Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
6863 results about "Friction coefficient" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
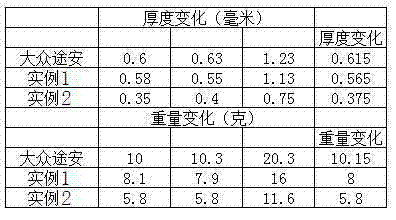
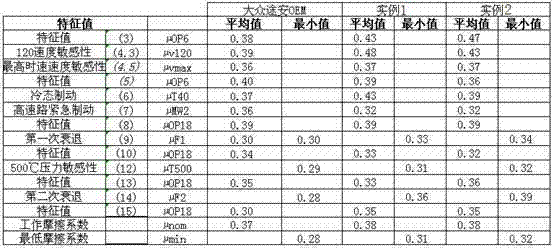
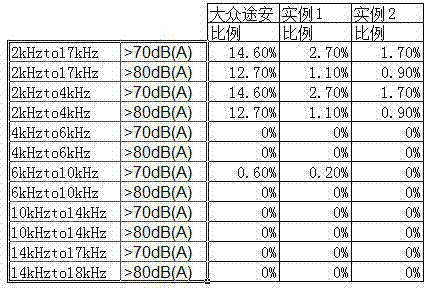
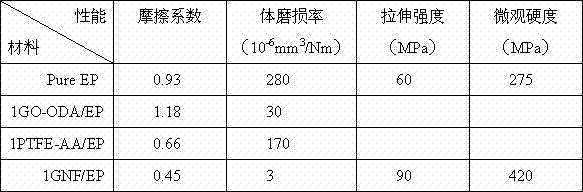
Coefficient of friction. The ratio of the force of friction between an object and a surface to the frictional force resisting the motion of the object.
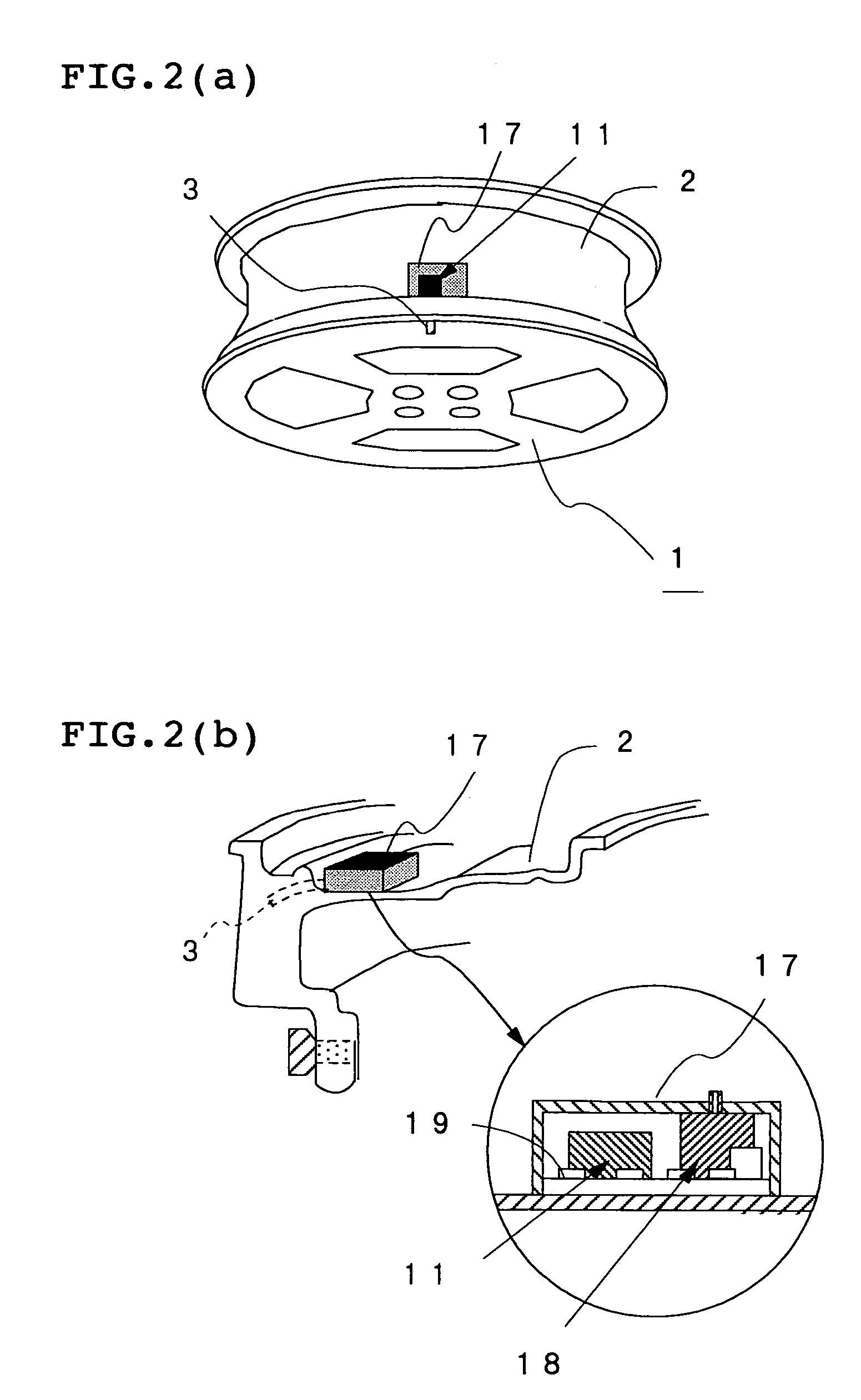
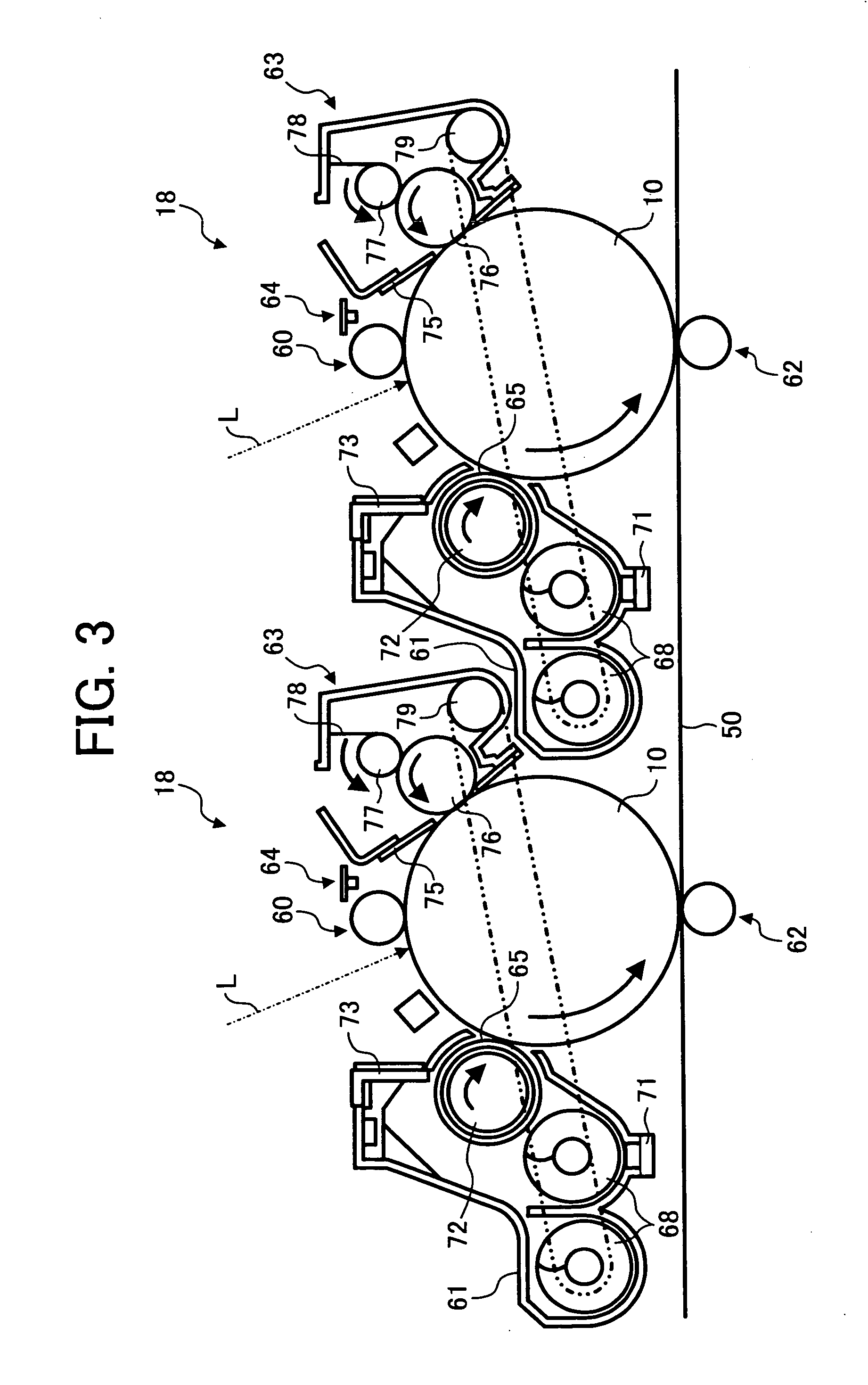
Sealing stopper for a syringe and a prefilled syringe
There can be provided a sealing stopper for a syringe, having very high sealing property and sliding property, and a prefilled syringe using this sealing stopper and capable of preserving a medicament for a long time and operating in easy and precise manner during injecting. This syringe is also excellent in sanitary and operating property during a step of formulation or preservation of a medicament. In this sealing stopper for a syringe, a surface of the rubber body is laminated with a tetrafluoroethylene resin film or ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene film having an average roughness Ra on the central line of the surface in a range of at most 0.05 mu m and a kinematic friction coefficient of at most 0.2.
