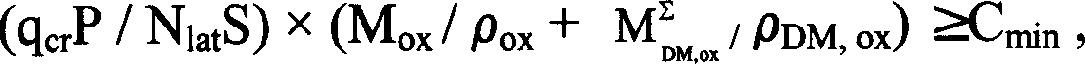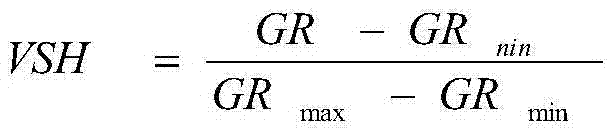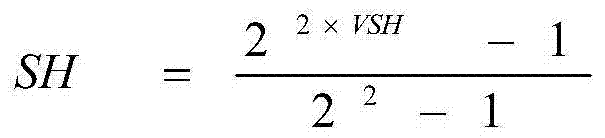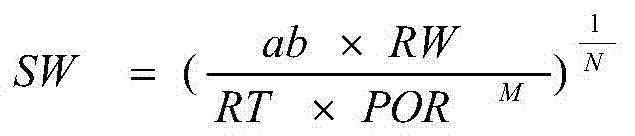Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1415 results about "Uranium" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Uranium is a chemical element with the symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Uranium is weakly radioactive because all isotopes of uranium are unstable; the half-lives of its naturally occurring isotopes range between 159,200 years and 4.5 billion years. The most common isotopes in natural uranium are uranium-238 (which has 146 neutrons and accounts for over 99% of uranium on Earth) and uranium-235 (which has 143 neutrons). Uranium has the highest atomic weight of the primordially occurring elements. Its density is about 70% higher than that of lead, and slightly lower than that of gold or tungsten. It occurs naturally in low concentrations of a few parts per million in soil, rock and water, and is commercially extracted from uranium-bearing minerals such as uraninite.
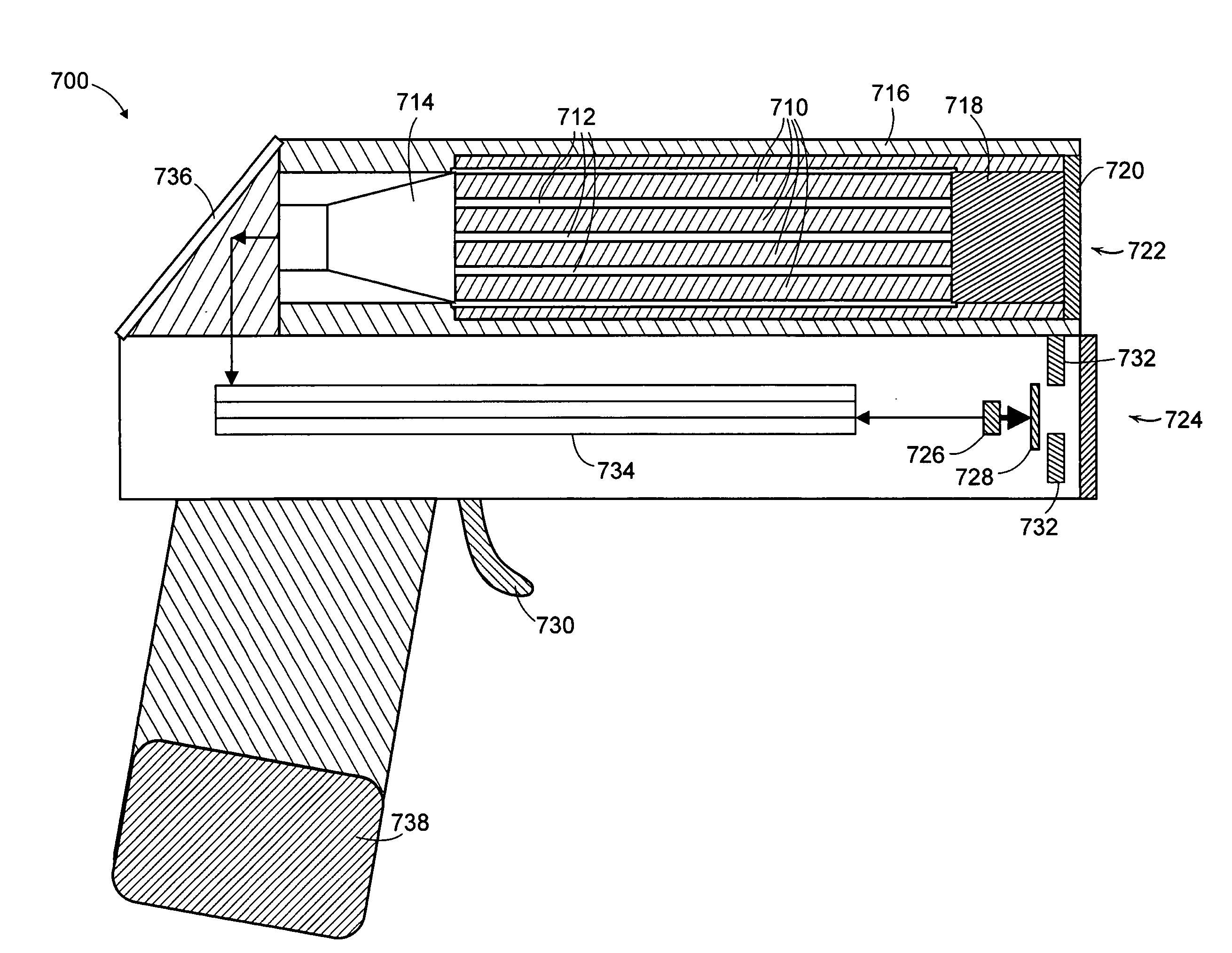
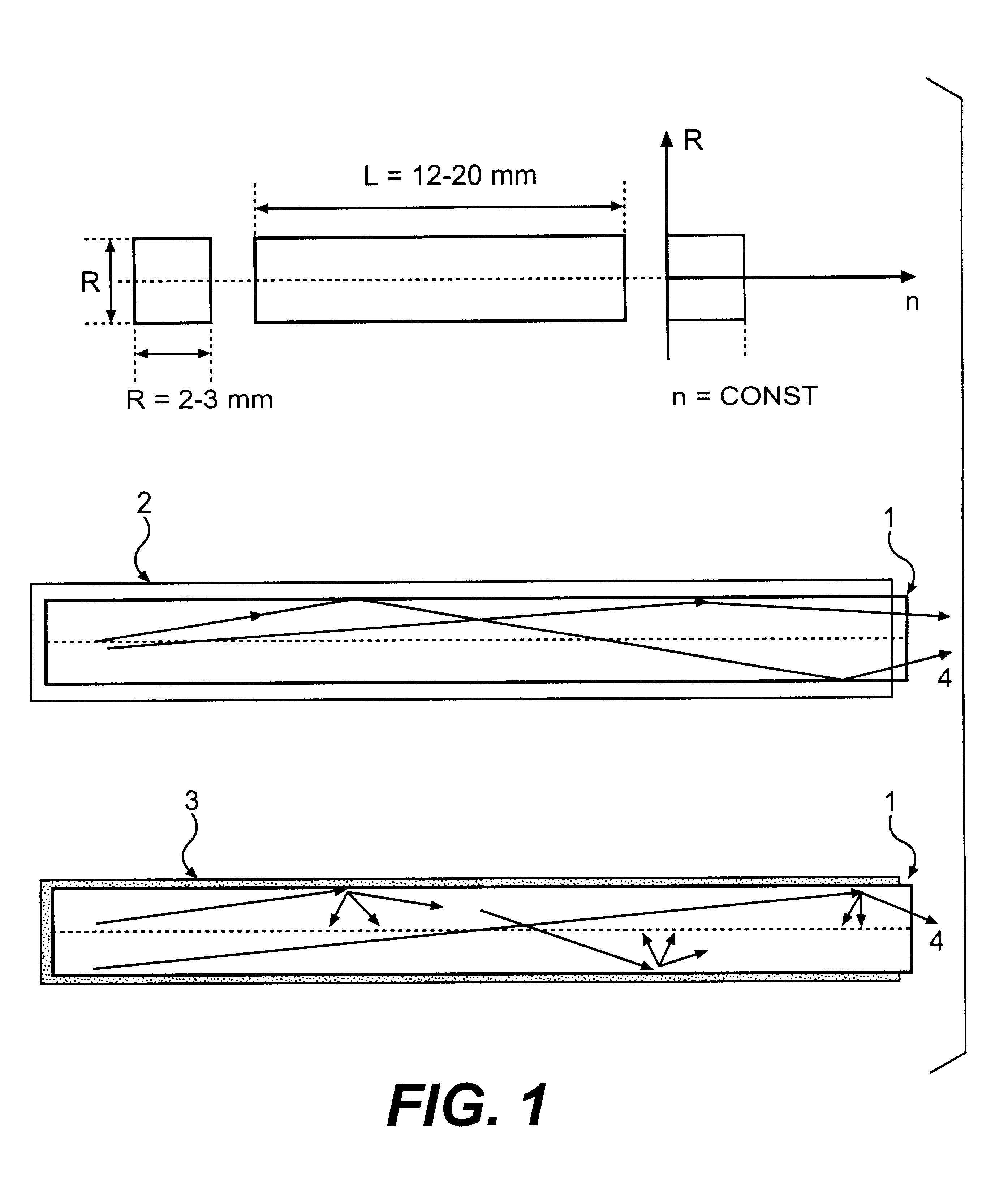
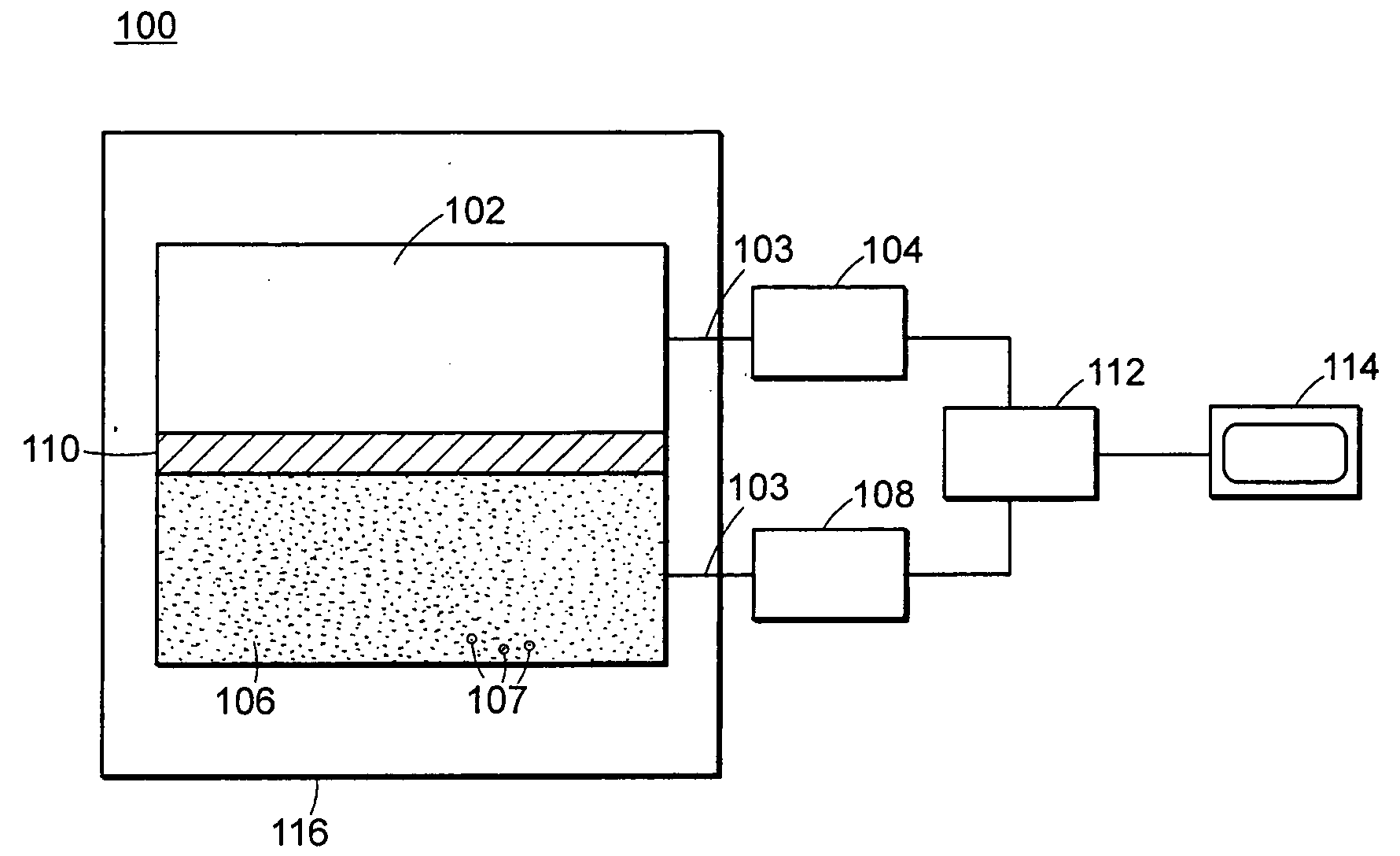
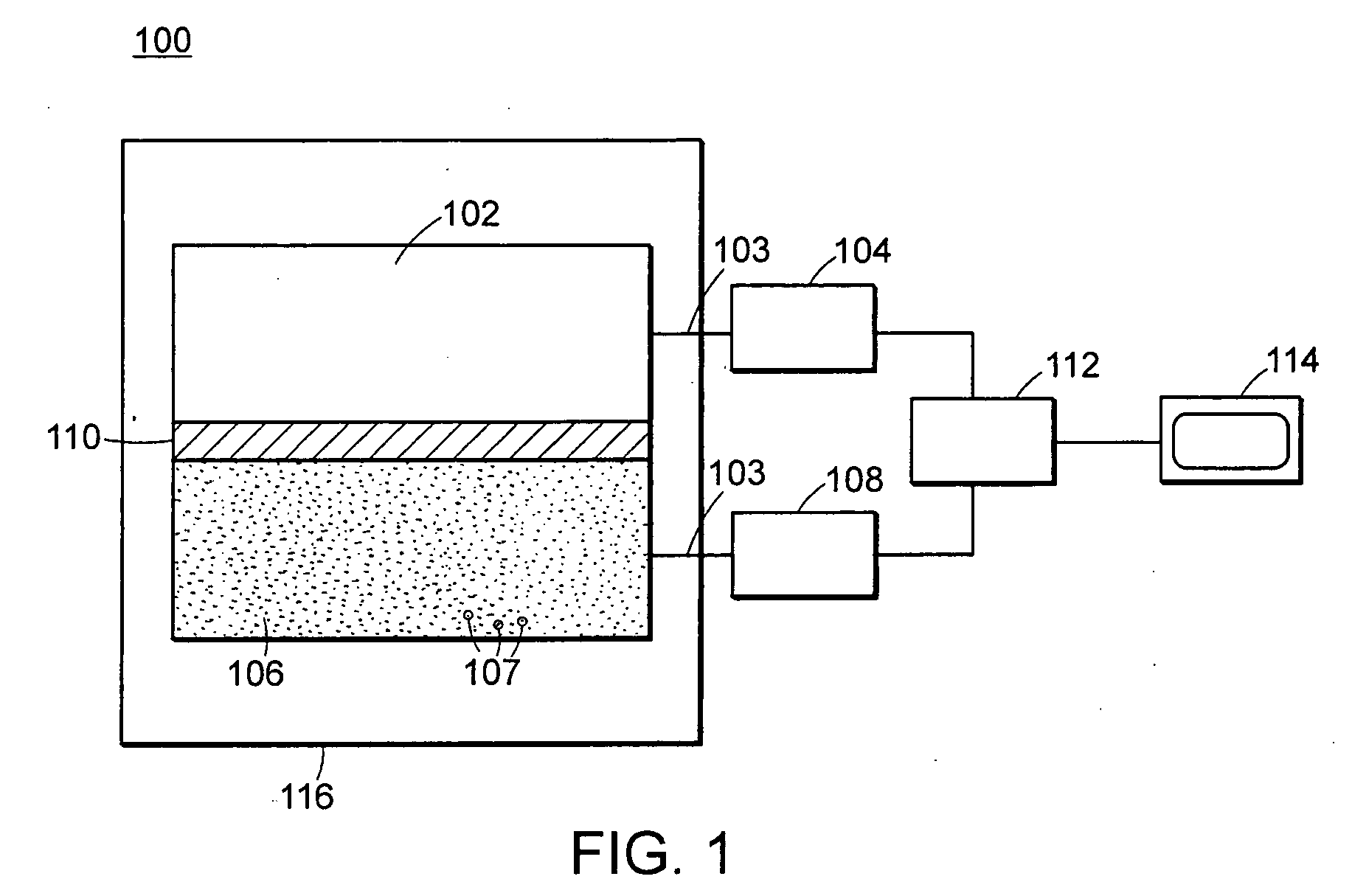
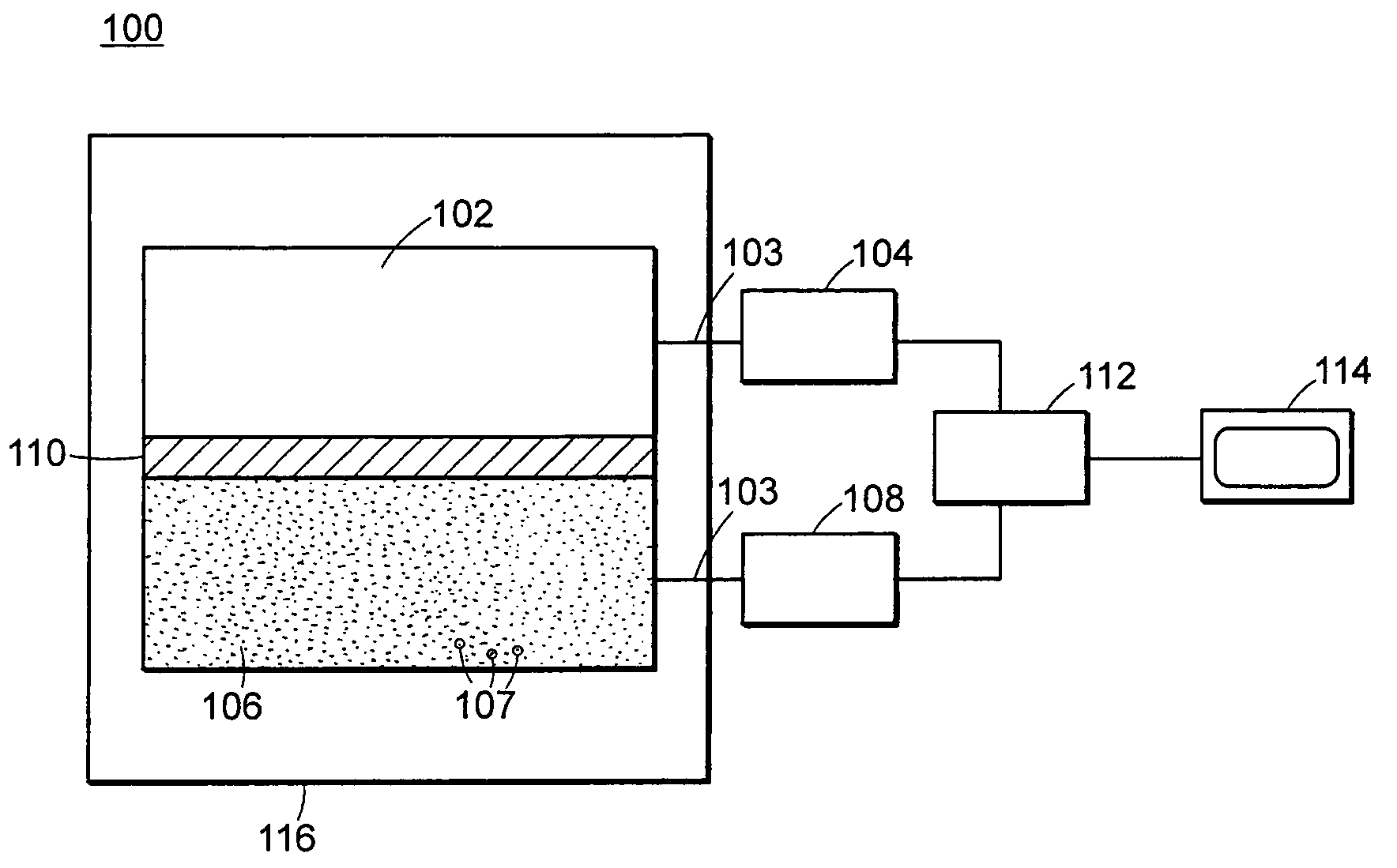
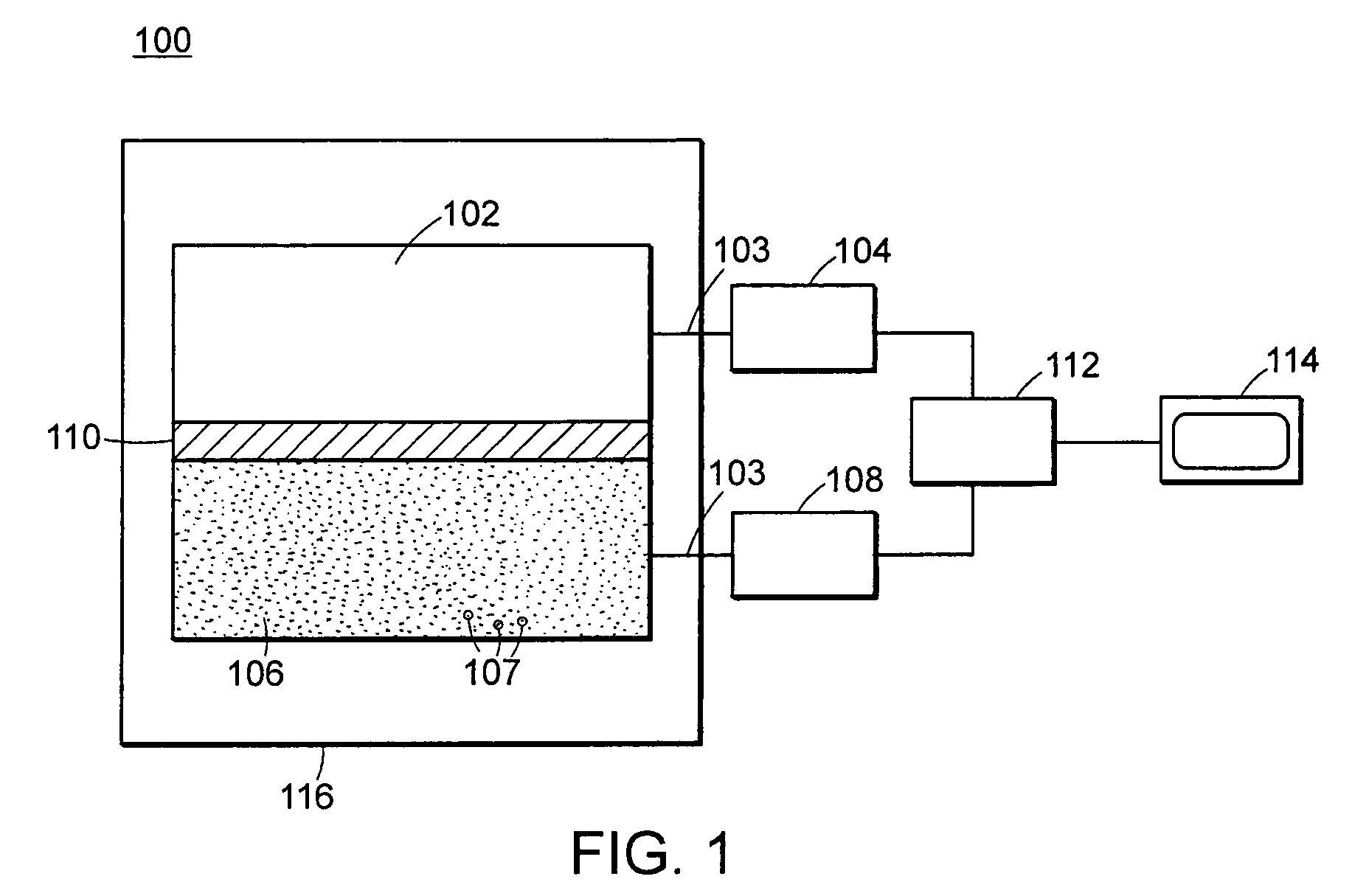
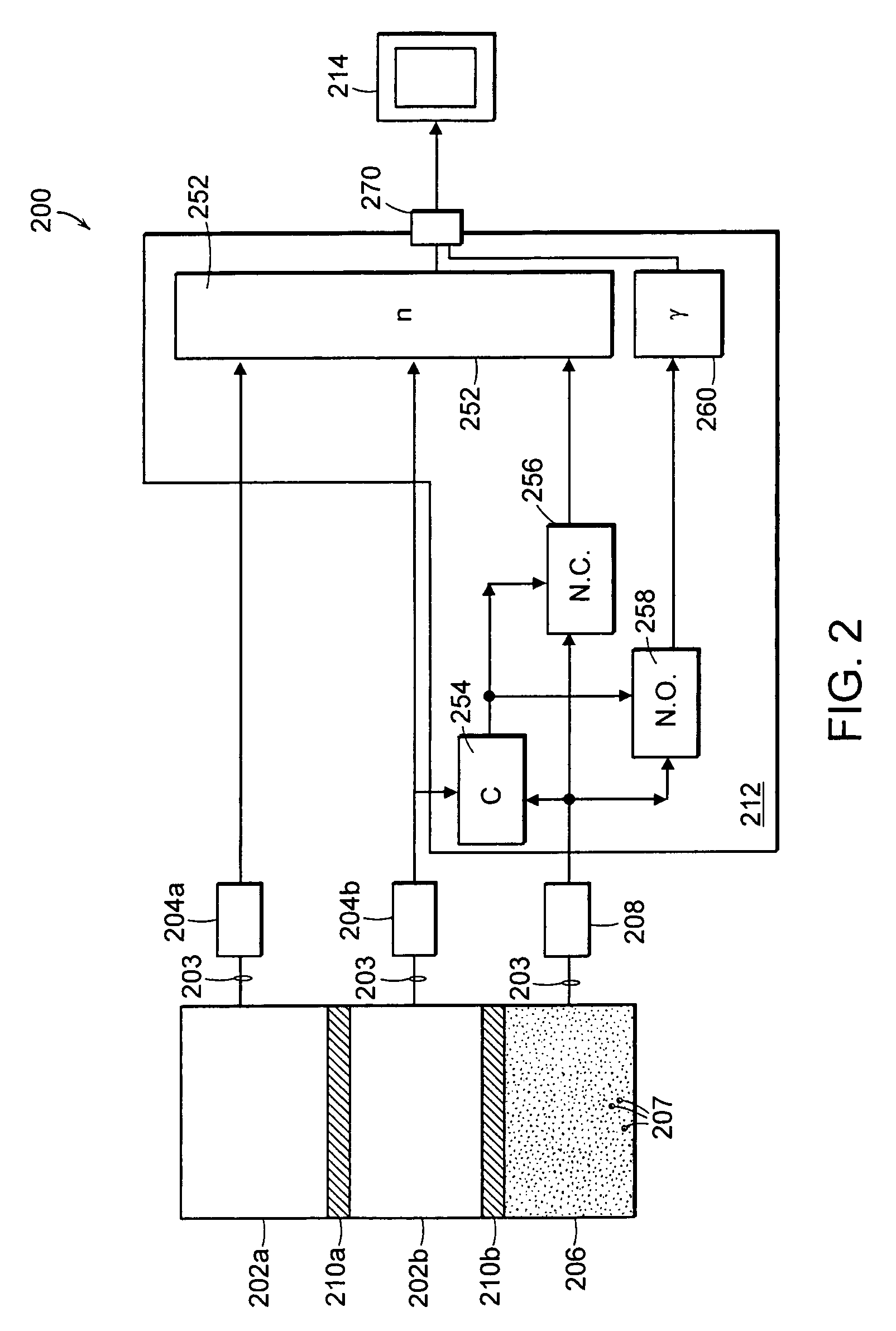
Neutron and gamma ray monitor
InactiveUS20050023479A1Light weightMore selectiveX-ray spectral distribution measurementMeasurement with scintillation detectorsNeutron emissionX-ray
