Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
156 results about "Pet scanner" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
PET scan. A positron emission tomography scan is a type of imaging test. It uses a radioactive substance called a tracer to look for disease in the body. A positron emission tomography (PET) scan shows how organs and tissues are working. This is different than MRI and CT scans. These tests show the structure of, and blood flow to and from organs.
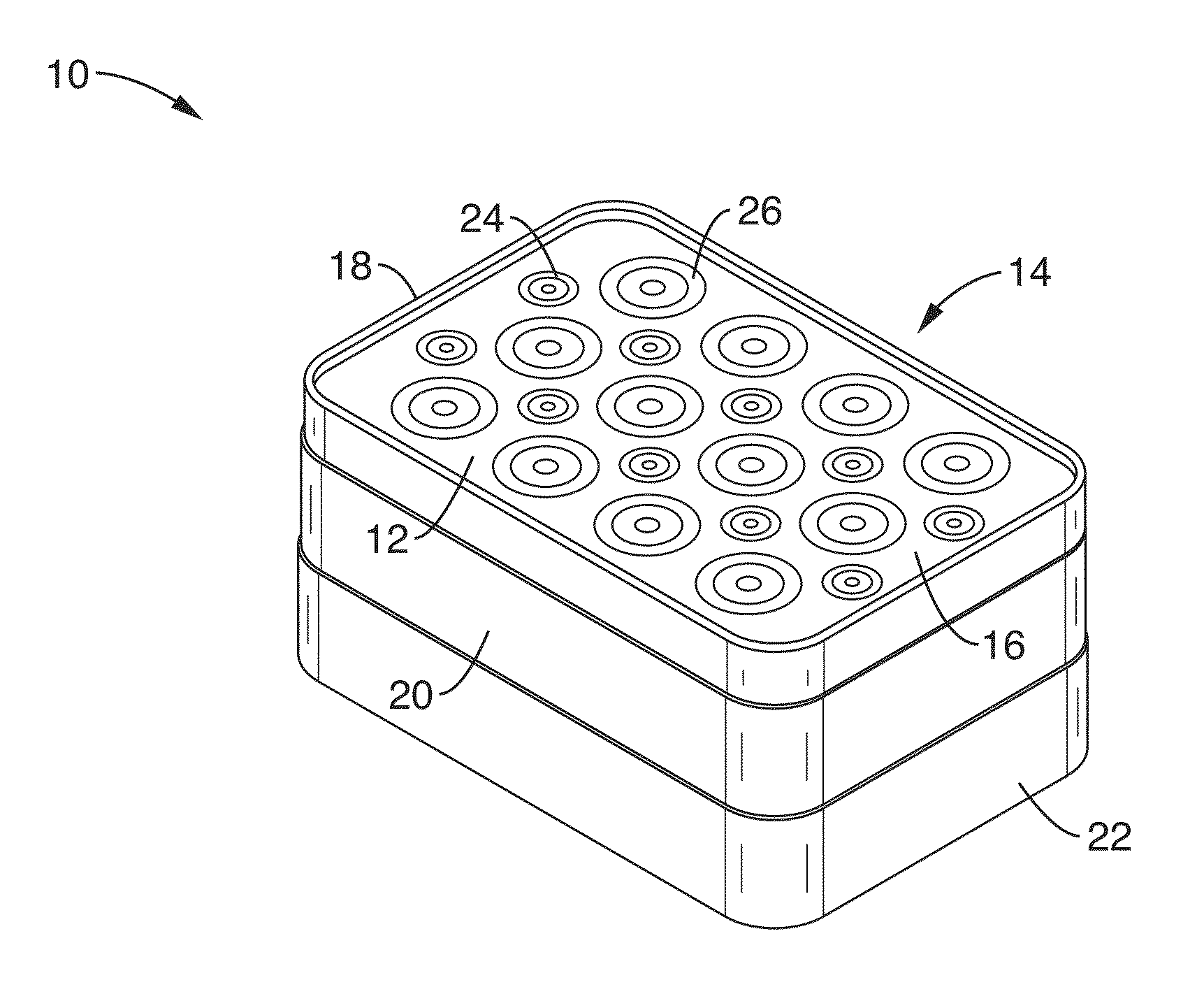
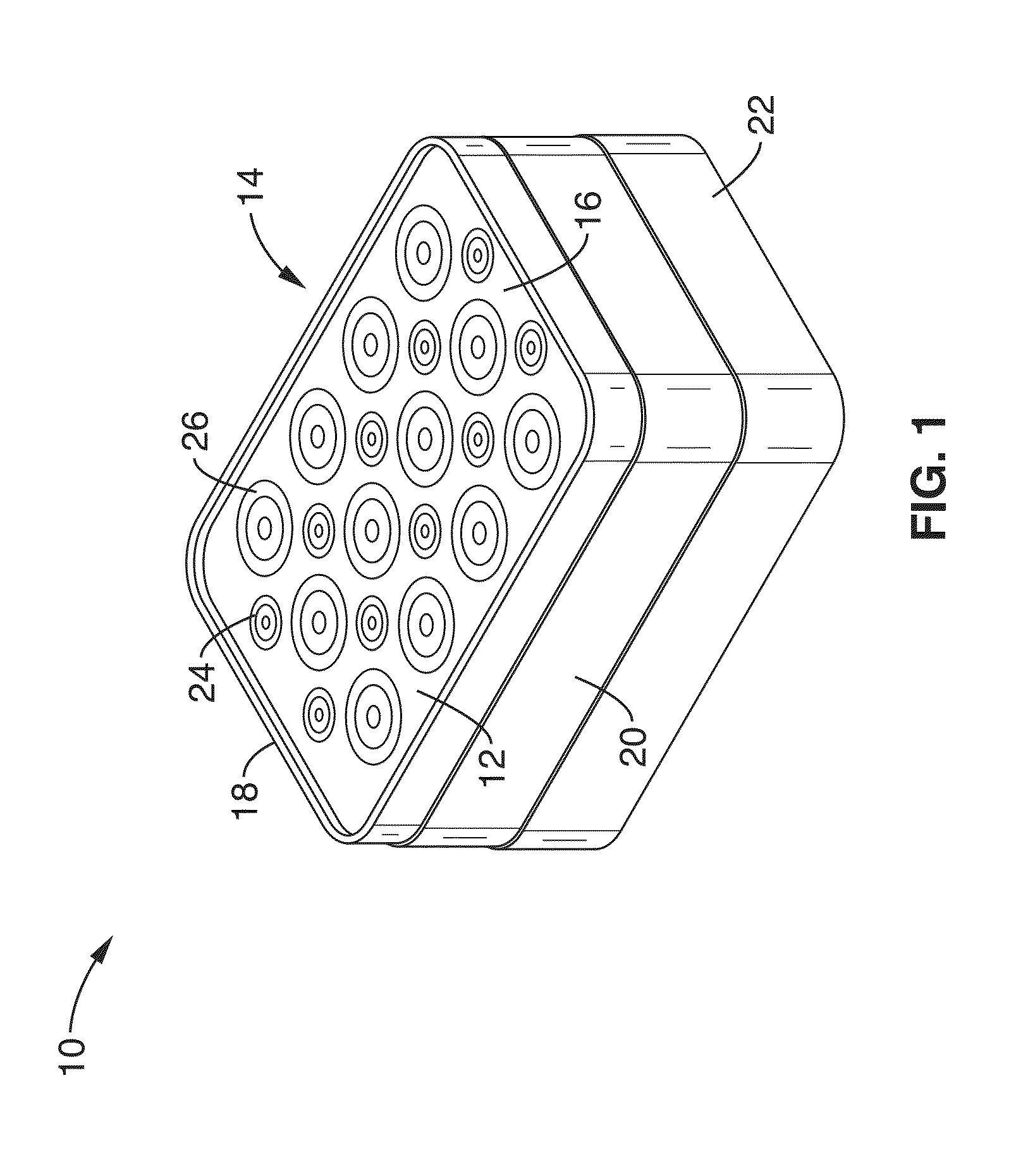
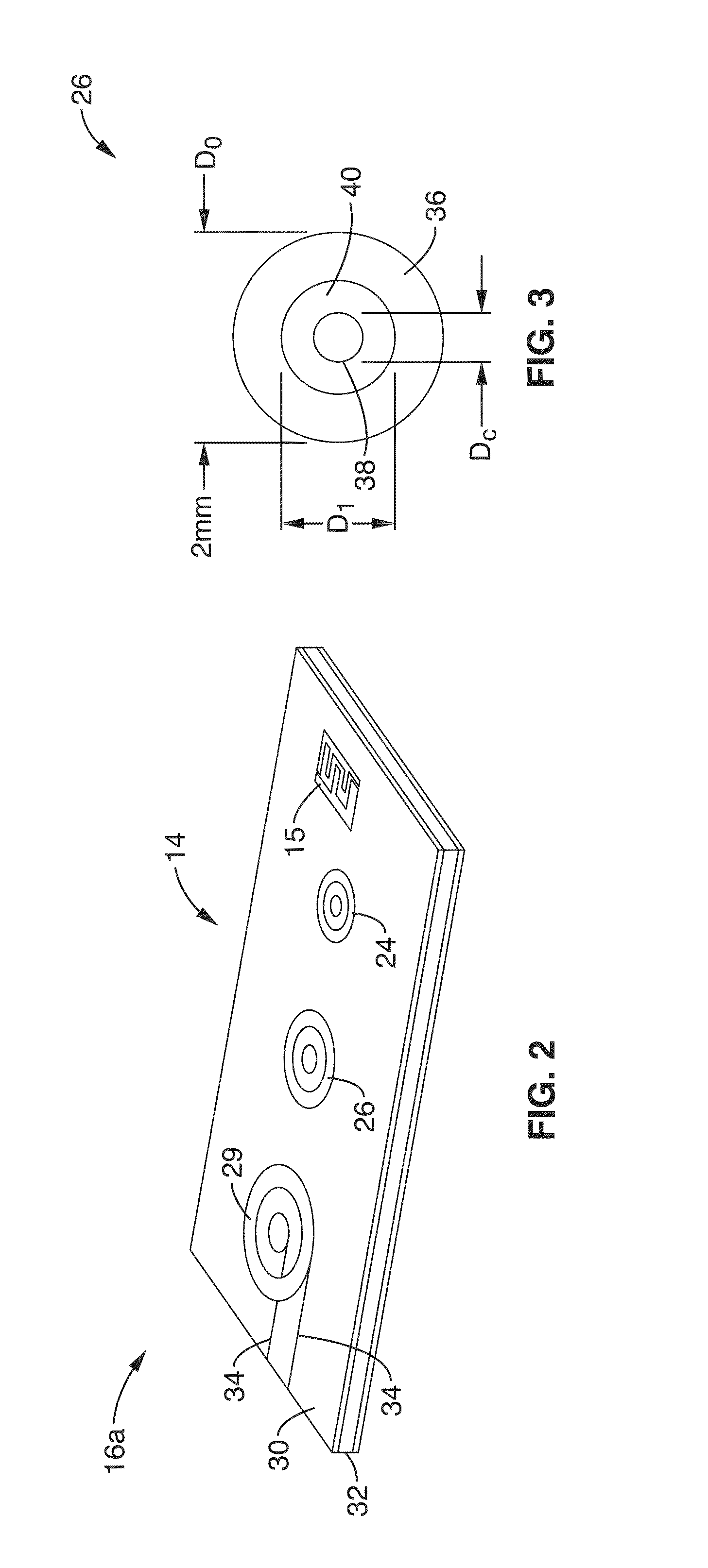
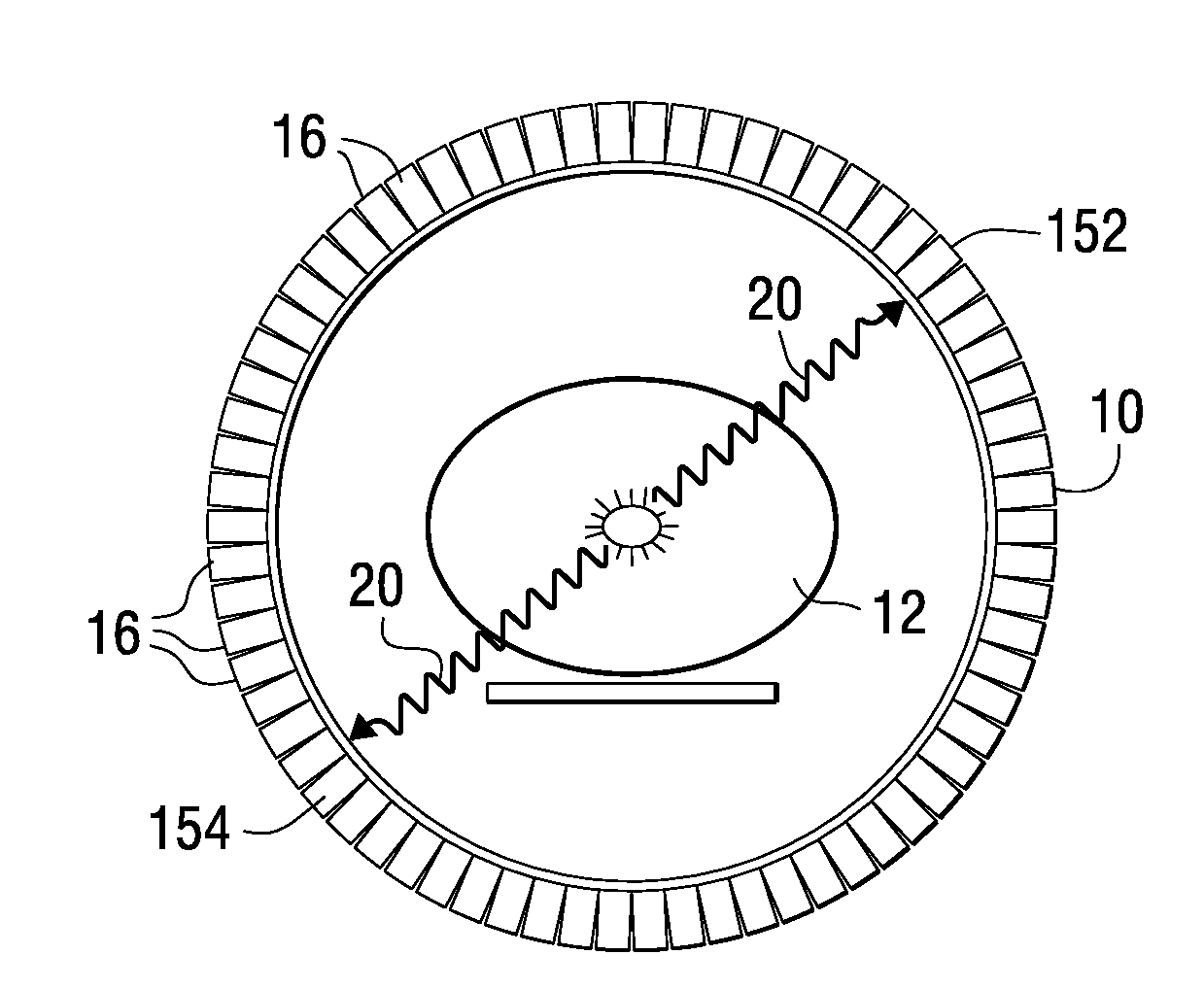
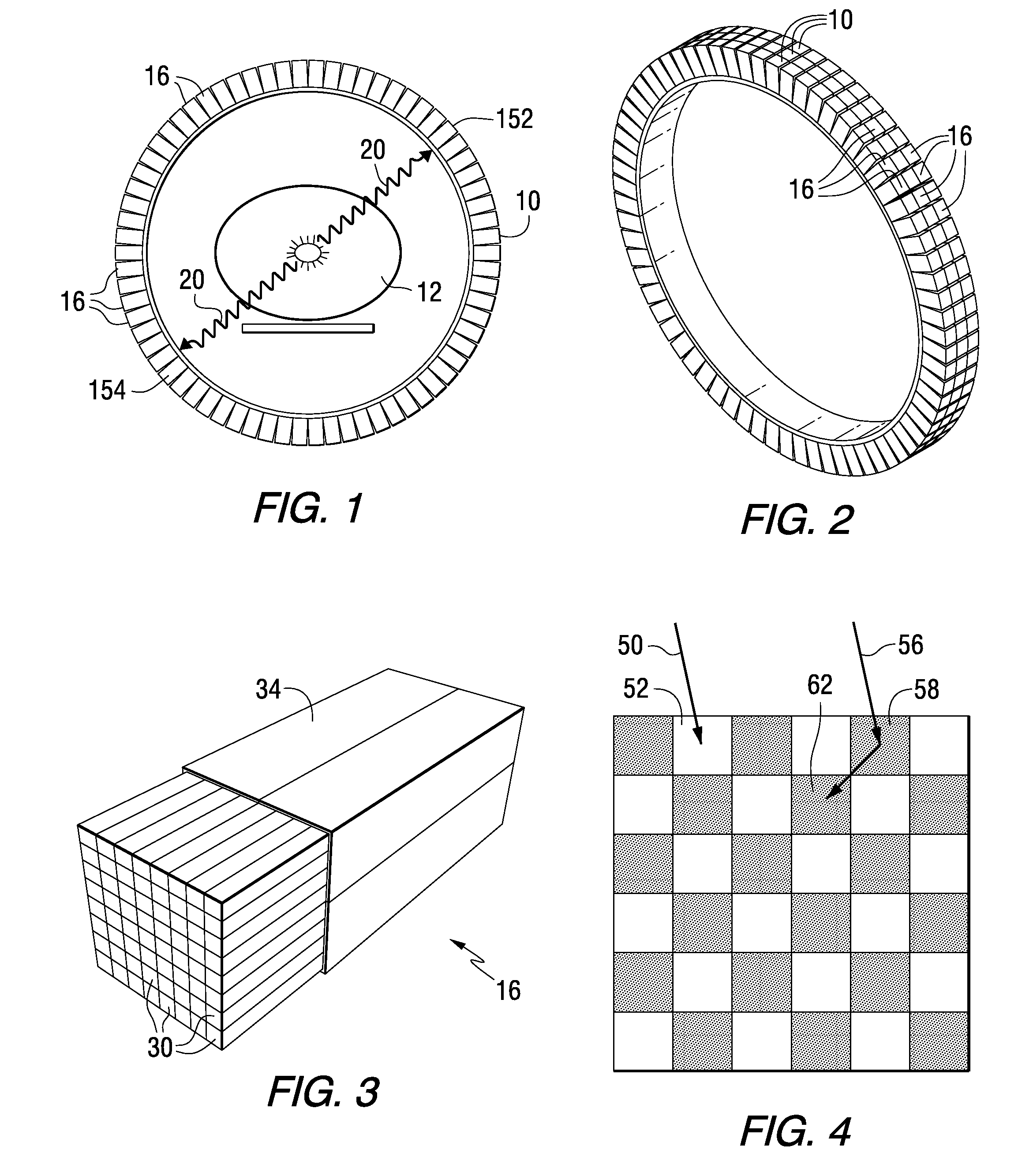
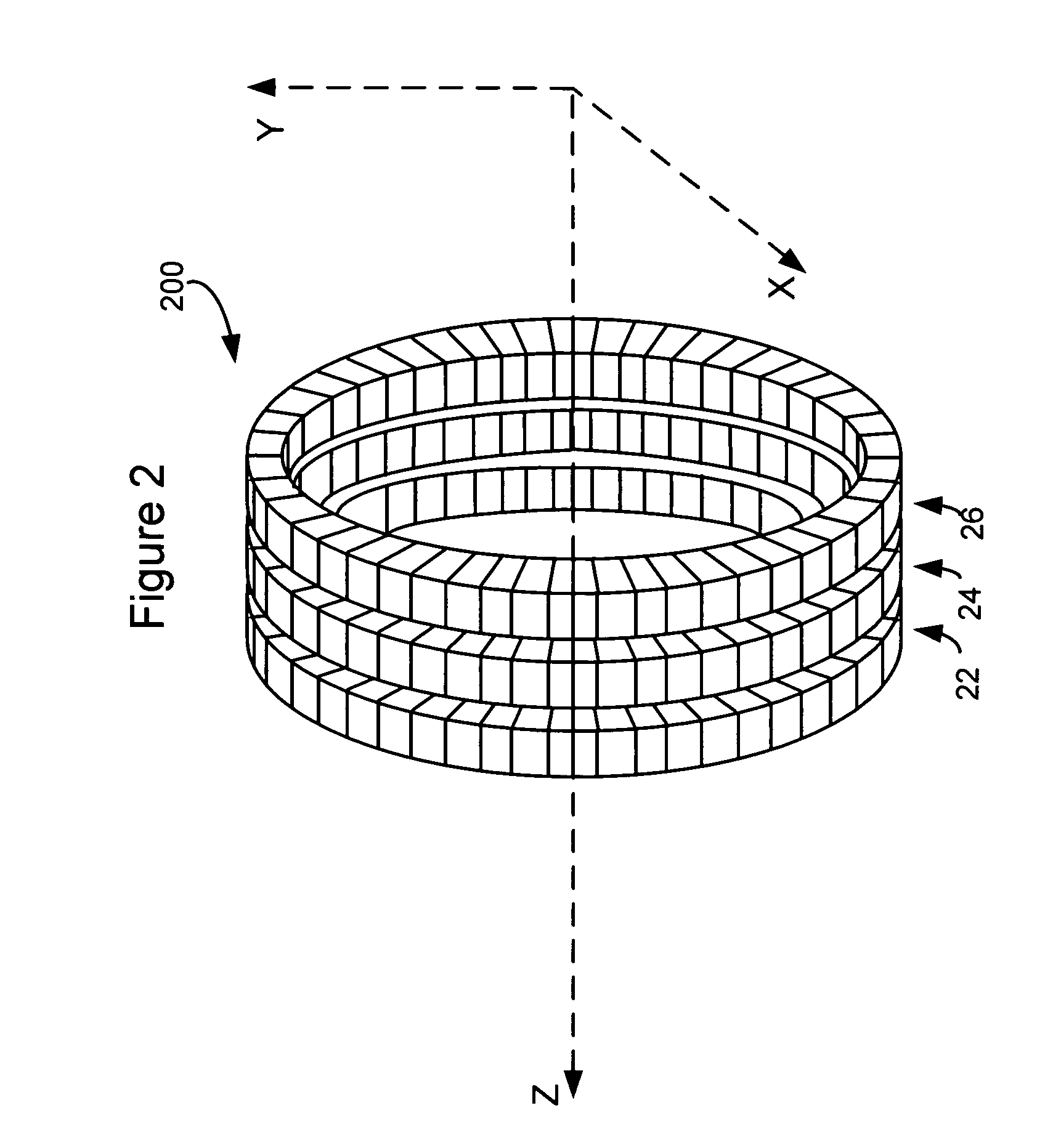
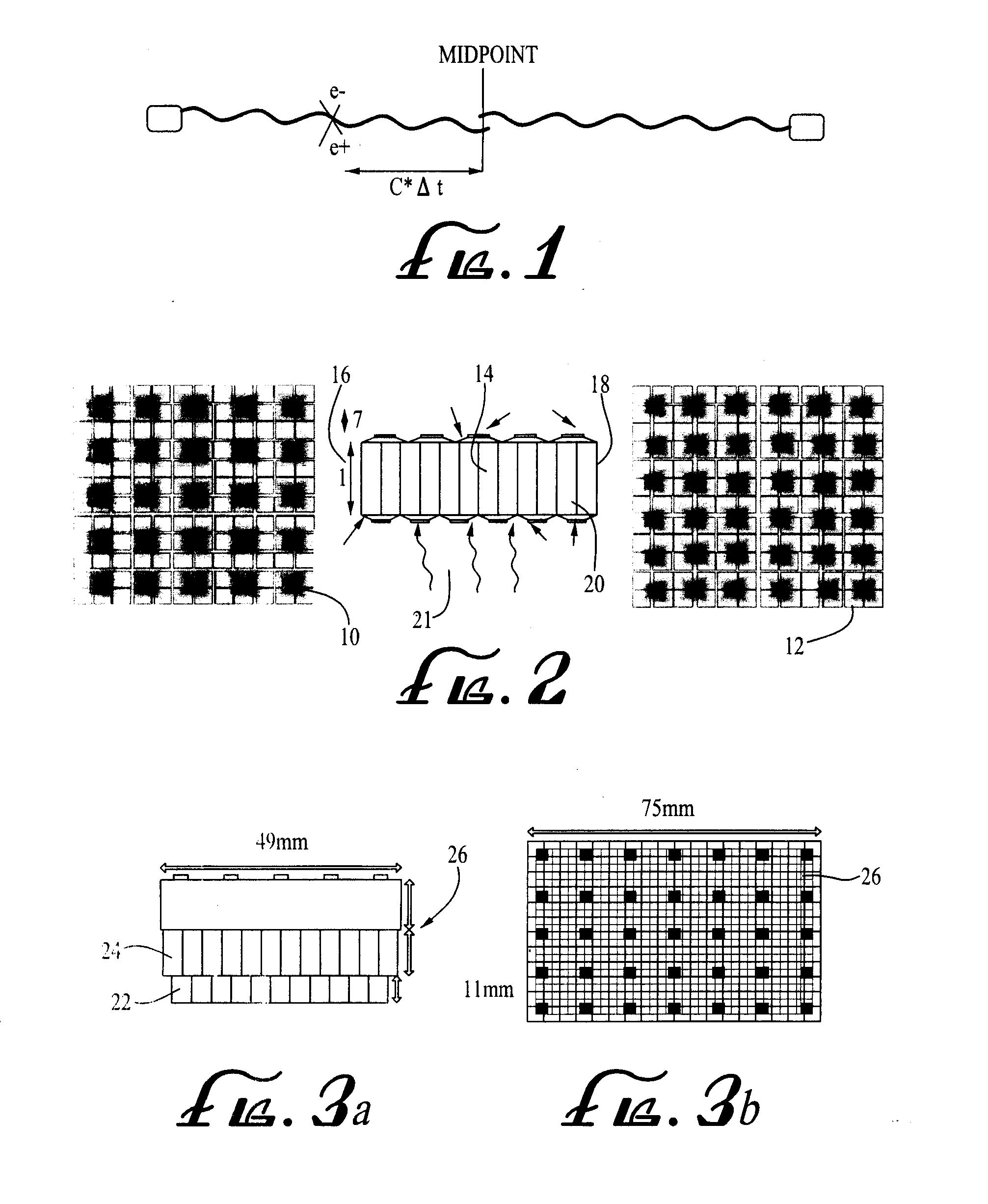
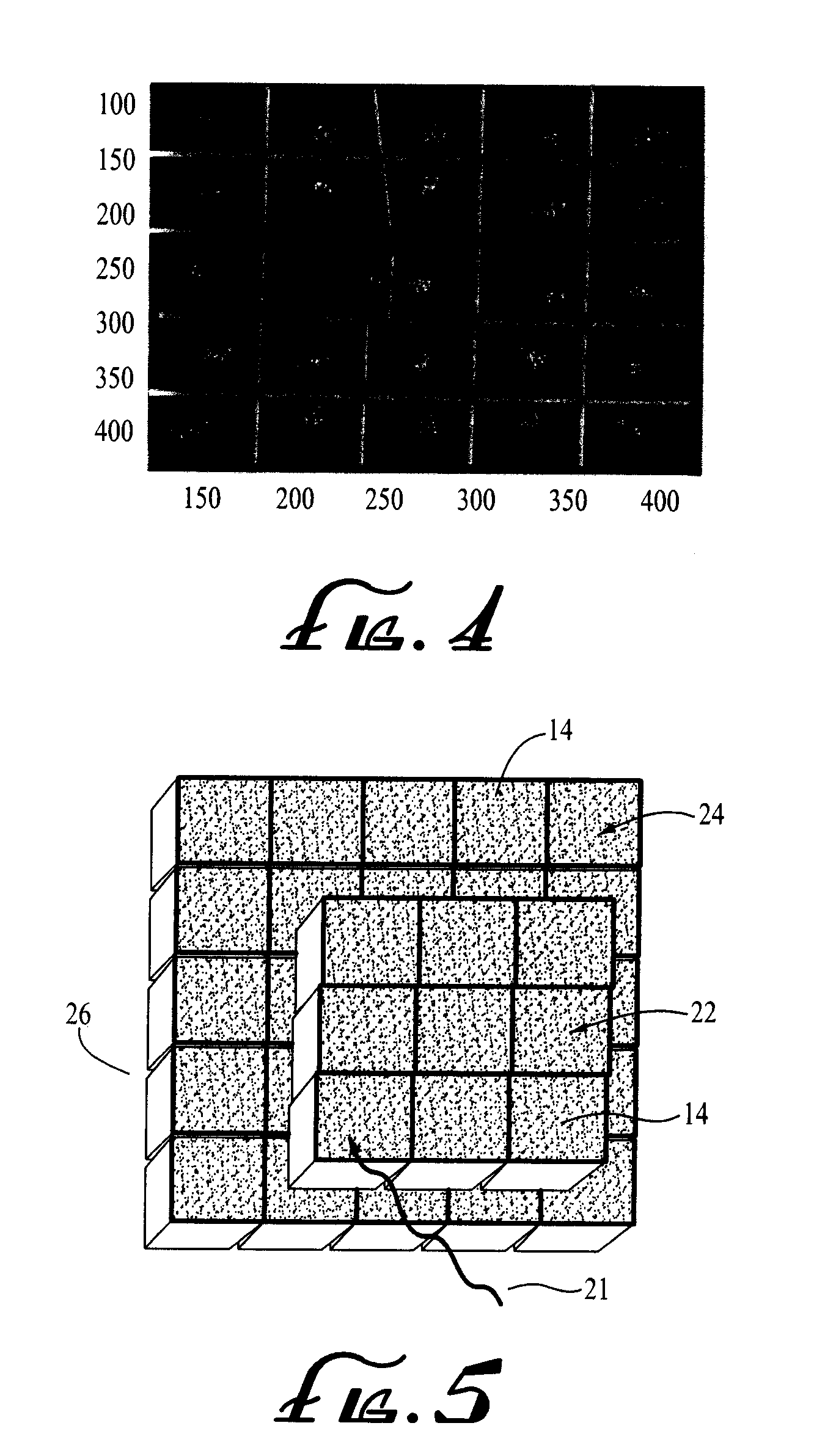
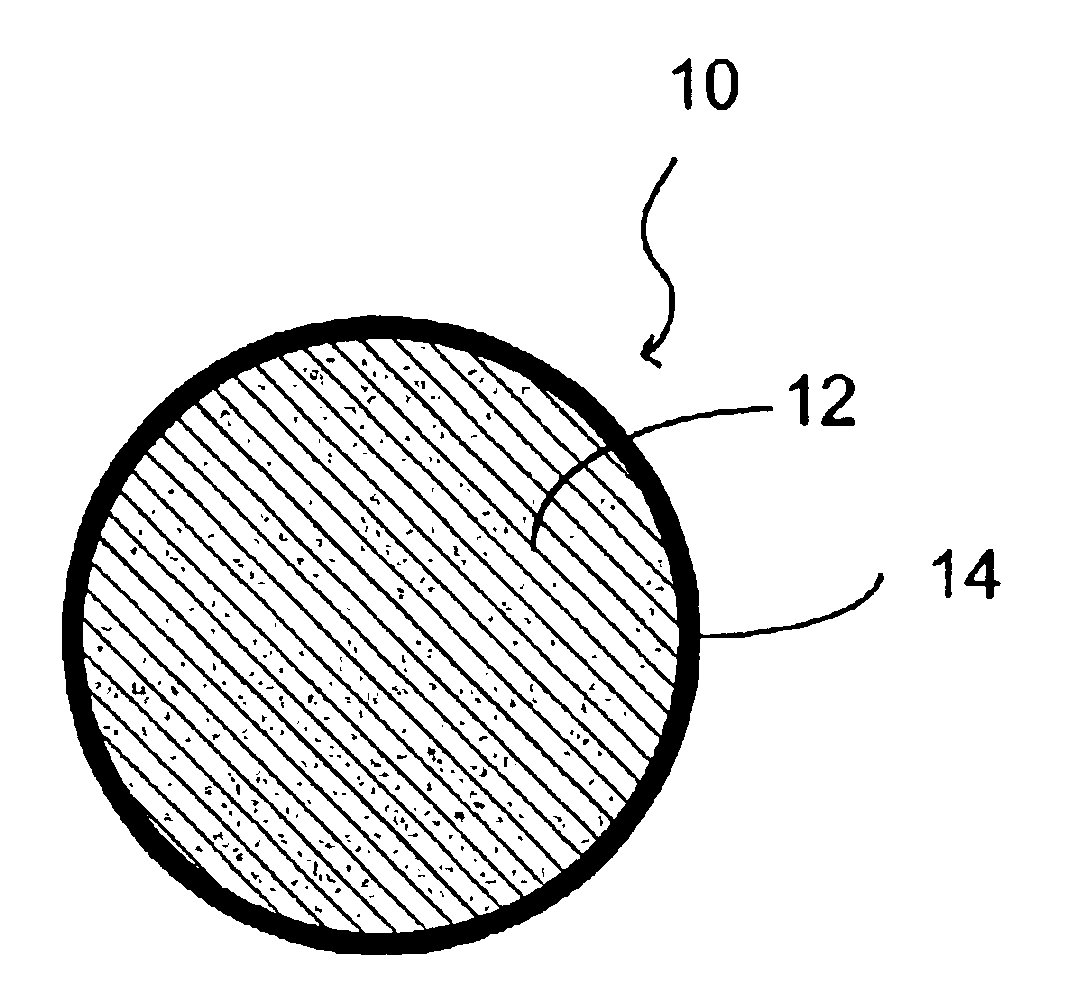
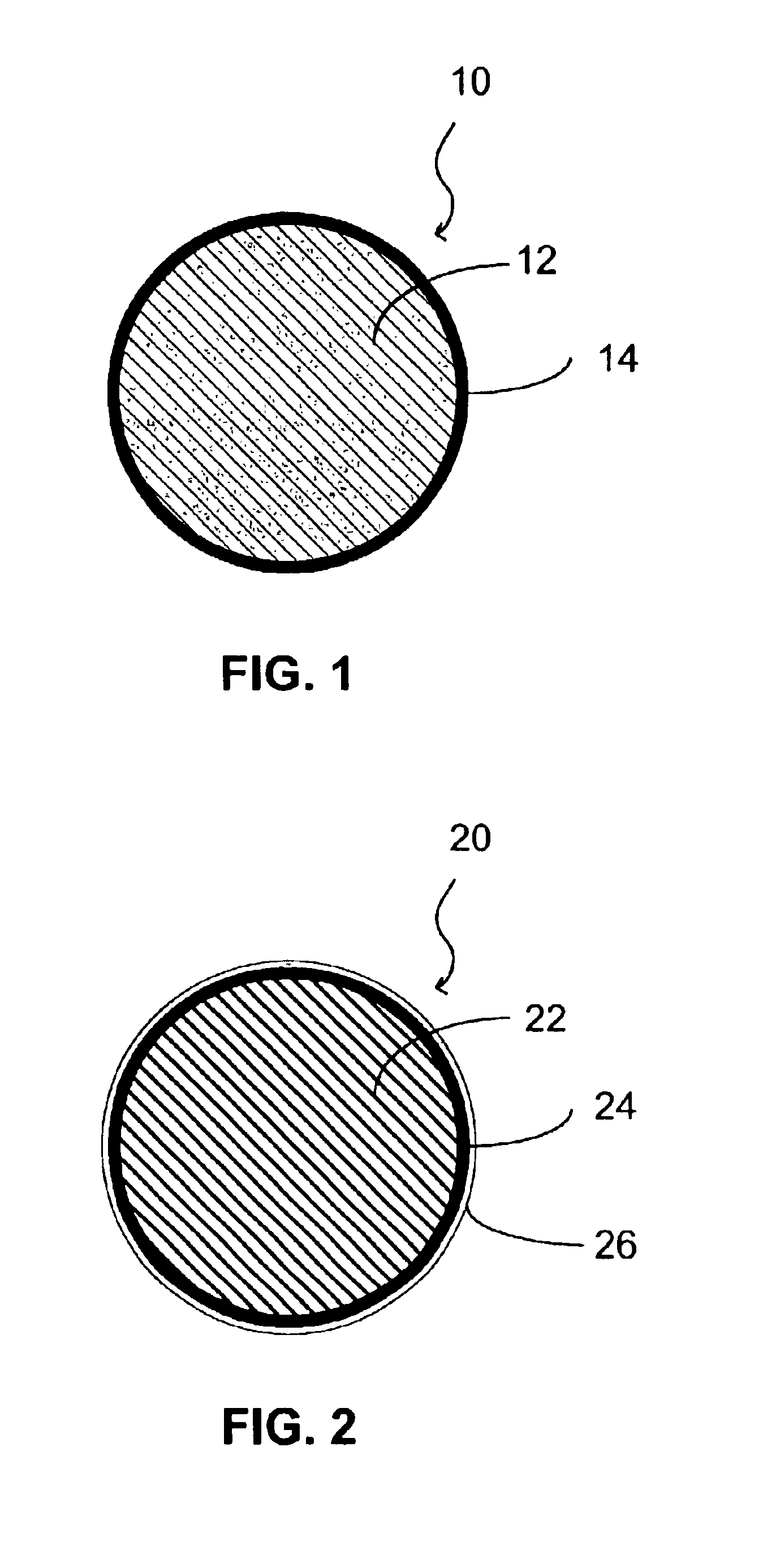
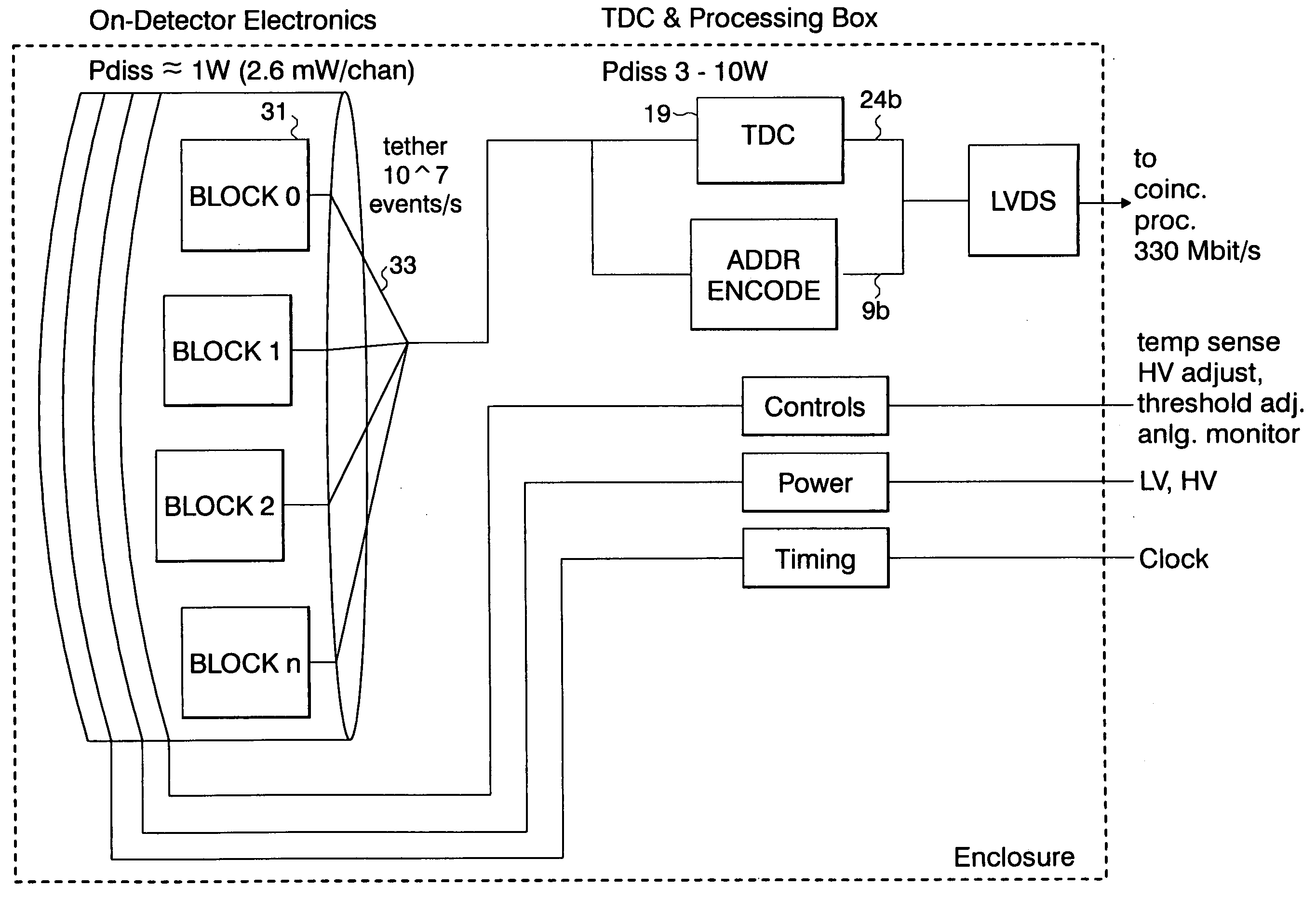
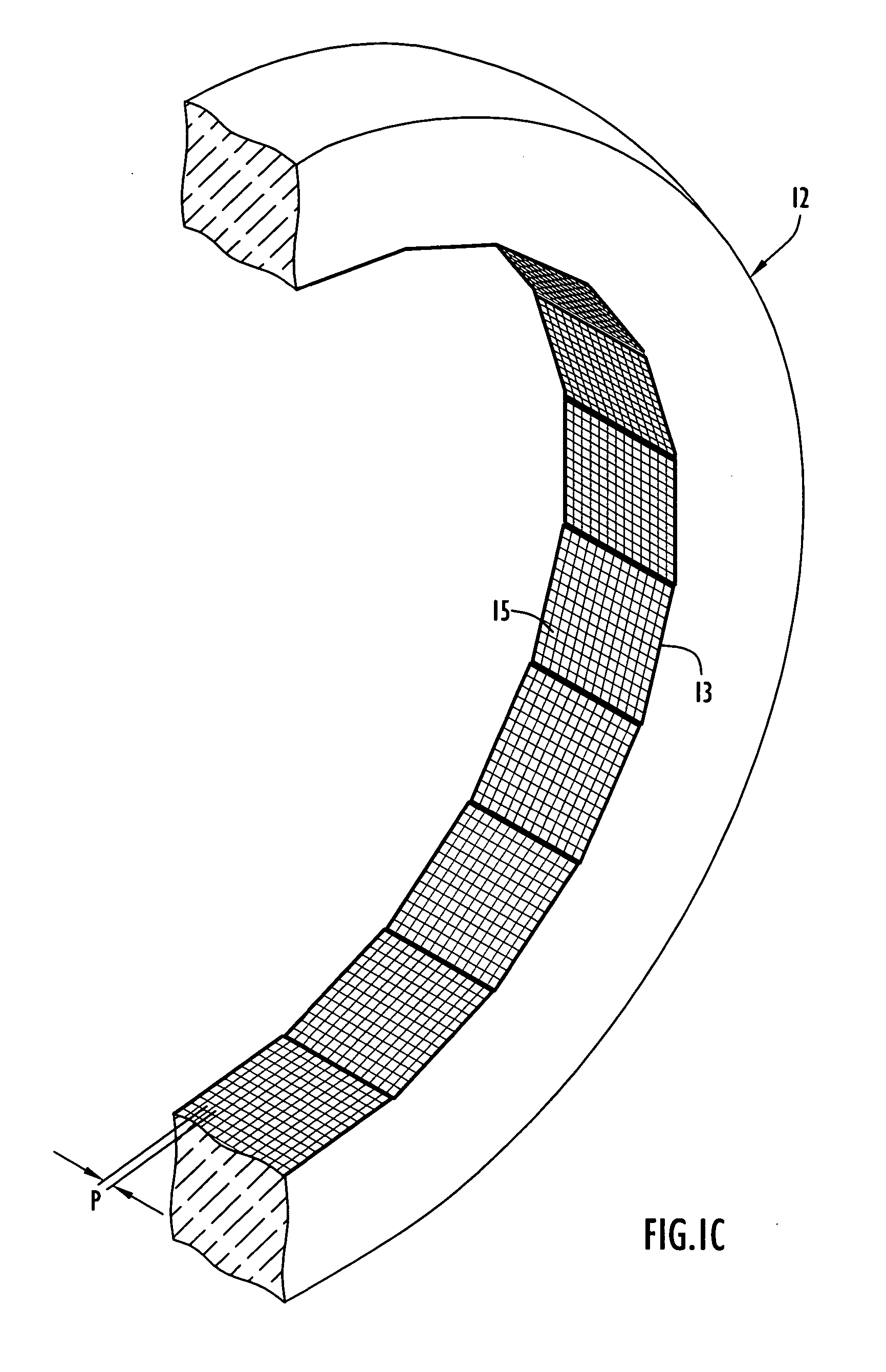
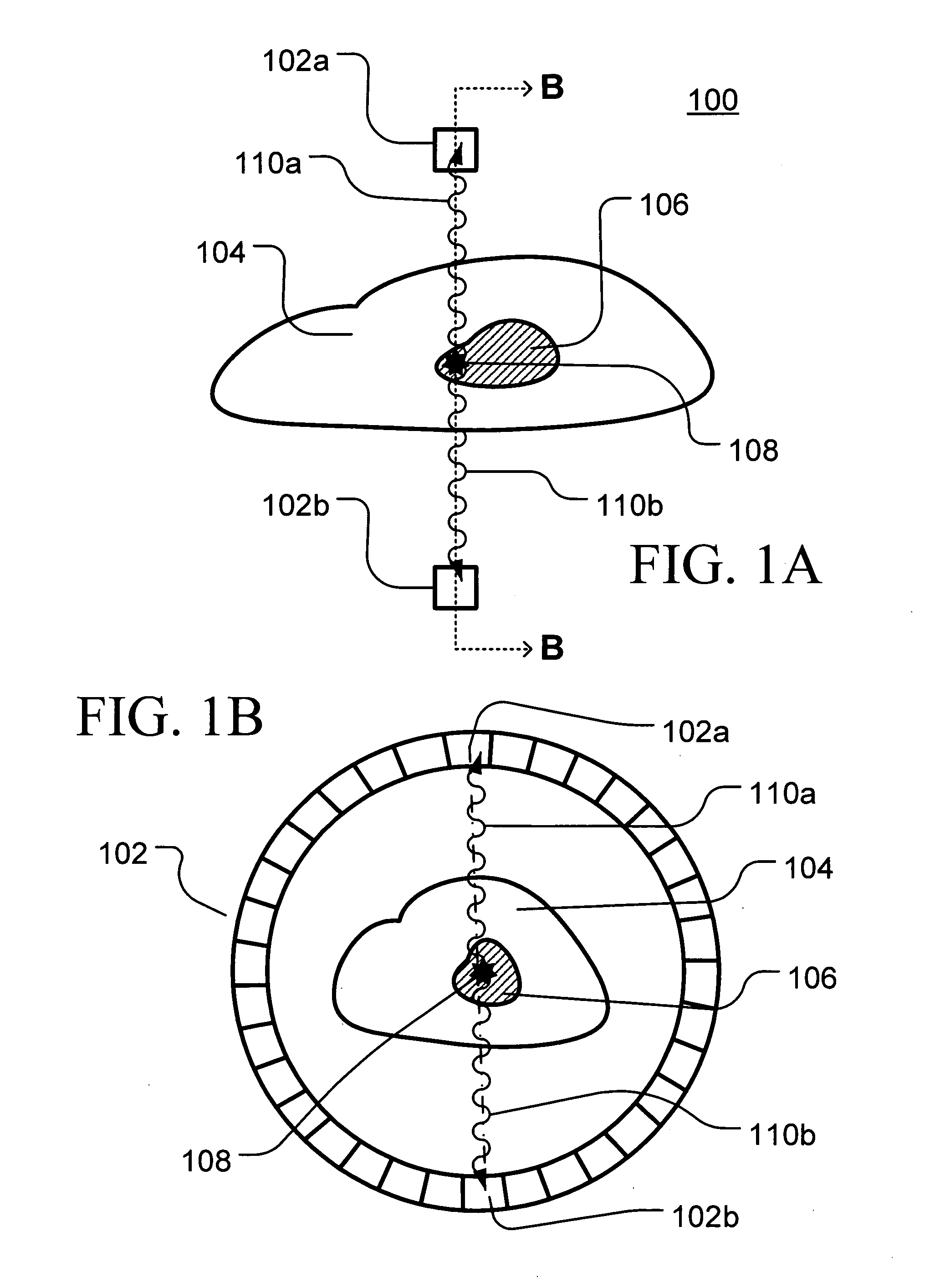
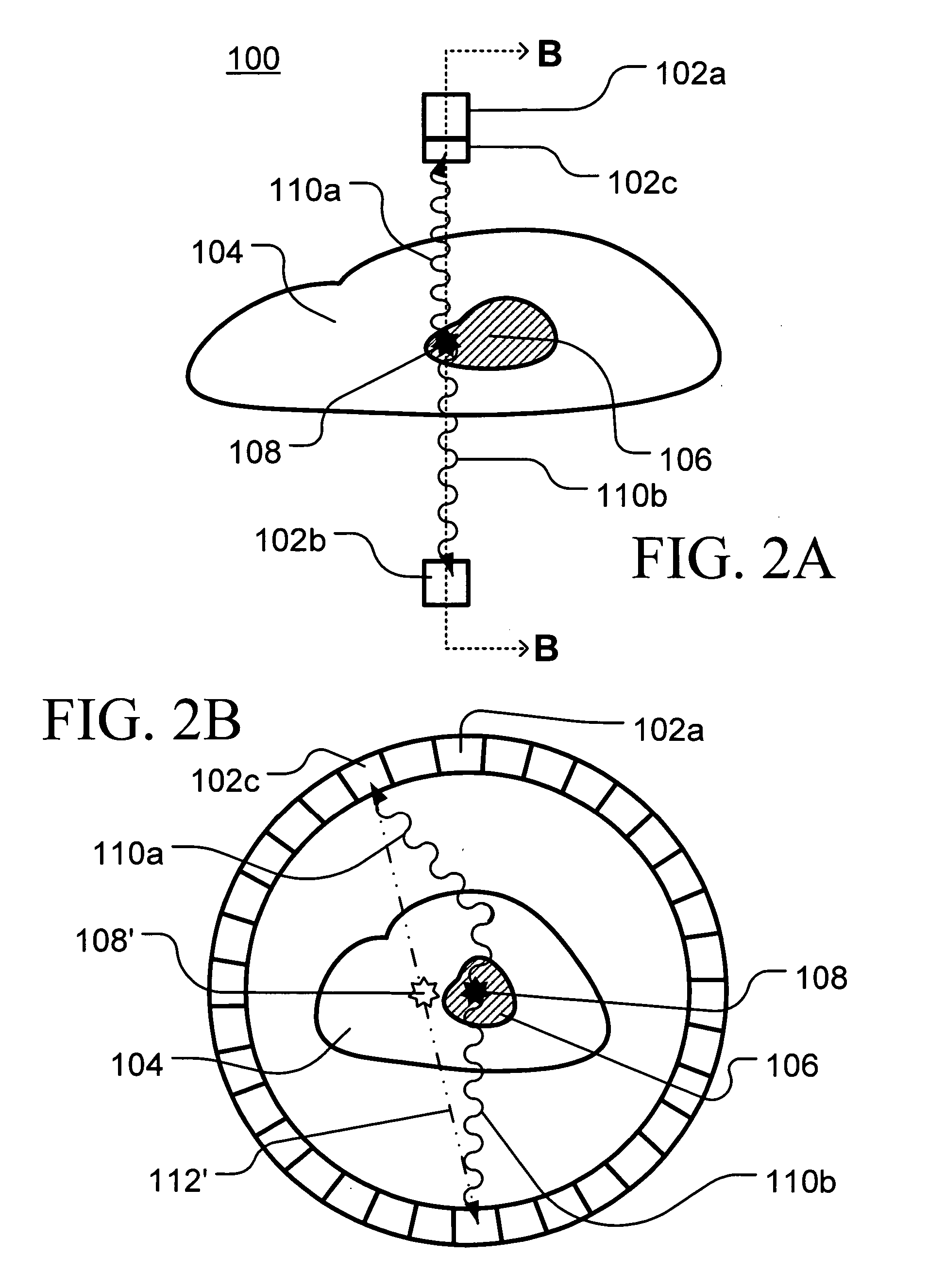
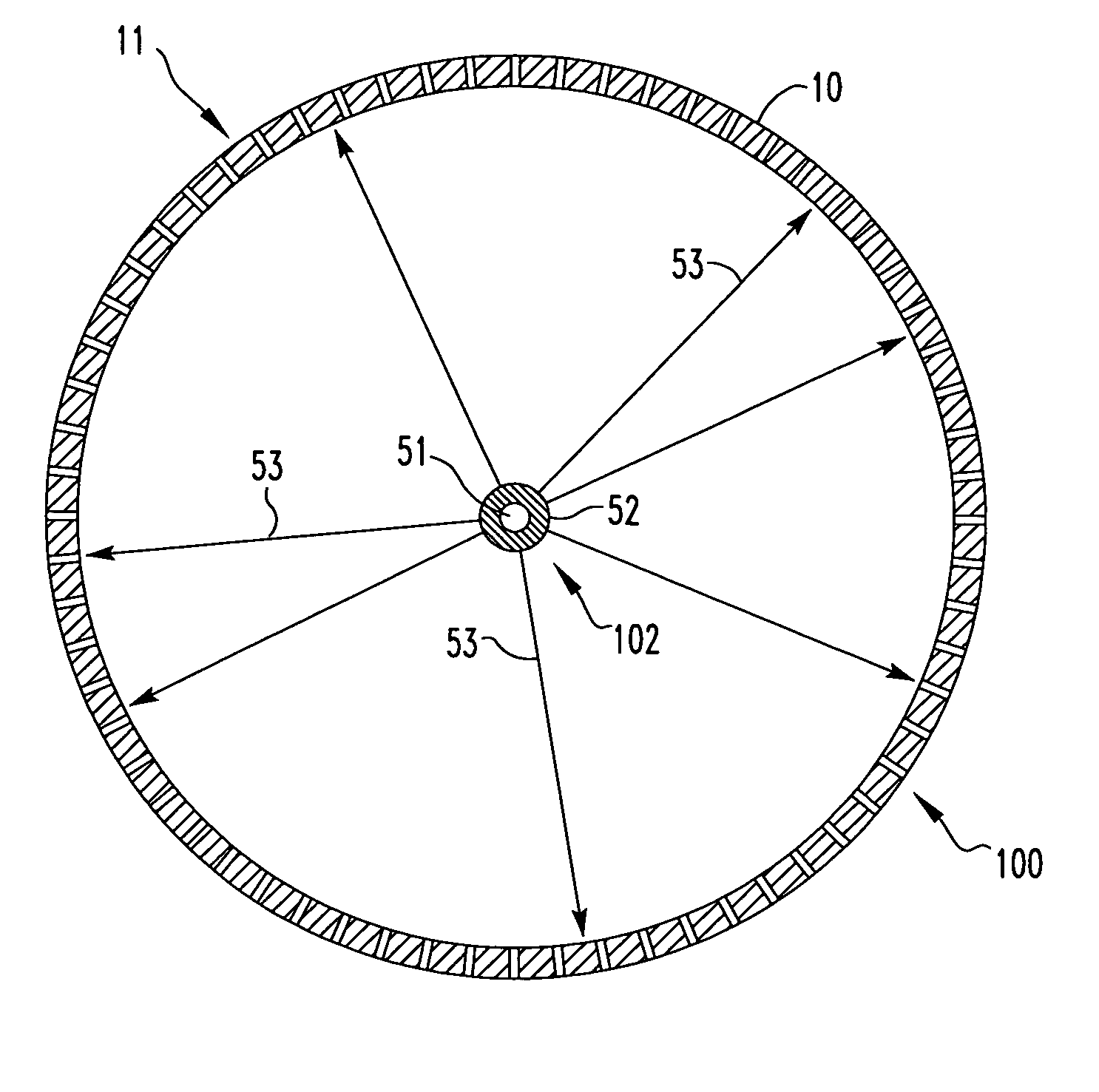
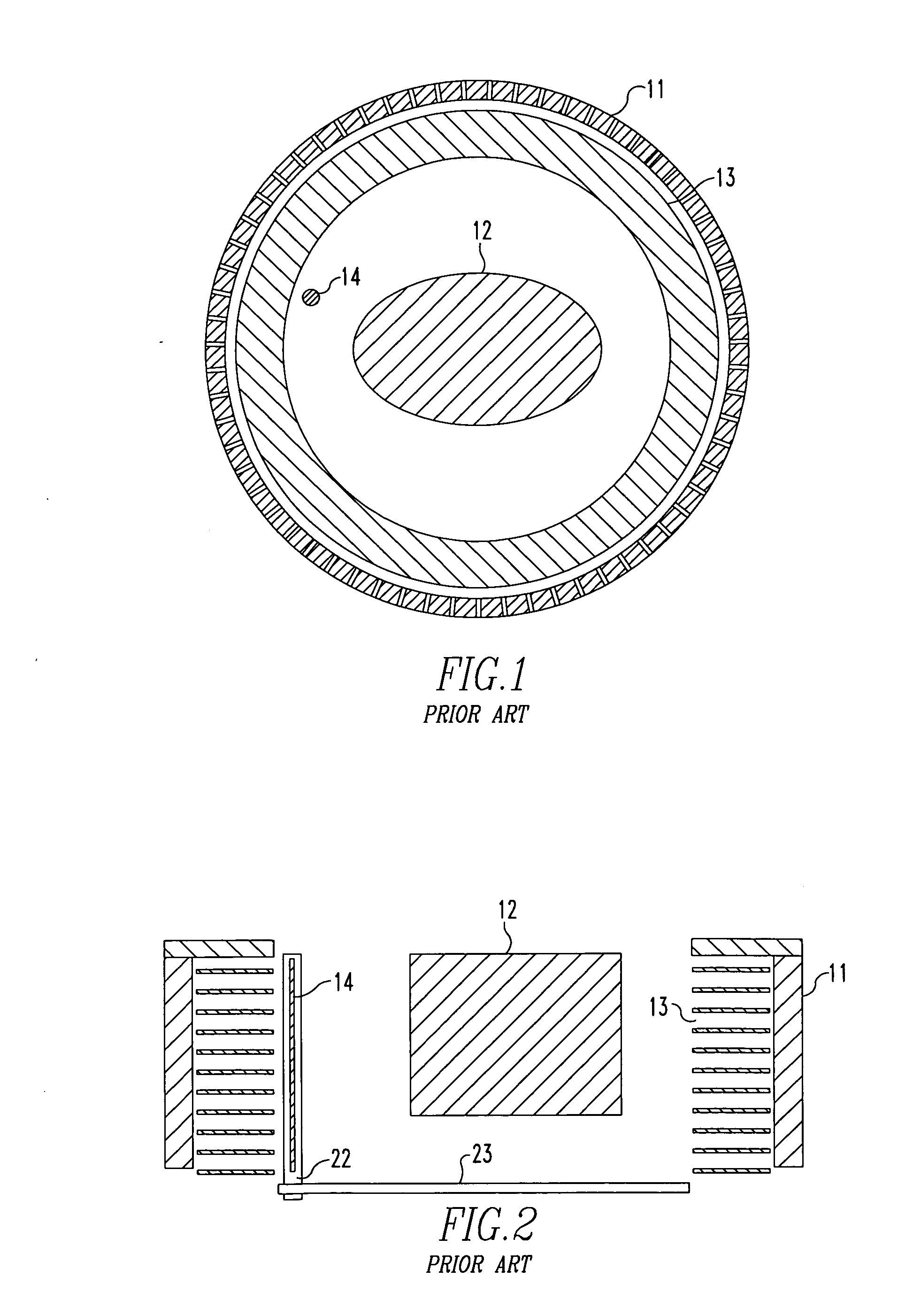
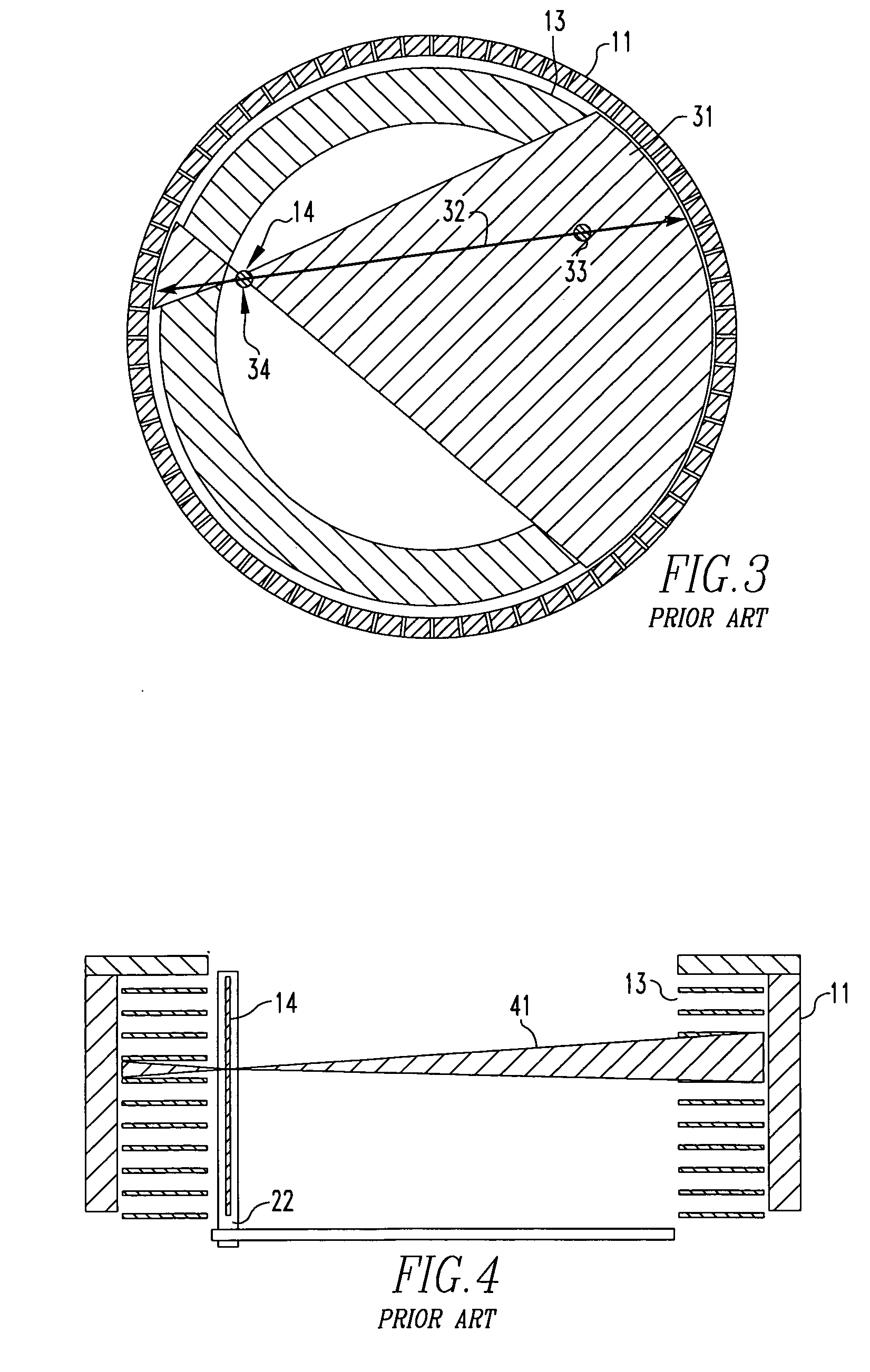
Method and apparatus for timing calibration in a PET scanner
InactiveUS20060102845A1Material analysis by optical meansX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentScintillatorPhysics
