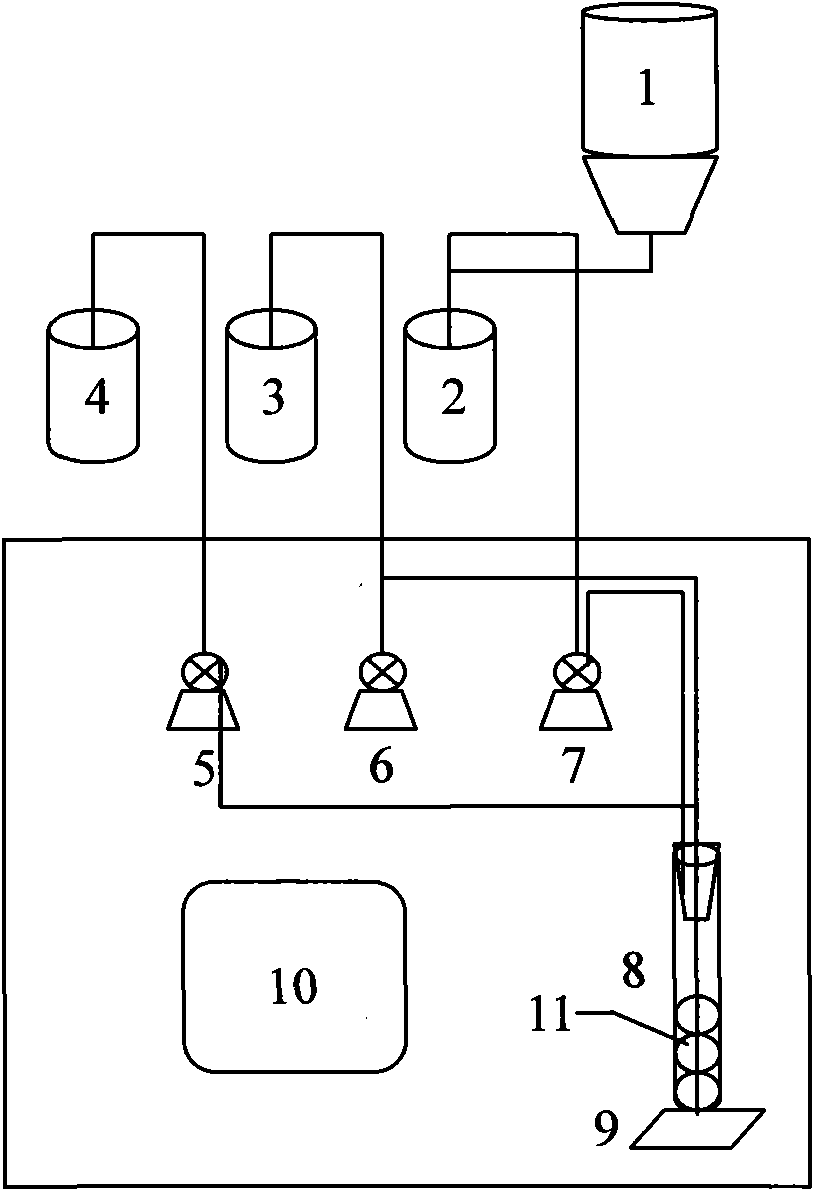
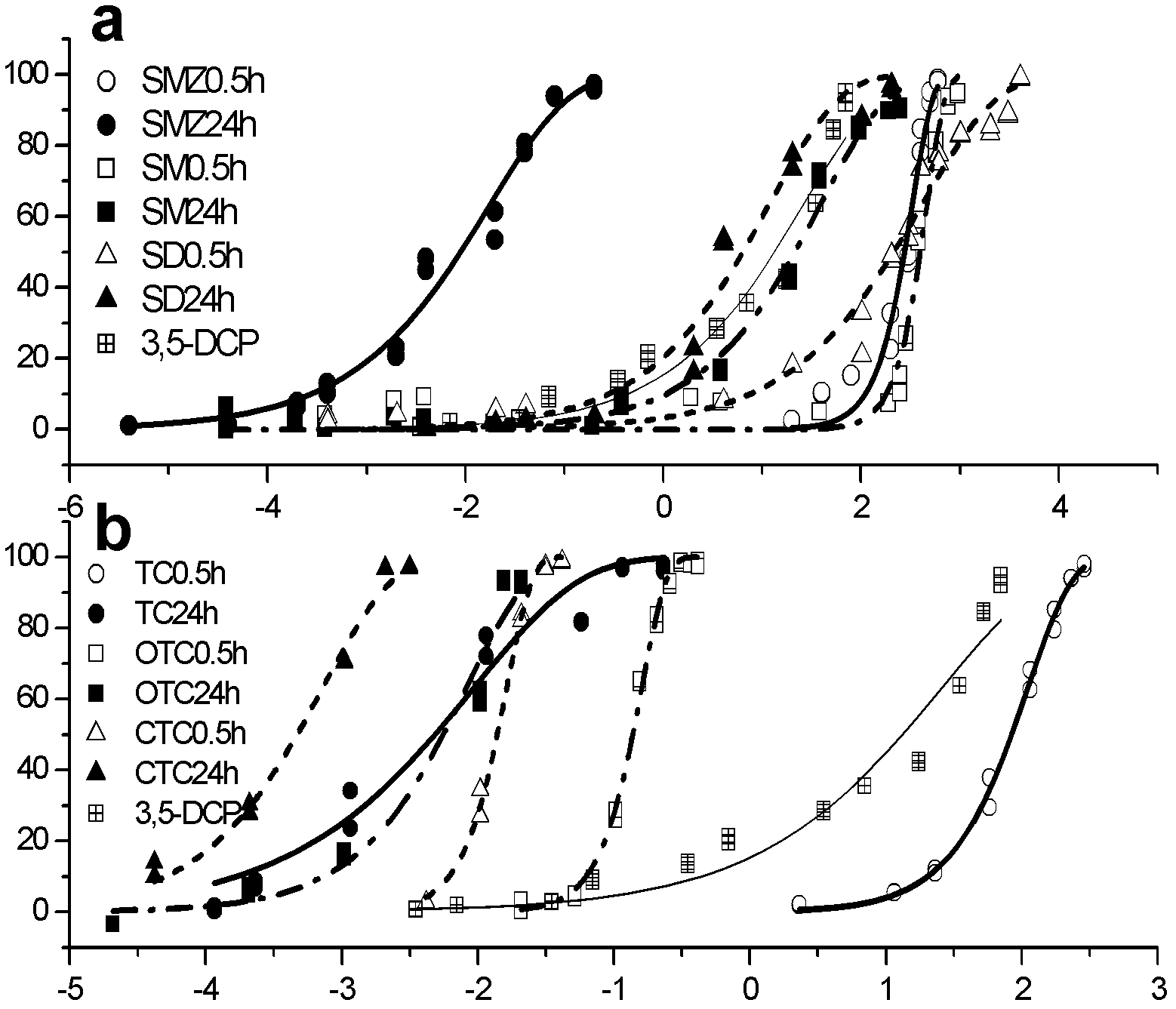
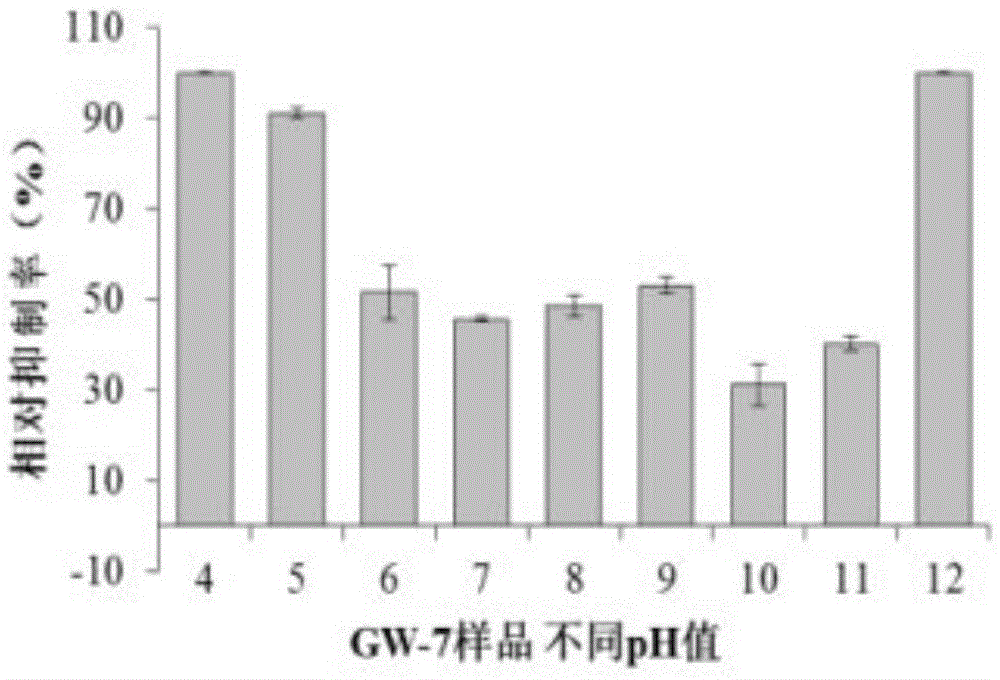
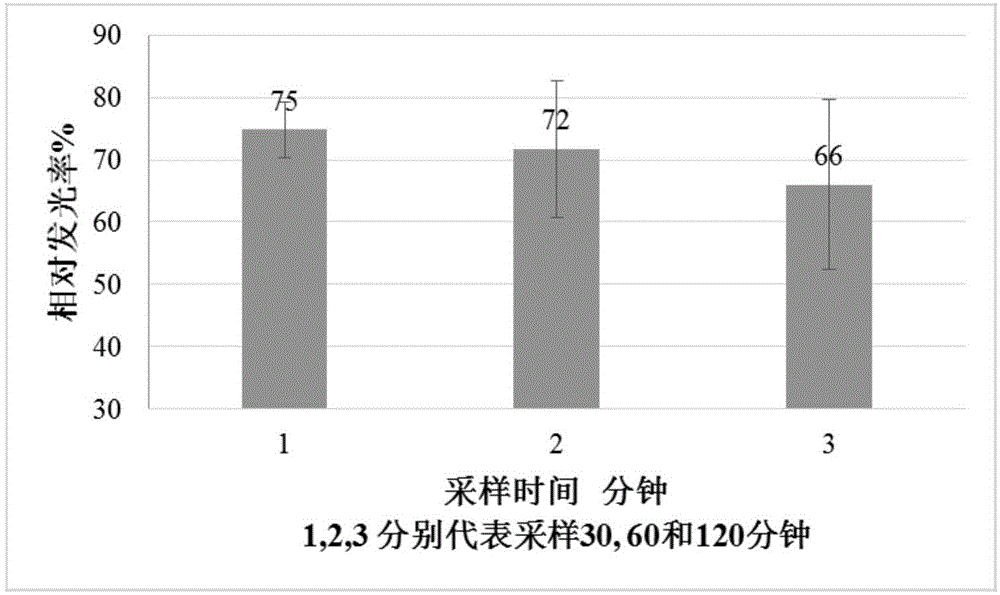
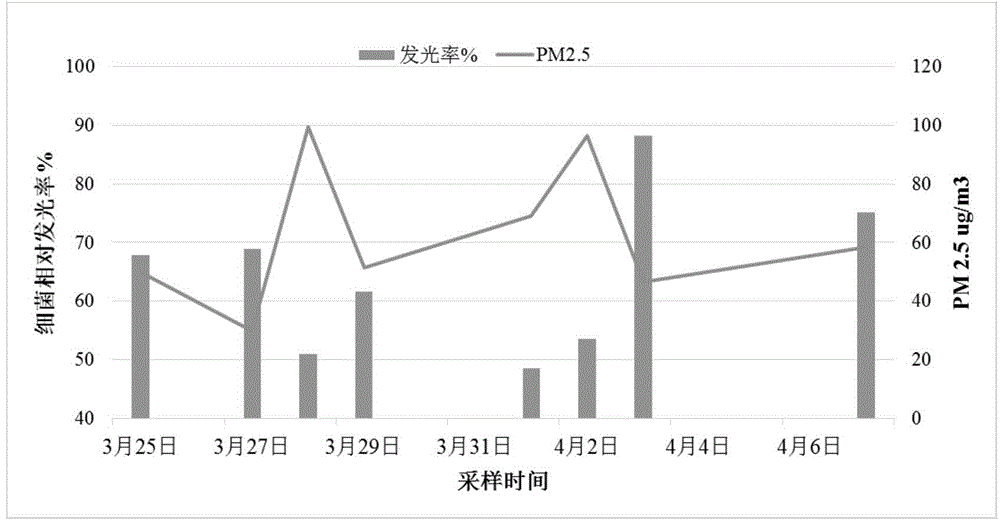
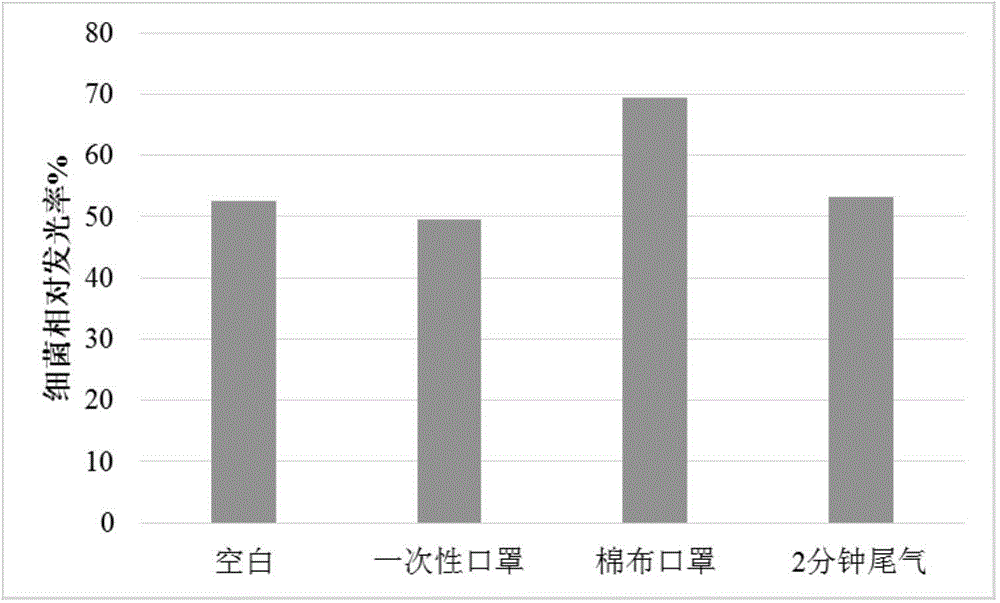
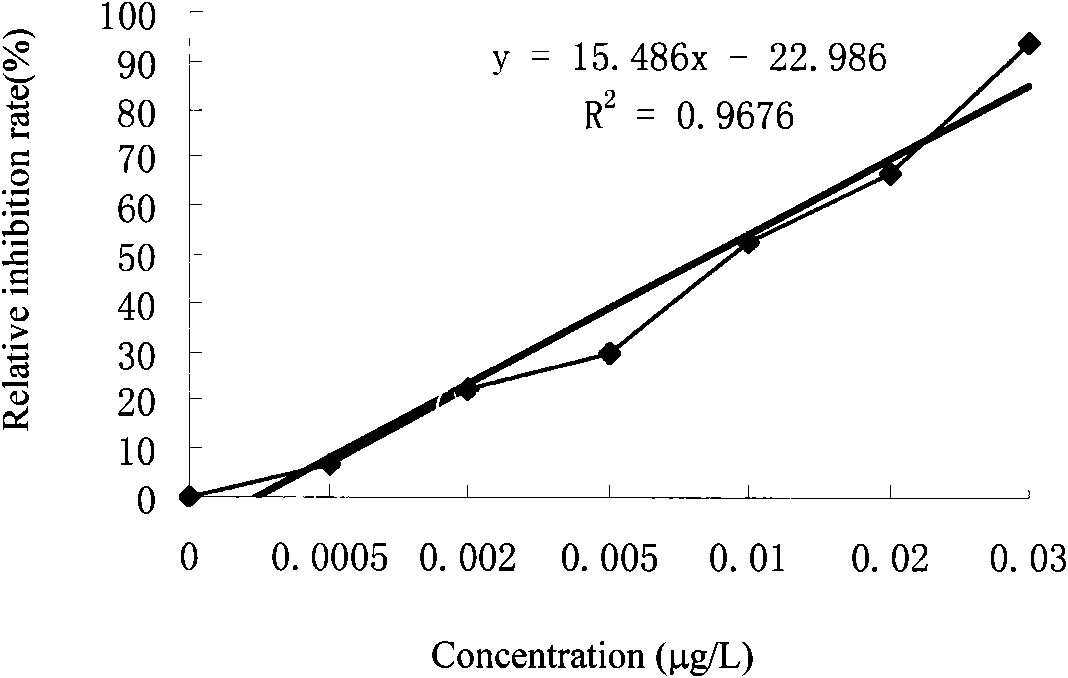
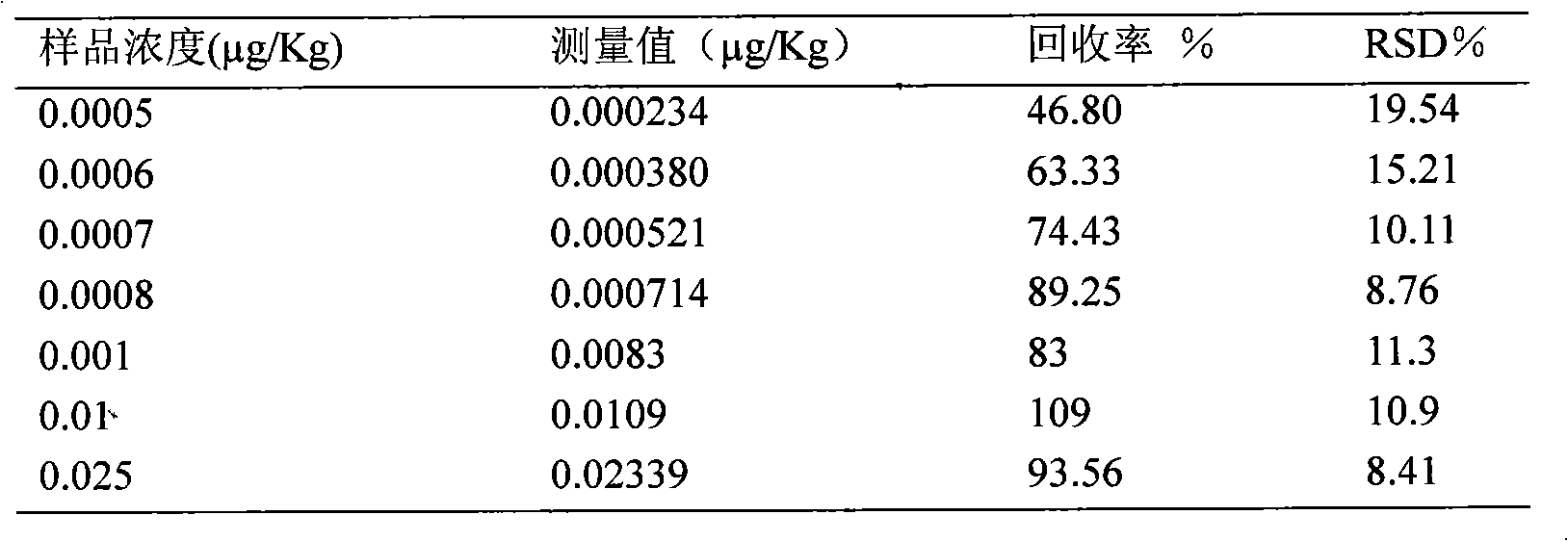
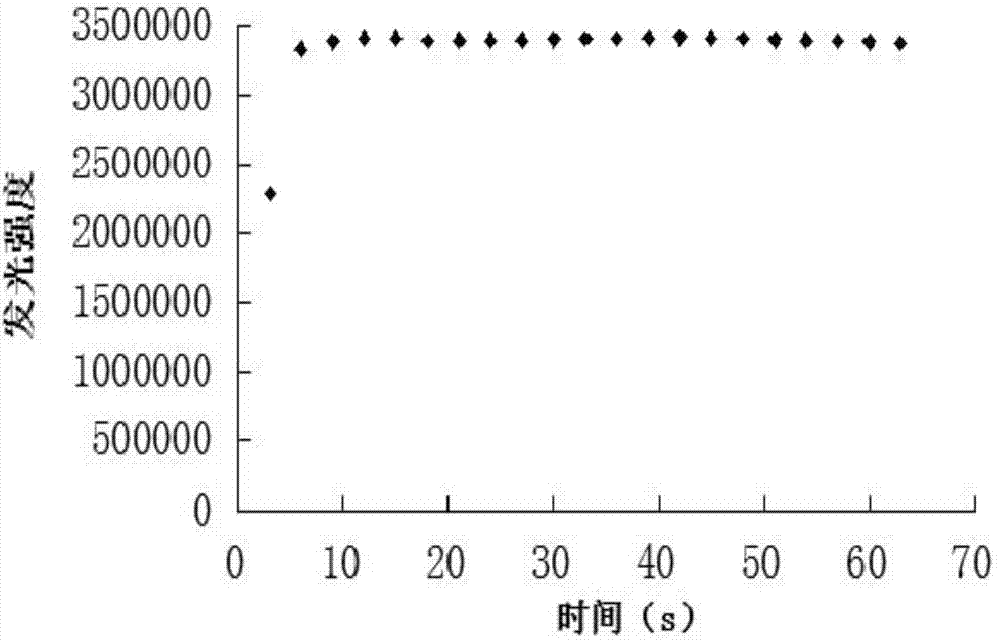
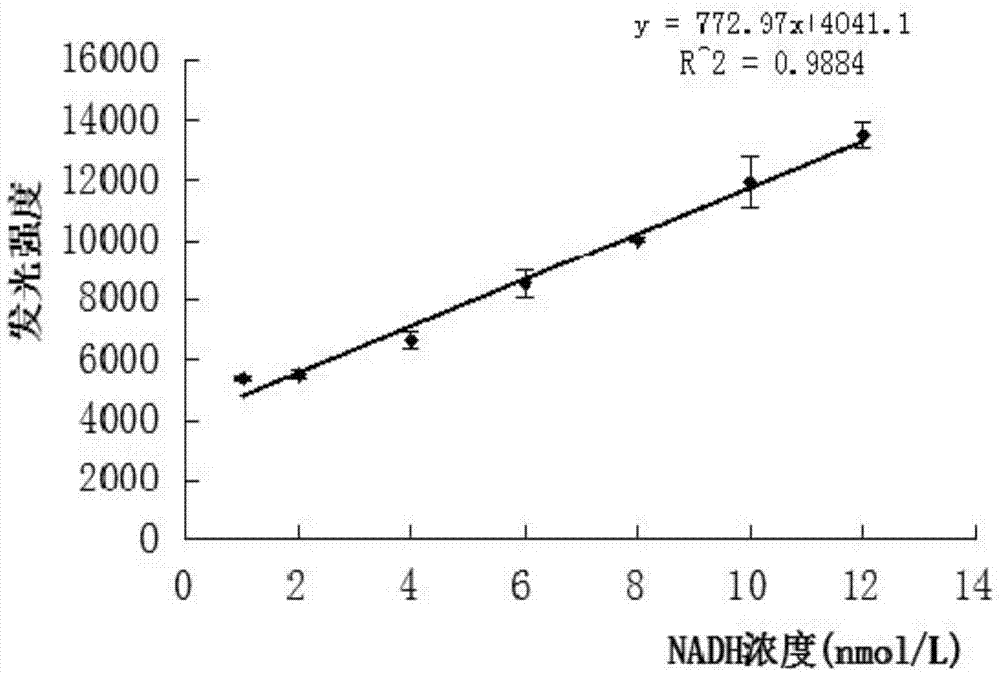
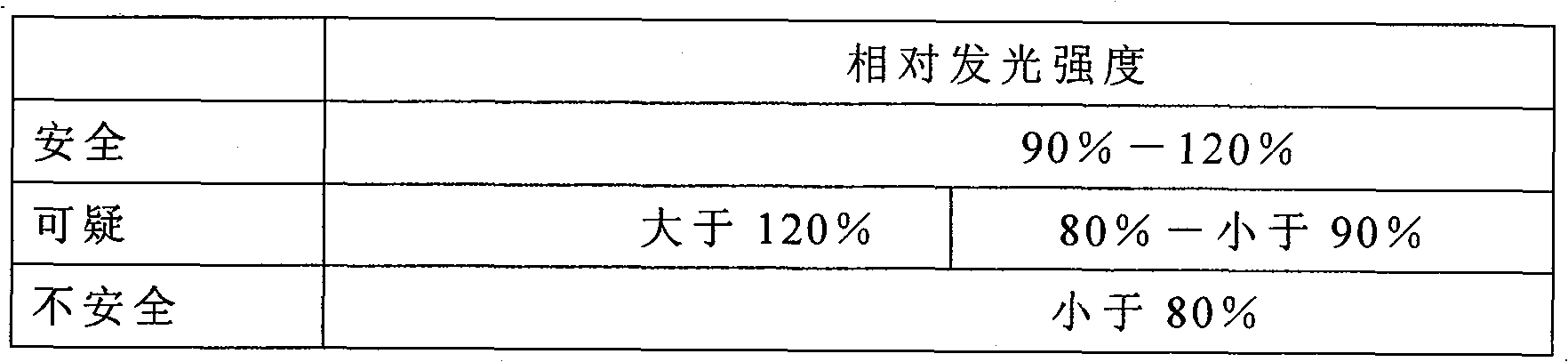
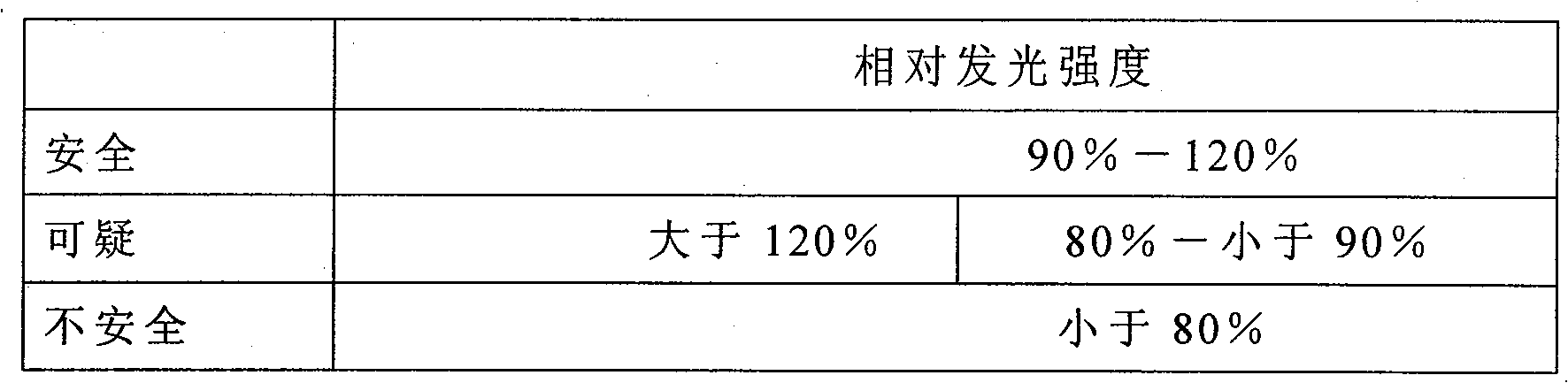
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
60 results about "Luminescent bacteria" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Luminescent bacteria emit light as the result of a chemical reaction during which chemical energy is converted to light energy. Luminescent bacteria exist as symbiotic organisms carried within a larger organism, such as many deep sea organisms, including the Lantern Fish, the Angler fish, certain jellyfish, certain clams and the Gulper eel. The light is generated by an enzyme-catalyzed chemoluminescence reaction, wherein the pigment luciferin is oxidised by the enzyme luciferase. The expression of genes related to bioluminescence is controlled by an operon called the lux operon.
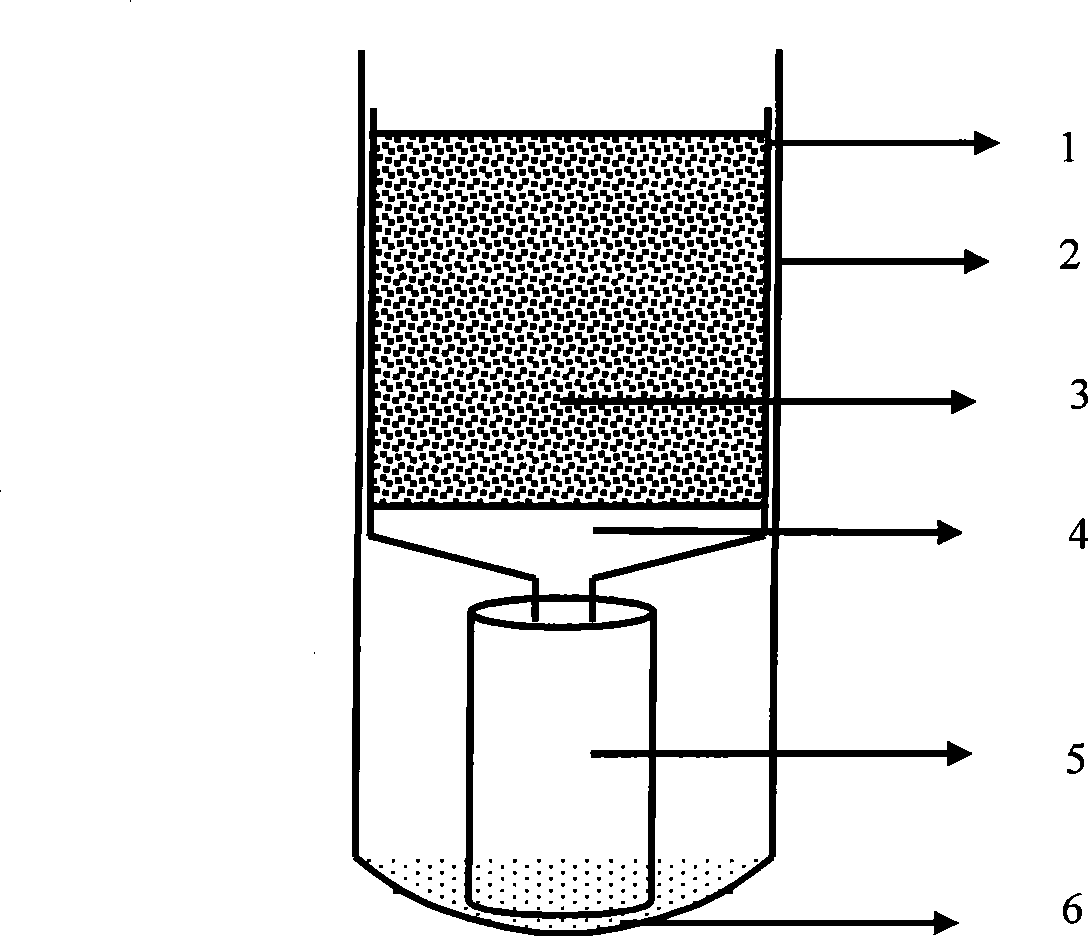
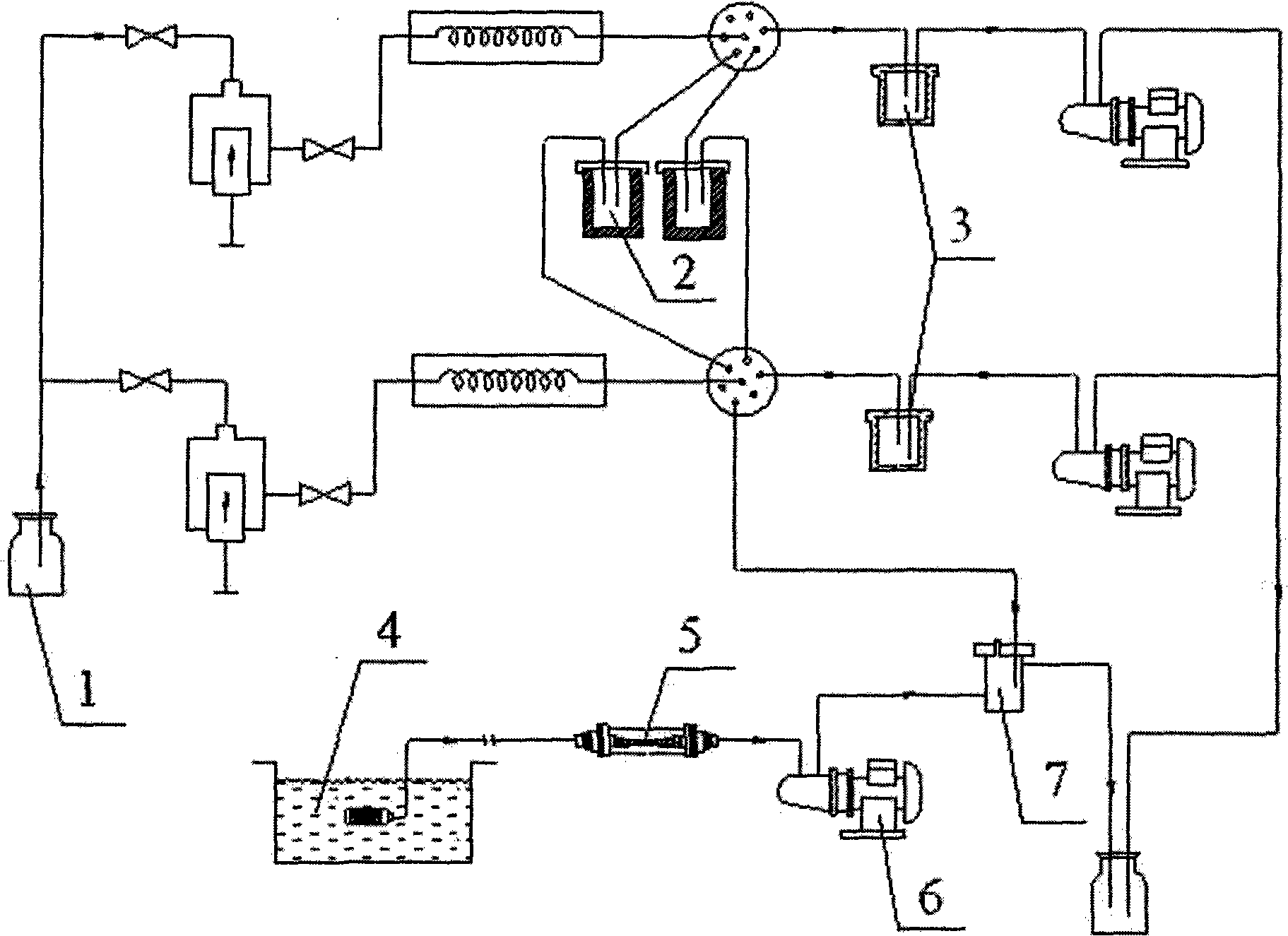
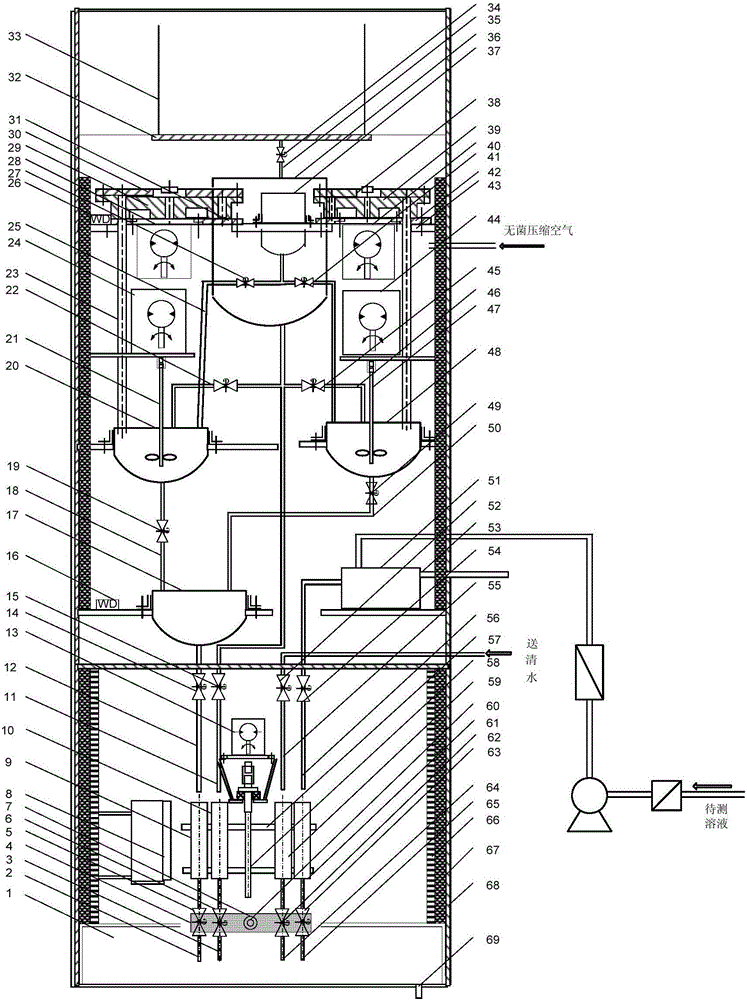
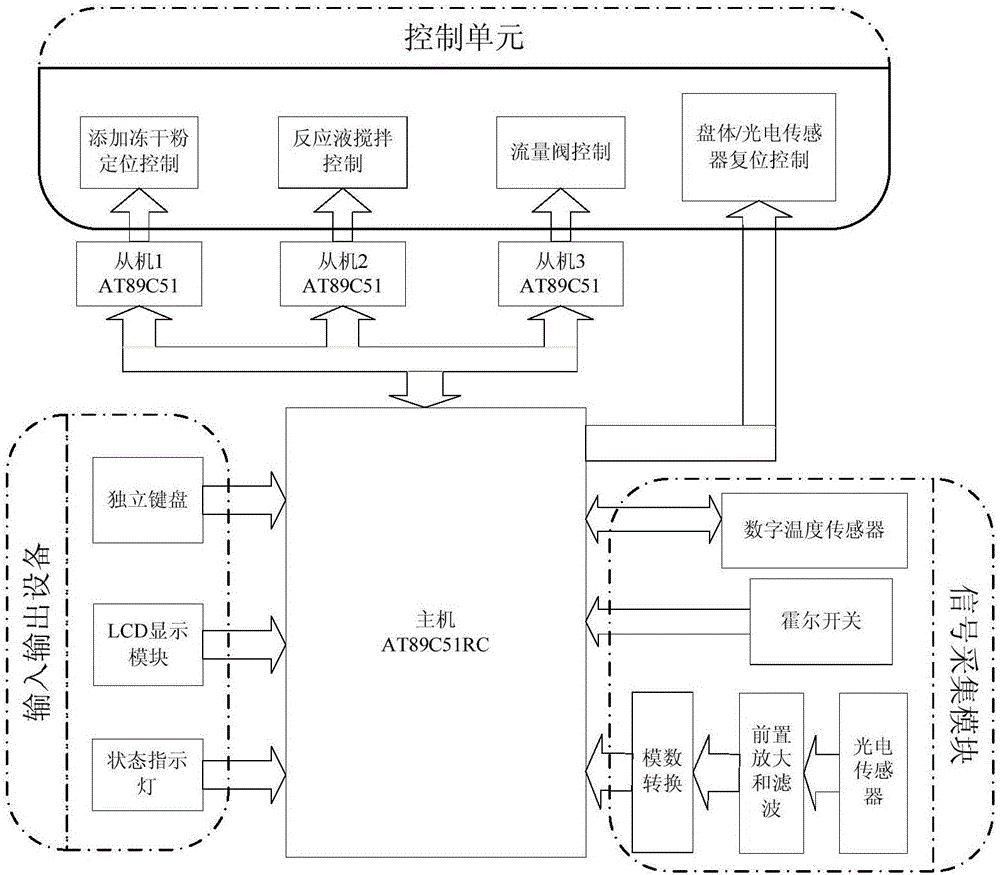
Online monitoring equipment and method for acute toxicity of water quality
InactiveCN101871927ASimple structureLow costBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsData displayLuminescent bacteria
The invention discloses online monitoring equipment for acute toxicity of water quality. The equipment comprises a luminescent bacteria continuous culture system, a sample feeding system, a liquid draining system, a photoelectric detection system and a data display system, and can realize automatic operation. The invention also discloses a method for performing online monitoring on the acute toxicity of the water quality by utilizing the equipment. The online monitoring equipment for the acute toxicity of the water quality of the invention has the characteristics of simple structure, low cost and convenient operation, and can be operated and maintained by non-professionals only after a simple training. By using the method, continuous and automatic acute toxicity monitoring of the water quality can be realized completely; sensitivity is equivalent to that of an international luminescent bacteria method; and monitoring steps are simplified greatly. By using the equipment and the method, an early warning is provided for a sudden environment accident and corresponding measures are taken timely so as to reduce loss greatly.
Owner:NANJING UNIV +1
Method for detecting acute toxicity of water environment by using ATP bioluminescence
