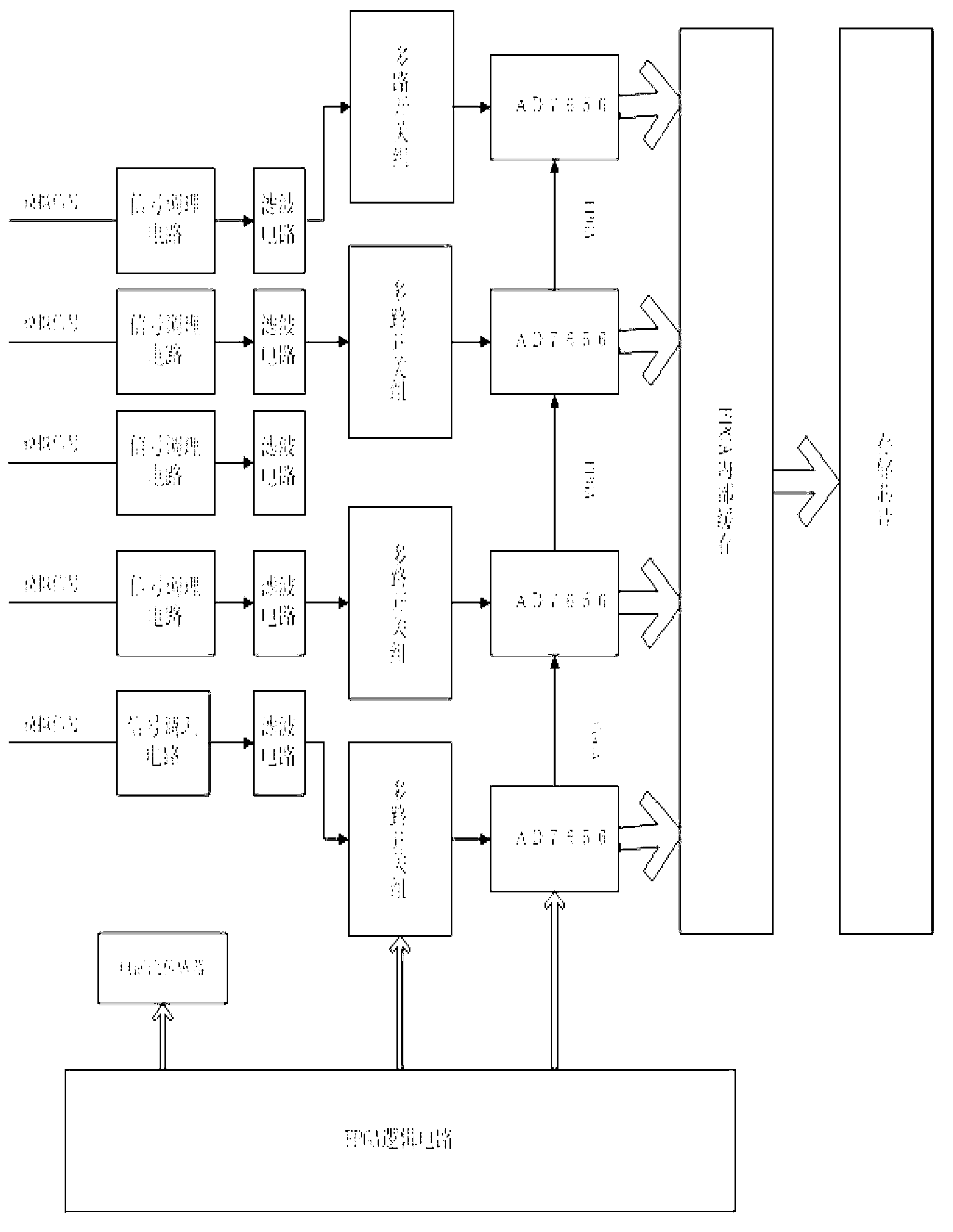
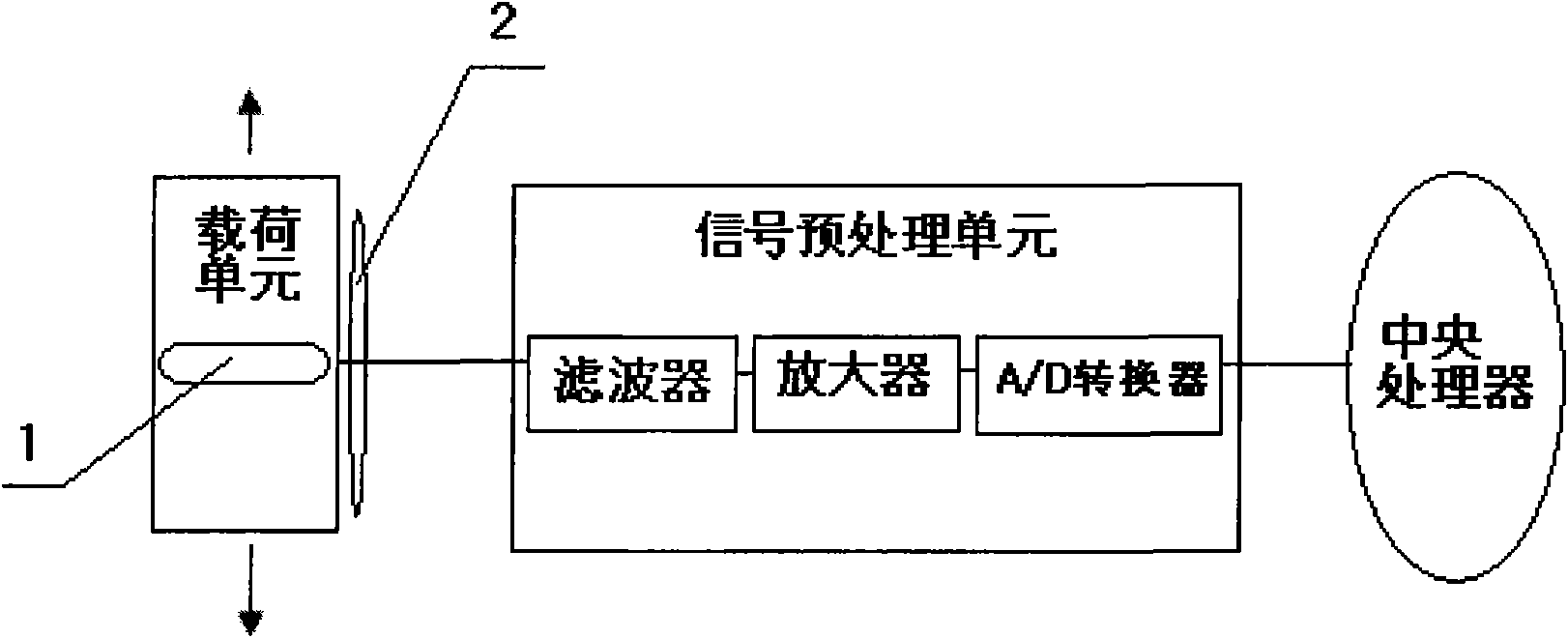
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
794 results about "Destructive testing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In destructive testing (or destructive physical analysis, DPA) tests are carried out to the specimen's failure, in order to understand a specimen's performance or material behavior under different loads. These tests are generally much easier to carry out, yield more information, and are easier to interpret than nondestructive testing. Destructive testing is most suitable, and economic, for objects which will be mass-produced, as the cost of destroying a small number of specimens is negligible. It is usually not economical to do destructive testing where only one or very few items are to be produced (for example, in the case of a building). Analyzing and documenting the destructive failure mode is often accomplished using a high-speed camera recording continuously (movie-loop) until the failure is detected. Detecting the failure can be accomplished using a sound detector or stress gauge which produces a signal to trigger the high-speed camera. These high-speed cameras have advanced recording modes to capture almost any type of destructive failure. After the failure the high-speed camera will stop recording. The captured images can be played back in slow motion showing precisely what happens before, during and after the destructive event, image by image.
Non-destructive testing of pipes
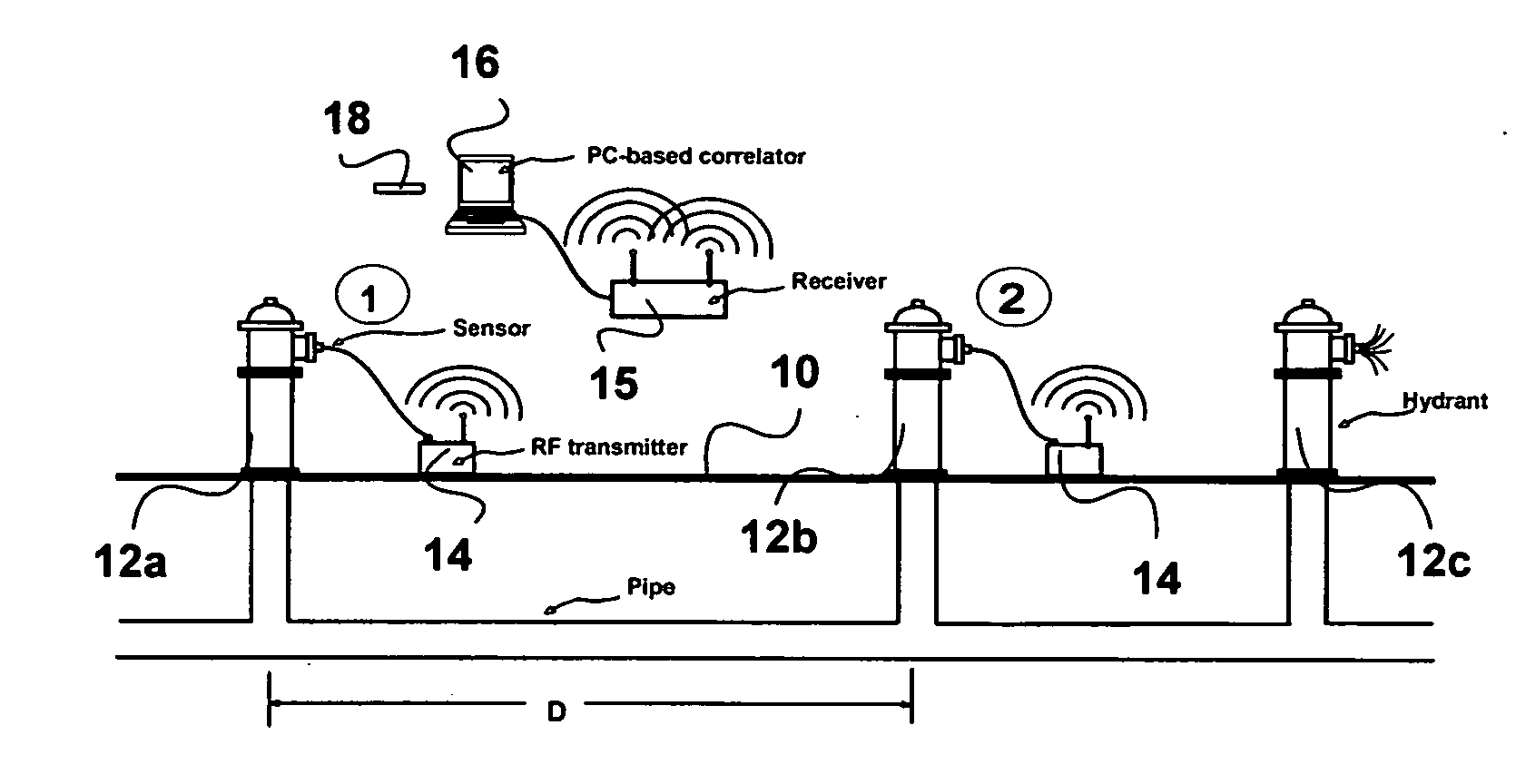
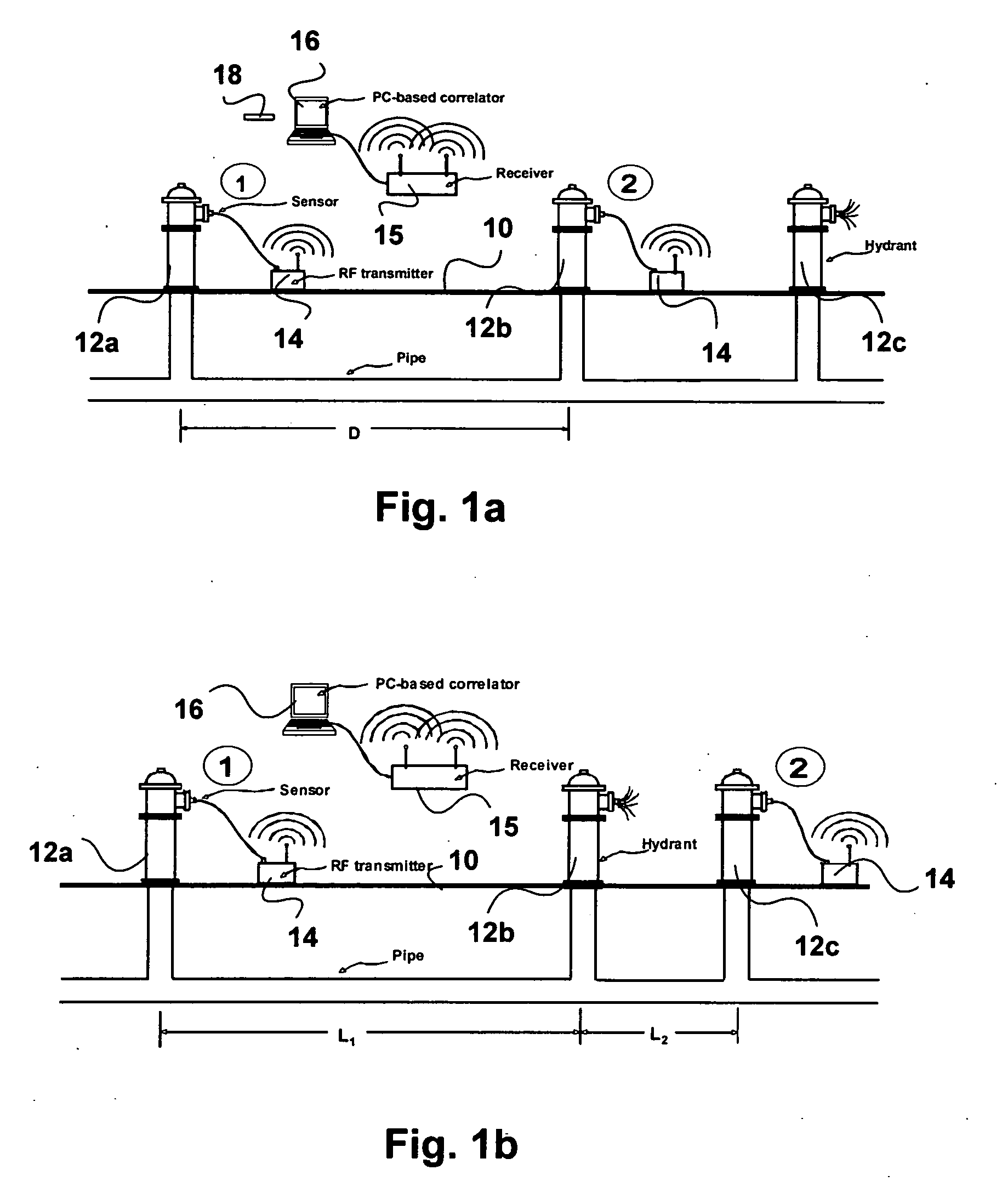
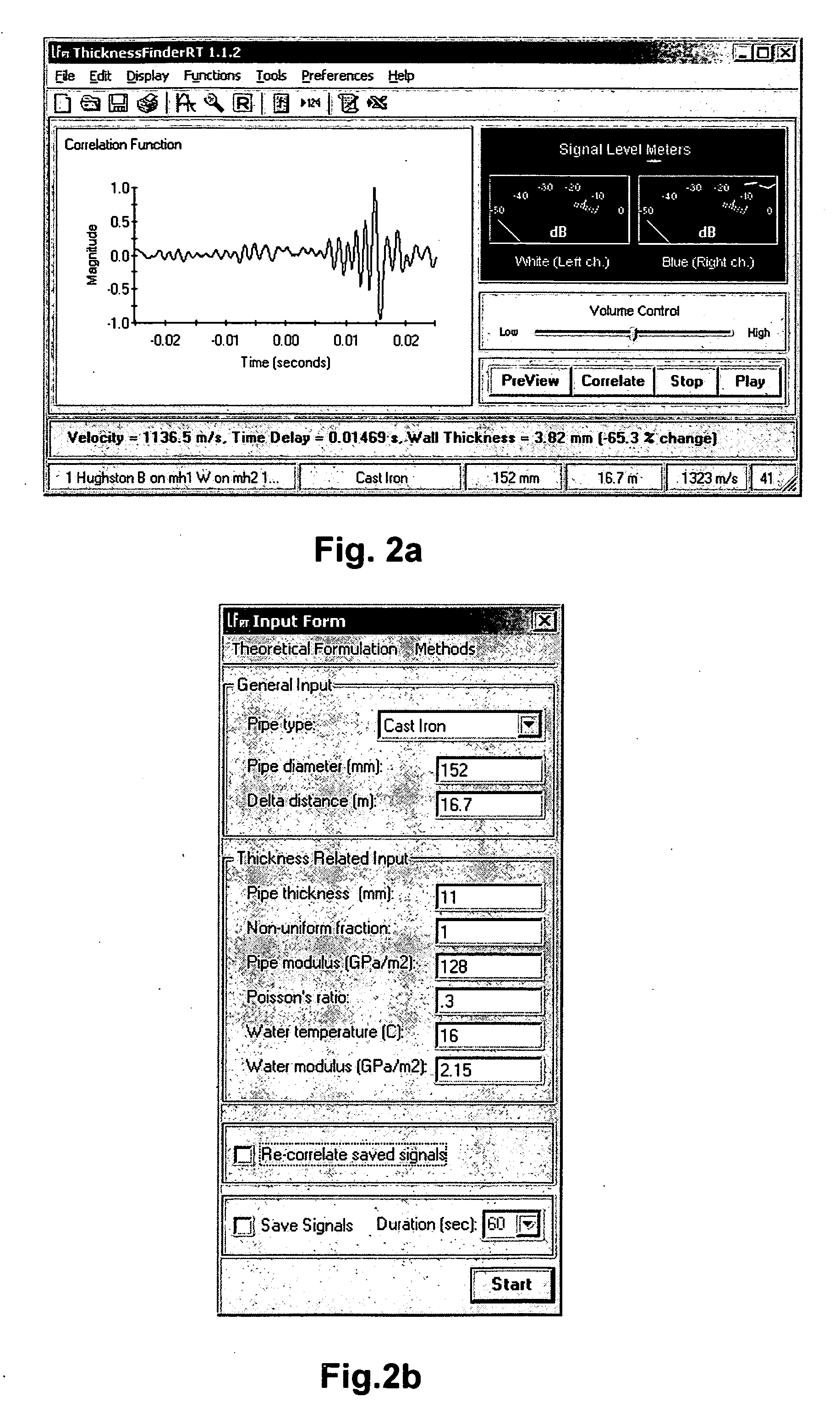
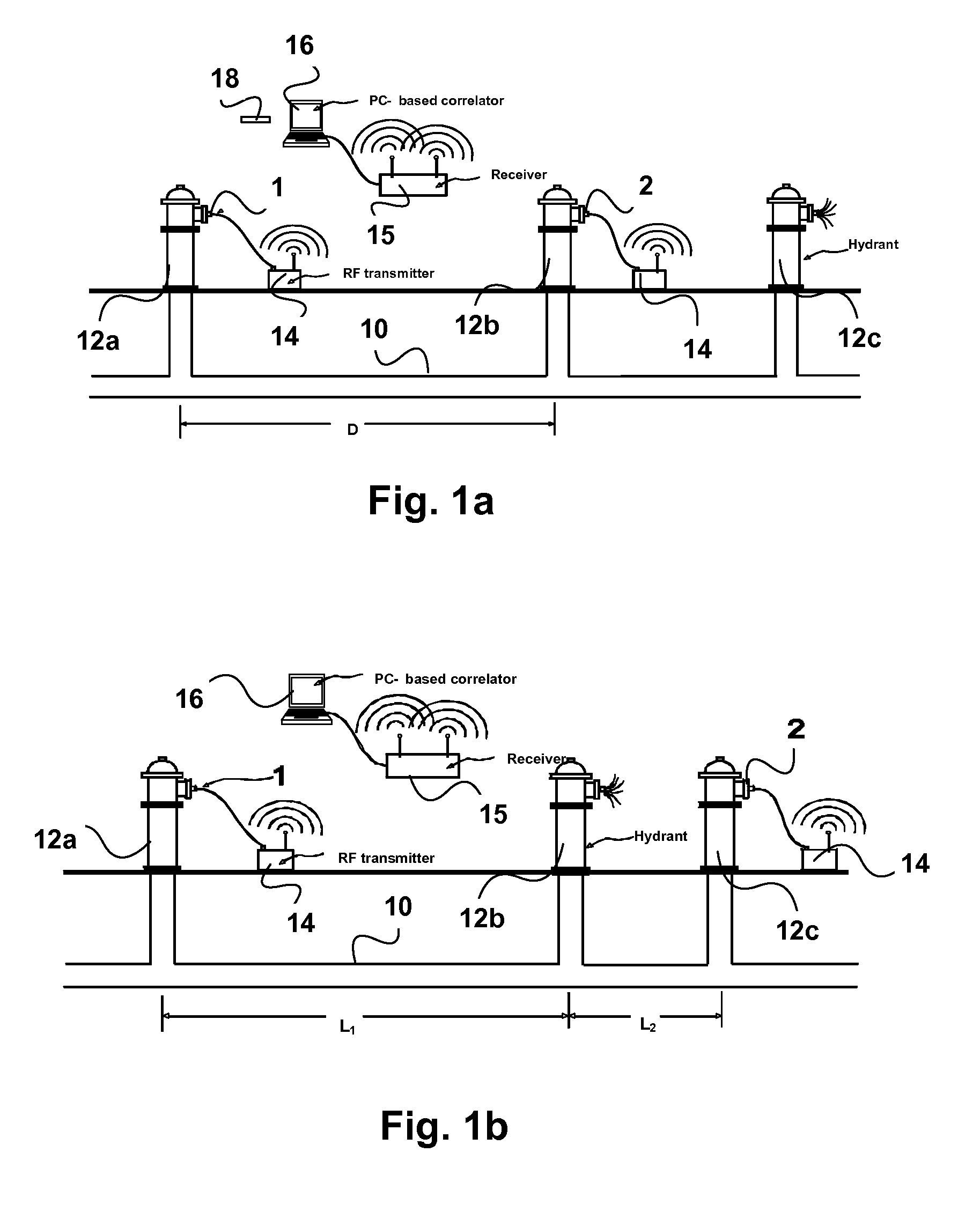
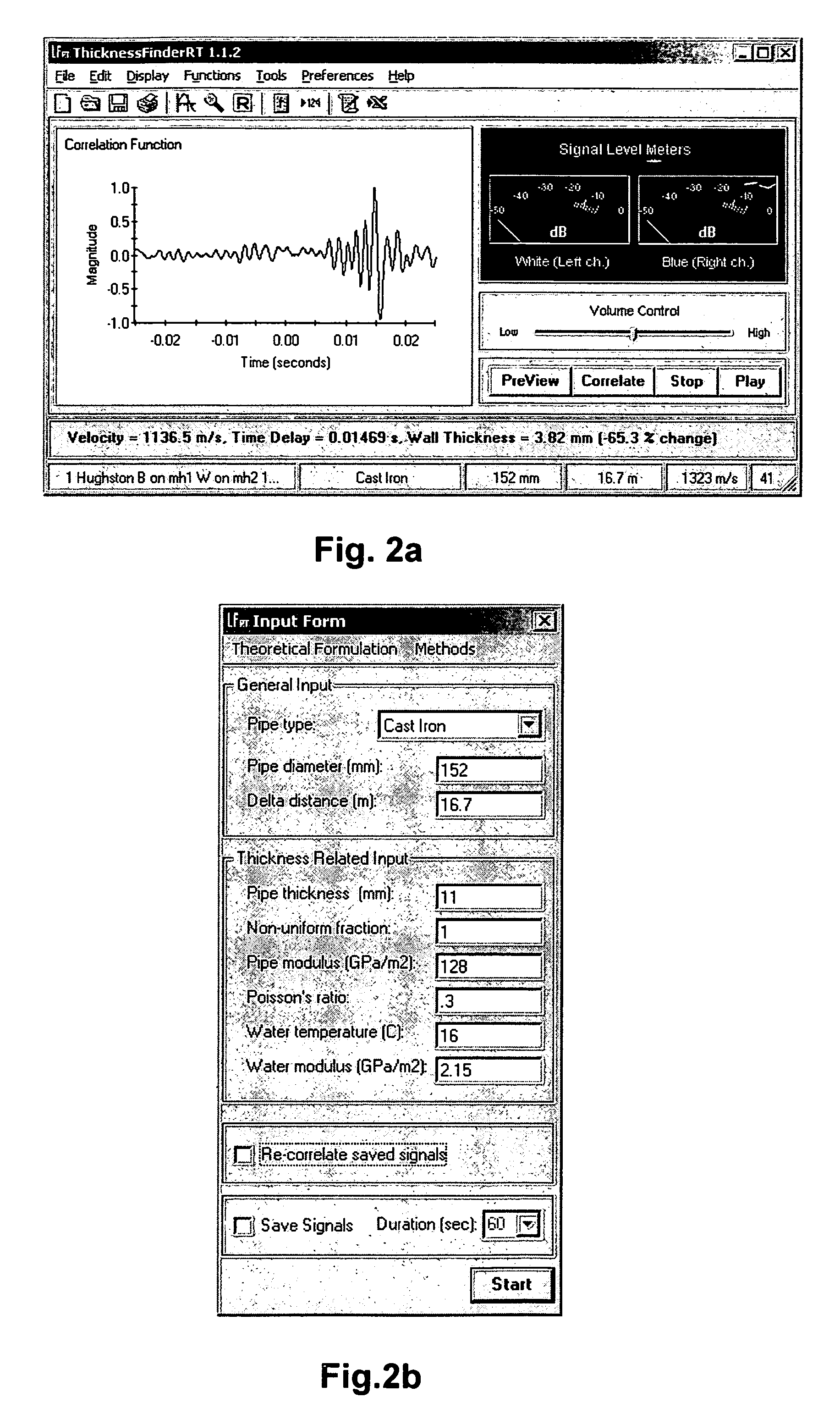
ActiveUS20060283251A1Easy to measureEasy to calculateAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesNon destructiveEngineering
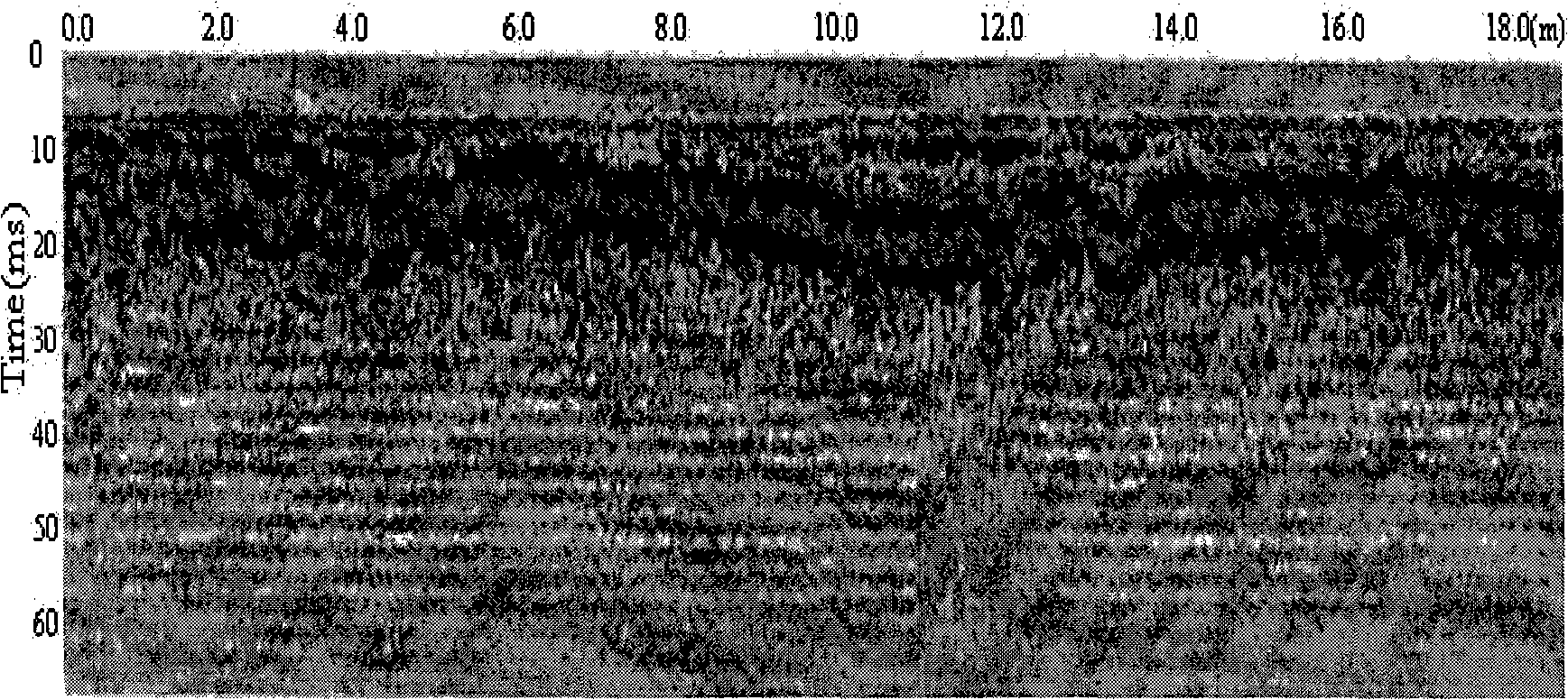
To perform a non-destructive condition assessment of a pipe carrying a fluid, an actual value representative of the propagation velocity of an acoustic disturbance propagating between two longitudinally separated points on the pipe is determined. A corresponding predicted value for the propagation velocity is computed as a function of at least one wall thickness parameter of the pipe by using a theoretical model for the propagation of acoustic waves in the pipe that assumes said pipe has a finite wall thickness with a predetermined circumferential thickness profile. The wall thickness parameter is then computed by matching the actual value with the predicted value, for example, by substituting the actual value in a formula predicting the theoretical value.
Owner:MUELLER INT LLC
Non-destructive testing and imaging
InactiveUS20050264796A1Optically investigating flaws/contaminationUsing optical meansNon destructivePixel value difference
A method of non-destructive testing includes non-destructively testing an object over a range of test levels, directing coherent light onto the object, directly receiving the coherent light substantially as reflected straight from the object, and capturing the reflected coherent light over the range of test levels as a plurality of digital images of the object. The method also includes calculating differences between pixel values of a plurality of pairs of digital images of the plurality of digital images, and adding the pixel value differences of the plurality of pairs of digital images to yield at least one cumulative differential image.
Owner:RAVEN ENG
Modular lamp head and assembly for non-destructive testing