Owner:DAIKYO SEIKO LTD
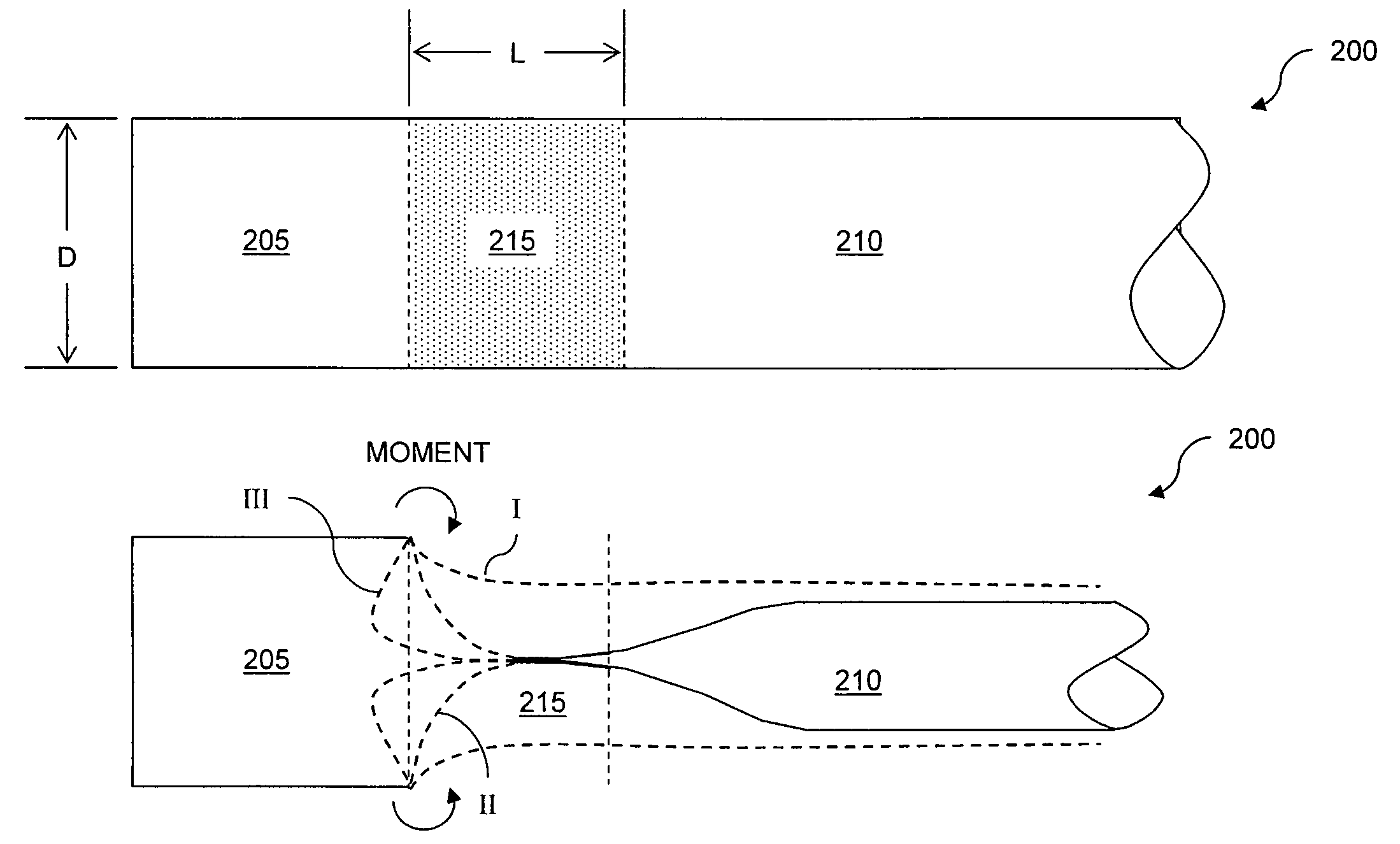
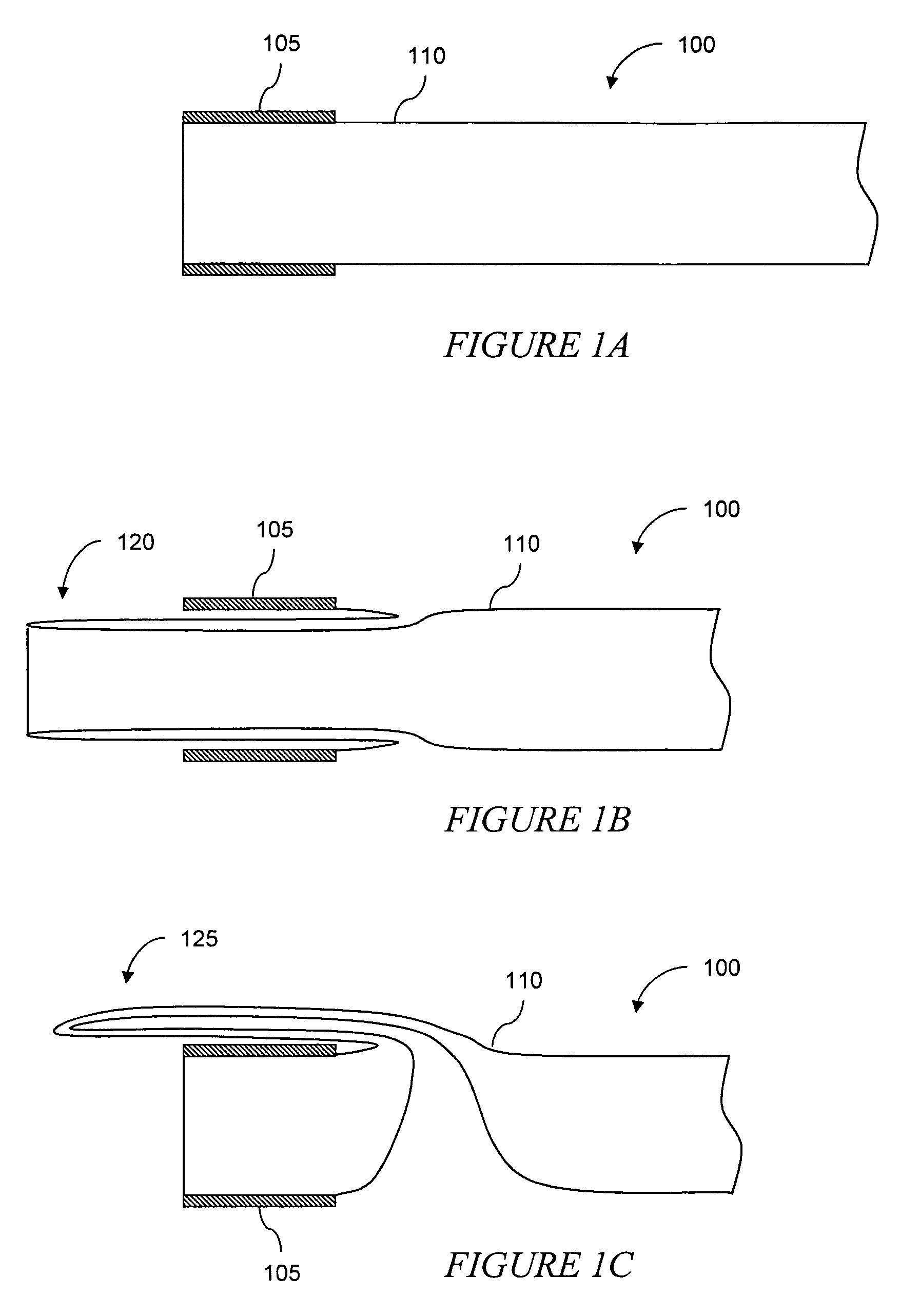
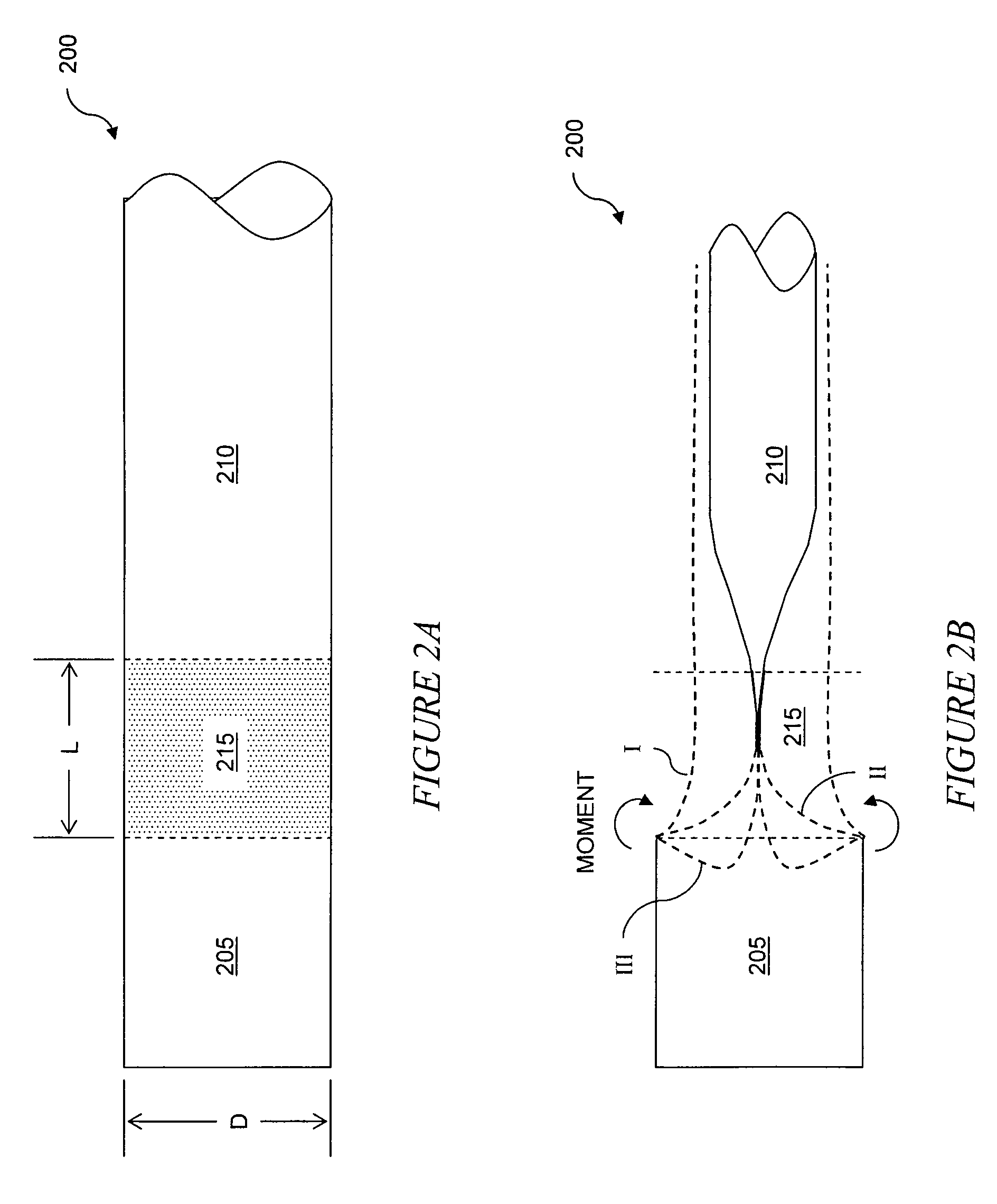
Anti-buckling sleeve
The invention relates to improved means for preventing buckling and therefore eversion of thin-walled, flexible, floppy gastrointestinal liners implanted in the digestive tract of an animal. The implantable devices include an anchor adapted for attachment within a natural body lumen and a thin-walled, floppy sleeve open at both ends and defining a lumen therebetween. A substantial length of the sleeve has material characteristics that result in the sleeve being prone to buckling and therefore eversion in the presence of retrograde pressures. Exemplary anti-buckling mechanisms provide an increased stiffness and / or an increased friction coefficient between the anchor and the proximal end of the sleeve to resist buckling and therefore eversion. In some embodiments, the anti-buckling mechanism is as a wire coupled along the substantial length of the sleeve.
