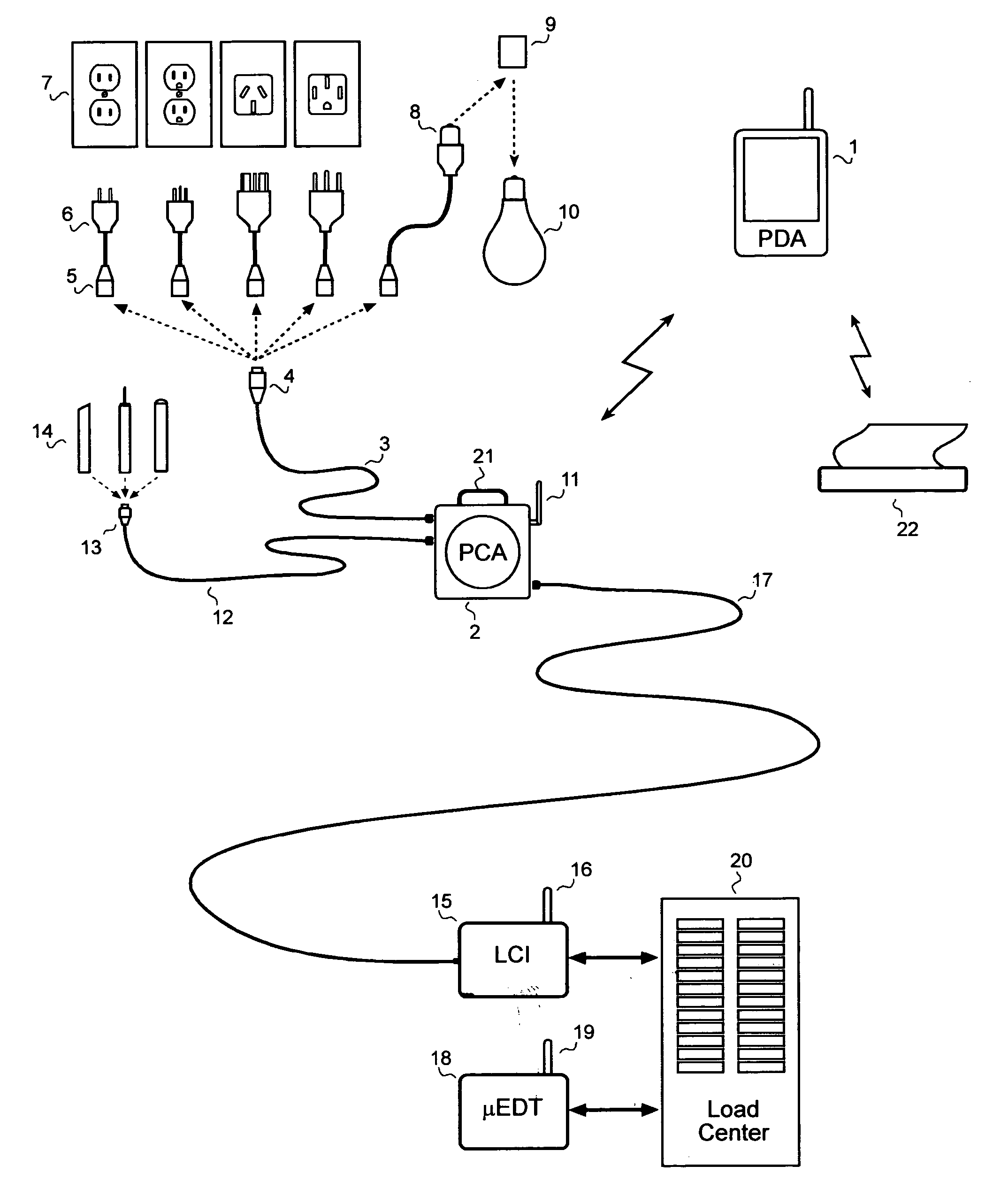
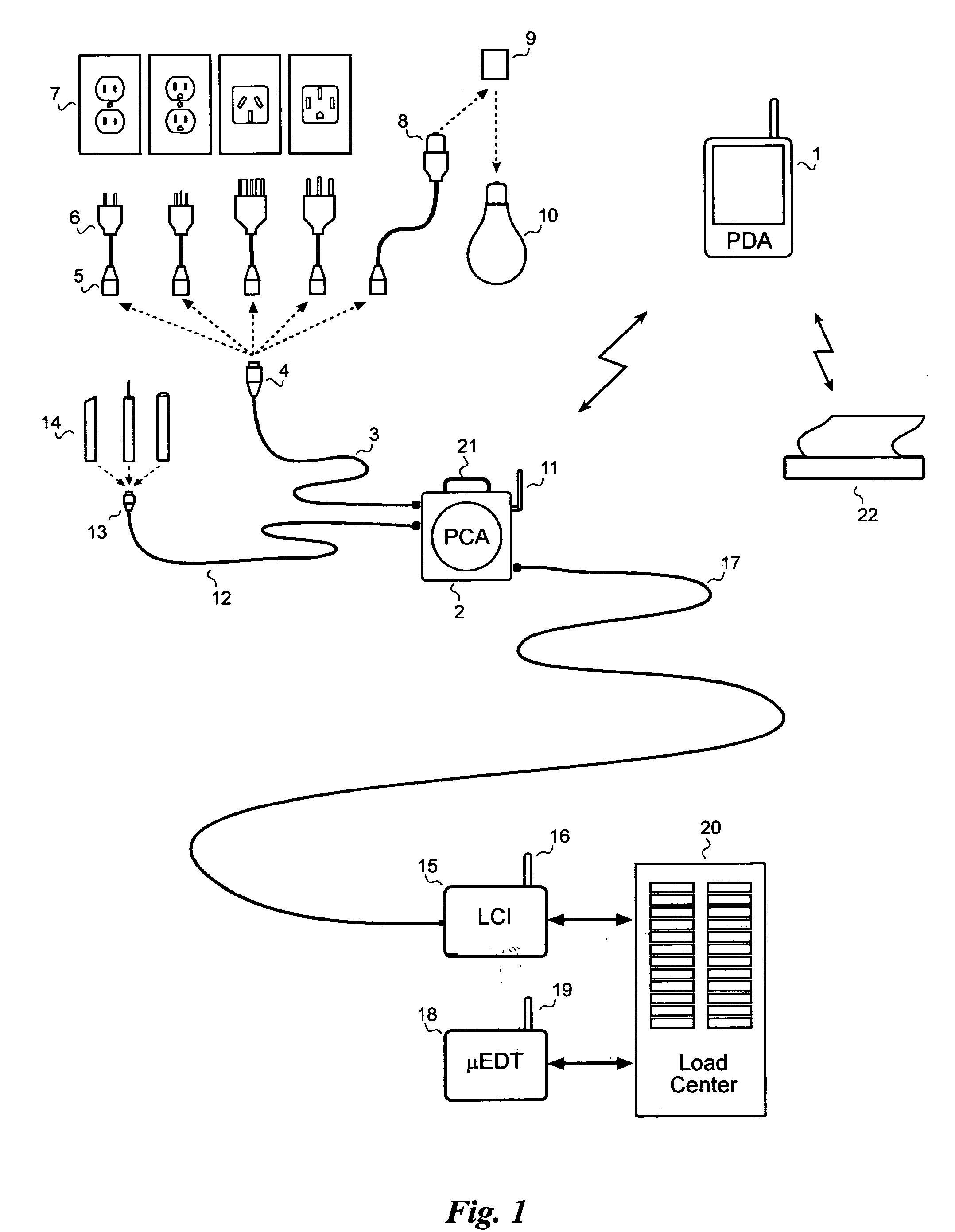
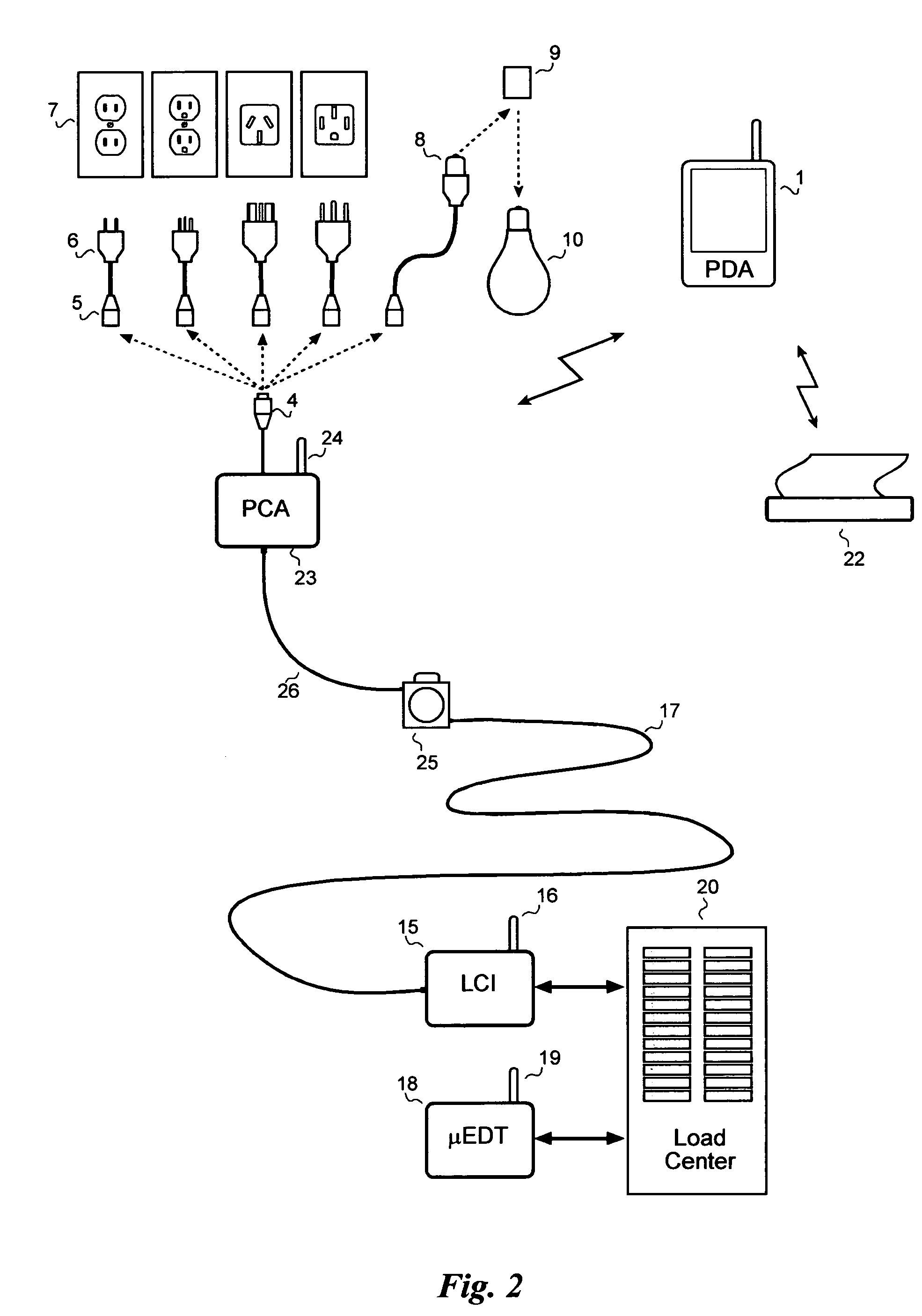
A system for testing and documenting the electrical wiring in a building, for example, comprises a Portable Circuit Analyzer (PCA) that is connected to the building's Load Center through an umbilical cord. The PCA is in wireless communication with a hand-held computer device, such as a personal digital assistant (PDA) as now widely available, provided with custom software according to the invention. The electrician connects the PCA in succession to each circuit in the building, operating each switch, and each fixture or appliance, while recording the test results of the circuit element on the PDA. The PCA measures the resistance and length of each circuit thus established. When the test process is completed, the PDA is enabled to generate a complete schematic diagram of the building, including, for example, an identification of the branch circuit to which each fixture, outlet, appliance, or other load or connection point is connected.
Owner:BLADES FREDERICK K
System and method for identifying and locating an acoustic event
InactiveUS6847587B2Improve “ view ”Eliminate riskDefence devicesDirection finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesEvent typeHost processor
A system and method for detecting, identifying, and fixing the location of the source of an acoustic event. The inventive system includes: a plurality of sensors dispersed at somewhat regular intervals throughout a monitored area; a communication network adapted to deliver information from the sensors to a host processor; and a process within the host processor for determining, from the absolute times of arrival of an event at two or more sensors, a position of the source of the event. Acoustic events are detected and analyzed at each sensor so that the sensor transmits over the network: an identifier for the sensor; an identifier for the type of event; and a precise absolute time of arrival of the event at the sensor. In a preferred embodiment, the system also identifies the type of weapon firing a gunshot.
Owner:SHOTSPOTTER +2
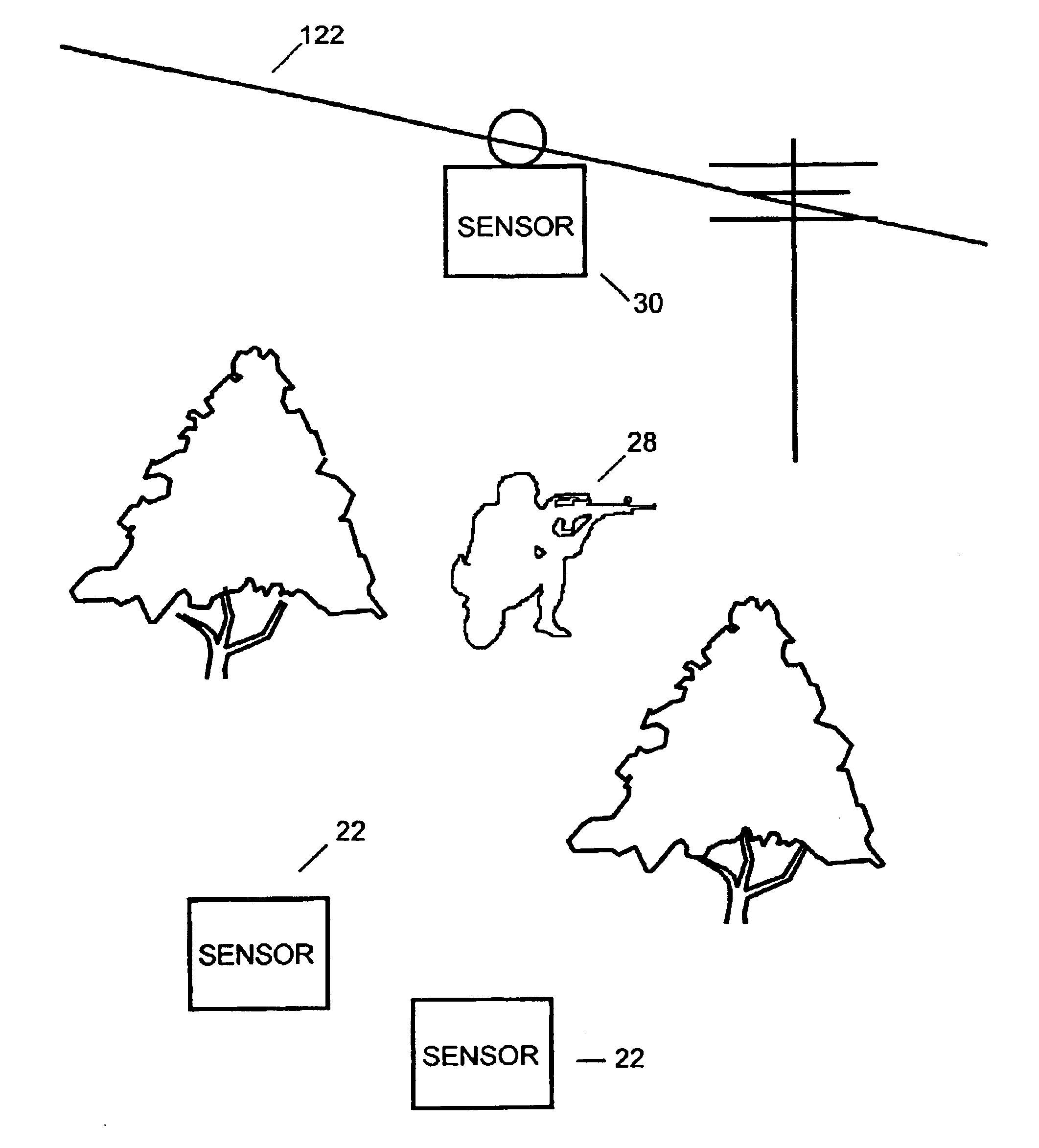
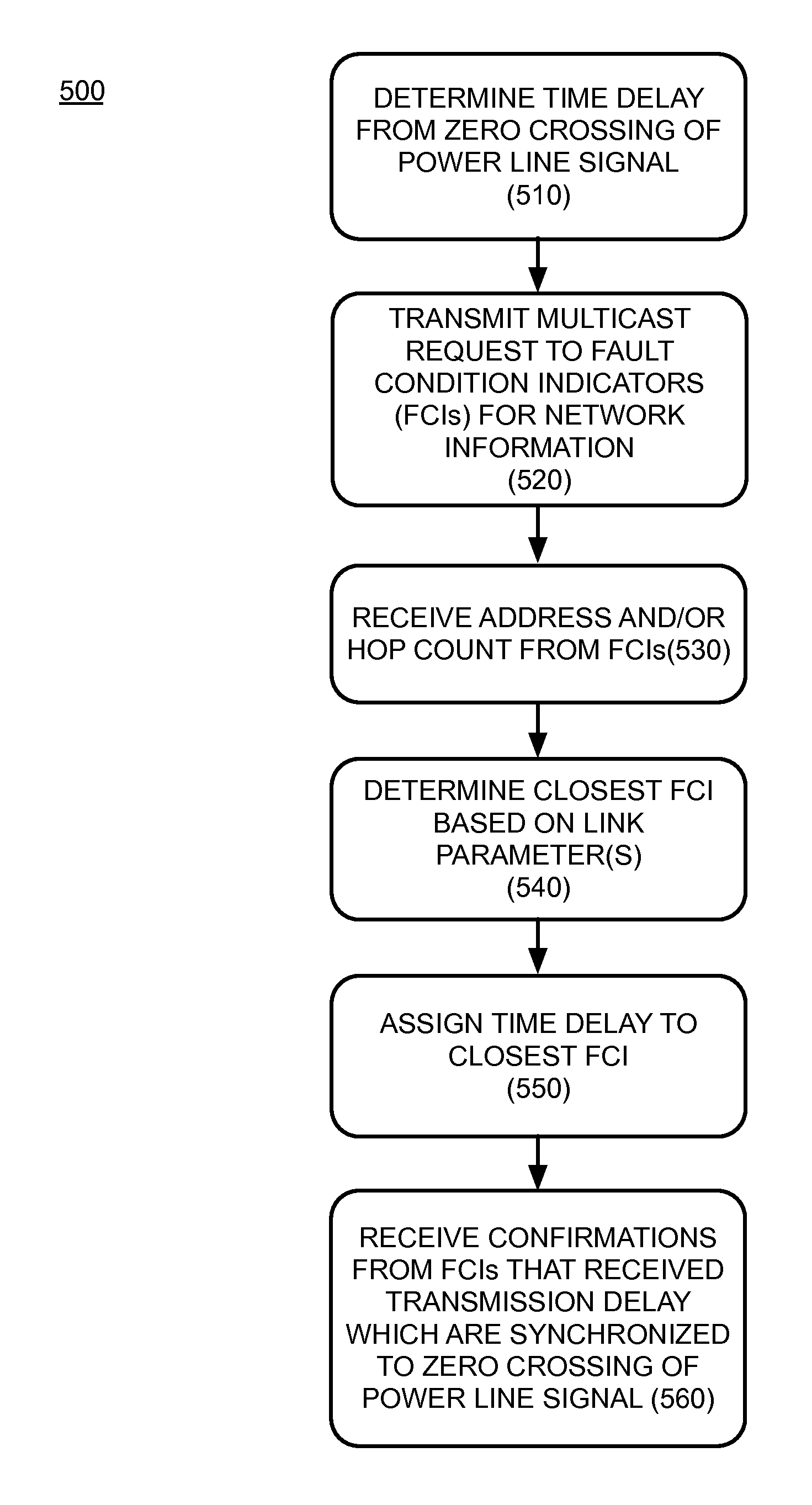
Wireless transmission synchronization using a power line signal
InactiveUS9413519B2Circuit arrangementsPower distribution line transmissionWireless transmissionTime delays
A gateway may be configured to synchronize transmissions of a plurality of faulted circuit indicators (FCIs). The gateway may determine a time delay from a zero crossing of a power line signal and obtain network information from the at least one FCI from the plurality of FCIs. The gateway may identify a proximate FCI that is closest to a gateway based on at least one link parameter, and assign the determined time delay to the proximate FCI. The gateway may receive confirmations that at least one FCI received the determined time delay, and has synchronized transmissions based on the determined time delay and the zero crossings of the power signal.
