Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3327 results about "Standing wave" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
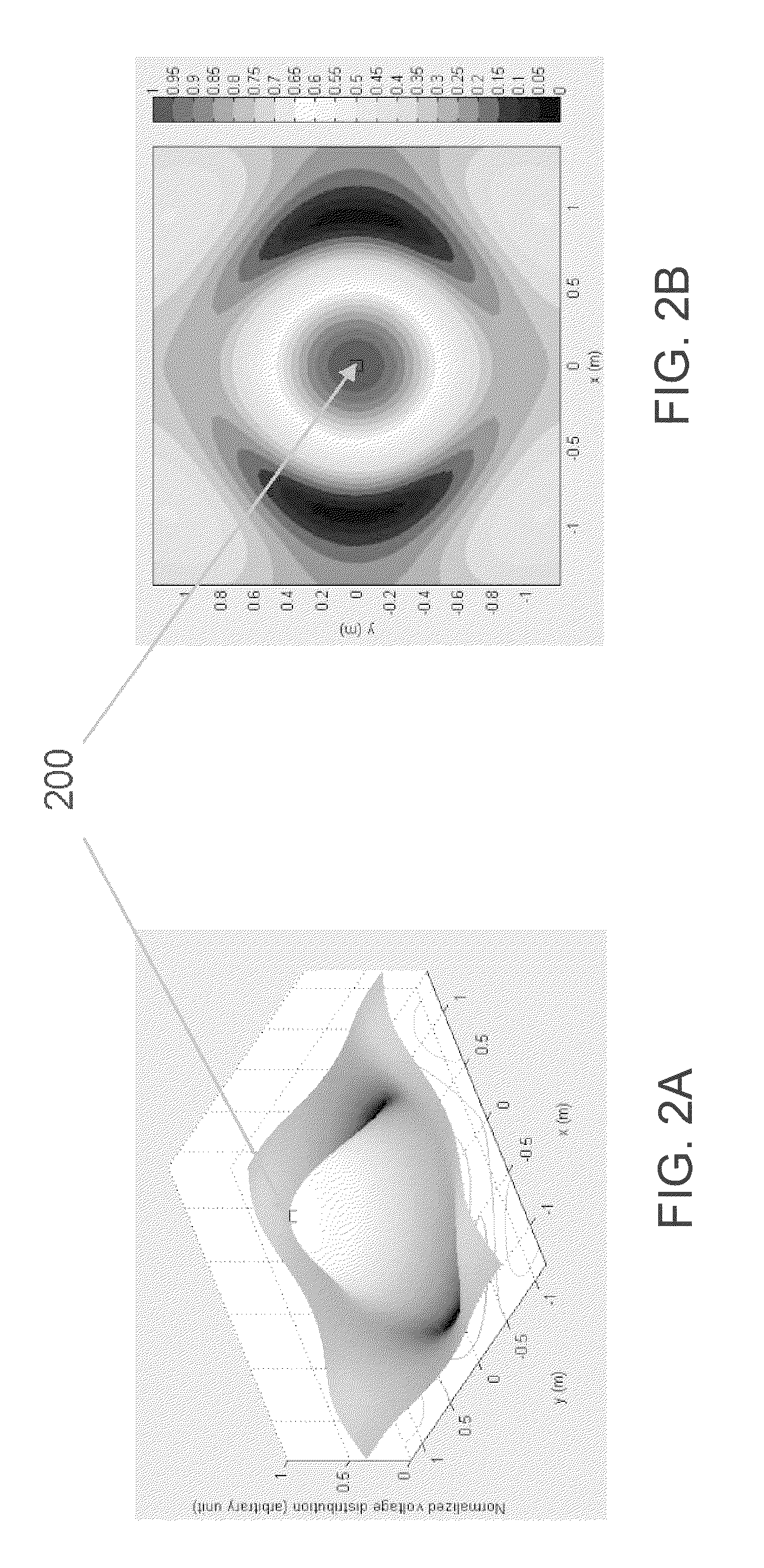
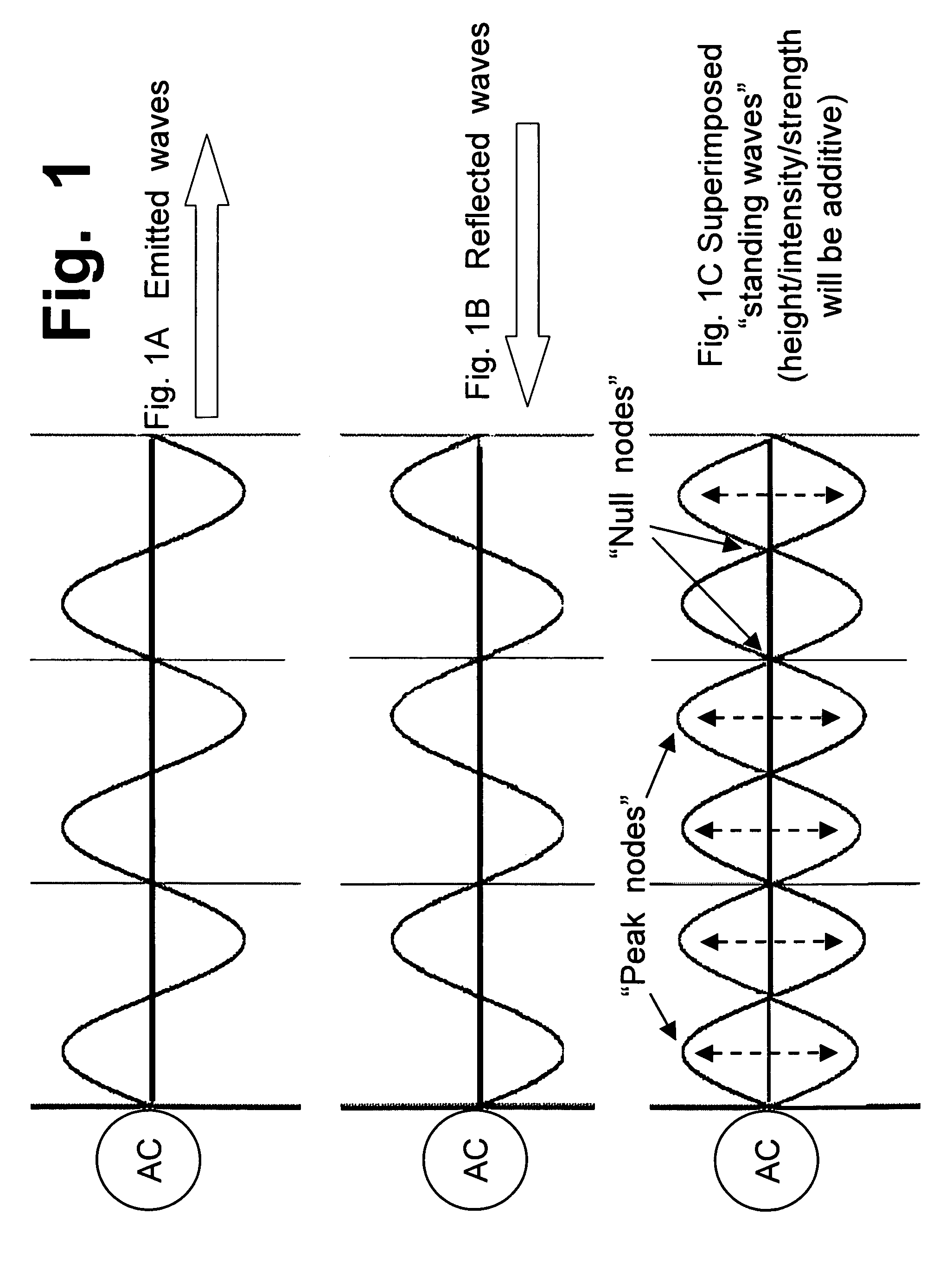
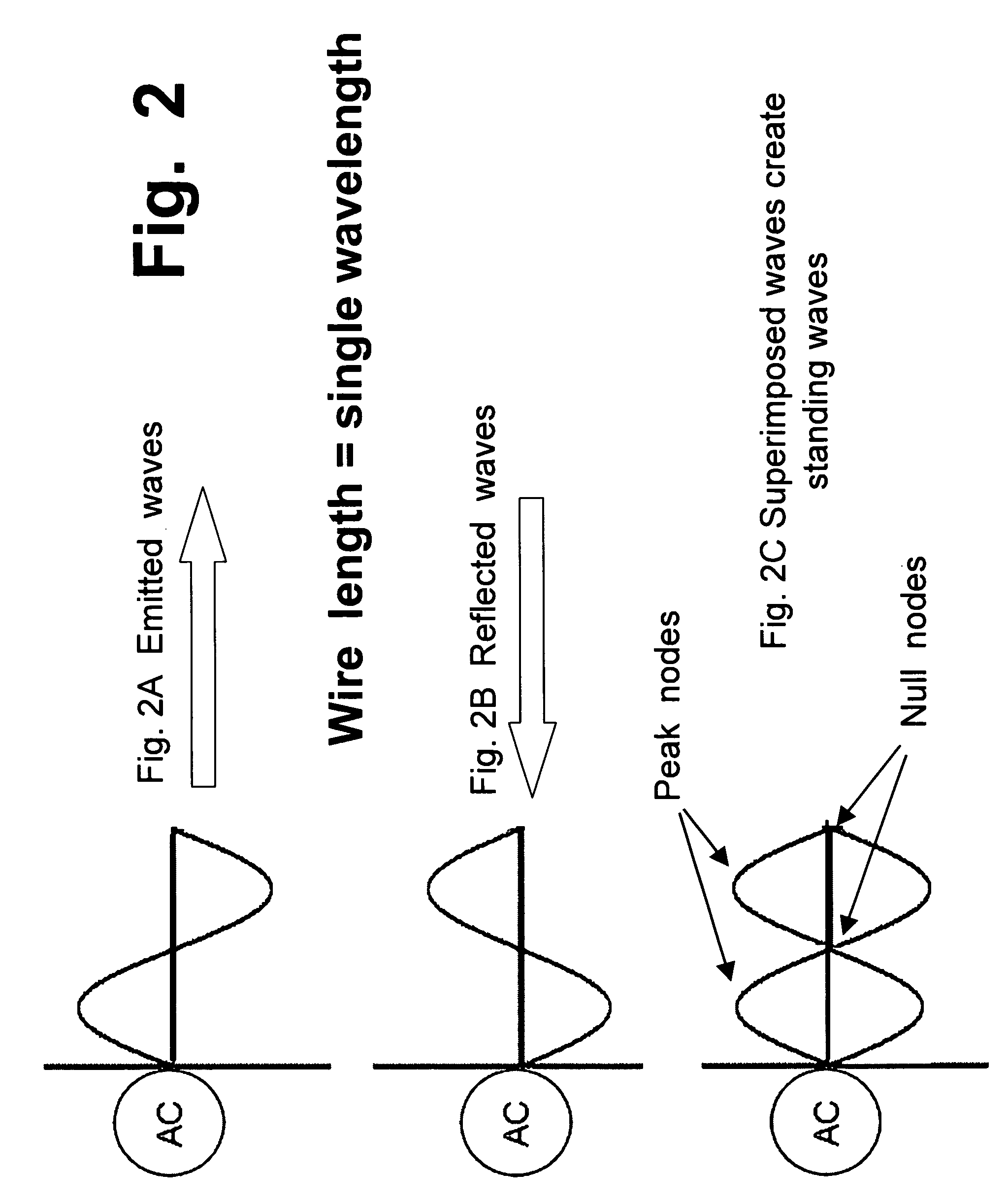
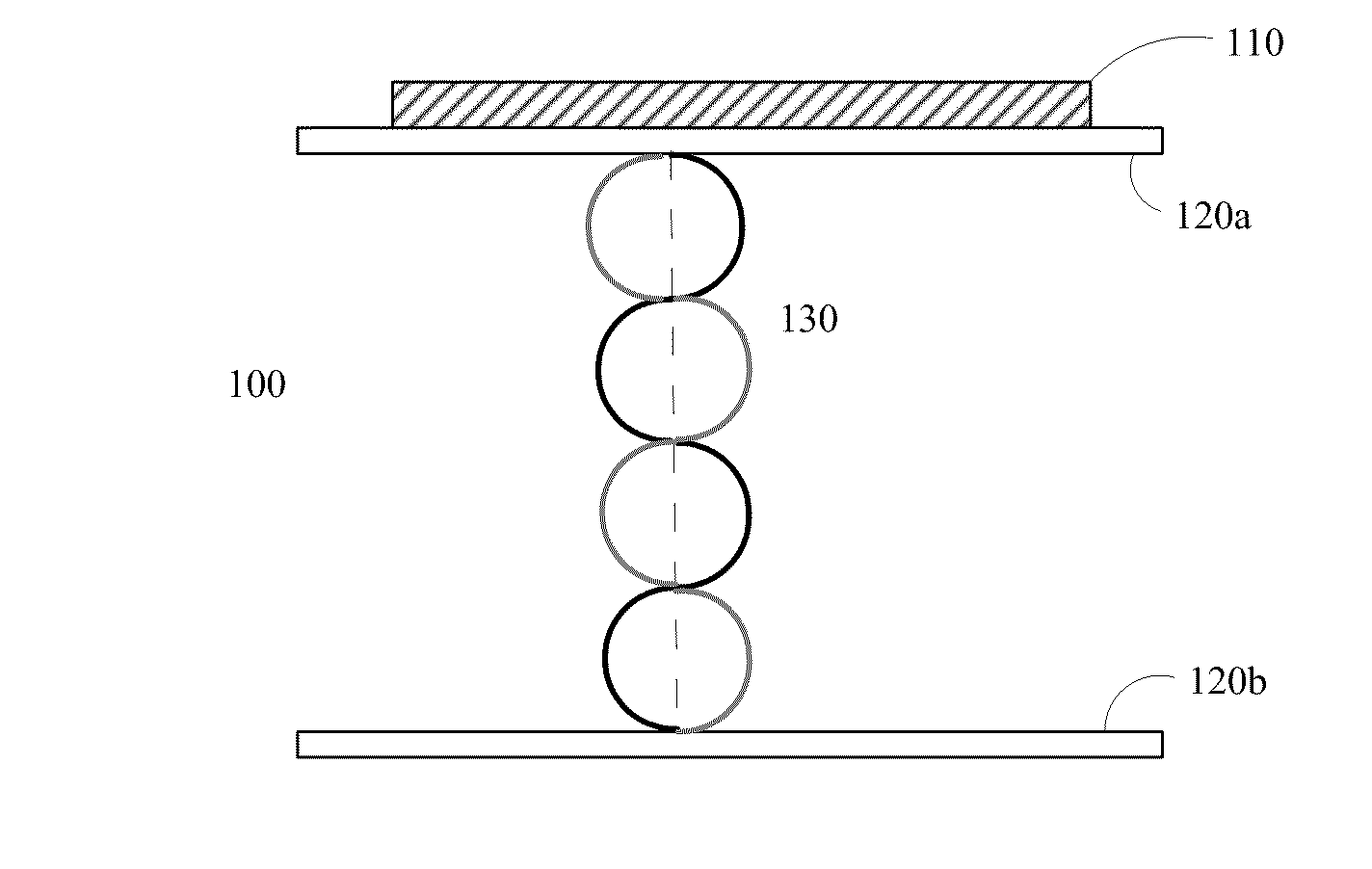
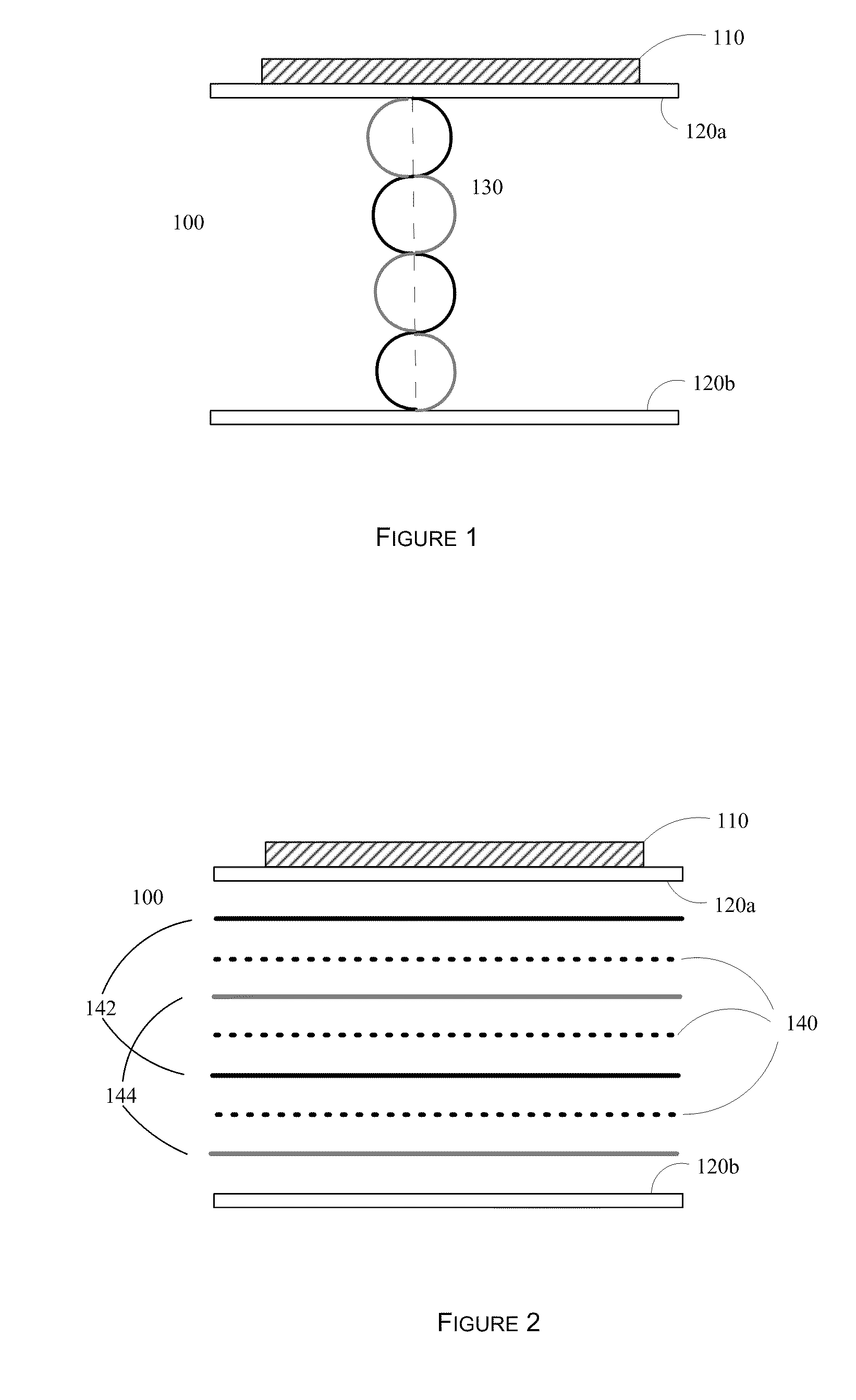
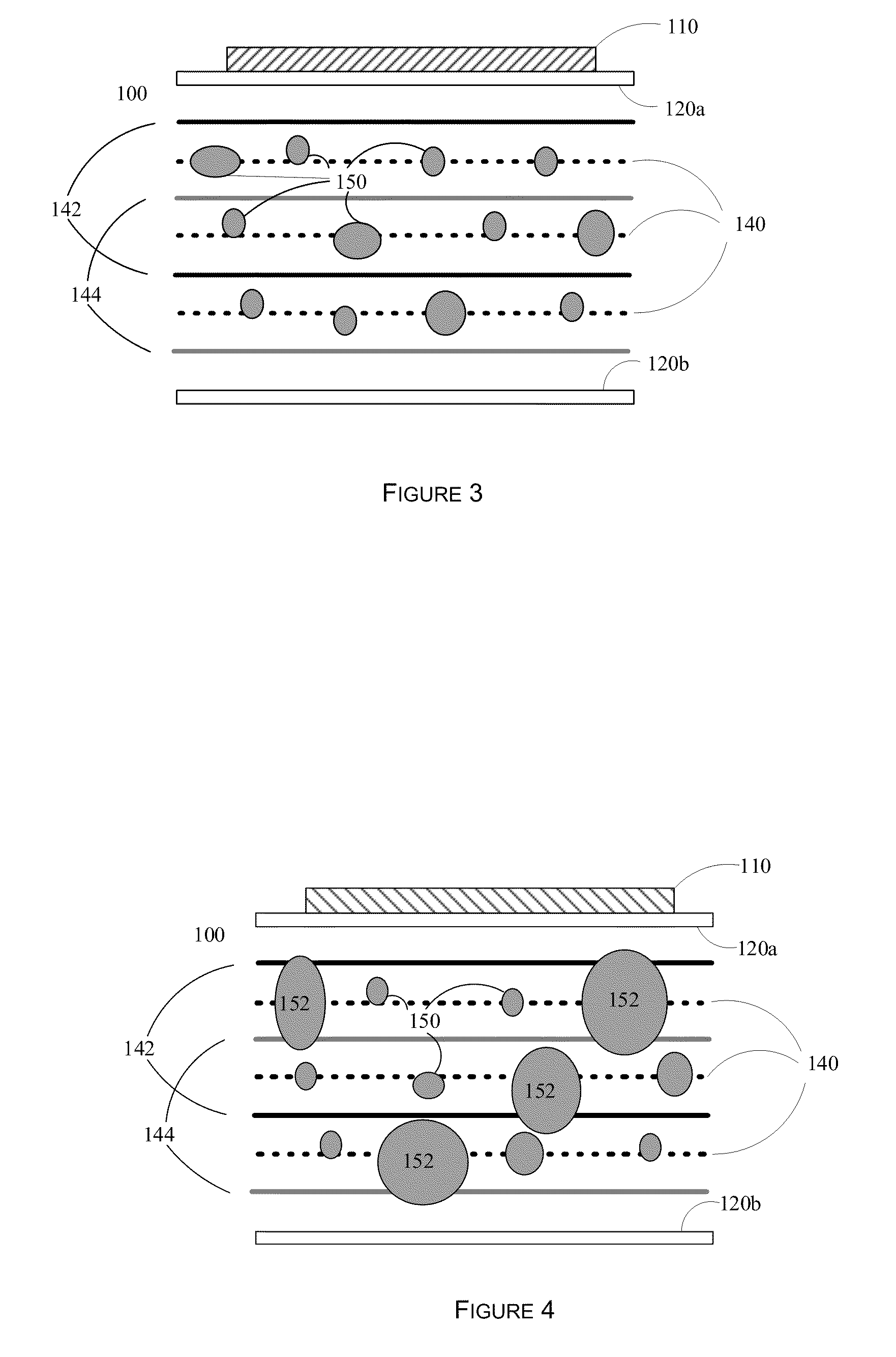
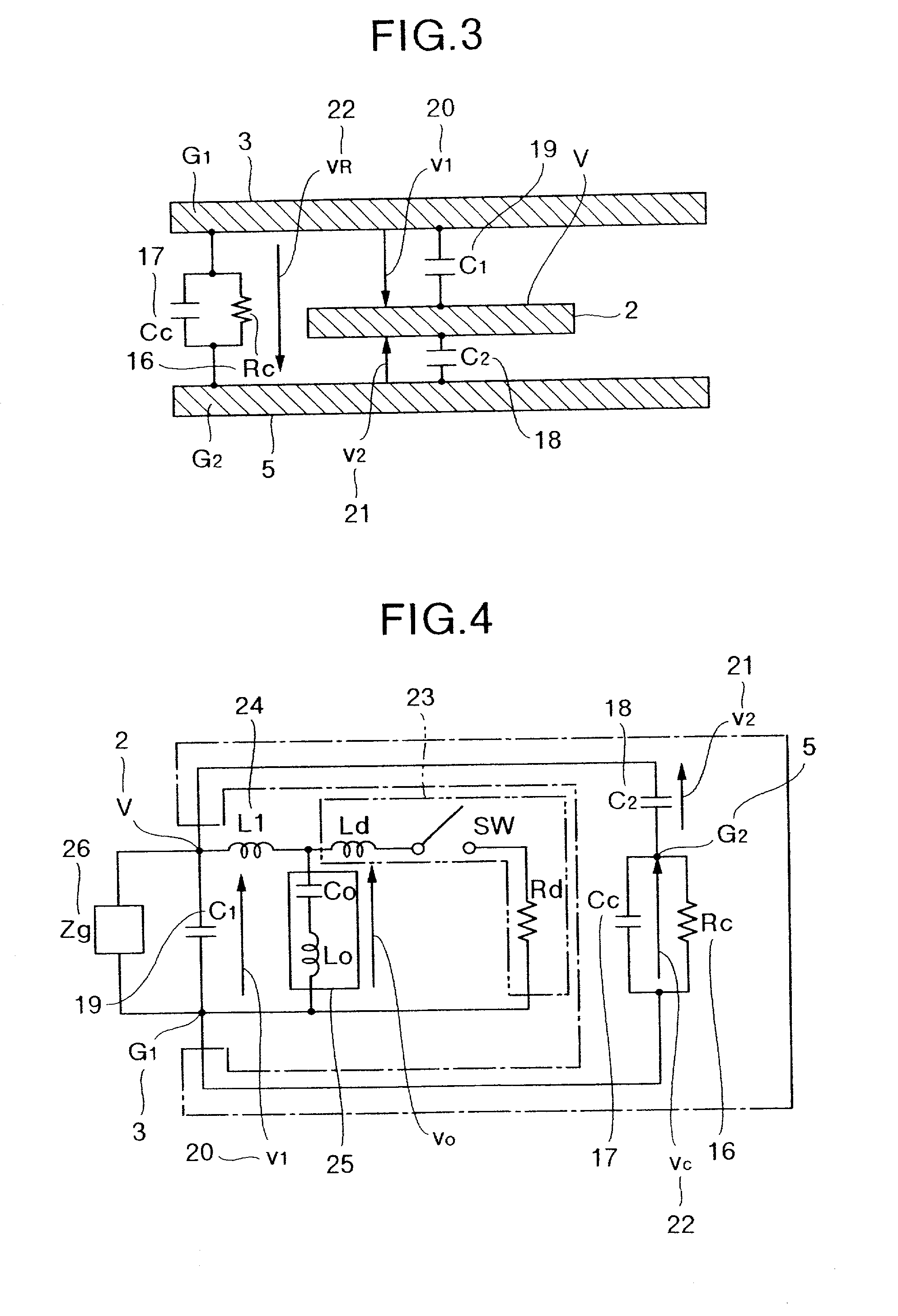
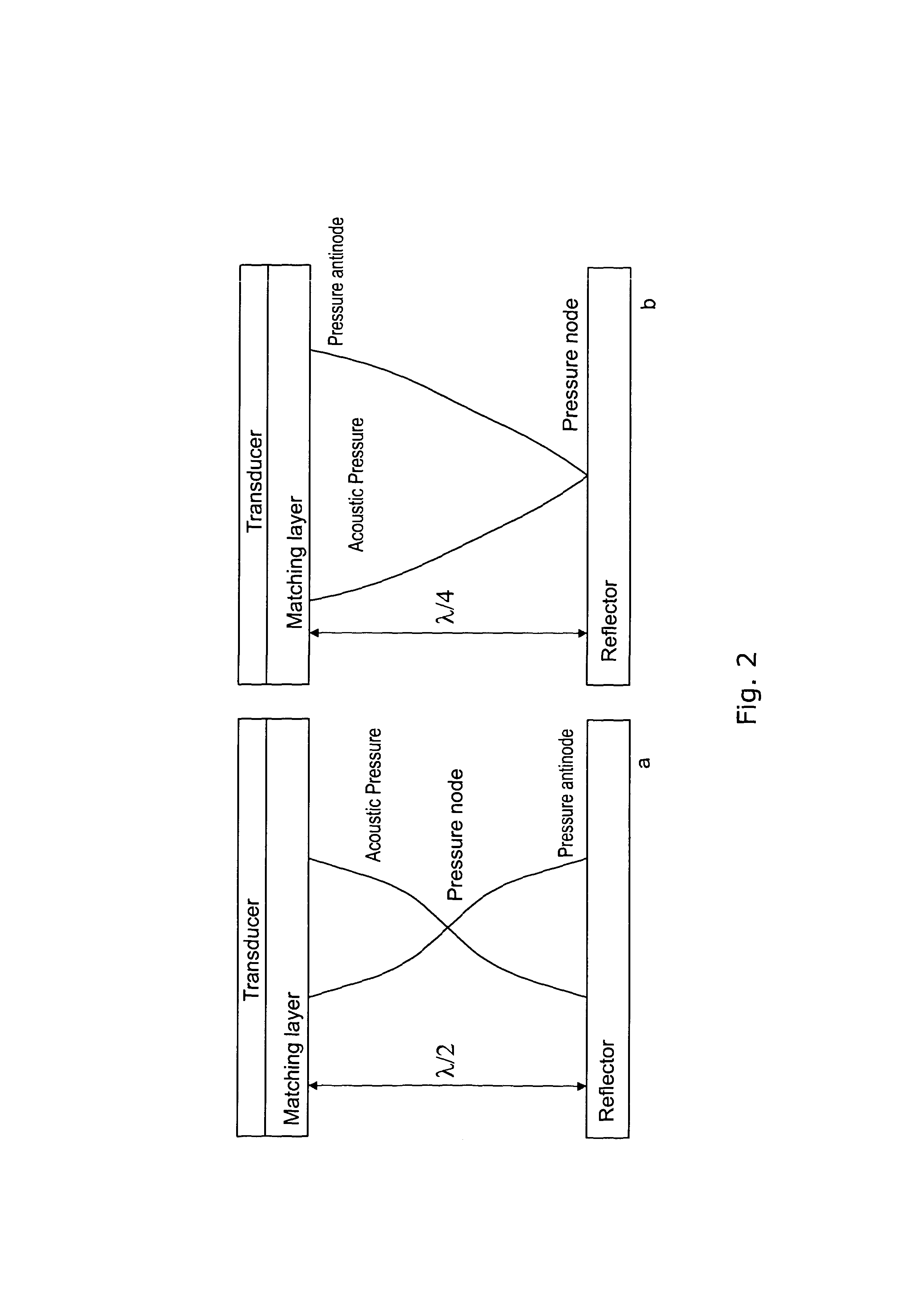
In physics, a standing wave, also known as a stationary wave, is a wave which oscillates in time but whose peak amplitude profile does not move in space. The peak amplitude of the wave oscillations at any point in space is constant with time, and the oscillations at different points throughout the wave are in phase. The locations at which the amplitude is minimum are called nodes, and the locations where the amplitude is maximum are called antinodes.
