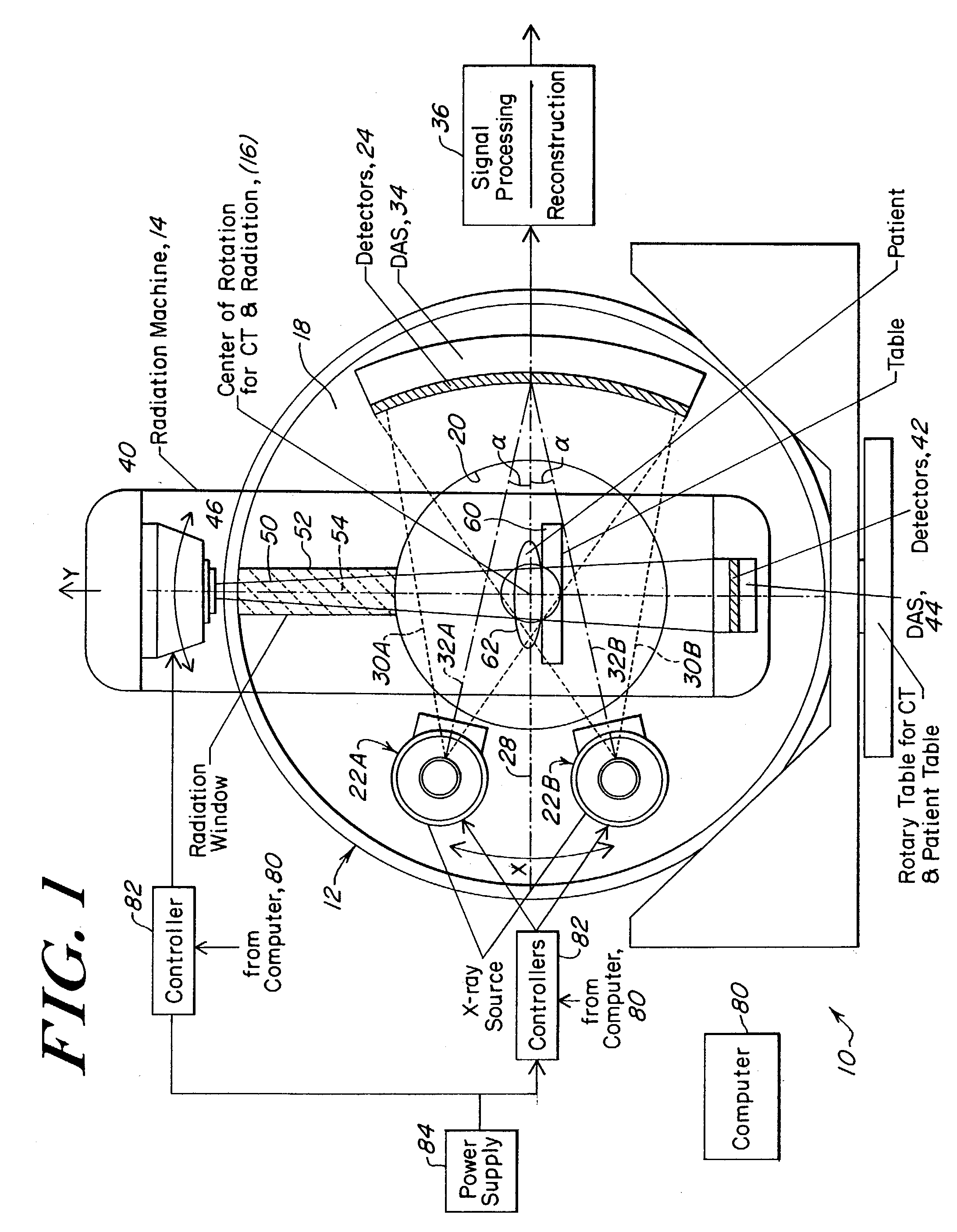
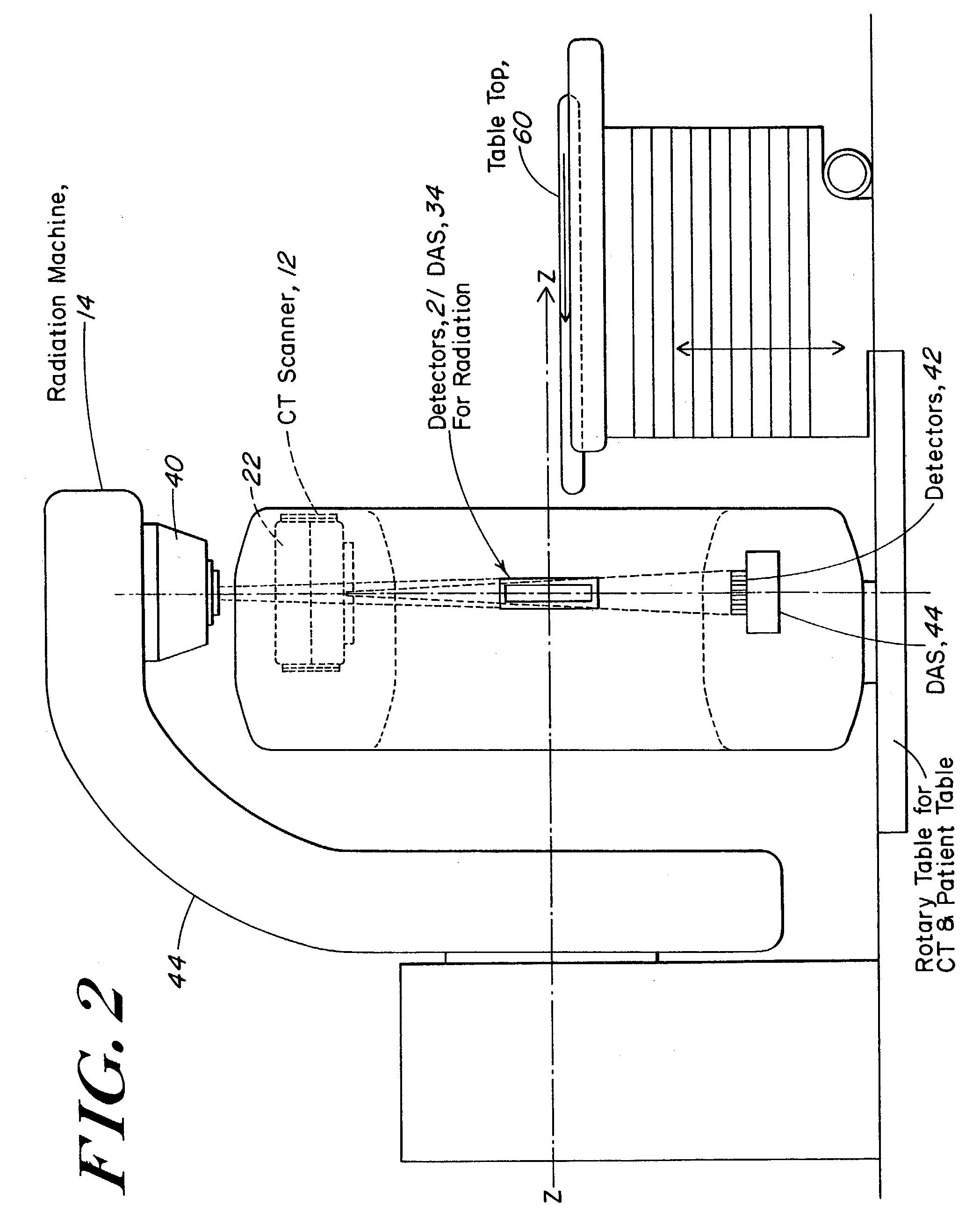
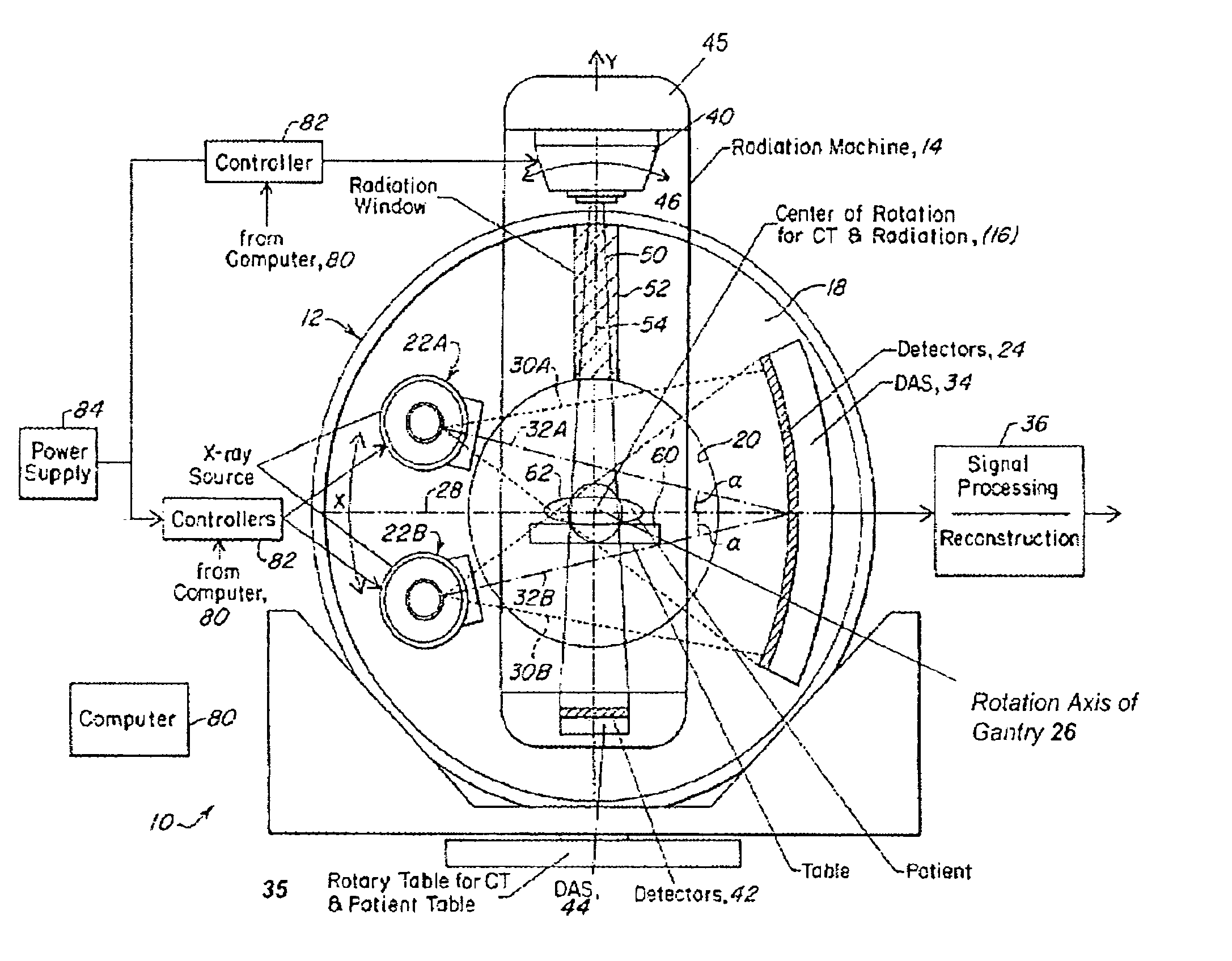
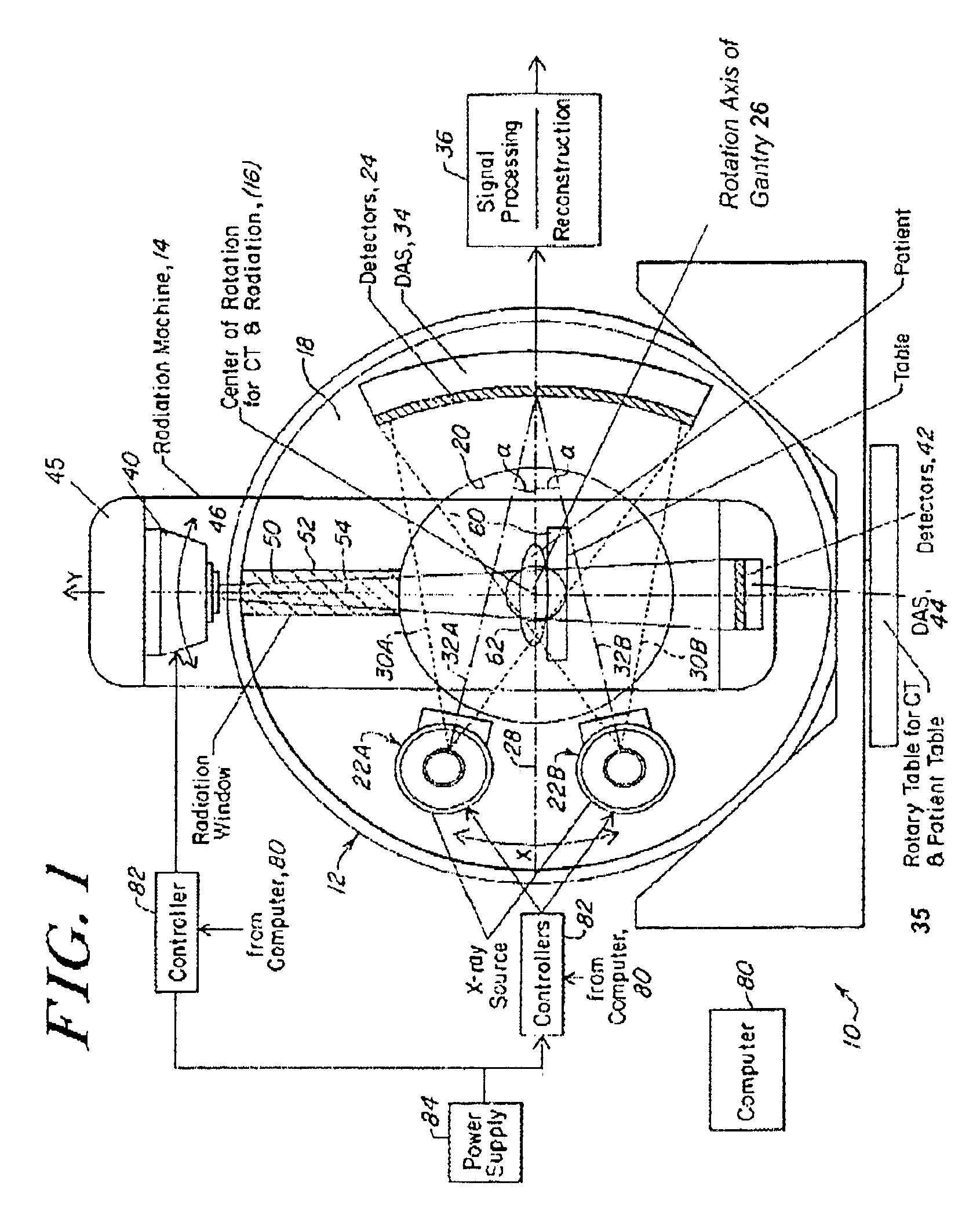
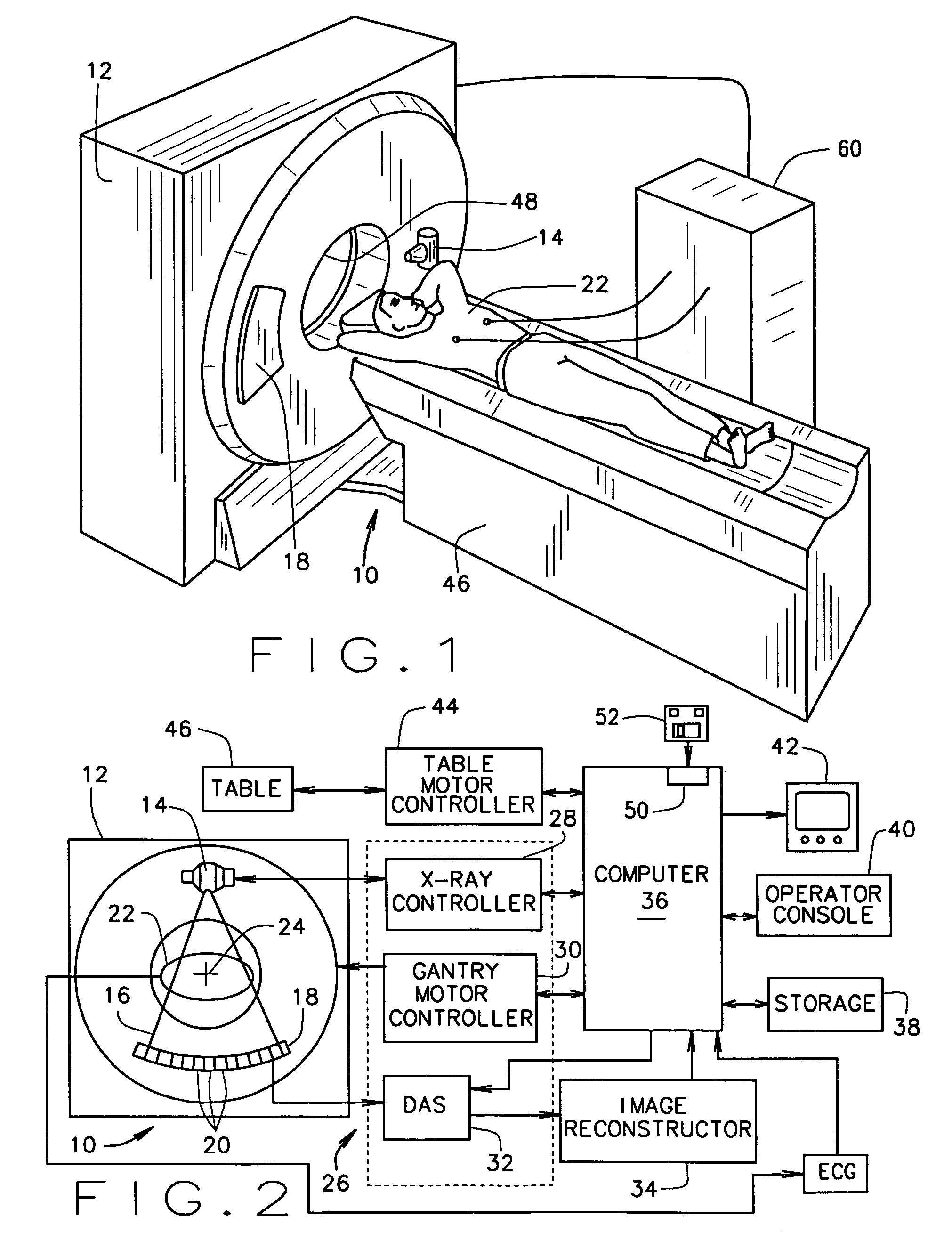
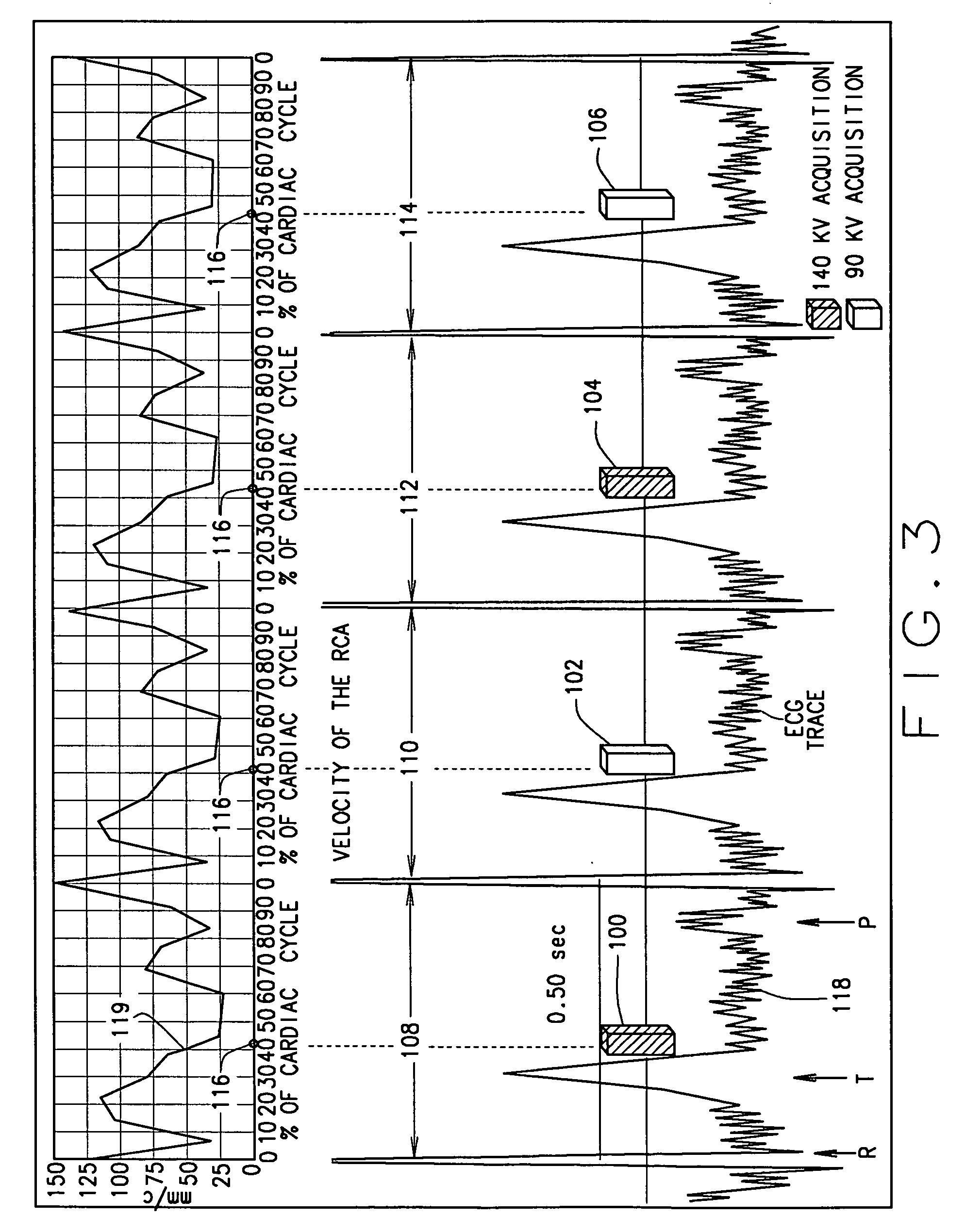
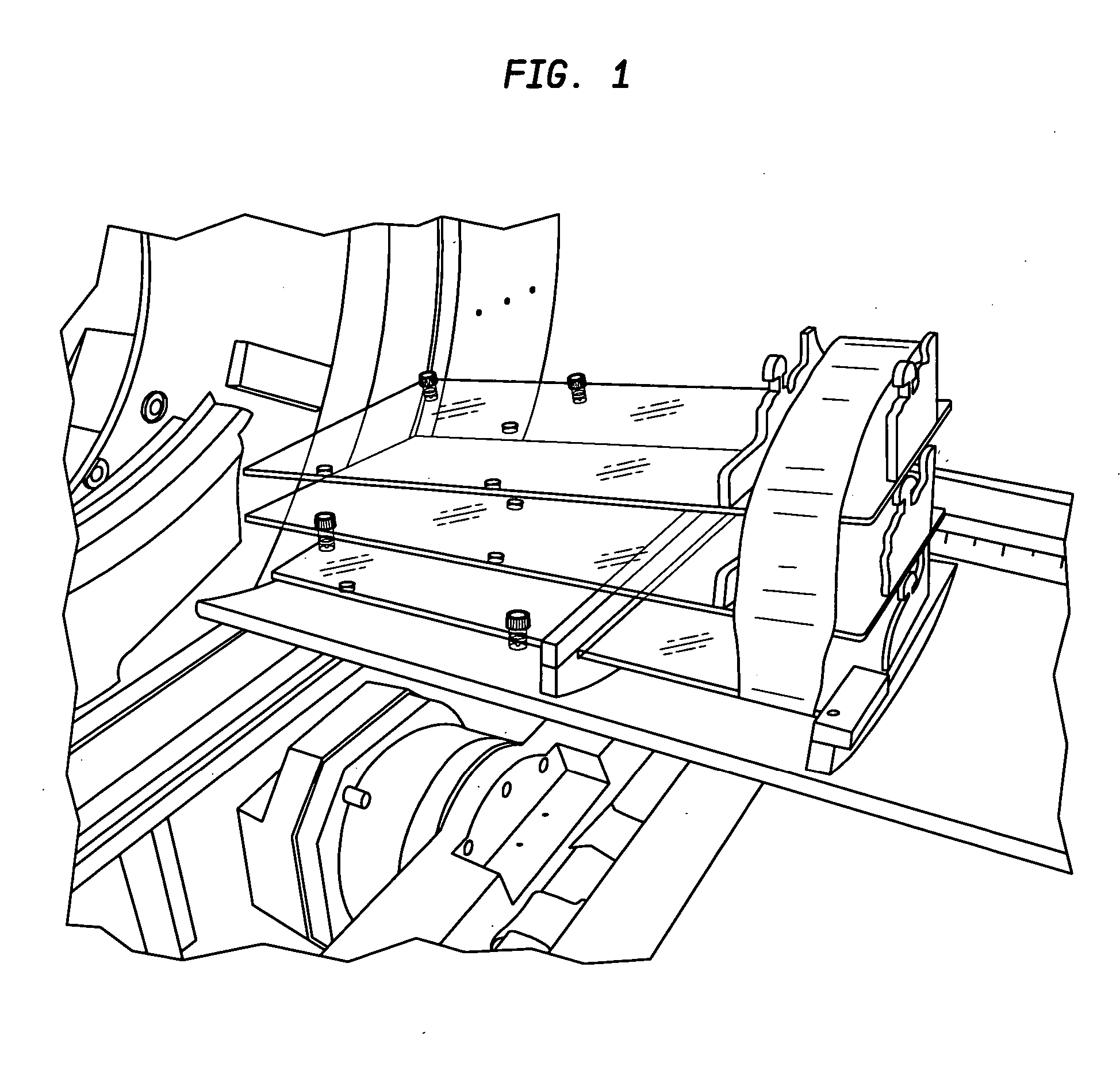
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1062 results about "Ct imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
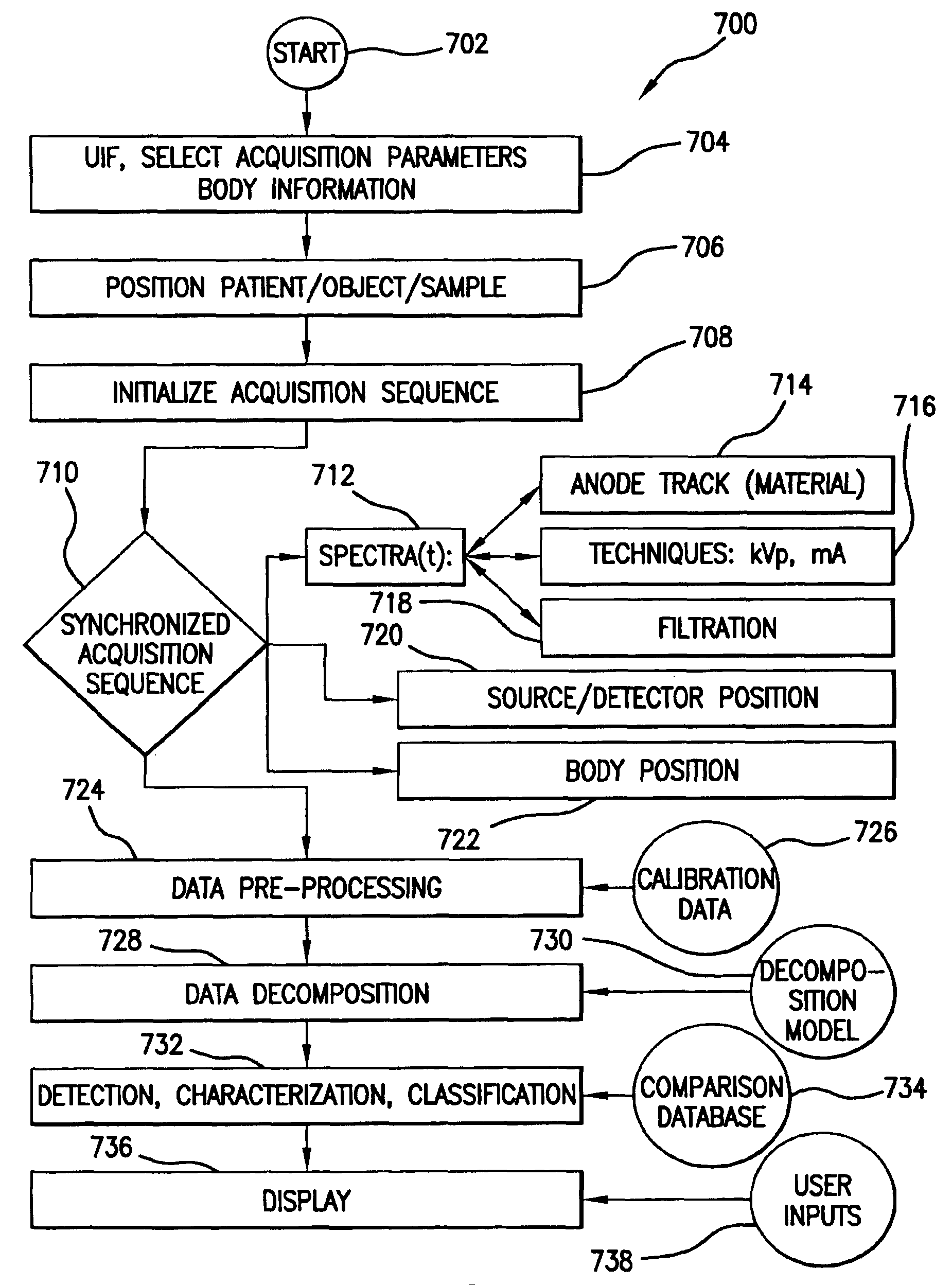
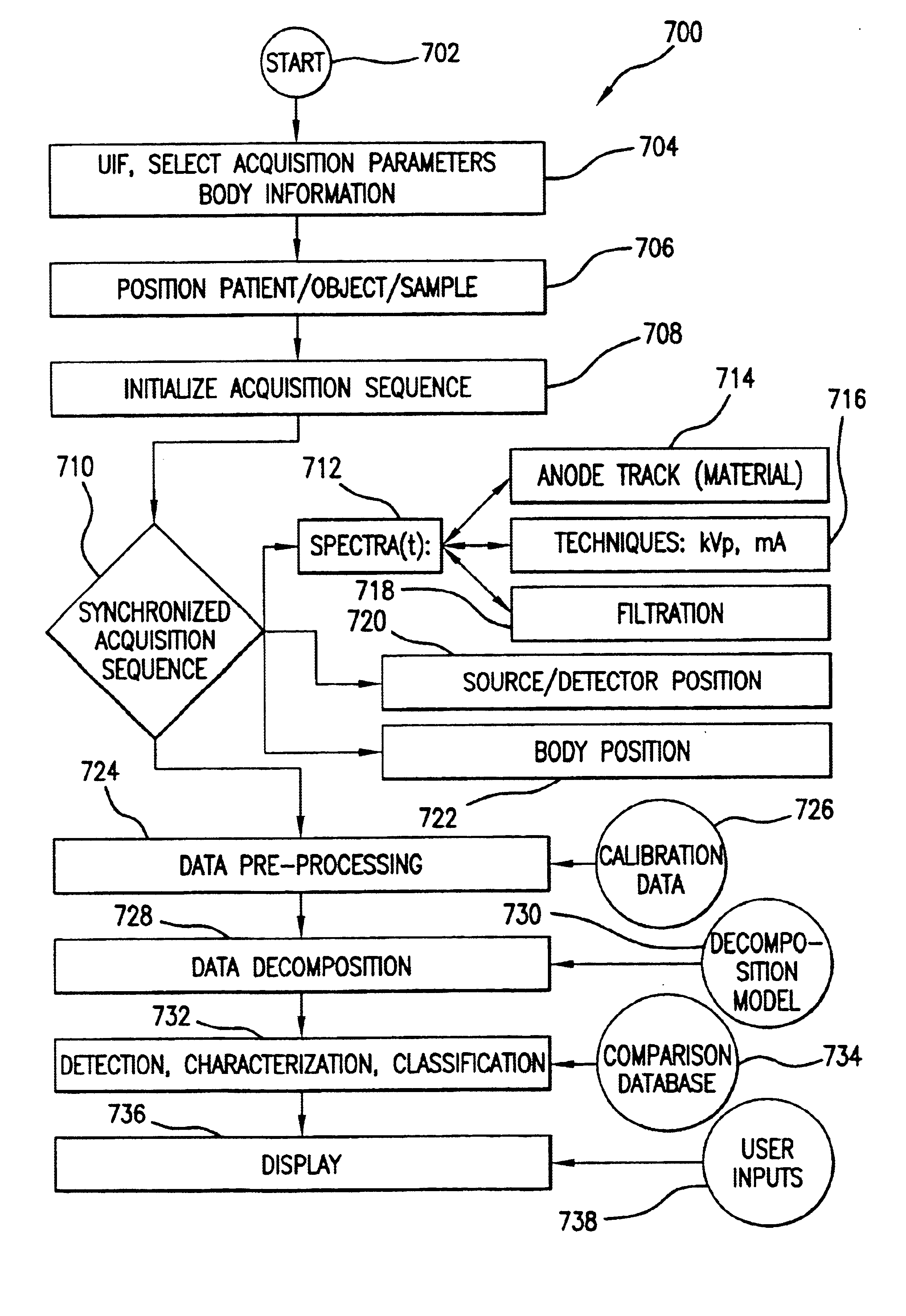
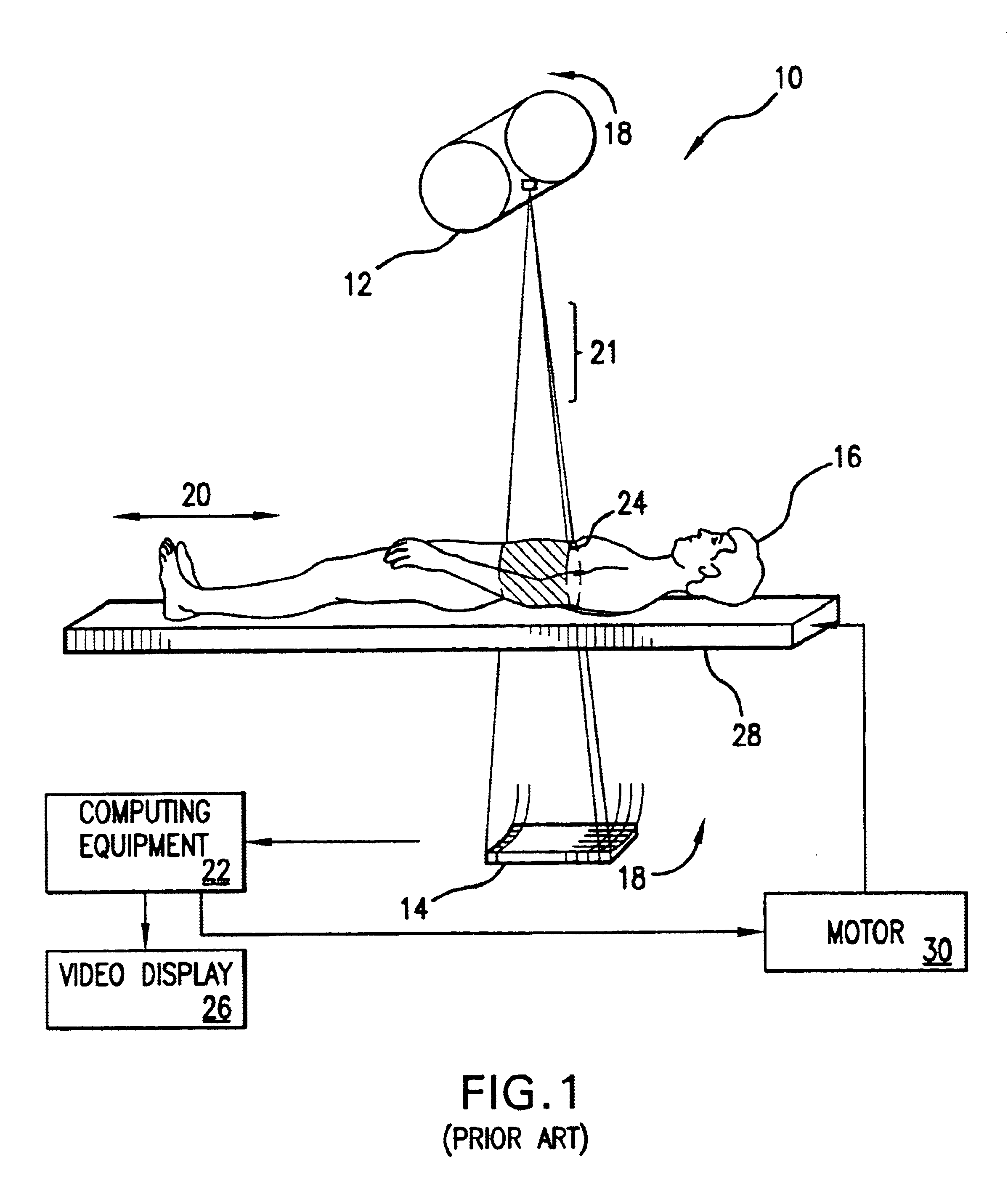
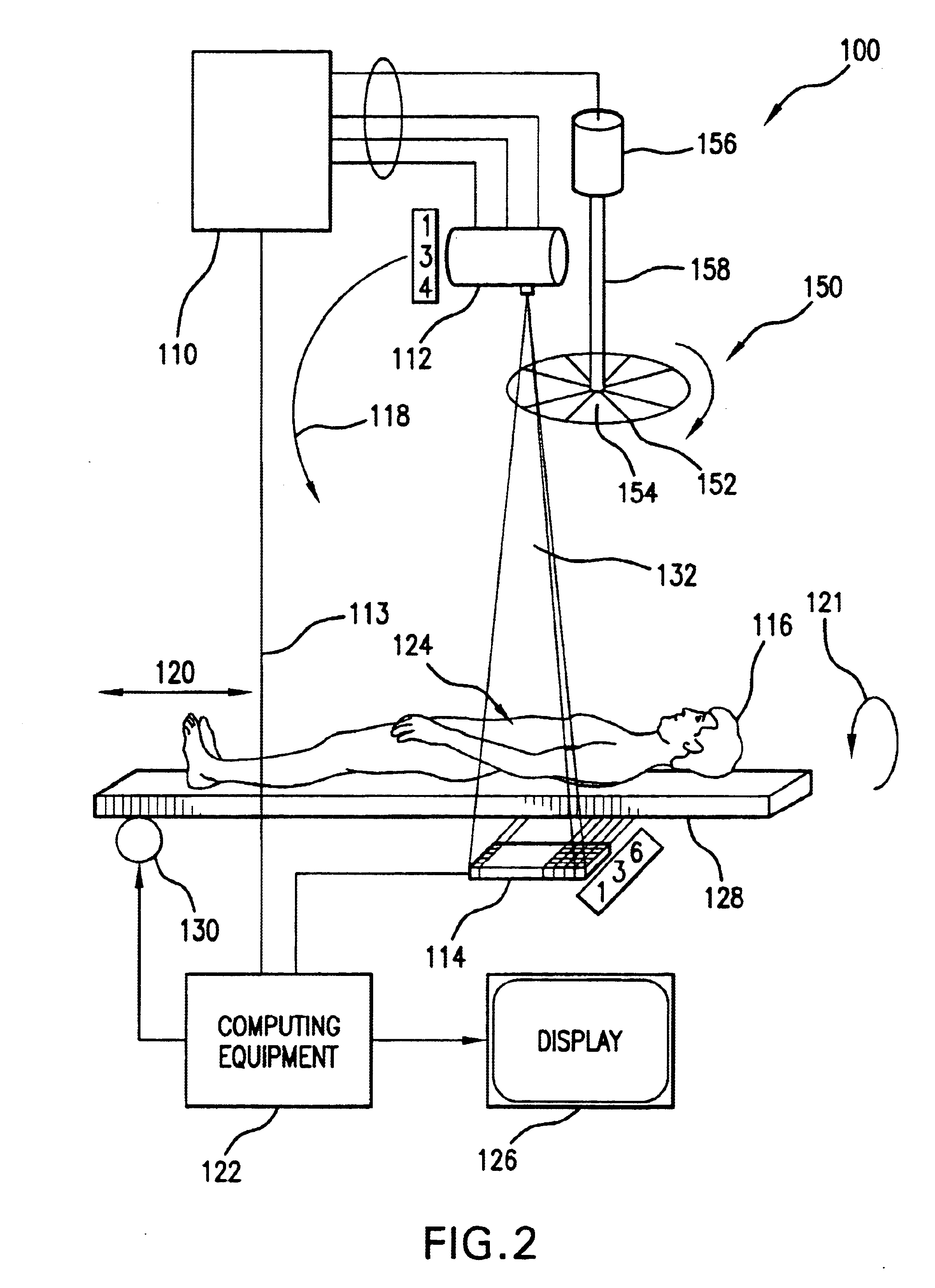
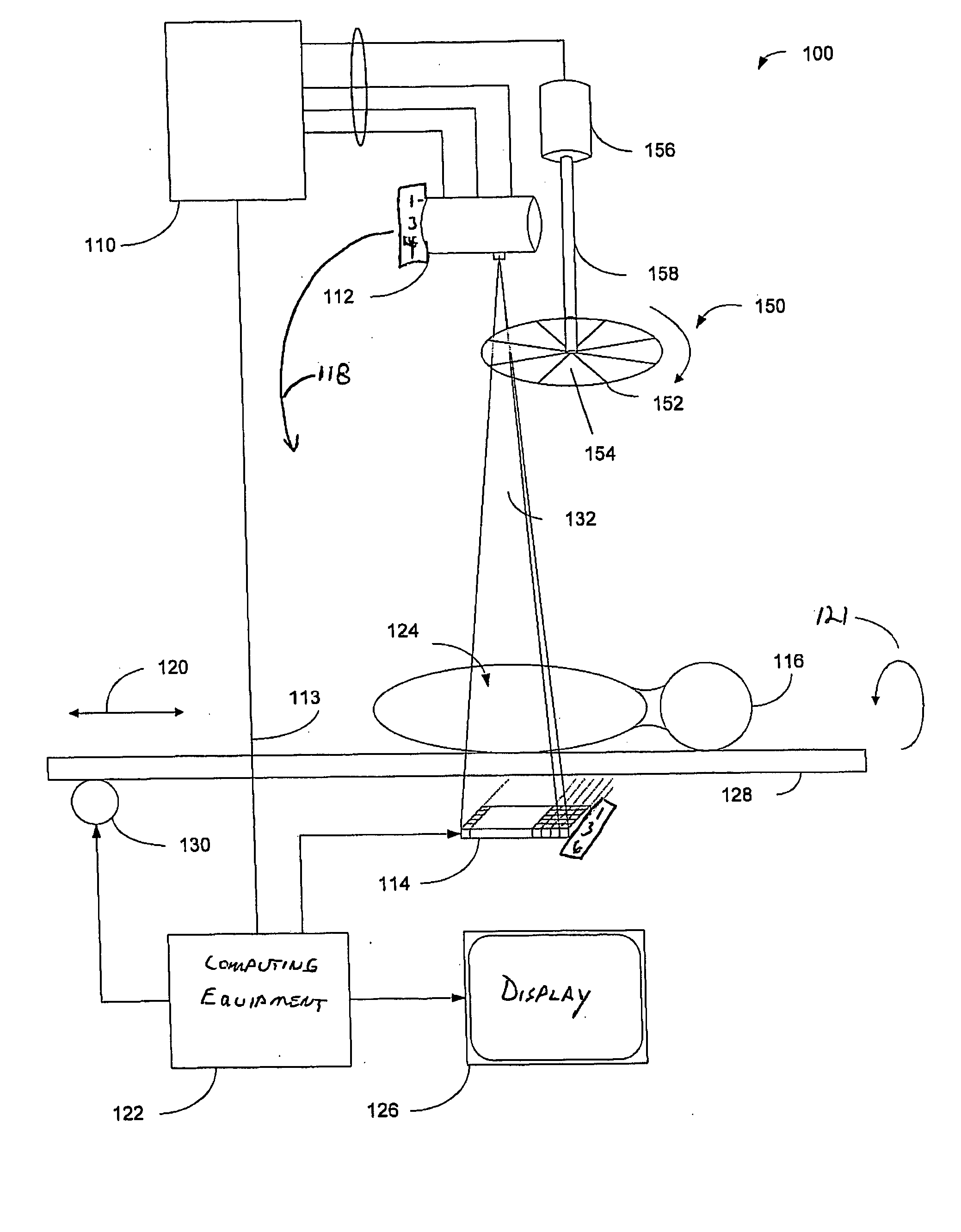
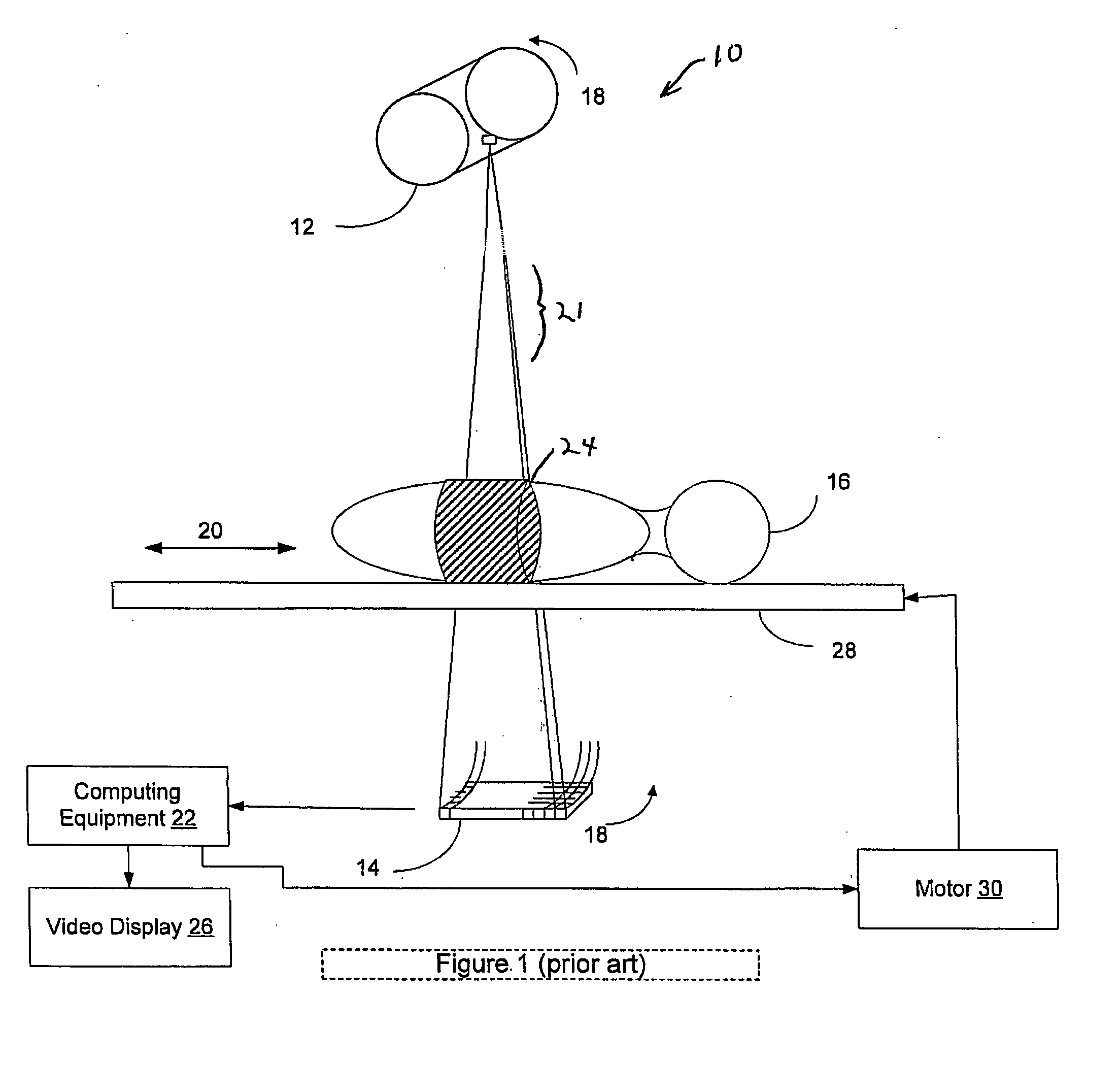
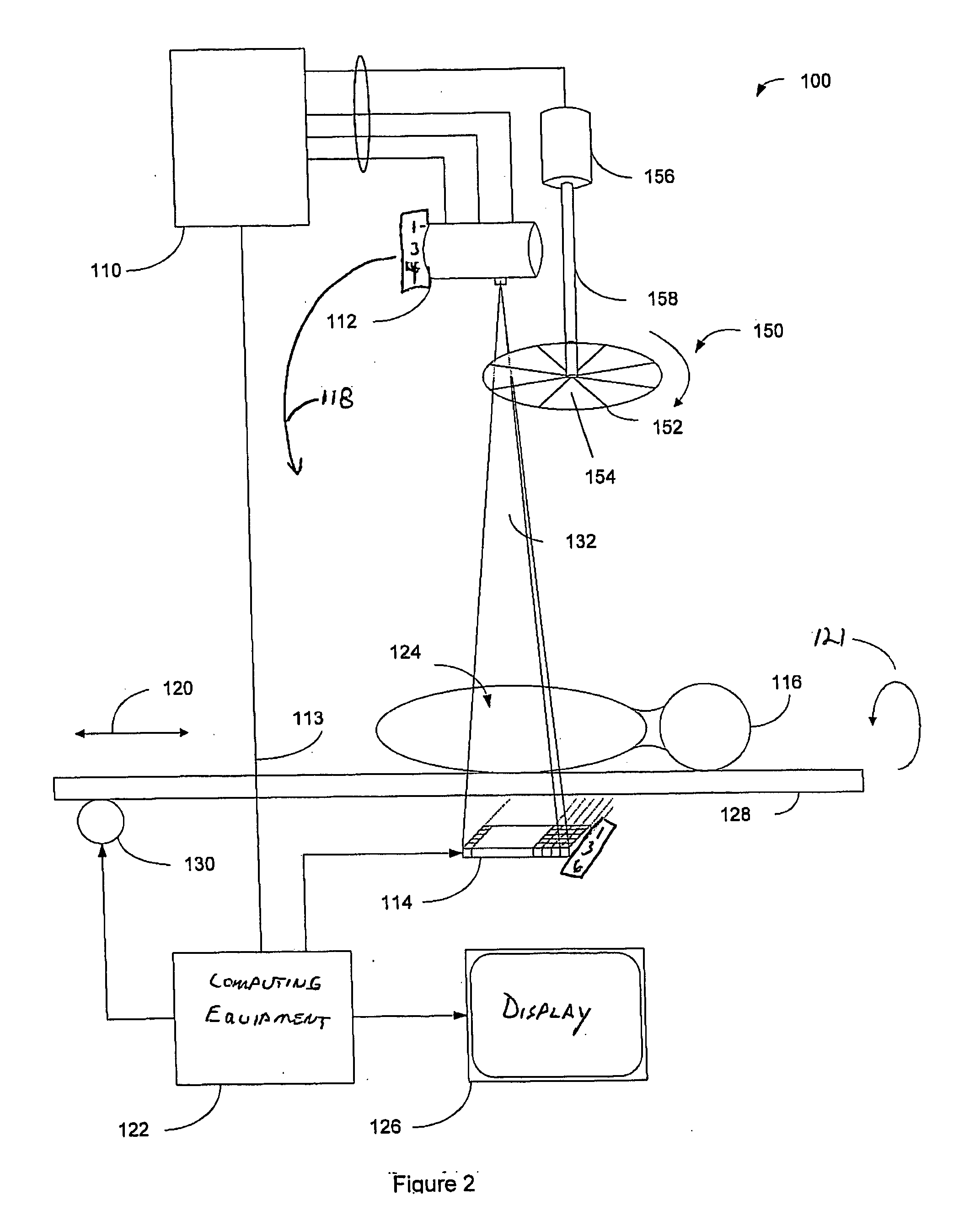
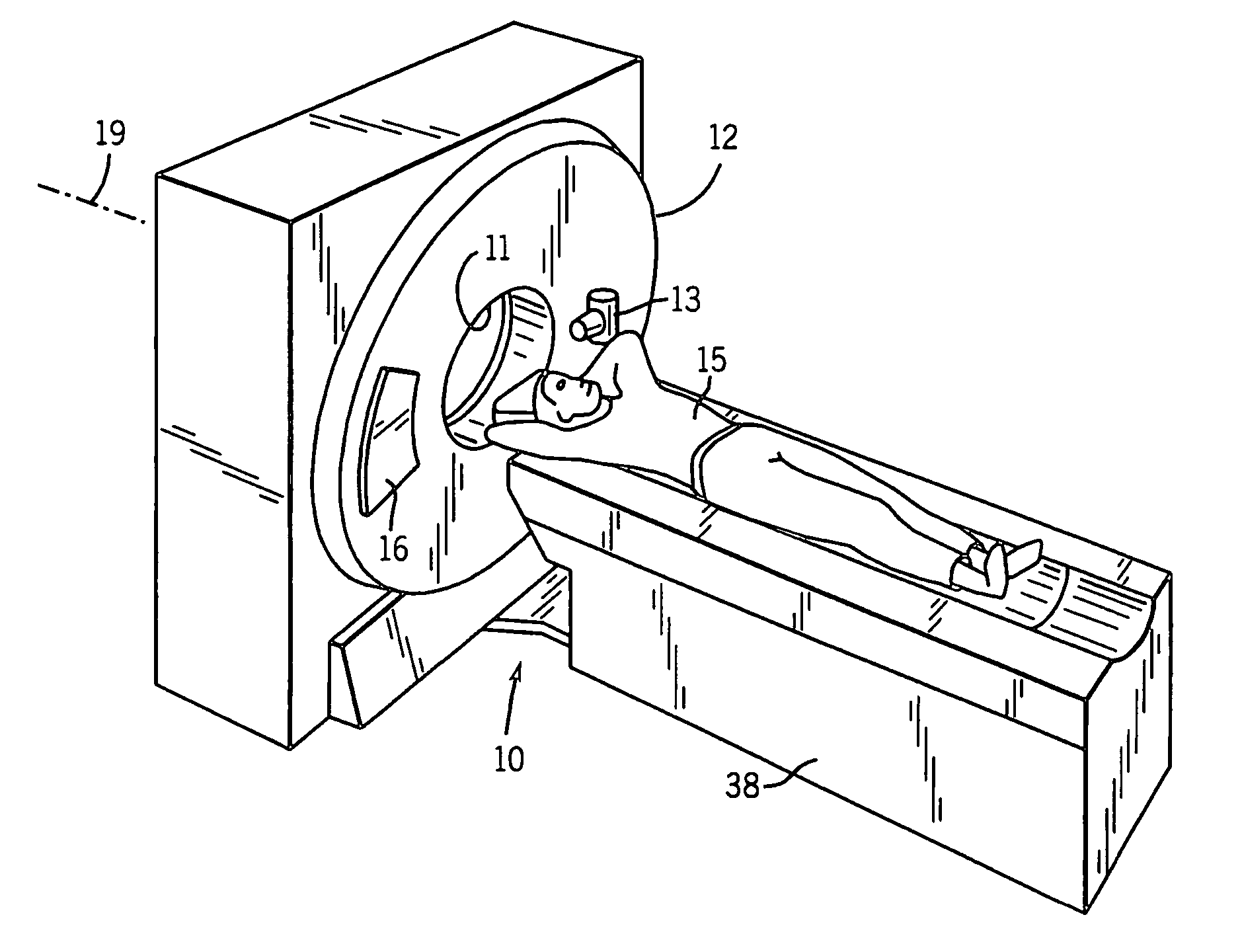
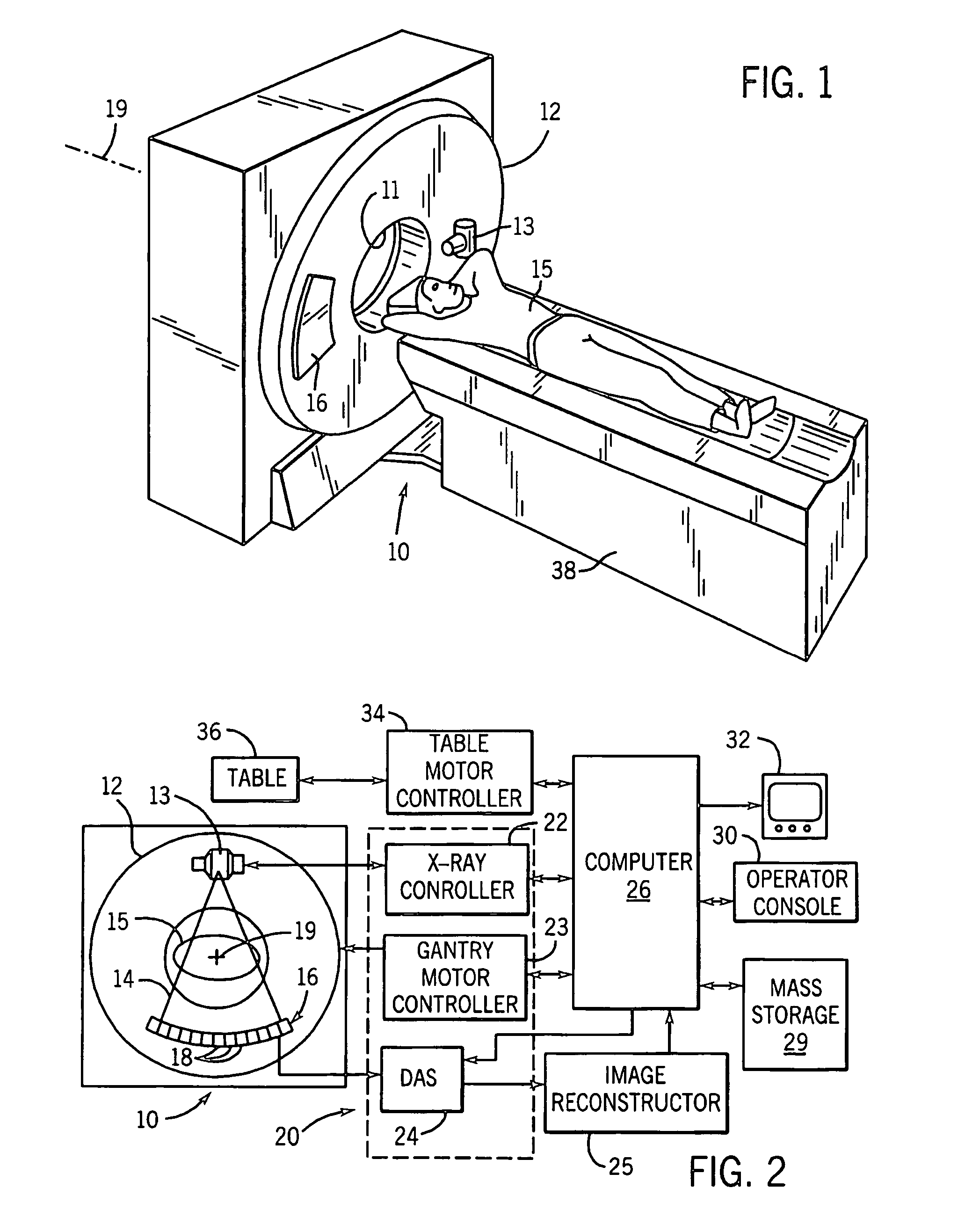
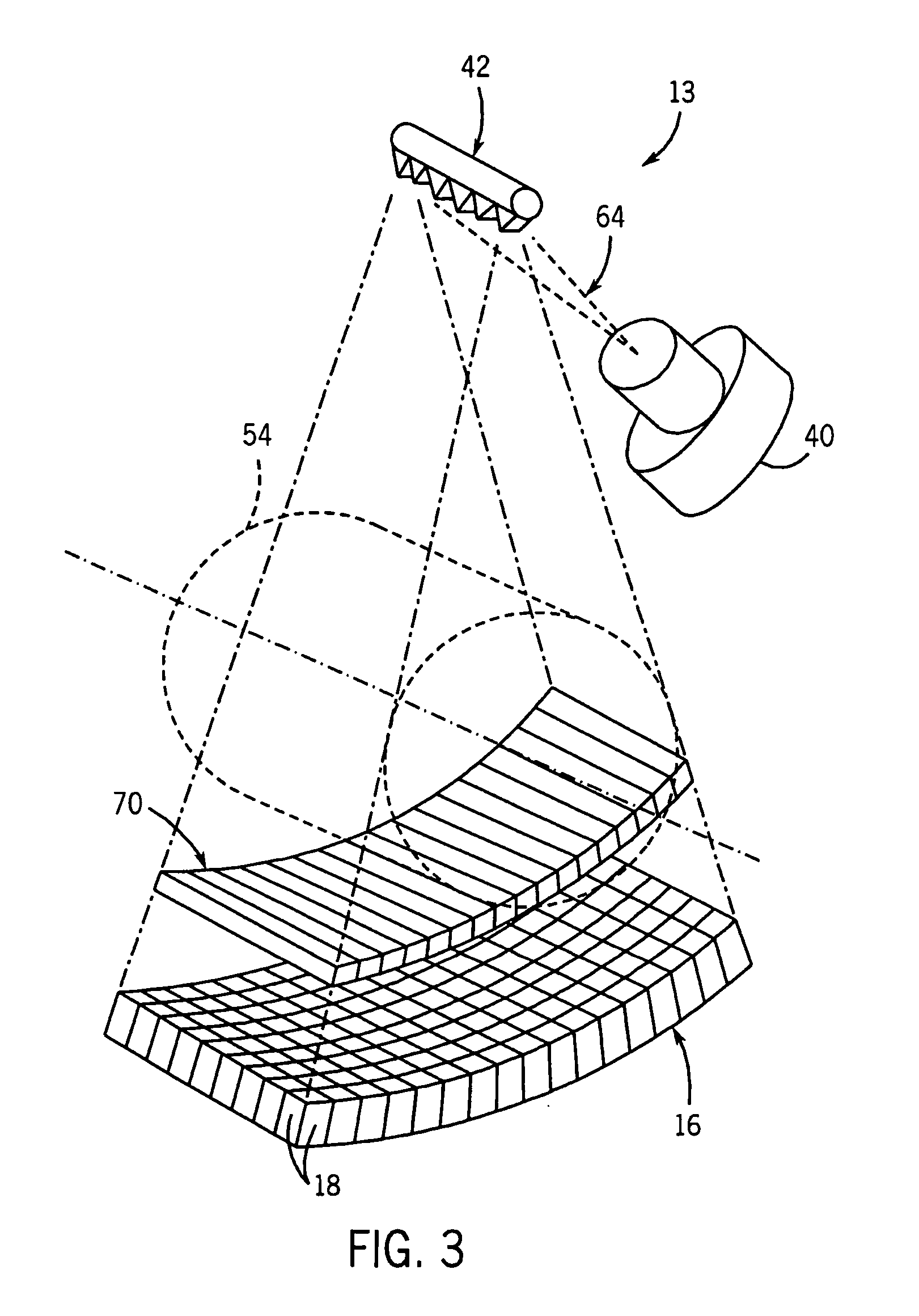
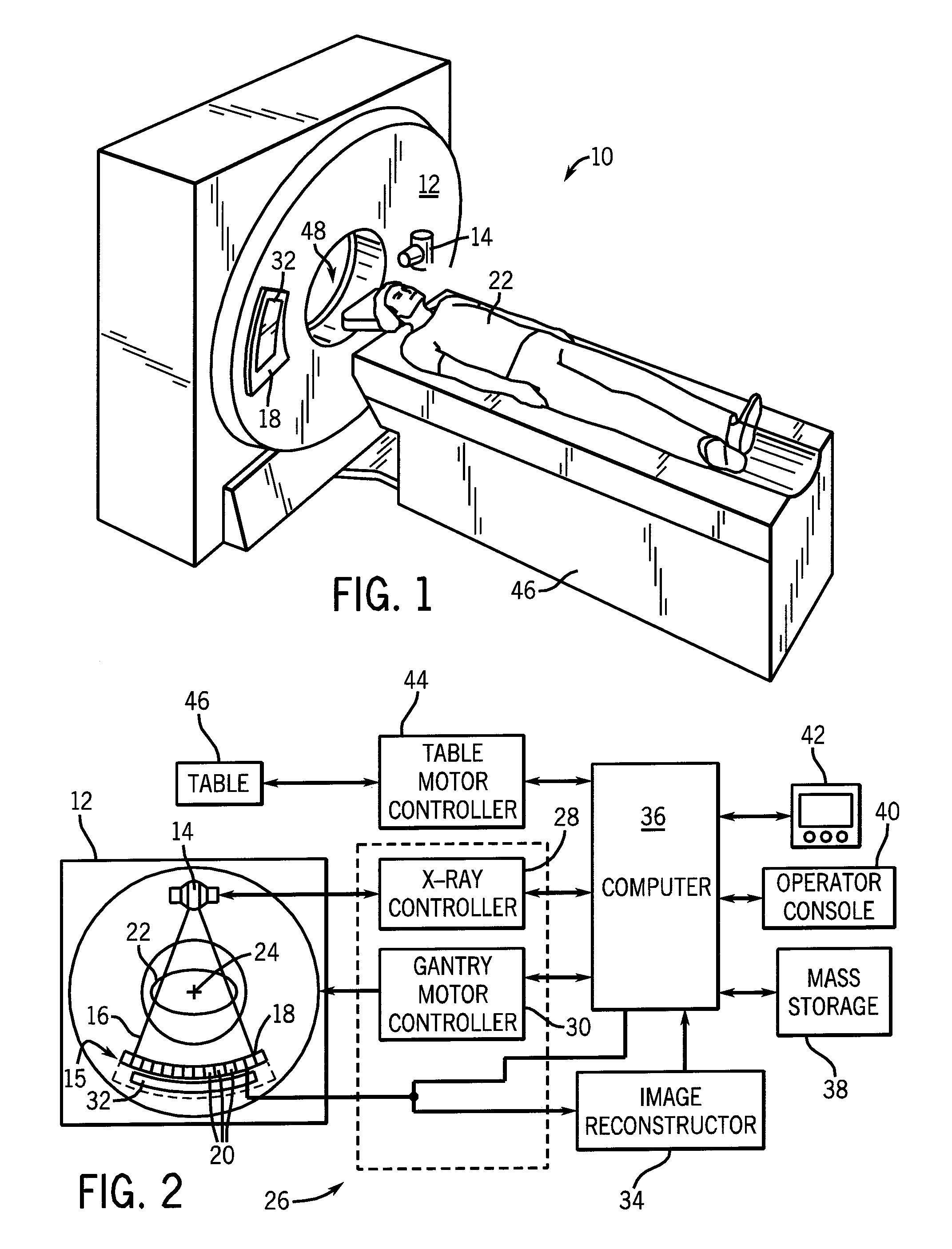
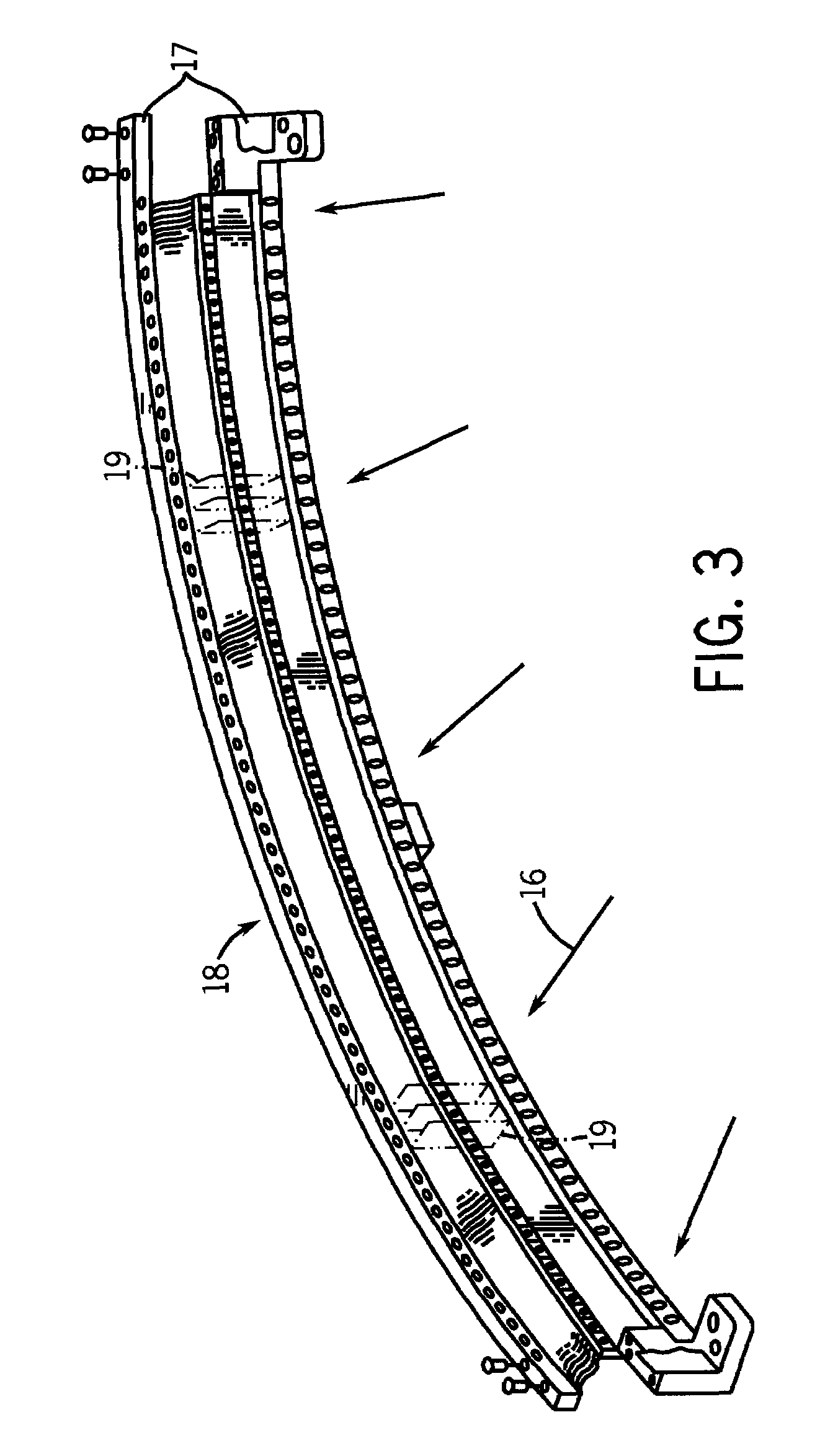
Dynamic multi-spectral X-ray projection imaging
InactiveUS6950492B2Good curative effectPromote resultsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingFiltrationX-ray
A multispectral X-ray imaging system uses a wideband source and filtration assembly to select for M sets of spectral data. Spectral characteristics may be dynamically adjusted in synchrony with scan excursions where an X-ray source, detector array, or body may be moved relative to one another in acquiring T sets of measurement data. The system may be used in projection imaging and / or CT imaging. Processed image data, such as a CT reconstructed image, may be decomposed onto basis functions for analytical processing of multispectral image data to facilitate computer assisted diagnostics. The system may perform this diagnostic function in medical applications and / or security applications.
Owner:FOREVISION IMAGING TECH LLC
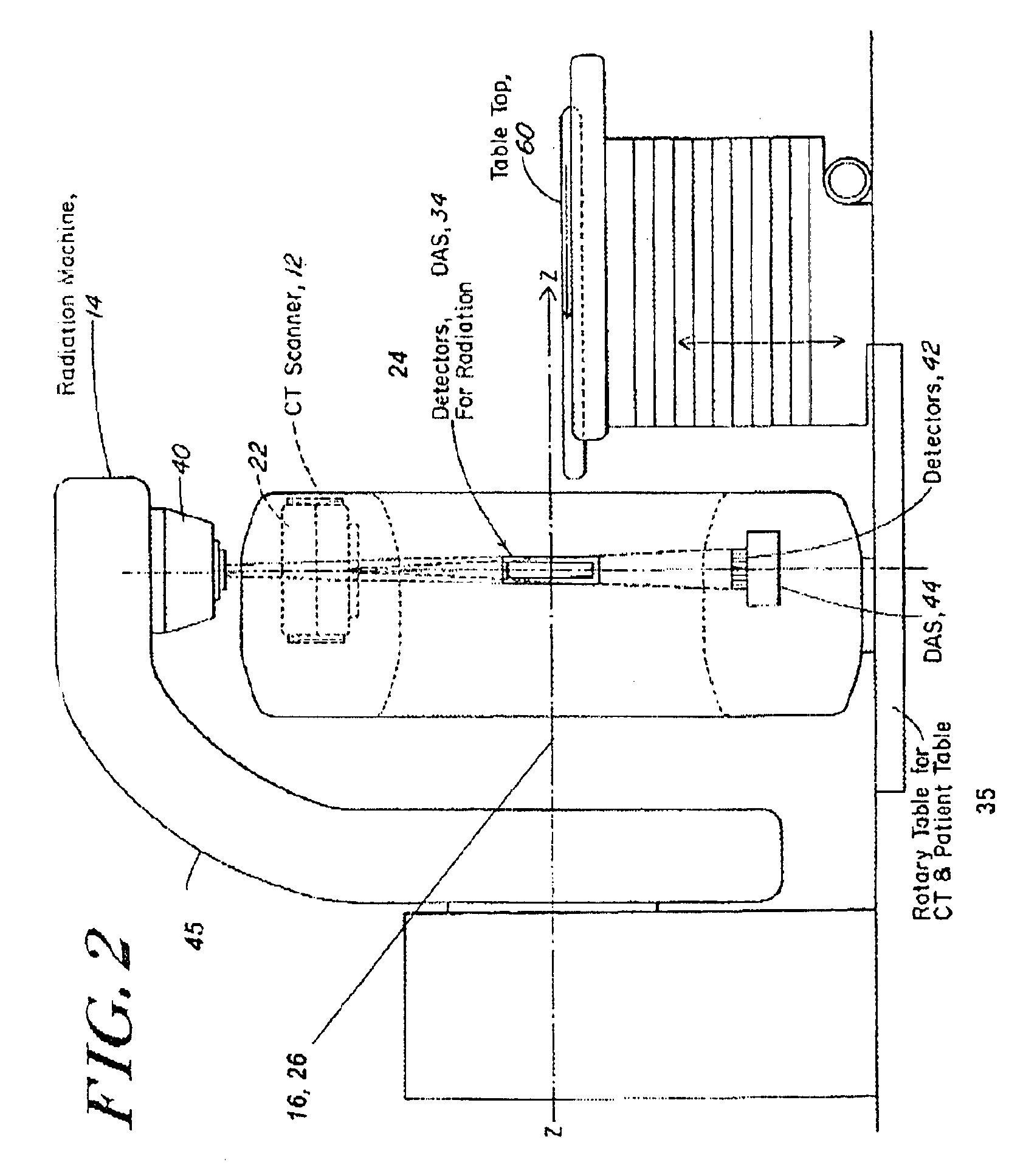
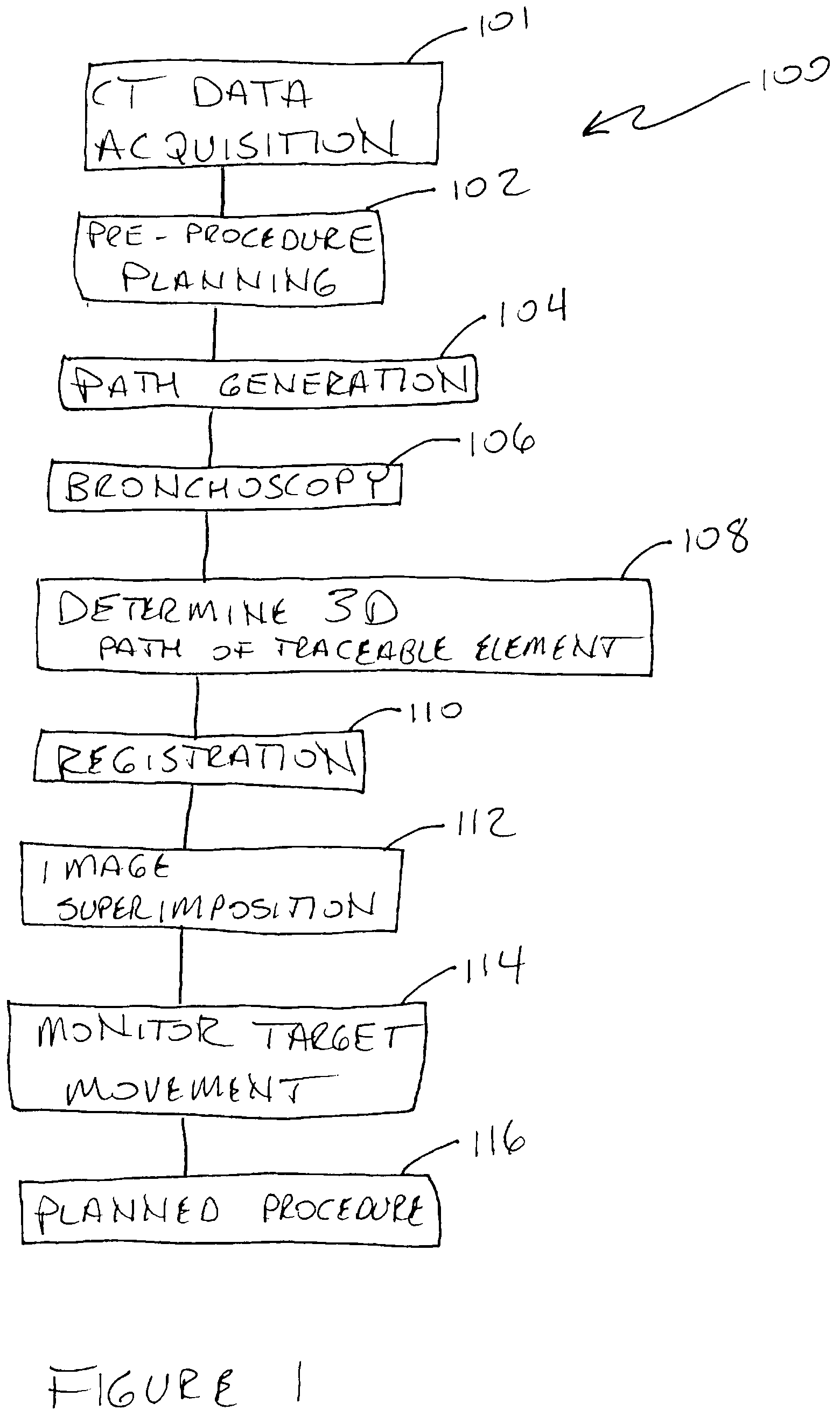
Combined radiation therapy and imaging system and method
InactiveUS20030048868A1X-ray/infra-red processesMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationX-rayRadiation therapy