An apparatus for selective radiation detection includes a neutron detector that facilitates detection of neutron emitters, e.g. plutonium, and the like; a gamma ray detector that facilitates detection of gamma ray sources, e.g., uranium, and the like; and / or an X-ray analyzer that facilitates detection of materials that can shield radioactive sources, e.g., lead, and the like.
Owner:THERMO NITON ANALYZERS
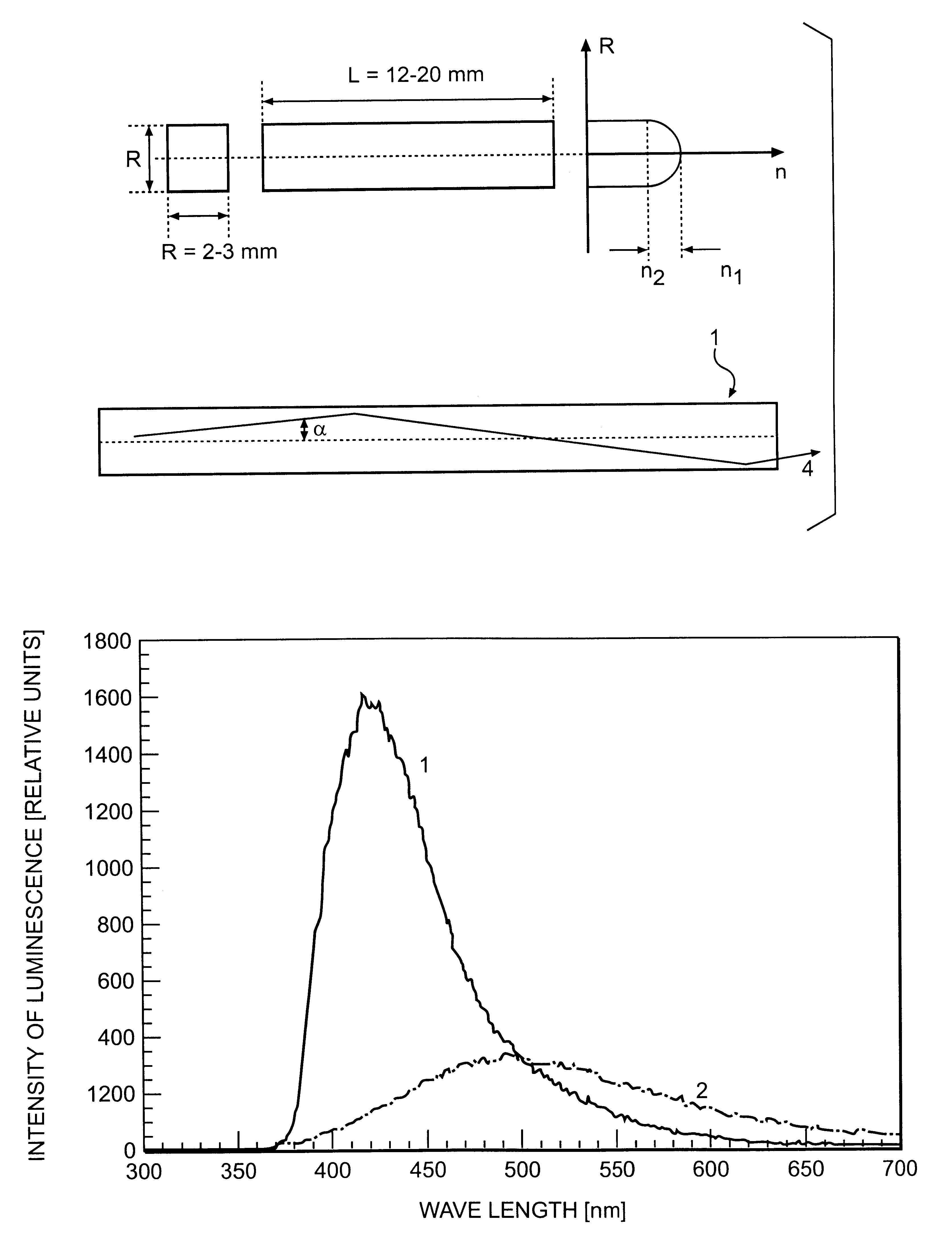
Scintillating substance and scintillating wave-guide element
InactiveUS6278832B1Improve light outputShorten the timePolycrystalline material growthOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingFiberAdditive ingredient
The invention is related to nuclear physics, medicine and oil industry, namely to the measurement of x-ray, gamma and alpha radiation; control for trans uranium nuclides in the habitat of a man; non destructive control for the structure of heavy bodies; three dimensional positron-electron computer tomography, etc.The essence of the invention is in additional ingredients in a chemical composition of a scintillating material based on crystals of oxyorthosilicates, including cerium Ce and crystallized in a structural type Lu2SiO5.The result of the invention is the increase of the light output of the luminescence, decrease of the time of luminescence of the ions Ce3+, increase of the reproducibility of grown crystals properties, decrease of the cost of the source melting stock for growing scintillator crystals, containing a large amount of Lu2O3, the raise of the effectiveness of the introduction of SCintillating crystal luminescent radiation into a glass waveguide fibre, prevention of cracking of crystals during the production of elements, creation of waveguide properties in scintillating elements, exclusion of expensive mechanical polishing of their lateral surface.
