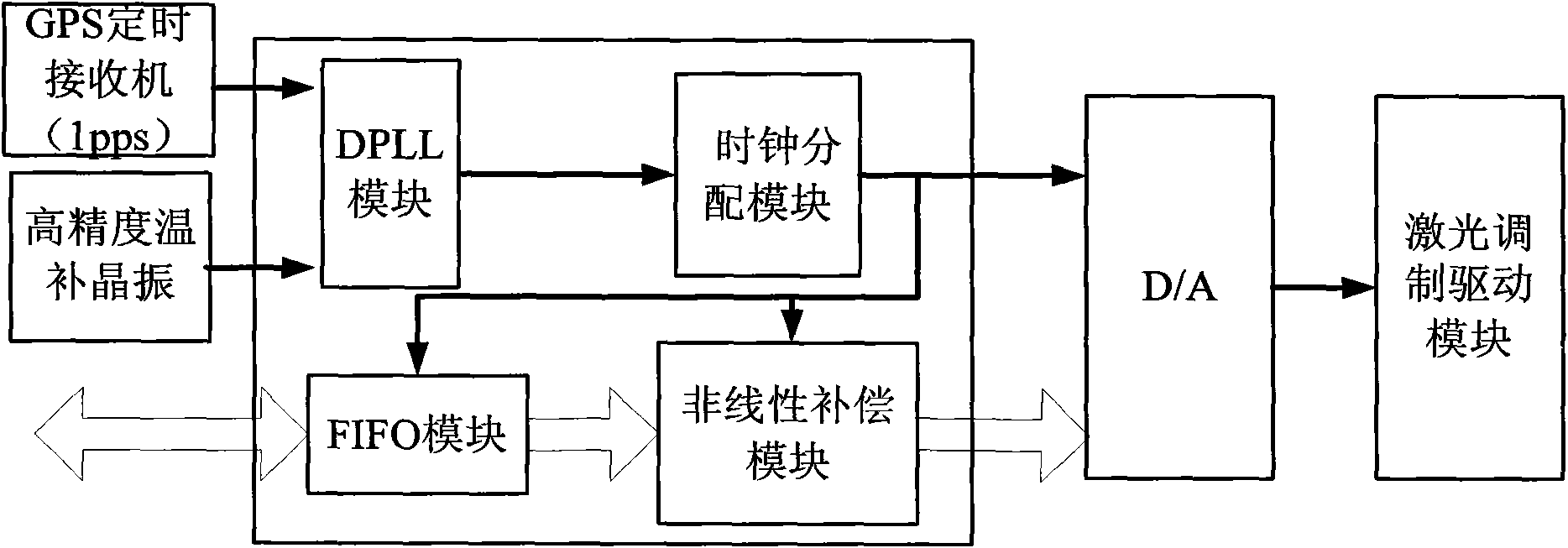
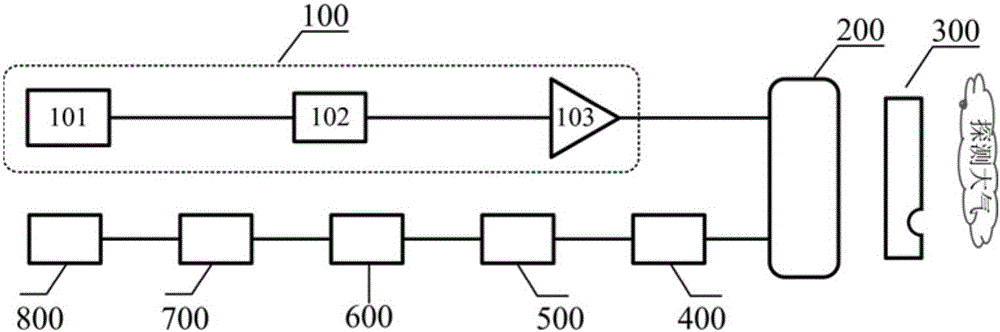
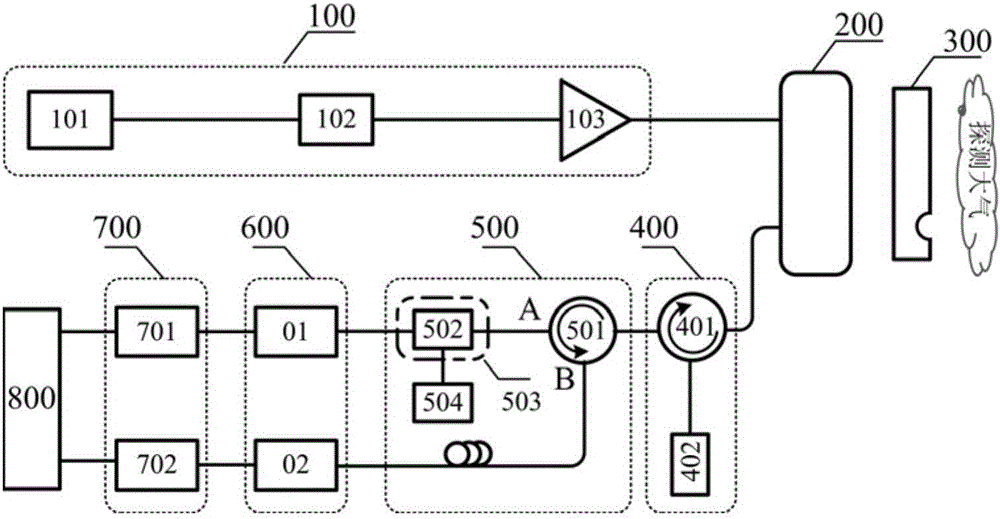
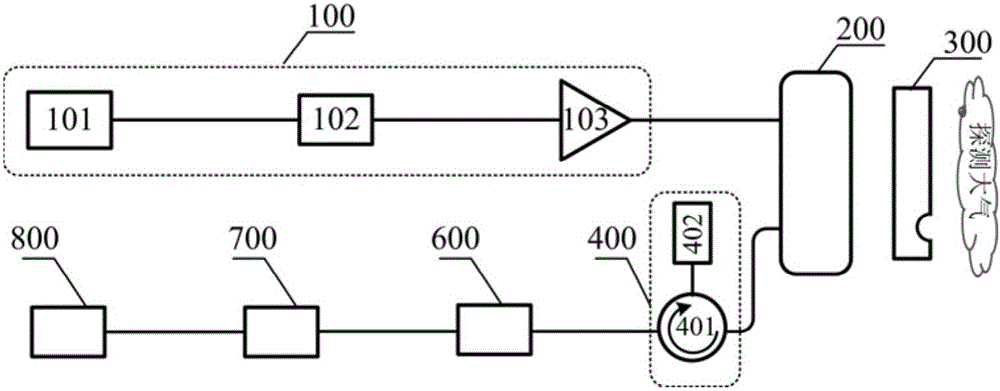
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
643 results about "Photon detection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
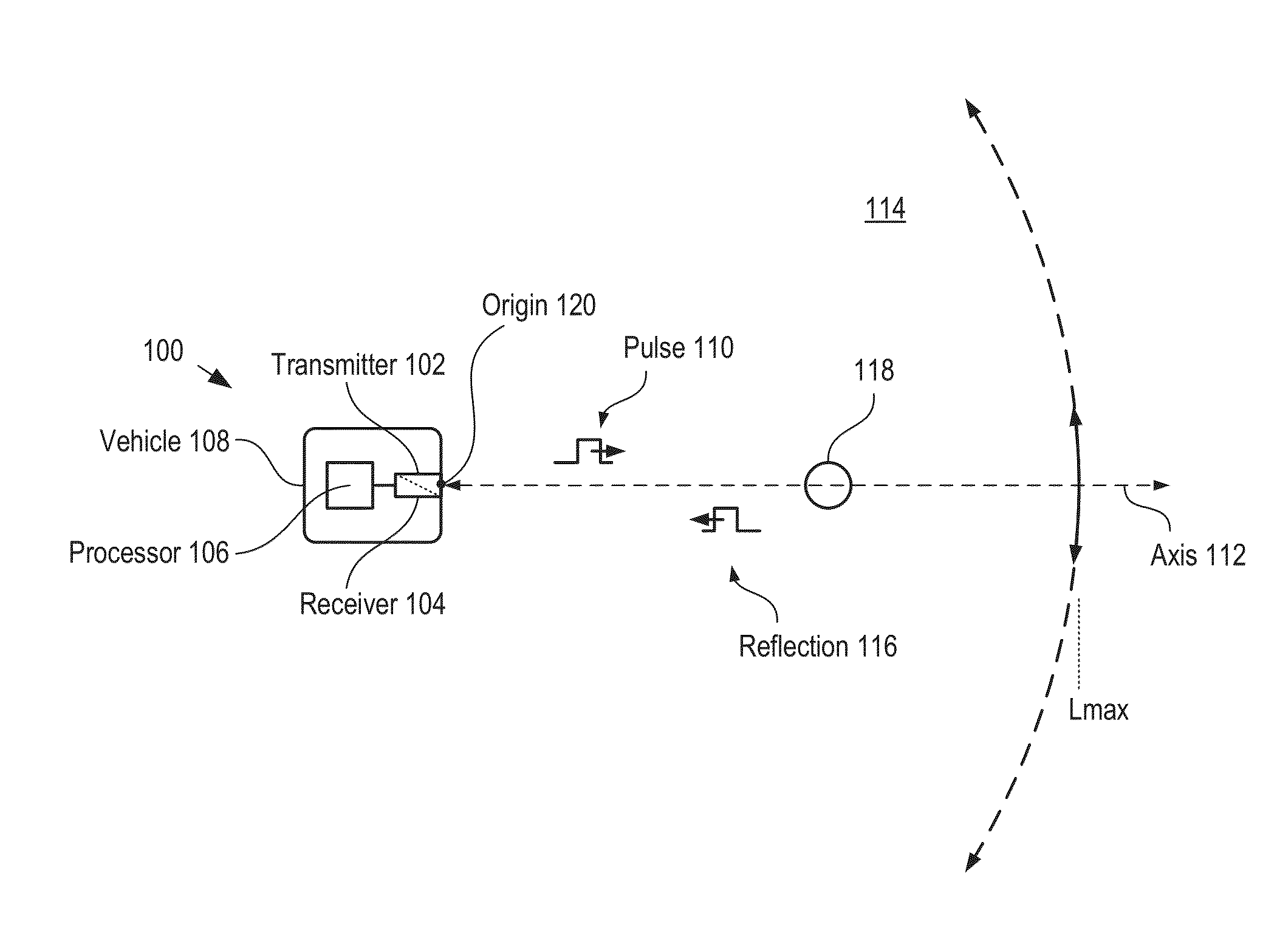
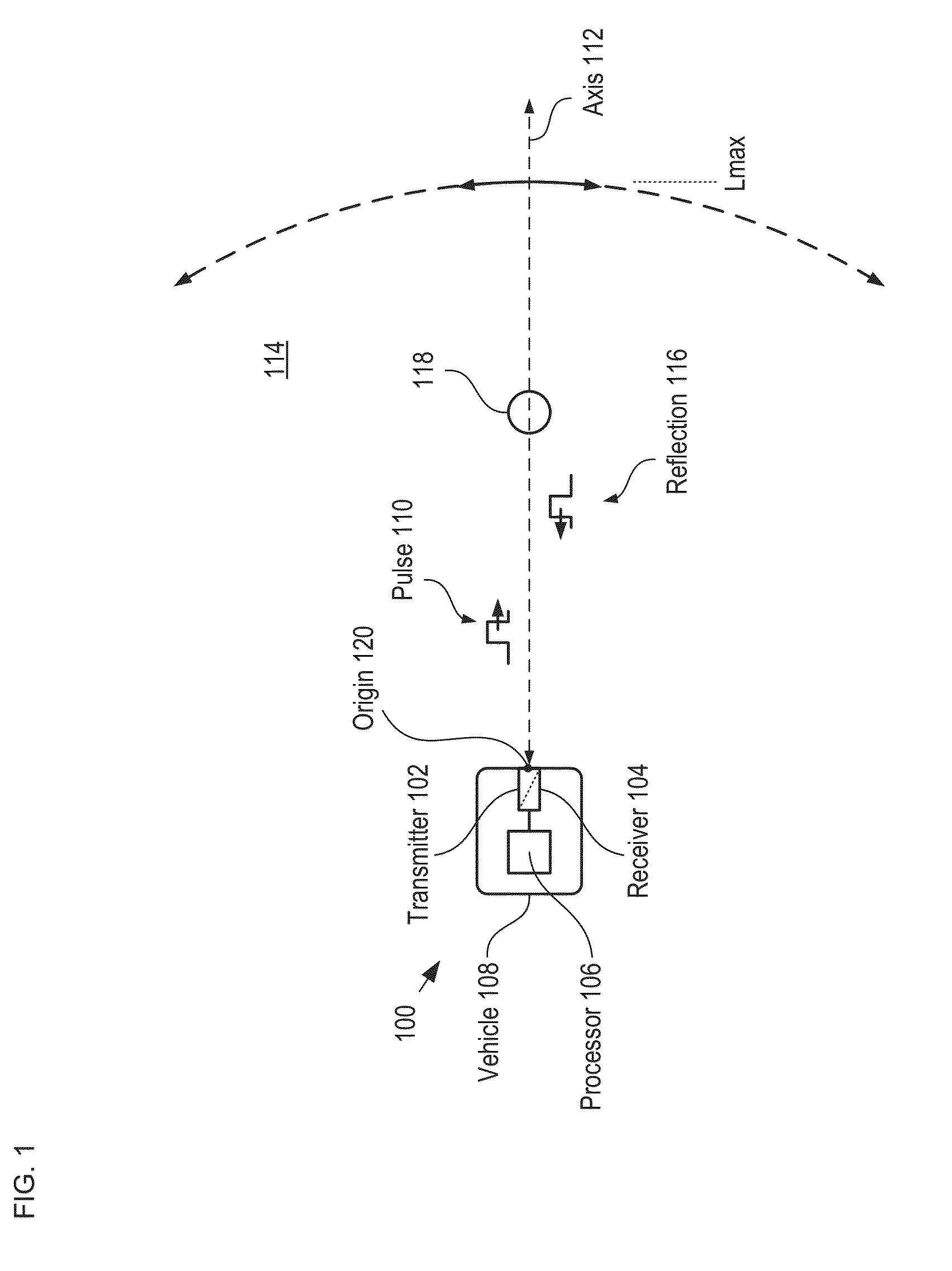
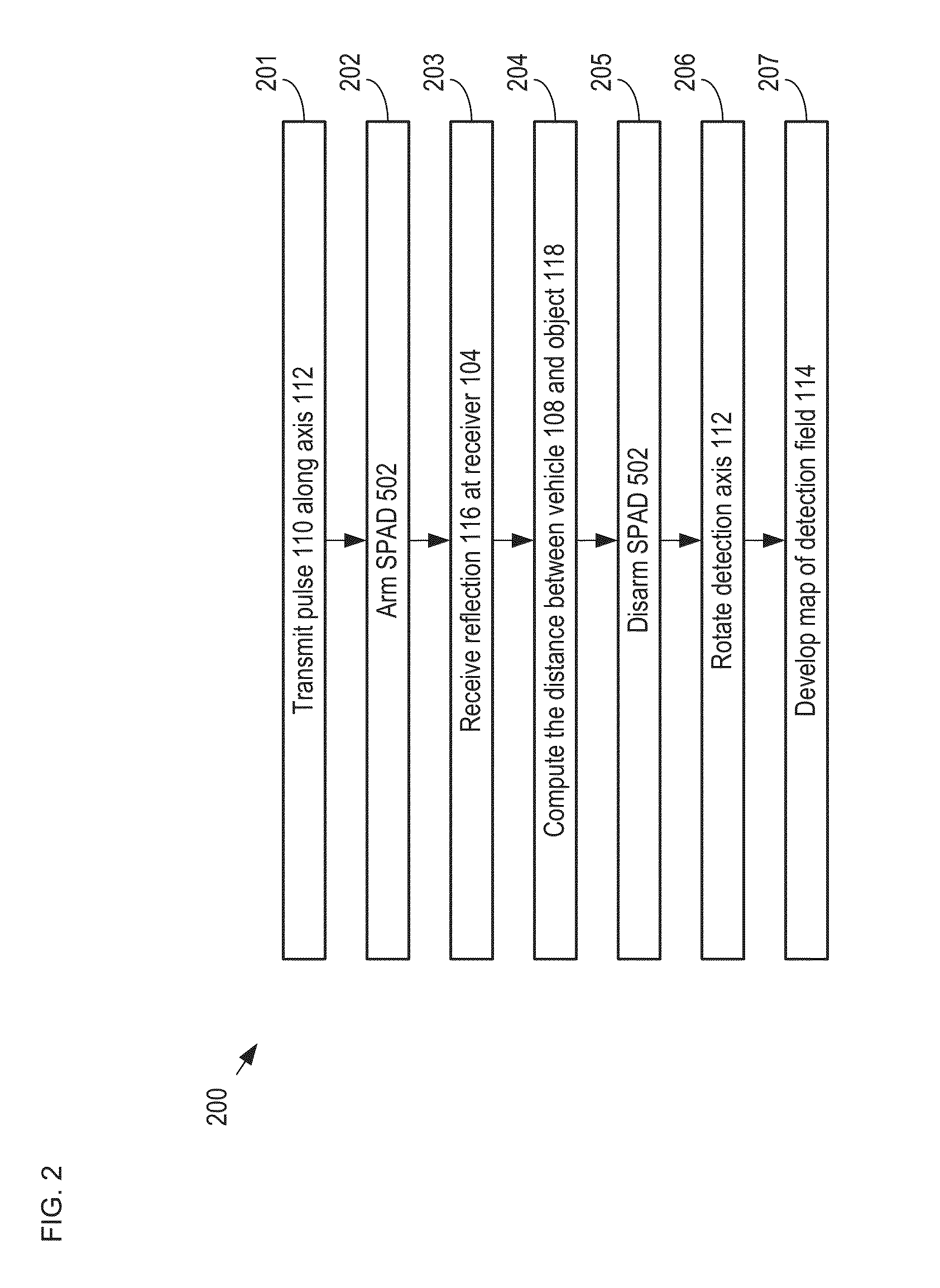
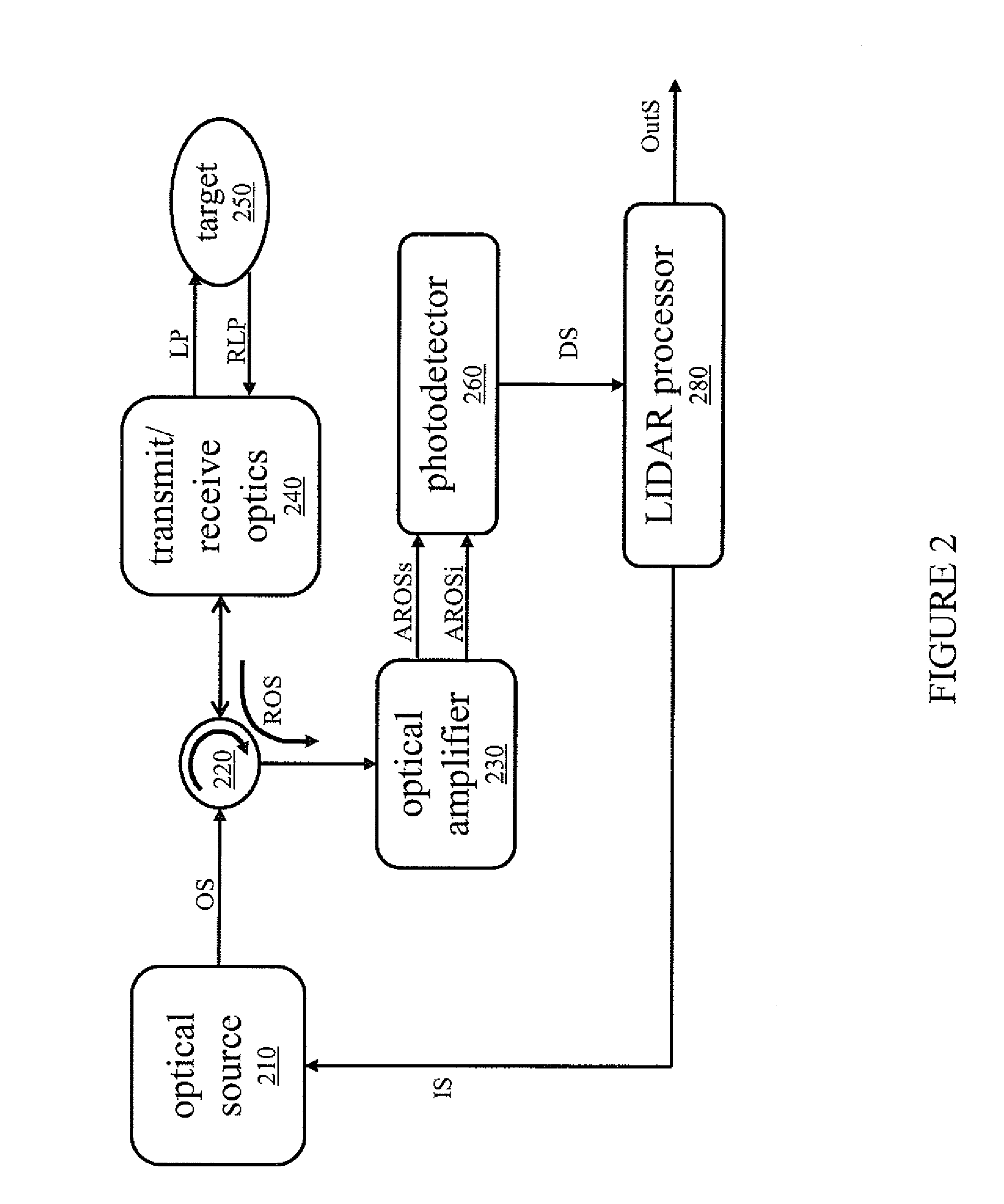
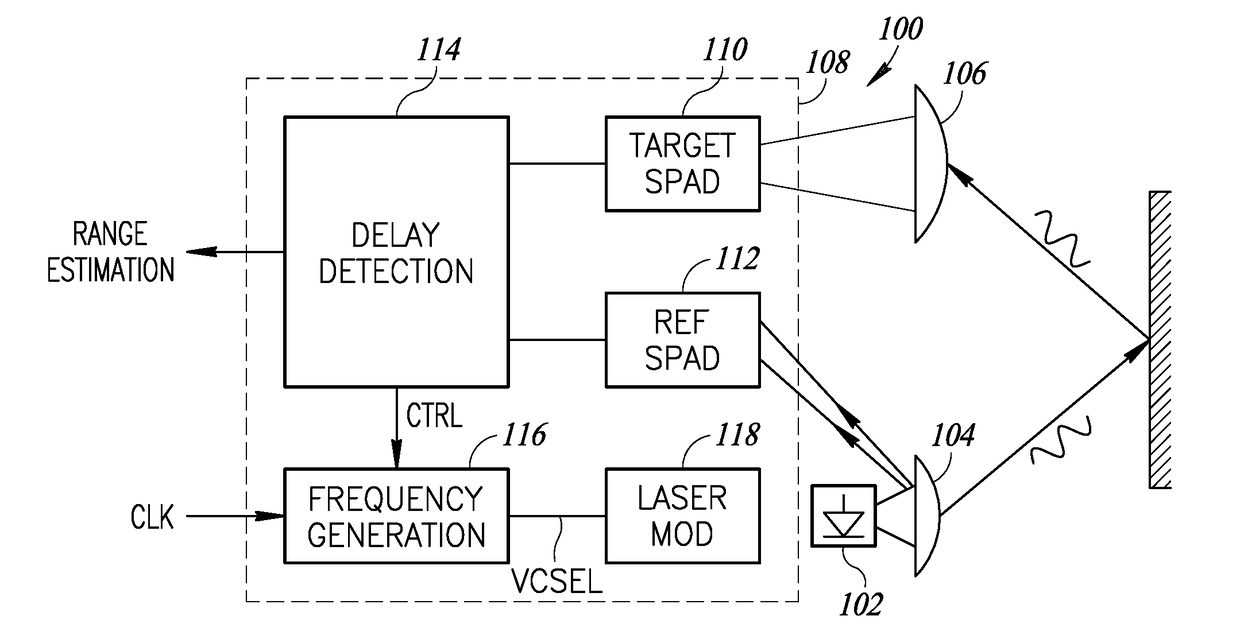
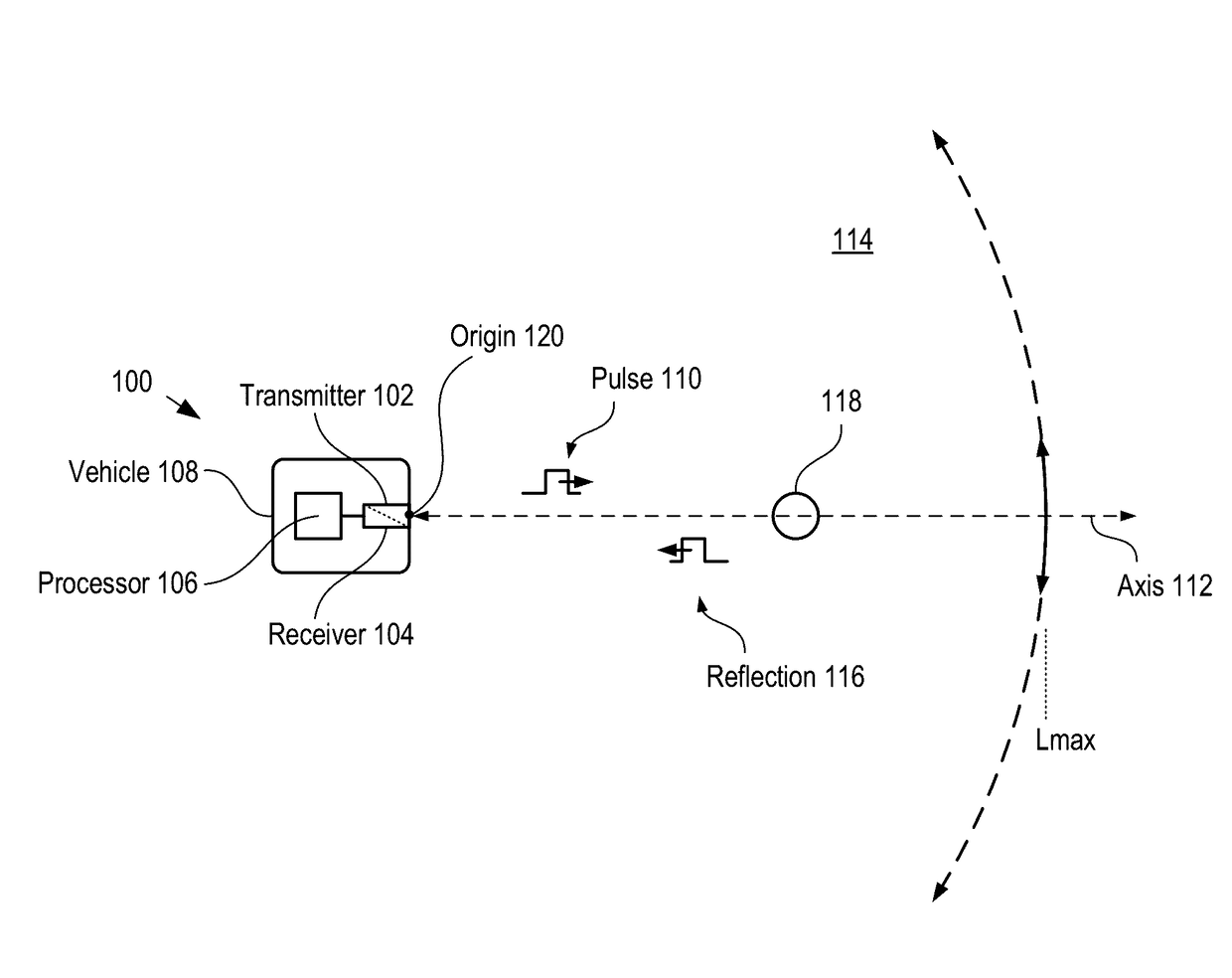
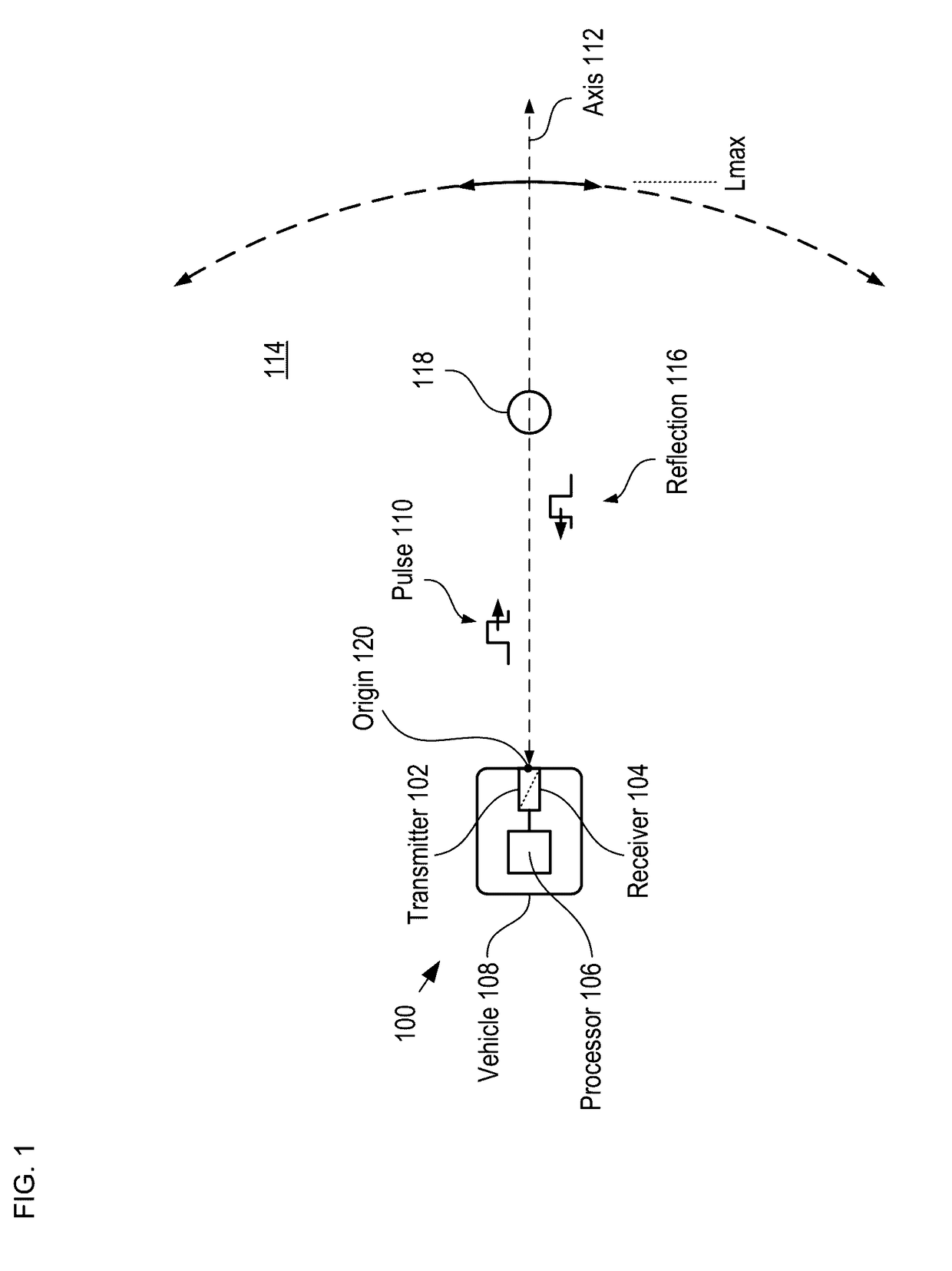
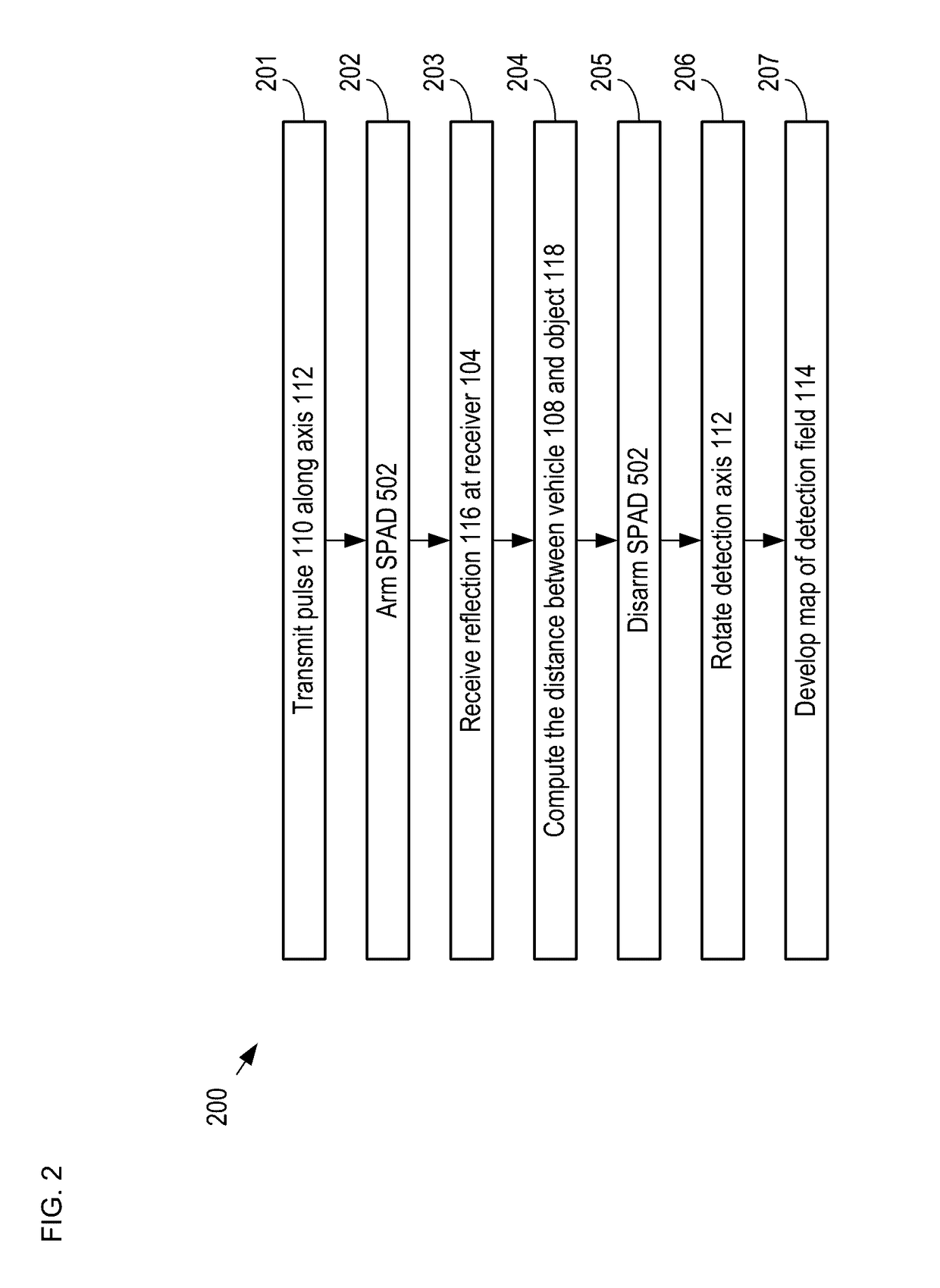
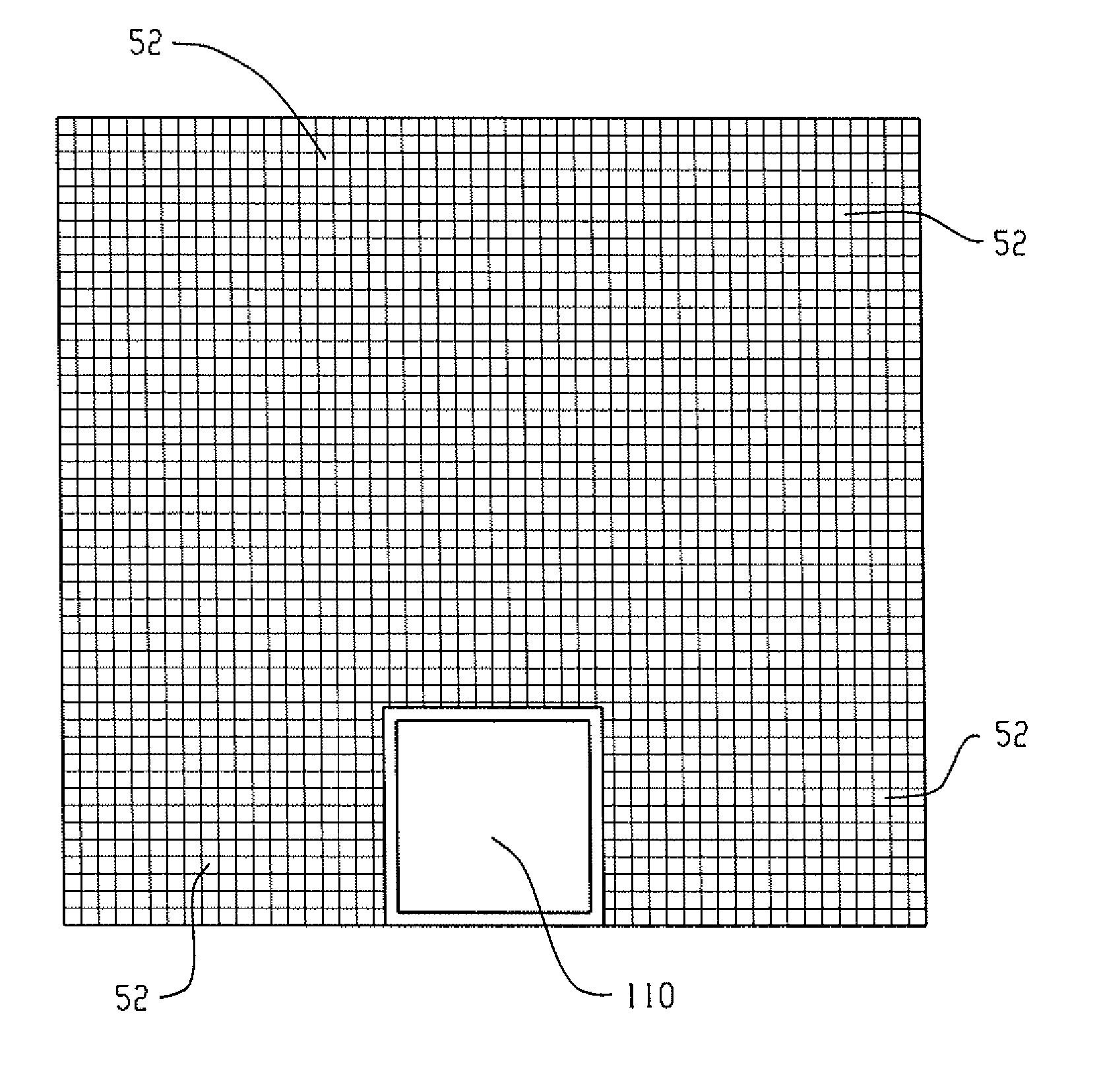
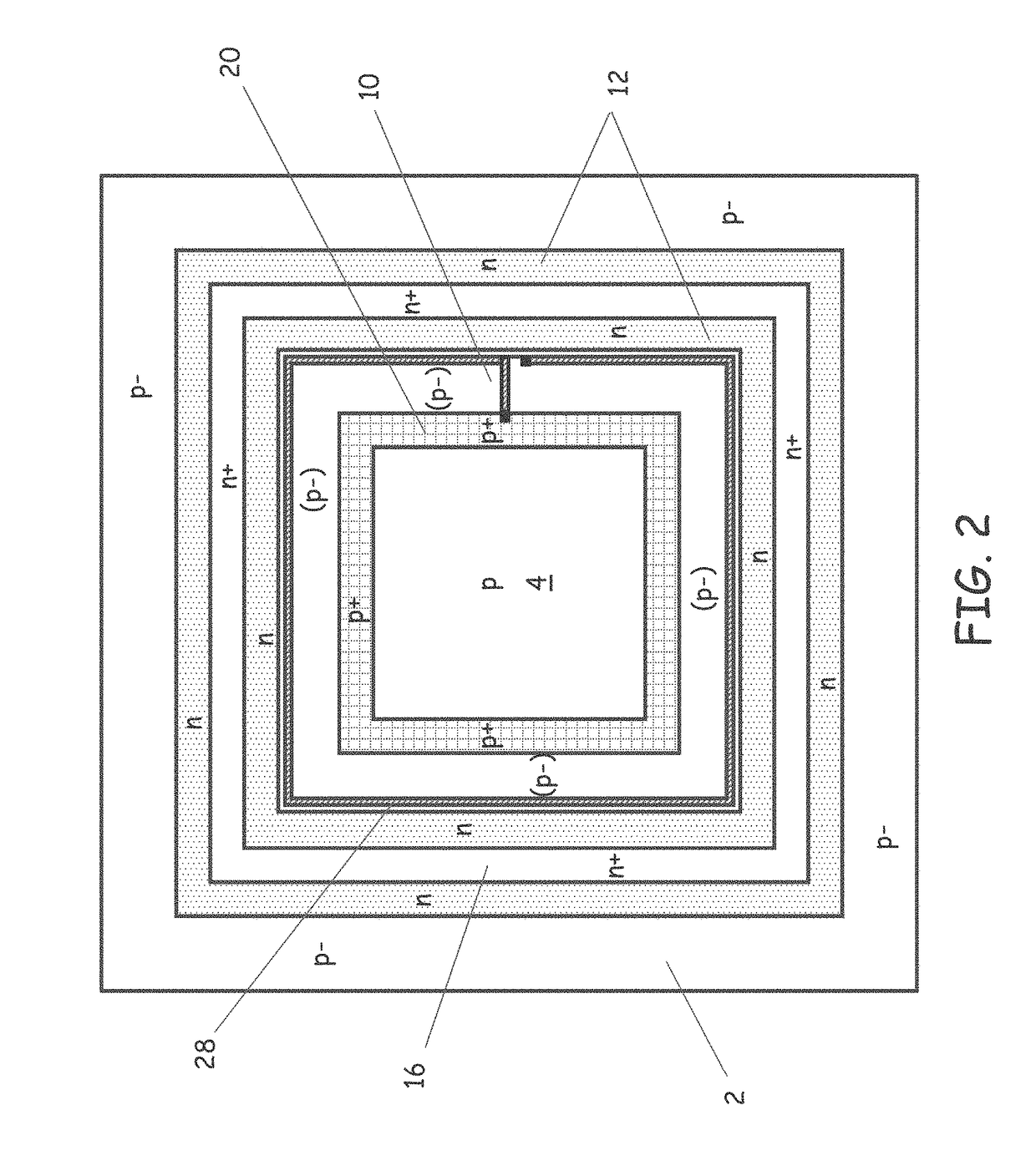
LiDAR System Comprising A Single-Photon Detector
ActiveUS20150192676A1Reduce impactHigh operating requirementsOptical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationWavelengthMulti dimensional
A method for developing a map of objects in a region surrounding a location is disclosed. The method includes interrogating the region along a detection axis with a series of optical pulses and detecting reflections of the optical pulses that originate at objects located along the detection axis. A multi-dimensional map of the region is developed by scanning the detection axis about the location in at least one dimension. The reflections are detected via a single-photon detector that is armed using a sub-gating scheme such that the single-photon detector selectively detects photons of reflections that originate only within each of a plurality of zones that collectively define the detection field. In some embodiments, the optical pulses have a wavelength within the range of 1350 nm to 1390 nm, which is a spectral range having a relatively high eye-safety threshold and a relatively low solar background.
Owner:LG INNOTEK CO LTD
Combined PET/MRI scanner
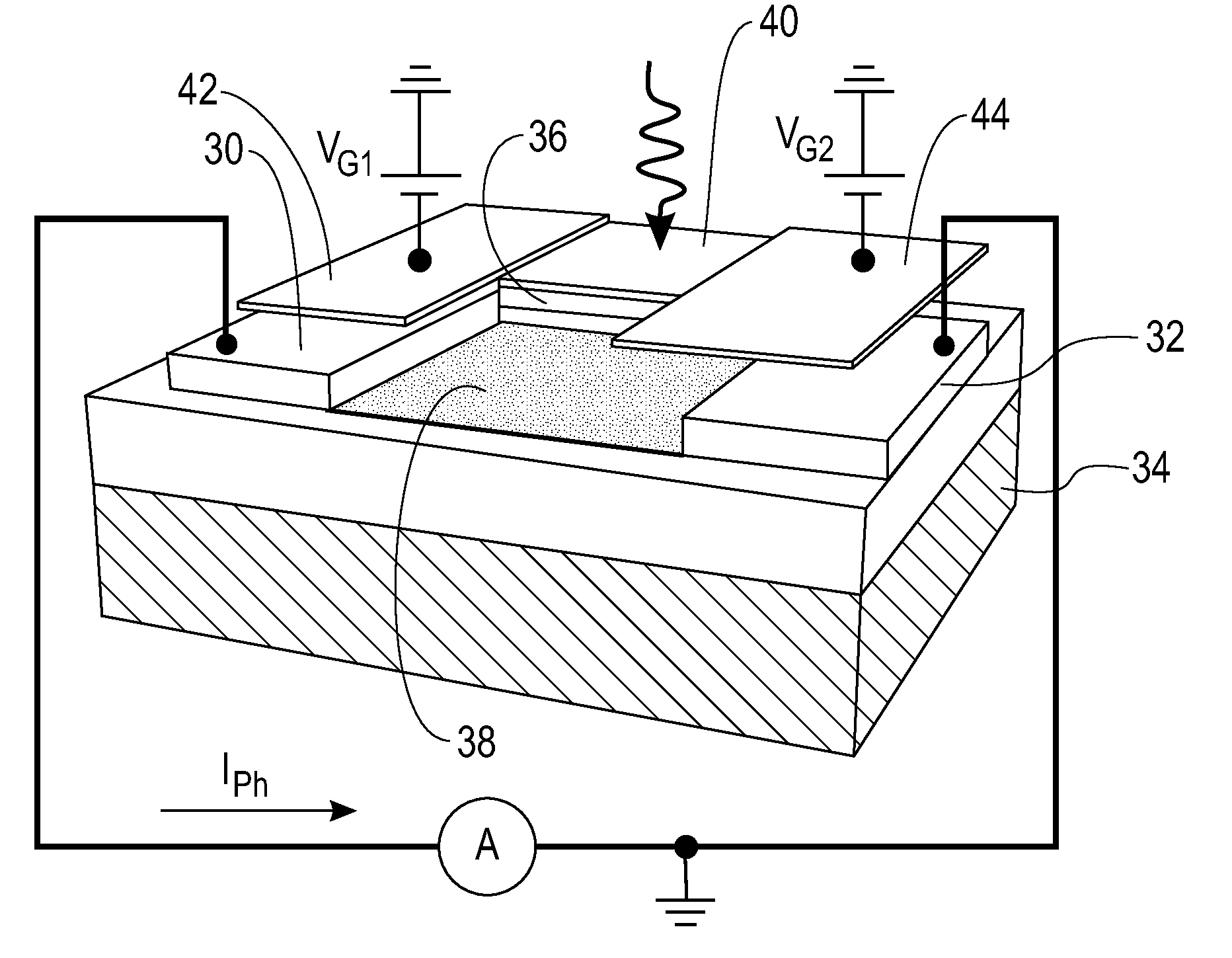
ActiveUS20050113667A1Reduce power consumptionExtension of timeMagnetic measurementsMaterial analysis by optical meansAudio power amplifierPhoton detection
A combined PET / MRI scanner generally includes a magnet for producing a magnetic field suitable for magnetic resonance imaging, a radiofrequency (RF) coil disposed within the magnetic field produced by the magnet and a ring tomograph disposed within the magnetic field produced by the magnet. The ring tomograph includes a scintillator layer for outputting at least one photon in response to an annihilation event, a detection array coupled to the scintillator layer for detecting the at least one photon outputted by the scintillator layer and for outputting a detection signal in response to the detected photon and a front-end electronic array coupled to the detection array for receiving the detection signal, wherein the front-end array has a preamplifier and a shaper network for conditioning the detection signal.
Owner:BROOKHAVEN SCI ASSOCS
Pulsed light optical rangefinder
ActiveUS20120075615A1Improve dynamic rangeAvoid saturationOptical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationPhoton detectionTime of flight
