Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
364 results about "Gamma ray detectors" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
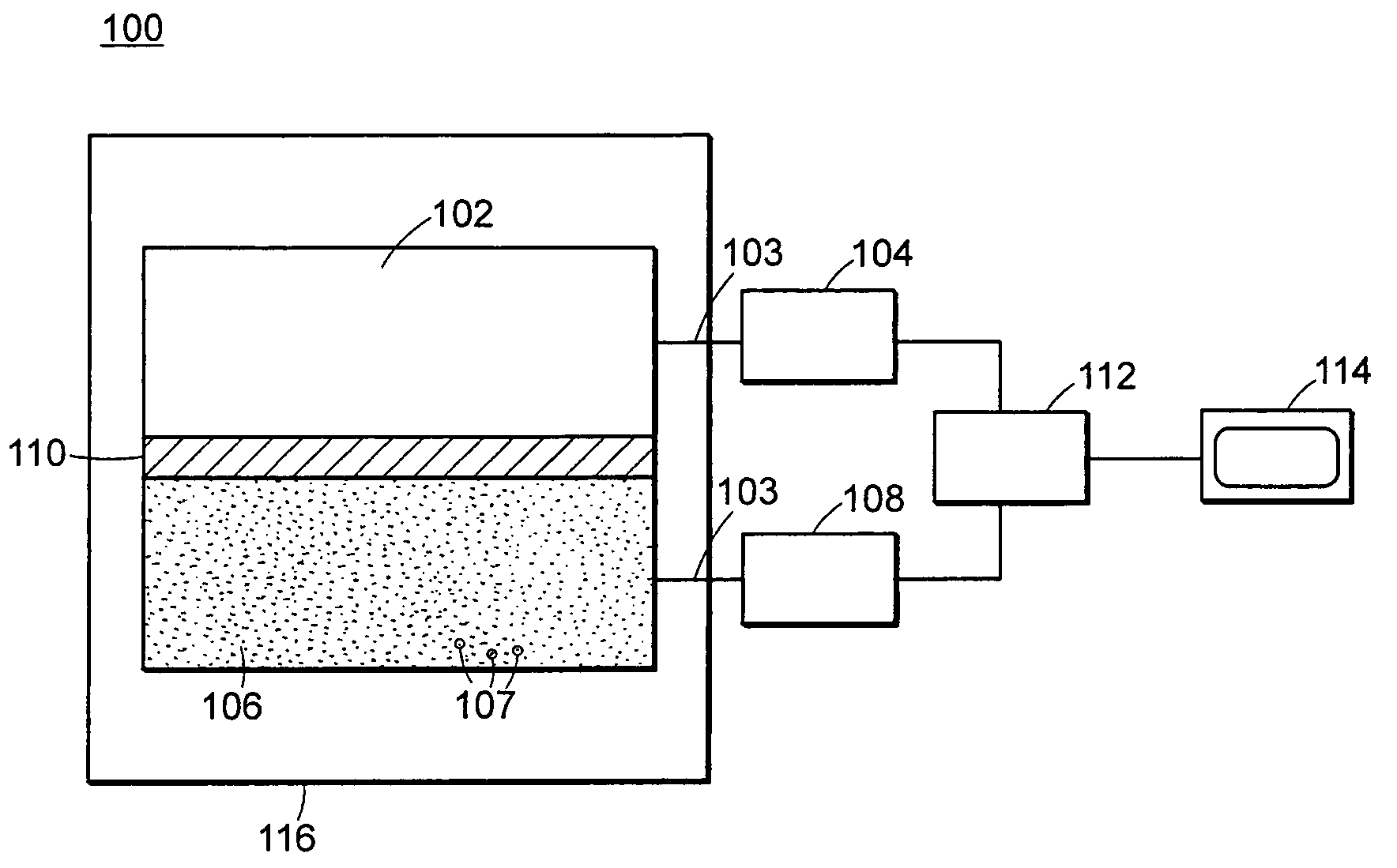
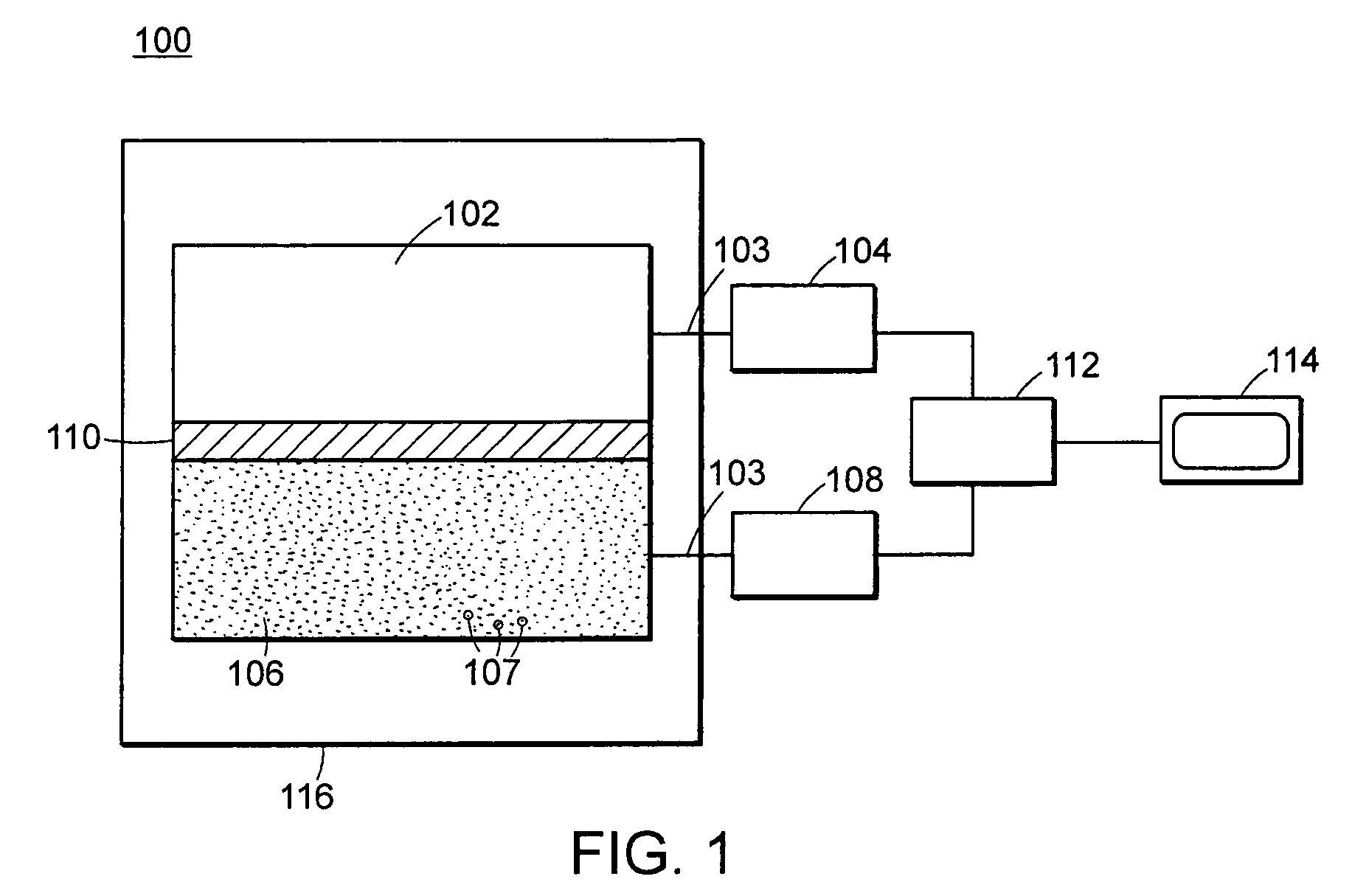
Detectors used for Gamma detection mainly exploit the property of it being an ionizing radiation i.e. gamma rays can ionize the medium they pass through. The trick is to count the no. of ionization and assess the radiation dose. Popular detectors include gas-filled detectors, semidonductor detectors and scintillation detectors.
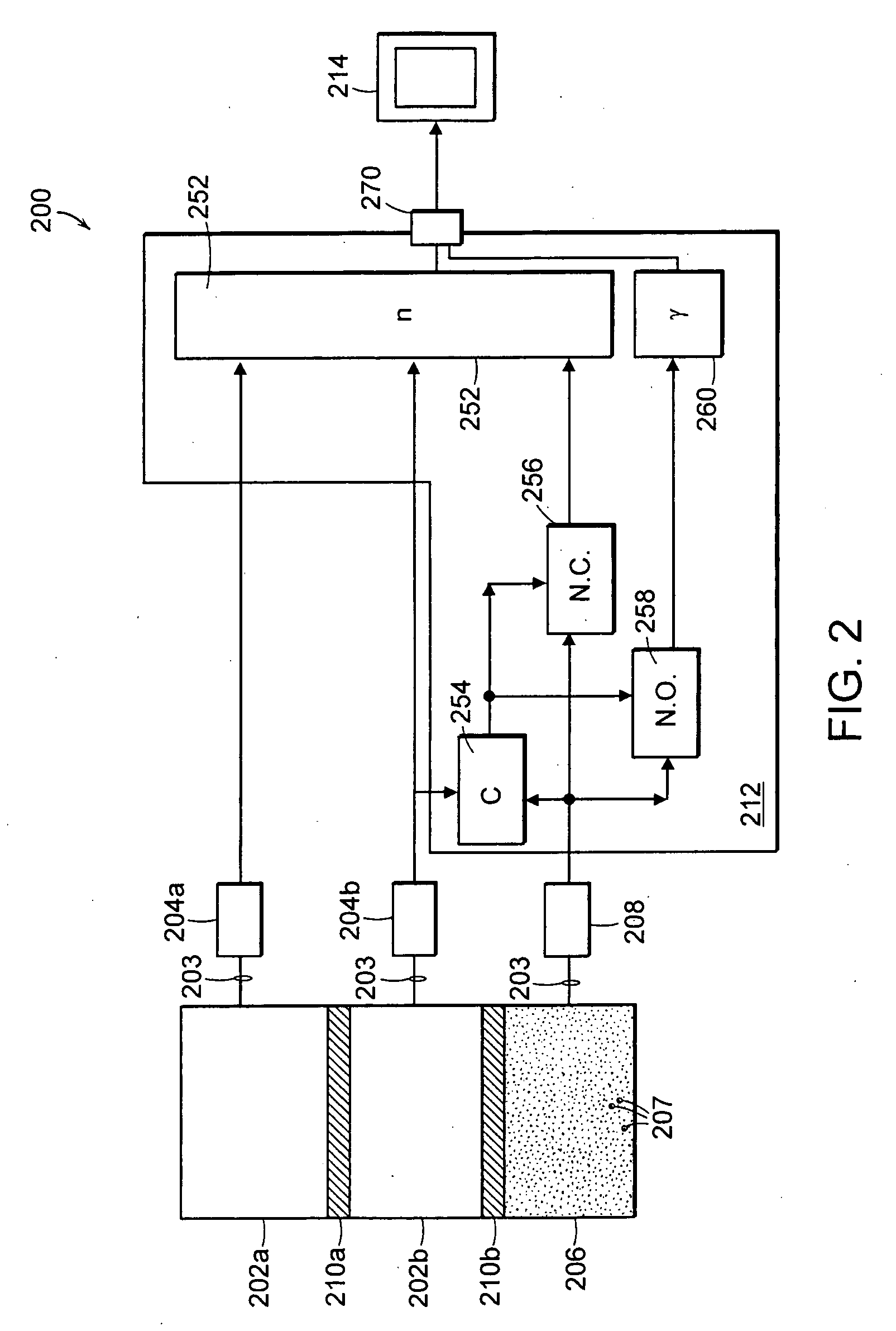
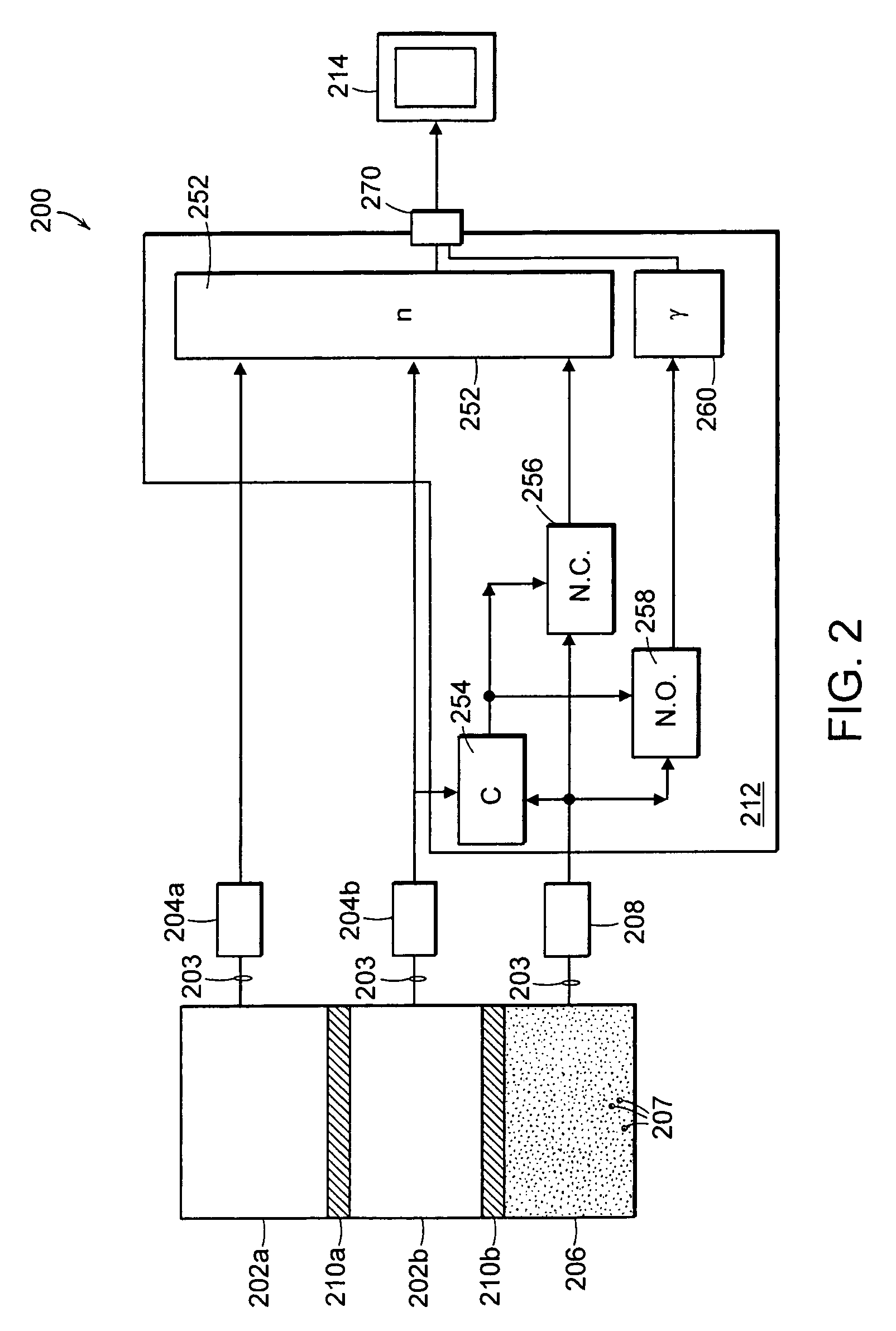
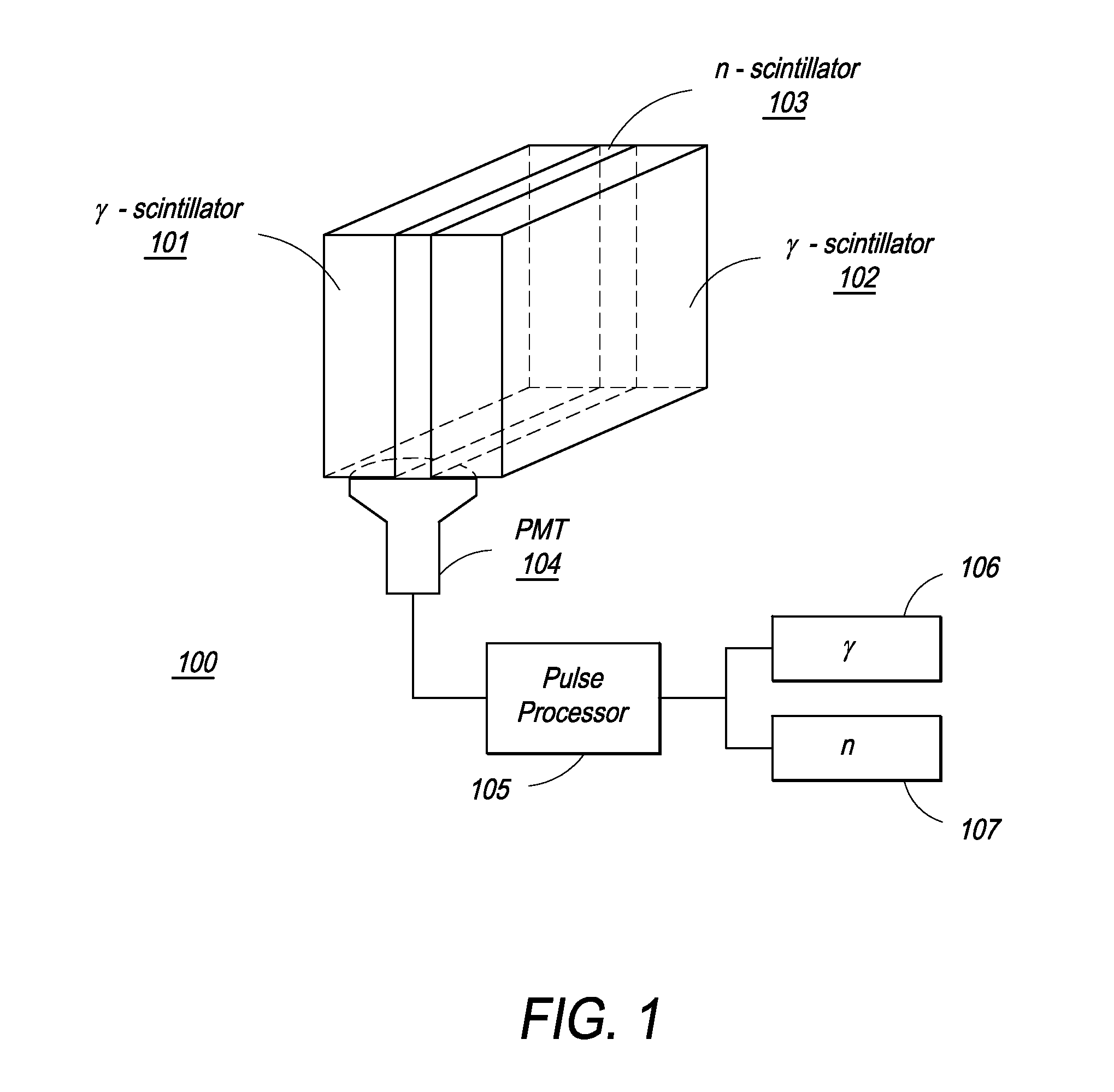
Neutron and gamma ray monitor
InactiveUS20050023479A1Light weightMore selectiveX-ray spectral distribution measurementMeasurement with scintillation detectorsNeutron emissionX-ray
An apparatus for selective radiation detection includes a neutron detector that facilitates detection of neutron emitters, e.g. plutonium, and the like; a gamma ray detector that facilitates detection of gamma ray sources, e.g., uranium, and the like; and / or an X-ray analyzer that facilitates detection of materials that can shield radioactive sources, e.g., lead, and the like.
Owner:THERMO NITON ANALYZERS
Stand-alone mini gamma camera including a localization system for intrasurgical use
ActiveUS8450694B2Surgical navigation systemsMaterial analysis by optical meansLocalization systemThe Internet
The invention relates to a portable mini gamma camera for intrasurgical use. The inventive camera is based on scintillation crystals and comprises a stand-alone device, i.e. all of the necessary systems have been integrated next to the sensor head and no other system is required. The camera can be hot-swapped to any computer using different types of interface, such as to meet medical grade specifications. The camera can be self-powered, can save energy and enables software and firmware to be updated from the Internet and images to be formed in real time. Any gamma ray detector based on continuous scintillation crystals can be provided with a system for focusing the scintillation light emitted by the gamma ray in order to improve spatial resolution. The invention also relates to novel methods for locating radiation-emitting objects and for measuring physical variables, based on radioactive and laser emission pointers.
Owner:GENERAL EQUIP FOR MEDICAL IMAGING SL +2
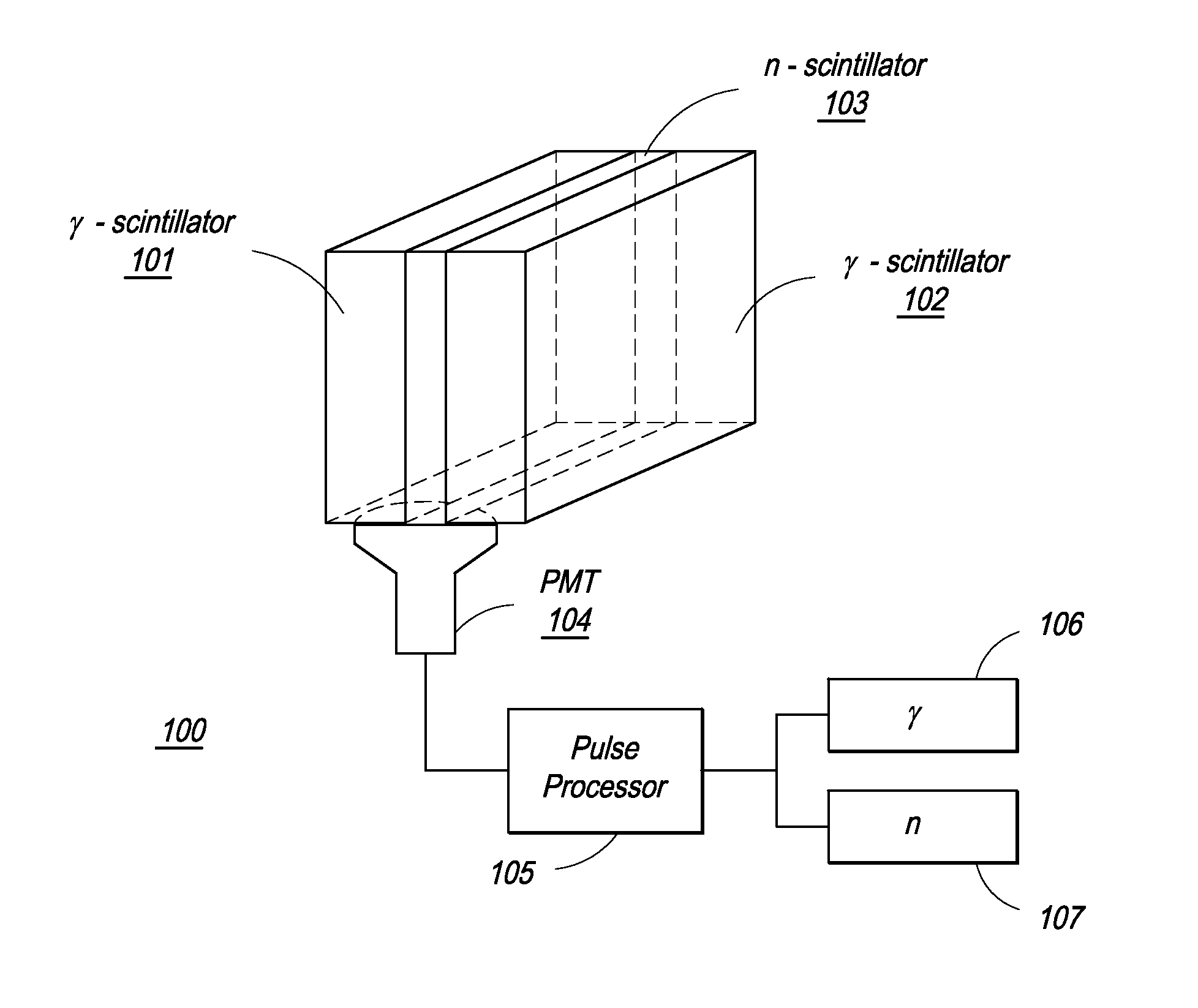
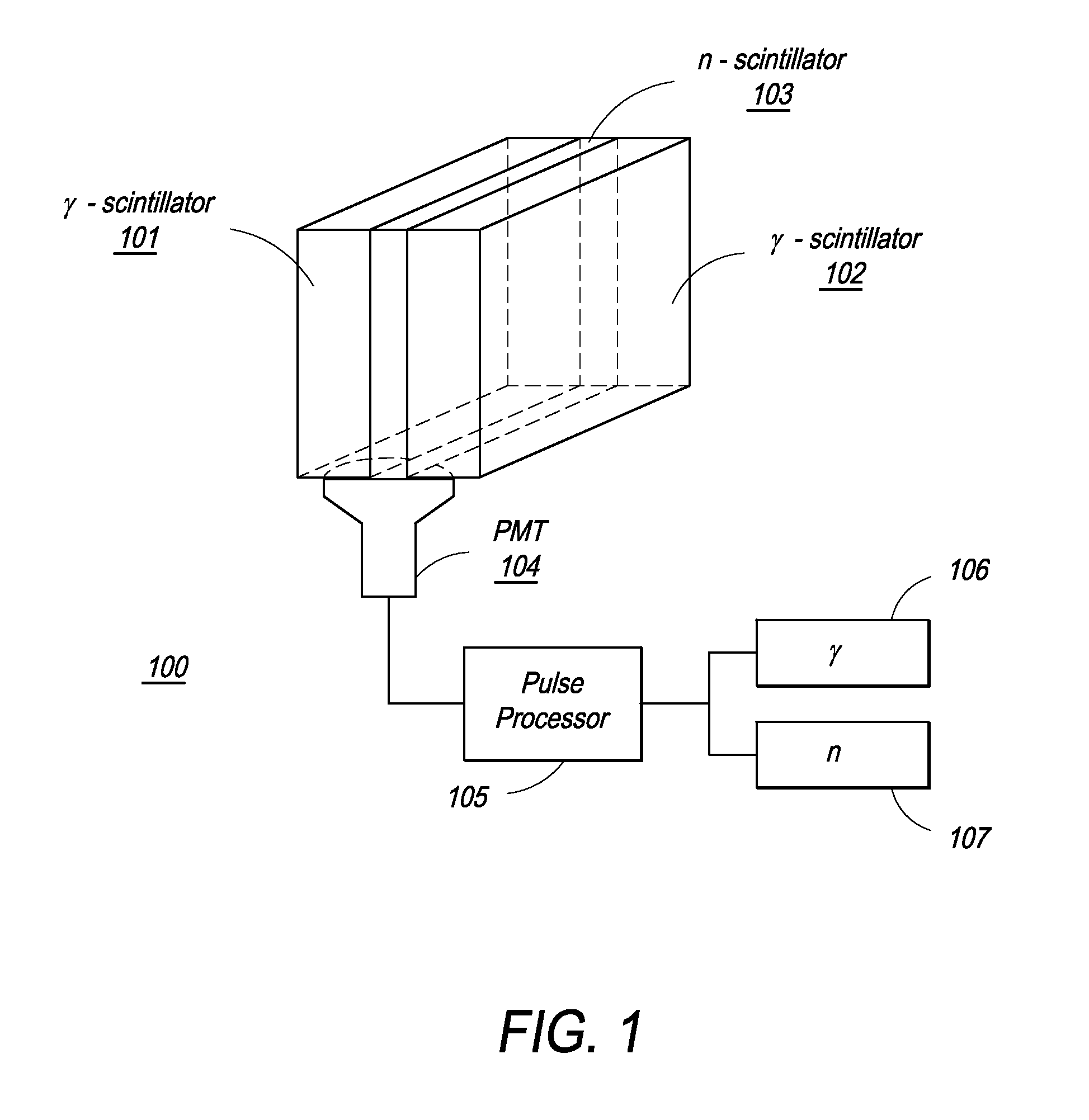
Composite Gamma-Neutron Detection System
ActiveUS20110204243A1Avoid cross contaminationMultiplier cathode arrangementsMeasurement with scintillation detectorsHeavy particleLight guide
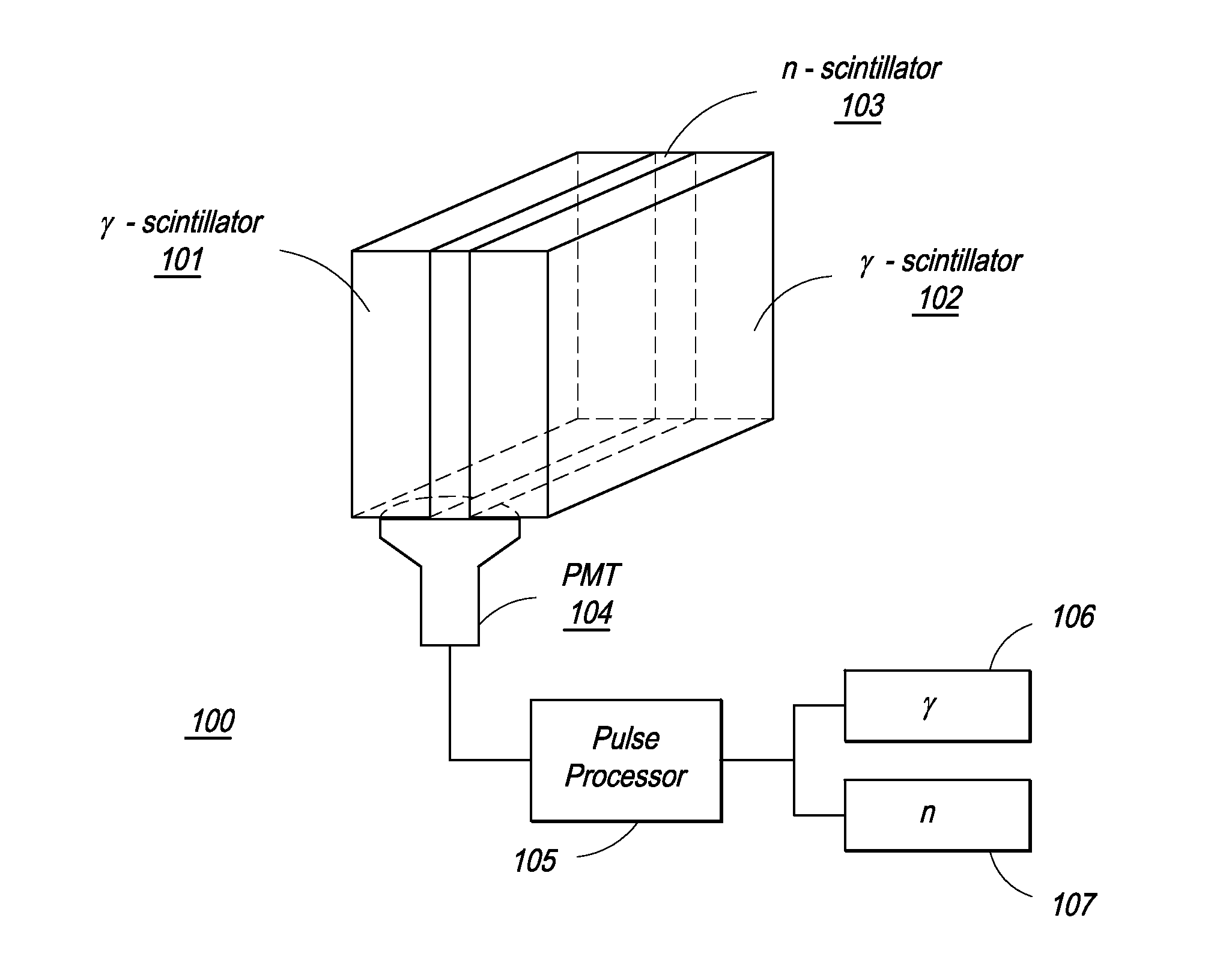
The present invention provides a gamma-neutron detector based on mixtures of thermal neutron absorbers that produce heavy-particle emission following thermal capture. The detector consists of one or more thin screens embedded in transparent hydrogenous light guides, which also serve as a neutron moderator. The emitted particles interact with the scintillator screen and produce a high light output, which is collected by the light guides into a photomultiplier tube and produces a signal from which the neutrons are counted. Simultaneous gamma-ray detection is provided by replacing the light guide material with a plastic scintillator. The plastic scintillator serves as the gamma-ray detector, moderator and light guide. The neutrons and gamma-ray events are separated employing Pulse-Shape Discrimination (PSD). The detector can be used in several scanning configurations including portal, drive-through, drive-by, handheld and backpack, etc.