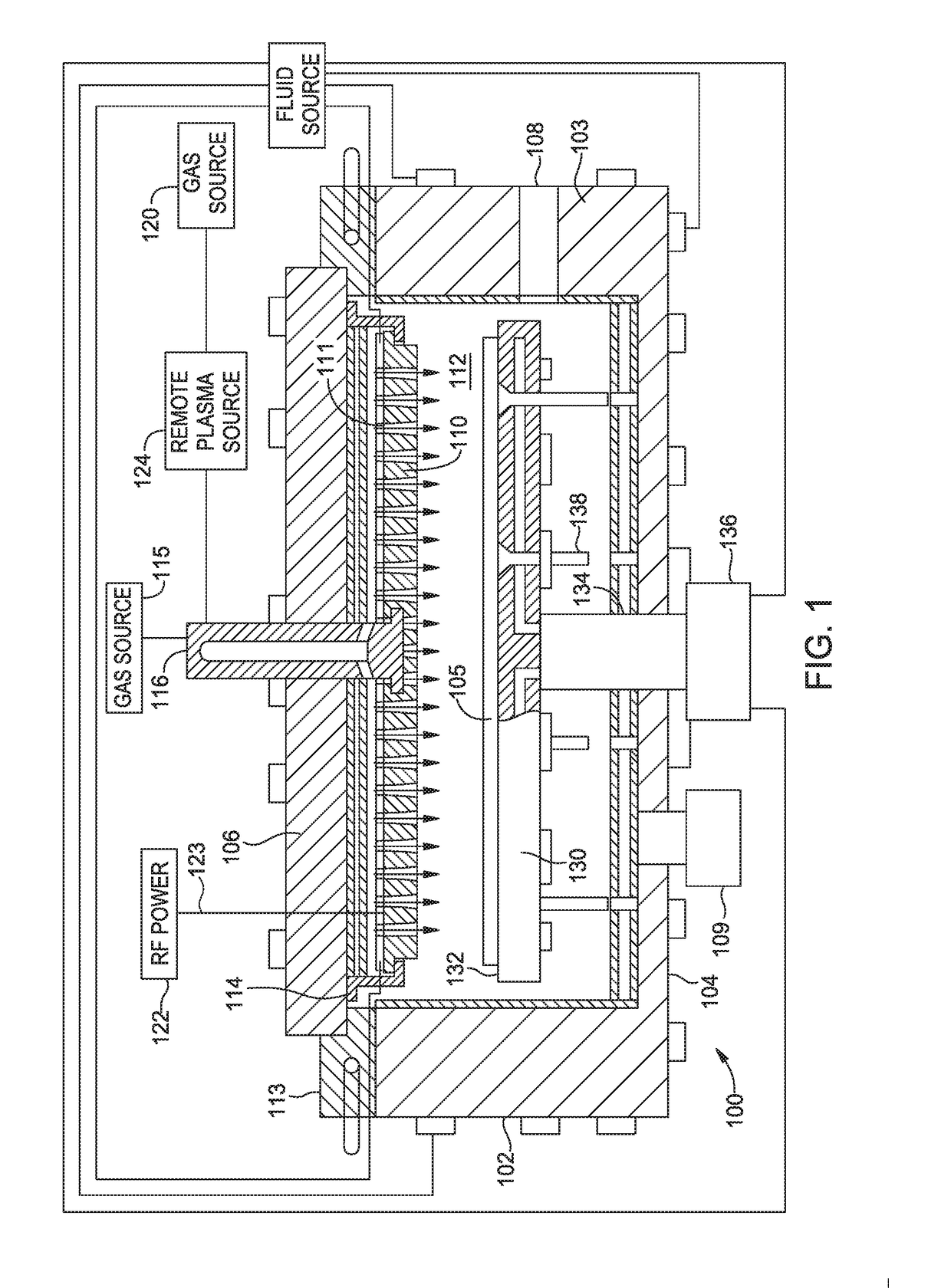
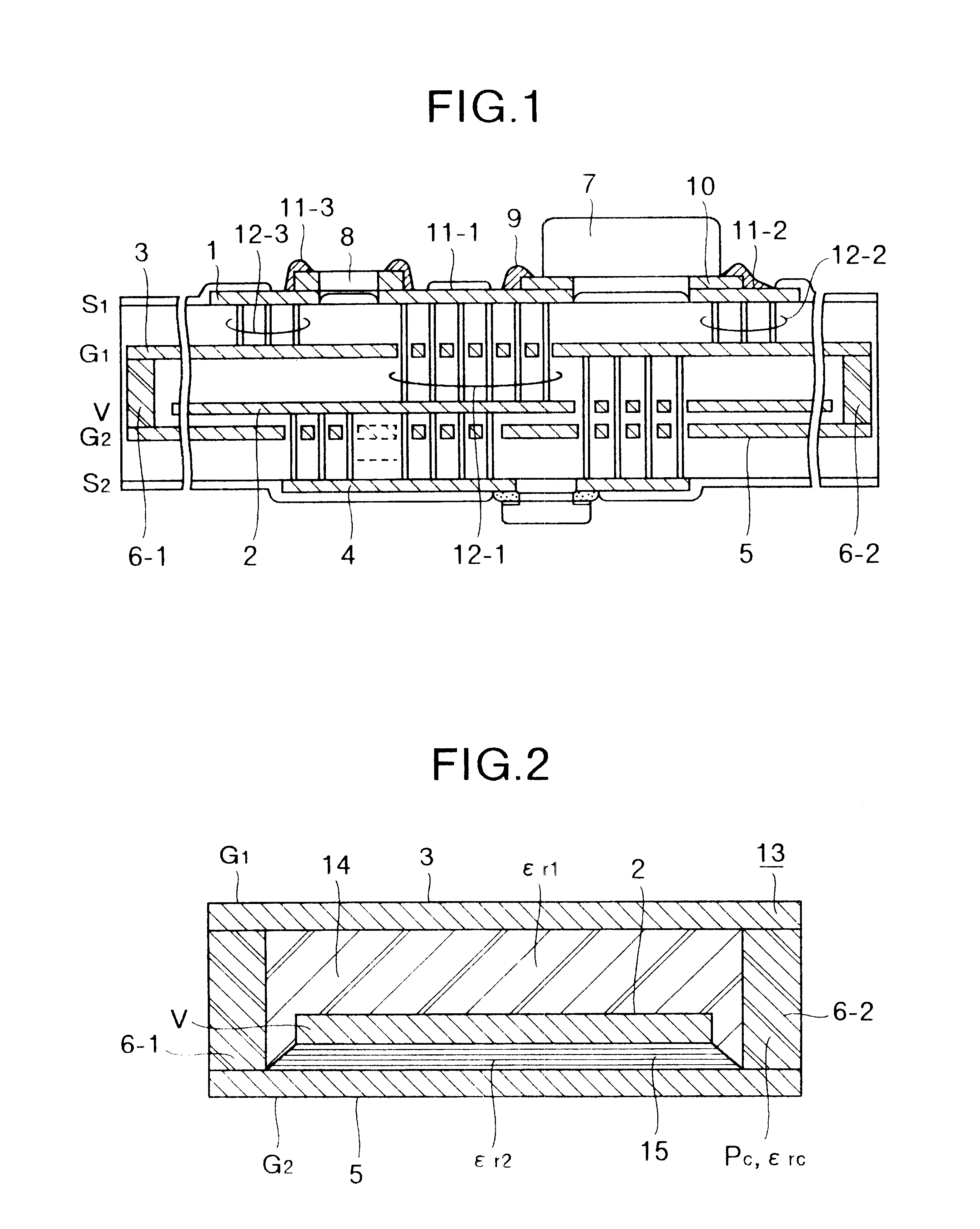
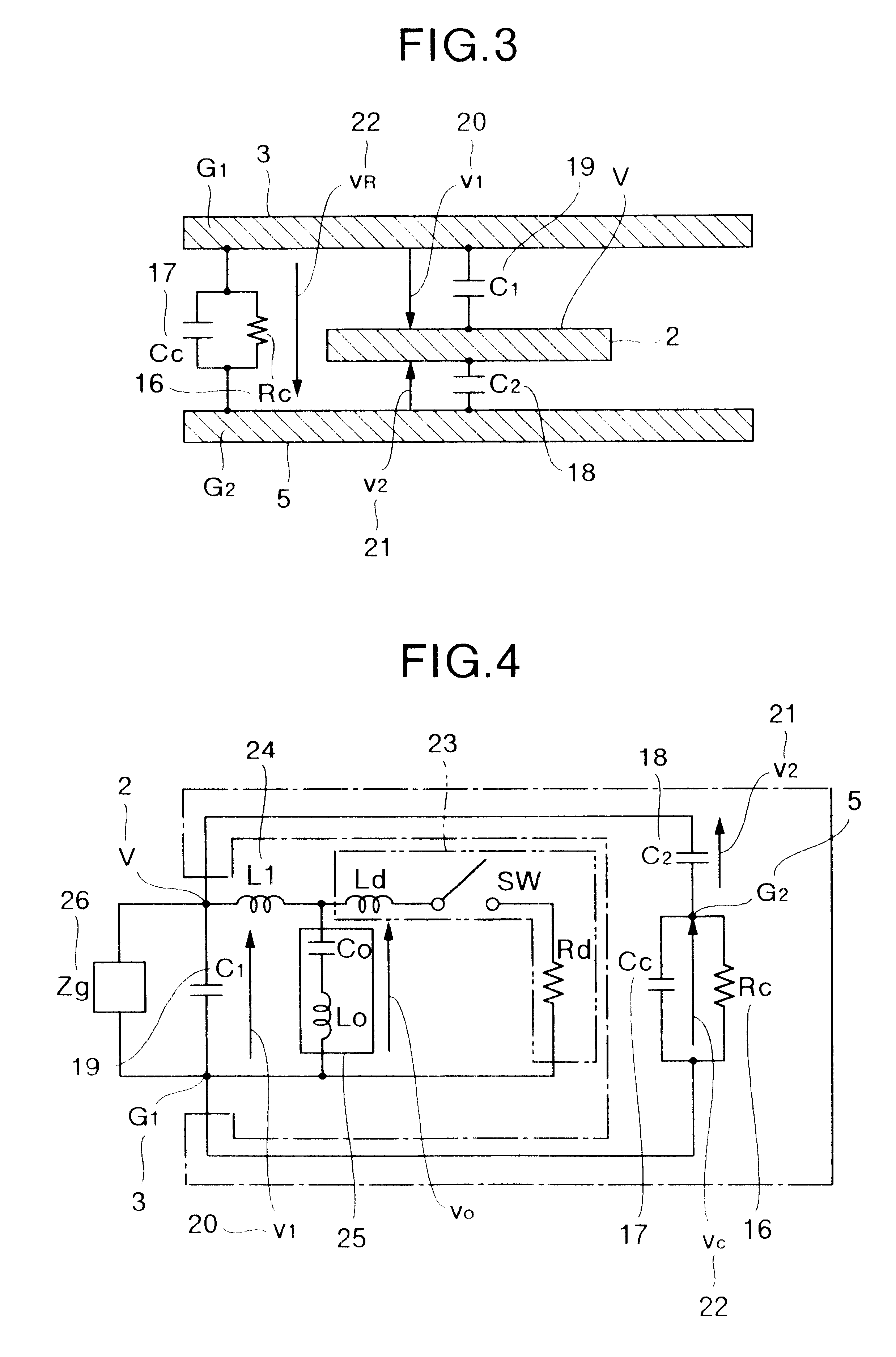
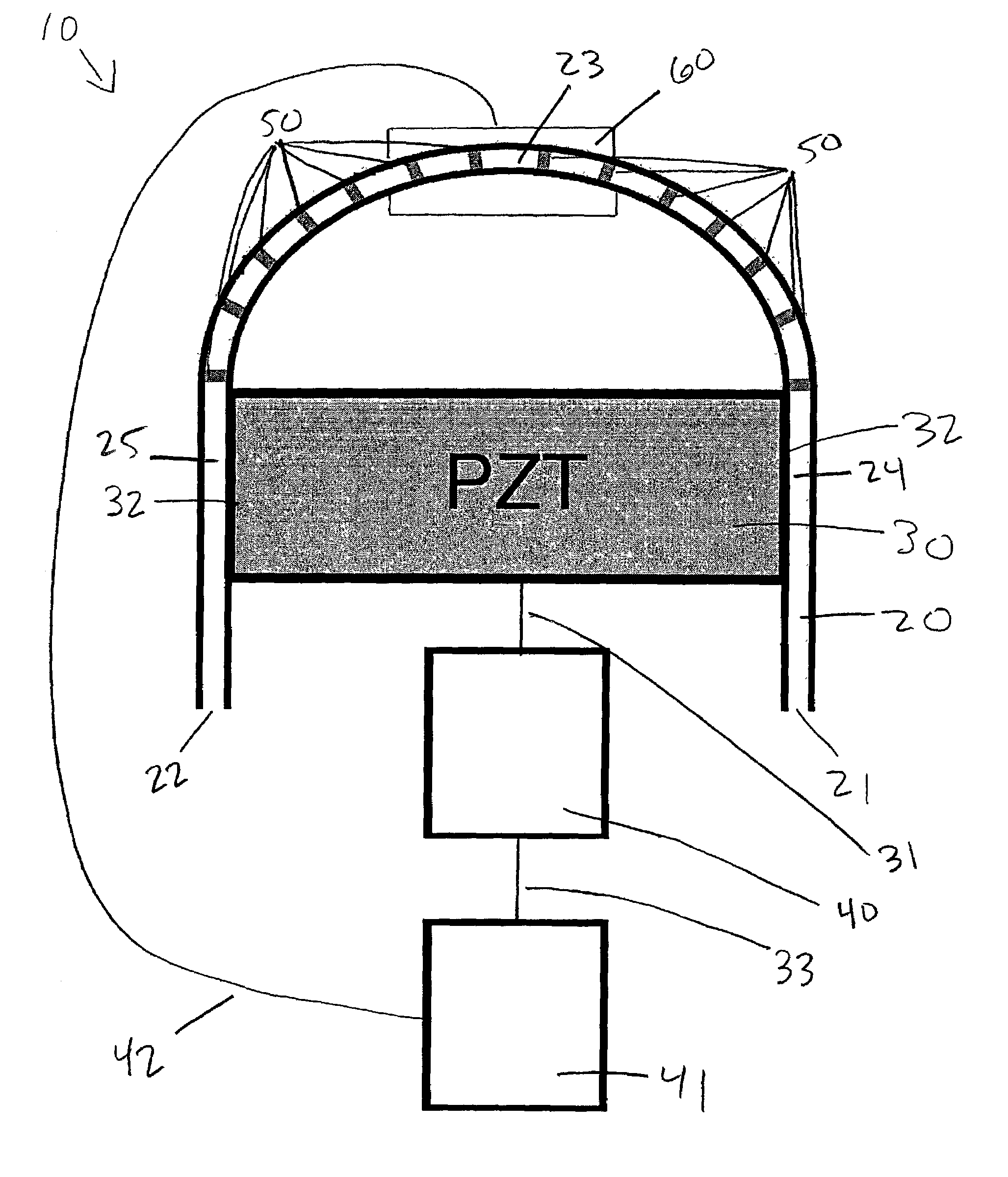
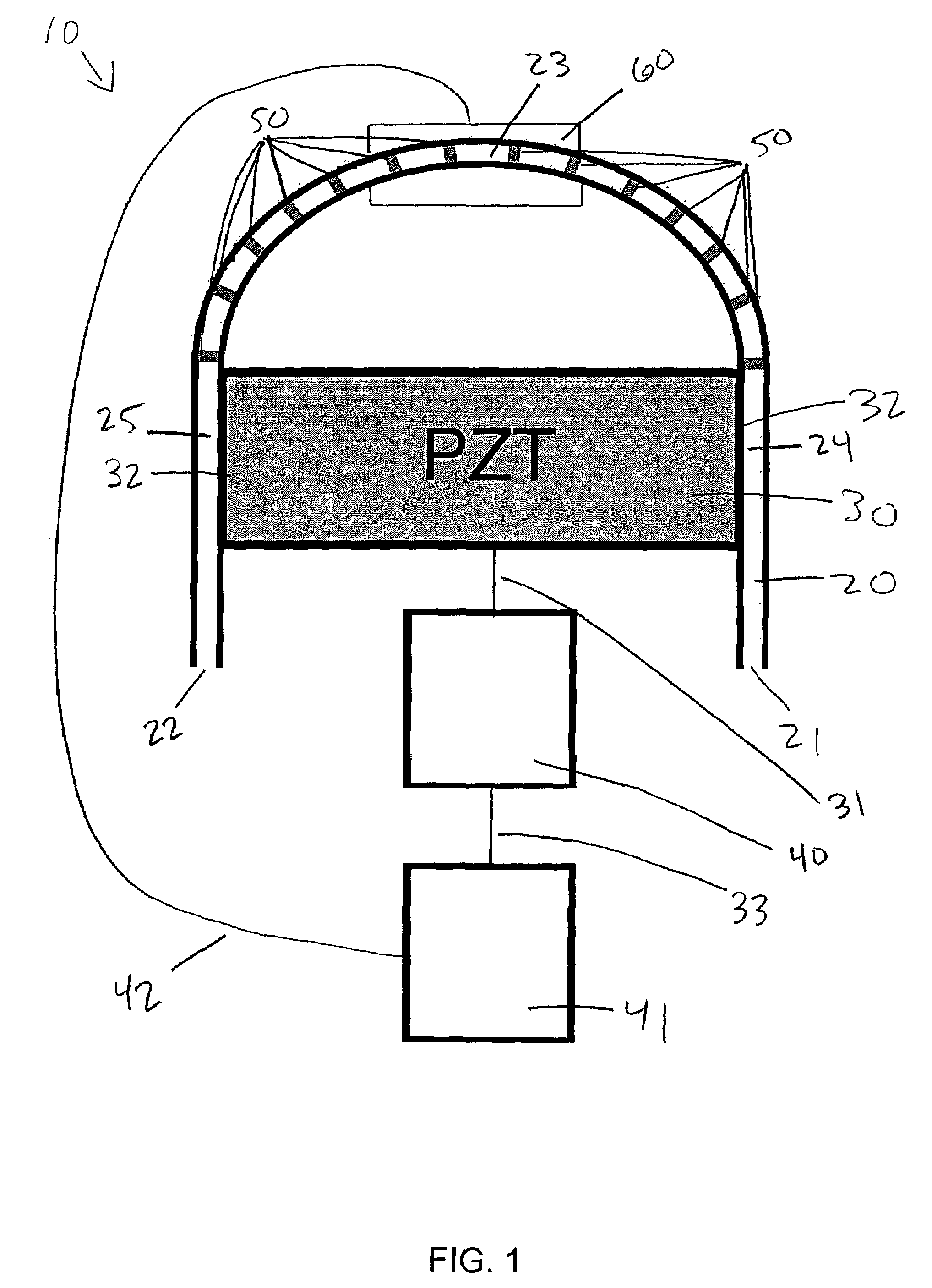
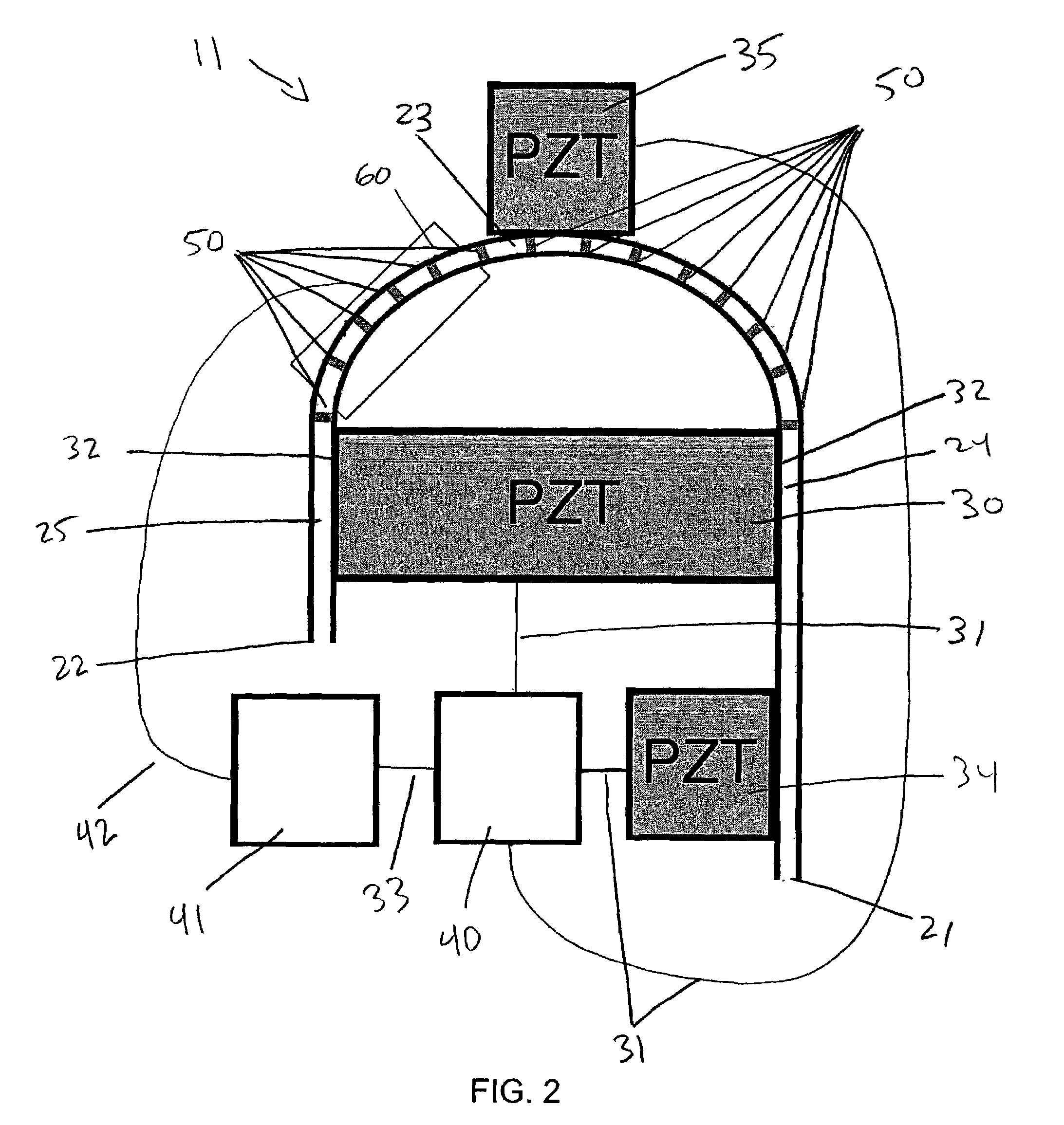
Method of controlling the film properties of PECVD-deposited thin films
ActiveUS20050255257A1Increase in hollow cathode effectIncrease surface areaElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPlasma densityEngineering
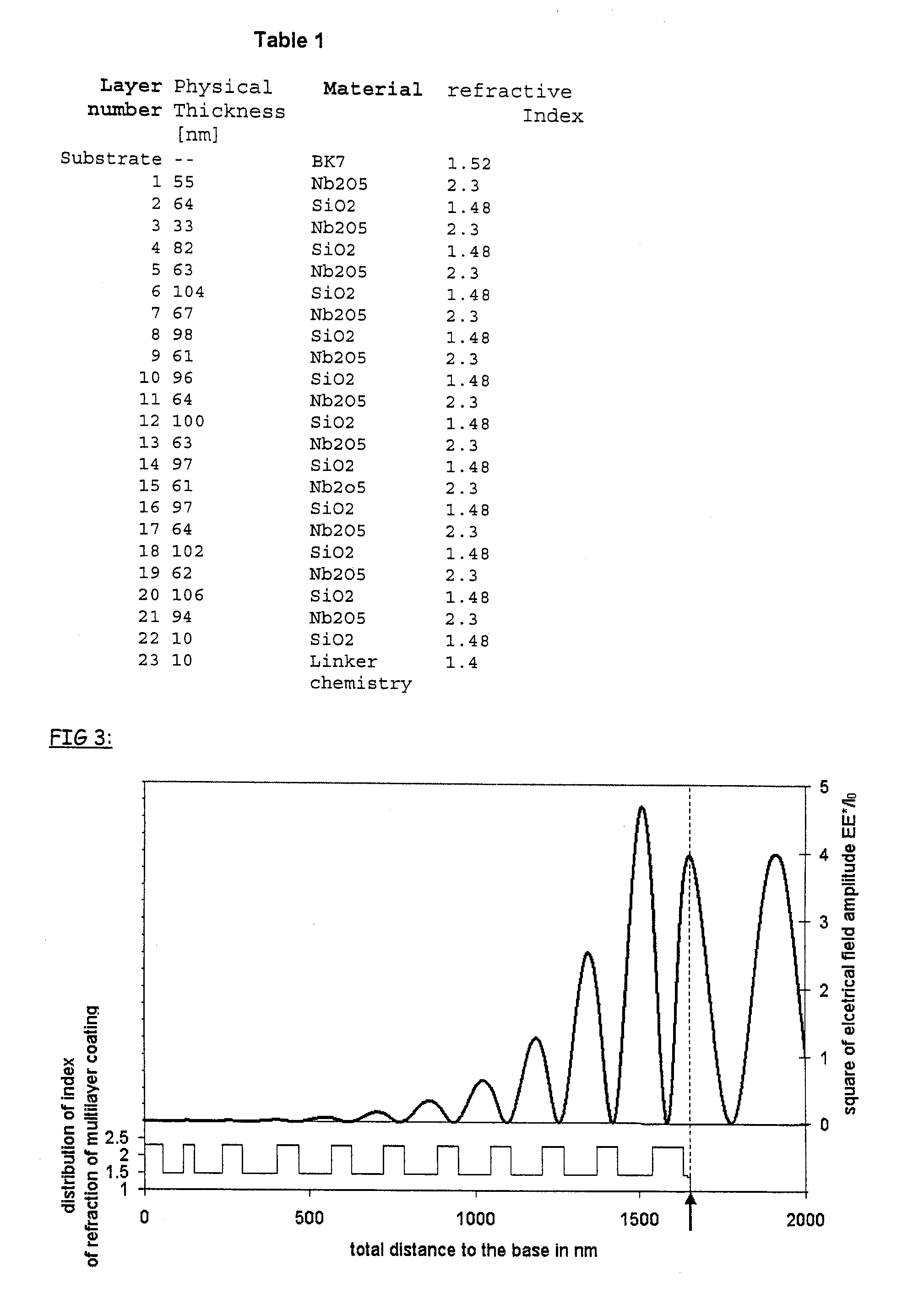
We have discovered methods of controlling a combination of PECVD deposition process parameters during deposition of thin films which provides improved control over surface standing wave effects which affect deposited film thickness uniformity and physical property uniformity. By minimizing surface standing wave effects, the uniformity of film properties across a substrate surface onto which the films have been deposited is improved. In addition, we have developed a gas diffusion plate design which assists in the control of plasma density to be symmetrical or asymmetrical over a substrate surface during film deposition, which also provides improved control over uniformity of deposited film thickness.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
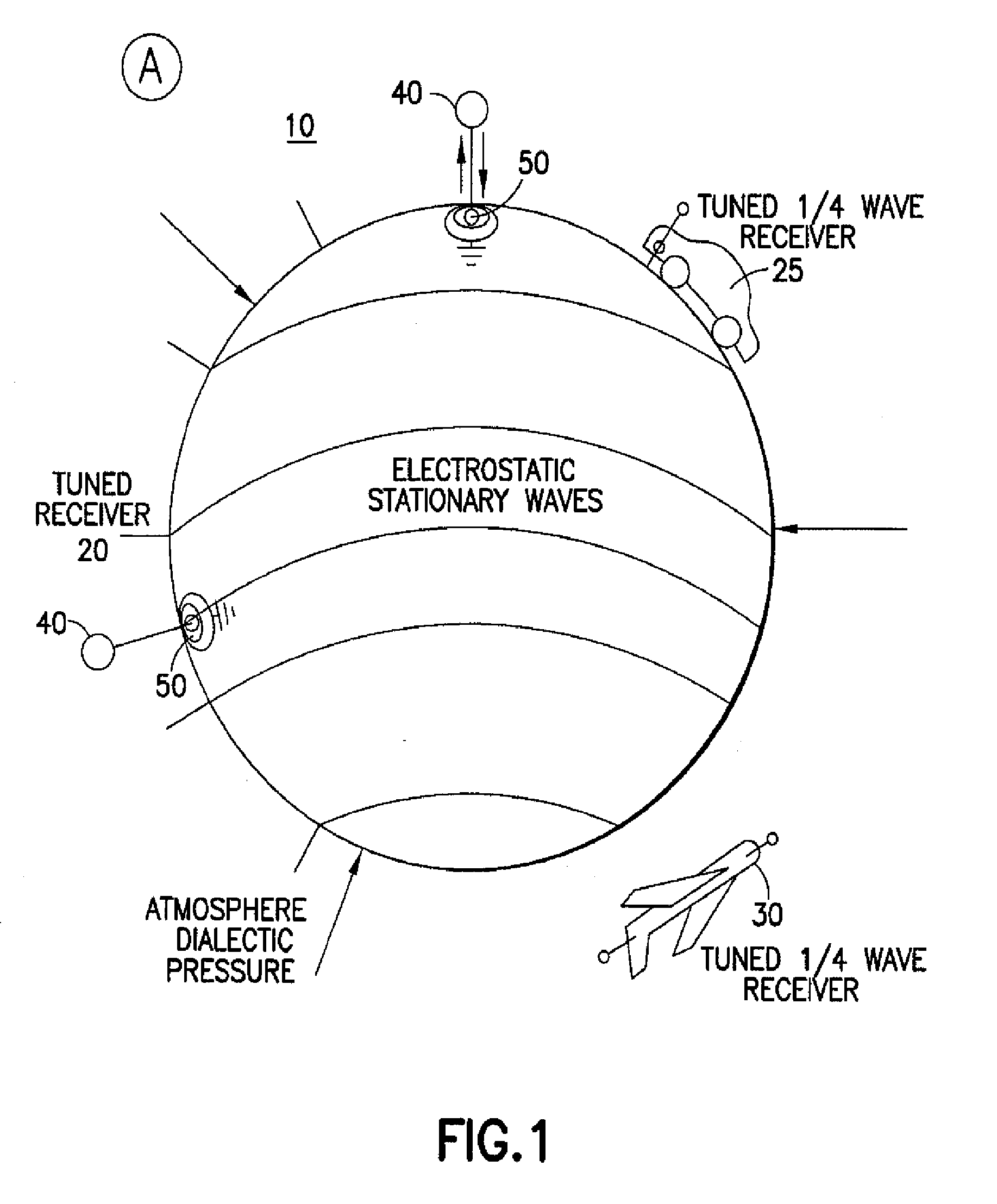
Wireless Energy Transfer System
InactiveUS20110156494A1Increase positive chargeHigh energyElectromagnetic wave systemTransformersEnergy transferTransmitted power
A system for transmitting power without wires or with no more than one connection, wherein communication is provided between an unlimited number of electronic devices, or to connect these devices to an unlimited number networks that are located externally to the system to thereby enable high speed voice and data communications over a single resonant connection At least one transmitter and one receiver are utilized, which may have the same or different configurations, such that an induced oscillating electπc current, which occurs at the resonant frequency of a transmitter, induces a standing wave The standing wave is tuned and “tapped” by a receiver having a coil or set of plates and receivers that are tuned to oscillate at the same frequency or one of its harmonics and, thus, absorb an electrical current and / or signals at the receiver
Owner:GOVERNING DYNAMICS LLC
Grooved backing plate for standing wave compensation
ActiveUS20170092469A1Electric discharge tubesChemical vapor deposition coatingPath lengthEngineering