A method of and system for locating a targeted region in a patient uses a CT imaging subsystem and a radiotherapy subsystem arranged so the targeted region can be imaged with the imaging system and treated with a beam of therapeutic X-ray radiation using a radiotherapy subsystem. The beam of therapeutic X-rays is in a plane that is substantially fixed relative to, and preferably coplanar with, a slice plane of the CT imaging subsystem so that the targeted region can be imaged during a planning phase, and imaged and exposed to the therapeutic X-rays during the treatment phase without the necessity of moving the patient.
Owner:ANLOGIC CORP (US)
Combined radiation therapy and imaging system and method
InactiveUS6914959B2X-ray/infra-red processesMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiologyNuclear medicine
A method of and system for locating a targeted region in a patient uses a CT imaging subsystem and a radiotherapy subsystem arranged so the targeted region can be imaged with the imaging system and treated with a beam of therapeutic X-ray radiation using a radiotherapy subsystem. The beam of therapeutic X-rays is in a plane that is substantially fixed relative to, and preferably coplanar with, a slice plane of the CT imaging subsystem so that the targeted region can be imaged during a planning phase, and imaged and exposed to the therapeutic X-rays during the treatment phase without the necessity of moving the patient.
Owner:ANLOGIC CORP (US)
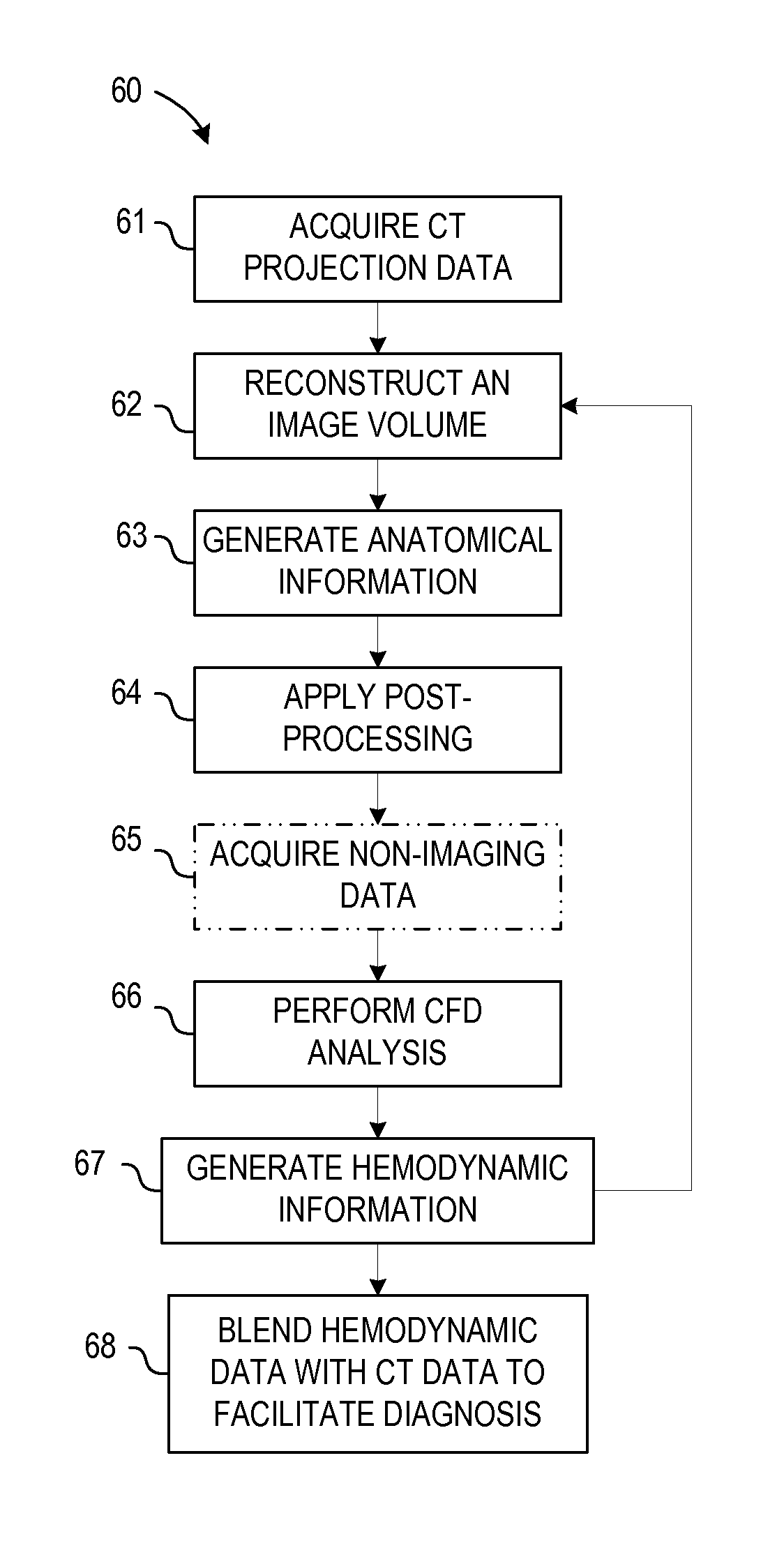
System and method for estimating vascular flow using ct imaging
A system and method for estimating vascular flow using CT imaging include a computer readable storage medium having stored thereon a computer program comprising instructions, which, when executed by a computer, cause the computer to acquire a first set of data comprising anatomical information of an imaging subject, the anatomical information comprises information of at least one vessel. The instructions further cause the computer to process the anatomical information to generate an image volume comprising the at least one vessel, generate hemodynamic information based on the image volume, and acquire a second set of data of the imaging subject. The computer is also caused to generate an image comprising the hemodynamic information in combination with a visualization based on the second set of data.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
