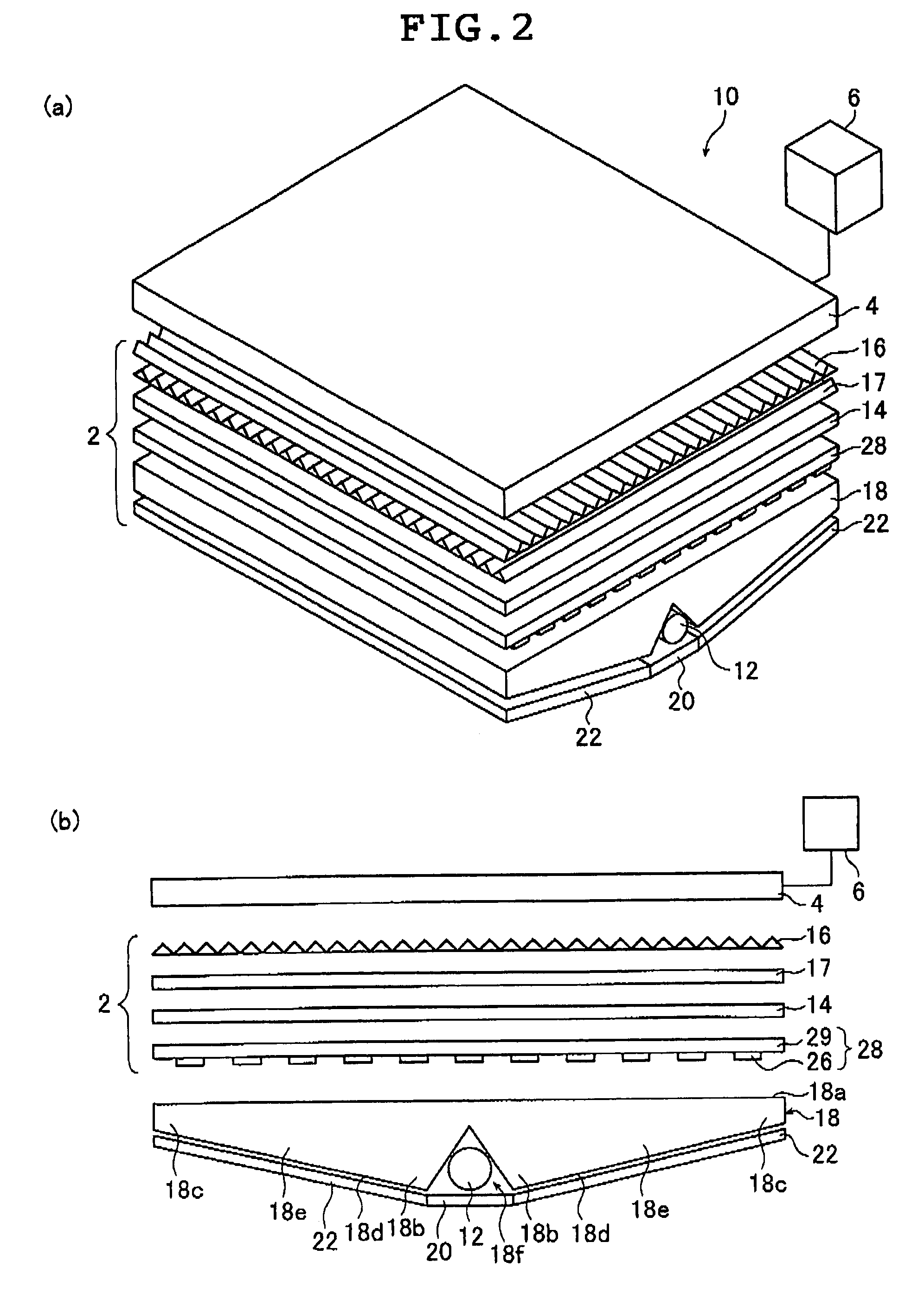
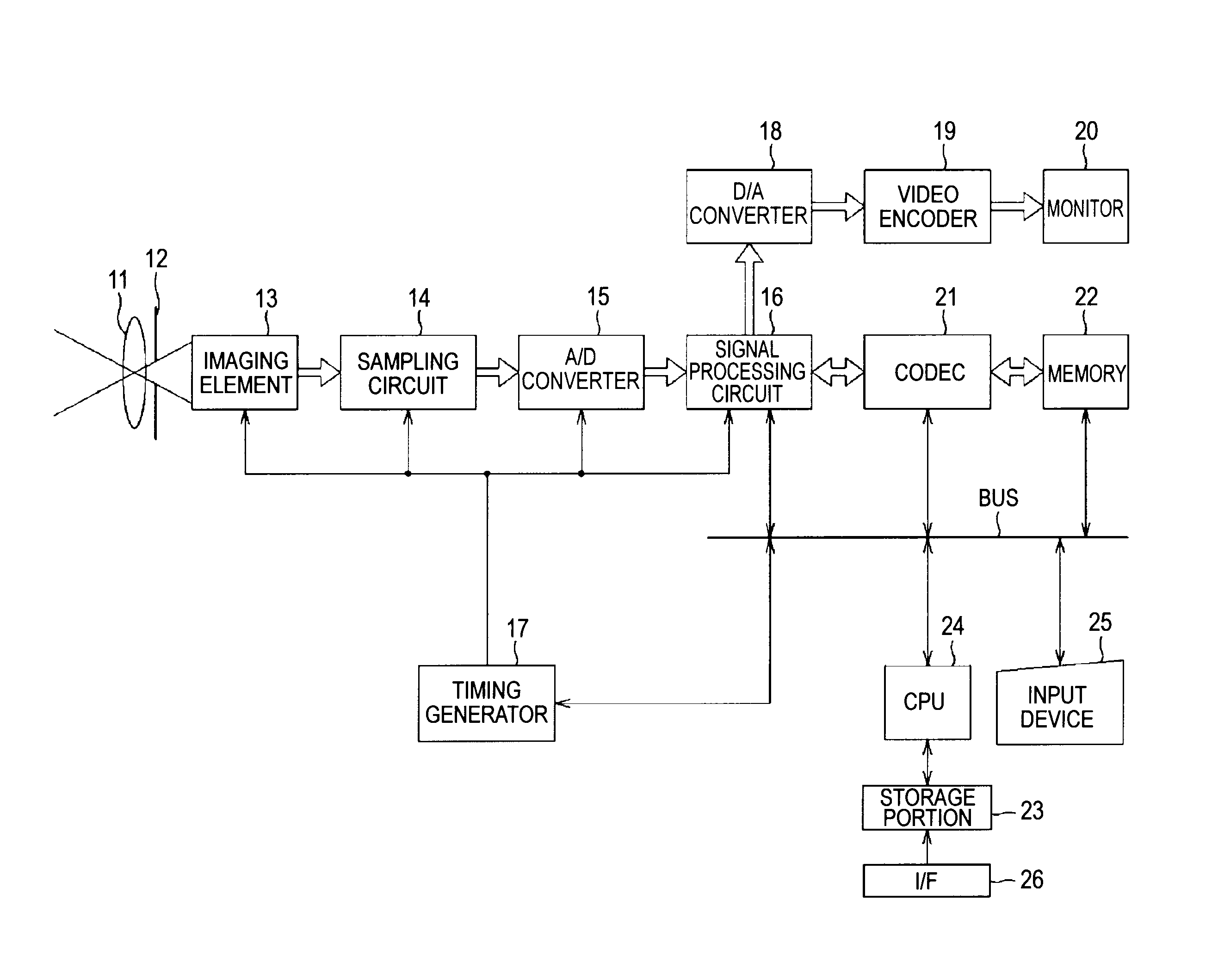
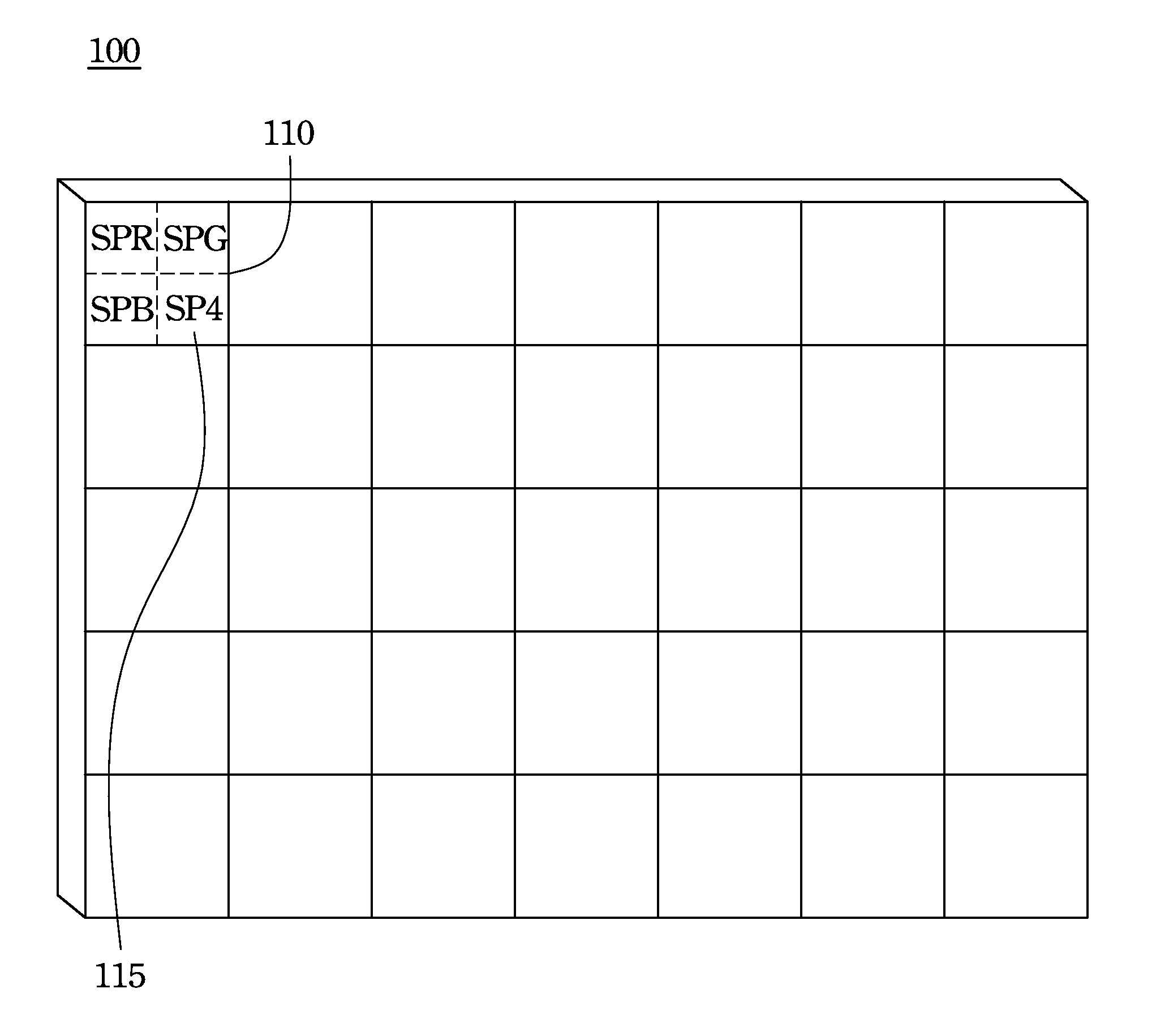
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
110 results about "Relative luminance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
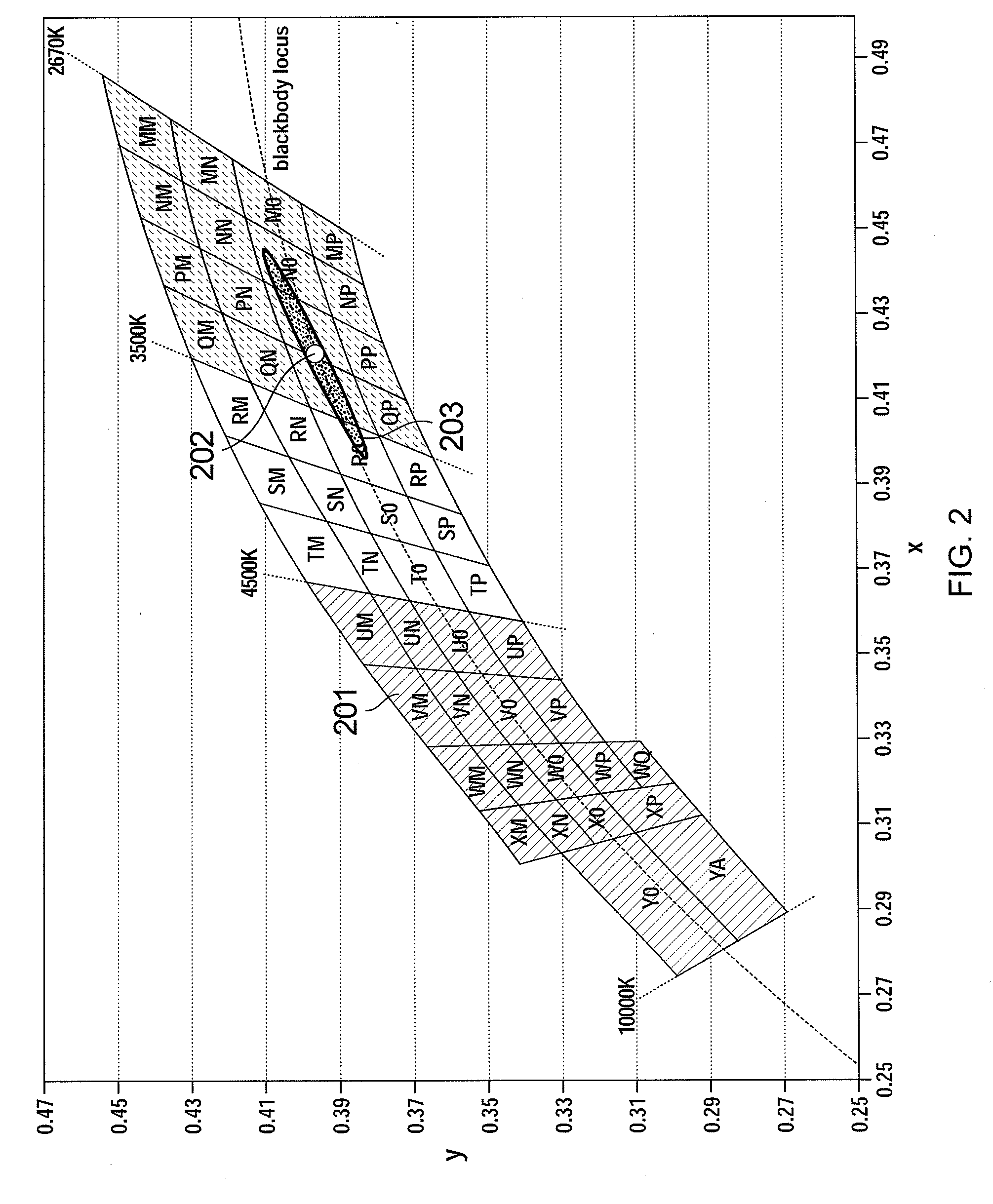
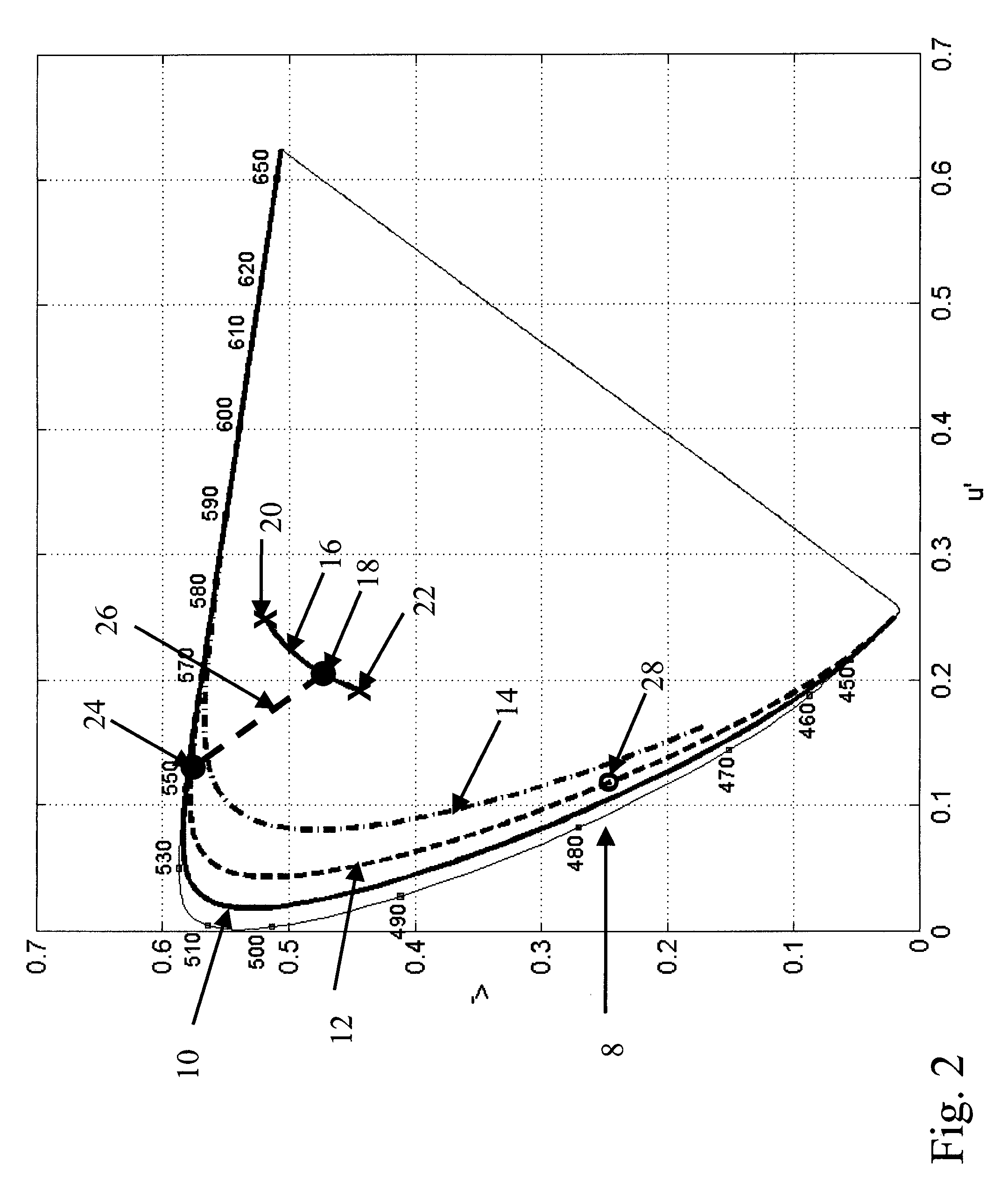
Relative luminance follows the photometric definition of luminance, but with the values normalized to 1 or 100 for a reference white. Like the photometric definition, it is related to the luminous flux density in a particular direction, which is radiant flux density weighted by the luminosity function y(λ) of the CIE Standard Observer.