An optical rangefinder based on time-of-flight measurement, radiates pulsed light toward an object (70), and receives reflected light from the object, the receiver operating in a photon counting mode, so as to generate a pulse for a detected photon. There is a variable probability of a photon detection on the receiver, and a controller (370, 380, 390; 365, 470, 475, 380, 390; 570, 580, 590, 390) controls the photon detection probability of the receiver, based on a light level. By controlling the detection probability according to a light level, the receiver can have an increased dynamic range, and without the expense of using optical components. This can apply even while detecting very weak signals since the receiver can still be in a photon counting mode while the detection probability is controlled. The light level can be indicated by an output of the receiver itself, or by another detector external to the receiver.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
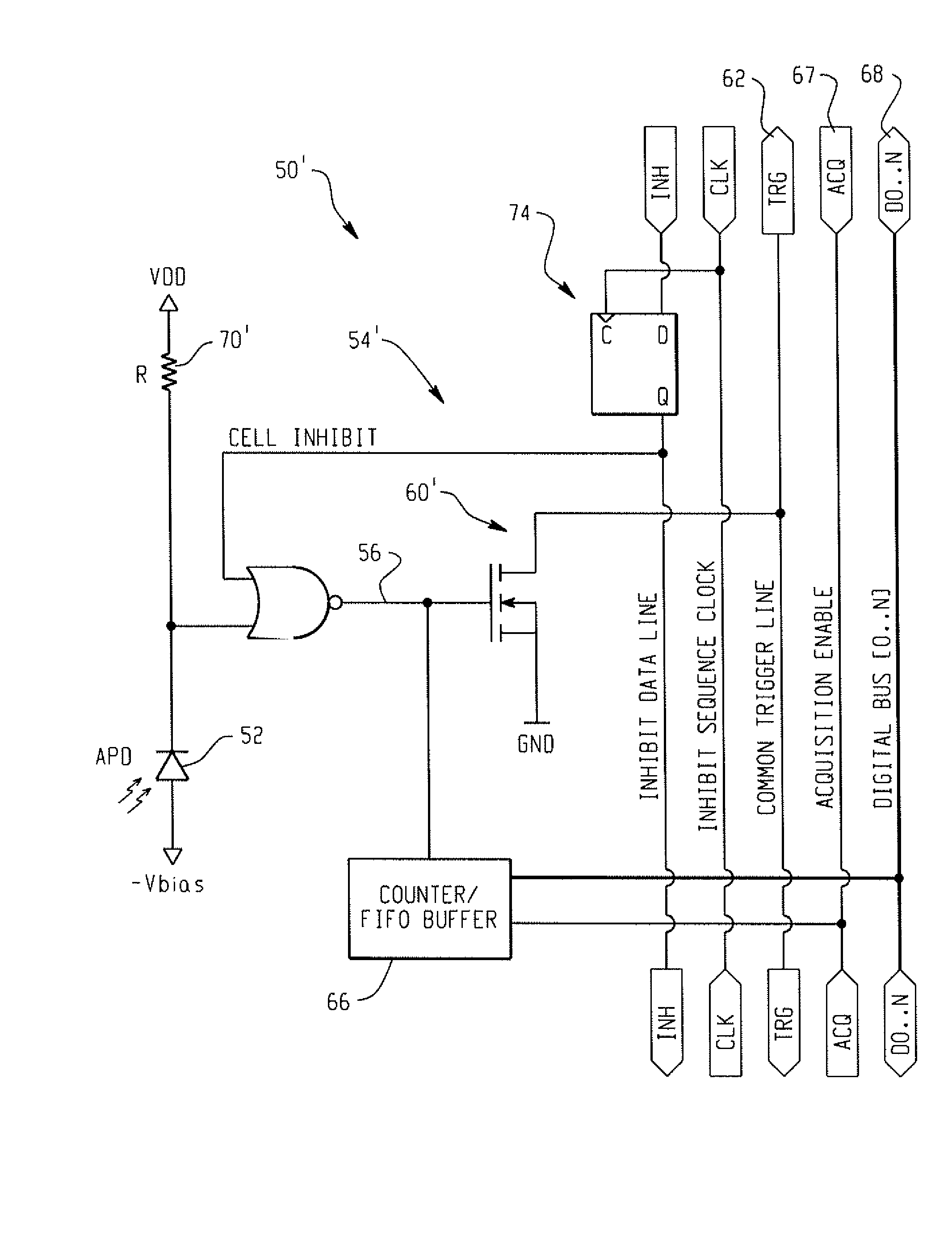
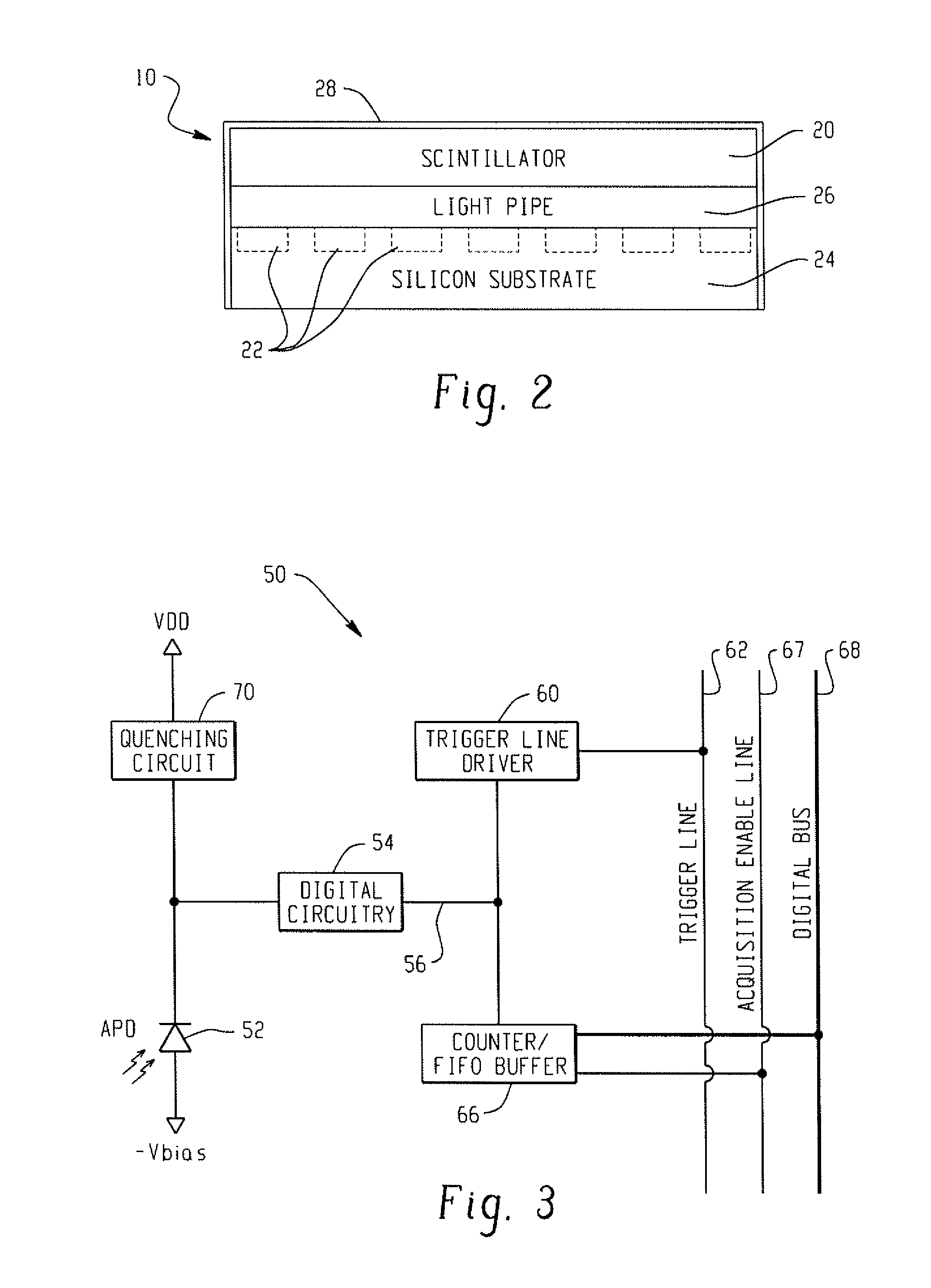
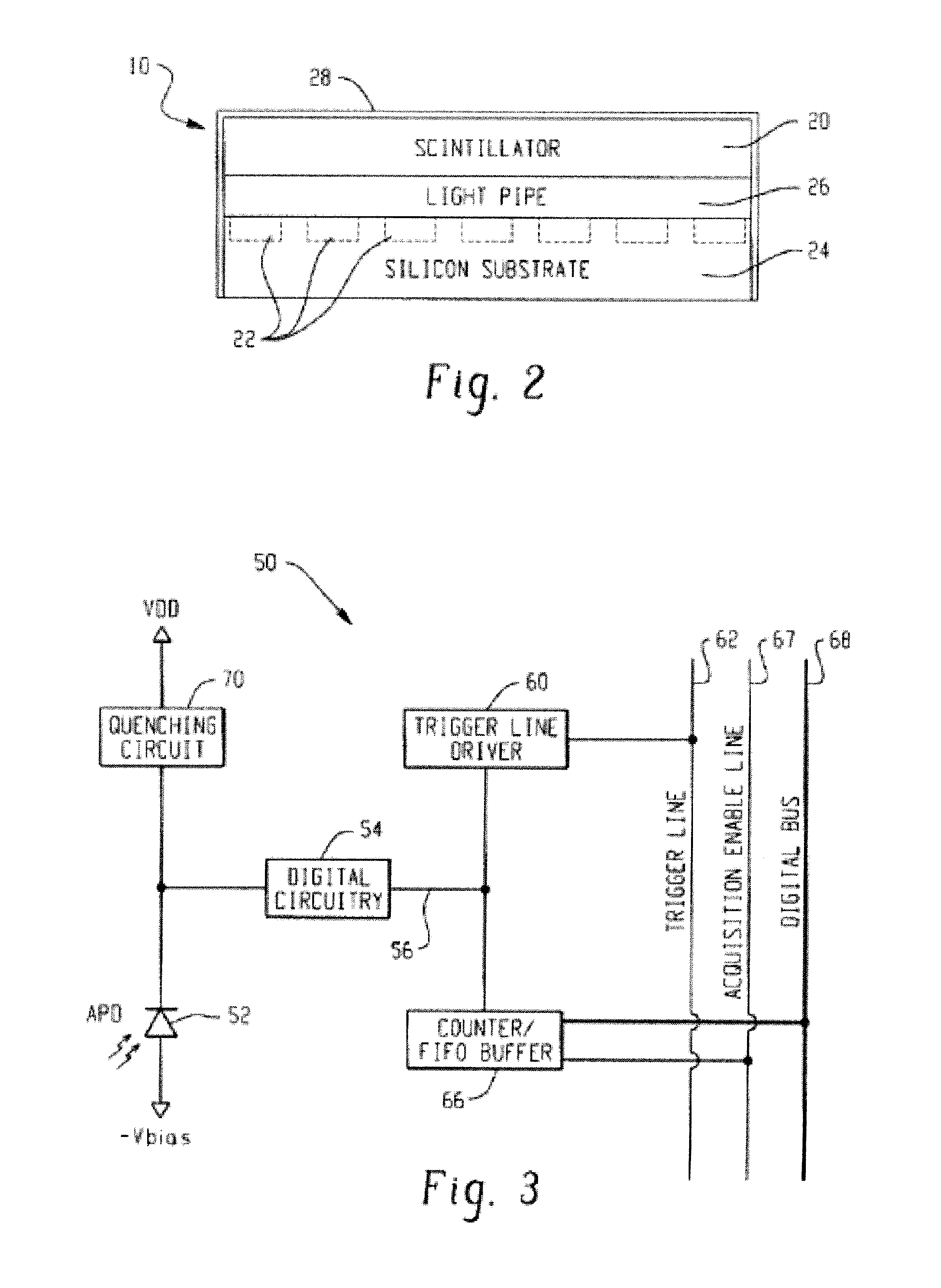
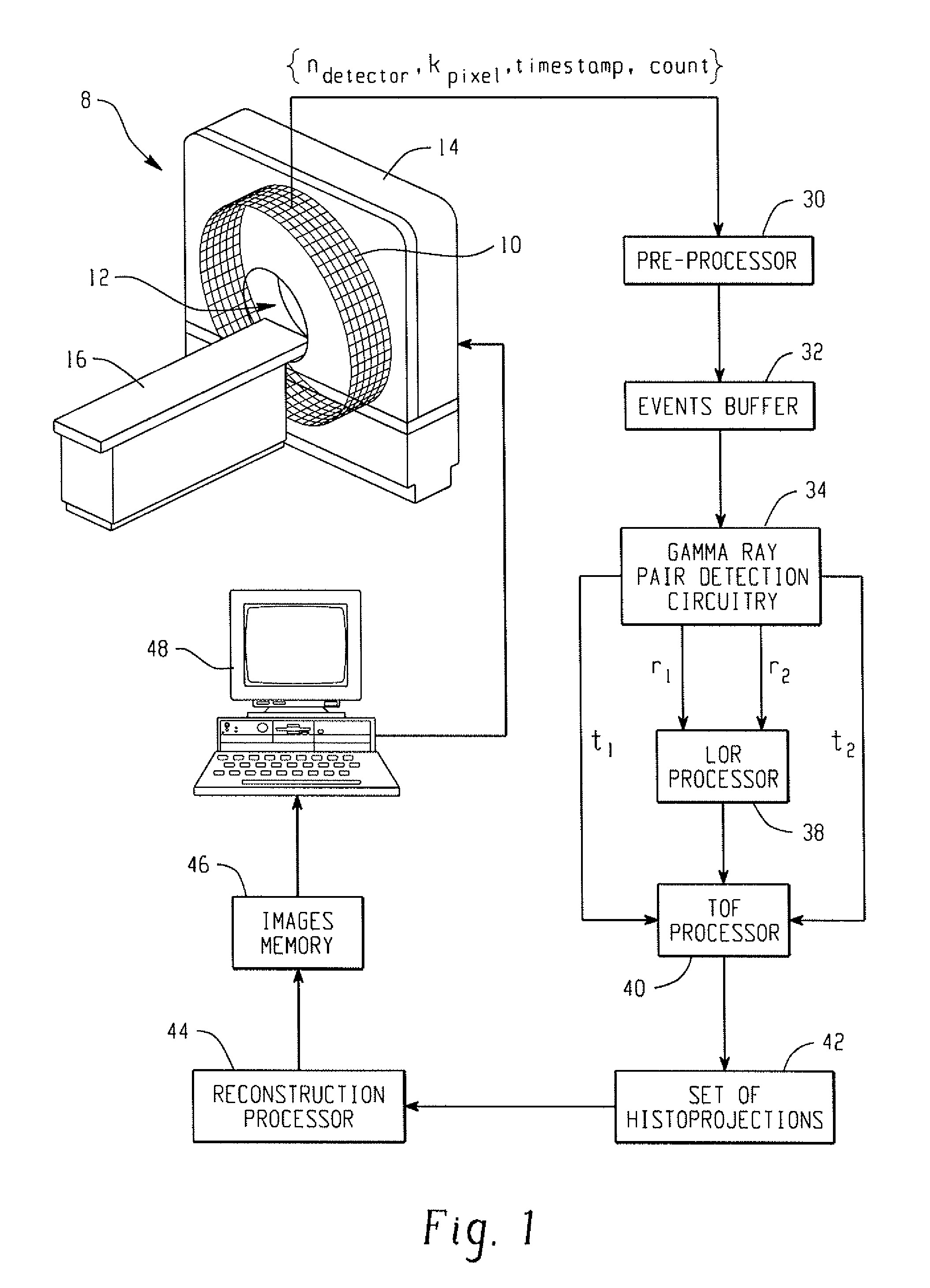
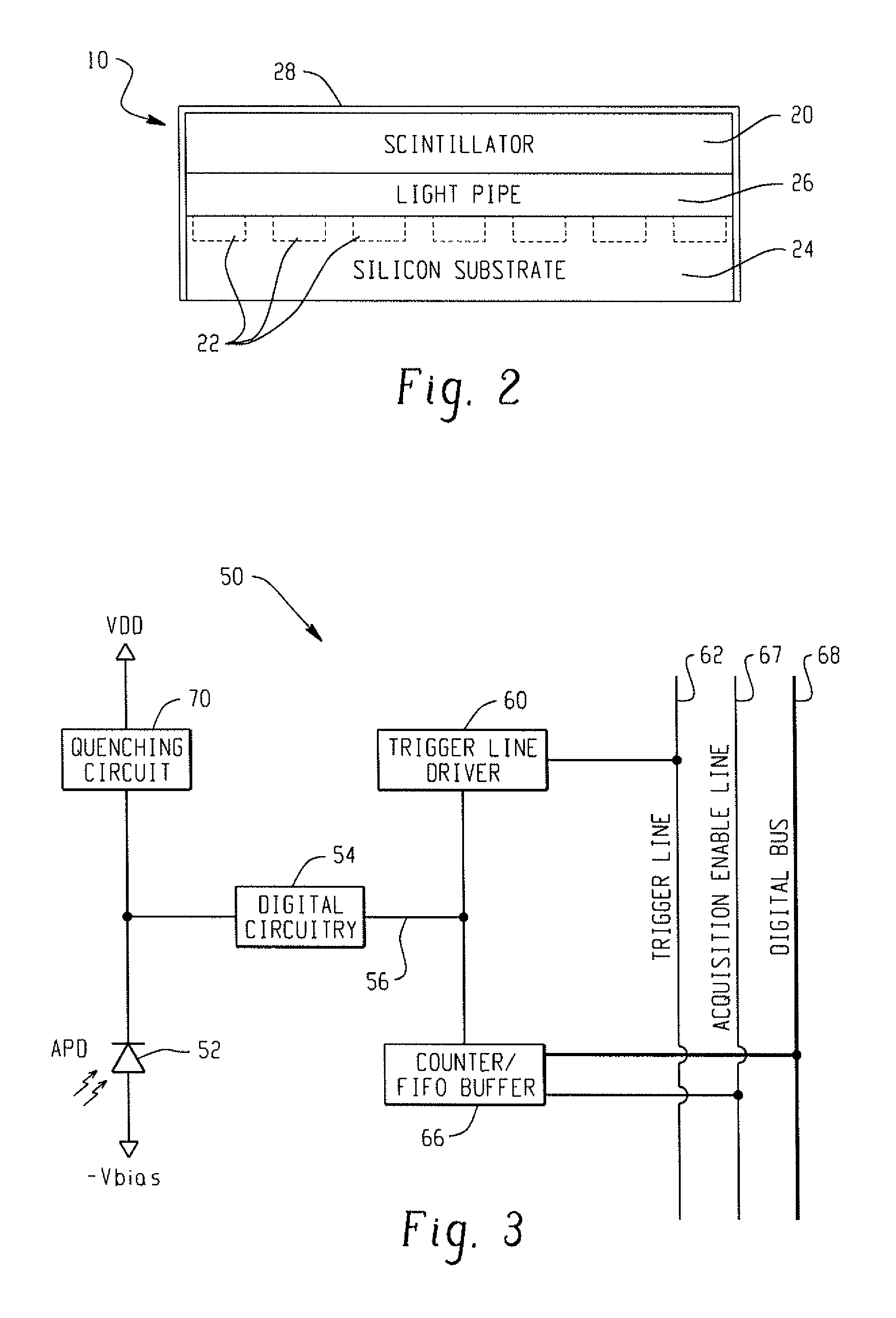
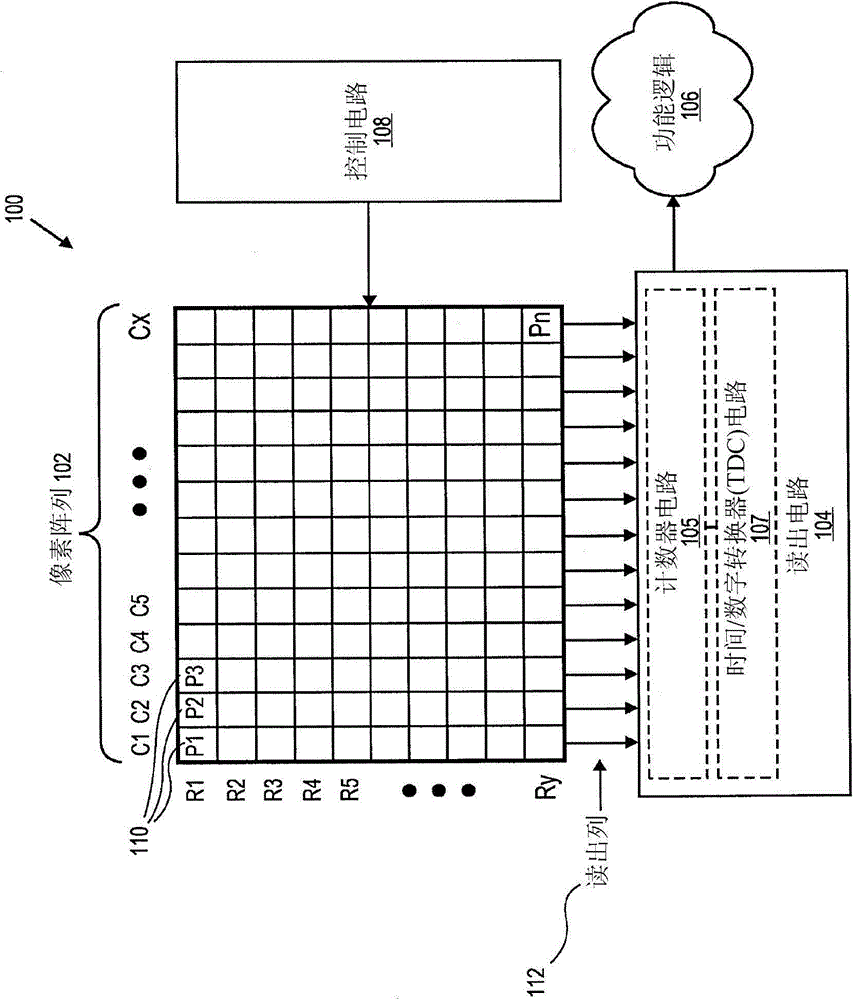
Digital silicon photomultiplier for TOF-PET
ActiveUS20080203309A1High data-rate radiation detectionImproved spatial detector resolutionMaterial analysis by optical meansTomographyQuiescent stateSilicon photomultiplier
A radiation detector includes an array of detector pixels each including an array of detector cells. Each detector cell includes a photodiode biased in a breakdown region and digital circuitry coupled with the photodiode and configured to output a first digital value in a quiescent state and a second digital value responsive to photon detection by the photodiode. Digital triggering circuitry is configured to output a trigger signal indicative of a start of an integration time period responsive to a selected number of one or more of the detector cells tranisitioning from the first digital value to the second digital value. Readout digital circuitry accumulates a count of a number of transitions of detector cells of the array of detector cells from the first digital state to the second digital state over the integration time period.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
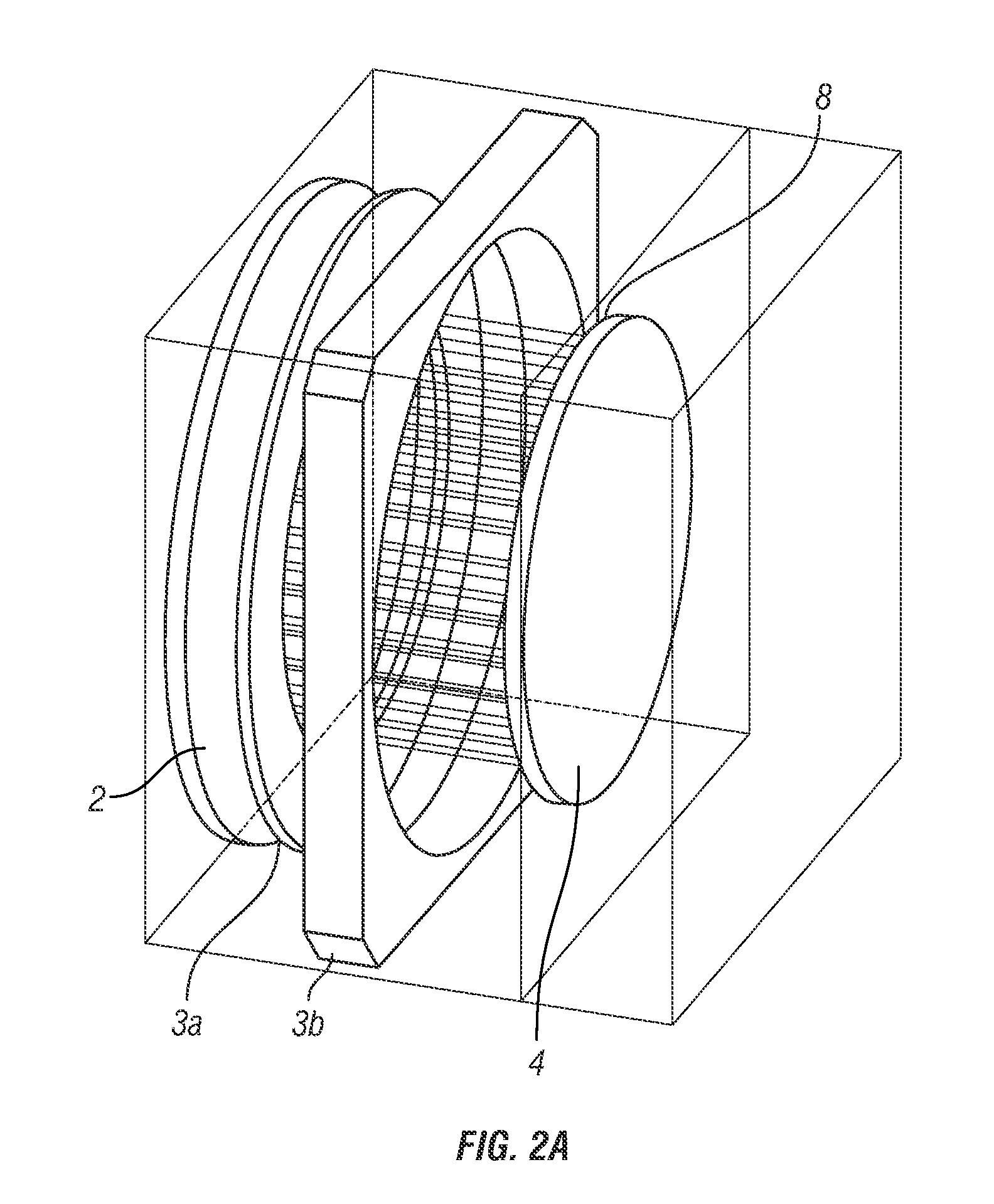
Superconducting Single Photon Detector
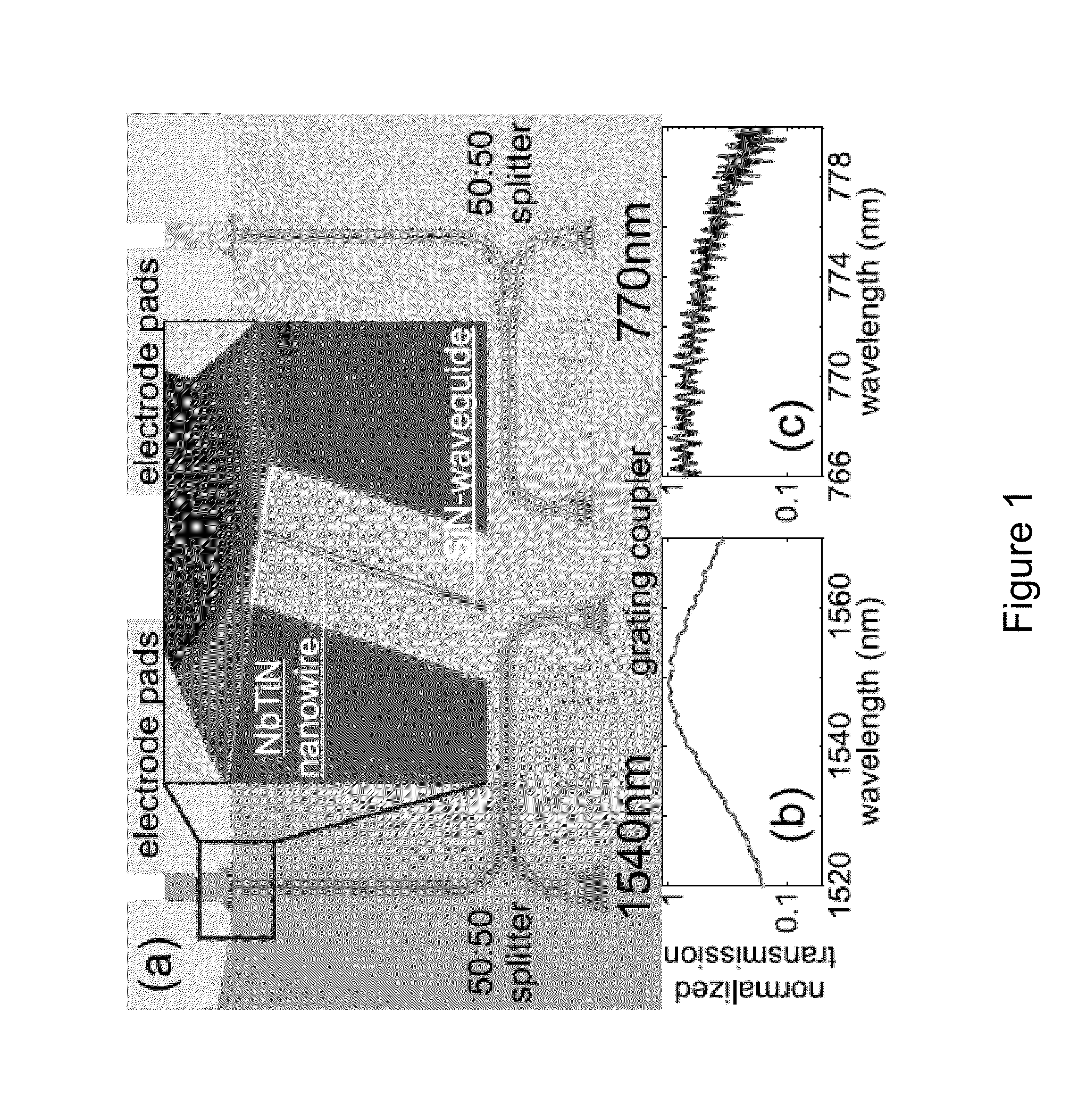
The present invention provides a device and system for high-efficiency and low-noise detection of single photons within the visible and infrared spectrum. In certain embodiments, the device of the invention can be integrated within photonic circuits to provide on-chip photon detection. The device comprises a traveling wave design comprising a waveguide layer and a superconducting nanowire atop of the waveguide.
Owner:YALE UNIV
System and method for nonlinear optical devices
InactiveUS9000347B2High sensitivityRadiation pyrometryPhase-affecting property measurementsAudio power amplifierPhoton detection
