Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3525 results about "Gamut" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
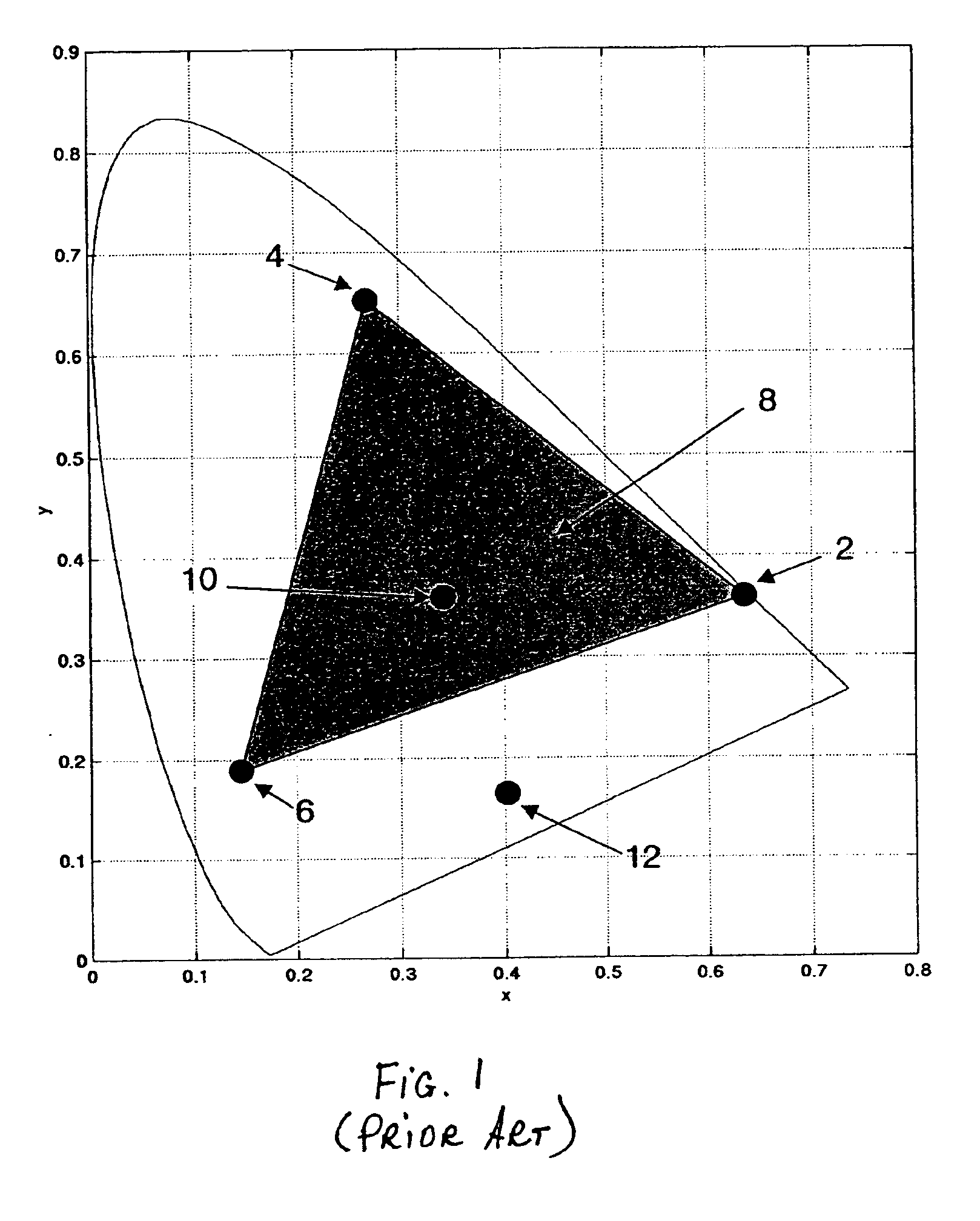
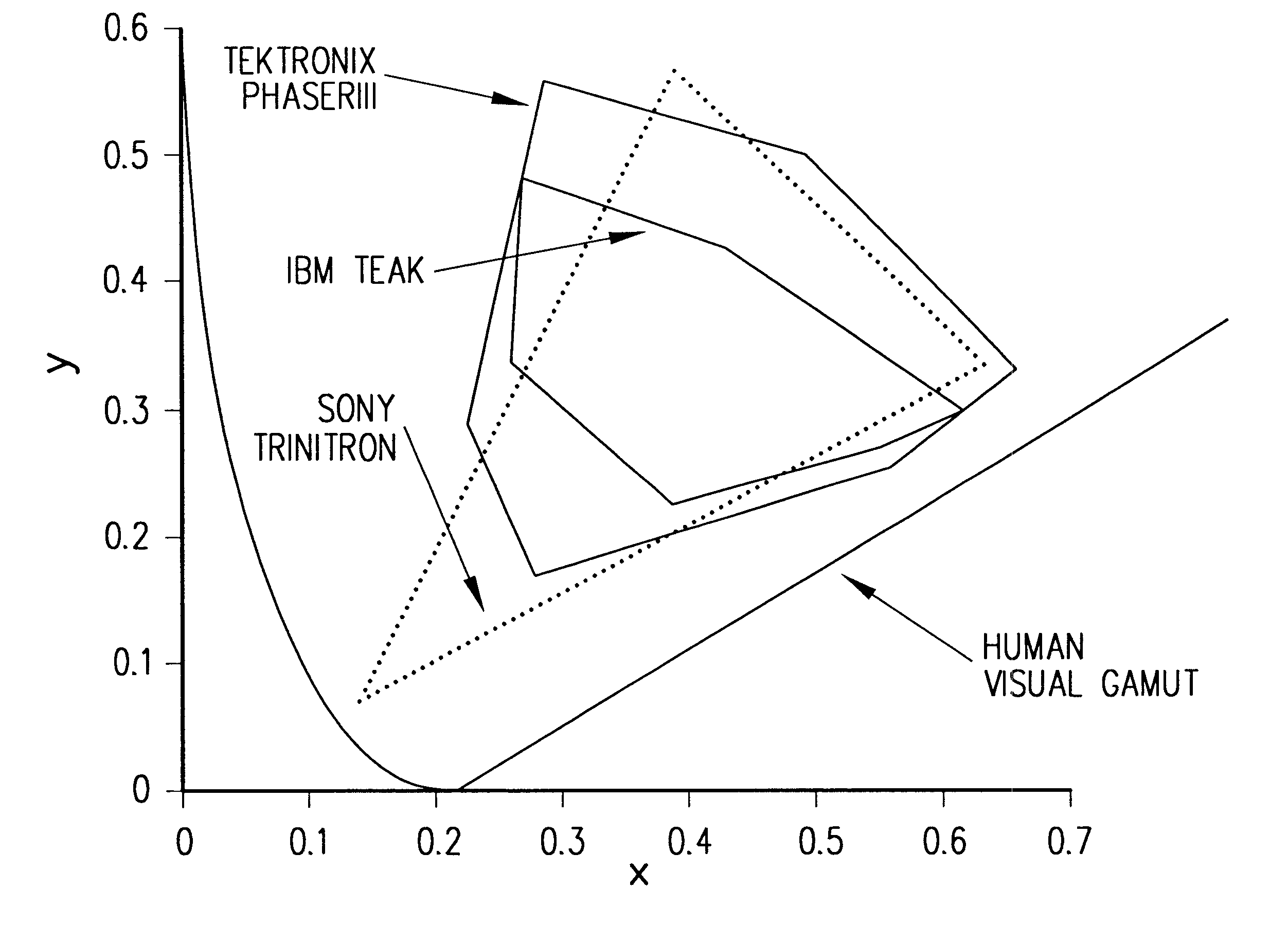
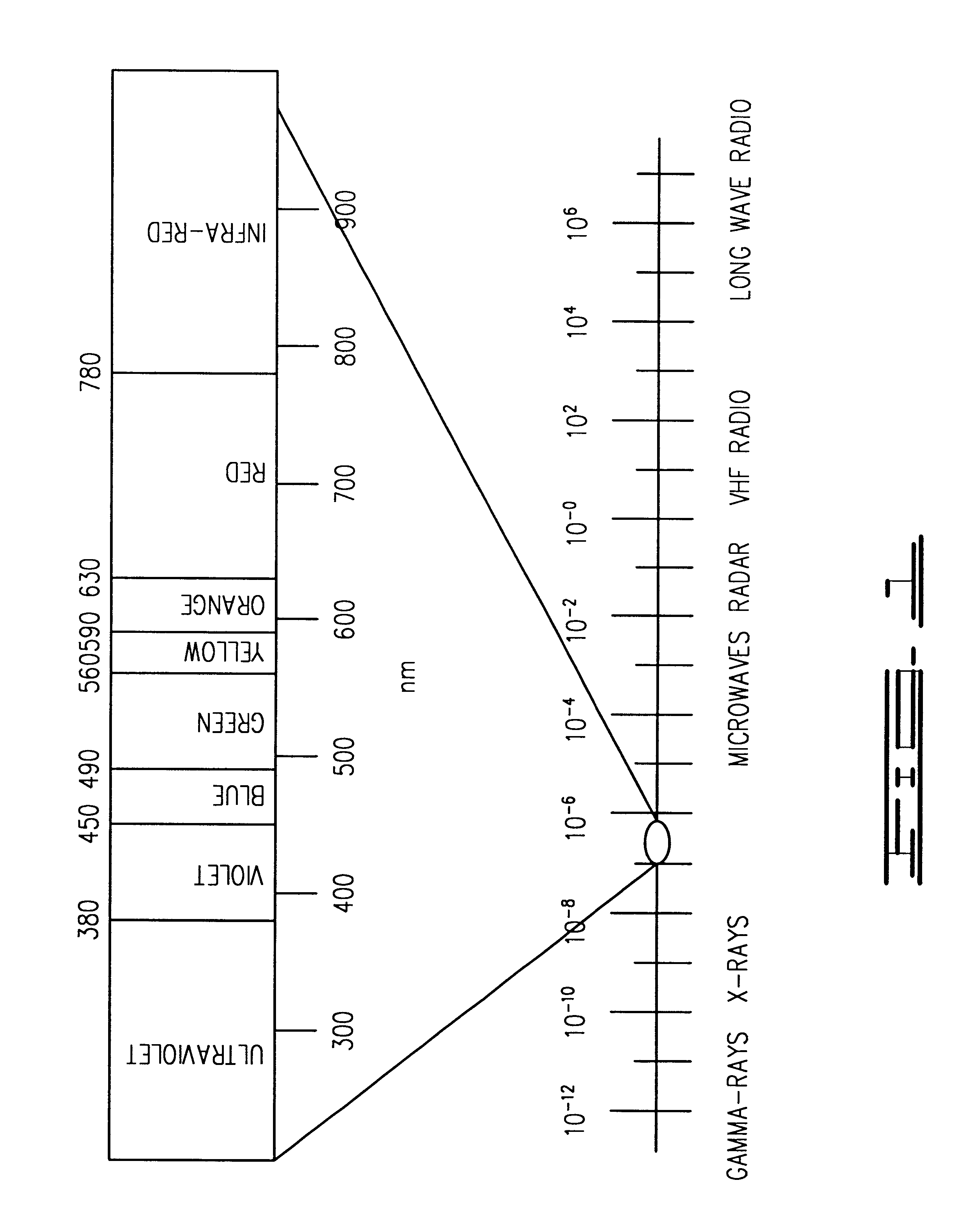
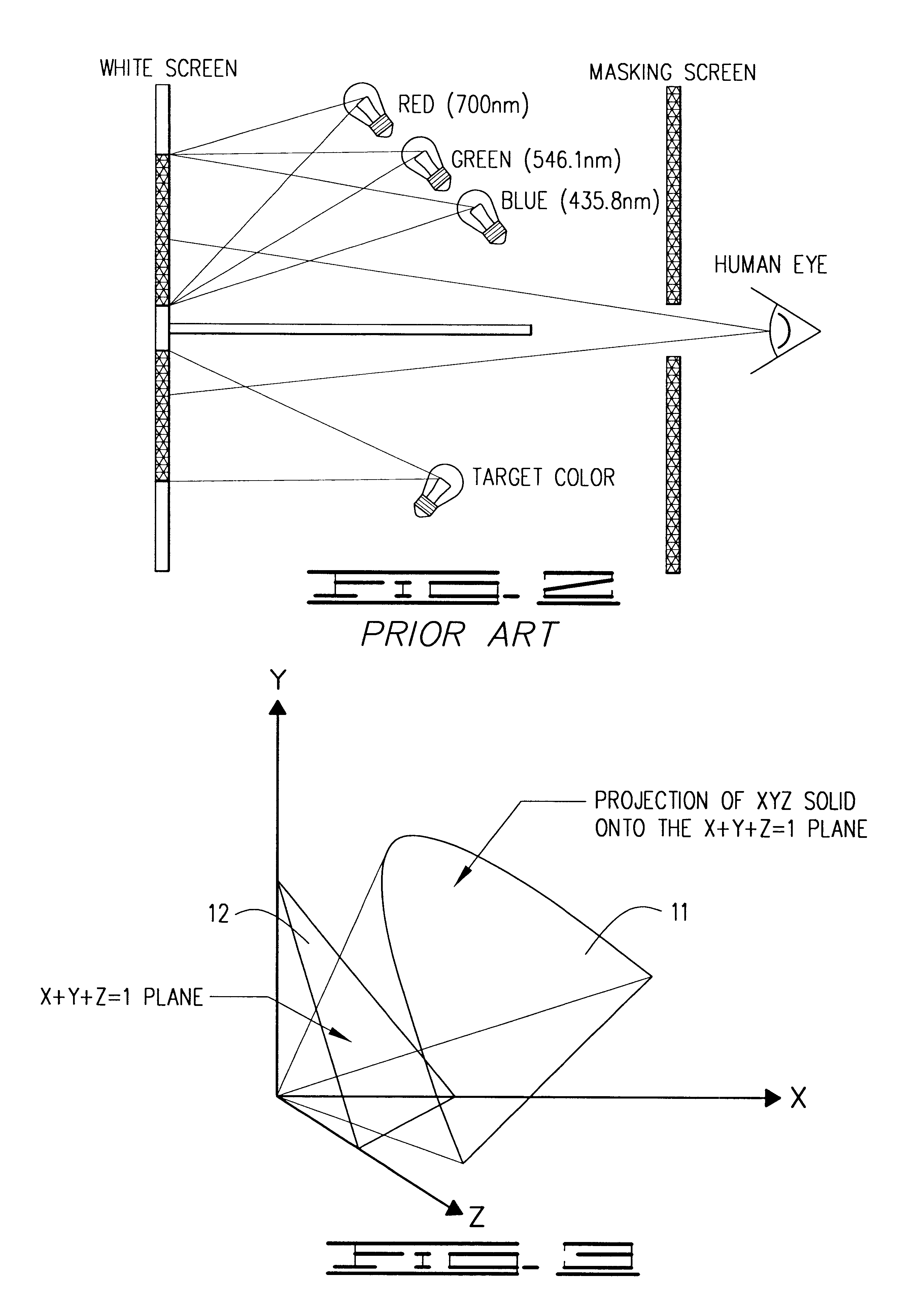
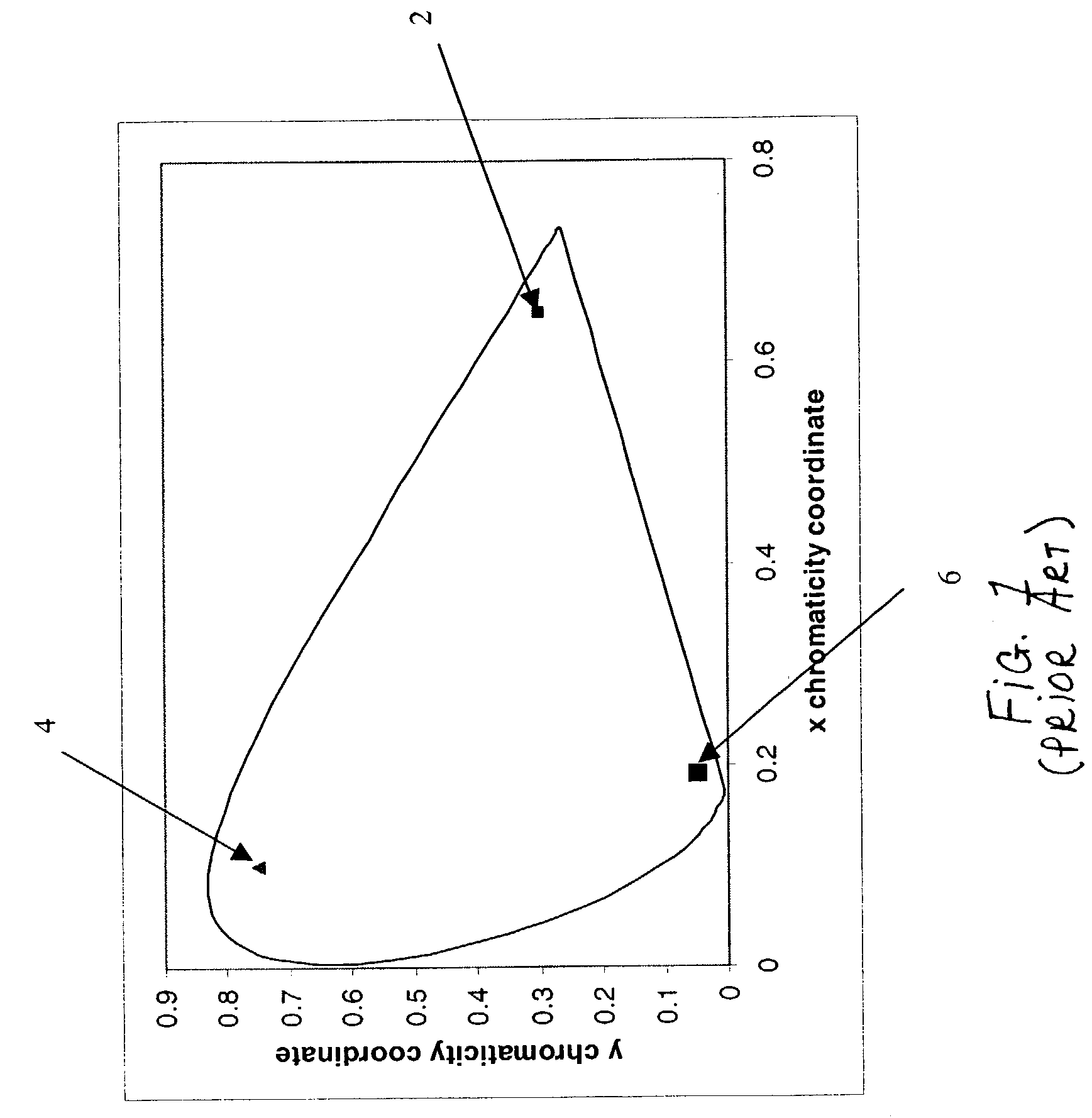
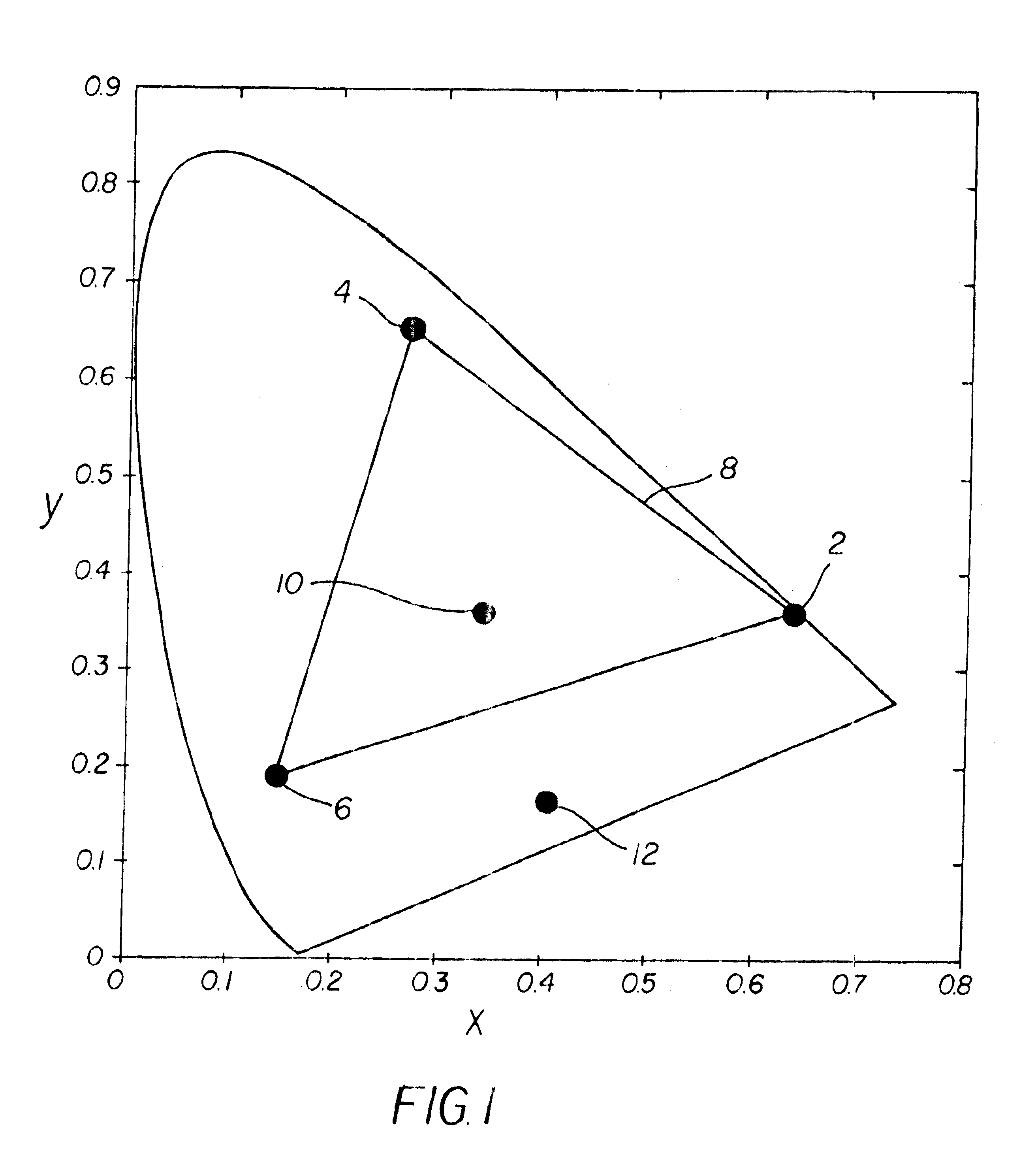
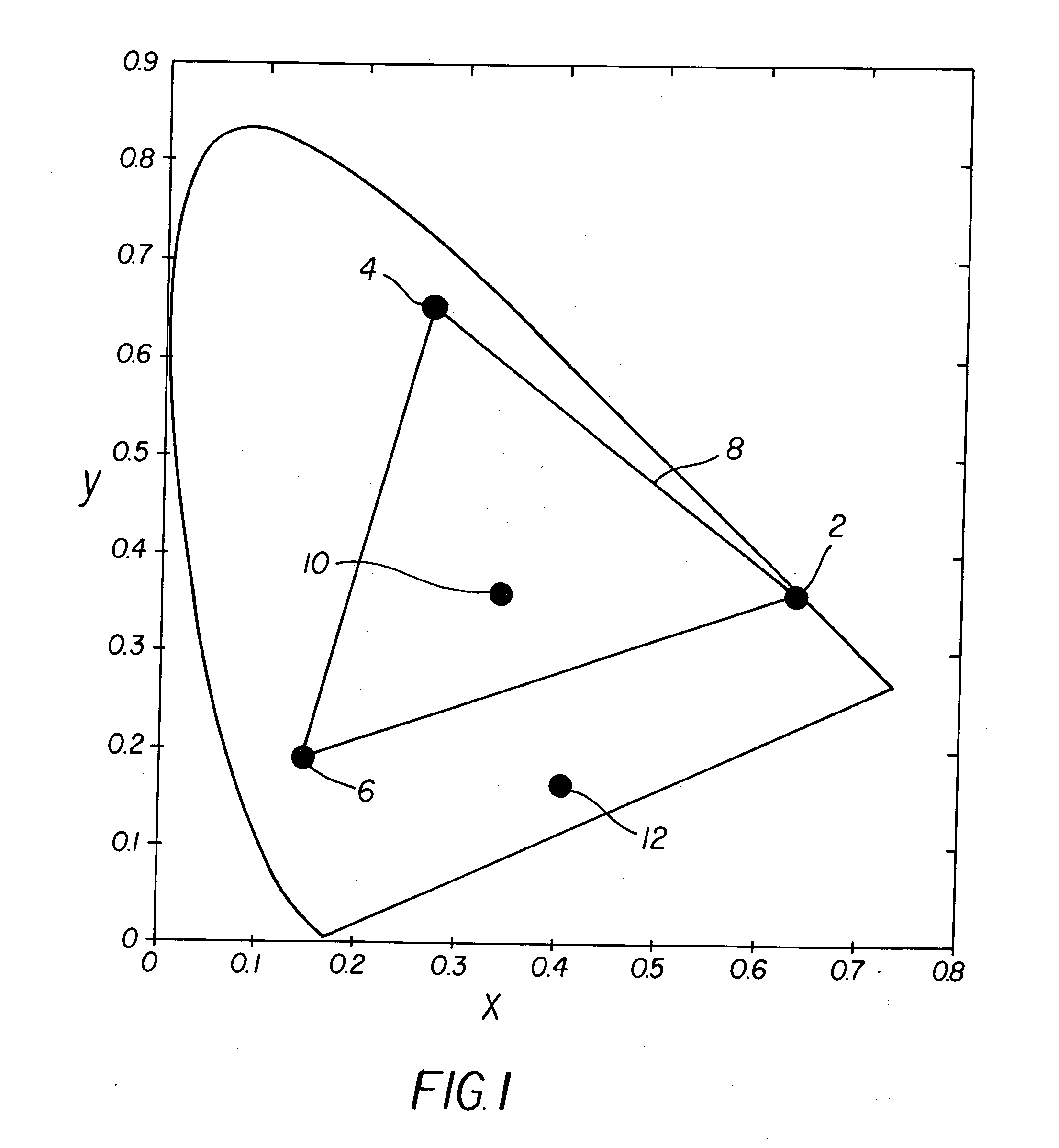
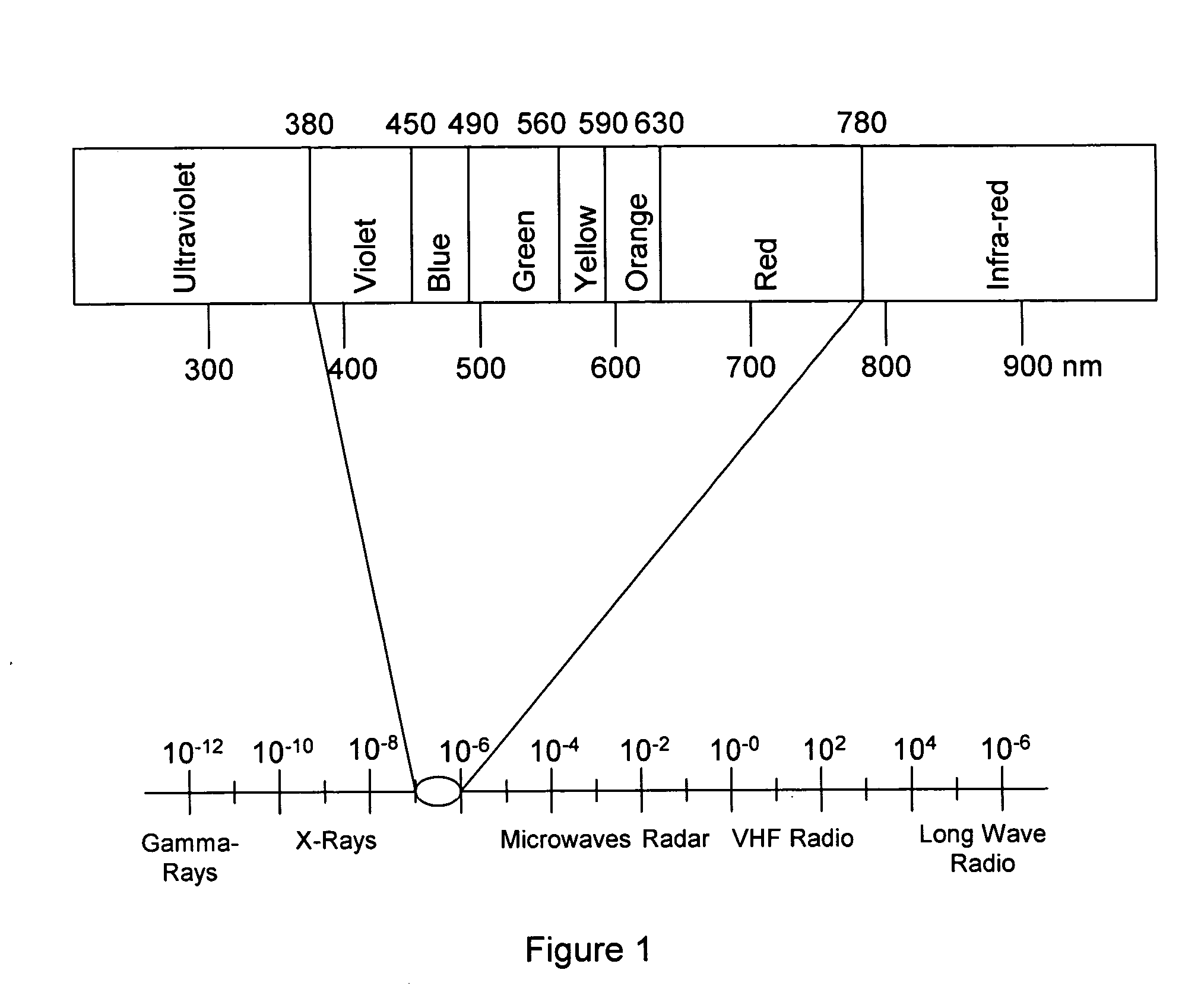
In color reproduction, including computer graphics and photography, the gamut, or color gamut /ˈɡæmət/, is a certain complete subset of colors. The most common usage refers to the subset of colors which can be accurately represented in a given circumstance, such as within a given color space or by a certain output device.