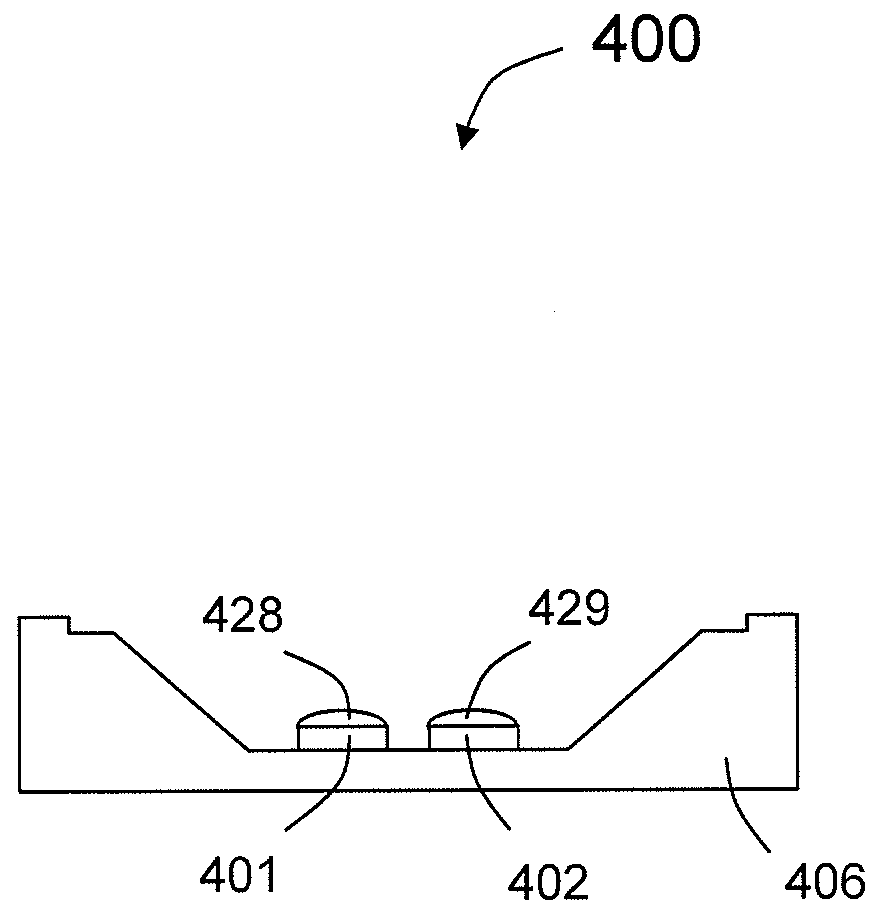
Color OLED display system having improved performance
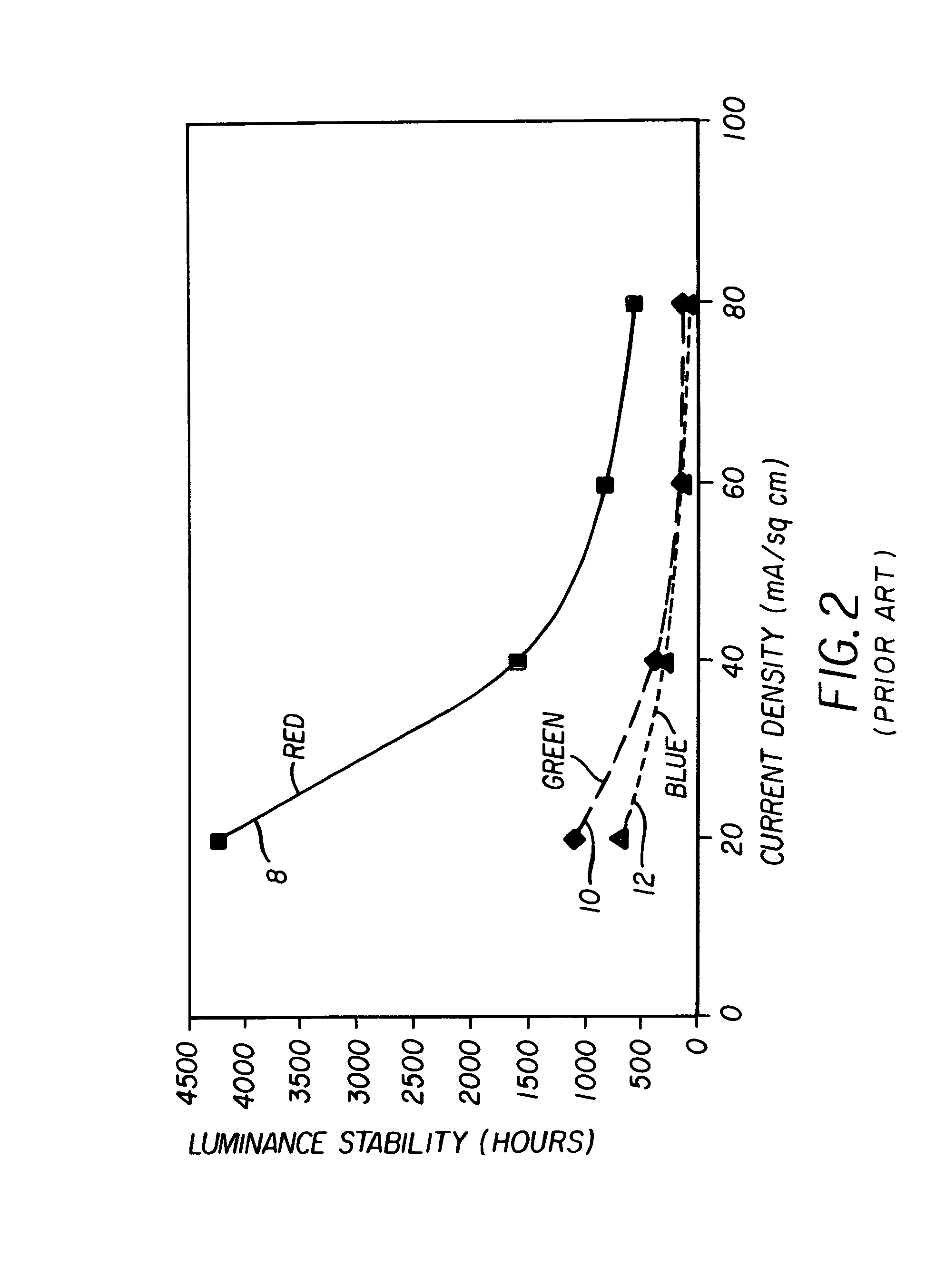
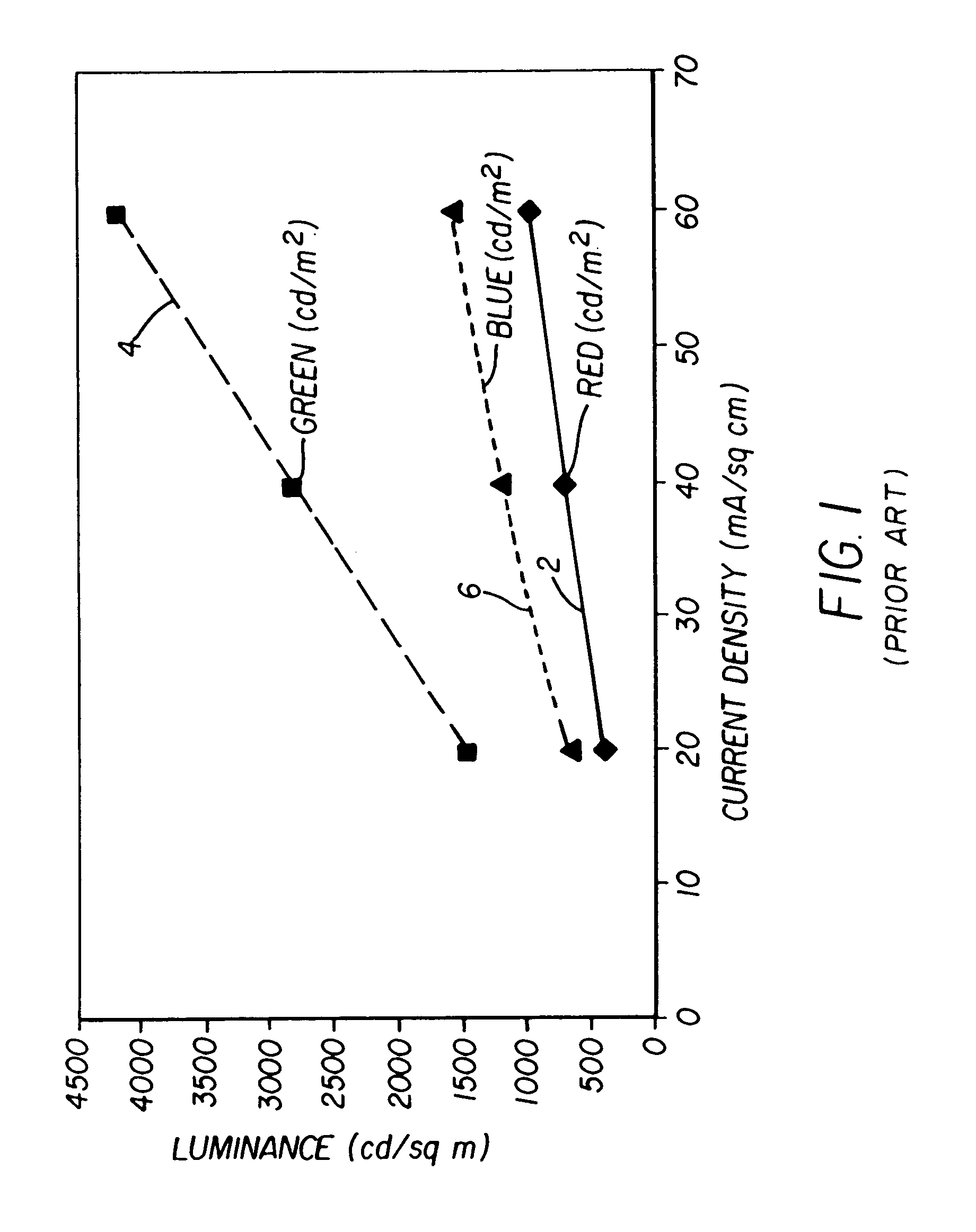
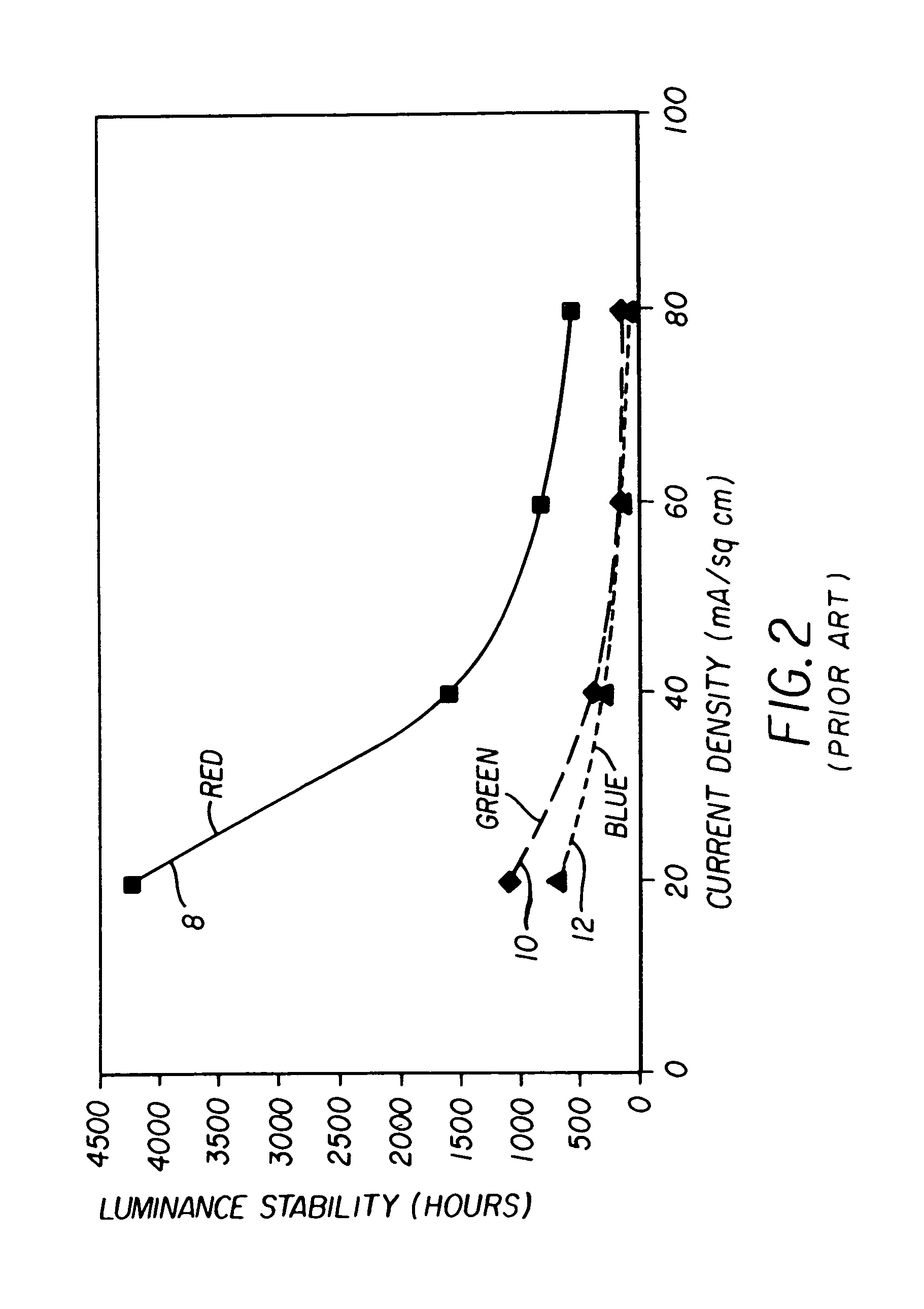
ActiveUS7397485B2Improve power efficiencyImproved display lifetimeSolid-state devicesDiodeGamutControl signal
An OLED display system includes a) an OLED display including an array of light emitting pixels, each pixel having a plurality of OLEDs for emitting different colors of light specifying a gamut wherein one of the OLEDs has a power efficiency or lifetime different from the power efficiency or lifetime of at least one of the other OLEDs; b) a control signal; and c) a display driver for receiving a color display signal representing a relative luminance and color to be produced for each pixel of the display and generating a converted color display signal for driving the OLEDs in the display, wherein the display driver is responsive to the control signal for controlling the color gamut saturation of light produced by the OLEDs to reduce power consumption or increase lifetime of at least one of the OLEDs.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
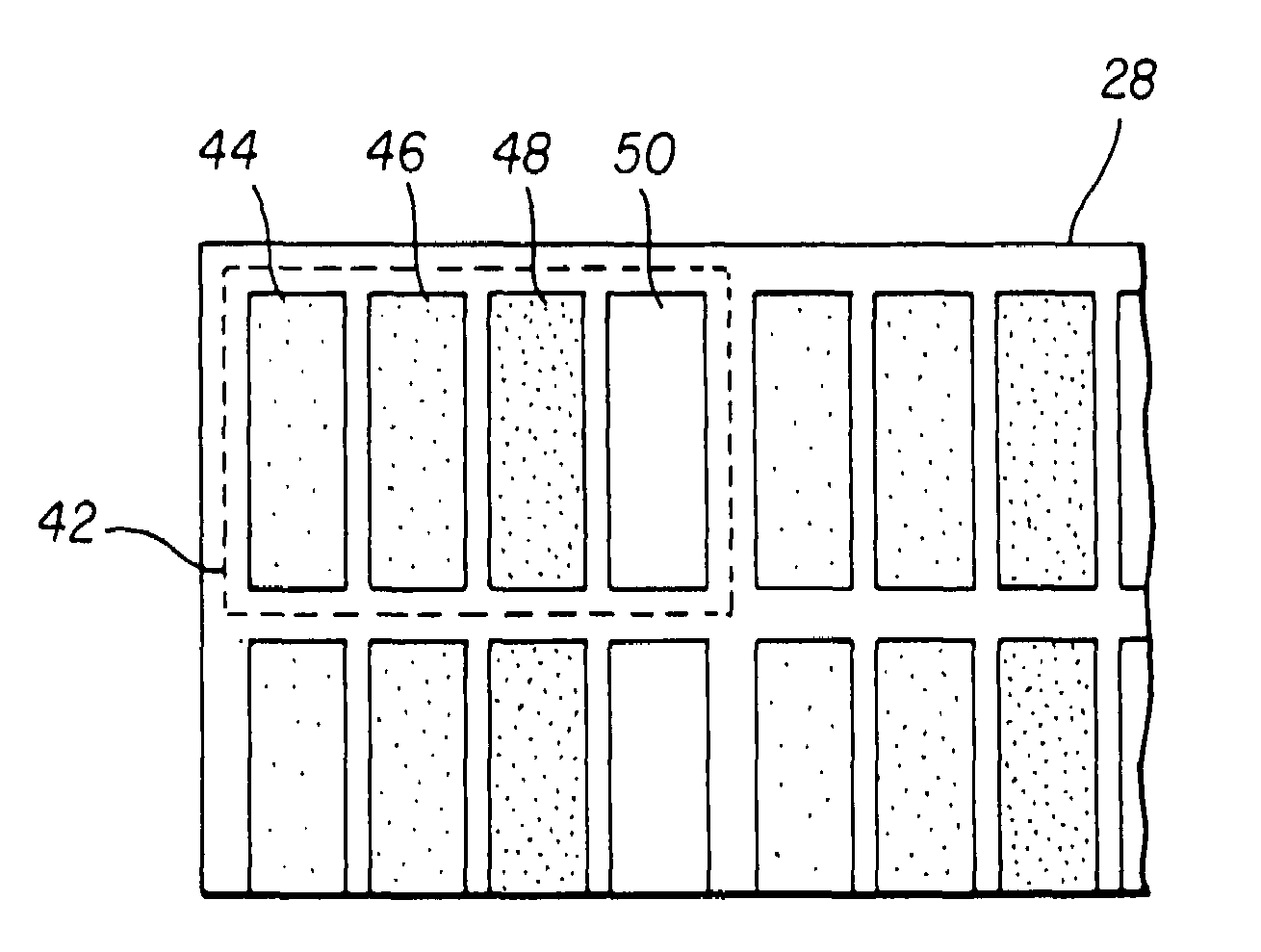
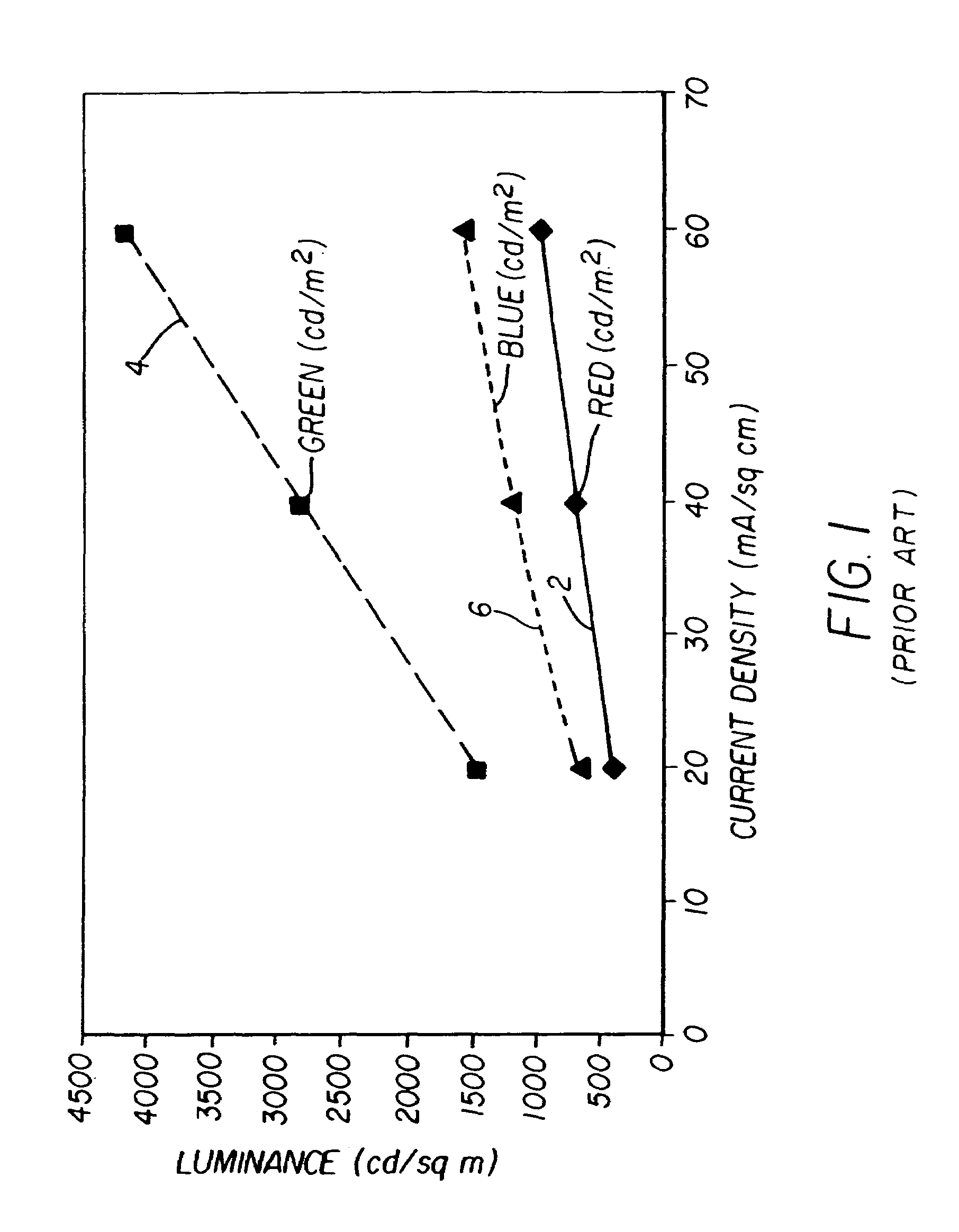
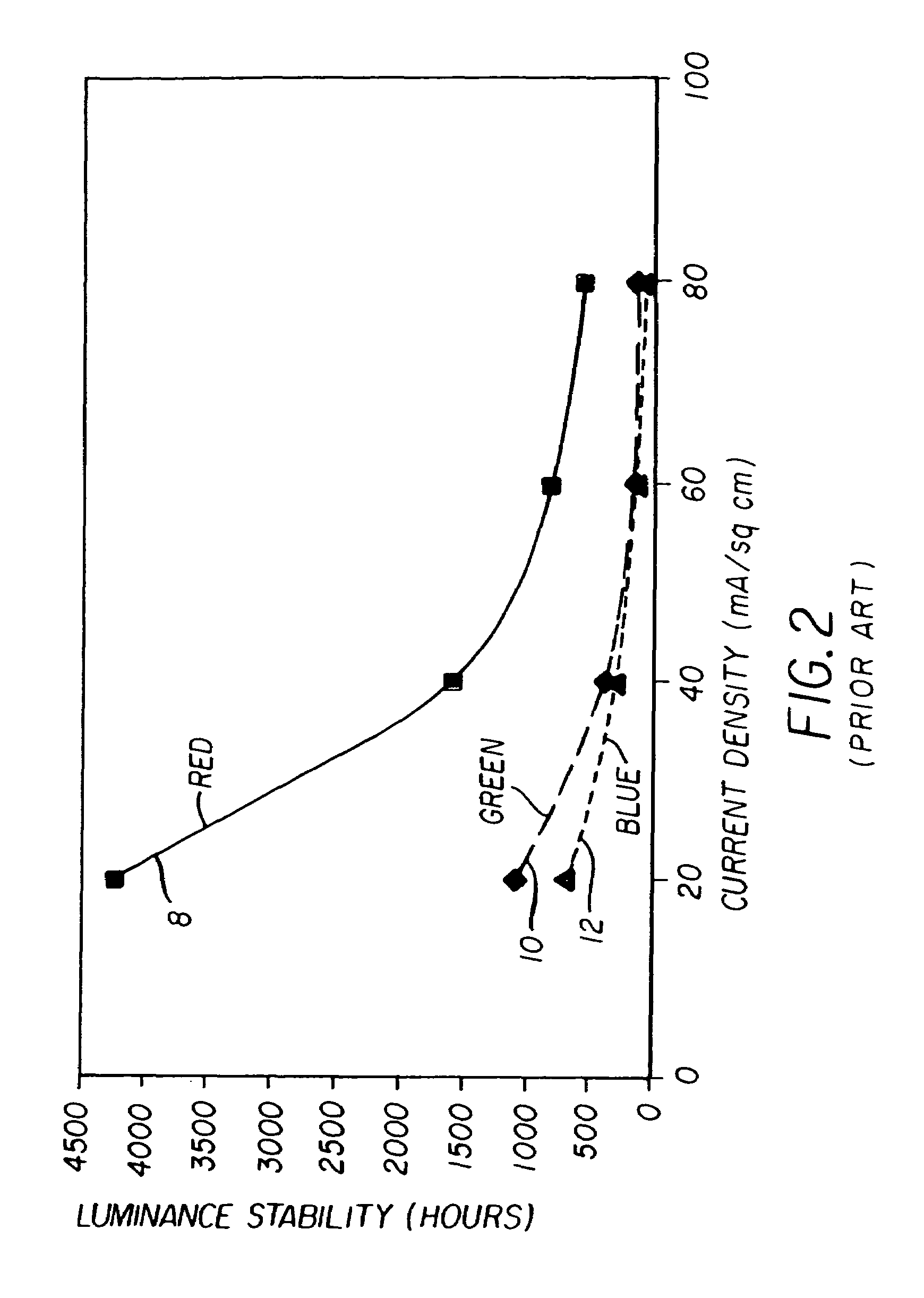
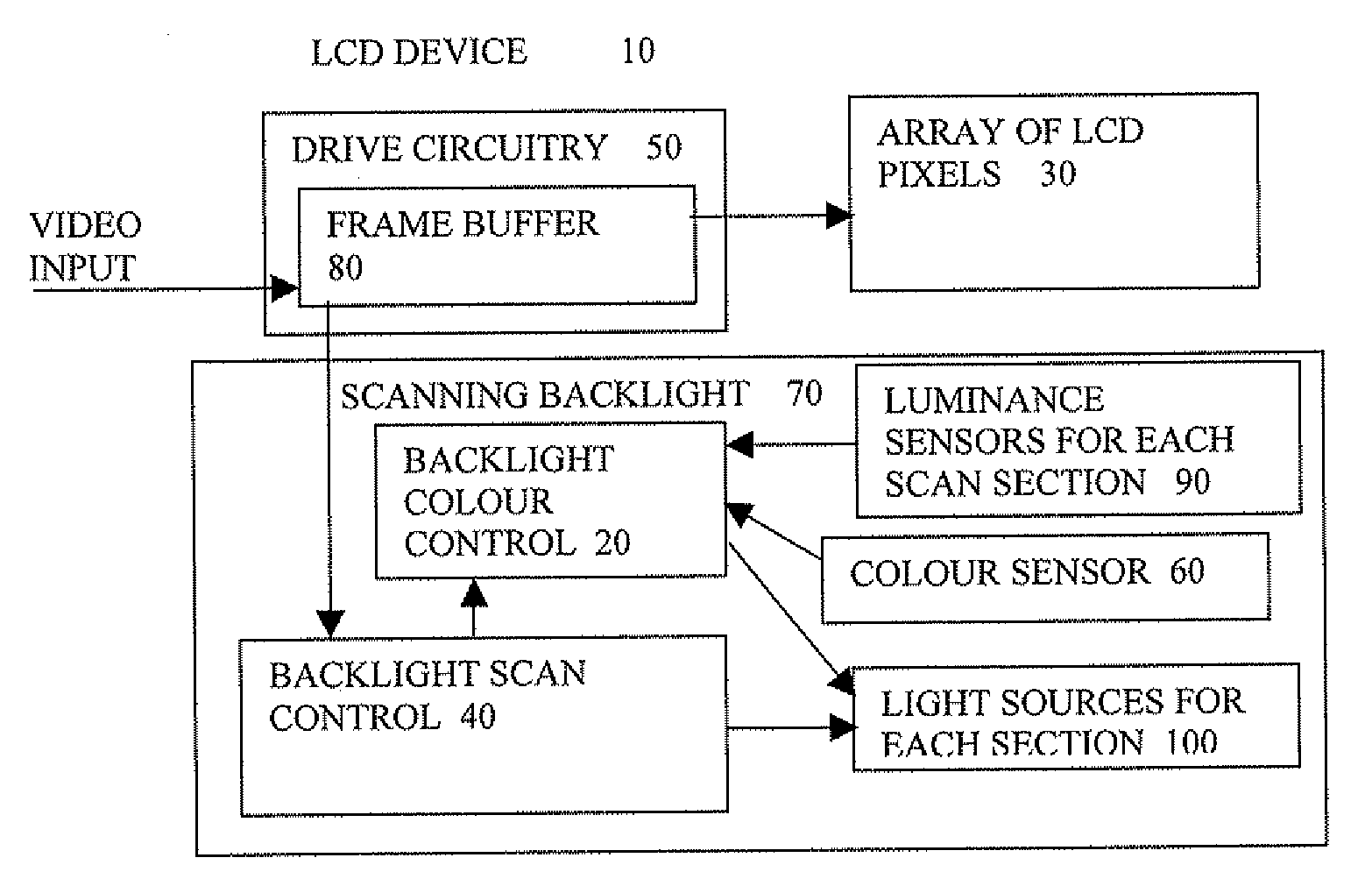
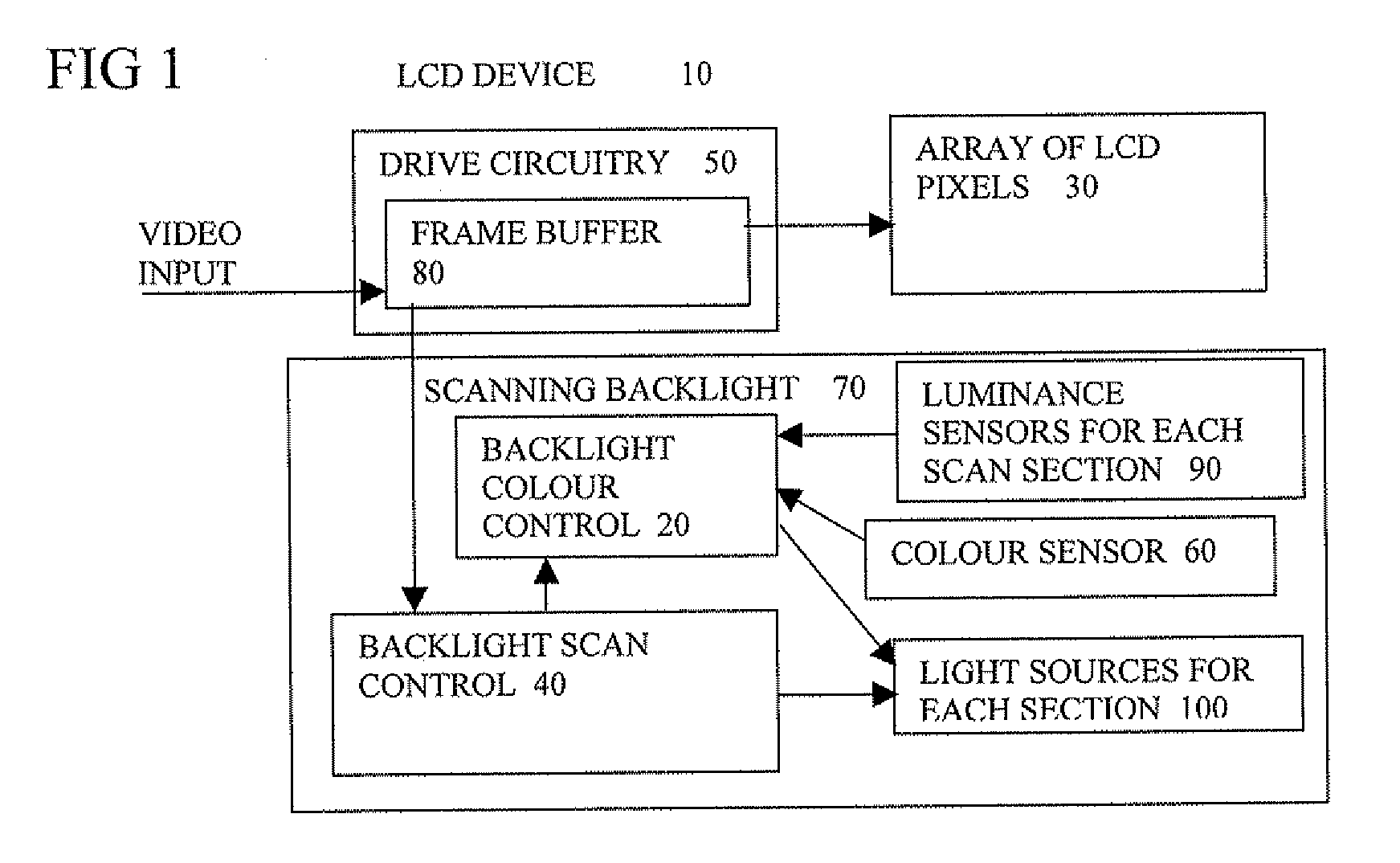
Scanning backlight color control
InactiveUS20090278789A1Without hindering display functionPrecise maintenanceStatic indicating devicesDisplay deviceRelative luminance
A scanning backlight (70) for a display, the backlight having a number of sections separately illuminated, a controller (20) to control the illuminating of the different sections at different times, and to control relative luminance levels of the different sections, and the backlight having a sensor (60) to detect a spectrum of the lighting, the controller being arranged to control a color of the illuminations of the different sections according to the detected spectrum. This combination can enable the color output to be maintained accurately without needing an external spectrometer, and control the uniformity of color in the different sections. This control can enable the specifications of any parts used to illuminate the sections to be relaxed, such as temperature and aging specifications, to keep the costs lower.