Owner:THOMAS & BETTS INT INC
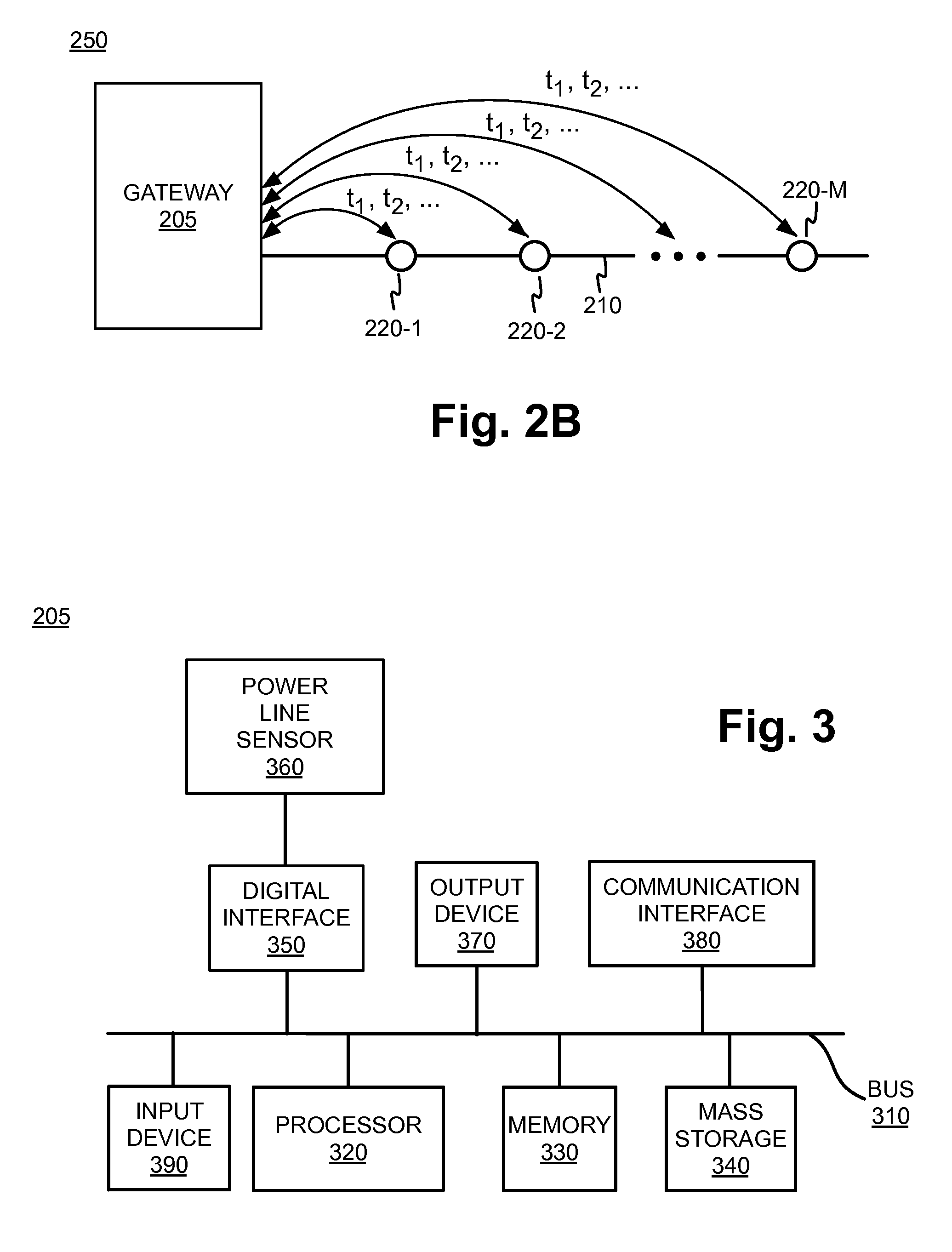
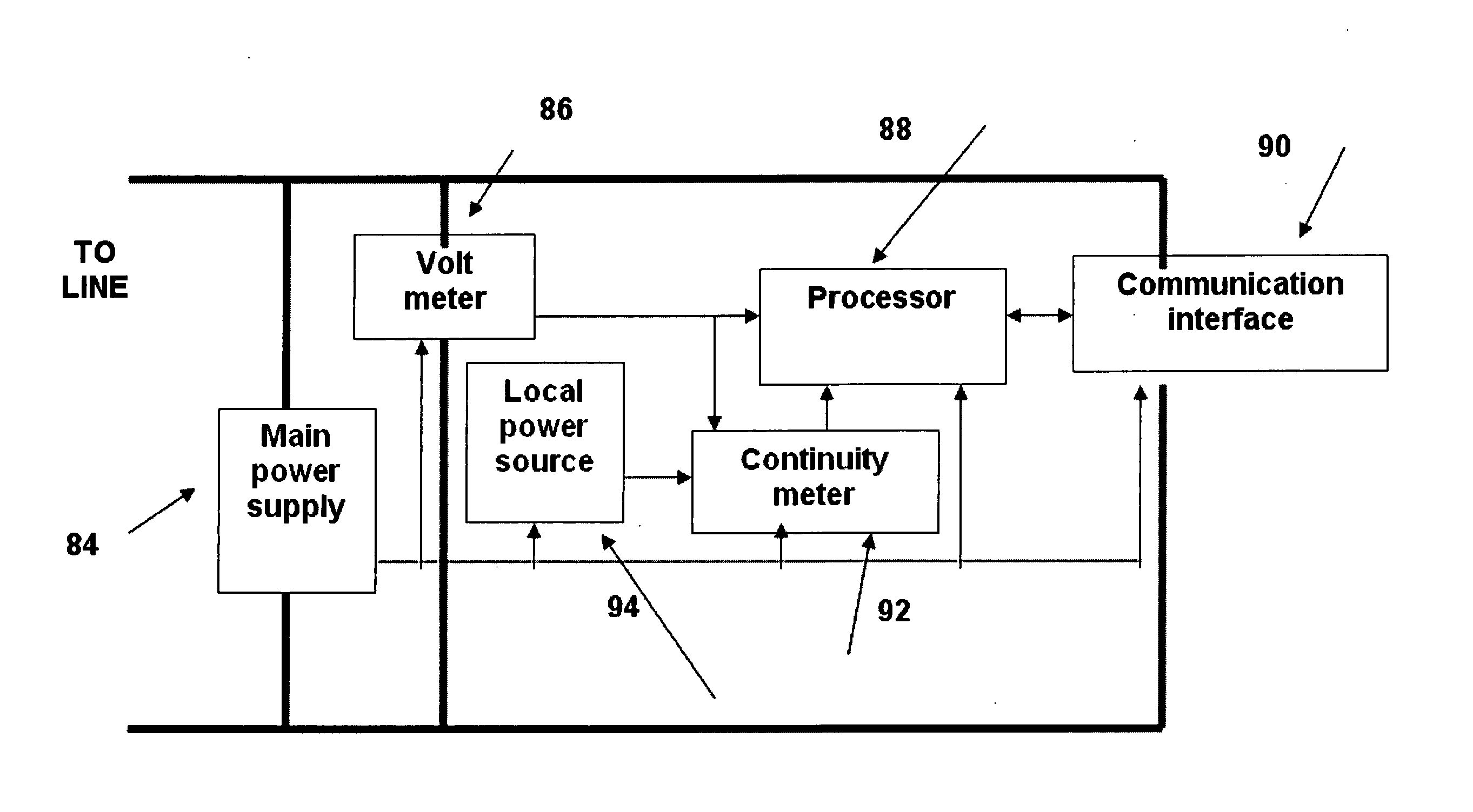
System, apparatus and method for detection of electrical faults
ActiveUS20060119368A1Low implementation costProtection is in progressDc network circuit arrangementsTesting dielectric strengthElectric forceElectrical Failure
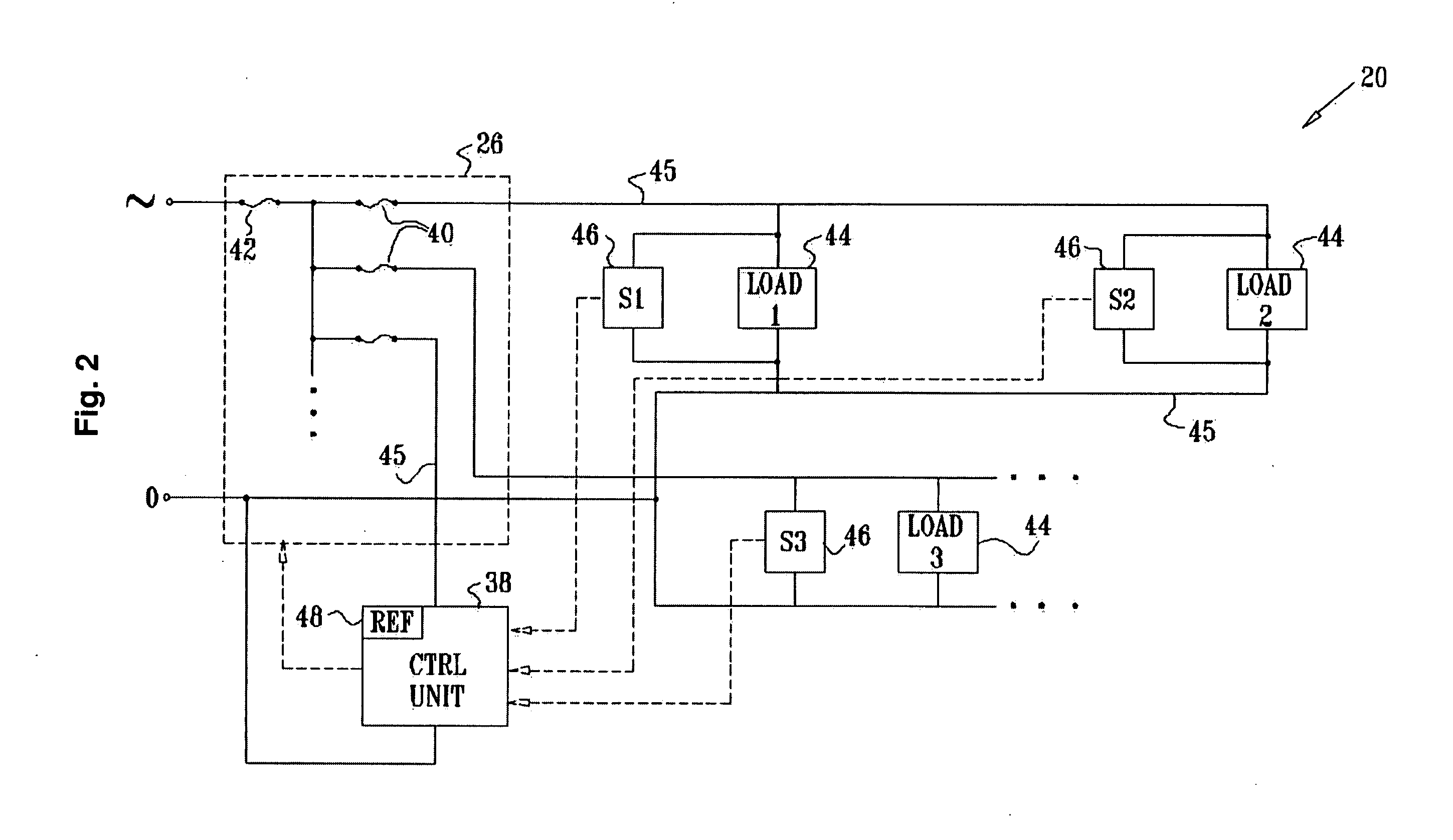
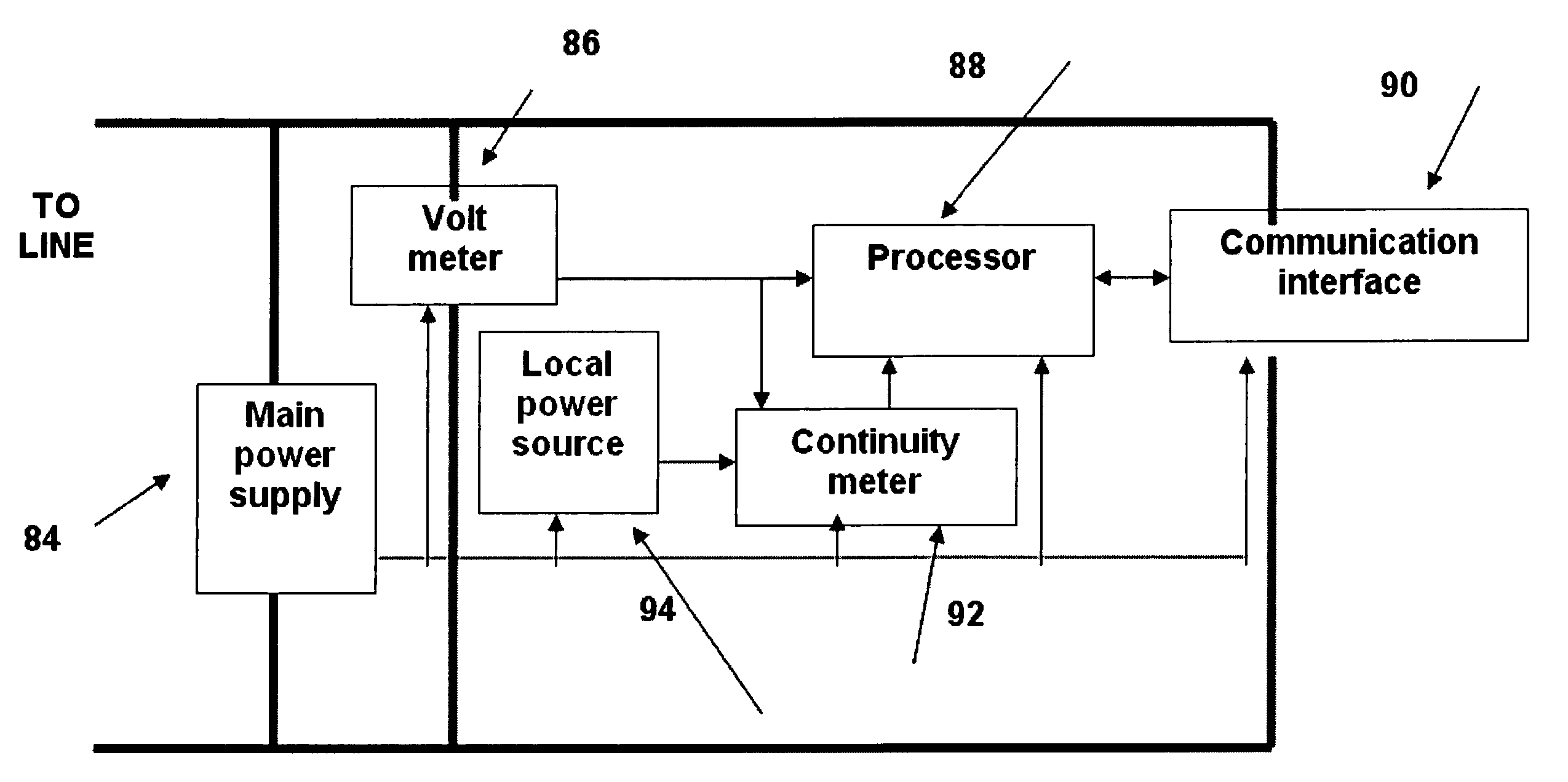
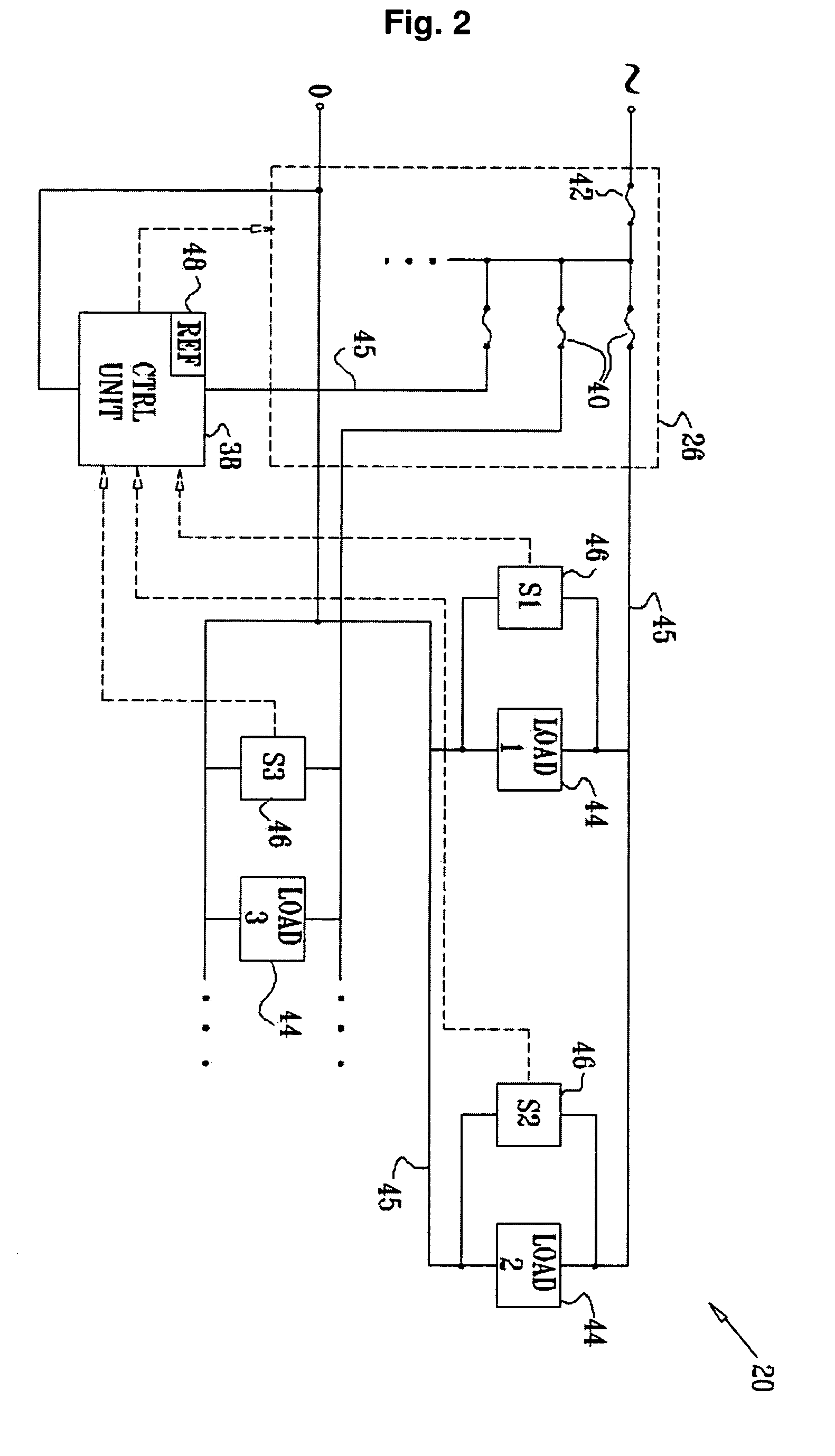
System for monitoring an electrical system of a facility includes one or more local sensing devices, each of which is adapted to be connected to the electrical system of the facility in proximity to a respective load that receives power from the electrical system so as to make local measurements of a voltage across the load continuity measurements of electrical-power presence at one or more points in the electrical system of said facility. A processing unit is adapted to receive and compare the local measurements to reference measurements of the voltage supplied to the facility, in order to detect a fault in the electrical system.
Owner:ISRA JUK ELECTRONICS
System, apparatus and method for detection of electrical faults
ActiveUS7282921B2Improve robustnessCheap and easy to implementDc network circuit arrangementsTesting dielectric strengthEngineeringElectric power
Owner:ISRA JUK ELECTRONICS
Method and system for detecting and locating single-phase ground fault on low current grounded power-distribution network
ActiveUS20160041216A1Accurate locationFault location by conductor typesShort-circuit testingThree-phaseElectric distribution network
A method and system for detecting and locating a single-phase ground fault on a low current grounded power-distribution network, comprising: respectively testing and picking up the voltage signals and current signals at multiple positions on each phase feeder (61), and determining the corresponding transient voltage signals and transient current signals according to the extraction of the voltage signals and the current signals (62); when the change in the transient voltage signals and the transient current signals exceeds a preset threshold (63), synchronously picking up the voltage signals and current signals at multiple positions on a three-phase feeder (64); calculating corresponding zero-sequence voltages and zero-sequence currents according to the voltage signals and current signals synchronously picked up at multiple positions on the three-phase feeder (65), and then extracting the steady-state signal and transient signal of the zero-sequence voltage and zero-sequence current at each position on the three-phase feeder (66); and determining a specific fault location on a faulty line according to the steady-state signal and the transient signal (67). The method effectively detects and displays a single-phase ground fault on a low current grounded power-distribution network.
Owner:BEIJING INHAND NETWORKS TECH
Monitoring electrical assets for fault and efficiency correction
A system and method of monitoring a plurality of electrical assets comprise an electricity distribution infrastructure, including a plurality of electrical asset sensors coupled to the electrical assets for monitoring an operating condition of the electrical assets as well as any fault conditions. The sensors may include a current transformer for obtaining a current waveform, a GPS receiver for applying a synchronized time-stamp to the waveform data, and a mesh network radio for transmitting the time-stamped waveform data. Data from the plurality of sensors may be encrypted and transmitted over a mesh network to one or more gateways that are in communication with a central command processor. In response to an abnormal operating condition of any electrical asset, the central command processor may determine a probable fault location, a probable fault type, and a fault response.
Owner:ACLARA TECH LLC
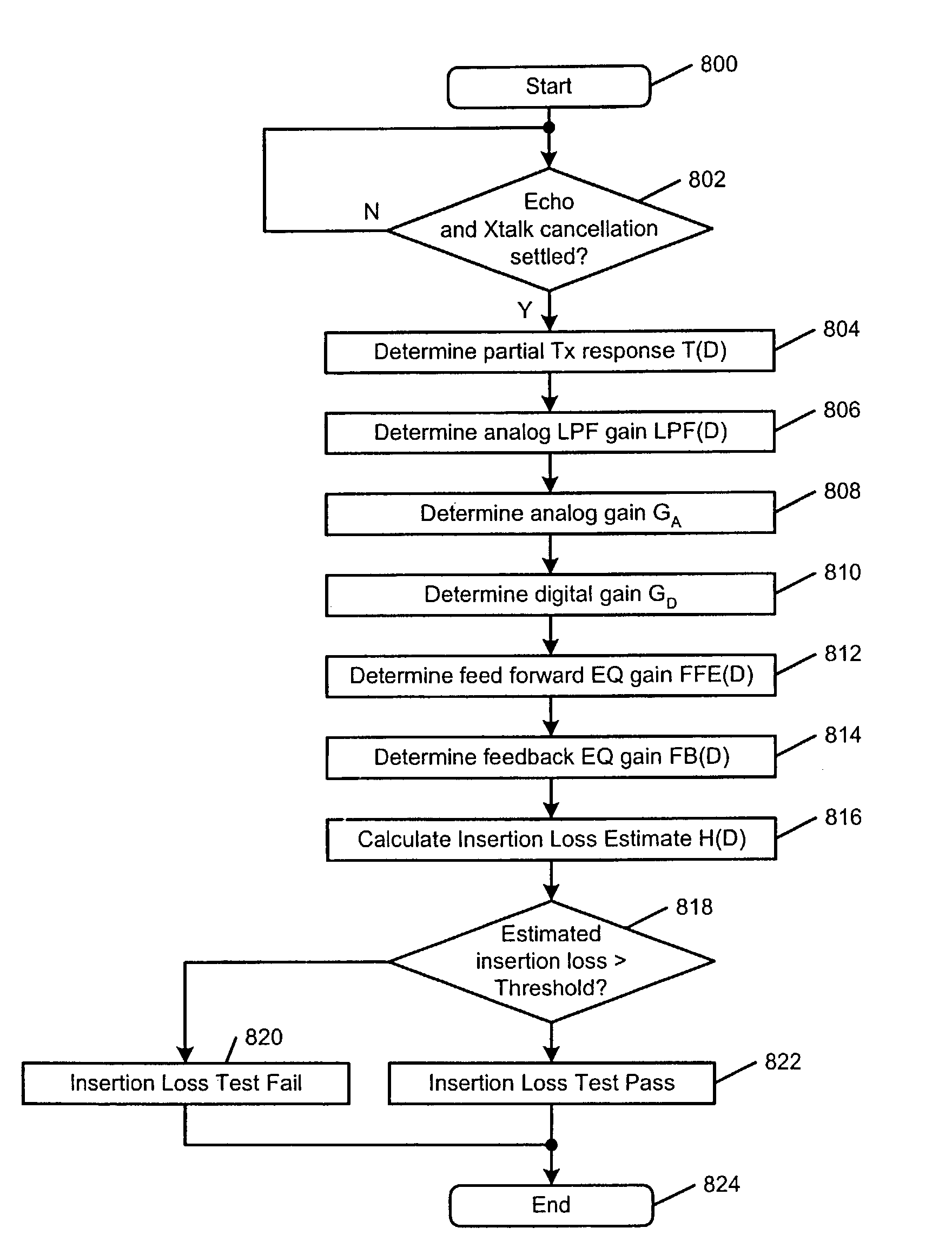
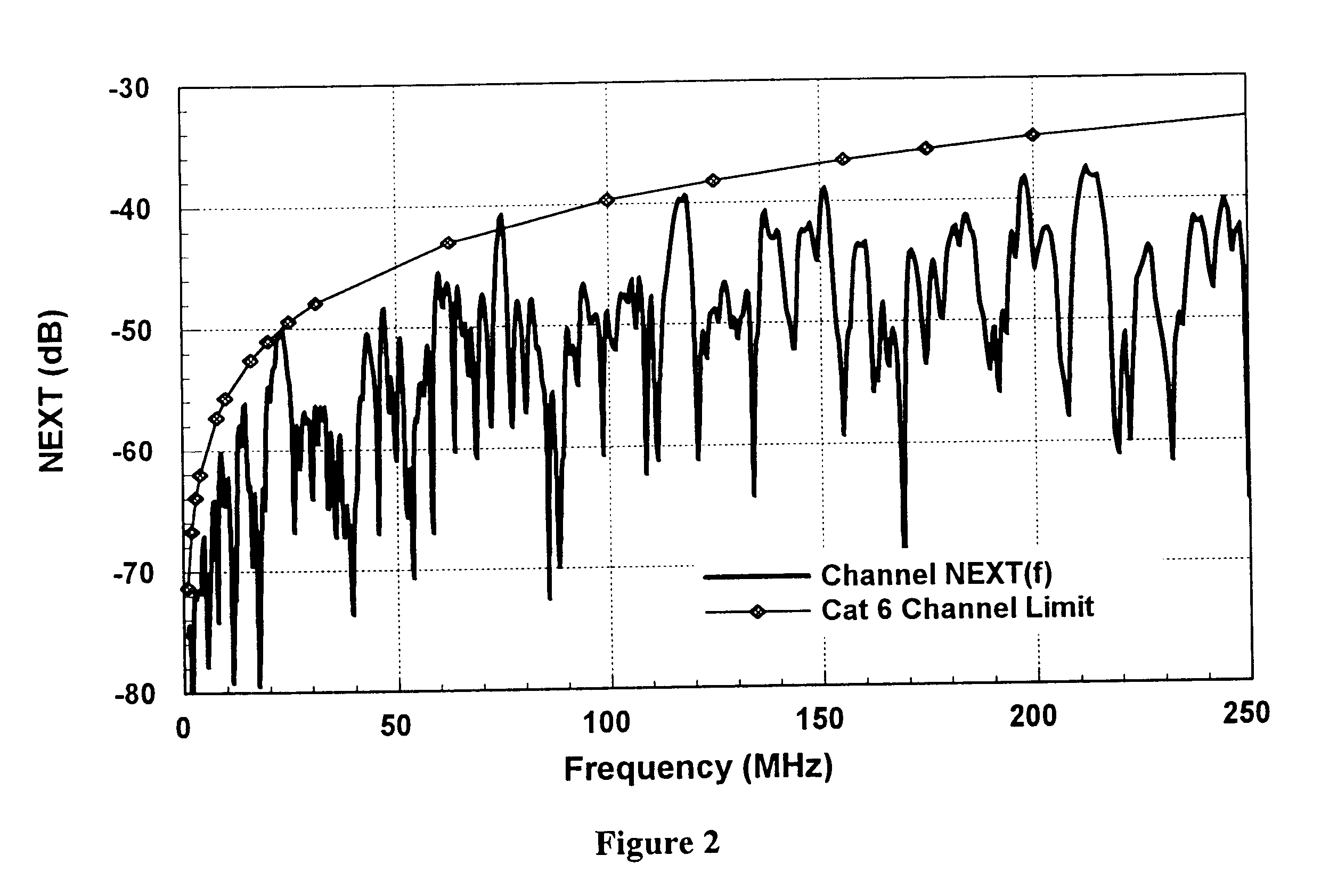
Cable tester with insertion loss and return loss estimators
InactiveUS6980007B1Fault location by conductor typesFault location by pulse reflection methodsInsertion lossEngineering
A physical layer device that communicates over a cable comprises a cable tester that determines a cable status, which includes an open status, a short status, and a normal status. The cable tester includes a pretest module that senses activity on the cable and selectively enables testing based on the sensed activity. A test module is enabled by the pretest module, transmits a test pulse on the cable, measures a reflection amplitude, calculates a cable length, and determines the cable status based on the measured amplitude and the calculated cable length. An insertion loss estimator communicates with the cable tester and estimates insertion loss of the cable. A return loss estimator communicates with the cable tester and estimates return loss of the cable based on gain parameters of the physical layer device.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Electrical wiring inspection system
InactiveUS7057401B2Electrical measurement instrument detailsElectric connection testingElectrical resistance and conductanceOperating energy
A system for testing and documenting the electrical wiring in a building, for example, includes a Portable Circuit Analyzer (PCA) that is connected to the building's Load Center through an umbilical cord. The PCA is in wireless communication with a hand-held computer device, such as a personal digital assistant (PDA) as now widely available, provided with custom software according to the invention. The electrician connects the PCA in succession to each circuit in the building, operating each switch, and each fixture or appliance, while recording the test results of the circuit element on the PDA. The PCA measures the resistance and length of each circuit thus established. When the test process is completed, the PDA is enabled to generate a complete schematic diagram of the building, including, for example, an identification of the branch circuit to which each fixture, outlet, appliance, or other load or connection point is connected.