Implementations described herein generally relate to components and methods used in plasma processing, and more specifically relate to grooved surfaces for controlling RF return path lengths in plasma processing chambers and methods for forming the same. In one implementation, a backing plate for a plasma processing chamber is provided. The backing plate comprises a rectangular body. The rectangular body has a front surface, a back surface opposing the front surface, a first axis perpendicular to a center of the rectangular body and a plurality of grooves formed in the front surface. At least one groove of the plurality of grooves has a first length across the groove in a first location and a second length across the groove in a second location.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
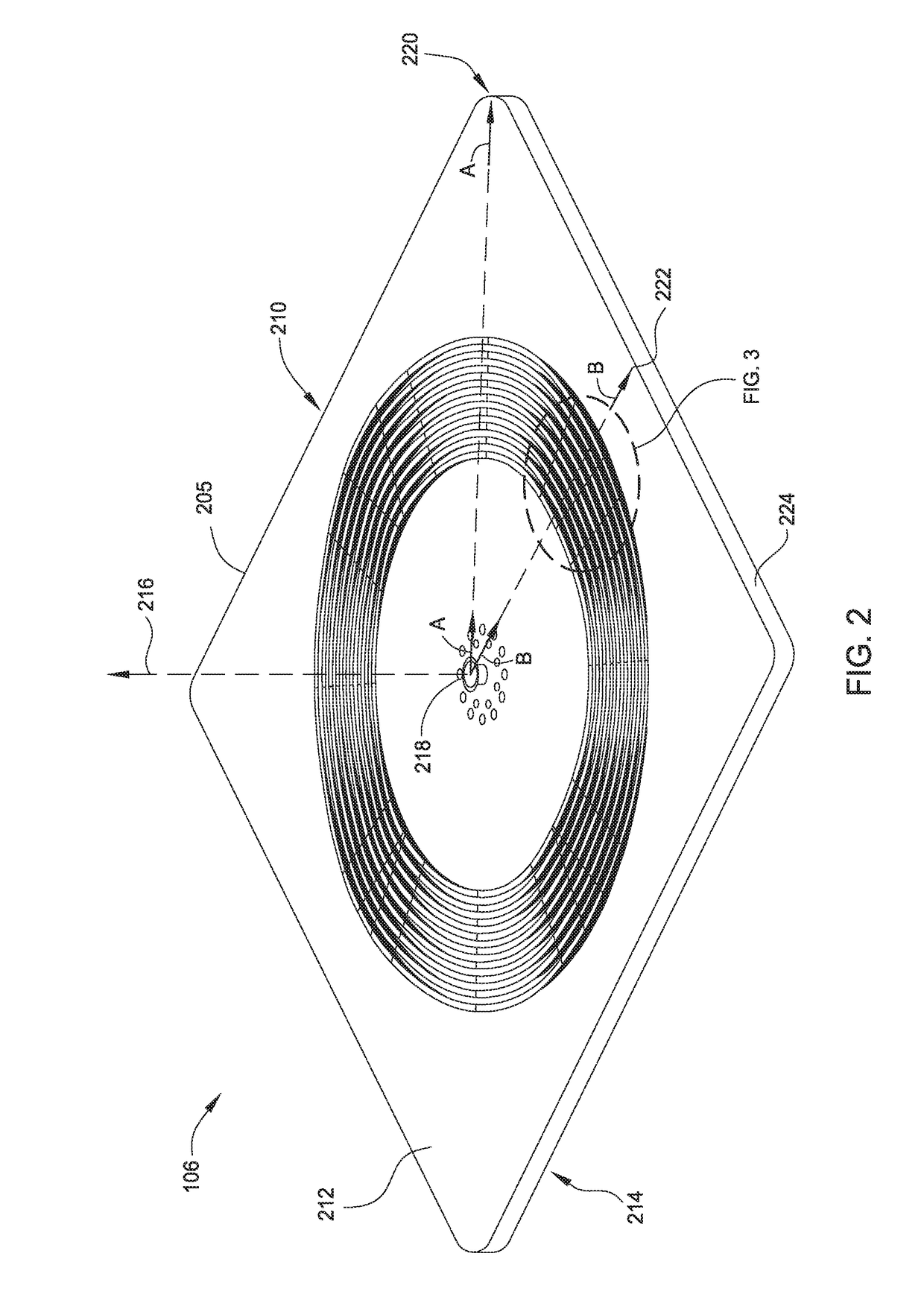
Forward throw antenna utility meter
InactiveUS20080129536A1Impedance matchingElectric signal transmission systemsElectrical measurementsTransceiverEngineering
Systems and methods are provided for a utility meter assembly comprising: a plurality of meter components configured for measuring and collecting data, wherein the meter components include a transceiver operative for signal communications over a network; a faceplate, configured such that meter reading information is displayed on the front of the faceplate; an exterior cover configured to enclose the meter components and the faceplate, wherein the faceplate is forward of the plurality of meter components; and an internal dipole antenna situated within the exterior cover, wherein the internal dipole antenna is beyond the front of the faceplate and toward the front of the utility meter assembly. The internal dipole antenna is typically situated away from the meter components, so as to minimize interference by the meter components. The internal dipole antenna is typically tuned for optimal matching impedance in an 850 MHz or 1900 MHz receiving band, so that the desired receiving band Standing Wave Ration (SWR) is achieved, and also a specified minimum radiated power threshold is maintained.
Owner:ITRON +1
Method of controlling the film properties of PECVD-deposited thin films
ActiveUS7785672B2Improve performanceImprove uniformityElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDiffusionPlasma density
We have discovered methods of controlling a combination of PECVD deposition process parameters during deposition of thin films which provides improved control over surface standing wave effects which affect deposited film thickness uniformity and physical property uniformity. By minimizing surface standing wave effects, the uniformity of film properties across a substrate surface onto which the films have been deposited is improved. In addition, we have developed a gas diffusion plate design which assists in the control of plasma density to be symmetrical or asymmetrical over a substrate surface during film deposition, which also provides improved control over uniformity of deposited film thickness.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Low-EMI electronic apparatus, low-EMI circuit board, and method of manufacturing the low-EMI circuit board.