InactiveCN101865850AResponsiveImprove test performanceChemiluminescene/bioluminescencePhotometryAcute toxicity testingLuminescent bacteria
The invention discloses a method for detecting the acute toxicity of water environment by using ATP bioluminescence. The method comprises the following steps: an ATP reaction reagent, luciferase, an ATP standard sample, and a water body to be detected are sequentially added in a reaction test tube, placing the reaction test tube in an ATP fluoroscope testing instrument to detect fluorescence intensity, the detection response time is 30s and the detection is served as an experimental group; the standard sample is replaced by distilled water, the detection is served as a control group; the experimental group and the control group are repeatedly detected for three times; and the toxicity of the water body is judged by calculating relative luminance K. The method of the invention has the characteristic of stable and sensitive test effect; and the effect of a luminescent bacteria test can be reached within 3 min of the testing time at most; and the response on organic toxic substances is more sensitive than the luminescent bacteria. In the invention, a portable ATP handholding instrument with a direct current power supply is adopted, thus the ATP handholding instrument is convenient to be carried and is suitable for site test.
Owner:NANJING UNIV +1
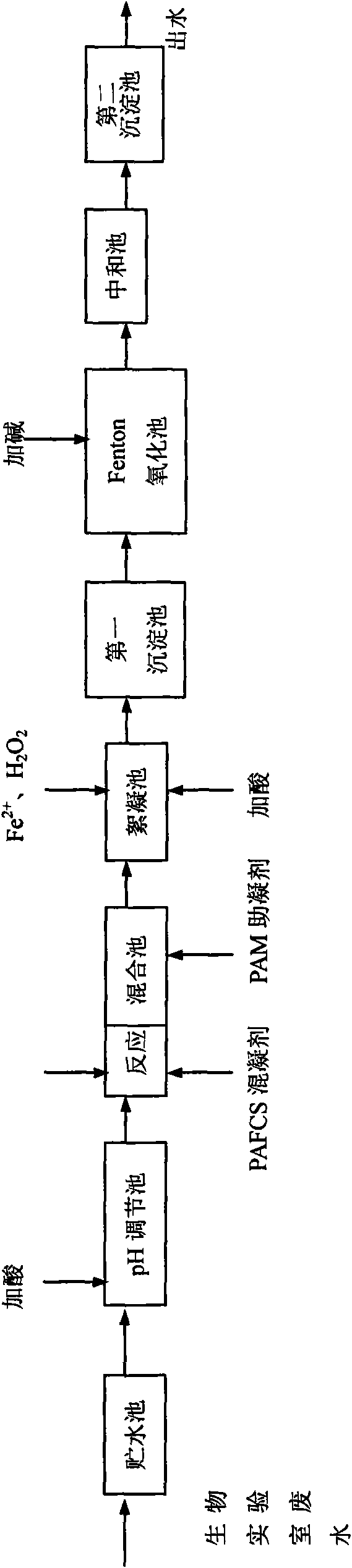
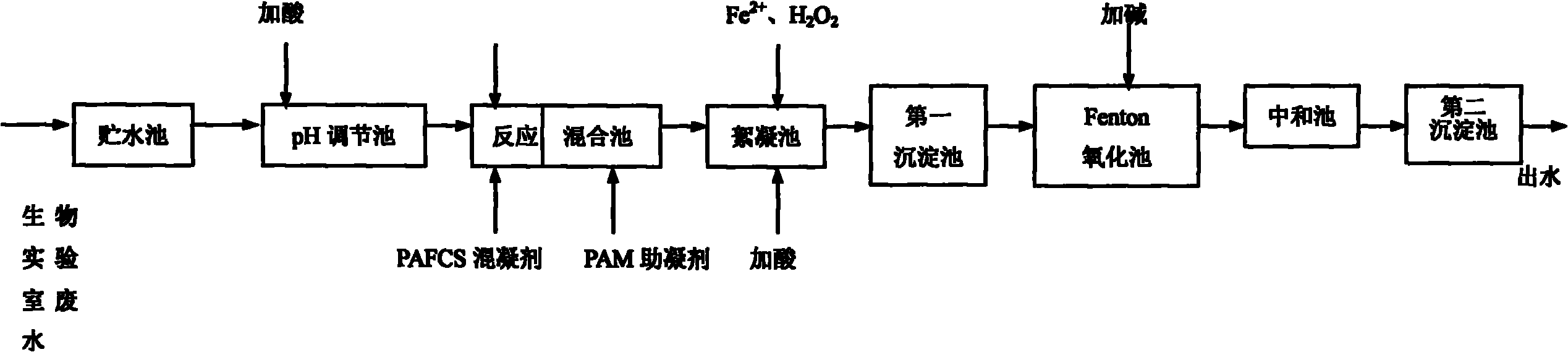
Method for treating biological laboratory wastewater
InactiveCN101851036ASolve new problems of biological pollutionAvoid it happening againMultistage water/sewage treatmentWater/sewage treatment by neutralisationLuminescent bacteriaChemical reaction
The invention belongs to the technical field of environmental protection, and relates to a method for treating biological laboratory wastewater. In the method, a pH regulator 30 percent dilute H2SO4 is adopted to perform preliminary sterilization; a chemical reactant calcium oxide, a coagulant polyaluminum ferric chlorine sulfate and a coagulant aid polyacrylamide are matched to perform coagulating sedimentation to remove pollutants in the biological laboratory wastewater; the method combines a Fenton oxidation method to fulfill the aim of continuously removing organic pollutants CODcr and LAS and has the effects of killing bacteria, removing ATP and reducing the biological toxicity; the pH of effluent is adjusted by using calcium hydroxide and the effluent is settled, and the CODcr and LAS concentration, NH3-N, T-N and T-P in the discharged biological laboratory wastewater reach or precede secondary discharge standard after measurement; and the removing rate of the total number of the bacteria reaches 100 percent, the index value of the biological activity of the bacteria is 0, and the biological toxicity index, namely the inhibition ratio of luminescent bacteria is less than 30 percent.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