Owner:BARCO NV
Color OLED display system
ActiveUS7184067B2Display deviceEfficient powerElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesColor imageGamut
An OLED display system includes a display device having an array of light emitting pixels, each pixel having a plurality of OLEDs for emitting different colors of light specifying a gamut and at least one additional OLED for emitting a color of light within the gamut, wherein the power efficiency of the additional OLED is higher than the power efficiency of at least one of the plurality of OLEDs; means for generating a control signal indicating an amount of contribution to the light output of the display provided by the additional OLEDs; and a display driver for receiving a standard color image signal representing relative luminance and color to be produced for each pixel of the display and generating a converted color image signal for driving the OLEDs in the display, the display driver being responsive to the control signal for controlling an amount of light produced by the additional OLEDs such that the power efficiency of the display may be increased and / or the rate of degradation of the display device may be decreased.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Color OLED display system having improved performance
An OLED display system includes an OLED display including an array of light emitting pixels, each pixel having a plurality of OLEDs for emitting different colors of light specifying a gamut and including at least one additional OLED within the gamut defined by the other OLEDs and wherein one of the OLEDs has a power efficiency or lifetime different from the power efficiency or lifetime of at least one of the other OLEDs; a control signal; and a display driver for receiving a color display signal representing a relative luminance and color to be produced for each pixel of the display and generating a converted color display signal for driving the OLEDs in the display at the relative luminance and color, wherein the display driver is responsive to the control signal for controlling the in-gamut mixing ratio of the OLEDs to reduce power consumption or increase lifetime of at least one of the OLEDs.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Image processing device and associated methodology of processing gradation noise
InactiveUS8411992B2Improve denoising effectAchieve denoisingImage enhancementTelevision system detailsComputational scienceImaging processing
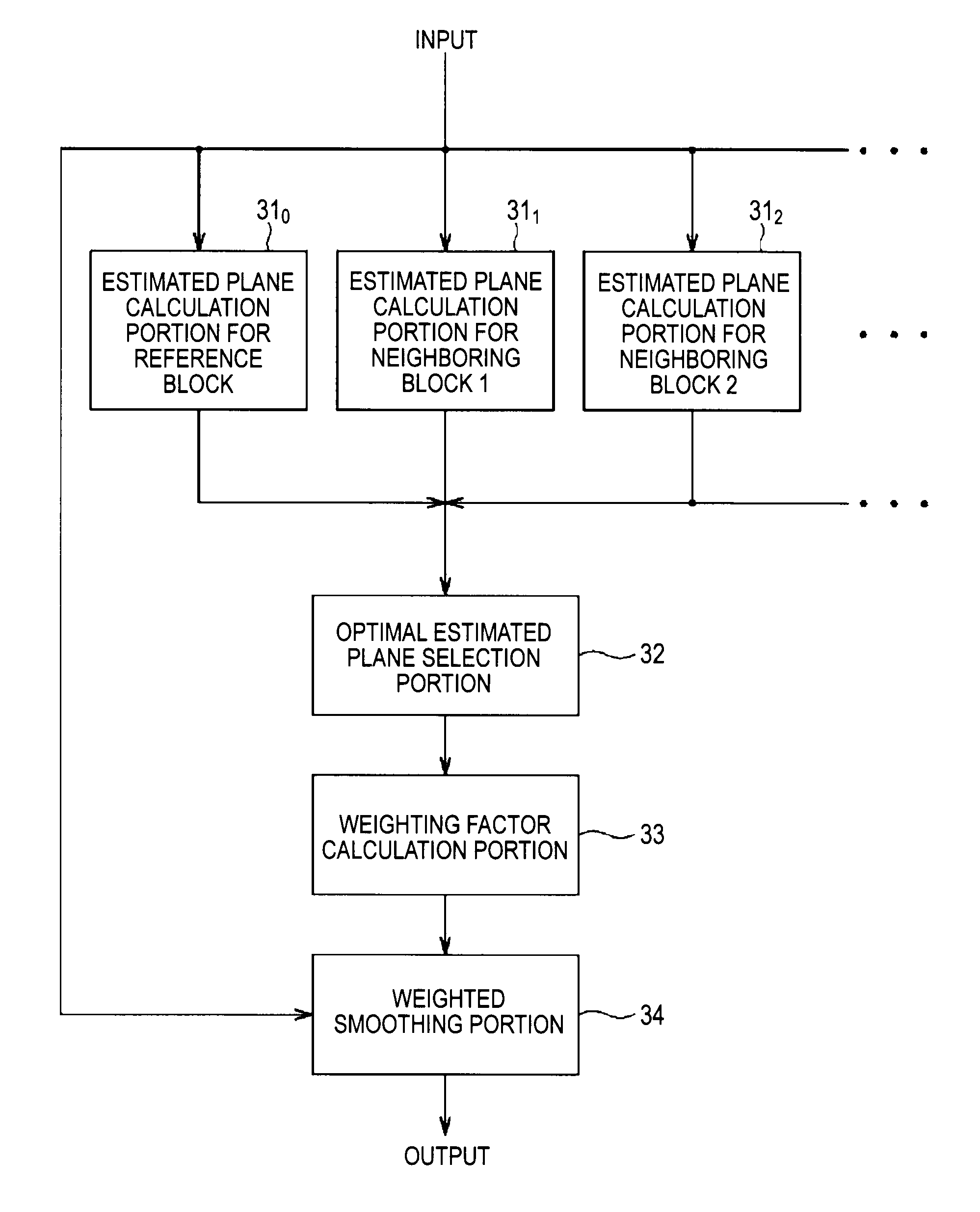
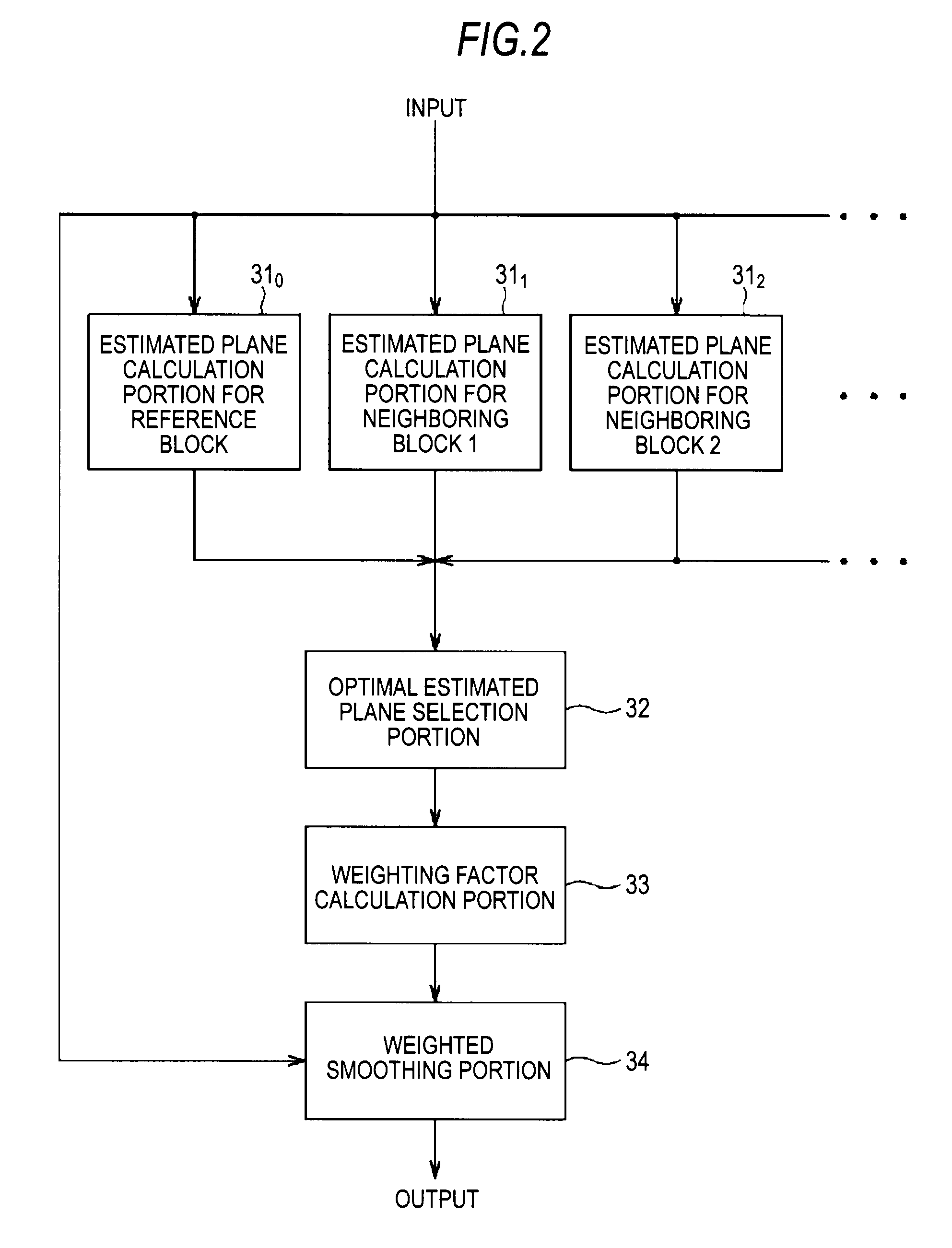
An image processing device includes: an estimated plane calculation portion calculating, for inputted image data, estimated planes defined by luminance values in blocks each containing a predetermined number of pixels including a reference pixel; an optimal estimated plane selection portion selecting an optimal estimated plane having a least summation of errors between luminance values of respective pixels in a block and an estimated plane among the estimated planes; a weighting factor calculation portion calculating a weighting factor for the reference pixel base on luminance values of the reference pixel and in the optimal estimated plane; and a weighted smoothing portion computing a sum of products of relative luminance differences between the luminance values of the respective pixels in the block and in the optimal estimated plane and the weighting factor for the reference pixel and adding a luminance value in the optimal estimated plane at a reference pixel position to a result of computation.
Owner:SONY CORP
Display device
ActiveUS20110074838A1Improve luminosityInhibition effectSolid-state devicesCathode-ray tube indicatorsDisplay deviceHemt circuits
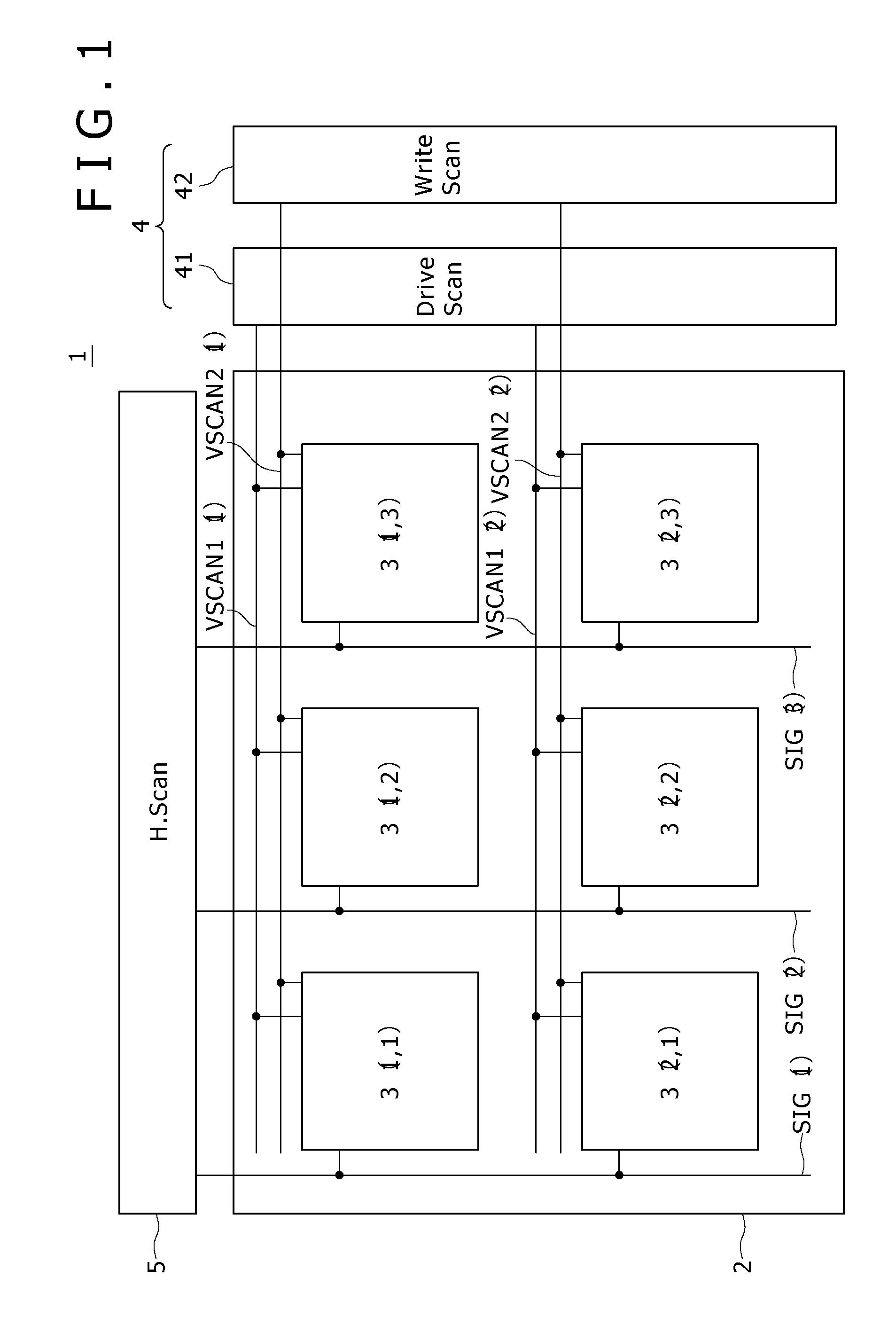
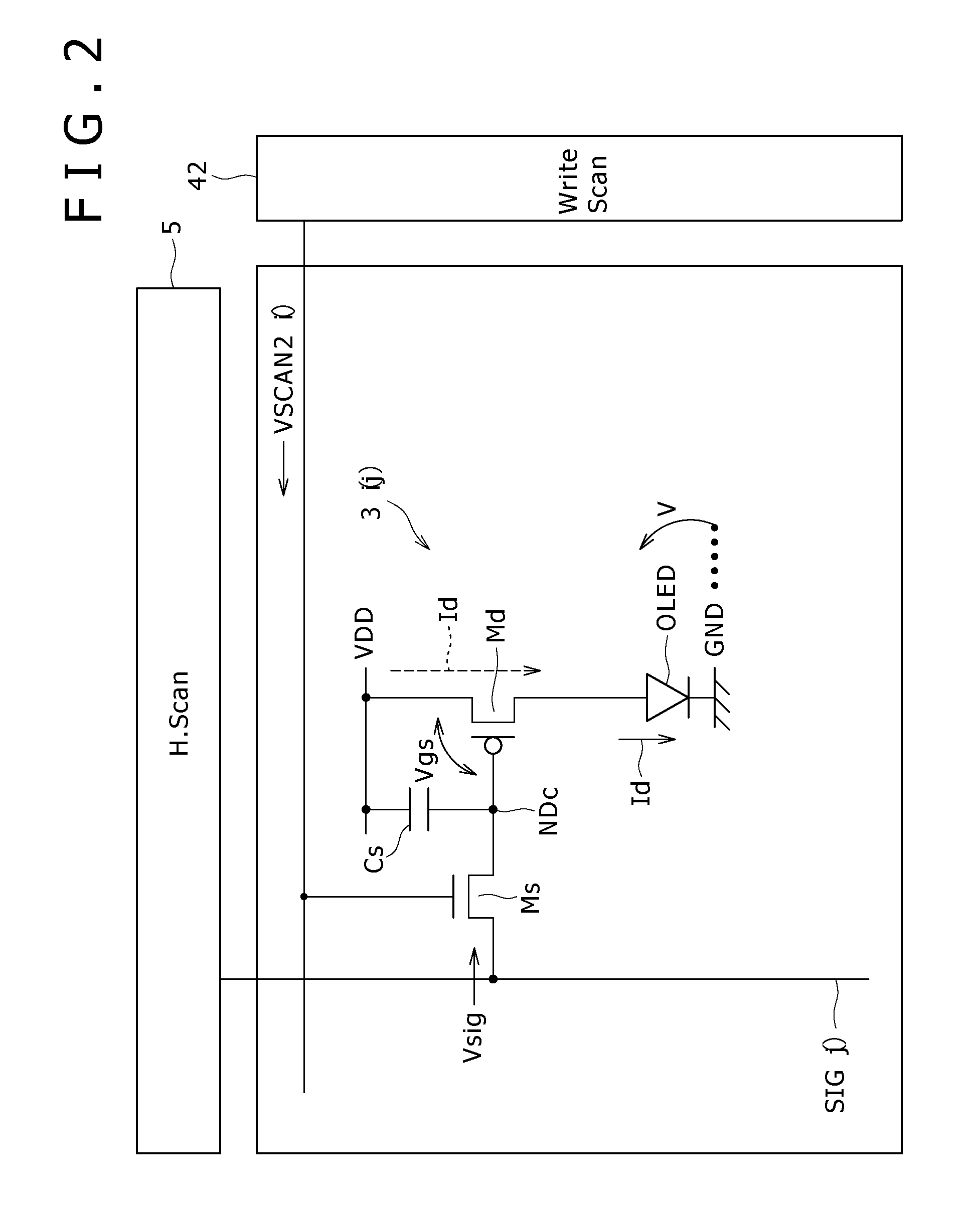