Owner:SOUTHBOURNE INVESTMENTS
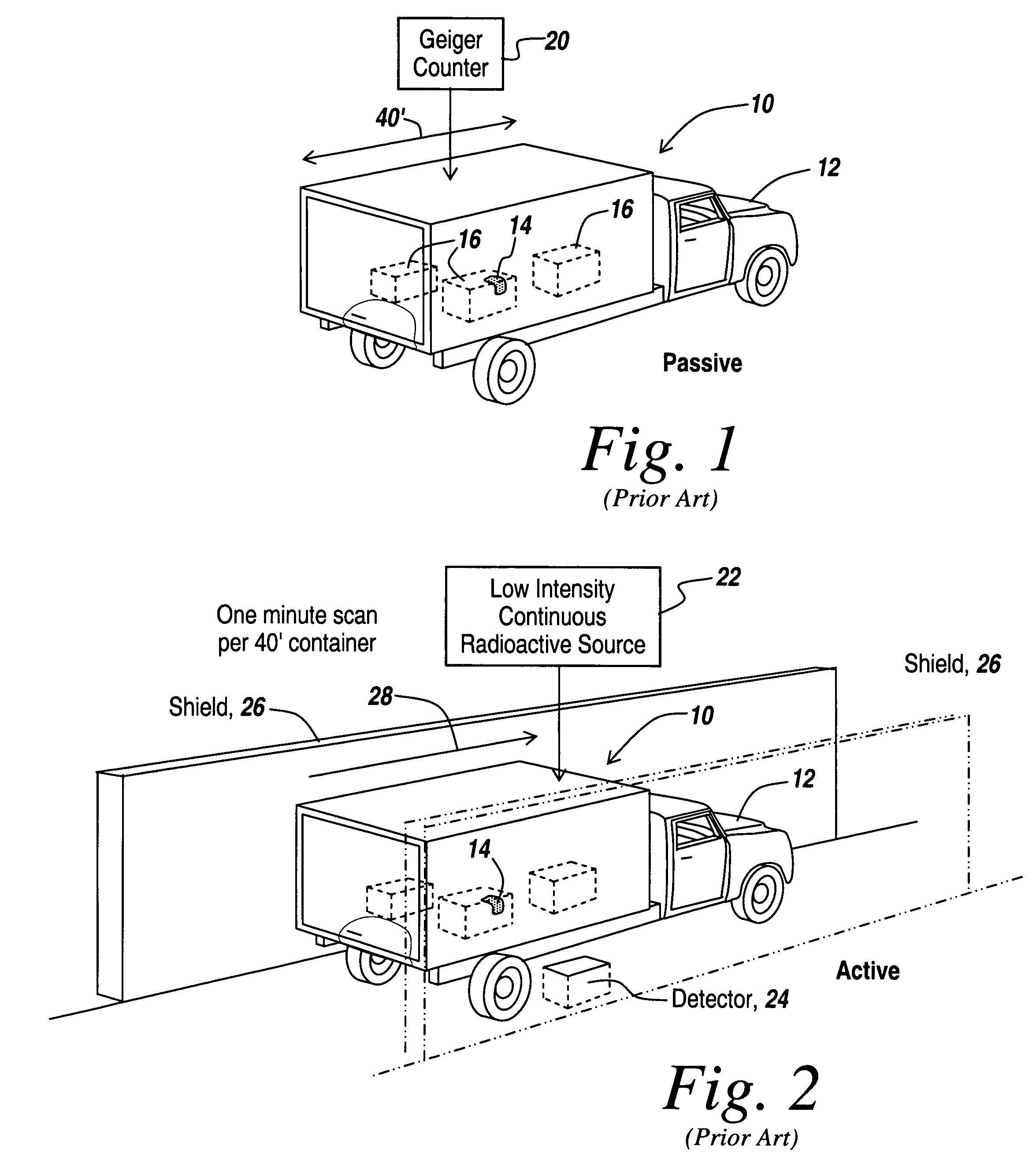
Method and apparatus for the safe and rapid detection of nuclear devices within containers
ActiveUS7379530B2Faster scan timeAccurate detectionX-ray apparatusMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationDisplay deviceHigh intensity
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
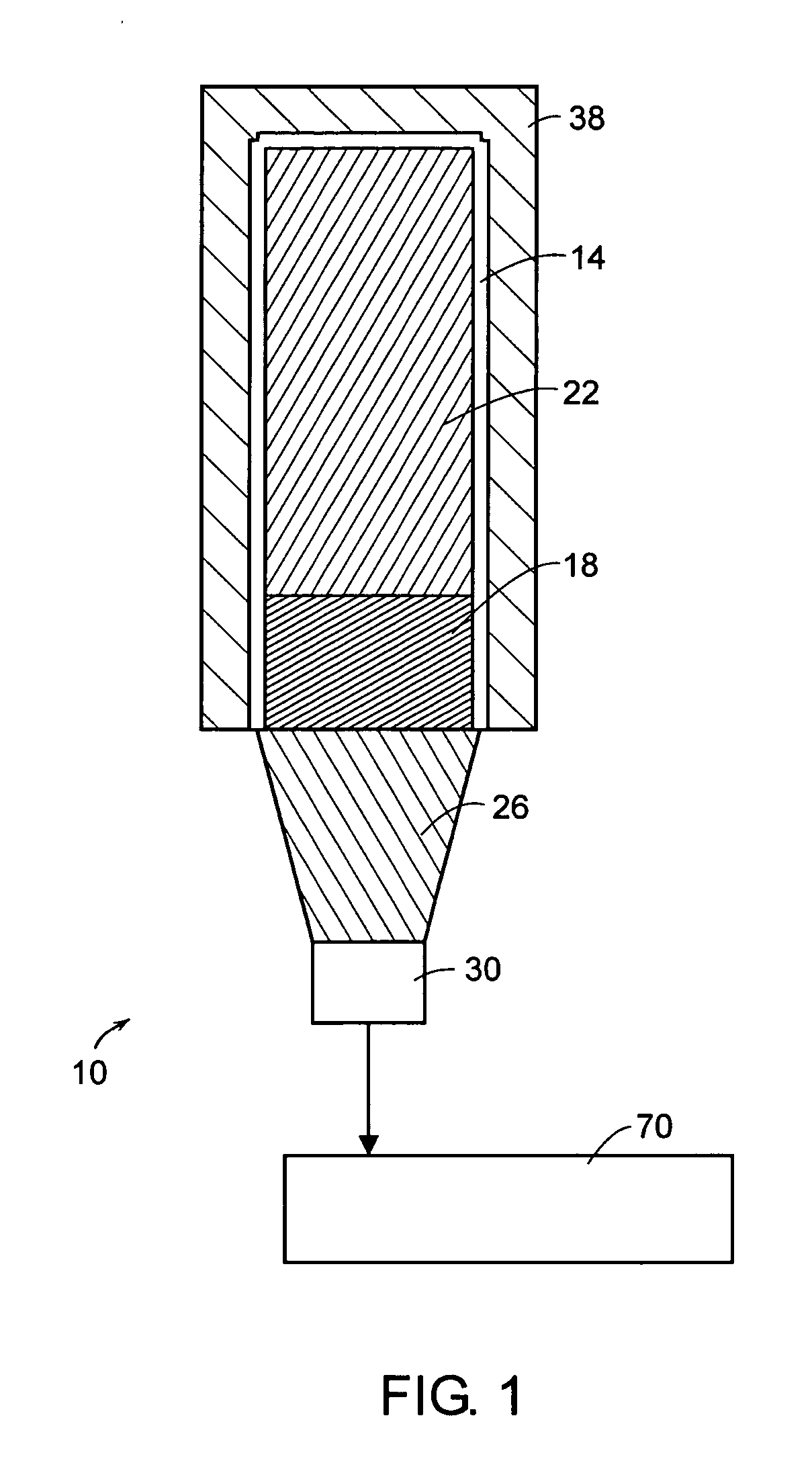
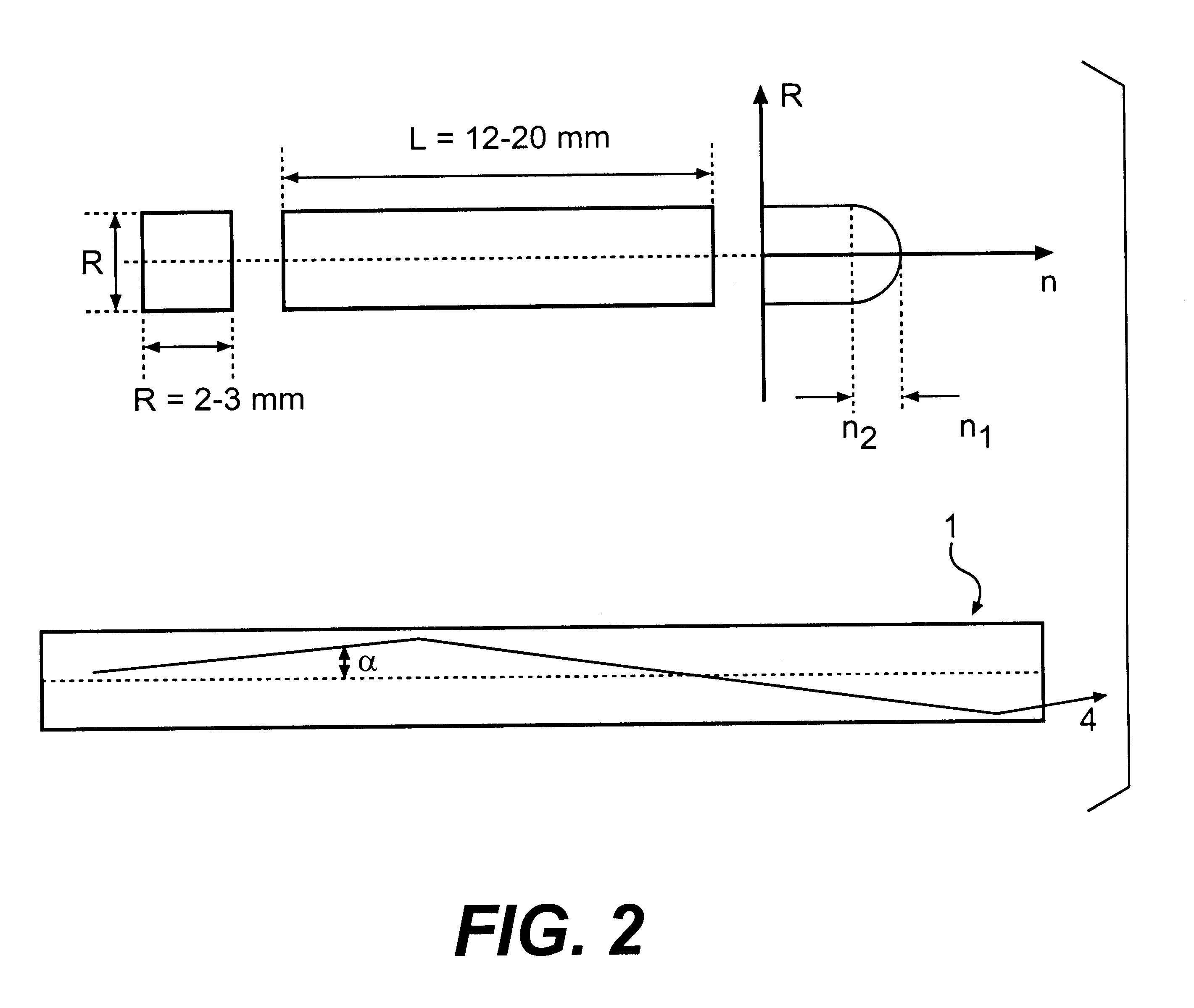
Neutron and gamma ray monitor
ActiveUS20070272874A1Easy to detectMeasurement with scintillation detectorsMaterial analysis by optical meansNeutron emissionLight guide
An apparatus for selective radiation detection includes a neutron detector that facilitates detection of neutron emitters, e.g. plutonium, and the like; a gamma ray detector that facilitates detection of gamma ray sources, e.g., uranium, and the like. The apparatus comprises a first light guide, optically coupled to a first optical detector; a second light guide, optically coupled to a second optical detector a sheet of neutron scintillator, opaque for incoming optical photons, said sheet of neutron scintillator sandwiched between the first and the second light guides. The second light guide comprises a gamma ray scintillator material.
Owner:THERMO NITON ANALYZERS
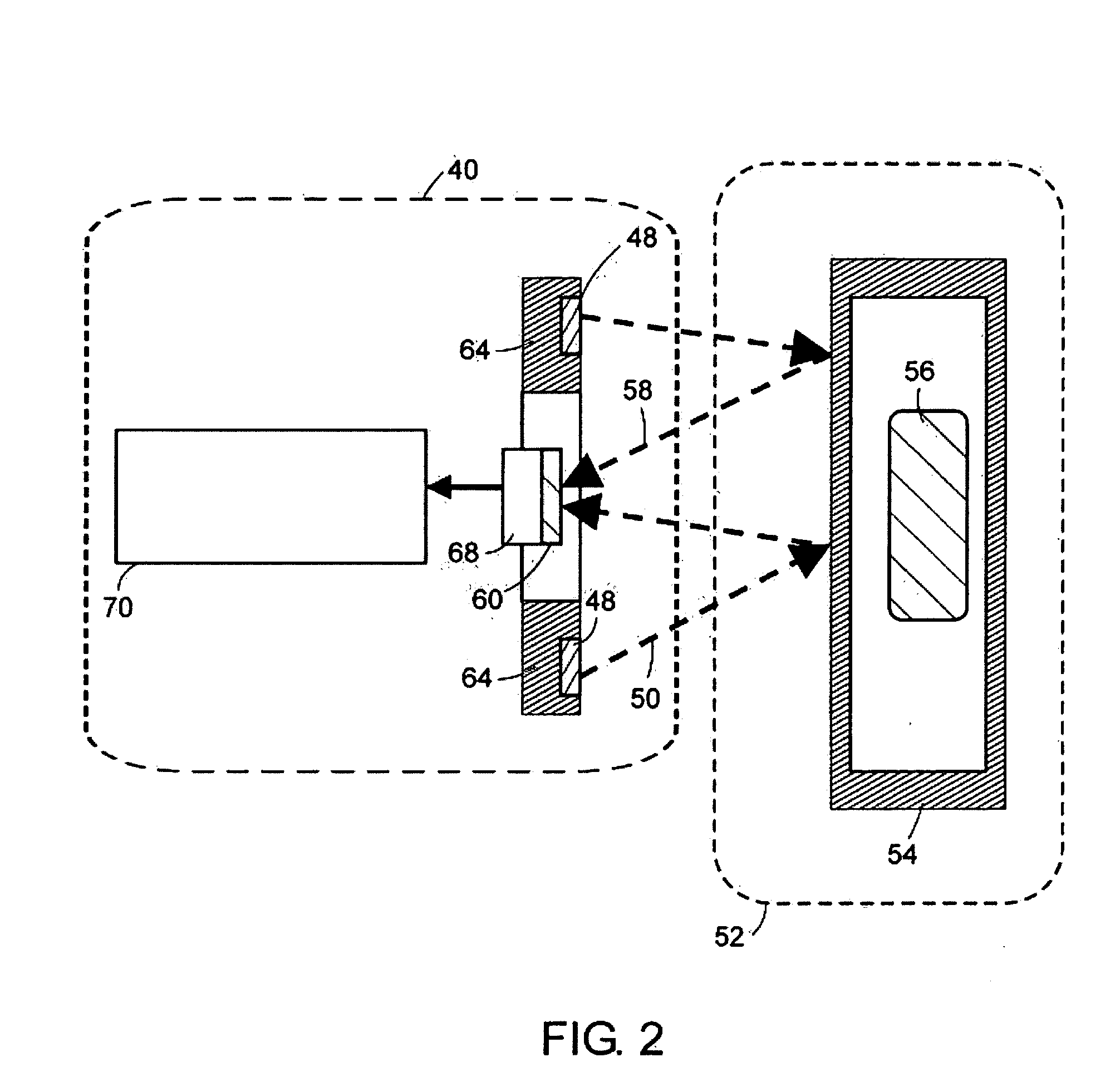
Neutron and gamma ray monitor
ActiveUS7525101B2Easy to detectMeasurement with scintillation detectorsMaterial analysis by optical meansNeutron emissionLight guide
Owner:THERMO NITON ANALYZERS
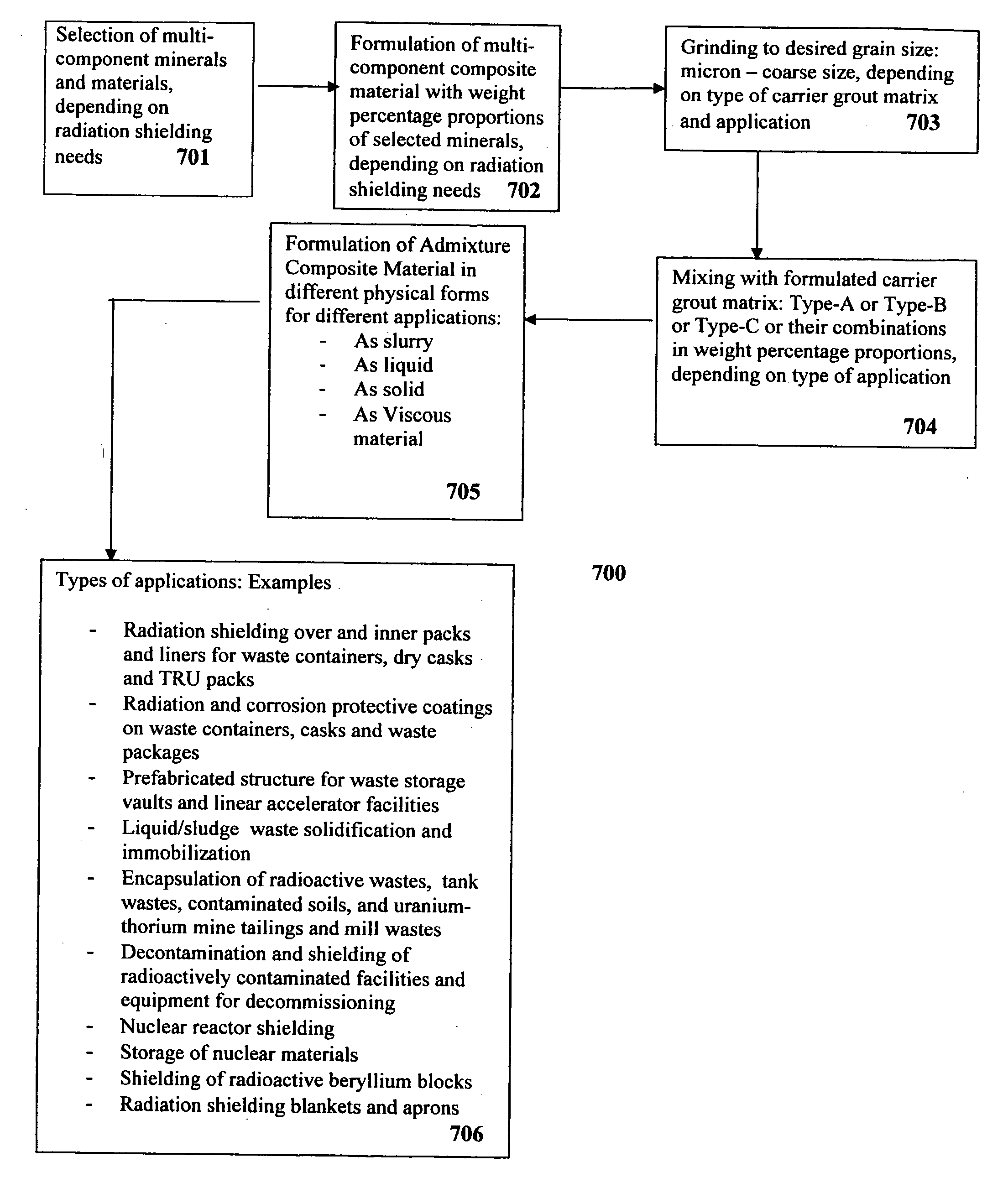
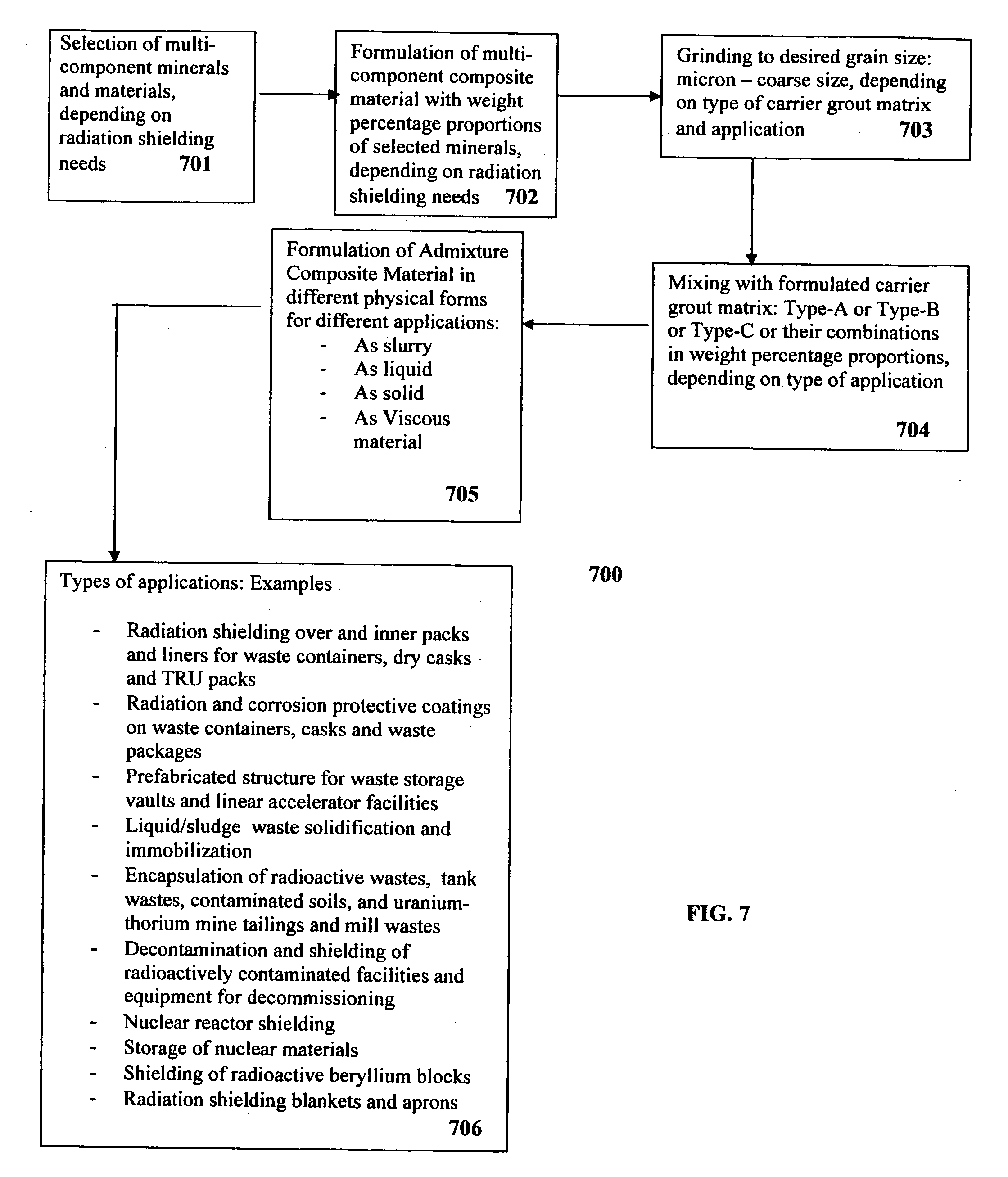
Composite materials and techniques for neutron and gamma radiation shielding
ActiveUS20050258405A1Safe and cost-effective managementIncrease volumeDiffusing elementsNuclear engineering solutionsPolymer modifiedRadioactive waste
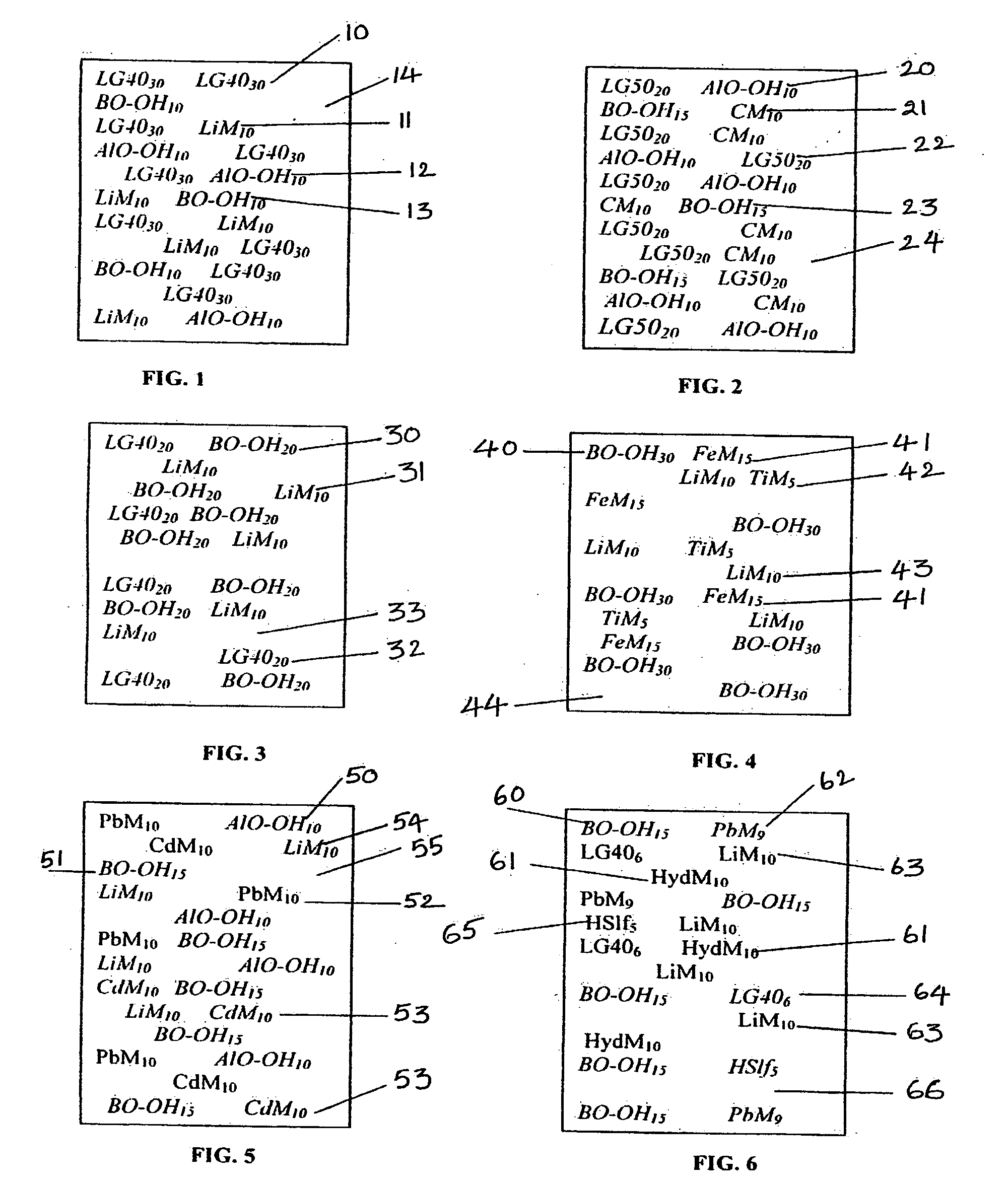
This invention deals with multi-component composite materials and techniques for improved shielding of neutron and gamma radiation emitting from transuranic, high-level and low-level radioactive wastes. Selective naturally occurring mineral materials are utilized to formulate, in various proportions, multi-component composite materials. Such materials are enriched with atoms that provide a substantial cumulative absorptive capacity to absorb or shield neutron and gamma radiation of variable fluxes and energies. The use of naturally occurring minerals in synergistic combination with formulated modified cement grout matrix, polymer modified asphaltene and maltene grout matrix, and polymer modified polyurethane foam grout matrix provide the radiation shielding product. These grout matrices are used as carriers for the radiation shielding composite materials and offer desired engineering and thermal attributes for various radiation management applications.