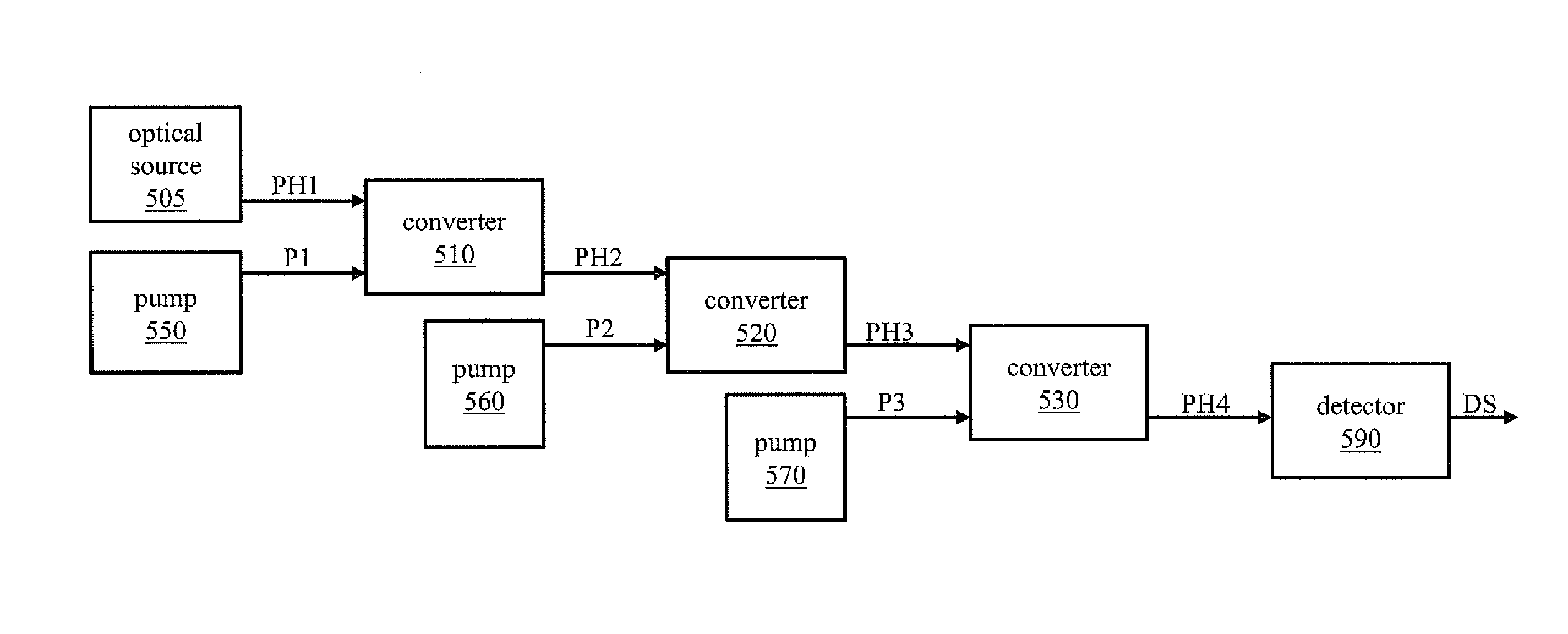
Systems for enhancing the sensitivity of detecting an optical signal using nonlinear optics and method of performing the same. In one embodiment, a single-photon detection system includes an optical amplifier realized in a waveguide, and a photodetector coupled to an output of the optical amplifier. A light detection and ranging system includes the optical amplifier coupled to an optical source and one photodetector. In another embodiment, a photodetection system includes a plurality of optical frequency converters, coupled to an optical source, that sequentially convert a wavelength of photons of the optical source to a final wavelength, and a single-photon photodetector coupled to the optical frequency converters to detect single photons produced by the optical source. In another embodiment, an optical sensor includes an optical pump, and a transducer including an optical ring cavity coupled to the optical pump and configured to utilize optical four-wave mixing to detect an external stimulus.
Owner:TELCORDIA TECHNOLOGIES INC
Method and system for fluorescence lifetime based sequencing
ActiveUS20150293021A1Wave based measurement systemsMicrobiological testing/measurementResistFlow cell
An integrated detection, flow cell and photonics (DFP) device is provided that comprises a substrate having an array of pixel elements that sense photons during active periods. The substrate and pixel elements form an IC photon detection layer. At least one wave guide is formed on the IC photo detection layer as a photonics layer. An optical isolation layer is formed over at least a portion of the wave guide. A collection of photo resist (PR) walls patterned to define at least one flow cell channel that is configured to direct fluid along a fluid flow path. The wave guides align to extend along the fluid flow path. The flow cell channel is configured to receive samples at sample sites that align with the array of pixel elements.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Sample collection and bioluminescent analysis system
ActiveUS20140004548A1Promote useReduce power consumptionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPhoton detectionPhoton counter
Methods and apparatus for evaluating the quality of an environment or process by measuring light emitted from a bioluminescent sample containing ATP, ADP, or alkaline phosphatase. The apparatus comprises a sample collection and analysis system used to collect a sample, mix reagents, react the sample, and collect it in a measurement chamber. The system includes an instrument having a photon detection assembly for use with the sample testing device and one or more probe assemblies that optically cooperate with the instrument. The instrument includes a dark chamber with a reflective interior surface which may be concave or preferably spherical, and a photon detection sensor such as a multi-pixel photon counter sensor. A substantially transparent portion of the probe assembly, and liquid contained therein, focus bioluminescence toward the photon detection sensor.