Owner:GI DYNAMICS
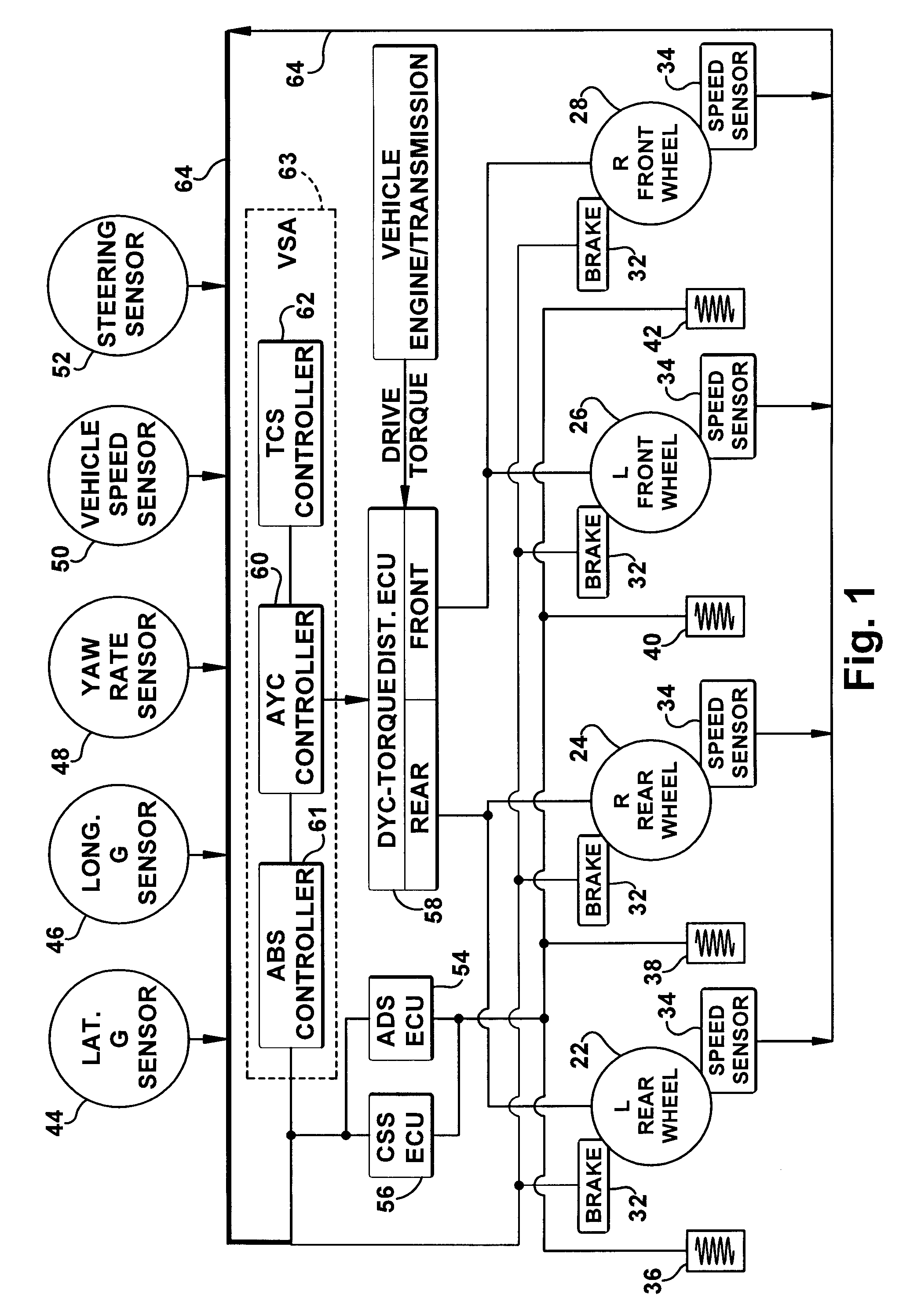
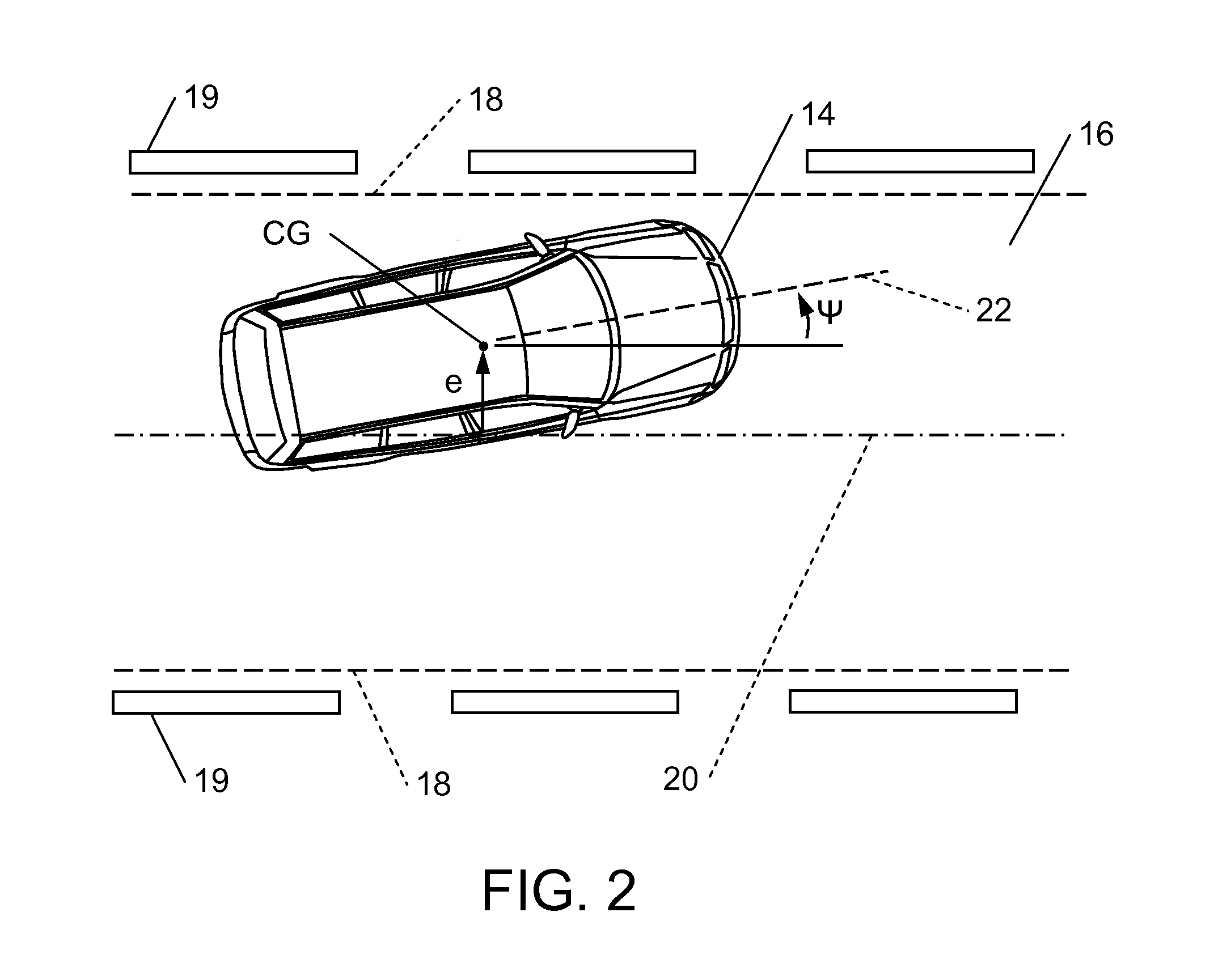
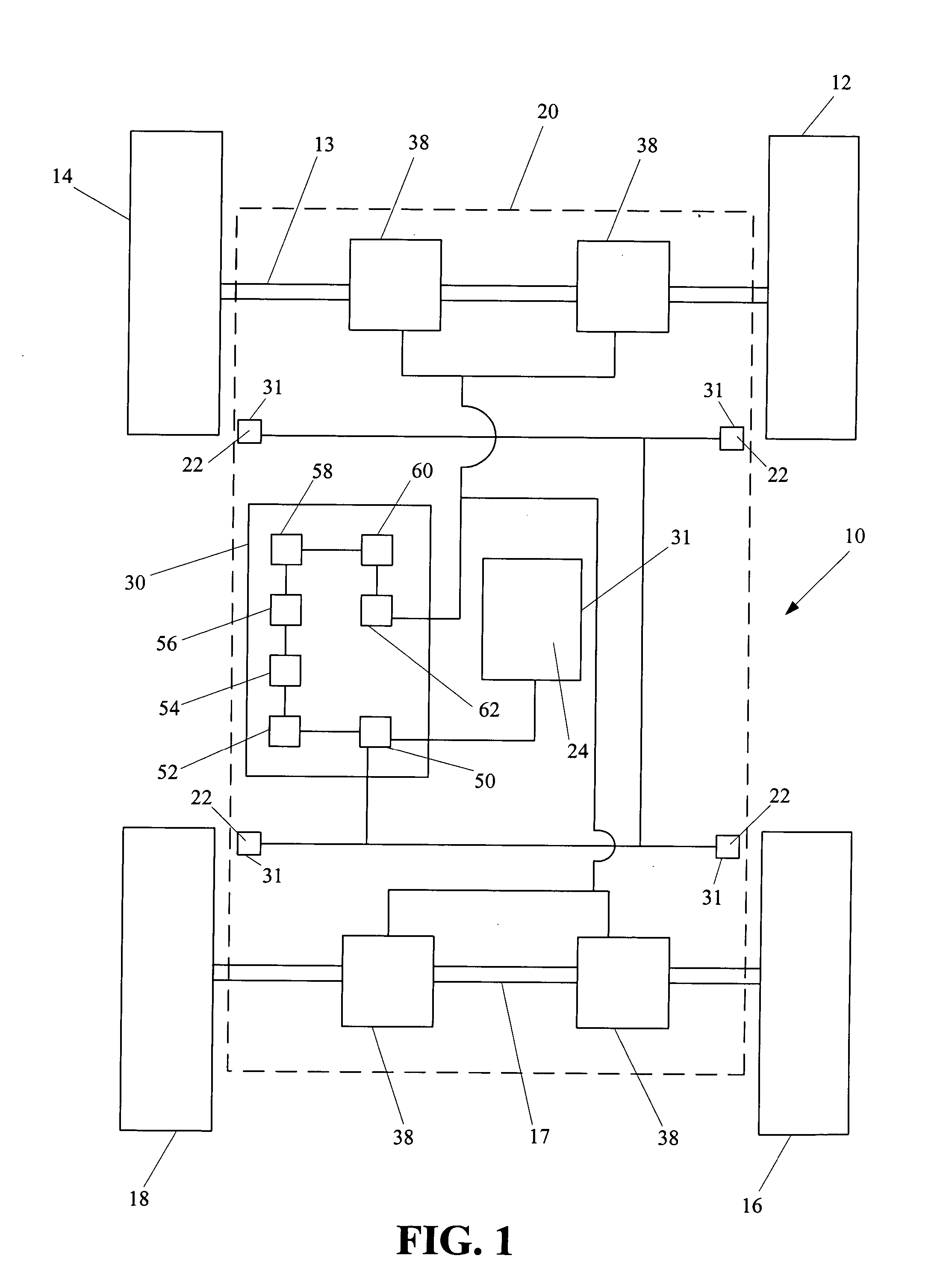
Vehicle systems control for improving stability
InactiveUS20080183353A1Improve vehicle stabilityDigital data processing detailsAnimal undercarriagesControl systemTraction control system
Improved methods of controlling the stability of a vehicle are provided via the cooperative operation of vehicle stability control systems such as an Active Yaw Control system, Antilock Braking System, and Traction Control System. These methods use recognition of road surface information including the road friction coefficient (mu), wheel slippage, and yaw deviations. The methods then modify the settings of the active damping system and / or the distribution of drive torque, as necessary, to increase / reduce damping in the suspension and shift torque application at the wheels, thus preventing a significant shift of load in the vehicle and / or improving vehicle drivability and comfort. The adjustments of the active damping system or torque distribution temporarily override any characteristics that were pre-selected by the driver.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
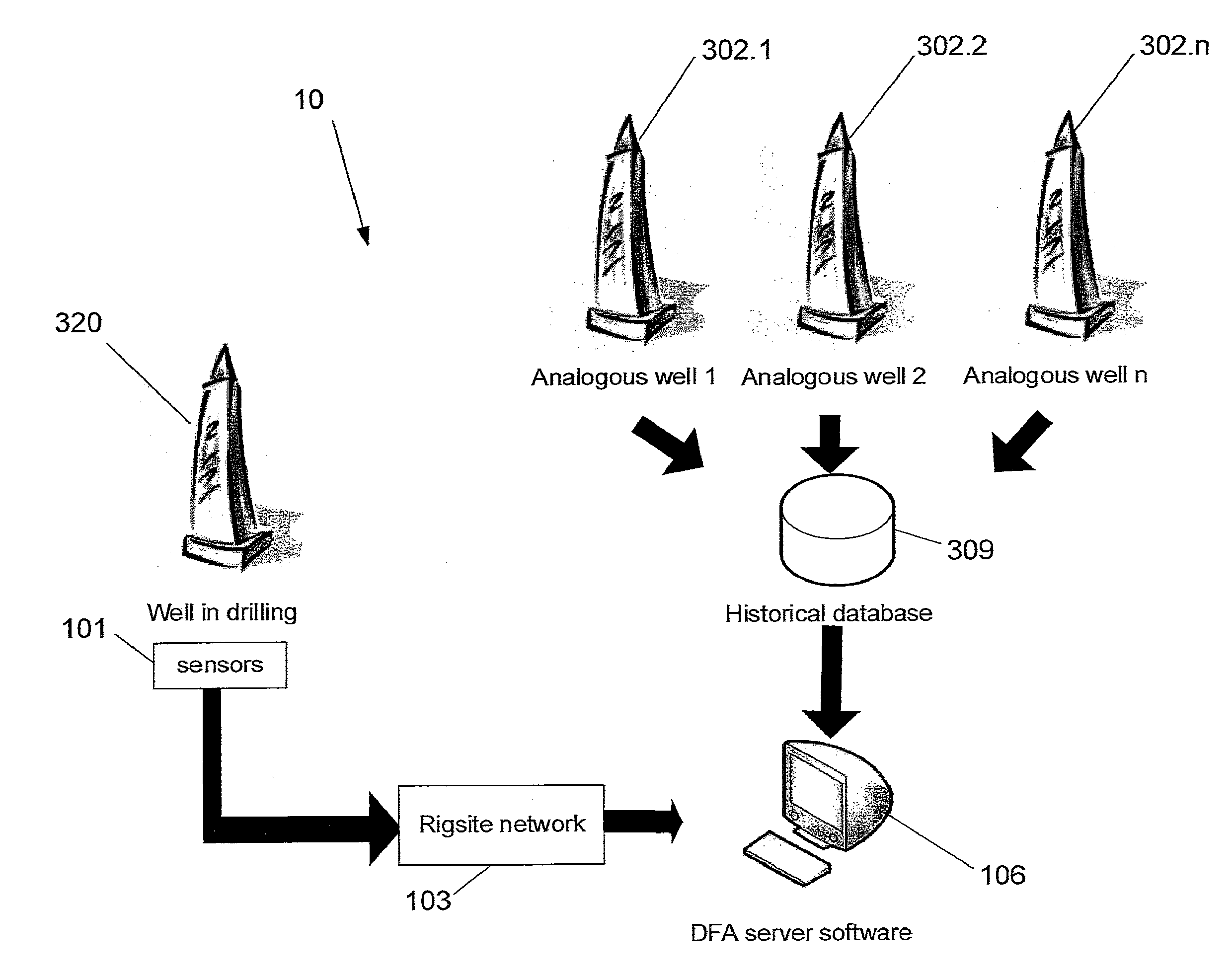
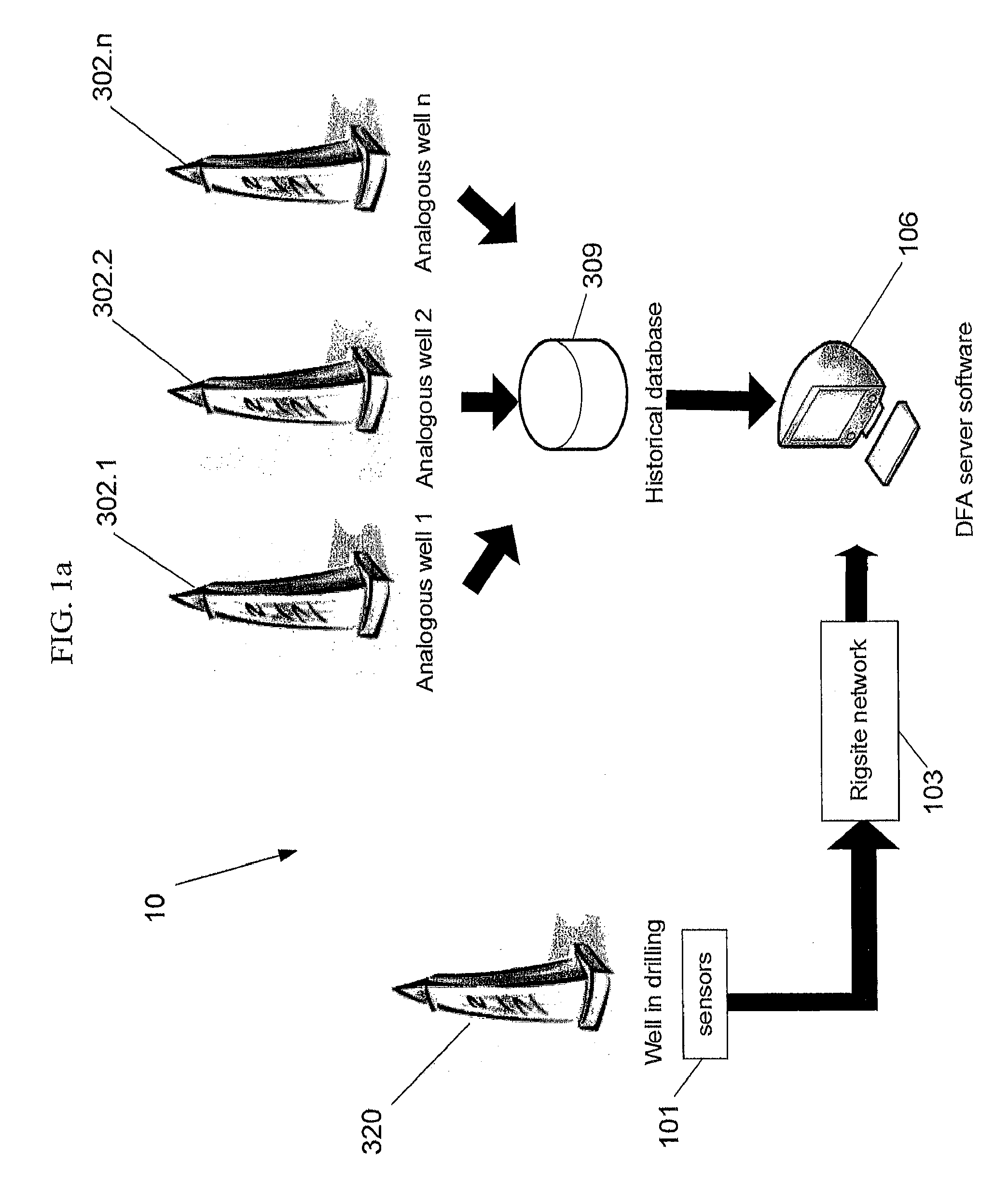
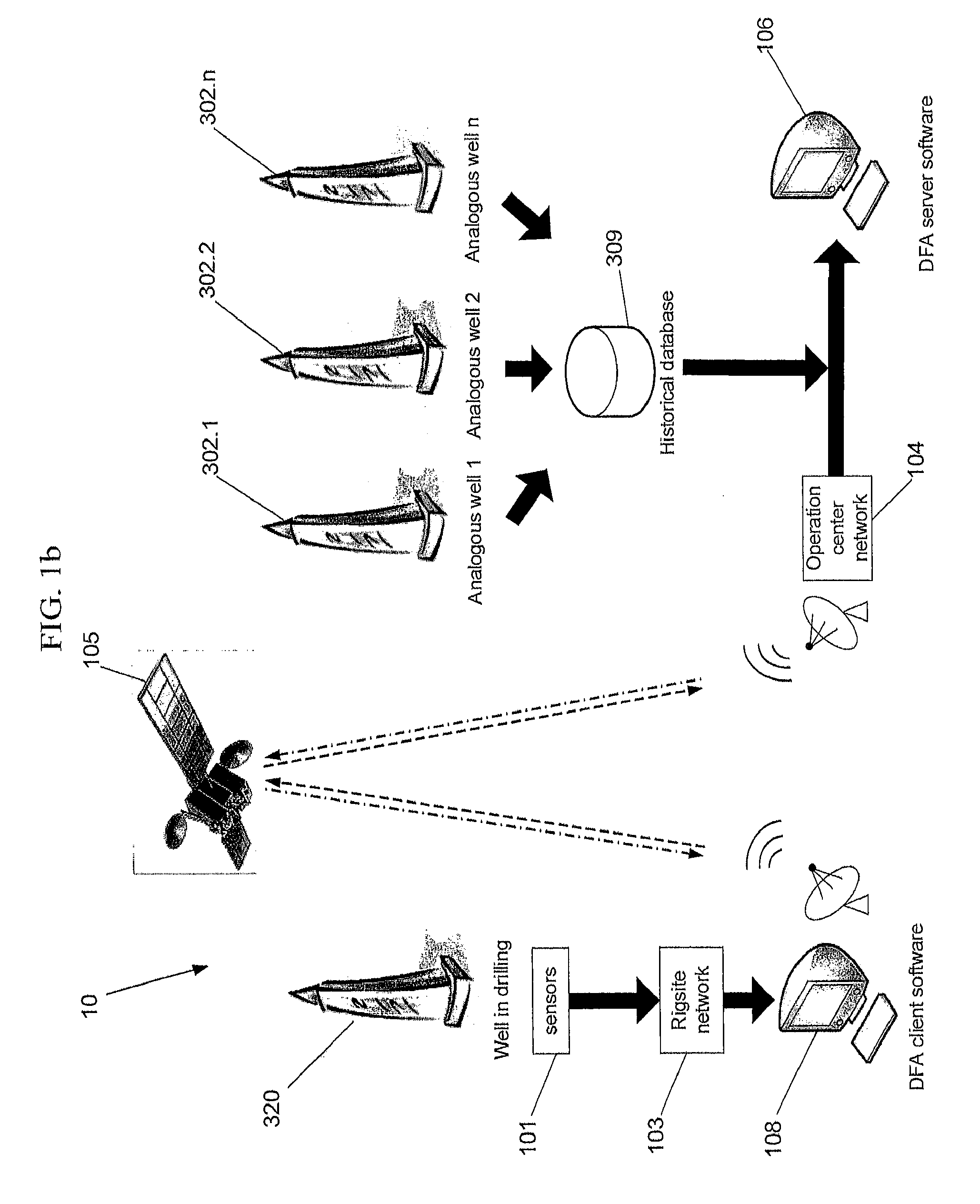
Methods and systems for improved drilling operations using real-time and historical drilling data
ActiveUS20140116776A1Maximized drilling rateLower Drilling CostsEarth drilling toolsMathematical modelsLithologyReal-time data
