Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
307 results about "Photon emission" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
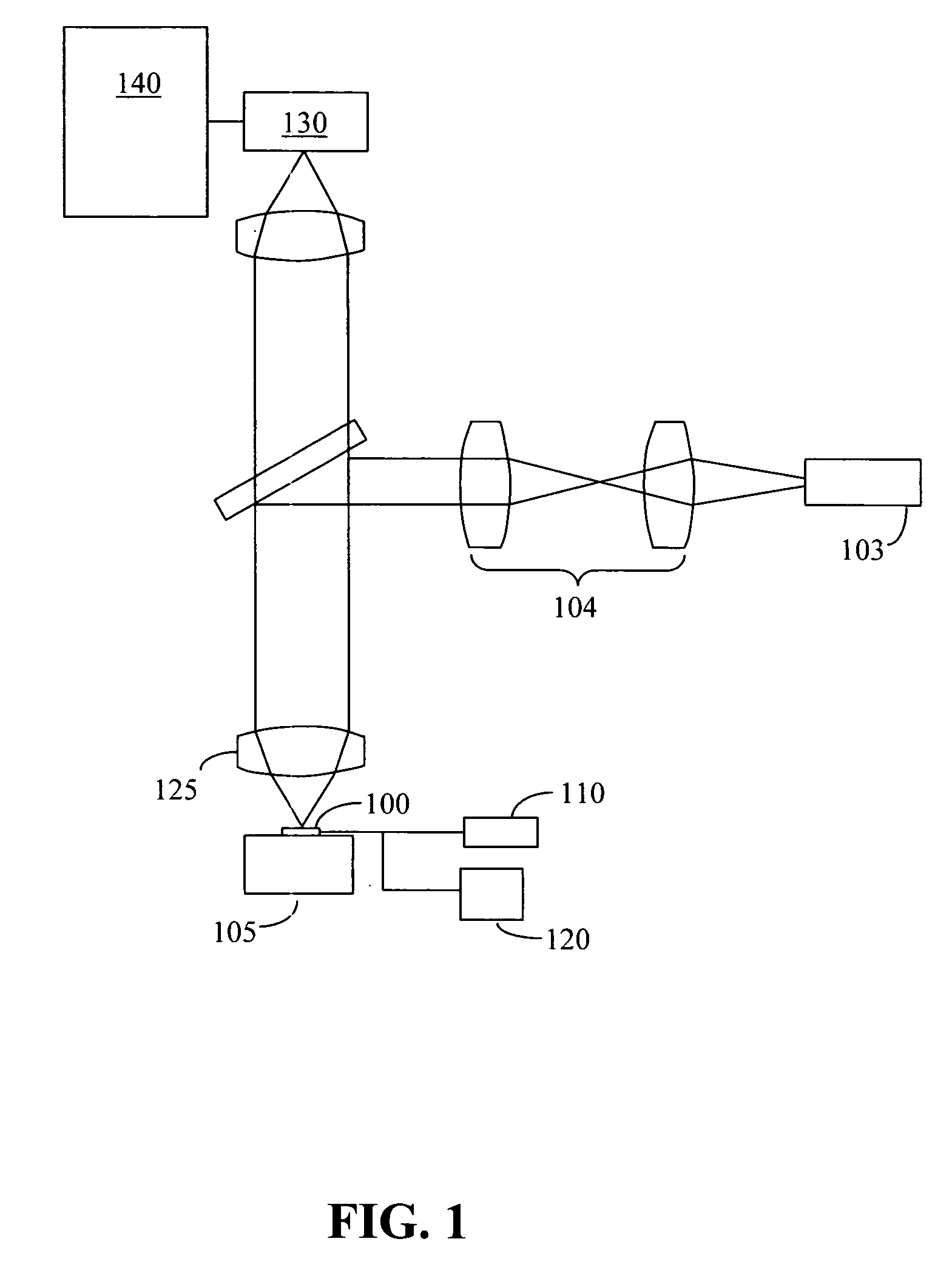
Photon Emission. Photon Emission Microscopy (PEM) or (EMMI) is a high efficient Failure Analysis technique for fault localization on IC's. In principle EMMI or PEM consists of a highly-sensitive CCD or InGaAs detector capable of detecting photons.
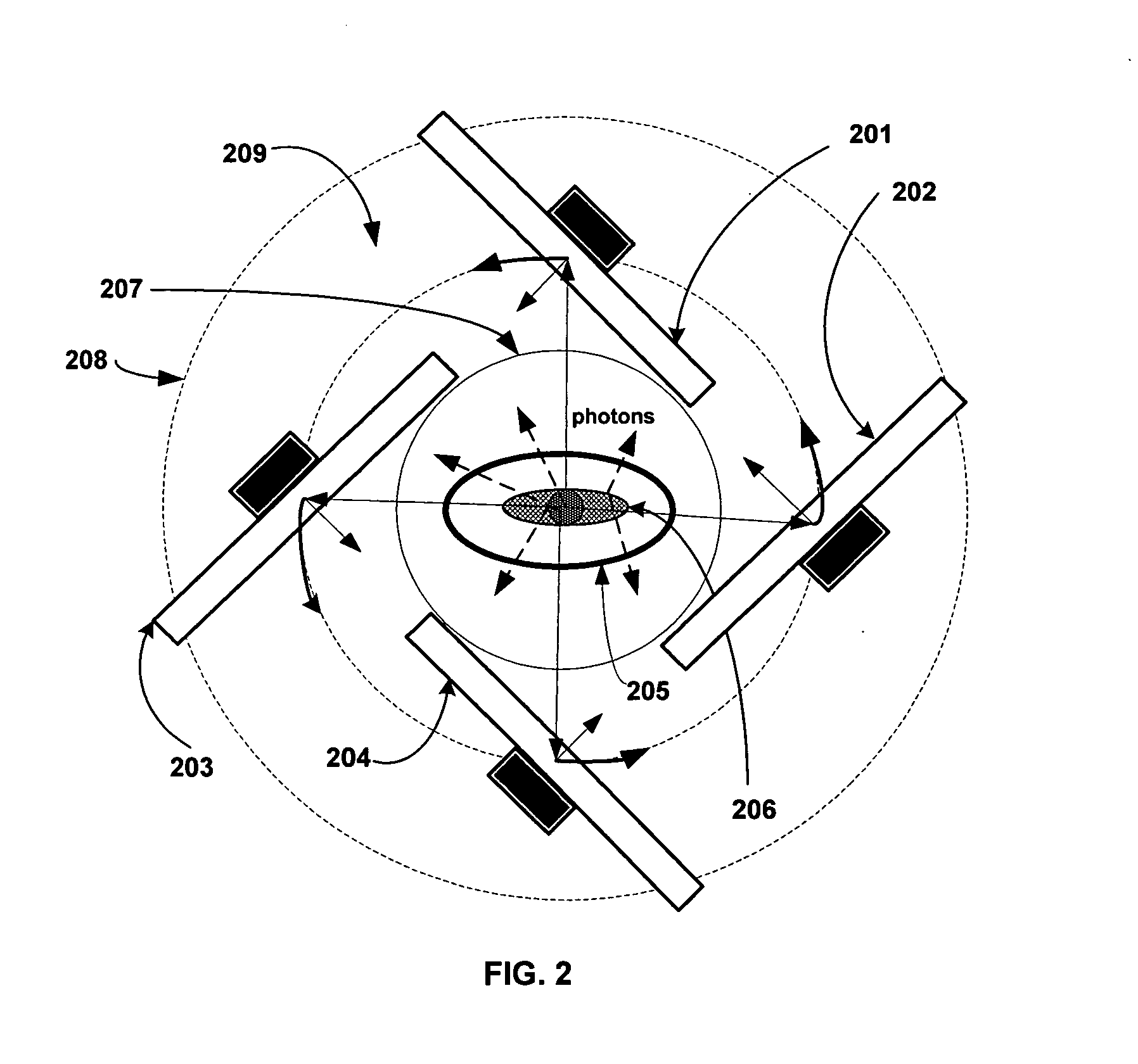
High definition lidar system
ActiveUS7969558B2More compactMore ruggedAngle measurementOptical rangefindersHigh definition tvPower coupling
Owner:VELODYNE LIDAR USA INC
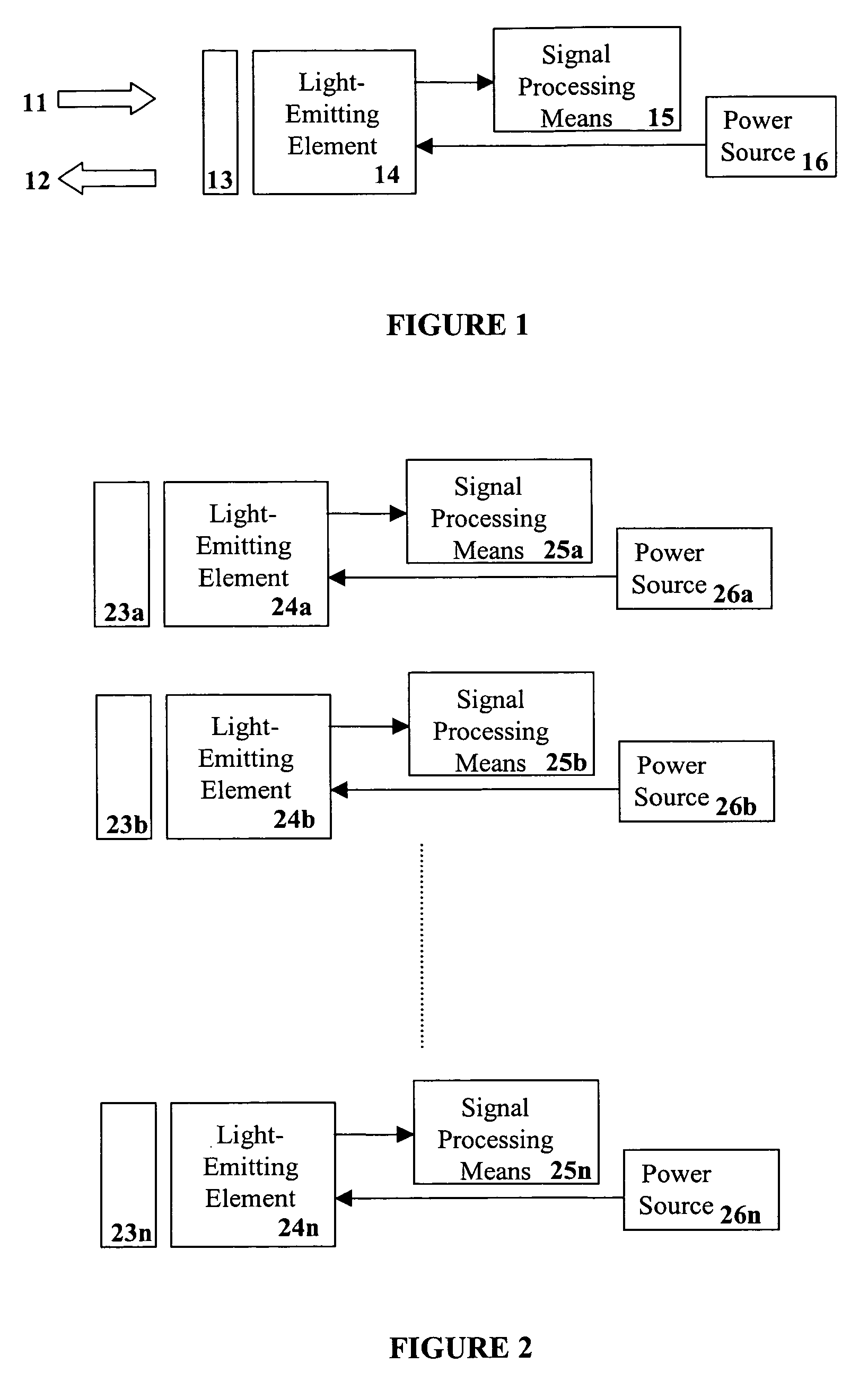
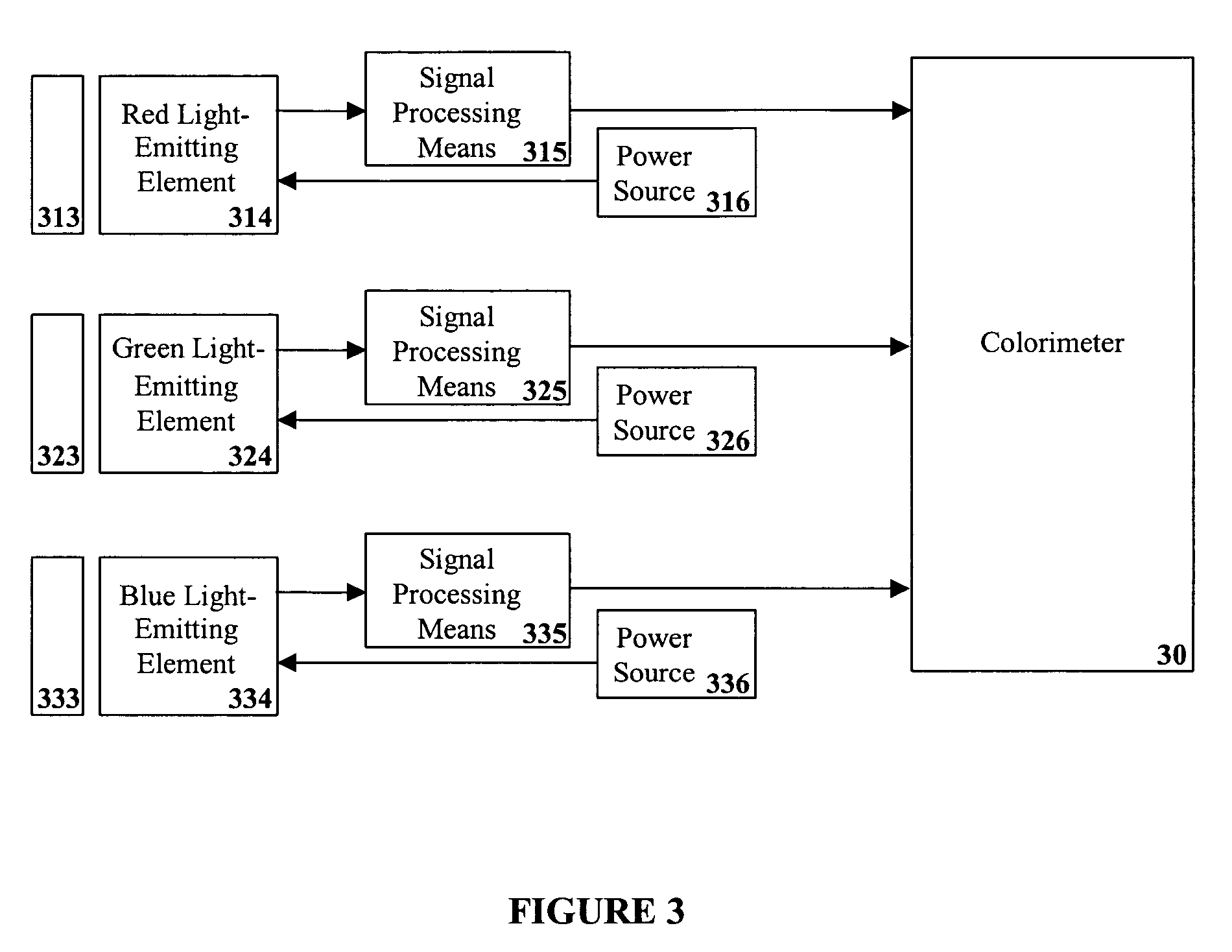
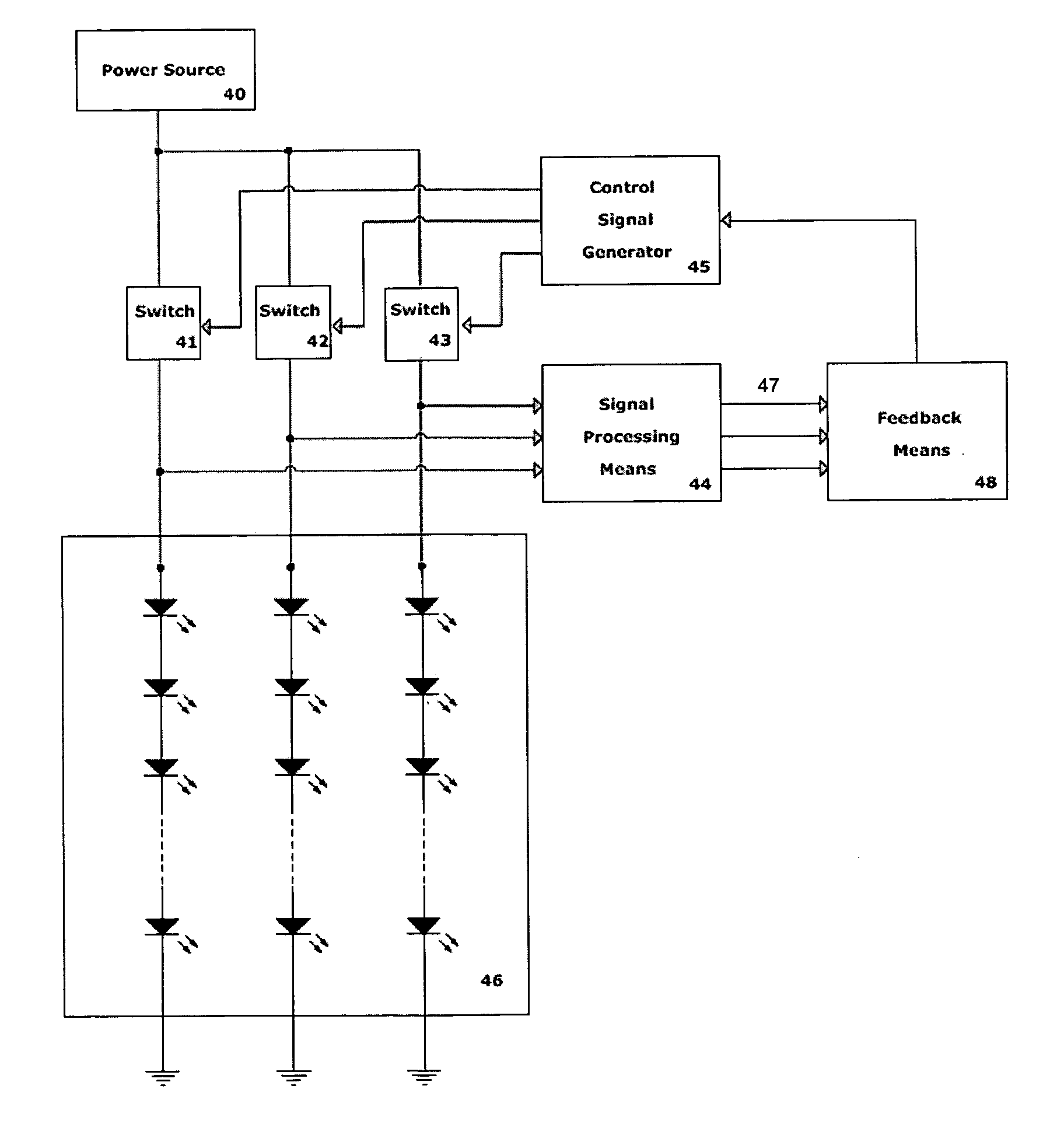
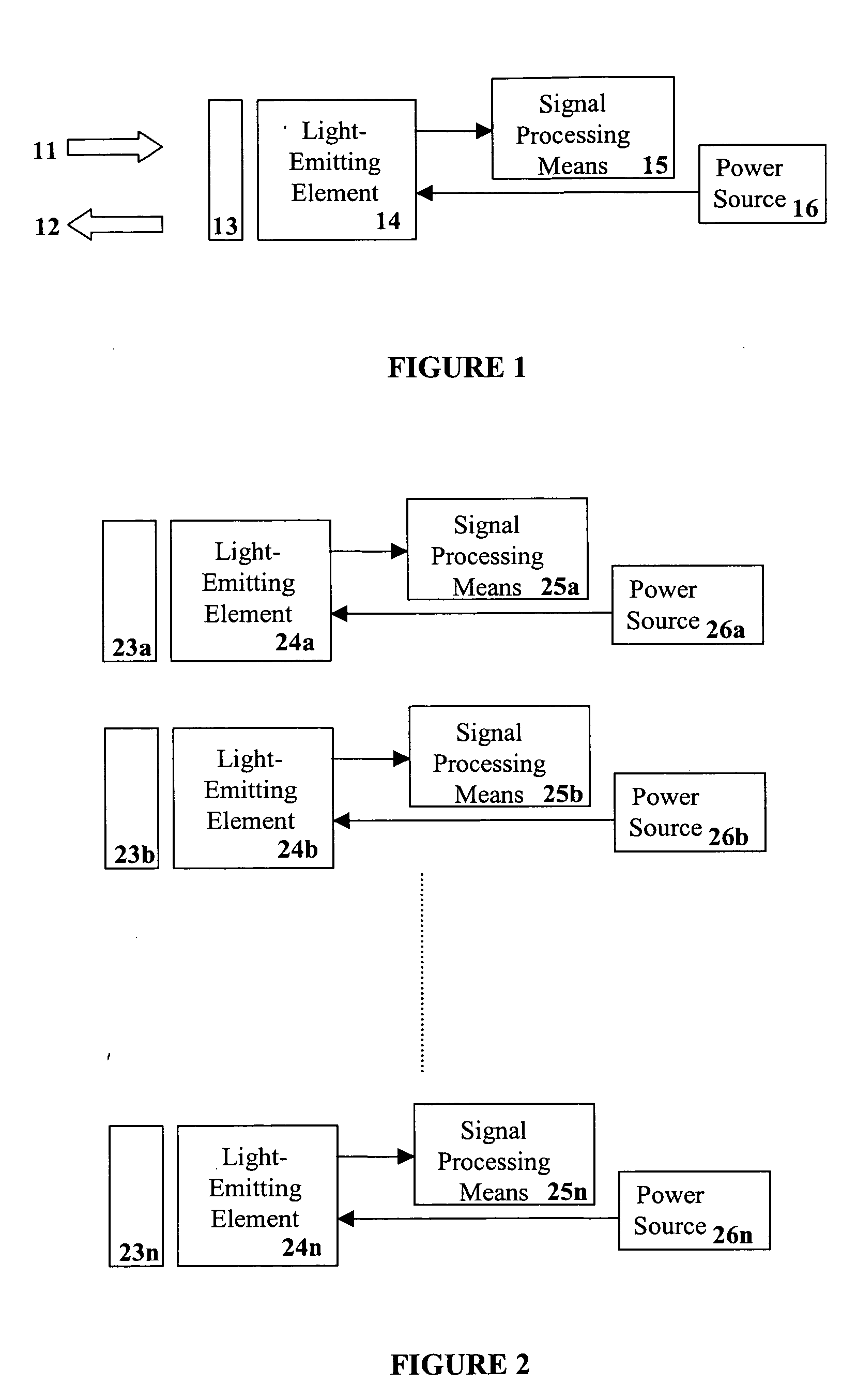
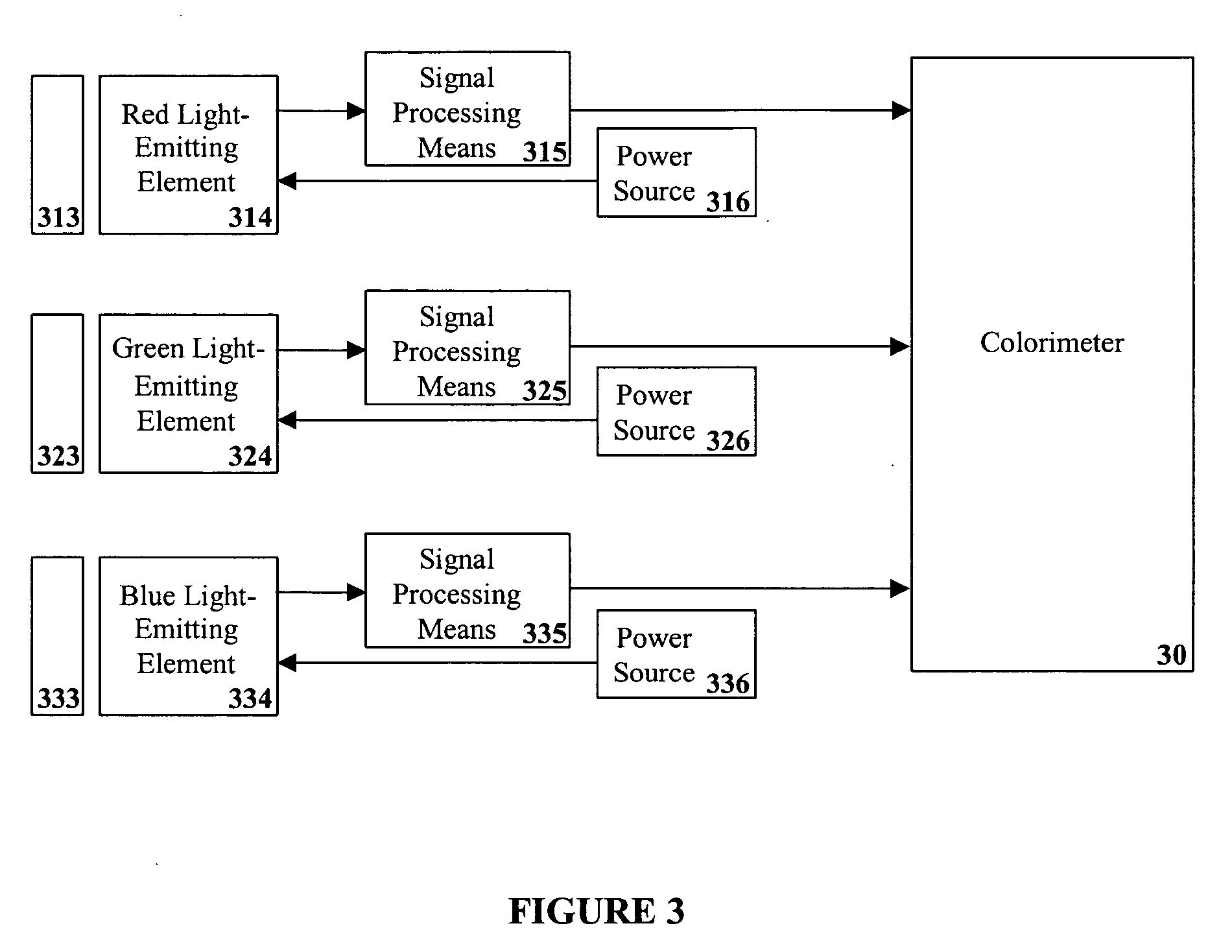
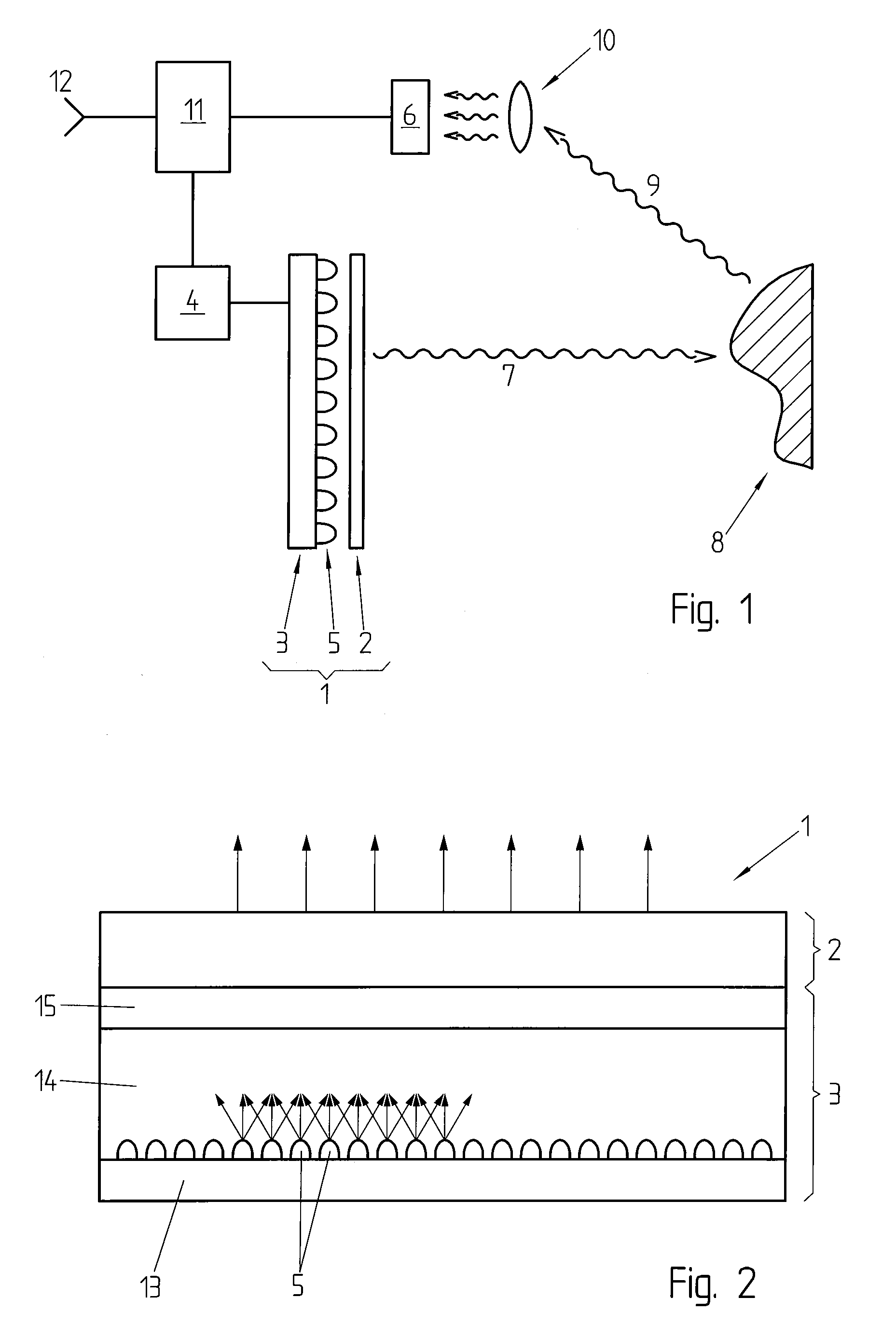
Lighting system including photonic emission and detection using light-emitting elements
The present invention provides a system and method for generating light using light-emitting elements and detecting the intensity and spectral power distribution of light using the same light-emitting elements as spectrally sensitive photodetectors. The light-emitting elements function in two modes, an ON mode and an OFF mode, wherein in the ON mode the light-emitting elements are activated and emit light of a particular frequency or range of frequencies. When in the OFF mode, the light-emitting elements are deactivated, wherein they do not emit light but serve to detect photons incident upon them thus generating an electrical signal representative of the intensity and spectral power distribution of the incident photons. The detected signal from the deactivated light-emitting elements can be used to provide photonic feedback to a lighting system, and thereby may be used to control the brightness and color balance of the lighting system. In addition, the light-emitting elements may be arranged such that no spectrally selective filters or optics are necessary to block or focus light onto the light-emitting elements when in the detection or OFF mode.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
Lighting system including photonic emission and detection using light-emitting elements
ActiveUS20060028156A1Electrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesPhoton emissionPhotodetector
The present invention provides a system and method for generating light using light-emitting elements and detecting the intensity and spectral power distribution of light using the same light-emitting elements as spectrally sensitive photodetectors. The light-emitting elements function in two modes, an ON mode and an OFF mode, wherein in the ON mode the light-emitting elements are activated and emit light of a particular frequency or range of frequencies. When in the OFF mode, the light-emitting elements are deactivated, wherein they do not emit light but serve to detect photons incident upon them thus generating an electrical signal representative of the intensity and spectral power distribution of the incident photons. The detected signal from the deactivated light-emitting elements can be used to provide photonic feedback to a lighting system, and thereby may be used to control the brightness and colour balance of the lighting system. In addition, the light-emitting elements may be arranged such that no spectrally selective filters or optics are necessary to block or focus light onto the light-emitting elements when in the detection or OFF mode.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