The invention is directed to a method and apparatus for timing calibration in a PET scanner. According to one embodiment, the invention relates to a method for timing calibration in a PET scanner having a plurality of scintillator blocks. The method comprises: detecting, in a first scintillator block, a first radiation event, wherein the first scintillator block time-stamps the first radiation event; detecting, in a second scintillator block that is adjacent to the first scintillator block, a second radiation event that corresponds to the first radiation event, wherein the second scintillator block time-stamps the second radiation event; and determining a timing characteristic of the first scintillator block with respect to the second scintillator block based on a comparison between the time-stamps of the first radiation event and the second radiation event.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Sem scanner sensing apparatus, system and methodology for early detection of ulcers
InactiveUS20130123587A1Increased risk of infectionHigh stage ulcer developmentDiagnostic recording/measuringPressure sensorsMultiplexingCapacitance
A handheld, conforming capacitive sensing apparatus configured to measure Sub-Epidermal Moisture (SEM) as a mean to detect and monitor the formation of pressure ulcers. The device incorporates an array of electrodes which are excited to measure and scan SEM in a programmable and multiplexed manner by a battery-less RF-powered chip. The scanning operation is initiated by an interrogator which excites a coil embedded in the apparatus and provides the needed energy burst to support the scanning / reading operation. Each electrode measures the equivalent sub-epidermal capacitance corresponding and representing the moisture content.