InactiveUS6353540B1Radiation suppressionHigh packageMagnetic/electric field screeningFinal product manufactureCapacitanceCountermeasure
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Mixing frequency at multiple feeding points
Embodiments disclosed herein generally relate to obtaining a substantially uniform plasma distribution within a large area processing chamber. For large area processing chambers that utilize RF voltages, standing waves can lead to deposition and / or etching non-uniformities. By applying RF voltage in at least two separate locations at two separate, but close frequencies with or without phase modulation, the wave interference pattern moves across the electrode. By moving the standing wave across the electrode, the plasma generated in the chamber can, over time, be substantially uniform.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method and apparatus for separating particles by size
InactiveUS7108137B2Easy to manufactureLow costWater/sewage treatment with mechanical oscillationsParticle size analysisUltrasonic radiationHigh pressure
A method and apparatus for separating a mixture of particles of various sizes in a capillary tube into groups by size using multiple forces of controlled amplitude. Ultrasonic radiation at a first selected frequency is applied to set up a standing pressure wave in the capillary tube, resulting in a first aggregating force which causes particles of all sizes to aggregate at positions within the capillary tube which correspond to nodes or anti-nodes of the standing wave. Transverse vibrations are also applied to the capillary tube. The frequency of the ultrasonic radiation is adjusted to reduce the magnitude of the first aggregating force. Inertial forces resulting from the transverse vibrations then cause the particles to separate by size. The apparatus and method allows a mixture of particles to be separated by size quickly, without requiring the use of high voltages.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Apparatus and method for separation of particles suspended in a liquid from the liquid in which they are suspended
InactiveUS20100078384A1Improve concentrationAvoid turbulenceSemi-permeable membranesLiquid separation by electricityUltrasonic sensorCompressibility
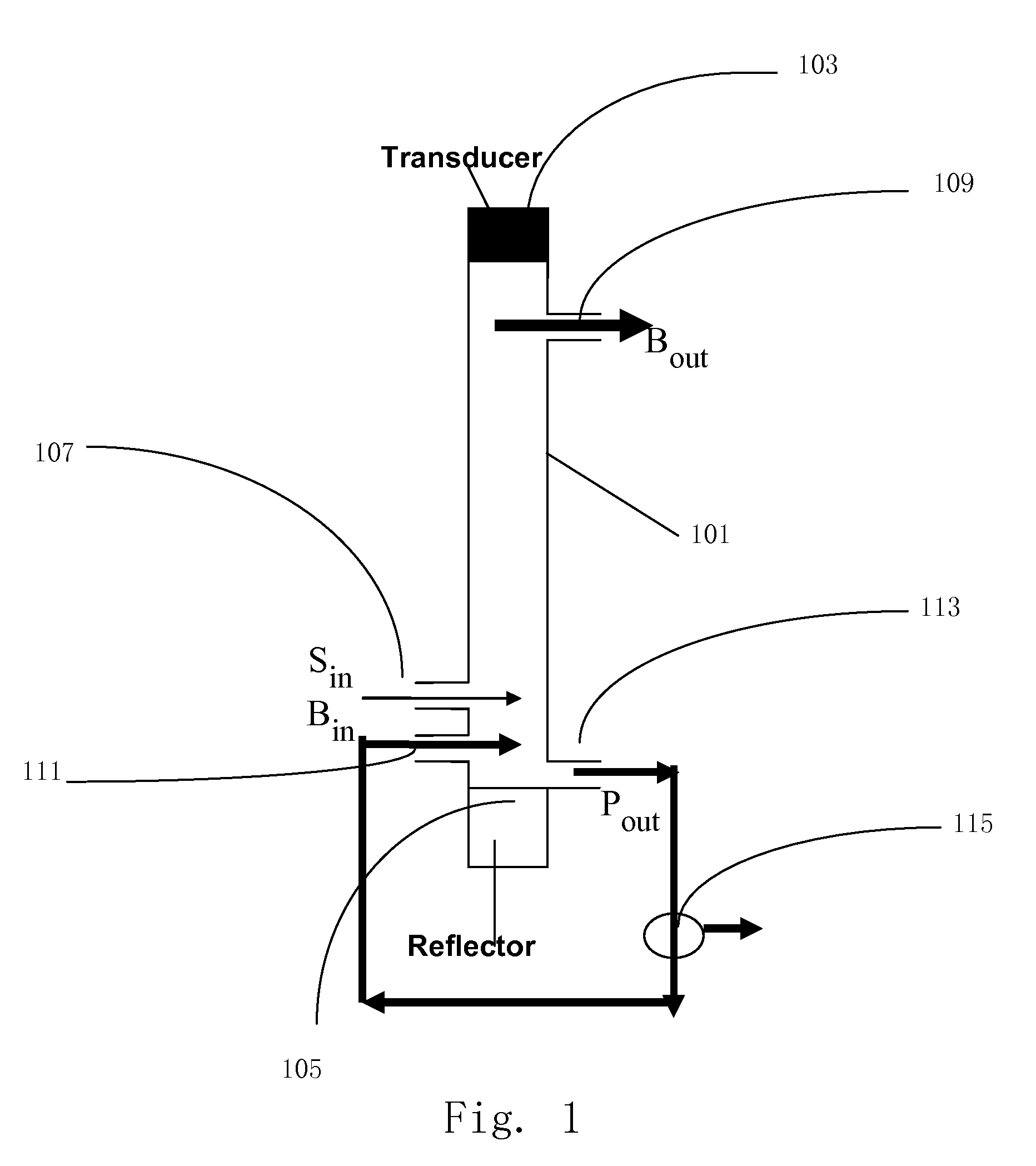
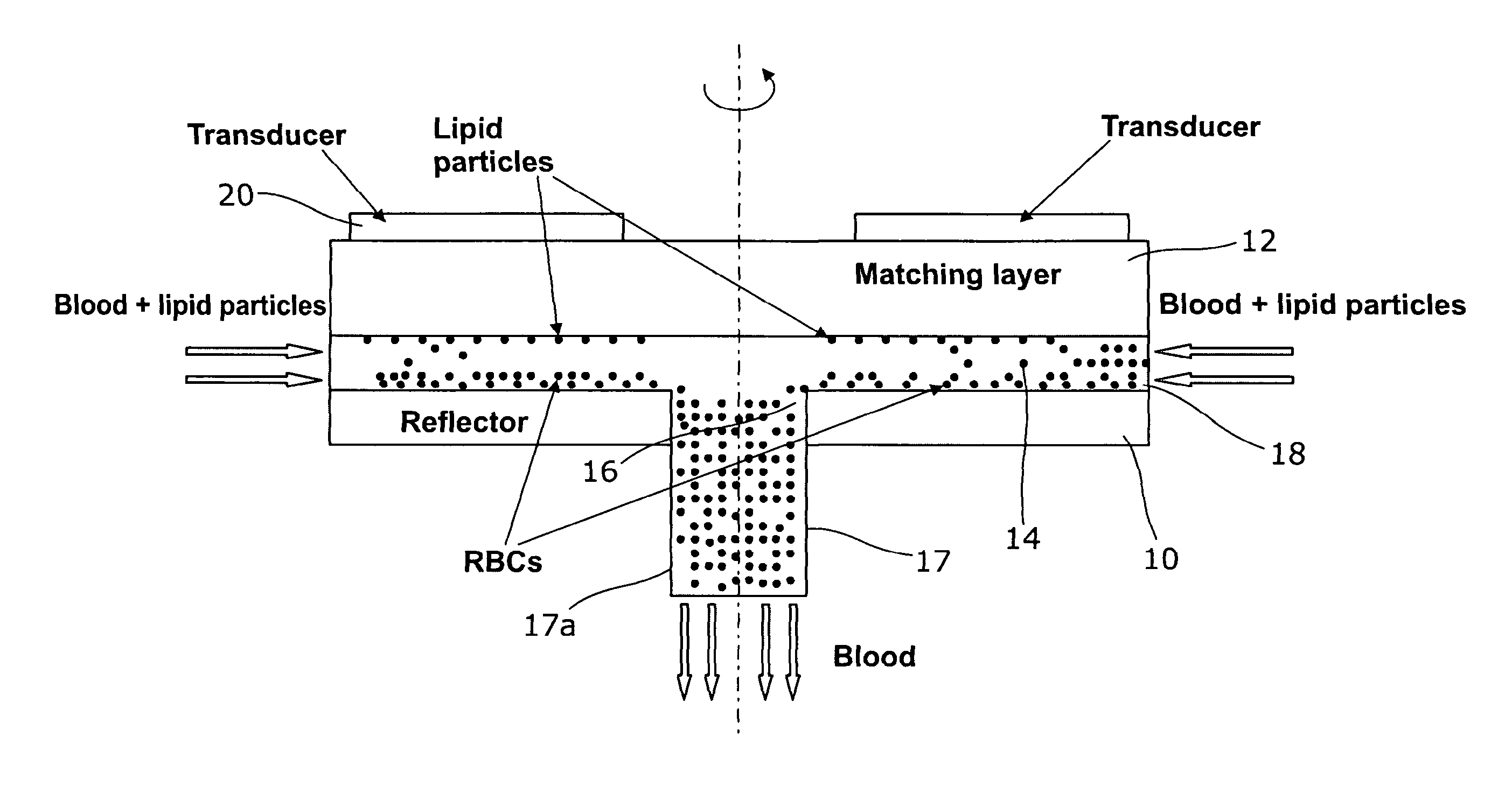
A method for separating, or removing, particulate material, e.g., blood cells, from a sample of fluid, e.g., whole blood of a patient, in which the particulate material is suspended. In the case of separating blood cells from blood plasma or blood serum, the resulting samples of blood plasma or blood serum can be used for in vitro diagnostic applications. In normal practice, a whole blood sample of a patient are provided and then introduced into an apparatus that contains a flow channel. An acoustic field, which contains acoustic standing waves from external ultrasonic transducers, is located within the flow channel. Laminar flow is maintained in the flow channel. Blood cells and platelets are separated from blood plasma or blood serum at the end of the flow channel and collected. The method described herein allows fluid components to differentially migrate to areas of preferred acoustic interaction. The parameters that affect separation of particles are size, density, compressibility of the particles, and the fluid surrounding the particles.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Electromagnetic systems with double-resonant spiral coil components
InactiveUS7973296B2Easy to operateHigh outputNuclear energy generationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitanceElectrical conductor
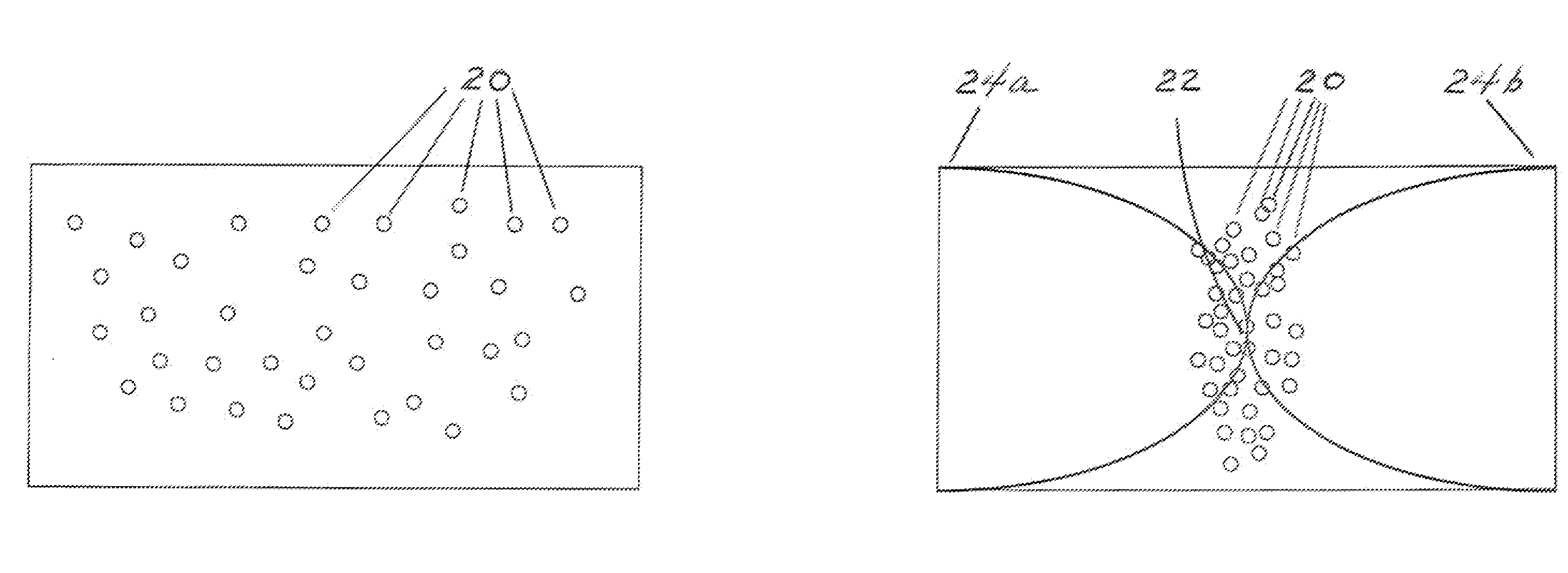
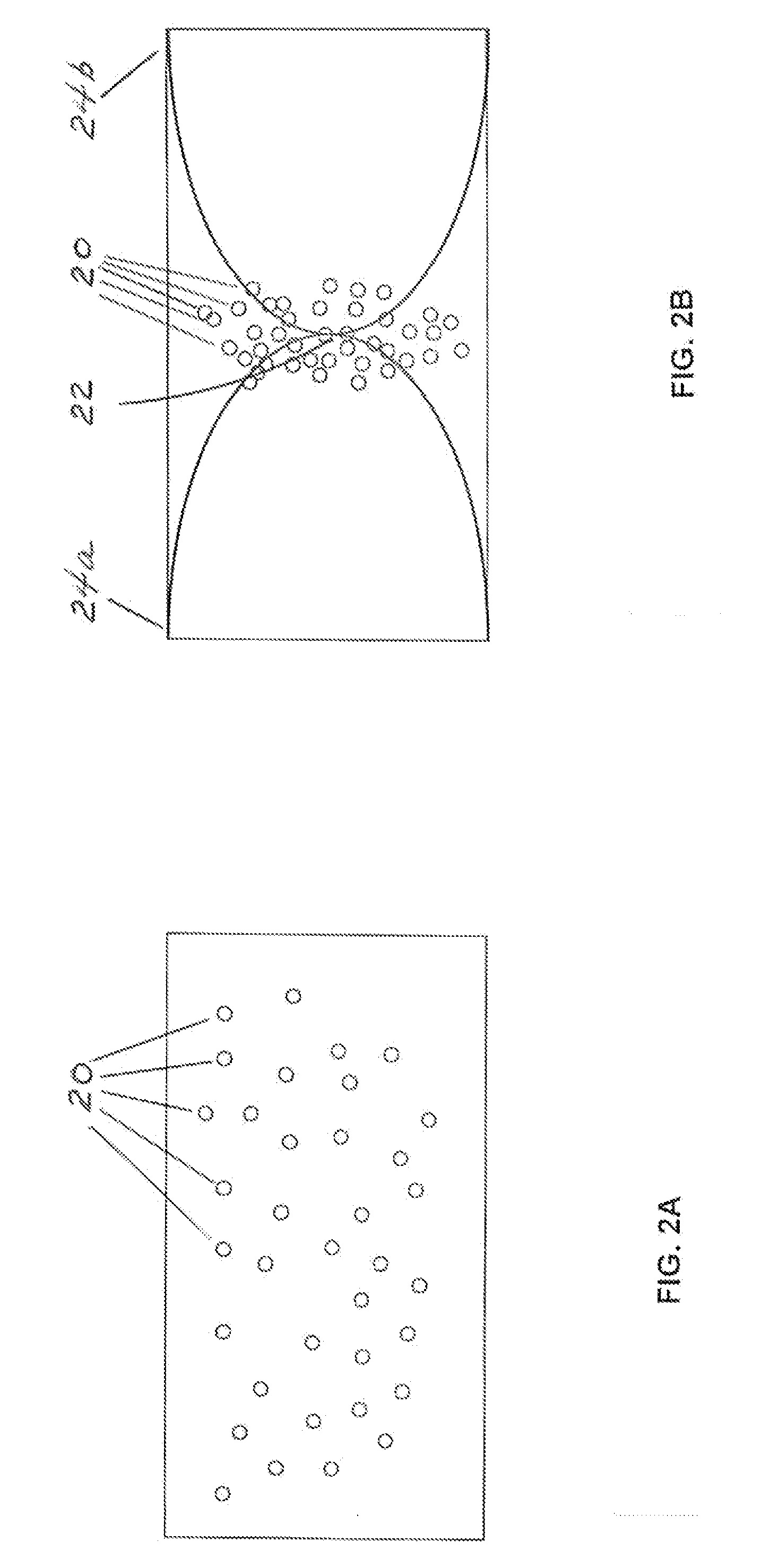
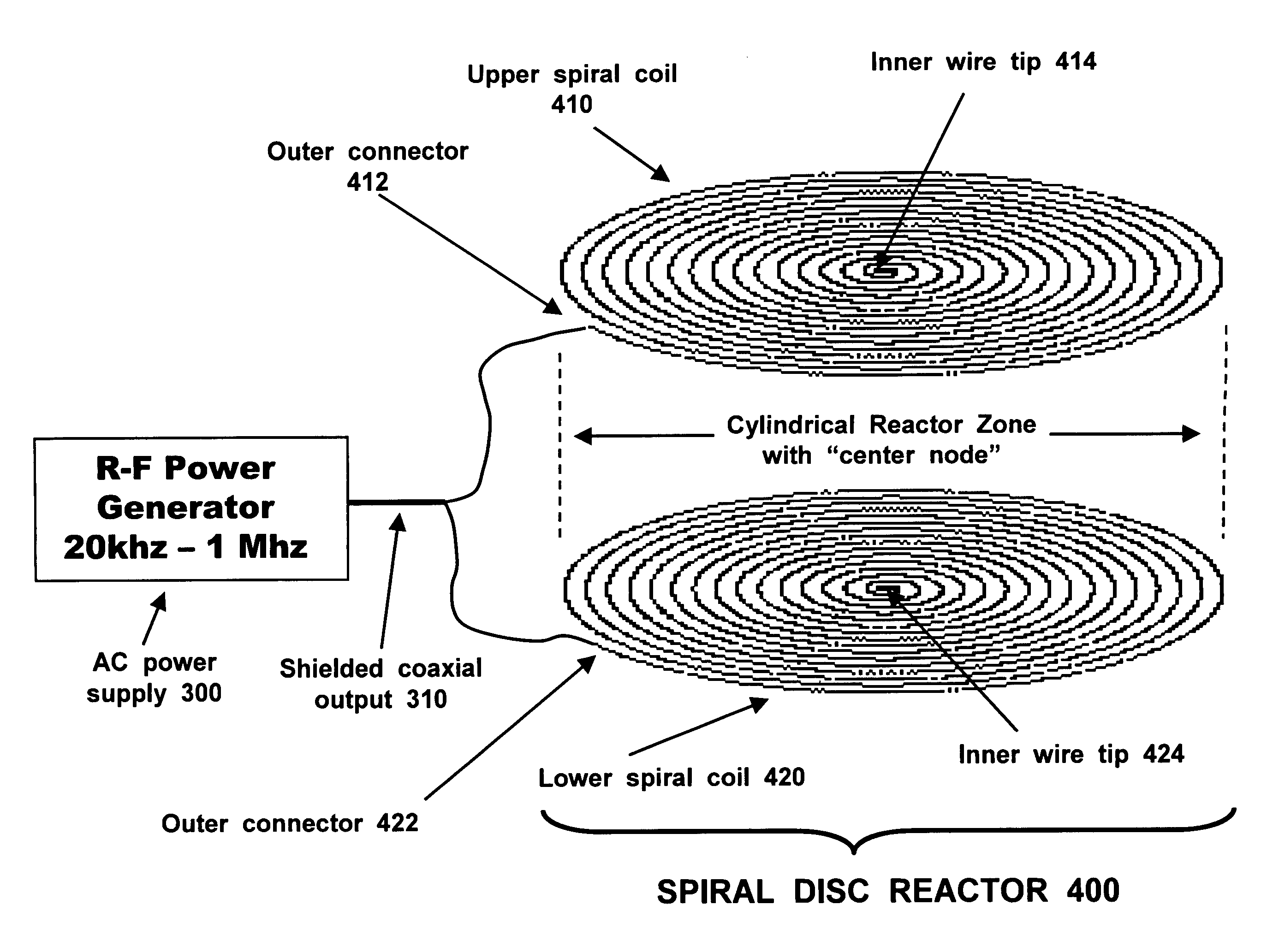
Spiral coils generate very powerful electromagnetic fields by operating with two different but simultaneous resonant behaviors. Quarter-wave resonance is established by adjusting the frequency (and wavelength) of a radiofrequency (RF) voltage source until the length of the spiral conductor is equal to ¼ of the wavelength of the alternating voltage. This generates an electromagnetic standing wave with at least one peak node and at least one null node. Inductive-capacitive (L / C) resonance is established by optimizing the thickness and width of the wire ribbon used to make the spiral coil. When inductance and capacitance are balanced, the current response will synchronize with the voltage input, creating in-phase behavior, minimal total impedance, and maximal power output. If two such coils are placed near each other, they will create an extremely powerful electromagnetic field between them, which can promote chemical and plasma reactions involving charged particles such as ions or plasma particles, possibly including nuclear fusion reactions.
Owner:TETRAHEED
Method and device for ultrasonically manipulating particles within a fluid
InactiveUS7846382B2Easy to operateAuxillary pretreatmentShaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersBiological particlesSolid phase extraction
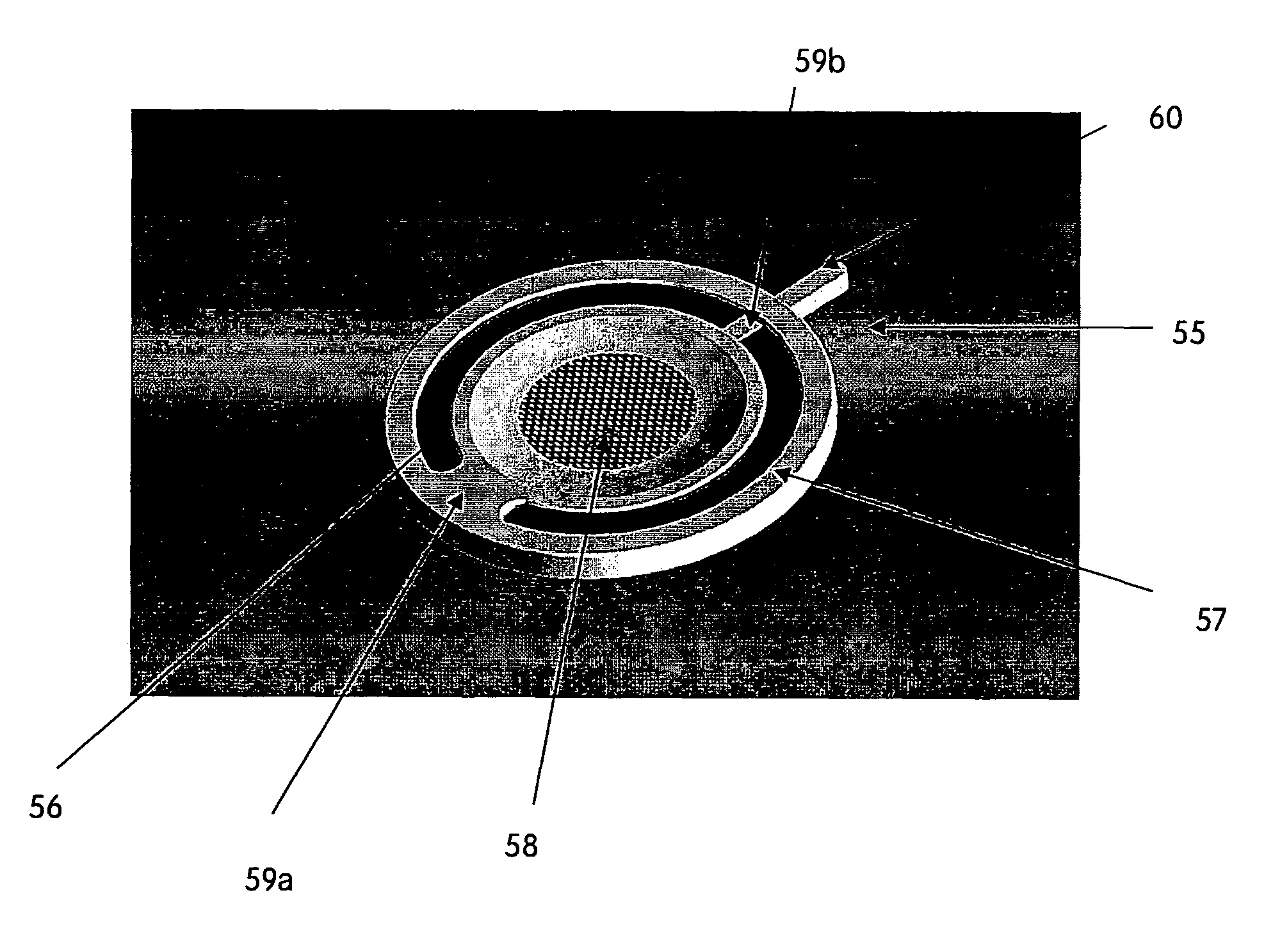
Fluid-handling methods and devices for ultrasonic manipulation of fluid-borne particles comprise a fluid-handling manifold and an ultrasonic particle manipulator defining an ultrasonic cavity within the manifold. Fluid-borne particles introduced into the manifold are manipulated by controlling ultrasonic standing waves at the ultrasonic cavity. Cavities having non-uniform configurations, asymmetric standing waves and / or multiple ultrasonic cavities within the manifold are operative to control the movement of the fluid-borne particles, optionally including collecting and holding such particles, transferring particles through an intersection from one channel to another, etc. Solid phase extraction (SPE) particles, biological particles and other fluid-borne particles can be manipulated within the fluid-handling manifold.
Owner:PROTASIS CORP
Nanocomposite microresonators
InactiveUS6876796B2High refractive indexGood optical performanceMaterial nanotechnologyNanomedicineIsolatorNanoparticle
A microresonator is provided that incorporates a composite material comprising a polymer matrix and nanoparticles dispersed therein. The microresonator includes the composite material having a shape that is bounded at least in part by a reflecting surface. The shape of the microresonator allows a discrete electromagnetic frequency to set up a standing wave mode. Advantageously, the polymer matrix comprises at least one halogenated polymer and the dispersed nanoparticles comprise an outer coating layer, which may also comprise a halogenated polymer. Methods for making composite materials and microresonators are also provided. Applications include, for example, active and passive switches, add / drop filters, modulators, isolators, and integrated optical switch array circuits.
