Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
69results about How to "Enhance excitation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
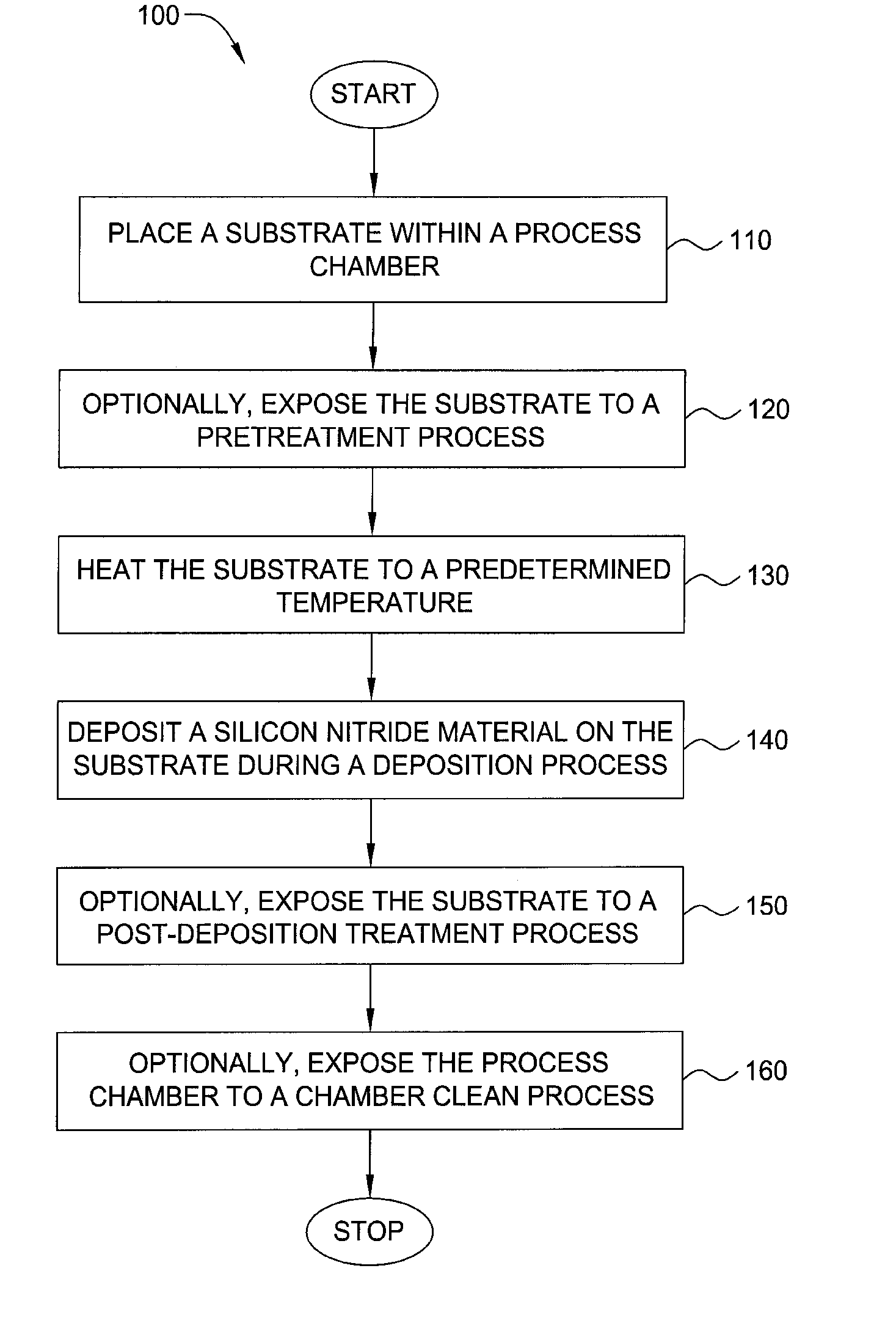
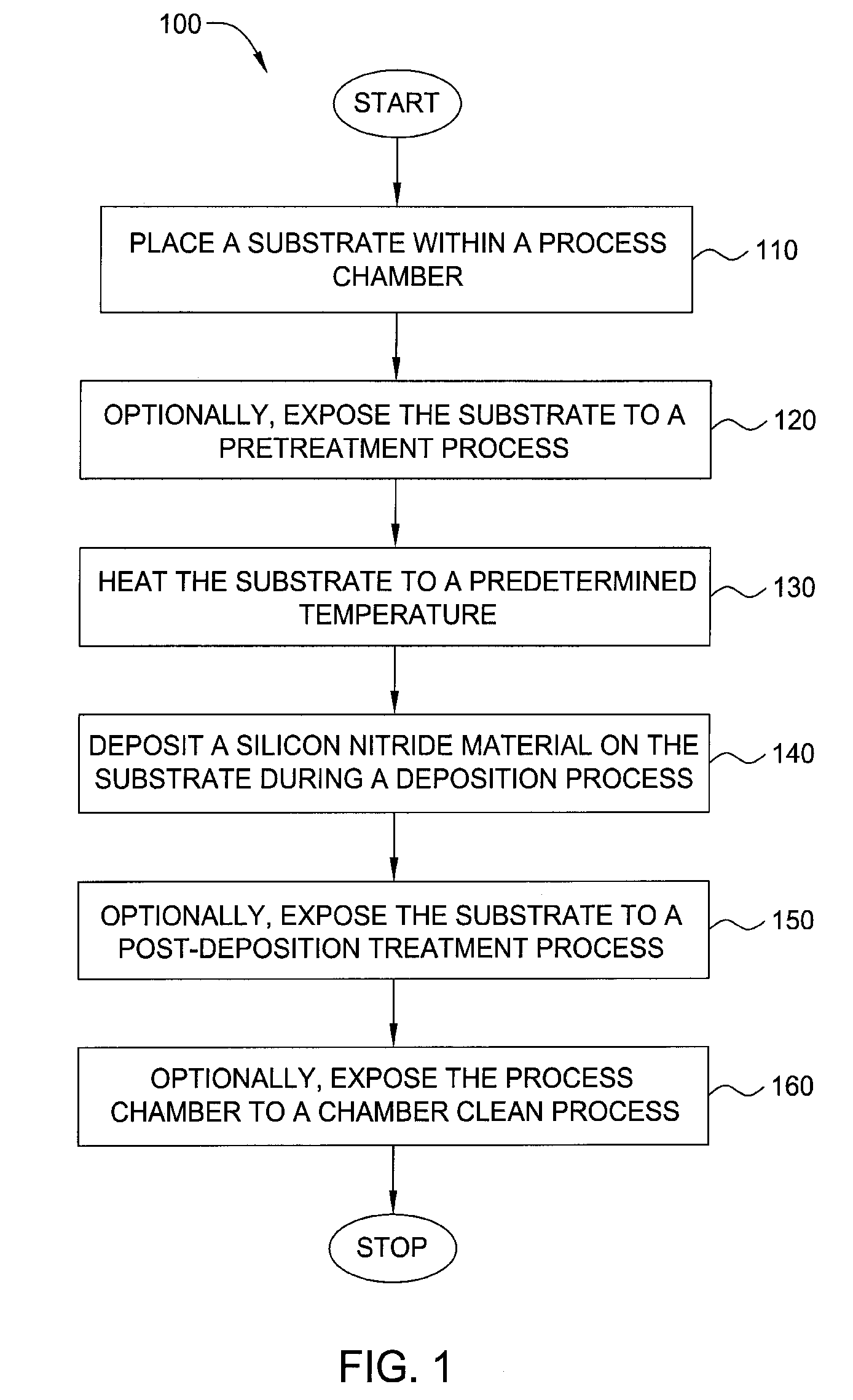
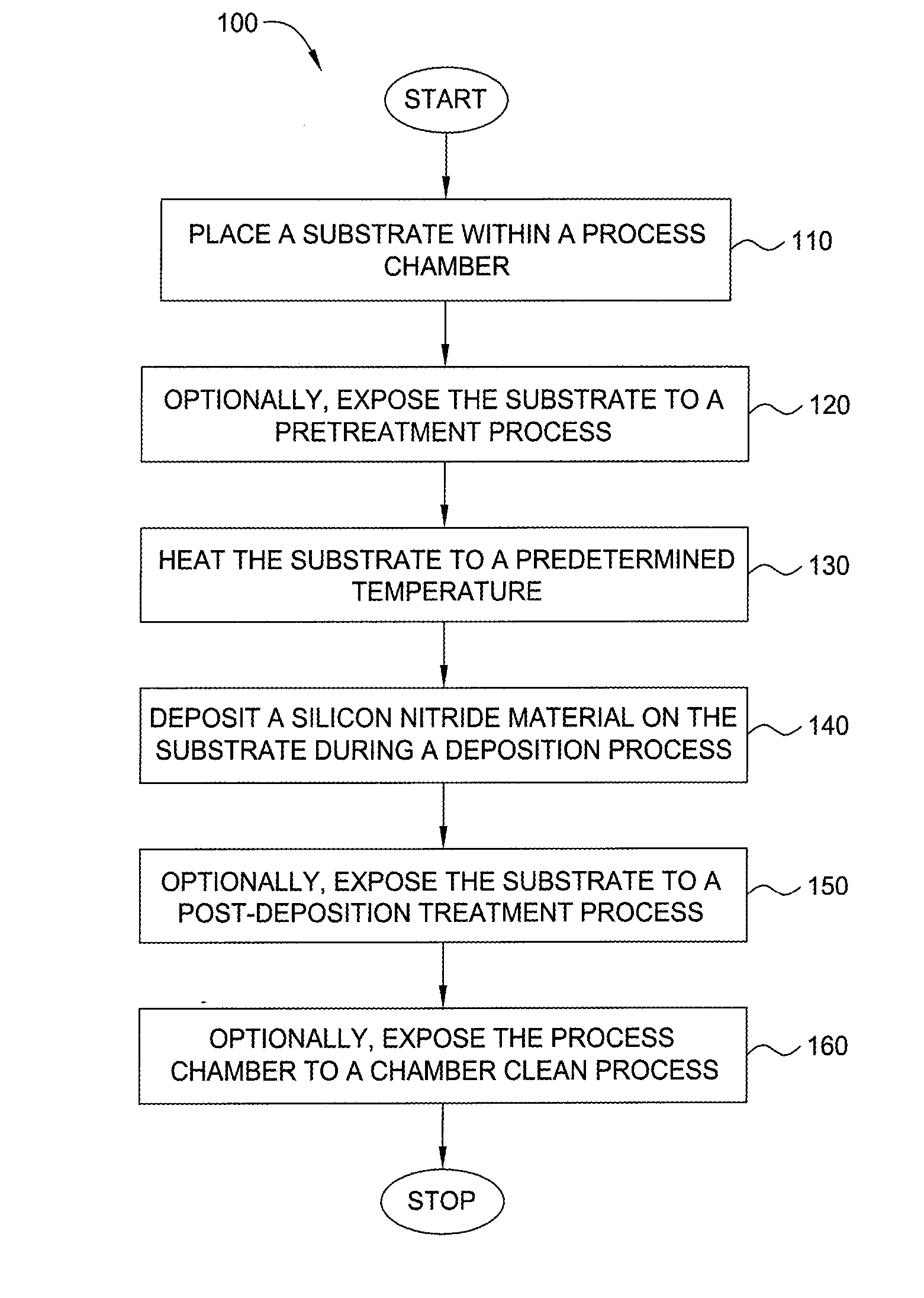
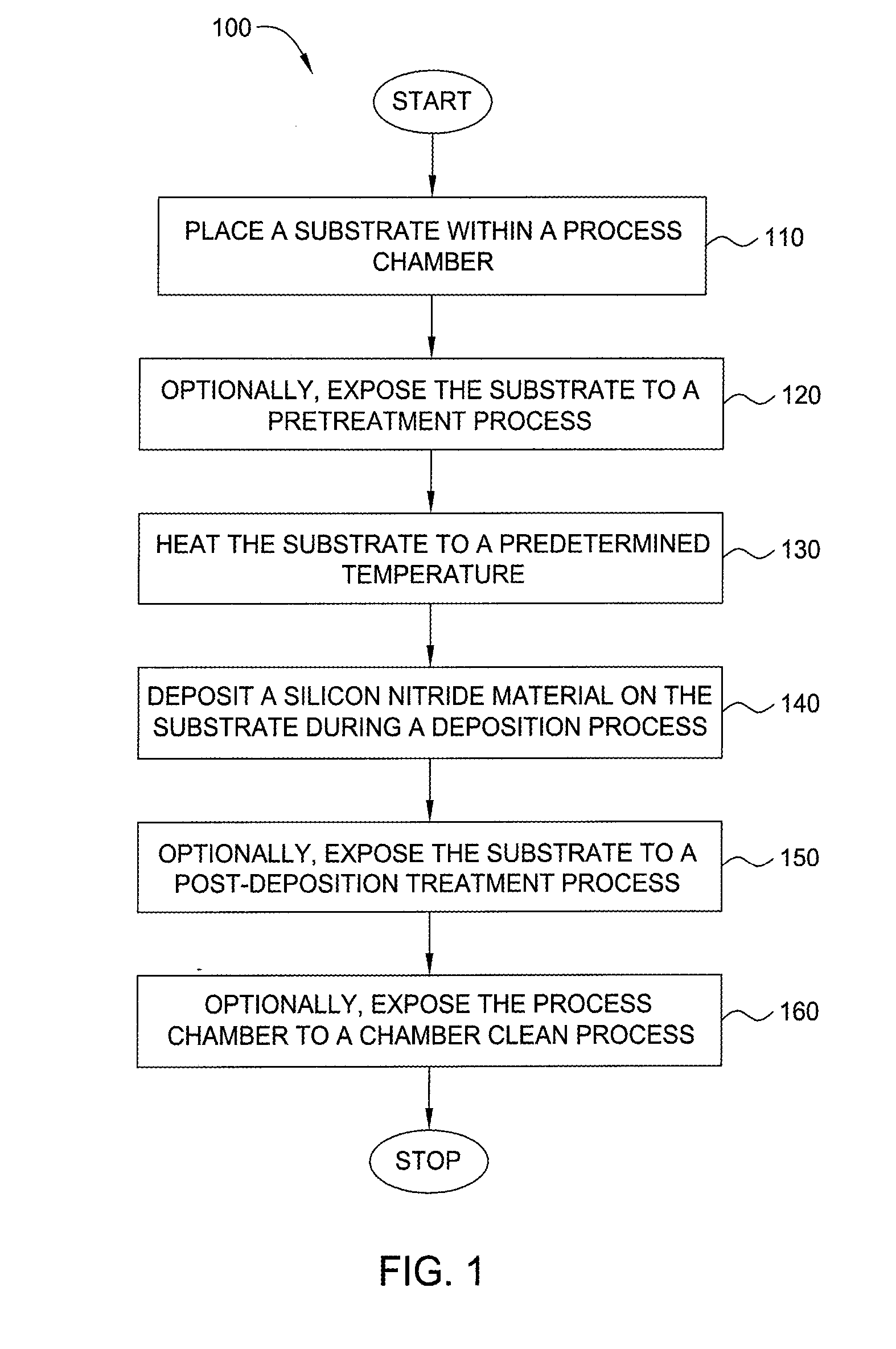
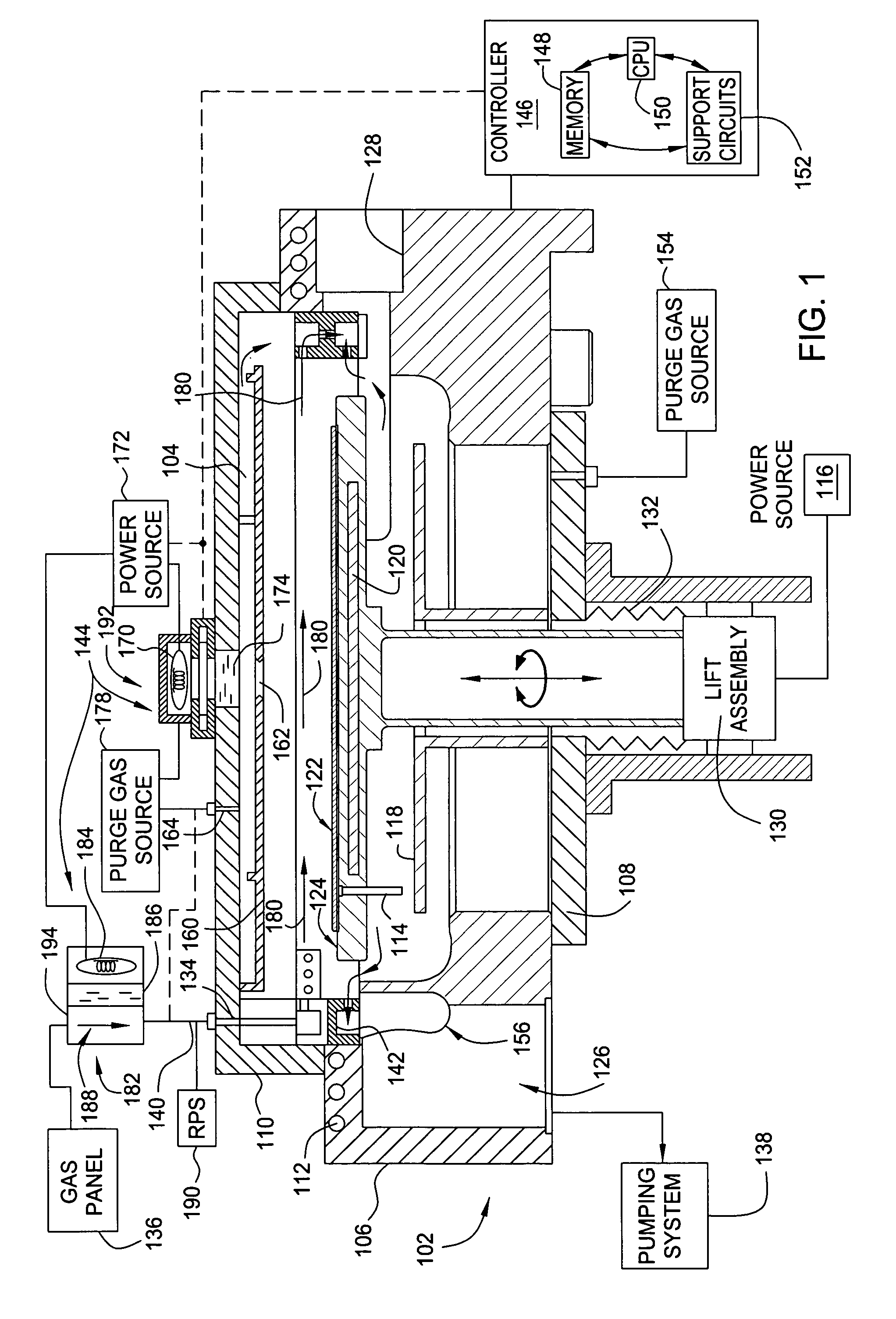
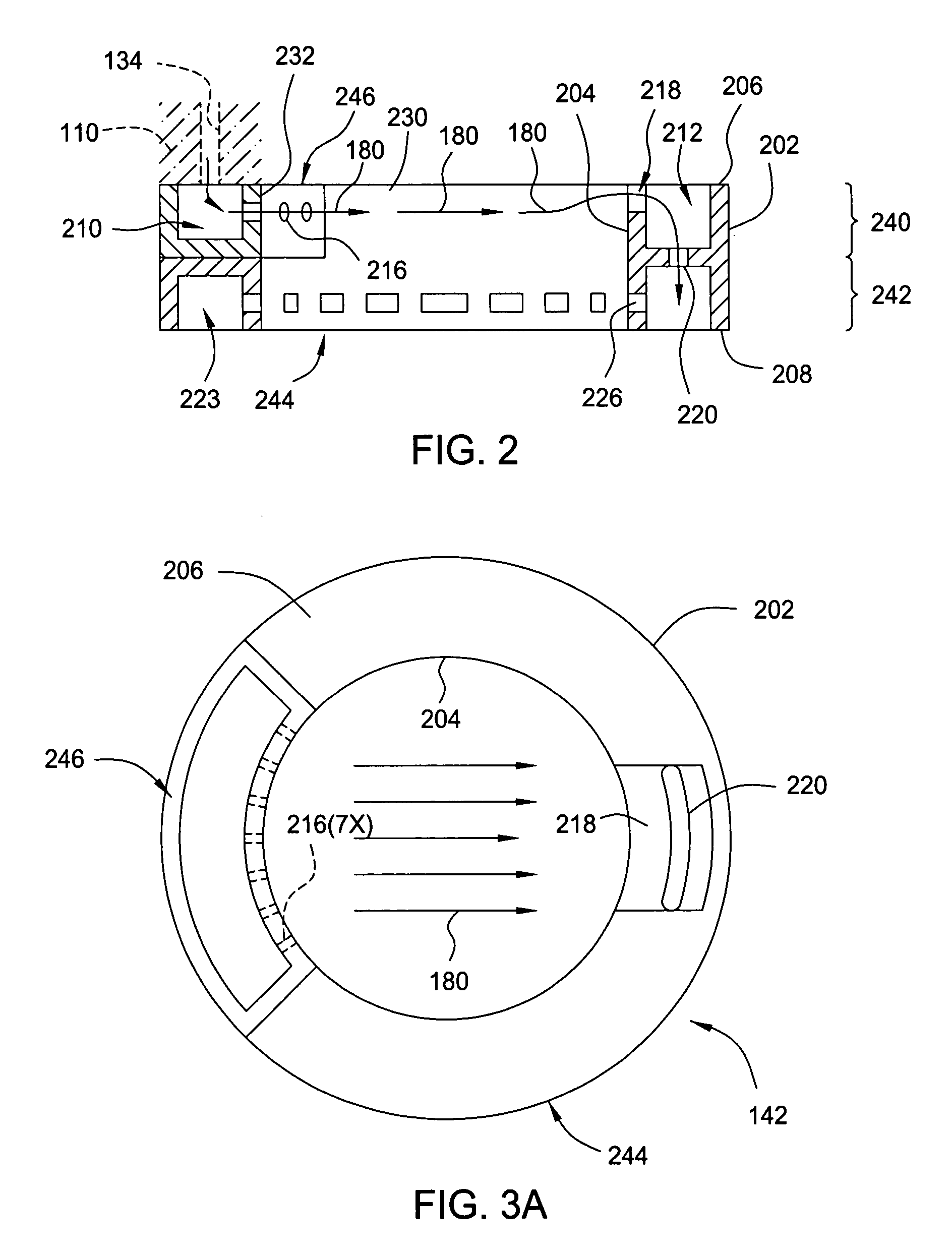
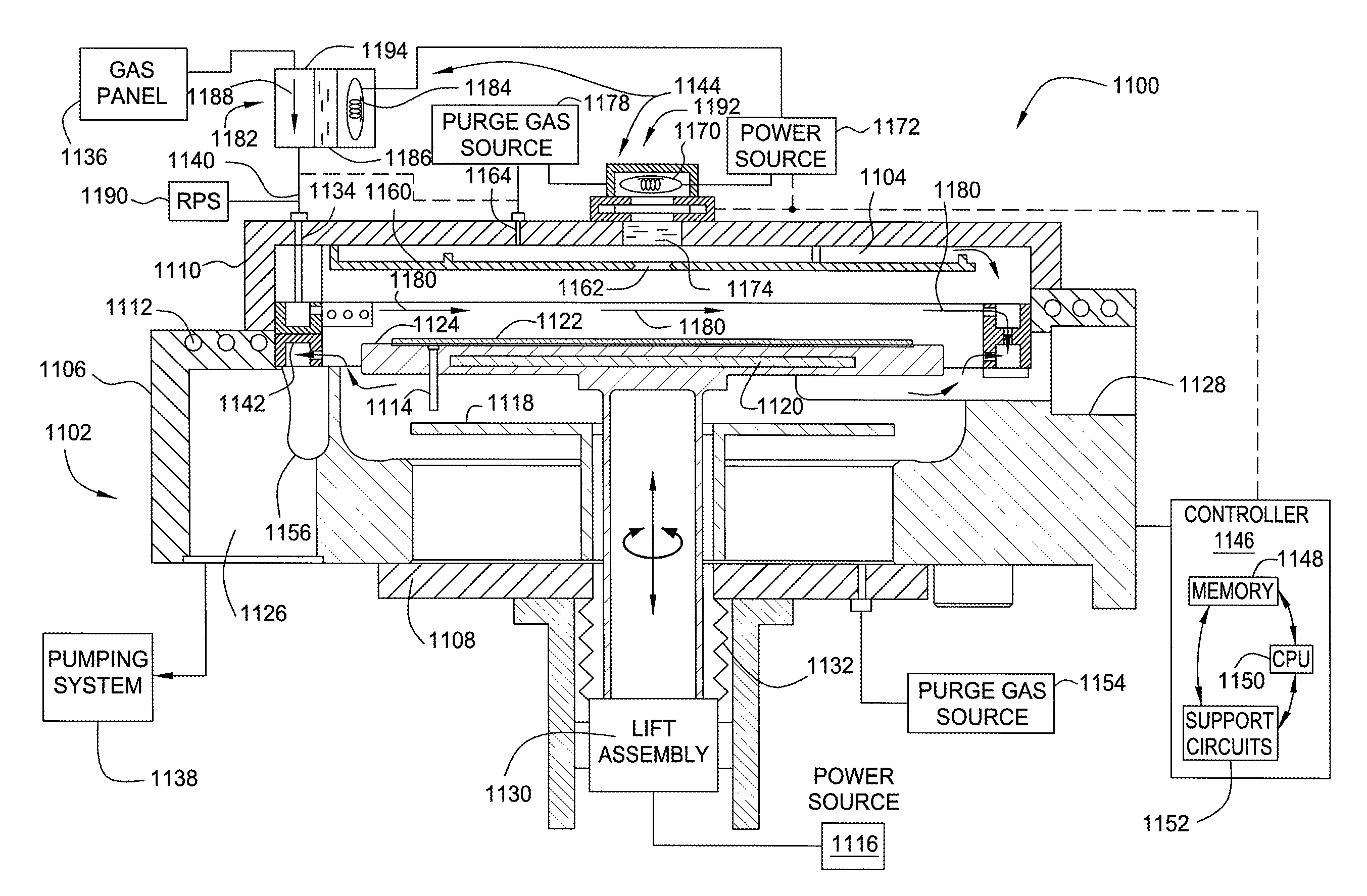
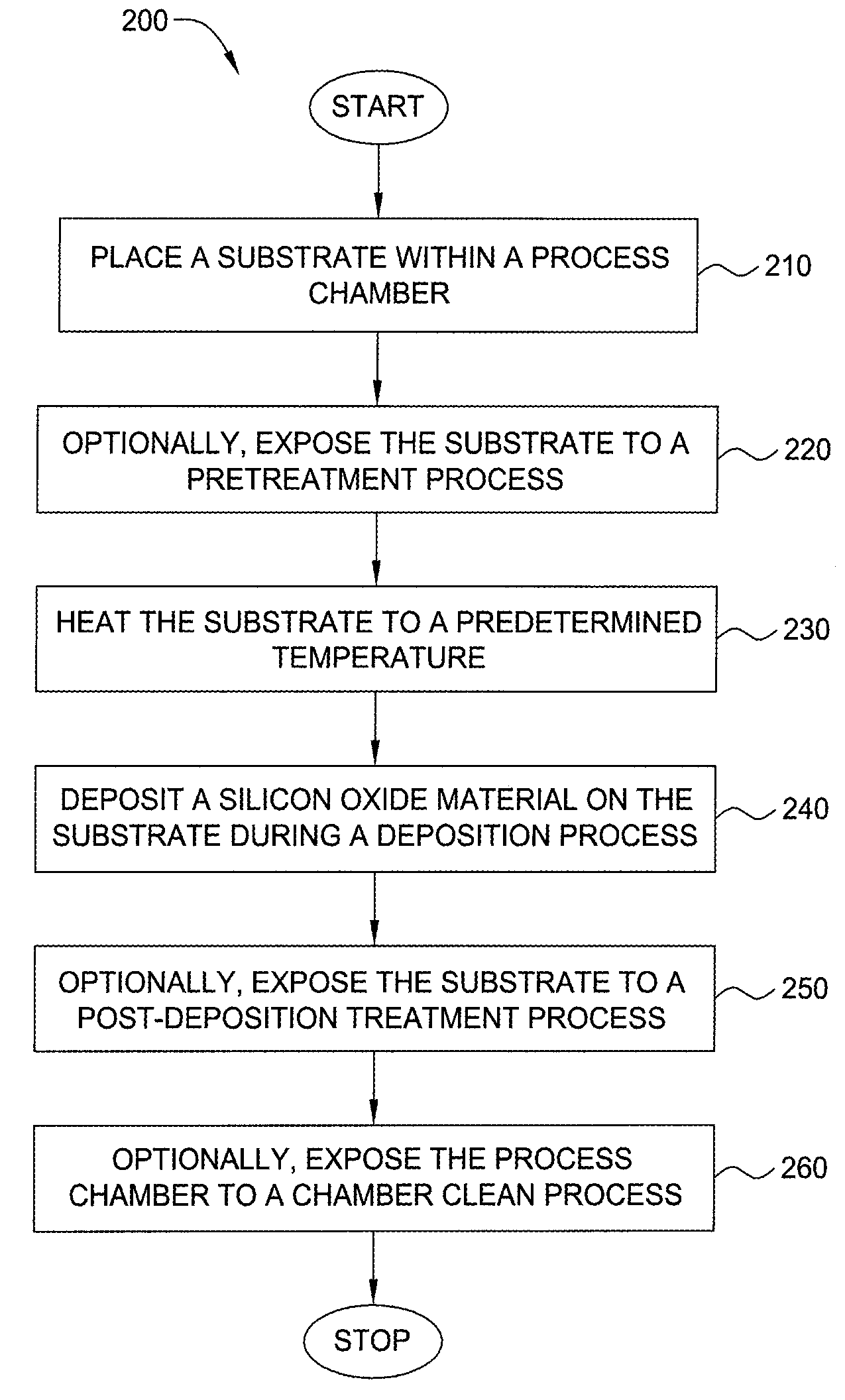
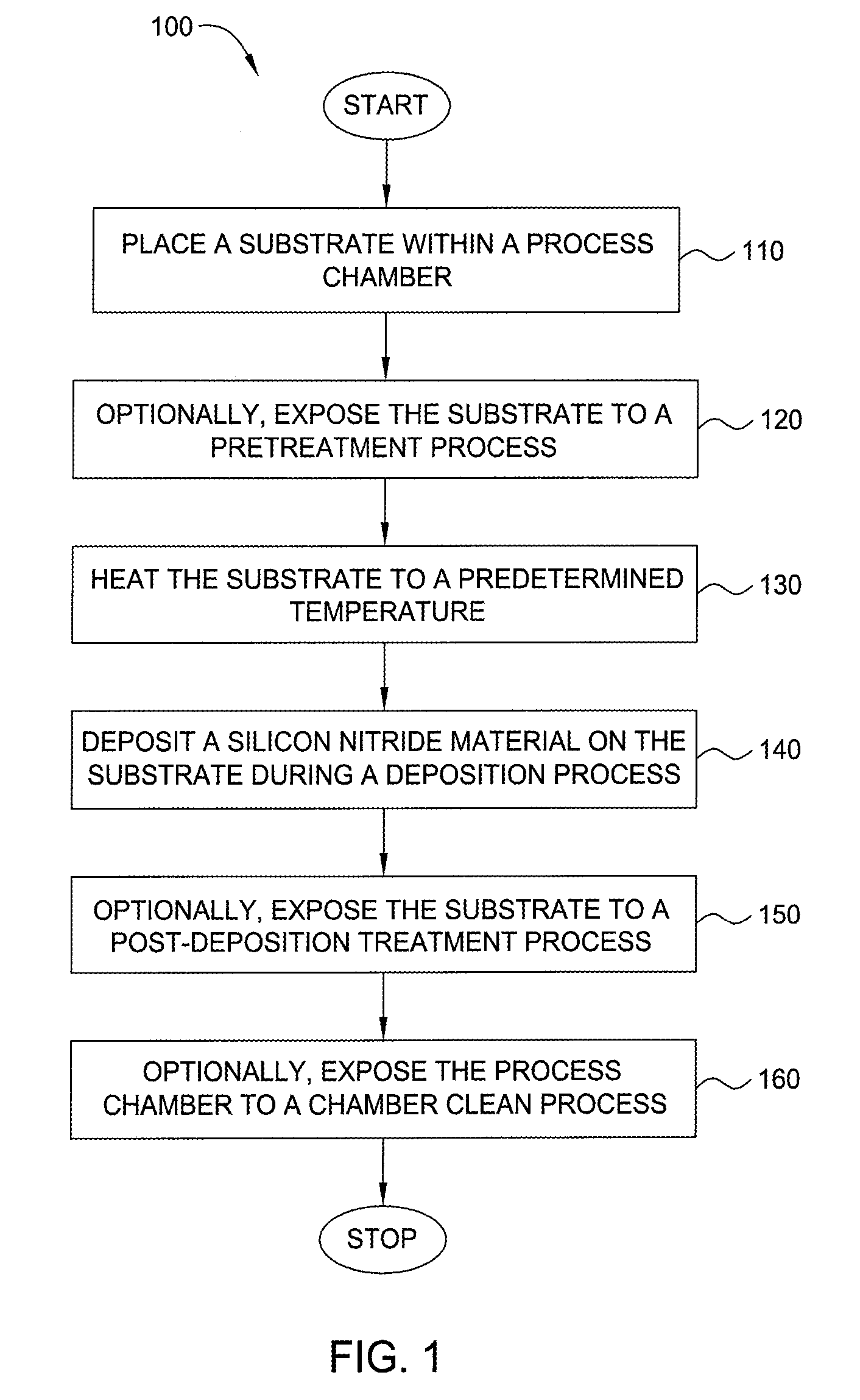
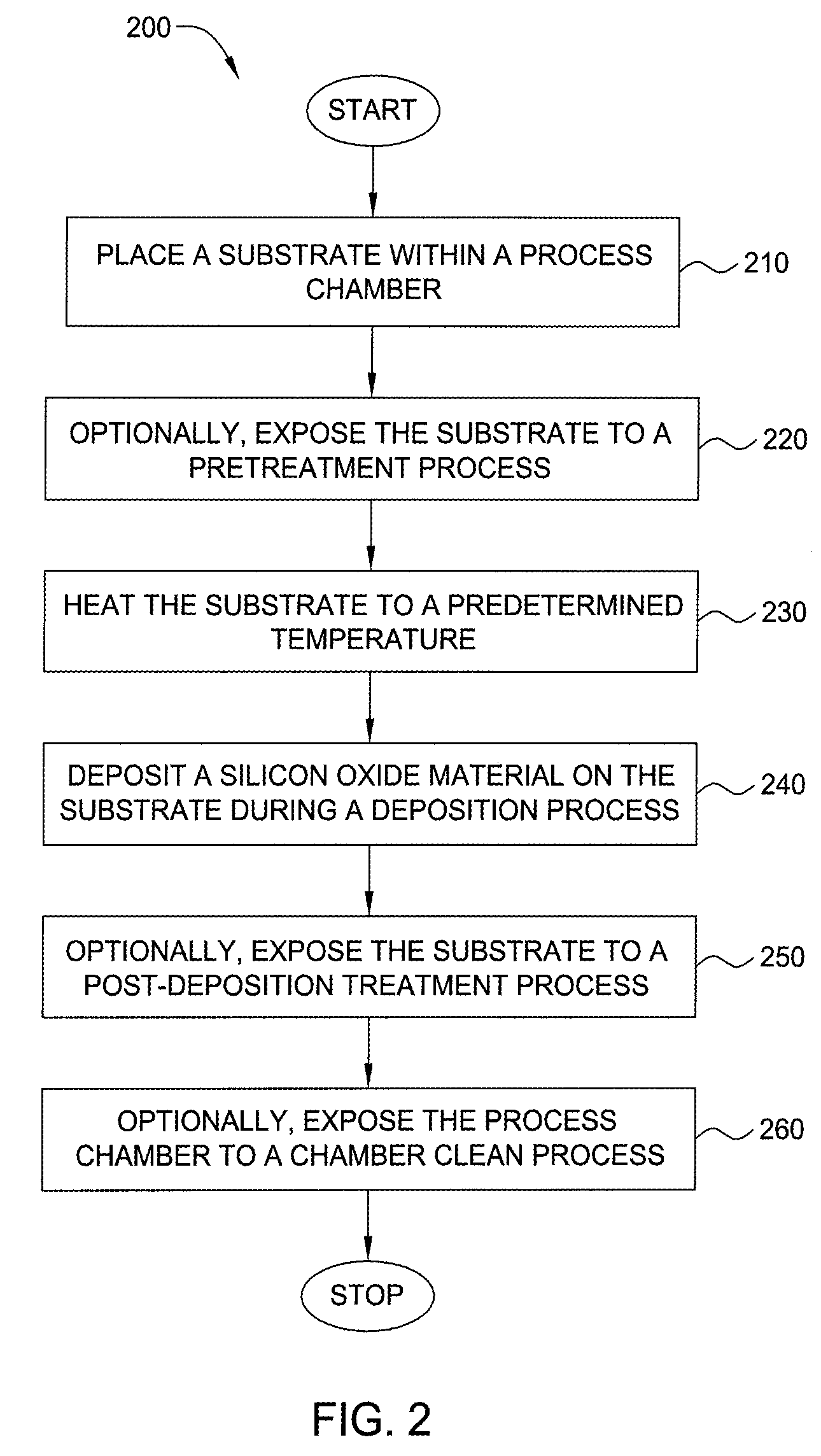
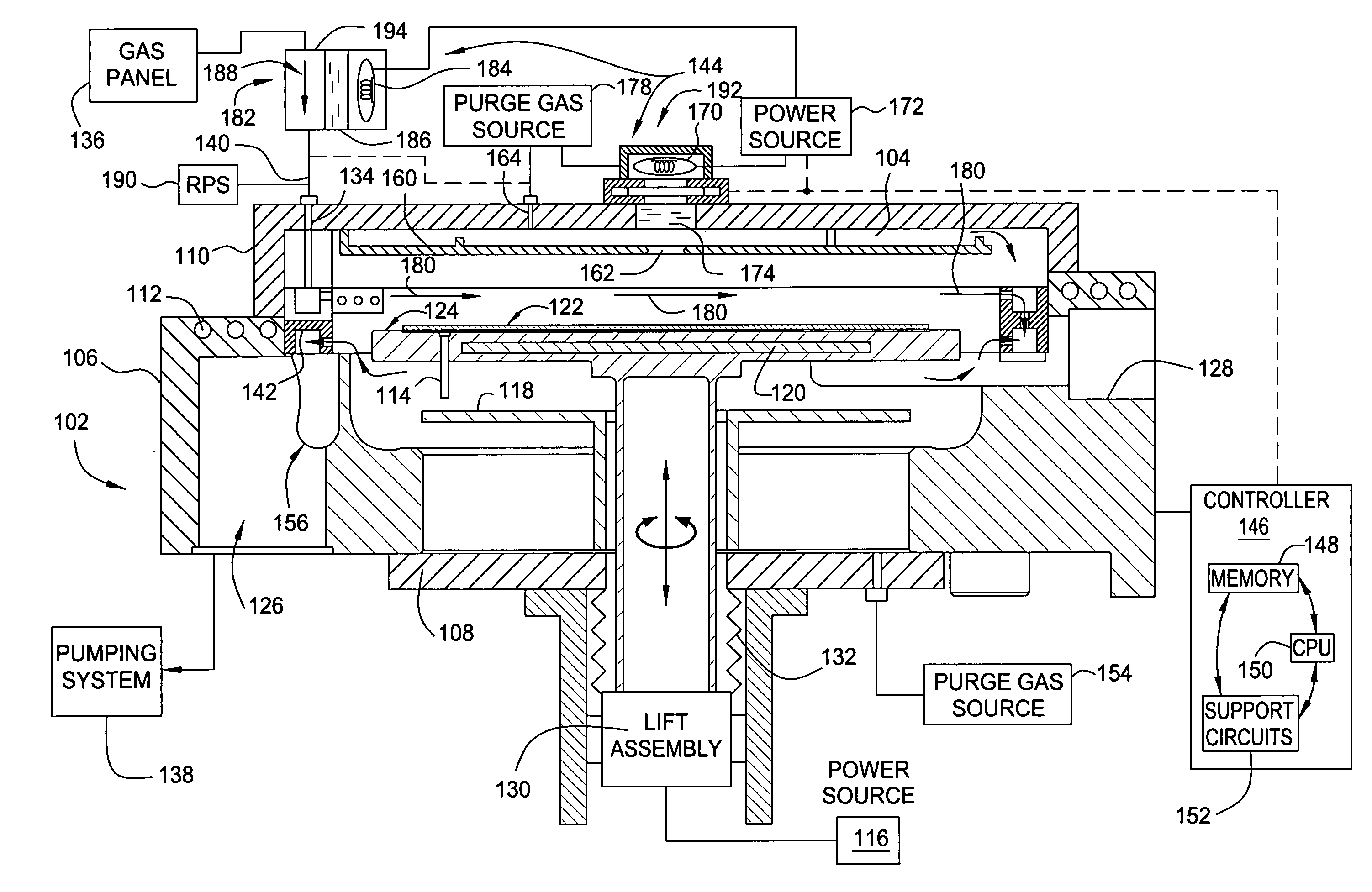
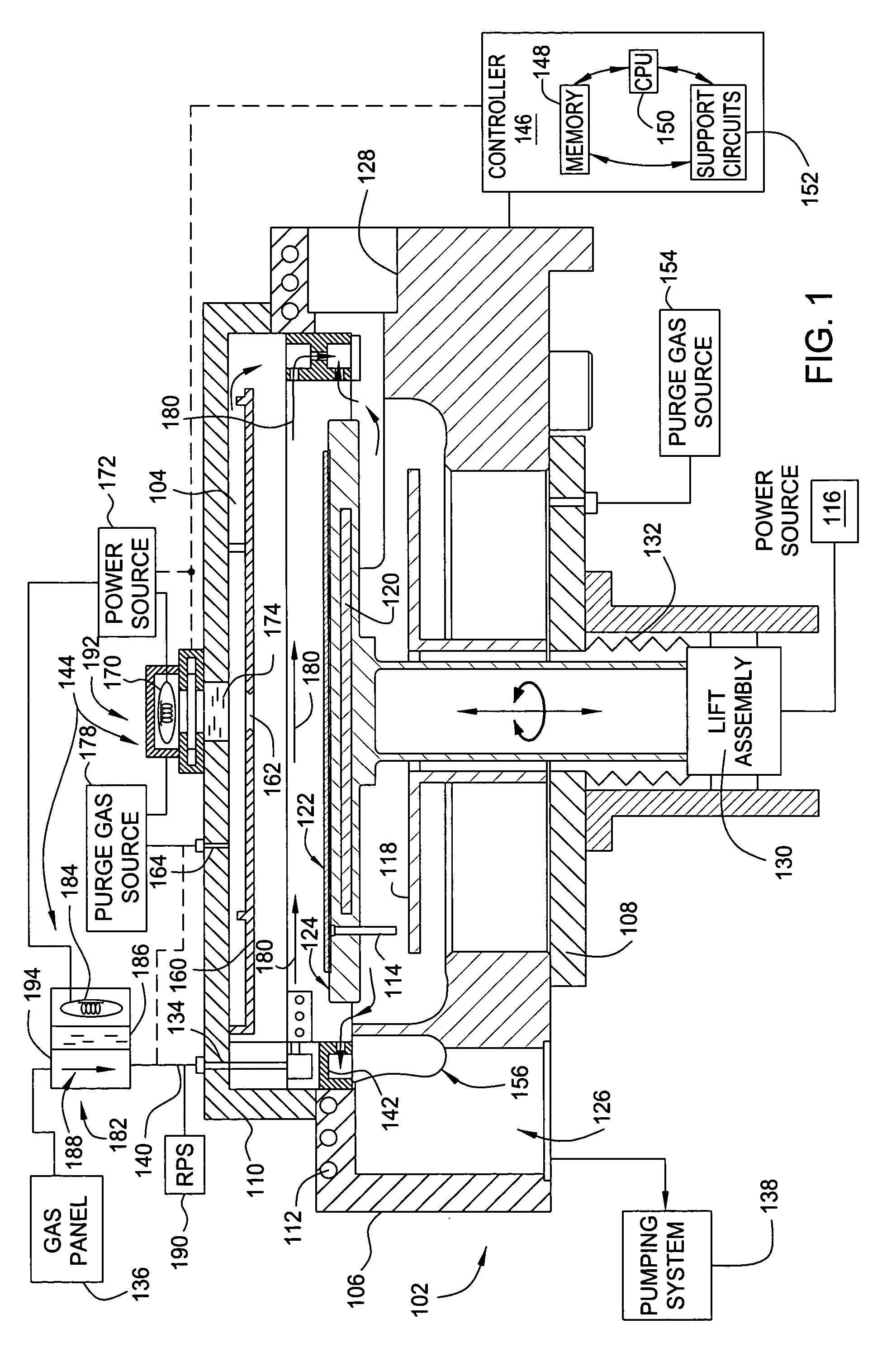
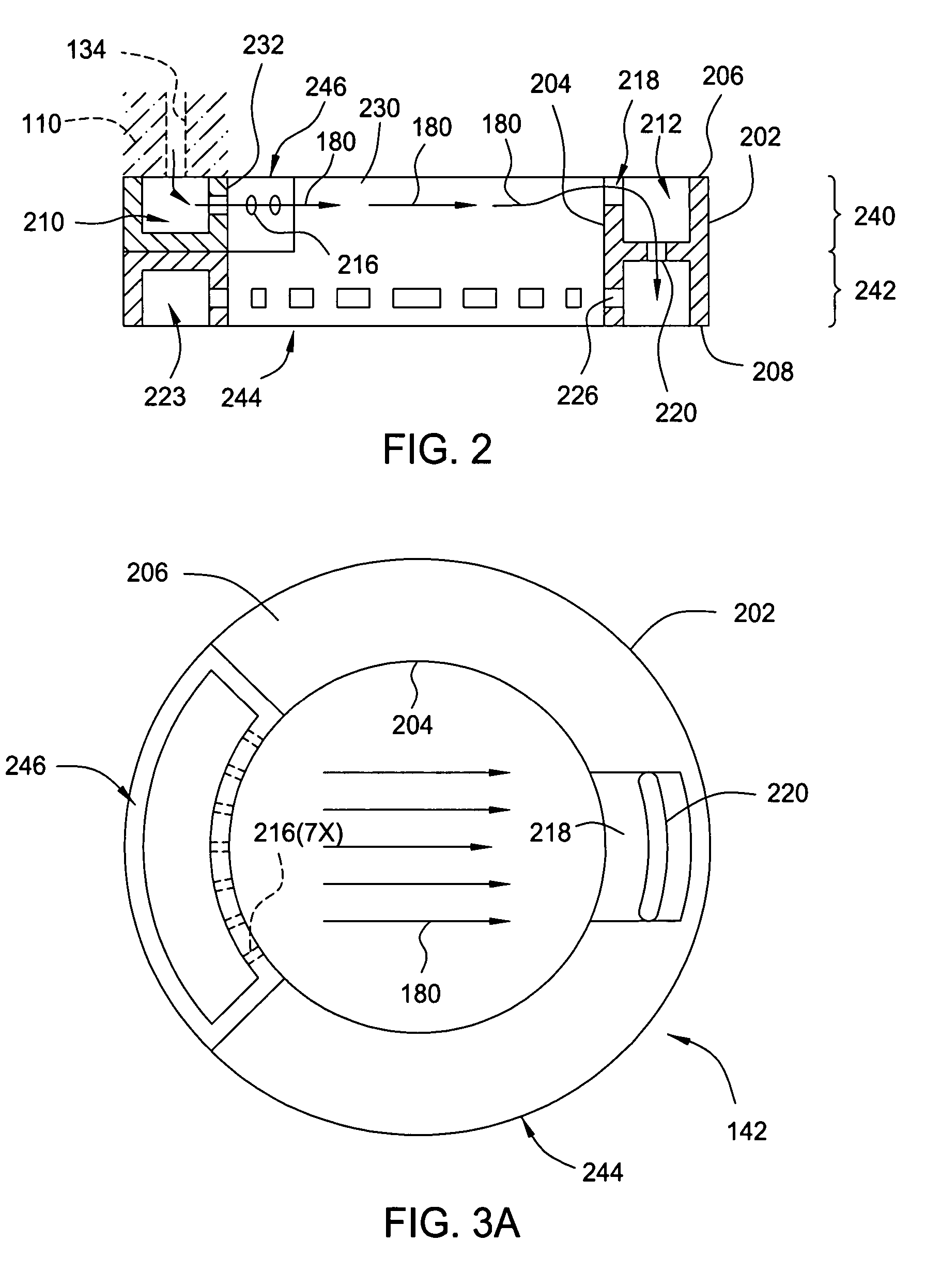
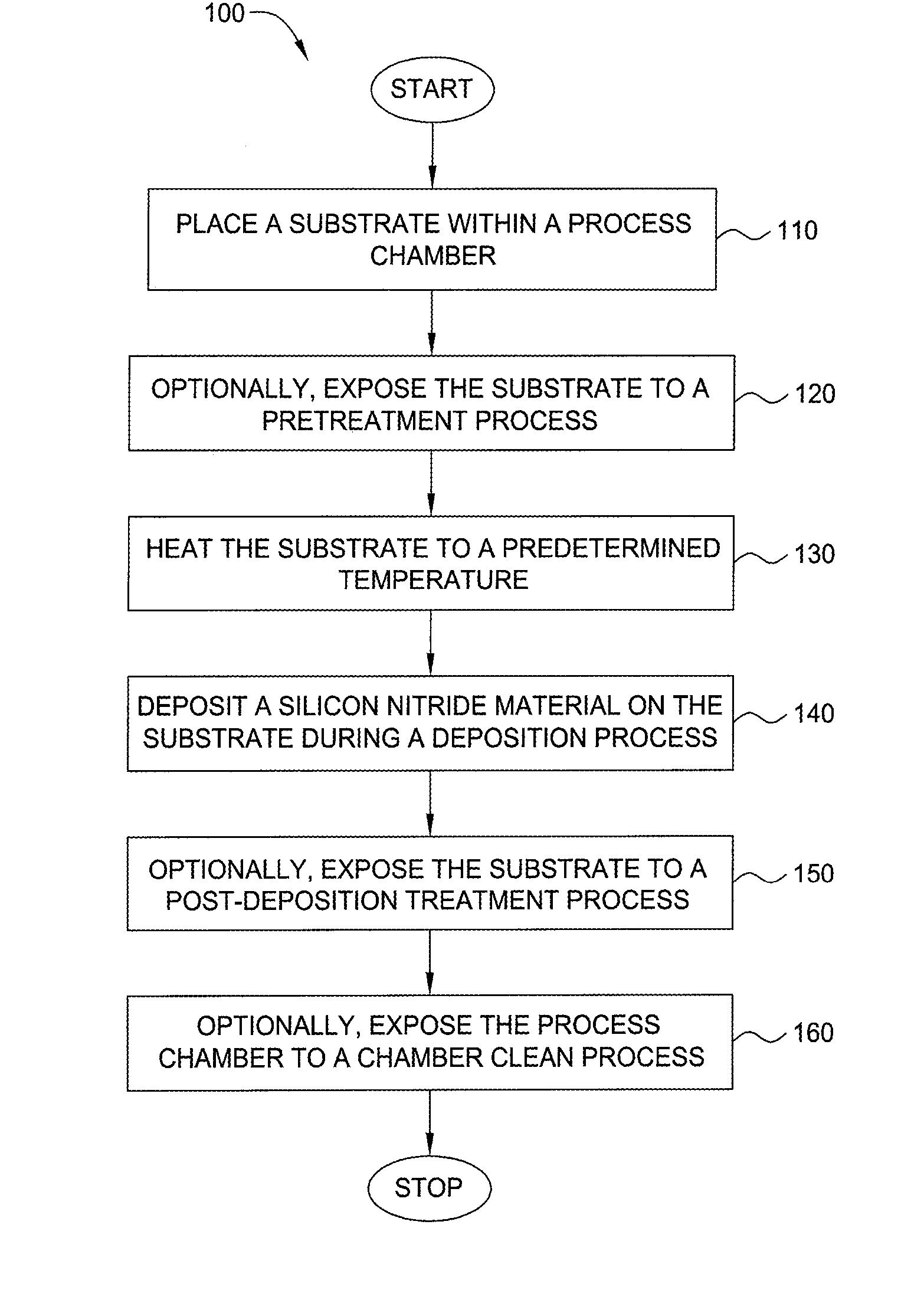
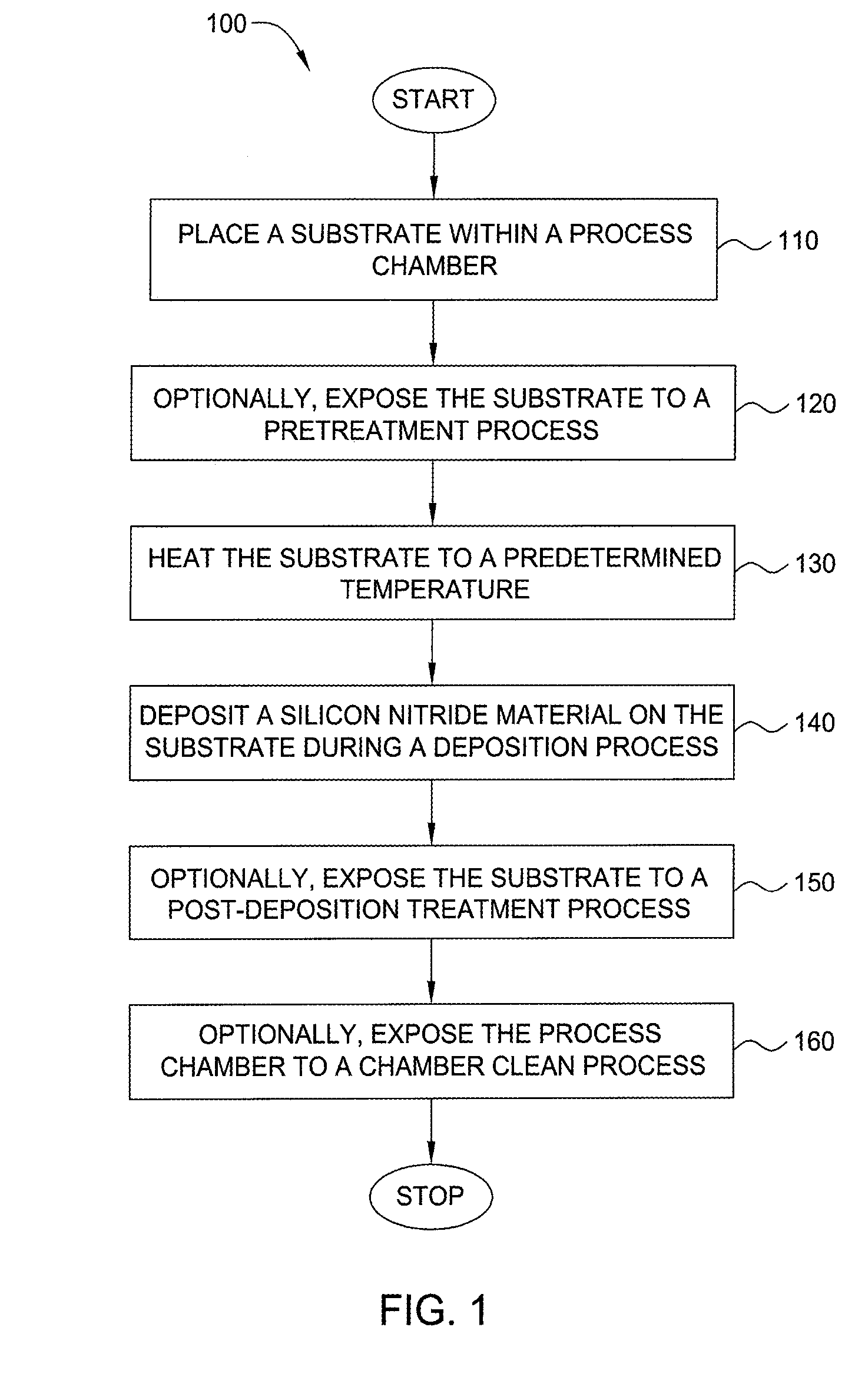
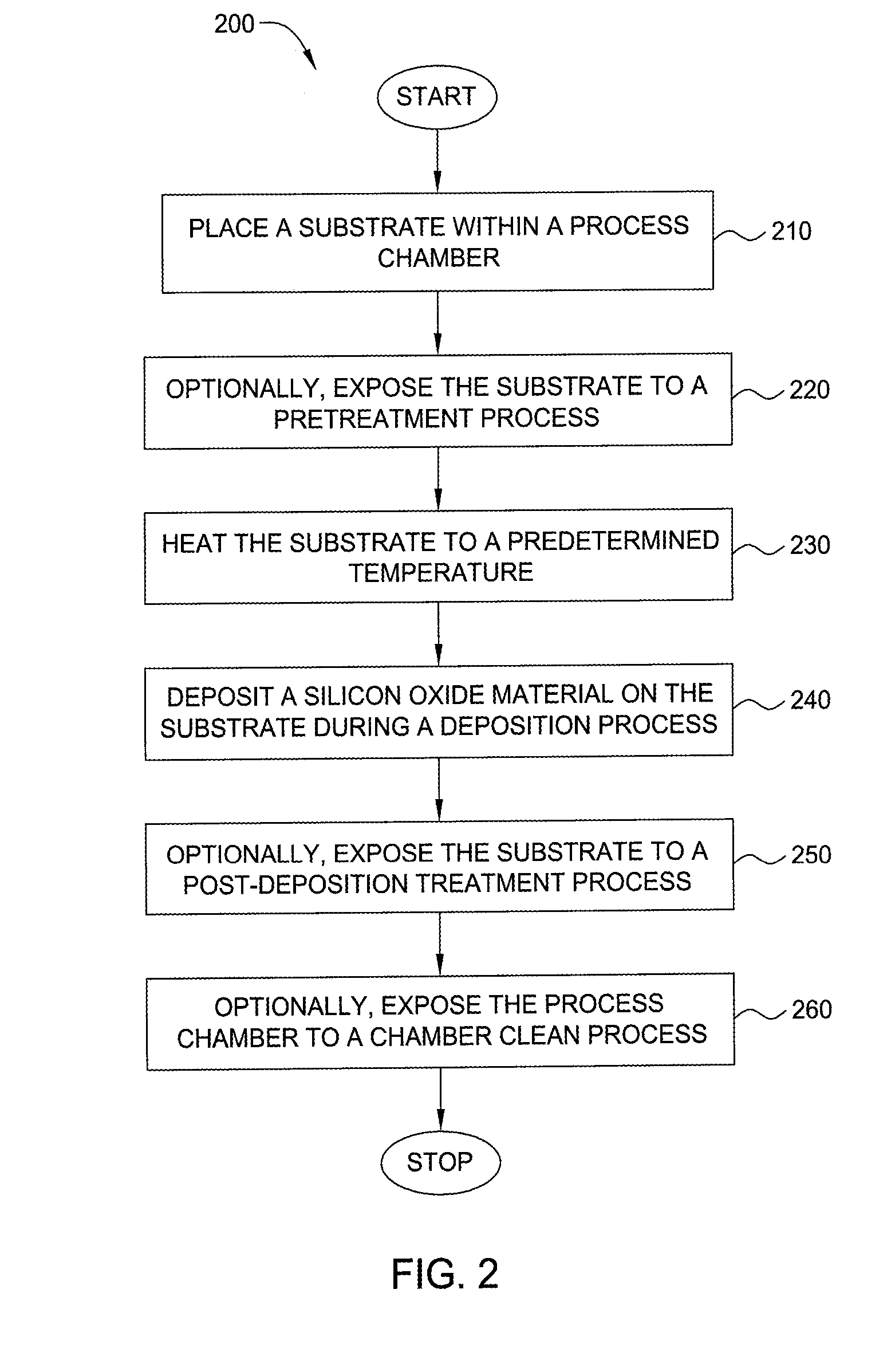
Method for forming silicon-containing materials during a photoexcitation deposition process
InactiveUS20060286774A1Enhance chamber cleaning processHigh surface energyPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingVolatilesSilicon oxide
Embodiments of the invention generally provide a method for depositing films or layers using a UV source during a photoexcitation process. The films are deposited on a substrate and usually contain a material, such as silicon (e.g., epitaxy, crystalline, microcrystalline, polysilicon, or amorphous), silicon oxide, silicon nitride, silicon oxynitride, or other silicon-containing materials. The photoexcitation process may expose the substrate and / or gases to an energy beam or flux prior to, during, or subsequent a deposition process. Therefore, the photoexcitation process may be used to pre-treat or post-treat the substrate or material, to deposit the silicon-containing material, and to enhance chamber cleaning processes. Attributes of the method that are enhanced by the UV photoexcitation process include removing native oxides prior to deposition, removing volatiles from deposited films, increasing surface energy of the deposited films, increasing the excitation energy of precursors, reducing deposition time, and reducing deposition temperature.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
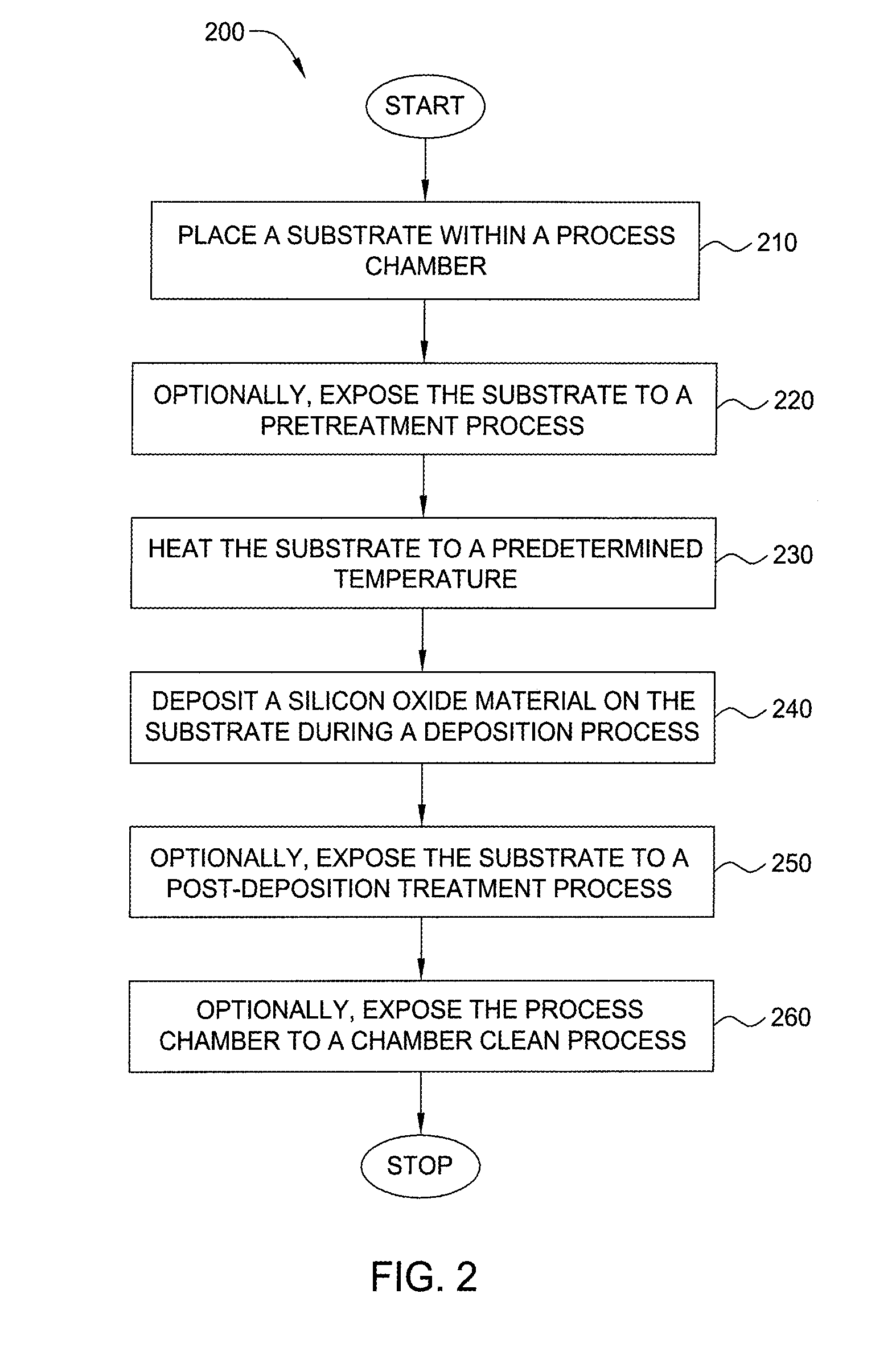
Method for forming silicon-containing materials during a photoexcitation deposition process
InactiveUS20060286775A1Enhance cleaning processIncreased surface energyPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSurface energyOxide
Embodiments of the invention generally provide a method for depositing films or layers using a UV source during a photoexcitation process. The films are deposited on a substrate and usually contain a material, such as silicon (e.g., epitaxy, crystalline, microcrystalline, polysilicon, or amorphous), silicon oxide, silicon nitride, silicon oxynitride, or other silicon-containing materials. The photoexcitation process may expose the substrate and / or gases to an energy beam or flux prior to, during, or subsequent a deposition process. Therefore, the photoexcitation process may be used to pre-treat or post-treat the substrate or material, to deposit the silicon-containing material, and to enhance chamber cleaning processes. Attributes of the method that are enhanced by the UV photoexcitation process include removing native oxides prior to deposition, removing volatiles from deposited films, increasing surface energy of the deposited films, increasing the excitation energy of precursors, reducing deposition time, and reducing deposition temperature.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
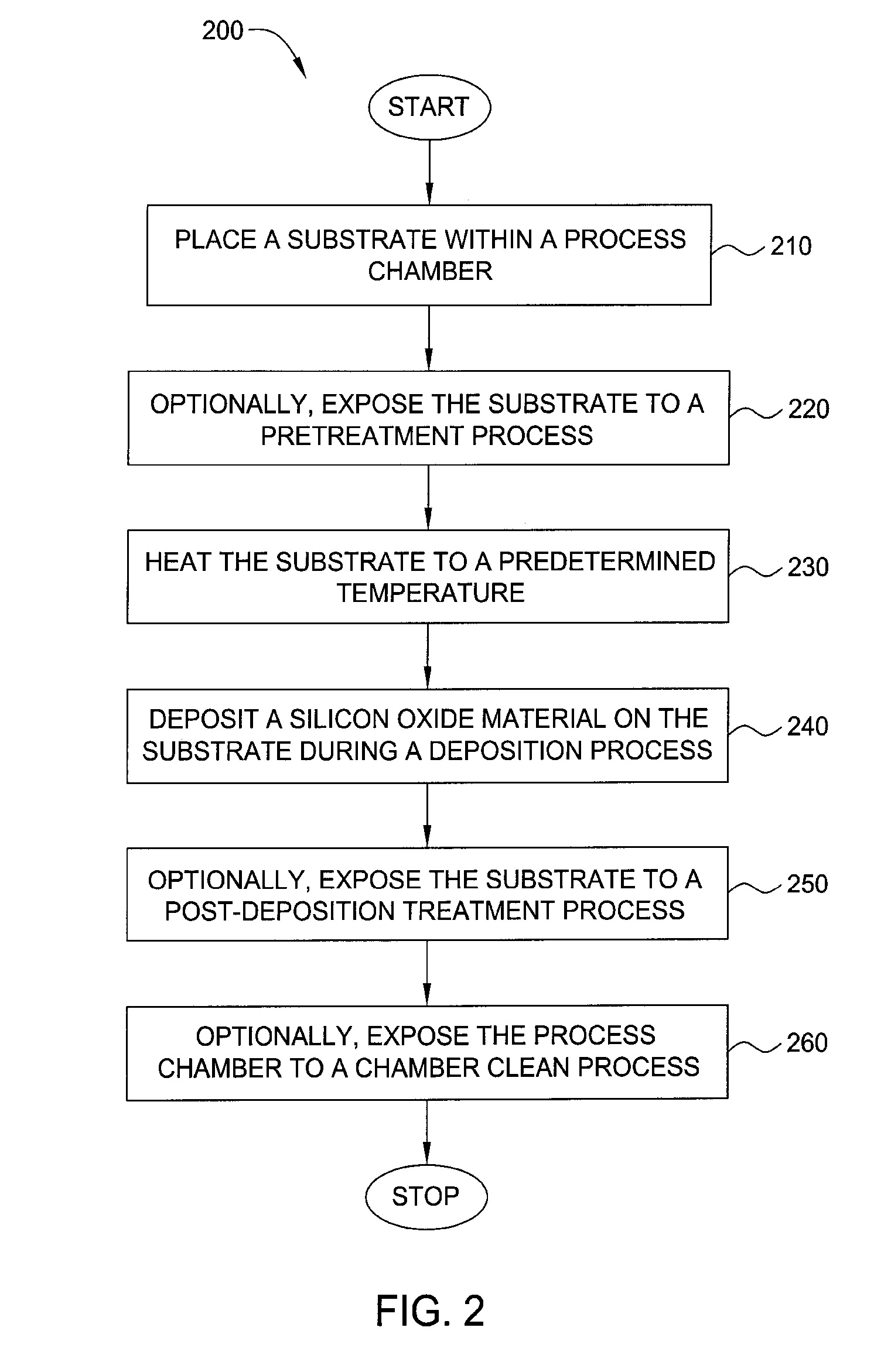
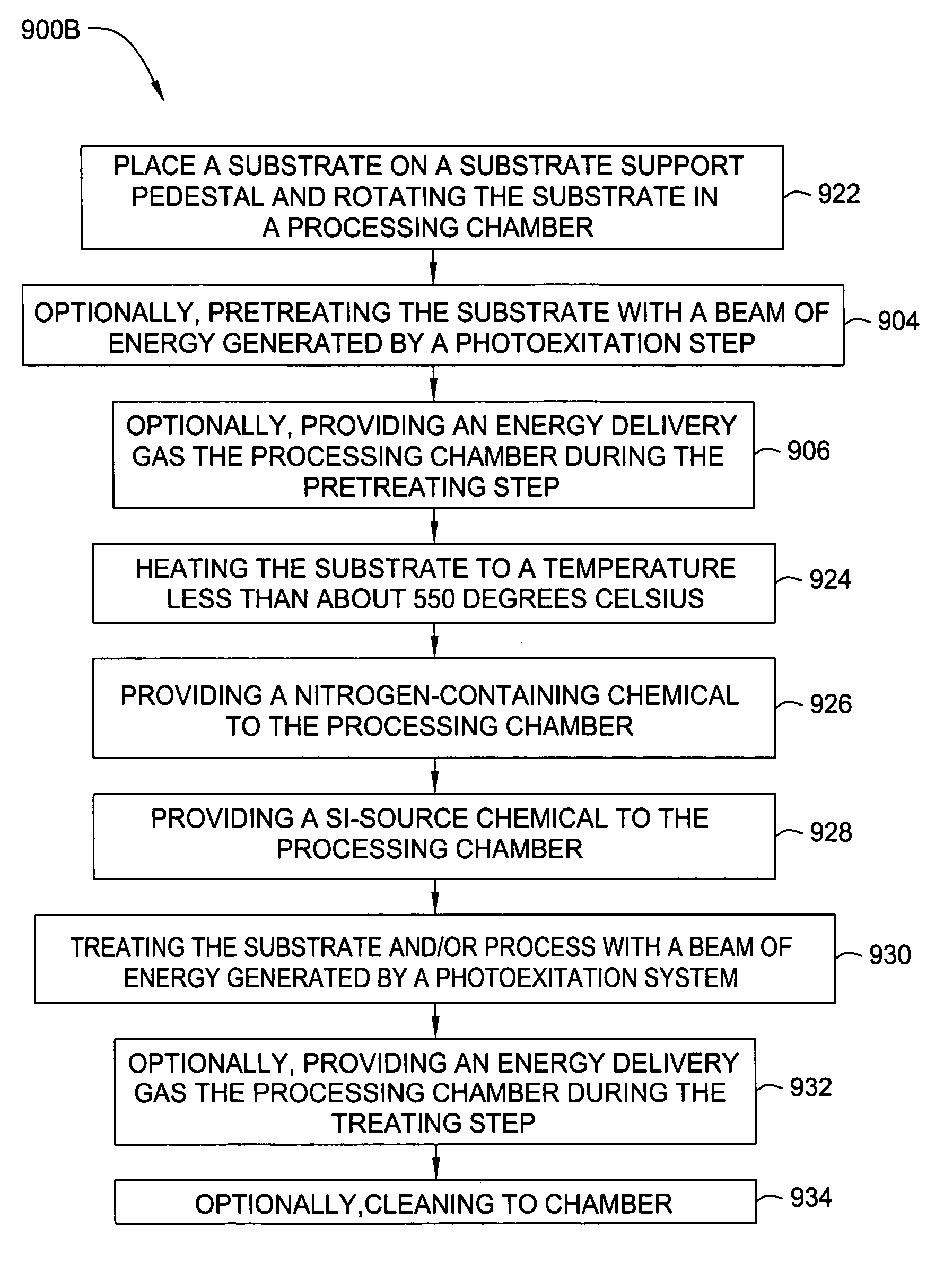
Method for silicon based dielectric deposition and clean with photoexcitation
InactiveUS20060286819A1Enhancing chamber cleaningSpeed up the processSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingDielectricCompound (substance)
