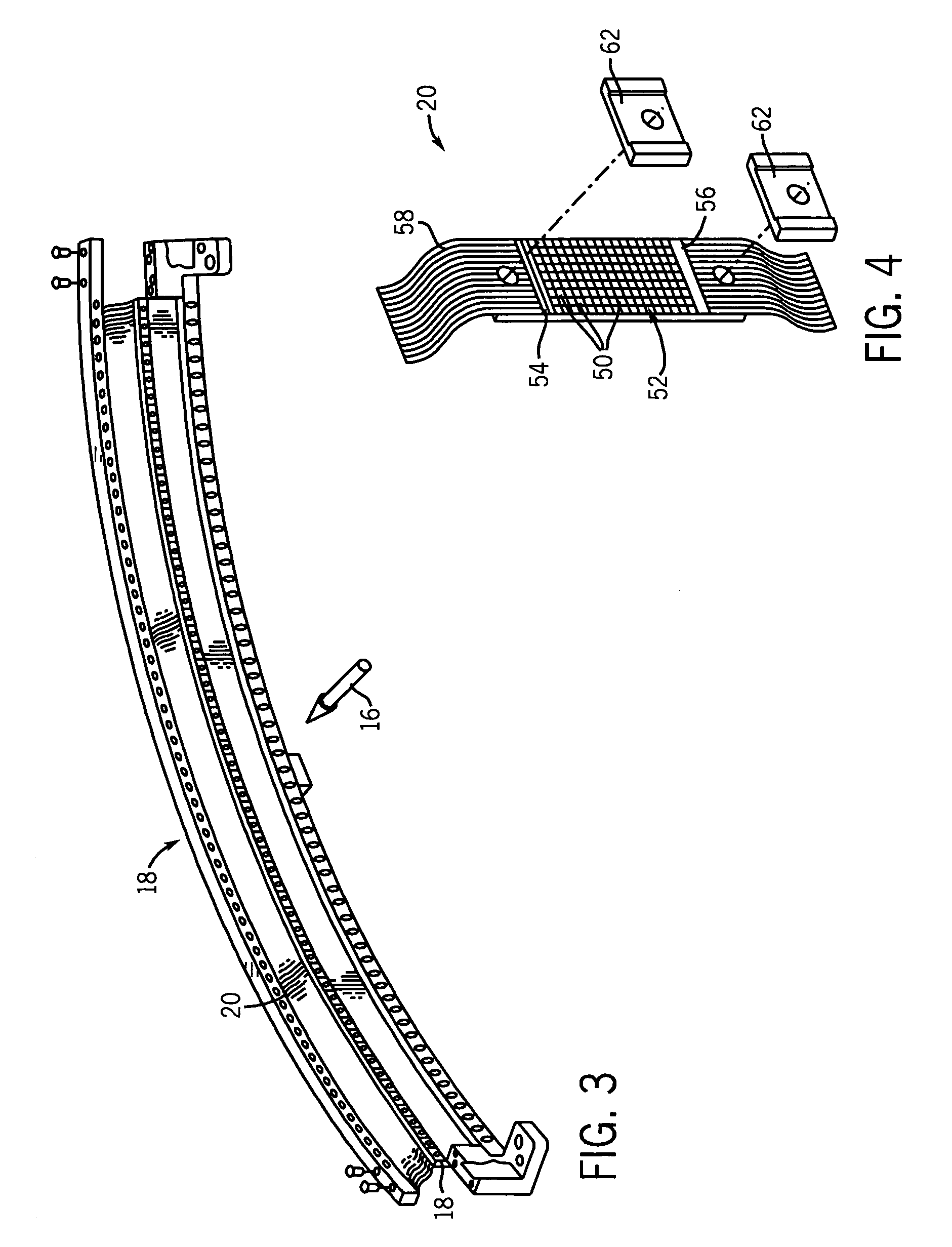
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
641 results about "Counting rate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
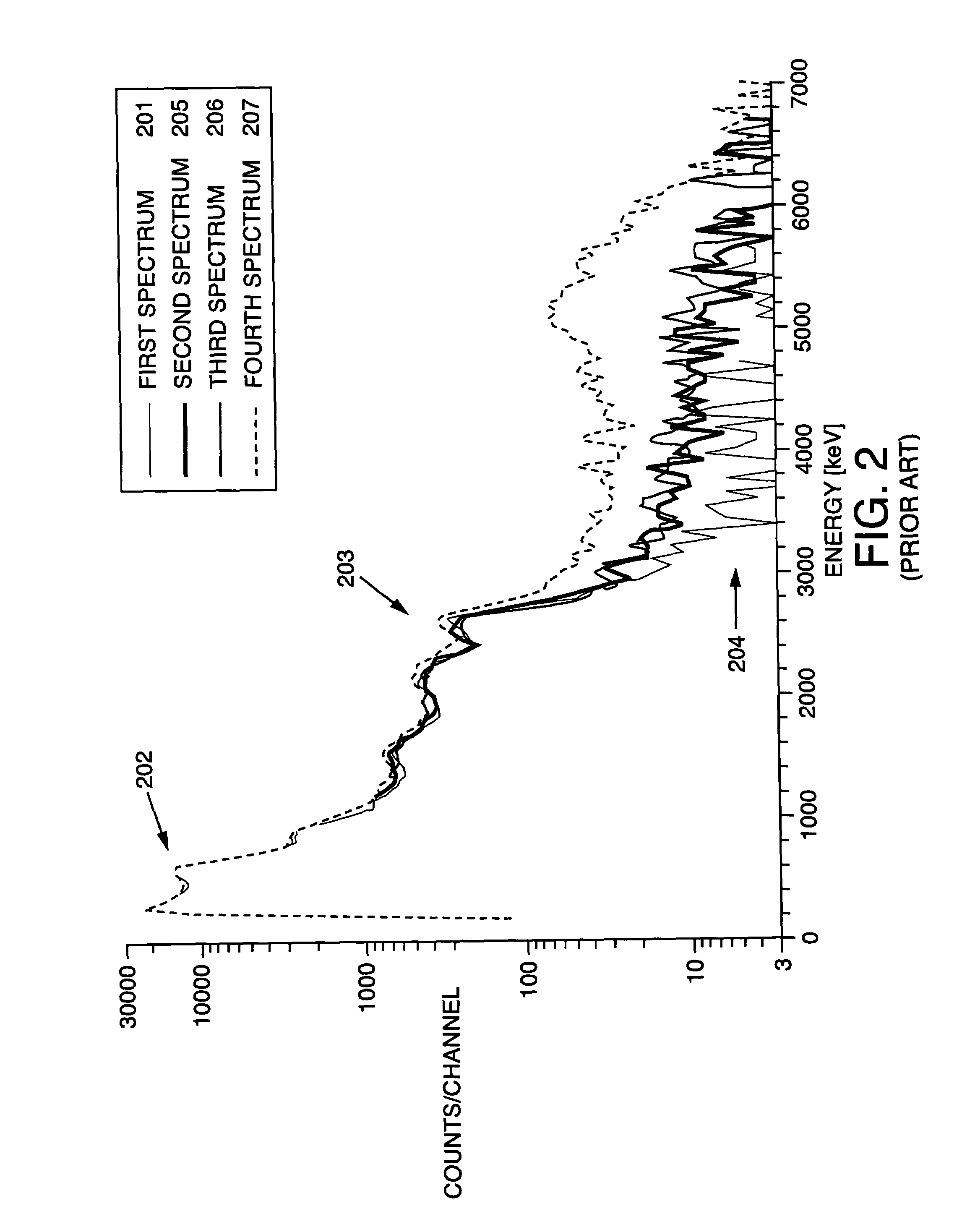
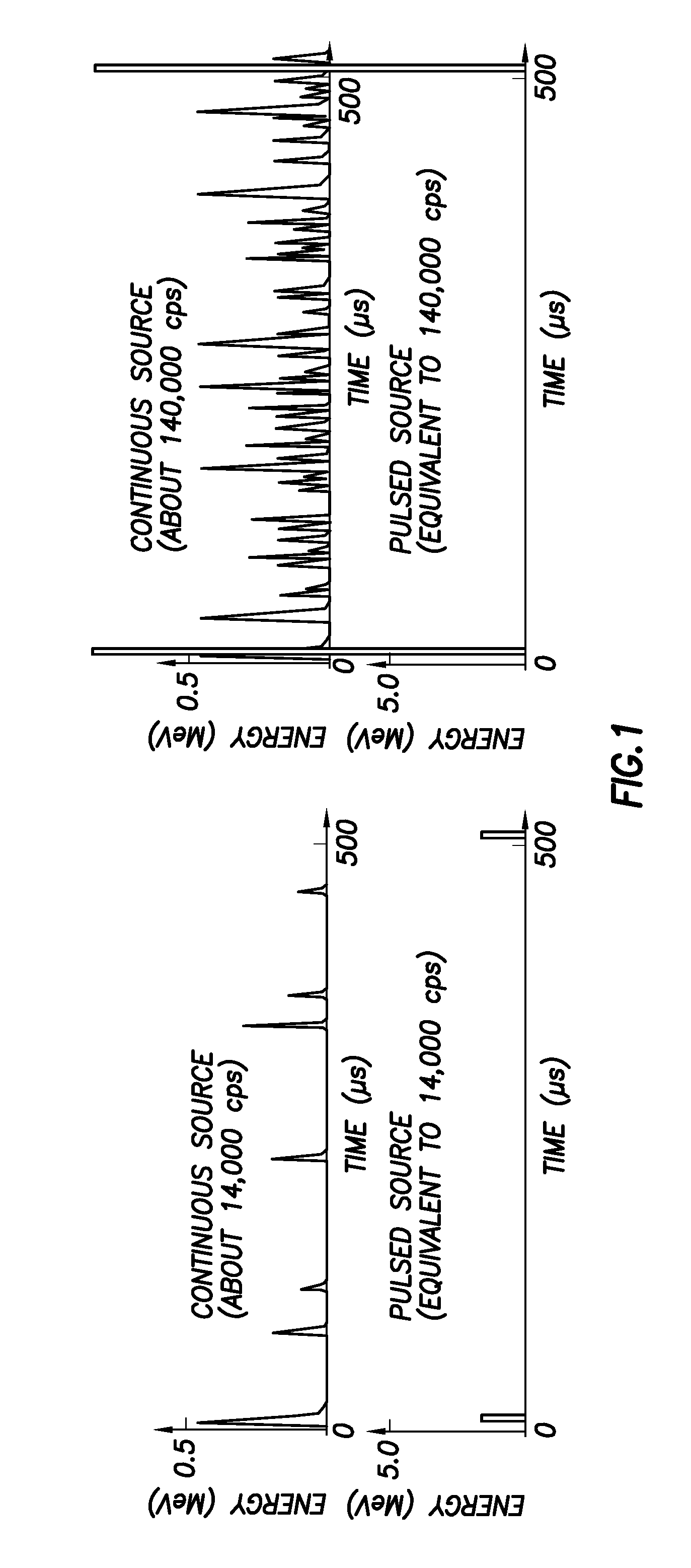
Counting rate. [′kau̇nt·iŋ ‚rāt] (physics) The average rate of occurrence of events as observed by means of a counting system.
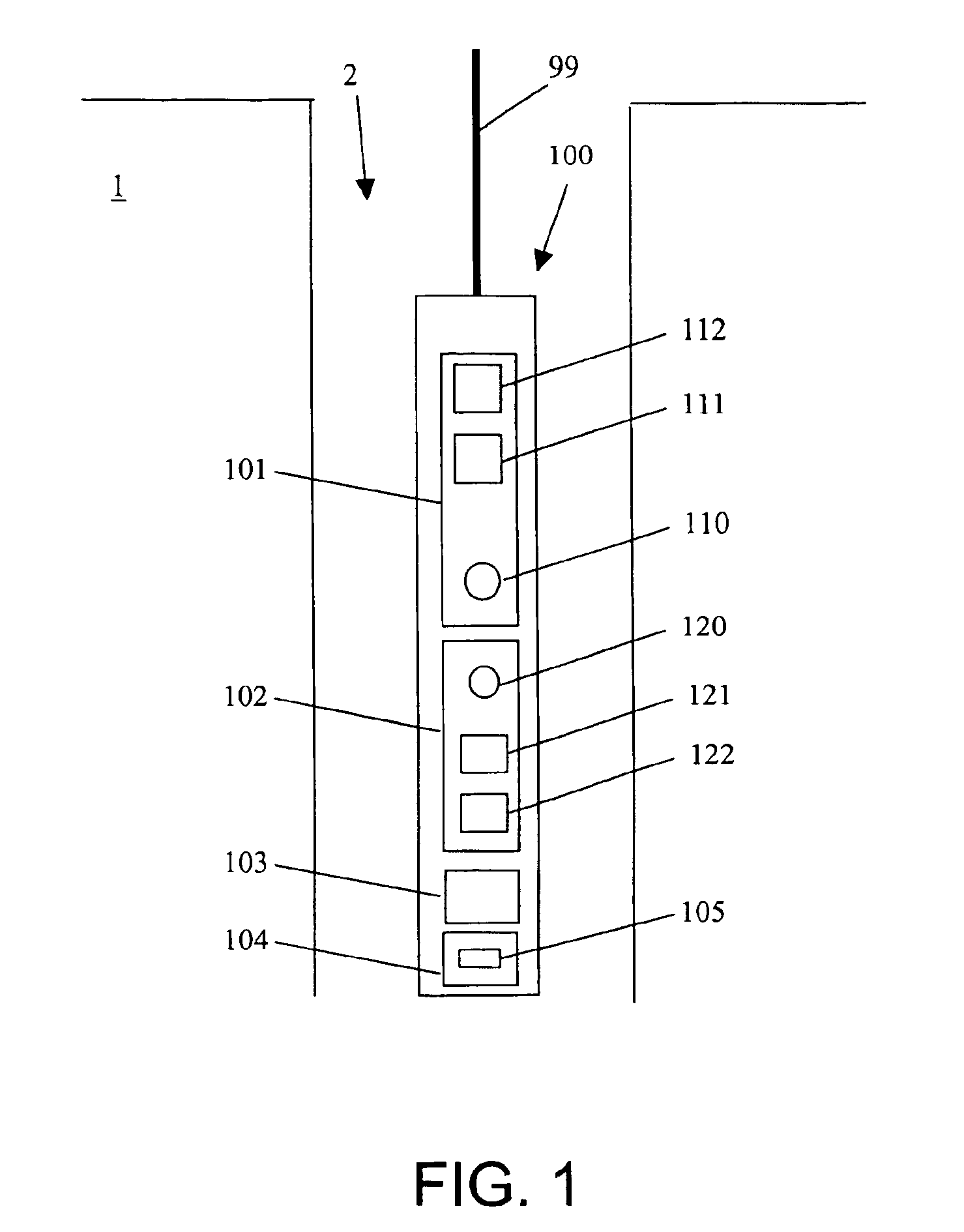
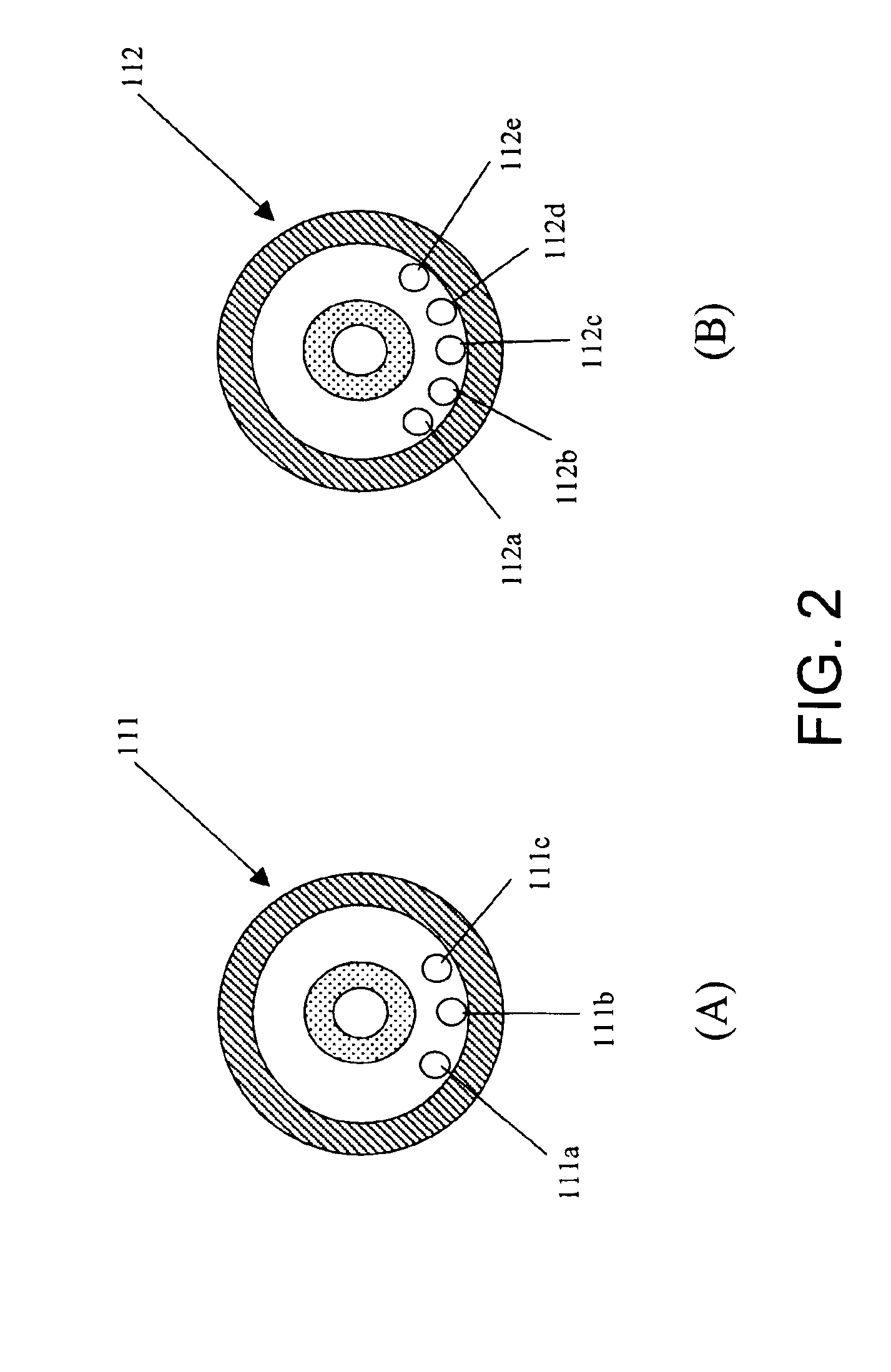
Direct conversion energy discriminating CT detector with over-ranging correction
ActiveUS20060056581A1Reduce the impactImprove visualizationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingCounting rateSemiconductor materials
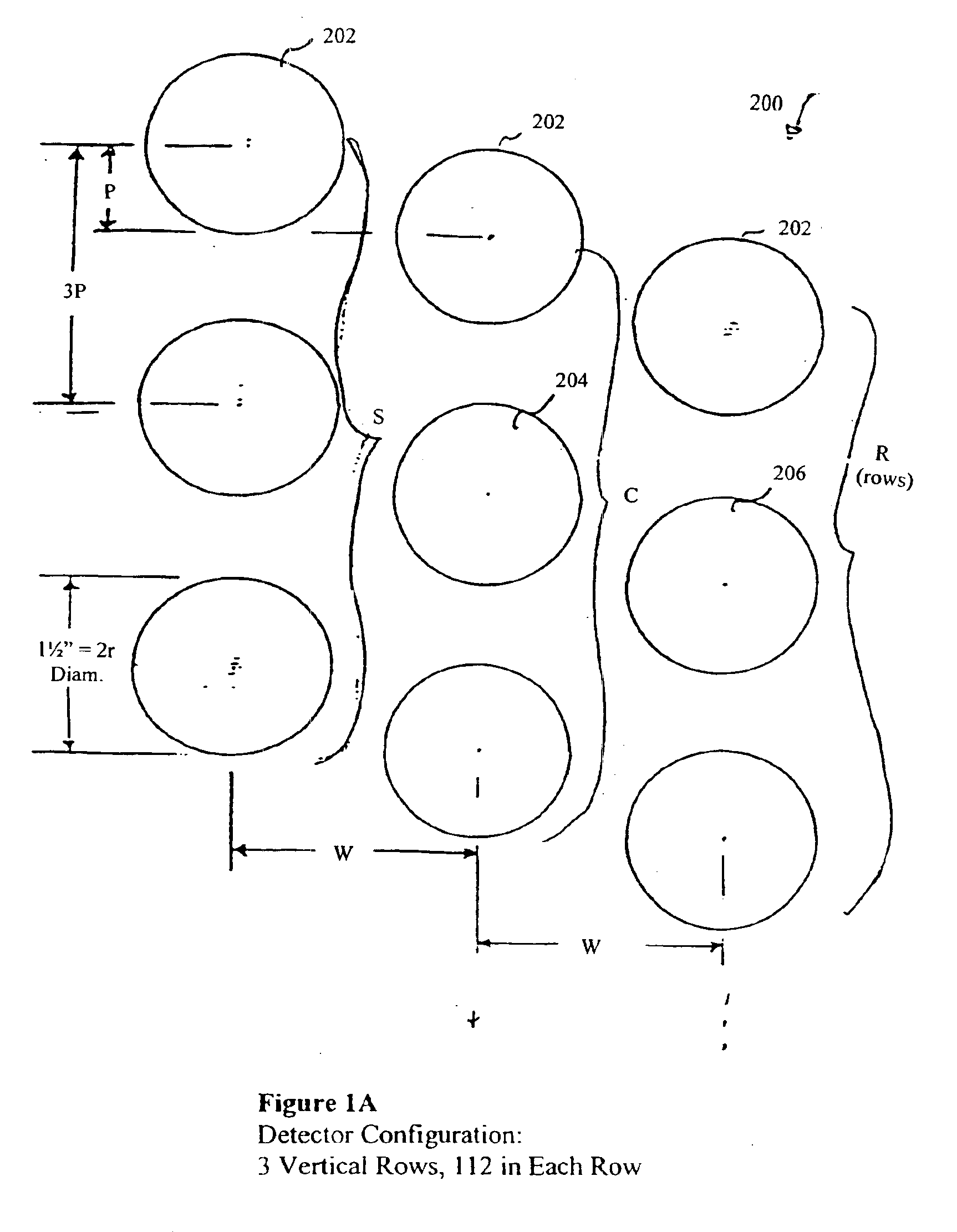
A CT detector capable of energy discrimination and direct conversion is disclosed. The detector includes multiple layers of semiconductor material with the layers having varying thicknesses. The detector is constructed to be segmented in the x-ray penetration direction so as to optimize count rate performance as well as avoid saturation. The detector also includes variable pixel pitch and a flexible binning of pixels to further enhance count rate performance.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Density detection using real time discrete photon counting for fast moving targets
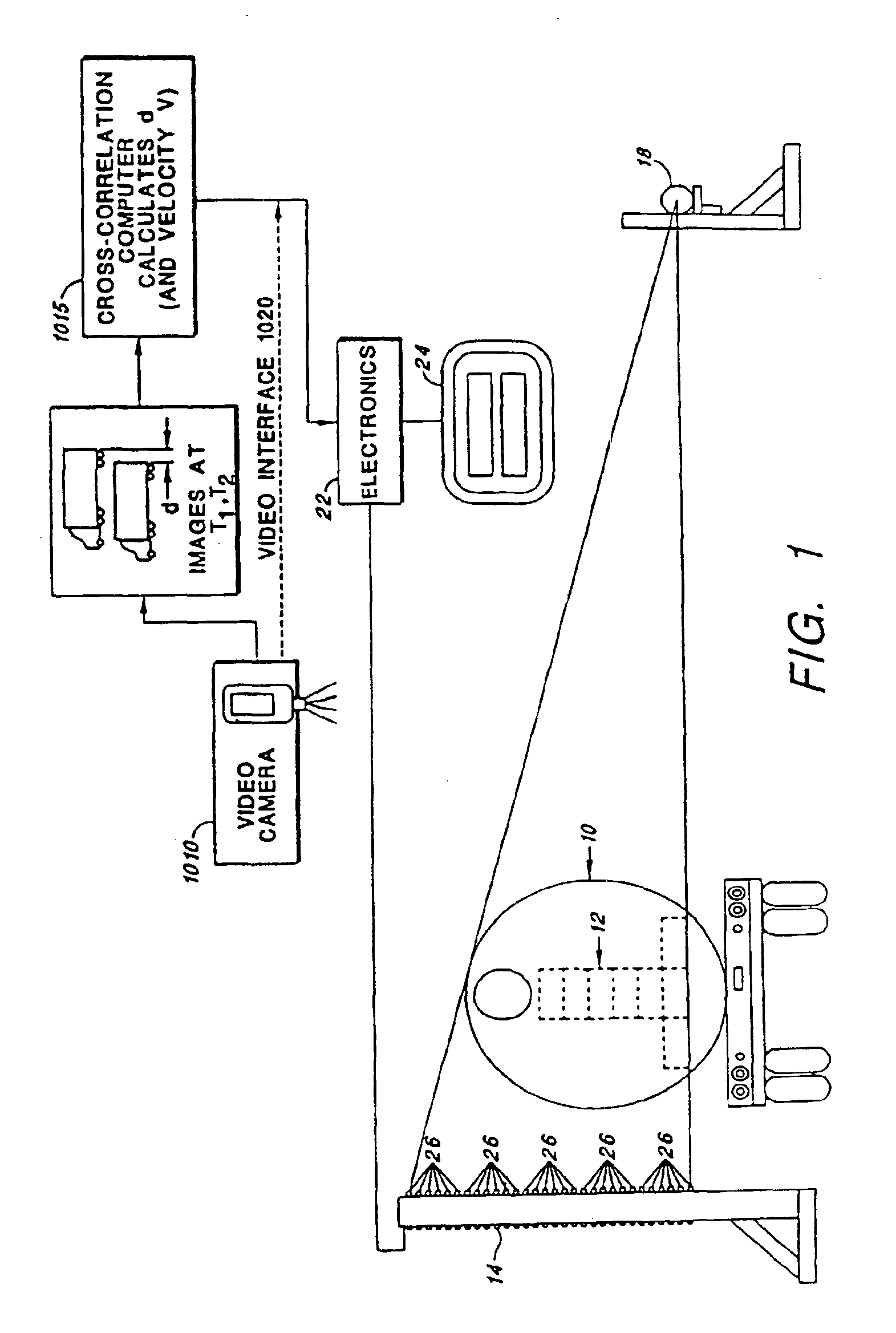
A system for detecting and graphically displaying a contents of a fast-moving target object comprises: a radiation source, having a position such that at least a portion of radiation emitted from the radiation source passes through the fast-moving target object, the fast-moving target object having a variable velocity and acceleration while maintaining a substantially constant distance from the radiation source and being selected from the group consisting of: a vehicle, a cargo container and a railroad car; a velocity measuring device configured to measure the variable velocity of the fast-moving target object; a detector array comprising a plurality of photon detectors, having a position such that at least some of the at least a portion of the radiation passing through the target object is received thereby, the detector array having a variable count time according to the variable velocity and a grid unit size; a counter circuit coupled to the detector array for discretely counting a number of photons entering individual photon detectors, the counter circuit measuring a count rate according to a contents within the fast-moving target object; a high baud-rate interface coupled to the counter circuit for sending count information from the counter circuit at a rate fast enough to support real-time data transfer therethrough; and a processor coupled to the velocity measuring device and to the high-baud-rate interface, receiving count information from the high baud-rate interface and generating distortion-free image data in real time as a function of the count information and the variable velocity. A method for using the system is also disclosed.