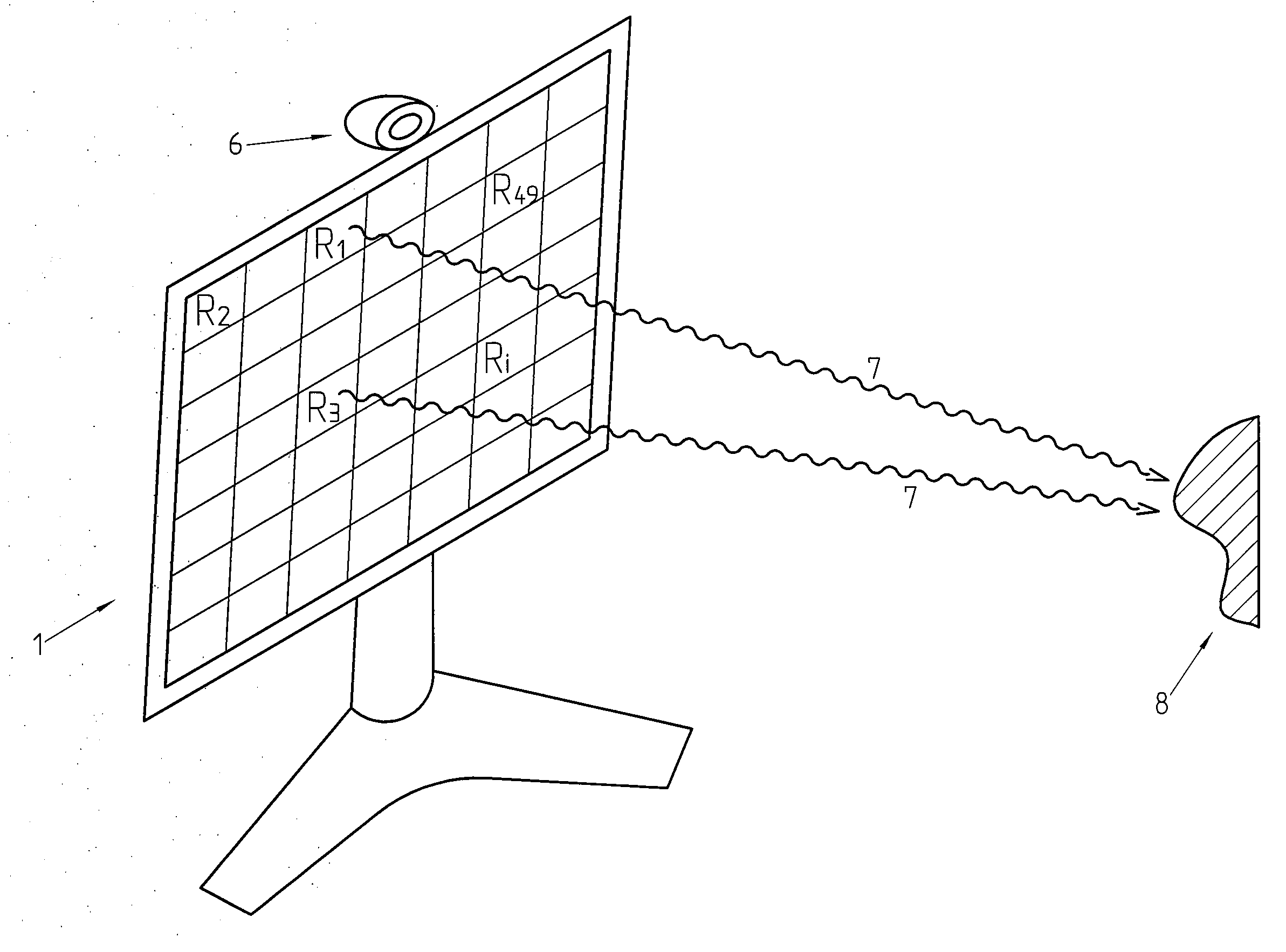
Time-of-flight based imaging system using a display as illumination source
InactiveUS20110037849A1Easy to implementLow cost configurationColor television detailsClosed circuit television systemsElectronic systemsPhoton emission
The present invention concerns a time-of-flight based imaging system comprising a photon emitter used as an illumination source; a photon sensor (6); an electronic system for delivering a signal depending on the reception time of photons by said photon detector, characterized in that an electronic display (2) is used as said photonic source.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Lighting system with high and improved extraction efficiency
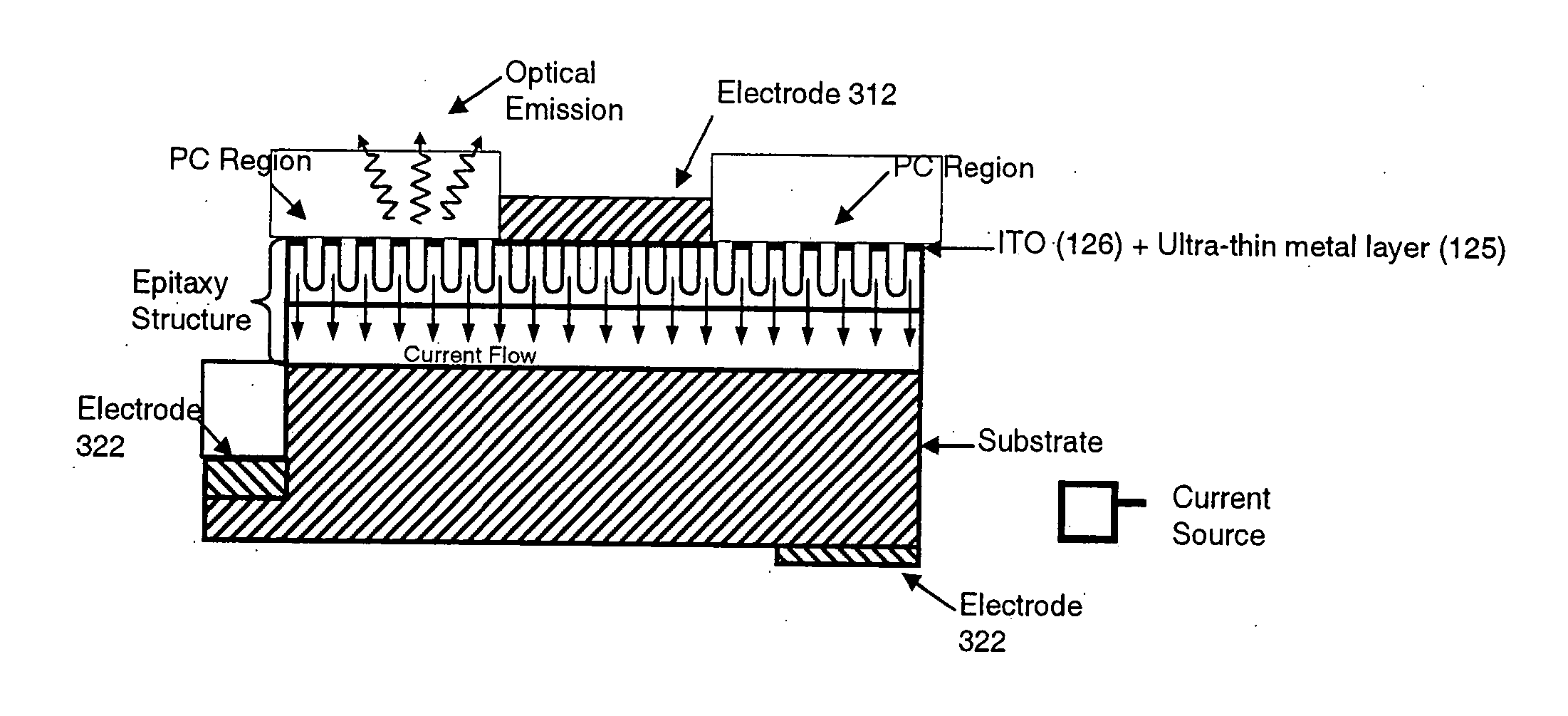
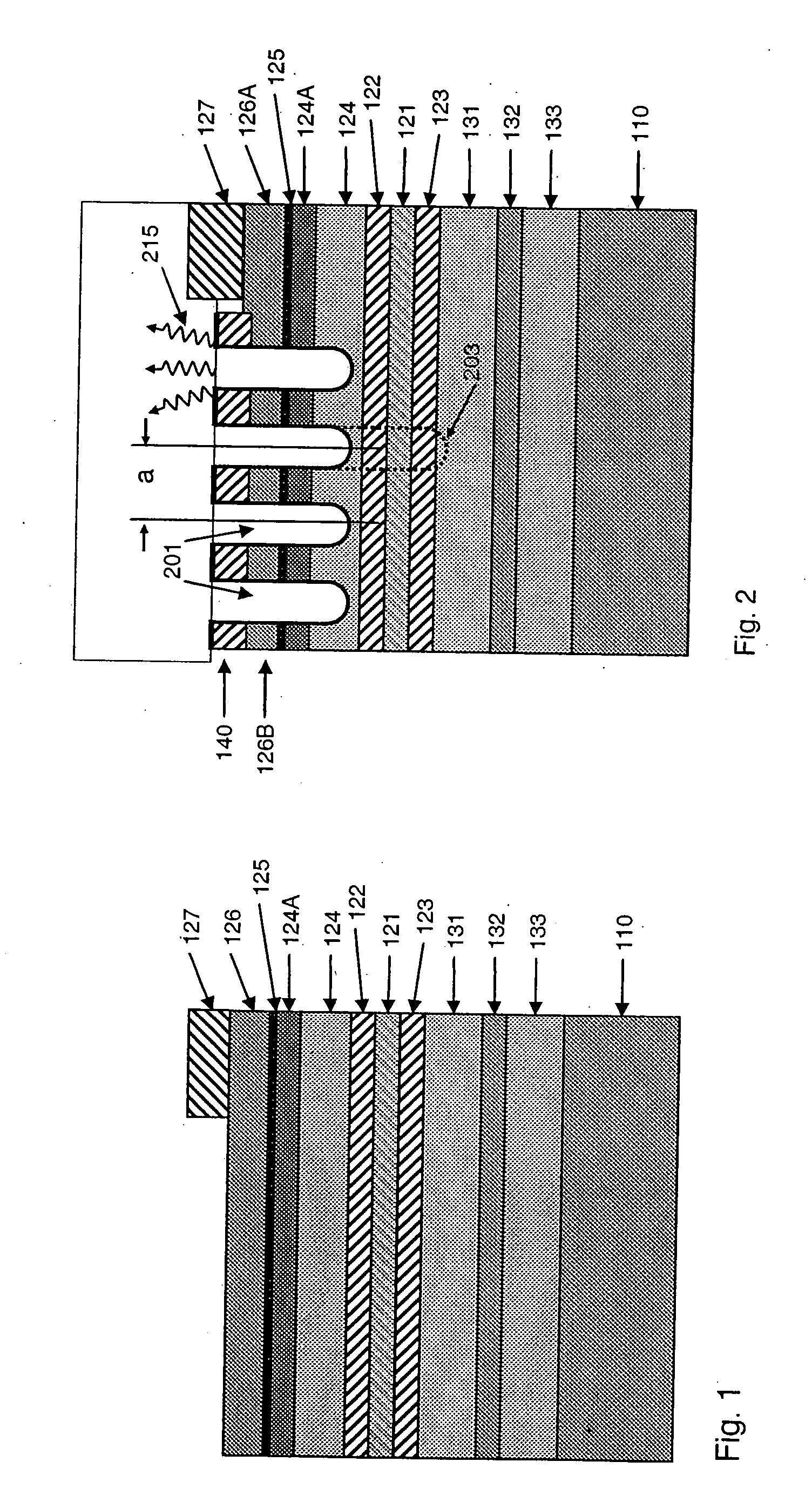
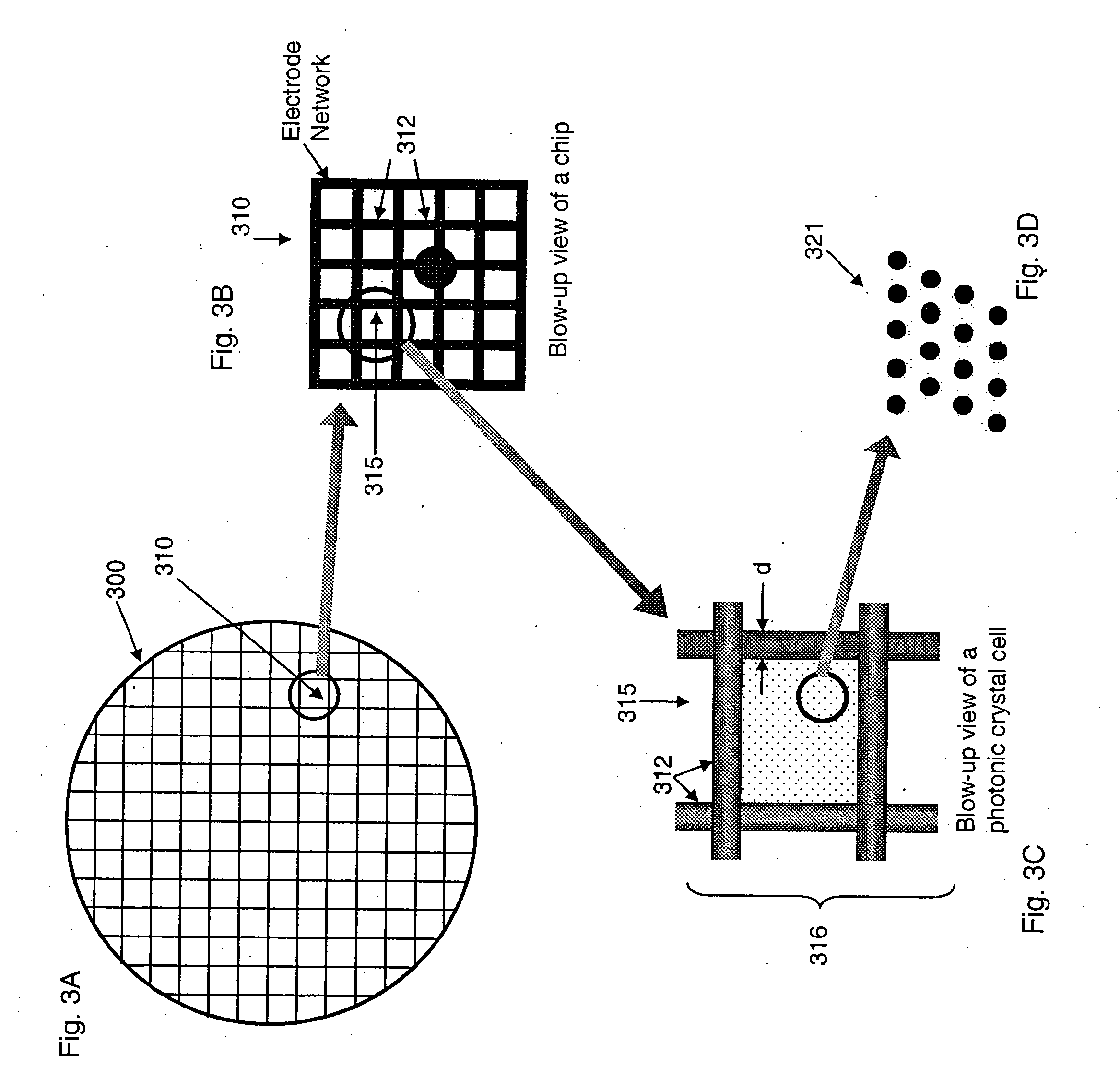
InactiveUS20050173714A1Efficient extractionImprove performanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotonic crystalPhoton emission
In an epitaxial structure of a solid state lighting system, electrical current injection into the active layer is used to excite the photon emission. The present invention employs a unique waveguide layer in the epitaxial structure for trapping the light generated by the active layer in the fundamental waveguide mode. Multiple photonic crystal regions with different characteristics located either outside or inside one or more current injection regions extract photons from the waveguide layer(s). The present invention creates solid state lighting with high optical output and high power efficiency.
Owner:DICON FIBEROPTICS
Integration of photon emission microscope and focused ion beam
InactiveUS20060012385A1Vacuum gauge using ionisation effectsFault location by increasing destruction at faultPhoton emissionIon beam
An integrated FIB / PEM apparatus and method for performing failure analysis on integrated circuits. In-situ failure analysis is enabled by integrating Photon Emission Microscopy into a Focused Ion Beam system, thereby improving throughput and efficiency of Failure Analysis. An iterative method is described for identifying and localizing fault sites on the circuit.
Owner:DCG SYST
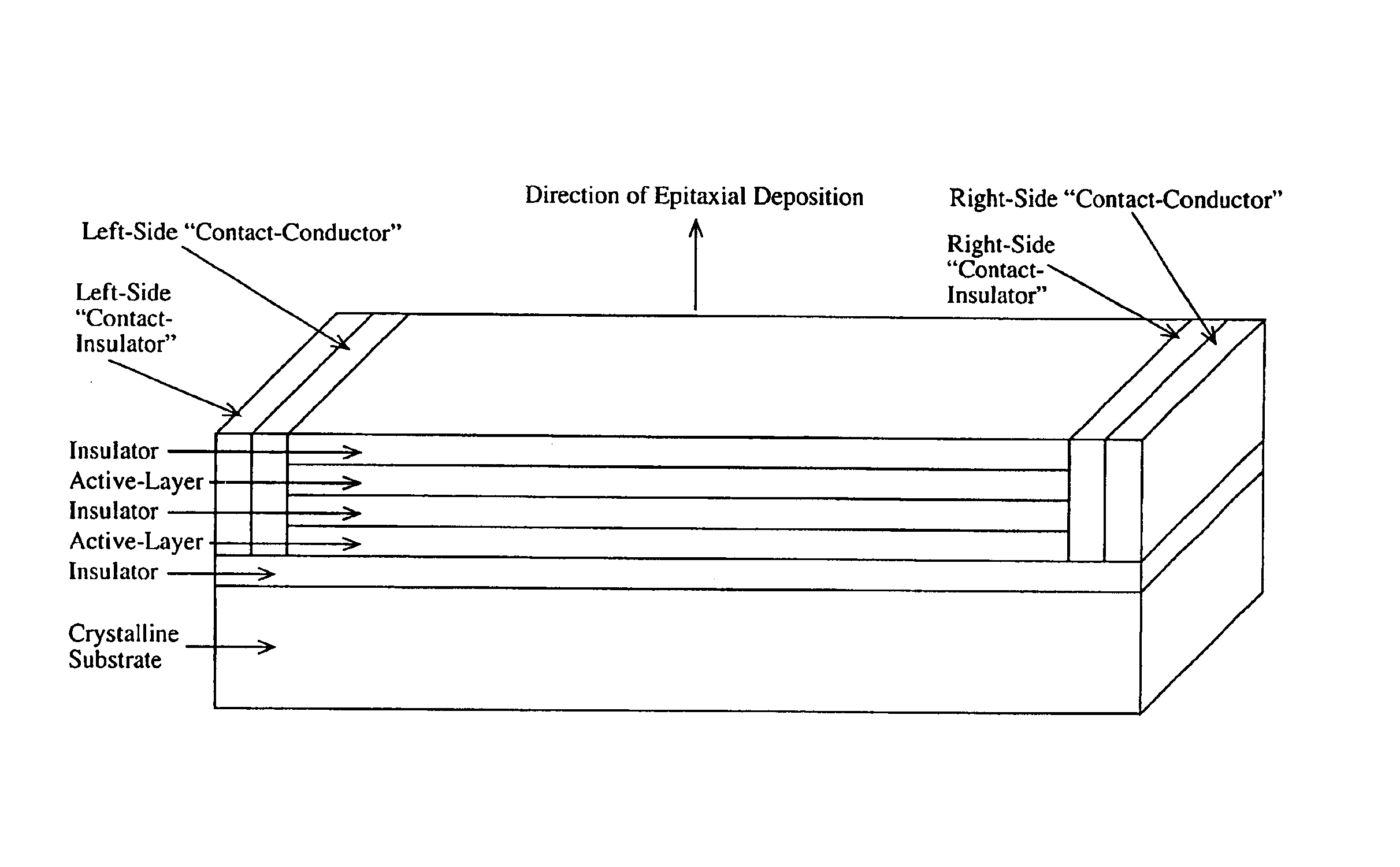
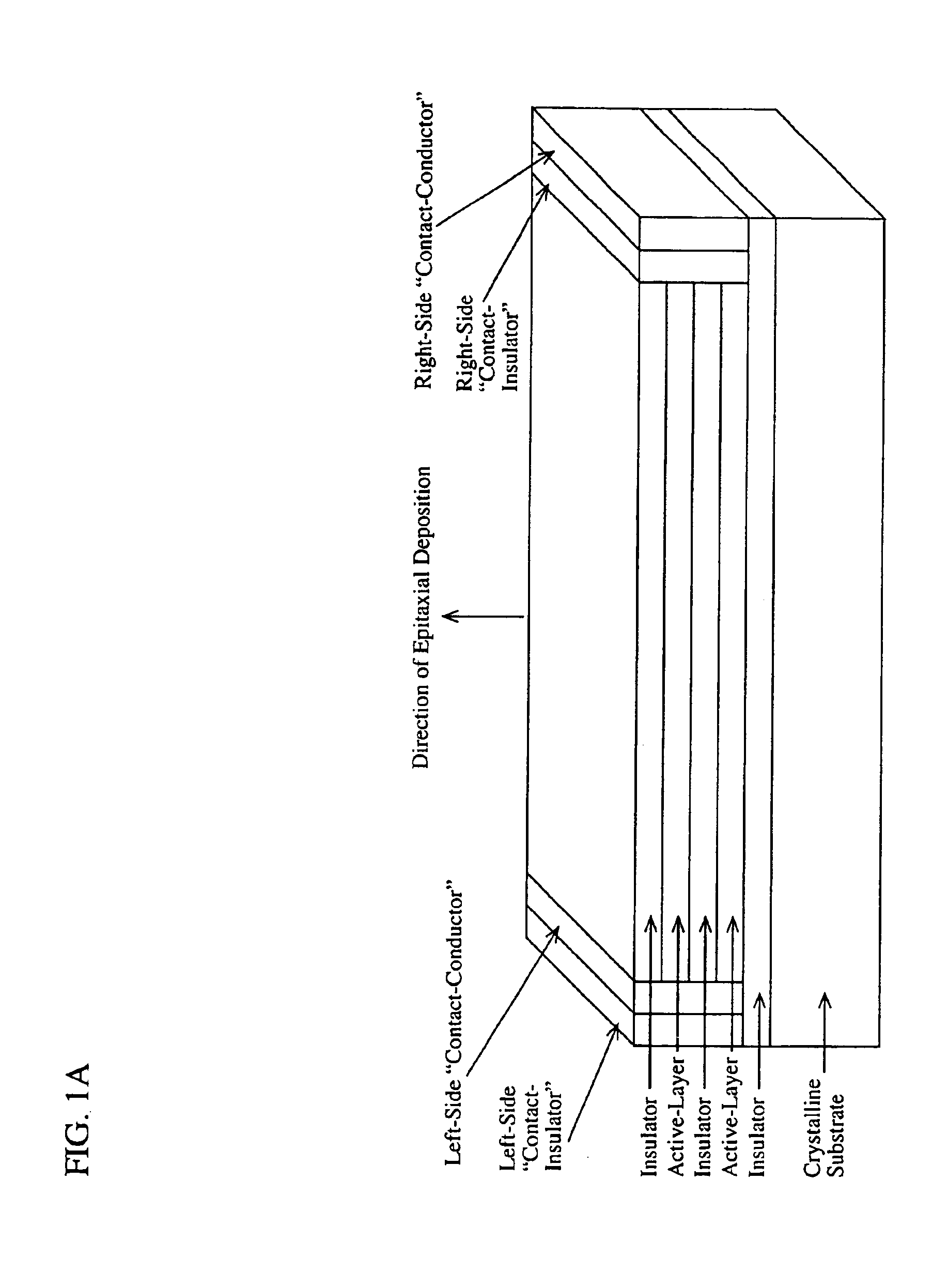
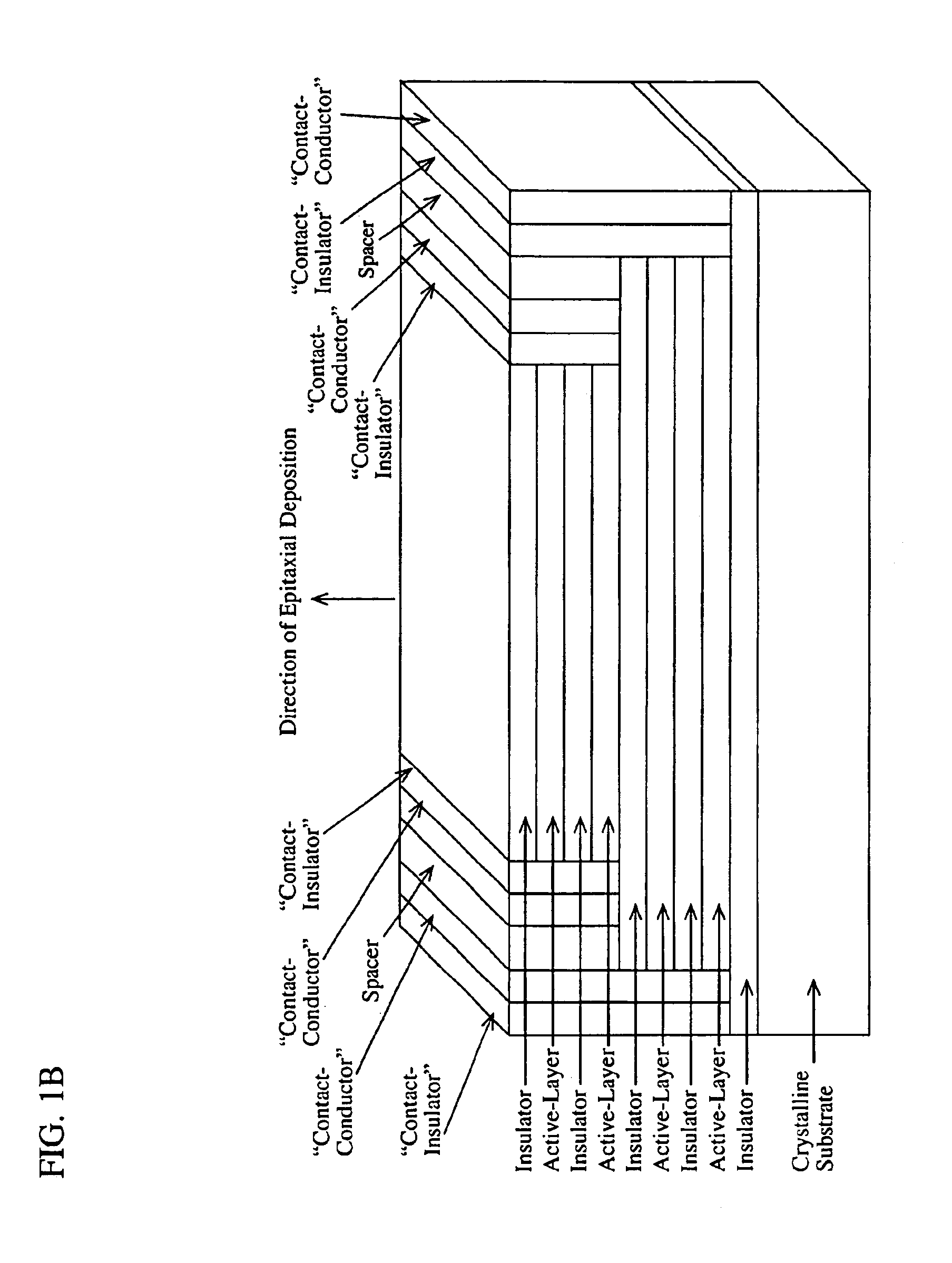
Wavelength-selective photonics device
InactiveUS6891869B2Wide rangeOvercome limitationsSolid-state devicesNanoopticsPhoton emissionPhotonics
A device comprising a number of different wavelength-selective active-layers arranged in a vertical stack, having band-alignment and work-function engineered lateral contacts to said active-layers, consisting of a contact-insulator and a conductor-insulator. Photons of different energies are selectively absorbed in or emitted by the active-layers. Contact means are arranged separately on the lateral sides of each layer or set of layers having the same parameters for extracting charge carriers generated in the photon-absorbing layers and / or injecting charge carriers into the photon-emitting layers. The device can be used for various applications: wavelength-selective multi-spectral solid-state displays, image-sensors, light-valves, light-emitters, etc. It can also be used for multiple-band gap solar-cells. The architecture of the device can be adapted to produce coherent light.