Owner:PHOTON
Device and method for separation
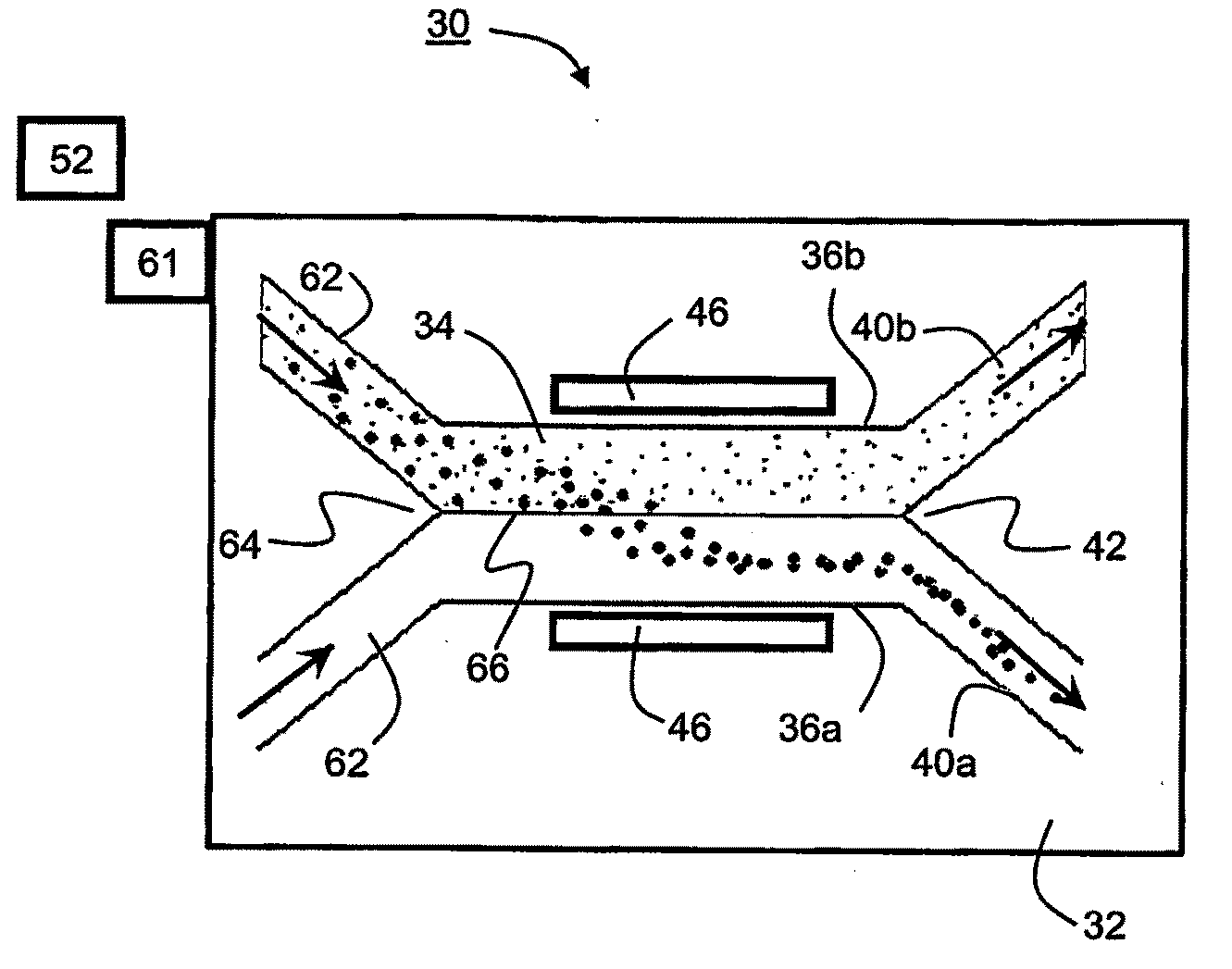
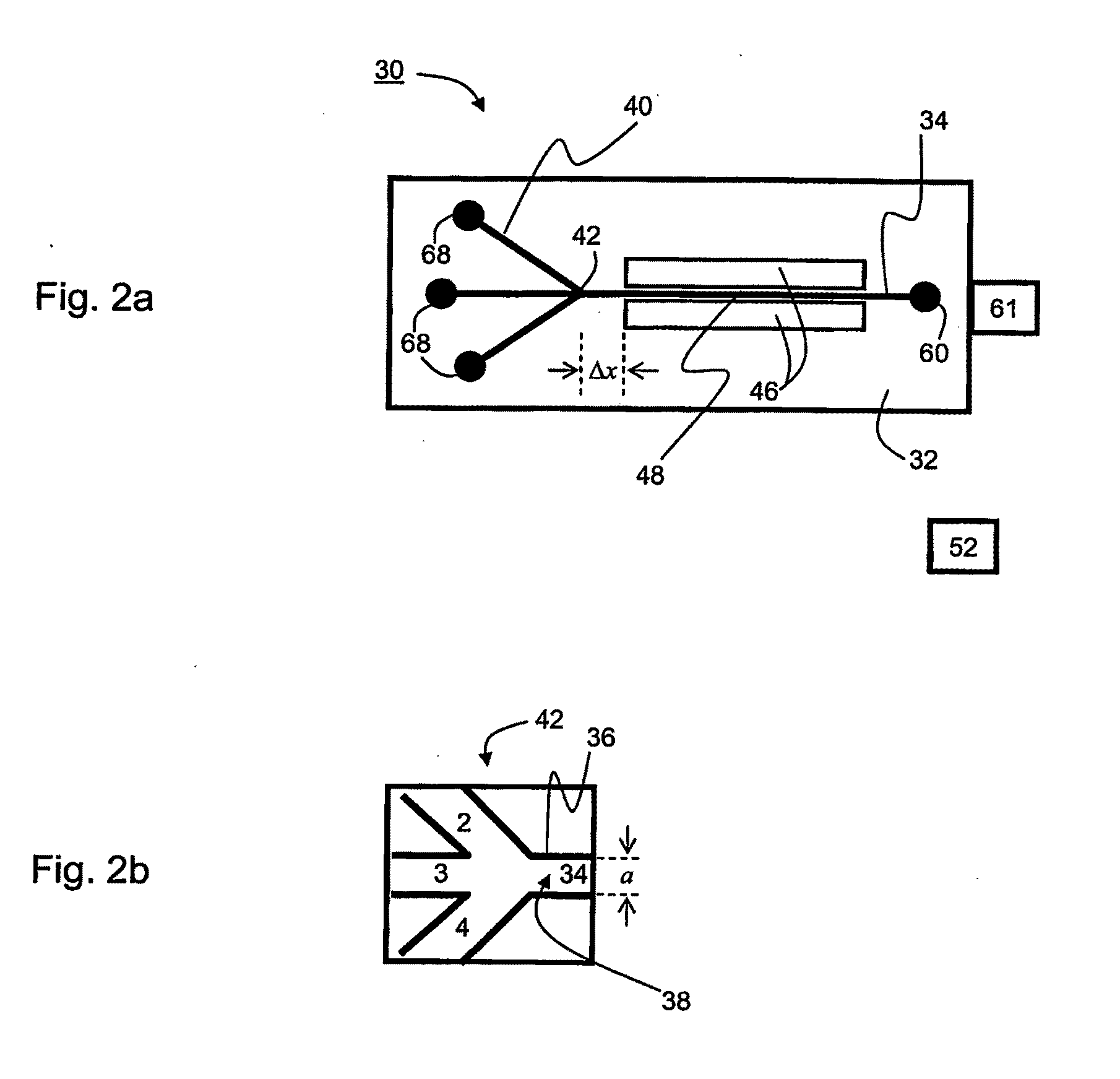
InactiveUS20040069717A1Raise the possibilityHigh particle separationOther blood circulation devicesHaemofiltrationElectricityEngineering
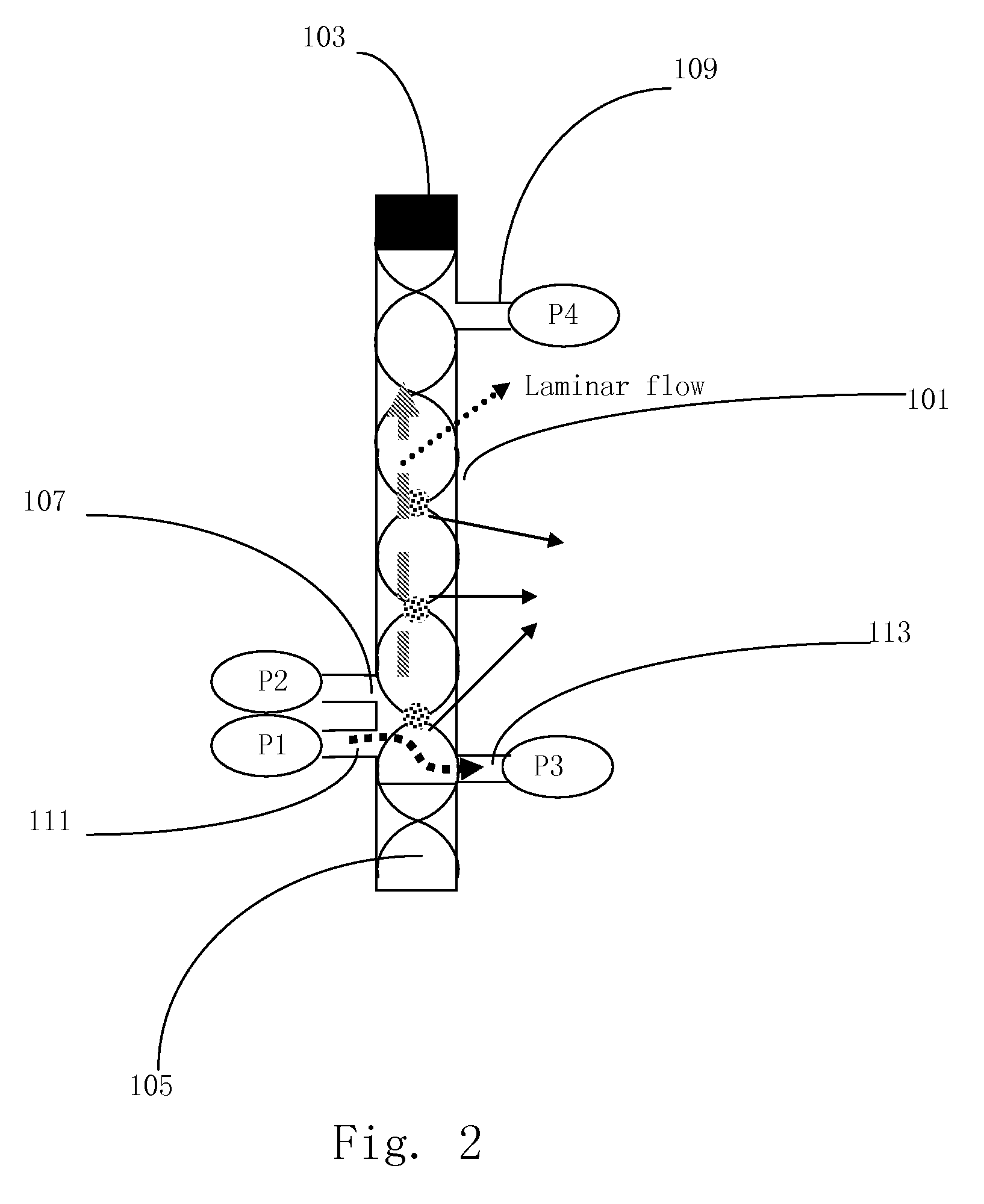
The present invention provides a device and a method for separating particles from fluids using ultrasound, laminar flow, and stationary wave effects comprisinga micro-technology channel system with an integrated branching point or branching fork, and a single ultrasound source. One of the characteristics of the invention is that the single ultrasound source, which generates the standing waves, excites the complete structure including the channel system. No special reflectors or the like are needed. Extremely thin dividers can separate the flow, thereby enhancing the effectiveness of the device. The device could be manufactured in silicon and the ultrasound energy could preferably be delivered by a piezoelectric element.
Owner:ERYSAVE
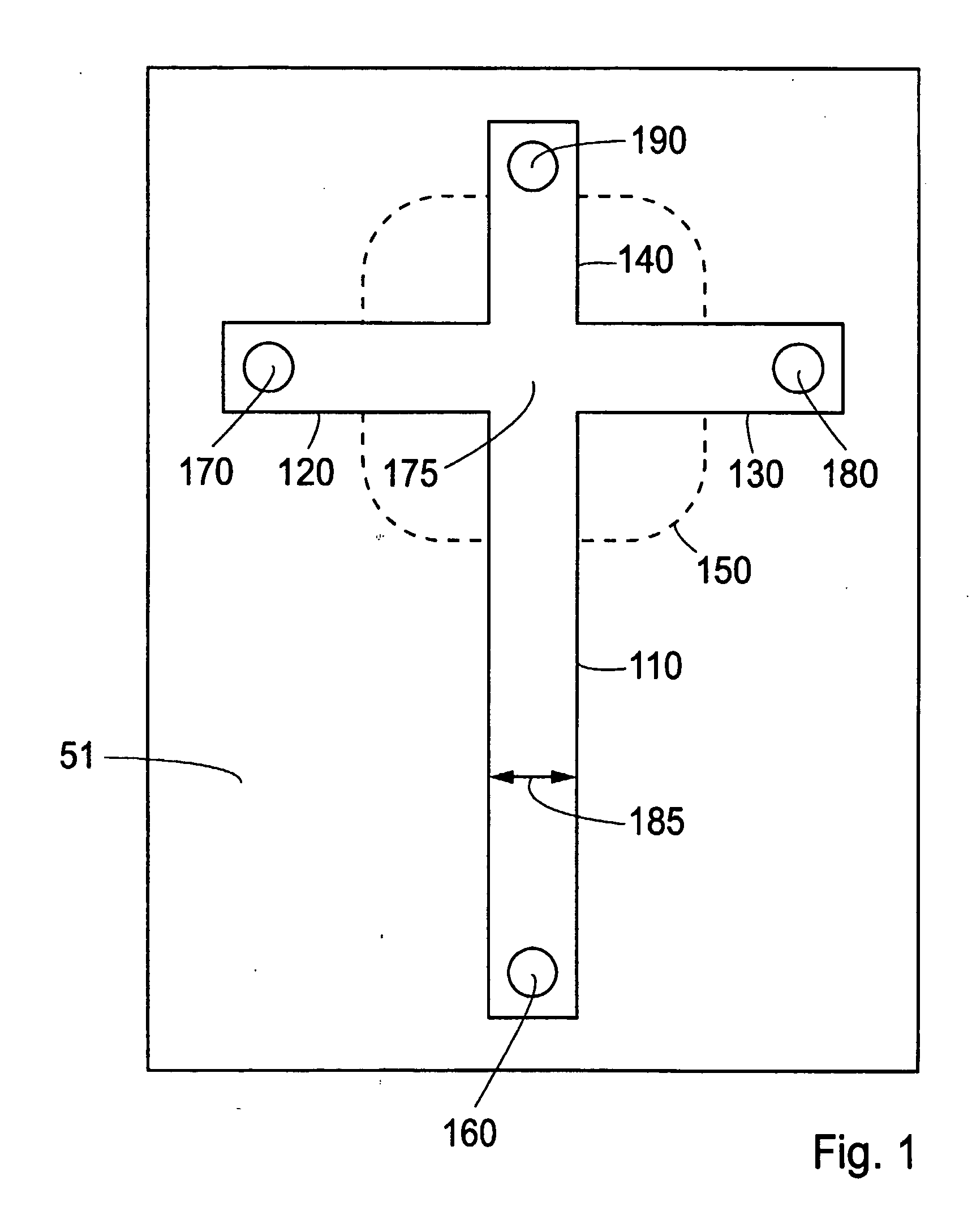
Micro-electro-mechanical gyroscope
InactiveUS6516665B1High sensitivityEasy to detectPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesImpedence networksElectricityGyroscope
A gyroscope comprises a piezoelectric substrate having a surface. Disposed on the surface are a resonator transducer, a pair of reflectors, a structure such as a metallic dot, and a sensor transducer. The resonator transducer creates a first surface acoustic wave on the surface. The pair of reflectors reflects the first surface acoustic wave to form a standing wave within a region of the surface between the pair of reflectors. The structure is disposed on the surface within the region, wherein a Coriolis force acting upon the structure creates a second surface acoustic wave. The sensor senses the second surface acoustic wave and provides an output indicative thereof.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Resonant cavity biosensor
InactiveUS20060182659A1Improve throughputAvoid complex processRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryResonant cavityBiosensor
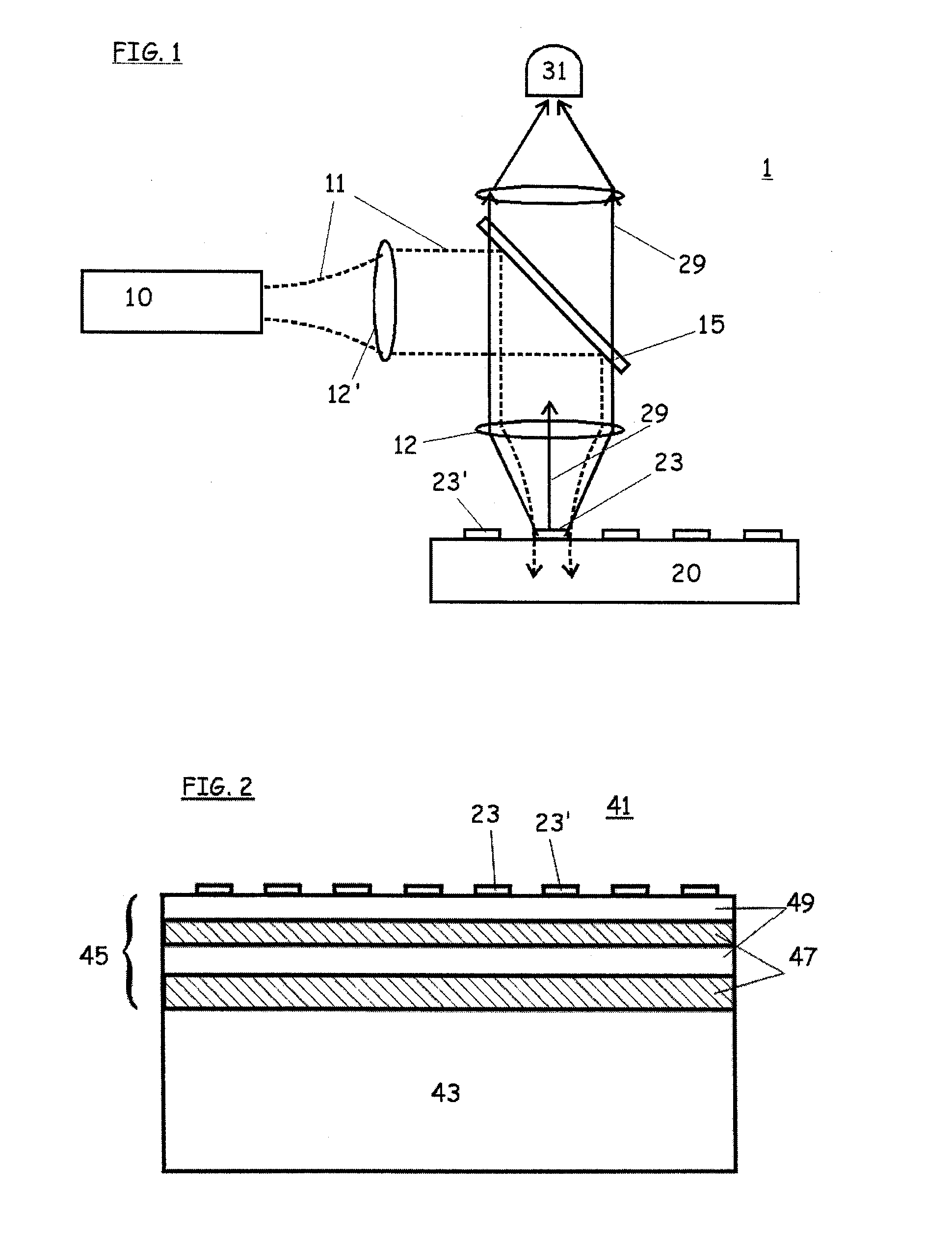
An assay system having a channel bounded by first and second reflective surfaces adapted to accommodate a fluid material therebetween and defining a plurality of regions in an array between those surfaces with each region defining a resonant cavity and adapted to receive a capturing material on a surface thereof whereby a source of radiation illuminates each region to provide a standing wave of radiation of within the cavity indicative of binding of said capturing agent to material under investigation, a binding thereof being detected in response to radiation from each cavity indicative of a change in the standing wave pattern.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
Device and Method For Particle Manipulation in Fluid
InactiveUS20100193407A1Water/sewage treatment with mechanical oscillationsLaboratory glasswaresPlanar substrateEngineering
A device for manipulating particles present in a fluid medium is disclosed. The device comprises a planar substrate, formed with at least one primary microchannel to allow passage of the fluid medium therethrough. The primary microchannel(s) has walls and a base and being in fluid communication with a plurality of secondary microchannels via at least one branching point. The device further comprises one or more ultrasound transmission pairs, positioned at opposite sides of the walls to generate ultrasound waves propagating through the fluid medium, substantially parallel to the planar substrate, such as to form a standing wave within the primary microchannel.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Ultrasonic filtration for cmp slurry
InactiveUS20100206818A1Water/sewage treatment with mechanical oscillationsSedimentation separationFiltrationSlurry
The present invention relates to semiconductor processing. In particular, it relates to a tunable ultrasonic filter and a method of using the same for more effective separation of large particles from slurry. In one embodiment a standing wave is produced in the filter and large particles are accumulated at the nodes of the standing waves while the slurry is flowed out of the filter.