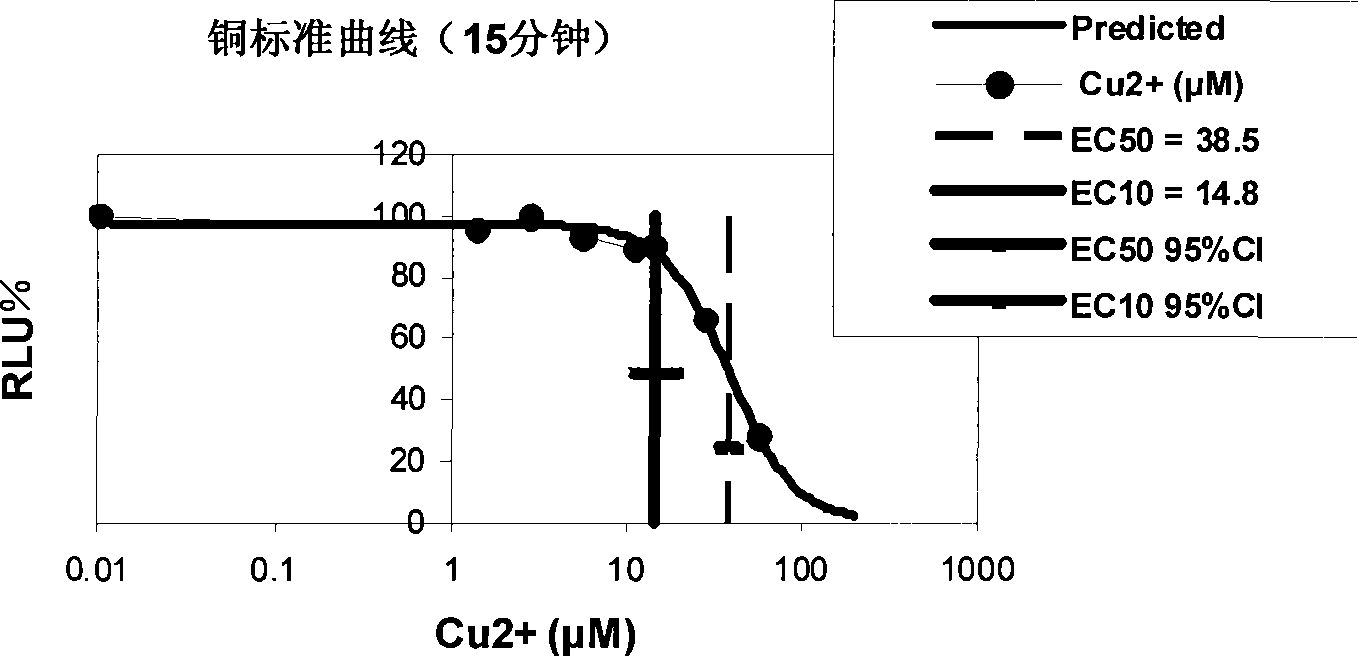
Method for detecting acute toxicity of copper-contaminated soil by using fresh water photobacteria
InactiveCN101487798AAvoid restrictionsNatural Luminous PropertiesChemiluminescene/bioluminescencePreparing sample for investigationLuminescent bacteriaAcute toxicity testing
The invention relates to a detection method in the technical field of environmental monitoring, specifically a method for detecting acute toxicity of copper contaminated soil by using fresh water luminescent bacteria. The method overcomes the limitations that seawater luminescent bacteria is applied in the detection of acute toxicity in soil sample. The specific method uses fresh water luminescent bacteria as bacteria for detection, and includes the following steps: in the first step, soil background soil is used for preparing bacteria suspension of fresh water luminescent bacteria; in the second step, a double-chamber centrifuge method is used for extracting soil pore space water; and in the third step, the toxicity of the soil sample is detected.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
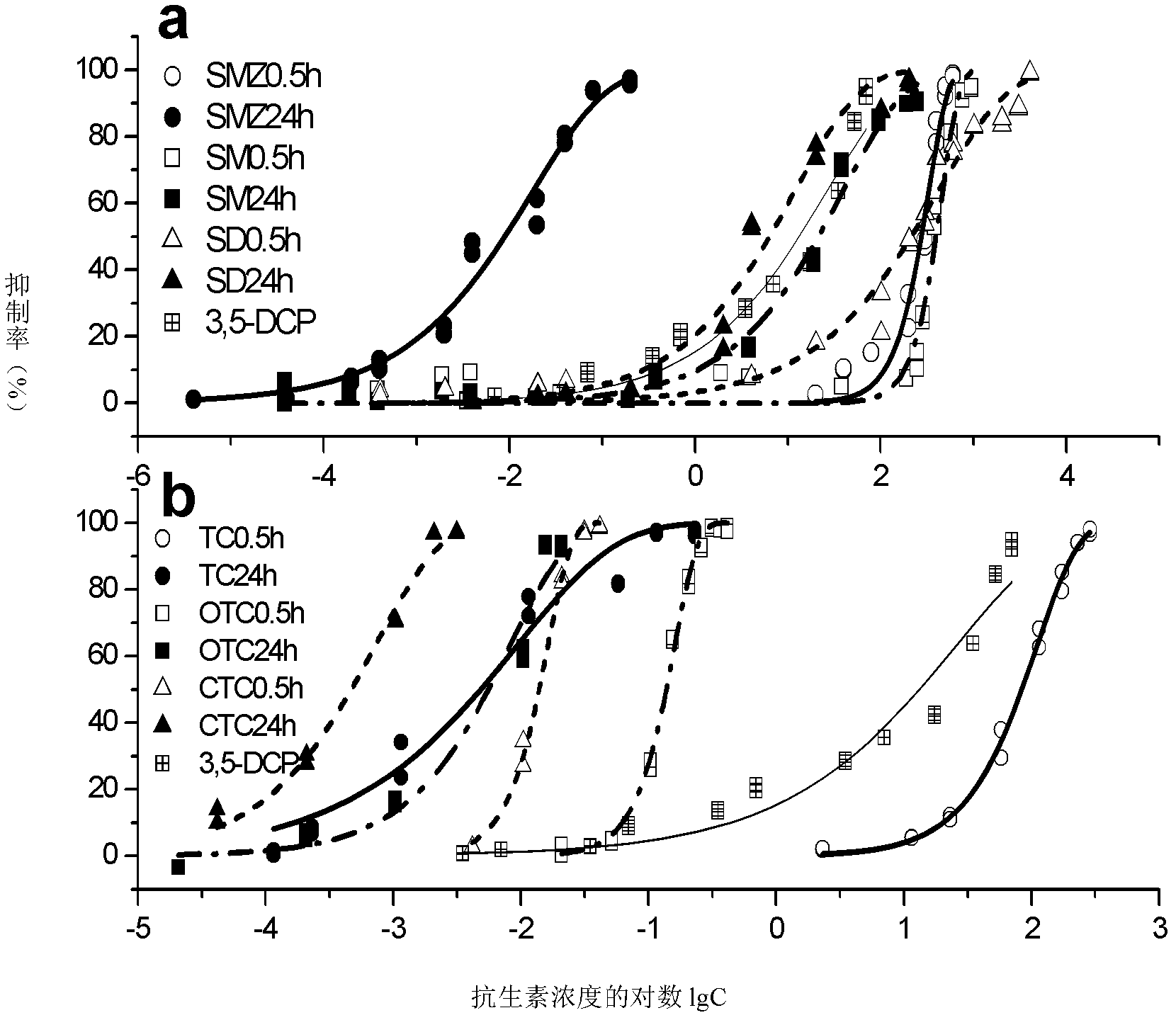
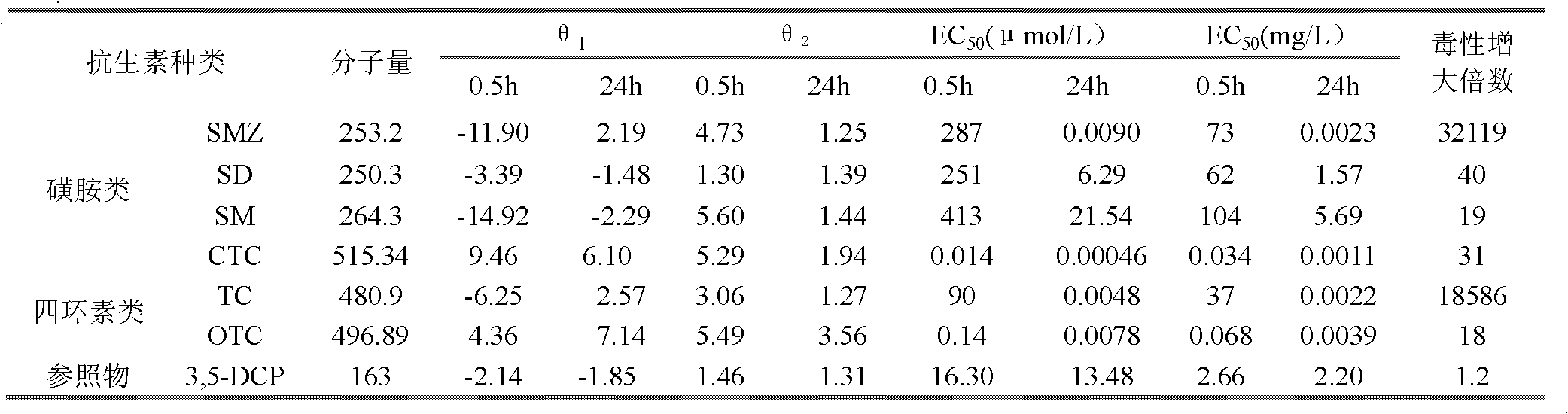
Method for detecting toxicity of antibiotic-type substances by utilizing luminous bacteria
InactiveCN102634564AProlong the action timeGuaranteed normal proliferationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological organismBacteria
The invention provides a method for detecting toxicity of antibiotic-type substances by utilizing luminous bacteria. The method comprises the following step of: prolonging the action time of antibiotic-type substances and the luminous bacteria to12-36 hours, preferably 24 hours. In the technical scheme provided by the invention, the action time of the antibiotic-type substances and the luminous bacteria is prolonged, so that the proliferation of the luminous bacteria during the period is ensured; and through the method, good timeliness of the accurate characterization of the biotoxicity of antibiotic can be realized, the detection result is more accurate on the basis of guaranteeing the timeliness, and the detection of toxicity delay of antibiotic-type pollutants is realized.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
Method for evaluating water quality health risk with chromium ion as standard toxic substance
ActiveCN102175828AToxicity AccurateToxicity results are easily harmonizedMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansLuminescent bacteriaWater quality
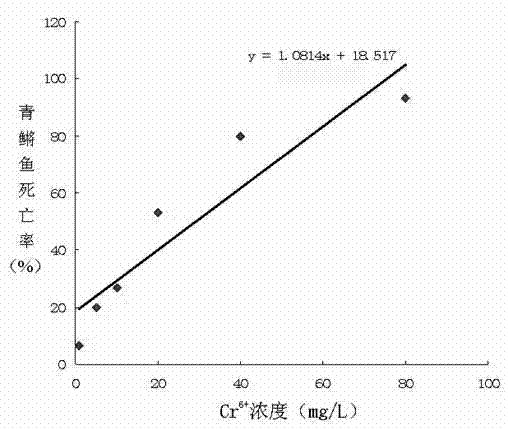
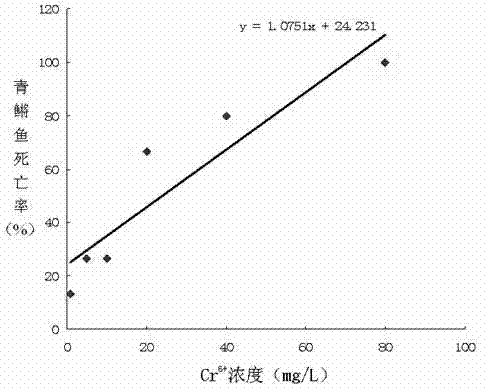