Owner:RAPISCAN SYST INC (US)
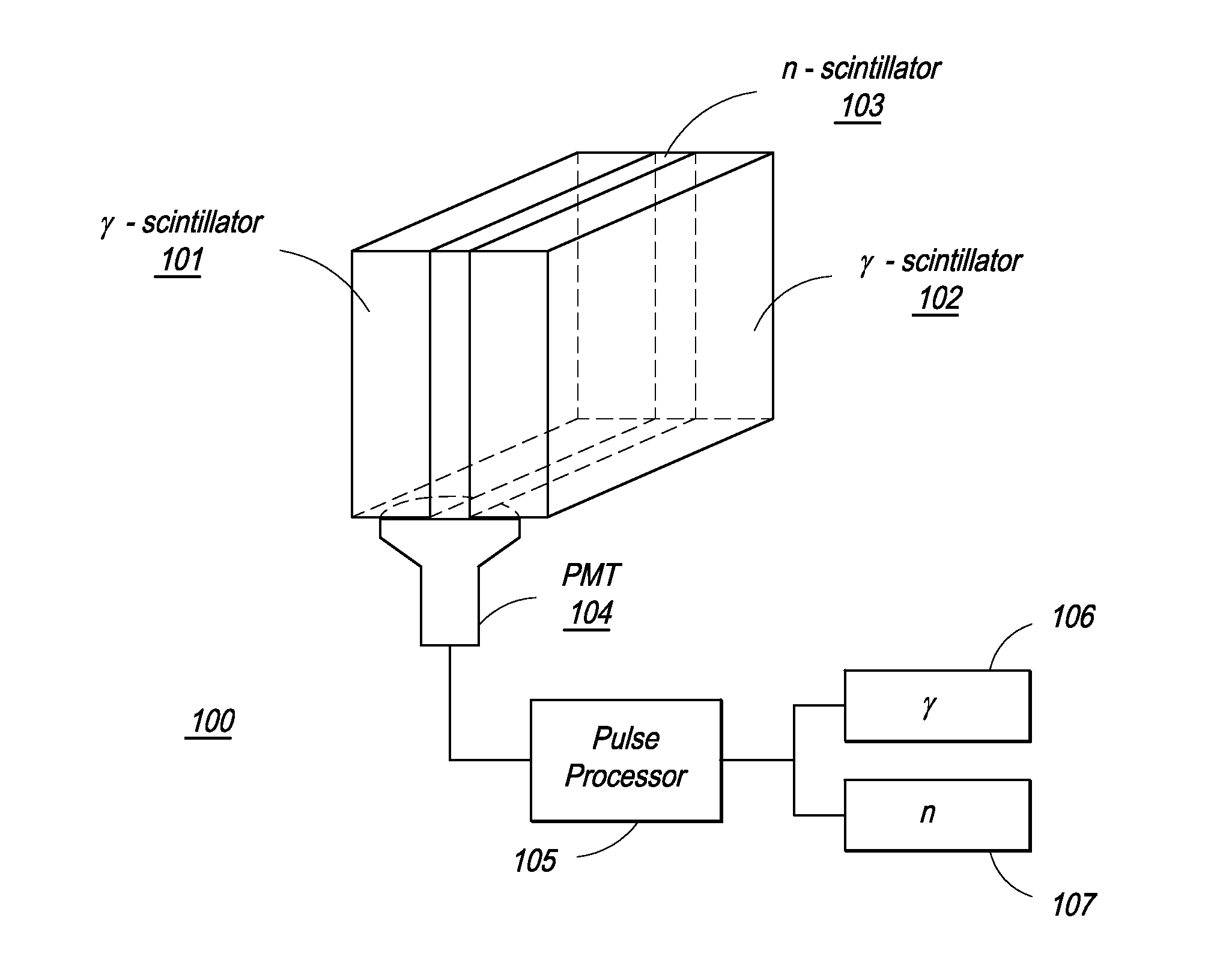
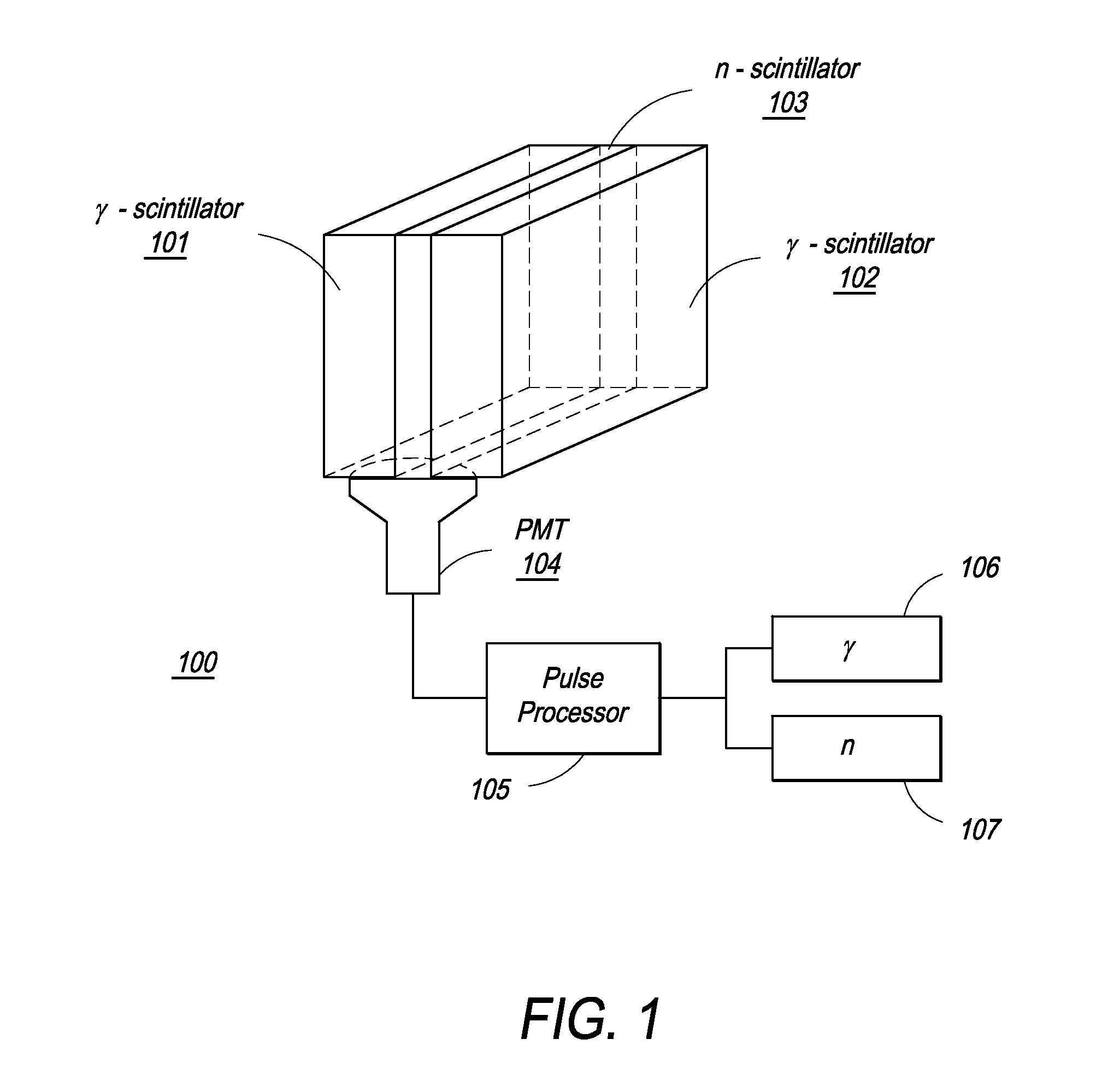
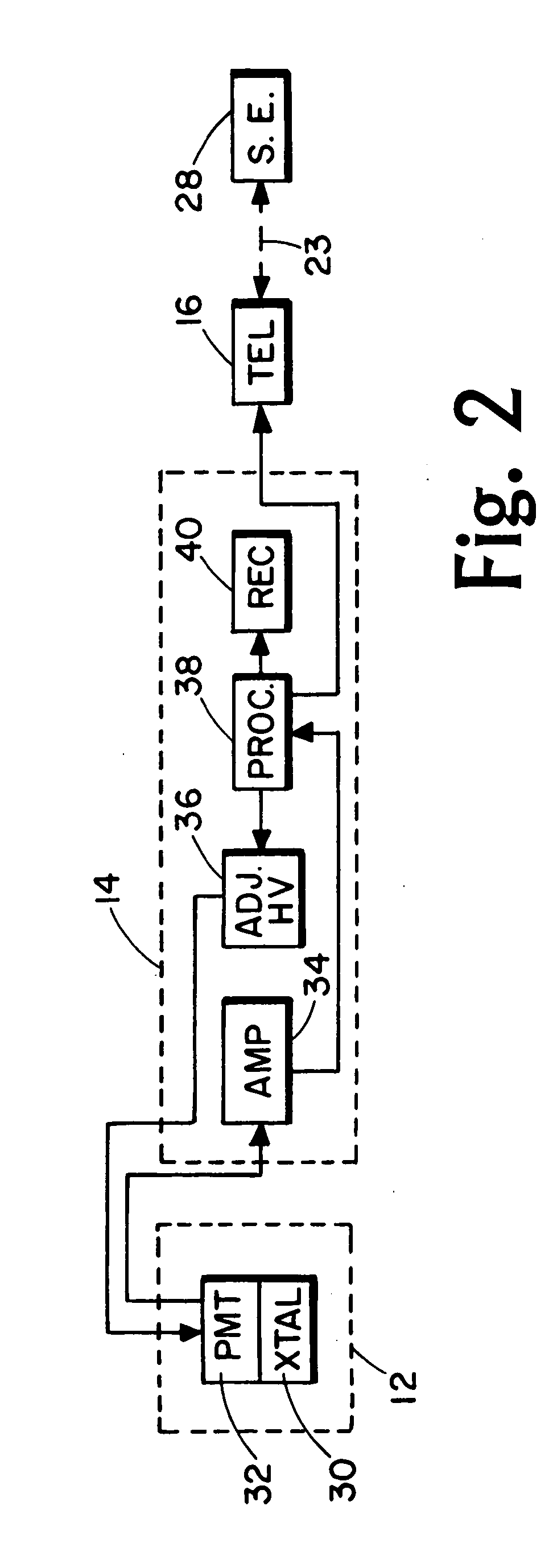
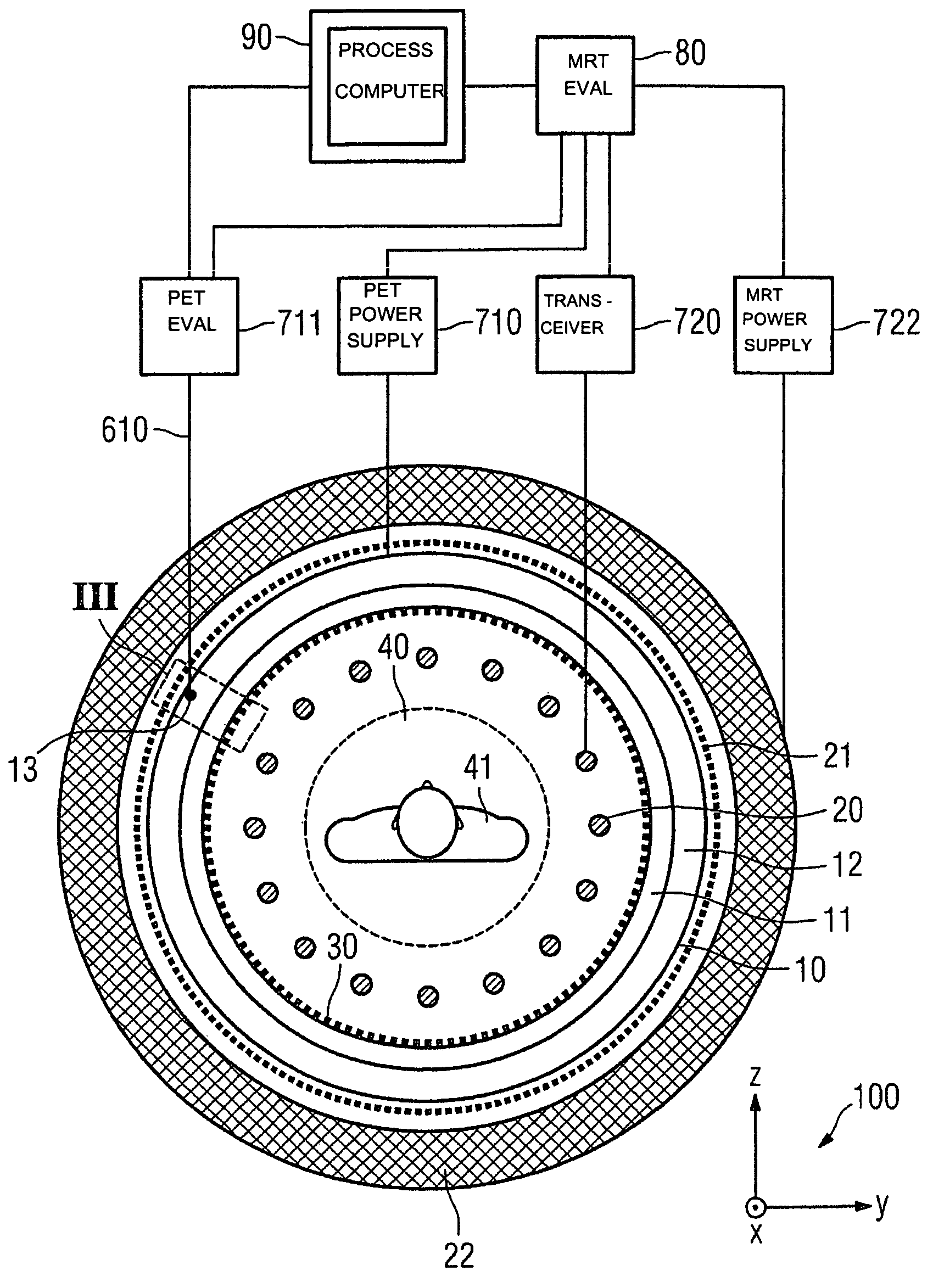
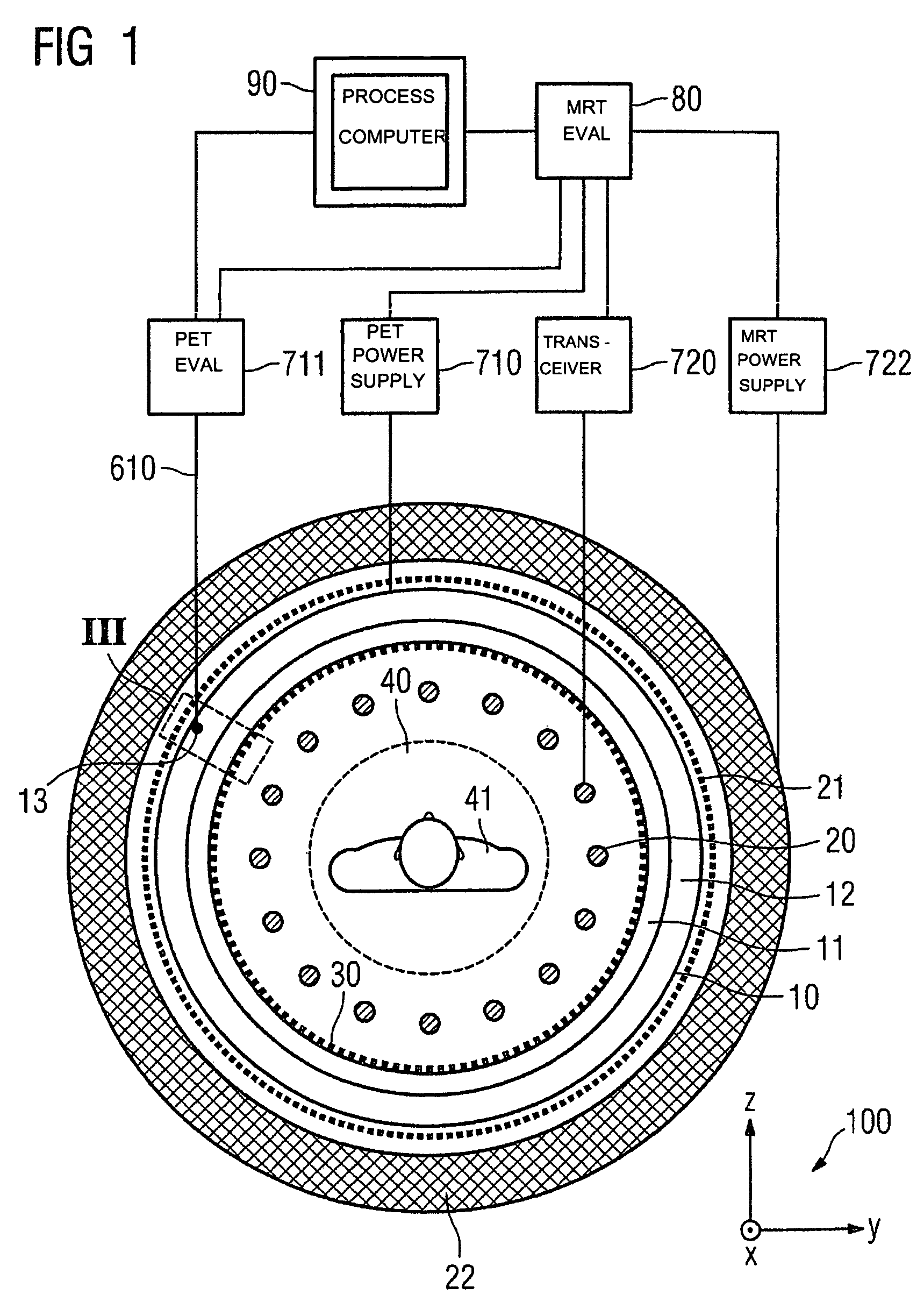
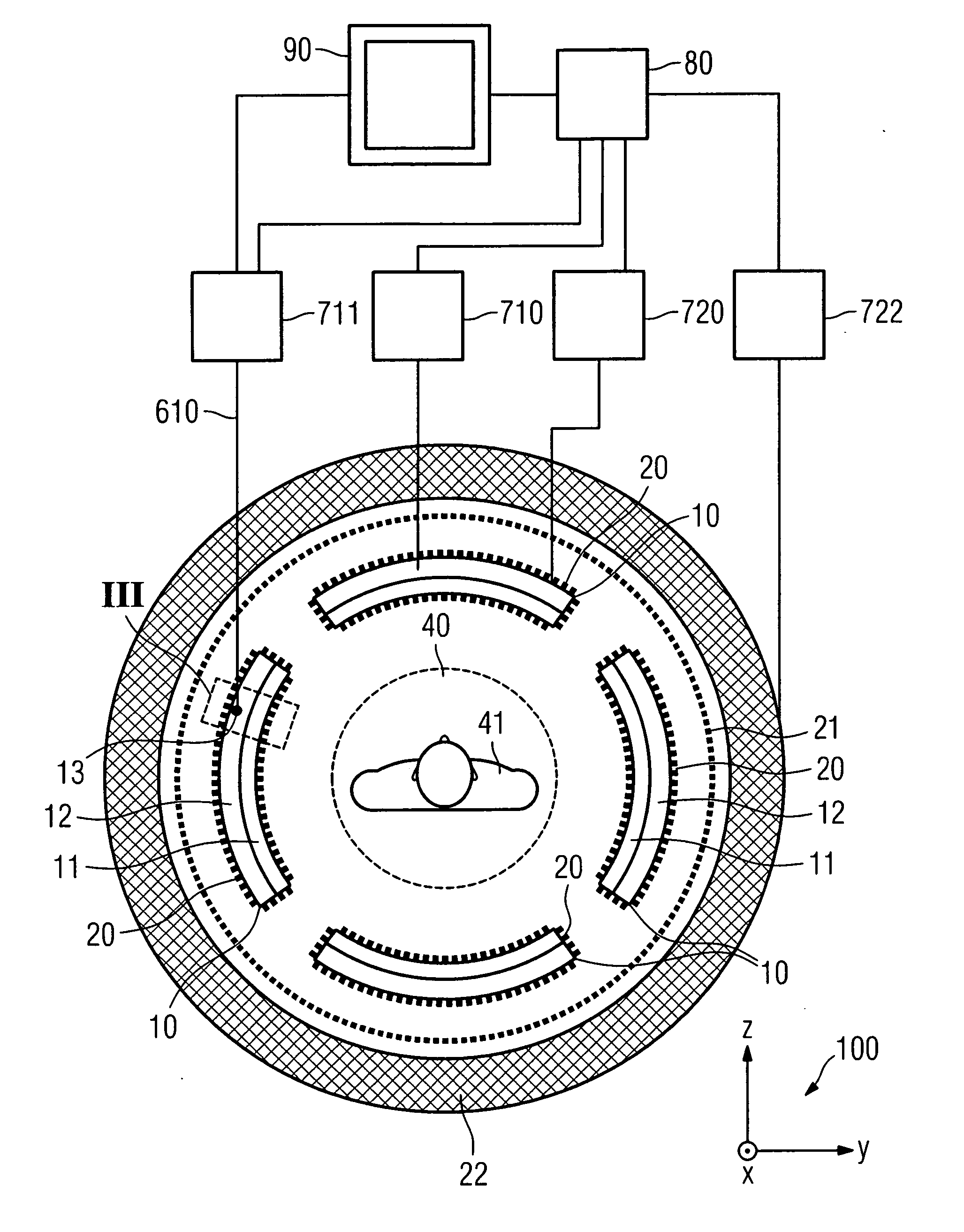
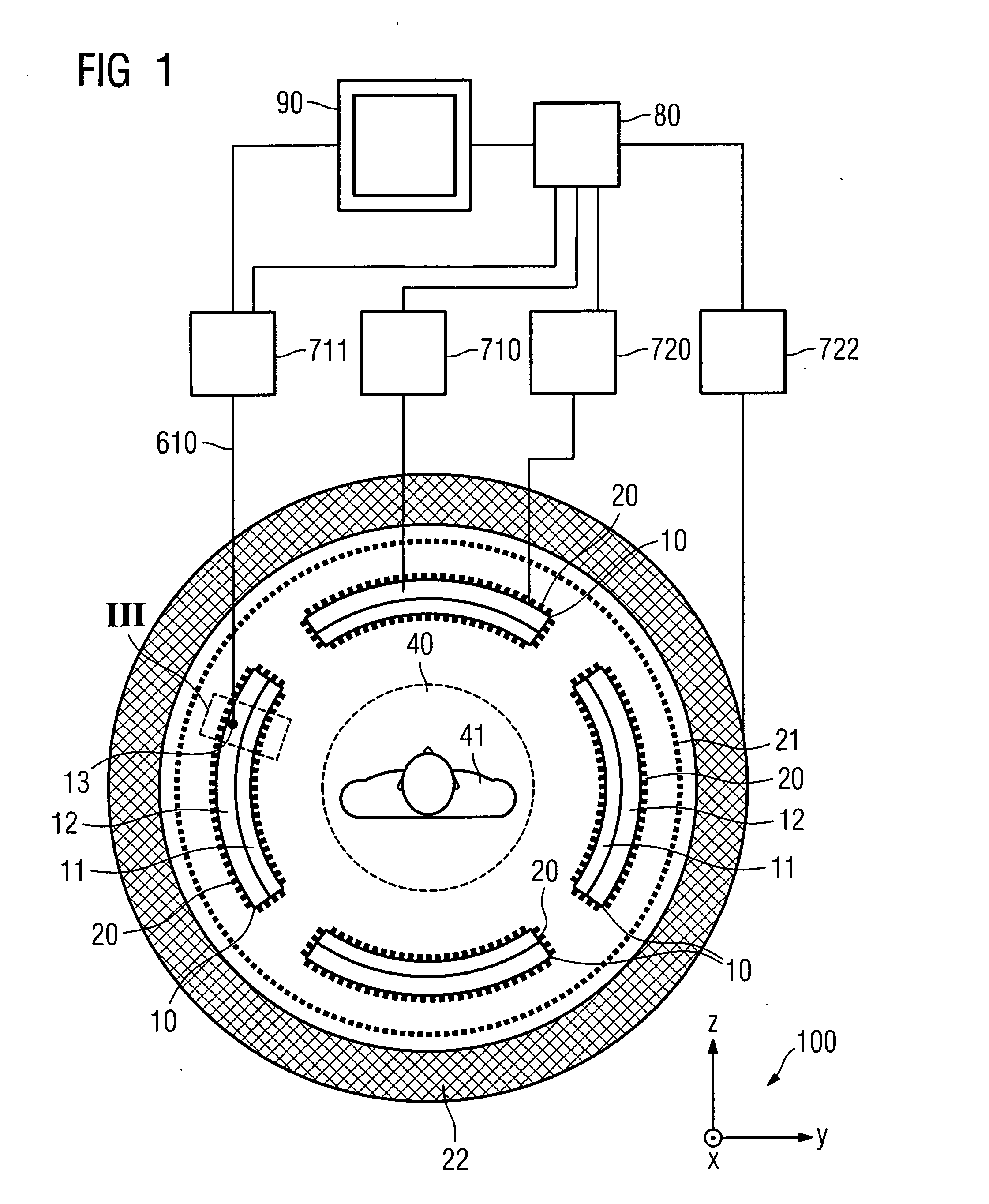
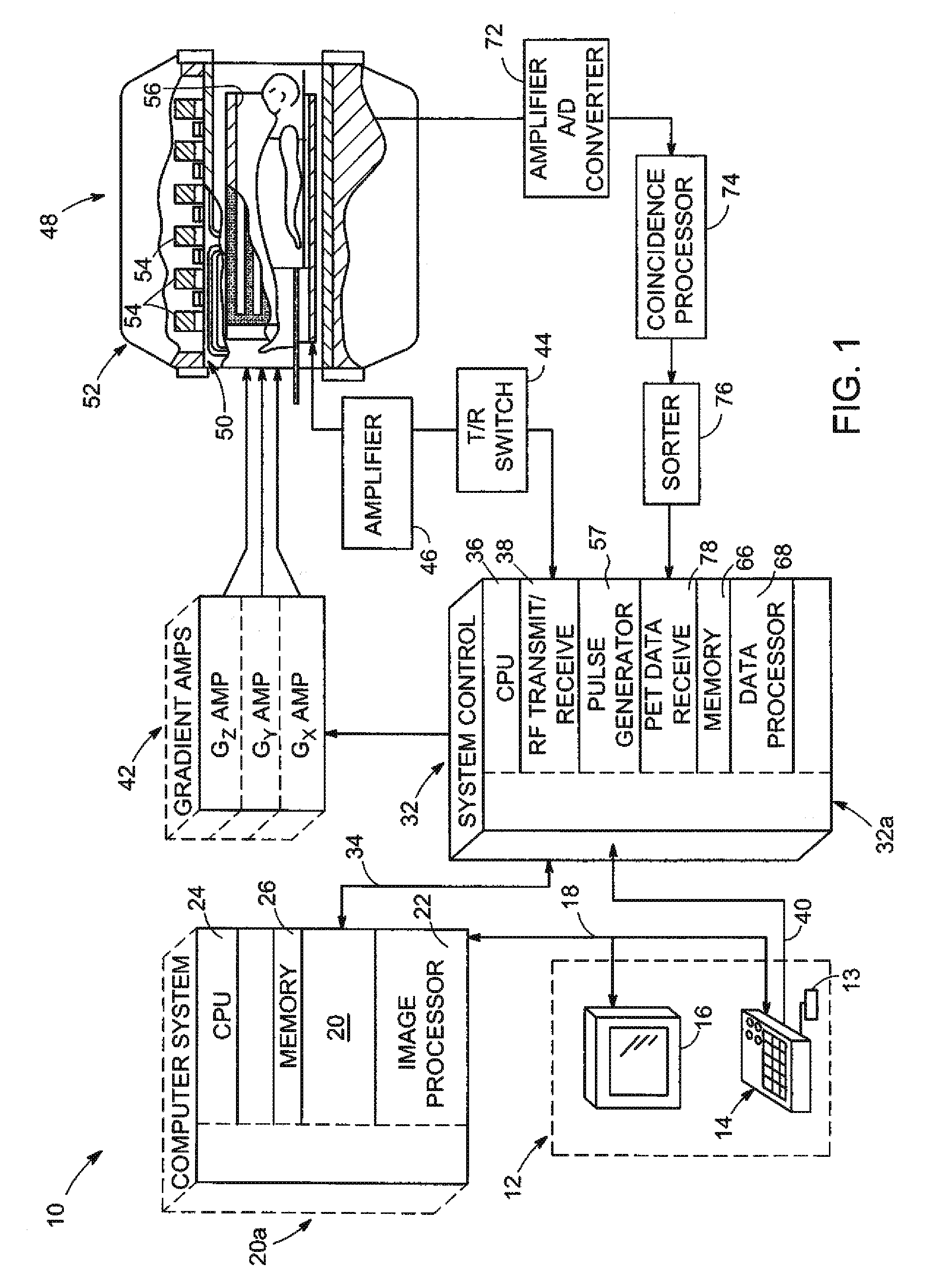
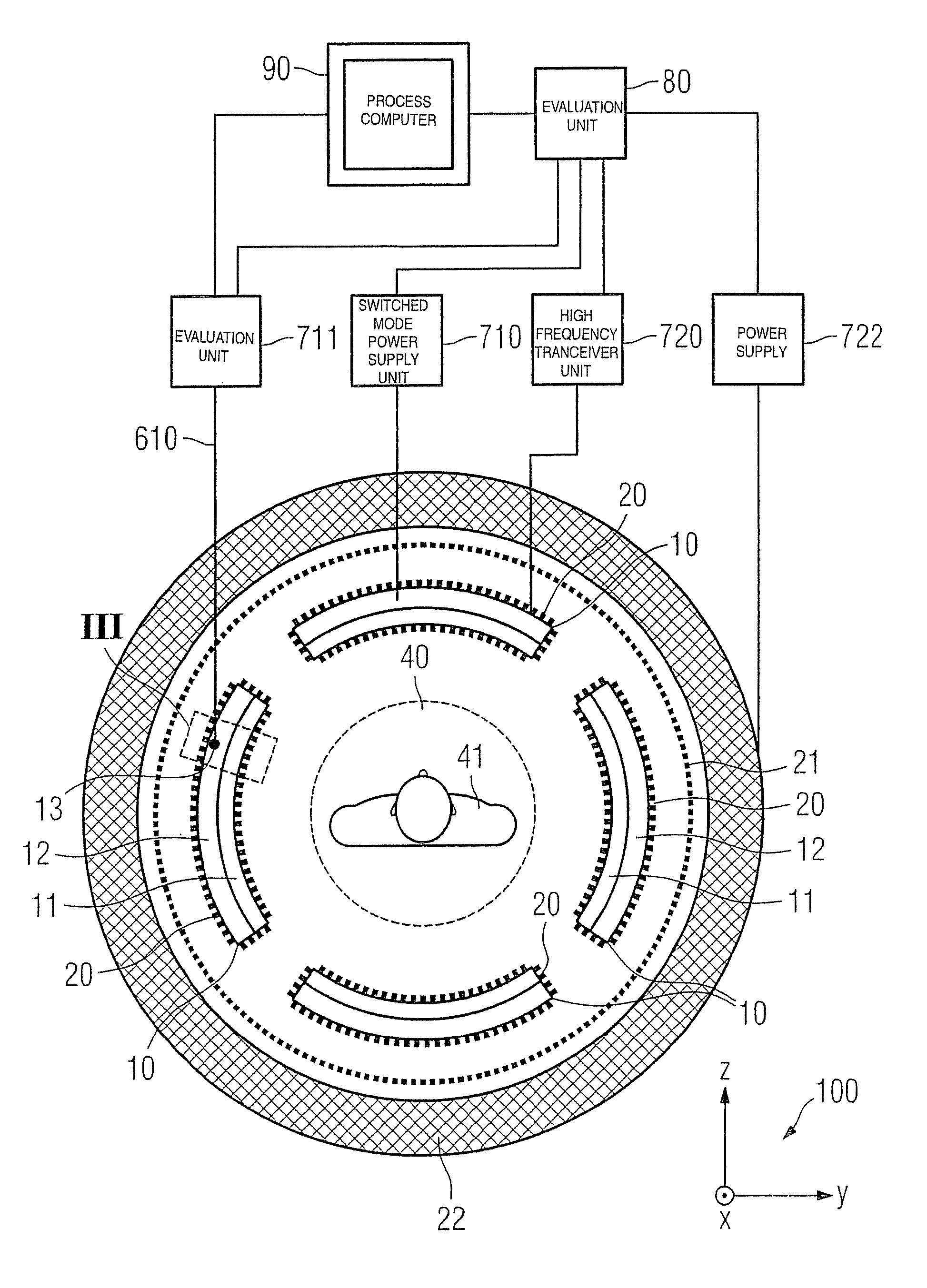
Combined positron emission tomography and magnetic resonance tomography unit
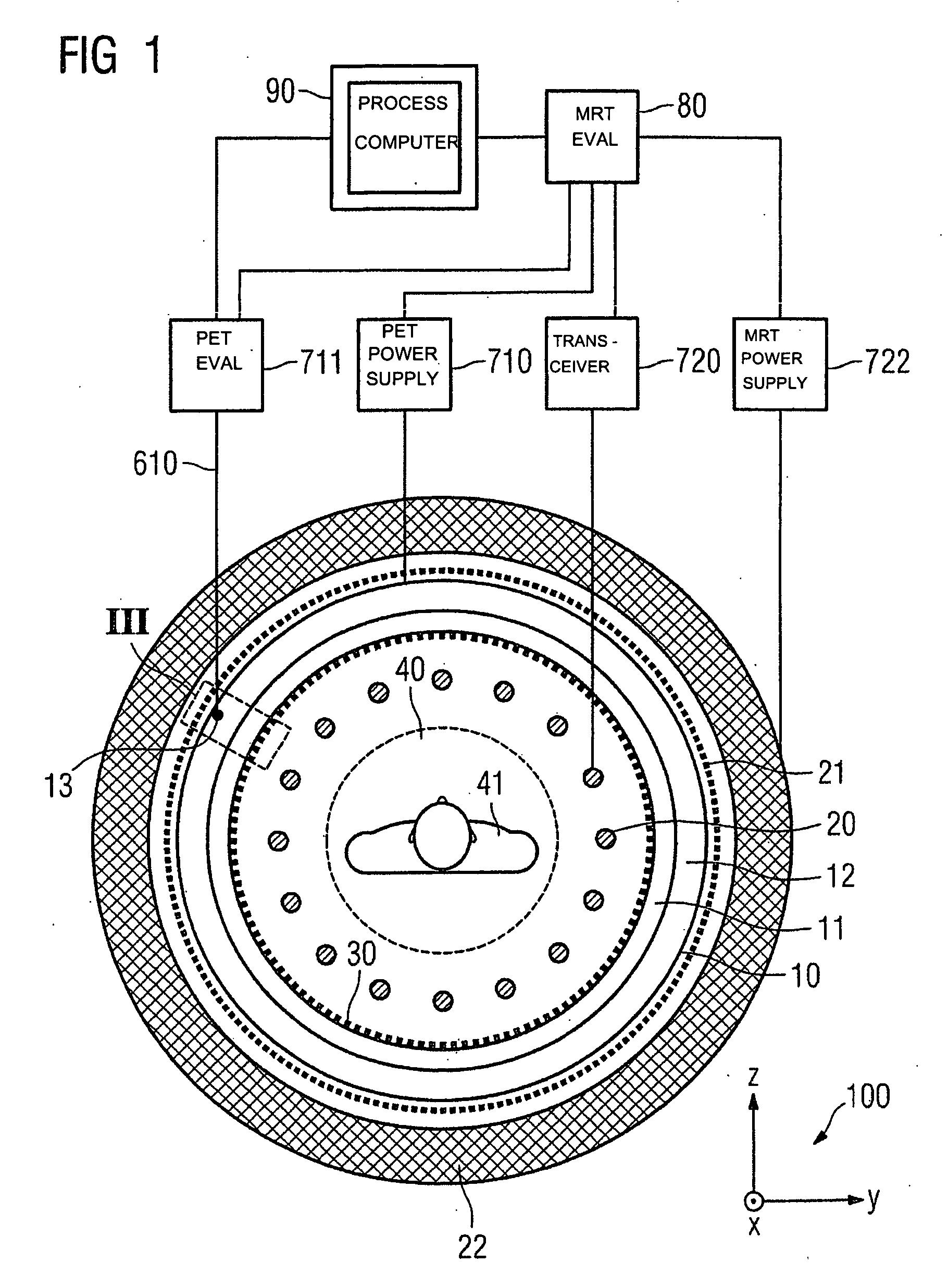
InactiveUS20060251312A1Save spaceShorten the timeMagnetic measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionPositron emission tomography unitElectron
Combined positron emission tomography and magnetic resonance tomography unit for imaging an examination object in an examination space, comprising a positron emission tomography unit that has a unit part assigned to the examination space, and a first evaluation unit for evaluating the electric signals for a positron emission tomography image of the examination object. The unit part in this case comprises a gamma ray detector with an assigned electronics unit. Furthermore, the combined unit comprises a magnetic resonance tomography unit and a second evaluation unit for evaluating the magnetic resonance signals for a magnetic resonance image of the examination object. The magnetic resonance unit in this case has a high frequency antenna device as well as a gradient coil system, the high frequency antenna device being arranged nearer to the examination space than the gradient coil system, as well as a high frequency shield arranged between the gradient coil system and the high frequency antenna device. The positron emission tomography unit part is arranged in this case between the high frequency shield and the high frequency antenna device, and is provided, at least on the side facing the high frequency antenna device, with a shielding cover that is caused by the high frequency antenna device and is opaque to high frequency radiation.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Neutron and gamma ray monitor
ActiveUS20070272874A1Easy to detectMeasurement with scintillation detectorsMaterial analysis by optical meansNeutron emissionLight guide
An apparatus for selective radiation detection includes a neutron detector that facilitates detection of neutron emitters, e.g. plutonium, and the like; a gamma ray detector that facilitates detection of gamma ray sources, e.g., uranium, and the like. The apparatus comprises a first light guide, optically coupled to a first optical detector; a second light guide, optically coupled to a second optical detector a sheet of neutron scintillator, opaque for incoming optical photons, said sheet of neutron scintillator sandwiched between the first and the second light guides. The second light guide comprises a gamma ray scintillator material.