Owner:SAYALA DASHARATHAM
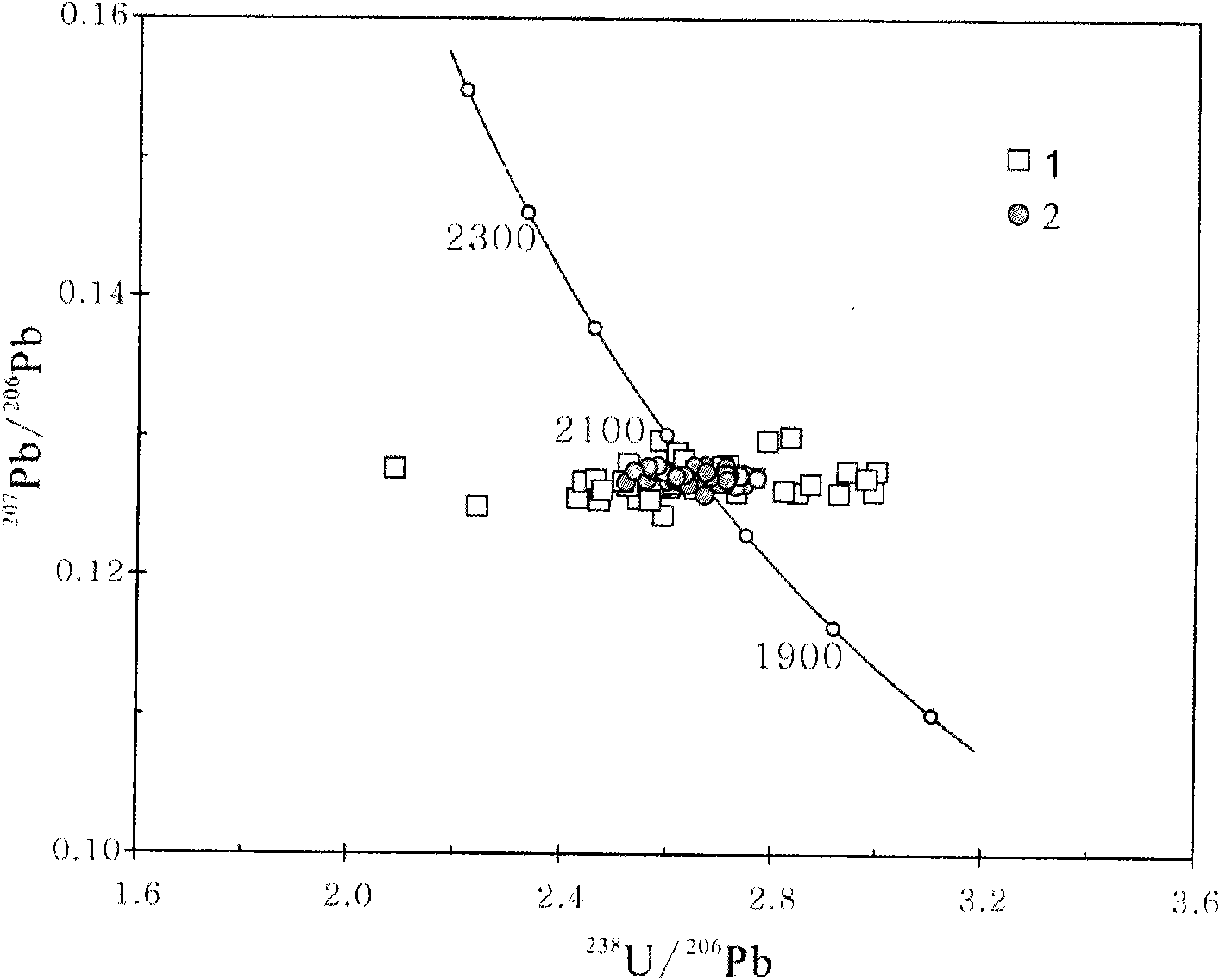
Method for determining U-Pb age of zircon sample
InactiveCN106908510AAdvantages of measurement accuracyImprove spatial resolutionMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSpectrographMass analyzer
The invention discloses a method for determining the U-Pb age of a zircon sample. The method comprises the steps as follows: the zircon sample and a standard substance are made into a sample target; solid sol is obtained through laser ablation; the solid sol is loaded in a multi-receiving inductive coupled plasma mass spectrograph ion source (plasma) for ionization, and primary ions are obtained; the primary ions pass through an electric field and a magnetic field of a mass spectrograph to realize dual-focusing of energy and direction and arrive at an ion detection system; the original U-Pb ratio of the primary ions of the zircon sample and the zircon standard substance is detected and calculated; the original U-Pb ratio of the zircon sample is corrected by using the standard U-Pb ratio of zircon, and the corrected U-Pb ratio of the zircon sample is obtained; the U-Pb age of the zircon sample is calculated by using the corrected U-Pb ratio. The method has high precision and high sensitivity, has the low sample content requirement, has small ablation depth, and can be used for spatial high-resolution U-Pb age determination of zircon with the ablation diameter smaller than 10 mum.
Owner:INST OF GEOLOGY & GEOPHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Molten nuclear fuel salts and related systems and methods
InactiveUS20160189813A1Improve power densityImprove the level ofFuel elementsNuclear energy generationPresent methodChloride
This disclosure describes nuclear fuel salts usable in certain molten salt reactor designs and related systems and methods. Binary, ternary and quaternary chloride fuel salts of uranium, as well as other fissionable elements, are described. In addition, fuel salts of UClxFy are disclosed as well as bromide fuel salts. This disclosure also presents methods and systems for manufacturing such fuel salts, for creating salts that reduce corrosion of the reactor components and for creating fuel salts that are not suitable for weapons applications.