Owner:BRUIN BIOMETRICS +1
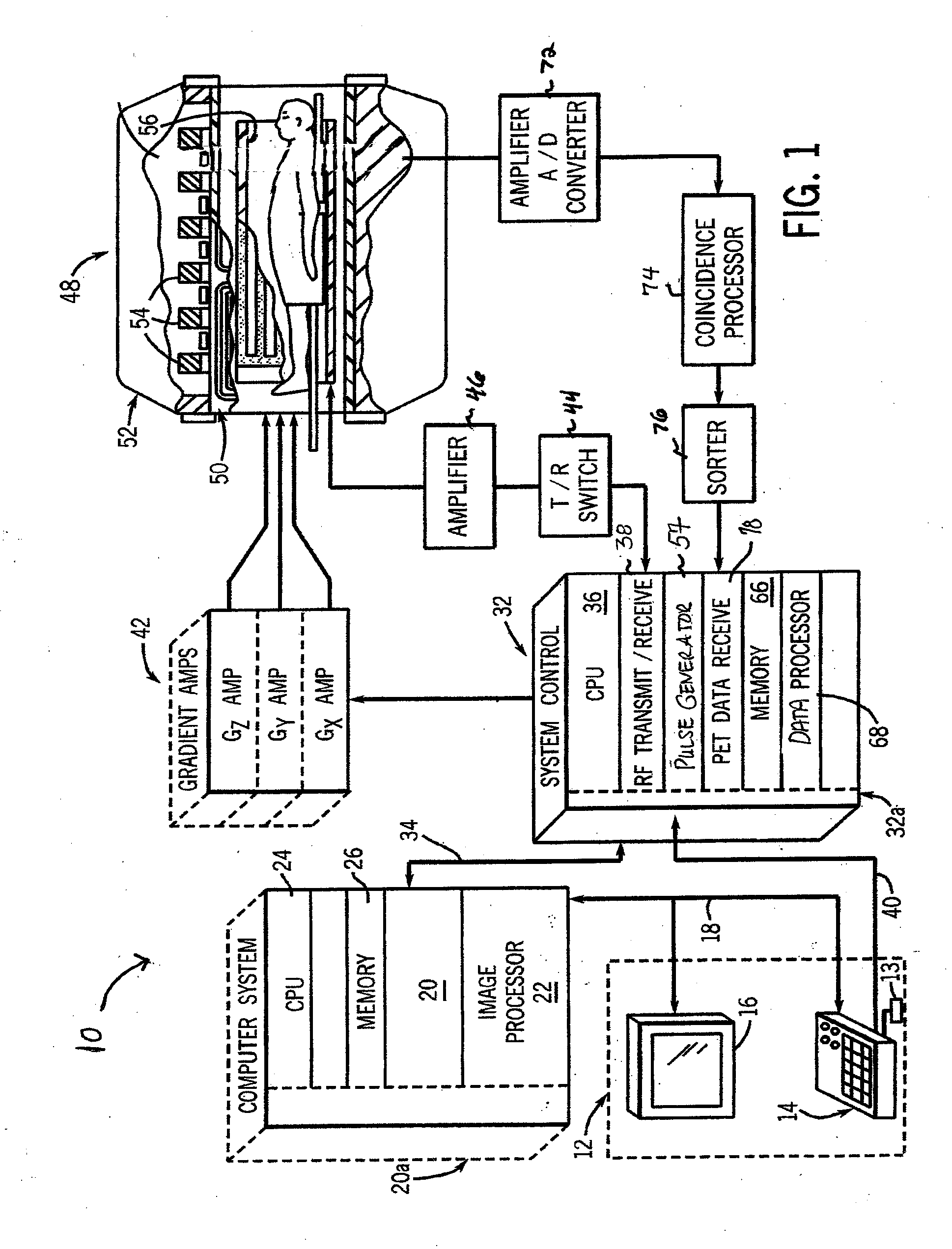
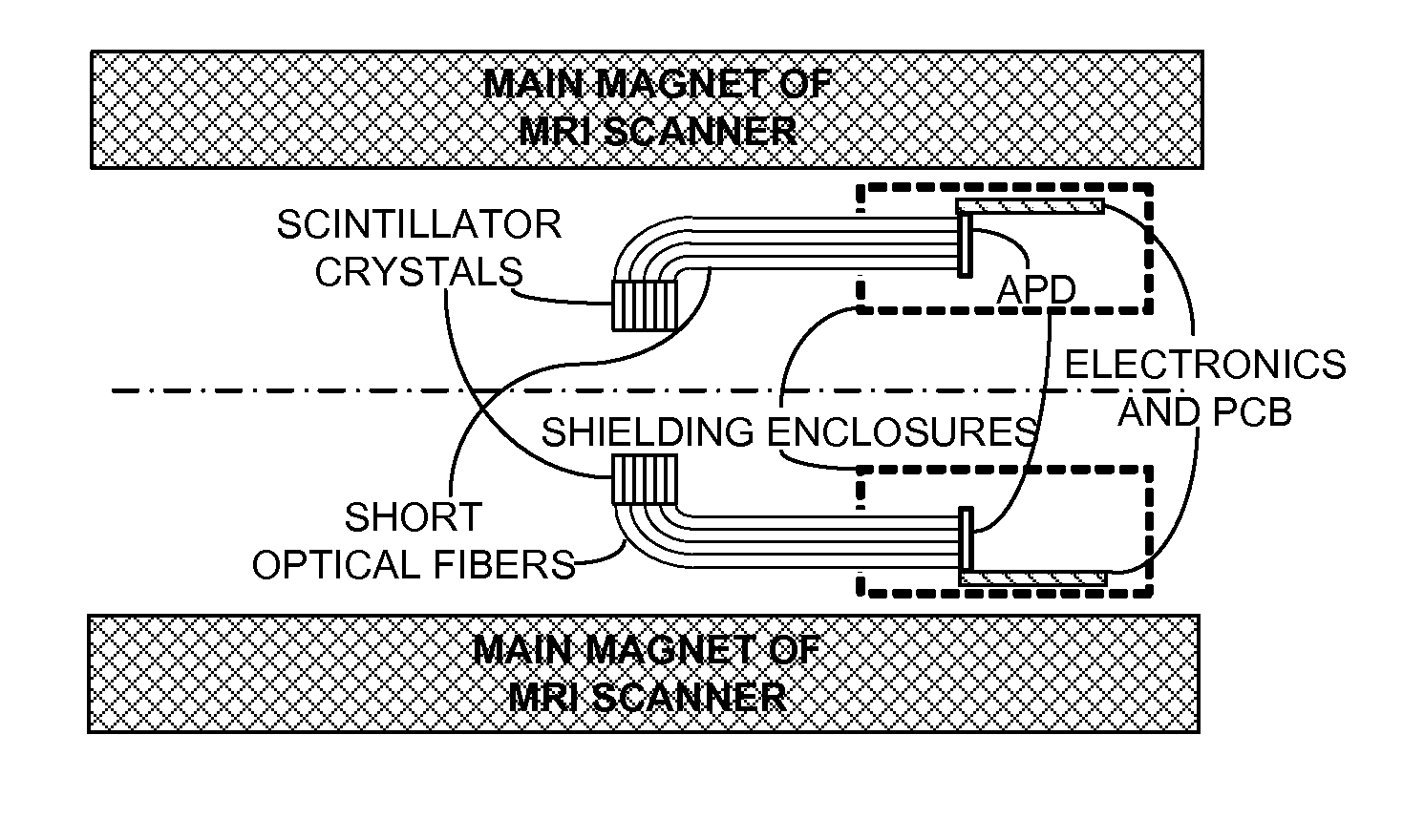
System and apparatus for detecting gamma rays in a pet/mri scanner
ActiveUS20080265887A1Material analysis by optical meansElectric/magnetic detectionPhotodetectorRadio frequency
A gamma ray detector ring for a combined positron emission tomography (PET) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system is integrated into a radio frequency (RF) coil assembly such that the detector ring is integrated with a RF shield. Each gamma ray detector in the detector ring includes a scintillator component that emits light when a gamma ray is detected and a photodetector component designed to be sensitive to the frequency of light produced by the scintillator. A RF shield may be integrated into a detector ring such that the RF shield is positioned between the scintillator and photodetector components of each detector, thereby saving valuable radial space within the imaging system. Multiple such detector rings may be located adjacent to one another to increase axial coverage and enable three-dimensional PET imaging techniques.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
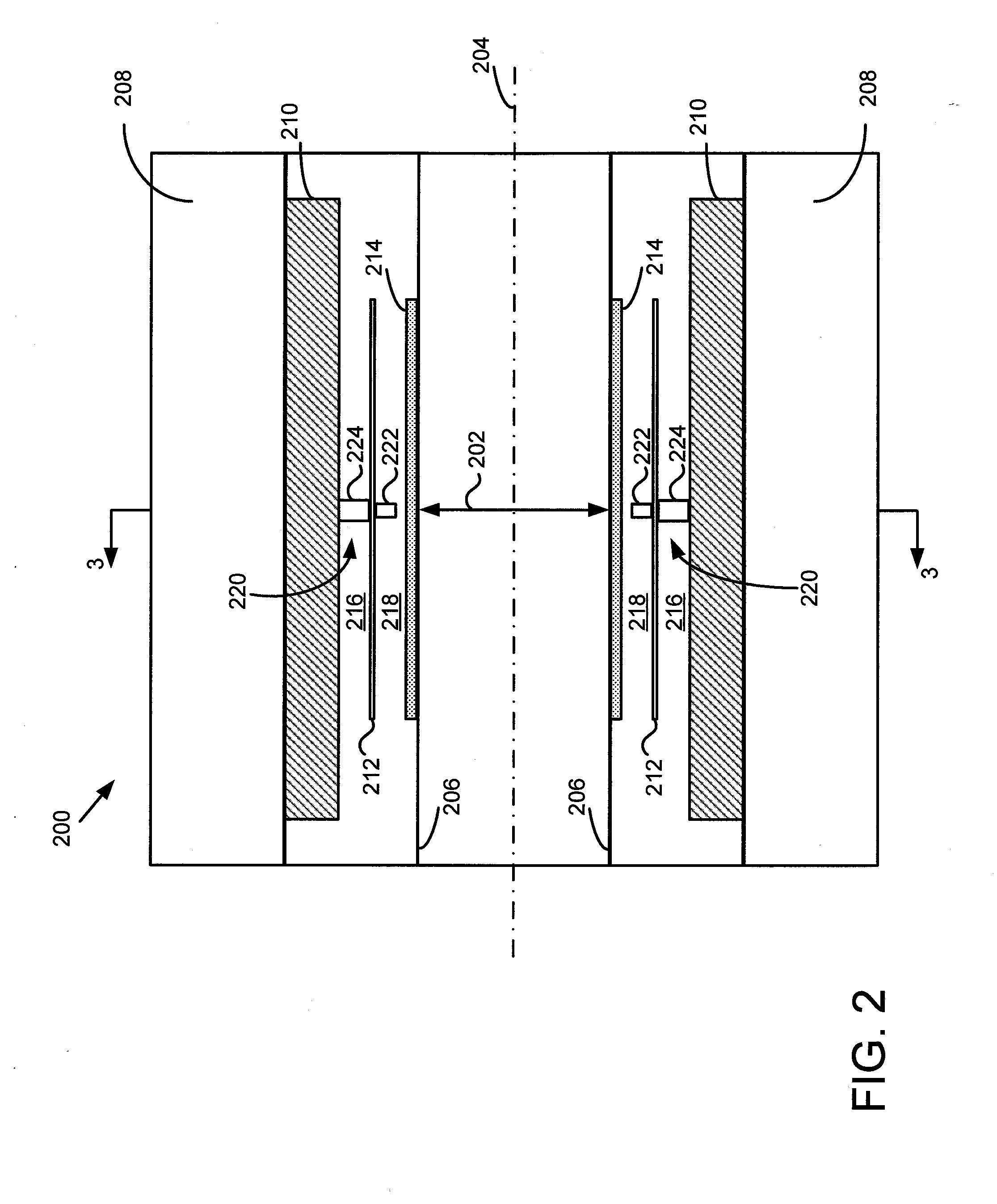
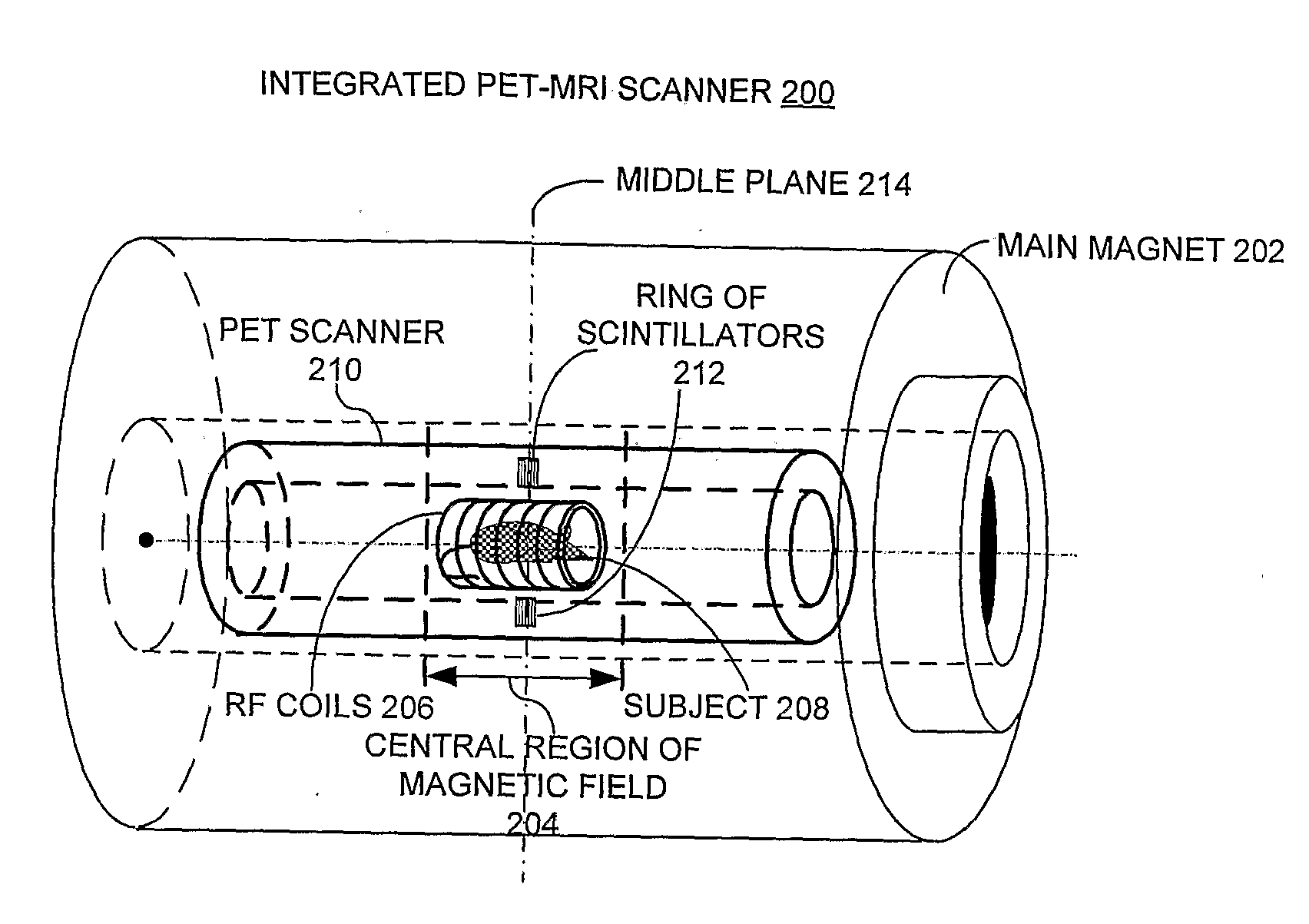
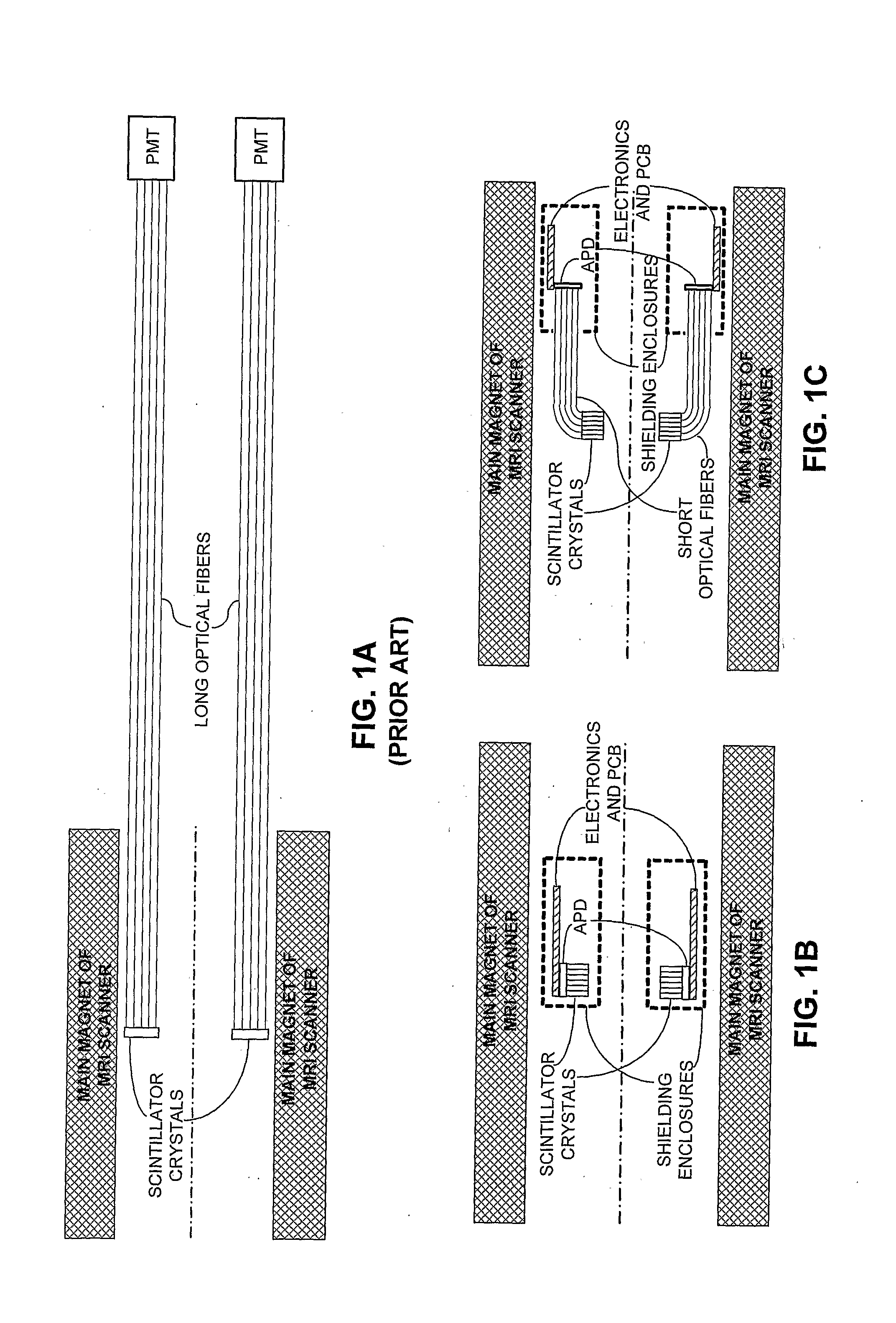
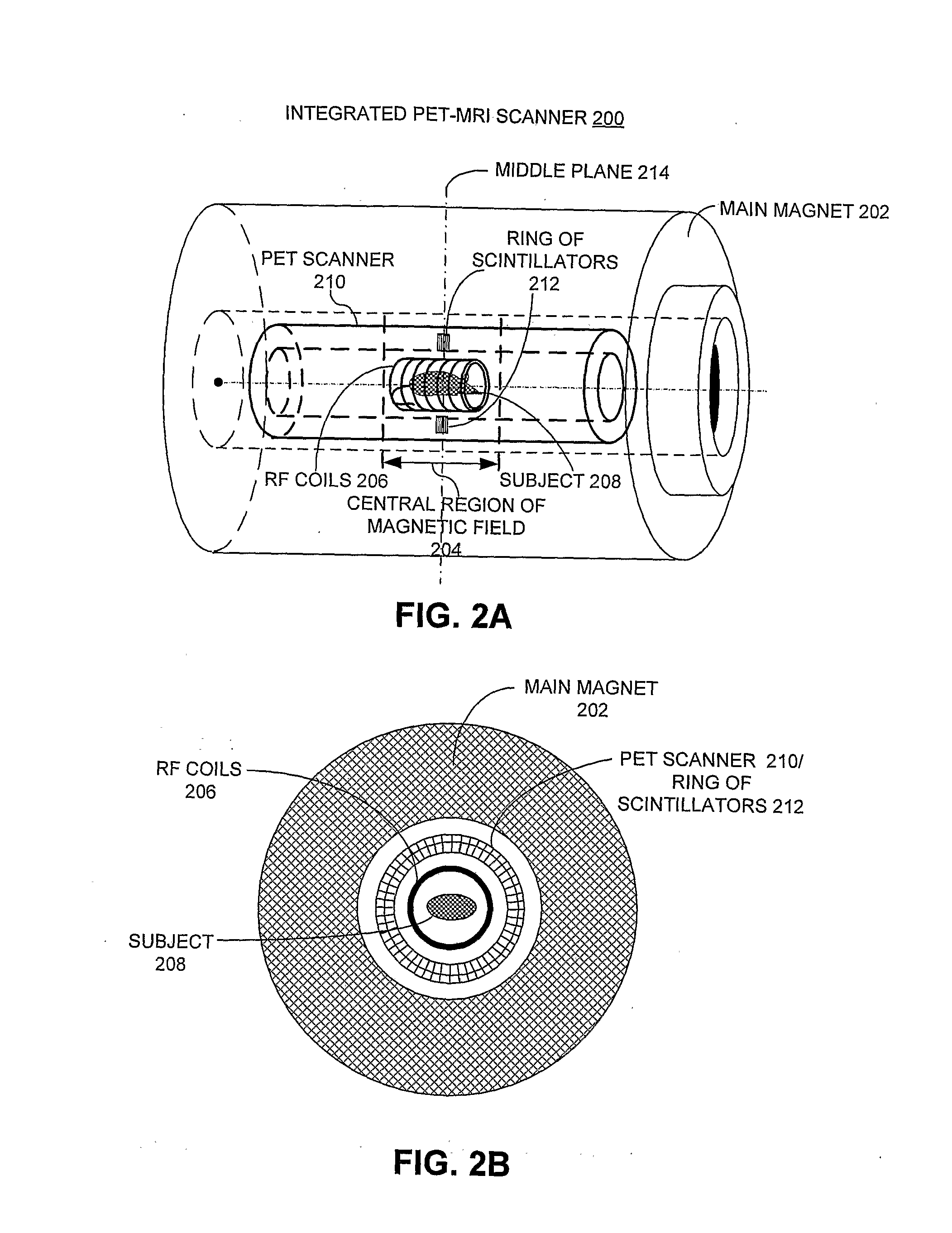
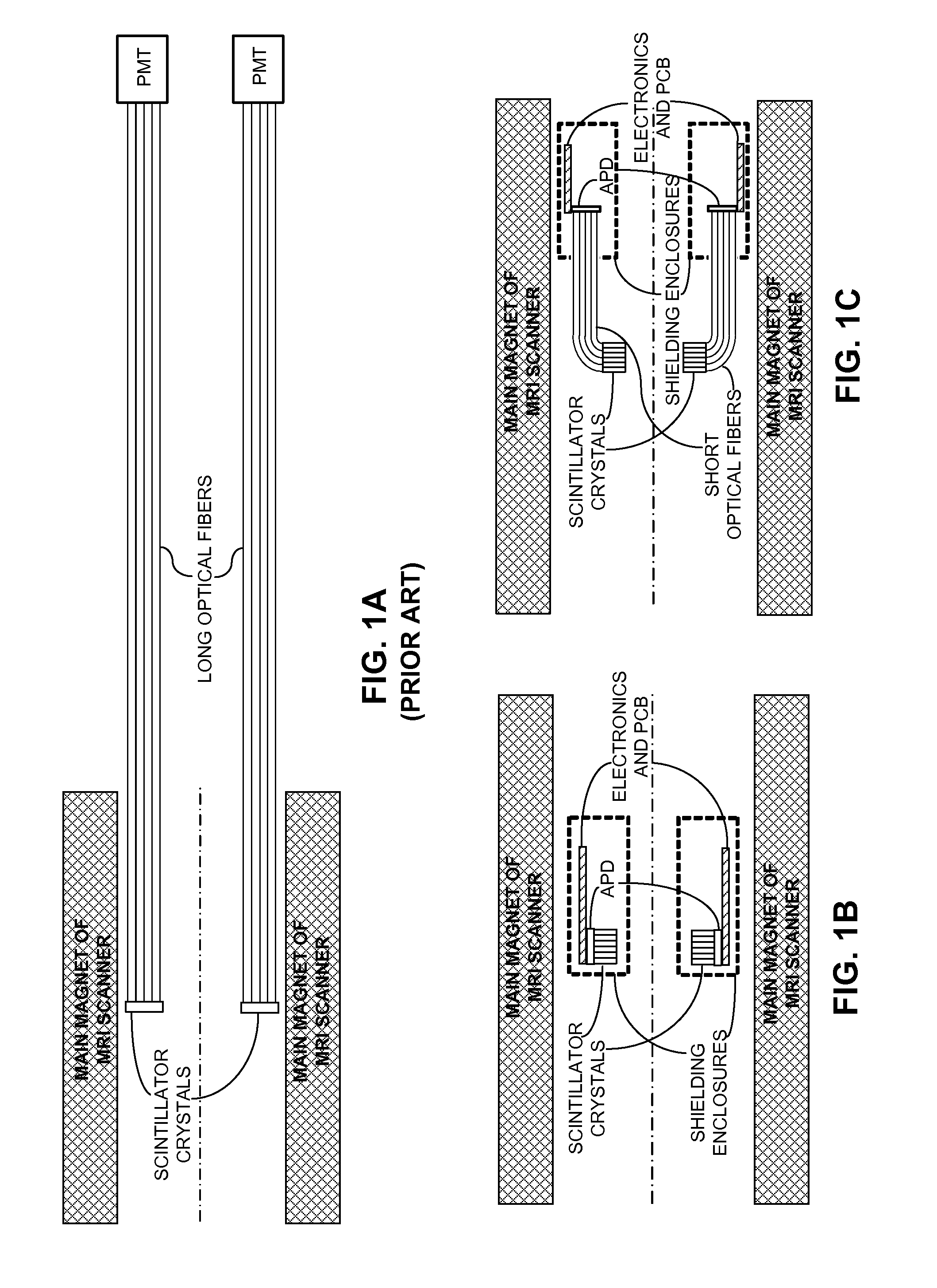
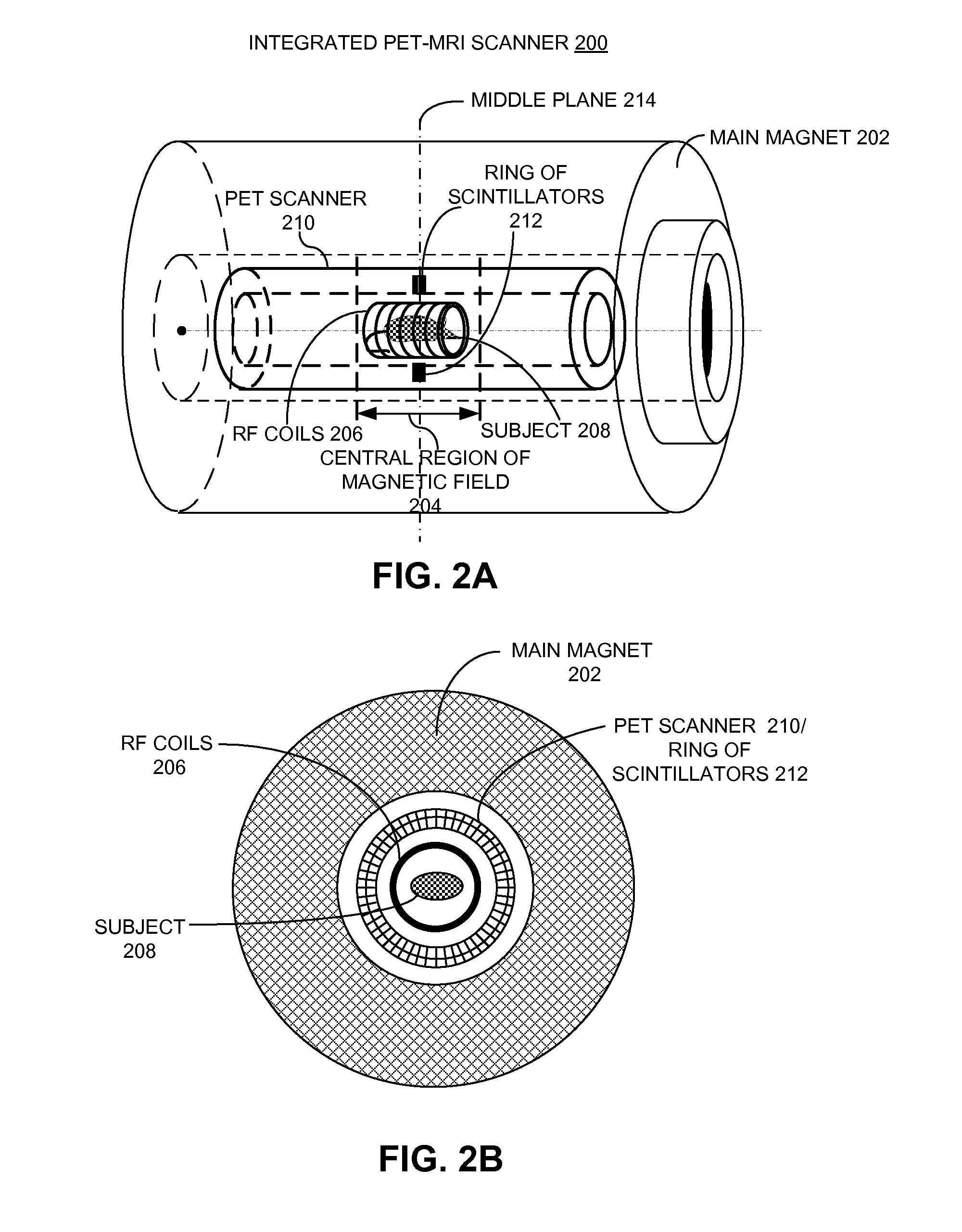
Integrated Pet-Mri Scanner
InactiveUS20080214927A1Reduce electromagnetic interferenceEasy to storeMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
One embodiment of the present invention provides an integrated PET-MRI scanner. This integrated scanner includes a main magnet that generates a magnetic field, wherein images of the subject is generated in a central region of the magnetic field. It also includes a PET scanner which is enclosed by the main magnet. The PET scanner further comprises: (1) at least one ring of scintillators, which is situated in the central region of the magnetic field and, (2) one or more photodetectors, which are coupled to the ring of scintillators, so that the one or more photodetectors are outside the central region of the magnetic field. The integrated scanner also includes radio-frequency (RF) coils which are enclosed by the PET scanner. By keeping the photodetectors and associated circuitry outside the central region of the magnetic field, the integrated scanner reduces the electromagnetic interference (EMI) between the PET scanner and the MRI scanner.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
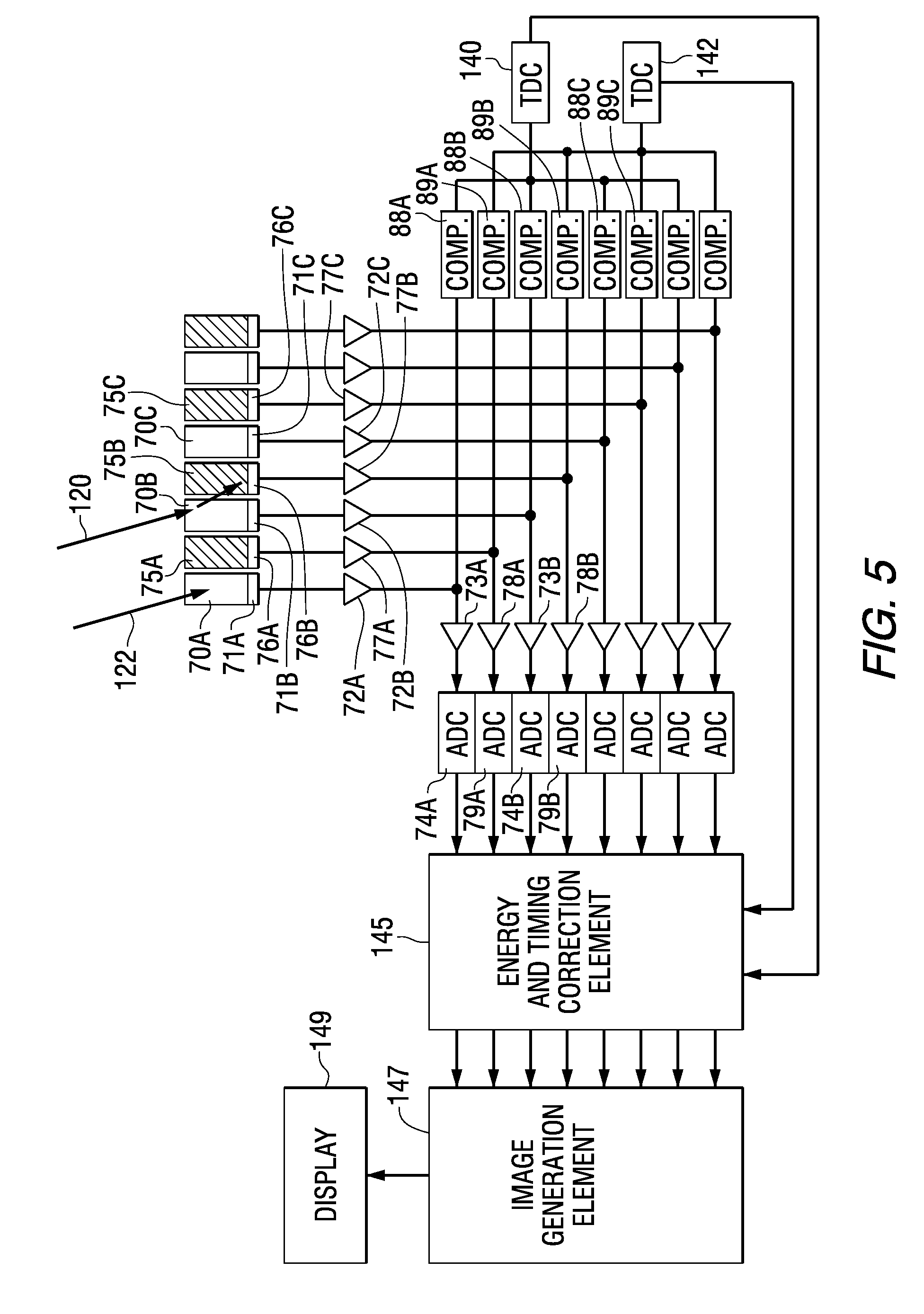
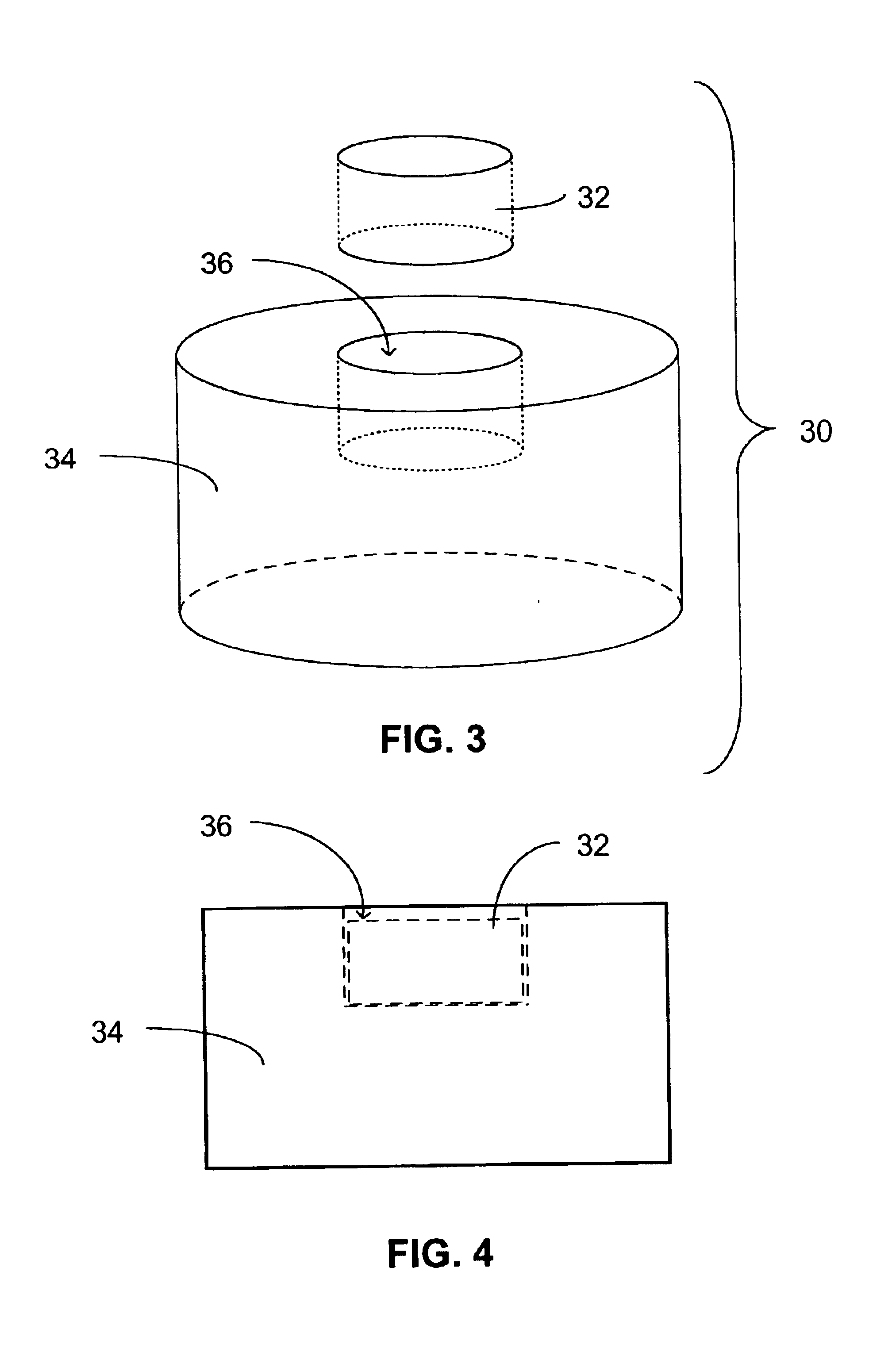
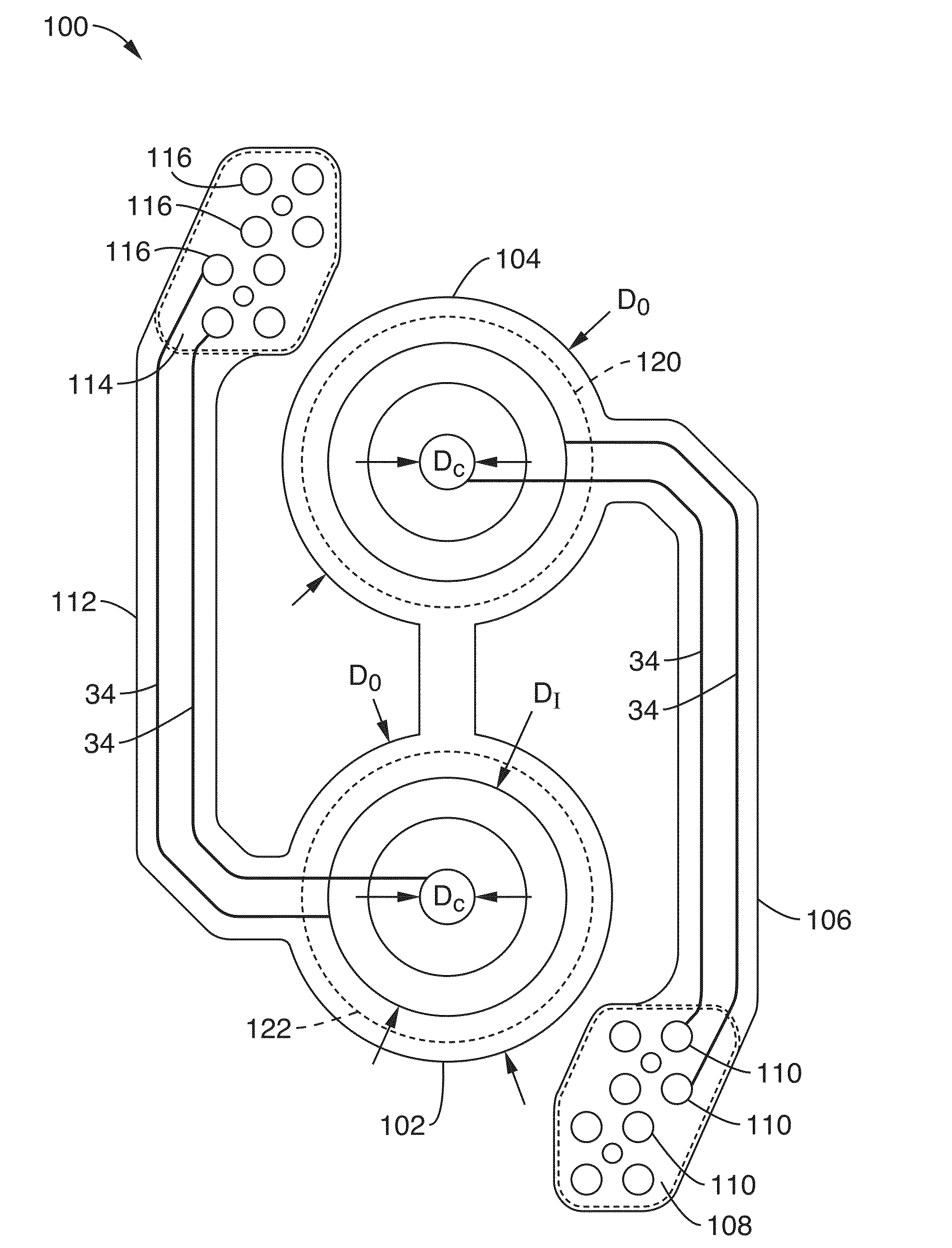
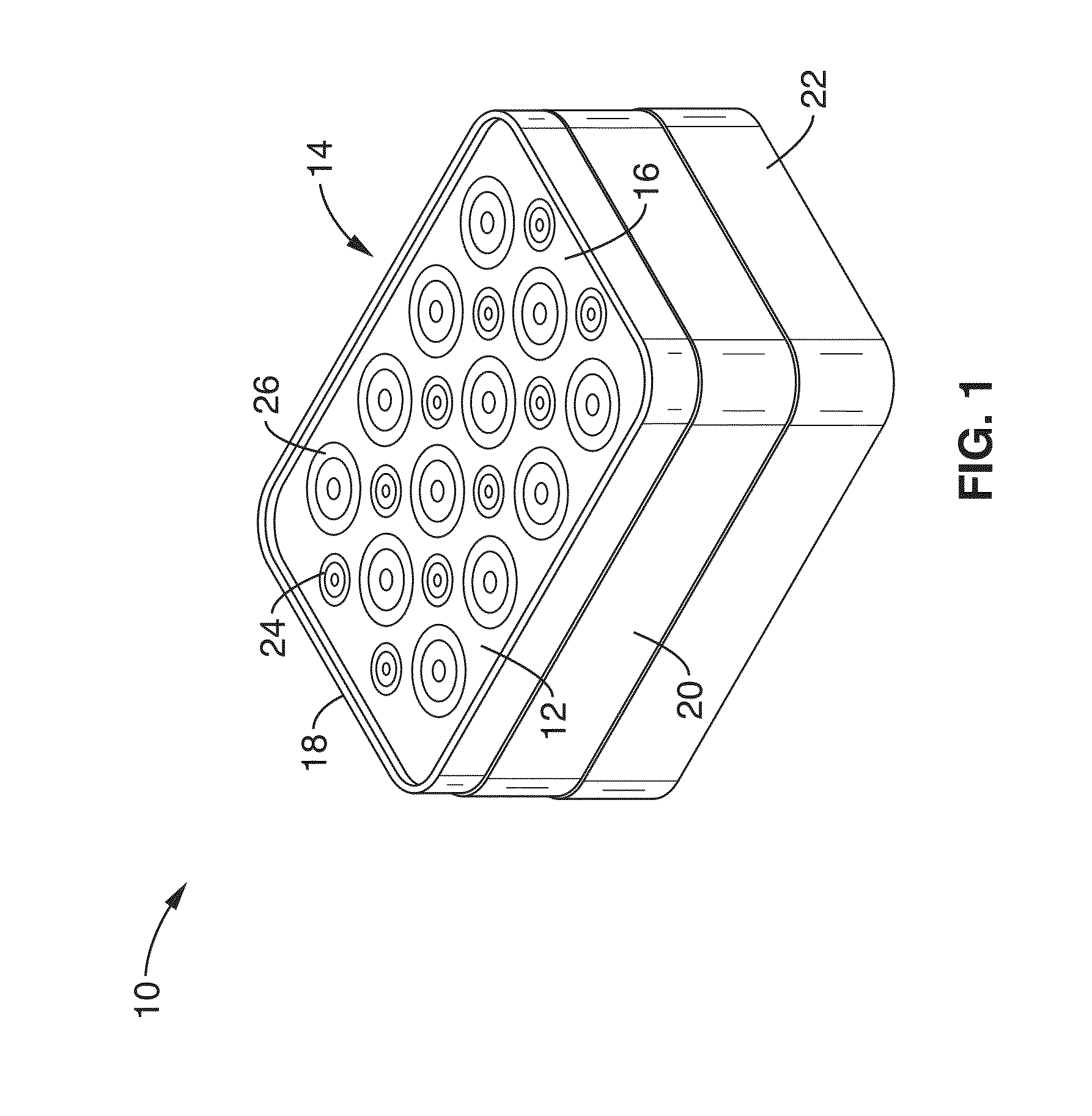
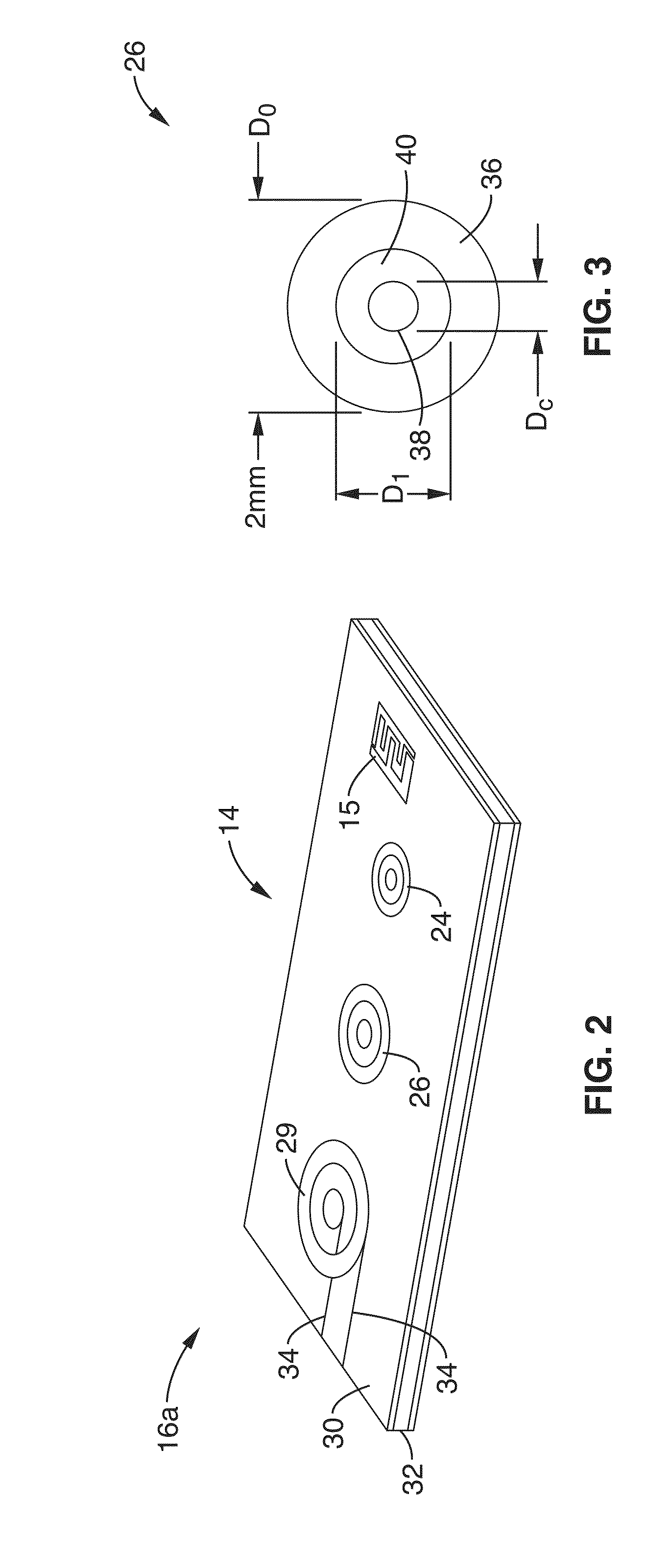
Multiplexing readout scheme for a gamma ray detector
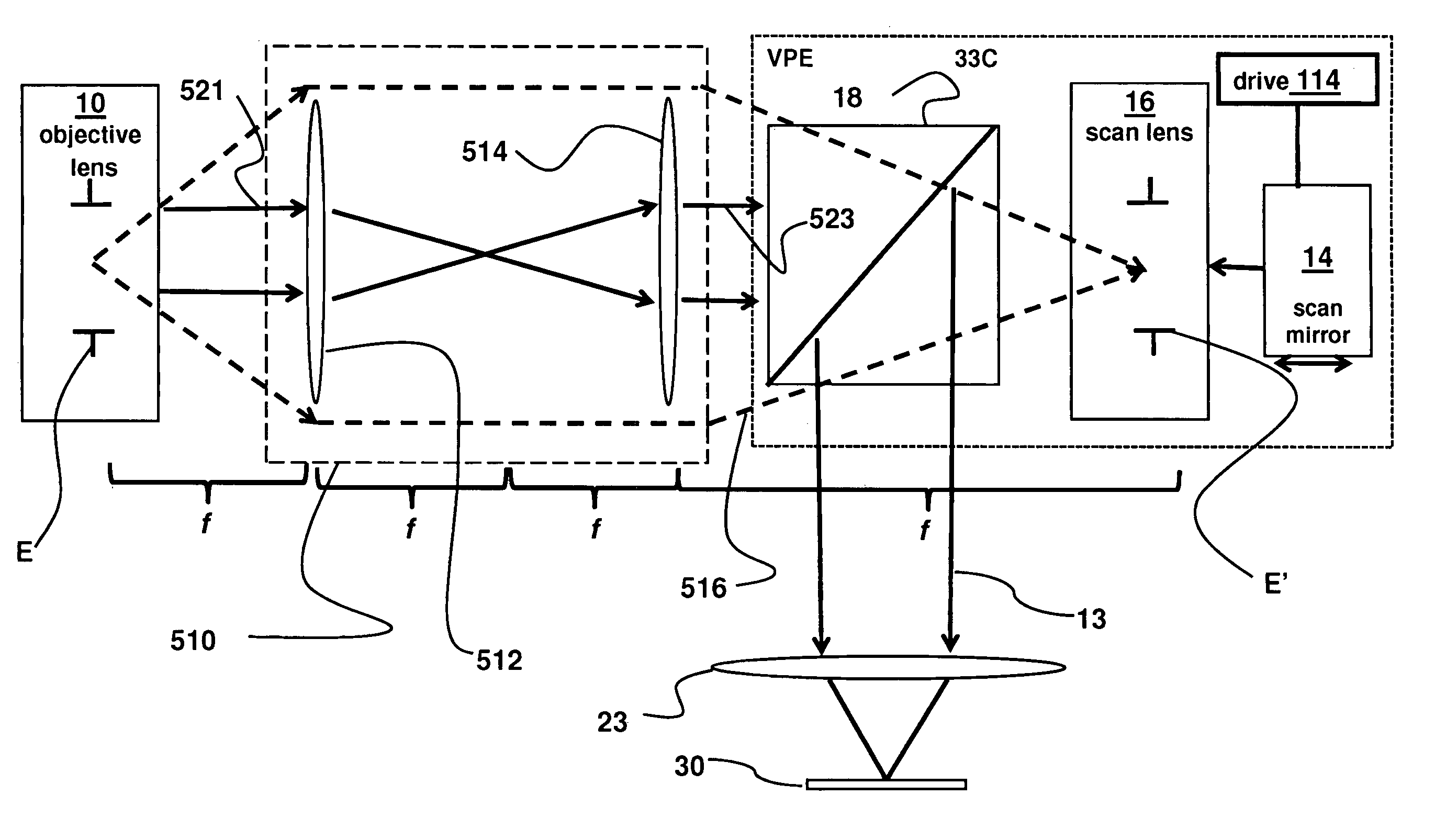
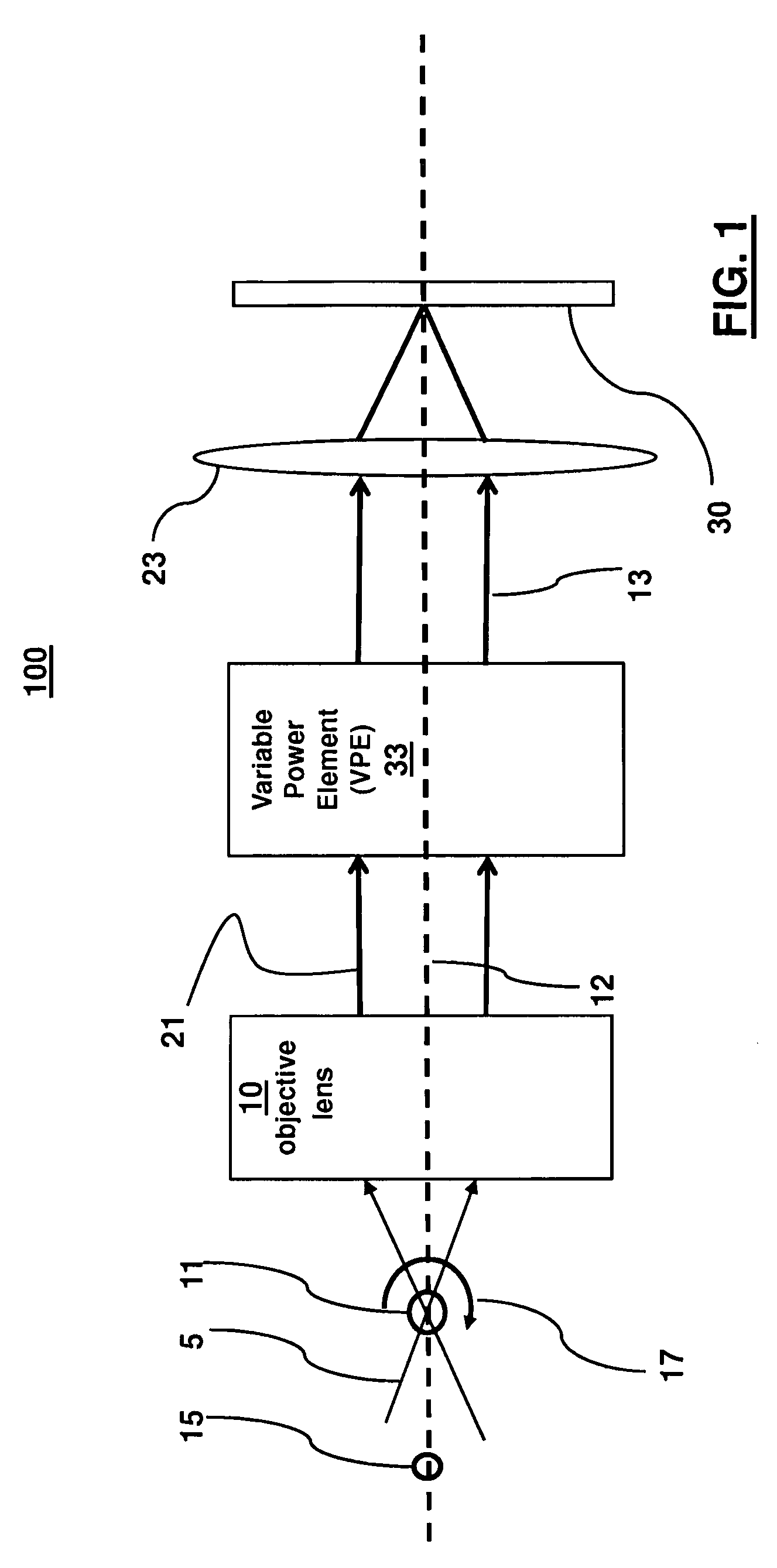
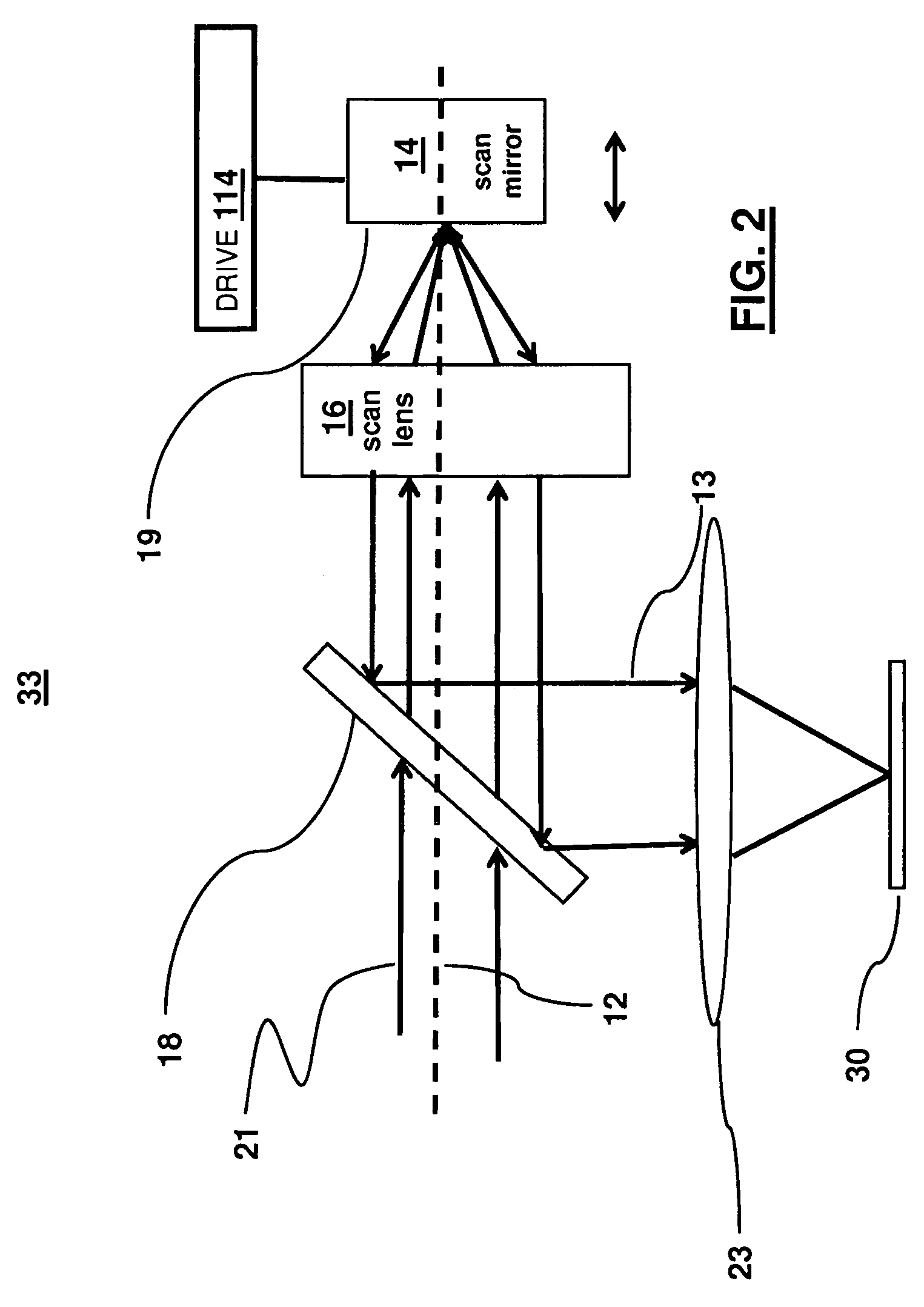
A method for producing a PET image of a tissue using a PET scanner, the scanner comprising a plurality of scintillation crystals (70X / 75X) and a plurality of detectors (71X / 76X). The method comprises forming a first crystal group (160X) including a first subset of the plurality of crystals; forming a second crystal group (164X) including a second subset of the plurality of crystals, wherein crystals comprising the first crystal group (160X) are different from crystals comprising the second crystal group (164X); converting a first beam (120) striking one or more crystals of the first crystal group (70X / 160X) to a first electrical signal (94); converting a second beam striking one or more crystals of the second crystal group (75X / 164X) to a second electrical signal (98), wherein the second beam is scattered from the first beam; determining one or both of a first and a second timing relationship, wherein the first timing relationship (Δt2) is a time interval between a value of the first electrical signal (94) and a time reference (t1), and the second timing relationship (Δt3) is a time interval between a value of the second electrical signal (98) and the time reference (t1); correcting the second electrical signal (98) to produce a corrected second electrical signal using a correction factor derived from at least one of the first and the second timing relationships to compensate for energy in the second signal scattered from the first signal; and creating an image of the tissue (12) using the corrected second electrical signal.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method for improving clinical data quality in positron emission tomography