Owner:THERMO NITON ANALYZERS
Neutron and gamma ray monitor
ActiveUS7525101B2Easy to detectMeasurement with scintillation detectorsMaterial analysis by optical meansNeutron emissionLight guide
Owner:THERMO NITON ANALYZERS
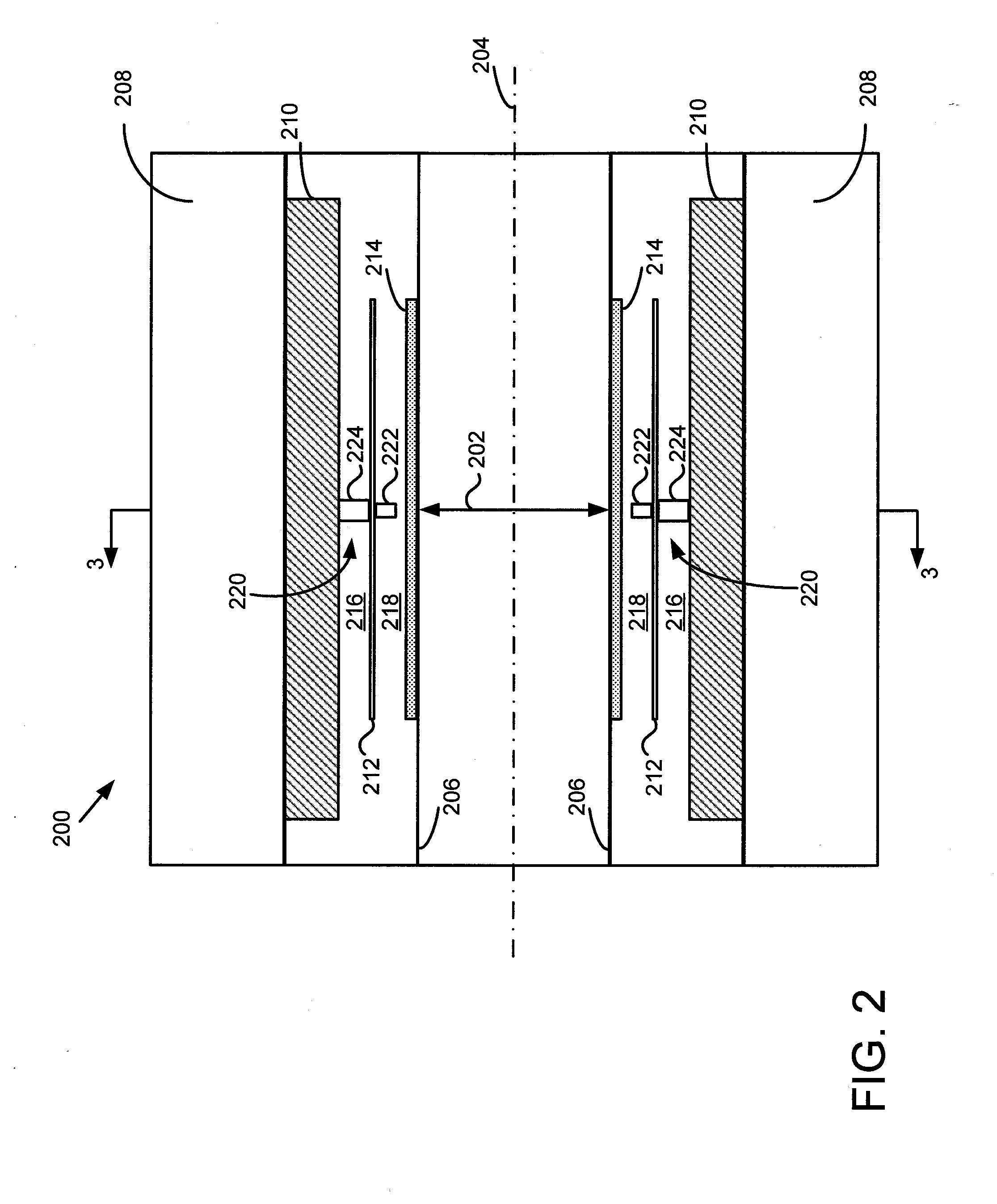
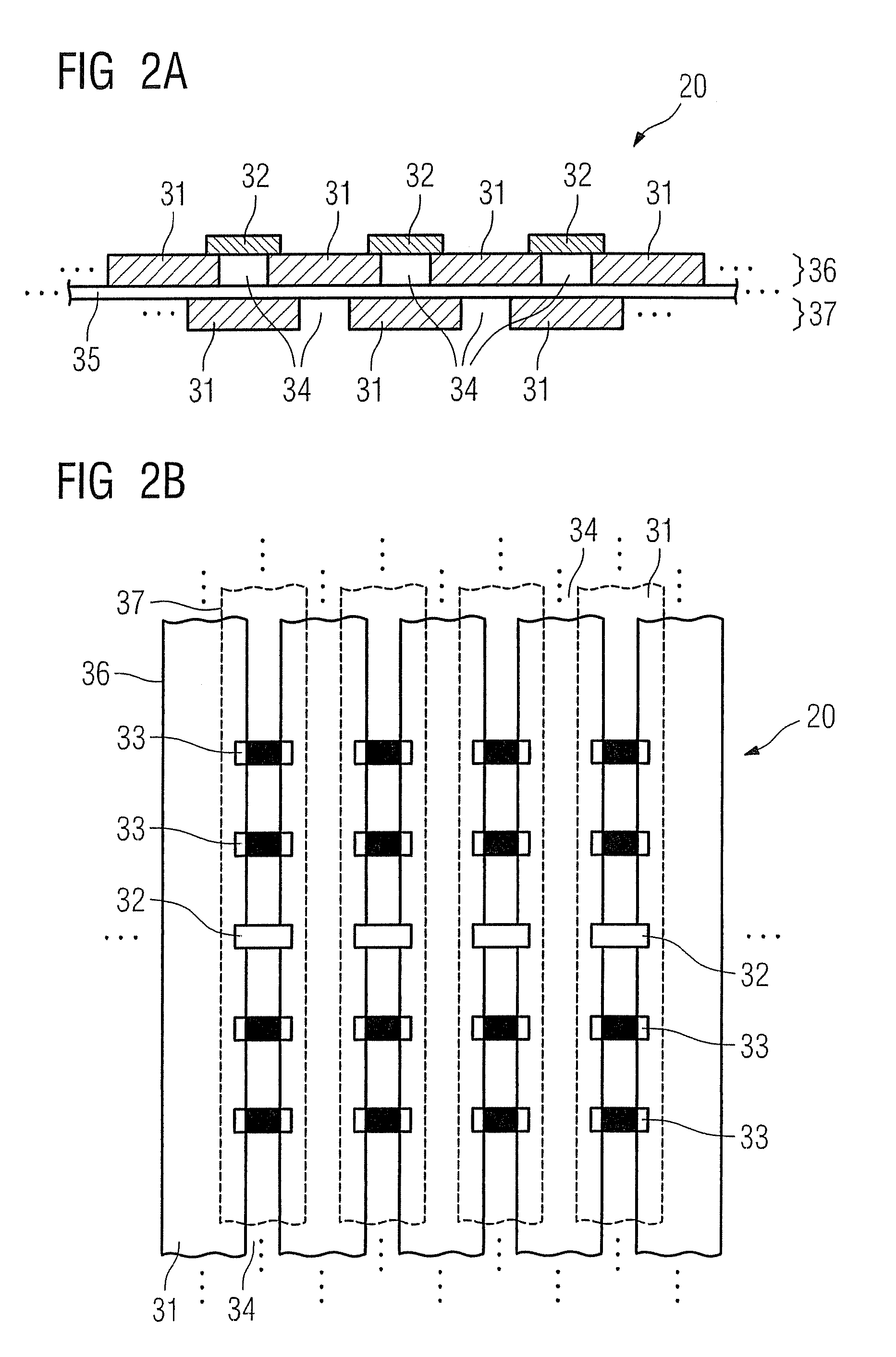
Gamma ray detector modules
InactiveUS7223981B1Reduce in quantityLow profileSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansSemiconductor chipInterposer
A radiation detector assembly has a semiconductor detector array substrate of CdZnTe or CdTe, having a plurality of detector cell pads on a first surface thereof, the pads having a contact metallization and a solder barrier metallization. An interposer card has planar dimensions no larger than planar dimensions of the semiconductor detector array substrate, a plurality of interconnect pads on a first surface thereof, at least one readout semiconductor chip and at least one connector on a second surface thereof, each having planar dimensions no larger than the planar dimensions of the interposer card. Solder columns extend from contacts on the interposer first surface to the plurality of pads on the semiconductor detector array substrate first surface, the solder columns having at least one solder having a melting point or liquidus less than 120 degrees C. An encapsulant is disposed between the interposer circuit card first surface and the semiconductor detector array substrate first surface, encapsulating the solder columns, the encapsulant curing at a temperature no greater than 120 degrees C.
Owner:CREATIVE ELECTRON
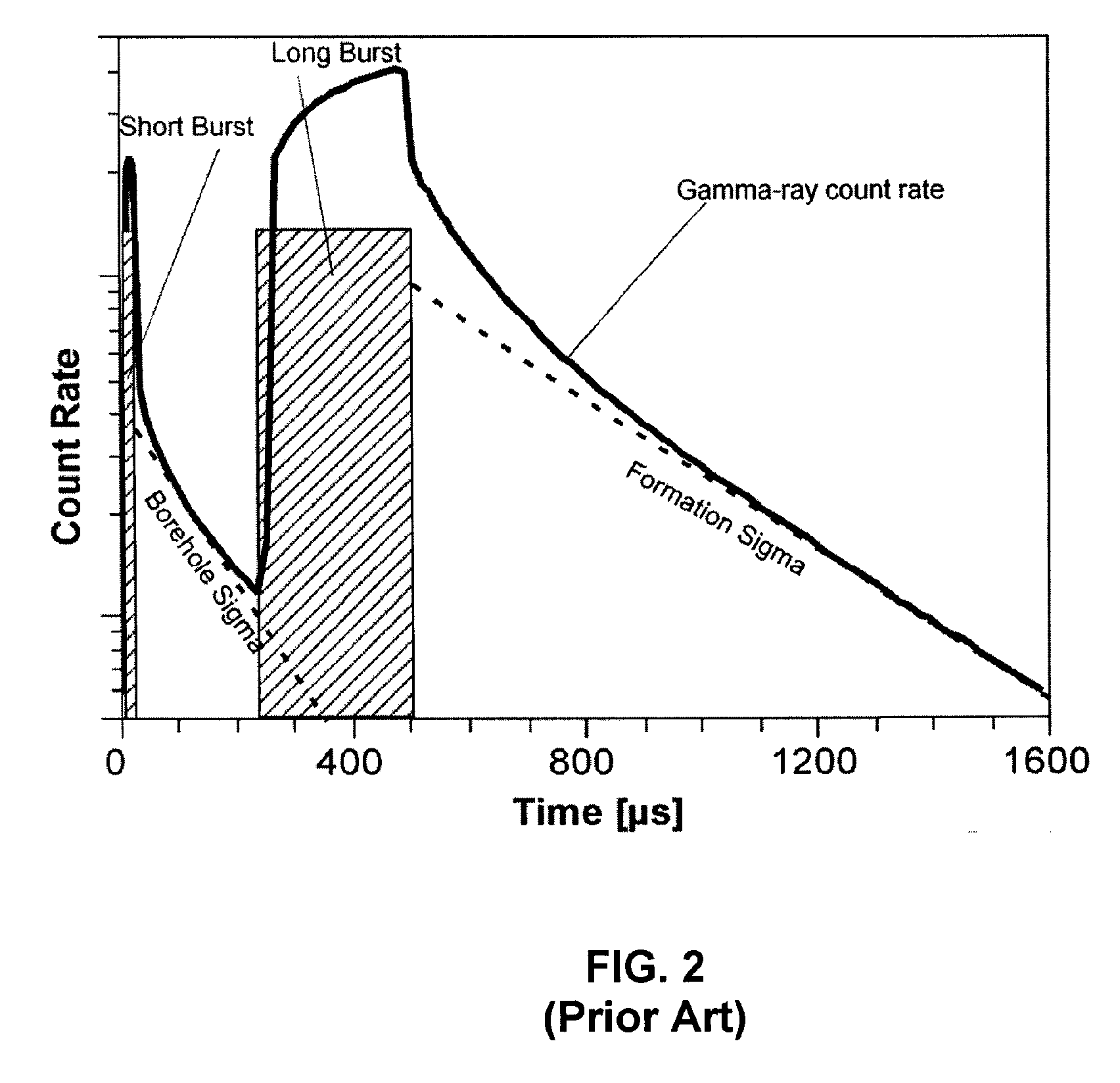
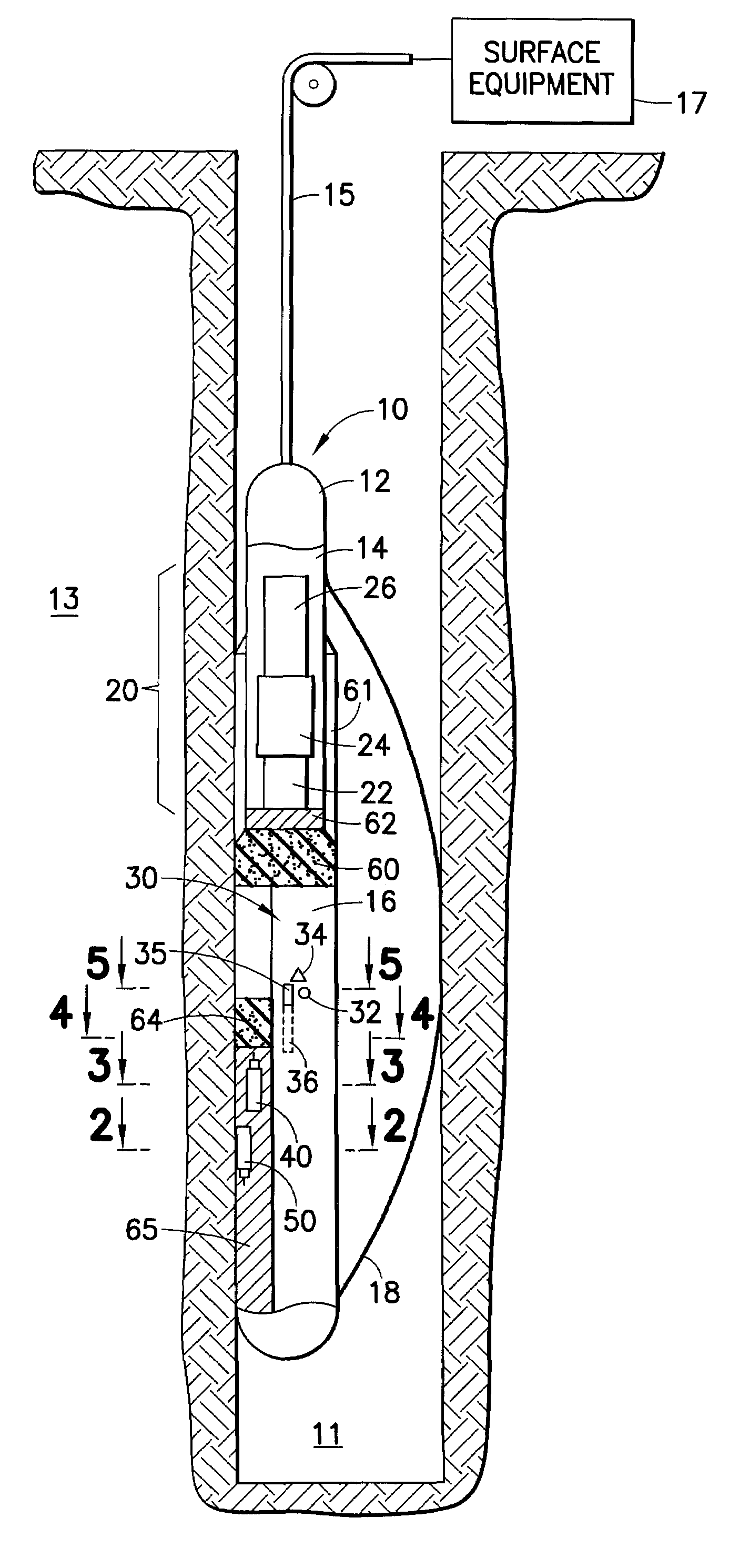
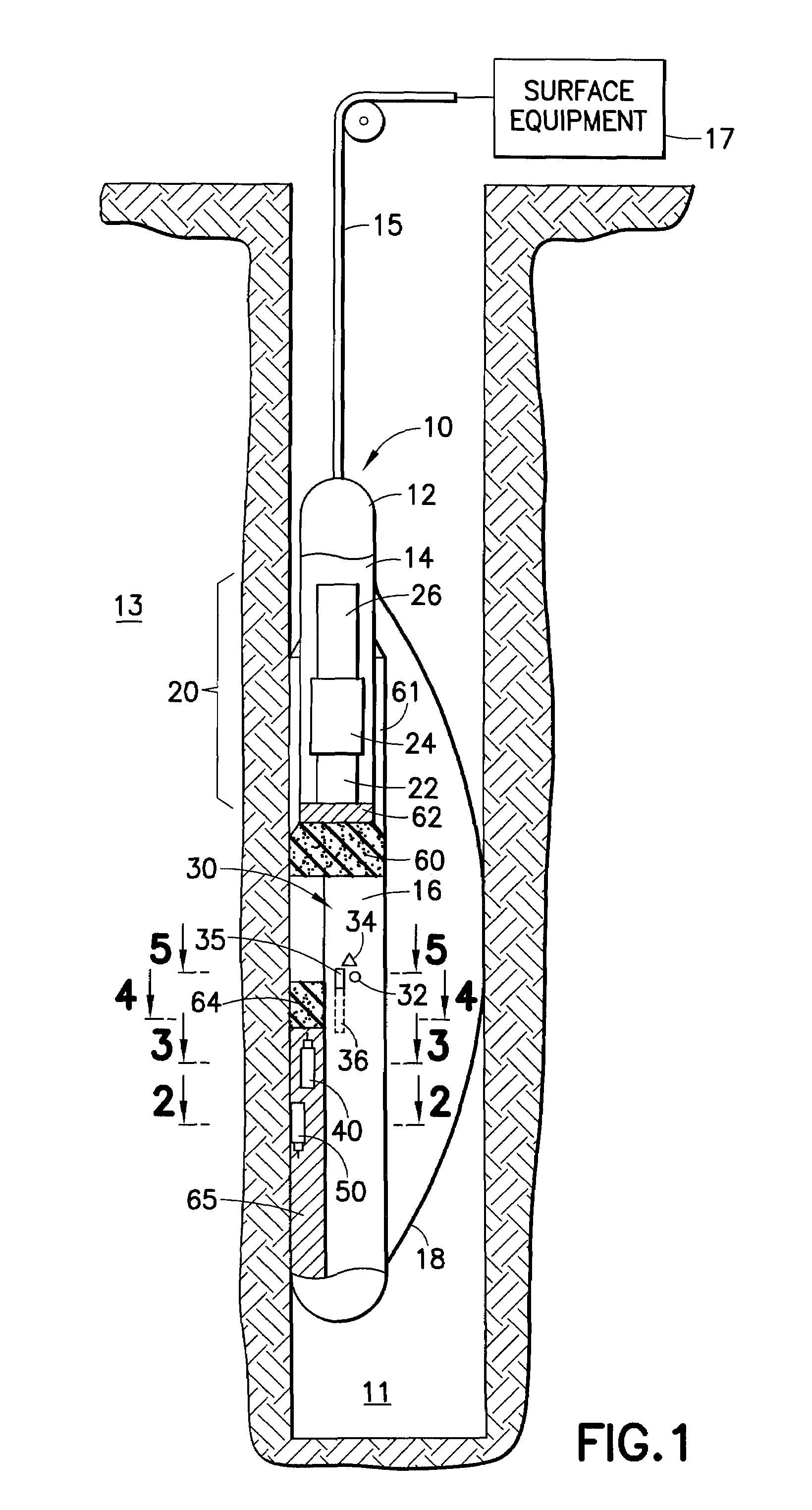
Gamma radiation spectral logging system and method for processing gamma radiation spectra
ActiveUS20070284518A1Radiation measurementNuclear radiation detectionGamma ray detectorsMathematical relationship
A gamma ray logging system and a method of calibrating a detected gamma radiation spectrum. The gamma ray logging system includes a gamma ray detector for detecting gamma radiation, an analyzer for generating a detected gamma radiation spectrum from the detected gamma radiation, and a processor which is configured to perform a calibration of the detected gamma radiation spectrum. The method of calibrating the detected gamma radiation spectrum includes selecting at least two data points from the detected gamma radiation spectrum, determining a mathematical relationship from the selected data points, and using the mathematical relationship to generate a calibrated gamma radiation spectrum from the detected gamma radiation spectrum.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
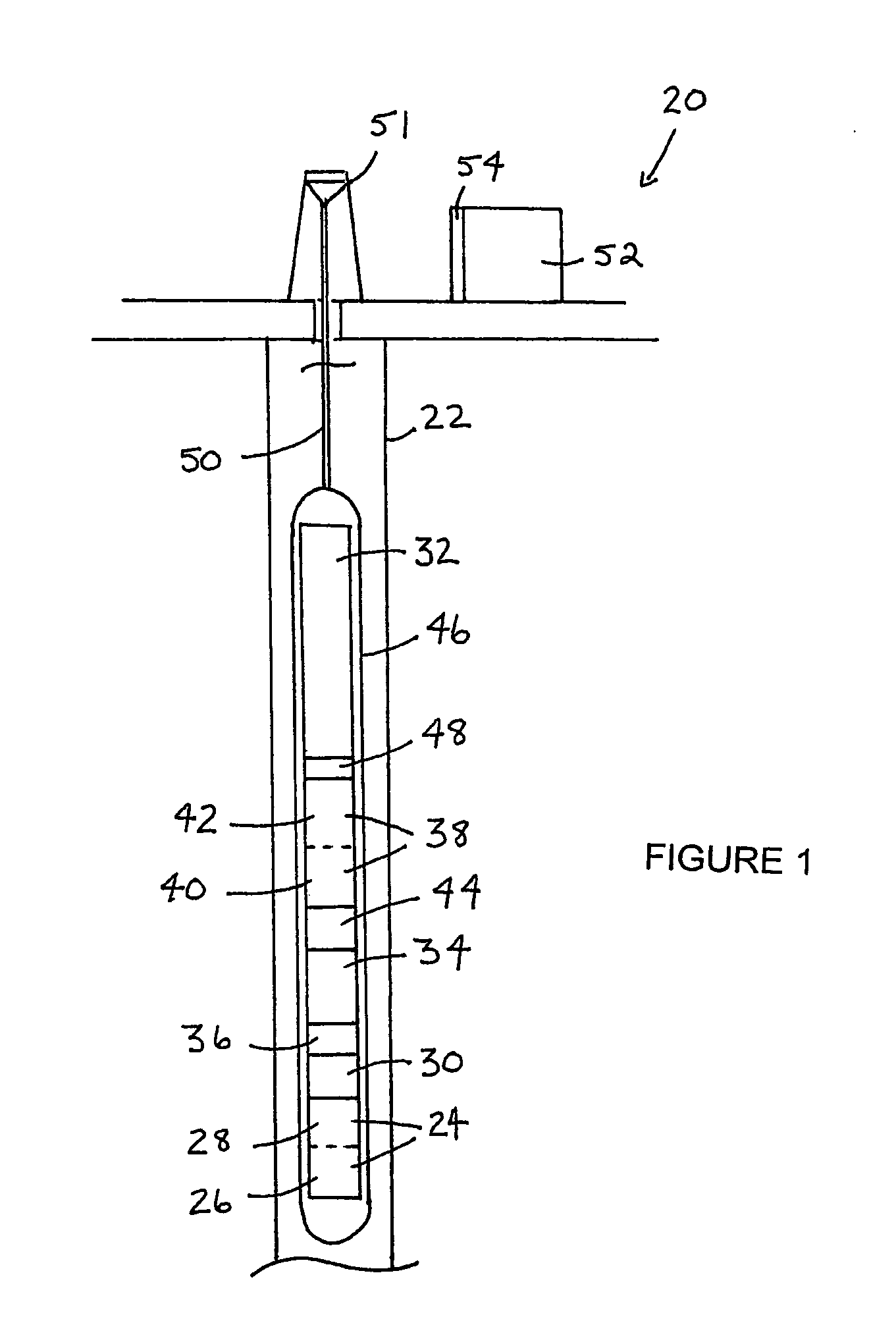
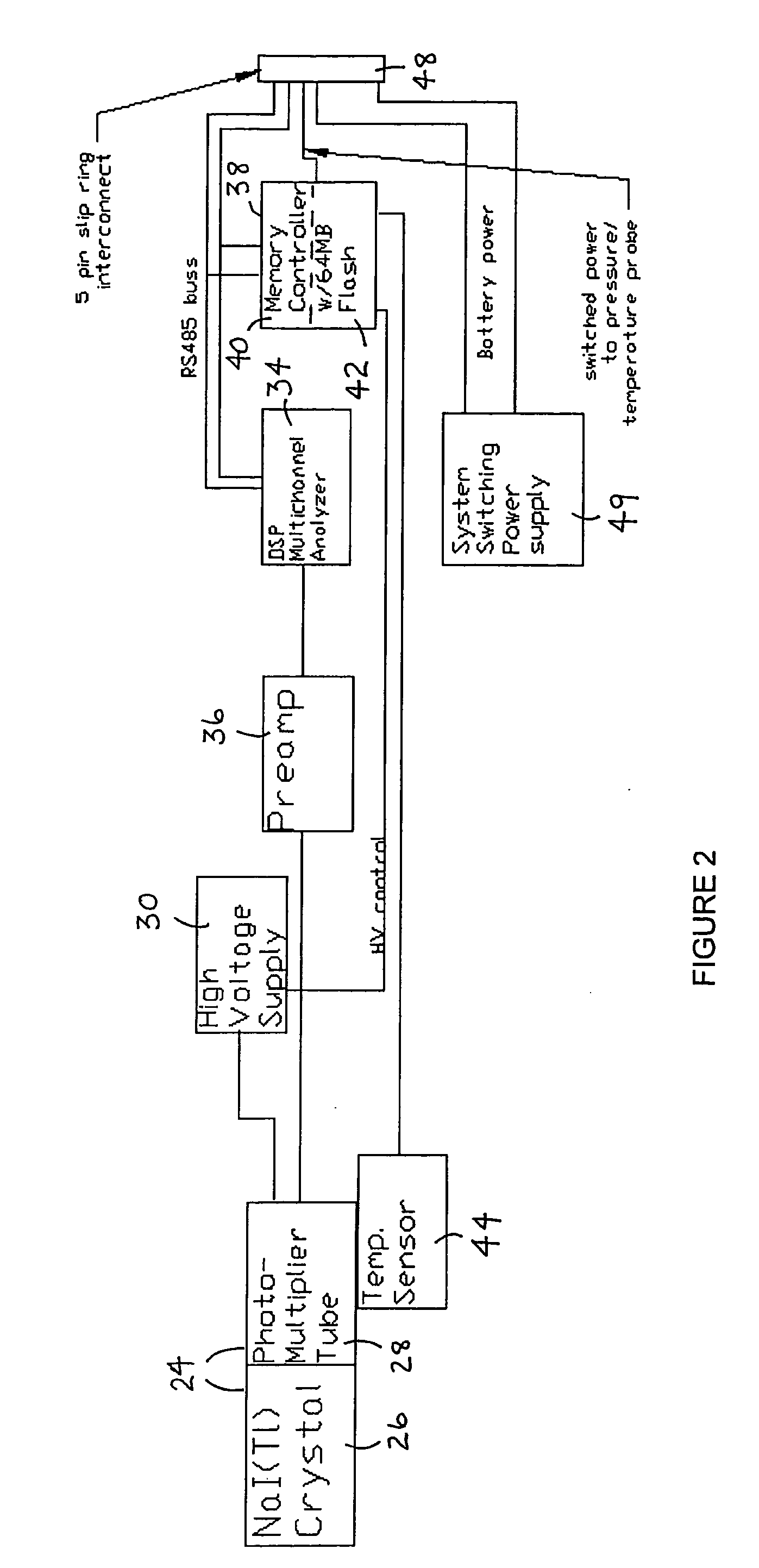
Spectral gamma ray logging-while-drilling system
ActiveUS20050199794A1Minimize degradationMaximizing counting rateCalibration apparatusBorehole/well accessoriesPotassiumDrilling system
A method for determining concentrations of naturally occurring radioactive elements in earth formation by analysis of gamma ray energy spectra measured by at least one gamma ray detector while the borehole is being drilled. Gain of the gamma ray detector is controlled automatically through analysis of the spectra. The one or more gamma ray detectors are disposed at the periphery of the downhole instrumentation to maximize sensitivity. Elemental concentrations of naturally occurring radioactive elements such as potassium, uranium and thorium are measured either as a function of depth in the borehole, or as a function of aximuthal sectors around the borehole wall, or as a function of both depth and azimuthal sectors.