Methods and systems are described for improved drilling operations through the use of real-time drilling data to predict bit wear, lithology, pore pressure, a rotating friction coefficient, permeability, and cost in real-time and to adjust drilling parameters in real-time based on the predictions. The real-time lithology prediction is made by processing the real-time drilling data through a multilayer neural network. The real-time bit wear prediction is made by using the real-time drilling data to predict a bit efficiency factor and to detect changes in the bit efficiency factor over time. These predictions may be used to adjust drilling parameters in the drilling operation in real-time, subject to override by the operator. The methods and systems may also include determining various downhole hydraulics parameters and a rotary friction factor. Historical data may be used in combination with real-time data to provide expert system assistance and to identify safety concerns.
Owner:RESOURCE ENERGY SOLUTIONS
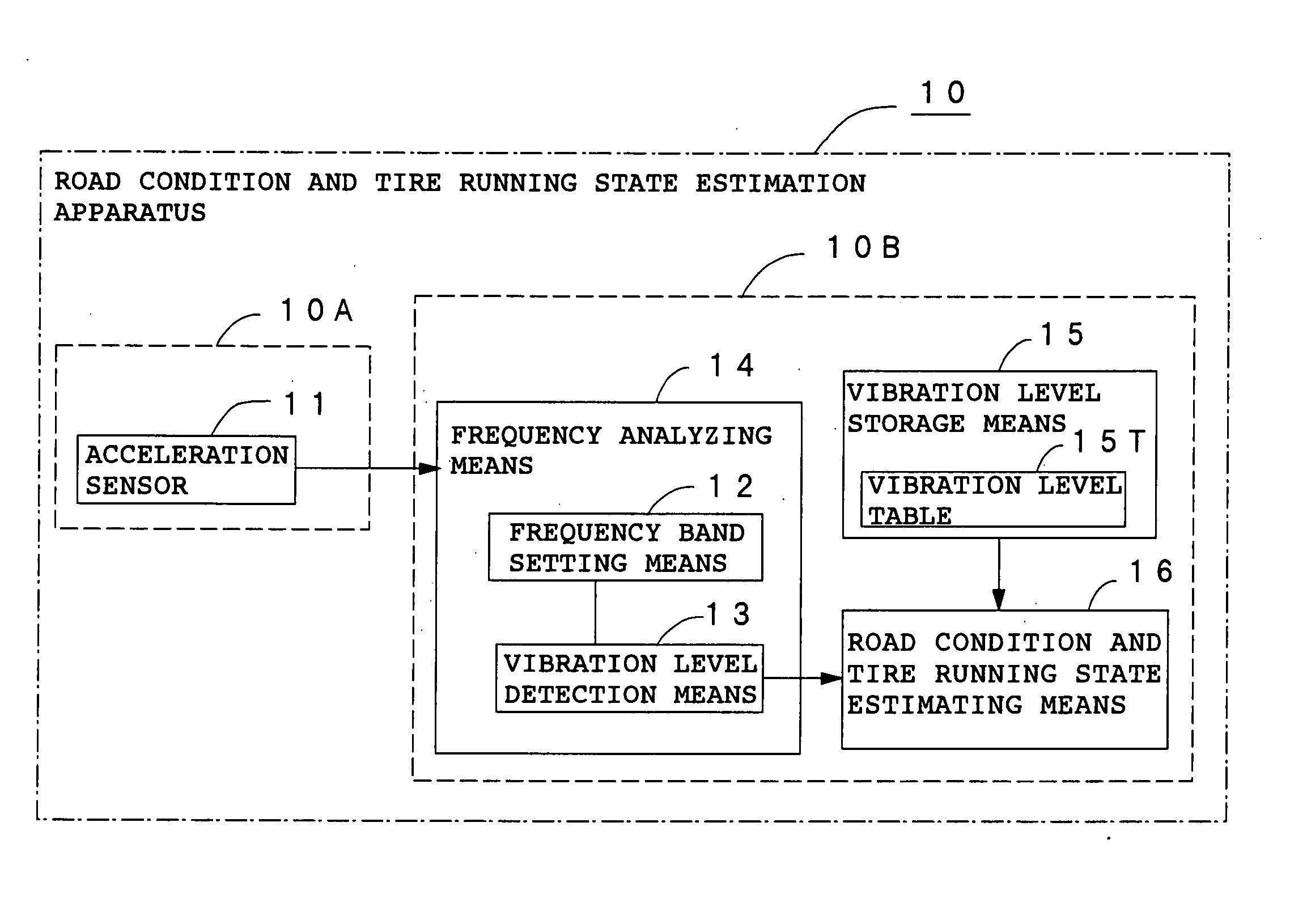
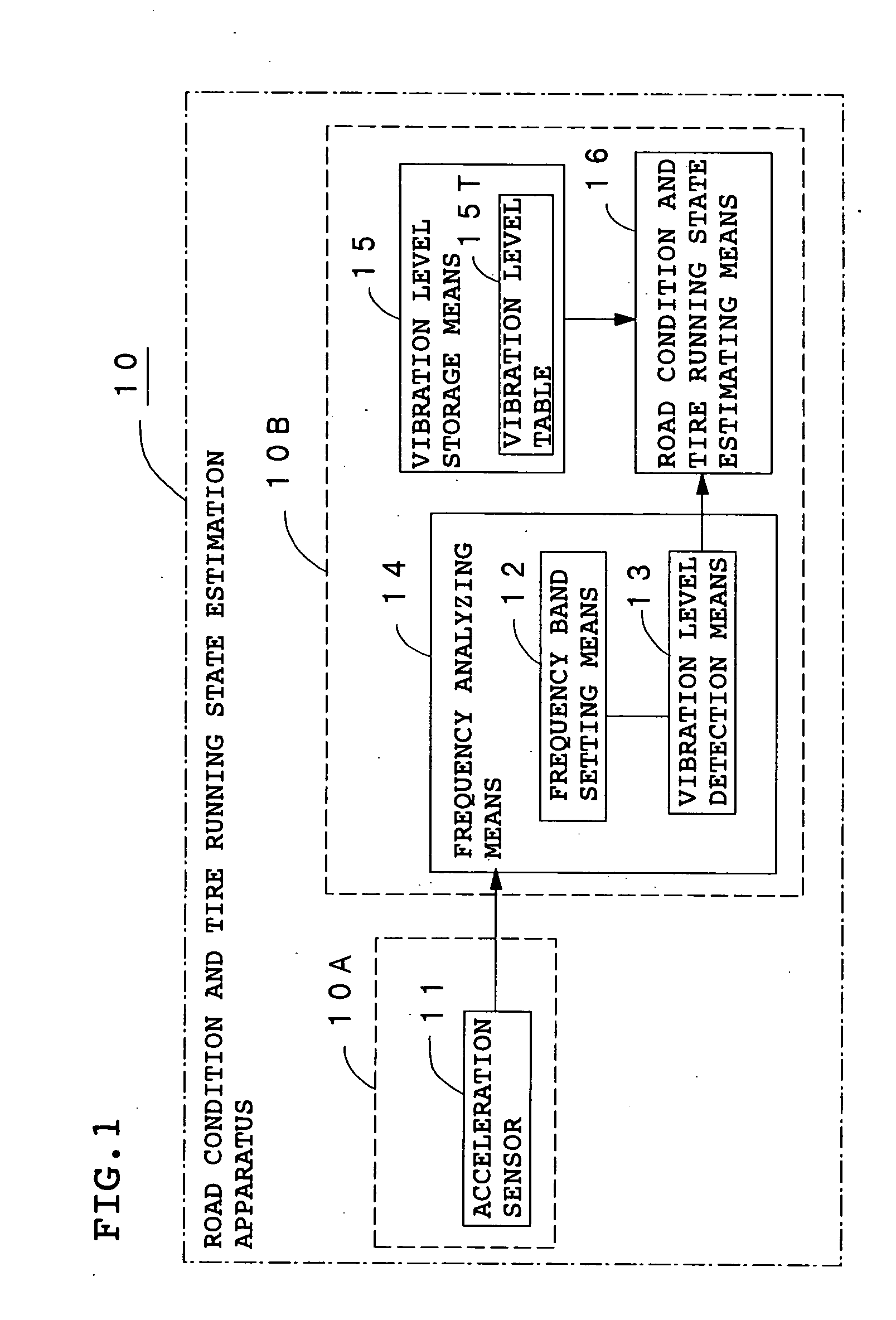
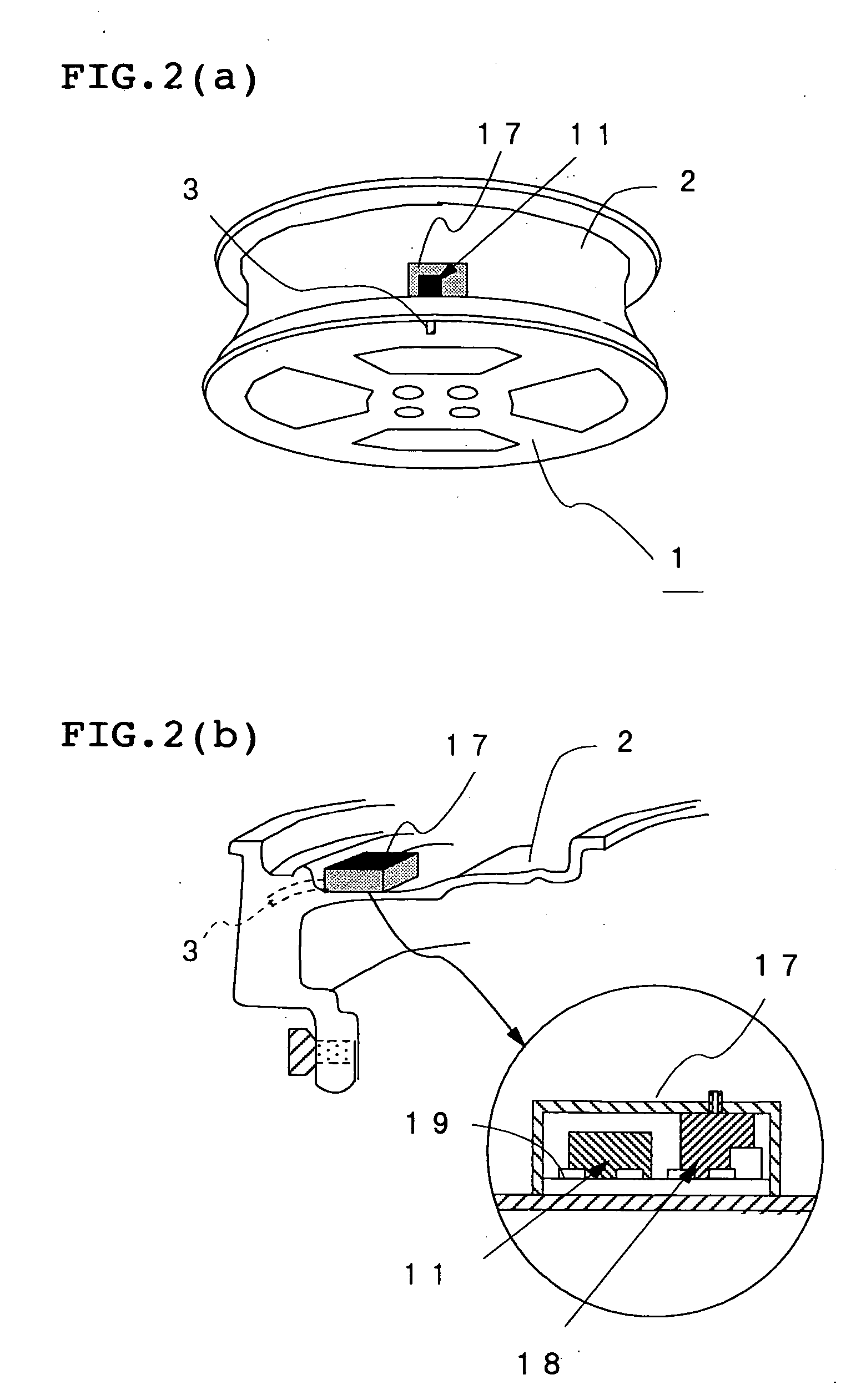
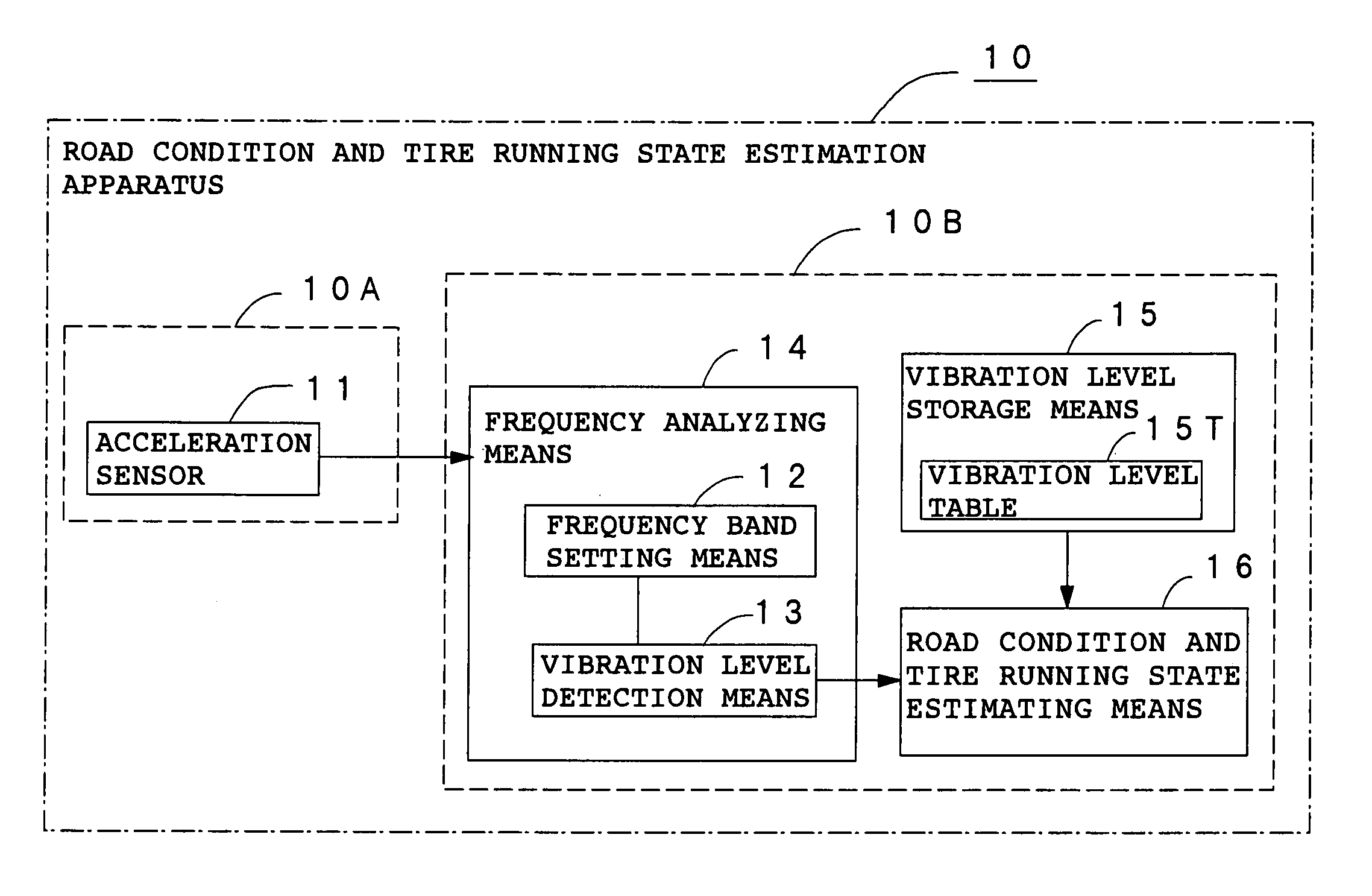
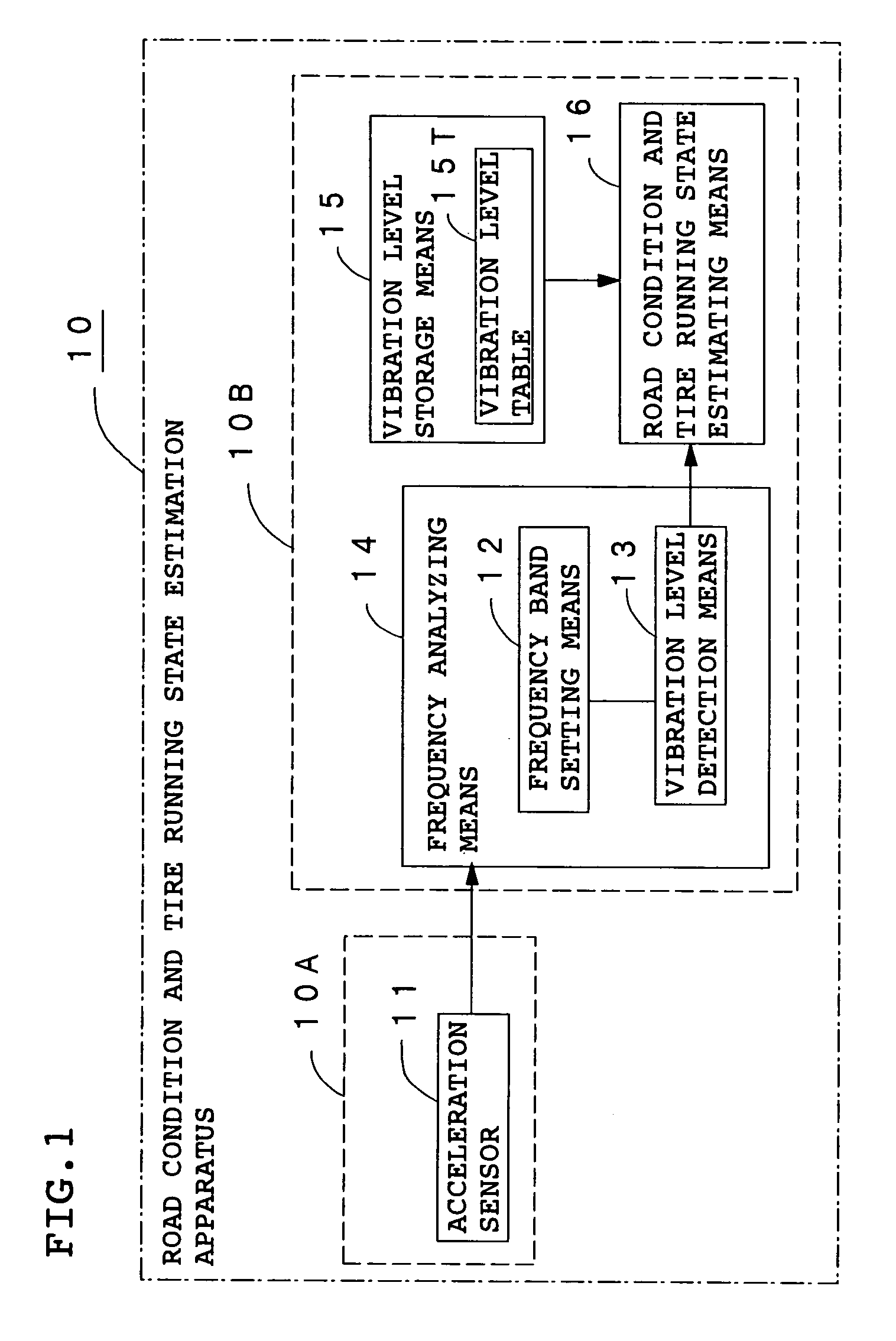
Method and apparatus for estimating road surface state and tire running state, abs and vehicle control using the same
InactiveUS20050085987A1Accurate estimateRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesDigital data processing detailsRoad surfaceVehicle control
The frequency of an information signal indicative of the vibration of a wheel detected by an acceleration sensor 11 mounted to a wheel 1 or the frequency of an information signal indicative of a change in the pressure of a gas in a tire detected by a pressure sensor 31 installed in the tire is analyzed by frequency analyzing means 14 (34), the band value of the obtained vibration spectrum or pressure change spectrum is detected, and a vibration level or pressure change level at the detected frequency band is compared with a