A lamp module for use in non-destructive testing and inspection. The module including a module body with a front and rear end, and a side wall. The module body includes a mounting chamber located within the side walls. A plurality of LEDs are mounted within the chamber and oriented to so as to emit light out of the front end of the body. At least one LED emits light having a wavelength selected to produce fluorescence of an illuminated material. A fan is mounted to the body to dissipate heat generated by the LEDs when the fan is activated. Electrical connectors extend out of the body and are electrically connected to the LEDs and the fan for supplying current. The module can be installed in various structures or systems, including in a luminaire, an overhead light housing or a track light system.
Owner:SPECTRO UV LLC
Evaluation method of semiconductor layer, method for fabricating semiconductor device, and storage medium
InactiveUS6128084AImprove throughputEasy to detectSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementPolarisation-affecting propertiesSpectral patternPhase difference
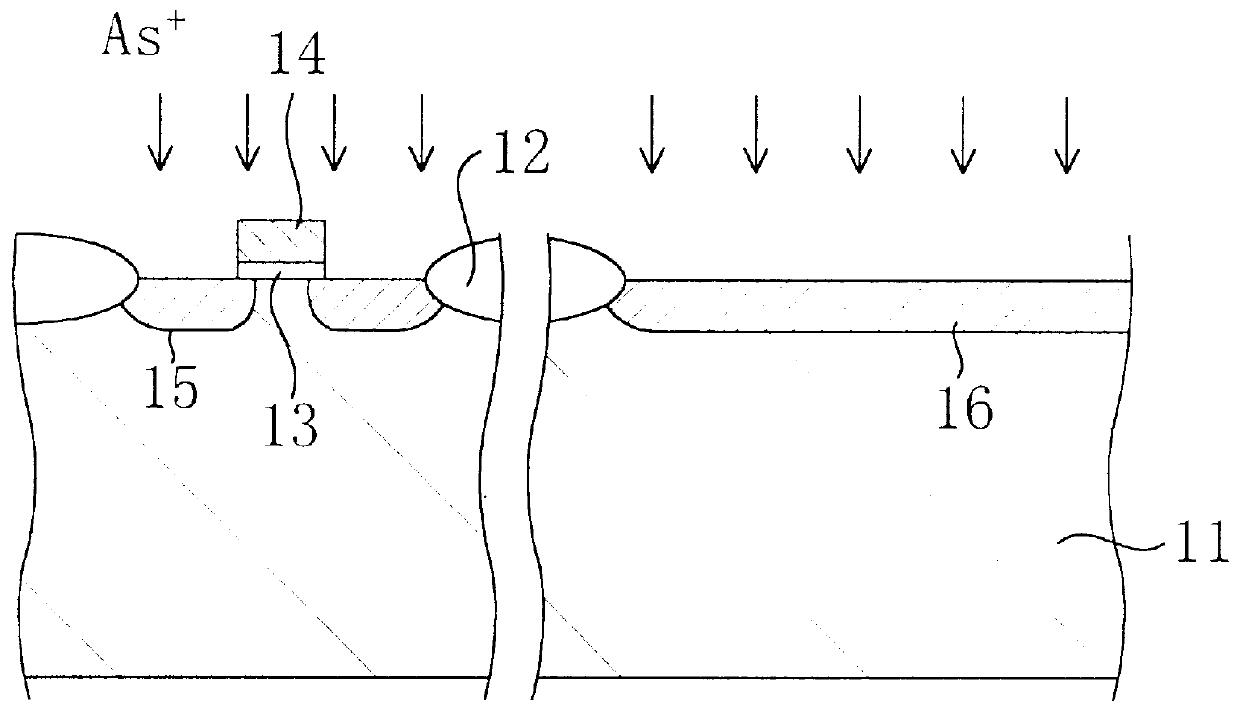
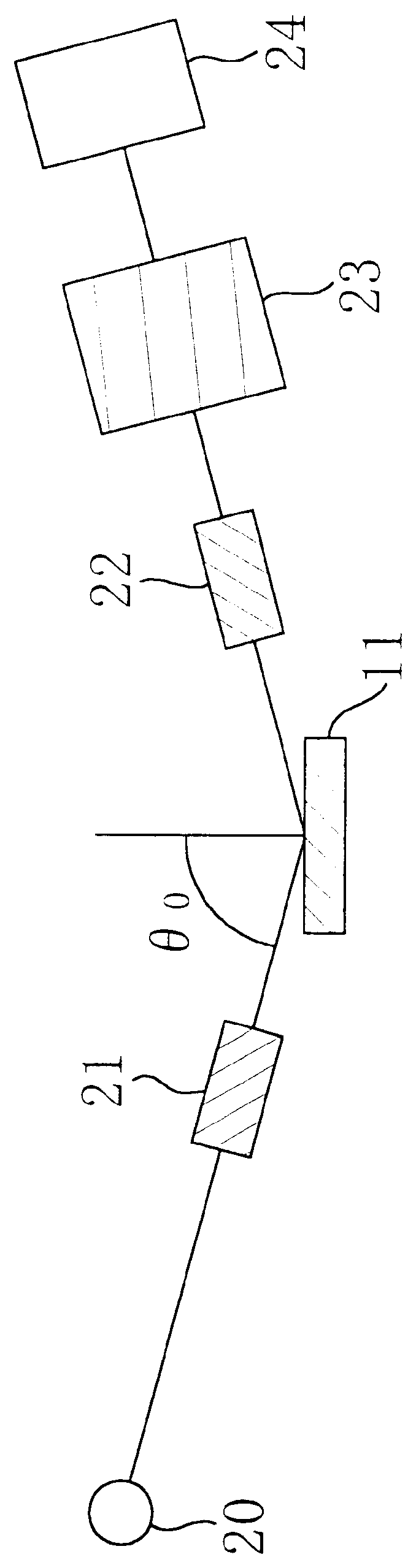
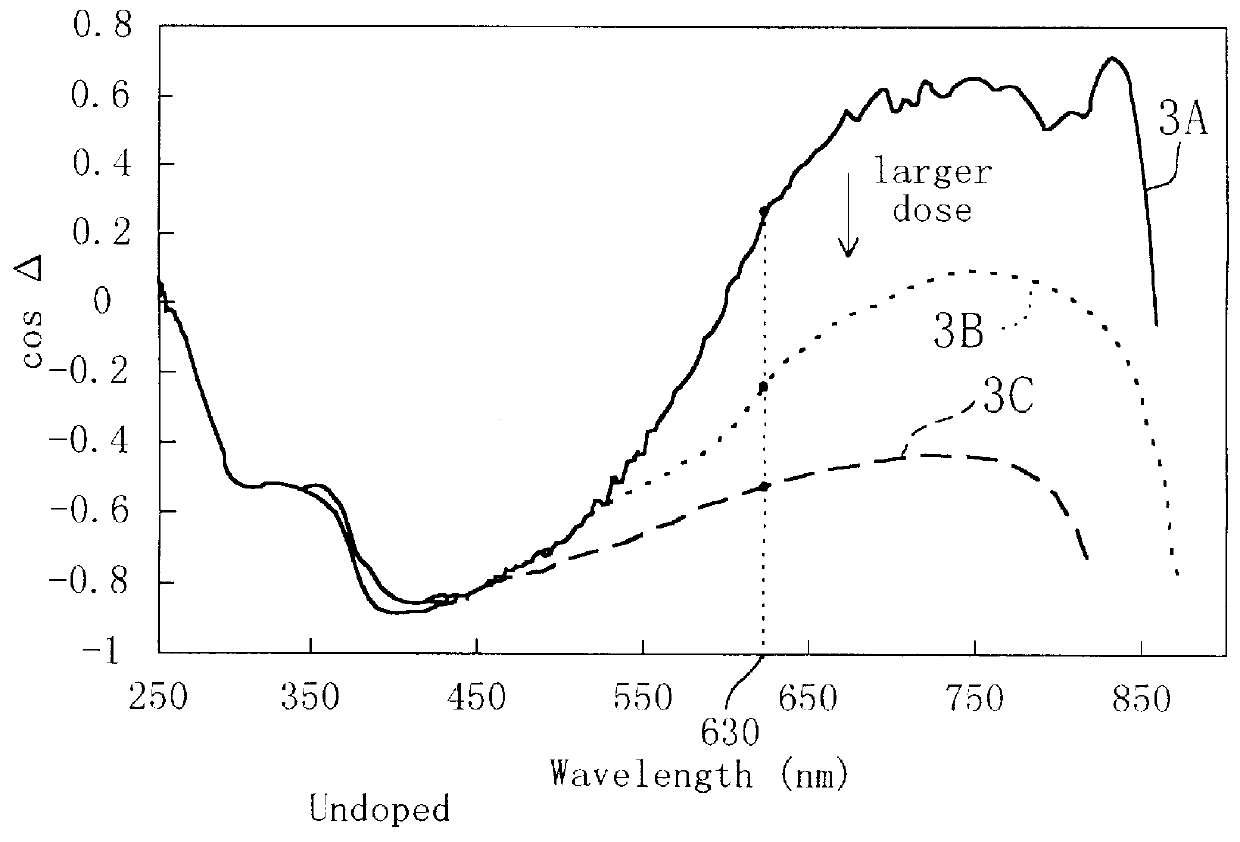
PCT No. PCT / JP98 / 02567 Sec. 371 Date Jan. 13, 1999 Sec. 102(e) Date Jan. 13, 1999 PCT Filed Jun. 10, 1998 PCT Pub. No. WO98 / 57146 PCT Pub. Date Dec. 17, 1998Measurement light, which has been emitted from a Xe light source (20) and then linearly polarized by a polarizer (21), is made to be incident at a tilt angle on a region in a silicon substrate (11) with crystallinity disordered by the implantation of dopant ions. And the spectra of cos DELTA and tan psi are measured with a variation of the measurement light, where DELTA is a phase difference between respective components in p and s directions as to the light reflected as an elliptically-polarized ray, and psi is a ratio between the amplitudes of these components. By correlating in advance the spectral patterns of cos DELTA and so on with the thickness of an amorphous region through a destructive test or the like, or by paying special attention to characteristic parts of the patterns of cos DELTA and so on, the thickness or the degree of disordered crystallinity of the amorphous region is estimated. Also, since a variation in the thickness of the amorphous region can be identified based on a variation of cos DELTA before and after a heat treatment, a temperature of the heat treatment can be sensed based on the variation of the thickness. Thus, an evaluation method allowing for nondestructive estimation of the thickness and the degree of disorder of a region, having crystallinity disordered by implanting dopant ions into a semiconductor region at a high level, can be provided.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Non-destructive testing of pipes
ActiveUS7328618B2Easy to measureEasy to calculateAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesNon destructiveEngineering
To perform a non-destructive condition assessment of a pipe carrying a fluid, an actual value representative of the propagation velocity of an acoustic disturbance propagating between two longitudinally separated points on the pipe is determined. A corresponding predicted value for the propagation velocity is computed as a function of at least one wall thickness parameter of the pipe by using a theoretical model for the propagation of acoustic waves in the pipe that assumes said pipe has a finite wall thickness with a predetermined circumferential thickness profile. The wall thickness parameter is then computed by matching the actual value with the predicted value, for example, by substituting the actual value in a formula predicting the theoretical value.