Owner:LEIDOS
Method for Cement Evaluation with Acoustic and Nuclear Density Logs
Method for evaluating cement quality in a cased well. A density log of the well is obtained using, for example, a GammaRay sources and detectors (51). The detector count rates are inverted to provide initial estimates of cement density and thickness (53). Acoustic waveform data are obtained from the well using an acoustic logging tool (52). The acoustic data are inverted (54-56), using the initial estimates of cement density and thickness obtained from the density logs, and an updated density log is inferred. Cement images are obtained from the updated density log, and cement bond quality can be estimated (57).
Owner:GUO PINGJUN +1
CT detector fabrication process
ActiveUS6953935B1Reduce the impactImprove visualizationPhotometry using reference valueX-ray/infra-red processesCounting rateX-ray
A CT detector capable of energy discrimination and direct conversion is disclosed. The detector includes multiple layers of semiconductor material with the layers having varying thicknesses. The detector is constructed to be segmented in the x-ray penetration direction so as to optimize count rate performance as well as avoid saturation.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
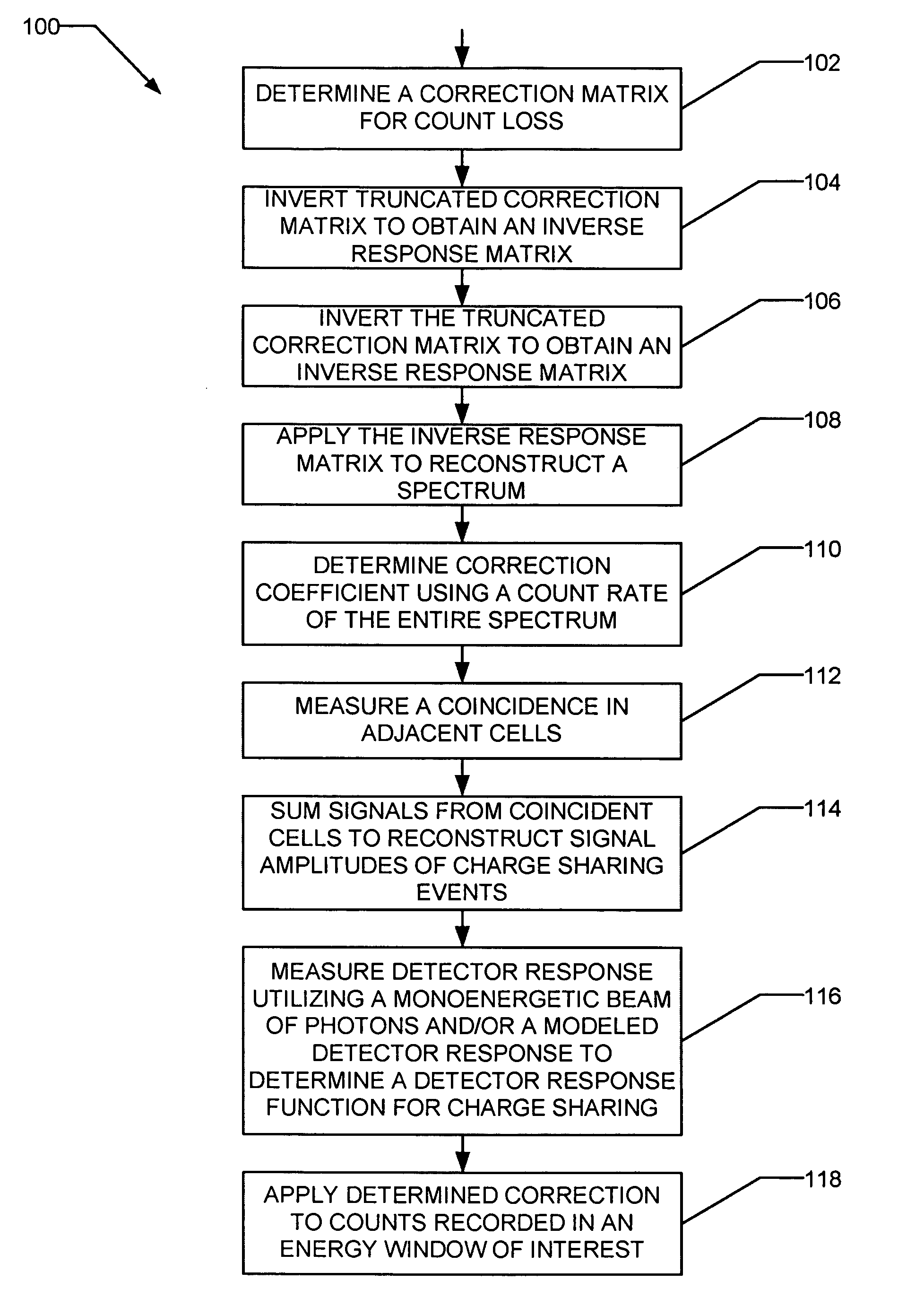
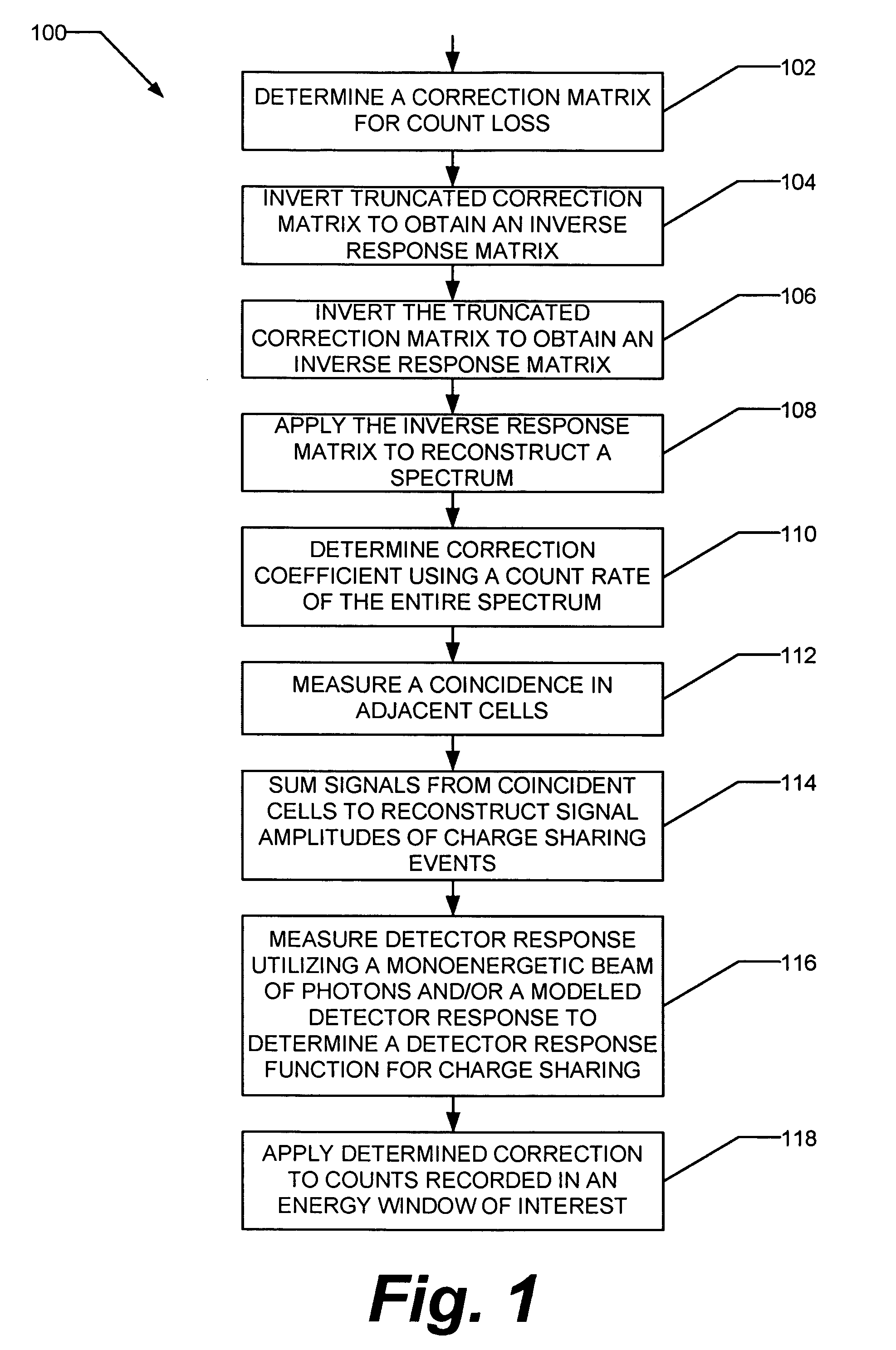
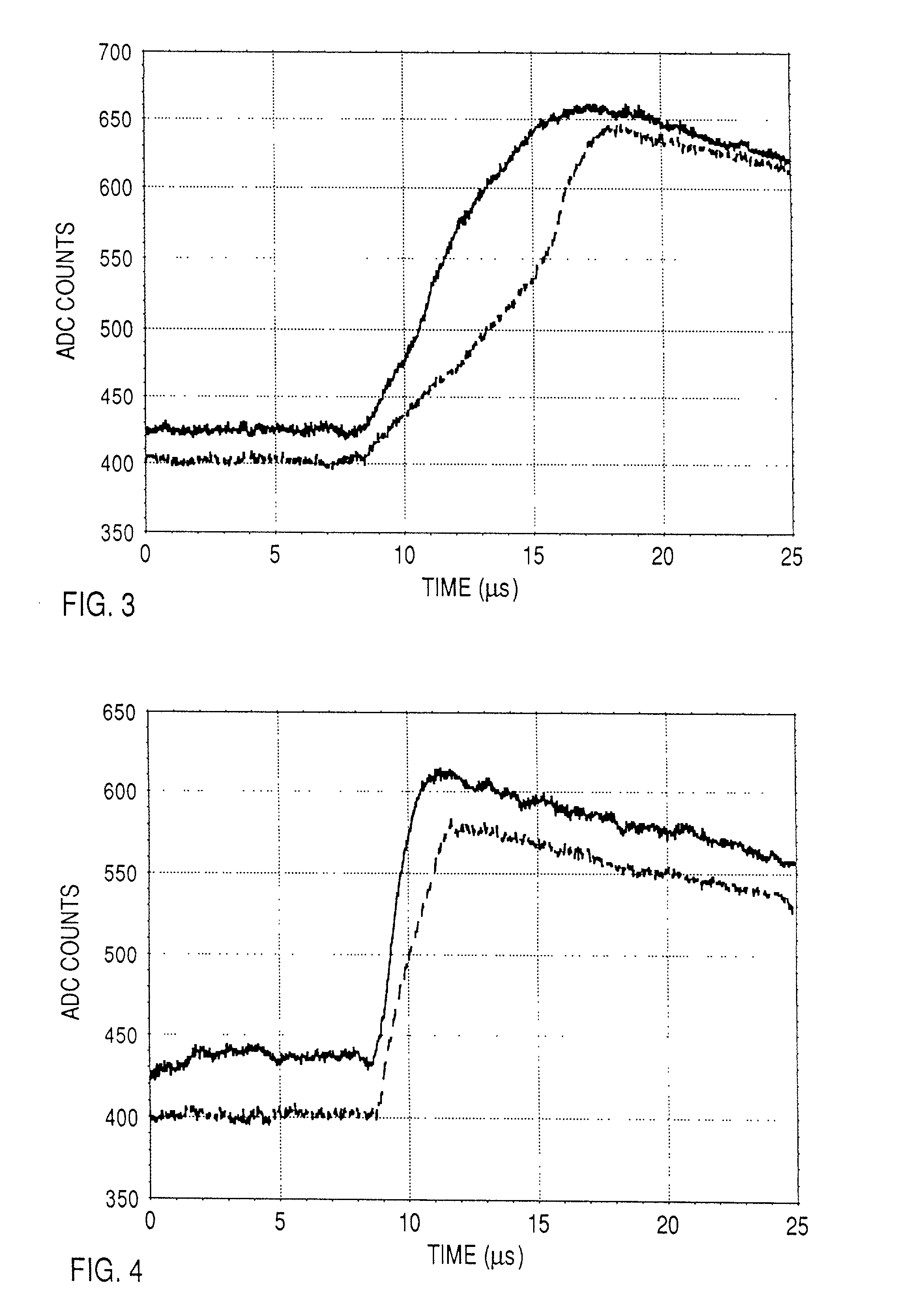
Method and apparatus for correction of pileup and charge sharing in x-ray images with energy resolution
ActiveUS7208739B1Reduce distortion problemsMaterial analysis by optical meansX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentCounting rateEnergy window
A method for correcting at least one of pileup effects or charge sharing effects in multi-cell photon counting detectors includes determining a correction coefficient using a count rate of an entire spectrum and applying the determined correction to the counts recorded in an energy window of interest.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
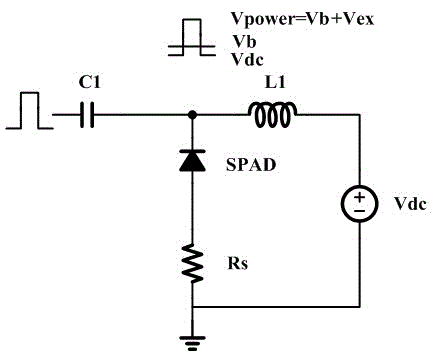
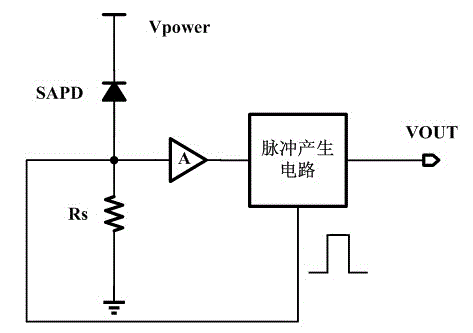
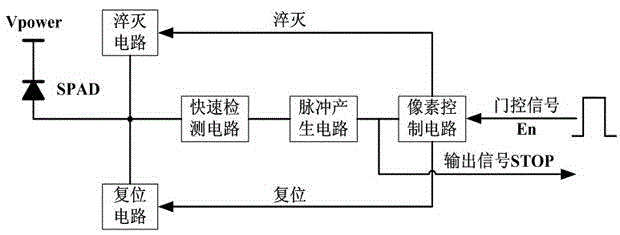
Integrated gating active quenching/restoring circuit
InactiveCN103148950AReduce detection noiseImprove reliabilityInstrumentsCounting rateSingle-photon avalanche diode
The invention discloses an integrated gating active quenching / restoring circuit. The integrated gating active quenching / restoring circuit comprises a quick detection circuit, a pulse generation circuit, a pixel control circuit, a quenching circuit and a restoring circuit, wherein the quick detection circuit is used for processing a detected anode current signal of an SPAD (Single Photon Avalanche Diode) into a pulse signal, the pulse signal can be output through the pulse generation circuit, the pixel control circuit is controlled by an output signal and a gating signal of the pulse generation circuit, the restoring circuit and the quenching circuit are respectively controlled by outputs of the pixel generation circuit, outputs of the restoring circuit and the quenching circuit can be fed back to an anode of the SPAD, and the restoring and the quenching of the SPAD can be controlled. According to the integrated gating active quenching / restoring circuit disclosed by the invention, by adopting a gating control method, the dark counting rate of the SPAD can be effectively reduced, the quenching time can be controlled by the pulse generation circuit, and the integrated gating active quenching / restoring circuit has the advantages of compact area and low power consumption.
Owner:THE 44TH INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GROUP CORP
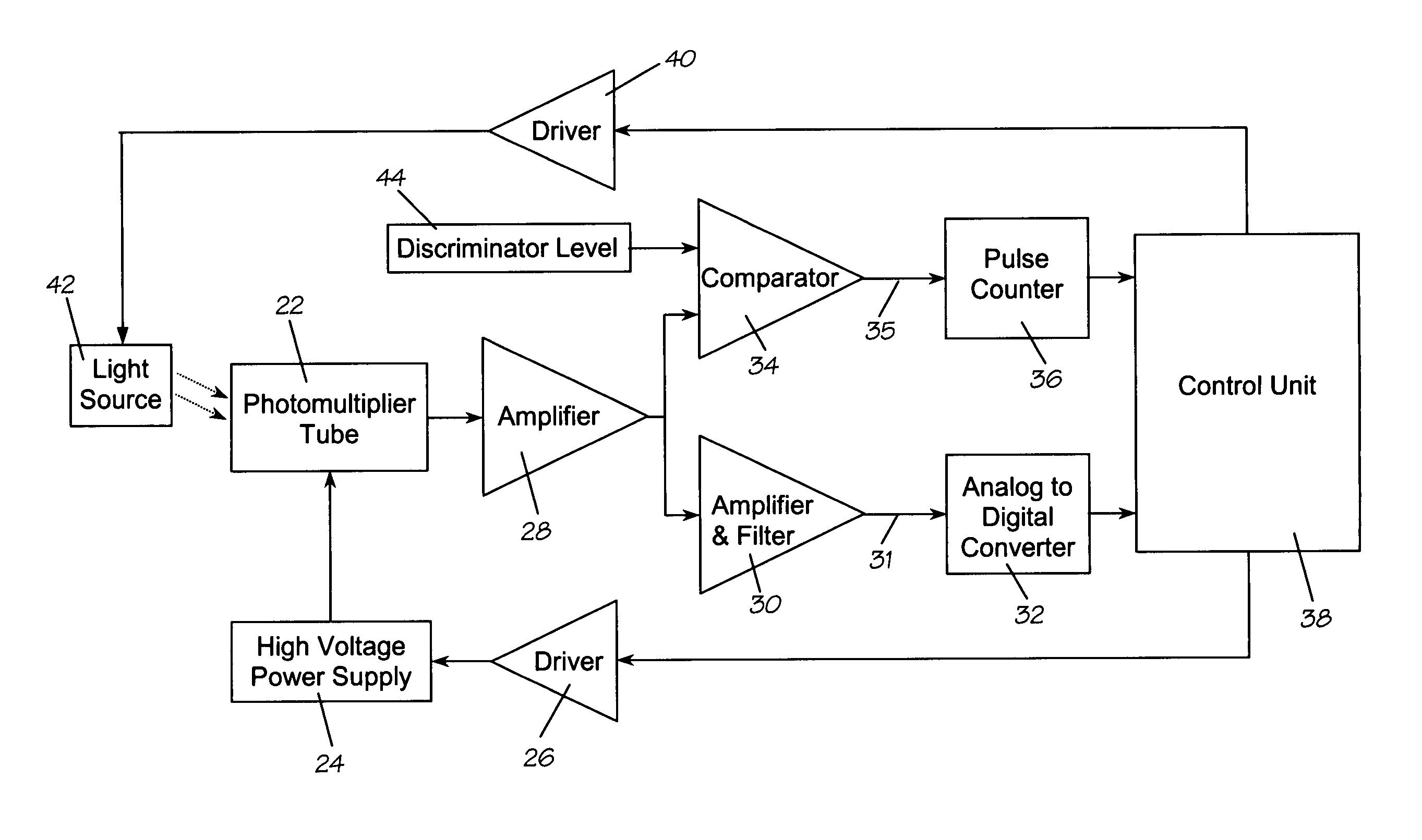
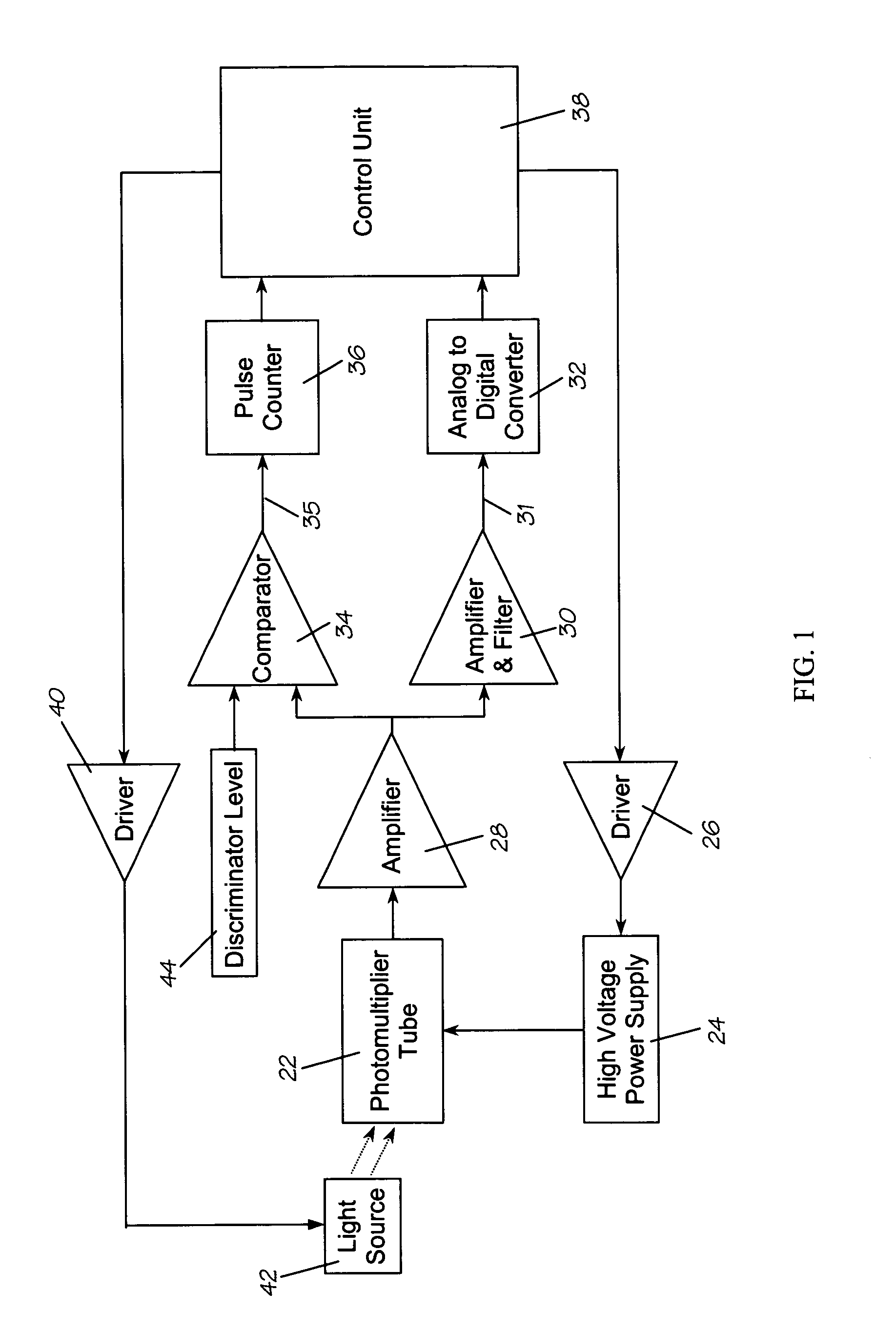
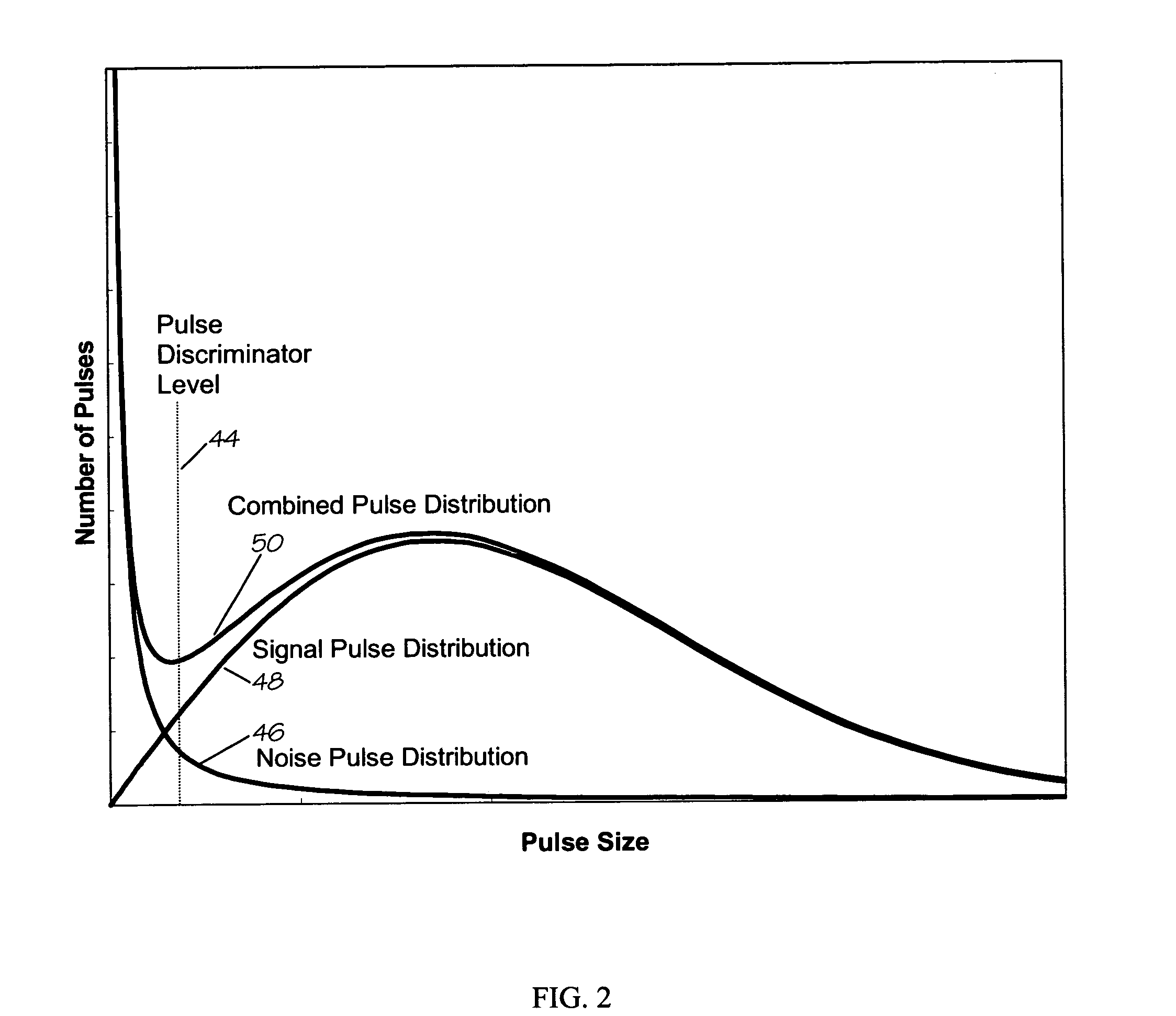
Photomultiplier tube gain stabilization for radiation dosimetry system
InactiveUS7157681B1Low costSmall sizePhotometry using reference valueMaterial analysis by optical meansDosimetry radiationDosimeter
Methods and means for measuring and adjusting the gain of a photomultiplier tube (PMT), or other photo-detector with electron multiplication gain, for the purpose of achieving accurate light measurement, such as in a luminescent radiation dosimeter reader. With a PMT illuminated by a light emitting diode or other light source, the PMT output signal is measured in two modes, signal integration and photon pulse counting. The measured PMT gain is calculated as the ratio of the integrated signal to the photon pulse count. The PMT high voltage may be adjusted to cause the measured PMT gain to correspond to an established calibration gain value, or the data from the PMT may be adjusted to compensate the deviation of the measured PMT gain from the calibration gain value. The light source may be a controllable light source that can be adjusted to provide a specific photon count rate output as measured by the PMT. This invention provides for maintaining light measurement calibration without requiring temperature stabilization or a fixed light source.