vibration level table 15T showing the relationship between road friction coefficient μ and vibration level stored in vibration level storage means 15, or a pressure change level table 35T showing the relationship between road friction coefficient μ and pressure change level stored in pressure change level storage means 35 to estimate a road friction coefficient μ. Therefore, it is possible to estimate the value of road friction coefficient μ accurately and improve the safety of a car.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
Method and apparatus for estimating road surface state and tire running state, ABS and vehicle control using the same
InactiveUS7203579B2Accurate estimateRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesDigital data processing detailsRoad surfaceVehicle control
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
Magnetic recording medium comprising a magnetic layer having specific thickness, surface roughness and friction coefficient
InactiveUS6921592B2Reduce space lossReduce error rateMagnetic materials for record carriersBase layers for recording layersSurface roughnessNon magnetic
A magnetic recording medium comprising a non-magnetic support, at least one primer layer formed on one surface of the non-magnetic support, a magnetic layer formed on the primer layer, and a backcoat layer formed on the other surface of the non-magnetic support, wherein the magnetic layer has a thickness of 0.30 μm or less and a centerline average surface roughness Ra of 3.2 nm or less, and (P1−P0) is 30 nm or less and (P1-P20) is 5 nm or less in which P0 is an averaged height of projections of the magnetic layer, and P1, P2, - - - and P20 are heights of the highest, the second highest, - - - and the 20th highest projections of the magnetic layer, respectively.