InactiveUS20050129170A1Improving clinical data qualitySimple calculationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingData signalData quality
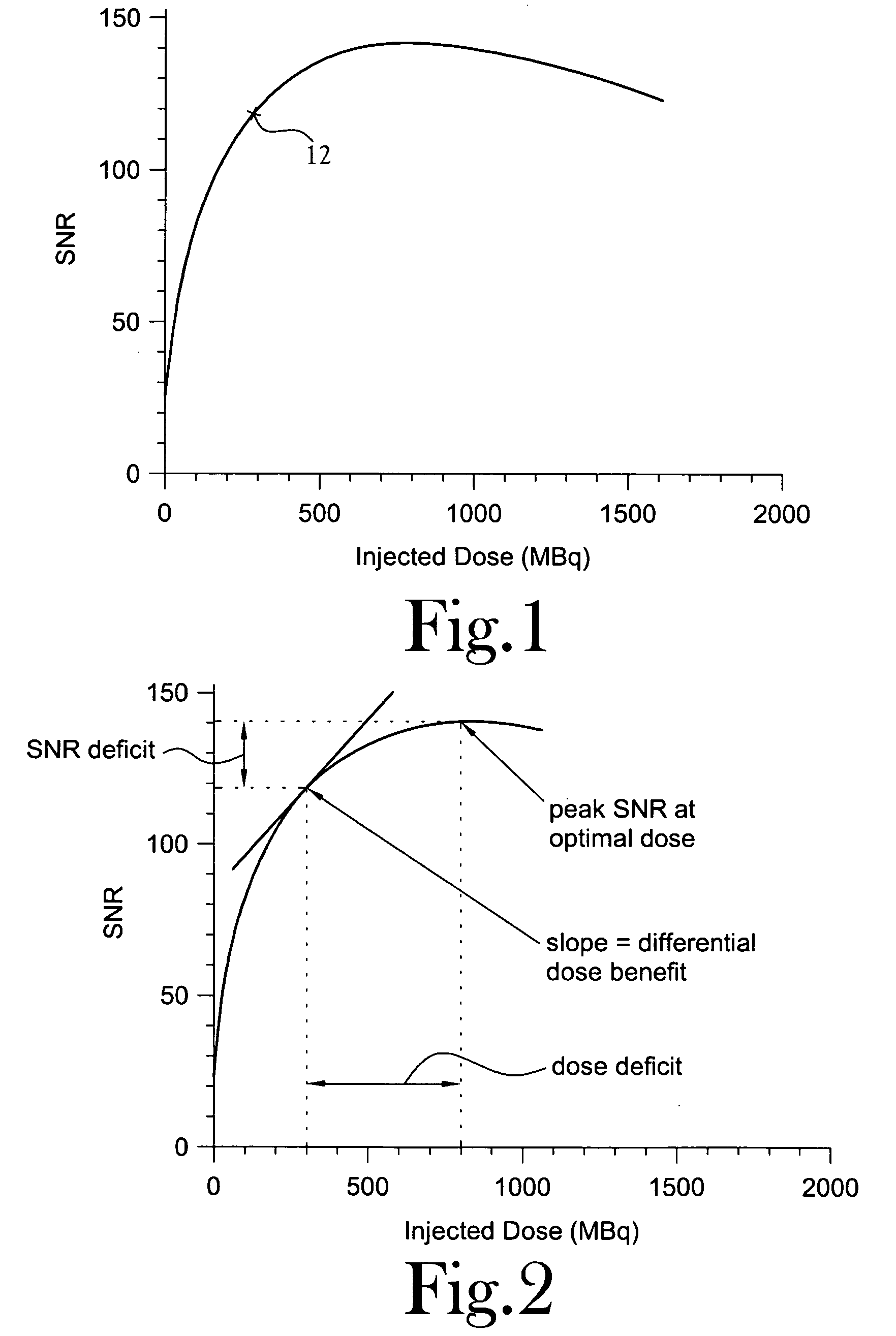
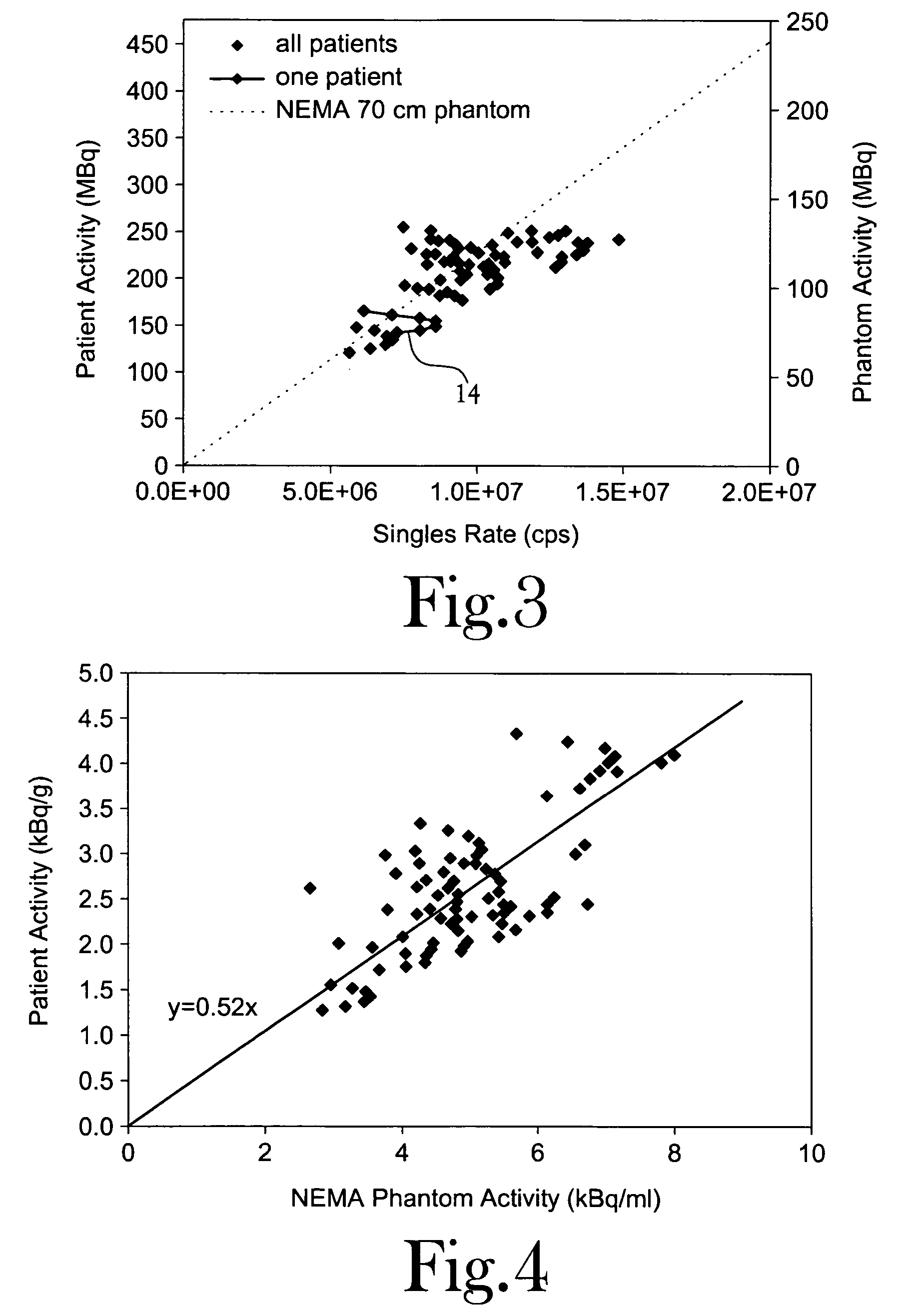
A method for improving clinical data quality in Positron Emission Tomography (PET). The method provides for the processing of PET data to accurately and efficiently determine a data signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) corresponding to each individual clinical patient scan, as a function of a singles rate in a PET scanner. The method relates an injected dose to the singles rate to determine SNR(Dinj), and provides an accurate estimate of a quantity proportional to SNR, similar in function to the SNR(Dinj). Knowledge of SNR(Dinj) permits determination of peak SNR, optimal dose, SNR deficit, dose deficit, and differential dose benefit. The patient dose is fractionated, with a small calibration dose given initially. After a short uptake, the patient is pre-scanned to determine T, S, and R. An optimal dose is then determined and the remainder injected.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Technique for reconstructing PET scan images
ActiveUS7381959B2Material analysis by optical meansX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentComputer scienceCoincidence
The invention is directed to a technique for reconstructing PET scan images. According to one embodiment, the invention relates to a method for reconstructing PET scan images. The method comprises: detecting a plurality of coincidence events in a PET scanner; storing data associated with the plurality of coincidence events in a chronological list based on a detection time for each of the plurality of coincidence events; generating correction data based on scatter coincidence events and random coincidence events in the plurality of coincidence events; and reconstructing one or more PET scan images based at least in part on the chronological list of data and the correction data.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
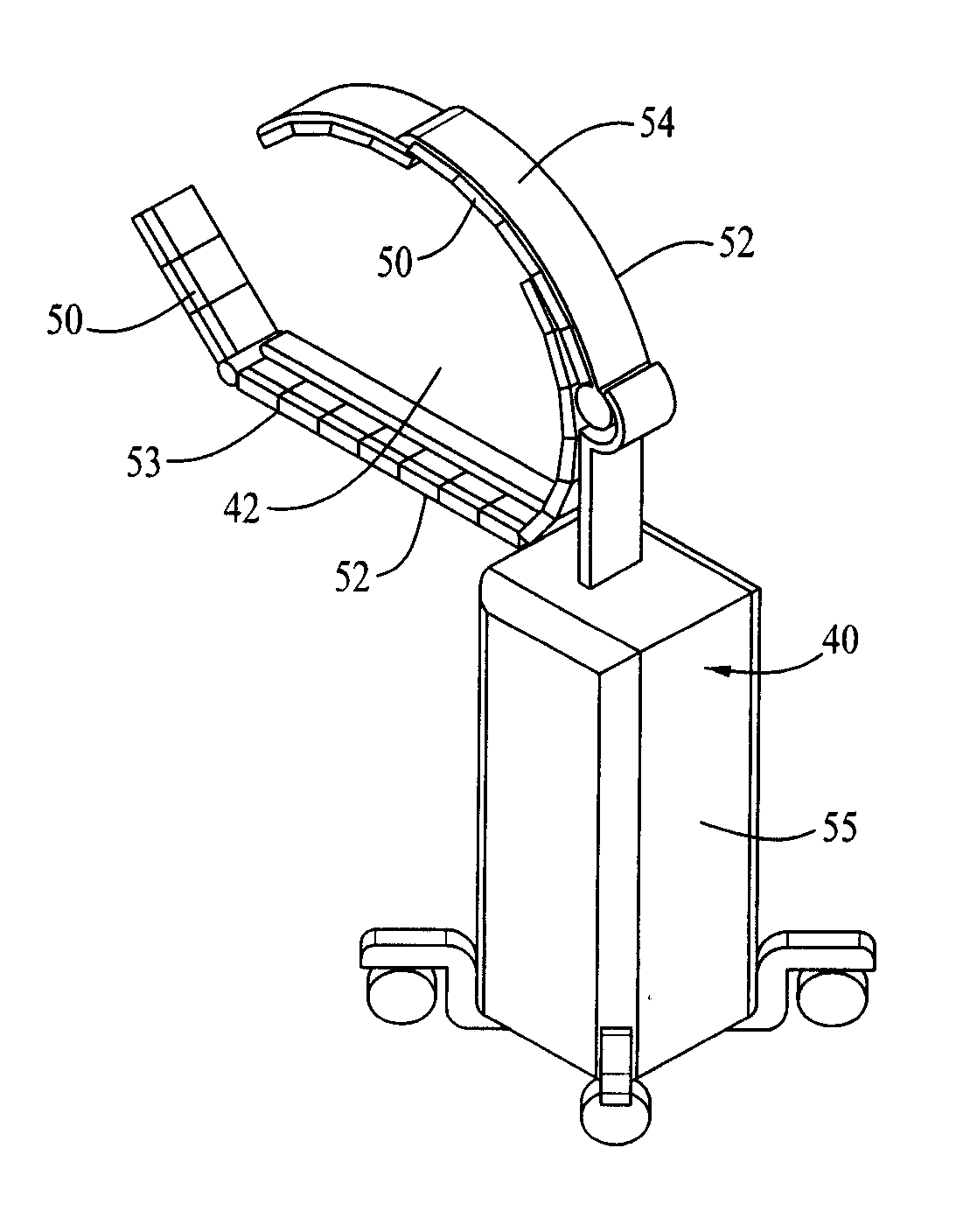
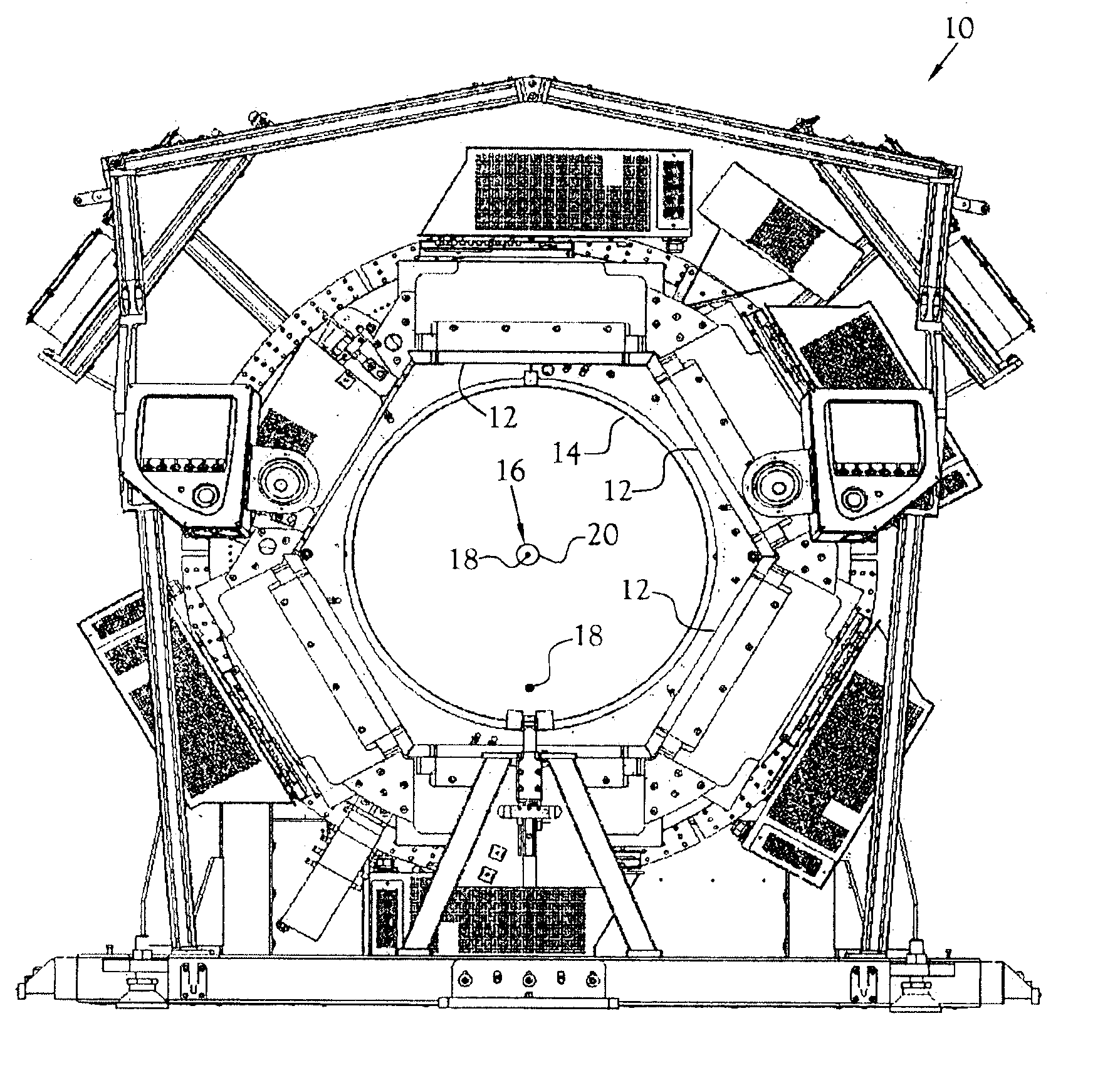
Portable pet scanner for imaging of a portion of the body
A mobile PET scanner for use in bed side or a surgical environment comprises a mobile support base, with first and a second arm arms extending therefrom. The first arm is configured for placement under a table supporting an individual while the second arm is substantially parallel to and above said first arm with the individual being located between the first and second arms. Multiple module blocks are positioned along the length of the first and second arm. Each modules block comprises scintillators with solid state silicone multipliers or multi-pixel photon counters attached thereto. Positrons emitted from radiation labeled tissue within the individual's body impinge on the multiple scintillators to generate. The photons from each of the scintillator are received by each of a solid state silicone multipliers or multi-pixel photon counters associated therewith and an electrical signal representative of the received photons is then generated. The electrical signal output from each of the solid state silicone multipliers or multi-pixel photon counters is then transmitted to a computerized data collection and analysis system, which substantially instantaneously generates a visual image on a screen showing the location within the individuals body emitted the photons. This image can be coordinated with a photo image or a CT image showing the same portion of the individual's body.
Owner:INTRAMEDICAL IMAGING LLC
Multimodal imaging sources
A multimodal source for imaging with at least one of a gamma camera, a positron emission tomography (PET) scanner and a single-photon-emission computed tomography (SPECT) scanner, and at least one of a computed tomography (CT) scanner, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scanner and optical scanner. The multimodal source has radioactive material permanently incorporated into a matrix of material, at least one of a material that is a target for CT, MRI and optical scanning, and a container which holds the radioactive material and the CT, MRI and / or optical target material. The source can be formed into a variety of different shapes such as points, cylinders, rings, squares, sheets and anthropomorphic shapes. The material that is a target for gamma cameras, PET scanners and SPECT scanners and / or CT, MRI and / or optical scanners can be formed into shapes that mimic biological structures.