Embodiments of the invention generally provide a method for depositing films using photoexcitation. The photoexcitation may be utilized for at least one of treating the substrate prior to deposition, treating substrate and / or gases during deposition, treating a deposited film, or for enhancing chamber cleaning. In one embodiment, a method for depositing silicon and nitrogen-containing film on a substrate includes heating a substrate disposed in a processing chamber, generating a beam of energy of between about 1 to about 10 eV, transferring the energy to a surface of the substrate; flowing a nitrogen-containing chemical into the processing chamber, flowing a silicon-containing chemical with silicon-nitrogen bonds into the processing chamber, and depositing a silicon and nitrogen-containing film on the substrate.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method for forming silicon-containing materials during a photoexcitation deposition process
InactiveUS7651955B2Easy to cleanHigh surface energyPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAutoxidationDeposition temperature
Embodiments of the invention generally provide a method for depositing films or layers using a UV source during a photoexcitation process. The films are deposited on a substrate and usually contain a material, such as silicon (e.g., epitaxy, crystalline, microcrystalline, polysilicon, or amorphous), silicon oxide, silicon nitride, silicon oxynitride, or other silicon-containing materials. The photoexcitation process may expose the substrate and / or gases to an energy beam or flux prior to, during, or subsequent a deposition process. Therefore, the photoexcitation process may be used to pre-treat or post-treat the substrate or material, to deposit the silicon-containing material, and to enhance chamber cleaning processes. Attributes of the method that are enhanced by the UV photoexcitation process include removing native oxides prior to deposition, removing volatiles from deposited films, increasing surface energy of the deposited films, increasing the excitation energy of precursors, reducing deposition time, and reducing deposition temperature.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method for forming silicon-containing materials during a photoexcitation deposition process
InactiveUS7648927B2Easy to cleanHigh surface energyPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAutoxidationDeposition temperature
Embodiments of the invention generally provide a method for depositing films or layers using a UV source during a photoexcitation process. The films are deposited on a substrate and usually contain a material, such as silicon (e.g., epitaxy, crystalline, microcrystalline, polysilicon, or amorphous), silicon oxide, silicon nitride, silicon oxynitride, or other silicon-containing materials. The photoexcitation process may expose the substrate and / or gases to an energy beam or flux prior to, during, or subsequent a deposition process. Therefore, the photoexcitation process may be used to pre-treat or post-treat the substrate or material, to deposit the silicon-containing material, and to enhance chamber cleaning processes. Attributes of the method that are enhanced by the UV photoexcitation process include removing native oxides prior to deposition, removing volatiles from deposited films, increasing surface energy of the deposited films, increasing the excitation energy of precursors, reducing deposition time, and reducing deposition temperature.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method for treating substrates and films with photoexcitation
InactiveUS7601652B2Easy to cleanSpeed up the processSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingNitrogenCompound (substance)