A display device according to the present invention includes pixel units. Each of the pixel units is made up of N consecutive pixels. One of N (N≧3) colors including R (red), G (green) and B (blue) is assigned to each of the N pixels. Each of the N pixels includes a sampling transistor Ms, drive transistor Md, holding capacitor Cs and light-emitting element (organic light-emitting diode OLED). Of the N pixels, a specific color pixel that is susceptible to a dark dot (e.g., B) or that has the highest relative luminosity factor (e.g., G) has more sets of pixel circuit elements including the drive transistor Md, holding capacitor Cs and organic light-emitting diode OLED than other color pixels and has two or more sets thereof.
Owner:JOLED INC
Liquid crystal display
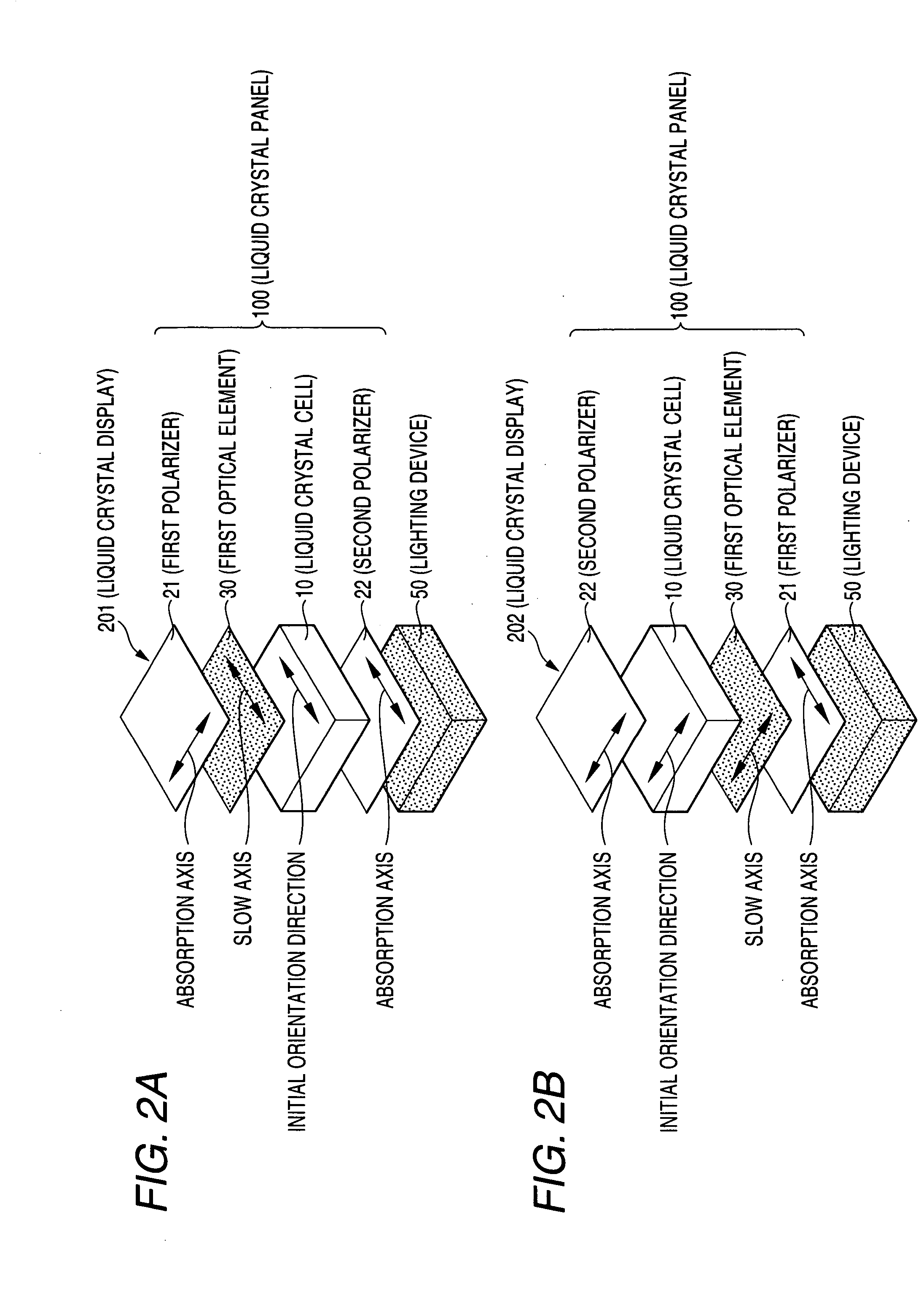
ActiveUS20070211199A1Small color shiftReduce the effect of colorNon-linear opticsEffect lightRelative luminance
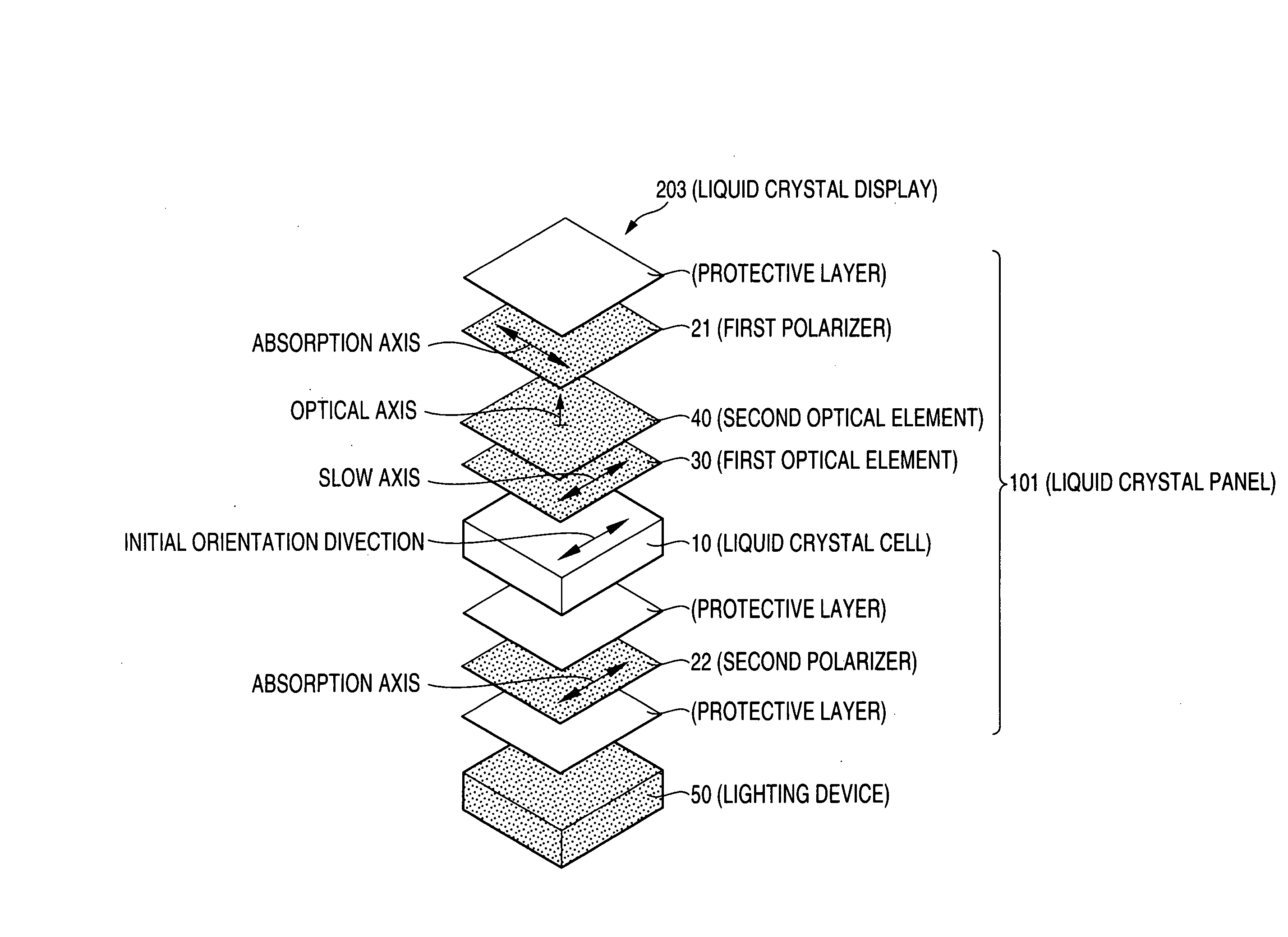
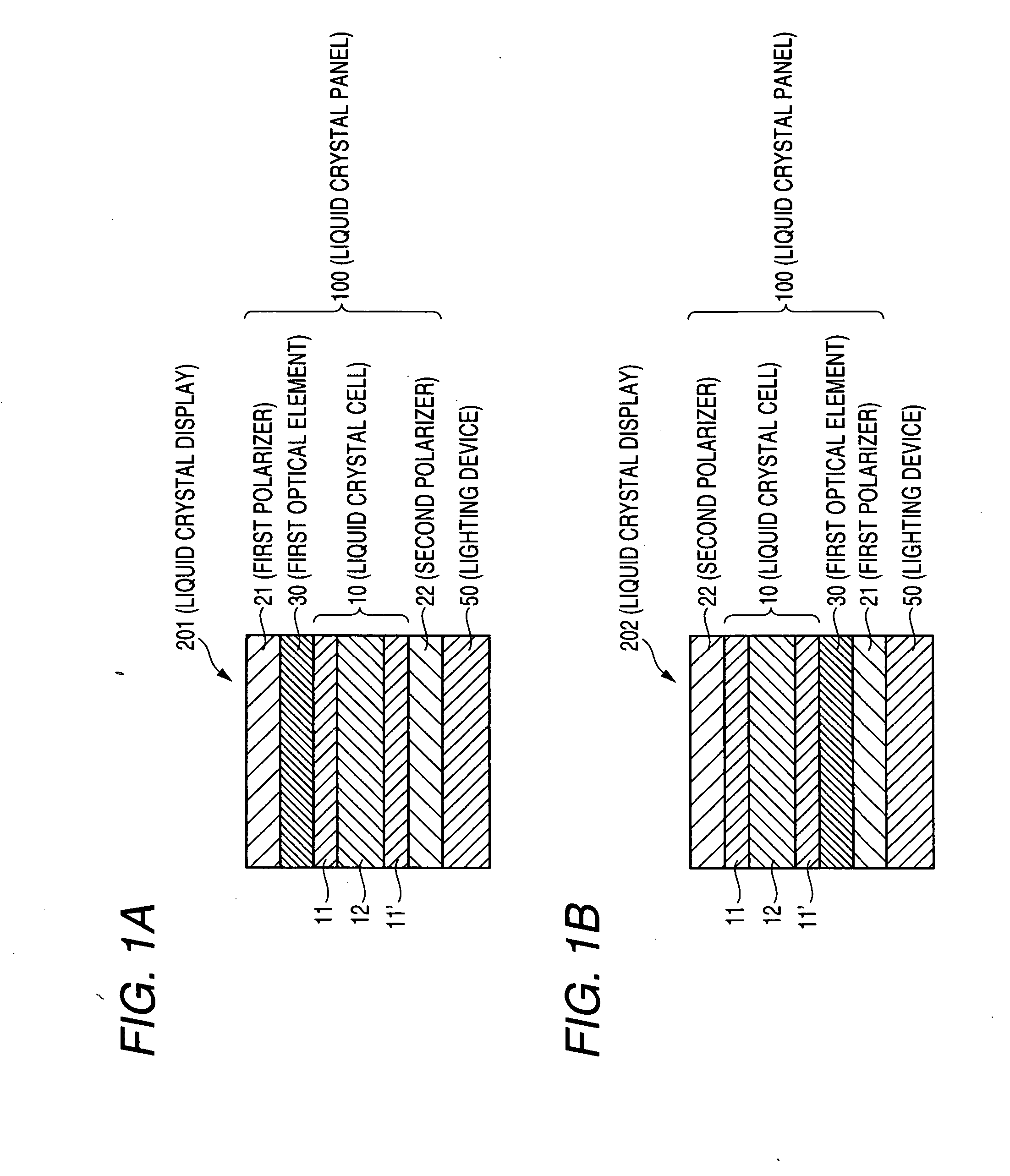
The present invention provides a liquid crystal display including: a liquid crystal panel; and a lighting device disposed on one side of the liquid crystal panel, the liquid crystal panel including: a liquid crystal cell; a first polarizer disposed on one side of the liquid crystal cell; a second polarizer disposed on the other side of the liquid crystal cell; and a first optical element disposed between the liquid crystal cell and the first polarizer; the absorption axis direction of the first polarizer being substantially perpendicular to the absorption axis direction of the second polarizer, the first optical element having an optical indicatrix having a relationship of nx≧nx>ny, the lighting device having: a maximum value of luminance in the wavelength range of 550±50 nm; and a relative luminance at a wavelength of 450 nm is 0.28 or less.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
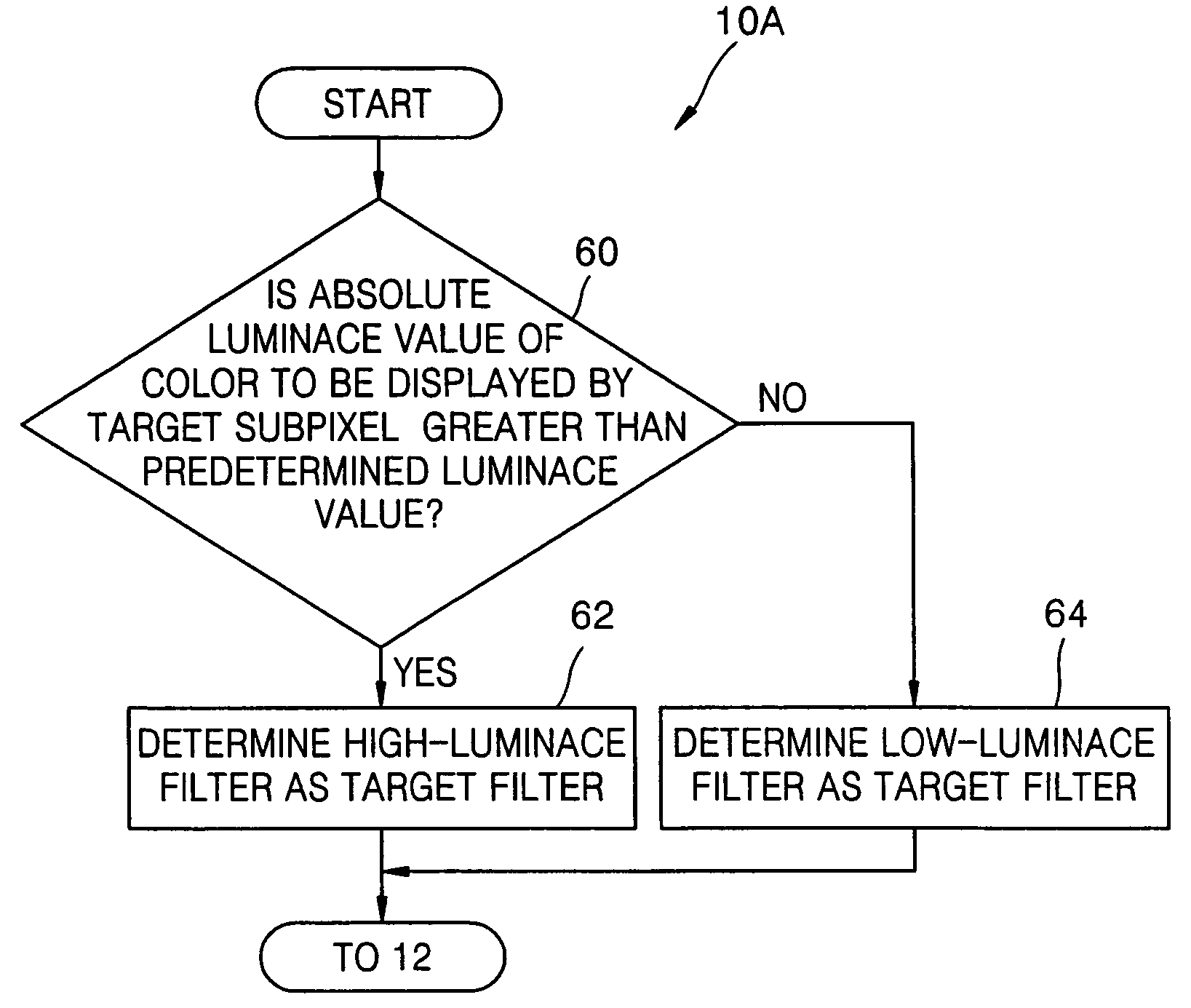
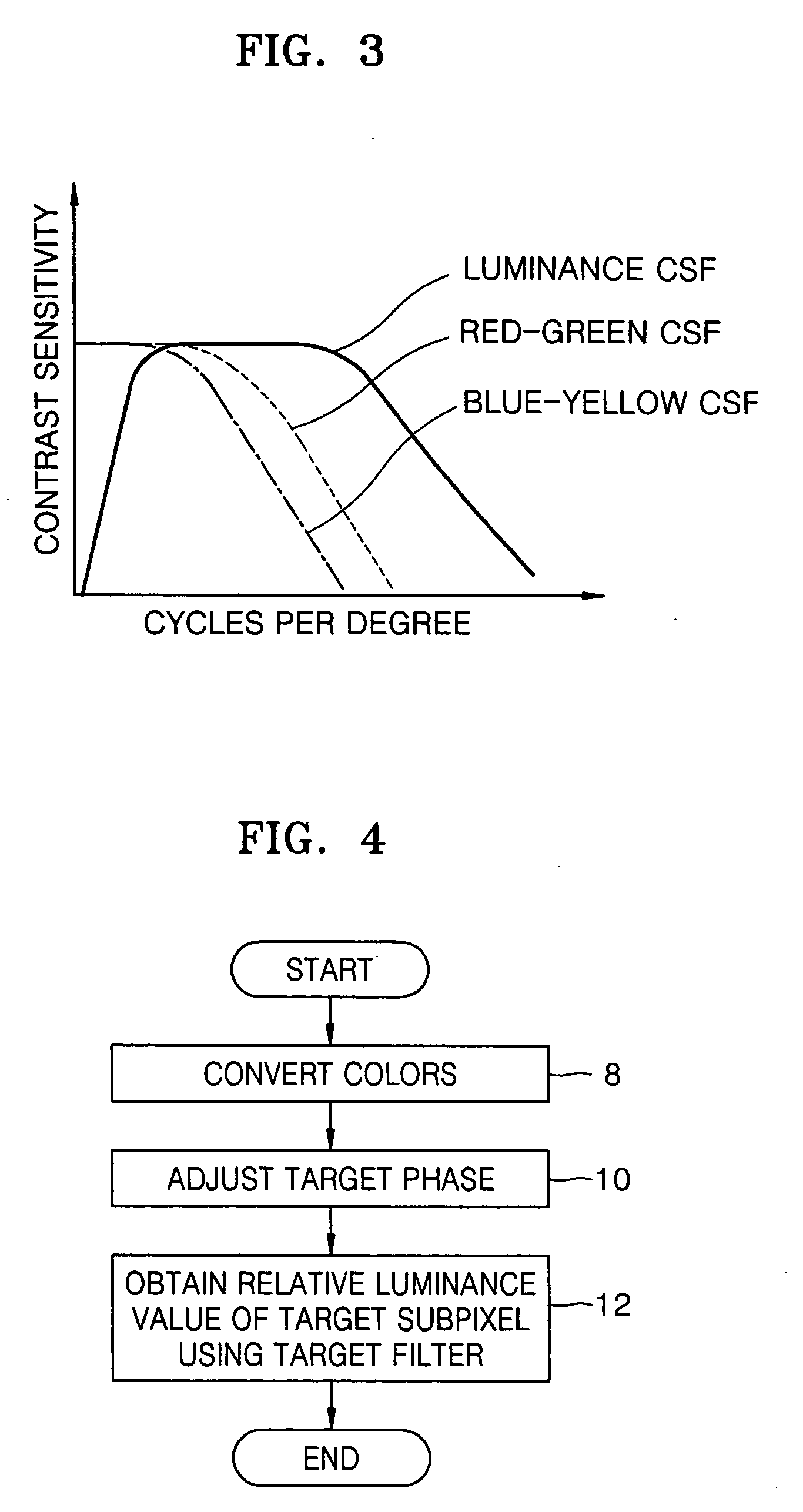
Method and apparatus for displaying image and computer-readable recording medium for storing computer program
ActiveUS20050062767A1Minimize color fringeMinimize colorTelevision system detailsCathode-ray tube indicatorsRelative luminanceLightness
A method and apparatus for displaying an image using a display pixel including at least one subpixel displaying one among four or more colors, and a computer-readable recording medium for storing a computer program for performing the method. A target phase of a target subpixel is adjusted using a difference between an absolute luminance value of a color to be displayed by the target subpixel and an absolute luminance value of a color to be displayed by at least one subpixel adjacent to the target subpixel. A relative luminance value of the target subpixel is obtained from a relative luminance value of at least one image pixel using a target filter having the adjusted target phase as a center of the target filter.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and apparatus for adapting chromatic compensation
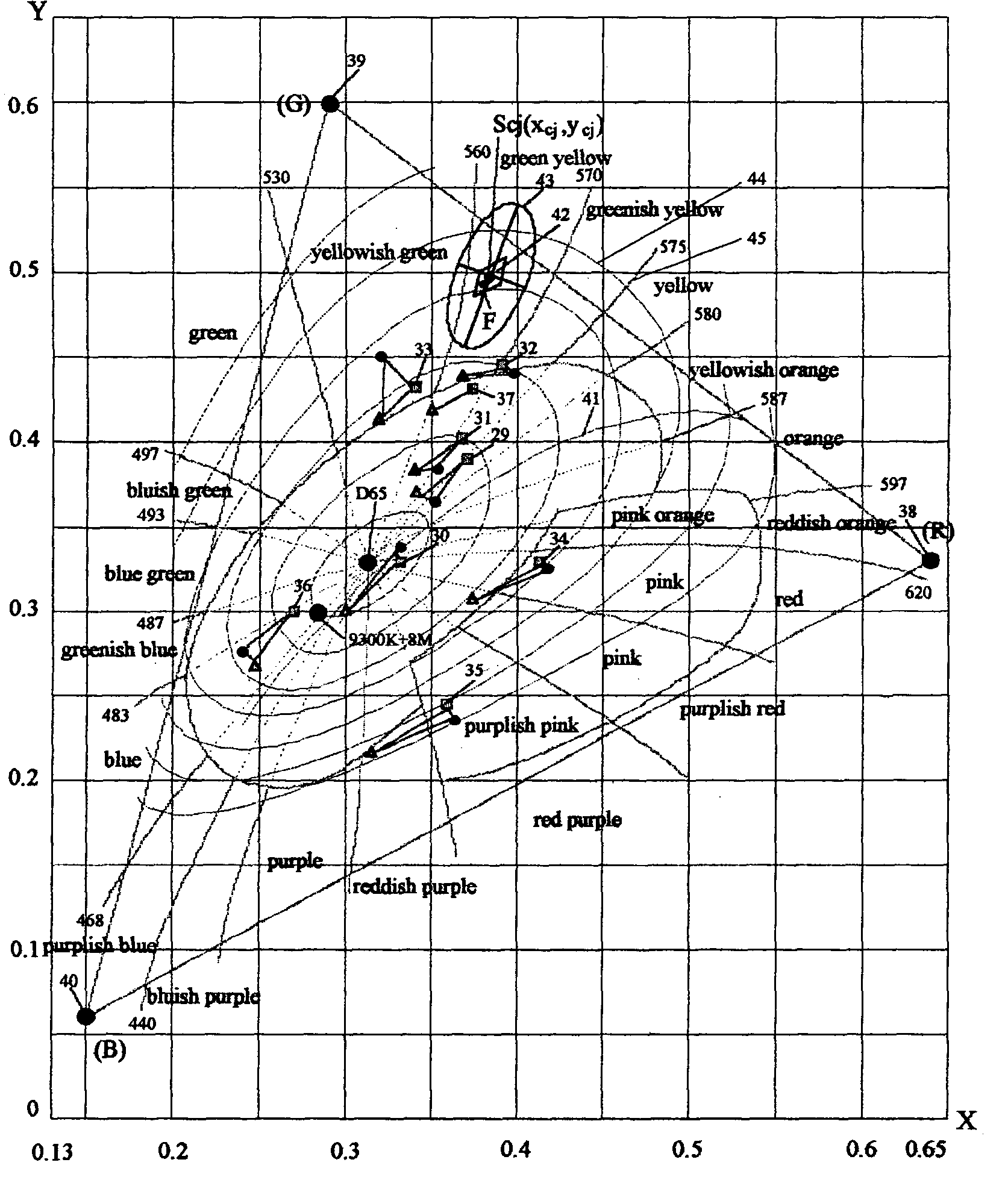
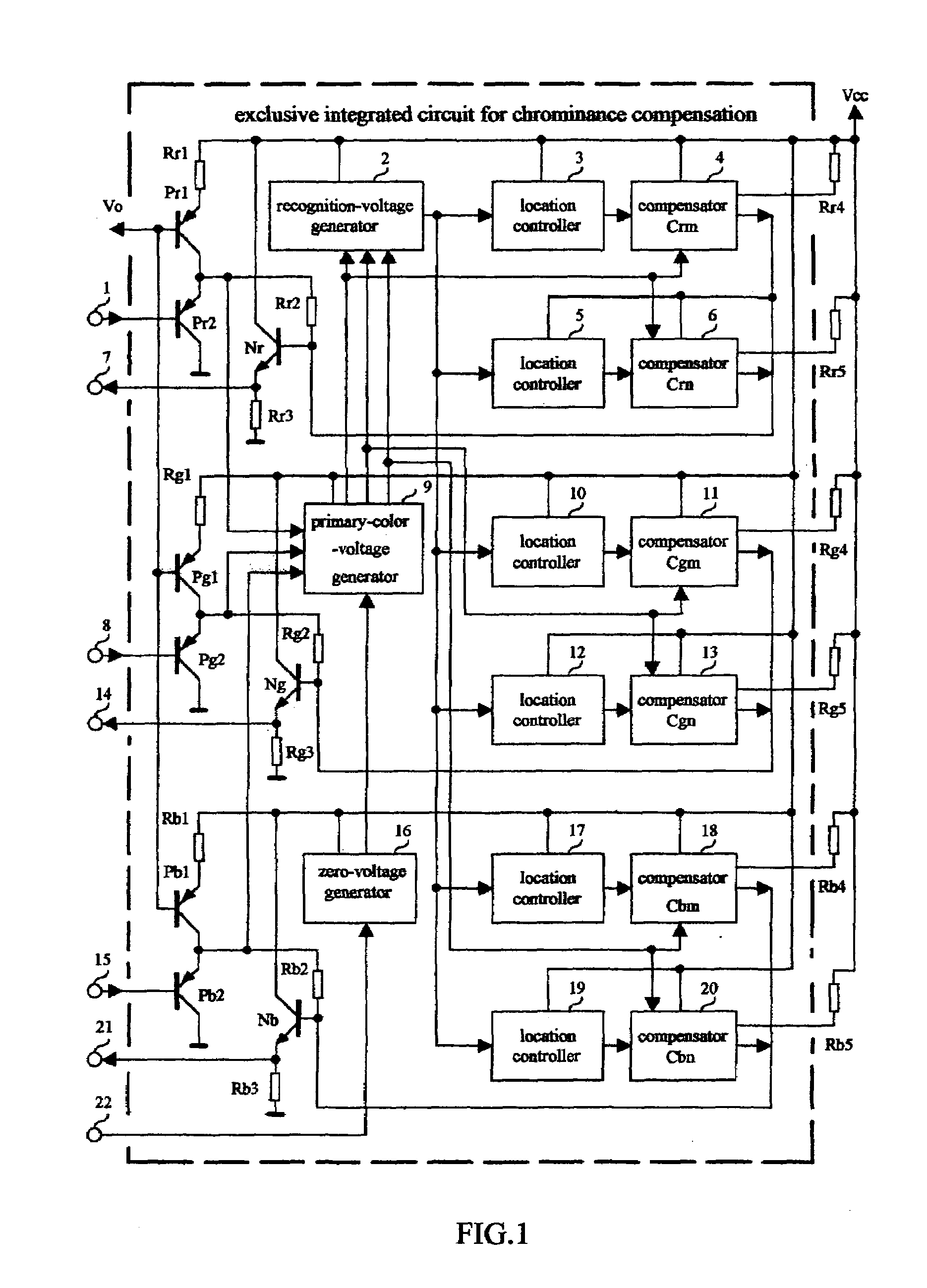
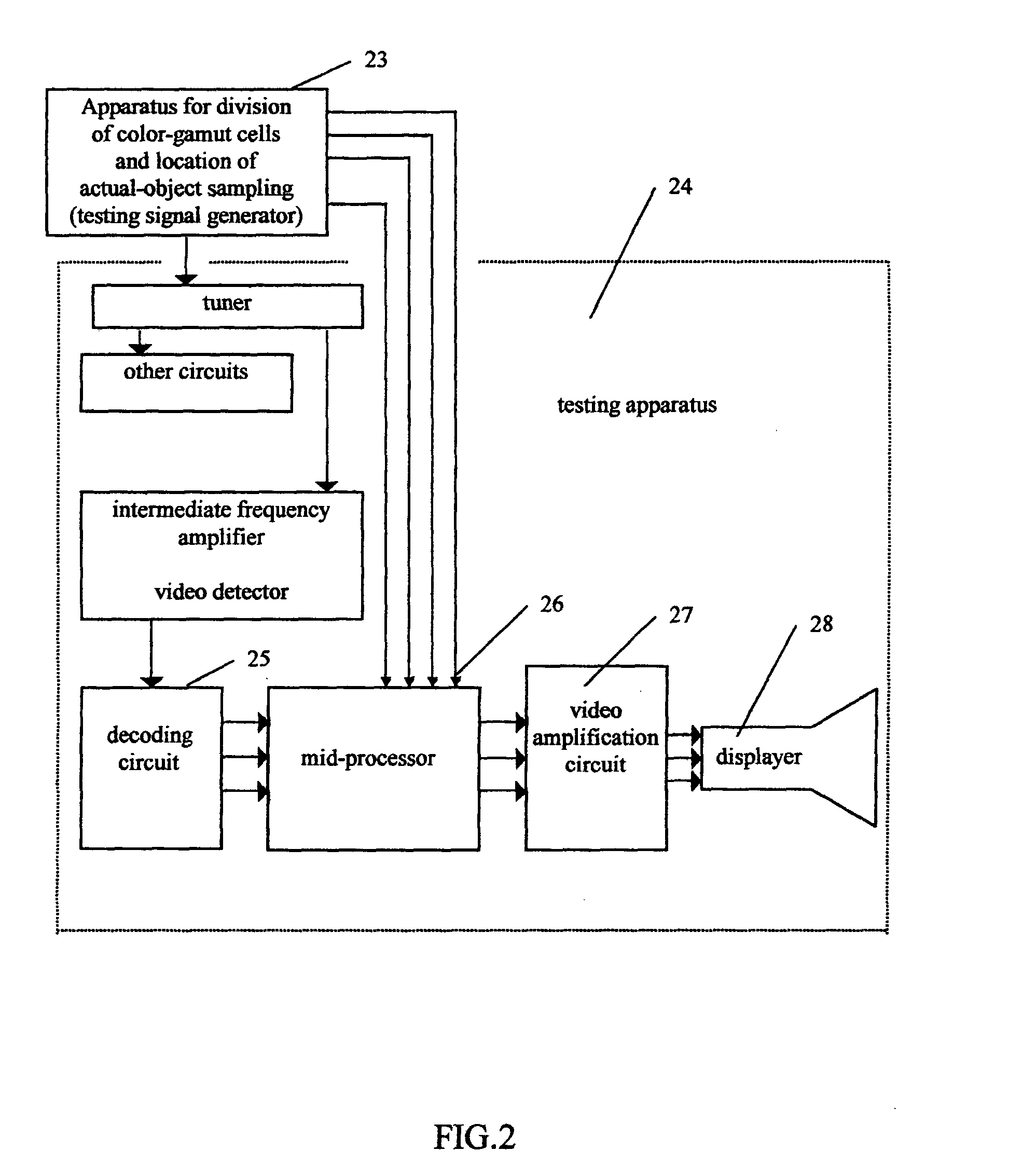
The present invention relates to a method and an apparatus for adaptive compensation of chrominance, aiming at the optimization of colors of electronic images. The invention includes the experimental data obtained when the best viewing effects are achieved, the division of color-gamut cells according to visual characteristics, the preset compensation characteristics that have different amplifications for different color-gamut cells, the real-time recognition of color-gamut cells that the signals belong to, and appropriate compensation that is done according to the color-gamut cells. The characteristic of the compensation is that each pixel gets its own amplification dynamically, which makes the dominant wavelength, chroma and relative brightness of all the image colors meet the requirement of best self-adaptive color reproduction automatically. As a result, colorful images with high qualities can be acquired. The present invention eliminates the local inferior chrominance distortion that inevitable for existing products and improves the equipment's adaptability to the receiving environments.