Owner:ISO SCI LAB
Method and apparatus for timing calibration in a PET scanner
InactiveUS7129495B2Material analysis by optical meansX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentScintillatorPhysics
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
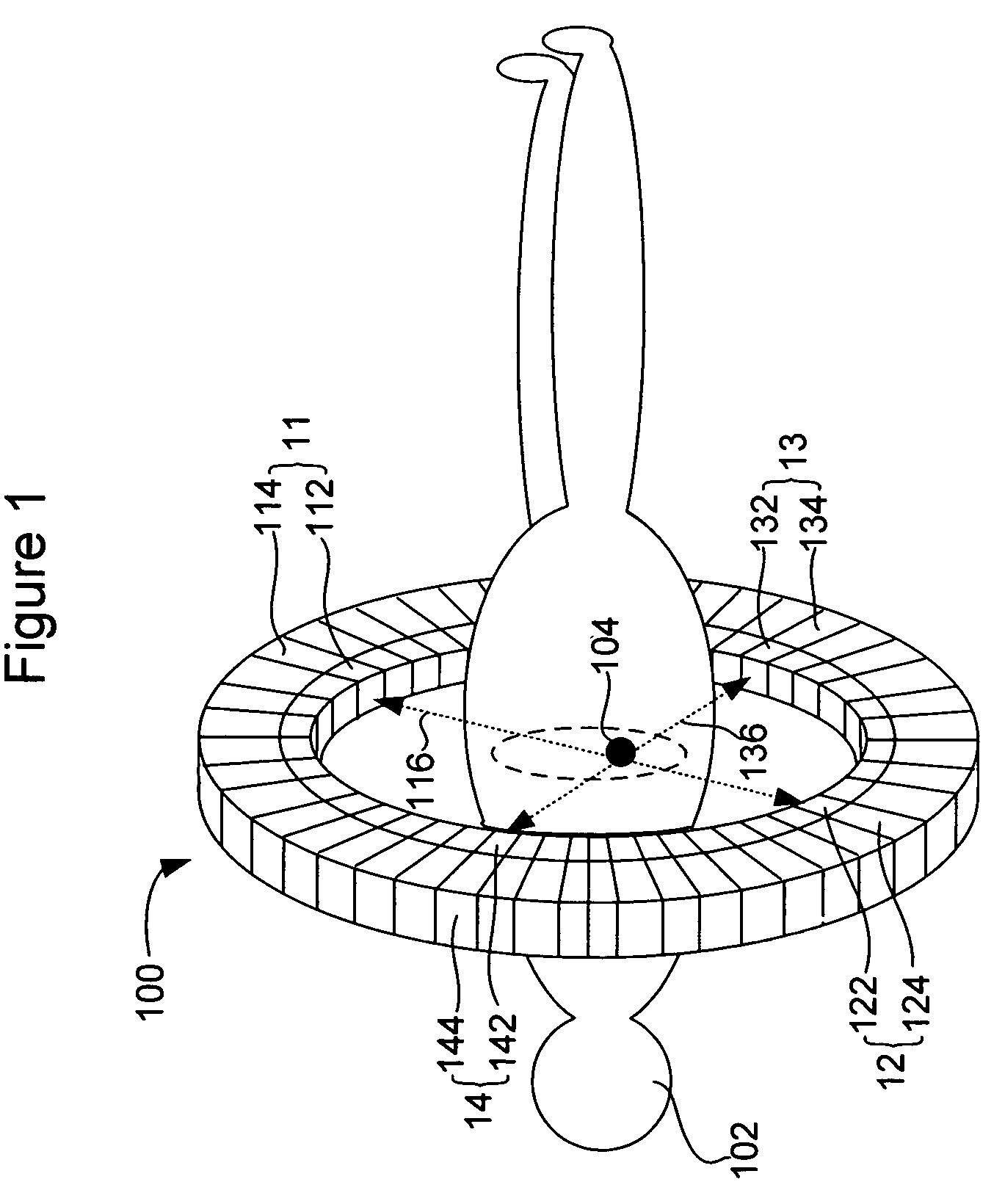
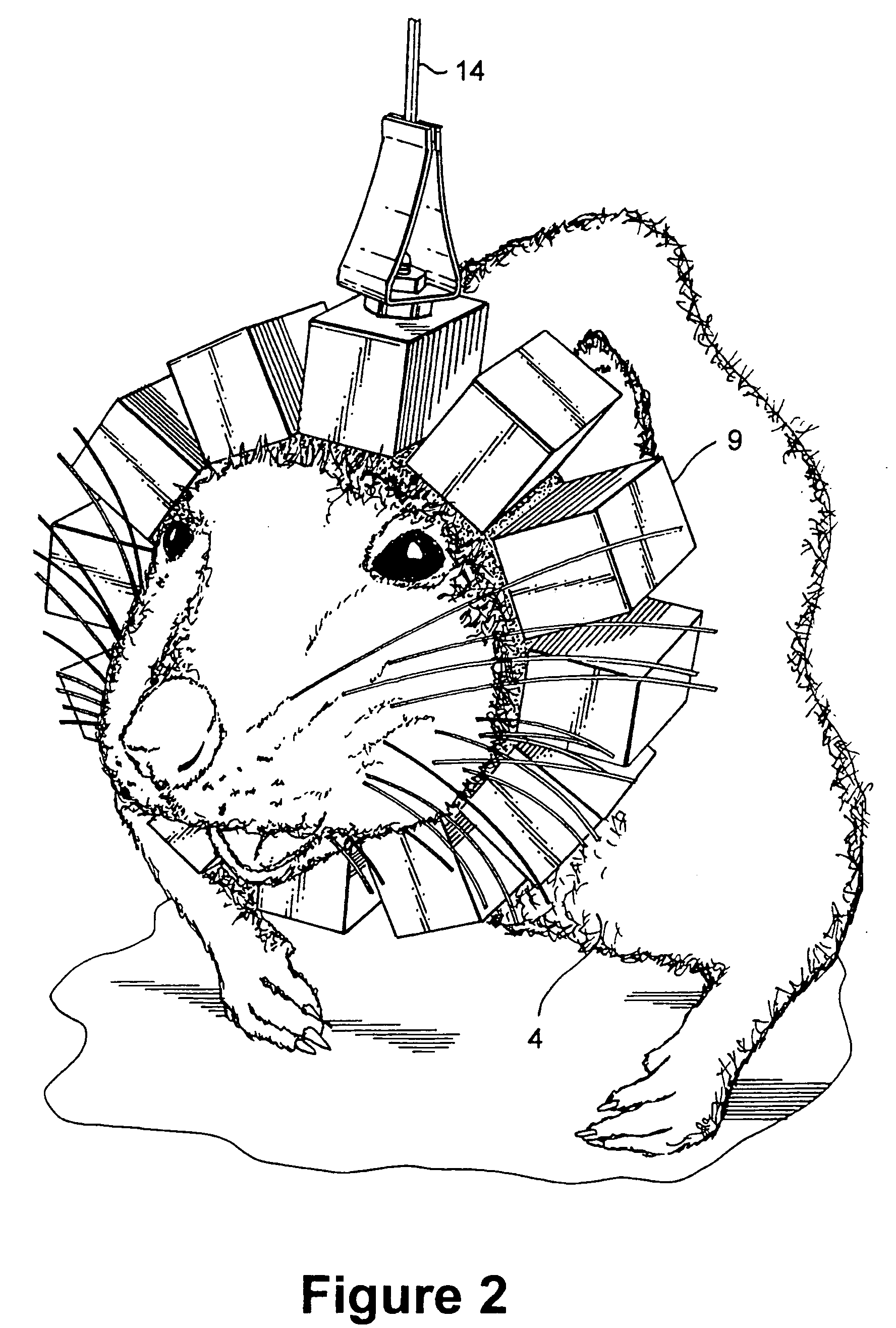
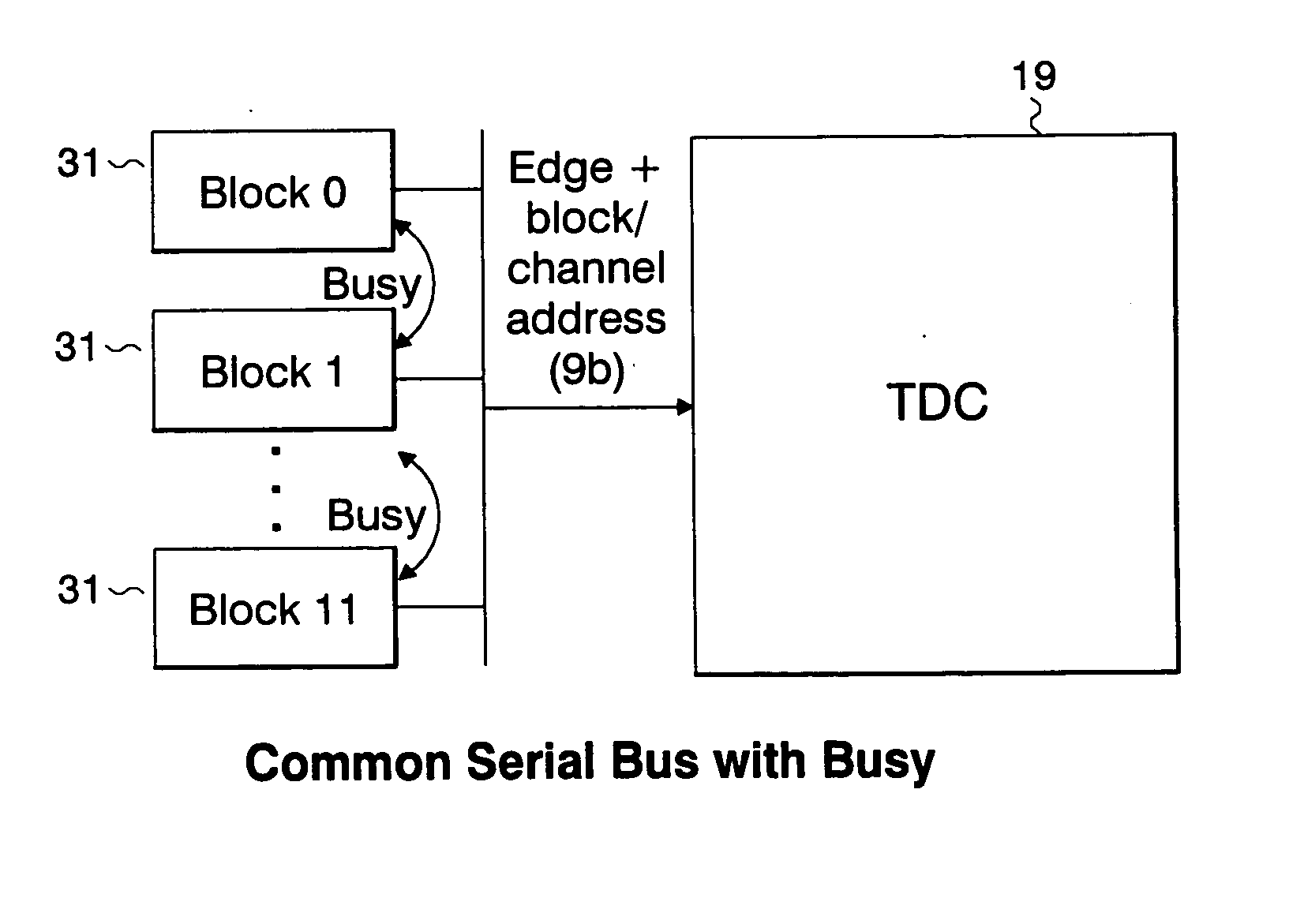
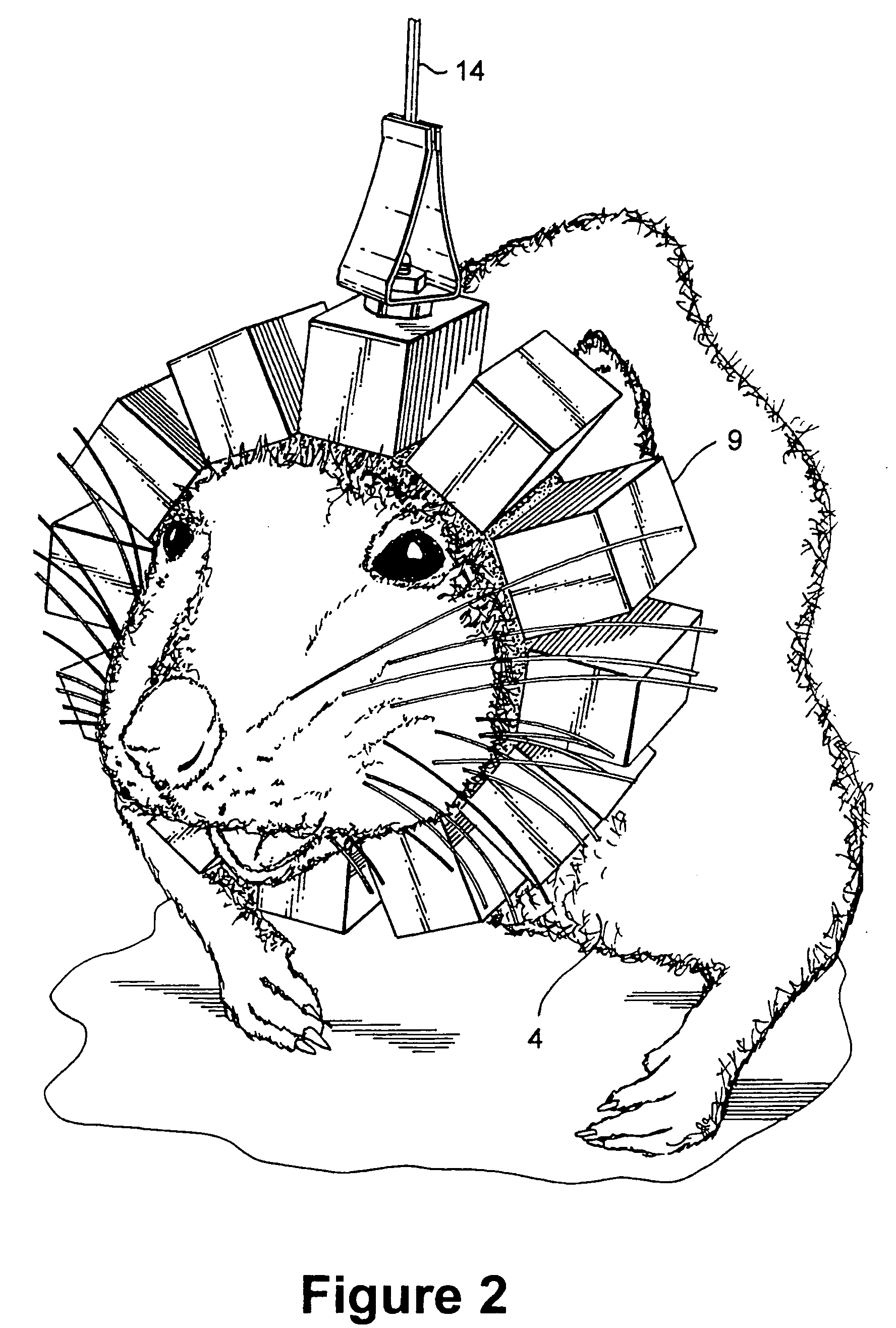
Compact conscious animal positron emission tomography scanner
ActiveUS20050082486A1Reduce power consumptionMagnetic measurementsHandling using diaphragms/collimetersSerial transferEngineering
A method of serially transferring annihilation information in a compact positron emission tomography (PET) scanner includes generating a time signal for an event, generating an address signal representing a detecting channel, generating a detector channel signal including the time and address signals, and generating a composite signal including the channel signal and similarly generated signals. The composite signal includes events from detectors in a block and is serially output. An apparatus that serially transfers annihilation information from a block includes time signal generators for detectors in a block and an address and channel signal generator. The PET scanner includes a ring tomograph that mounts onto a portion of an animal, which includes opposing block pairs. Each of the blocks in a block pair includes a scintillator layer, detection array, front-end array, and a serial encoder. The serial encoder includes time signal generators and an address signal and channel signal generator.
Owner:BROOKHAVEN SCI ASSOCS
Sem scanner sensing apparatus, system and methodology for early detection of ulcers
ActiveUS20140288397A1Increased risk of infectionHigh stage ulcer developmentDiagnostic recording/measuringPressure sensorsMultiplexingCapacitance
A handheld, conforming capacitive sensing apparatus configured to measure Sub-Epidermal Moisture (SEM) as a mean to detect and monitor the formation of pressure ulcers. The device incorporates an array of electrodes which are excited to measure and scan SEM in a programmable and multiplexed manner by a battery-less RF-powered chip. The scanning operation is initiated by an interrogator which excites a coil embedded in the apparatus and provides the needed energy burst to support the scanning / reading operation. Each electrode measures the equivalent sub-epidermal capacitance corresponding and representing the moisture content.
Owner:BRUIN BIOMETRICS +1
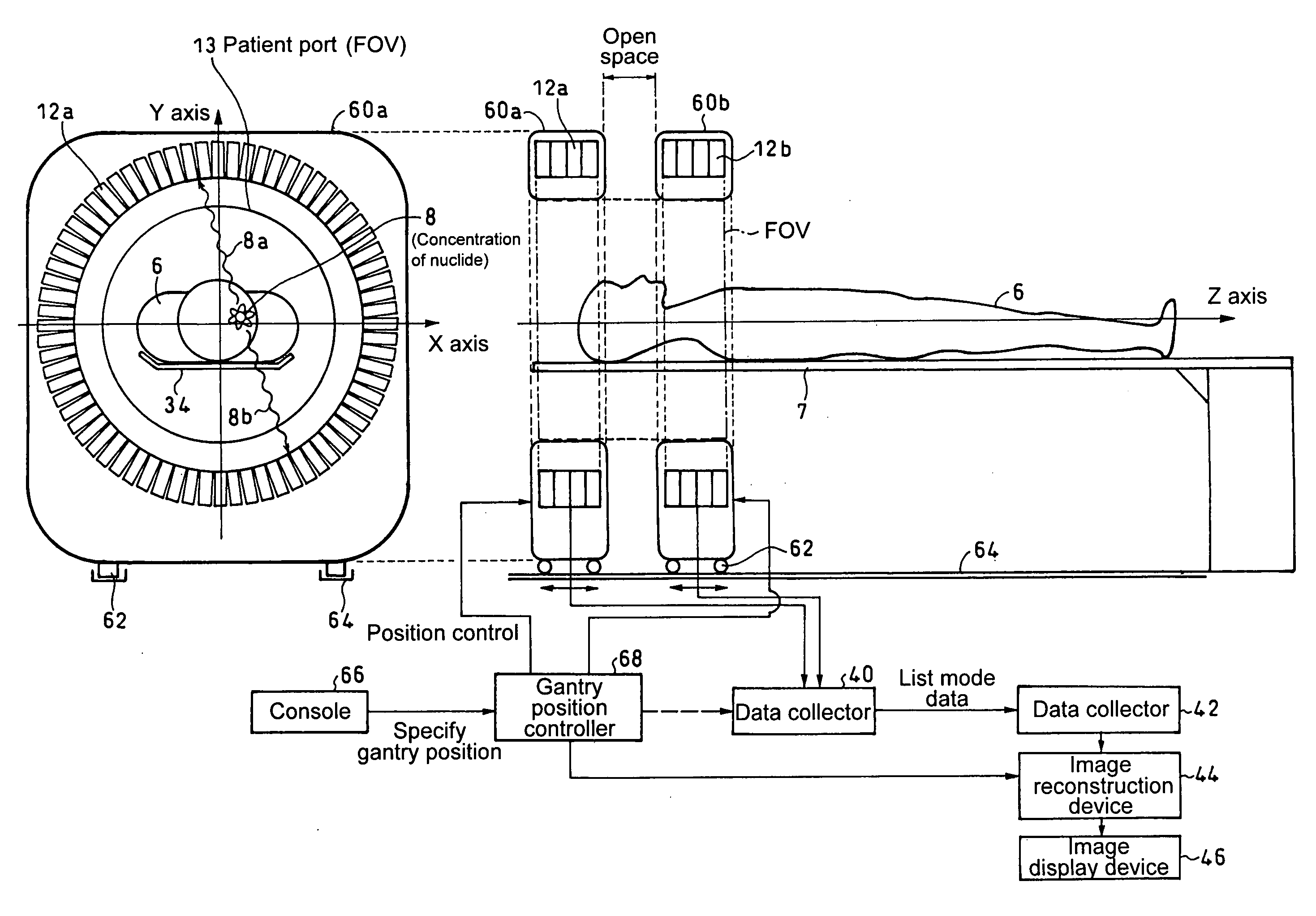
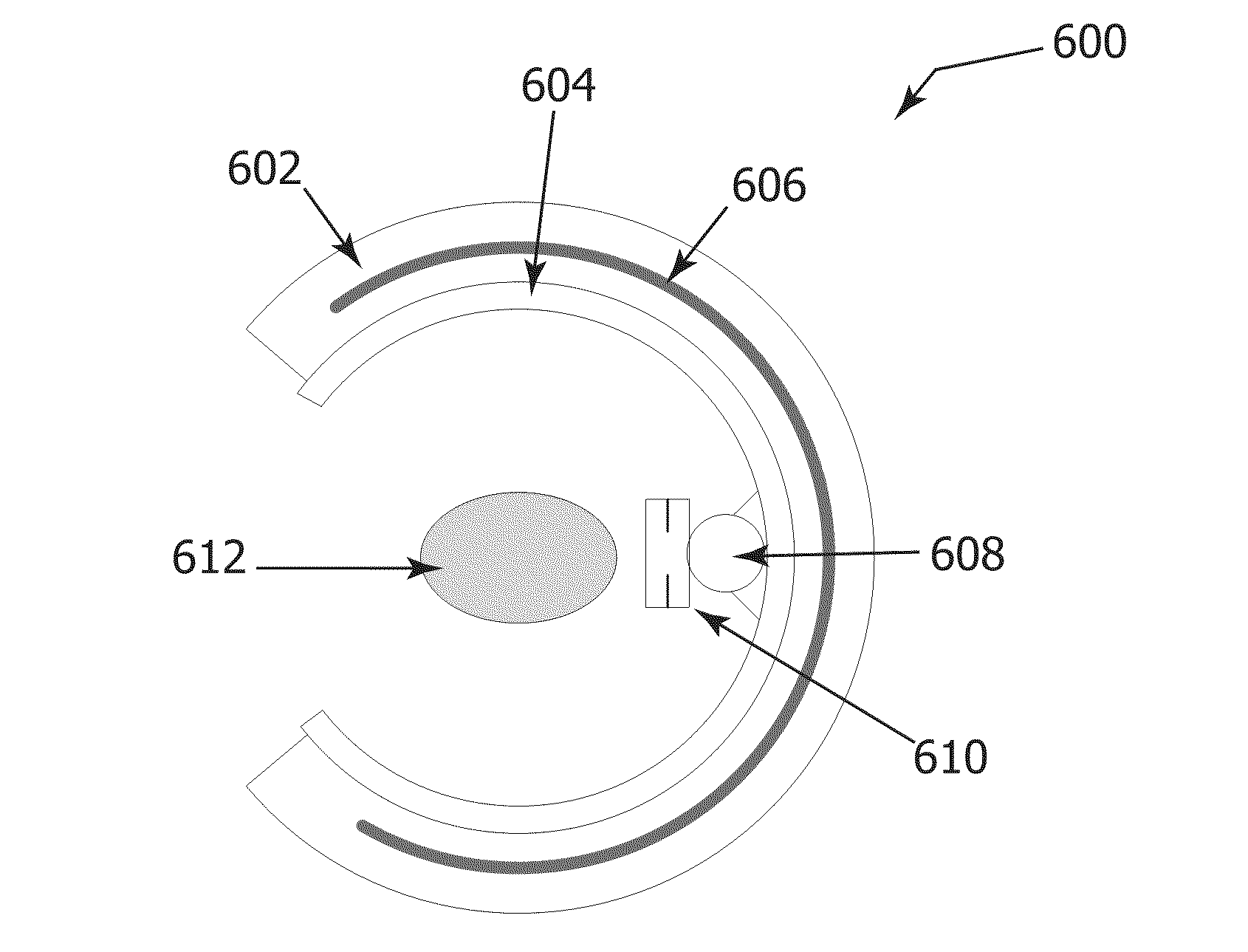
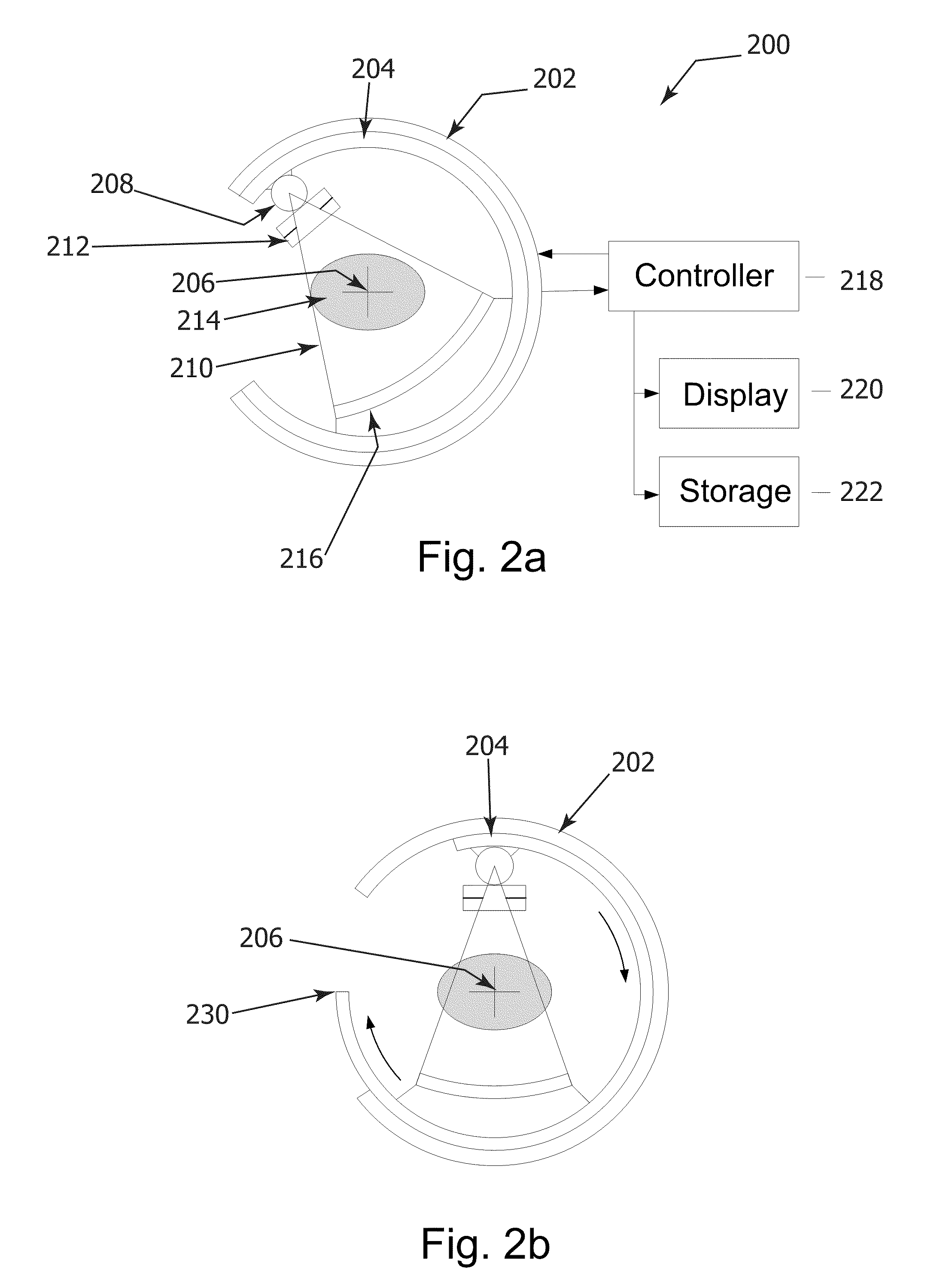
Pet scanner and image reconstruction method thereof
InactiveUS20100128956A1Reduce image qualityEasily gain accessMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationImage analysisComputed tomographyBody axis
A plurality of detector rings in which detectors arranged densely or spatially in a ring shape or in a polygonal shape are arranged, with an open space kept in the body axis direction, coincidences are measured for some of or all of detector pairs connecting the detector rings apart from the open space to perform three-dimensional image reconstruction, thereby imaging the open space between the detector rings as a tomographic image. Therefore, the open space is secured, with the deteriorated quality of an image suppressed, thus making it possible to easily gain access to a patient under PET scanning from outside a gantry and also provide irradiation of particle beams for cancer treatment as well as X-ray CT scanning.
Owner:NAT INST FOR QUANTUM & RADIOLOGICAL SCI & TECH
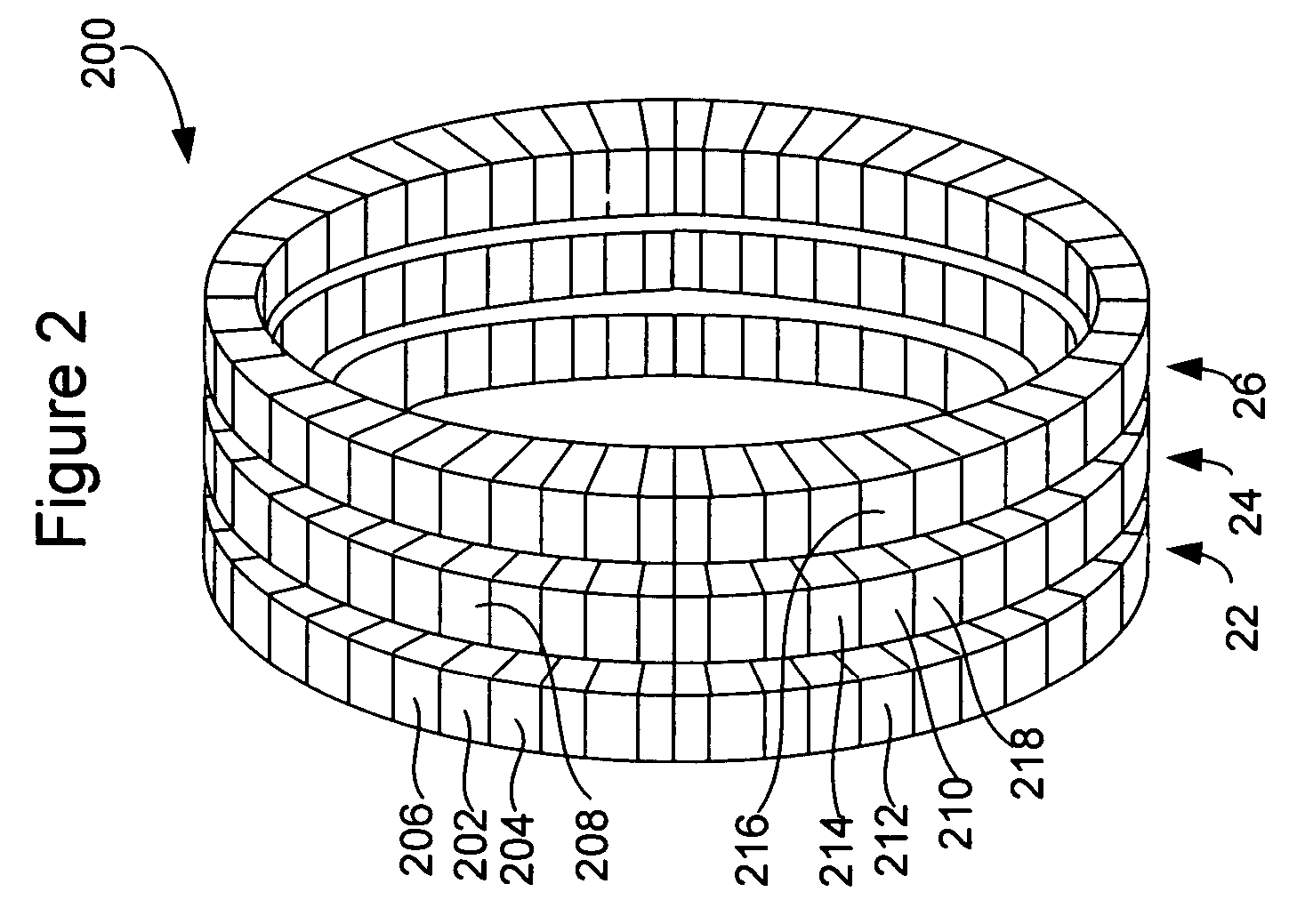
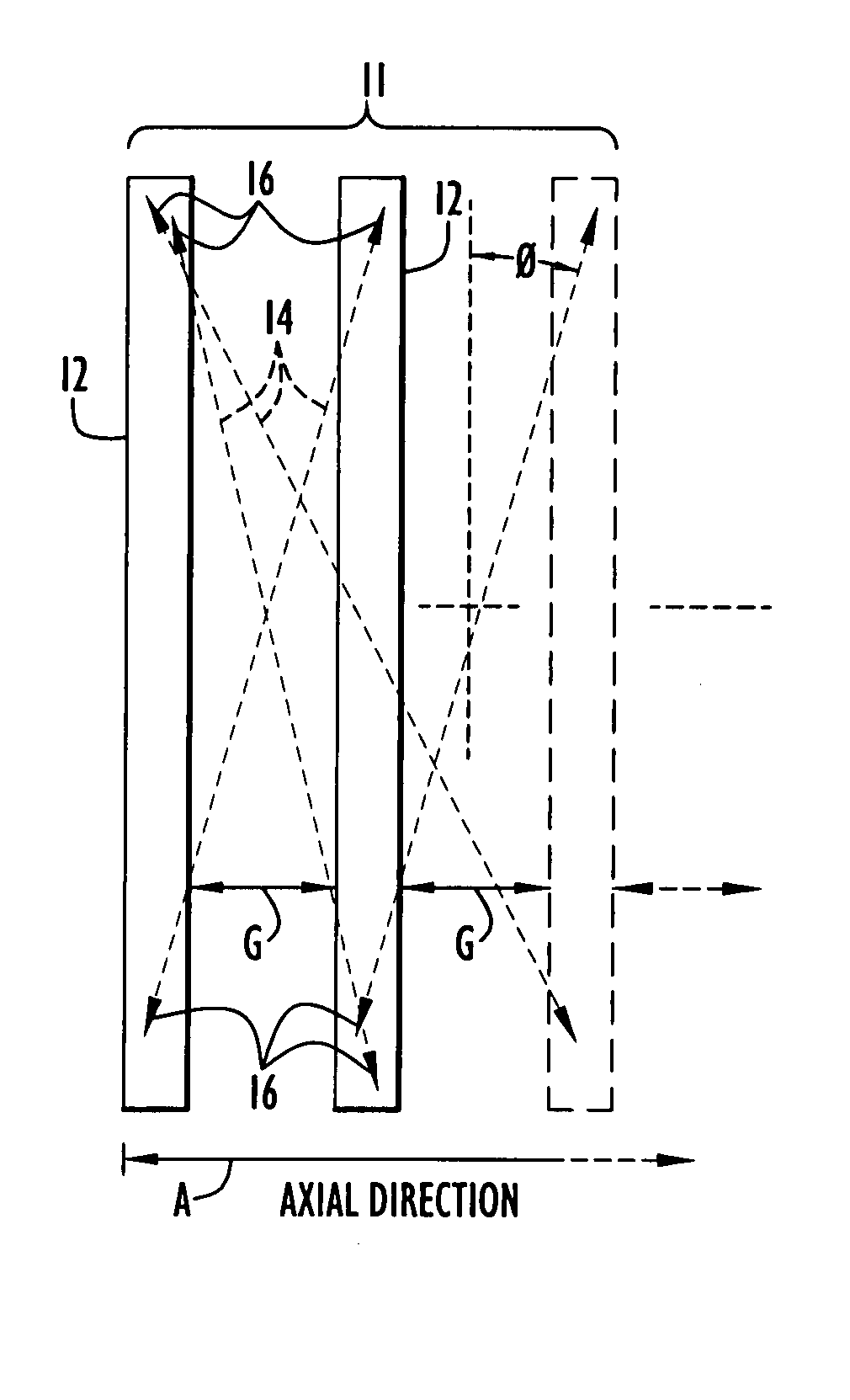
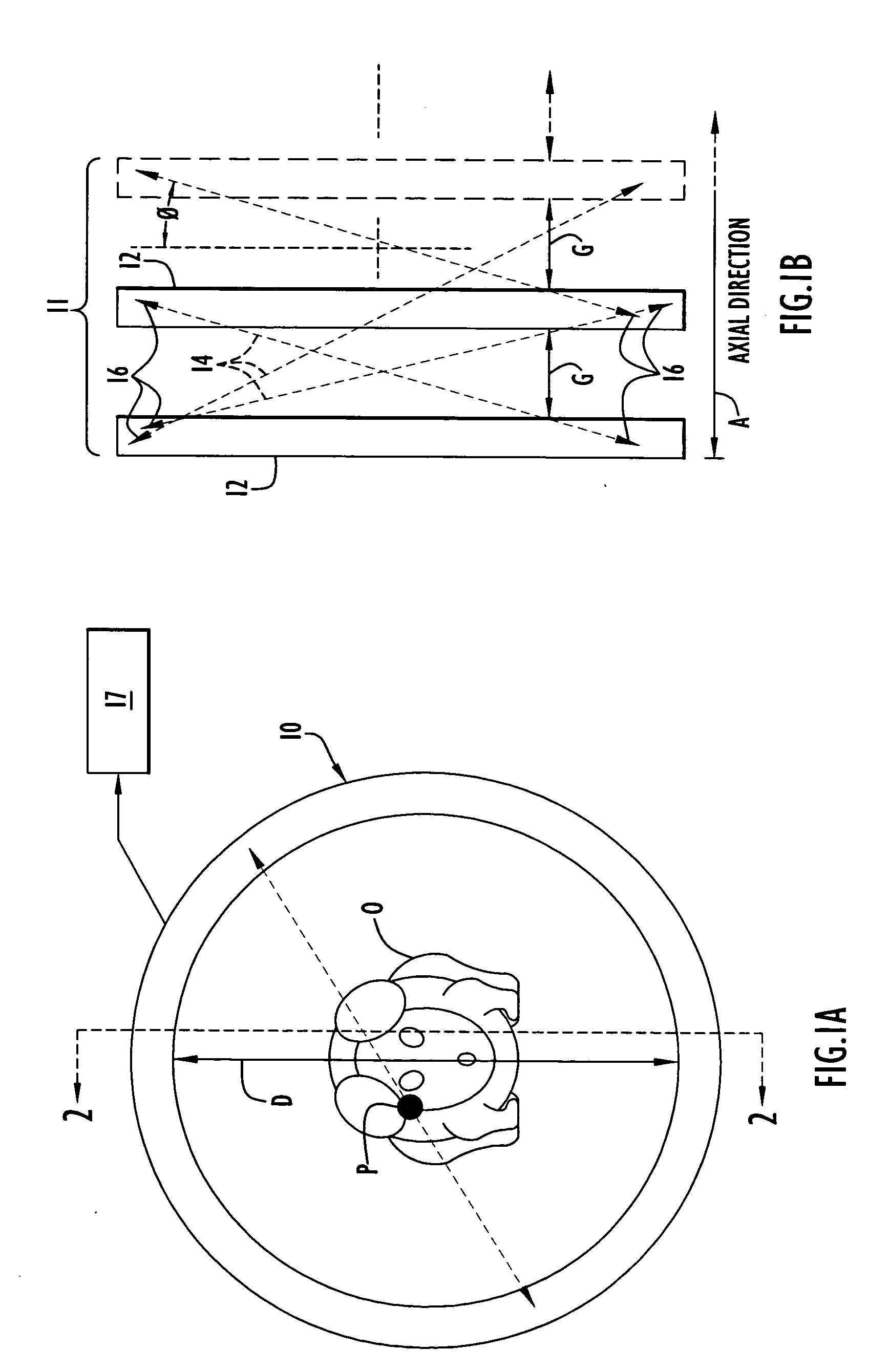
Tomography scanner with axially discontinuous detector array
InactiveUS20050109943A1Avoid the needEffect of gap can be minimizedMaterial analysis by optical meansX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentSmall animalDetector array
A tomography scanner has intentionally designed, well defined gaps between detector rings with image reconstruction obtained with the use of conventional tomography data processing. The scanner is particularly advantageous as a small animal PET scanner.