Embodiments of the invention generally provide a method for depositing films using photoexcitation. The photoexcitation may be utilized for at least one of treating the substrate prior to deposition, treating substrate and / or gases during deposition, treating a deposited film, or for enhancing chamber cleaning. In one embodiment, a method for depositing silicon and nitrogen-containing film on a substrate includes heating a substrate disposed in a processing chamber, generating a beam of energy of between about 1 to about 10 eV, transferring the energy to a surface of the substrate; flowing a nitrogen-containing chemical into the processing chamber, flowing a silicon-containing chemical with silicon-nitrogen bonds into the processing chamber, and depositing a silicon and nitrogen-containing film on the substrate.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method for forming silicon-containing materials during a photoexcitation deposition process
InactiveUS20060286776A1Enhance chamber cleaning processHigh surface energyPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingVolatilesSilicon oxide
Embodiments of the invention generally provide a method for depositing films or layers using a UV source during a photoexcitation process. The films are deposited on a substrate and usually contain a material, such as silicon (e.g., epitaxy, crystalline, microcrystalline, polysilicon, or amorphous), silicon oxide, silicon nitride, silicon oxynitride, or other silicon-containing materials. The photoexcitation process may expose the substrate and / or gases to an energy beam or flux prior to, during, or subsequent a deposition process. Therefore, the photoexcitation process may be used to pre-treat or post-treat the substrate or material, to deposit the silicon-containing material, and to enhance chamber cleaning processes. Attributes of the method that are enhanced by the UV photoexcitation process include removing native oxides prior to deposition, removing volatiles from deposited films, increasing surface energy of the deposited films, increasing the excitation energy of precursors, reducing deposition time, and reducing deposition temperature.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Optical substrate for enhanced detectability of fluorescence
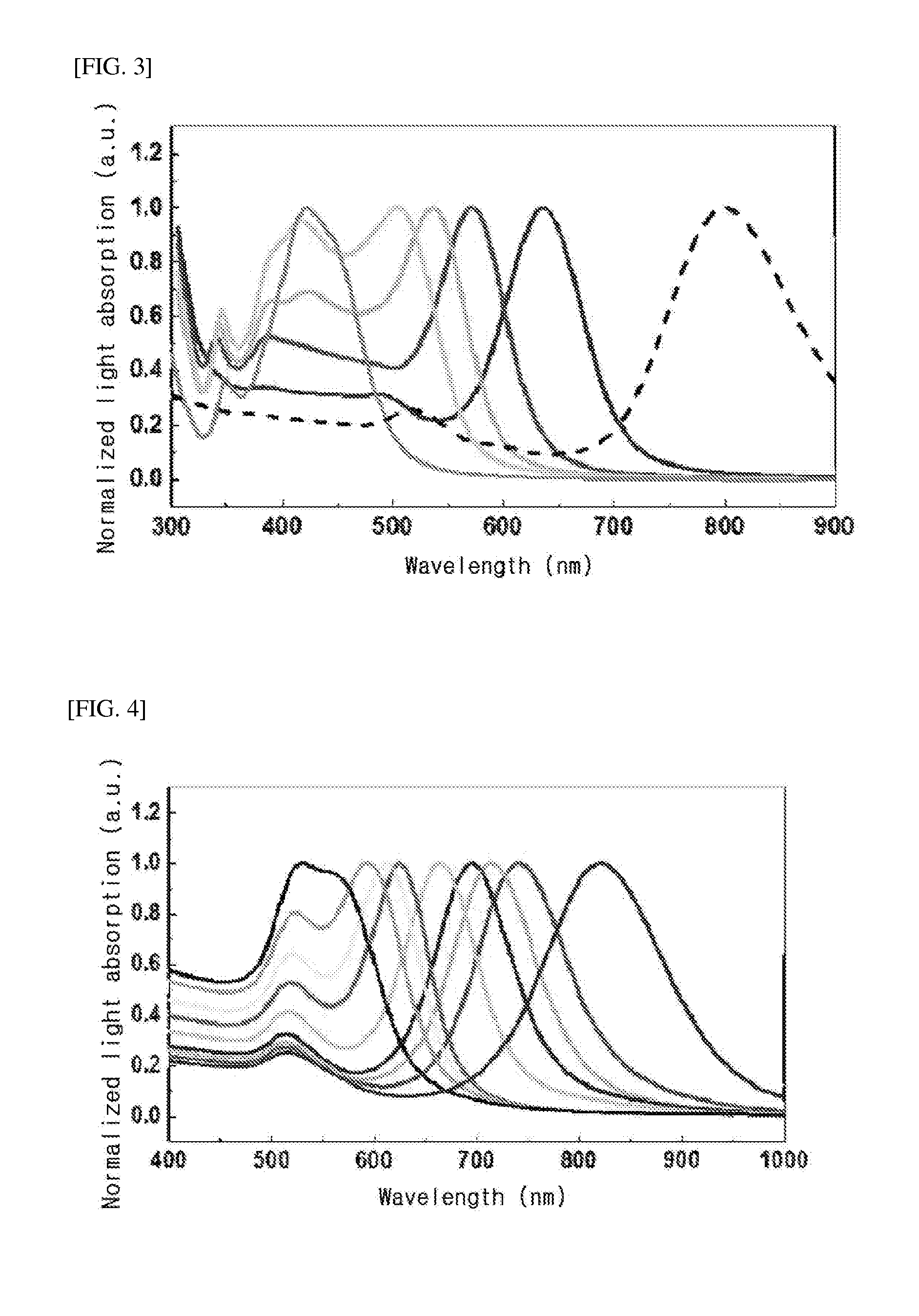
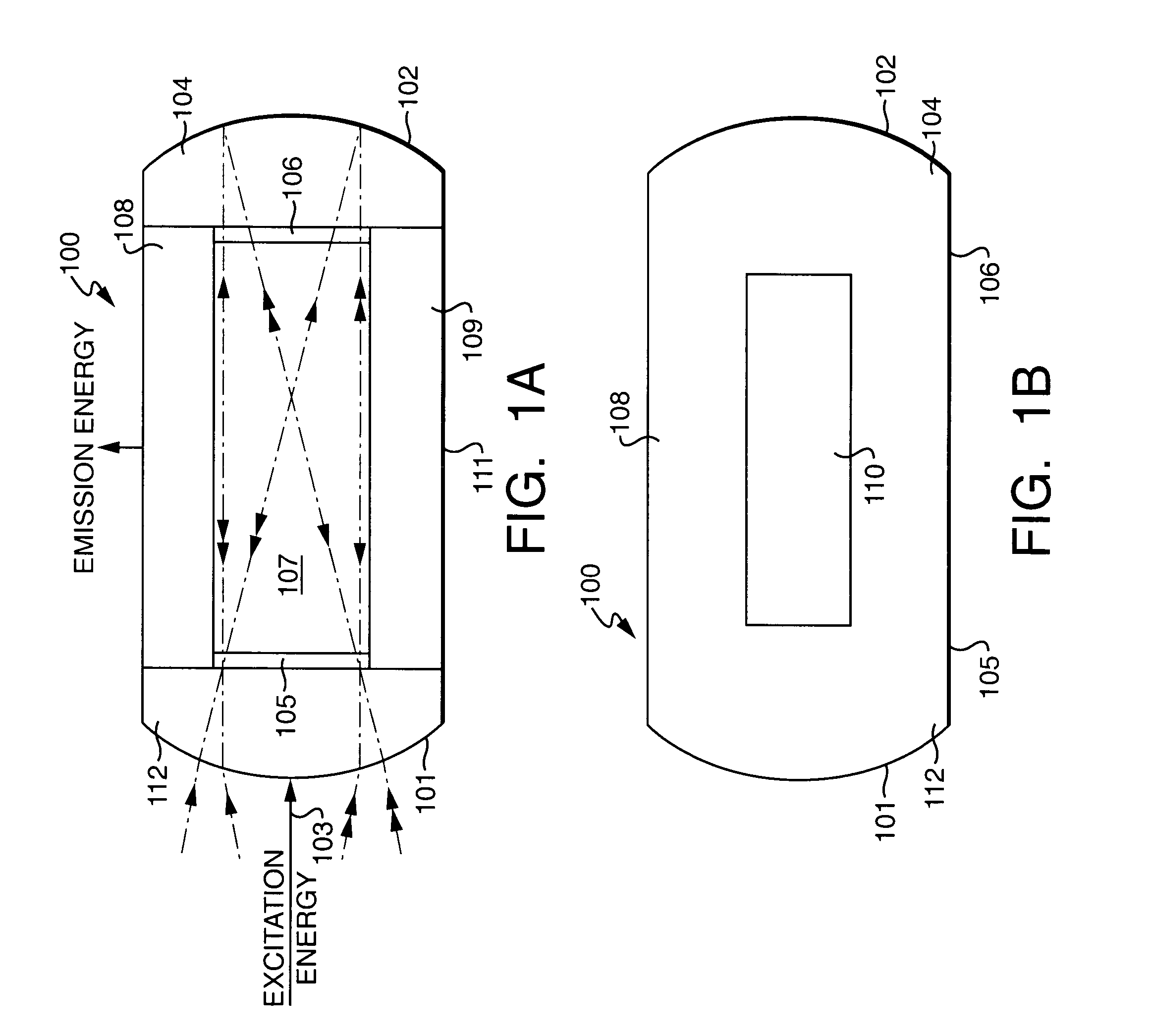
InactiveUS20070188746A1Accelerate emissionsEnhance excitationRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationFluorescenceRefractive index
Owner:OERLIKON TRADING AG TRUEBBACH
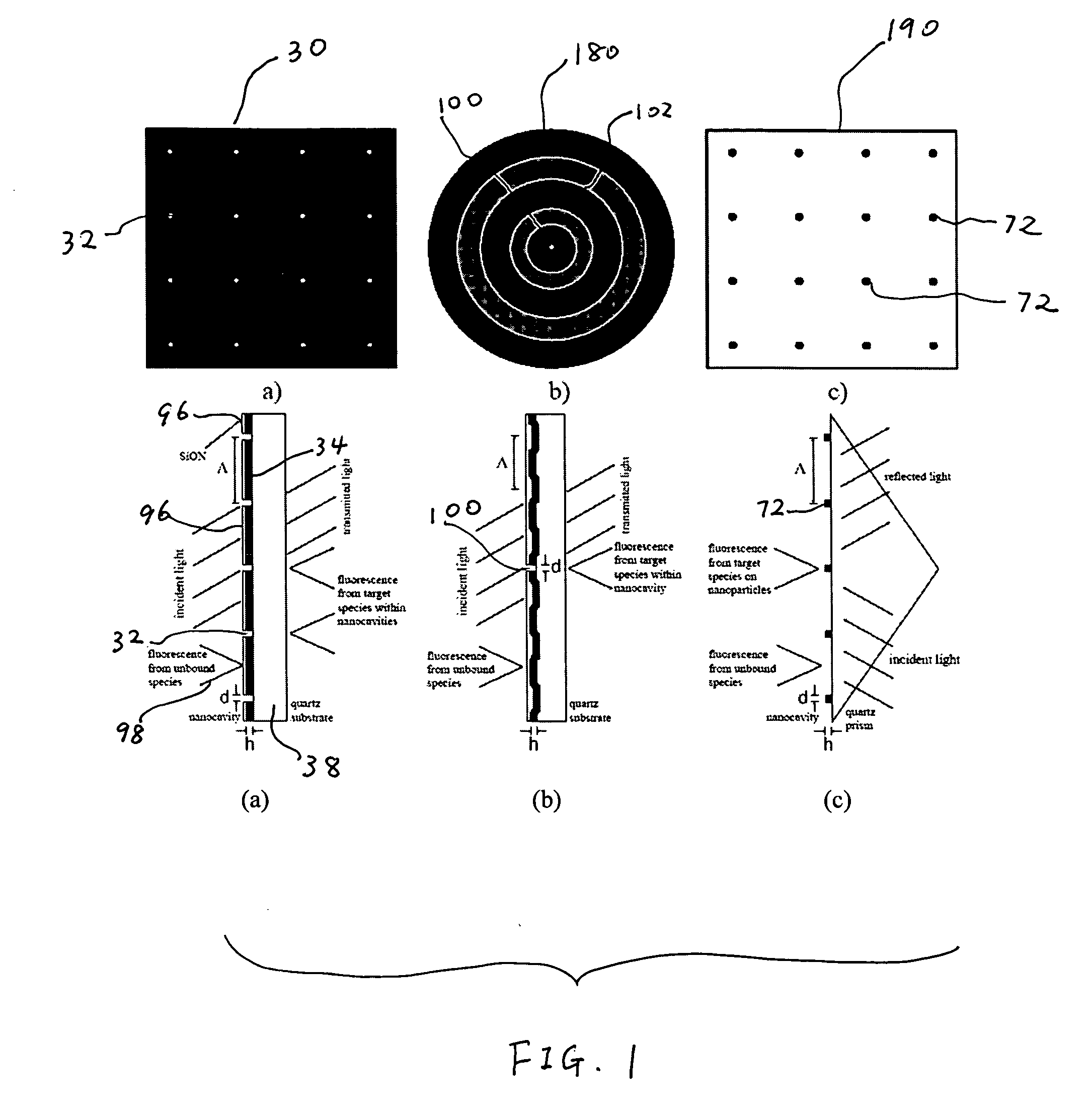
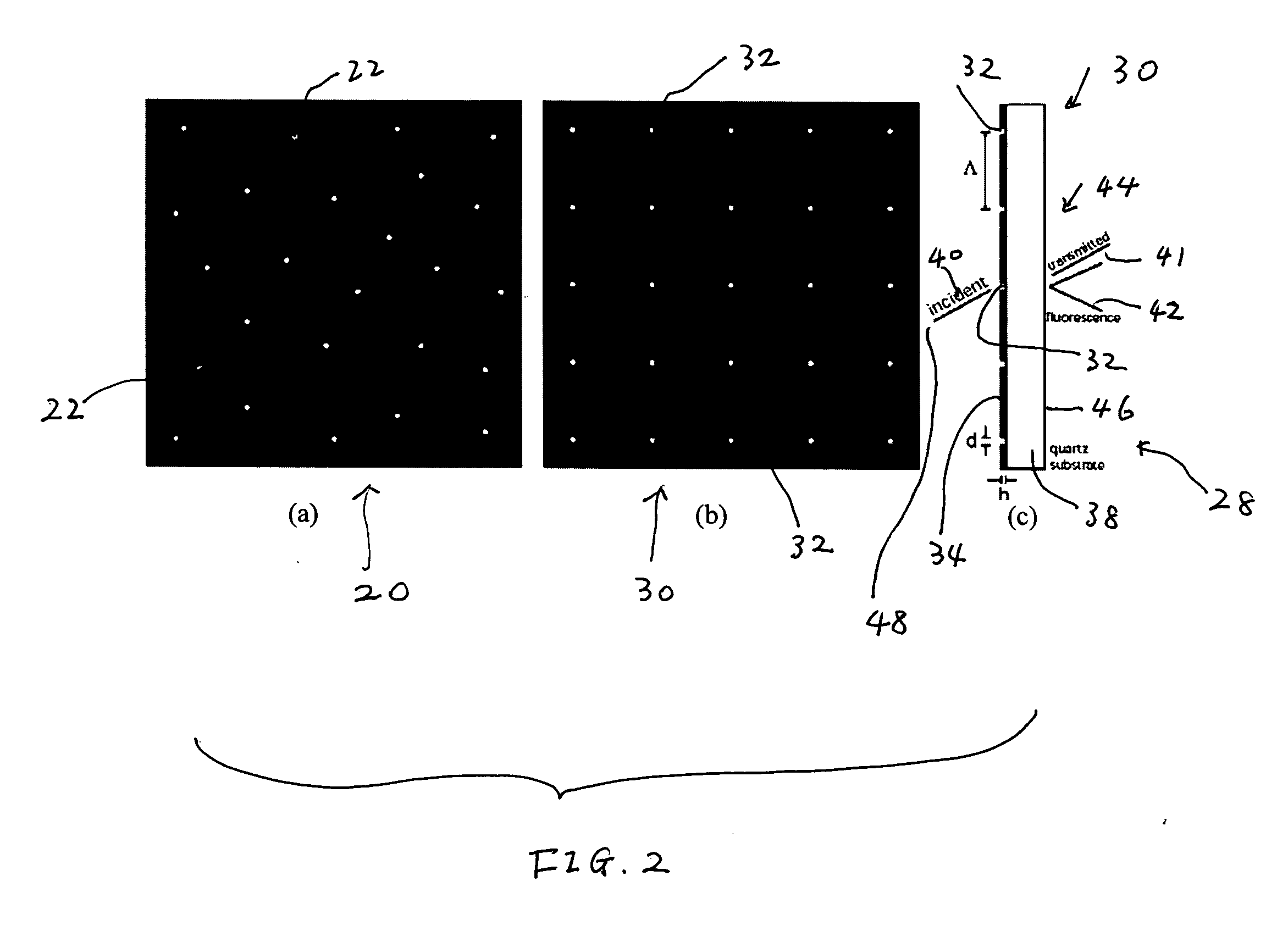
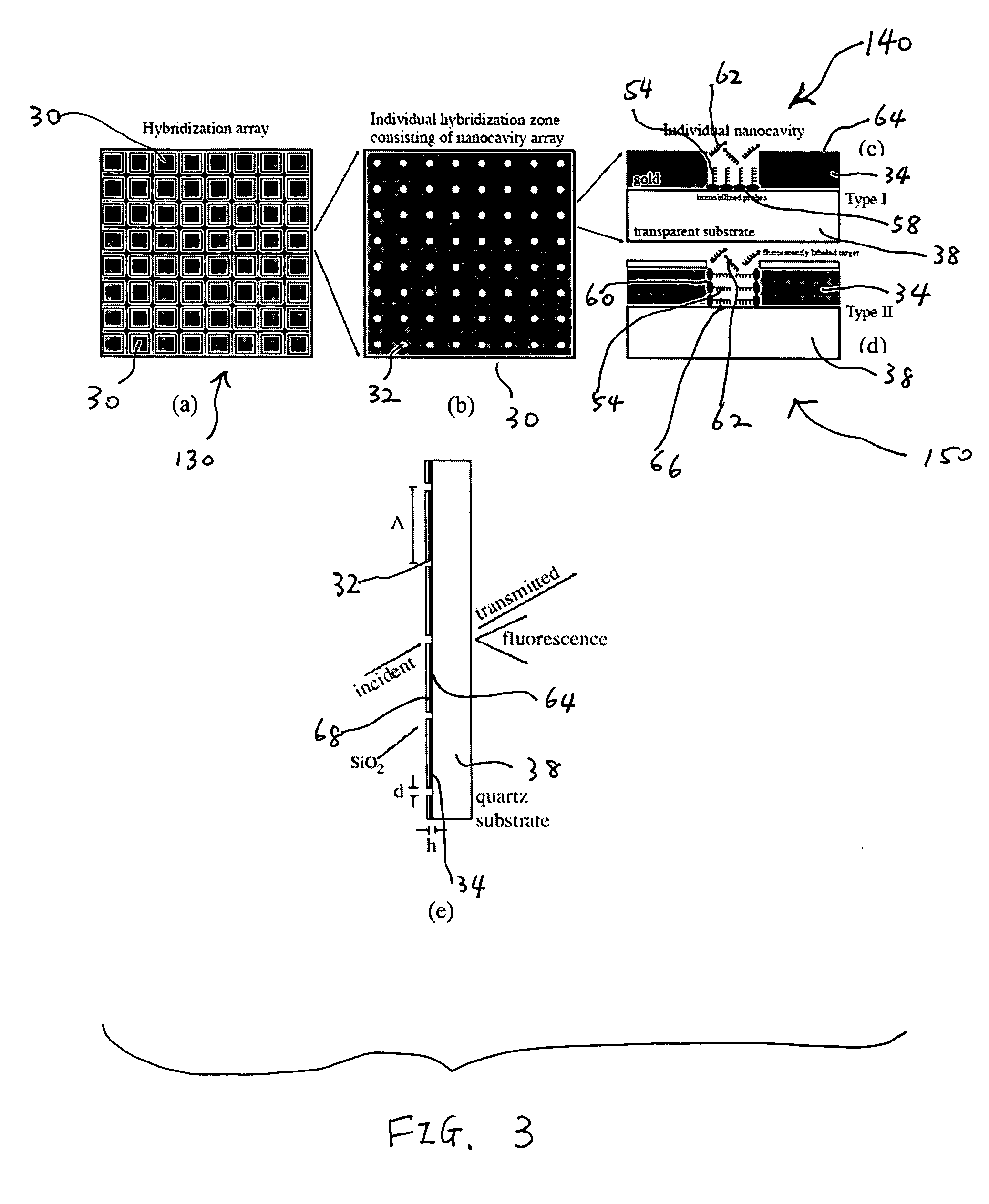
Biosensors including metallic nanocavities
InactiveUS20100256016A1Increase homogeneityReduce amountMaterial nanotechnologyLibrary screeningPhysicsAssay technique
A biomolecular assay includes a substrate with a metallic layer on at least one surface thereof. The metallic film includes nanocavities. The nanocavities are configured to enhance signals that are representative of the presence or amount of one or more analytes in a sample or sample solution, and may be configured to enhance the signal by a factor of about two or more or by a factor of about three or more. Such signal enhancement may be achieved with nanocavities that are organized in an array, randomly positioned nanocavities, or nanocavities that are surrounded by increased surface area features, such as corrugation or patterning, or nanocavities that have quadrilateral or triangular shapes with tailored edge lengths, or with a plurality of nanoparticles. Methods for fabricating biomolecular substrates and assay techniques in which such biomolecular substrates are used are also disclosed.
Owner:THE UNIV OF UTAH
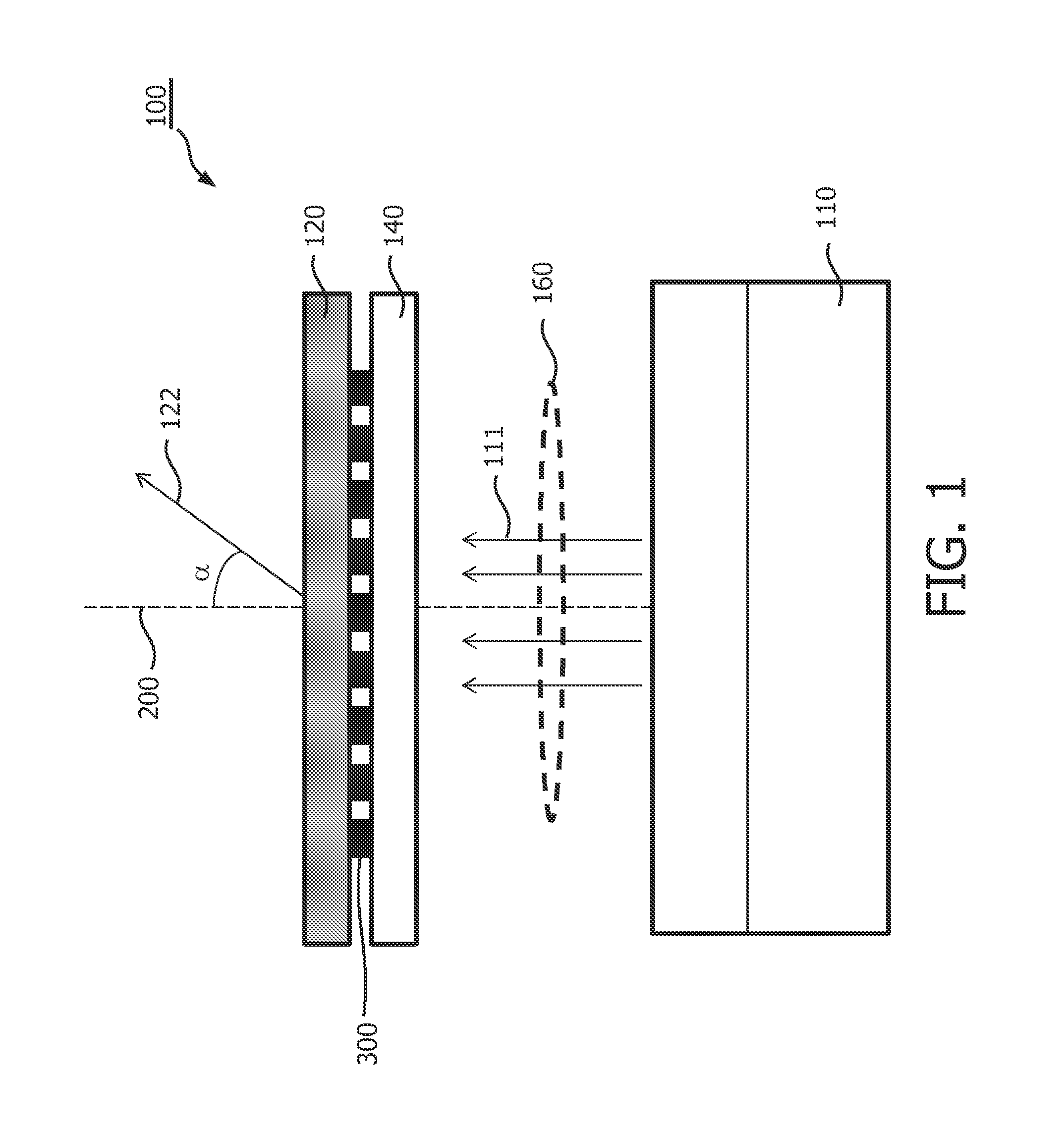
Illumination device
ActiveUS20130286633A1Improving wavelength conversion processEnhanced couplingProjectorsDiffraction gratingsResonancePhosphor
