Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
106 results about "Fluoroscope" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
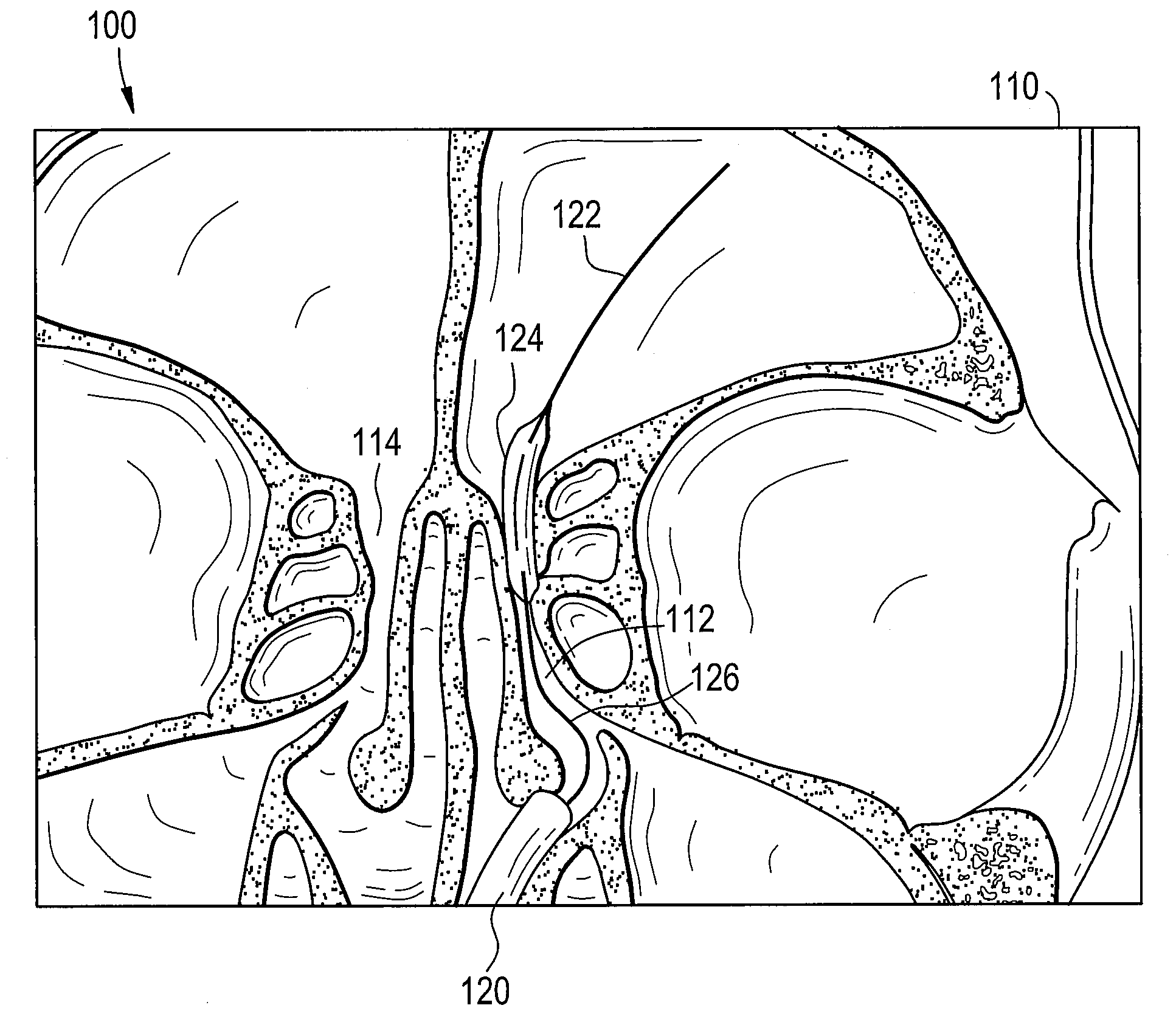
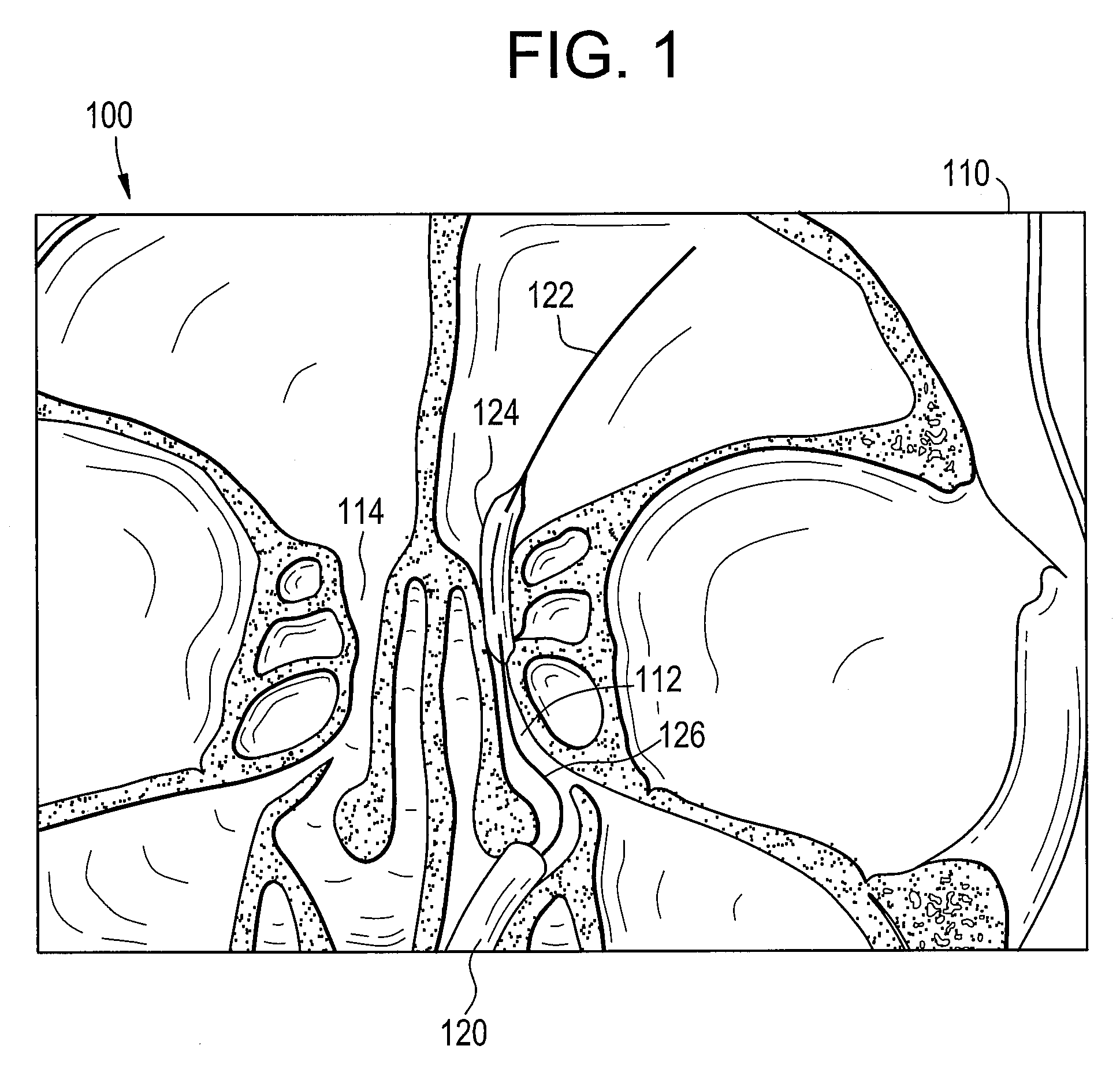
An x-ray machine that makes it possible to see internal organs in motion.
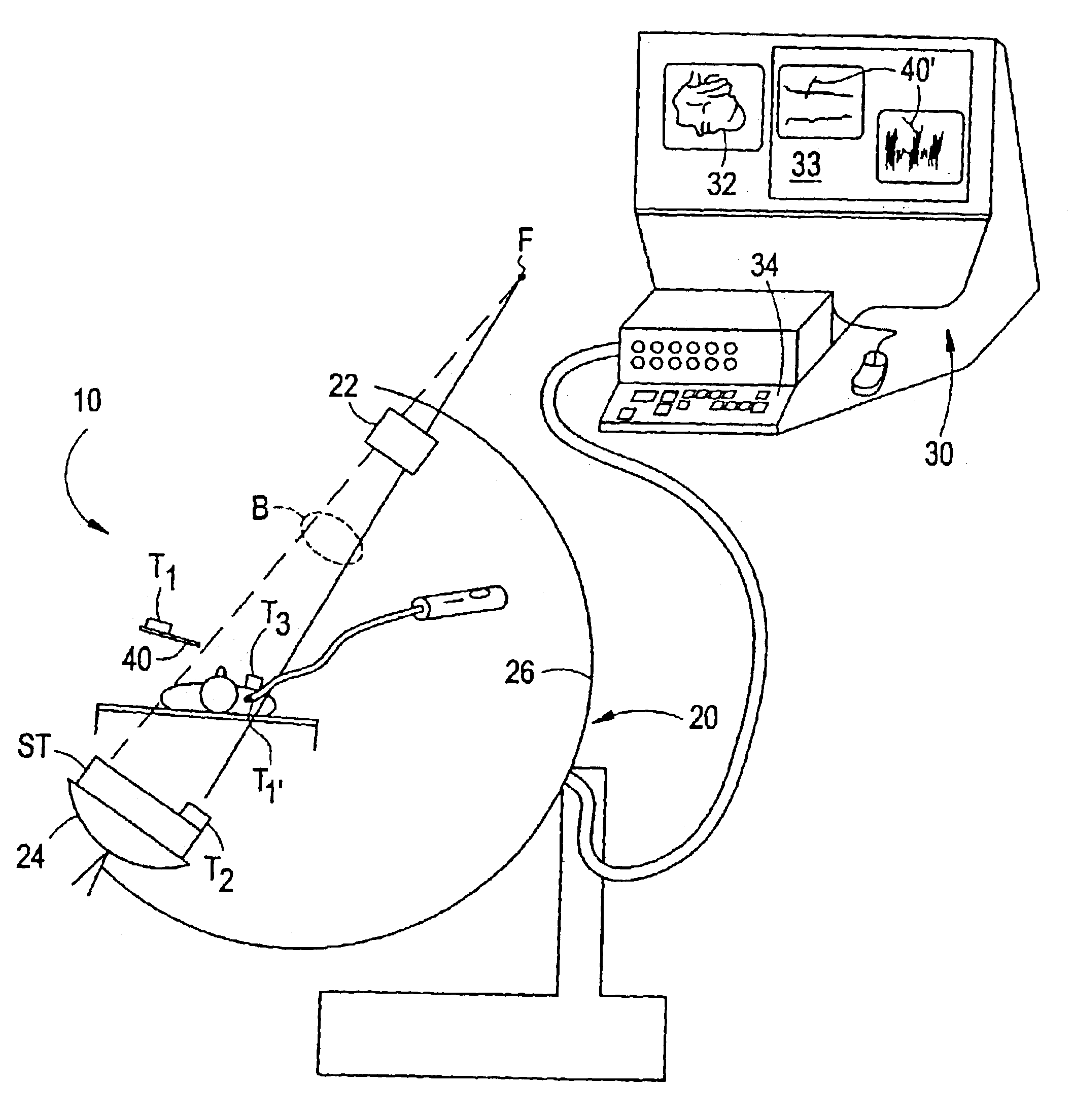
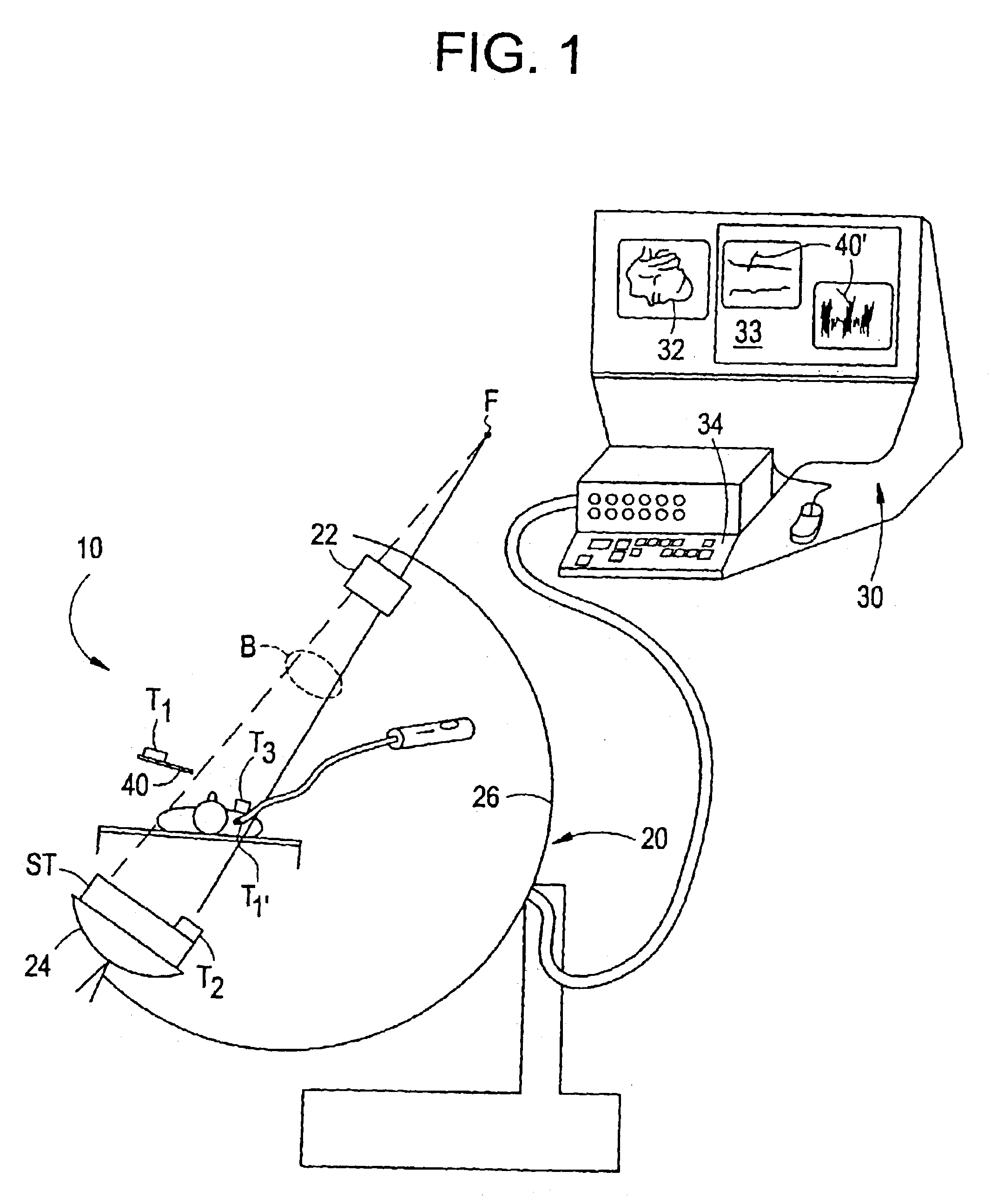
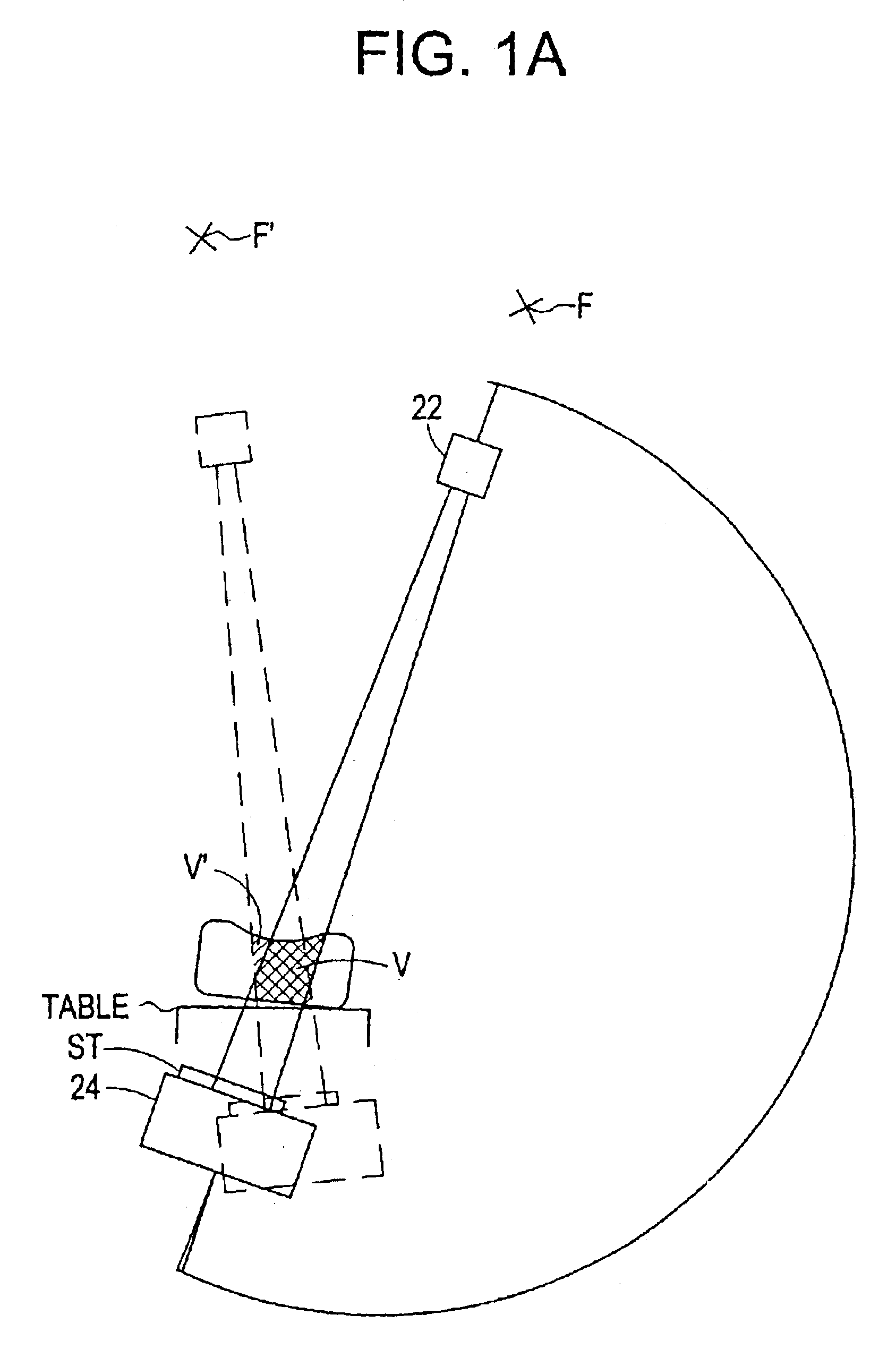
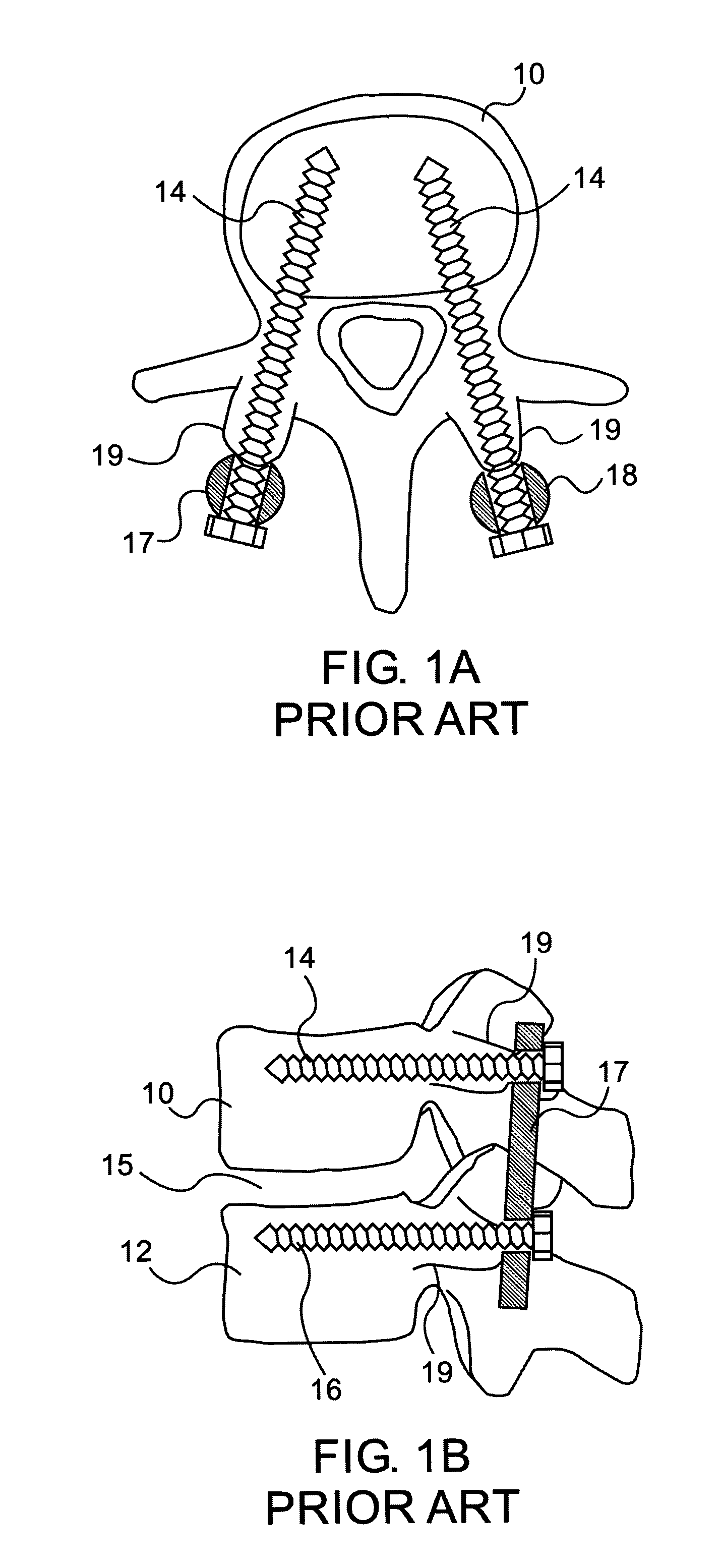
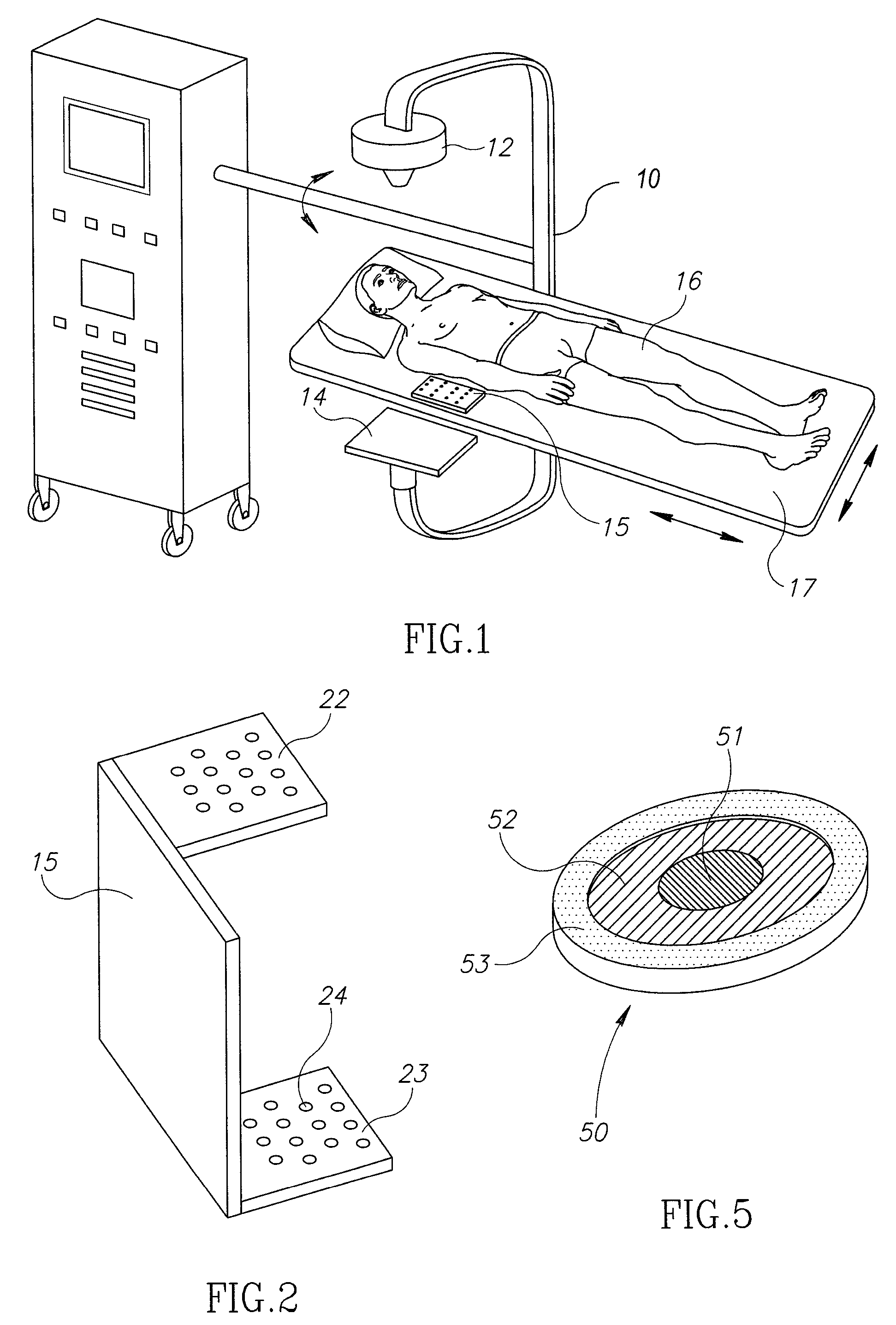
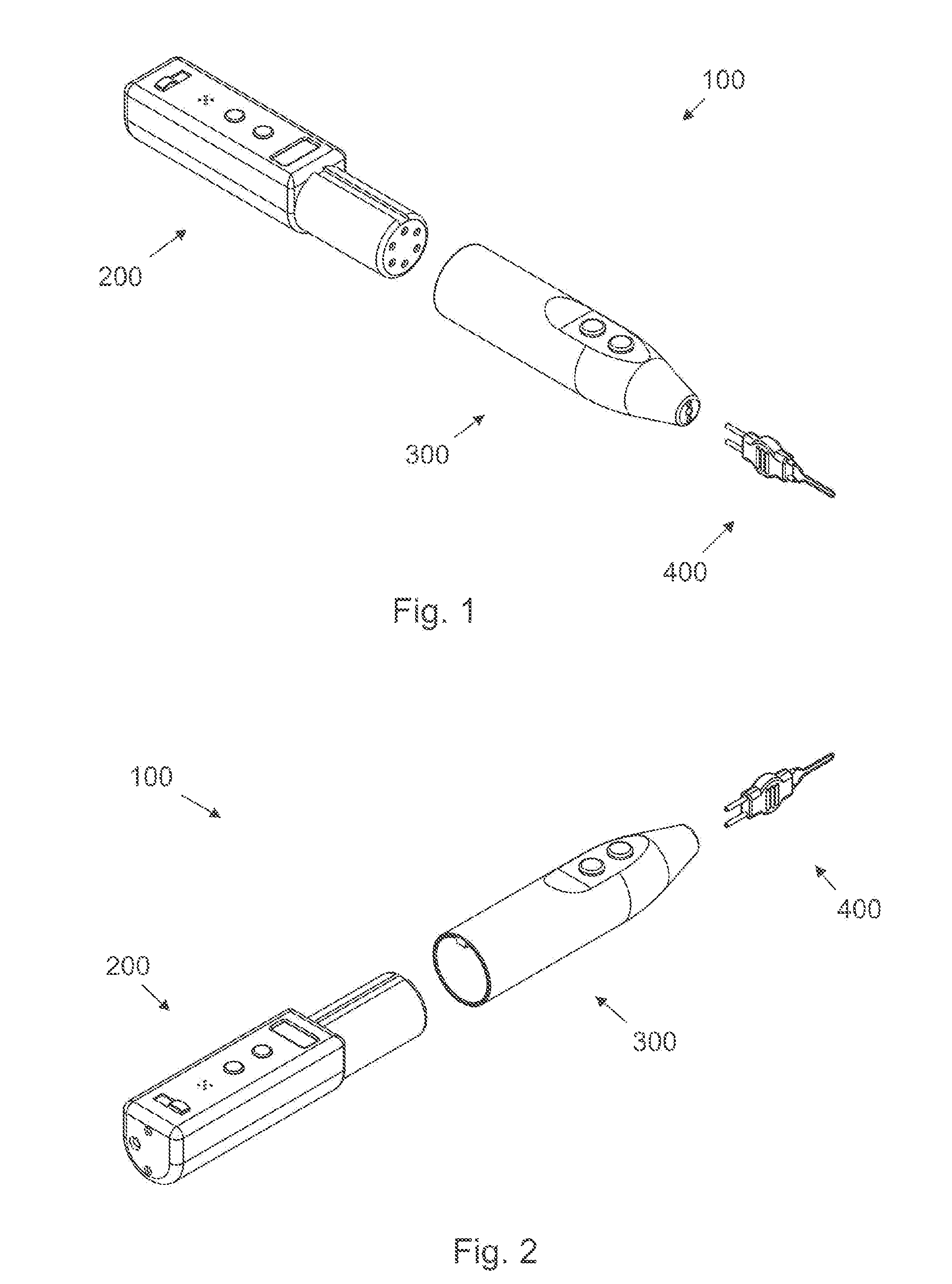
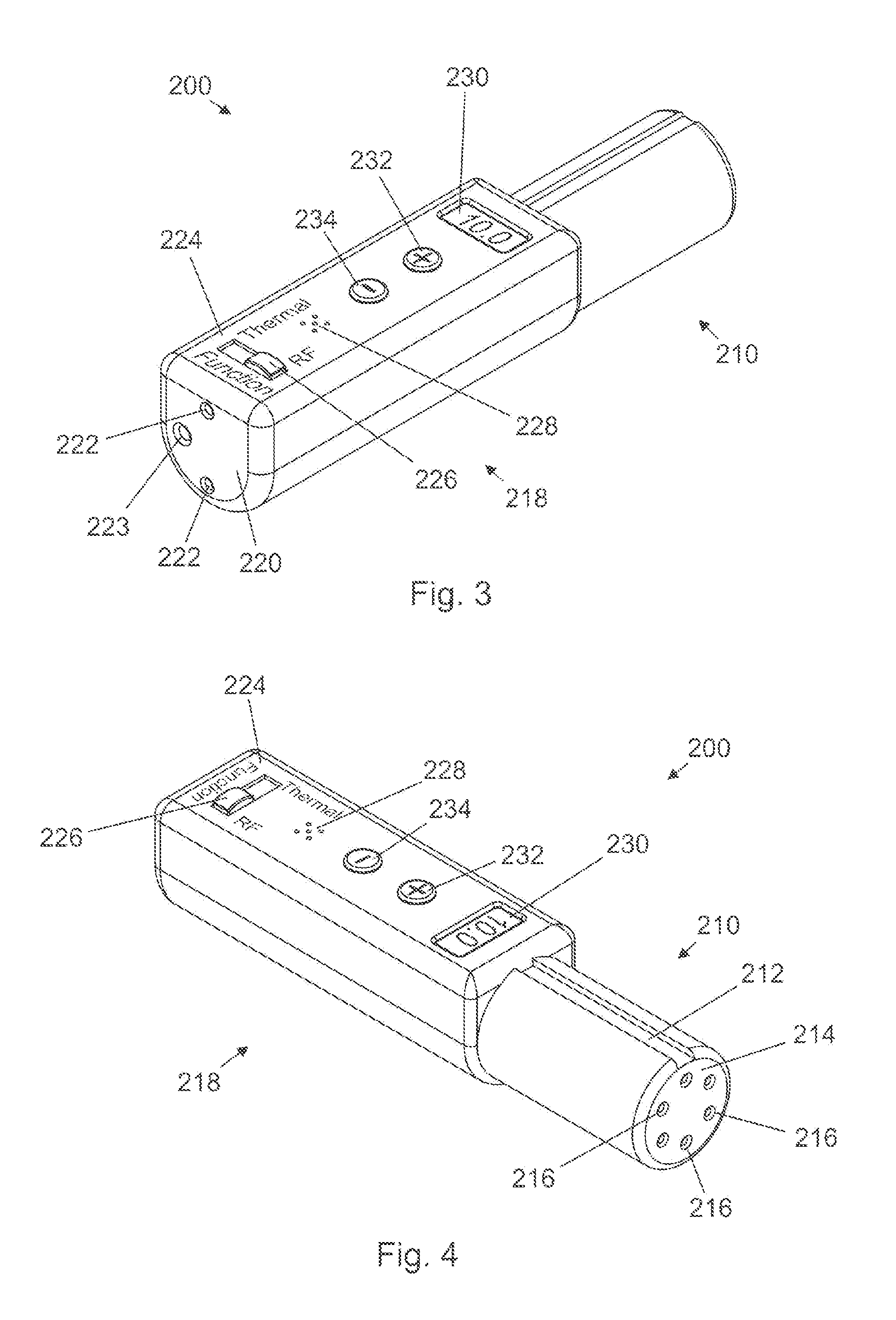
Fluoroscopic tracking and visualization system
InactiveUS6856827B2Quickly and accurately determineImprove accuracyX-ray spectral distribution measurementX-ray/infra-red processesDisplay deviceComputer vision
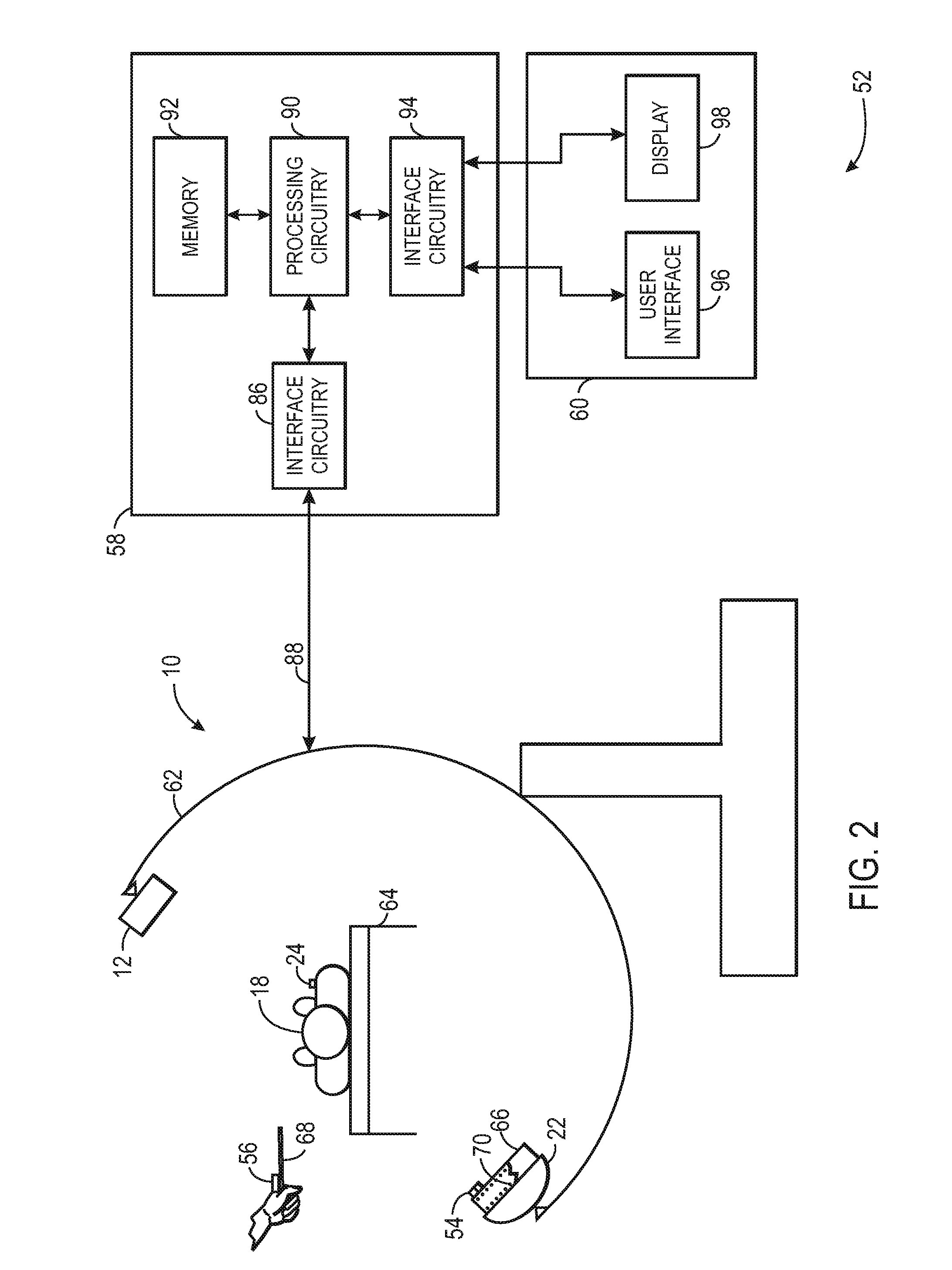
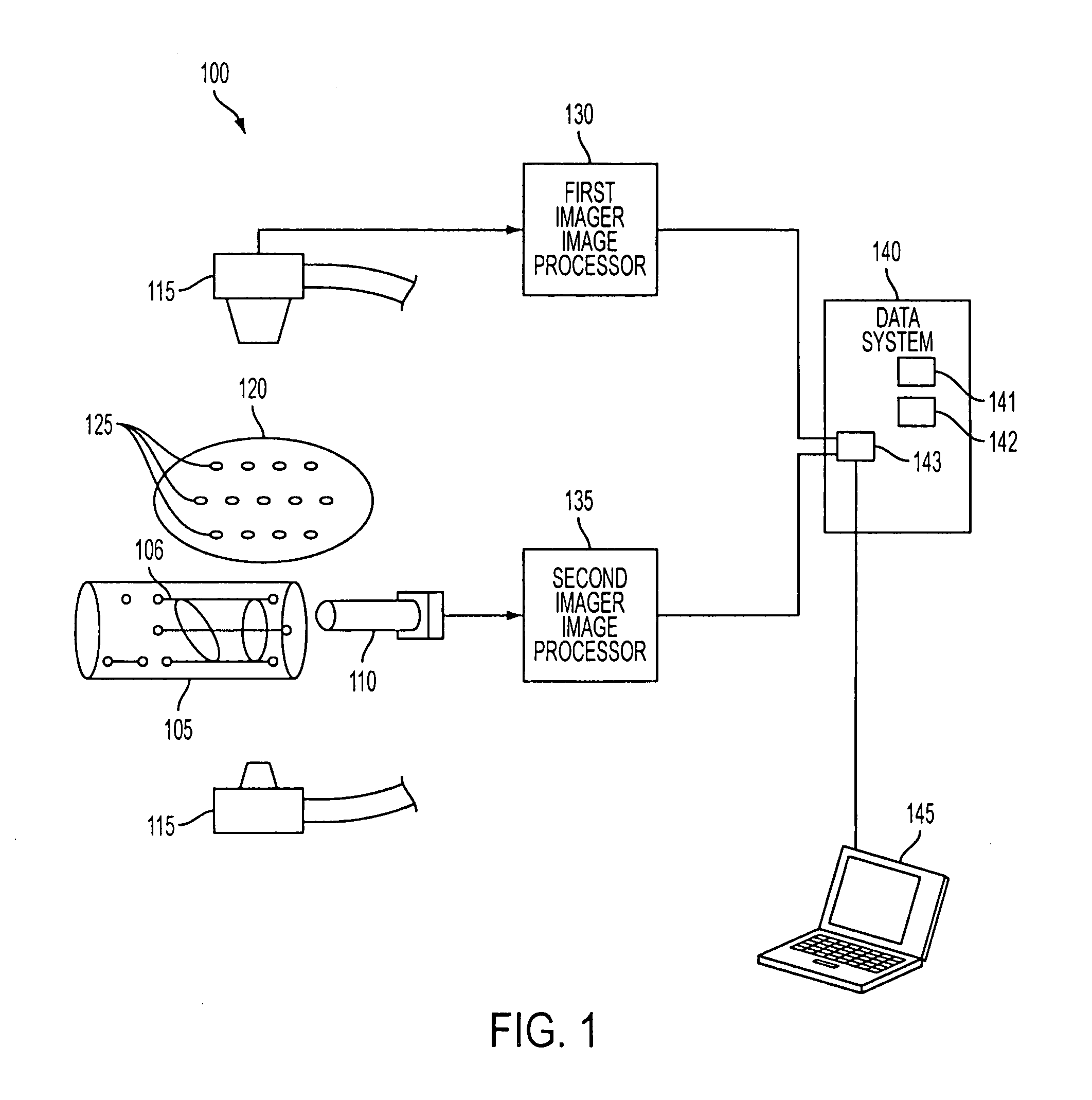
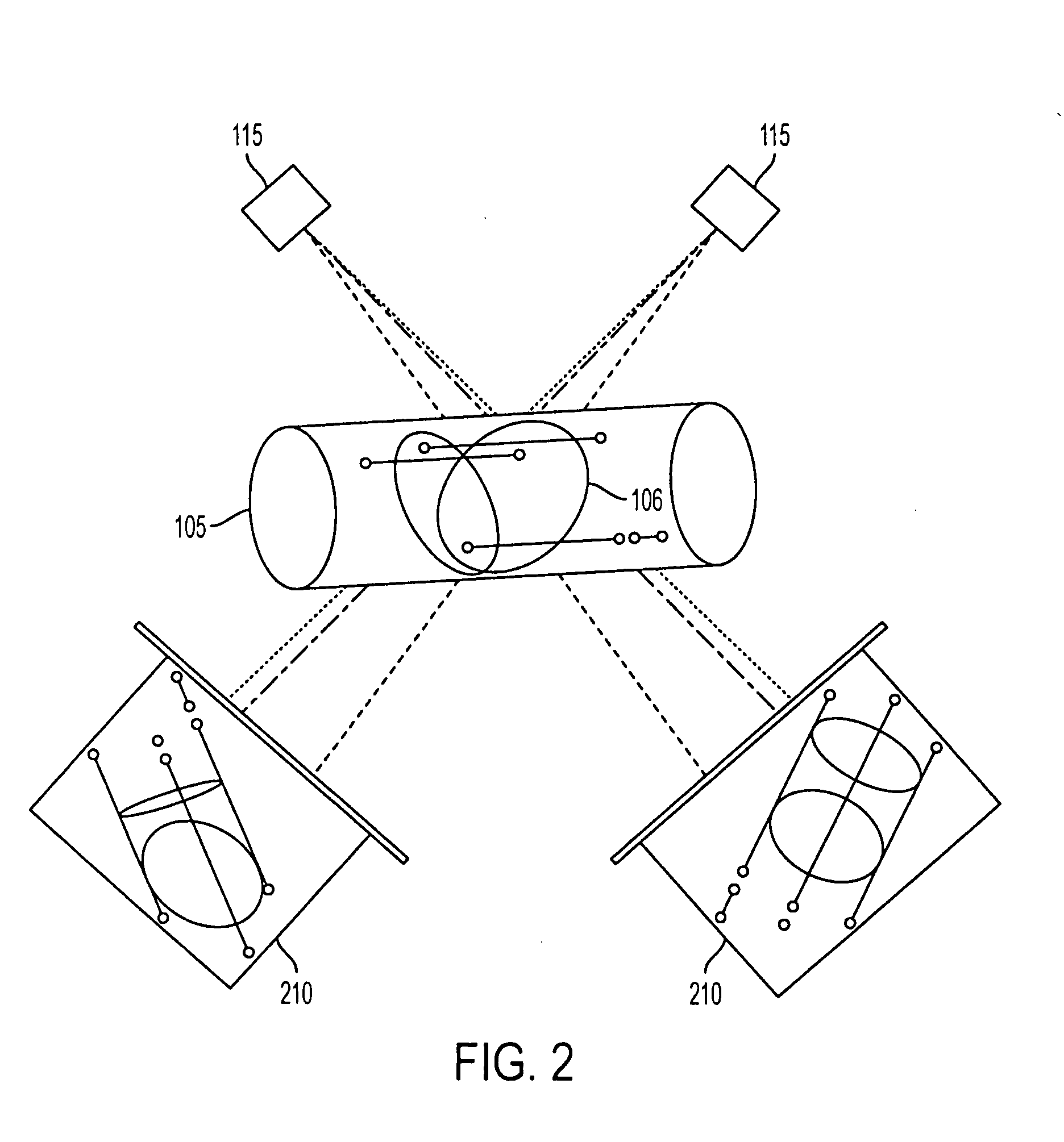
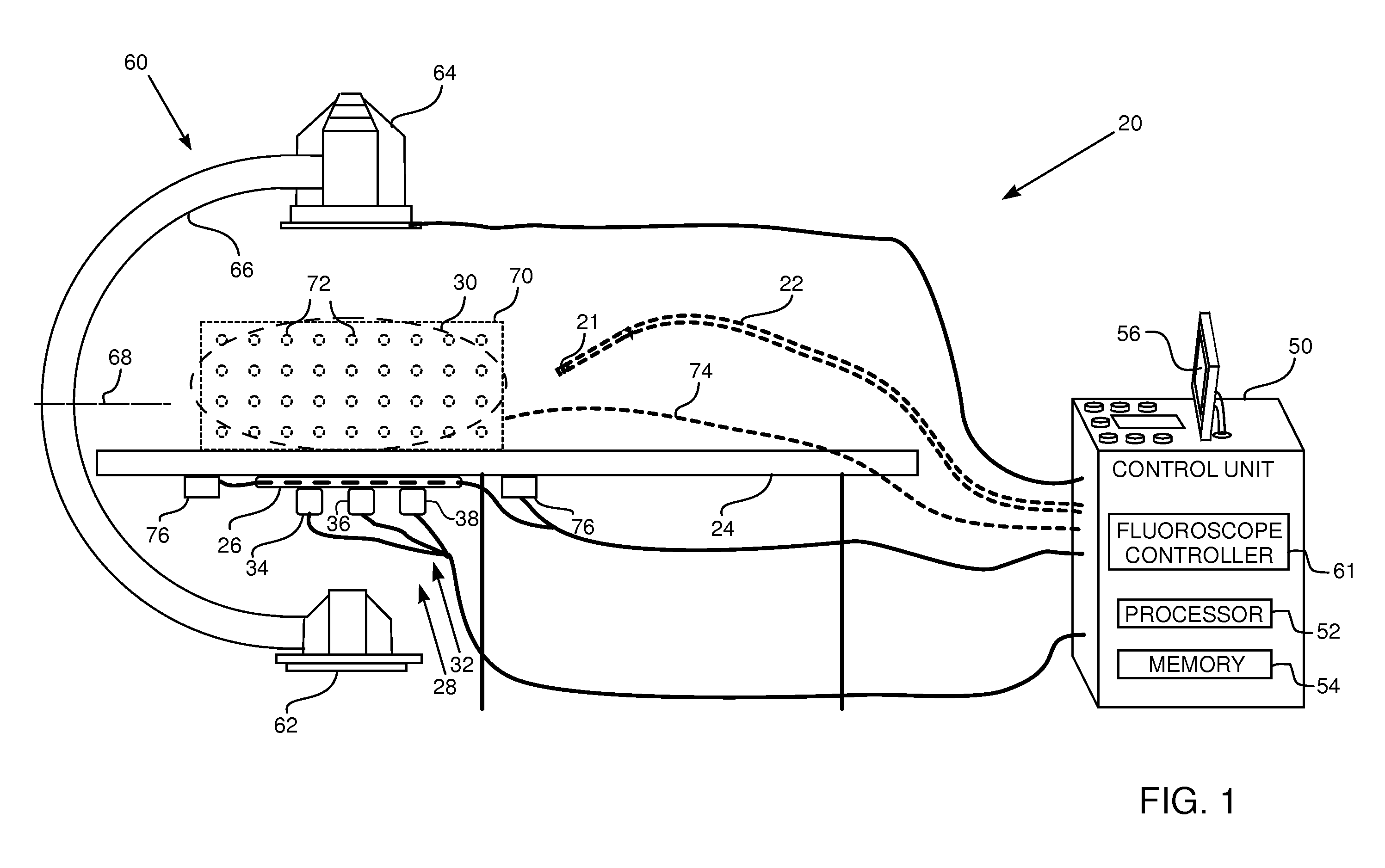
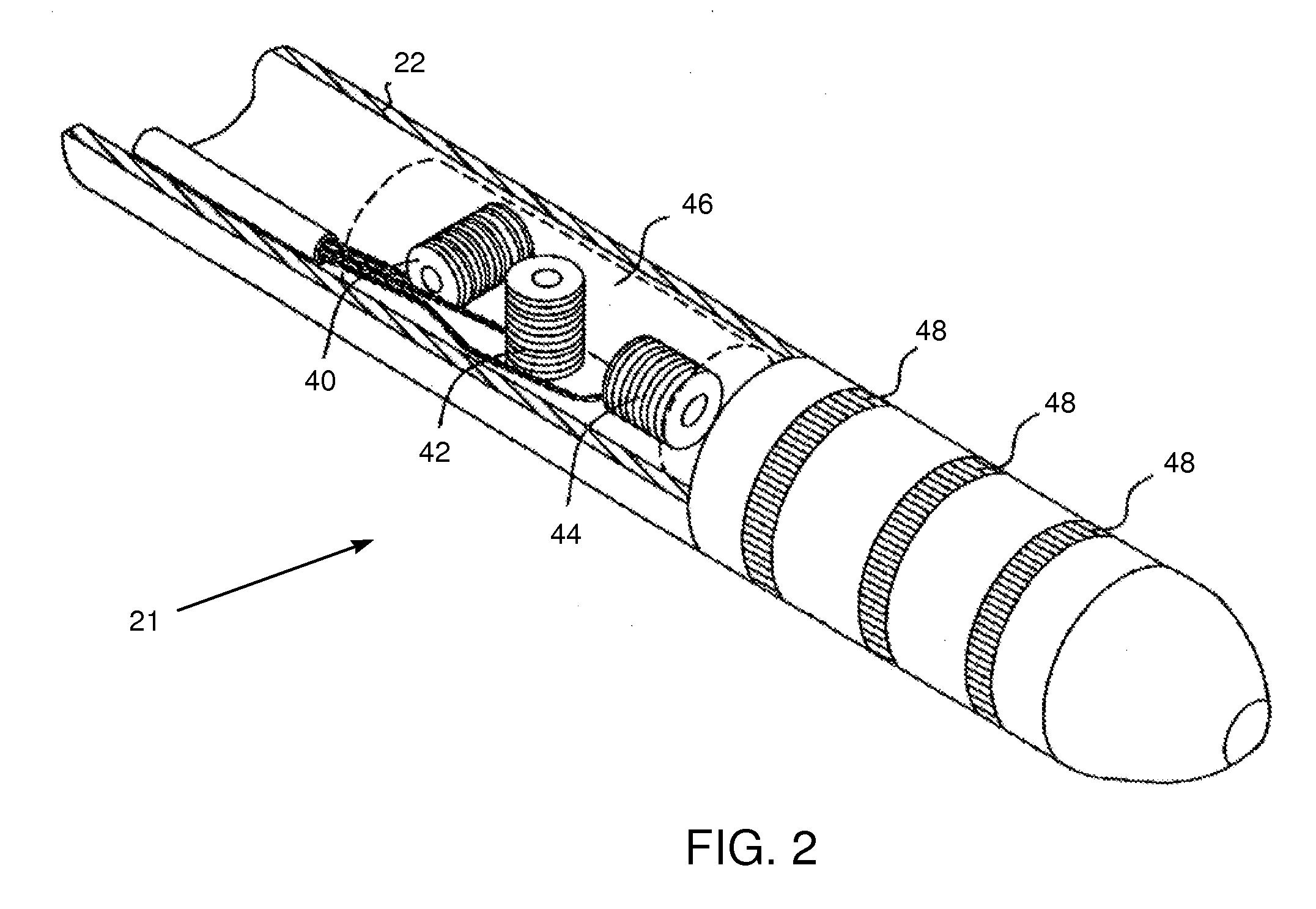
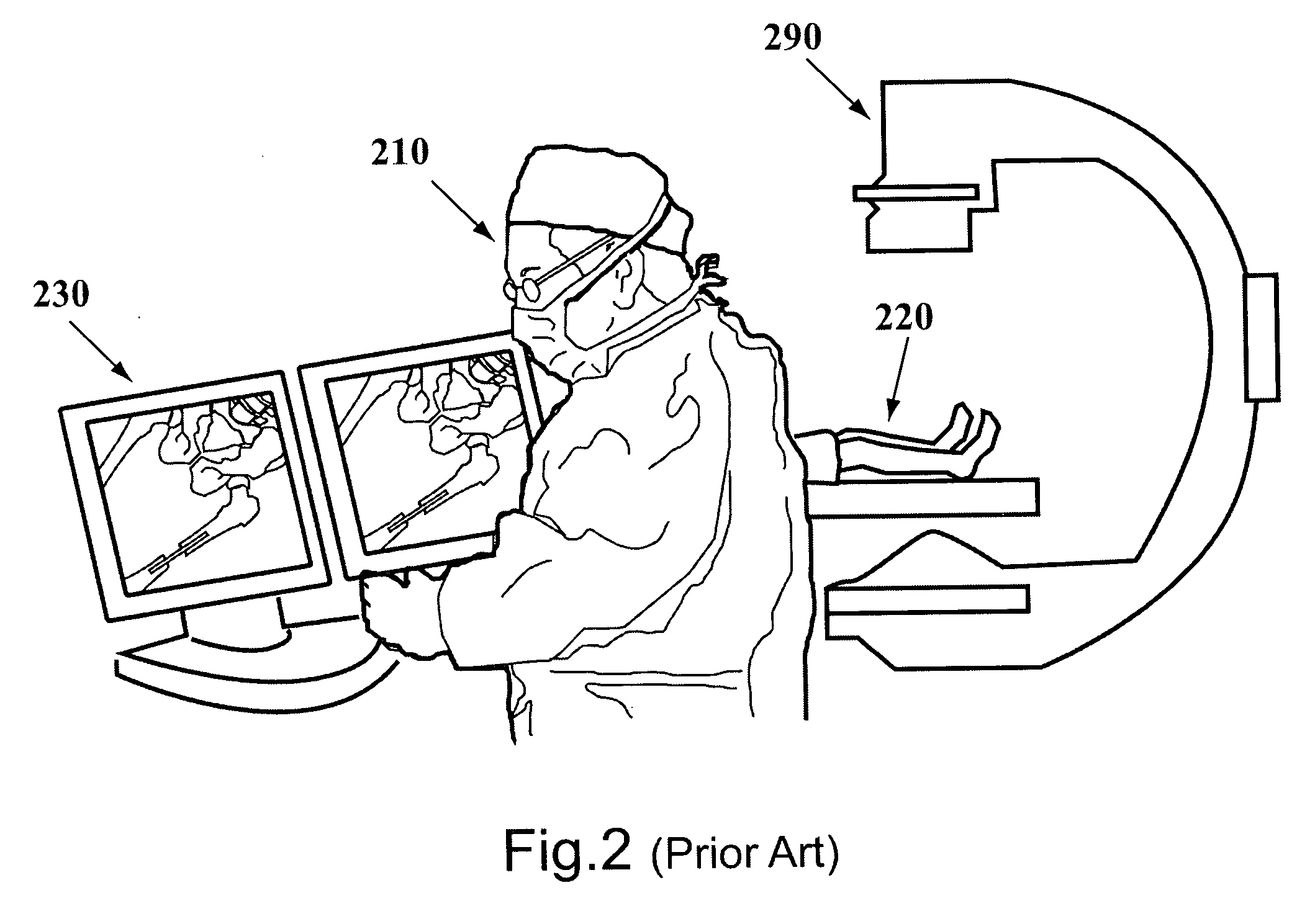
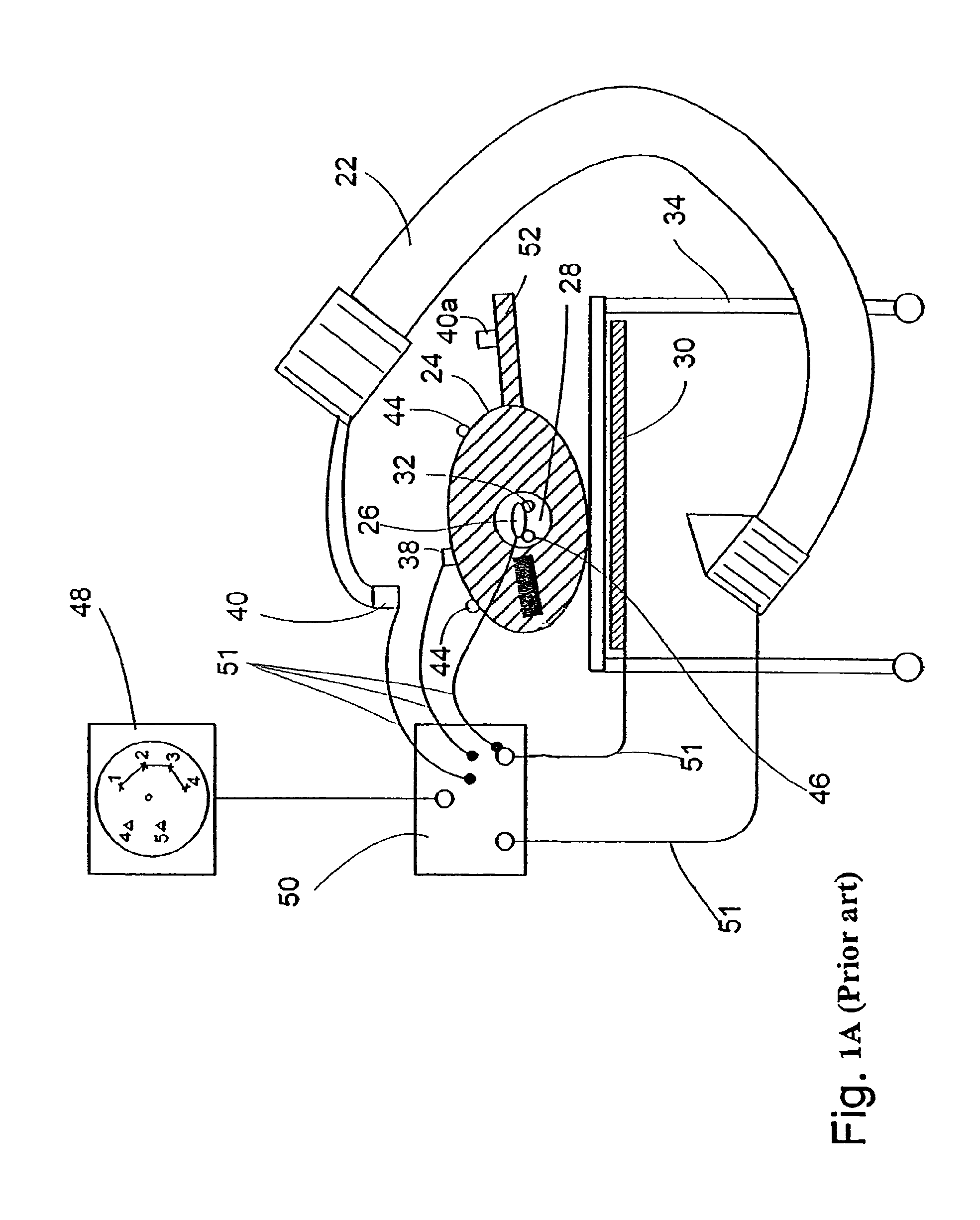