Owner:TRIDENT IMAGING
Optical tomography system with high-speed scanner
Owner:VISIONGATE
Integrated PET-MRI scanner
InactiveUS7835782B2Reduce electromagnetic interferenceEasy to storeMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
One embodiment of the present invention provides an integrated PET-MRI scanner. This integrated scanner includes a main magnet that generates a magnetic field, wherein images of the subject is generated in a central region of the magnetic field. It also includes a PET scanner which is enclosed by the main magnet. The PET scanner further comprises: (1) at least one ring of scintillators, which is situated in the central region of the magnetic field and, (2) one or more photodetectors, which are coupled to the ring of scintillators, so that the one or more photodetectors are outside the central region of the magnetic field. The integrated scanner also includes radio-frequency (RF) coils which are enclosed by the PET scanner. By keeping the photodetectors and associated circuitry outside the central region of the magnetic field, the integrated scanner reduces the electromagnetic interference (EMI) between the PET scanner and the MRI scanner.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
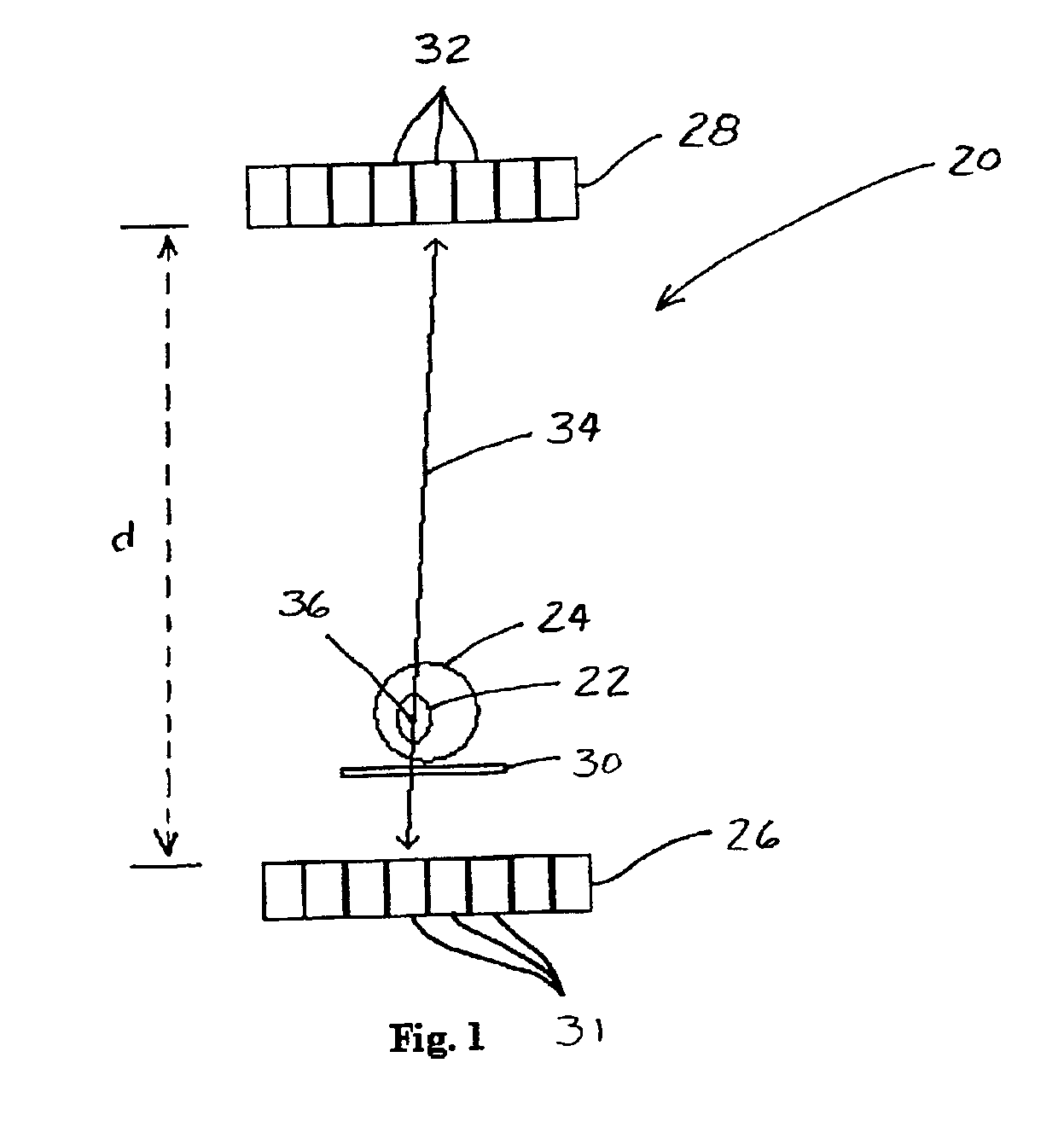
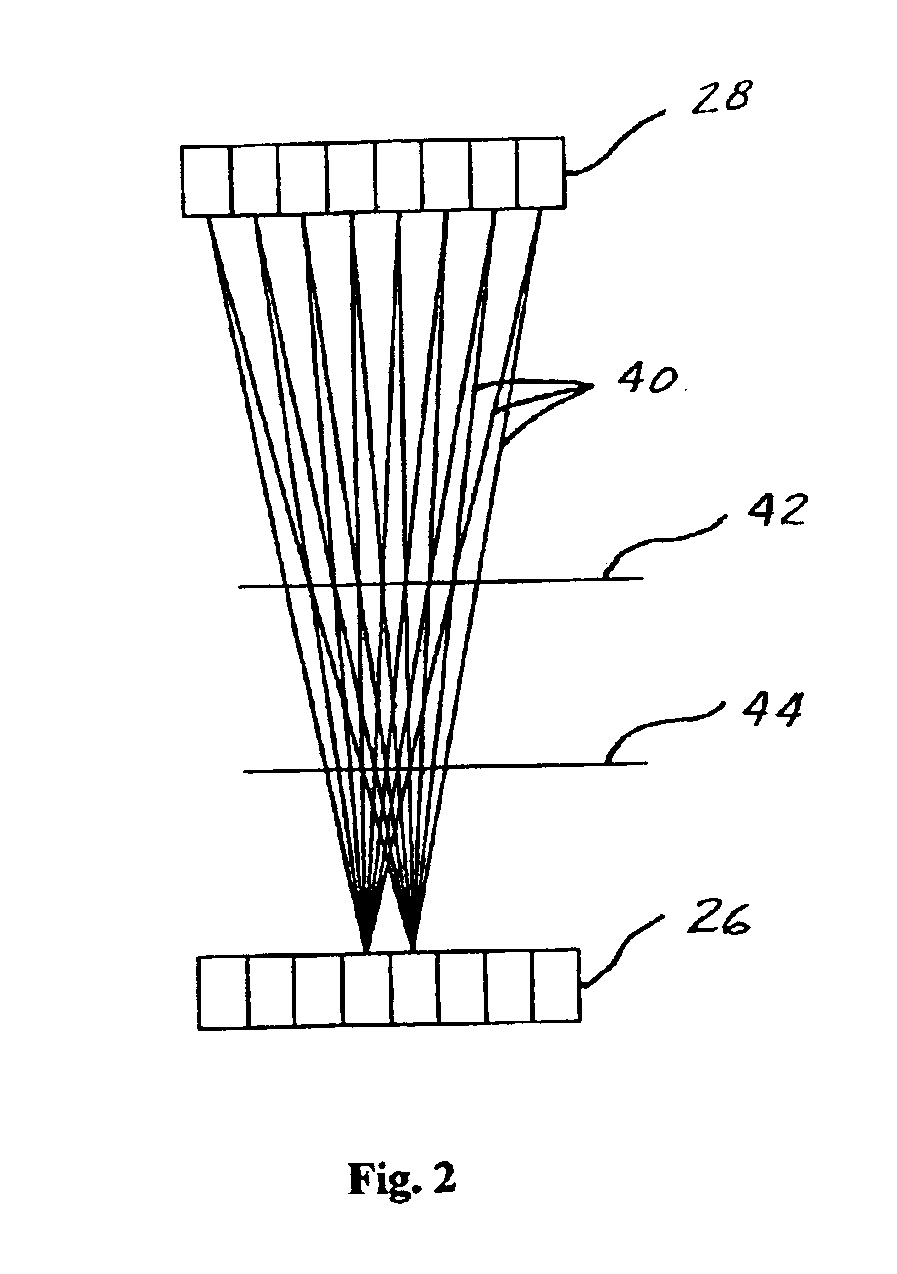
Method and apparatus for increasing spatial resolution of a pet scanner
InactiveUS6946658B2Improve imaging resolutionImprove spatial resolutionMaterial analysis by optical meansRadiation intensity measurementDetector arrayElectron
A method and apparatus for increasing the resolution of a Positron Emission Tomography scanner. The method and apparatus comprise elements and acts for centering a region of interest of an object at a point between first and second detector arrays which is at least about ten percent closer to the first detector array than to the second detector array.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
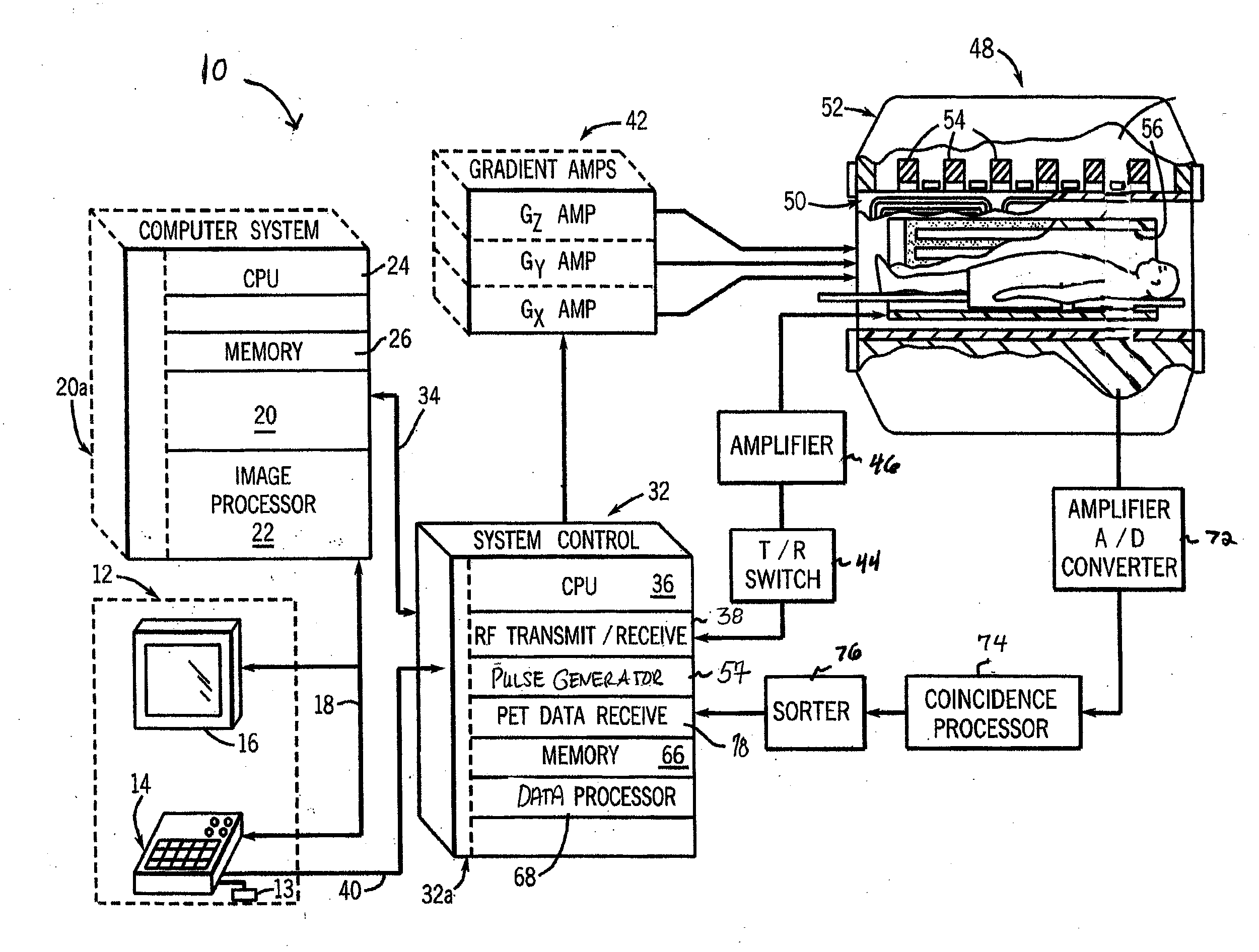
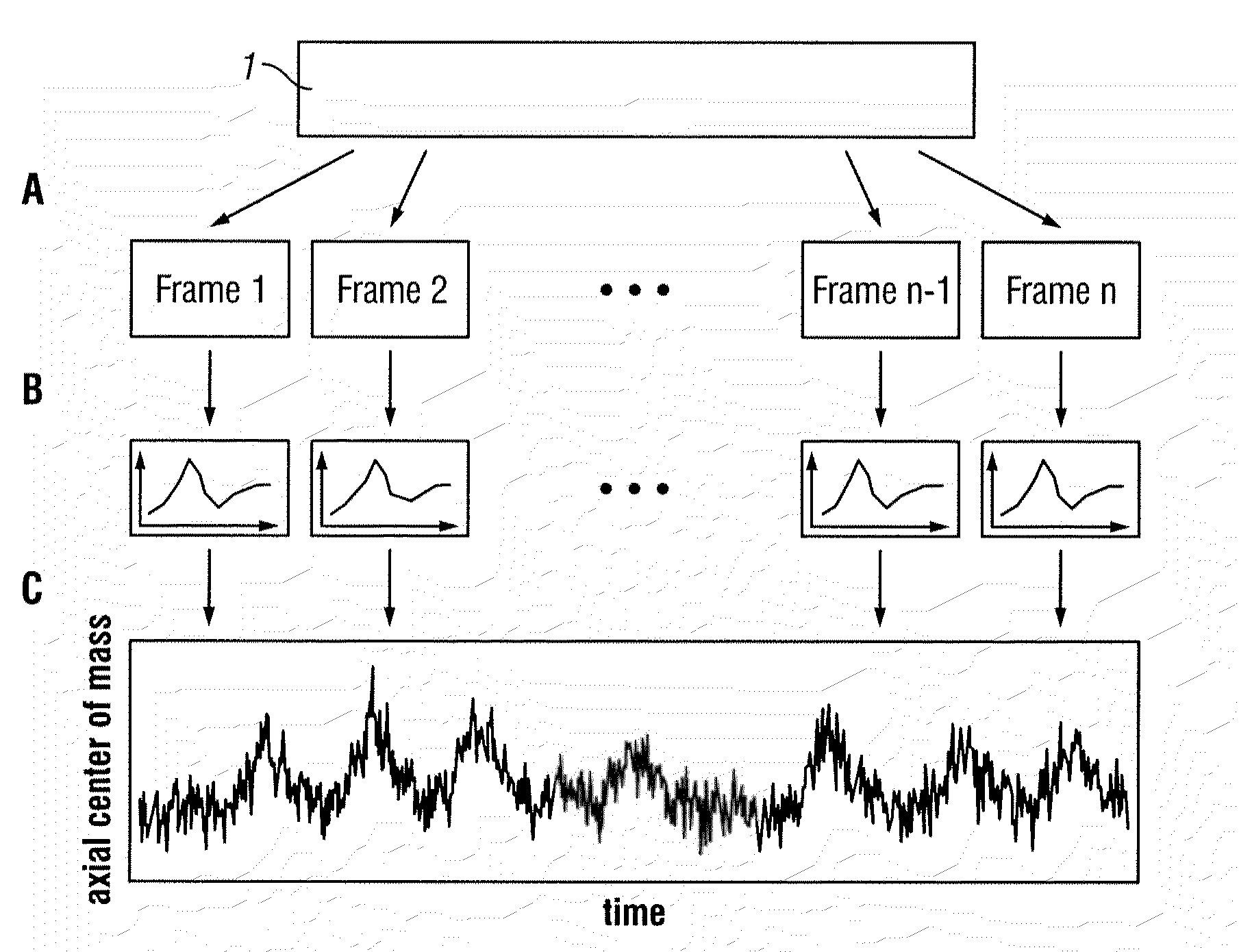
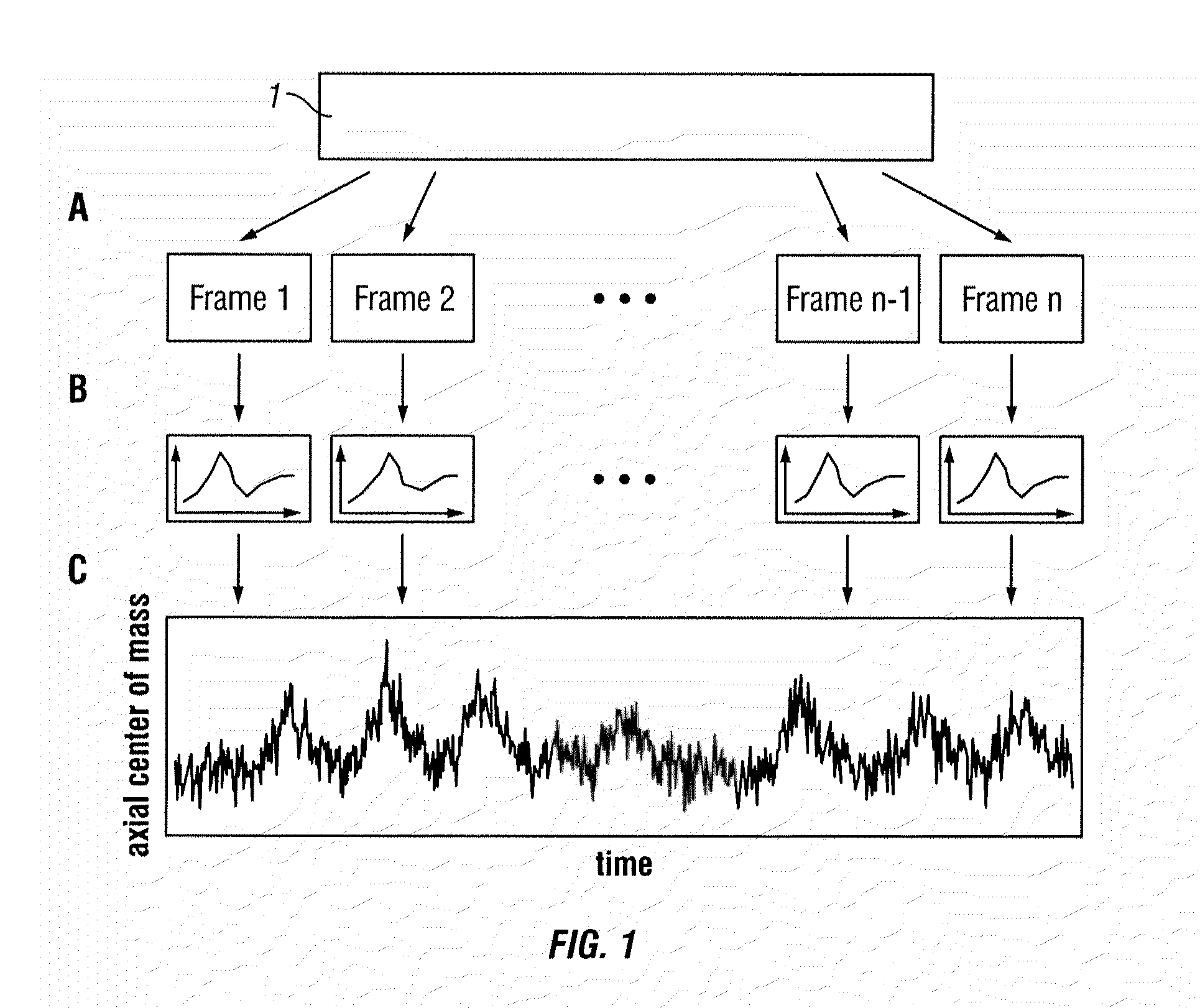
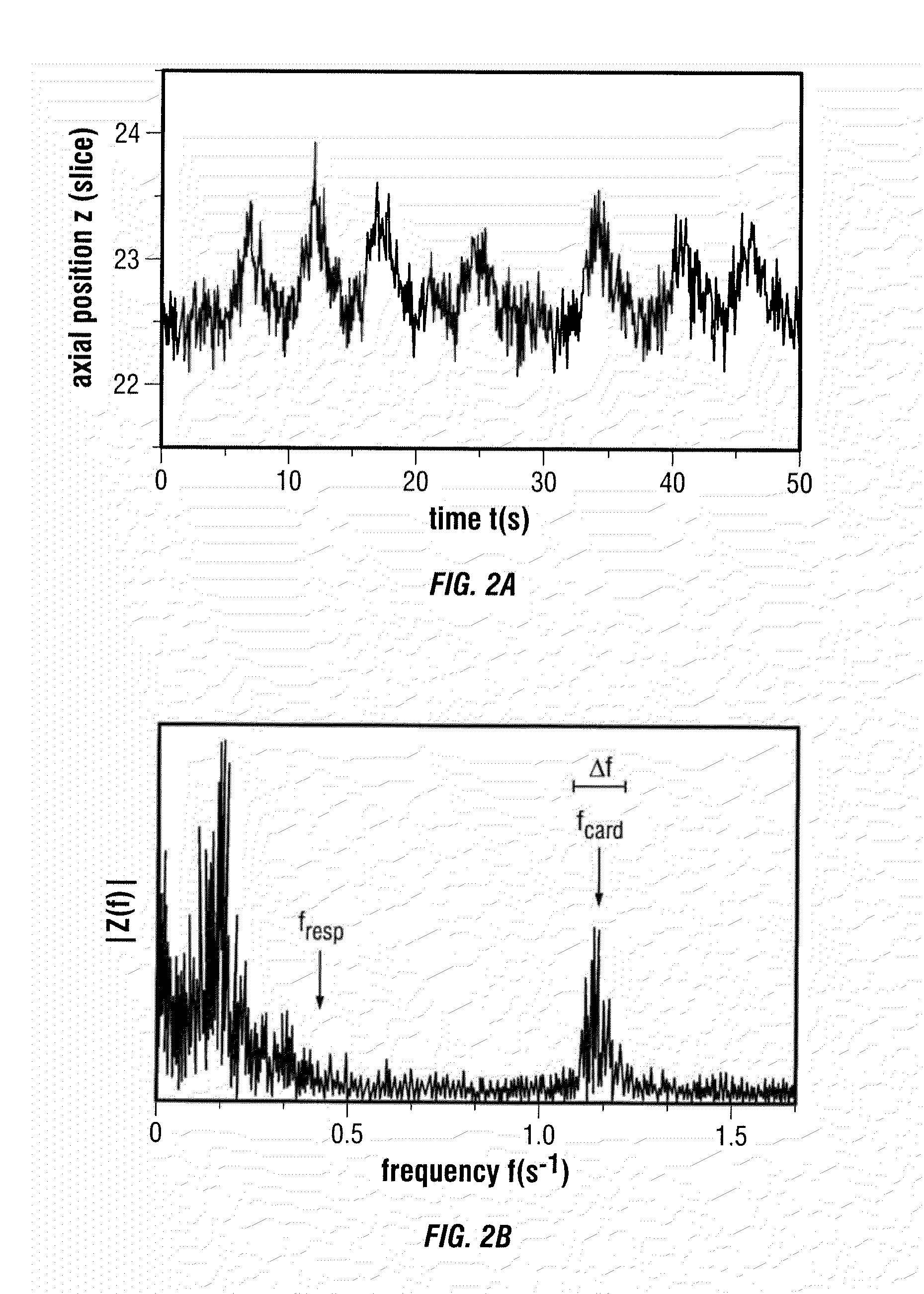
List Mode-Based Respiratory and Cardiac Gating in Positron Emission Tomography
InactiveUS20100067765A1Health-index calculationCharacter and pattern recognitionFrequency spectrumData stream
According to a preferred embodiment, the invention provides a method for extracting internal organ motion from positron emission tomography (PET) coincidence data, the method comprising the following steps: generating a data stream of PET coincidence data using the list mode capability of a PET scanner; dividing the data stream into time frames of a given length; computing a histogram A(i, t) of an axial coincidence distribution for a set of time frames; computing the axial center of mass z(t) for each of the time frames in the set of time frames based on the histogram A(i, t); transforming z(t) into the frequency domain; determining either the frequency contribution caused by respiratory motion, given by fresp, or the frequency contribution caused by heart contractions, given by fcard and Δf, identified in the frequency spectrum |Z(f)|; and carrying out further processing of Z(f) leading to curves zresp(t) and zcard(t) with which a gating sequence is established.
Owner:UNIVERSLTAT MUNSTER +1
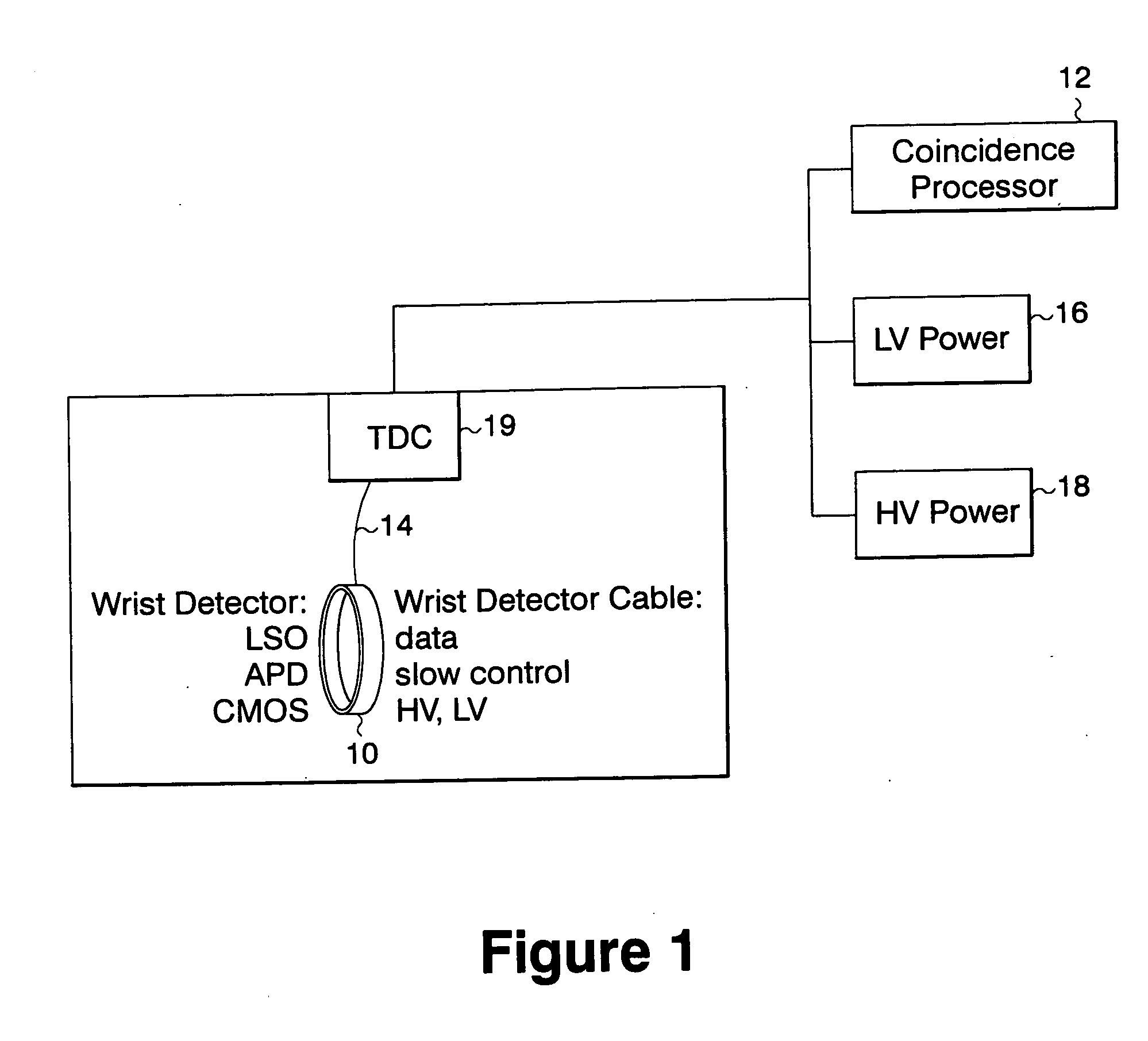
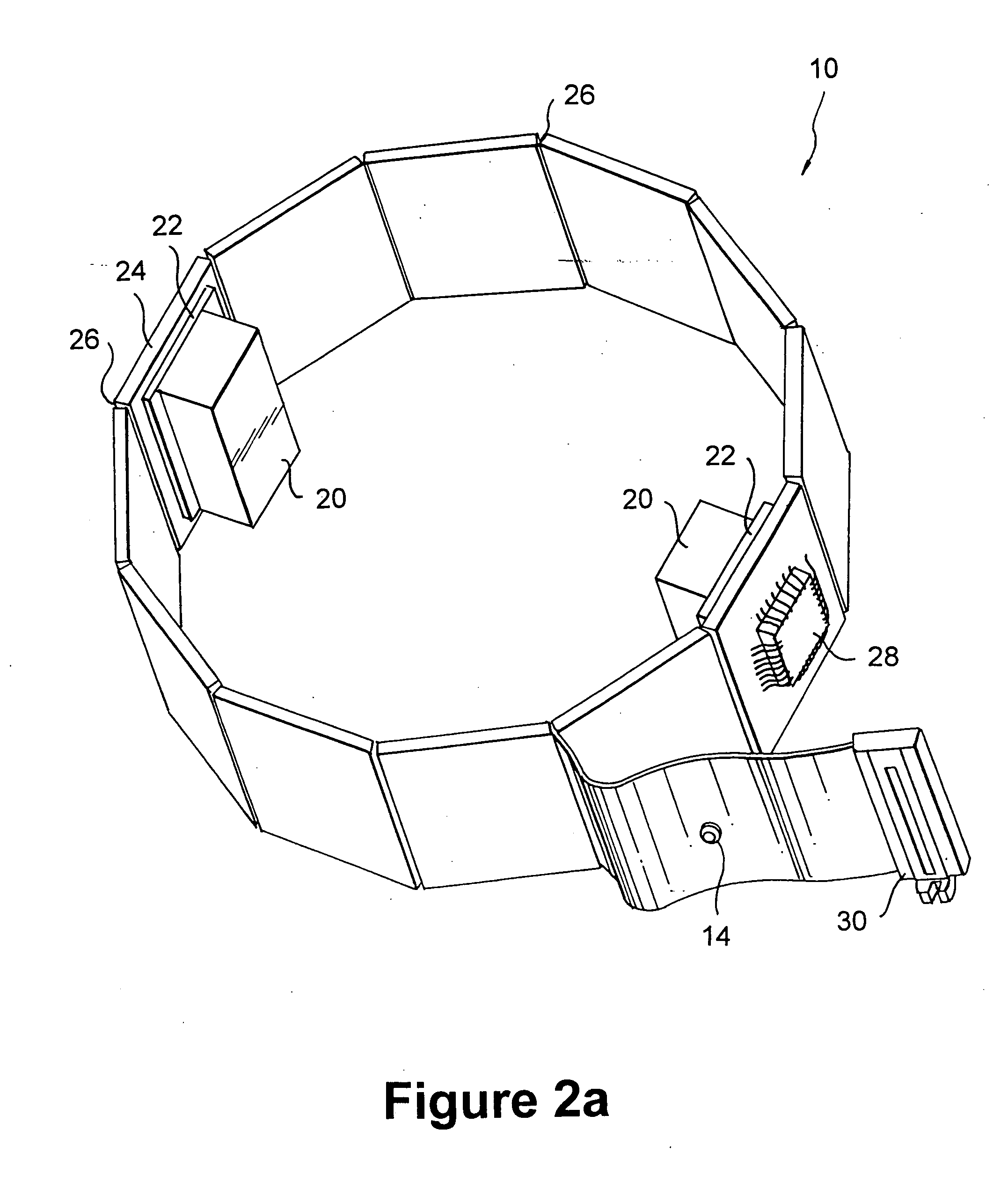
Positron emission tomography wrist detector
ActiveUS20050167599A1Less discomfortAccurate measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansTomographySignal generatorCompanion animal
A method of serially transferring annihilation information in a compact positron emission tomography (PET) scanner includes generating a time signal representing a time-of-occurrence of an annihilation event, generating an address signal representing a channel detecting the annihilation event, and generating a channel signal including the time and address signals. The method also includes generating a composite signal including the channel signal and another similarly generated channel signal concerning another annihilation event. An apparatus that serially transfers annihilation information includes a time signal generator, address signal generator, channel signal generator, and composite signal generator. The time signal is asynchronous and the address signal is synchronous to a clock signal. A PET scanner includes a scintillation array, detection array, front-end array, and a serial encoder. The serial encoders include the time signal generator, address signal generator, channel signal generator, and composite signal generator.
Owner:BROOKHAVEN SCI ASSOCS
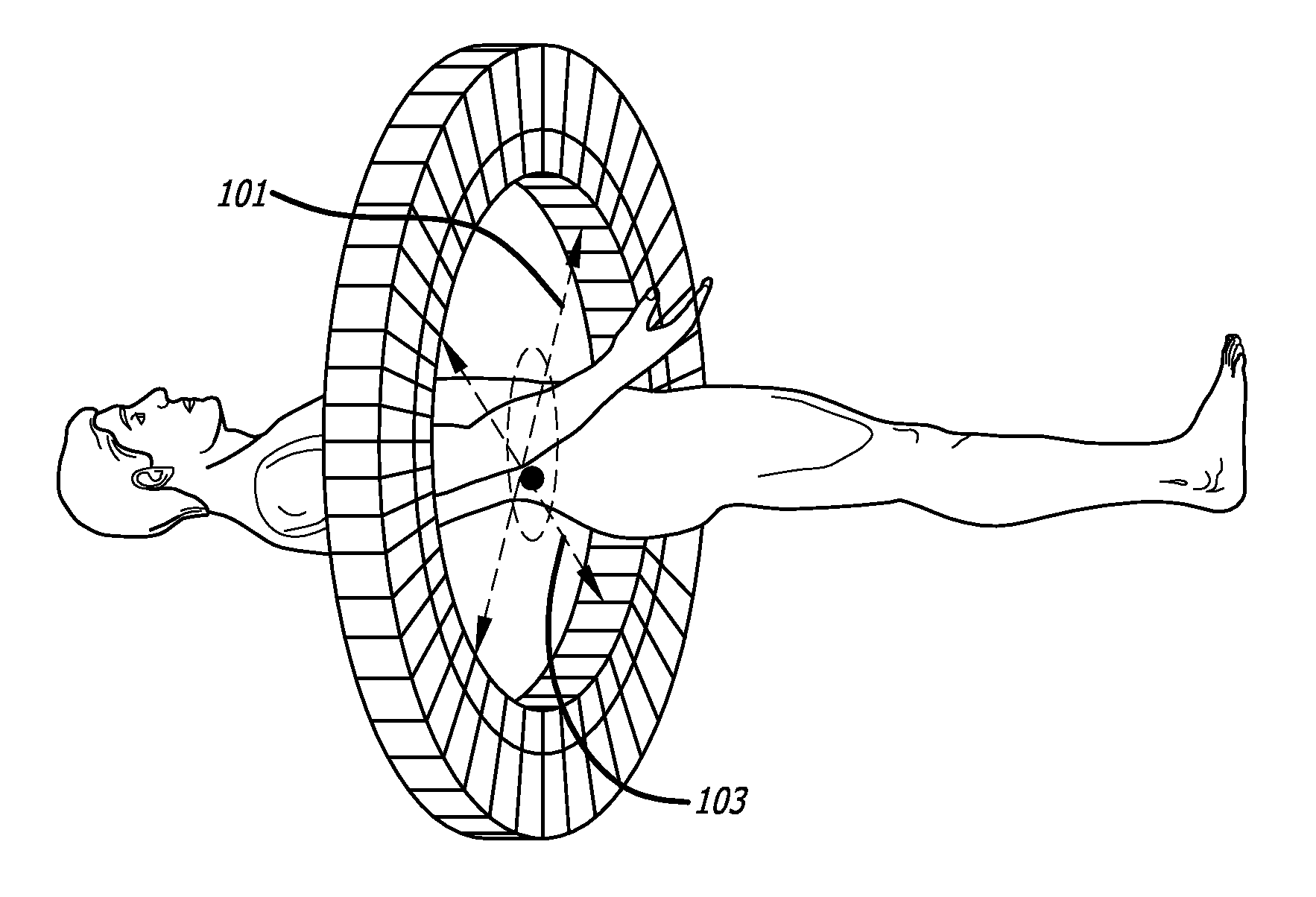
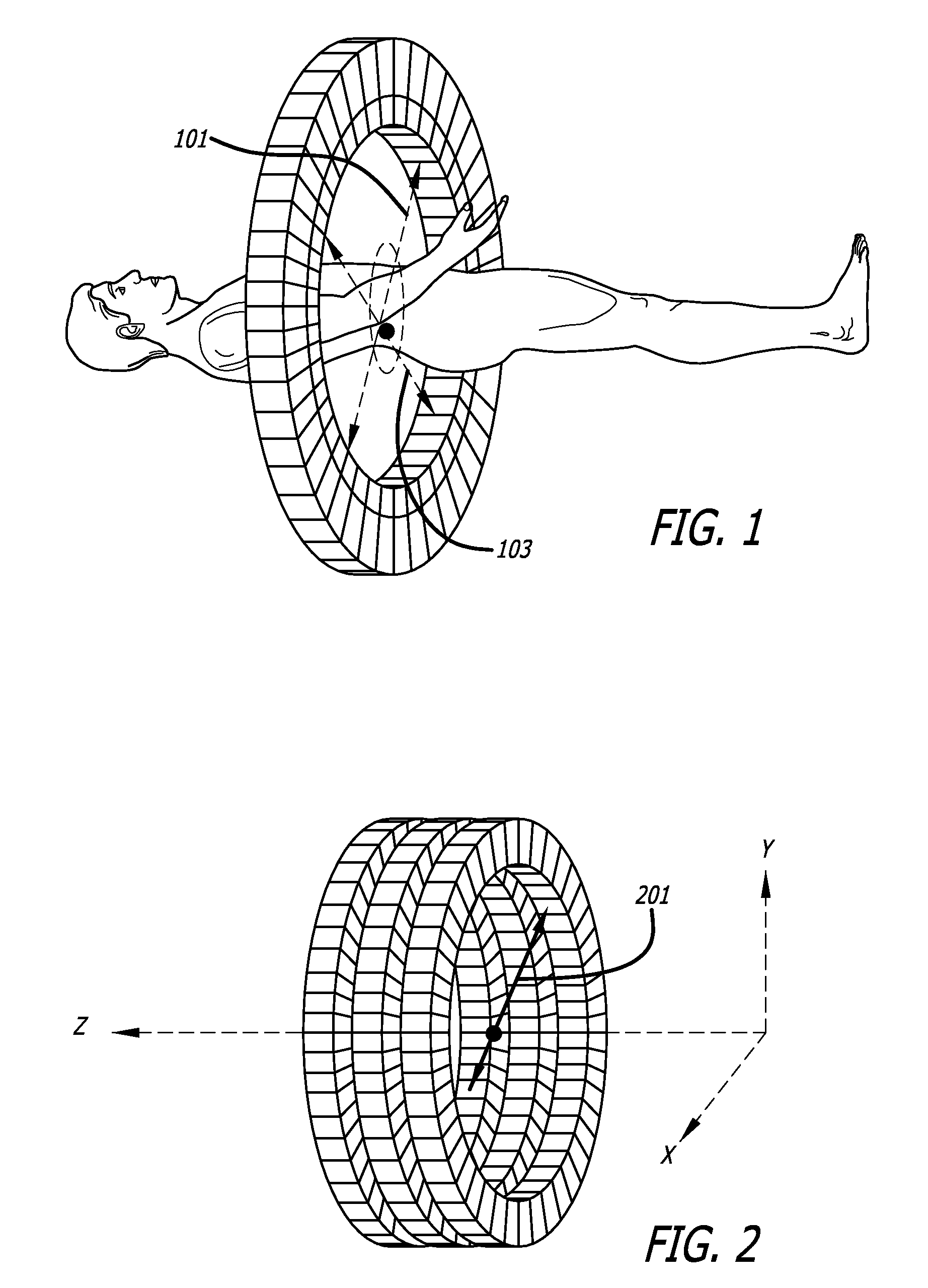
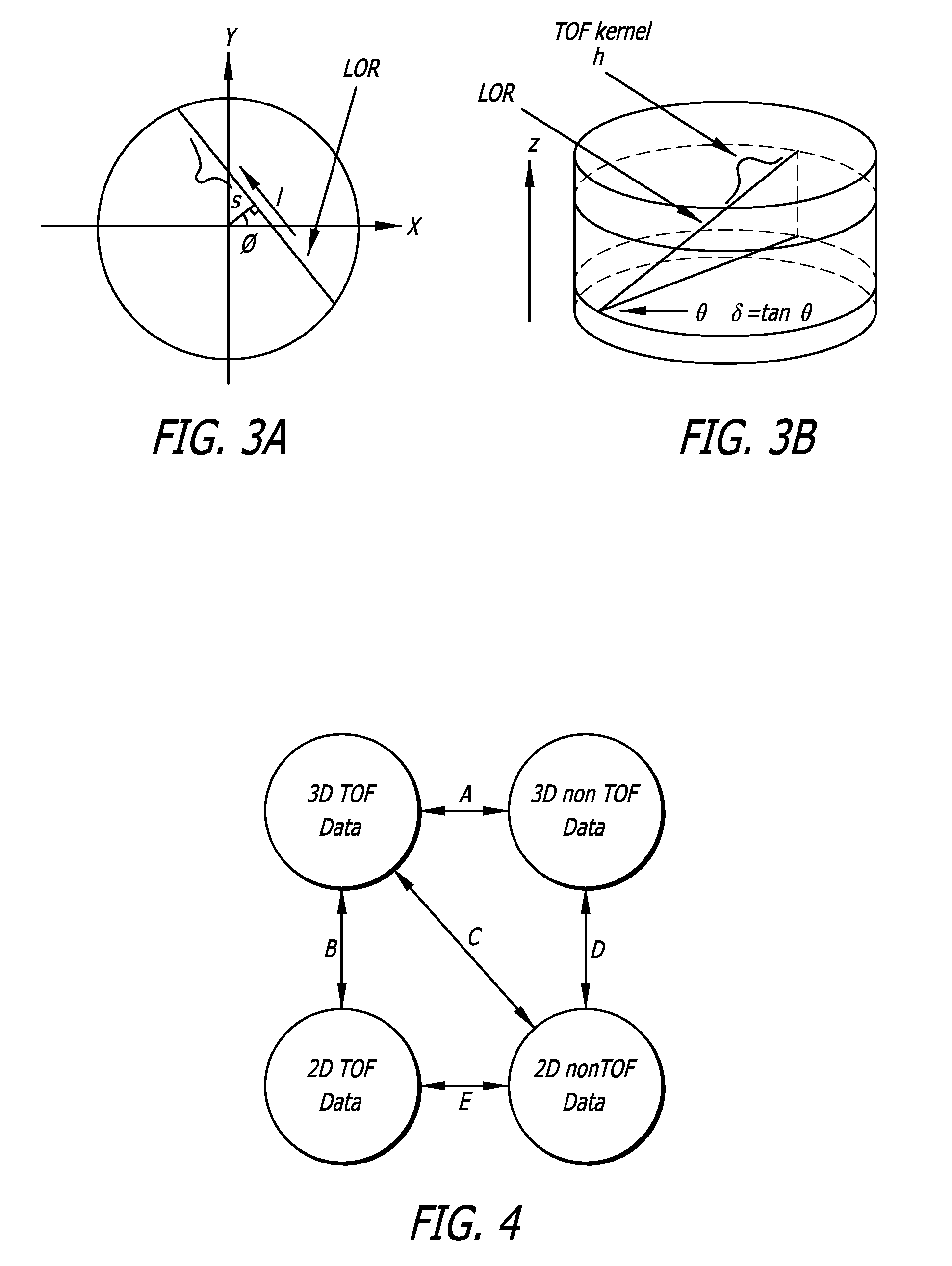
Exact and approximate rebinning of time-of-flight pet positron emission tomography data
InactiveUS20100098312A1Increase redundancyReduce dimensionalityReconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionCompanion animalComputer science
A technique for processing of data from time-of-flight (TOF) PET scanners. The size of TOF PET data may be reduced without significant loss of information through a process called rebinning. The rebinning may use the Fourier transform properties of the measured PET data, taken with respect to the time-of-flight variable, to perform data reduction. Through this rebinning process, TOF PET data may be converted to any of the following reduced representations: 2D TOF PET data, 3D non-TOF PET data, and 2D non-TOF PET data. Mappings may be exact or approximate. Approximate mappings may not require a Fourier transform in the axial direction which may have advantages when used with PET scanners of limited axial extent. Once TOF PET data is reduced in size using this rebinning, PET images may be reconstructed with hardware and / or software that is substantially less complex and that may run substantially faster in comparison to reconstruction from the original non-rebinned data.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
System for selecting true coincidence events in positron emission tomography
InactiveUS20060138332A1High sensitivityImprove resolutionMaterial analysis by optical meansX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentAngle of incidencePositron annihilation
Provided are new methods for enhancing the selection of true (T) annihilation events relative to the inclusion of true scattered (TS) and random (R) annihilation events in PET tomographs and thereby improving the sensitivity and / or resolution of PET scanners. The methods include reconstruction of Compton scattering interactions in the γ-ray detectors for determining the angles of incidence of the γ-rays received at the detectors and may utilize γ-ray polarization effects and electron recoil data associated with positron annihilation and Compton scattering. The use of the γ-ray polarization effects provides an improved ability for selecting data corresponding to T events while simultaneously suppressing data corresponding to TS and R events during PET applications.