Proposed is an illumination device (100), comprising a light source (110) such as an LED or a laser diode, a wavelength conversion medium (120) such as a phosphor, and a periodic antenna array (300) made of a highly polarisable material such as a metal. The light source emits primary wavelength light that at least partially is converted in secondary wavelength light by the wavelength conversion medium. The periodic antenna array is positioned in close proximity to the wavelength conversion medium and functions to enhance the efficiency of the absorption and / or emission processes in the wavelength conversion medium through the coupling of the incident primary wavelength light or the emitted secondary light to surface lattice resonances that arise from the diffractive coupling of localized surface plasmon polaritons in the individual antennas of the array. This is especially advantageous for forming low étendue illumination device suitable for use in projection systems, or for controlling the directionality, the polarization, and / or the color of the secondary wavelength light.
Owner:LUMILEDS
Method for treating substrates and films with photoexcitation
InactiveUS20060286820A1Enhancing chamber cleaningSpeed up the processSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingNitrogenCompound (substance)
Embodiments of the invention generally provide a method for depositing films using photoexcitation. The photoexcitation may be utilized for at least one of treating the substrate prior to deposition, treating substrate and / or gases during deposition, treating a deposited film, or for enhancing chamber cleaning. In one embodiment, a method for depositing silicon and nitrogen-containing film on a substrate includes heating a substrate disposed in a processing chamber, generating a beam of energy of between about 1 to about 10 eV, transferring the energy to a surface of the substrate; flowing a nitrogen-containing chemical into the processing chamber, flowing a silicon-containing chemical with silicon-nitrogen bonds into the processing chamber, and depositing a silicon and nitrogen-containing film on the substrate.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
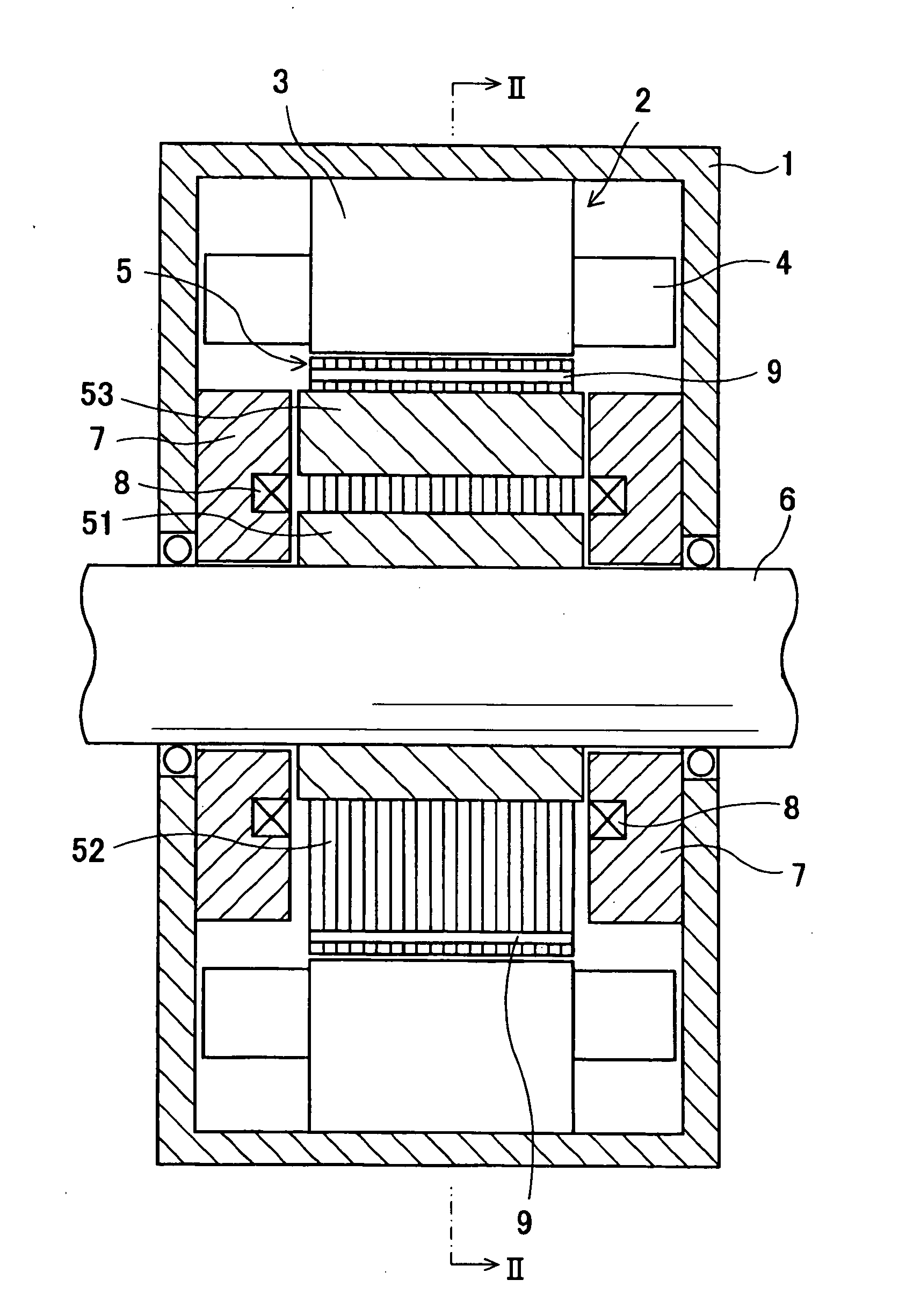
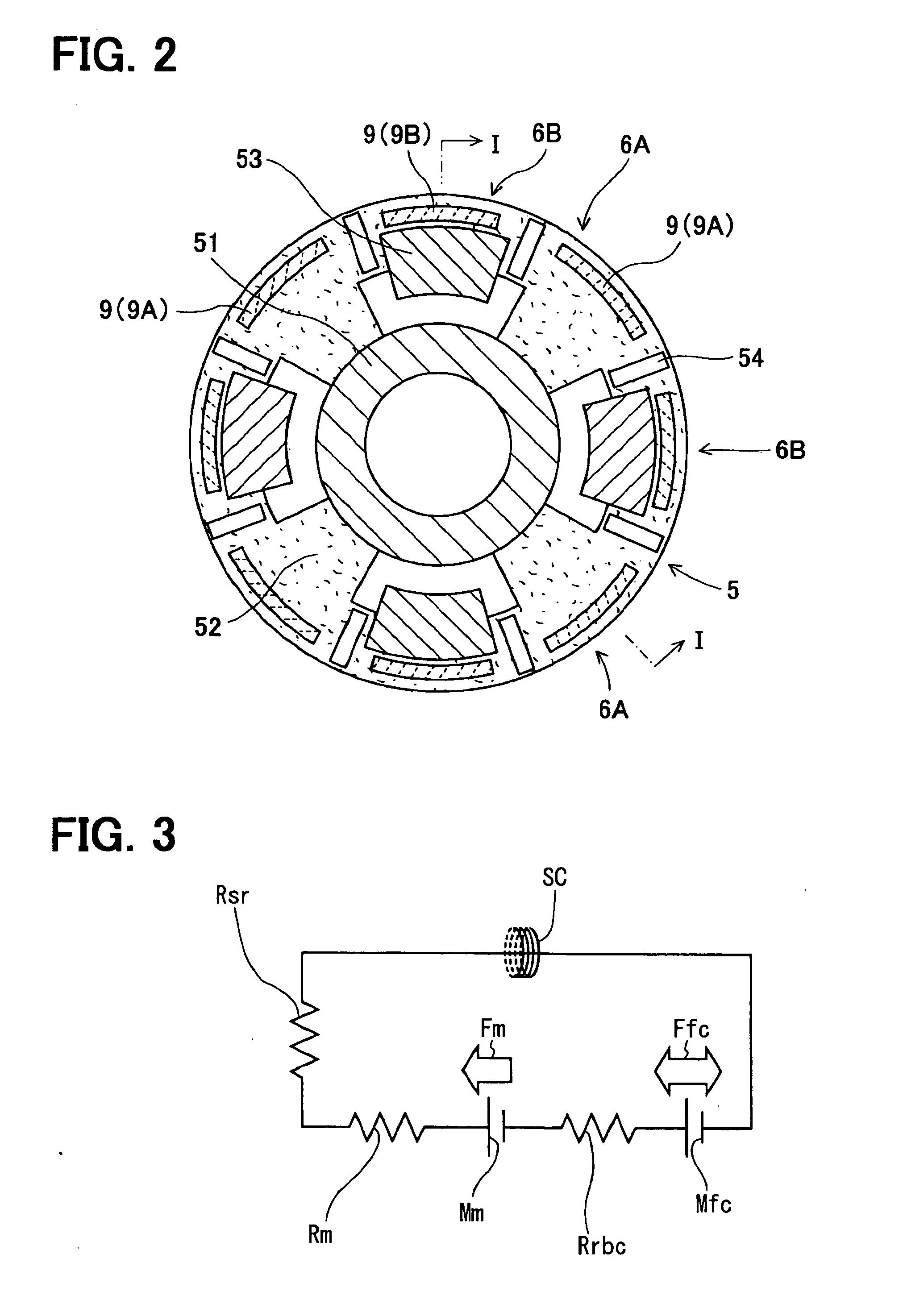
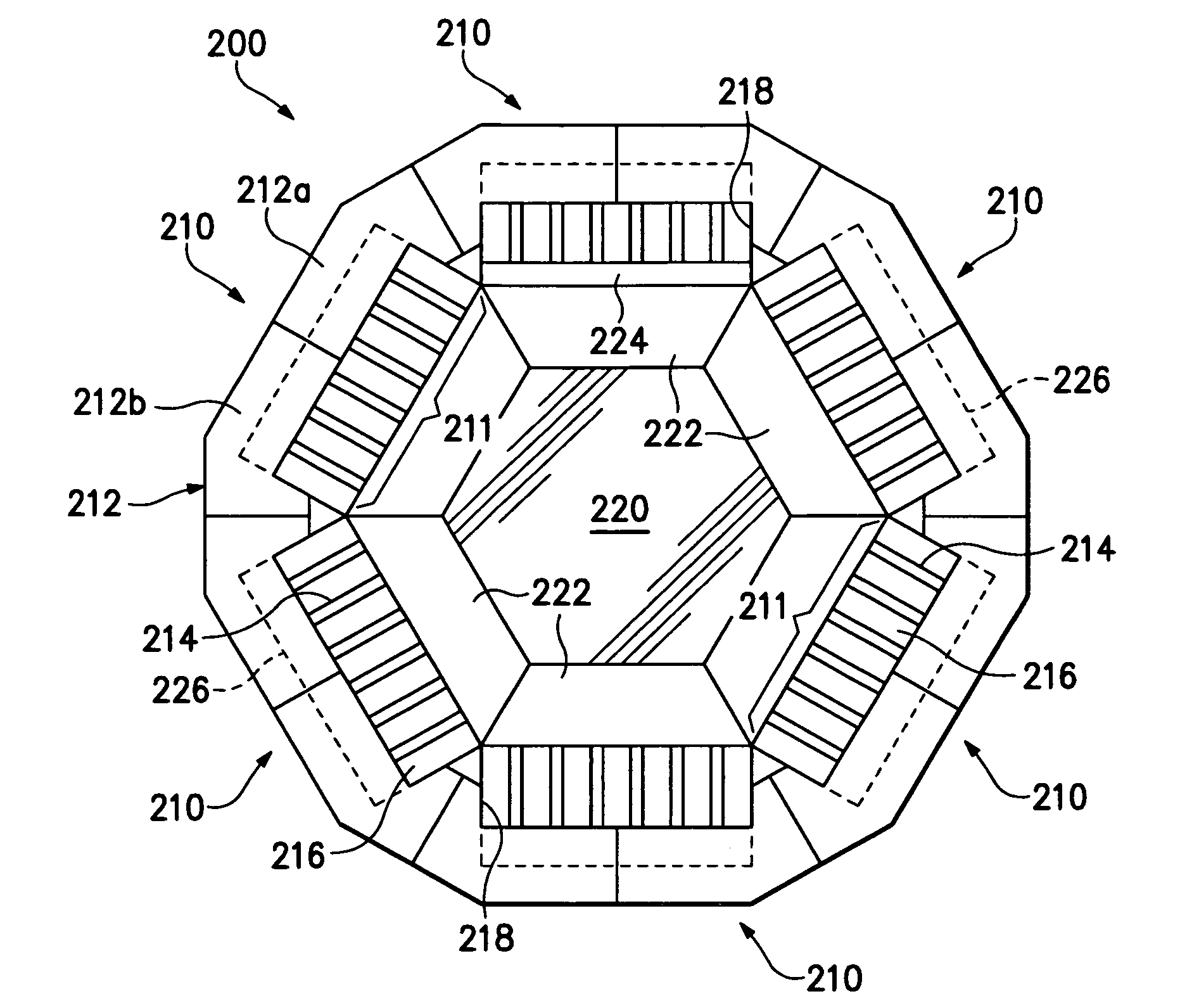
Hybrid-type synchronous machine
InactiveUS20090295249A1Low efficiencyMagnetization is eliminatedSynchronous generatorsWindingsHybrid typeElectric machine
A rotor core has permanent magnets. Magnetic flux of the permanent magnet of an even-numbered rotor magnetic pole part is guided in an axial direction by an axial magnetic path member. Magnetic flux of the permanent magnet of an odd-numbered rotor magnetic pole part is guided into a soft magnetic inner cylindrical part. The axial end faces of the inner cylindrical part and the axial magnetic path member protrude from the rotor core in the axial direction and face a stationary magnetic path member with a small gap therebetween. The amount of magnetic flux of the magnet, which the permanent magnet applies to a stator core is adjusted by an excitation current of an excitation coil wound on the stationary magnetic path member.
Owner:DENSO CORP +1
Treatment of adhd
InactiveUS20100087422A1Robust and well tolerated effectEliminate the effects ofBiocideSenses disorderStimulantMood stabilisers
A method is described for treating attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), by administering to the individual an anti-epileptic mood stabiliser at a dose which is sub-therapeutic for mood stabilisation, optionally in combination with a psychostimulant. Also described is a method of improving reading comprehension and / or fluency in an individual suffering from learning difficulties which method comprises administering to the individual an anti-epileptic mood stabiliser.