Owner:CHARTERED SEMICONDUCTOR MANUFACTURING
Apparatus and method for filter cleaning by ultrasound, backwashing and filter movement during the filtration of biological samples
InactiveUS8273253B2Minimises fouling and clogging of filterImprove overall efficiency and accuracyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCyclic processVacuum pressure
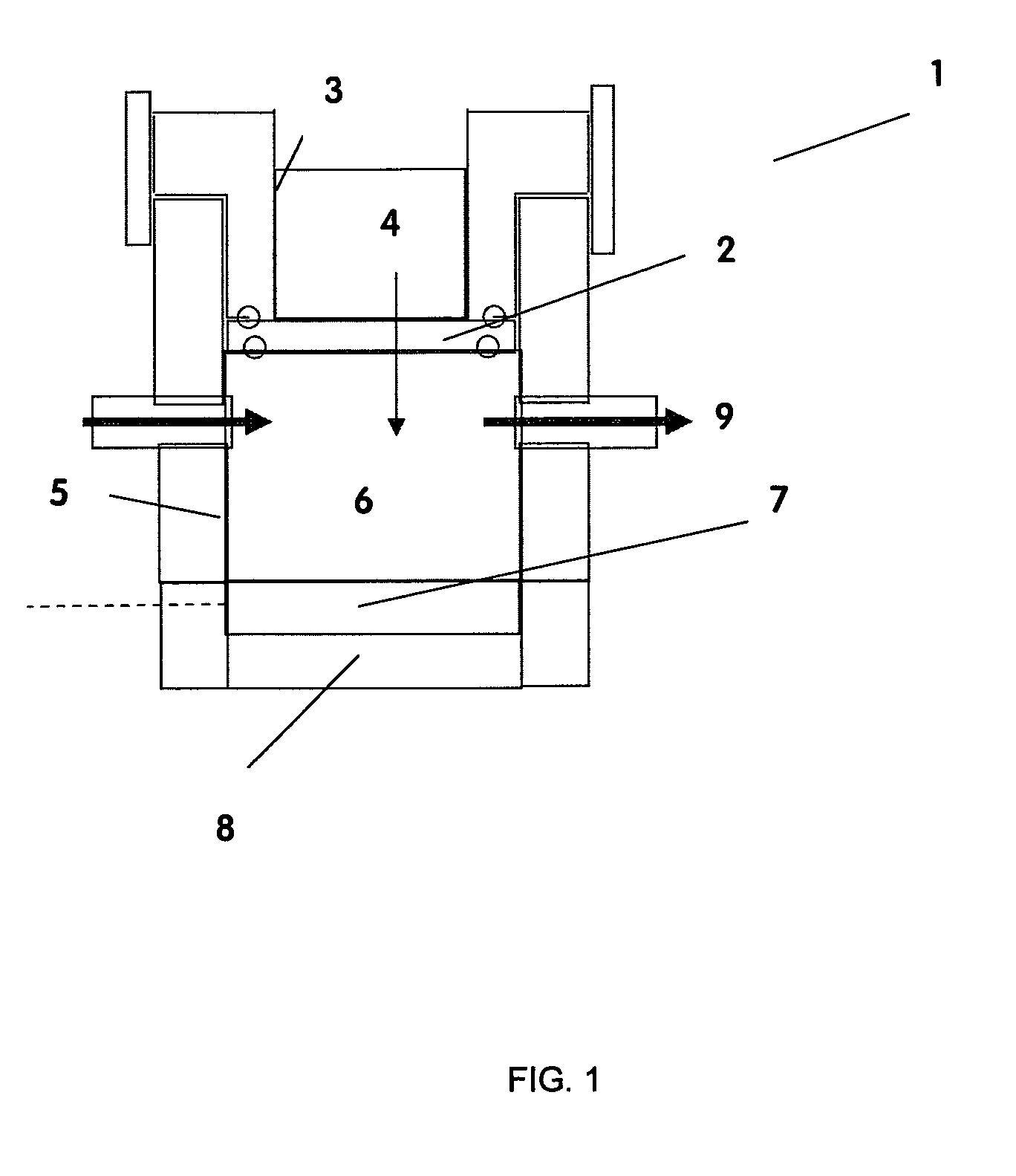
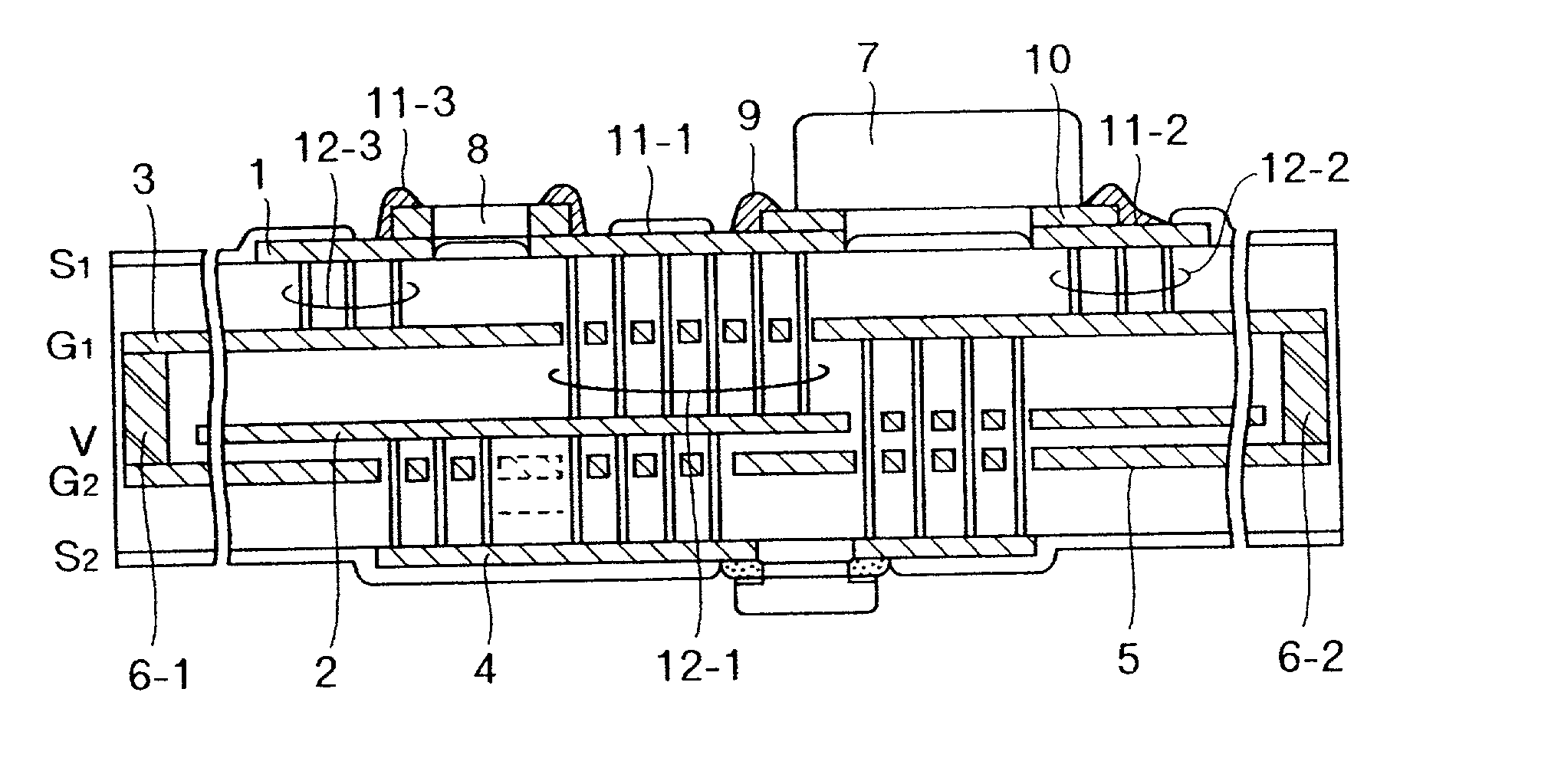
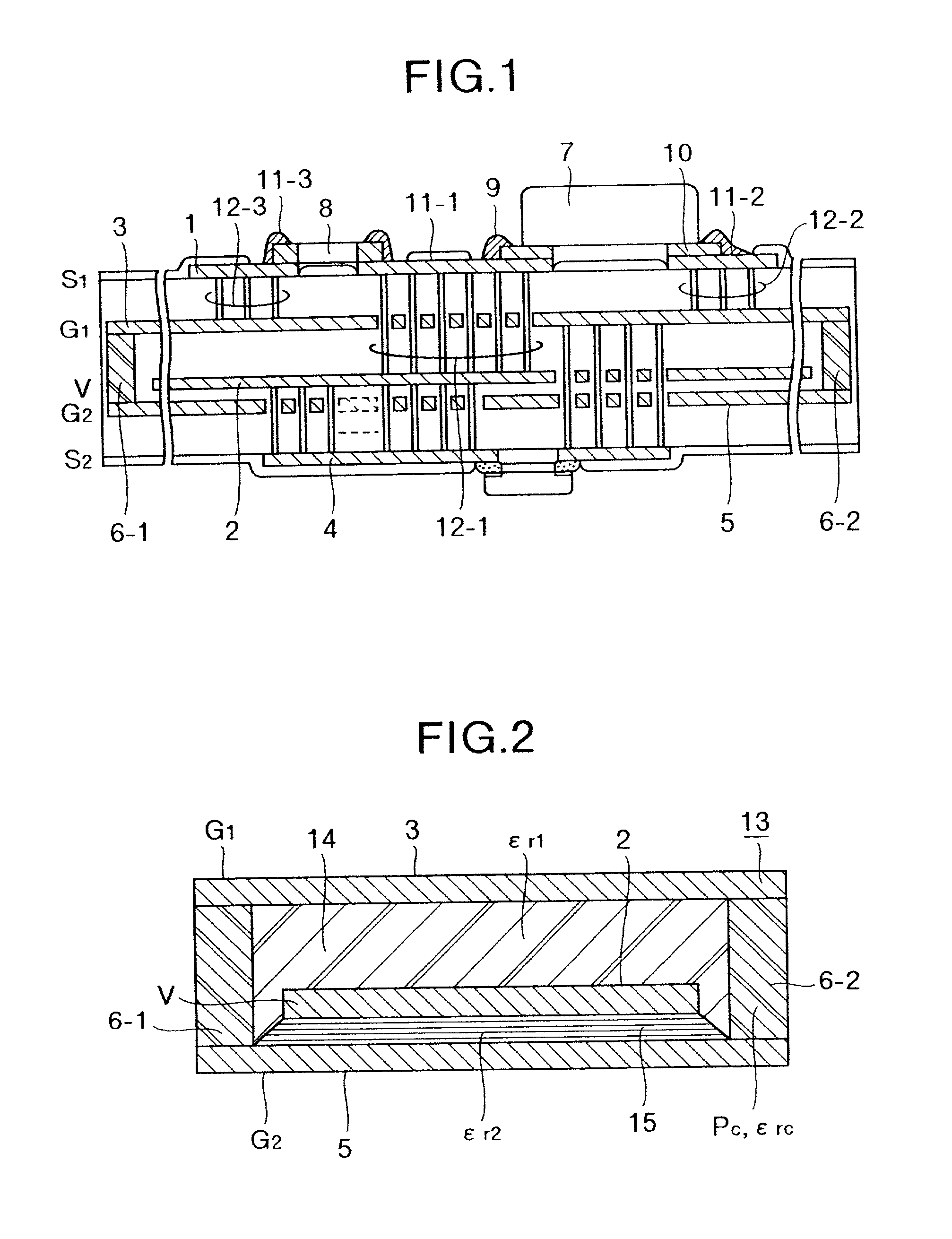
The present application is directed to the separation of—a solid fraction from a fluid sample particularly a therapeutic cellular fraction from a biological sample such as a bone marrow sample by a porous filter (2) which separates a filtration unit (1) into an upper pre-filtration chamber (3) into which a fluid sample (4) requiring cell separation is introduced and a lower post-filtration chamber (5) into which a fluid (6) capable of transmitting an acoustic standing wave is introduced. An acoustic element (8) is coupled to a substrate (7) which is located within and at the bottom of the lower chamber (5) and which resonates in response to the acoustic generating element (8) and generates a standing wave through the two fluid phases and the filter to agitate the sample (4). Simultaneously, a cyclic process of vacuum draw (9). causes movement of the sample (4) downwards through the filter (2). Vacuum pressure, fluid flow rate and frequency of vibration are controlled from a remote unit housing appropriate pumps and valves.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
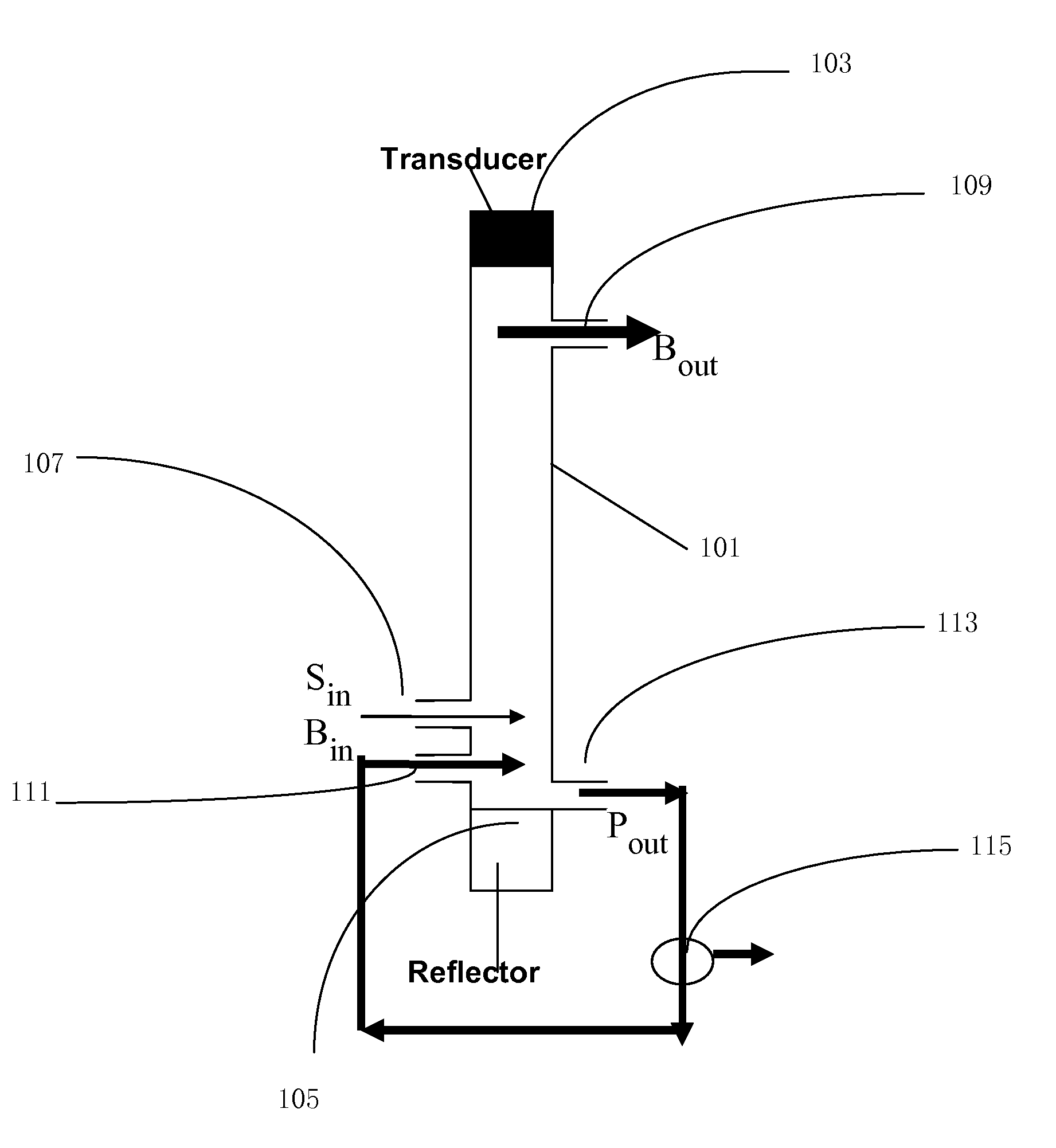
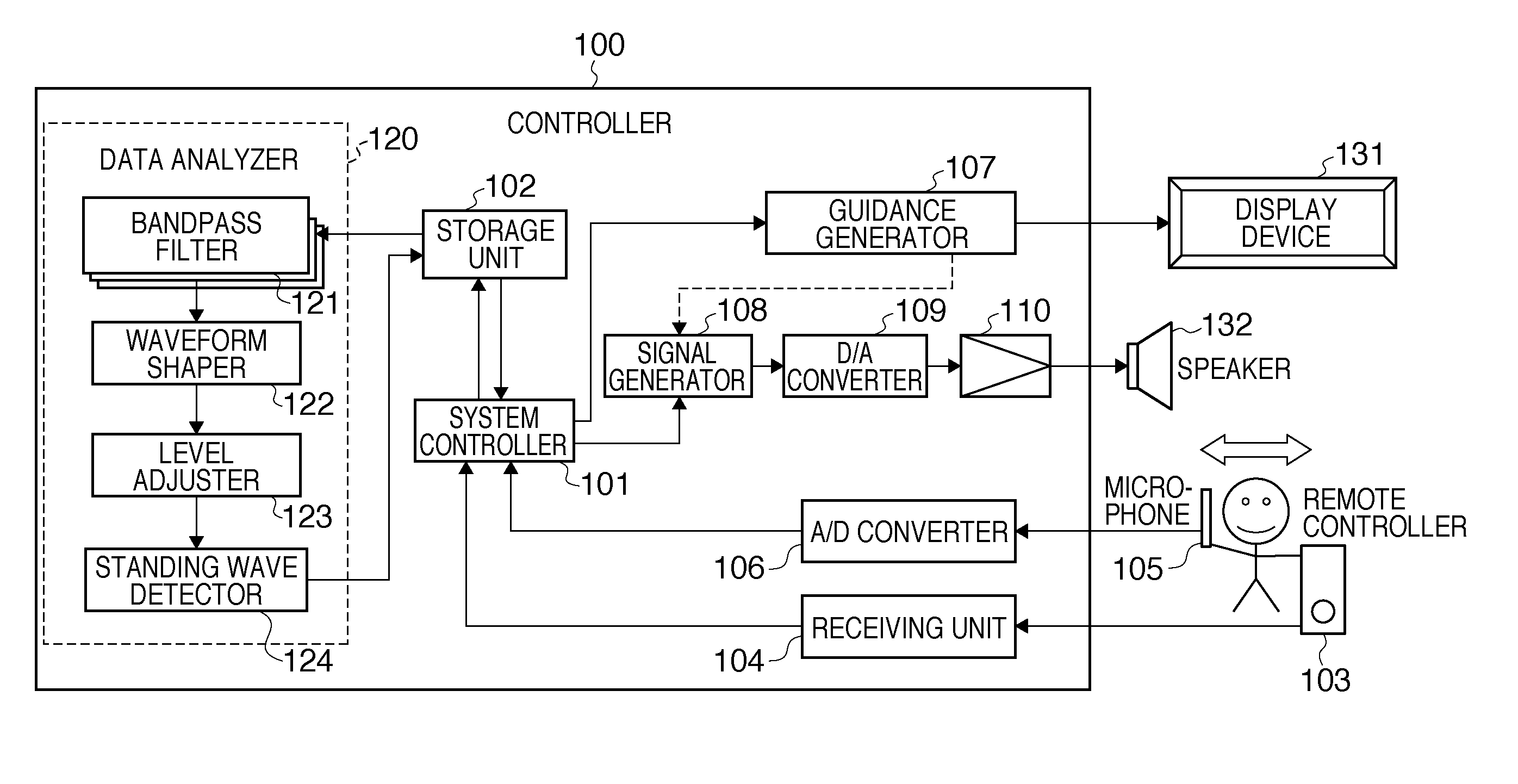
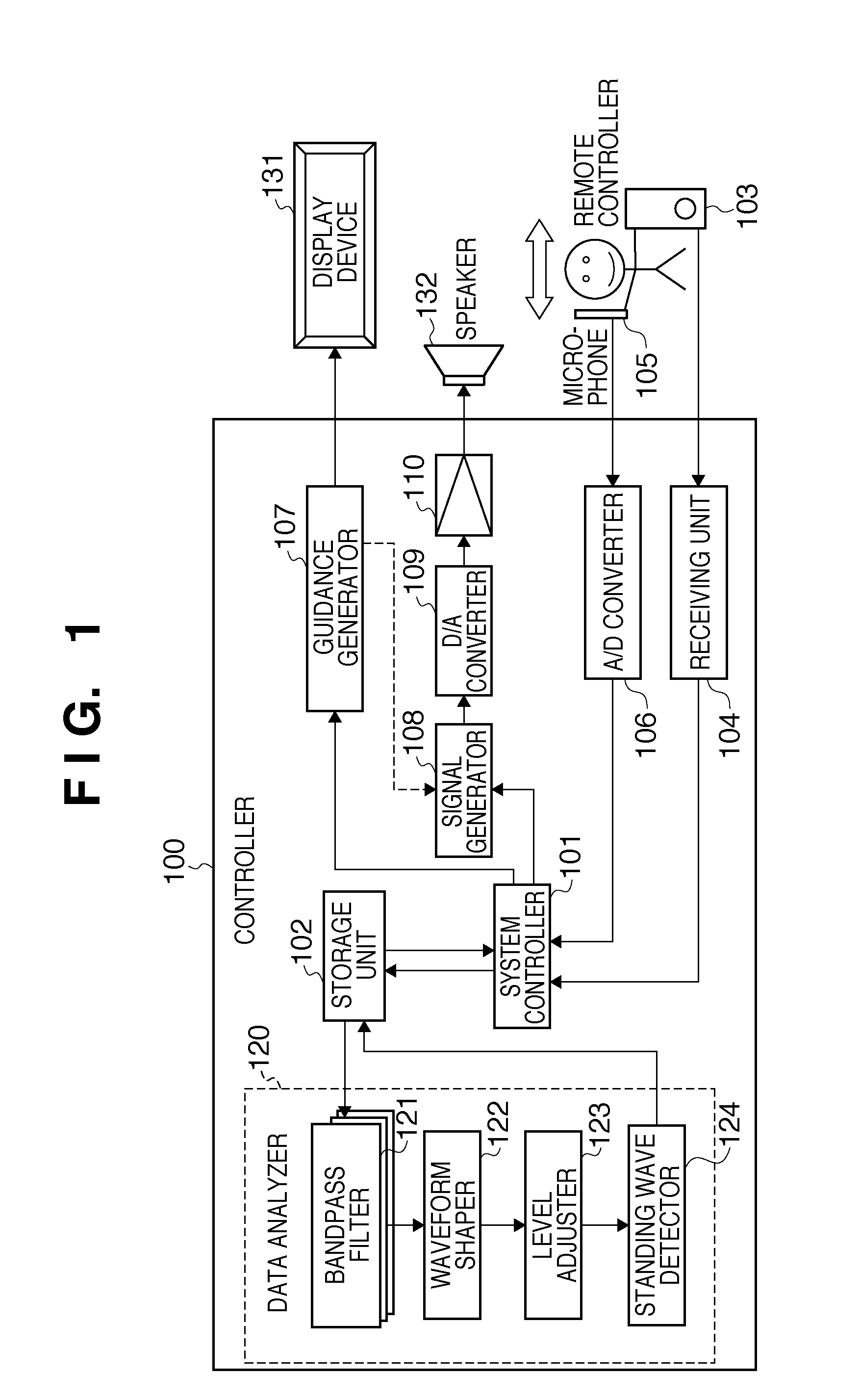
Standing wave detection apparatus and method of controlling the same
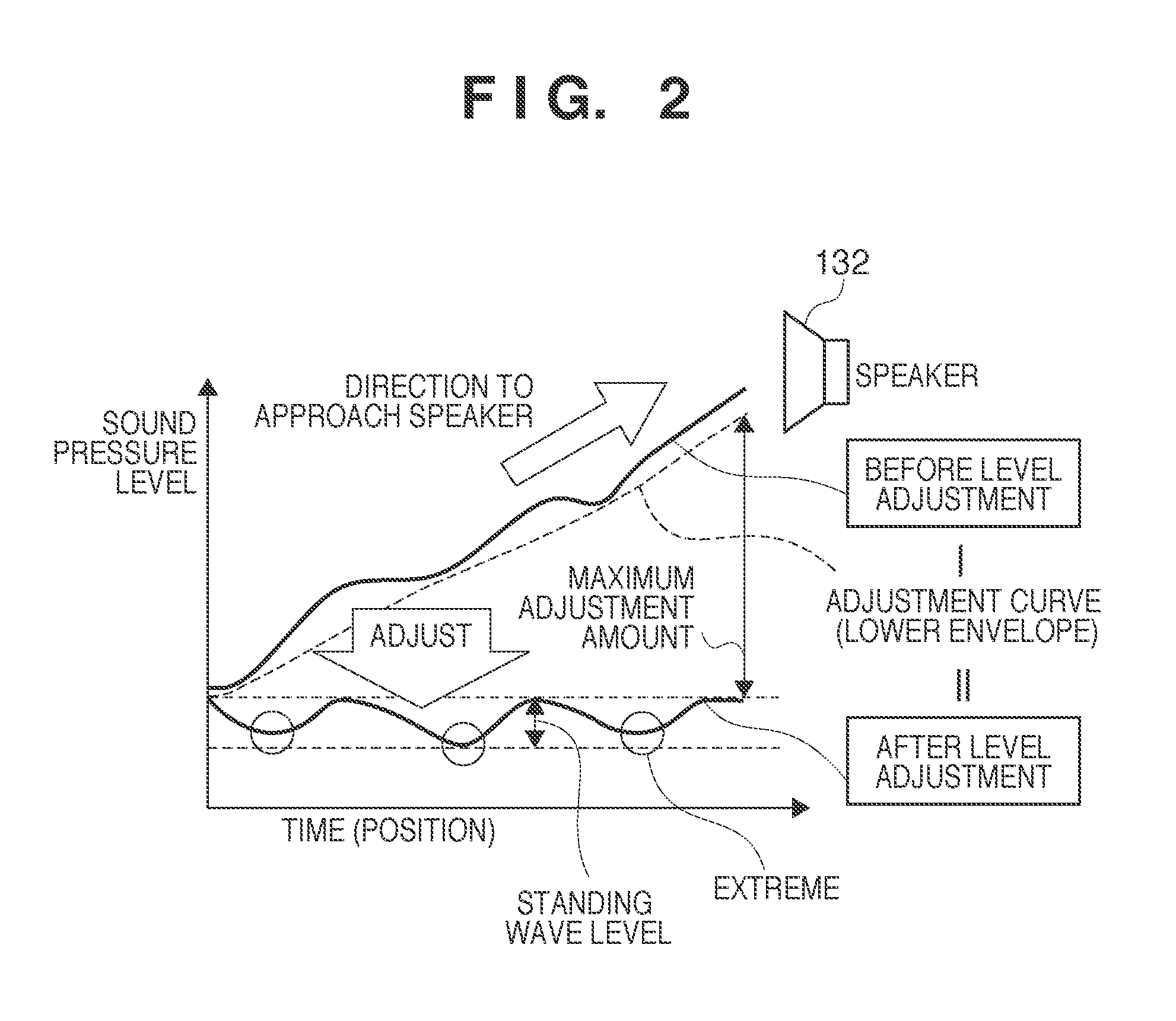
To efficiently detect a standing wave generated in a room, a standing-wave detection apparatus for detecting a standing wave in a predetermined space, comprises: a sound-receiving unit adapted to receive a sound generated from a sound source arranged in the predetermined space; a storage unit adapted to store time series sound pressure level data acquired by the sound-receiving unit during movement along a path in the predetermined space; an adjustment unit adapted to adjust the time series sound pressure level data stored in the storage unit, based on an adjustment curve determined using a lower envelope of the time series sound pressure level data stored in the storage unit; and a detection unit adapted to detect an existence position of a standing wave in the predetermined space based on the adjusted time series sound pressure level data.
