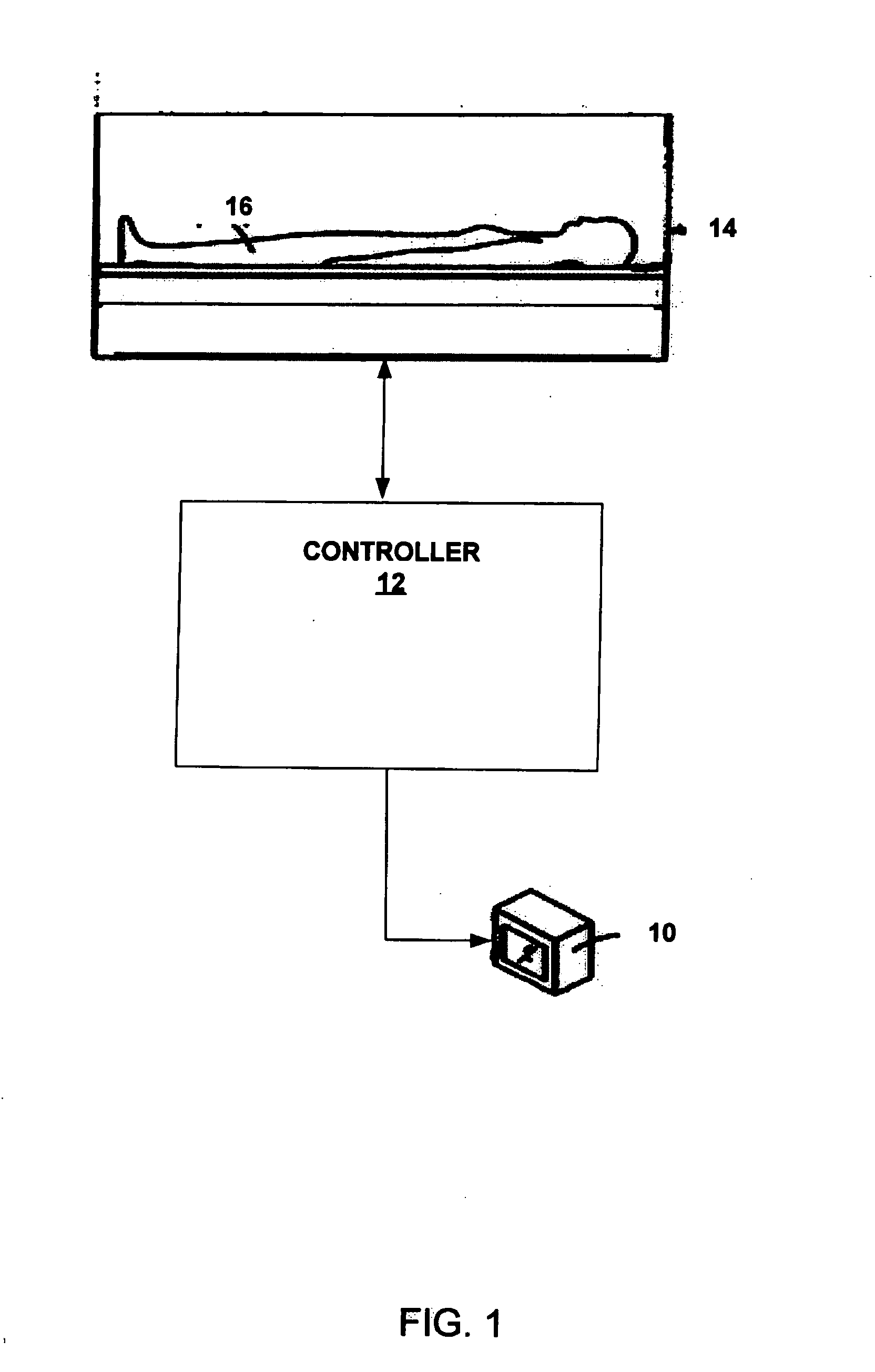
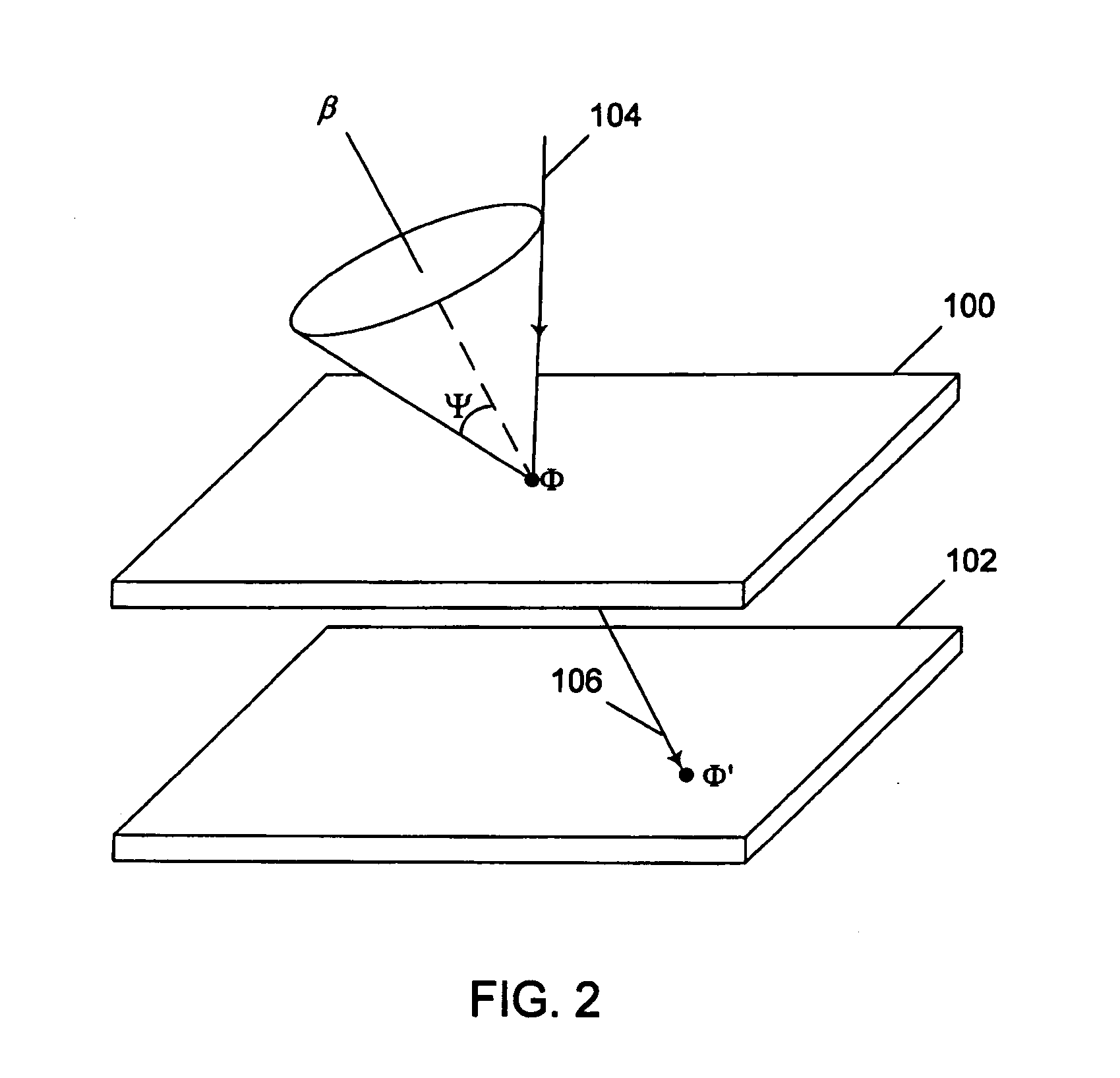
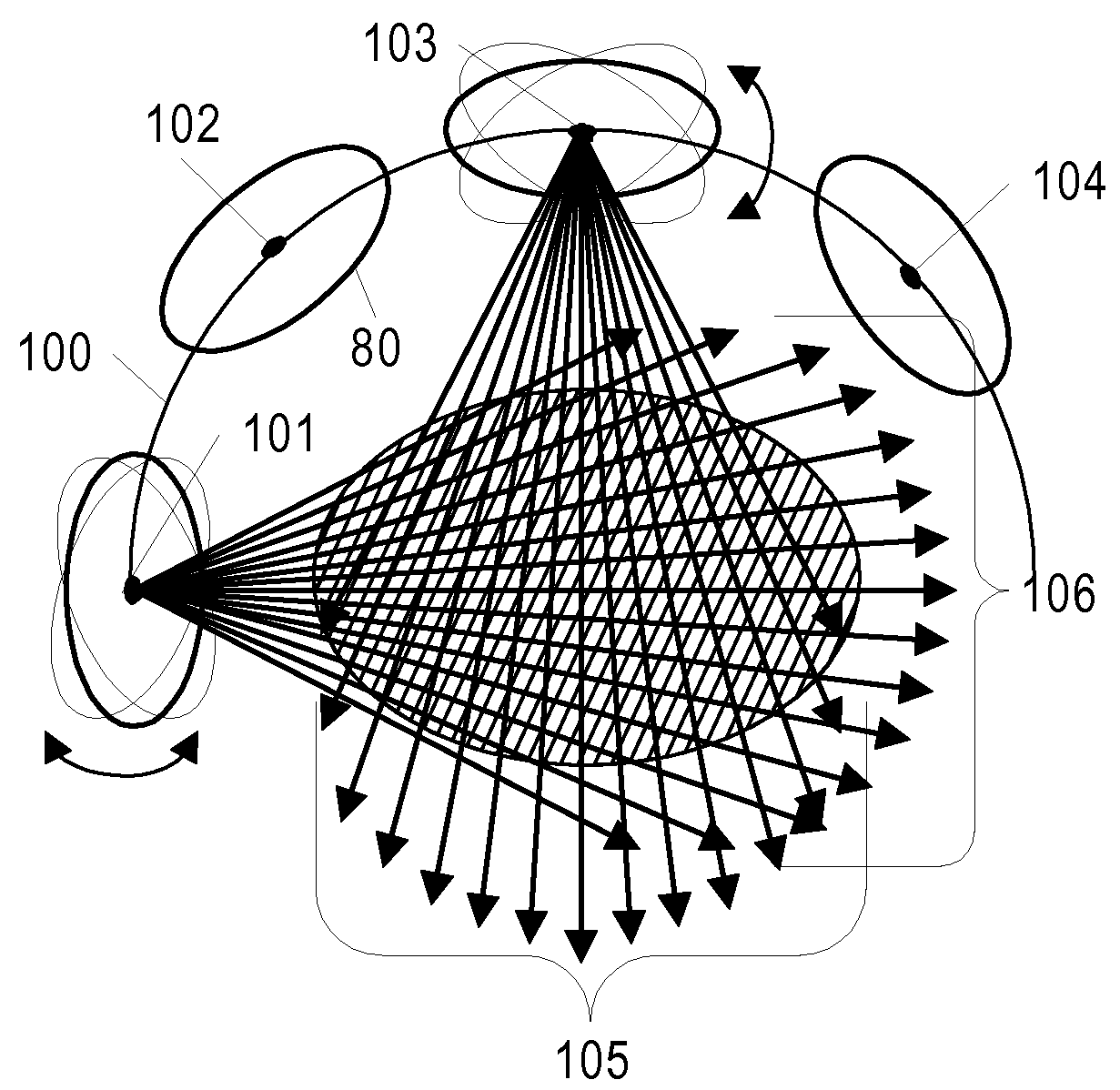
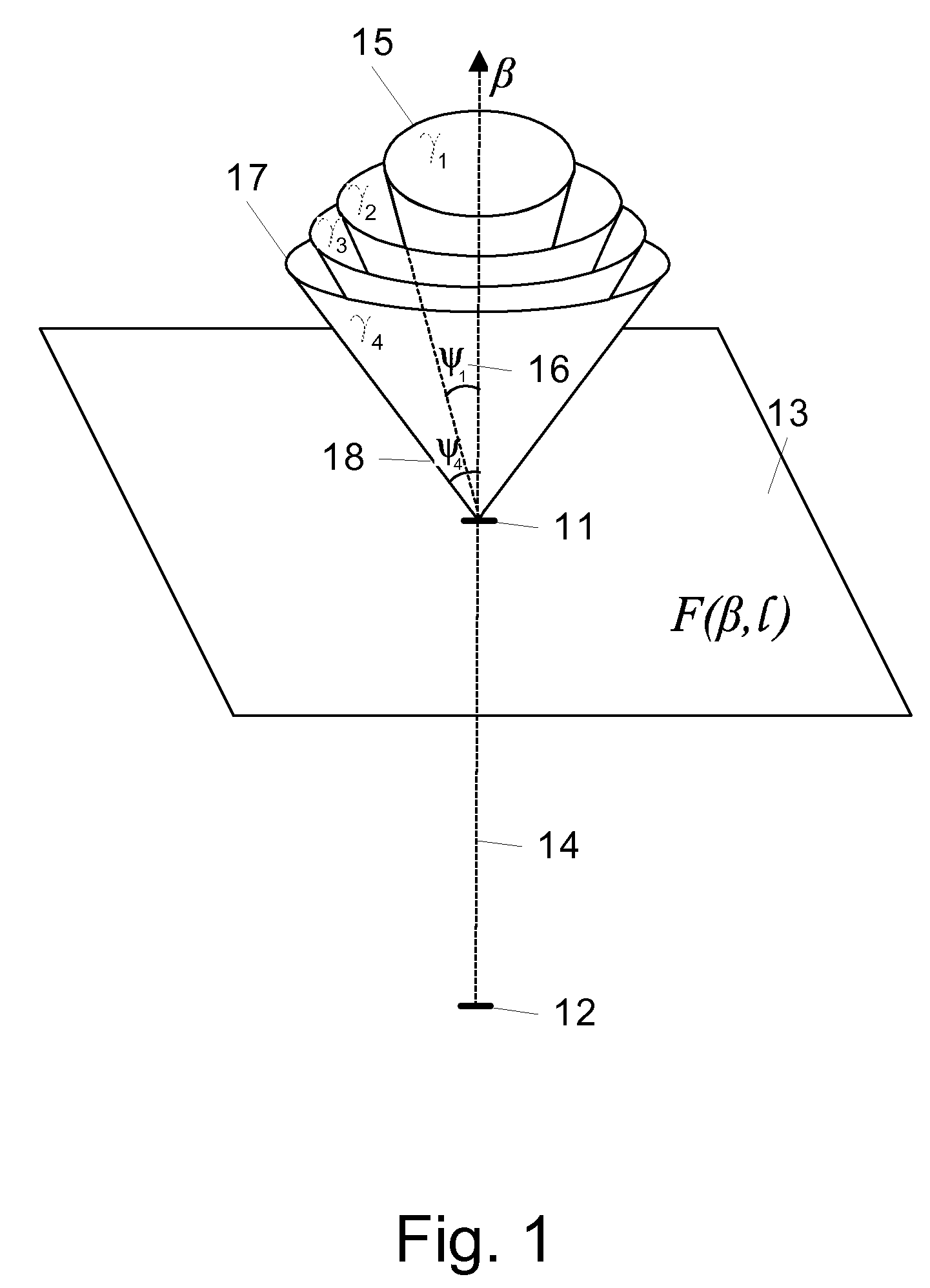
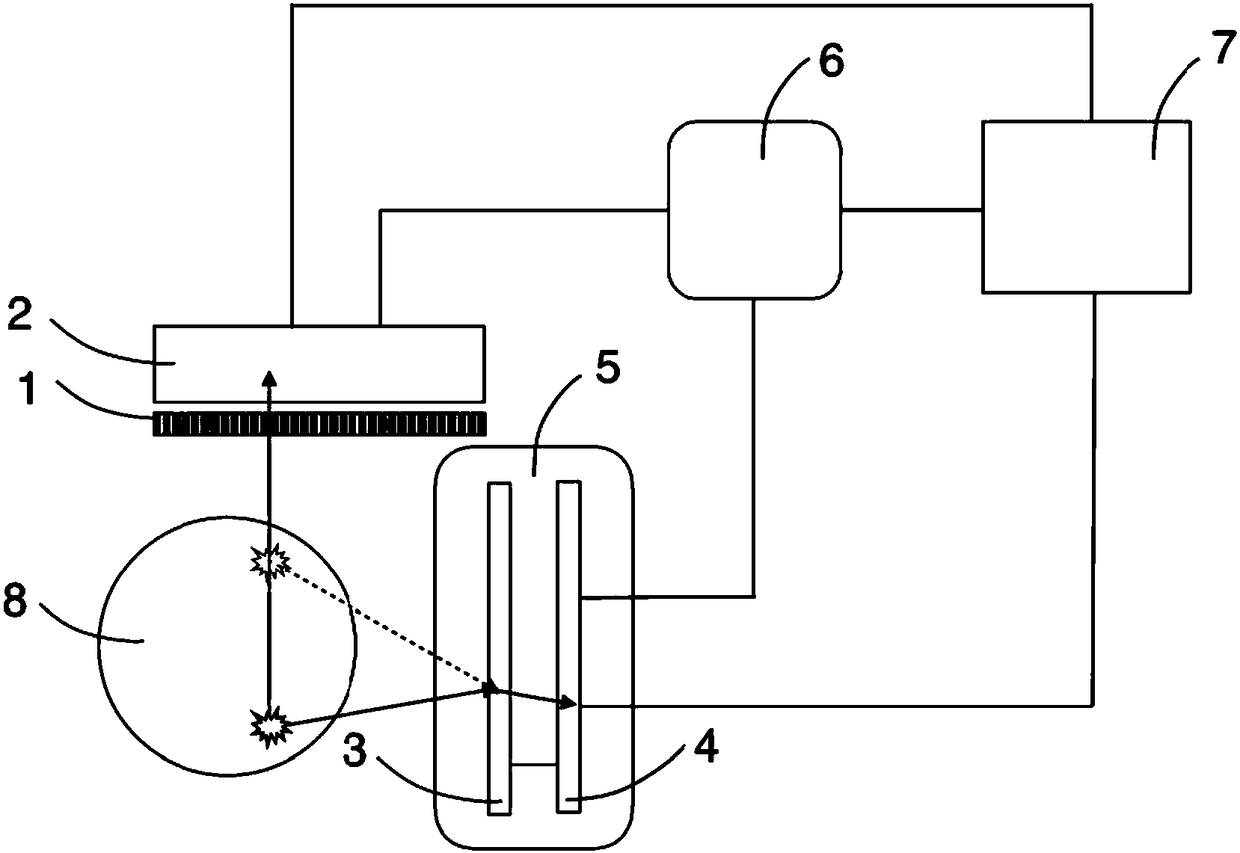
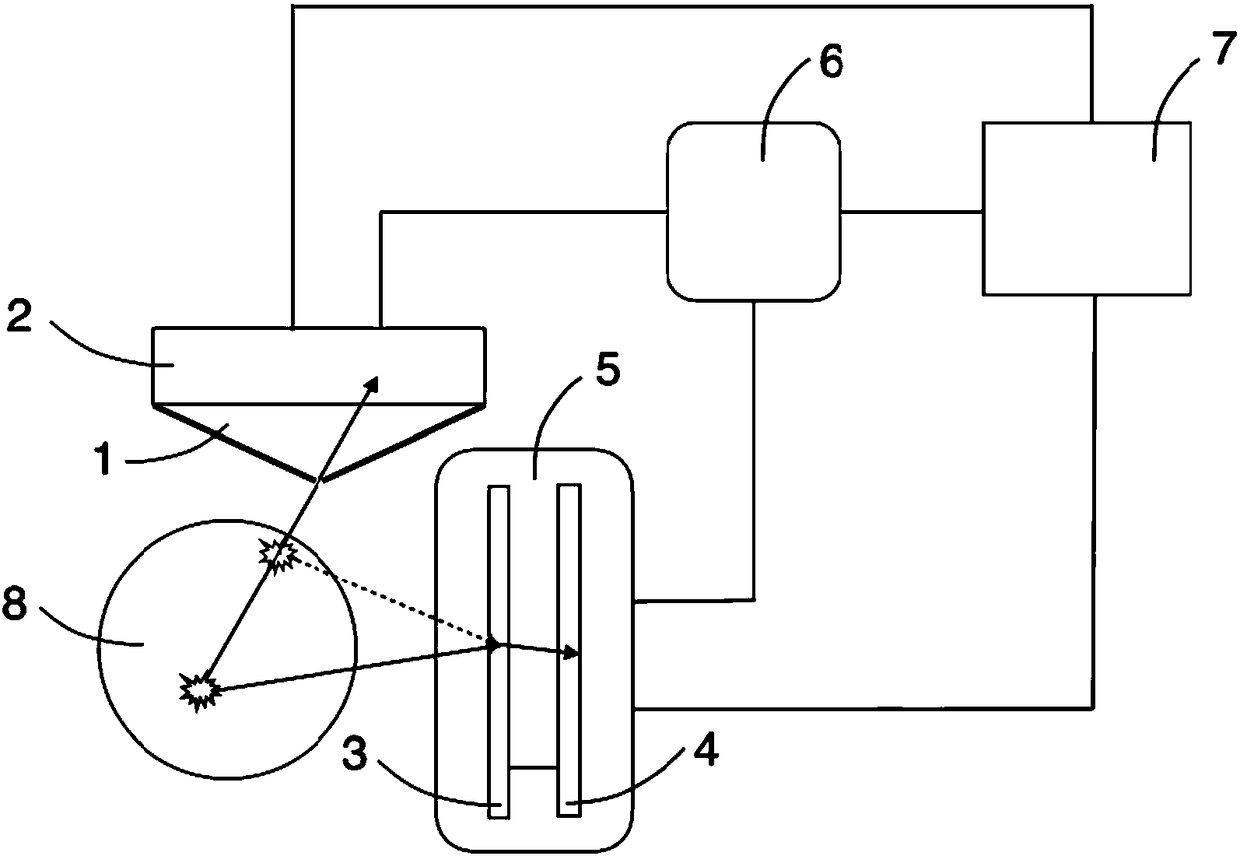
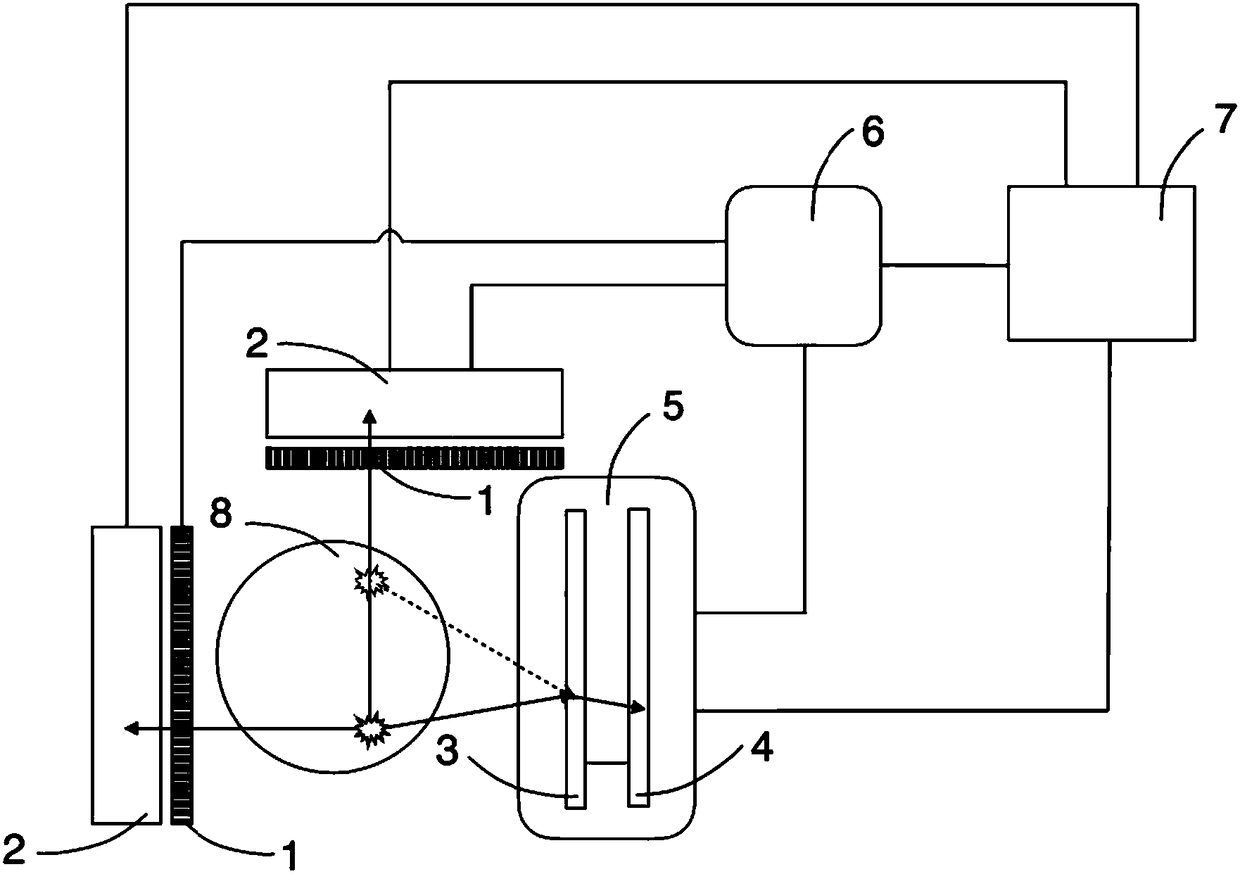
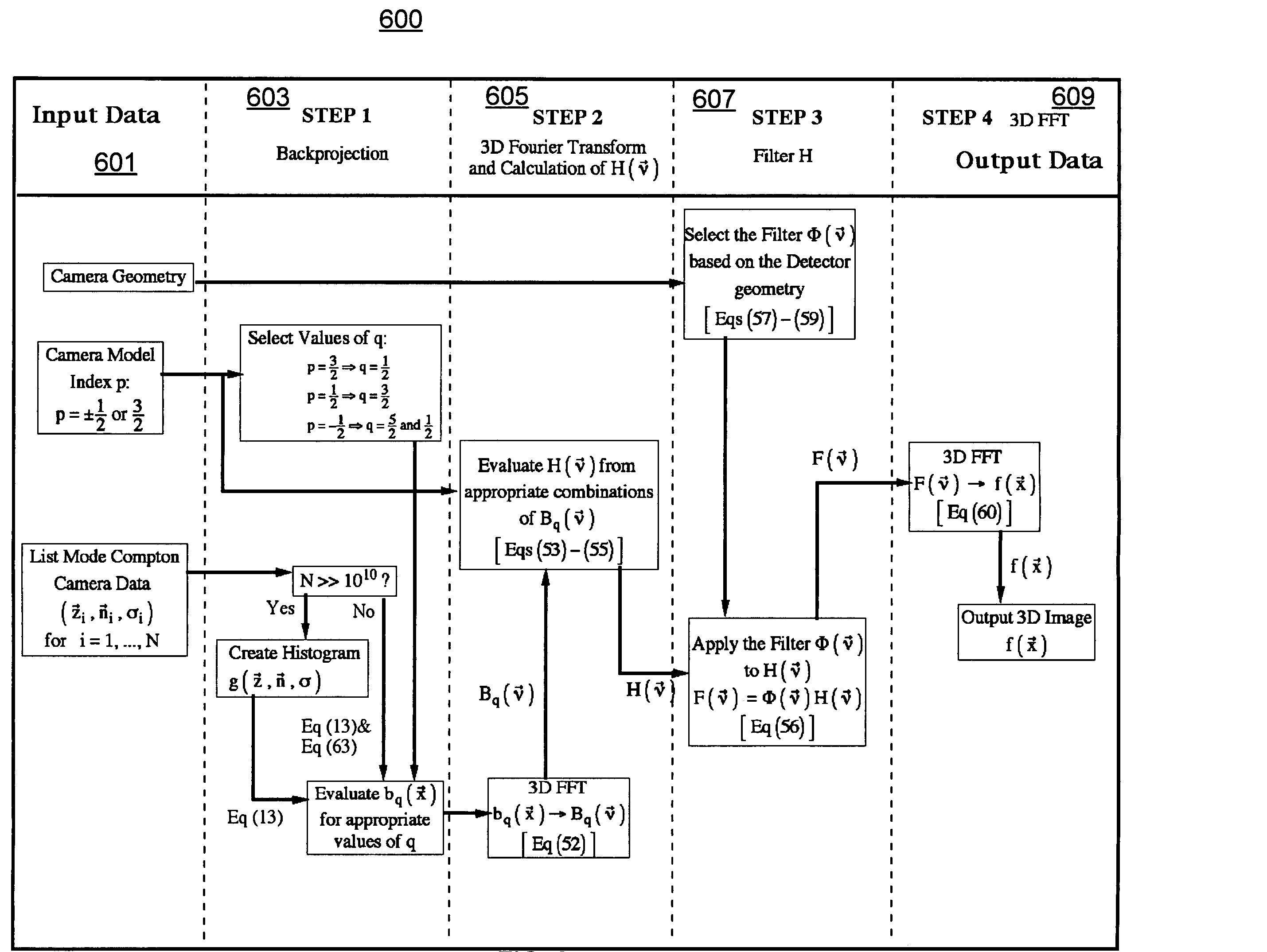
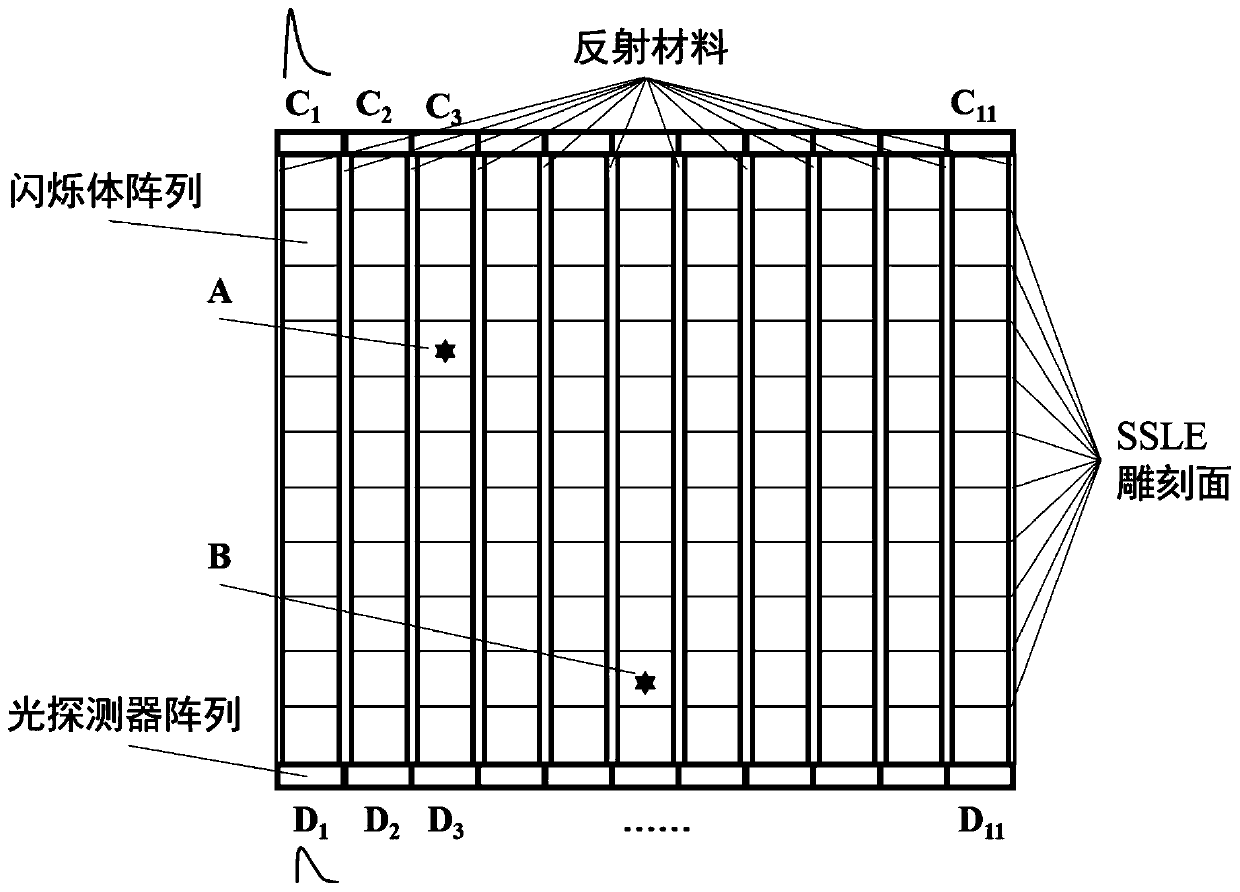
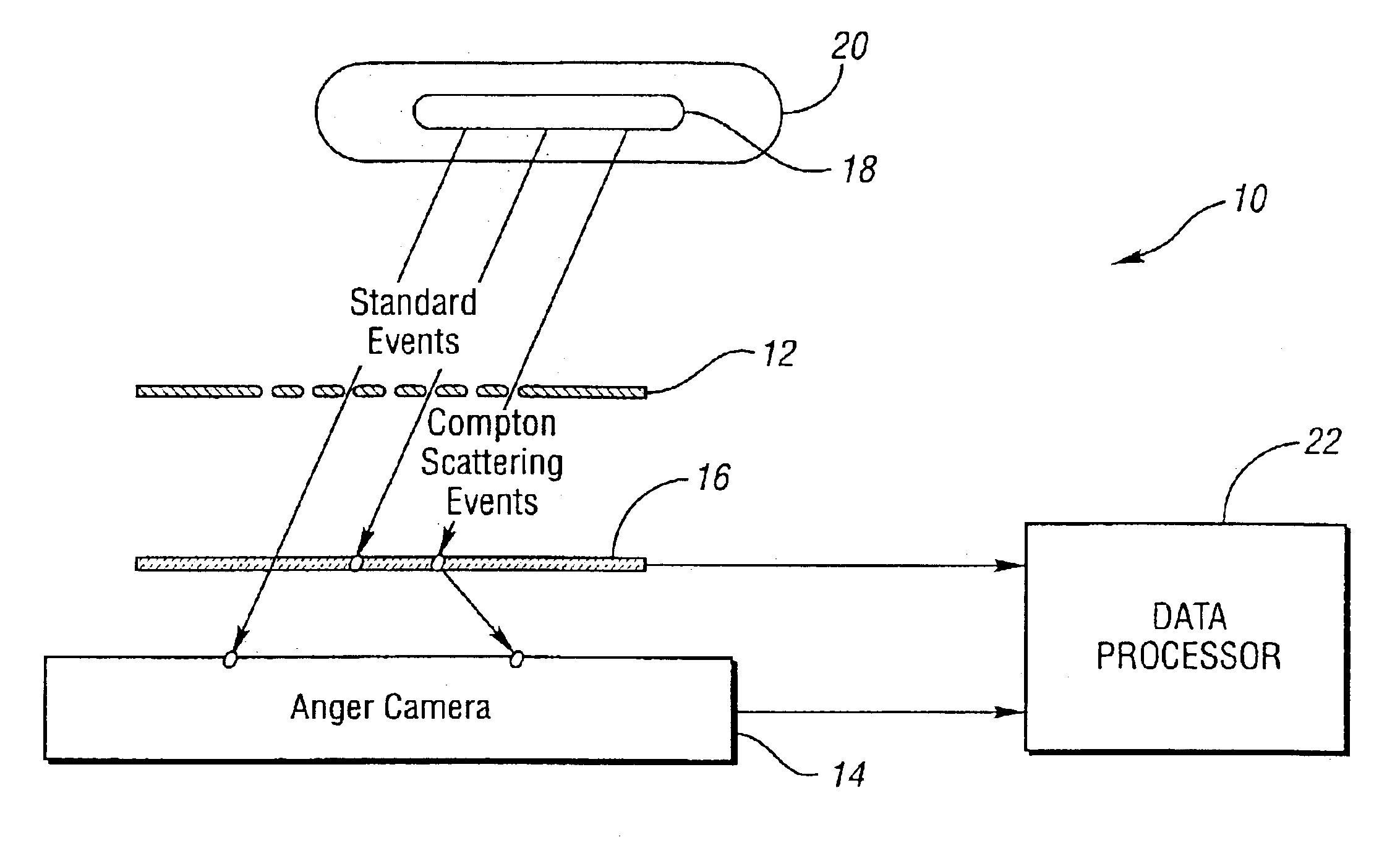
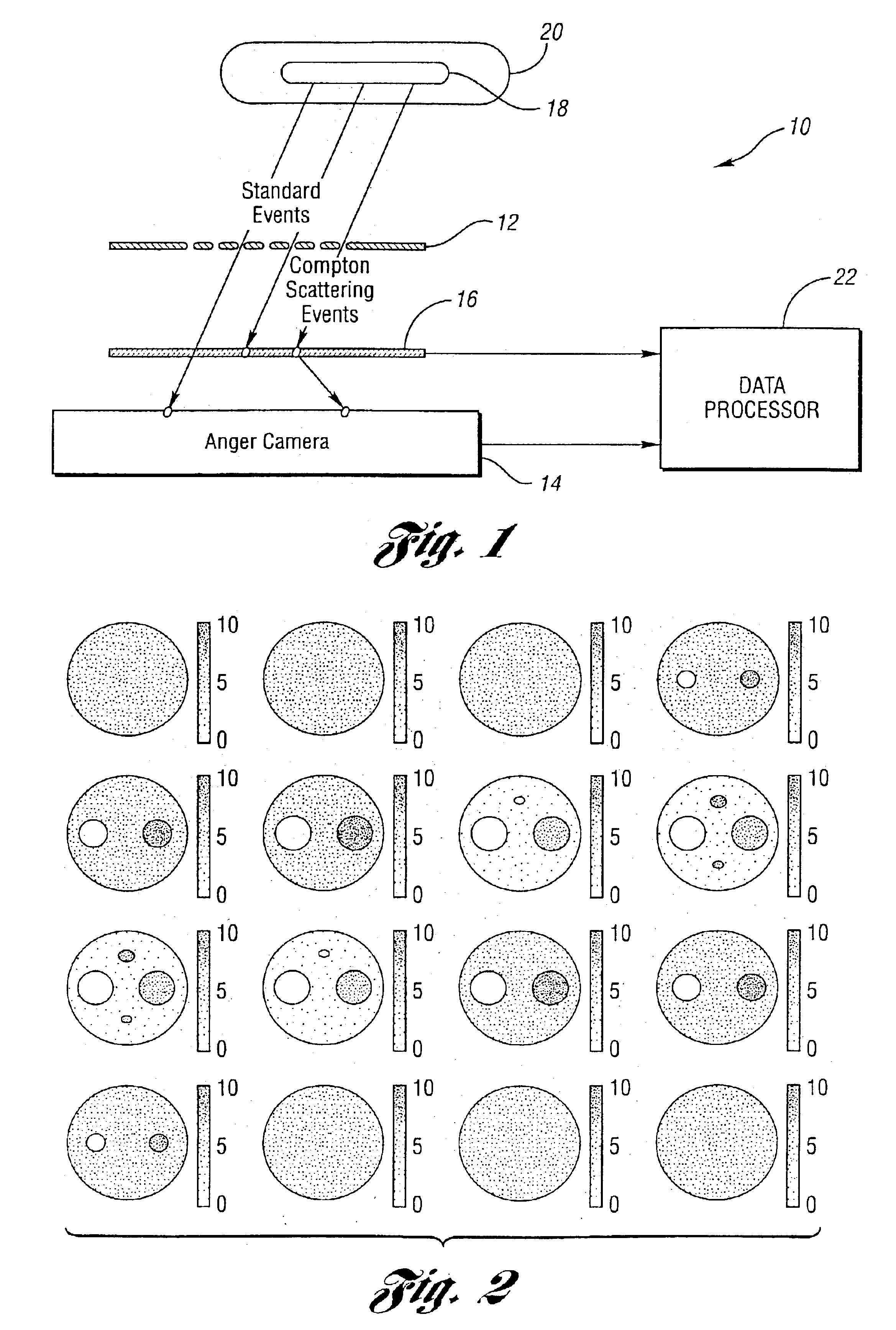
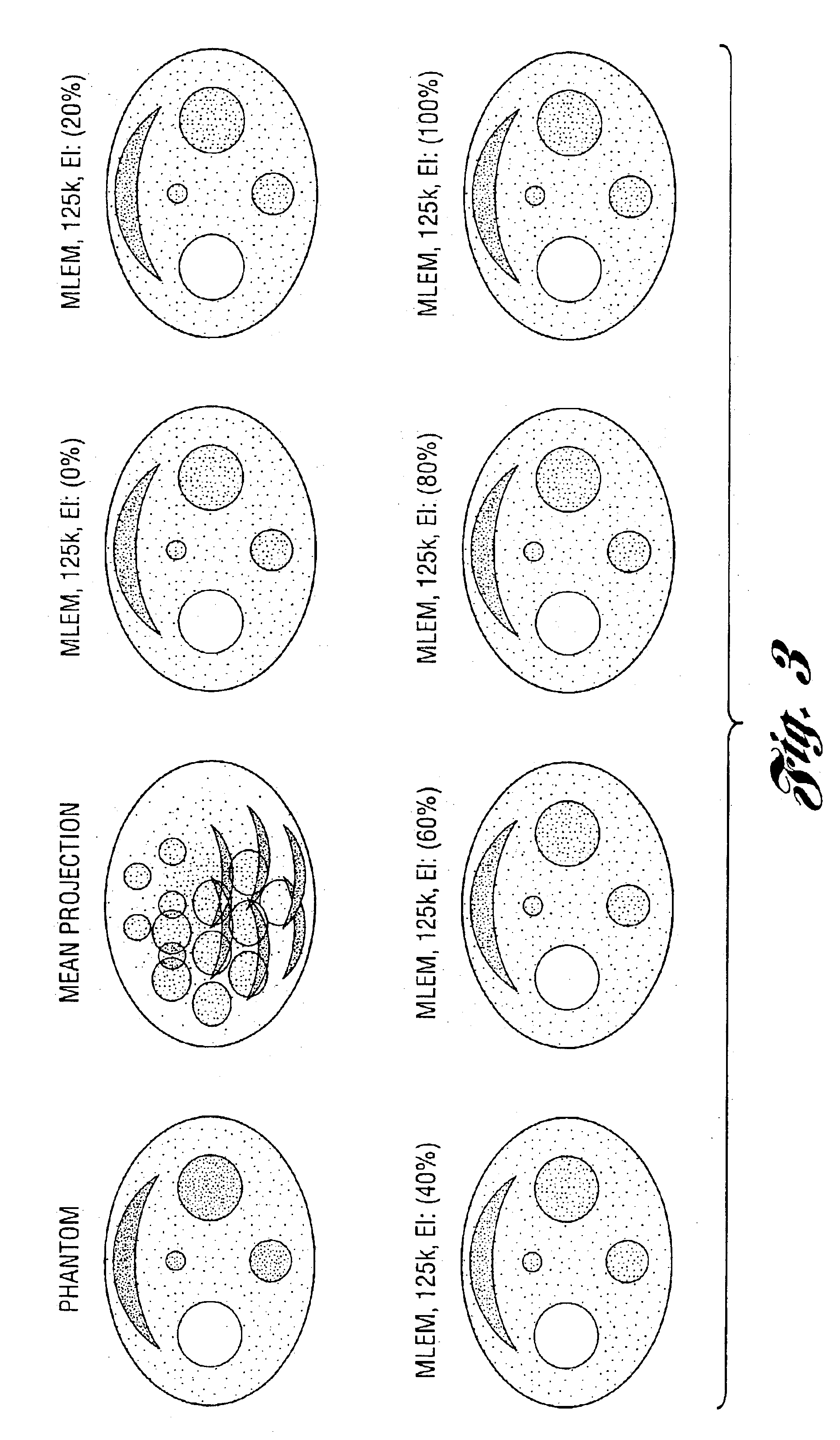
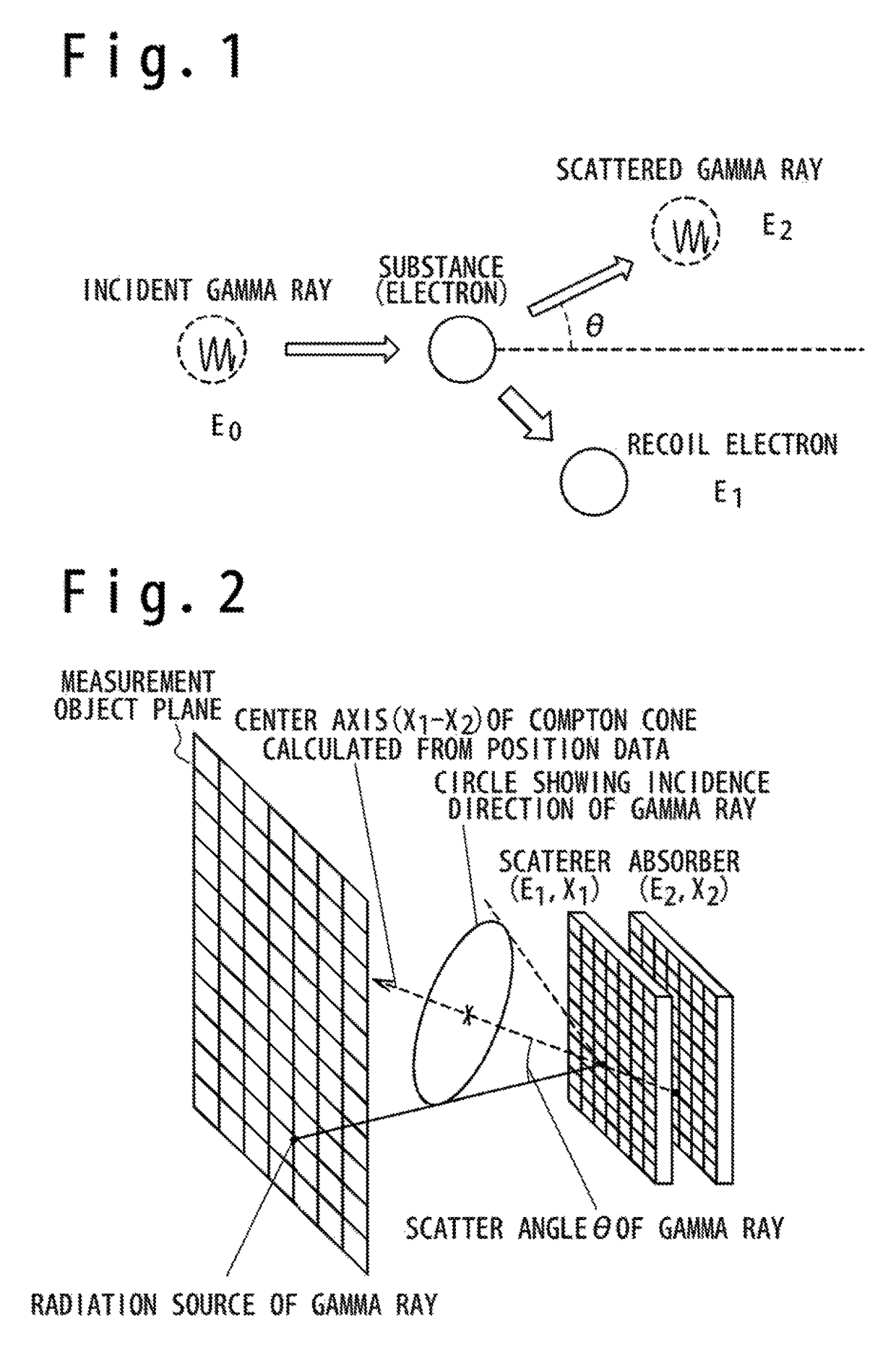
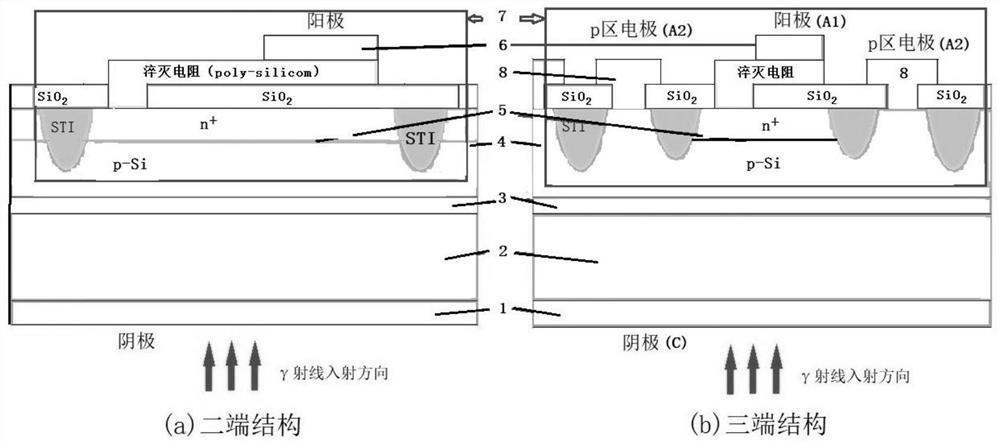
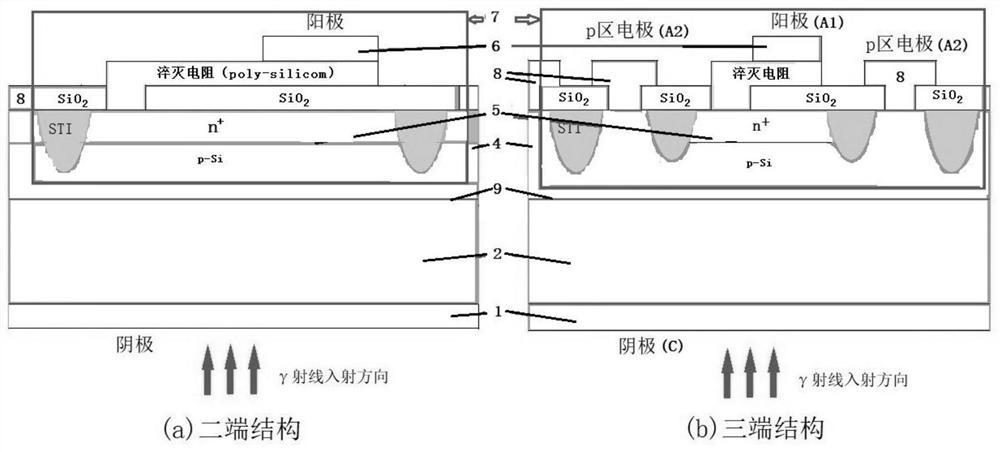
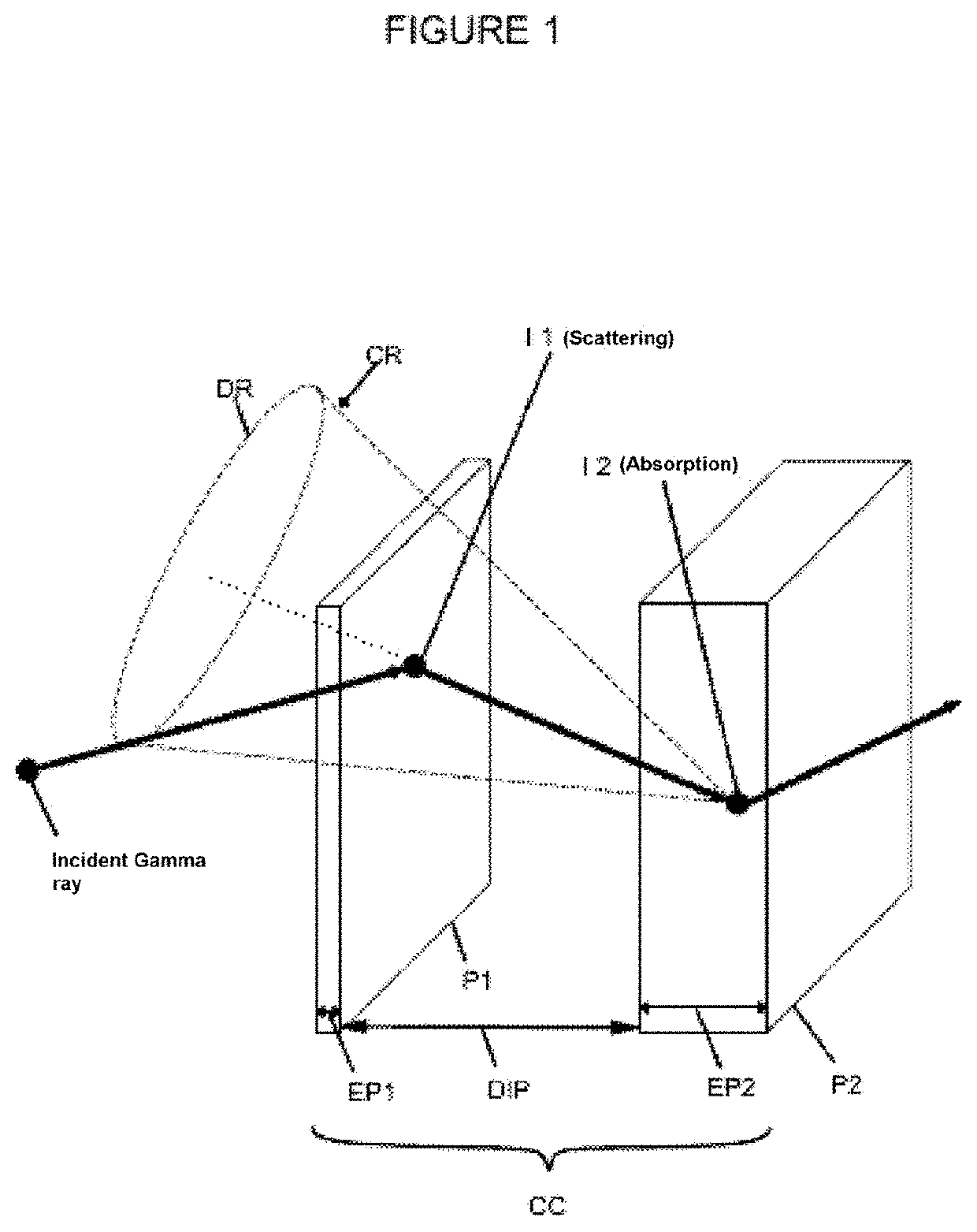
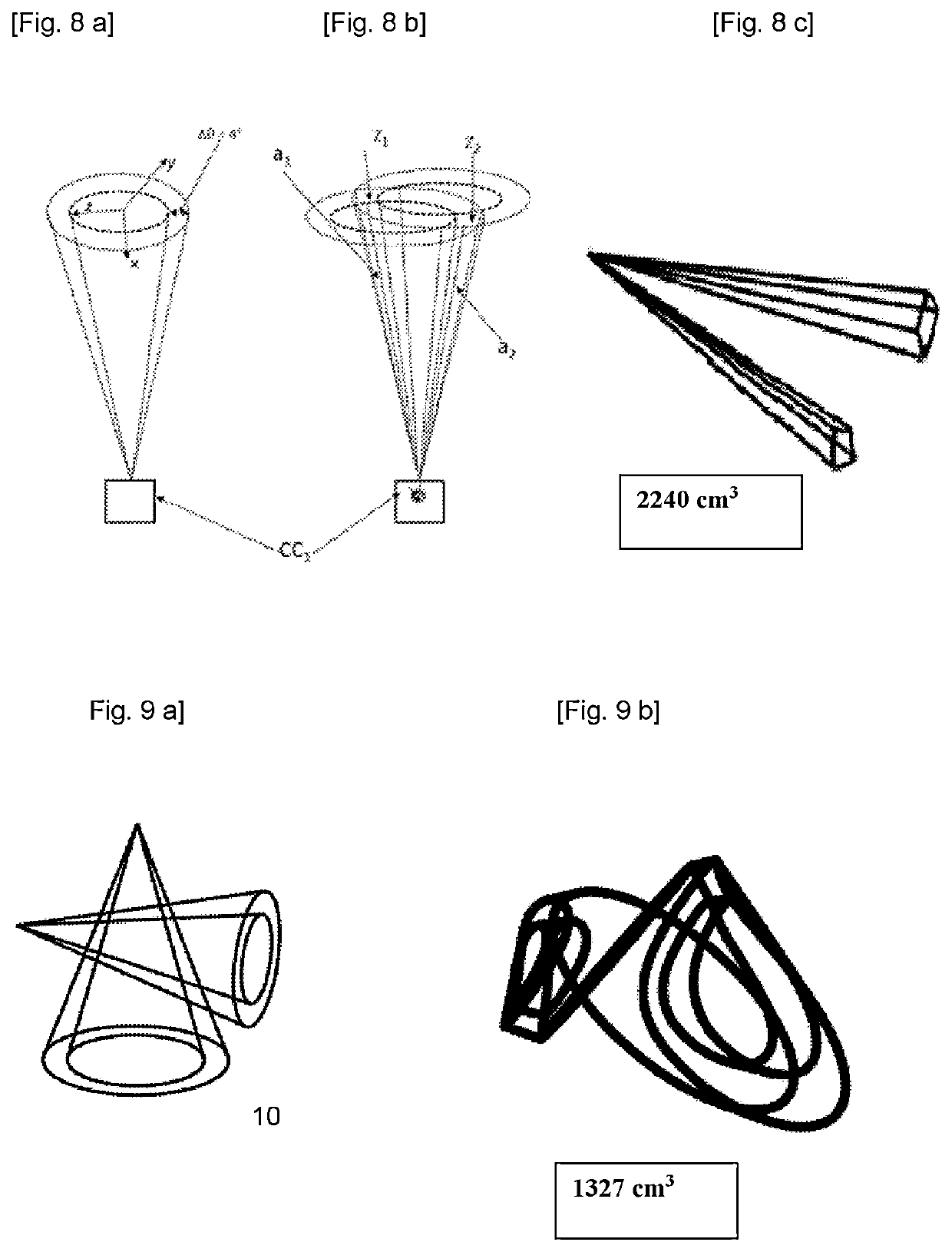