Owner:BLADES FREDERICK K
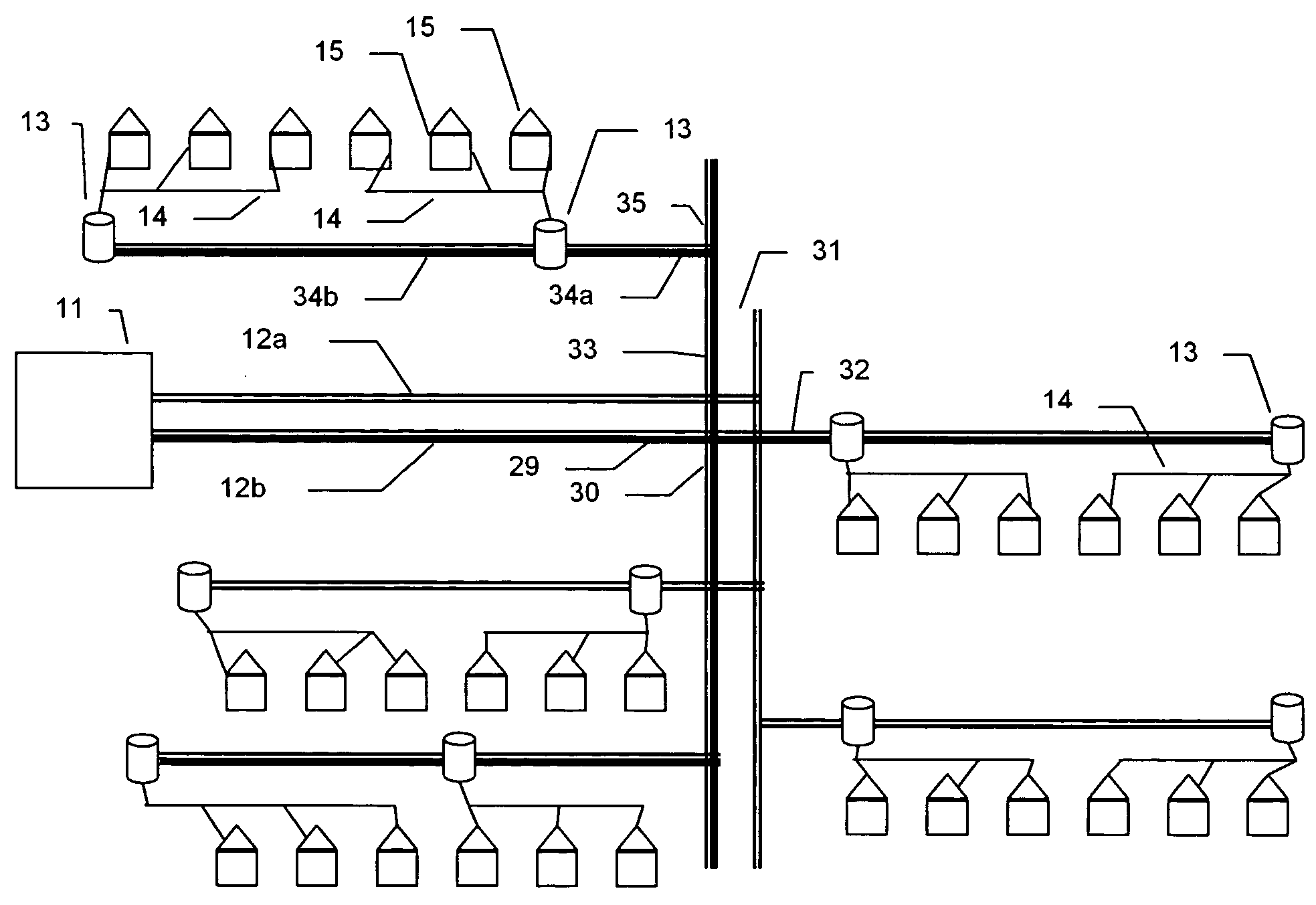
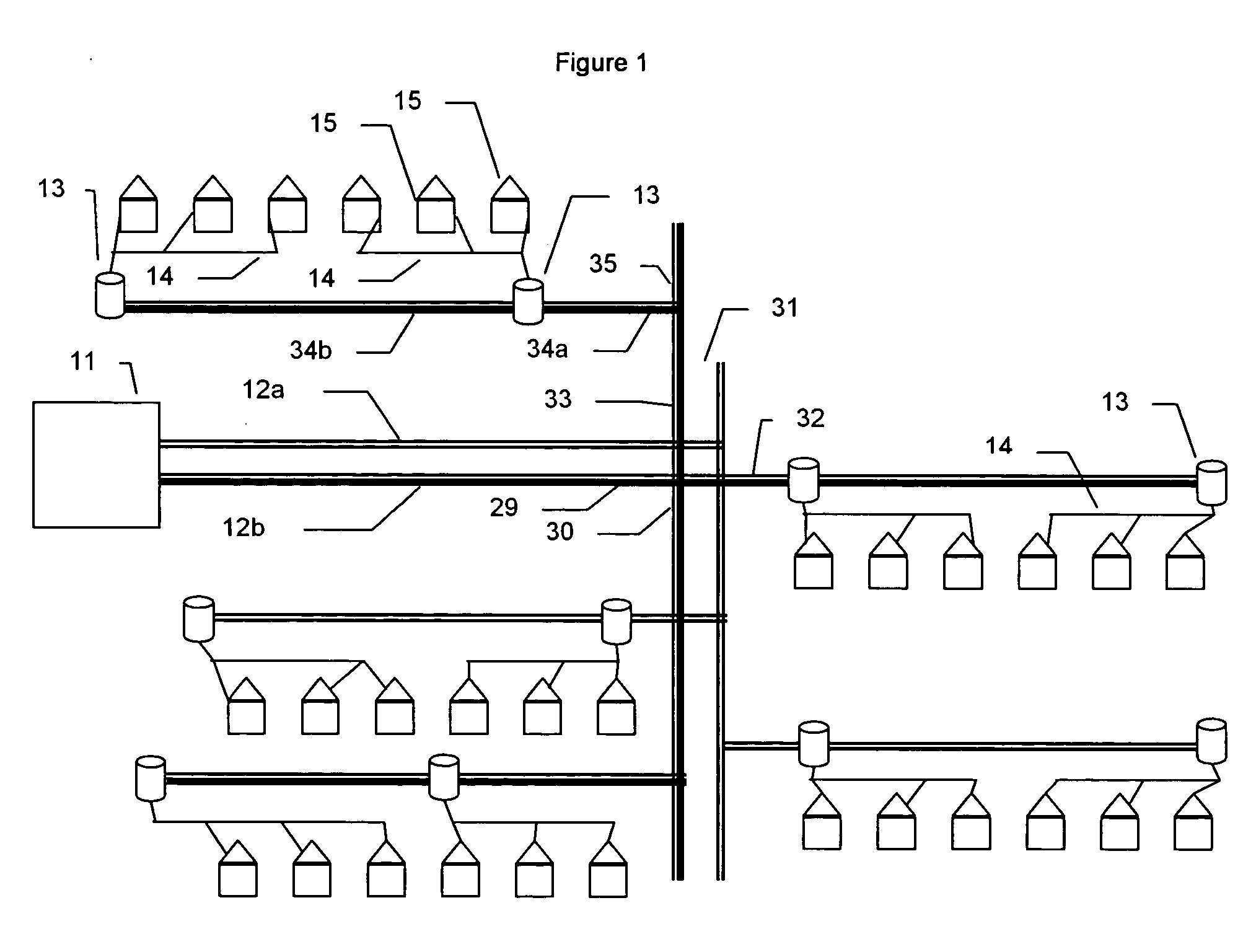
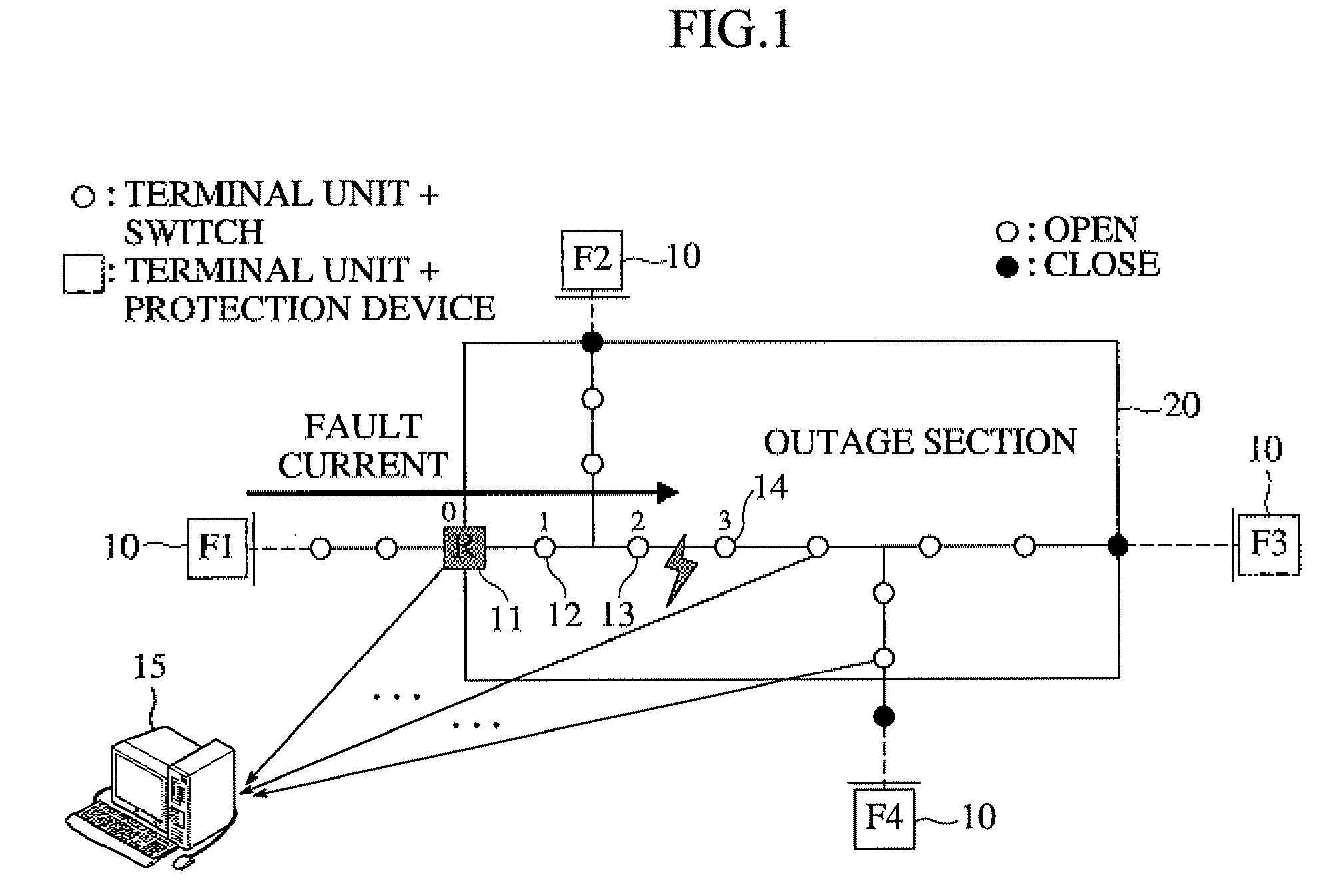
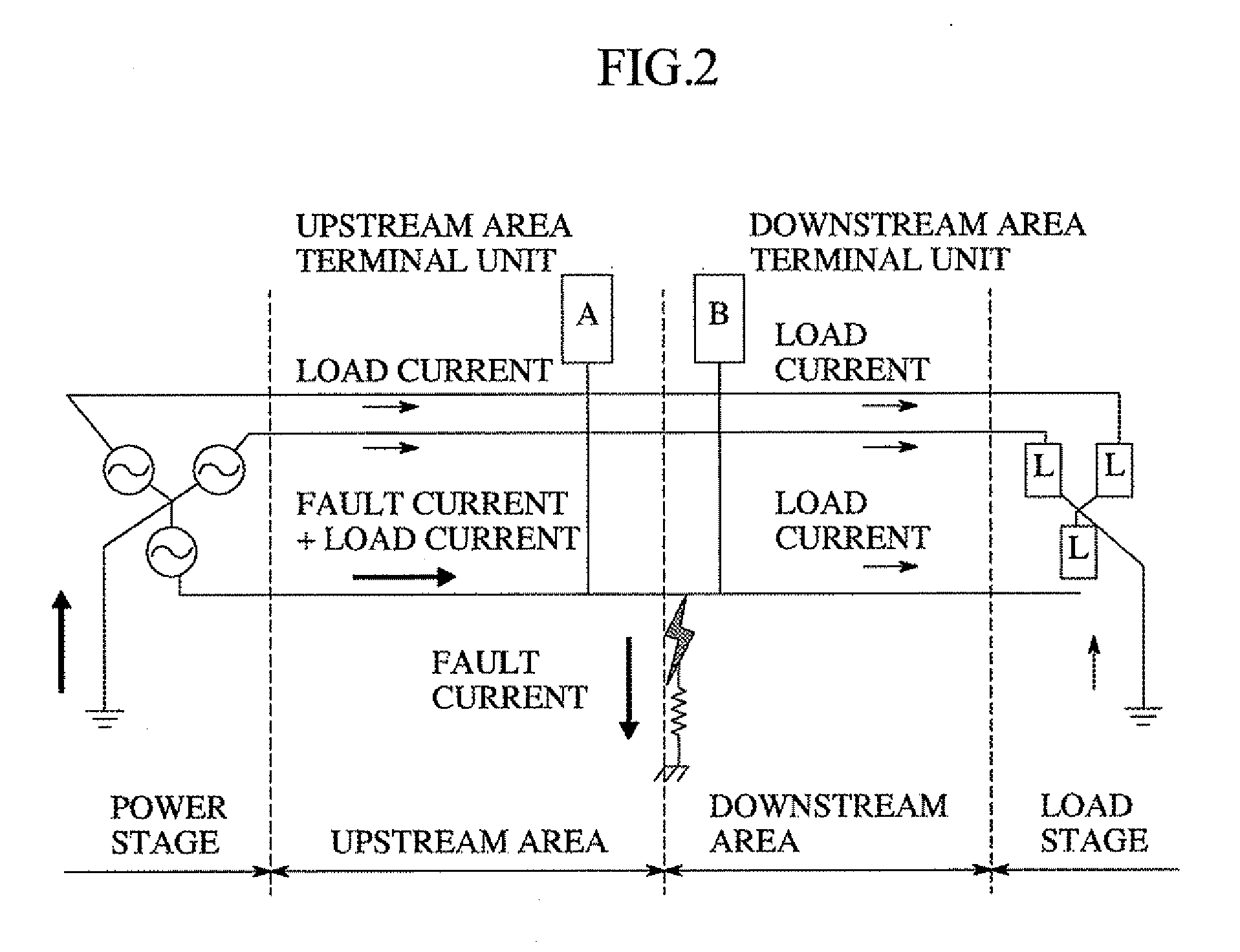
Method of Generating Fault Indication in Feeder Remote Terminal Unit for Power Distribution Automation System
InactiveUS20080211511A1Fault location by conductor typesEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionDistribution systemVoltage
The present invention relates to a method of generating fault indication in a feeder remote terminal unit for a power distribution automation system. The method is performed in a distribution system that includes a plurality of feeder remote terminal units, which are installed in respective sections of a line and are configured to measure voltage, current and a phase difference of the line, and a central control unit for determining whether a fault occurs and controlling operation of the feeder remote terminal units. In the method, phases are measured by each of the feeder remote terminal units. The phase of a zero-sequence current is compared with that of a zero-sequence voltage. A direction of a fault current is calculated, and fault indication information is generated in the calculated direction of the fault current.
Owner:MYONGJI UNIV IND & ACAD COOPERATION FOUND
System and method for locating a fault on ungrounded and high-impedance grounded power systems
InactiveUS20030085715A1Structural/machines measurementFault location by conductor typesElectric power distributionDistribution power system
A fault is located in a power distribution system having a line frequency. The power distribution system includes a plurality of phases, at least one feeder, and each feeder includes at least one segment. The fault is located by detecting a faulted phase from the plurality of phases of the power distribution system. A measurement signal having a measurement frequency is injected into the detected faulted phase, the measurement frequency being a different frequency than the line frequency. The fault location is determined for a selected segment based on at least one measured residual current corresponding to the injected signal and a predetermined relative impedance of the power distribution system.