Owner:GOSFORTH CENT HLDG
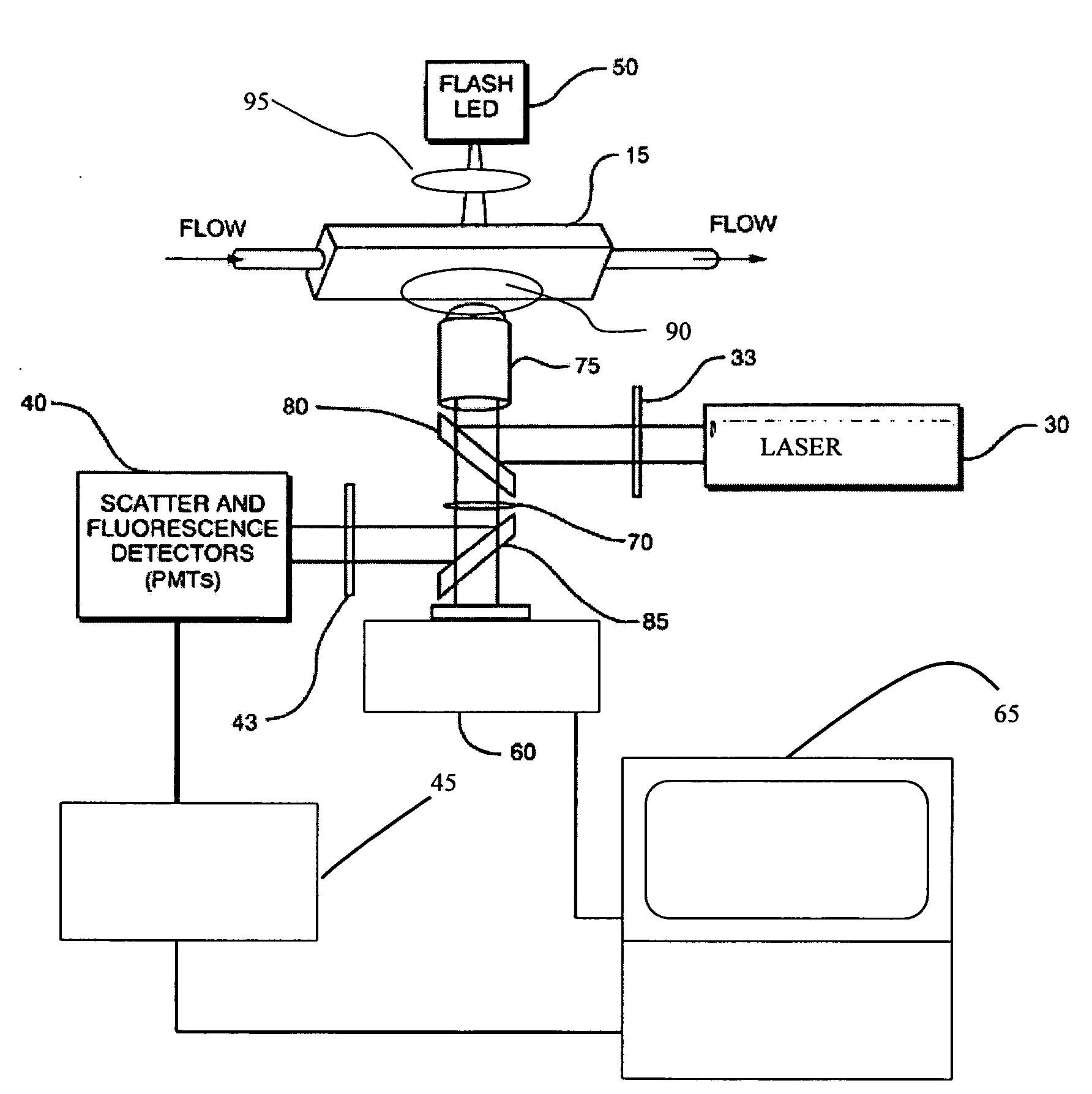
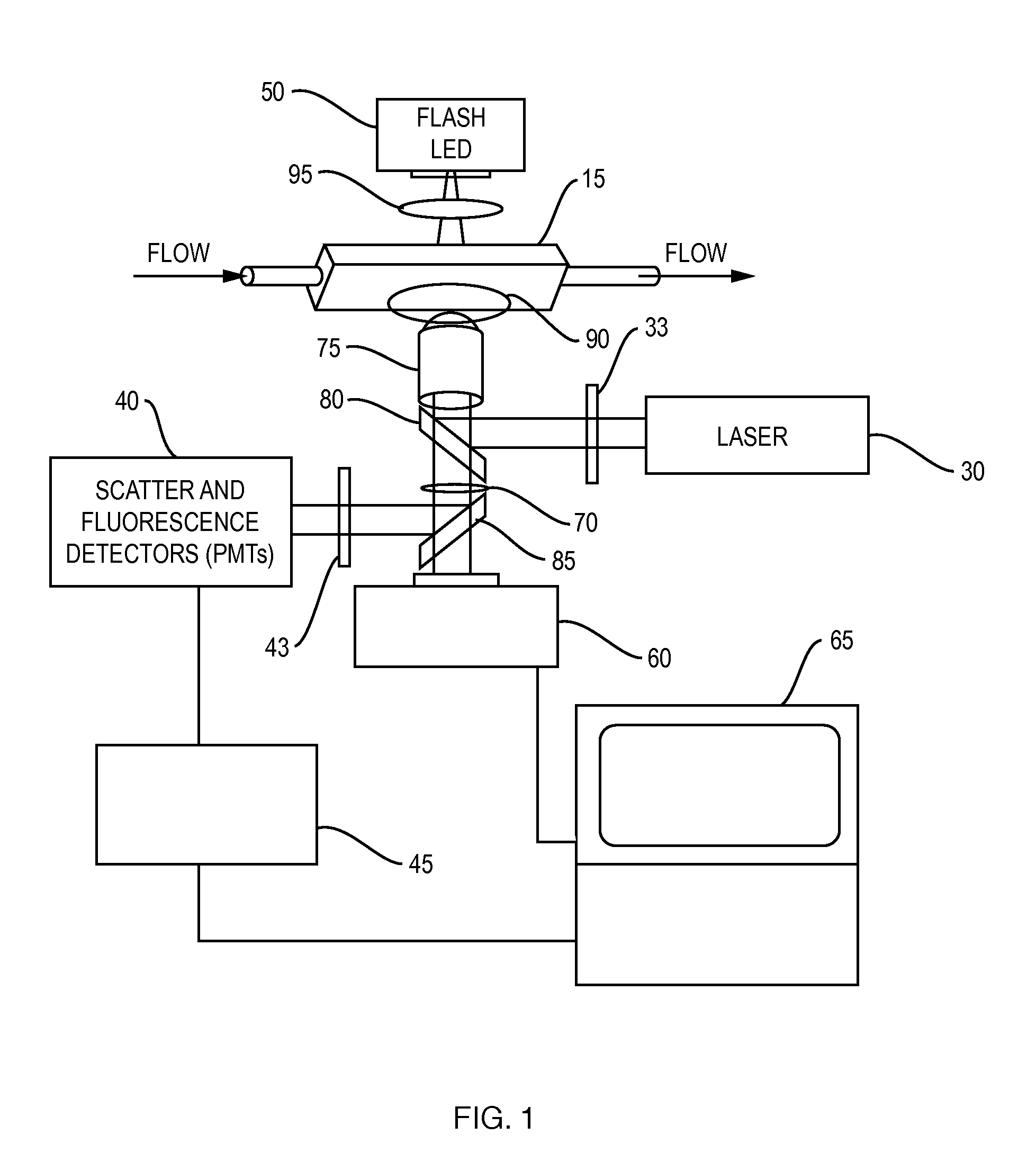
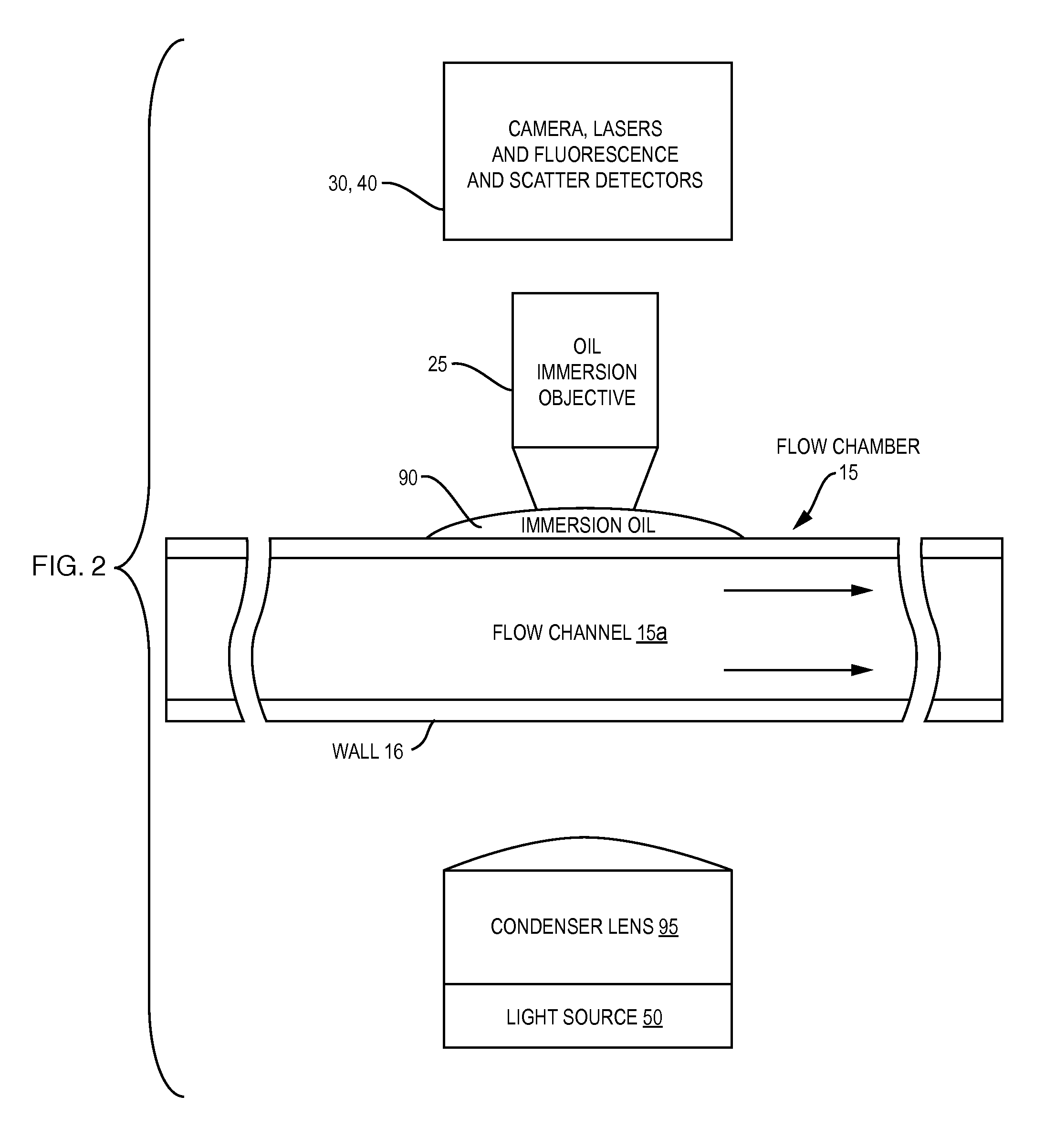
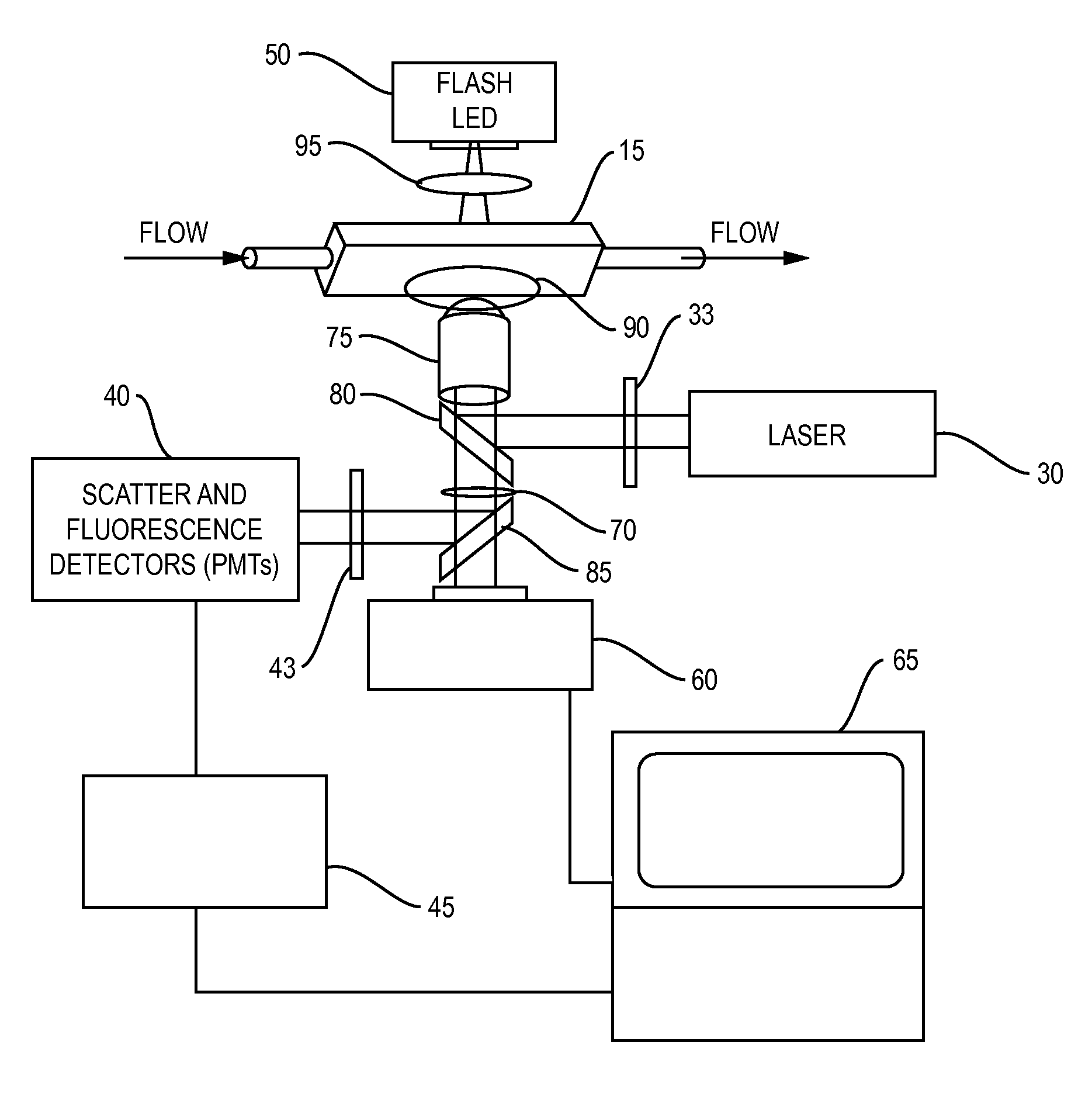
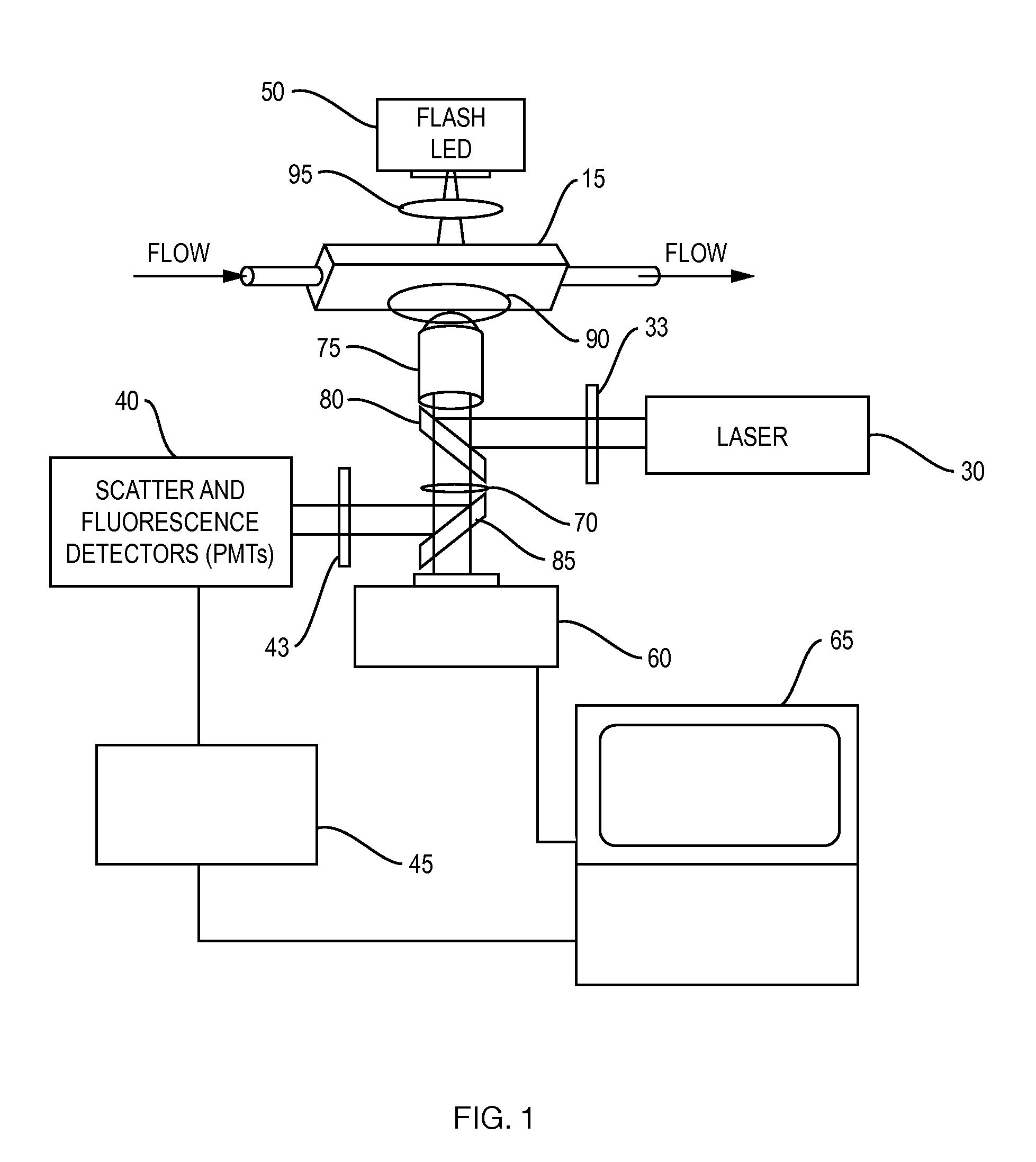
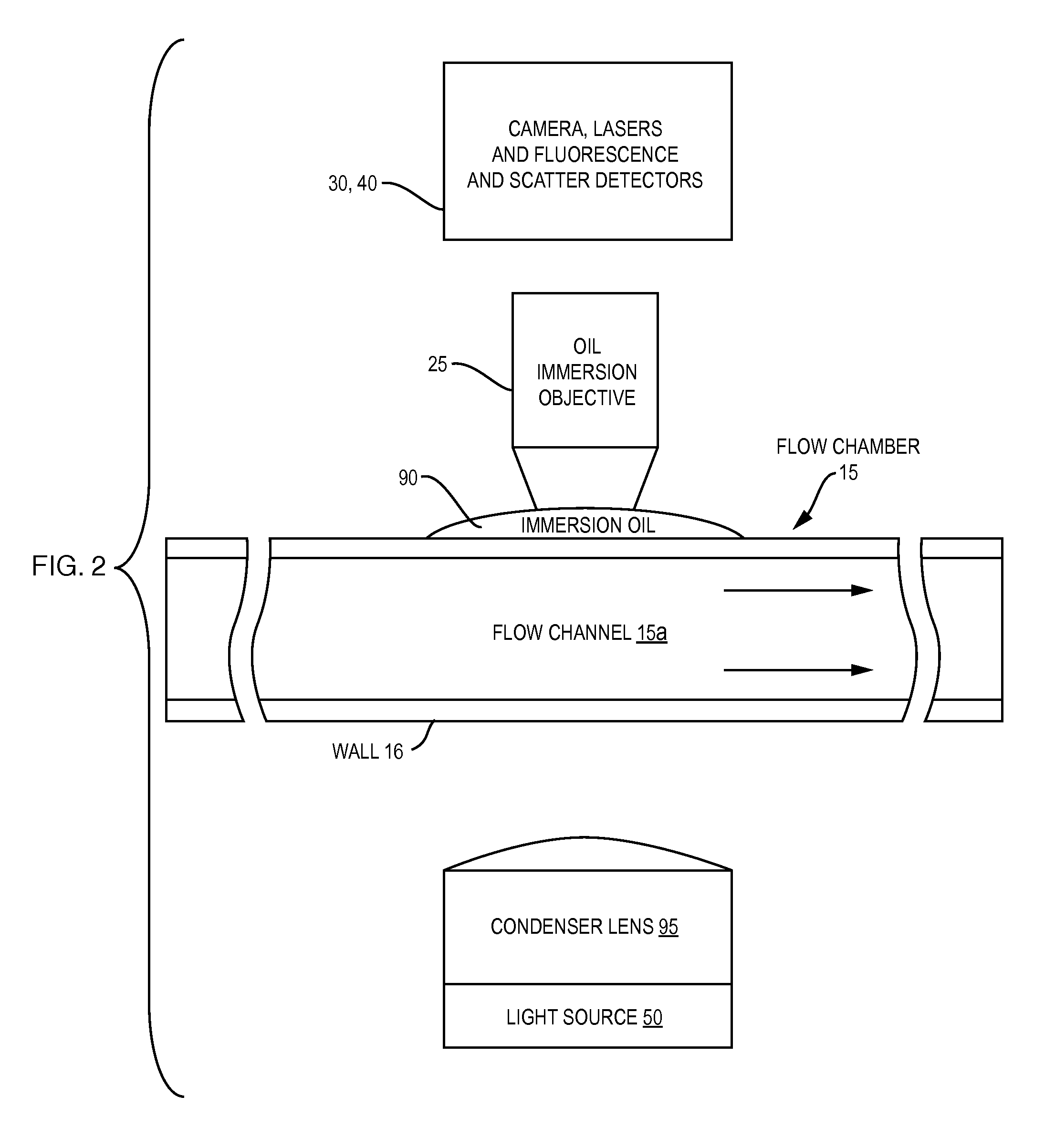
Oil-immersion enhanced imaging flow cytometer
ActiveUS20090273774A1High resolutionImprove analytical abilityRadiation pyrometryNanoparticle analysisFluorescenceHigh numerical aperture
A flow chamber, imaging objective, condenser and imaging light source as part of an optical system includes an oil-immersion objective and high numerical aperture condenser matched to a rectangular flow chamber. The oil-immersion objective and flow chamber include a high index of refraction immersion oil so as to enhance the optical resolution and optical coupling therethrough. The imaging light source generates light which passes through the condenser, the flow chamber and then the objective before being focused onto an imaging camera. Fluorescence excitation passes through the objective to the flow chamber where the oil immersion configuration enhances the focus and collection of the light back through the objective.
Owner:YOKOGAWA FLUID IMAGING TECH INC
Oil-immersion enhanced imaging flow cytometer
ActiveUS7796256B2Easy to collectEnhance excitationRadiation pyrometryNanoparticle analysisHigh numerical apertureFluorescence
A flow chamber, imaging objective, condenser and imaging light source as part of an optical system includes an oil-immersion objective and high numerical aperture condenser matched to a rectangular flow chamber. The oil-immersion objective and flow chamber include a high index of refraction immersion oil so as to enhance the optical resolution and optical coupling therethrough. The imaging light source generates light which passes through the condenser, the flow chamber and then the objective before being focused onto an imaging camera. Fluorescence excitation passes through the objective to the flow chamber where the oil immersion configuration enhances the focus and collection of the light back through the objective.