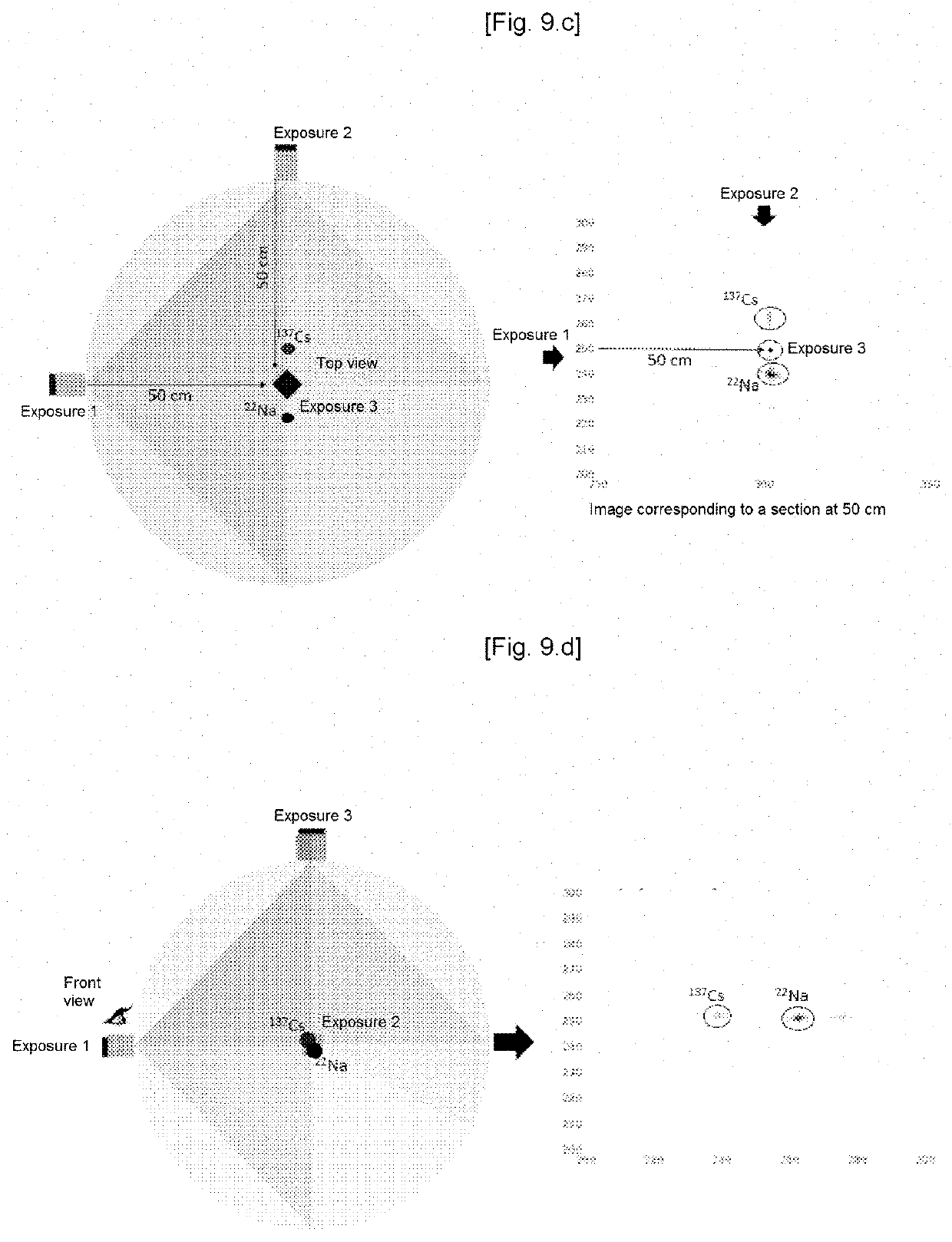
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
34 results about "Compton camera" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
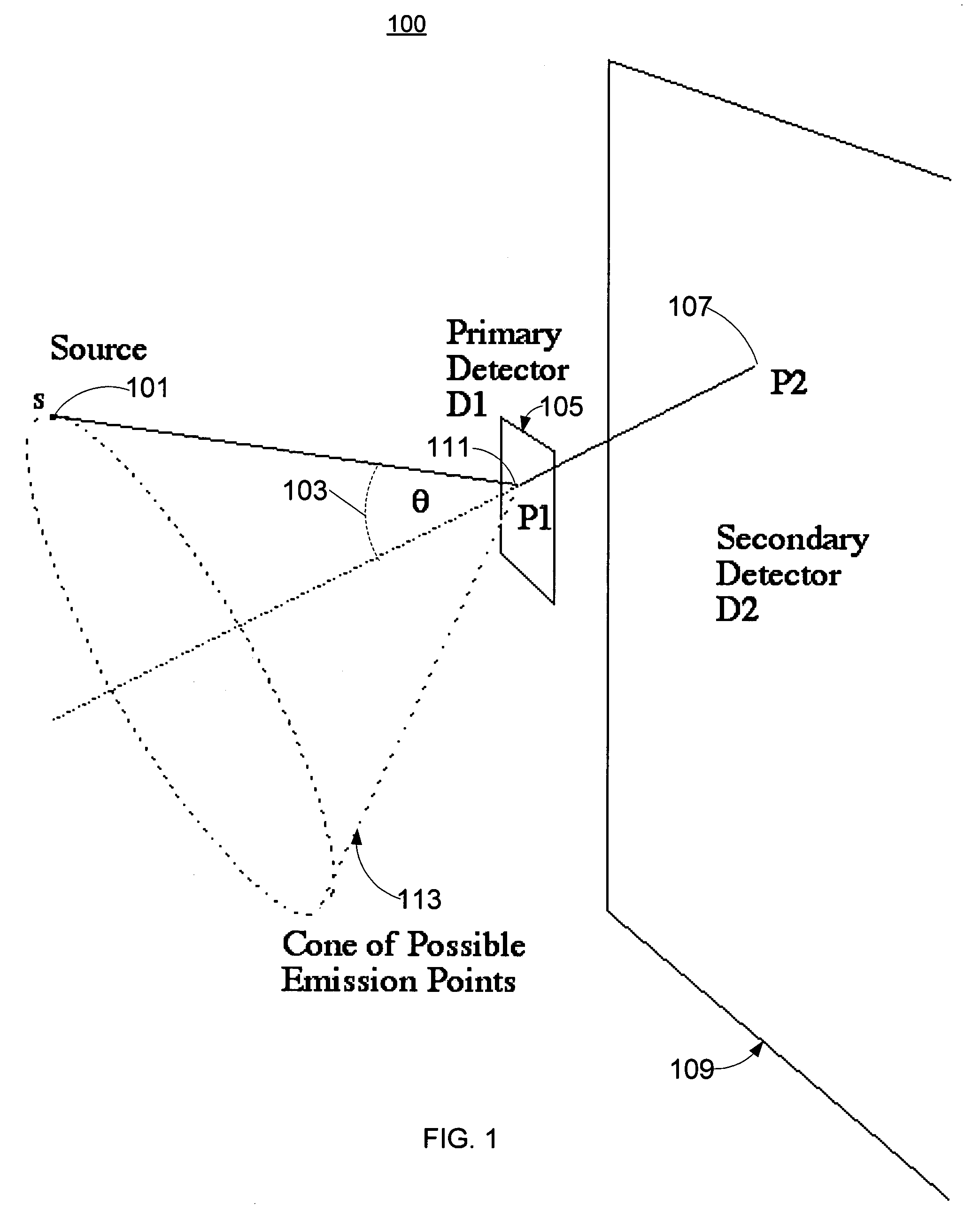
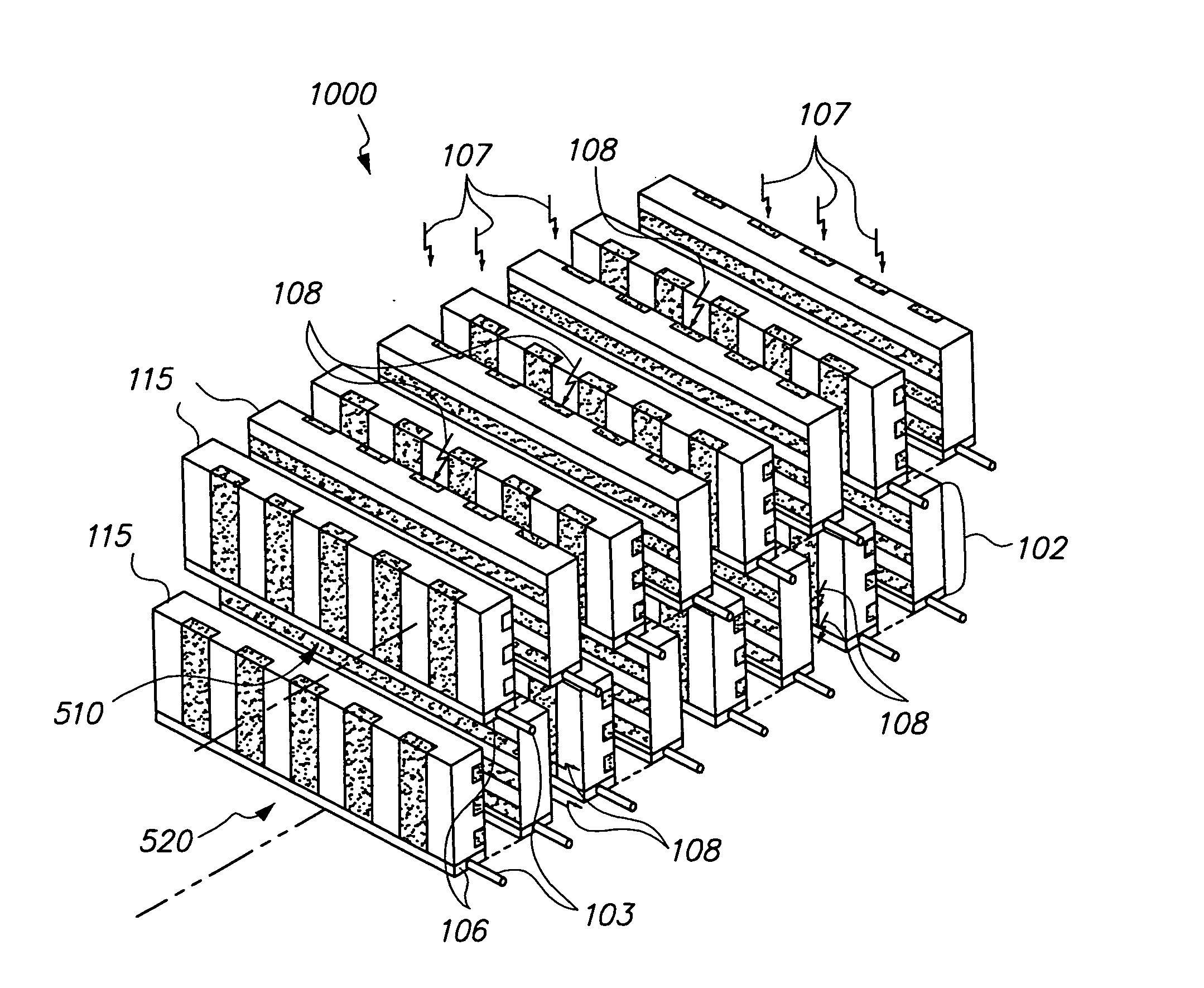
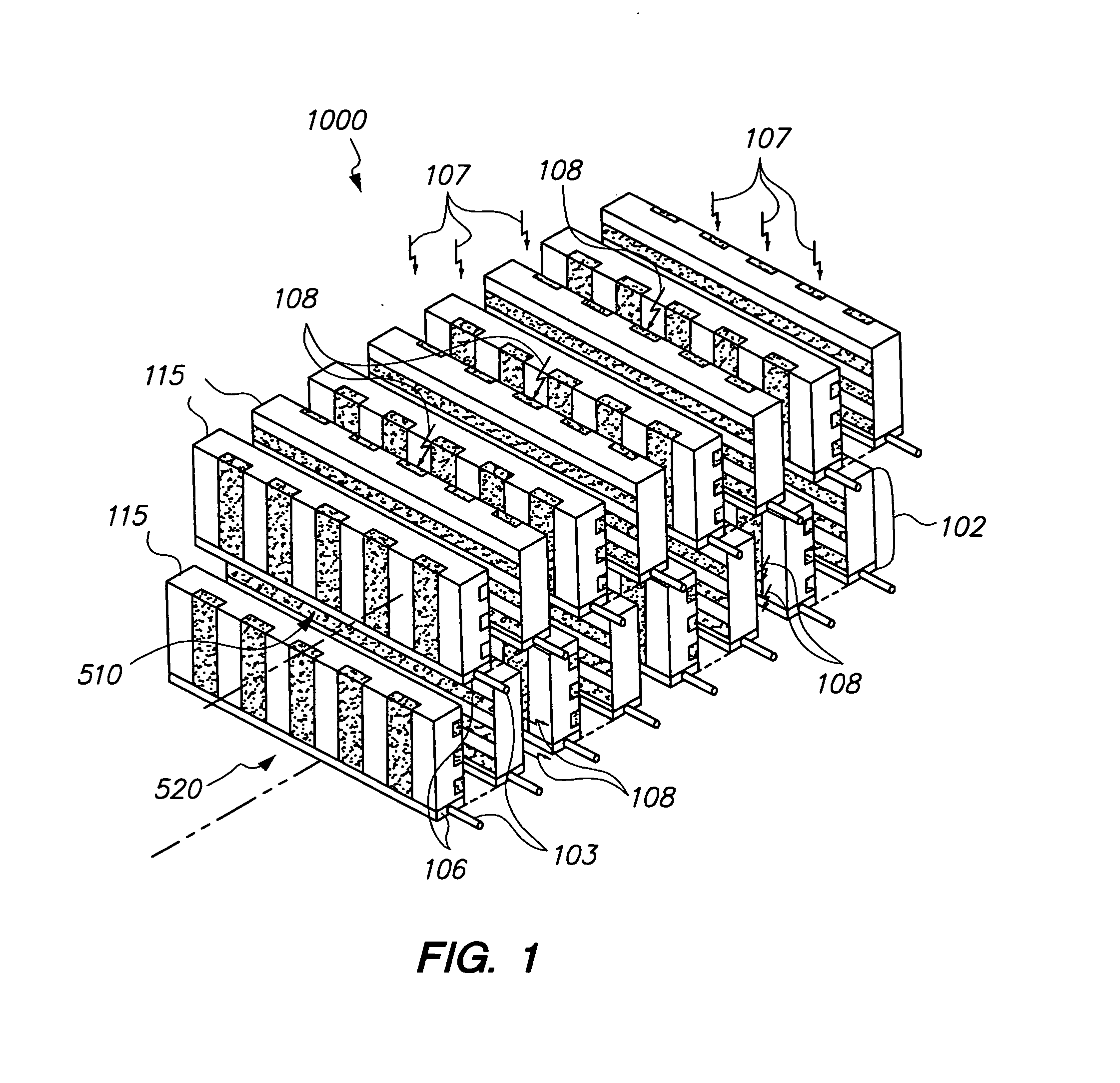
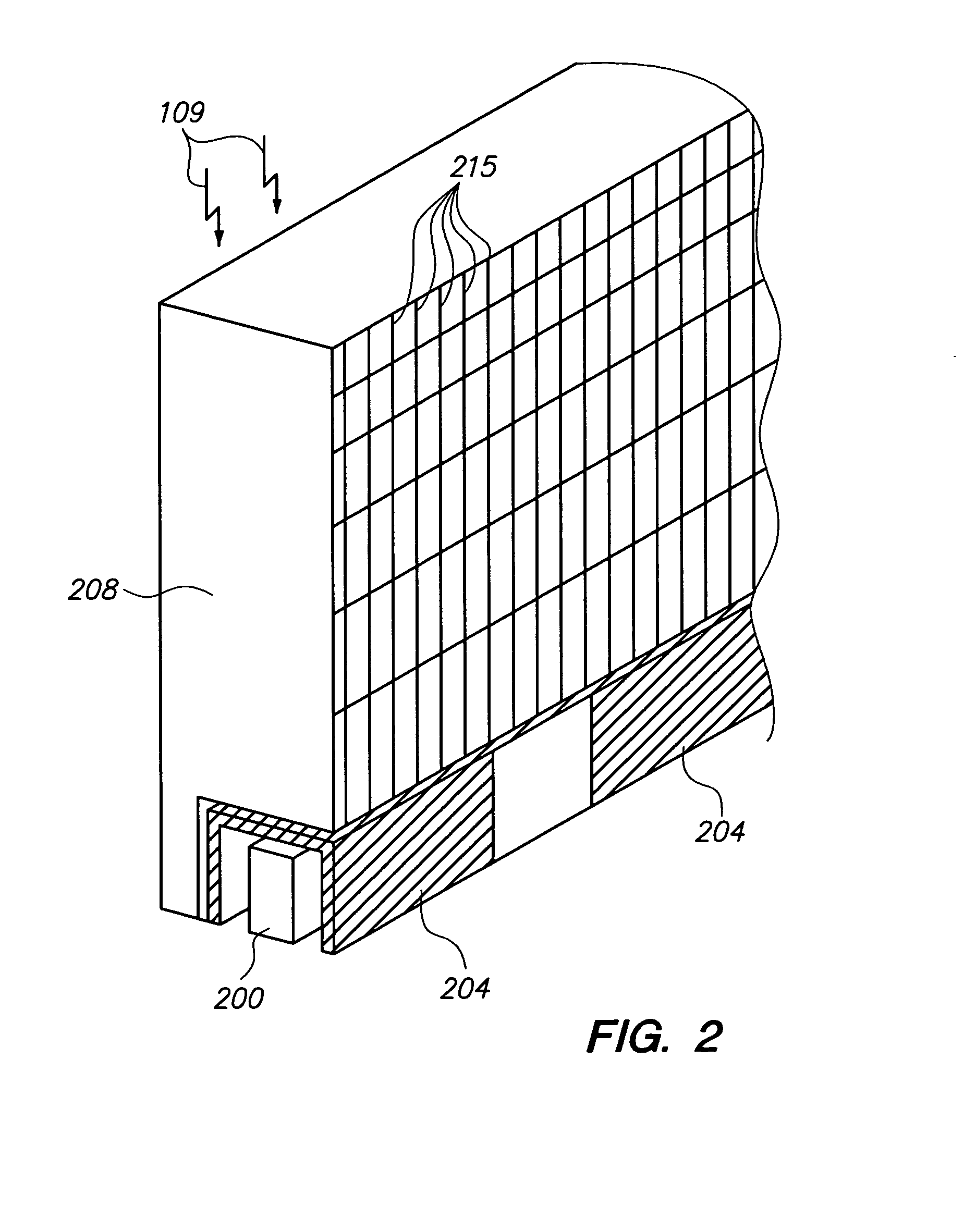
Radiation detectors
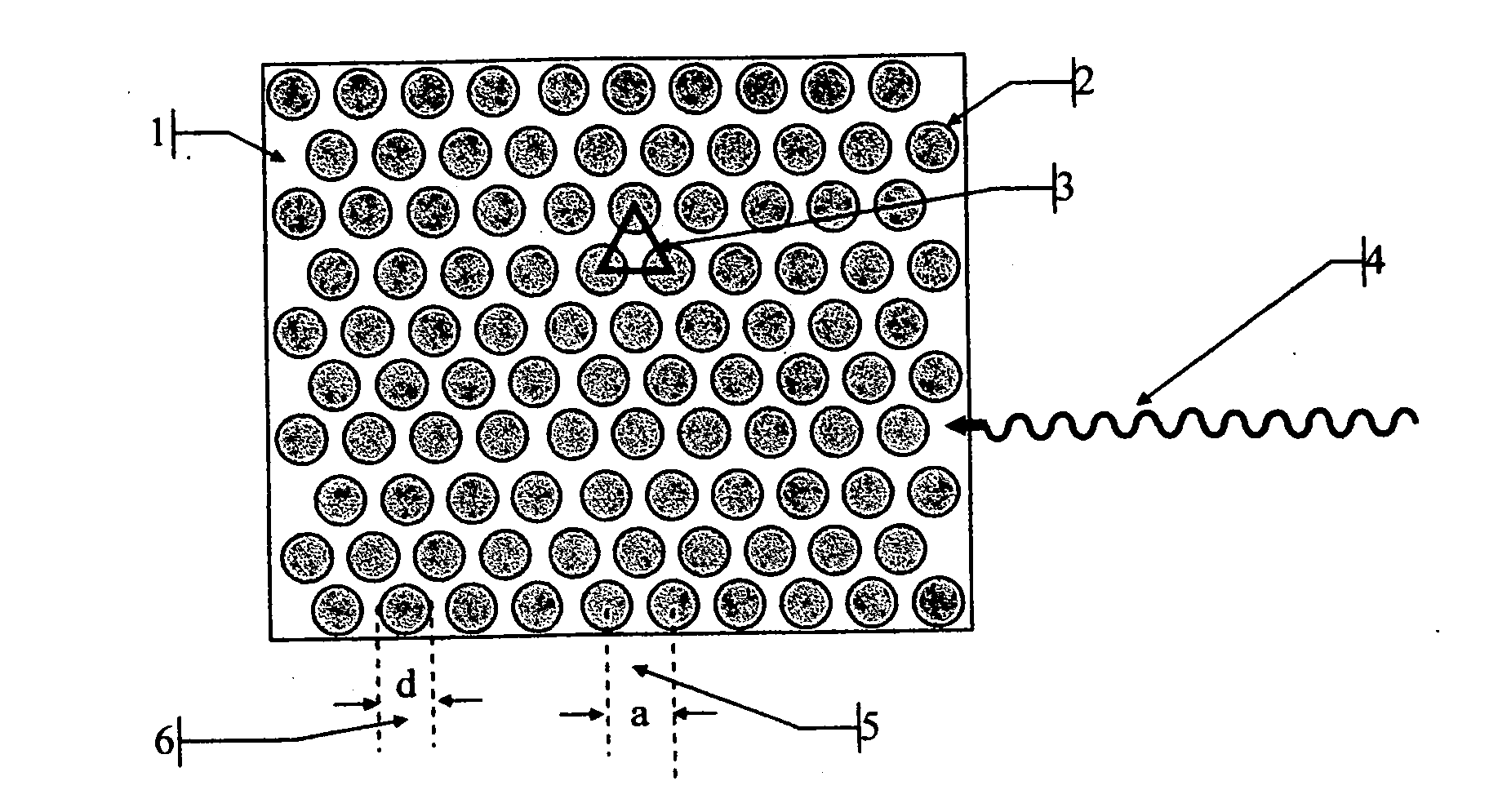
InactiveUS20060202125A1Thinner sliceImprove spatial resolutionMaterial analysis by optical meansNanoopticsRecoil electronPhotonic bandgap
The invention consists in structuring scintillation radiation detectors as Photonic Bandgap Crystals or 3D layers of thin filaments, thus enabling extremely high spatial resolutions and achieving virtual voxellation of the radiation detector without physical separating walls. The ability to precisely measure the recoil electron track in a Compton camera enables to assess the directions of the gamma rays hitting the detector and consequently dispensing with collimators that strongly reduce the intensity of radiation detected by gamma cameras. The invention enables great enhancements of the capabilities of gamma cameras, SPECT, PET, CT and DR machines as well as their use in Homeland Security applications. Methods of fabrication of such radiation detectors are decribed.
Owner:SUHAMI AVRAHAM
Compton camera detector systems for novel integrated compton-Pet and CT-compton-Pet radiation imaging
The invention provides novel Compton camera detector designs and systems for enhanced radiographic imaging with integrated detector systems which incorporate Compton and nuclear medicine imaging, PET imaging and x-ray CT imaging capabilities. Compton camera detector designs employ one or more layers of detector modules comprised of edge-on or face-on detectors or a combination of edge-on and face-on detectors which may employ gas, scintillator, semiconductor, low temperature (such as Ge and superconductor) and structured detectors. Detectors may implement tracking capabilities and may operate in a non-coincidence or coincidence detection mode.