Owner:MUELLER INT LLC
Method and apparatus for non-destructive testing of fruit internal quality based on optical properties
InactiveCN1837788AHigh precisionImprove detection accuracyUsing optical meansColor/spectral properties measurementsNon destructiveOptical property
This invention relates to a method and apparatus for non-destructive testing of fruit internal quality based on optical properties. The device comprises a send unit, an analysis and process unit to evaluate the fruit referred to a stored quality prediction model, a signal control unit to send the fruit position and size information to the detection system with command format, an illumination system to provide stable and optimal-strength light, a detection system to obtain and send the transmitted spectrum information for fruit inner quality to the analysis and process unit, a fruit grade-outlet, a size detection device, and a coder. This invention improves on-line detection speed and precision.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Fast checking method for pipe defect and nondestructive testing apparatus
InactiveCN101173911AQuick scanImprove detection efficiencyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wave generationNon destructiveComputerized system
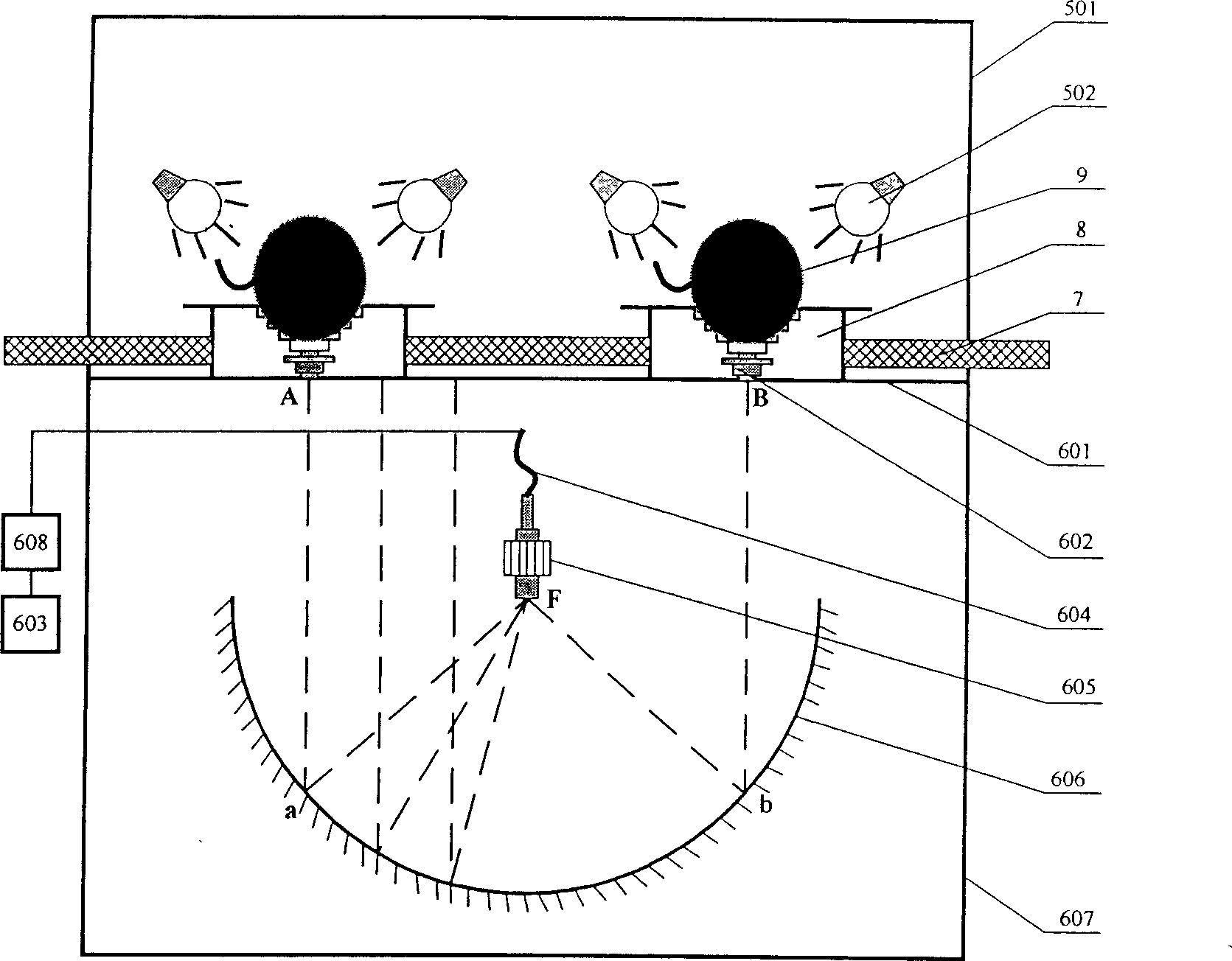
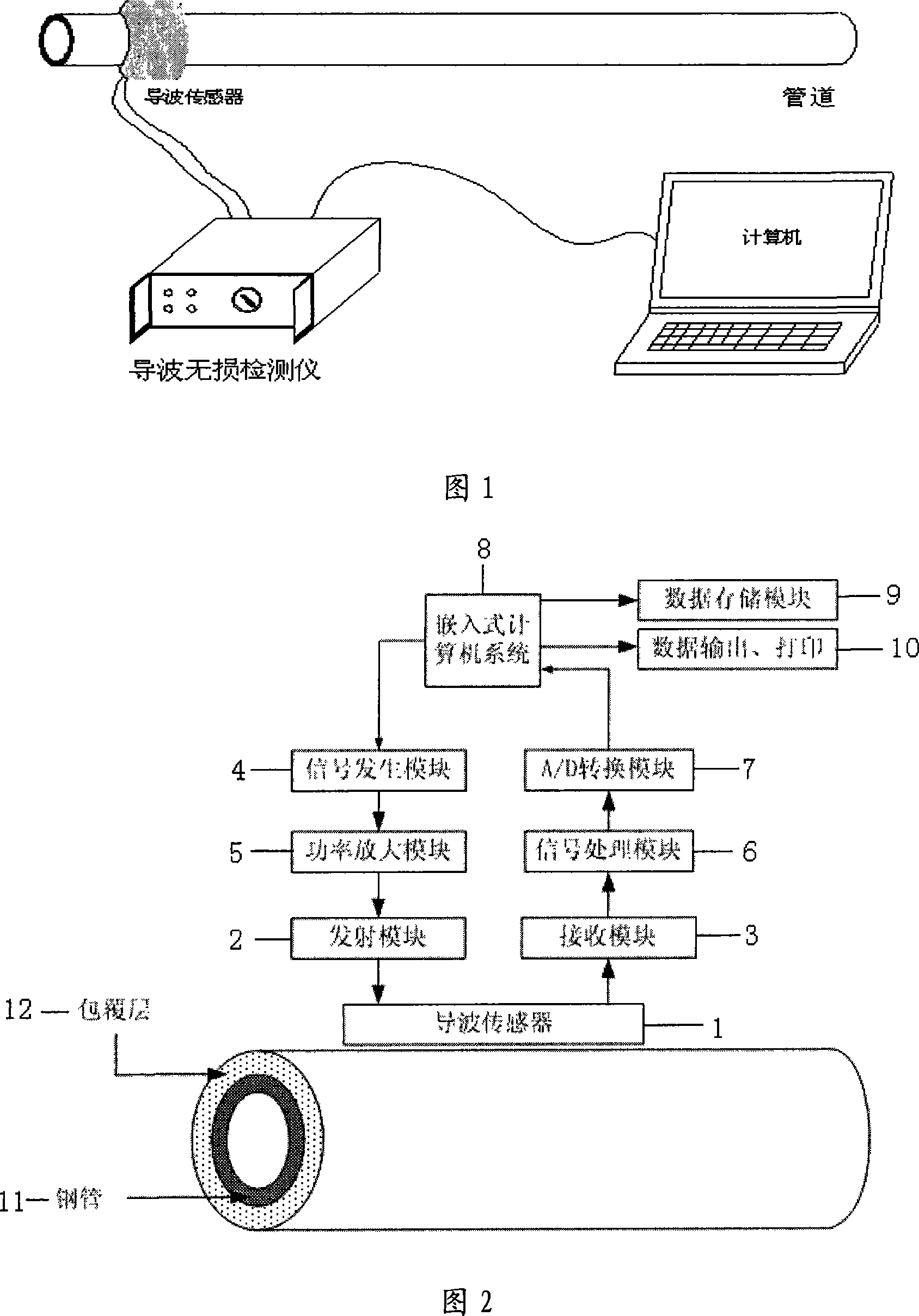
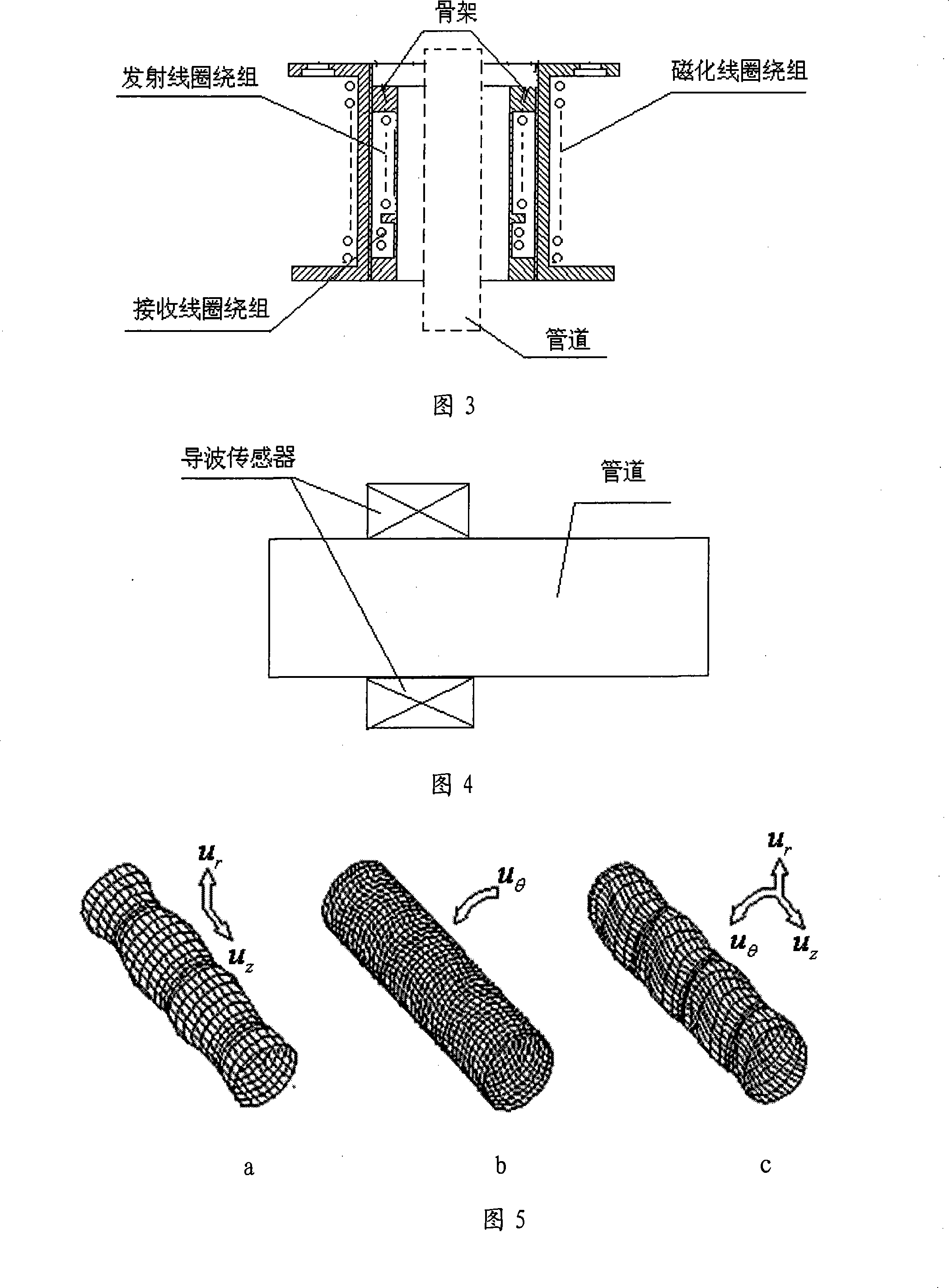
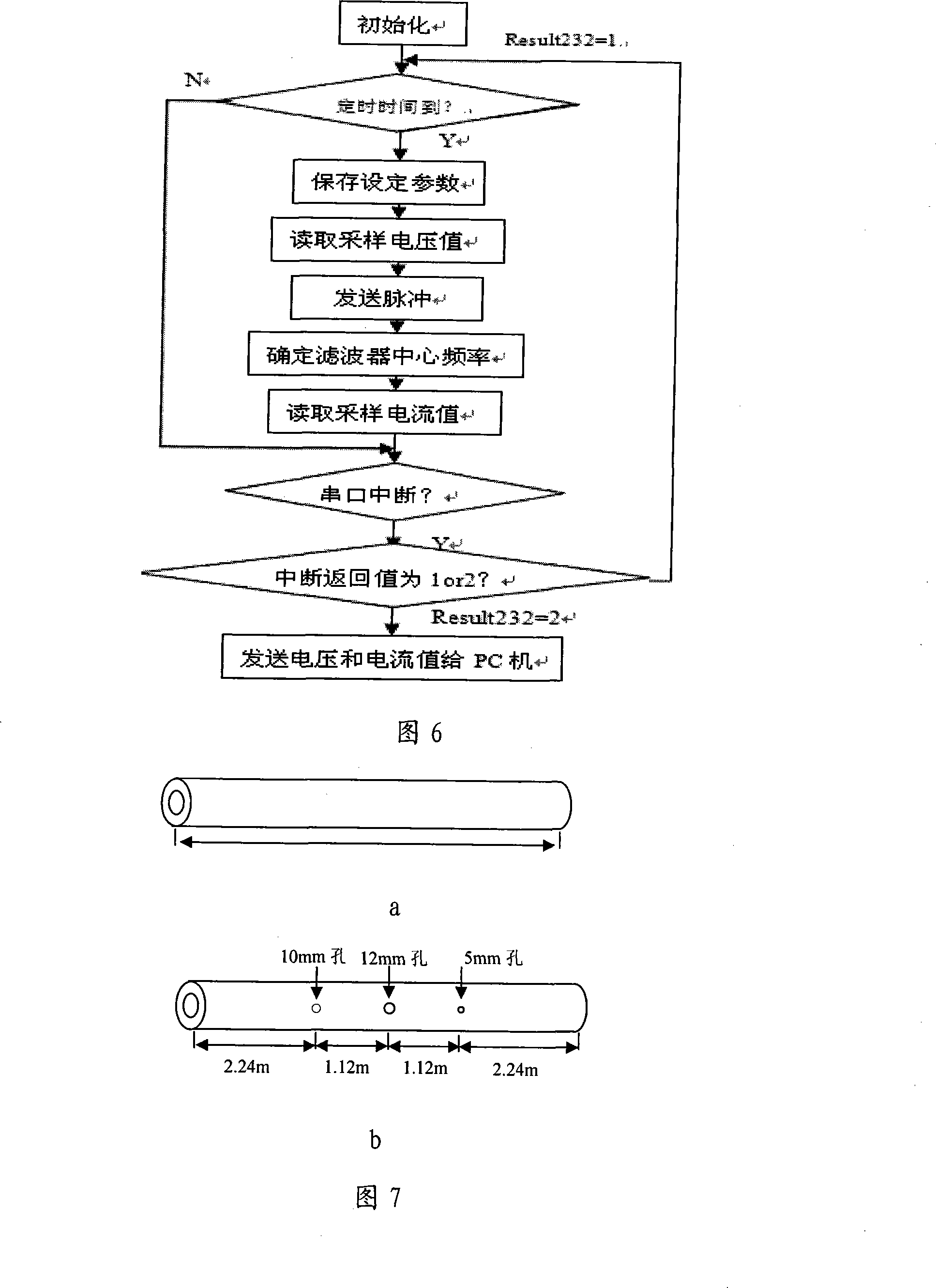
The invention relates to a fast scanning method of pipeline drawbacks and a non-destructive detection device, which is more particularly suitable for fast scanning and non-destructive detection of drawbacks of the pipelines with insulation. The invention is composed of a guided wave sensor, a transmitting module, a receiving module, a signal generating module, a power amplifying module, a signal processing module, an A / D conversion module and an built-in computer system. The invention is suitable for comprehensive detection of drawbacks of pipelines with different diameters, detection of long distance pipelines, and detection of pipelines in inaccessible places. The invention has the advantages of fast and large-scale detection ability without contact, high efficiency; overcoming a plurality of limitations of the conventional non-destructive detection method; overcoming the restriction conditions of oil pollution, fouling, bending or heat insulation protective layer, judging and locating the drawbacks of the pipelines, reducing the maintenance range, avoiding unnecessary disassembly and replacement, reducing the intensity of artificial detection, and saving the human and material resource. In addition, the invention can achieve on-line monitoring, and evaluate the health condition of the element or predicts the service life of the element.