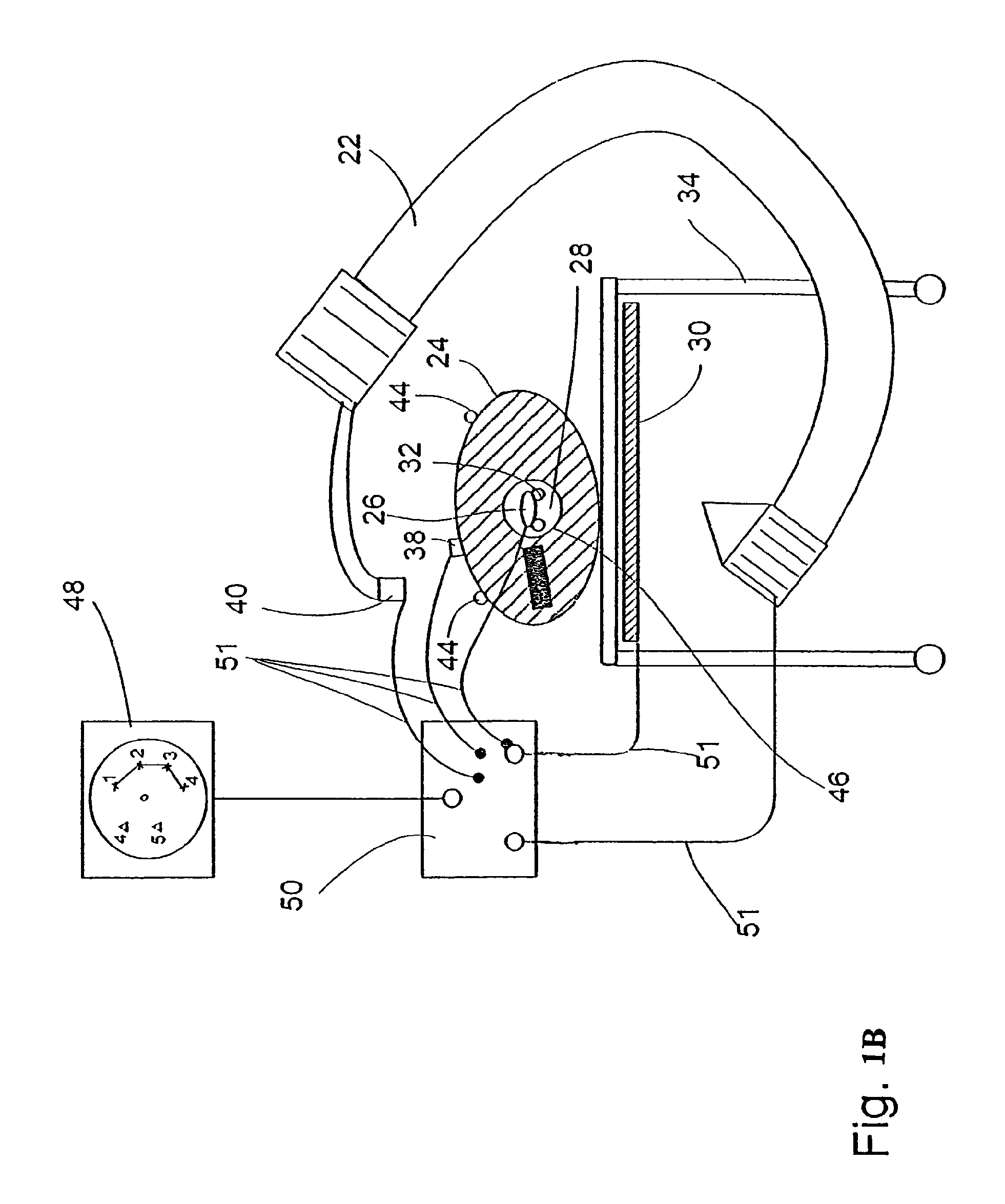
A system for surgical imaging and display of tissue structures of a patient, including a display and an image processor for displaying such images in coordination with a tool image to facilitate manipulation of the tool during the surgical procedure. The system is configured for use with a fluoroscope such that at least one image in the display is derived from the fluoroscope at the time of surgery. A fixture is affixed to an imaging side of the fluoroscope for providing patterns of an of array markers that are imaged in each fluoroscope image. A tracking assembly having a plurality of tracking elements is operative to determine positions of said fixture and the patient. One of the tracking elements is secured against motion with respect to the fixture so that determining a position of the tracking element determines a position of all the markers in a single measurement.
Owner:STRYKER EURO HLDG I LLC +1
Fluoroscopic image guided orthopaedic surgery system with intraoperative registration
InactiveUS7130676B2Safely determineCheck the accuracy of the procedureSurgical navigation systemsDiagnostic recording/measuringFluoroscopic imagingFluoroscopic image
A fluoroscopic image guided surgery system, comprising a C-arm fluoroscope for obtaining fluoroscopic images of an object bone, the C-arm fluoroscope including at least one set of emitters; a reference bar capable of attaching to an object bone, the reference bar including emitters; a surgical instrument for performing an operation, the instrument including emitters; a digitizer system in communication with the at least one set of emitters of the C-arm fluoroscope, the emitters of the reference bar, and the emitters of the surgical instrument so that the digitizer system can determine a position of each of the C-arm fluoroscope, the reference bar, and the surgical instrument; and a single fiducial marker for attachment to an object bone, the single fiducial marker being visible in the fluoroscopic images for determining a position of an object bone relative to the digitizer system.