Owner:MINNESOTA IMAGING & ENG
Radiation detectors
InactiveUS7304309B2Improve efficiencyEasy accessMaterial analysis by optical meansNanoopticsRecoil electronPhotonic bandgap
The invention consists in structuring scintillation radiation detectors as Photonic Bandgap Crystals or 3D layers of thin filaments, thus enabling extremely high spatial resolutions and achieving virtual voxellation of the radiation detector without physical separating walls. The ability to precisely measure the recoil electron track in a Compton camera enables to assess the directions of the gamma rays hitting the detector and consequently dispensing with collimators that strongly reduce the intensity of radiation detected by gamma cameras. The invention enables great enhancements of the capabilities of gamma cameras, SPECT, PET, CT and DR machines as well as their use in Homeland Security applications. Methods of fabrication of such radiation detectors are described.
Owner:SUHAMI AVRAHAM
Method and system for improved image reconstruction and data collection for compton cameras
InactiveUS20050211909A1Efficient and accurateReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis by optical meansPattern recognitionCollections data
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Compton camera configuration and imaging method
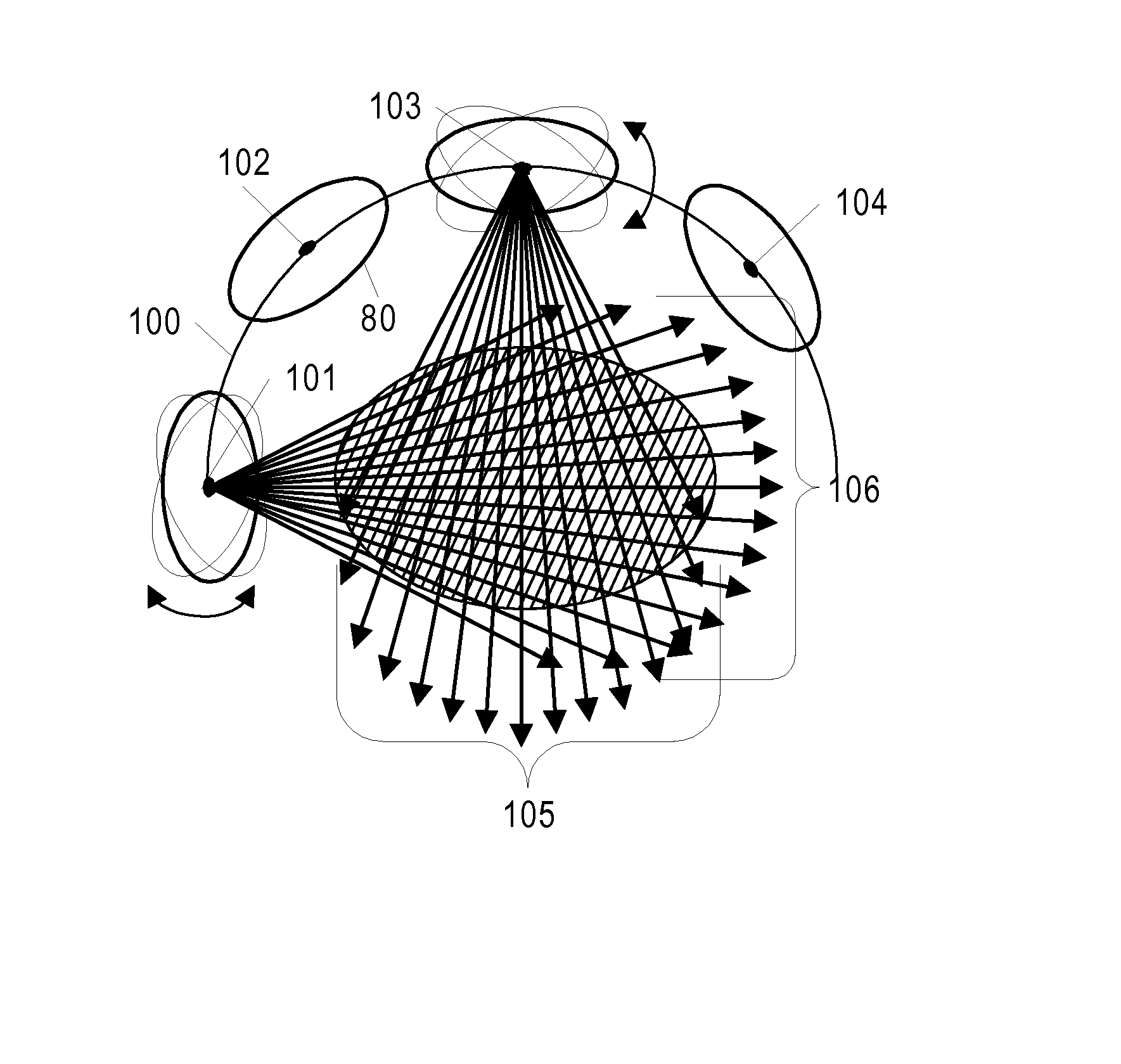
An approach for the selection of Compton camera shapes, configurations, positions, orientations, trajectory paths, and detector element sets is provided for collecting data for analysis using the surface integral and integral-of-line-integral methods of reconstruction Compton data. Methods are introduced for (1) selecting one or more imaging lines through a radioactive distribution for which approximations of integrals of radioactivity are to be derived, (2) selecting and using Compton camera relative positions, relative orientations, and detector element sets that “correspond to” the selected imaging lines to collect the needed data; and (3) deriving approximations of integrals of radioactivity along those imaging lines. This methodological approach is used to reconstruct line integrals, cross-sections, local volumes, parallel projections, and cone-beam projections of radioactive distributions.
Owner:SMITH BRUCE D
Single plane compton camera
InactiveUS20120043467A1Improve detection efficiencyCompact layoutHandling using diaphragms/collimetersMaterial analysis by optical meansHigh probabilityDetector array
A single plane Compton telescope uses a coplanar array of detectors to determine the direction of a radiation source. Detector materials and dimensions may have comparable Compton scattering and photoelectric absorption probabilities, so scattered photons have a high probability of escape from the detector in which the initial interaction occurs, while being absorbed in adjacent detectors. Energy information from coincident interactions between two detectors defines a bearing plane that contains the radiation source; by comparing these interactions in two non-parallel directions, the source is localized to a line representing the intersection of two bearing planes. Energies may be summed to determine the initial photon energy. The array may be of a single detector type or an arrangement of different detector types. The array may be a stationary, planar configuration of at least three detectors, or a linear array of at least two detectors that is rotatable within a selected plane.
Owner:GUEORGUIEV ANDREY +4
Multi-gamma photon coincidence imaging system and method
ActiveCN108523916ASmall doseSimplified Reconstruction AlgorithmComputerised tomographsTomographyReconstruction algorithmCoincidence
The invention discloses a multi-gamma photon coincidence imaging system and a multi-gamma photon coincidence imaging method, and belongs to the technical field of emission computed tomography. The system comprises a time coincidence module, a computer platform, at least one first probe consisting of a collimator and a gamma photon detector as well as at least one second probe consisting of front and back Compton camera detectors; and each probe detects multiple gamma photons radiated by radionuclide to form a multi-gamma photon coincidence event. According to the imaging method, the range of the position where the radionuclide decays is shrunk into a plurality of intersection points of a projection line determined by the gamma photon event detected by the first probe in the multi-gamma photon coincidence event as well as a protection conical surface determined by the gamma photon event detected by the second probe, and a certain number of multi-gamma photon coincidence events are accumulated to obtain the images, distributed in the detected range, of the radionuclide. The reconstruction algorithm is simplified, the detection efficiency is improved, the signal-to-noise ratio of thereconstructed image is increased, and demand on the total count of the gamma photons is reduced.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Filtered backprojection algorithms for compton cameras in nuclear medicine
InactiveUS7015477B2Reconstruction from projectionSolid-state devicesMathematical modelComputer science
The present invention provides methods and apparatuses for constructing observed data from a Compton camera in order to provide a three-dimensional image of a radiopharmaceutical source distribution within a patient. No intermediate two-dimensional images are formed. Observed data may be analyzed by a processor in order to construct a three-dimensional image representing the source distribution. An idealized mathematical model may express the observed Compton camera data in terms of an integral over the source distribution. An exact analytic inversion is then found for this idealized model. The new analytic solutions arise from a generalization of the integral equation used to model the Compton camera. The kernel of the integral equation is modified by the introduction of an index p that describes the effect of source distance from the camera.
Owner:GUNTER DONALD LEE
Compton camera detector systems for novel integrated compton-Pet and CT-compton-Pet radiation imaging
Owner:MINNESOTA IMAGING & ENG
Compton Camera Configuration and Imaging Method
InactiveUS20080224061A1Radiation/particle handlingMaterial analysis by optical meansComputer scienceIntegral method
An approach for the selection of Compton camera shapes, configurations, positions, orientations, trajectory paths, and detector element sets is provided for collecting data for analysis using the surface integral and integral-of-line-integral methods of reconstruction Compton data. Methods are introduced for (1) selecting one or more imaging lines through a radioactive distribution for which approximations of integrals of radioactivity are to be derived, (2) selecting and using Compton camera relative positions, relative orientations, and detector element sets that “correspond to” the selected imaging lines to collect the needed data; and (3) deriving approximations of integrals of radioactivity along those imaging lines. This methodological approach is used to reconstruct line integrals, cross-sections, local volumes, parallel projections, and cone-beam projections of radioactive distributions.
Owner:SMITH BRUCE D
Filtered back-projection algorithm for Compton telescopes
InactiveUS7345283B2Reconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis by optical meansBack projectionCelestial sphere
A method for the conversion of Compton camera data into a 2D image of the incident-radiation flux on the celestial sphere includes detecting coincident gamma radiation flux arriving from various directions of a 2-sphere. These events are mapped by back-projection onto the 2-sphere to produce a convolution integral that is subsequently stereographically projected onto a 2-plane to produce a second convolution integral which is deconvolved by the Fourier method to produce an image that is then projected onto the 2-sphere.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Scintillator array detector and three-dimensional position resolution method in Compton scattering imaging
InactiveCN109782326AHigh resolutionDOI effect is goodRadiation intensity measurementGamma photonNuclear radiation