Owner:WEATHERFORD CANADA
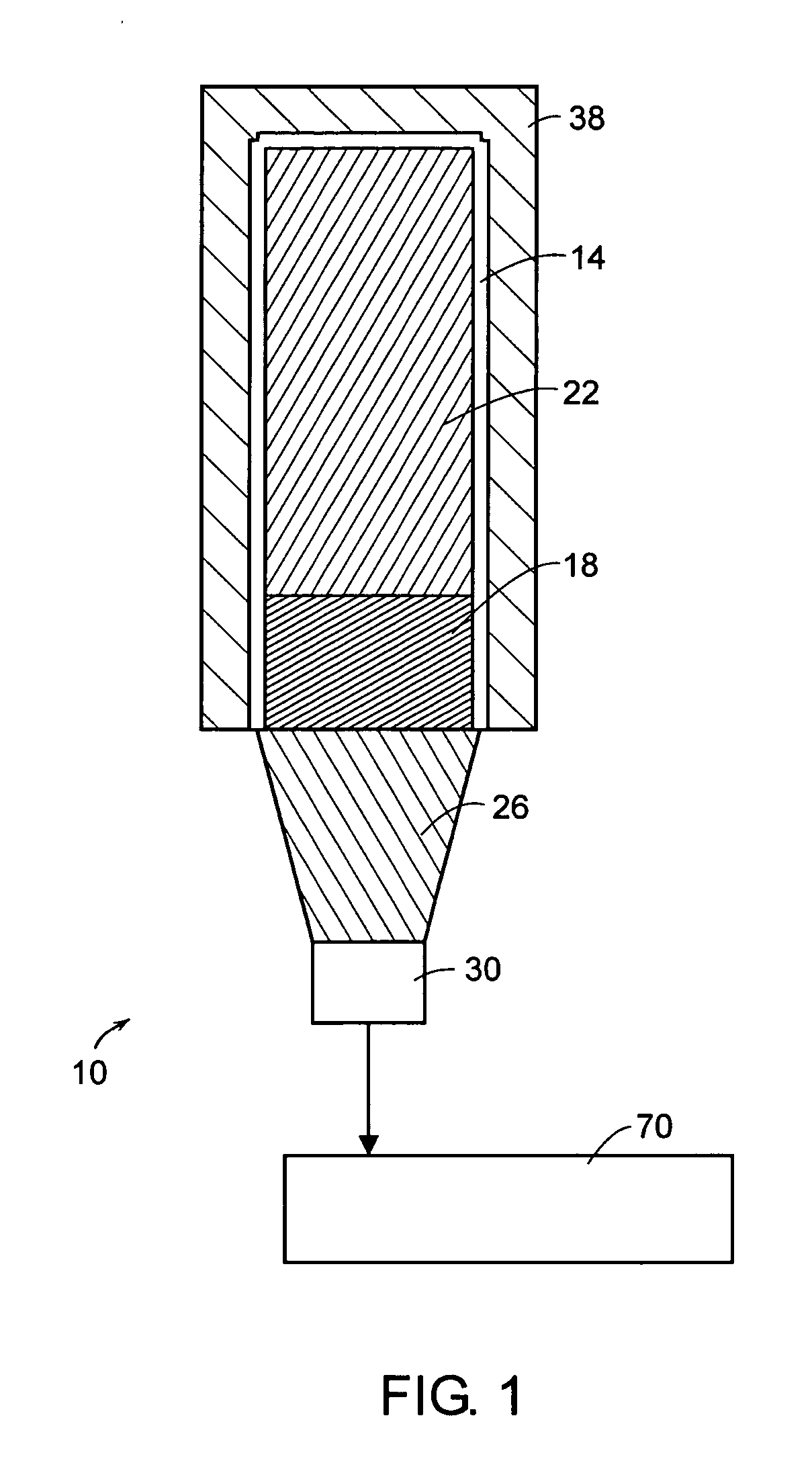
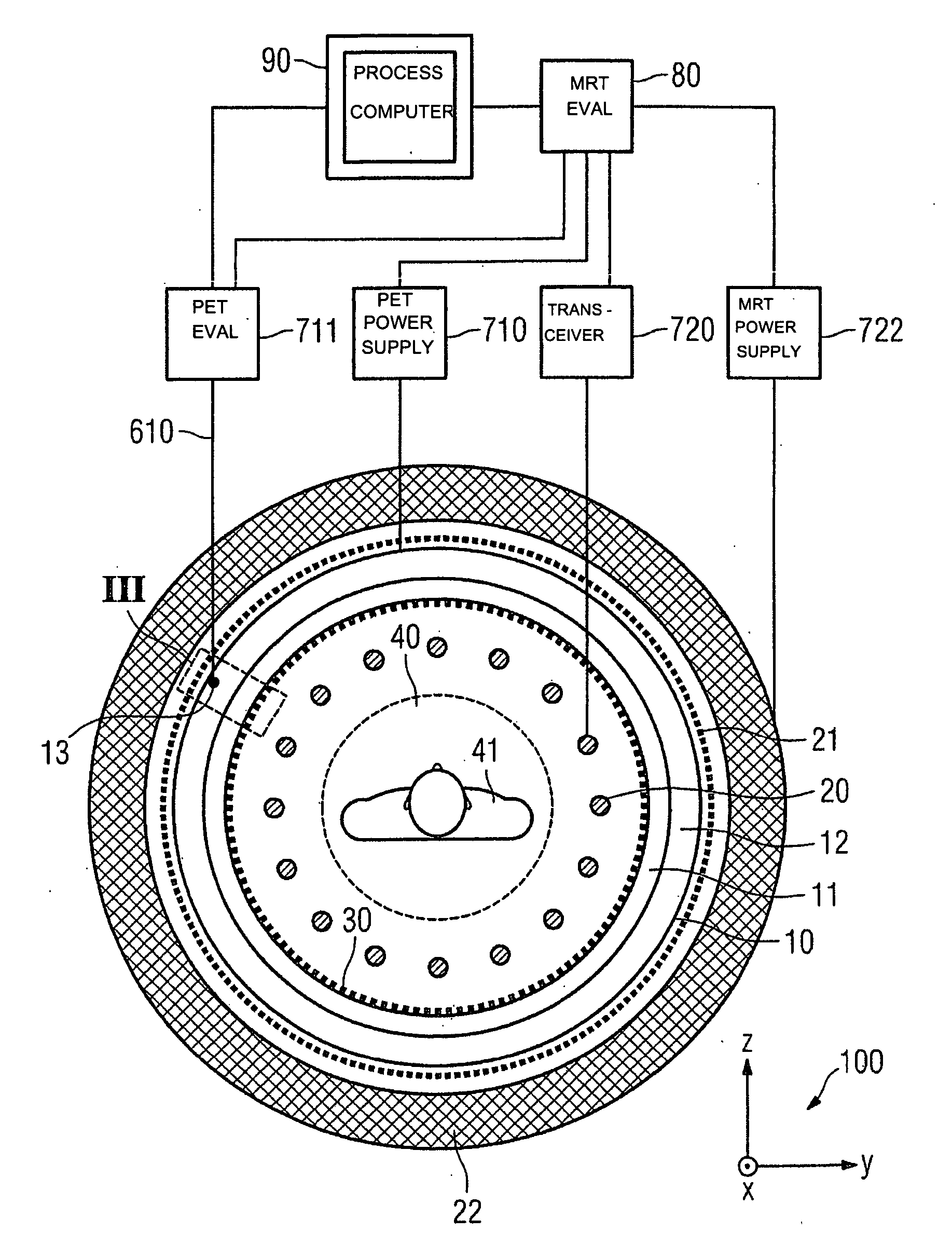
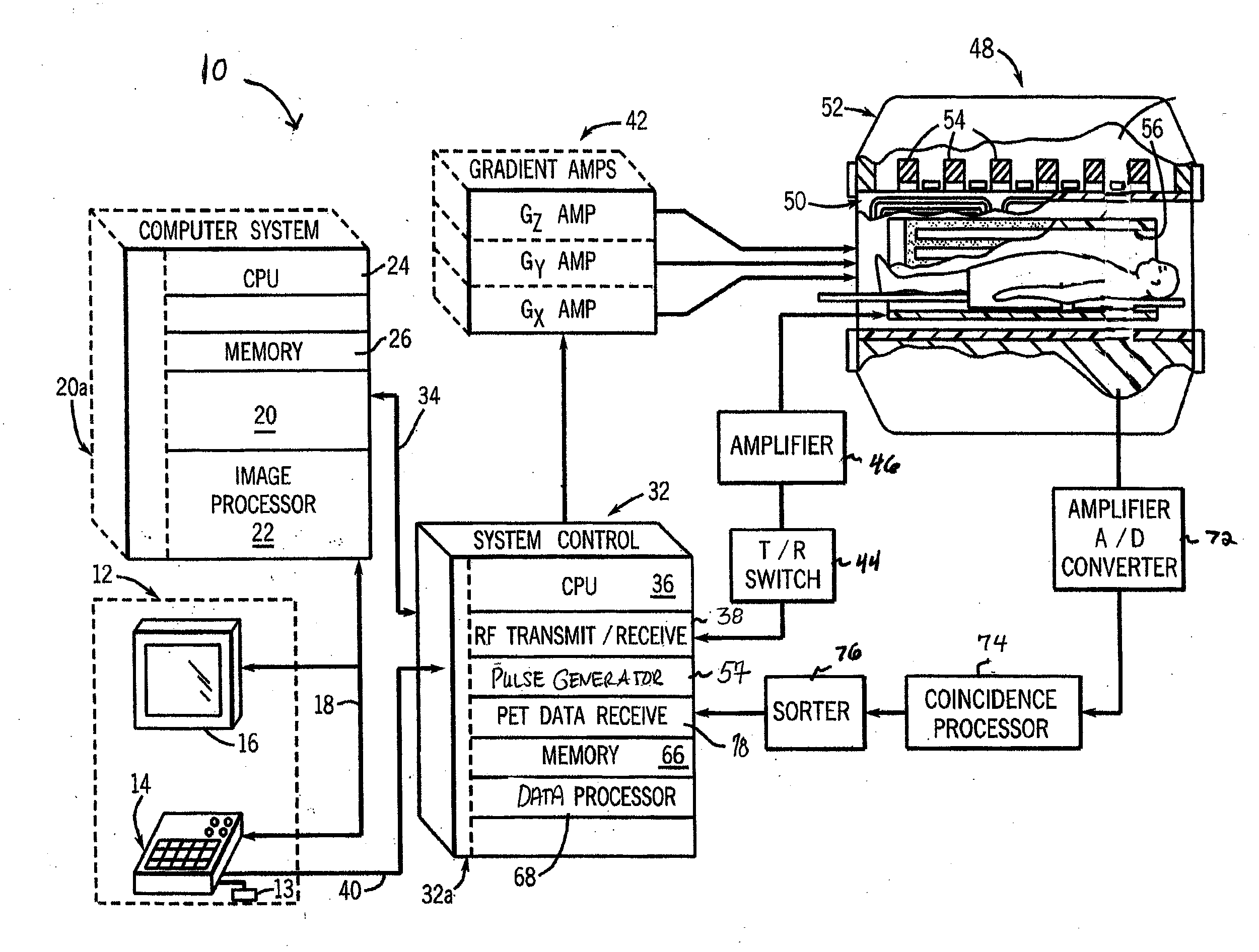
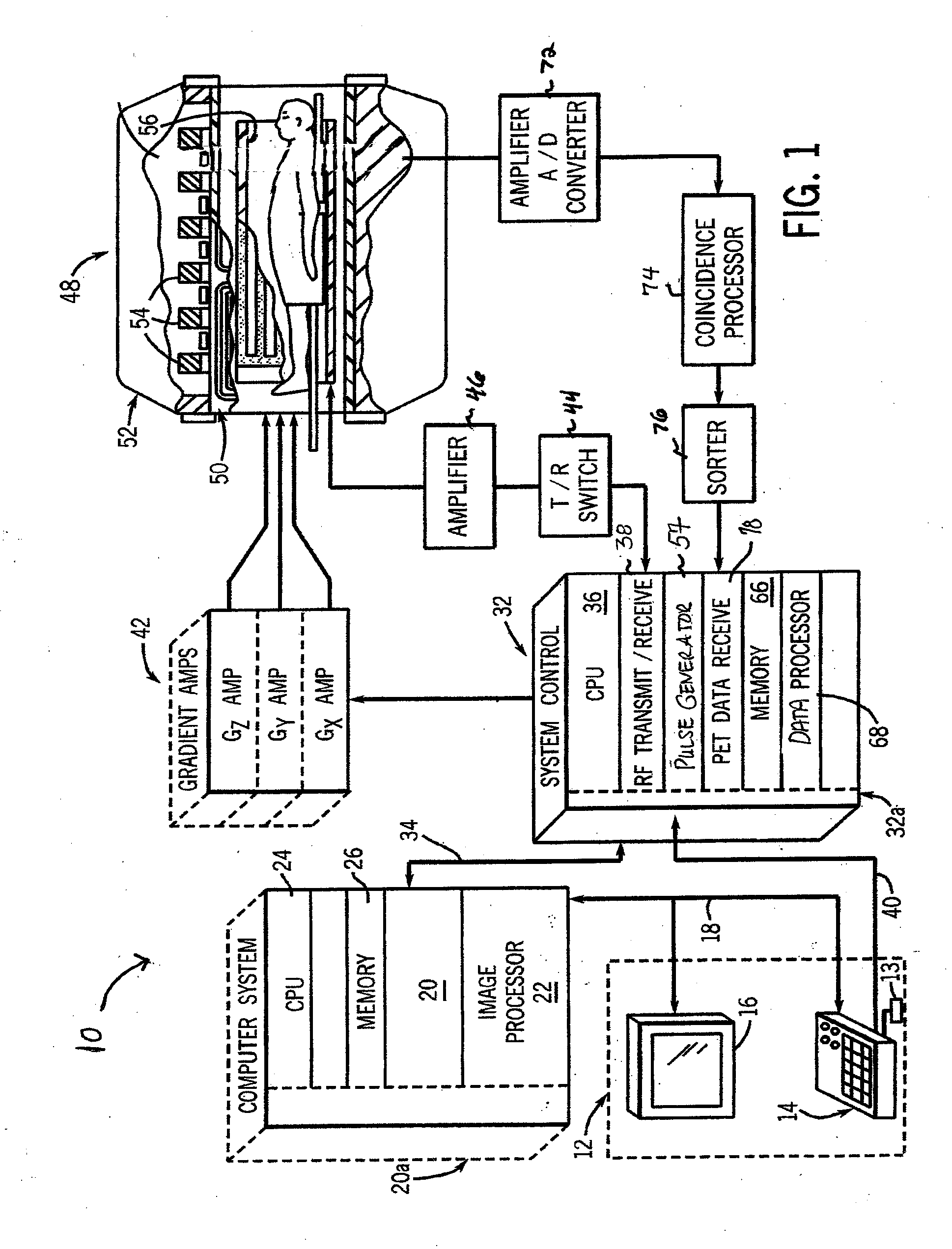
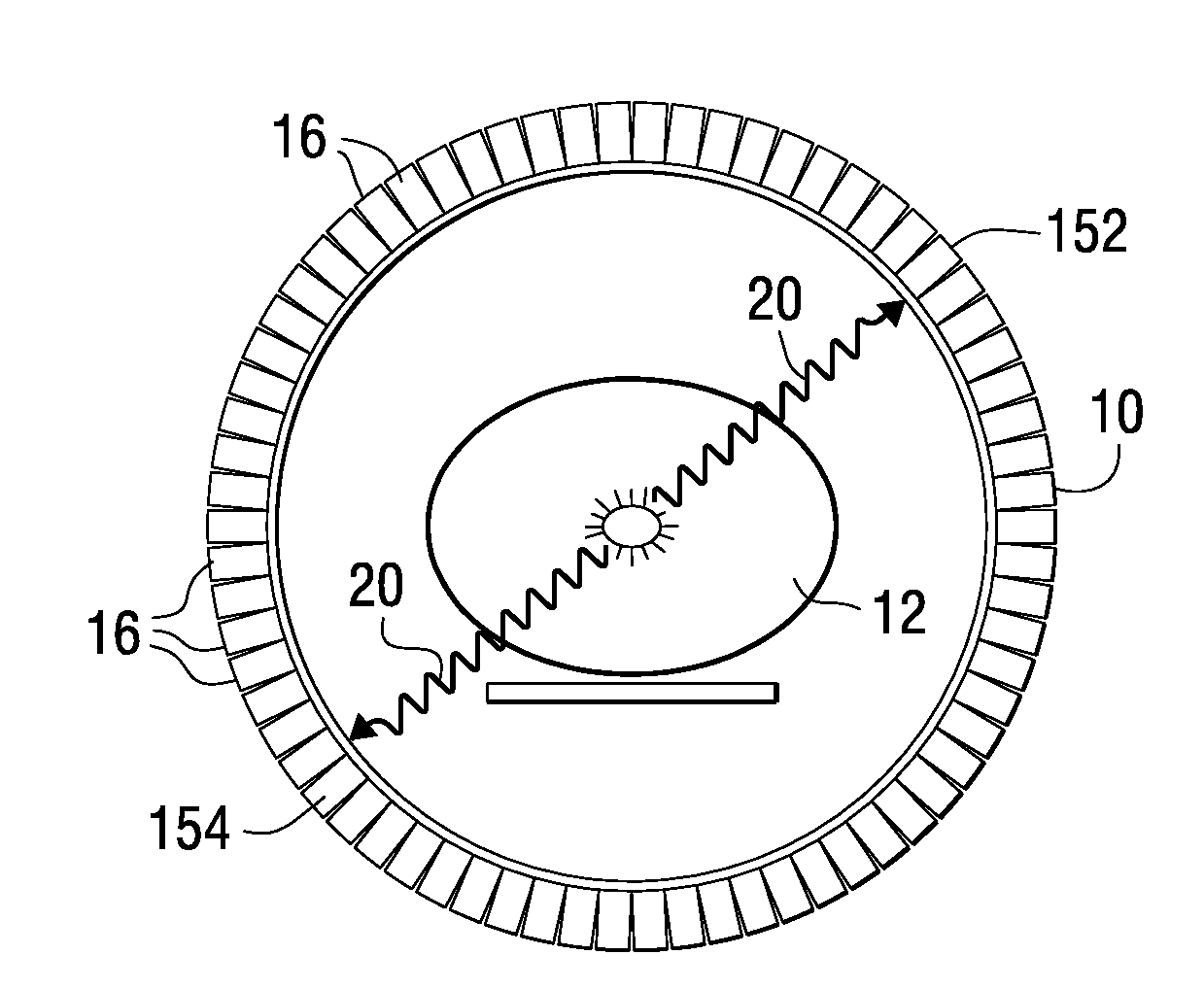
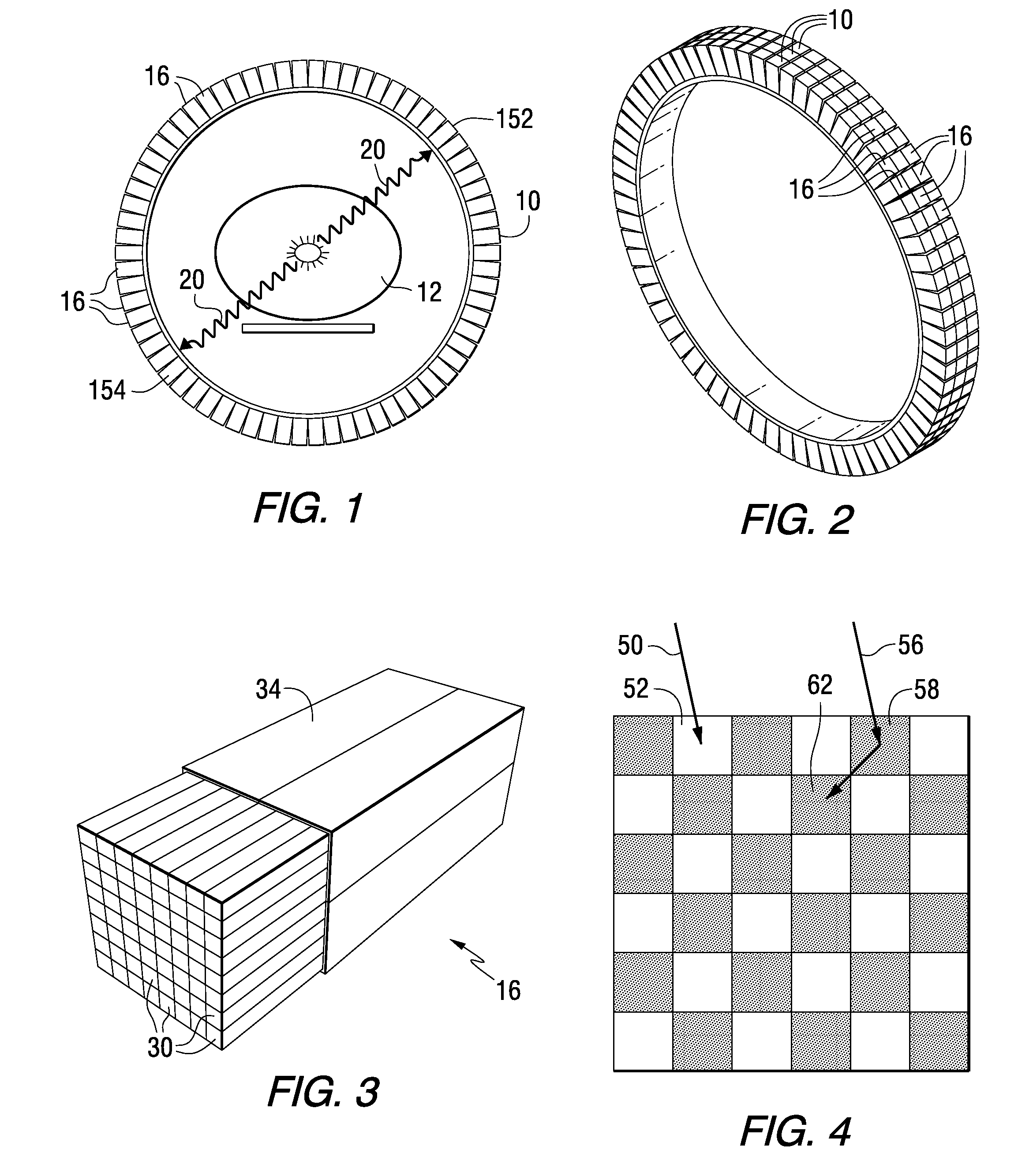
System and apparatus for detecting gamma rays in a pet/mri scanner
ActiveUS20080265887A1Material analysis by optical meansElectric/magnetic detectionPhotodetectorRadio frequency
A gamma ray detector ring for a combined positron emission tomography (PET) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system is integrated into a radio frequency (RF) coil assembly such that the detector ring is integrated with a RF shield. Each gamma ray detector in the detector ring includes a scintillator component that emits light when a gamma ray is detected and a photodetector component designed to be sensitive to the frequency of light produced by the scintillator. A RF shield may be integrated into a detector ring such that the RF shield is positioned between the scintillator and photodetector components of each detector, thereby saving valuable radial space within the imaging system. Multiple such detector rings may be located adjacent to one another to increase axial coverage and enable three-dimensional PET imaging techniques.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Nuclear imaging using three-dimensional gamma particle interaction detection
InactiveUS20050023474A1High resolutionReduce uncertaintySolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansDetector arrayPerformed Imaging
An improved method of, and apparatus for, nuclear imaging takes advantage of the ability to determine the depth of gamma ray / electron interaction within a semiconducting gamma ray detector to determine the (most highly probable) location of the first gamma ray / electron interaction within the detector. Lines of interaction constructed between opposing detector arrays, extending between the location of the first gamma ray / electron interaction in each detector associated with the coincident detection of gamma radiation, permits a positron-emitting object of interest to be imaged according to protocols known in the art, but with better spatial resolution than previously believed to have been known.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
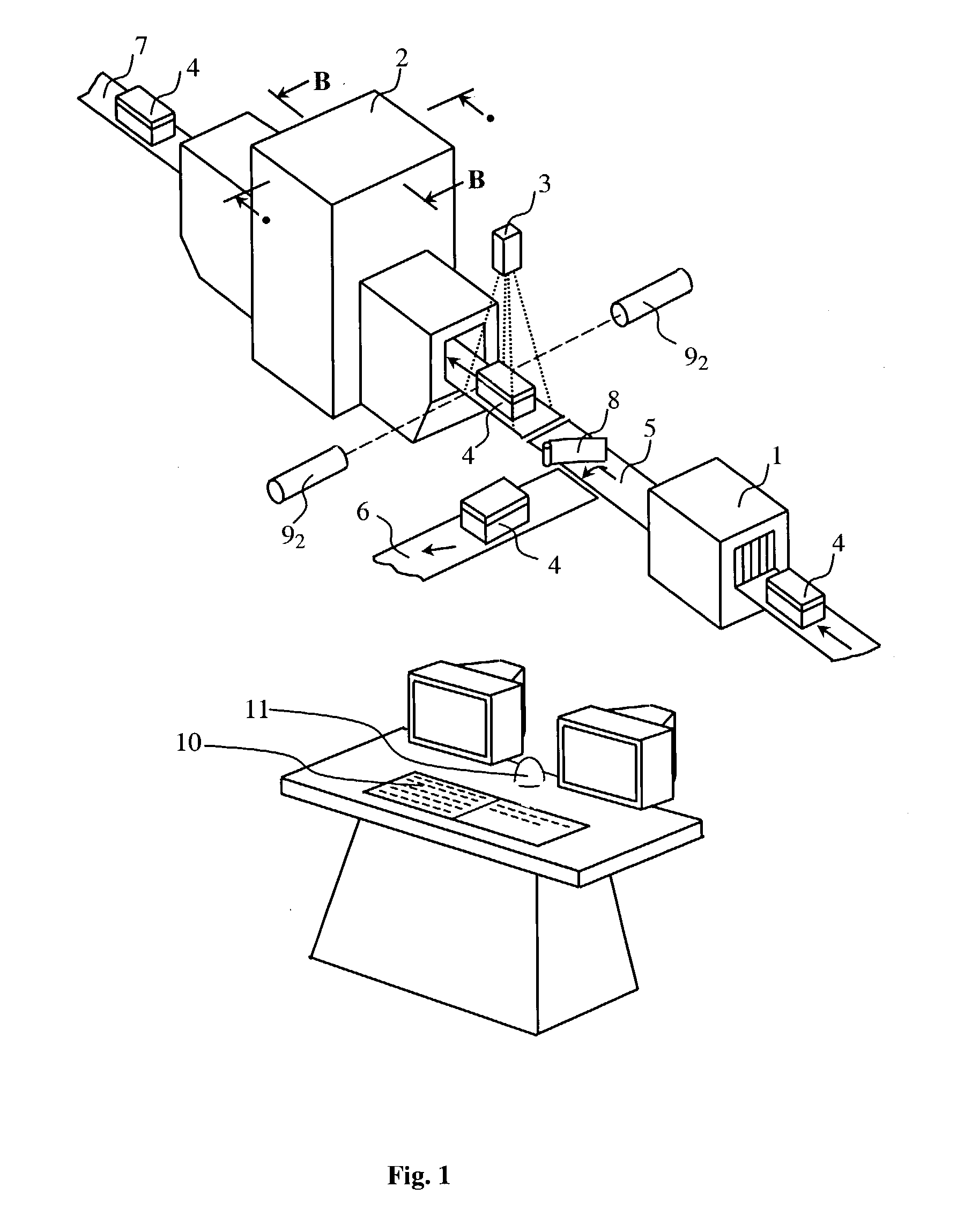
Method for detecting an explosive in an object under investigation
InactiveUS20030147484A1Increases radiation levelReduce riskConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsMaterial analysis by optical meansNeutron irradiationX-ray
A method for detecting an explosive in an object under investigation involves the initial X-ray irradiation of the object under investigation, e.g. a piece of luggage or mailing, and forming its X-ray images; using the X-ray images to detect areas with a high density of organic materials and identifying articles therein; determining the location, dimensions and supposed mass of an unidentified article; determining and forming a directional pattern of the neutron radiator corresponding to the dimensions of the unidentified article. The method further includes subsequent thermal neutron irradiation of the area with the unidentified article; recording gamma-ray quanta having the energy of 10.8 MeV and cascade gamma-ray quanta with energies of 5.534 and 5.266 MeV by at least two gamma-ray detectors; counting of simultaneously recorded pairs of cascade gamma-ray quanta; determination of the overall gamma-ray intensity, taking into account weight factors in readings of the detectors; determination of the threshold value for the overall gamma-ray intensity basing on the supposed mass of explosive being detected; and making a decision in the event the threshold value of overall gamma-ray intensity is exceeded. When checking small-size objects, the neutron irradiation step is preceded by replacing the ambient air by a gaseous medium not containing nitrogen.