Owner:QUANTUM SEMICON
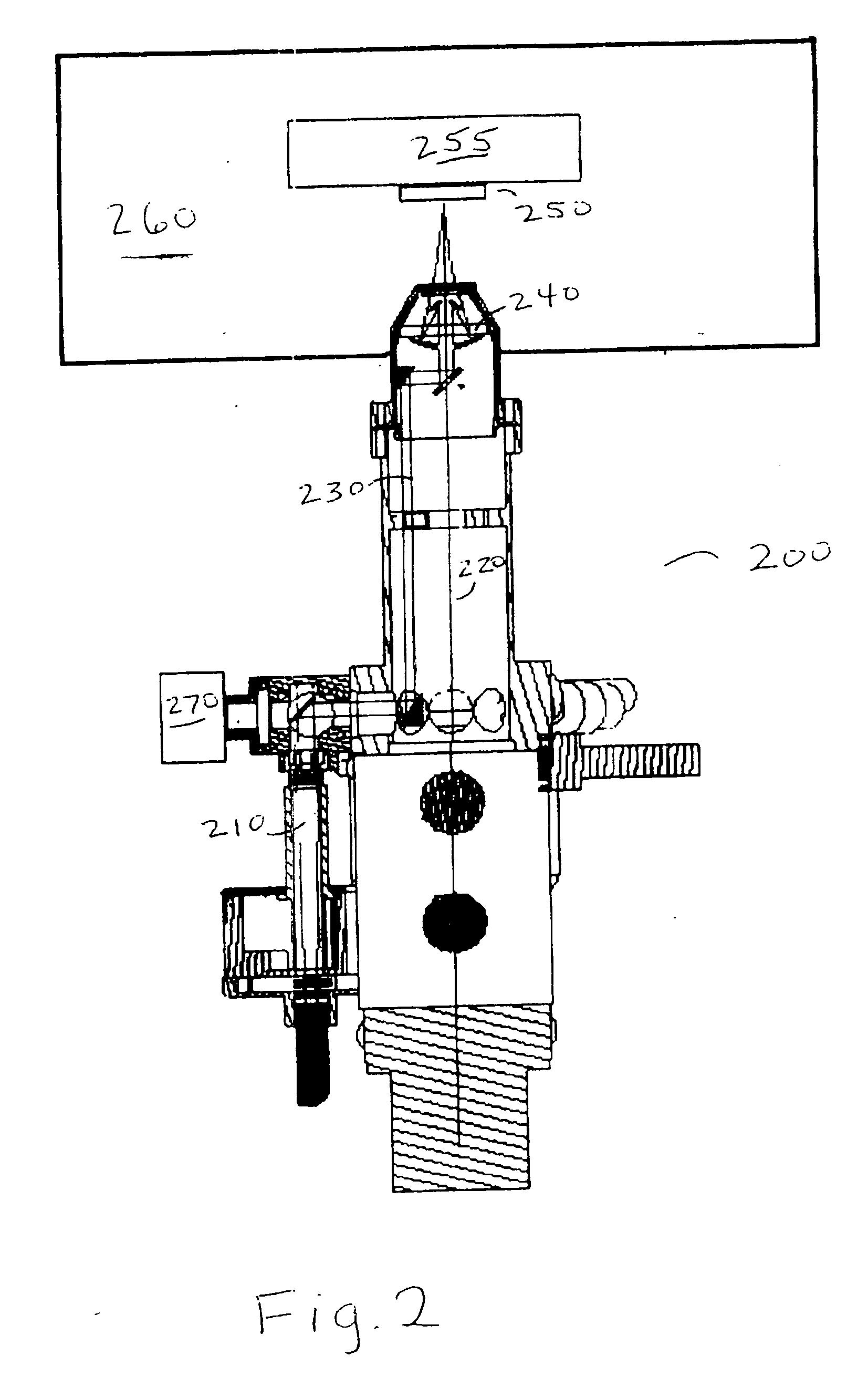
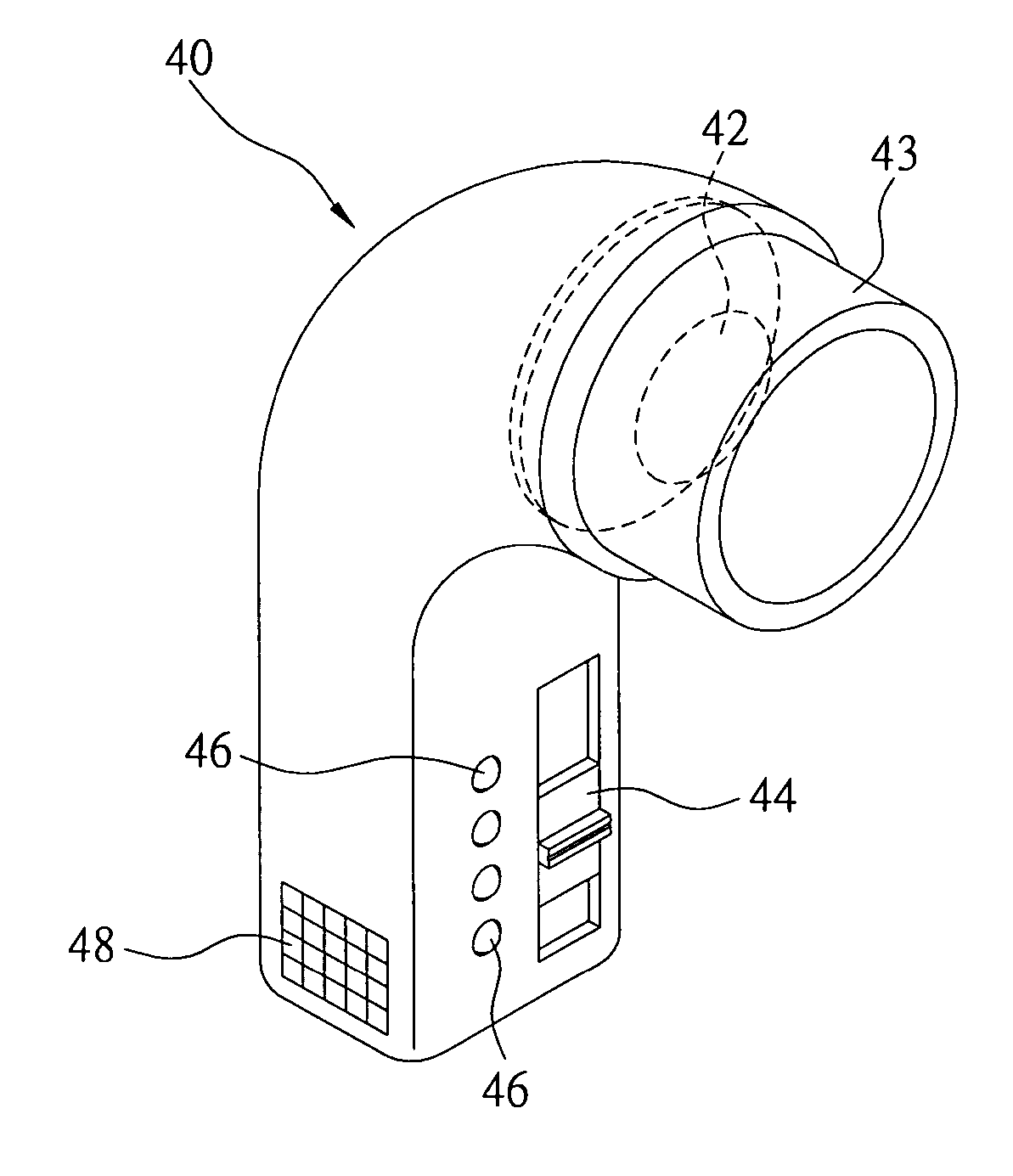
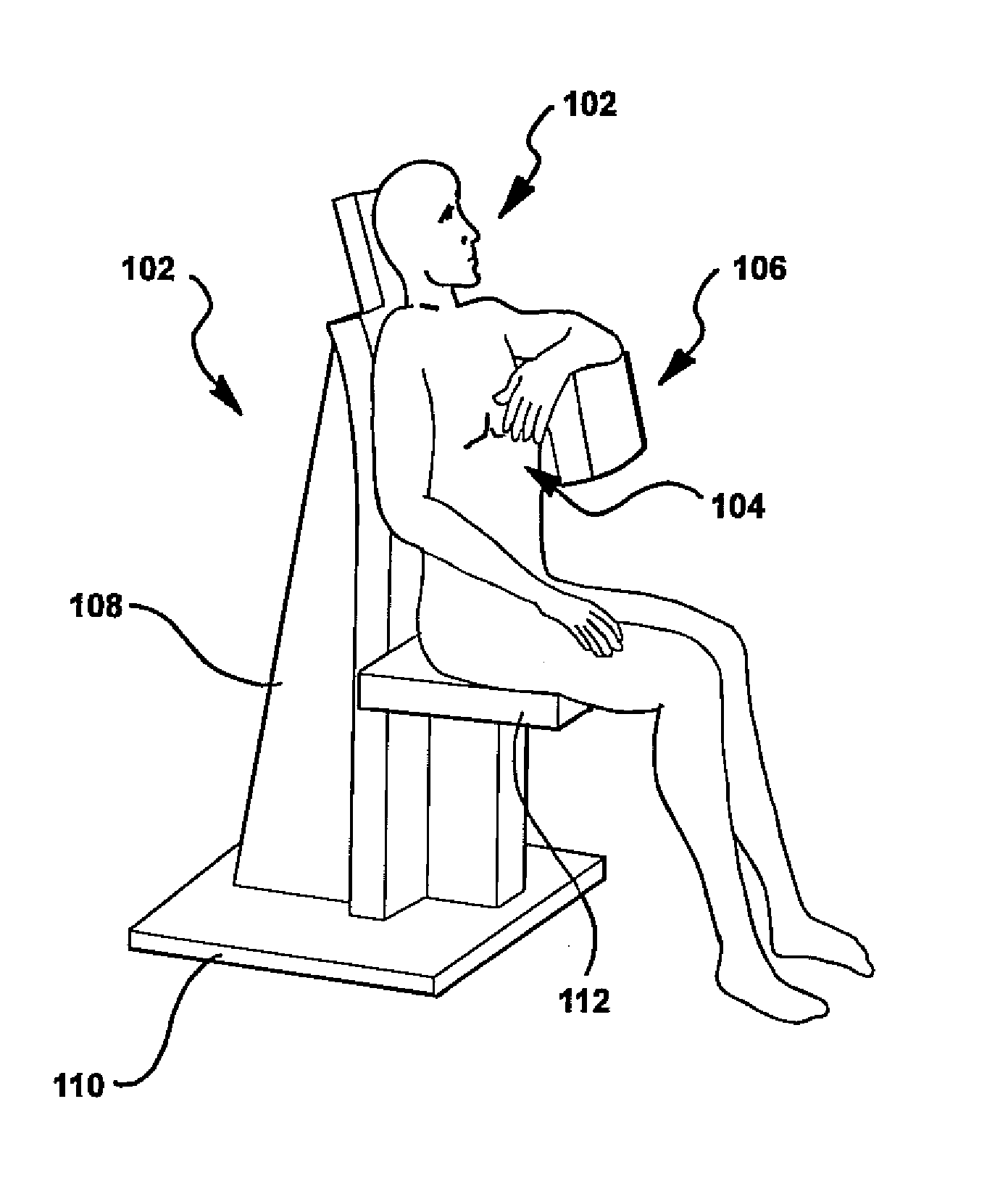
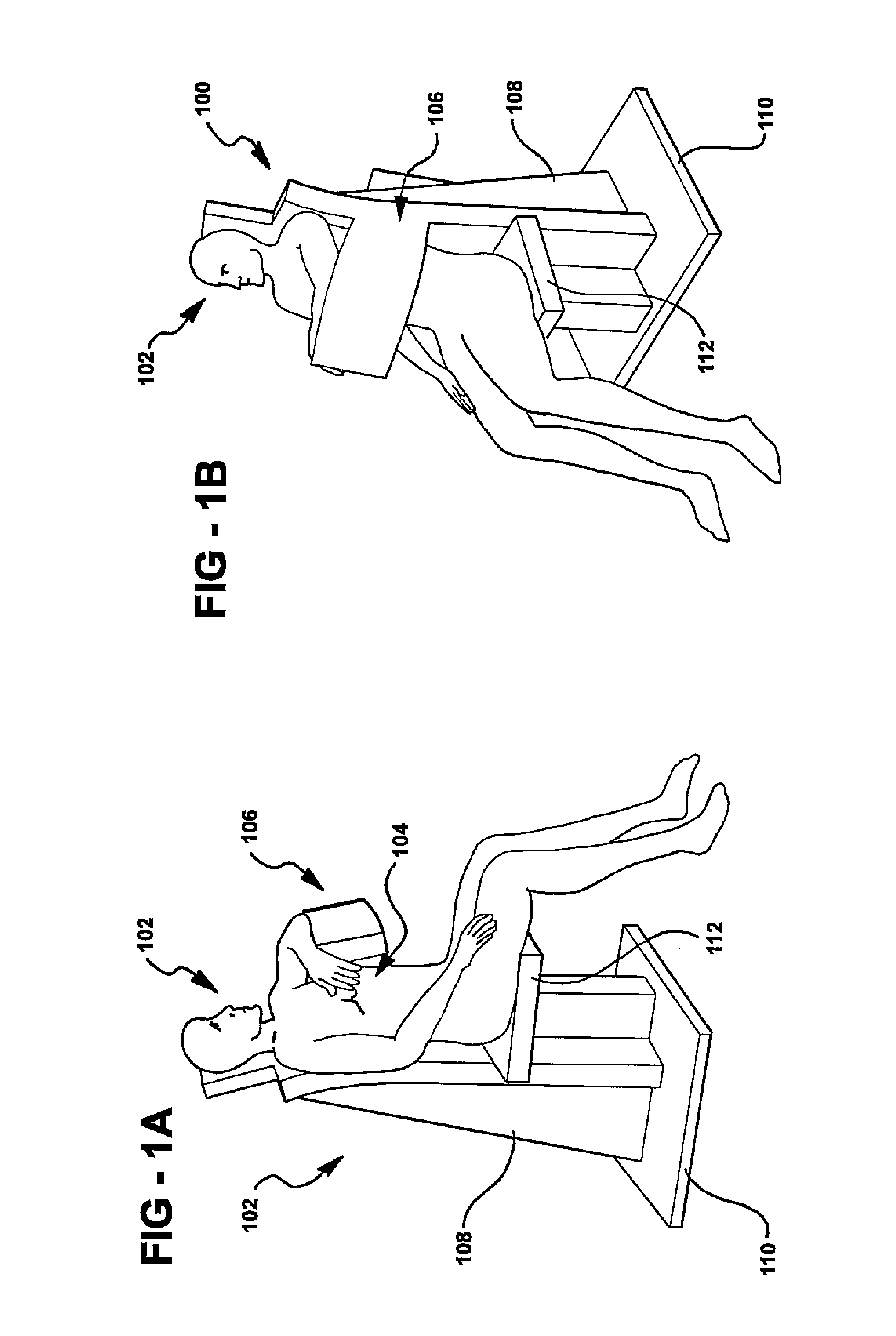
Portable medical and cosmetic photon emission adjustment device and method using the same
The present invention describes a portable medical and cosmetic photon emission adjustment device with the control of dose of photon and a method for using the same. A light source for medical treatment is positioned in a portable device to adjust the dose of photon emission by a dose adjustment device. The dose adjustment device has a microprocessor for processing and transmitting control signals and instruction signals. The dose adjustment device is used to control a plurality of light sources. The light source can be a high power light-emitting diode (LED) or a laser diode, and is combined with a set of lenses to achieve light convergence or light dispersion.
Owner:LIN WUN CHEN
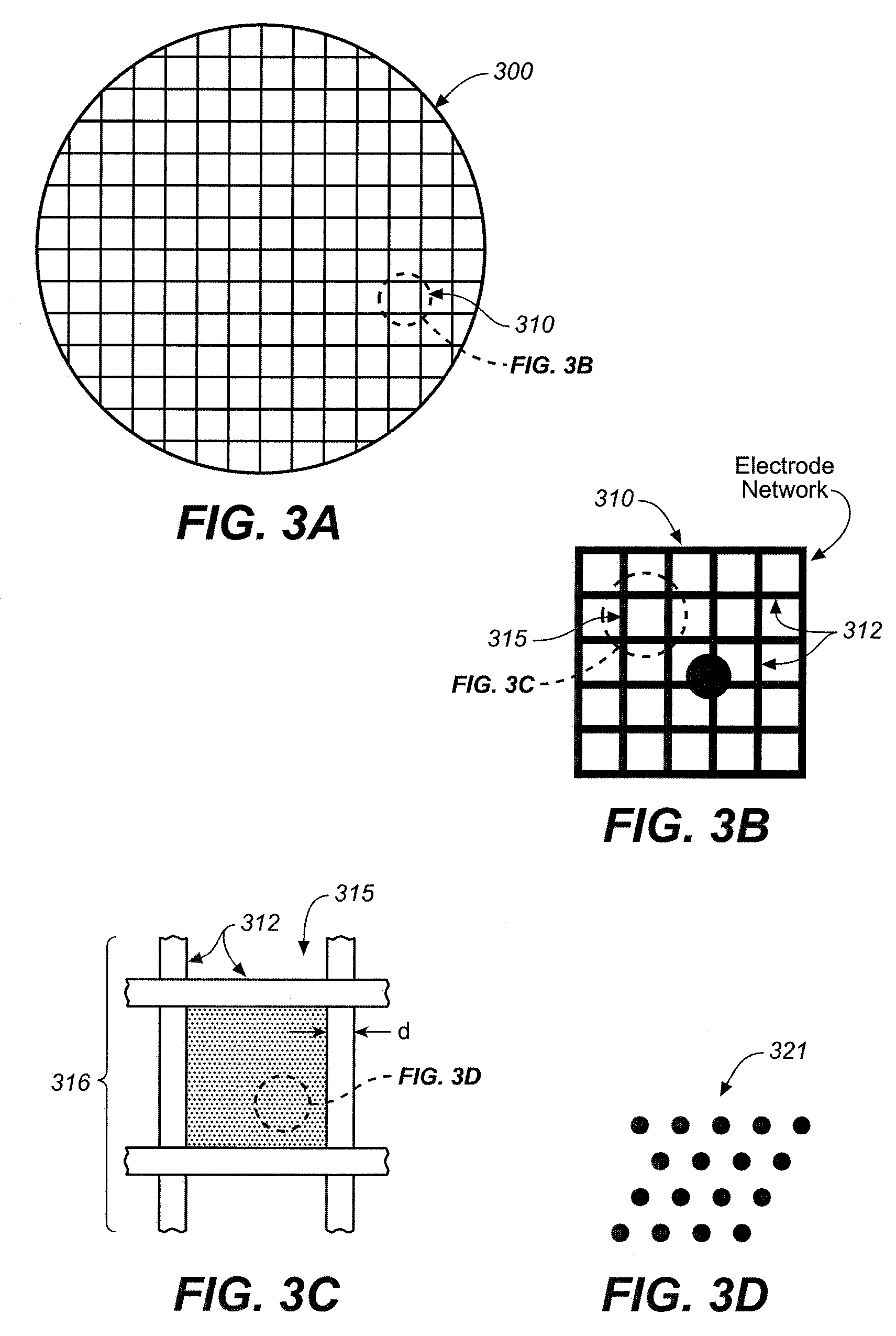
Reflective substrate and algorithms for 3D biochip
ActiveUS7198901B1Eliminates major background artifact emissionEnhanced signalBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDielectricElectricity
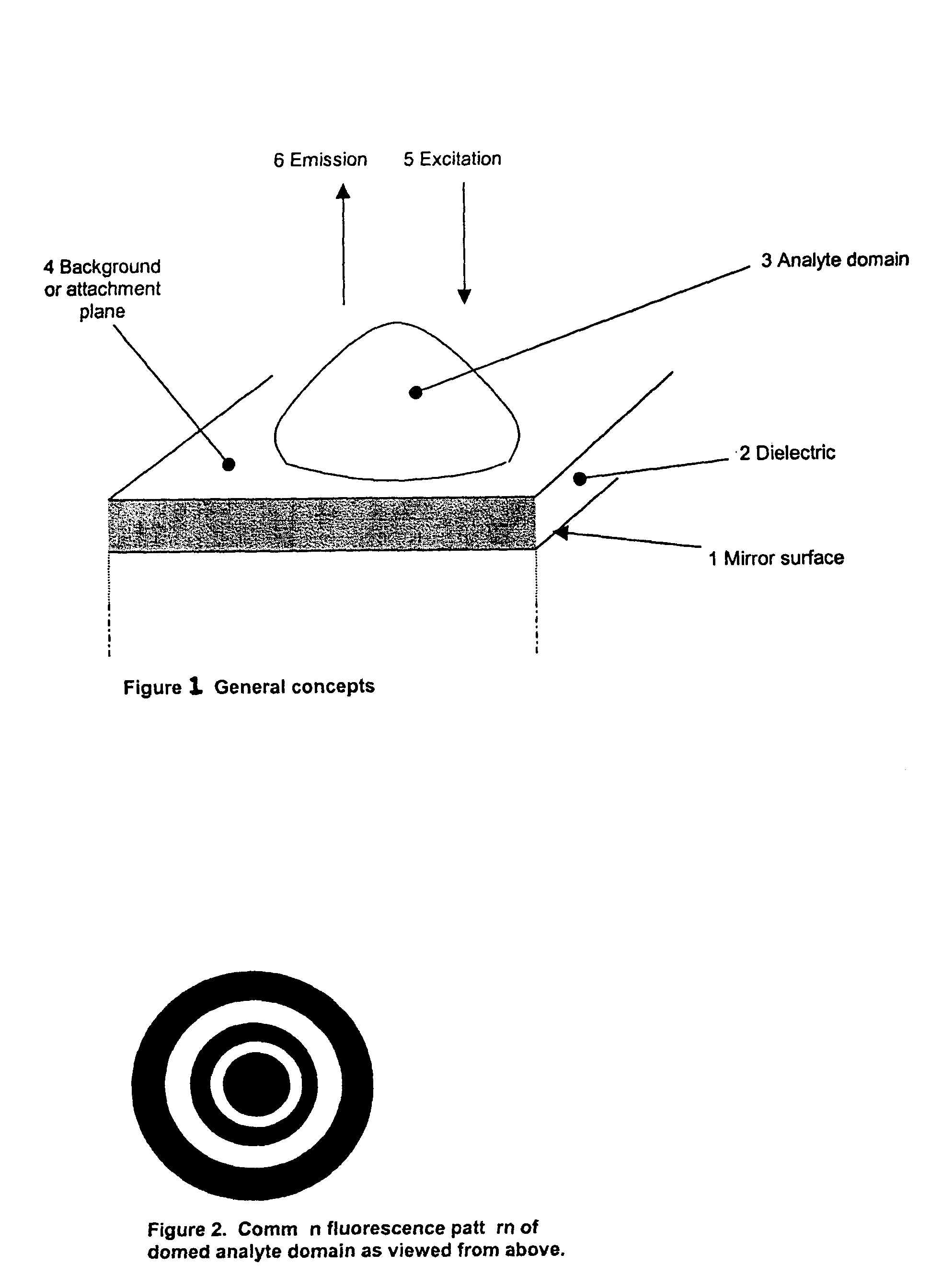
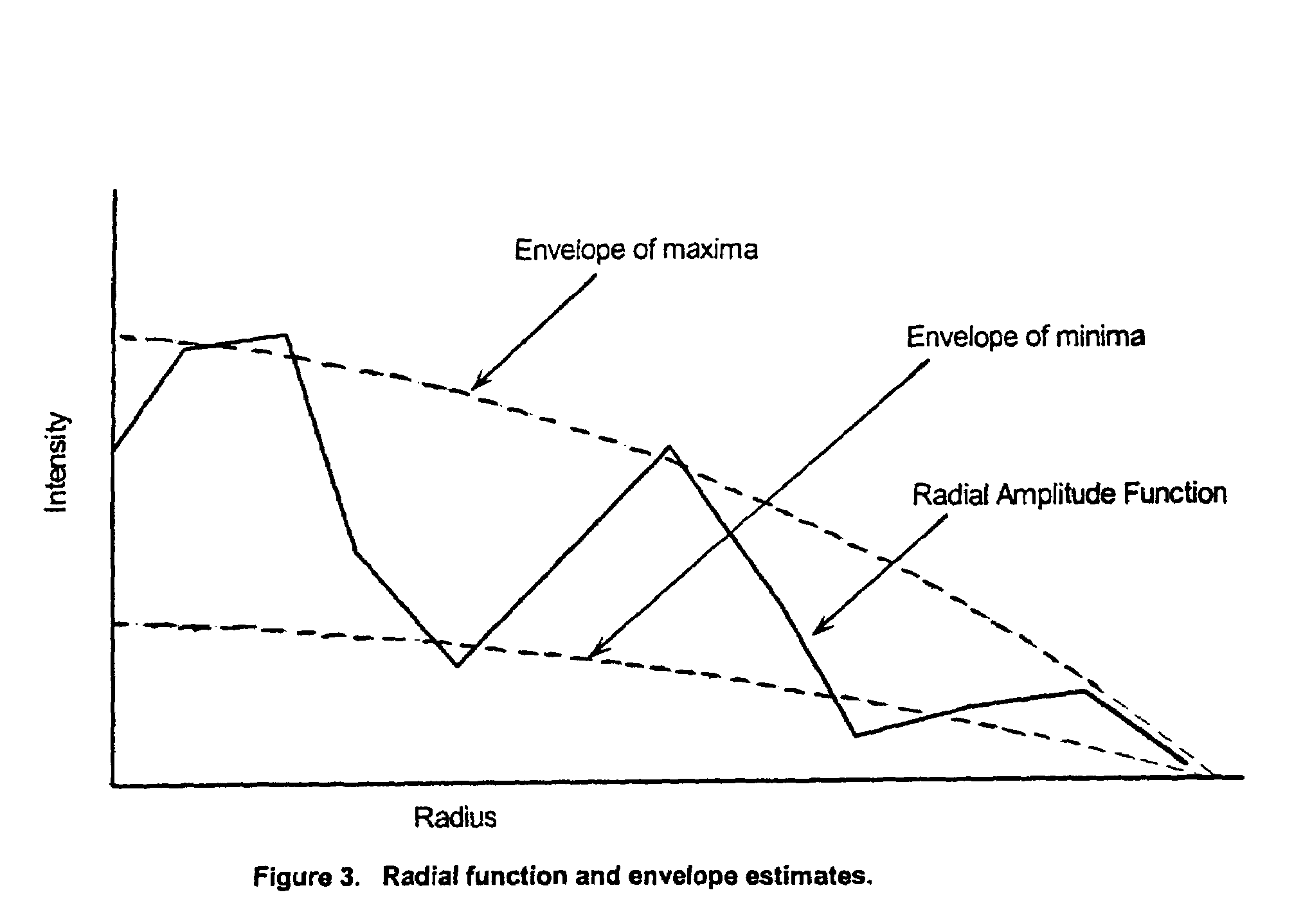
A reflective substrate is used to amplify the photon signal captured from overlying analyte domains containing photon emitters. The reflective substrate provides substantial desired signal amplification of the photon emissions from each domain via interference effects induced in the incident excitation and / or emission energies. A dielectric is interposed between the domains and the reflective surface, which has a thickness such that substantial destructive interference occurs with respect to emission photons or excitation photons or both at the attachment surface. When analyte domains have a three-dimensional structure such that a significant fraction of their volume extends at least ¼ wavelength above the attachment surface provided by the dielectric, substantial constructive signal amplification can take place of signals generated within the analyte domains. Destructive interference relating to emissions arising from the plane of attachment surface yields significant reduction in spurious background emissions.
Owner:BIOCEPT INC
Quantum processing device
ActiveUS20140291490A1High efficiency in photon collectionAttenuation bandwidthQuantum computersNanoinformaticsPhoton emissionPhoton detection
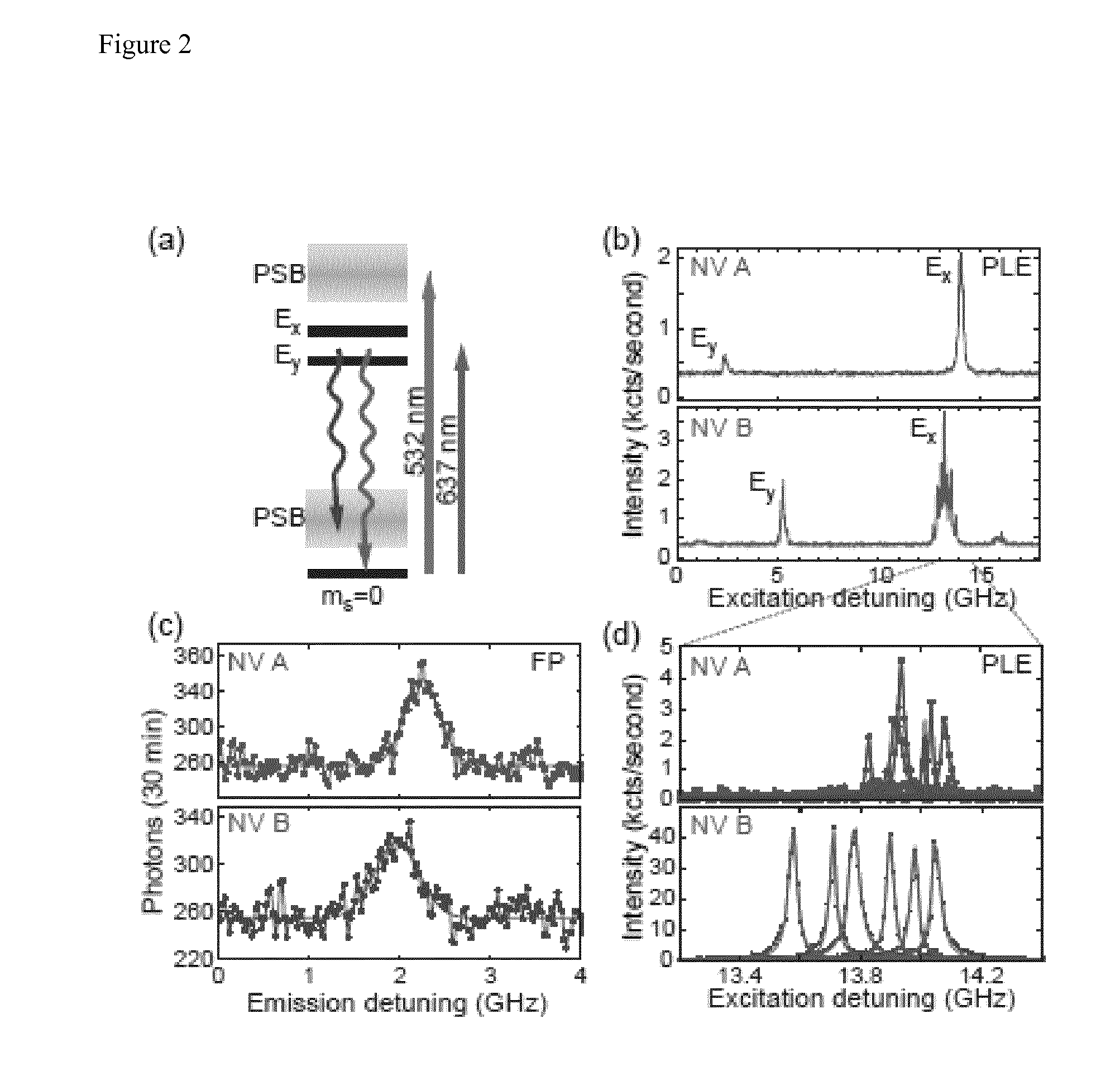
A device for achieving multi-photon interference, said device comprising: at least two solid state photon emitters, each solid state photon emitter comprising nuclear and electron spin states coupled together, each solid state photon emitter being configured to produce photon emission comprising a photon emission peak, wherein the photon emission peaks from different solid state photon emitters have a first frequency difference between peak intensities, and wherein the electron spin states of each solid state photon emitter are resolvable; an excitation arrangement configured to individually address the at least two solid state photon emitters; a plurality of optical out coupling structures wherein each solid state photon emitter is provided with an associated optical out coupling structure; a tuning arrangement configured to reduce the first frequency difference between the peak intensities of the photon emission peaks from the at least two solid state photon emitters to a second frequency difference which is smaller than the first frequency difference; a photon interference arrangement configured to overlap photon emissions from the at least two solid state emitters after tuning; and a detector arrangement configured to detect photon emissions from the at least two solid state emitters after tuning and passing through the photon interference arrangement, wherein the detector arrangement is configured to resolve sufficiently small differences in photon detection times that tuned photon emissions from the at least two solid state emitters are quantum mechanically indistinguishable resulting in quantum interference between indistinguishable photon emissions from different solid state photon emitters.