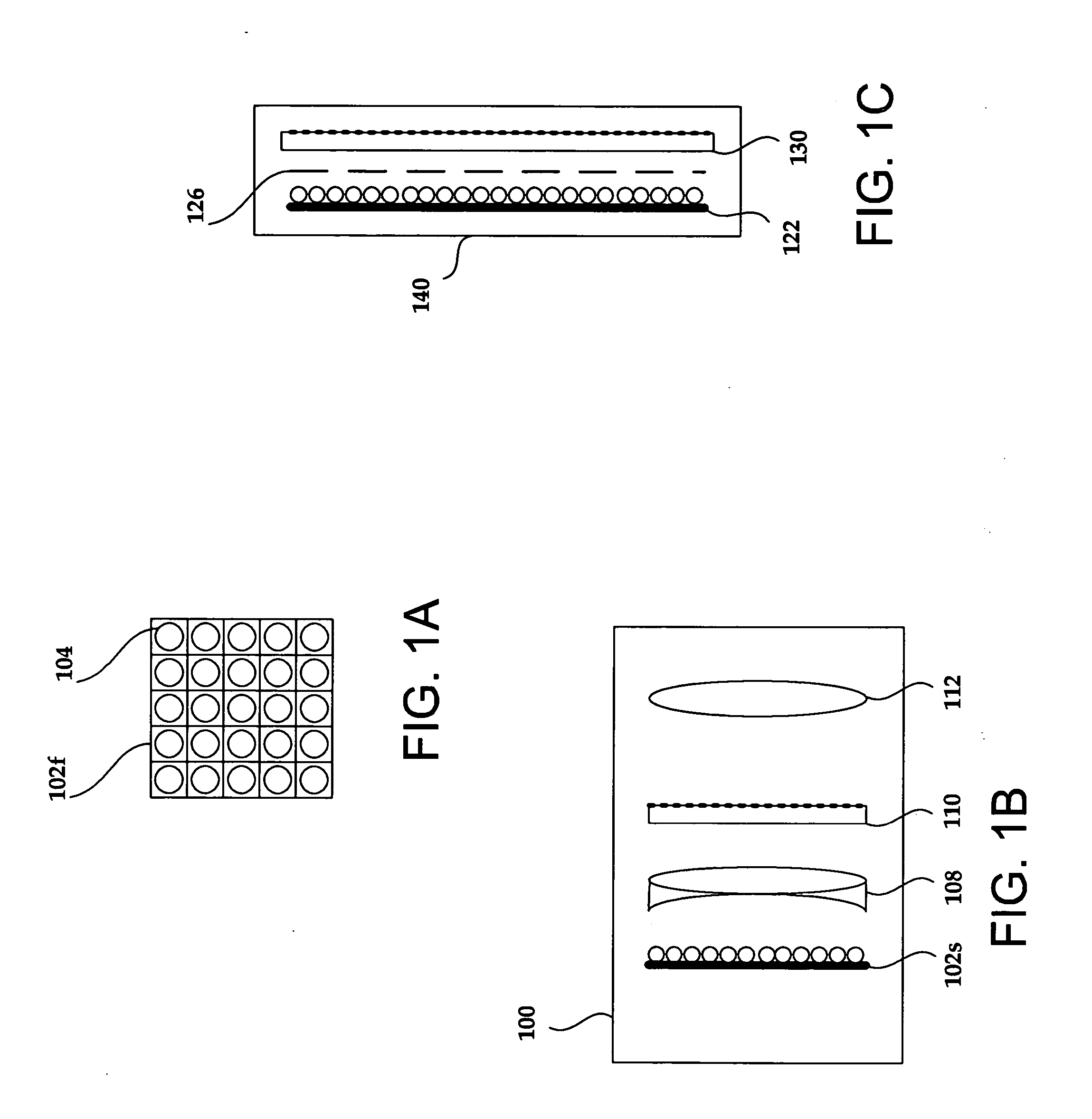
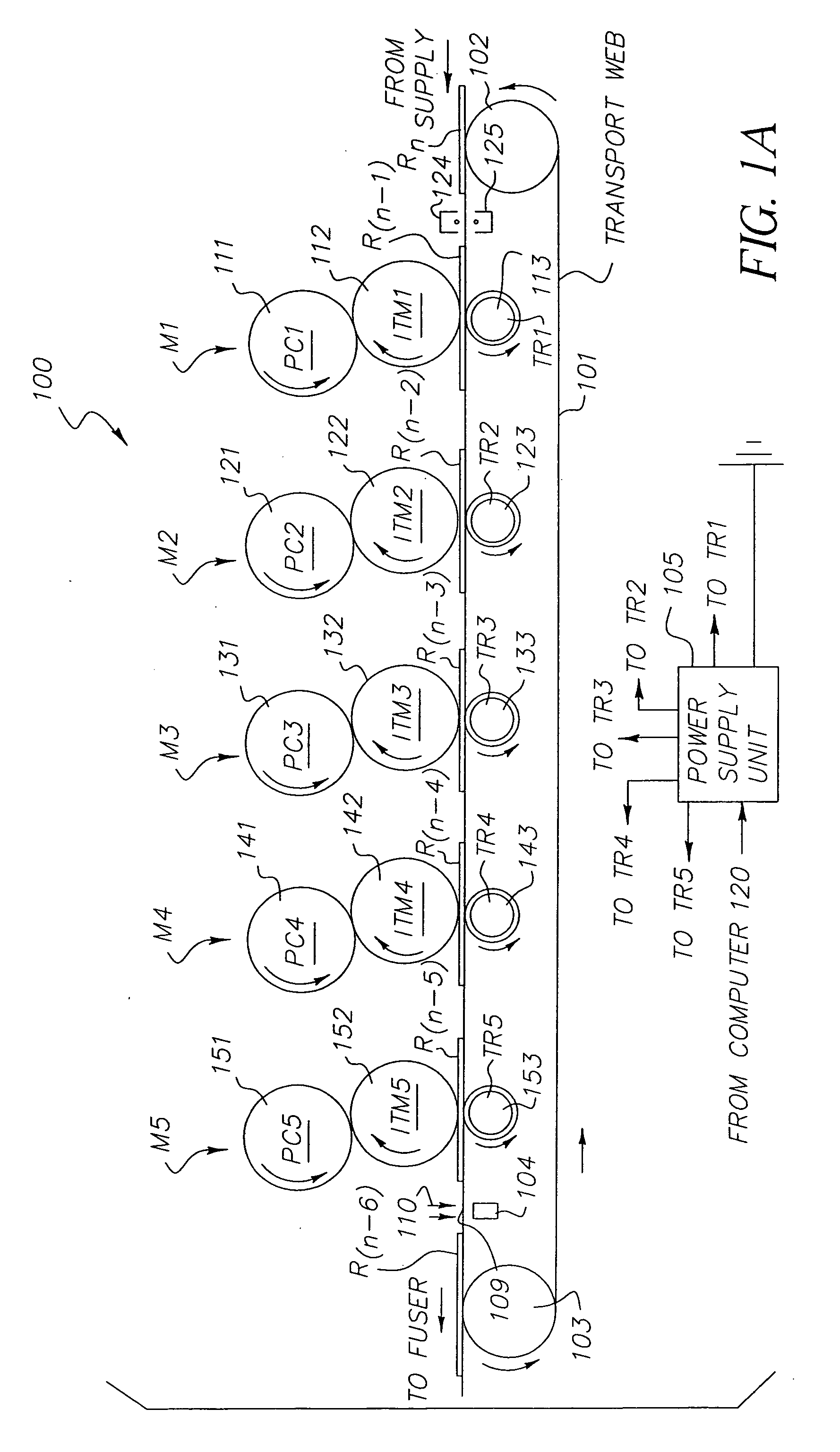
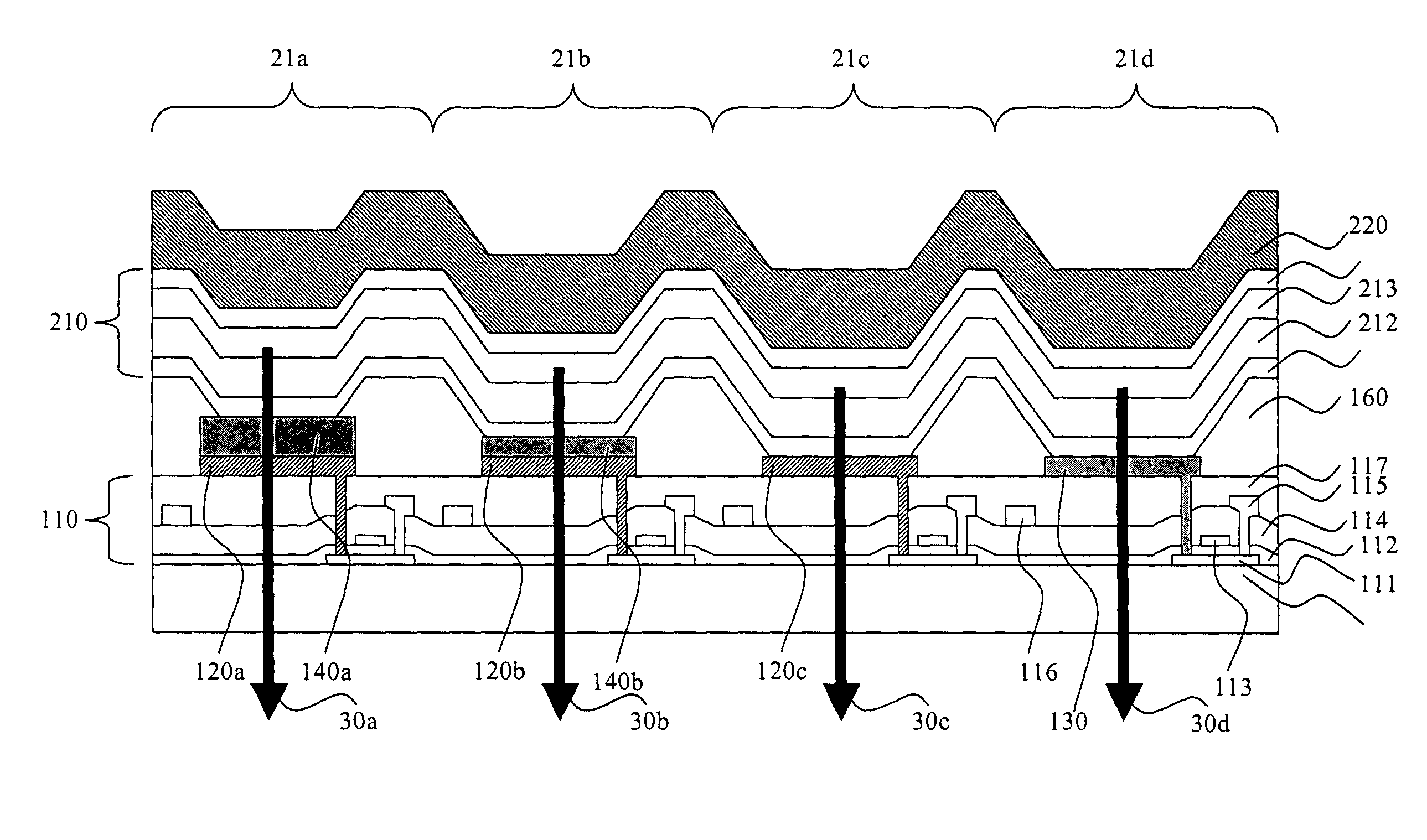
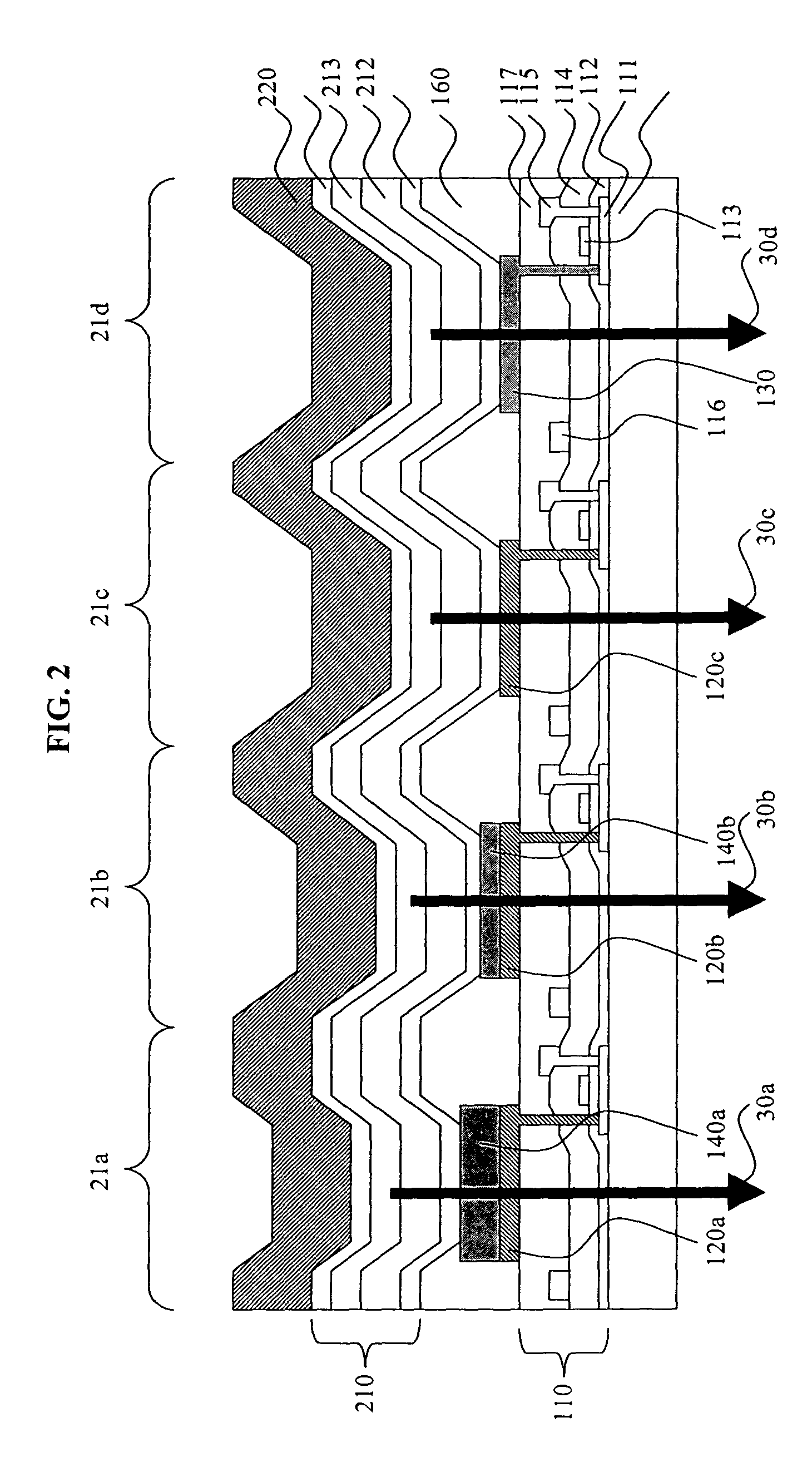
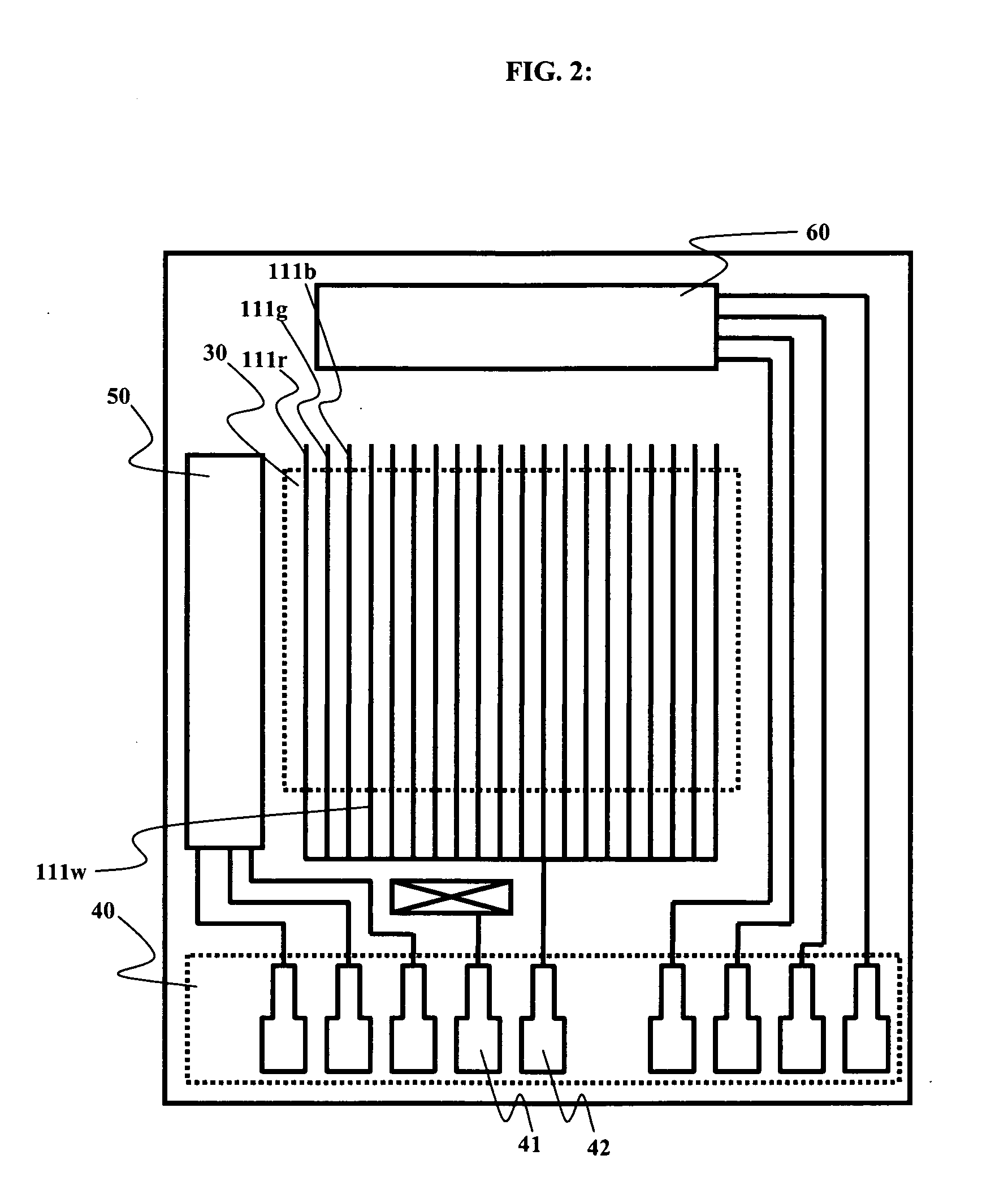
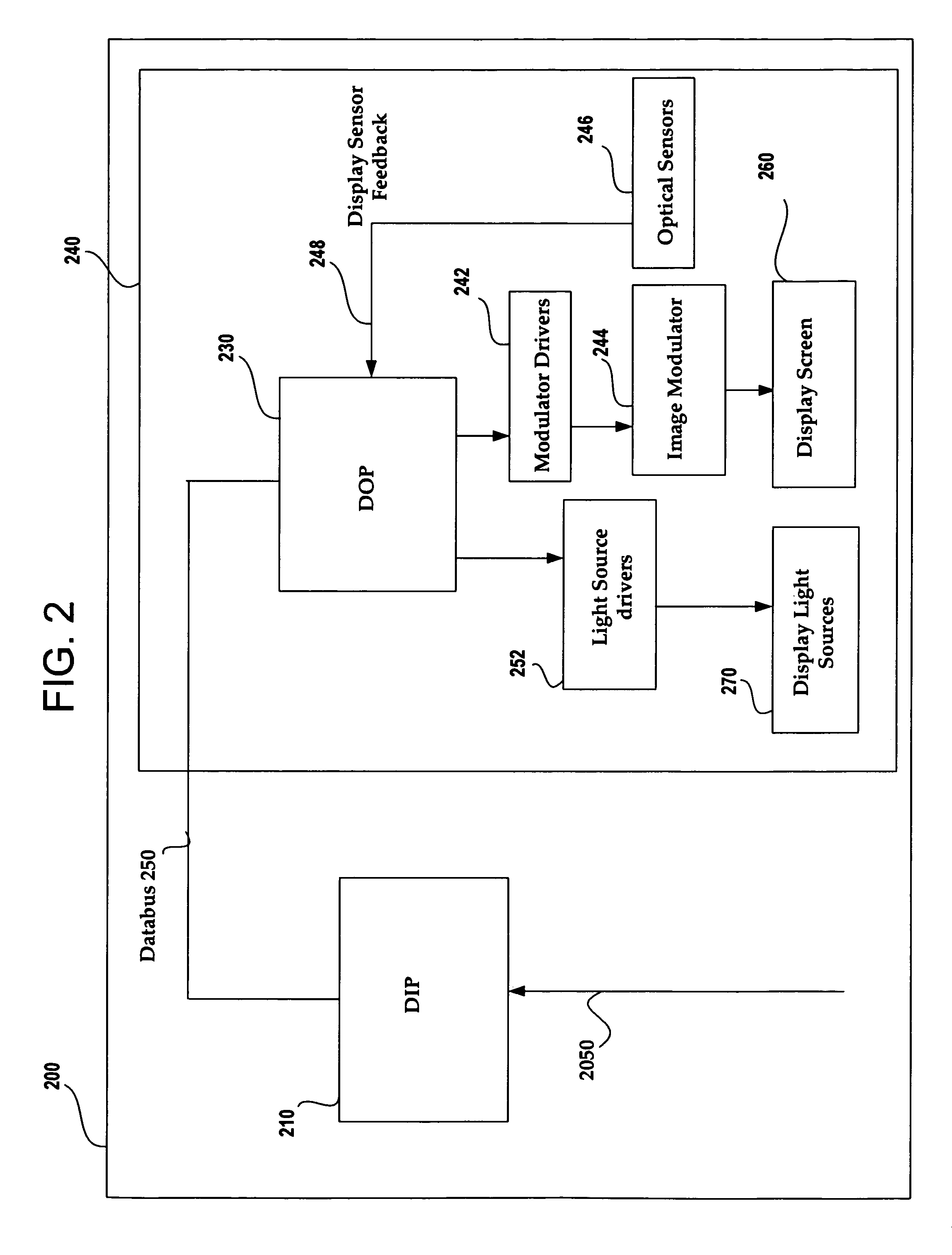
Field sequential light source modulation for a digital display system
ActiveUS20070035707A1Improve display qualityHigh resolutionTelevision system detailsStatic indicating devicesData streamImaging processing
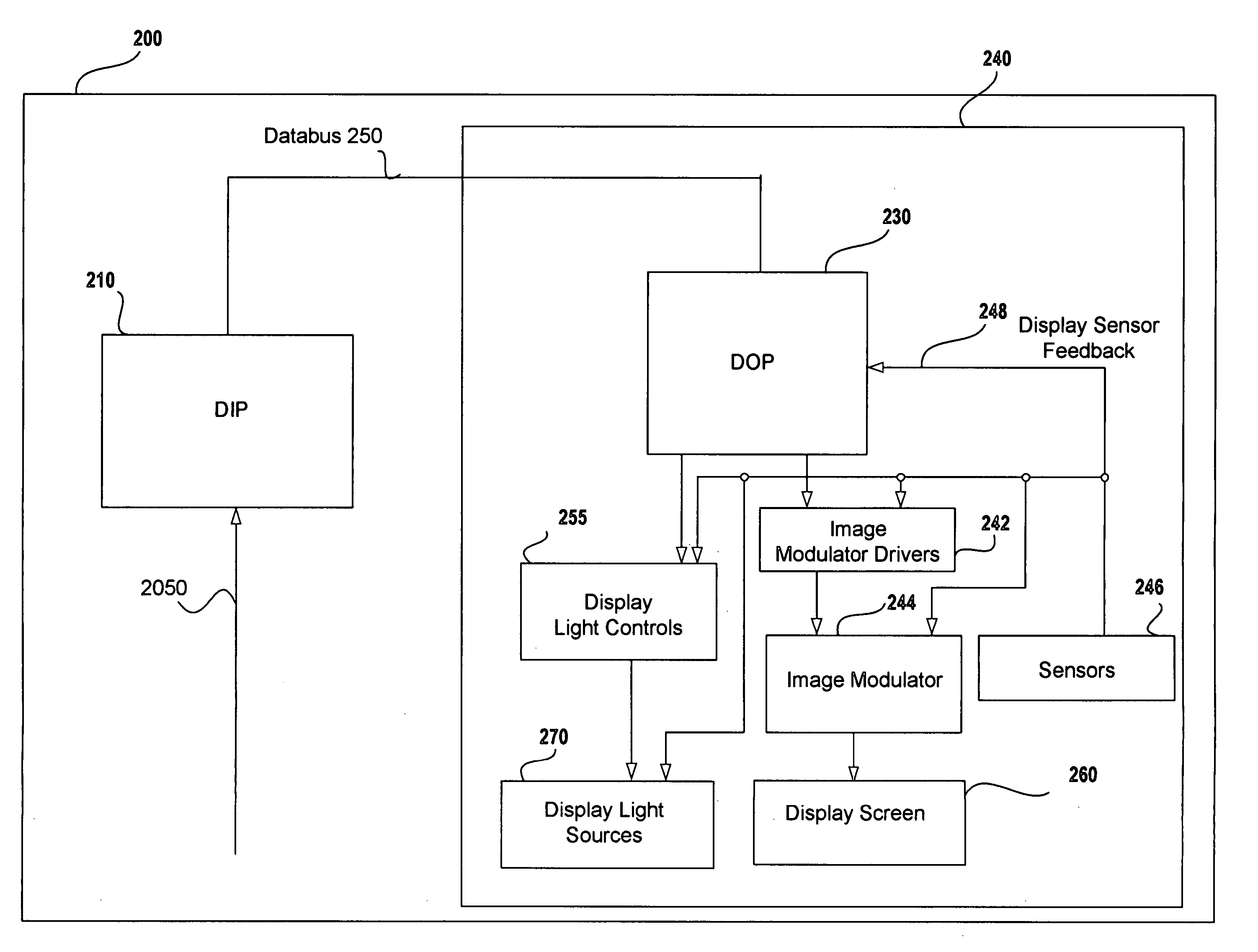
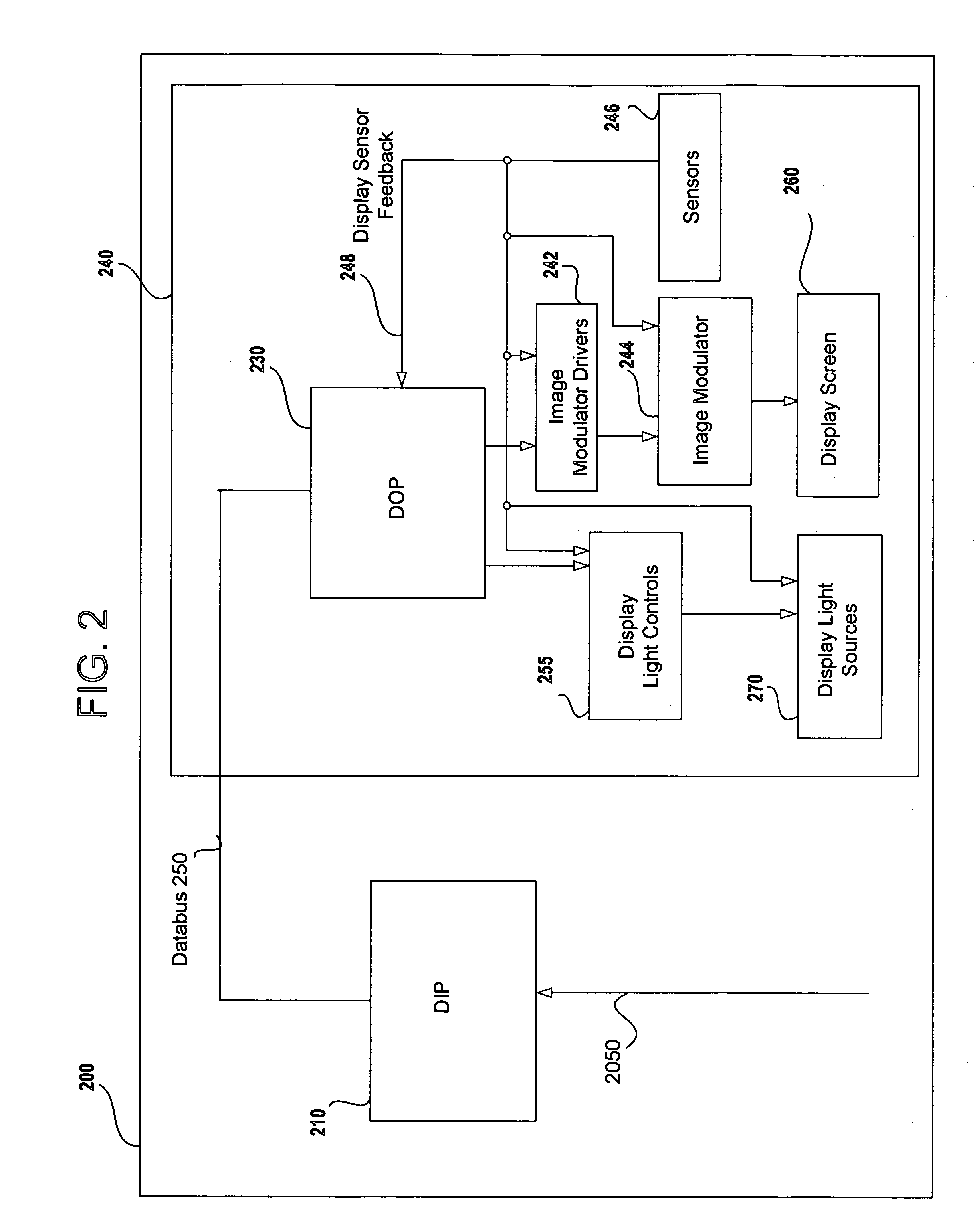
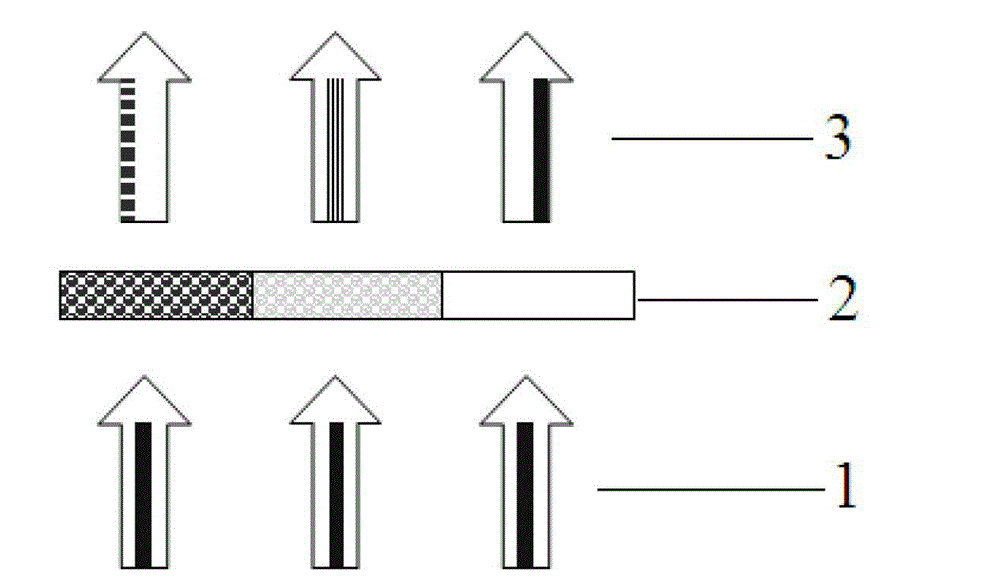
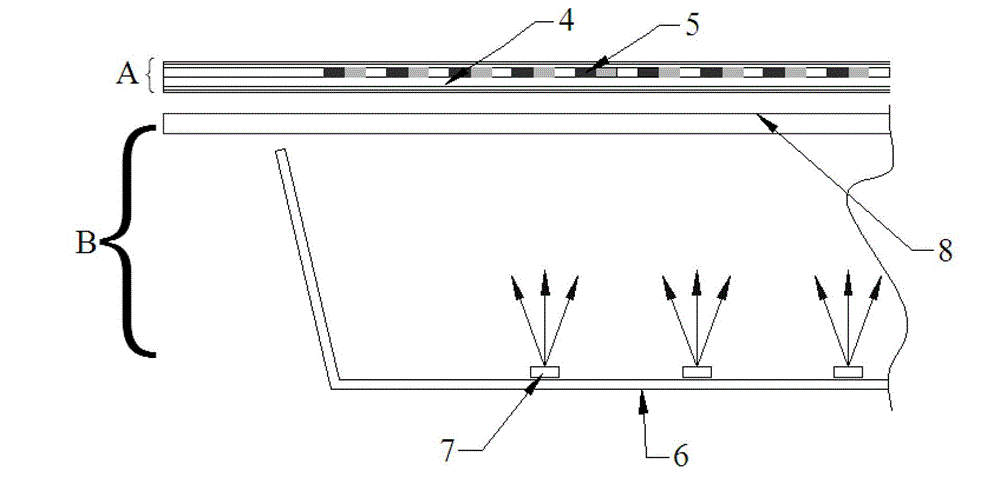
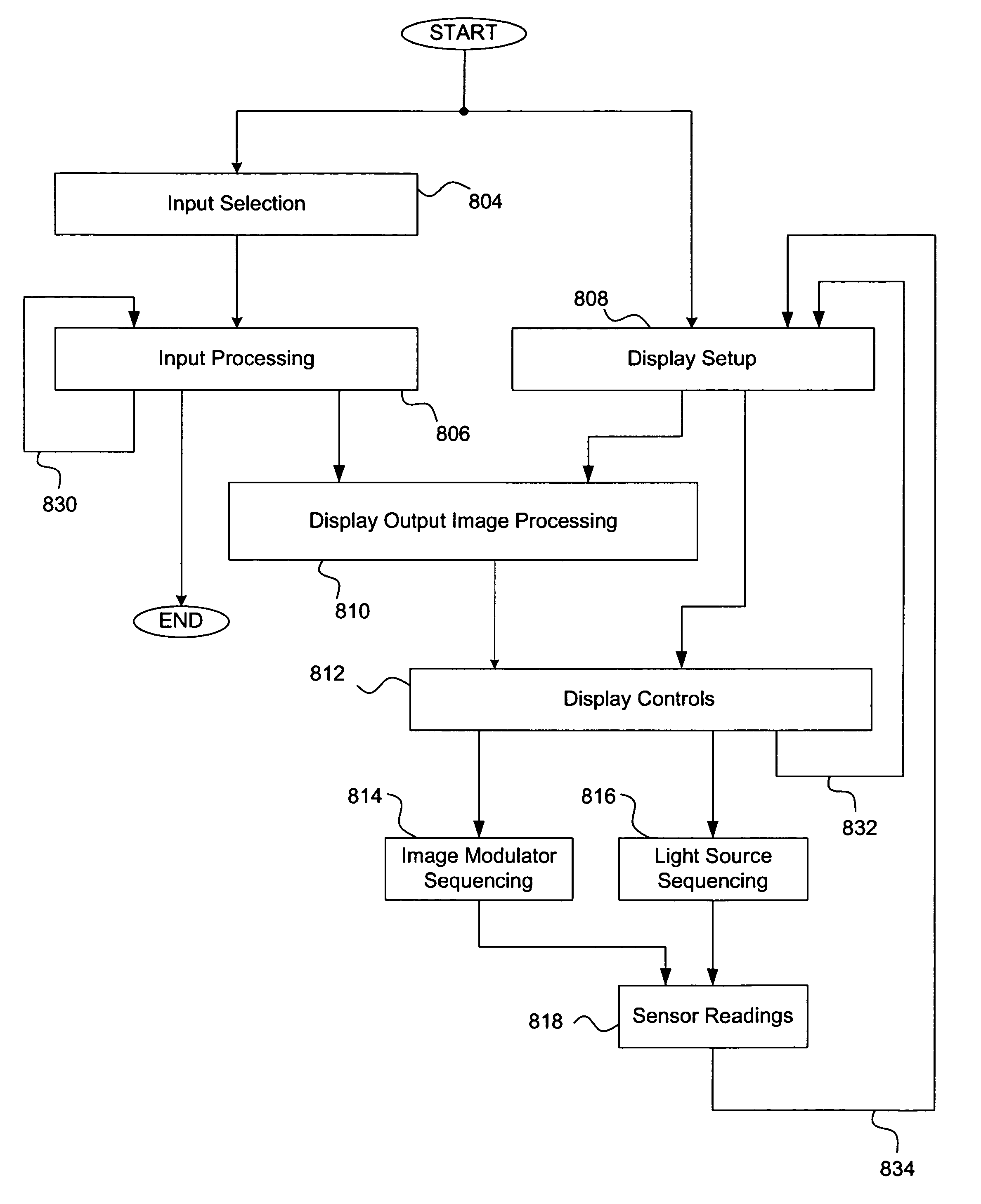
A digital display system consists of an image modulator and multiple light modulators. An image processing system processes an incoming data stream, scans processed data to an image modulator and controls for the light modulators. Other user inputs and sensors are used to affect the processing and controls. The timing for scanning the processed data into the image modulators is controlled along with the intensity and wavelength of the light modulators. The display system may implement a spatial and temporal image processing, digital shutter controls, rolling shutter controls, sequential color output, adaptive dynamic sensor feedback, frame rate matching, motion compensated field sequencing and a variety of other techniques to produce a high quality display output. The resulting display has improved image consistency, enhanced color gamut, higher dynamic range and is better able to portray high motion content.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
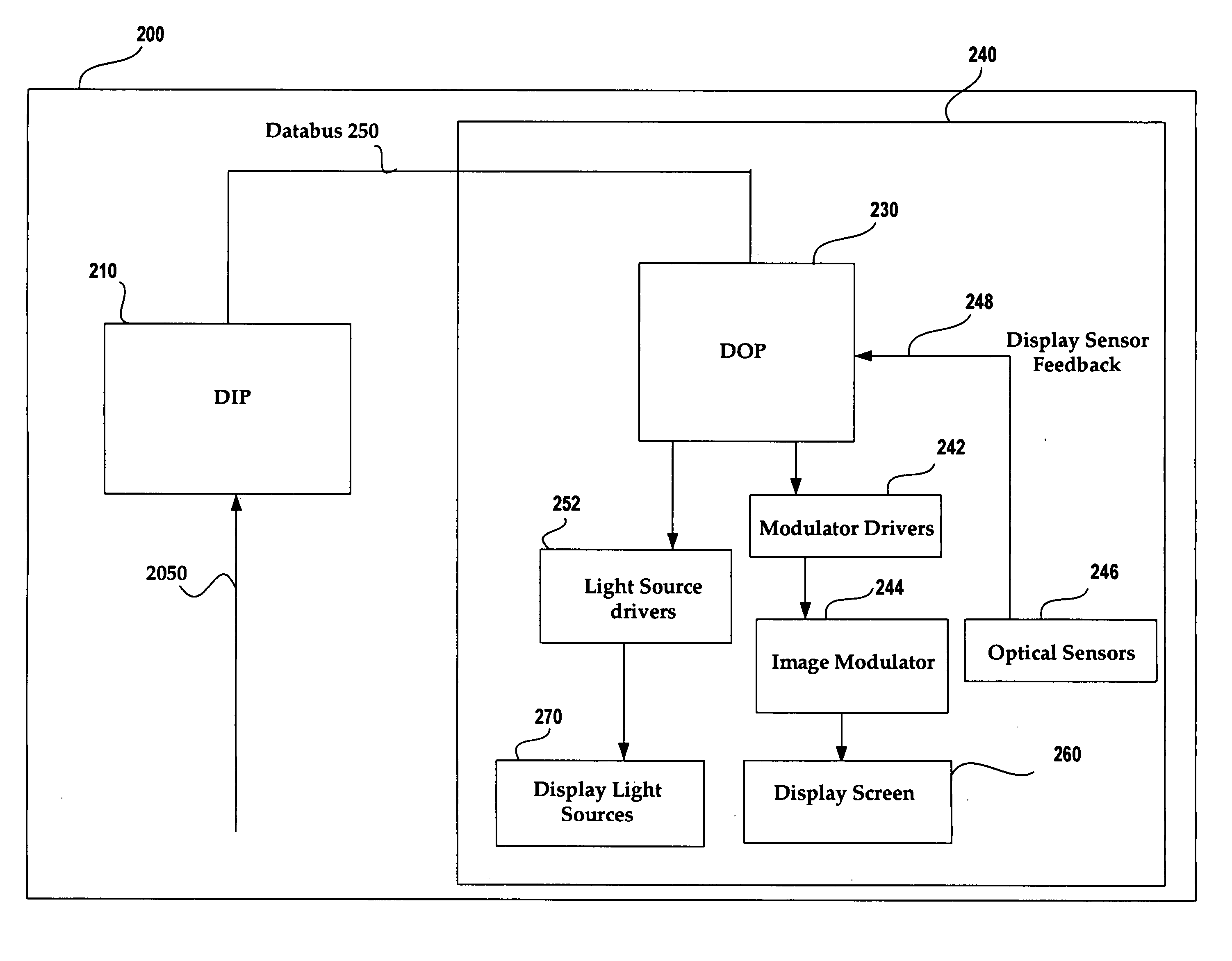
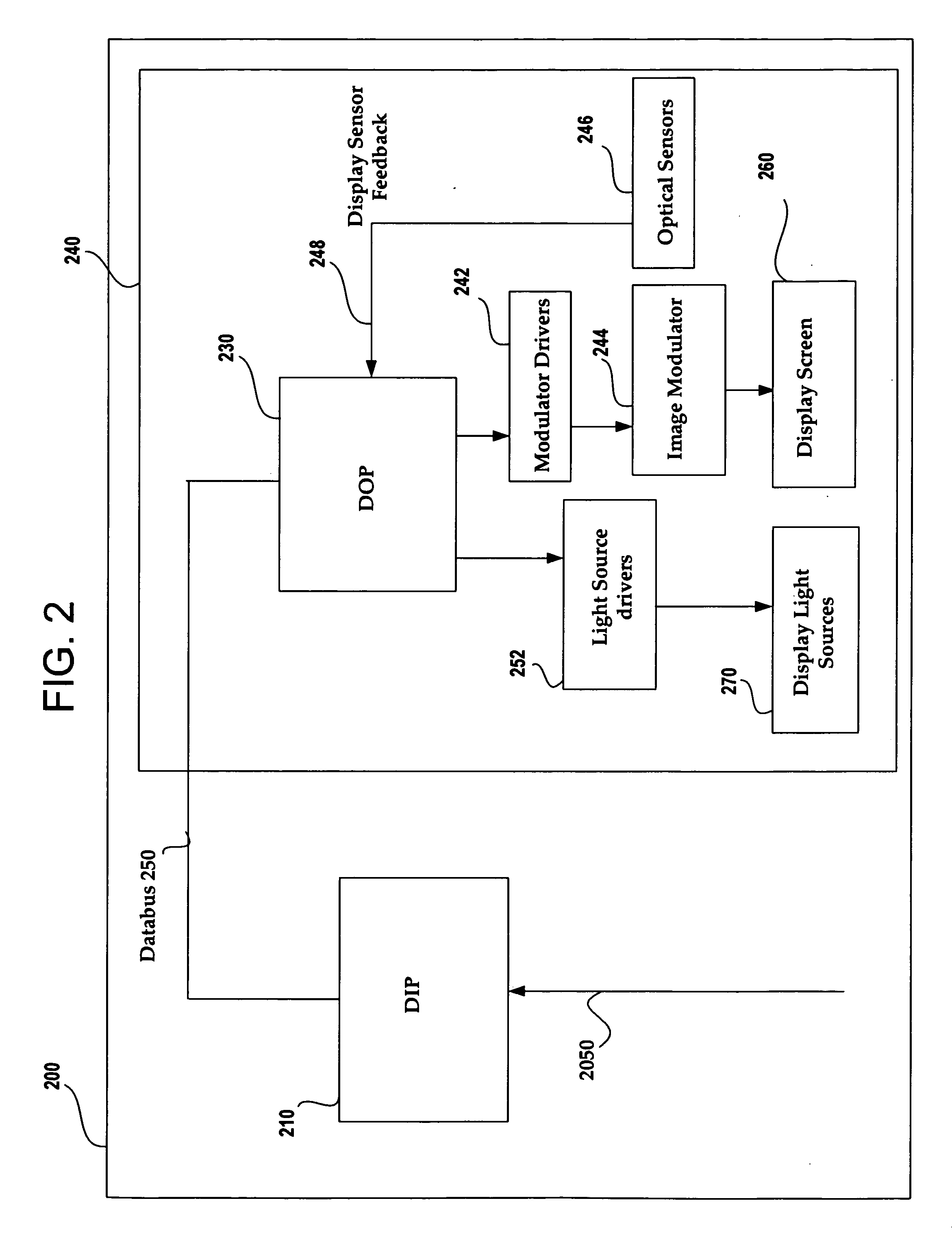
Image and light source modulation for a digital display system
ActiveUS20070035706A1Improve display qualityImprove consistencyTelevision system detailsProjectorsDisplay deviceSystem configuration
Image processing enhances display quality by controlling both the image modulator and the light sources to produce the best possible visual images. The image processing system utilizes a combination of user inputs, system configuration, design information, sensor feedback, pixel modulation information, and lighting control information to characterize the display environment on a per pixel basis. This per pixel characterization information is combined with one or more frames of the incoming real time display data. The image processing system processes each incoming pixel and produces a modified corresponding output pixel. Each pixel of each frame is processed accordingly. In addition to producing modified output pixels, the image processing system produces control information for the light sources. The light source control information can control individual lamps, tubes or LEDs, or can control a block or subset of the light sources. The resulting display has improved image consistency, enhanced color gamut, higher dynamic range and is better able to portray high motion content.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