Owner:NAVAL UNIV OF ENG PLA
Device and method for detecting defects of inner and outer walls of pipeline based on three-axis magnetic flux leakage and eddy current
ActiveCN102798660ASave electricityImprove detection qualityMaterial magnetic variablesNon destructiveElectricity
The invention relates to a device and a method for detecting defects of inner and outer walls of a pipeline based on three-axis magnetic flux leakage and eddy current, and belongs to the technical field of non-destructive testing. The device comprises a magnetic flux leakage detector, a data processing and storing device, a power supply, at least three odometer wheels and an eddy current detector, wherein the eddy current detector consists of an eddy current sensor and is a device used for detecting the defects on inner and outer surfaces of the pipeline. According to the device provided by the invention, a magnetic flux leakage detection method and an eddy current detection method are combined by using different characteristics of the magnetic flux leakage detection method and the eddy current detection method, so that the function of distinguishing the defect of the inner wall from the defects of the outer wall is realized; and in addition, the method provided by the invention is favorable in detection quality and simple in operation and can be widely applied to non-destructive detection of oil transmission pipelines in the industrial fields of petroleum, petrifaction and the like.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
X-ray tomogram imaging device
InactiveCN103096804AImprove resolutionEasy to useImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionX-rayCt imaging
An X-ray tomogram imaging device (1) of the present invention is provided with an X-ray tube (31) and a direct conversion-type detector (32). The X-ray tube and the detector are supported so as to be independently rotatable of each other along a curved trajectory by way of support means (21, 311, and 312). Scanning and image reconstruction are performed under instruction from a computer (11). The X-ray tube and the detector are moved independently of each other along the trajectory so that X-ray radiation is consistently transmitted at a desired angle through a desired cross-section of an object to be imaged. A panorama image of the cross-section is generated using frame data, and using the frame data and the panorama image, a tomogram is generated in which the focus in the object to be imaged has been optimized and distortion caused by differences in the angles of the paths of the X-ray radiation has been suppressed. The present invention can be implemented as an apparatus for such applications as medicine, including dentistry, and destructive testing. In addition, the present invention can also have functionality for CT imaging.
Owner:TAKARA TELESYST
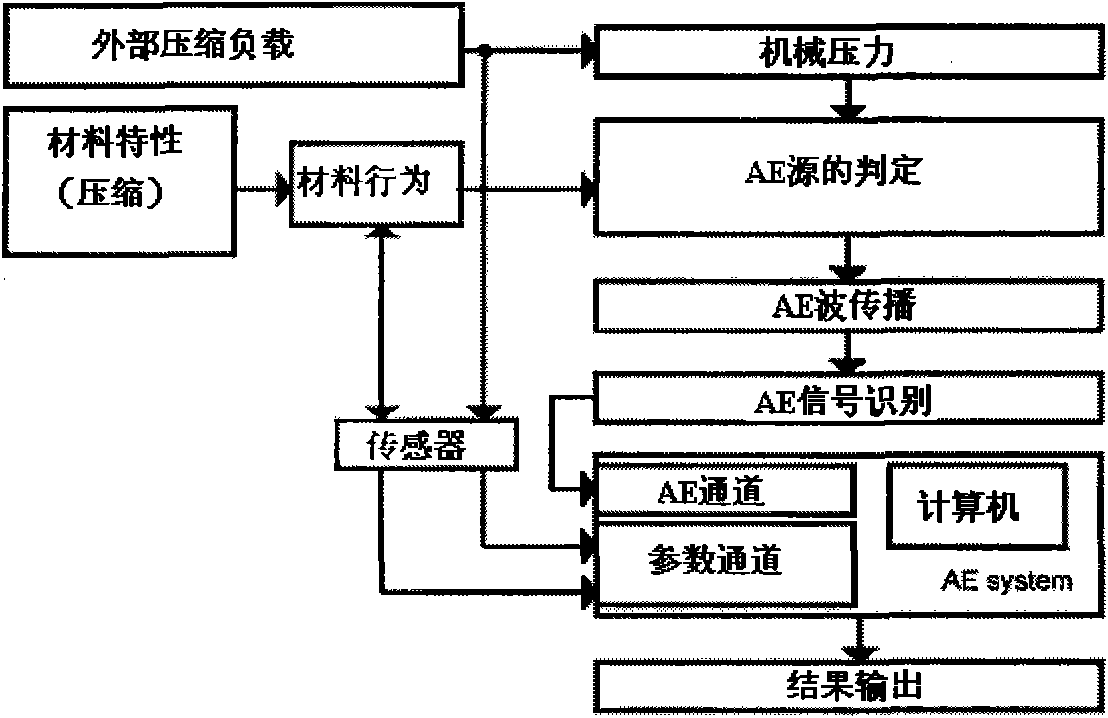
Nondestructive testing system and testing analysis method for three-dimensional braided composite material
InactiveCN102109498ARealize the whole dynamic monitoringShow damage characteristicsMaterial analysis using acoustic emission techniquesFrequency spectrumAcoustic emission
The invention provides an acoustic-emission-technology-based nondestructive testing system and an acoustic-emission-technology-based nondestructive testing method for a three-dimensional braided composite material. In the method, an acoustic emission signal generated by the composite material under external loading is received by an acoustic emission sensor and then is digitized, and the damaged condition of the material is further analyzed. By the method, a unilateral stretching experiment of the carbon fiber three-dimensional braided composite material is dynamically monitored all the way by the acoustic emission technology; and the method proves that the number of the acoustic emission events has good correlation with damage evolution of the carbon fiber composite material; through the spectrum analysis of the carbon fiber three-dimensional braided composite material, the final damage to the material is caused by fibrous fracture and damage frequencies show the damage characteristics of the material; different types of damage modes are well described through the spectrum analysis, and frequency ranges of all peak values can be detailed further, so that more detailed explanation for damage types and mechanisms can be given; and the fracture modes of the material can be analyzed by using acoustic emission characteristic parameters.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Cable fault detection and aging analysis method
The invention discloses a cable fault detection and aging analysis method. According to the insulation resistance oscillation theory of the frequency domain, the cable fault detection and aging analysis method is characterized in that a fault location model is established by analyzing the oscillation characteristics of frequency domain impedance on the basis of oscillation wave spectrum analysis of the frequency domain impedance acquired by a non-destructive test system or a destructive test system, and then test oscillation impedance spectrum defect is compared with an internal simulation curve, so that long-distance accurate fault location can be realized, and the fault types can be also effectively distinguished. Compared with the prior art, the method not only is capable of realizing accurate multipoint positioning of faults, but also is capable of carrying out fault type recognition and insulation aging state analysis; in the whole detection and analysis processes, artificial experience is hardly depended; the method is suitable for a cable with the length of 1m-1,000km, and is especially suitable for a cable with the length of more than hundreds of kilometers.
Owner:GAUSS ELECTRONICS TECH
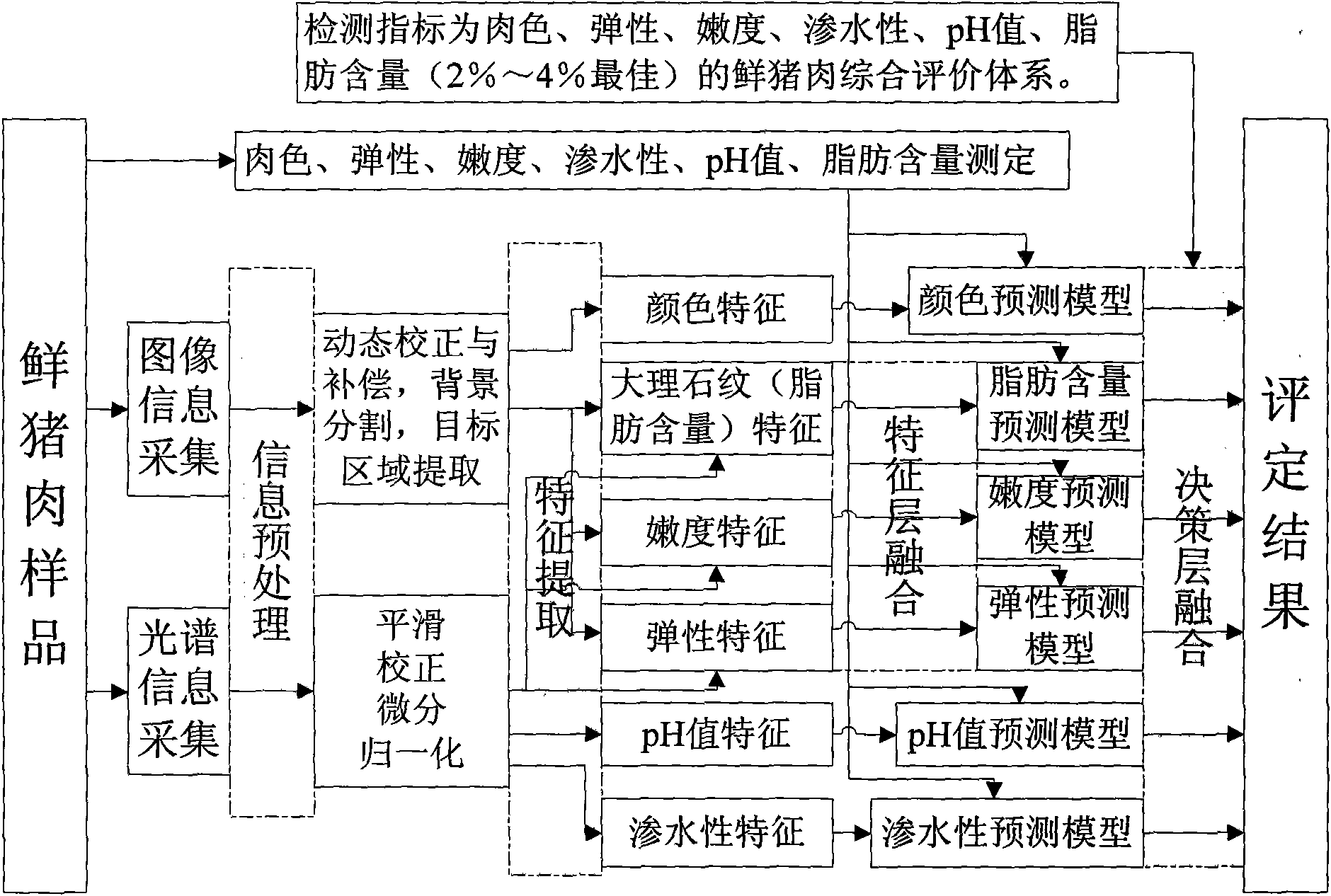
Meat online non-destructive testing method and apparatus based on fusion of image and spectrum information
InactiveCN101551341AFree laborEliminate human subjective factorsMaterial analysis by optical meansCharacter and pattern recognitionNon destructiveOptical property
The invention discloses a meat online non-destructive testing method and apparatus based on fusion of image and spectrum information, including a conveyor belt, a spectrum collection room, an image collection room, a camera mounted beam, an imaging source, a camera, a Y type optical fiber, a spectrograph, a data processing PC, two photosensors, a motor and a conveyor belt bracket. Through online collection of meat image and spectrum information, collecting feature information of characteristic meat quality, establishing a fused quantification prediction model based on image characteristics, spectrum characteristics and characteristics layer data of image and spectrum, using the obtained quantification prediction model to combine with quality evaluation system to establish a decision layer data fusion model based on image and spectrum for testing meat online. The invention uses complementarity and redundancy of the image information and the spectrum information to implement classification of materials and quality test during meat producing process according to optical feature of meat, which improving production efficiency.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method of non-destructively testing a work piece and non-destructive testing arrangement
InactiveUS20080141778A1Eliminate needExact correlationVibration measurement in solidsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesNon destructivePositioning system
A method of non-destructively testing a work piece is disclosed, wherein the work piece is placed within an active field of a positioning system; a frame of reference of the work piece is established based on the geometry of the work piece in the coordinates of the positioning system; the geometry of the work piece is detected by determining the position of specific transponders, which are fixed to the work piece, by the positioning system or the geometry of the work piece is detected by scanning at least parts of the contour of the work piece with a transponder of the positioning system; testing data is acquired for the work piece with a non-destructive testing probe, which comprises a transponder of the positioning system, while the position of the testing probe is recorded by the positioning system; the position of the testing probe is transformed into an intrinsic position defined with respect to the frame of reference of the work piece; and the intrinsic position of the testing probe is assigned to the testing data recorded at the respective position. Moreover, a non-destructive testing arrangement is provided.
Owner:SIEMENS GAMESA RENEWABLE ENERGY AS
Laser speckle tire non-destructive detector and non-destructive testing method utilizing the same
InactiveCN1632543ASimple structureReduce testing costsPhase-affecting property measurementsVehicle tyre testingNon destructiveFull field
This invention discloses a laser speckle tyre lossless detector. The detector is located in the test room of the vacuum device and is connected with a vertical and level and rotation laser speckle probes through test moving structure. Under the test prove there is tyre automatic position device to supporting and positioning and there is door in the sidewall of the test room. This invention also provides a method for lossless test and the laser speckle tyre loss detector can test the inner defection of the products and can be used in quality test of space flight field.
Owner:GUANGZHOU SCUT BESTRY TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Rapid determination of fatigue failure based on temperature evolution
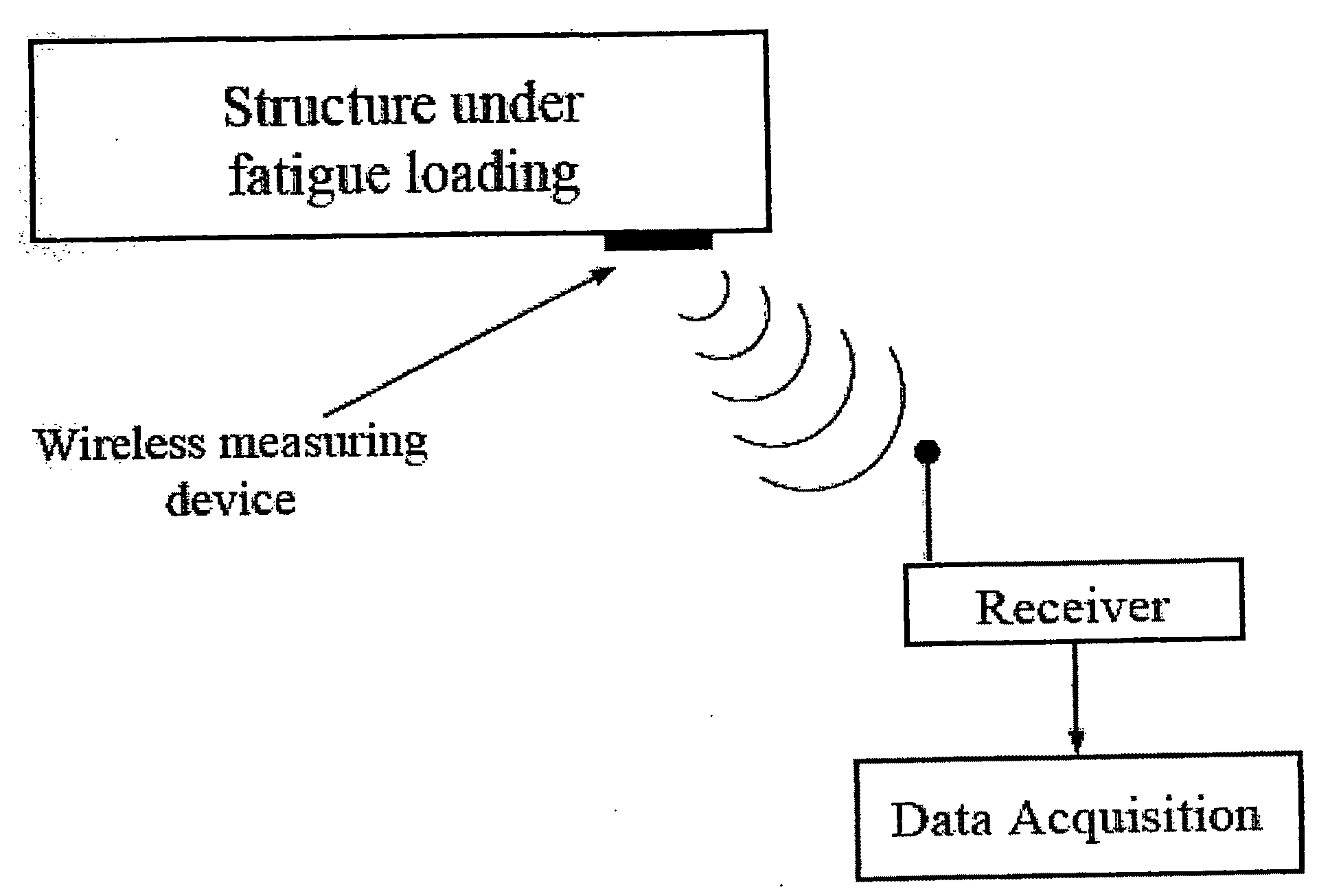
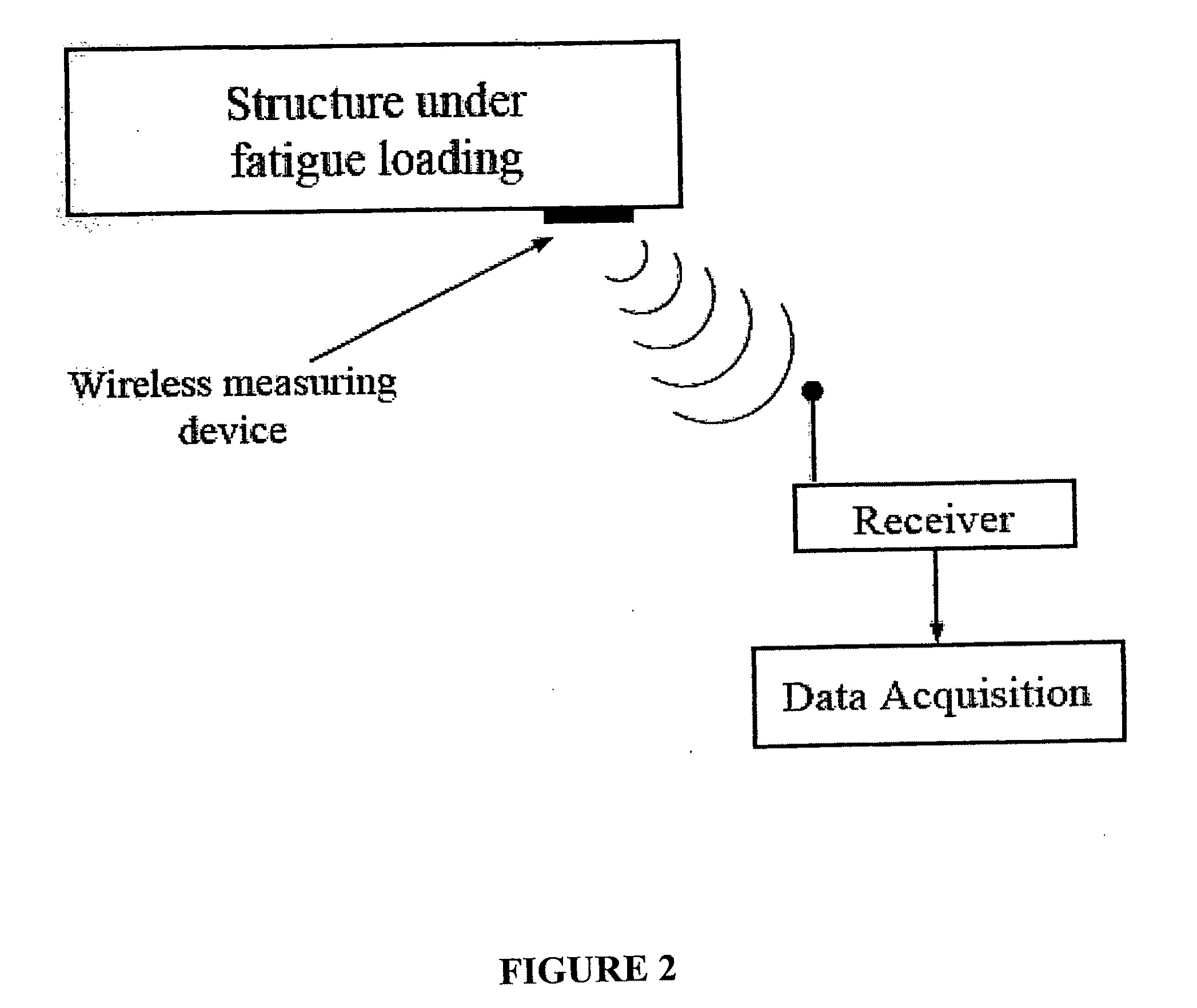
InactiveUS20090048788A1Efficient use ofAvoid catastrophic failureMeasurement gaugesAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceEngineeringUsage analysis
A method and apparatus are disclosed for predicting the service life of a metallic structure subjected to cyclic loading. Such structures experience fatigue, which can lead to failure after a number of loading cycles. The disclosed invention allows for an accurate prediction of the number of cycles to failure for a metallic structure by observing the slope of the rise in surface temperature of the structure after the cyclic loading has begun. The method of this invention provides early and accurate predictions of service life and does not require destructive testing. The method and apparatus of the present invention may be installed on working equipment, thus providing service life predictions for materials in real world use. The invention uses an empirically derived relationship that was confirmed using analytical relationships and material properties. The derived formula uses two constants that may be determined empirically using a disclosed process. The constants also may be estimated mathematically. The apparatus may include a wireless temperature sensor mounted on the metallic structure of interest and a data analysis unit to perform the needed calculations.