Owner:BEIDA GISOFT +1
Method for detecting subaqueous acute biological toxicity using photobacteria
InactiveCN101131384AReduce usageHigh test sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceToxicantWater quality
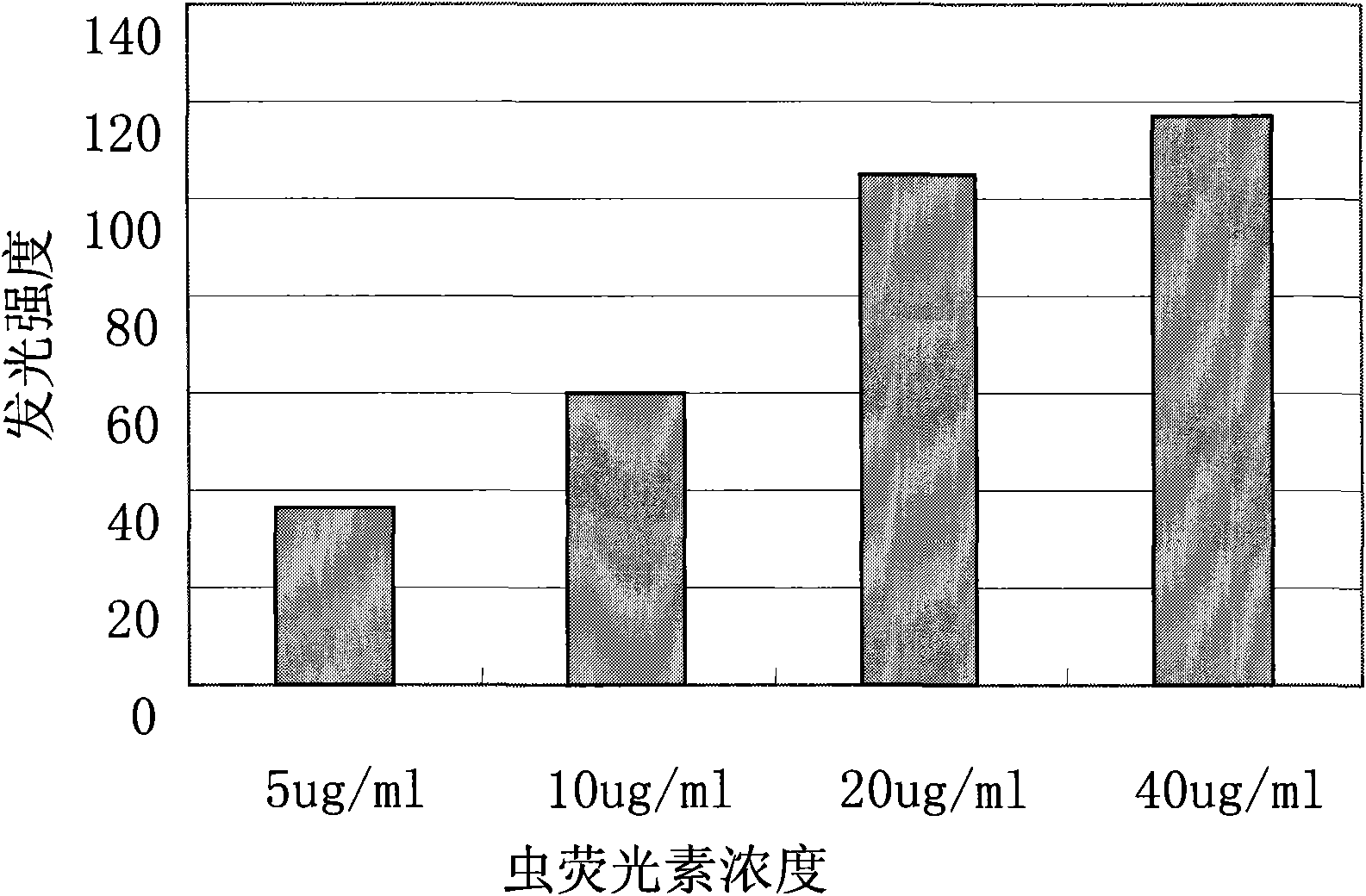
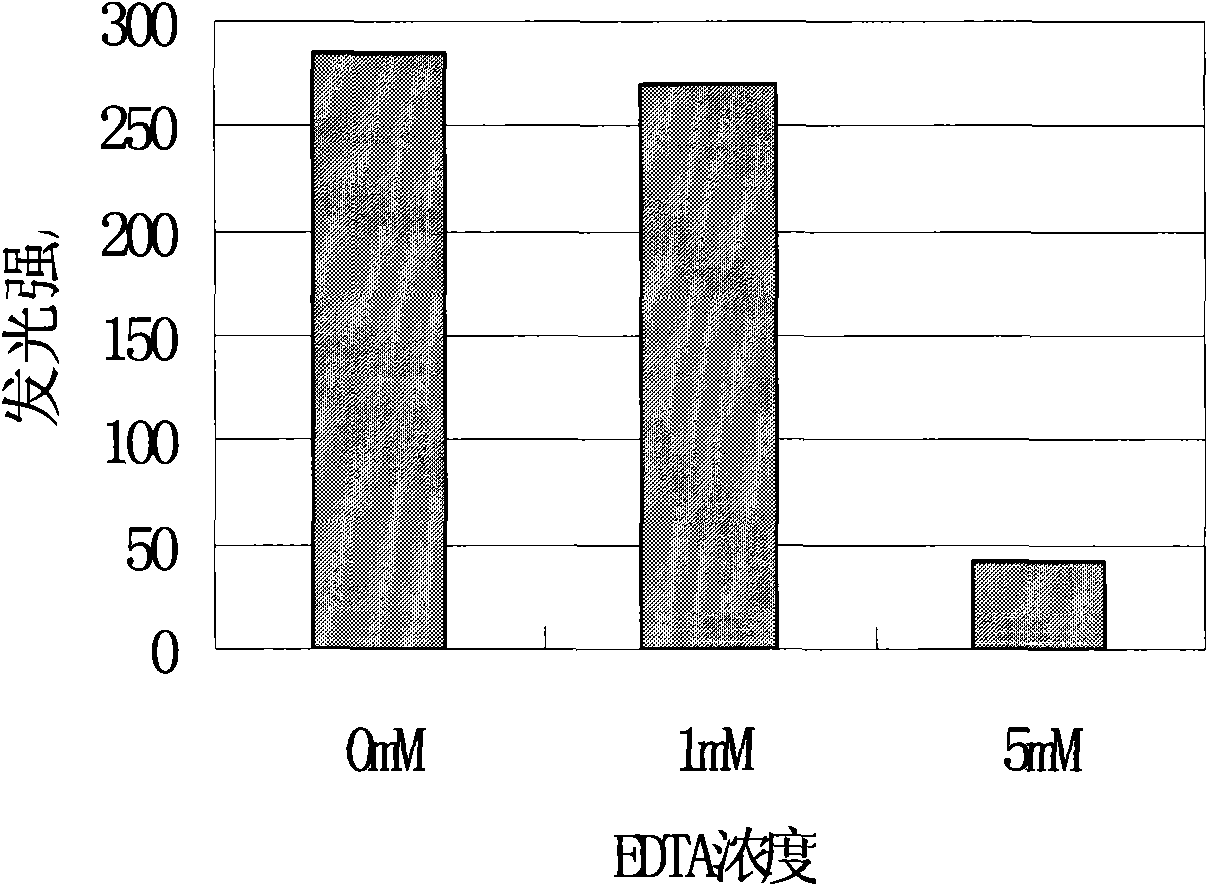
A method to detect the acute biology toxicity by the photobacterium is to prepare the new photobacterium culture firstly, then to adjust the pH of tested water: the pH is 4.5 when the Cu density is higher than other metal and organic matter; the pH is 5.4 when the water sample does not contain Cu and other metal density is higher than the organic matter; the pH is 7.0 when the organic matter in water is higher than metal density. The ZnSO4 is as reference toxicity and matching a series of standard solution which are set in tube which is added in the photobacterium culture and detect the relative luminance. The luminance change of test water is expressed by the relative luminance. The computing formula is: the sample relative luminance = sample tube luminance / reference tube luminance. The invention uses the photobacterium not the toxicity to detect the acute biology toxicity of water.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
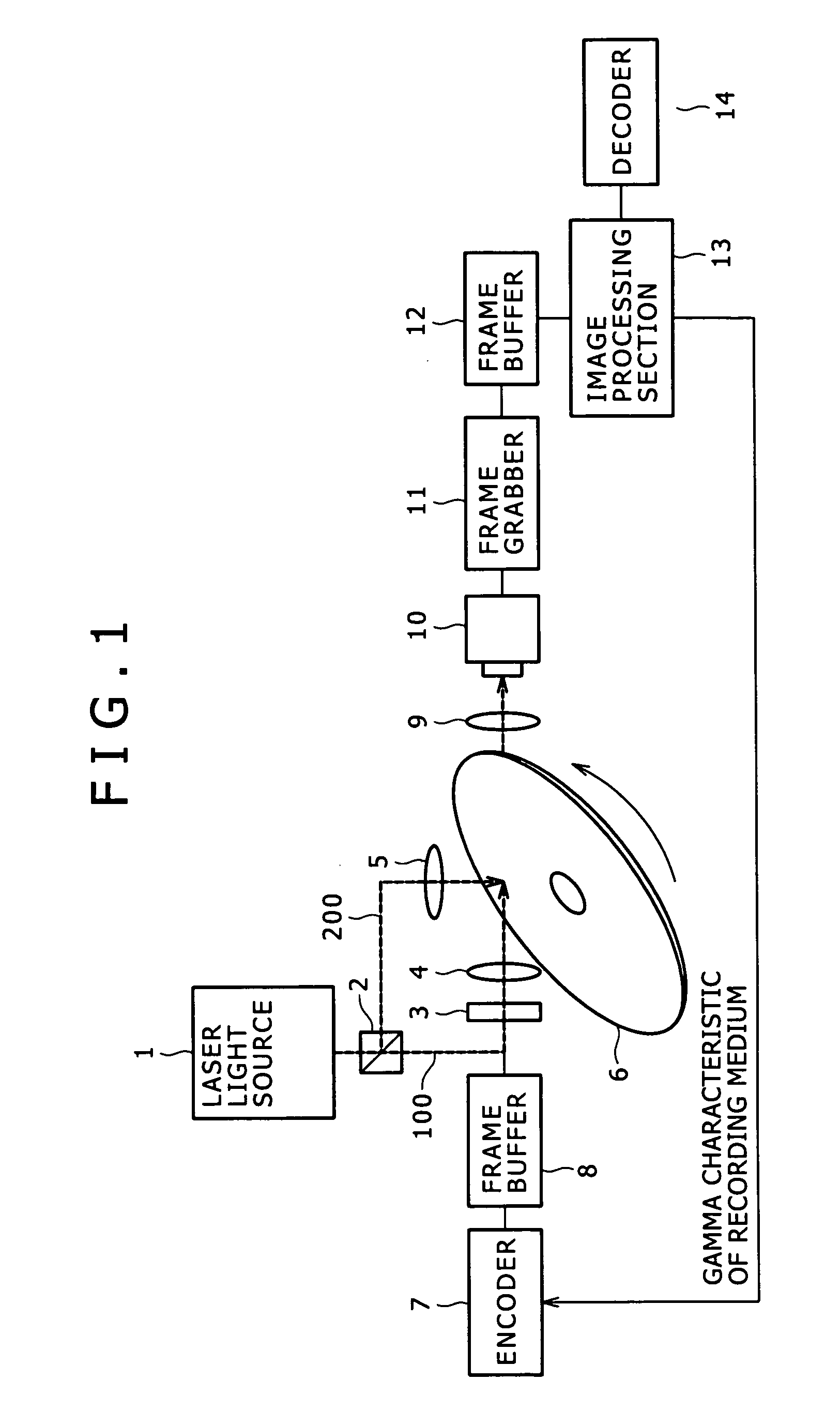
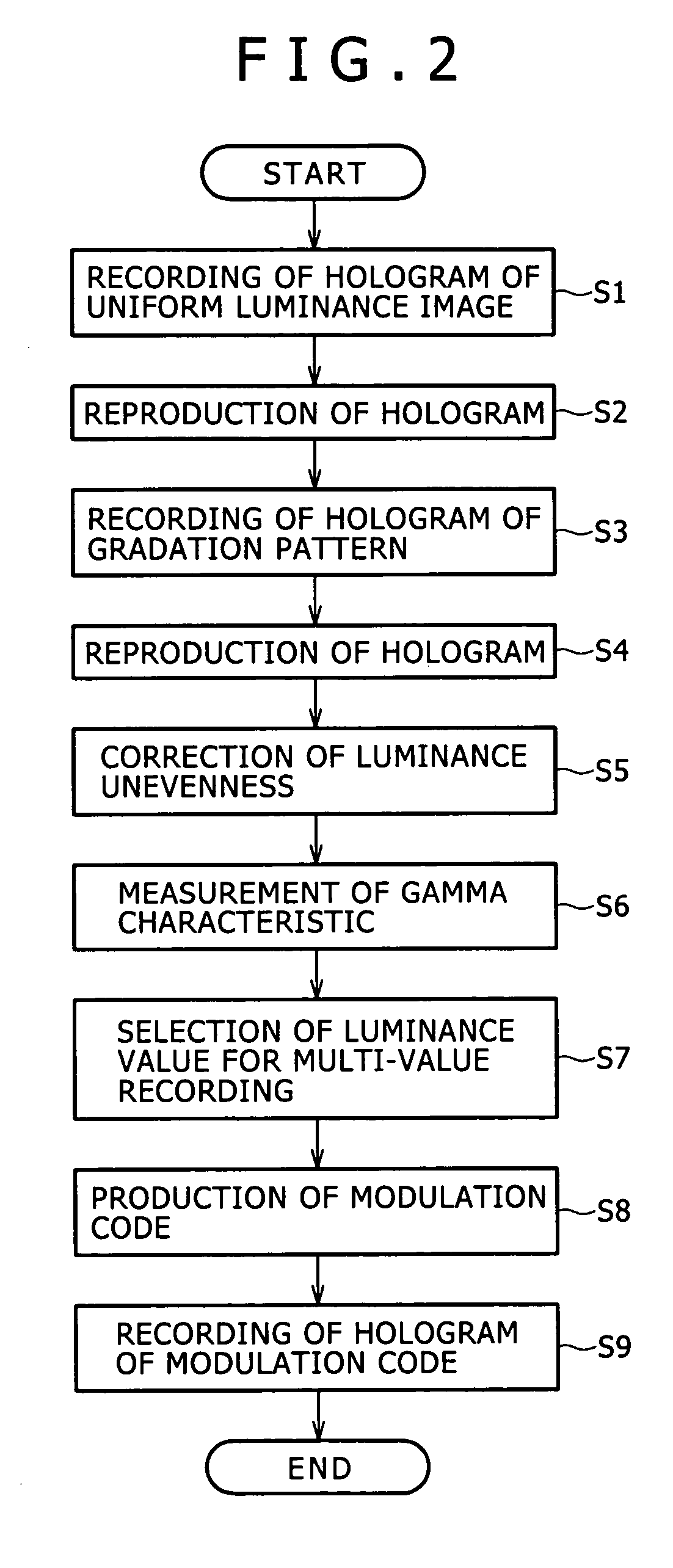
Hologram recording and reproduction method, hologram recording and reproduction apparatus, and hologram recording medium
InactiveUS20050185233A1Good repeatabilityReduce error rateRecord information storageSignal processing using self-clocking codesSpatial light modulatorModulation pattern
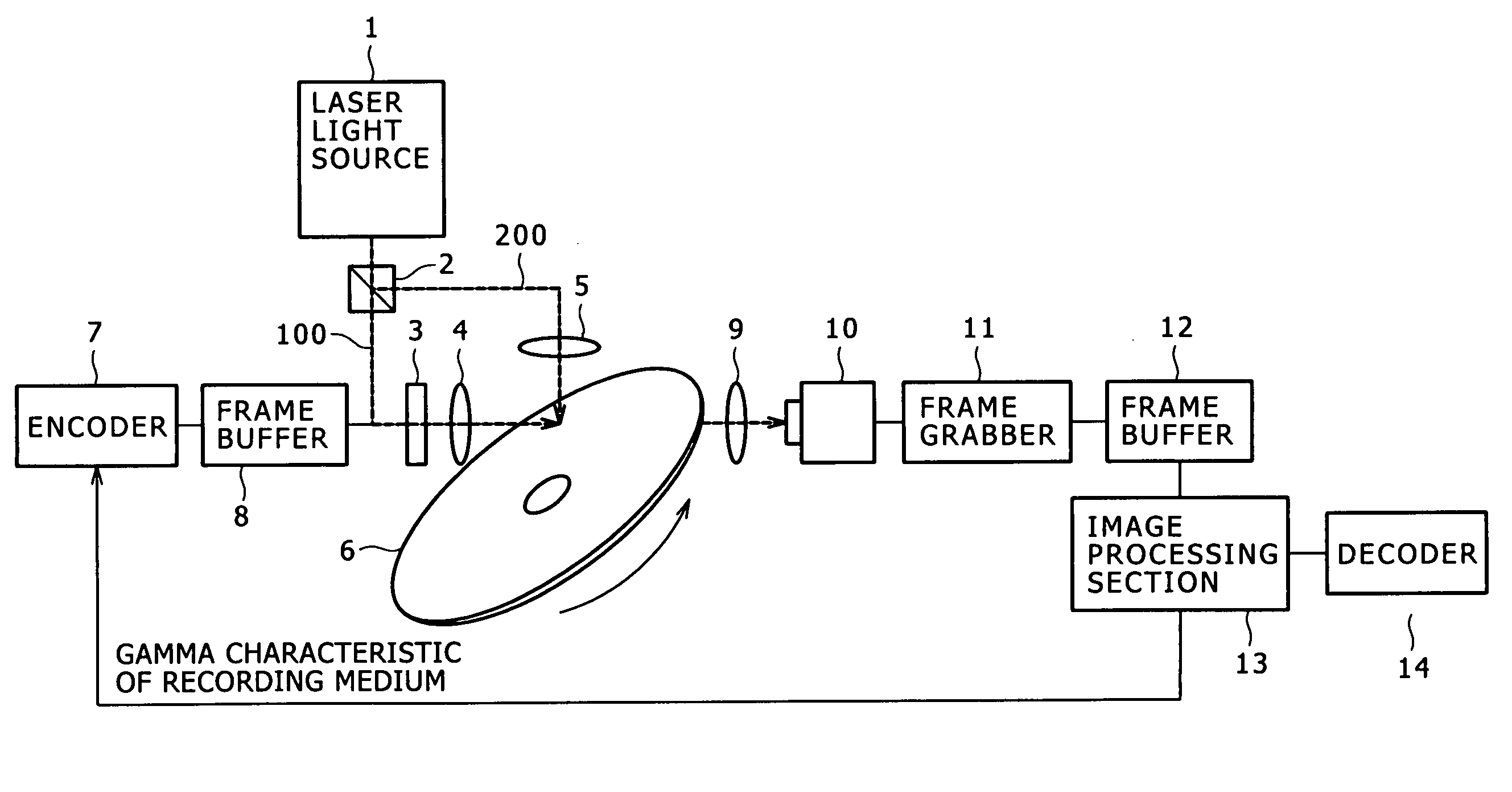
A method and apparatus is disclosed which can reproduce multi-value data with high reproducibility from a hologram recording medium having data recorded in multi-values therein and can reduce the error rate of reproduction data. A reference gradation pattern is recorded in a medium, and luminance unevenness of a gradation pattern obtained by reproducing the gradation pattern is corrected. A gamma characteristic of the medium is determined based on the reproduction gradation pattern, and a modulation pattern produced using easily separable luminance values determined based on the gamma characteristic is displayed on a spatial light modulator to record data in multi-values into the medium. Thereupon, the data are oversampled and recorded, and a block of the reproduced data is decoded depending upon a sequence of relative luminance levels of pixels in the block to decode the entire reproduced multi-value data.
Owner:SONY CORP
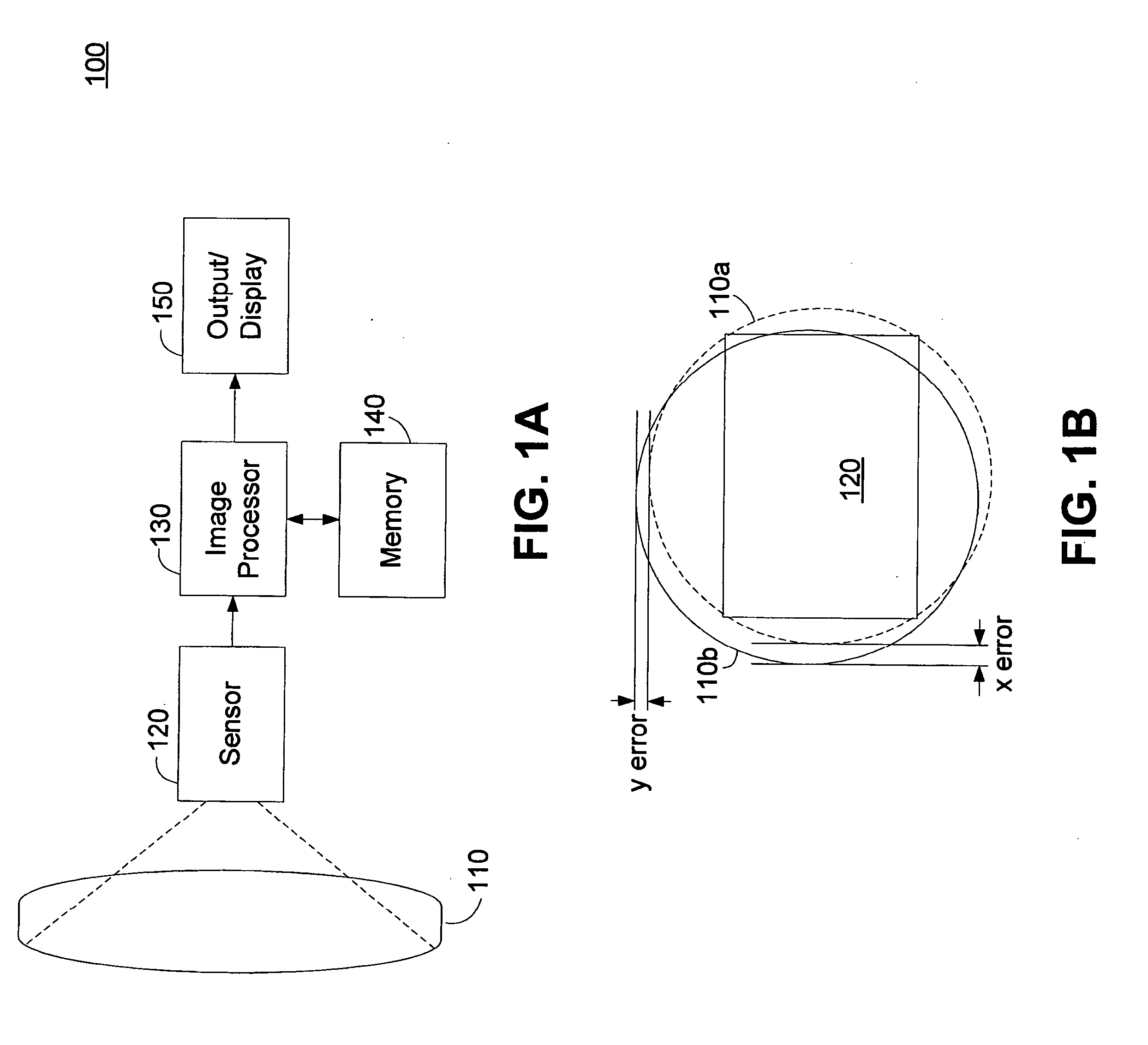
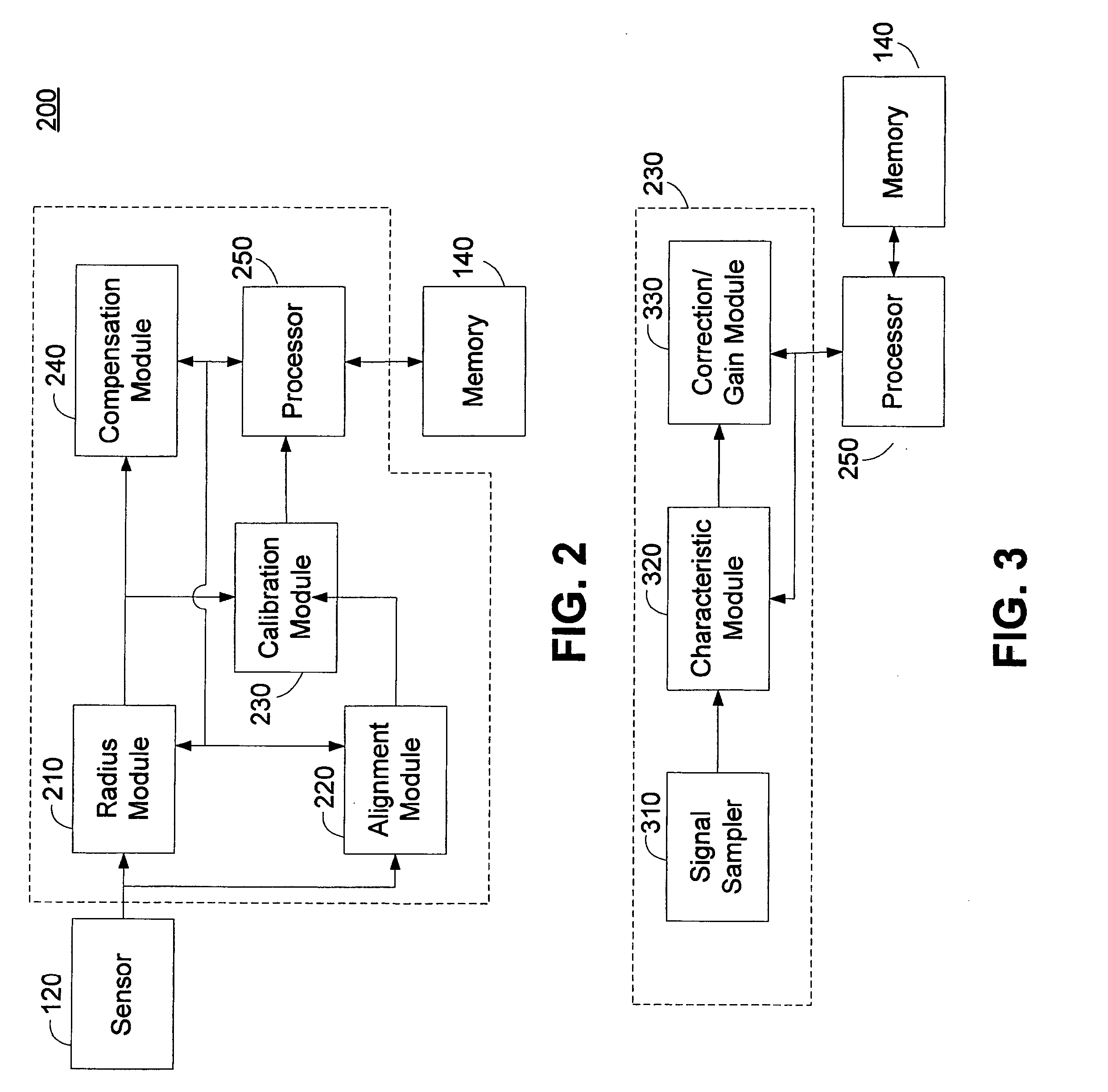
Lens roll-off correction method and apparatus
Brightness and color tone shift distortion of captured images by a non-ideal lens can be compensated by applying an inverse transfer function to the captured image. An estimate of the lens transfer function can be measured based on a radius from a center of the lens. The lens transfer function can be measured by capturing a flat field image. The center of the lens can be determined based on a relative brightness maximum. The relative brightness of the captured flat field image can then be measured as a function of radius to generate a lens response curve. Separate response curves can be measured for each color component. A correction curve can be determined as the inverse of the response curve. The correction curve can be applied to subsequent captured images to compensate for lens degradation.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
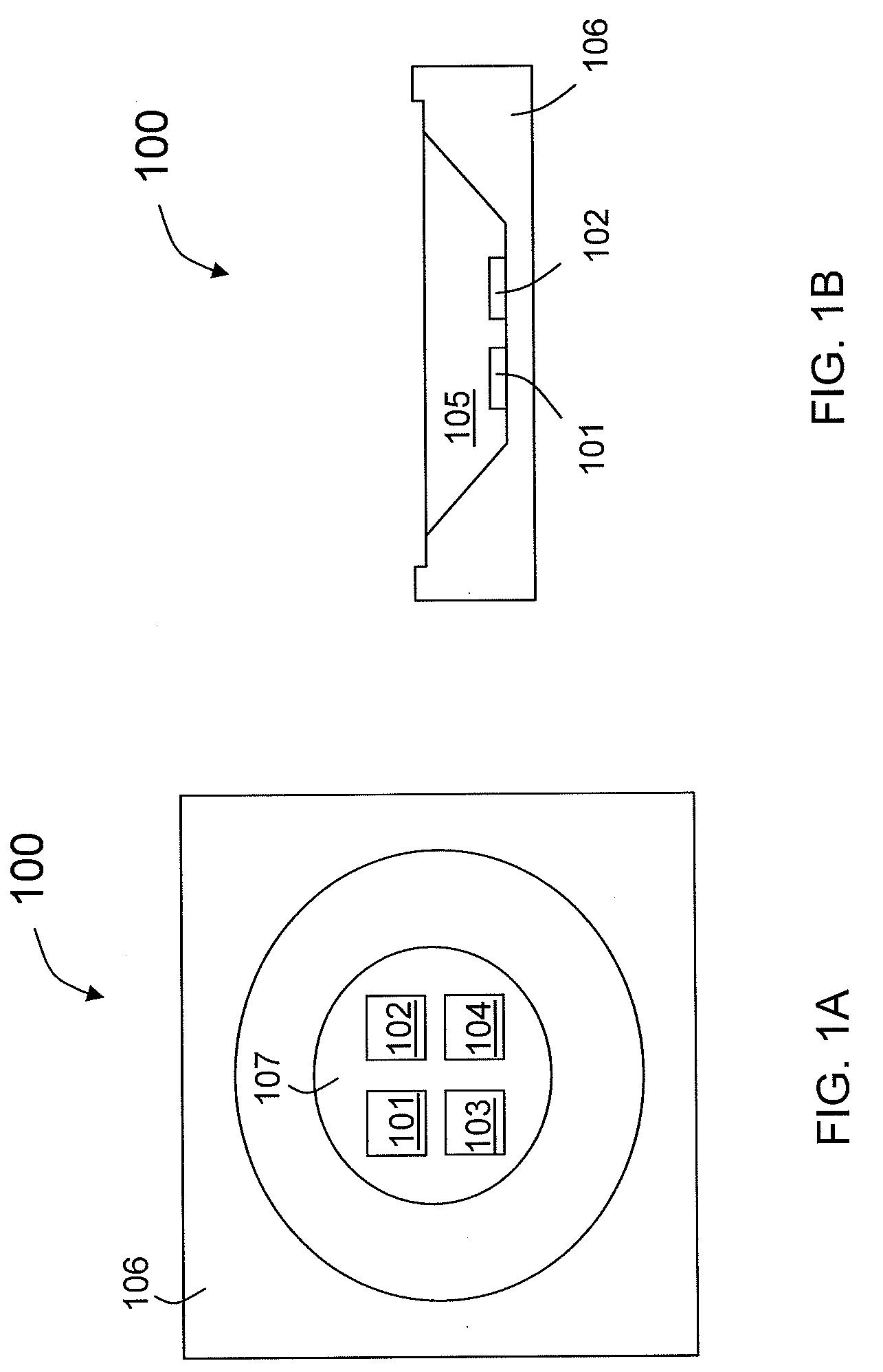
Lighting Apparatus Having Multiple Light-Emitting Diodes With Individual Light-Conversion Layers
ActiveUS20100259924A1Improve light outputReduce manufacturing costElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesLight equipmentPhosphor
A lighting apparatus includes a combination of LED dice that emit light of a first color and a wavelength-shifting material (e.g., phosphor) that converts light of the first color to light of a second color. An appropriate combination of light of the first color and light of the second color can be used to produce light of a target color. In an embodiment, LED dice in the lighting apparatus are divided into two groups. Each LED die in the first group is combined with less wavelength-shifting material than needed to produce light of the target color, while each LED die in the second group is combined with more wavelength-shifting material than needed to produce light of the target color. As a result, the two groups produce light having colors on opposite sides of the target color in the International Commission on Illumination (CIE) chromaticity diagram. In some embodiments, the target color and color variations of both groups are on one straight line in the CIE chromaticity diagram, although it is to be understood that there might be small scattering within the groups. By adjusting the relative brightness of the two groups, the target color can be obtained.