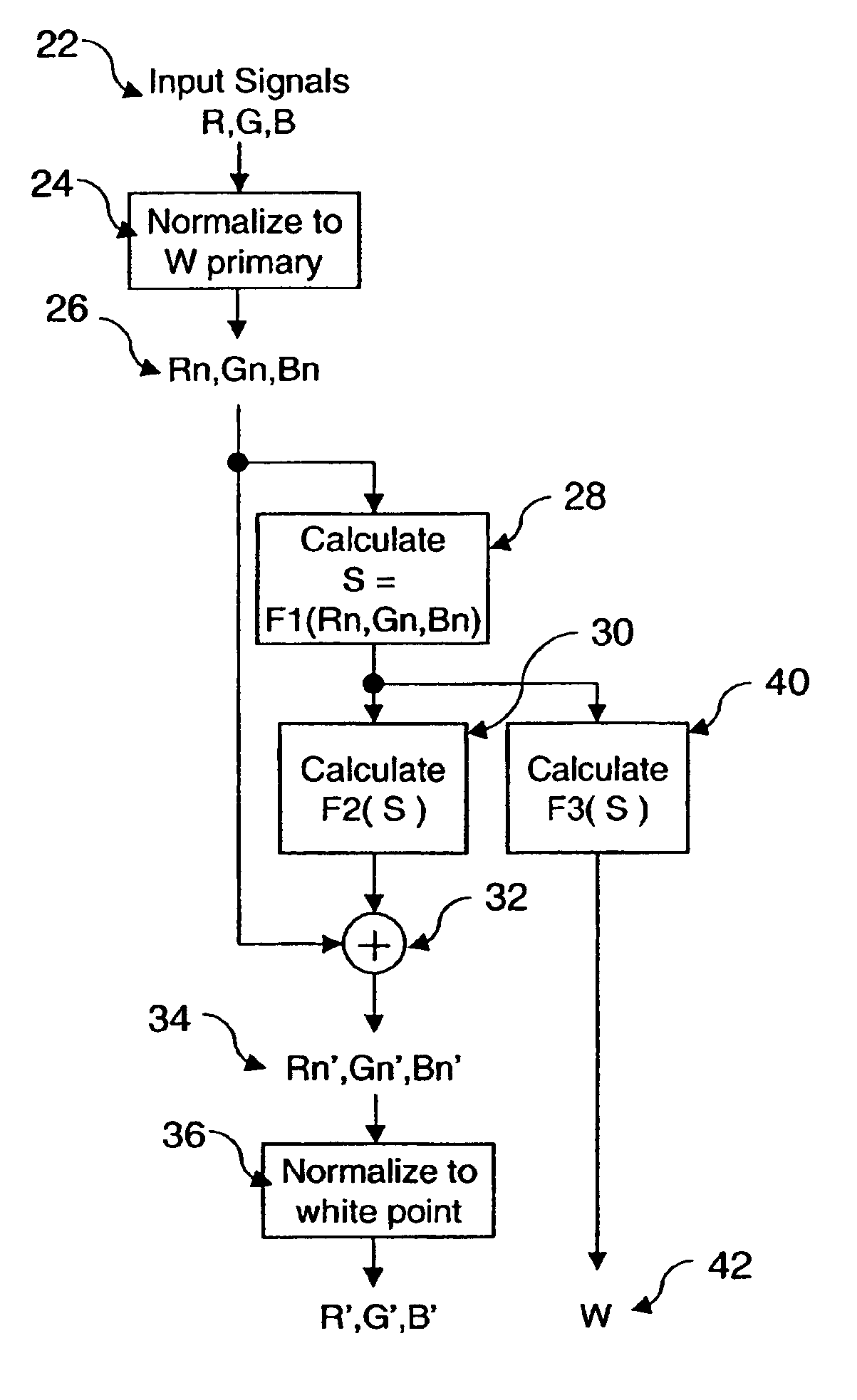
Method for transforming three color input signals to four or more output signals for a color display
InactiveUS6897876B2Preserve accuracyLife expectancyColor signal processing circuitsCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionGamut
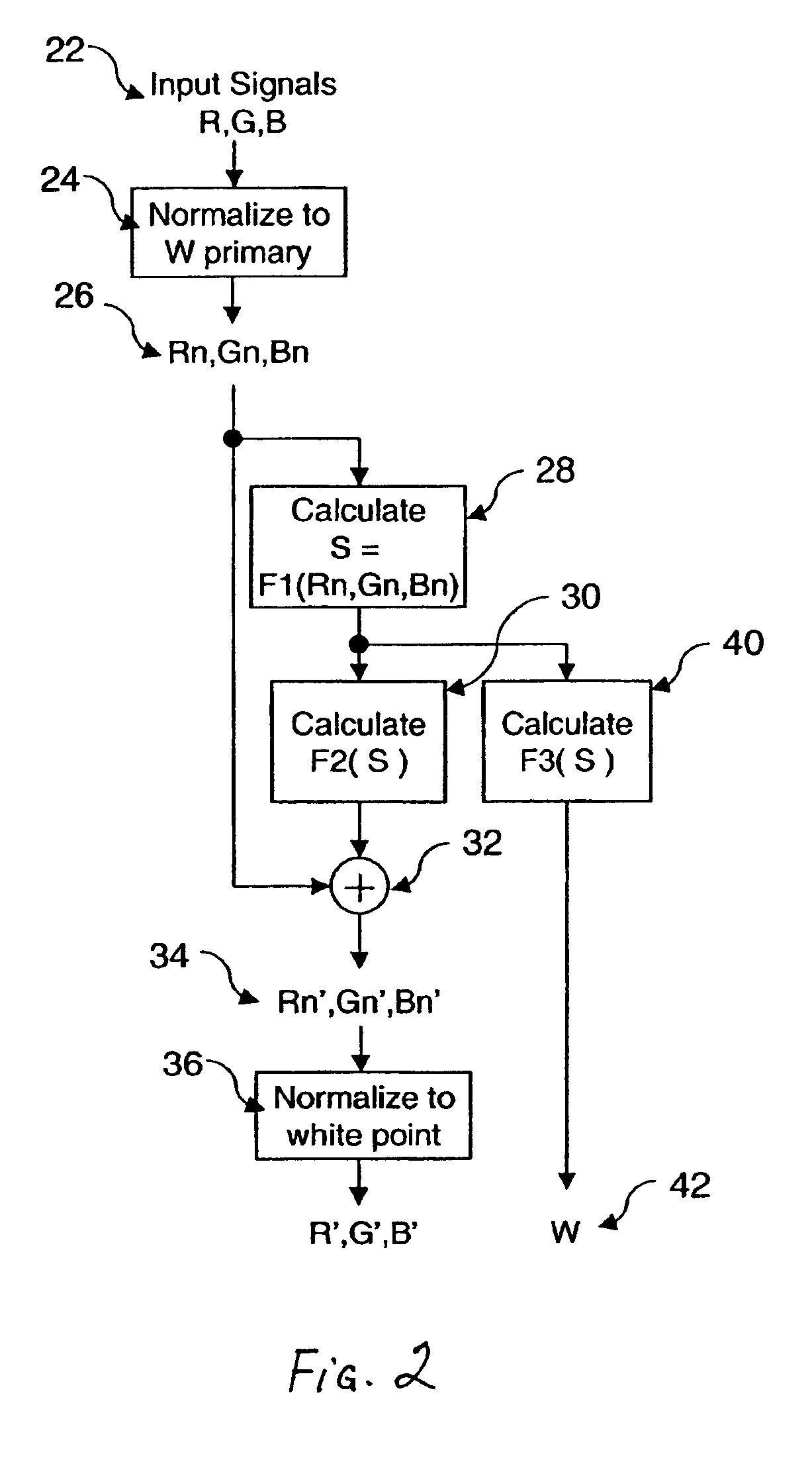
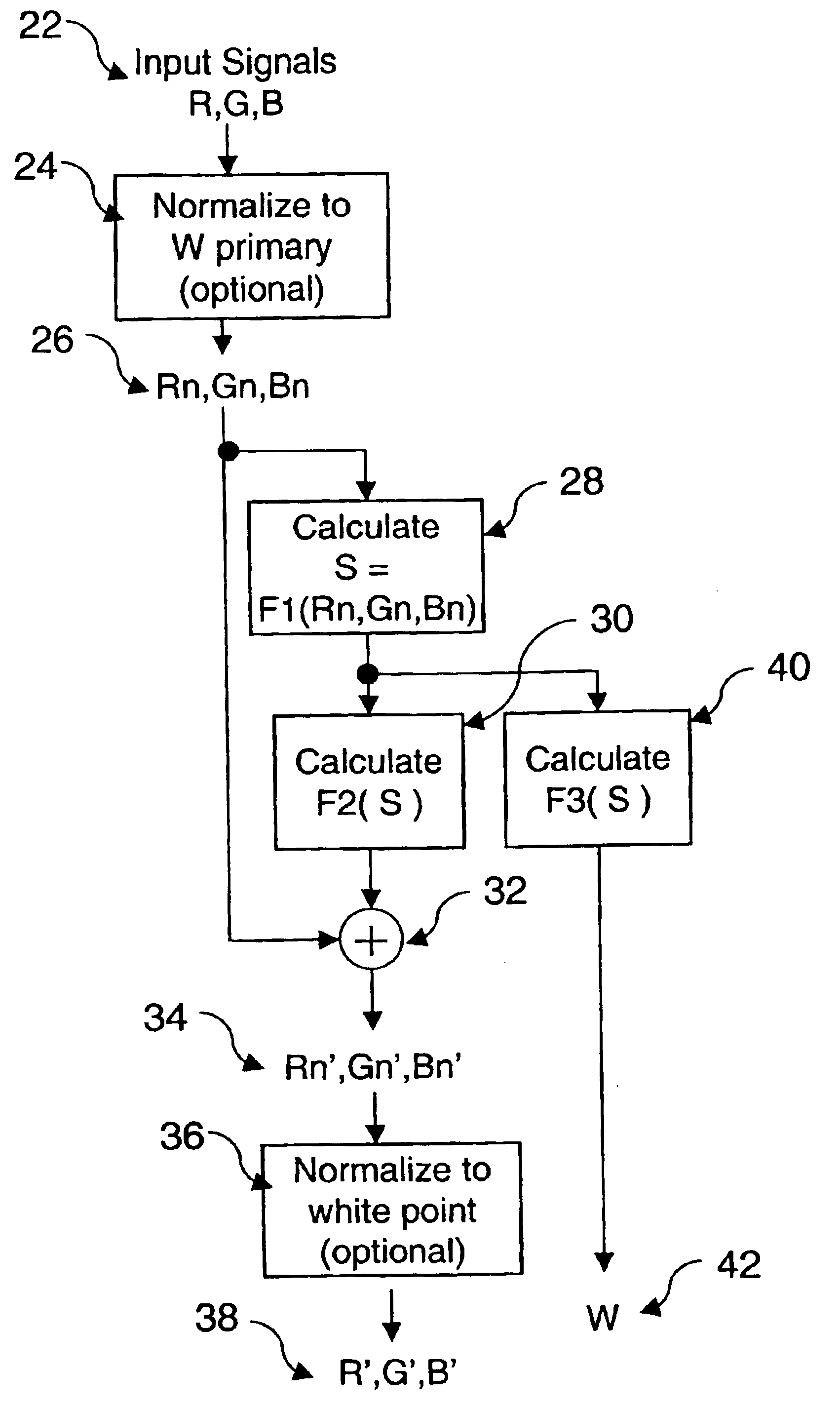
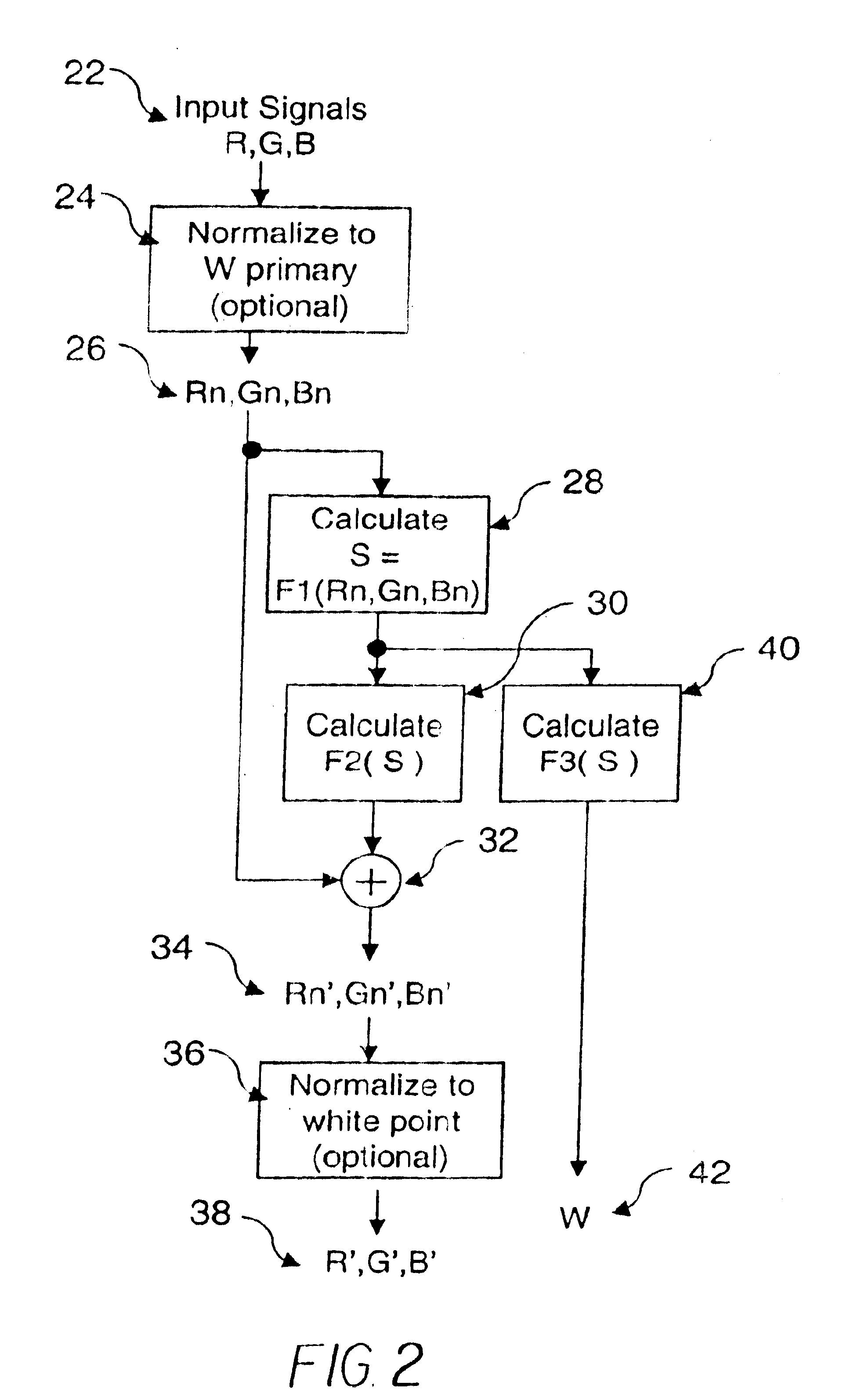
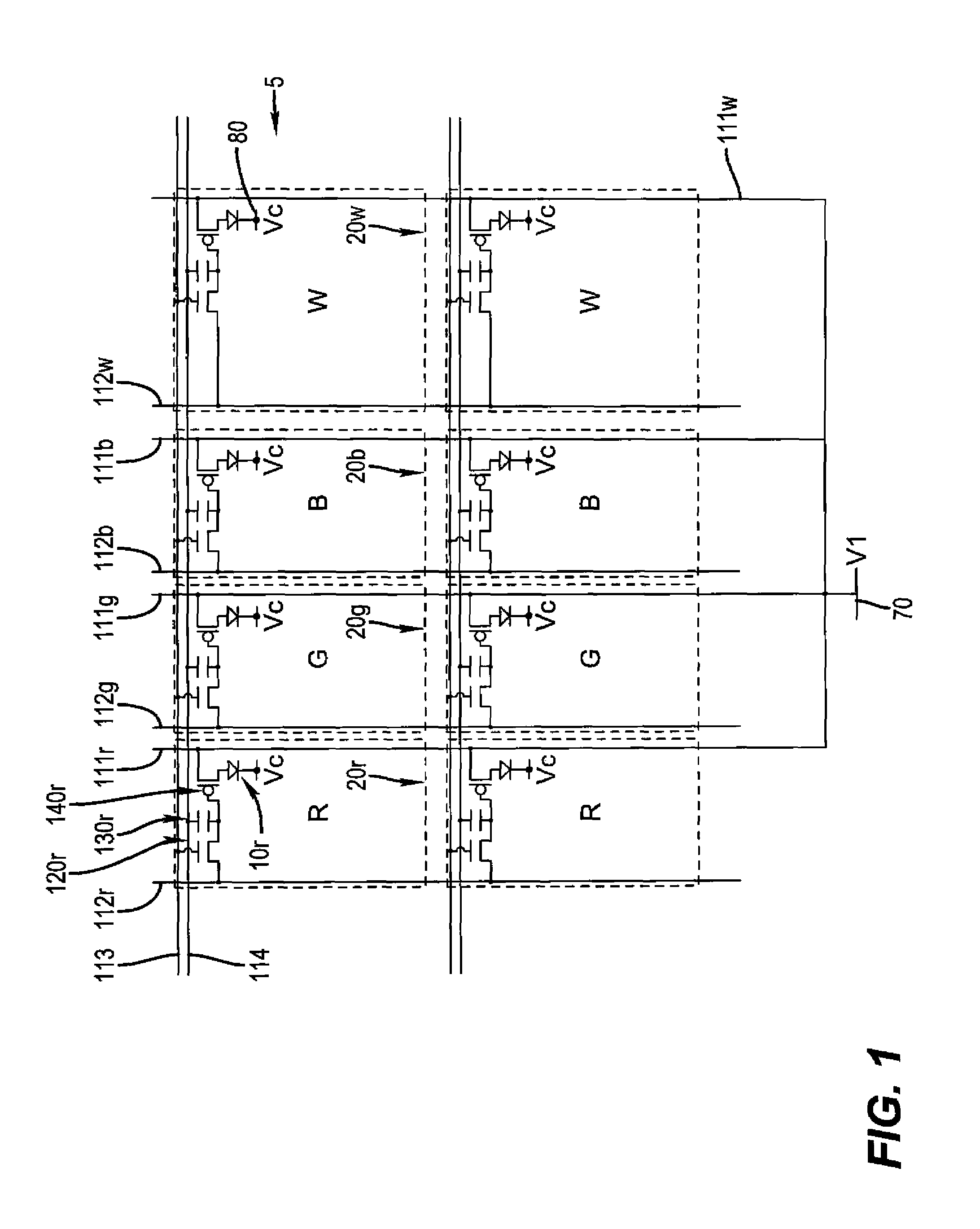
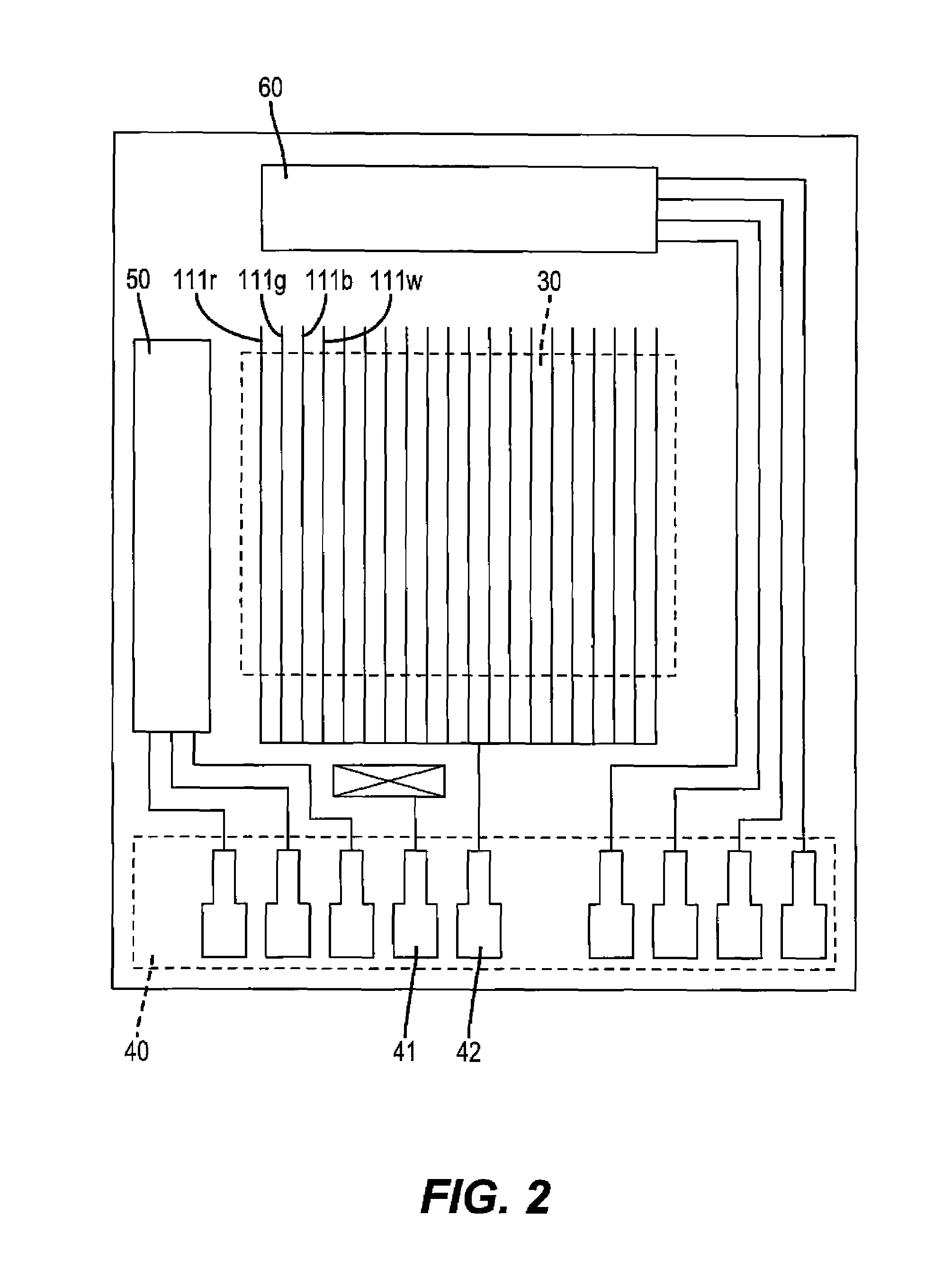
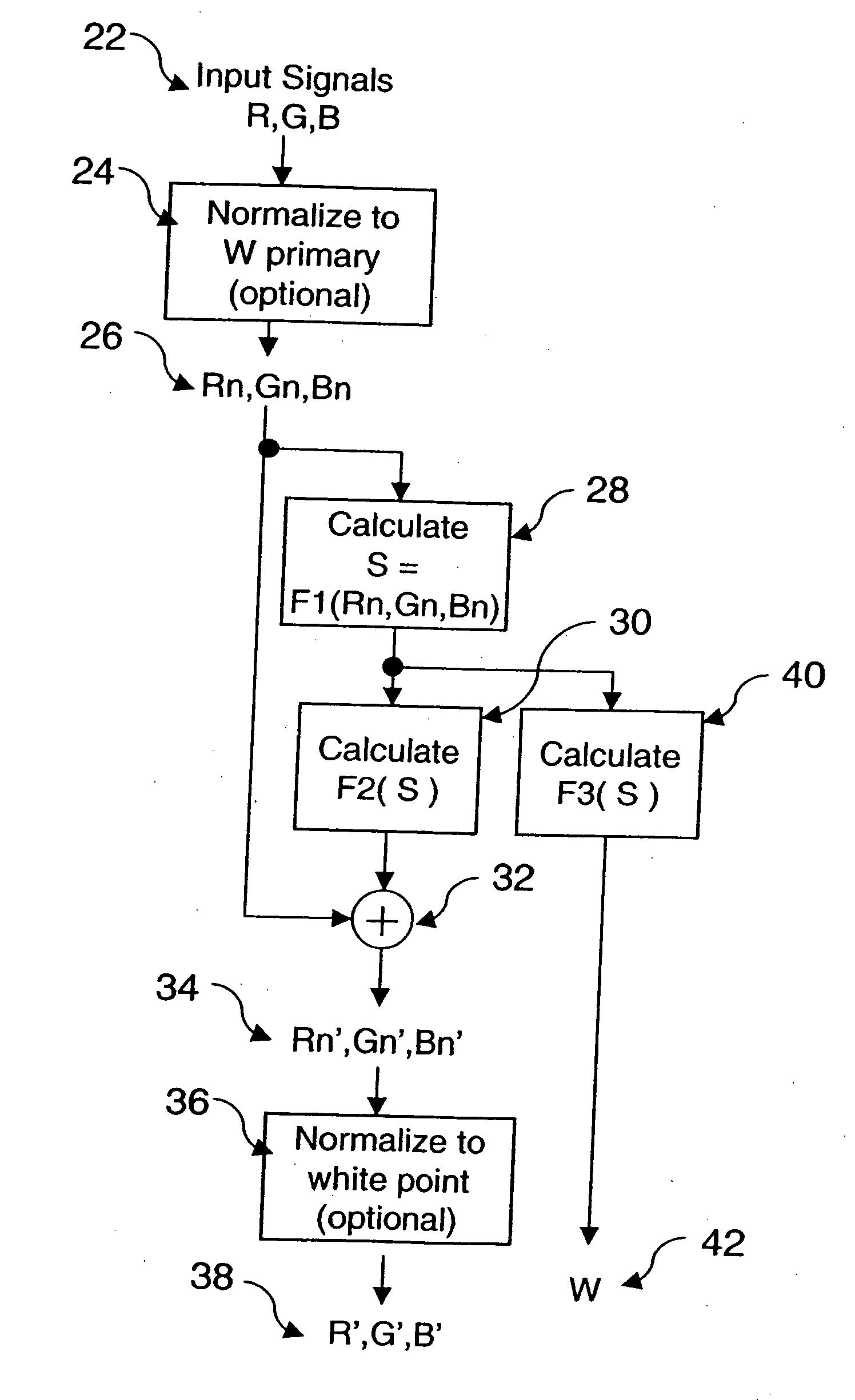
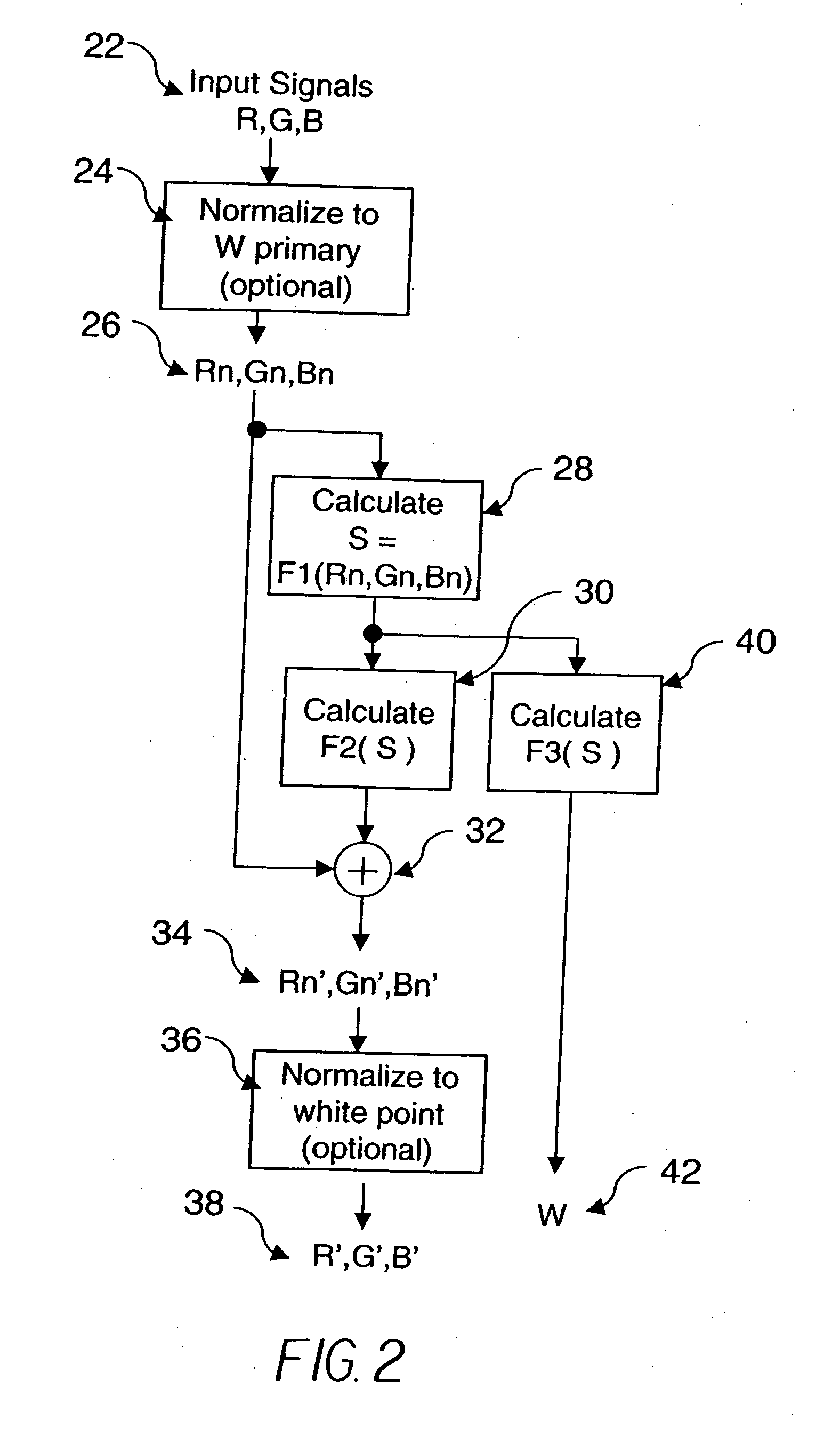
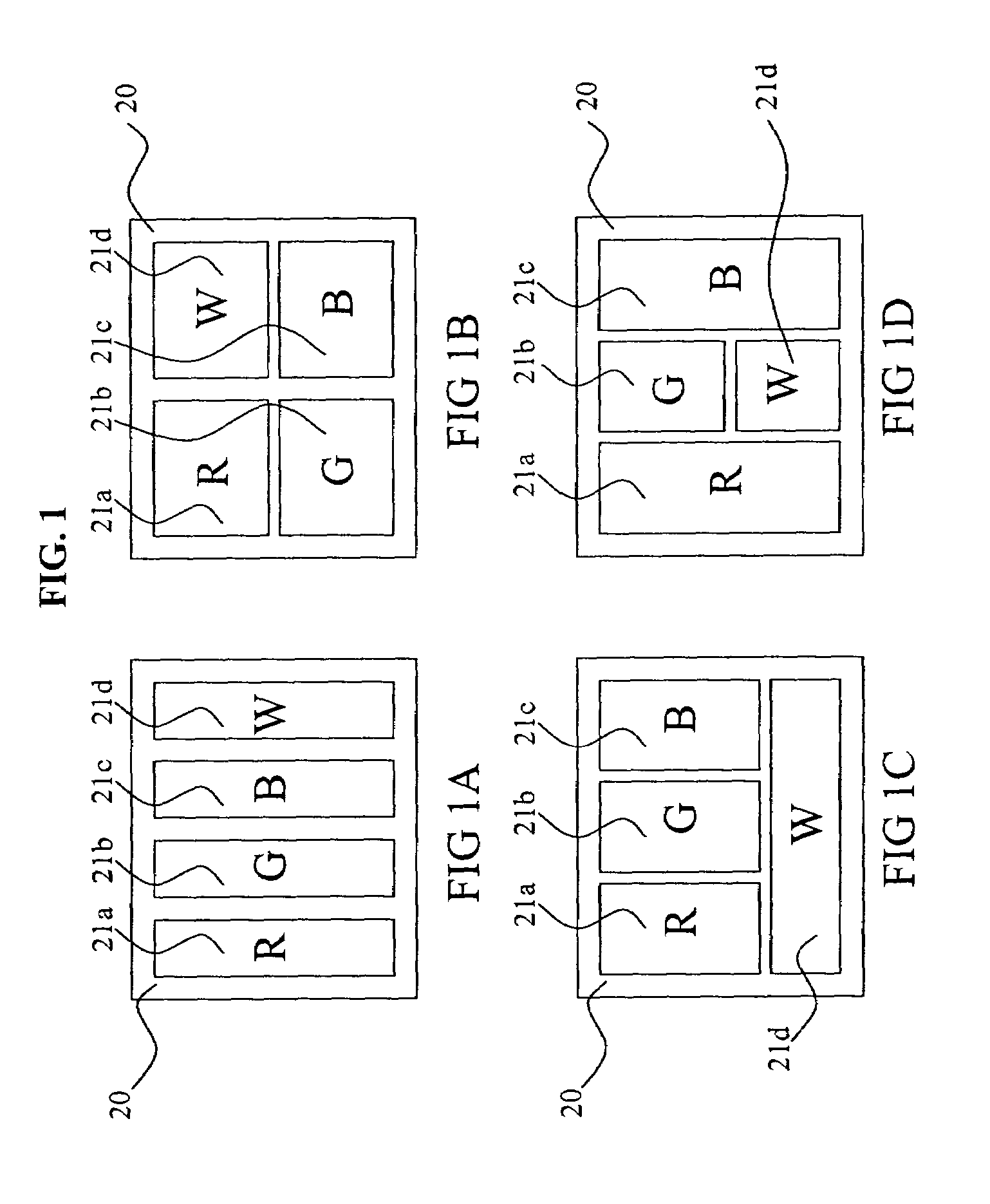
A method for transforming three color input signals (R, G, B) corresponding to three gamut defining color primaries to four color output signals (R′, G′, B′, W) corresponding to the gamut defining color primaries and one additional color primary W for driving a display having a white point different from W includes the steps of: normalizing the color input signals (R,G,B) such that a combination of equal amounts in each signal produces a color having XYZ tristimulus values identical to those of the additional color primary to produce normalized color signals (Rn,Gn,Bn); calculating a common signal S that is a function F1 of the three normalized color signals (Rn,Gn,Bn); calculating a function F2 of the common signal S and adding it to each of the three normalized color signals (Rn,Gn,Bn) to provide three color signals (Rn′,Gn′,Bn′); normalizing the three color signals (Rn′,Gn′,Bn′) such that a combination of equal amounts in each signal produces a color having XYZ tristimulus values identical to those of the display white point to produce three of the four color output signals (R′,G′,B′); and calculating a function F3 of the common signal S and assigning it to the fourth color output signal W.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Color printer characterization using optimization theory and neural networks
InactiveUS6480299B1Digitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsPattern recognitionICC profile