Owner:SCI & TECHN CENT RATEC
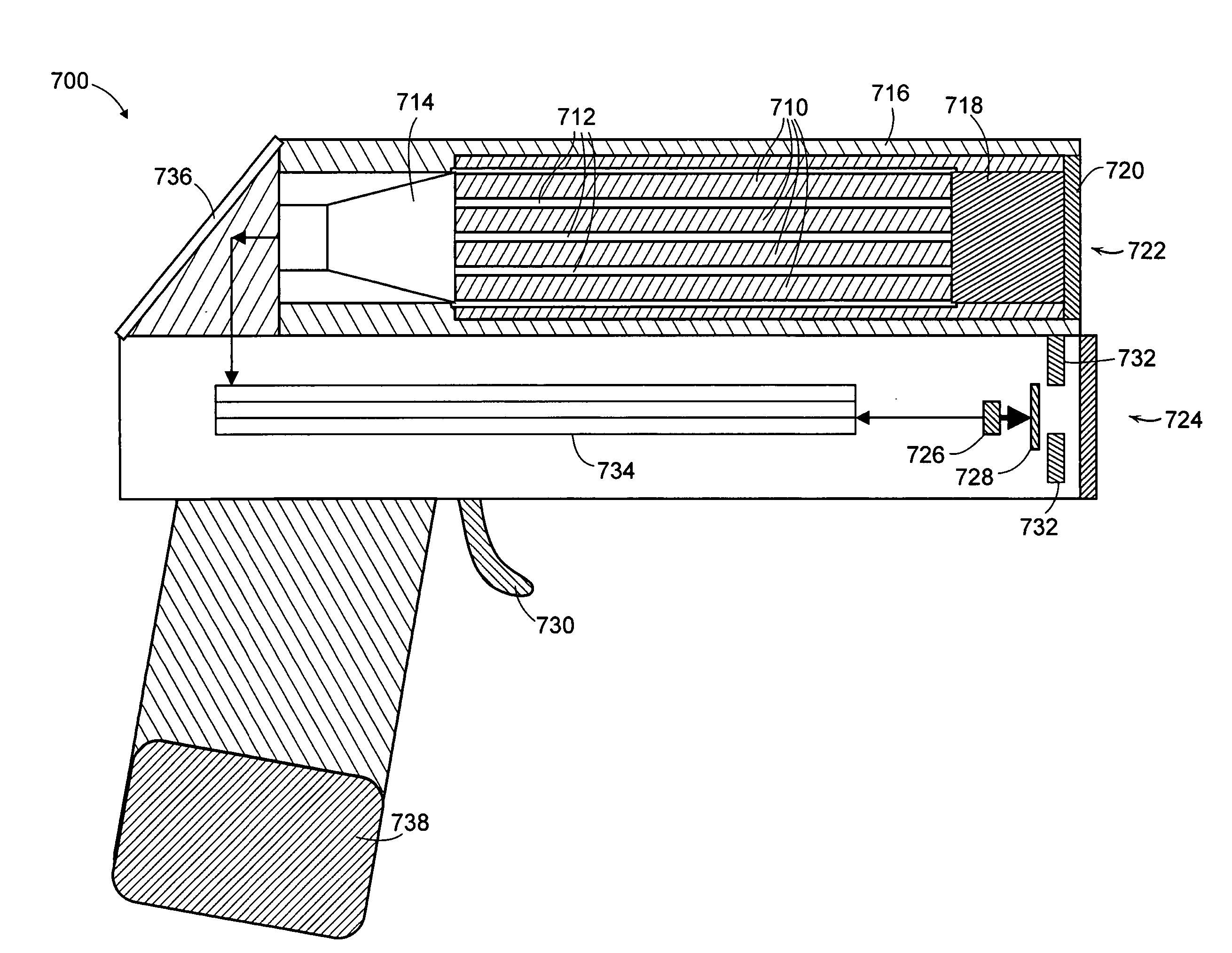
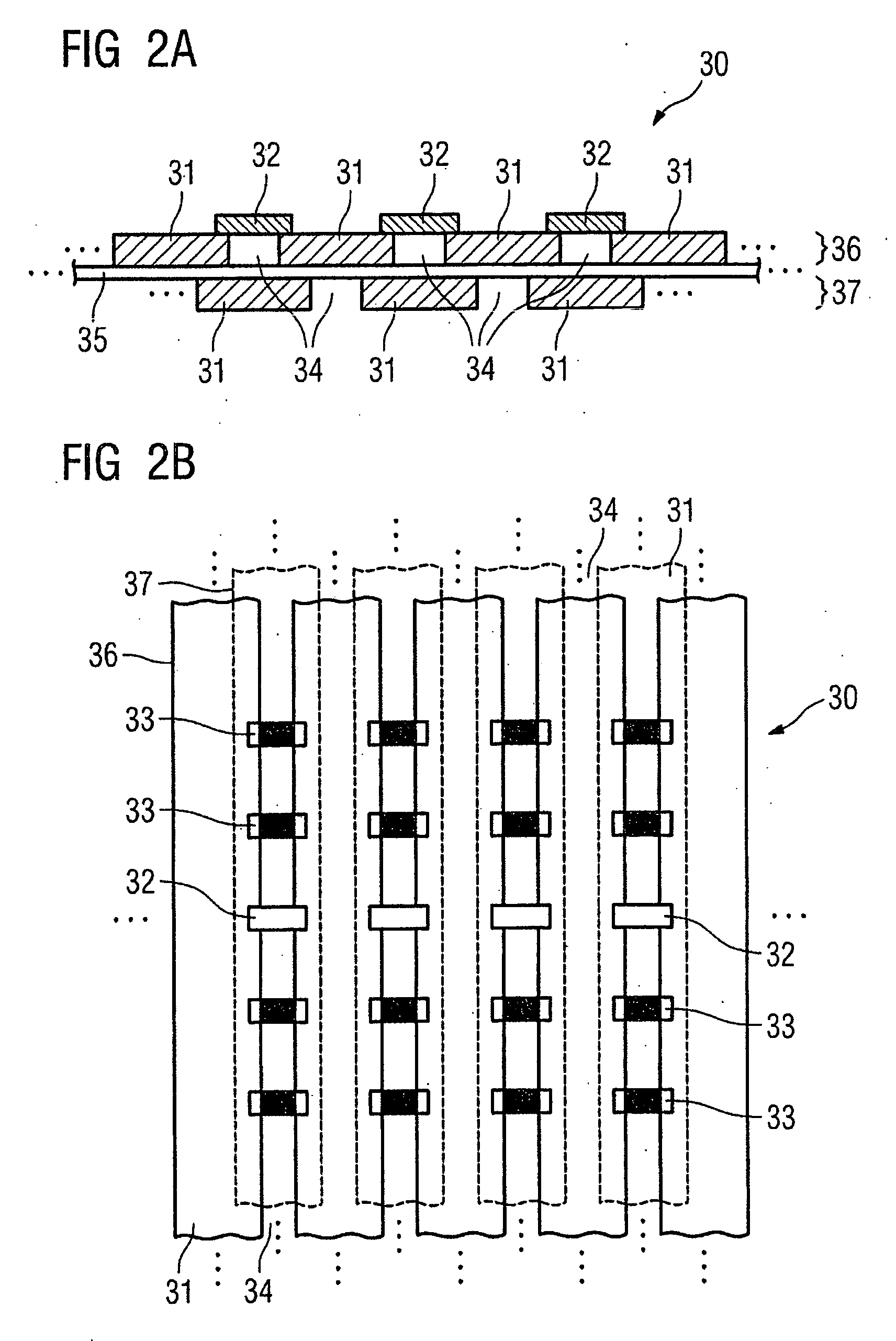
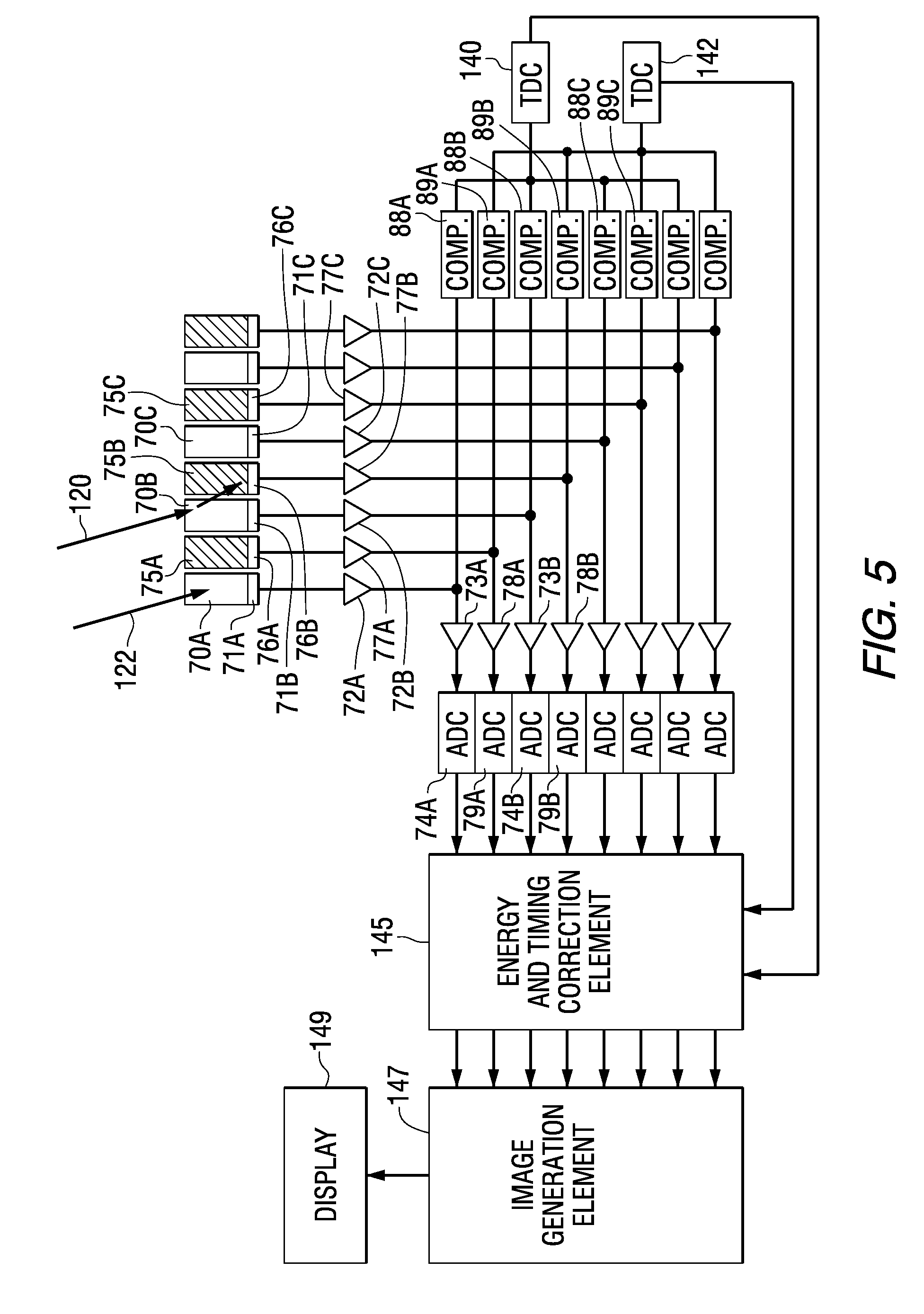
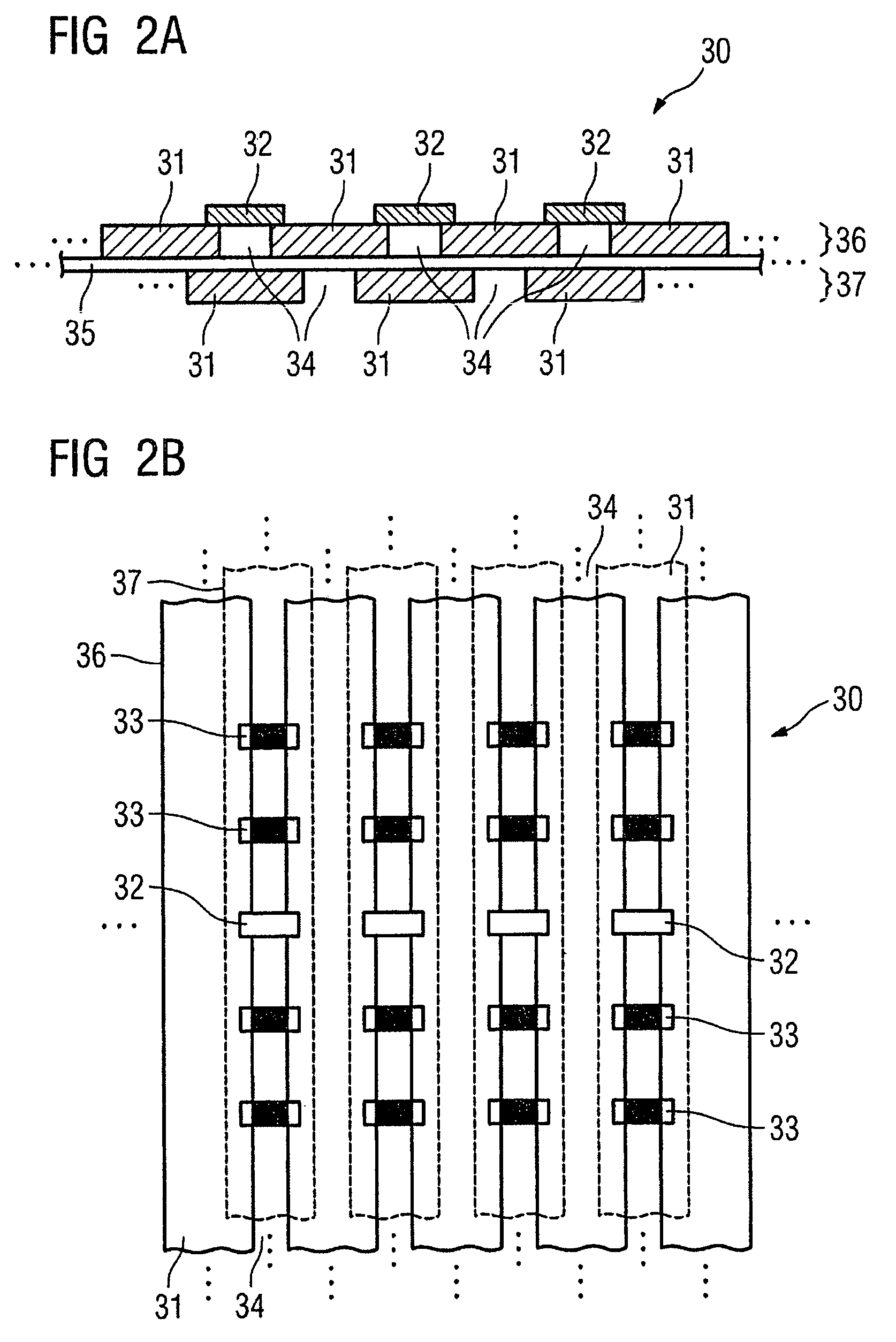
Multiplexing readout scheme for a gamma ray detector
A method for producing a PET image of a tissue using a PET scanner, the scanner comprising a plurality of scintillation crystals (70X / 75X) and a plurality of detectors (71X / 76X). The method comprises forming a first crystal group (160X) including a first subset of the plurality of crystals; forming a second crystal group (164X) including a second subset of the plurality of crystals, wherein crystals comprising the first crystal group (160X) are different from crystals comprising the second crystal group (164X); converting a first beam (120) striking one or more crystals of the first crystal group (70X / 160X) to a first electrical signal (94); converting a second beam striking one or more crystals of the second crystal group (75X / 164X) to a second electrical signal (98), wherein the second beam is scattered from the first beam; determining one or both of a first and a second timing relationship, wherein the first timing relationship (Δt2) is a time interval between a value of the first electrical signal (94) and a time reference (t1), and the second timing relationship (Δt3) is a time interval between a value of the second electrical signal (98) and the time reference (t1); correcting the second electrical signal (98) to produce a corrected second electrical signal using a correction factor derived from at least one of the first and the second timing relationships to compensate for energy in the second signal scattered from the first signal; and creating an image of the tissue (12) using the corrected second electrical signal.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
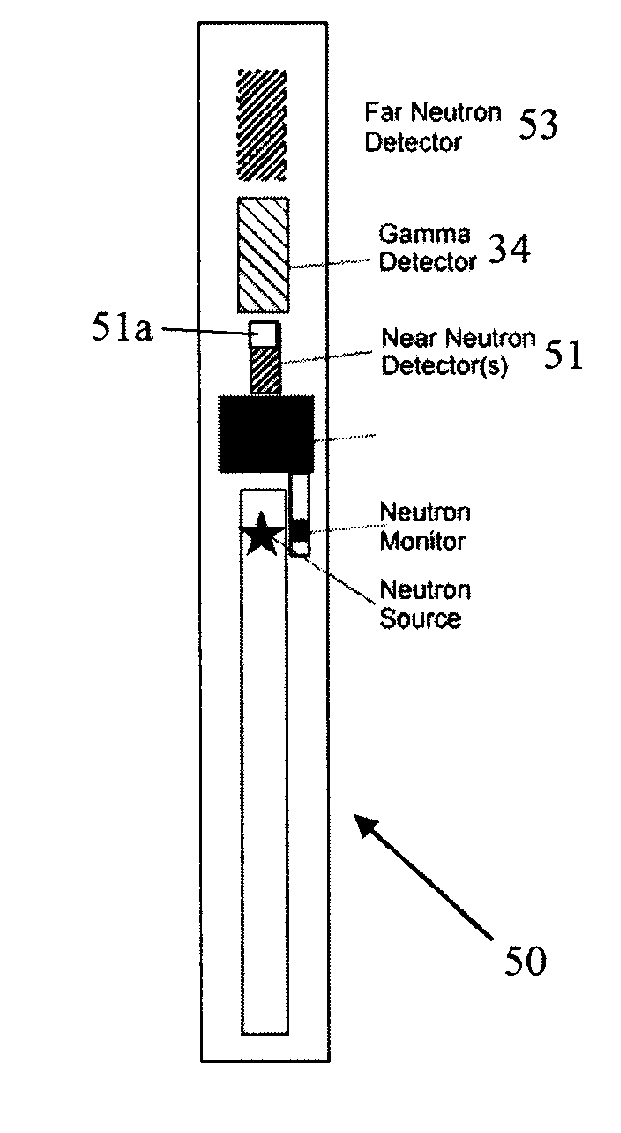
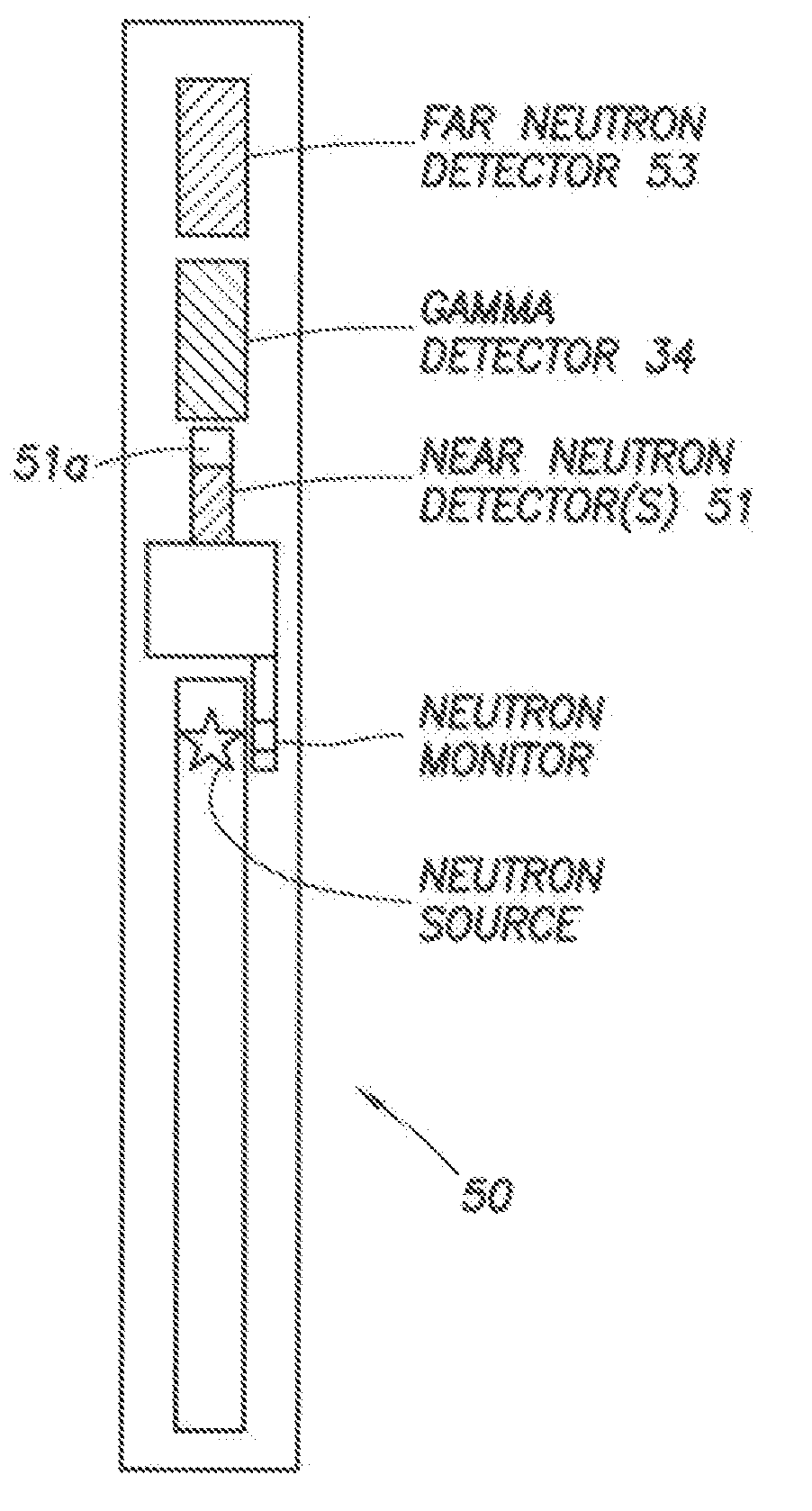
Sigma/porosity tools with neutron monitors
A tool for formation logging includes a support configured for movement in a borehole; a neutron source disposed on the support; a neutron monitor disposed on the support and configured to monitor an output of the neutron source; a gamma-ray detector disposed on the support and spaced apart from the neutron source; and a shielding material disposed between the gamma-ray detector and the neutron source.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
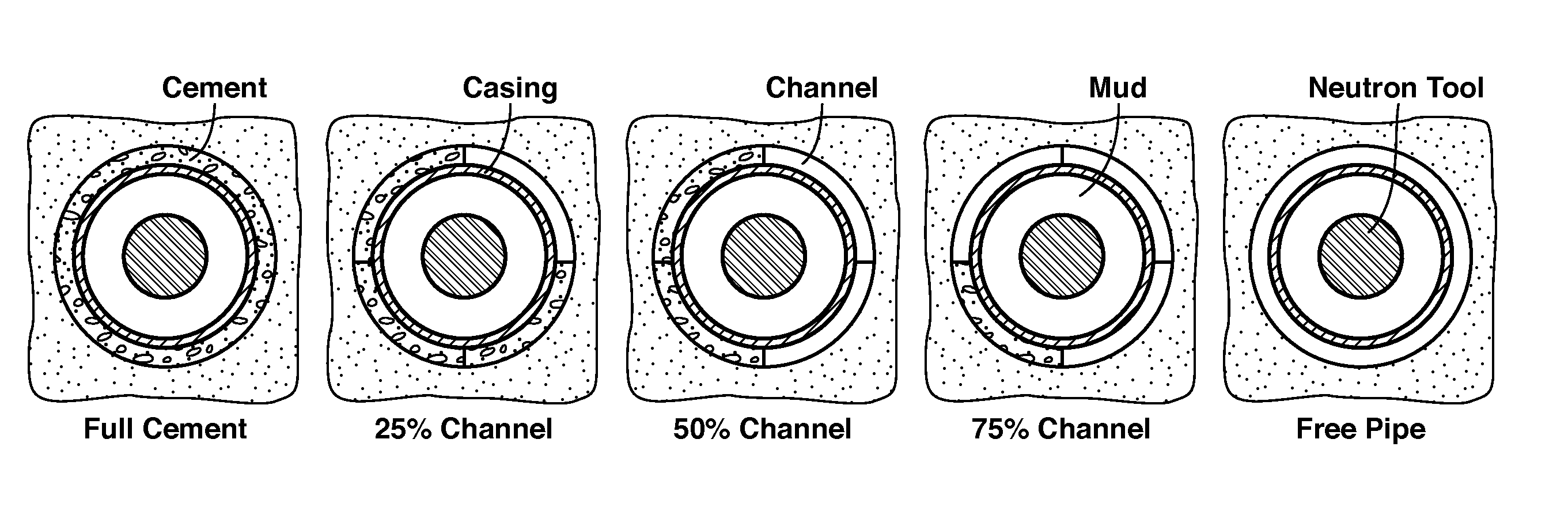
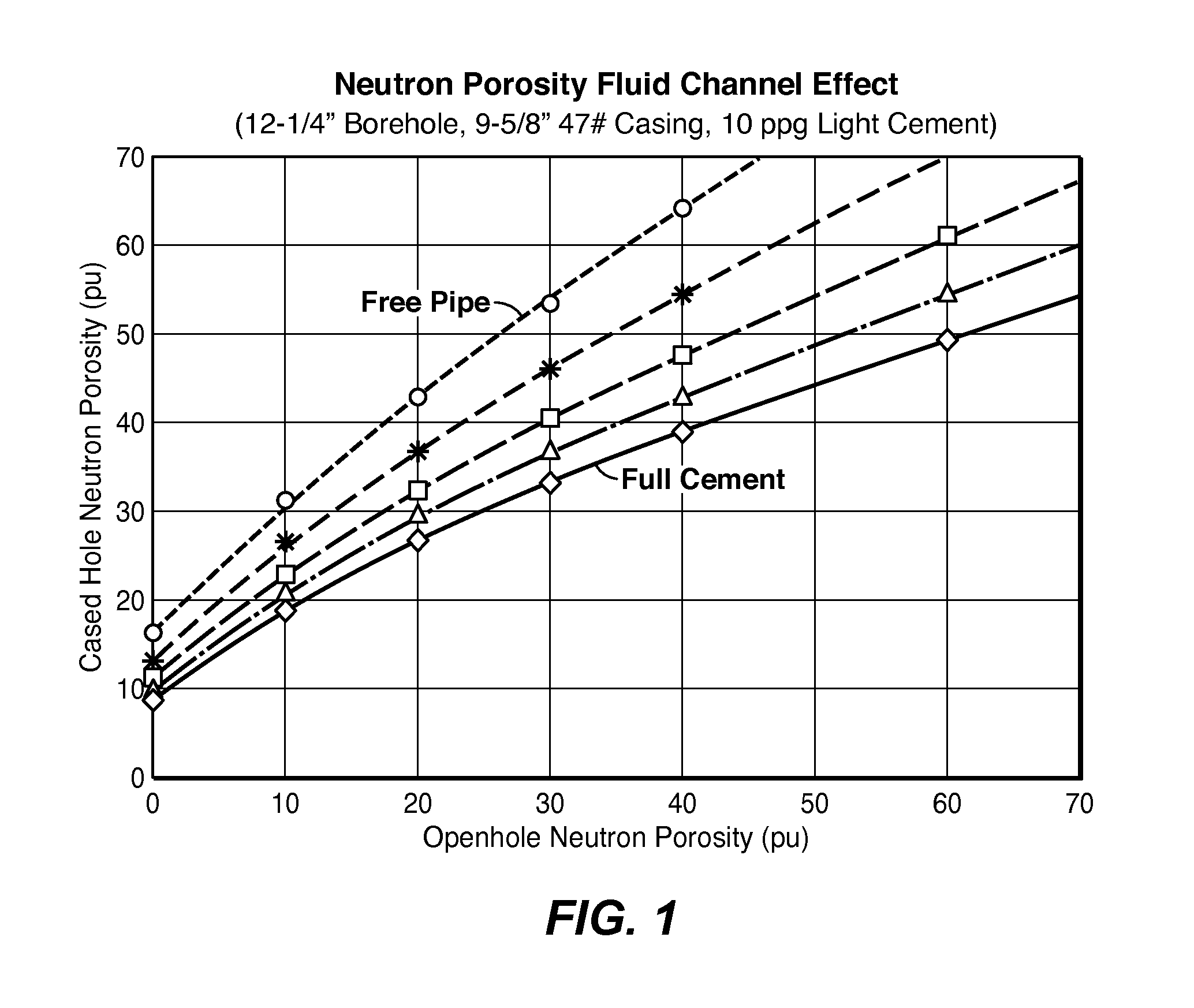
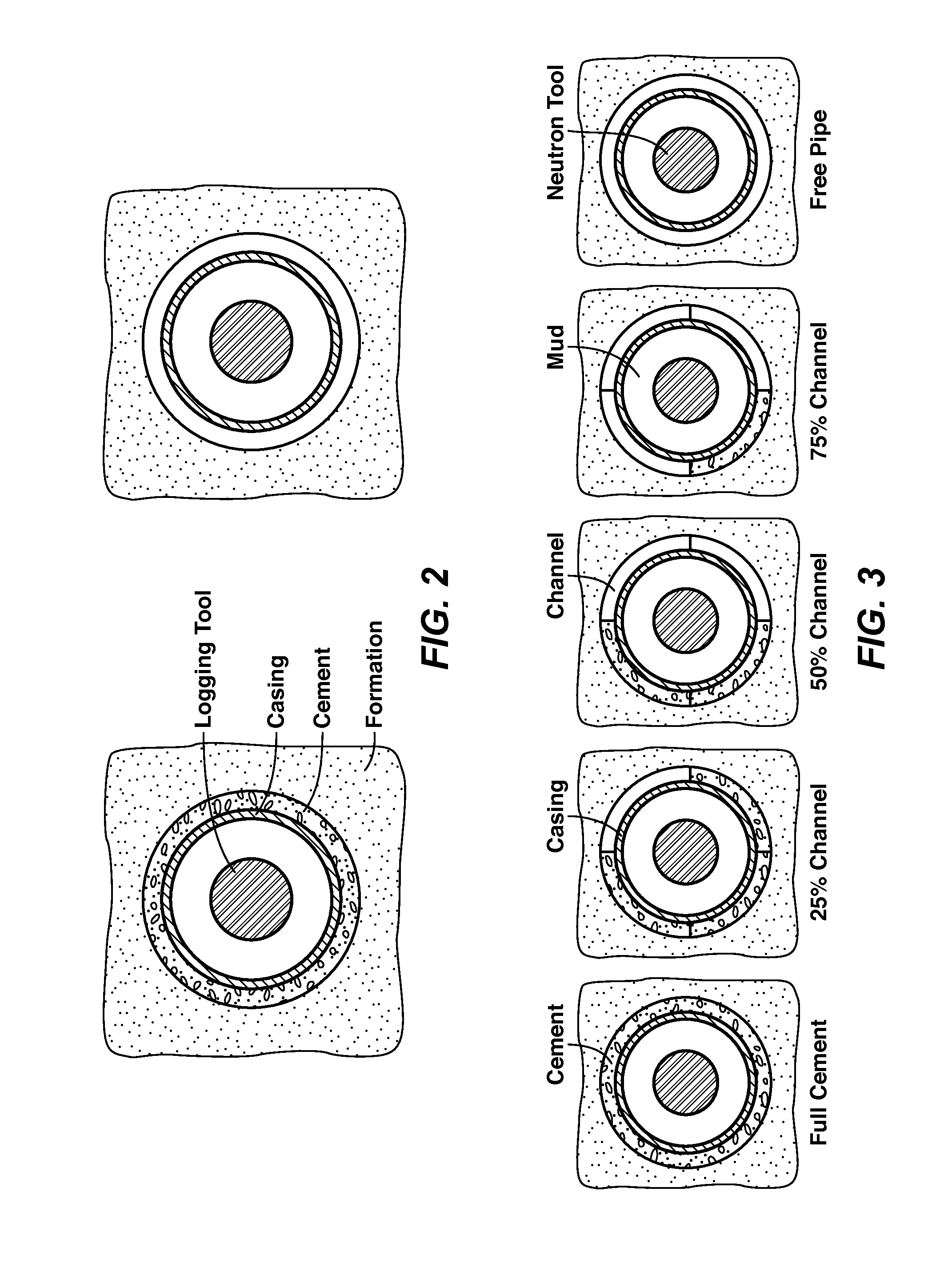
Method For Cement Evaluation With Neutron Logs
ActiveUS20130345983A1Effective approachEasy to explainElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingConstructionsNeutron porosityMulti parameter
Method for evaluating cement integrity in a cased well environment using a logging tool that has a neutron source and one or more neutron or gamma ray detectors. Neutron porosity logs are obtained from the well before (42) and after (41) casing. This log data along with well dimensions and material composition parameters are the input quantities to a multi-parameter database (43) that is constructed by computer modeling or laboratory experiments to relate volume fraction for fluid filled channels in the cement sheath to the input quantities. The channel volume fraction (45) corresponding to the input quantities is identified or interpolated (44) from the multi-parameter database.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
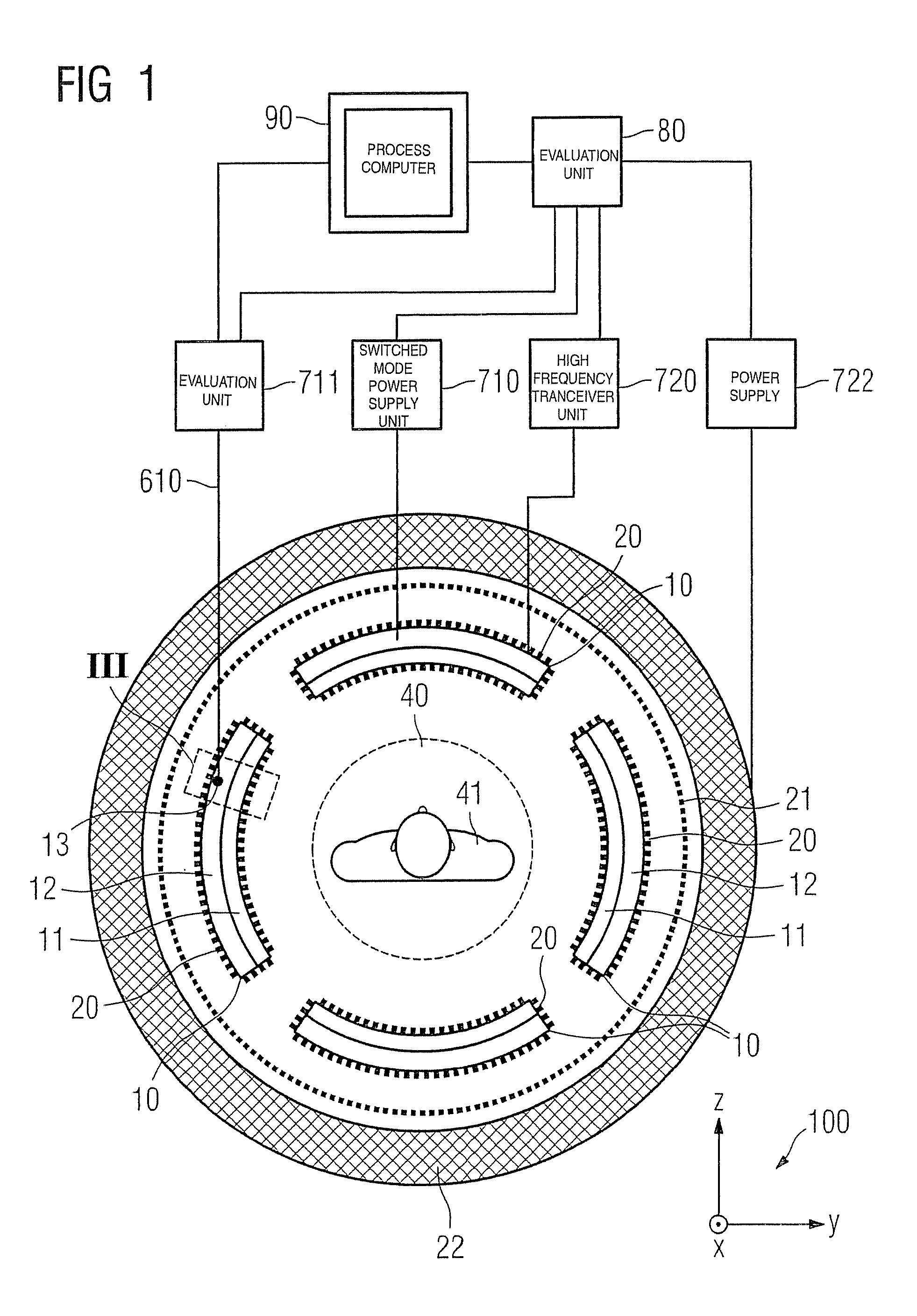
Combined positron emission tomography and magnetic resonance tomography unit
InactiveUS7522952B2Save spaceShorten the timeMagnetic measurementsMaterial analysis by optical meansResonanceTomography
A combined PET / MRI tomography unit has a PET unit with a unit part assigned to the examination space, and a first evaluation unit for evaluating the PET electric signals. The unit part has a gamma ray detector. The combined unit has an MRI unit and a second evaluation unit for evaluating MRI signals. The MRI unit has a high frequency antenna as well as a gradient coil system, the high frequency antenna device being arranged nearer to the examination space than the gradient coil system, as well as a high frequency shield arranged between the gradient coil system and the high frequency antenna device. The PET unit part is arranged between the high frequency shield and the high frequency antenna device. A shielding cover for the high frequency antenna device faces the high frequency antenna device. The shielding cover is opaque to high frequency radiation.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Combined positron emission tomography and magnetic resonance tomography unit