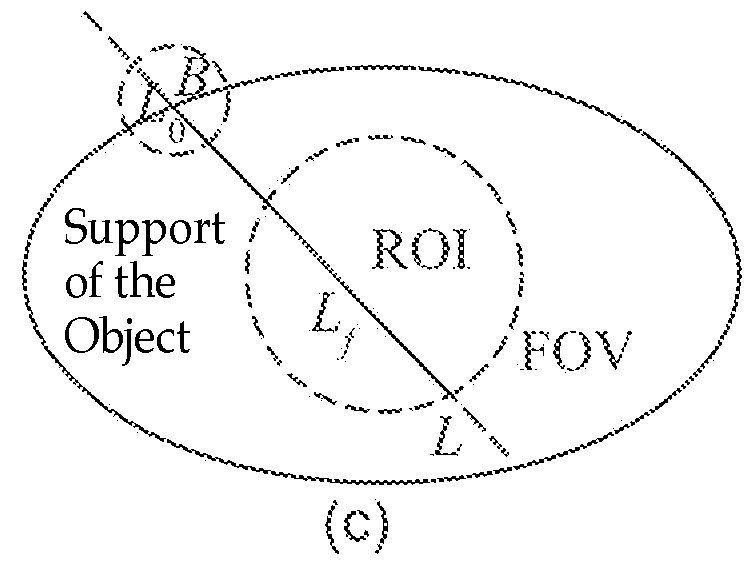
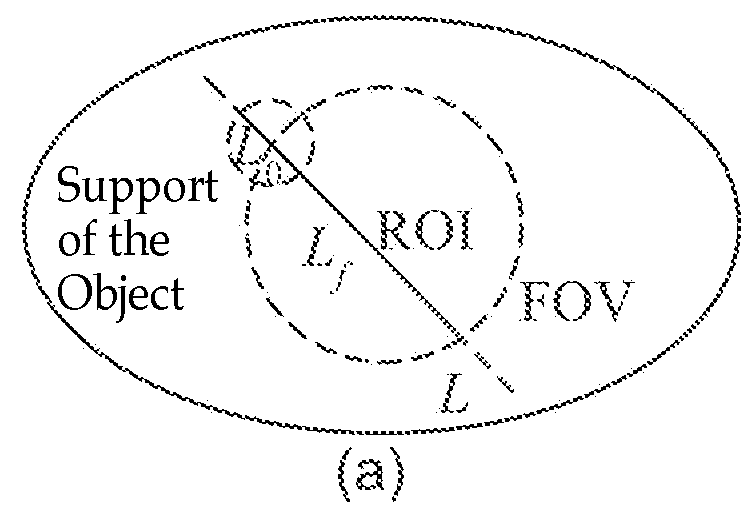
Computer tomography imaging device and method
ActiveUS9380984B2Increase speedReduce hardware costsReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationX-rayTomography
The present invention discloses a method for performing CT imaging on a region of interest of an object under examination, comprising: acquiring the CT projection data of the region of interest; acquiring the CT projection data of region B; selecting a group of PI line segments covering the region of interest, and calculating the reconstruction image value for each PI line segment in the group; and combining the reconstruction image values in all the PI line segments to obtain the image of the region of interest. The present invention further discloses a CT imaging device using this method and a data processor therein. Since the 2D / 3D slice image of the region of interest can be exactly reconstructed and obtained as long as the X-ray beam covers the region of interest and the region B, it is possible to use a small-sized detector to perform CT imaging on the region of interest at any position of a large-sized object, which reduces to a great extent the radiation dose of the X-ray during the CT scanning.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Dynamic multi-spectral CT imaging
InactiveUS6950493B2Good curative effectPromote resultsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingX-rayDetector array
A multispectral X-ray imaging system uses a wideband source and filtration assembly to select for M sets of spectral data. Spectral characteristics may be dynamically adjusted in synchrony with scan excursions where an X-ray source, detector array, or body may be moved relative to one another in acquiring T sets of measurement data. The system may be used in projection imaging and / or CT imaging. Processed image data, such as a CT reconstructed image, may be decomposed onto basis functions for analytical processing of multispectral image data to facilitate computer assisted diagnostics. The system may perform this diagnostic function in medical applications and / or security applications.