Owner:BOARD OF SUPERVISORS OF LOUISIANA STATE UNIV & AGRI & MECHANICAL COLLEGE
Synthetic nondestructive detecting method for hidden dangers of levee
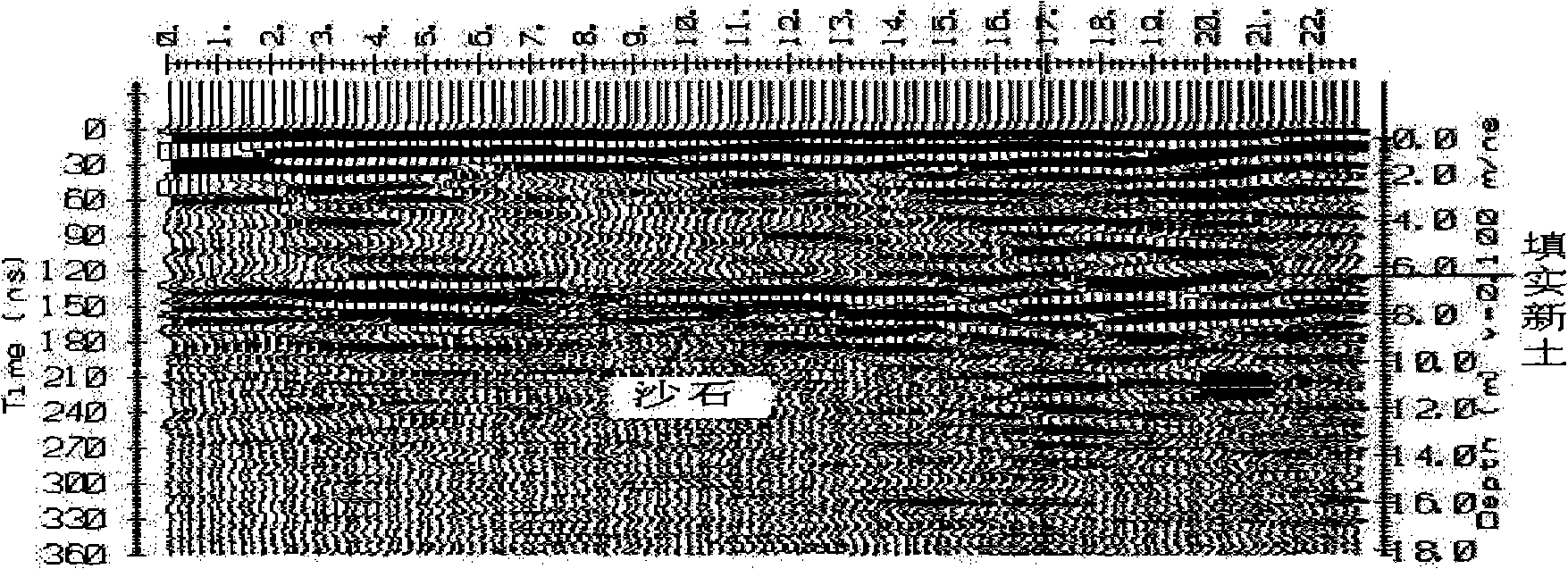
InactiveCN101295027AComprehensive detectionDetailed detectionDetection using electromagnetic wavesRadar resolutionNon destructive
The invention relates to a levee hidden trouble integrated non-destructive testing method. Geological radar is adopted to carry out general survey to the levee to find out whether an abnormal levee section exists according to the characteristics of high resolution, high detecting speed, no damage to an object to be tested and high anti-interference capability of the geological radar. At the abnormal levee section, detailed survey is carried out by integrating the characteristics of rich exploration information, convenient interpretation and strong exploring capability of a high intensity resistivity method and the characteristic of a seismic method that the sandy clay physical mechanics characteristics which are relevant to the shearing strength and the compressive strength of the levee sandy clay such as levee crack, collapse and sinkage, etc. can be reflected, and the property and scope of the abnormal section of the levee are determined. The method of the invention overcomes the limitation exists in a single physical geography non-destructive detecting method when levee detecting is carried out, thus roundly and accurately grasping the abnormal information of the levee and realizing the integrated detecting of the levee hidden troubles.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Device and method for 3D-printing part model reverse-calculating through layer-by-layer detecting and defect positioning
ActiveCN107175329AAvoid Destructive TestingAdditive manufacturing apparatusOptically investigating flaws/contaminationThree dimensional shapeLaser beams
The invention discloses a device and method for 3D-printing part model reverse-calculating through layer-by-layer detecting and defect positioning. The device comprises a scanning galvanometer, a half transparent and half reflecting mirror, an optical filter, a laser head, a high-speed camera, a controller and the like. The scanning galvanometer is used for controlling a laser beam to melt metal powder selectively, and molten pool radiation is reflected into the high-speed camera by the half transparent and half reflecting mirror and transformed into pictorial information to be transmitted to the controller. According to the device and method for 3D-printing part model reverse-calculating through layer-by-layer detecting and defect positioning, the device conducts monitoring on powder melting in the SLM machining process in an aiming mode, and feeds back to a computer software interface, molten pool characteristics of different positions are reflected in real time, the outline of each molten layer is measured accurately, and a part model is obtained through a reverse-calculating mode; and comparing and analyzing are conducted on the model and an original three-dimensional model, errors between a metal 3D printed part and original model data at the aspects of precision and dimension is obtained; the positions and the three-dimensional shapes of internal defects in the 3D printing process can be acquired precisely, and a destructive test aiming at the part in the later period of part printing is avoided.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
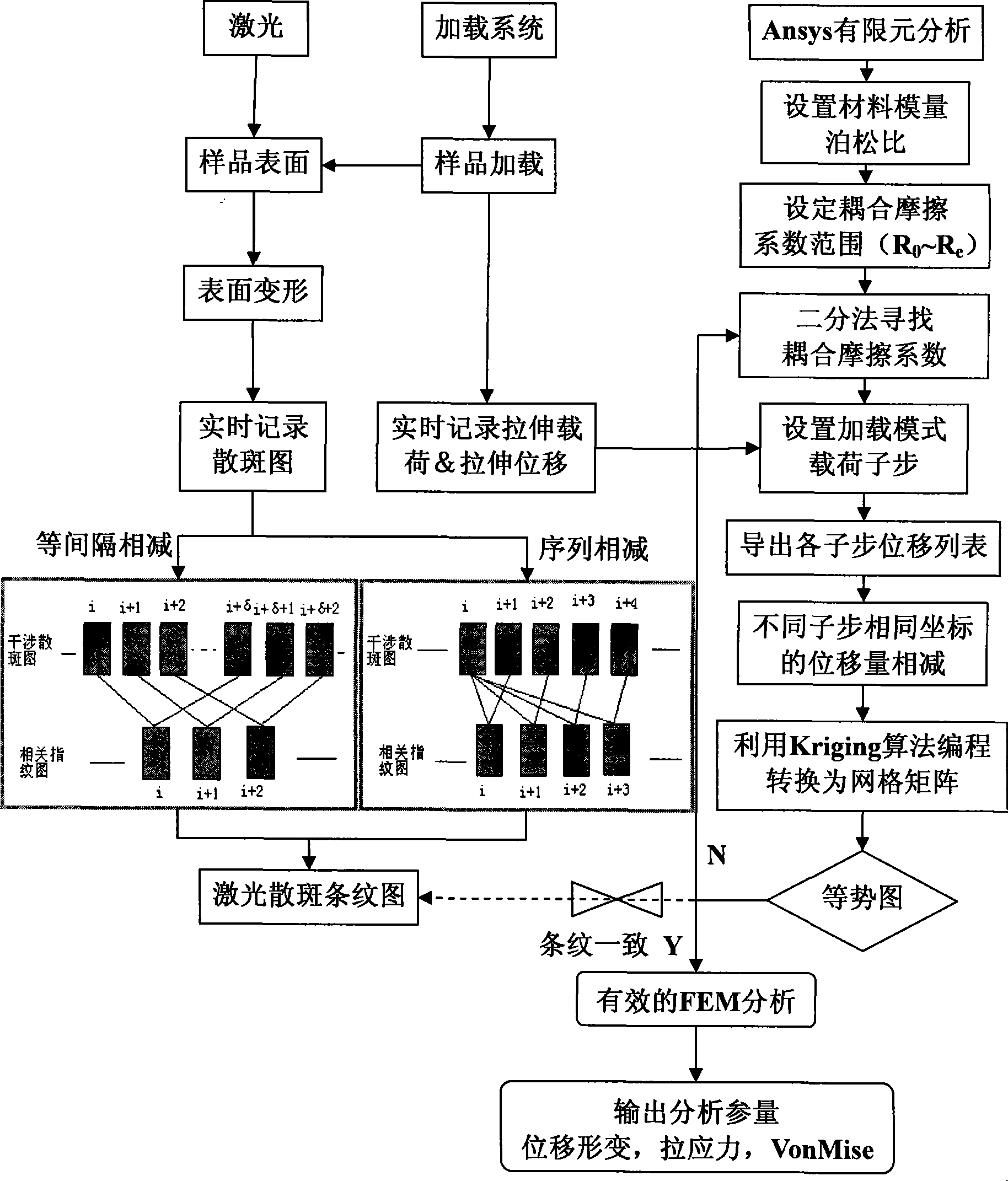
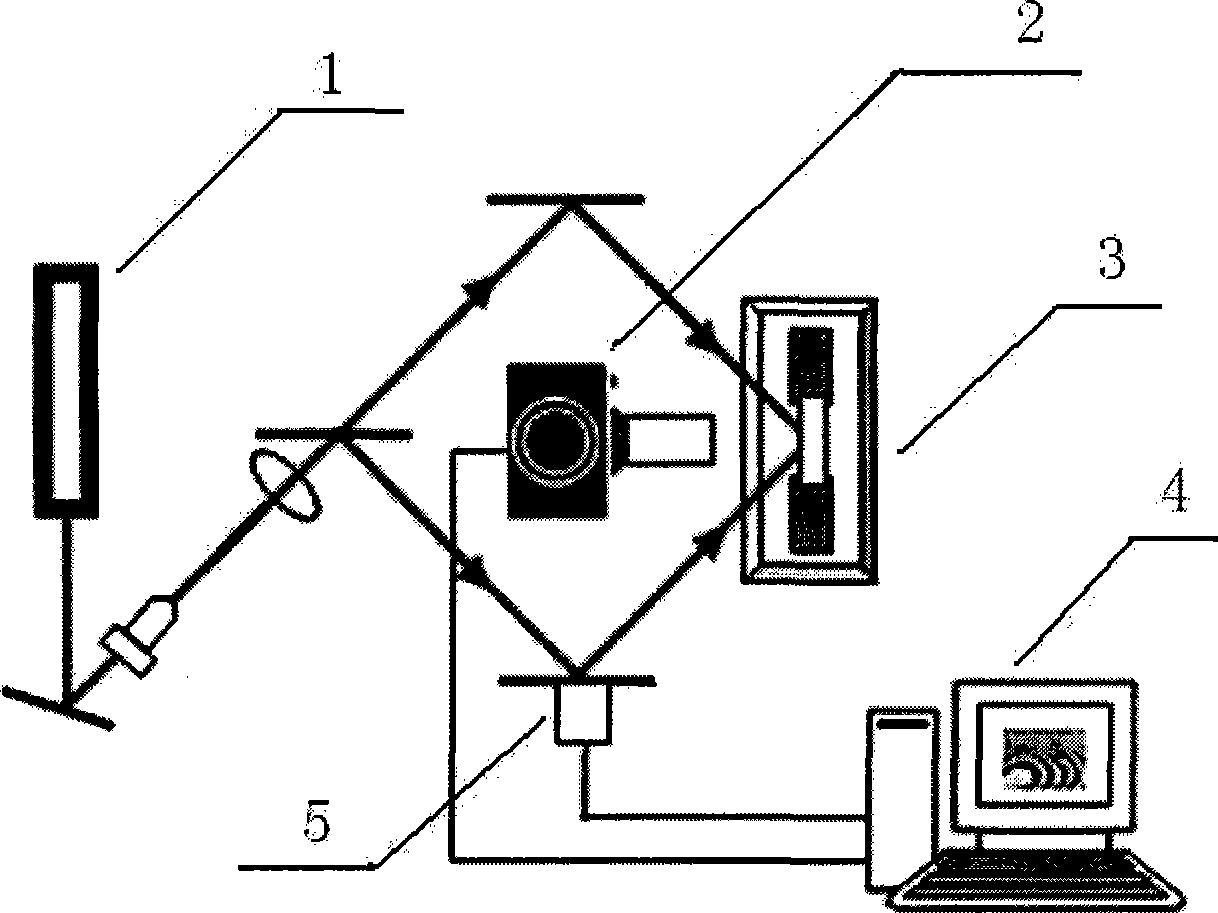
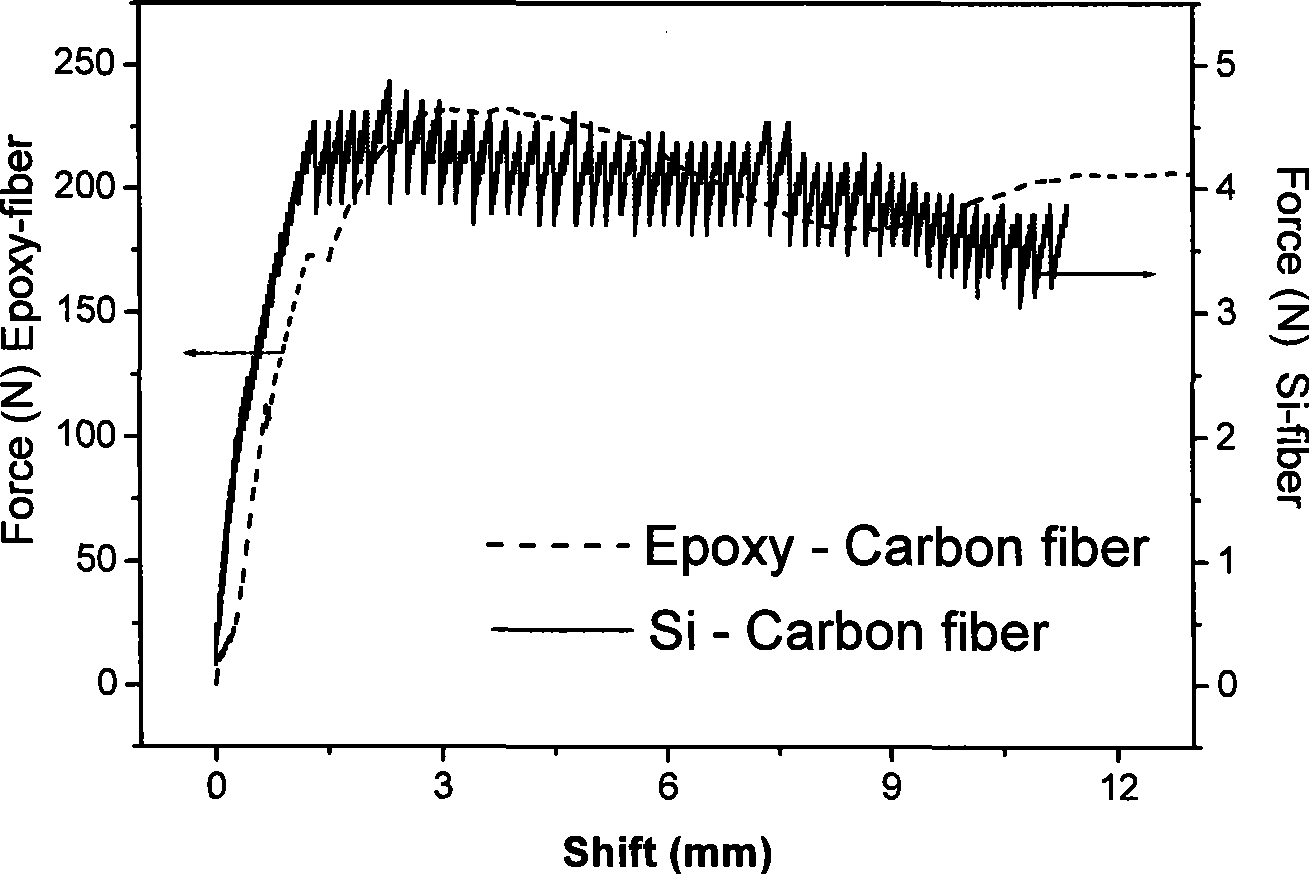
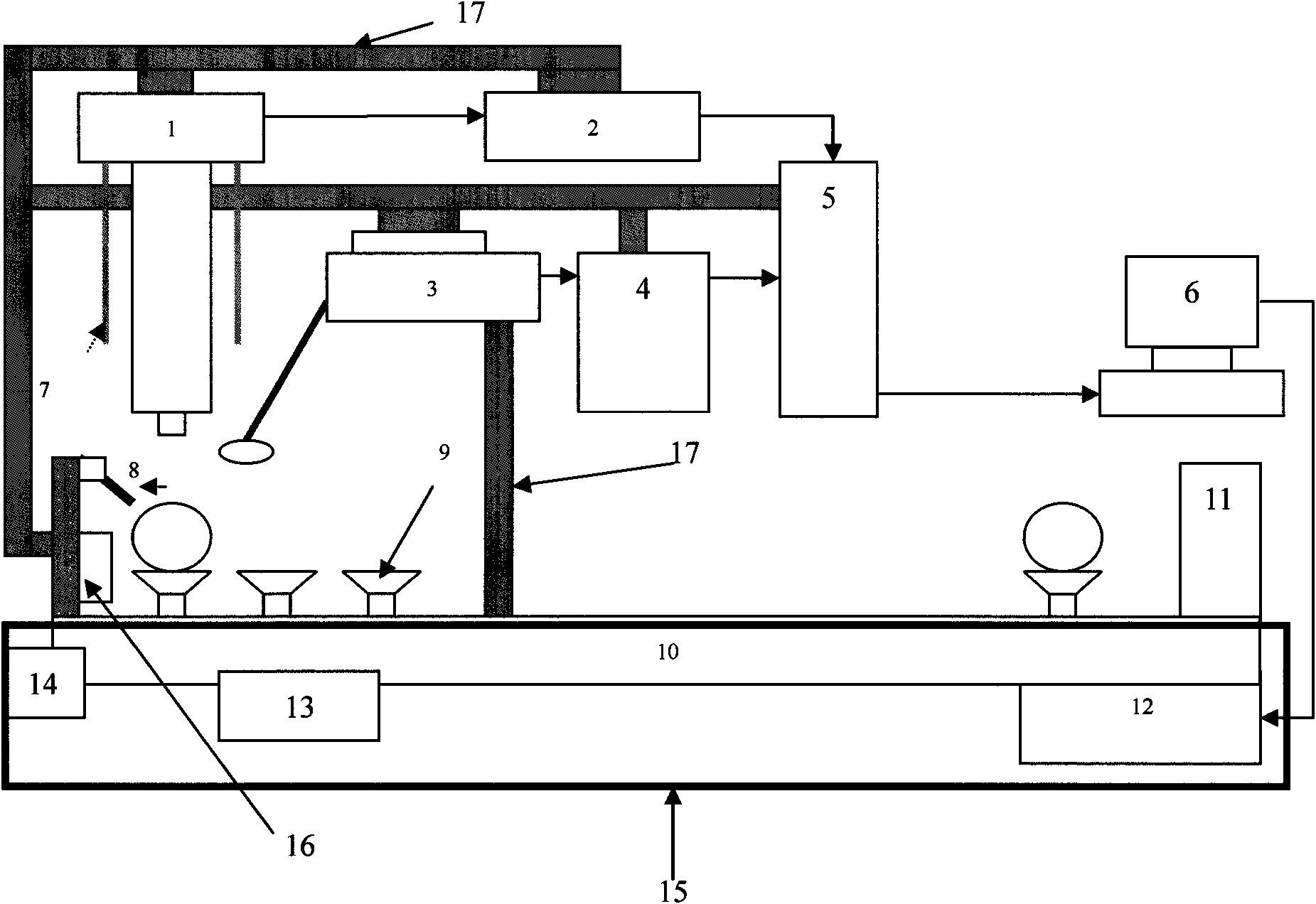
Method for quantitatively analyzing material interface properties by combining non-destructive testing and definite element modelling
InactiveCN101545849AImprove stressReal-time observation of mesoscopic damage behaviorMaterial analysis by optical meansUsing optical meansNon destructiveFiber
The invention relates to a method for quantitatively analyzing material interface properties by combining non-destructive testing and definite element modelling. In the method, by loading a composite material, a non-destructive testing system records a loading variable; and at the same time, a finite element method correspondingly simulates the whole loading process of a test piece according to intrinsic properties, modulus, tensile strength, Poisson ratio and the like of the material so as to find a simulation state corresponding to the non-destructive testing variable and further obtain comprehensive analysis results, including various physical quantities reflecting the material interface properties such as friction coefficient between fibers and a matrix, stress, straining, counterforce and the like, in the simulation state. The non-destructive testing high-precision method verifies partial parameters of finite element analysis, and the finite element analysis provides more comprehensive analysis results. The method has the advantages of high sensitivity, credible quantitative values and no need of damaging an adhesive layer.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
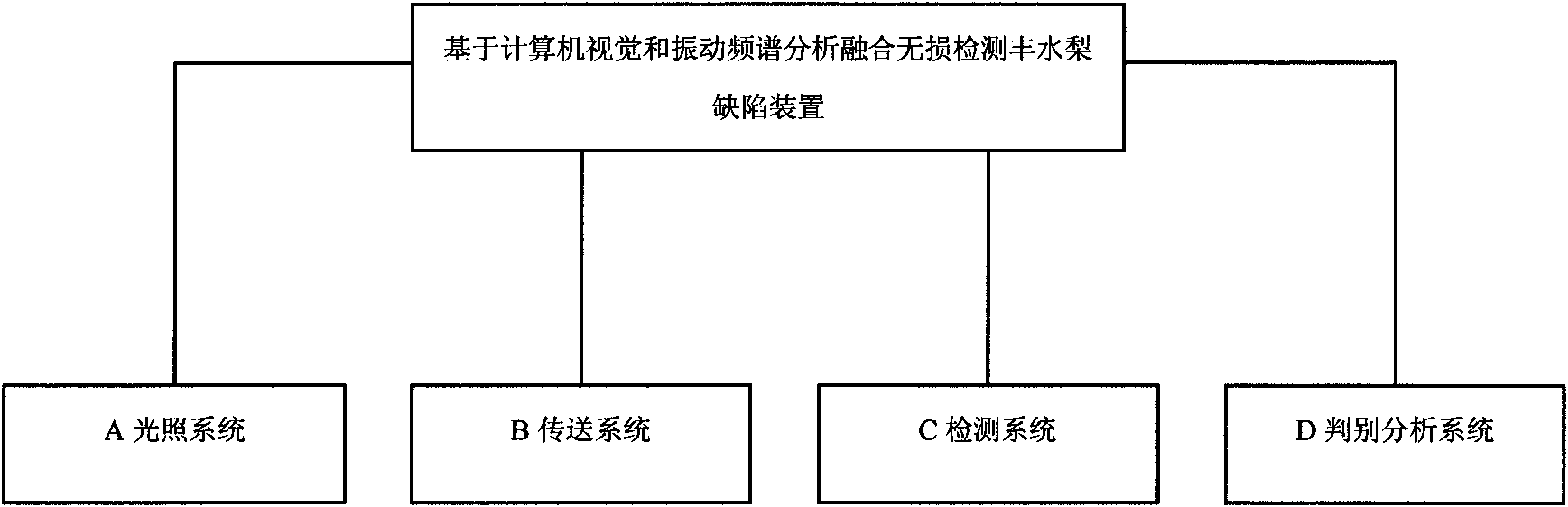
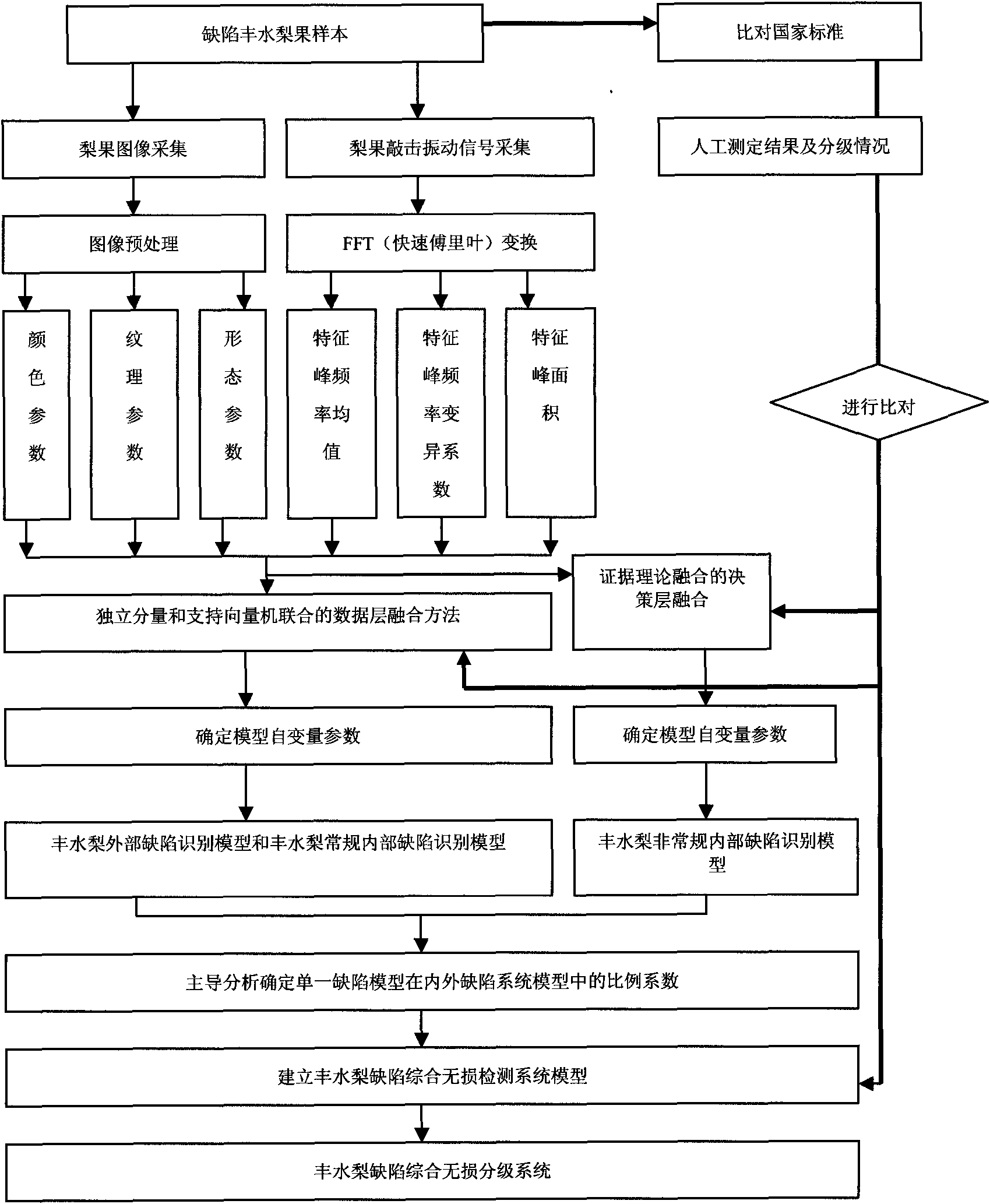
Device for nondestructive testing of defects of hoxiu pears and use method
InactiveCN101603927AComprehensive recognitionFast NDTMaterial analysis by optical meansSortingFrequency spectrumFourier transform on finite groups
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for performing non-destructive detection on evolution of three-dimensional carbonation depth of cement-based material through X-ray scanning
InactiveCN102590242AIntegrity guaranteedGuaranteed accuracyPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationPorosityObject based