Owner:TETZLAFF WOLFGANG
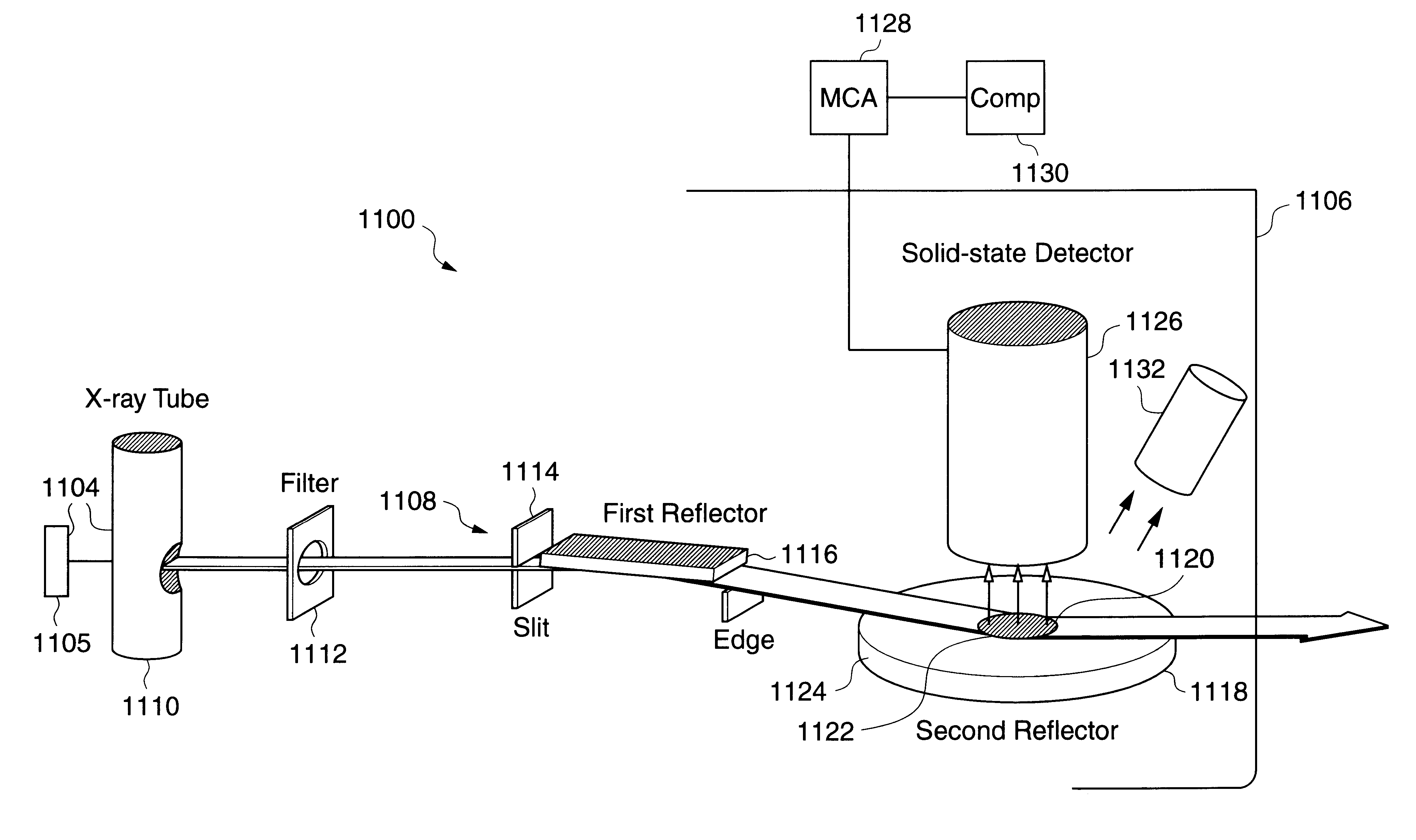
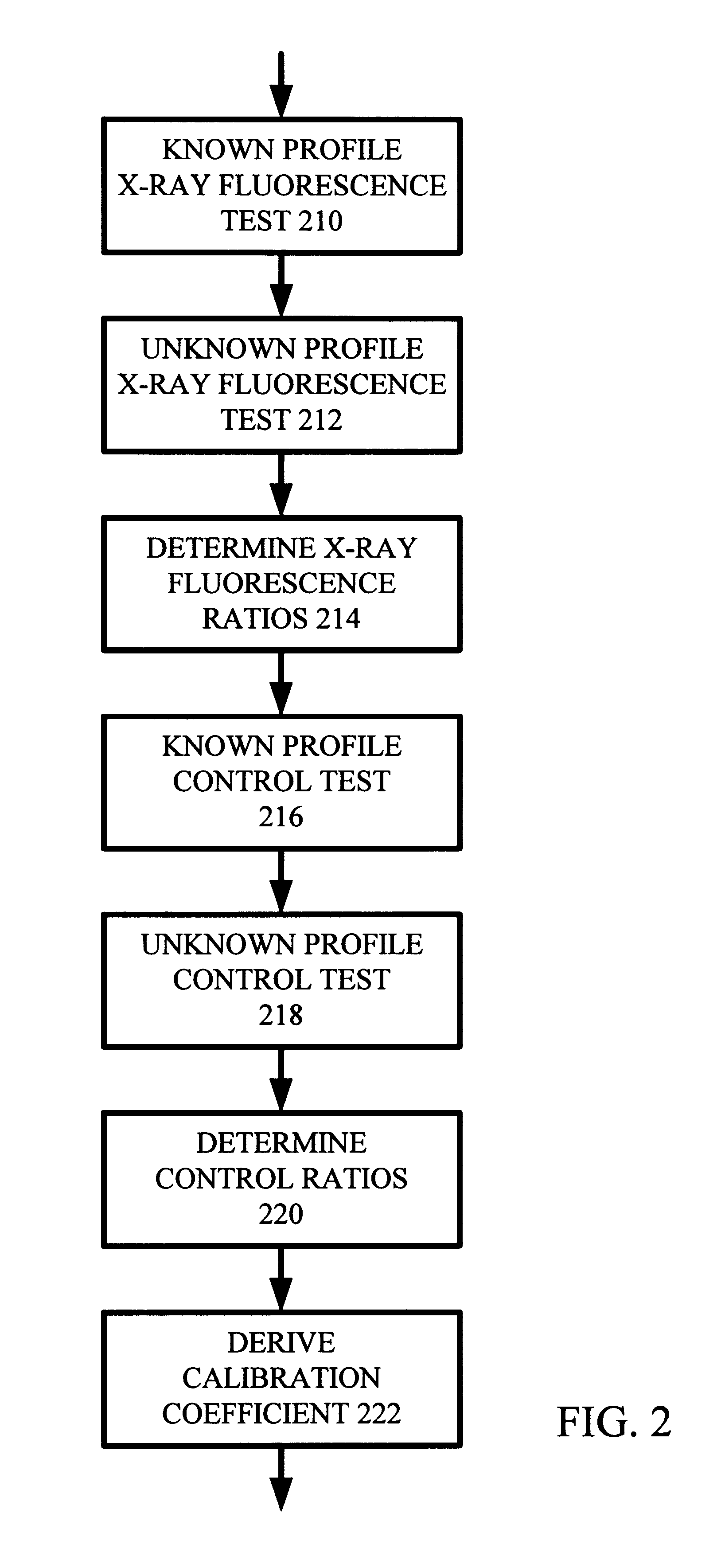
Depth profile metrology using grazing incidence X-ray fluorescence
InactiveUS6173036B1X-ray spectral distribution measurementUsing wave/particle radiation meansMetrologyMicro-X-ray fluorescence
For small angles that are near critical angle, a primary incident X-ray beam has excellent depth resolution. A series of X-ray fluorescence measurements are performed at varying small angles and analyzed for depth profiling of elements within a substrate. One highly useful application of the X-ray fluorescence measurements is depth profiling of a dopant used in semiconductor manufacturing such as arsenic, phosphorus, and boron. In one example, angles are be varied from 0.01° to 0.20° and measurements made to profile arsenic distribution within a semiconductor wafer. In one embodiment, measurements are acquired using a total reflection X-ray fluorescence (TXRF) type system for both known and unknown profile distribution samples. The fluorescence measurements are denominated in counts / second terms and formed as ratios comparing the known and unknown sample results. The count ratios are compared to ratios of known to unknown samples that are acquired using a control analytical measurement technique. In one example the control technique is secondary ion mass spectroscopy (SIMS) so that the count ratios from the TXRF-type measurements are compared to ratios of integrals of SIMS profiles. In another example, the TXRF-type measurement ratios are compared to simulation profiles of known samples. Integrals of the SIMS profile that vary as a function of depth into the substrate correspond to the grazing incidence angles of the TXRF-like measurement and respective count rates.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
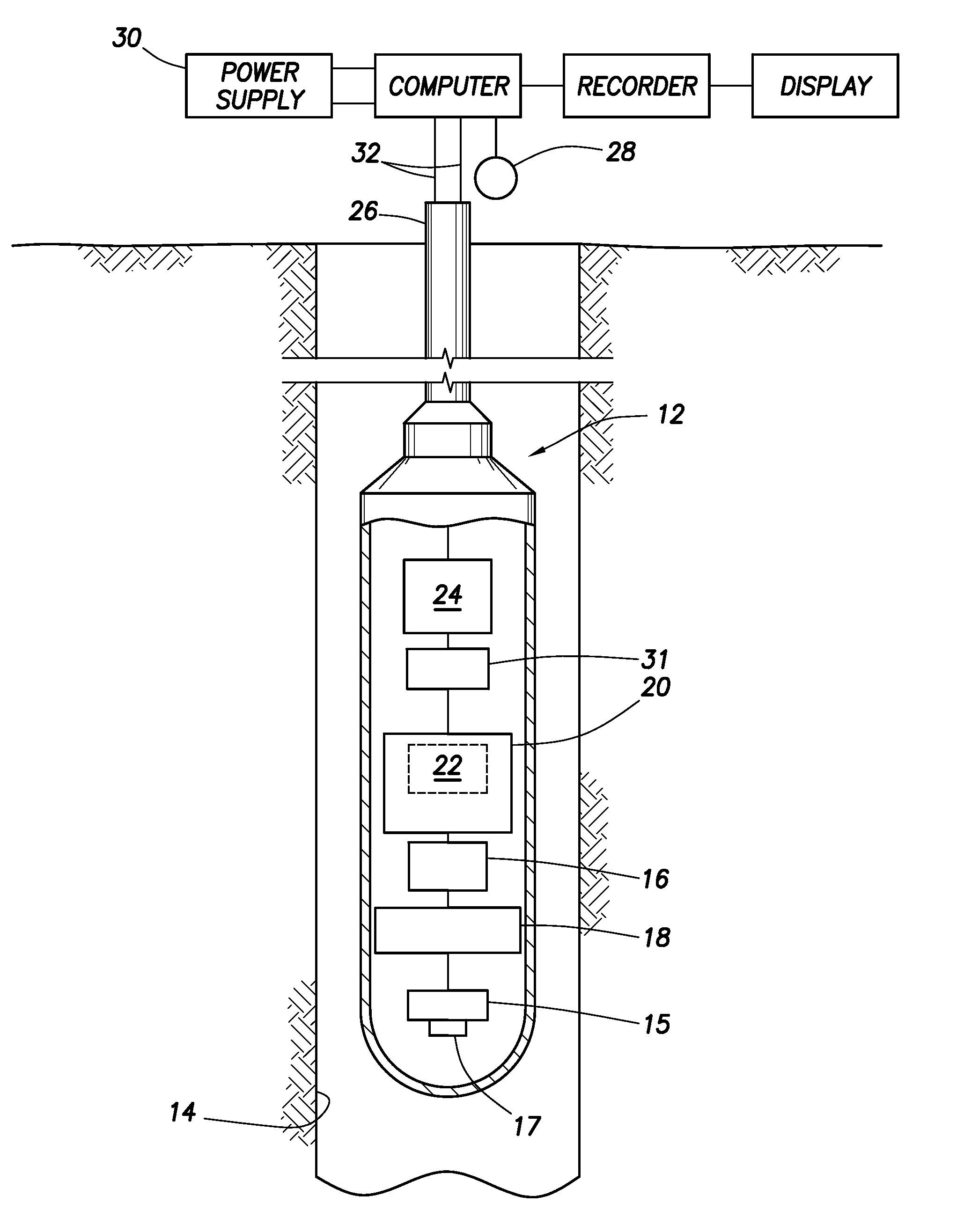
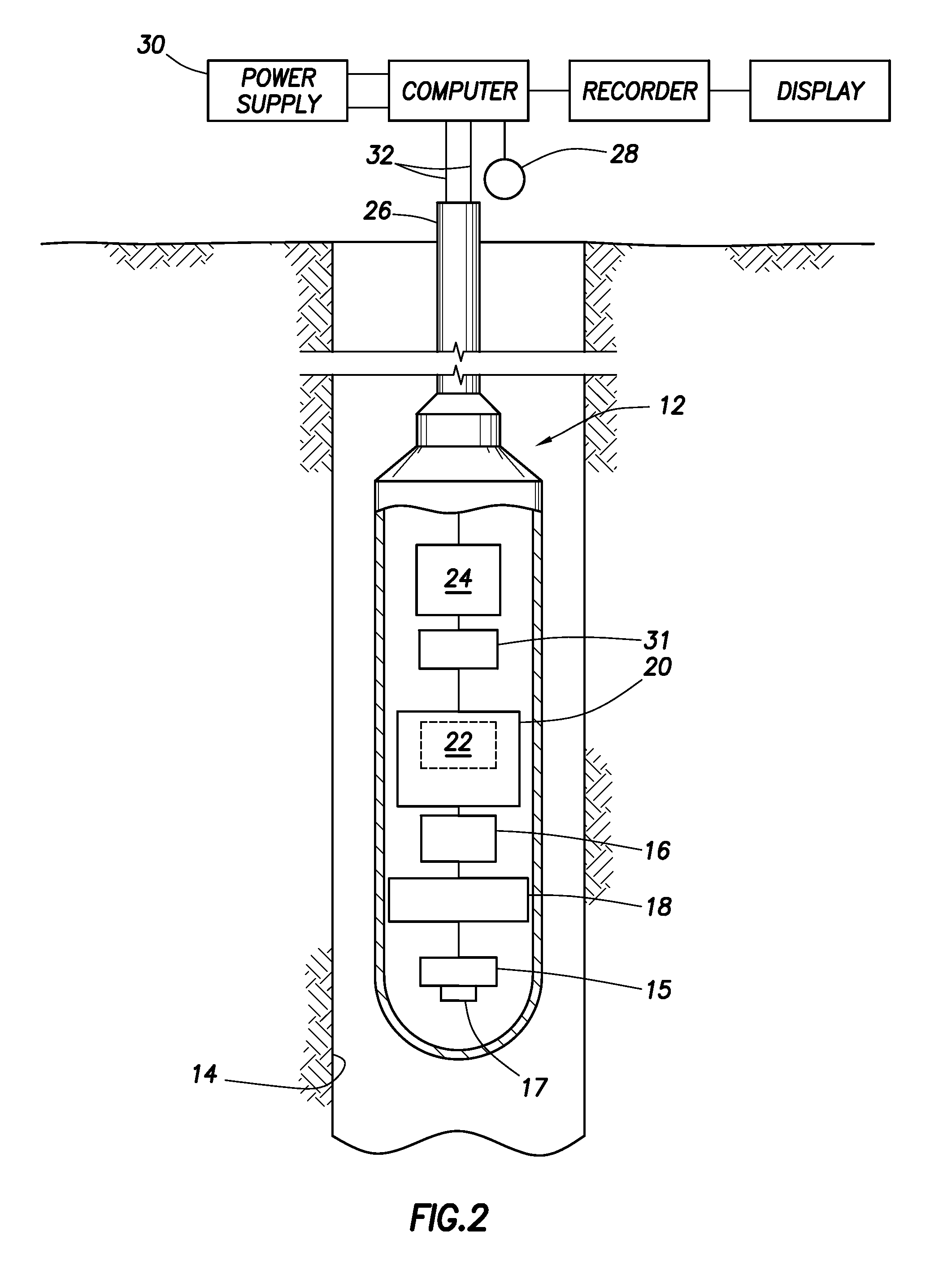
Method and apparatus for measuring well characteristics and formation properties
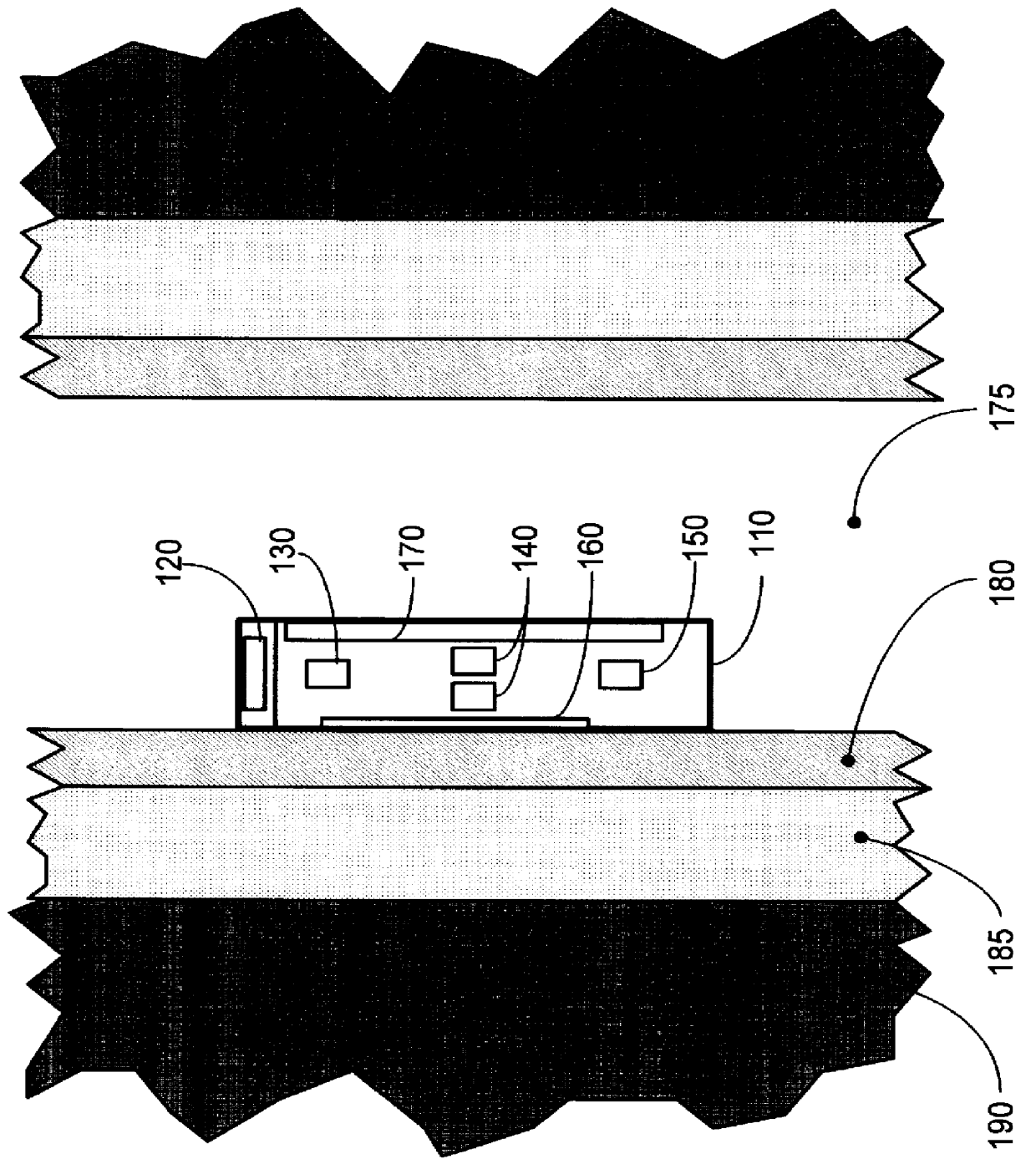
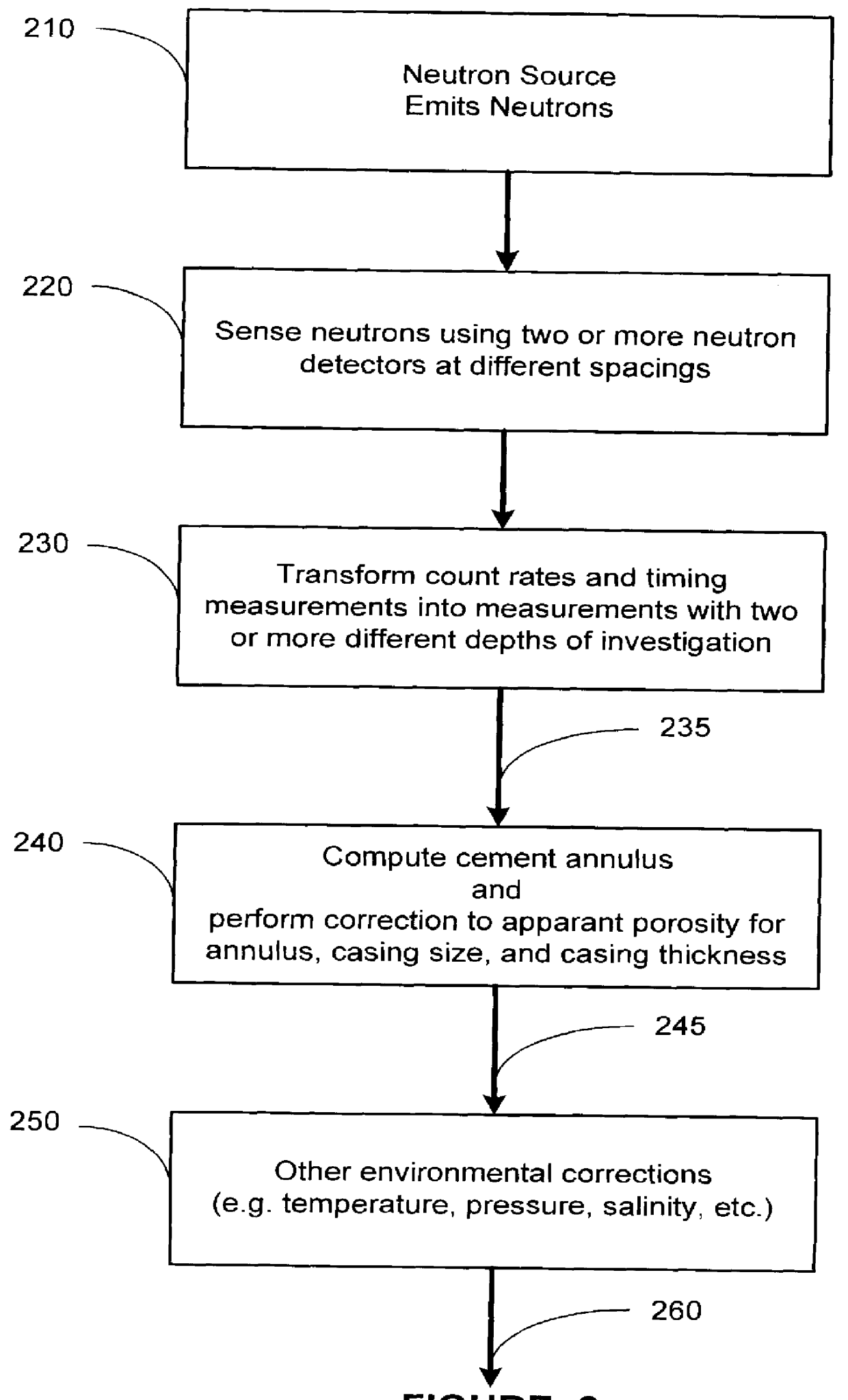
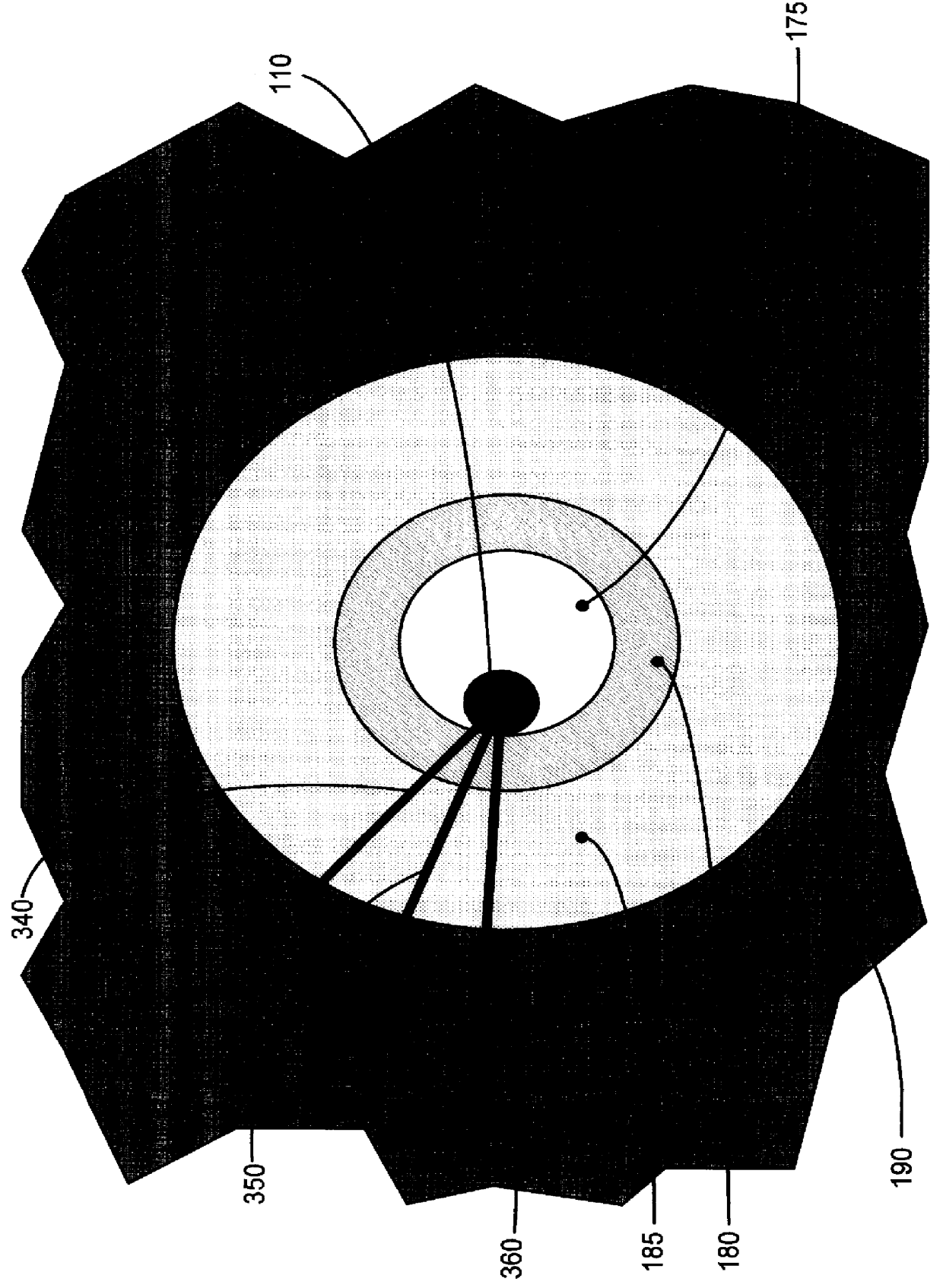
InactiveUS6032102AElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismology for water-loggingCounting ratePorosity
The present invention provides for method and an apparatus for determining the porosity of a geological formation surrounding a cased well. The method further comprises of generating neutron pulses that release neutrons into an area adjacent the well, from a neutron source. Neutrons are sensed and a plurality of neutron detector count rates is acquired using at least two neutron source to neutron detector spacings. A timing measurement is acquired at one of the spacings to measure a first depth of investigation. A ratio of the neutron detector count rates is acquired to measure a second