The invention discloses a scintillator array detector and a three-dimensional position resolution method in Compton scattering imaging. The method comprises the following steps: 1) enabling gamma photons to be incident to the scintillator array detector; 2) determining two-dimensional coordinate information (X, Y) of the action position of the gamma photons in the scintillator array according to the number of the responded photodetector pixel in the photodetector array; and 3) determining third-dimensional coordinate information Z of the action position of the gamma photons in the scintillatorarray according to the amplitude ratio f=X1 / (X1+X2) of output signals (X1, X2) of the responded light detector and a lookup table obtain three-dimensional coordinates (X, Y, Z) of the action positionof the gamma photons, wherein X1 and X2 are corresponding top surface and bottom surface optical detector output signals when gamma photons act on the scintillator strip detection unit i. According to the invention, the detection efficiency of a Compton camera and the imaging precision of the nuclear radiation hot spot are improved.
Owner:INST OF HIGH ENERGY PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method and system for generating an image of the radiation density of a source of photons located in an object
InactiveUS6881959B2Improve image qualitySolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansMultiplexingImaging quality
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Filtered back-projection algorithm for compton telescopes
InactiveUS20070145278A1Reduced feasibilityReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis by optical meansBack projectionEngineering
A method for the conversion of Compton camera data into a 2D image of the incident-radiation flux on the celestial sphere includes detecting coincident gamma radiation flux arriving from various directions of a 2-sphere. These events are mapped by back-projection onto the 2-sphere to produce a convolution integral that is subsequently stereographically projected onto a 2-plane to produce a second convolution integral which is deconvolved by the Fourier method to produce an image that is then projected onto the 2-sphere.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method and system for improved image reconstruction and data collection for compton cameras
InactiveUS7262417B2Reconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis by optical meansPattern recognitionCollections data
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Imaging system and method based on gamma radiation detection
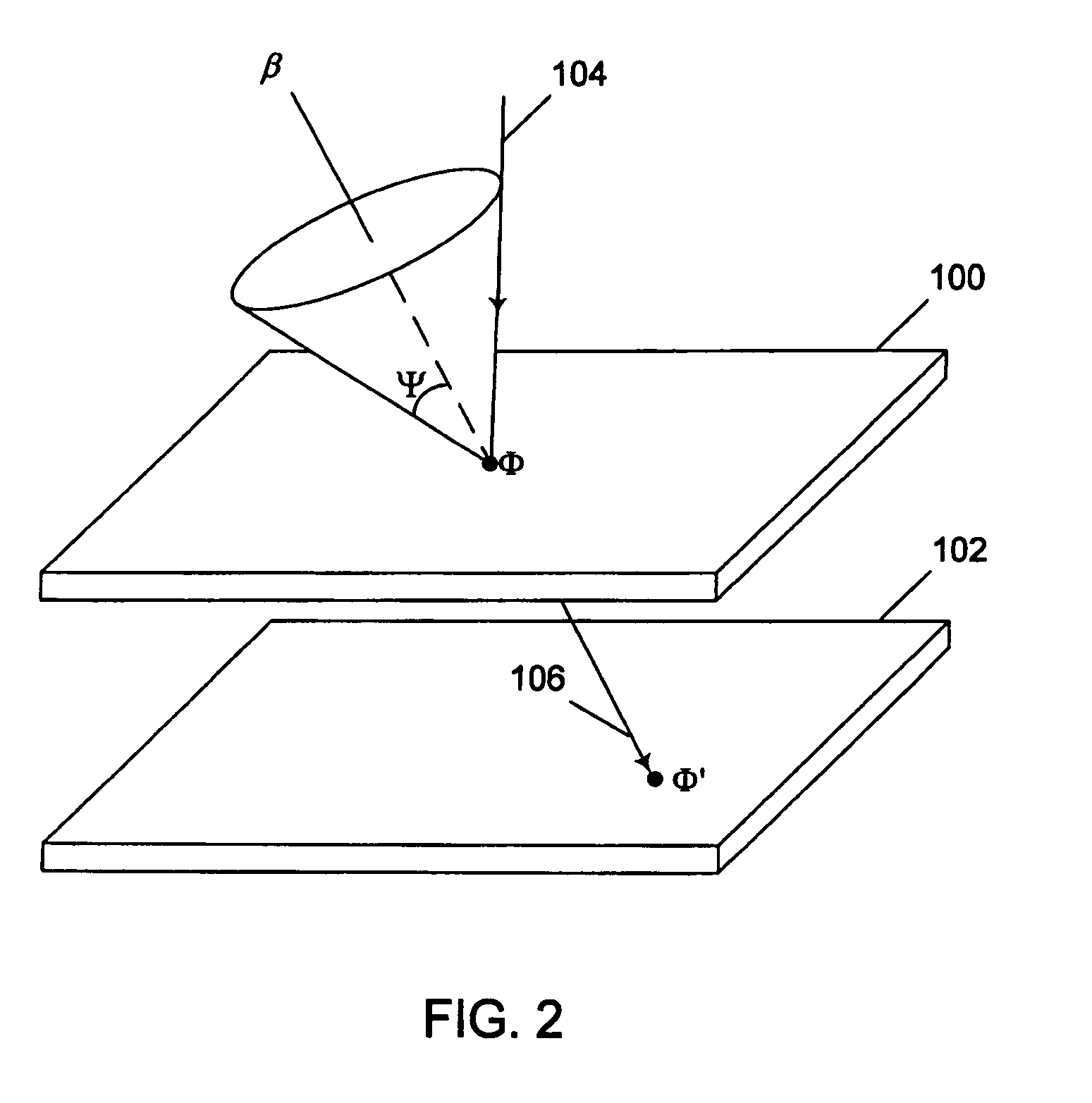
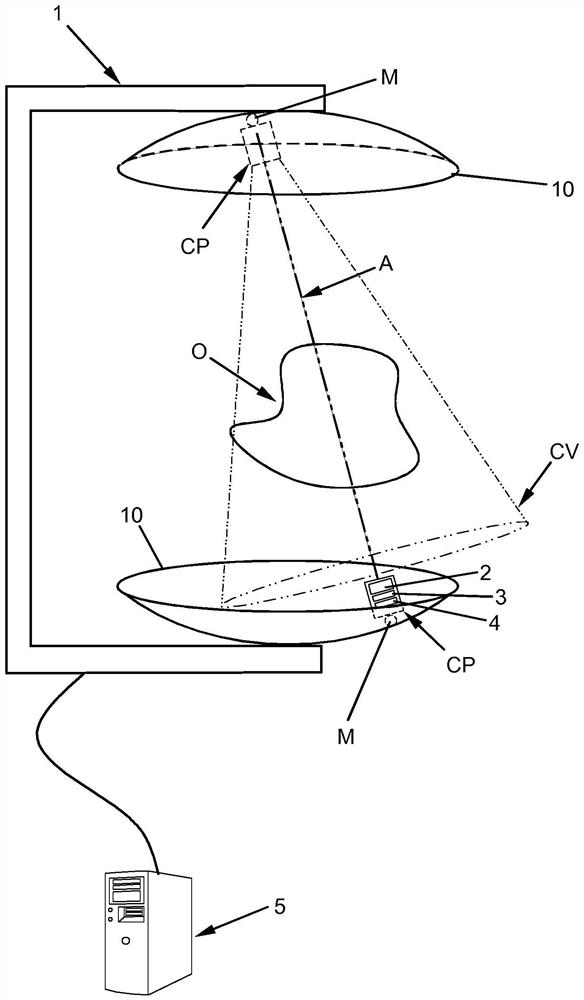
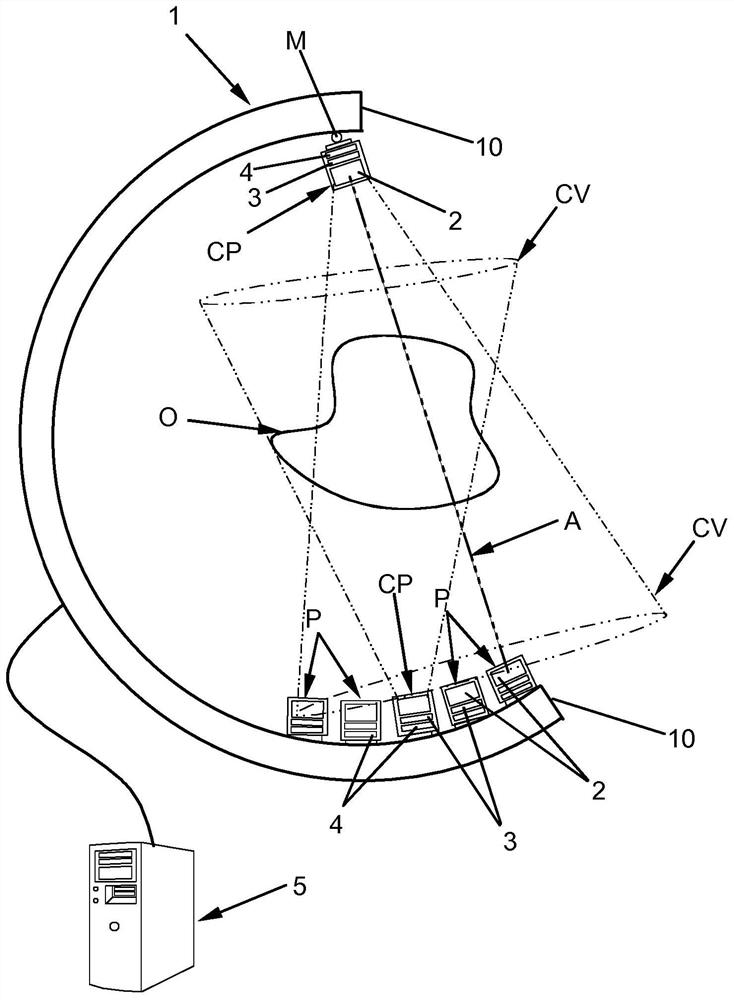
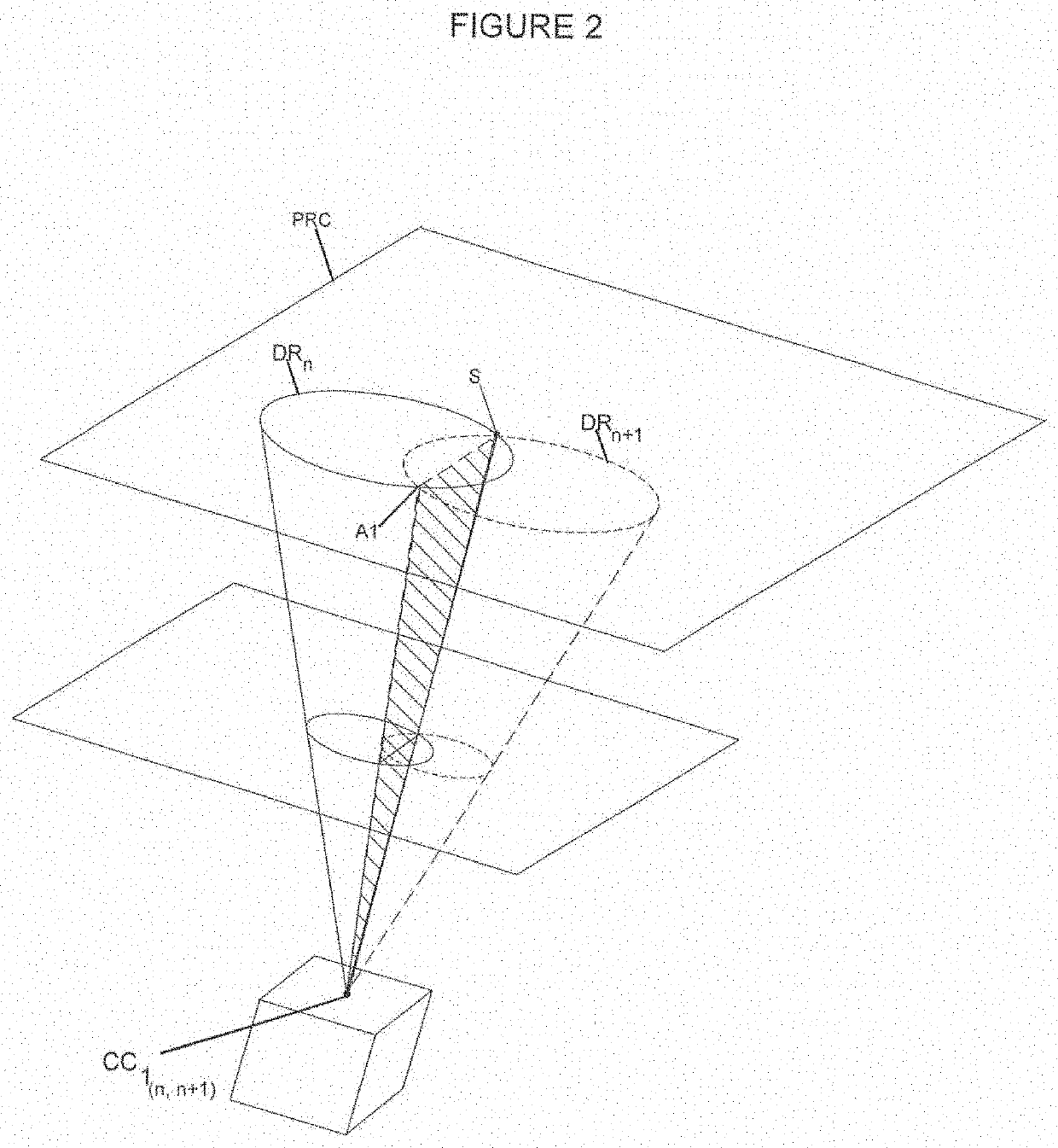
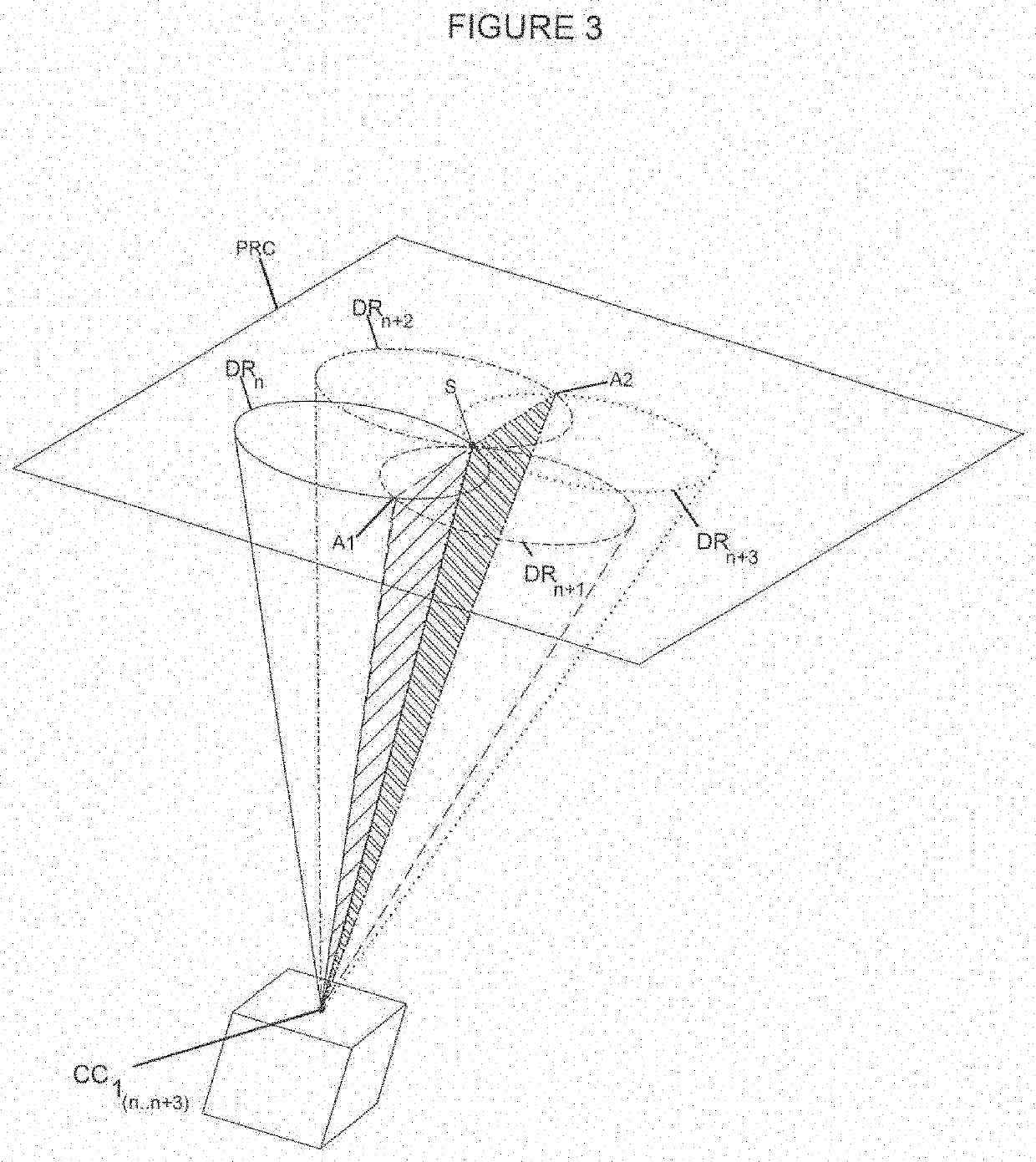
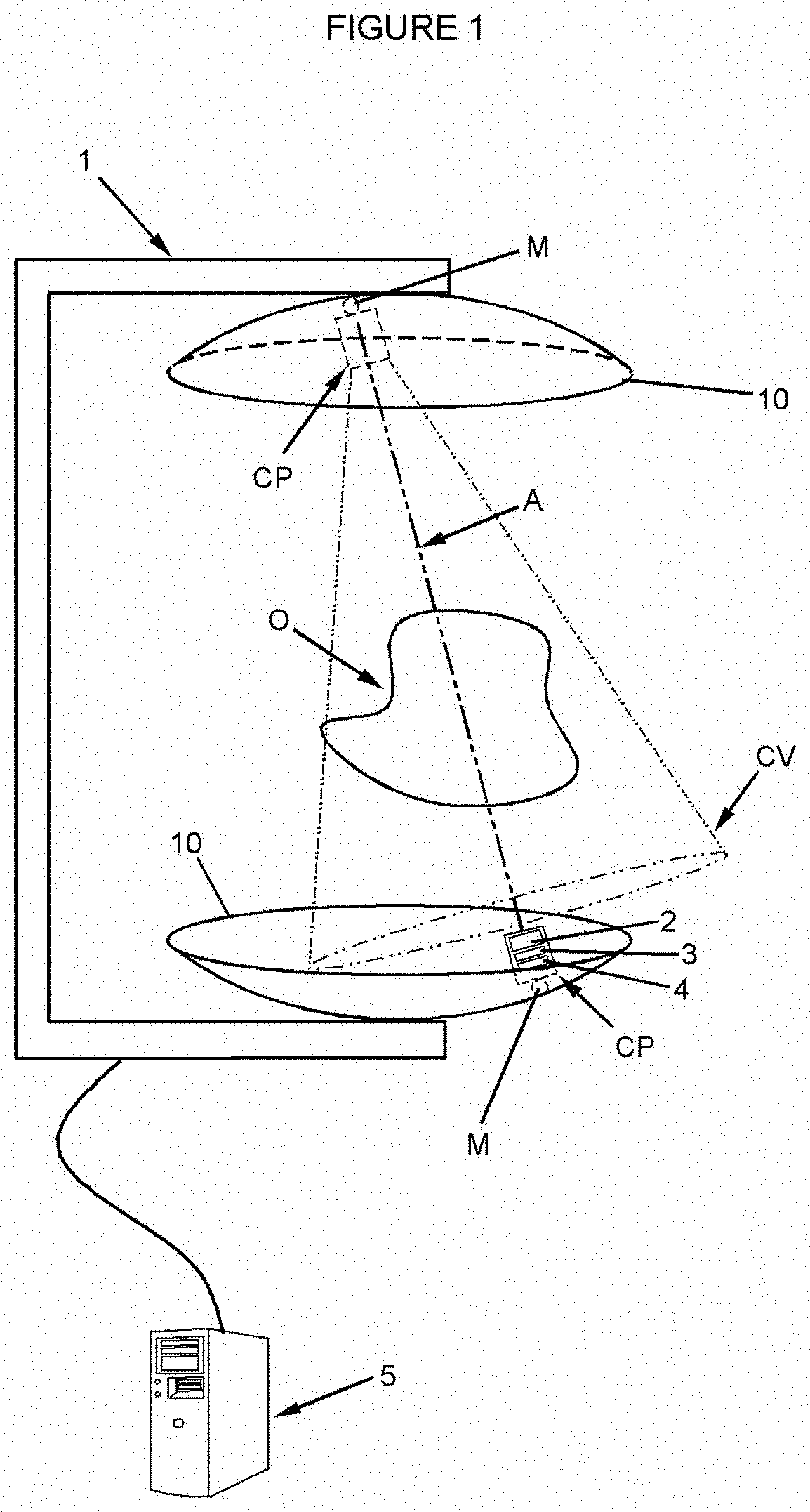
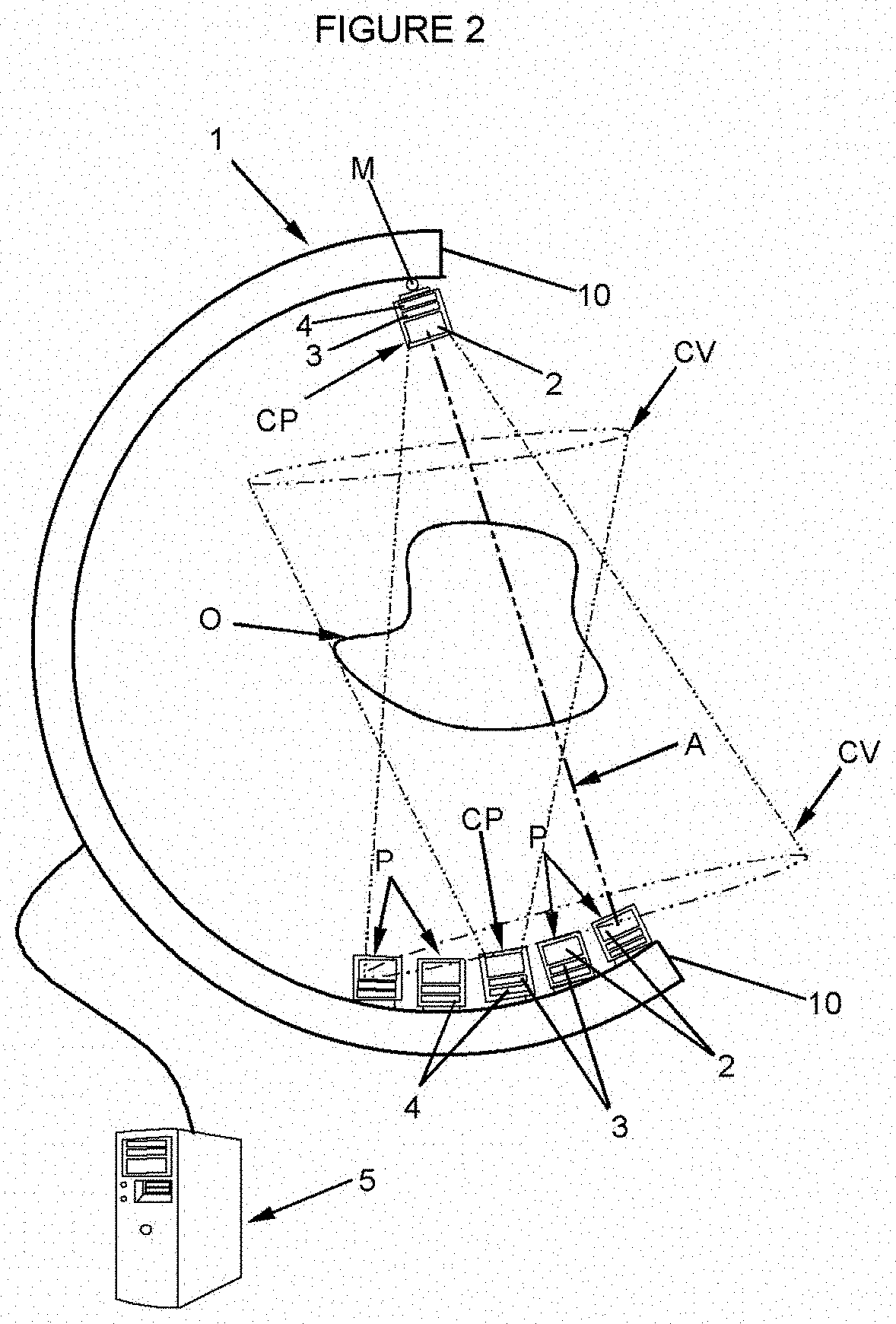
PendingCN112470039ASave spaceMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationTomographyNuclear engineeringField of view
The present invention relates to an imaging system and method based on gamma radiation detection, comprising at least one processing unit (5) which analyses at least one signal supplied by at least one set of detection modules (CP, P) mounted on a frame and comprising: at least one Compton-camera-type module having a field of view (CV) directed towards a volume defined by the frame, and at least one pair of coincidence-detection PET modules, positioned diametrically opposite one another on the chassis and defining an imaging axis (A), said processing unit (5) analysing the signal from the Compton-type module in order to determine the intersection between the imaging axis (A) and the field of view (CV) and to determine the optimal locations and / or orientations for the different detection modules (CP, P) on the chassis so that the imaging axis (A) passes through the gamma radiation source in the object (O) to be imaged.
Owner:法国放射性废物管理局 +1
Camera compton multi-capture et procede d'imagerie
InactiveUS20200400593A1Reduce the numberReduce computing timeMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentEngineeringMechanical engineering
The present invention concerns a device, system and method of use of a multi-capture Compton camera, characterised by the use of at least two capture centres having separate positions.
Owner:DAMAVAN IMAGING +1
System and method for imaging by gamma radiation detection
ActiveUS20210199821A1Remove signal noiseEliminate detectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationComputerised tomographsNuclear medicineField of view
A system and method for imaging by gamma radiation detection having at least one processing unit analyzing at least one signal provided by at least one set of detection modules mounted on a frame and including, on the one hand, at least one module of Compton camera type having a field of view directed towards a volume delimited by the frame and, on the other hand, at least one pair of coincidence detection PET modules, diametrically opposite to each other on the frame and defining an imaging axis, the processing unit analyzing the signal derived from the Compton-type module to determine the intersection of the imaging axis with the field of view and to determine the optimal orientations and / or locations of the various detection modules on the frame so that the imaging axis passes through the source of the gamma radiation in the object to be imaged.
Owner:A N D R A +1
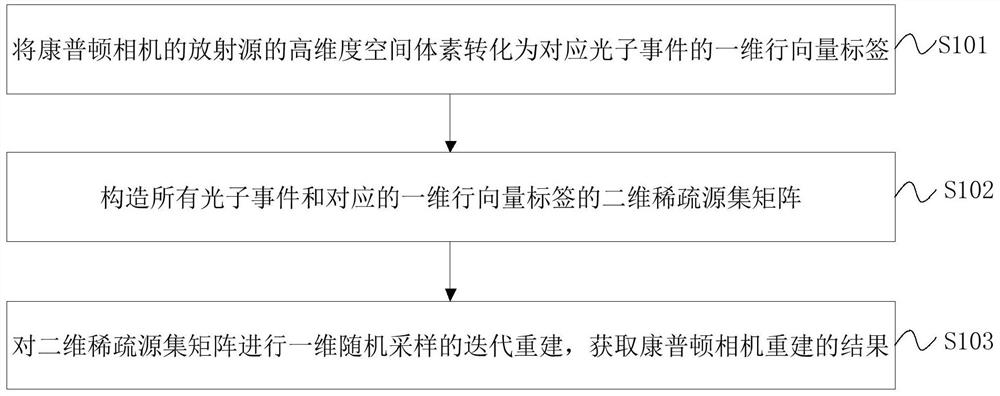
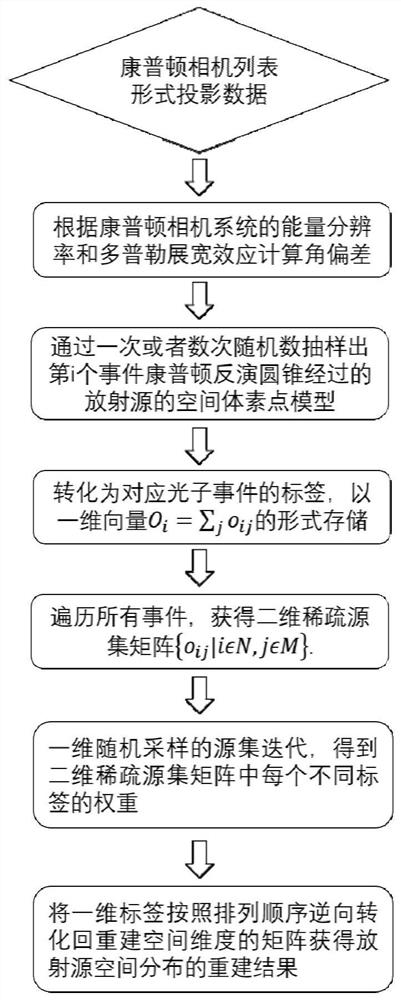
Method and device for realizing Compton camera reconstruction by constructing sparse source set matrix
PendingCN114581547AShort timeRemove background noiseReconstruction from projectionComplex mathematical operationsVoxelComputation complexity
The invention discloses a method and device for realizing Compton camera reconstruction by constructing a sparse source set matrix, electronic equipment and a storage medium, and the method comprises the steps: converting a high-dimensional space voxel of a radioactive source of a Compton camera into a one-dimensional row vector tag of a corresponding photon event; constructing a two-dimensional sparse source set matrix of all photon events and corresponding one-dimensional row vector labels; and performing iterative reconstruction of one-dimensional random sampling on the two-dimensional sparse source set matrix to obtain a Compton camera reconstruction result. According to the embodiment of the invention, the calculation amount of Compton camera reconstruction is greatly reduced, the calculation complexity is lower, and the time consumption in the high-dimension and high-precision reconstruction of the Compton camera is shorter. Therefore, the problems of large calculation amount, high calculation complexity, long time consumption in calculation and low calculation precision during Compton camera reconstruction in the prior art are solved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Methods for increasing the sensitivity of gamma-ray imagers
InactiveUS8110810B2Improve imaging efficiency and accuracyIncrease the number ofSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansImage resolutionSemiconductor detector
Methods are presented that increase the position resolution and granularity of double sided segmented semiconductor detectors. These methods increase the imaging resolution capability of such detectors, either used as Compton cameras, or as position sensitive radiation detectors in imagers such as SPECT, PET, coded apertures, multi-pinhole imagers, or other spatial or temporal modulated imagers.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Radiation detector and compton camera
The present disclosure concerns a charge-accumulation radiation detector that includes a semiconductor device and specifies an incident time and energy of radiation from a transferred image signal. The radiation detector includes a semiconductor substrate and electrodes disposed on both sides of the semiconductor substrate, and includes a plurality of charge accumulation units inside the semiconductor substrate. The plurality of charge accumulation units is each configured to accumulate charges generated by radiation incident on the semiconductor substrate. The charges accumulated in the charge accumulation units are readable to outside through at least one of the electrodes.