Owner:ELEMENT SIX TECH LTD
Methods Circuits Devices Assemblies Systems and Functionally Associated Machine Executable Code for Light Detection and Ranging Based Scanning
InactiveUS20180081038A1Reduce field of viewIncreases beam spreadElectromagnetic wave reradiationPhoton emissionPhotonics
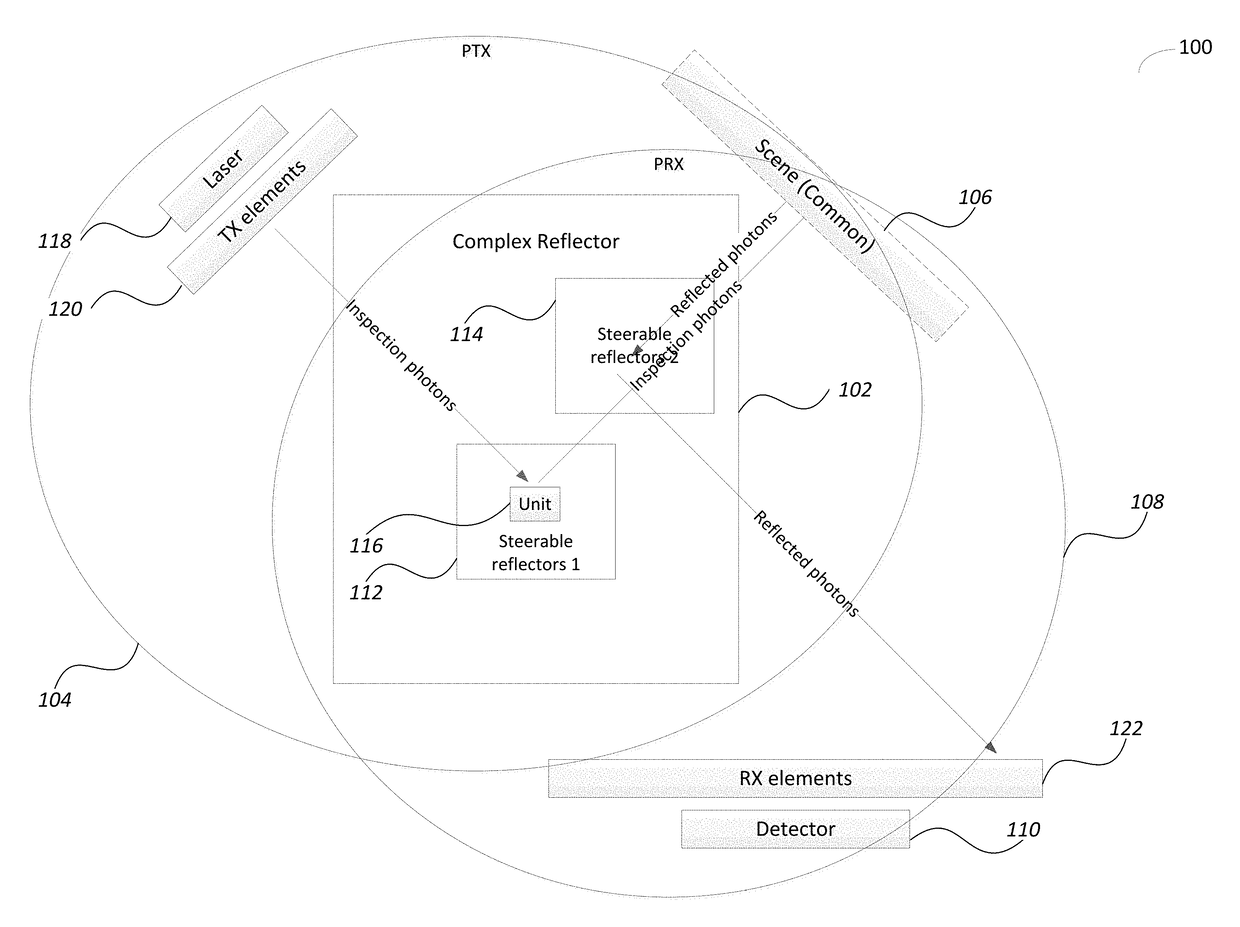
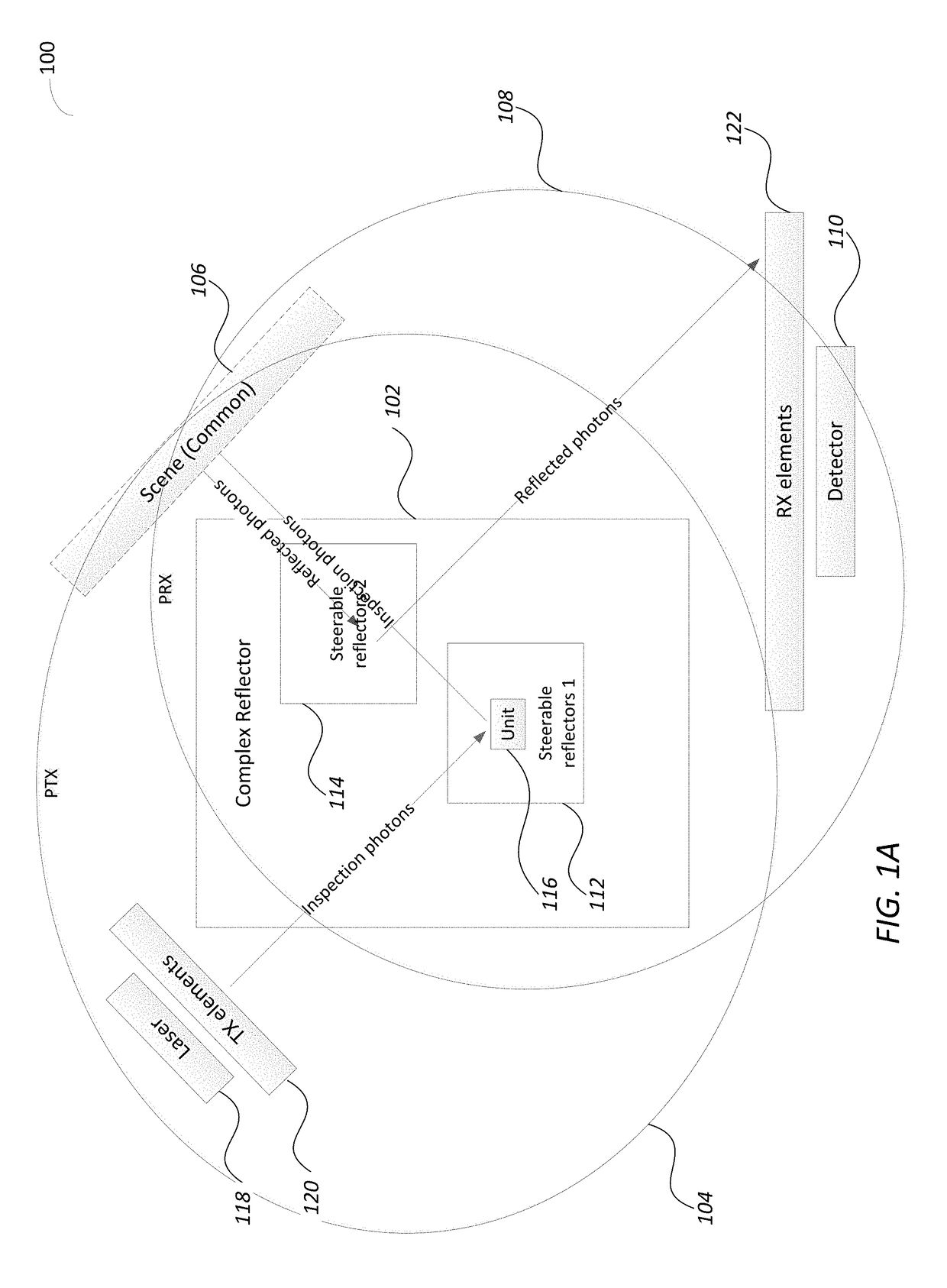
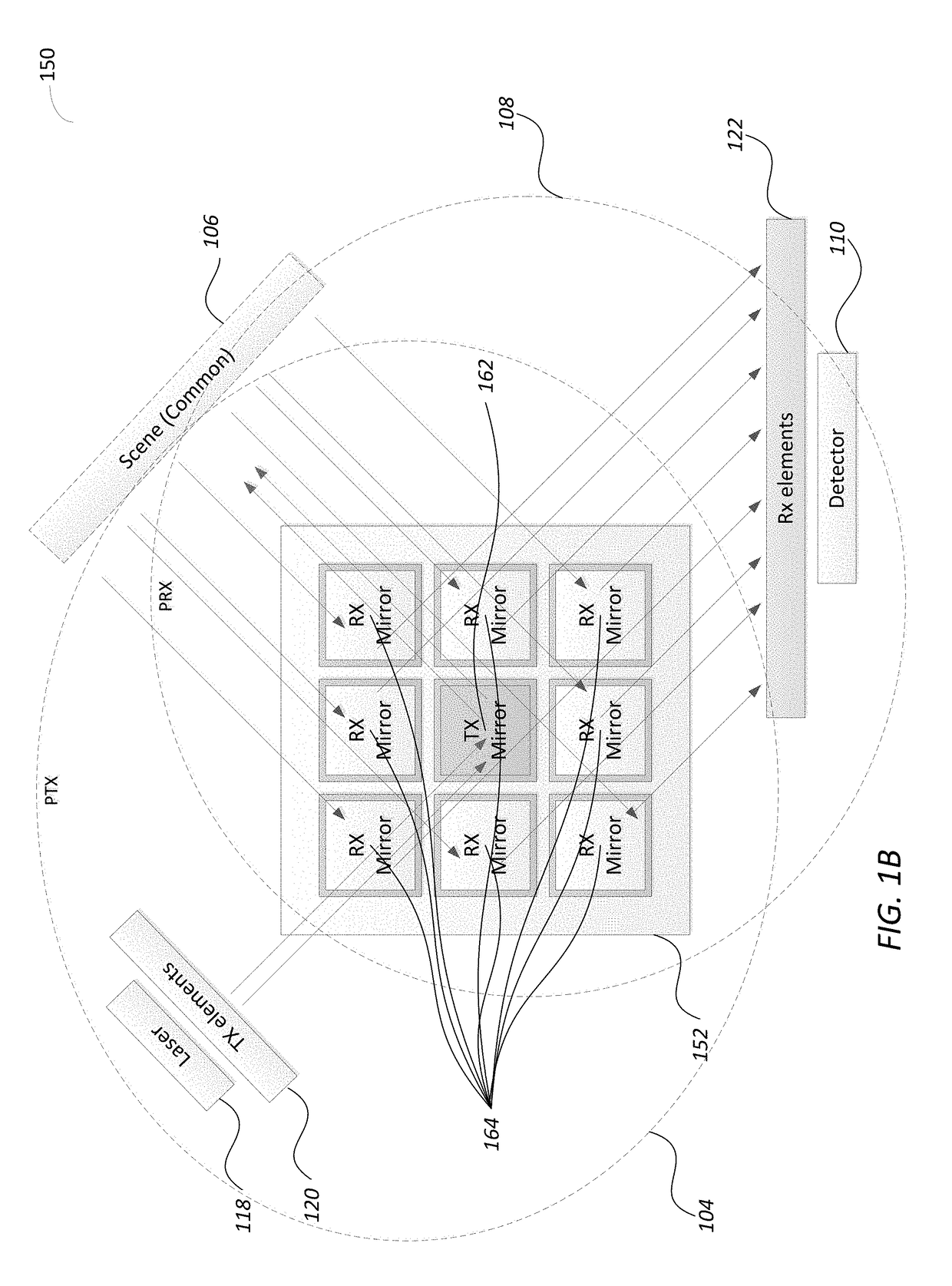
Disclosed is a light detection and ranging (Lidar) device including a photonic pulse emitter assembly including one or more photonic emitters to generate and focus a photonic inspection pulse towards a photonic transmission (TX) path of the Lidar device, a photonic detection assembly including one or more photo sensors to receive and sense photons of a reflected photonic inspection pulses received through a receive (RX) path of the device, a photonic steering assembly located along both the TX and the RX paths and including a Complex Reflector (CR) made of an array of steerable reflectors, where a first set of steerable reflectors are part of the TX path and a second set of steerable reflectors are part of the RX path.
Owner:INNOVIZ TECH LTD
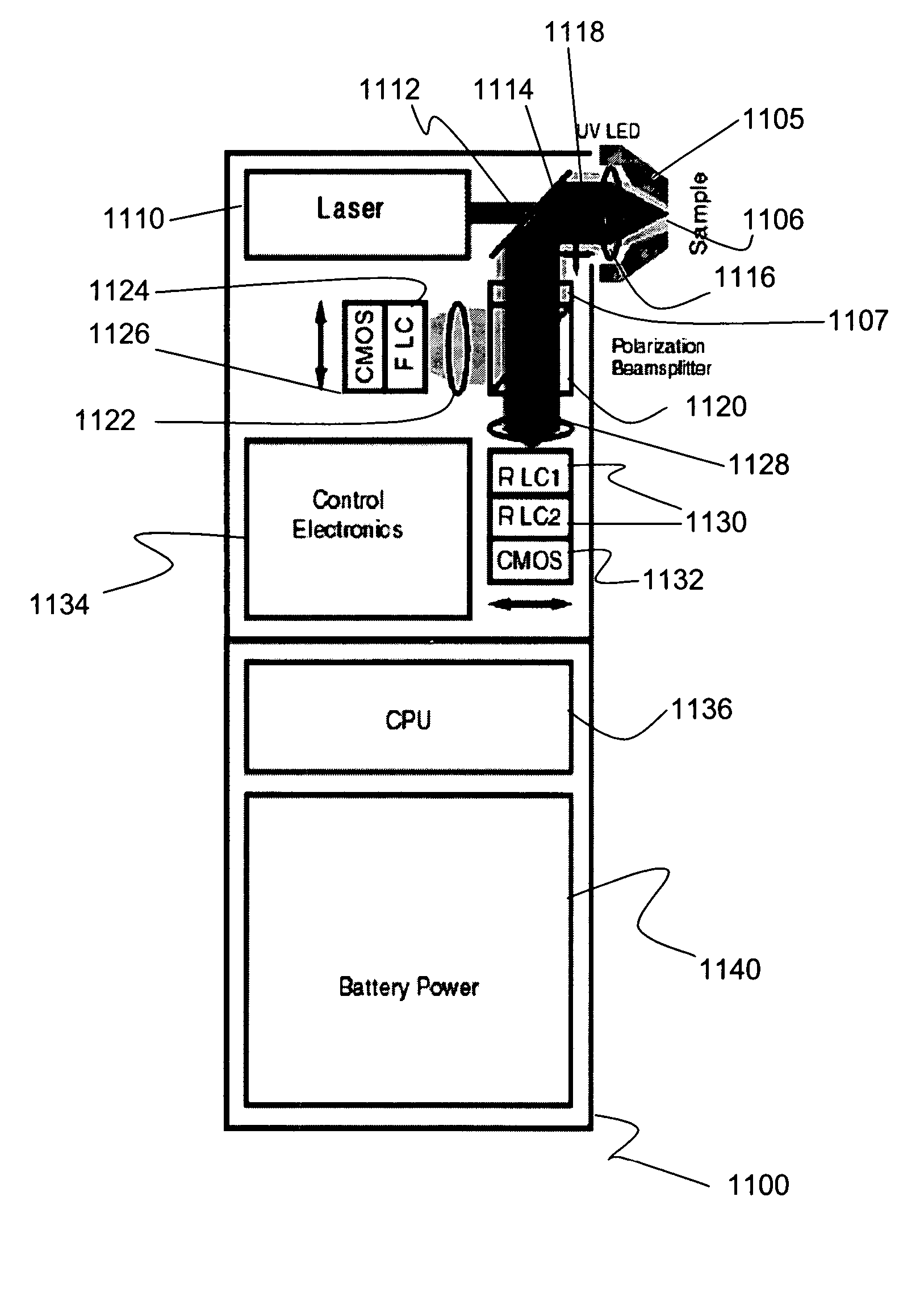
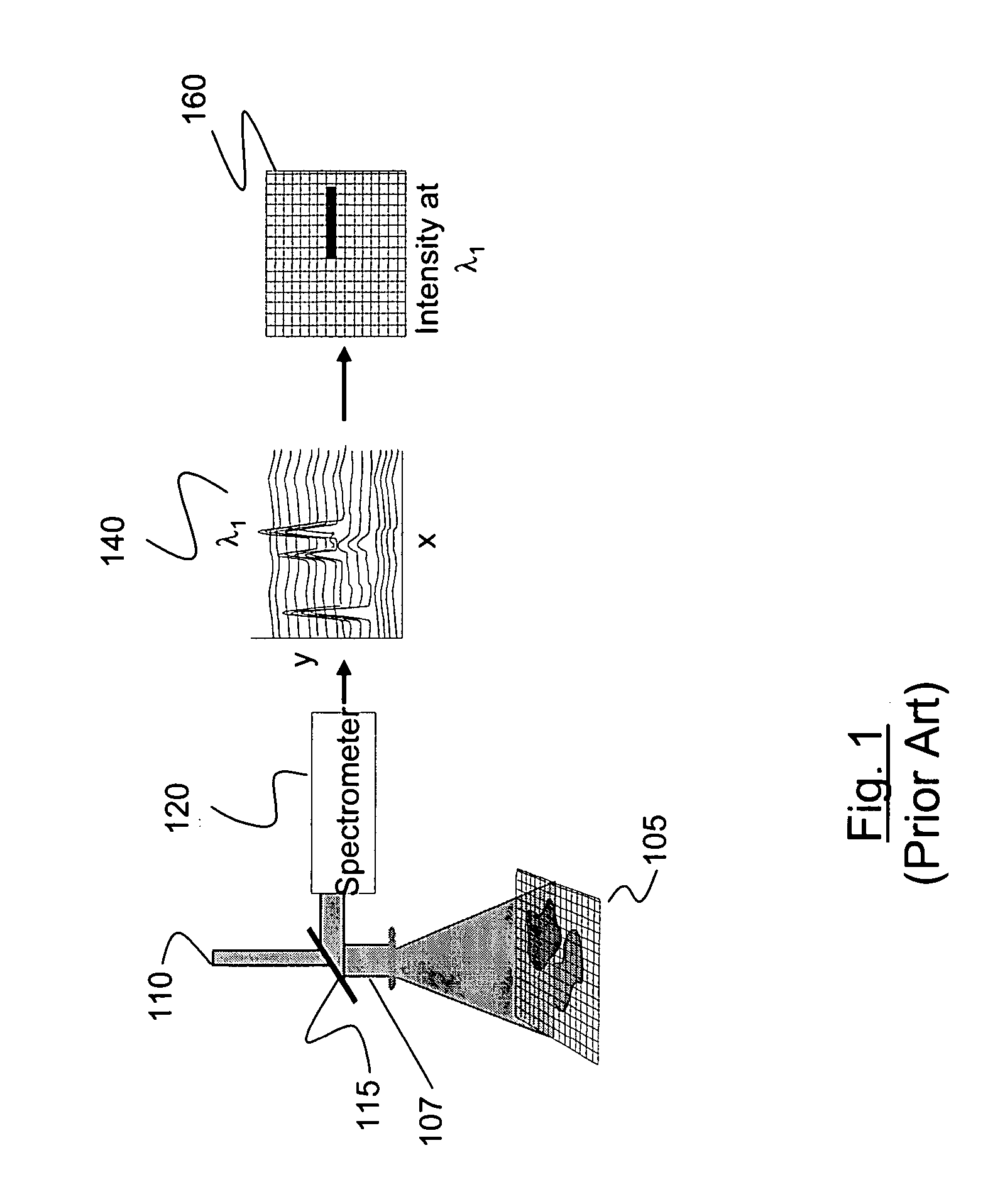
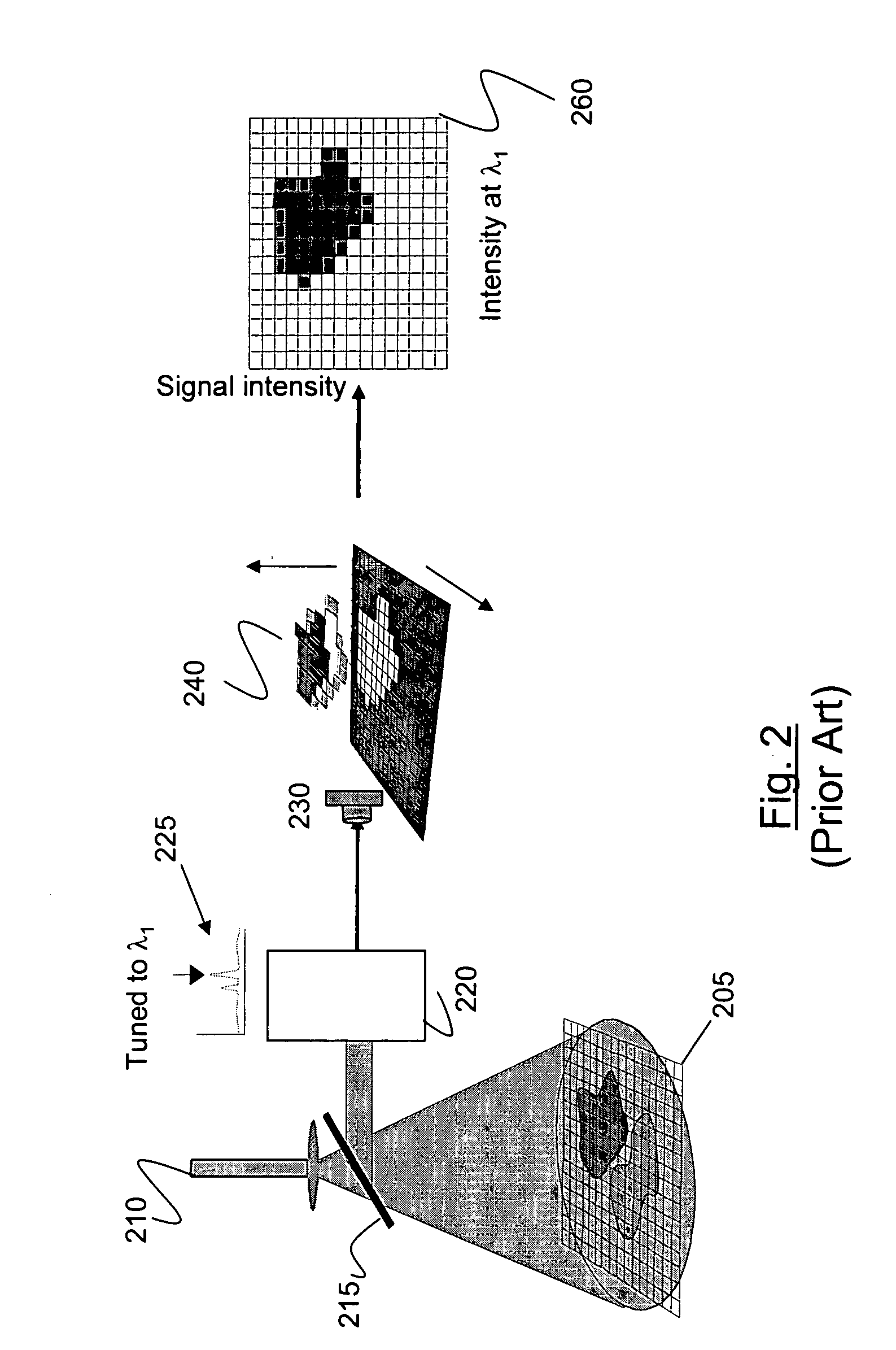
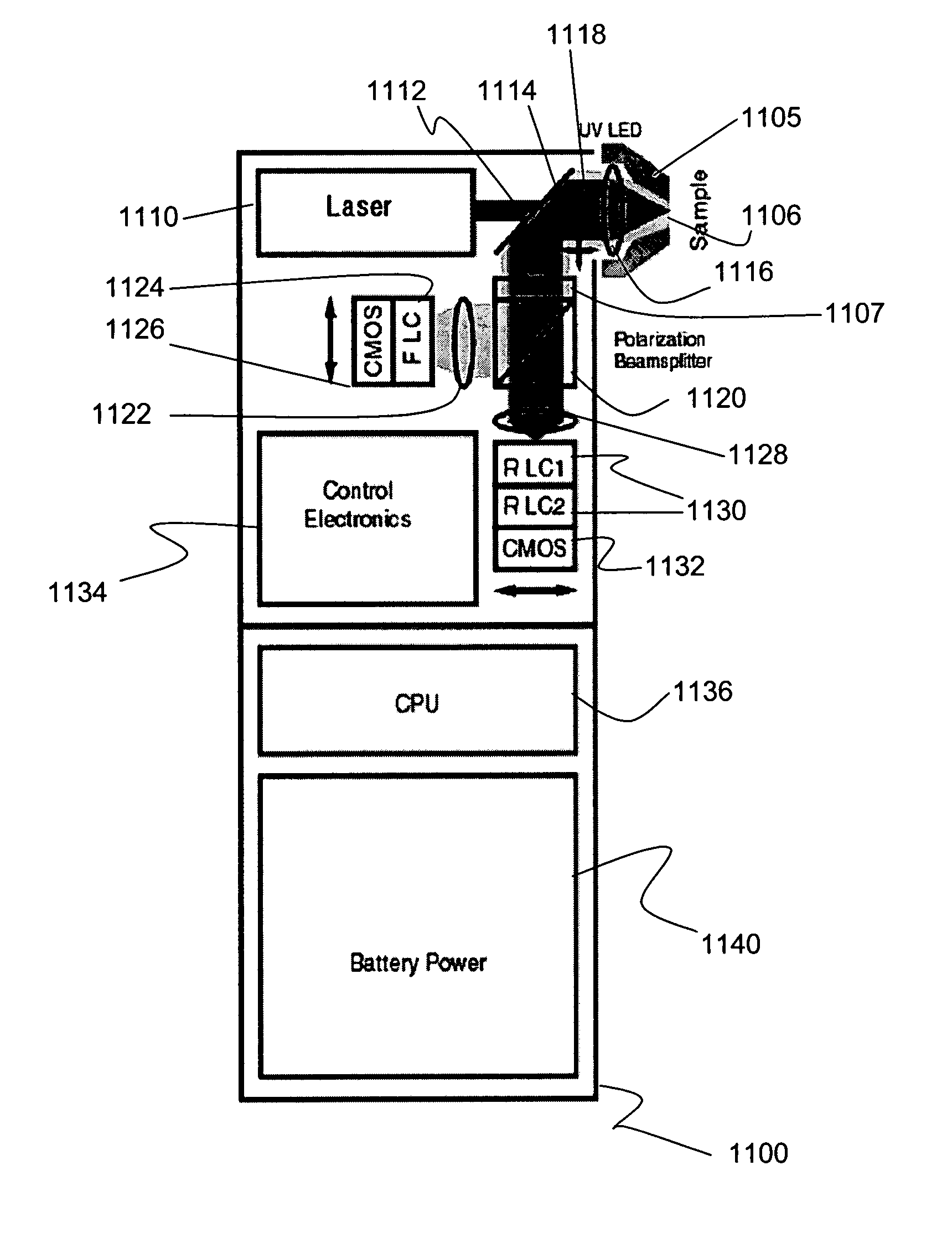
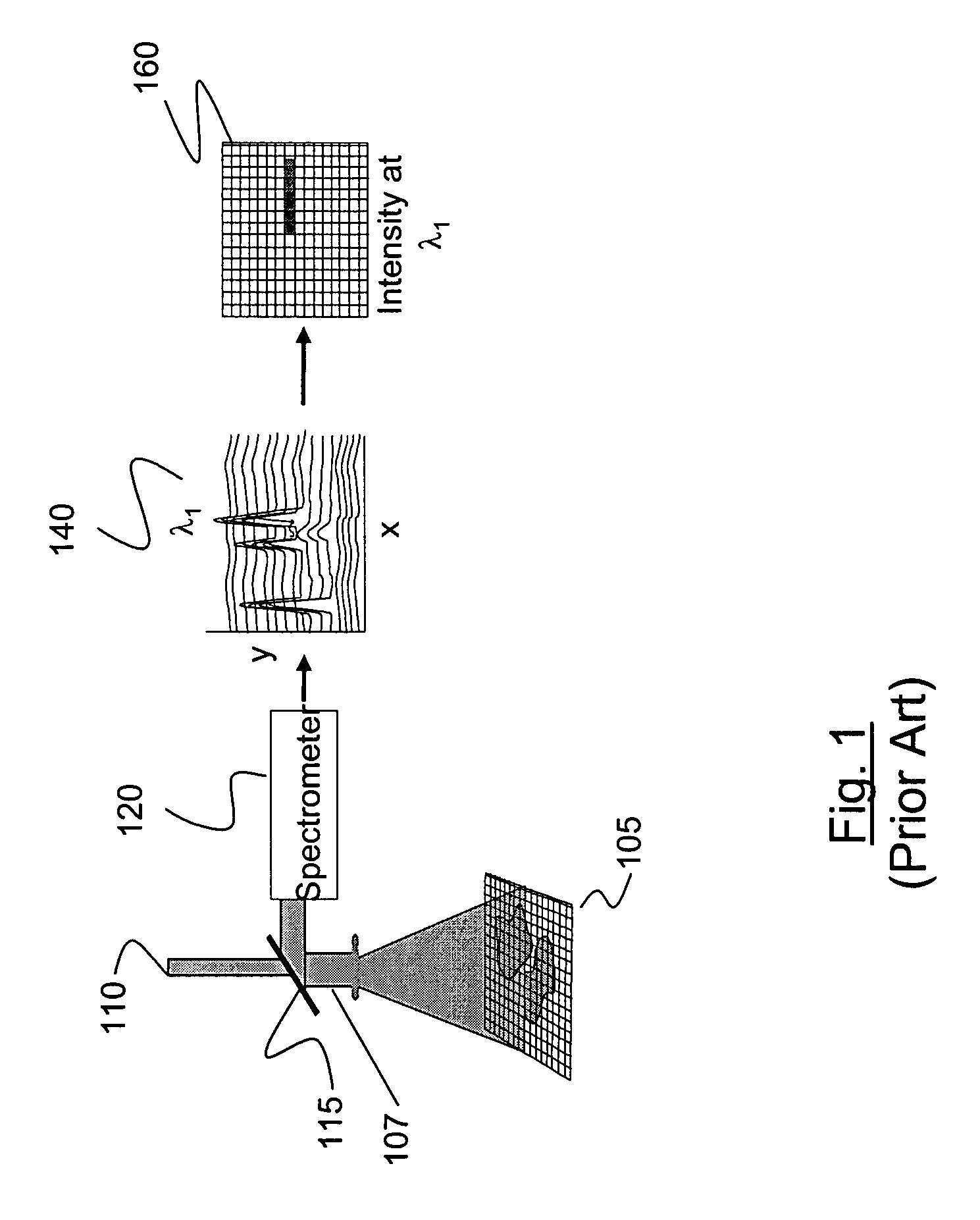
Method and apparatus for compact dispersive imaging spectrometer
ActiveUS20050030533A1Radiation pyrometryRaman/scattering spectroscopyPhoton emissionPhoton scattering
The disclosure generally relates to a method and apparatus for compact dispersive imaging spectrometer. More specifically, one embodiment of the disclosure relates to a portable system for obtaining a spatially accurate wavelength-resolved image of a sample having a first and a second spatial dimension. The portable system can include a photon emission source for sequentially illuminating a plurality of portions of said sample with a plurality of photons to produce photons scattered by the sample. The photon emission source can illuminate the sample along the first spatial dimension for each of plural predetermined positions of the second spatial dimension. The system may also include an optical lens for collecting the scattered photons to produce therefrom filtered photons, a dispersive spectrometer for determining a wavelength of ones of the filtered photons, a photon detector for receiving the filtered photons and obtaining therefrom plural spectra of said sample, and a processor for producing a two dimensional image of said sample from the plural spectra.