depth of investigation. An apparent porosity is calculated using the timing measurements and the ratios of neutron count rates. The effect of a well casing on the calculated apparent porosity is determined in response to at least one of the ratio of neutron detector count rates and the timing measurement. A cement annulus is computed based on the ratios of neutron count rates and the timing measurement. A formation porosity is calculated by performing a correction to the apparent porosity for the casing and the cement annulus.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
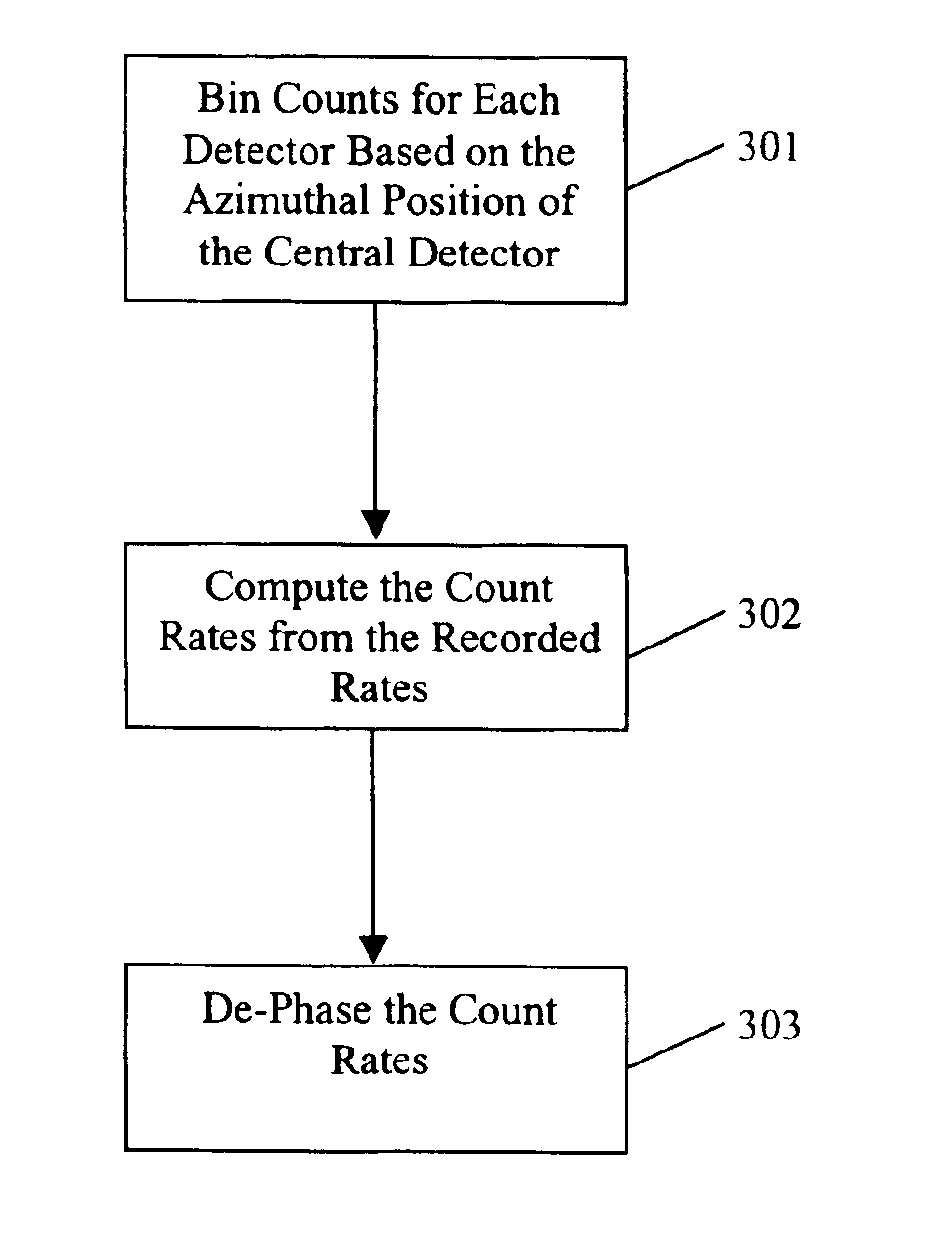
Formation evaluation through azimuthal measurements
A method for formation logging includes acquiring measurements of neutron-induced signals having azimuthal information using a neutron tool; processing the measurements into a plurality of azimuthal sector data for each acquisition interval; and deriving a selected parameter from the plurality of azimuthal sector data. A logging tool includes a housing adapted to move in a borehole; a circuitry having memories for storing neutron-induced measurements; a neutron source disposed in the housing; and at least one detector bank disposed in the housing spaced apart from the neutron source, wherein each of the at least one detector bank comprises at least one detector disposed around a periphery of the housing such that the at least one detector is more sensitive to signals from an azimuthal direction, and wherein count rates detected by each of the at least one detector are separately stored in the memories.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
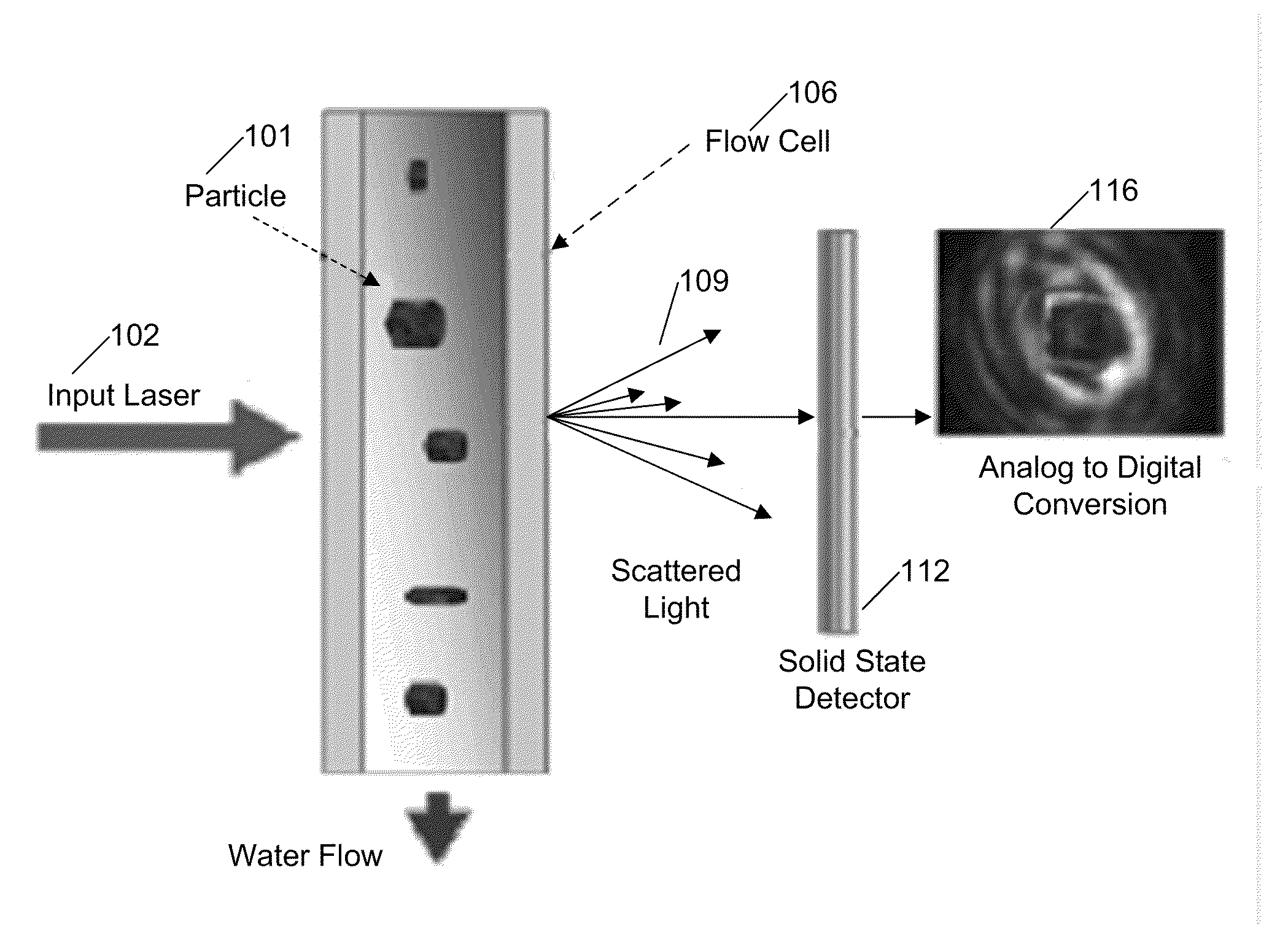
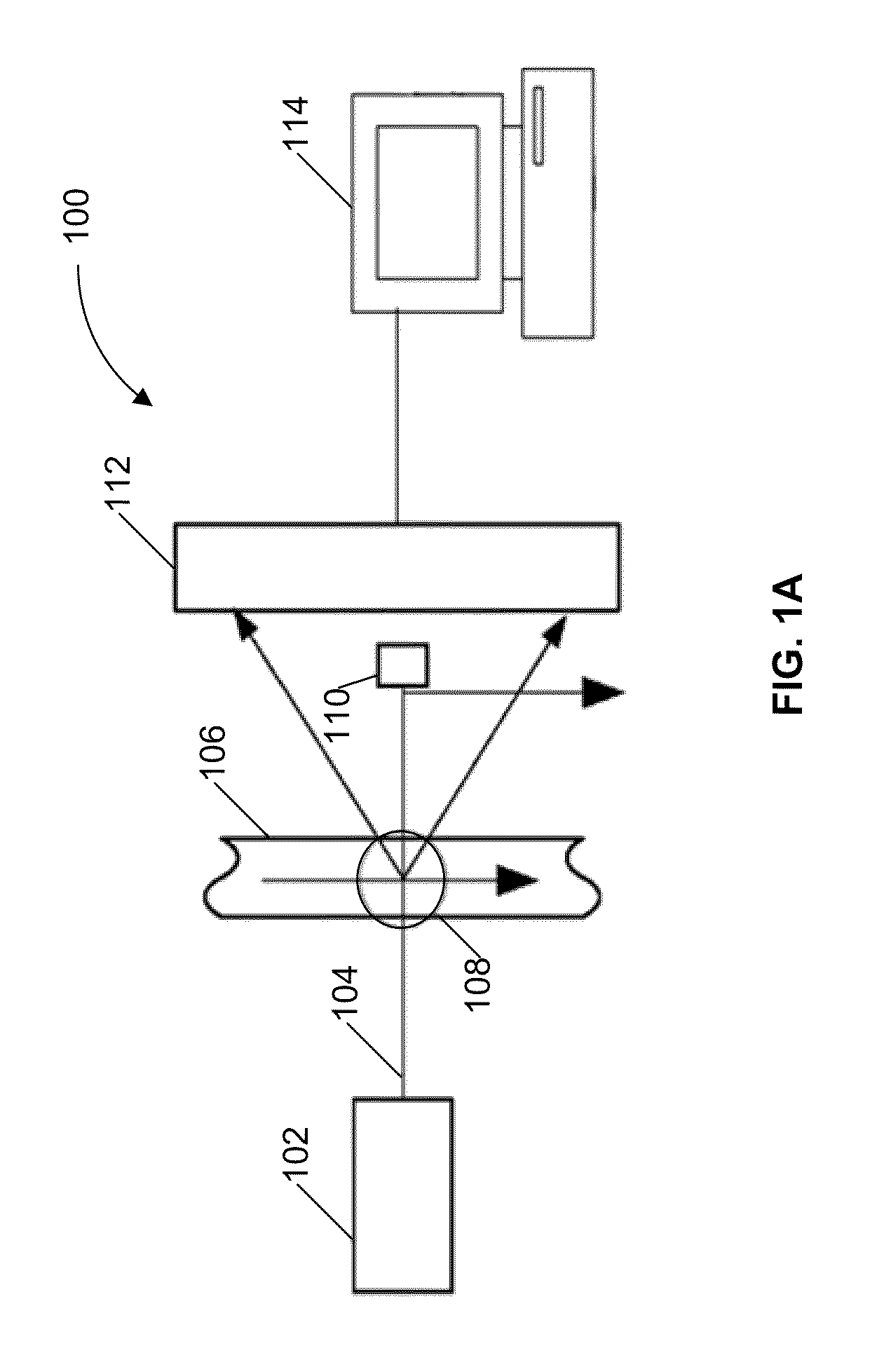
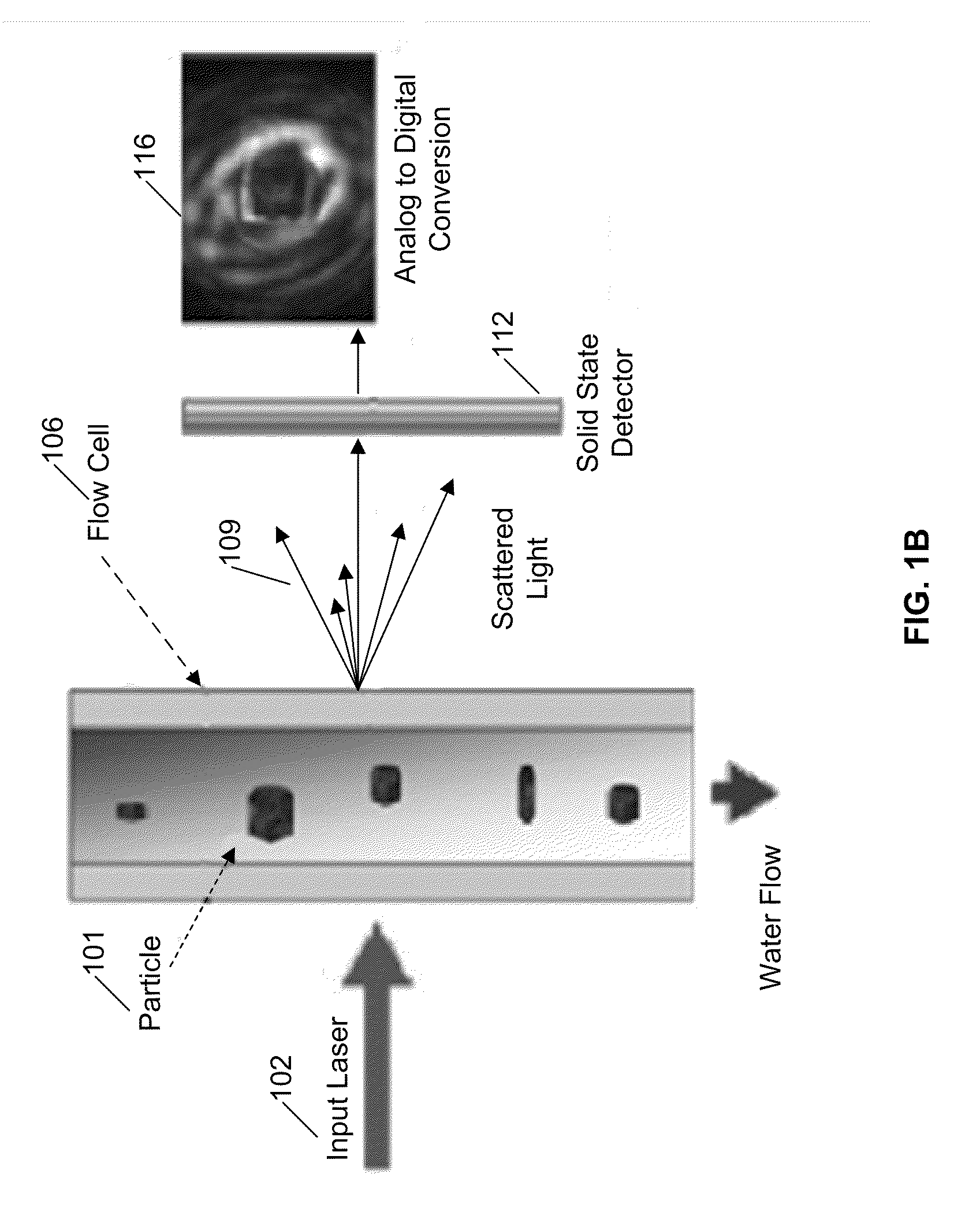
Systems and methods for detecting normal levels of bacteria in water using a multiple angle light scattering (MALS) instrument
InactiveUS20110066382A1Scattering properties measurementsParticle size analysisWater useLiquid medium
A particle detection system uses a camera to produce a picture based on the scattered light generated by a particle in a liquid medium, when a laser beam is incident on the particle. These pictures are then automatically analyzed through the use of a processing system (e.g., a computer). The processing system is configured to record the forward scattering intensity (e.g., amplitude) and the picture of the scattered light rays to generate a classification of the particle causing the scattering. Count rate and trends of the classified particles are monitored to detect a change that is representative of the overall health safety of the water or by knowing the levels of bacteria in process water, such as Reverse Osmosis (RO) feed water, reject brine, and product water, the operator may better monitor the life and condition of the RO membrane.