Owner:ABB INC
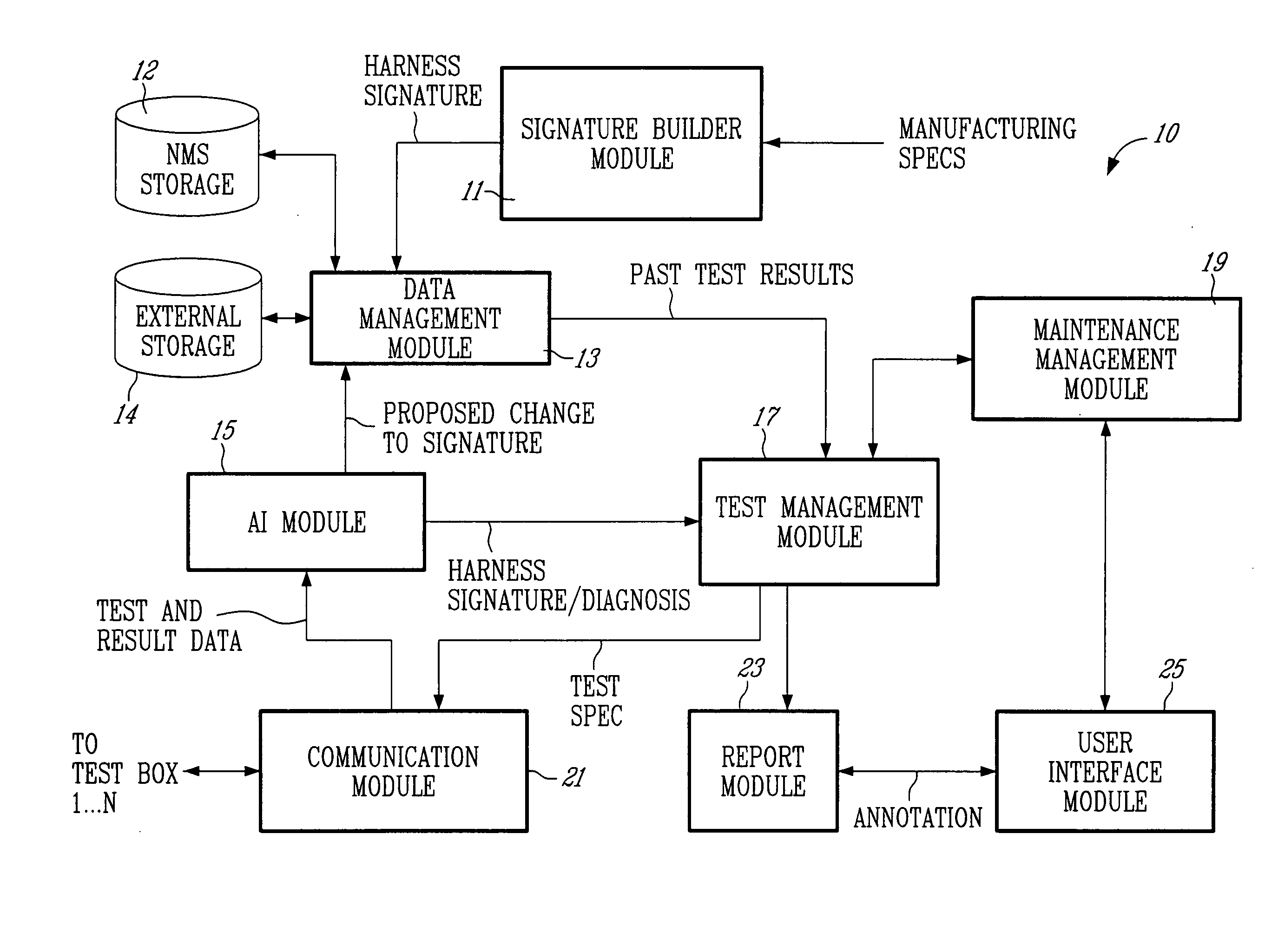
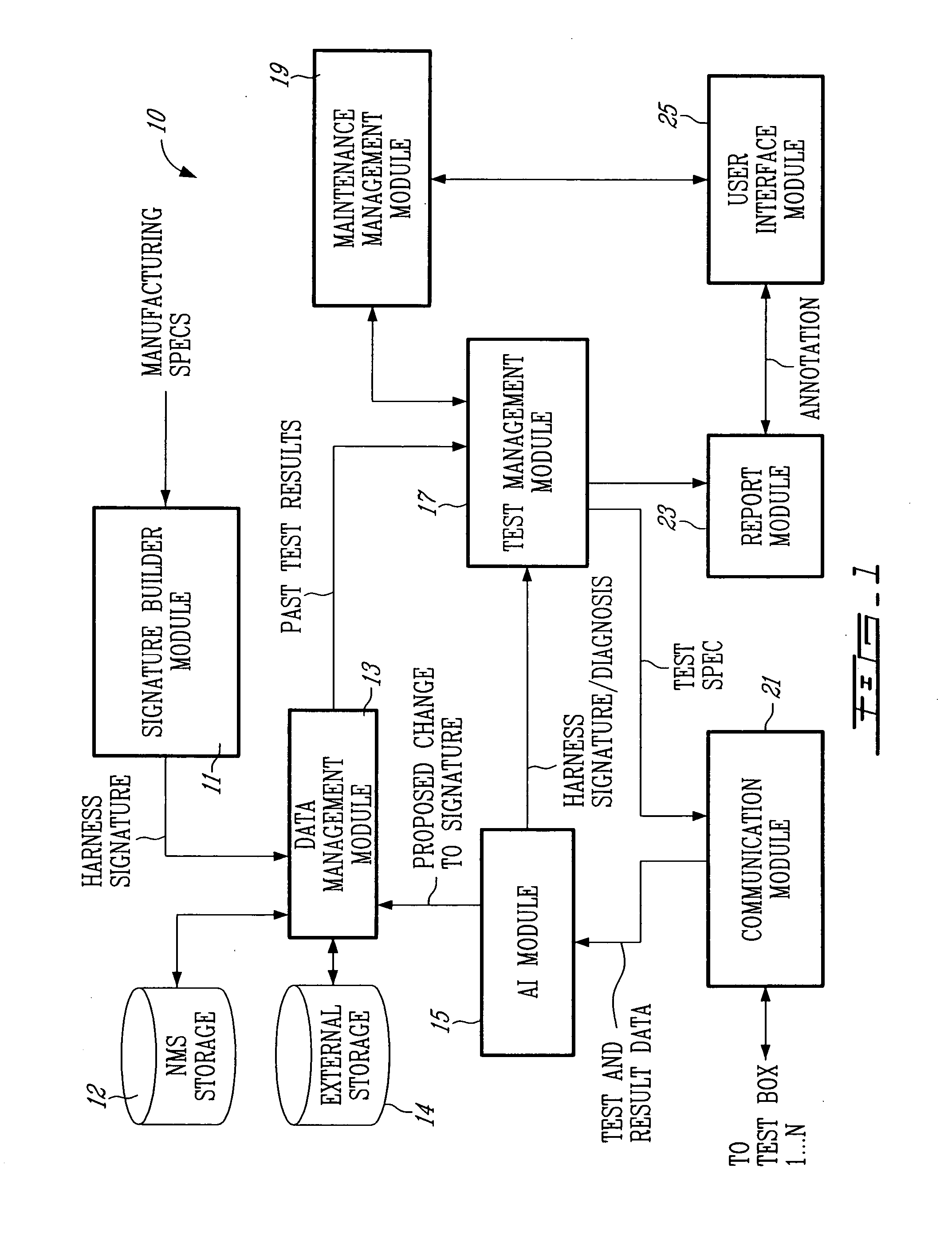
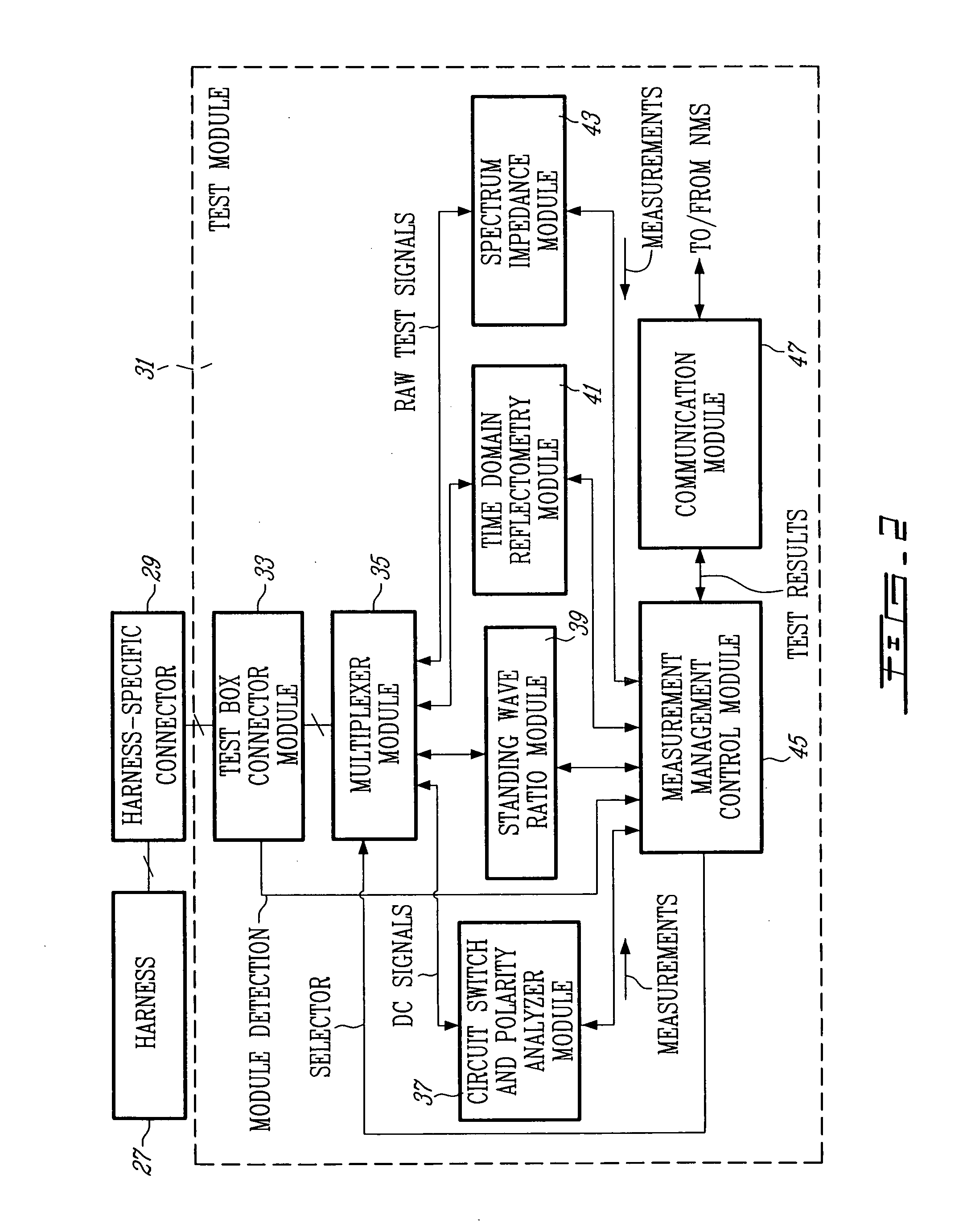
Wireless portable automated harness scanner system and method therefor
ActiveUS20060043976A1Shorten the timeLow costResistance/reactance/impedenceFault location by conductor typesTest measurementEngineering
A method for testing an installed wiring harness is provided. The method comprises providing a signal source testing module at a first node in the wiring harness and a measurement termination testing module at a second node in the wiring harness. A central management module for controlling the testing modules coordinates the testing modules to send testing signals for performing tests and recording test measurements of the installed wiring harness. The testing modules send the test measurements to the management module.
Owner:ZIOTA TECH
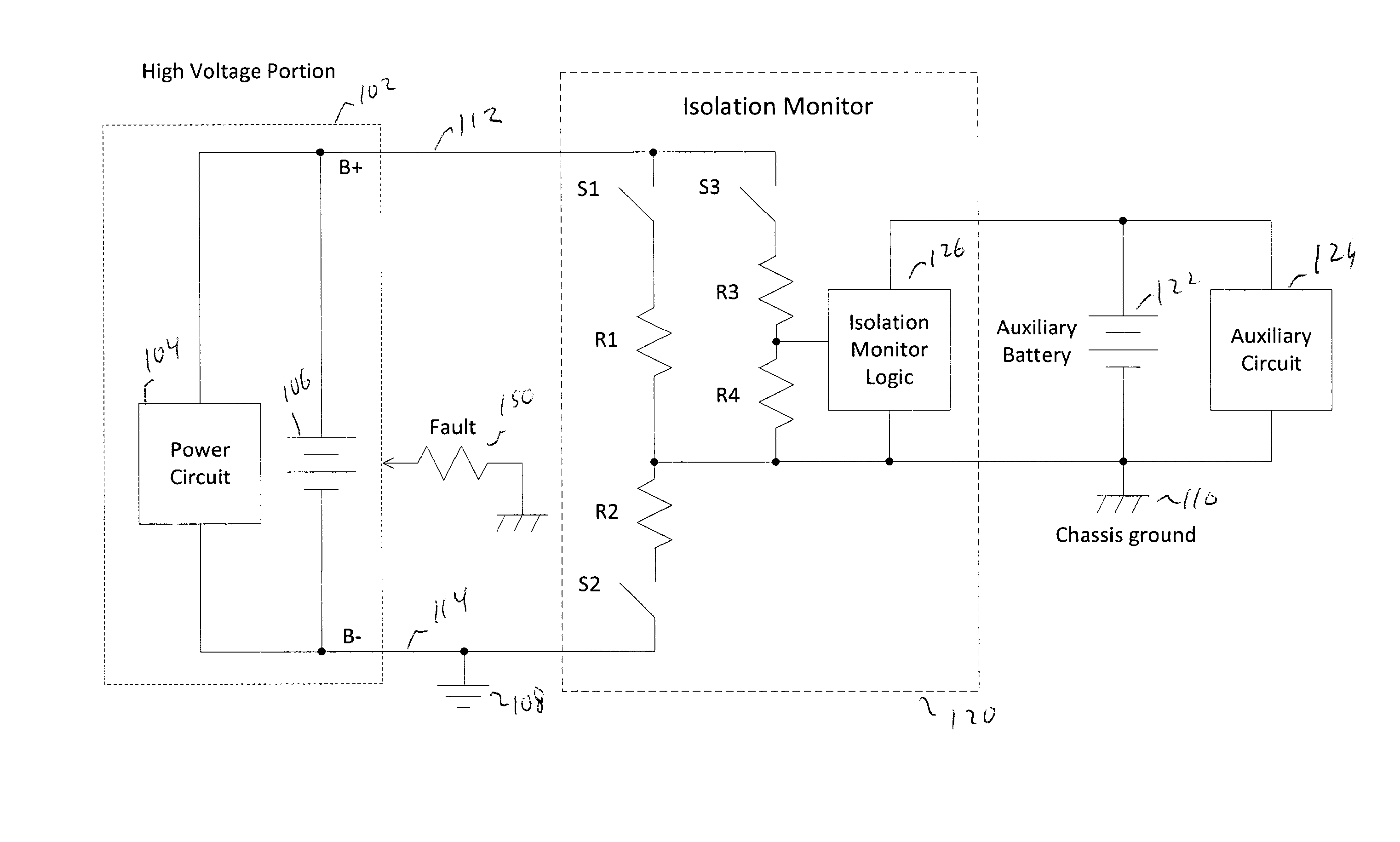
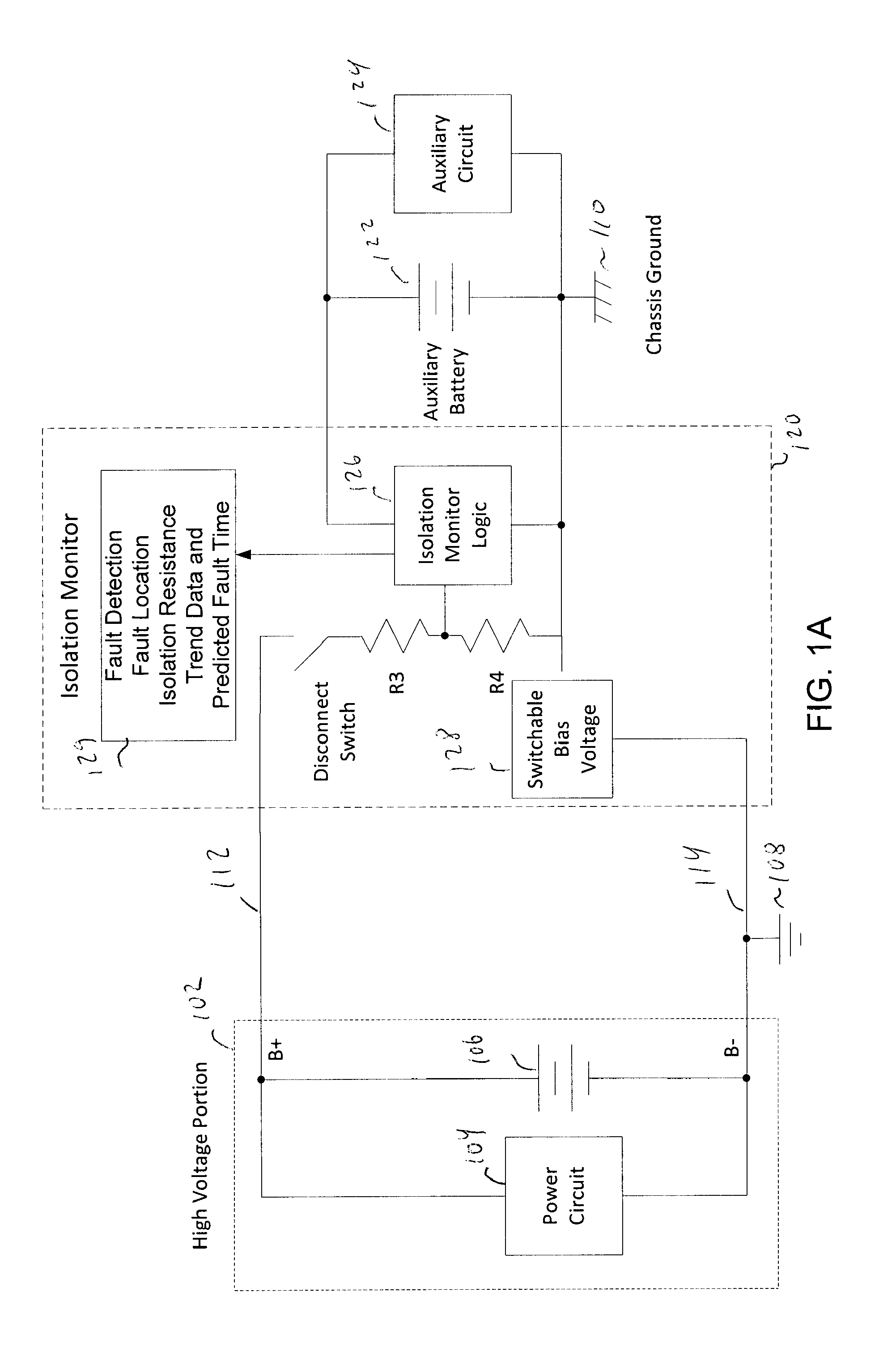
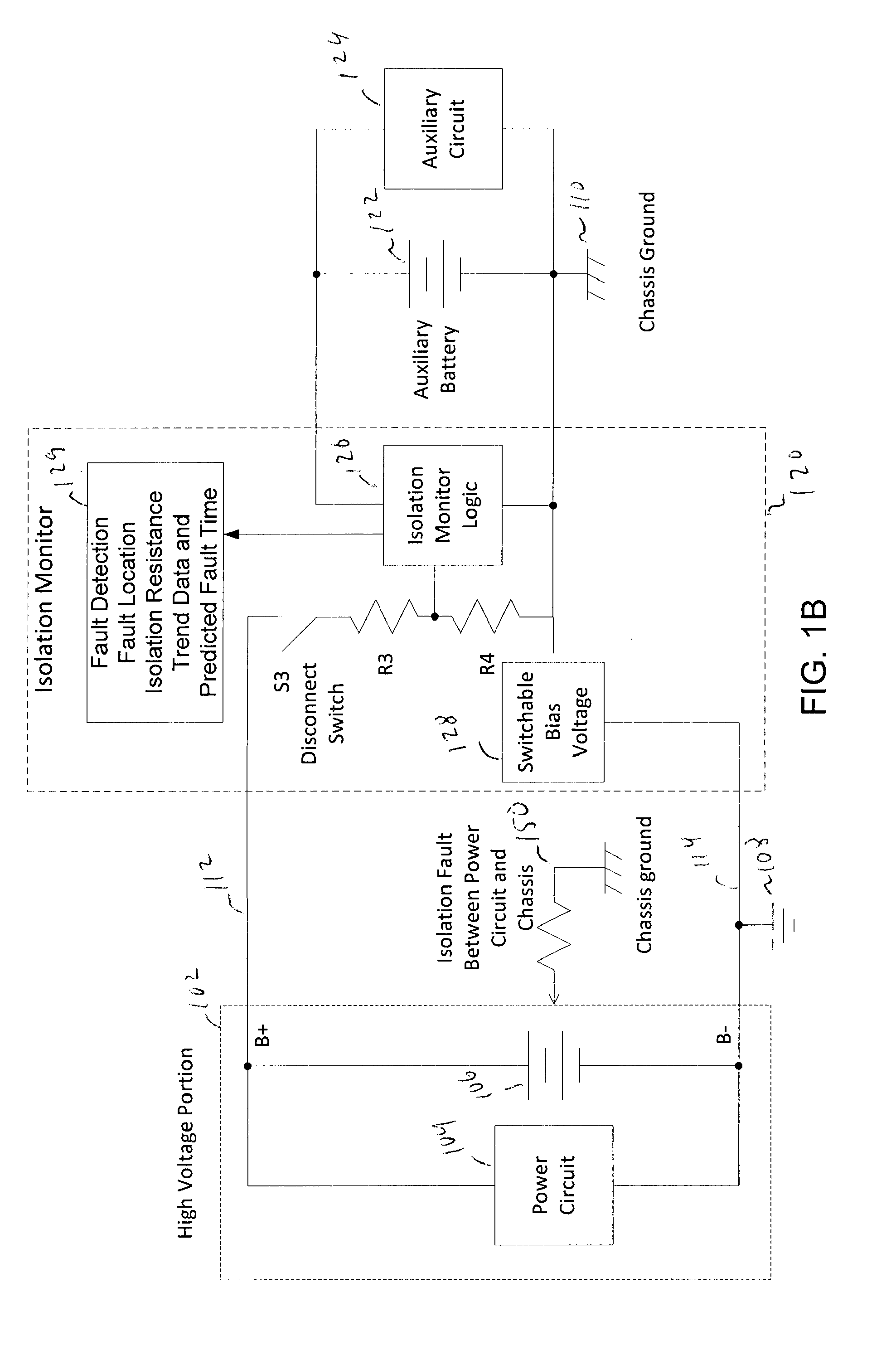
Isolation monitor
ActiveUS20130300430A1Electric devicesOperating modesElectrical resistance and conductanceEngineering
An isolation monitor is disclosed in which a switchable bias voltage is imposed on a chassis ground. An isolation voltage is measured when a bias voltage is applied. When there are no electrical faults, the isolation voltage swings up and down to known values. When a fault occurs, the isolation voltage will not to swing to the known values, and thus the isolation resistance can be measured and alarm generated if the isolation resistance falls below a threshold value.
Owner:CURTIS INSTRUMENTS INC
Method and apparatus for adaptive cancellation of responses in cabling
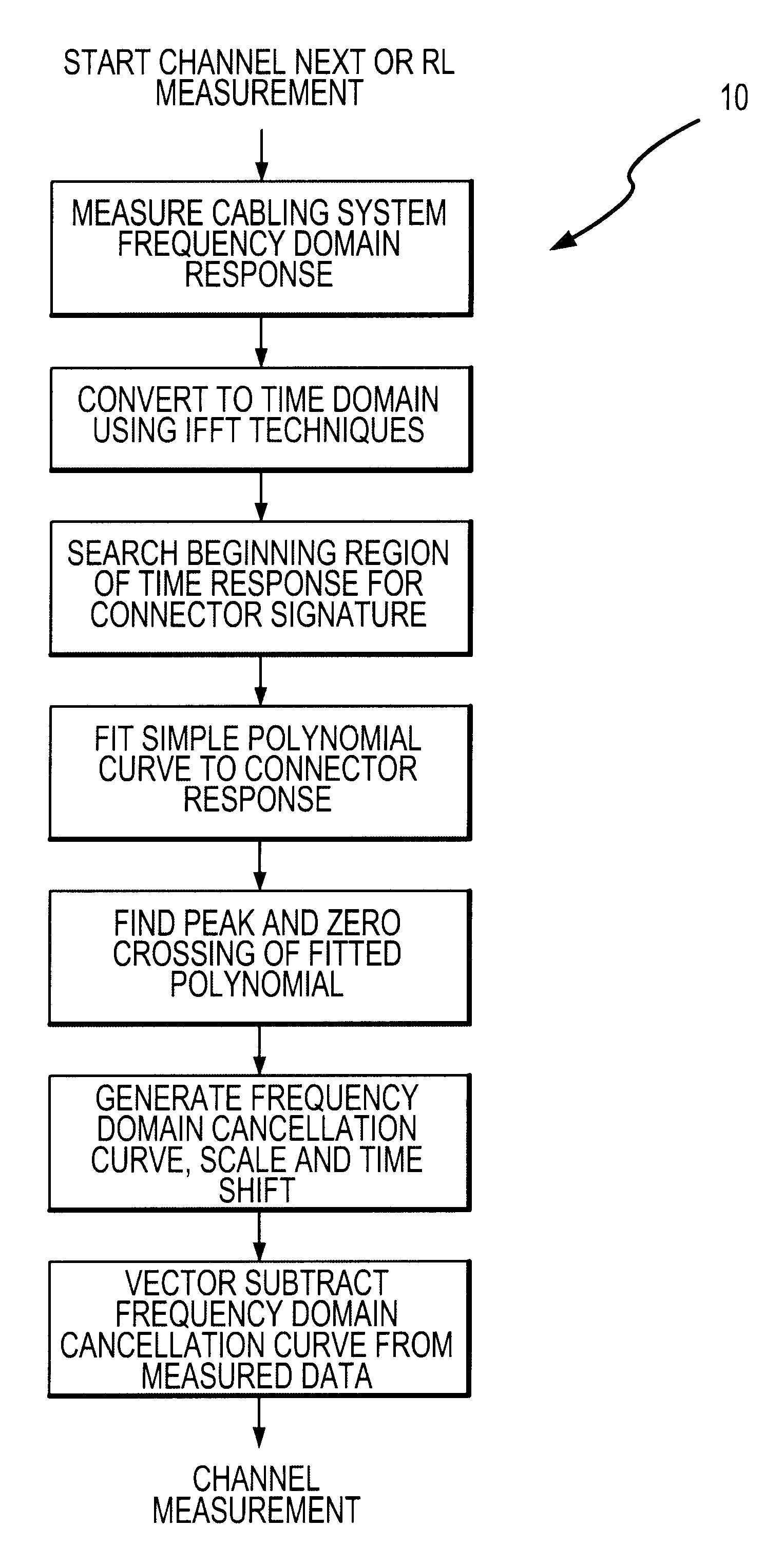
InactiveUS6522152B1Resistance/reactance/impedenceFault location by conductor typesSignal responseTime domain
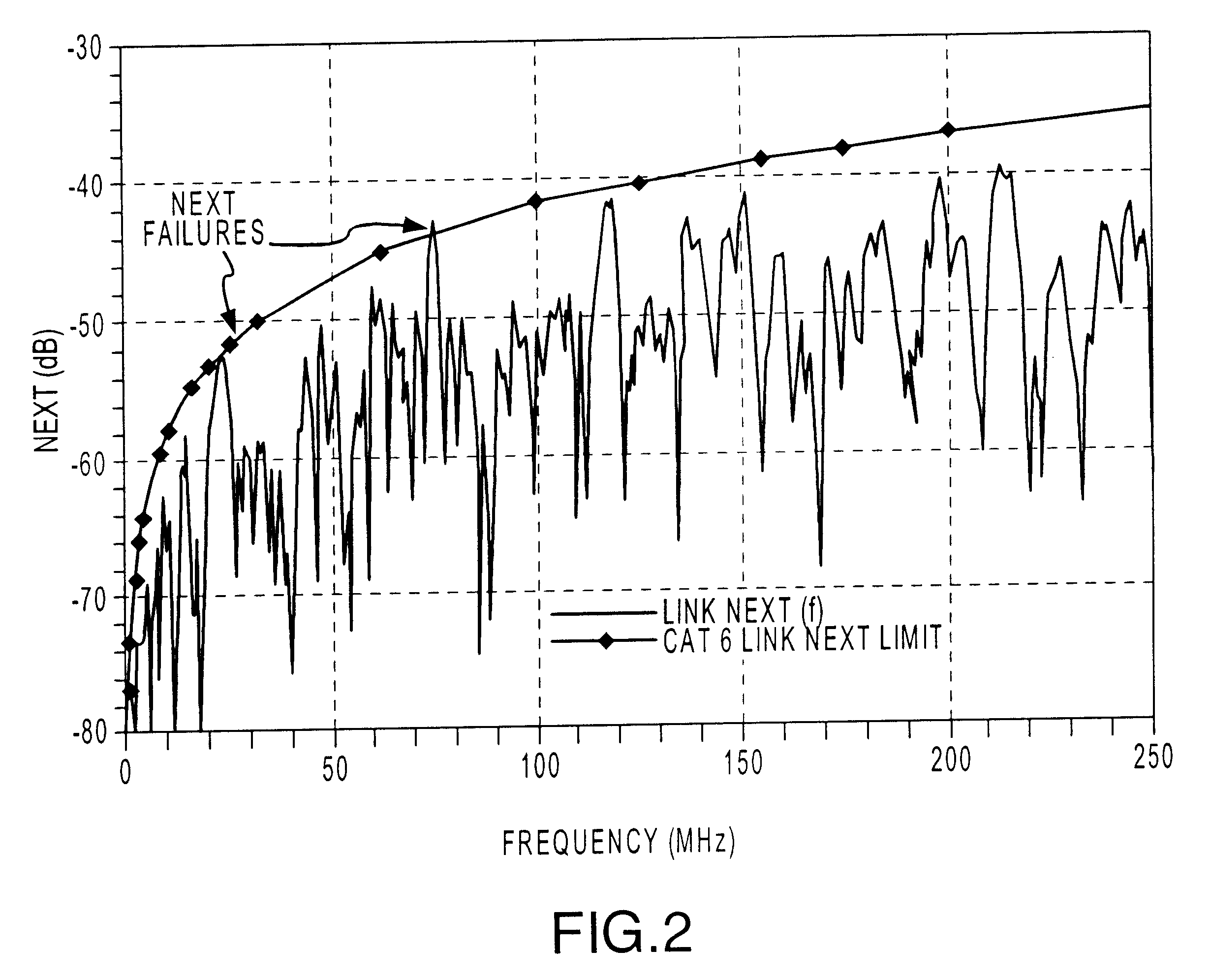
An Adaptive Vector Cancellation method which uses time domain data for an instrument connection to estimate magnitude, phase, and time position of a signal response such as NEXT or Return Loss associated with the connection. Based on the estimate of the amplitude and time of the connection response, a suitable full-bandwidth frequency response that corresponds to a point source of NEXT or Return Loss is determined. This calculated connector response is then scaled to an appropriate magnitude, phase and time shifted to the estimated position of the actual connection. The scaled / shifted response is then vectorially combined with the measured sweep data to suitably cancel the connection contribution to NEXT and / or Return Loss. Thus, the amount of NEXT or return loss existing in the user's patch cord is preserved, while the NEXT or return loss due to the instrument connection is suitably suppressed. Correction is done in the frequency domain, over the full bandwidth of the measured data.