Owner:BIOCONTROL SYST
Digital silicon photomultiplier for TOF PET
ActiveUS8395127B1High data-rate radiation detectionImproved spatial detector resolutionSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansQuiescent stateSilicon photomultiplier
A radiation detector includes an array of detector pixels each including an array of detector cells. Each detector cell includes a photodiode biased in a breakdown region and digital circuitry coupled with the photodiode and configured to output a first digital value in a quiescent state and a second digital value responsive to photon detection by the photodiode. Digital triggering circuitry is configured to output a trigger signal indicative of a start of an integration time period responsive to a selected number of one or more of the detector cells transitioning from the first digital value to the second digital value. Readout digital circuitry accumulates a count of a number of transitions of detector cells of the array of detector cells from the first digital state to the second digital state over the integration time period.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
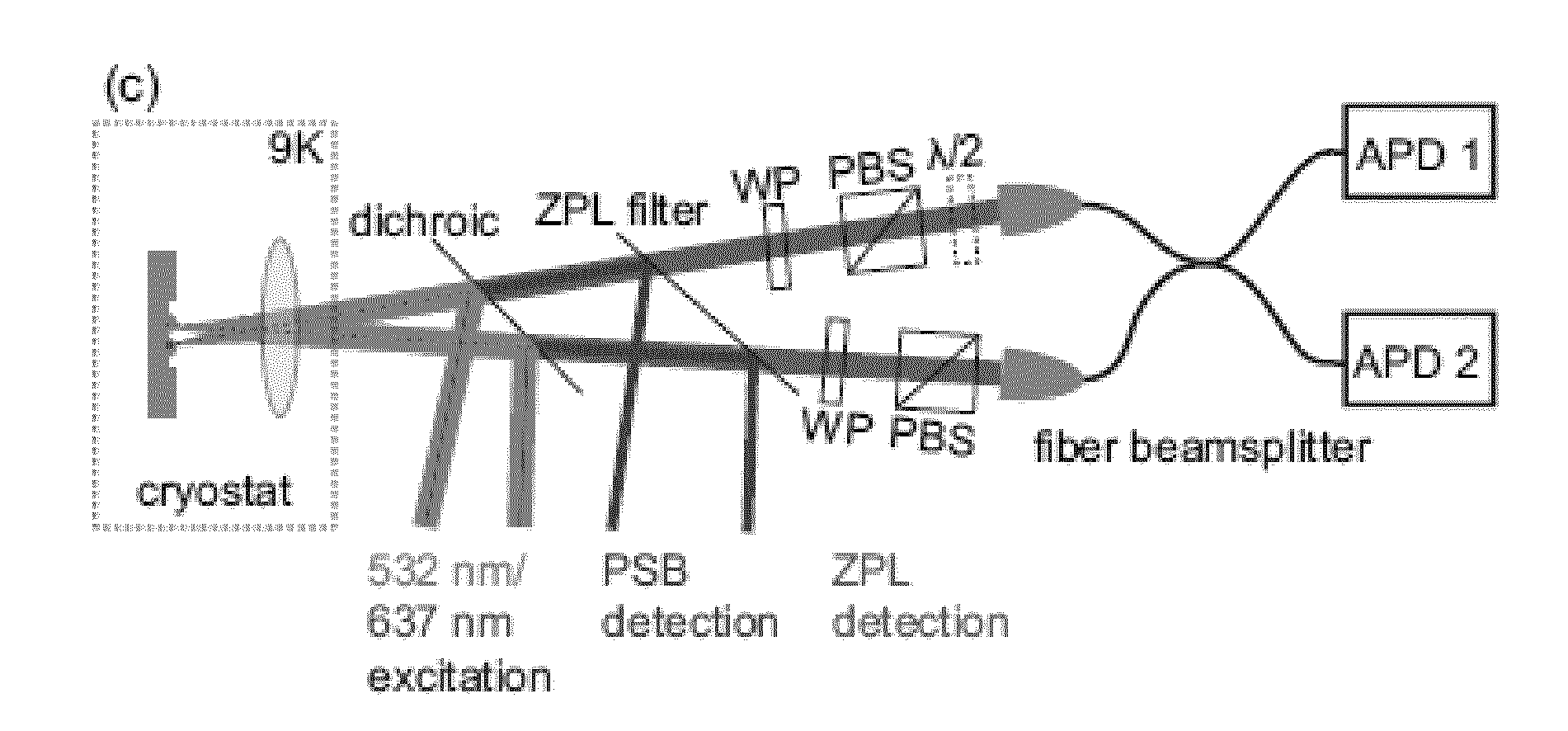
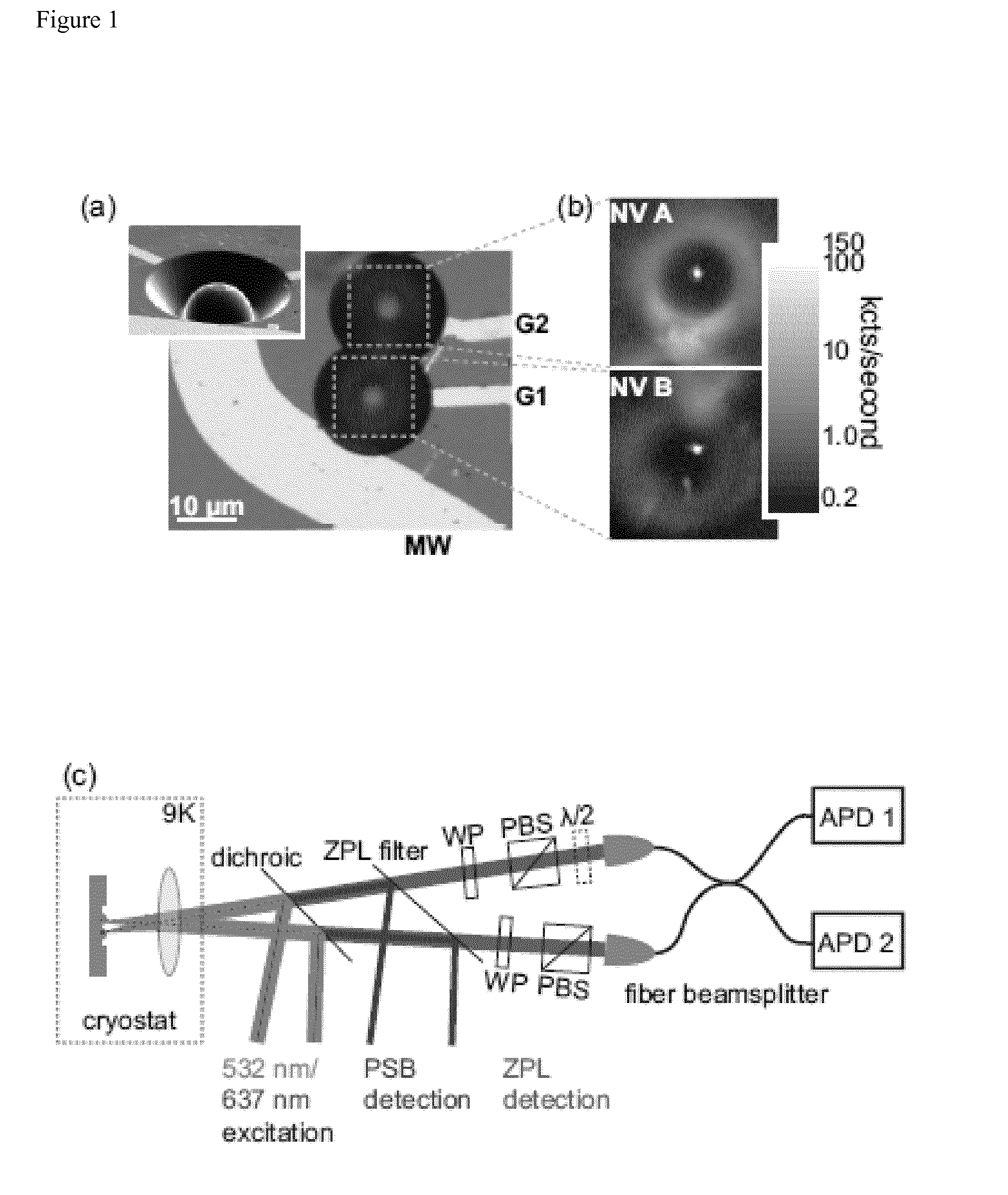
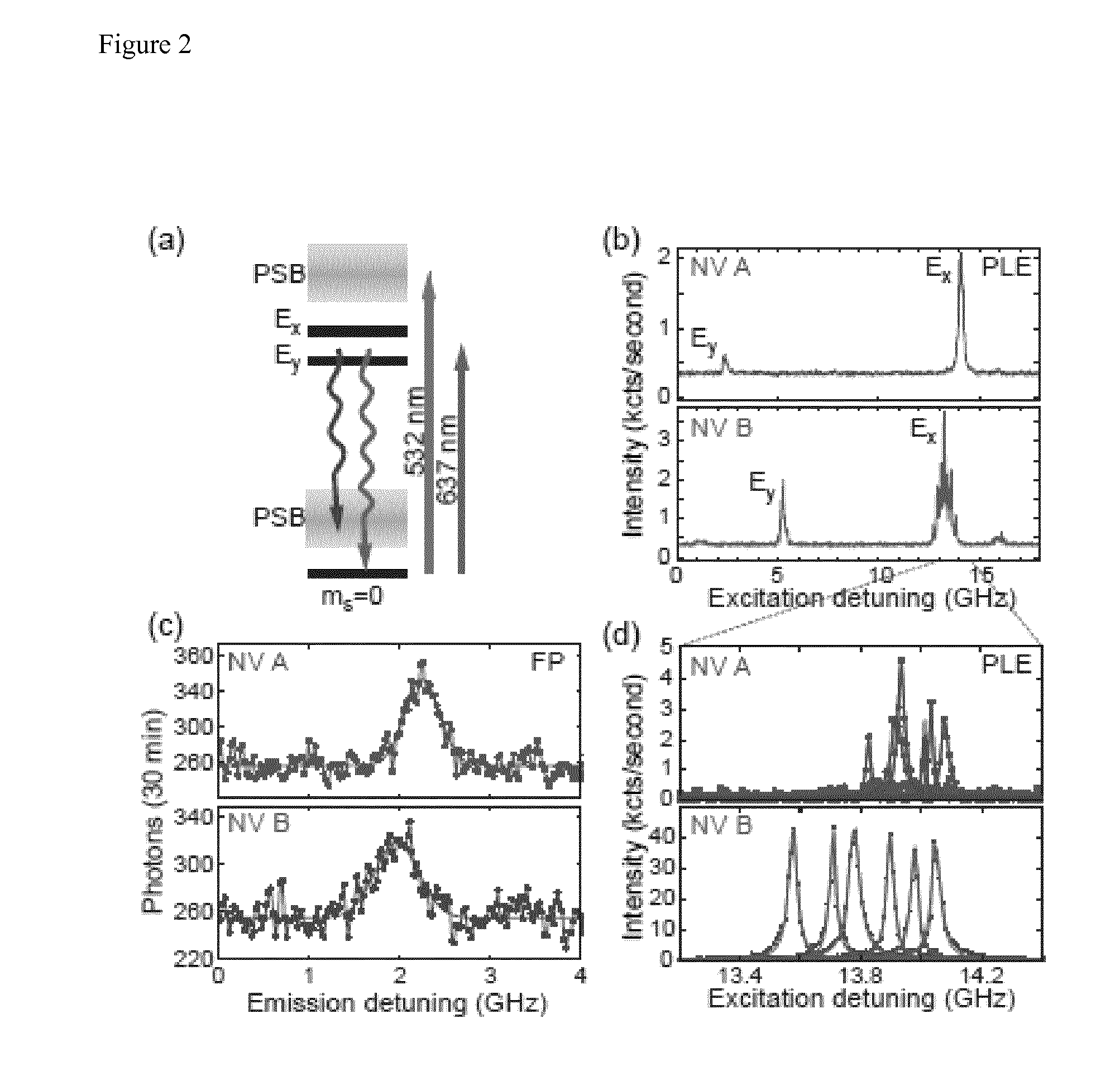
Quantum processing device
ActiveUS20140291490A1High efficiency in photon collectionAttenuation bandwidthQuantum computersNanoinformaticsPhoton emissionPhoton detection
A device for achieving multi-photon interference, said device comprising: at least two solid state photon emitters, each solid state photon emitter comprising nuclear and electron spin states coupled together, each solid state photon emitter being configured to produce photon emission comprising a photon emission peak, wherein the photon emission peaks from different solid state photon emitters have a first frequency difference between peak intensities, and wherein the electron spin states of each solid state photon emitter are resolvable; an excitation arrangement configured to individually address the at least two solid state photon emitters; a plurality of optical out coupling structures wherein each solid state photon emitter is provided with an associated optical out coupling structure; a tuning arrangement configured to reduce the first frequency difference between the peak intensities of the photon emission peaks from the at least two solid state photon emitters to a second frequency difference which is smaller than the first frequency difference; a photon interference arrangement configured to overlap photon emissions from the at least two solid state emitters after tuning; and a detector arrangement configured to detect photon emissions from the at least two solid state emitters after tuning and passing through the photon interference arrangement, wherein the detector arrangement is configured to resolve sufficiently small differences in photon detection times that tuned photon emissions from the at least two solid state emitters are quantum mechanically indistinguishable resulting in quantum interference between indistinguishable photon emissions from different solid state photon emitters.
Owner:ELEMENT SIX TECH LTD
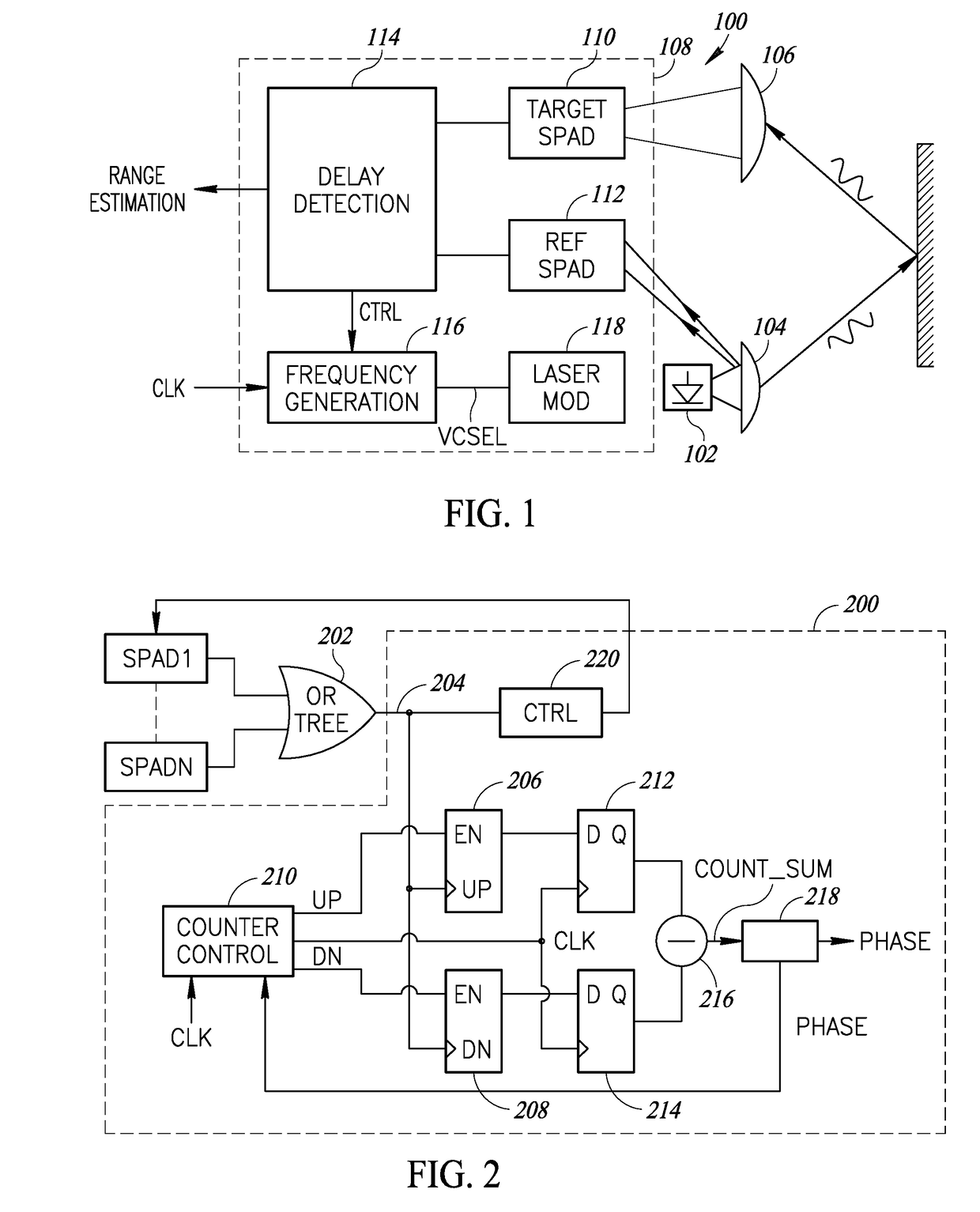
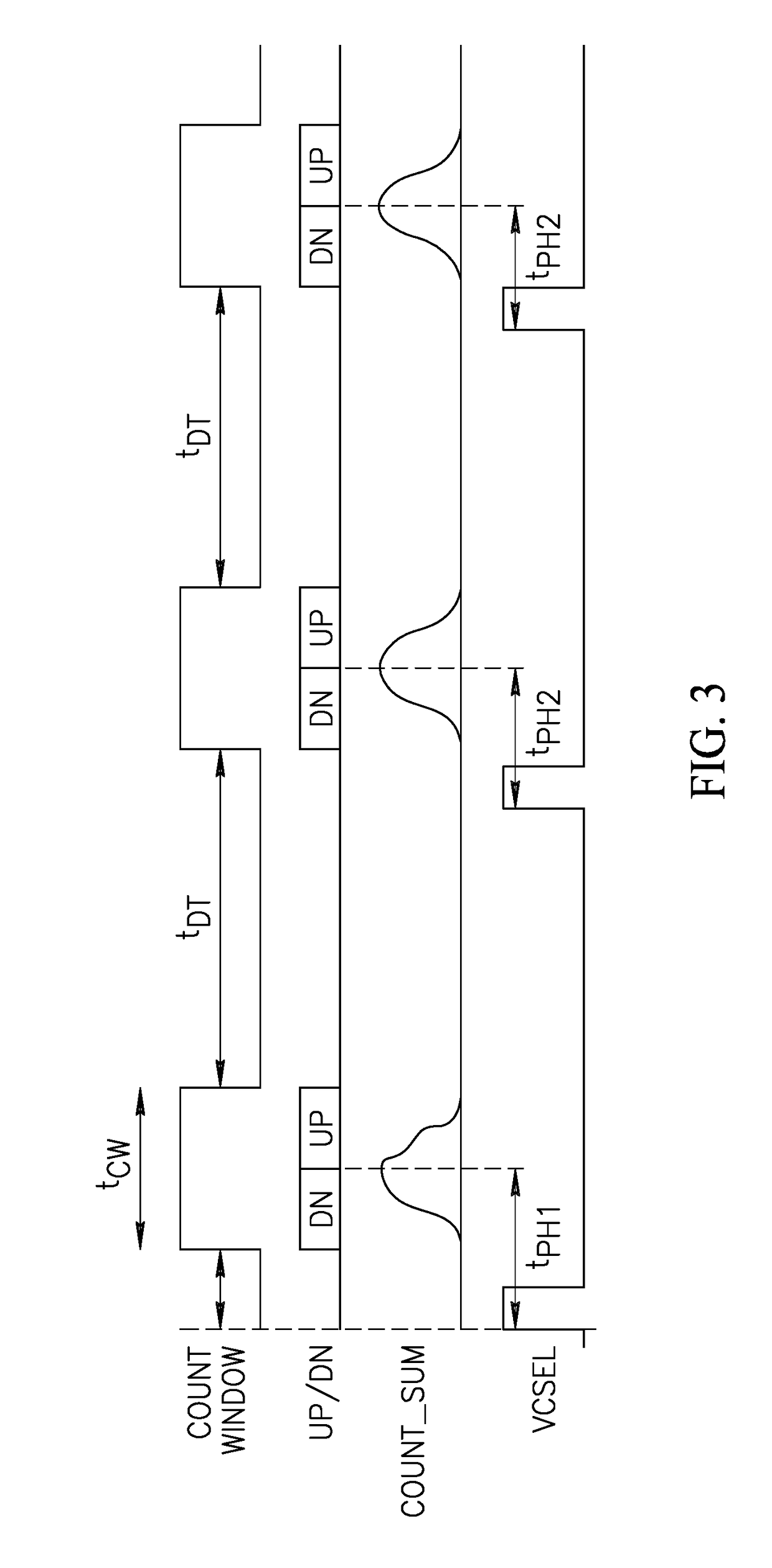
Ranging device with imaging capability
ActiveUS20170139041A1Problem be addressSolid-state devicesRadiation controlled devicesComputer sciencePhoton detection
A ranging device includes an array of photon detection devices adapted to receive an optical signal reflected by an object in an image scene. First and second logic devices are adapted to respectively combine the outputs of first and second pluralities of the photon detection devices. A first range detection circuit is coupled to outputs of the first and second logic devices and a first counter is coupled to the output of the first logic device and adapted to generate a first pixel value by counting events generated by the first plurality of photon detection devices. A second counter is coupled to the output of the second logic device and is adapted to generate a second pixel value by counting events generated by the second plurality of photon detection devices. The first and second pixel values may be used in estimating a range to the object in the image scene.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS (GRENOBLE 2) SAS
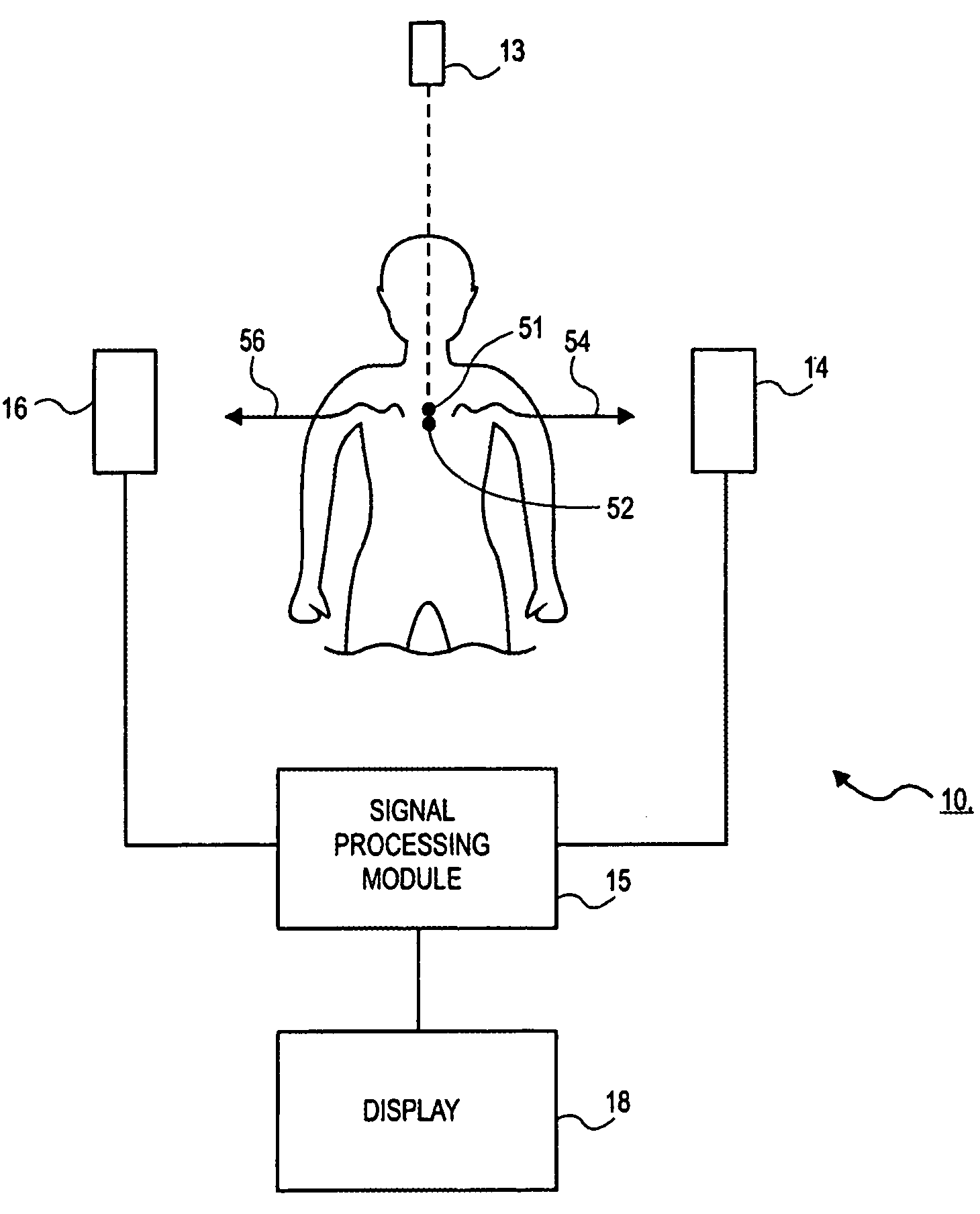
Imaging apparatus and method with event sensitive photon detection
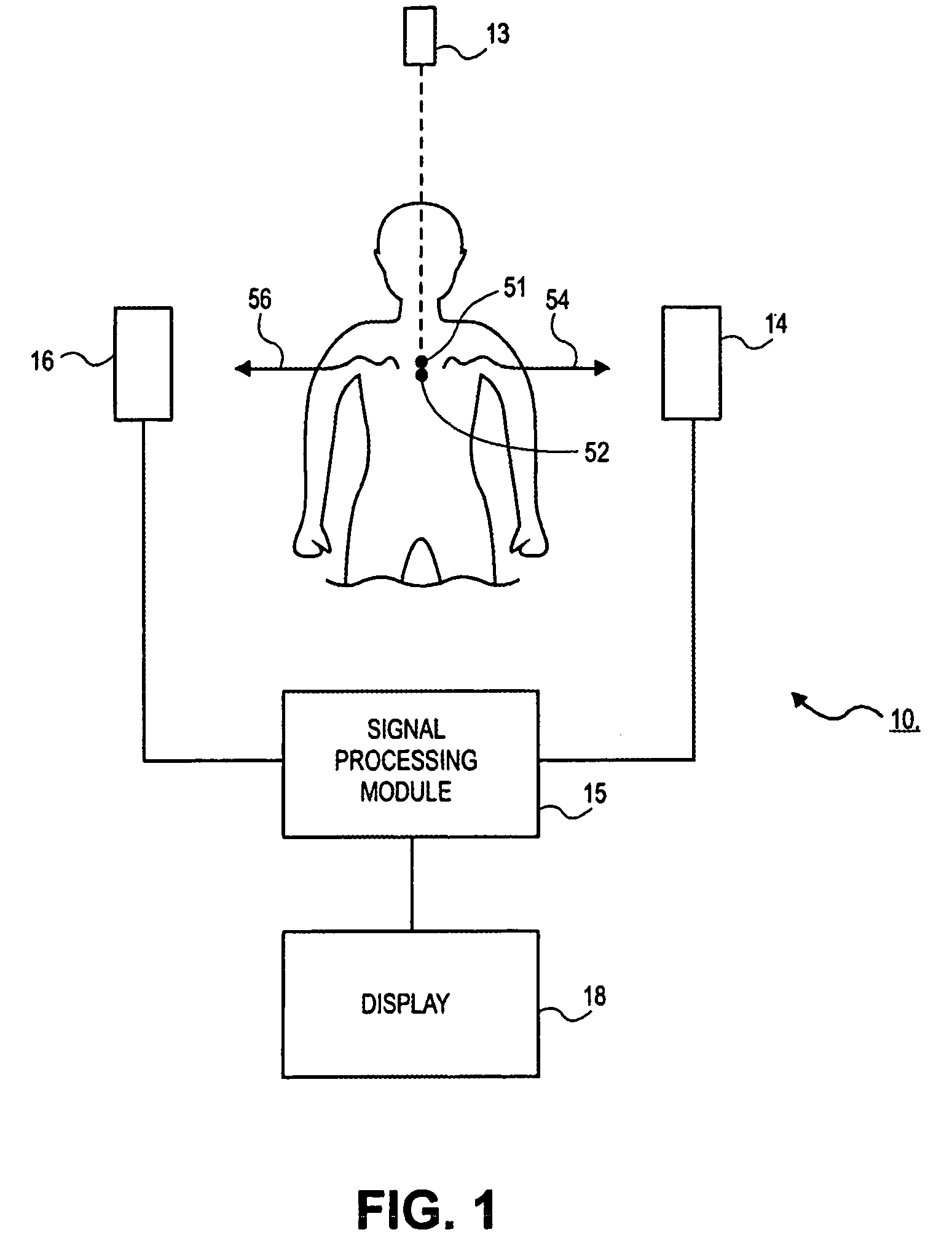
InactiveUS7078699B2Accurate detectionImprove signal-to-noise ratioRadiation/particle handlingMaterial analysis by optical meansTemporal resolutionHigh rate
An imaging apparatus (10) includes a photon detector (20) and an accessing circuit (44) coupled thereto. The photon detector (20) detects photons and generates signals in response thereto. The accessing circuit (44) reads out the signals from the photon detector (20) at a sufficiently high rate so that it operates in an event sensitive mode. The apparatus (10) also includes a signal processing module (15) for processing the signals and generating data regarding the images of the object. In accordance with various embodiments of the present invention, the signal processing module (15) may include a spatial resolution circuit (56), a photon energy resolution circuit (57), a temporal resolution circuit (58), or any combination thereof.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
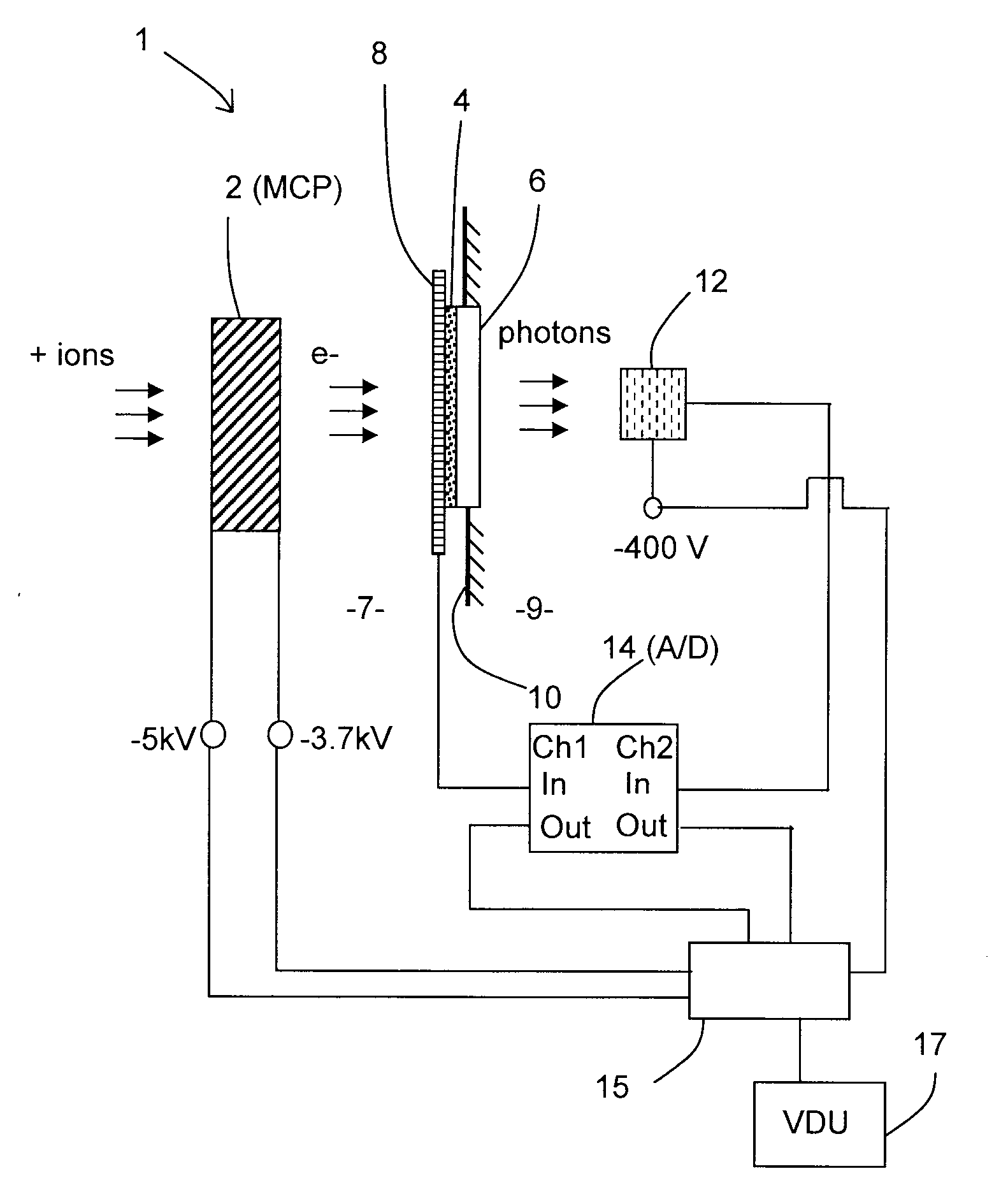
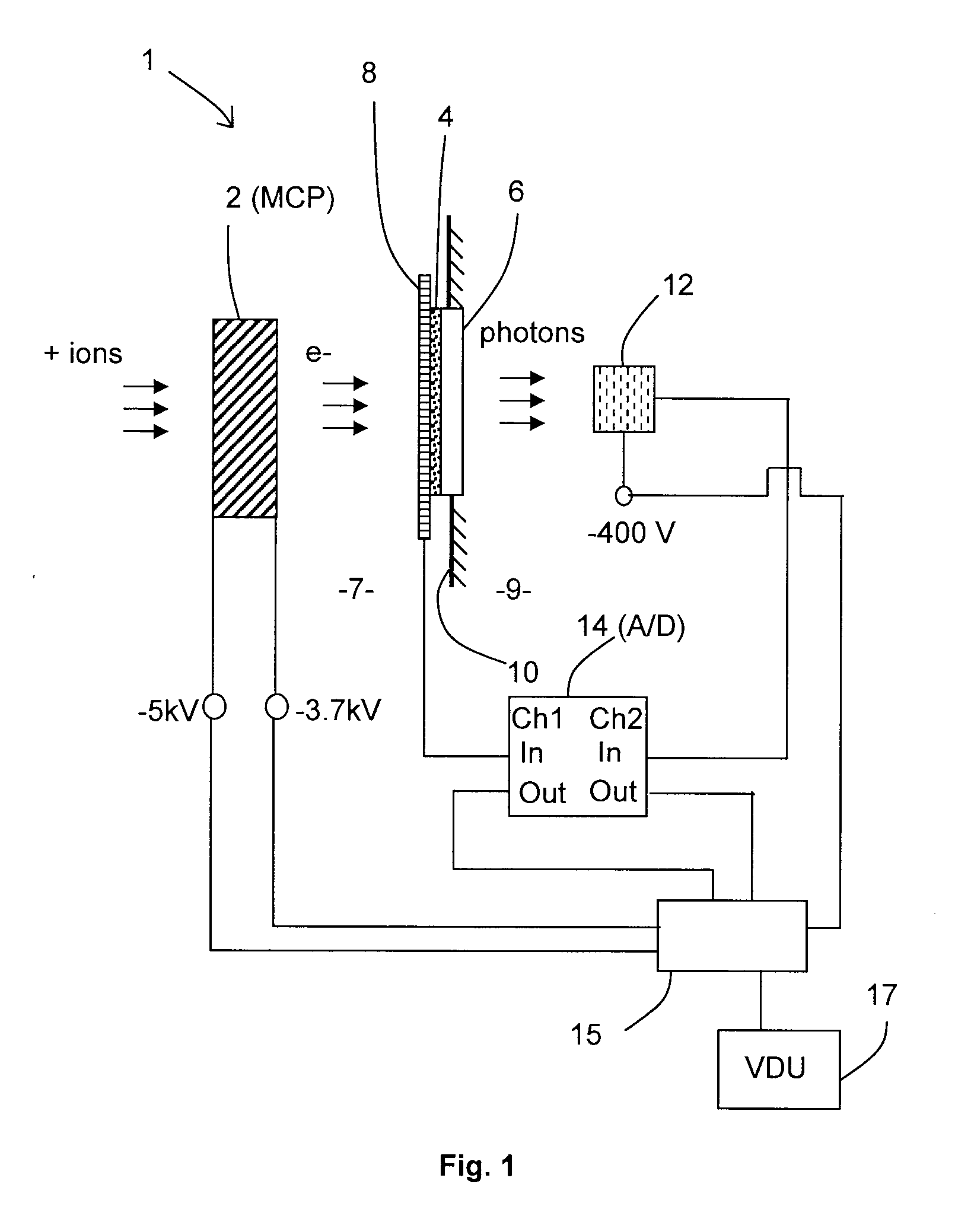
Detection Apparatus for Detecting Charged Particles, Methods for Detecting Charged Particles and Mass Spectrometer
ActiveUS20110095177A1Improve dynamic rangeProlong lifeTime-of-flight spectrometersSpectrometer detectorsPhoton detectionCharged particle detectors
Embodiments of the invention provide a detection apparatus for detecting charged particles having a secondary particle generator for generating secondary charged particles in response to receiving incoming charged particles, a charged particle detector for receiving and detecting secondary charged particles generated by the secondary particle generator, a photon generator for generating photons in response to receiving secondary charged particles generated by the secondary particle generator, and a photon detector for detecting the photons generated by the photon generator.