Owner:TERRAPOWER
Apparatus for positioning and cooling lining layer of damaged LWR nuclear reactor
InactiveCN1585034AImprove melt fluidityImprove cooling conditionsNuclear energy generationEmergency protection arrangementsCore catcherNuclear reactor
The invention relates to apparatus for positioning and cooling melting lining layer when the melting lining layer flows out of the reactor shell during accident. The improvements of invention are described as following: the design of the cooling lining layer trap which has steel basket shell and arranged in sub-reactor, wherein sacrifice material is filled in the steel basket for diluting the component containing uranium and steel component of the lining layer; the shape (arrangement) of the sacrifice material in reactor core; the choice for optimum number of the sacrifice material; installation of guiding device used for the lining layer flowing into the reactor core trap. Especially, the thickness of bottom of the cooling jacket is larger than the thickness of the side wall thereof for no less than 30%, and the cooling jacket inclines to its center for 10 to 20 degree; the diluent and sacrifice material is made into blocks packed in steel shell.
Owner:V·B·哈本斯基 +17
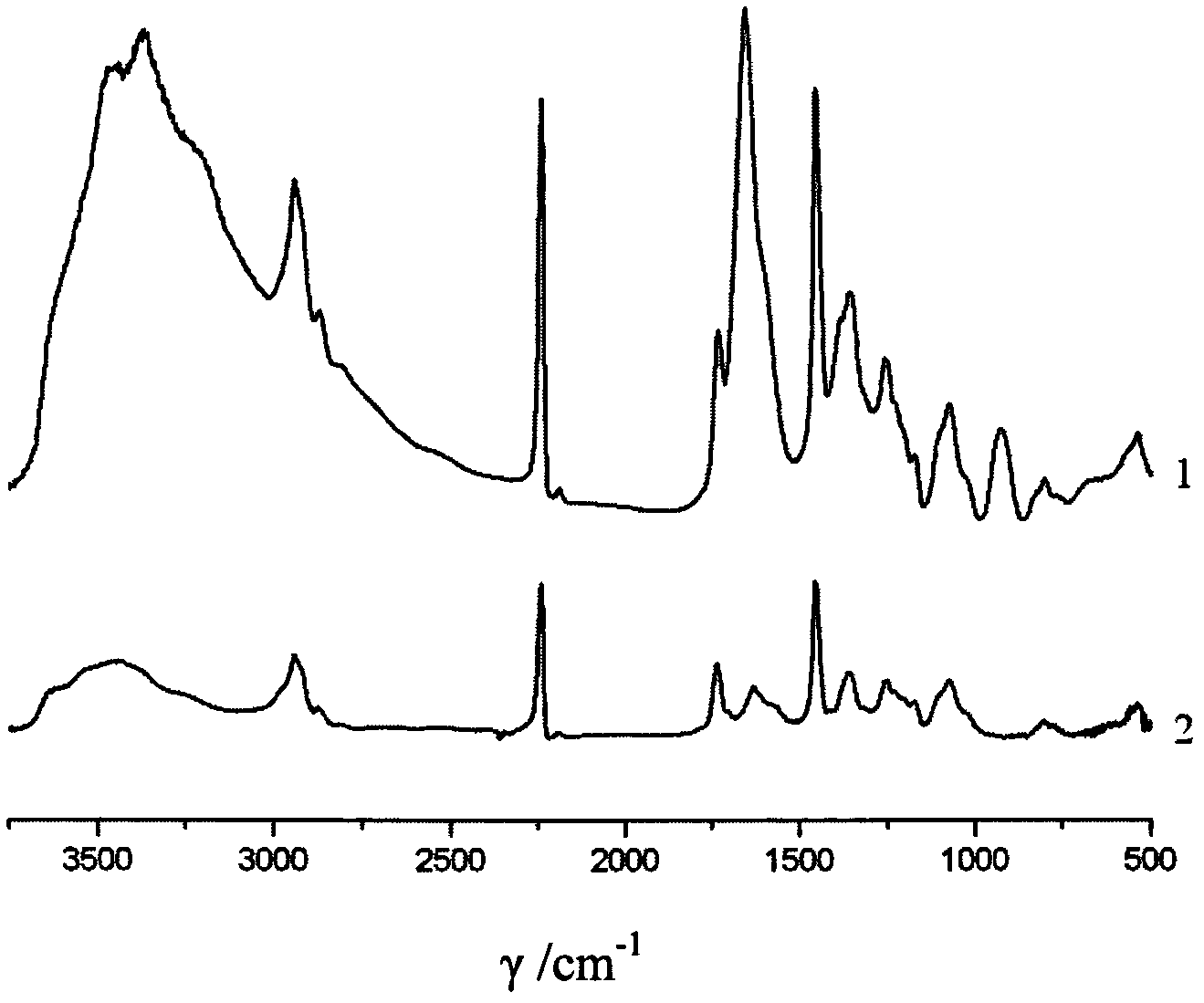
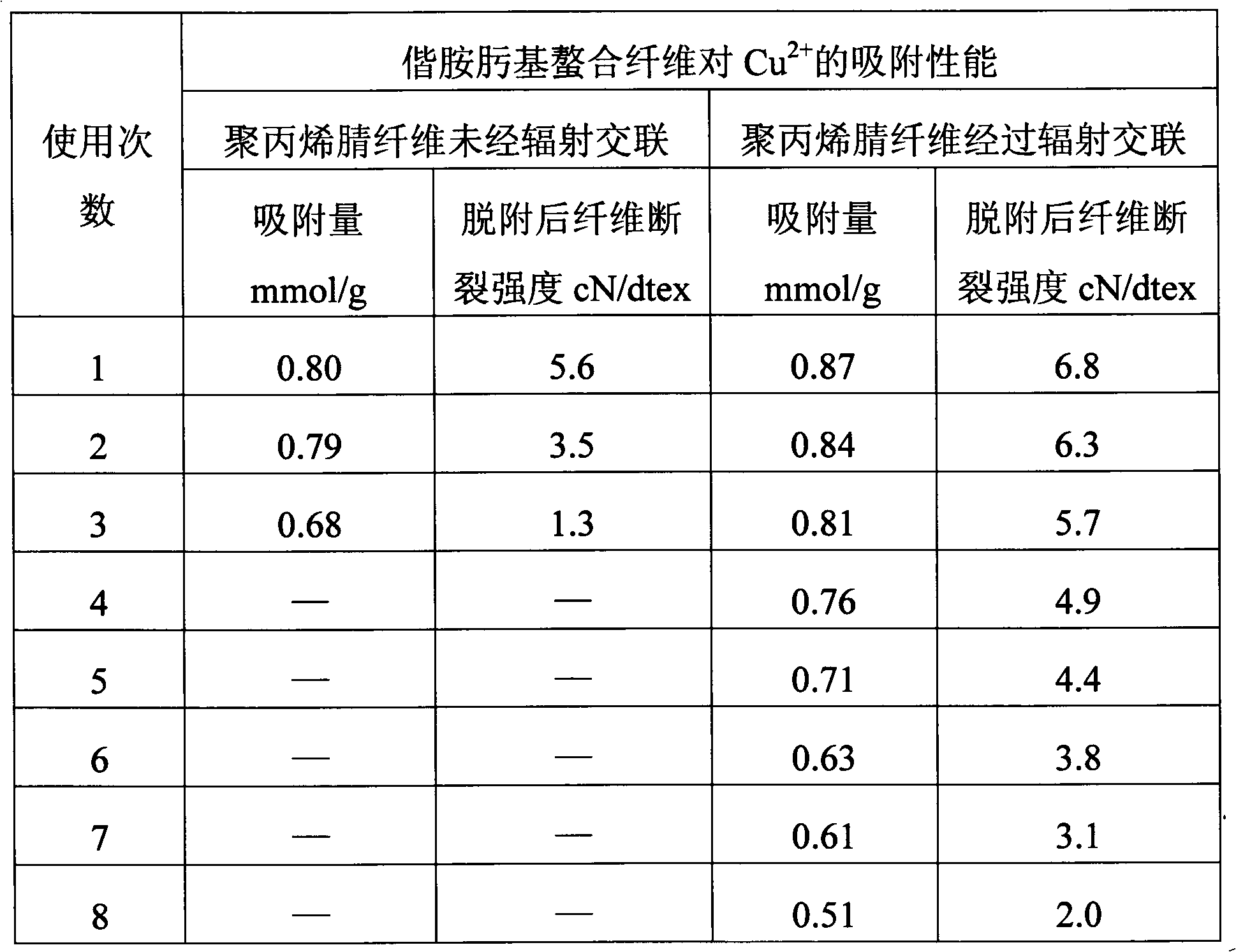
Amidoxime-based chelate polyacrylonitrile fiber and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN102587117AImprove mechanical propertiesImprove performanceOther chemical processesPhysical treatmentCross-linkIndustrial waste water
The invention provides an amidoxime-based chelate polyacrylonitrile fiber and its preparation method. The preparation method of the amidoxime-based chelate polyacrylonitrile fiber comprises the following steps that 1, polyacrylonitrile fibers are subjected to irradiation cross-linking under the conditions of an inert gas atmosphere and an irradiation amount of 20 to 2000kGy; and 2, the polyacrylonitrile fibers subjected to irradiation cross-linking undergo an amidoximation reaction. The invention also provides a use of the amidoxime-based chelate polyacrylonitrile fiber as a metal ion adsorption material. Through the preparation method which is simple relatively, the amidoxime-based chelate polyacrylonitrile fiber which has good mechanical properties, high fiber breaking strength, a long reuse life and stable performances and is damaged difficultly is obtained. The amidoxime-based chelate polyacrylonitrile fiber can be utilized as a metal ion adsorption material, is suitable for the fields of purification of industrial waste water or slag, or extraction of uranium of seawater, has excellent effects of adsorbing multiple metal ions, and can greatly reduce an industrial cost.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF APPLIED PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
In-situ uranium leaching and mining treatment method by adding O2 into CO2
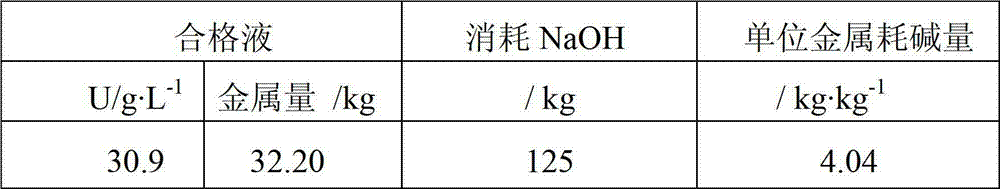
The invention provides an in-situ uranium leaching and mining treatment method by adding O2 into CO2. The invention comprises the steps of (1) adding O2 into leaching solution, then injecting an underground mine-water contained layer into a liquid injection pipeline, and preparing the leaching solution by adopting different oxygenation concentrations according to different underground leaching periods; (2) adding 100-300mg / L of CO2 into the leaching solution containing uranium; (3) conducting ion exchange adsorption on the leaching solution containing uranium, adopting macroporous styrene strong-base anion exchange resin, adsorbing to obtain saturated resin adsorption tail solution; and (4) washing saturated resin by adopting an eluting agent, and then analyzing uranyl carbonate ion solution to obtain Na2U2O7 sediment slurry and sediment mother liquor. According to the method, a high-temperature heating device is eliminated, so that the energy consumption and equipment investment are lowered greatly, the alkali consumption is lowered, control parameters are refined, the consumption of alkali is saved, and the production cost is lowered.