A color management method / apparatus generates image color matching and International Color Consortium (ICC) color printer profiles using a reduced number of color patch measurements. Color printer characterization, and the generation of ICC profiles usually require a large number of measured data points or color patches and complex interpolation techniques. This invention provides an optimization method / apparatus for performing LAB to CMYK color space conversion, gamut mapping, and gray component replacement. A gamut trained network architecture performs LAB to CMYK color space conversion to generate a color profile lookup table for a color printer, or alternatively, to directly control the color printer in accordance with the a plurality of color patches that accurately. represent the gamut of the color printer. More specifically, a feed forward neural network is trained using an ANSI / IT-8 basic data set consisting of 182 data points or color patches, or using a lesser number of data points such as 150 or 101 data points when redundant data points within linear regions of the 182 data point set are removed. A 5-to-7 neuron neural network architecture is preferred to perform the LAB to CMYK color space conversion as the profile lookup table is built, or as the printer is directly controlled. For each CMYK signal, an ink optimization criteria is applied, to thereby control ink parameters such as the total quantity of ink in each CMYK ink printed pixel, and / or to control the total quantity of black ink in each CMYK ink printed pixel.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Method and apparatus for printing using a tandem electrostatographic printer
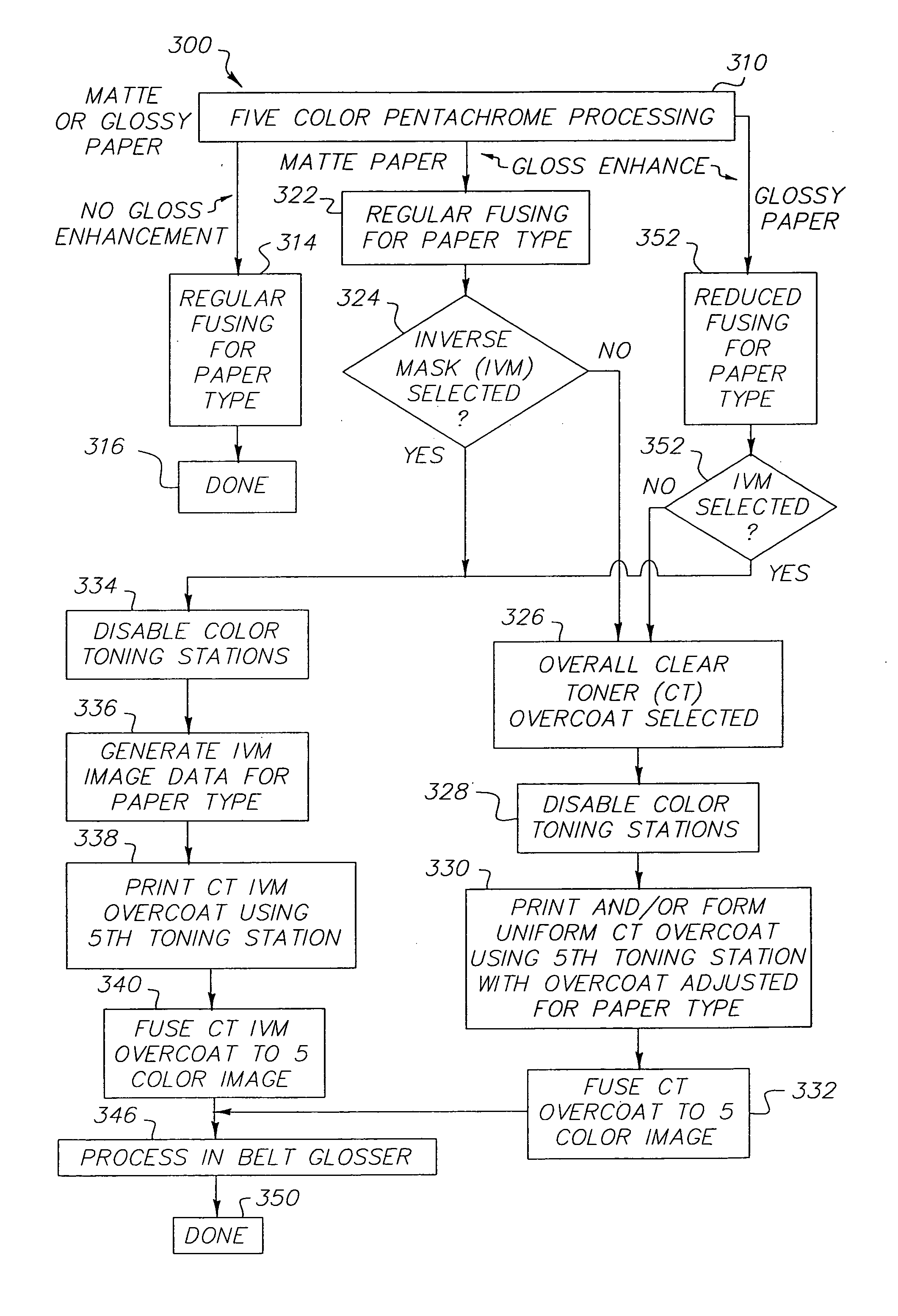
ActiveUS20060133870A1High glossImprove color gamutElectrographic process apparatusElectrographic processes using charge patternColor imageGamut
A tandem color electrostatographic printer apparatus has five or more color printing stations or modules for applying respective color separation toner images to a receiver member to form a pentachrome color image in a single pass. A fuser station fuses the pentachrome color image. A clear toner overcoat is then applied to the fused pentachrome toner image and enhanced glossing of the image is provided by a belt glosser to improve color gamut.
Owner:MIDWEST ATHLETICS & SPORTS ALLIANCE LLC
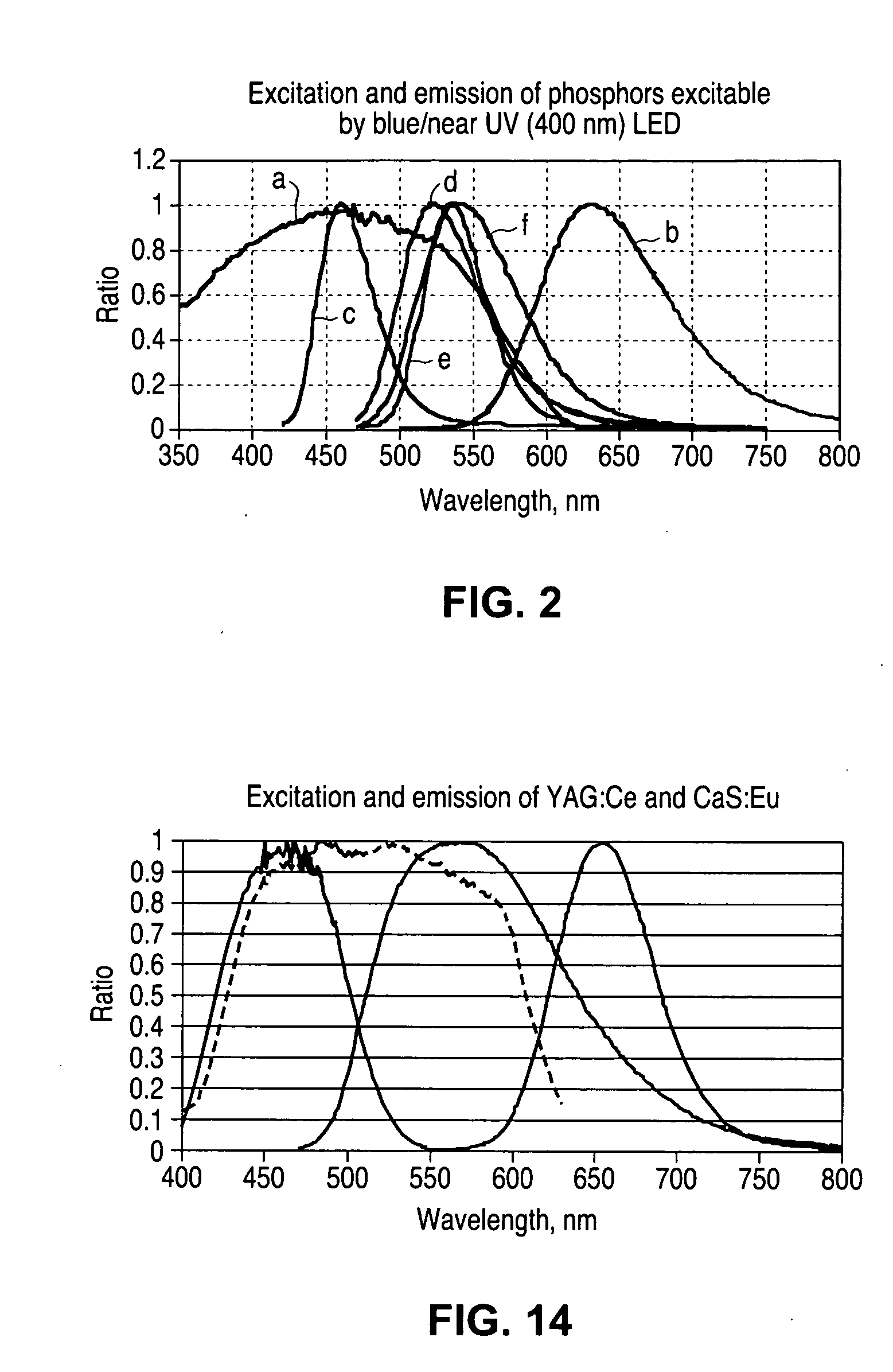
Wavelength converted semiconductor light emitting devices
ActiveUS20050184638A1Discharge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesGamutColor rendering index
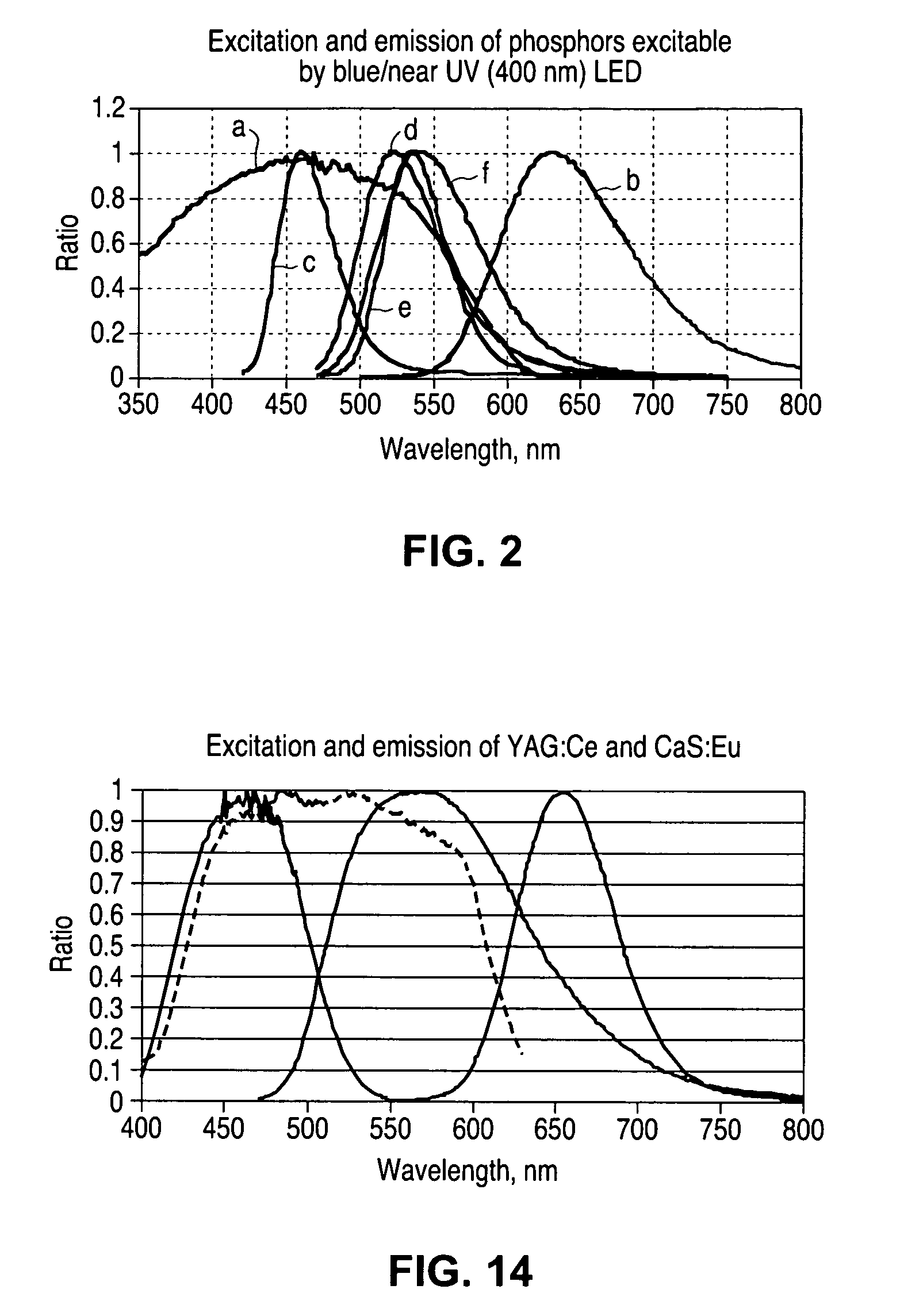
In a wavelength converted semiconductor light emitting device with at least two wavelength converting materials, the wavelength converting materials in the device are arranged relative to the light emitting device and relative to each other to tailor interaction between the different wavelength converting materials in order to maximize one or more of the luminous equivalent, color rendering index, and color gamut of the combined visible light emitted by the device.