Owner:JMAR LLC A DELAWARE LLC
Semi-chromatography gamma scanning method for low-medium radioactive waste barrel measurement
ActiveCN104714245AHigh measurement accuracyTomoscanX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentCounting rateLow-level waste
The invention provides a semi-chromatography gamma scanning method for low-medium radioactive waste barrel measurement. A rotary platform, a detector platform, a detector with a collimator, a transmission source platform, a transmission source, a shielding part of the transmission source and an analysis module are adopted in the method. A waste barrel is divided into multiple section layers in the height direction, the waste barrel is rotated, surface distribution of radioactive point sources on the section layers is changed into linear distribution of ring sources in the radius direction, the detector conducts measurement at different section layer heights and different eccentric positions in the section layers, an equation set reflecting the mutual relation between the detector counting rate and the activity of nuclide in annular grids is established, the equation set is solved, distribution of the activity of the radioactive nuclide in the waste barrel in the diameter direction and the height direction of the barrel is acquired, and the total activity of the radioactive nuclide in the waste barrel is acquired through summation. The method is high in measurement accuracy, short in measurement time and high in practical value and application prospect.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method and apparatus for acquiring radiation data
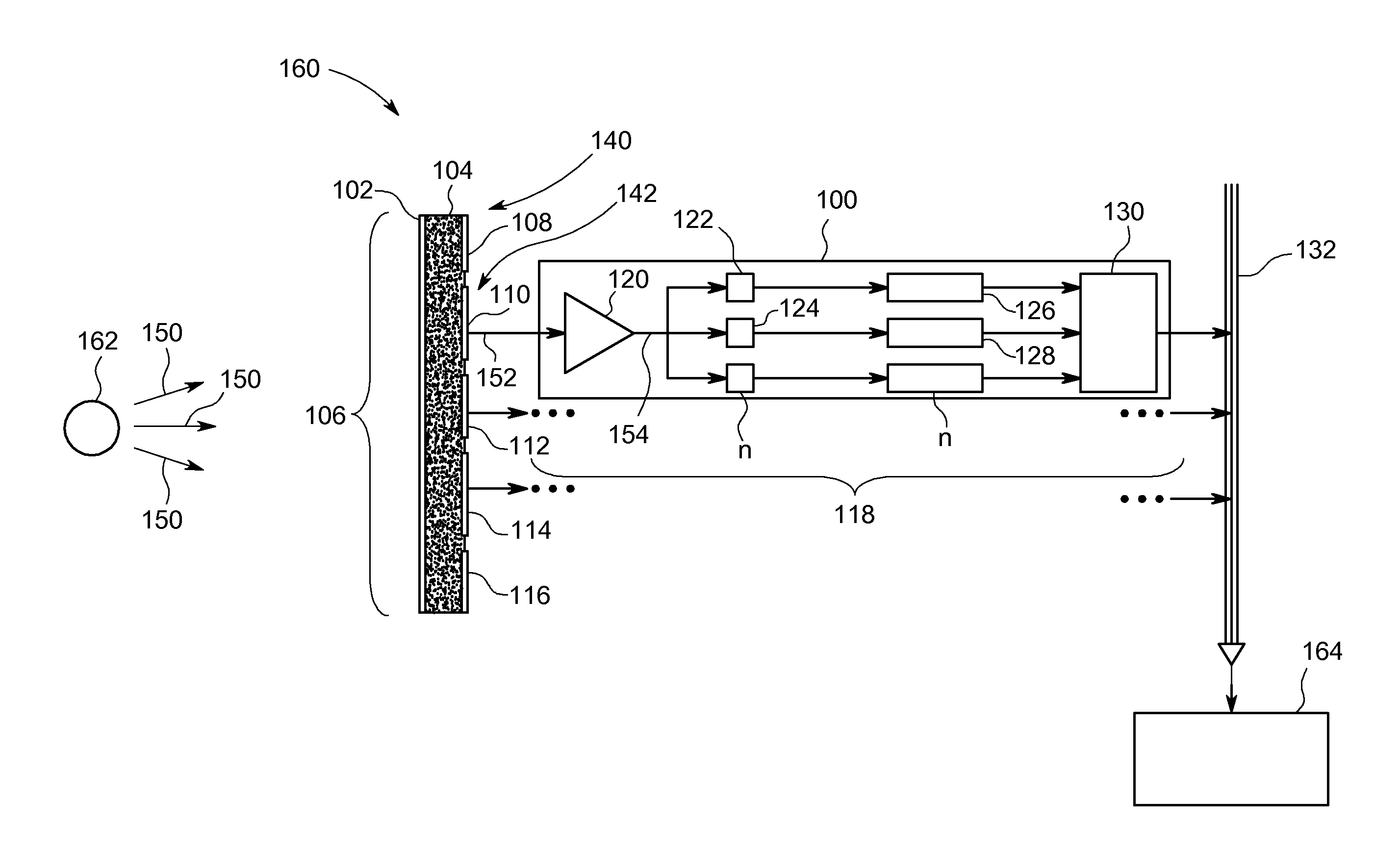
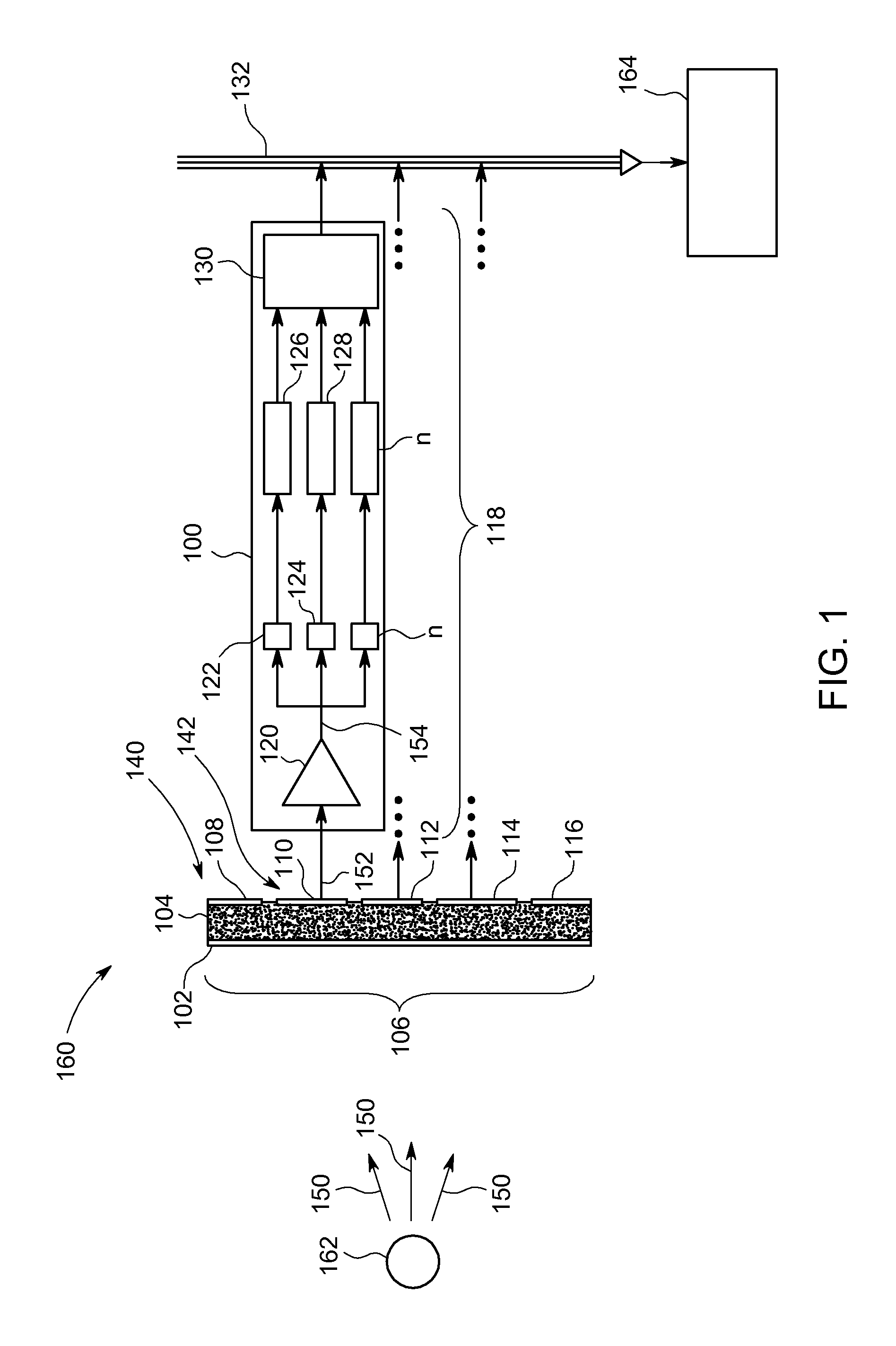
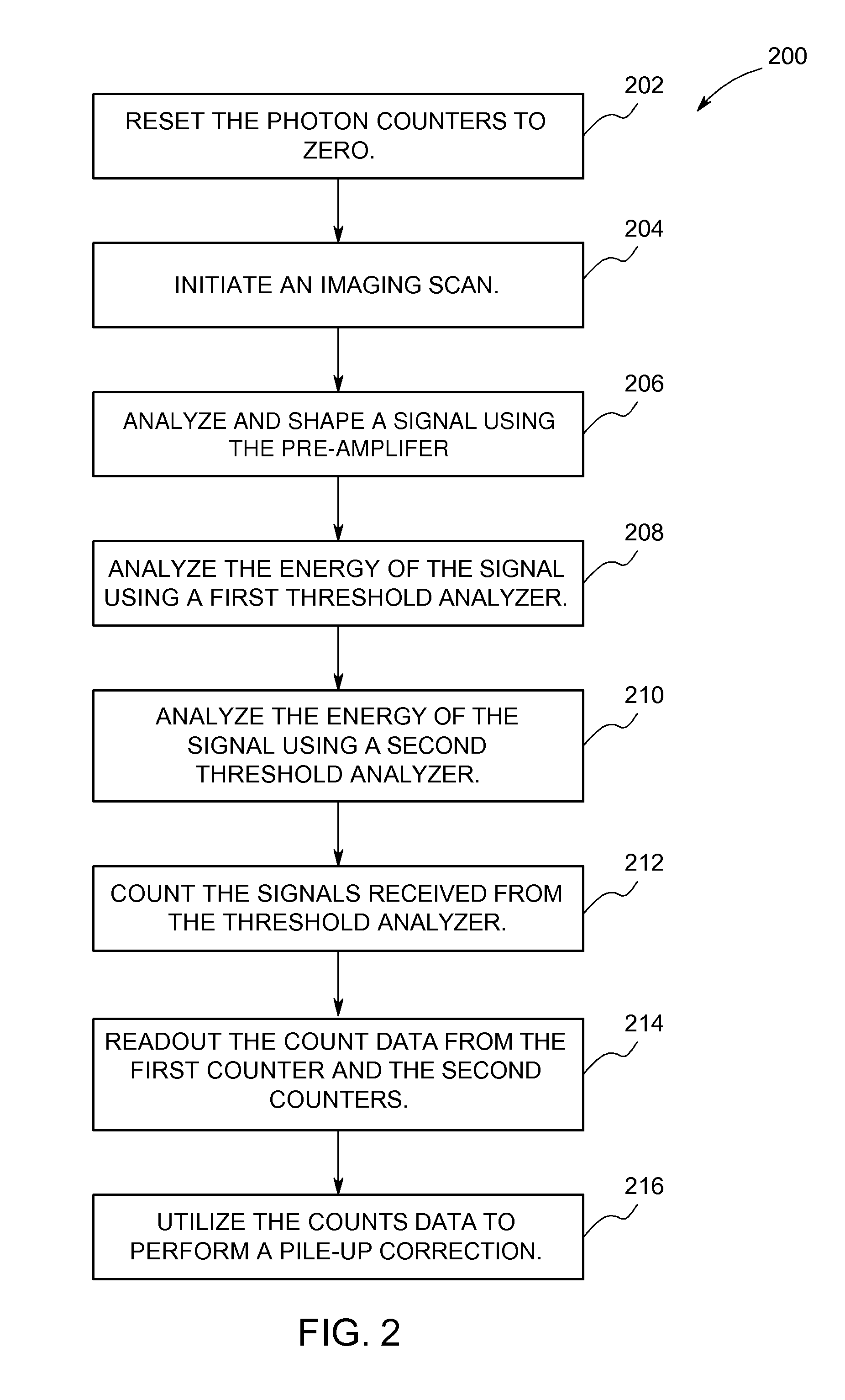
ActiveUS20110155899A1Raise countMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMicrobiological testing/measurementCounting rateCounting Number
Method and apparatus for extending a count rate capability of a detector array. The method includes receiving photons at a detector array, counting the photons that are above a first energy threshold using a first counter, counting the photons that are above a different second energy threshold using a second counter, and calculating a pile-up estimate using the photon counts from the first and second counters.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method for operation of a counting radiation detector with improved linearity
ActiveUS20050123090A1Improve linearityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingCounting rateActual count
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Downhole gamma-ray detection
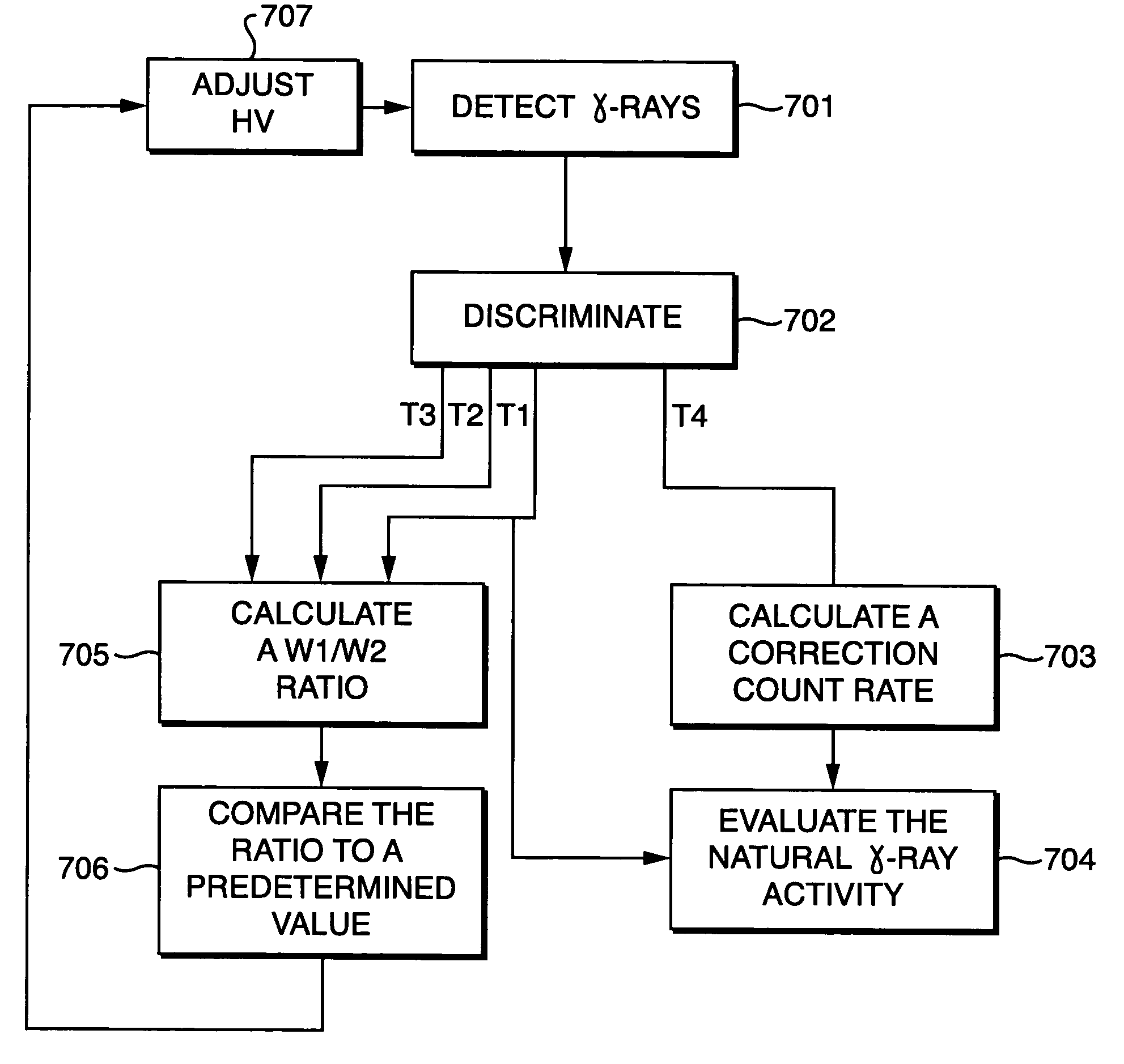
ActiveUS7081616B2Reduce detectionSpread the wordX-ray spectral distribution measurementSolid-state devicesCounting rateGamma ray detection
A method for evaluating a natural gamma-ray activity within a borehole, comprises the steps of:stabilizing the gain according to a method for stabilizing a gain of a gamma-ray detector for use in a downhole logging tool;determining an interval count rate, the interval count rate corresponding to gamma-rays having an energy within a predetermined correction interval;calculating a correction count rate from the determined interval count rate; andusing the correction count rate to evaluate the natural gamma-ray activity.The method for stabilizing the gain of the gamma-ray detector for use in the downhole logging tool, comprises the steps of:processing a backscatter peak of a full gamma spectrum such that the backscatter peak constitutes a reference peak;determining a first rate, the first rate corresponding to gamma-rays having an energy within a first predetermined energy interval;determining a second rate, the second rate corresponding to gamma-rays having an energy within a second predetermined energy interval; andthe first predetermined energy interval and the second predetermined energy interval straddle the backscatter peak.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
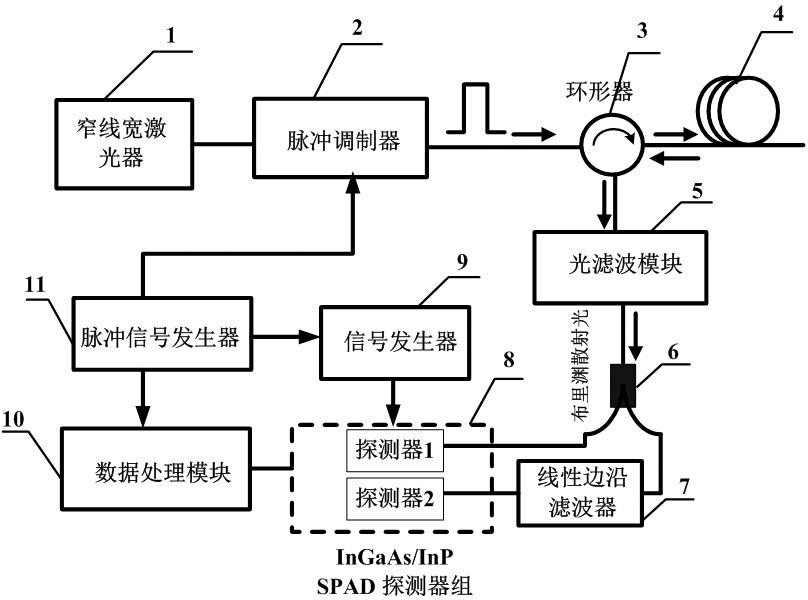
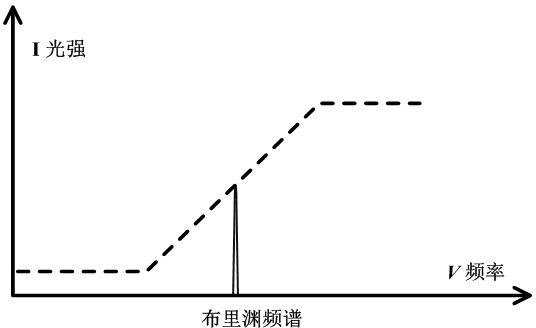
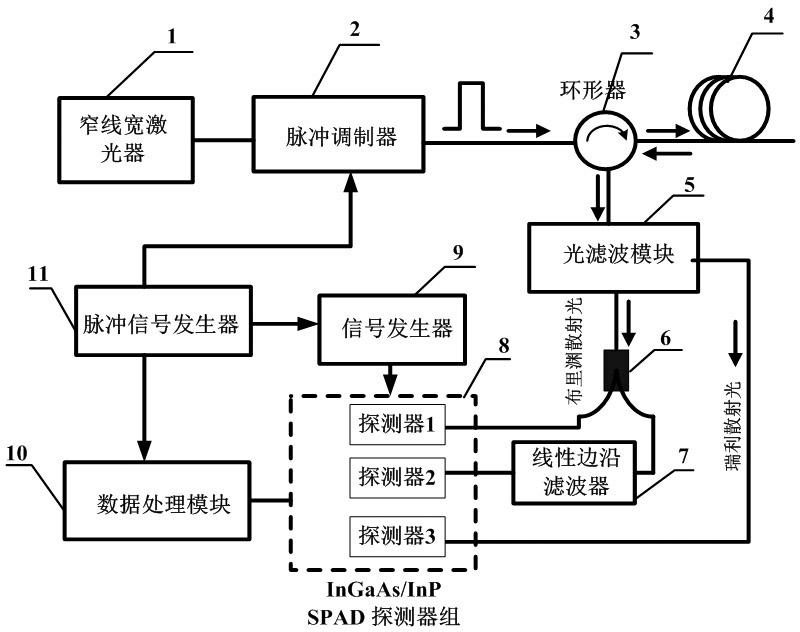
Brillouin optical time domain reflectometer for single-photon detection based on edged filter method
InactiveCN102620857ASimple structureReduce volumeThermometers using physical/chemical changesUsing optical meansTime correlationPhoton detection
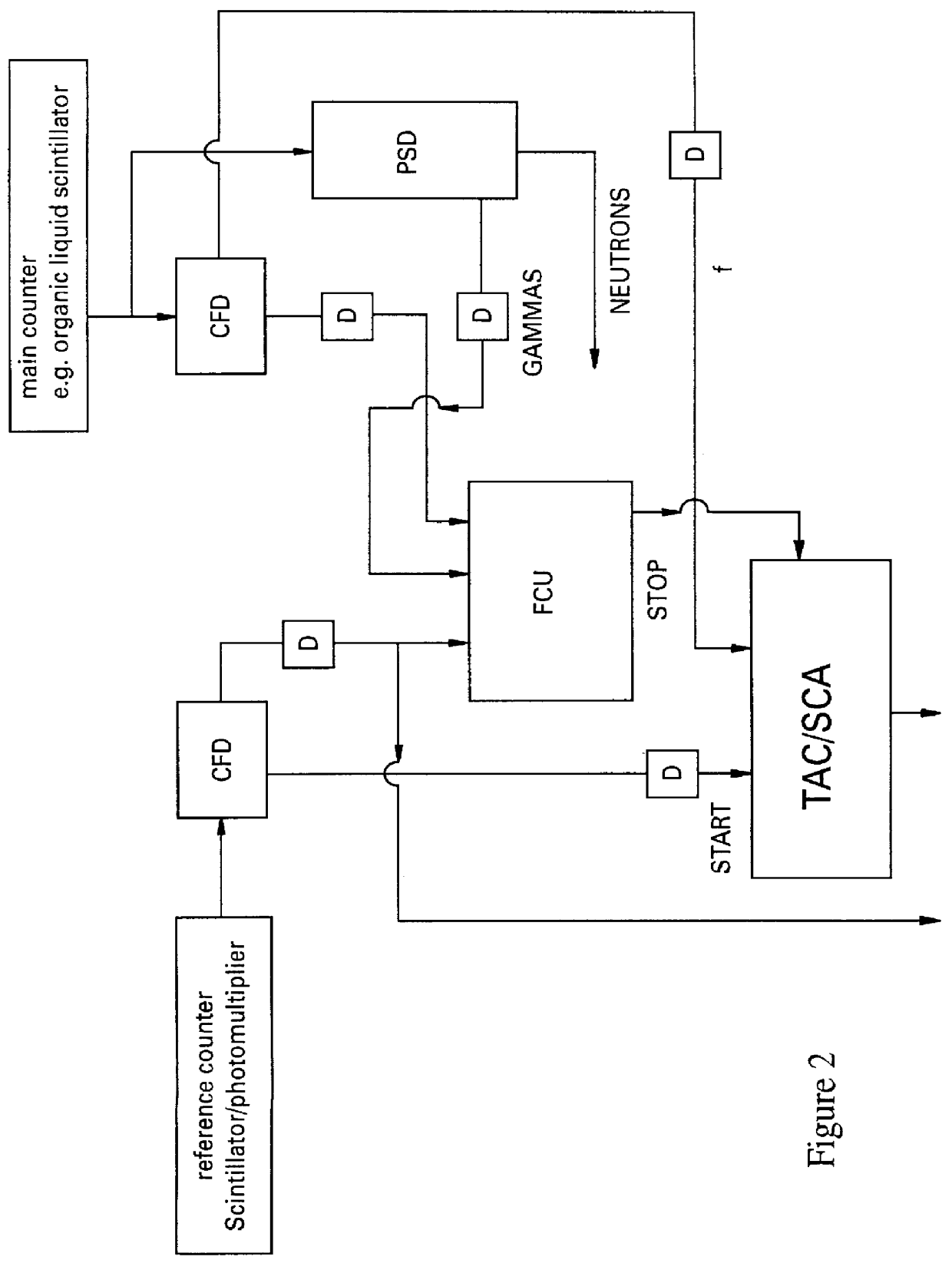
The invention discloses a Brillouin optical time domain reflectometer for single-photon detection based on an edged filter method, which comprises a narrow linewidth laser (1), a pulse modulator (2), a circulator (3), a sensing optical fiber (4), an optical fiber module (5), 3dB coupler (6), a linear edged filter (7), an InGaAs / InP SPAD (single-photon avalanche diode) detector group (8), a signal generator (9), a data processing module (10) and a pulse signal generator (11), wherein the InGaAs / InP SPAD detector group (8) includes two or three InGaAs / InP SPAD detectors. The InGaAs / InP SPAD detector group with a high counting rate and high sensitivity is used as a detection unit, Brillouin frequency shift information is acquired by the edged filter method, time correlation single-photon counting technology is adopted by the data processing module (10), limitations on the bandwidth and sensitivity of a traditional detector are broken through, spatial resolution and measuring precision of the reflectometer can be simultaneously improved, and temperature and strain are simultaneously sensed.
Owner:NANJING FAAIBO OPTOELECTRONICS TECH
Digital pileup waveform processing method and system
ActiveCN102073059AImprove signal-to-noise ratioReduce lossPulse descriminationX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentCounting rateSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The invention discloses a digital pileup waveform processing method and a digital pileup waveform processing system. The method comprises the following steps of: determining a pulse rising edge area, and judging whether a pulse has a pileup waveform or not according to a time interval between adjacent pulse rising edges; and dividing a digital waveform determined as pileup according to the risingedge and the falling edge of the pulse, reconstructing single event pulse waveforms in turn by using the divided waveform, and extracting single pulse information from the reconstructed waveforms. The invention also discloses the pileup waveform processing system, which comprises a pileup waveform discrimination module, a pulse waveform division module and a pulse waveform reconstruction module. By the method and the system, the pileup pulse waveform can be effectively discriminated, each single event pulse waveform in the pileup is accurately reconstructed, information such as energy, time, amplitude, decay time constant, position and the like of the single event pulse is accurately recovered, and the counting rate of a system under high activity, and the signal-to-noise ratio of a measuring result are improved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
System and method for monitoring the stability of a scintillation detector
InactiveUS6064068AX-ray spectral distribution measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansCounting rateLight beam
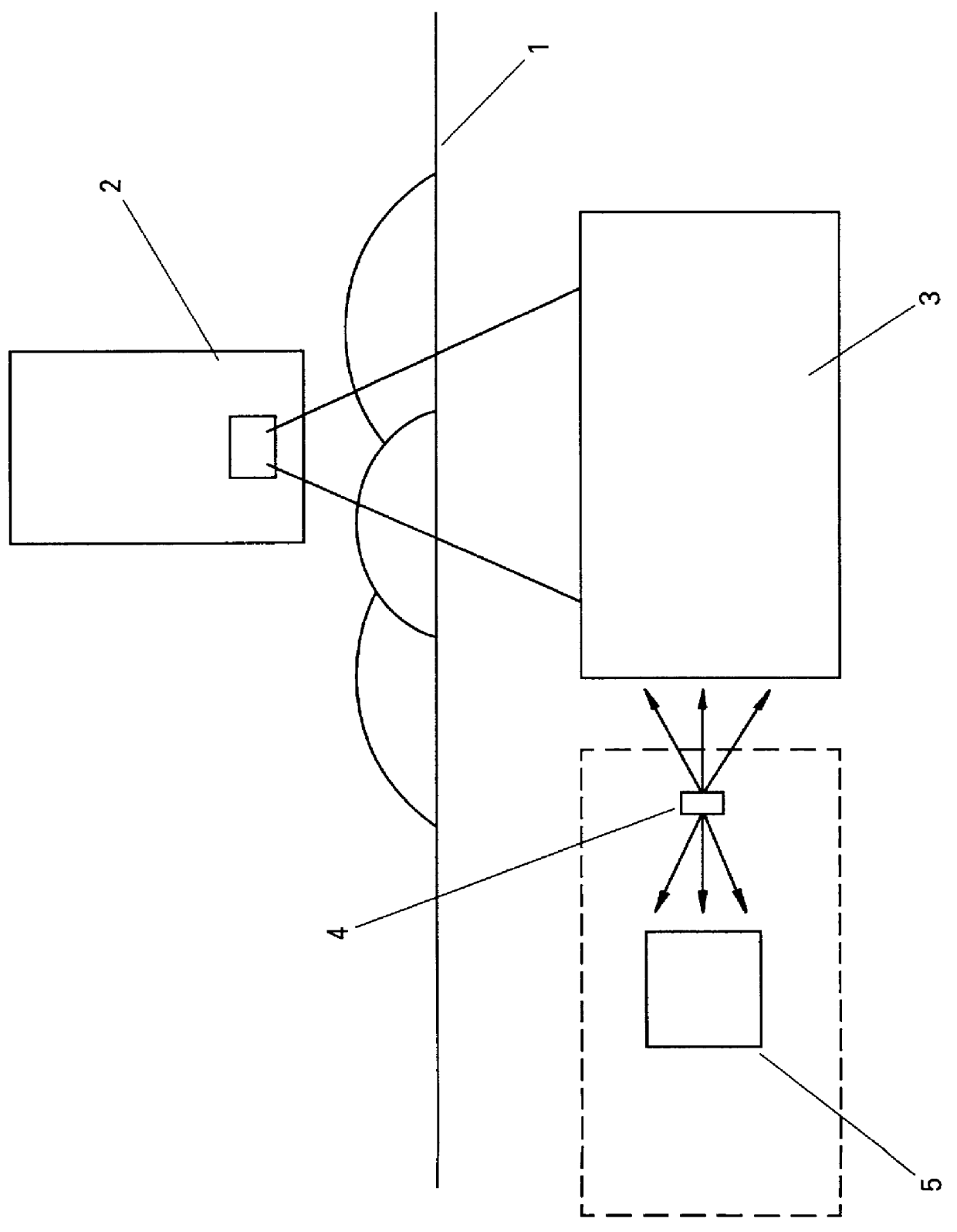
A system for on-line monitoring the stability of a scintillation detector, comprises means providing two beams of gamma rays from a subsidiary source which are distinguishable because of their time relationship from the primary source. The two beams are of similar energies but are oriented in different directions, with one directed into the scintillation detector and one acting as a reference beam and directed to a reference beam counter. The ratio of the detector-count rate for the timed events to the reference count rate is compared to provide an indication of any drift in the scintillation detector.