Owner:BEIJING RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF CHEMICAL ENGINEERING AND METALLURGY
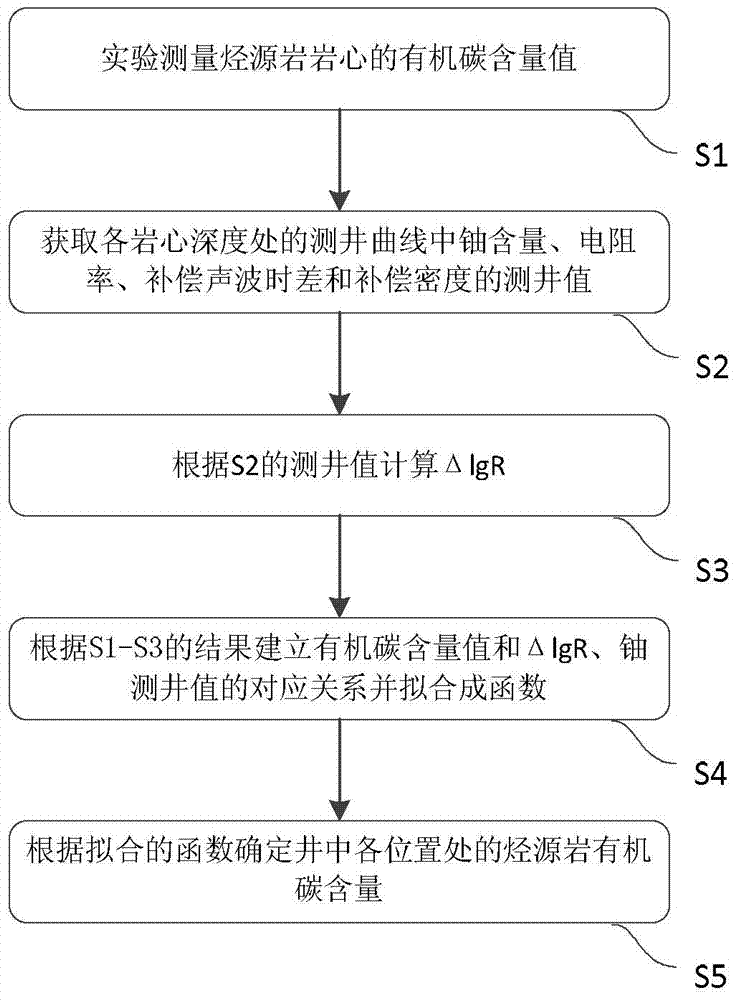
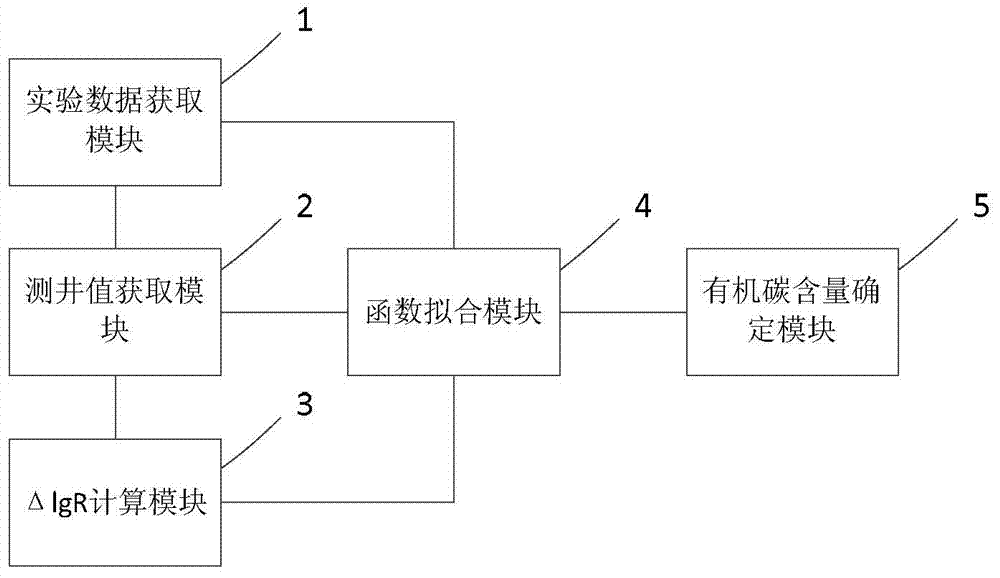
Method and device for determining content of organic carbon in hydrocarbon source rock
The invention provides a method for determining the content of organic carbon in hydrocarbon source rock. The method comprises the following steps: S1. experimentally measuring the content of organic carbon of a hydrocarbon source rock core; S2. acquiring the log values of uranium content, resistivity, compensated sonic time difference and compensated density in logging curves at rock core depths; S3. calculating delta lgR according to the log values of S2; S4. establishing the correspondence relation between the content value of organic carbon and the delta IgR as well as uranium log value according to the results of S1 to S3, and fitting into a function; S5. according to the fitted function, determining the content of organic carbon of hydrocarbon source rock at all positions of a log. The invention provides a device embodiment for determining the content of organic carbon in hydrocarbon source rock. According to the method and the device for determining the content of organic carbon in hydrocarbon source rock, the content of organic carbon is determined based on combination of uranium logging curves and delta lgR, the accuracy of the calculation results is high, and the method and the device have obviously practically application effects in the calculation on the content of organic carbon in the hydrocarbon source rock.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
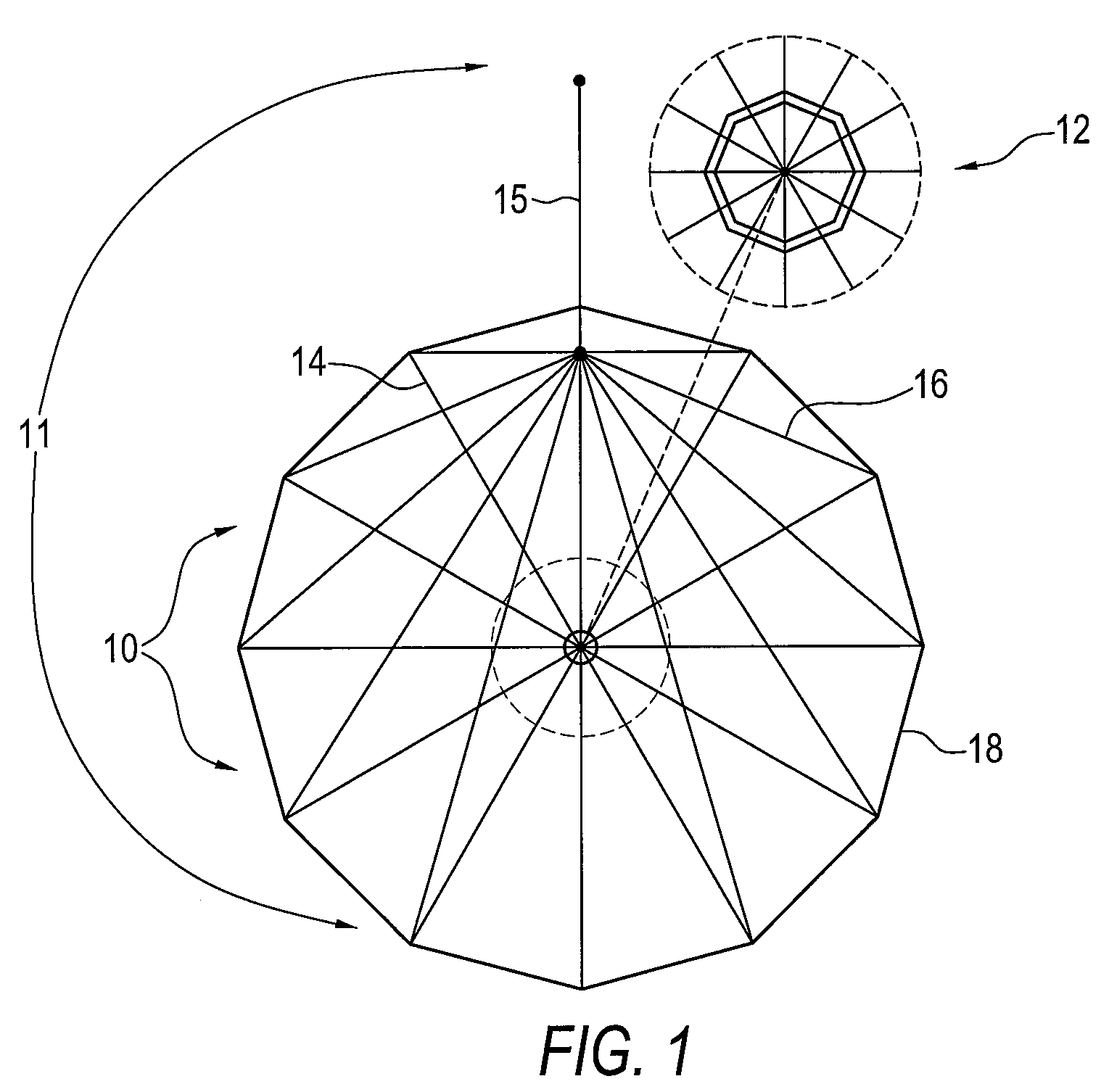
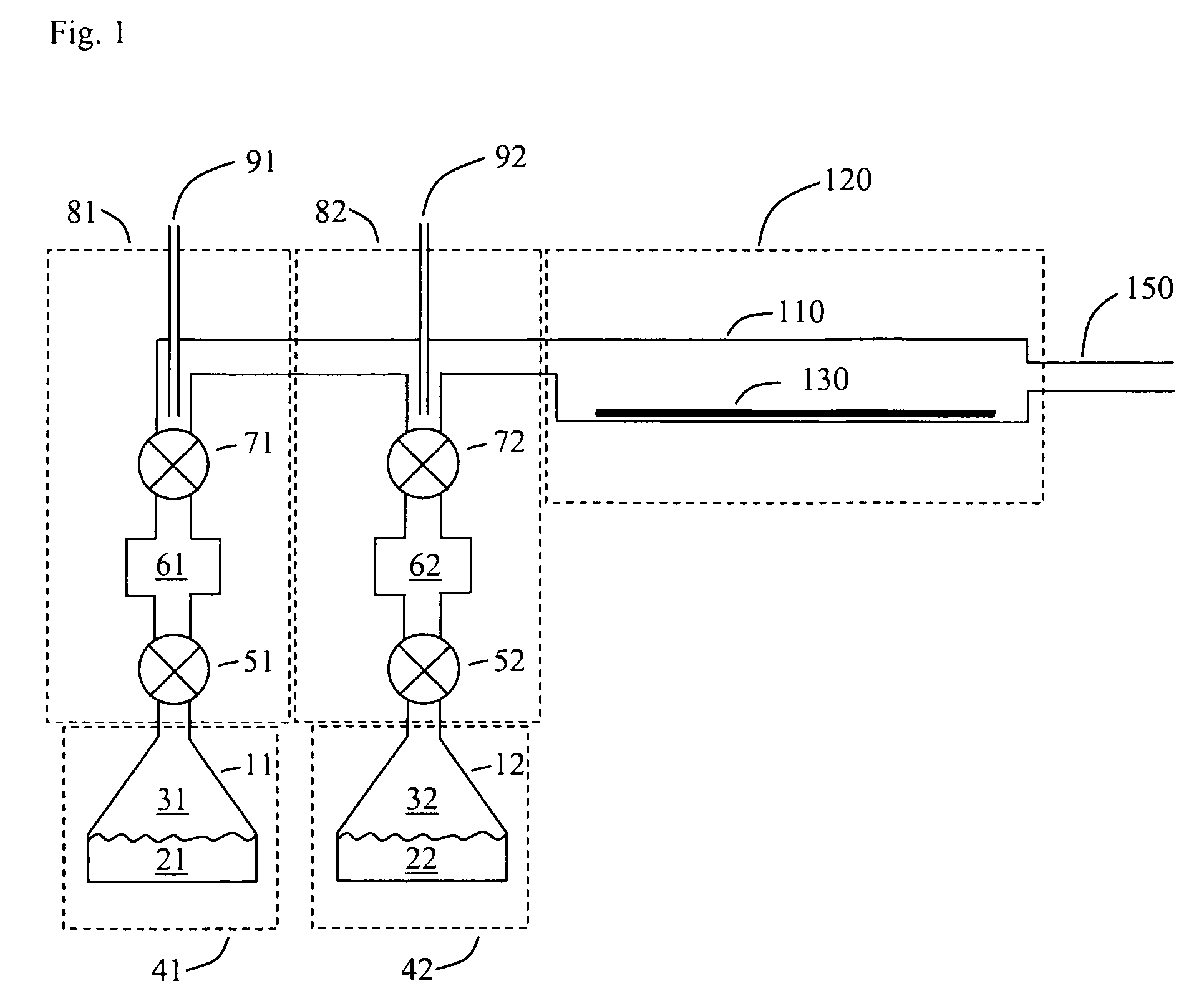
Large airborne time-domain electromagnetic transmitter coil system and apparatus
ActiveUS7948237B2Acoustic wave reradiationElectric/magnetic detection for transportElectromagnetic launchTransmitter coil
An airborne time domain electromagnetic survey system is provided. The system and apparatus of the present invention are able to address the interest in exploring base metals and uranium deposits at depths approaching 1 kilometer. It encompasses a transmitter coil having a large magnetic dipole moment, flight stability, which is light weight, compatible with small helicopters, and can be transported, setup and repaired in the field. It is of a semi-rigid modular structure that can decrease the incidence of damage or breakage during take-off or landing in rough terrain.
Owner:GEOTECH
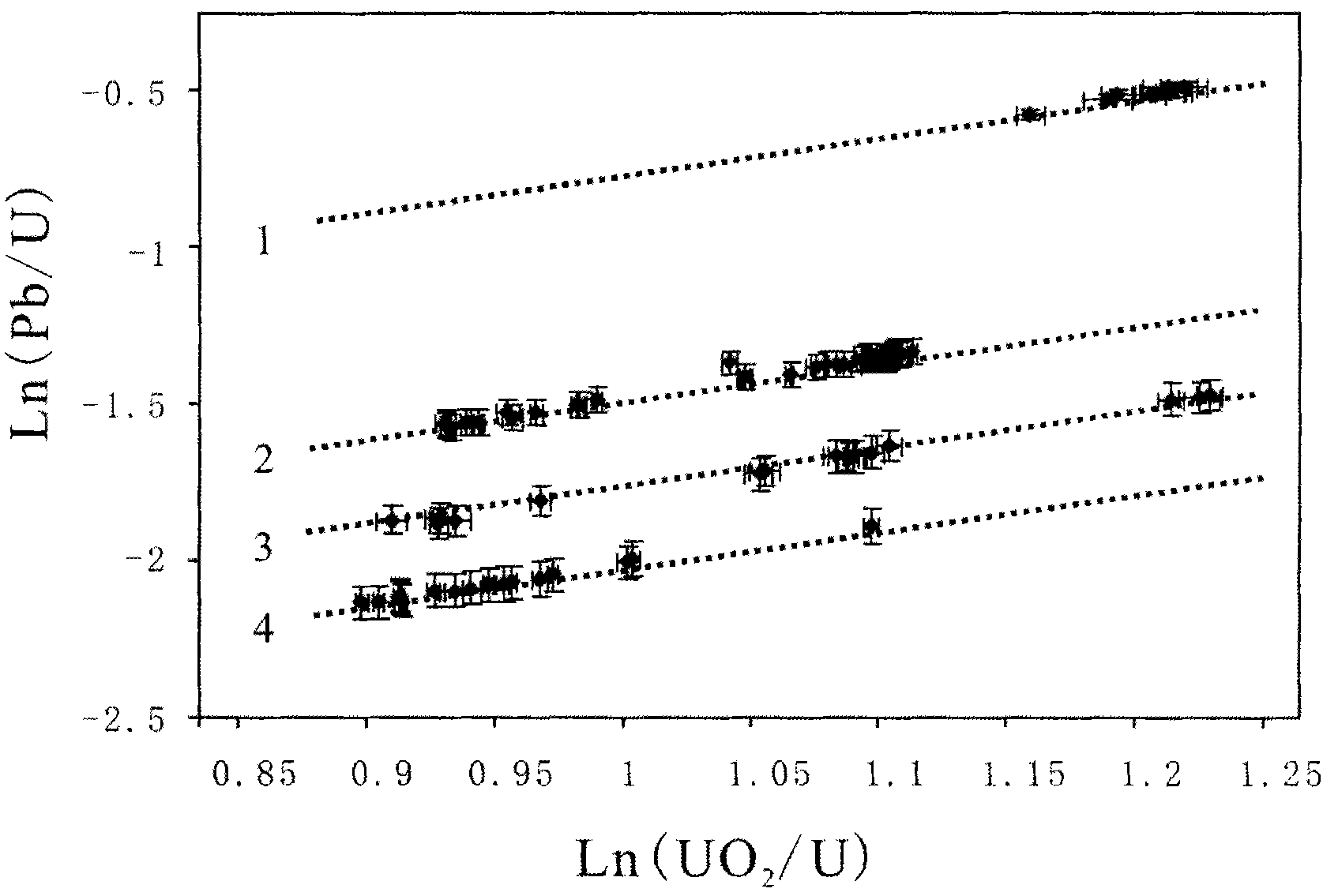
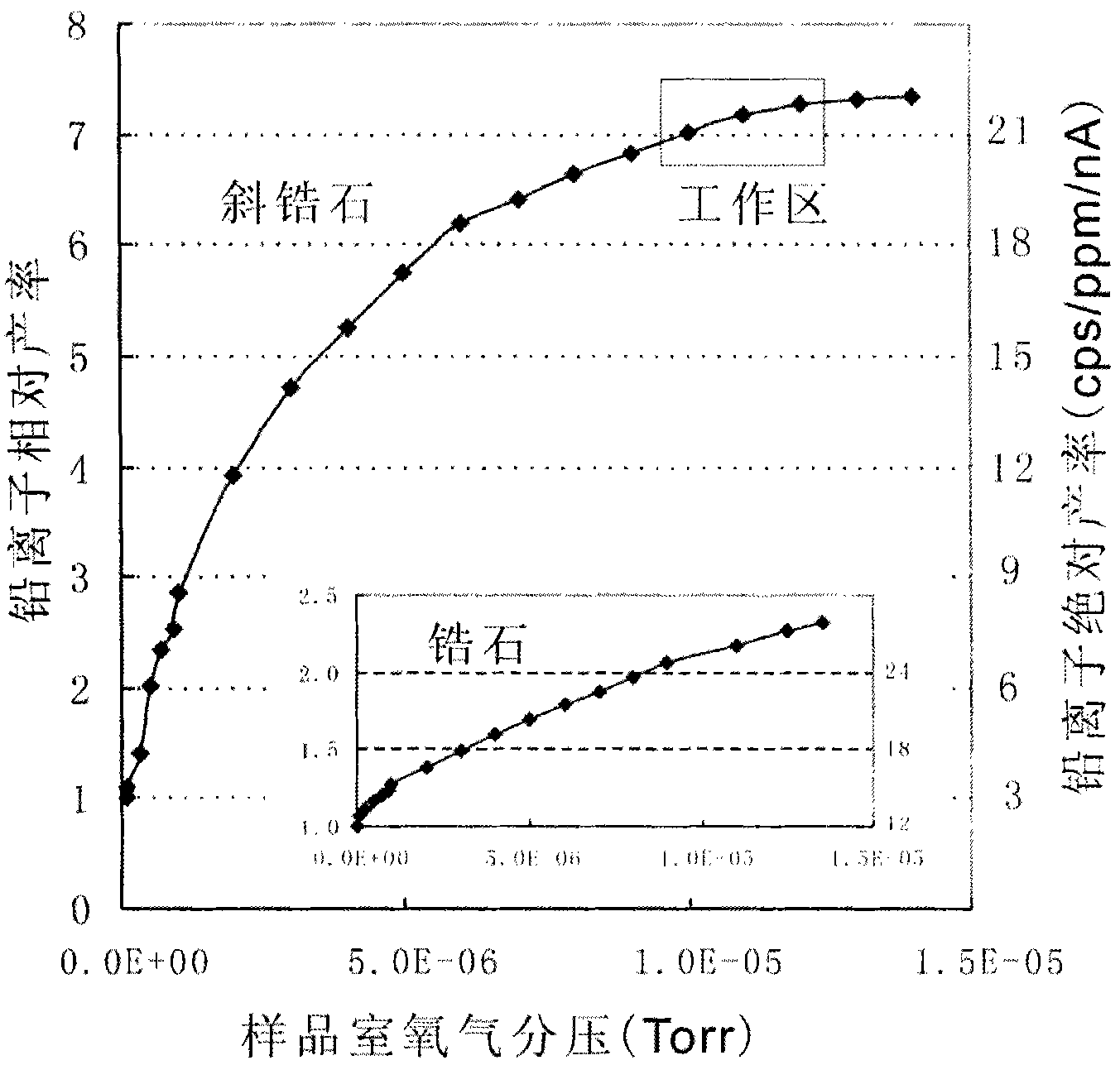
Method for uranium lead dating of baddeleyite by using secondary ion mass spectroscopy
InactiveCN102141539ASuppresses the "optical axis effect"Increased ionization yieldMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansFractionationMass analyzer
The invention discloses a method for determining uranium lead age of baddeleyite by using secondary ion mass spectroscopy, which belongs to the field of secondary ion mass spectroscopy dating method in geochronology and particularly relates to a method applied to a large secondary ion mass spectrometer having oxygen blowing conditions. In the measurement method described by the invention, the degree of vacuum in a sample cavity of the spectrometer is enabled to reach 1E-8Torr at first, and an oxygen leak valve is then opened to blow the oxygen with the purity of 99.99% to the surface of the sample so that the oxygen partial pressure of the sample cavity reaches 1E-5Torr. The method of the invention can reduce the optical axis effect, which is exhibited by secondary ion mass spectroscopy during the uranium-lead dating of baddeleyite, to be below 2%, thus the accuracy of uranium-lead age when the baddeleyite is subjected to secondary ion mass chromatographic analysis is significantly improved. After uranium-lead measurement ratio is obtained, uranium-lead fractionation correction is performed by adopting a linear relation between ln(Pb+ / U+) and ln(UO2+ / U+) in order to obtain accurate age.