Owner:SOFAMOR DANEK PROPERTIES
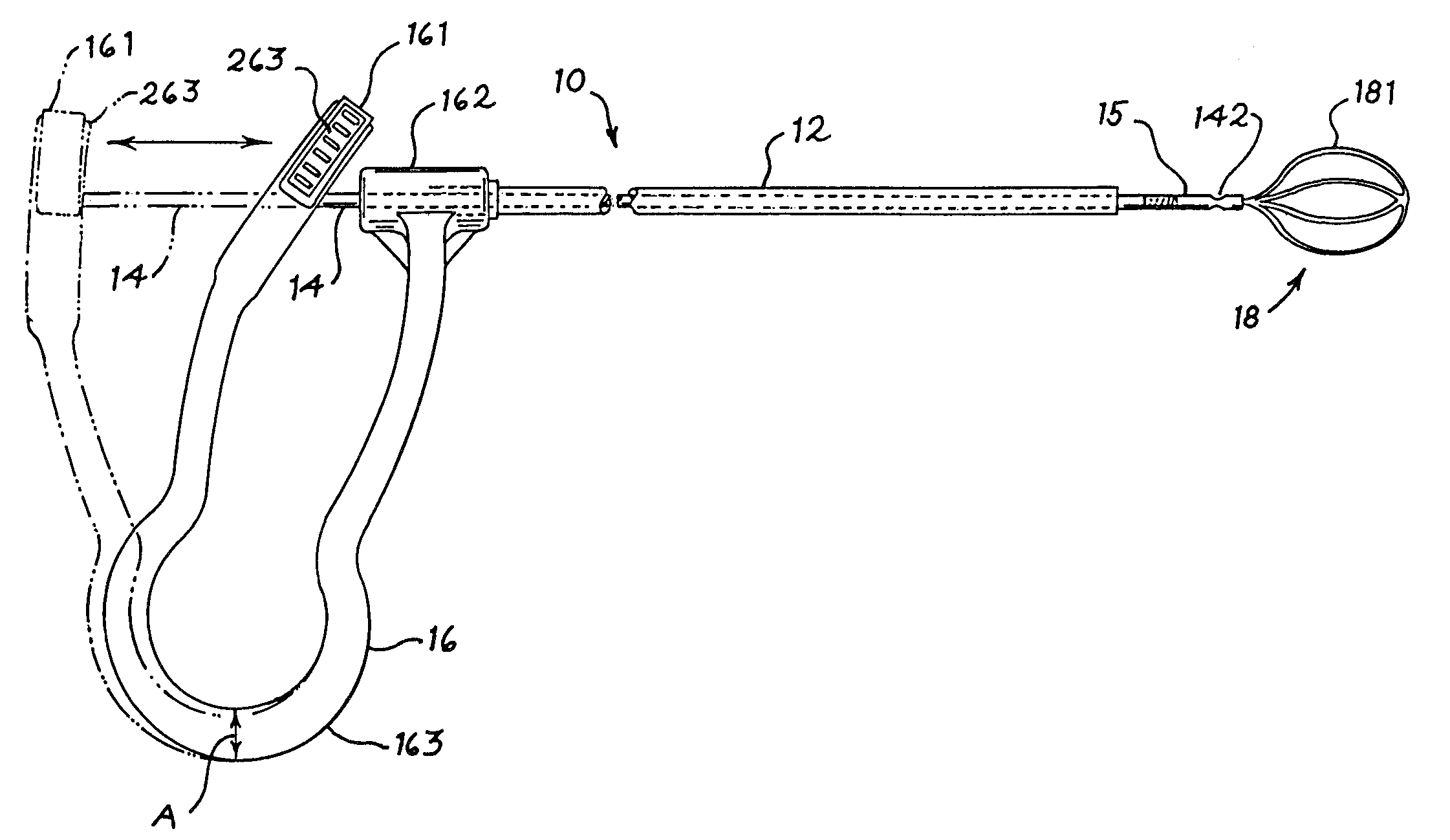
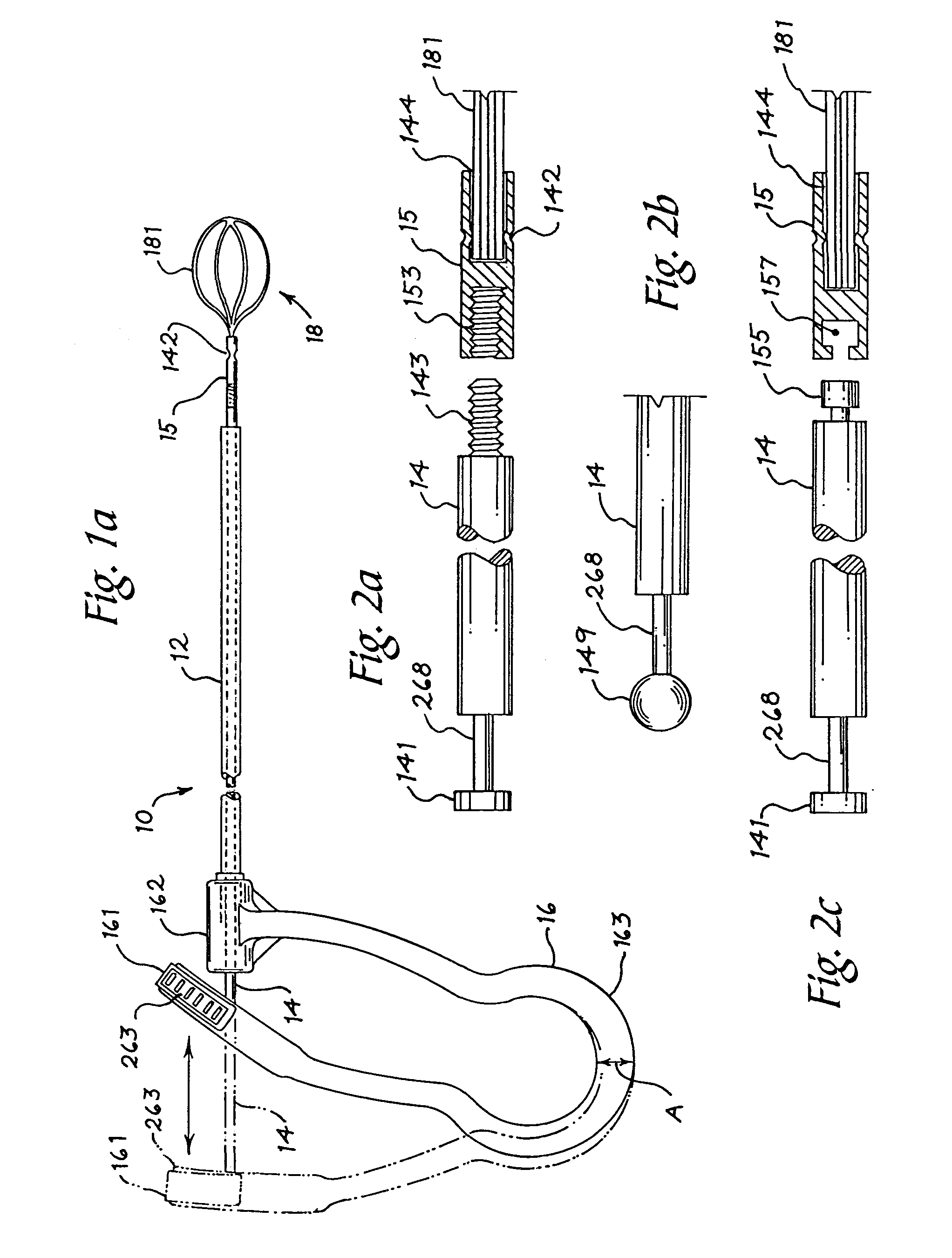
Systems and methods for transnasal dilation of passageways in the ear, nose and throat
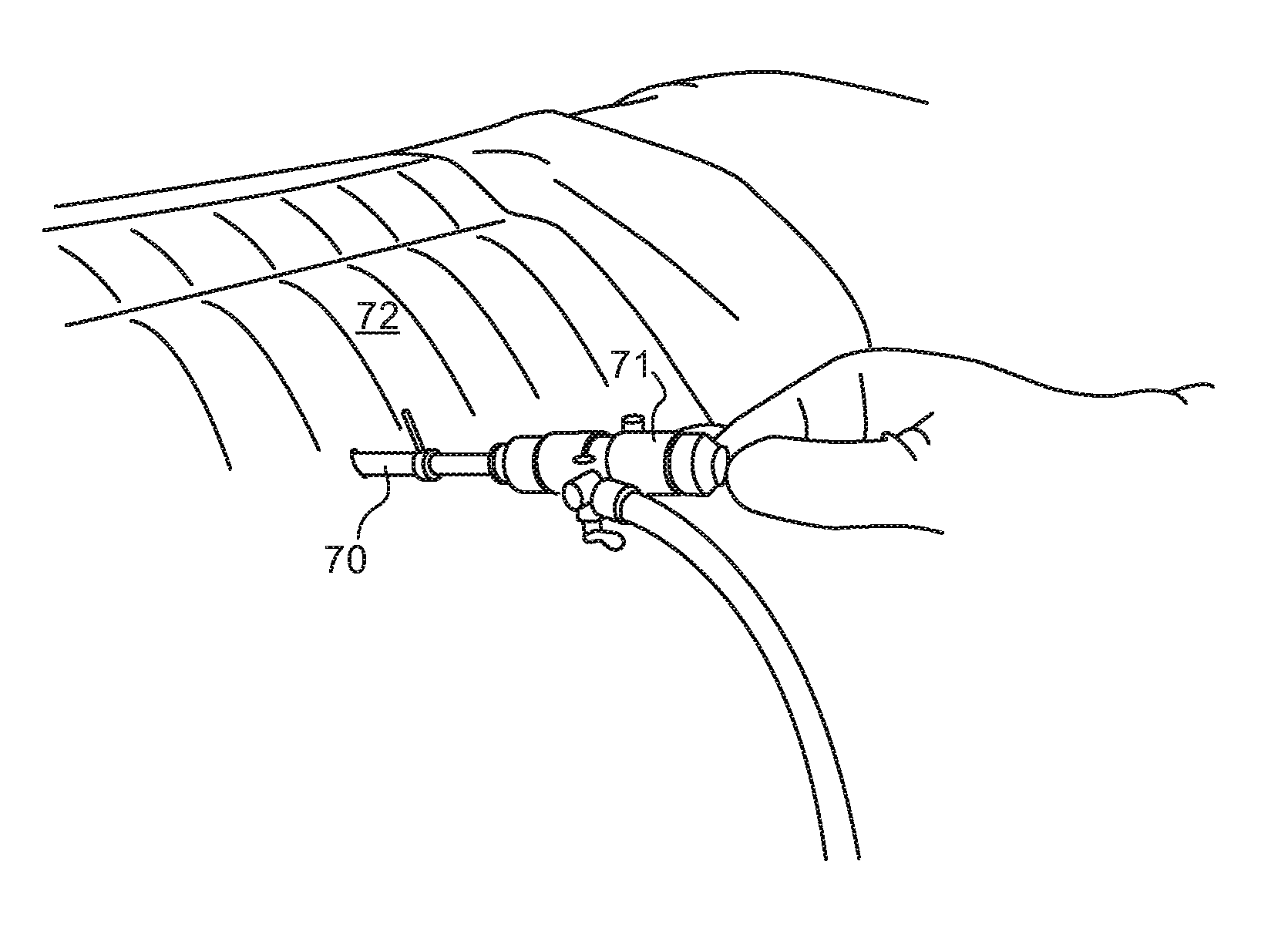
Devices, systems and methods useable for dilating the ostia of paranasal sinuses and / or other passageways within the ear, nose or throat. A dilation catheter device and system is constructed in a manner that facilitates ease of use by the operator and, in at least some cases, allows the dilation procedure to be performed by a single operator. Additionally, the dilation catheter device and system may be useable in conjunction with an endoscope and / or a fluoroscope to provide for easy manipulation and positioning of the devices and real time visualization of the entire procedure or selected portions thereof. In some embodiments, an optional handle may be used to facilitate grasping or supporting a device of the present invention as well as another device (e.g., an endoscope) with a single hand.
Owner:ACCLARENT INC
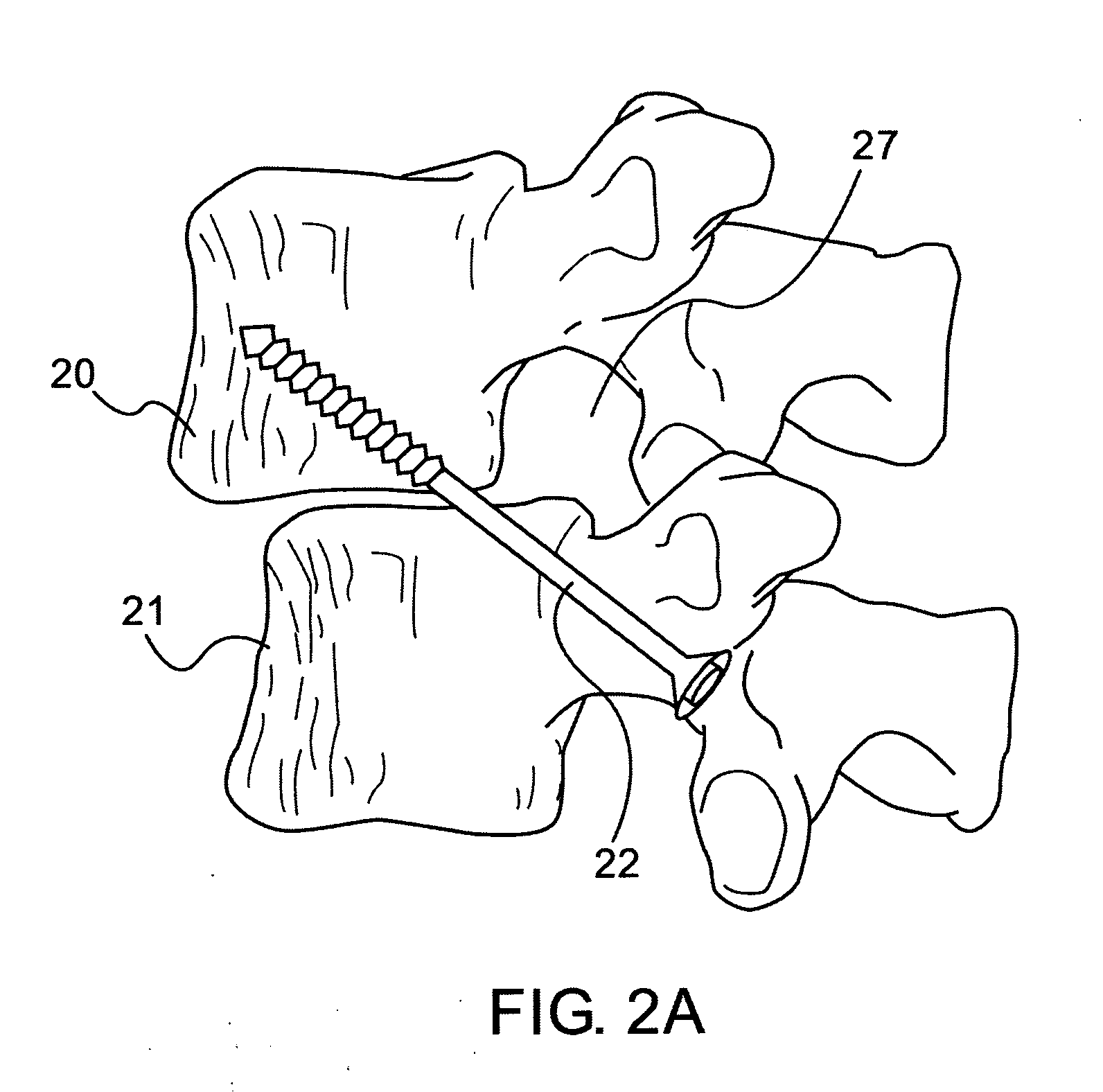
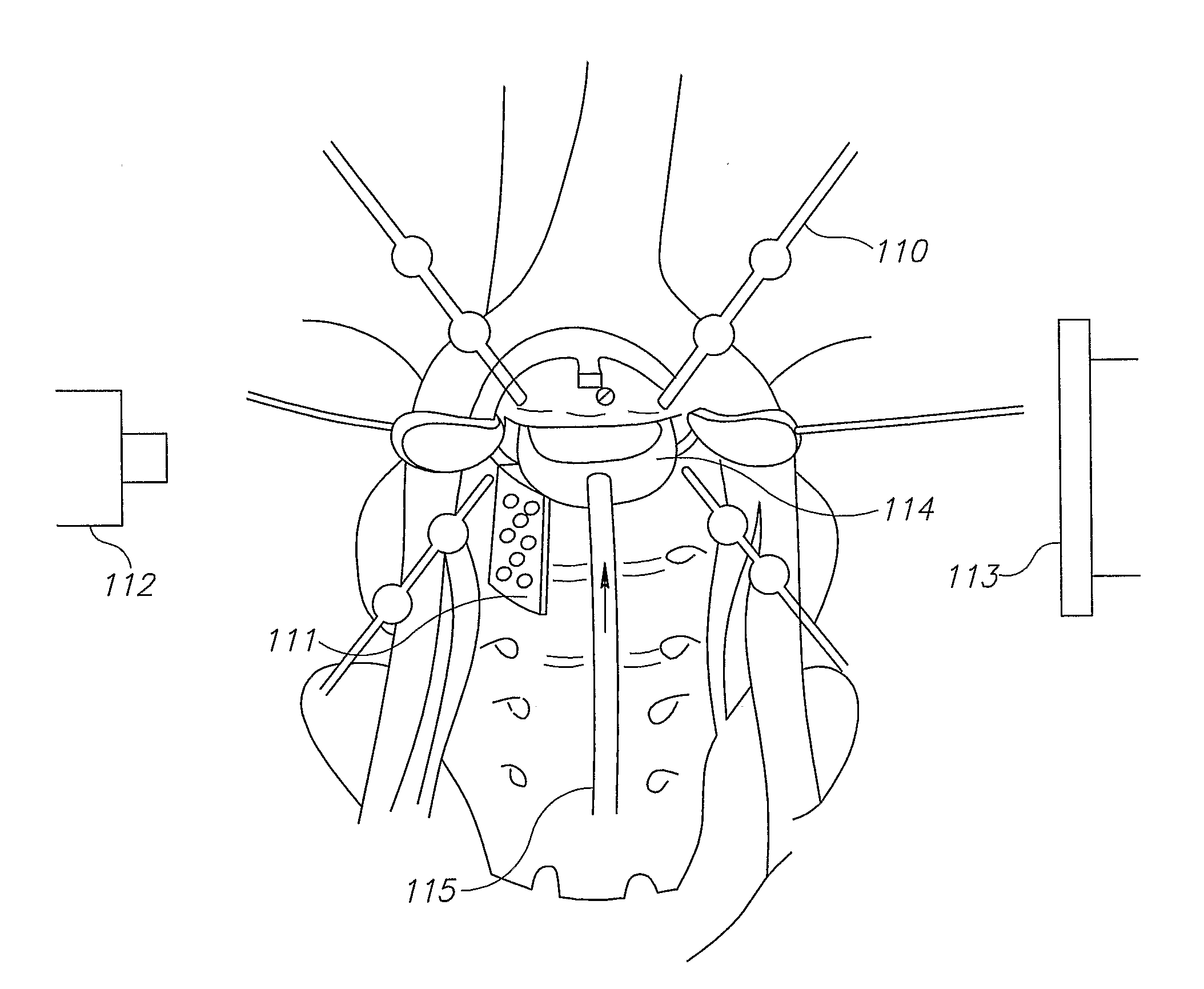
Robot guided oblique spinal stabilization
ActiveUS8992580B2Less traumaticImprove accuracyInternal osteosythesisSurgical needlesRobotic systemsMinimally invasive procedures