Owner:INST OF GEOLOGICAL & NUCLEAR SCI
Gamma energy spectrum-based method for identifying clay shale reservoir and uranium ore occurrence on spot
ActiveCN102621588AQuick identificationQuick evaluationNuclear radiation detectionCounting rateUranium ore
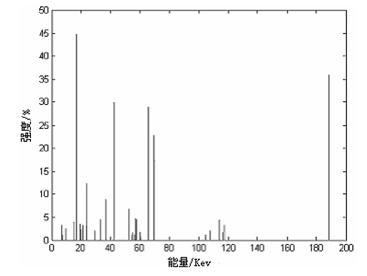
The invention relates to a gamma energy spectrum-based method for identifying clay shale reservoir and uranium ore occurrence on the spot, which comprises the following steps that: rock debris in corresponding depth of drilling fluid is continuously sampled or a core acquired through the core drilling is sampled according to corresponding depths; the rock debris sample or the core sample is placed into a matched lead tank, and a gamma energy spectrum probe is used for measuring the rock debris sample or the core sample inside the lead tank; then counting rates and activity of uranium (U), radium (Ra), thorium (Th) and kalium (K) and a total gamma value are acquired according to the measurement result, so that the real content of U(Ra), Th and K in the rock can be calculated; and finally, a variation curve of the contents of U(Ra), Th and K is drawn according to the calculation results, and the clay shale reservoir and the uranium ore occurrence are identified according to variation characteristics of the curve. Gamma energy spectrum measurement and analysis on rock debris or the core which are acquired from the drilling are directly performed, so that the clay shale reservoir and the uranium ore occurrence can be rapidly identified and evaluated. The method is an economical and efficient method. The gamma energy spectrum measurement is performed on the drilling site, so that influence of an external environment on the rock sample can be avoided, and the accuracy of the measurement result can be guaranteed.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
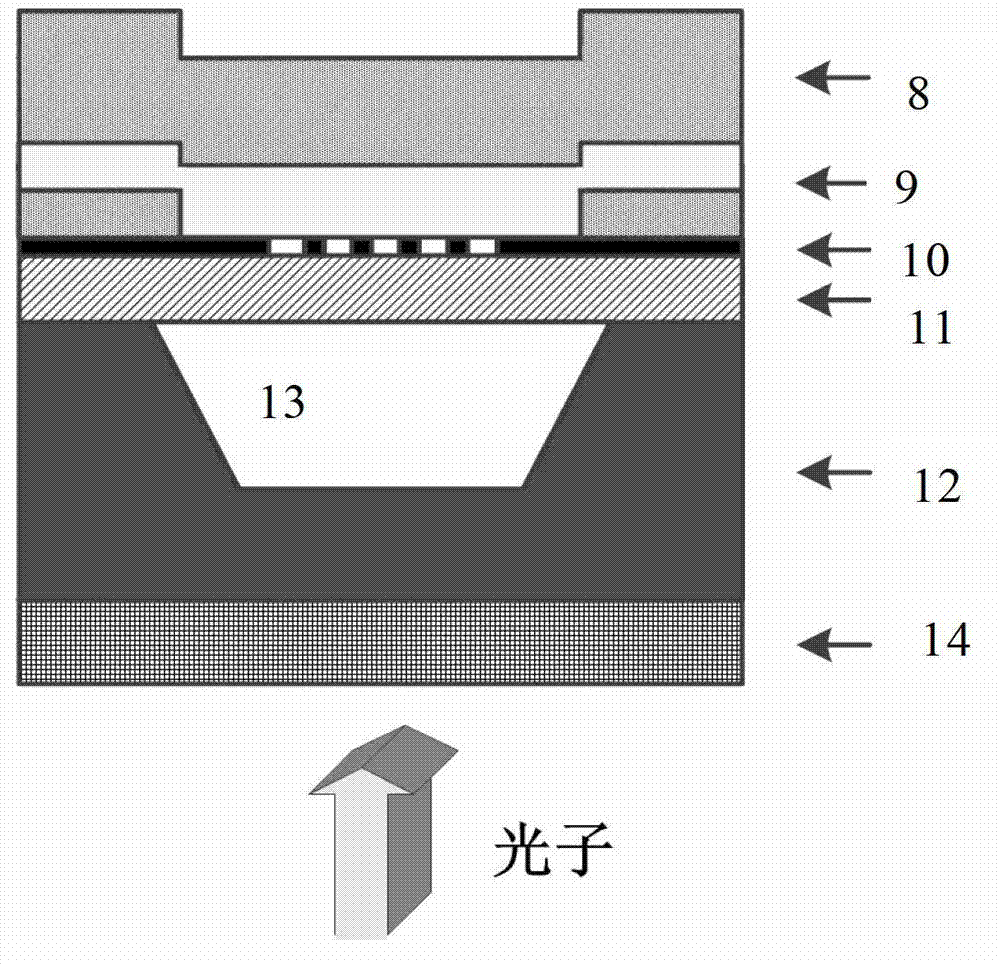
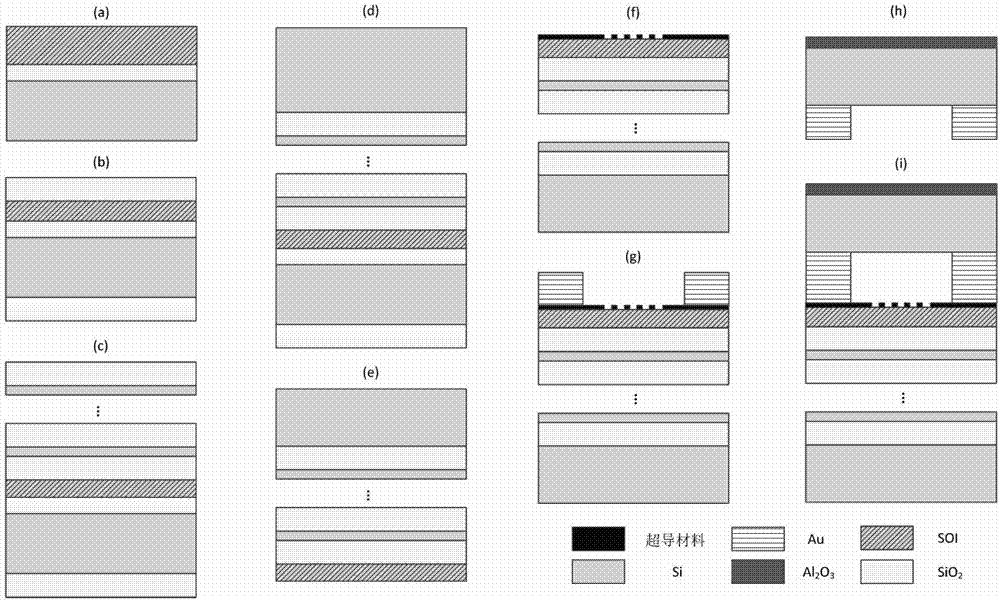
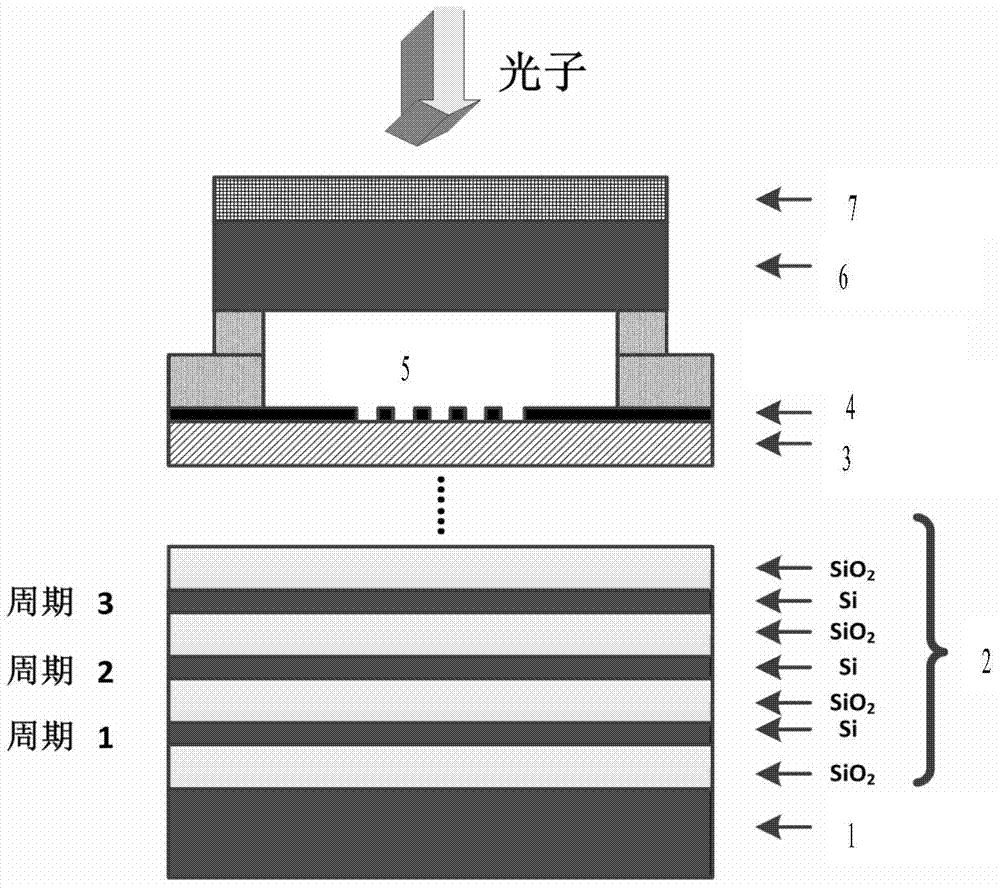
High-speed superconducting nanowire single-photon detector (SNSPD) with strong absorption structure and preparation method of high-speed SNSPD
ActiveCN102829884AHigh quality growthImprove absorption rateInstrumentsCounting rateQuantum efficiency
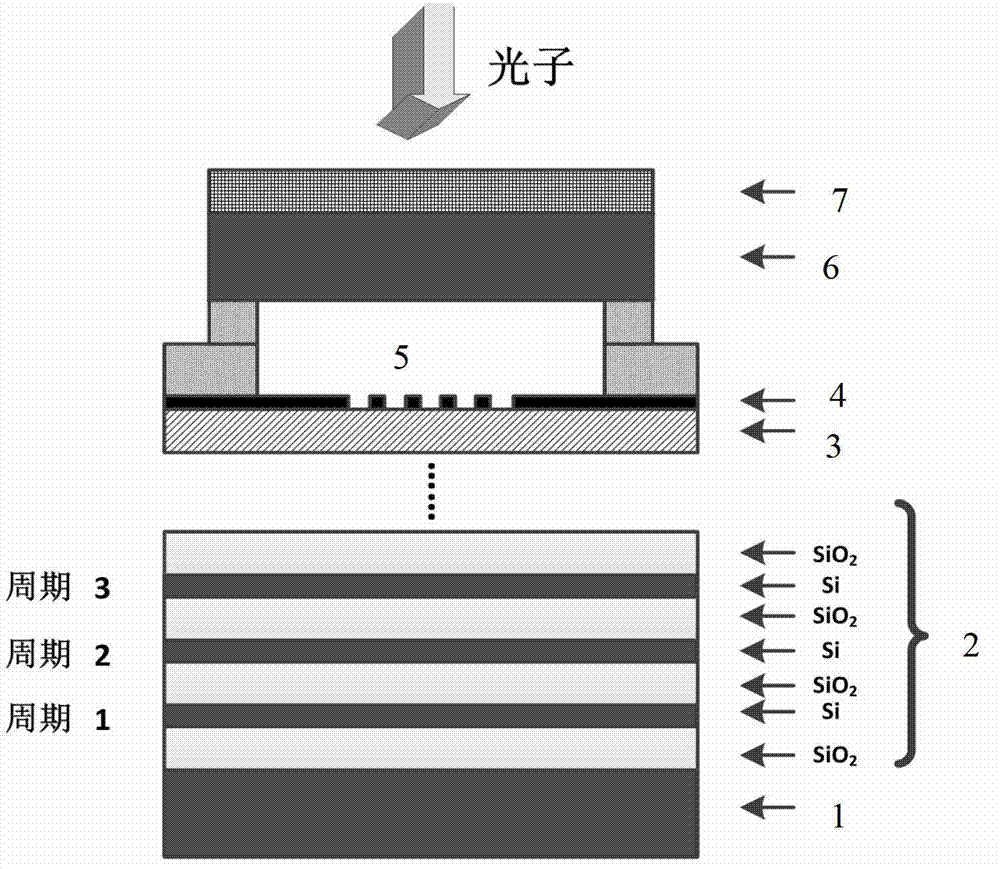
The invention discloses a high-speed superconducting nanowire single-photon detector (SNSPD) with a strong absorption structure and a preparation method of the high-speed SNSPD with the strong absorption structure. The SNSPD is capable of further improving the photon absorptivity of superconducting nanowires based on an incident medium with a high refractive index and an air cavity structure. Compared with the prior art and according to the high-speed SNSPD, under the condition that the nanowires are made of superconducting ultrathin membranes with the same material and the same thickness, nearly 100% of absorptivity can be realized through a lower duty ratio, and the difficulty of electron beams in the exposure steps is reduced greatly, thereby particularly being more beneficial to the preparation of the ultrathin nanowires; and meanwhile, by adopting a silicon on insulator (SOI) substrate, the high-quality growth of the superconducting ultrathin membranes can be ensured simultaneously without affecting the intrinsic quantum efficiency of the detector. In addition, under the condition that the large effective detection area is ensured equally, as the total length of the required nanowires is reduced obviously, the maximum counting rate of the detector can be improved, and the probability of occurring defects during preparation process is decreased notably.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
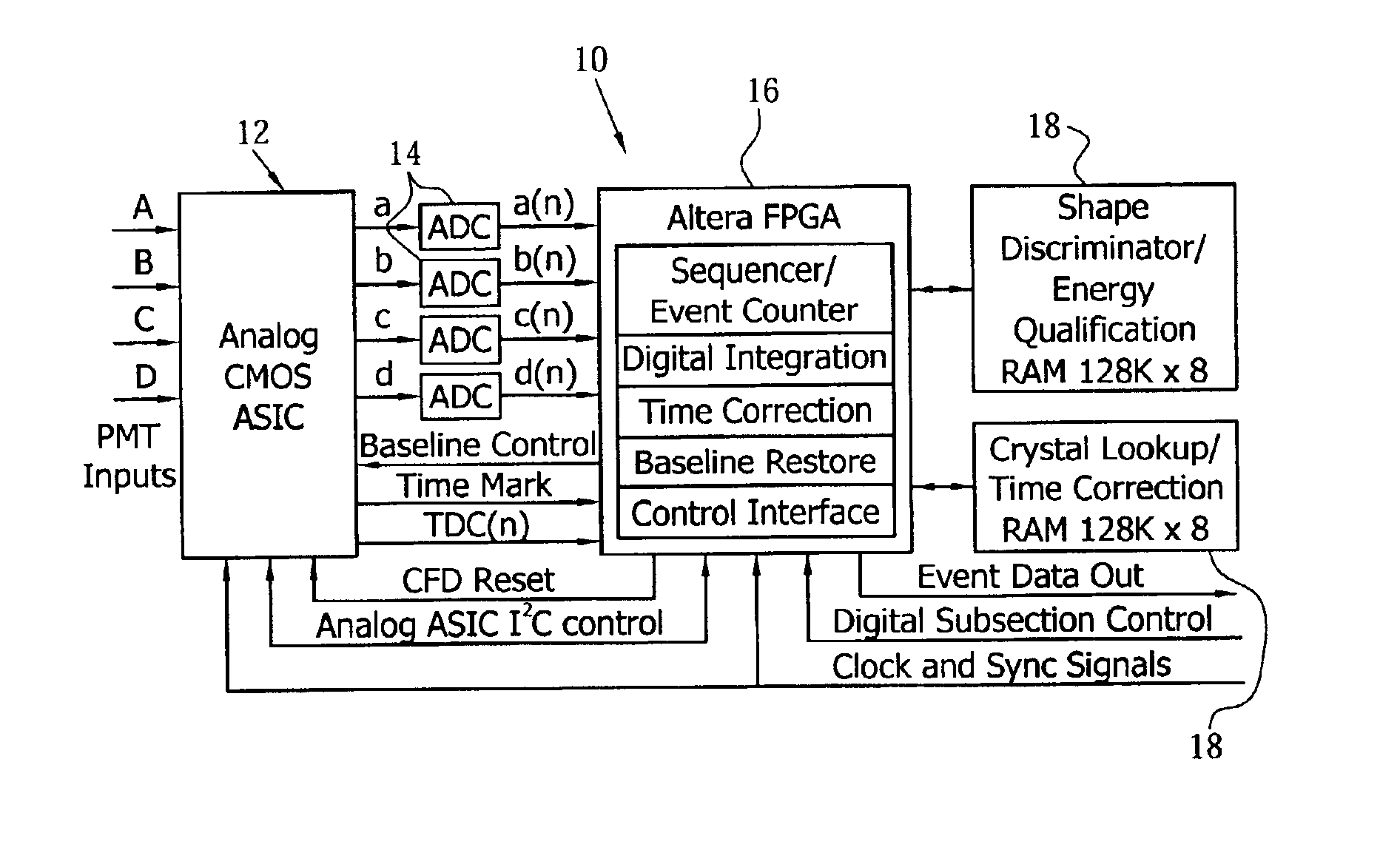
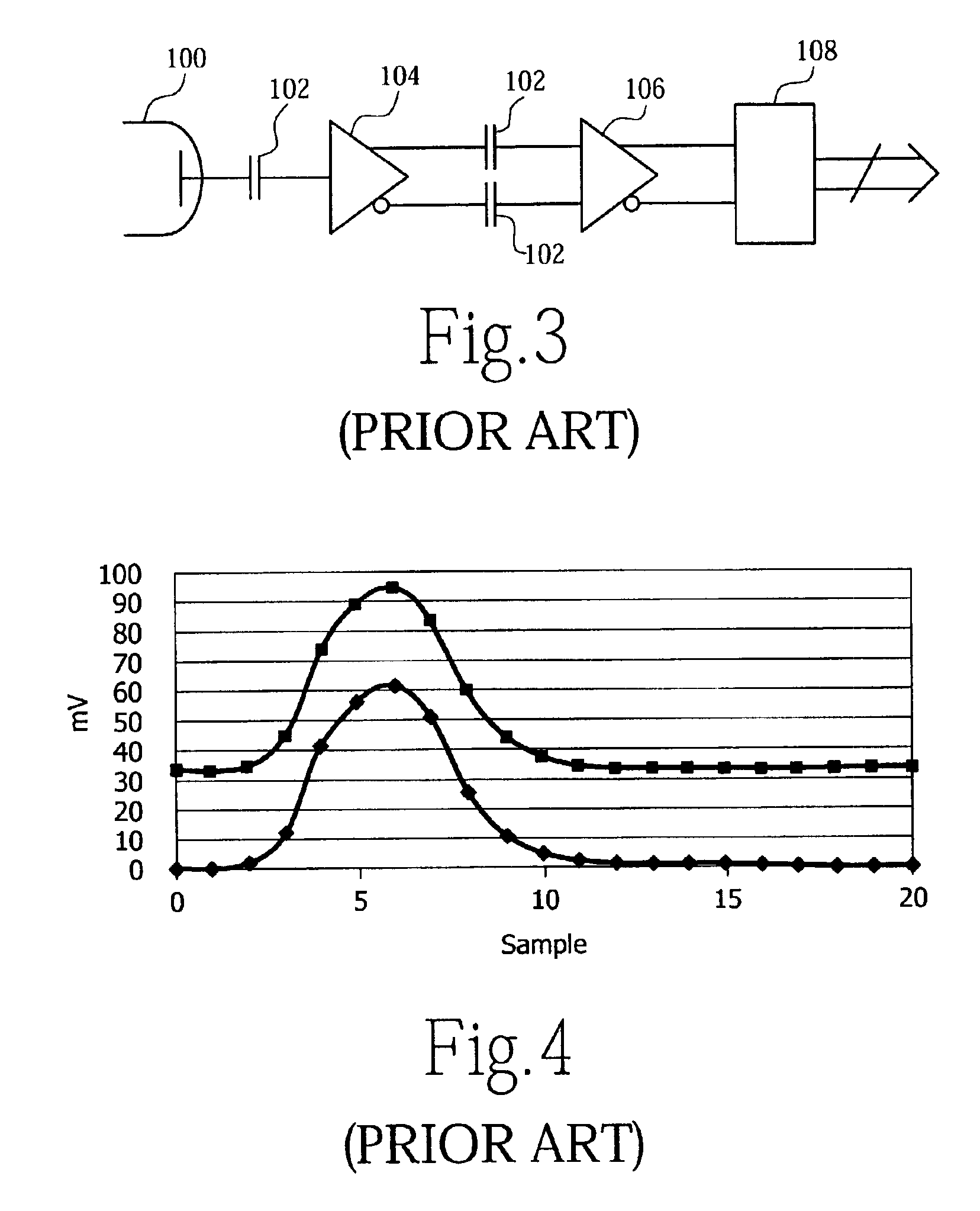
Baseline correction in PET utilizing continuous sampling ADCs to compensate for DC and count rate errors
ActiveUS6903344B2Low costImprove performanceMaterial analysis by optical meansTomographyCounting rateNegative feedback
A method and apparatus for determining and correcting the baseline of a continuously sampled signal for use in positron emission tomography. The method employs continuous signal sampling to determine the signal level at time t(0) so that an accurate determination of an integrated signal may be calculated, resulting in an accurate energy estimate for an ac-coupled, continuously-sampled signal at various count rates. The device includes a front-end electronics processing channel including primarily an analog CMOS ASIC, a bank of ADCs, an FPGA-based digital sequencer, and two RAMs. The processing electronics perform continuous digital integration of PMT signals to obtain normalized position and energy. Continuous baseline restoration (BLR) is used, wherein the baseline of the signal pulses are placed at mid-scale by continuously sampling the ADC, thus always making available the past history. A correction signal is generated for use in negative feedback control of the baseline.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Methods for sourceless density downhole measurement using pulsed neutron generator
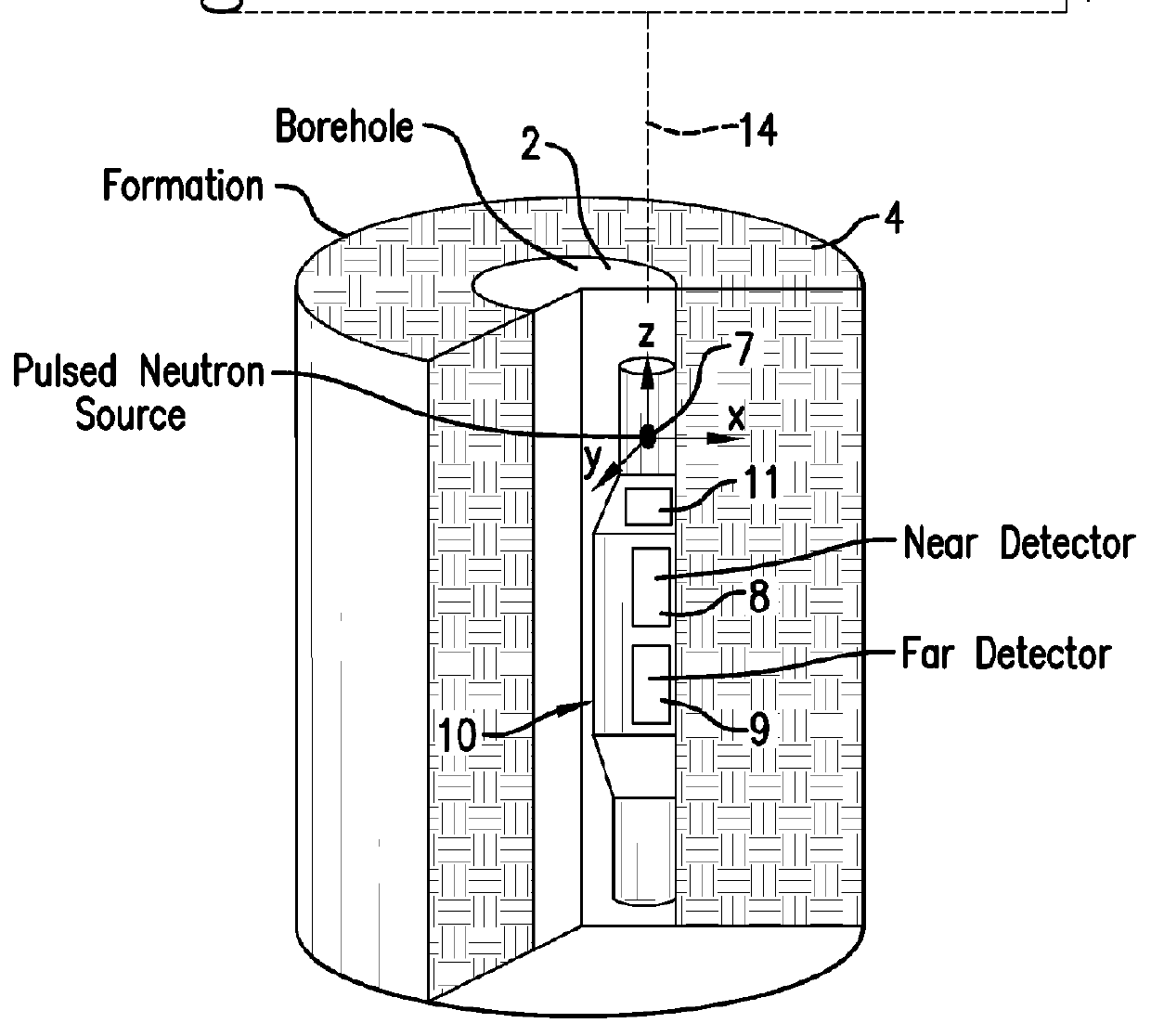
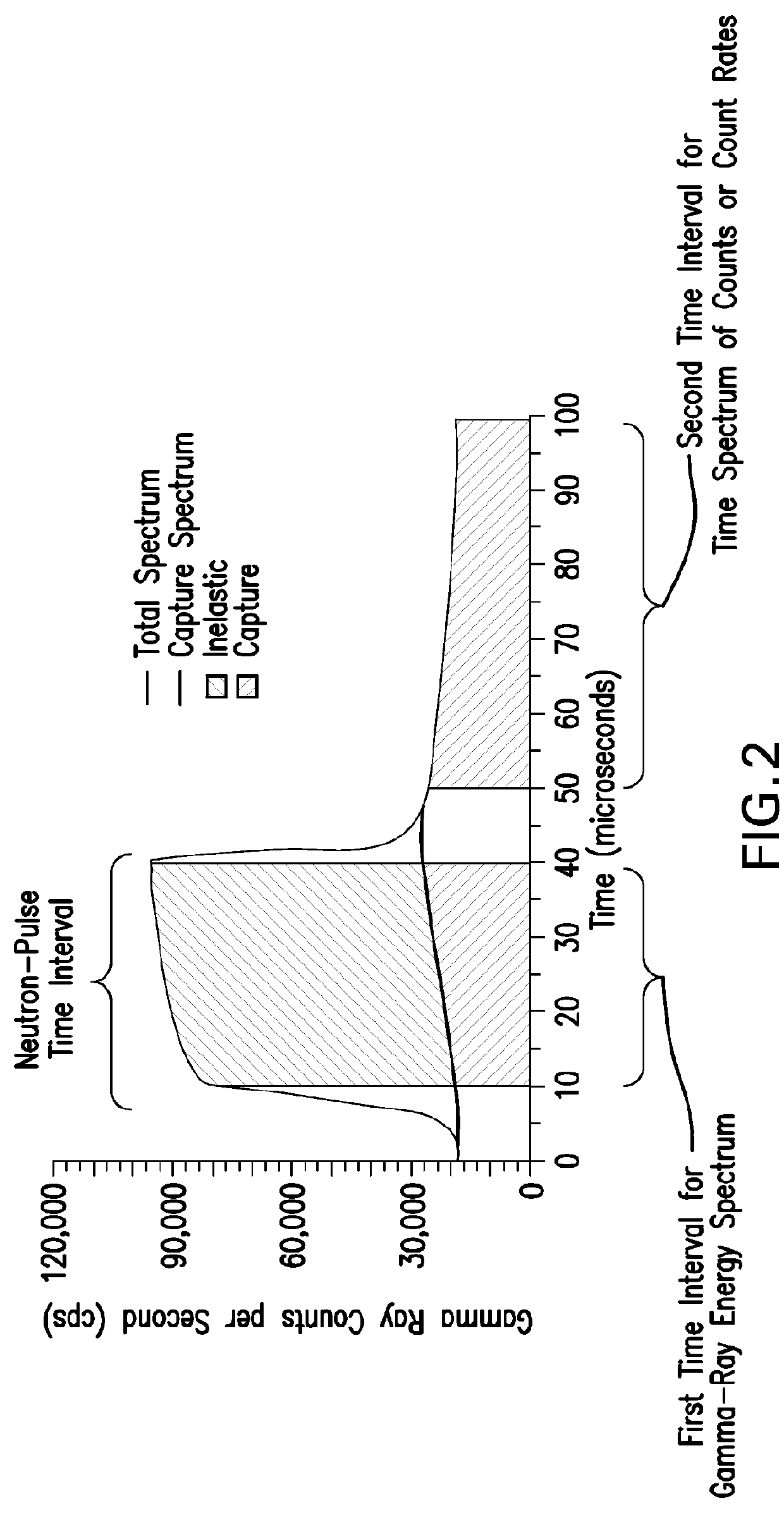
InactiveUS20130048849A1Radiation intensity measurementNuclear radiation detectionInelastic scatteringCounting rate
Disclosed is a method for estimating a density of an earth formation penetrated by a borehole. The method includes: emitting a pulse of fast neutrons into the formation during a neutron-pulse time interval; detecting gamma-rays due to inelastic scattering and thermal capture of the emitted neutrons in the formation to provide a gamma-ray energy spectrum due to the inelastic scattering and the thermal capture during a first time interval within the neutron-pulse time interval and to provide a time spectrum of counts or count rates due to thermal capture during a second time interval occurring after the neutron-pulse time interval; determining a macroscopic capture cross section of the formation from a decay in the time spectrum of counts or count rates; determining an elemental weight fraction from the gamma-ray energy spectrum; and estimating the density of the formation using the macroscopic capture cross section and the elemental weight fraction.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
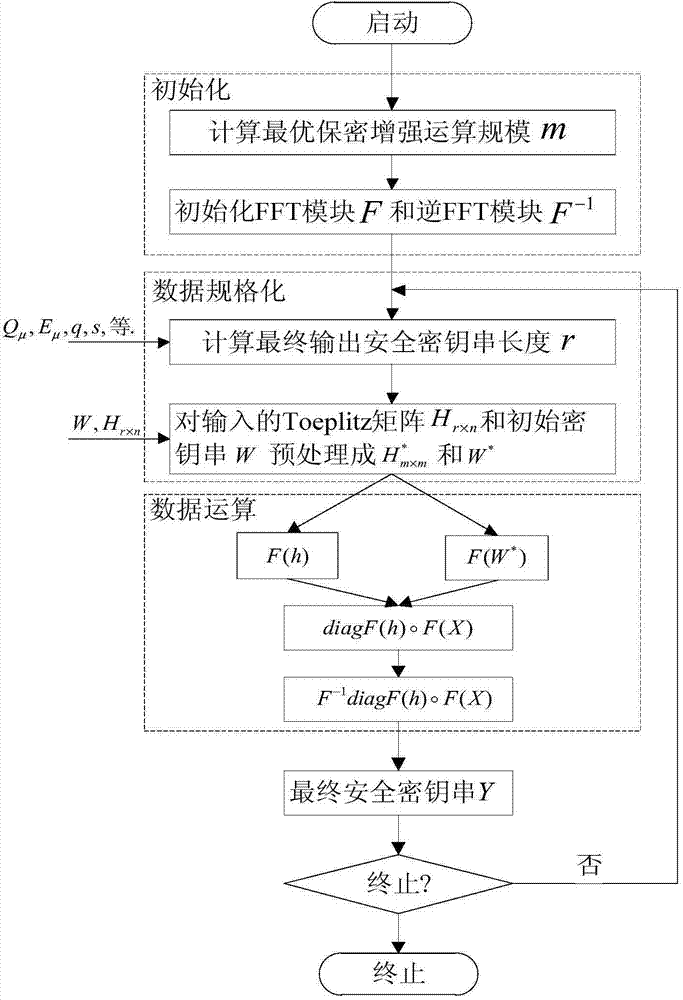