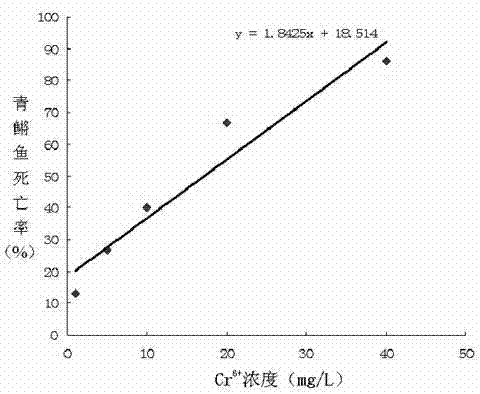
The invention relates to a method for evaluating water quality health risk with a chromium ion as a standard toxic substance, comprising the following steps: a toxicity test is conducted on biological fish, if dead fish occurs in 96h, Cr<6+> concentration is used for representing water quality toxicity, and if dead fish does not occur, a luminescent bacteria toxicity test is conducted; if the luminescent inhibition rate is higher than 40%, the Cr<6+> concentration is used for representing the water quality toxicity, and if the luminescent inhibition rate is lower than 40%, an SOS / umu test is conducted; if a test result is positive reaction, the Cr<6+> concentration is used for representing the water quality toxicity, and if a test result is negative reaction, a broad bean root tip micronucleus test is conducted; and if a micronucleus permillage ratio is more than 1.5, the Cr<6+> concentration is used for representing the water quality toxicity, and if the micronucleus permillage ratio is less than 1.5, a unicellular gel electrophoresis test is conducted and the Cr<6+> concentration is used for representing the water quality toxicity. In the invention, the steps are closely related to each other so that both the low pollutant content and the high pollutant content in water quality can be detected, the detection time is shorter, the result is accurate and easy to unify, and quantification evaluation of the water quality toxicity can be realized.
Owner:济南市供排水监测中心
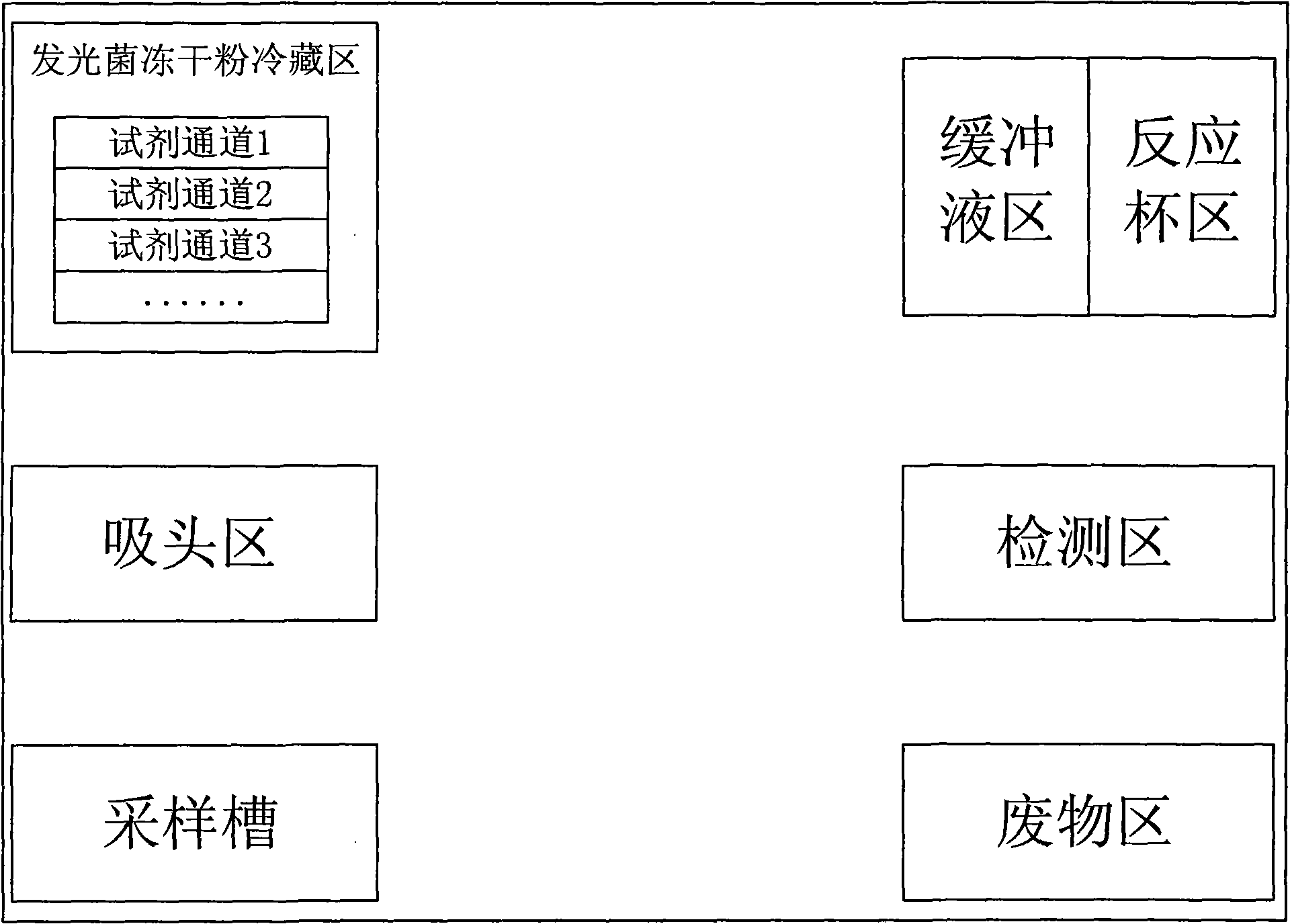
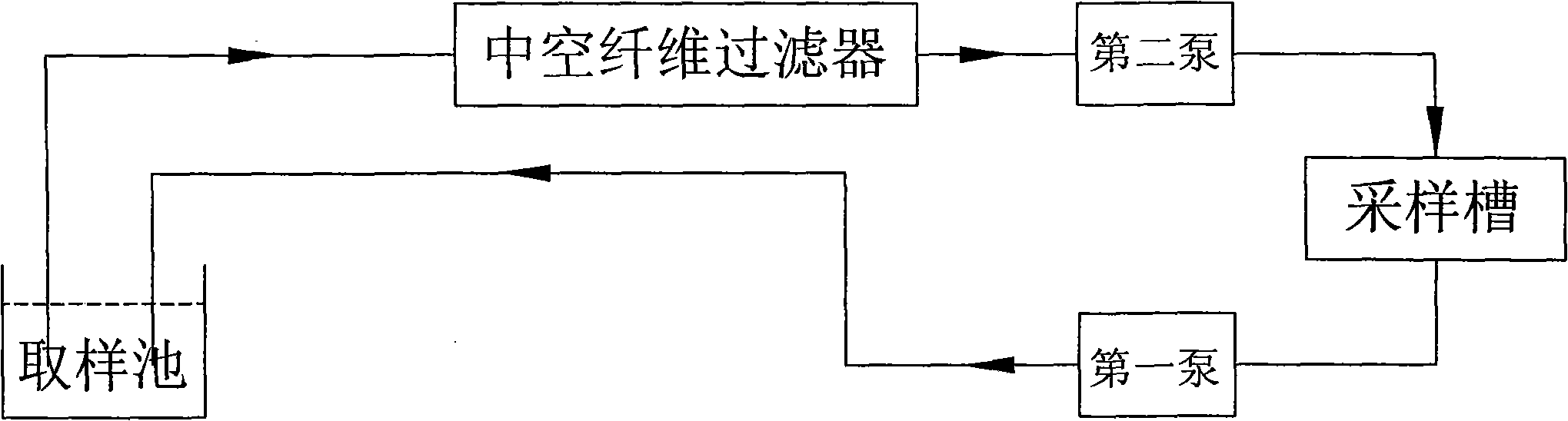
Water quality toxicity detector
InactiveCN101571534AAvoid cross infectionEliminate cross-contaminationChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceTesting waterLuminescent bacteriaWater quality
The invention discloses a water quality toxicity detector, which comprises the following parts which are mutually independent: a luminescent bacteria storing region, a sampling groove connected with acirculation pipeline, a sucker region used for storing disposable suckers, a detection region used for reacting luminescent bacteria and a water sample and detecting, and a mechanical arm capable ofmoving back and forth among the luminescent bacteria storing region, the sampling groove, the sucker region and the detection region. Because the parts are separated, the regions are not connected through pipelines, the transportation of substances is realized through the mechanical arm, and the cross infection among regions is avoided. In addition, the suckers and reaction cups for detection aredisposable, so that the problems of cross contamination of strains and cross contamination of samples to be detected are prevented; and apparatus do not need a washing fluid to wash, so that zero cross contamination is truly realized.