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Screw thread adhesion abrasion resisting self-lubricating coating and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101125995APrevent Adhesive WearReduce coefficient of frictionPolyurea/polyurethane coatingsEpoxy resin coatingsWear resistantSolvent
The invention relates to a self-greasing paint which can prevent screw thread from sticking and wearing and a preparation method thereof. The self-greasing paint which can prevent screw thread from sticking and wearing is a two-component self-greasing paint that consists of a component A and a component B. Component A consists of raw materials with weight proportion of 40-90 percent of film-forming material, 5-60 percent of solid greasing material, 0-10 percent of additive, 0-50 percent of solvent, 0-10 percent of color paint and 0-10 percent of filling while component B consists of raw materials with weight proportion of 50-100 percent of curing agent and 0-50 percent of solvent. The weight ratio of component A and component B is 1 to 0.1-5. The friction coefficient of the coat formed by the paint is low and the paint has self greasing function, anti-sticking and wearing resistant performances; the invention reduces and even avoids the use of grease and solves pollution problem caused by grease. The self-greasing paint is applicable to various mechanical parts such as bolt, screw, etc., in particular to screw threads of oil pipe, cashing and drill rod, etc. that are special for oil industry.
Owner:王新虎
Eversion resistant sleeves
ActiveUS7766973B2Reduce coefficient of frictionIncrease stiffnessOesophagiIntravenous devicesImplanted deviceSurgery