The invention provides a method for performing non-destructive detection on evolution of the three-dimensional carbonation depth of a cement-based material through X-ray computerized tomography and relates to a novel detection method for the carbonation depth of a cement-based material. The main principle is that: an image is reconstructed by acquiring ray attenuation information of a rotary object based on an X-ray source; a carbonized region and a non-carbonized region of the cement-based material are distinguished according to difference of gray value; and the defects in the traditional pHmethod of phenolphthalein alcohol solution are overcome. Under the condition of not damaging a test piece, the evolution process of the three-dimensional carbonation depth of the cement-based material along with the time is detected. By the method, flaw space distribution in the carbonation process, the flaw volume, the flaw closing area, the evolution law of porosity and hole dimensional distribution and the topological properties, such as connectivity, sinuosity and the like, of the hole can be achieved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Methods and Apparatus for the Non-Destructive Detection of Variations in a Sample
InactiveUS20080180111A1Radiation pyrometryResistance/reactance/impedenceNon destructivePosition dependent
Non-invasive THz spectroscopic apparatus and methods are provided for detecting and / or identifying constituents such as variations in a structural entity where chemical or biological entities can reside. Position dependent scattering of THz radiation is employed to image voids and defects in the internal structure of samples, enabling the determination of contamination, spoilage or readiness of products such as wine in sealed containers.
Owner:NEW JERSEY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Method and apparatus for non-destructive testing of a seed
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for non-destructive testing of a seed. In various embodiments, the method may comprise vibrating the seed to orient the seed on an axis, identifying a location of a known feature of the seed, determining a sample location on the seed based on the location of the known feature, and performing a non-destructive testing procedure on the seed proximate the sample location. In one embodiment, the method may comprise removing a sample portion of the seed from the sample location without damaging the embryo of the seed. Accordingly, the viability of the seed may be maintained while allowing for subsequent testing on the sample portion of the seed.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
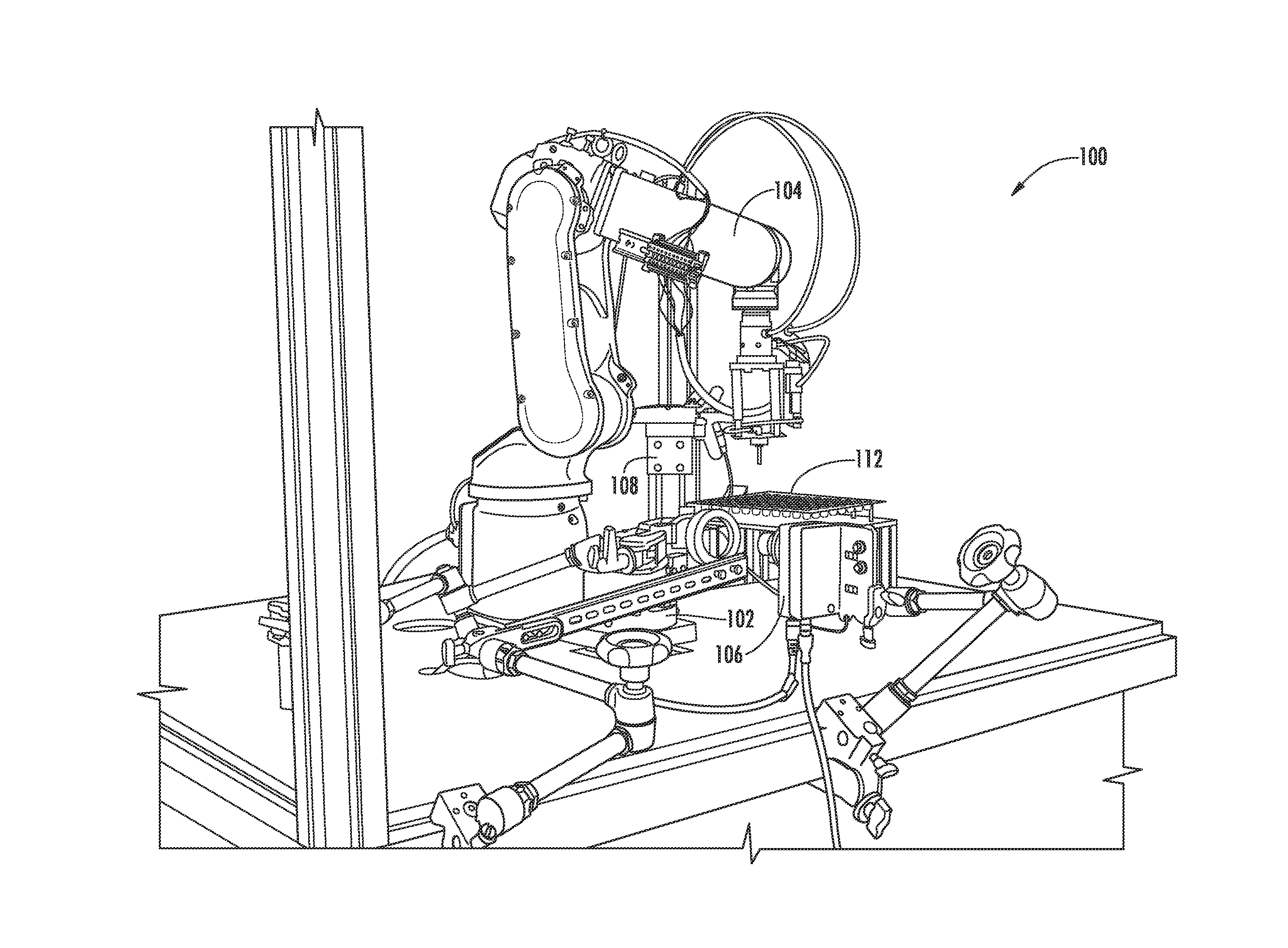
Device for the non-destructive testing of parts in a turbomachine
ActiveUS20110018530A1Easy to moveEasy positioningMagnetic property measurementsMaterial magnetic variablesNon destructiveEngineering
Device for the non-destructive testing of parts of a turbomachine motor, comprising a longitudinal rod carrying at its distal end a longitudinal finger carrying a retractile or deployable flexible blade supporting an inspection probe, this blade being guided in axial translation on the finger between a retracted position in which it extends along the finger and an advanced or deployed position in which it extends in front of the finger.
Owner:SN DETUDE & DE CONSTR DE MOTEURS DAVIATION S N E C M A
Crop biomass nondestructive testing image acquisition and processing device and testing method
InactiveCN102565061ARealize non-destructive testingSimple stepsMaterial analysis by optical meansCamera controlPrediction algorithms
The invention discloses a crop biomass nondestructive testing image acquisition and processing device and a testing method and aims at providing the crop biomass nondestructive testing image acquisition and processing device which is low in manufacturing and use costs and the testing method which is simple and convenient. The crop biomass nondestructive testing image acquisition and processing device comprises two camera height adjusting devices, a background wall, a calibration board, a lifting adjusting device, a seedling placing platform, a test bed and an image data acquisition, processing and analysis system. The image data acquisition, processing and analysis system comprises two charge coupled device (CCD) digital cameras and a computer. The camera control module of the computer is used for acquiring, displaying and storing the acquired images; and statistical analysis of the data is conducted through a biomass prediction algorithm module to finally obtain a crop biomass prediction model. The crop biomass nondestructive testing image acquisition and processing device and the testing method are suitable for the nondestructive testing of fresh biomass or dry biomass of potted crops or the biomass tracking and measurement of a single crop in the entire growth period.
Owner:SHENYANG AGRI UNIV
Rotating Array Probe System for Nondestructive Testing
ActiveCN102262129AMachine part testingAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesNon destructiveControl system
A device is disclosed for performing non-destructive inspection and testing (NDT / NDI) of an elongated test object, wherein the inspection system includes: a test object conveyor for conveying the test object along a longitudinal conveyance path; a probe assembly including phased-array probes, the probe assembly being configured to induce signals in the test object and sense echoes reflected from the test object; a probe assembly conveyor configured to movably support the probe assembly, to move the probe assembly on a circumferential path about the test object; and a control system coupled to the test object conveyor and to the probe assembly conveyor and configured to allow data acquisition by and from the phased-array probes while, simultaneously, the test object moves along the longitudinal path and the phased-array probes move on the circumferential path. The test system may include phased-array probes of different types to optimize detecting faults or cracks in the test object which extend in different directions.