Owner:LUMILEDS
Color OLED display with improved power efficiency
ActiveUS7230594B2Improve power efficiencyDesirable color gamutSolid-state devicesDiodeGamutDisplay device
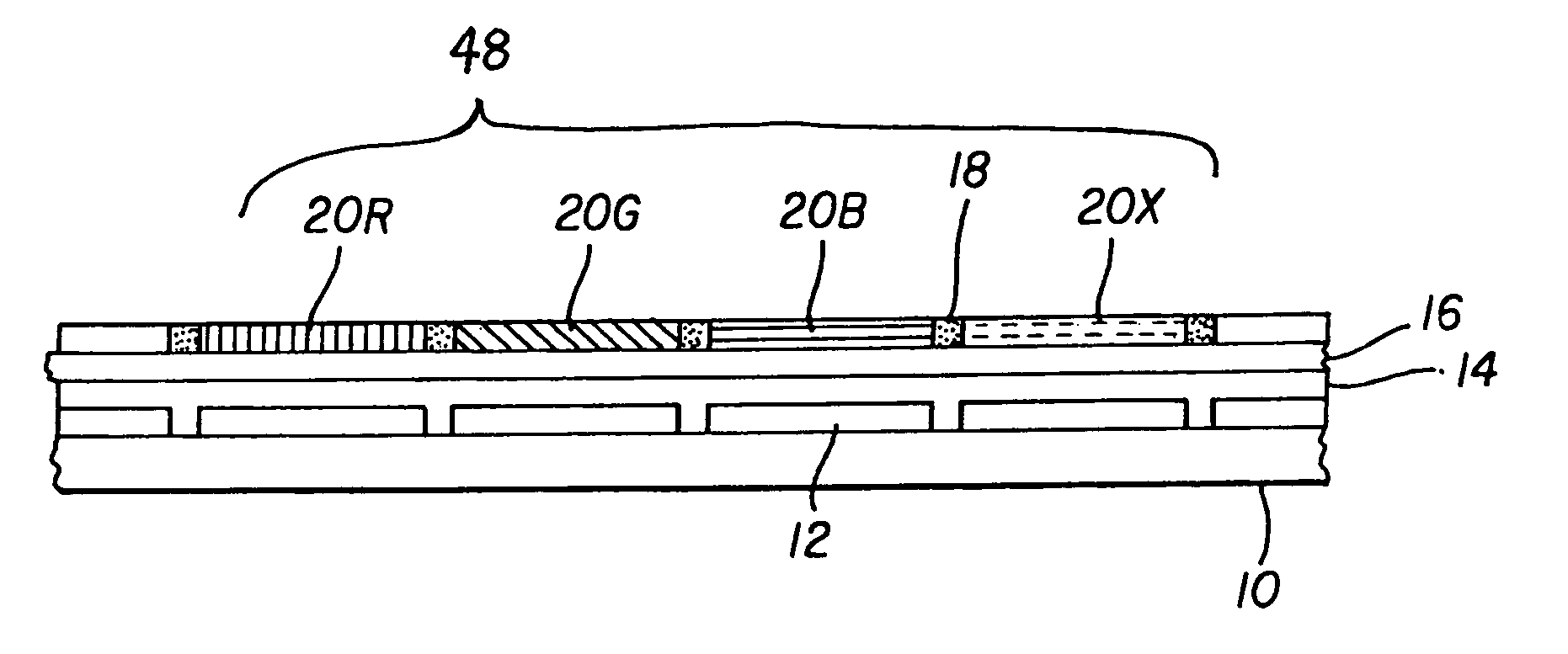
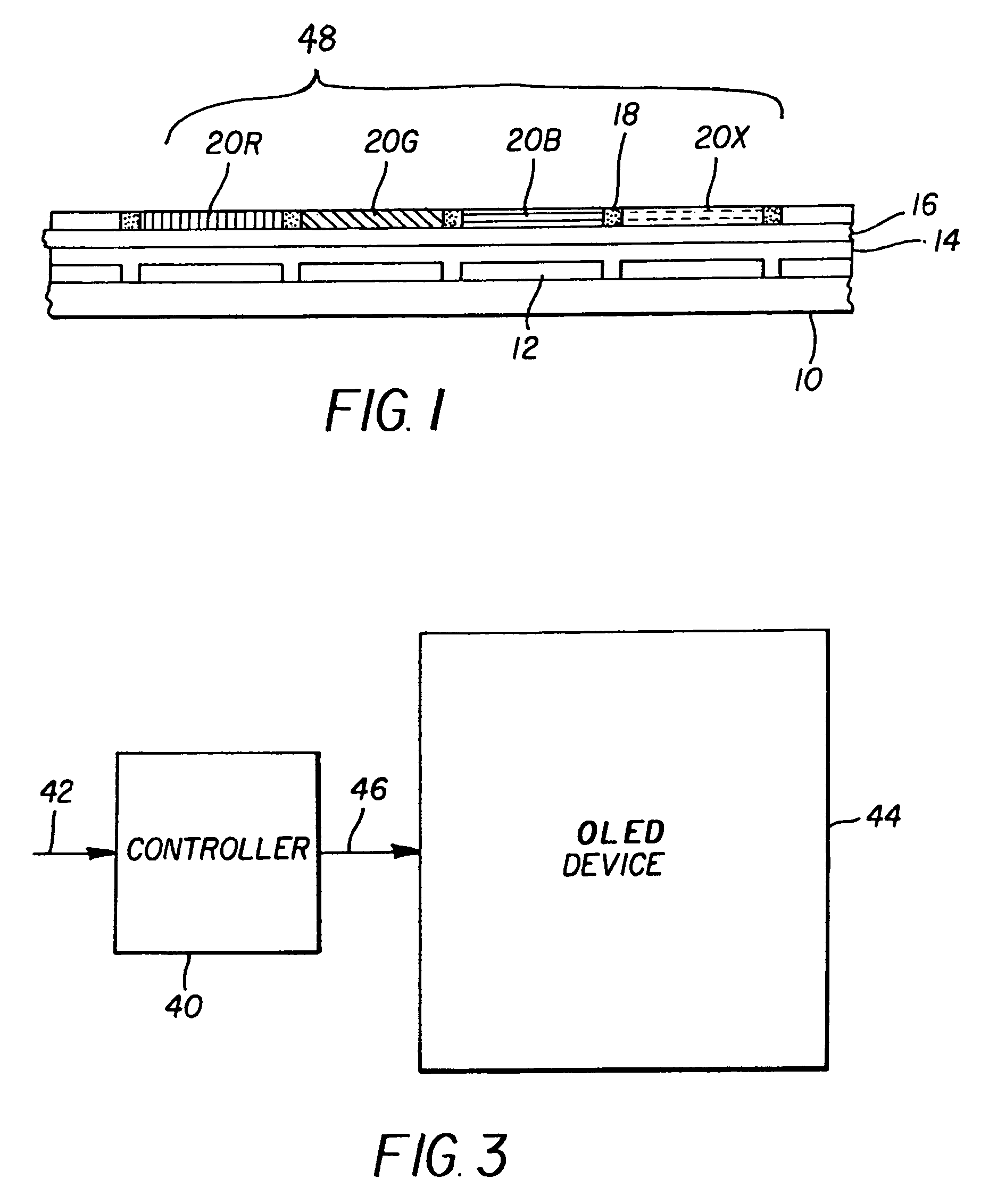
An OLED display device includes an array of light emitting pixels, each pixel having three or more OLEDs for emitting different colors of light specifying a gamut and at least one additional OLED for emitting a color of light within the gamut, wherein the power efficiency of the additional OLED is higher than the luminance efficiency of at least one of the three or more OLEDs; and means for driving the OLEDs in the pixels to produce a given color and luminance at a reduced power usage.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Method for transforming three colors input signals to four or more output signals for a color display
ActiveUS6885380B1Efficient methodCathode-ray tube indicatorsPictoral communicationPattern recognitionGamut
A method for transforming three color input signals (R, G, B) corresponding to three gamut defining color primaries to four color output signals (R′, G′, B′, W) corresponding to the gamut defining color primaries and one additional color primary W for driving a display having emitters that emit light corresponding to the to the four color output signals including calculating a common signal value S as a function F1 of the three color input signals (R,G,B) for a current and neighboring pixels; determining a final common signal value S′ based upon the common signals for the current and neighboring pixels; calculating the three color signals (R′,G′,B′) by calculating a value of a function F2 of the final common signal value S′ and adding it to each of the three color input signals (R,G,B); and calculating the output signal W as a function F3 of the final common signal value S′.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Perovskite/polymer composite luminescent material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104861958ASimple and fast operationLow costNanoopticsLuminescent compositionsPhotoluminescenceStructural formula
The invention relates to a perovskite / polymer composite luminescent material and a preparation method thereof, which belong to the technical field of composite materials and luminescent materials, wherein the structural formula of the perovskite is R1NH3AB3 or (R2NH3)2AB4, A and B form a ligand octahedral structure, R1NH3 or R2NH3 are filled into gaps of the ligand octahedral structure which is formed through the A and the B, R1 is methyl, R2 is a long-chain organic molecular group, the A is any one of metal Ge, Sn, Pb, Cu, Mn, Sb and Bi, the B is any one of Cl, Br and I. The perovskite / polymer composite luminescent material which is made through the preparation method is high in luminescent intensity, high in luminescent color purity, excellent in light and thermal stability and excellent chemical resistant property and mechanical property, and lays the foundation for theory research and application of the perovskite / polymer composite luminescent material in high-performance photoluminescence devices, flexible display, lasers, nonlinear optical devices. The preparation method can obtain composite materials which can cover a whole visible region through luminescent wavelengths, and has wide application prospect in the fields of wide gamut light emitting diode (LED) and high performance displays and the like.
Owner:ZHIJING NANOTECH CO LTD
OLED display with improved power performance
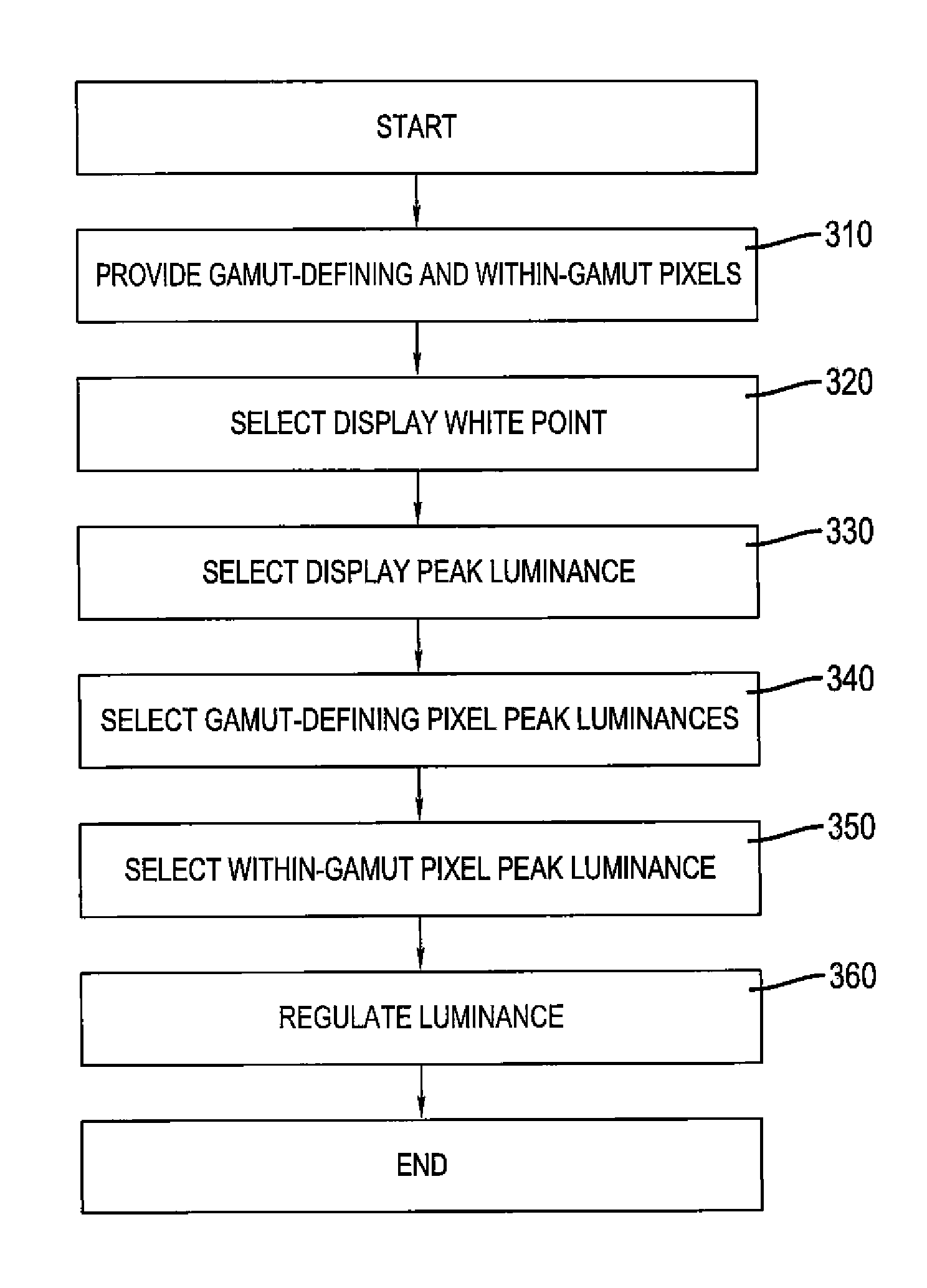
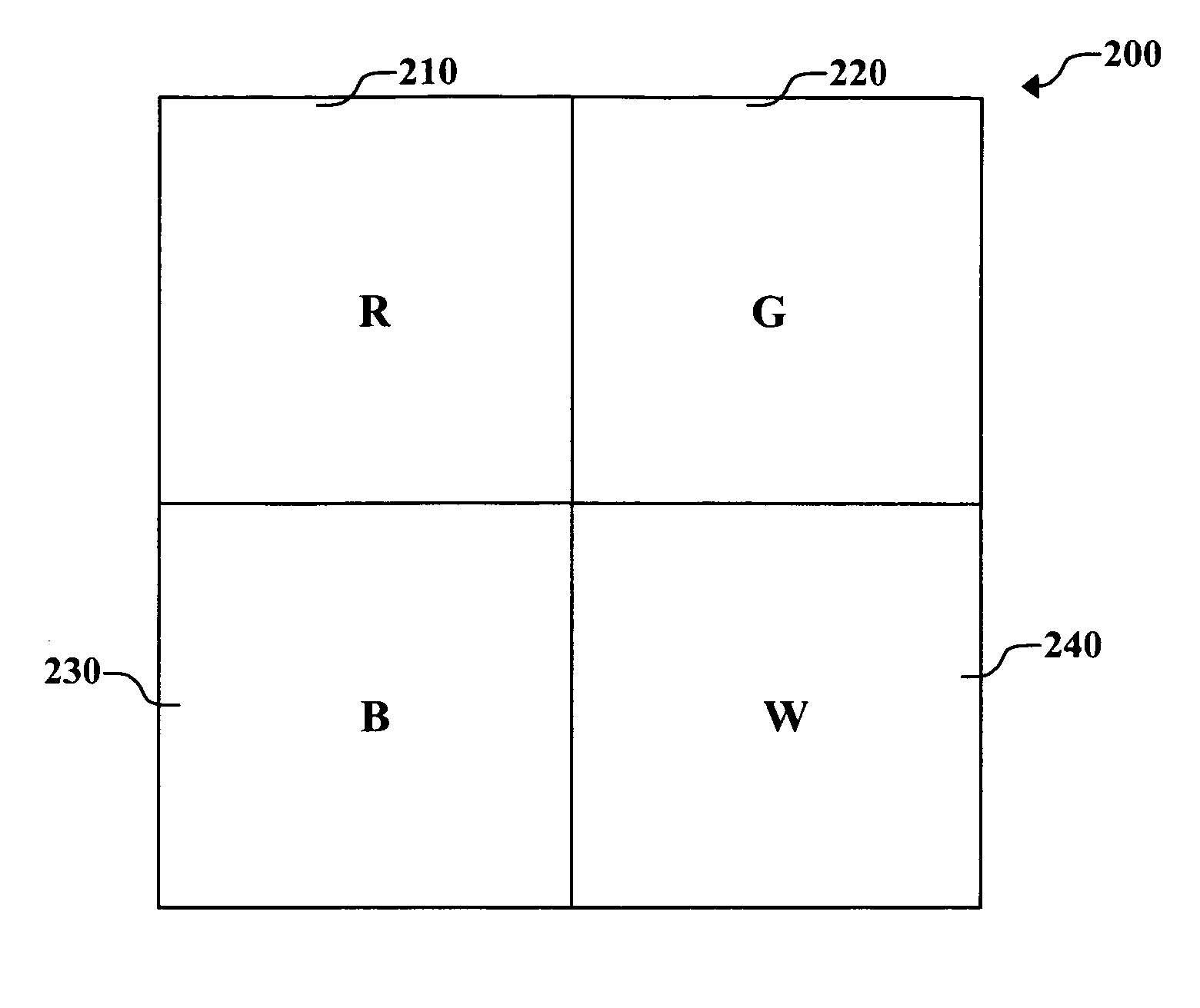
An OLED display for producing a full color image, comprising a plurality of at least four different colored pixels including three different colored addressable gamut-defining pixels and a fourth addressable within-gamut pixel, each pixel having an organic light-emitting diode with first and second electrodes and one or more organic light-emitting layers provided between the electrodes; the OLED display having a selected display white point, display peak luminance, gamut-defining pixel peak luminances and within-gamut pixel peak luminance; and drive circuitry for regulating luminance of the organic light-emitting diode of each of the colored pixels wherein the sum of the gamut-defining pixel peak luminances is less than the display peak luminance.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Method for transforming three colors input signals to four or more output signals for a color display
InactiveUS20050099426A1Efficient methodCathode-ray tube indicatorsPictoral communicationPattern recognitionGamut
A method for transforming three color input signals (R, G, B) corresponding to three gamut defining color primaries to four color output signals (R′, G′, B′, W) corresponding to the gamut defining color primaries and one additional color primary W for driving a display having emitters that emit light corresponding to the to the four color output signals including calculating a common signal value S as a function F1 of the three color input signals (R,G,B) for a current and neighboring pixels; determining a final common signal value S′ based upon the common signals for the current and neighboring pixels; calculating the three color signals (R′,G′,B′) by calculating a value of a function F2 of the final common signal value S′ and adding it to each of the three color input signals (R,G,B); and calculating the output signal W as a function F3 of the final common signal value S′.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Methods and apparatus for color uniformity
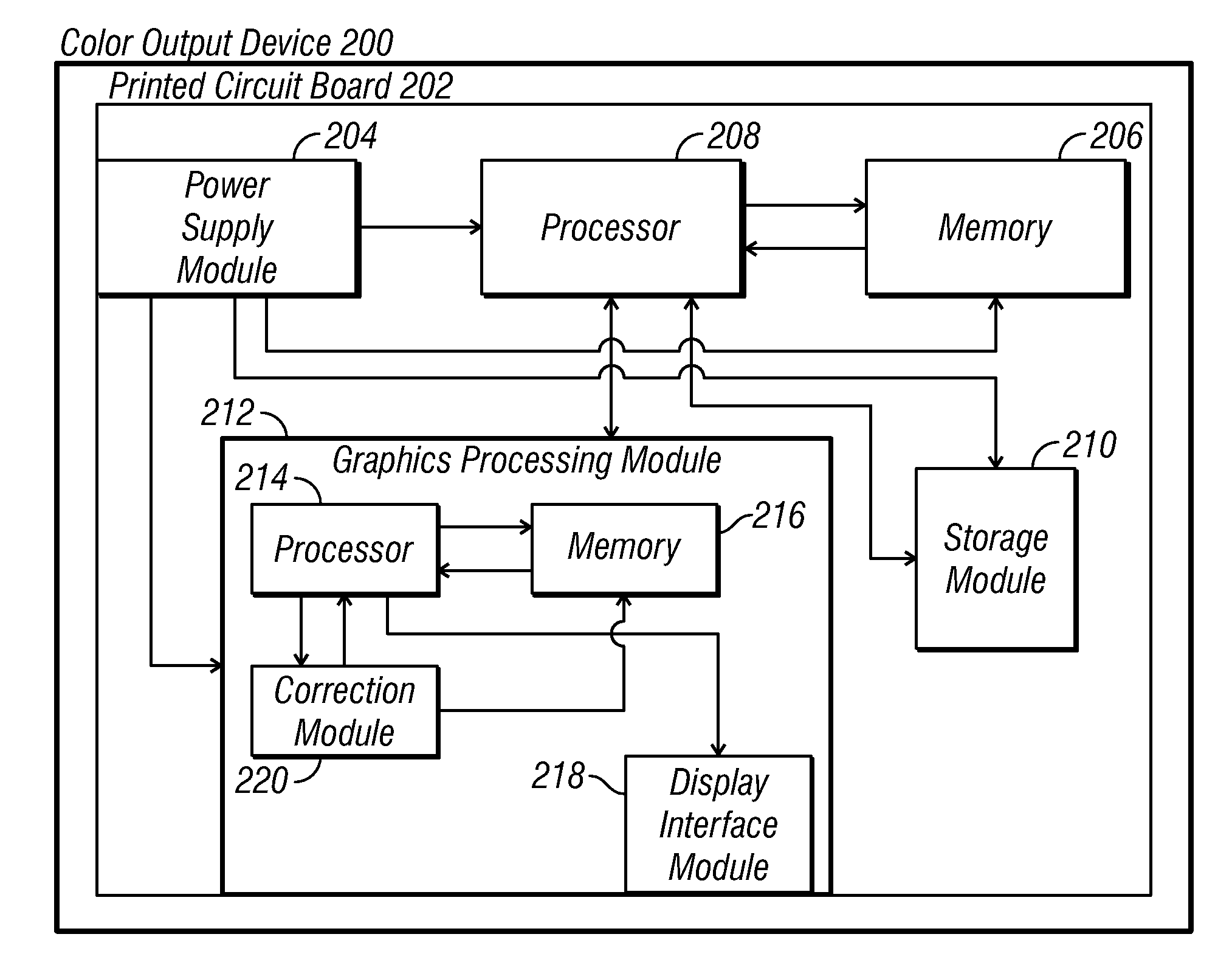
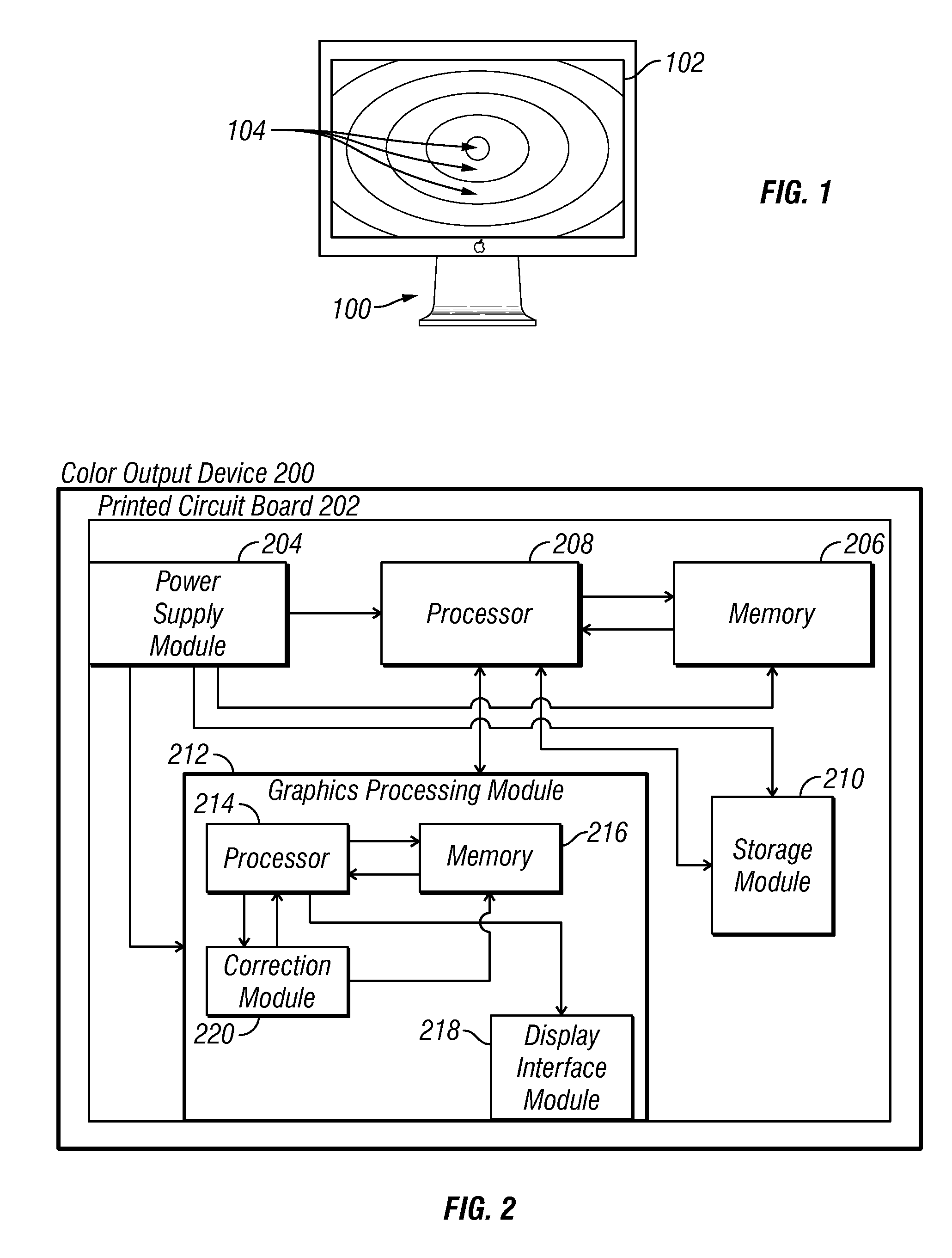
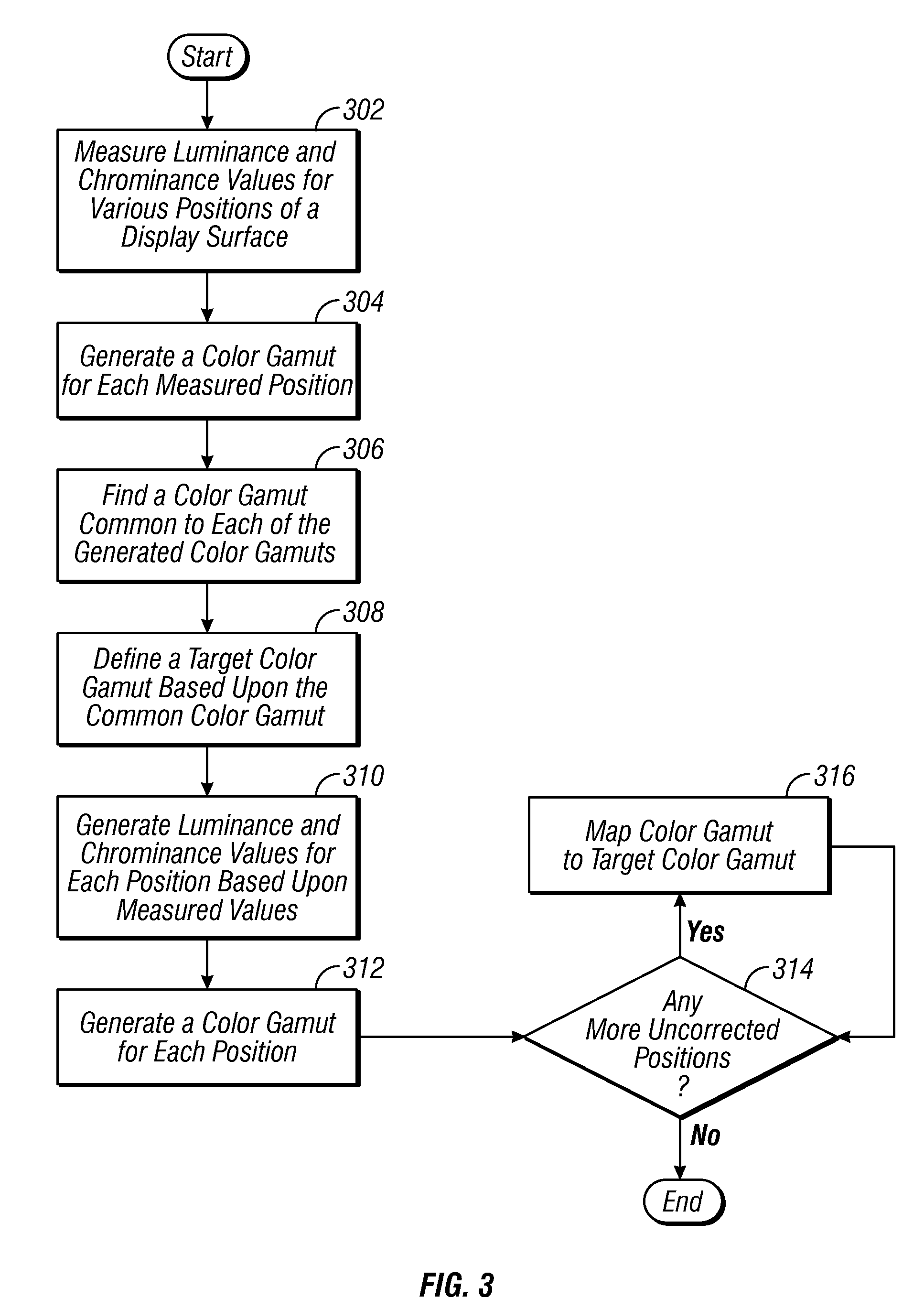
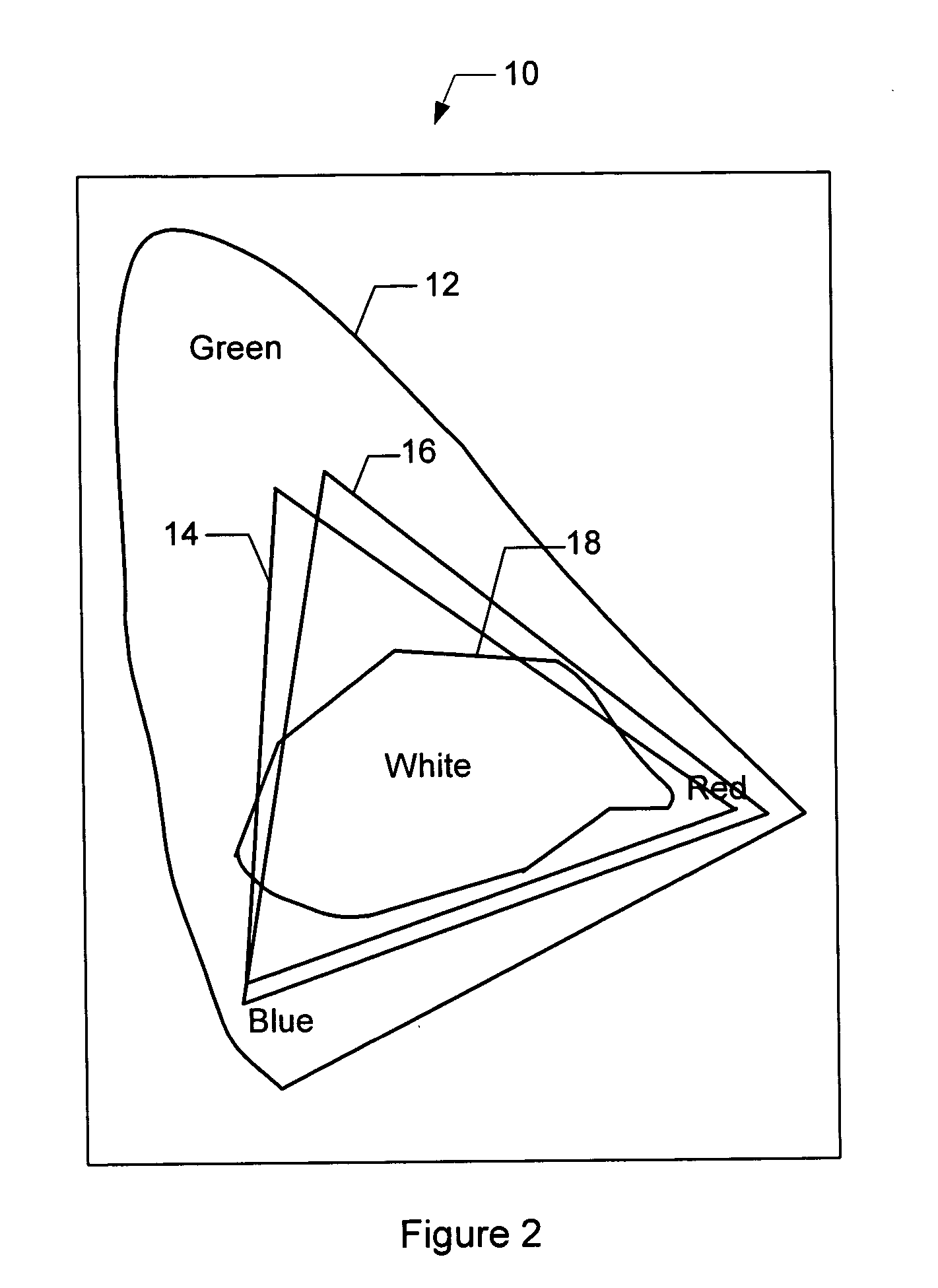
Methods and apparatus for achieving color and luminance uniformity in color output devices. In one embodiment, measurements of luminance and chrominance are taken at various regions of the display surface for a range of color inputs. Using the collected data, a color volume is formed for each of the measured regions. This color volume comprises a set of all colors producible at the measured region. The color volumes for each of the measured regions are then used to generate a common color gamut, i.e., a volume of colors that are producible in each of the measured regions. A gamut mapping can then be performed for all or a portion of the positions on the display surface to a target color gamut. Input data for the gamut mapping process may be determined by conventional interpolative techniques.