Owner:ADVANCED APPLIED PHYSICS SOLUTIONS
Compact conscious animal positron emission tomography scanner
ActiveUS7126126B2Reduce power consumptionMagnetic measurementsMaterial analysis by optical meansEngineeringTime signal
A method of serially transferring annihilation information in a compact positron emission tomography (PET) scanner includes generating a time signal for an event, generating an address signal representing a detecting channel, generating a detector channel signal including the time and address signals, and generating a composite signal including the channel signal and similarly generated signals. The composite signal includes events from detectors in a block and is serially output. An apparatus that serially transfers annihilation information from a block includes time signal generators for detectors in a block and an address and channel signal generator. The PET scanner includes a ring tomograph that mounts onto a portion of an animal, which includes opposing block pairs. Each of the blocks in a block pair includes a scintillator layer, detection array, front-end array, and a serial encoder. The serial encoder includes time signal generators and an address signal and channel signal generator.
Owner:BROOKHAVEN SCI ASSOCS
Methods apparatus assemblies and systems for implementing a ct scanner
InactiveUS20110122990A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingCt scannersEngineering
Disclosed is a Computer Tomography (CT) system including a gantry having first and second semicircular support elements which are concentric with one another. Each of the first and second semicircular support elements has a missing sector and at least one of the missing sectors may be of an angle of 180 degrees or less. A controller may be adapted to regulate relative rotational positions between said first and second support elements.
Owner:ARINETA
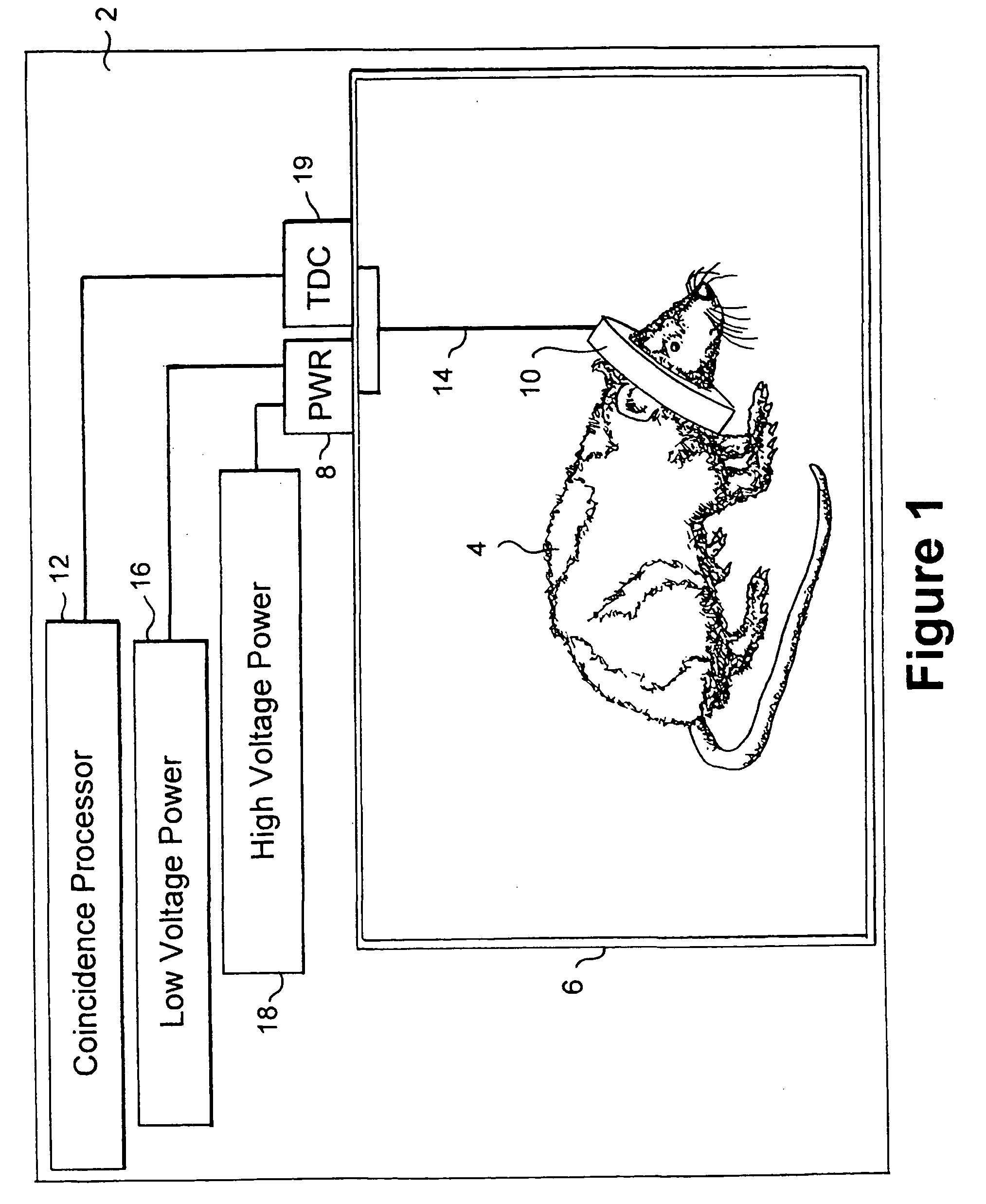
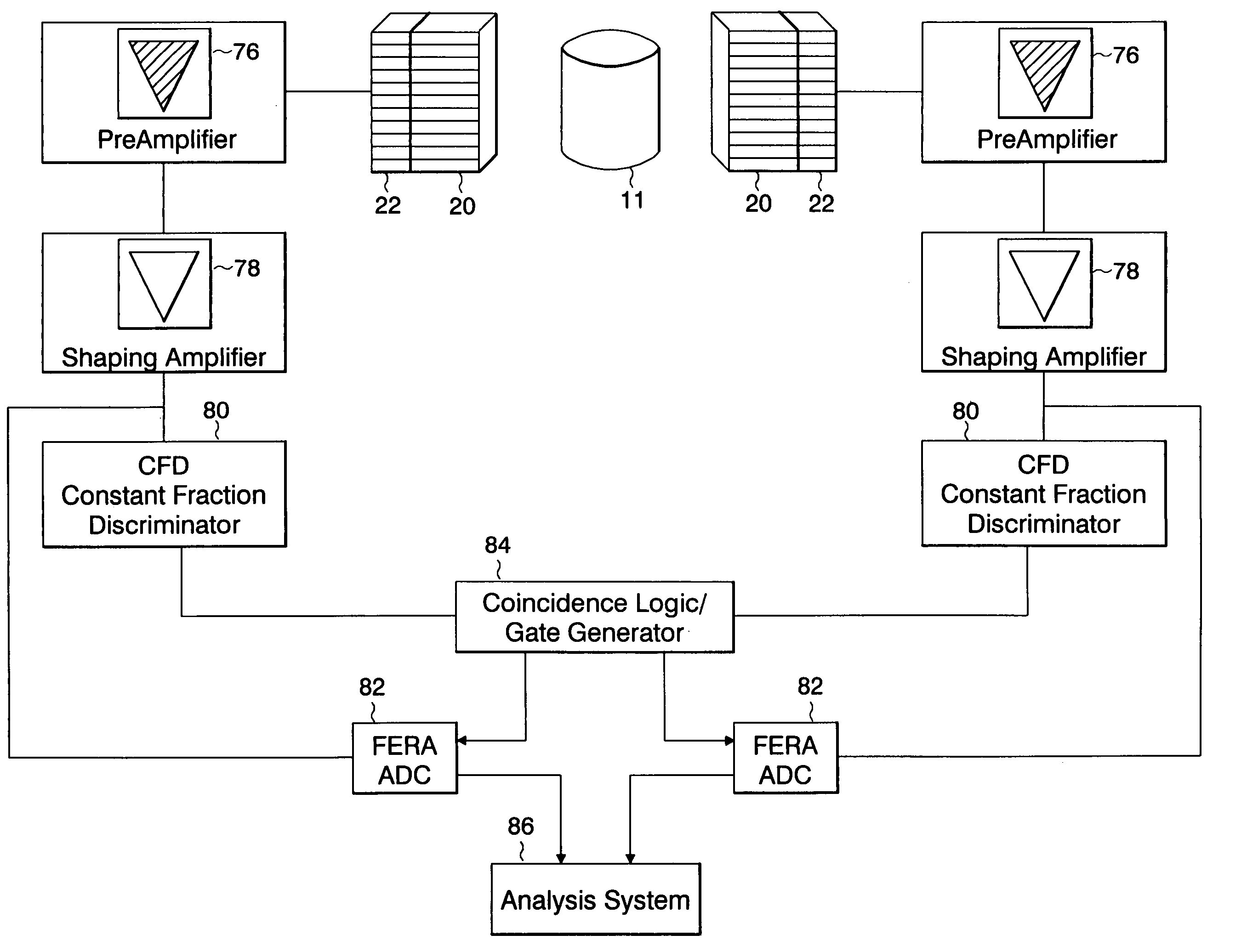
Instrument and method to facilitate and improve the timing alignment of a pet scanner
InactiveUS20070131857A1Long half-lifeMaterial analysis by optical meansCalibration apparatusEngineeringScintillator
A system for providing the timing alignment for a scanner. The system includes a removable source and detector assembly which is placed near the centre of the scanner when in use. The source includes a long-lived positron emitting radioactive source. The radioactive source is in close contact with a fast plastic scintillator or other mechanism of detecting the ionization due to positron decay. A method for reading out the precise time at which the surrounding medium detects the ionization due to positron decay. A mechanism for using this time as a reference clock unto which the detectors in the scanner can be aligned.
Owner:SCANWELL SYST
Normalization apparatus for panel detector PET scanners
A normalization apparatus and method for a PET scanner with panel detectors for obtaining an estimate of a normalization array, for correction for count rate effects on the normalization array, and for measurement of the relation between the normalization array and the count rate. The method of the present invention is based on two quasi-independent radial and axial components, which are count rate dependent due to sensitivity changes across the detector blocks. A scatter source is disposed at the center of the FOV and a scatter-free source is disposed at the outer edge of the FOV. The method computes the normalization array through several steps which evaluate the geometric profile, the axial profile, and the correction factor. A count rate correction is introduced to extend the normalization array to any count rate.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
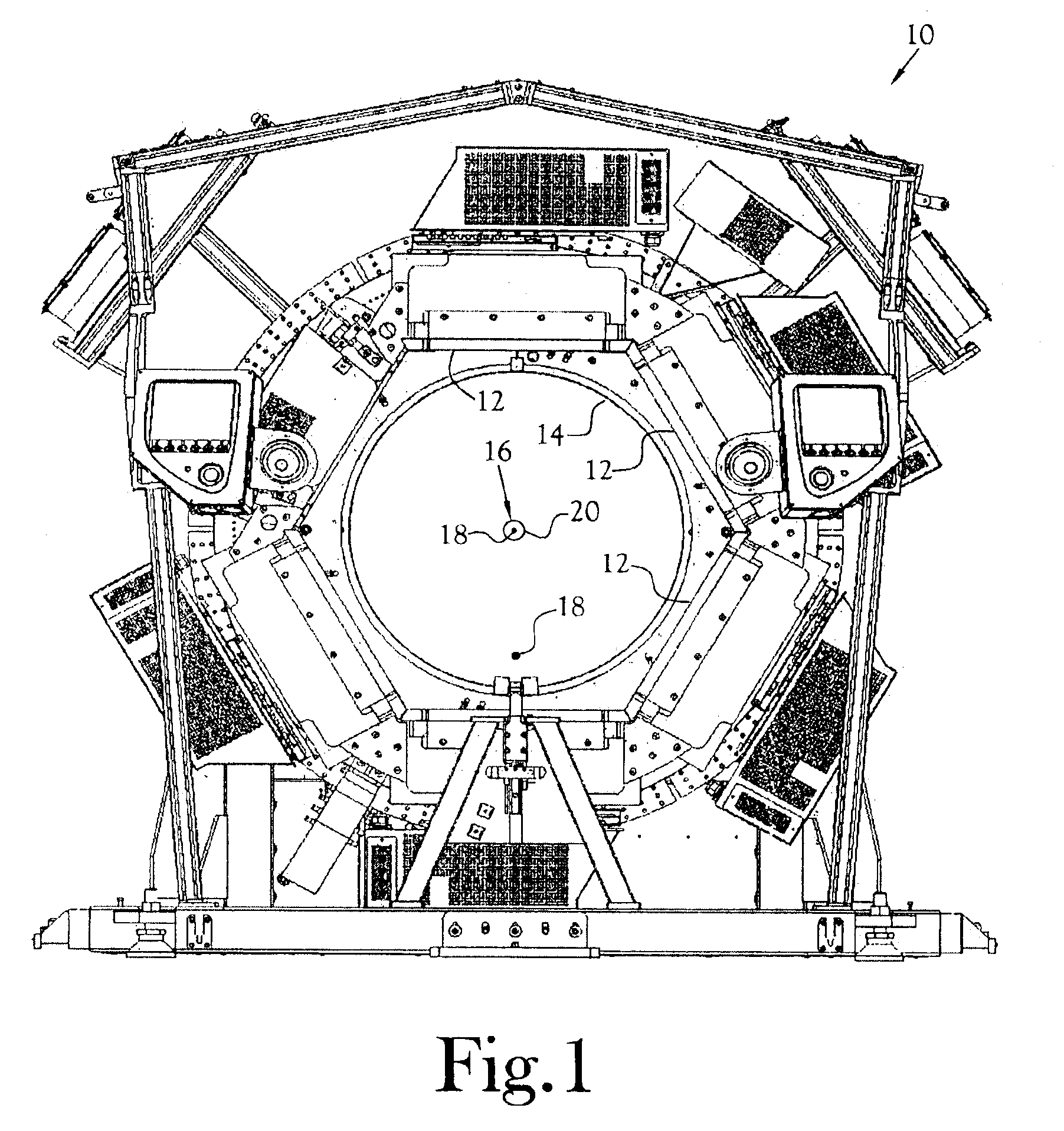
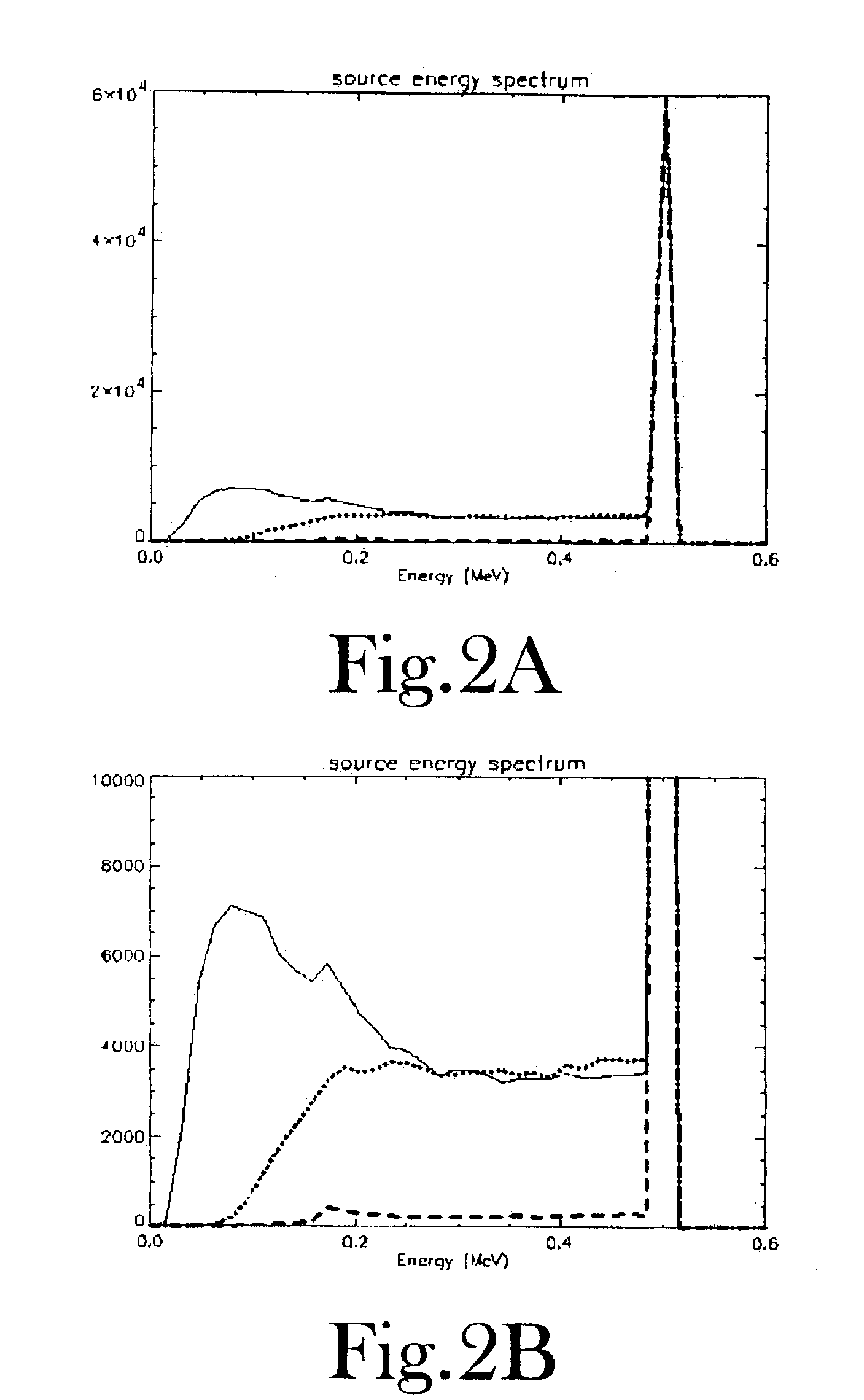
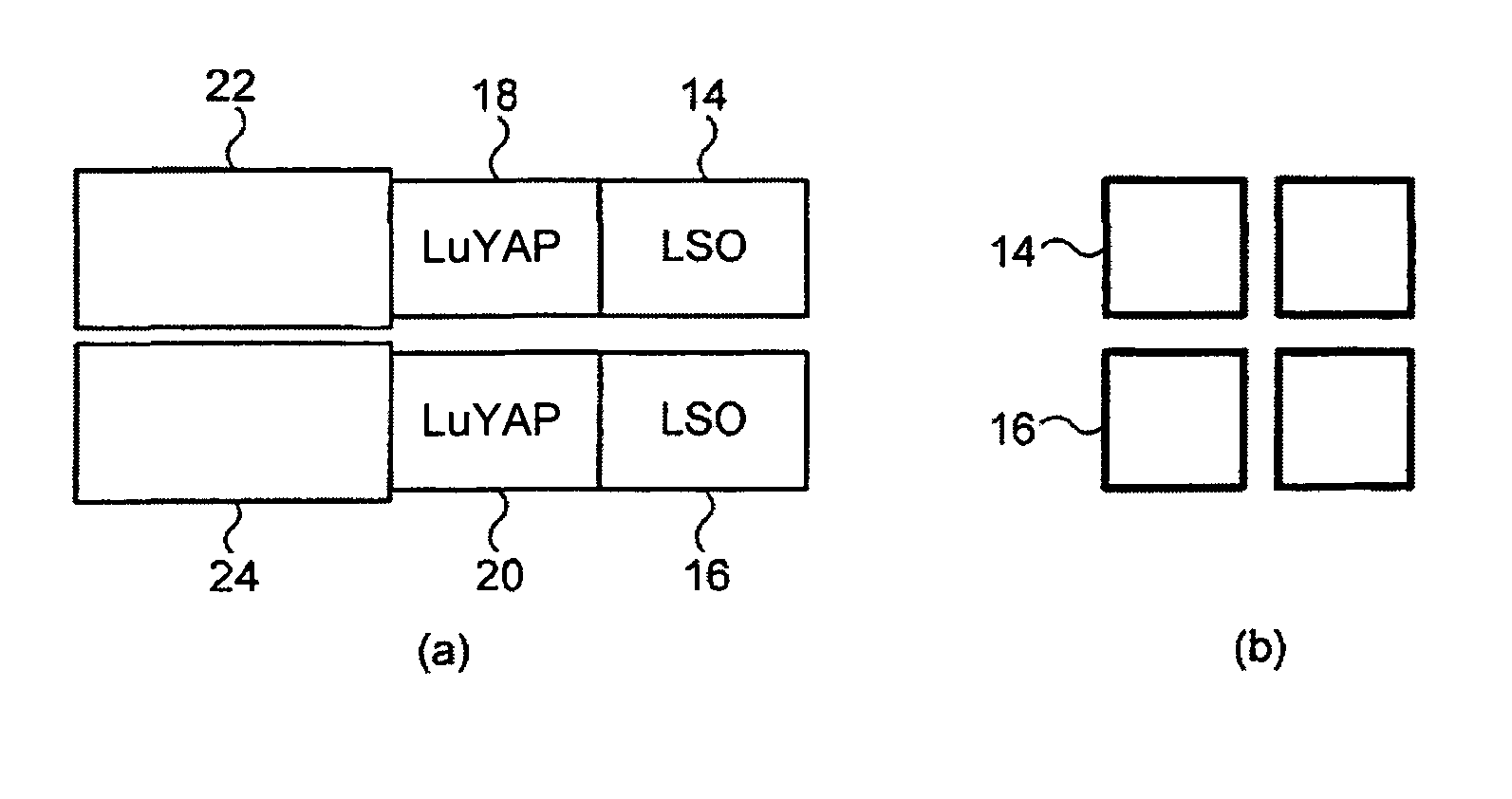
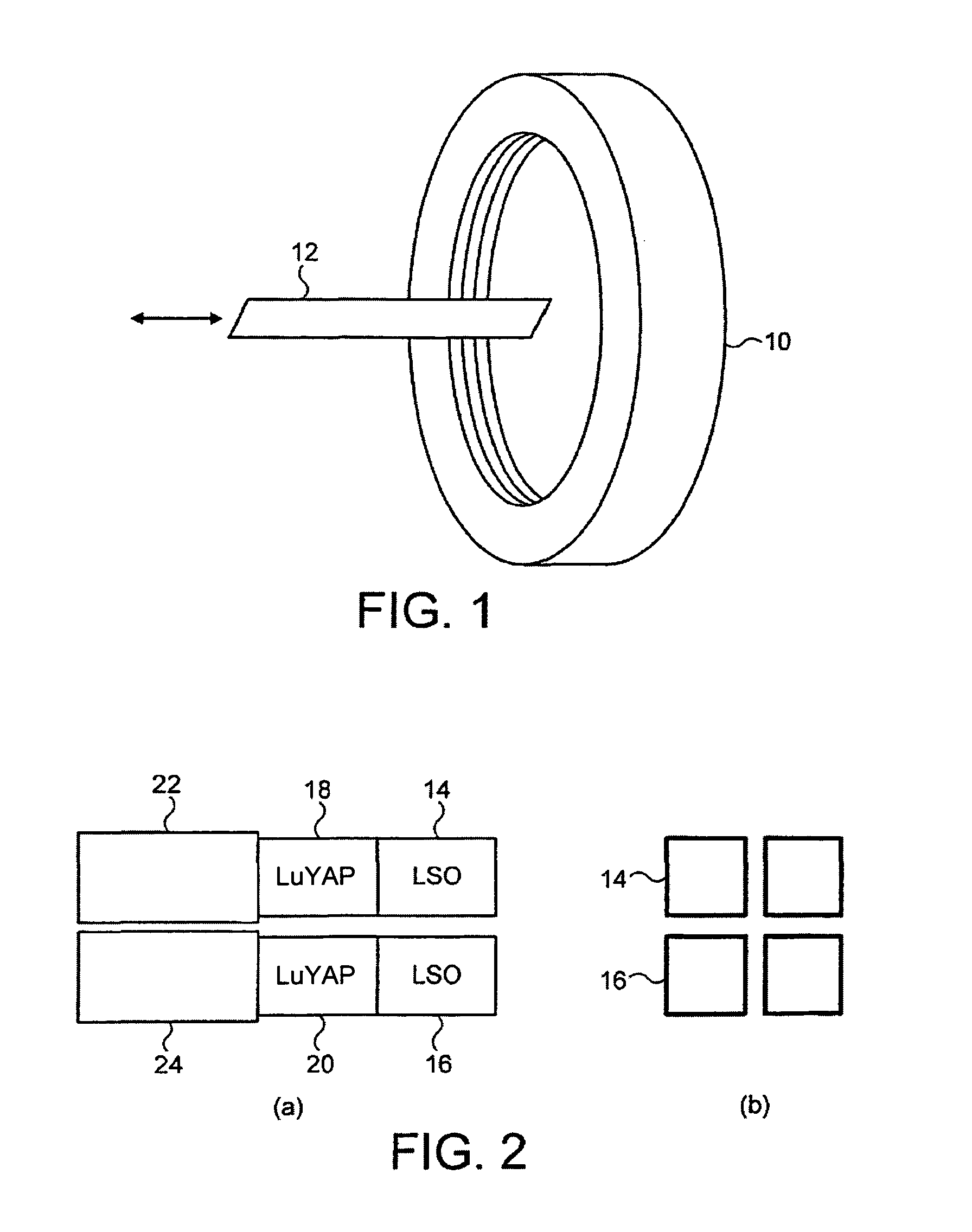
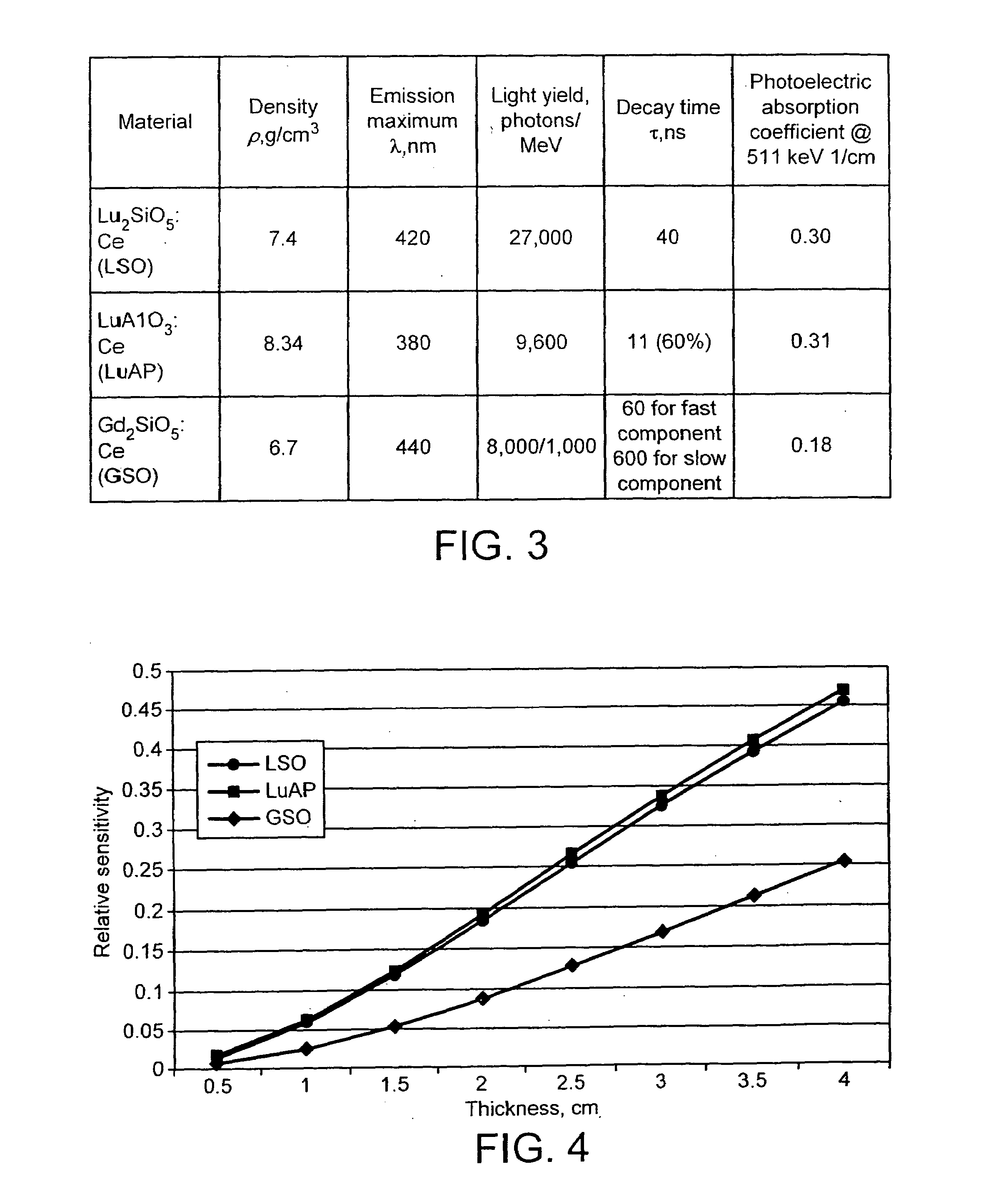
PET scanner
A positron emission camera comprising a plurality of scintillators, wherein the scintillators include LuAlO3:Ce (LuxY1−xAP where 0.5≦x≦0.995) based crystals (18,20). In particular, the scintillation crystals (18,20) are LuxY1−xAP where 0.5≦x≦0.995.