Owner:JIAXING QUEST LIFE SCI
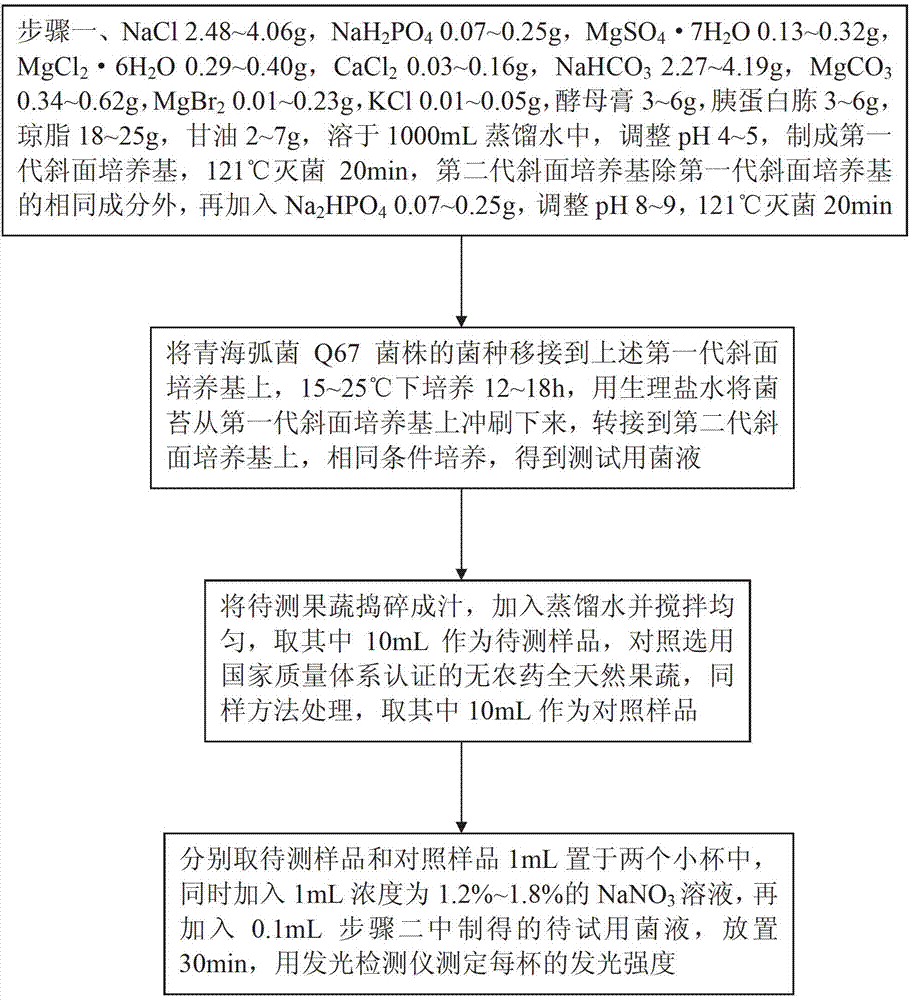
Method for testing biotoxicity of oil-field wastewater by employing vibrio qinghaiensis Q67
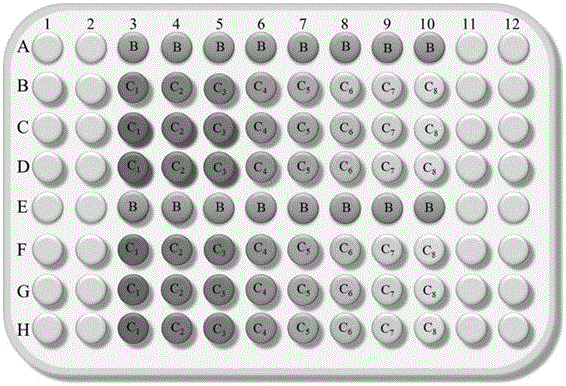
ActiveCN106755286ASolve the problem of not being able to express the biological toxicity of oil production wastewaterExperimental results are stableMicrobiological testing/measurementBioindicator SpeciesLuminous intensity
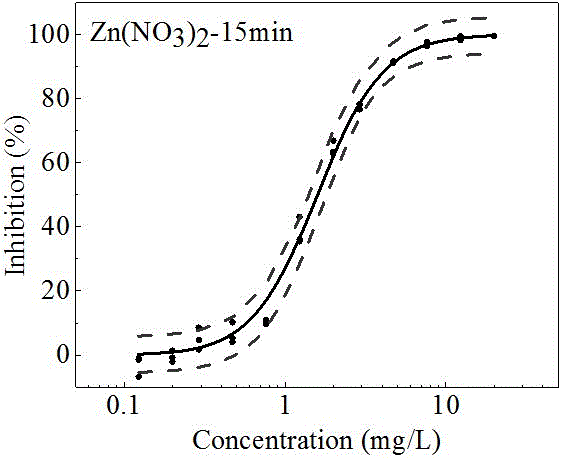
The invention discloses a method for testing biotoxicity of oil-field wastewater by employing vibrio qinghaiensis Q67. The oil-field wastewater is taken as test wastewater, the vibrio qinghaiensis Q67 is taken as a bioindicator and a 96-pore microwell plate is taken as a carrier; by adopting a 96-pore microwell plate analyzing method, the luminous intensity is detected by adopting a microwell plate spectraphotometer; and the luminescent inhibition rate is calculated by using the luminous intensity of an experiment group and a control group and Zn(NO3)2 is set as a toxic reference substance, thereby judging the biotoxicity of the oil-field wastewater. According to the method, the toxicity of the oil-field wastewater is detected and analyzed by using a microplate method; and the comprehensive toxicity of the oil-field wastewater is judged through calculating the luminescent inhibition rate of luminescent bacteria; the problem that conventional physicochemical indexes cannot represent the biotoxicity of the oil-field wastewater is solved; the method is fast, sensitive and convenient to popularize and apply; the selected toxic reference substance Zn(NO3)2 is steady in experiment result, low in price and medium in toxicity.
Owner:GUILIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Quick luminescent bacteria supported based on signal molecule
InactiveCN102250771AEasy to synthesizeShorten the timeMicroorganism based processesMicroorganism preservationLuminescent bacteriaSignalling molecules
The invention discloses quick luminescent bacteria supported based on signal molecule. The quick luminescent bacteria supported based on signal molecule are characterized in that: luminescent bacteria freeze-dried powder is prepared by mixing bacterial mud obtained by centrifuging 10ml of Vibrio fischeri at the concentration of 10<9> / ml and 1ml of cryoprotective agent, and performing freeze drying, and is stored at -20DEG C for 6 months; and the cryoprotective agent is prepared by dissolving 15g of nonfat milk, 5g of glycerol and 12.5g of trehalose in 100ml of signal molecule solution. The invention has the advantages that: by adding signal molecules, the synthesis of luciferase can be promoted, so that the time for the luminescent bacteria freeze-dried powder to restore stable luminescence is shortened from the original 15-30 minutes to 5 minutes; and by adding the composite cryoprotective agent, more bacteria can keep the integrity of cellular structures and the activity of cells during freezing and drying, and can be revived under proper conditions.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Method for detecting acute toxicity of rare earth tailing pond surrounding groundwater pollution by using freshwater luminescent bacteria
InactiveCN105588831AWide range of pH requirementsSensitive and accurate detectionChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceTesting waterEcological environmentAcute toxicity testing
The invention discloses a method for detecting acute toxicity of rare earth tailing pond surrounding groundwater pollution by using freshwater luminescent bacteria. The freshwater luminescent bacteria are Vibrio qinghaiensis Q67; the method comprises steps as follows: a to-be-detected sample is treated and diluted, and the pH value is adjusted; an activated Vibrio qinghaiensis Q67 solution is added to the to-be-detected sample for a reaction; meanwhile, a diluent for dilution replaces the to-be-detected sample to serve as a contrast; the luminescent intensity of the to-be-detected sample and the luminescent intensity of the contrast are detected by a bioluminescence tester; the result is calculated, standard reference poison ZnSO4 is set, and the toxicity effect is judged according to the result. The method is rapid, sensitive, accurate and convenient to popularize and apply. Meanwhile, Vibrio qinghaiensis, the freshwater luminescent bacteria, is used as a test strain, and the influence caused by salinity required by marine luminescent bacteria on luminescence is avoided. The reference poison is ZnSO4, and the influence on the ecological environment and human health is reduced.
Owner:INST OF URBAN ENVIRONMENT CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for performing low-dosage radiant biology early warning by utilizing luminous bacteria
The invention relates to a method for performing low-dosage radiant biology early warning by utilizing luminous bacteria. According to the method, a dosage-effect relationship between a radiant dosage acceptable by the bacteria and a luminous intensity can be established by utilizing a sensitivity of the luminous bacteria to the low-dosage radiation, and the luminous intensity of the bacteria has positive correlation with the activity of luminous elements such as fluorescein, luciferase and ATP in the bacterial cells. Therefore, through calculation of a luminous intensity suppression ratio of the luminous bacteria, the comprehensive toxicity of the low-dosage radiation for the luminous bacteria can be estimated, and a biology early warning method is established. The method for performing low-dosage radiant biology early warning by utilizing the luminous bacteria has multiple advantages of being convenient, simple and fast to operate, low in cost, high in sensitivity, good in accuracy, low in environment risk and the like.
Owner:NANHUA UNIV
Method for detecting comprehensive toxicity offresh meat, fresh milk and food
InactiveCN101071103ARapid responseHigh detection sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceBacteroidesLuminous intensity
The invention provides a method of detecting comprehensive toxicity of fresh meat and milk, belonging to food safety and environmental protection technical fields. On given conditions, the luminous bacteria's luminous intensity changes with the outside world's content of poison. The detection of comprehensive toxicity of the fresh meat and milk includes three steps: luminous bacteria preparations, testing sample preparation, the luminous bacteria detection. The freluminous bacteria is freshwater luminous bacteria - Qinghai Vibrio Q67 strain together. The fresh meat leaching fluid samples or fresh milk is mixed with Qinghai bacterium Vibrio Q67 Strain together. Through the detection of the Qinghai Vibrio Q67 strains luminous intensity the comprehensive toxicity of all toxicology together can be determined, then to measure if the food is safe to eat. It is quick, sample to detect comprehensive toxicity, and have high detection sensitivity and broad scope.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Sewage detecting method
ActiveCN109946433AImprove recycling efficiencyChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceWater/sewage treatment by ion-exchangeLuminescent bacteriaSewage treatment
The invention relates to a sewage detecting method comprising: sampling a sewage sample at a sewage discharge place, carrying out extraction on one part of sewage sample by using dichloromethane, carrying out dissolving by using DMSO, placing the processed sample in a refrigerator and storing the sample at a low temperature, and detecting the sewage sample by using luminescent bacteria toxicity testing; recycling and reusing the sewage directly under the condition of not detecting the toxicity in the sewage; spraying a sewage treatment agent uniformly at a sewage outlet and carrying out sampling detection again under the condition of detecting the toxicity in the sewage; and carrying out deep detection on the sewage sample placed in the refrigerator under the condition of detecting the toxicity in the sewage; and recycling and reusing the sewage directly under the condition of not detecting the toxicity in the sewage. Therefore, the sewage dosage can be evaluated preliminary from the perspective of toxicity; and secondary evaluation is performed after preliminary treatment against toxicity, so that the efficiency of sewage recovery is improved.
Owner:天津市宇驰检测技术有限公司
Detection method for acute biological toxicities of pollutants on dust-haze day
InactiveCN105987898AComprehensive toxicity applicableThe detection process is fastChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceLuminescent bacteriaAcute toxicity testing
The invention discloses a detection method for acute biological toxicities of pollutants on a dust-haze day. The detection method specifically comprises the following steps that air samples on the dust-haze day are collected and dissolved in sterile water, the light intensity of the air pollutants dissolved in water is measured through freshwater luminescent bacteria-Qinghai vibrio Q67, and the comprehensive acute toxicity effect of the air pollutants on the dust-haze day on bionts is detected through comparison with a blank group. Compared with other biological acute toxicity testing methods, the detection method has the advantages that the luminous bacterial method used for measuring the acute biological toxicities of the dust-haze day is high in sensitivity and high in detection speed, a result can be obtained within 0.5 h, and the levels of the acute biological toxicities of the air pollutants can be judged. The detection method has actual application value for detection and prevention of comprehensive toxicities of the air pollutants on the dust-haze day.
Owner:SHANGHAI NAN YANG MODEL HIGH SCHOOL
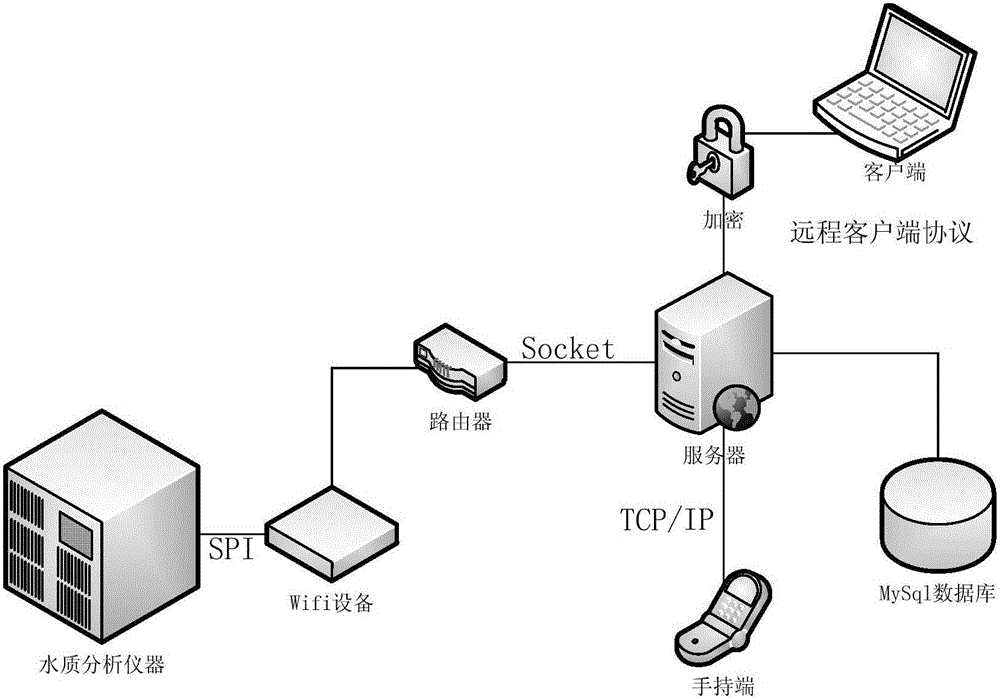
Remote online water quality monitoring method based on curve fitting and toxicological analytical algorithm
ActiveCN105973877APredicting Toxic Substance CompositionPredicted concentrationChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceLuminous intensityLuminescent bacteria
The invention provides a remote online water quality monitoring method based on a curve fitting and toxicological analytical algorithm. The method comprises the following steps: a water quality comprehensive biological toxicity analyzer is used for monitoring inhibition degree of toxic substances in sampling liquid on luminescence intensity of bioluminescent bacilli; luminescence intensity information is sent to a remote server; data processing of the luminescence intensity information is carried out by the server in order to determine class of pollution of sewage toxicity; and result information is searched on a remote client. Compared with the prior art, the improved curve fitting algorithm is implanted, a Fabonacci method is used for further optimizing each coefficient of an improved curve fitting model, in order to realize prediction of components and concentrations of toxic substances; at the same time, the effects of magnetic stirring time, culture temperature, culture time, exposure duration, and pH value range on the result measured value are also considered, the influences of each condition on biological toxicity tests of luminescent bacteria are analyzed, so that measurement precision and stability of the analyzer are improved, and remote online monitoring is realized.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
Method for detecting residual pesticidal toxicity in fruits and vegetables
ActiveCN103076319AQuick checkAccurate detectionChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceLuminescent bacteriaFood safety
The invention relates to the field of food safety, in particular to a method for detecting residual pesticidal toxicity in fruits and vegetables. The method for detecting the residual pesticidal toxicity in the fruits and the vegetables is characterized by comprising the following steps: preparing luminescent bacteria, preparing a detection sample, performing luminescent detection on the luminescent bacteria, mixing a fruit and vegetable sample to be detected with strain liquid of a vibrio qinghaiensis Q67 strain, and judging the residual pesticidal toxicity in the detected fruit and vegetable sample. By the method, the detection time of the residual pesticidal toxicity in the detected fruit and vegetable sample is shortened and the stable luminescent time of the vibrio qinghaiensis Q67 strain is prolonged.