Owner:APPLE INC
OLED device having microcavity gamut subpixels and a within gamut subpixel
ActiveUS7030553B2Improve efficiencyLow costIncadescent screens/filtersDischarge tube luminescnet screensGamutOrganic layer
An OLED device including an array of light emitting pixels, each pixel including subpixels having organic layers including at least one emissive layer that produces light and spaced electrodes, and wherein there are at least three gamut subpixels that produce colors which define a color gamut and at least one subpixel that produces light within the color gamut produced by the gamut subpixels; and wherein at least one of the gamut subpixels includes a reflector and a semitransparent reflector which function to form a microcavity.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
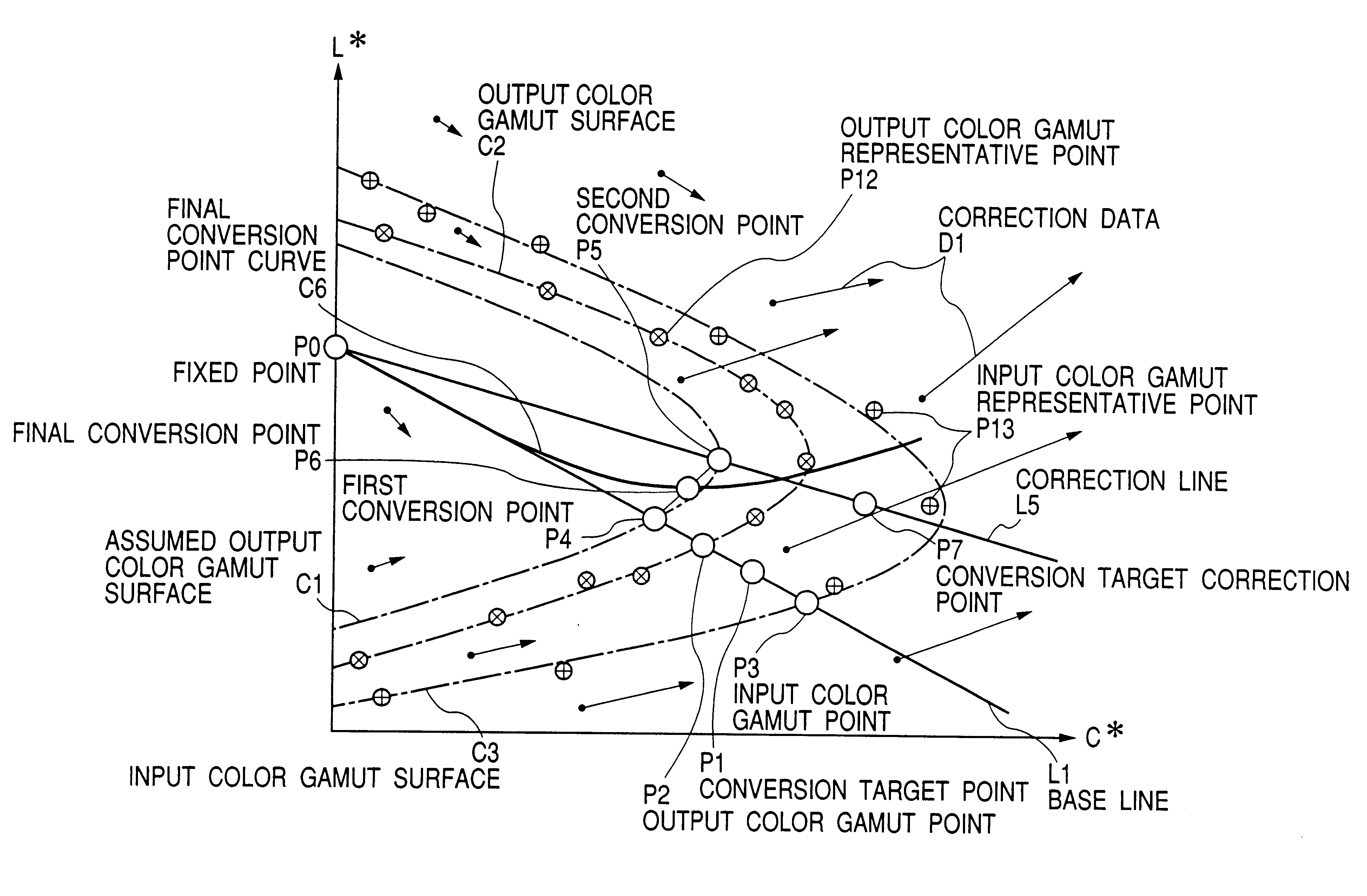
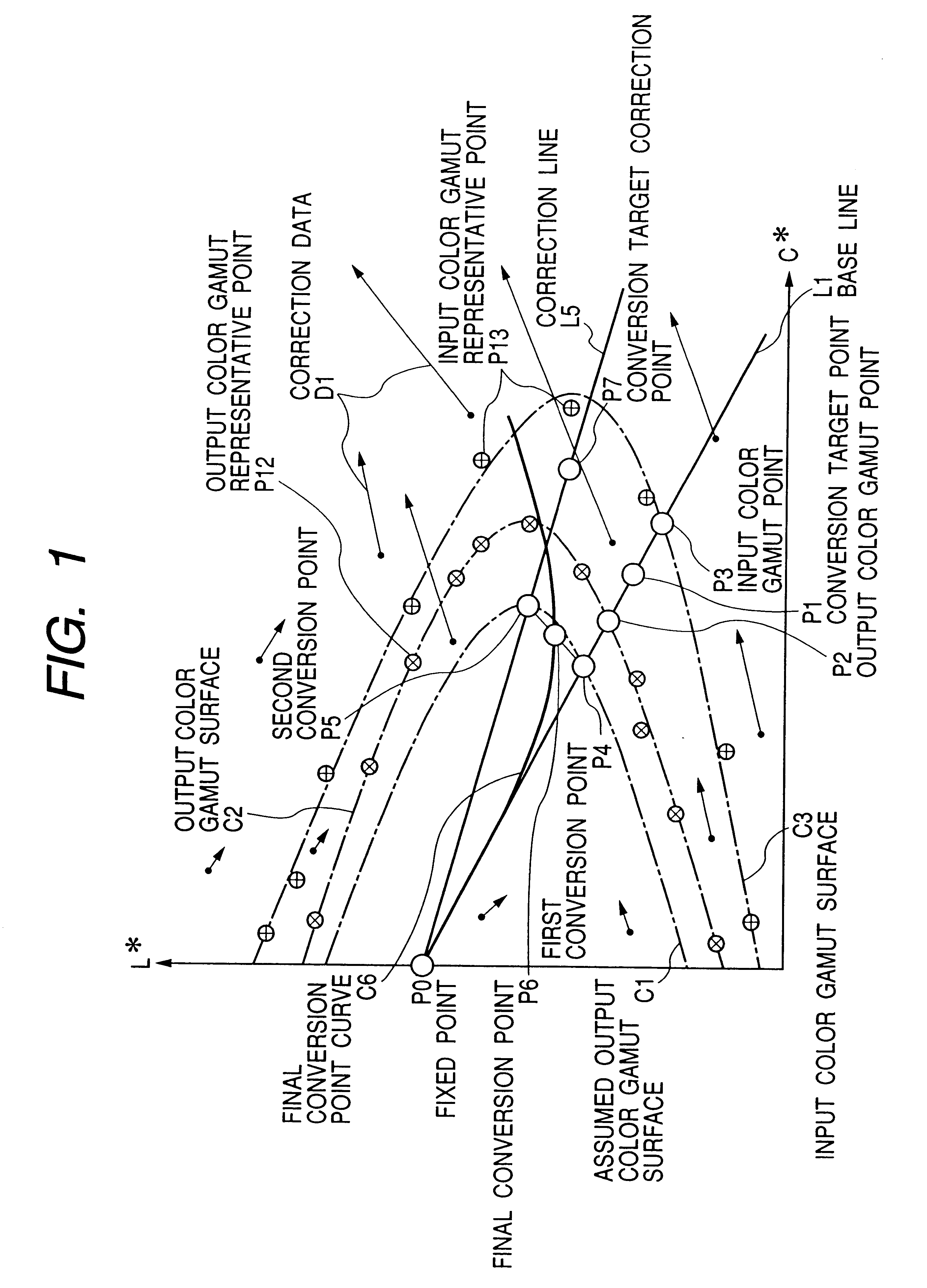
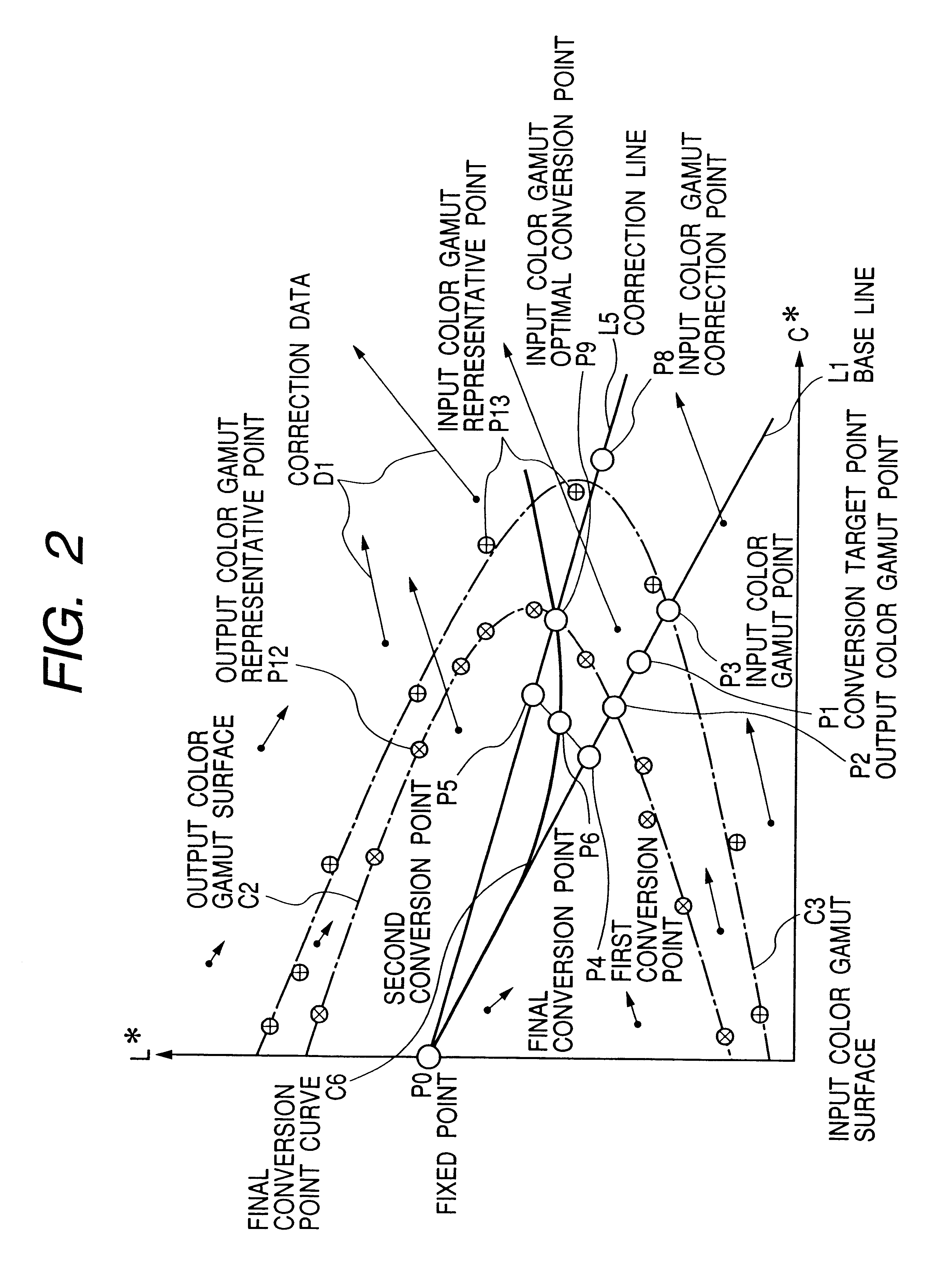
Systems, methods, and computer program products for converting between color gamuts associated with different image processing devices
InactiveUS20050185200A1Digitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsImaging processingGamut
The present invention provides systems, methods, and computer program products for performing color gamut mapping between different color gamuts on a pixel basis. A set of desired parameters is initially defined representing the desired color gamut transformation to which the color values of the pixel are to be mapped. The parameters describe the best-fit lines for the portions of the curve for the gamut transform to which the specific parameters are applied. The present invention next maps the color values used for the pixel in the first color gamut and the color values used for the pixel in the second gamut to the parameters of the transform. The present invention performs mapping by isolating portions of a curve and approximating those portions of the curve with a best straight-line fit. This method of mapping from one color gamut to another color gamut is less computationally intensive than conventional methods.
Owner:ZIH CORP
Color OLED display system having improved performance
ActiveUS7397485B2Improve power efficiencyImproved display lifetimeSolid-state devicesDiodeGamutControl signal
An OLED display system includes a) an OLED display including an array of light emitting pixels, each pixel having a plurality of OLEDs for emitting different colors of light specifying a gamut wherein one of the OLEDs has a power efficiency or lifetime different from the power efficiency or lifetime of at least one of the other OLEDs; b) a control signal; and c) a display driver for receiving a color display signal representing a relative luminance and color to be produced for each pixel of the display and generating a converted color display signal for driving the OLEDs in the display, wherein the display driver is responsive to the control signal for controlling the color gamut saturation of light produced by the OLEDs to reduce power consumption or increase lifetime of at least one of the OLEDs.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
OLED device with improved power consumption
ActiveUS20070164664A1Improve power efficiencyLow working voltageDischarge tube luminescnet screensStatic indicating devicesGamutEngineering
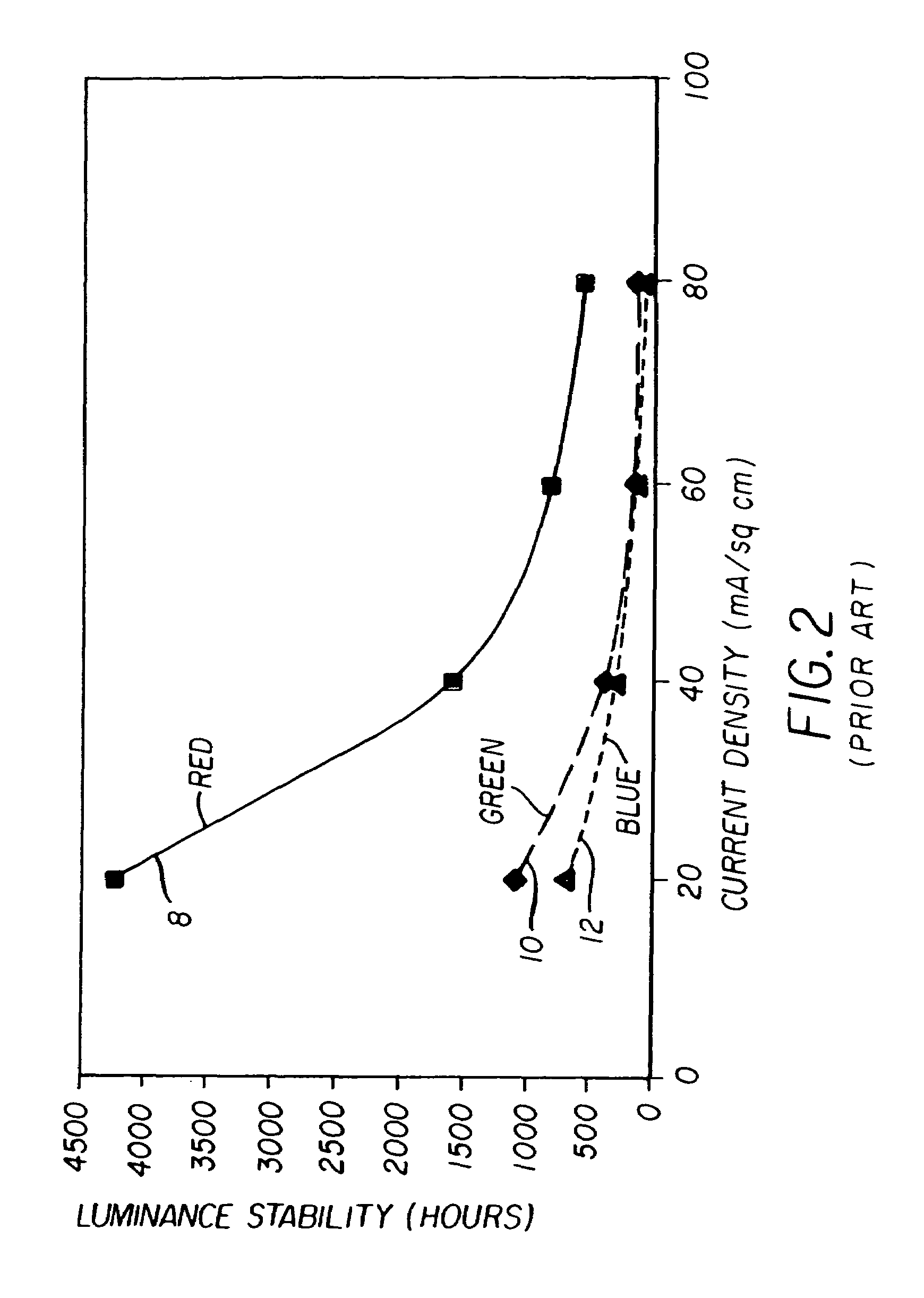
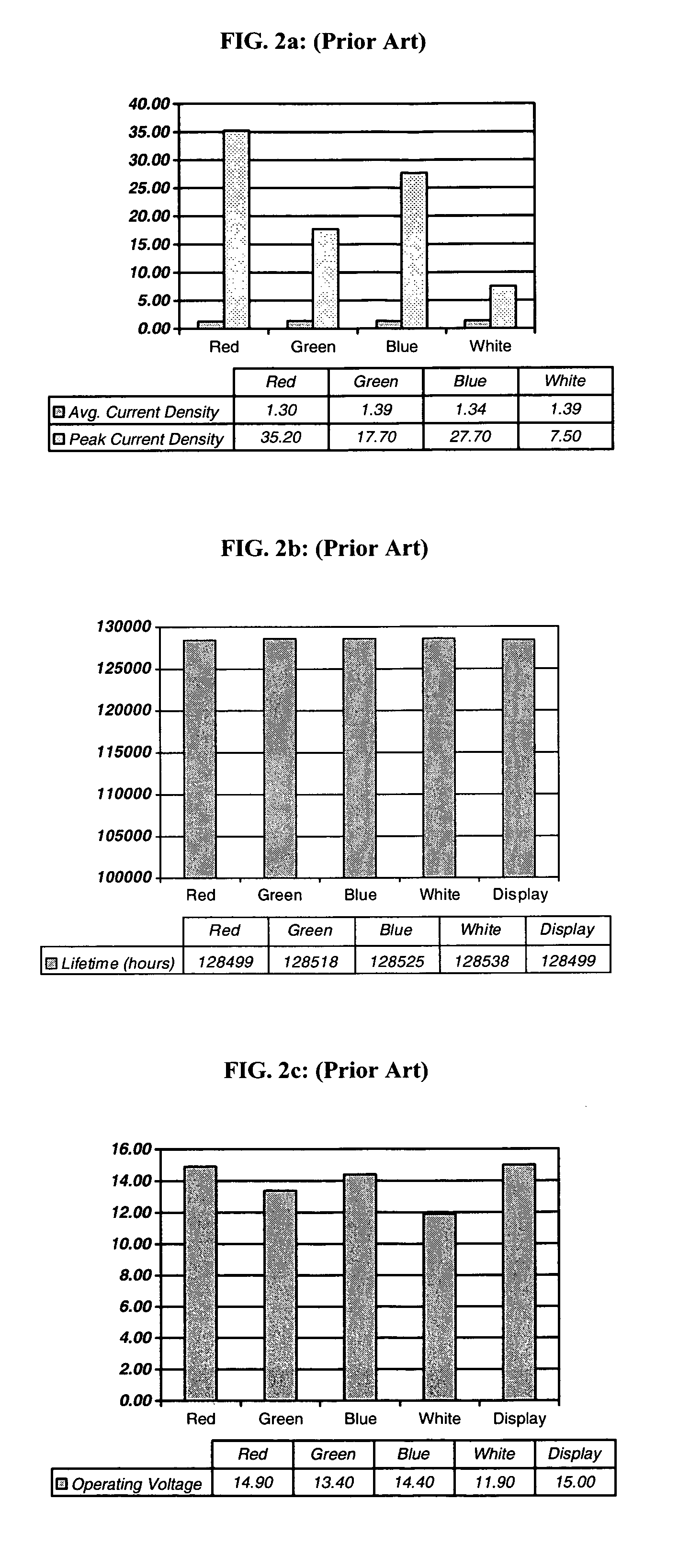
A method for making an OLED device, comprising: providing a plurality of subpixels of different colors, including at least three gamut-defining subpixels, each subpixel requiring an operating voltage which is based on the maximum current density required by that subpixel; selecting the display operating voltage to be equal to or greater than the maximum required subpixel operating voltage; and selecting the area of the subpixels to reduce the maximum required subpixel operating voltage, thereby reducing the display operating voltage so as to reduce power consumption in the device.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Color OLED device having improved performance
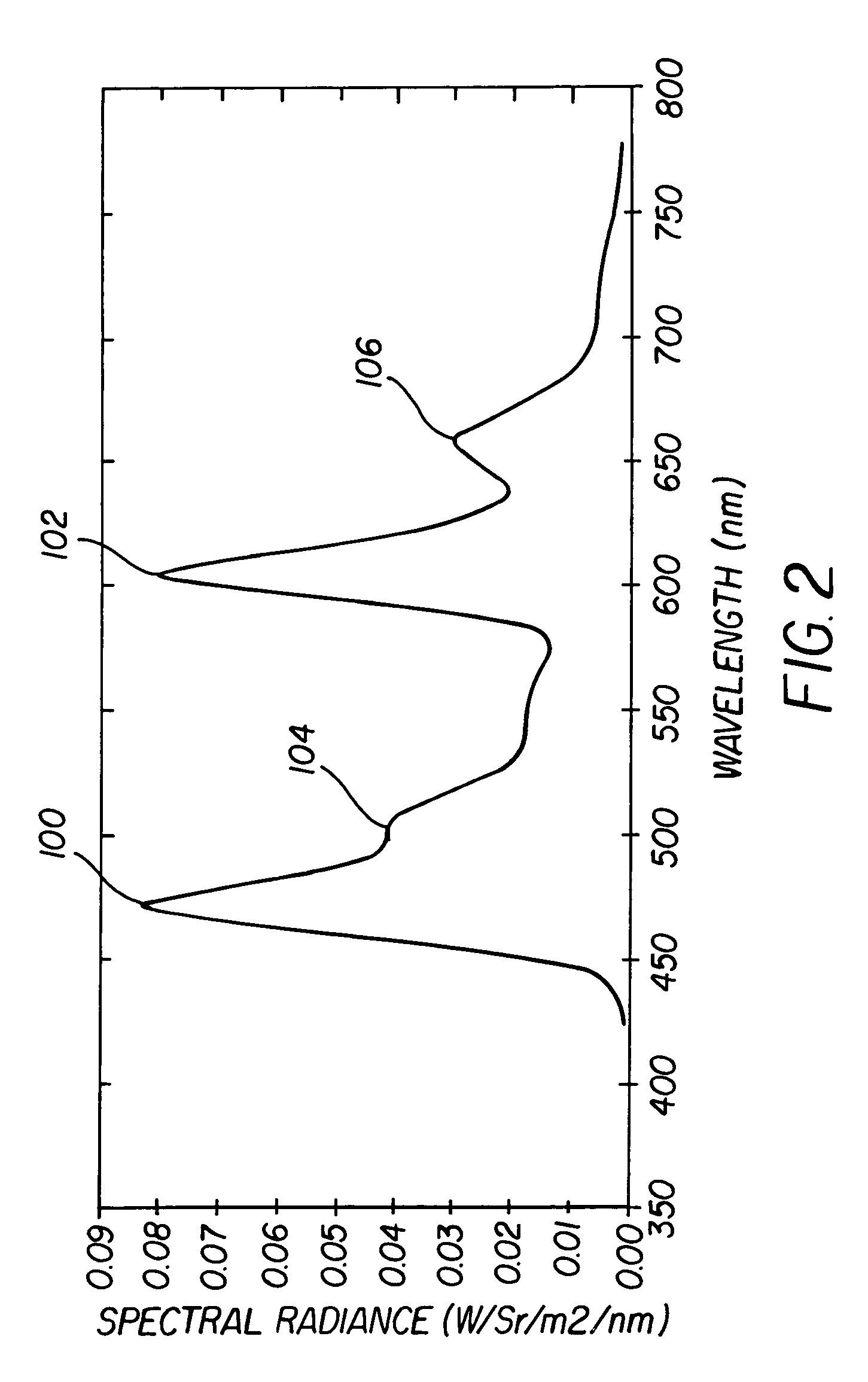
ActiveUS7091523B2Improve color gamutElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesGamutBroadband
A color OLED device is described having one or more pixels, at least one pixel comprising: four or more light-emitting elements, each light-emitting element comprising one or more layers of electroluminescent organic material producing a broadband light having a variable frequency-dependent luminous efficacy emission spectrum, and each light-emitting element further comprising a filter for filtering the broadband light and emitting a different color of light; wherein the different colors of light emitted by three of the light-emitting elements specify a first color gamut of the OLED device, and an additional one or more of the light-emitting elements emit at least one additional different color of light and wherein the frequency range of the filter of the additional light emitting element is matched to a portion of the broadband light frequency range having a radiant intensity greater than the radiant intensity of the frequency range of at least one of the filters of the three light-emitting elements specifying the first color gamut of the OLED device, and the additional one or more light emitting elements having luminous efficiency greater than that of at least one of the three light emitting elements specifying the first color gamut.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Scalable audio coding/decoding method and apparatus without overlap of information between various layers
InactiveUS6108625AEasy to useImprove sound qualityError detection/correctionSpeech analysisComputer architectureGamut
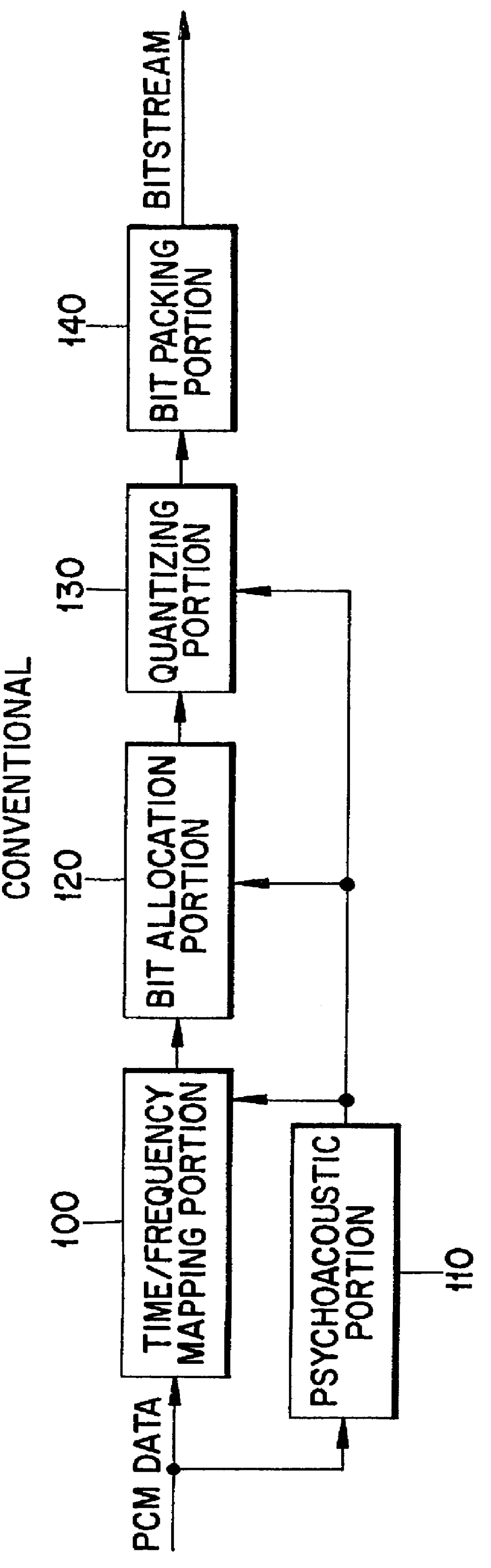
A scalable audio coding / decoding method and apparatus are provided. The coding method includes the steps of (a) signal-processing input audio signals and quantizing the same for each predetermined coding band; (b) coding the quantized data corresponding to the base layer within a predetermined layer size; (c) coding the quantized data corresponding to the next enhancement layer of the coded base layer and the remaining quantized data uncoded and belonging to the enhancement layer, within a predetermined layer size; and (d) sequentially performing the layer coding steps for all layers, wherein the steps (b), (c) and (d) each comprise the steps of: (i) obtaining gamut bit allocation information representing the number of bits of the quantized data corresponding to the respective subbands belonging to a layer to be coded; (ii) obtaining the number of bits allocated to the respective subbands within each subband size of the layers; (iii) generating an index representing the presence of quantized data for predetermined frequency components forming the subbands for the quantized data corresponding to the number of allocated bits; and (iv) generating bitstreams by coding the quantized data corresponding to the gamut bit allocation information, quantization step size, index and number of bits allocated to the respective subbands, by a predetermined coding method.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
OLED display with improved power performance
An OLED display for producing a full color image, comprising a plurality of at least four different colored pixels including three different colored addressable gamut-defining pixels and a fourth addressable within-gamut pixel, each pixel having an organic light-emitting diode with first and second electrodes and one or more organic light-emitting layers provided between the electrodes; the OLED display having a selected display white point, display peak luminance, gamut-defining pixel peak luminances and within-gamut pixel peak luminance; and drive circuitry for regulating luminance of the organic light-emitting diode of each of the colored pixels wherein the sum of the gamut-defining pixel peak luminances is less than the display peak luminance.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Color OLED display with improved power efficiency
ActiveUS20050212728A1Reduce power consumptionExtended service lifeCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingGamutDisplay device