The invention relates to improved means for preventing eversion and subsequent obstruction of thin-walled, floppy gastrointestinal liners implanted in the digestive tract of an animal. The implantable devices include an anchor adapted for attachment within a natural body lumen and a thin-walled, floppy sleeve open at both ends and defining a lumen therebetween. A substantial length of the sleeve has material characteristics that result in the sleeve being prone to eversion in the presence of retrograde pressures. Exemplary eversion-resistant features provide an increased stiffness and / or an increased friction coefficient between the anchor and the proximal end of the sleeve to resist eversion. In some embodiments, the eversion-resistant feature includes an anti-buckling element, such as a wire coupled along the substantial length of the sleeve.
Owner:GI DYNAMICS INC
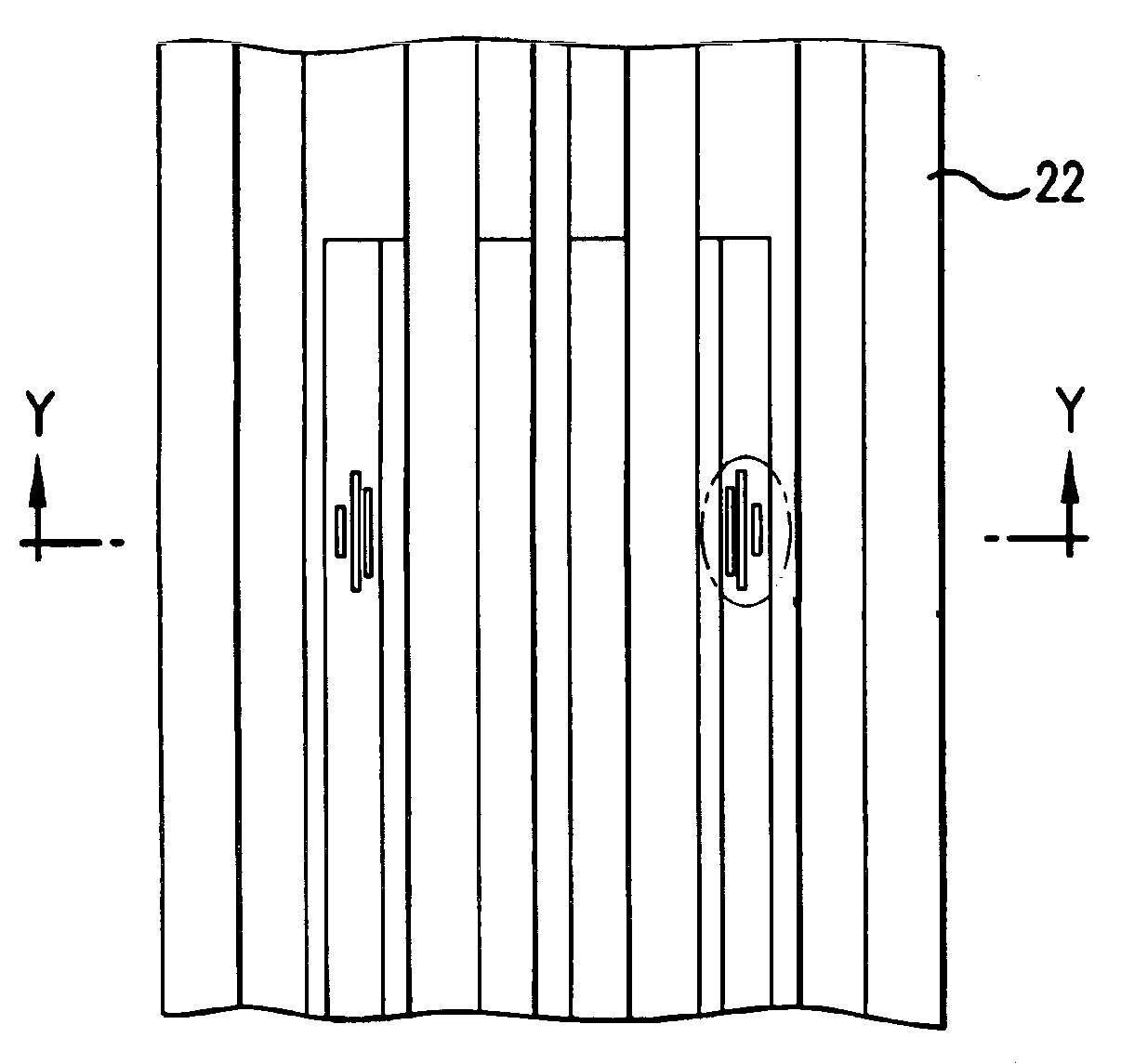
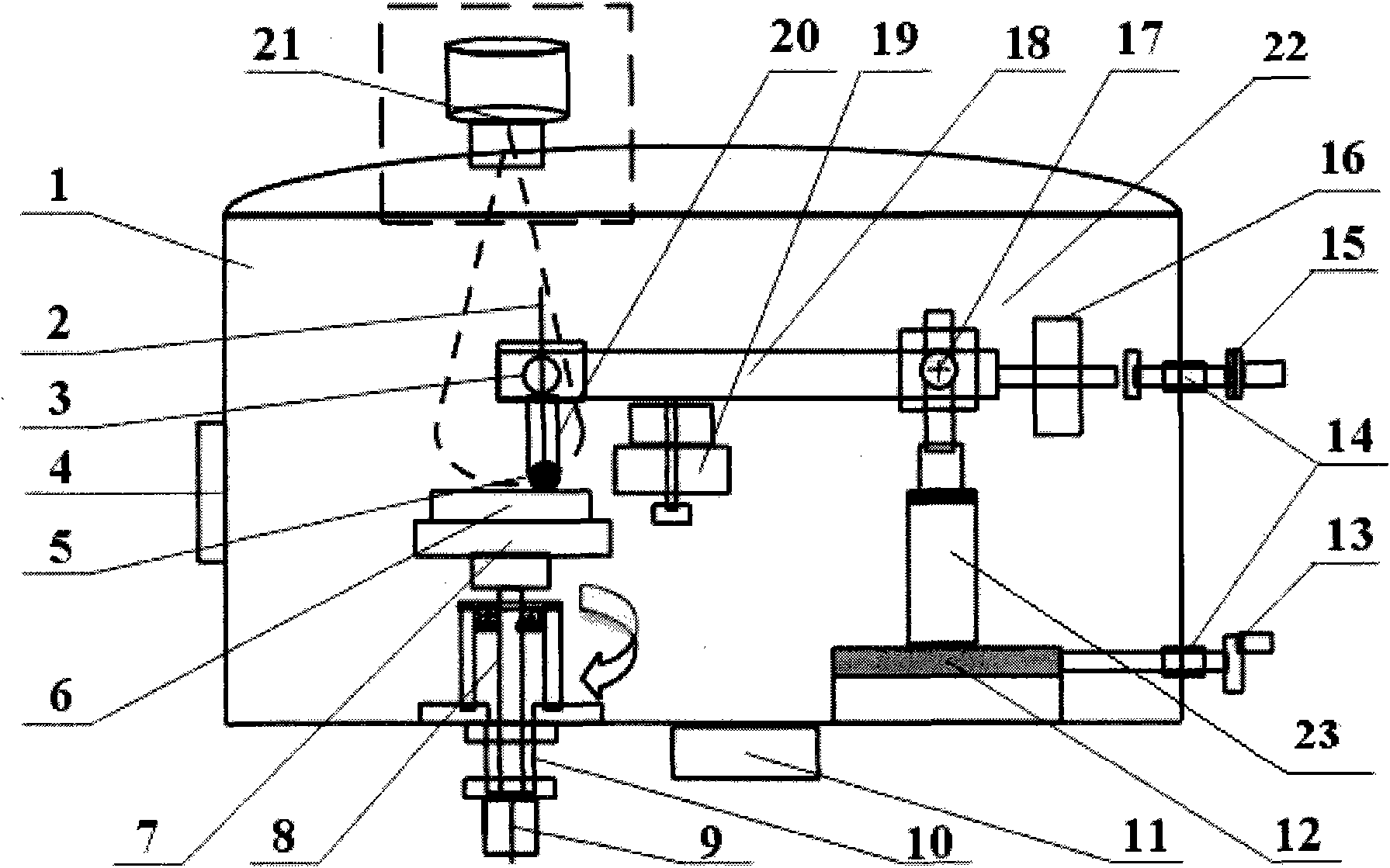
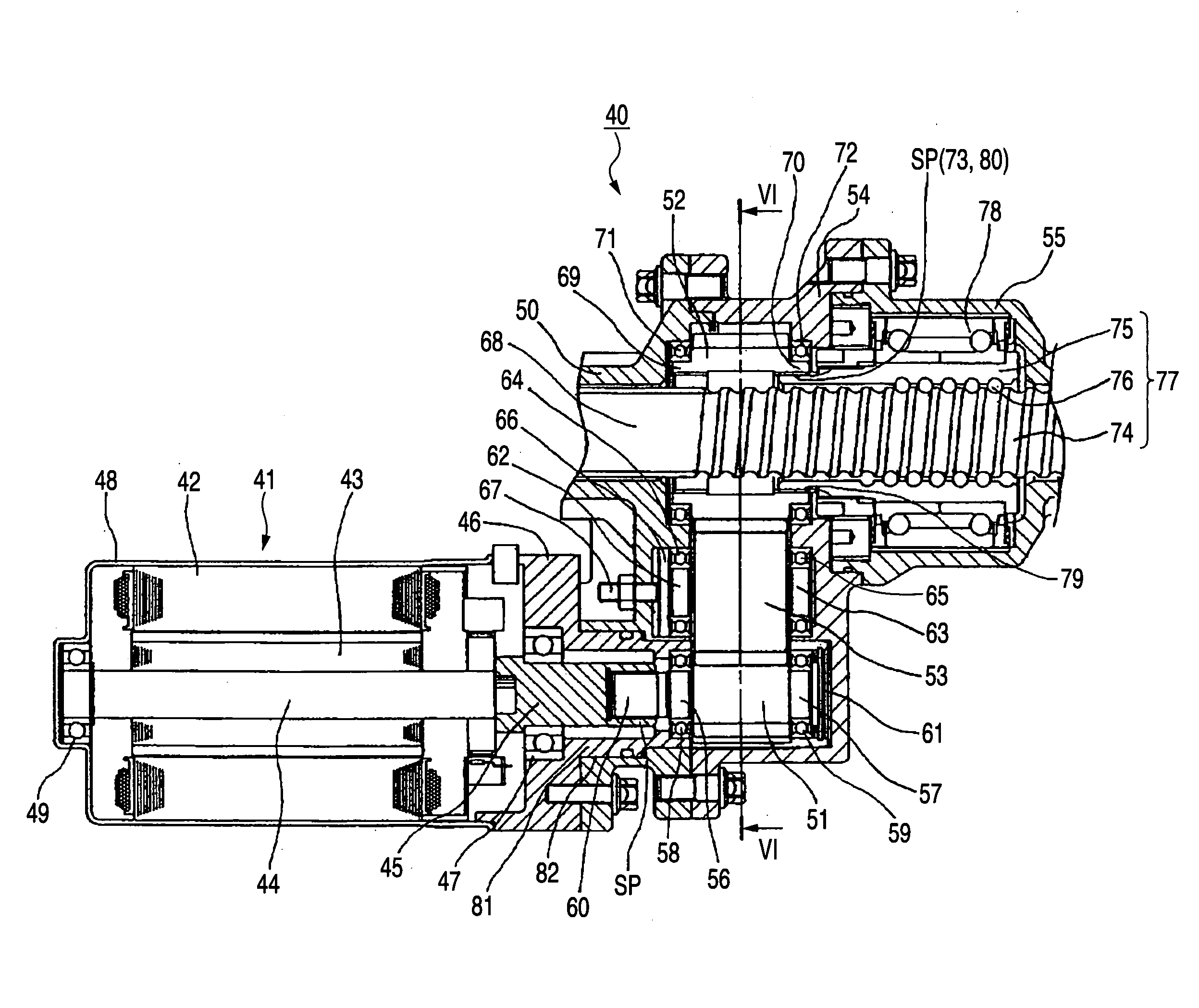
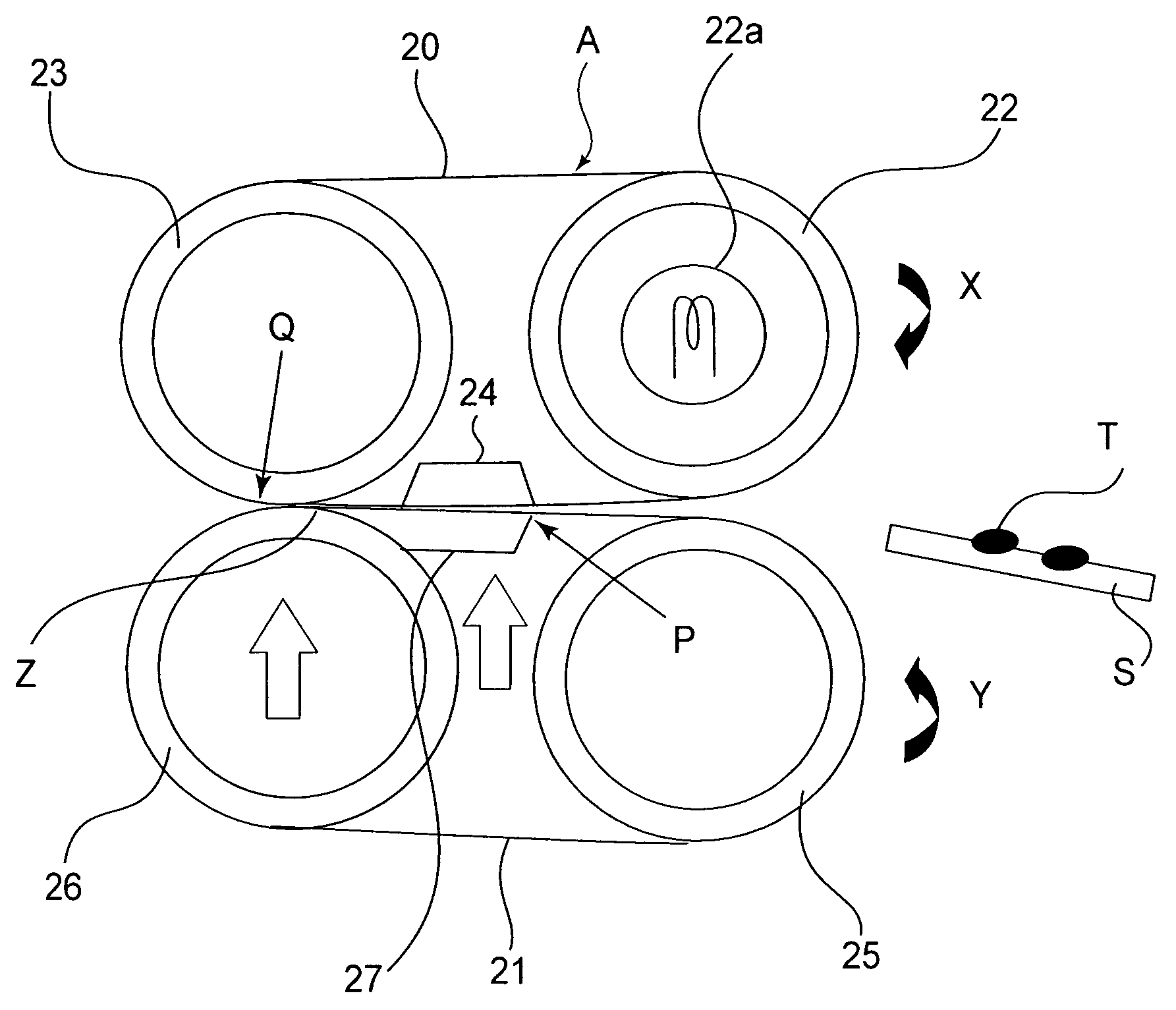
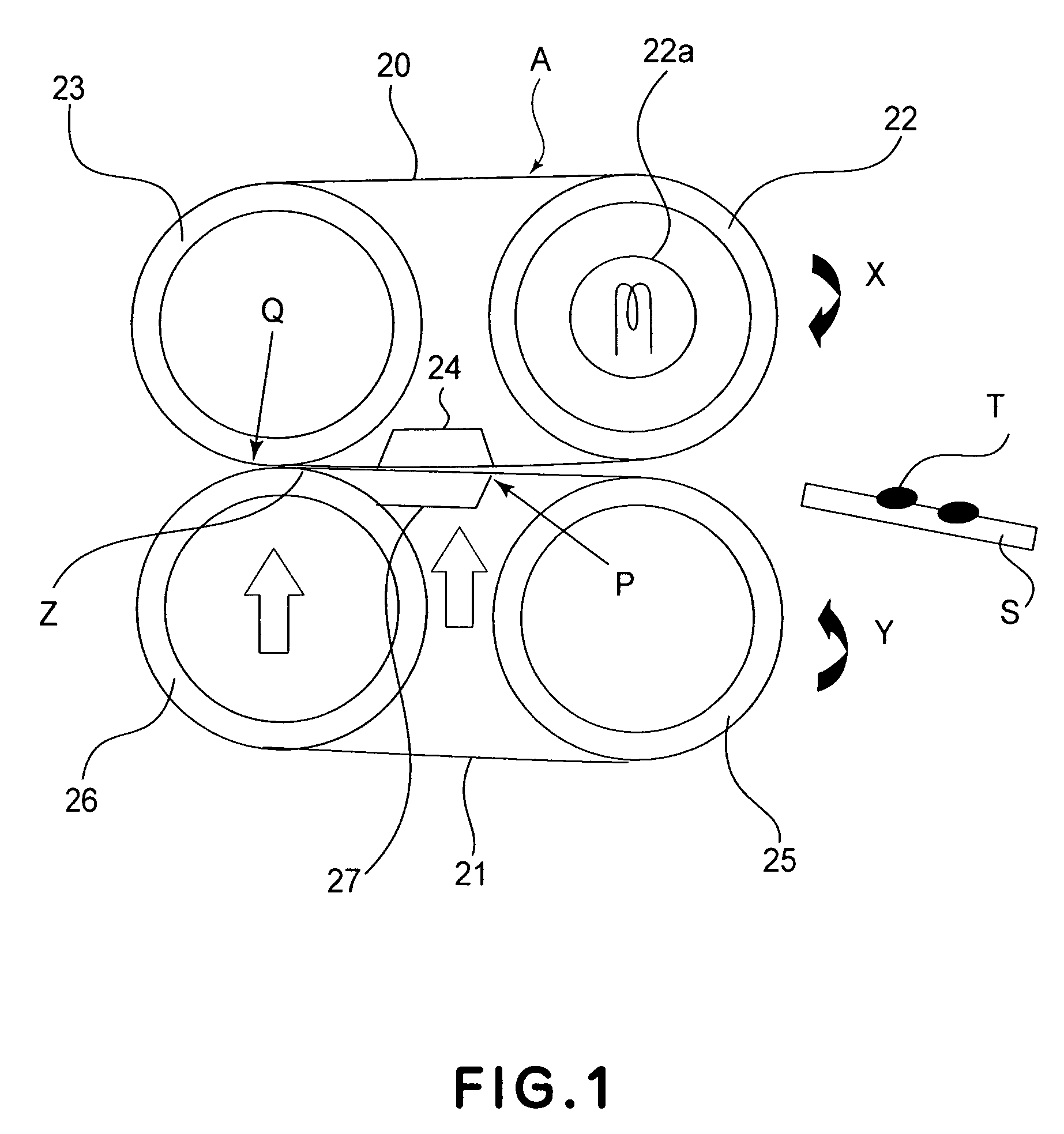
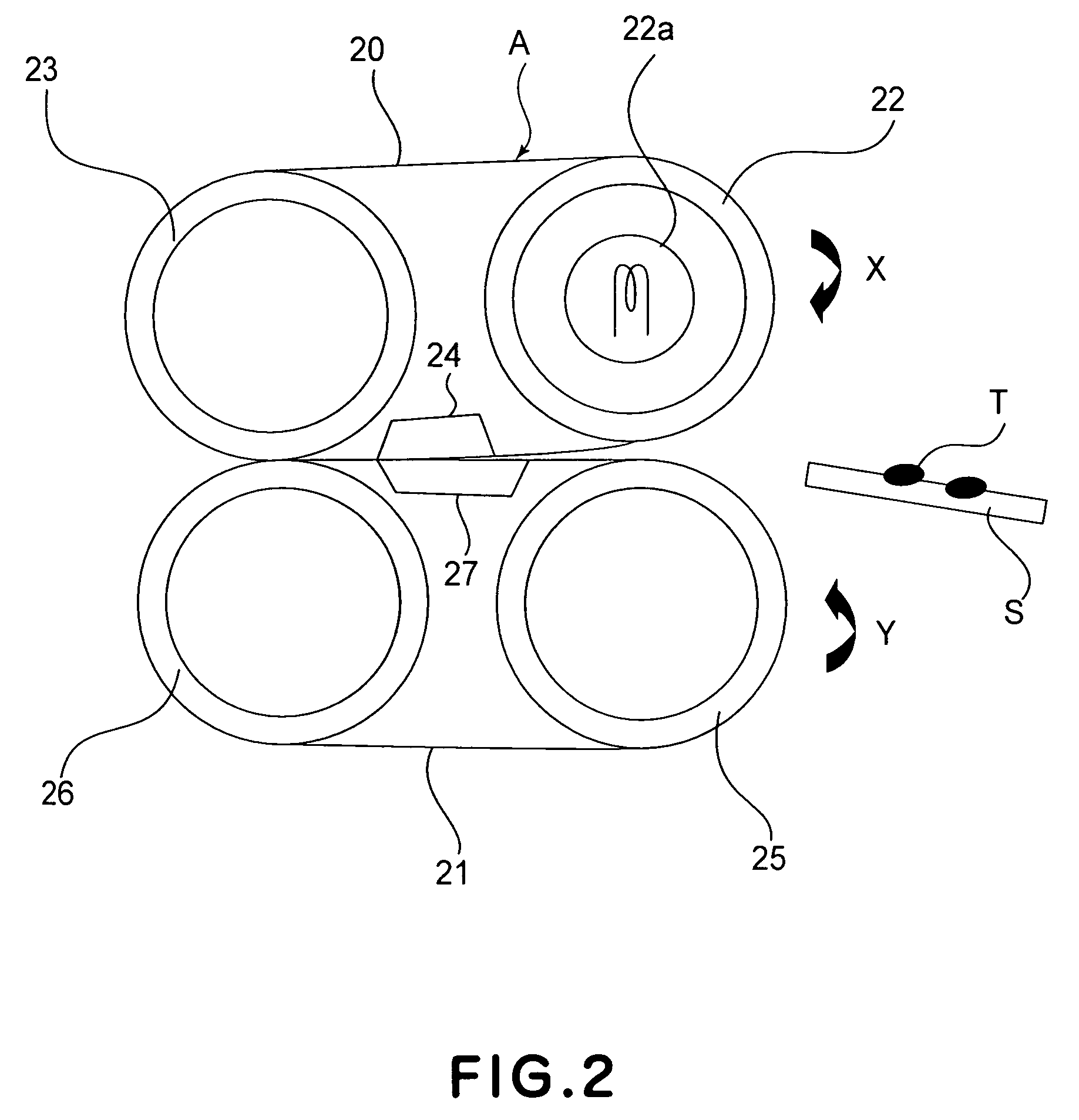
Multifunctional vacuum friction and wear testing machine
ActiveCN102759489APrecise position adjustmentAvoid time costInvestigating abrasion/wear resistanceDrivetrainEngineering
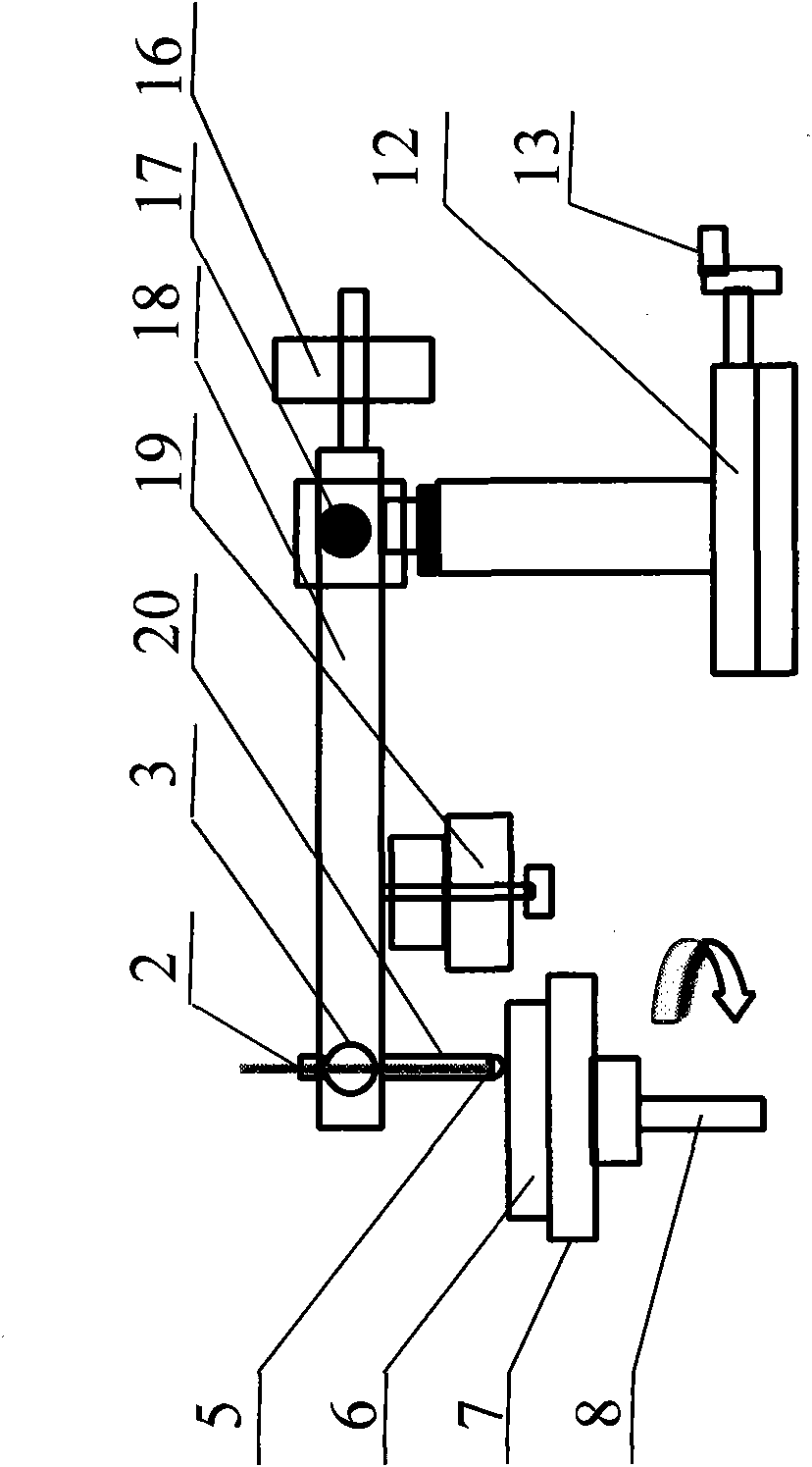
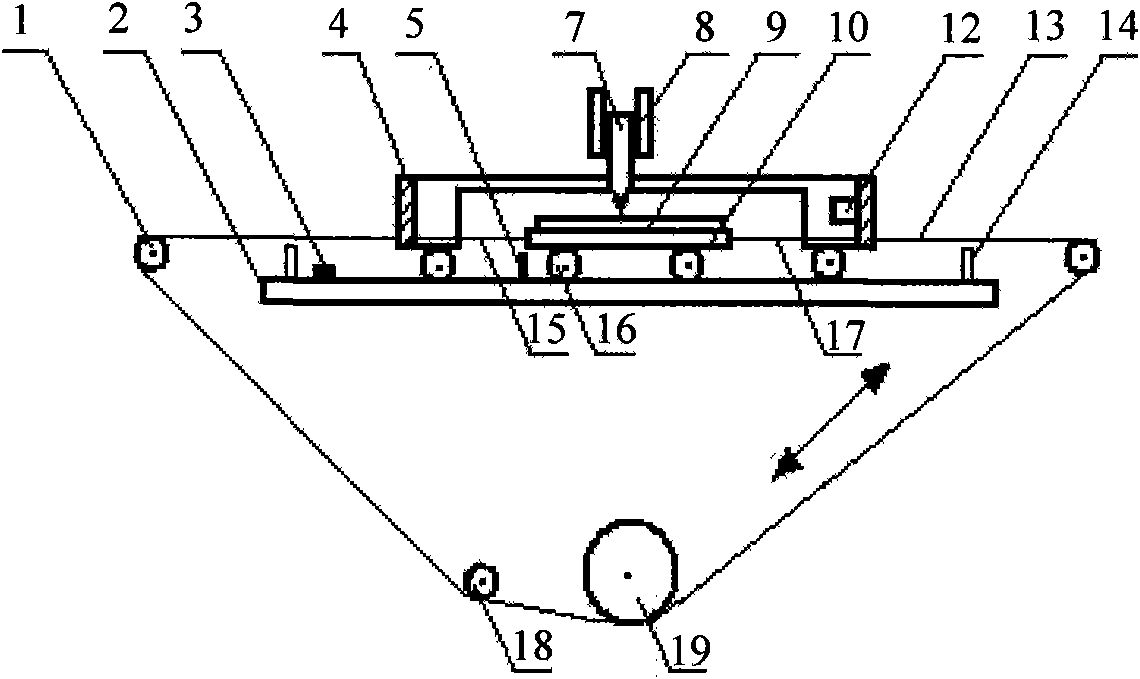
The invention provides a multifunctional vacuum friction and wear testing machine, which not only can simulate special environmental atmospheres such as vacuum, radiation and corrosion, but also can conduct tribology tests in a relatively wide speed and load range by using various contact manners (ball-disc and pin-disc). The multifunctional vacuum friction and wear testing machine mainly comprises a vacuum system, a friction and wear system, a power transmission system, a control system, and the like, wherein the friction