Owner:CHEMIMAGE TECH
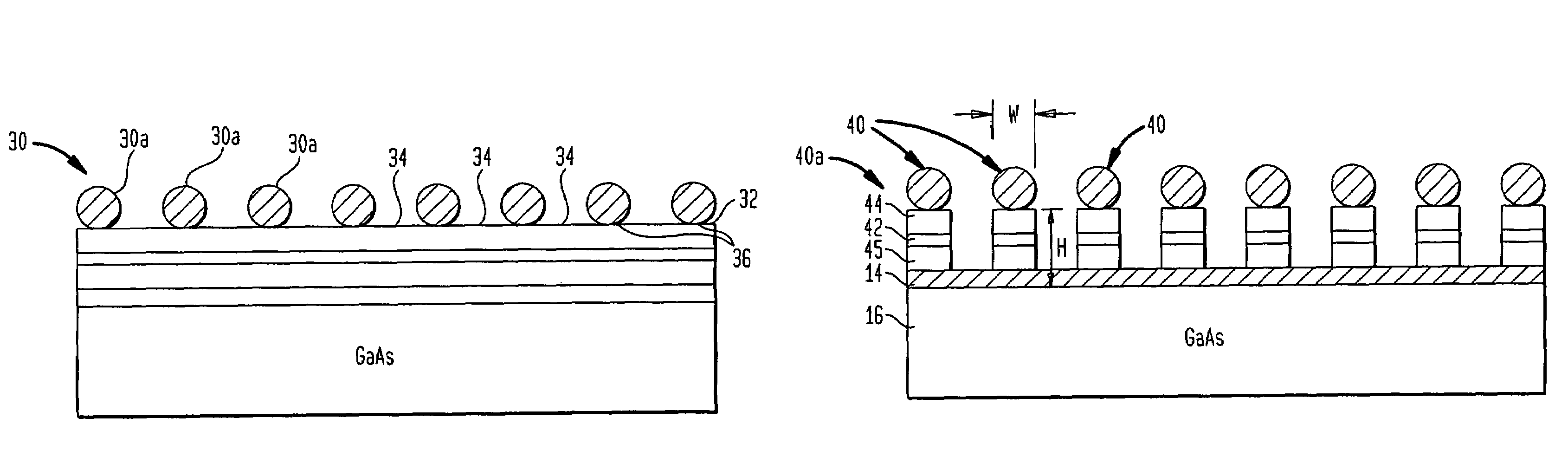
Precision synthesis of quantum dot nanostructures for fluorescent and optoelectronic devices
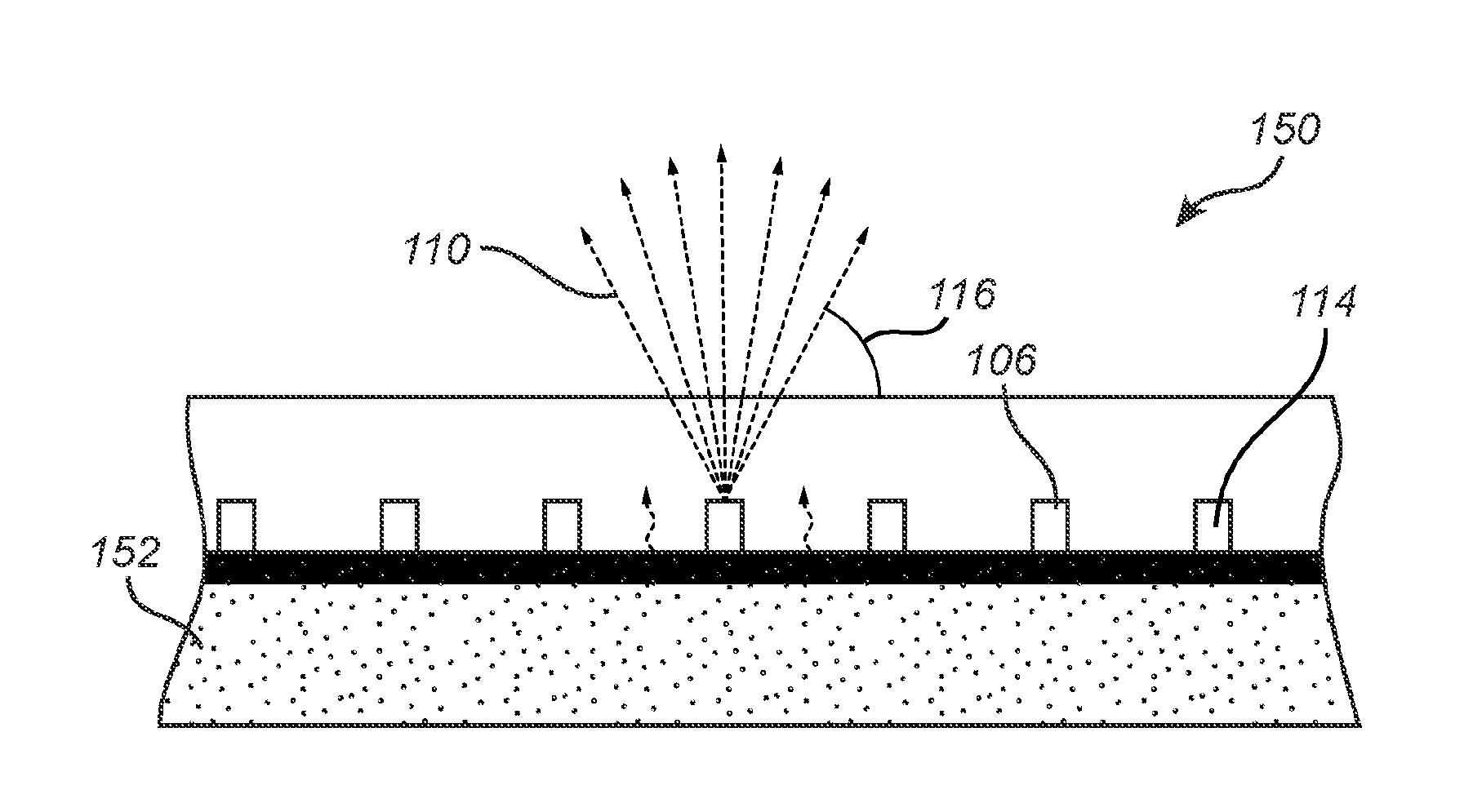
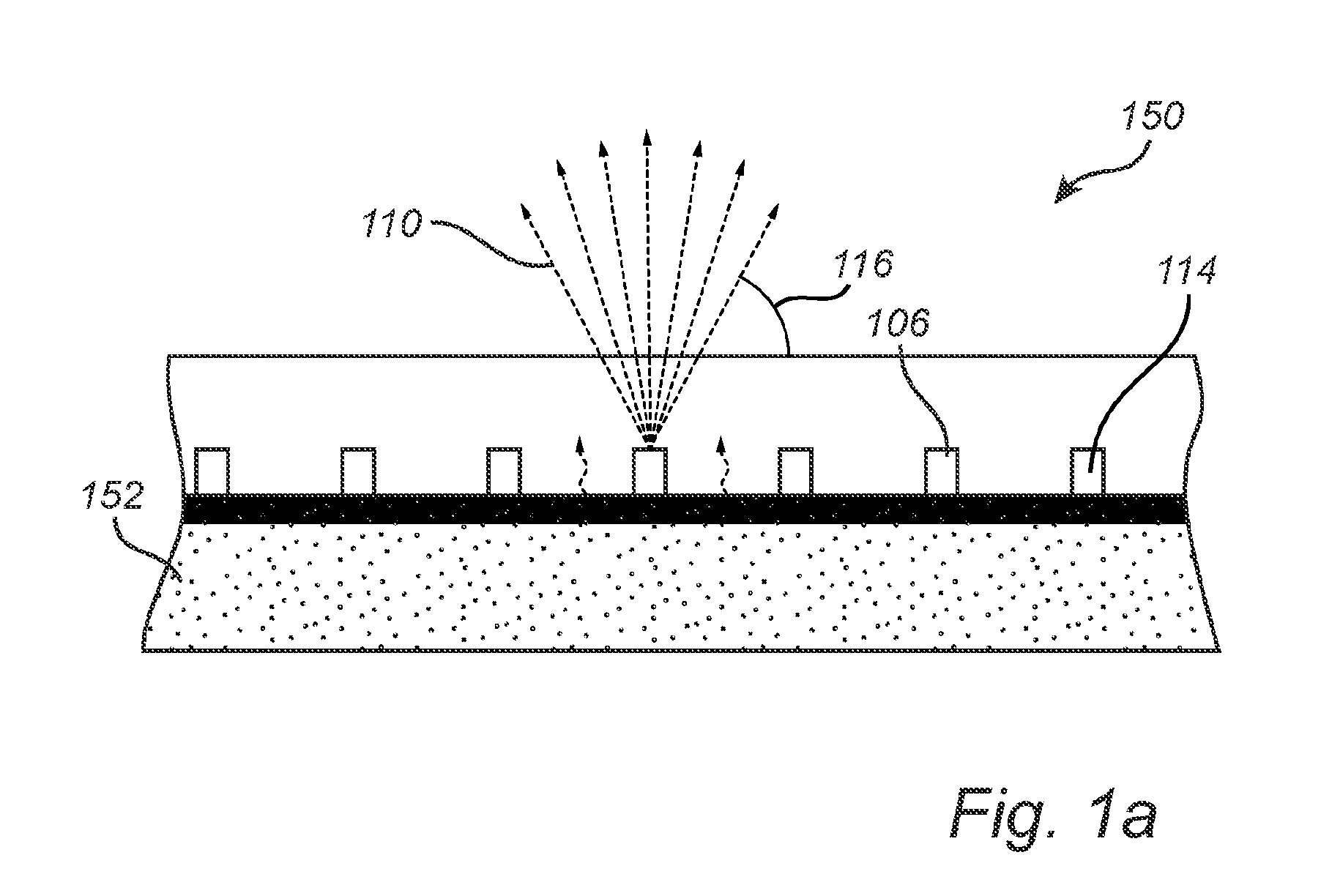
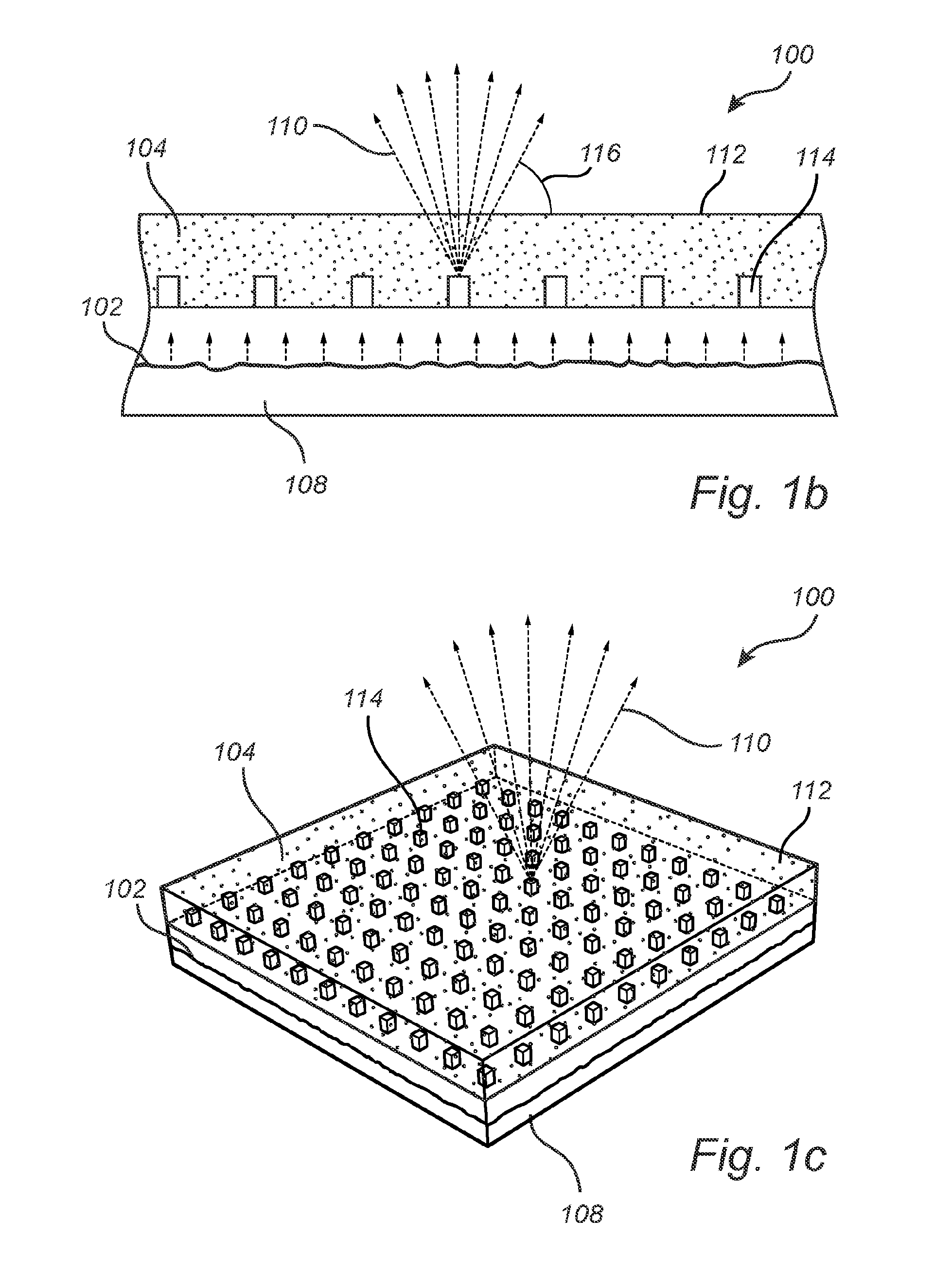
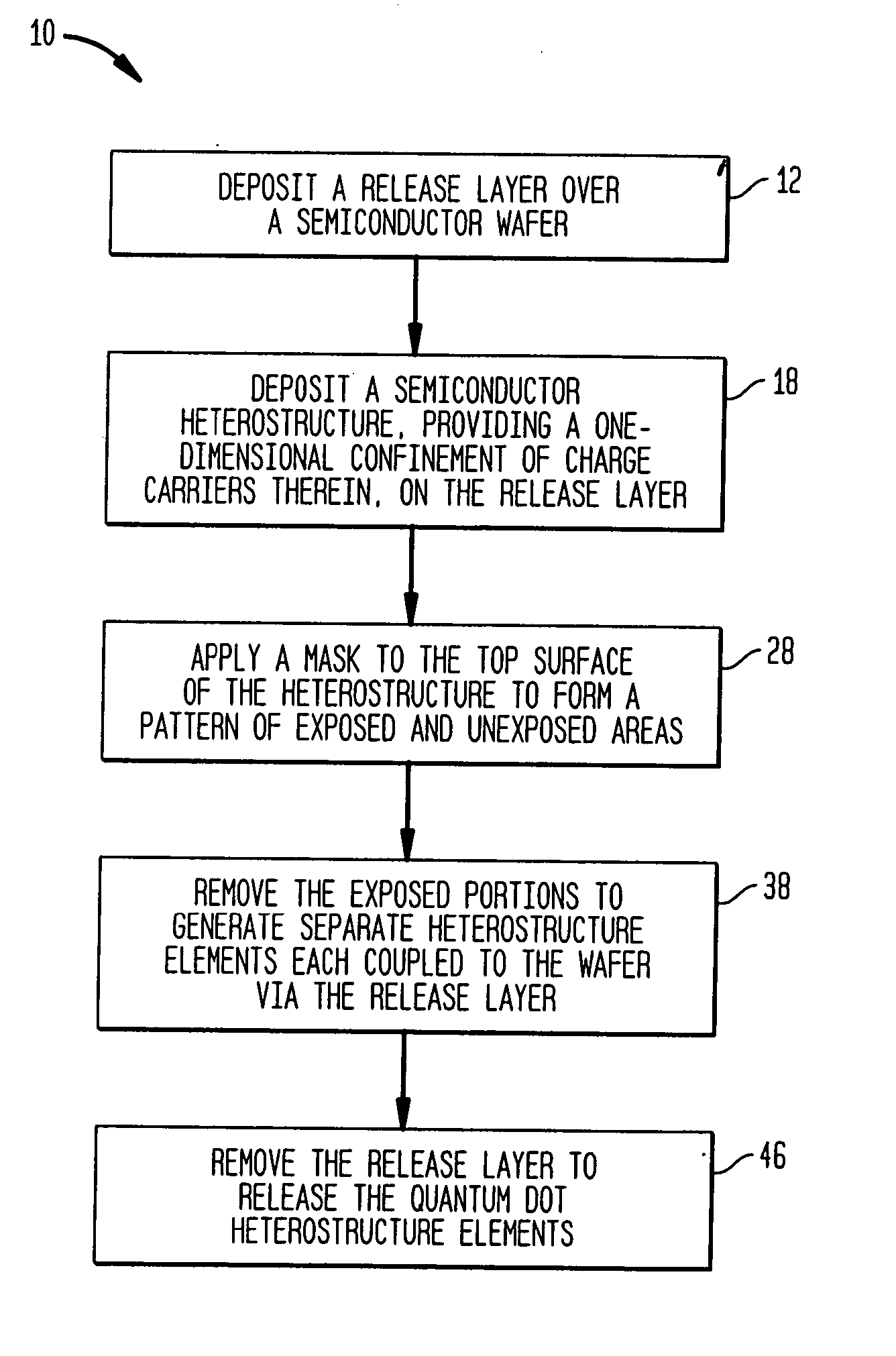
InactiveUS7306963B2Good size uniformityNanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhoton emissionFluorescence
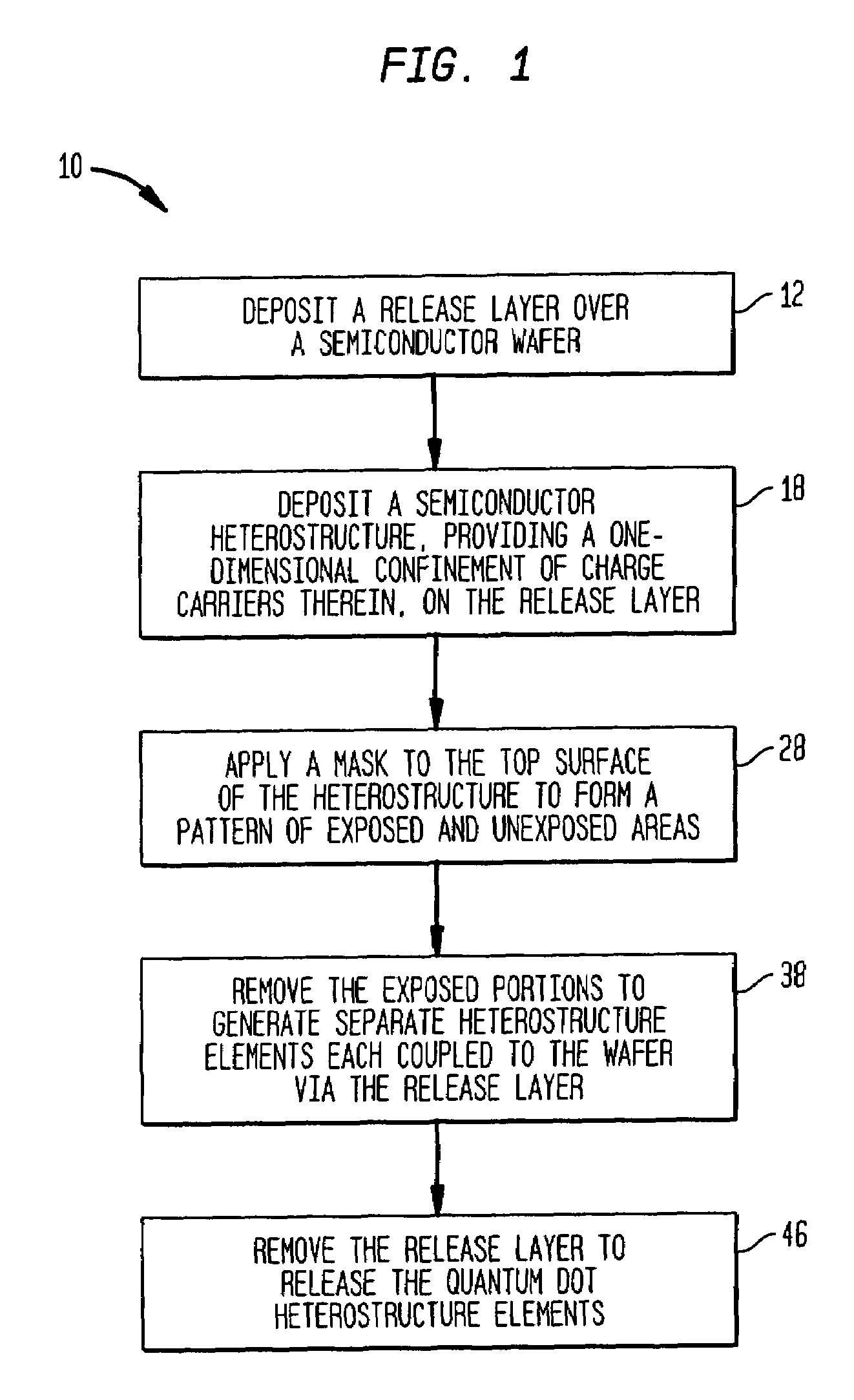
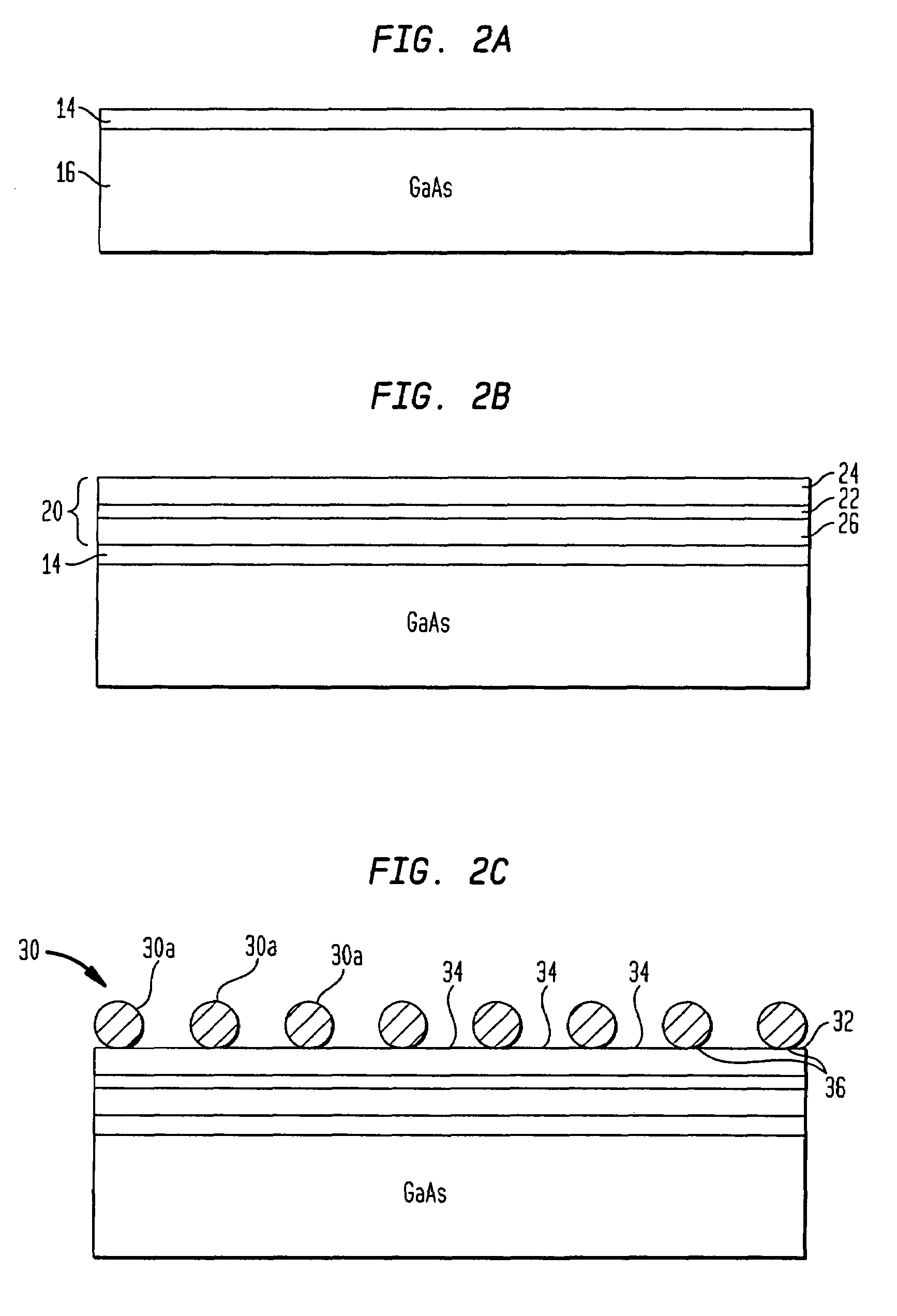
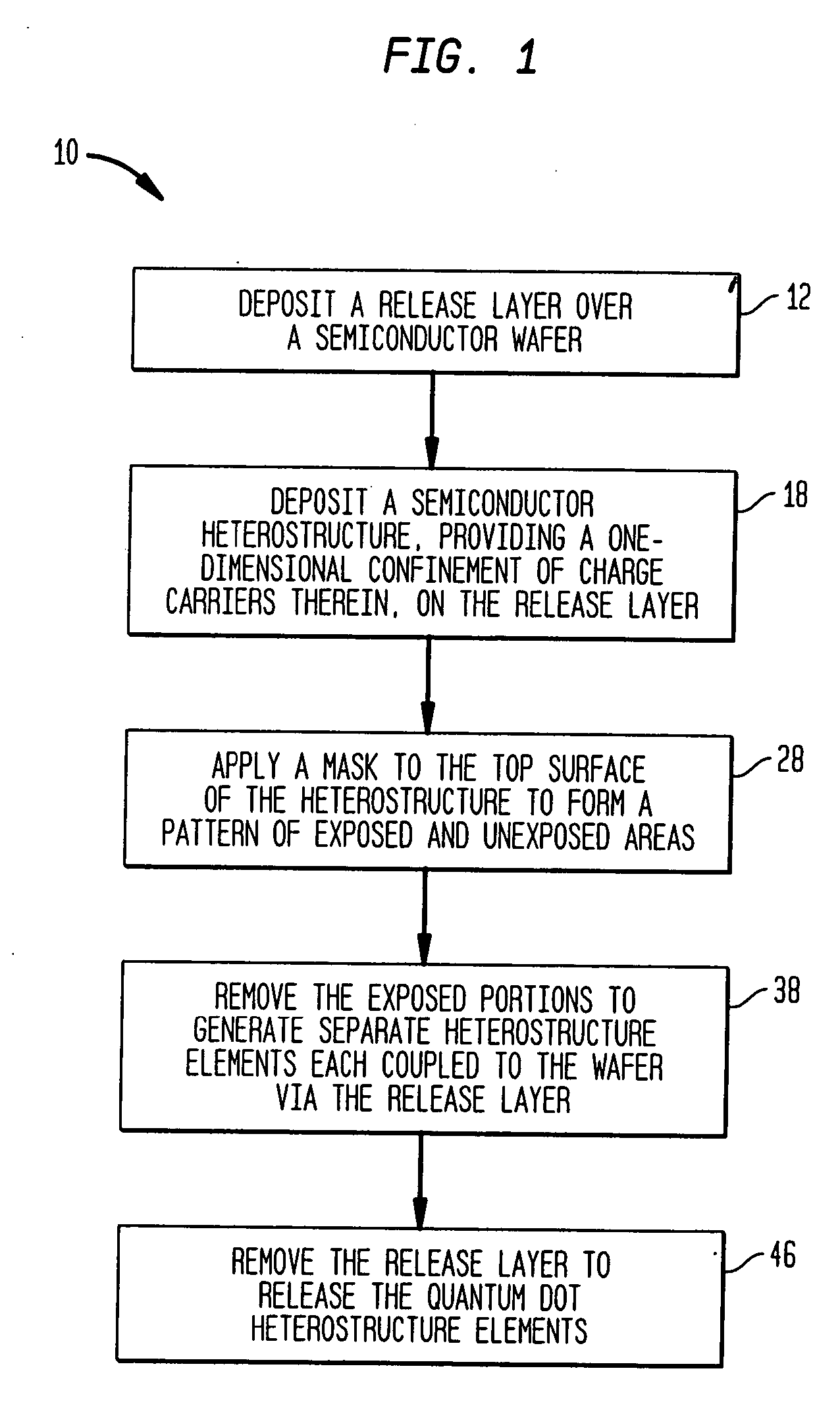
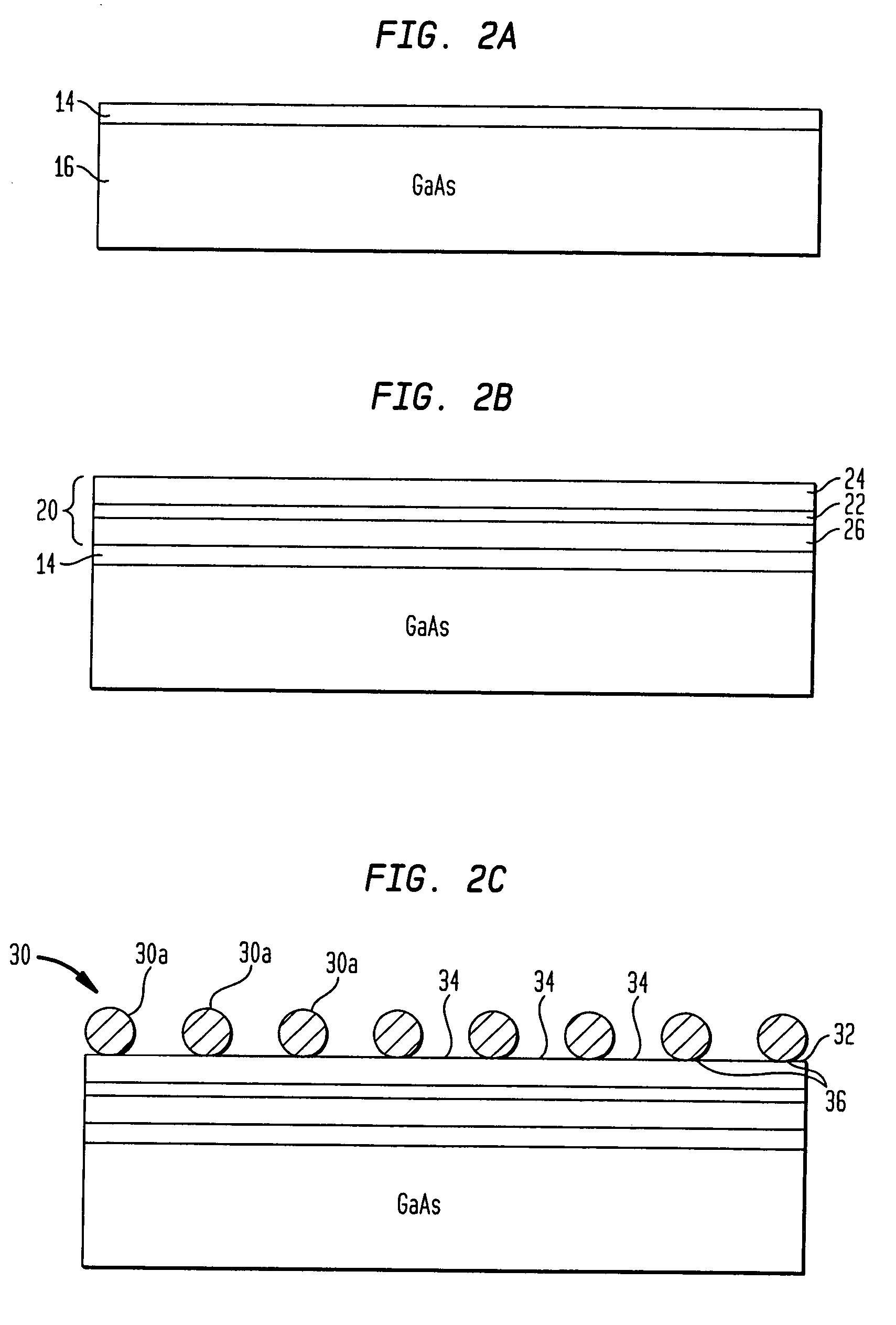
Methods are disclosed generally directed to design and synthesis of quantum dot nanoparticles having improved uniformity and size. In a preferred embodiment, a release layer is deposited on a semiconductor wafer. A heterostructure is grown on the release layer using epitaxial deposition techniques. The heterostructure has at least one layer of quantum dot material, and optionally, one or more layers of reflective Bragg reflectors. A mask is deposited over a top layer and reactive ion-beam etching applied to define a plurality of heterostructures. The release layer can be dissolved releasing the heterostructures from the wafer. Some exemplary applications of these methods include formation of fluorophore materials and high efficiency photon emitters, such as quantum dot VCSEL devices. Other applications include fabrication of other optoelectronic devices, such as photodetectors.