Owner:LEDENGIN
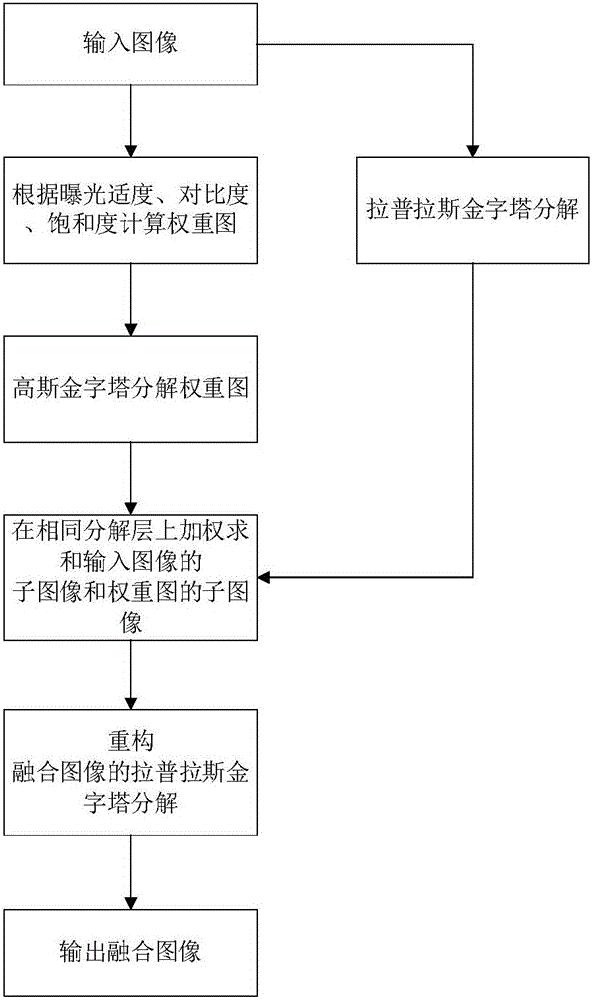
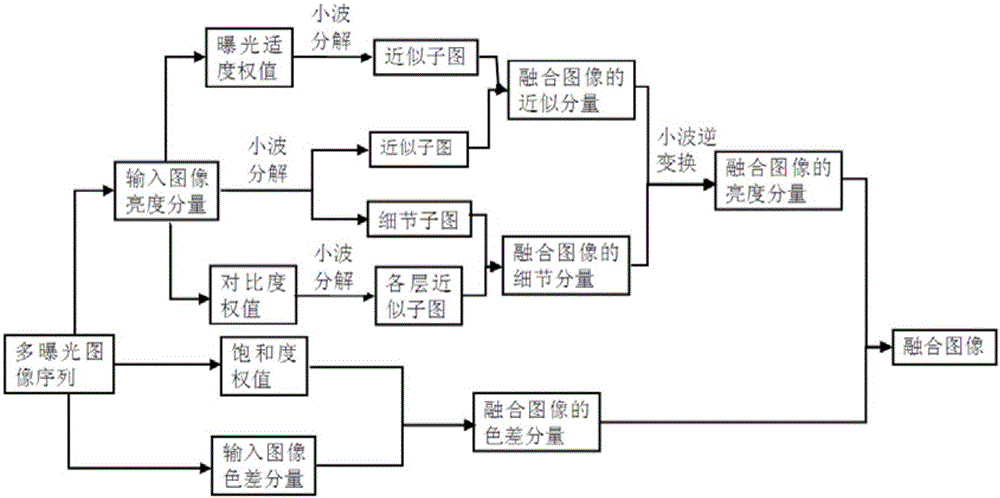
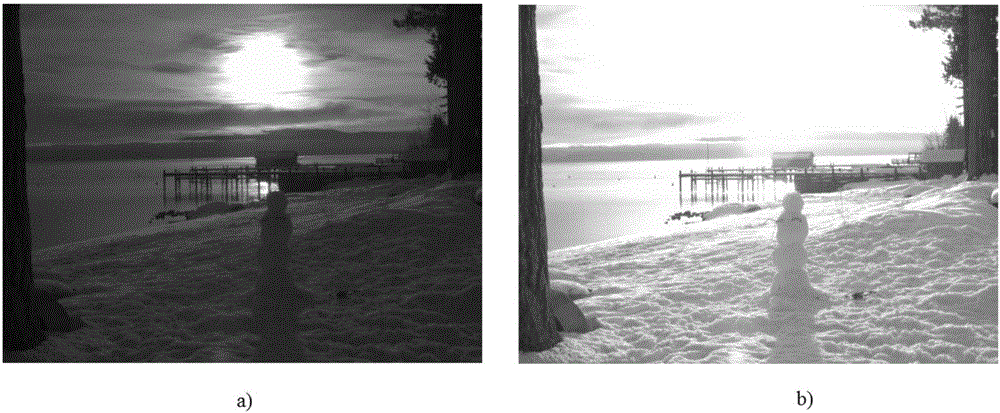
Multi-exposure image fusion method based on wavelet transform
ActiveCN106127718AAvoid lossIncrease exposureImage enhancementImage analysisRelative luminanceWavelet transform
The invention provides a multi-exposure image fusion method based on wavelet transform. A relative luminance relationship between pixels is described using maximum and minimum images of a brightness mean, and the relative luminance relationship is introduced into exposure moderation weight calculation to avoid brightness flip of a fused image and improve the overall contrast of the fused image; according to the method, hierarchical wavelet transform is carried out on a luminance component, an exposure moderation weight graph and a contrast weight graph, weight fusion is carried out on an approximate subgraph of the image luminance components by using the approximate subgraph of the exposure moderation weight graph, the weight fusion is carried out on a detail subgraph of the image luminance components by using the approximate subgraph of the adjusted contrast weight graph, details of different scales are enhanced in different scales, therefore areas on both sides of a strong edge of the fused image can be well exposed while the detail contrast is improved, and loss of the details is avoided.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Electroluminescent white light emitting device
InactiveUS20090002349A1Reduced color accuracyReduce power consumptionEnergy efficient ICTLight source combinationsControl signalRelative luminance
A white-light-emitting electroluminescent device includes light-emitting elements for emitting different colors of light, wherein one of the light-emitting elements has a luminous efficacy greater than the luminous efficacy of at least one of the other light-emitting elements. The different colors of light combine to form white light. Also included is a driver for receiving a color signal representing a relative luminance and color produced by the electroluminescent device. The driver is responsive to a converted control signal when controlling the color accuracy of the light produced by the light-emitting elements to ultimately reduce the power consumption of the white light-emitting electroluminescent device.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
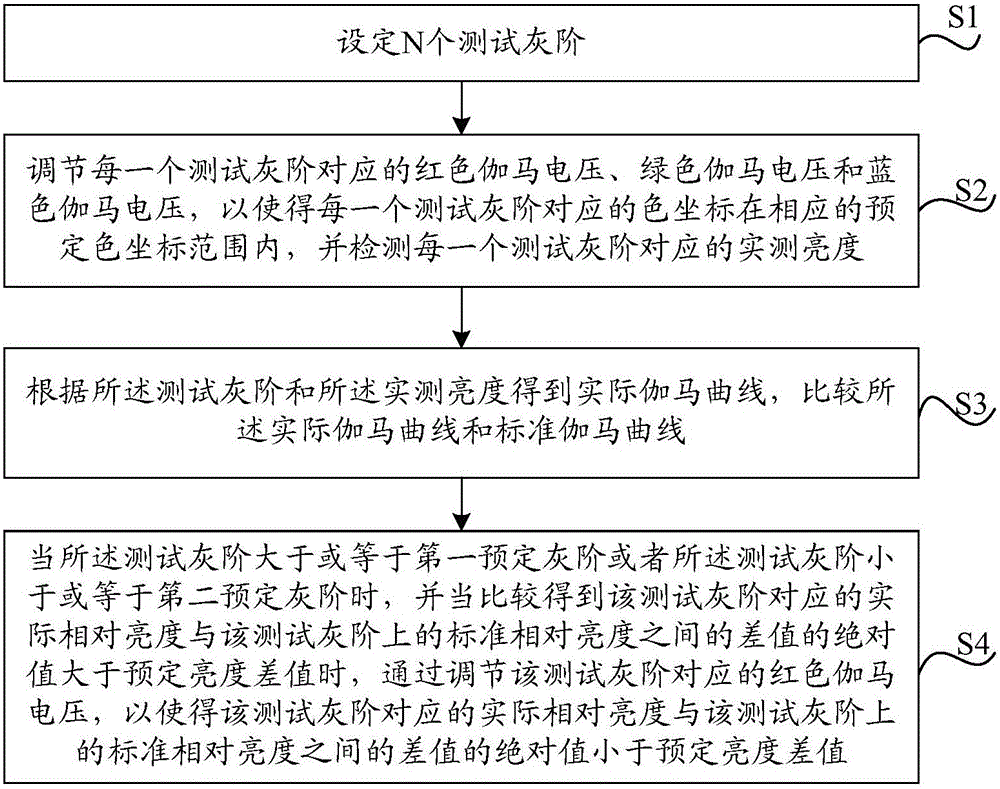
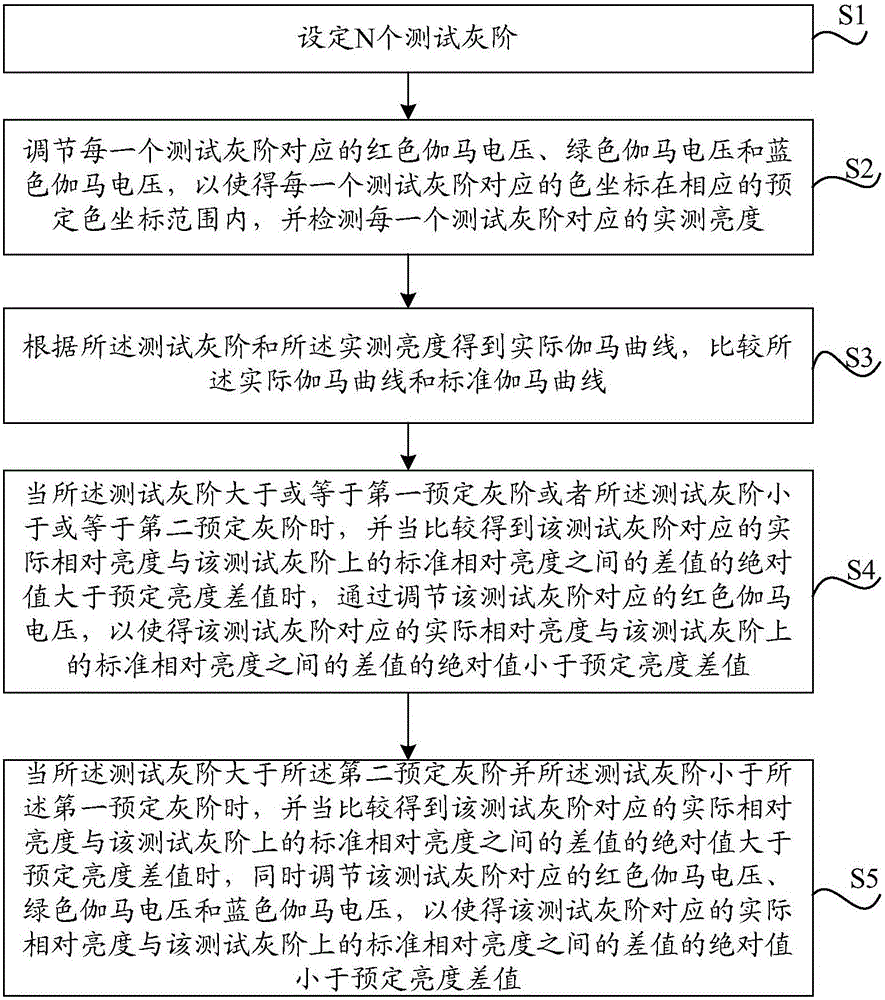
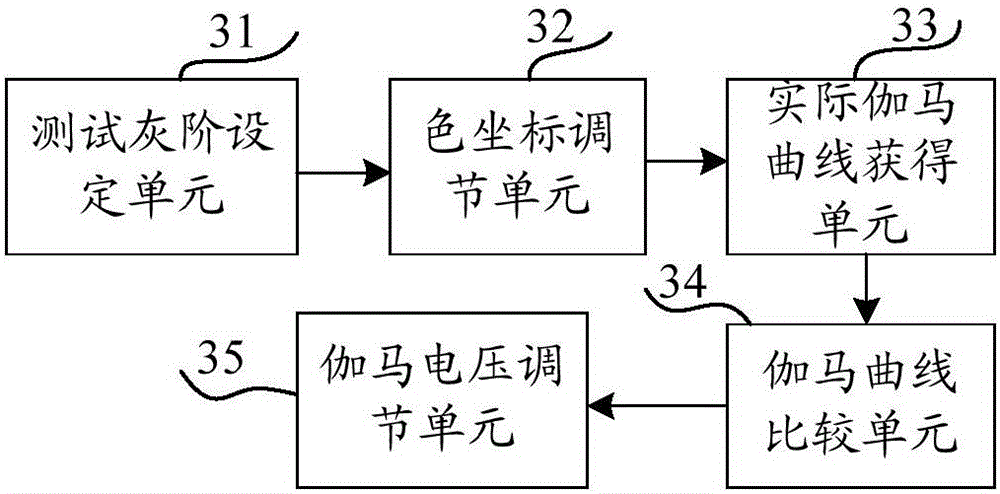
Gamma curve adjusting method and device and display device
The invention provides a gamma curve adjusting method and device and a display device. The gamma curve adjusting method comprises the following steps: setting N testing gray scales; adjusting until a corresponding chromaticity coordinate of each testing gray scale is in a corresponding preset chromaticity coordinate range and detecting actually measured brightness corresponding to each testing gray scale; obtaining an actual gamma curve according to the testing gray scales and the actually measured brightness; and when the testing gray scales are greater than or equal to a first preset gray scale or smaller than or equal to a second preset gray scale, adjusting red gamma voltages corresponding to the testing gray scales so that an absolute value of difference between the corresponding actual relative brightness of the testing gray scales and the standard relative brightness of the testing gray scales is smaller than preset brightness difference. By the gamma curve adjusting method and device and the display device in an embodiment of the invention, the gamma curve can be corrected, and requirements of chromaticity coordinates can be met.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD +1
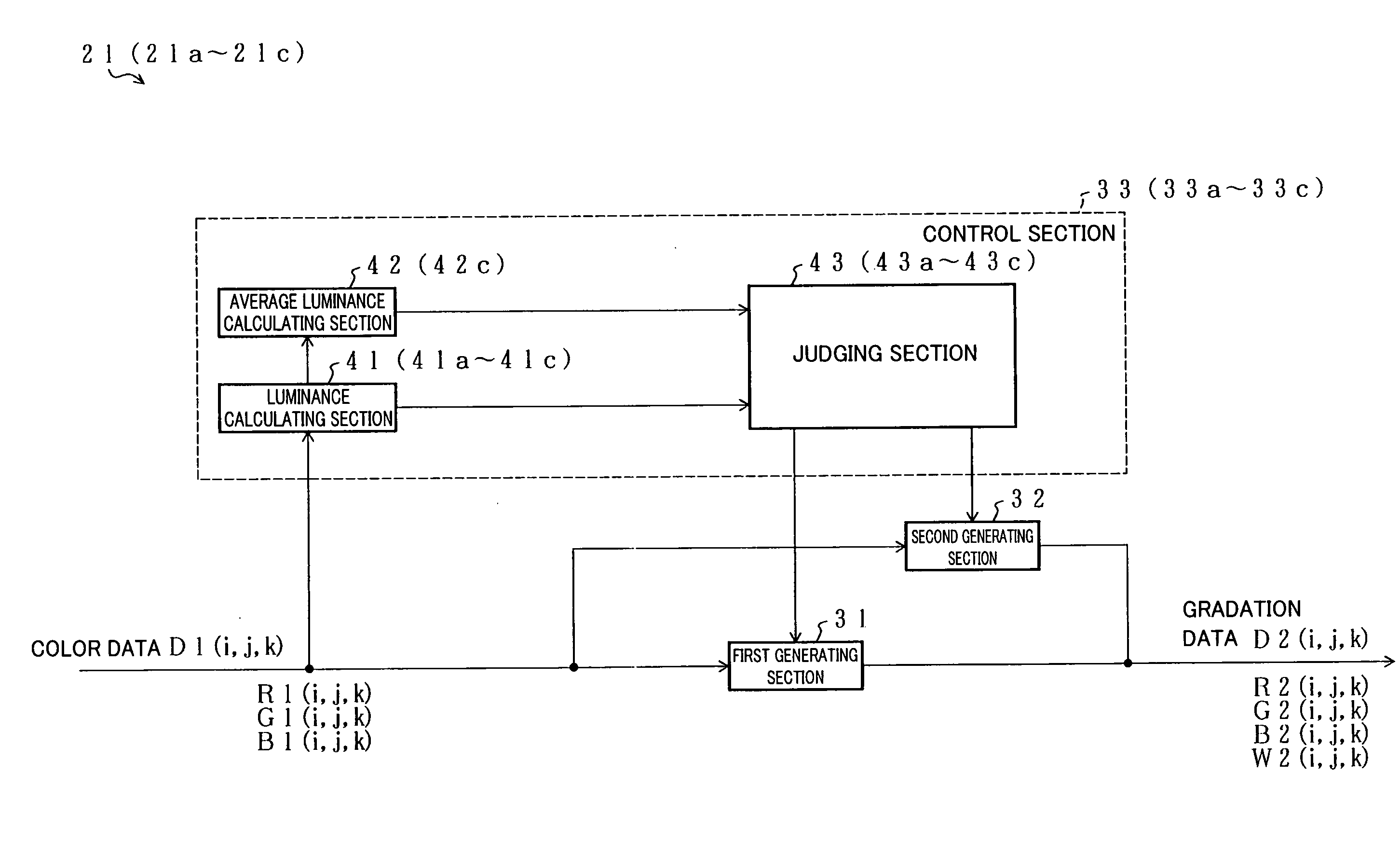
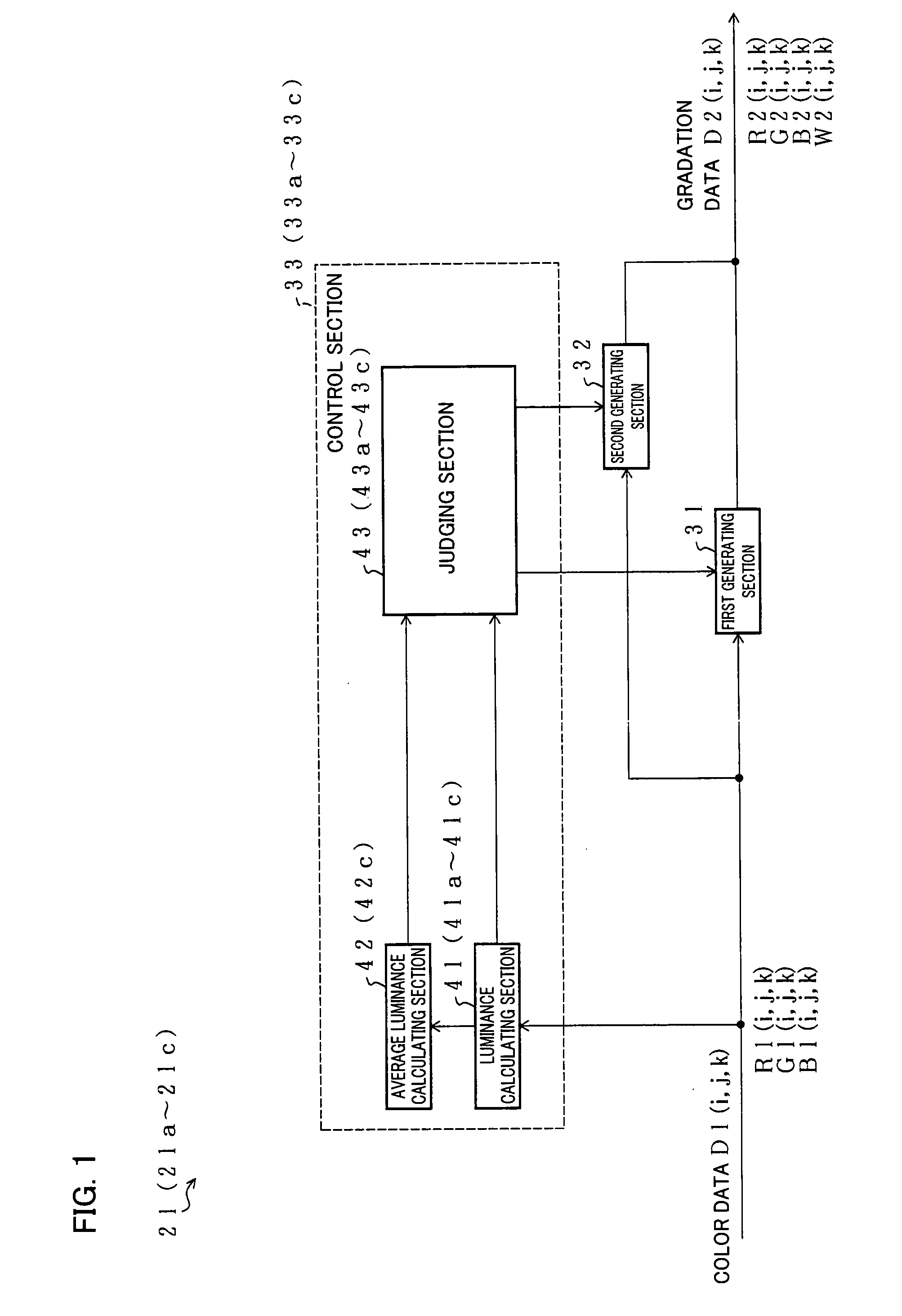
Display Apparatus Driving Method, Display Apparatus Driving Device, Program Therefor, Recording Medium Storing Program, and Display Apparatus
InactiveUS20080211801A1Less clearLess realisticCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingComputer graphics (images)Gradation
A control section is disclosed which divides a display screen into small regions, evaluates the relative brightness of each of the small regions in accordance with color data to be inputted as color data by which each pixel is displayed, and determines whether or not the display screen has a first small region that is brighter than the other small regions by a predetermined degree. Furthermore, the control section causes a first generating device to generate gradation data for use in the first small region, and causes a second generating device to generate gradation data for use in the other small regions. Even if the second generating section receives the same color data as the first generating section does, the second generating section limits the luminance of a W sub-pixel as compared to the first generating section. With this, the first small region can be displayed more strikingly brightly, so that a clearer, more realistic, and more appealing image can be displayed. This makes it possible to realize a display apparatus capable of displaying a clearer, more realistic, and more appealing image.