An OLED display device includes: an array of light emitting pixels, each pixel having red, green, and blue OLEDs and at least one additional colored OLED that expands the gamut of the display device relative to the gamut defined by the red, green and blue OLEDs, wherein the luminance efficiency or the luminance stability over time of the additional OLED is higher than the luminance efficiency or the luminance stability over time of at least one of the red, green, and blue OLEDs; and means for selectively driving the OLEDs with a drive signal to reduce overall power usage or extend the lifetime of the display while maintaining display color accuracy. In accordance with various embodiments, the present invention provides a color display device with improved power efficiency, longer overall lifetime, expanded color gamut with accurate hues, and improved spatial image quality.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Image processing method and image processing apparatus
InactiveUS6724507B1More colorColour-separation/tonal-correctionPictoral communicationColor imageColor transformation
Provided is an image processing method and a apparatus of converting a color input image or a partial region thereof in accordance with a color gamut of a color image output apparatus is provided. The method and apparatus is characterized in that only the region requiring color gamut compression can be put to color gamut compression depending on the distribution of an input image, that the direction of the color gamut compression can be controlled continuously for each of the regions; the amount of the color gamut compression can be controlled continuously including clipping, that when color gamut compression is conducted by a color converter of a multi-dimensional DLUT interpolating calculation type, an excessively unnecessary color gamut compression can be avoided particularly upon clipping, and that there is enabled correction for visual bending in iso-hue lines caused by distortion of a color space in each of the regions of the color space.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
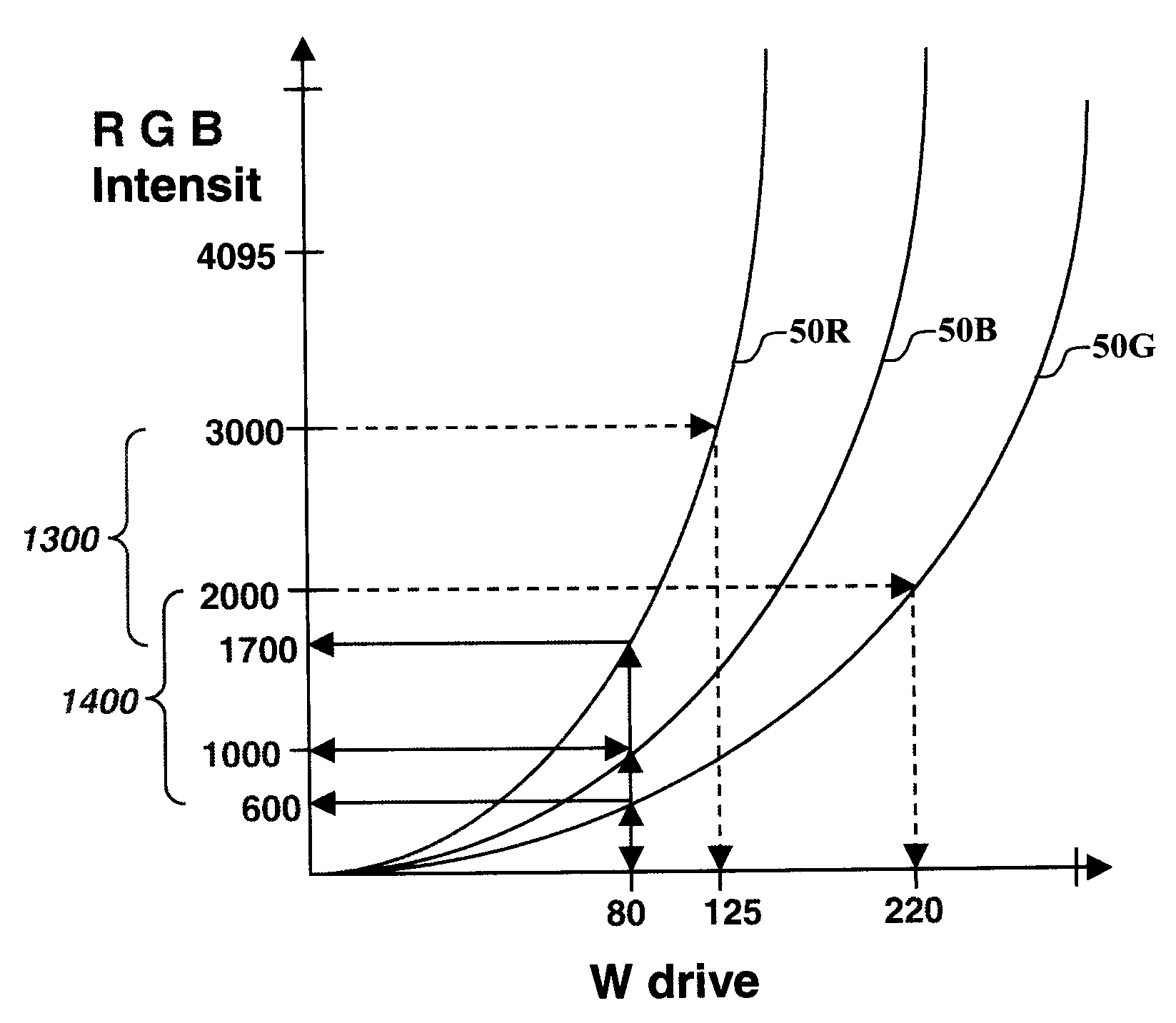
Method for input-signal transformation for rgbw displays with variable w color
InactiveUS20080252797A1Easy to measureSmall memoryColor signal processing circuitsStatic indicating devicesGamutDisplay device
A method for transforming three color-input signals (R, G, B) corresponding to three gamut-defining color primaries of a display to four color-output signals (R′, G′, B′, W) corresponding to the gamut-defining color primaries and one additional primary of the display, where the additional primary has color that varies with drive level, comprising: a) determining a relationship between drive level of the additional primary and intensities of the three gamut-defining primaries which together produce equivalent color over a range of drive levels for the additional primary; and b) employing the three color-input signals R, G, B and the relationship defined in a) to determine a value for W of the four color-output signals, and modification values to be applied to one or more of the R, G, B components of the three color-input signals to form the R′, G′, B′ values of the four color-output signals.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
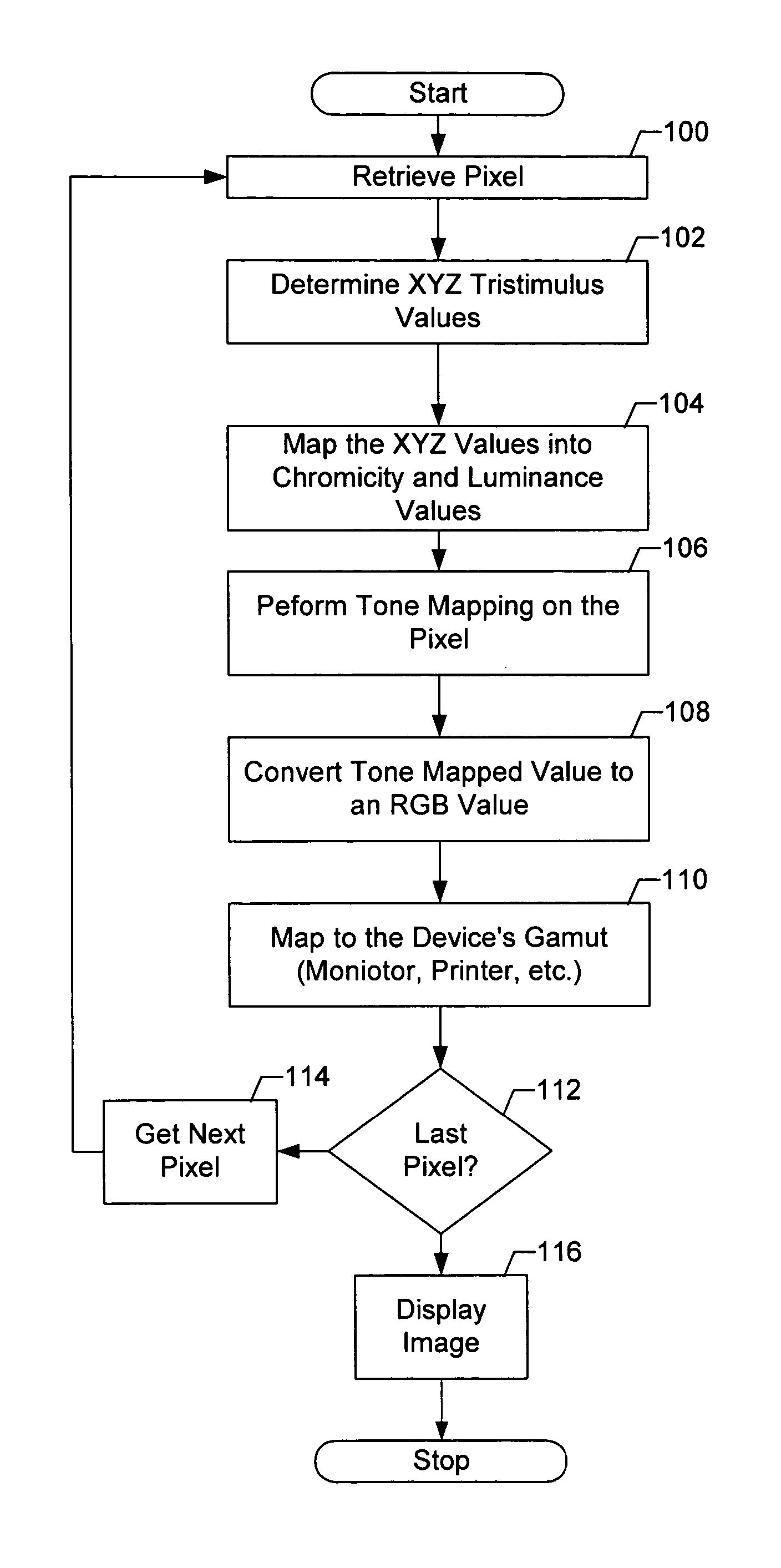
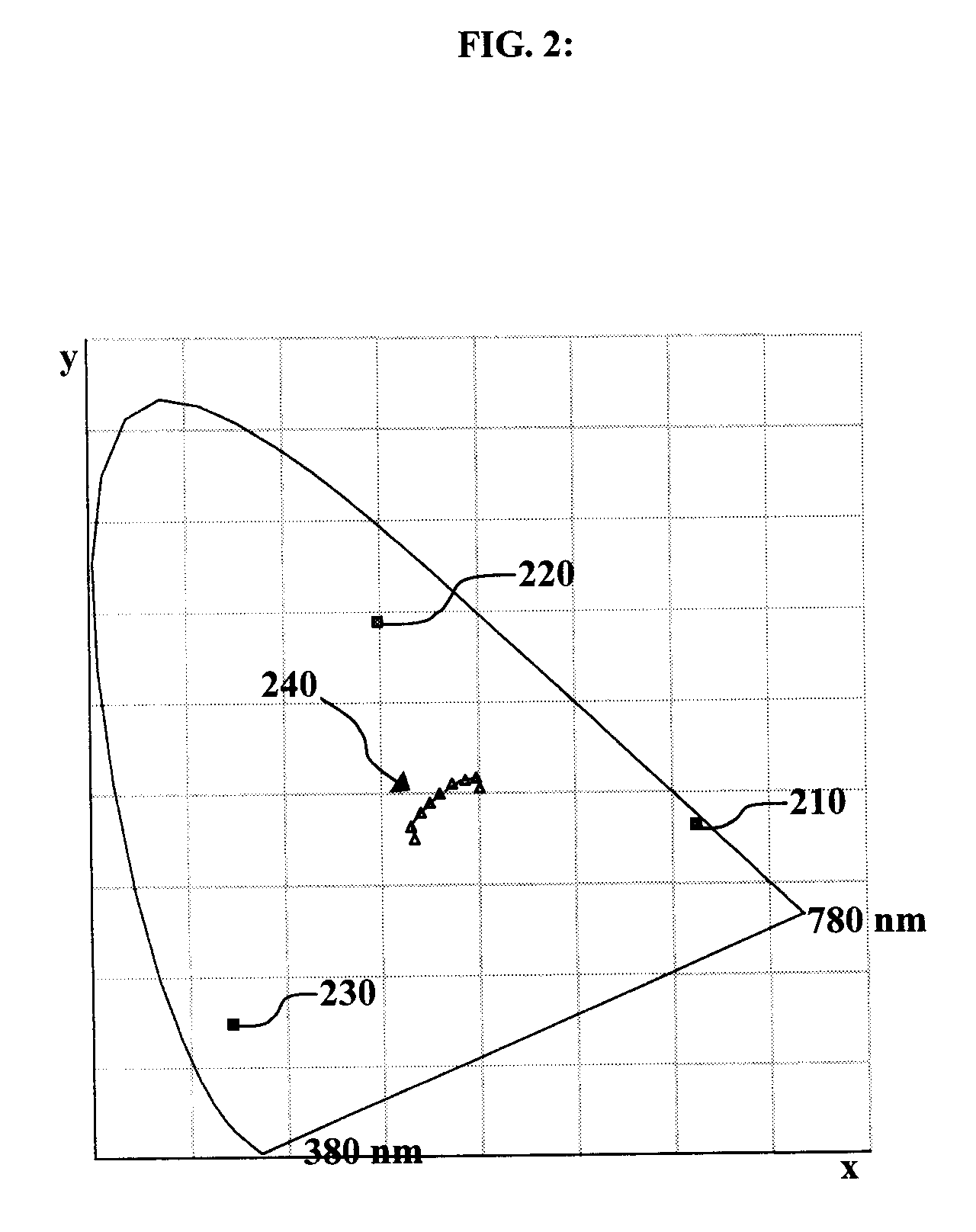
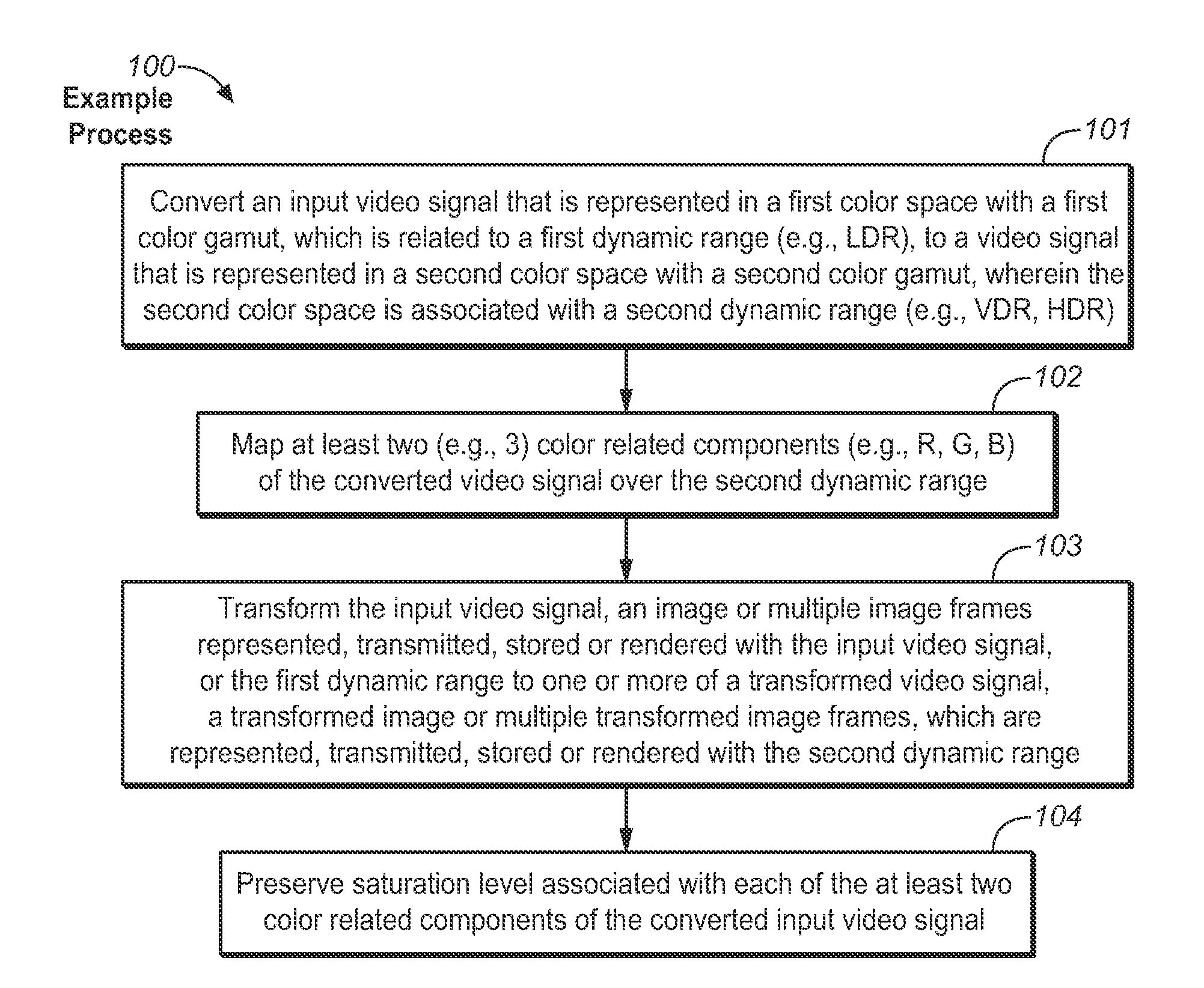
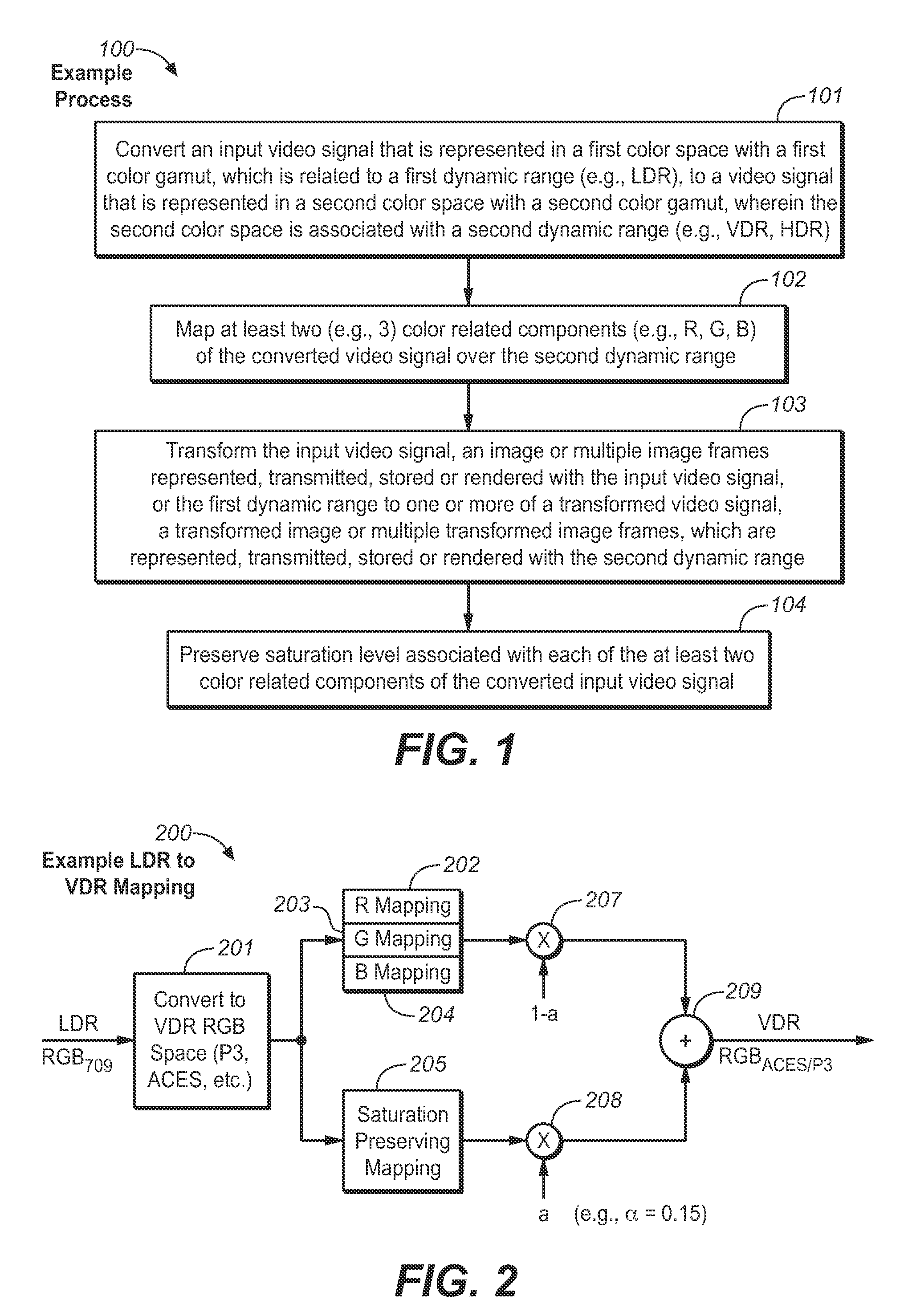
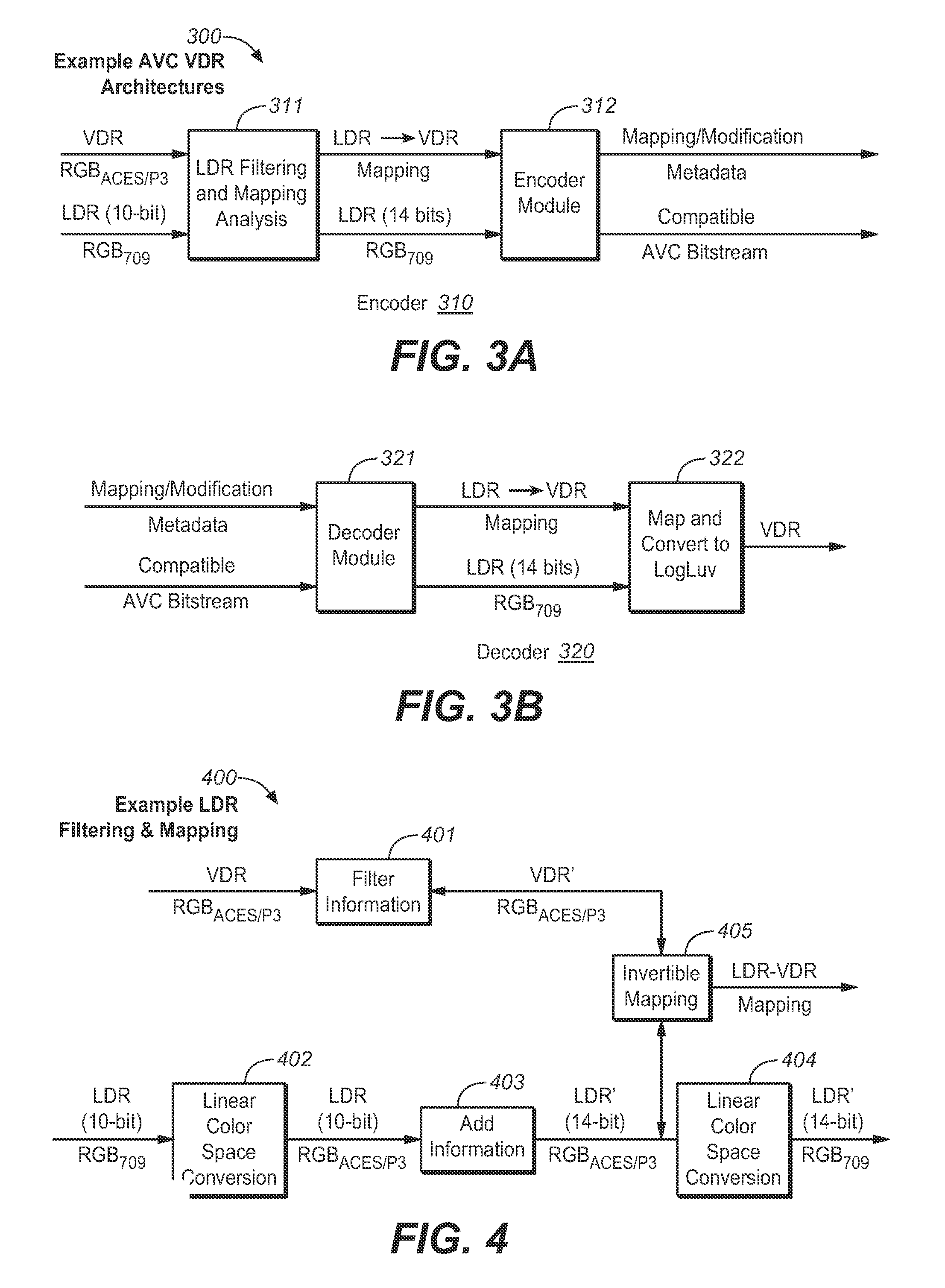
Quality Assessment for Images that Have Extended Dynamic Ranges or Wide Color Gamuts
A first video signal is accessed, and represented in a first color space with a first color gamut, related to a first dynamic range. A second video signal is accessed, and represented in a second color space of a second color gamut, related to a second dynamic range. The first accessed video signal is converted to a video signal represented in the second color space. At least two color-related components of the converted video signal are mapped over the second dynamic range. The mapped video signal and the second accessed video signal are processed. Based on the processing, a difference is measured between the processed first and second video signals. A visual quality characteristic relates to a magnitude of the measured difference between the processed first and second video signals. The visual quality characteristic is assessed based, at least in part, on the measurement of the difference.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Quantum dot color filter, liquid crystal panel and display device
The invention relates to the technical field of display, which discloses a quantum dot color filter, a liquid crystal panel and a display device. The quantum dot color filter is used for the liquid crystal panel. The liquid crystal panel is provided with a plurality of pixels, wherein each pixel is provided with a plurality of sub-pixels. Each sub-pixel corresponds to a color. The color filter comprises sub-areas in one-to-one correspondence to the sub-pixels. At least one sub-area is formed by quantum dot materials. Light generated by the quantum dot materials activated is as same as the corresponding sub-pixel in color. According to the invention, the color filter of a display is formed by the quantum dot materials, and a red, or green, or blue filter is made of quantum dot materials which generate red, or green, or blue light through photoexcitation, so that the utilization ratio of a backlight source is improved, and meanwhile, colored light with higher purity can be obtained. Therefore, the quantum dot display can realize high color gamut and low power consumption of color display.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD
Image and light source modulation for a digital display system
ActiveUS7404645B2Improve display qualityImprove consistencyTelevision system detailsProjectorsDisplay deviceSystem configuration
Image processing enhances display quality by controlling both the image modulator and the light sources.The image processing system utilizes a combination of user inputs, system configuration, design information, sensor feedback, pixel modulation information, and lighting control information to characterize the display environment on a per pixel basis. This per pixel characterization information is combined with one or more frames of the incoming real time display data. The image processing system processes each incoming pixel and produces a modified corresponding output pixel. Each pixel of each frame is processed accordingly.The image processing system also produces control information for the light sources. The light source control information can control individual lamps, tubes or LEDs, or can control a block or subset of the light sources. The resulting display has improved image consistency, enhanced color gamut, higher dynamic range and is better able to portray high motion content.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
LED backlighting system with closed loop control
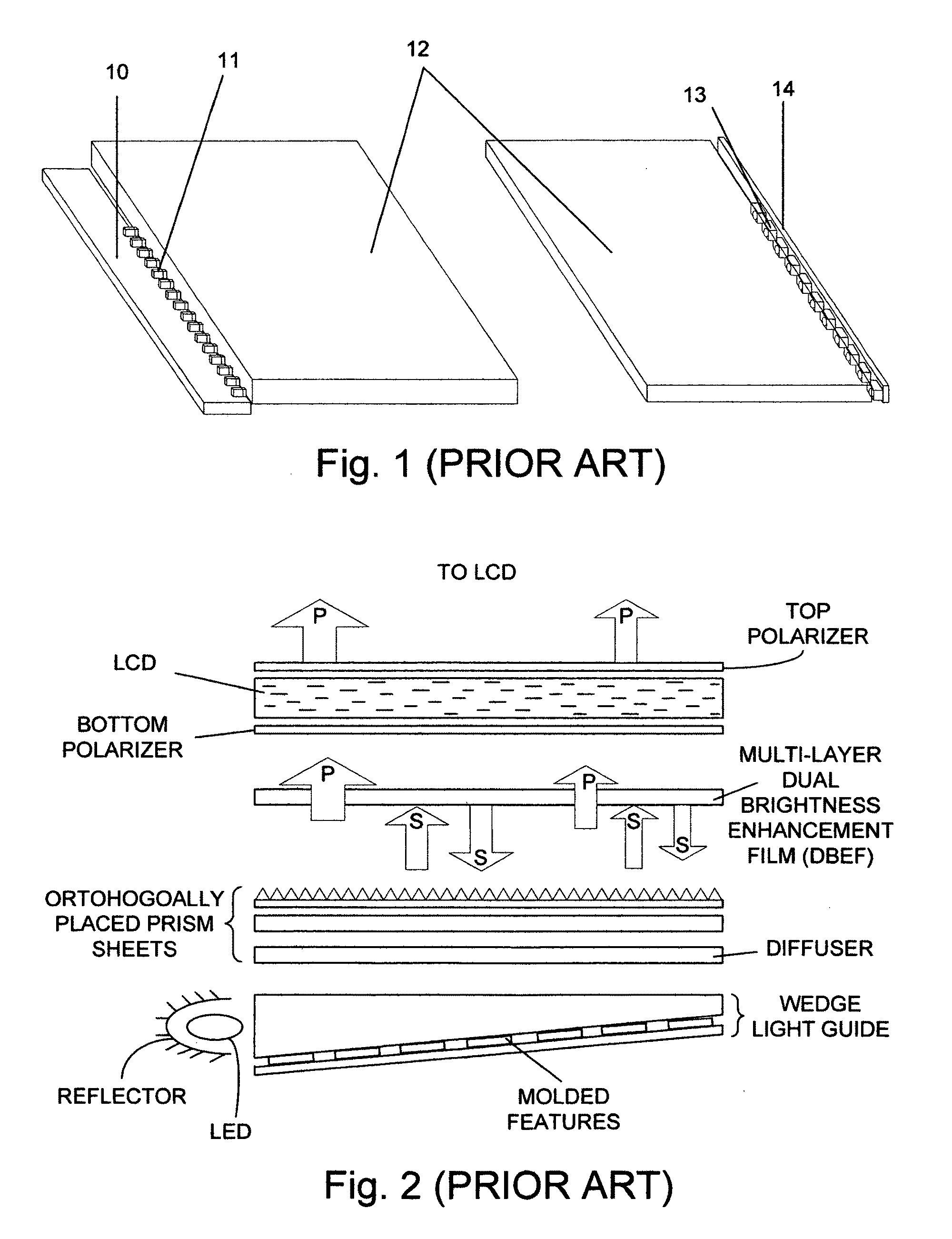
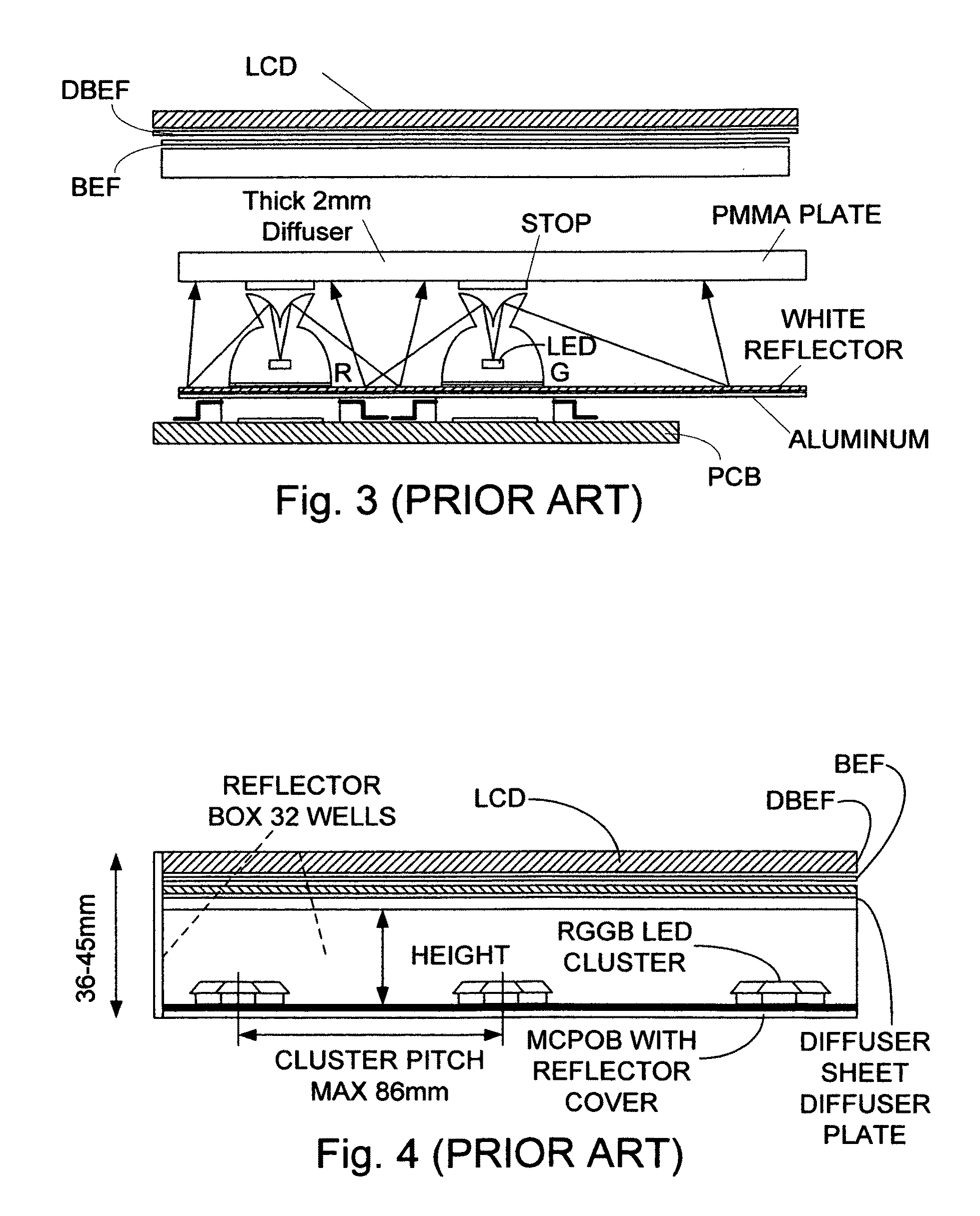
InactiveUS20090122533A1Improve homogeneityReduce intensityNon-electric lightingPoint-like light sourceOn boardDisplay device
A light emitting diode (LED) based illumination system with particular application to large scale side lighted liquid crystal displays (LCD). The invention uses on board closed loop intensity control in conjunction with red, green and blue (R,G,B) LED die and a hybrid non-imaging optical system to overcome substantial temperature dependence, loss in intensity with time, increased system cost and complexity, and decreased dynamic range. The invention obtains a large color gamut in excess of 110% of the NTSC (National Television System Committee) recommendation. A high performance thermal management design, the use of “chip on board” technology, compact and efficient collection optics, and on board closed loop intensity control increase and maintain luminous performance and decrease cost relative to less efficient RGB LED approaches. One or more line sources can be generated for applications other than in lighting LCD displays.