InactiveUS20060250133A1Reduce power lossGood delayMagnetic measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionElectrical conductorDevice form
A positron emission tomography unit (PET), having a unit part assigned to an examination space and a first evaluation unit, is combined with a magnetic resonance tomography unit (MRT). The unit part of the PRT includes at least two gamma ray detector units with in each case an assigned electronics unit. The MRT includes a second evaluation unit, a gradient coil system and a high frequency antenna device formed as a stripline antenna device having at least two conductors. The high frequency antenna device is arranged nearer to the examination space than the gradient coil system with a high frequency shield between the gradient coil system and the high frequency antenna device. Each conductor of the stripline antenna device respectively includes a gamma ray detector unit with an assigned electronics unit. The conductors of the stripline antenna device are configured for the respective gamma ray detector units and their assigned electronics units as shielding covers that are caused by the high frequency antenna device and are opaque to high frequency radiation. An examination object in the examination space can be imaged by the combined positron emission tomography and magnetic resonance tomography unit.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
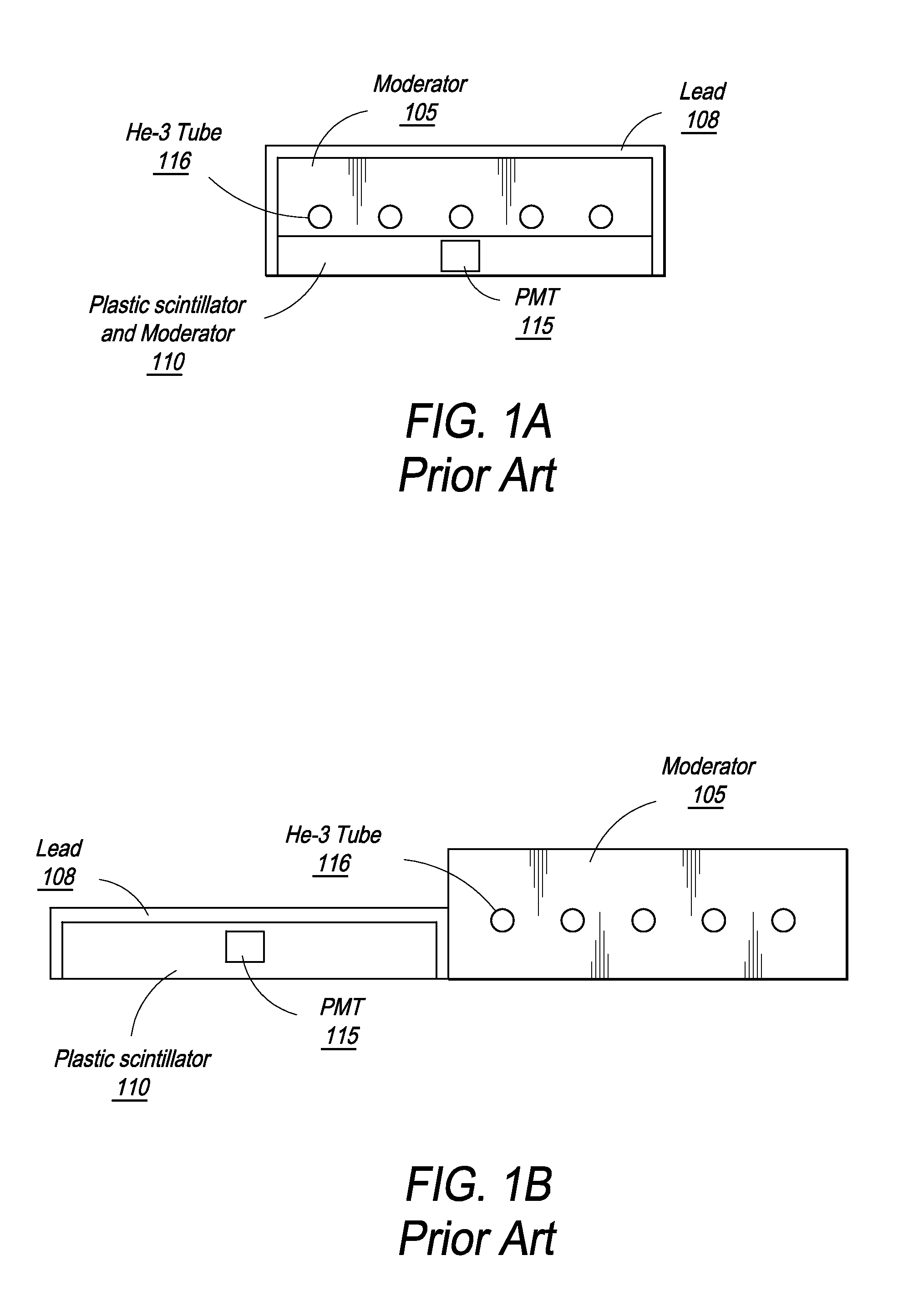
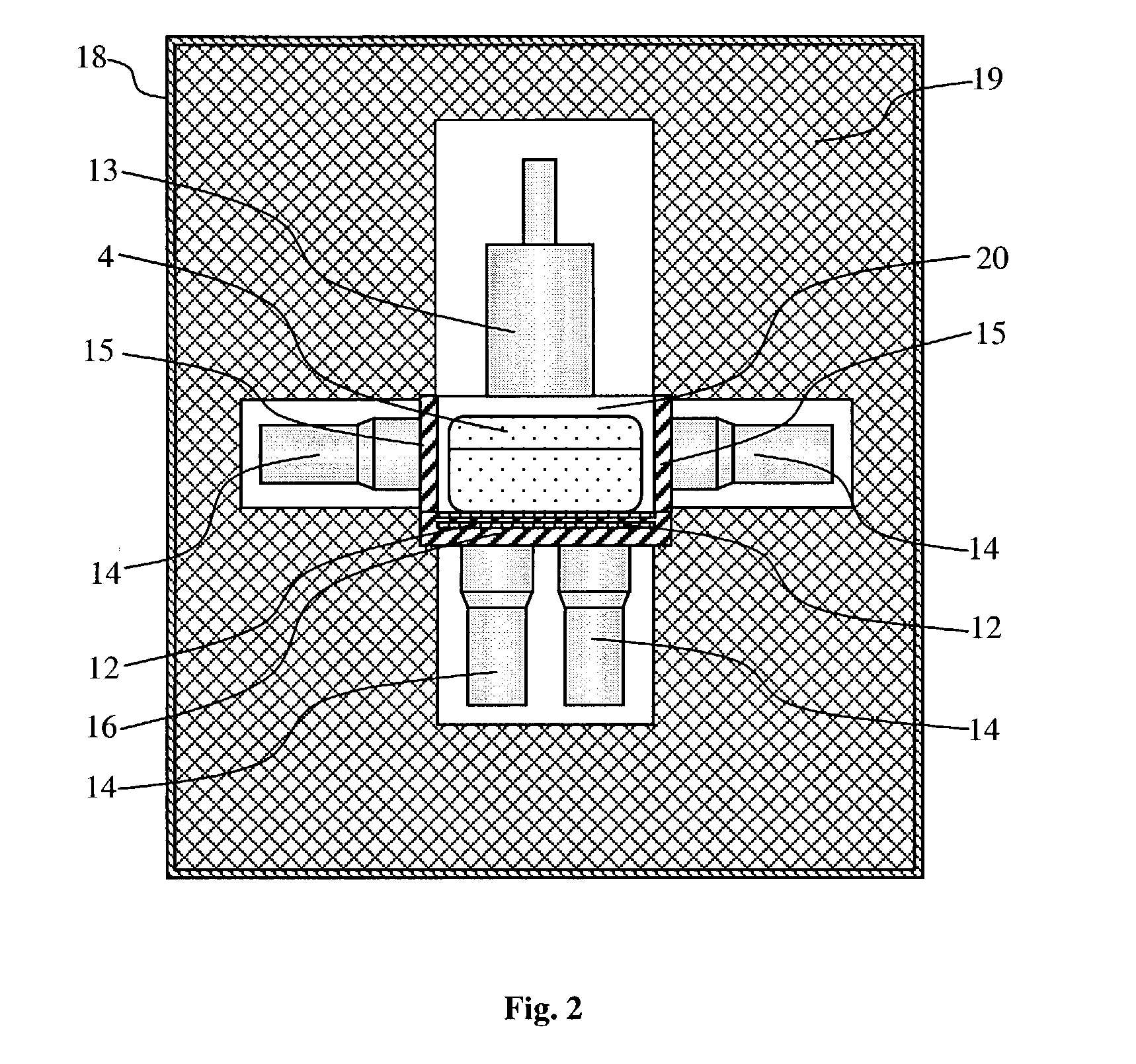
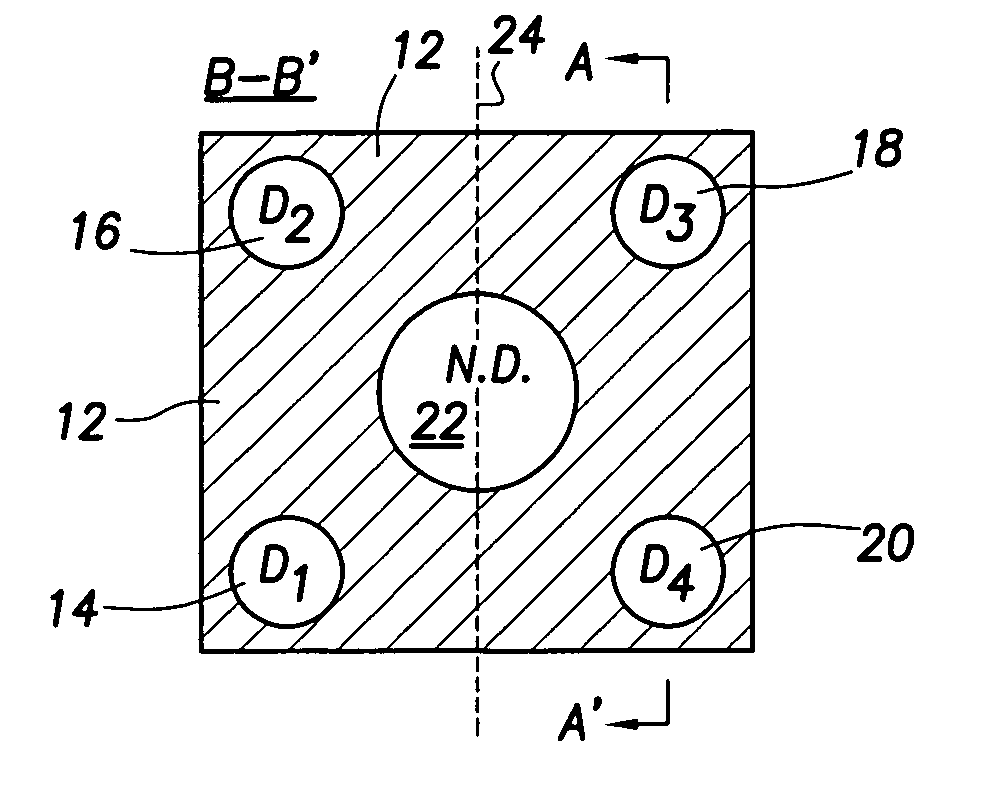
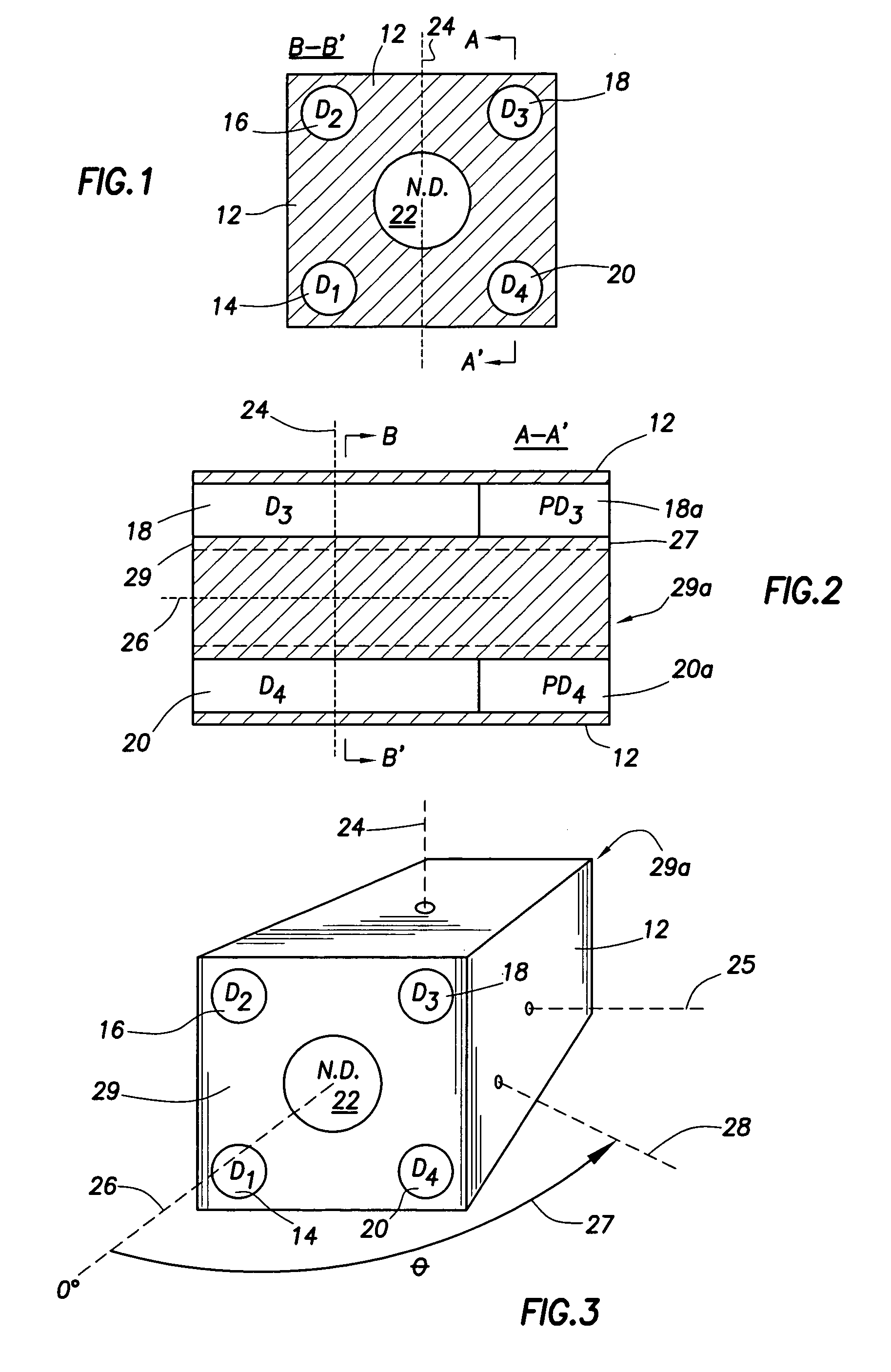
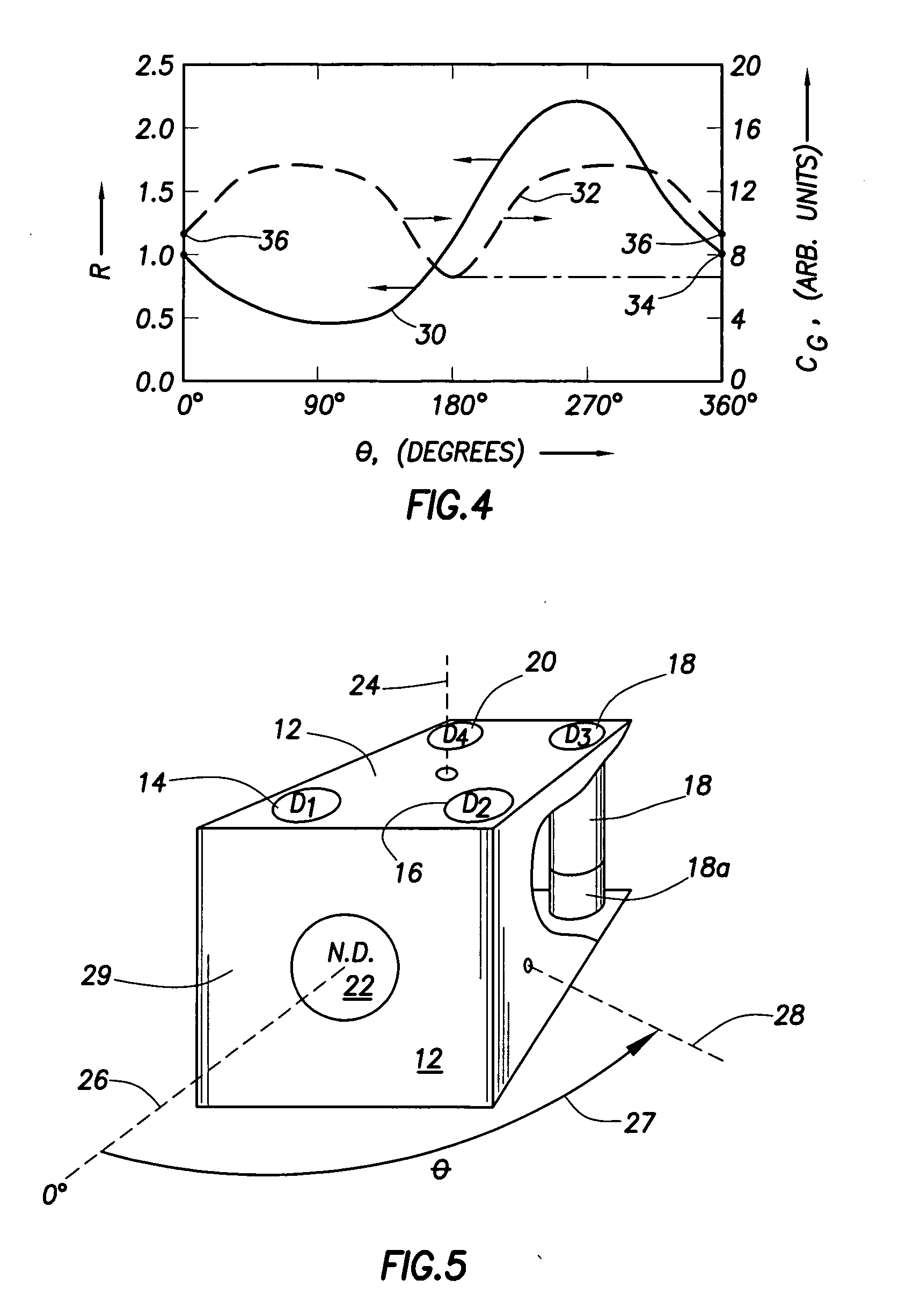
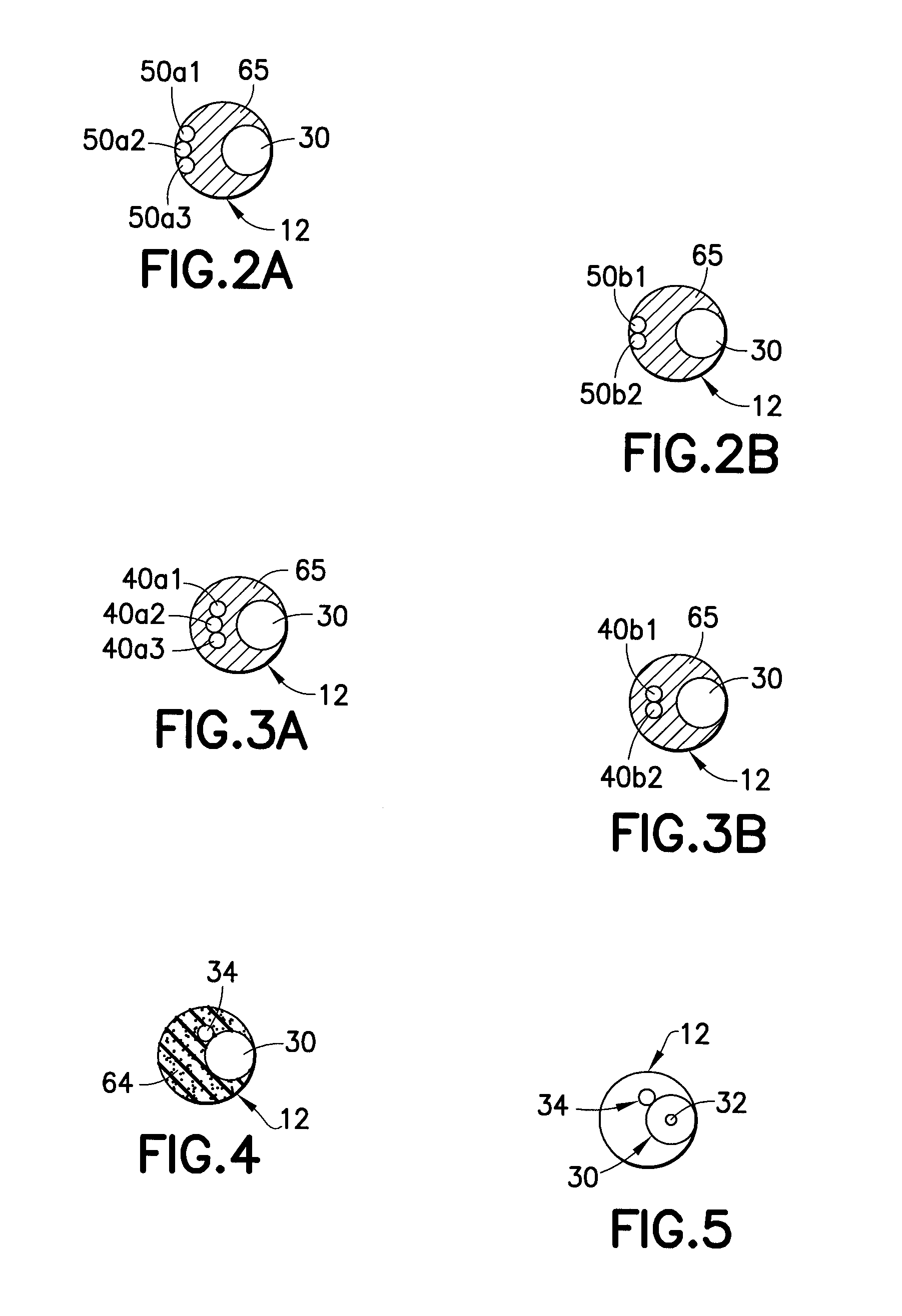
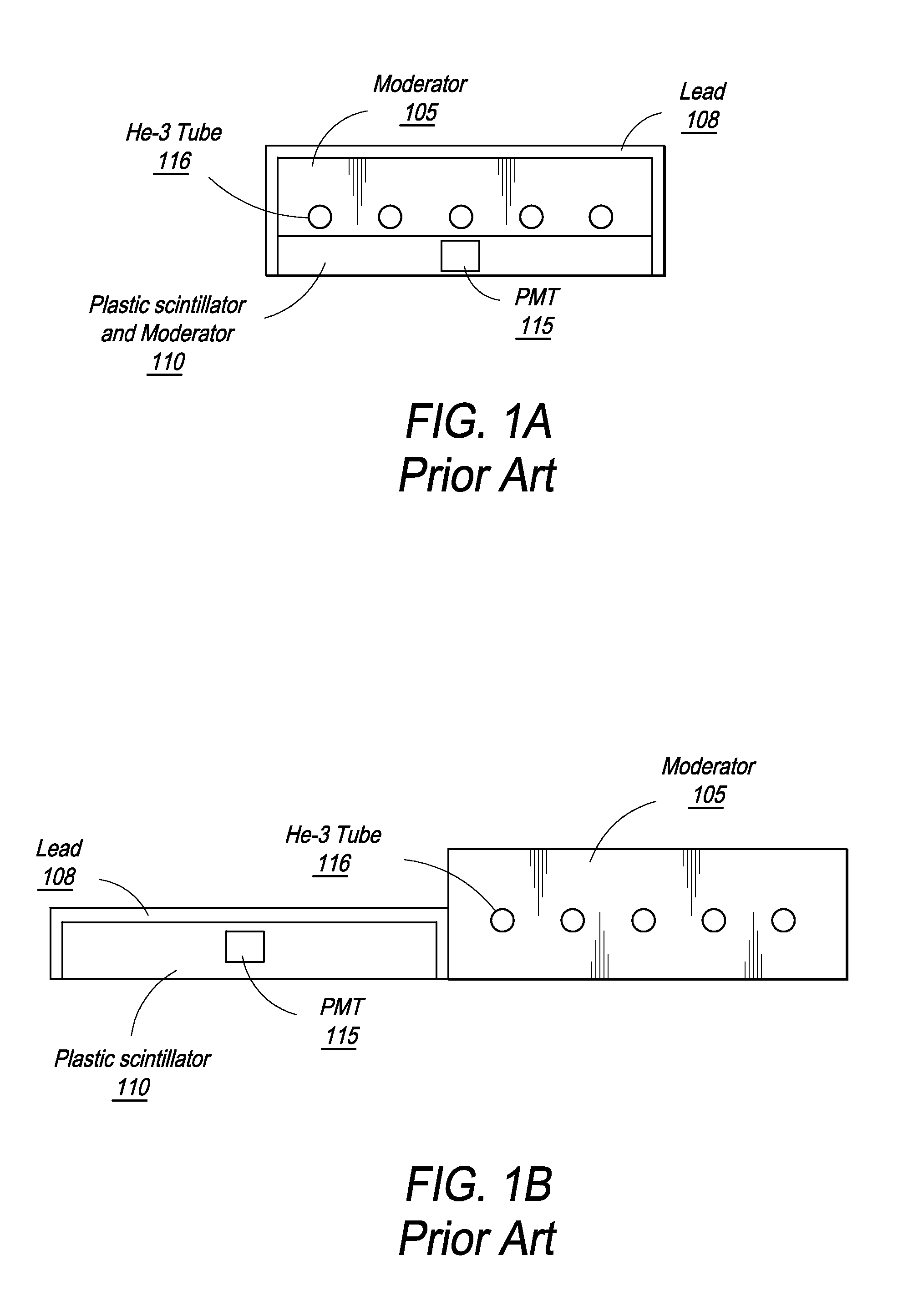
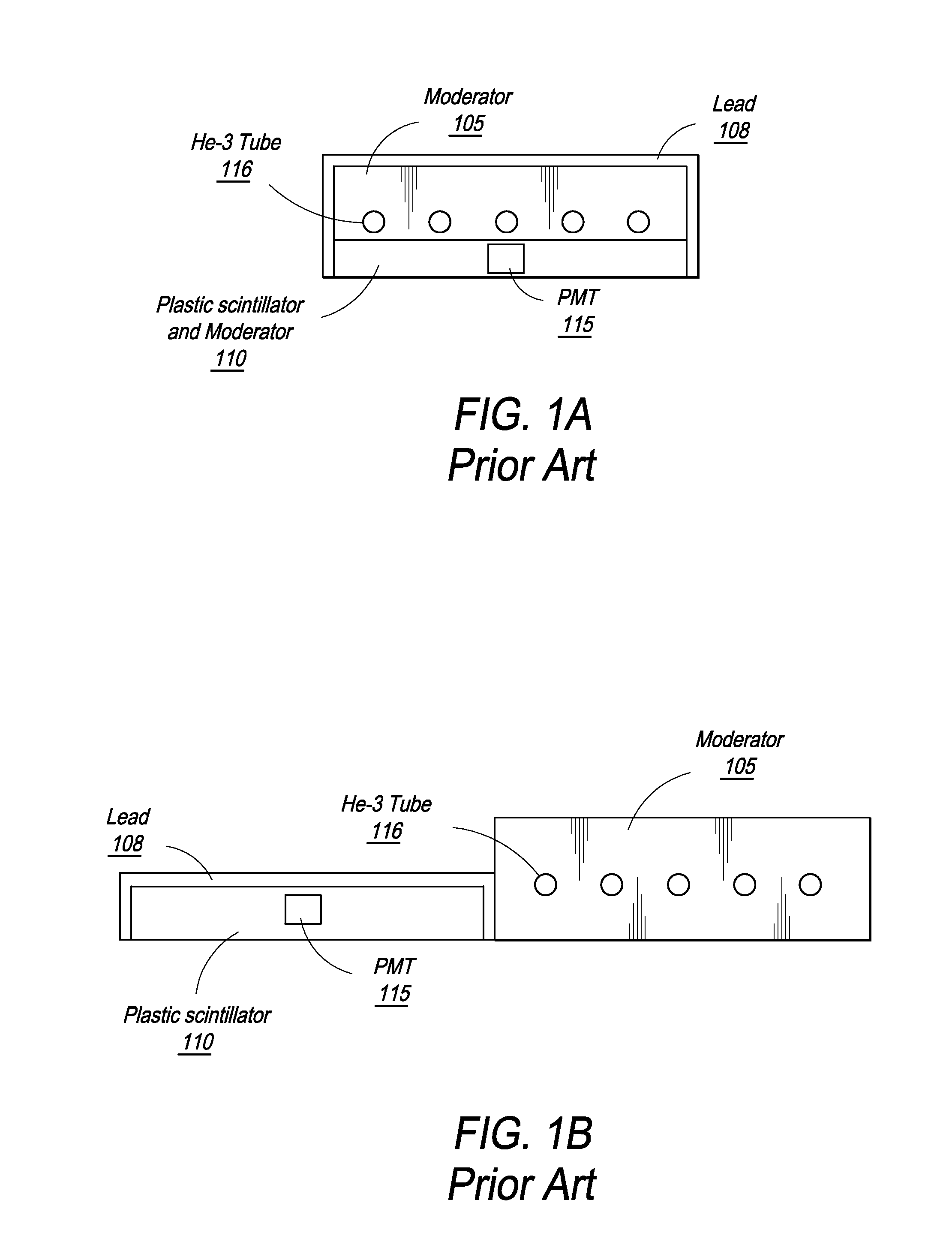
Neutron/gamma ray survey instrument with directional gamma ray sensitivity
ActiveUS20050121618A1High detection sensitivitySufficient thermalizationMaterial analysis by optical meansPhotometry using electric radiation detectorsSurvey instrumentMeasuring instrument
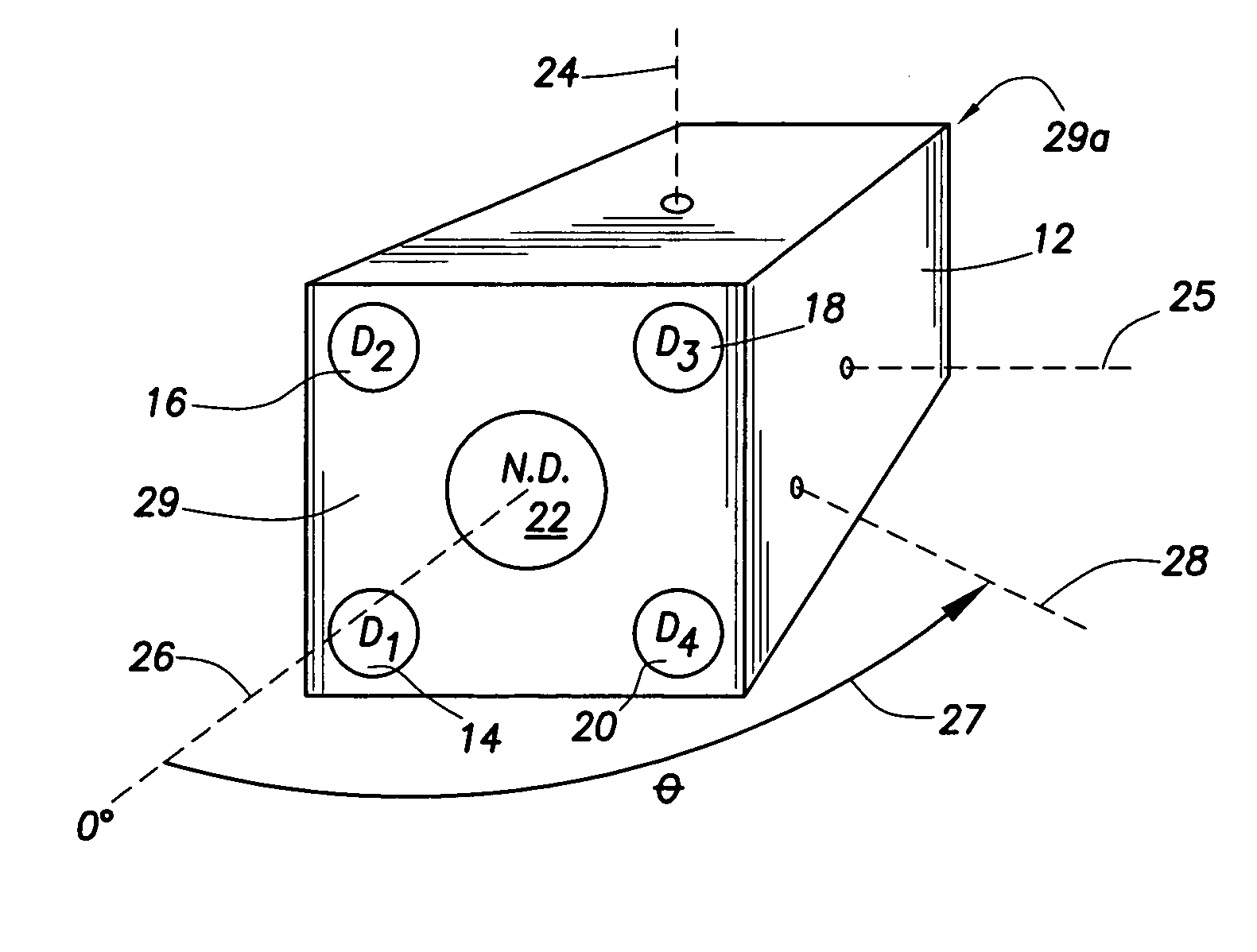
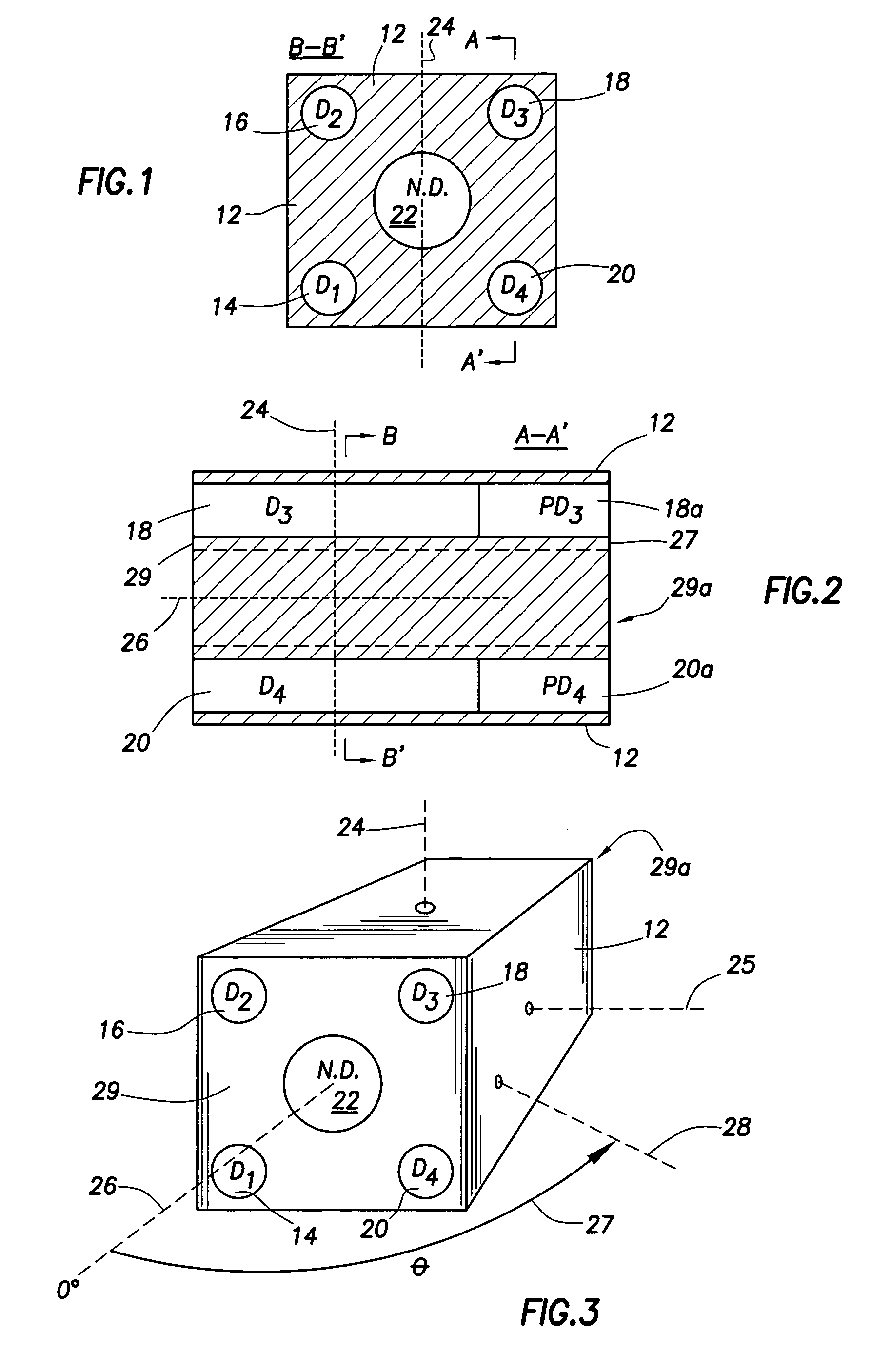
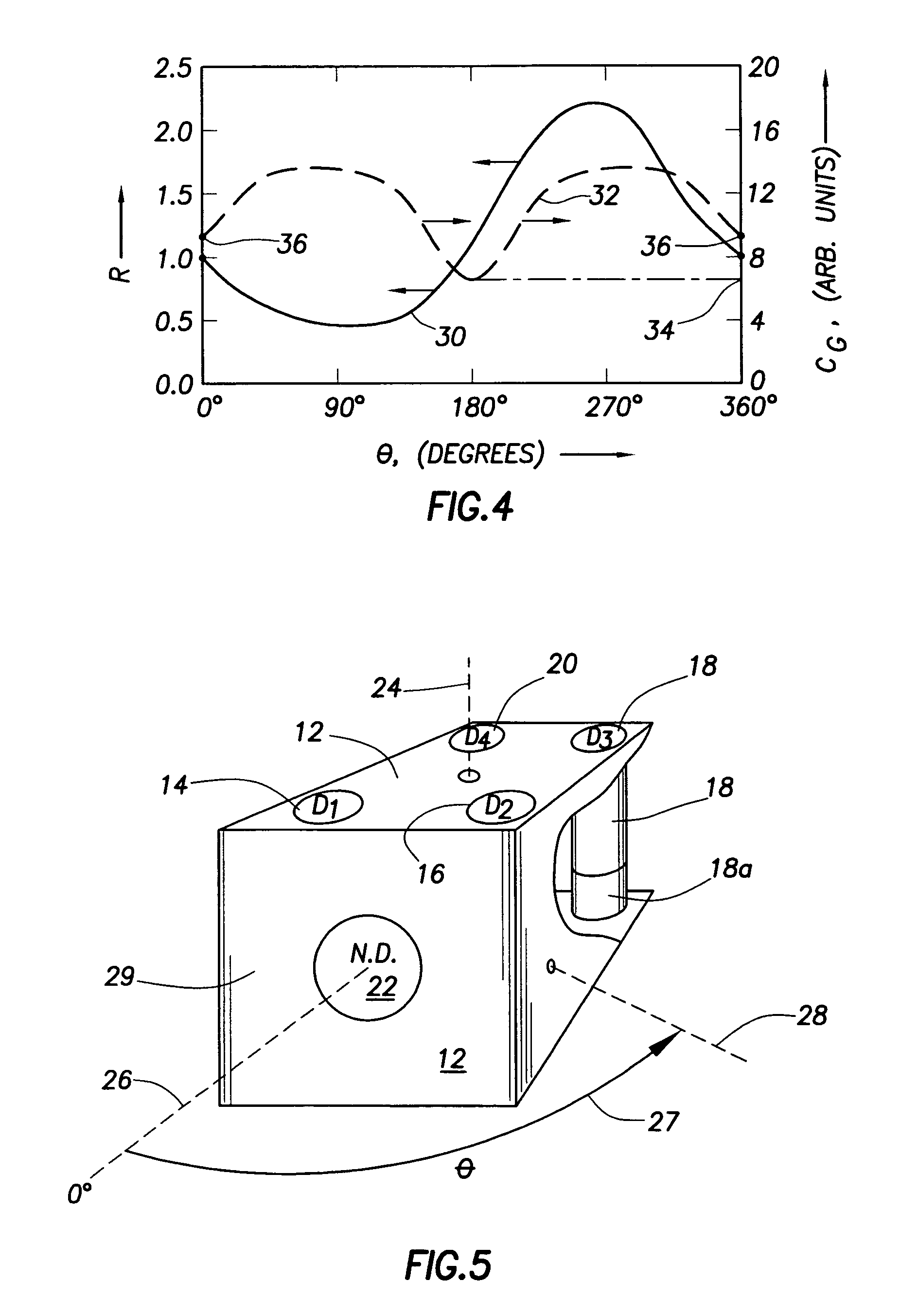
A portable survey instrument and methodology yield intensity of neutron radiation, intensity of gamma radiation, and a direction of impinging gamma radiation. The instrument uses a neutron detector surrounded by an essentially rectangular moderator with preferably four gamma ray detectors disposed symmetrically about the neutron detector and within the moderator. Material and dimensions of the moderator are selected so that the neutron-measurement is equally sensitive to fast and thermal neutrons. The moderator also induces angular responses to the gamma ray detectors. Responses of the gamma ray detectors are combined to yield a parameter indicative of the angular position of a source. The survey instrument is portable and suited for hand held use.
Owner:DELTA EPSILON INSTR
Sigma/porosity tools with neutron monitors
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
System and apparatus for detecting gamma rays in a PET/MRI scanner
ActiveUS7667457B2X/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentElectric/magnetic detectionPhotodetectorRadio frequency
A gamma ray detector ring for a combined positron emission tomography (PET) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system is integrated into a radio frequency (RF) coil assembly such that the detector ring is integrated with a RF shield. Each gamma ray detector in the detector ring includes a scintillator component that emits light when a gamma ray is detected and a photodetector component designed to be sensitive to the frequency of light produced by the scintillator. A RF shield may be integrated into a detector ring such that the RF shield is positioned between the scintillator and photodetector components of each detector, thereby saving valuable radial space within the imaging system. Multiple such detector rings may be located adjacent to one another to increase axial coverage and enable three-dimensional PET imaging techniques.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
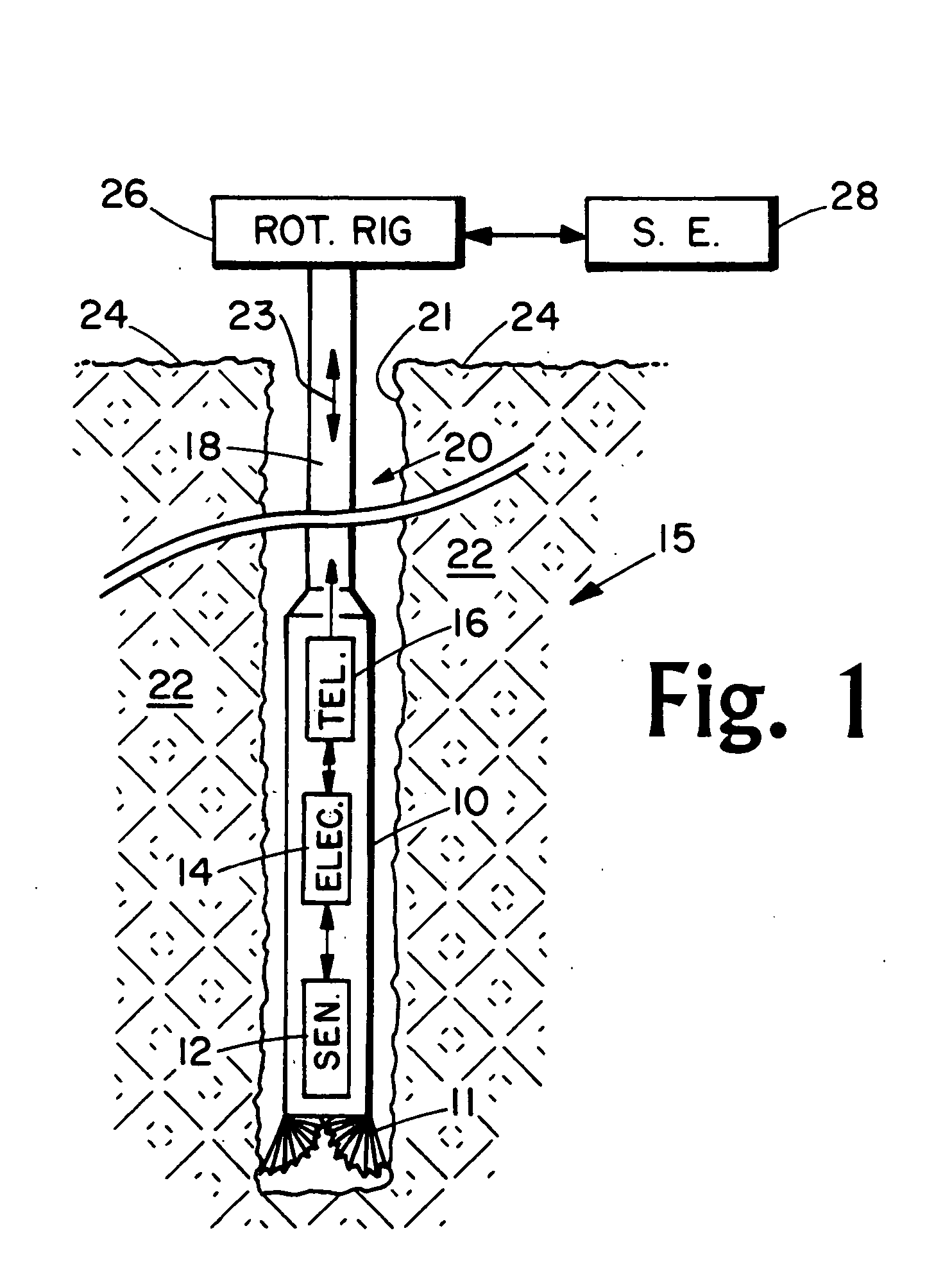
Well logging apparatus and method for measuring formation properties