Owner:INST OF GEOLOGY & GEOPHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
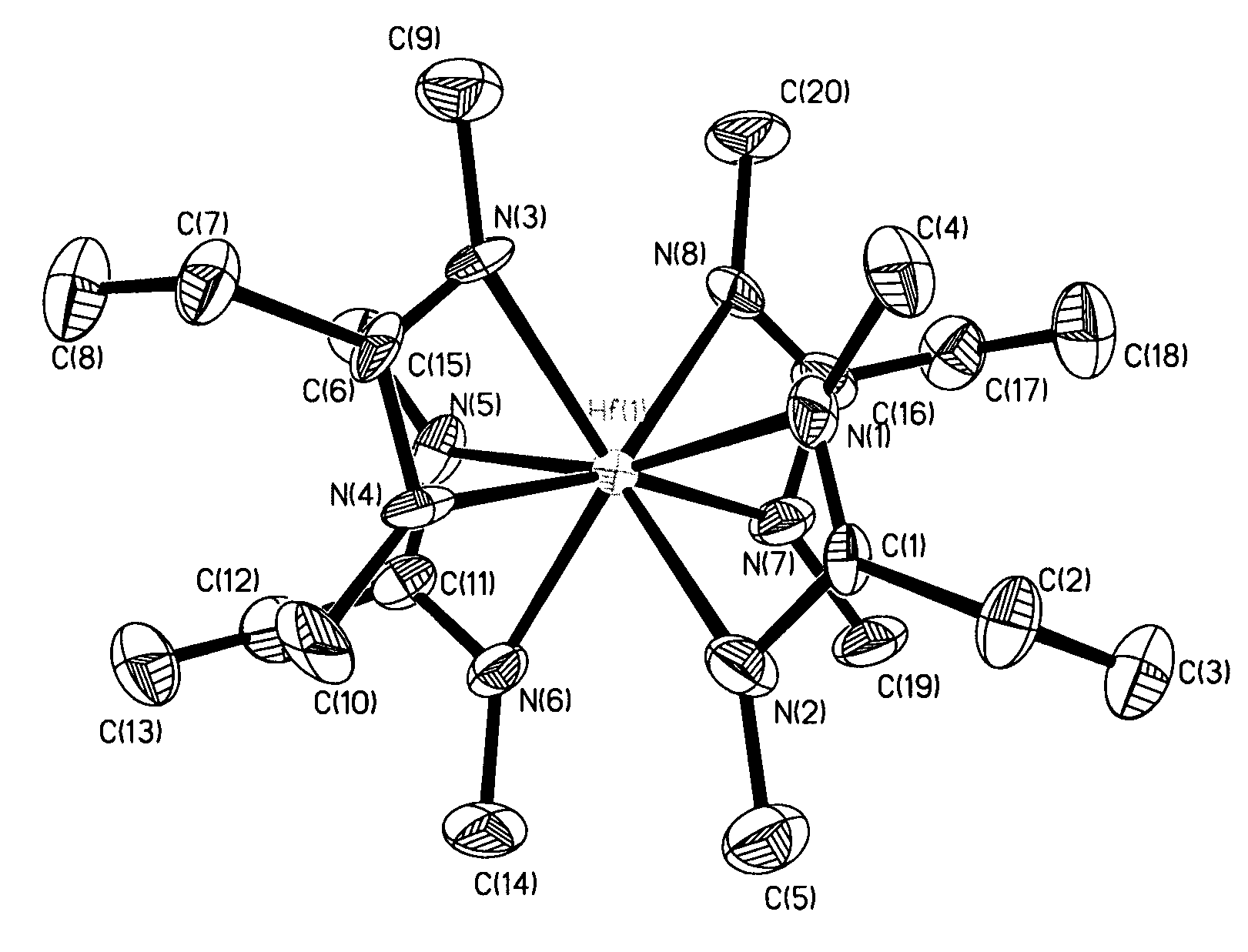
Metal (IV) tetra-amidinate compounds and their use in vapor deposition
ActiveUS7638645B2Group 4/14 organic compounds without C-metal linkagesGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsGas phaseNiobium
Metal(IV) tetrakis(N,N′-dialkylamidinates) were synthesized and characterized. Exemplary metals include hafnium, zirconium, tantalum, niobium, tungsten, molybdenum, tin and uranium. These compounds are volatile, highly stable thermally, and suitable for vapor deposition of metals and their oxides, nitrides and other compounds.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Process using rare earths to remove oxyanions from aqueous streams
ActiveUS7338603B1Efficiently and effectively removedReduce the concentration of pollutantsWater/sewage treatment by ion-exchangeRadioactive contaminantsCation-exchange capacityParticulates
Oxyanions of various contaminant elements, such as chromium, antimony, molybdenum, tungsten, vanadium and uranium, are removed from water and other aqueous feeds by treating the feed with (1) a sorbent comprising one or more rare earth compounds, usually mixed or supported on particulate solids having a cation exchange capacity less than 20 milliequivalents per 100 grams or (2) an aqueous solution of one or more soluble rare earth compounds.
Owner:SECURE NATURAL RESOURCES LLC
Nuclear reactor core capable of improving neutron flux rate
ActiveCN101447238AHigh fluence rateNuclear energy generationShieldingNuclear reactor coreNuclear reactor
The invention discloses a nuclear reactor core capable of improving neutron flux rate; the core is a circular structure; the center of the core is a Be thermal neutron well region, the circumference of which is a fuel component region, the circumference of which is a Be reflecting layer; the whole core is a circular structure. The maximum thermal neutron flux rate of the central Be thermal neutron well region can be over twice larger than that of the fuel region ; as the thermal neutron well region can be provided with fuel component with high uranium content, the fuel component center can form fast neutron region, therefore, the generated fission neutron has high flux rate.
Owner:NUCLEAR POWER INSTITUTE OF CHINA
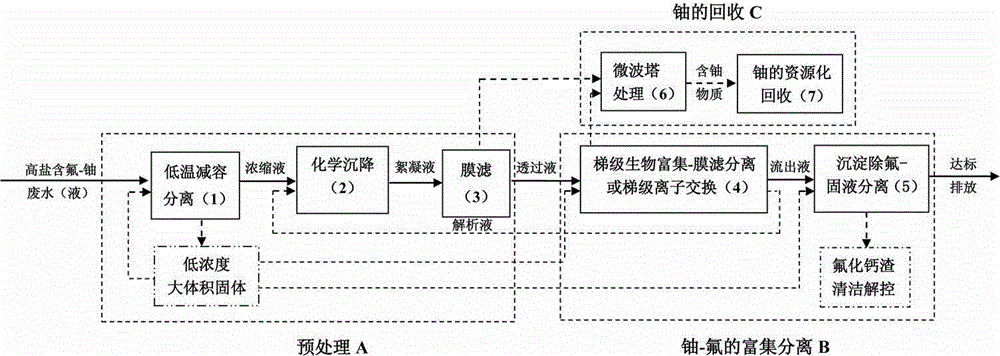
Method for deeply purifying and recovering hyperhaline fluoric-u radioactive waste solution
ActiveCN104835545AReduce lossesImprove efficiencyWater/sewage treatment by ion-exchangeWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisLiquid wasteRecovery method
The invention discloses a method for deeply purifying and recovering hyperhaline fluoric-U radioactive waste solution. The method comprises three sequent treatment phases including pretreatment, enrichment and separation of U-F and recovery of U, and can be further finely divided into 7 treatment units, including lower temperature reduction separation, chemical sedimentation, film filtering, step-grade organism enrichment-film filtering separation or step ion exchange, deposit fluorine removal solid-liquid separation, microwave tower treatment and resource recovery of U; under the condition that the salinity of waste solution to be treated is 0.1-10%, the initial U concentration is 0.1-1000mg / L, and the fluorine concentration is 0.01-15g / L, after treatment, the concentration of U is not larger than 0.05mg / L, the concentration of the fluorine is not higher than 10mg / L, and the recovery rate of U is larger than 90%. The method for deeply purifying and recovering hyperhaline fluoric-U radioactive waste solution is suitable for treating hyperhaline fluoric-U radioactive waste solution and the resource recovery of radioactive U.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH
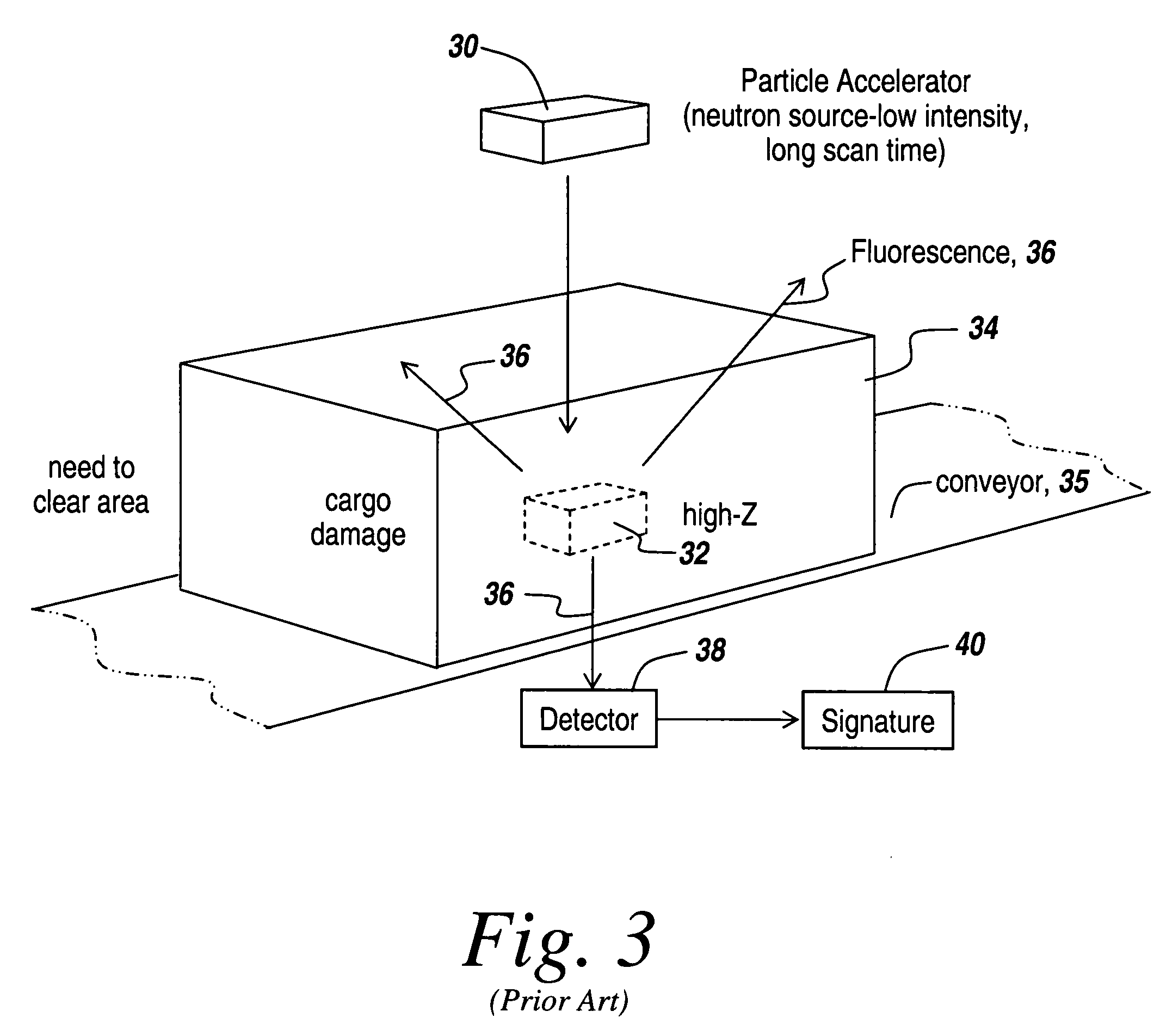
Method and apparatus for the safe and rapid detection of nuclear devices within containers
ActiveUS20070237294A1Faster scan timeAccurate detectionX-ray apparatusMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationHigh intensityGamma ray
A safe, reliable and rapid system for the detection of nuclear materials within containers includes the use of pulsed high-intensity gamma rays that can penetrate a container and its contents and can be detected outside the container to provide a display in which high-Z material, including lead, uranium, plutonium and other nuclear substances that absorb gamma rays are detected as black regions on the display. In one embodiment, orthogonal pulsed gamma ray beams illuminate the container from two different directions to provide three-dimensional slices from which the existence and location of nuclear threat materials can be ascertained in as little as four seconds for a 40-foot container.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Shale gas physical geography quick evaluation method
InactiveCN104500049AEasy to mineSolve the very inconvenient problem of miningInformaticsInstrumentsKerogenWell logging
The invention discloses a shale gas physical geography quick evaluation method. The geologic factors of production of shale gas are as follow: clay, kerogen, porosity, water saturation and permeability, and according to the above geologic factors, evaluation calculation with different models is performed: in the conventional well logging interpretation, the content of clay is calculated by a uranium-free gamma ray curve; the formation of kerogen is mostly in the reduction environment with relatively high content of the radioactive element U, so that a peak appears in the natural gamma ray curve, and as the density of kerogen is relatively low, TOC is integrally calculated with several methods; the value of porosity is calculated by a neutron-density crossplot, and the amount of minerals in rock can also be calculated through correction of the crossplot; the water saturation is calculated by the Archie's formula; and the permeability is calculated according to regression of porosity, and only the shale segment reservoir bed is subjected to regression. The shale gas physical geography production factors can be quickly and accurately calculated, and the results are accurate.
Owner:CHENGDU CHUANGYUAN OIL & GAS TECH DEV
High -throughput electrorefiner for recovery of u and u/tru product from spent fuel
ActiveUS20110180409A1Improve throughputEliminate useElectrolysis componentsPhotography auxillary processesElectrolysisPotential difference
The present invention provides a method of simultaneously removing uranium and transuranics from metallic nuclear fuel in an electrorefiner. In the method, a potential difference is established between the anode basket and solid cathode of the electrorefiner, thereby creating a diffusion layer of uranium and transuranic ions at the solid cathode, a first current density at the anode basket, and a second current density at the solid cathode. The ratio of anode basket area to solid cathode area that is selected based on the total concentration of uranium and transuranic metals in a molten halide electrolyte in the refiner and the effective thickness of the diffusion layer at the solid cathode, such that the established first and second current densities result in both codeposition of uranium and transuranic metals on the solid cathode and oxidation of the metallic nuclear fuel in the anode basket. Deposited material on the solid cathode is removed, and the first current density at the anode basket is maintained to prevent substantial oxidation of the anode basket during operation of the electrorefiner.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
Anidoximated globular lignin macroporous chelate adsorption resin and preparation technique thereof
ActiveCN101357324ABroaden the development pathConducive to the mobilization of comprehensive utilizationOther chemical processesBlack liquorAcrylonitrile
The invention discloses an amidoxime spherical lignin chelate adsorbing resin and a preparation method thereof. A spherical lignin bead is prepared by adopting reversed-phase suspension polymerization techniques of programmed heating, crosslinking and solidification and taking concentrated pulping black liquor or concentrated pulping red liquor as a raw material. The spherical lignin bead is grafted with copolymerized acrylonitrile through further amidoxime to obtain the spherical lignin chelate adsorbing resin which has the grain-size average pore size of 5-150nm, the uniformity coefficient of not more than 1.30, the specific surface area of 30-480m<2> / g, the water content of 55-75%, the bulk density of 0.60-0.73g / ml, the bulk volume of 2.25-5.80ml / g, the amidoxime group content of 6.51-15.85mmol / g and the chelate adsorption capacity of 5-15 mmol / g. The method of the invention is simple for operation, has low production cost, is expected to be of value in the practical application to the enrichment recovery of noble metals and the extraction of uranium from seawater.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Methods for manufacturing porous nuclear fuel elements for high-temperature gas-cooled nuclear reactors
Methods for manufacturing porous nuclear fuel elements for use in advanced high temperature gas-cooled nuclear reactors (HTGR's). Advanced uranium bi-carbide, uranium tri-carbide and uranium carbonitride nuclear fuels can be used. These fuels have high melting temperatures, high thermal conductivity, and high resistance to erosion by hot hydrogen gas. Tri-carbide fuels, such as (U,Zr,Nb)C, can be fabricated using chemical vapor infiltration (CVI) to simultaneously deposit each of the three separate carbides, e.g., UC, ZrC, and NbC in a single CVI step. By using CVI, a thin coating of nuclear fuel may be deposited inside of a highly porous skeletal structure made, for example, of reticulated vitreous carbon foam.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Preparation method of amidoxime group uranium extraction sorbent
InactiveCN101596449AHigh mechanical strengthImprove adsorption capacityOther chemical processesUranium compoundsAlcoholSorbent
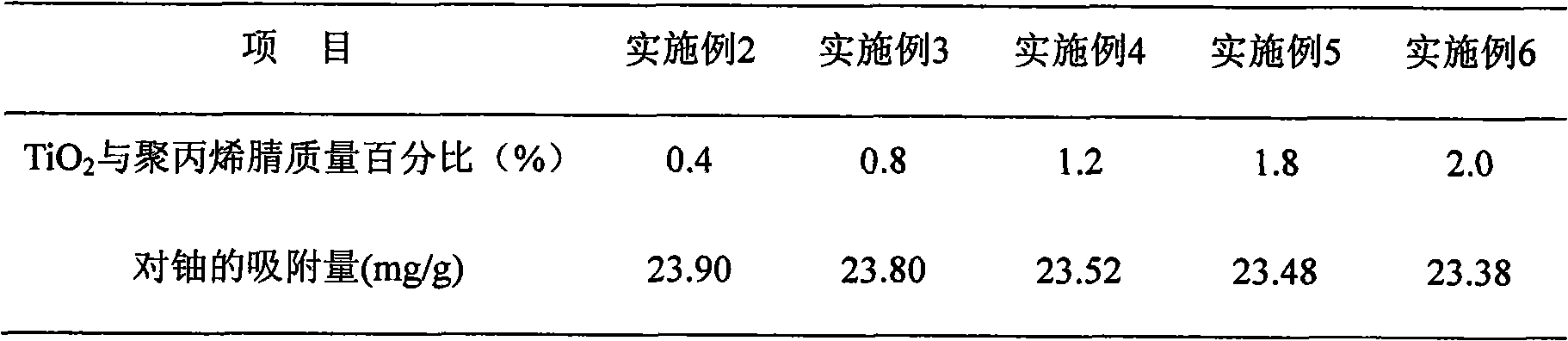
The invention discloses a preparation method of amidoxime group uranium extraction sorbent, comprising the following steps: firstly, adopting polyacrylonitrile powder as a raw material, producing uranium extraction sorbent containing amidoxime group by amidoximation; adding titanium dioxide sol which is prepared by the sol-gel method for blending to ensure that the weight percent of titanium dioxide and polyacrylonitrile is 0.4-2.0%; producing hybridized amidoxime group uranium extraction sorbent by water washing, alcohol washing and drying. The invention has the advantages that the amidoxime group uranium extraction sorbent material which is hybridized with titanium dioxide has higher mechanical strength, higher adsorption quantity of uranium, and higher adsorption selectivity to uranium in the presence of calcium and magnesium ions.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Method for treating uranium-containing waste water
InactiveCN101597113ASimple methodEasy to operateWater contaminantsMultistage water/sewage treatmentFlocculationWastewater
A method for treating uranium-containing waste water comprises uranium removal and phosphorus removal two techniques, firstly adding uranium removing agent in a uranium removal tank of uranium-containing waste water according to that the mass concentration ratio of uranium to uranium removing agent is 2-20 to 1, stirring and settling the uranium-containing waste water in the uranium removal tank, processing solid-liquid separation to the flocculated waste water through plate sedimentation tank to remove the uranium in the uranium-containing waste water, so that the uranium removal reaches up to 99%, and then, adding lime milk clarifying solution in the flocculation basin, stirring, settling and solid-liquid separation to remove the phosphorus in the waste water, in which the phosphorus removal reaches up to 99.99%. At last, supernatant is added with acid to regulate the pH value to 6 to 9 in the regulating tank.
