Method for testing biotoxicity of oil-field wastewater by employing vibrio qinghaiensis Q67
A technology for oil extraction wastewater and Vibrio qinghai, which is applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial determination/inspection, etc., can solve problems such as no wastewater toxicity discharge indicators, etc., and achieves easy popularization and application, stable experimental results, and moderate toxicity. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
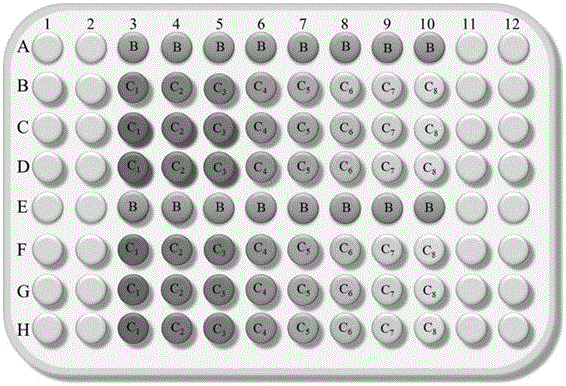
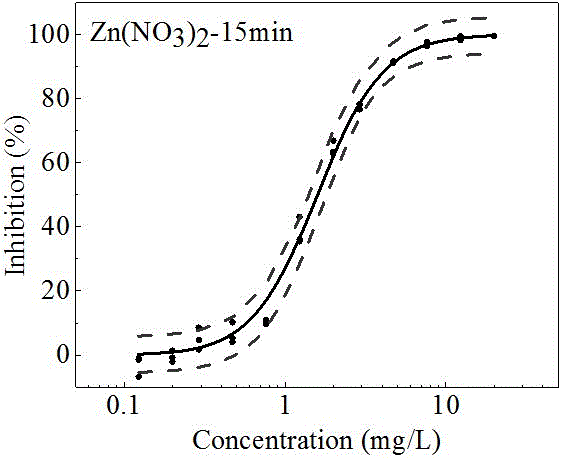
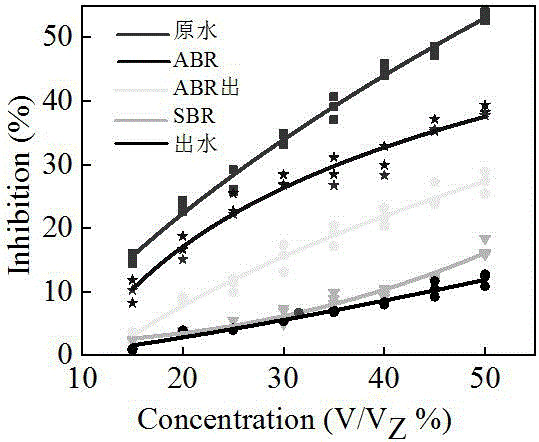
[0019] The wastewater samples to be tested in this embodiment are taken from the various treatment process sections of oil production wastewater in a certain petroleum Weizhou terminal treatment plant. The five sampling points are: raw water, ABR pool water, ABR pool effluent, SBR pool water and effluent. The samples were tested as follows:
[0020] (1) Take the oil production wastewater of each process section as the test wastewater and perform pretreatment:
[0021] After the oil production wastewater is transported to the terminal treatment plant through pipelines, it is biochemically treated by the combined process of anaerobic baffle reactor and activated sludge method, and the wastewater treated by biochemical method is transported to the clear water tank and then discharged outside the plant. In order to avoid the influence of turbid wastewater on the experimental results, the sample to be tested was filtered with a 0.45 μm filter membrane and stored in a refrigerator a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com