Owner:FOREVISION IMAGING TECH LLC
Dynamic multi-spectral imaging with wideband seletable source
InactiveUS20040264628A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingFiltrationX-ray
A multispectral X-ray imaging system uses a wideband source and filtration assembly to select for M sets of spectral data. Spectral characteristics may be dynamically adjusted in synchrony with scan excursions where an X-ray source, detector array, or body may be moved relative to one another in acquiring T sets of measurement data. The system may be used in projection imaging and / or CT imaging. Processed image data, such as a CT reconstructed image, may be decomposed onto basis functions for analytical processing of multispectral image data to facilitate computer assisted diagnostics. The system may perform this diagnostic function in medical applications and / or security applications.
Owner:FOREVISION IMAGING TECH LLC
Ct system for use in multi-modality imaging system
InactiveUS20120256092A1Reduced footprintMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingImaging qualityX-ray
A computed tomography (CT) imaging system is disclosed. The CT imaging system may be used in a multi-modality imaging context or other context. In one embodiment, the CT imaging system provides for both fast rotation of the rotating X-ray source and detection components and low dose of X-rays generated by the source providing several clinical and economic benefits such as low dose and sufficient image quality and no or insignificant investment in room shielding associated with diagnostic CT dose.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method for dynamic prior image constrained image reconstruction
ActiveUS20090161933A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioHigh resolutionReconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic Radiology ModalityTemporal resolution
A method for reconstructing a high quality image from undersampled image data is provided. The image reconstruction method is applicable to a number of different imaging modalities. Specifically, the present invention provides an image reconstruction method that incorporates an appropriate prior image into the image reconstruction process. Thus, one aspect of the present invention is to provide an image reconstruction method that requires less number of data samples to reconstruct an accurate reconstruction of a desired image than previous methods, such as, compressed sensing. Another aspect of the invention is to provide an image reconstruction method that produces a time series of desired images indicative of a higher temporal resolution than is ordinarily achievable with the imaging system. For example, cardiac phase images can be produced with high temporal resolution (e.g., 20 milliseconds) using a CT imaging system with a slow gantry rotation speed.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
CT-Enhanced Fluoroscopy
ActiveUS20080262342A1Quality improvementPrecise positioningGuide needlesMedical devicesNuclear medicineCt imaging
Real-time, enhanced imaging of remote areas, too minute for CT imaging, is made possible through a probe having a radiopaque tip as well as radiopaque volume markers. When deployed, the markers outline the space containing the tip such that both the tip and the volume containing the tip are viewable on a fluoroscope. This device may be used in conjunction with or independently of 3-D volumes created from CT scans and 3-D tip sensors.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
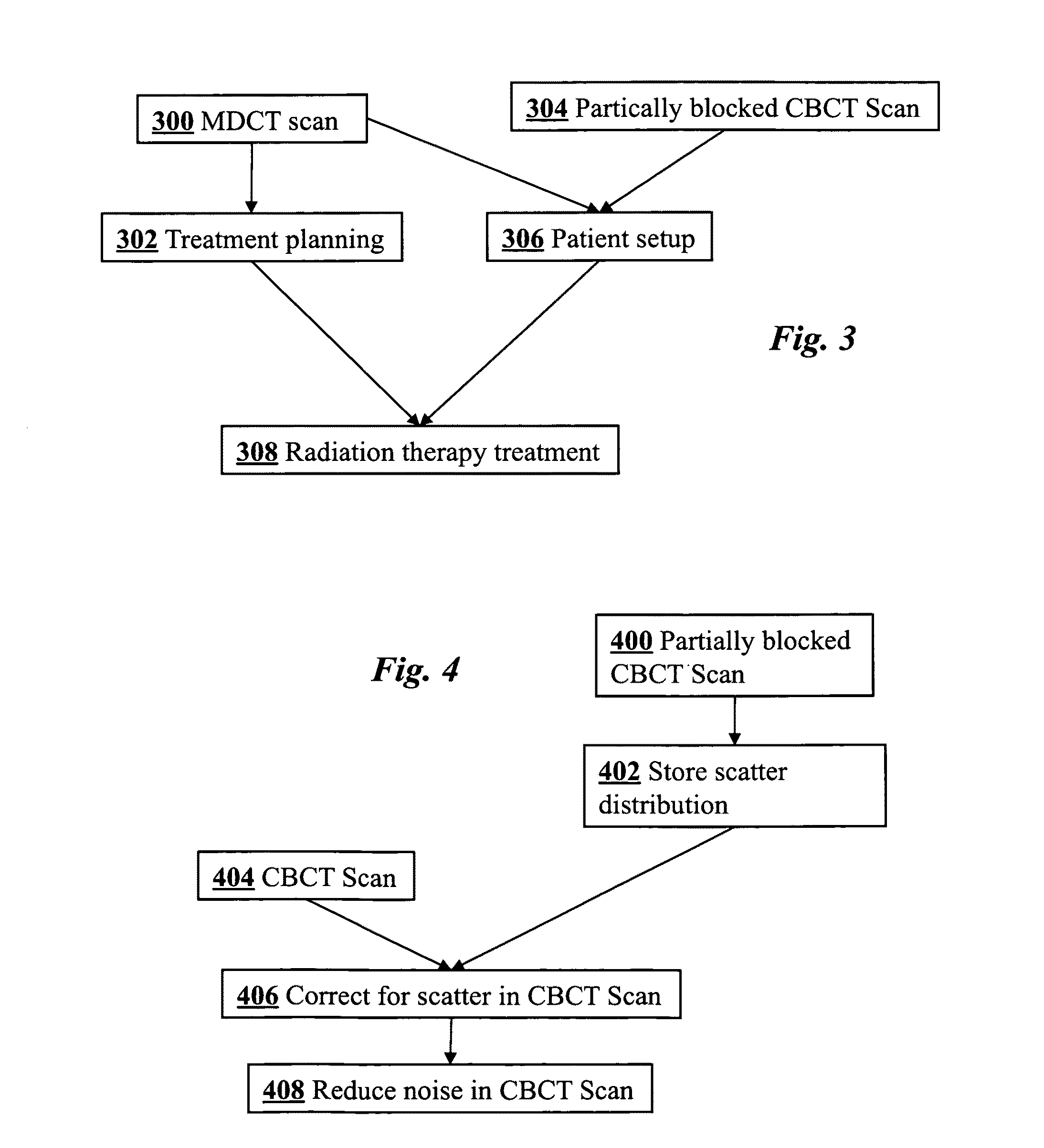
Cone-beam CT imaging scheme
InactiveUS20090225932A1Reduce noiseReduce doseReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationImaging qualityCbct imaging
A general imaging scheme is proposed for applications of CBCT. The approach provides a superior CBCT image quality by effective scatter correction and noise reduction. Specifically, in its implementation of CBCT imaging for radiation therapy, the proposed approach achieves an accurate patient setup using a partially blocked CBCT with a significantly reduced radiation dose. The image quality improvement due to the proposed scatter correction and noise reduction also makes CBCT-based dose calculation a viable solution to adaptive treatment planning.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
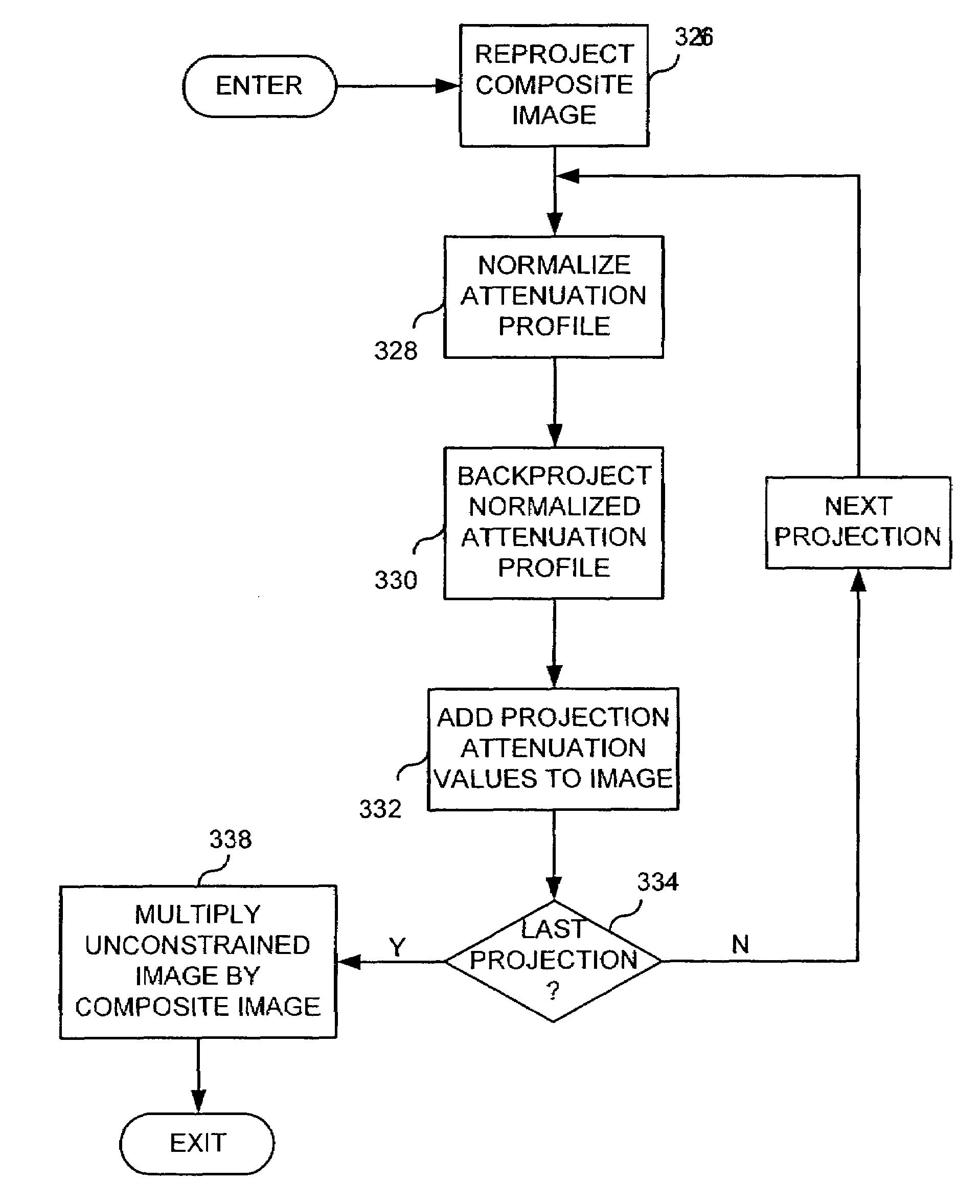
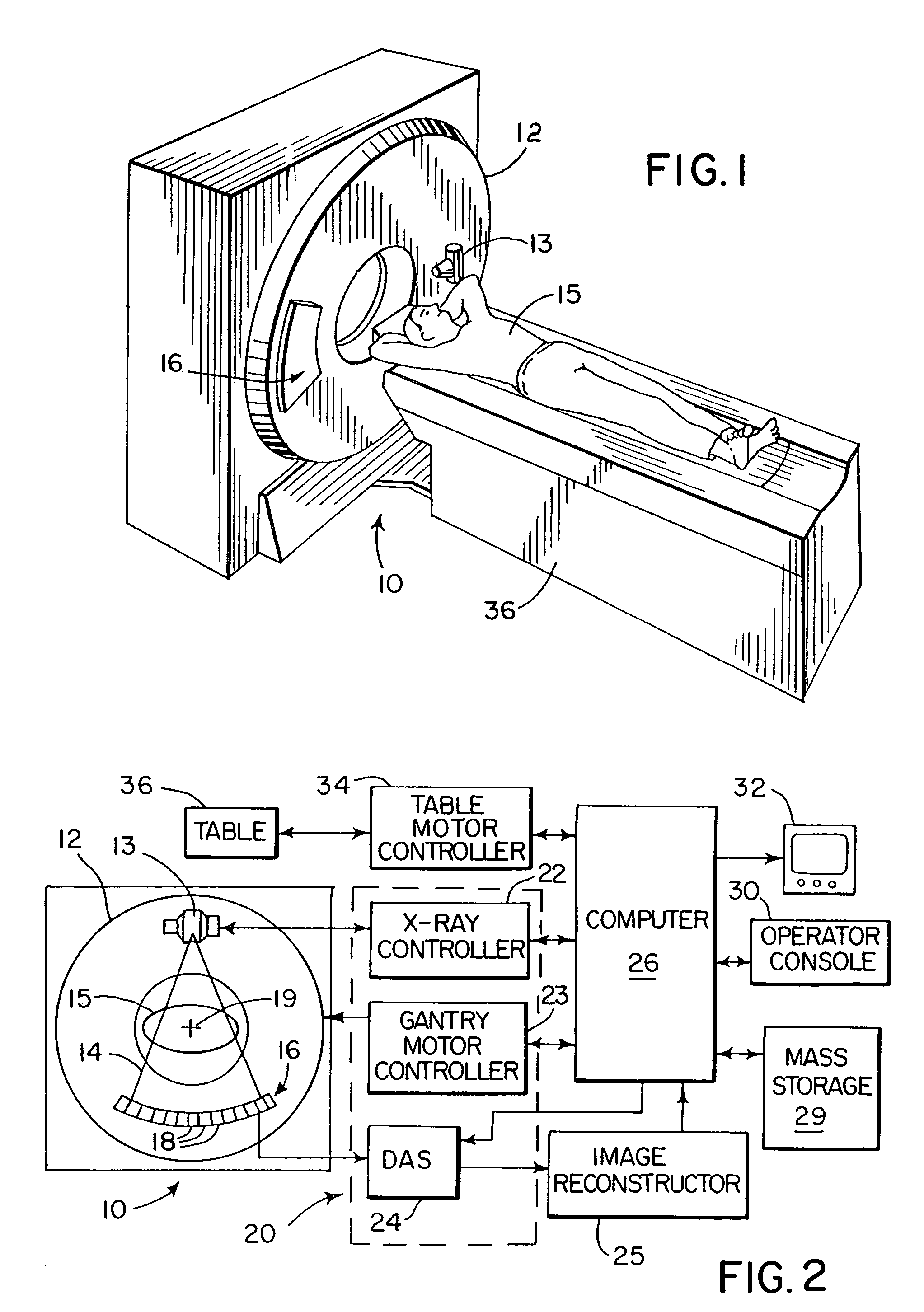
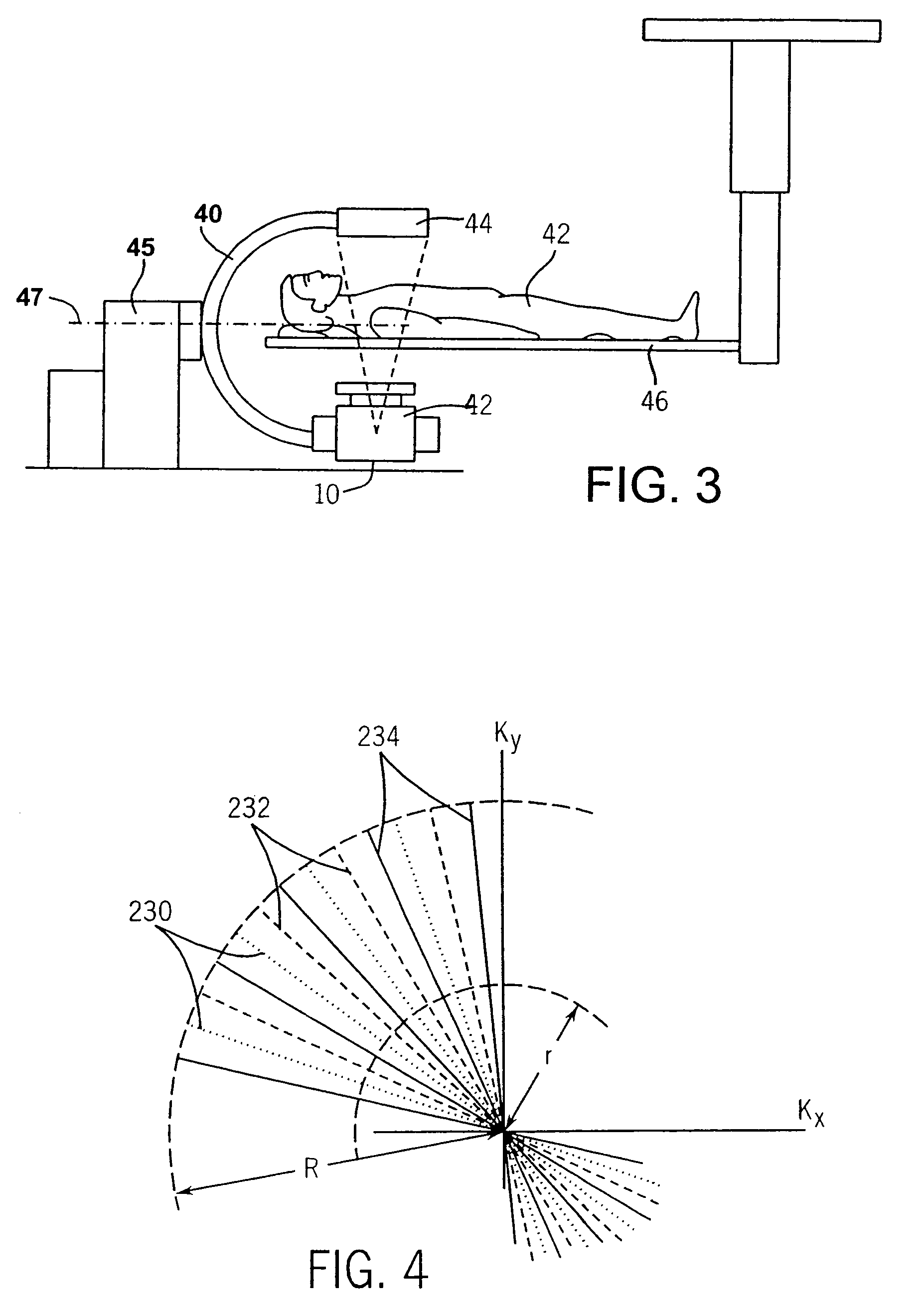
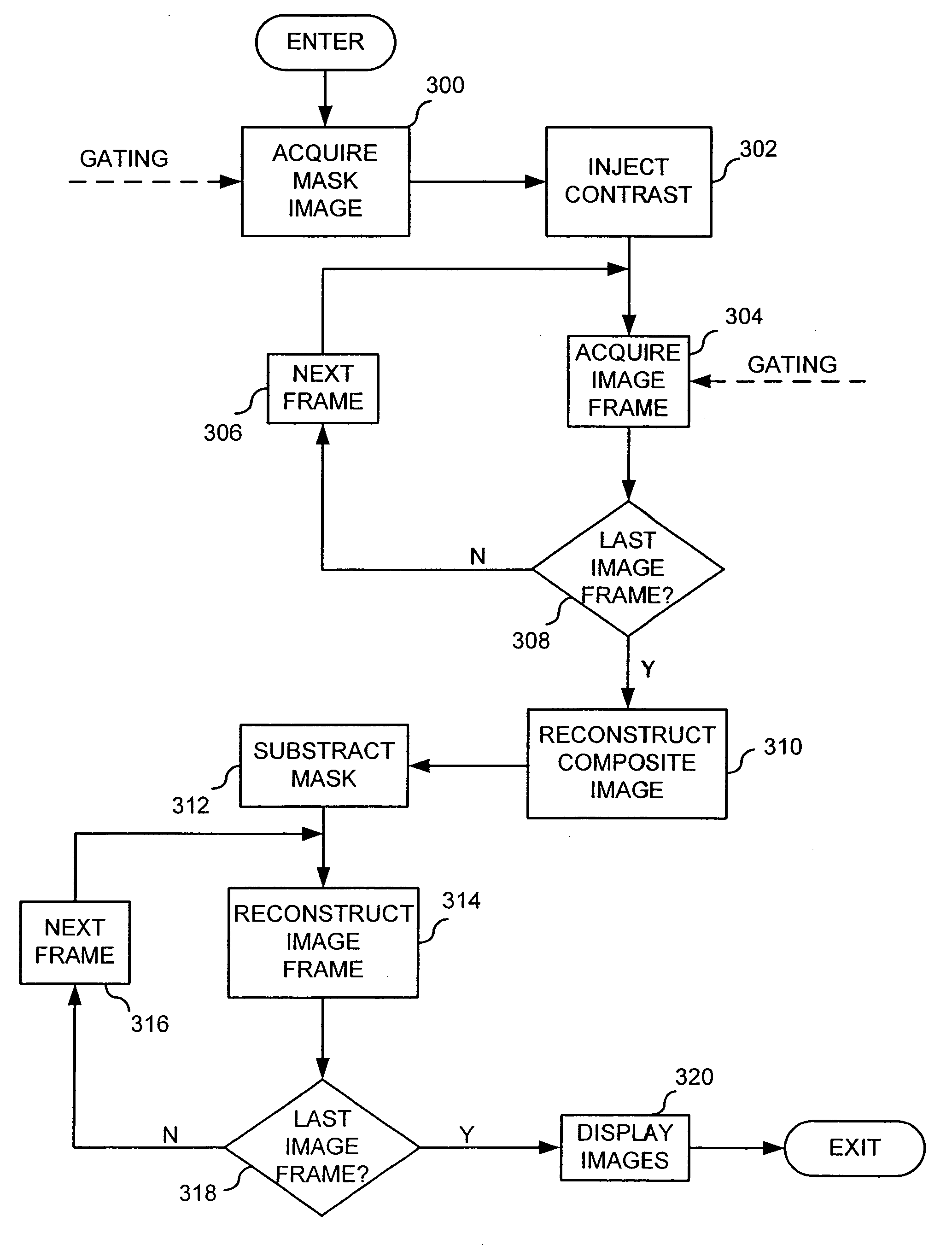
Backprojection reconstruction method for CT imaging
ActiveUS7545901B2Simple methodLower doseReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiologyBack projection
Two-dimensional or three-dimensional, time-resolved CT frame images are acquired during a dynamic study of a subject. A composite image is produced and this is used to reconstruct each CT frame image by weighting the backprojection of each projection view acquired for that image frame by the corresponding value in the composite image. This weighted backprojection enables artifact-free image frames to be produced with far fewer projection views of the subject. The composite image may be reconstructed from views acquired separately, or it may be produced by combining views acquired during the course of the dynamic study.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Backprojection reconstruction method for CT imaging
ActiveUS20070009080A1Improved image reconstructionImprove time resolutionReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiologyBack projection
Two-dimensional or three-dimensional, time-resolved CT frame images are acquired during a dynamic study of a subject. A composite image is produced and this is used to reconstruct each CT frame image by weighting the backprojection of each projection view acquired for that image frame by the corresponding value in the composite image. This weighted backprojection enables artifact-free image frames to be produced with far fewer projection views of the subject. The composite image may be reconstructed from views acquired separately, or it may be produced by combining views acquired during the course of the dynamic study.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
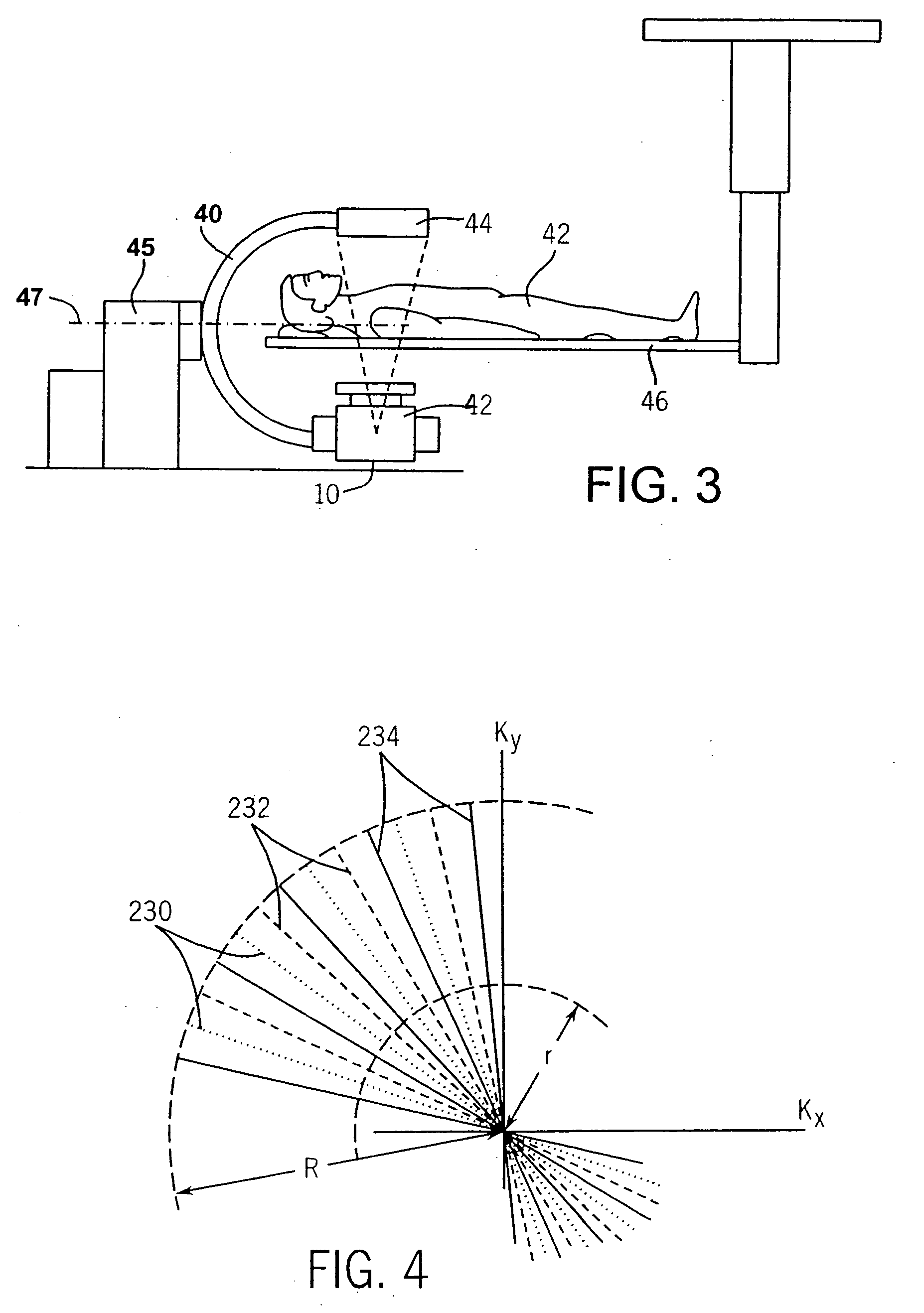
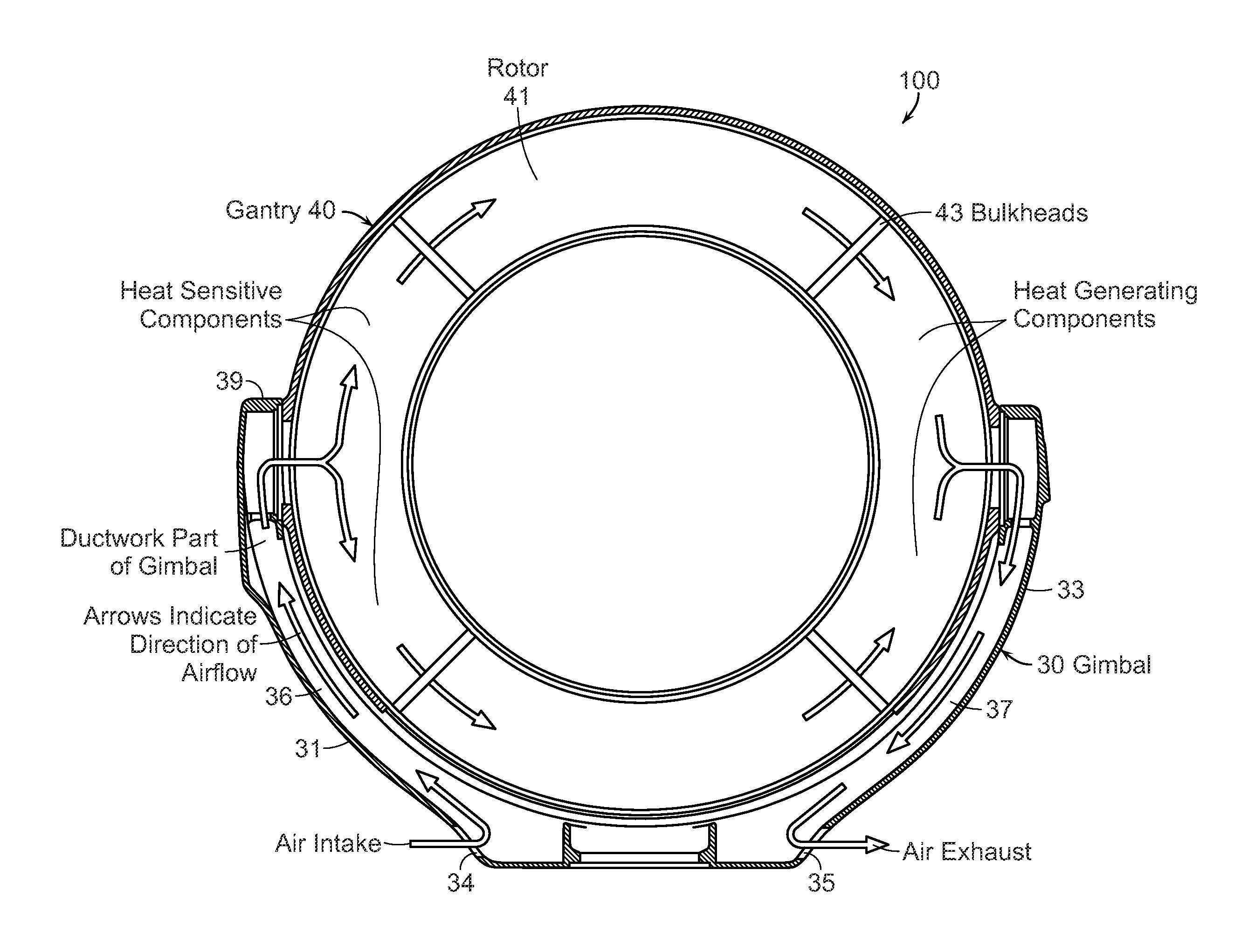
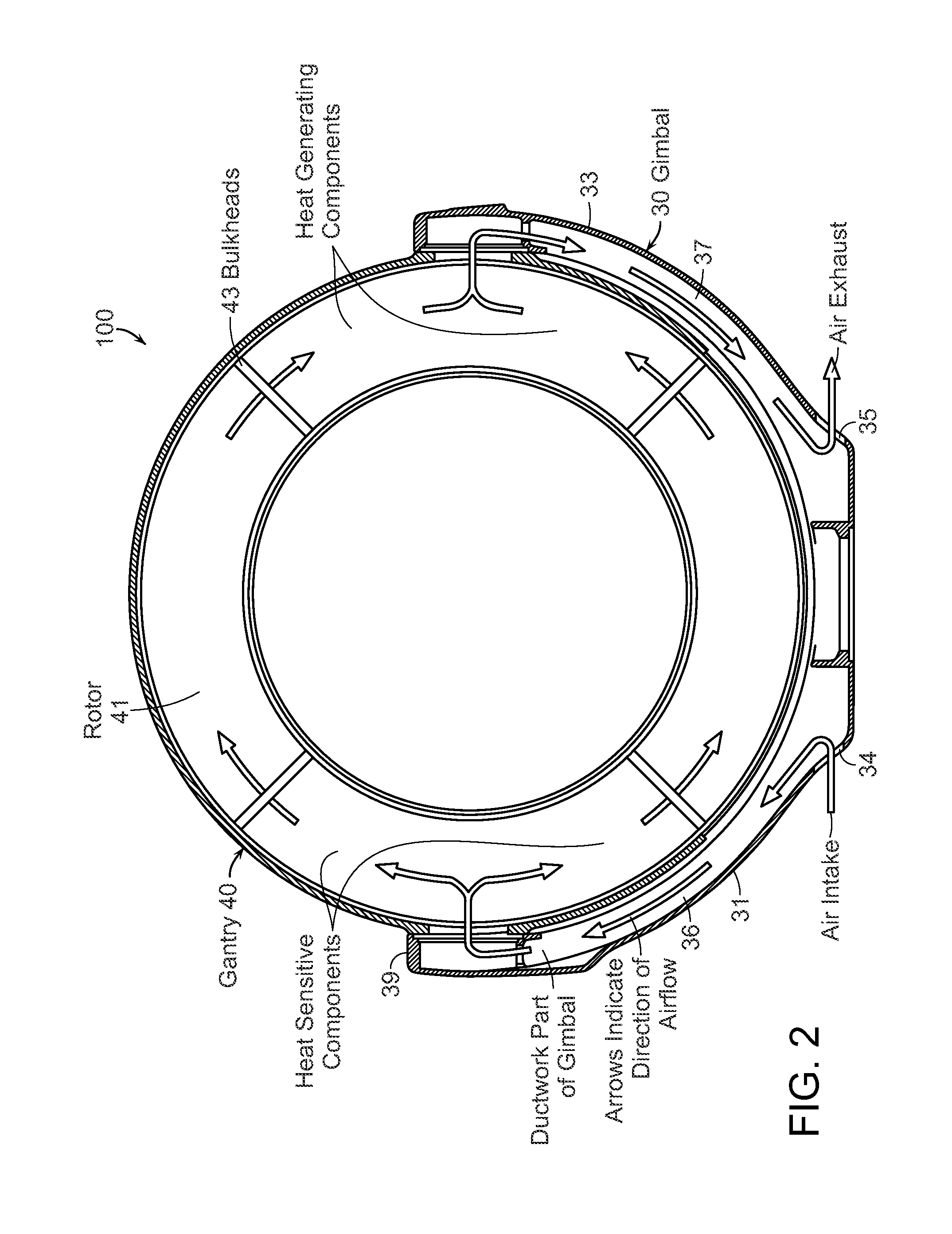
Diagnostic imaging apparatus with airflow cooling system
ActiveUS20110228910A1Susceptible to effectIncrease airflowMachines/enginesDiagnostic recording/measuringEngineeringCt imaging
A diagnostic imaging system, which can be a mobile or stationary surgical CT imaging system or an MRI system, comprises an internal airflow cooling system that includes an air intake opening and an air outtake opening that are positioned near the ground and direct air flow away from the sterile surgical field.