Owner:NANHUA UNIV
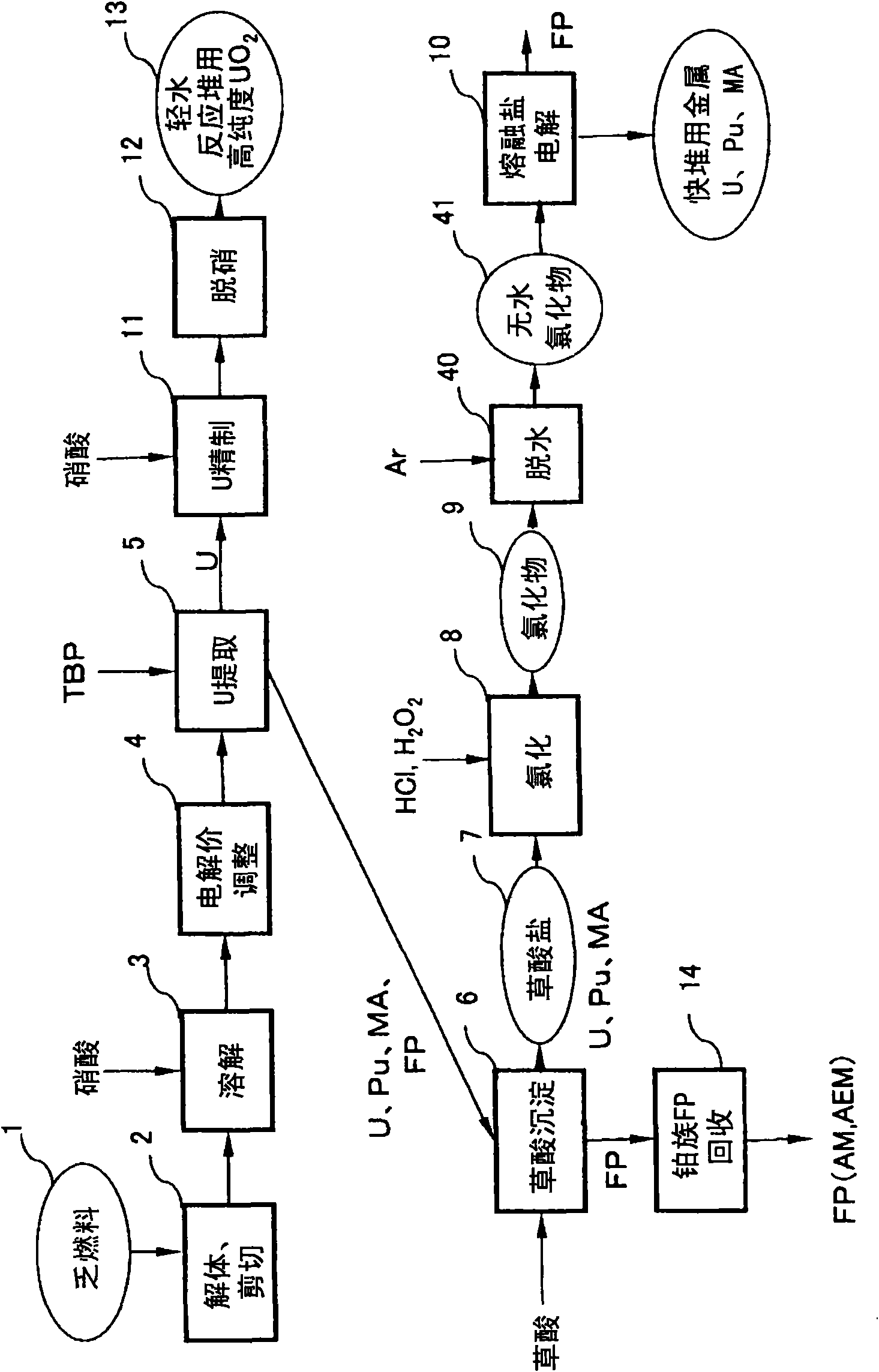
Spent fuel reprocessing method
InactiveCN101593566AHigh non-diffusionNuclear energy generationNuclear elementsFuel reprocessingElectrolysis
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Method and device for measuring the relative proportions of plutonium and uranium in a body
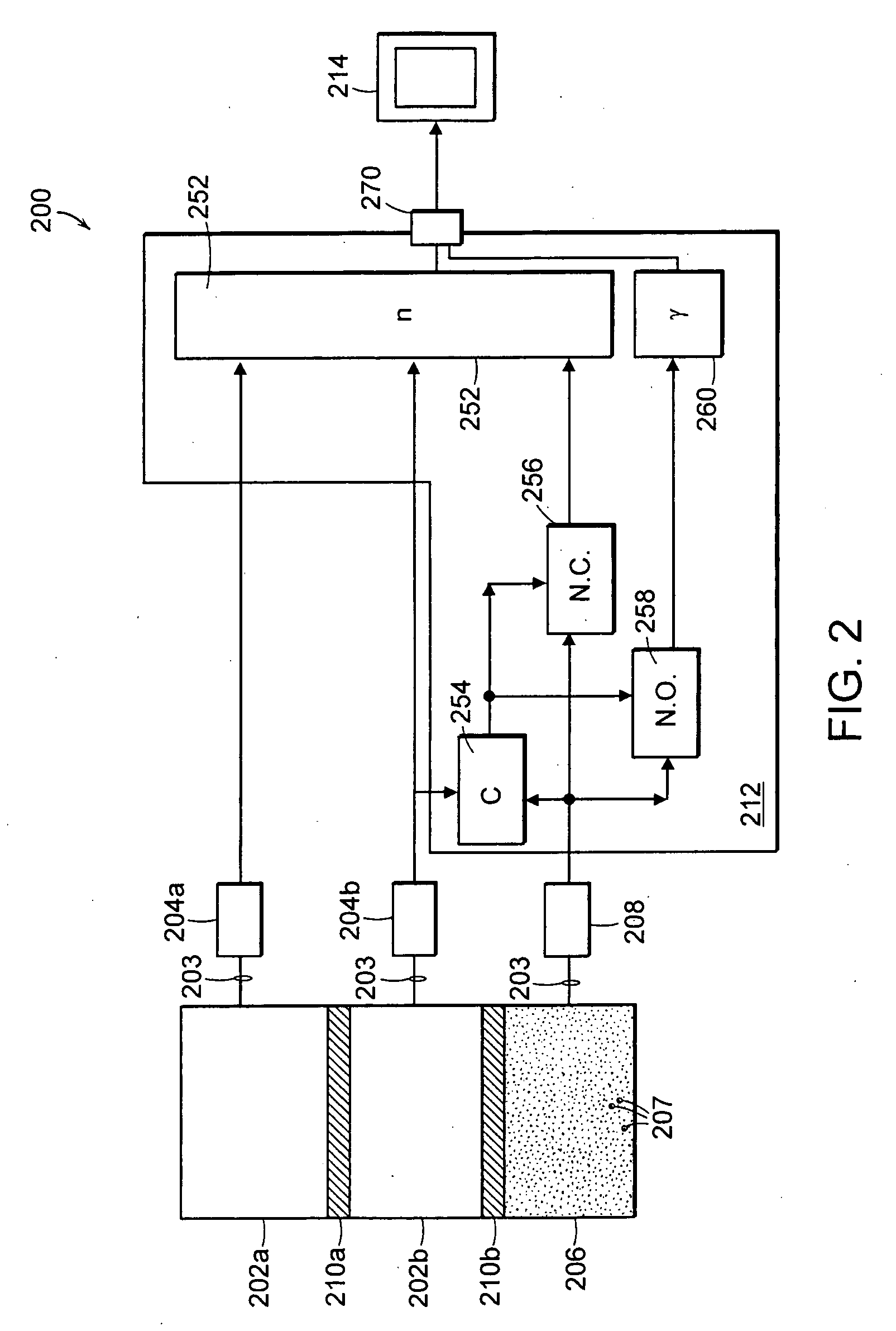
InactiveUS6452992B1Change timeConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentDelayed neutronNeutron
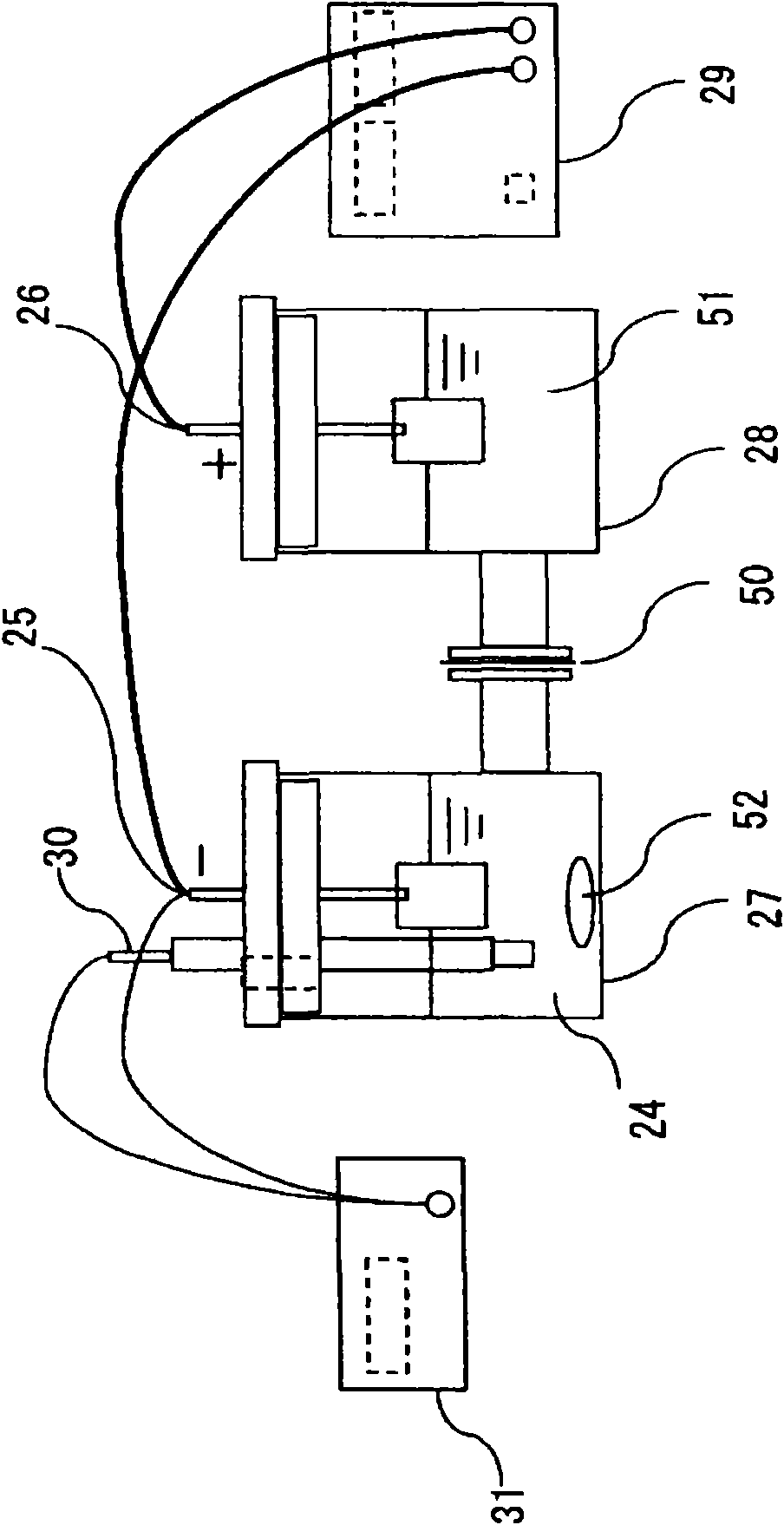
The invention relates a device for measuring the relative proportions of uranium and plutonium in a radioactive package (16), having:a source of photons (10) for irradiating the package,at least one delayed neutron detector (18) able to deliver counting signals for neutrons emitted by the package,means (22, 30) of acquiring counting signals, able to establish a decrease over time in the neutrons emitted, characteristic of the radioactive package,calculation means (32) for comparing the decay characteristic of the radioactive package with the respective characteristic decays of uranium and plutonium and for establishing relative proportions of uranium and plutonium in the package.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Method for producing porcelain granule light weight aggregate with sewage sludge
InactiveCN101195534ANot easy to precipitatePromote generationSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningCeramic materials productionSludgeExpanded clay aggregate
A method for preparing ceramsite light aggregate by utilizing sludge belongs to solid waste treatment, proposal and resource technical field, which produces dry sludge through thermal drying dehydrated mud cake whose moisture percentage is 75-85%, wherein the dry sludge is broken and sieved through 45 mm screen, 18-25% fly ash by mass of the dry sludge is charged to stir, the stirred hybrid material is injected in the powder tablet compressing machine to squeeze and mould under the pressure of 8 Mpa to obtain ceramsite light aggregate blank, the blank is heated to 350 DEG C and is stayed for 20 min in order to lead to volatilize and exhaust completely and is calcined under the temperature of 1080-1100 DEG C for 30 min and is cooled to indoor temperature naturally, and then the ceramsite light aggregate is obtained. The invention for processing living sewage and sludge improves strength of the calcined product, and saves the calcined energy consumption greatly. The obtained ceramsite light aggregate is compact in uranium face, light in weight, high in strength, and satisfies national standard GB / T17431.2-1998, which can be used in the projects such as buildings, roads, bridges and the like.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Refractory superalloys
Refractory superalloys consist essentially of a primary constituent selected from the group consisting of iridium, rhodium, and a mixture thereof, and one or more additive elements selected from the group consisting of niobium, tantalum, hafnium, zirconium, uranium, vanadium, titanium and aluminum, and the superalloys having a microstructure containing an FCC-type crystalline structure phase and an L12-type crystalline structure phase are precipitated. Preferably the amount of additive element(s) is 2 to 22 atom %.
Owner:NATIONAL RESEARCH INSTITUTE FOR METALS SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY AGENCY
Large airborne time-domain electromagnetic transmitter coil system and apparatus
An airborne time domain electromagnetic survey system is provided. The system and apparatus of the present invention are able to address the interest in exploring base metals and uranium deposits at depths approaching 1 kilometer. It encompasses a transmitter coil having a large magnetic dipole moment, flight stability, which is light weight, compatible with small helicopters, and can be transported, setup and repaired in the field. It is of a semi-rigid modular structure that can decrease the incidence of damage or breakage during take-off or landing in rough terrain.
Owner:GEOTECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com