Owner:YOKOGAWA FLUID IMAGING TECH INC
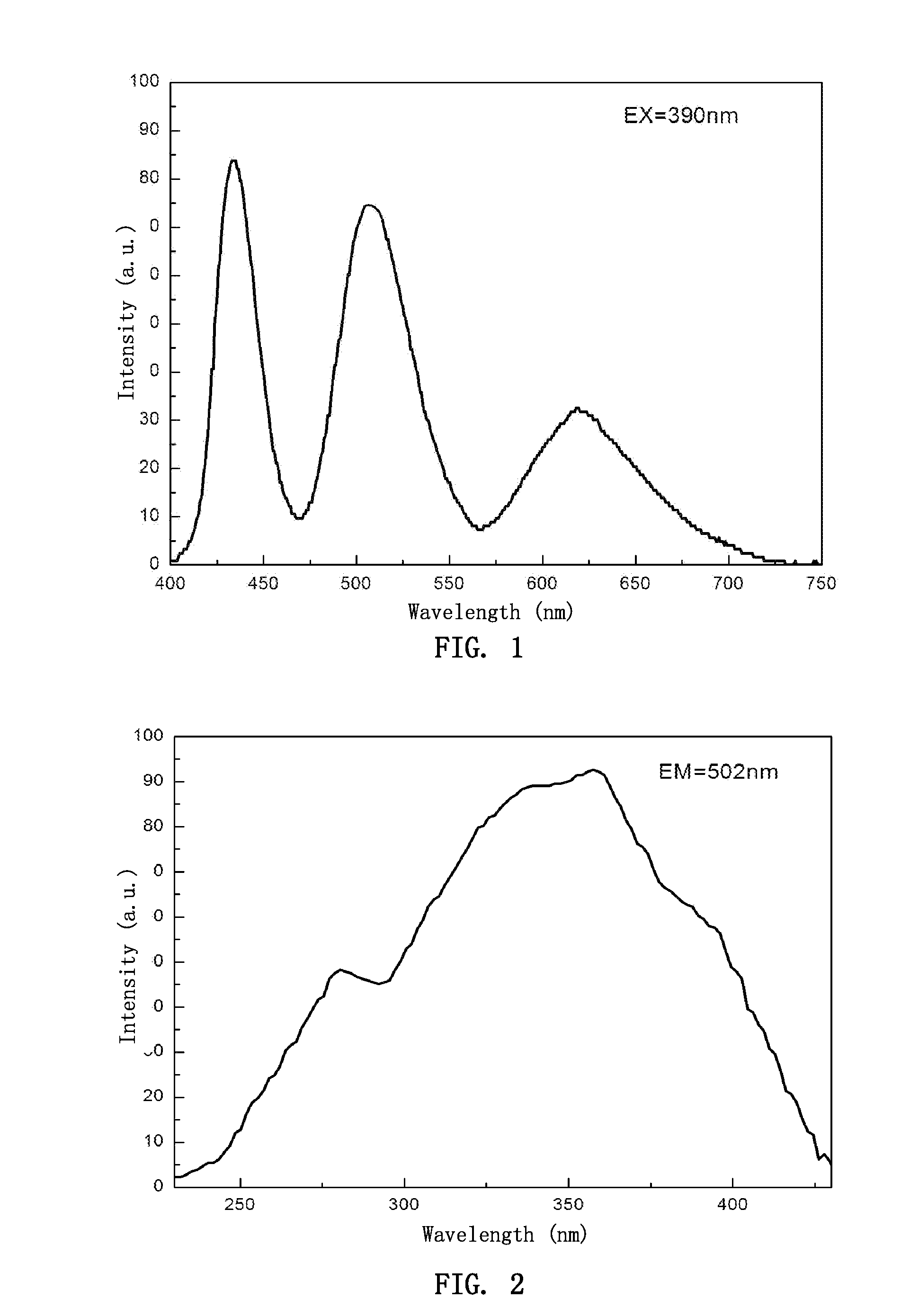
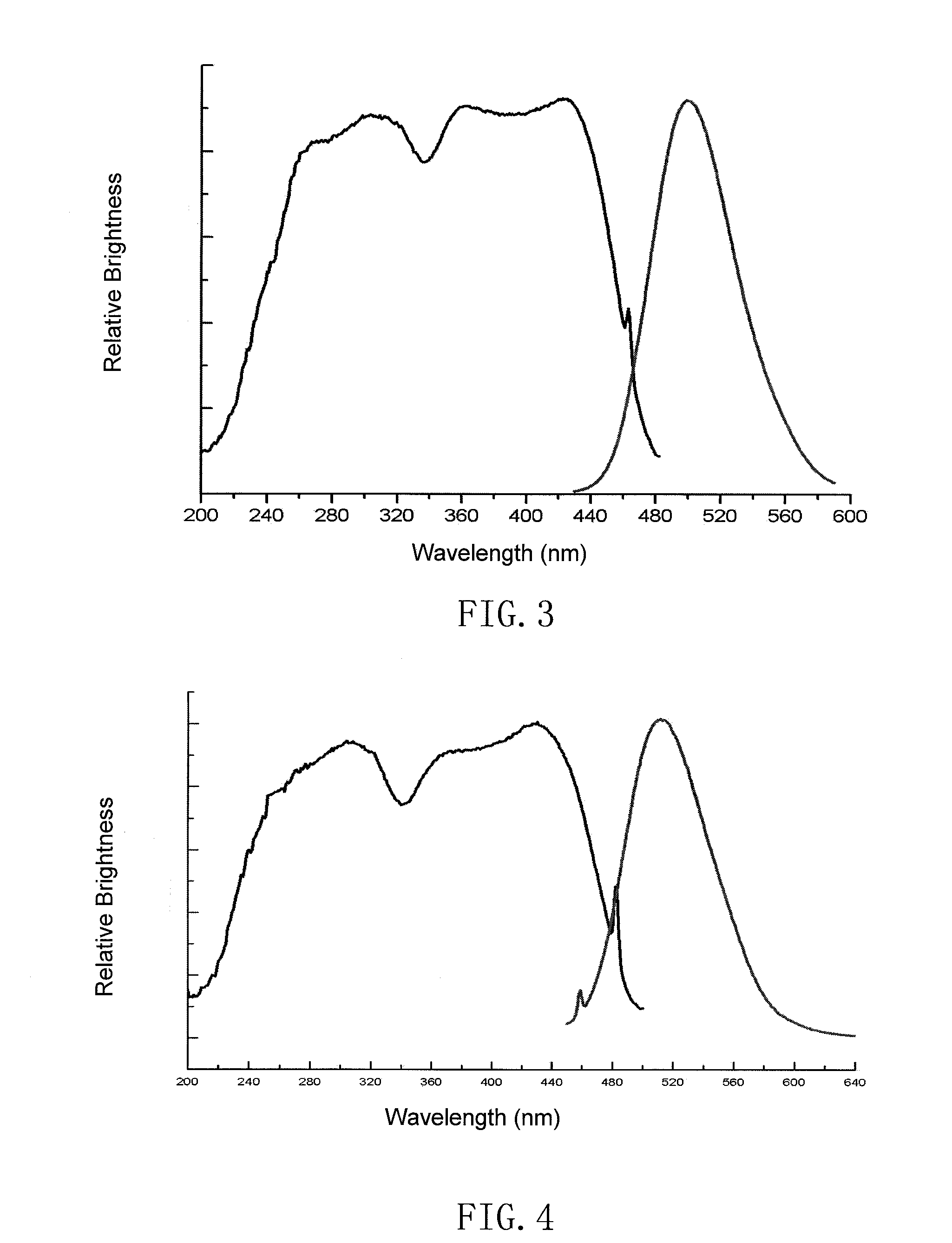
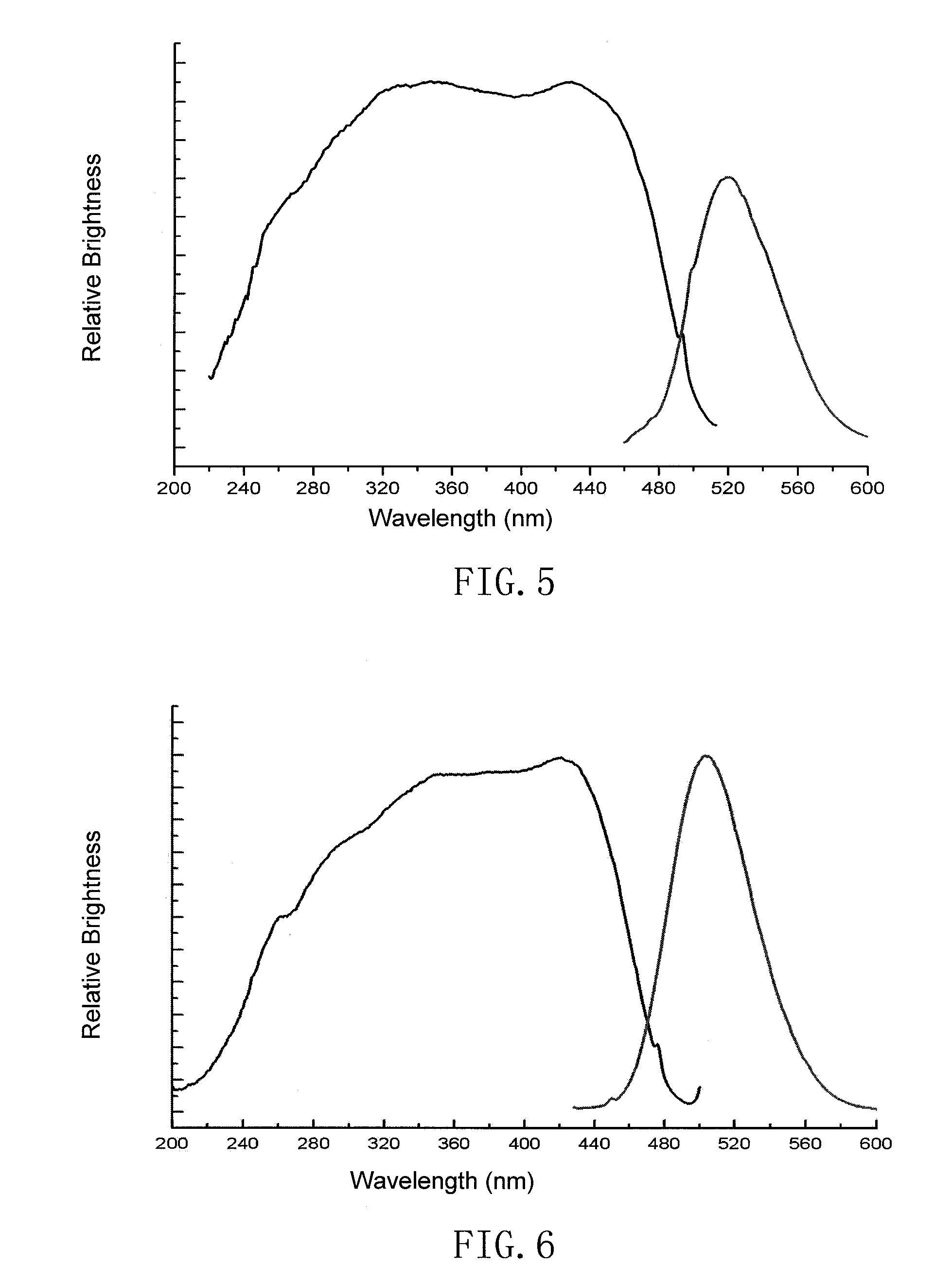
Silicate base luminescent materials having multiple emission peaks, processes for preparing the same and light emitting devices using the same
ActiveUS20100052513A1High light conversion efficiencyImprove aging resistanceDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsLight emitting deviceLight-emitting diode
A silicate luminescent material excitable by an excitation light source having emissions in UV to blue light region, a process for producing the same, and a white light emitting device. The luminescent material has an emission spectrum with at least two peaks in a range of from 370 to 760 nm, and has a general chemical composition formula of aAO.bA′O.cSiO2:xEu.yLn.zM.δN, wherein A is selected from the group consisting of Sr, Ca, Ba, and combinations thereof; A′ is selected from the group consisting of Mg, Zn, and combinations thereof; Ln is selected from the group consisting of Nd, Dy, Ho, Tm, La, Ce, Er, Pr, Bi, Sm, Sn, Y, Lu, Ga, Sb, Tb, Mn, Pb and combinations thereof; M is one or a combination of halogen ions; N is selected from the group consisting of Li+, Na+, K+, Ag+, and combinations thereof; and a, b, c, x, y, z, and δ are molar coefficients.
Owner:DALIAN LUMINGLIGHT SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
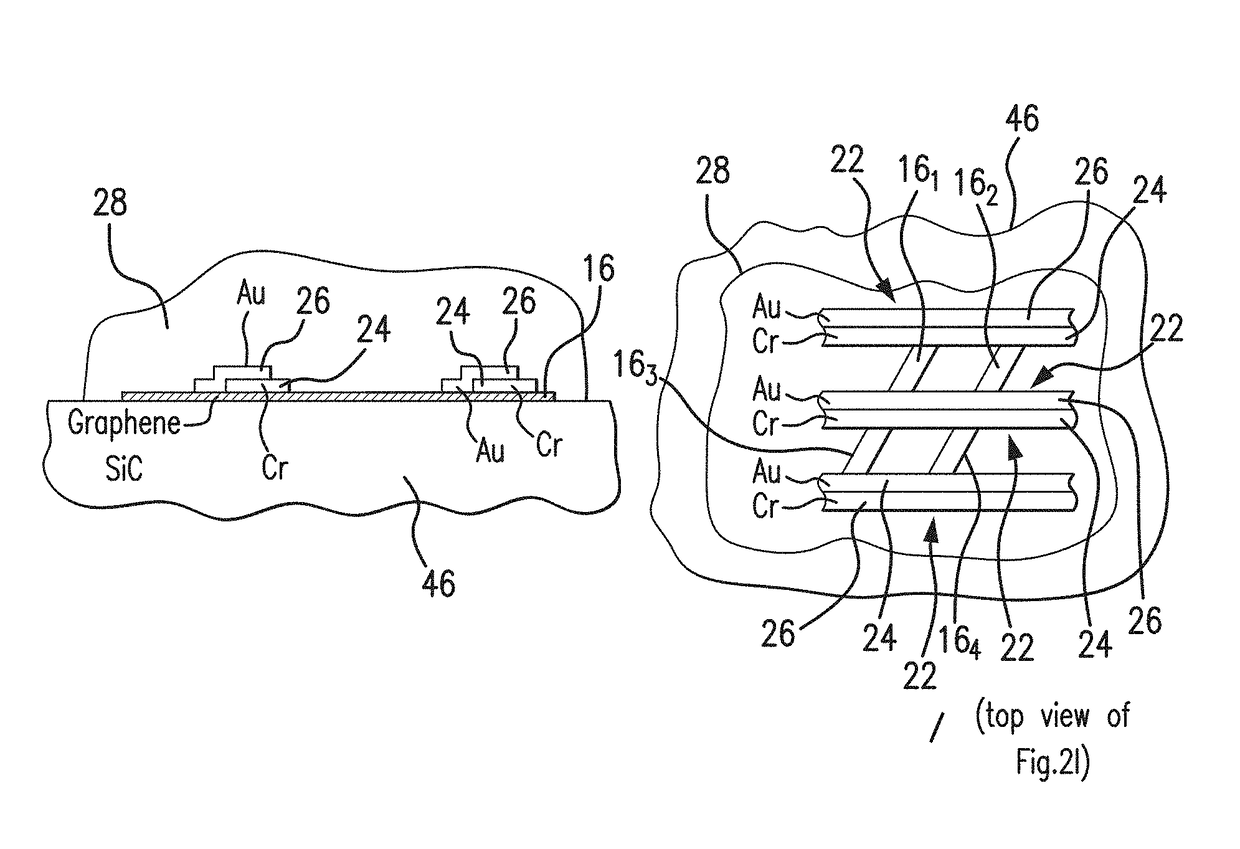
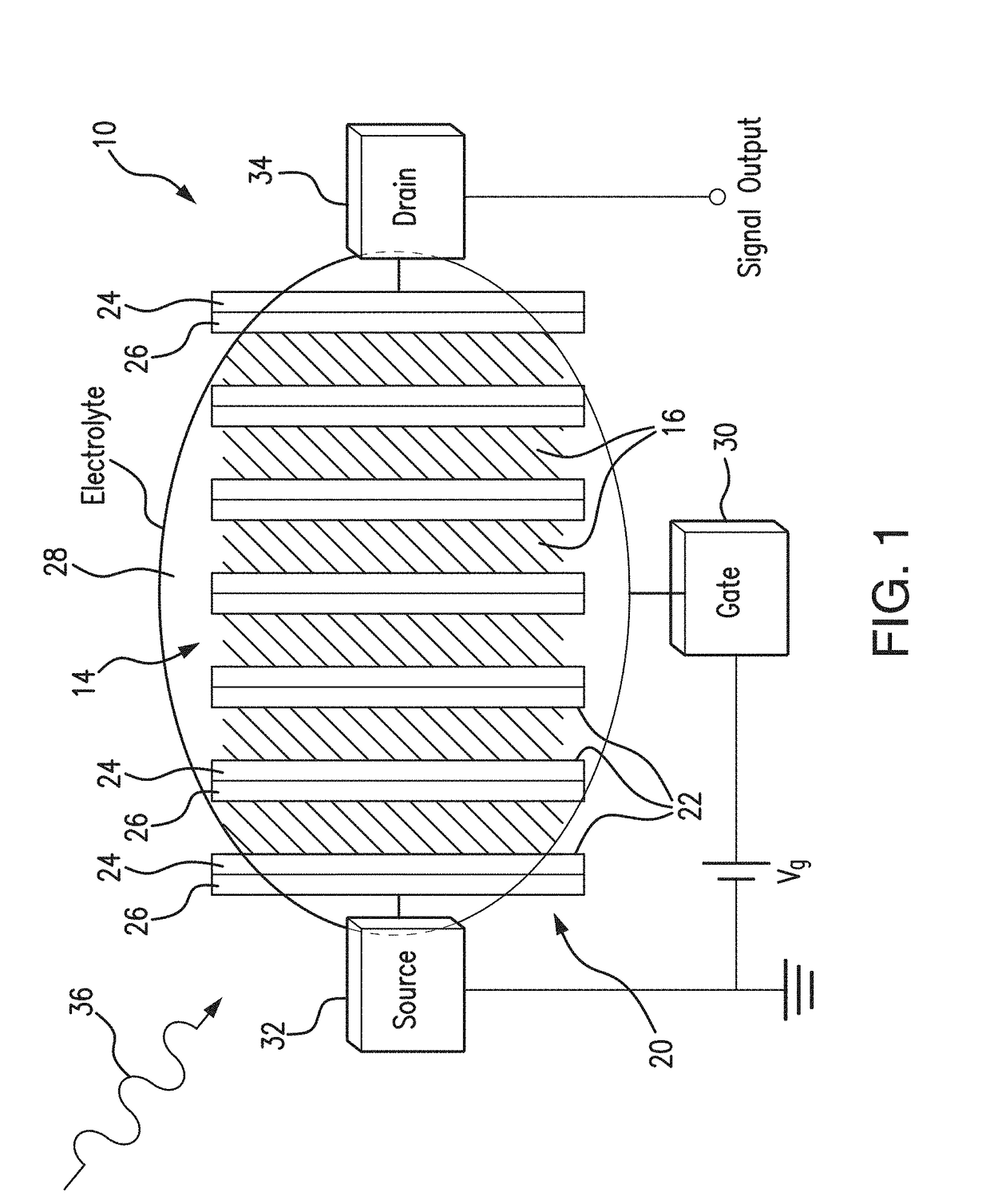
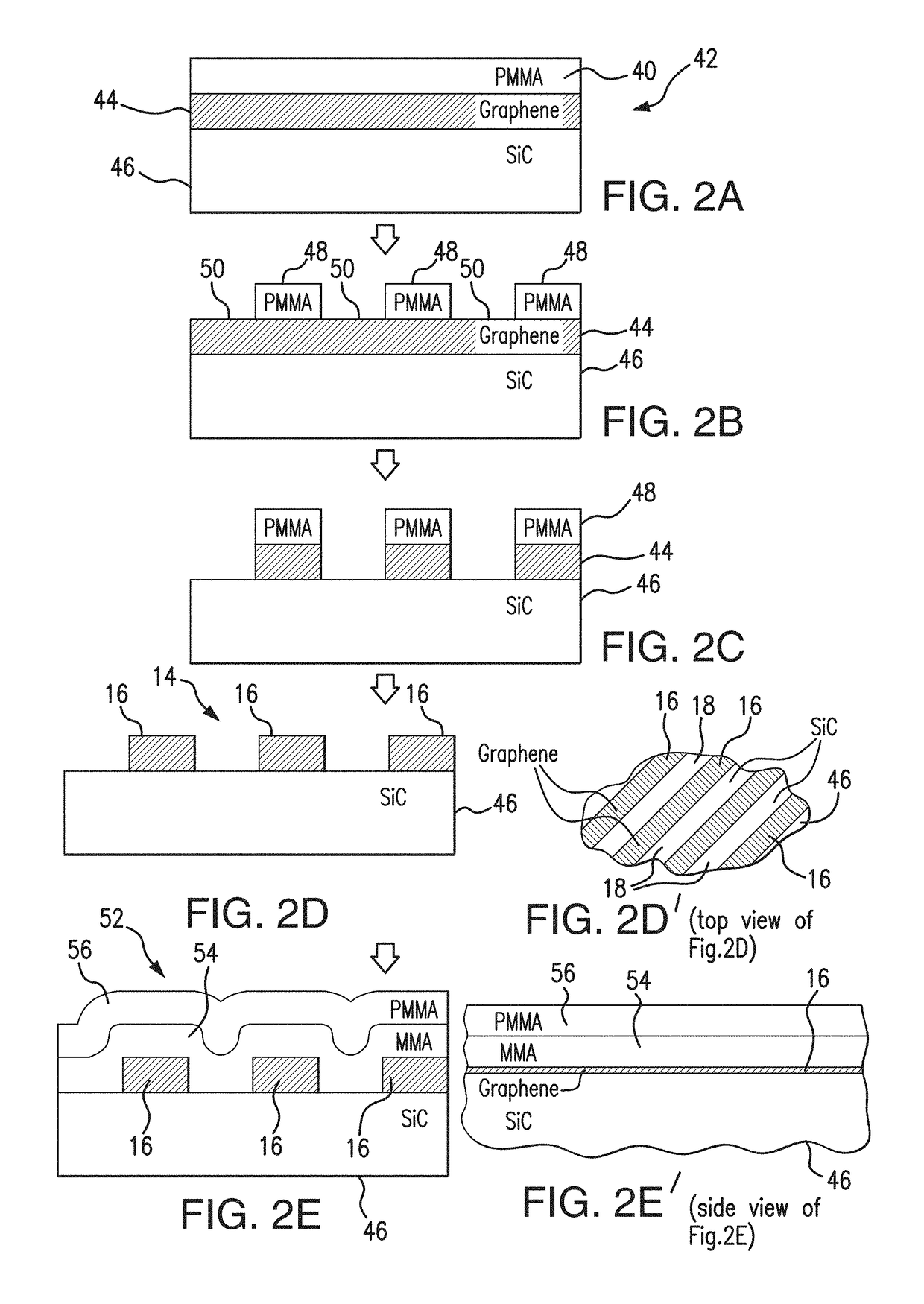
Plasmon-enhanced terahertz graphene-based photodetector and method of fabrication
ActiveUS20180047856A1Improve responsePromote absorptionMaterial nanotechnologyWave amplification devicesMetallic electrodePhotodetector
A plasmon-enhanced terahertz graphene-based photodetector exhibits an increased absorption efficiency attained by utilizing a tunable plasmonic resonance in sub-wavelengths graphene micro-ribbons formed on SiC substrate in contact with an array of bi-metallic electrode lines. The orientation of the graphene micro-ribbons is tailored with respect to the array of sub-wavelengths bi-metallic electrode lines. The graphene micro-ribbons extend at the angle of approximately 45 degrees with respect to the electrode lines in the bi-metal electrodes array. The plasmonic mode is efficiently excited by an incident wave polarized perpendicular to the electrode lines, and / or to the graphene micro-ribbons. The absorption of radiation by graphene is enhanced through tunable geometric parameters (such as, for example, the width of the graphene micro-ribbons) and control of a carrier density in graphene achieved through tuning the gate voltage applied to the photodetector.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
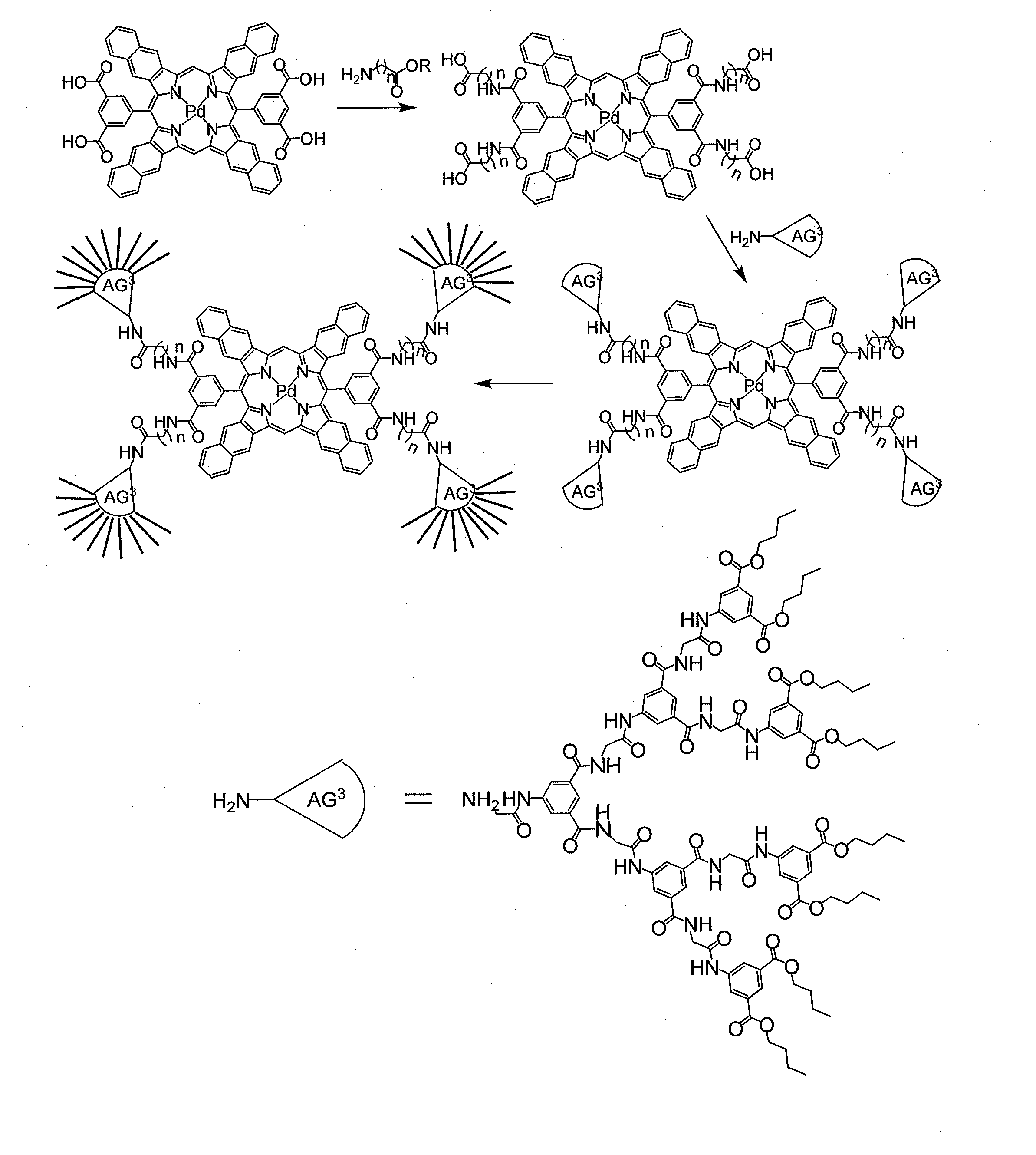
Phosphorescent Molecules for Measuring Oxygen and Imaging Methods
ActiveUS20130224874A1Simple structureImprove chemical structureGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsBiological testingDendrimerSinglet oxygen
Oxygen levels in biological tissue or systems can be measured by the phosphorescence quenching method using phosphorescent porphyrin probes, also referred to as a dendritic oxygen probes, with controllable quenching parameters and defined biodistributions. Provided are a “next generation” of oxygen sensors with substantially improved phosphorescence emission for better imaging capabilities, ease of use, increasing the quantum efficiency (phosphorescence intensity) and extending their range of applicability including constructing a class of oxygen sensors for making measurements in organic media. In addition, provided are methods for synthesizing new porphyrin constructs in which the porphyrin is made less flexible and more planar, changing with decrease internal quenching, and thereby increasing the phosphorescence emission used for oxygen sensing. Additional methods are provided for structurally modifying the dendrimer used to encapsulate the porphyrin phosphor to provide internal quenching of singlet oxygen molecules formed during oxygen measurements.