A logging tool includes an elongated body housing a neutron source and at least one neutron detector positioned along one side of the neutron source. Some embodiments of the logging tool include at least one gamma ray detector longitudinally separated from and to one end of the neutron source, and may be used to make simultaneous gamma ray and neutron logging measurements. In some embodiments, the logging tool also includes a (n, 2n)-neutron shield positioned to one end of the neutron detector, longitudinally between the neutron detector and the neutron source.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
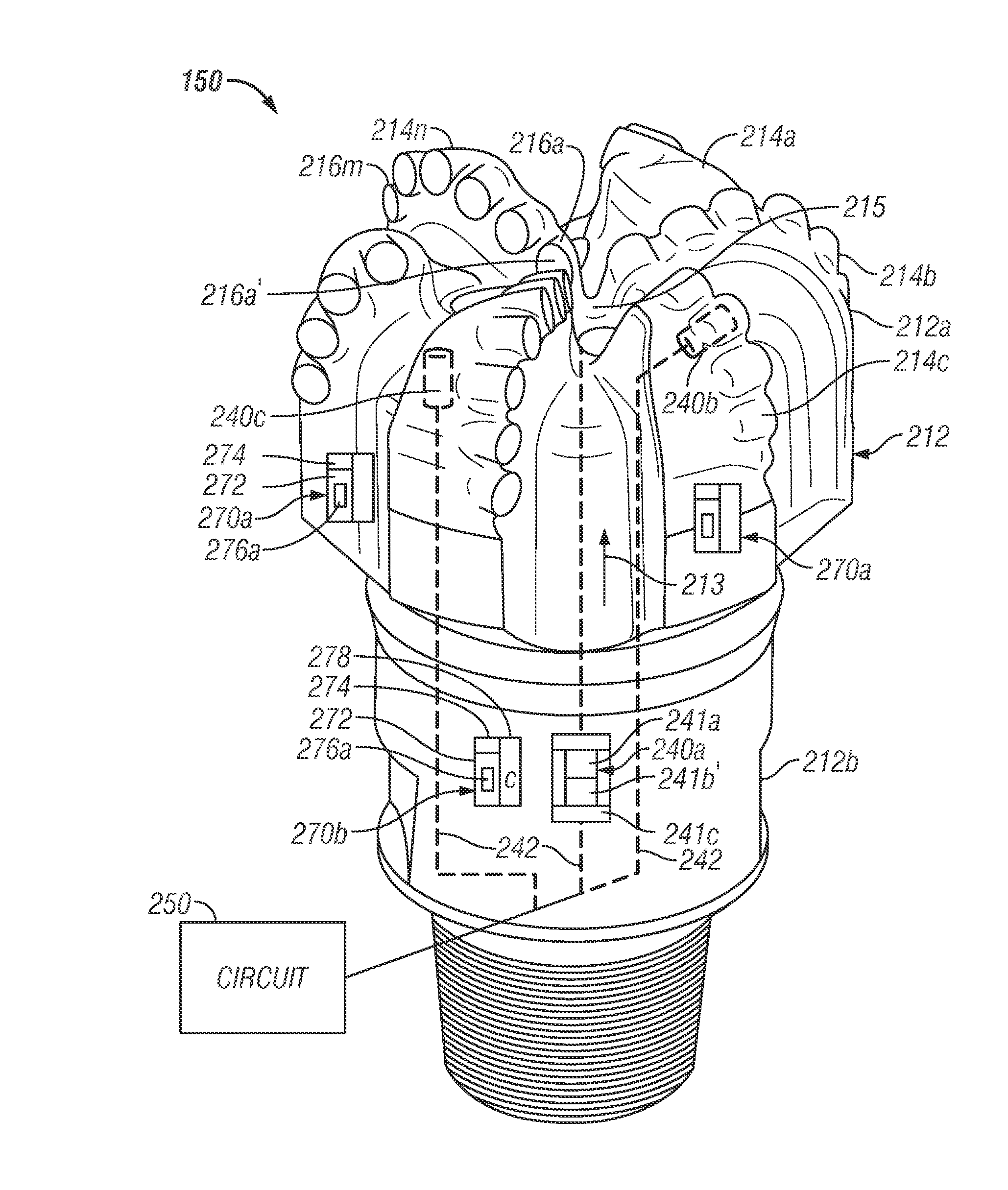
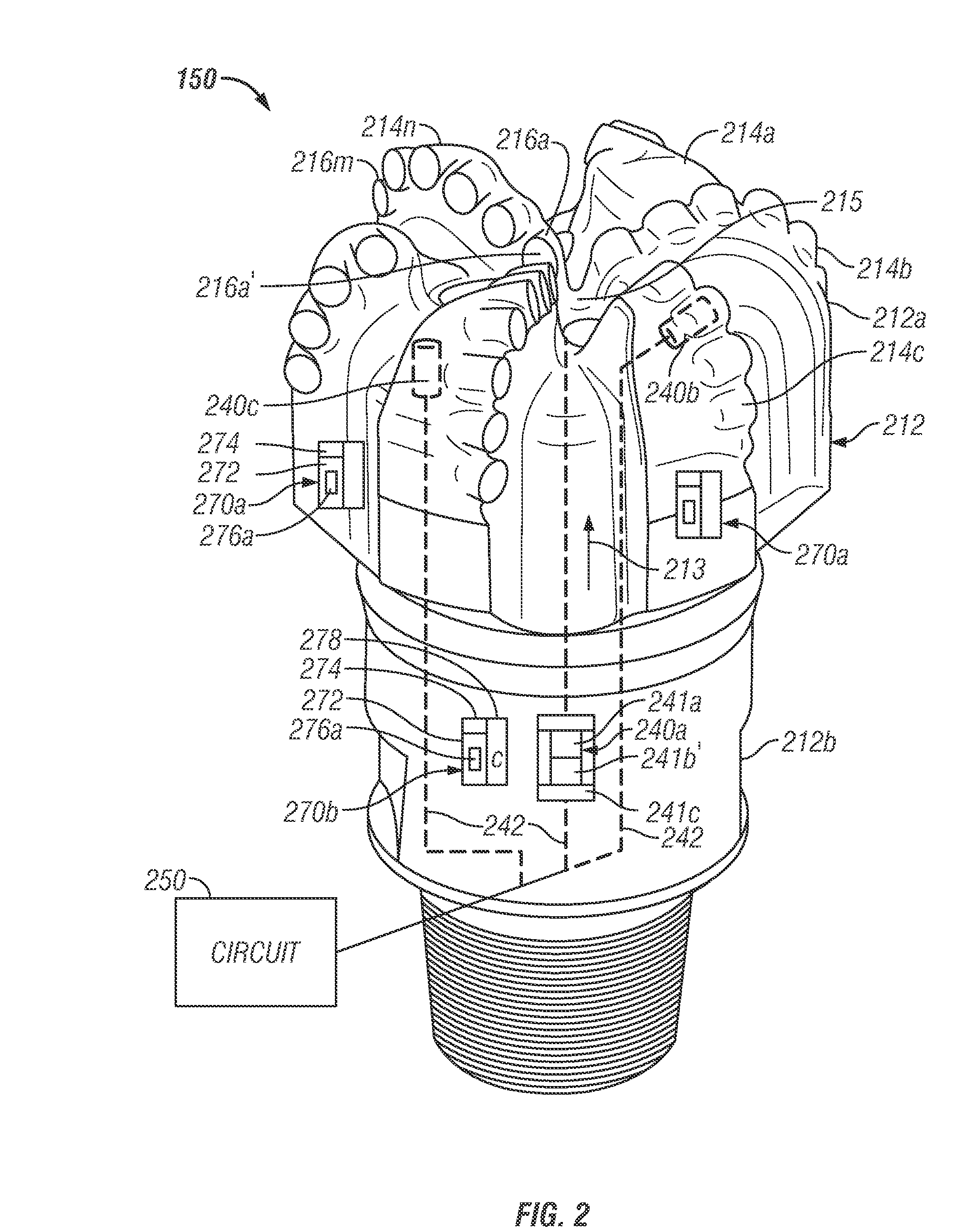
Formation Evaluation Using a Bit-Based Active Radiation Source and a Gamma Ray Detector
A drill bit made according to one embodiment includes a source configured to induce radiation into a formation during drilling of a wellbore and a sensor in the drill bit configured to detect radiation from the formation responsive to the radiation induced by the source. The drill bit may further include a circuit configured to process signals received from the sensor to estimate a property of the formation.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Neutron/gamma ray survey instrument with directional gamma ray sensitivity
ActiveUS7026627B2High detection sensitivityLow cross sectionMaterial analysis by optical meansPhotometry using electric radiation detectorsNuclear engineeringNeutron radiation
A portable survey instrument and methodology yield intensity of neutron radiation, intensity of gamma radiation, and a direction of impinging gamma radiation. The instrument uses a neutron detector surrounded by an essentially rectangular moderator with preferably four gamma ray detectors disposed symmetrically about the neutron detector and within the moderator. Material and dimensions of the moderator are selected so that the neutron measurement is equally sensitive to fast and thermal neutrons. The moderator also induces angular responses to the gamma ray detectors. Responses of the gamma ray detectors are combined to yield a parameter indicative of the angular position of a source. The survey instrument is portable and suited for hand held use.
Owner:DELTA EPSILON INSTR
Composite gamma-neutron detection system
ActiveUS8389941B2Avoid cross contaminationMultiplier cathode arrangementsMeasurement with scintillation detectorsHeavy particleLight guide
The present invention provides a gamma-neutron detector based on mixtures of thermal neutron absorbers that produce heavy-particle emission following thermal capture. The detector consists of one or more thin screens embedded in transparent hydrogenous light guides, which also serve as a neutron moderator. The emitted particles interact with the scintillator screen and produce a high light output, which is collected by the light guides into a photomultiplier tube and produces a signal from which the neutrons are counted. Simultaneous gamma-ray detection is provided by replacing the light guide material with a plastic scintillator. The plastic scintillator serves as the gamma-ray detector, moderator and light guide. The neutrons and gamma-ray events are separated employing Pulse-Shape Discrimination (PSD). The detector can be used in several scanning configurations including portal, drive-through, drive-by, handheld and backpack, etc.
Owner:RAPISCAN SYST INC (US)
Combined positron emission tomography and magnetic resonance tomography unit
InactiveUS7323874B2Save spaceShorten the timeMagnetic measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionElectrical conductorDevice form
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Composite gamma-neutron detection system
InactiveUS20140197321A1Avoid cross contaminationMeasurement with scintillation detectorsPhotometryHeavy particleLight guide
The present invention provides a gamma-neutron detector based on mixtures of thermal neutron absorbers that produce heavy-particle emission following thermal capture. The detector consists of one or more thin screens embedded in transparent hydrogenous light guides, which also serve as a neutron moderator. The emitted particles interact with the scintillator screen and produce a high light output, which is collected by the light guides into a photomultiplier tube and produces a signal from which the neutrons are counted. Simultaneous gamma-ray detection is provided by replacing the light guide material with a plastic scintillator. The plastic scintillator serves as the gamma-ray detector, moderator and light guide. The neutrons and gamma-ray events are separated employing Pulse-Shape Discrimination (PSD). The detector can be used in several scanning configurations including portal, drive-through, drive-by, handheld and backpack, etc.