Owner:EUROPEAN ORGANIZATION FOR NUCLEAR RESEARCH
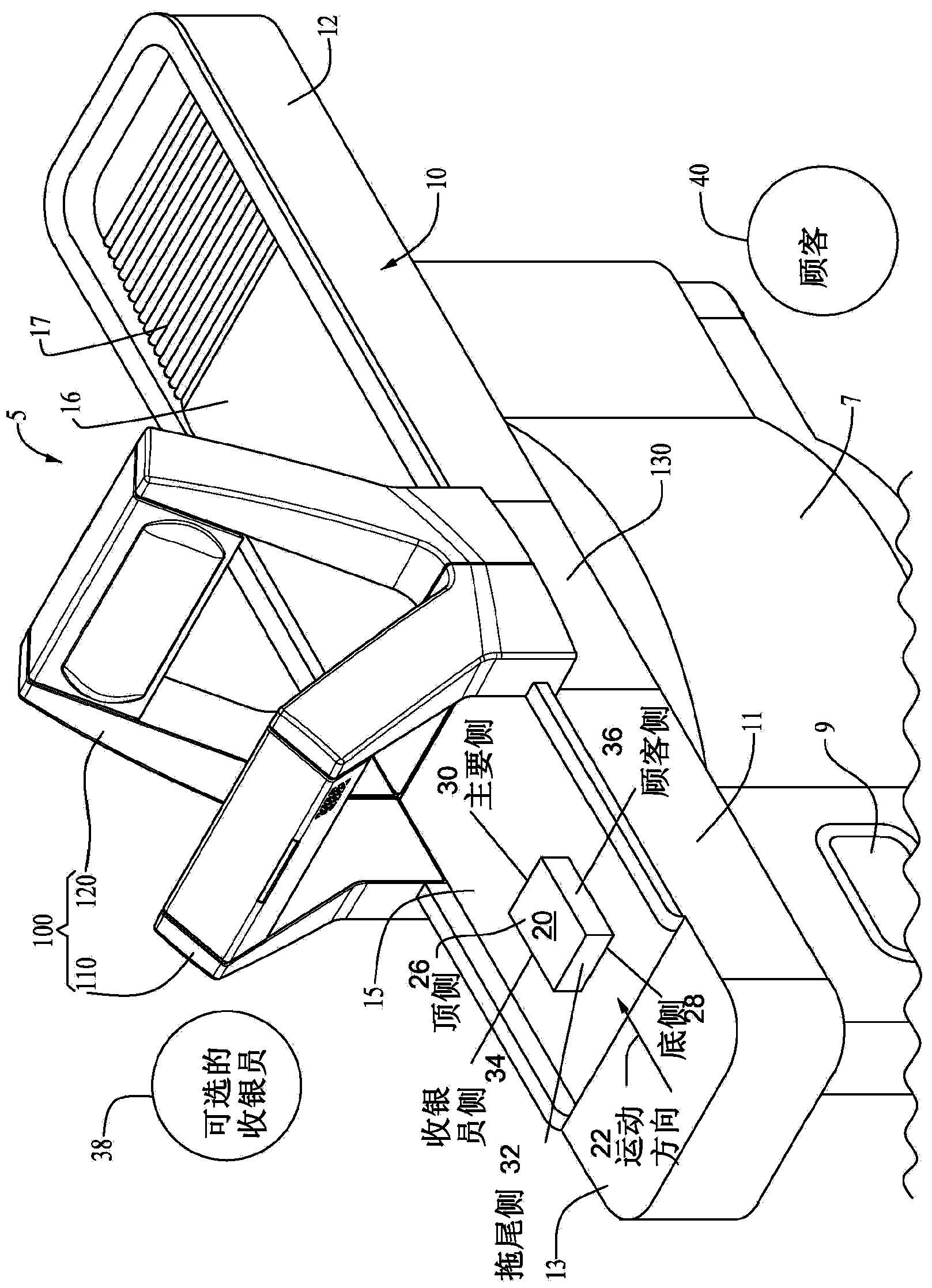
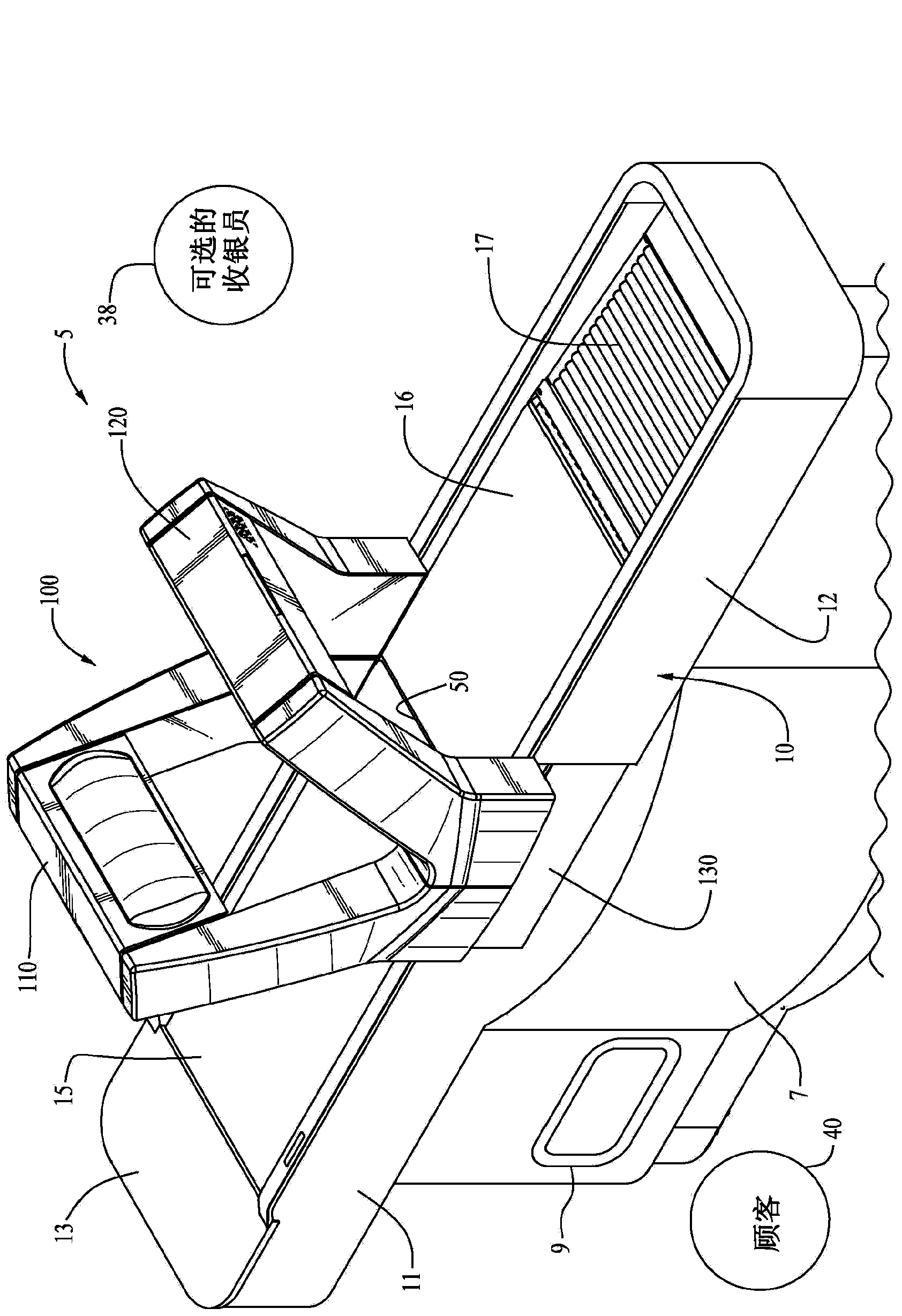
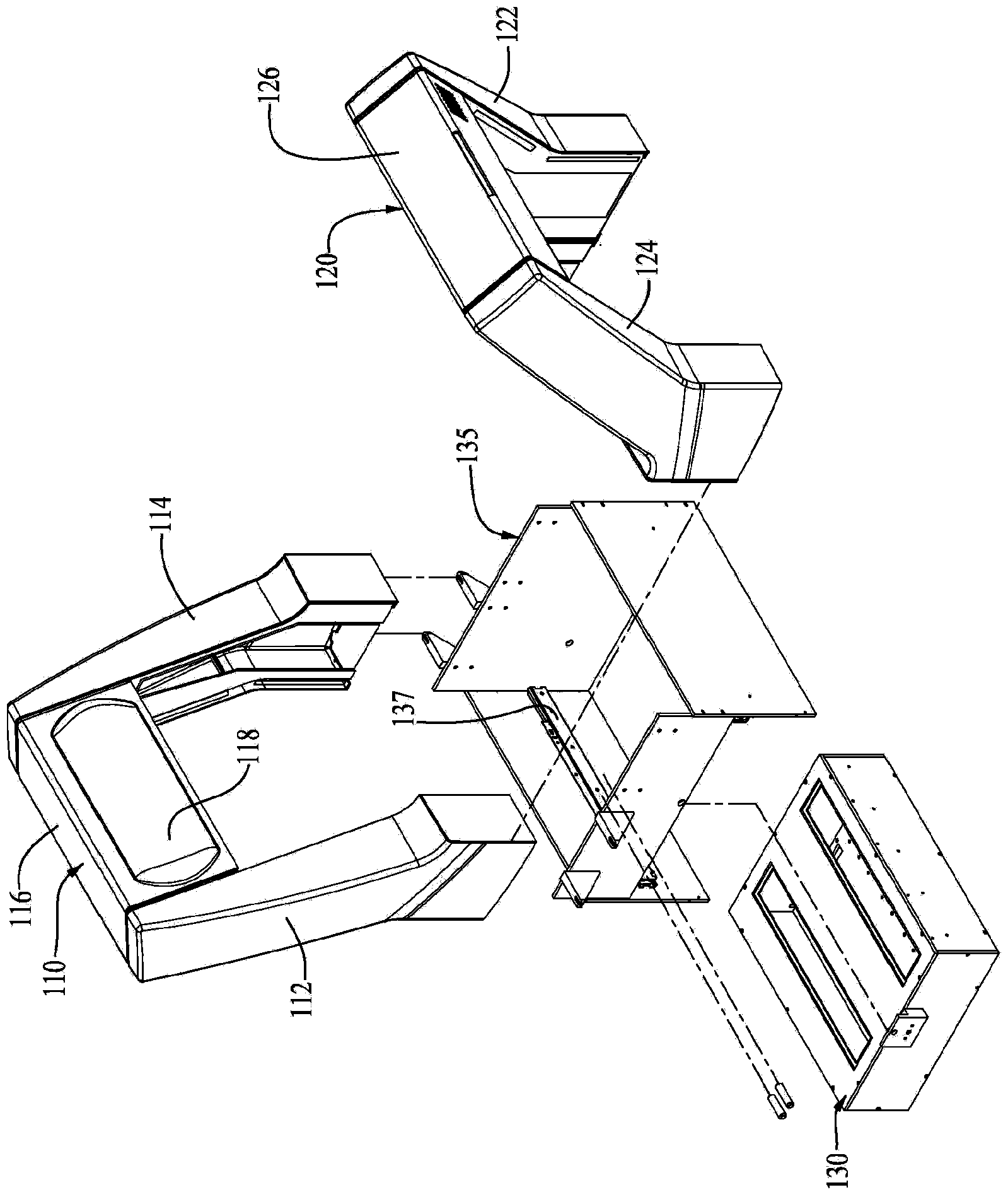
Tunnel or portal scanner and method of scanning for automated checkout
Systems and methods for data reading, which in one configuration is directed to an automated optical code data reader (5) in the form of a tunnel or portal scanner (100, 500) having an open architecture configured with front and rear inverted U-shaped arches (110, 120), a plurality cameras (some or most of which having multiple fields of view) (150, 160, 170, 180, 192 / 194, 250, 260, 270, 280, 300, 310, 320, 330) in each of the arches for reading the top five sides of an item (20) being passed by a conveyor (15 / 16) through a read region formed by the arches, and a bottom reader (130) including one or more cameras (410, 420) under the conveyor for reading a bottom side of the item through a gap (50) in the conveyors as the item is passed over the gap. Also disclosed are specific imaging schemes for providing effective views of the items with a minimum number of cameras.
Owner:DATALOGIC ADC
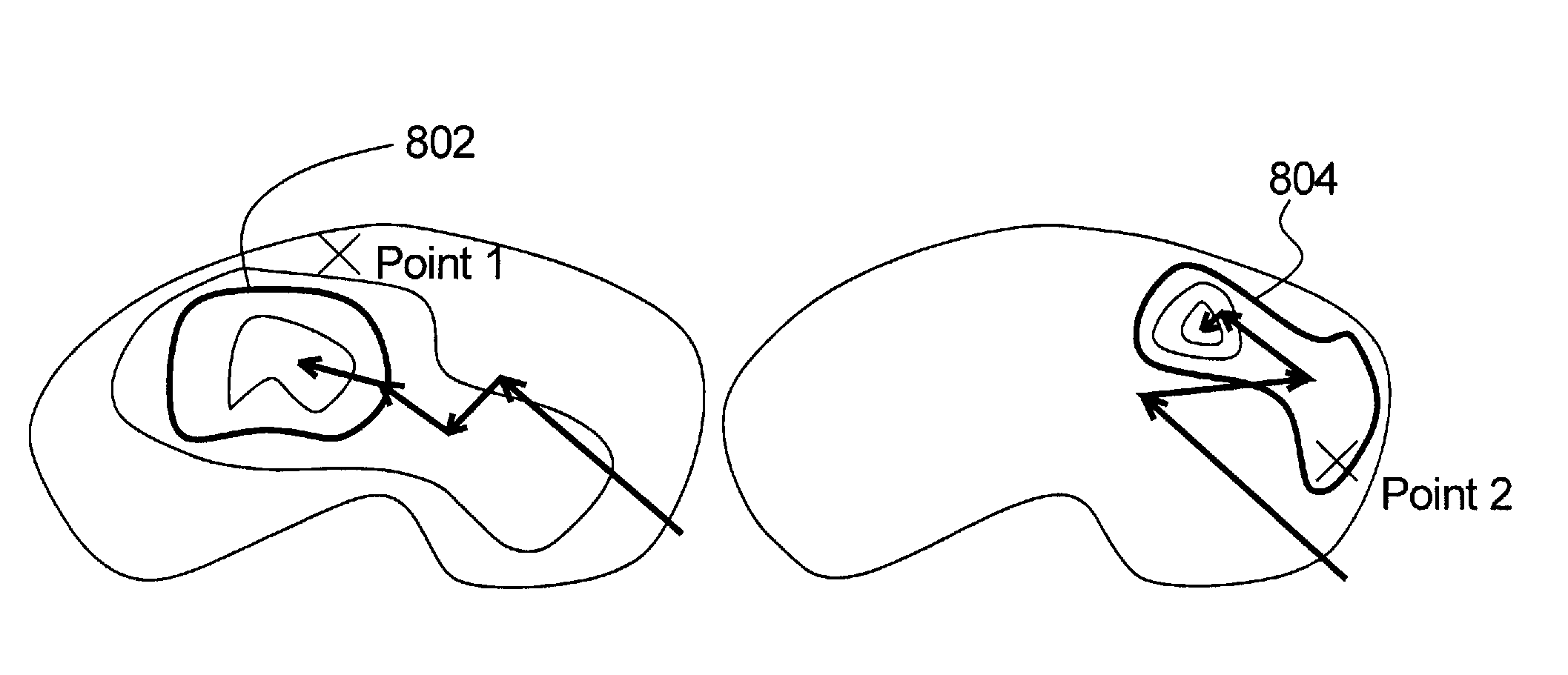
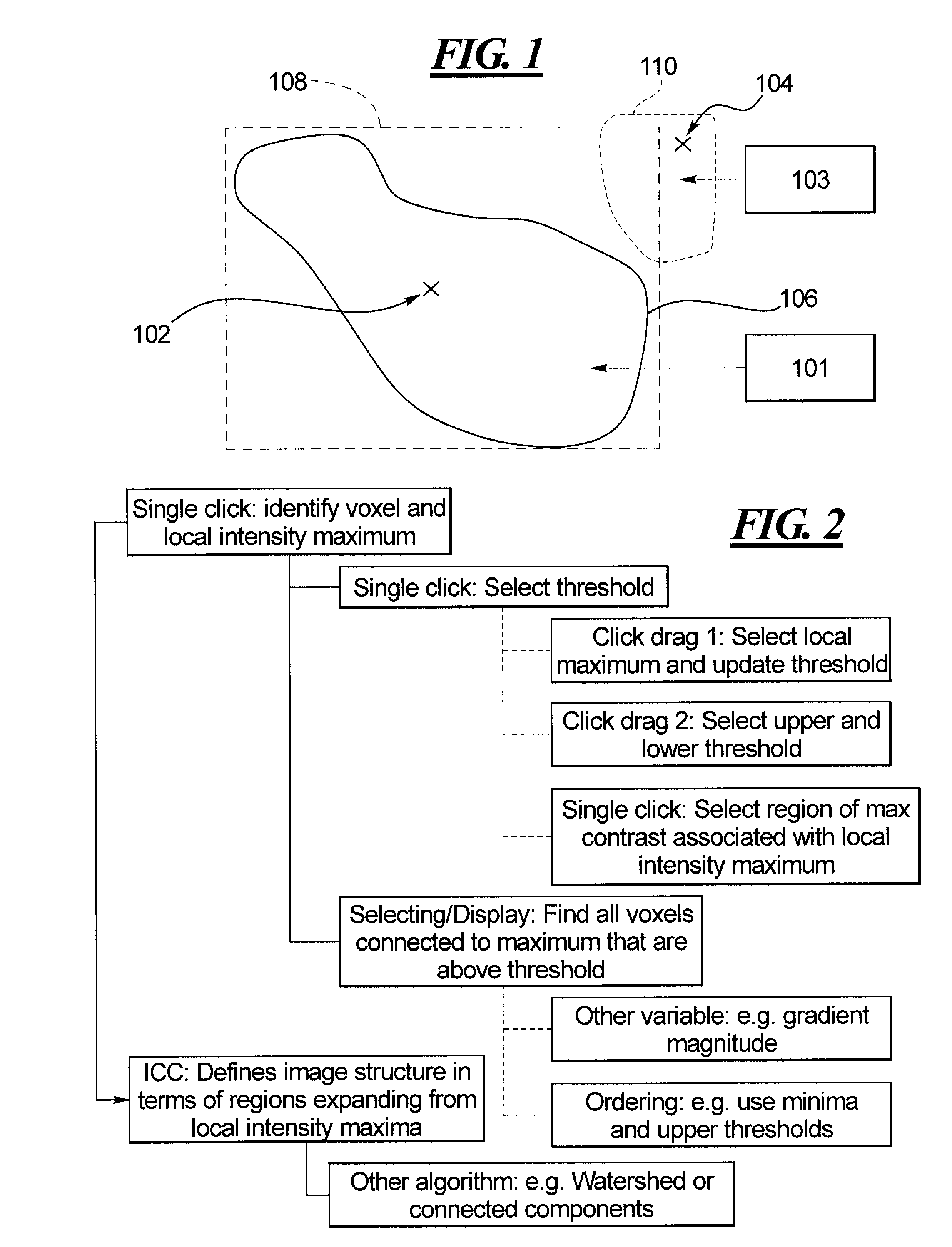
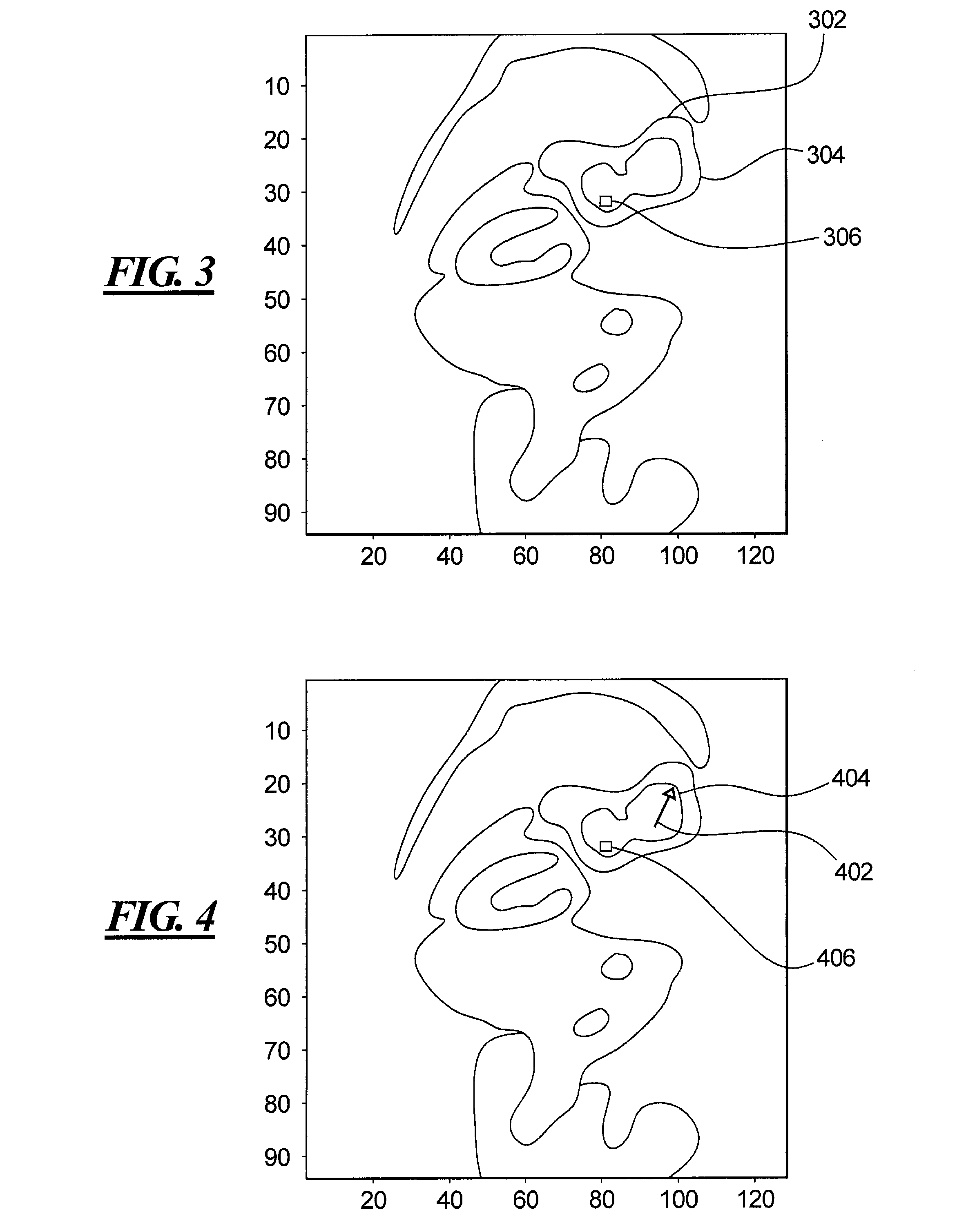
Method and apparatus for identifying regions of interest in a medical image
ActiveUS20100088644A1Avoid inclusionsSimple definitionImage enhancementImage analysisVoxelMedical imaging
In a method and apparatus for identifying regions of interest in medical images of a subject, in particular images captured by a medical imaging apparatus, such as a PET scanner, a list of voxels of the image is obtained, and sorted according to a first variable. A user-selection of an initial voxel in the image is then registered, and at least one voxel or group of voxels from the sorted list is selected as a region of interest, according to a property of the at least one voxel or group in relation to the user-selected initial voxel. The image may be pre-processed to generate the sorted list of voxels, following which the user selection of the initial voxel is registered.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Multi-doped lutetium based oxyorthosilicate scintillators having improved photonic properties
InactiveCN104508192ALow costIncrease concentrationPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsHigh energyCerium
The present invention relates to a set of multi-doped cerium-activated scintillation materials of the solid solutions on the basis of the rare earth silicate, comprising lutetium and having compositions represented by the chemical formulas: (Lu2-w-x+2yAwCexSi1-y)1-zMezJjOq and (Lu2-w-x-2yAwCexSi1+y)1-zMezJjOq. The invention is useful for detection of elementary particles and nuclei in high-energy physics, nuclear industry; medicine, Positron Emission Tomography (TOF PET and DOI PET scanners) and Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT), Positron Emission Tomography with Magnetic Resonance imaging (PET / MR); X-ray computer fluorography; non-destructive testing of solid state structure, including airport security systems, the Gamma-ray systems for the inspection of trucks and cargo containers.
Owner:ZECOTEK PHOTONICS INC
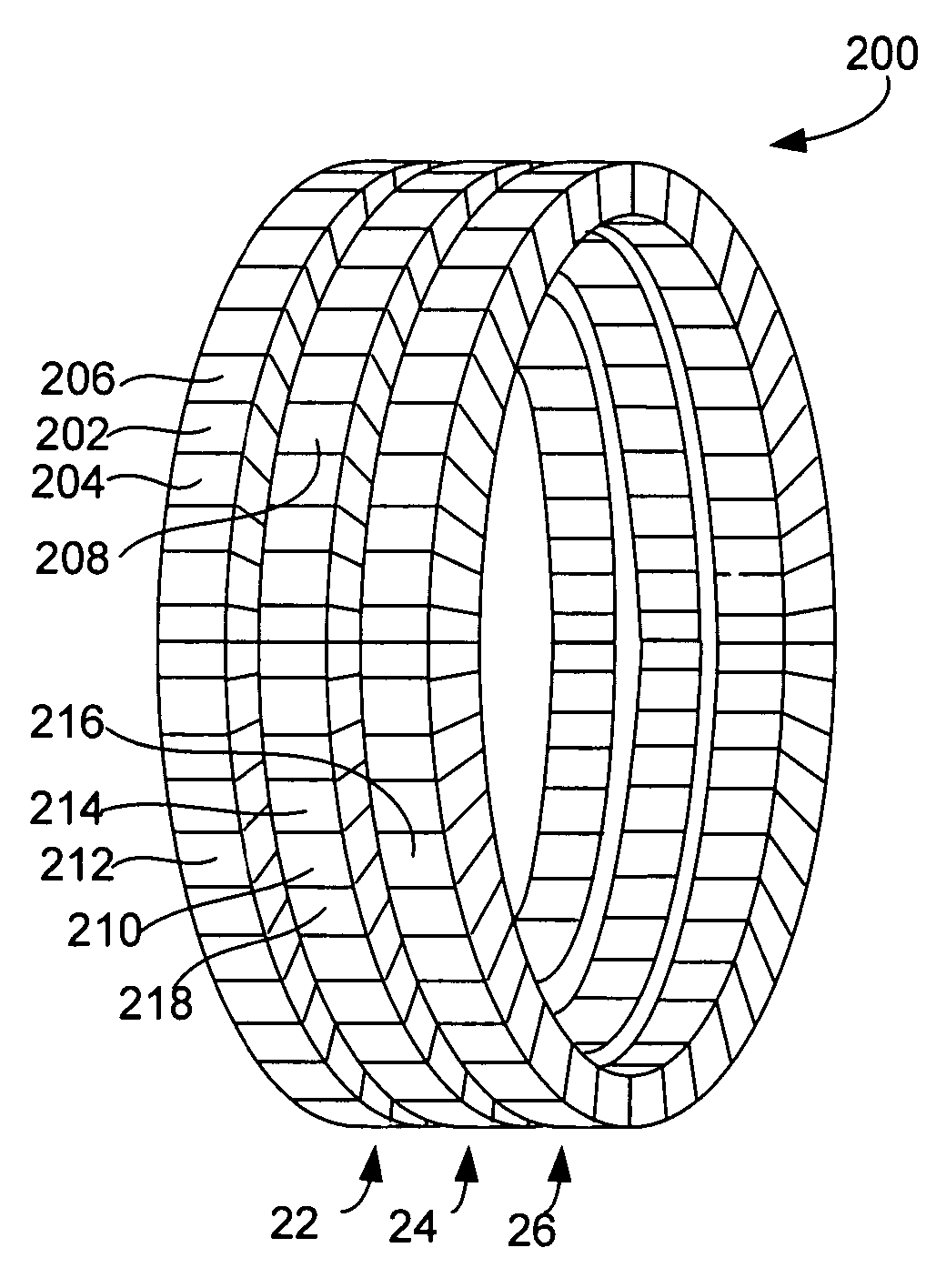
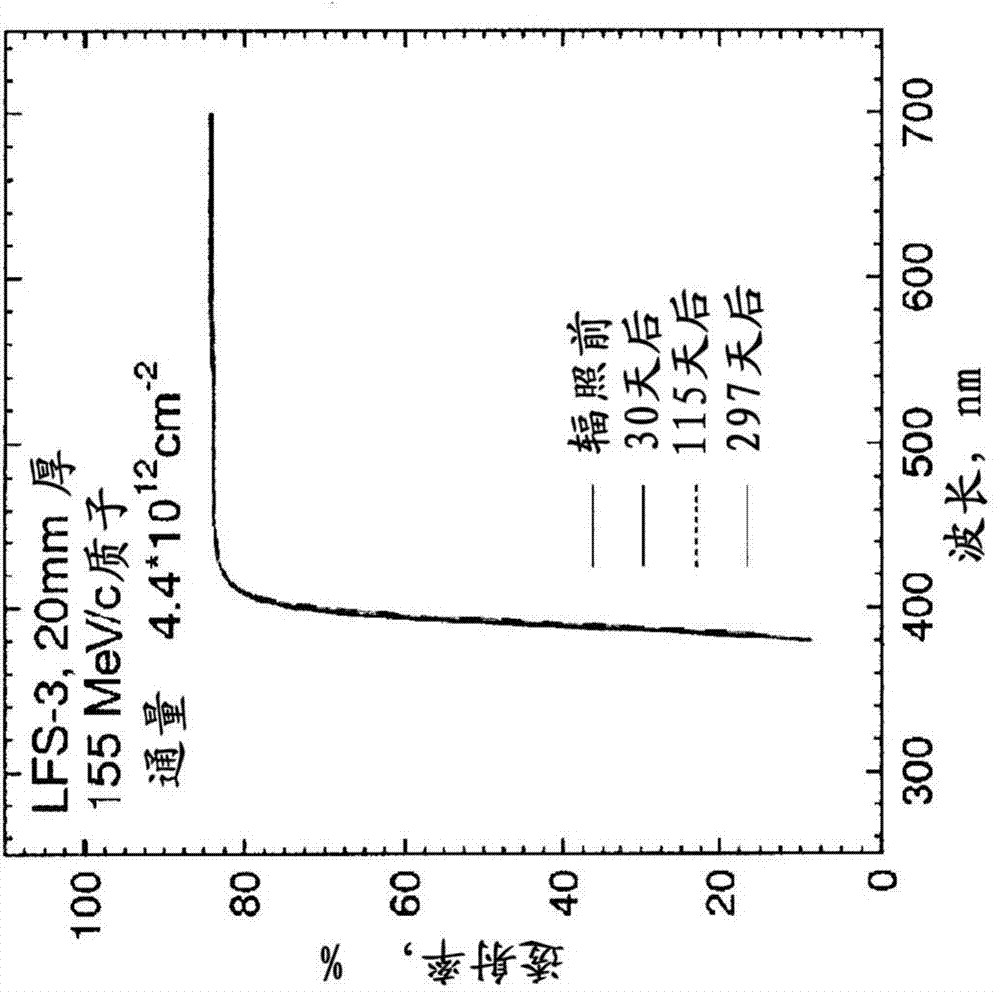
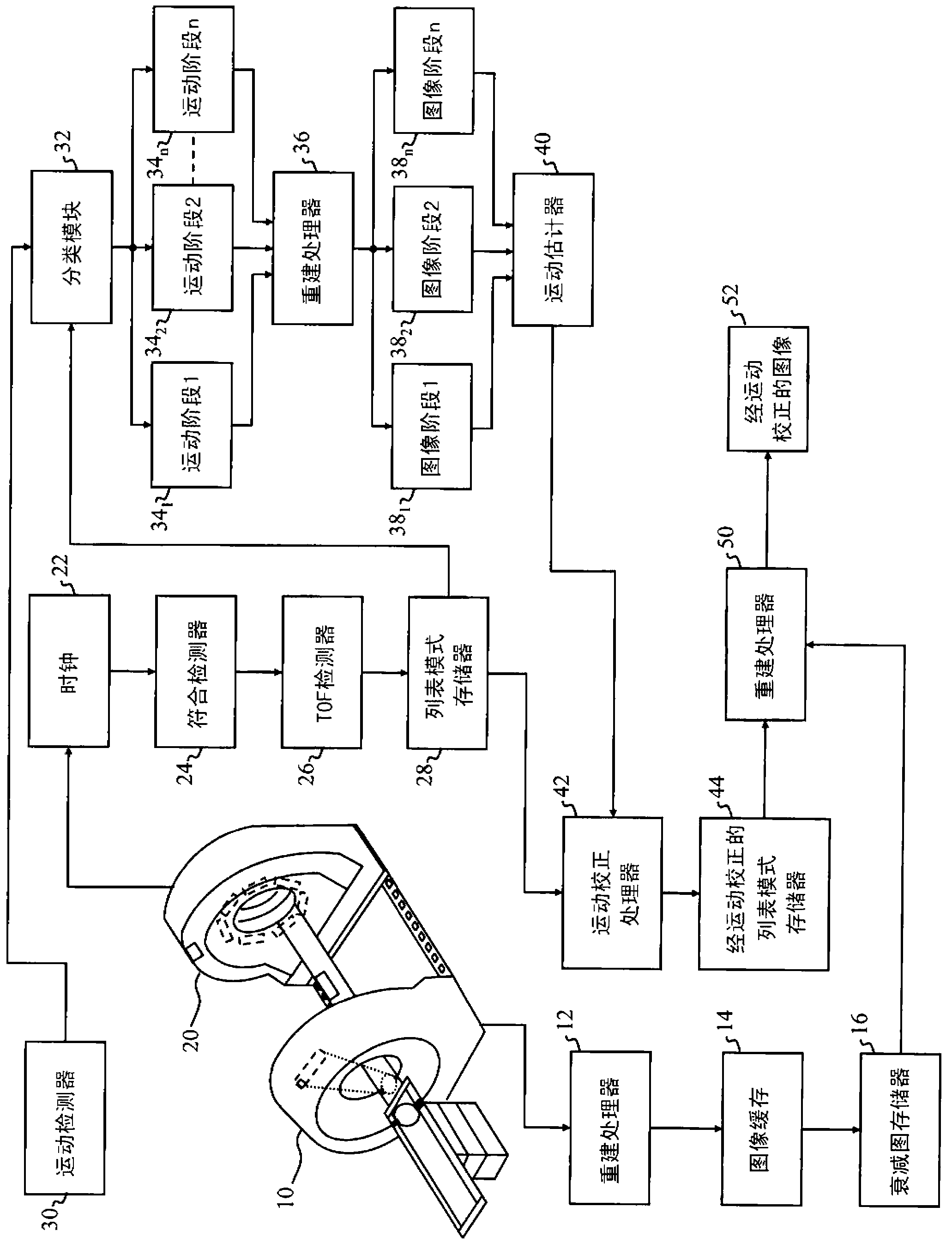
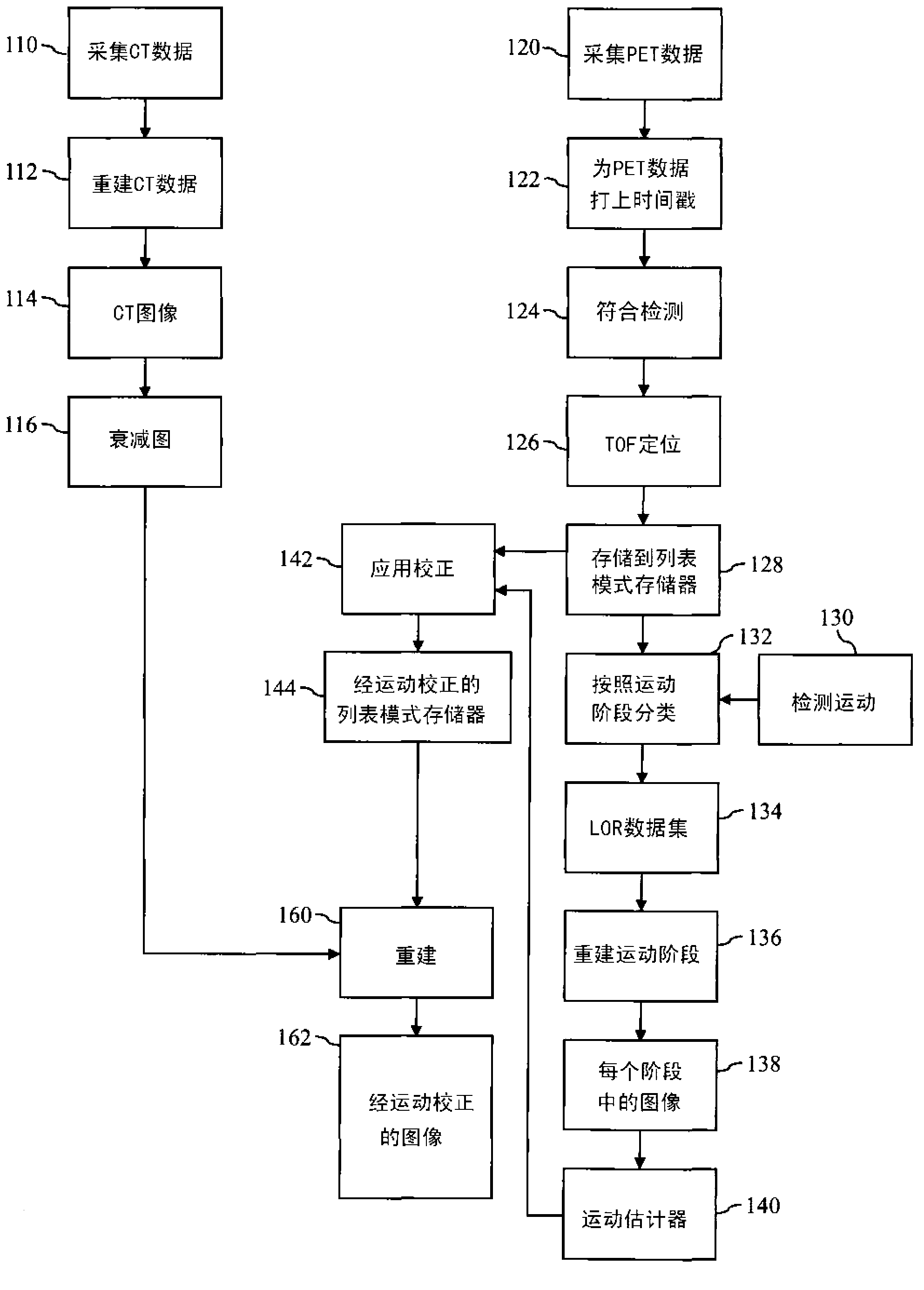
Method and apparatus to detect and correct motion in list-ode pet data with a gated signal
ActiveCN103282941AIdentify and monitor radiation intakeIdentify and monitor washoutReconstruction from projectionImage generationLines of responseMotion detector
A PET scanner (20, 22, 24, 26) generates a plurality of time stamped lines of response (LORs). A motion detector (30) detects a motion state, such as motion phase or motion amplitude,of the subject during acquisition of each of the LORs. A sorting module (32) sorts the LORs by motion state and a reconstruction processor (36) reconstructs the LORs into high spatial, low temporal resolution images in the corresponding motion states. A motion estimator module (40) determines a motion transform which transforms the LORs into a common motion state. A reconstruction module (50) reconstructs the motion corrected LORs into a static image or dynamic images, a series of high temporal resolution, high spatial resolution images.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com