Owner:OLYMPUS NDT
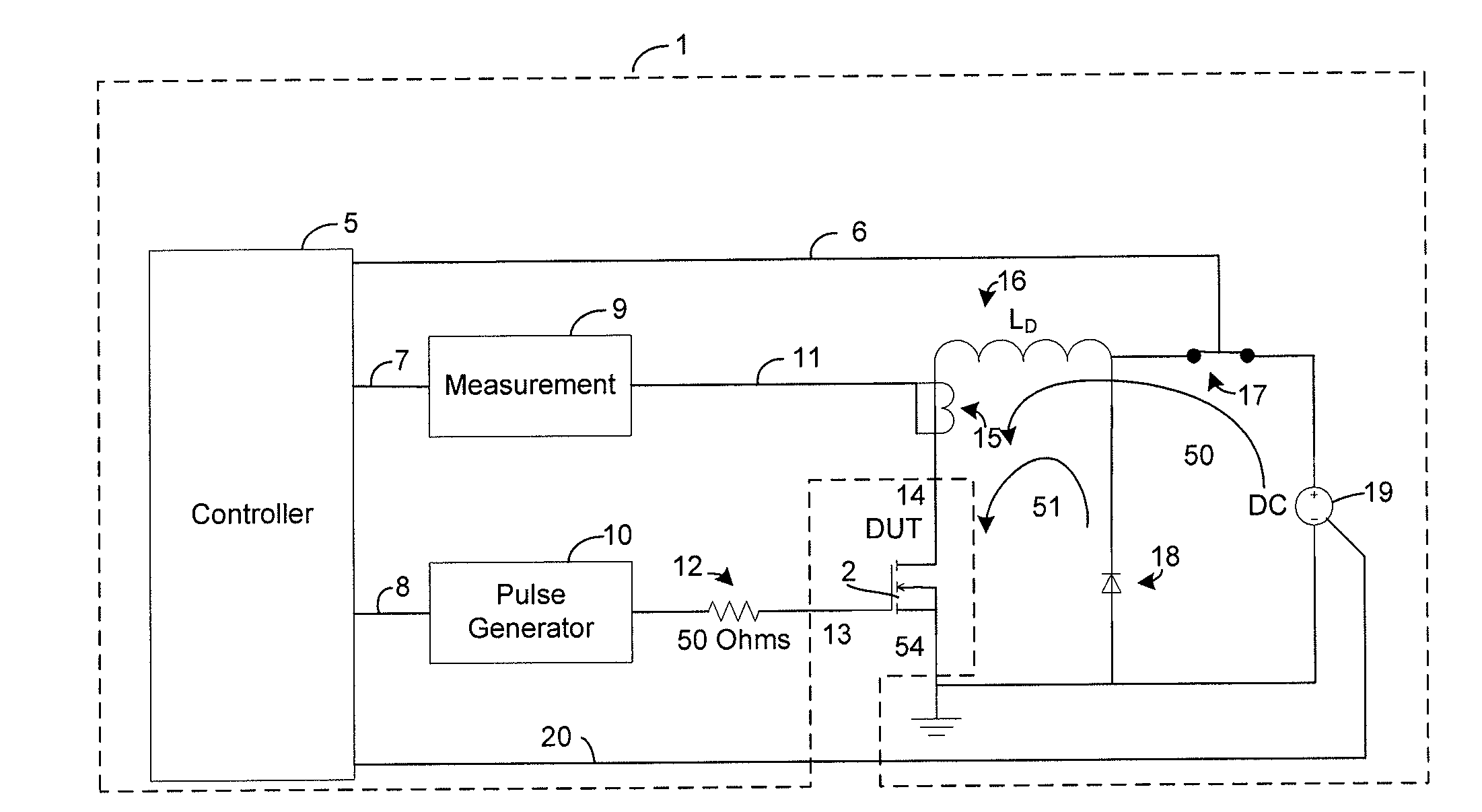
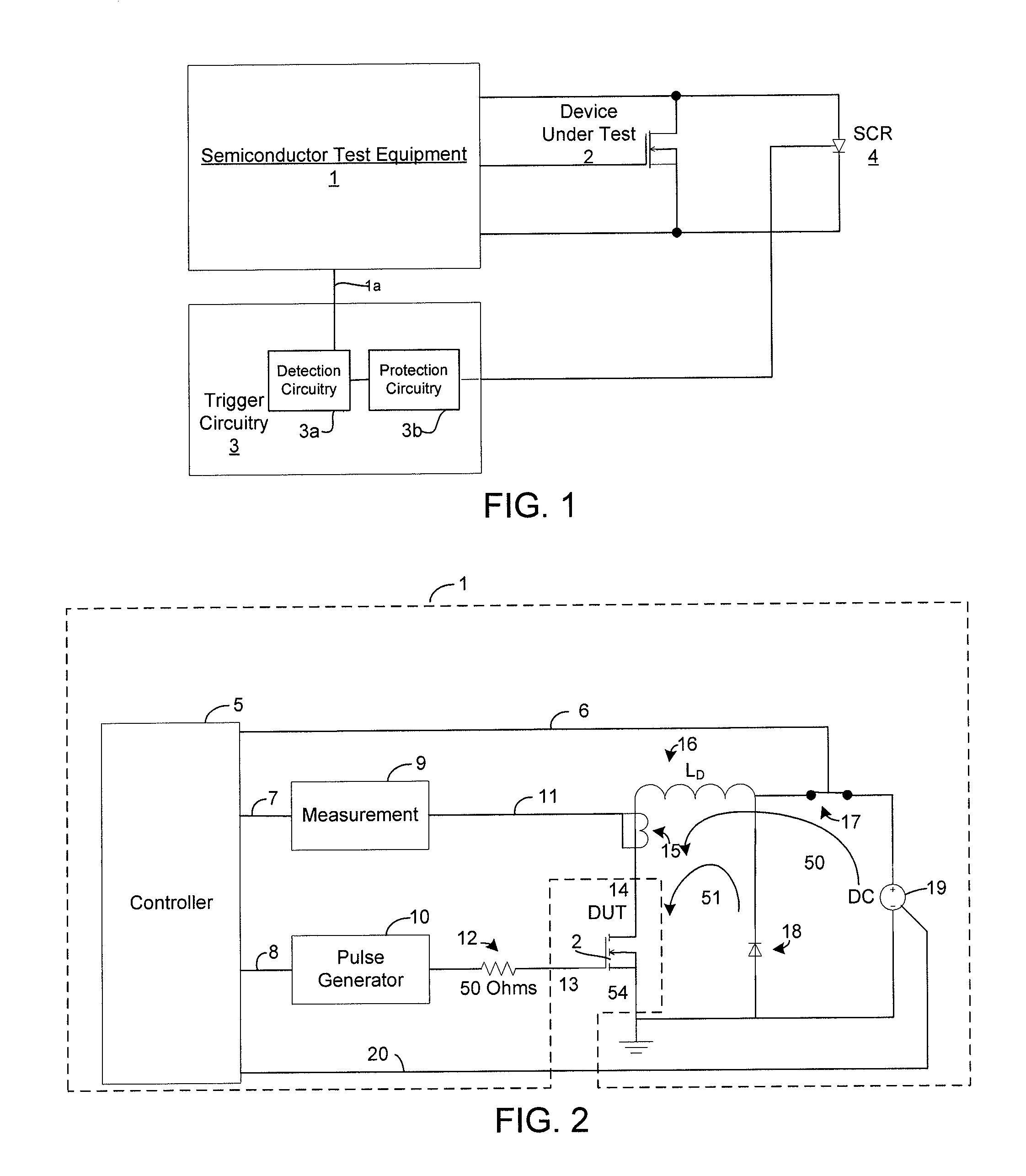
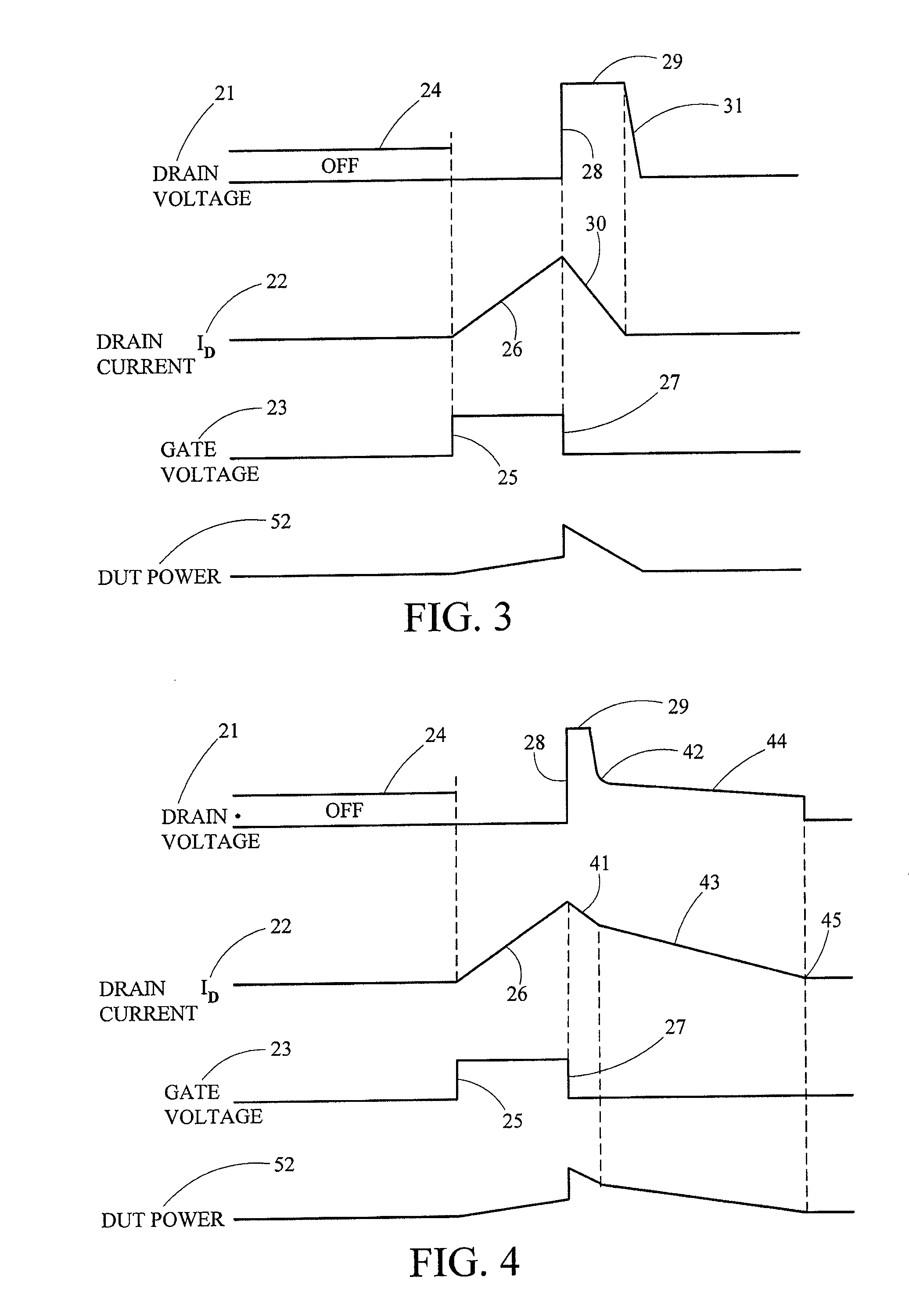
Damage reduction method and apparatus for destructive testing of power semiconductors
ActiveUS20130027067A1Limit damage theretoControl damageFault location by increasing destruction at faultShort-circuit testingEngineeringPower test
A device and method for limiting damage to a semiconductor device under test when the semiconductor device fails during a high current, or high power test is provided. The occurrence of a failure of the device under test is detected, and power applied to the semiconductor device is diverted through a parallel path element upon detection of failure of the semiconductor device.
Owner:INTEGRATED TECH
Non-destructive testing systems and method used for detecting a metal-containing object through X-ray detection
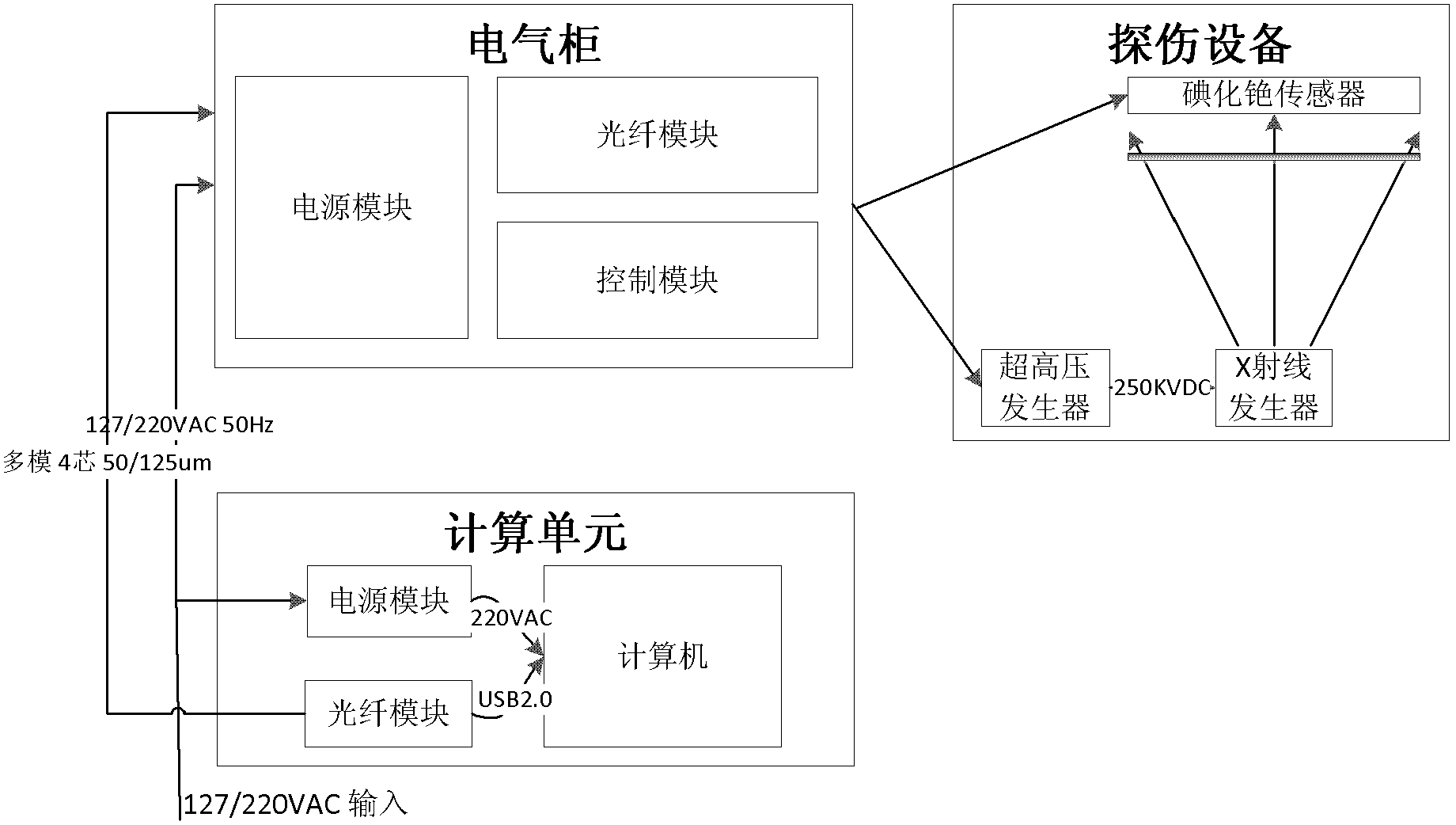
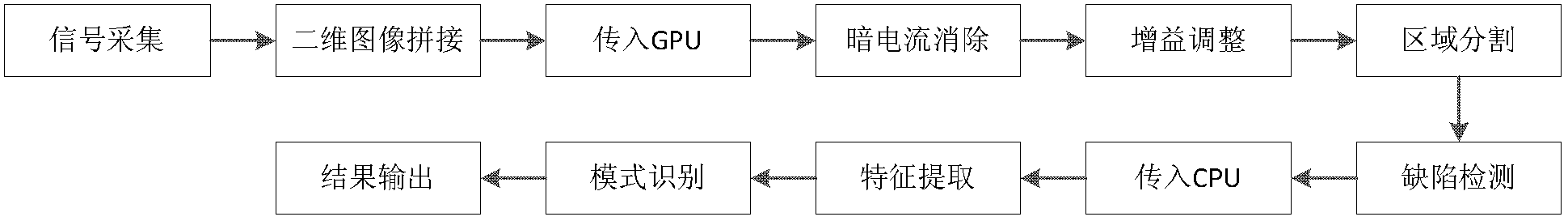
InactiveCN102937599AExtend your lifeMeet the testing requirementsMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationEnergy variationInternal memory
The invention discloses a non-destructive testing systems and a non-destructive testing method used for detecting a metal-rope-containing detection target through X-ray detection. The system comprises: an ultrahigh-voltage generator, an X-ray generator, a cesium iodide sensor, an optical fiber module, a controlling module, a computer, and a power supply module. The method comprises the steps that: one-dimensional energy variation data is recorded; a two-dimensional image is spliced; the image is transferred into a GPU; dark current is eliminated; gain adjustment is carried out; metal region segmentation is carried out; defect detection is carried out; the result is transferred to a computer internal memory; feature extraction is carried out; mode recognition is carried out; and the result is outputted. According to the invention, through X-ray processing, GPU calculating, and image processing algorithms, defects such as low detection precision, long feedback cycle, offline spot-check, low efficiency, and the like of other methods are solved. The system and the method provided by the invention can satisfy requirements of various terminal users such as belt manufacturers, mines, ports, power plants, steel plants, cement plants, and the like.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Performance Curve Generation For Non-Destructive Testing Sensors
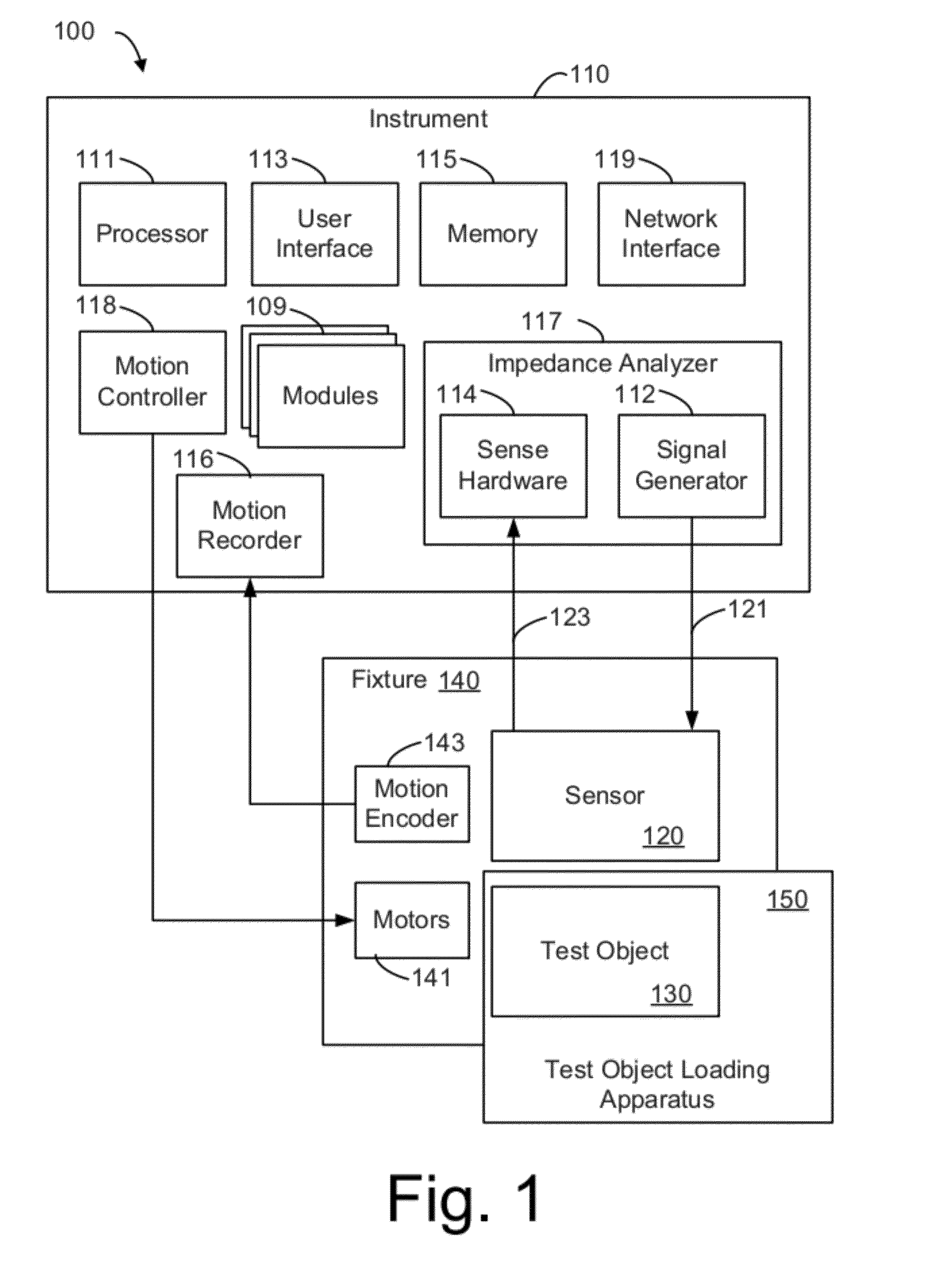
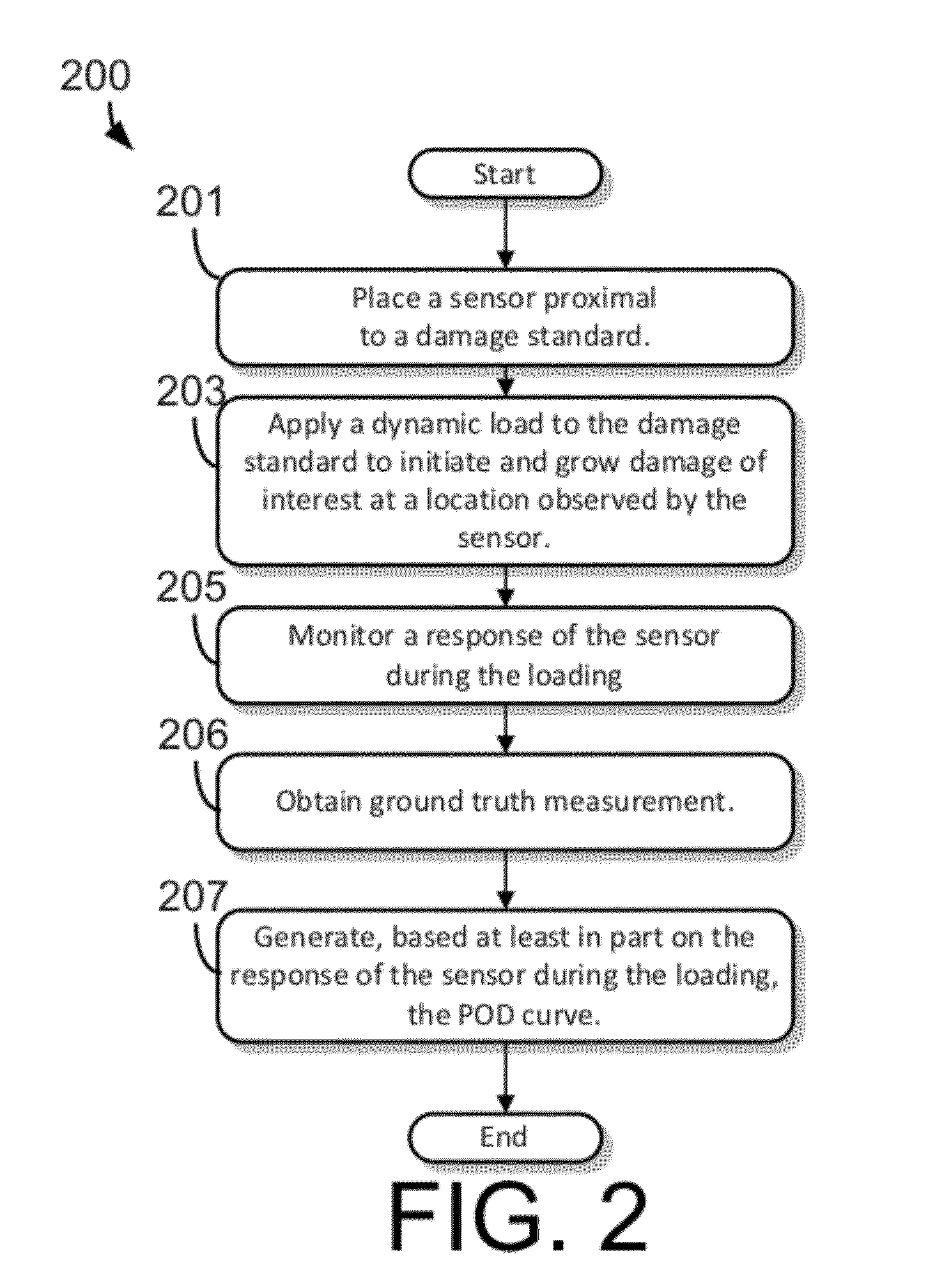
ActiveUS20120271824A1Easily damagedImprove performanceUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wave generationDigital data processing detailsGround truthMultiple sensor
Methods and apparatus for enhancing performance curve generation, damage monitoring, and improving non-destructive testing performance. Damage standards used for performance curve generation are monitored using a non-destructive testing (NDT) sensor during a damage evolution test performed with the standard. The evolution test may be intermittently paused to permit ground truth data to be collected in addition to the NDT sensor data. A damage evolution model may be used to estimate ground truth data during the intervening periods of the damage evolution test. The NDT sensor data and ground truth data are used to generate performance curves for the NDT system. Multiple sensors may be monitored at multiple locations on the damage standard and multiple damage evolution tests may be performed with multiple damage standards.