Owner:OXYGEN ENTERPRISES
Resonant switching power source device
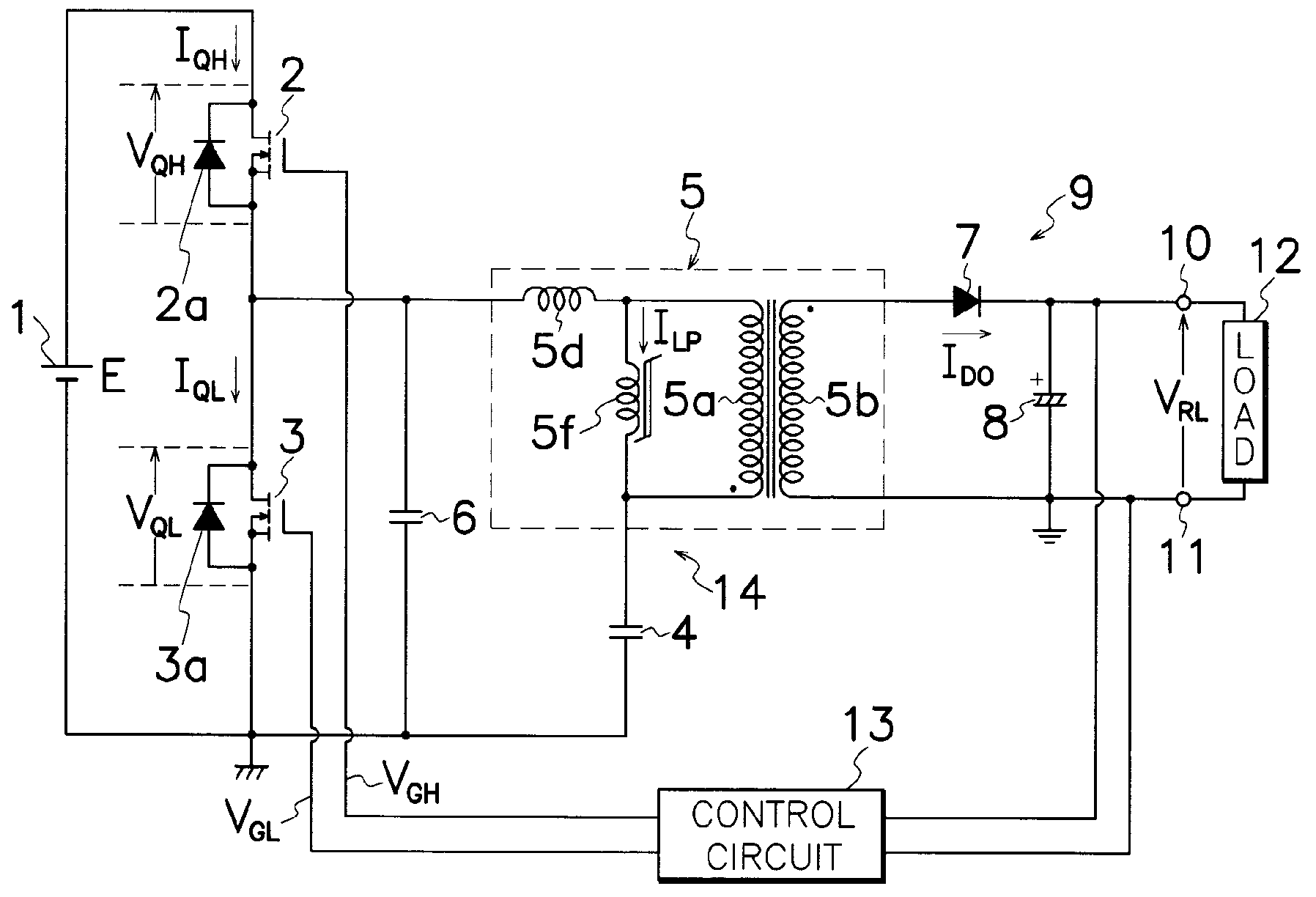
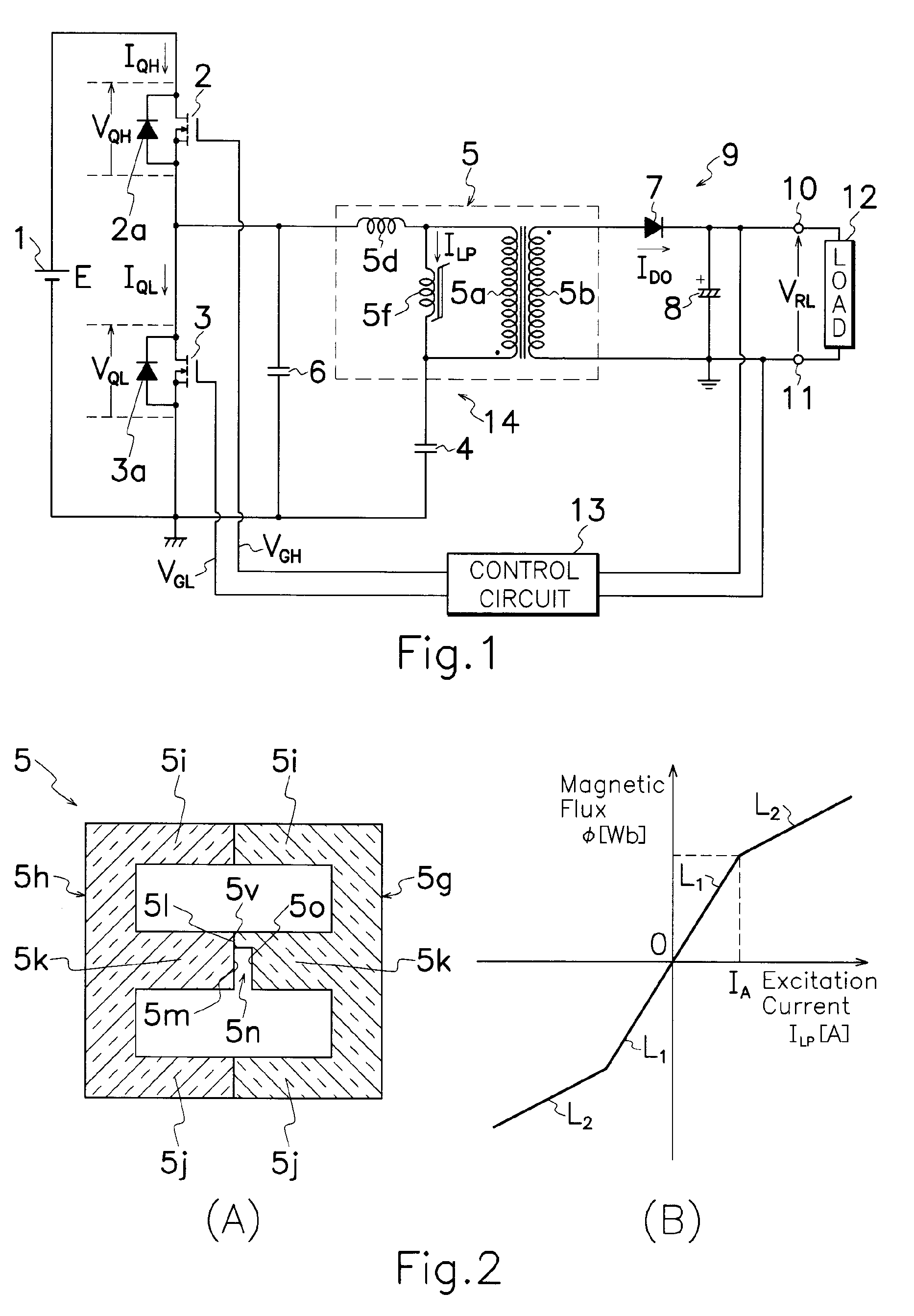
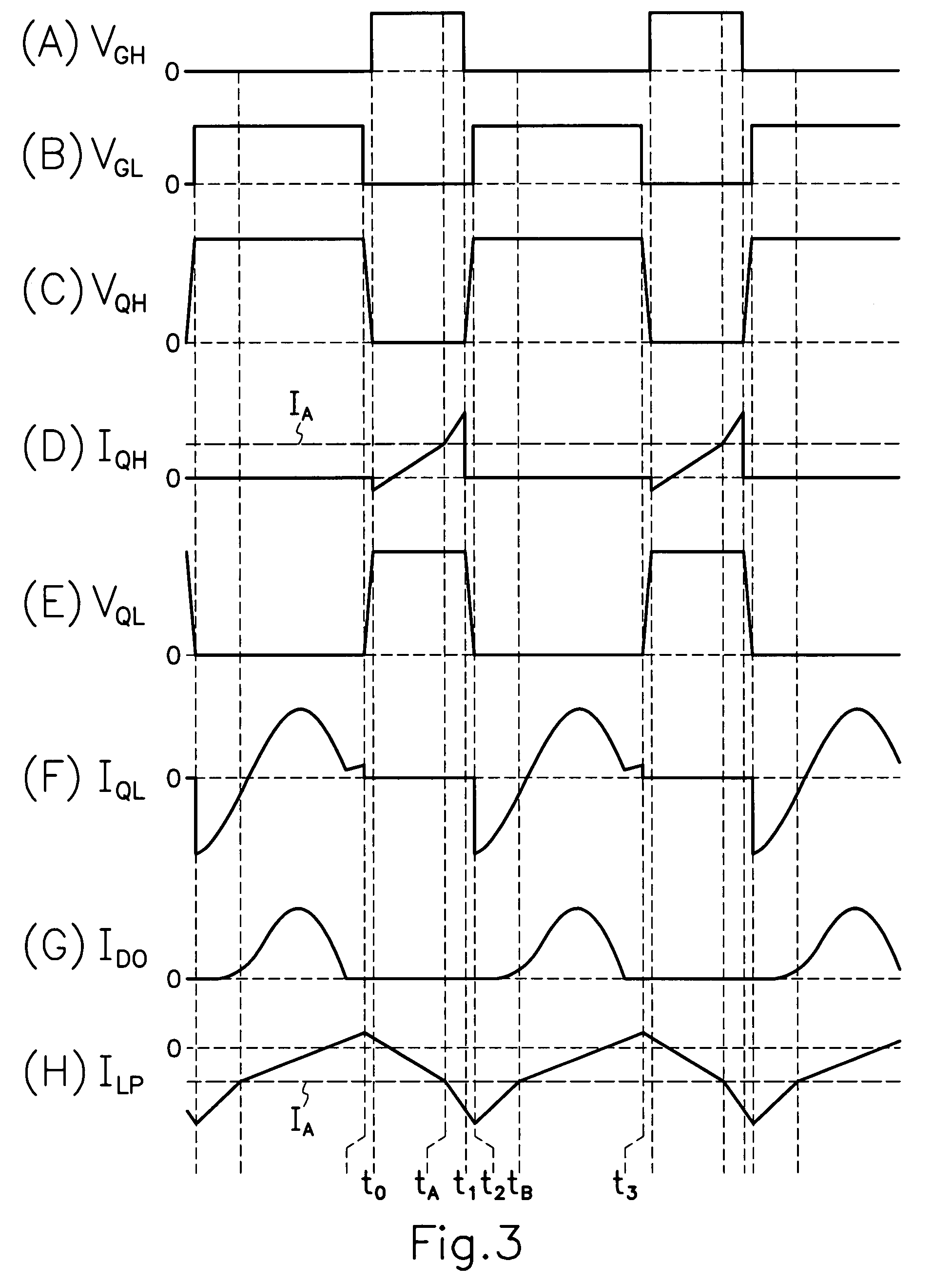
InactiveUS20070195562A1Reducing excitation currentReduce power lossEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionTransformerExcitation current
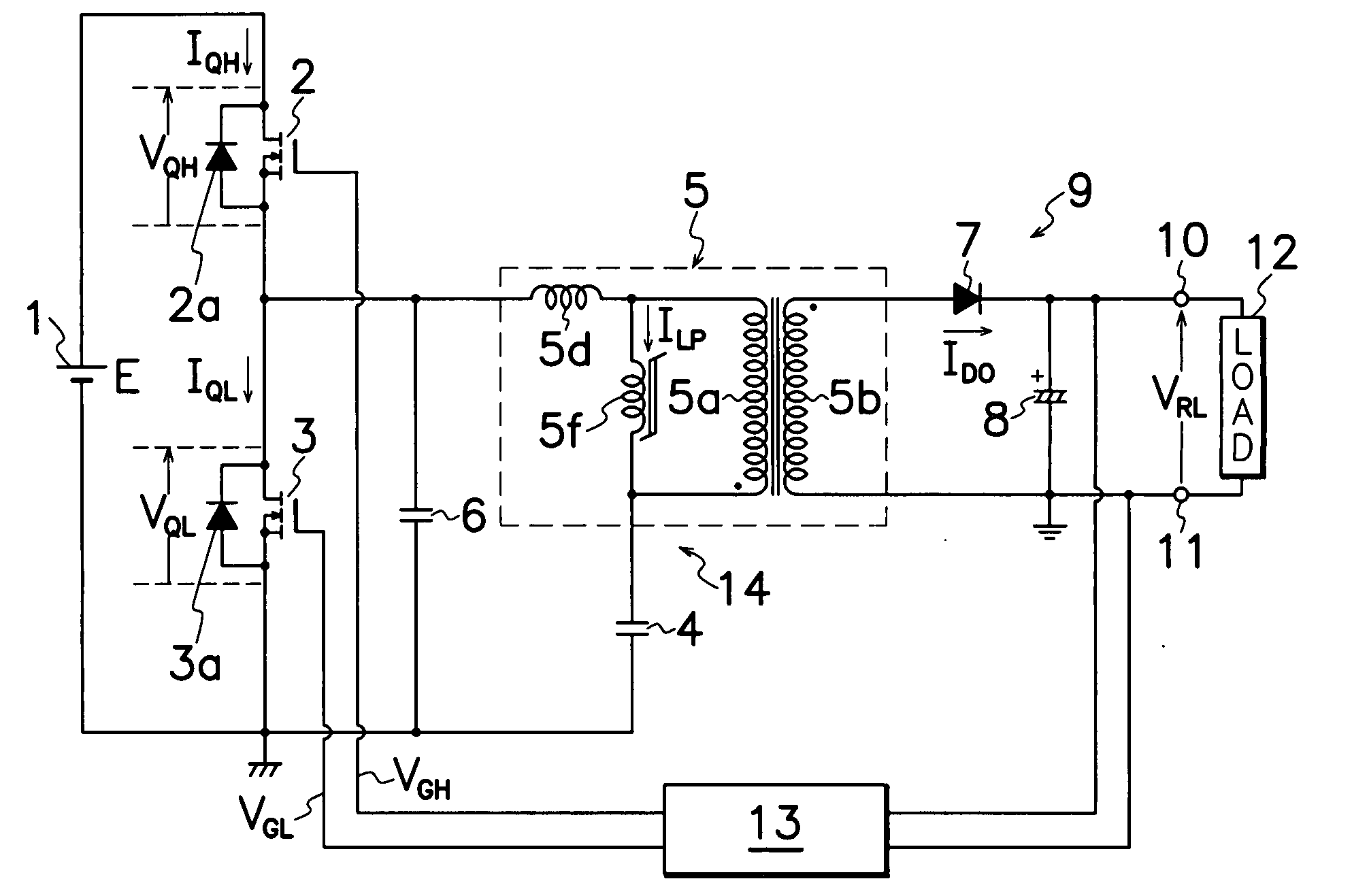
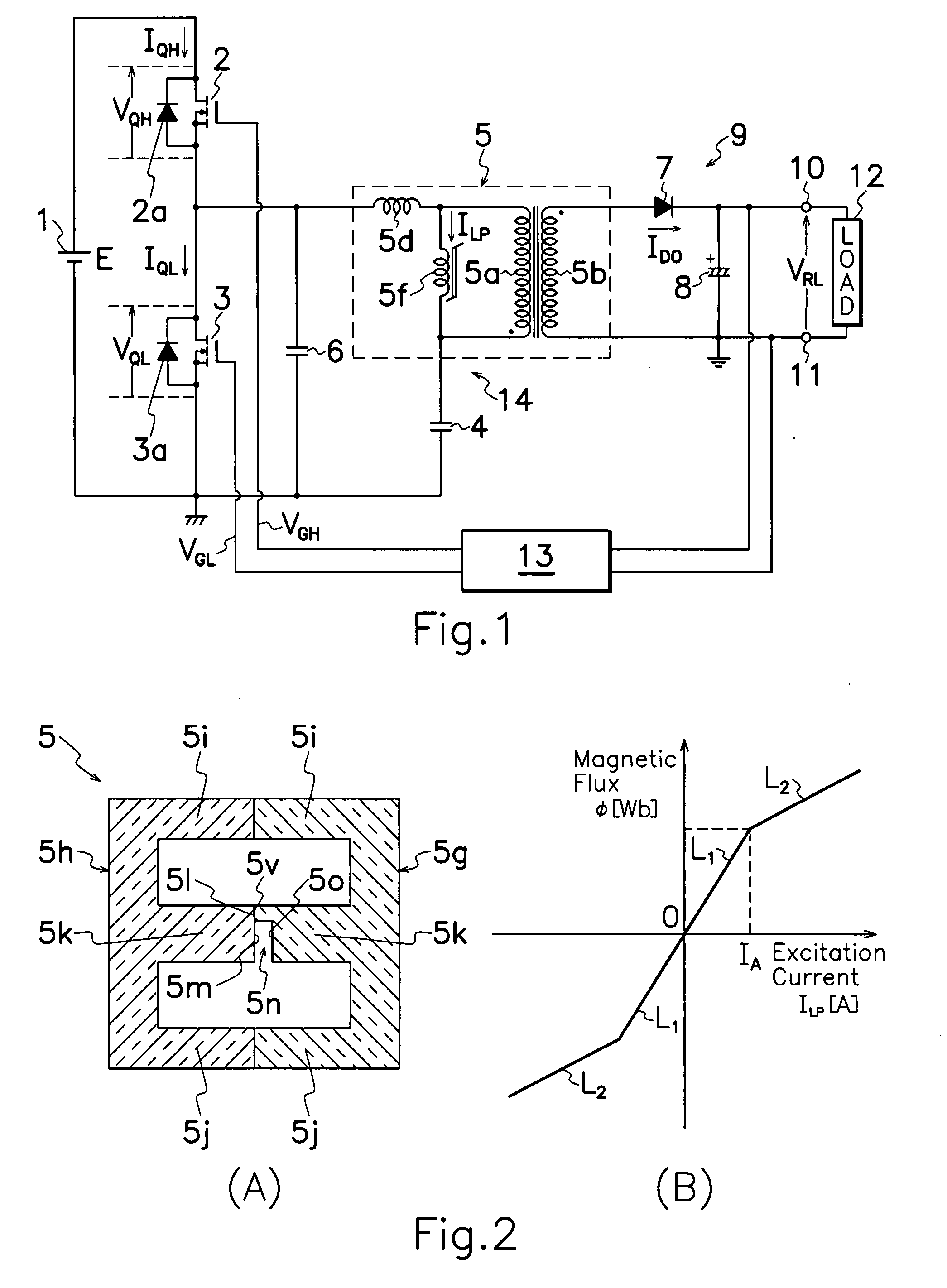
The transformer 5 used for the present invention, comprises a core of E-shaped first and second core halves 5g, 5h coupled together in opposed relation to each other to form a closed magnetic circuit or circuits for supporting primary and secondary windings 5a, 5b wound around first and second core halves 5g, 5h; and a gap 5n defined between end surfaces 5l, 5m of first and second core halves 5g, 5h by spaced relation of end surfaces 5l, 5m to also form a reduced section area 5v by contacting the end surfaces 5l, 5m. When a large amount of electric current flows through resonant series circuit 14, reduced section area 5v comes to magnetic saturation to reduce an excitation inductance 5f of transformer 5, more increase excitation current ILP and thereby perform steady operation in any load condition. When a small amount of electric current flows through resonant series circuit 14, excitation inductance 5f of transformer 5 is increased to repress excitation current ILP, thereby reducing power loss during light or no load to improve power conversion efficiency during light load.
Owner:SANKEN ELECTRIC CO LTD
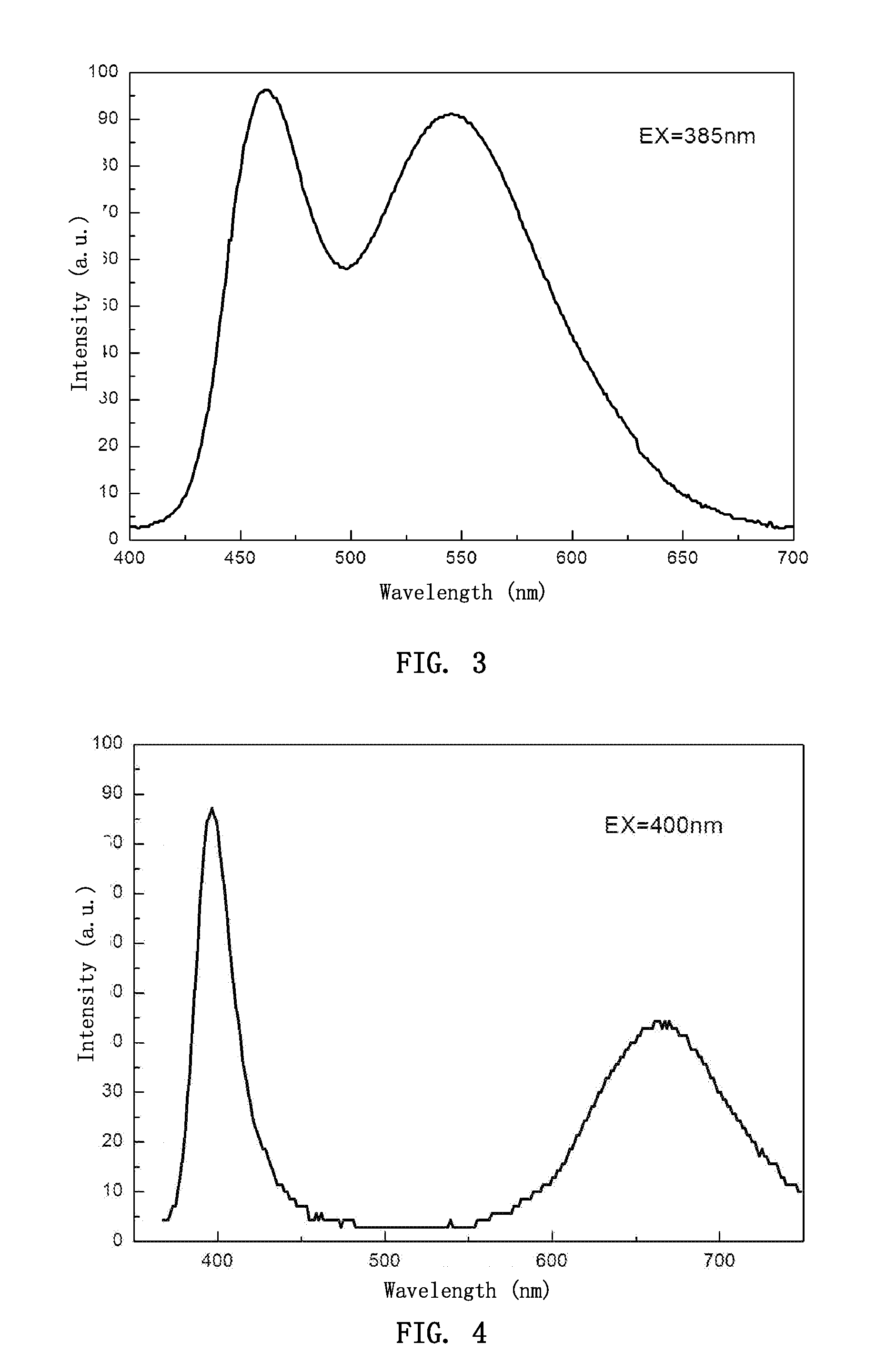
Silicate phosphor and its manufacture method as well as light-emitting device using the same
ActiveUS20080031797A1Wide rangeHigh light conversion efficiencyDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsPhosphorUltraviolet
The invention relates to an ultraviolet to green light region silicate phosphor capable of being excited by radiation light source and its manufacturing method, particularly to white and multicolor systems light-emitting device. The material has luminous color in the range from blue to red color system. The essential composition of the phosphor is aMO.bM′O.SiO2.cR:xEu.yLn.zLv.δLm, wherein M is an element or a combination of elements selected from the group consisting of Sr, Ca, Ba and Zn; M′ is an element or a combination of elements selected from the group consisting of Mg, Cd and Be; R is one or two of B2O3 and P2O5; Ln is an element or a combination of elements selected from the group consisting of Nd, Dy, Ho, Tm, La, Ce, Er, Pr, Bi, Sm, Sn, Y, Lu, Ga, Sb, Tb, Mn and Pb; Lv is an element or a combination of elements selected from the group consisting of Cl, F, Br, I and S; Lm is an element or a combination of elements selected from the group consisting of Li, Na and K
Owner:DALIAN LUMINGLIGHT SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
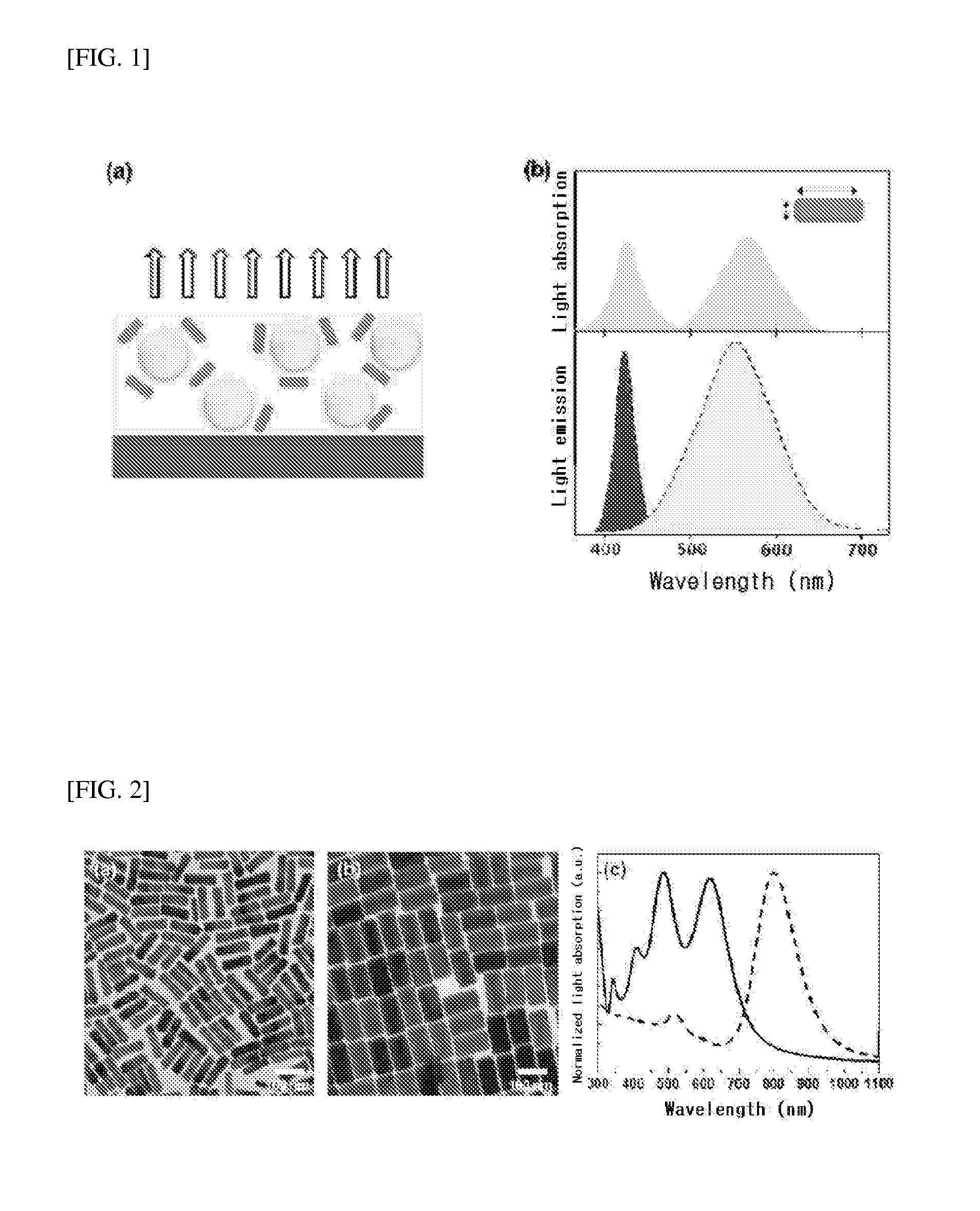
Light conversion light-emitting device with enhanced light luminescence efficiency using anisotropic metal nanoparticles
ActiveUS20150155449A1Increase brightnessLight conversion efficiency can be improvedIndividual molecule manipulationSolid-state devicesWavelengthLight emitting device
There is provided a light-emitting device with enhanced luminescence efficiency, which simultaneously exhibits excitation enhancement and emission enhancement of a light-emitting material by controlling two or multiple surface plasmon resonance bands of anisotropic metal nanoparticles to be formed in a near ultraviolet light range and a visible light range and optimizing overlapping of a wavelength of a near ultraviolet or blue light source with an absorption wavelength and an emission wavelength of the light-emitting material. There is also provided a light-emitting device with improved color gamut and luminance, which simultaneously exhibit emission enhancement of different types of light-emitting materials by controlling two or multiple surfaces plasmon resonance bands of anisotropic metal nanoparticles to be overlapped with absorption and emission wavelengths of two or more light-emitting materials having different emission wavelengths from one another.
Owner:HANWHA TOTALENERGIES PETROCHEMICAL CO LTD
Scalable thermally efficient pump diode systems
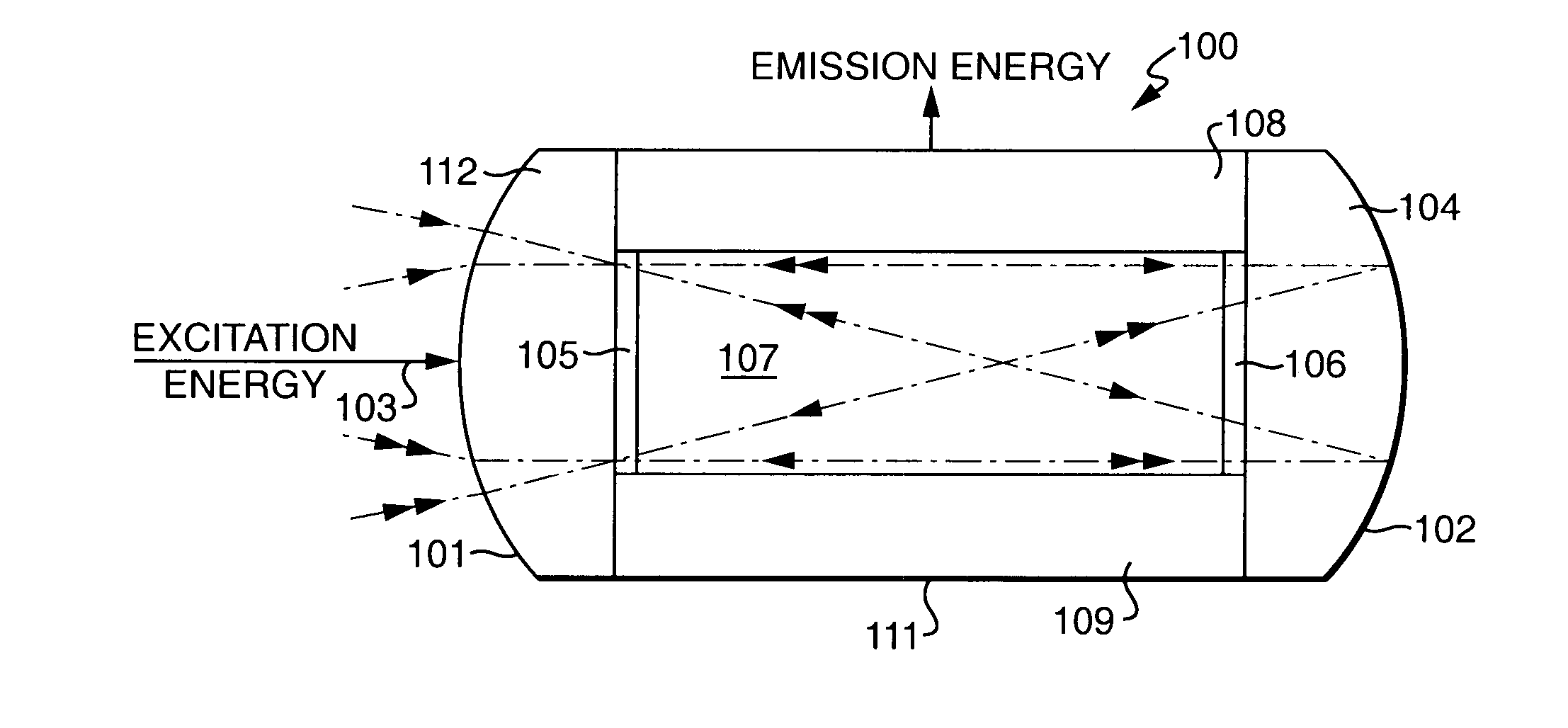
ActiveUS7529286B2Significant energy lossLow costExcitation process/apparatusSemiconductor lasersEngineeringLaser
Scalable, thermally efficient pump diode systems. These systems may include an arrangement of pump diodes and thermally conductive spacers mounted within a single indentation in a substrate or substrate clamps, so as to provide enhanced heat removal from the system. These systems also may include a plurality of such pump diode assemblies mounted, in a symmetric or partially symmetric arrangement, around a lasing medium in a diode pumped laser system, to improve heat removal and / or excitation of the medium.