Owner:MICROTEST
Method for diagnosing performance problems in cabling
InactiveUS6433558B1Resistance/reactance/impedenceFault location by conductor typesTime domainTime limit
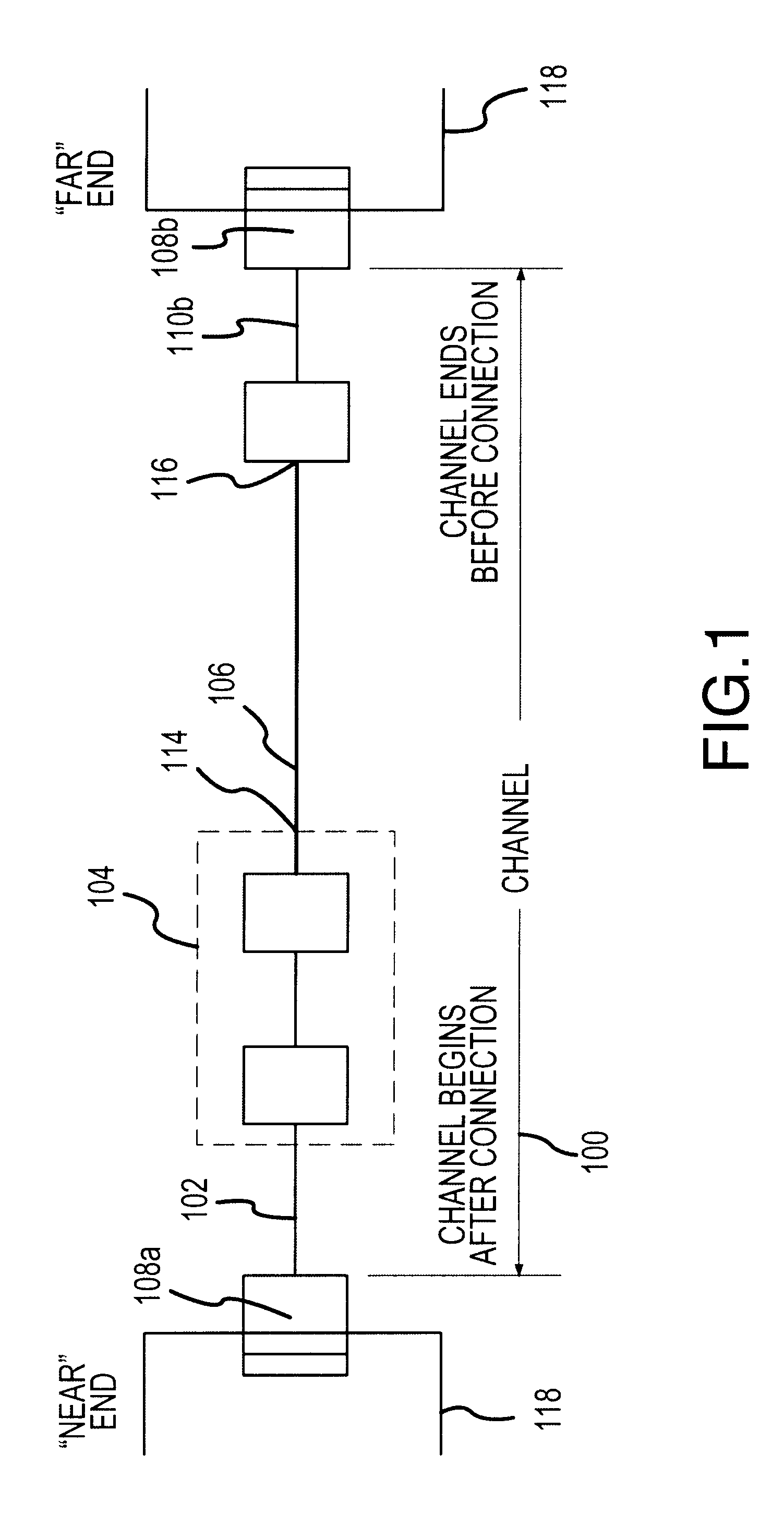
The present invention provides methods for using time domain analysis of NEXT, Return Loss and the like, in conjunction with the application of time or distance referenced limits to verify and determine compliance of the performance requirements of connections in a typical link. Time domain analysis of NEXT, Return Loss data and the like, suitably provides the performance characteristics of a link as a function of time or distance. When coupled with time or distance performance curves for connections, it can be determined if the transmission fault is at a connection or in the cable. The time limit curves for connections can be generated based on the frequency domain performance requirements for connecting hardware of a specific level of performance. The connection time limit curves thus provide an interpretation means to determine if the connection is within performance standards, allowing improved isolation of the fault condition.
Owner:MICROTEST
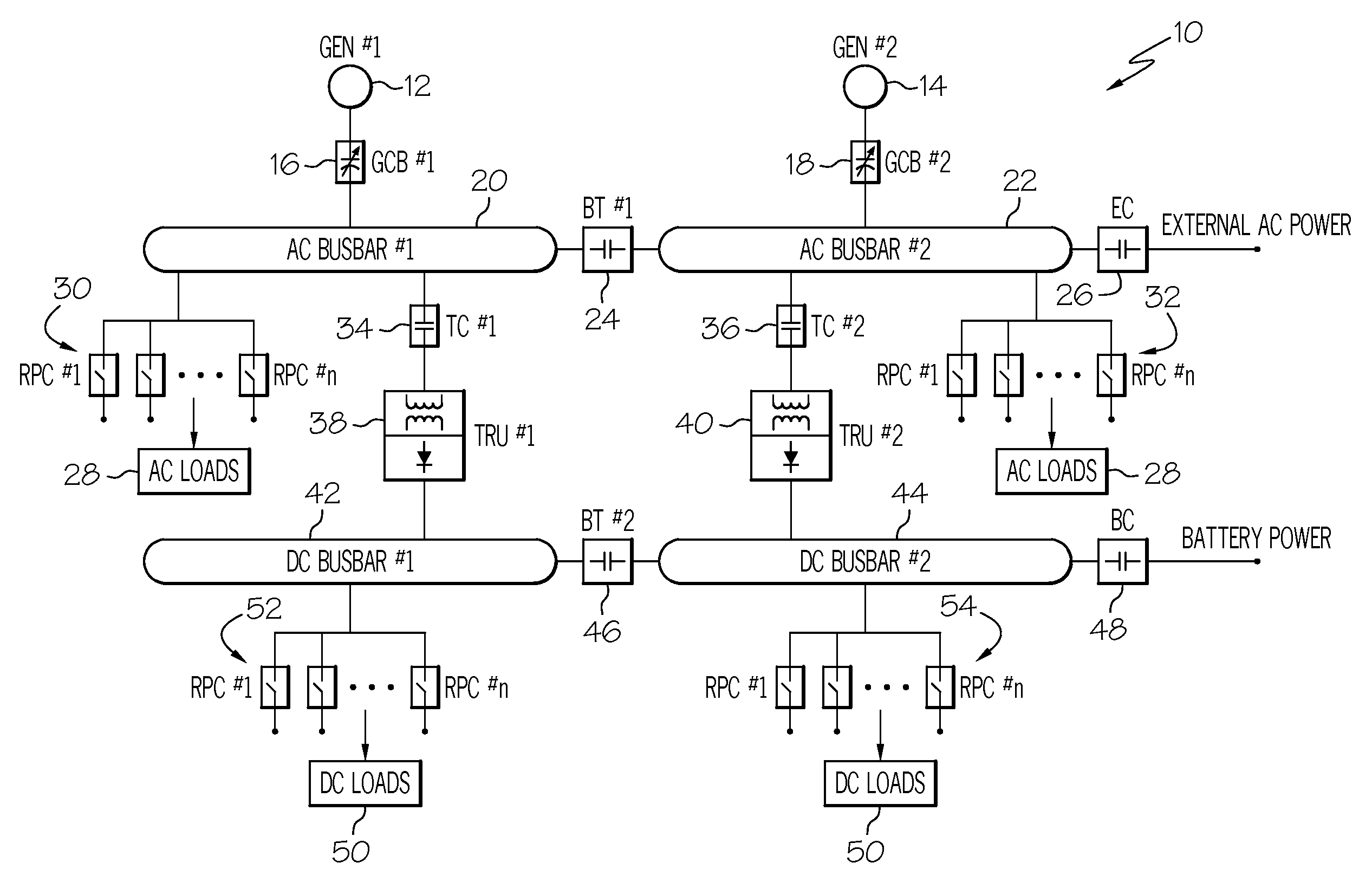
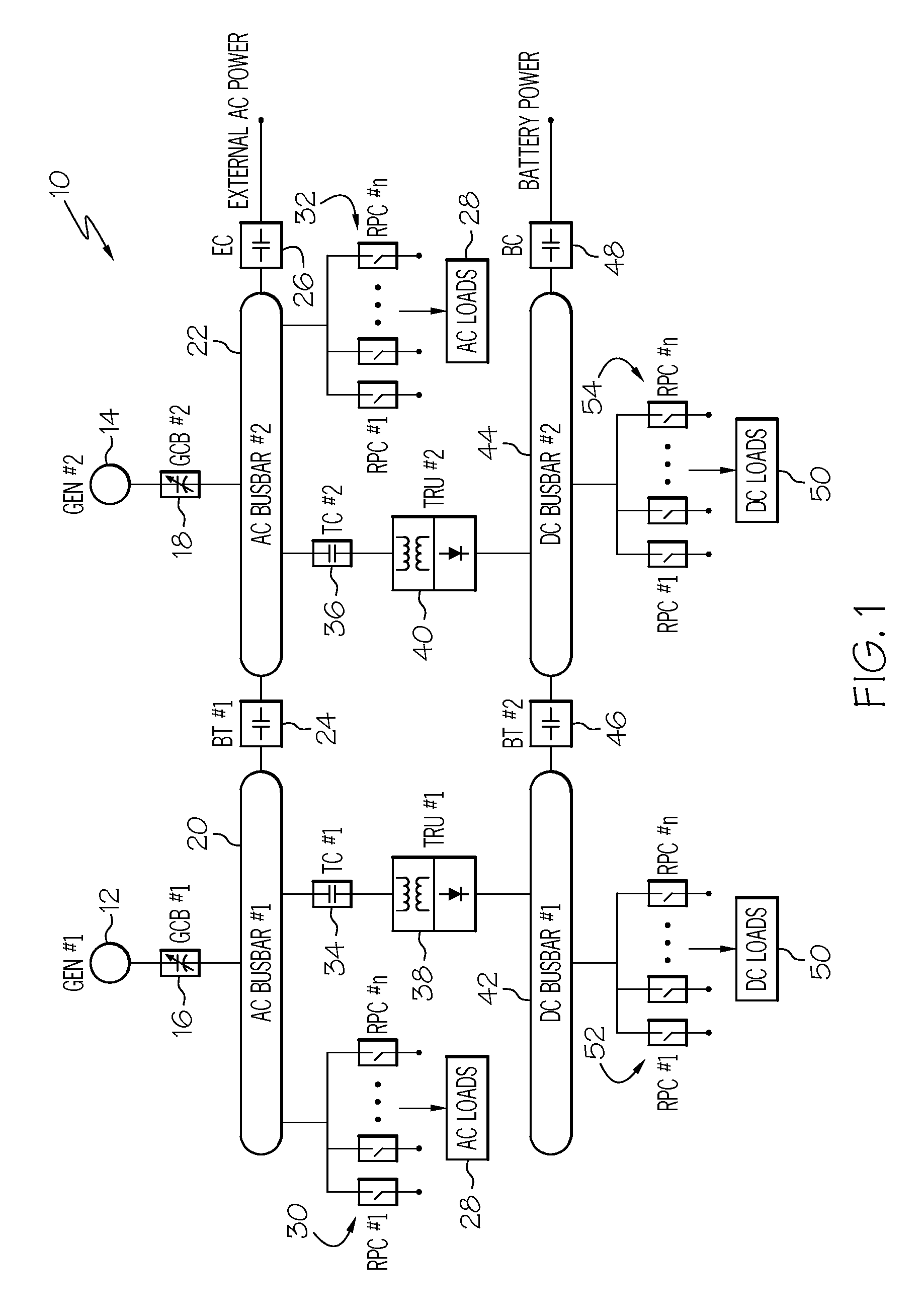
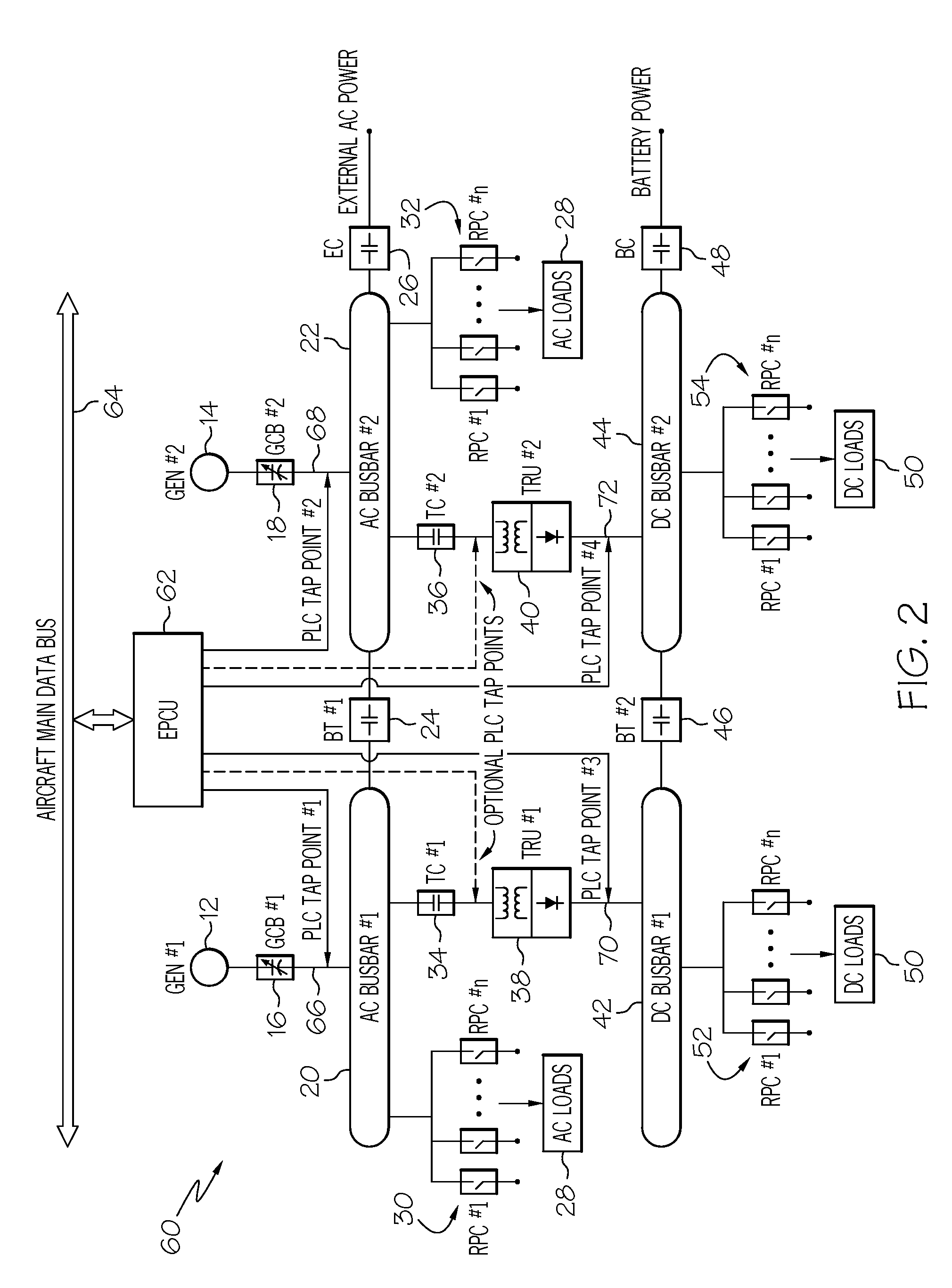
Power line communication based aircraft power distribution system with real time wiring integrity monitoring capability
InactiveUS20090228223A1Systems with measurements/testing channelsLock network applicationsTime domainDistribution power system