Owner:INNOVATIONS & OPTICS
Electro-optic displays, and method for driving same
ActiveUS20050152022A1Improve economyCheap preparationNon-linear opticsOptical elementsElectro-opticsGamut
Electro-optic media are disclosed containing a plurality of types of electro-optic media within a single layer. The media provide blinking displays, displays in which images appear transiently and displays having a wider color gamut than conventional electro-optic displays
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
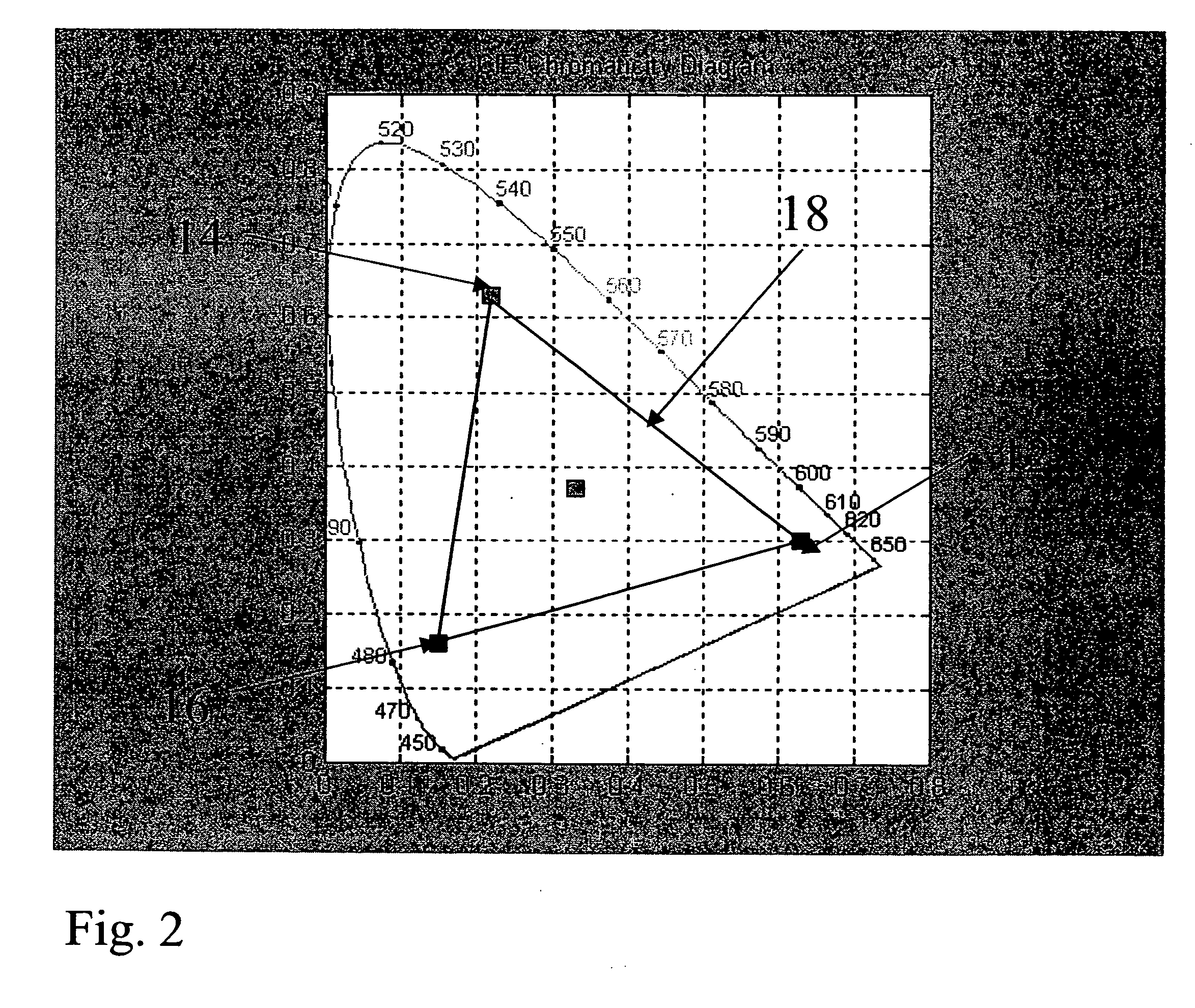
Color image reproduction with accurate inside-gamut colors and enhanced outside-gamut colors
InactiveUS6400843B1Good colorHigh chromaColor signal processing circuitsColor television signals processingPattern recognitionColor image
A color image reproduction system achieves higher-quality color reproduction by improving the utilization of colors within the gamut of an output device that are not in the gamut of an input device. This is accomplished by a device-dependent compensation transformation that maps a second set of colors in both the gamut of an input device and the gamut of the output device into a first set of colors in the gamut of the output device but not in the gamut of the input device. The compensation transformation may be derived in a number of ways that entail identifying the first and second sets of colors and then determining one or more scaling factors that map the second set of colors into a union of the first and second sets of colors.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
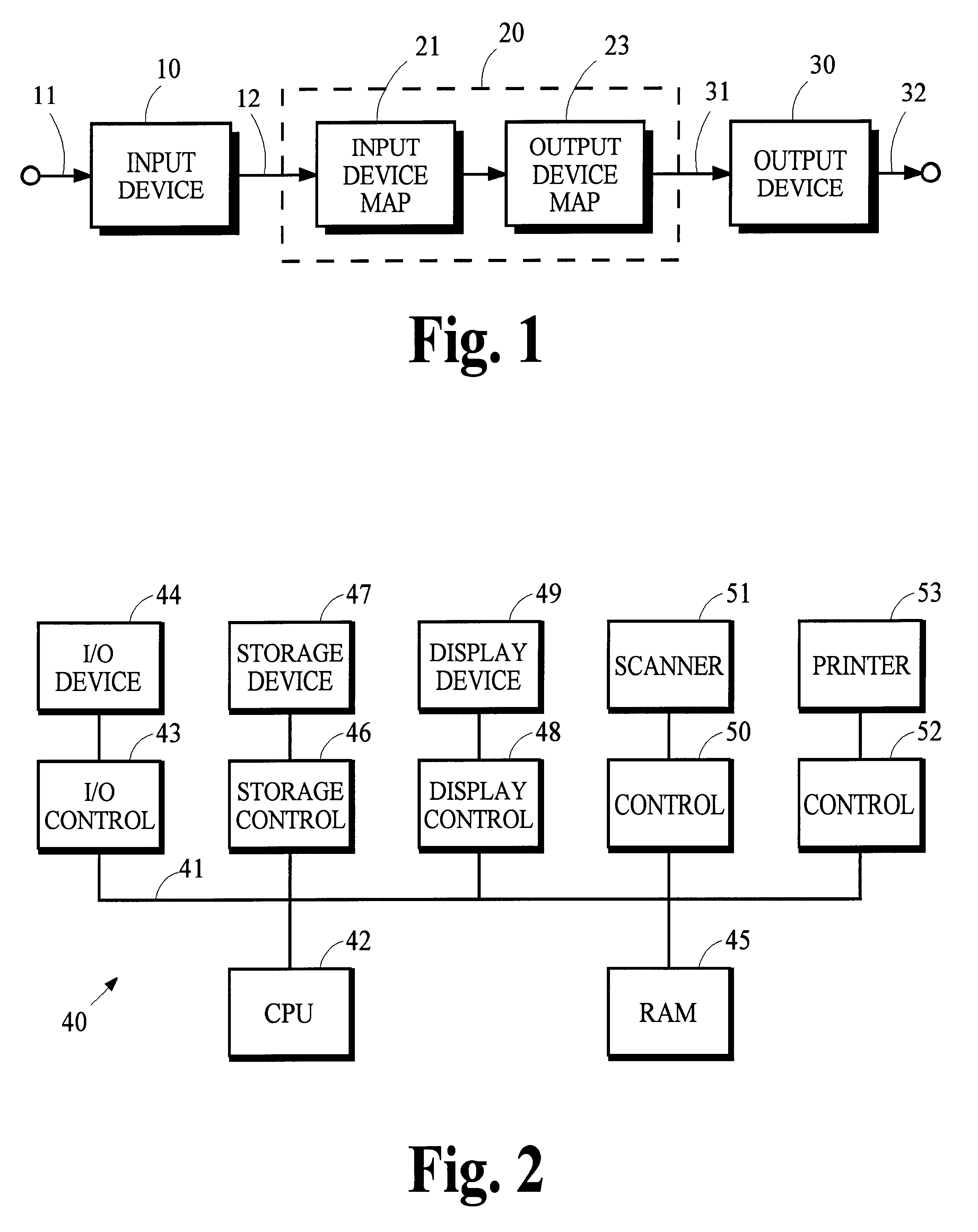
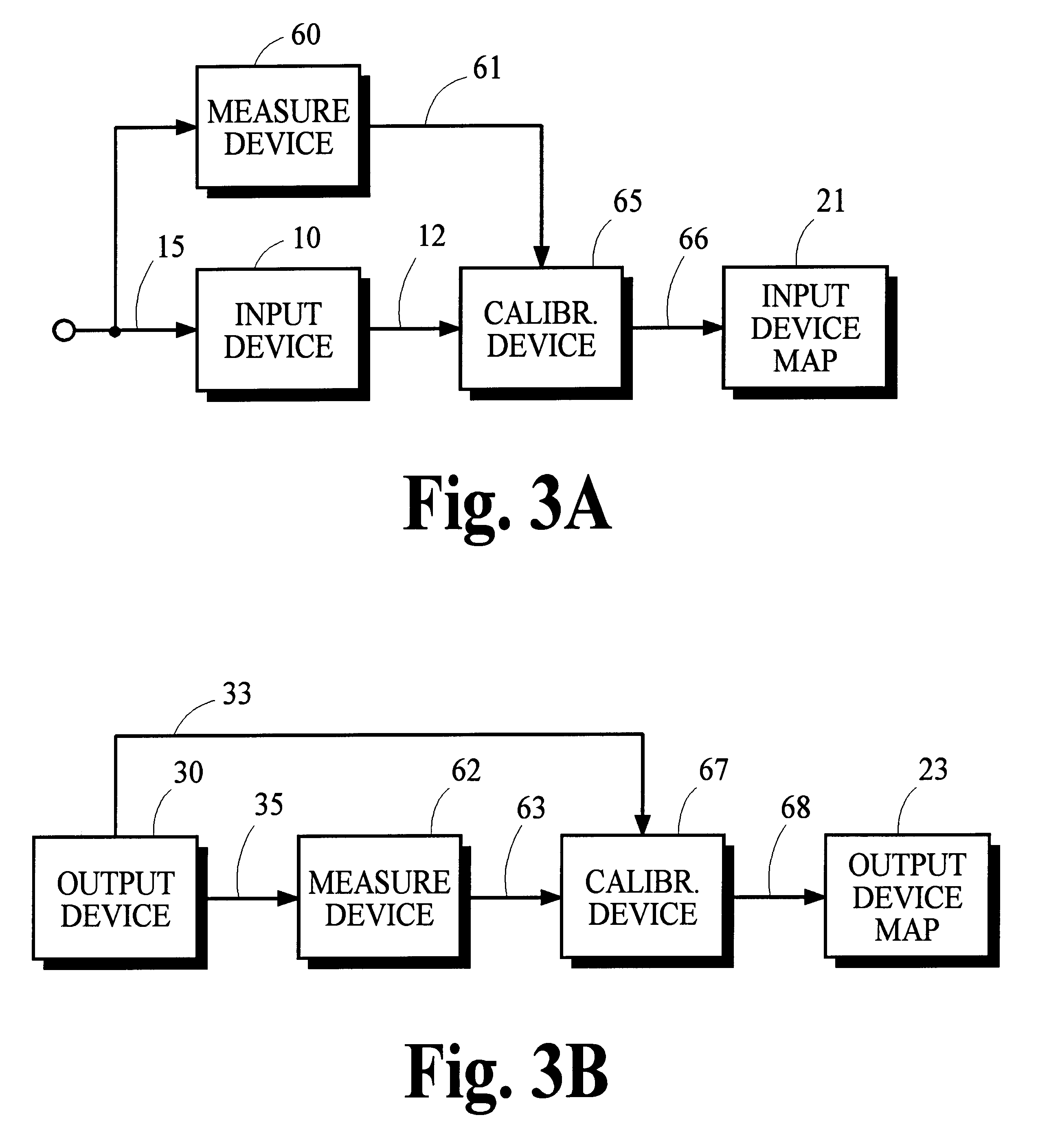
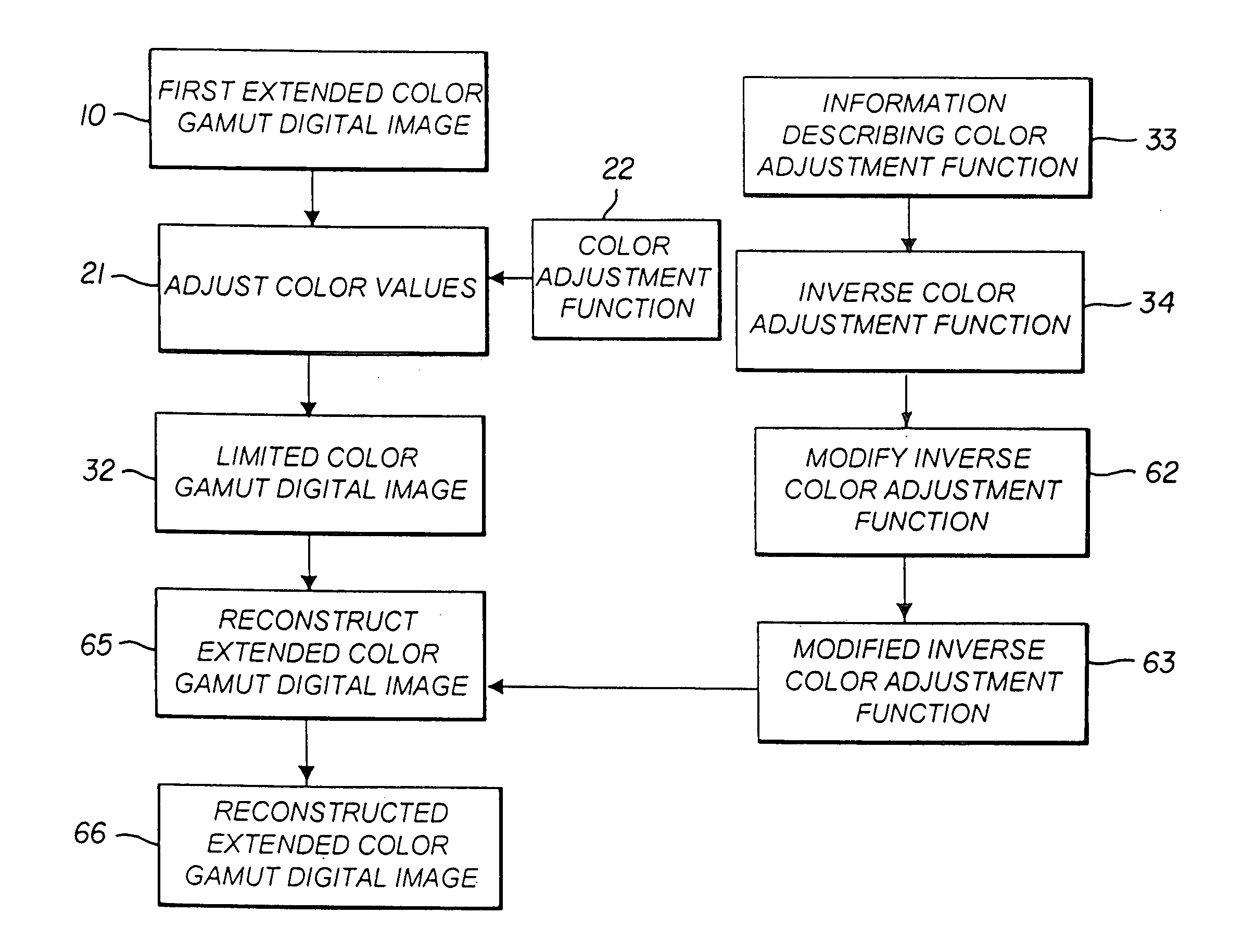
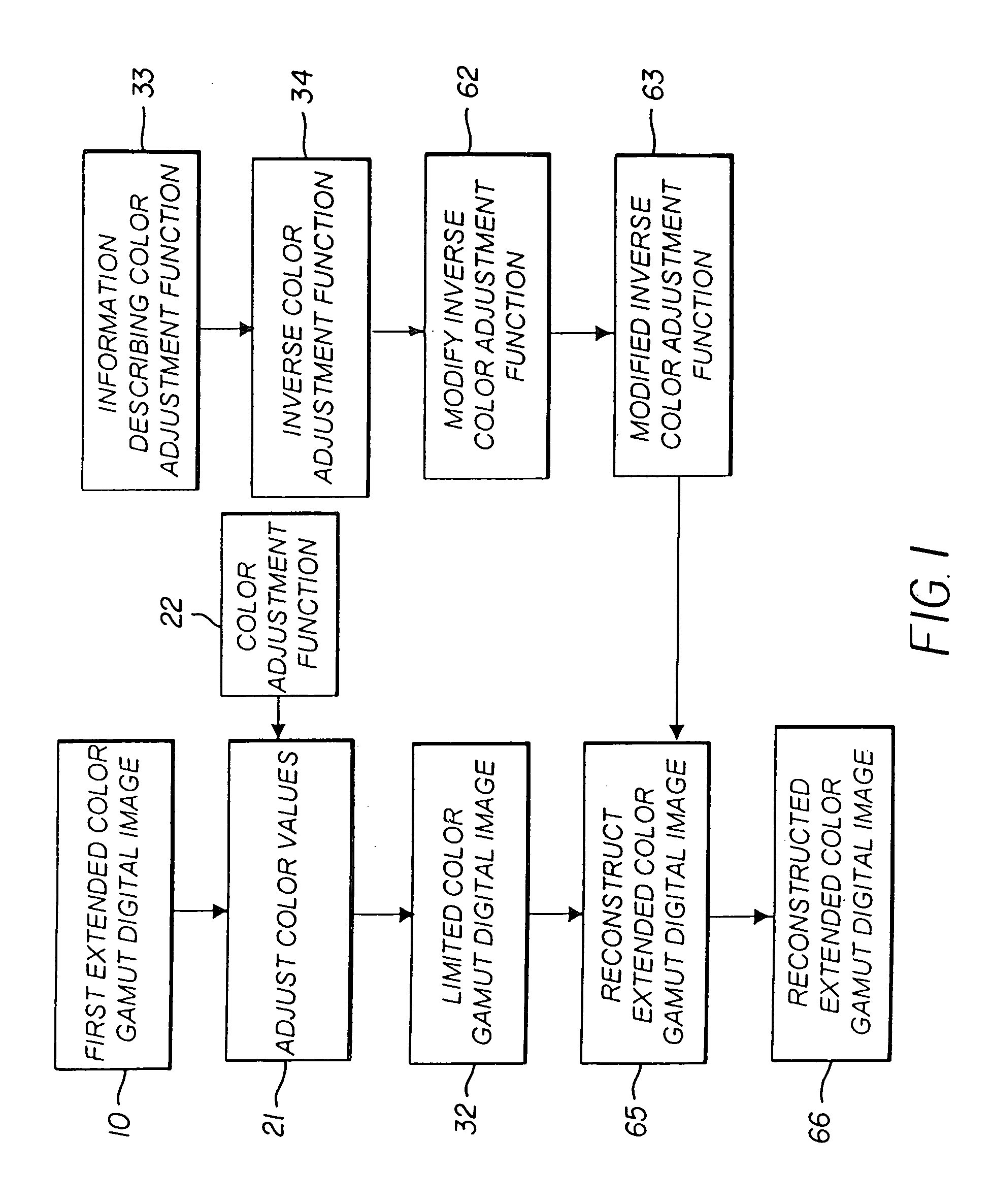
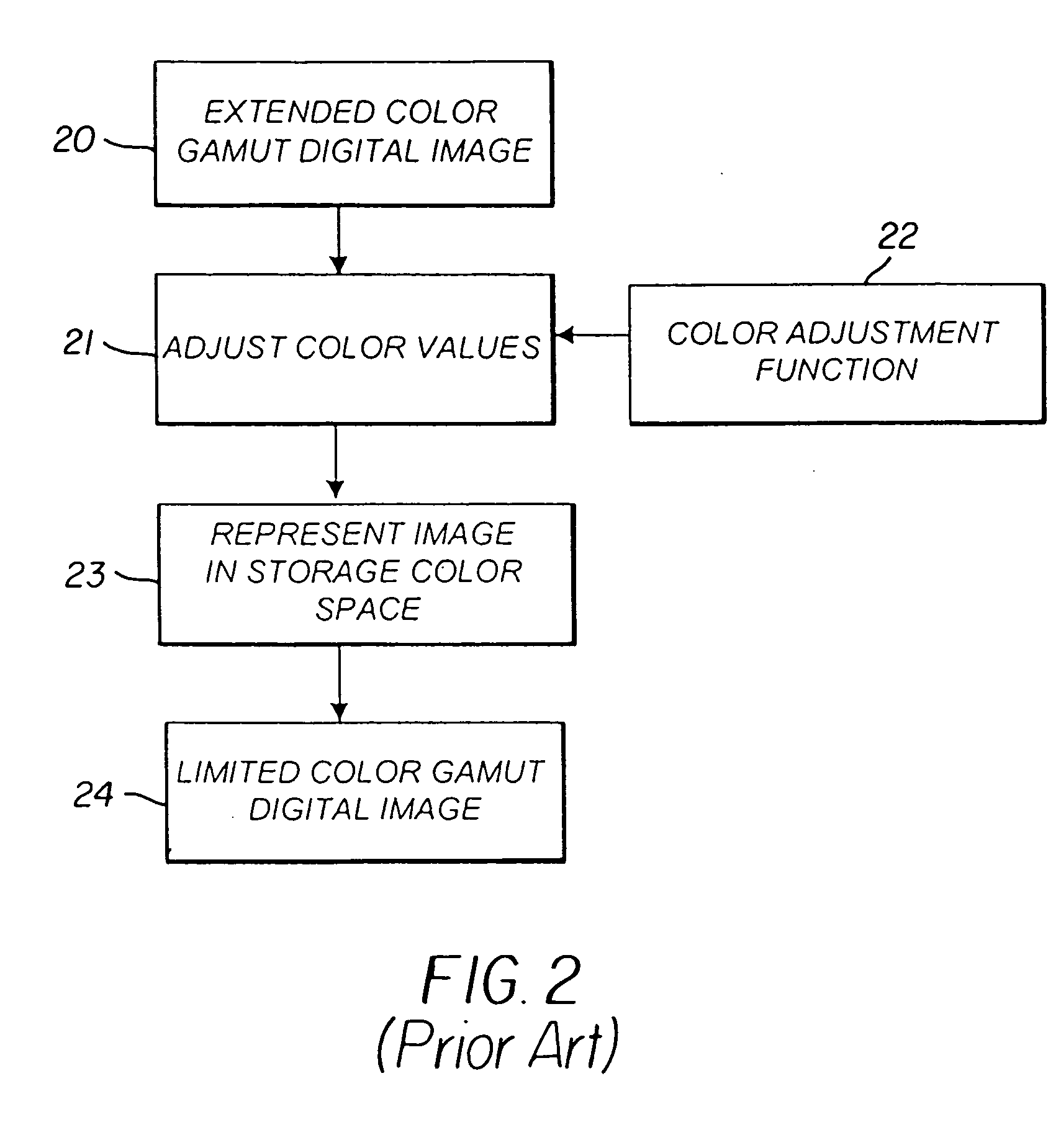
Constructing extended color gamut digital images from limited color gamut digital images
InactiveUS20050152597A1Reduced color saturationPromote lowerDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsGamutColor saturation
A method for reconstructing an extended color gamut digital image from a limited color gamut digital image includes transforming the limited color gamut digital image in the particular limited color gamut color space to a reference color space forming a limited color gamut digital image in a reference color space; providing a modified inverse color adjustment function which, when such function operates on the limited color gamut digital image in the reference color space, produces the reconstructed extended color gamut digital image having reduced highlight color saturation for highlight color values when compared with corresponding color values of the initial extended color gamut image; and operating on the limited color gamut digital image in the reference color space with the modified inverse color adjustment function to form the reconstructed extended color gamut digital image having reduced levels of color contouring and quantization artifacts.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com