Owner:D DIODE
Biosensors including metallic nanocavities
InactiveUS9012207B2Enhanced couplingInhibition of excitementMaterial nanotechnologyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteNanoparticle
A biomolecular assay includes a substrate with a metallic layer on at least one surface thereof. The metallic film includes nanocavities. The nanocavities are configured to enhance signals that are representative of the presence or amount of one or more analytes in a sample or sample solution, and may be configured to enhance the signal by a factor of about two or more or by a factor of about three or more. Such signal enhancement may be achieved with nanocavities that are organized in an array, randomly positioned nanocavities, or nanocavities that are surrounded by increased surface area features, such as corrugation or patterning, or nanocavities that have quadrilateral or triangular shapes with tailored edge lengths, or with a plurality of nanoparticles. Methods for fabricating biomolecular substrates and assay techniques in which such biomolecular substrates are used are also disclosed.
Owner:THE UNIV OF UTAH
Resonant switching power source having first and second switching elements connected in series to a DC power source
InactiveUS7643314B2Reducing excitation currentReduce power lossEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionExcitation currentTransformer
The transformer 5 used for the present invention, comprises a core of E-shaped first and second core halves 5g, 5h coupled together in opposed relation to each other to form a closed magnetic circuit or circuits for supporting primary and secondary windings 5a, 5b wound around first and second core halves 5g, 5h; and a gap 5n defined between end surfaces 5l, 5m of first and second core halves 5g, 5h by spaced relation of end surfaces 5l, 5m to also form a reduced section area 5v by contacting the end surfaces 5l, 5m. When a large amount of electric current flows through resonant series circuit 14, reduced section area 5v comes to magnetic saturation to reduce an excitation inductance 5f of transformer 5, more increase excitation current ILP and thereby perform steady operation in any load condition. When a small amount of electric current flows through resonant series circuit 14, excitation inductance 5f of transformer 5 is increased to repress excitation current ILP, thereby reducing power loss during light or no load to improve power conversion efficiency during light load.
Owner:SANKEN ELECTRIC CO LTD
Multipole coils
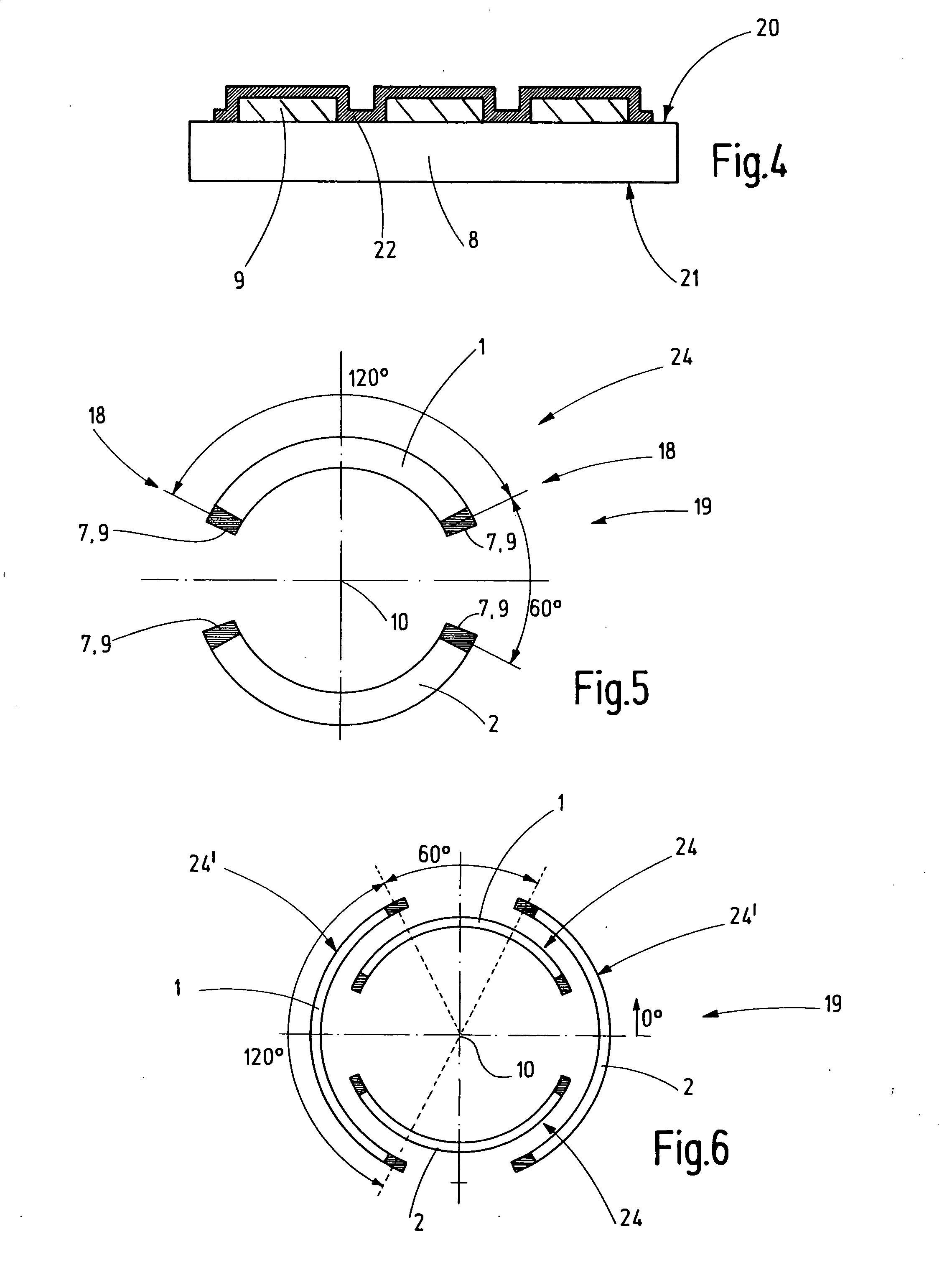
InactiveUS20090079531A1Improve cooling effectIncrease currentCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesMagnetic discharge controlElectrical conductorFlexible electronics
Multipole coils (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6) comprise at least two coils (1, 2) which are disposed to concentrically enclose an imaginary axis (10). Multipole coils (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6) of this type are designed in such a fashion that effective fields can be generated in the area of an imaginary axis (10) when little installation space is available, and the multipole coils can be reproducibly manufactured with high precision. This is achieved in that, for each coil (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6), at least one winding (7) is disposed on a flexible printed circuit board (8) through disposed strip conductors (9), and the printed circuit board (8) is rolled in at least one printed circuit board layer (11, 12, 13, 14).
Owner:CEOS CORRECTED ELECTRON
Fluorescent proteins, their production and use
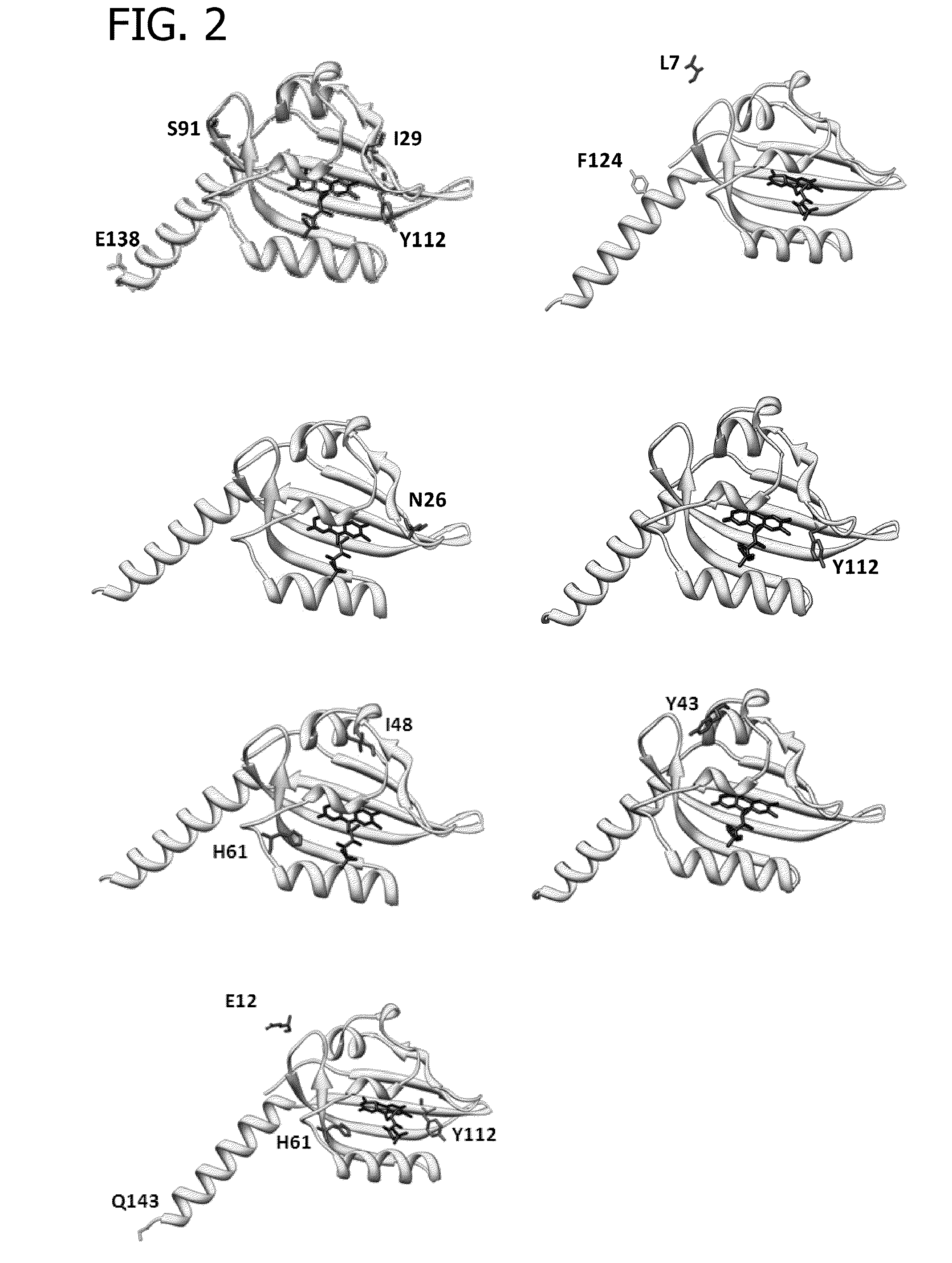
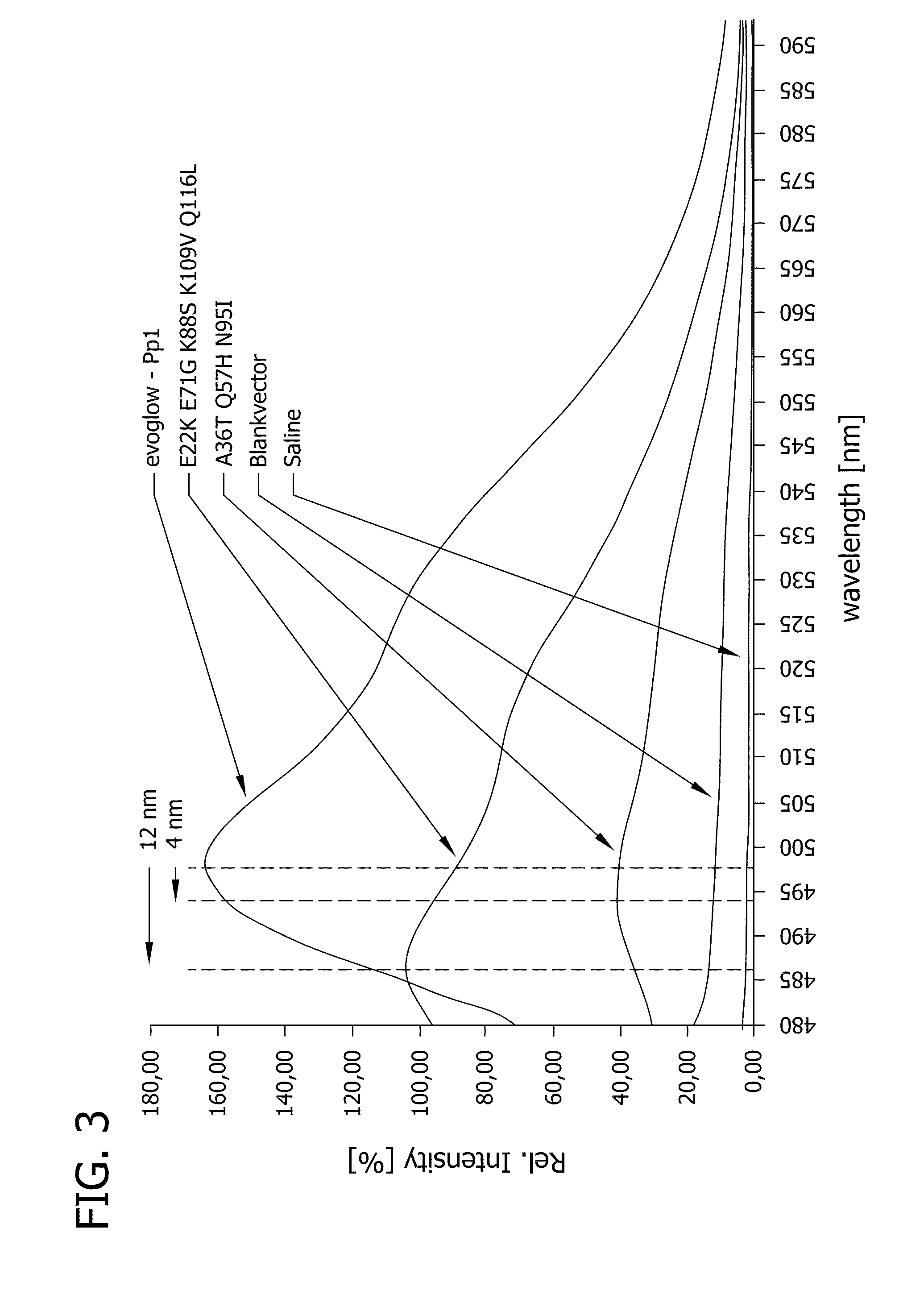
InactiveUS20100304435A1Enhance excitationHigh yieldUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPeptide/protein ingredientsQuantum yieldAmino acid substitution
The present invention provides variants of fluorescent proteins, which are improved with regard to their properties for use as reporter proteins and / or in analytics. In particular, variants of fluorescent proteins are provided, which fluoresce brighter, show improved quantum yield and / or have shifted excitation or emission spectra. The fluorescent proteins according to the invention comprise in their LOV domain besides the substitution of a cysteine with an amino acid that does not covalently bind FMN at least one further point mutation.
Owner:EVOCATAL
Air Gap Servo for Optical Recording
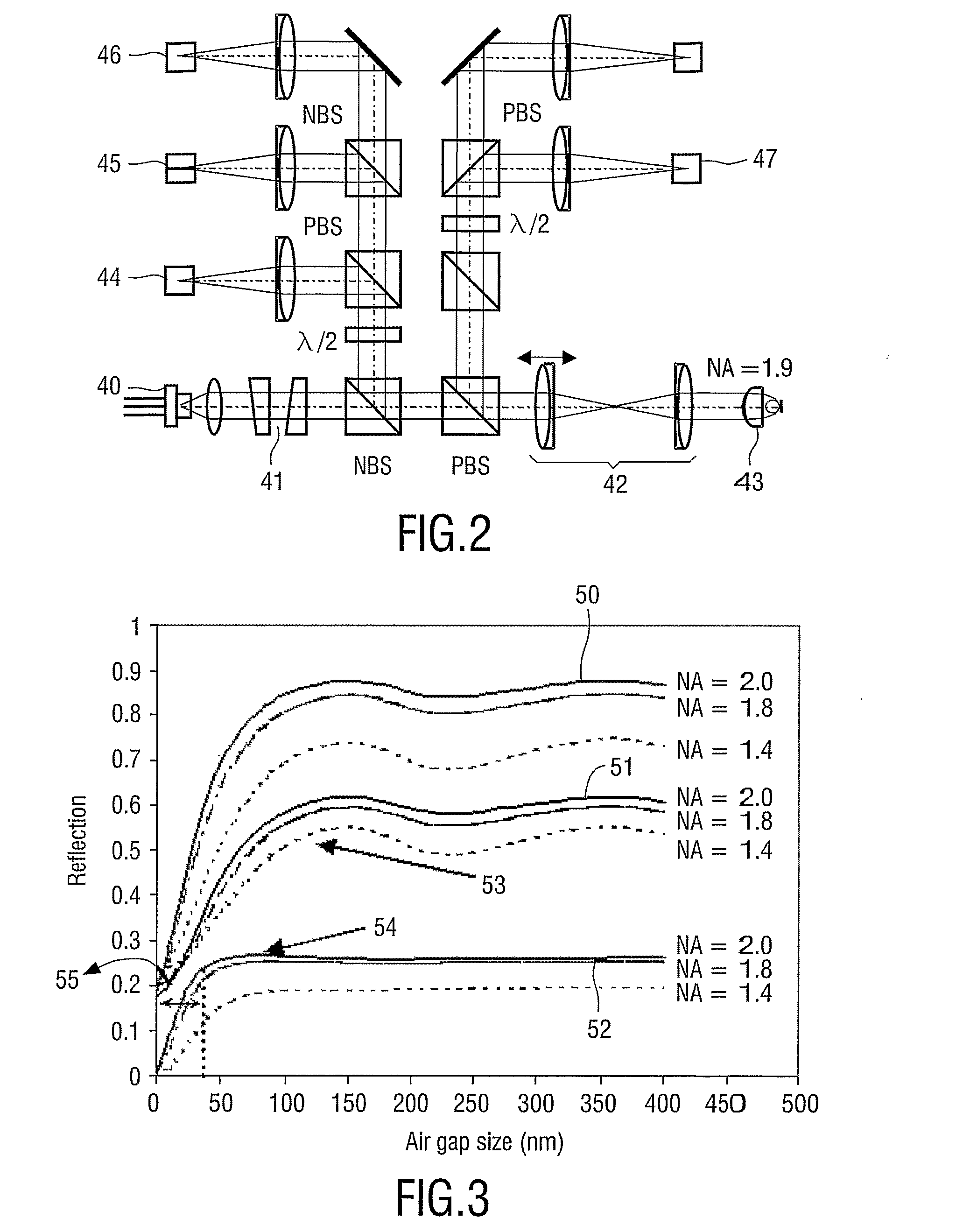
InactiveUS20080267036A1Reduce riskReduce readRecord information storageOptical beam guiding meansClosed loopEngineering
A device reads and / or records marks in a track on a record carrier via near field optical recording. The device has a head including a lens to be positioned at a near field distance from a surface of the record carrier. An air gap controller is for controlling an air gap between the lens and the surface, and has an approach mode for bringing the lens from a remote distance in the far field (72) to the near field distance. Thereto the controller provides an increasing periodical excitation signal (73) for generating a sequence of approach instants (77) at which the lens approaches the surface. At the approach instants the lens has substantially zero velocity (76). The sequence of approach instants brings the lens subsequently closer to the surface. When the lens enters in the near field range (71) at one of the approach instants (77), the air gap controller is switched to closed loop mode.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Display device using quantum dot film
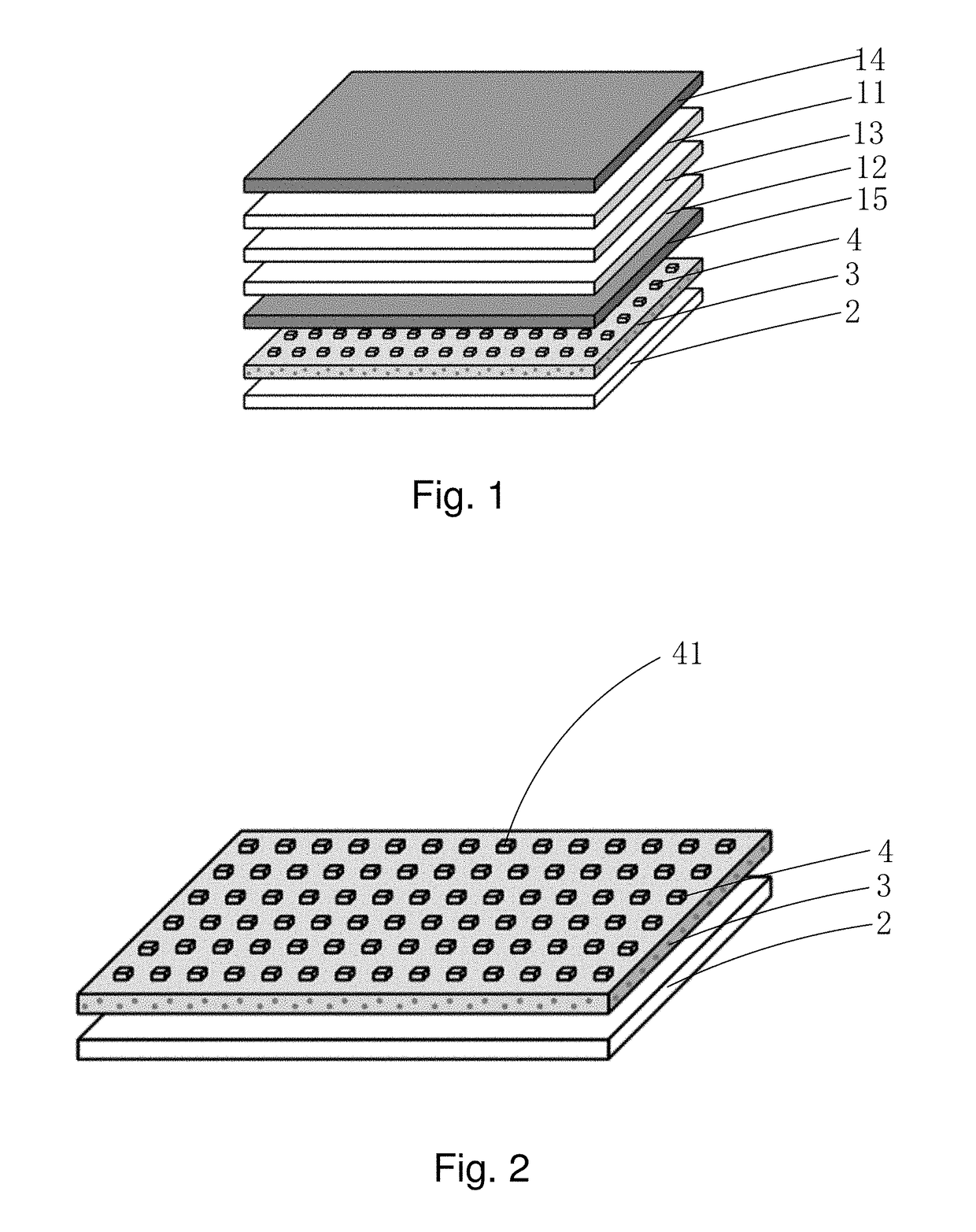
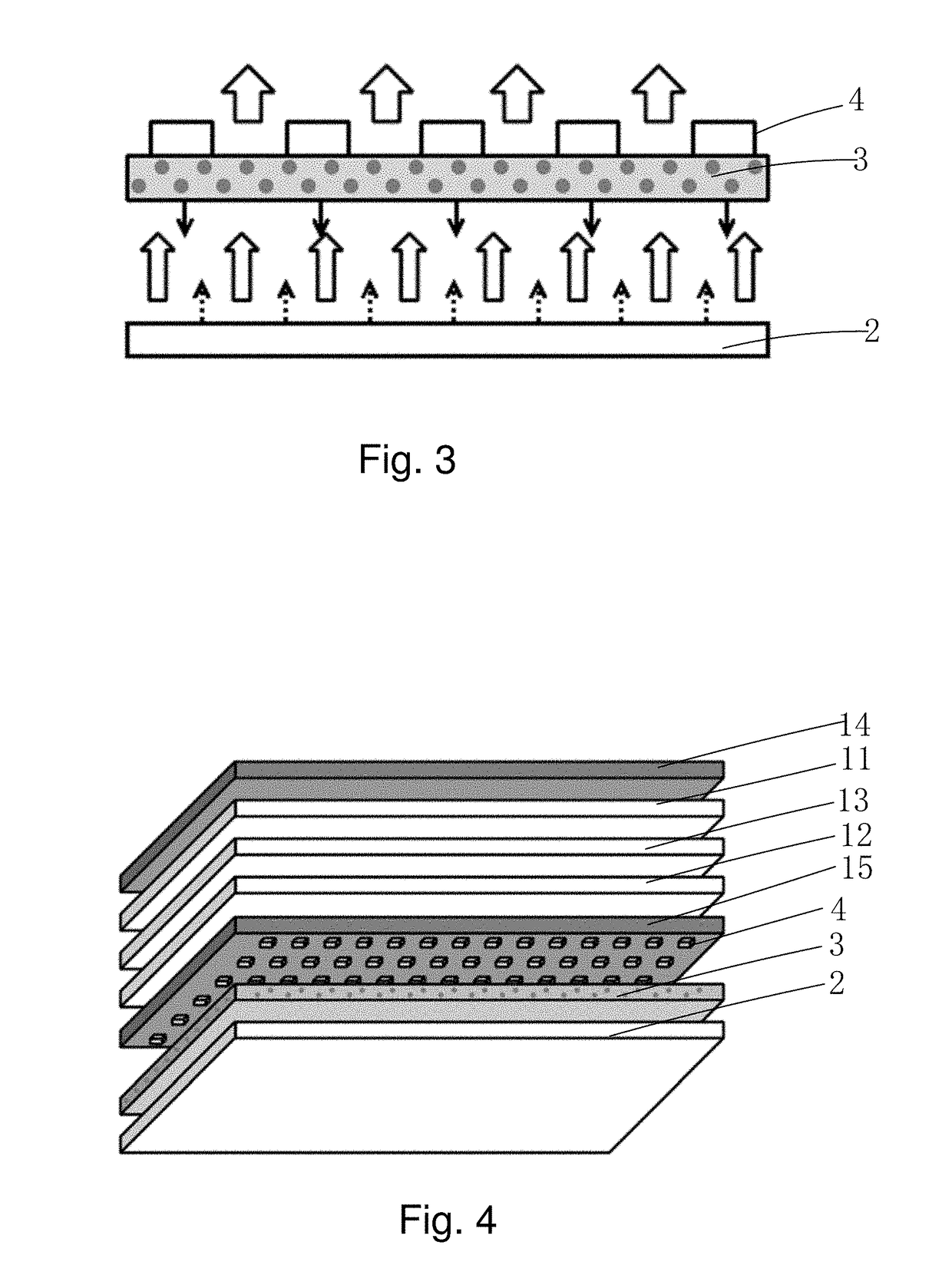
ActiveUS20170261812A1Expand the range of displayImprove excitation efficiencyNon-linear opticsGamutQuantum dot
The present invention provides a display device using a quantum dot film, including a display panel, a backlight module (2) located under the display panel, a quantum dot film (3) located between the display panel and the backlight module (2), and a plurality of reflector units (41) located between the quantum dot film (3) and the display panel. The quantum dot film (3) can be excited by light emitting from the backlight module to give off excitation light. The liquid crystal panel includes therein a black matrix. The plurality of reflector units (41) is arranged to correspond to the black matrix. The display device using a quantum dot film of the present invention has a wide color gamut range and has good image quality and high quantum dot excitation rate and utilization of backlighting.
Owner:SHENZHEN CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Fluorescence detector geometry
InactiveUS20050046834A1Great detection sensitivityNon-linearity be avoidRadiation pyrometryRaman/scattering spectroscopyMonochromatorLong axis
Excitation light of a selected wavelength from an excitation monochromator is directed along the long axis of a flow cell containing the sample to be analyzed, generating fluorescence. An emission monochromator is positioned at right angles to the plane of the excitation monochromator and receives the fluorescence from the flow cell utilizing optical components positioned such that the entrance slit of the emission monochromator is aligned with the long axis of the emission window. The intensity of the output from the flow cell is further maximized by positioning a retro-reflecting mirror at the end of the flow channel to effectively double the path-length of the excitation beam, and a reflecting surface on the side of the cell opposite the emission window to increase the collection efficiency and thereby increase the sensitivity of the detector.
Owner:WATERS TECH CORP
Hybrid photovoltaically active layer and method for forming such a layer
InactiveUS20090065056A1Extension of timeIncrease powerElectric discharge tubesFinal product manufactureCharge carrier mobilityActive layer
A “hybrid” photovoltaically active layer is homogenous (in a direction parallel to the major surfaces of the layer) with respect to film constituents, but is non-homogenous with respect to photovoltaic properties. First regions exhibit high absorptivity, while second regions that are perpendicular to the major surfaces of the layer exhibit a higher carrier mobility. The method for forming the layer includes one or all of chemical vapor deposition, the hollow cathode effect, and high power DC pulsing.
Owner:SUB ONE TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com