Owner:MOBIUS IMAGING
X-ray tomogram imaging device
InactiveUS20150305696A1High resolutionImprove usabilityImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionSoft x rayX-ray
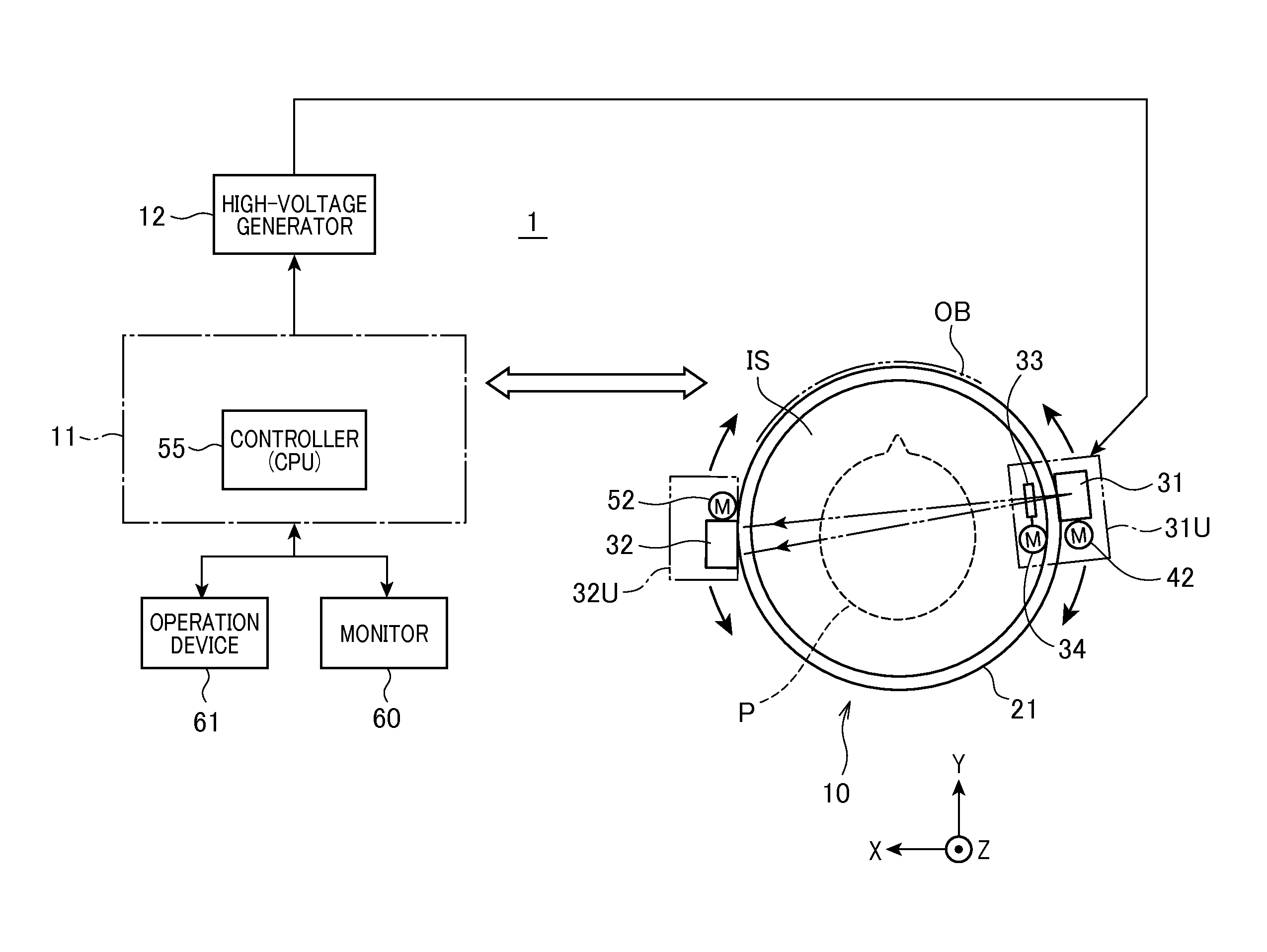
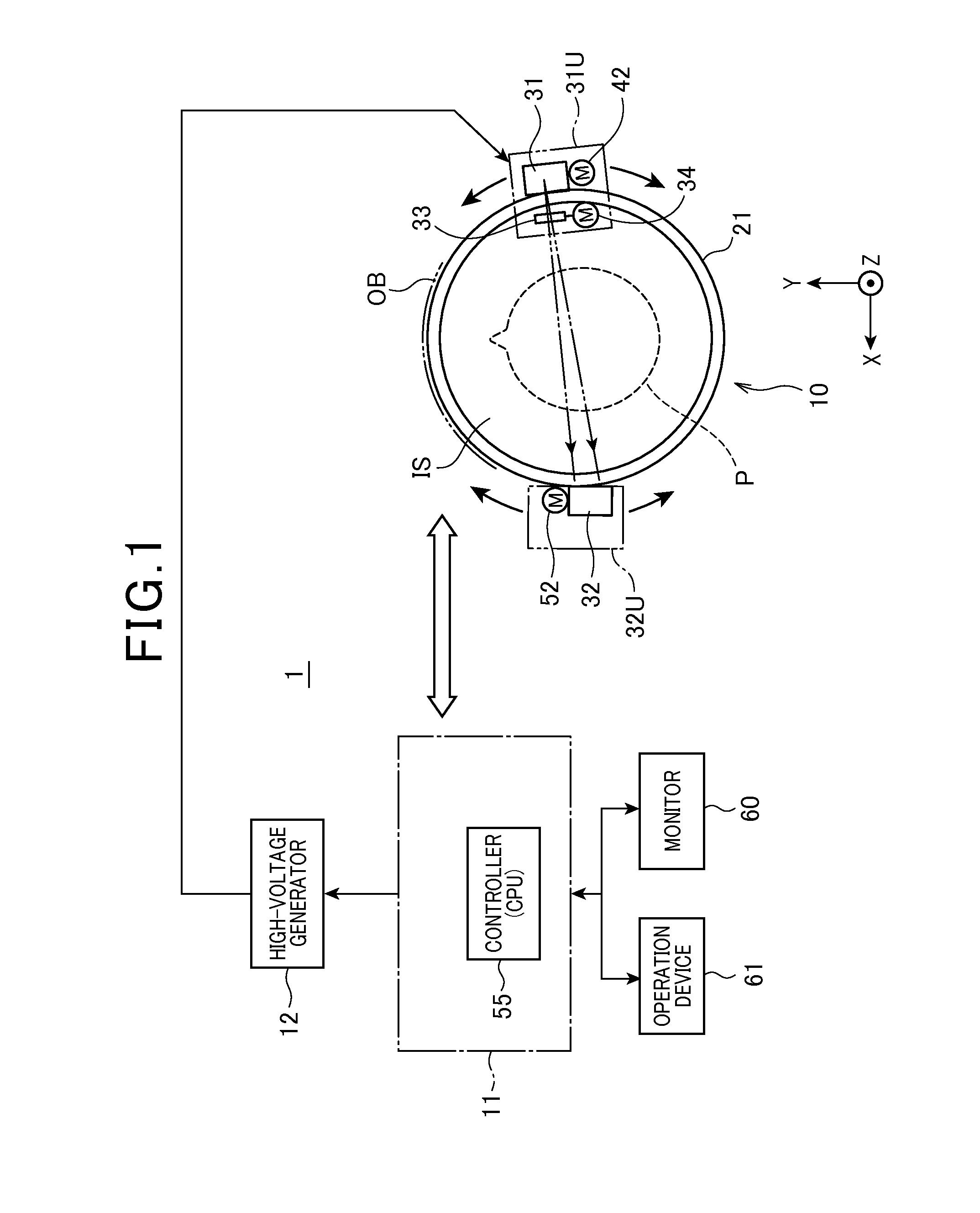
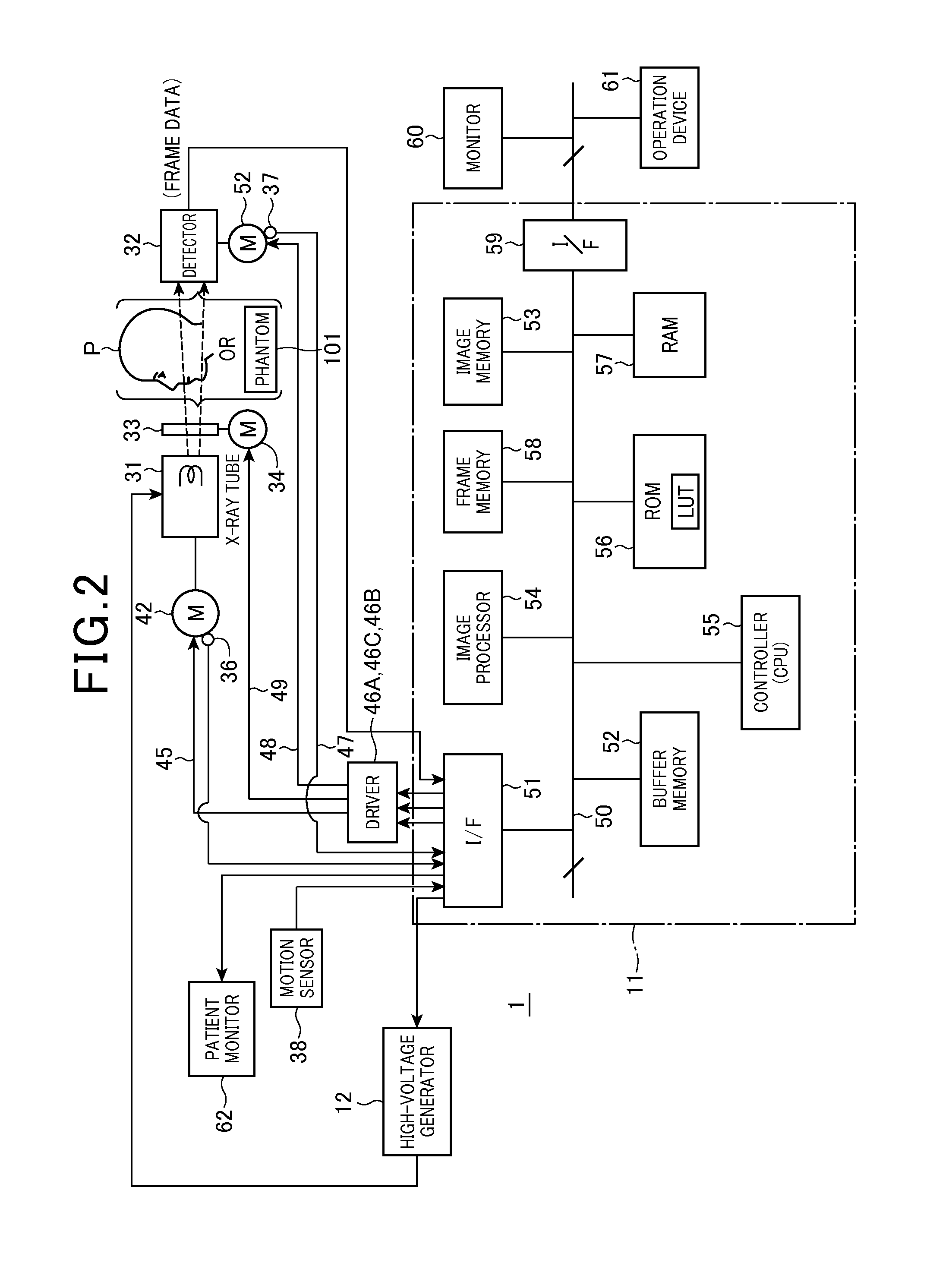
An X-ray tomographic imaging apparatus includes an X-ray and a direct conversion type of detector. The X-ray tube and the detector are supported by the support means so as to be rotatable along curved orbits mutually independently. Under instructions from a computer, scans and image reconstruction are performed. The X-ray tube and the detector are moved along the orbits mutually independently so that X-ray beams are always transmitted through a desired tomographic plane of an object at desired angles. Acquired frame data are used to produce a panoramic image of the plane, while the frame data and the panoramic image are used to produce a tomographic image in which structural components of the object are optically focused and distortions caused due to differences in X-ray paths are suppressed. The apparatus can be used as devices for dental, medical diagnosis and nondestructive inspection, and can have a CT imaging function.
Owner:TAKARA TELESYST
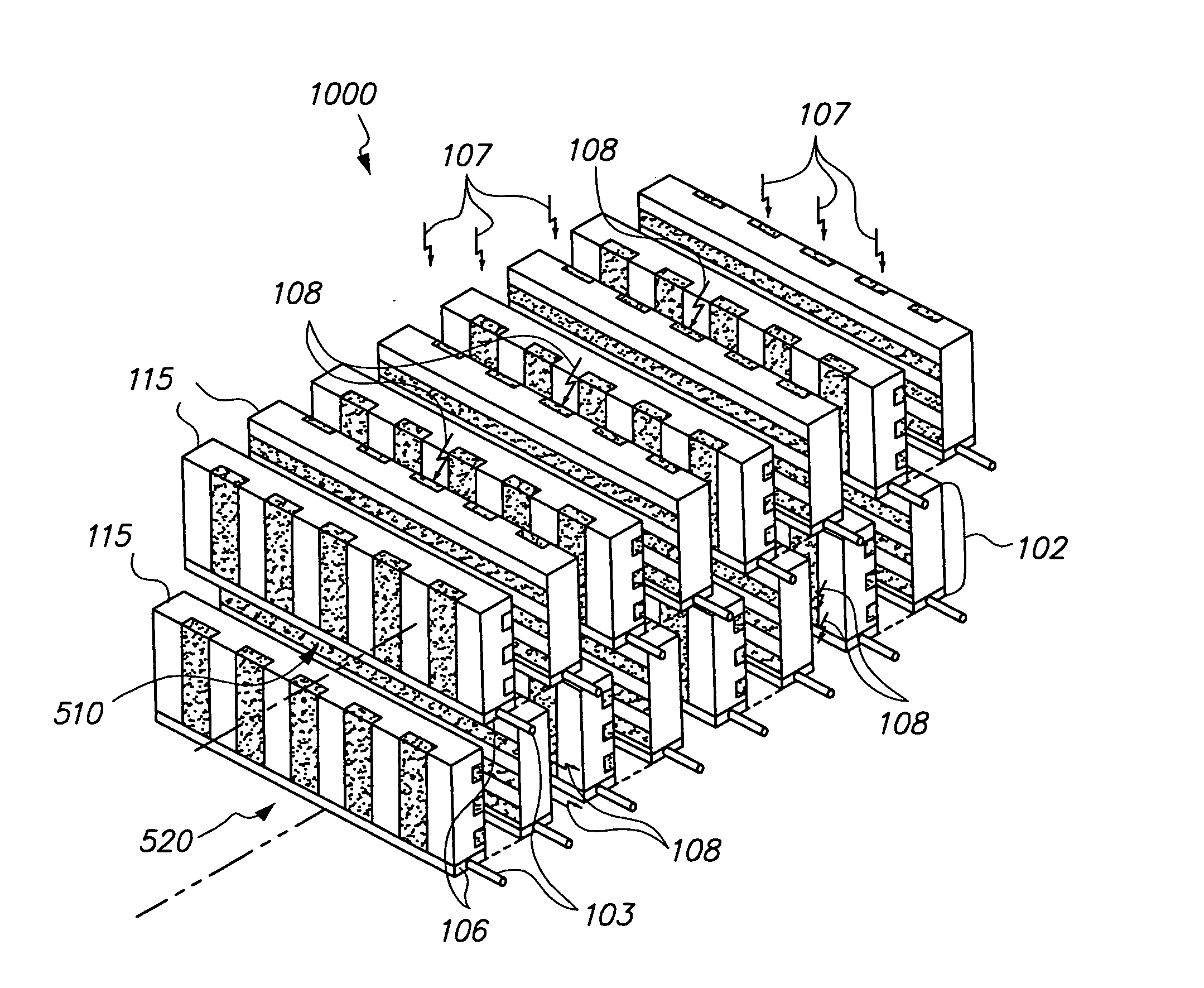
Compton camera detector systems for novel integrated compton-Pet and CT-compton-Pet radiation imaging
The invention provides novel Compton camera detector designs and systems for enhanced radiographic imaging with integrated detector systems which incorporate Compton and nuclear medicine imaging, PET imaging and x-ray CT imaging capabilities. Compton camera detector designs employ one or more layers of detector modules comprised of edge-on or face-on detectors or a combination of edge-on and face-on detectors which may employ gas, scintillator, semiconductor, low temperature (such as Ge and superconductor) and structured detectors. Detectors may implement tracking capabilities and may operate in a non-coincidence or coincidence detection mode.