Owner:SPIRE
Time resolved emission spectral analysis system
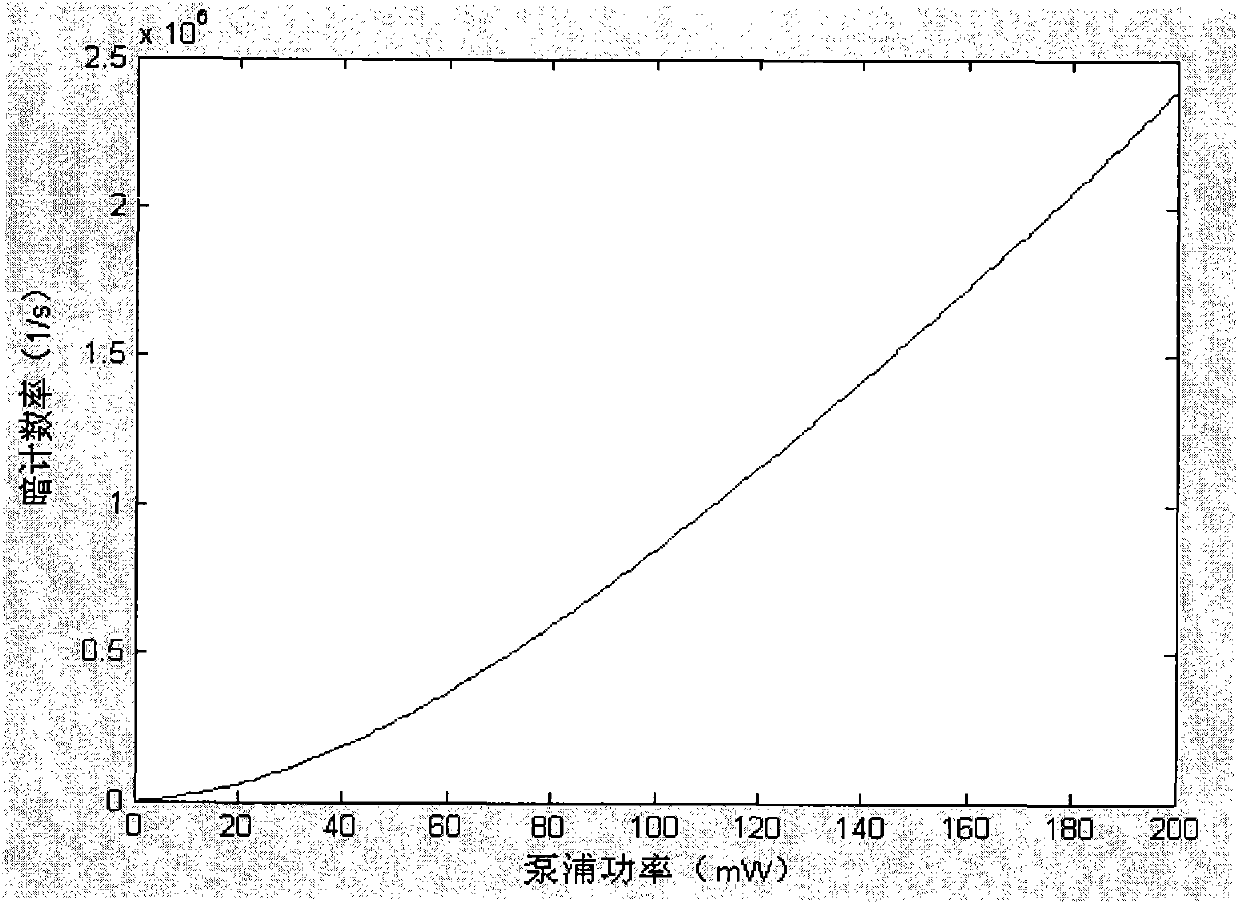
InactiveUS20050002028A1Improve spatial resolutionReduce noiseRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationPhoton emissionWavelength filter
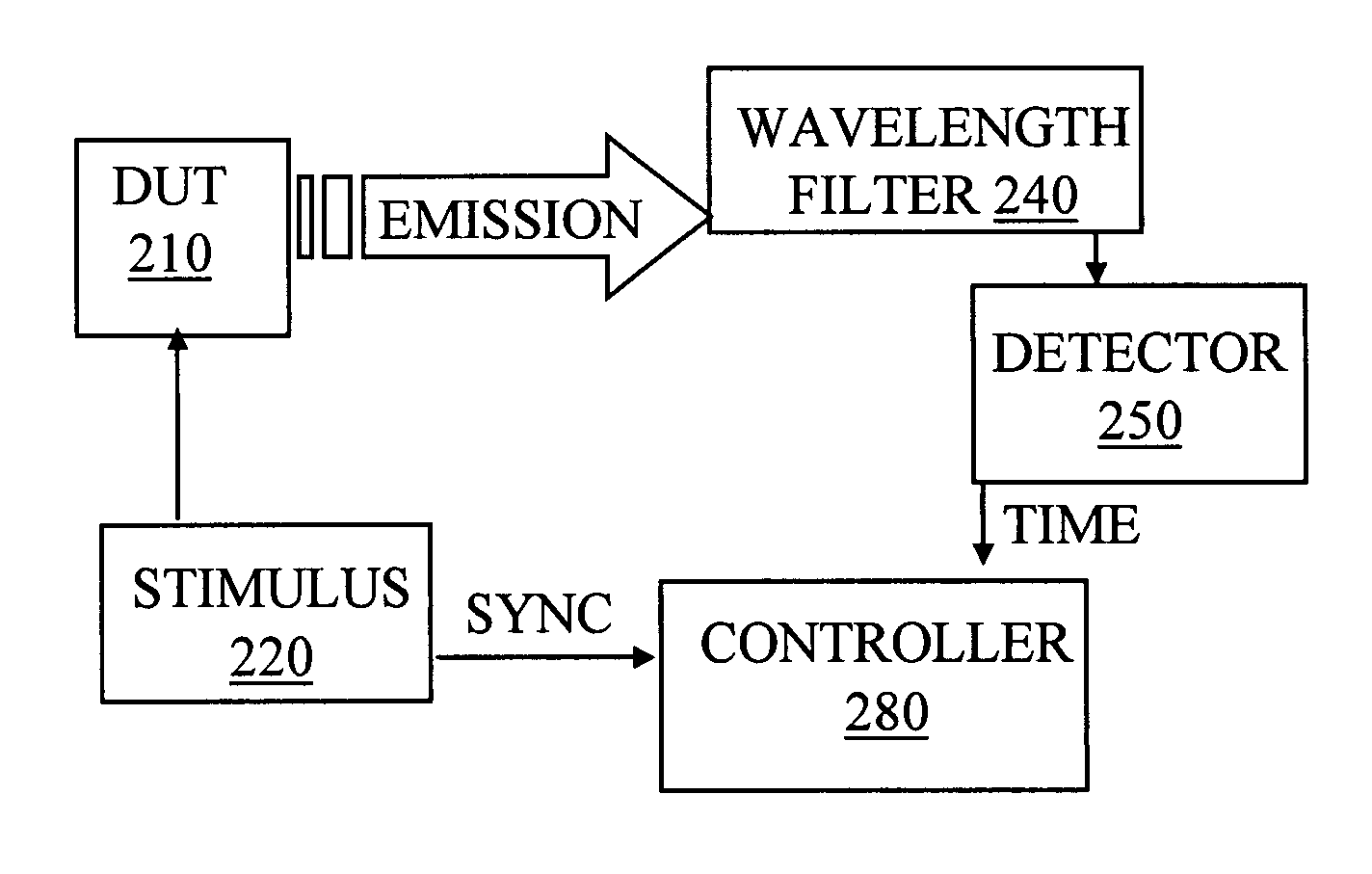
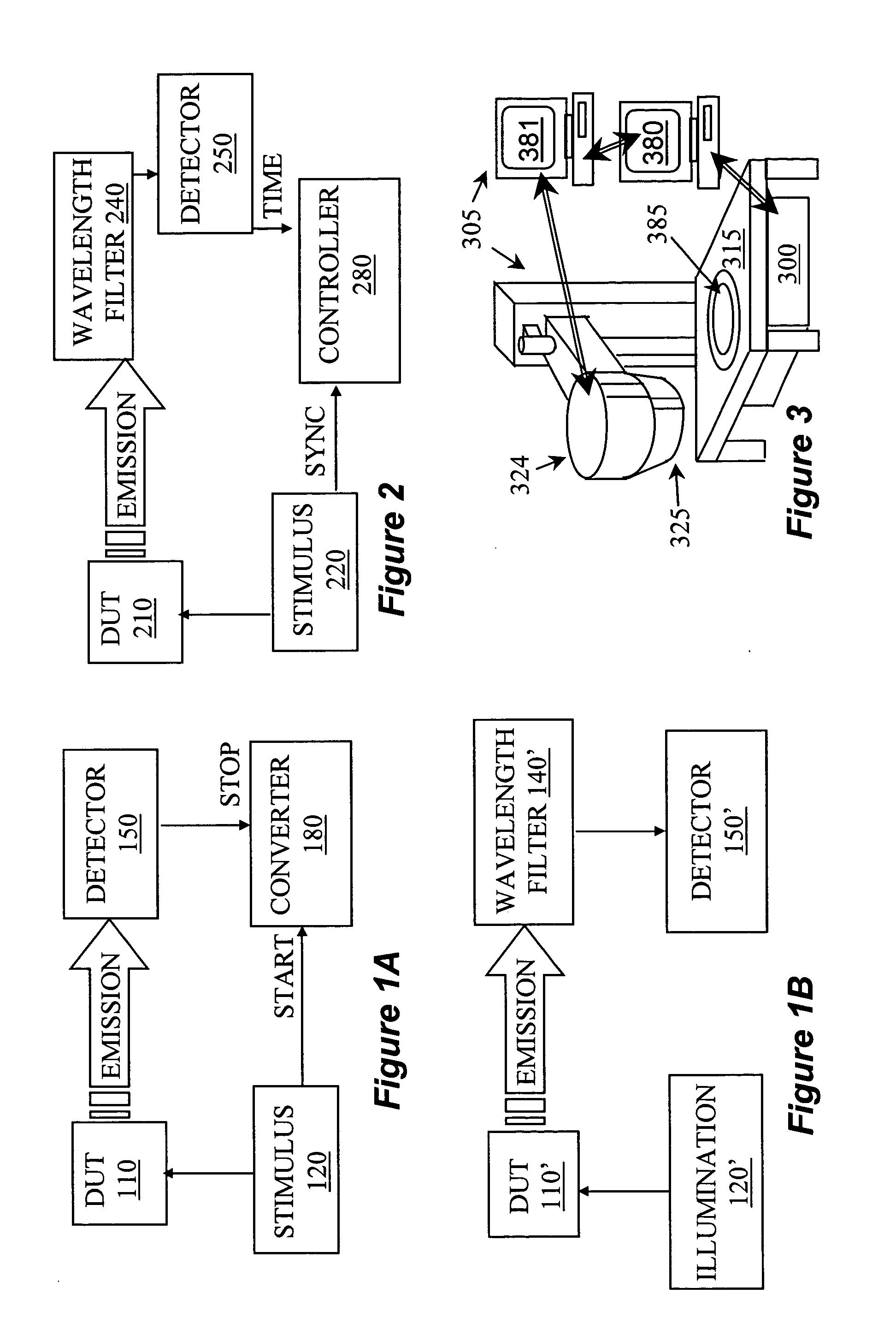
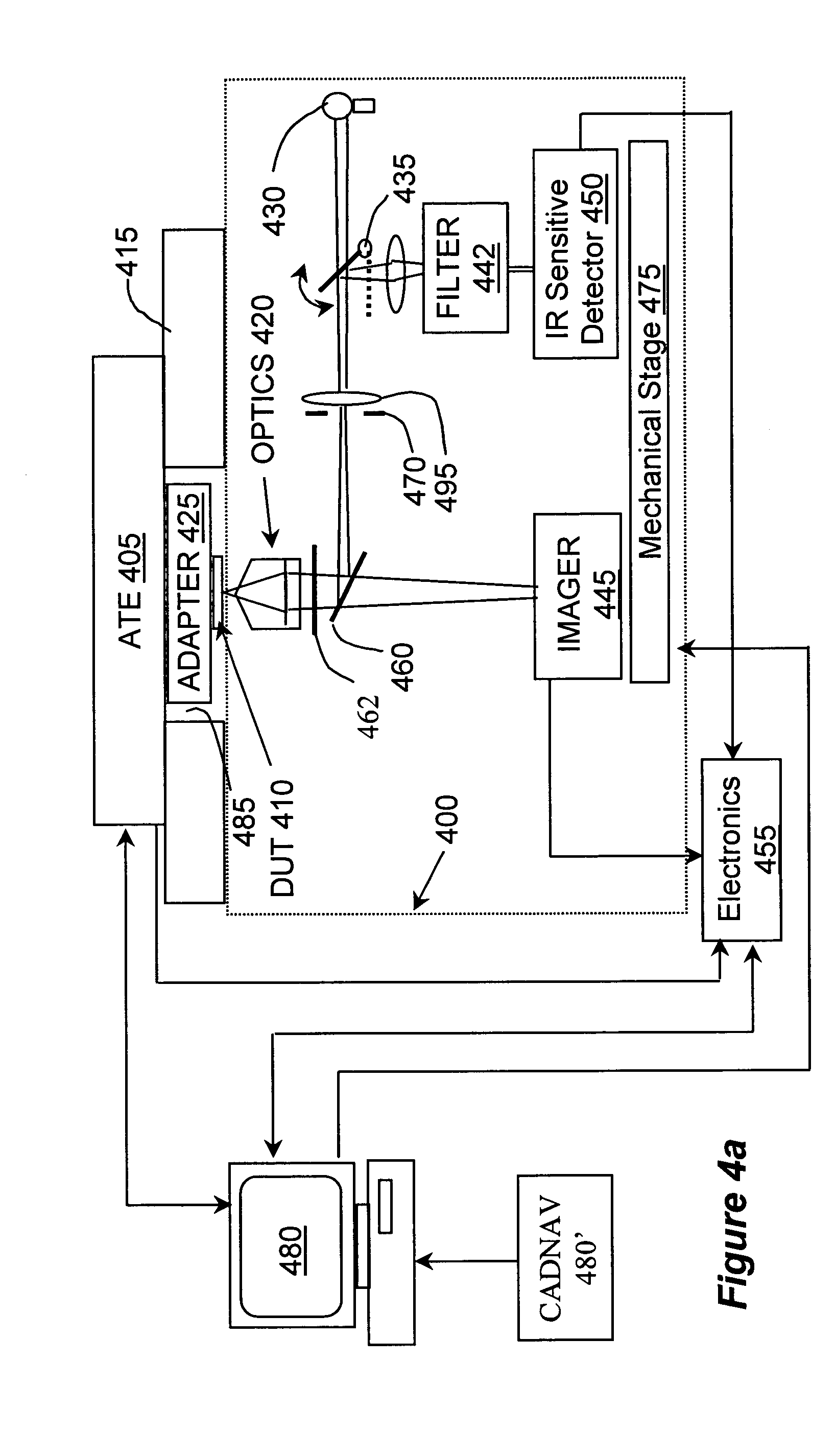
A system for temporal and spectral resolved detection of photon emission from an integrated circuit is disclosed. A DUT is stimulated by a conventional ATE, so that its active devices emit light. The signal from the ATE is also sent to the system's computer as a synchronization signal. The light emitted from the switching devices is passed through a wavelength filter. Selected bands of wavelengths are then passed to respective detector(s) and the detector(s) response with respect to the time correlated ATE stimulus is studied.
Owner:ONTONICS
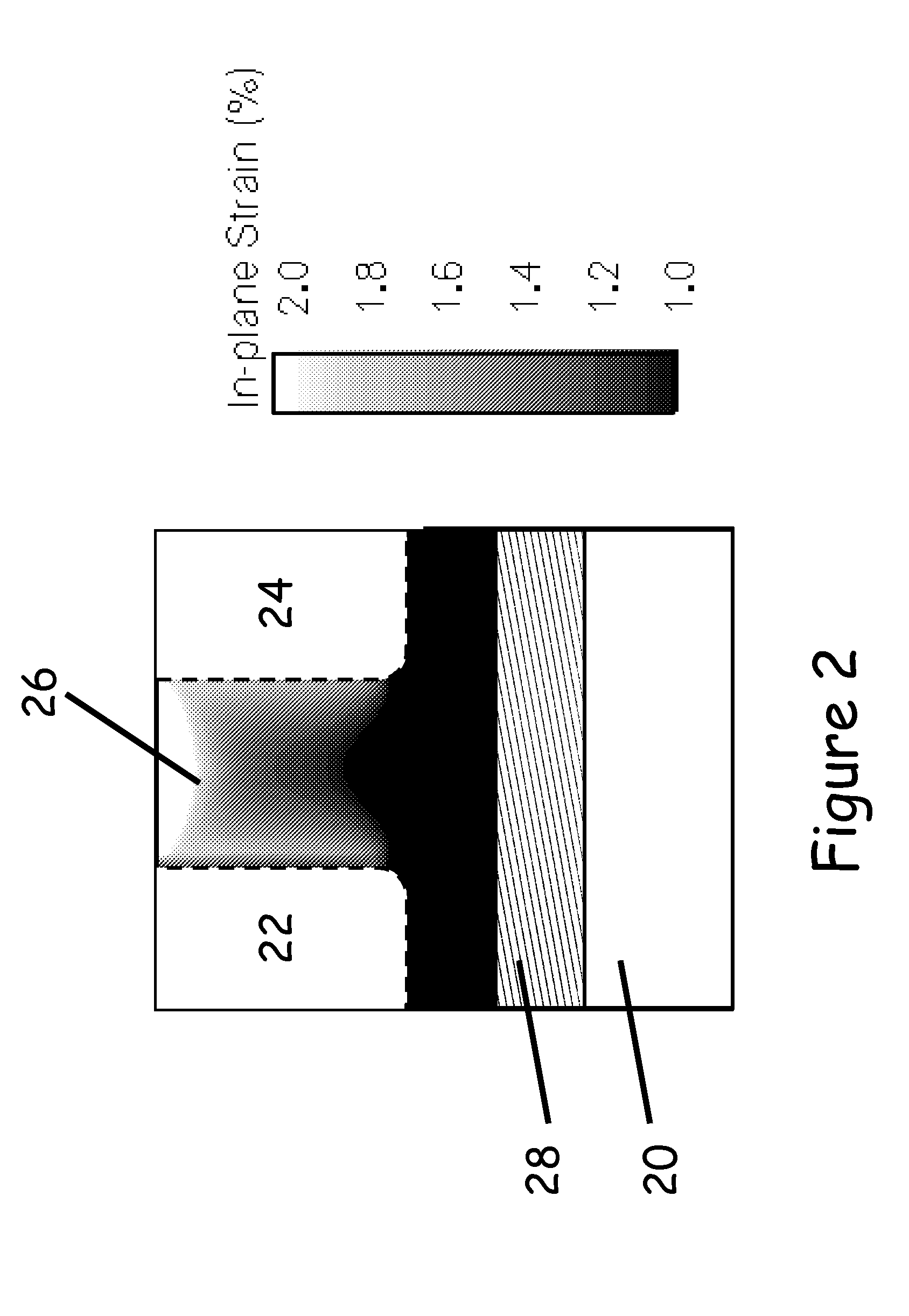
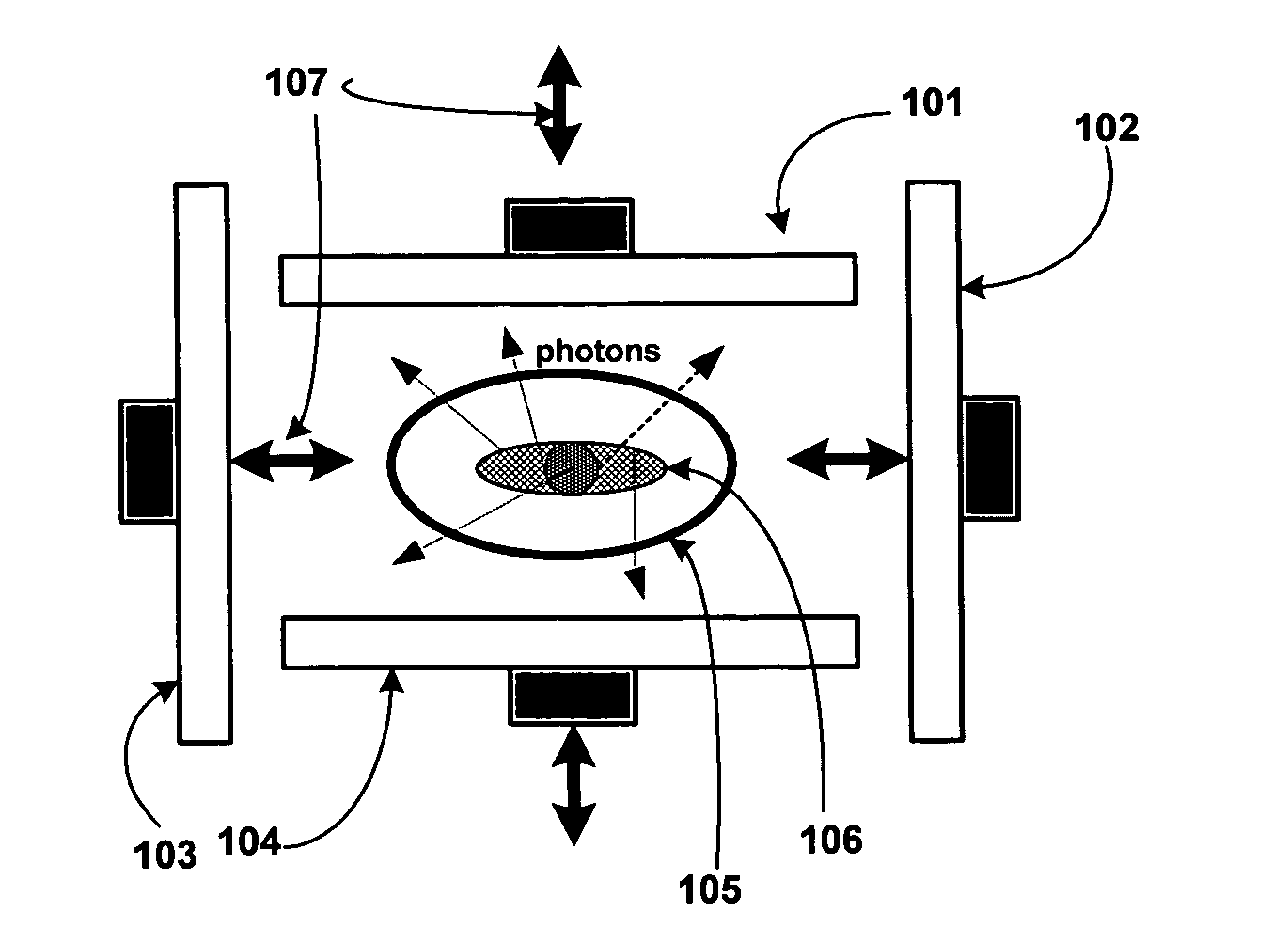
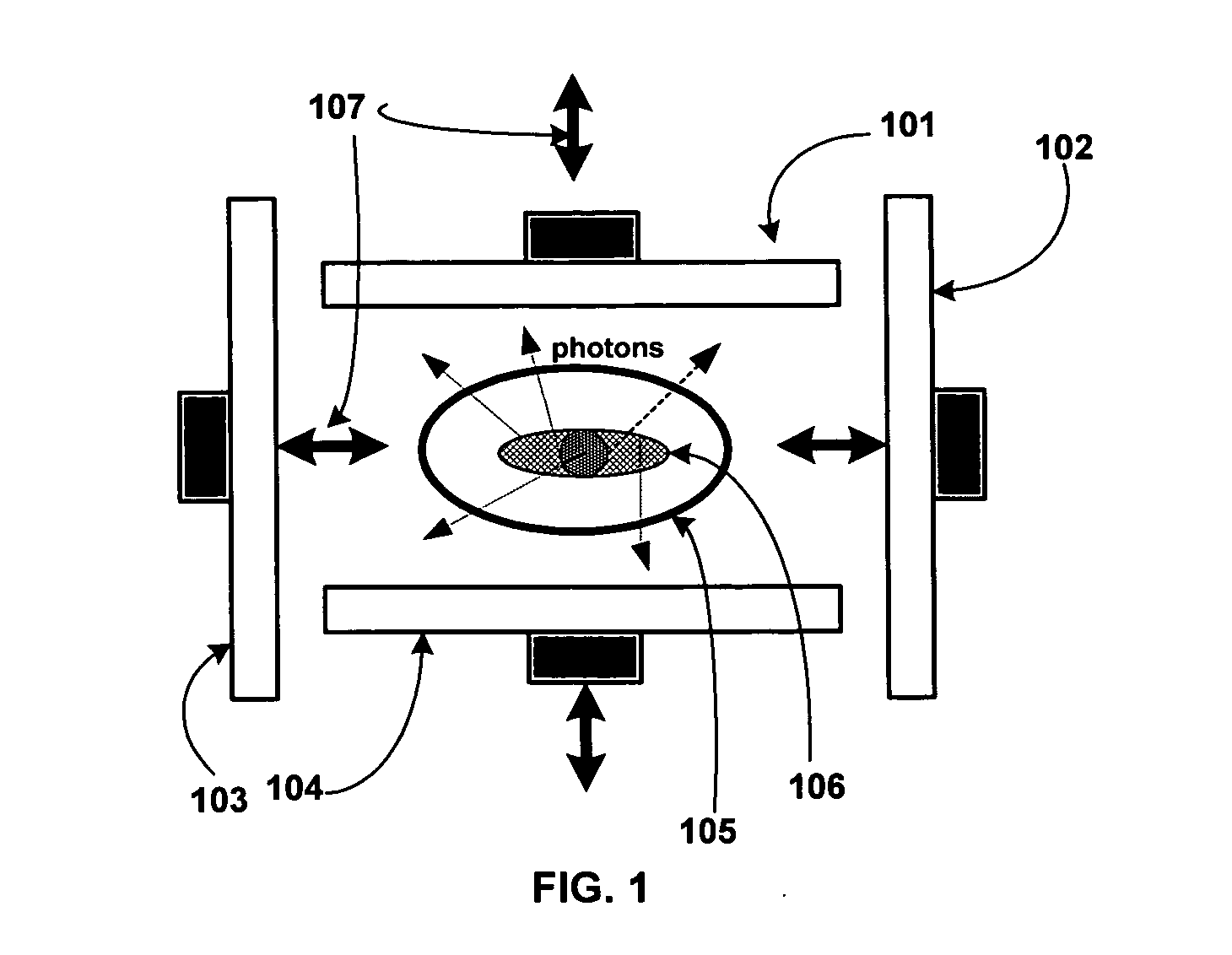
Tensile strained semiconductor photon emission and detection devices and integrated photonics system
Tensile strained germanium is provided that can be sufficiently strained to provide a nearly direct band gap material or a direct band gap material. Compressively stressed or tensile stressed stressor materials in contact with germanium regions induce uniaxial or biaxial tensile strain in the germanium regions. Stressor materials may include silicon nitride or silicon germanium. The resulting strained germanium structure can be used to emit or detect photons including, for example, generating photons within a resonant cavity to provide a laser.