Owner:通标标准技术服务有限公司
Growth effect and acute and chronic toxicity detection method of luminous bacteria
InactiveCN110441292AAvoiding Ignoring Delayed Toxicity of Test SubstancesThe detection effect is comprehensive and accurateChemiluminescene/bioluminescencePreparing sample for investigationBiotechnologyLuminescent bacteria
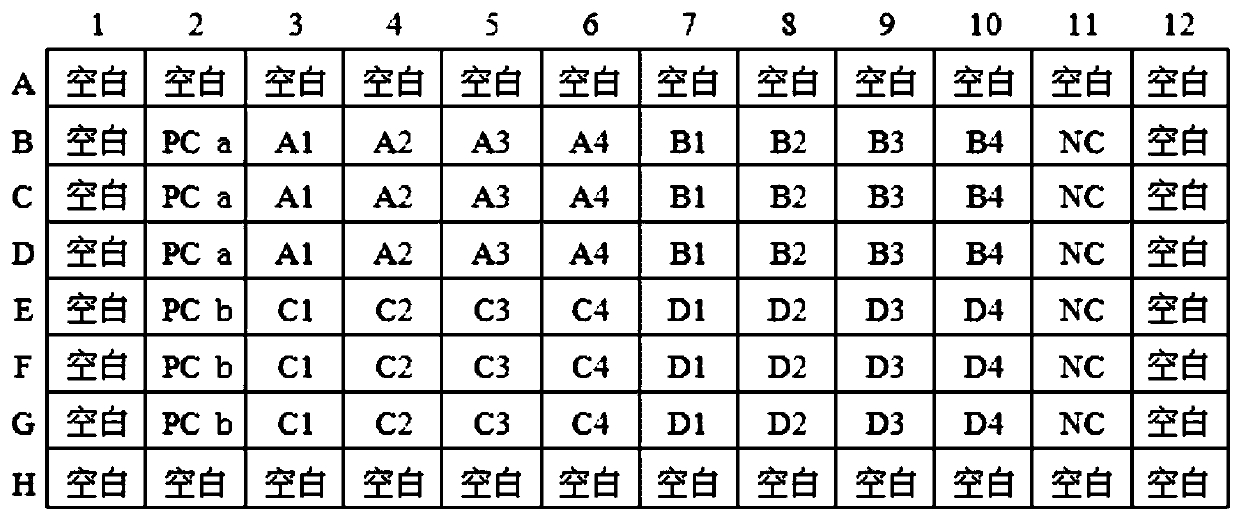
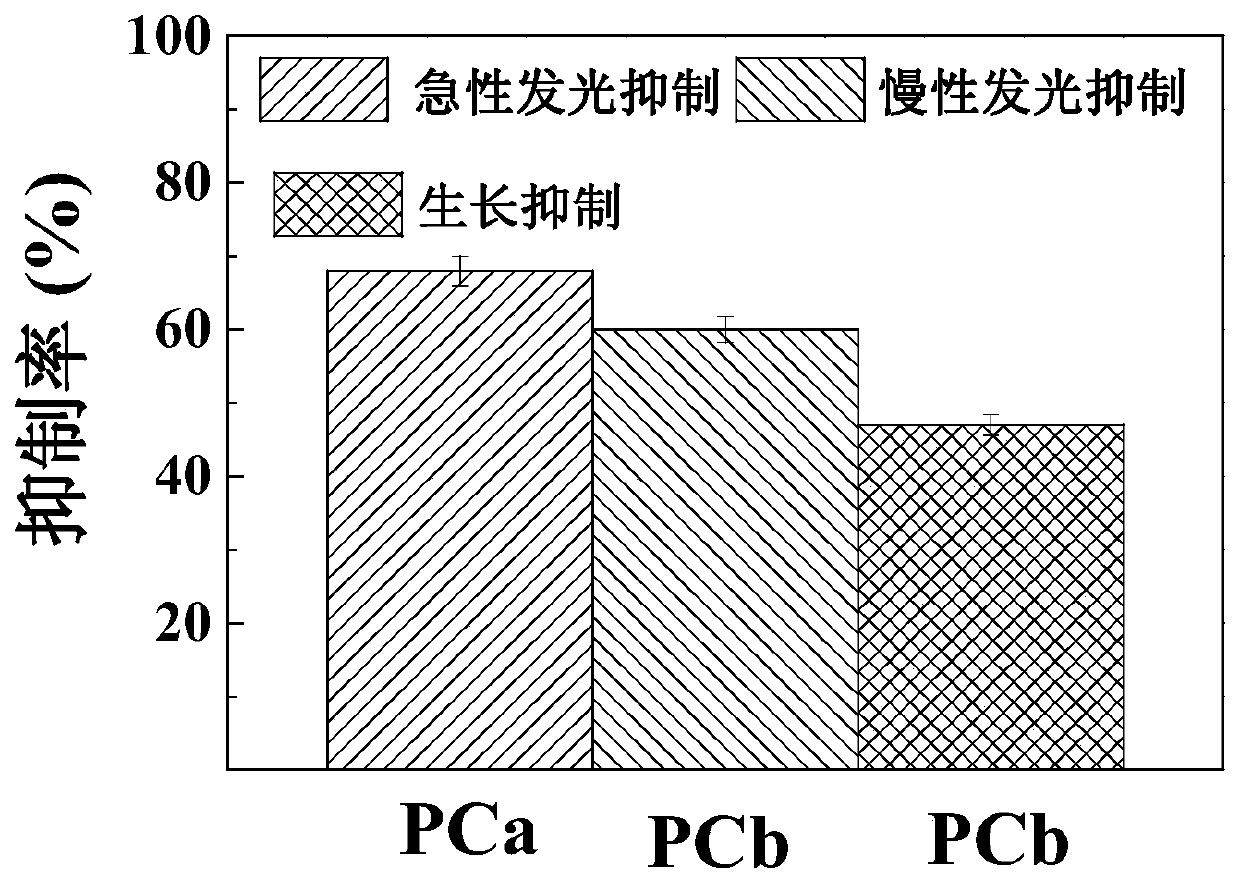
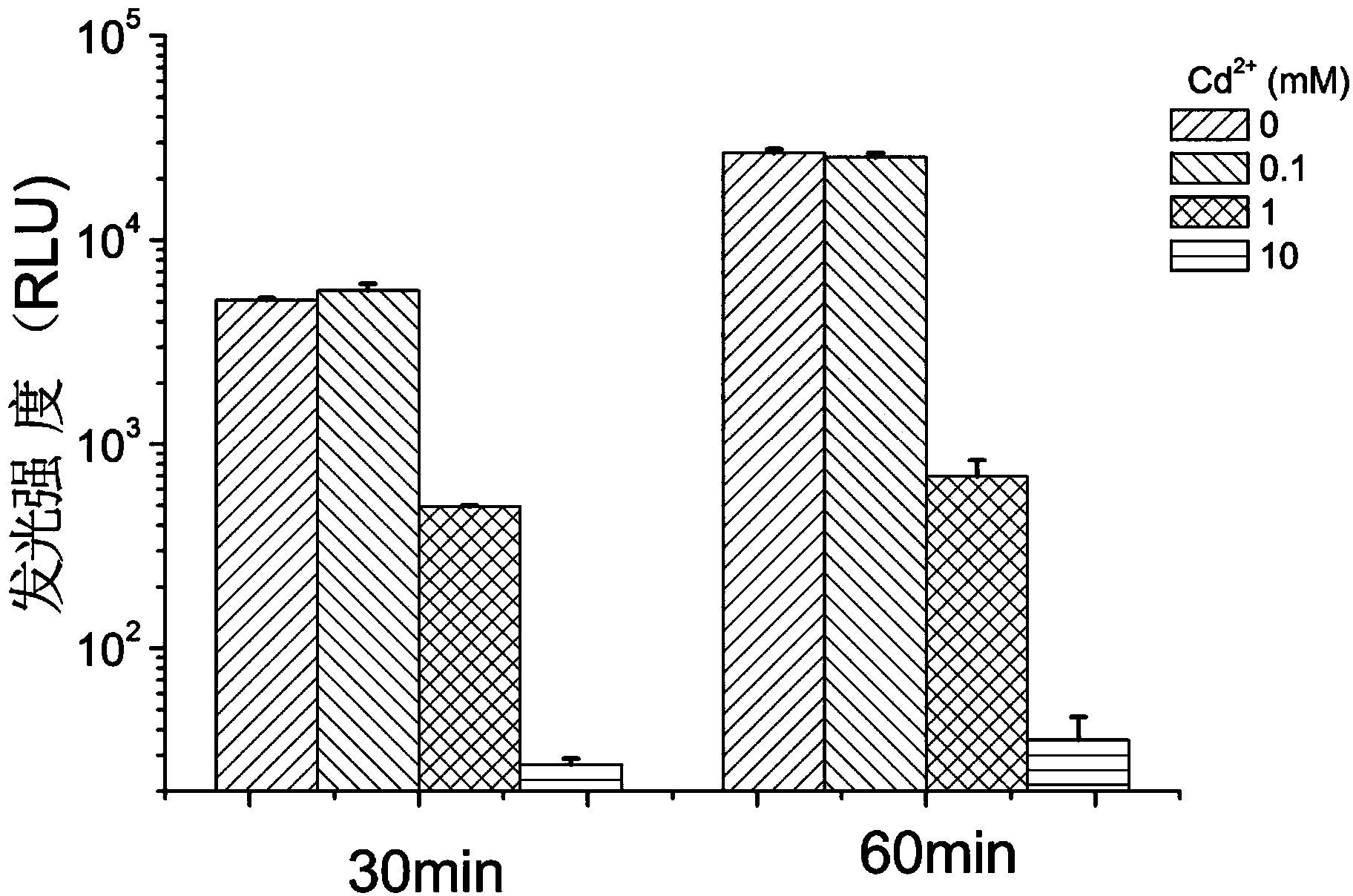
The invention discloses a growth effect and acute and chronic toxicity detection method of luminous bacteria. The method comprises the steps of: preparing an experiment sample, a negative control sample and a positive control sample; preparing a luminous bacteria solution; adding the luminous bacteria solution into a 96-pore cell culture board, then placing the 96-pore cell culture board on a microplate reader, and measuring an initial optical density value and an initial bioluminescence value 30 minutes later; adding the experiment sample, the negative control sample and the positive controlsample into the luminous bacteria solution, measuring the optical density value and the bioluminescence value every 30 minutes within the first 1 hour, and then measuring the optical density value and the bioluminescence value every 1h, and performing the test for not less than 24h; obtaining an optical density mutation time and a bioluminescence mutation time; and calculating an acute luminescence inhibition rate, a chronic luminescence inhibition rate and a growth inhibition rate. The growth effect and acute and chronic toxicity detection method disclosed by the invention can be used for simultaneously evaluating the growth effect, and acute and chronic toxic effects of a test substance on the luminous bacteria, the accuracy is high, high throughput of the toxicity test is achieved, andthe test efficiency is high.
Owner:NANJING COLLEGE OF INFORMATION TECH
A luminescent bacterium freeze-drying protective agent, freeze-dried powder and application of the freeze-dried powder in on-line monitoring of comprehensive toxicity of water quality
InactiveCN111566199AHigh live bacteriaGood for production researchBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyLuminescent bacteria
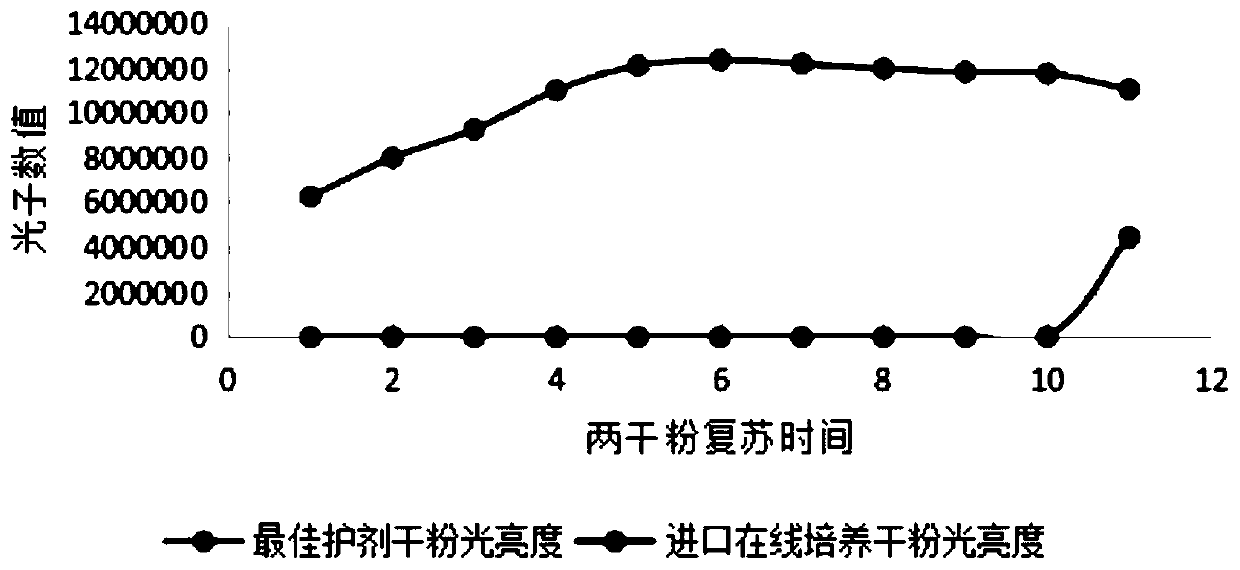
The invention discloses a luminescent bacterium freeze-drying protective agent, freeze-dried powder and application of the freeze-dried powder in on-line monitoring of comprehensive toxicity of waterquality. Each L of the luminous bacterium freeze-drying protective agent is composed of the following components: 100-200g of skim milk, 20-120g of cane sugar, 10-60g of sodium chloride and the balance of water. The luminescent bacterium freeze-dried powder is prepared by adding a luminescent bacterium freeze-drying protective agent into a luminescent bacterium solution. The luminescent bacteriumfreeze-drying protective agent or the luminescent bacterium freeze-dried powder can be used as a detection preparation for on-line water quality toxicity monitoring. The resuscitated luminous bacterium freeze-dried powder is refrigerated in a strain storage cup at 4 DEG C, can be used for an online toxicity monitoring instrument for 15 days, can replace an imported freeze-drying protective agent,reduces the operation cost of reagent consumables of the online toxicity monitoring instrument, improves the continuous and stable operation of the online toxicity monitoring instrument, and plays a role in biotoxicity early warning for the safety of water quality.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Luminescent bacteria test paper for rapidly detecting water quality biotoxicity and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103105388AImprove portabilityIncreased sensitivityChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceLuminescent bacteriaLiquid state
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological analysis and detection and in particular relates to luminescent bacteria test paper for rapidly detecting water quality biotoxicity and a preparation method thereof. The luminescent bacteria test paper is prepared by the following steps: taking a common test paper material as a substrate, coating luminescent bacteria through hydrogel, solidifying the coating luminescent bacteria from a liquid state to a solid state under the irradiation of an ultraviolet lamp, and fixing the solid luminescent bacteria on the test paper. The test paper is thrown into a water body to be detected, the initial luminous amount value of the luminescent bacteria and the luminous amount value of the luminescent bacteria (in the water body) within 15 minutes or 30 minutes on the test paper are compared so as to obtain the light-inhibiting rate, so that the water quality biotoxicity is detected. The method has the characteristics of rapidness, high efficiency, convenience, low cost and the like, also has high sensitivity and high tolerance to external condition change and is suitable for rapid on-site toxicity detection in various water environments.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Fish and photogenic bacterium-based comprehensive toxicity online analyzer
InactiveCN106645611AIncreased sensitivityLearn about pollutionTesting waterLuminescent bacteriaOrganism
The invention provides a fish and photogenic bacterium-based comprehensive toxicity online analyzer. The analyzer comprises a sampling unit, a bacterium storage chamber, a reaction chamber, a salt solution unit, a detection unit, a control unit and a fish pond, wherein the detection unit comprises a dual-optical-path detection module and a behavior monitor; fish behaviors are monitored by the dual-optical-path detection module and the behavior monitor by utilizing a method of luminescent bacteria. The biological toxicity of a water body is determined by combining two methods, so that a sensitive, simple and convenient method with high repeatability for testing biological toxicity of environmental pollutant is realized, and the pollution situation of a water environment can be better known.