A power line communication-based aircraft power distribution system may allow for both power line communication (PLC) technology and spread spectrum time domain reflectometry (SSTDR) technology to be utilized in aircraft power distribution systems to achieve key maintenance functions. Unlike conventional power distribution systems, which may, for example, use only SSTDR for fault detection, the present invention includes a hardware platform that may allow both the PLC and the SSTDR to be utilized in aircraft power distribution systems to achieve key maintenance functions, such as real time wire fault location, and cost and weight savings. Further, unlike conventional power distribution systems, which may only detect and locate damage in feeder conductor wire sections before the power is applied to the load, the power distribution system of the present invention may permit real time wire fault location.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
UAV Constraint in Overhead Line Inspection
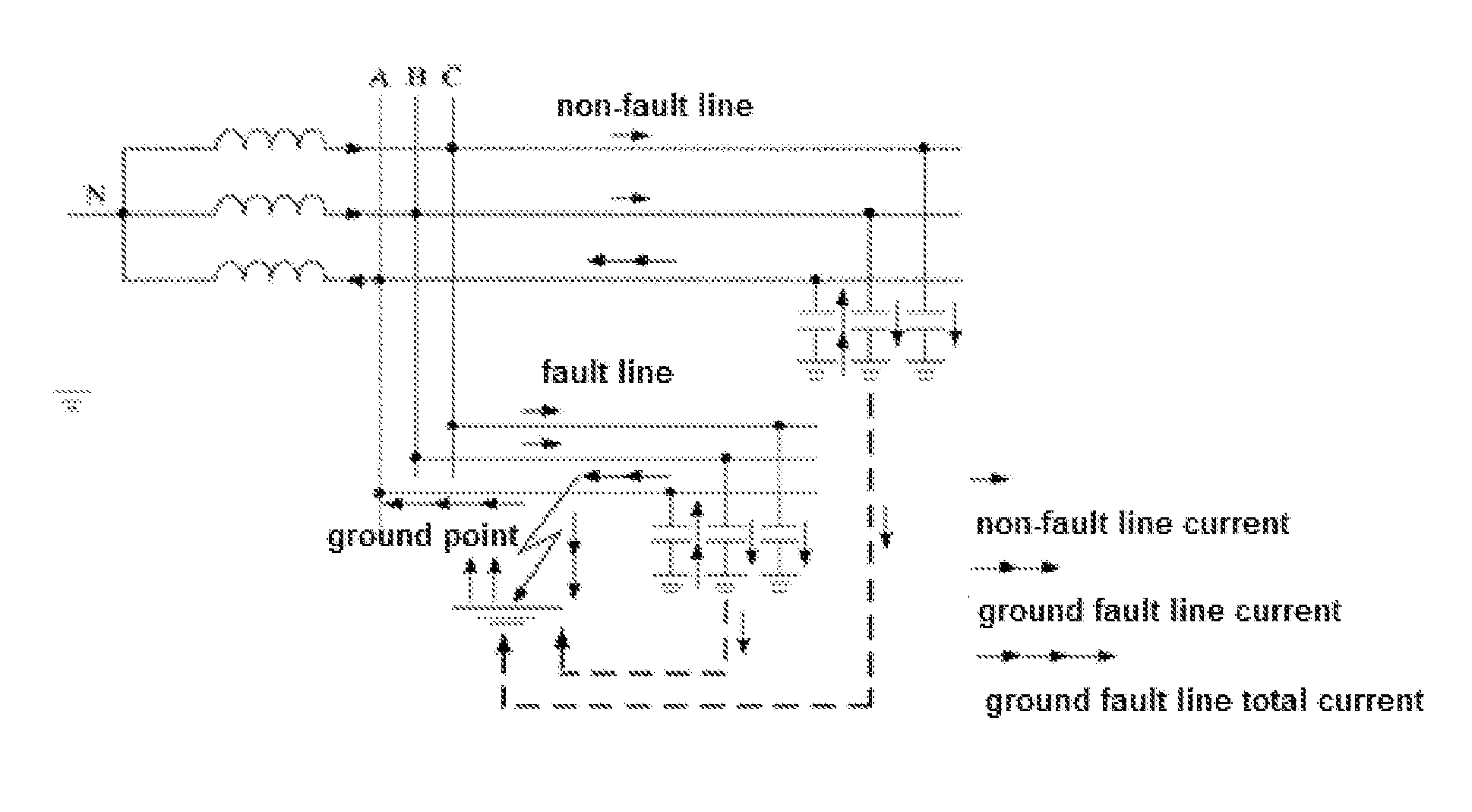
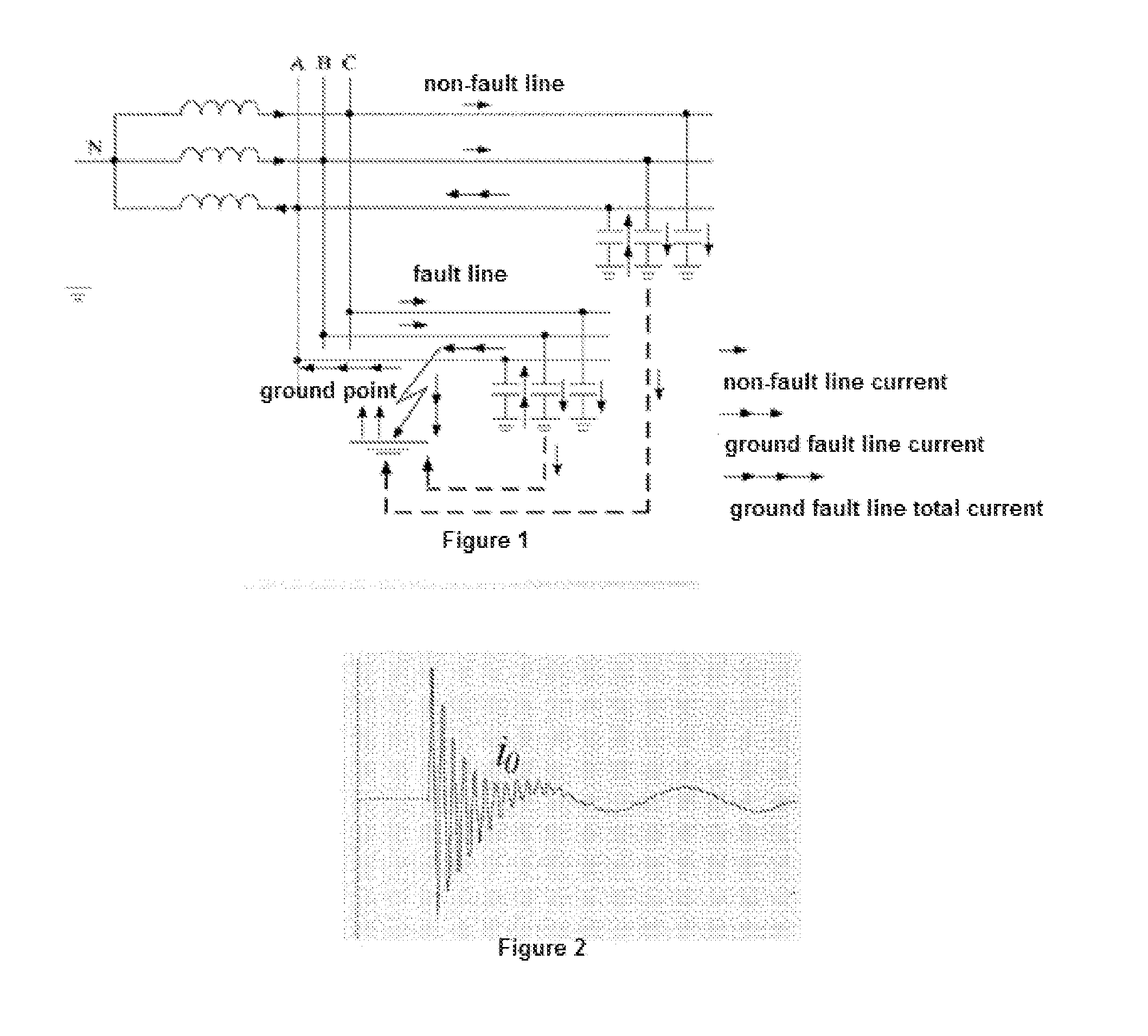
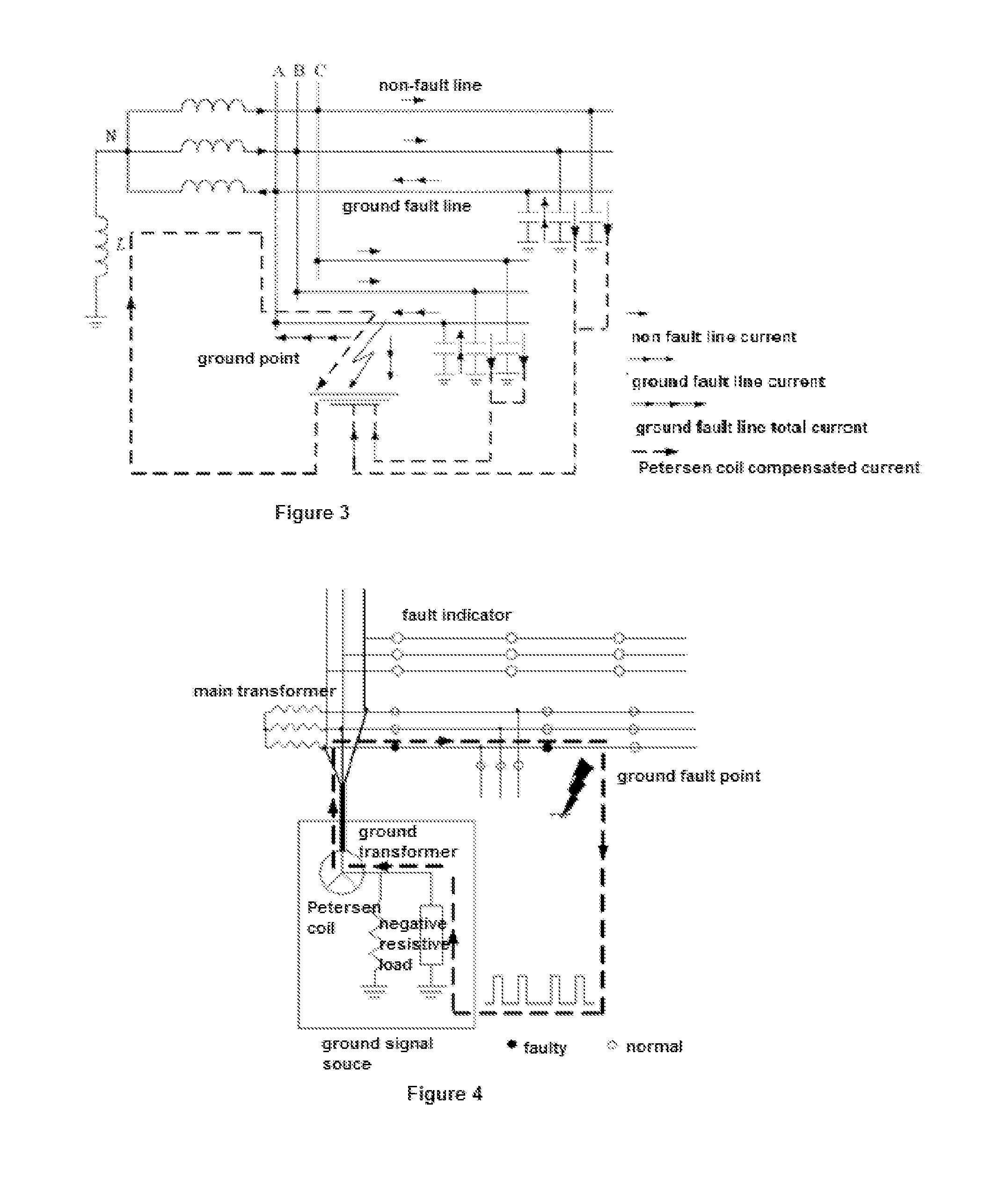
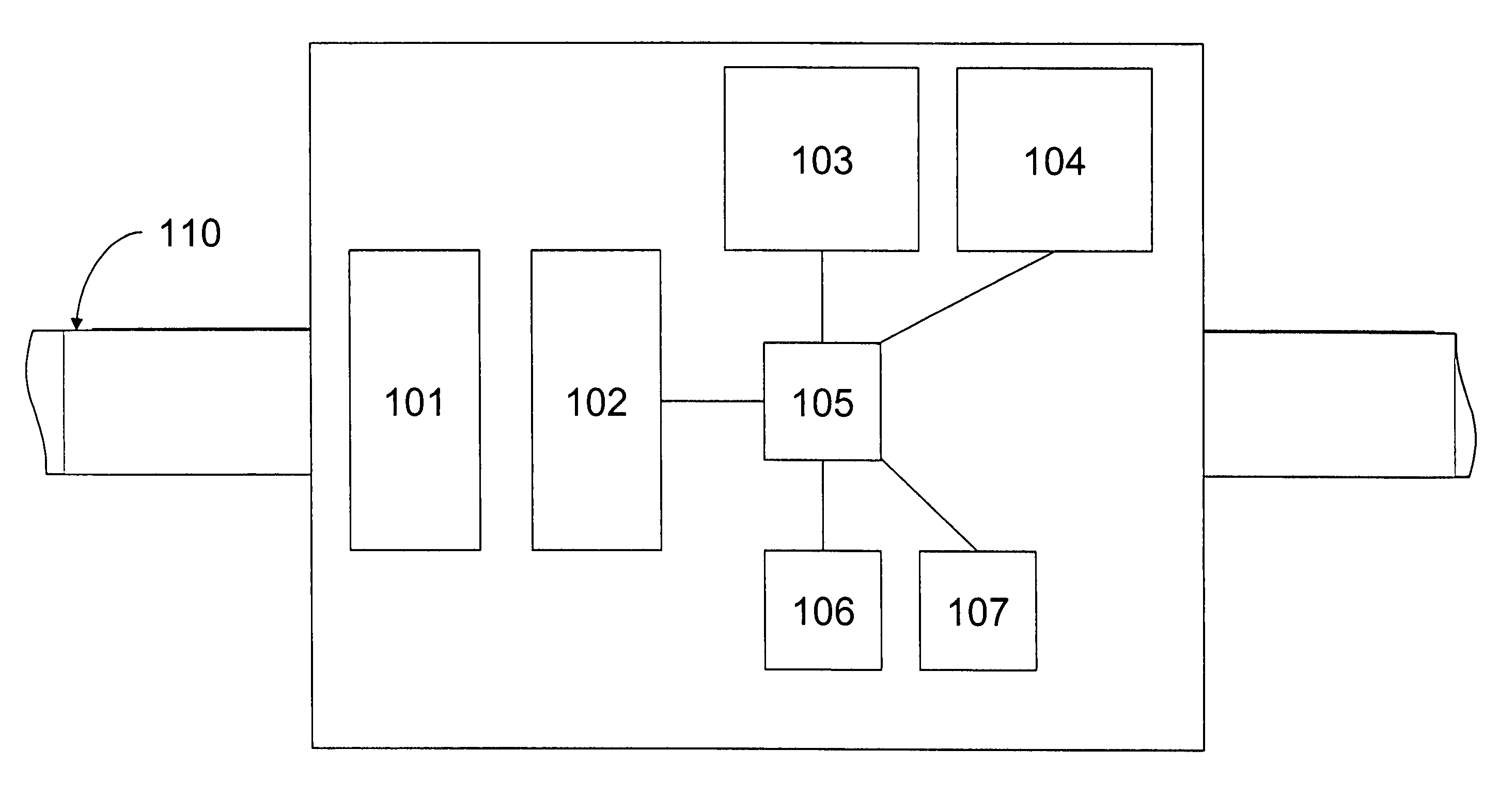
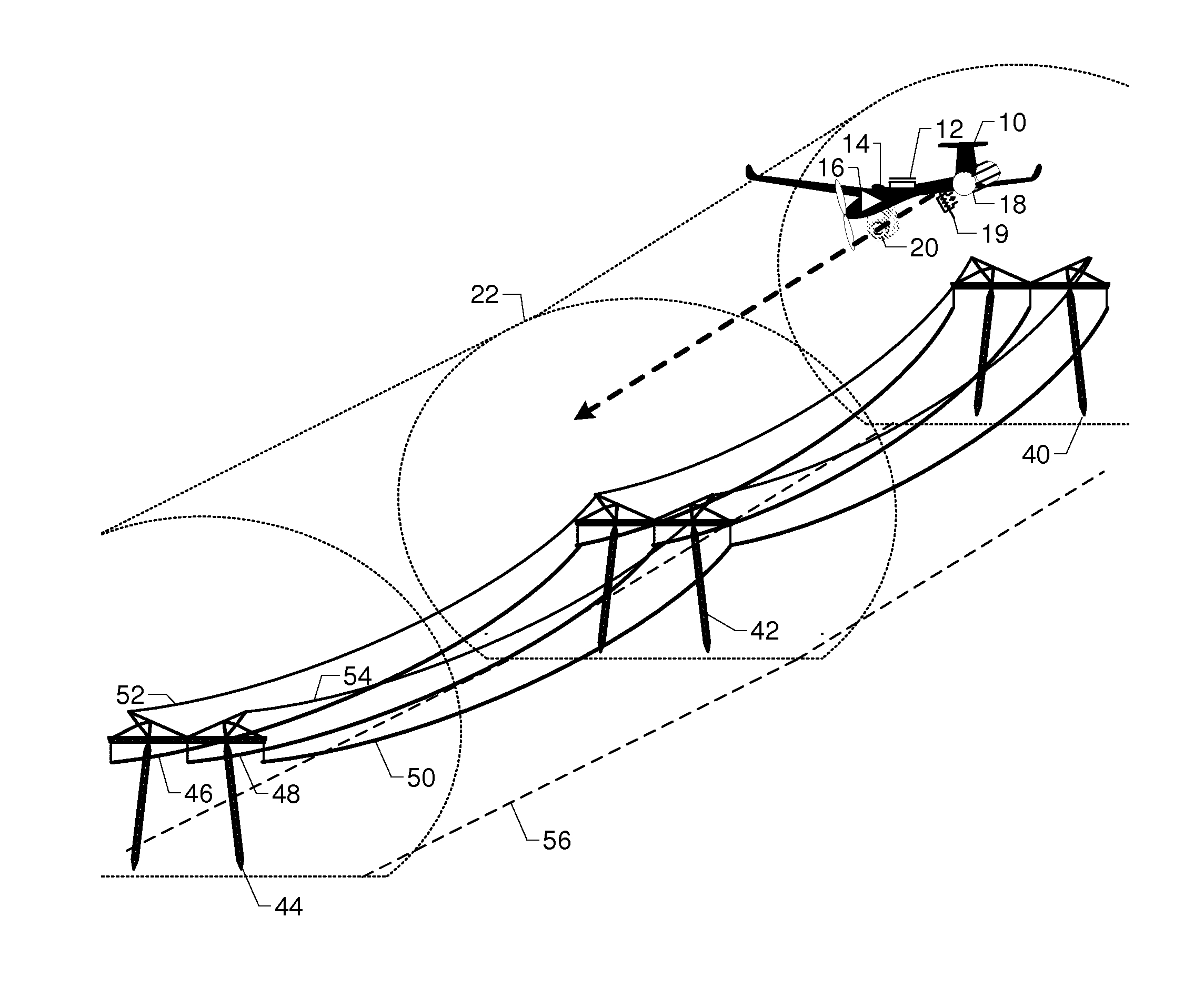
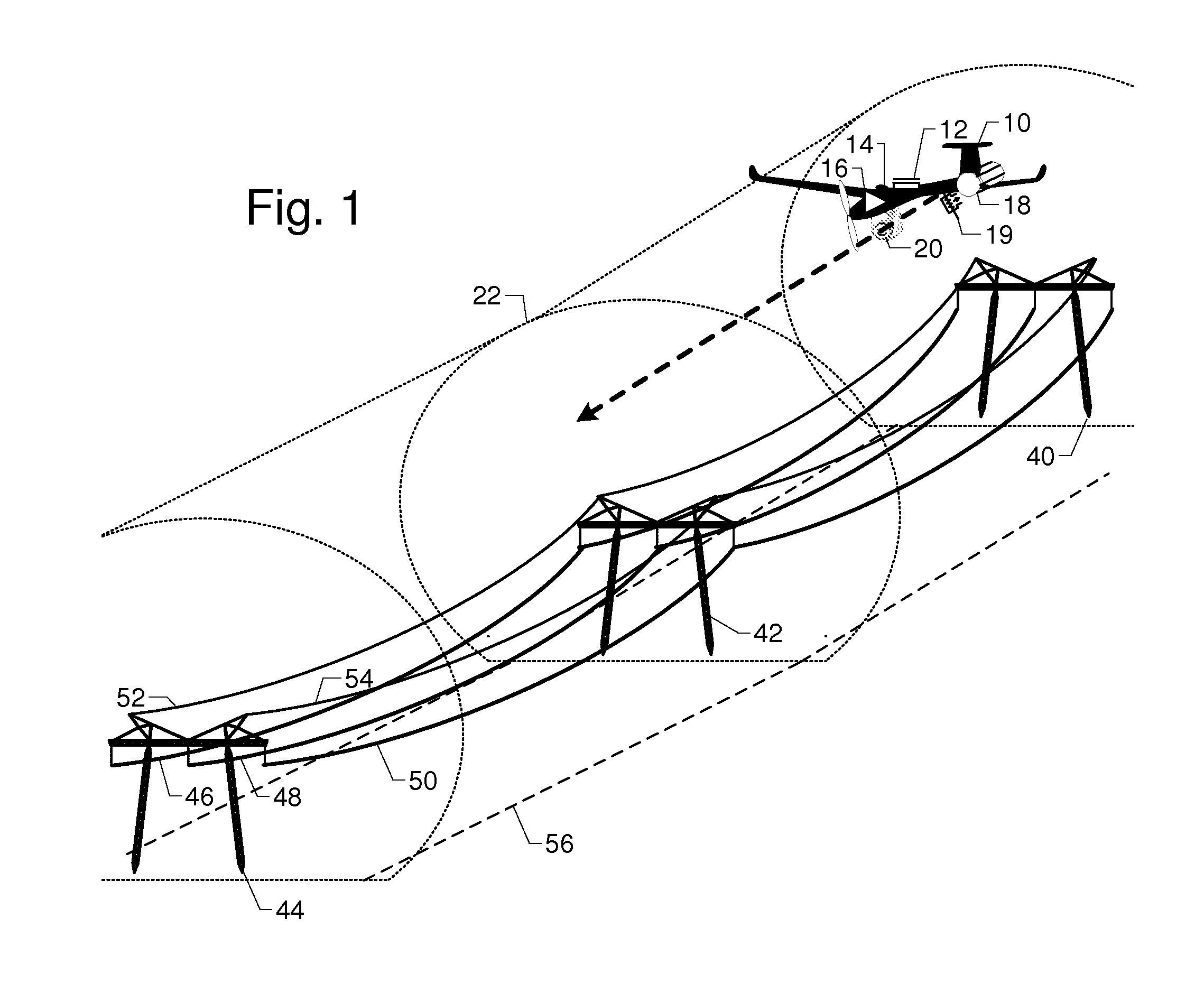
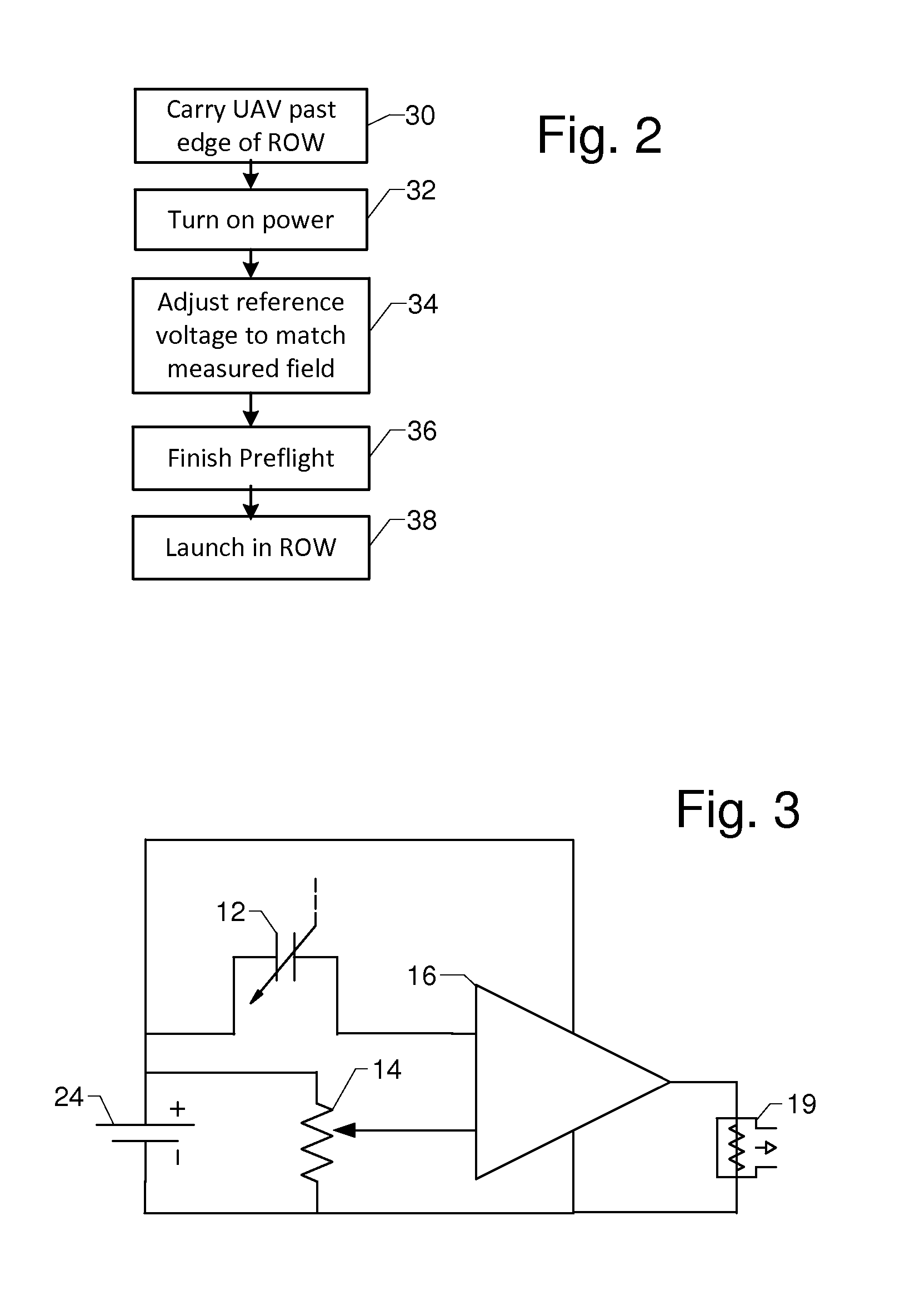
FIG. 1 shows airframe 10 with electromagnetic field sensor 12, adjustable reference electromagnetic field strength 14, comparator 16, parachute 18, parachute trigger 19, and inspection camera 20 inspecting a transmission line corridor containing towers 40, 42, and 44, phase conductors 46, 48, and 50, and shield wires 52 and 54. Reference electromagnetic field strength 14 is adjusted before the flight to set the minimum electromagnetic field strength before parachute trigger 19 deploys parachute 18. The reference electromagnetic field strength 14 corresponds to a radius, and thus virtual tunnel 22, outside of which airframe 10 cannot fly without deploying parachute 18, regardless of the state of the autopilot, GPS signal, or radio link.