Owner:SHARP KK
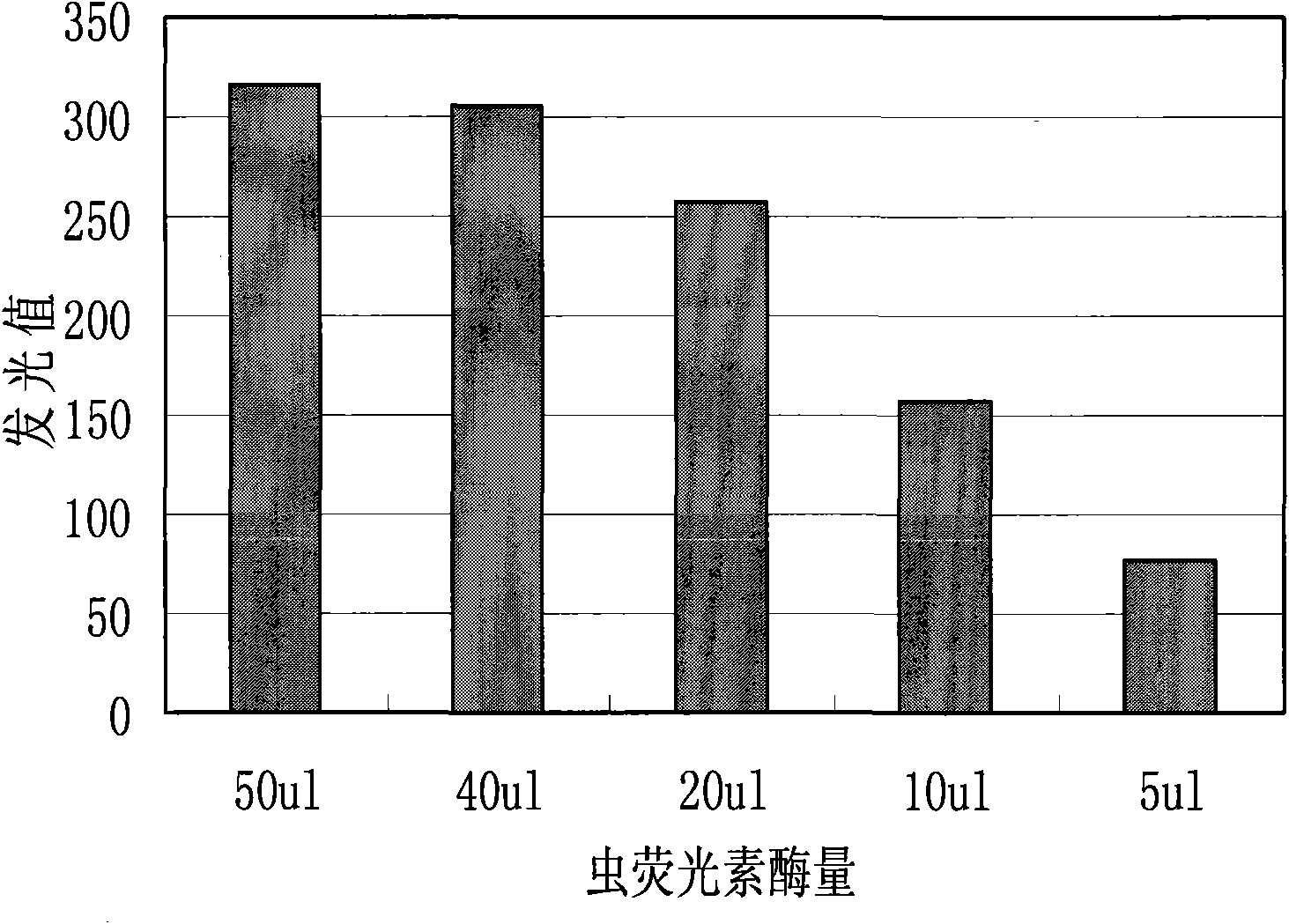
Method for detecting acute toxicity of water environment by using ATP bioluminescence
InactiveCN101865850AResponsiveImprove test performanceChemiluminescene/bioluminescencePhotometryAcute toxicity testingLuminescent bacteria
The invention discloses a method for detecting the acute toxicity of water environment by using ATP bioluminescence. The method comprises the following steps: an ATP reaction reagent, luciferase, an ATP standard sample, and a water body to be detected are sequentially added in a reaction test tube, placing the reaction test tube in an ATP fluoroscope testing instrument to detect fluorescence intensity, the detection response time is 30s and the detection is served as an experimental group; the standard sample is replaced by distilled water, the detection is served as a control group; the experimental group and the control group are repeatedly detected for three times; and the toxicity of the water body is judged by calculating relative luminance K. The method of the invention has the characteristic of stable and sensitive test effect; and the effect of a luminescent bacteria test can be reached within 3 min of the testing time at most; and the response on organic toxic substances is more sensitive than the luminescent bacteria. In the invention, a portable ATP handholding instrument with a direct current power supply is adopted, thus the ATP handholding instrument is convenient to be carried and is suitable for site test.
Owner:NANJING UNIV +1
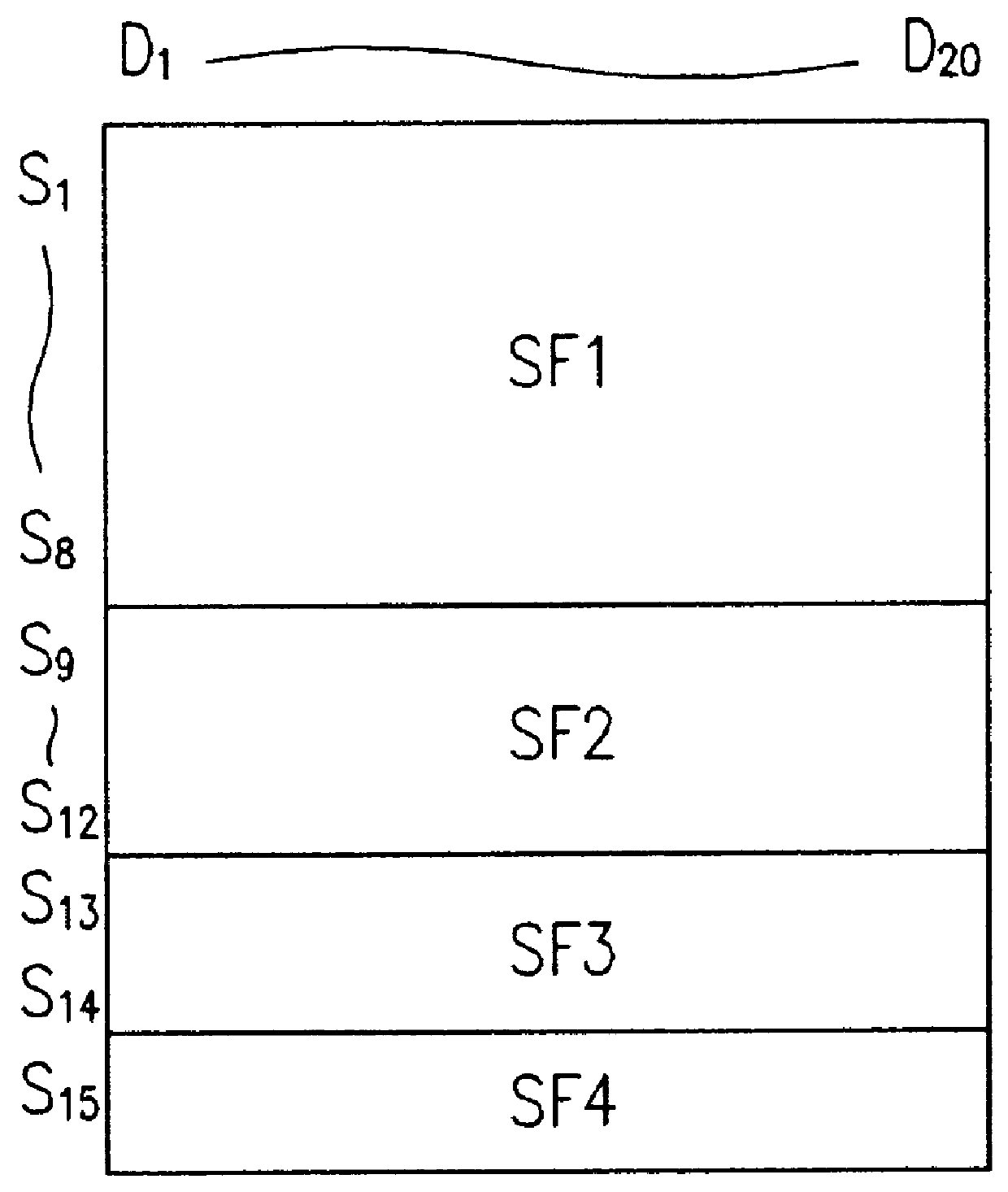
Circuit of driving plasma display device and gray scale implementing method
Driving circuit for plasma display device and a gray scale implementing method therefor are provided. The method includes the steps of (1) dividing total horizontal lines of one frame into XxY subframes according to a relative luminance ratio, (2) dividing each frame into X subfields and allotting Y different subframes to each subfield, and (3) supplying corresponding gray scale data while sequentially erasing each XxY horizontal lines during one horizontal period from the first horizontal electrode lines to the last Nth horizontal electrode lines, included in Y different subframes allotted to each subfield by repeatedly driving X subfields and scanning the same, thereby implementing a display picture of 2XxY gray scales. At least two scanning and sustaining drivers are provided, and one frame is divided into one or more subfields by the drivers, different subframes are allotted to each subfield and then X subfields are repeatedly driven. In other words, since a plurality of horizontal lines to be scanned at a time in a sub-frame method are separately scanned, the overall scanning frequency is decreased. Thus, gray scales exceeding 256 levels can be easily implemented under a stabilized system. Also, flickers caused by the sub-field method can be eliminated. Further, luminance and contrast of a display picture can be improved.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Mosaic removing method and device
InactiveCN103841388AHigh color reproductionRestore true colorColor signal processing circuitsGeometric image transformationImaging processingRelative luminance
The embodiment of the invention provides a mosaic removing method and device, and relates to the technical field of image processing. The mosaic removing method improves the color reproduction effect of pixels and is better in pixel actual color restoration effect. The method comprises the steps that gradients of a current position pixel in a plurality of preset directions are obtained and a gradient threshold is determined according to the gradients in the preset directions; relative luminance component information of the current position pixel is determined; according to the relative luminance component information of the current position pixel, color values of the current position pixel in various target directions are obtained, wherein the target directions are the directions, where the gradients of the current position pixel are smaller than the gradient threshold, in the preset directions; according to the color values of the current position pixel in all the target directions, an average color value is calculated; according to known color component values of the current position pixel and the average color value of the current position pixel, missing color component values of the current position pixel are obtained; according to the known color component values and the missing color component values, the current position pixel is output.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Transmittance adjuster unit, a planar illumination device, a liquid crystal display device using the same, and a method of arranging transmittance adjusters
ActiveUS7556391B2Reduce brightnessLuminance unevenness being efficientlyMeasurement apparatus componentsOptical light guidesLiquid-crystal displayRelative luminance
A transmittance adjuster unit includes multiple transmittance adjusters arranged in a predetermined pattern, if the pattern density is ρ(x, y), the maximum luminance Fmax of the light emitted from the light emission plane of a planar illumination device when the unit is not provided is 1, the minimum luminance is Fmin, and the relative luminance with respect to the maximum luminance Fmax of the light emitted from a predetermined position (x, y) of the emission plane is F(x, y), the relationship between the luminance F(x, y) and the pattern density ρ(x, y) satisfies the following expression: ρ(x, y)=c{F(x, y)−Fmin} / (Fmax−Fmin), wherein 0.5≦c≦1. This unit is thin and lightweight, and can reduce unevenness of the luminance without reducing the average luminance of the incident light. The planar illumination device includes the transmittance adjuster unit and a liquid crystal display device includes the planar illumination device.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Image processing device, image processing method, program, and imaging device
InactiveUS20100177982A1Improve denoising effectAchieve denoisingImage enhancementTelevision system detailsImaging processingRelative luminance
An image processing device includes: an estimated plane calculation portion calculating, for inputted image data, estimated planes defined by luminance values in blocks each containing a predetermined number of pixels including a reference pixel; an optimal estimated plane selection portion selecting an optimal estimated plane having a least summation of errors between luminance values of respective pixels in a block and an estimated plane among the estimated planes; a weighting factor calculation portion calculating a weighting factor for the reference pixel base on luminance values of the reference pixel and in the optimal estimated plane; and a weighted smoothing portion computing a sum of products of relative luminance differences between the luminance values of the respective pixels in the block and in the optimal estimated plane and the weighting factor for the reference pixel and adding a luminance value in the optimal estimated plane at a reference pixel position to a result of computation.
Owner:SONY CORP
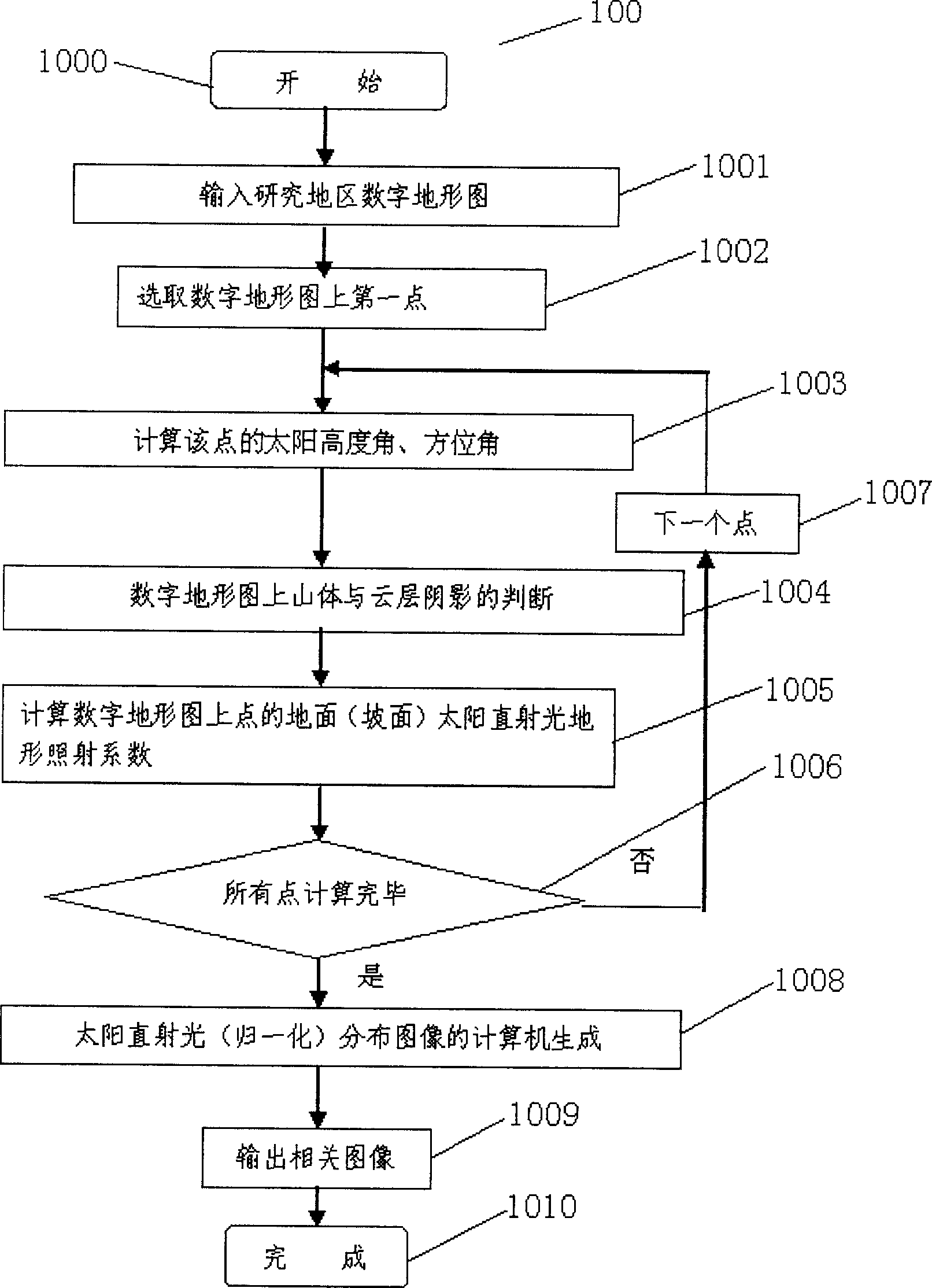
Computerized generation method for sunlight normalized distribution image on rough ground
The invention relates to a method for generating the graph of sunlight normalized distribution on concave-convex ground, by computer. It comprises: based on GIS, it uses the sun altitude angle / azimuth angle, the digital map (digital ground mode) and the geography coordinate (latitude and longitude) at each point, to use computer point-to-point calculate the sunlight ground irradiate factor at each point of digital map; at last, transforms the sunlight ground irradiate factor at each point into the sunlight distribution map. The inventive sun light distribution map can express the sunlight relative luminance at each point of natural ground that affected by the landform; it can be used in the landform effect correct of sunlight of remote sensing graph, the prediction of radar detecting effect, digital simulation, etc.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
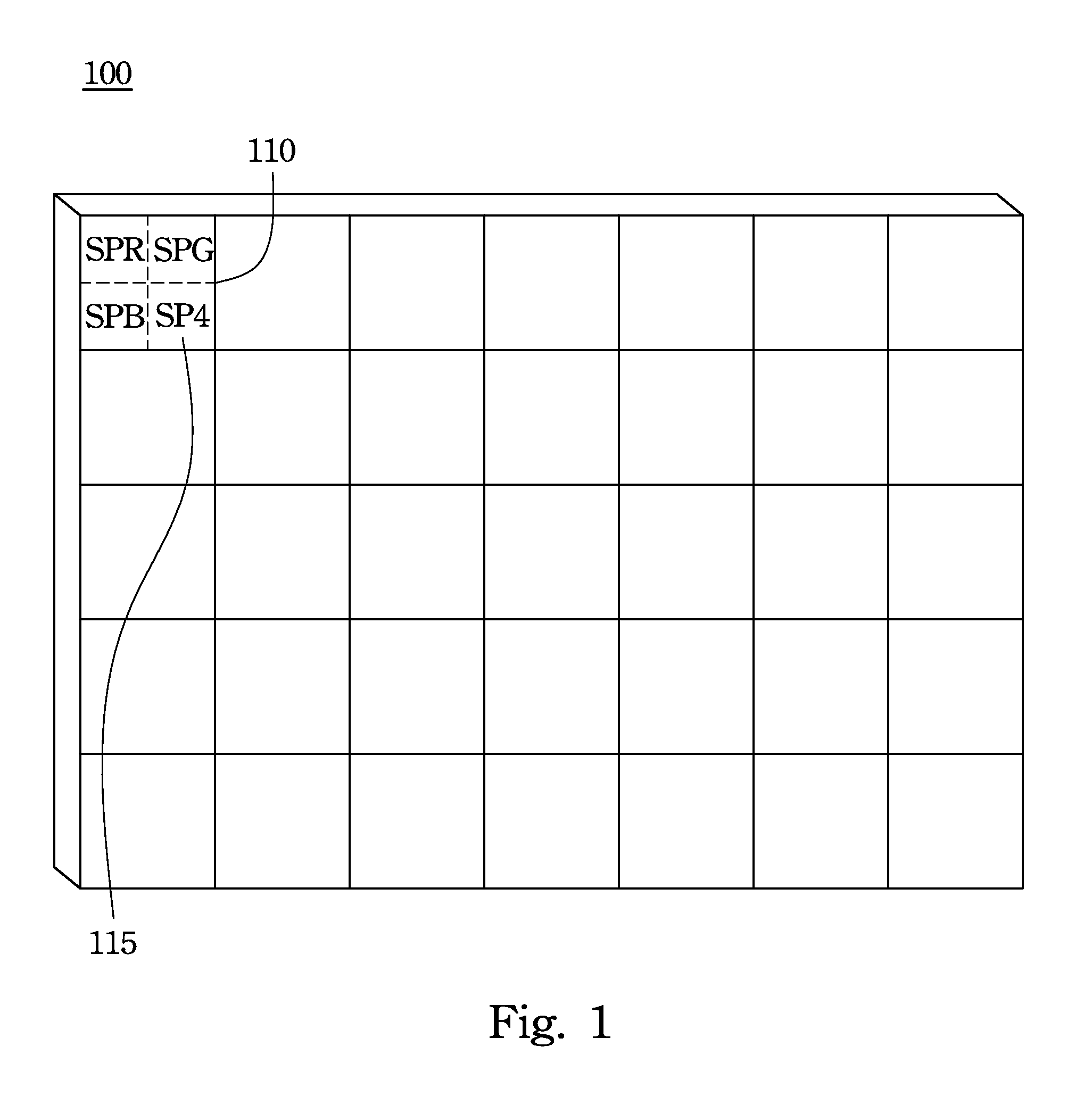
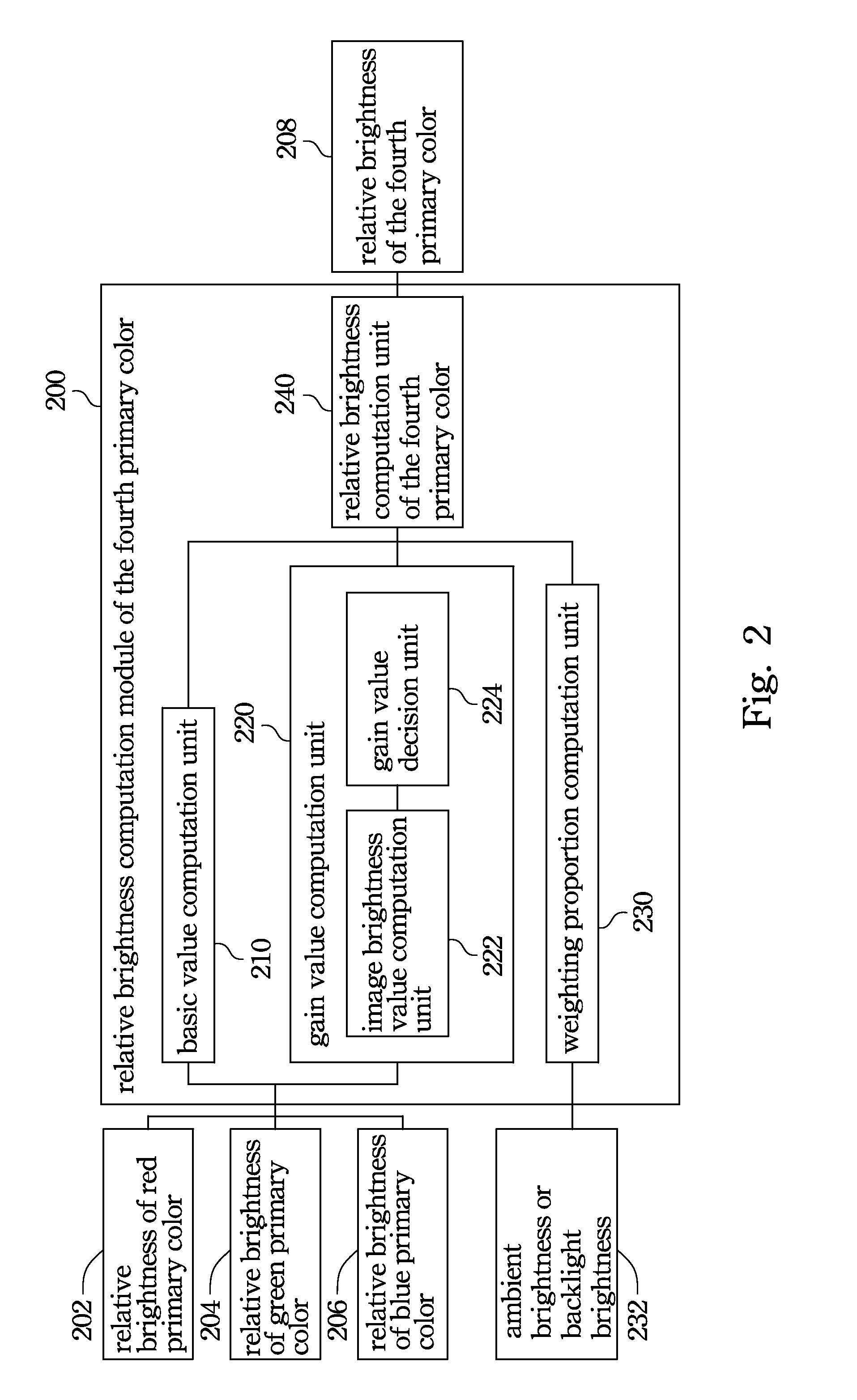
Four-Primary Color Display Device and Method for Calculating Relative Brightness of Fourth Primary Color
InactiveUS20130120468A1Improve readabilityImage brightnessTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsDisplay deviceRelative luminance
A four-primary color display device and a method for calculating relative brightness of a fourth primary color are provided. The display device includes plural pixels and a relative brightness computation module of the fourth primary color for calculating relative brightness of that color. The pixel has at least four sub-pixels for displaying red, green, blue and the fourth primary color respectively. The relative brightness computation module of the fourth primary color includes a basic value computation unit, a gain value computation unit, a weighting proportion computation unit and a relative brightness computation unit of the fourth primary color.
Owner:CHUNGHWA PICTURE TUBES LTD
Transparent screen and video image projection system comprising same
ActiveUS20180180982A1Satisfactory visibilitySuitable for useTelevision system detailsDiffusing elementsRelative luminanceEngineering
[Problem] Provided is a transparent screen which satisfies both the visibility of the projection light and the transmission light by anisotropically scattering and reflecting the projection light emitted from a light source.[Solving means] A transparent screen according to the present invention comprises a light diffusion layer including a binder and microparticles,said transparent screen having a scattered light brilliance profile characterized to meet the following conditions A to C:A: the emitted light relative brilliance in the 0° direction is from 50 to 95, when the entered light relative brilliance is 100;B: the emitted light relative brilliance in the ±5° direction is 1.1 or less, when the emitted light relative brilliance in the 0° direction is 100; andC: the emitted light relative brilliance in the ±50° direction is 0.0005 or higher, when the emitted light relative brilliance in the 0° direction is 100;when the brilliance is Y from the XYZ color system measured with a goniophotometer.