Owner:JENTEK SENSORS
Destructive testing apparatus and method for simulating tunnel going through oblique displaced active fault
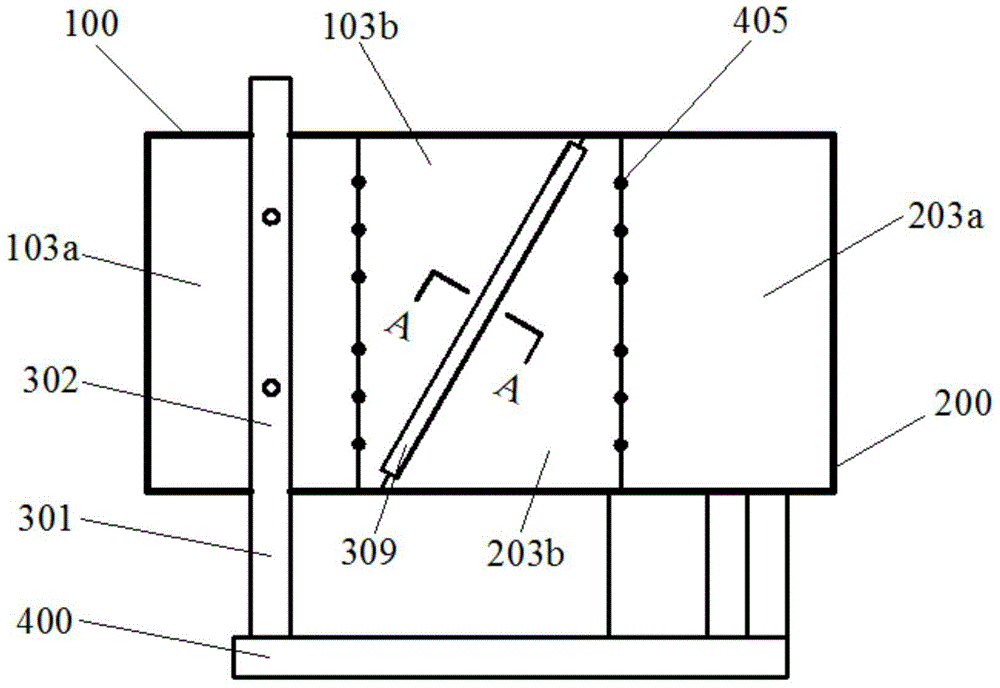
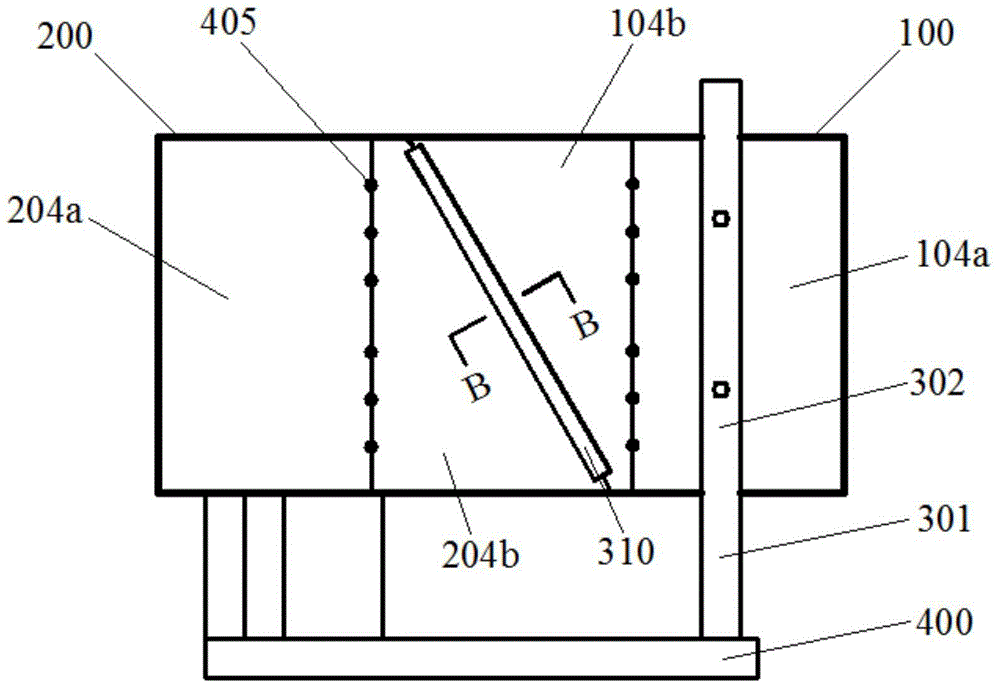
ActiveCN105785468AGuaranteed operational safetyThe test data is accurate and reliableGeological measurementsActive faultLeft half
The invention discloses a destructive testing apparatus and method for simulating tunnel going through oblique displaced active fault. The apparatus is mainly configured in that: a lidless model testing sample box is composed of a movable left half box 100 and a fixed right half box 200; the movable left half box 100 is connected to the fixed right half box 200 through a front bilateral sliding pair 309 and a rear bilateral sliding pair 310; a left bottom plate 102 of the left half box hinges an upper end of a vertically loading apparatus 307, and a lower end of the vertically loading apparatus 307 is connected to a horizontal moving platform 308 which can move forward and backward to the left side of a pedestal 400; a left front plate 103 and right front plate of the left half box cling closely and respectively to a front horizontal loading apparatus 302 and a rear horizontal loading apparatus. The apparatus can implement a tunnel structure and spatial positions of multiple dip angles and multiple crossing angles among active faults, simulates stress states and destructive methods of the tunnel structure in a more accurate manner so as to provide more reliable testing data for the design and construction of going through fault tunnel structure.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Metal surface defect image recognition non-destructive testing device and method
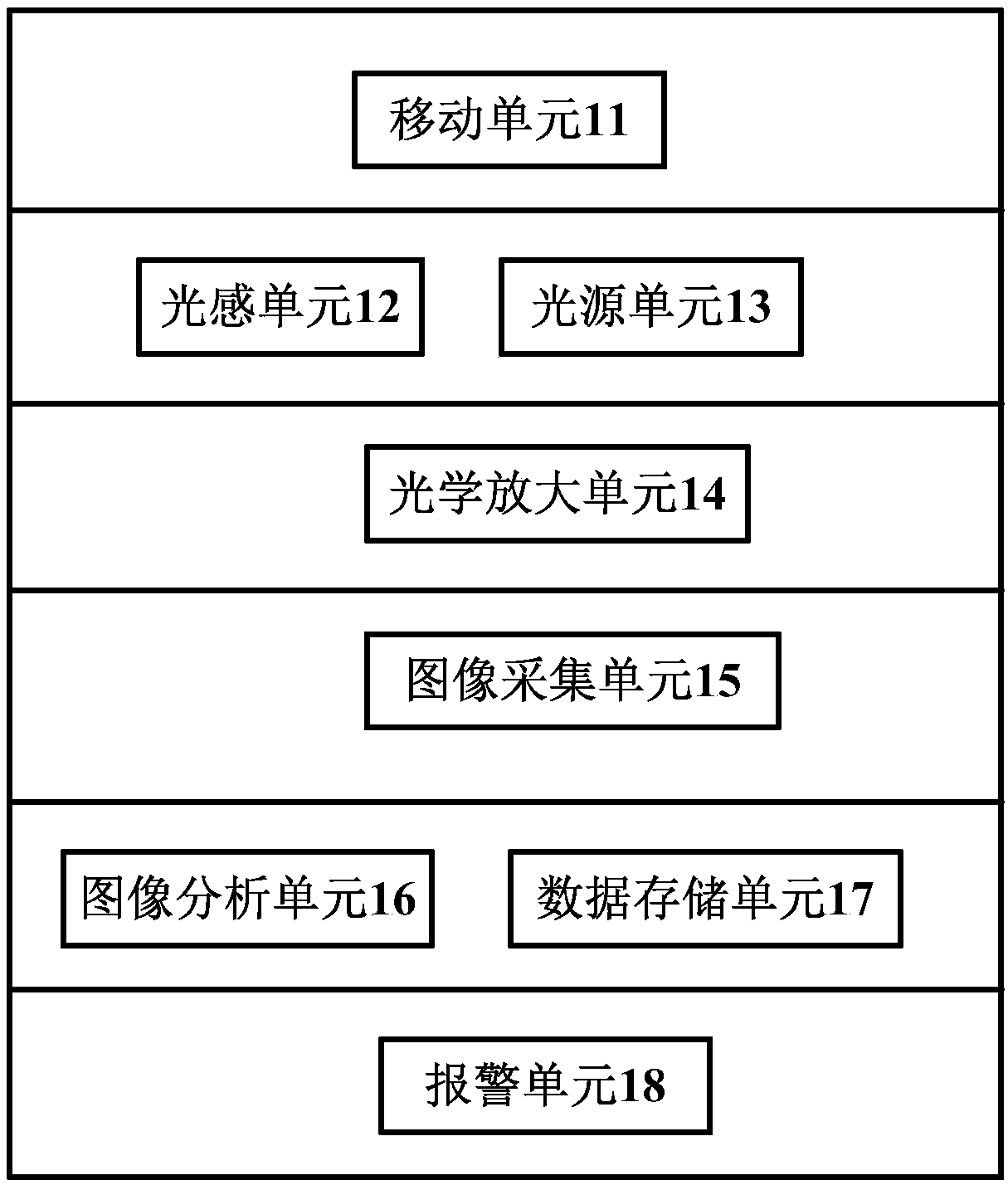
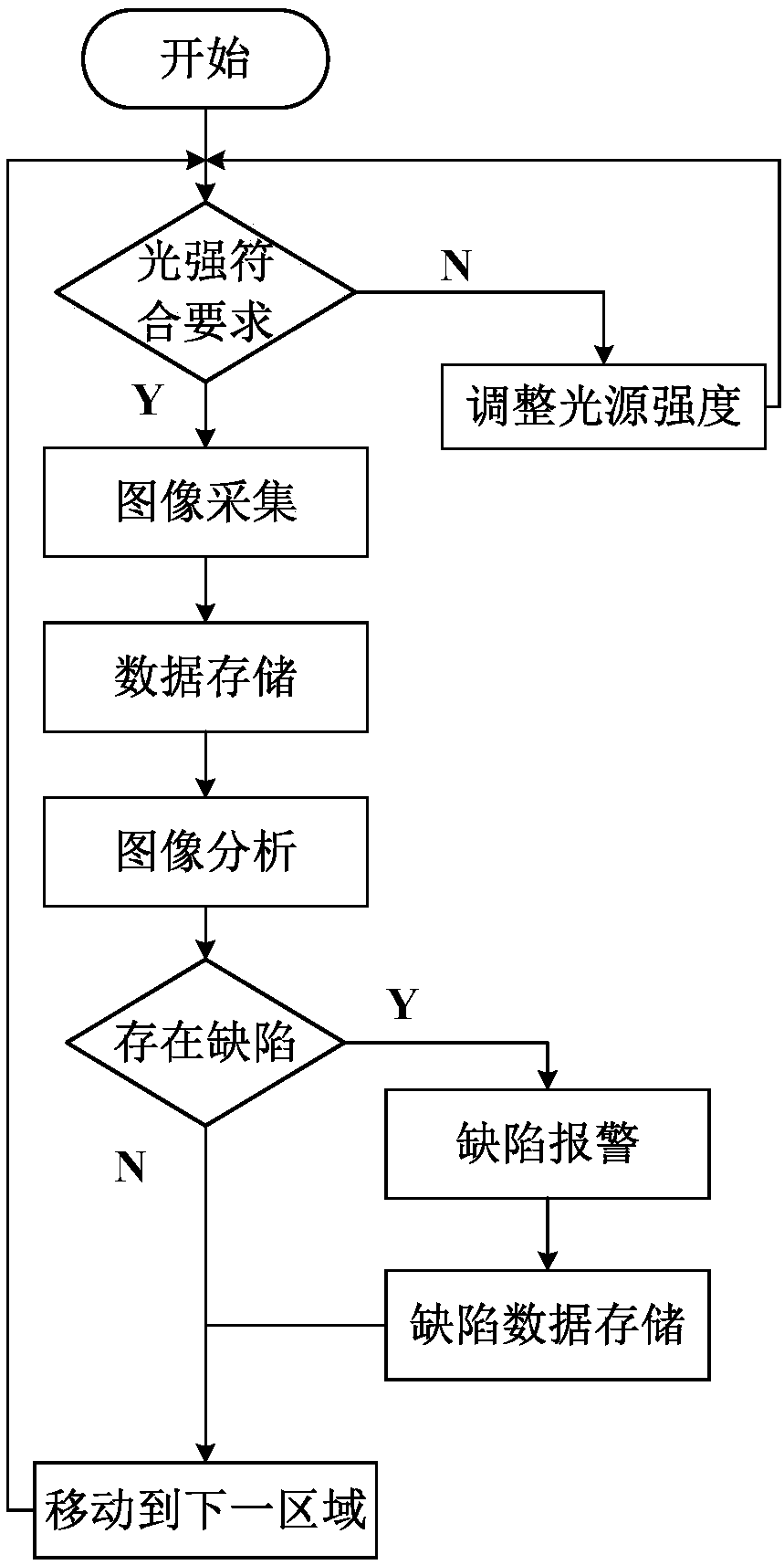
ActiveCN107782733AExpand the scope of detectionModerate brightnessOptically investigating flaws/contaminationNon destructiveImaging analysis
The invention discloses a metal surface defect image recognition non-destructive testing device and method, and relates to the field of automatic metal surface defect testing. The device comprises a mobile unit, a light sensation unit, a light source unit, an optical amplification unit, an image acquisition unit, an image analysis unit, a data storage unit and an alarm unit, wherein the light sensation unit and the light source unit ensure suitable brightness of an acquired image in a tested area, the optical amplification unit is used for optically amplifying the acquired image, the image acquisition unit acquires the image, the image analysis unit analyzes the acquired image in the tested area and judges whether defects exist or not, the data storage unit stores data needed by running ofthe device, the acquired image and analysis results, and the alarm unit gives an alarm for a tested problem area. Metal surfaces can be full-automatically tested, the tested area is large, the testing method is simple and rapid, and testing time and labor cost are reduced.
Owner:NO 719 RES INST CHINA SHIPBUILDING IND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com