Owner:CANON KK
A multi-gamma photon coincidence imaging system and method
ActiveCN108523916BSmall doseSimplified Reconstruction AlgorithmComputerised tomographsTomographyGamma photonNuclear engineering
The invention discloses a multi-gamma photon coincidence imaging system and a multi-gamma photon coincidence imaging method, and belongs to the technical field of emission computed tomography. The system comprises a time coincidence module, a computer platform, at least one first probe consisting of a collimator and a gamma photon detector as well as at least one second probe consisting of front and back Compton camera detectors; and each probe detects multiple gamma photons radiated by radionuclide to form a multi-gamma photon coincidence event. According to the imaging method, the range of the position where the radionuclide decays is shrunk into a plurality of intersection points of a projection line determined by the gamma photon event detected by the first probe in the multi-gamma photon coincidence event as well as a protection conical surface determined by the gamma photon event detected by the second probe, and a certain number of multi-gamma photon coincidence events are accumulated to obtain the images, distributed in the detected range, of the radionuclide. The reconstruction algorithm is simplified, the detection efficiency is improved, the signal-to-noise ratio of thereconstructed image is increased, and demand on the total count of the gamma photons is reduced.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
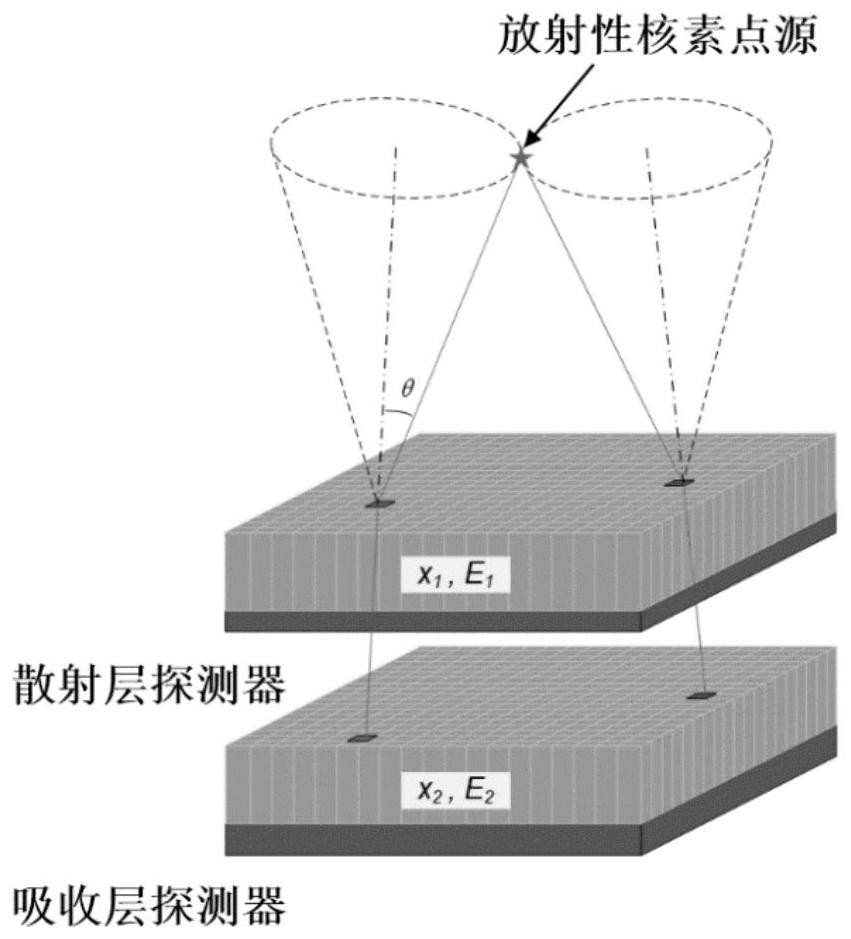
Radiation measuring apparatus and radiation measuring method
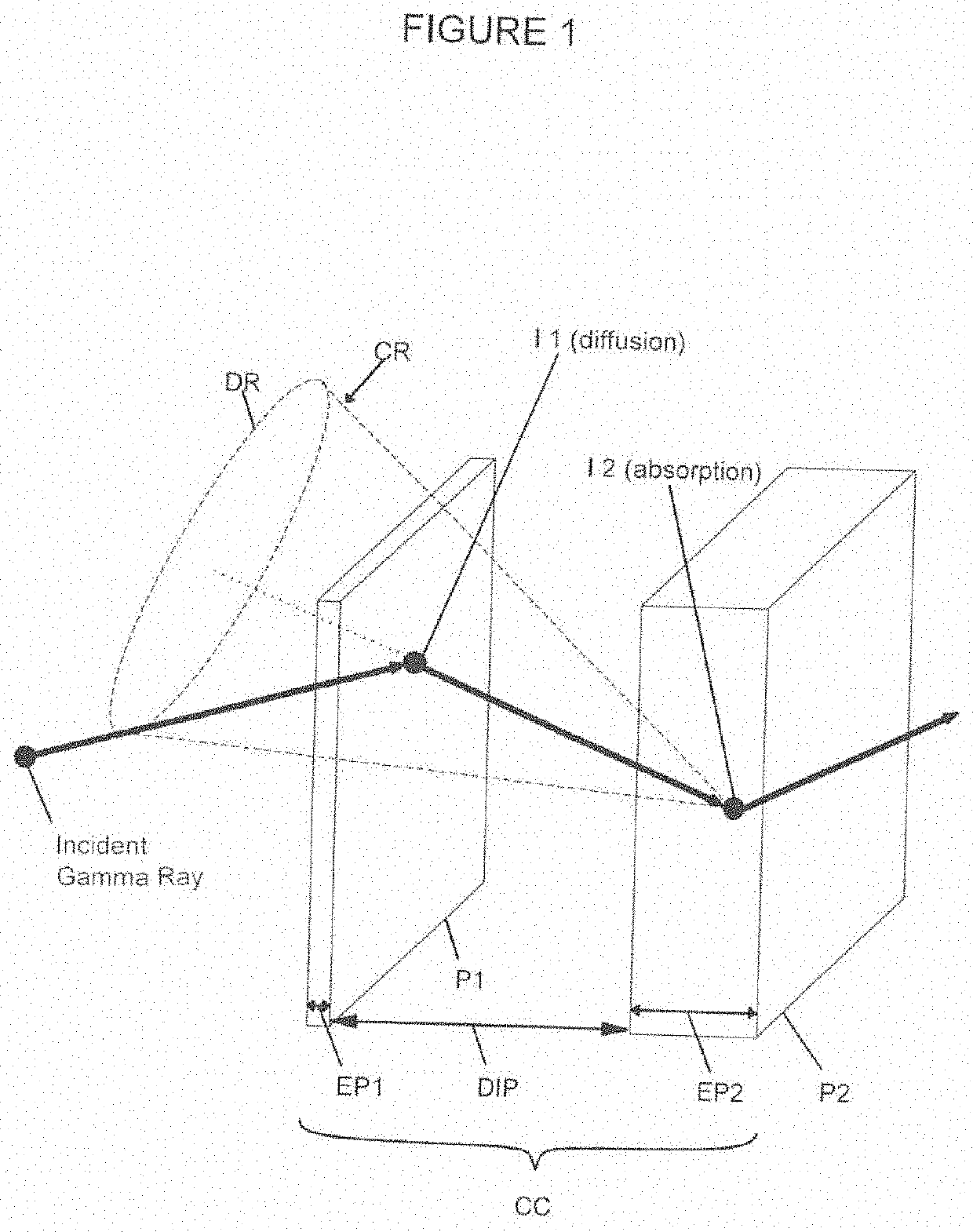
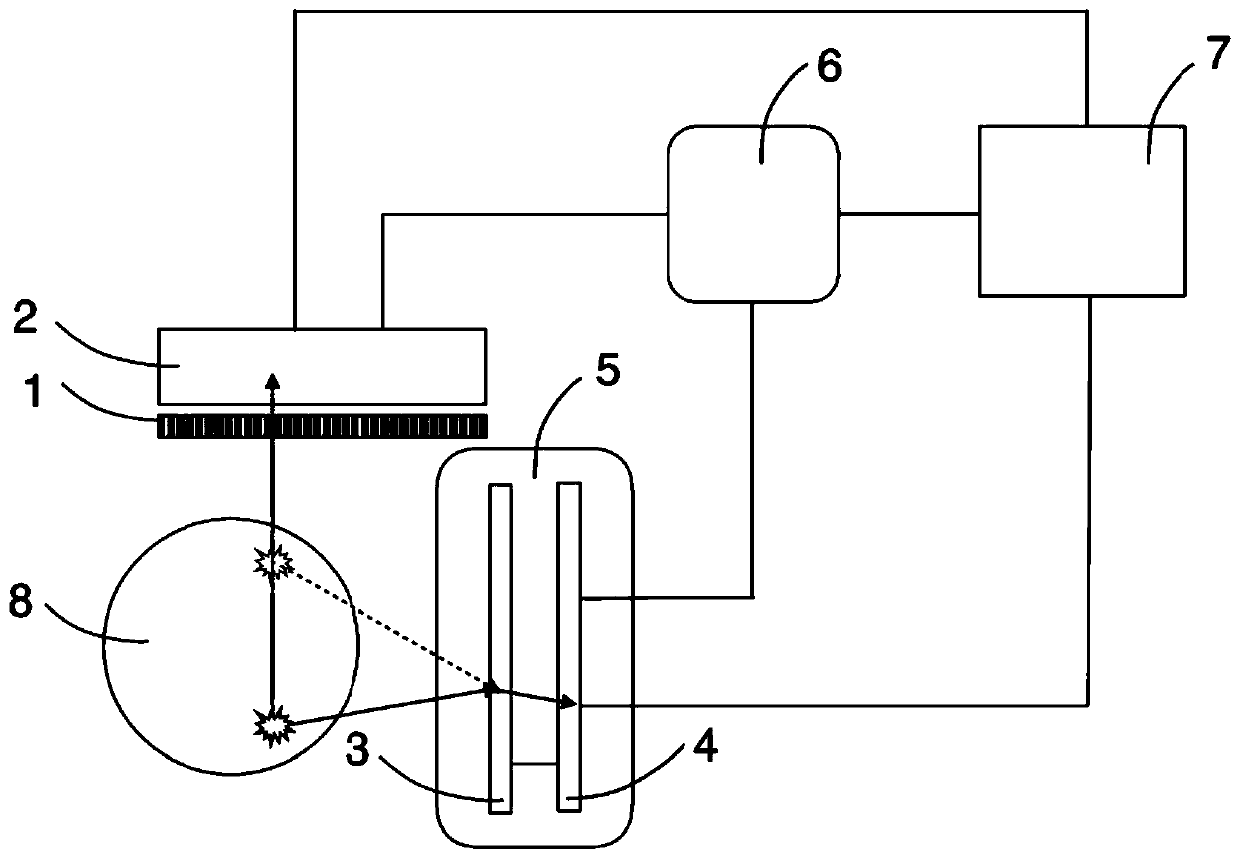
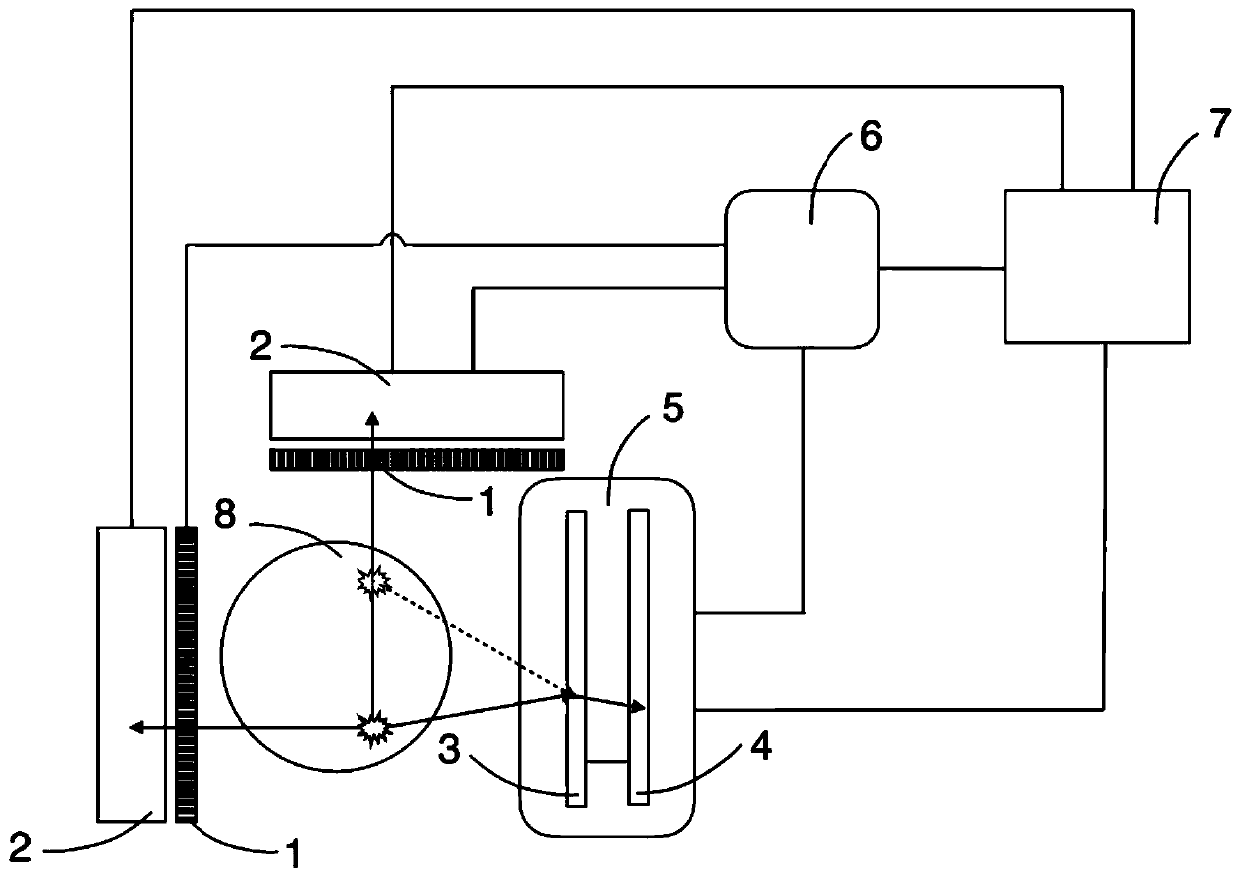
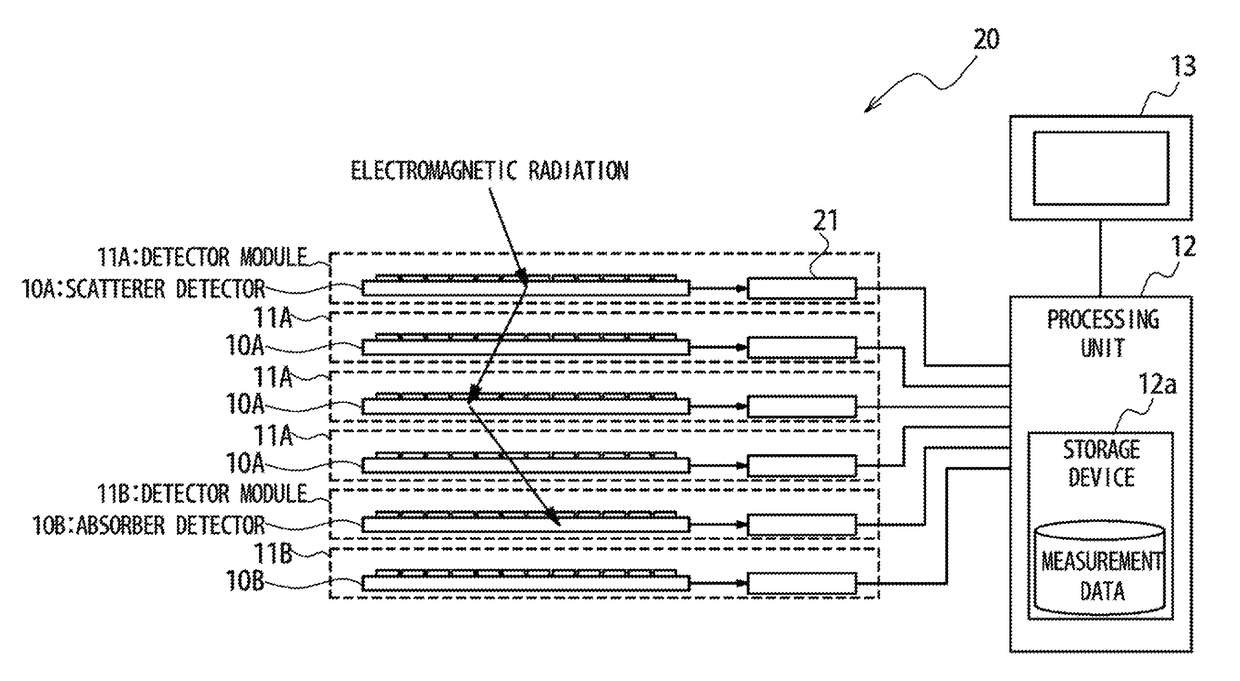
A radiation measuring apparatus (20) includes a scatterer detector (10A), an absorber detector (10B) and a processing unit (12). Pixel electrodes (2) of the scatterer detector (10A) and the absorber detector (10B) are arranged such that a distance between centers of two neighbor pixel electrodes (2) is smaller than a mean free path of a recoil electron generated in the Compton scattering of an electromagnetic radiation. The processing unit (12) specifies and incidence direction of the electromagnetic radiation based on a recoiling direction to which the recoil electron recoils. In this way, an electron tracking-type Compton camera is realized which confines the incidence direction of the electromagnetic radiation by using the recoiling direction of the recoil electron in a Compton camera using a semiconductor detector.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD +2
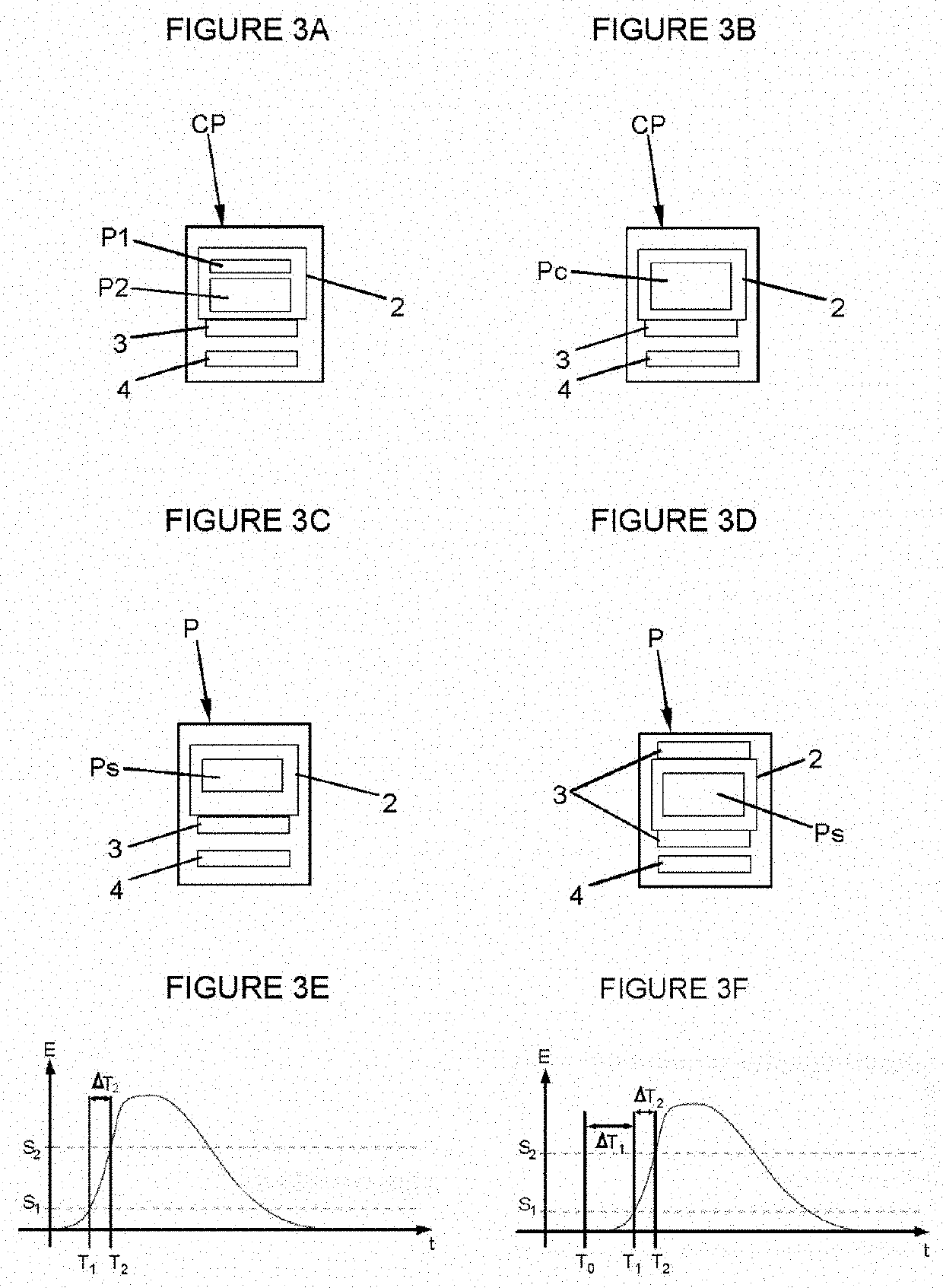
Compton camera system and method for detecting gamma radiation
ActiveUS10509134B2Promote reconstructionReduce noiseImage analysisRadiation intensity measurementGamma photonPhotovoltaic detectors
A Compton camera system and method for detecting gamma radiation, comprising a gamma radiation source, at least one fast scintillator plate P1 of which the rise time to peak light is less than 1 ns, having a thickness greater than or equal to 5 mm, equipped with an array of segmented photodetectors (5) and a dedicated fast-reading microelectronic means. The system is characterised in that it is capable of measuring the spatial and temporal coordinates (X, Y, Z, T) and energy E at at least two successive positions of a gamma photon when said photon undergoes Compton scattering at a first point A before being absorbed at a second point B, by recognising circles of non-scattered photons corresponding to each scintillation interaction. The system has a module for estimating a valid Compton event. The detection system has two scintillator plates P1 and P2.