Owner:ENEOS CORP
Transmittance Adjuster Unit, A Planar Illumination Device, A Liquid Crystal Display Device Using The Same, And A Method Of Arranging Transmittance Adjusters
ActiveUS20080089091A1Luminance unevenness being efficientlyReduce brightnessMechanical apparatusMeasurement apparatus componentsLiquid-crystal displayTransmittance
A transmittance adjuster unit includes multiple transmittance adjusters arranged in a predetermined pattern, if the pattern density is ρ(x, y), the maximum luminance Fmax of the light emitted from the light emission plane of a planar illumination device when the unit is not provided is 1, the minimum luminance is Fmin, and the relative luminance with respect to the maximum luminance Fmax of the light emitted from a predetermined position (x, y) of the emission plane is F(x, y), the relationship between the luminance F(x, y) and the pattern density ρ(x, y) satisfies the following expression: ρ(x, y)=c{F(x, y)−Fmin} / (Fmax−Fmin), wherein 0.5≦c≦1. This unit is thin and lightweight, and can reduce unevenness of the luminance without reducing the average luminance of the incident light. The planar illumination device includes the transmittance adjuster unit and a liquid crystal display device includes the planar illumination device.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Reflective transparent screen and image projection apparatus provided with same
ActiveCN108292090ALarge field of viewVivid imageTelevision system detailsDiffusing elementsRelative luminanceTransmittance
The invention provides a reflective transparent screen that is capable of achieving both visibility of projected light and visibility of transmitted light by anisotropically diffusing and reflecting the projected light emitted from a light source. A reflective transparent screen according to the present invention is provided with a light diffusing layer including a binder and fine particles, wherein reflective transparent screen is characterized in that the total light transmittance is at least 60%, the parallel light transmittance is at least 50%, and the diffused reflected light luminance profile measured by a goniophotometer satisfies the following conditions A and B. A: when light enters at an angle of 45 degrees with respect to the direction parallel to a screen surface and the luminance at 135 degrees in the regular reflection direction is 100, the relative luminance of diffused reflected light at 90 degrees is at least 0.001. B: when the light enters at the angle of 45 degrees with respect to the direction parallel to the screen surface and the luminance at 135 degrees in the regular reflection direction is 100, the relative luminance of diffused reflected light at 120 degrees is at least 0.01.
Owner:JXTJ NIPPON OIL & ENERGY CORP
Image sensing system and correction method
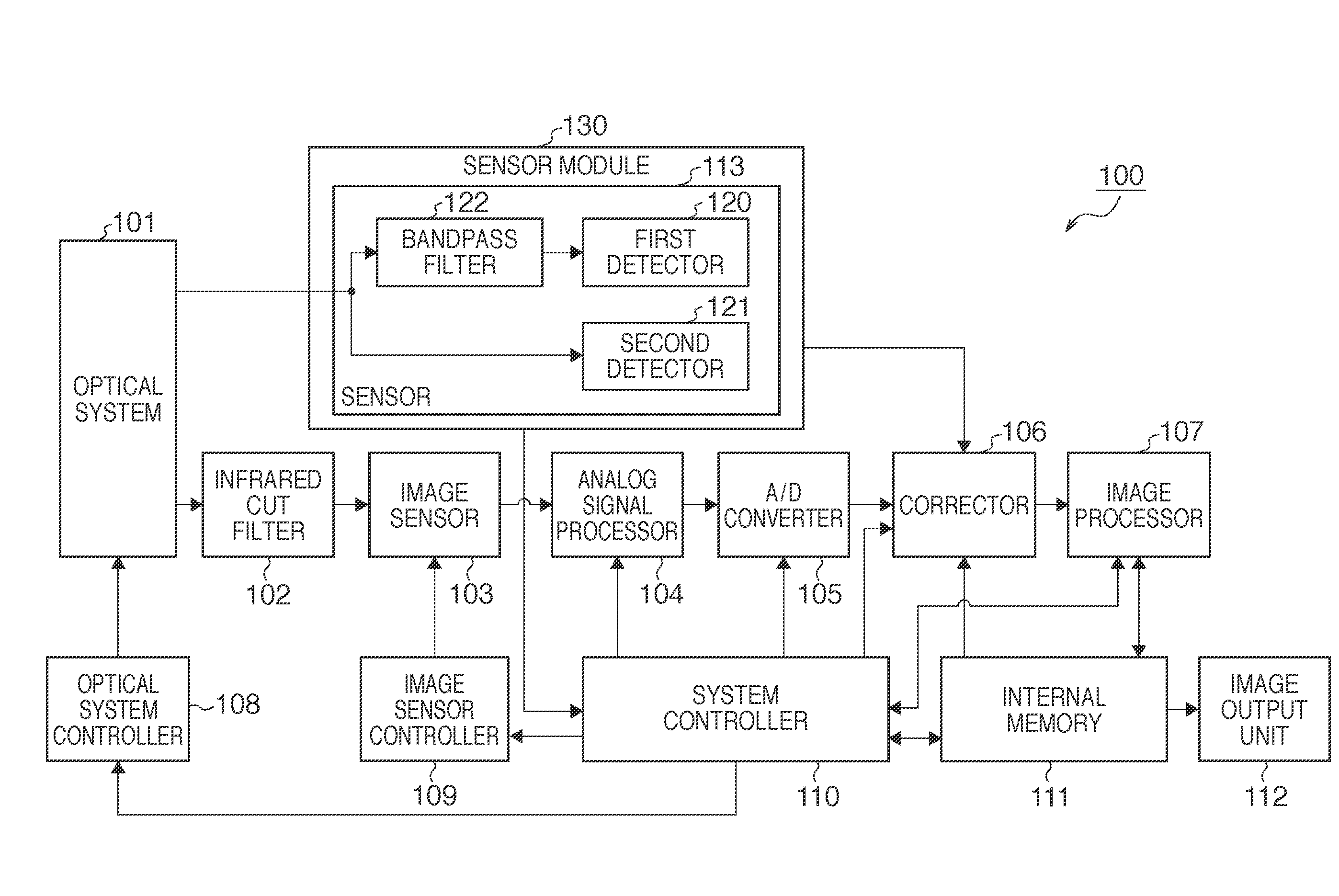
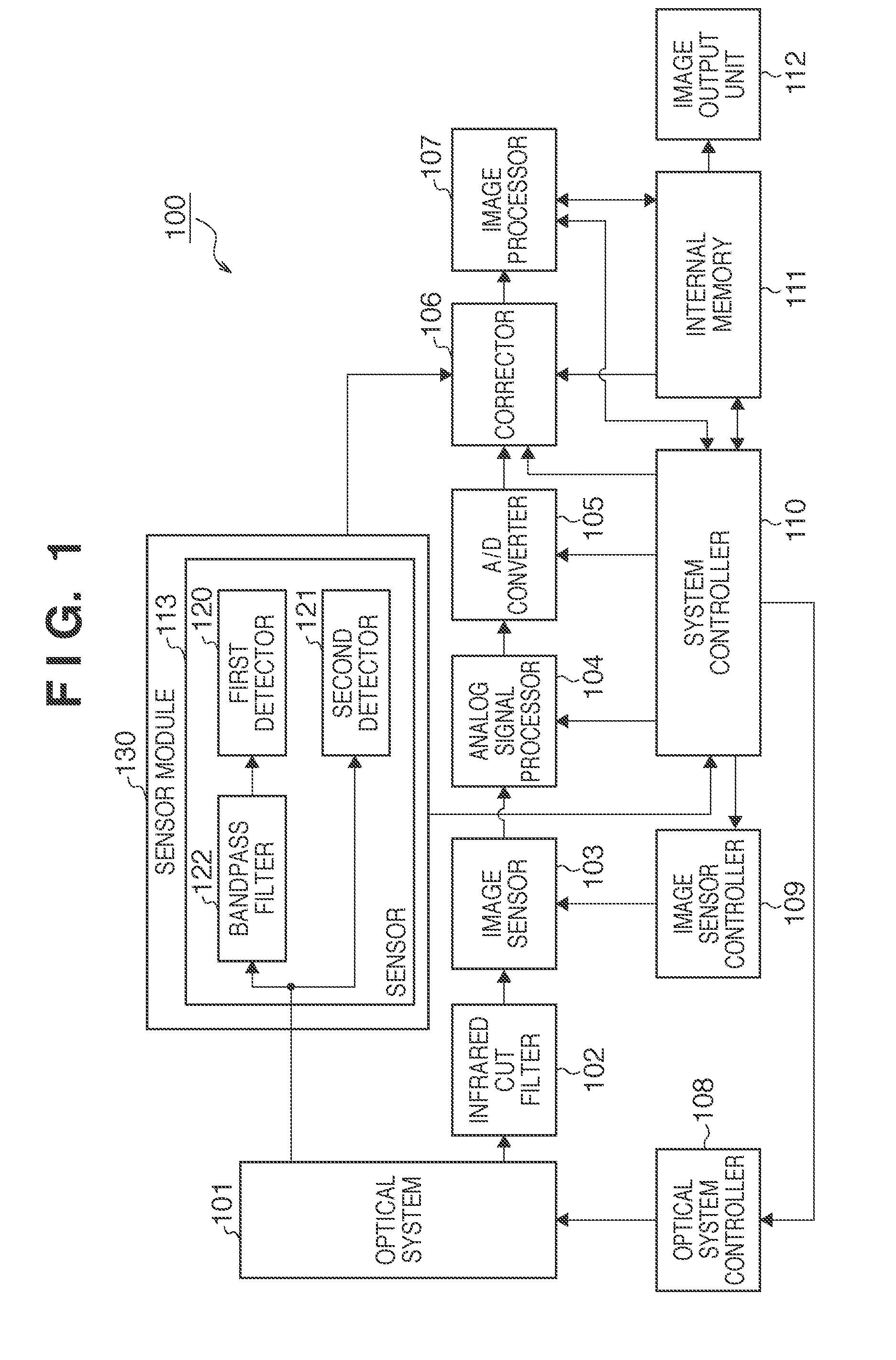
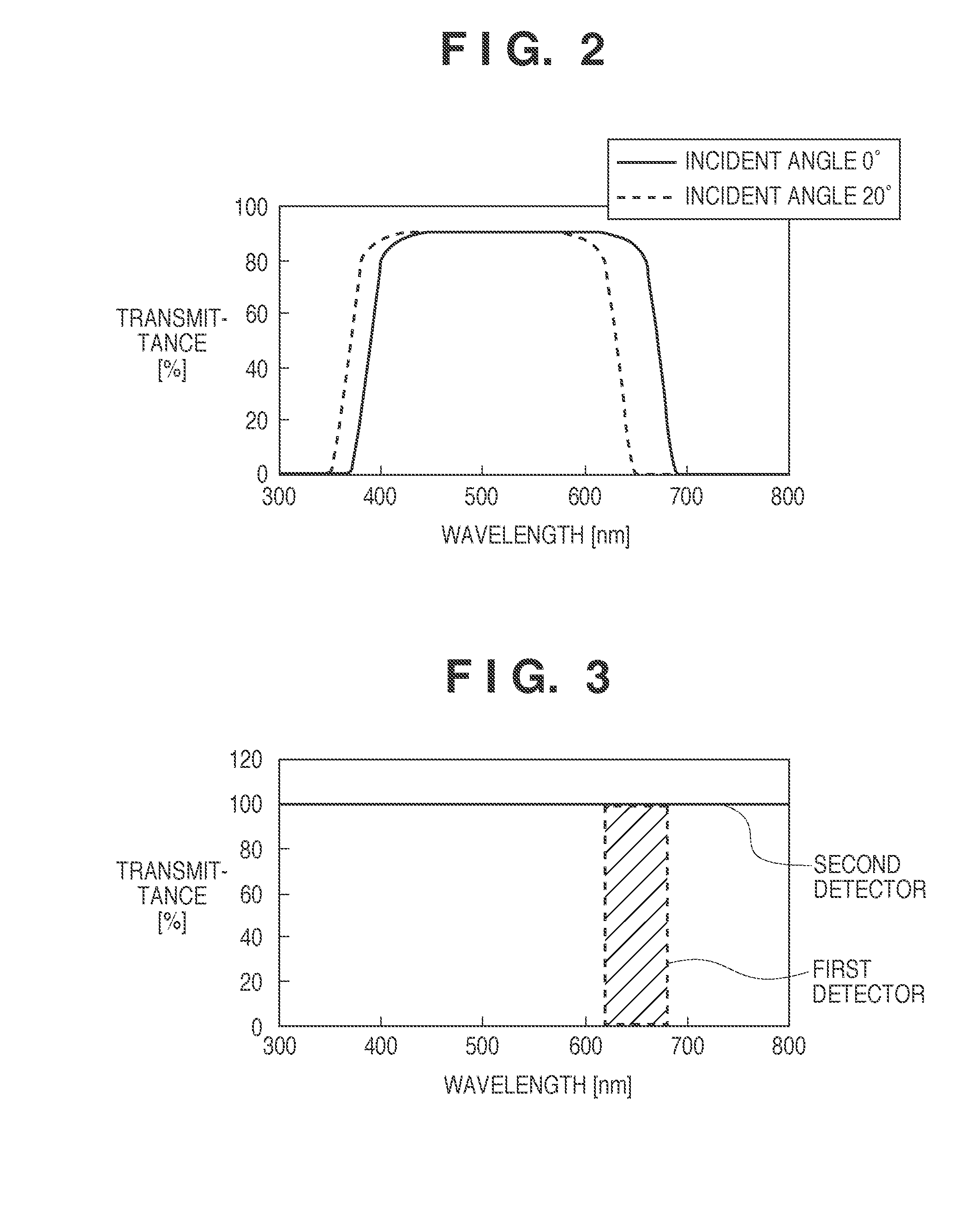
InactiveUS20110090379A1Improve accuracyAccurate detectionColor signal processing circuitsSolid-state device signal generatorsRelative luminanceLength wave
An image sensing system comprises an image sensor having an image sensing surface, a filter arranged between the image sensing surface and an optical system which forms an image of an object on the image sensing surface, a sensor configured to detect a luminance of the object in a band in the vicinity of a cutoff wavelength of the filter relative to an average luminance of the object via the optical system, and a corrector configured to execute color shading correction of the image, sensed by the image sensor, using a color shading correction coefficient determined by the relative luminance detected by the sensor.
Owner:CANON KK
Plasma display and its driving method
InactiveUS7180481B2Improve performanceLower ratioStatic indicating devicesRelative luminanceComputer science
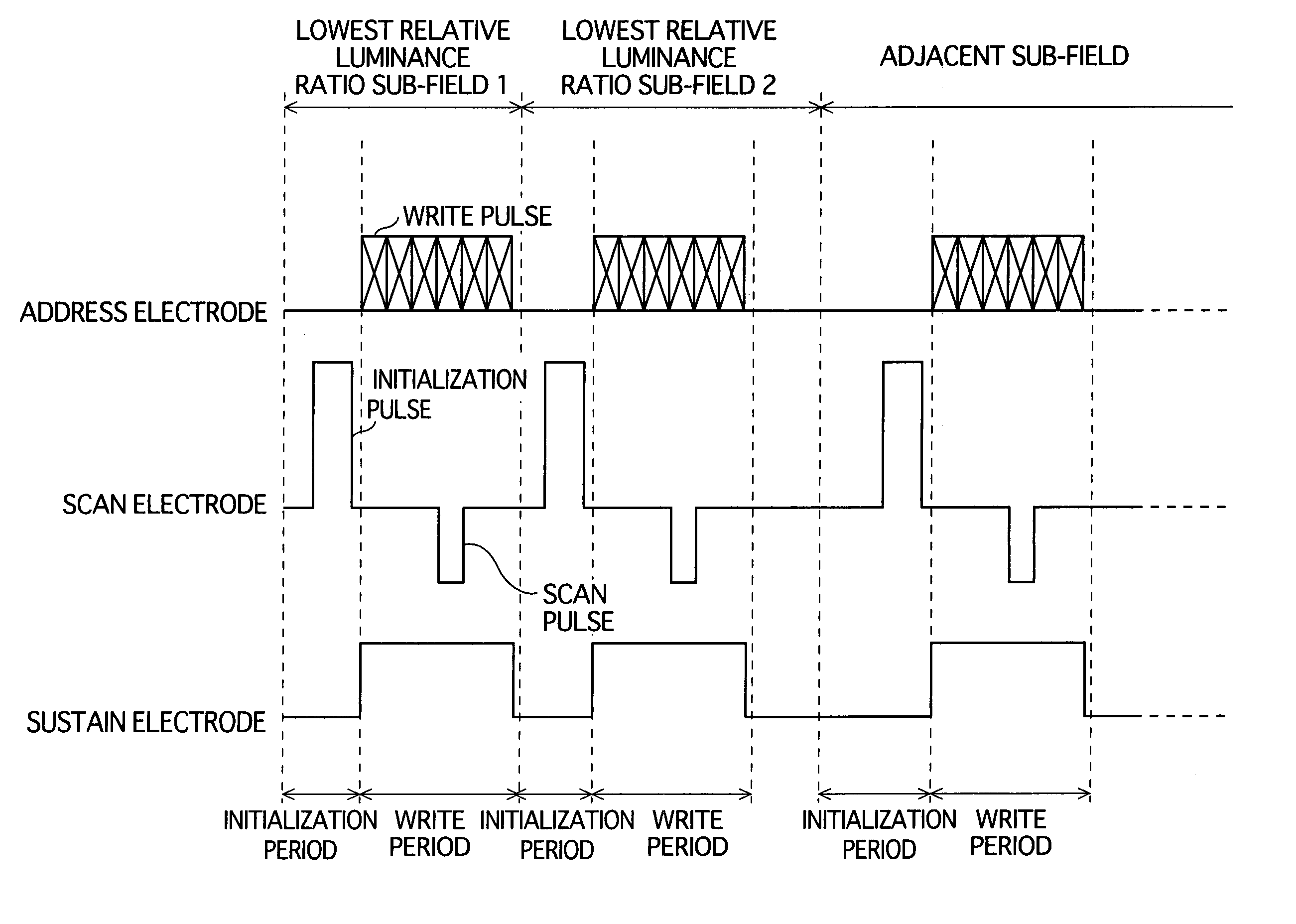
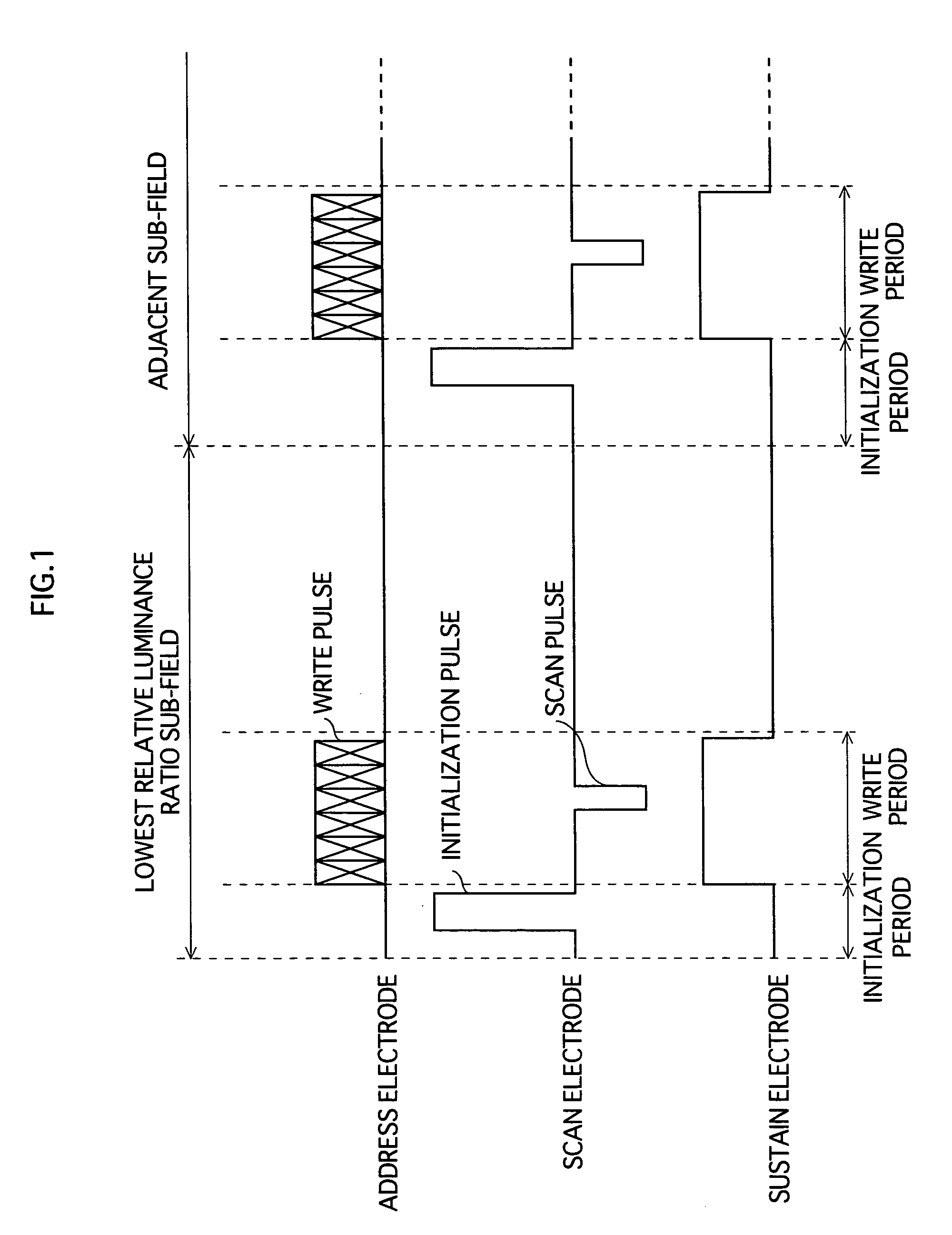
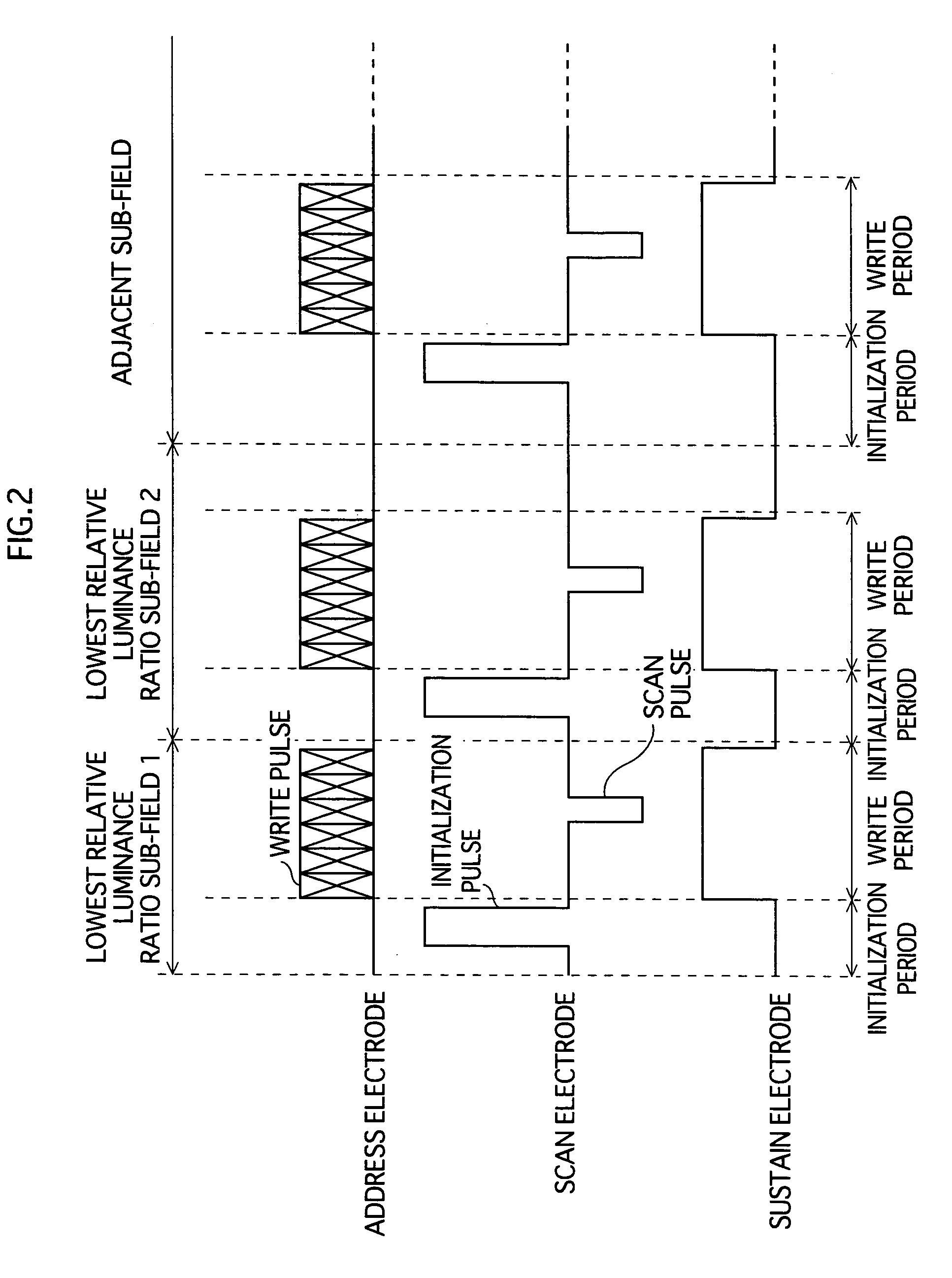
A PDP display apparatus driving method for performing multi-level gradation display by constituting one frame of a plurality of subfields assigned different weights, wherein in a subfield in which a relative luminance ratio corresponds to a lowest weight, display is performed according to discharges in two periods only, the periods being an initialization period and a write period.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Diffusion plate
ActiveCN107430219AGood appearanceSimple structureDiffusing elementsLensFine structureOptical property
A diffusion plate (1) according to the present invention is characterized by having a plurality of fine structures (microlenses (2)) each having at least two lens functions arranged on the principle surface (S1) thereof, and enabling diffused light within a desired diffusion angle range to have substantially uniform intensity, wherein when the average pitch of the fine structures is P and the standard deviation of relative luminance of the fine structures in the respective front surface directions is Sk, P<=200 [mu]m, Sk >= 0.005, and P * P * Sk <= 400 [mu]m2 are satisfied. Accordingly, the present invention can provide a diffusion plate having a simple configuration which exhibits optical properties of low luminance unevenness and low color unevenness, and also exhibits favorable exterior appearance quality at a time of image projection.
Owner:KURARAY CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com