Owner:MINNESOTA IMAGING & ENG
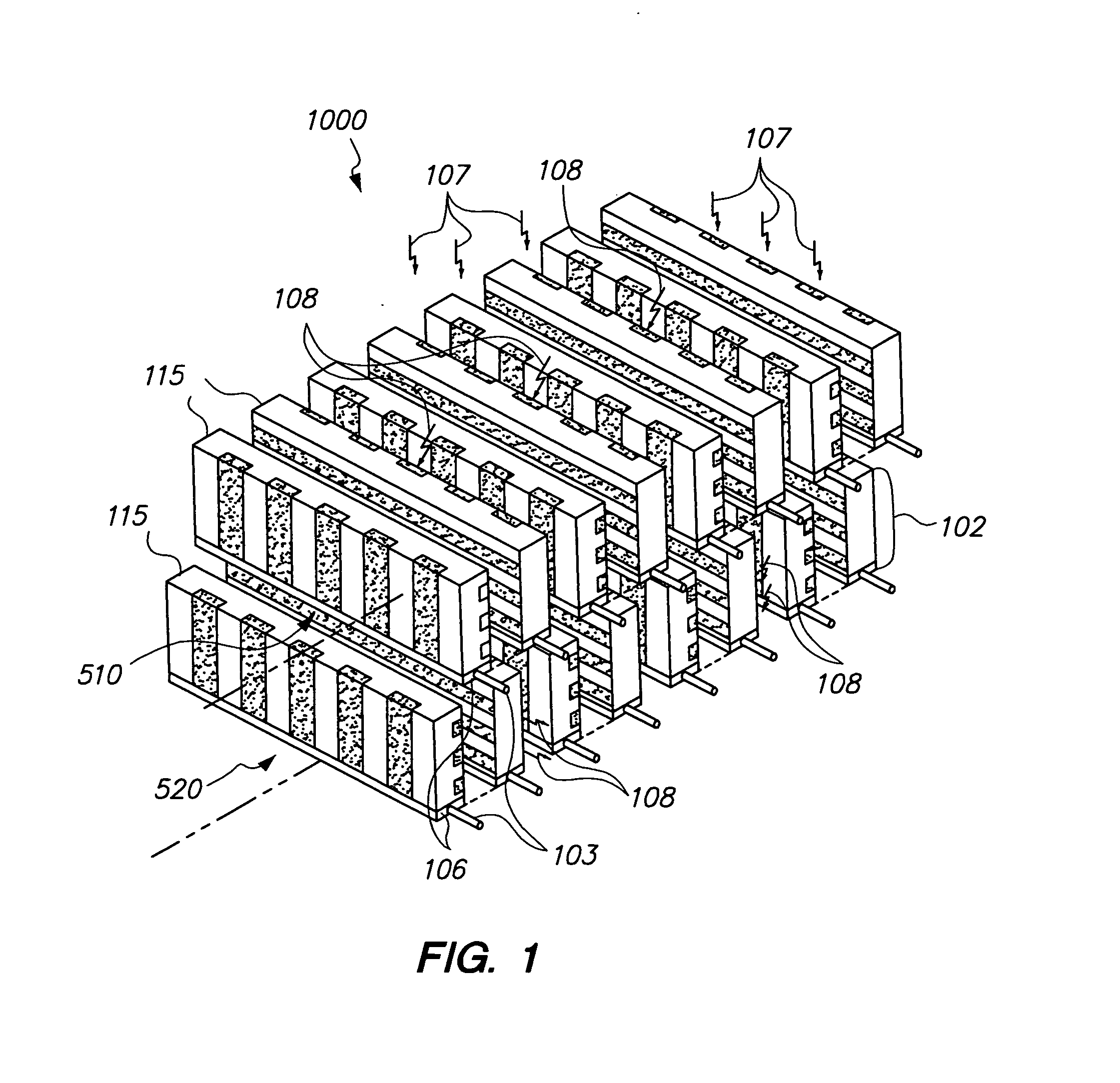
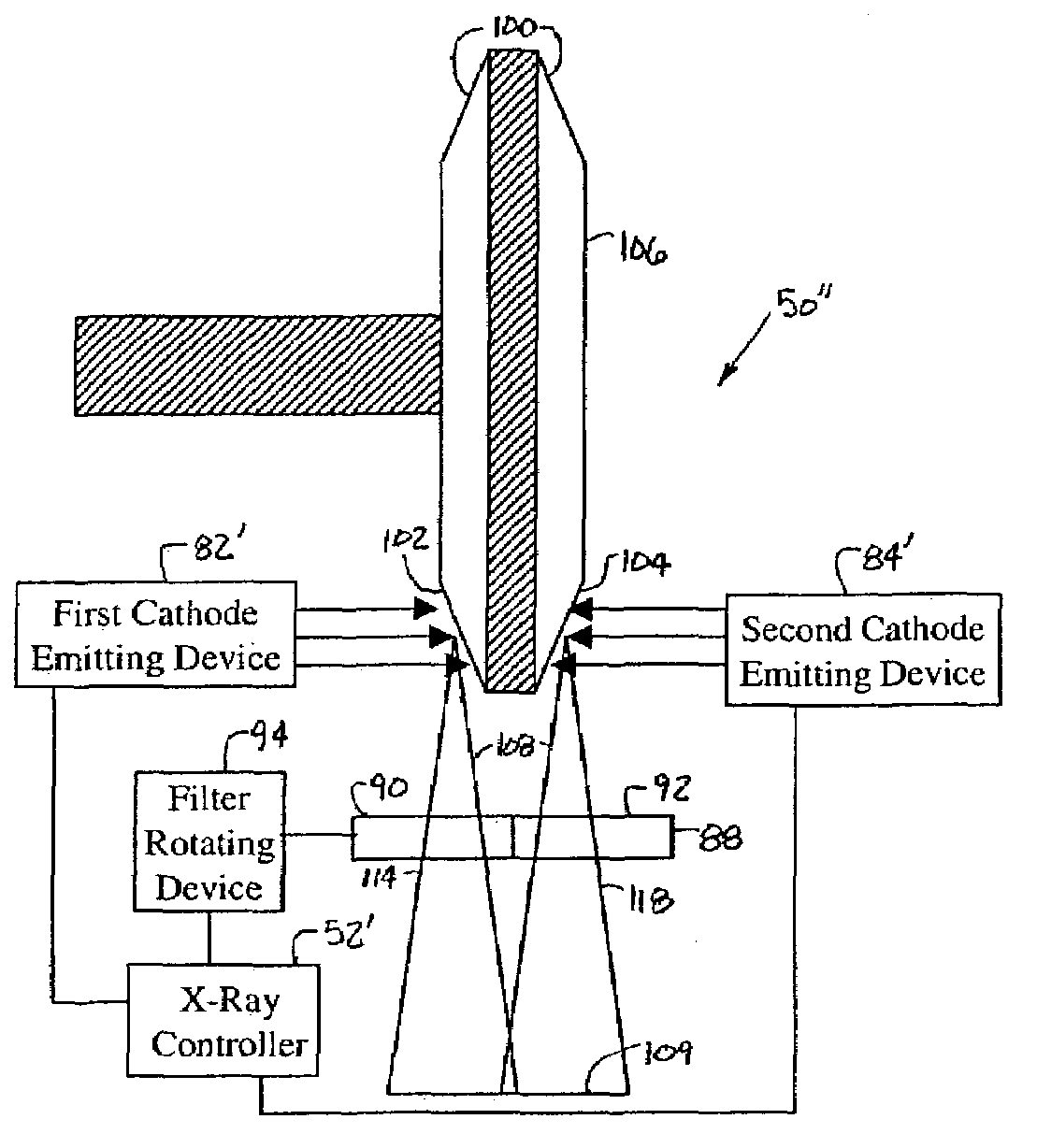
CT imaging system with multiple peak x-ray source
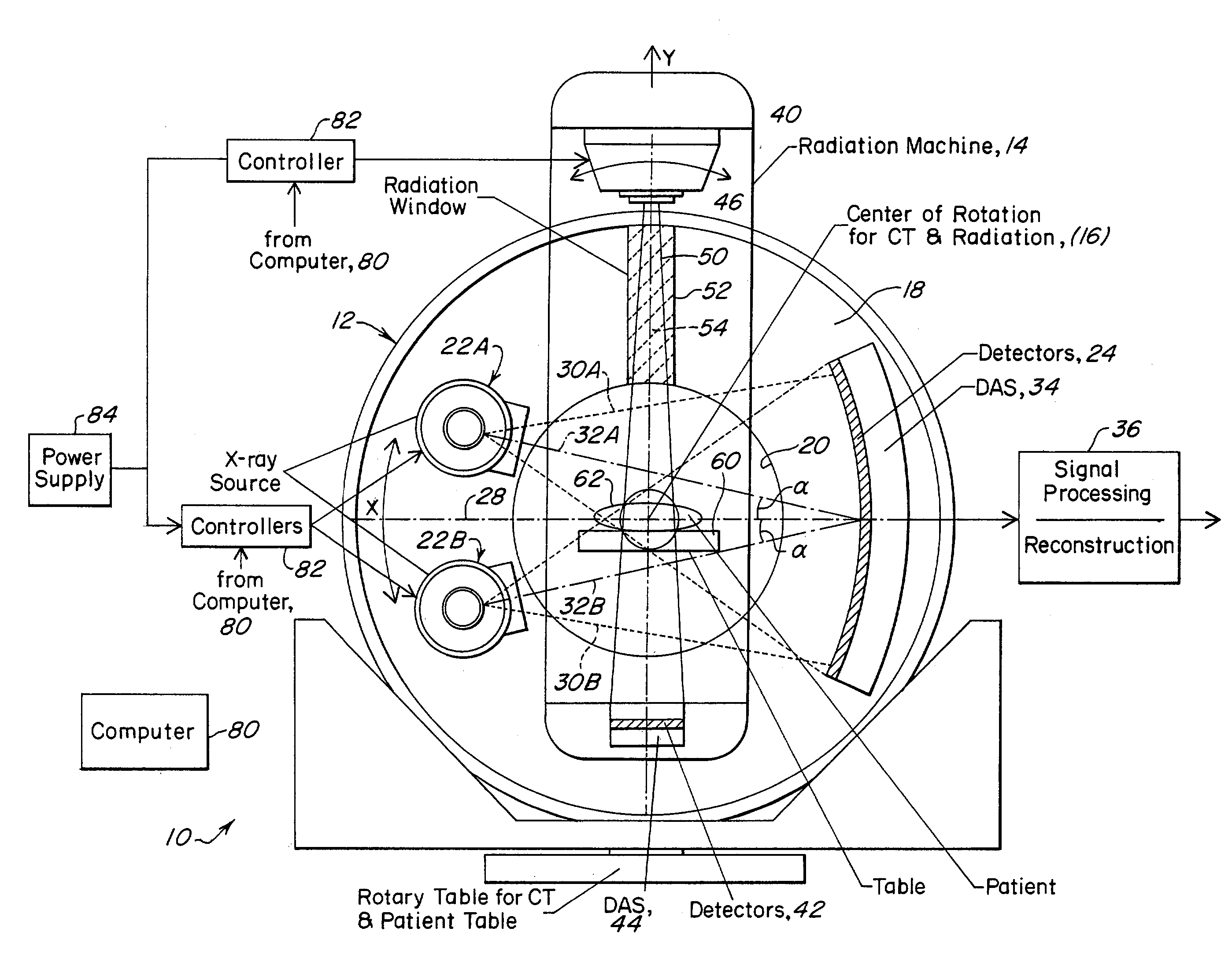
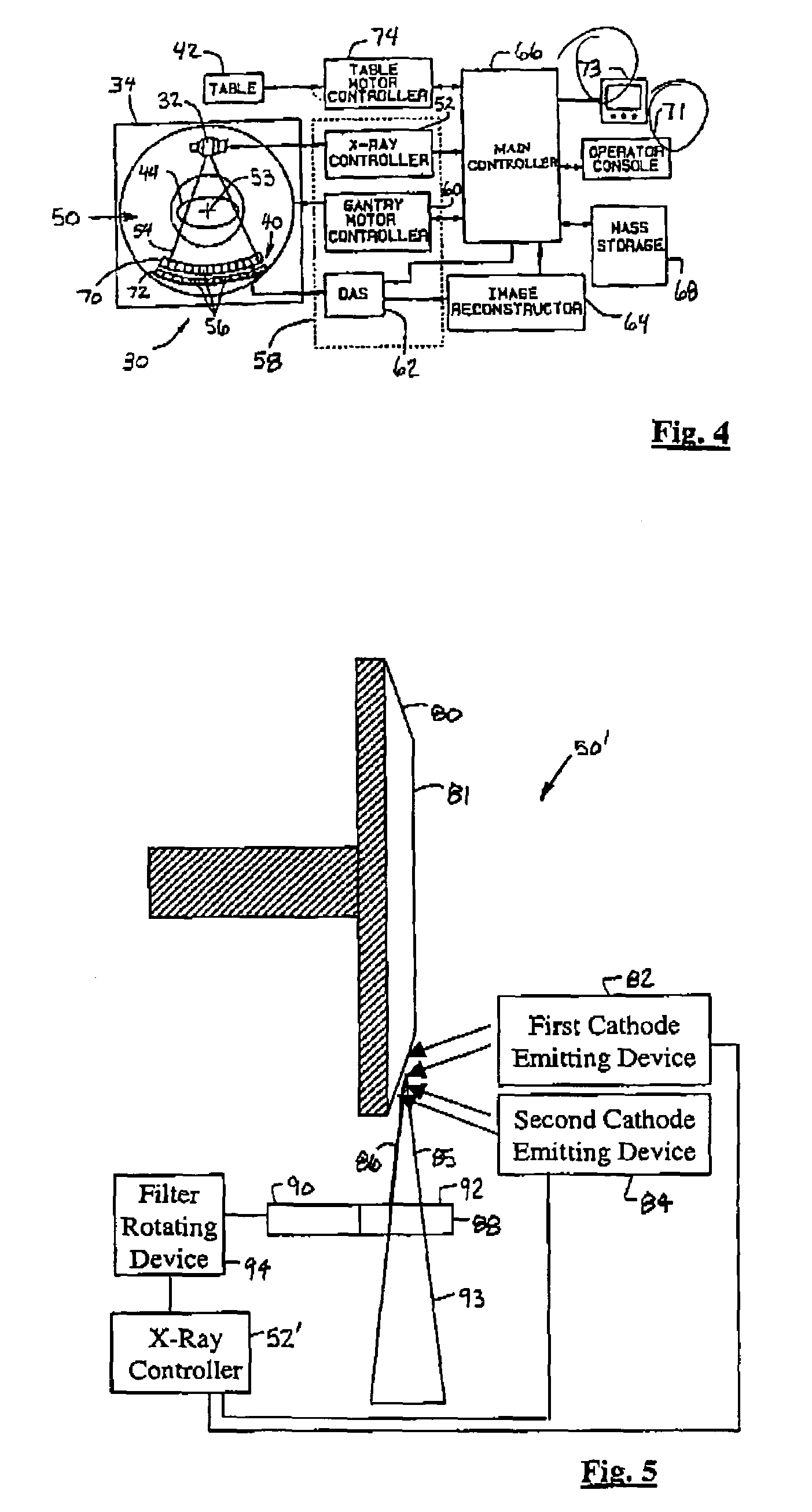
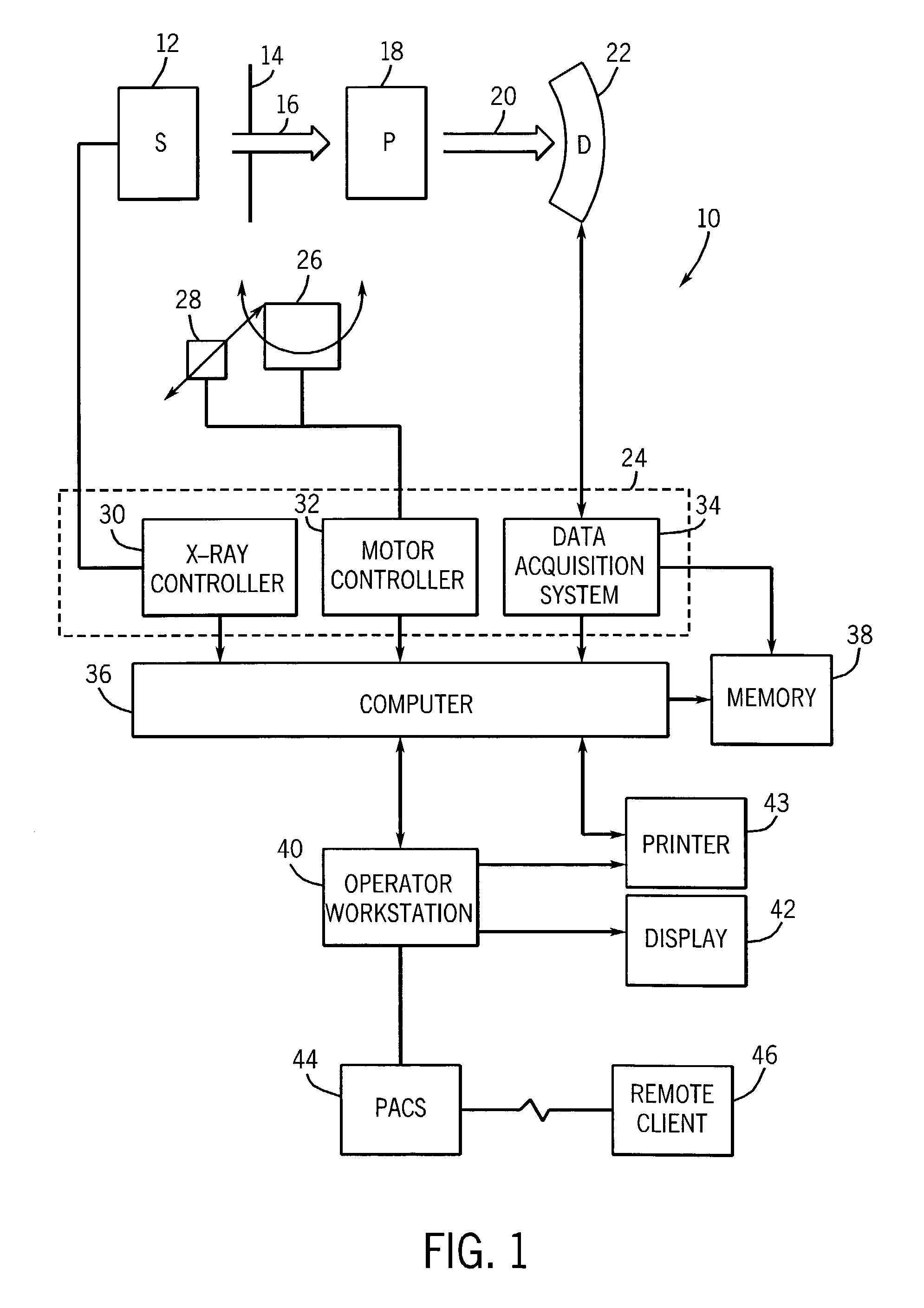
ActiveUS7120222B2Increase spacingImprove usabilityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingSoft x rayX-ray
An x-ray source (32) for performing energy discrimination within an imaging system (10) includes a cathode-emitting device (82) emitting electrons and an anode (81) that has a target (80) whereupon the electrons impinge to generate an x-ray beam (93) with multiple x-ray quantity energy peaks (116 and 120). A method of performing energy discrimination in the imaging system (10) includes emitting the electrons. The x-ray beam (93) with the x-ray quantity energy peaks (116 and 120) is generated. The x-ray beam (93) is directed through an object (44) and is received. An x-ray image having multiple energy differentiable characteristics is generated in response to the x-ray beam (93).
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
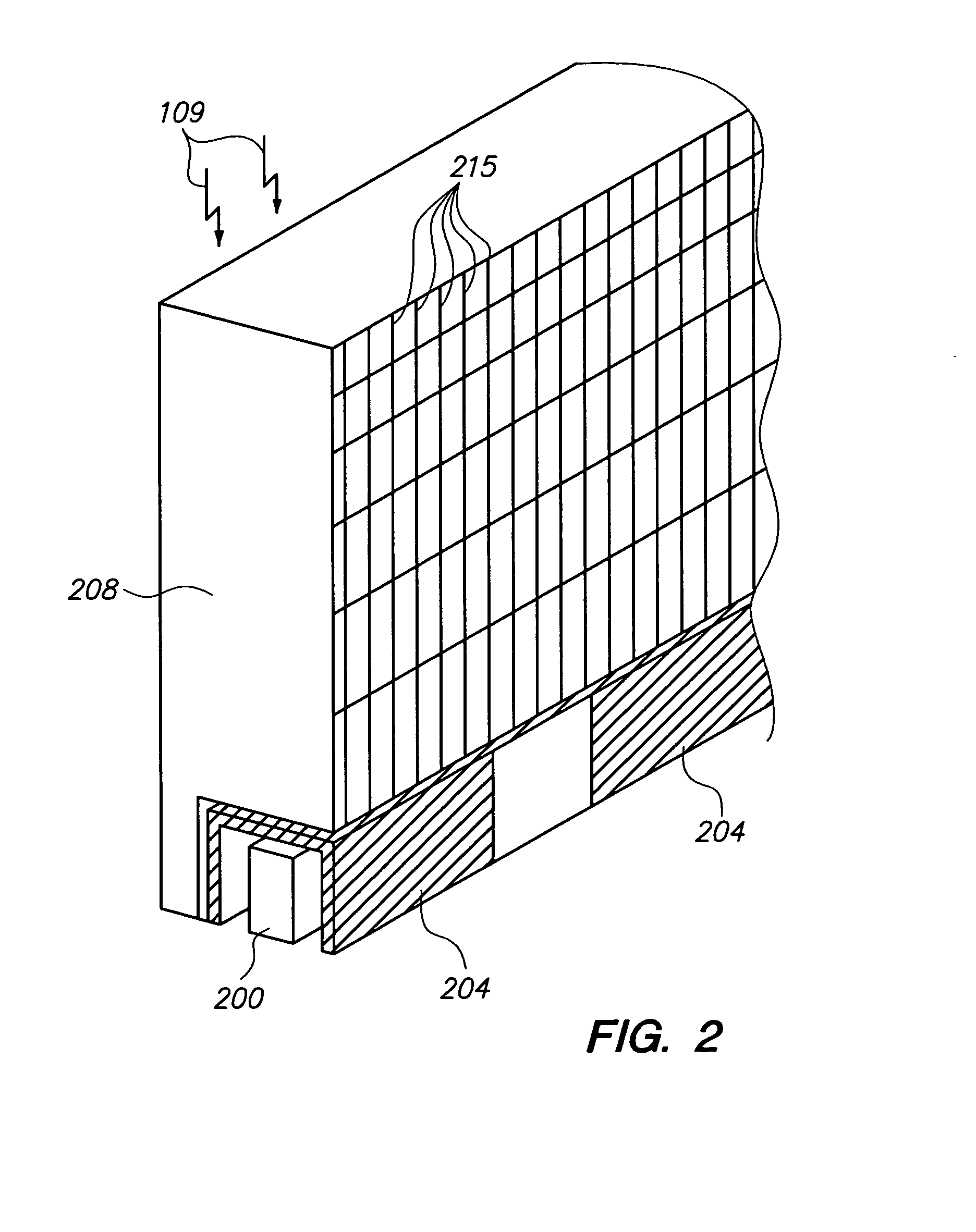
CT detector having a segmented optical coupler and method of manufacturing same
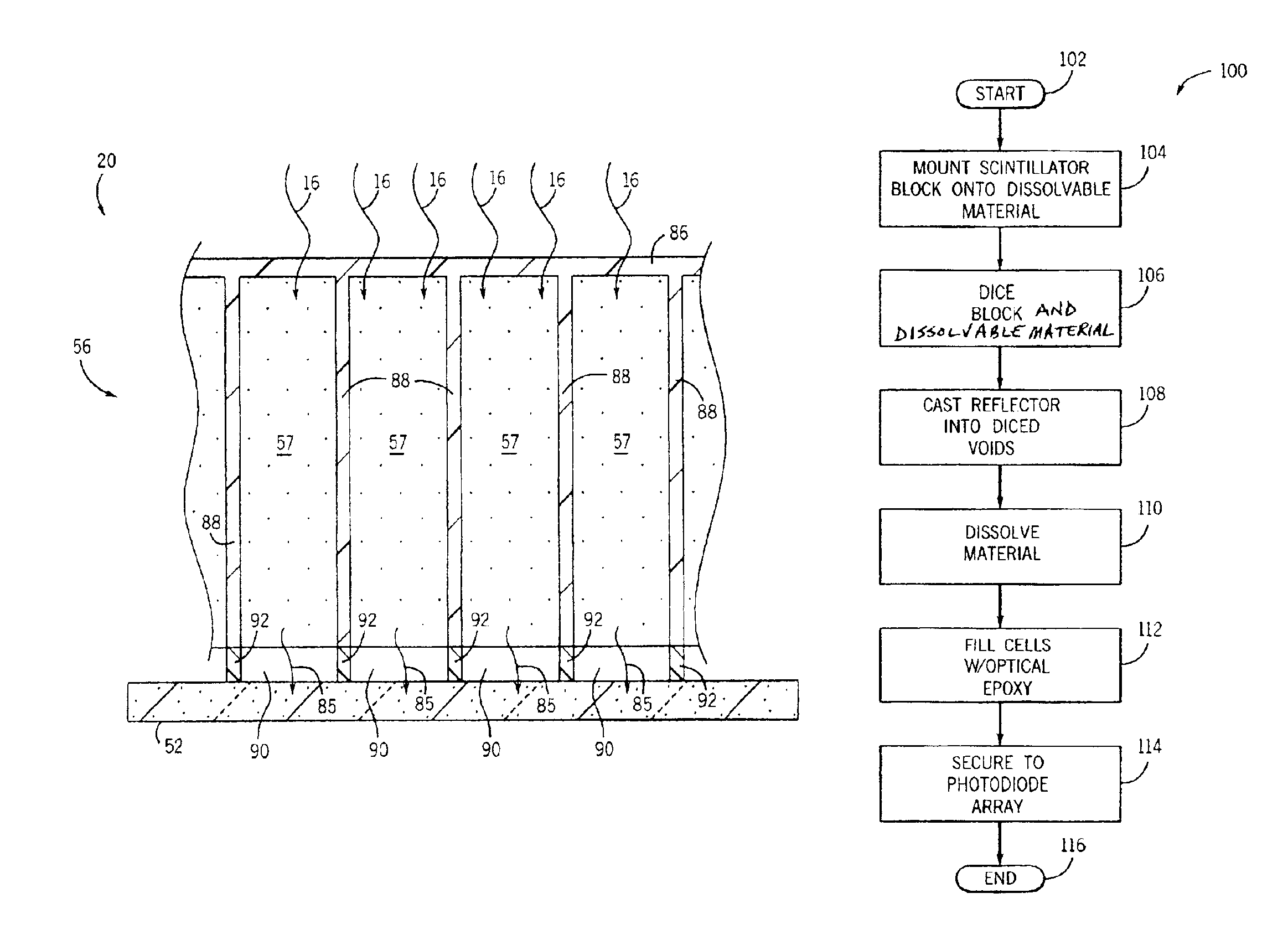
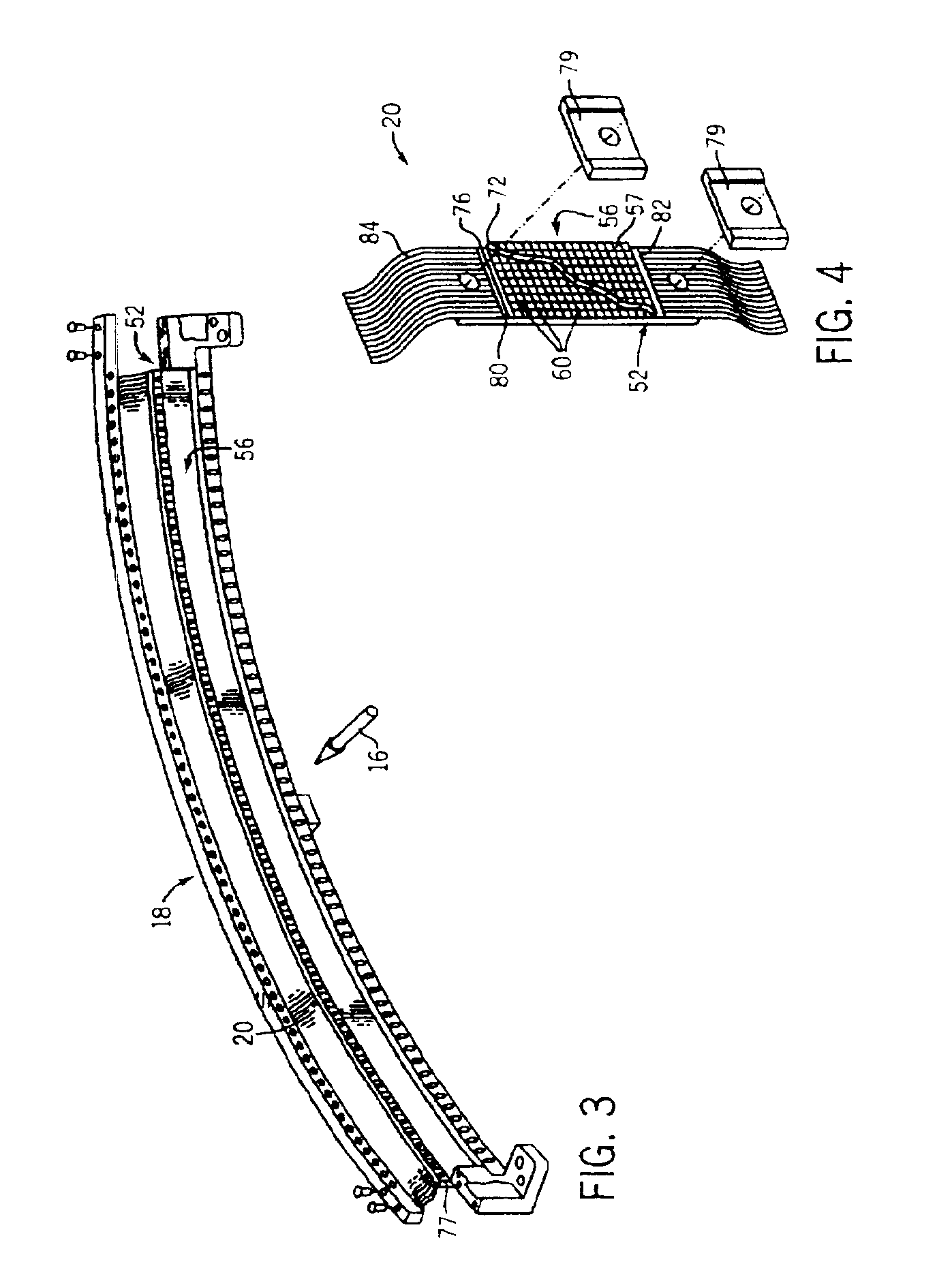
InactiveUS6933504B2Light collection efficiency is improvedReduce crosstalkMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingEpoxyScintillator
The present invention is a directed to a CT detector for a CT imaging system that incorporates a segmented optical coupler between a photodiode array and a scintillator array. The segmented optical coupler also operates as a light collimator which improves the light collection efficiency of the photodiode array. The segmented optical coupler is defined by a series of reflector elements that collectively form a plurality of open cells. The open cells form light transmission cavities and facilitate the collimation of light from a scintillator to a photodiode. The cavities may be filled with optical epoxy for sealing to the photodiode array.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Computed tomography with z-axis scanning
InactiveUS20050100126A1Reduce relative motionShort time intervalMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingTwo dimensional detectorX-ray
A CT imaging system includes a two-dimensional detector array and an x-ray source that both revolve around the subject during a scan. The x-ray source produces a cone beam of x-rays and the focal point of this cone beam is electrically moved to different locations along the z-axis to increase the z-axis extent of the ROI that can be imaged without patient table movement. Different focal point scan patterns are described for a variety of different clinical applications.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC +1
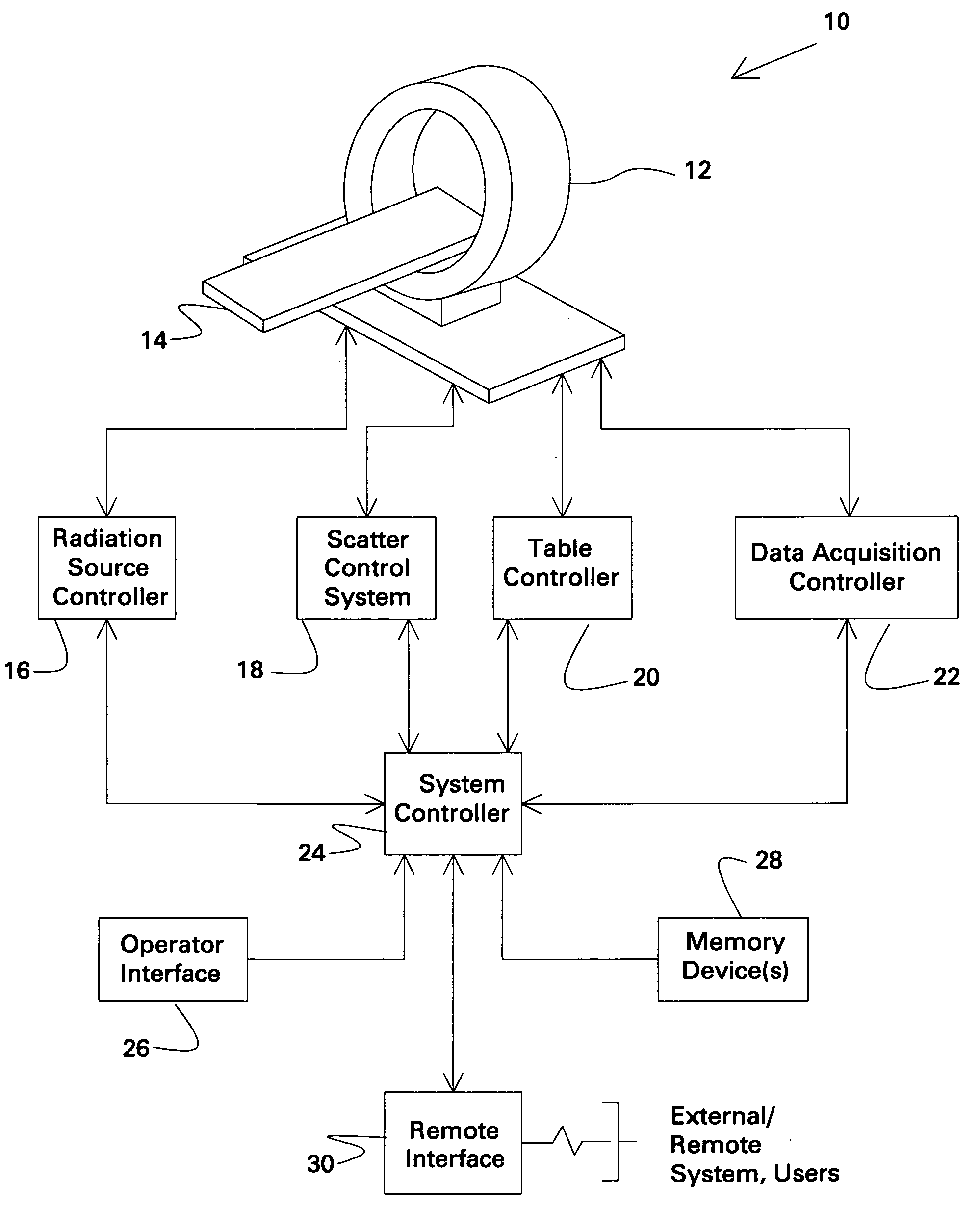
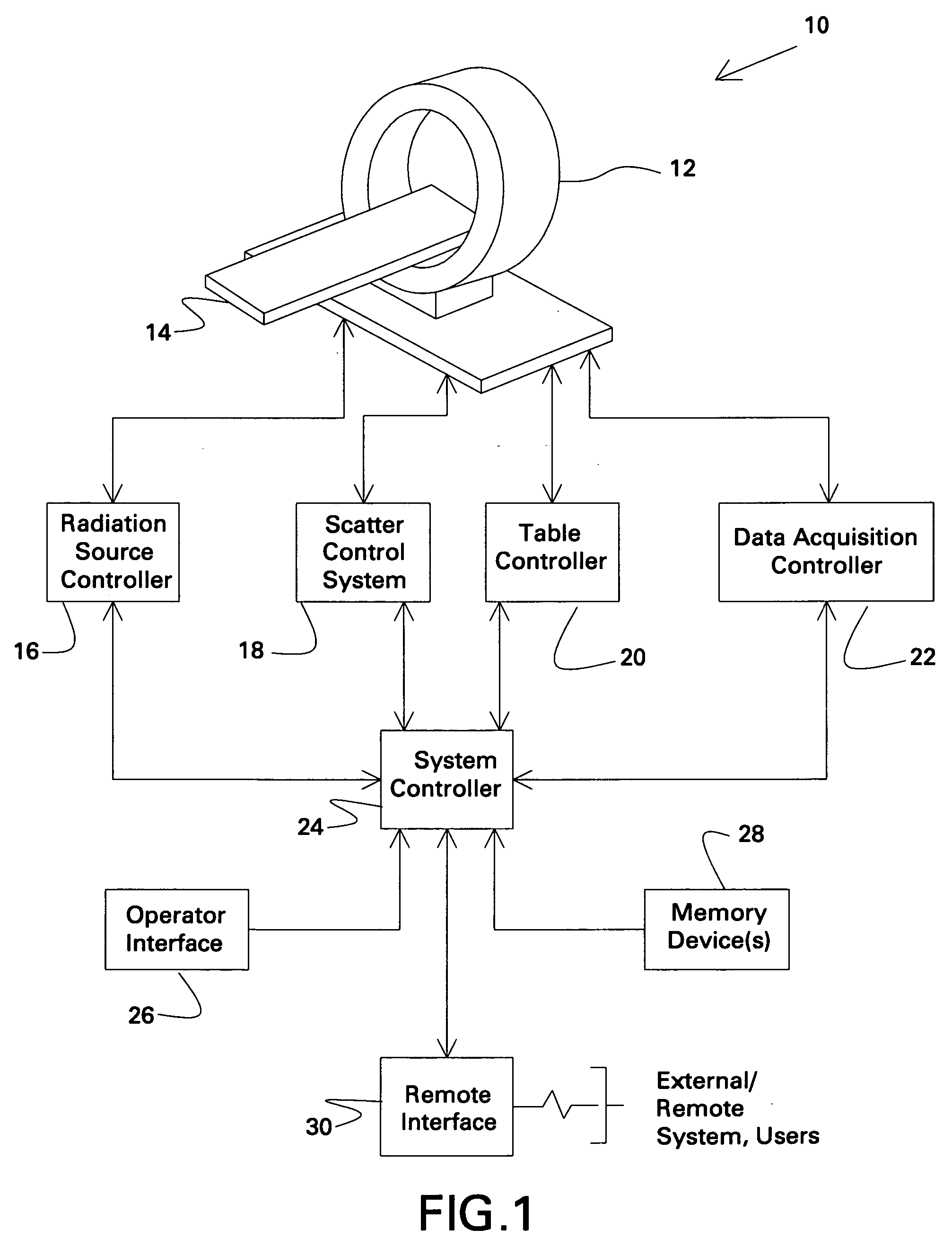
Scatter control system and method for computed tomography
ActiveUS20060023832A1Reduce dispersionDose utilizationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationHandling using diaphragms/collimetersControl systemX-ray
Various configurations for scatter reduction and control are provided for CT imaging. These configurations include an imaging system having a stationary detector extending generally around a portion of an imaging volume and a distributed X-ray source placed proximal to the stationary detector for radiating an X-ray beam toward the stationary detector. A scatter control system is further provided that is configured to adaptively operate in cooperation with the stationary detector and the distributed X-ray source to focally align collimator septa contained therein to the X-ray beam at a given focal point and to provide X-ray beam scatter control.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
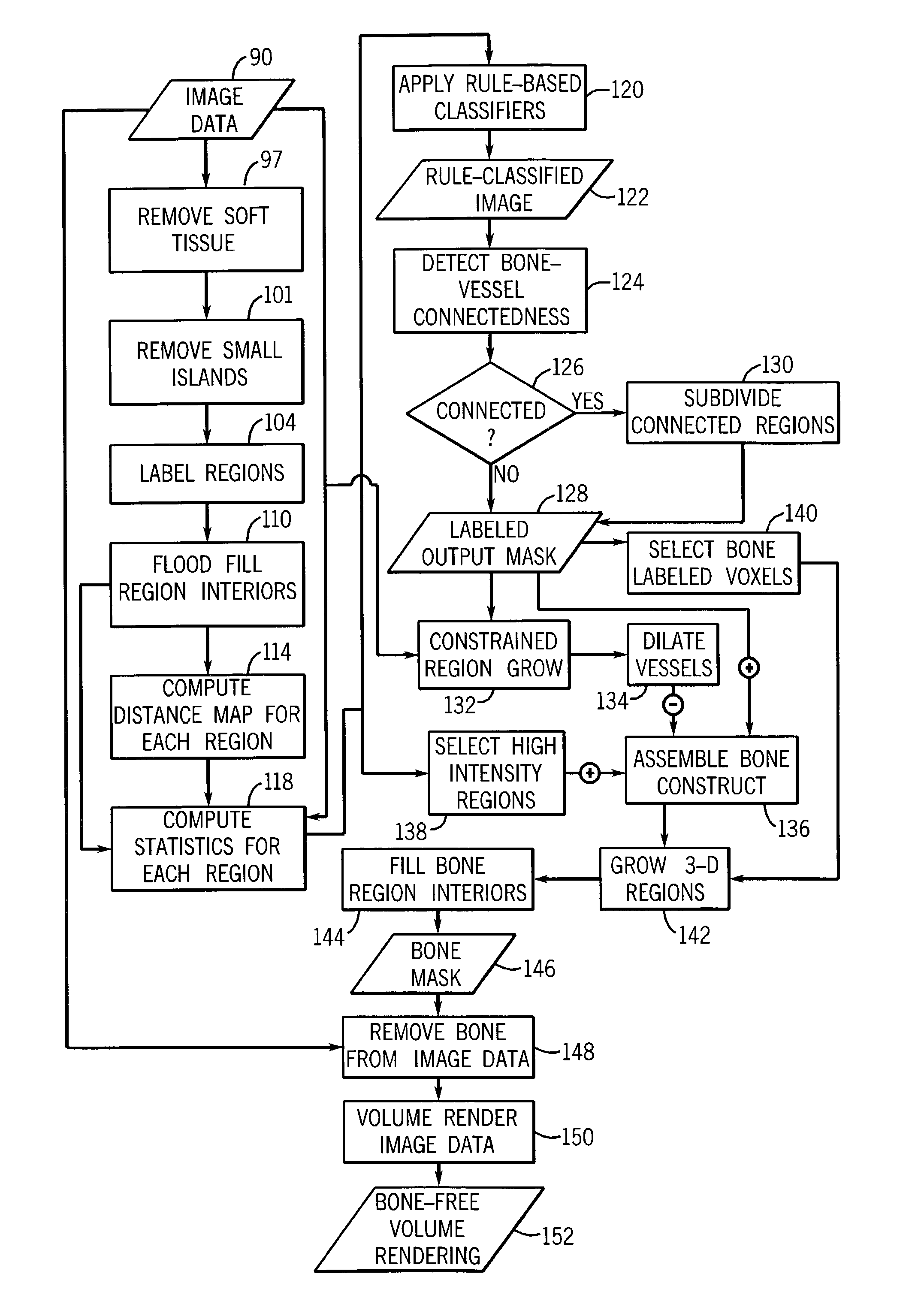
Method and apparatus for removing obstructing structures in CT imaging
InactiveUS7123760B2Image enhancementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationData setLabeled data
A technique is provided for automatically identifying regions of bone or other structural regions within a reconstructed CT volume data set. The technique identifies and labels regions within the data set and computes various statistics for the regions. A rule-based classifier processes the statistics to classify each region. Incidental connections between disparate regions are eliminated. A structure mask, such as a bone mask, is then constructed after exclusion of regions of interest, such as a vascular map. The structure mask may then be used to construct a volume rendering free of the structure, such as bone-free.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