Owner:VAN CRUYNINGEN IZAK JAN +1
System and method of locating ground fault in electrical power distribution system
ActiveUS20060125486A1Fault location by conductor typesEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionCurrent sensorDistribution power system
A method for locating a ground fault in an electrical power distribution system includes providing a plurality of current sensors at a plurality of locations in the electrical power distribution system. The method further includes detecting a ground fault in the electrical power distribution system. Current is monitored at a plurality of locations in the electrical power distribution system via the current sensors and a test signal is introduced into the electrical power distribution system via a test signal generating device. The plurality of locations are monitored to locate the ground fault between a location at which the test signal is detected and a downstream location at which the test signal is not detected.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
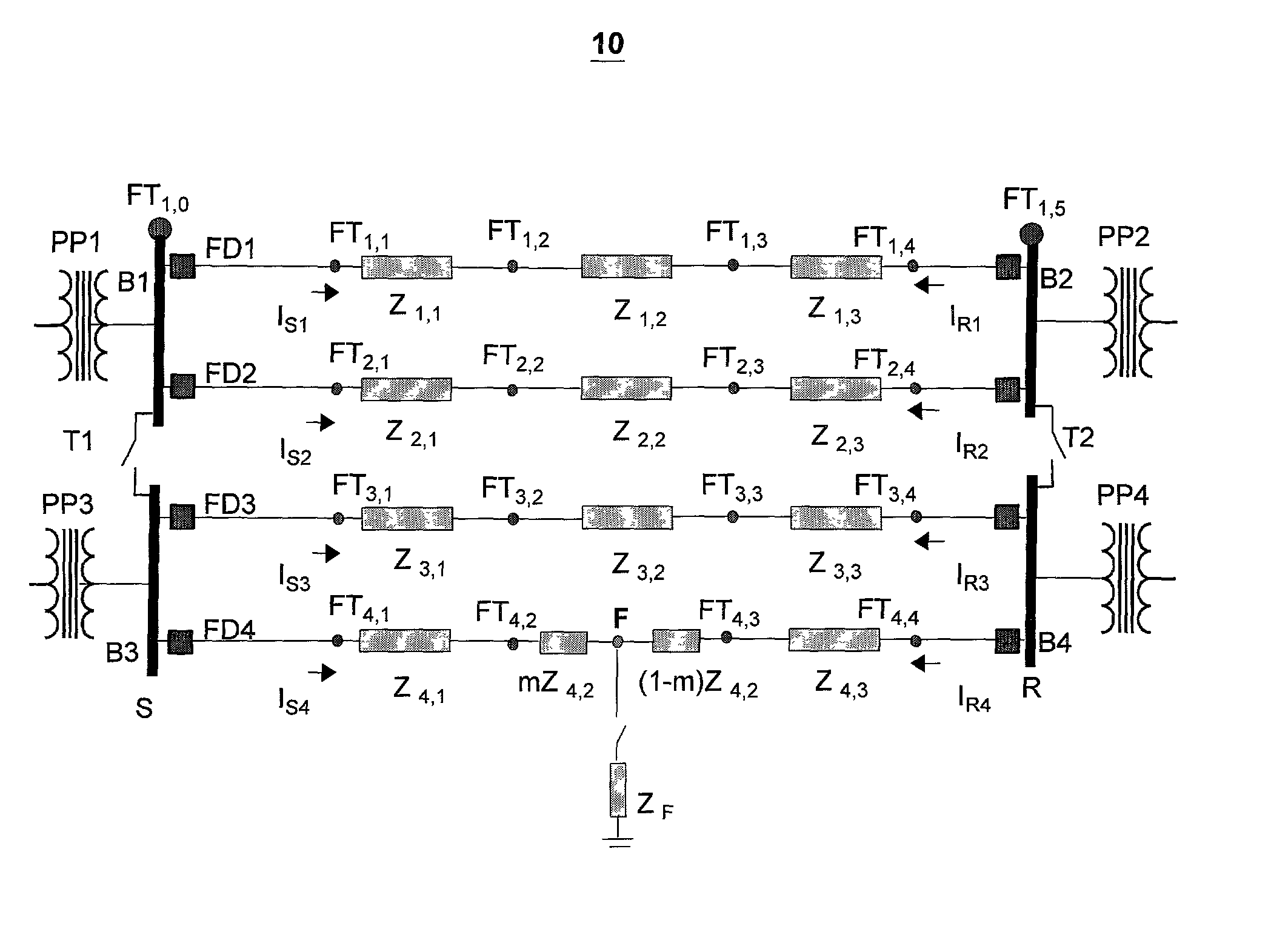
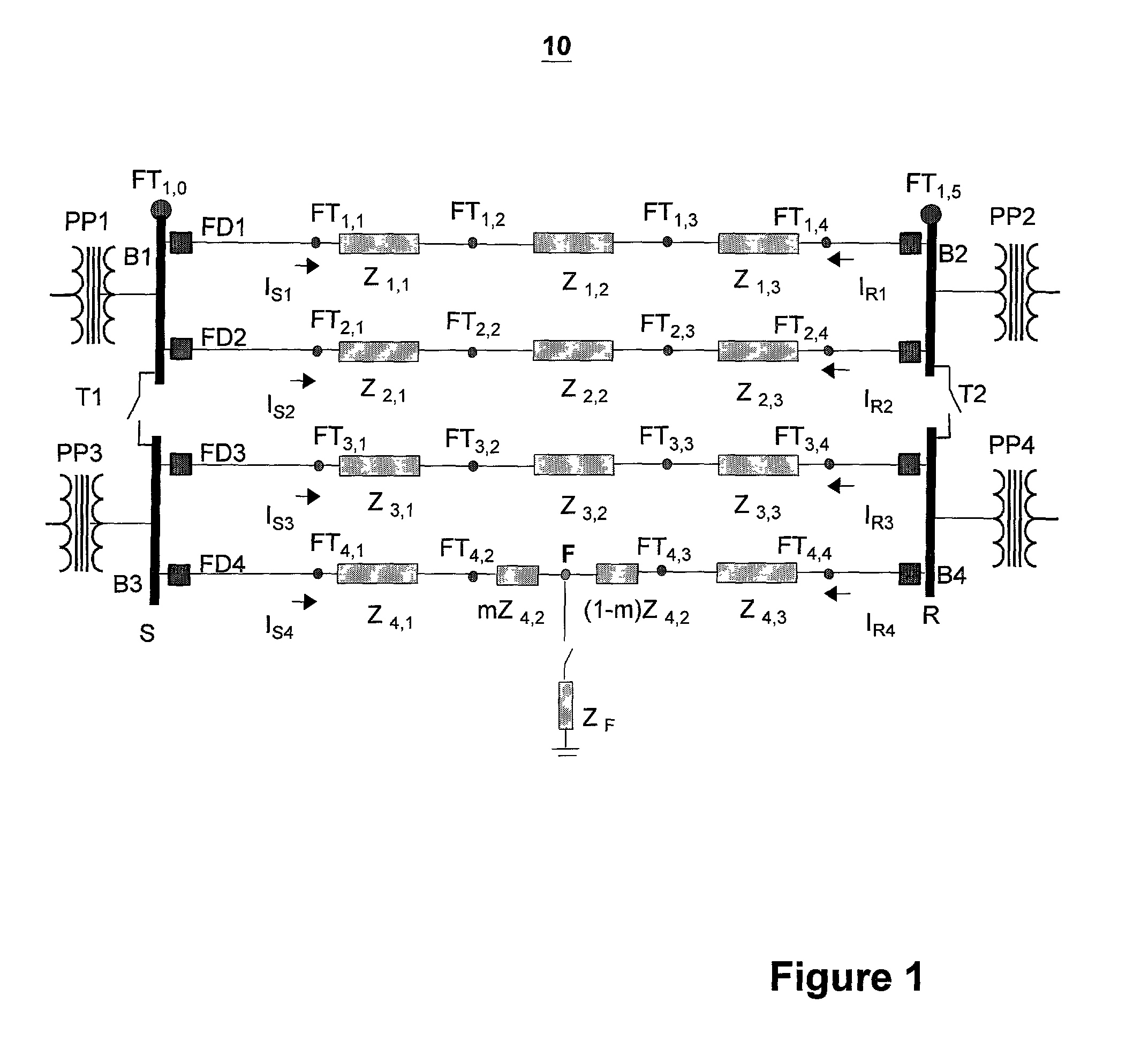
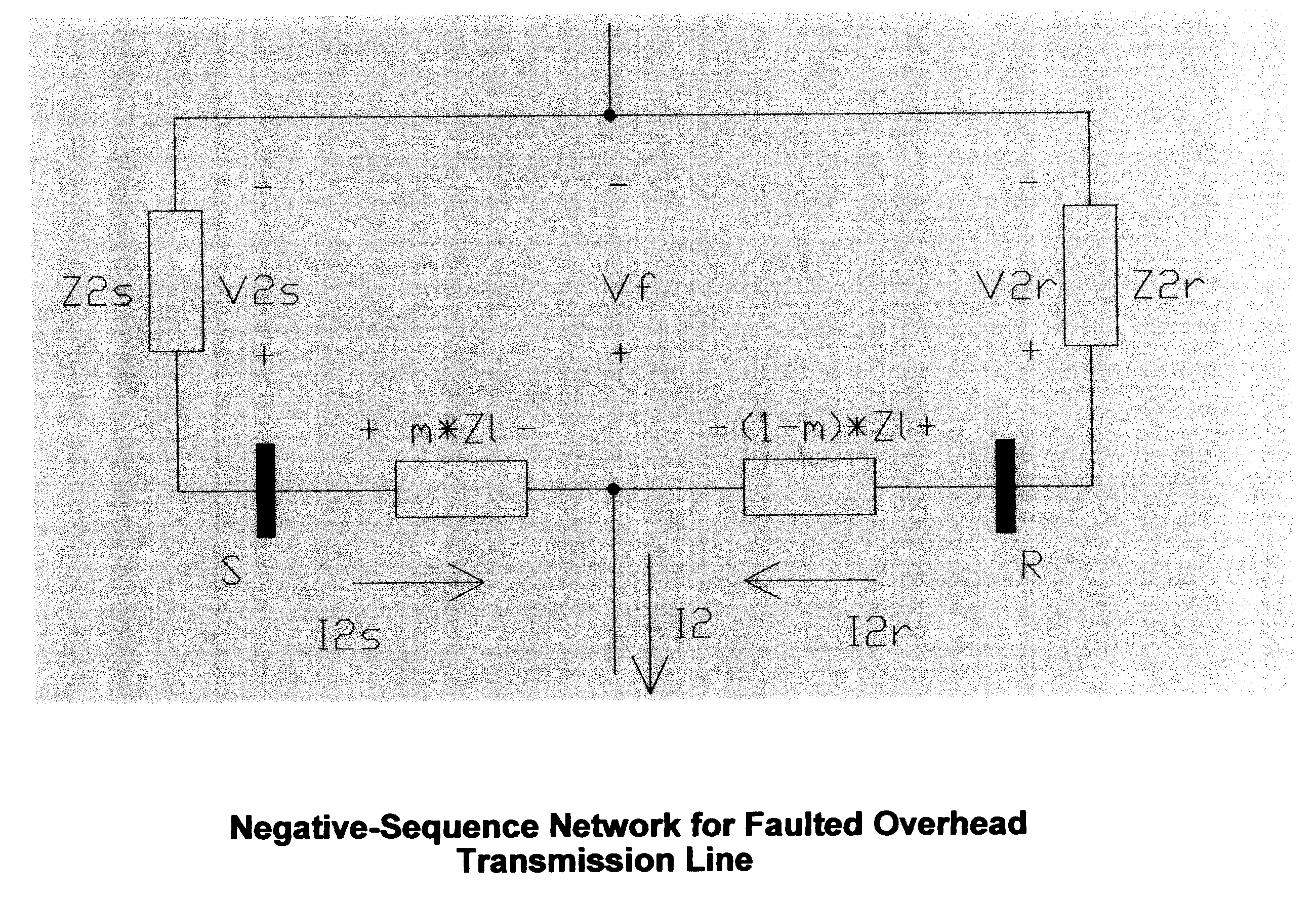
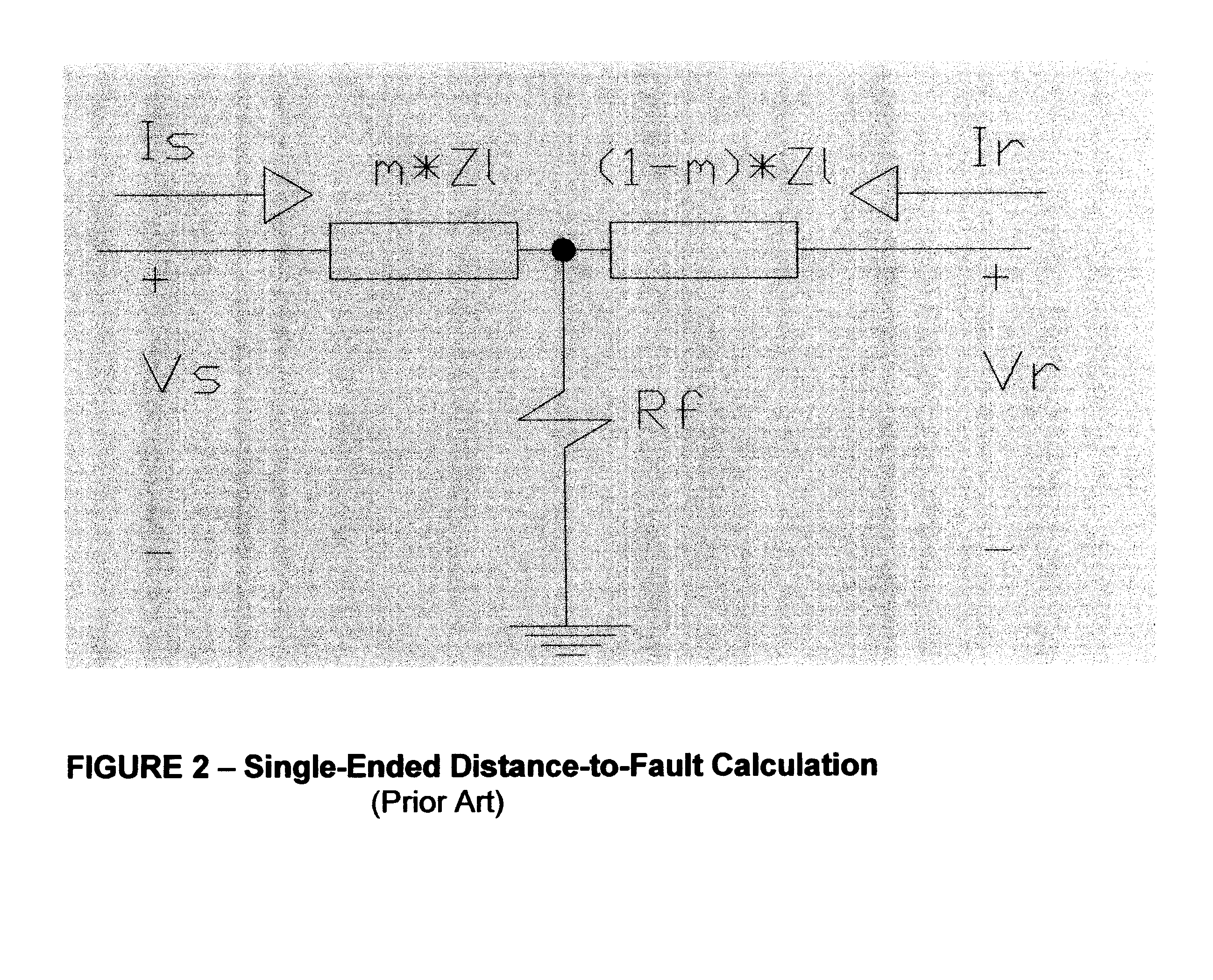
Double-ended distance-to-fault location system using time-synchronized positive-or negative-sequence quantities
InactiveUS6879917B2Avoid problemsNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementFault location by conductor typesLightning strikeHigh pressure
When a disturbance (for example, lightning strike) occurs on a high-voltage overhead transmission line, the line must be checked for any possible damage. If the distance-to-fault is known, line crews can be quickly dispatched for any necessary repair. The present invention is a fault location method and system that uses filtered, time-synchronized positive- or negative-sequence voltage and current measurements from both ends of the overhead transmission line to determine the exact distance to the fault with respect to either end.
Owner:PROGRESS ENERGY CAROLINAS
Real time dynamic physics simulation device of flexible DC transmission system
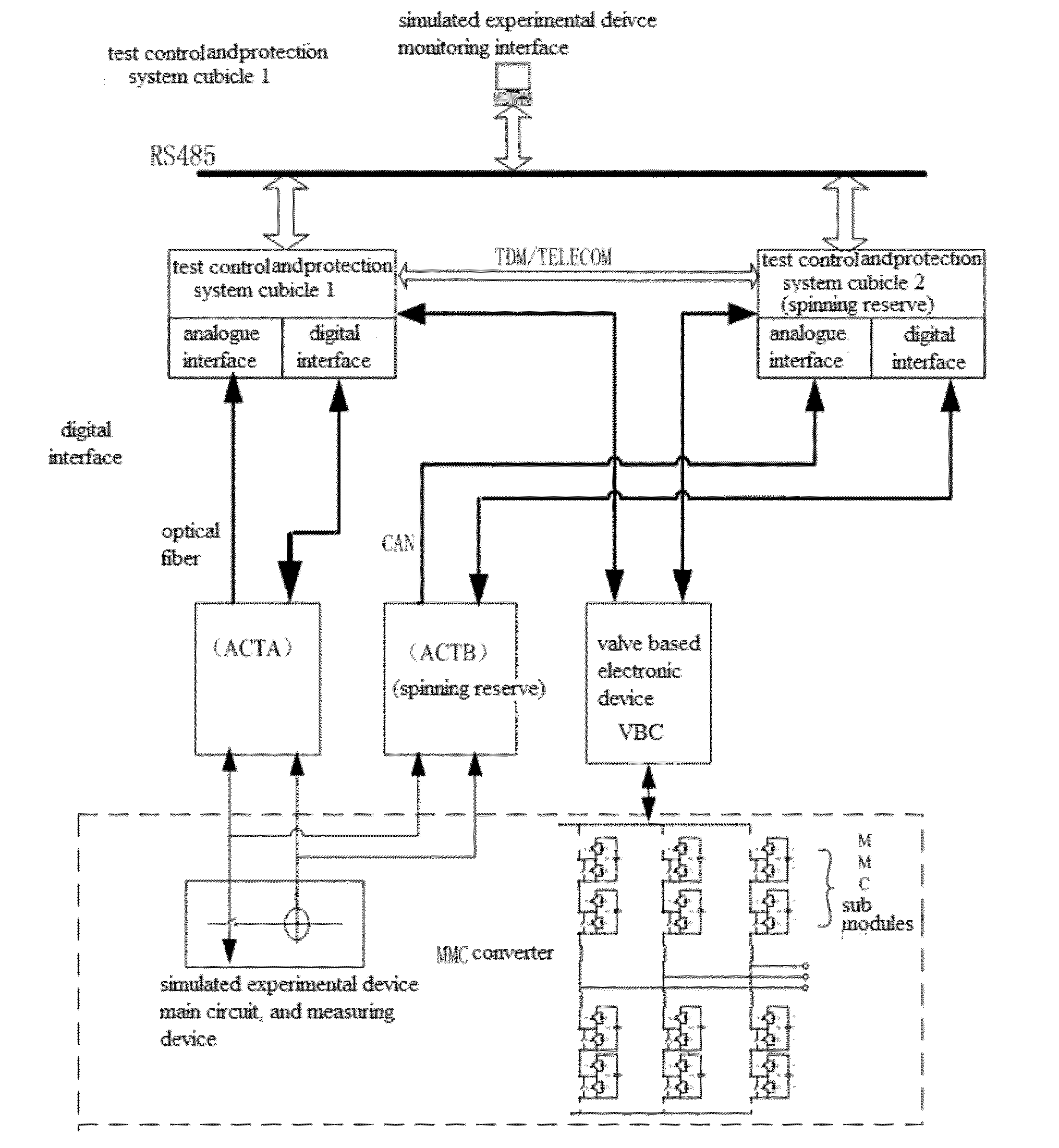
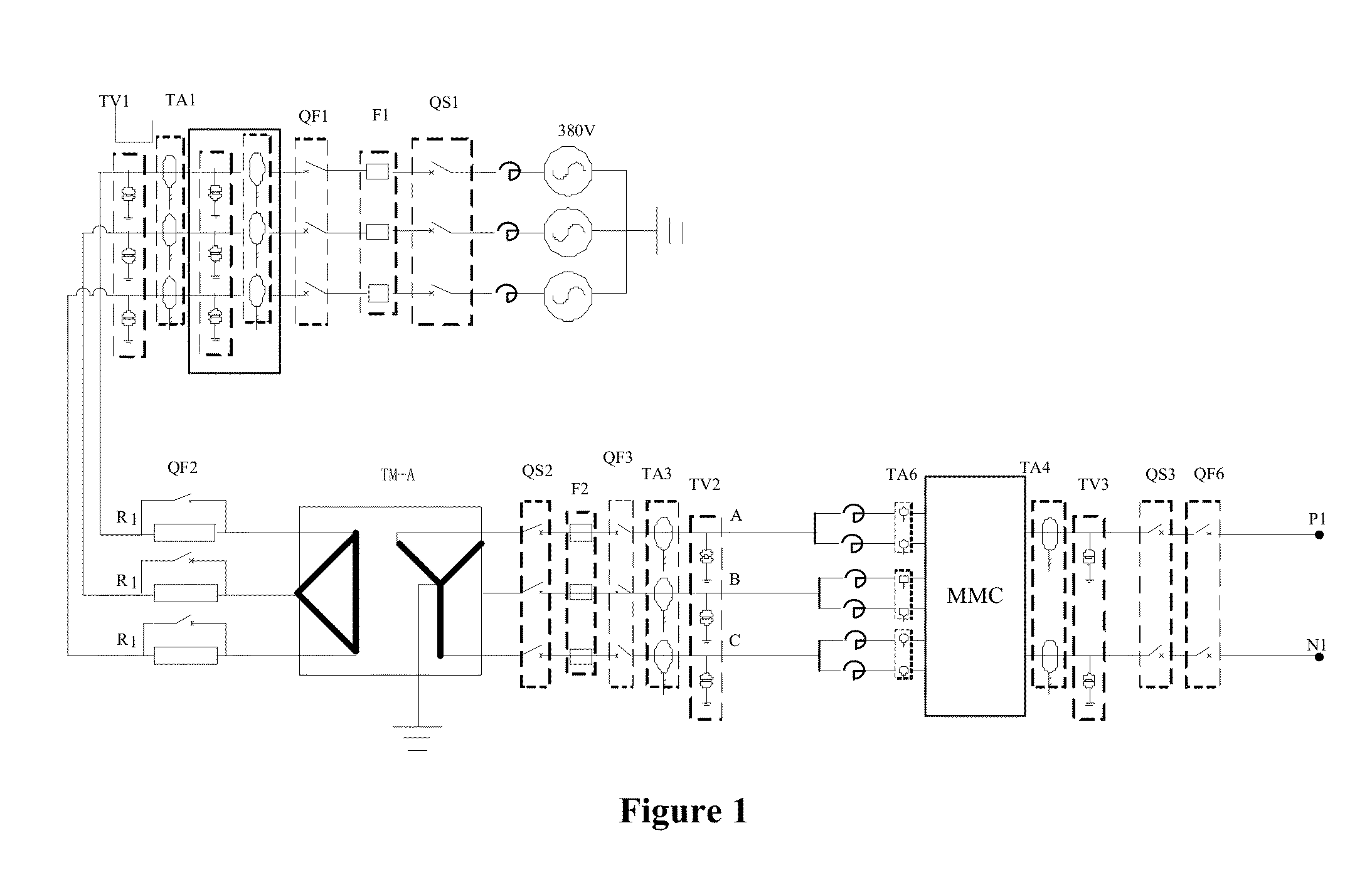
ActiveUS20140129195A1Accurately understand operation characteristicAccurate understandingFault location by conductor typesComputation using non-denominational number representationControl systemTransformer
The present invention relates to a real time dynamic physics simulation device of flexible DC transmission system. The device includes simulated converter transformer, simulated AC field, simulated DC field, simulated converter reactor, simulated converter, and measurement and control cabinet chassis; the simulated AC field includes the vacuum switch I, the contactor I, resistors and the vacuum switch II connected orderly; the simulated DC field includes successively connected the vacuum switch contactor III and II; the simulated AC field is connected with said measurement and control cabinet chassis; Said converter transformer is set between said resistors and said vacuum switch II; Said simulated converter reactors and said simulated converter connected are set between the vacuum switch II and the vacuum switch III. The present invention can accurately simulate different voltage level flexible DC transmission system based on modular multilevel converter (MMC-HVDC), able to accurately understand the operation characteristics of MMC-HVDC and the dynamic responds to the instruction of the control system.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
Diagnostic methods for electrical cables utilizing axial tomography
ActiveUS20080048668A1Easy to identifyPrecise positioningFault location by conductor typesFault location by pulse reflection methodsElectrical conductorEngineering
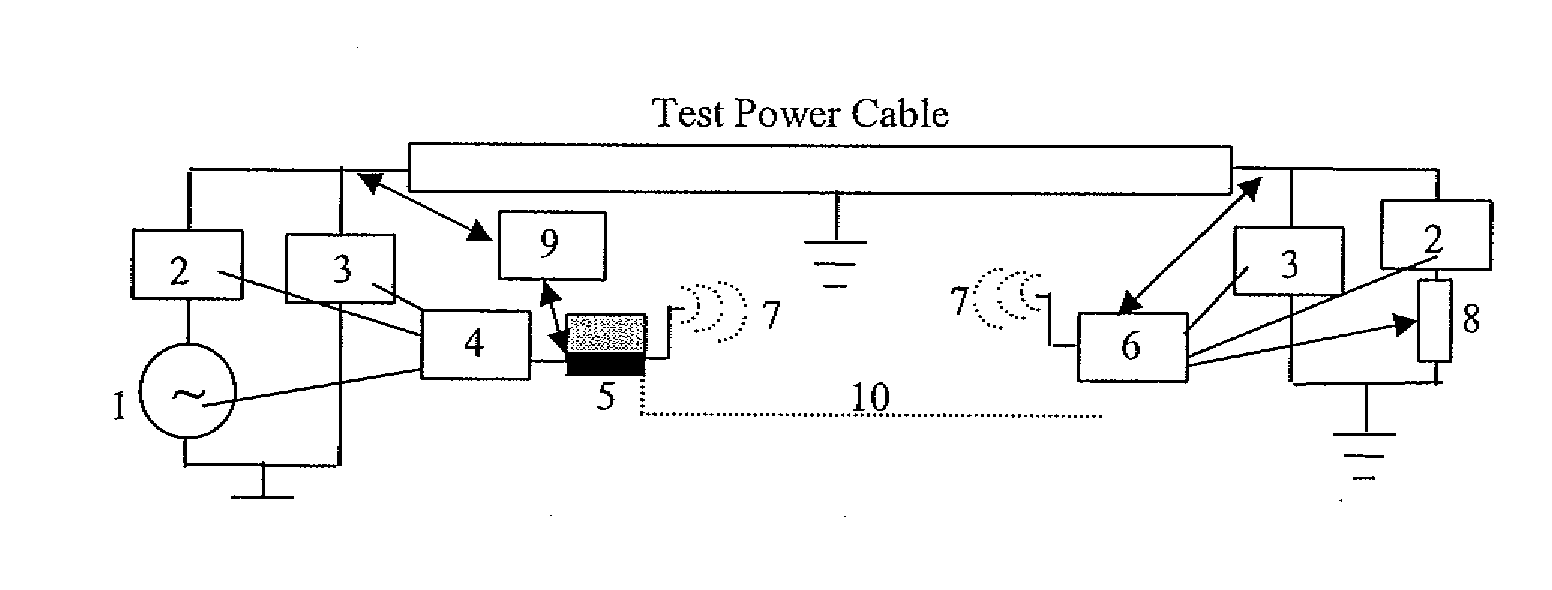
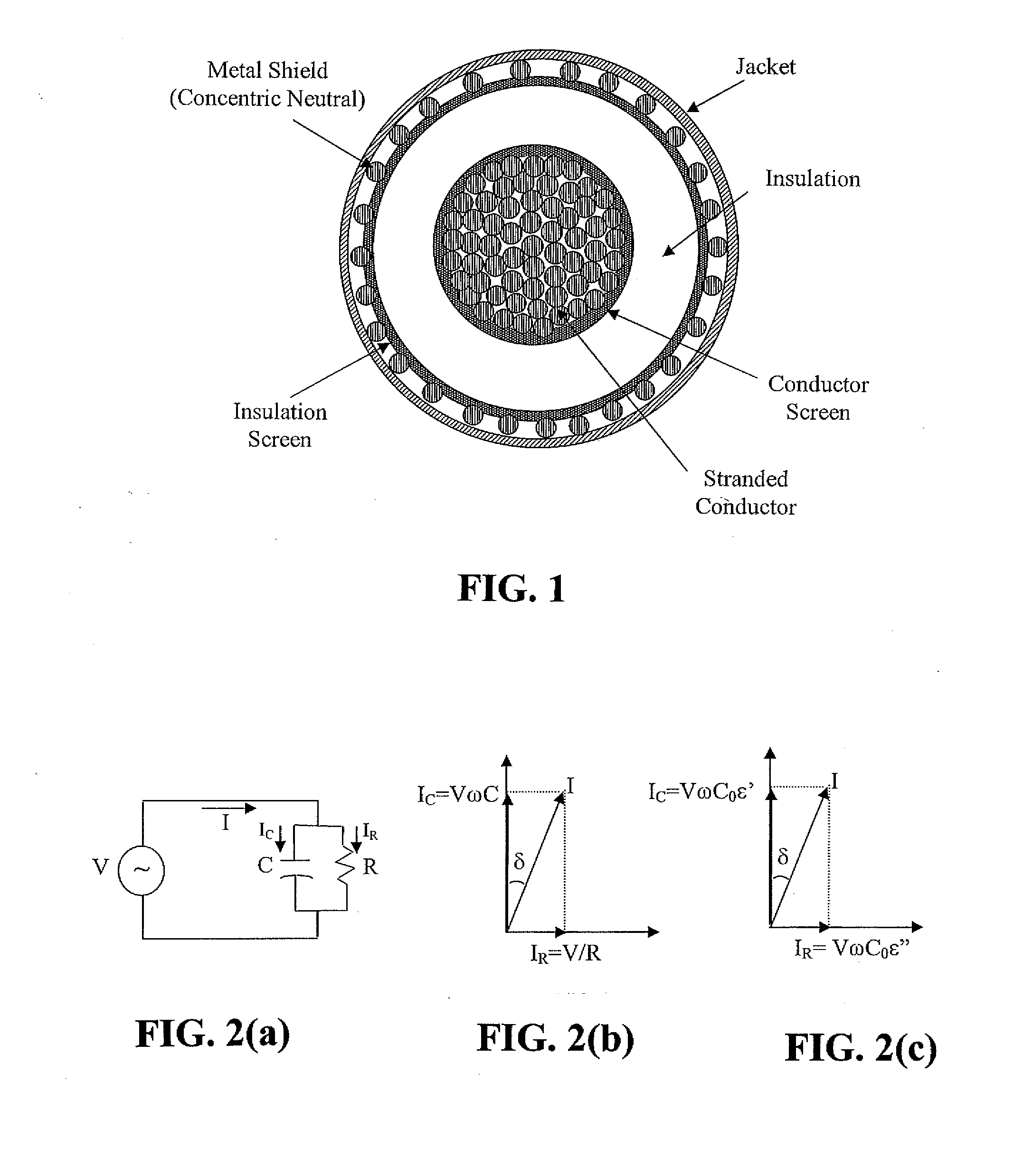
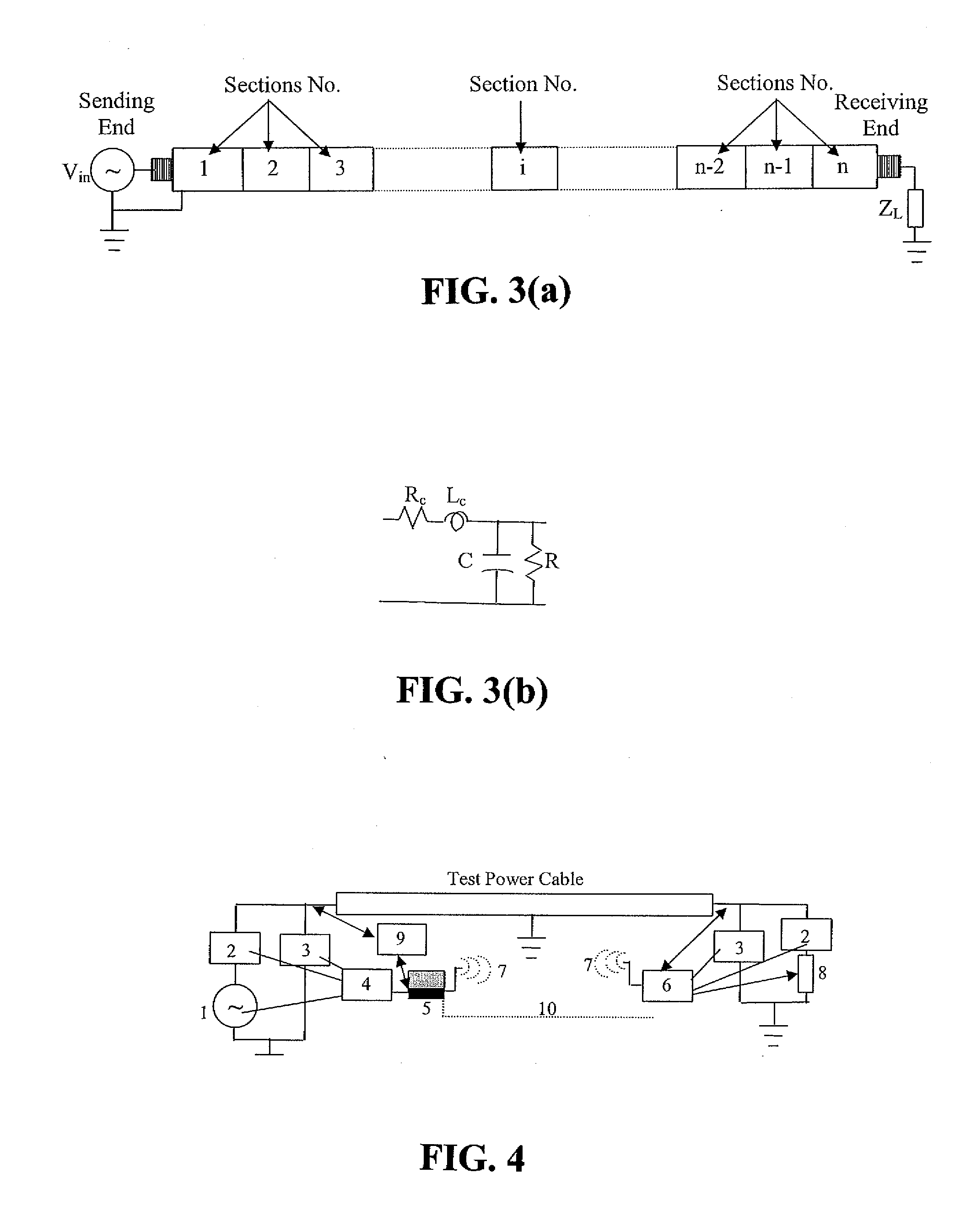
Cable diagnostic test methods, systems and apparatus are disclosed that utilize “standing wave” principles to facilitate identification and location of insulation defect(s) along a power cable. The methods / systems measure dissipation factors and dielectric constants associated with the power cable insulation and the impedance of the power cable conductor at any number of points or sections along the axial length of the cable. In an exemplary embodiment, the disclosed method involves (i) connecting an alternating voltage source to a cable at a “sending end” thereof; (ii) applying a voltage to the cable at a first frequency to set up a traveling wave along the cable that is reflected at the “receiving end” thereof; (iii) permitting a standing wave pattern to be established along the cable by the traveling wave and the reflection thereof; (iv) measuring the total complex power loss (Sin) at the sending end of the cable; (v) calculating the standing wave voltage at any point / section of the cable based on the load impedance (ZL) connected at the receiving end of the cable, and the characteristic impedance (ZO) of the cable, or the measured / calculated cable parameters for the first frequency of the voltage source, (vi) repeating the foregoing steps while one of: (1) varying at least one of: the load impedance (ZL) connected at the receiving end of the cable, the first frequency of the voltage source; the output impedance of the voltage source, a combination of the load impedance (ZL), the output impedance of the voltage source and the first frequency of the voltage source, and combinations thereof; (2) interchanging sending and receiving cable ends; and (3) a combination thereof, and (vii) determining a dissipation factor (tan δ) and a dielectric constant (∈′), for the insulation, and an impedance, for the conductor at predetermined points / sections along the axis of the cable.