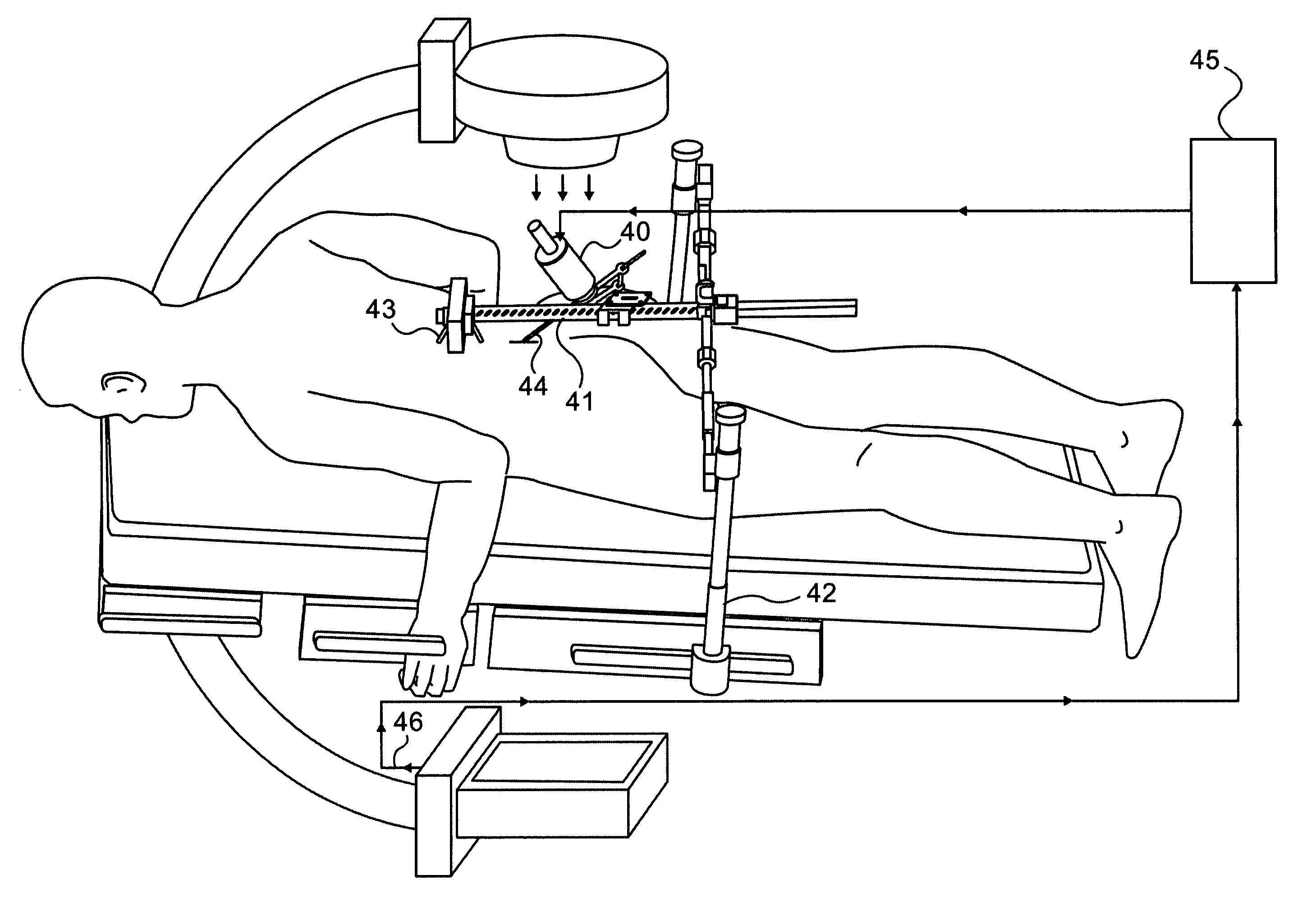
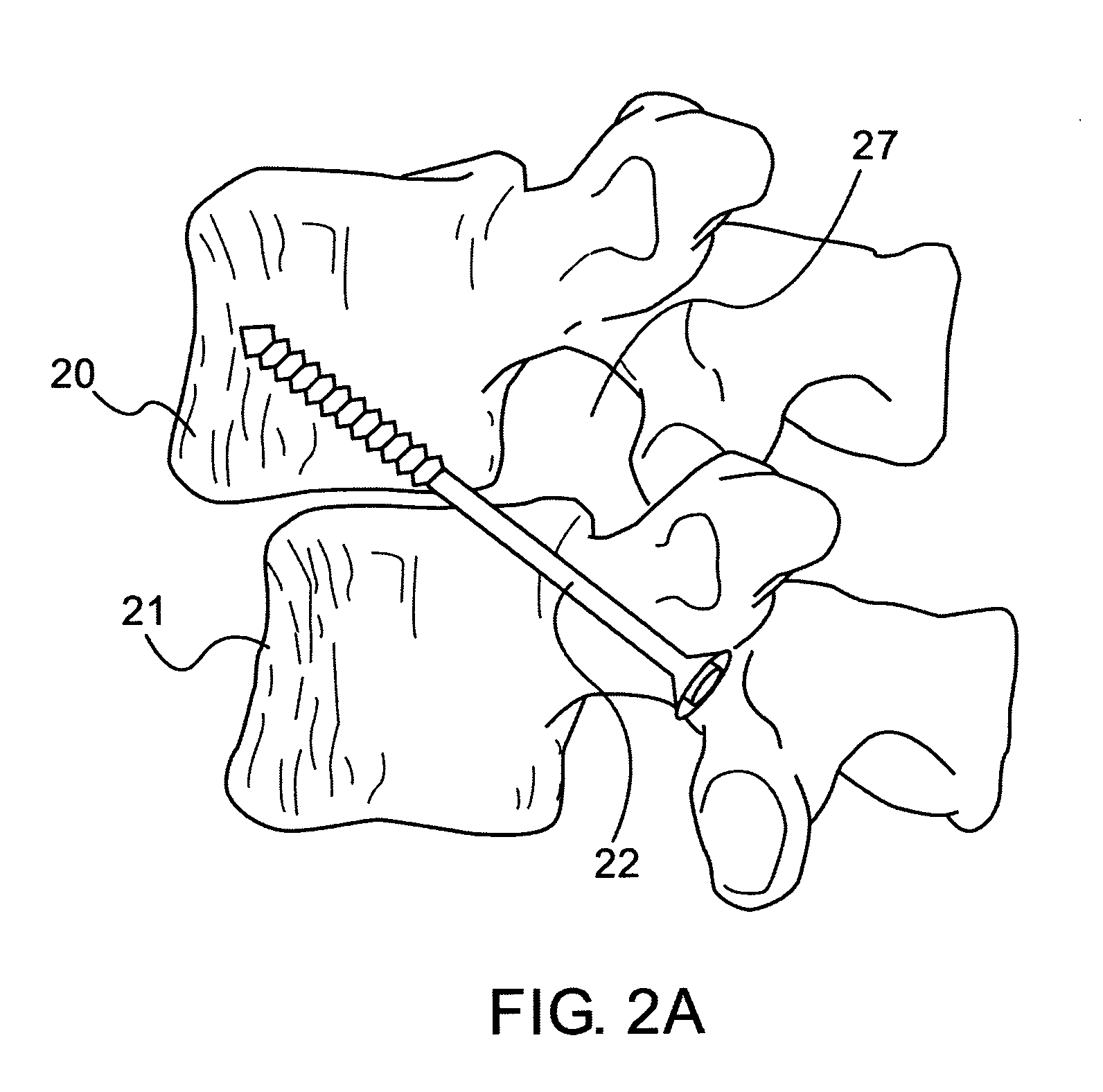
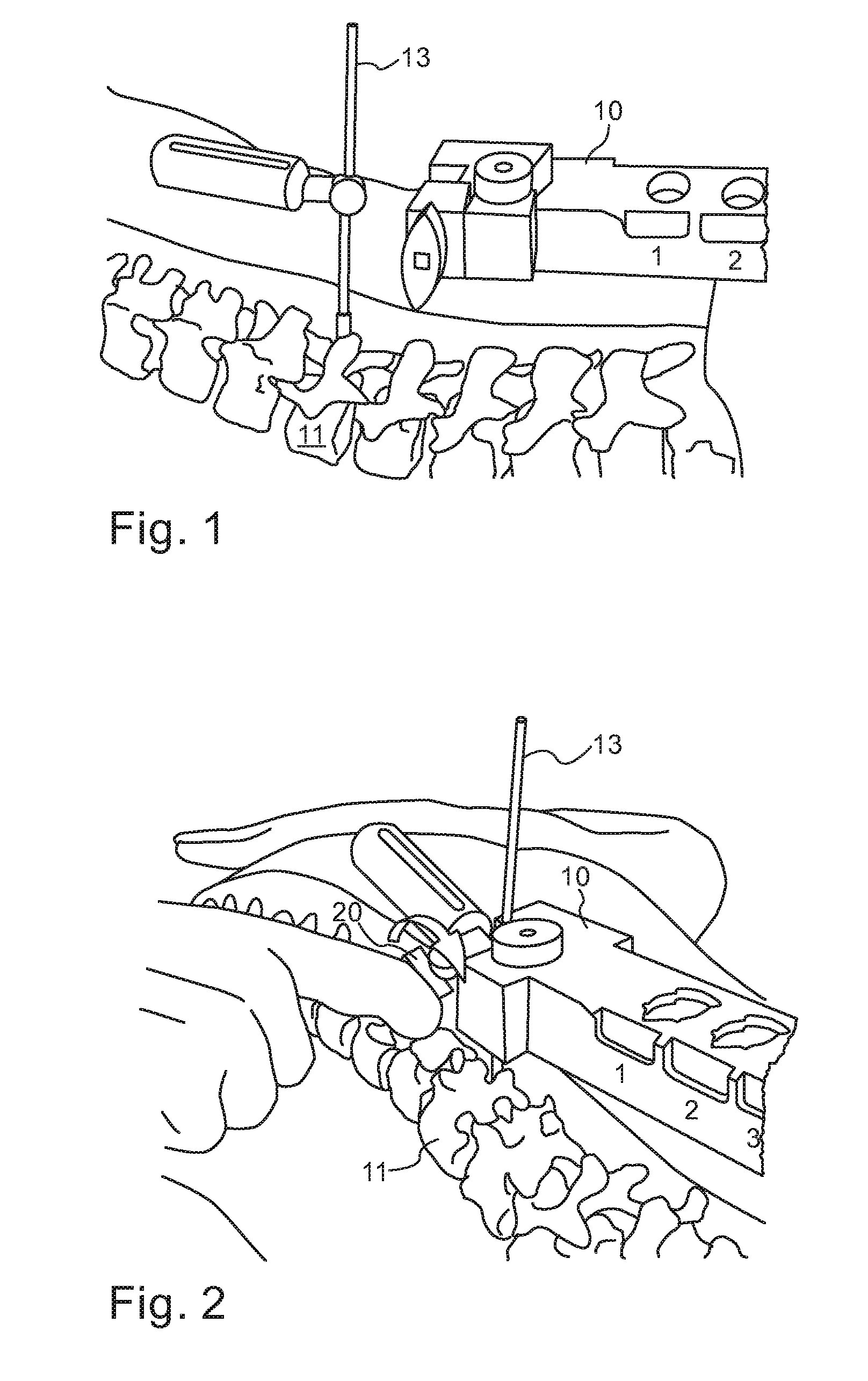
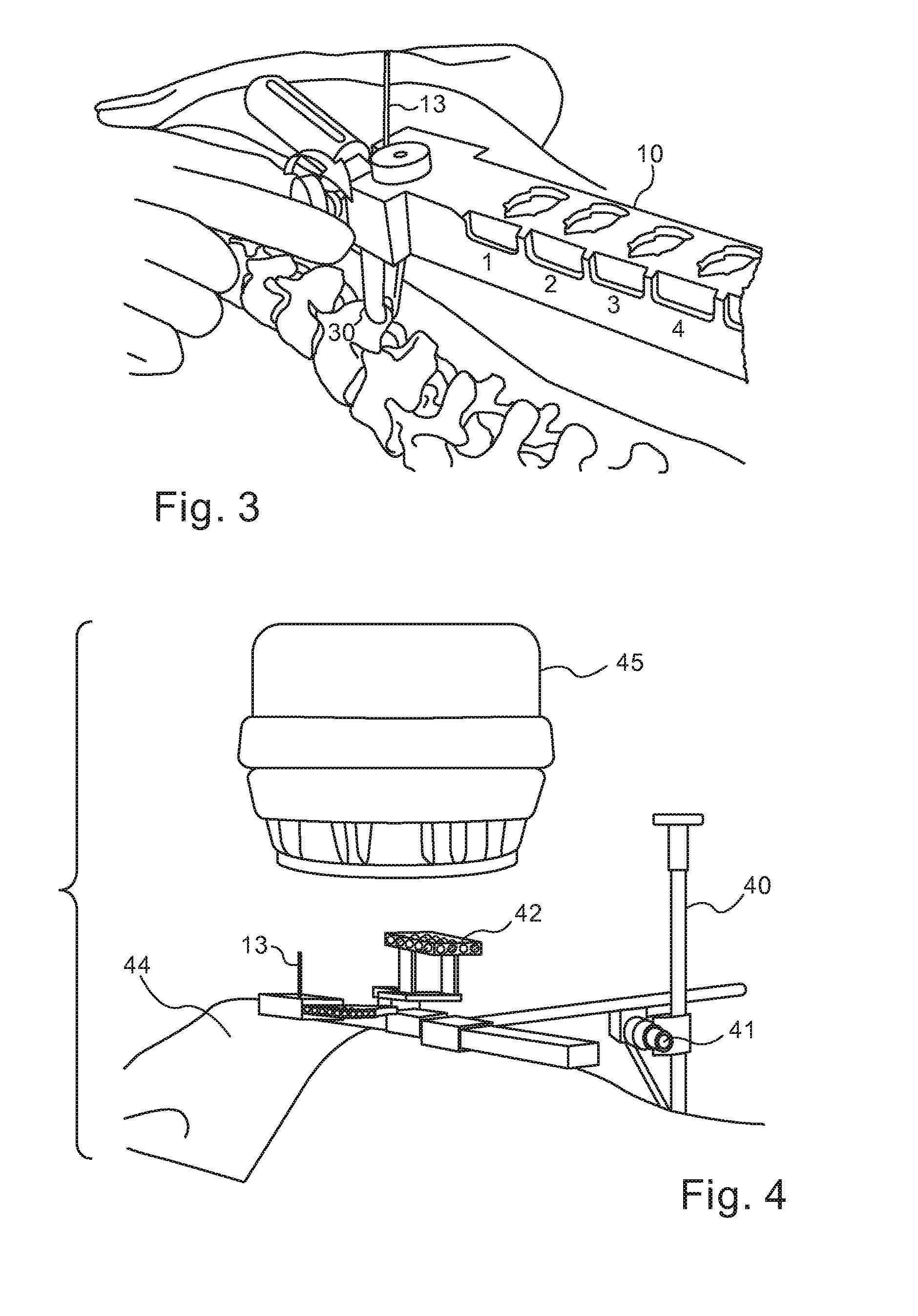
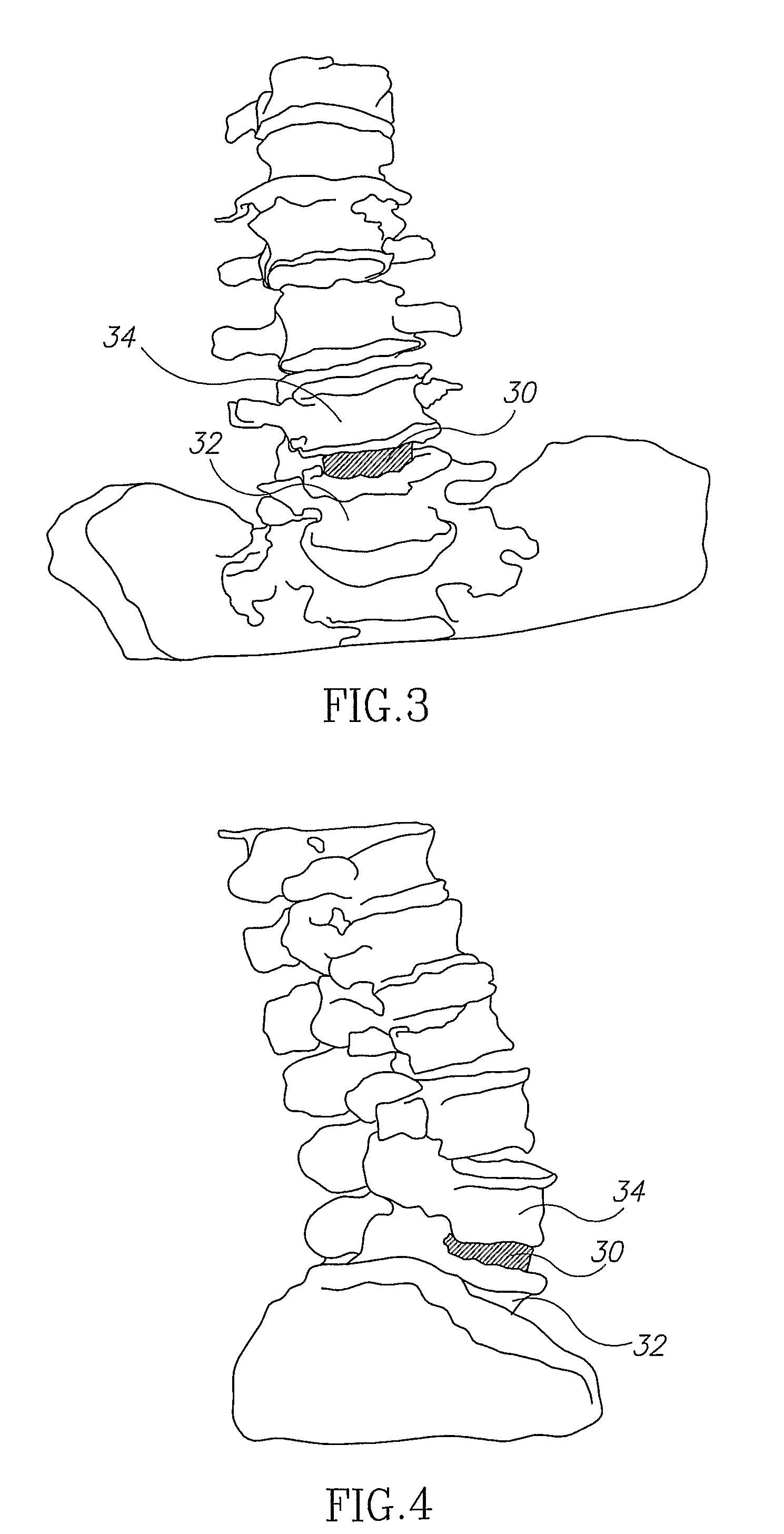
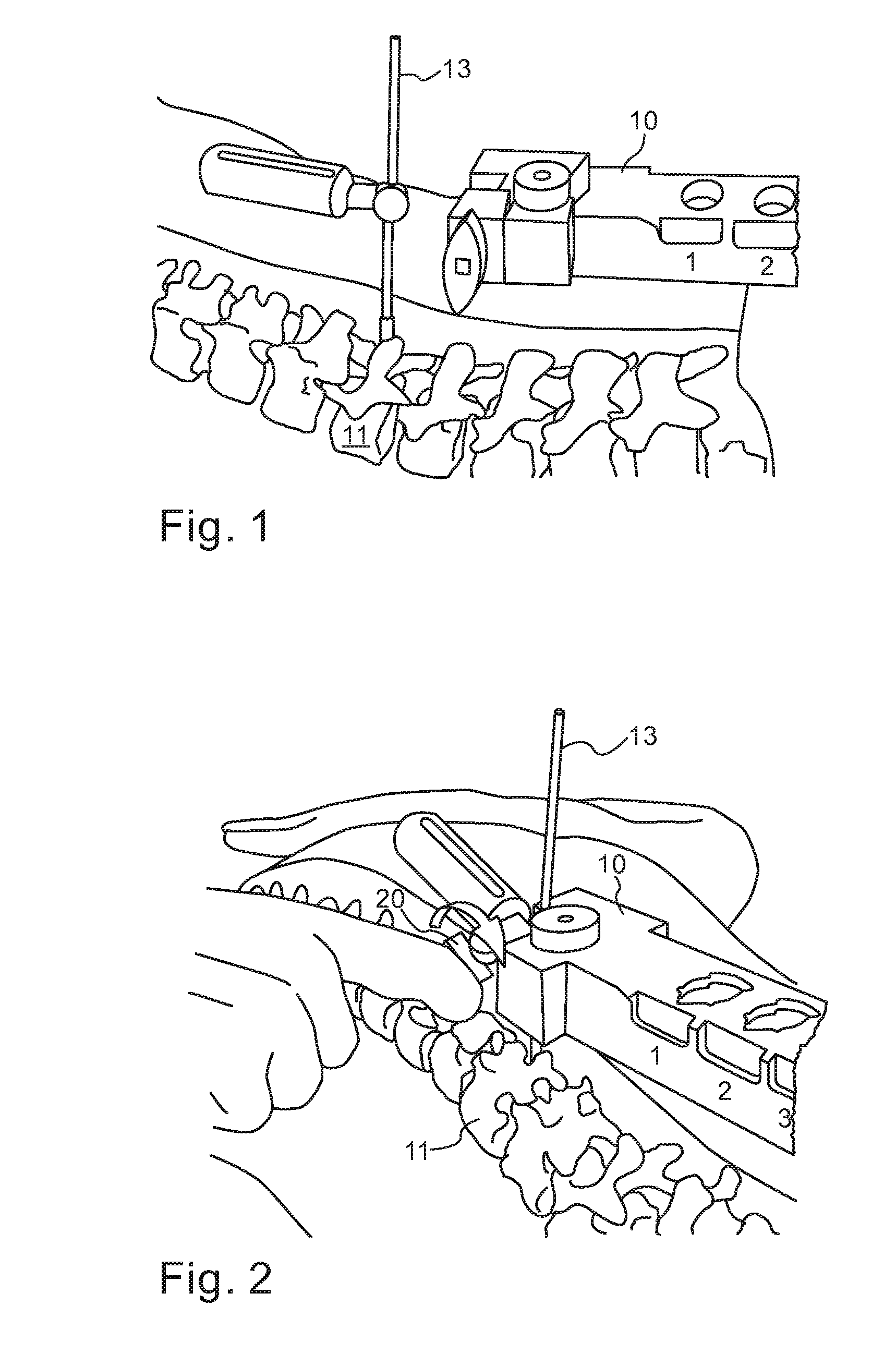
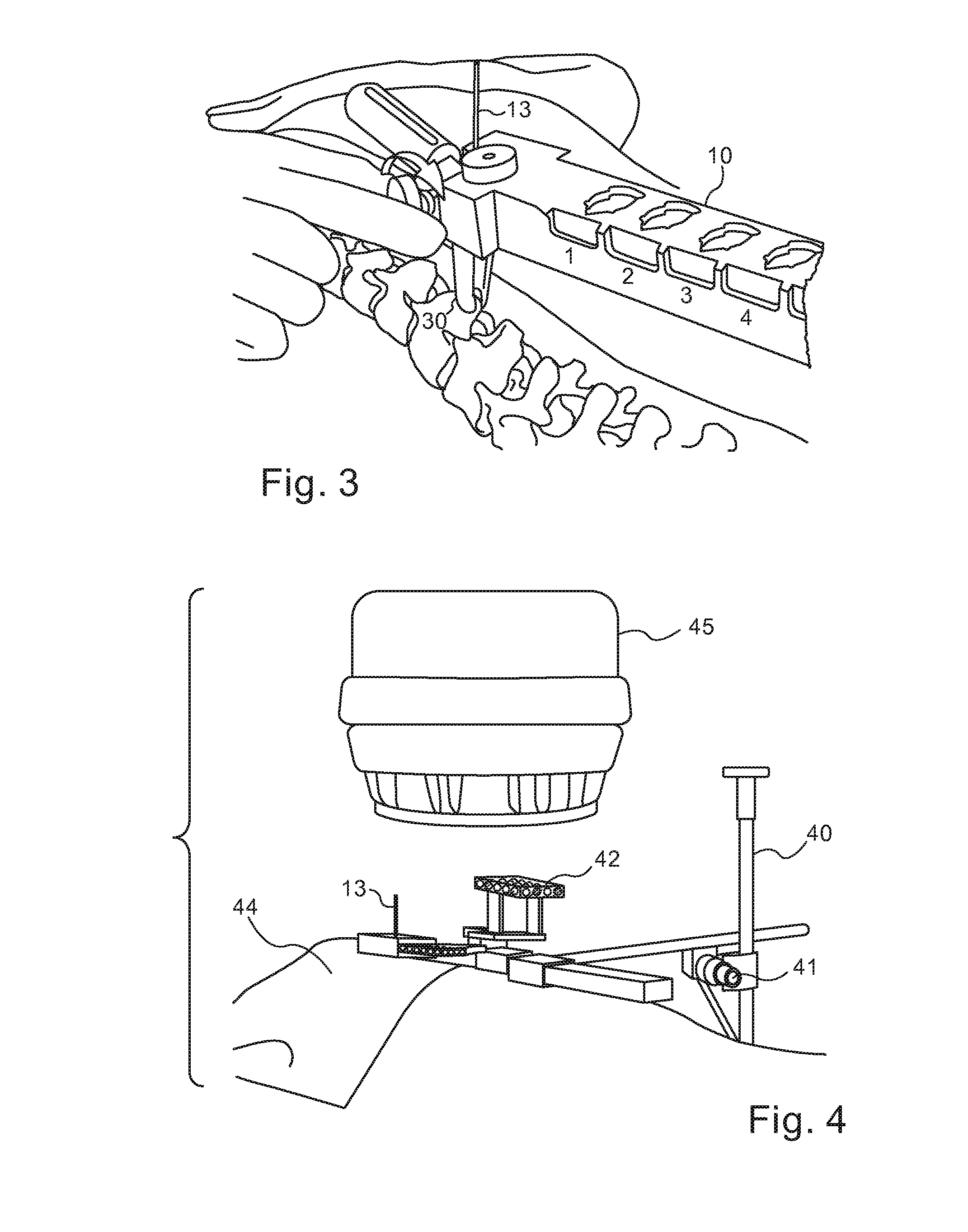
A robotic system for performing minimally invasive spinal stabilization, using two screws inserted in oblique trajectories from an inferior vertebra pedicle into the adjacent superior vertebra body. The procedure is less traumatic than such procedures performed using open back surgery, by virtue of the robot used to guide the surgeon along a safe trajectory, avoiding damage to nerves surrounding the vertebrae. The robot arm is advantageous since no access is provided in a minimally invasive procedure for direct viewing of the operation site, and the accuracy required for oblique entry can readily be achieved only using robotic control. This robotic system also obviates the need for a large number of fluoroscope images to check drill insertion position relative to the surrounding nerves. Disc cleaning tools with flexible wire heads are also described. The drilling trajectory is determined by comparing fluoroscope images to preoperative images showing the planned path.