Owner:CANON KK
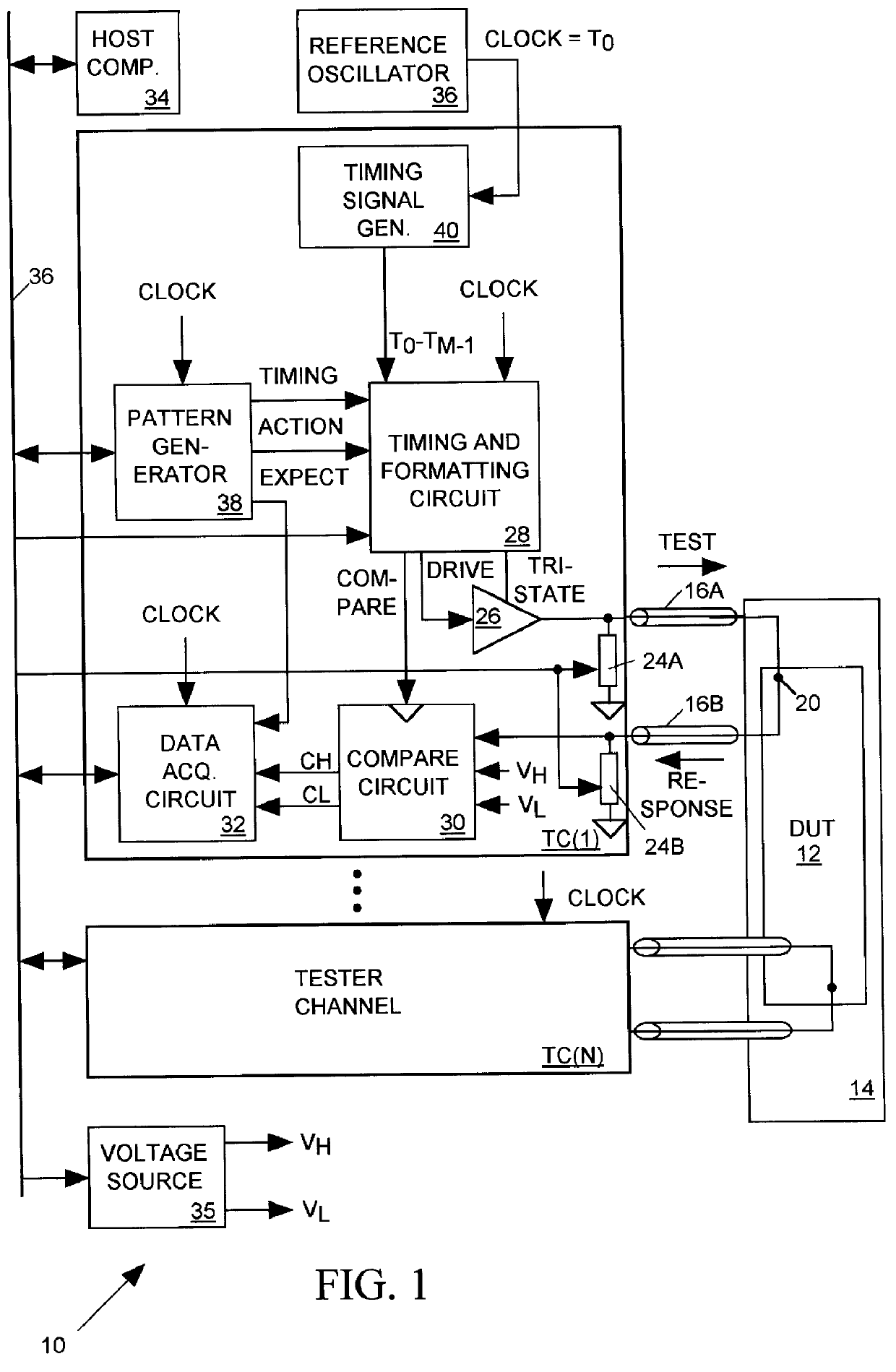
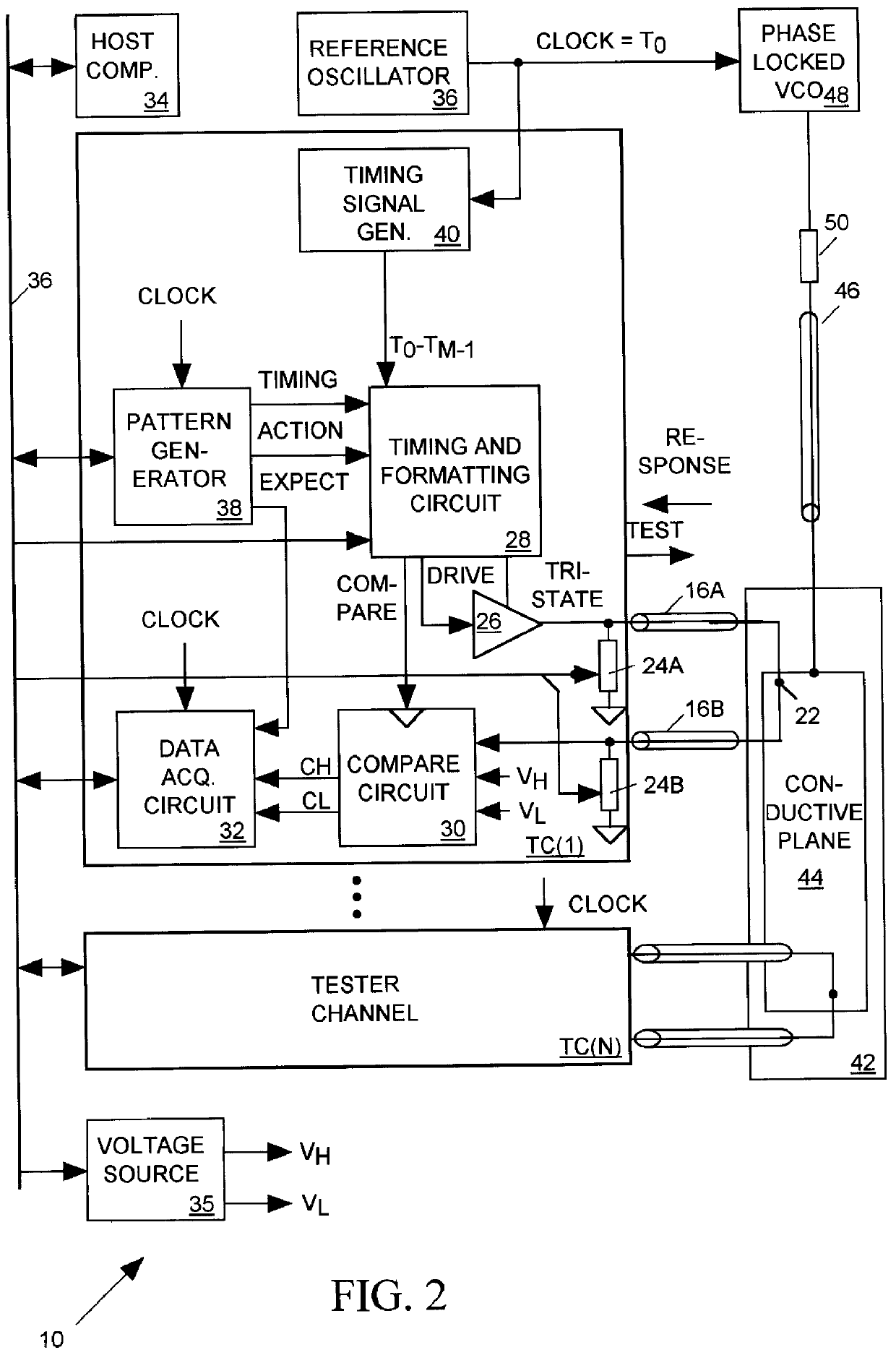
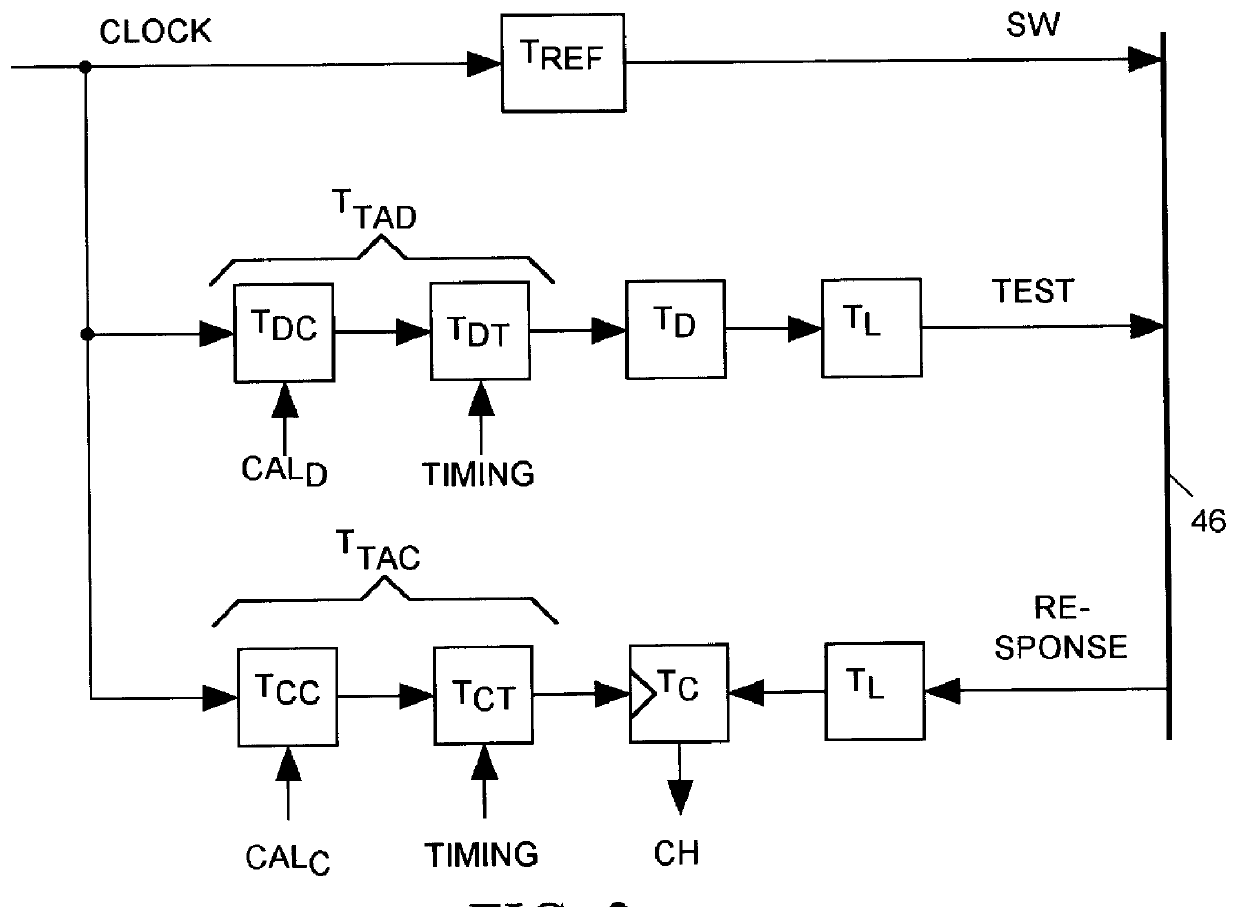
Salphasic timing calibration system for an integrated circuit tester
InactiveUS6105157AQuickly and easily calibratingDigital circuit testingError detection/correctionTester deviceEngineering
An integrated circuit tester produces an output TEST signal following a pulse of a reference CLOCK signal with a delay that is a sum of an inherent drive delay and an adjustable drive delay. The tester also samples an input RESPONSE signal following a pulse of the reference CLOCK signal with a delay that is a sum of an inherent compare delay and an adjustable compare delay. The inherent drive and compare signal path delays within an integrated circuit tester are measured by first connecting a salphasic plane to transmission lines that normally convey signals between the tester and terminals of an integrated circuit device under test. A standing wave signal appearing on that salphasic plane is phase locked to the CLOCK signal so that a zero crossing of the standing wave occurs at a fixed interval after each pulse of the CLOCK signal. Each transmission line concurrently conveys the standing wave to the tester to provide timing references for measuring the inherent drive and compare signal path delays within the tester. Transmission line signal paths are also measured. Delays are added to the drive and compare signal paths to compensate for the measured inherent drive, compare and transmission line delays.
Owner:CREDENCE SYSTEMS
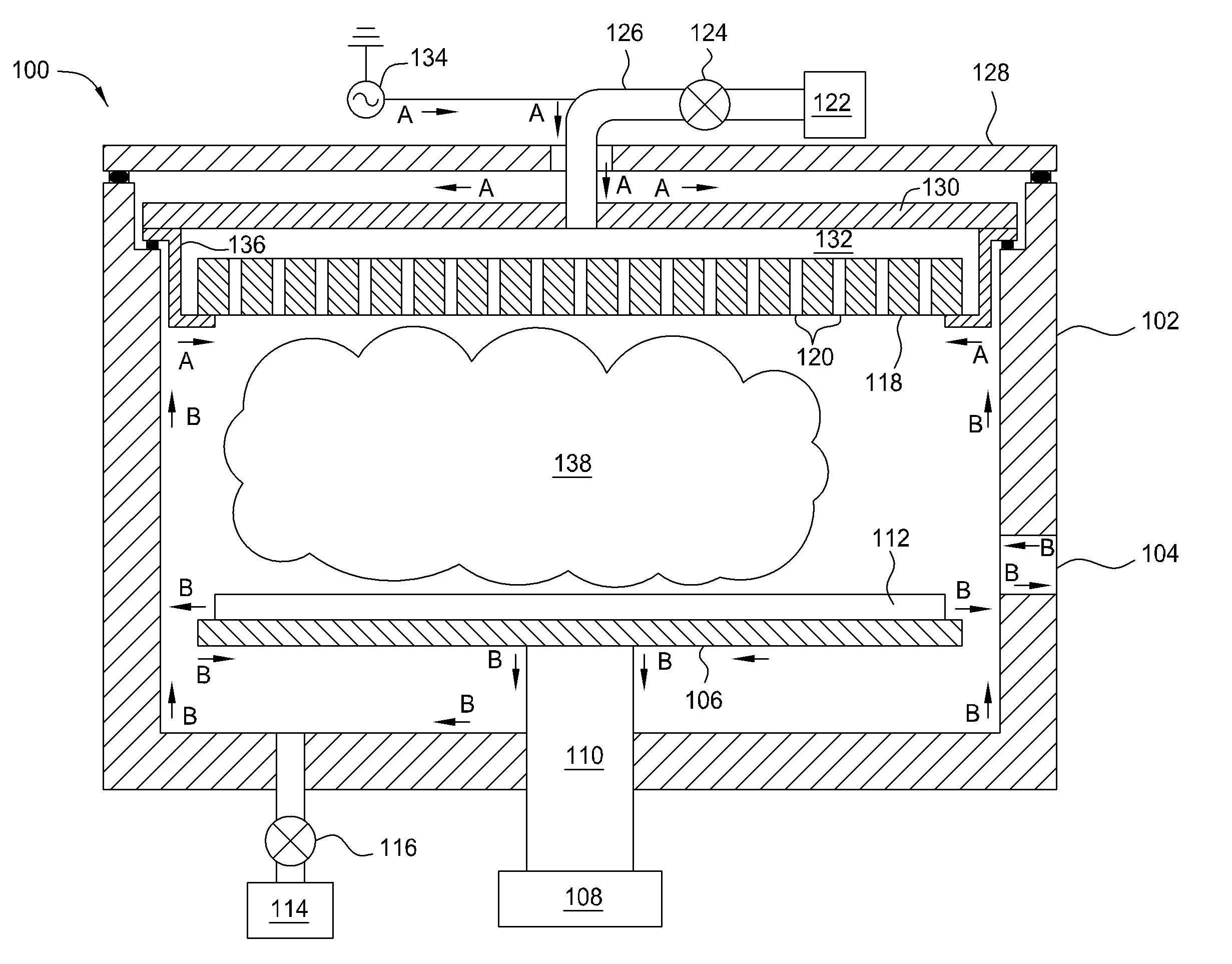
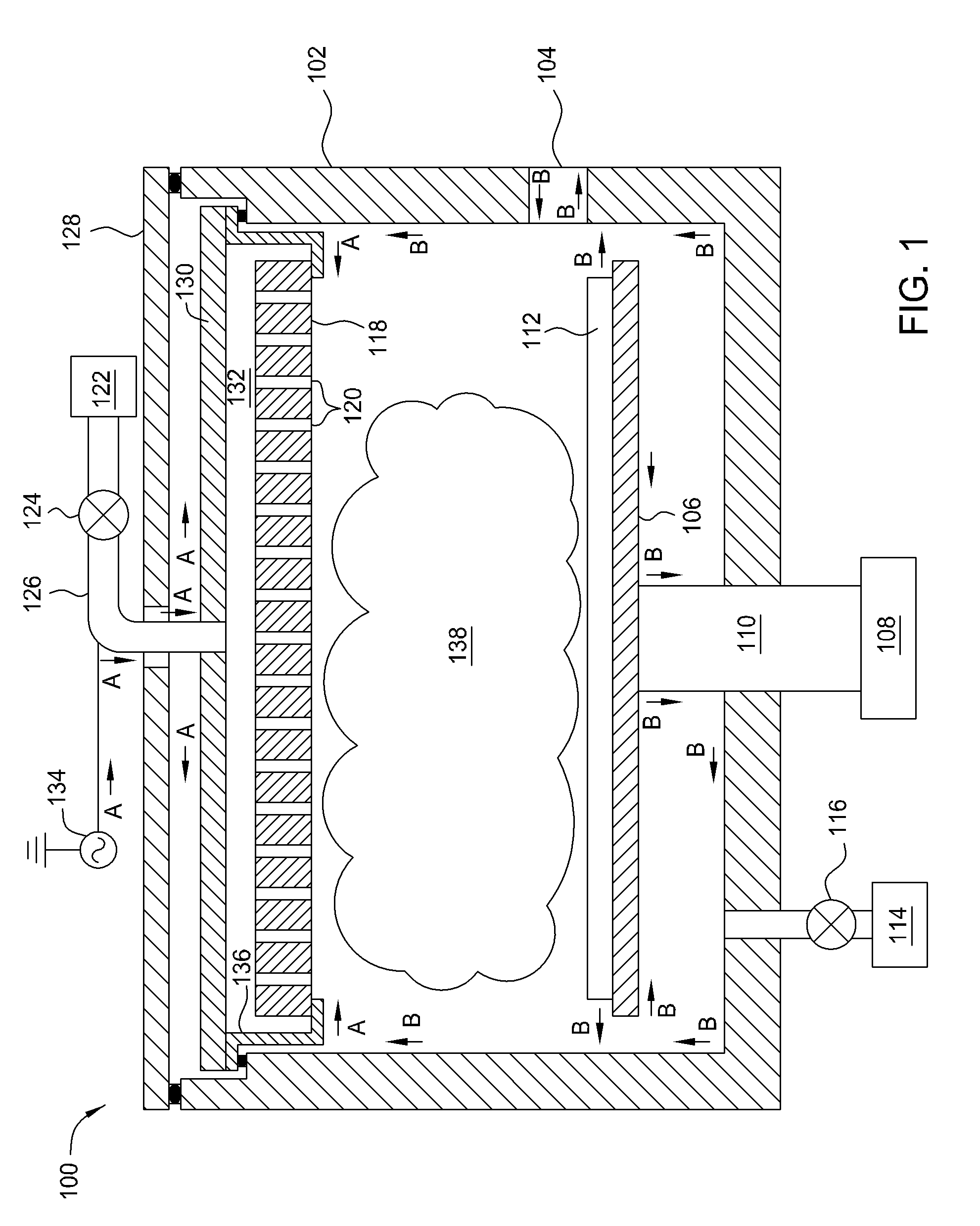
High pressure rf-dc sputtering and methods to improve film uniformity and step-coverage of this process
Embodiments of the invention generally provide a processing chamber used to perform a physical vapor deposition (PVD) process and methods of depositing multi-compositional films. The processing chamber may include: an improved RF feed configuration to reduce any standing wave effects; an improved magnetron design to enhance RF plasma uniformity, deposited film composition and thickness uniformity; an improved substrate biasing configuration to improve process control; and an improved process kit design to improve RF field uniformity near the critical surfaces of the substrate. The method includes forming a plasma in a processing region of a chamber using an RF supply coupled to a multi-compositional target, translating a magnetron relative to the multi-compositional target, wherein the magnetron is positioned in a first position relative to a center point of the multi-compositional target while the magnetron is translating and the plasma is formed, and depositing a multi-compositional film on a substrate in the chamber.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Selective lysing of cells using ultrasound
ActiveUS20110166551A1Easily maintaining sterilityReduce riskBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCell membraneUltimate tensile strength
Described are embodiments that employ ultrasonic energy to selectively lyse larger adipose cells in a suspension containing adipose cells of different sizes resulting in a suspension in which the only viable cells are the small adipose cells and stem cells. Embodiments provide for generating an acoustic standing wave field of sufficient intensity and proper geometry, that high shear stress is induced on the cell membranes of cells larger than a predetermined size. The remaining small adipose cells can be physically separated from the suspension after the suspension is subjected to the acoustic standing wave field.