Owner:武汉联宇技术股份有限公司
Surgical smoke biological toxicity evaluation method
InactiveCN106568902AEndocrine disrupting toxicity sensitivityThe biological toxicity evaluation results are comprehensive, true and reliableAnalysing gaseous mixturesLuminescent bacteriaDeficient mouse
The invention discloses a surgical smoke biological toxicity evaluation method. The method comprises the following steps: A, evaluating the in-vitro biological toxicity of luminescent bacteria; B, evaluating the in-vivo biological toxicity of ApoE gene-deficient mice exposed to surgical smoke; and C, evaluating the genetic toxicity of surgical smoke through micronucleus test. The method of the invention has the advantages of quickness and efficiency, accuracy and quantification, realness and reliability, multi-level evaluation, and the like, and has very high practical value and a broad market prospect. The method gets away from the embarrassing situation in which the biological toxicity of surgical smoke cannot be tested fully, and is expected to become an important way of evaluation and test for controlling surgical smoke pollution.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
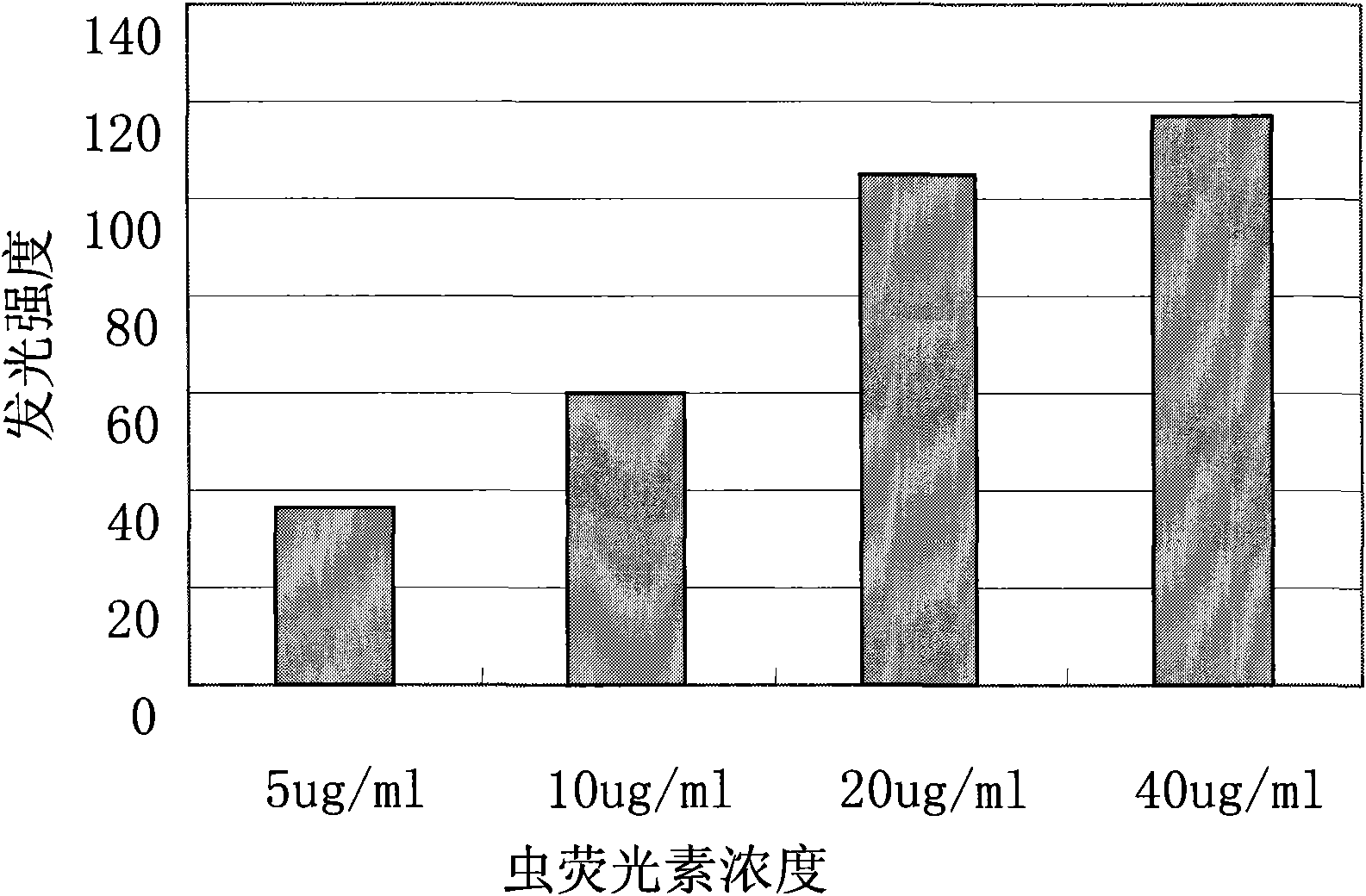
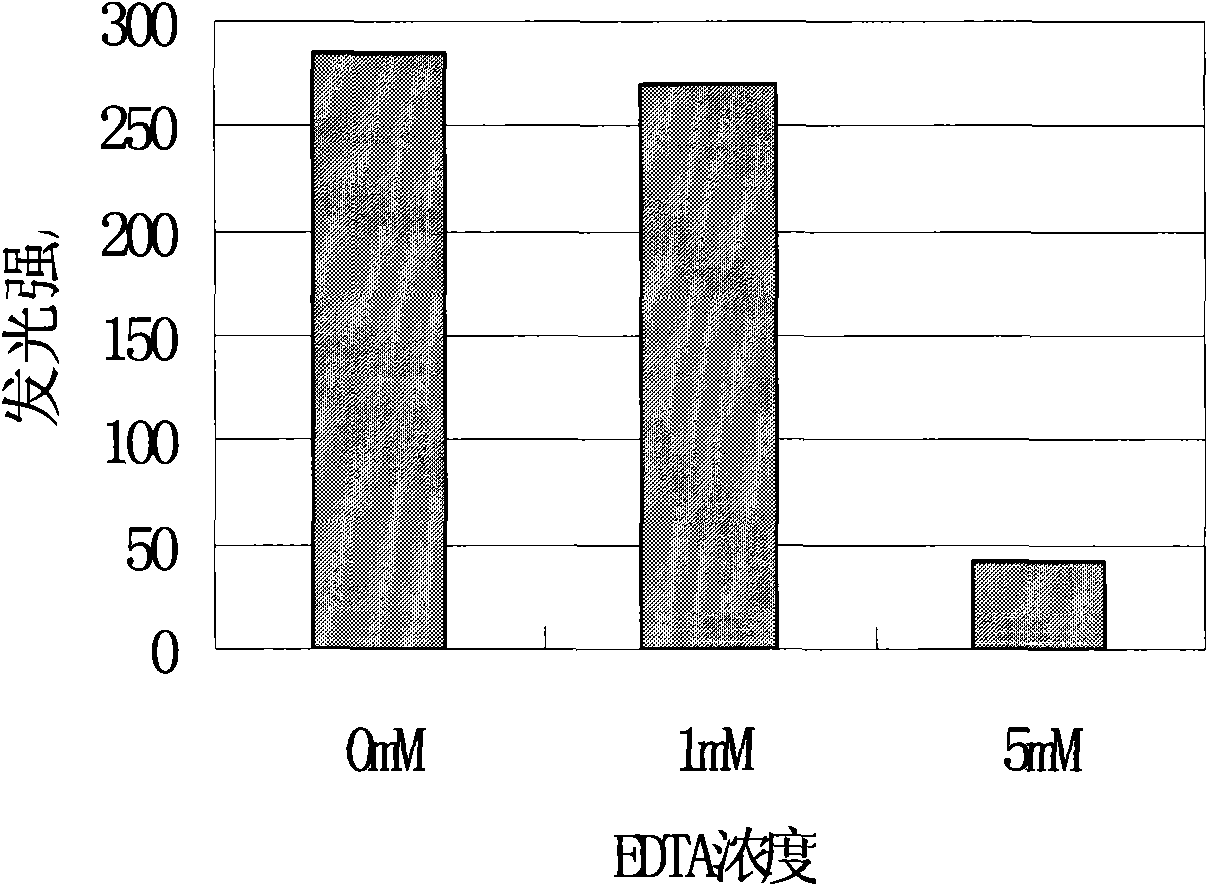
Quantitative detection of heavy metal mercury by using luciferase and FMN:NADH oxido-reductase
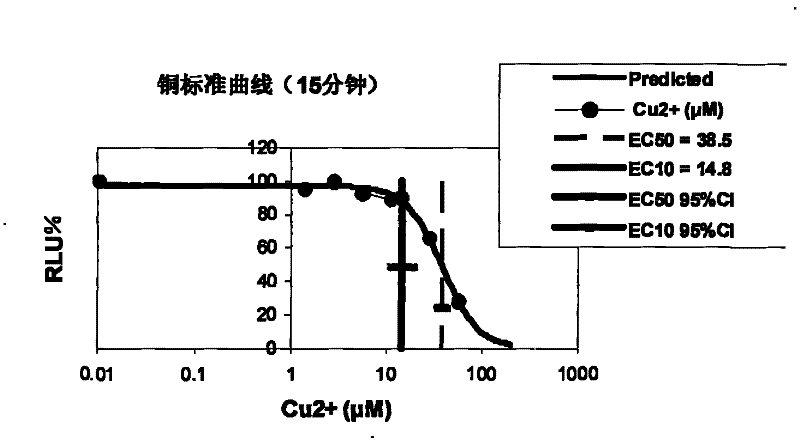
InactiveCN101625322ARealize quantitative detectionStable LuminescenceFluorescence/phosphorescenceLuminescent bacteriaEnzyme system
The invention aims at using luminous bacteria strain Photobacterium leiognathi YL endoenzyme luciferase derived from marine environment and FMN:NADH oxido-reductase to detect mercury quantitatively. A strain of luminous bacterial YL derived from marine environment separated and purified in the invention is gram-negative bacilli and is verified as Photobacterium leiognathi. China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC for short) is authorized to preserve the bacteria strain on Dec 27, 2006, with the preservation number being M 206139. The 16SrDNA gene sequence of the bacteria strain has already been submitted to the GenBank nucleotide sequence database with the accession number being EF017227. By extracting luminous bacteria endoenzyme luciferase and FMN-NADH oxido-reductase coarse enzyme preparation, the invention establishes a luciferase: FMN-NADH oxido-reductase invitro luminous system, realizes the expression of the luciferase: FMN-NADH oxido-reductase dual-enzyme system outside a living cell, and measures the concentration of mercury in virtue of the inhibition of the heavy metal mercury against the luminescence of the dual-enzyme system. The invention realizes the expression of the luciferase: FMN-NADH oxido-reductase outside the living cell and establishes the luciferase: FMN-NADH oxido-reductase invitro luminous system. The system has stable luminous performance, high luminous and strength and simple and feasible substrate mixture ratio, and can realize the quantitative detection of mercury. The use of the invention to detect mercury is characterized by low cost, simple and convenient operation, high sensitivity and the like, and can meet the requirement of rapid quantitative detection of mercury.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Photobacterium leiognathi luciferase, gene coding photobacterium leiognathi luciferase, and applications of photobacterium leiognathi luciferase
ActiveCN104845986AGood linear relationshipReduce testing costsBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementLuminescent bacteriaRecombinant escherichia coli
The present invention relates to a photobacterium leiognathi luciferase, a gene coding the photobacterium leiognathi luciferase, and applications of the photobacterium leiognathi luciferase, and belongs to the technical field of biology. The present invention provides a photobacterium leiognathi luciferase gene, which can achieve efficient expression in escherichia coli and can be used for quantitative NADH detection so as to provide possibility for replacement of the luminescent bacteria double enzyme system detection. According to the present invention, with the introduction of the photobacterium leiognathi luciferase gene LuxAB, the conditions are optimized to make the exogenous luciferase protein achieve the efficient expression in the escherichia coli, the escherichia coli RosettaDE3 contains high activity FMN-NADH oxidoreductase so as to achieve the in vitro luminescence of the recombinant escherichia coli double enzyme body, and the obtained product is used for NADH detection.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Method for detecting comprehensive toxicity of fresh meat, fresh milk and food
InactiveCN101071103BRapid responseHigh detection sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceBiotechnologyBacteroides
The invention provides a method of detecting comprehensive toxicity of fresh meat and milk, belonging to food safety and environmental protection technical fields. On given conditions, the luminous bacteria's luminous intensity changes with the outside world's content of poison. The detection of comprehensive toxicity of the fresh meat and milk includes three steps: luminous bacteria preparations, testing sample preparation, the luminous bacteria detection. The freluminous bacteria is freshwater luminous bacteria - Qinghai Vibrio Q67 strain together. The fresh meat leaching fluid samples or fresh milk is mixed with Qinghai bacterium Vibrio Q67 Strain together. Through the detection of the Qinghai Vibrio Q67 strains luminous intensity the comprehensive toxicity of all toxicology together can be determined, then to measure if the food is safe to eat. It is quick, sample to detect comprehensive toxicity, and have high detection sensitivity and broad scope.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Recombinant luminous bacteria and application thereof
ActiveCN104140943AAvoiding the False Positive ProblemEasy to operateBacteriaChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceBacteroidesLuminescent bacteria
The invention discloses recombinant luminous bacteria and application of the recombinant luminescent bacteria. According to the recombinant luminescent bacteria, the R genes in mer genes and a regulation and control recognition element composed of o / p loci are inserted in the upstream of luminous genes lacking a starting element on a carrier and led into recipient bacteria so that the recombinant luminous bacteria can be obtained. The recombinant luminous bacteria with mercury specific response serve as testing strains, and the bioavailability range of mercury concentration in water can be judged according to luminous intensity. Compared with a traditional physicochemical detection method, the method is low in cost, easy to operate, high in result reliability and capable of achieving automatic online detection easily without special high-precision analytical instruments and detecting devices, the method can be applied to the field of environmental water quality monitoring and has great economical and beneficial significance in early warning and monitoring of mercury pollutants.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Disposable cartridge for automatic and continuous water quality monitoring
Provided is a disposable cartridge for use in assaying an analyte in an automated water quality monitoring analyzer comprising: (a)a platform; (b)array of containers for separately containing at least one reagent, a buffer and a freeze dried preparation of luminescent bacteria, said containers being mounted on said platform; (c)reaction chamber mounted on said platform and configured for being moved between said containers, such that said reagent, said buffer and said freeze dried preparation of luminescent bacteria are conveyed to said reaction chamber in a predetermined sequence such that light detectable by said analyzer is emitted; (d)fluid transferring means for fluid transfer and mixing between said containers, reaction chamber, and analyzer; (e)conveying means for moving said cartridge to predetermined positions within said automated water quality monitoring analyzer for enabling analysis of said analyte.