Owner:ILTIS ALAIN
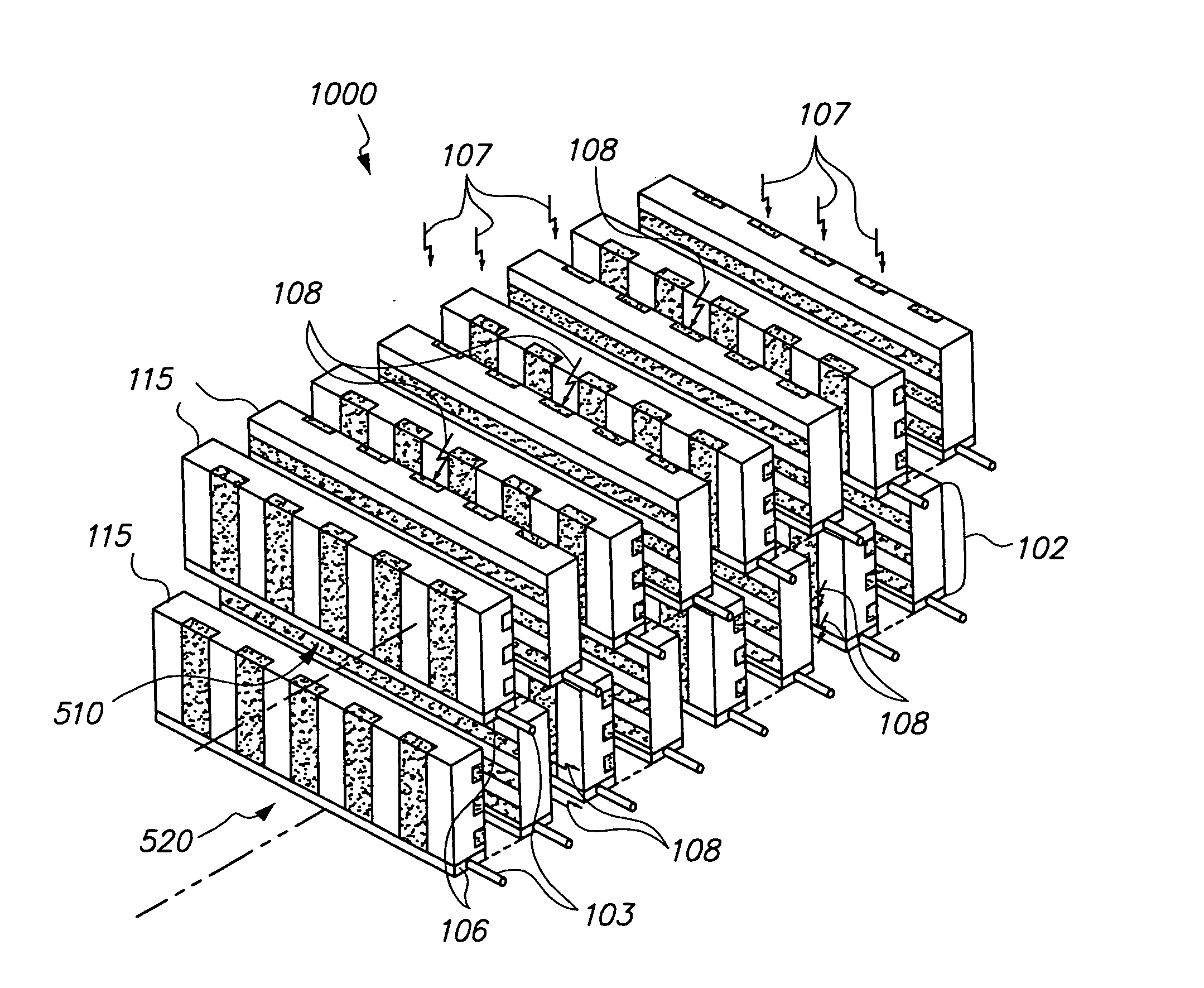
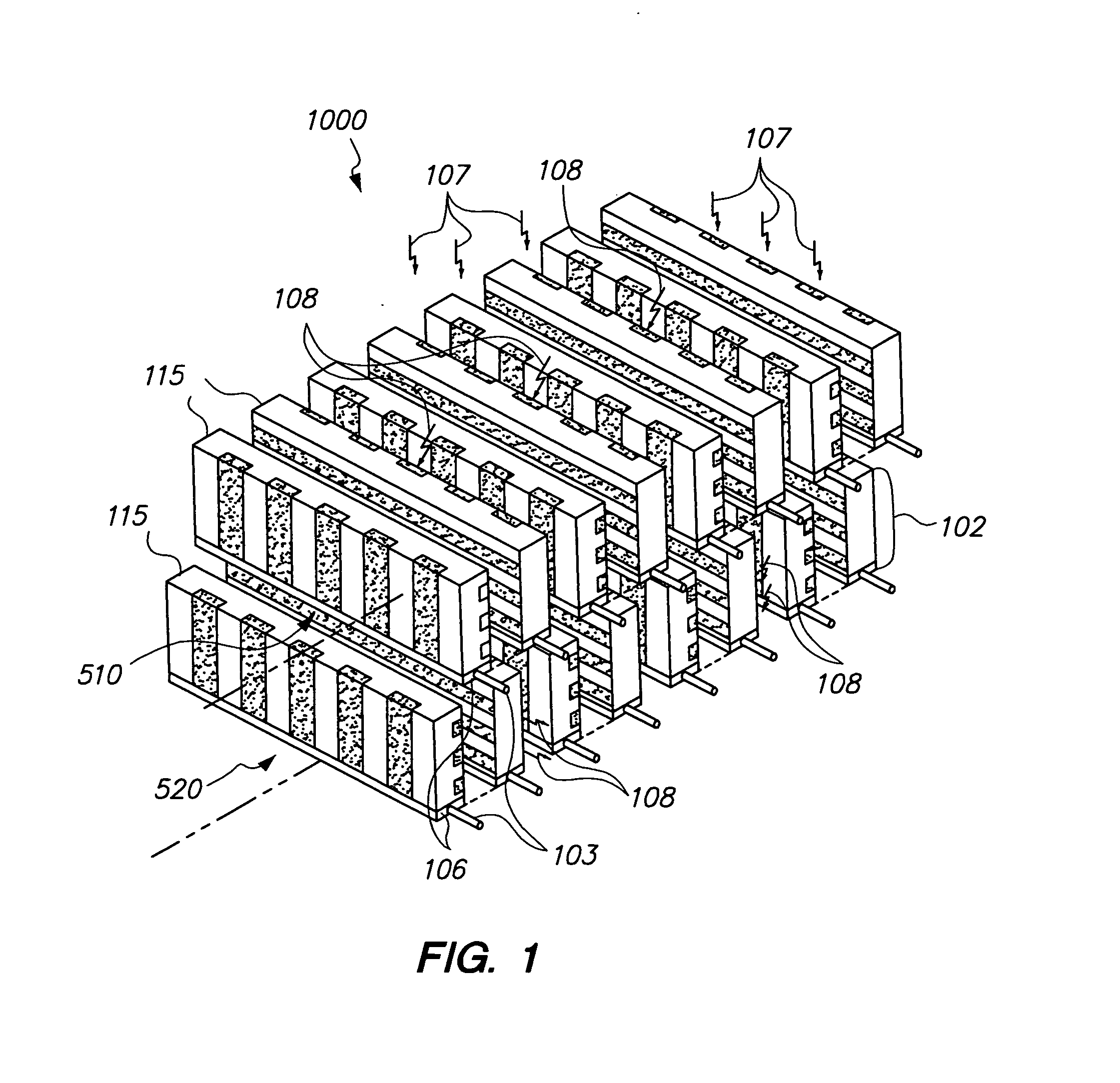
Compton camera with segmented detection modules
A Compton camera for medical imaging is divided into segments (11) with each segment (11) including part of the scatter detector (12), part of the catcher detector (13), and part of the electronics (14). The different segments (11) may be positioned together to form the Compton camera arcing around part of the patient space. By using segments (11), any number of segments (11) may be used to fit with a multi-modality imaging system.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
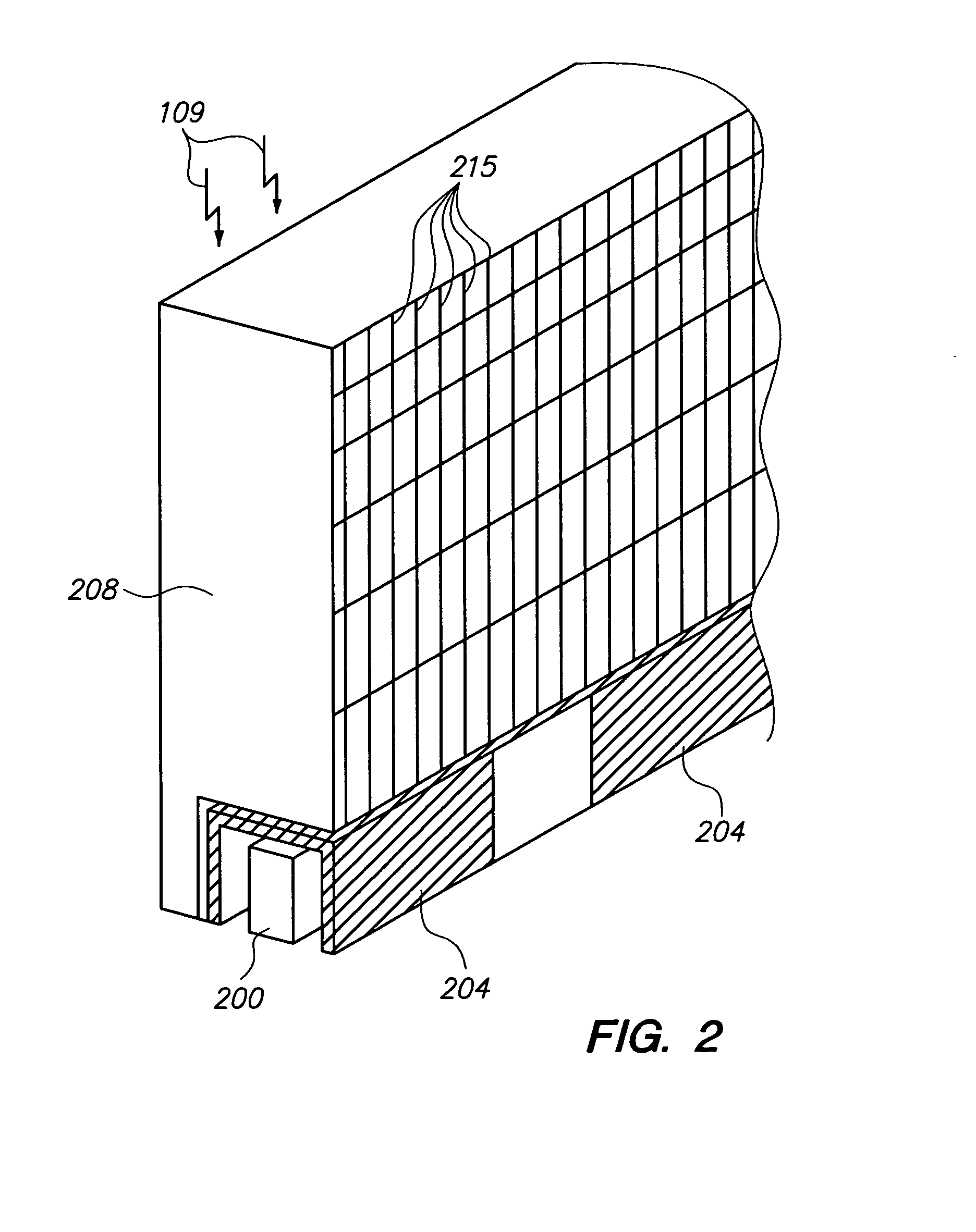
Adaptive compton camera for medical imaging
PendingCN112512427APatient positioning for diagnosticsComputerised tomographsImaging qualityMedical imaging
To optimize image quality and / or sensitivity, a Compton camera is adaptable. The scatter and / or catcher detectors (12, 13) may move closer to and / or further away from a patient and / or each other. Thisadaptation allows a balancing of image quality and sensitivity by altering the geometry.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Cadmium zinc telluride/silicon gamma ray X-ray detector and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN112133775AHigh detection sensitivityImprove detection efficiencyX-ray spectral distribution measurementRadiation intensity measurementPhoton emissionHigh energy
The invention discloses a cadmium zinc telluride / silicon gamma ray X-ray detector and a preparation method thereof. The detector provided by the invention has high detection sensitivity and high detection efficiency, and is a composite cadmium zinc telluride-silicon detector with absorption and multiplication region separation. According to the invention, a CZT wafer and SiPM are bonded together,the CZT wafer is used as an absorption region for detecting nuclear radiation, the SiPM is used as a multiplication and amplification region of a carrier, and the CZT / Si nuclear radiation detector with an absorption region and a multiplication region separated and high detection sensitivity is formed. When a SiPM structure is adopted, the whole device is used as a high-sensitivity detector; and when a single APD unit or a part of APD units are used as pixel units, the detector can be used as a high-sensitivity pixel detector. A detection device with single photon counting capability, high energy resolution, high spatial resolution, high time resolution, high detection sensitivity and high detection efficiency is provided for imaging instruments of a next generation Compton gamma camera, asingle photon emission computed tomography instrument and a positron emission tomography instrument.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
NEAR 2Pi COMPTON CAMERA FOR MEDICAL IMAGING
PendingCN112512428APatient positioning for diagnosticsComputerised tomographsEngineeringMedical imaging
To capture more emitted photons with a Compton camera, the scatter detector (12) is tilted (non-orthogonal angle) relative to a radial from the isocenter of the imaging system. The tilt creates a greater volume for scatter interaction. To capture more scatter photons, the catcher detector (13) is non-planar, such as a multi-faced detector at least partially surrounding a volume behind the scatterdetector (12). The tilted scatter detector (12) alone, the non-planar catcher detector (13) alone, or the tilted scatter detector (12) and the non-planar catcher detector (13) are used in the Comptoncamera.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Method for radionuclide identification by utilizing Compton scattering case statistics
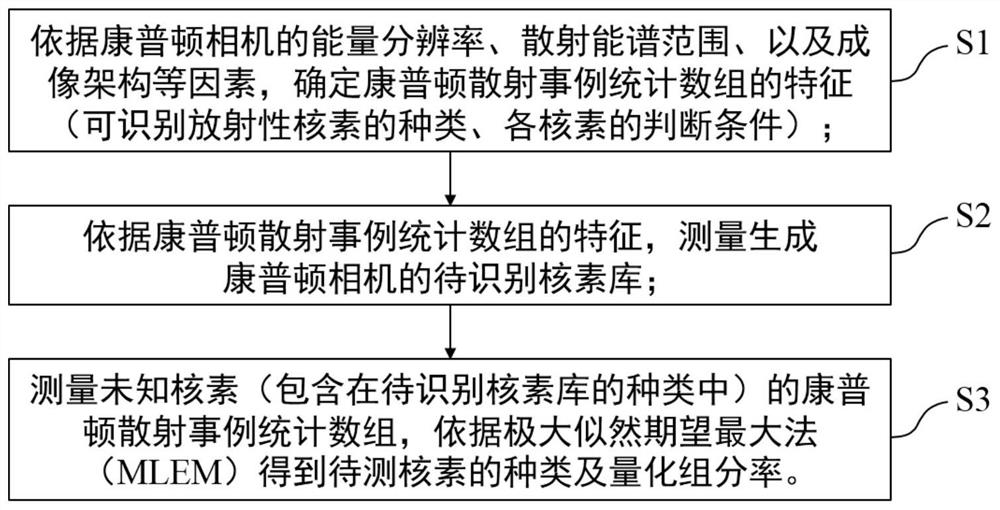
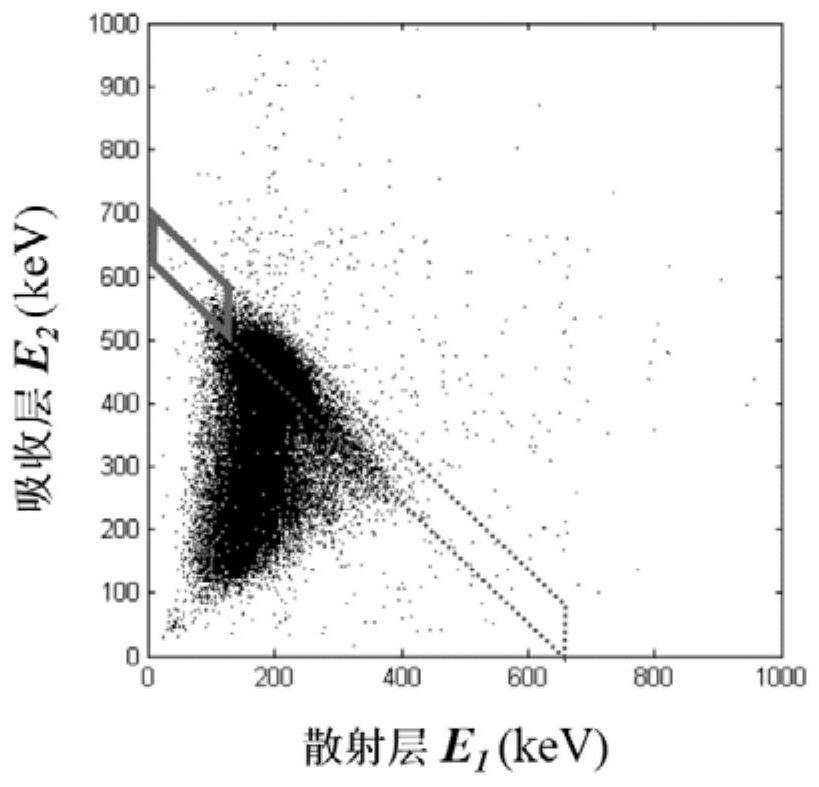
ActiveCN111880211AImprove recognition efficiencyX-ray spectral distribution measurementComplex mathematical operationsCounting rateNuclear engineering
The invention discloses a method for radionuclide identification by utilizing Compton scattering case statistics. The method comprises the following steps: 1) measuring and generating a nuclide library to be identified of target equipment by utilizing the characteristics of a Compton scattering case statistical array determined by the target equipment, wherein the target device is a device capableof obtaining Compton scattering cases; 2) testing unknown nuclide contained in the to-be-identified nuclide library by utilizing the target equipment to obtain a to-be-tested Compton scattering casestatistical array; 3) calculating the probability density vi of the counting rate of each element i in the to-be-tested Compton scattering case statistical array relative to the multiple of the background condition; 4) obtaining the type and quantitative component rate of the nuclide to be measured according to a maximum likelihood expectation maximization method. According to the invention, quantitative identification of unknown radionuclides by the Compton camera can be realized.
Owner:INST OF HIGH ENERGY PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Imaging method using jointly a pet reconstruction and a compton reconstruction, preferably in 3D compton
PendingUS20220357291A1Overcomes drawbackImprove accuracyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentComputer graphics (images)Radiology
Owner:DAMAVAN IMAGING +1
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com