Owner:INSTR MFG
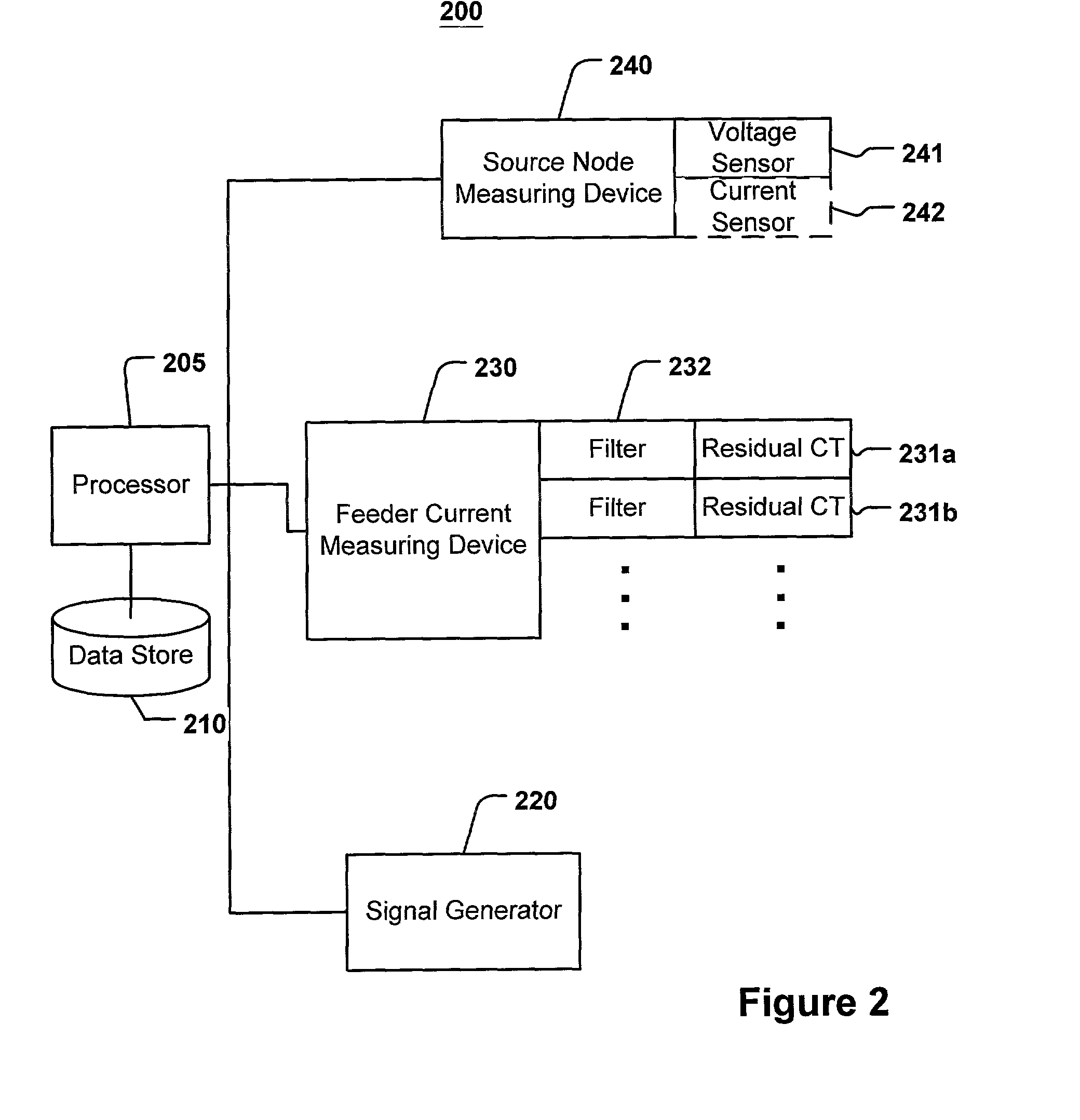
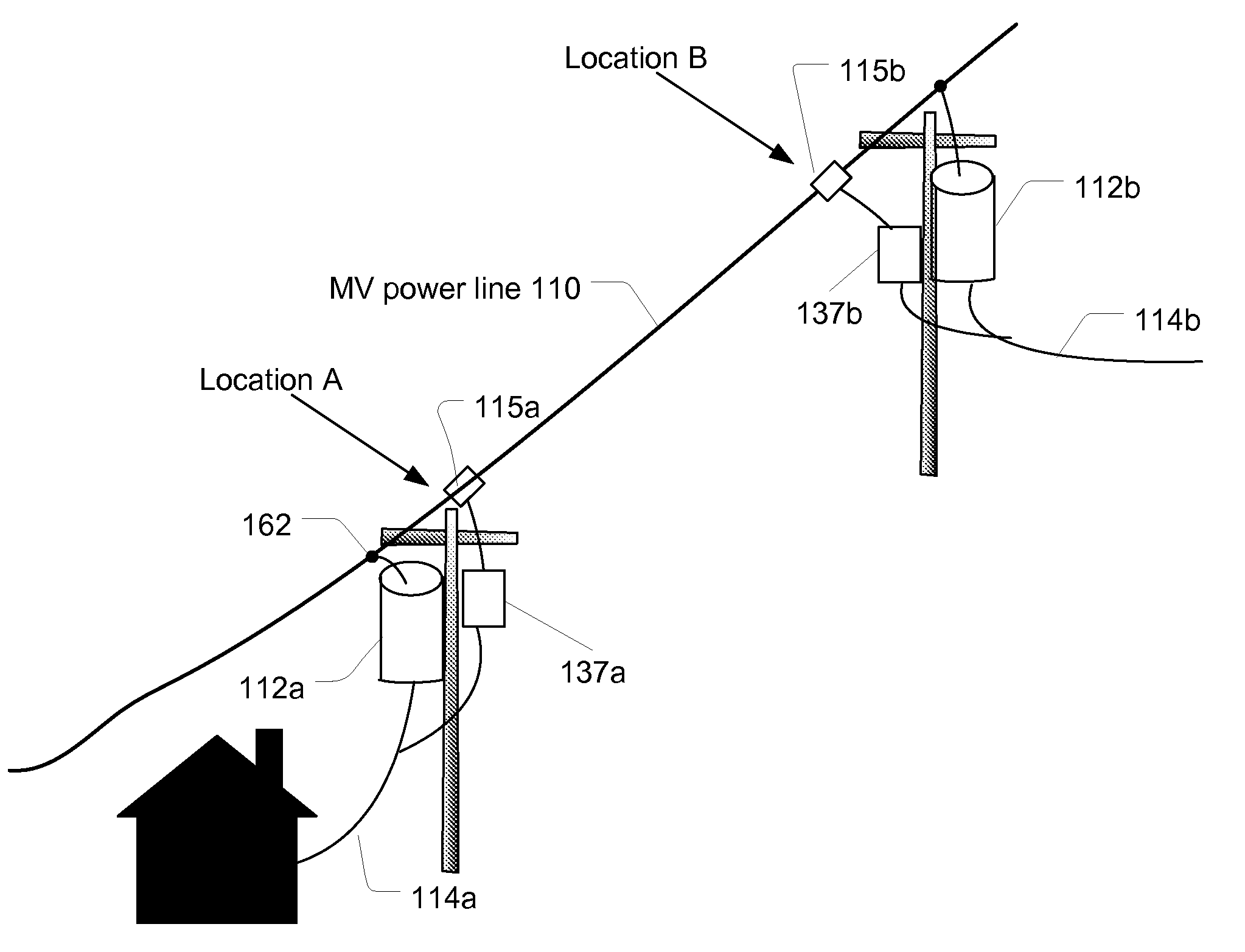
System and method for determining the impedance of a medium voltage power line
InactiveUS7714592B2Fault location by conductor typesImpedence measurementsElectric powerImpedance variation
A system and method of detecting changes in the impedance of a segment of medium voltage power line is provided. In one embodiment, the method comprises receiving voltage data comprising data of the voltage of the power lines at locations at a plurality of different points in time, receiving current data that comprises data of the current flowing between adjacent locations at the plurality of points in time, intermittently determining an impedance of the power lines between adjacent locations based on the voltage data and current data, monitoring the impedance of the power lines between adjacent locations over time, and providing a notification of a change in the impedance of a power line between adjacent locations upon detection of a change in the impedance beyond a threshold change.
Owner:CURRENT TECH
Arc detection and prevention in a power generation system
ActiveUS9647442B2Service lifeLow costTesting dielectric strengthDc network circuit arrangementsElectrical and Electronics engineeringPower generation system
A method for arc detection in a system including a photovoltaic panel and a load connectible to the photovoltaic panel with a DC power line. The method measures power delivered to the load thereby producing a first measurement result of the power delivered to the load. Power produced by the photovoltaic panel is also measured, thereby producing a second measurement result of power produced by the photovoltaic panel. The first measurement result is compared with the second measurement result thereby producing a differential power measurement result. Upon the differential power measurement result being more than a threshold value, an alarm condition may also be set. The second measurement result may be modulated and transmitted over the DC power line.
Owner:SOLAREDGE TECH LTD
Distribution network line fault section positioning method based on full-waveform information
ActiveCN104155582AHigh sensitivityImprove reliabilityEmergency protective circuit arrangementsFault location by conductor typesPhase currentsCorrelation function
The invention discloses a distribution network line fault section positioning method based on full-waveform information. For the grounding fault, line selection is carried out through extreme value points of a cross-correlation function of the bus zero-sequence voltage and all outgoing line zero-sequence currents, and positioning is carried out according to the adjacent detection point zero-sequence current waveform standard drift rate of the whole action process of a fault occurrence and compensation device; for the interphase fault, line selection is carried out according to the overcurrent information obtained before action of a relay protection device, and positioning is carried out according to the adjacent detection point fault phase current waveform standard drift rate. The waveform data of the whole action process of a fault and arc extinction device are utilized, the current ubiquitous problems that when a small current grounding system encounters the single-phase grounding phase, the fault current is weak, the reliability is poor, and the sensitivity is low can be well solved, and meanwhile the system cannot get interference.
Owner:SHANGHAI MAINE ENERGY TECH CO LTD
System and Method For Determining The Impedance of a Medium Voltage Power Line
InactiveUS20090115427A1Fault location by conductor typesImpedence measurementsElectric powerLine segment
A system and method of detecting changes in the impedance of a segment of medium voltage power line is provided. In one embodiment, the method comprises receiving voltage data comprising data of the voltage of the power lines at locations at a plurality of different points in time, receiving current data that comprises data of the current flowing between adjacent locations at the plurality of points in time, intermittently determining an impedance of the power lines between adjacent locations based on the voltage data and current data, monitoring the impedance of the power lines between adjacent locations over time, and providing a notification of a change in the impedance of a power line between adjacent locations upon detection of a change in the impedance beyond a threshold change.
Owner:CURRENT TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com