Owner:CHECK LIGHT
Method for rapidly detecting veterinary drug residues in animal products by using luminescent bacteria
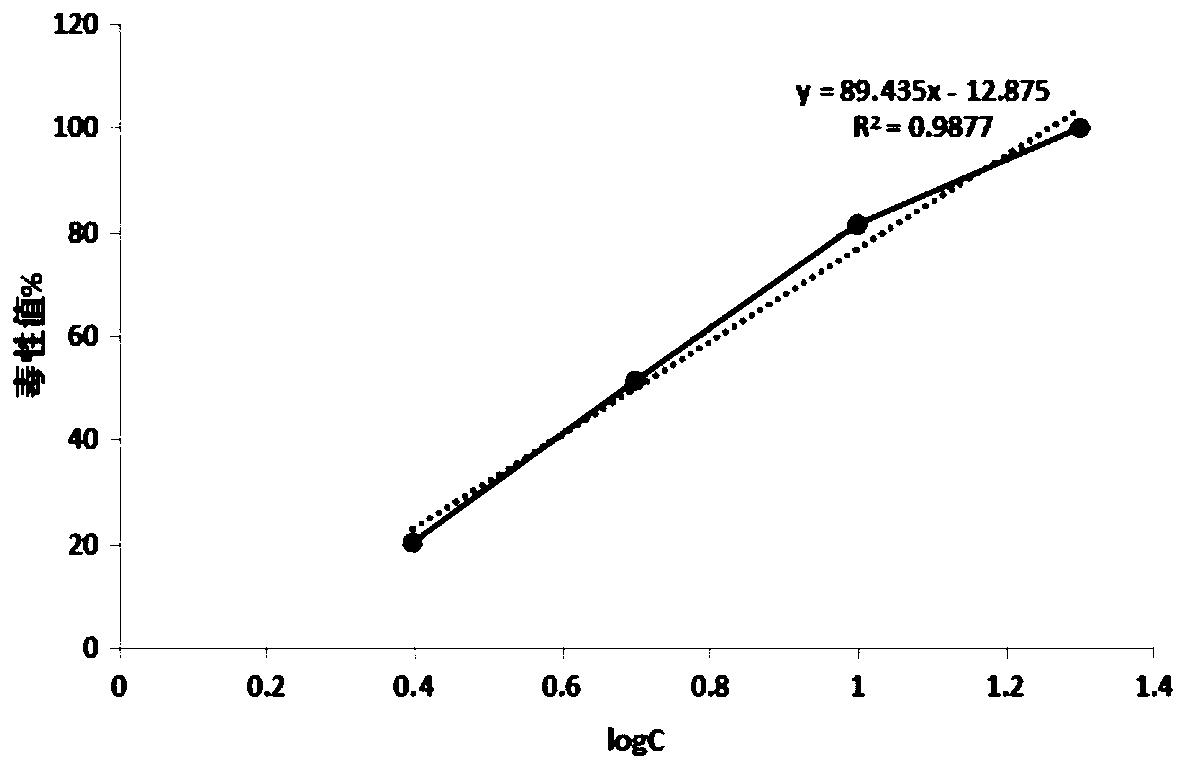
The invention discloses a method for rapidly detecting veterinary drug residues in animal products by using luminescent bacteria. Vibrio qinghaiensis Q67 and brilliant luminescent bacterium T3 are used as toxicity test strains, by measuring relative luminescence intensity at different mass concentrations and the half inhibitory effect concentration (EC50) of ten veterinary drugs of the vibrio qinghaiensis Q67 and the brilliant luminescent bacterium T3 in the ten common veterinary drugs such as sulfonamides, furans and quinolones, the law of function of the ten veterinary drugs on the luminescent bacteria and acute toxic effects in animal products are studied; secondary universal composite test design and statistical method is adopted to study the combined toxicity of various quinolone veterinary drugs against the vibrio qinghaiensis and reveal the total toxic effects and interactions of the various quinolone veterinary drugs during coexisting; the law of action and acute toxic effectsof the veterinary drug residues in pork extracts against the vibrio qinghaiensis are preliminarily explored; and therefore, a theoretical basis for establishing a method for detecting the veterinary drug residues by the luminescent bacteria and a safety evaluation system for the animal products is provided. According to the method for rapidly detecting the veterinary drug residues in the animal products by using the luminescent bacteria, materials used in the method for rapidly detecting the veterinary drug residues in the animal products by using the luminescent bacteria is cheap and easy toobtain, and the route is simple, and the requirements of the ministry of agriculture for detecting the sulfonamides veterinary drugs in the animal products are met.
Owner:JIANGSU WEI LING BIOCHEM TECH CO LTD
Water quality integration toxicity detection paper chip
InactiveCN109633115APrecise flow controlEasy to operateChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceLaboratory glasswaresInlet channelLuminescent bacteria
The invention discloses a water quality integration toxicity detection paper chip. The paper chip comprises a paper substrate possessing hydrophobicity, and detection units and a recovery unit which have hydrophilia and pass through the paper substrate. After the paper substrate is folded along a folding line, a cover plate area, a first transition area, a second transition area, and a bottom plate isolation area are superposed. There are at least two detection units, and each detection unit comprises a liquid inlet, a detection zone, a first transition liquid inlet zone, a first transition detection zone, a recovery liquid addition channel, a second transition liquid inlet zone, a second transition detection zone and a liquid inlet channel. The recovery unit comprises a recovery liquid addition port and a recovery fluid transition zone. A microfluidic paper chip technology is combined with a luminescent bacteria detection mehtod, luminous bacteria is prestored in a specific area in the chip, a bacteria liquid does not need to be prepared during detection and an operation process is simplified. The luminous bacteria and a paper chip are combined, the chip is small and a current situation that existing detection cost is high so that popularization in a grassroots level and families is difficult can be solved.
Owner:HANGZHOU TINKER BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Method for detecting acute toxicity of copper-contaminated soil using freshwater luminescent bacteria
InactiveCN101487798BAvoid restrictionsNatural Luminous PropertiesChemiluminescene/bioluminescencePreparing sample for investigationBacteroidesEnvironmental monitor
The invention relates to a detection method in the technical field of environmental monitoring, in particular to a method for detecting the acute toxicity of copper-contaminated soil by using freshwater luminescent bacteria, which overcomes the limitations of the application of seawater luminescent bacteria in the detection of acute toxicity of soil samples. The specific method selects freshwater luminescent bacteria as the bacteria for detection, including the following steps: the first step: prepare the bacterial suspension of freshwater luminescent bacteria with the soil background solution; the second step, extract the soil pore water by double-chamber centrifugation; the third step, Testing soil samples for toxicity.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
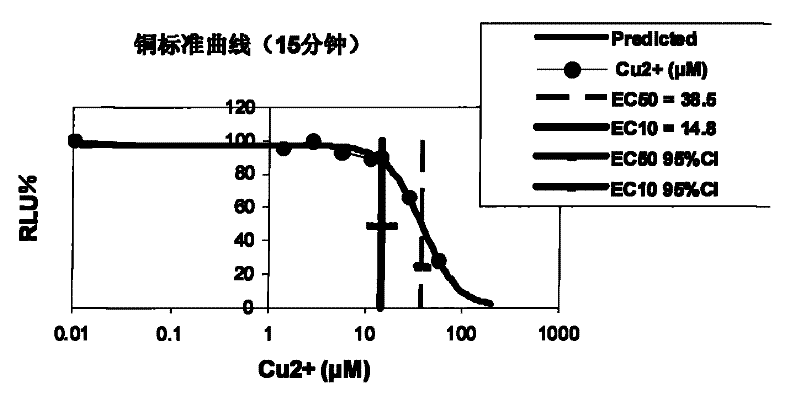
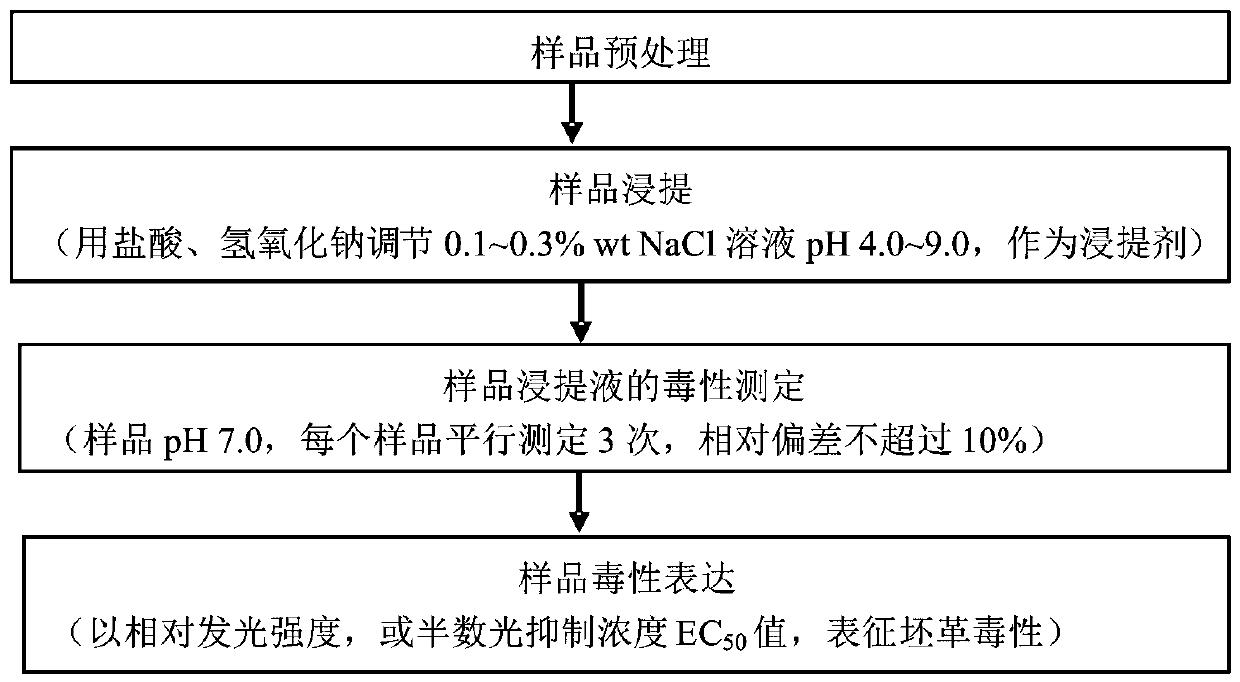
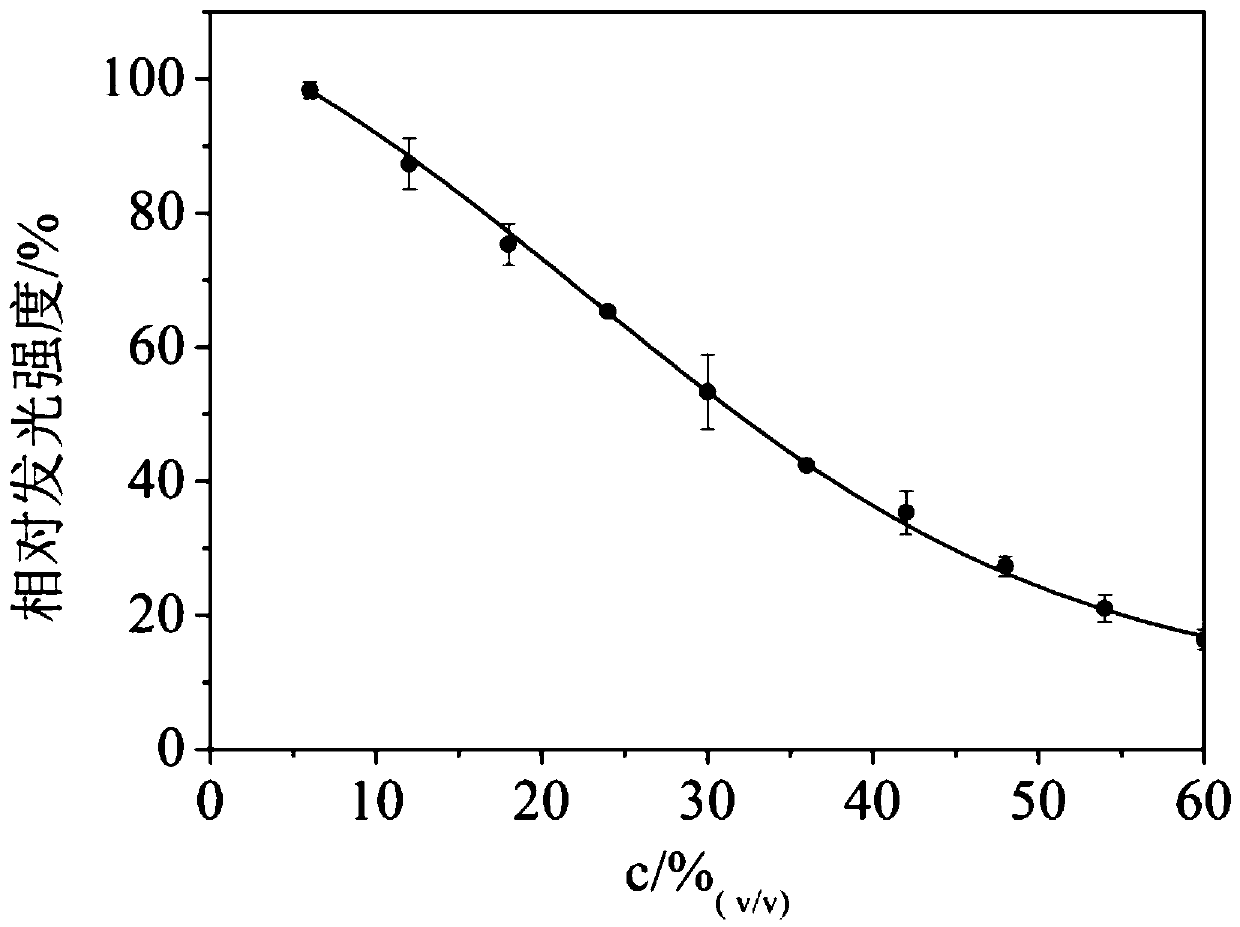
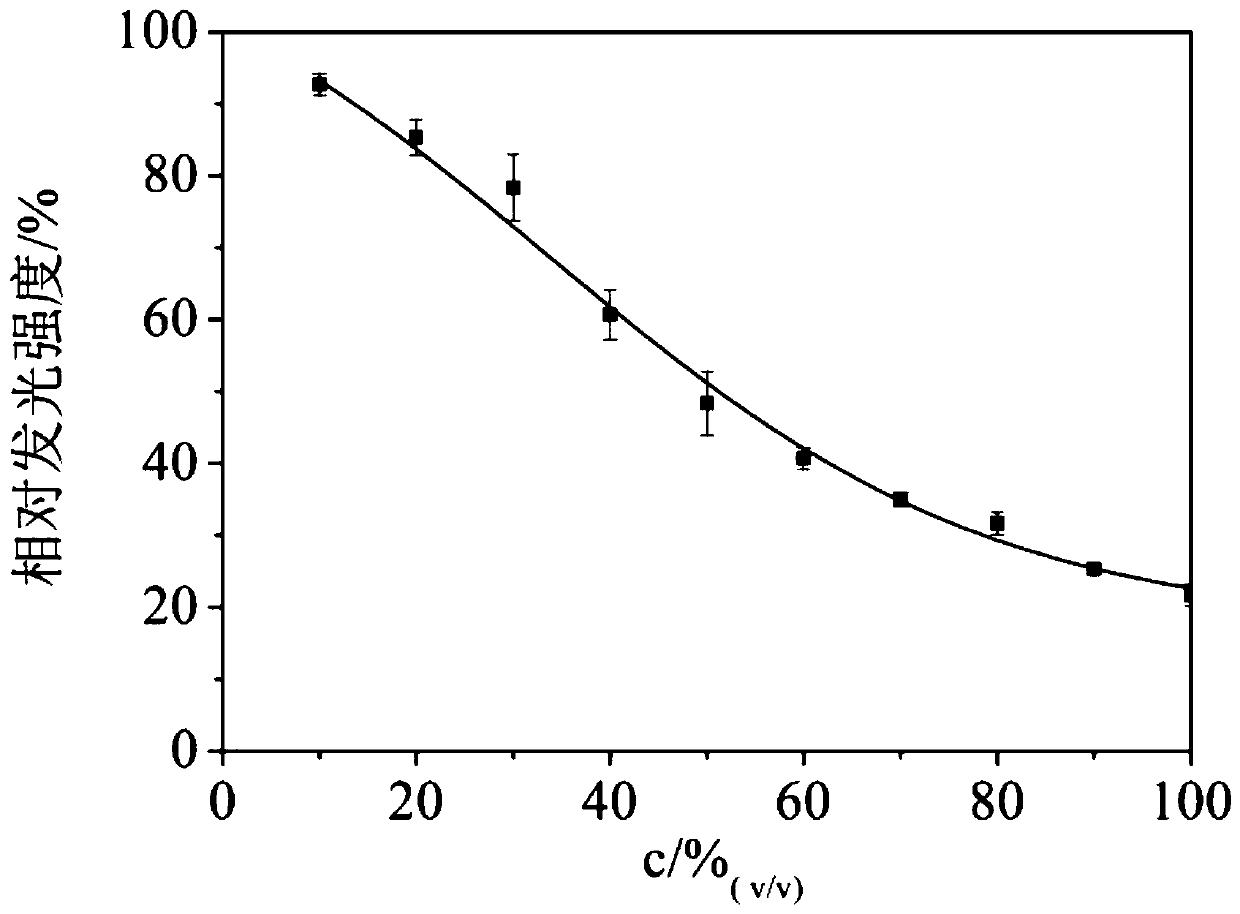
Detection method of crust leather comprehensive toxicity
PendingCN110607340ALow costHigh sensitivityBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementLuminous intensityLuminescent bacteria
The invention discloses a method for detecting crust leather comprehensive toxicity by luminescent bacteria. The method comprises the steps that a NaCl solution with the concentration being lower than2.5% wt is used as an extracting agent to extract weakly bound chemicals from crust leather, and a crust leather extraction solution is obtained; NaCl is added into the extraction solution to make the concentration of the extraction solution be 2.5% wt, and pH is adjusted to be 7.0; or the NaCl solution of 2.5% wt is used for diluting the extraction solution to a suitable concentration gradient,and pH is adjusted to be 7.0; a toxicity test sample is obtained; the cultured luminescent bacteria are taken, a sample solution is added, still standing is conducted after even mixing, and the luminous intensity is measured; and expression of sample toxicity is conducted, specifically, a NaCl solution of 2.5% wt is taken as a blank, and the relative luminous intensity and the half relative luminous intensity concentration EC50 of a mixture after still standing are measured. According to the method, the NaCl solution is used as the extracting agent to extract toxic substances in the crust leather sample, the comprehensive toxicity of the extraction solution is directly detected by a toxicity detector, a convenient method for detection of comprehensive toxicity of the crust leather is constructed, and the shortcomings of a traditional method are avoided.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com