Owner:THERMO FISHER SCI BREMEN
Superconducting single photon detector
The present invention provides a device and system for high-efficiency and low-noise detection of single photons within the visible and infrared spectrum. In certain embodiments, the device of the invention can be integrated within photonic circuits to provide on-chip photon detection. The device comprises a traveling wave design comprising a waveguide layer and a superconducting nanowire atop of the waveguide.
Owner:YALE UNIV
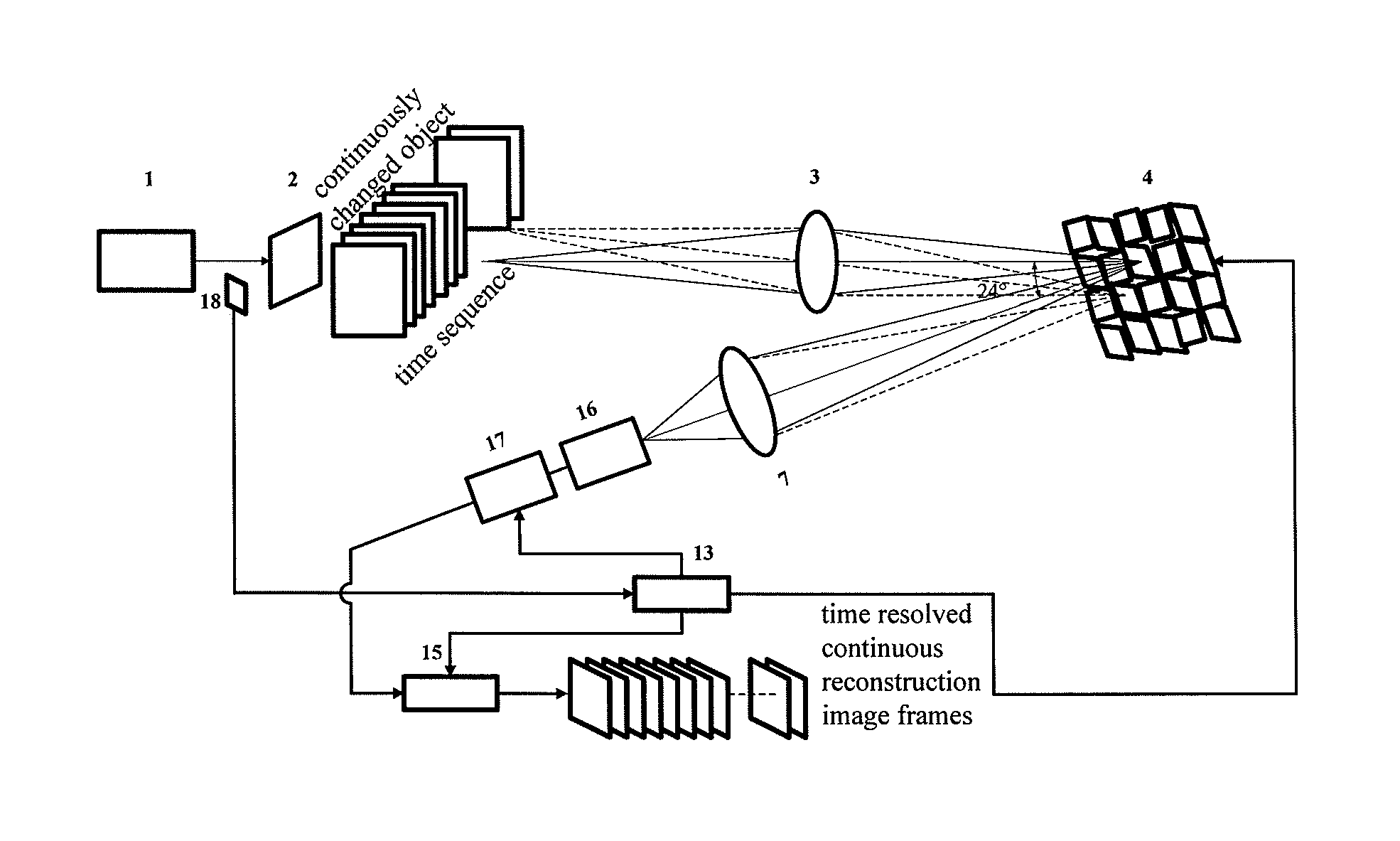
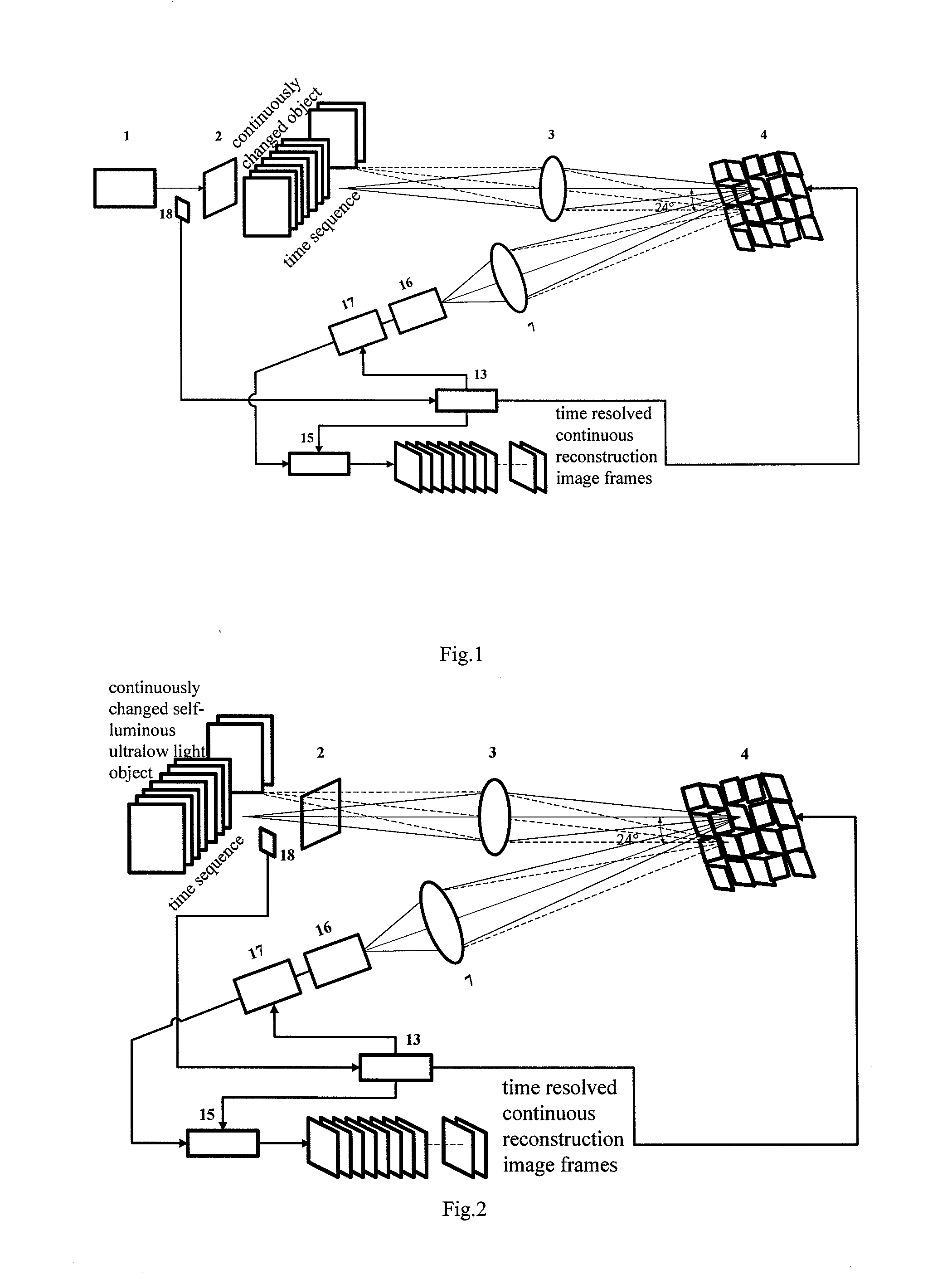
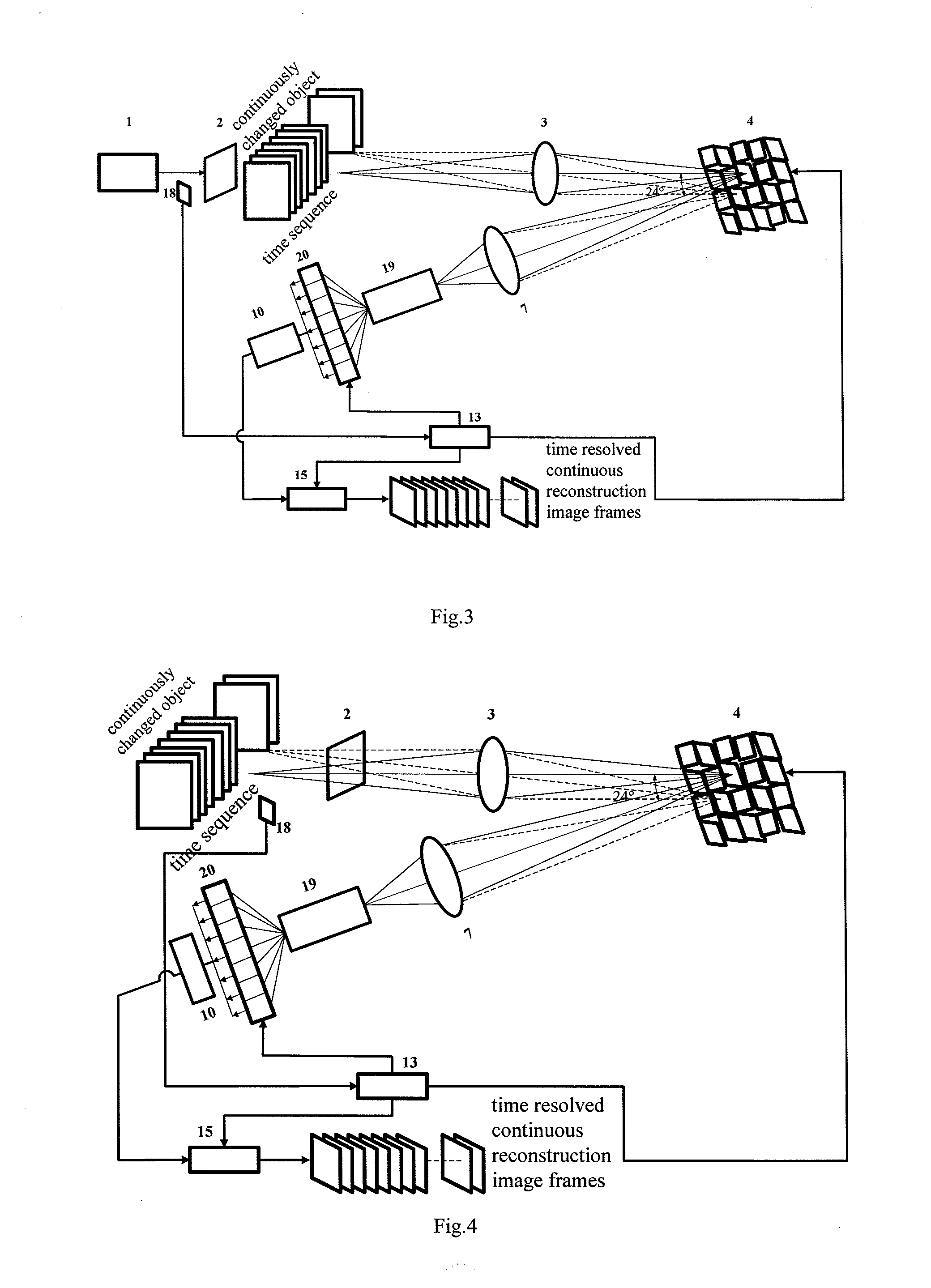
Time-Resolved Single-Photon or Ultra-Weak Light Multi-Dimensional Imaging Spectrum System and Method
InactiveUS20140253713A1Improve reconstruction qualityShorten recovery timeColor television detailsClosed circuit television systemsSpatial light modulatorGrating
A single-photon or ultra-weak light multi-D imaging spectral system and method. In order to realize rough time resolution, a time-resolved single-photon counting 2D imaging system for forming color or grey imaging is provided. Moreover, in order to realize high-precision time resolution, the system comprises a light source, an imaging spectral measurement unit, an electric detection unit, a system control unit and an algorithm unit. The light carrying information of an object is imaged on a spatial light modulator and randomly modulated according to compressed sensing theory, emergent light of a grating is collected using a point or array single-photon detector, the number of photons and photon arrival time are recorded, and reconstruction is carried out using the compressed sensing algorithm and related algorithm of the spectral imaging. The system provides single-photon detection sensitivity, high time resolution and wide spectral range, and can be applied in numerous new high-tech industries.
Owner:CENT FOR SPACE SCI & APPLIED RES
LiDAR system comprising a single-photon detector
ActiveUS9625580B2Reduce impactHigh operating requirementsOptical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationPhoton detectionLength wave
A method for developing a map of objects in a region surrounding a location is disclosed. The method includes interrogating the region along a detection axis with a series of optical pulses and detecting reflections of the optical pulses that originate at objects located along the detection axis. A multi-dimensional map of the region is developed by scanning the detection axis about the location in at least one dimension. The reflections are detected via a single-photon detector that is armed using a sub-gating scheme such that the single-photon detector selectively detects photons of reflections that originate only within each of a plurality of zones that collectively define the detection field. In some embodiments, the optical pulses have a wavelength within the range of 1350 nm to 1390 nm, which is a spectral range having a relatively high eye-safety threshold and a relatively low solar background.
Owner:LG INNOTEK CO LTD
Digital silicon photomultiplier for TOF-PET
ActiveUS7723694B2Improve manufacturing yieldReduce sensitivityMaterial analysis by optical meansTomographyQuiescent stateSilicon photomultiplier
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
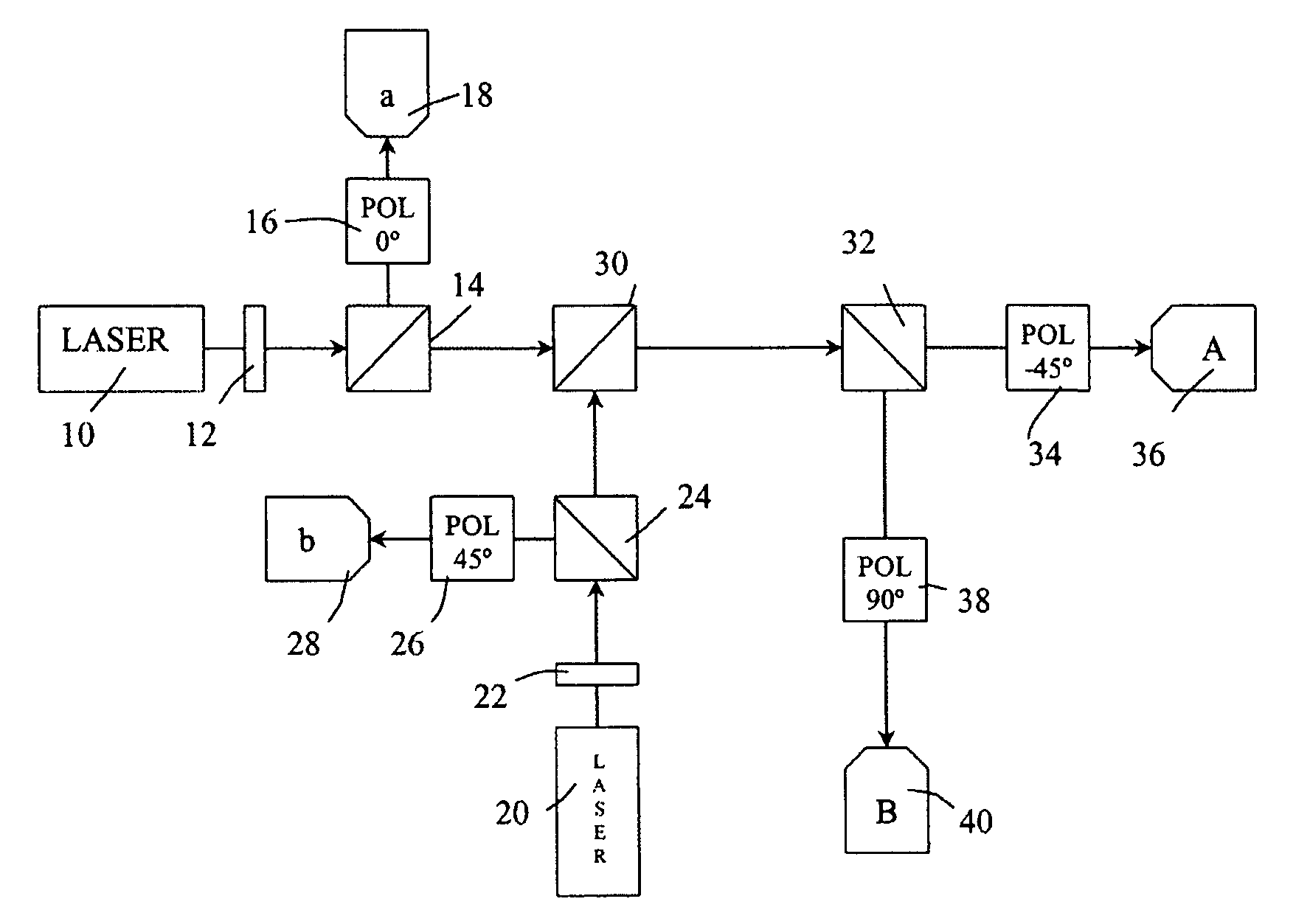
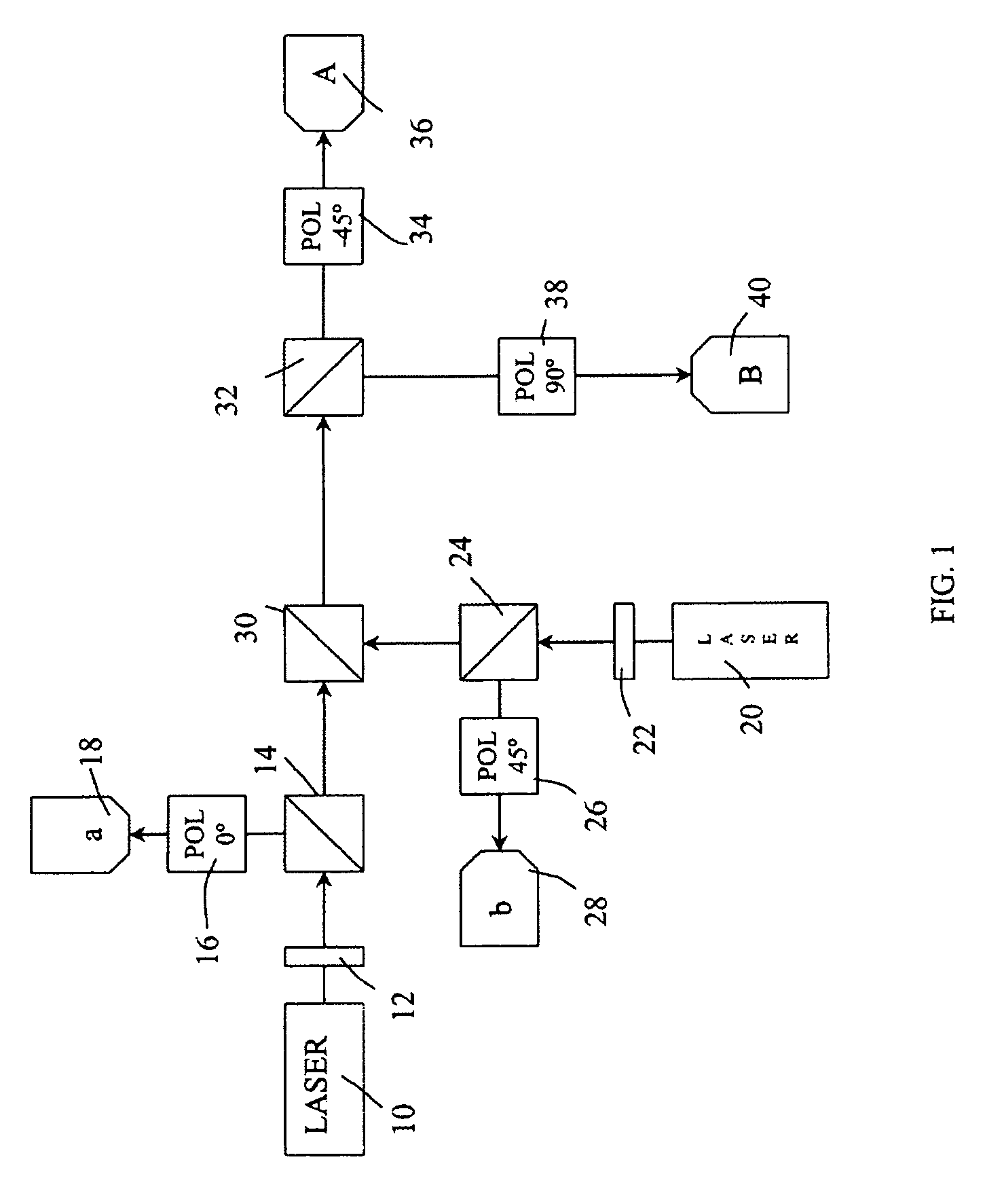
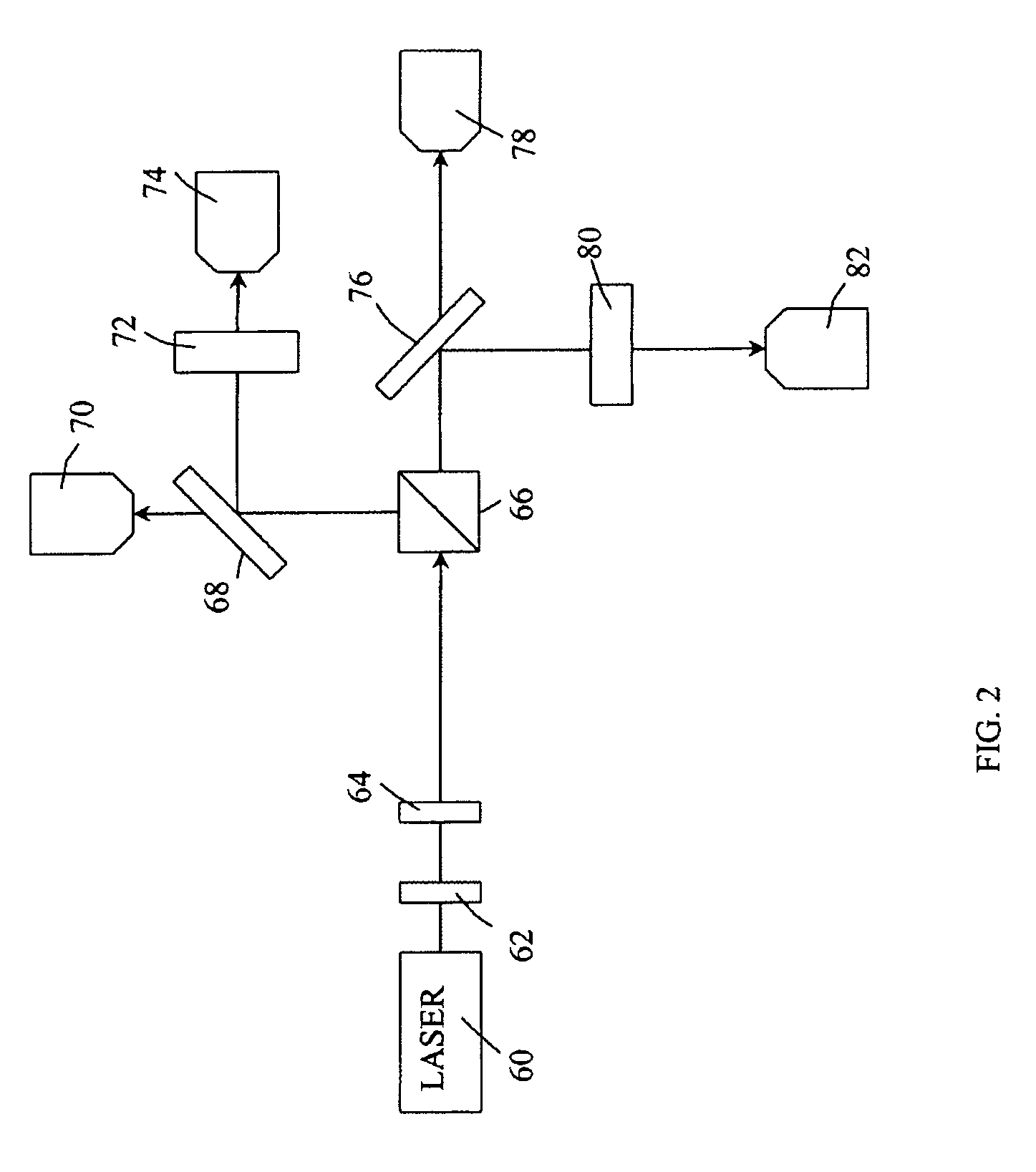
Entangled quantum communications and quantum imaging
InactiveUS7536012B1Synchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesComputer hardwareSecure communication
An apparatus for generating a shared quantum key between a sender and a receiver comprises a sending apparatus which generates entangled photon pairs, and a receiving apparatus. A shared quantum key can be generated using temporal coincidences between photon detection events. For example, coincidences may be determined between sender and receiver photon detection events using detection data shared through a non-secure communications link between the sender and receiver. The quantum key can be used in encrypted communications. Similar apparatus and methods can be used for quantum imaging.