Quantum secret key distribution privacy amplification method supporting large-scale dynamic changes
ActiveCN104506313AIncrease flexibilityEasy to handleKey distribution for secure communicationCounting rateData operations
The invention discloses a quantum secret key distribution privacy amplification method supporting large-scale dynamic changes. The method includes the steps of firstly, conducting initialization, wherein the optimal operation scale m of an FFT module is calculated according to the actual running parameters of a quantum secret key distribution system when the privacy amplification method is started, and the initialization scale is an FFT operation and inverse FFT operation module of m; secondly, normalizing data, wherein the final security secret key length r is calculated according to the detector counting rate Q mu of the quantum secret key distribution system, the quantum bit error rate E mu, the corrected weak security secret key length n and the security parameter s of the quantum secret key distribution system, and normalizing an initial secret key string and a Toeplitz matrix according to the parameter m, the parameter n and the parameter r; thirdly, conducting data operation, wherein the operation process of the Toeplitz matrix and the initial secret key string is operated through the FFT technology, the first r items of the calculation result are taken to form a result vector, namely, the final security secrete key. The method has the advantages of being high in flexibility, better in processing performance, and the like.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
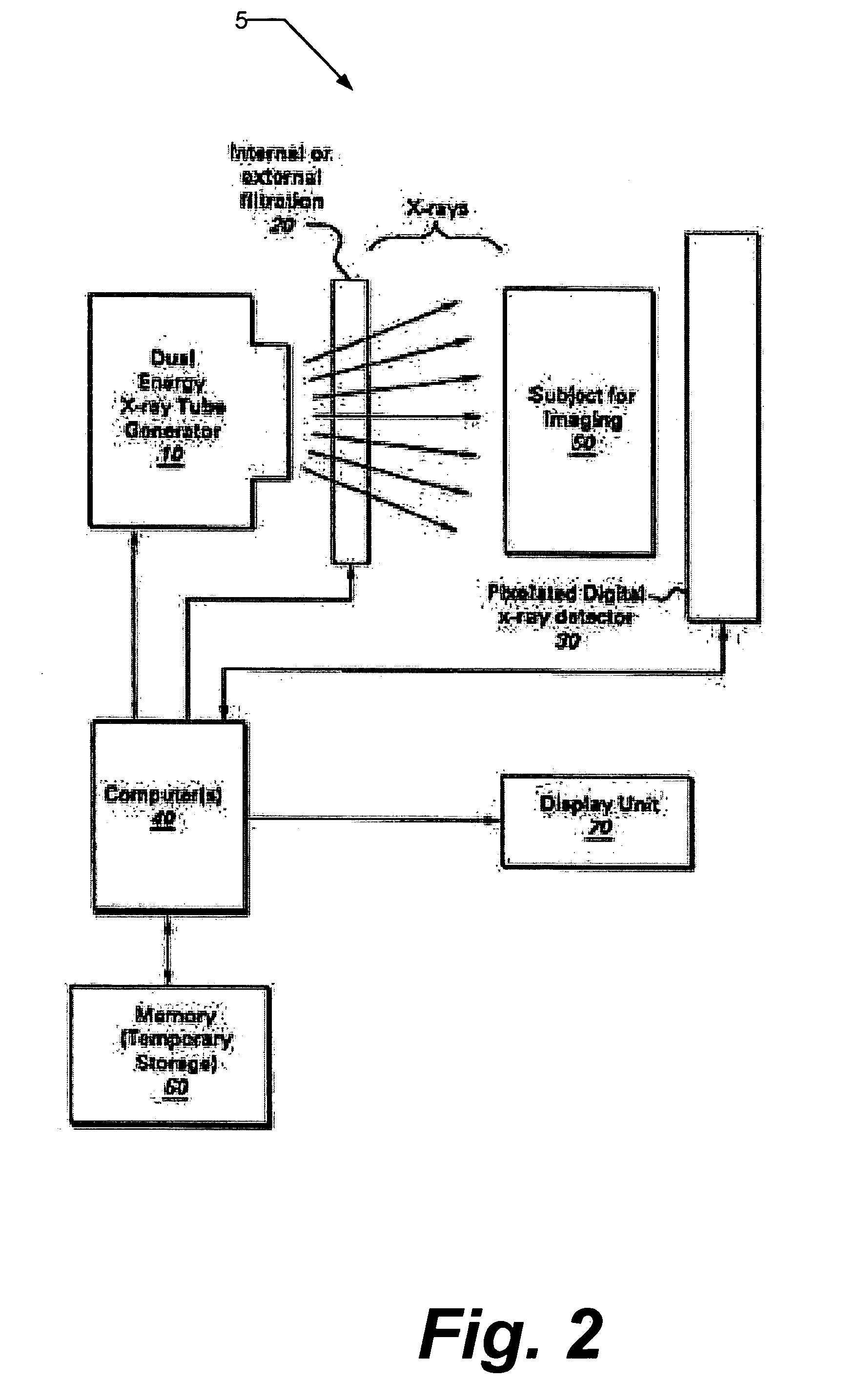
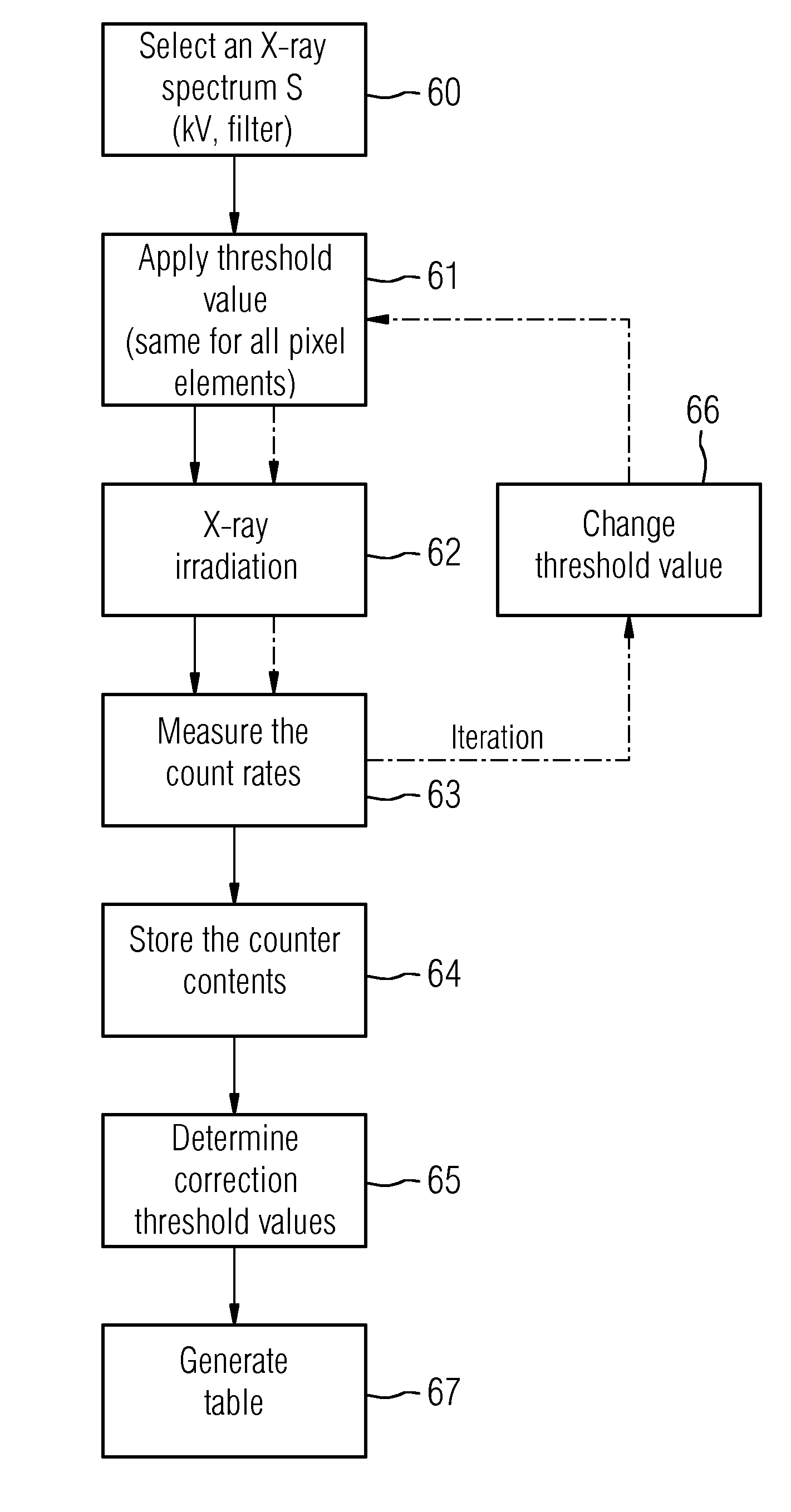
Method for Calibrating a Counting Digital X-Ray Detector, X-Ray System for Performing Such a Method and Method for Acquiring an X-Ray Image
ActiveUS20140185781A1Improve automationImprove image qualityX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentCounting rateSoft x ray
A method for calibrating a counting digital X-ray detector includes performing a threshold value scan in at least one defined X-ray spectrum for irradiating the X-ray detector, which includes a matrix composed of pixel elements, storing count rates of the pixel elements as a function of respective applied threshold values, and from results of a measurement of count rates of the pixel elements, determining or calculating individual correction threshold values for the individual pixel elements. The individual correction threshold values correct a threshold value that is to be applied to the pixel elements for the defined X-ray spectrum such that threshold value noise is reduced.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
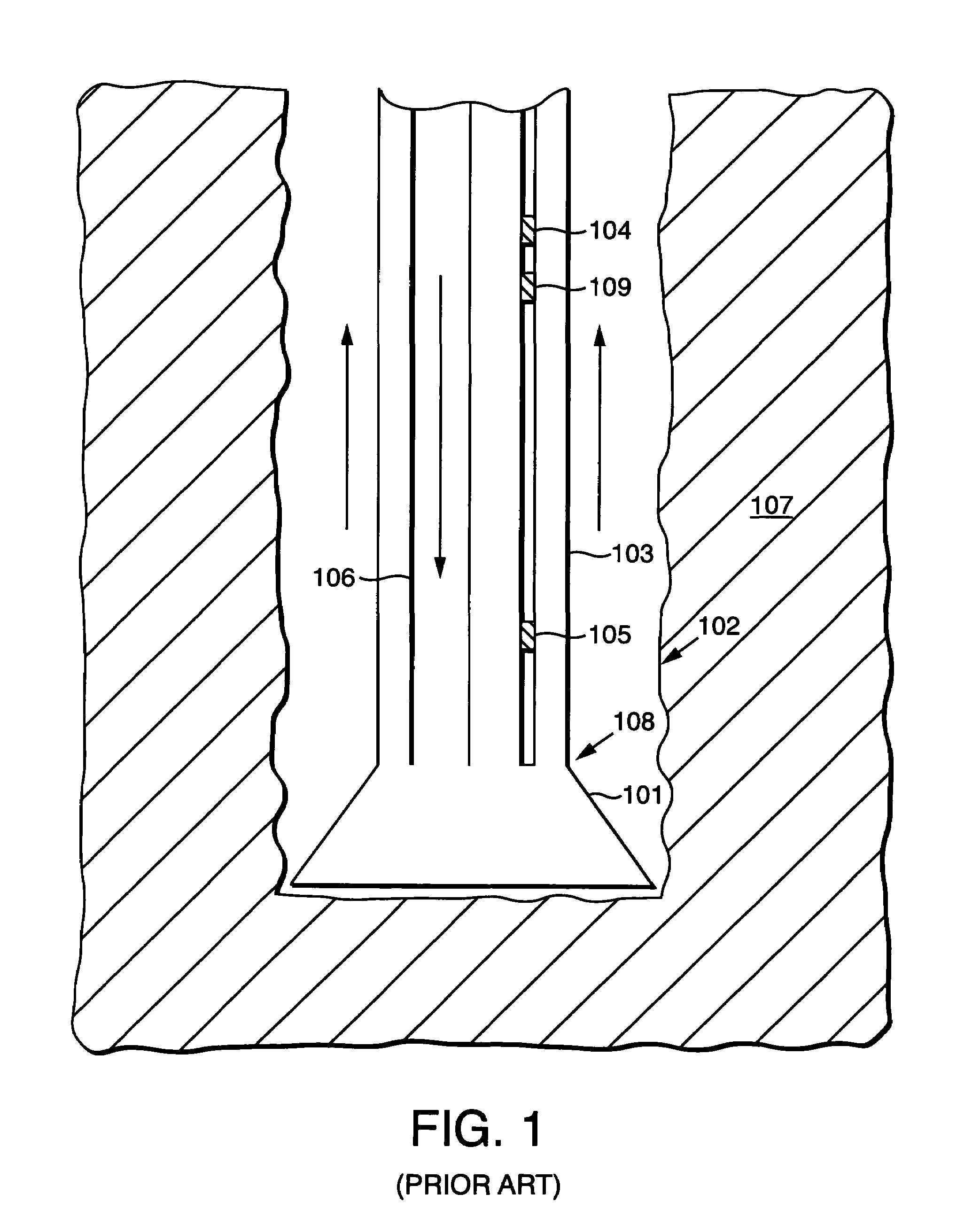
Ultra-low background gas-filled alpha counter
InactiveUS20030040877A1Reduce rateLow count rateSolid-state devicesAmplifiers controlled by lightParallel plateLarge sample
A method and counter for reducing the background counting rate in gas-filled alpha particle counters wherein the counter is constructed in such a manner as to exaggerate the differences in the features in preamplifier pulses generated by collecting the charges in ionization tracks produced by alpha particles emanating from different regions within the counter and then using pulse feature analysis to recognize these differences and so discriminate between different regions of emanation. Thus alpha particles emitted from the sample can then be counted while those emitted from the counter components can be rejected, resulting in very low background counting rates even from large samples. In one embodiment, a multi-wire ionization chamber, different electric fields are created in different regions of the counter and the resultant difference in electron velocities during charge collection allow alpha particles from the sample and counter backwall to be distinguished. In a second embodiment, a parallel-plate ionization chamber, the counter dimensions are adjusted so that charge collection times are much longer for ionization tracks caused by sample source alpha particles than for those caused by anode source alpha particles. In both embodiments a guard electrode can be placed about the anode's perimeter and secondary pulse feature analysis performed on signal pulses output from a preamplifier attached to this guard electrode to further identify and reject alpha particles emanating from the counter's sidewalls in order to further lower the counter's background.
Owner:WARBURTON WILLIAM K
Pulsed X-Ray Signal Processing
ActiveUS20090150077A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismology for water-loggingCounting rateX-ray
Method and system for analyzing electrical pulses contained in a pulse train signal representative of the interaction of x-ray bursts with a nuclear detector configured for subsurface disposal. The pulse train signal is sampled to form a digitized signal. The total energy deposited at the detector during an x-ray burst is determined from the digitized signal, and a count rate of x-ray pulses from the burst is determined. A subsurface parameter is determined using the total energy deposit.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
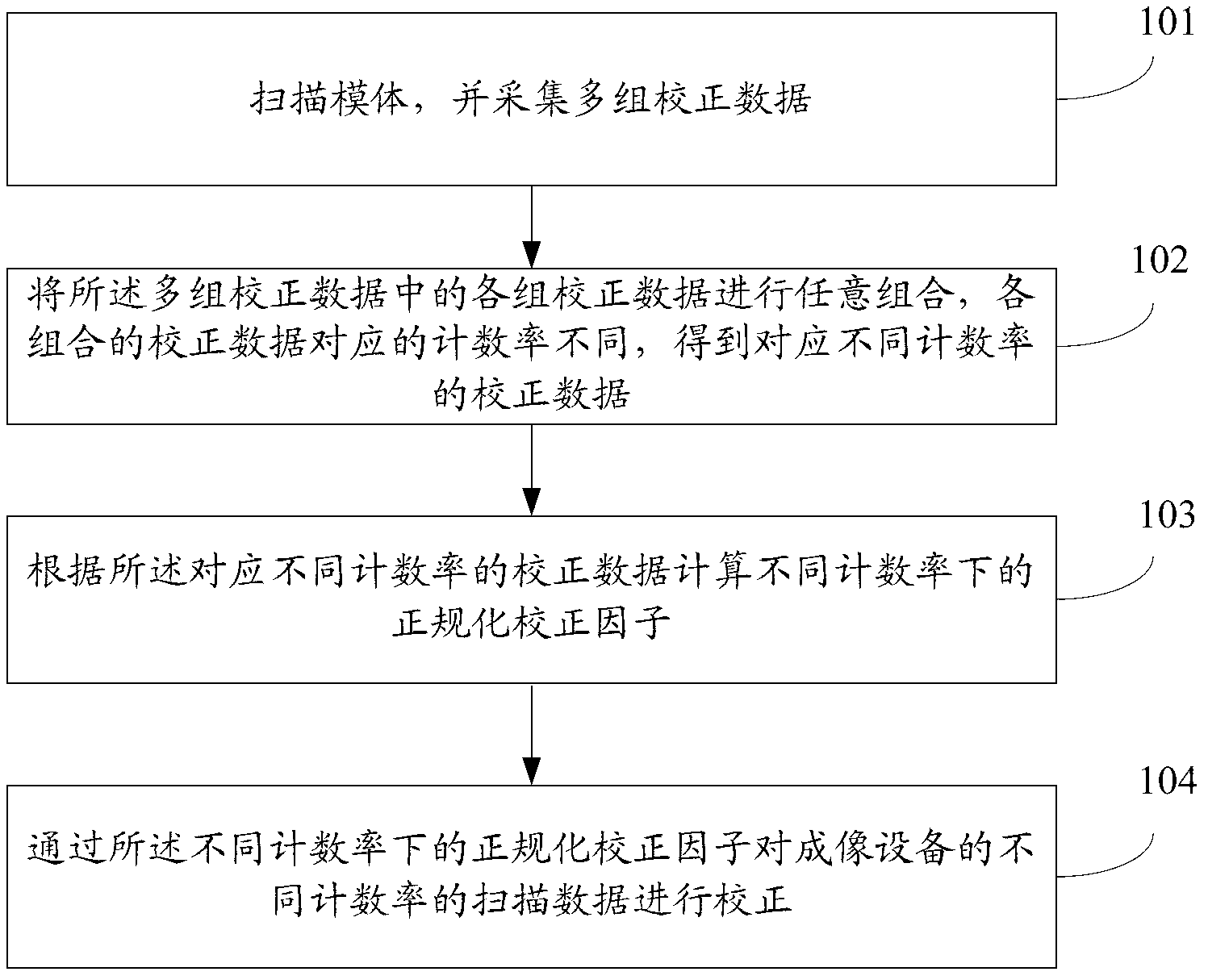
Method and device for normal correction of scanning data in imaging equipment
ActiveCN103315763APrevent Image ArtifactsReduce acquisition timeComputerised tomographsTomographyCounting rateAcquisition time
An embodiment of the invention discloses a method and a device for normal correction of scanning data in imaging equipment. The method includes scanning a model and acquiring a plurality of groups of correction data; optionally combining the groups of correction data to obtain correction data combinations corresponding to different counting rates, thus obtaining correction data corresponding to the different counting rates; calculating normal correction factors under the different counting rates according to the correction data corresponding to the different counting rates; and correcting scanning data different in counting rate in the imaging equipment through the normal correction factors under the different counting rates. The method and the device according to the embodiment have the advantages that acquisition time of correction data can be shortened and the problem of image artifacts caused by mismatch of the counting rates is also avoided.