Owner:MAZOR ROBOTICS
Systems and methods that facilitate minimally invasive spine surgery
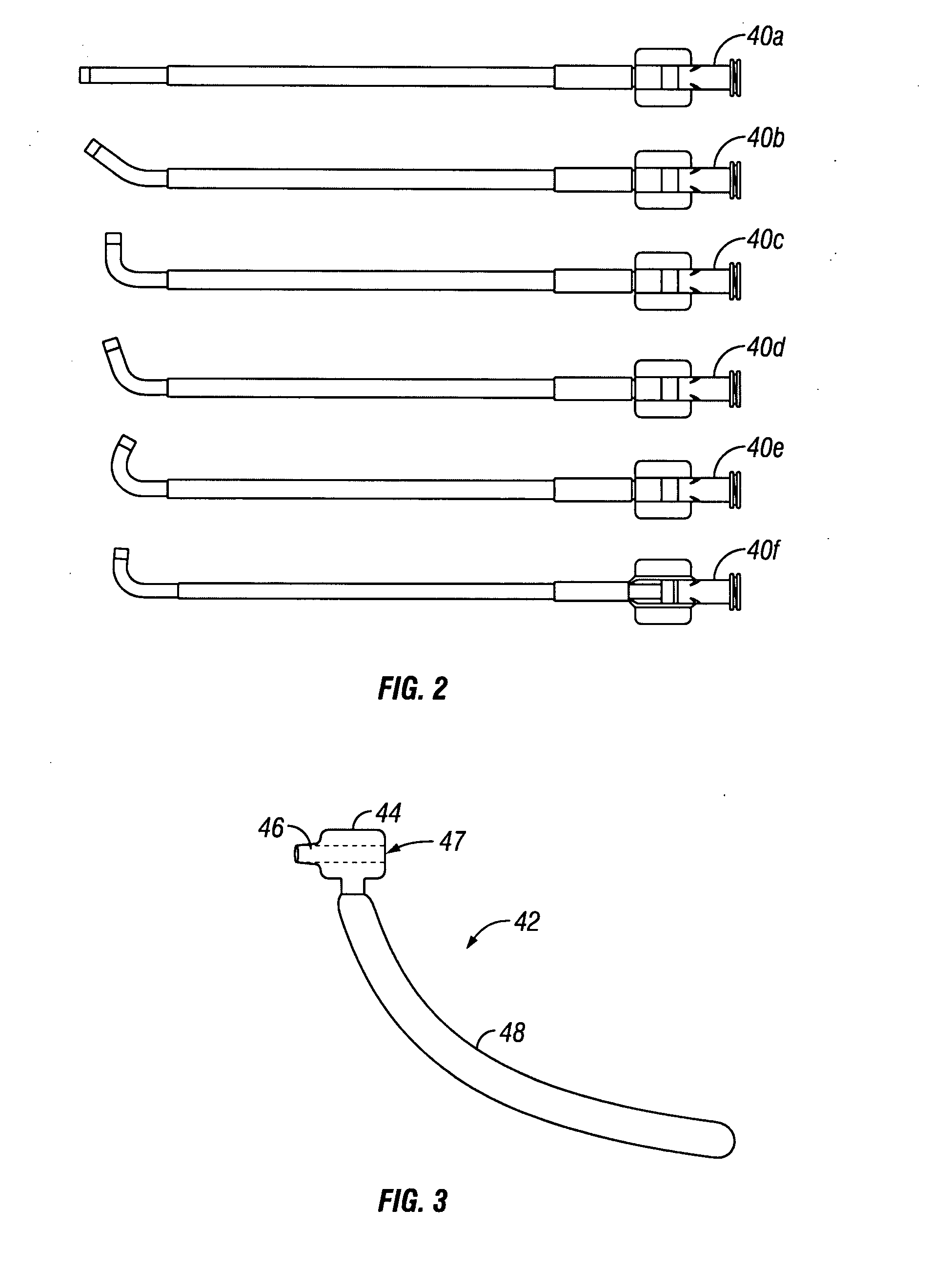
A system and method that facilitates minimally invasive spine surgery. The system includes screw preparation instruments that include a targeted guide with a laser attached to a fluoroscope, at least one polyaxial screw and rod guidance instruments that selectively insert the at least one polyaxial screw within the spine. The screw preparation instruments include an awl, a hand-held drill or tap, a ball-tipped probe, a cannulated depth gauge ruler, and a hexagonal screwdriver. Each screw preparation instrument have respective handles marked with a targeting guide oriented along respective central axes of the instruments. The rod guidance instruments include a rod with a tapered tip, a T-handle rod holder, a T-handle alignment guide, an alignment marker sleeve, a flexible alignment marker with a polyaxial head, and a template rod.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC
C-arm computerized tomography system
ActiveUS9044190B2Reducing effect of motion of C-armCharacter and pattern recognitionX-ray apparatusData setVideo sequence
Owner:MAZOR ROBOTICS
Intra-operative registration for navigated surgical procedures
ActiveUS8694075B2Surgical navigation systemsCharacter and pattern recognition3d imagePatient registration
A navigation system for use during a surgical procedure is provided. The navigation system is configured to use electromagnetic tracking data produced by electromagnetic tracking devices and 2D image data produced by a fluoroscope to intra-operatively register 2D images of a patient to a pre-operative 3D image of the patient. In some implementations, a surgeon may be able to perform an interventional or surgical procedure guided by the navigation system.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC
Robotic guided endoscope
ActiveUS9125556B2Level accuracyReduce traumaEndoscopesComputerised tomographsSurgical robotEngineering
Owner:MAZOR ROBOTICS
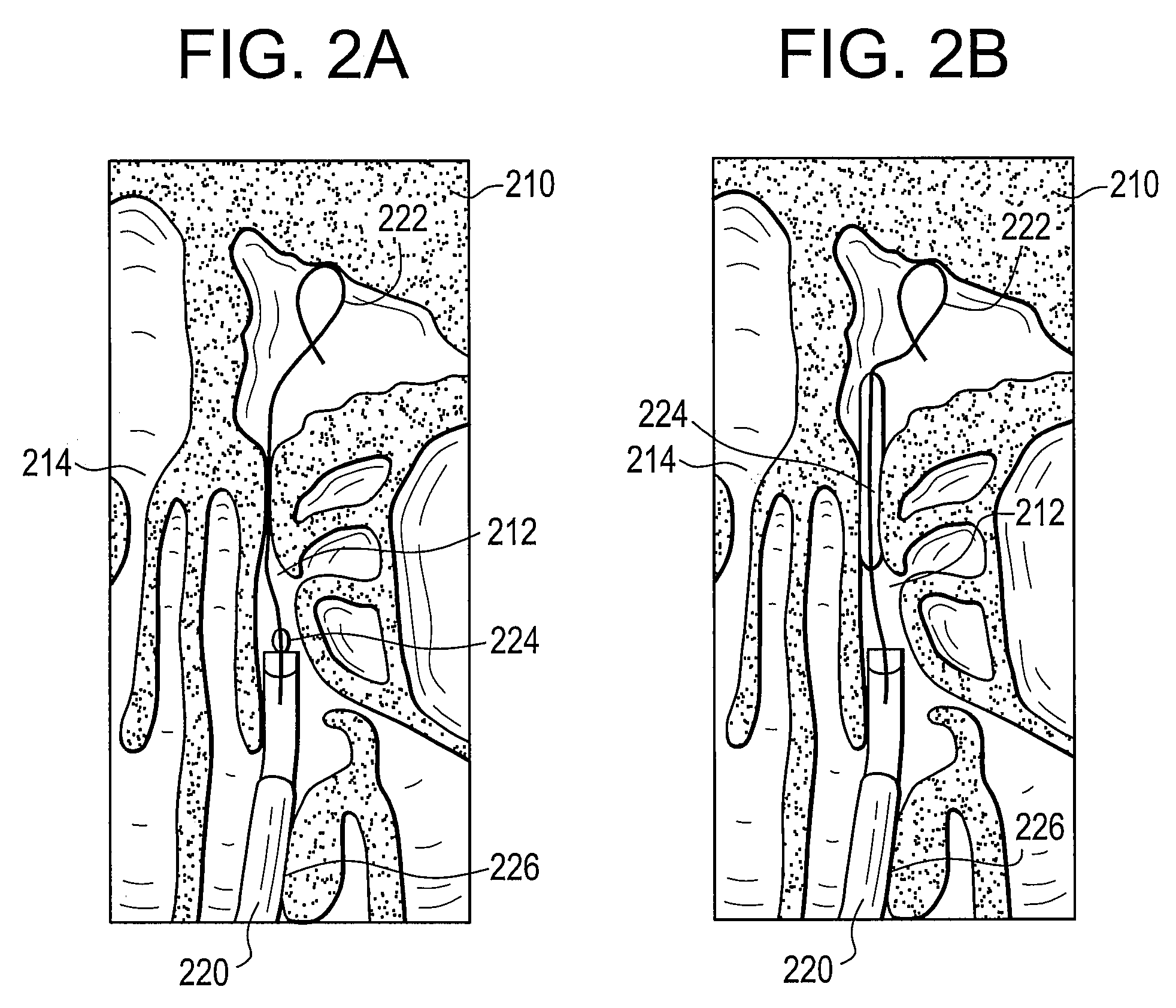
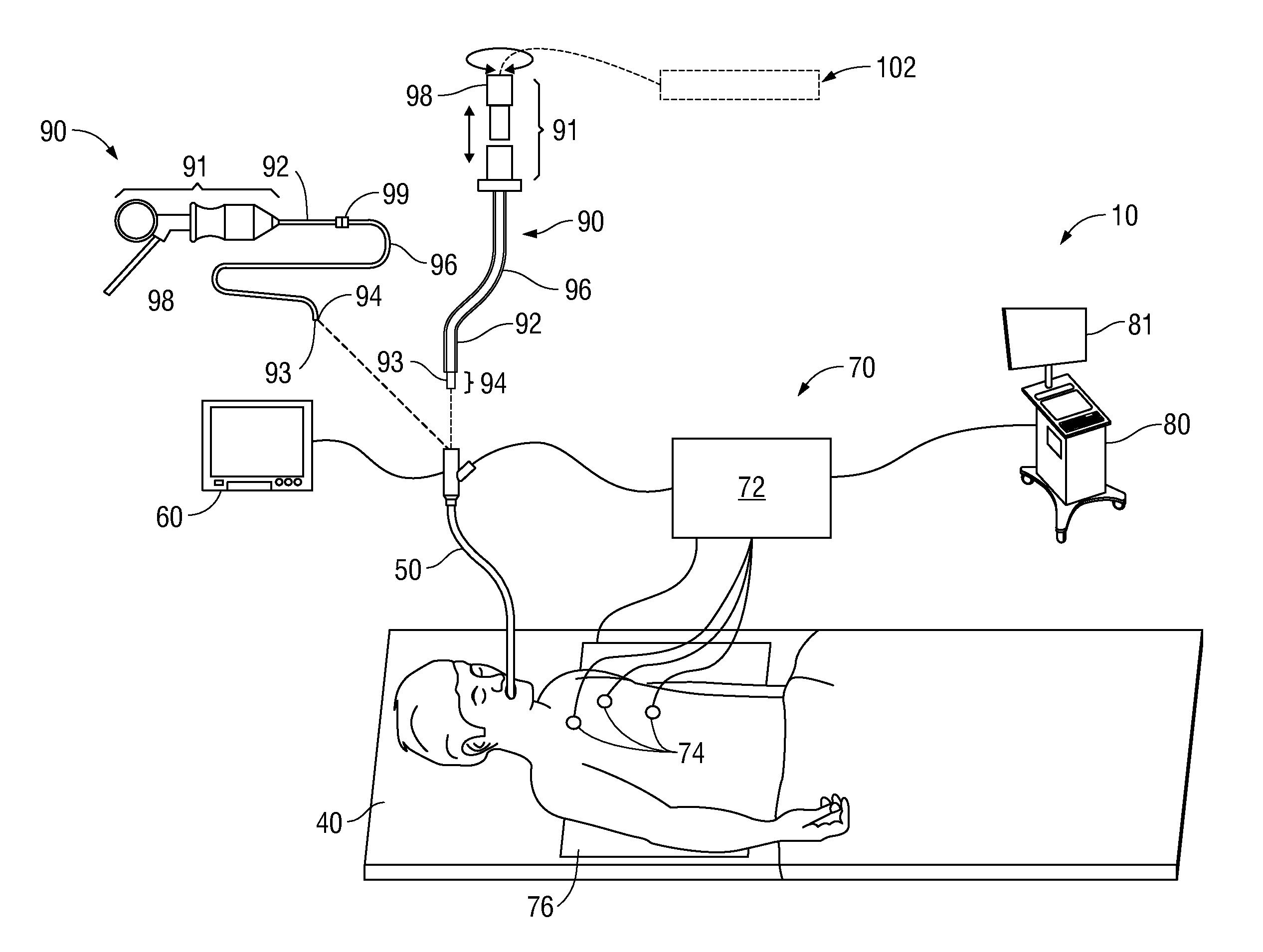
System and Method for Use of Fluoroscope and Computed Tomography Registration for Sinuplasty Navigation
InactiveUS20090080737A1Improved medical device navigationStentsSurgeryMethod of imagesIonising radiation exposure
Certain embodiments of the present invention provide systems and methods of improved medical device navigation. Certain embodiments include acquiring a first image of a patient anatomy, a second image of patient anatomy, and creating a registered image based on the first and second images. Certain preferred embodiments teach systems and methods of automated image registration without the use of fiducial markers, headsets, or manual registration. Thus the embodiments teach a simplified method of image registration that allows a medical device to be navigated within a patient anatomy. Furthermore, the embodiments teach navigating a medical device in a patient anatomy with reduced exposure to ionizing radiation. Additionally, the improved systems and methods of image registration provide for improved accuracy of the registered images.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Image registration of multiple medical imaging modalities using a multiple degree-of-freedom-encoded fiducial device
ActiveUS20080262345A1Easy to controlImprove visualizationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryDiagnostic Radiology ModalityX-ray
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
Method and apparatus for visualizing anatomical structures
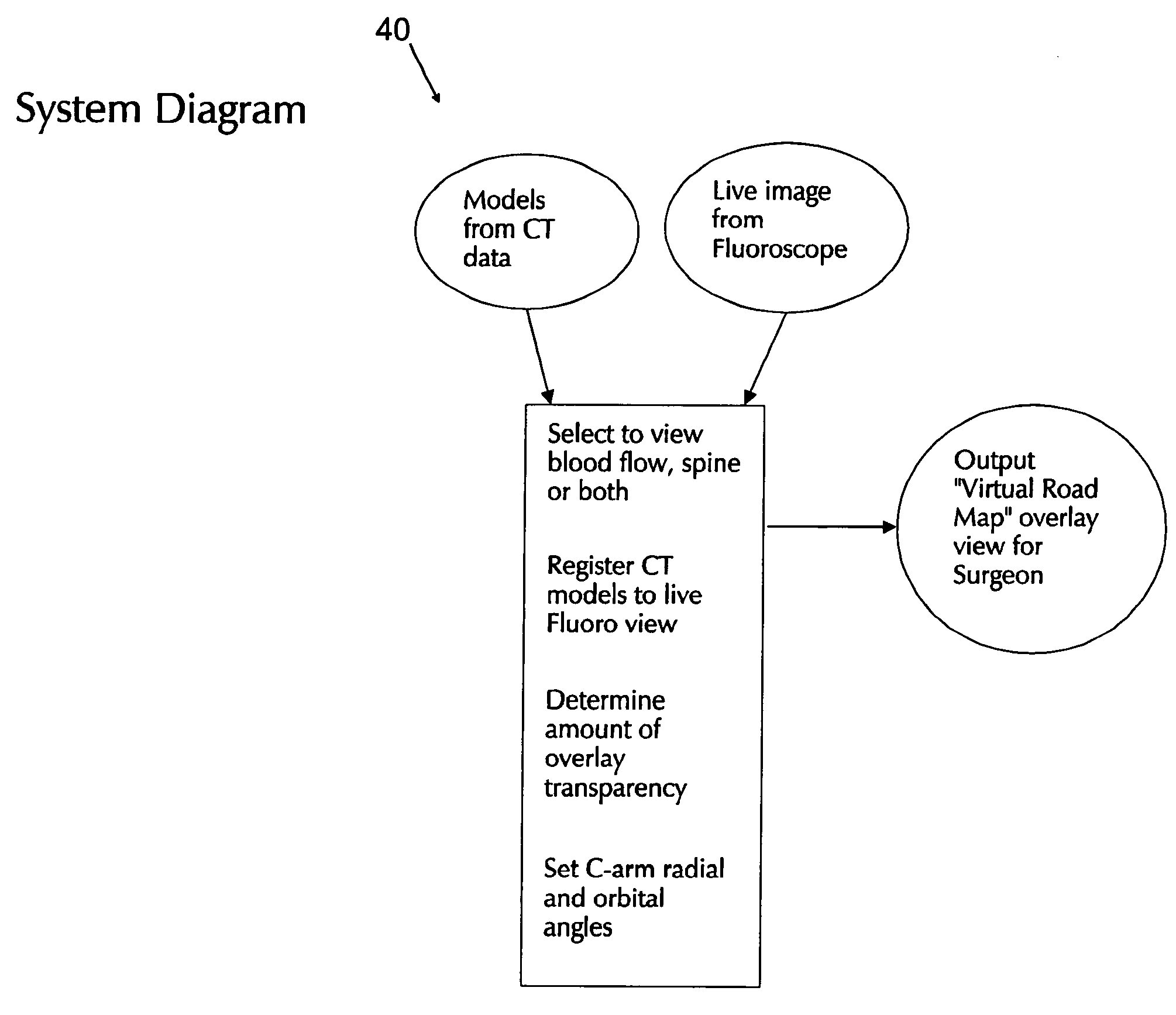
Apparatus and method for producing a virtual road map of a patient's vascular anatomy comprising a virtual 3D model of the patient's vascular and bony structure in proper registration with one another, a fluoroscope for providing real-time images of the bony structure of the patient, registration apparatus for placing the virtual 3D model in proper registration with the patient space of the fluoroscope, bone mask subtraction apparatus for generating a bone mask of the bony structure, and subtracting the same from the real-time images, whereby to create modified fluoroscope images omitting bony structure, and image generating apparatus for generating the virtual road map comprising a composite image combining (i) images of the virtual 3D structure representing the vascular structure, and (ii) modified fluoroscope images omitting bony structure, wherein the images of the virtual 3D structure representing vascular structure are in proper registration with the modified fluoroscope images omitting bony structure.
Owner:ASTUTE IMAGING LLC
CT-Enhanced Fluoroscopy
ActiveUS20080262342A1Quality improvementPrecise positioningGuide needlesMedical devicesNuclear medicineCt imaging
Real-time, enhanced imaging of remote areas, too minute for CT imaging, is made possible through a probe having a radiopaque tip as well as radiopaque volume markers. When deployed, the markers outline the space containing the tip such that both the tip and the volume containing the tip are viewable on a fluoroscope. This device may be used in conjunction with or independently of 3-D volumes created from CT scans and 3-D tip sensors.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
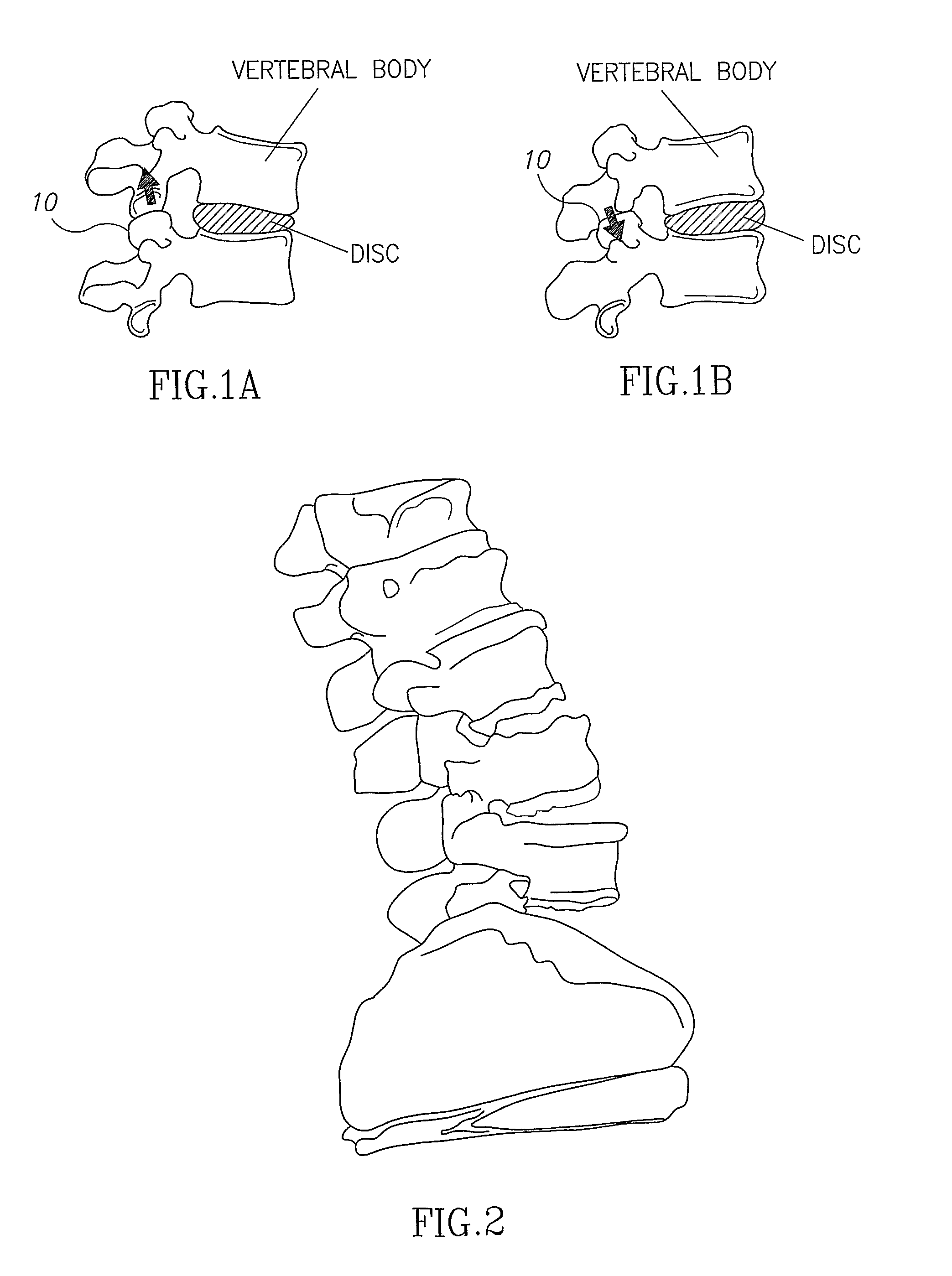
Devices and methods for stabilizing a spinal region
InactiveUS20100114098A1Strengthening intervertebral spaceIncrease spacingInternal osteosythesisEar treatmentComputed tomographyOuter Cannula
Disclosed are apparatuses and methods for delivering implants through a posterior aspect of a vertebral body such as a pedicle and placing the implant or performing a procedure into the anterior aspect of the vertebral body. A representative apparatus includes an outer cannula, and advancer tube and a drill assembly. It is envisioned that at least one of the outer cannula, the advancer tube or the drill assembly can be viewed in vivo using for example, a CT scan or fluoroscope. The present invention is also directed to an apparatus for forming an arcuate channel in bone material. The apparatus includes and advancer tube and a drill assembly.
Owner:K2M
Robot Guided Oblique Spinal Stabilization
ActiveUS20110319941A1Less traumaticImprove accuracyInternal osteosythesisSurgical needlesSpinal columnSurgical department
A robotic system for performing minimally invasive spinal stabilization, using two screws inserted in oblique trajectories from an inferior vertebra pedicle into the adjacent superior vertebra body. The procedure is less traumatic than such procedures performed using open back surgery, by virtue of the robot used to guide the surgeon along a safe trajectory, avoiding damage to nerves surrounding the vertebrae. The robot arm is advantageous since no access is provided in a minimally invasive procedure for direct viewing of the operation site, and the accuracy required for oblique entry can readily be achieved only using robotic control. This robotic system also obviates the need for a large number of fluoroscope images to check drill insertion position relative to the surrounding nerves. Disc cleaning tools with flexible wire heads are also described. The drilling trajectory is determined by comparing fluoroscope images to preoperative images showing the planned path.