Owner:SOLTA MEDICAL
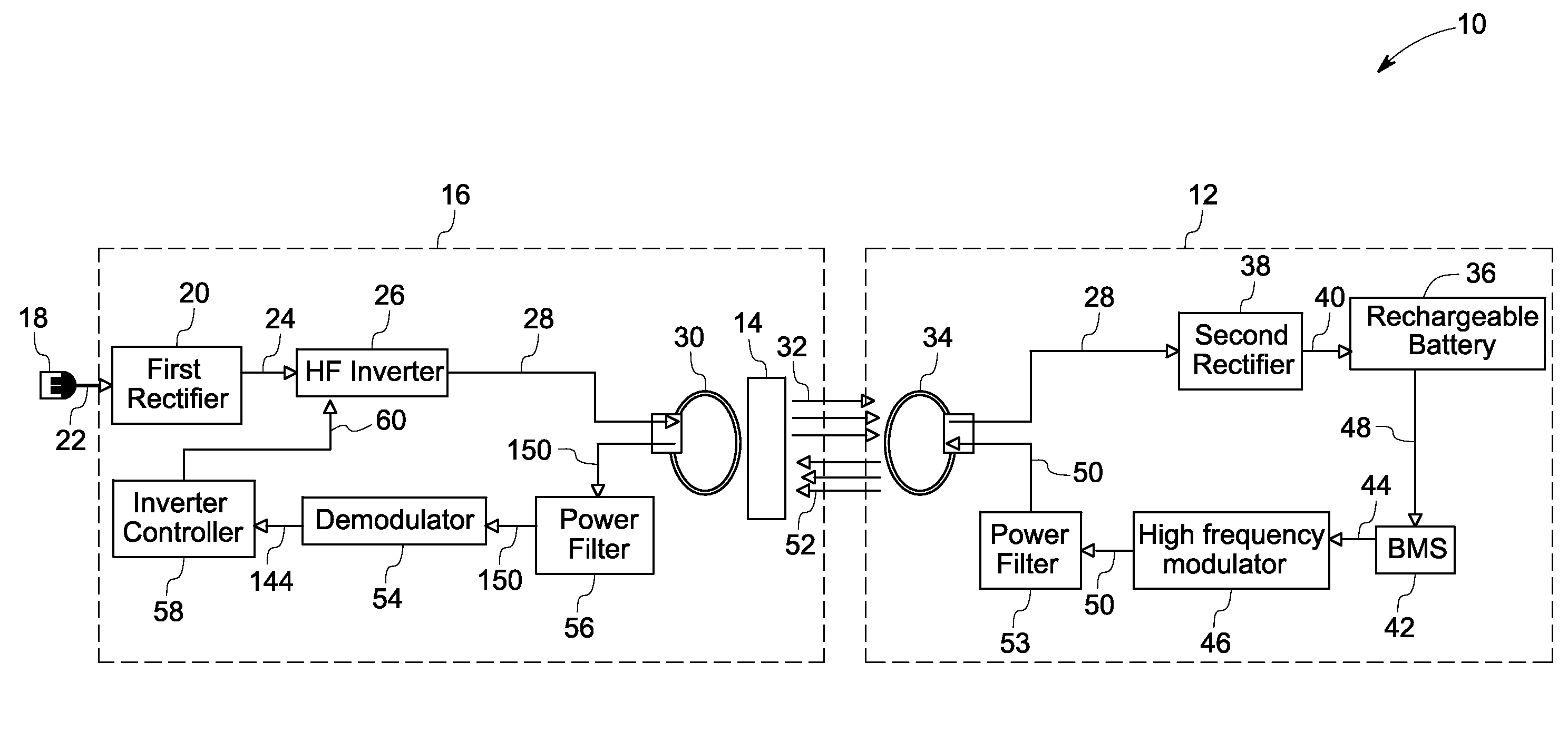
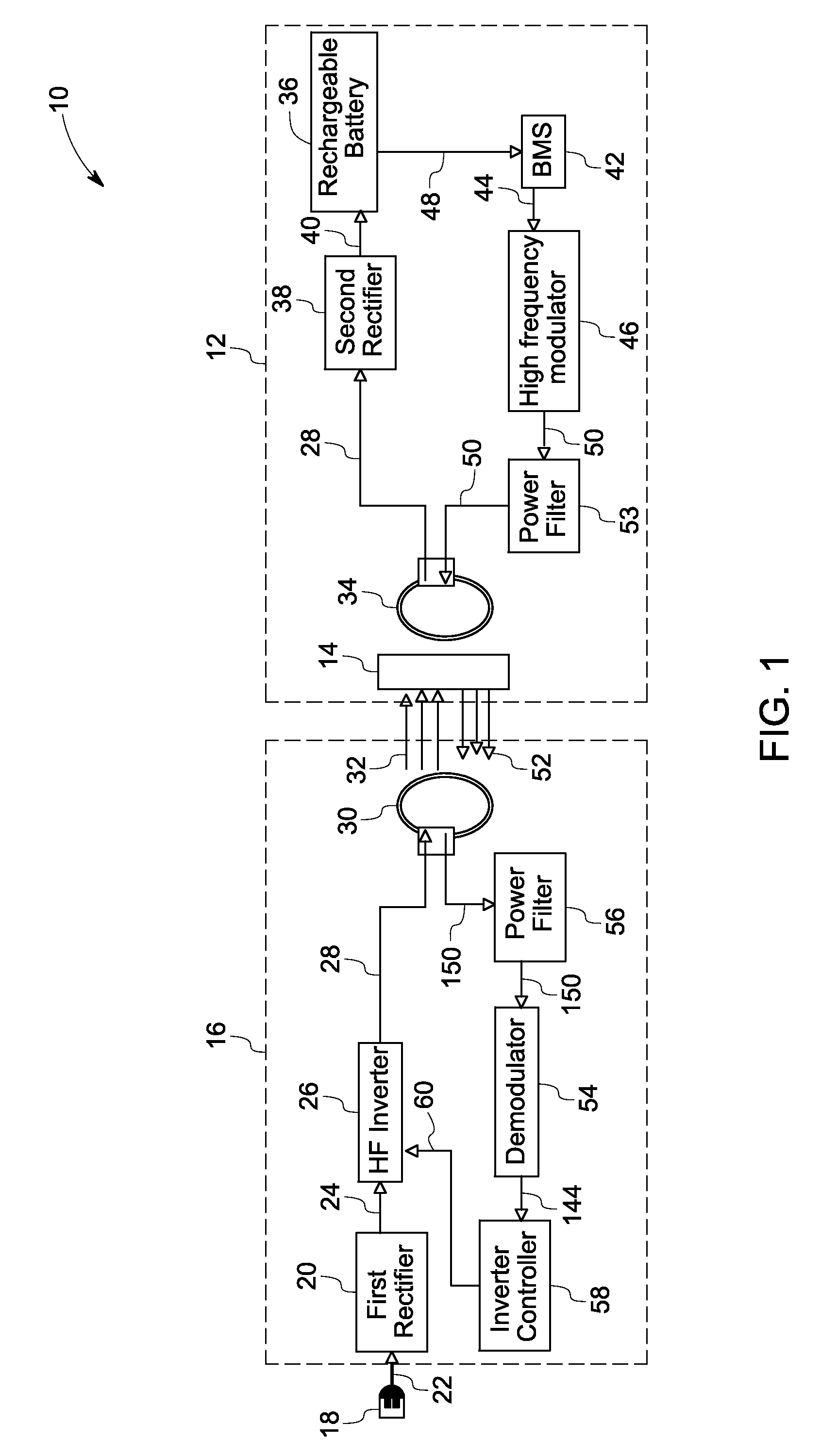
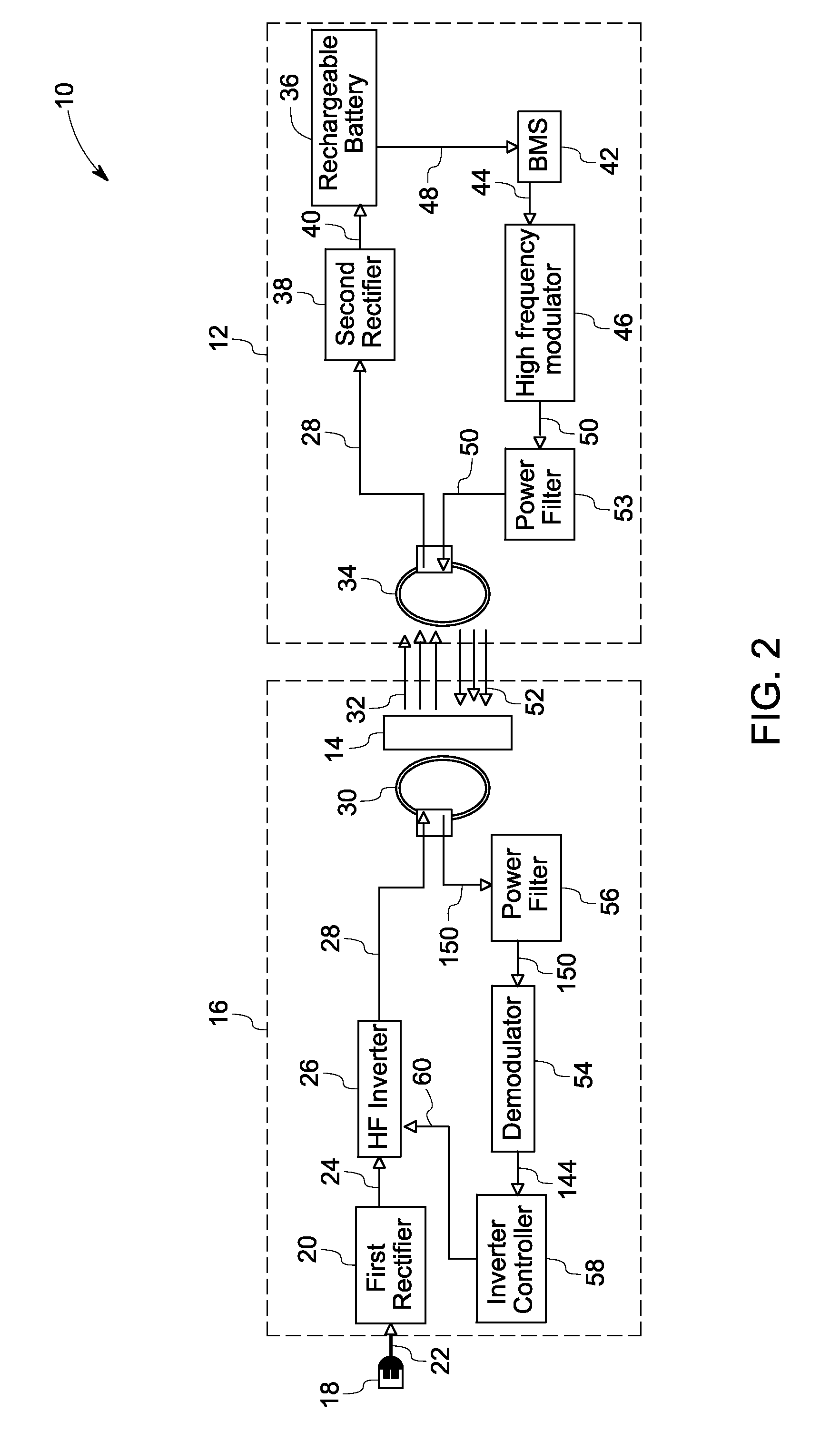
System and method for contactless power transfer in implantable devices
ActiveUS20120245649A1Enhanced couplingNear-field transmissionEar treatmentElectric power transmissionCoupling
A system and method for contactless power transfer in implantable devices for charging rechargeable batteries disposed within the implantable devices are provided. The system includes a first coil electrically couplable to a power source, wherein the first coil is configured to produce a magnetic field. The system further includes a second coil electrically coupled to the rechargeable battery disposed within the implantable device and configured to receive power from the first coil via the magnetic field and to transfer the power to the rechargeable battery. The system also includes a field focusing element disposed between the first coil and the second coil and configured as a self resonant coil having a standing wave current distribution to focus the magnetic field onto the second coil and enhance the coupling between the first coil and the second coil.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Noise suppression method for wave filter
ActiveUS7057476B2Eliminate signalWeaken energyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesImpedence networksThin-film bulk acoustic resonatorHarmonic vibration
A noise suppression method of a wave filter used to eliminate standing wave signal interferences in the acoustic wave filter consisted by a plurality of film bulk acoustic resonators (FBARs). The method is to provide a plurality of scatterers in the structured consisted by the FBARs, thereby creating an band-gap structure due to the material characteristics difference, which consequently generates a destructive interfering effect to the transverse higher harmonics vibration within a specific operating frequency range, and ultimately decreases or even eliminates any parasitic effects. Therefore, within the operation frequency range of this band-gap structure, abnormal signals created by any transverse wave modes cannot exist. In addition, an acoustic shield can be provided by phononic crystal structures between different FBARs, thus acoustic shielding any mutual interference within the operation frequency range.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Modular standing frame
A modular standing frame is described herein. The modular standing frame has a chair module adapted to raise and lower a user between sitting and standing postures without inducing shear between the user and the seat and seat back of the chair module. The chair module may be selectively coupled to one of a glider module adapted to provide walking-type exercise to a standing user, a workstation module that provides a work surface for a sitting or standing user, and a mobility module that allows the standing frame to be moved about by a user much like a wheel chair.
Owner:ALTIMATE MEDICAL
Method and apparatus for enhanced resolution microscopy of living biological nanostructures
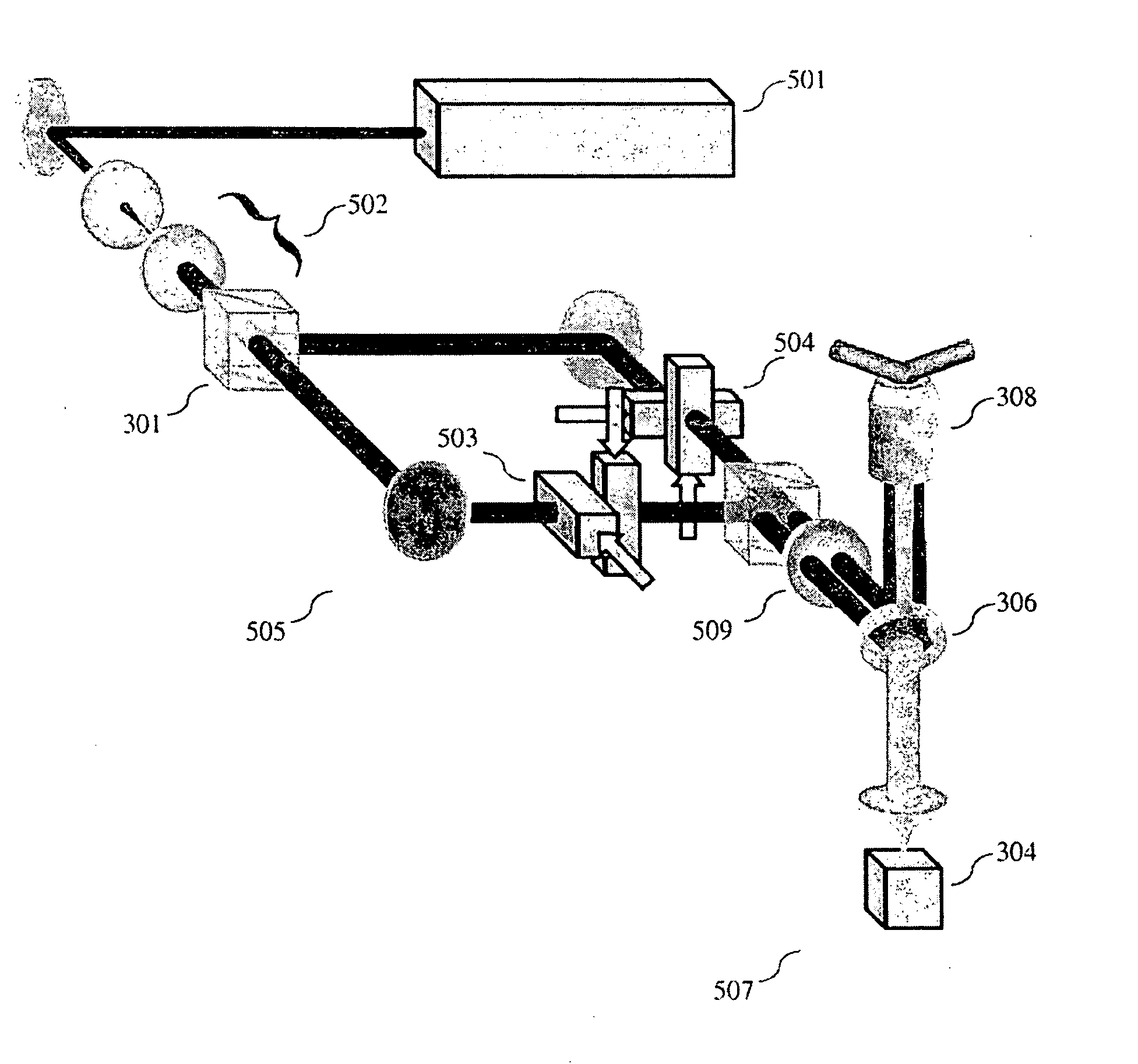
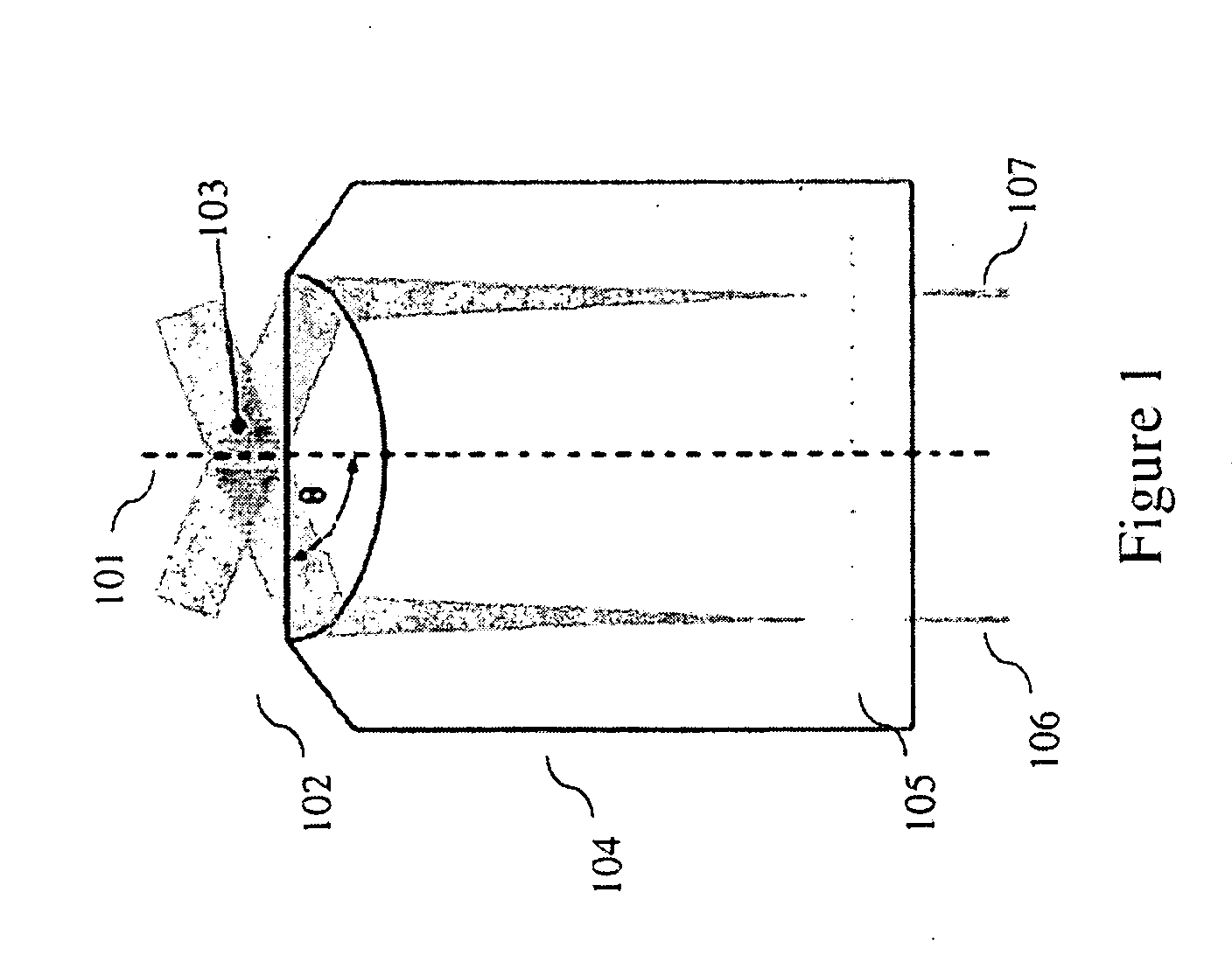
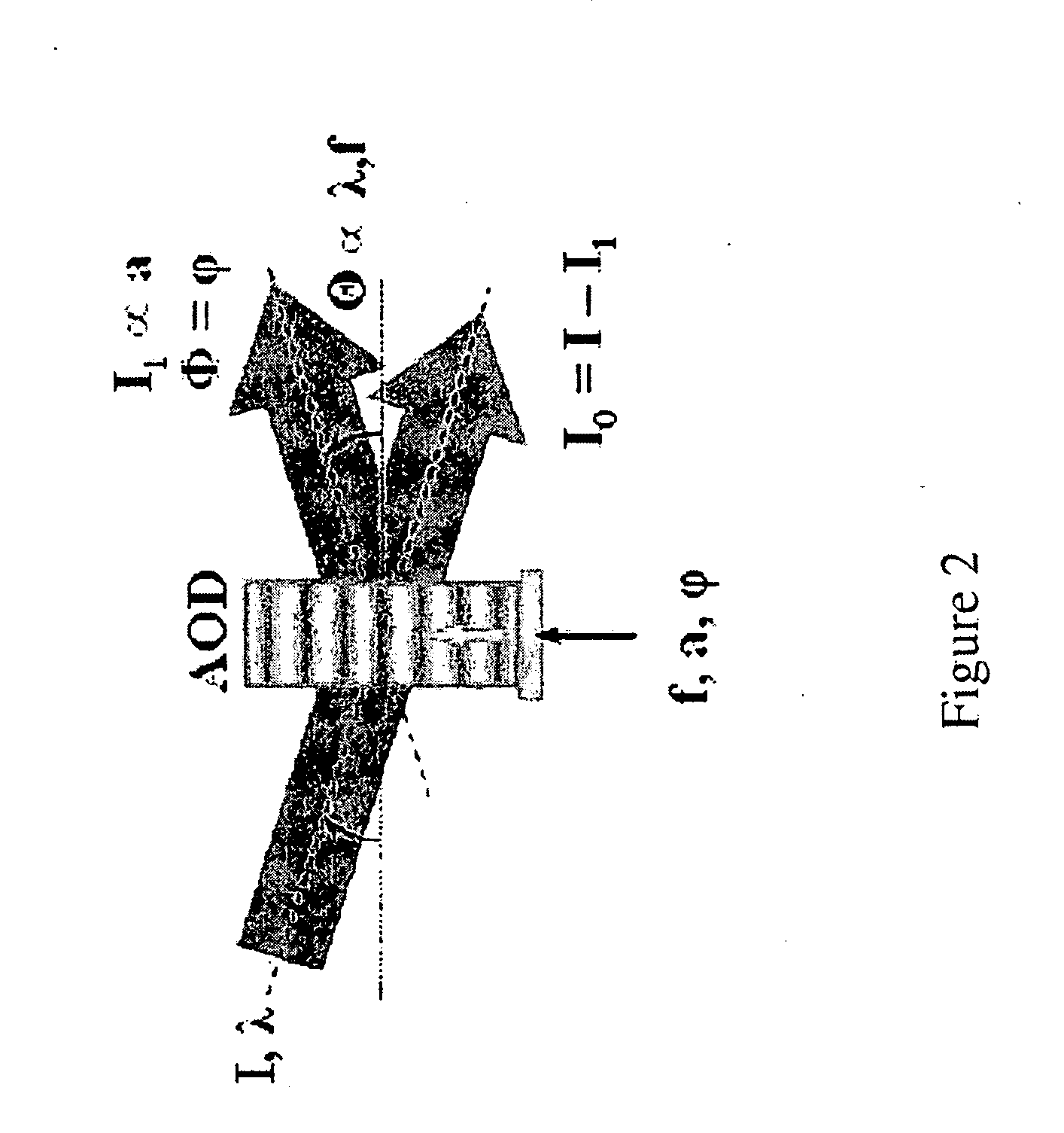
The present invention is a method and apparatus that utilizes an inertia-free diffraction mechanism to control both phase and rotation of the standing wave pattern that results in super-resolution at unparalleled imaging speeds. In some embodiments of the present inventions, AODs are utilized to control period, phase, and rotation of the SW pattern in contrast to the commonly used mechano-optical principles. This allows 2D (and 3D) super-resolution imagining at high stability and speed not limited by mechanical constraints. The present invention can be utilized, for example, for real time observations of dynamic processes in living cells.
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE +1
Unbalanced-to-balanced converter
An unbalanced-to-balanced converter (balun) comprising three distributed-constant lines. In one distributed-constant line, a standing wave is generated. Disposed adjacent thereto is another distributed-constant line to which the power of the standing wave is transferred. A signal input to the unbalanced-to-balanced converter is divided into two signals having phases 180 degrees apart and the same level.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Optical substrate for enhanced detectability of fluorescence
InactiveUS20070188746A1Accelerate emissionsEnhance excitationRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationFluorescenceRefractive index
Owner:OERLIKON TRADING AG TRUEBBACH
Low-EMI electronic apparatus, low-EMI circuit board, and method of manufacturing the low-EMI circuit board
InactiveUS20020015293A1Suppress spurious radiationIncrease costMagnetic/electric field screeningFinal product manufactureCapacitanceCountermeasure
A low-EMI circuit which realizes a high mounting density by converting the potential fluctuation of a power supply layer with respect to a ground layer which occurs on switching an IC device etc., into Joule's heat in the substrate without using any parts as a countermeasure against the EMI. Its structure, a circuit board using it, and a method of manufacturing the circuit board are also disclosed. Parallel plate lines in which the Q-value of the stray capacitance between solid layers viewed from the power supply layer and ground layer is equivalently reduced and which are matchedly terminated by forming a structure in which a resistor (resistor layer) and another ground layer are provided in addition to the power supply layer and the ground layer on a multilayered circuit board. A closed shield structure is also disclosed. This invention can remarkably suppress unwanted radiation by absorbing the potential fluctuation (resonance) which occurs in a power supply loop by equivalently reducing the Q-value of the stray capacitance, absorbing the standing wave by the parallel plate lines matchedly terminated and, closing and shielding the parallel plate lines.
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
Acoustic separators
InactiveUS20130175226A1Water/sewage treatment with mechanical oscillationsSeparation devicesTransducerEngineering
An acoustic separator comprises: two parallel chamber walls defining a separation chamber therebetween, each chamber wall defining one side of the chamber; inlet means through which fluid can flow into the chamber; and outlet means through which fluid can flow out of the chamber. One of the chamber walls includes a transducer arranged to transmit pressure waves across the chamber towards the other of the chamber walls which in turn is arranged to reflect the pressure waves to set up a standing wave in the chamber. The outlet means defines an opening in one of the sides of the chamber.
Owner:ISIS INNOVATION LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com