System and method of CT imaging with second tube/detector patching
ActiveUS7433443B1Reduce the impactIncrease contrastMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingX-rayCt imaging
A CT imaging system includes a rotatable gantry having an opening to receive an object to be scanned, a first x-ray emission source attached to the rotatable gantry and configured to emit x-rays toward the object, and a second x-ray emission source attached to the rotatable gantry and configured to emit x-rays toward the object. A first detector is configured to receive x-rays that emit from the first x-ray emission source, and a second detector configured to receive x-rays that emit from the second x-ray emission source. A first portion of the first detector is configured to operate in an integration mode and a first portion of the second detector is configured to operate in at least a photon-counting mode.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
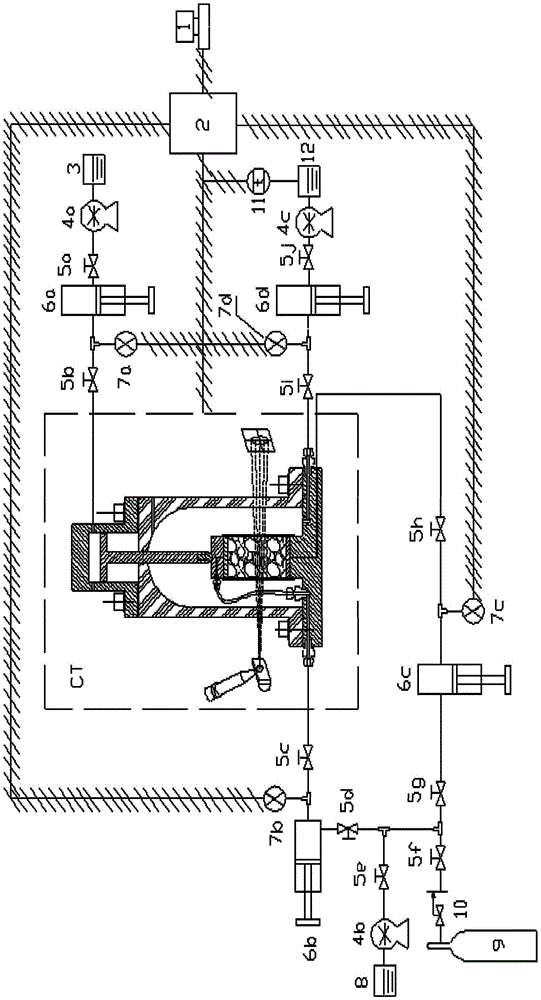
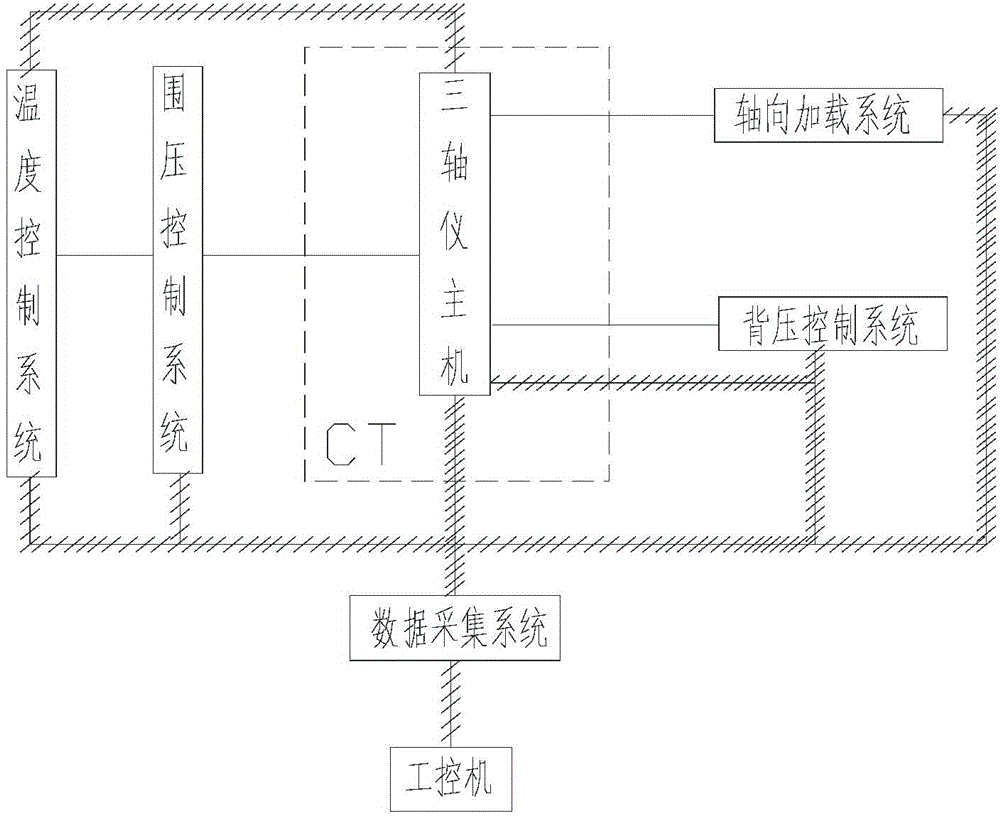
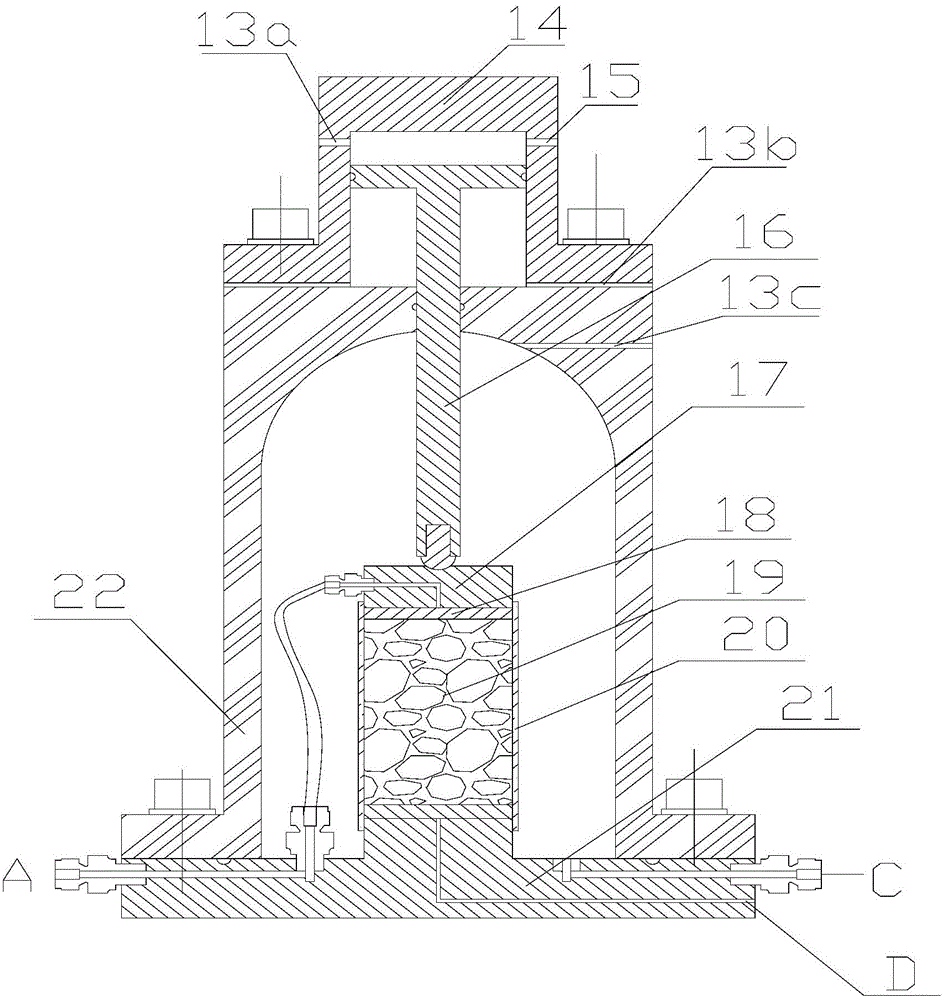
Visual natural gas hydrate sediment mechanical property testing apparatus
ActiveCN104155188AGet macroGet propertiesMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesOcean bottomDecomposition
The invention relates to a visual natural gas hydrate sediment mechanical property testing apparatus, belonging to the field of the measurement of basic natural gas hydrate physical properties. The visual natural gas hydrate sediment mechanical property testing apparatus mainly comprises an automatic-pressing triaxial apparatus main machine, an axial loading system, a confining pressure control system, a backpressure control system, a temperature control system, a data collection system and an X-ray CT (computed tomography) imaging system. The low-temperature high-pressure hydrate triaxial apparatus is organically combined with the X-ray CT imaging system, so that the testing on macro and micro mechanical properties of natural gas hydrate sediments can be synchronously carried out. The visual natural gas hydrate sediment mechanical property testing apparatus can simulate a stress state of a real reservoir stratum, macro and micro mechanical property data of the natural gas hydrate sediments can be acquired, the important significance on disclosing a deformation mechanism of the natural gas hydrate reservoir stratum and a triggering mechanism of geological hazards such as submarine landslide caused by the decomposition of natural gas hydrate can be realized, and an important guiding function for safely and high efficiently exploiting the natural gas hydrate can be realized.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Photon counting CT detector using solid-state photomultiplier and scintillator
ActiveUS7403589B1Improved saturation characteristicHigh gainMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingPhoton counting detectorX-ray
A detector module for a CT imaging system includes a scintillator to convert x-rays to optical photons. The scintillator is optically coupled to a solid-state photomultiplier with internal gain to receive the optical photons and convert them into a corresponding electrical signal output.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
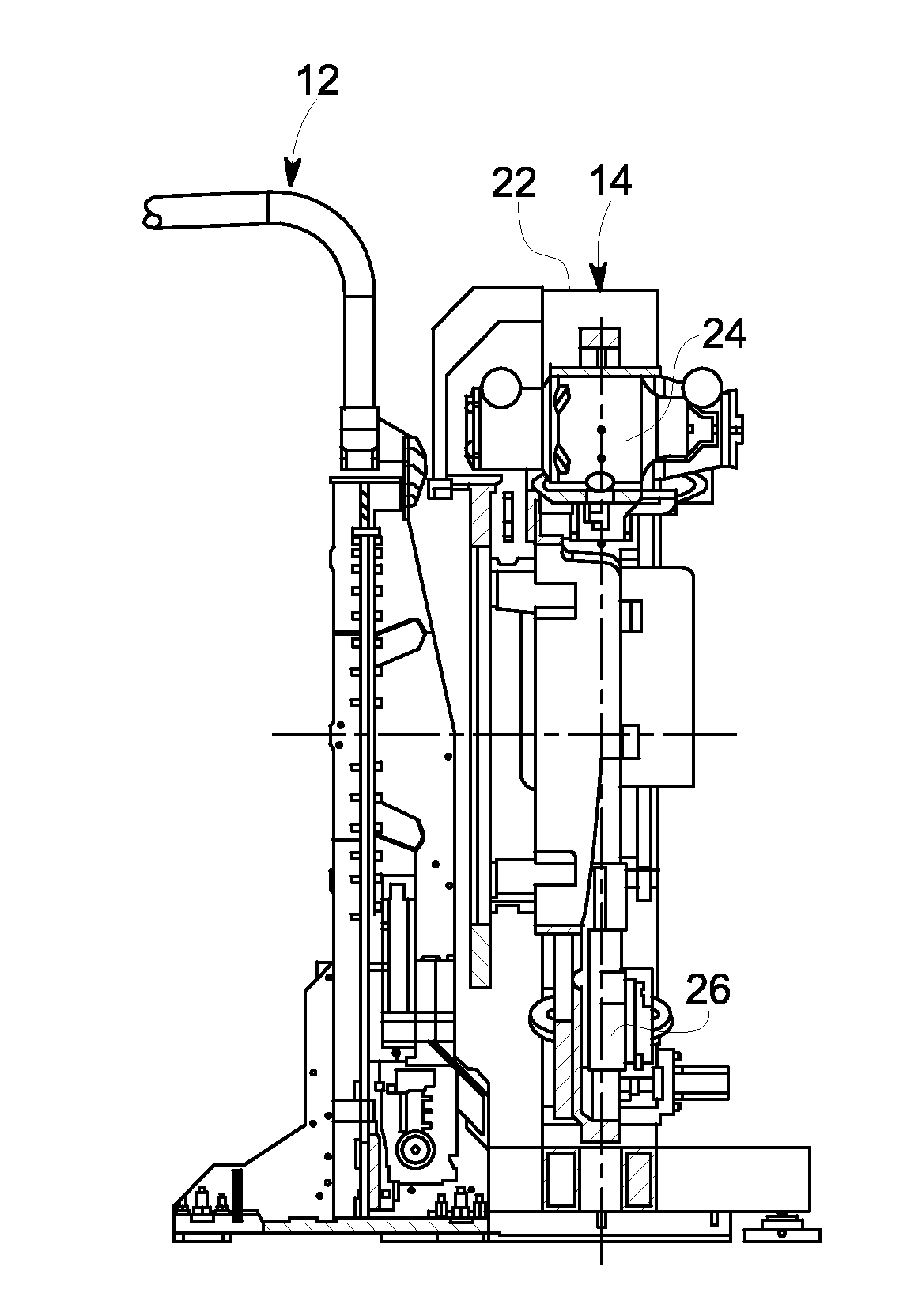
Mobile Computerized Tomography (CT) imaging system with cordless and wireless capabilities
ActiveUS20070183588A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationPatient positioning for diagnosticsOn boardEngineering
A mobile CT imaging system comprising a frame; a CT imaging unit mounted to the frame, wherein the CT imaging unit is adapted to scan anatomical objects and generate images of the same; a transport mechanism mounted to the frame, wherein the transport mechanism comprises a fine movement mechanism for moving the CT imaging unit precisely, relative to the patient, during scanning; an on-board networking unit mounted to the frame, wherein the on-board networking unit is adapted to connect the CT imaging unit to a workstation, hospital PACs system or other IT network without requiring the use of conventional physical cabling during the same; and an on-board power unit mounted to the frame, wherein the on-board power unit is adapted to provide the electrical power needed to operate the CT imaging unit, transport mechanism and networking unit without requiring the use of conventional physical cabling during the same.