Owner:ACORN SEMI LLC
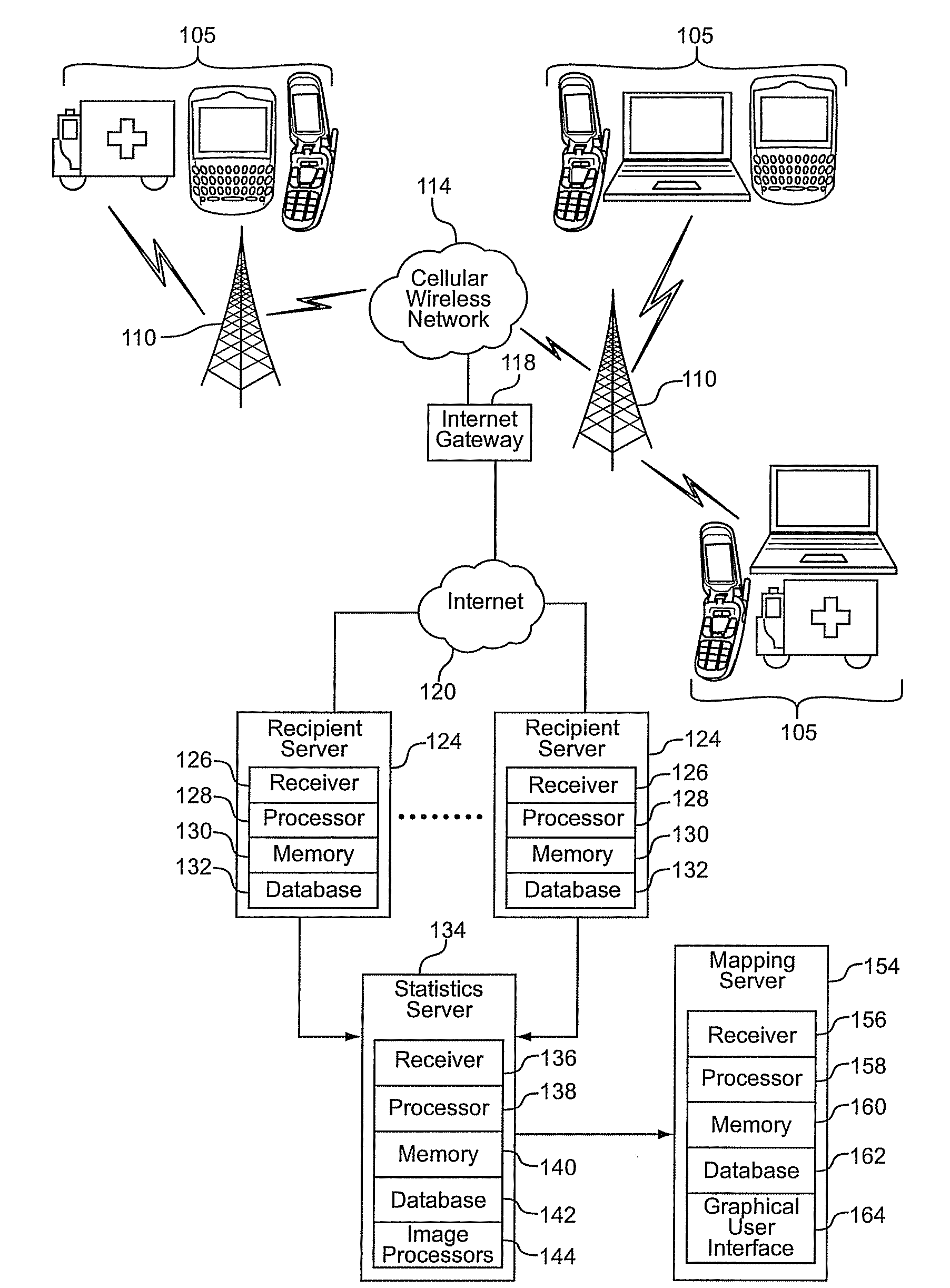
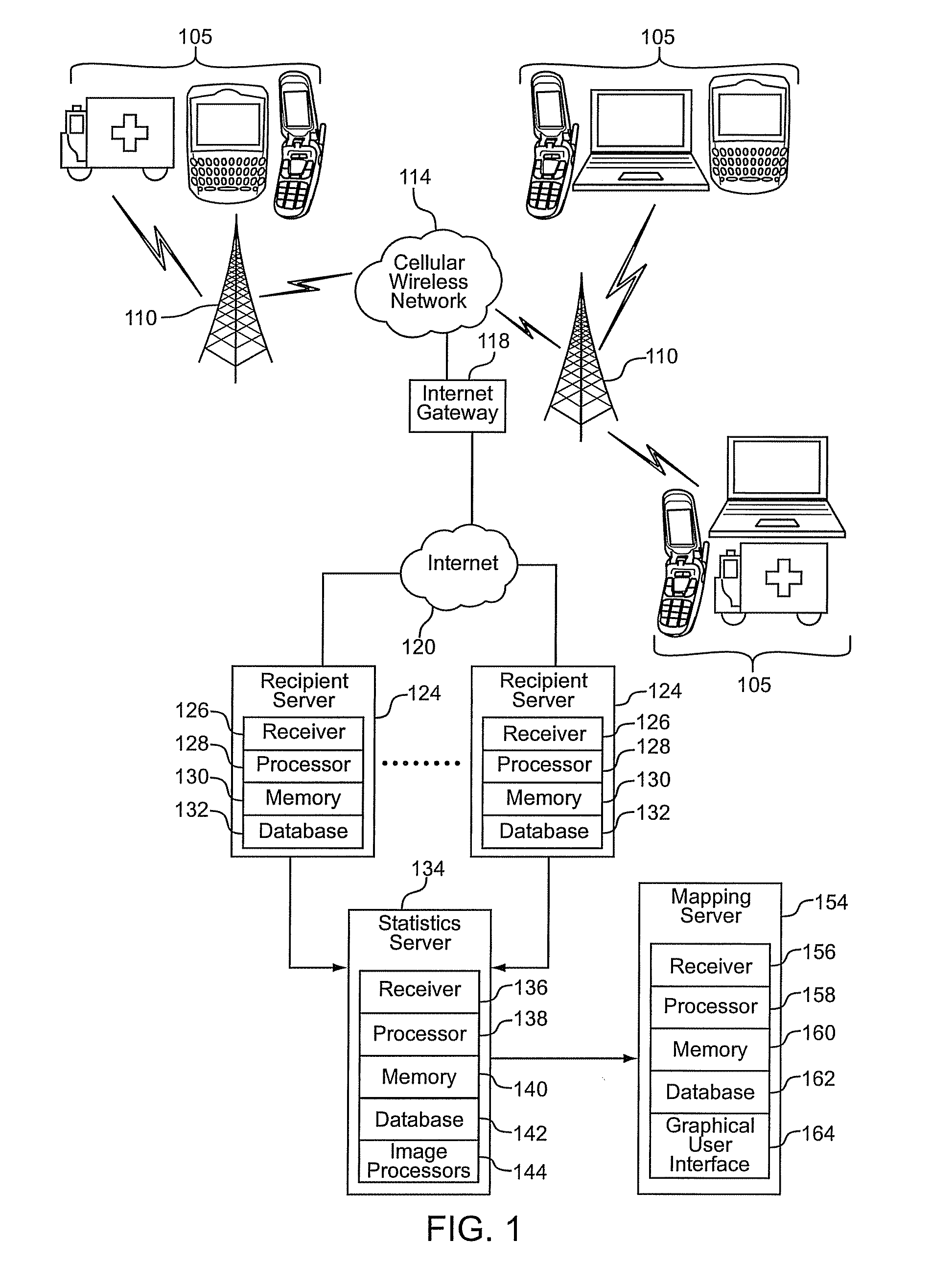
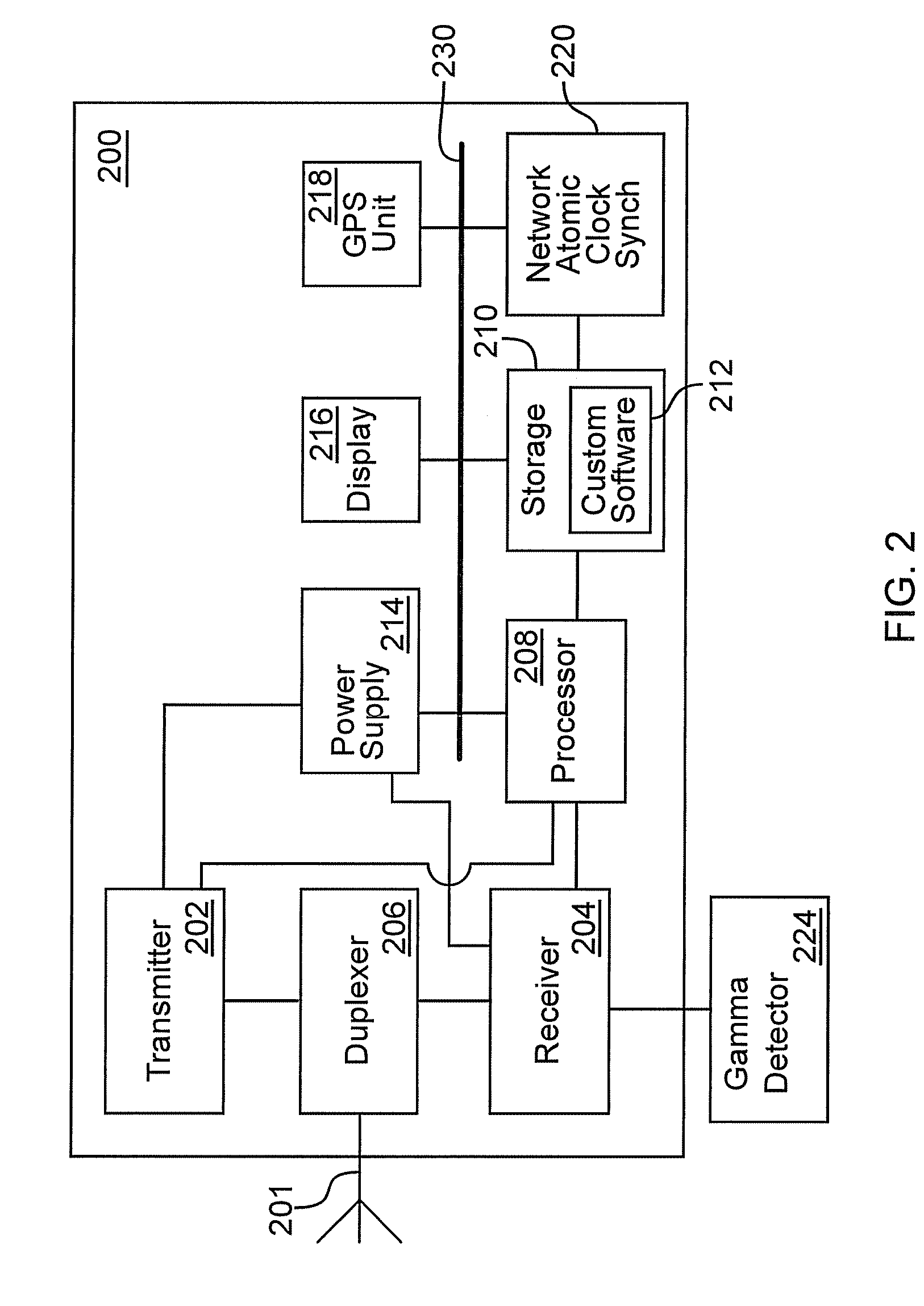
Nuclear detection via a system of widely distributed low cost detectors
A radiation detection system includes many receivers to continuously receive radiation emission data from at least some of a sufficient density of dispersed detectors capable of communicating geo-positions and photon emission counts over a network; the data includes gamma intensities, time stamps, and geo-positions. A processor builds digital image data of the received radiation data for a geographic area by treating gamma-ray proton data from each dispersed detector as a pixel in a low-light image. The processor continuously executes a plurality of statistical computational analyses on the digital image data to separate detected radiation signals from random, undesired signal noise, and known signal noise or sources. The statistical computational analyses include match-filter and / or other convolution techniques. An interface reports to a user when the computational analyses result in detection of a radiation signal and reports a location of one or more of the dispersed detectors that contribute to the detection.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
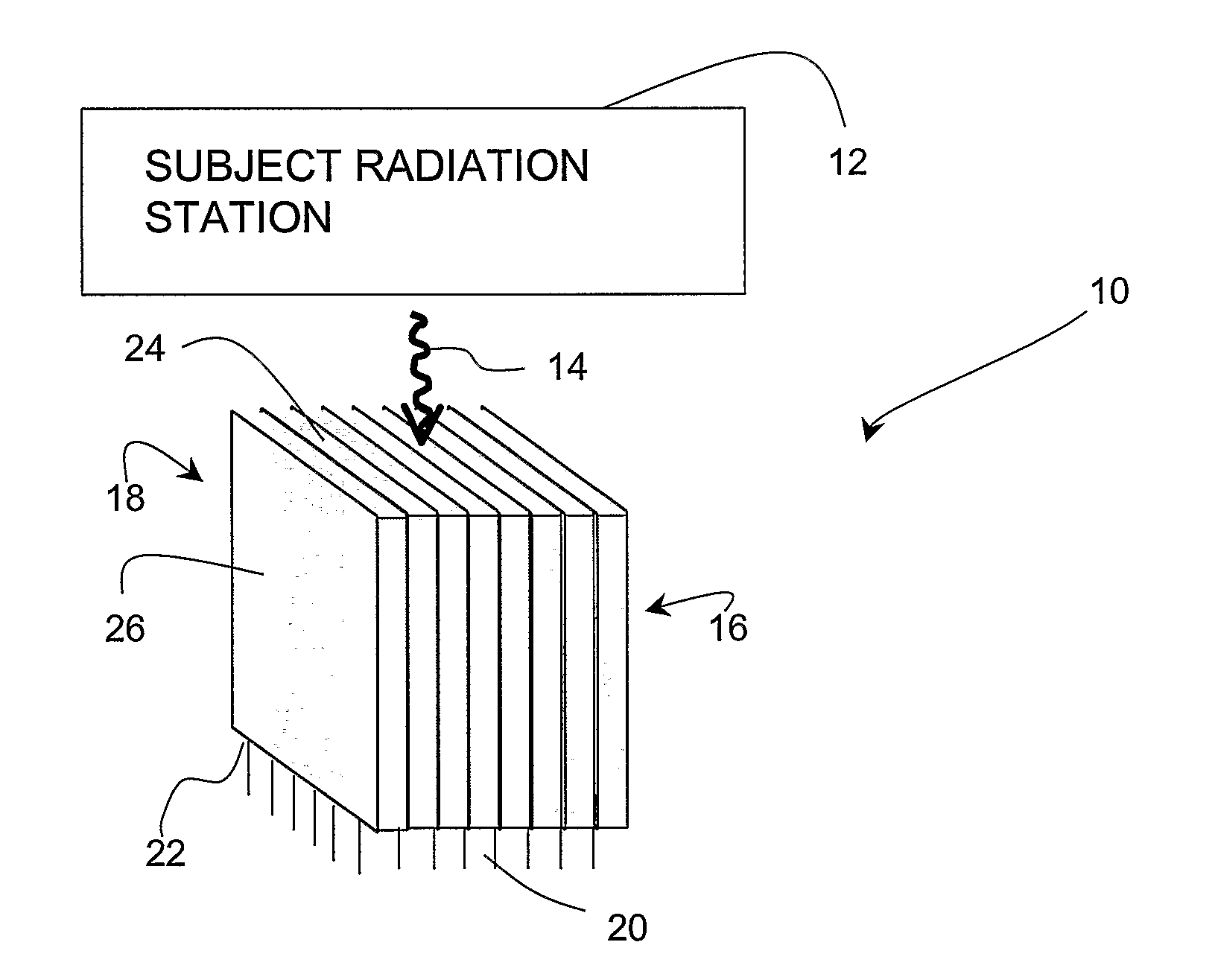
Semiconductor Crystal High Resolution Imager
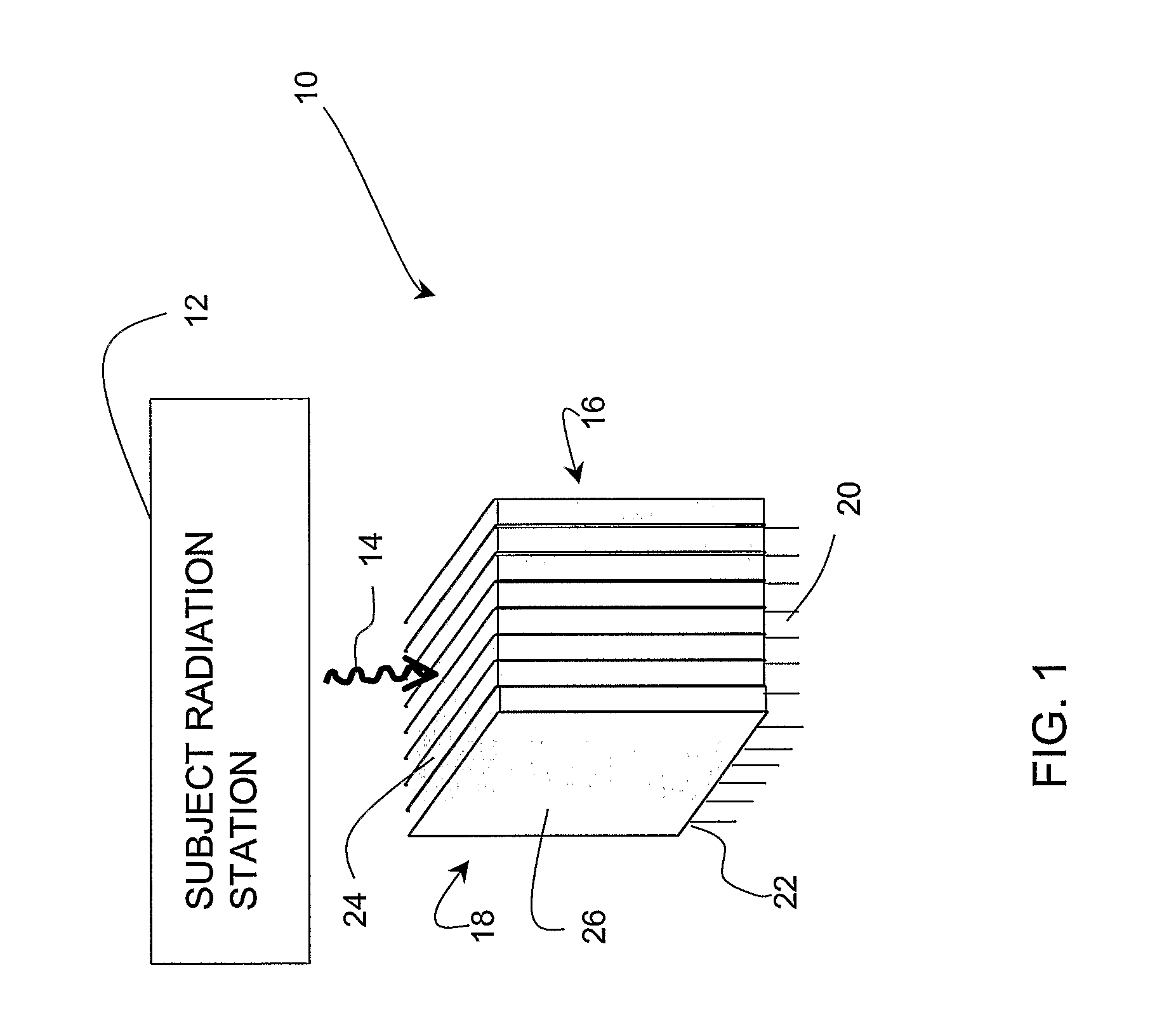
ActiveUS20080042070A1Television system detailsSolid-state devicesPhoton emissionHigh resolution imaging
A radiation imaging device (10). The radiation image device (10) comprises a subject radiation station (12) producing photon emissions (14), and at least one semiconductor crystal detector (16) arranged in an edge-on orientation with respect to the emitted photons (14) to directly receive the emitted photons (14) and produce a signal. The semiconductor crystal detector (16) comprises at least one anode and at least one cathode that produces the signal in response to the emitted photons (14).
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Method and apparatus for compact birefringent interference imaging spectrometer
The disclosure relates to a method and apparatus for a compact birefringent interference imaging spectrometer. More specifically, the disclosure relates to a portable system for obtaining a spectrum of a sample. The portable system may include a first photon emission source for illuminating the sample with a first plurality of photons to thereby produce photons scattered by the sample; an optical lens for collecting the scattered photons; a filter for receiving the collected scattered photons and providing therefrom filtered photons; a first photon detector for receiving the filtered photons and obtaining therefrom a spectrum of the sample; and a rejection filter for blocking the photons from said first photon emission source from entering said first photon detector. The disclosure additionally relates to methods of using such portable systems.
Owner:CHEMIMAGE TECH LLC
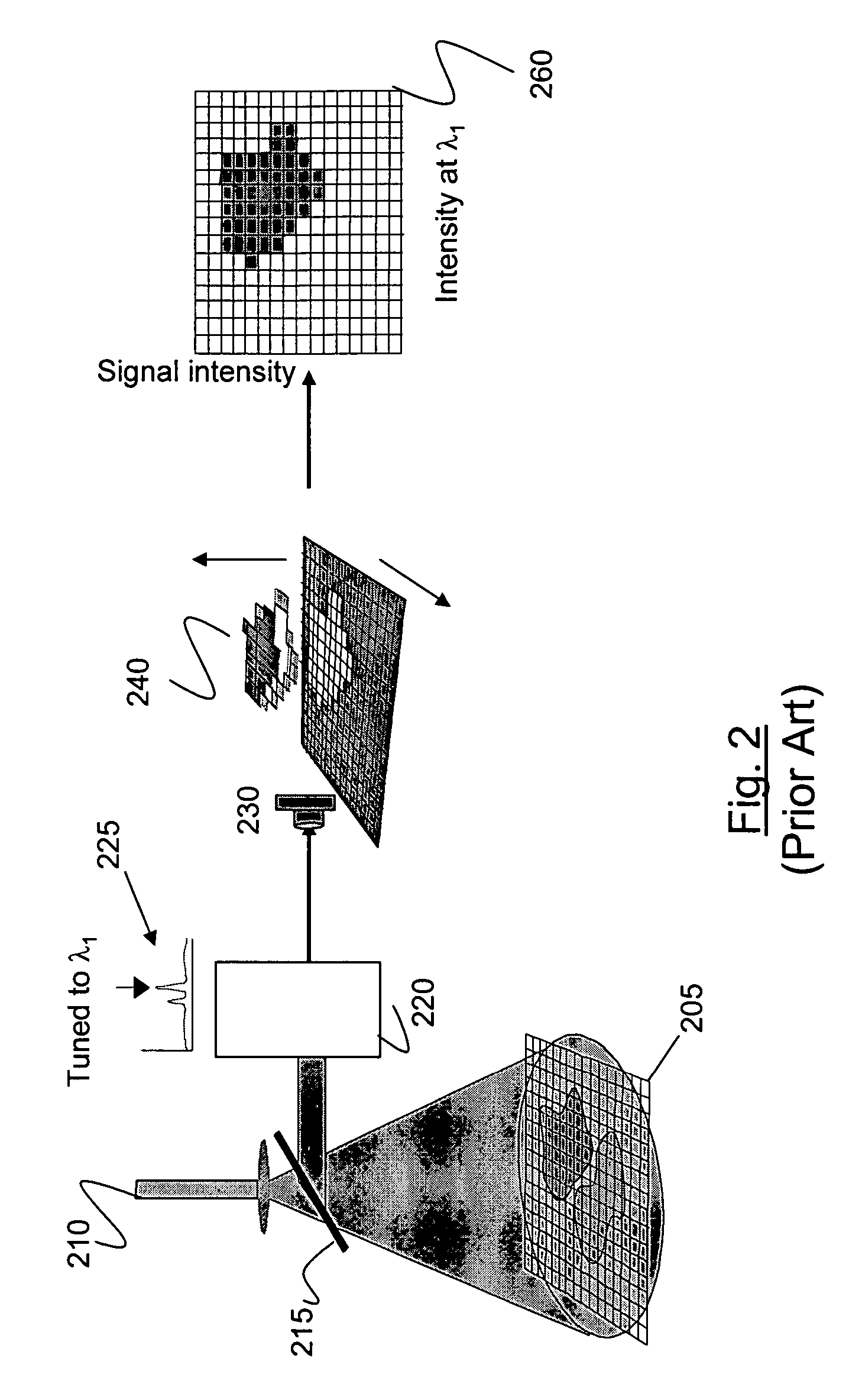
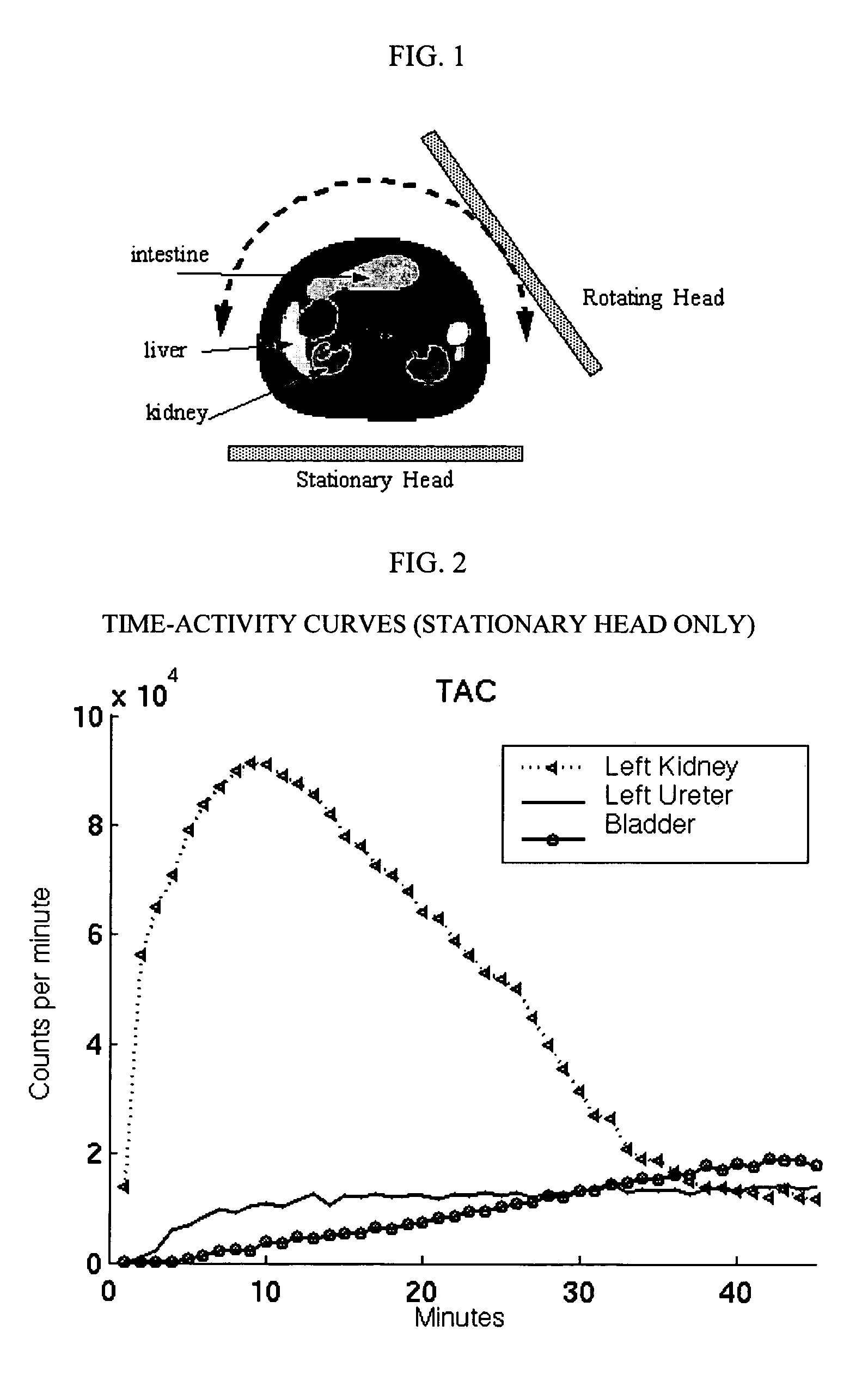
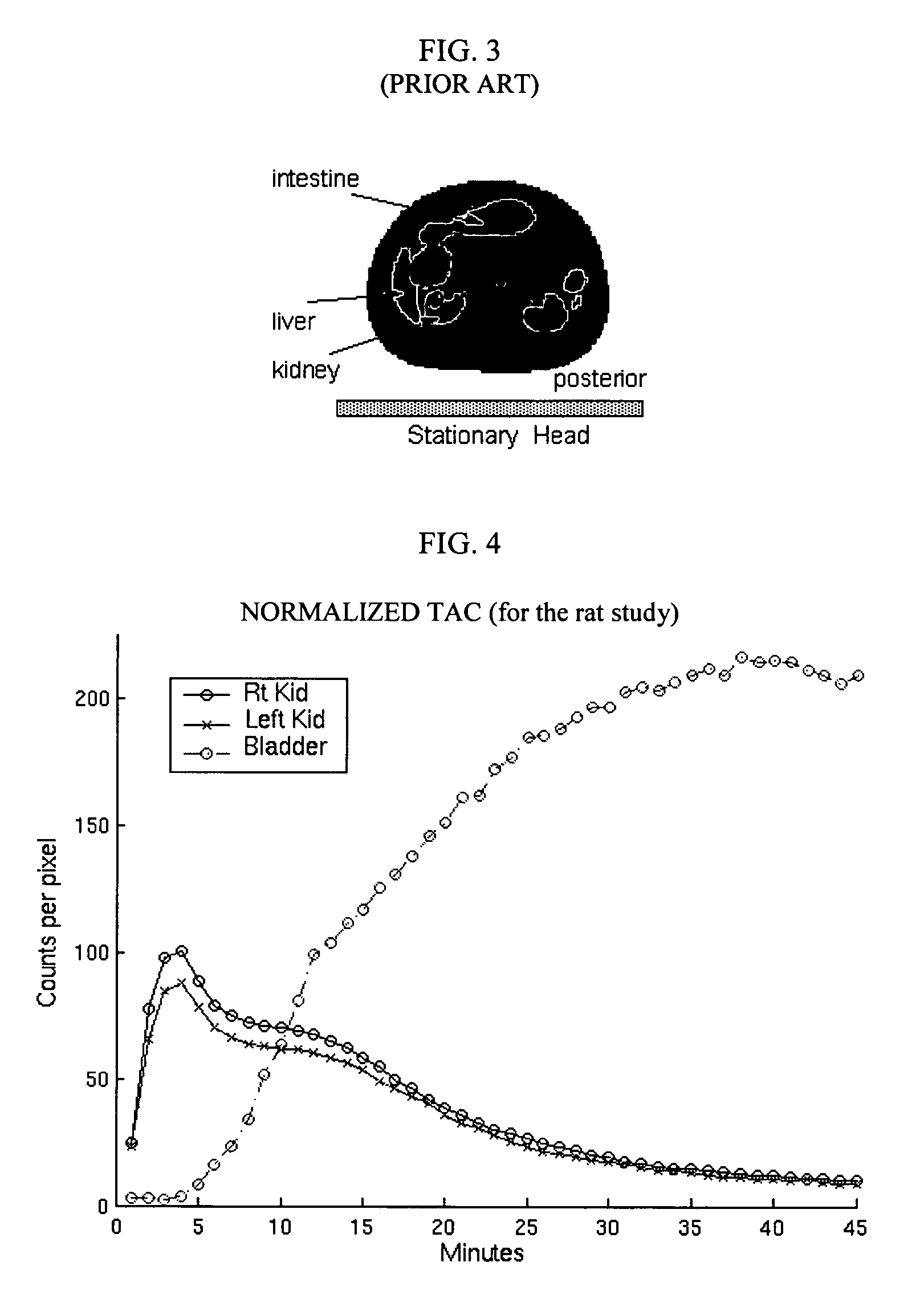
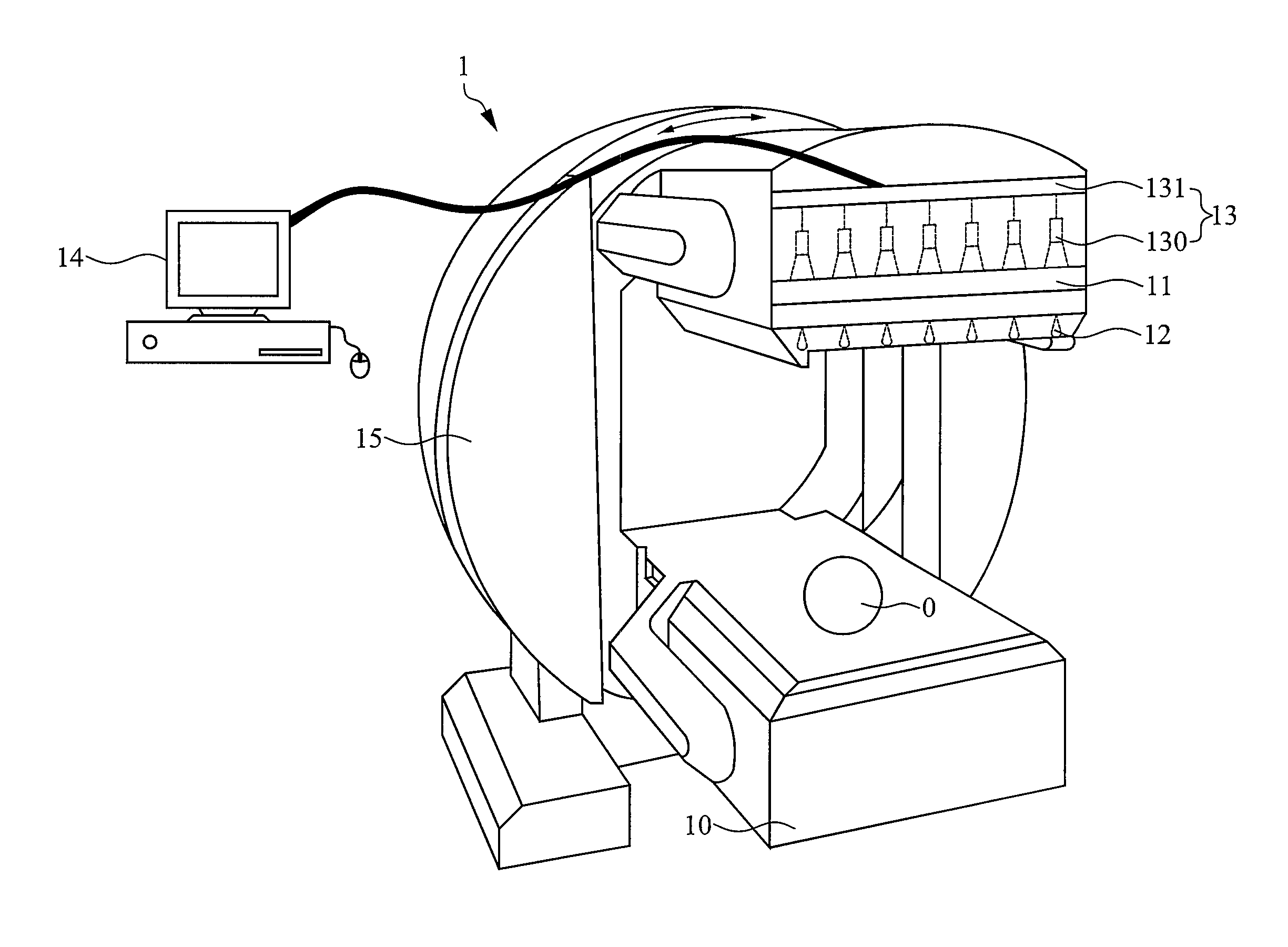
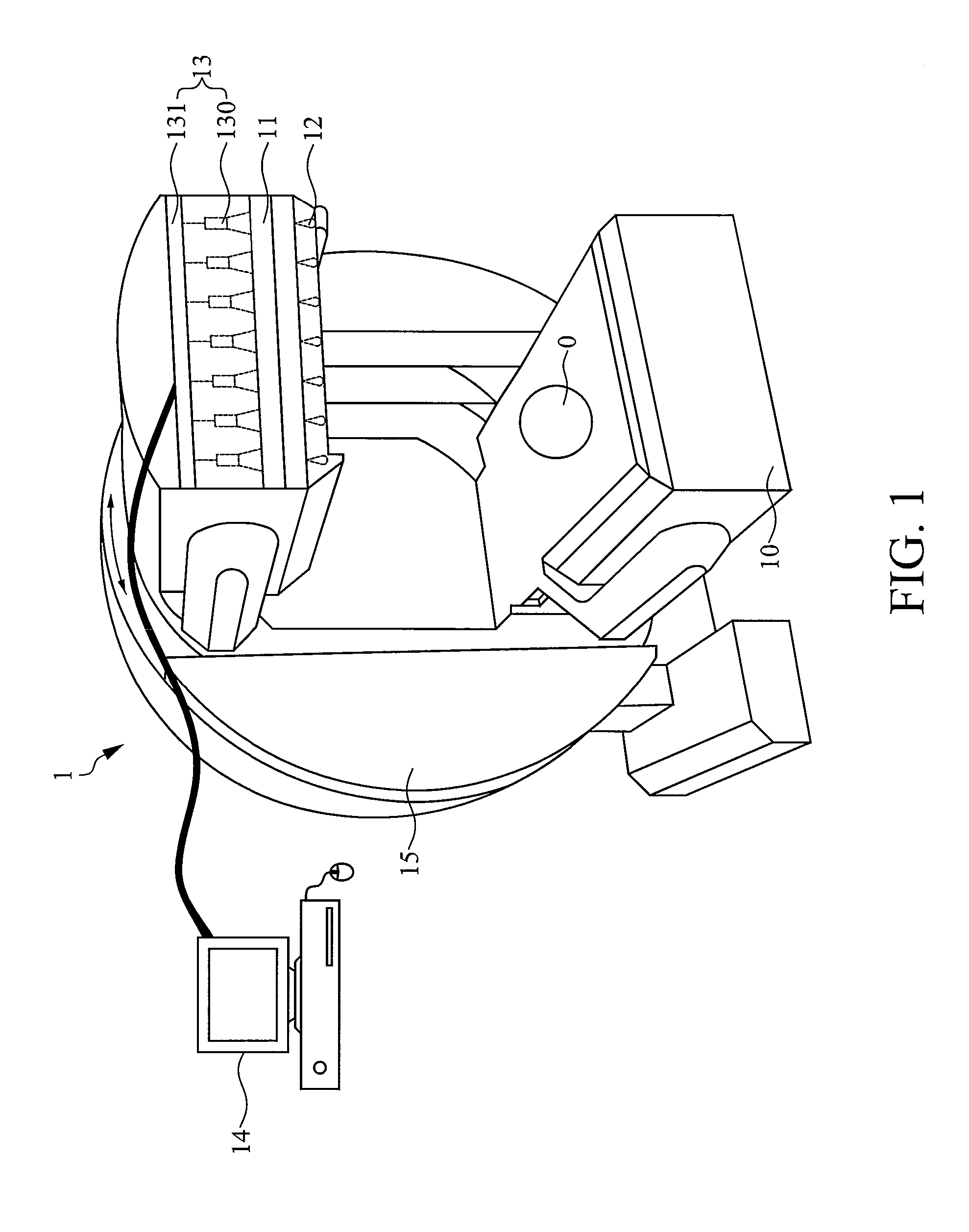
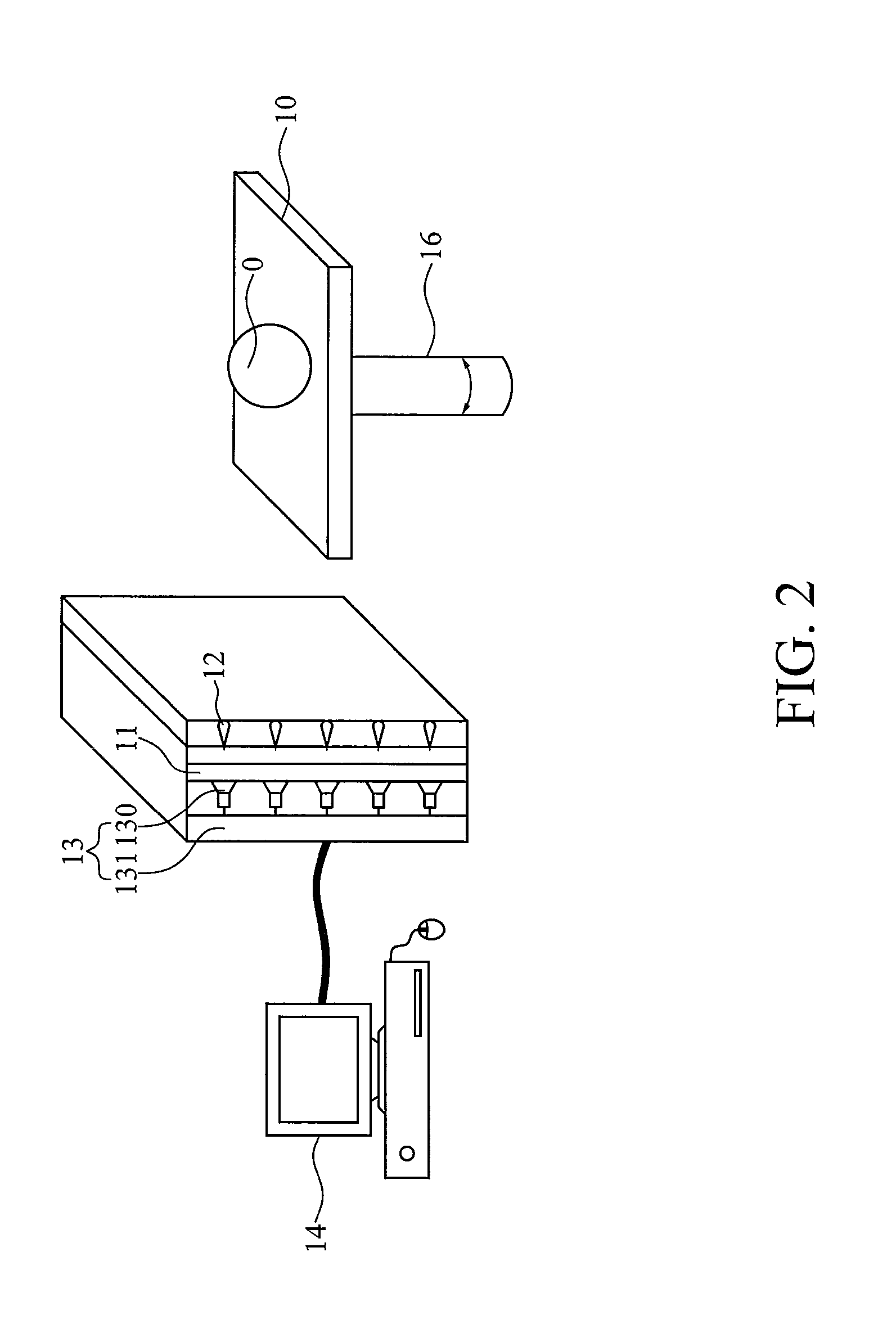
Fast dynamic imaging protocol using a multi-head single photon emission computed tomography system
ActiveUS7468513B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingPhoton emissionData acquisition
An imaging system for acquiring multi-dimensional tomographic image data of an object, the imaging system having (1) a plurality of detectors to acquire image data, the detectors coupled to a supporting structure, wherein at least one of the detectors is adapted to move relative to the object during image data acquisition and wherein the detectors are adapted to rotate independently of each other, provided that image data from the detectors are collected concomitantly during a study time and (2) a data analyzer adapted to acquire and / or reconstruct the image data.