Owner:MAZOR ROBOTICS
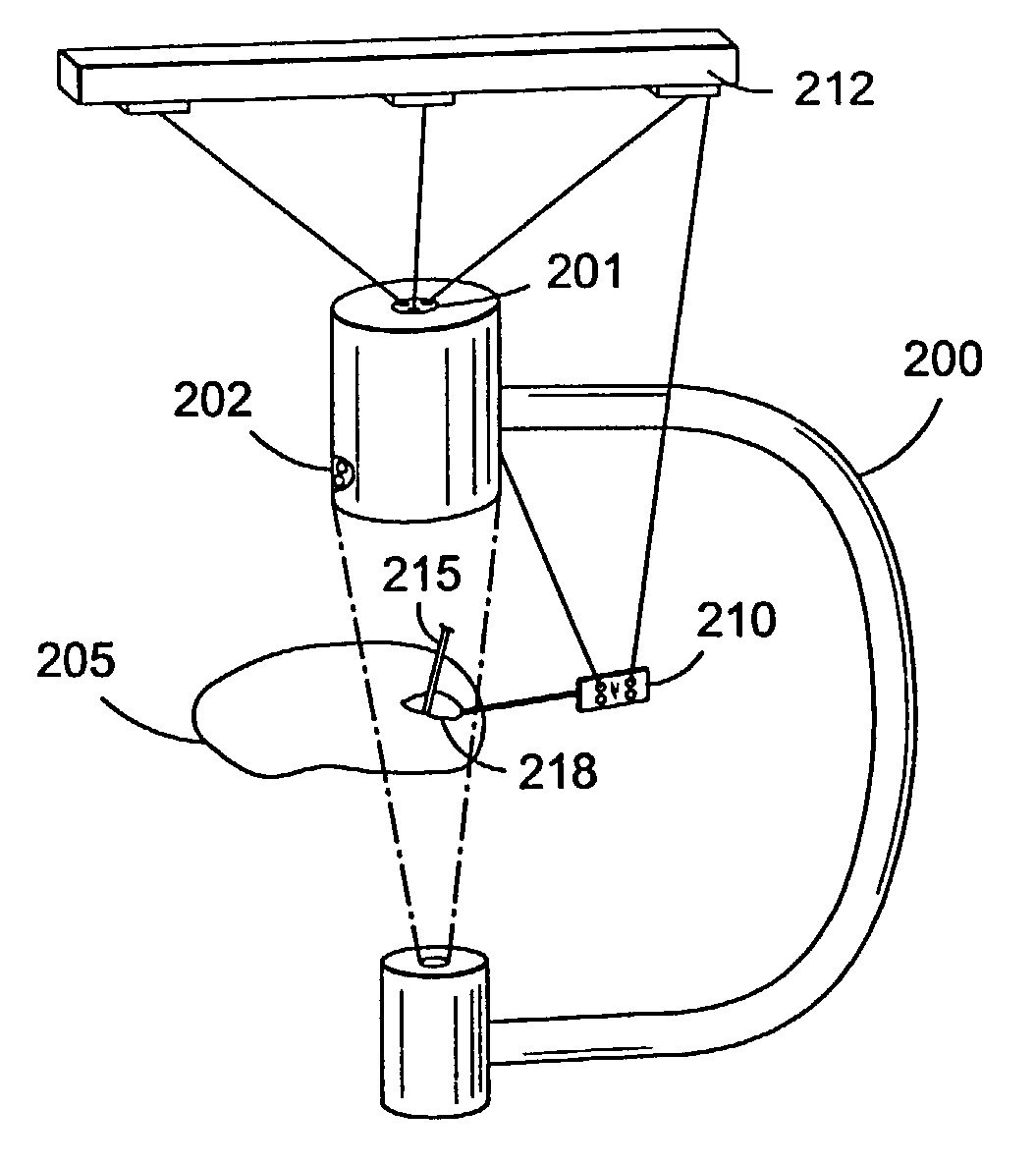
Fluoroscopic pose estimation
Methods and systems for registering three-dimensional (3D) CT image data with two-dimensional (2D) fluoroscopic image data using a plurality of markers are disclosed. In the methods and systems, a lateral angle and a cranial angle are searched for and a roll angle is computed. 3D translation coordinates are also computed. The calculated roll angle and 3D translation coordinates are computed for a predetermined number of times successively. After performing the calculations, the 3D CT image data is overlaid on the 2D fluoroscopic image data based on the lateral angle, the cranial angle, the roll angle, and the 3D translation coordinates.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Compensation for magnetic disturbance due to fluoroscope
ActiveUS20120165656A1Surgical navigation systemsUsing electrical meansMagnetic disturbanceCondensed matter physics
A method, consisting of generating, using a plurality of magnetic transmitters, a magnetic field in a region and introducing a field perturbing element into the region. The method includes characterizing multiple images of each magnetic transmitter in the field perturbing element, and calculating a reaction magnetic field in the region based on the characterized images. The method further includes positioning a probe in the region and measuring a perturbed magnetic field at the probe, and determining a location of the probe in response to the measured perturbed magnetic field and the calculated reaction magnetic field.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER (ISRAEL) LTD
Devices and methods for stabilizing a spinal region
InactiveUS8579903B2Increase spacingInternal osteosythesisEar treatmentComputed tomographyOuter Cannula
Owner:K2M
Automatically Determining 3D Catheter Location and Orientation Using 2D Fluoroscopy Only
ActiveUS20130243153A1Improve accuracy and effectivenessMinimize impactX-ray/infra-red processesElectrocardiographyVideo fluoroscopyLiving body
A method for automatically determining the 3D position and orientation of a radio-opaque medical object in a living body using single-plane fluoroscopy comprising capturing a stream of digitized 2D images from a single-plane fluoroscope (10), detecting the image of the medical object in a subset of the digital 2D images, applying pixel-level geometric calculations to measure the medical-object image, applying conical projection and radial elongation corrections (31) to the image measurements, and calculating the 3D position and orientation of the medical object from the corrected 2D image measurements.
Owner:APN HEALTH
Systems for treating disorders of the ear, nose and throat
Devices, systems and methods useable for dilating the ostia of paranasal sinuses and / or other passageways within the ear, nose or throat. A dilation catheter device and system is constructed in a manner that facilitates ease of use by the operator and, in at least some cases, allows the dilation procedure to be performed by a single operator. Additionally, the dilation catheter device and system may be useable in conjunction with an endoscope and / or a fluoroscope to provide for easy manipulation and positioning of the devices and real time visualization of the entire procedure or selected portions thereof. In some embodiments, an optional handle may be used to facilitate grasping or supporting a device of the present invention as well as another device (e.g., an endoscope) with a single hand.
Owner:ACCLARENT INC
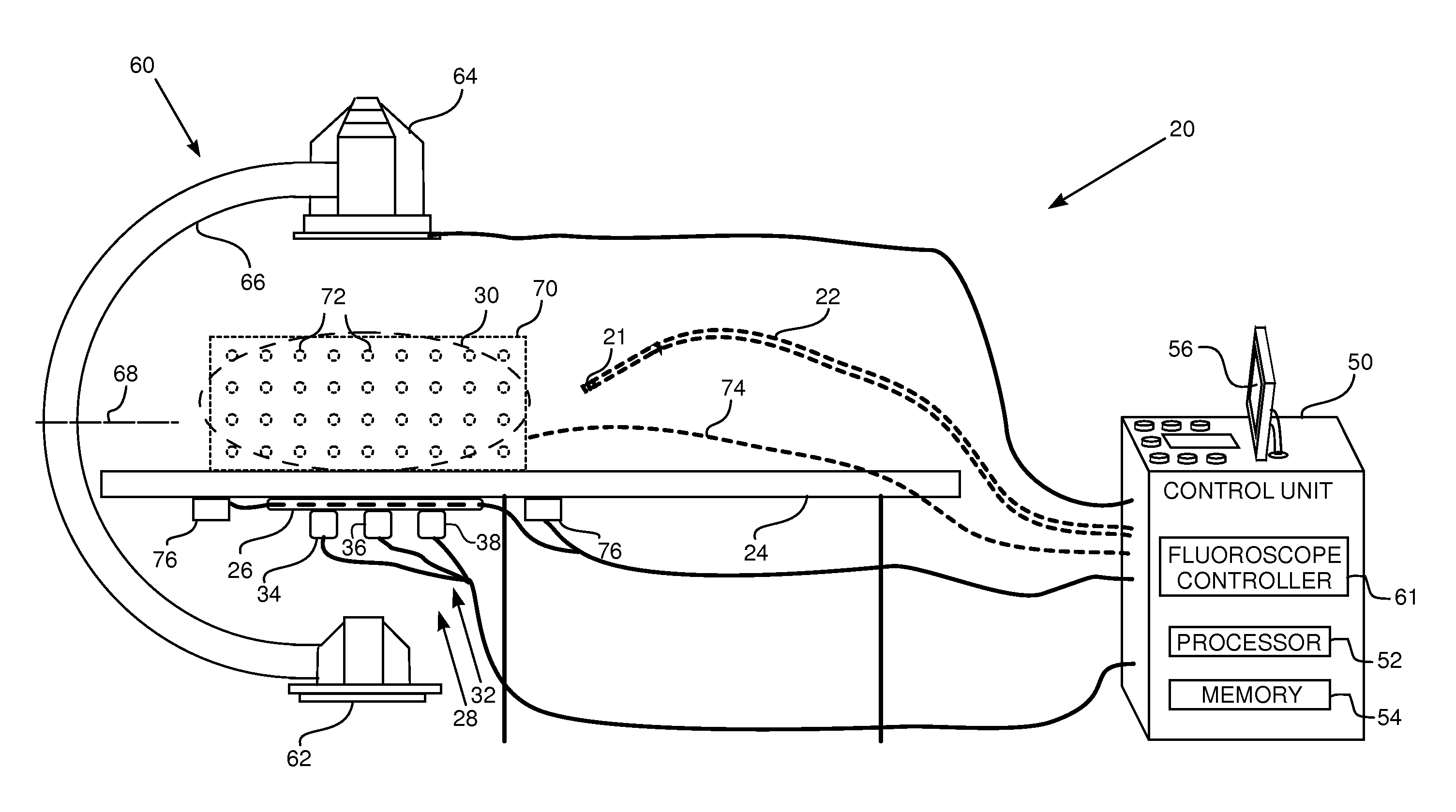
Surgical targeting system
A targeting device for providing a series of coordinates / lines within a sheet of sterile, flexible material with an adherent surface which is applied to the skin (after suitable surgical preparation). The sheet is non-porous and may have a topical antiseptic on the side which is applied to the skin. A fluoroscope or roentgenographic image of the portion of the body to which the adherent film is applied will show the underlying skeletal and radiopaque elements as well as the overlying surgical grid. Once the targeting device is applied, the coordinates on the grid lines are clearly visible on the surface of the skin as well as on the fluoroscopic or radiographic image and by knowing the direction of the fluoroscopic or radiographic beam, the operator will be able to thereby correlate a specific locus on the skin with an underlying skeletal element or other underlying radiopaque structure. By applying the targeting device to the part of the body in a circumferential or nearly circumferential manner, and utilizing a radiolucent operating room table, and a radiograph or C-arm fluoroscope, targeting techniques using the targeting device can be utilized at surgery. Multiple targeting or percutaneous procedures can be performed at the same sitting with the application of a single device.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Apparatus for providing visual data during an operation
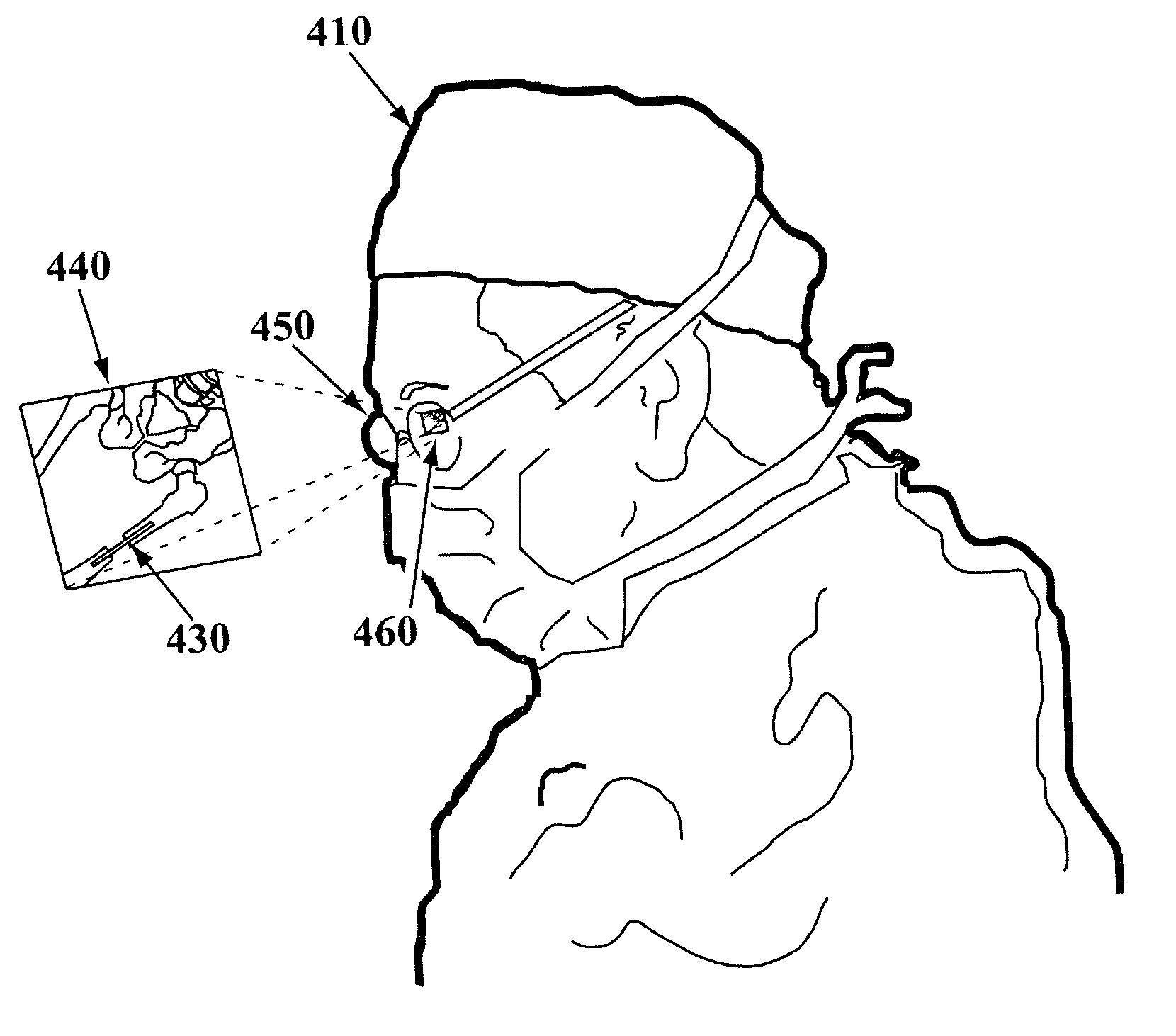
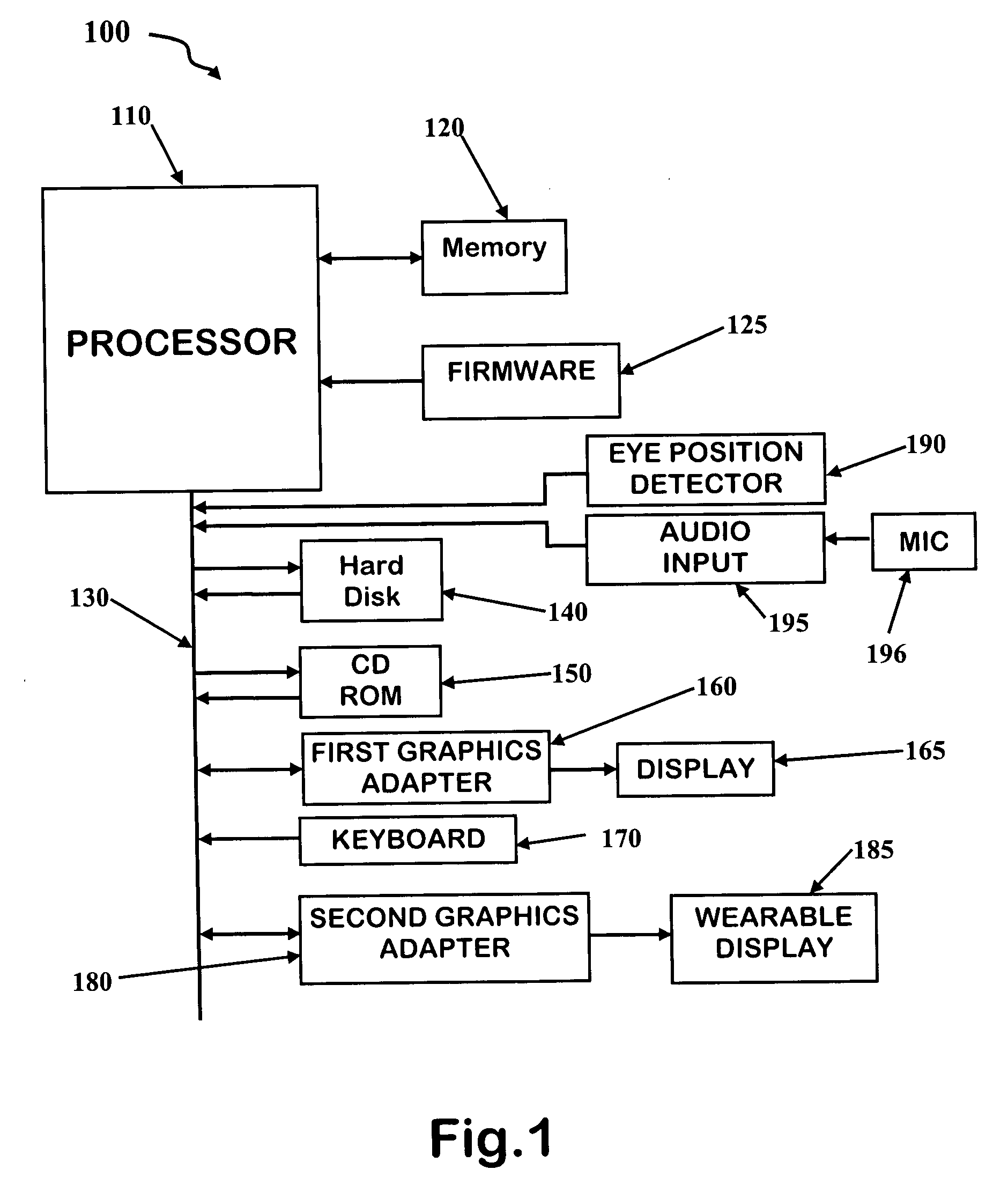
A method and apparatus for providing visual data during an operation is described, comprising a processing base with memory and storage; a source of images such as x-rays and fluoroscopes; and a personally worn display such as a heads-up display. The display provides images of x-rays; fluoroscopic images; ultrasound images; and the like within the field of vision of the person or persons performing detailed medical procedures.
Owner:IAQUINTO JOHN M
Portable electrosurgical instruments and method of using same
InactiveUS20140081256A1Easy to adaptEasily manipulatedSurgical instruments for heatingOn boardElectrical connection
In contrast to instruments of the prior art that require bulky, cumbersome and / or costly electrical connections and energy sources, instruments designed in accordance with the instant disclosure are both portable and self-powered. The electrosurgical instruments of the present invention are not limited to a particular use or construction and can be adapted for operation with or without a patient return electrode (sometimes referred to as return pad or plate), in dry or wet fields, in the presence of bodily fluids (such as blood saliva and more), electrically conductive or non-conductive fluids. They may further be optionally equipped or configured for irrigation and or aspiration of liquids, gases or cryogenics, either external, remote or on-board. The electrode component of the electrosurgical instrument of the present invention may be monopolar, bipolar, or multipolar and may optionally include one or more floating electrodes. The electrosurgical instruments of the present invention may be single use (disposable) or multi-use (reusable) and can be compatible with various image-guiding systems, like fluoroscopic, ultrasound and others.
Owner:ELECTROMEDICAL ASSOCS
Handle for interchangeable medical device
A rigid extractor is revealed, a rigid device for use in percutaneous procedures to remove kidney stones directly from the kidneys. The rigid extractor uses a handle fixed to an outer rigid cannula, and an inner cannula to control an extraction device that may be removable from the inner cannula. The extractor is desirably used with a fluoroscope, in which the surgeon maneuvers the extractor with the aid of a view of the operating field provided by the fluoroscope. The surgeon then maneuvers the extractor to grasp the kidney stones and remove from the patient. The extractor may also be used with a nephroscope. The device may be used with a removable extraction device such as a basket, a grasper a pair of jaws, or a pair of scissors.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
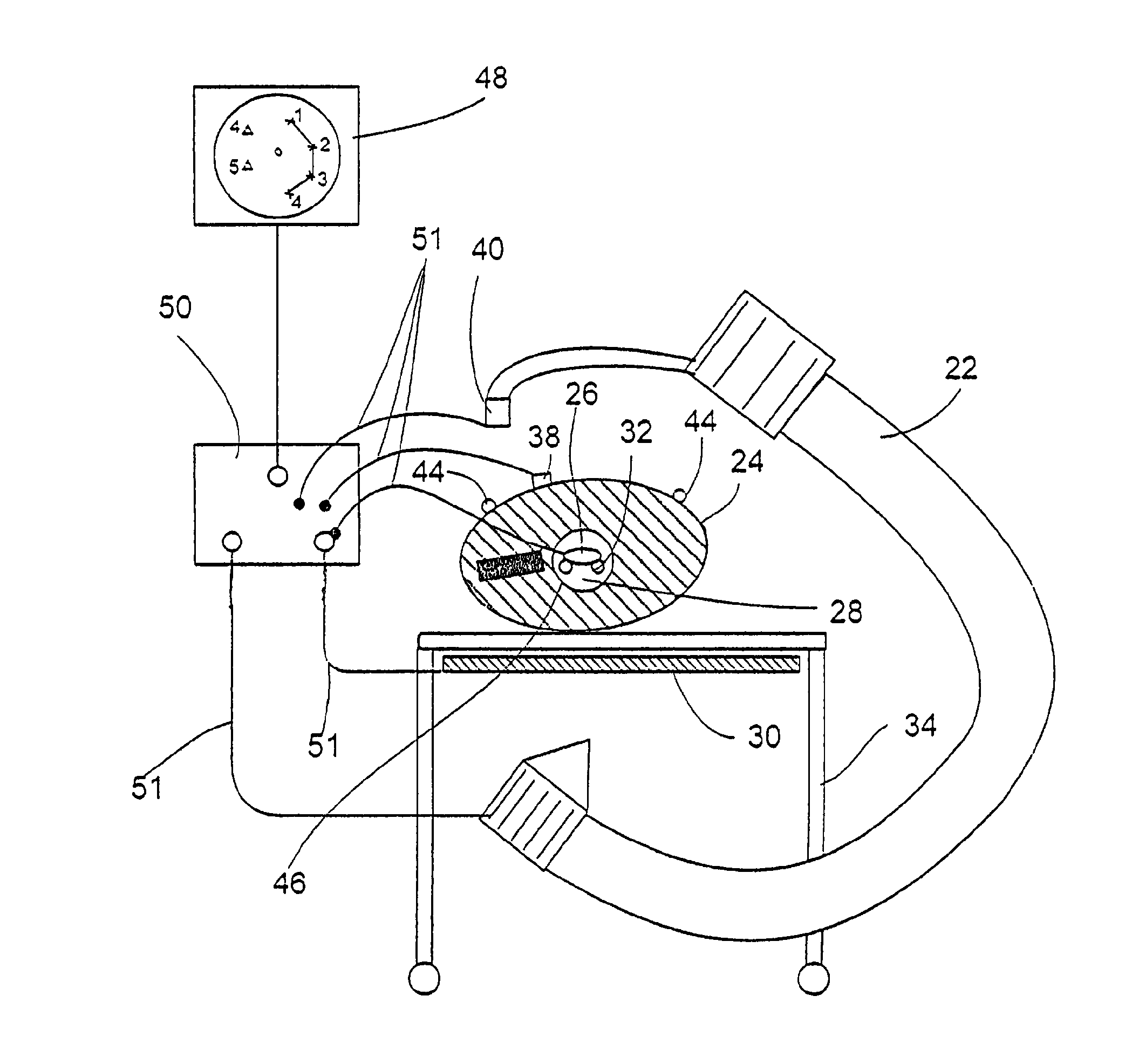
Fluoroscopy image verification
ActiveUS20060050988A1Negative effectMinimally invasiveX-ray/infra-red processesSurgical navigation systemsFluorescenceComputer-aided
A system and method for verifying the registration of a fluoroscopy image, wherein an artificial landmark array is introduced into a radiation path of a fluoroscopy apparatus, the landmark array being trackable by a computer assisted, medical navigation system. A fluoroscopy recording is produced with the aid of the fluoroscopy apparatus, and a spatial position of the artificial landmark array at the time the fluoroscopy recording is produced is detected and stored. The fluoroscopy recording is registered onto previously acquired body image data of the navigation system using marking points mapped on the fluoroscopy recording, wherein the marking points are maps of markings on the radiation source. Verification is based on a correspondence between an image shadow of the artificial landmark array on the fluoroscopy recording and a position of the landmark array at the time the recording was produced.