Owner:BENDAHAN JOSEPH +1
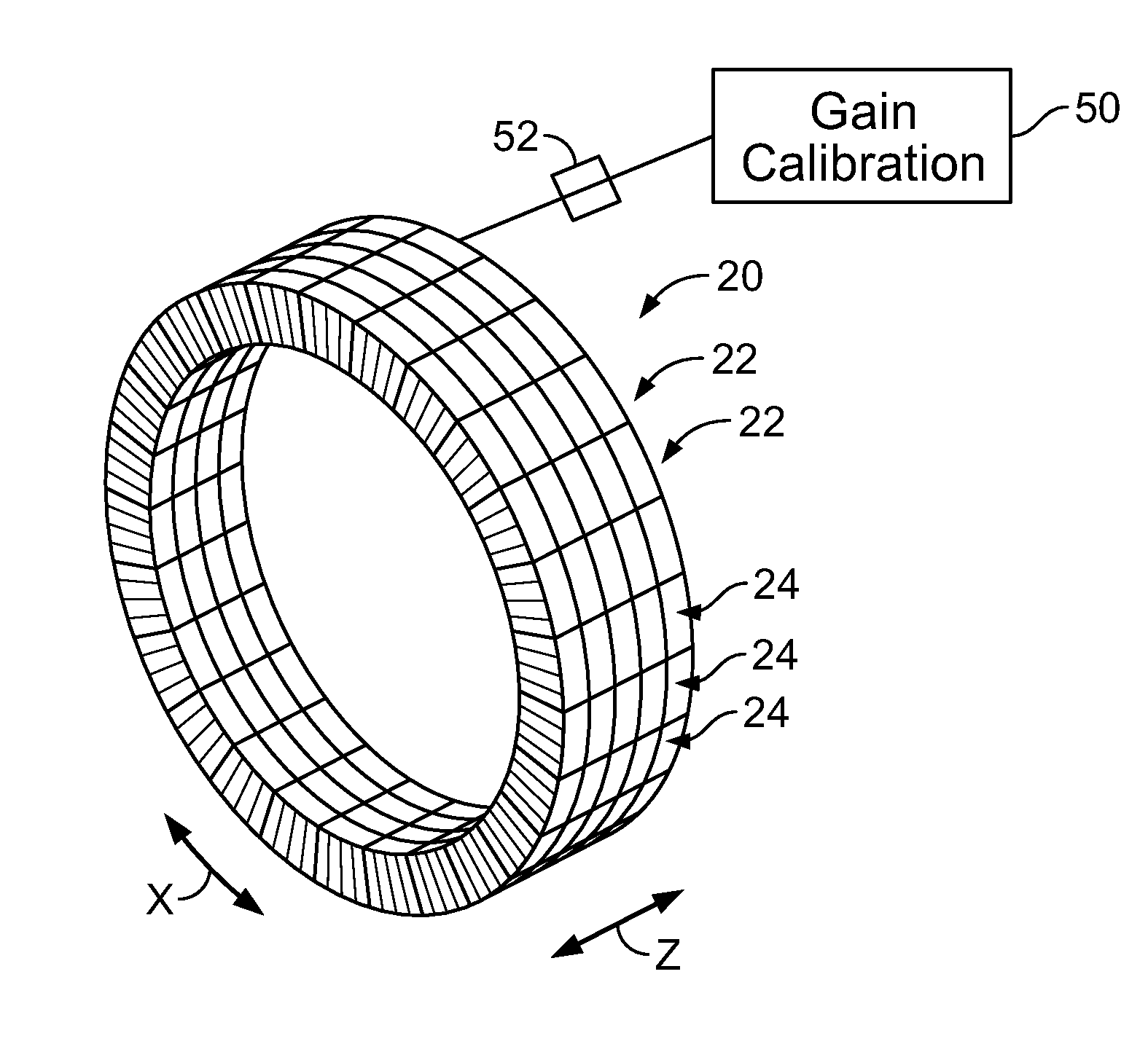
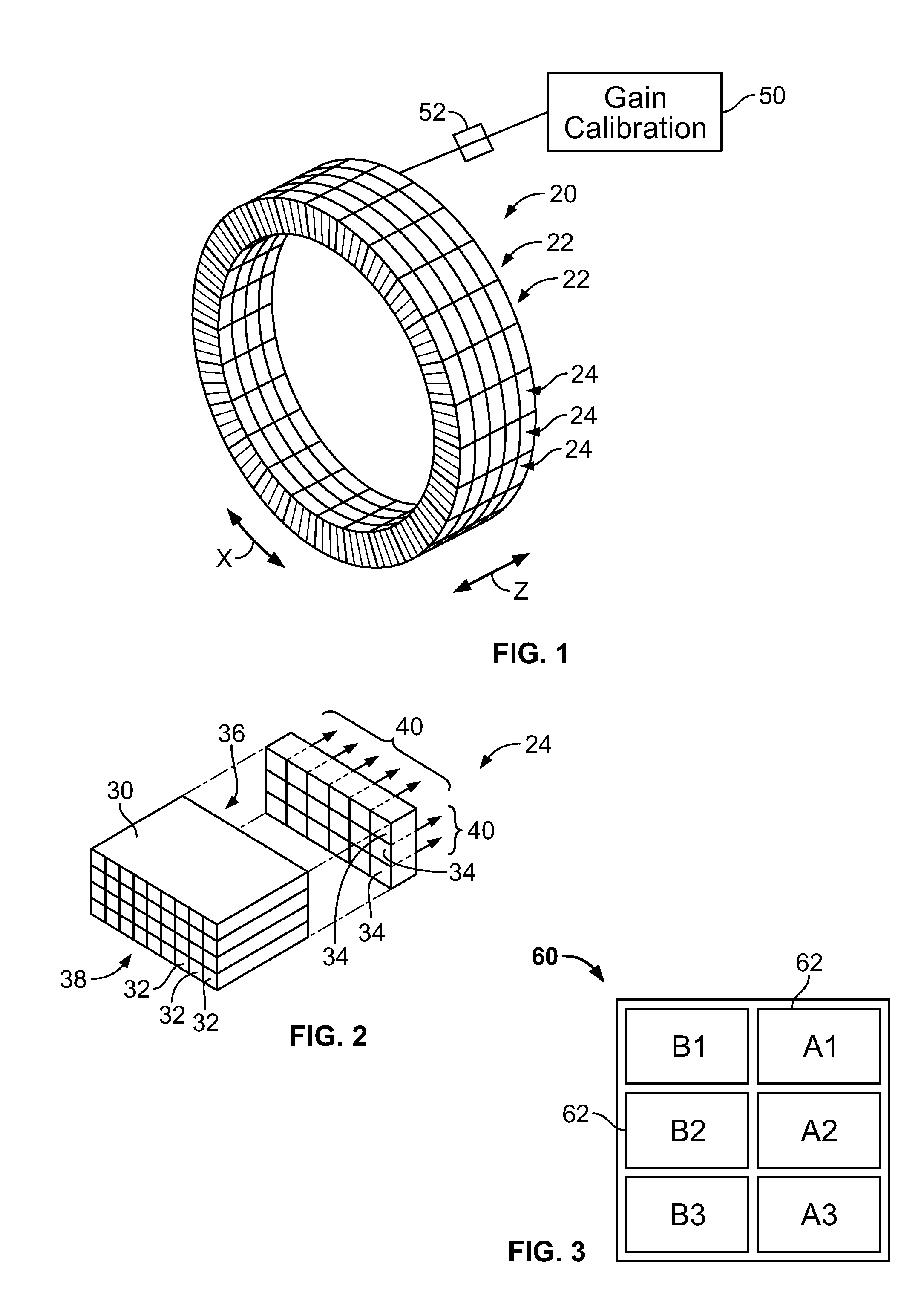
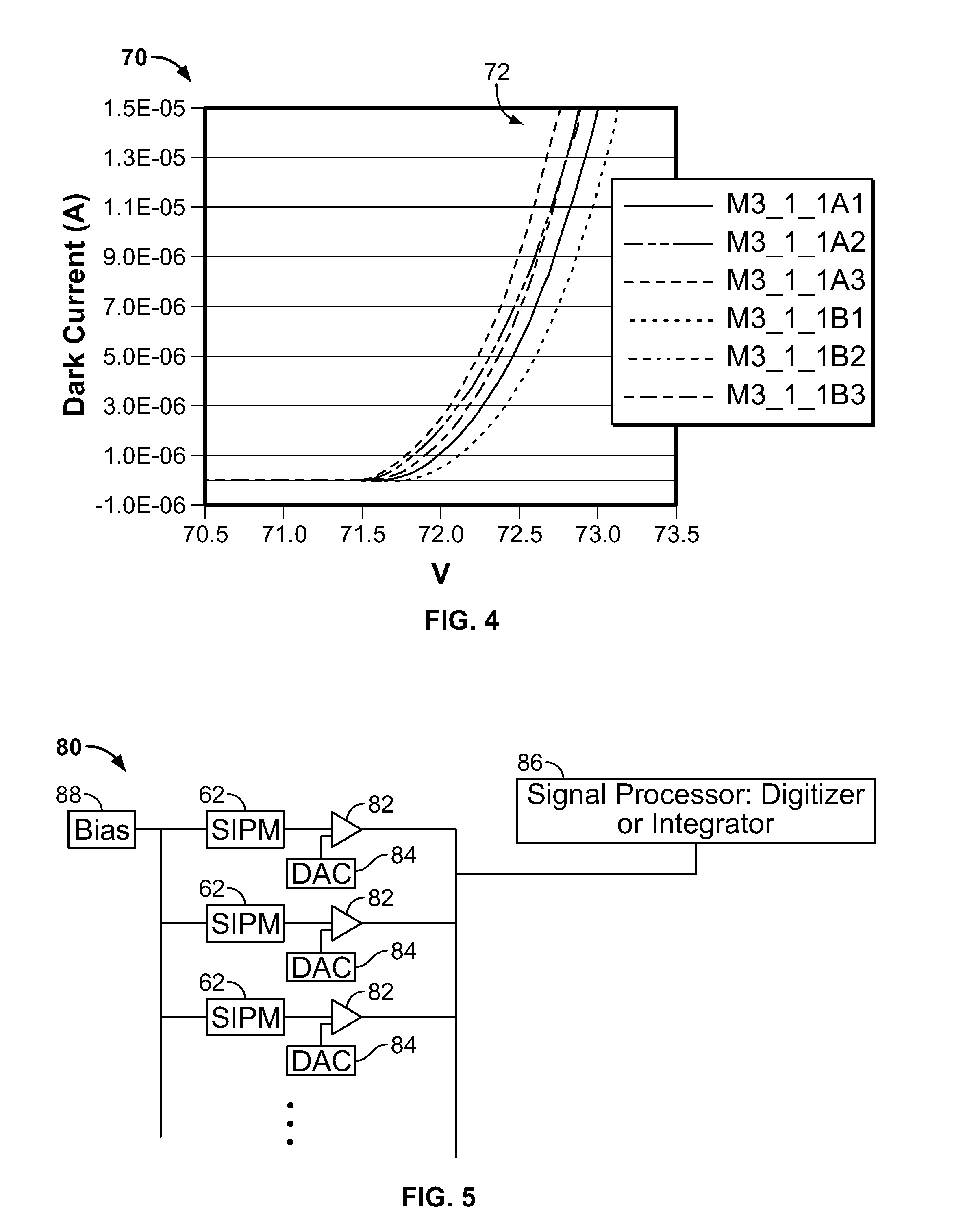
Methods and systems for gain calibration of gamma ray detectors
ActiveUS20130327932A1Material analysis by optical meansCalibration apparatusTransition pointCondensed matter physics
Methods and systems for gain calibration of a gamma ray detector are provided. One method includes measuring signals generated by one or more light sensors of a gamma ray detector, generating one or more derived curves using the measured signals as a function of bias voltage and identifying a transition point in the one or more derived curves. The method also includes determining a breakdown voltage of the one or more light sensors using the identified transition point and setting a bias of the one or more light sensors based on the determined breakdown voltage.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
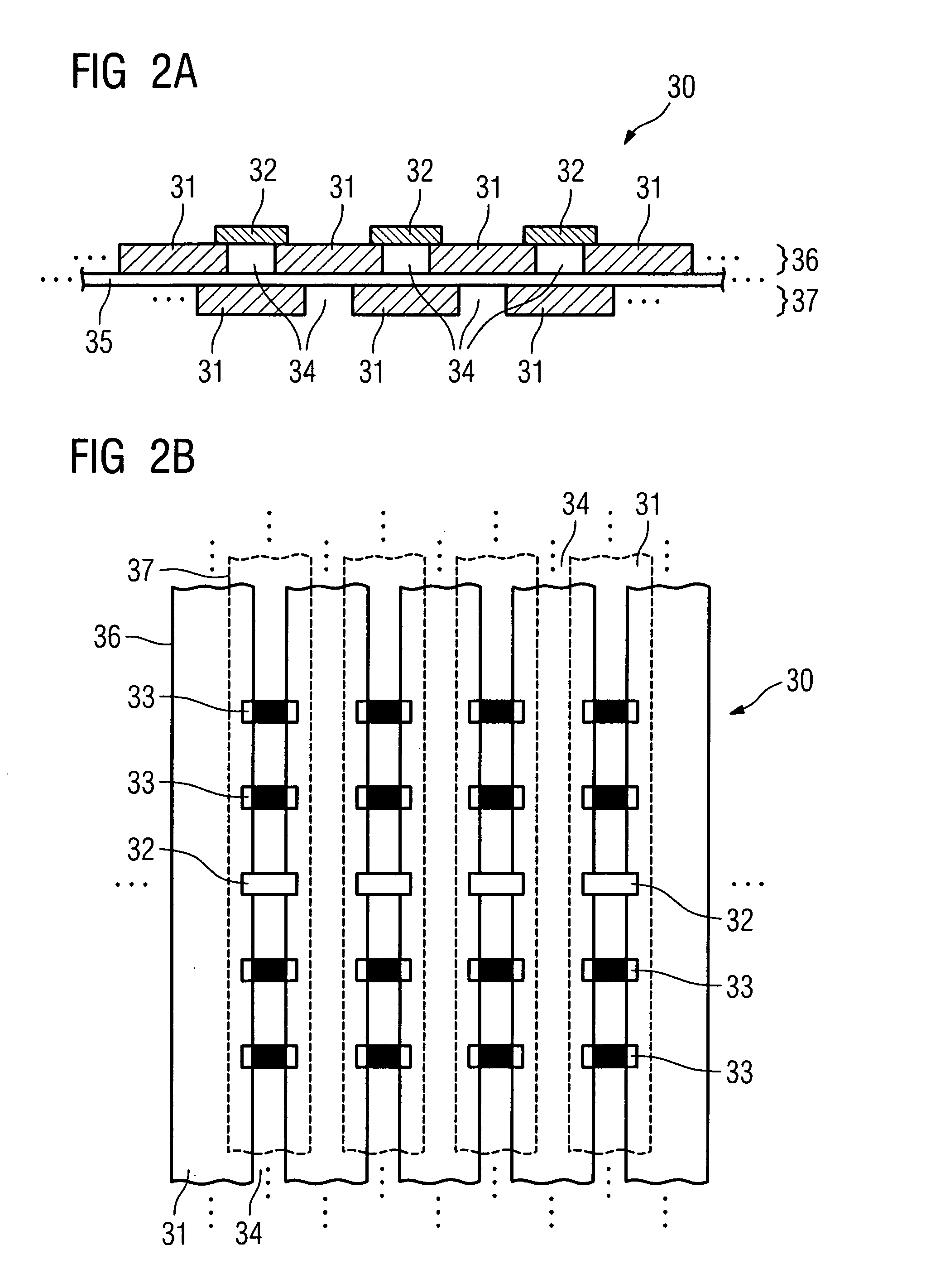
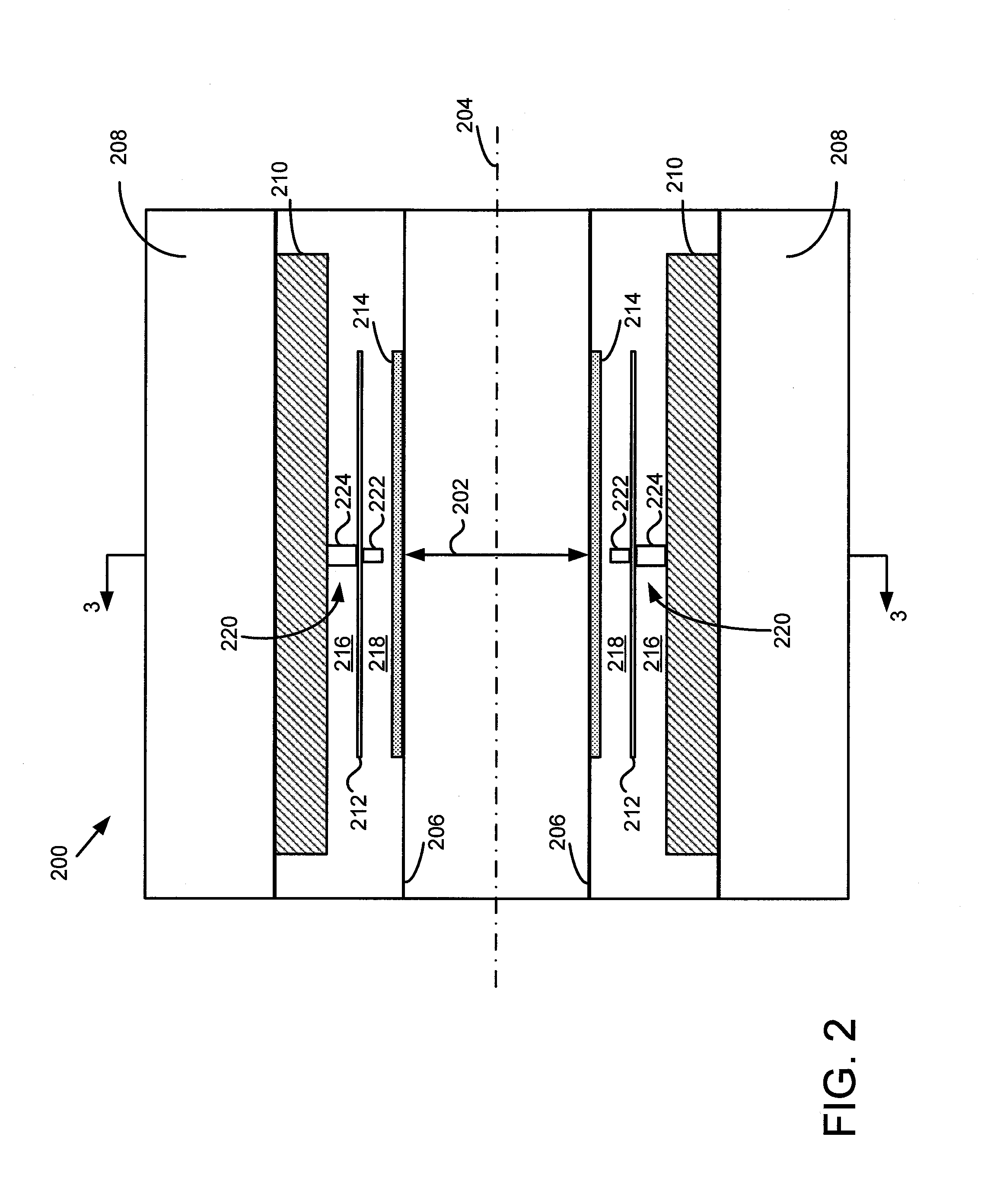
Novel scintillation detector array and associate signal processing method for gamma ray detection with encoding the energy, position, and time coordinaties of the interaction
InactiveUS20100012846A1Material analysis by optical meansTomographyPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
A gamma ray detector module includes at least one scintillation detector configured to operate in a dot-decoding mode, or at least two scintillation detectors configured to operate in a line-decoding mode, wherein the at least one scintillation detector is each coupled to a single photodetector, and wherein the at least two scintillation detectors are coupled to at least two photodetectors arranged substantially along a line; and at least four scintillation detectors configured to operate in a plane-decoding mode, wherein the at least four scintillation detectors are coupled to a plurality of photodetectors arranged in a two-dimensional array.
Owner:YU WANG
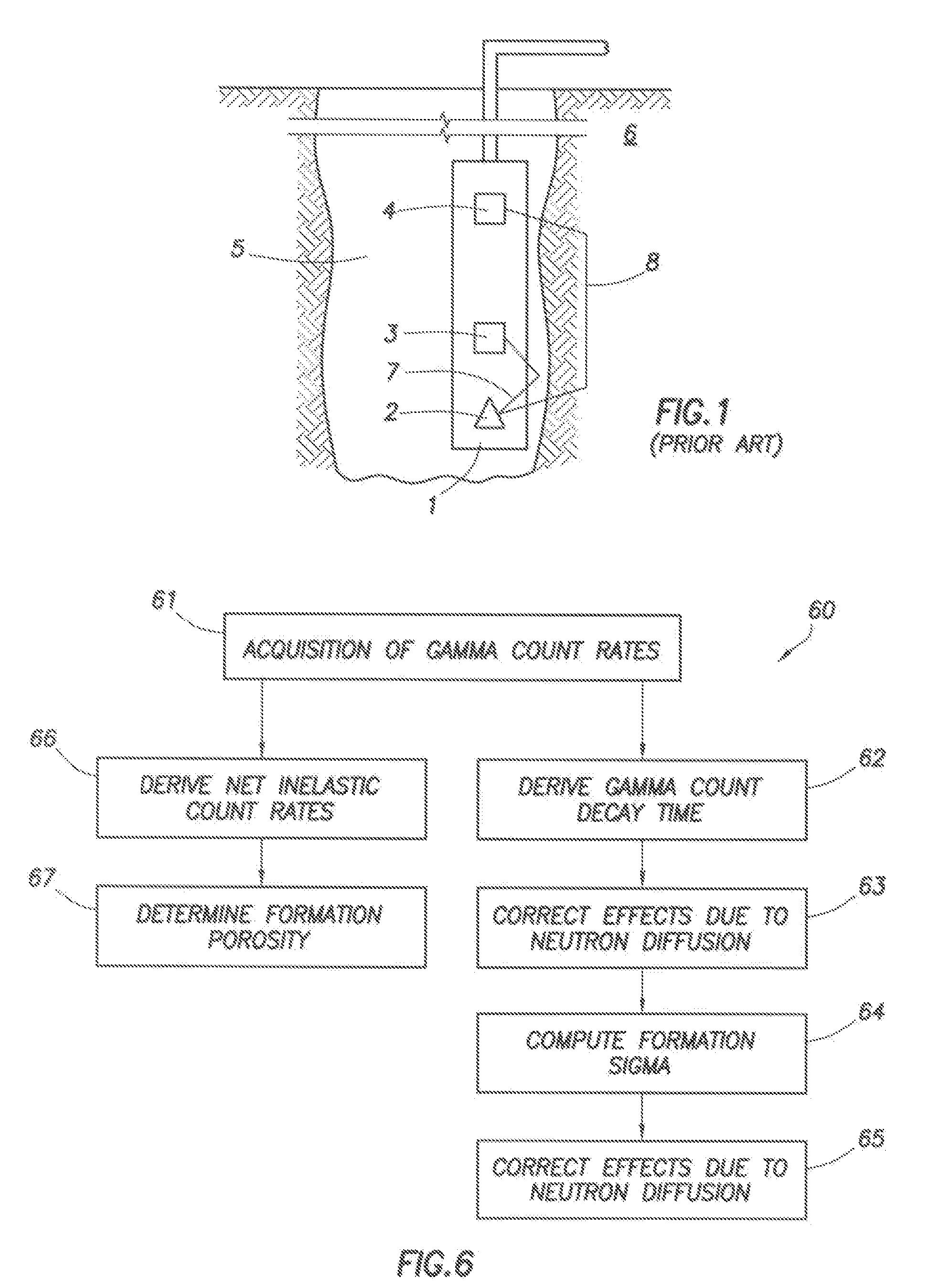
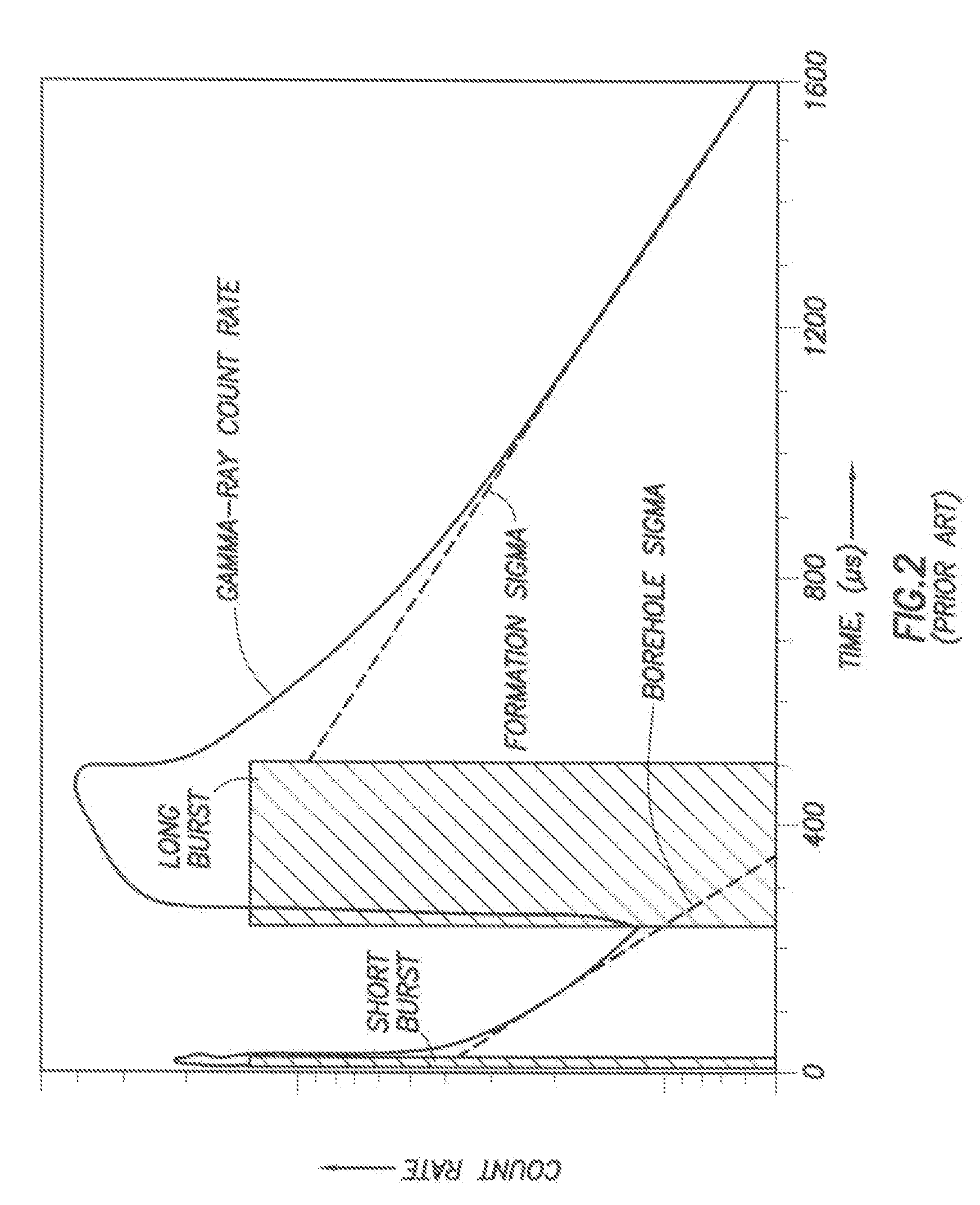
Apparatus and method for determining density, porosity and fluid saturation of formations penetrated by a borehole
InactiveUS6936812B2Reduce ambiguityMinimize adverse effectsNuclear radiation detectionInelastic scatteringFluid saturation
A borehole logging system for determining bulk density, porosity and formation gas / liquid fluid saturation of formation penetrated by a borehole. Measures of fast neutron radiation and inelastic scatter gamma radiation, induced by a pulsed neutron source, are combined with an iterative numerical solution of a two-group diffusion model to obtain the formation parameters of interest. Double-valued ambiguities in prior art measurements are removed by using the iterative solution of the inverted two-group diffusion model. The system requires two gamma ray detectors at different axial spacings from the source, and a single neutron detector axially spaced between the two gamma ray detectors. The system can be embodied as a wireline system or as a logging-while-drilling system.
Owner:PRECISION ENERGY SERVICES
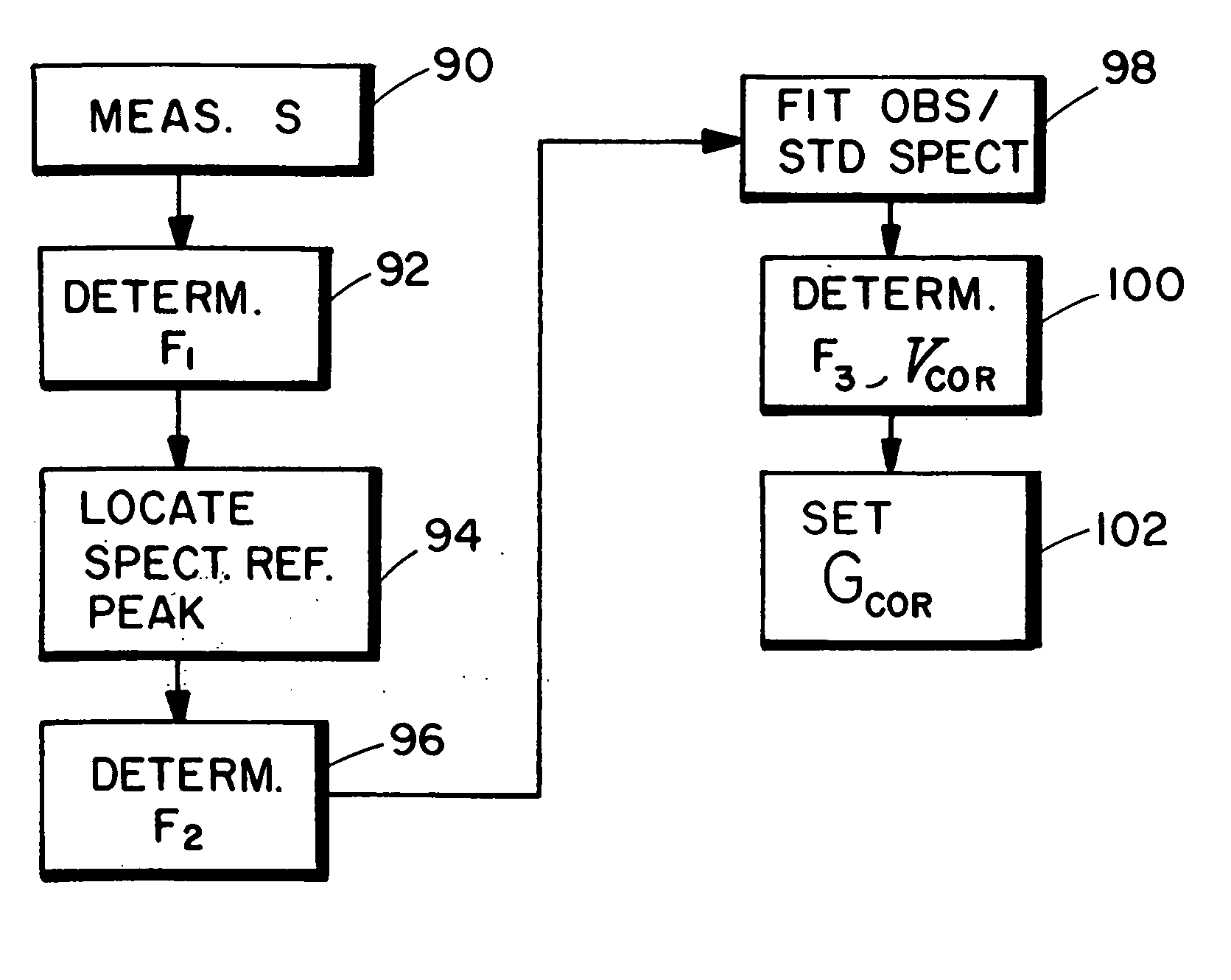
Downhole tool data correction method and apparatus
InactiveUS6289283B1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismology for water-loggingFrequency spectrumFtir spectra
A method and apparatus are provided for correcting gamma ray data representative of gamma ray energies for spectral degradation. The method and apparatus include degrading reference gamma ray spectra. At least one correction factor is calculated between the degraded gamma ray spectra and the reference gamma ray spectra. The gamma ray data are then corrected using a calculated correction factor. Another method is provided for determining a correction factor for correcting data representative of gamma ray energies for spectral degradation. The method includes disposing a downhole tool in a simulated environment representative of actual downhole conditions, the tool including a neutron source and at least one gamma ray detector. The temperature of at least one of the gamma ray detectors of the tool is then varied while the simulated environment is irradiated with neutrons emitted from the neutron source. Gamma ray energy signals are then detected at the at least one detector in response to gamma rays produced during nuclear reactions between the neutrons and materials in and of the simulated environment. A characteristic of the simulated environment is then determined along with a characteristic of the at least one detector. The determined characteristics of the simulated environment and of the at least one detector are then correlated to determine at least one correction factor.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com