Owner:SHENYANG INTELLIGENT NEUCLEAR MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
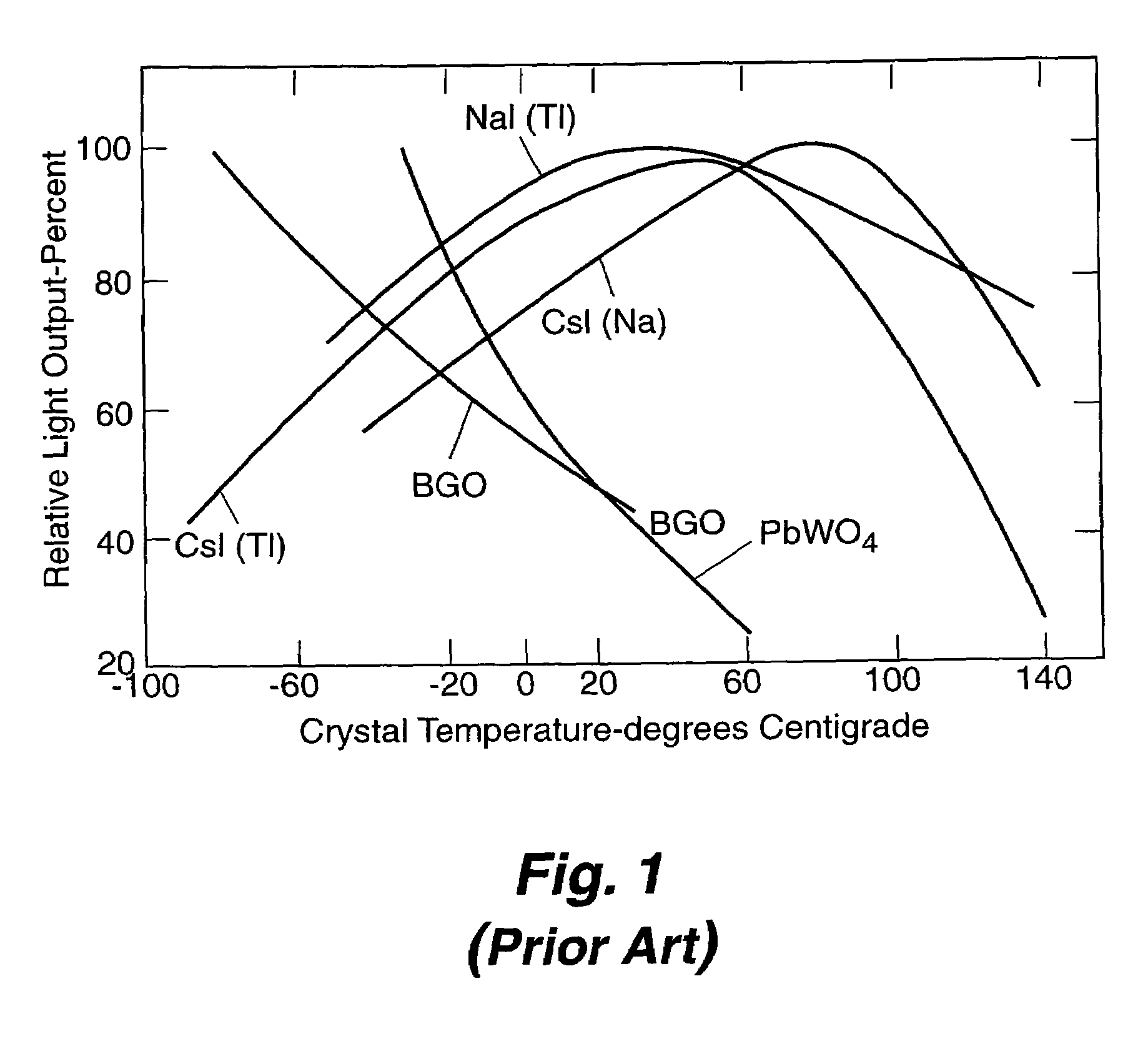
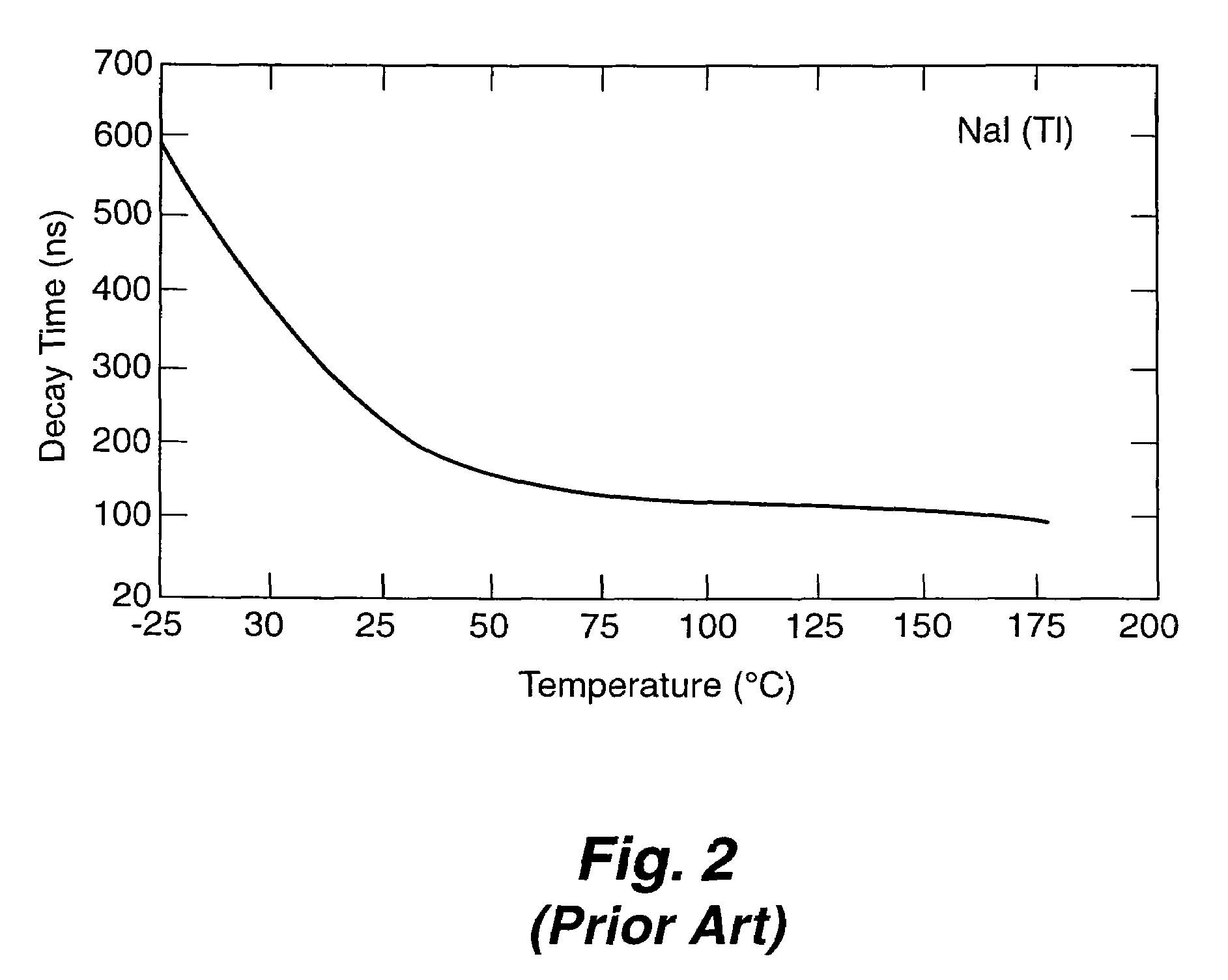
Apparatus and method for temperature correction and expanded count rate of inorganic scintillation detectors
InactiveUS7081626B2Increase count rateMaterial analysis by optical meansRadiation intensity measurementCounting rateSlow light
The present invention includes an apparatus and corresponding method for temperature correction and count rate expansion of inorganic scintillation detectors. A temperature sensor is attached to an inorganic scintillation detector. The inorganic scintillation detector, due to interaction with incident radiation, creates light pulse signals. A photoreceiver processes the light pulse signals to current signals. Temperature correction circuitry that uses a fast light component signal, a slow light component signal, and the temperature signal from the temperature sensor to corrected an inorganic scintillation detector signal output and expanded the count rate.
Owner:LOS ALAMOS NATIONAL SECURITY
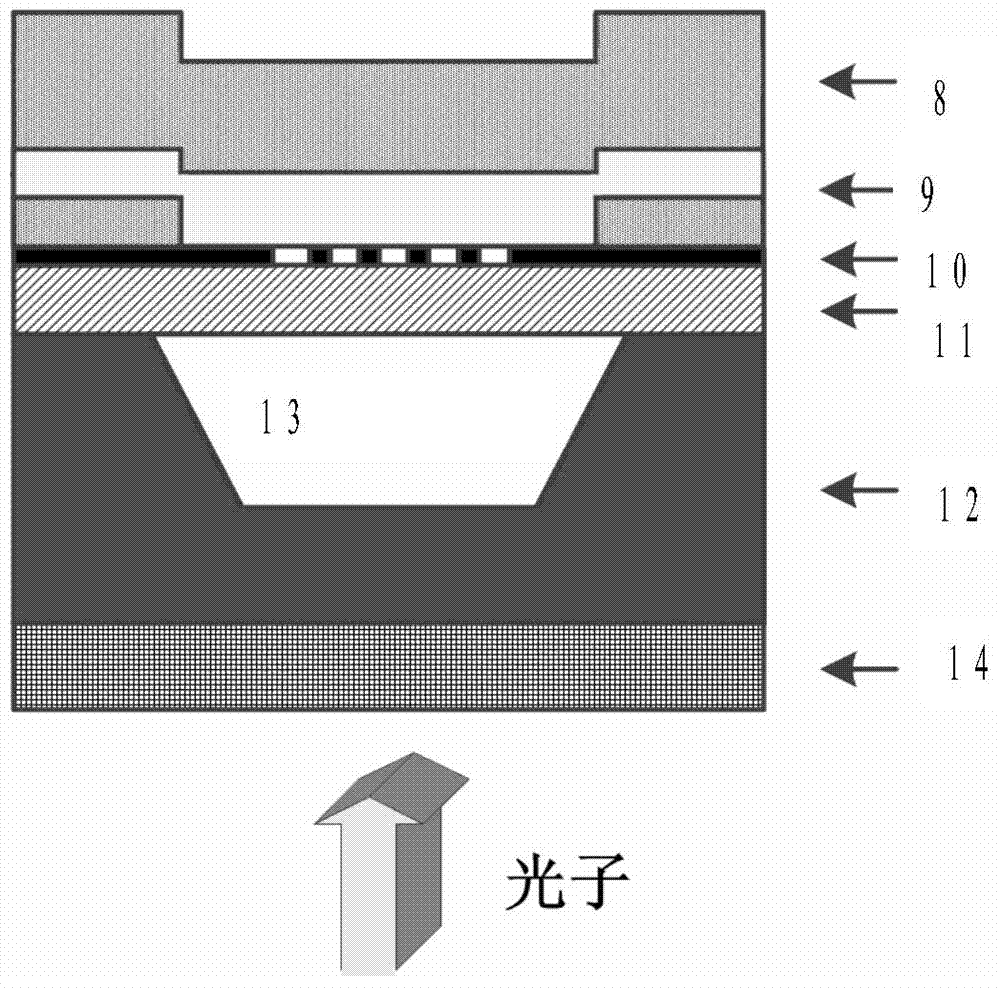
High-speed SNSPD with high-absorption structure and preparation method of high-speed SNSPD
ActiveCN103579405AHigh quality growthImprove absorption rateMaterial nanotechnologyFinal product manufactureCounting rateQuantum efficiency
The invention discloses high-speed SNSPD with a high-absorption structure and a preparation method of the high-speed SNSPD. The SNSPD is based on a high-refraction-index incident medium and an air cavity structure, and can further improve the photon absorption rate of superconducting nanowire, and compared with the prior art, the SNSPD can achieves approximate 100 percent absorption rate with lower duty ratio in the condition of nanowire made of superconducting ultrathin membrane made of the same material and having the same thickness, so that the difficulty in electron beam lithography steps is greatly lowered, the SNSPD is beneficial to the preparation of superfine nanowire, the high-quality growth of superconducting films can be guaranteed through the adoption of an SOI substrate, the intrinsic quantum efficiency of a detector is not affected; moreover, the highest counting rate of the detector can be enhanced as the total length of the required nanowire is obviously reduced in the condition that the same effective detection area is guaranteed, and the probability of defect occurrence during the preparation process is obviously reduced.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for operation of a counting radiation detector with improved linearity
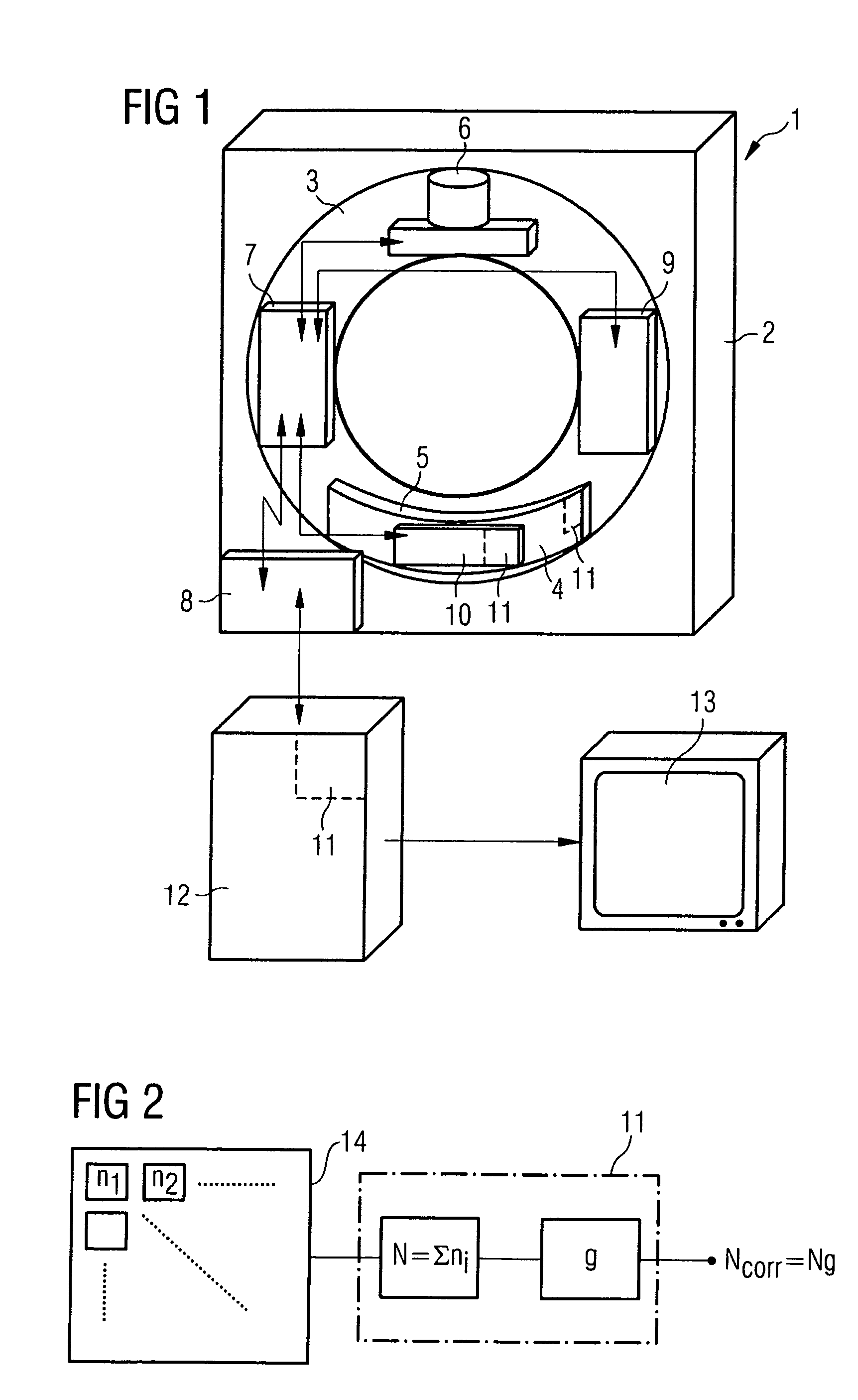
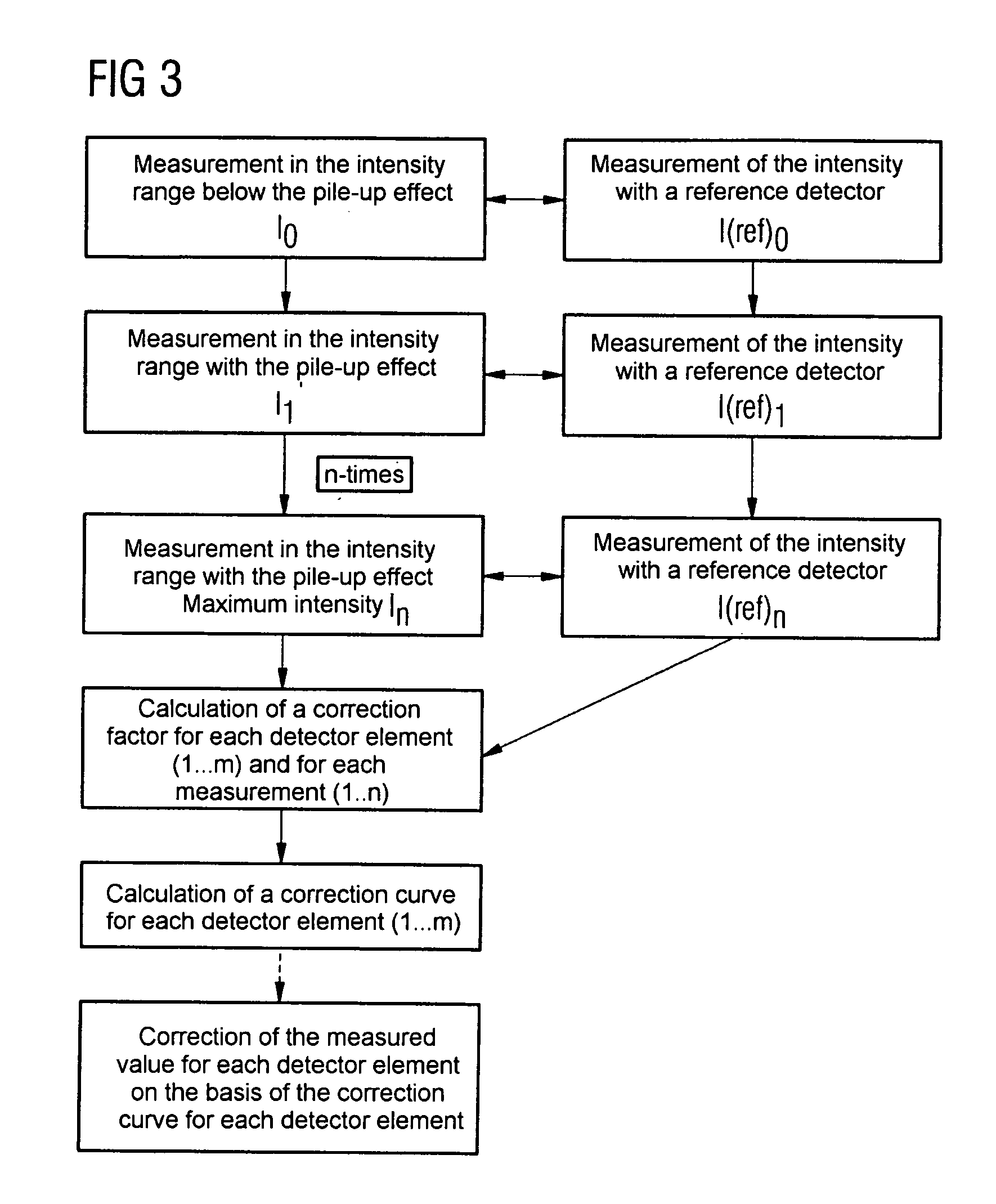
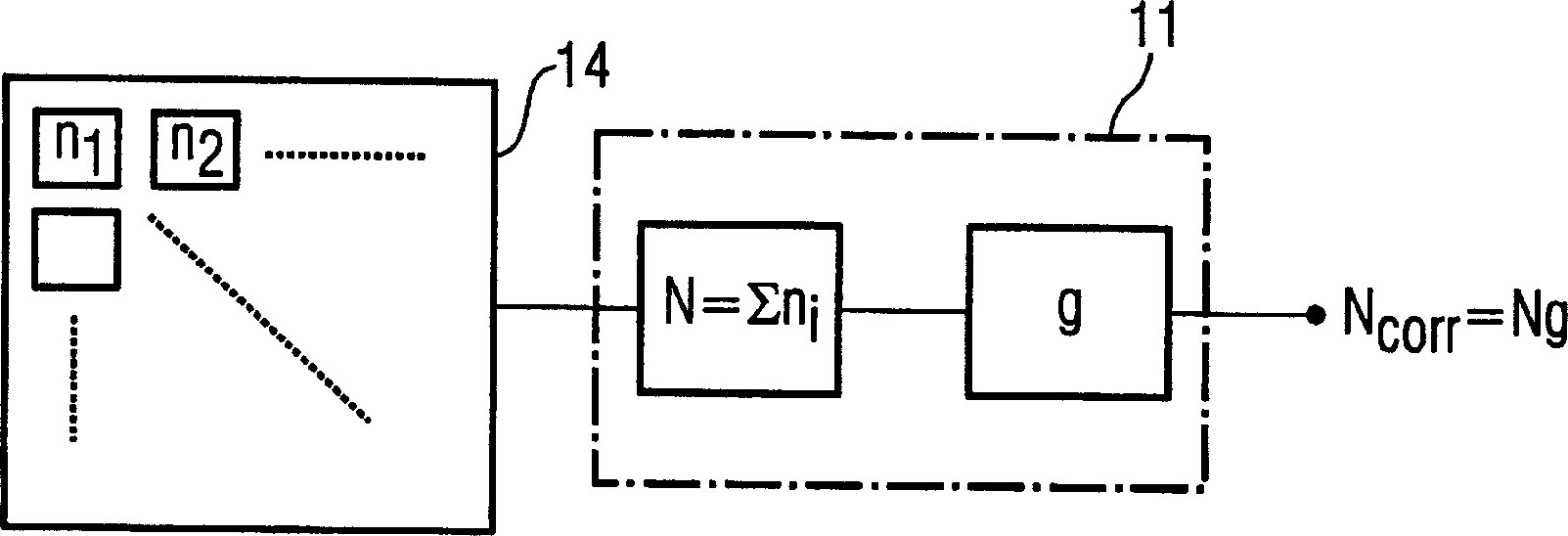
The invention relates to a method for operating a counting radiation detector, in particular a counting X-ray detector, with improved linearity, during operation each detector element (14) of the radiation detector (4) is counted depending on providing counting pulses at the counting rate of the number of ray quantum numbers occurring per time unit; converting the counting rate provided by each detector element (14) or part of the detector element (14) into an actual counting rate through a functional relationship, or Multiply by a correction factor that depends on the magnitude of the count rate. Correction coefficients are determined in advance for each detector element (14) or a subsection thereof for the calculation of the count rate due to the dead time of the detector element (14) to the actual number of radiation quanta present per time unit The deviation is corrected. The method of the invention improves the linearity of the counting radiation detector especially under high radiation intensity, and can also meet the linearity condition in X-ray CT equipment.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com