Owner:NEUROLOGICA CORP
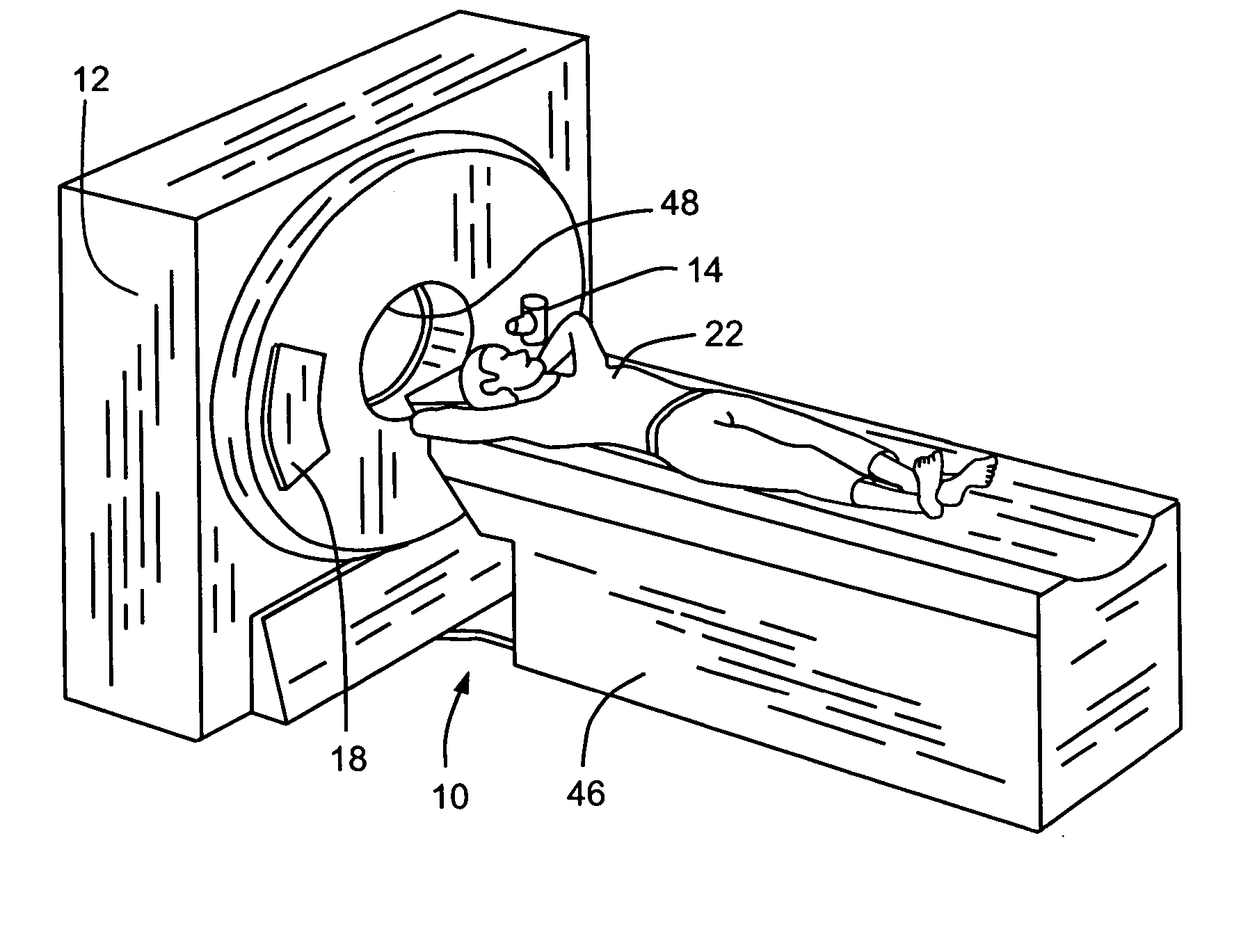
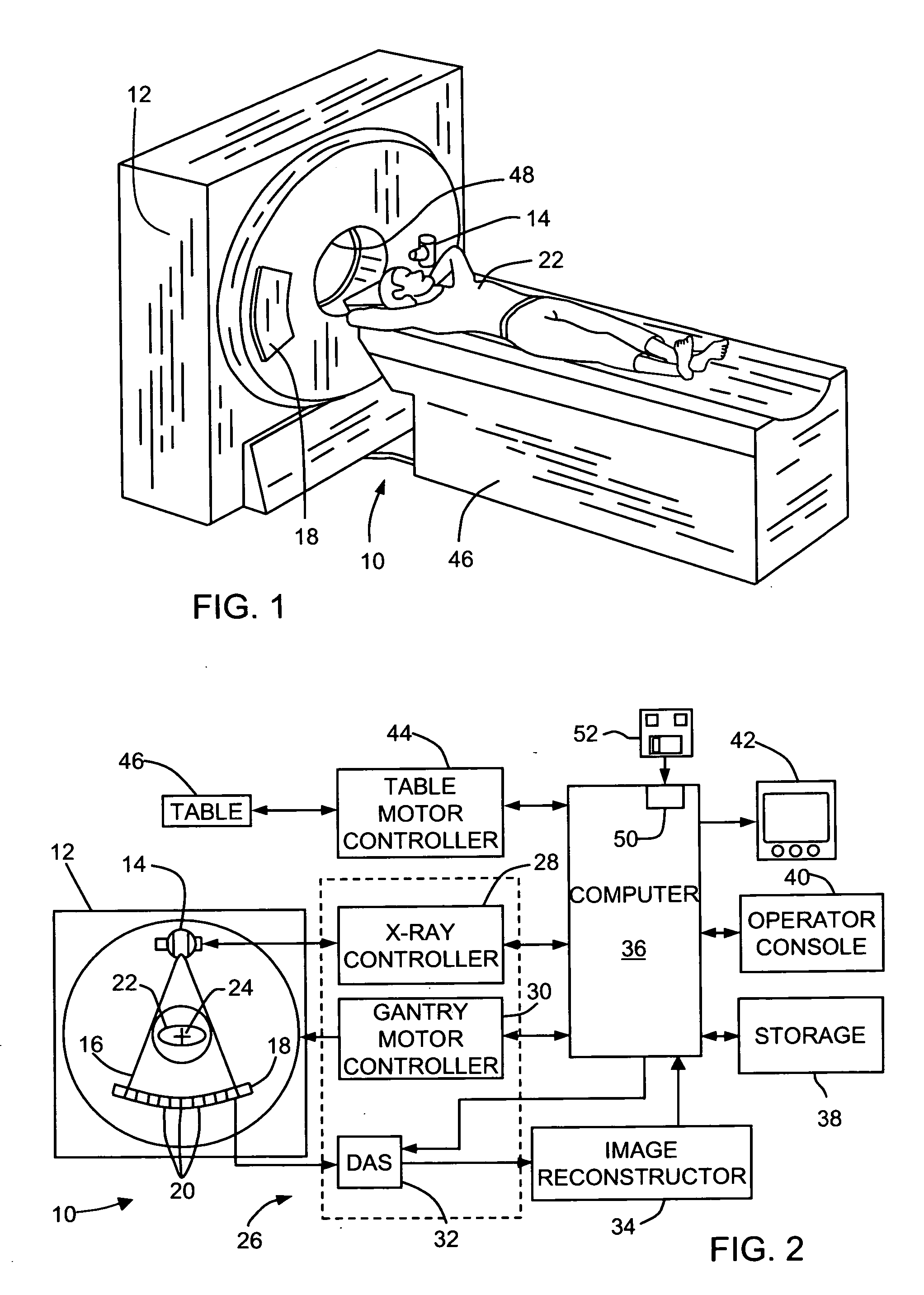
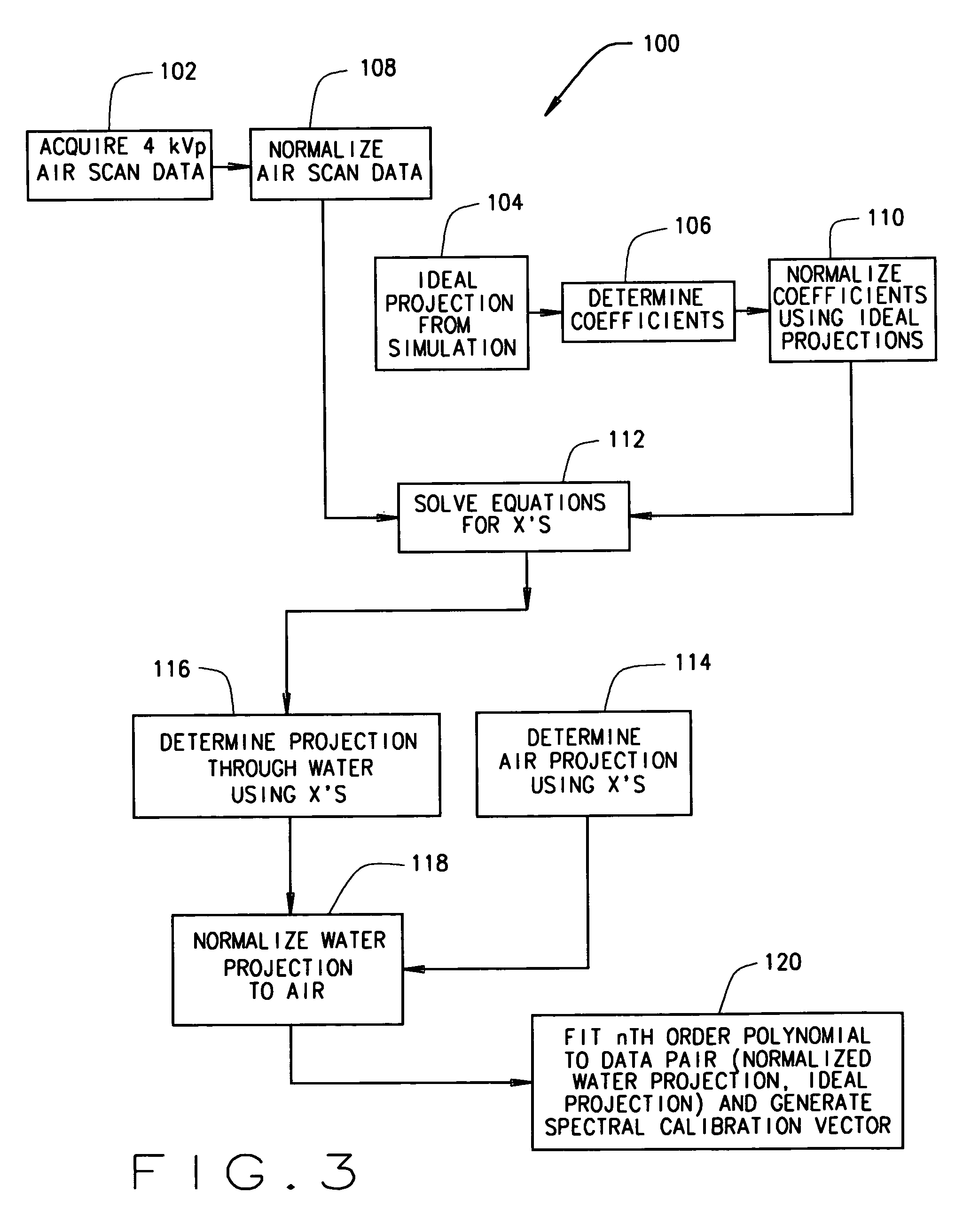
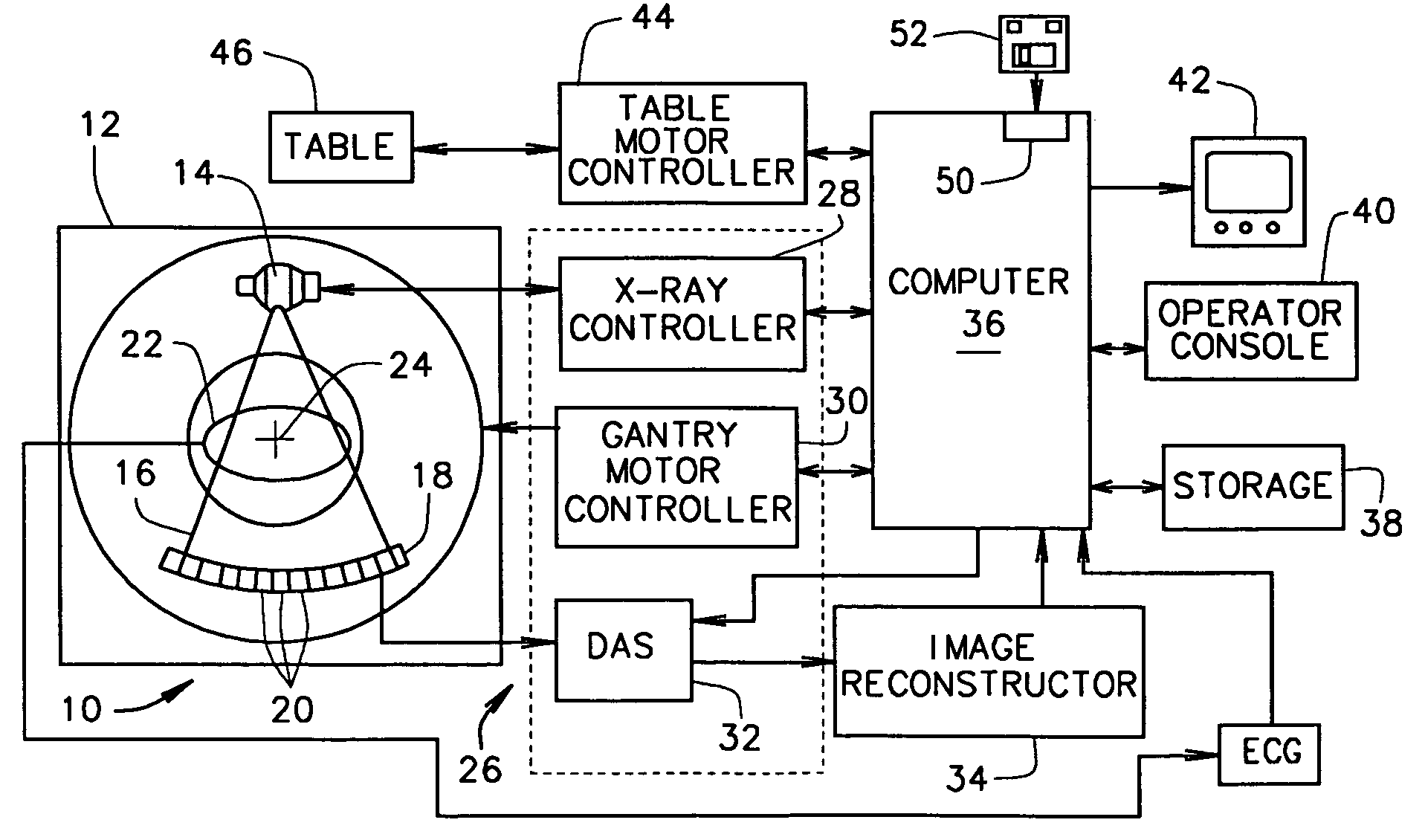
Method and apparatus for correcting for beam hardening in CT images
InactiveUS20060159223A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingRadiologyBeam hardening
A method for determining a correction for beam hardening in CT images includes obtaining air scans at a plurality of kVp's, determining detection efficiencies for detector elements of the CT imaging apparatus, and estimating projection values through a combination of at least two different materials of different thicknesses. The method further includes determining a transfer function that translates the estimated projection values into ideal projection values for at least two of the different materials and storing the transfer function as the beam hardening correction for images of the CT imaging apparatus.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Dual energy scanning protocols for motion mitigation and material differentiation
ActiveUS20070041490A1Reducing mis-registrationMinimal mis-registrationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingTomographyDual energy
A method for reducing mis-registration during multiple energy scanning on computed tomographic (CT) imaging systems or multiple energy electron beam tomographic (EBT) systems includes scanning a portion of a patient including a cyclically moving body part using a multiple energy computed tomographic (CT) imaging system or multiple energy electron beam tomographic (EBT) system having at least two different energies, monitoring the cyclically moving body part, and gating the multiple energy CT imaging system or multiple energy EBT system in accordance with the monitored cyclically moving body part so that acquisitions are acquired at at least two different kVps. The data acquired at the different kVps are then utilized to generate material decomposition images of the cyclically moving body part.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
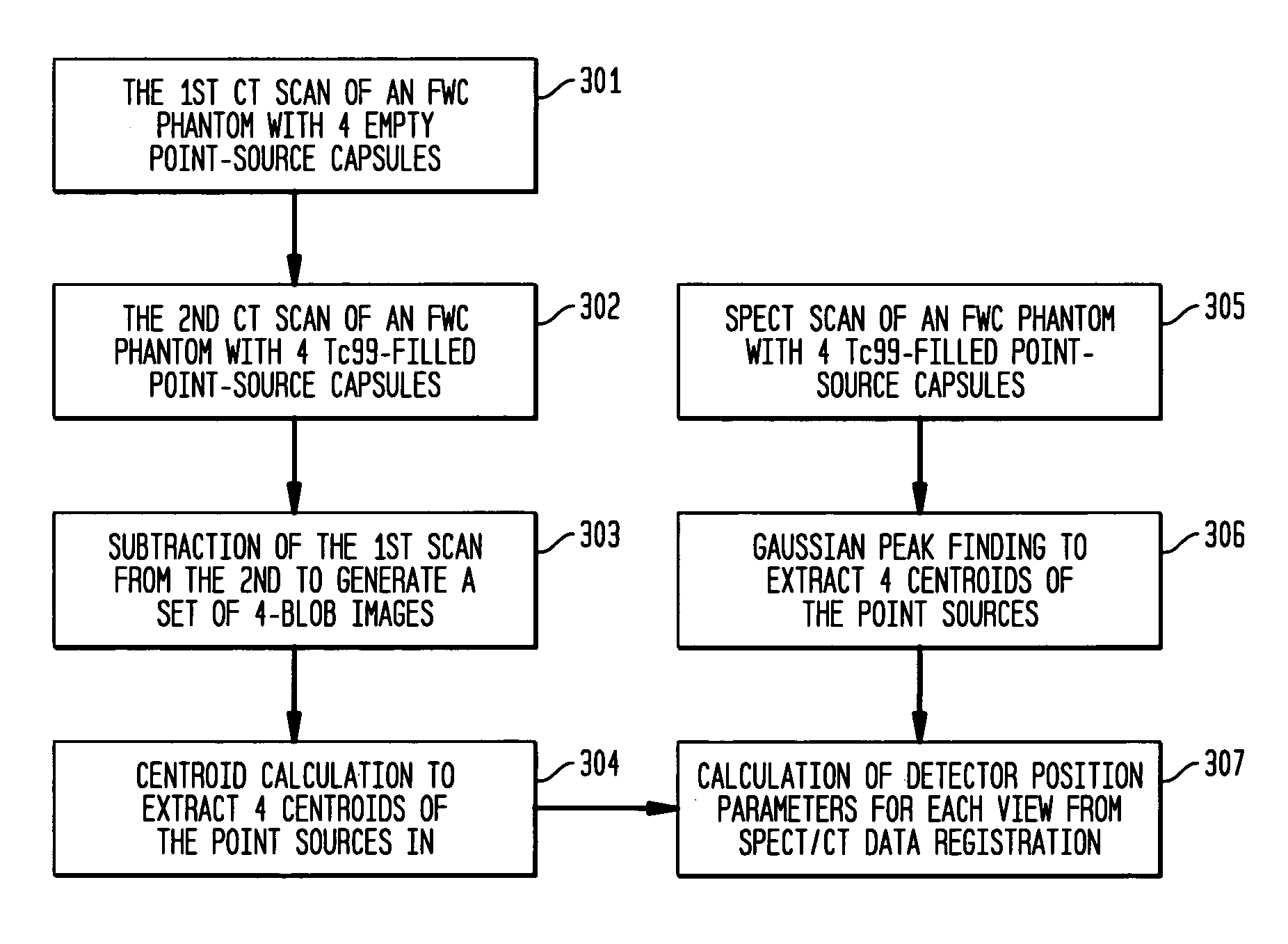
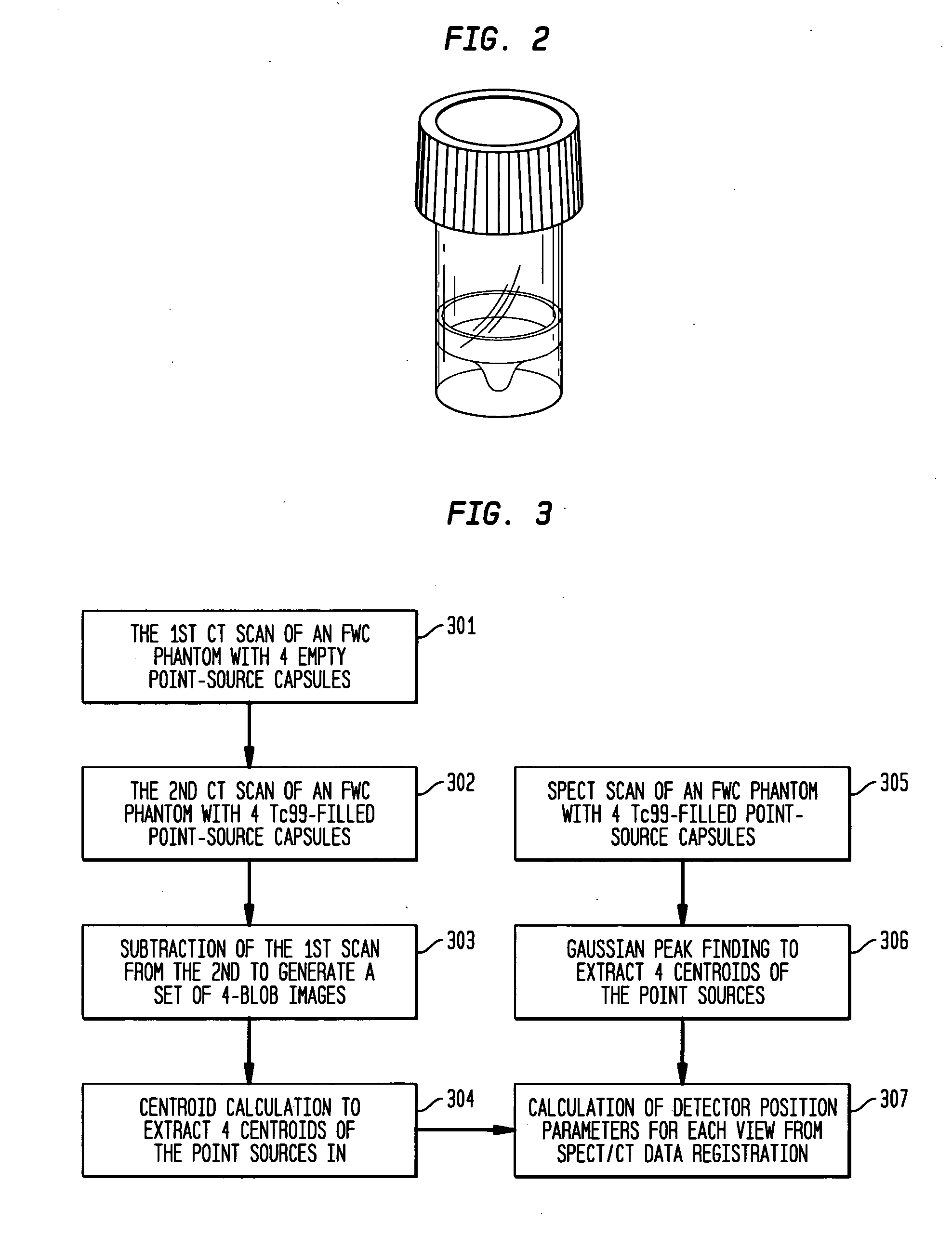
Detector head position correction for hybrid SPECT/CT imaging apparatus
ActiveUS20060214097A1Accurate image registrationSolve the real problemMaterial analysis by optical meansCalibration apparatusThree dimensional ctProjection image
A system and method provide for more accurate SPECT / CT image registration. CT data is utilized to establish a global spatial coordinate system of a common test phantom. The common test phantom is then used to obtain a set of point source nuclear images. Three-dimensional CT point source data is mapped to a two-dimensional image plane of corresponding point source data, to obtain a pair of intersecting projection cones that are used to obtain a set of detector head position correction parameters to correct detector head positioning in the CT coordinate system when obtaining SPECT projection images of the same object.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Medical examination device for CT imaging and for nuclear medical imaging
InactiveUS20110280364A1Enhance the imageSharp contrastMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingMedical imagingCt imaging
A medical examination device for CT imaging and for nuclear medical imaging is provided. The medical examination device has an essentially ring-shaped gantry with a CT imaging arrangement and a nuclear medical imaging arrangement. The gantry has an especially laterally arranged, fold-out or removable segment for creating an access opening to the interior of the gantry.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method And System Of Adaptive Control For Reducing Motion Artifacts And Patient Dose In Four Dimensional Computed Tomography
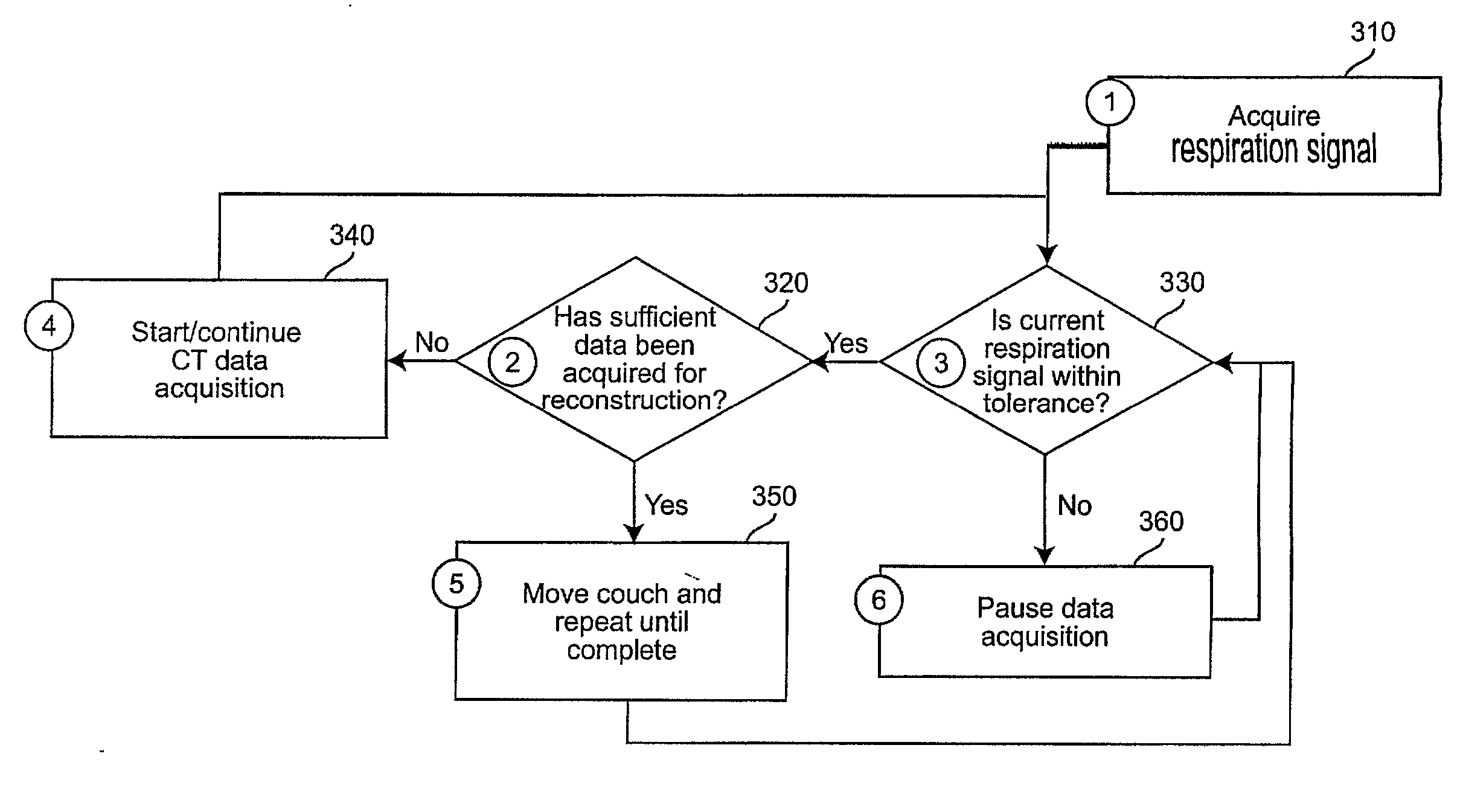
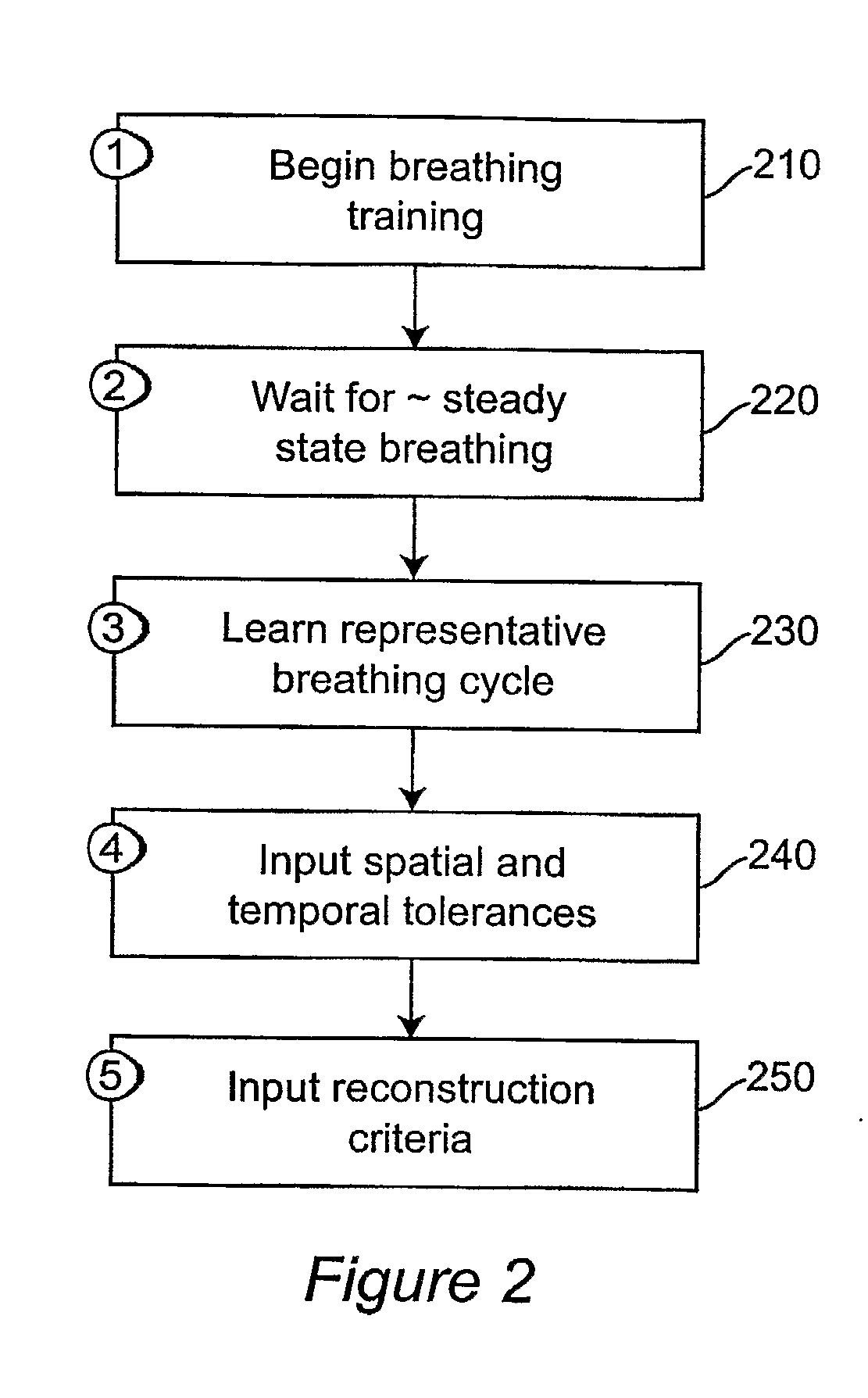
InactiveUS20070286331A1Weakening rangeMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingData acquisitionFour-Dimensional Computed Tomography
Motion artifacts and patient dose during 4D CT imaging are reduced by adaptive control of data acquisition. The respiration signal (310) and CT data acquisition (340) are linked, such that ‘bad’ data from erratic breathing cycles that cause artifacts is not acquired by pausing CT data acquisition (360) when erratic breathing is detected, and not resuming CT data acquisition until steady-state respiration is resumed. Training data is used to develop a tolerance envelope for a respiratory signal such that for erratic breathing cycles the respiratory signal is not within the tolerance envelope (330).
Owner:VIRGINIA COMMONWEALTH UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com