Owner:ARMY US SEC THE THE
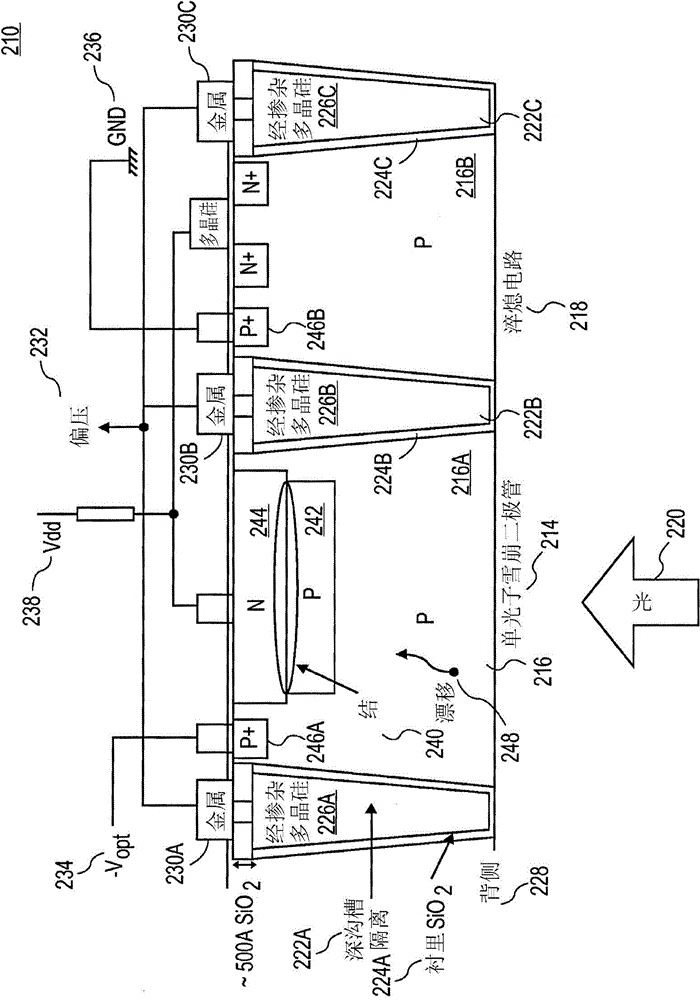
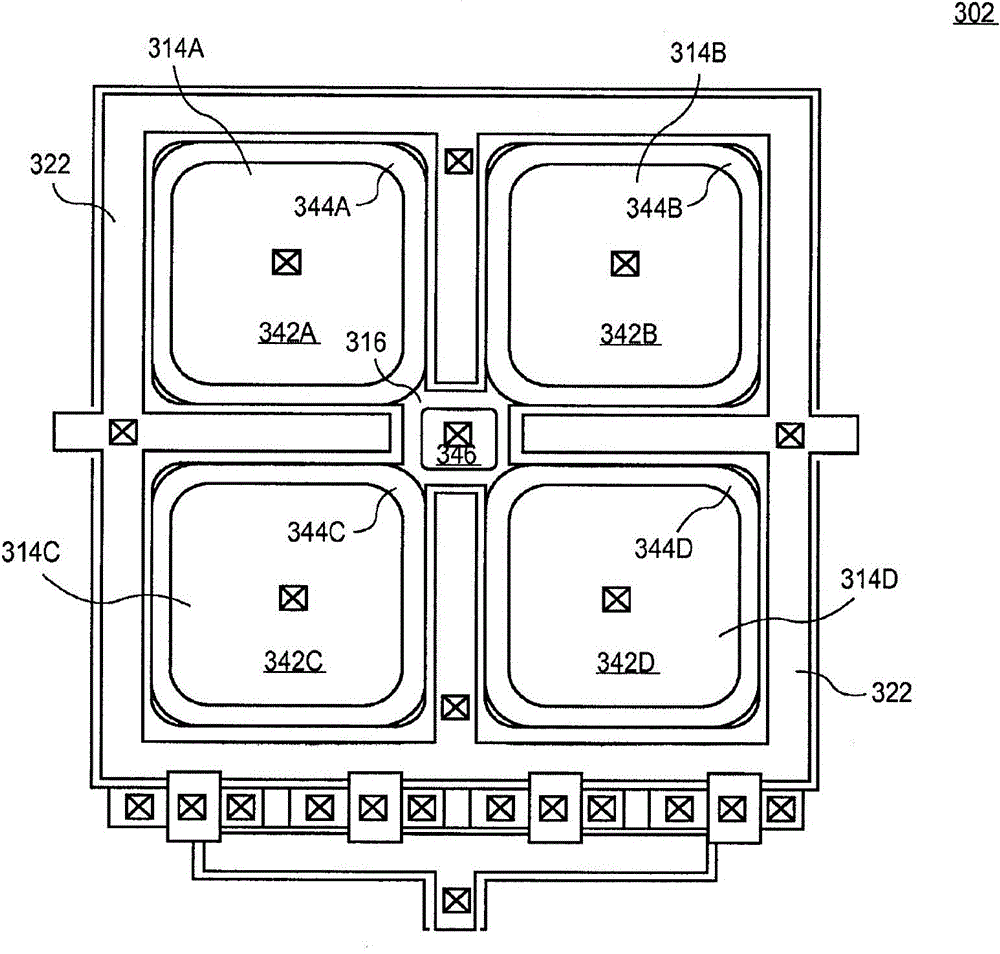
Enhanced photon detection device with biased deep trench isolation
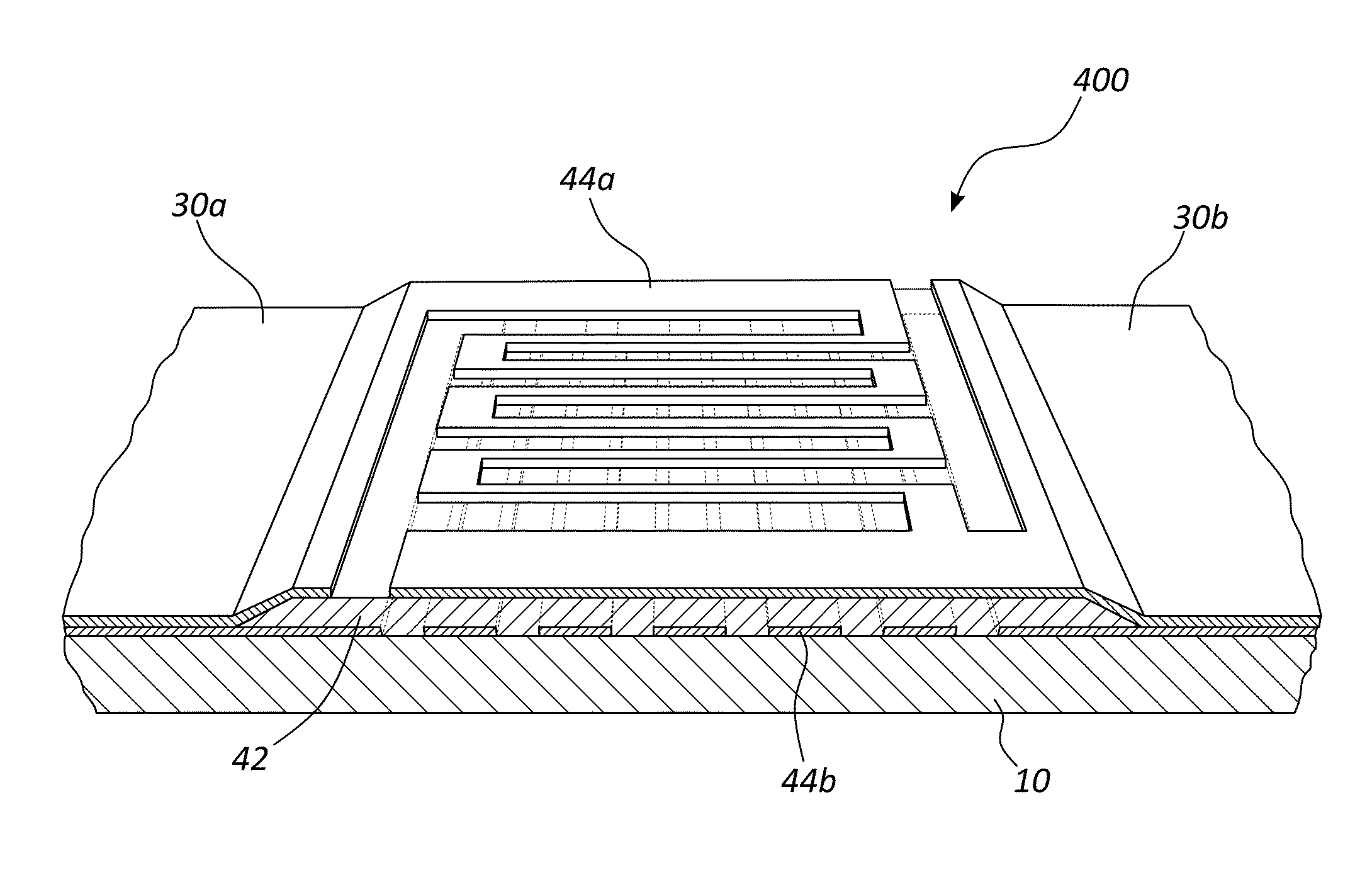
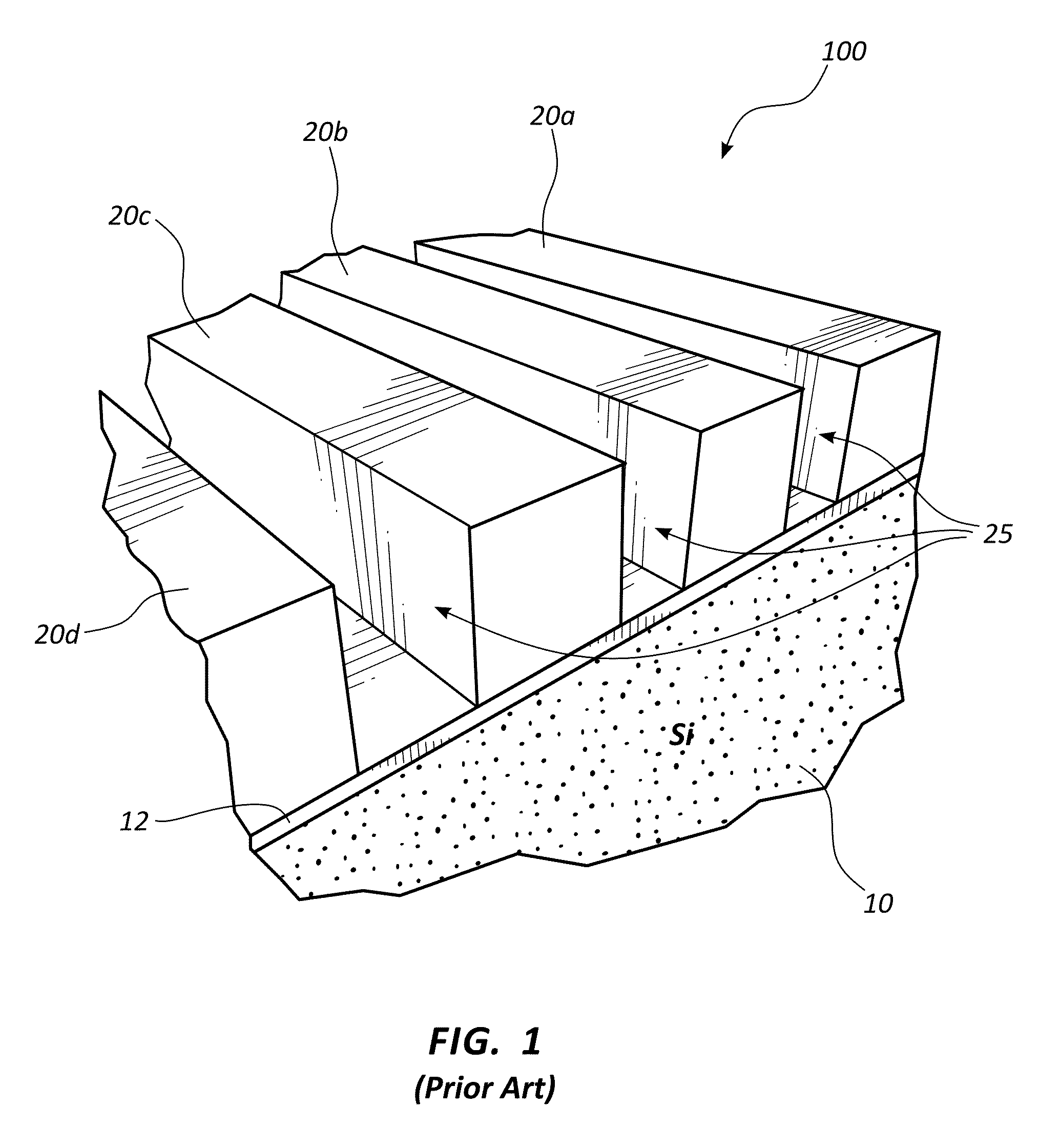
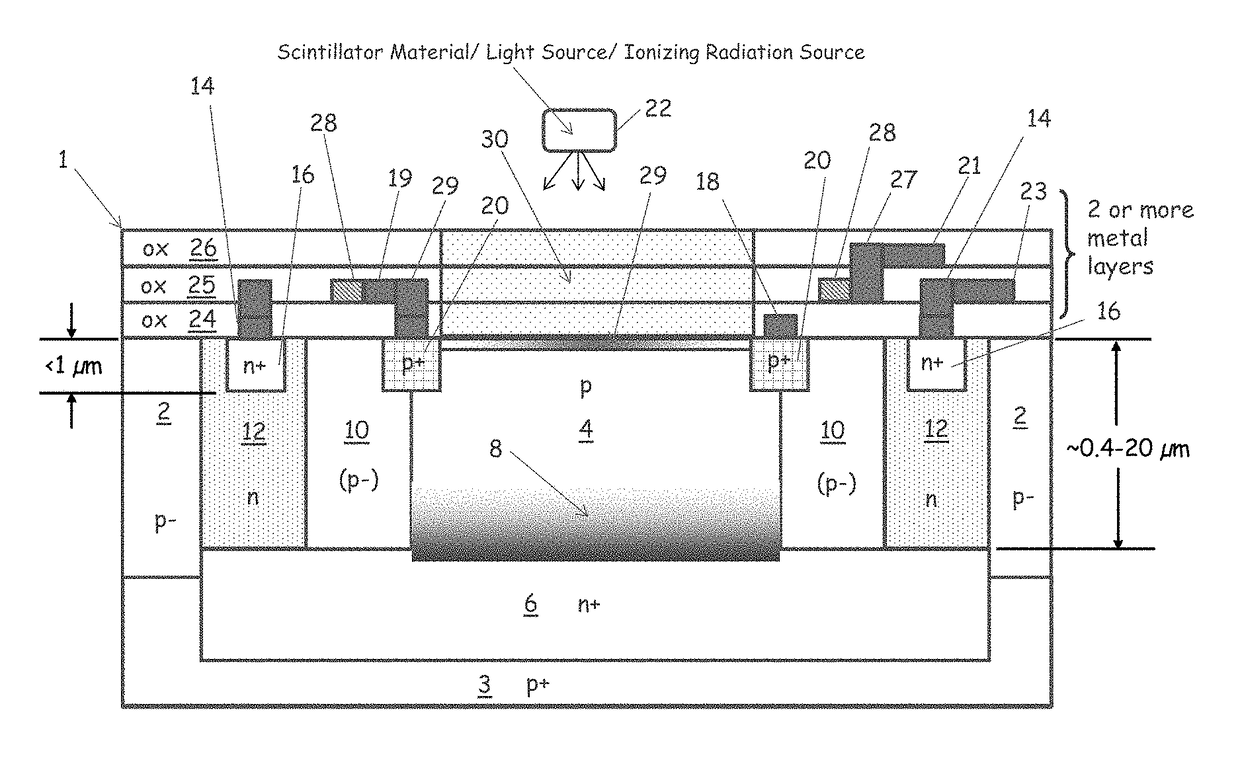
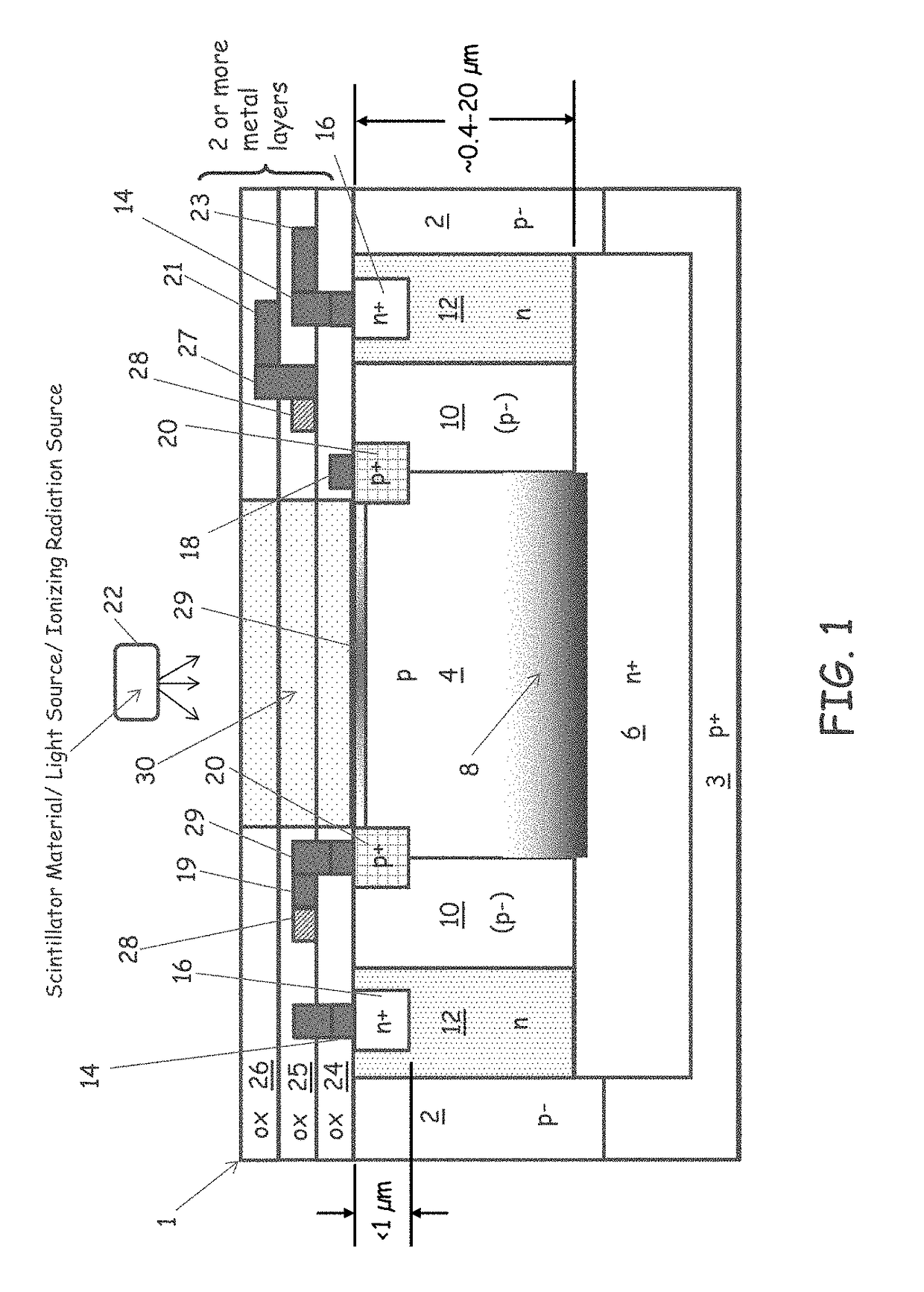
ActiveCN104103655ATelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor materialsPhoton detection
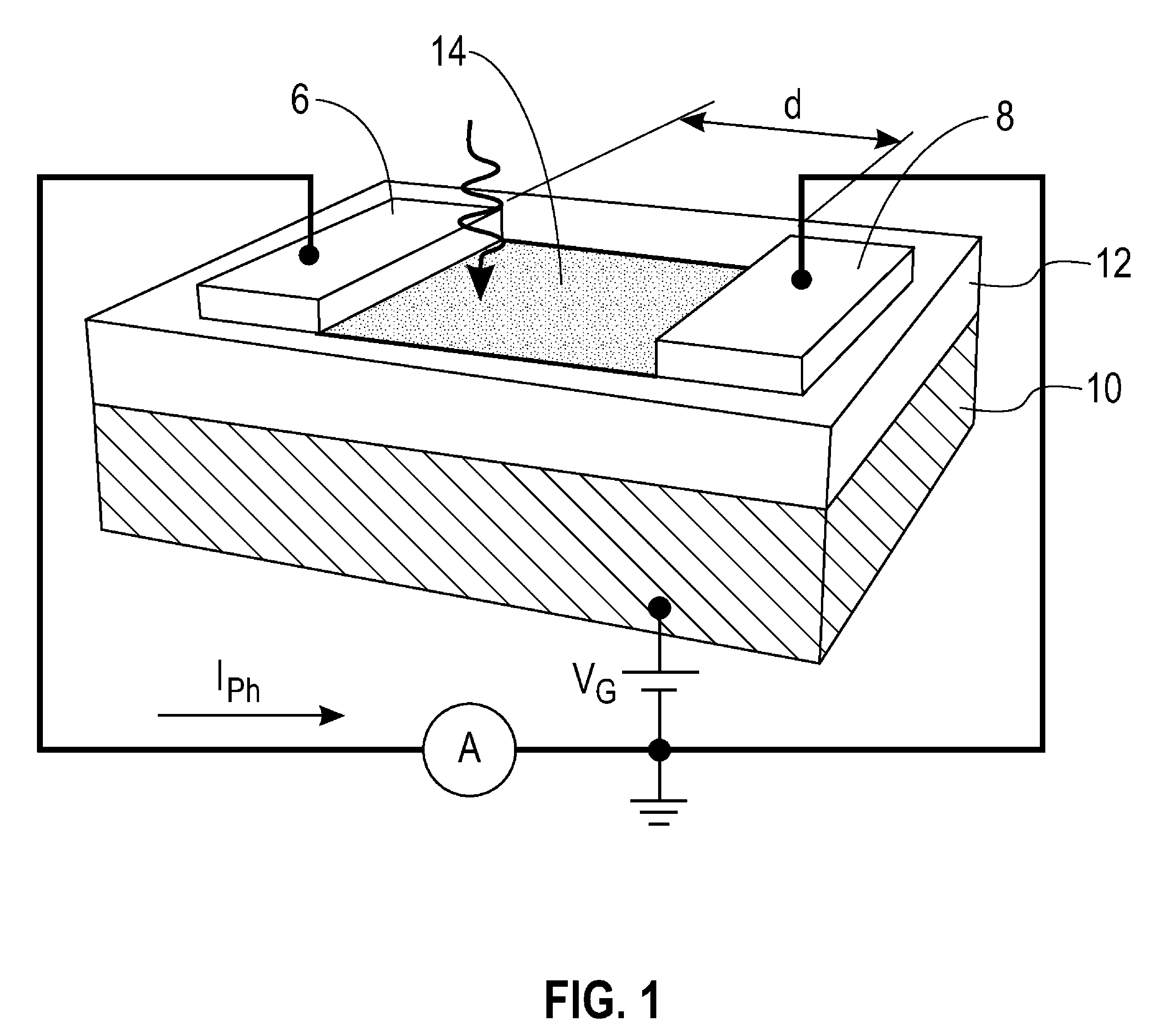
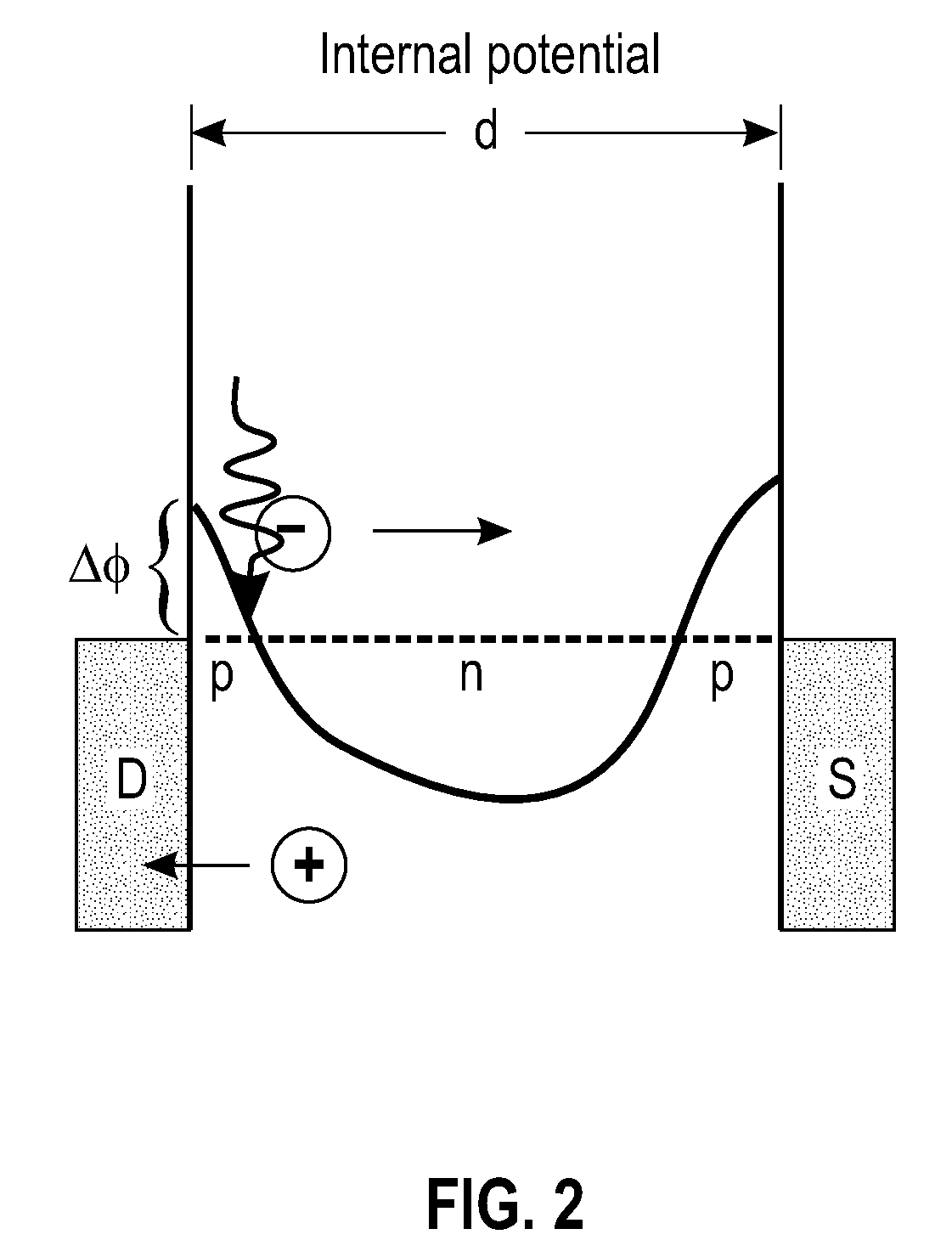
The invention relates to an enhanced photon detection device with biased deep trench isolation. The photon detection device includes a photodiode having a planar junction disposed in a first region of semiconductor material. A deep trench isolation (DTI) structure is disposed in the semiconductor material. The DTI structure isolates the first region of the semiconductor material on one side of the DTI structure from a second region of the semiconductor material on another side of the DTI structure. The DTI structure includes a dielectric layer lining an inside surface of the DTI structure and doped semiconductor material disposed over the dielectric layer inside the DTI structure. The doped semiconductor material disposed inside the DTI structure is coupled to a bias voltage to isolate the photodiode in the first region of the semiconductor material from the second region of the semiconductor material.