Owner:BRAINLAB
Fluoroscopy operator protection device
ActiveUS20090232282A1Patient positioning for diagnosticsX-ray tube vessels/containerX-rayRadiation shield
A radiation protection device attaches to the C-arm of a fluoroscope and shields and collimates the X-ray beam between the X-ray source and the patient and between the patient and the image intensifier. One embodiment has a radiation shield of X-ray opaque material that surrounds the C-arm of the fluoroscopy system, the X-ray source and the image intensifier. A padded slot fits around the patient's body. Another embodiment has conical or cylindrical radiation shields that extend between the X-ray source and the patient and between the patient and the image intensifier. The radiation shields have length adjustments and padded ends to fit the device to the patient. The radiation protection device may be motorized to advance and withdraw the radiation shields. A blanket-like radiation shield covers the patient in the area surrounding where the X-ray beam enters the body.
Owner:RADIACTION
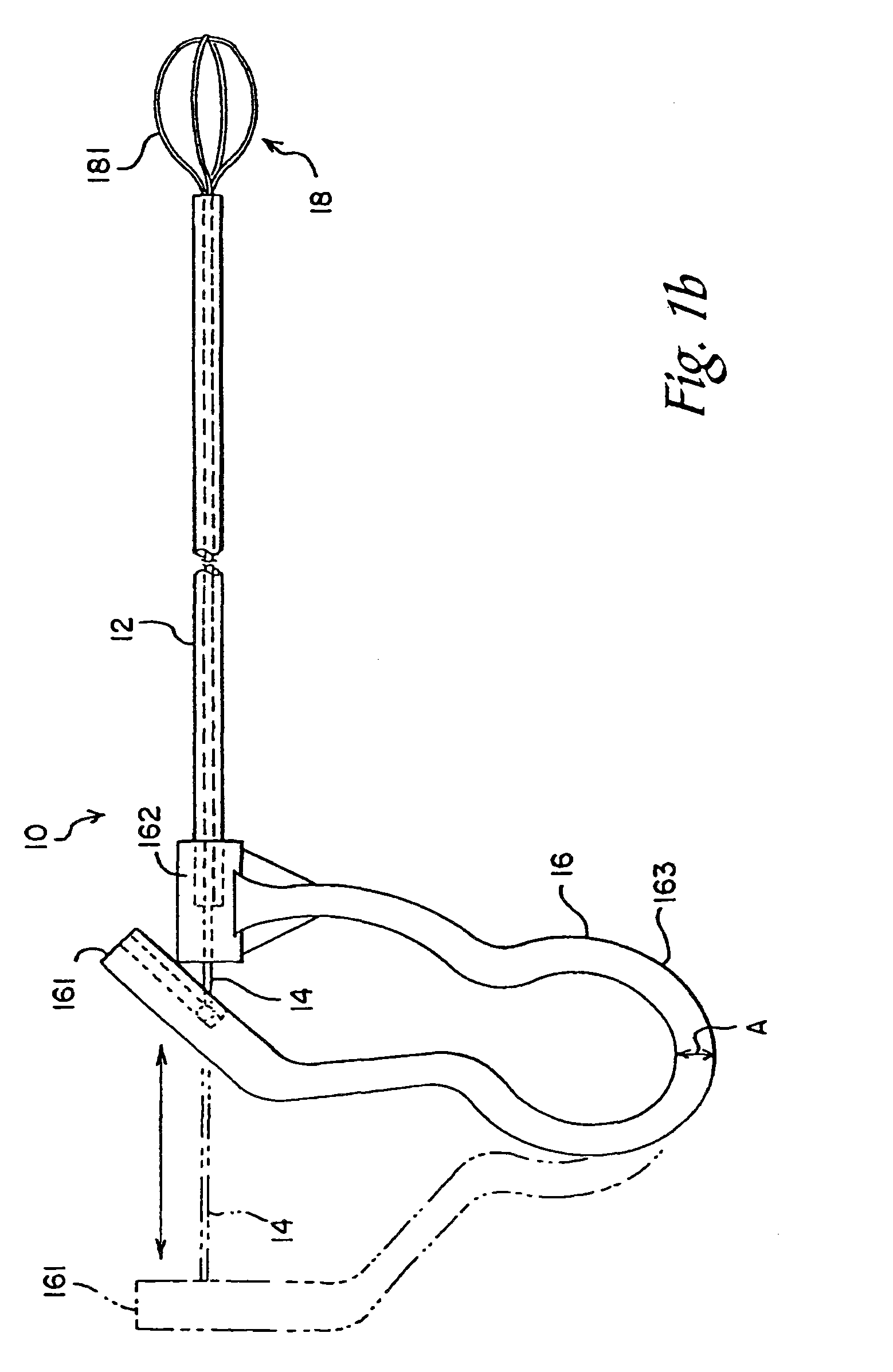
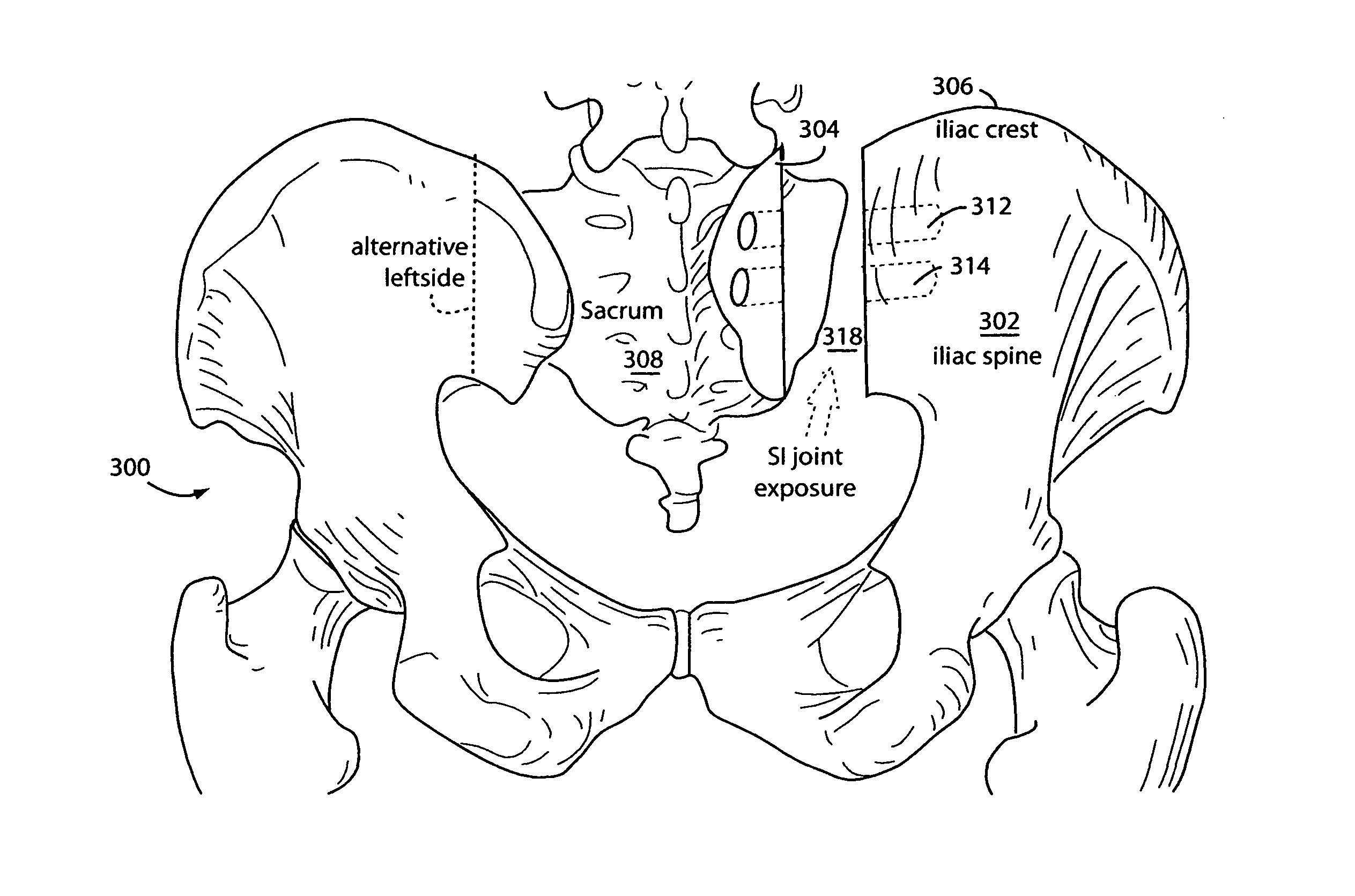
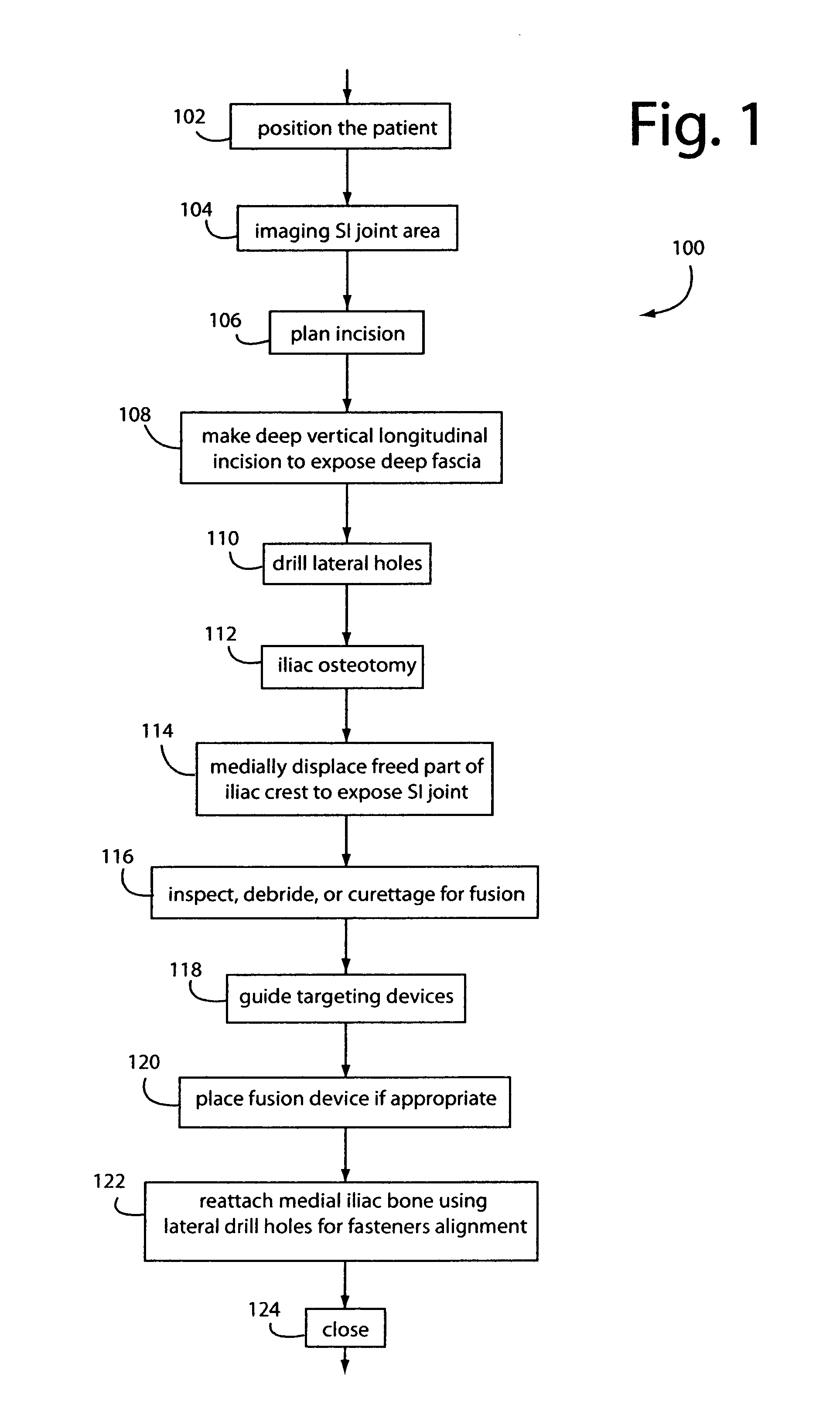
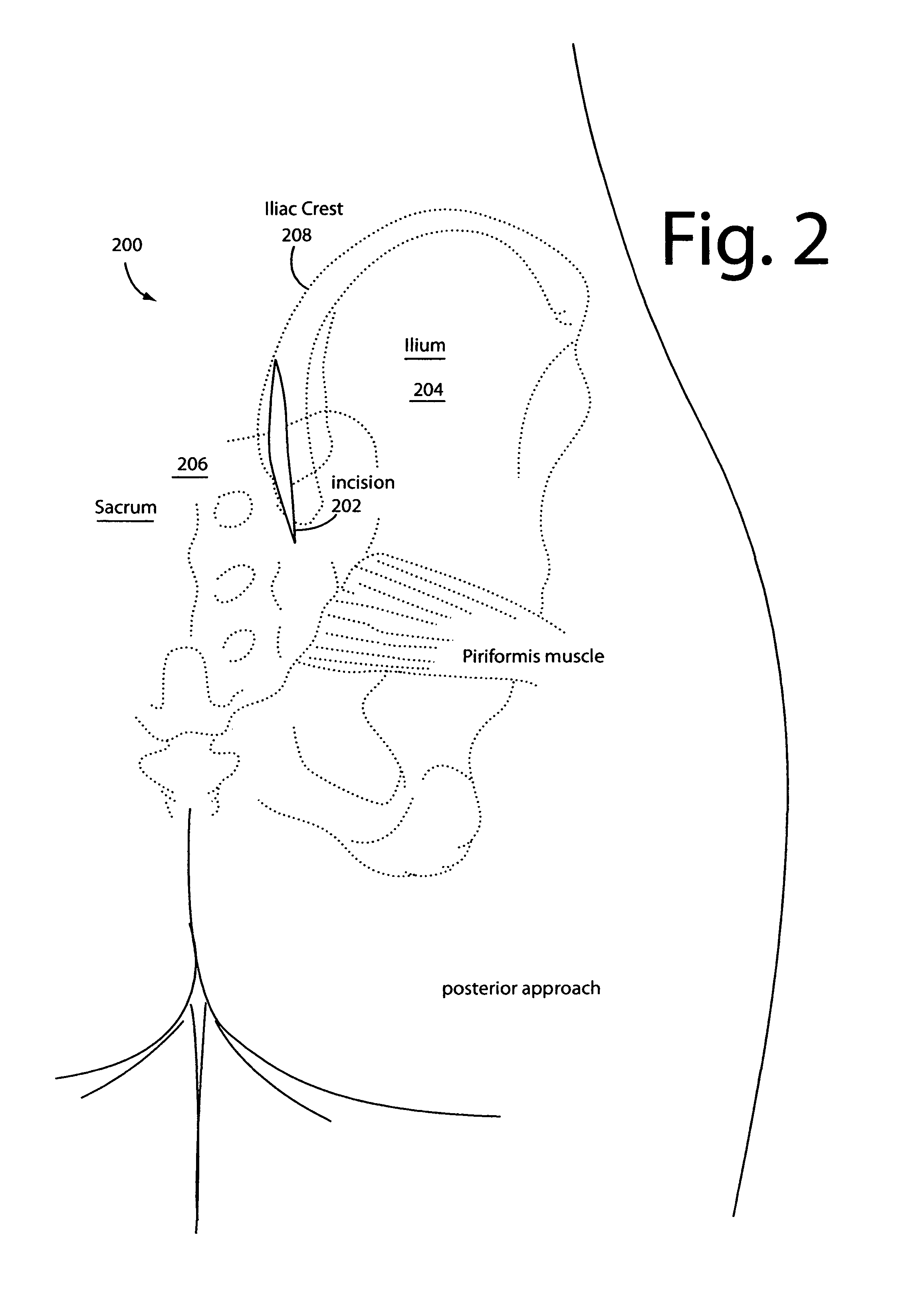
Sacroiliac joint exposure, fusion, and debridement
InactiveUS9452065B1Closure and subsequent healing are facilitatedEasy to placeJoint implantsSpinal implantsPosterior approachSacrum
A surgical method for exposure of the sacroiliac joint using a posterior approach begins with a longitudinal incision over the posterior iliac crest, centered on the posterior iliac spine. Holes which will be used to repair the iliac osteotomy are made obliquely from the medial to lateral to cross the plane of exposure. A cut through the bone is made lateral to the drill holes and centered over the sacroiliac complex with the aid of fluoroscope or radiograph imaging. The medial part of the iliac crest is freed from the back of the sacrum and displaced medially for the sacroiliac joint complex to be inspected, debrided, or curettaged for fusion. The closure and subsequent healing are facilitated by the predrilled oblique holes. These are used to re-attach the medial iliac bone to the remaining lateral ilium.
Owner:HILL ROBERT CHARLES
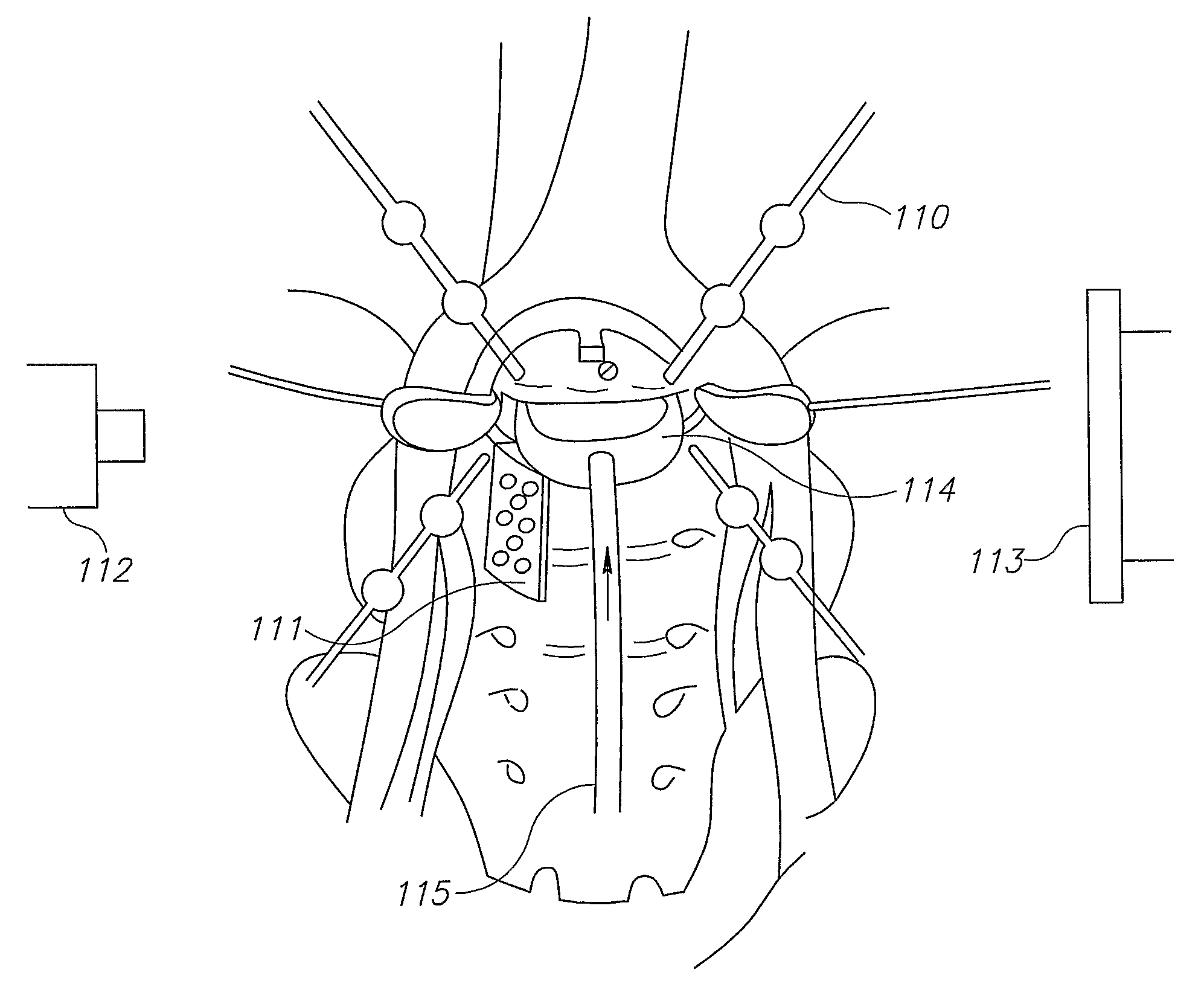
System for positioning of surgical inserts and tools
ActiveUS20100030232A1Improve accuracyPrecise positioningComputer-aided planning/modellingSpinal implantsSurgical operationSurgical site
A tracking and positioning system and method to enable the precise positioning of an object or tool relative to its surgical surroundings, and in accordance with preoperative CT images of the operating site. When used for artificial spinal disc positioning, the system comprises a computing system incorporating in memory the preoperative CT data showing the two vertebrae and the predetermined disc position between them; a 3-D target having radio-opaque markers for attaching to one of the vertebrae to define the position of the vertebra in an intra-operative fluoroscope image of the spine; a tool for intra-operative insertion of the artificial disc, and a registration system for relating the intra-operative fluoroscope image to the preoperative CT data, such that the predetermined disc position is displayed in the fluoroscope image of the subject, thereby enabling the surgeon to place the artificial disc accurately in its intended position.
Owner:MAZOR ROBOTICS
Methods and systems for performing medical procedures with reference to determining estimated dispositions for actual dispositions of projective images to transform projective images into an image volume
InactiveUS8565858B2Minimize the differenceCharacter and pattern recognitionCatheterCatheterElectromagnetic radiation
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
System for positioning of surgical inserts and tools
ActiveUS8394144B2Improve accuracyPrecise positioningComputer-aided planning/modellingSpinal implantsSurgical operationSurgical site
A tracking and positioning system and method to enable the precise positioning of an object or tool relative to its surgical surroundings, and in accordance with preoperative CT images of the operating site. When used for artificial spinal disc positioning, the system comprises a computing system incorporating in memory the preoperative CT data showing the two vertebrae and the predetermined disc position between them; a 3-D target having radio-opaque markers for attaching to one of the vertebrae to define the position of the vertebra in an intra-operative fluoroscope image of the spine; a tool for intra-operative insertion of the artificial disc, and a registration system for relating the intra-operative fluoroscope image to the preoperative CT data, such that the predetermined disc position is displayed in the fluoroscope image of the subject, thereby enabling the surgeon to place the artificial disc accurately in its intended position.
Owner:MAZOR ROBOTICS
Robotic guided endoscope
ActiveUS20130303883A1Reduce traumaLevel accuracyEndoscopesComputerised tomographsSurgical robotSurgery scheduling
Systems and methods for performing robotic endoscopic surgical procedures, according to a surgical plan prepared on a preoperative set of three dimensional images. The system comprises a surgical robot whose coordinate system is related to that of fluoroscope images generated intraoperatively, by using a three dimensional target having radio-opaque markers, attached in a predetermined manner to the robot or to another element to which the robot is attached, such as the spinal bridge or an attachment clamp. The robot is mounted directly or indirectly on a bone of the patient, thereby nullifying movement of the bone, or a bone tracking system may be utilized. The coordinate system of the intraoperative fluoroscope images may be related to the preoperative images, by comparing anatomical features between both image sets. This system and method enables the endoscope to be directed by the robot along the exact planned path, as determined by the surgeon.
Owner:MAZOR ROBOTICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com