Owner:THE CHILDRENS HOSPITAL OF PHILADELPHIA
Electron injection nanostructured semiconductor material anode electroluminescence method and device
ActiveUS20110297846A1Lower operating temperatureAccelerate emissionsElectroluminescent light sourcesPhotometryPhoton emissionSemiconductor materials
Embodiments of the invention include methods and devices for producing light by injecting electrons from field emission cathode across a gap into nanostructured semiconductor materials, electrons issue from a separate field emitter cathode and are accelerated by a voltage across a gap towards the surface of the nanostructured material that forms part of the anode. At the nanostructure material, the electrons undergo electron-hole (e-h) recombination resulting in electroluminescent (EL) emission. In a preferred embodiment lighting device, a vacuum enclosure houses a field emitter cathode. The vacuum enclosure also houses an anode that is separated by a gap from said cathode and disposed to receive electrons emitted from the cathode. The anode includes semiconductor light emitting nano structures that accept injection of electrons from the cathode and generate photons in response to the injection of electrons. External electrode contacts permit application of a voltage differential across the anode and cathode to stimulate electron emissions from the cathode and resultant photon emissions from the semiconductor light emitting nanostructures of the anode. Embodiments of the invention also include the usage of nanostructured semiconductor materials as phosphors for conventional planar LED and nanowire array light emitting diodes and CFL. For the use in conventional planar LEDs, the nanostructures may take the form of quantum dots, nanotubes, branched tree-like nanostructure, nanoflower, tetrapods, tripods, axial heterostructures nanowires hetero structures.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
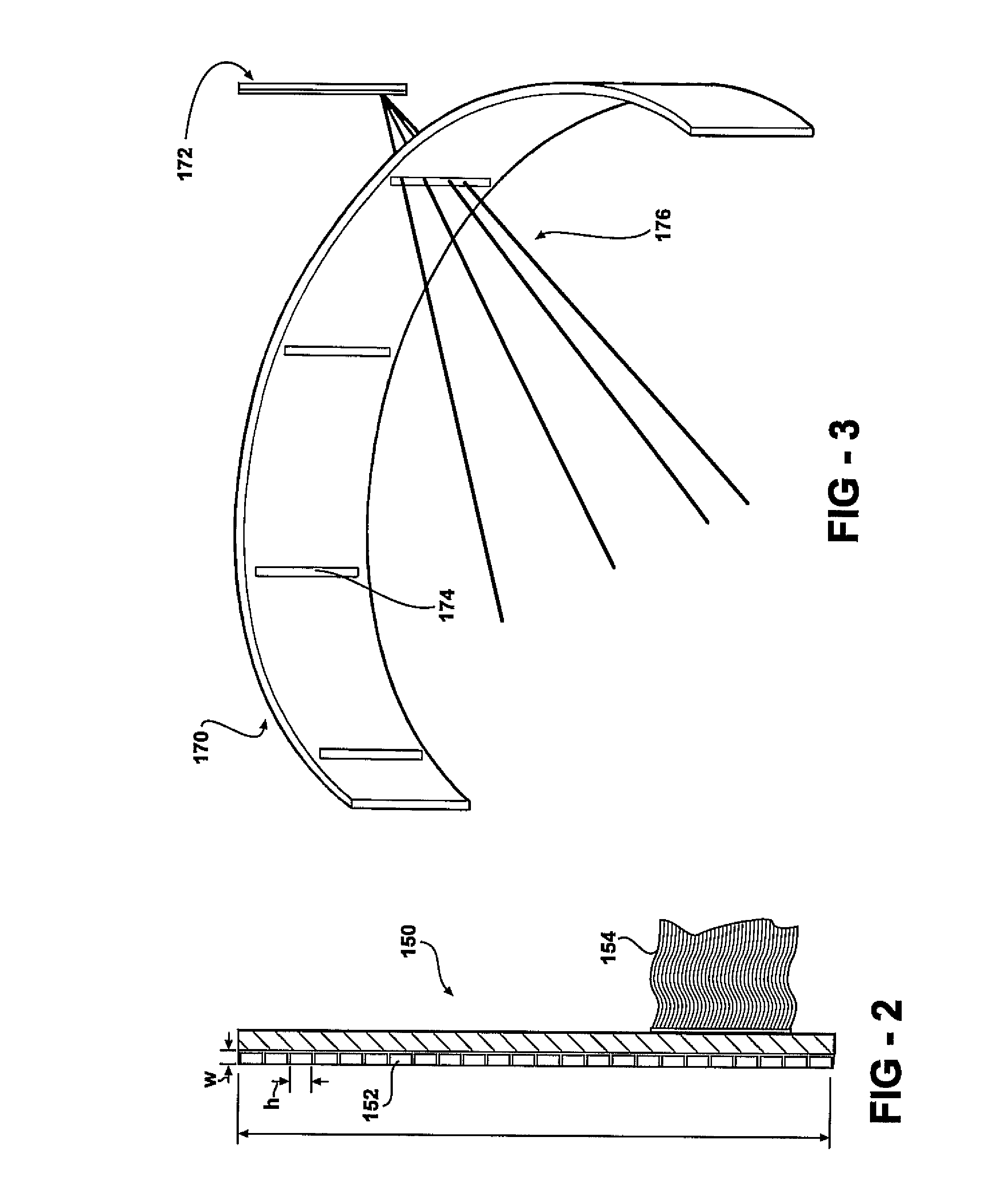
Light emitting system with high extraction efficency
ActiveUS7250635B2Improve performanceImprove light outputElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesElectricityPhoton emission
In an epitaxial structure of a solid state lighting system, electrical current injection into the active layer is used to excite the photon emission. The present invention employs a unique waveguide layer in the epitaxial structure for trapping the light generated by the active layer in the fundamental waveguide mode. Multiple photonic crystal regions located either outside or inside one or more current injection regions extract photons from the waveguide layer(s). This novel design optimizes the interplay of electrical pumping, radiation and optical extraction to increase the optical output to several times that of conventional LEDs. A transparent and conductive ITO layer is added to the surface of an epitaxial structure to reduce the interface reflection in addition to functioning as a current spreading layer. The present invention creates solid state lighting with high optical output and high power efficiency.
Owner:DICON FIBEROPTICS
Method and apparatus for high-sensitivity Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography
ActiveUS20110073763A1Facilitates higher qualityAccurate clinical diagnosisMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingPhoton emissionSystem matrix
A method and apparatus are disclosed for high-sensitivity Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT), and Positron Emission Tomography (PET). The apparatus includes a two-dimensional (2D) gamma detector array that, unlike a conventional SPECT machine, moves to different positions in a three-dimensional (3D) volume space near an emission source and records a data vector g which is a measure of gamma emission field. In particular, the 3D volume space in which emission data g is measured extends substantially along a radial direction r pointing away from the emission source, and unlike a conventional SPECT machine, each photon detector element in the 2D gamma detector array is provided with a very large collimator aperture. Data g is related to the 3D spatial density distribution f of the emission source, noise vector n, and a system matrix H of the SPECT / PET apparatus through the linear system of equations g=Hf+n. This equation is solved for f by a method that reduces the effect of noise.
Owner:SUBBARAO MURALIDHARA
X-ray pulsar navigation embedded simulation system based on semiconductor laser
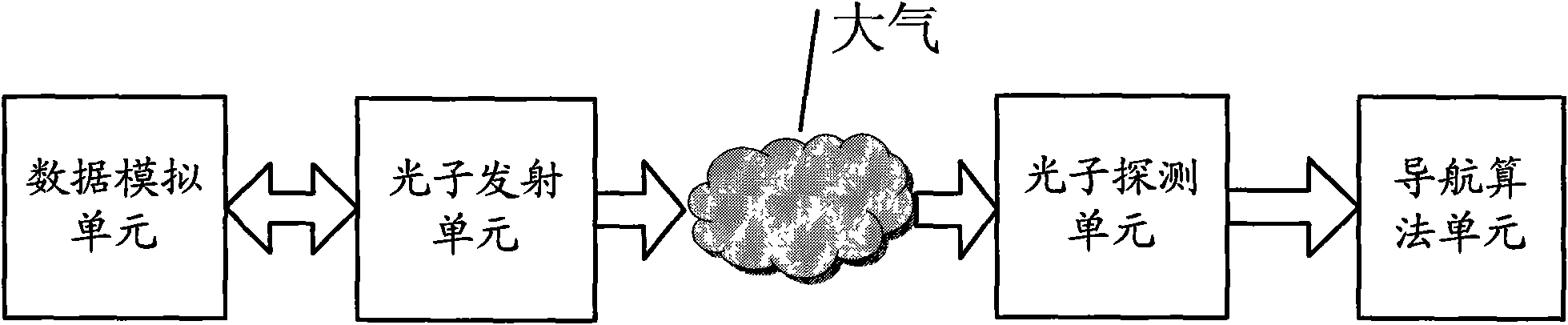
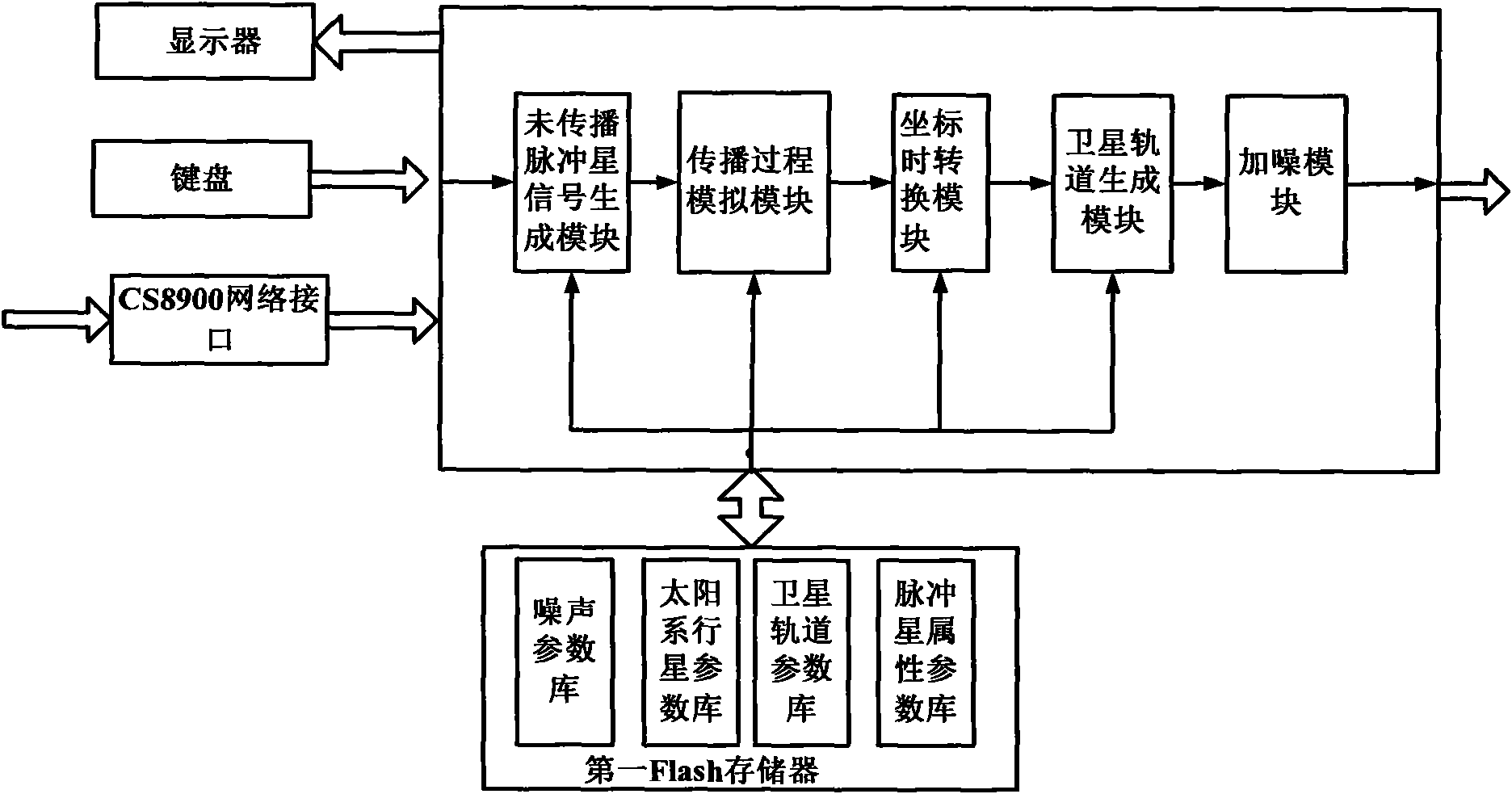
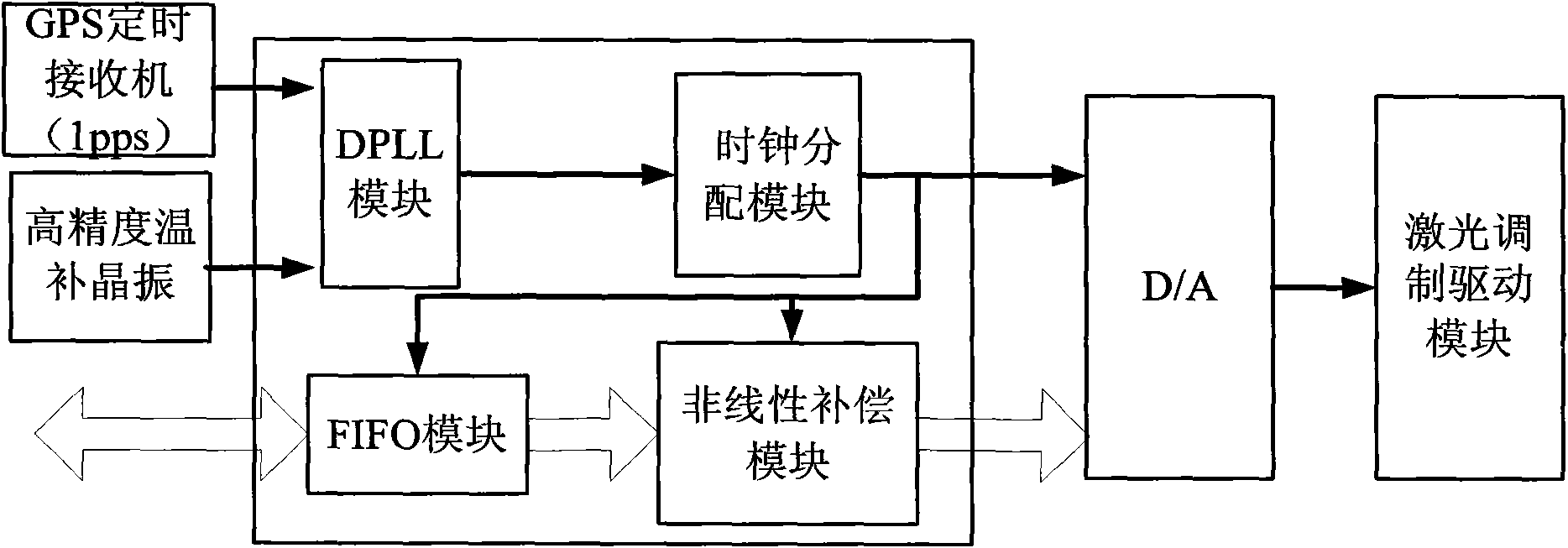
InactiveCN101608919AEasy to compare and analyzeHigh precisionInstruments for comonautical navigationNavigation by astronomical meansData simulationPhoton emission
The invention discloses an X-ray pulsar navigation embedded simulation system based on a semiconductor laser, which comprises a data simulation unit, a photon emission unit, a photon detection unit and a navigation test unit. The data simulation unit simulates X-ray pulsar radiation signal data, and sends the X-ray pulsar radiation signal data to the photon emission unit; the photon emission unit uses simulation data to modulate light intensity of a laser modulation laser, and radiate lasers to the atmosphere; the photon detection unit receives the lasers of the photon emission unit from the atmosphere, filters non-laser spectra components in background sunlight, and sends the received lasers to the navigation test unit after carrying out counting on the received lasers; and the navigation test unit carries out noise elimination, pulse profile accumulation, pulse arrival time measurement treatment on the data of the photon detection unit, and utilizes time measurement data to carry out a navigation test. The invention can provide a complete simulation experiment platform for obtaining navigation signals, signal processing, time synchronization and navigation design verification of navigation signals.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Solid state illumination device having plasmonic antenna array for anisotropic emission
ActiveUS20160161644A1Improve directionalityControl is possibleStability-of-path spectrometersLaser detailsPhoton emissionLocalized surface plasmon
There is provided an illumination device (100, 150, 200, 300) comprising: a periodic plasmonic antenna array (114), comprising a plurality of individual antenna elements (106) arranged in an antenna array plane, the plasmonic antenna array being configured to support surface lattice resonances at a first wavelength, arising from diffractive coupling of localized surface plasmon resonances in the individual antenna elements; a photon emitter (152) configured to emit photons at the first wavelength, the photon emitter being arranged in close proximity of the plasmonic antenna array such that at least a portion of the emitted photons are emitted by a coupled system comprising said photon emitter and said plasmonic antenna array, wherein the plasmonic antenna array is configured to comprise plasmon resonance modes being out-of plane asymmetric, such that light emitted from the plasmonic antenna array has an anisotropic angle distribution.
Owner:LUMILEDS
Precision synthesis of quantum dot nanostructures for fluorescent and optoelectronic devices
Methods are disclosed generally directed to design and synthesis of quantum dot nanoparticles having improved uniformity and size. In a preferred embodiment, a release layer is deposited on a semiconductor wafer. A heterostructure is grown on the release layer using epitaxial deposition techniques. The heterostructure has at least one layer of quantum dot material, and optionally, one or more layers of reflective Bragg reflectors. A mask is deposited over a top layer and reactive ion-beam etching applied to define a plurality of heterostructures. The release layer can be dissolved releasing the heterostructures from the wafer. Some exemplary applications of these methods include formation of fluorophore materials and high efficiency photon emitters, such as quantum dot VCSEL devices. Other applications include fabrication of other optoelectronic devices, such as photodetectors.
Owner:SPIRE
Method and system for quantum communication security
InactiveCN101820343AHighlight substantiveSignificant progressKey distribution for secure communicationCommunications securityPhoton emission
The invention relates to a method and a system for quantum communication security. An Alice terminal comprises a watchdog detector, an optical attenuator, a phase modulator, a reflector, a controller and a photon emitter; and a Bob terminal comprises a laser, a time division multiplex / demultiplex system, a phase modulator, a single photon detector, a controller, an optical switch and a reflector. The method and the system have the advantages that: (1) the two-way, stable and safe distribution of quantum keys is realized, the polarization and phase change of a single photon can be automatically compensated, and the aim of stable long-distance transmission is achieved; (2) the Alice terminal adopts the watchdog detector, on one hand, Trojan attack and intermediary attack can be detected by measuring the number of weak pulses reaching or leaving the Alice terminal, so that the communication security is improved greatly, and on the other hand, the communication speed and communication distance of the system are improved greatly; and (3) the Alice terminal and the Bob terminal can be adjusted and corrected respectively, can select mu independently without transmitting photons by means of unsafe optical fiber lines so as to ensure the system security.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Use of electromagnetic excitation or light-matter interactions to generate or exchange thermal, kinetic, electronic or photonic energy
The present disclosure concerns a means to use at least a form of electromagnetic excitation or light-matter interactions in a structure or material having one or more addressable frequencies to generate the exchange of thermal, kinetic, electronic or photonic energy. In some implementations this provides a means to use electromagnetic excitation or light-matter interactions to influence, cause, control, modulate, stimulate or change the state or phase of electrical, magnetic, optical or electromagnetic charge, emission, conduction, storage or similar properties. The method could include the use of light-matter interactions to generate electromagnetic excitation or light-matter interactions and concentrate extremely localized field effects or concentrated plasmonic field effects to cause an exchange of energy states in a material or structure. Said field effects could be used for excitation of surface electrons in metallic nanostructures causing said electrons to exchange energy states or said field effects could be used to mediate or stimulate photon emissions or to modulate photonic energy to excite or stimulate emissions of electrons. Said electron or photon emissions could be used to drive photochemical, photocatalysis, photovoltaic or thermophotovoltaic reactions.
Owner:DEFRIES ANTHONY +1
Single photon emission computed tomography system
InactiveUS20070007455A1Material analysis by optical meansTomographyPhoton attenuationPhoton emission
A single photon emission computed tomography system includes a detector assembly adjacent a field of view and a collimating assembly disposed between the detector assembly and the field of view. The collimating assembly includes at least two spaced-apart collimating vanes of photon-attenuating material. The system further includes a photon-blocking member disposed between the field of view and the detector. The blocking member has an aperture defined therethrough. The system further includes a mask disposed adjacent the detector assembly having at least one aperture defined therethrough. A displacement actuator moves the photon-blocking member relative to the detector assembly.
Owner:HIGHBROOK HLDG
Single photon emission computed tomography instrument and the operating method thereof
A single photon emission computed tomography instrument is provided, which has a platform, at least one detector, at least one beam stopper, a signal processing device and a computer. The at least one detector is disposed at one side of the platform, and the at least one beam stopper is disposed between the platform and the detector. The signal processing device is electrically communicated with the at least one detector, and the computer is electrically communicated with the signal processing device. The present disclosure further provides an operating method which the beam stopper is added or removed respectively while scanning an analyze by the single photon emission computed tomography instrument in different angles. The projection dataset emitted from the focus could be estimated by subtracting the projecting data without the beam stopper from that with the beam stopper, and high resolution image could be obtained by using image reconstruction program.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
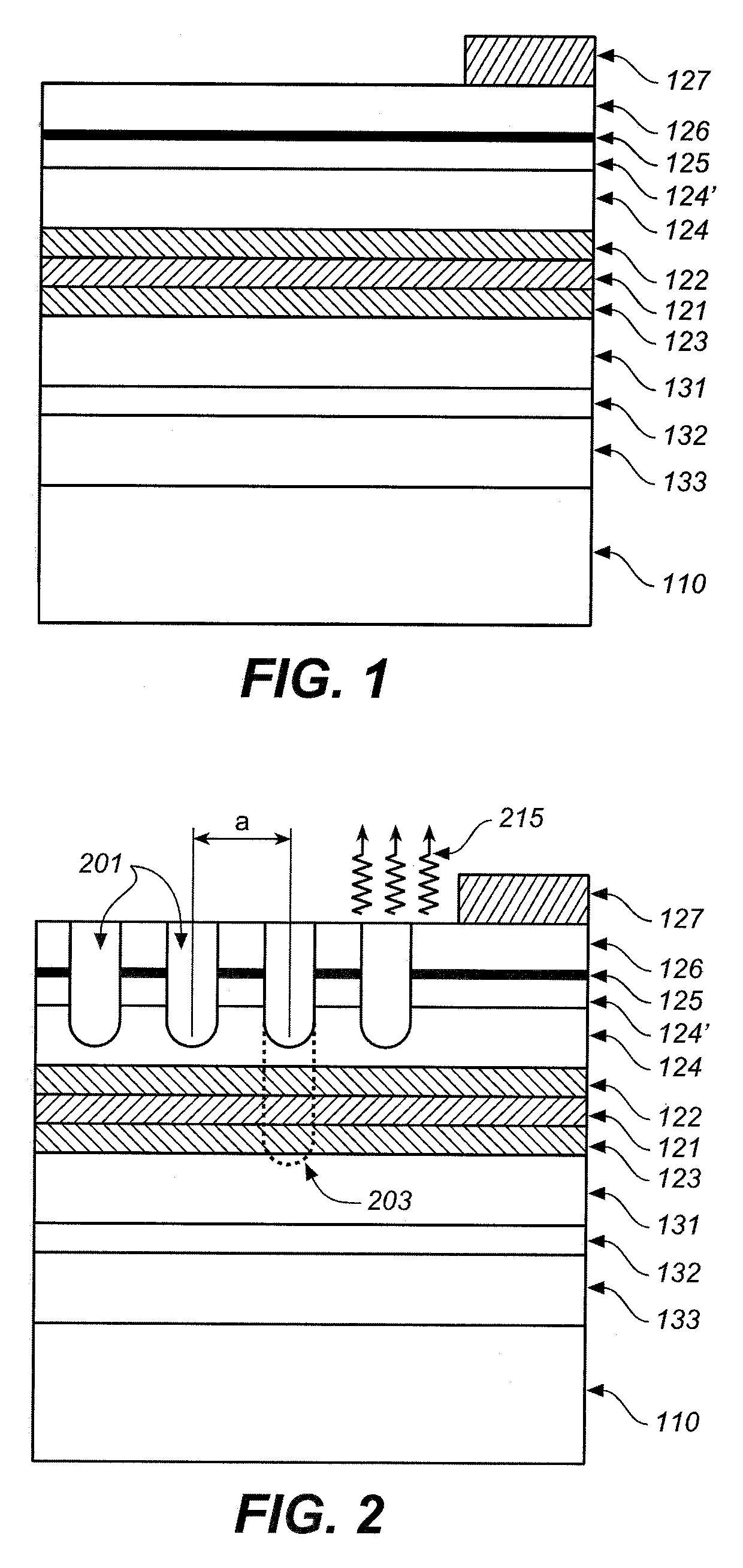
Organic electroluminescence device
ActiveUS20070205411A1Hole transporting ability is deterioratedDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsPhoton emissionOrganic electroluminescence
An organic electroluminescence device of multi-photon emission mode which includes plural light emission layers and at least one charge generation layer between a pair of electrodes, arranged in a film thickness direction thereof, wherein the charge generation layer includes at least one p-doped layer and at least one n-doped layer, and further includes an alkali metal layer and a layer containing a hole transport material between the p-doped layer and the n-doped layer. An organic electroluminescence device of multi-photon emission mode exhibiting little unevenness in luminance even in a large-area format electroluminescence device is provided.
Owner:UDC IRELAND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com