Owner:OMNIVISION TECH INC
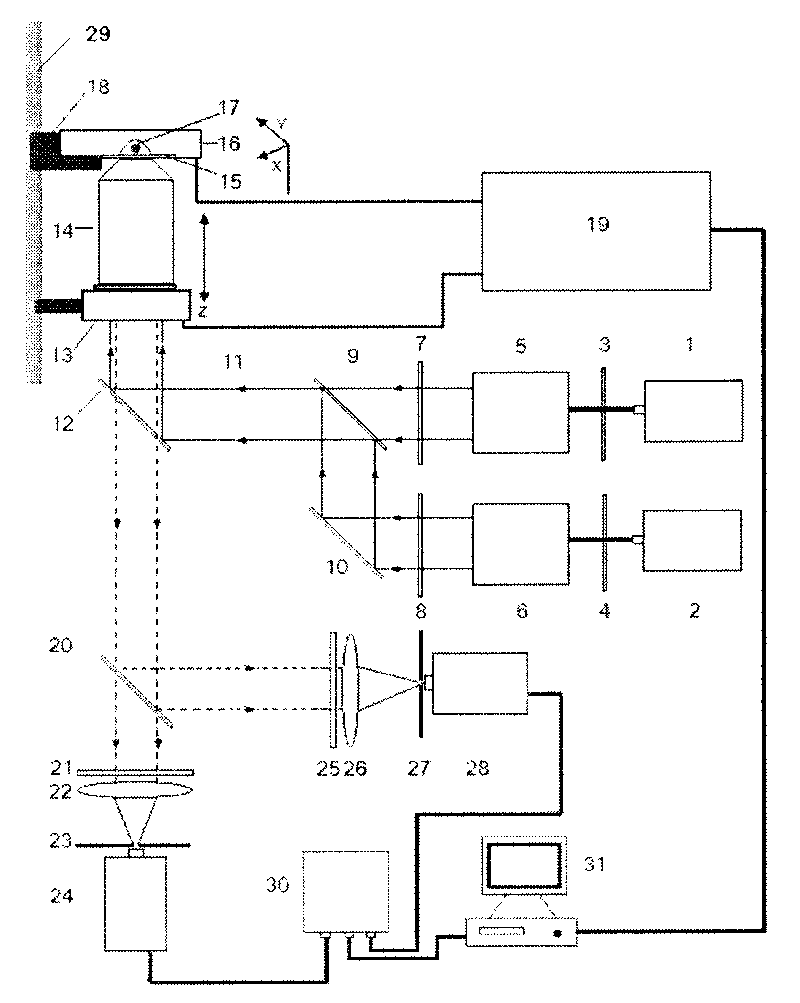
Lasing fluorescence scanning imaging-fluorescence correlation spectrum unimolecule detecting instrument
InactiveCN101718696AEasy to replaceEasy to operateFluorescence/phosphorescencePhoton detectionData acquisition
The invention relates to a lasing fluorescence scanning imaging-fluorescence correlation spectrum unimolecule detecting instrument. Cover glass or a sample cell is arranged on an X-Y scanning platform; a microscope objective is installed on a Z-direction locator. Expended laser is filtered by an excitation filter, and then reflected into the objective by a dichroic mirror, and finally radiated in a sample above the cover glass after being focused by the objective; the sample generates fluorescence; and the generated fluorescence is collected by the same objective, passes through the dichroic mirror, and stray light is filtered off by an emission filter, and finally the filtered fluorescence is focused by a focusing lens on a small hole which is coupled with a single photon detector; and a signal generated by the single photon detector enters a computer through a data acquisition card. In the computer, three-dimension displacement and positioning system control software control the X-Y scanning platform to do X-Y two-dimension movement, and the Z-direction locator controls the focus of the objective to do Z-direction movement, thereby forming the three-dimension scanning to the sample; and three-dimension space position information and the signal generated by the single photon detector construct three-dimension scanning images and fluorescence correlation spectrum curves in the computer.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
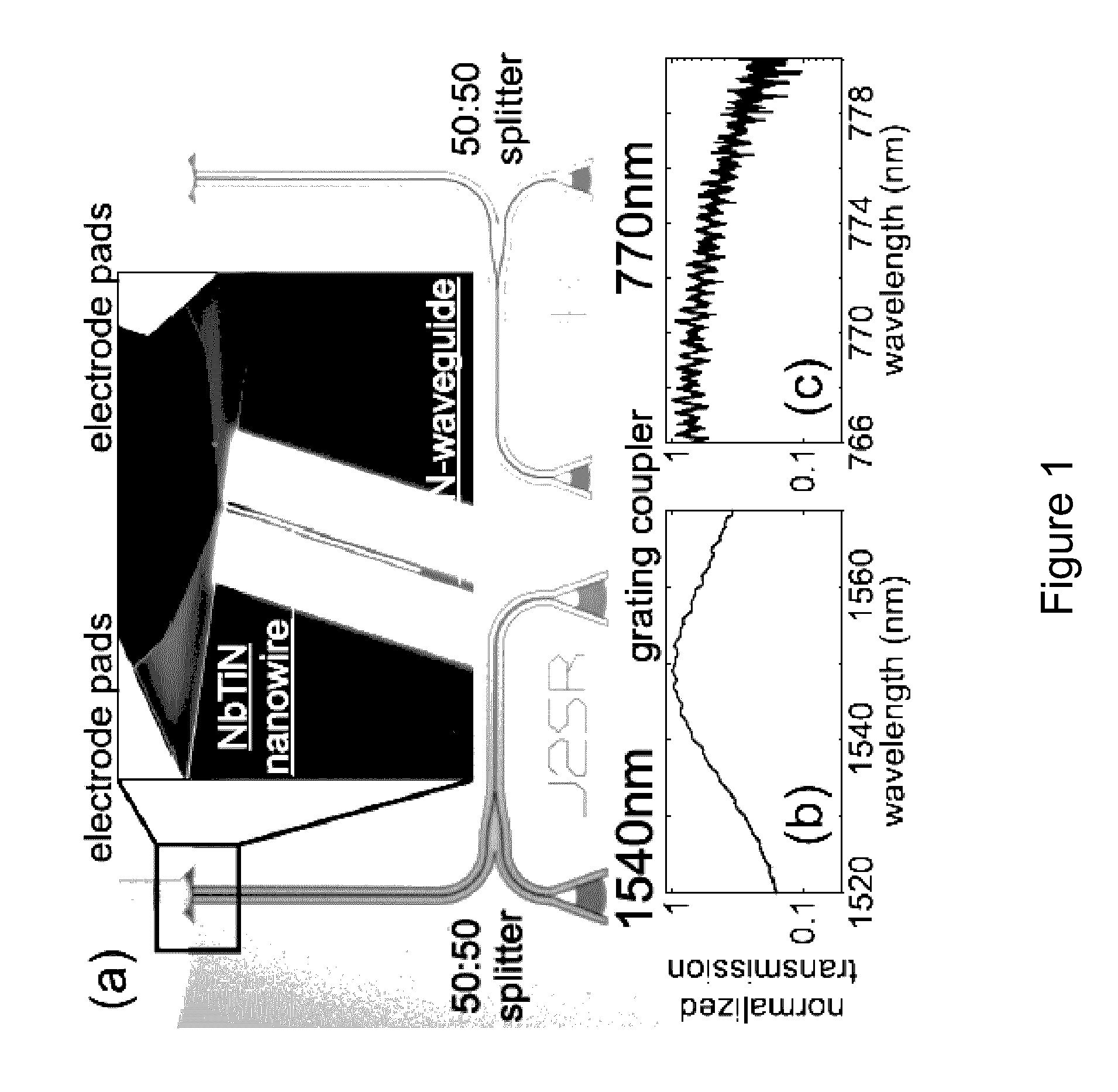
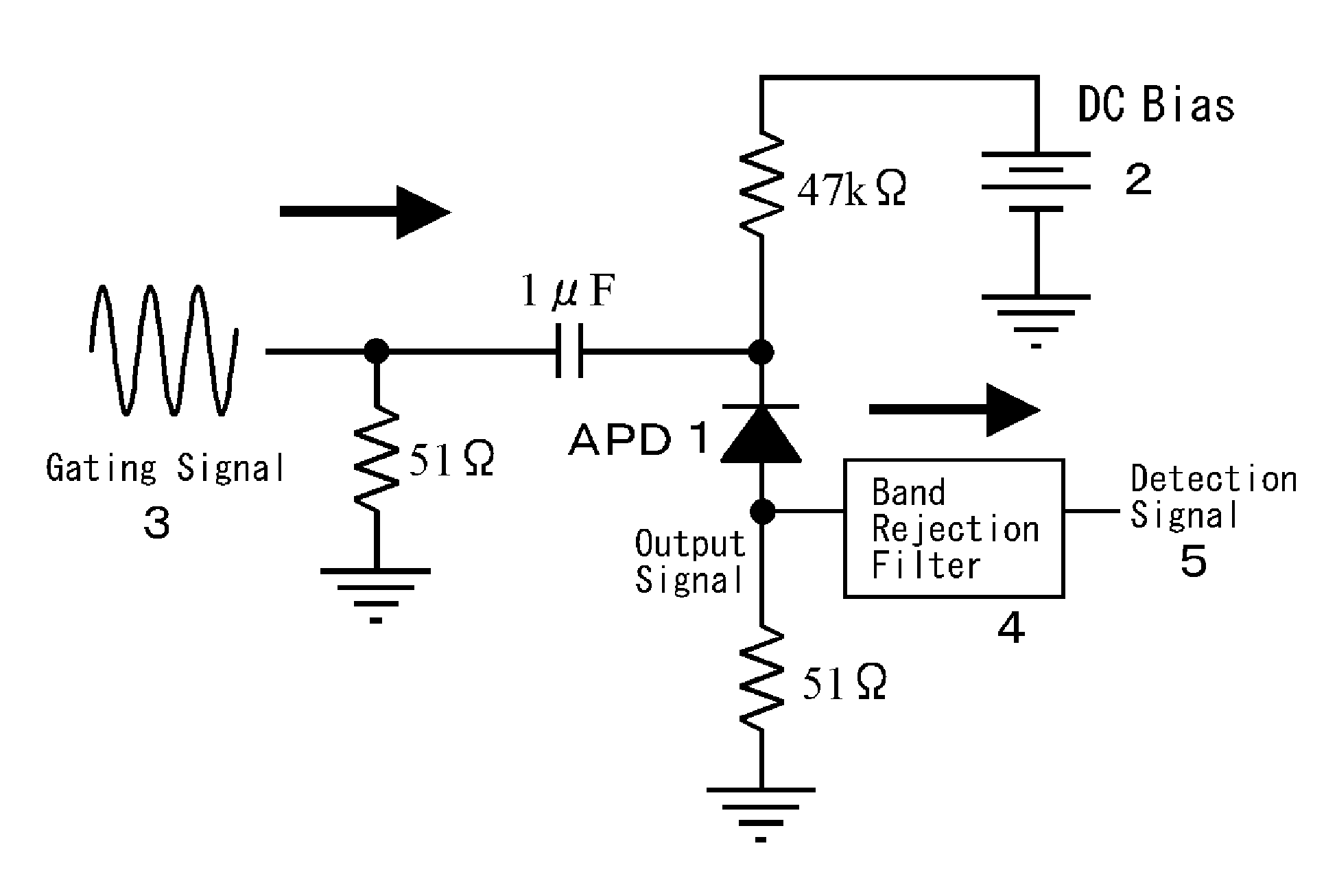
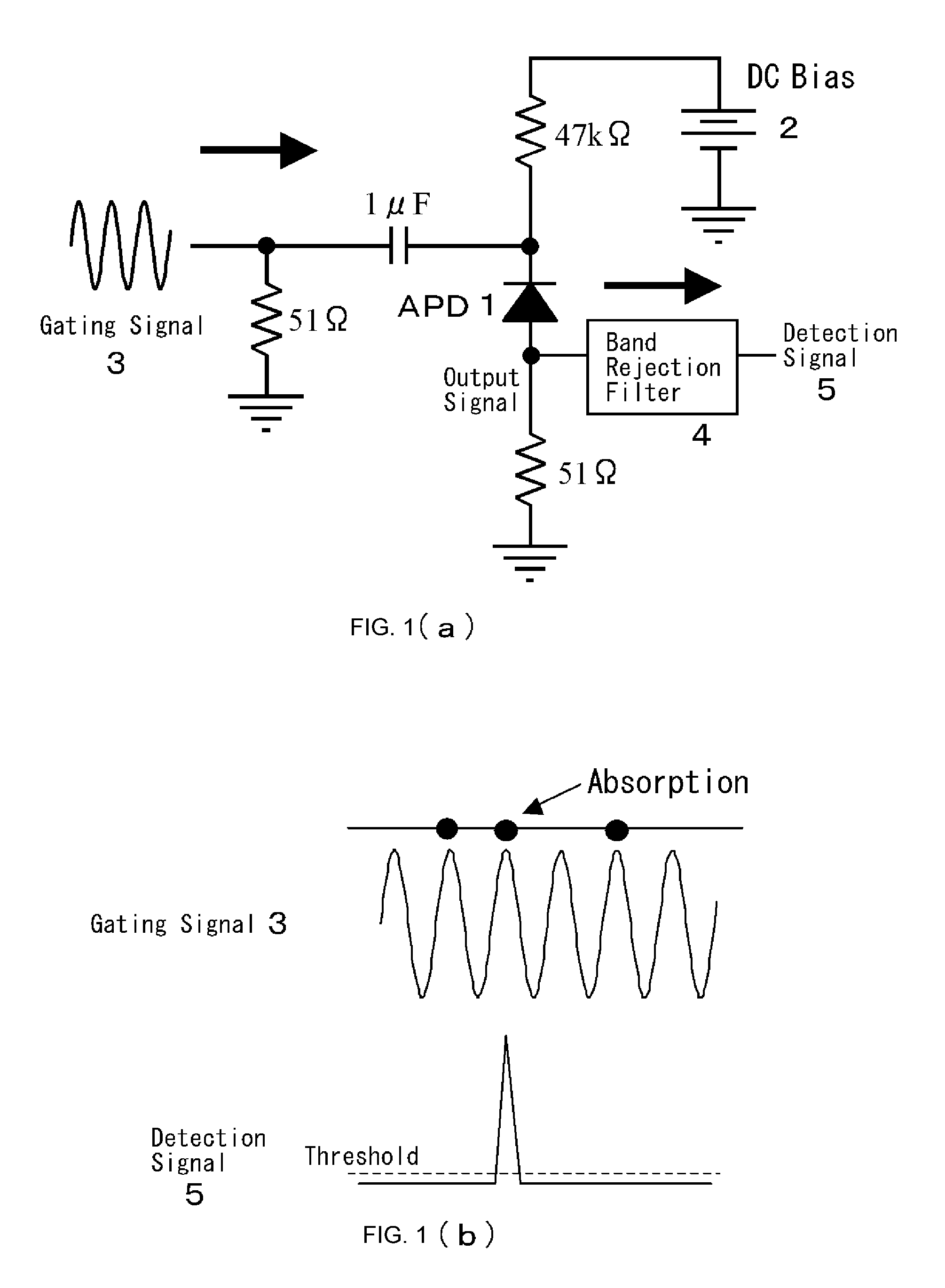
High-speed single-photon detector in telecommunication wavelength band
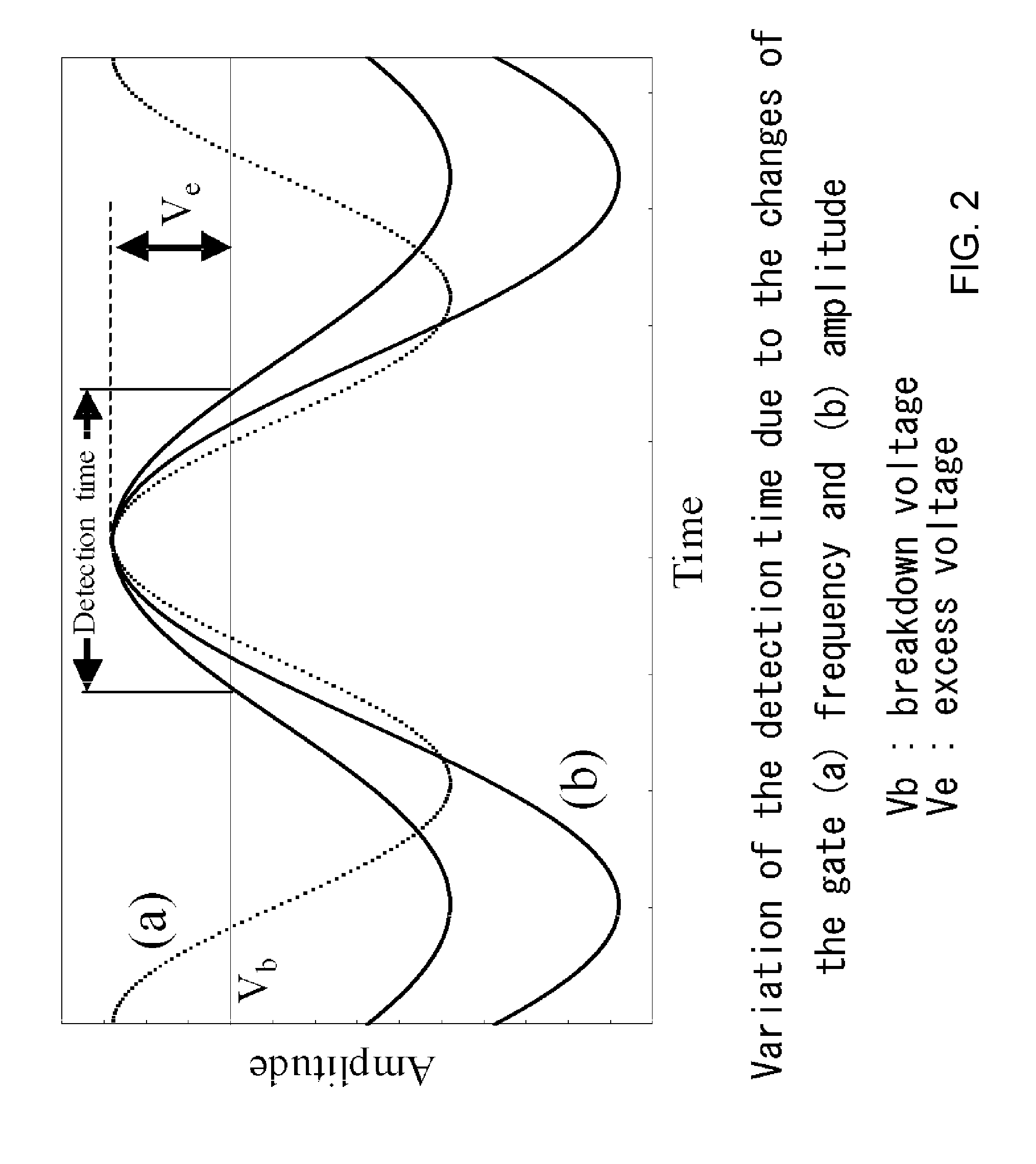
In order to operate a single photon detector in communication wavelength band at a high speed, a DC bias voltage 2 lower than the breakdown voltage is applied to an InGaAs / InP avalanche photodiode (APD) 1. A 500 MHz sine wave gating signal 3 is superimposed with the DC bias voltage 2 and applied to the APD 1 so as to exceed the breakdown voltage by about 4V in a fractional time of each period. The sine wave gating signal 3 passed through the APD 1 is substantially completely removed by a filter 4, thereby improving S / N and enabling to detect a single photon even if the avalanche multiplication time is shortened to reduce the after pulse and the detection period. As a result, it achieves to detect a single photon in the 1550 nm communication band at a high speed.
Owner:NIHON UNIVERSITY
Single and few-layer graphene based photodetecting devices
A photodetector which uses single or multi-layer graphene as the photon detecting layer is disclosed. Multiple embodiments are disclosed with different configurations of electrodes. In addition, a photodetector array comprising multiple photodetecting elements is disclosed for applications such as imaging and monitoring.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
Apparatus and methods for performing optical nanopore detection or sequencing
InactiveUS20140087474A1Reducing translocation speedReduced translocation speedMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansProtein translocationNanopore
Methods and systems for detecting or sequencing a biological molecule or polymer, e.g., a nucleic acid, are provided. Optical sequencing of a molecule may be performed utilizing an optical or photon detector operated in time delayed integration mode. In certain variations, the translocation rate of molecules through a, pore, nanopore or channel may be controlled or reduced by increasing the diameter of the molecules to allow for molecule detection or sequencing by optical or electrical detection. In certain variations, a plurality or an array of, pores, nanopores, or channels may be utilized to optically detect a plurality of molecules.
Owner:QUANTAPORE
High resolution, high pressure xenon gamma ray spectroscopy using primary and stimulated light emission
InactiveUS6486468B1Particle separator tubesMaterial analysis by optical meansPhoton detectionSpectroscopy
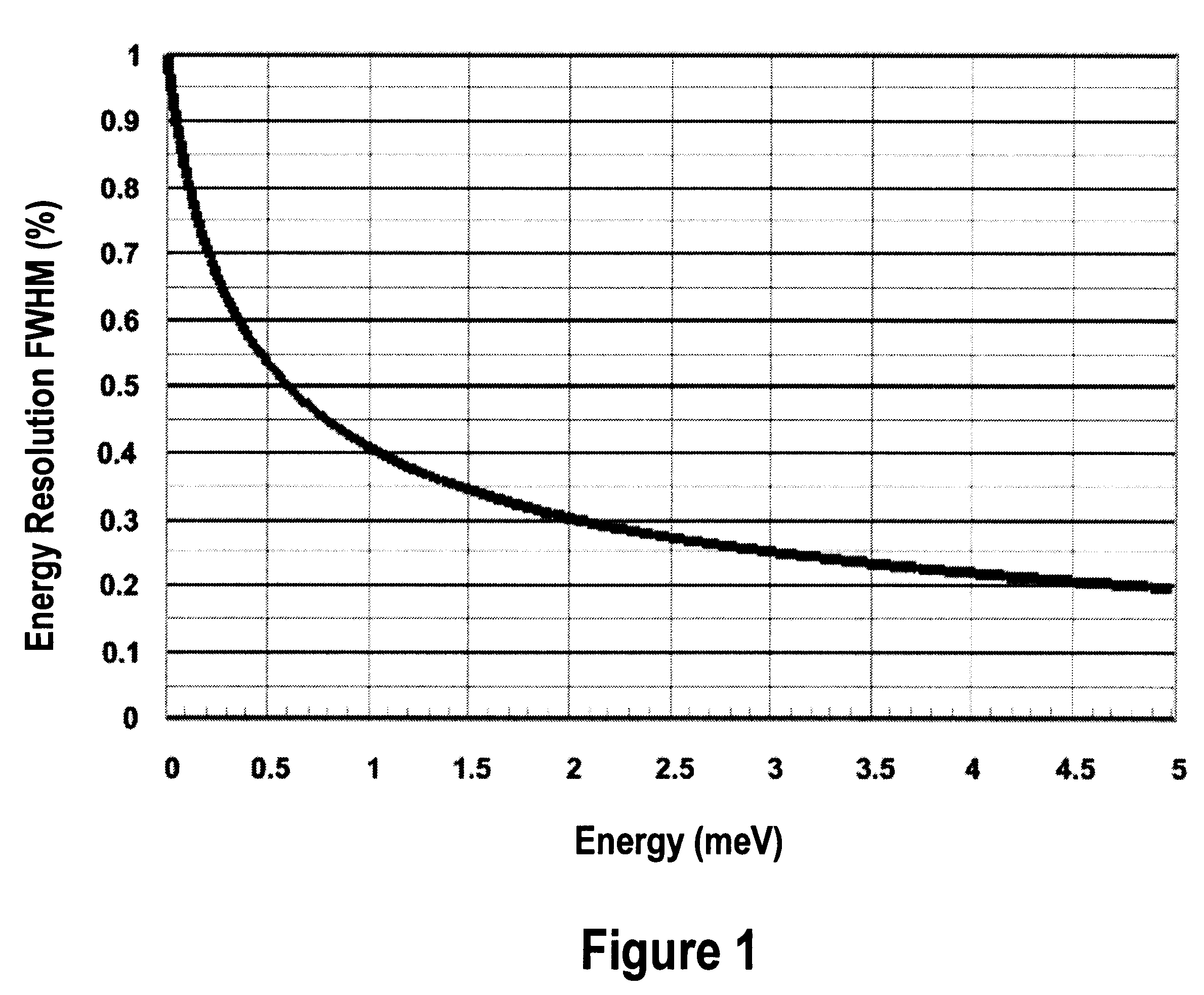
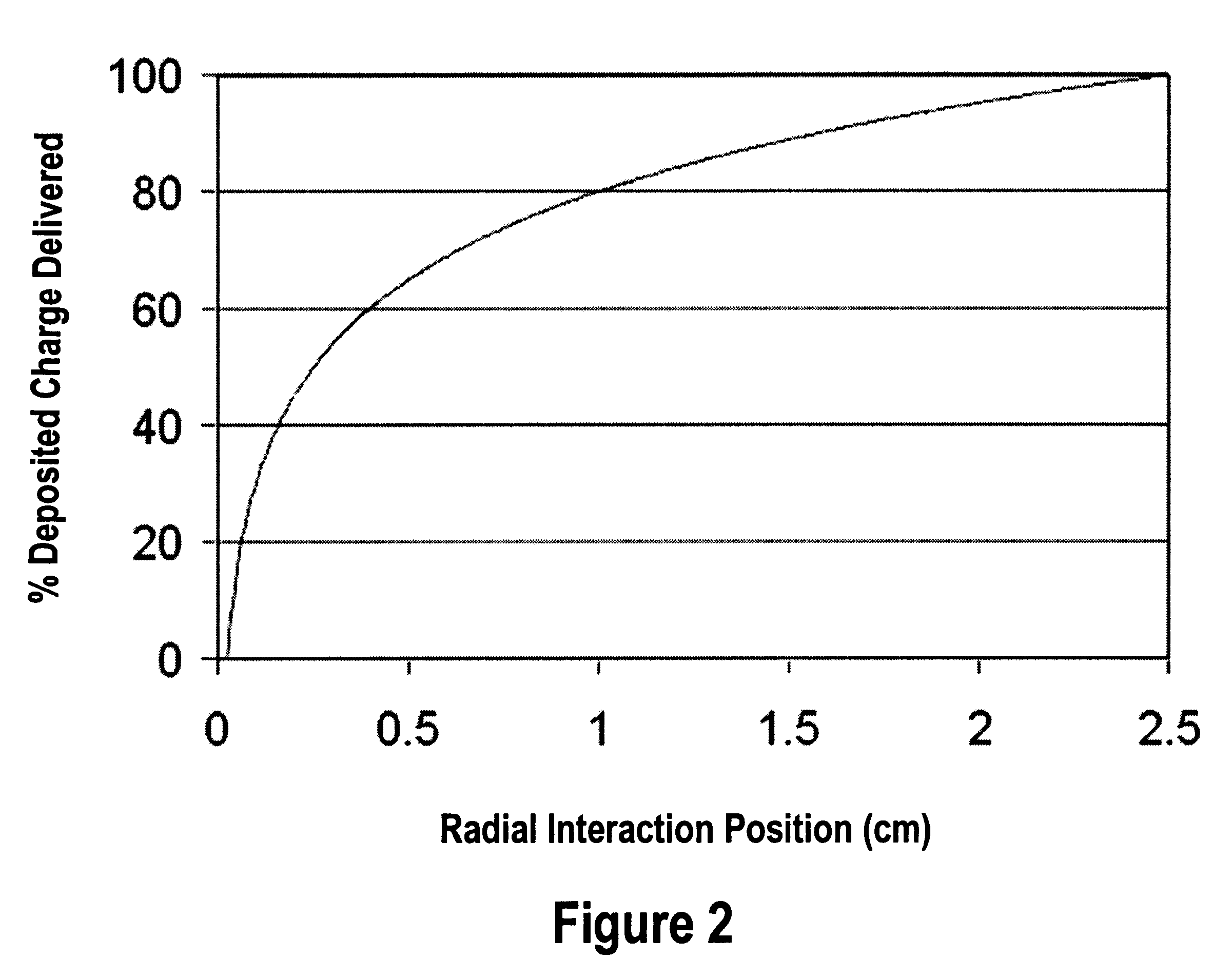
A design and readout of a xenon detection medium based device, which provides improved spectroscopic performance compared to currently commercially available devices. To achieve energy resolution improvement, a method to accurately measure radial spatial position for interacting events within a HPXe cylindrical detector is described using the plan as shown in FIG. 4. This is accomplished by utilization of light generated both at the gamma interaction site and at the collection point near the anode wire of the cylindrical detector. These light flashes are detected by a VUV photon detector. Light transmission is facilitated by incorporating a vacuum ultraviolet (VUV) light transparent window at least one end of the cylindrical ionization detector. With the known electron drift velocity in HPXe, the time between these two photopulses is sufficient to accurately determine the radial coordinate. Consequently, correction by electronic means for the electrostatic pulse dispersion using the expression graphed in FIG. 2 can be achieved in order to approach the true intrinsic energy resolution limit for HPXe.
Owner:PROPORTIONAL TECH
X-ray pulsar navigation embedded simulation system based on semiconductor laser
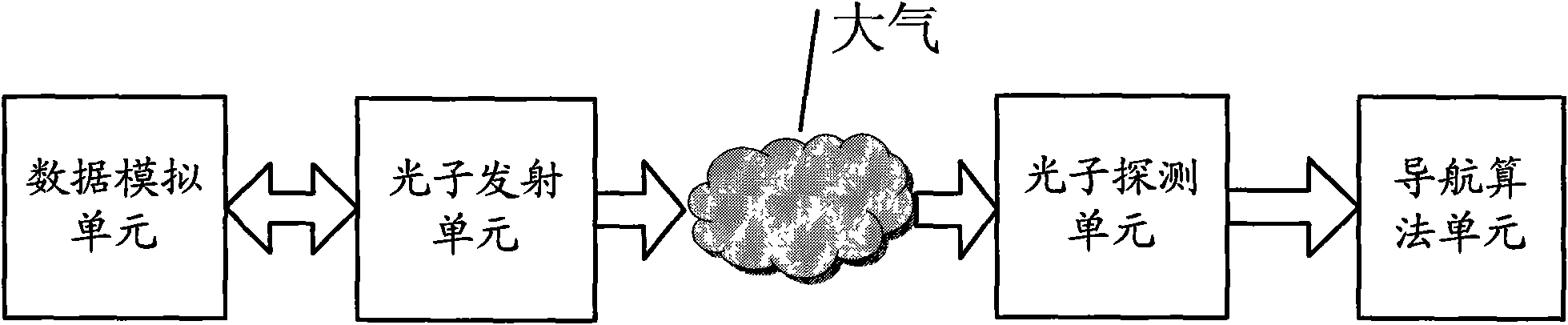
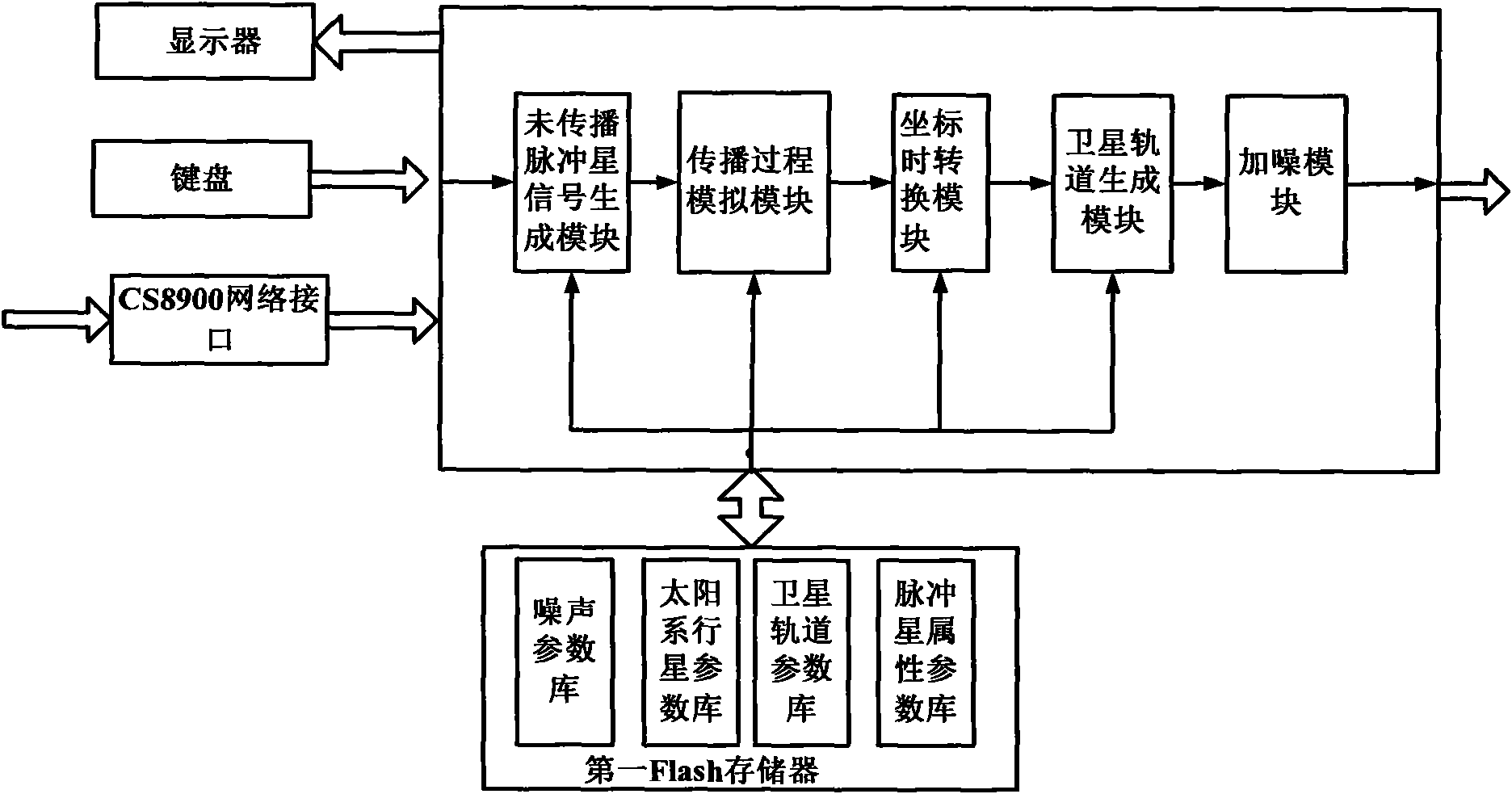
InactiveCN101608919AEasy to compare and analyzeHigh precisionInstruments for comonautical navigationNavigation by astronomical meansData simulationPhoton emission
The invention discloses an X-ray pulsar navigation embedded simulation system based on a semiconductor laser, which comprises a data simulation unit, a photon emission unit, a photon detection unit and a navigation test unit. The data simulation unit simulates X-ray pulsar radiation signal data, and sends the X-ray pulsar radiation signal data to the photon emission unit; the photon emission unit uses simulation data to modulate light intensity of a laser modulation laser, and radiate lasers to the atmosphere; the photon detection unit receives the lasers of the photon emission unit from the atmosphere, filters non-laser spectra components in background sunlight, and sends the received lasers to the navigation test unit after carrying out counting on the received lasers; and the navigation test unit carries out noise elimination, pulse profile accumulation, pulse arrival time measurement treatment on the data of the photon detection unit, and utilizes time measurement data to carry out a navigation test. The invention can provide a complete simulation experiment platform for obtaining navigation signals, signal processing, time synchronization and navigation design verification of navigation signals.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Atmospheric detection laser radar based on superconducting single-photon detector
ActiveCN106054209AImprove time resolutionHigh range resolutionElectromagnetic wave reradiationICT adaptationPhoton detectionOptical processing
The invention discloses an atmospheric detection laser radar based on a superconducting single-photon detector. Optical pulse emitted by a laser pulse generation unit points to a detected atmosphere through a transmitting telescope and a laser scanning unit, background noise of an atmospheric echo signal is filtered out by an optical preprocessing unit, an optical processing unit extracts atmospheric information, a superconducting single-photon detection unit detects the atmospheric echo signal, a data acquisition card collects the signal, and finally, a subsequent data inversion and display unit inverts and displays atmospheric parameter information. The atmospheric detection laser radar of the invention is different from the existing atmospheric detection laser radar in that the atmospheric detection laser radar of the invention uses a superconducting single-photon detector with low dark count, high quantum efficiency, wide wavelength response and low time jitter as a detection unit. By using the superconducting single-photon detector, the atmospheric detection laser radar has the advantages of high spatial resolution, high temporal resolution, large detection distance, high detection precision, and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method and apparatus for generating true random numbers by way of a quantum optics process
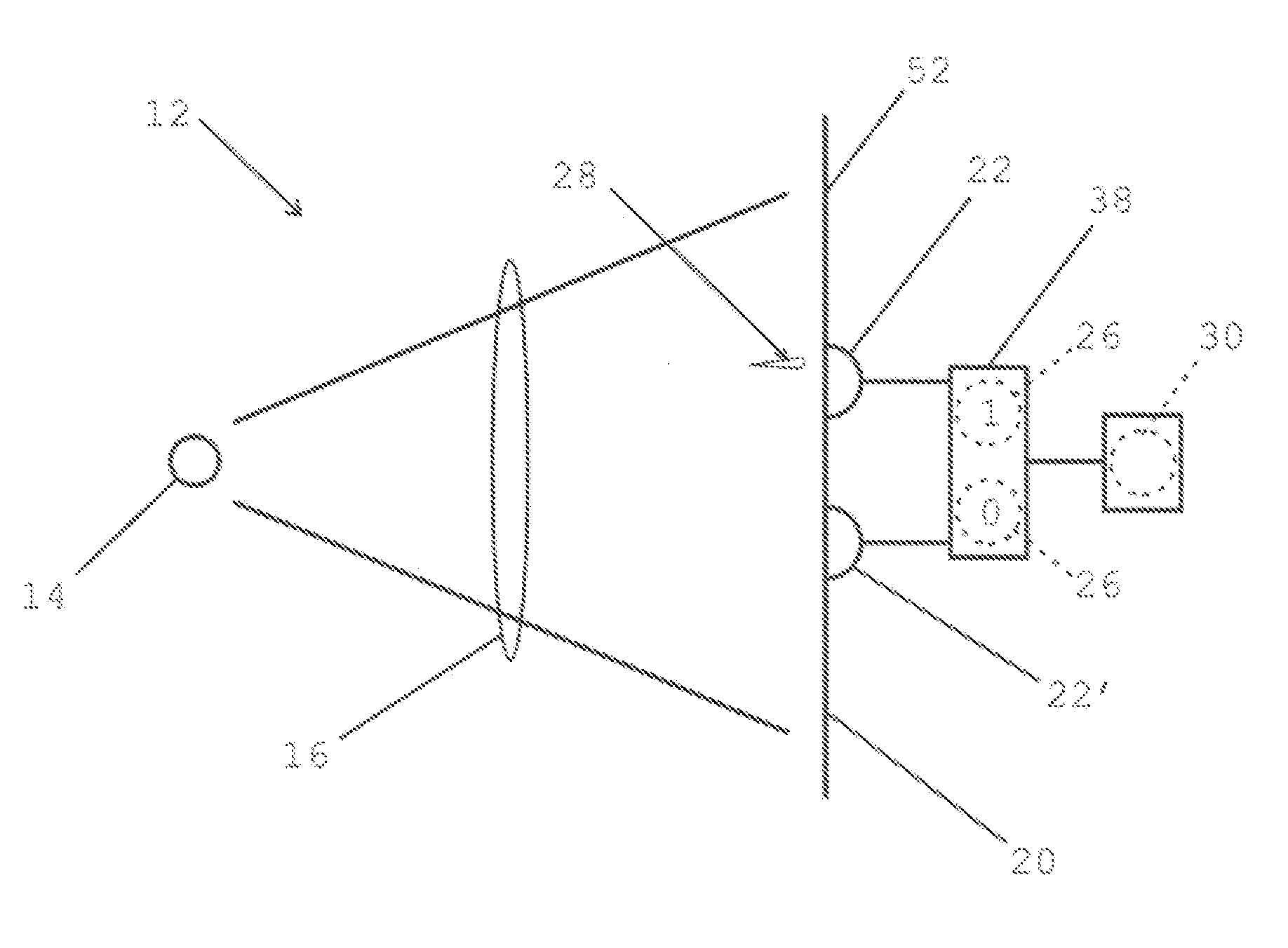
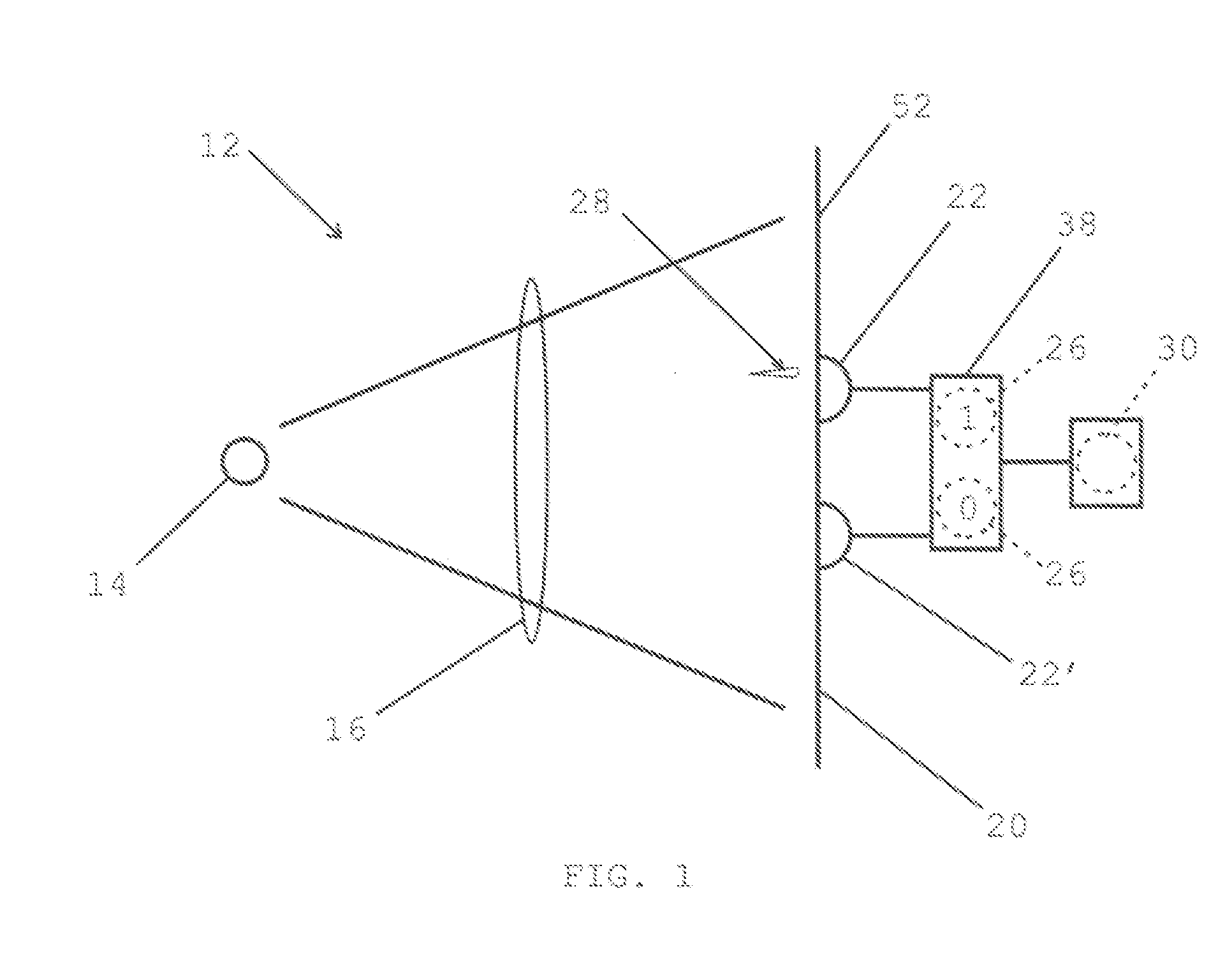
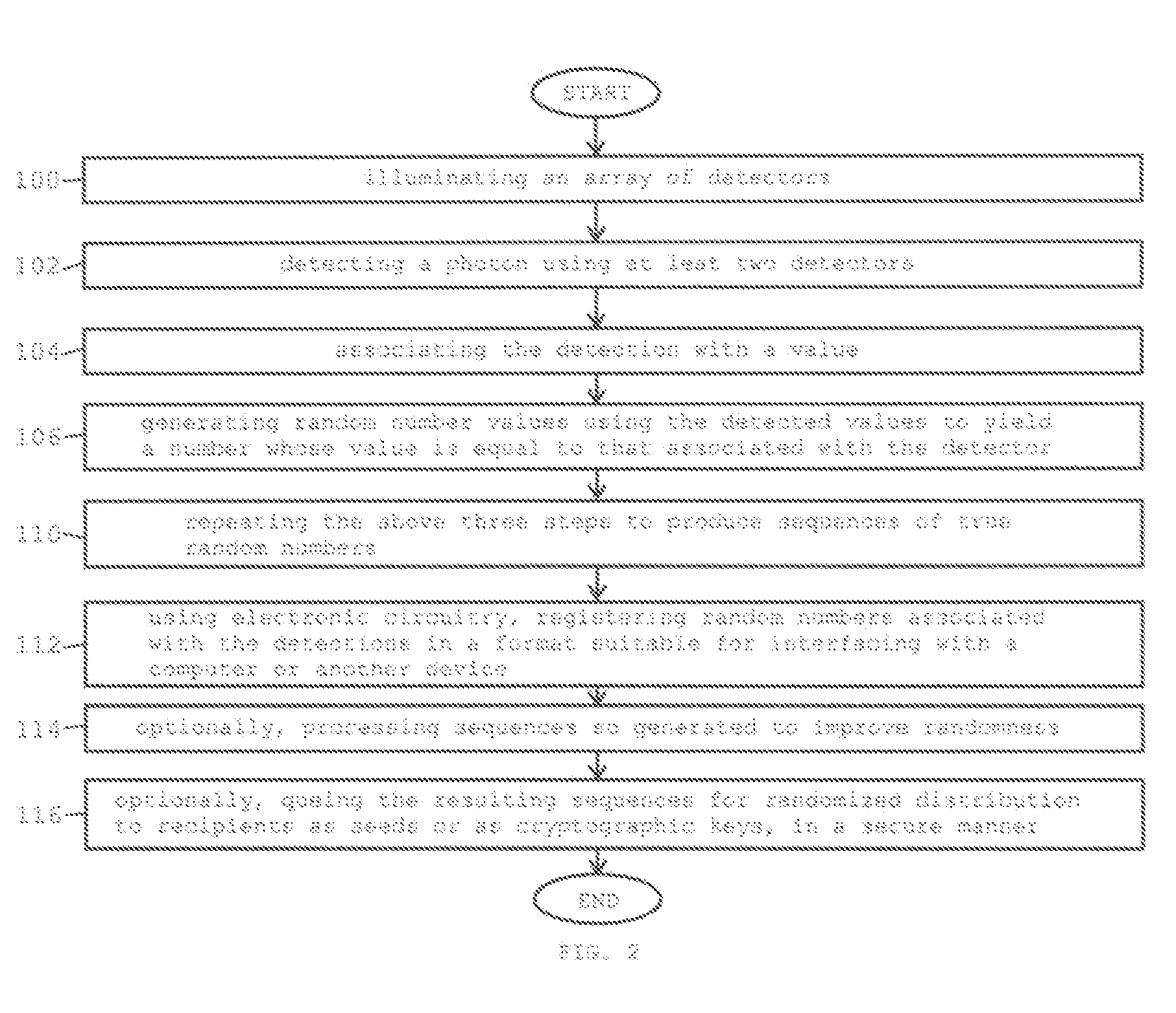
InactiveUS20070127718A1SpeedRandom number generatorsSecret communicationPhoton detectionDetector array
A method and apparatus for generating true random numbers by way of a quantum optics process uses a light source to produce a beam which illuminates a detector array. The detectors of the array are associated with random numbers values. Detection of a photon by one of the detectors yields a number whose value is equal to that associated with the detector. This procedure is repeated to produce sequences of true random numbers. The randomness of the numbers stems from the transverse spatial distribution of the detection probability of the photons in the beam. If the array comprises two detectors, the true random numbers produced are binary numbers. The process can be sped up using an array having pairs of two detectors. Using an array having more than two detectors also allows generating true random numbers of dimension higher than two. The primary object of the invention is to allow generating true random numbers by way of a quantum optics process.
Owner:ID QUANTIQUE SA
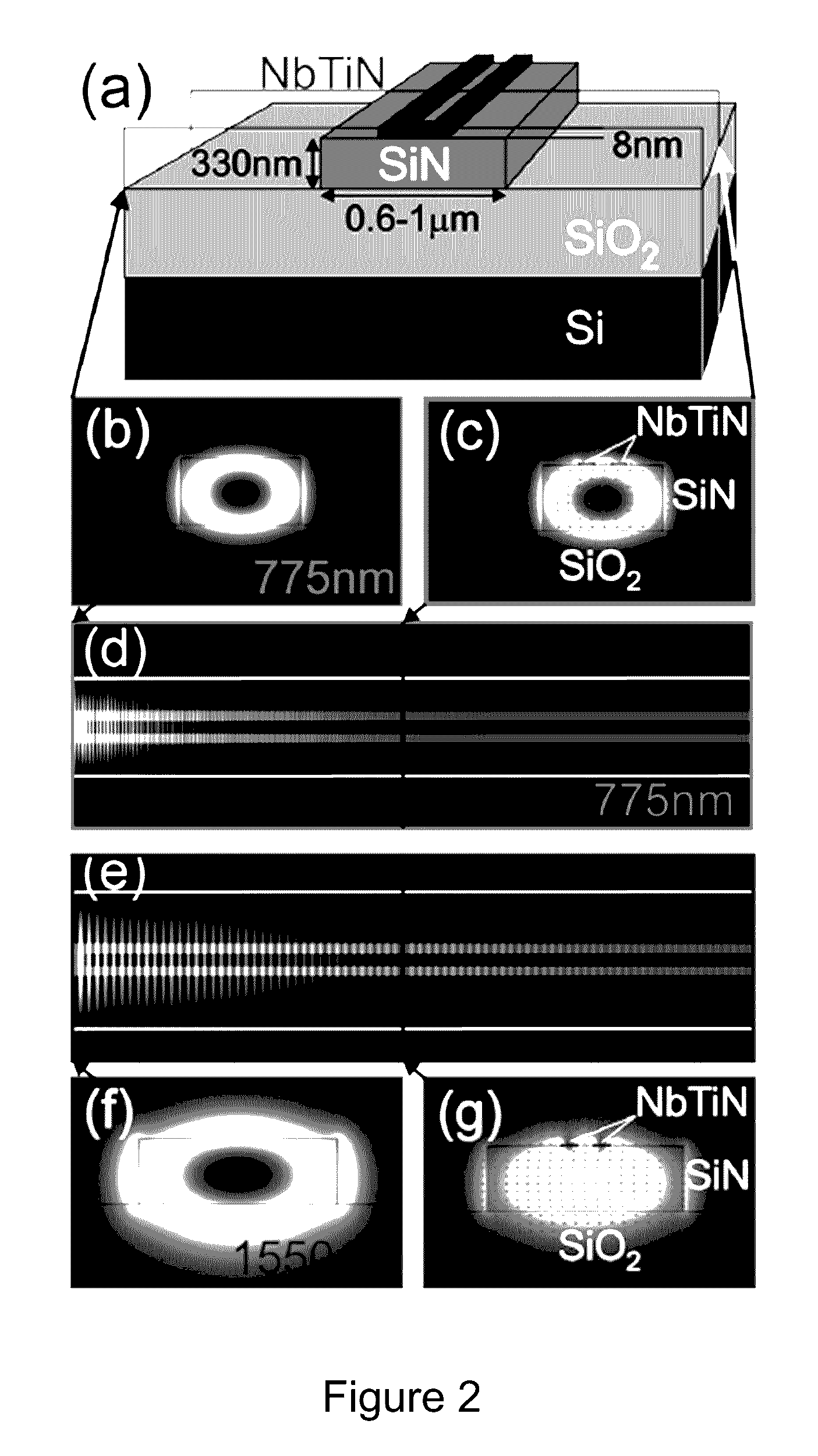
Efficient Polarization Independent Single Photon Detector
ActiveUS20140087952A1Improve quantum efficiencySuperconductors/hyperconductorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingQuantum efficiencyNanowire
A superconducting nanowire single photon detector (SN-SPD) microelectronic circuit is described which has higher quantum efficiency and signal-to-noise than any SN-SPD's known in the art. The material and configuration of the microelectronic circuit eliminates the polarization dependence and shows improved signal-to-noise over SN-SPD microelectronic circuits known in the art. The higher efficiency, polarization independence, and high signal-to-noise is achieved by vertically stacking two tungsten-silicide (TS) SN-SPDs and electrically connecting them in parallel. This structure forms a multilayer superconducting nanowire avalanche photo-detector (SNAP). A single photon detection device employing the multilayer (SNAP) microelectronic circuit demonstrates a peak system detection efficiency of 87.7% and a polarization dependence of less than 2%. This represents nearly an order of magnitude improvement in both system detection efficiency and reduction of polarization dependence compared to conventional SNSPDs.
Owner:GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF COMMERCE THE NAT INST OF STANDARDS & TEHCNOLOGY
Solid state photomultiplier using buried P-N junction
A device that detects single optical and radiation events and that provides improved blue detection efficiency and lower dark currents than prior silicon SSPM devices. The sensing element of the devices is a photodiode that may be used to provide single photon detection through the process of generating a self-sustained avalanche. The type of diode is called a Geiger photodiode or signal photon-counting avalanche diode. A CMOS photodiode can be fabricated using a “buried” doping layer for the P-N junction, where the high doping concentration and P-N junction is deep beneath the surface, and the doping concentration at the surface of the diode may be low. The use of a buried layer with a high doping concentration compared to the near surface layer of the primary P-N junction allows for the electric field of the depletion region to extend up near the surface of the diode. With a low doping concentration through the bulk of the diode, the induced bulk defects are limited, which may reduce the dark current. The resulting structure provides a diode with improved quantum efficiency and dark current.
Owner:RADIATION MONITORING DEVICES
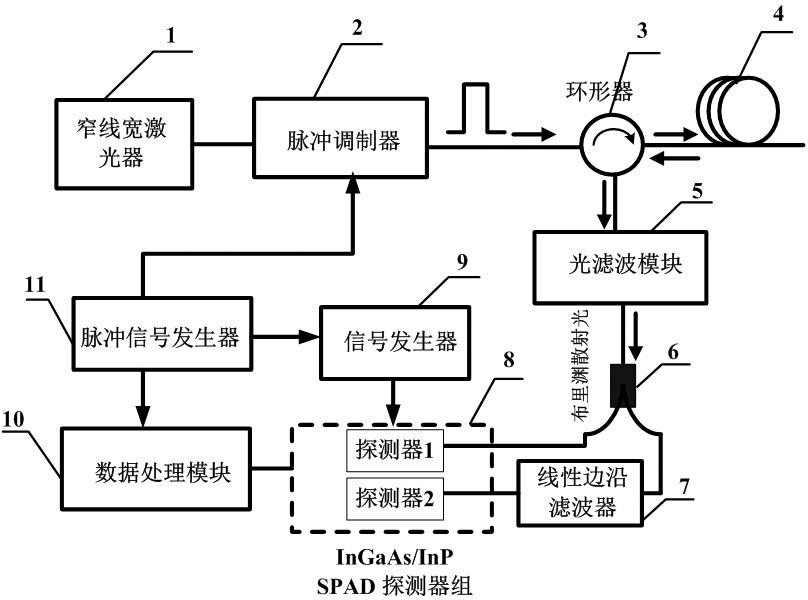
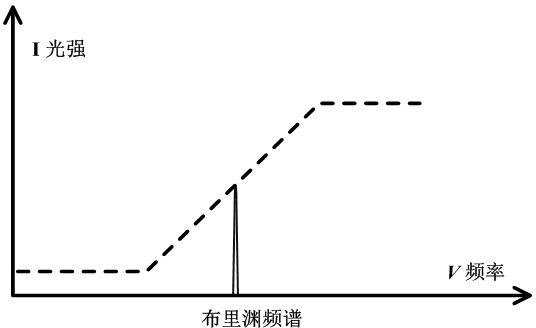
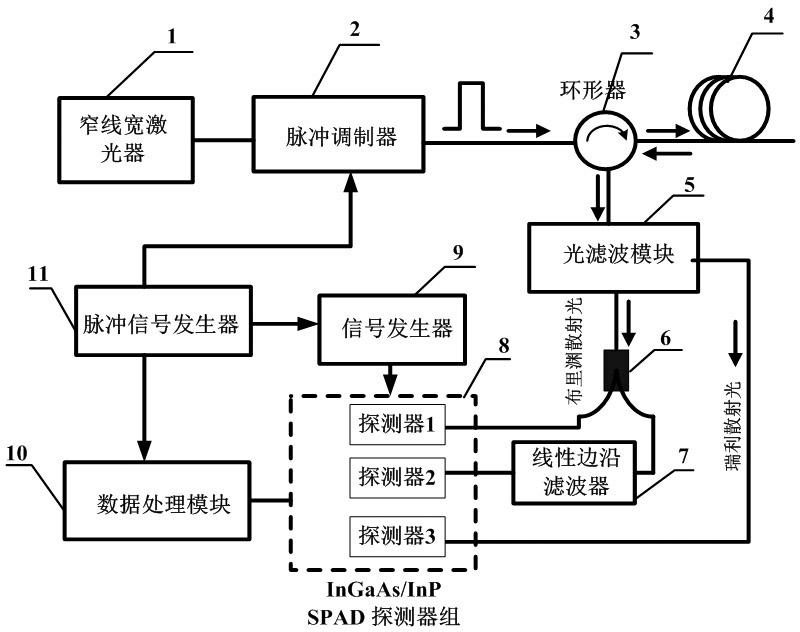
Brillouin optical time domain reflectometer for single-photon detection based on edged filter method
InactiveCN102620857ASimple structureReduce volumeThermometers using physical/chemical changesUsing optical meansTime correlationPhoton detection
The invention discloses a Brillouin optical time domain reflectometer for single-photon detection based on an edged filter method, which comprises a narrow linewidth laser (1), a pulse modulator (2), a circulator (3), a sensing optical fiber (4), an optical fiber module (5), 3dB coupler (6), a linear edged filter (7), an InGaAs / InP SPAD (single-photon avalanche diode) detector group (8), a signal generator (9), a data processing module (10) and a pulse signal generator (11), wherein the InGaAs / InP SPAD detector group (8) includes two or three InGaAs / InP SPAD detectors. The InGaAs / InP SPAD detector group with a high counting rate and high sensitivity is used as a detection unit, Brillouin frequency shift information is acquired by the edged filter method, time correlation single-photon counting technology is adopted by the data processing module (10), limitations on the bandwidth and sensitivity of a traditional detector are broken through, spatial resolution and measuring precision of the reflectometer can be simultaneously improved, and temperature and strain are simultaneously sensed.
Owner:NANJING FAAIBO OPTOELECTRONICS TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com