and wear system comprises a lever structure (22) used for fixing a test sample fixture (20) and capable of freely rotating in a horizontal direction and a vertical direction; the lever structure (22) comprises a cantilever beam (18) and a vertical arm (23) which are arranged in a perpendicular manner; the cantilever beam (18) is connected with the vertical arm (23) through a two degree of freedom bearing structure (17); positions of the cantilever beam (18) and the vertical arm (23) can be adjusted in the horizontal direction and the vertical direction through the control of a manipulator (15) and a hand wheel structure (13), so that the test sample fixture (20) can accurately move within two degrees of freedom; and a temperature sensor (2) and a pressure sensor (3) are mounted on the test sample fixture (20), so as to detect / monitor friction coefficients and temperature variations during the tribology tests.
Owner:ACADEMY OF ARMORED FORCES ENG PLA
Method for Controlling Vehicle Dynamics
InactiveUS20100114431A1Improve accuracy and reliabilityBrake system interactionsSteering initiationsVehicle dynamicsRoad surface
A method for controlling vehicle dynamics includes acquiring steering torque data indicative of forces acting on at least one tire of a vehicle and acquiring image data by capturing images of an area outside the vehicle. The friction coefficient between a tire of the vehicle and a road surface is determined as a function of vehicle data including at least the steering torque data. The lateral velocity of the vehicle is determined as a function of vehicle data including the steering torque data and / or the image data. A vehicle dynamics control is performed as a function of the lateral velocity and the friction coefficient.
Owner:VOLKSWAGEN GROUP OF AMERICA
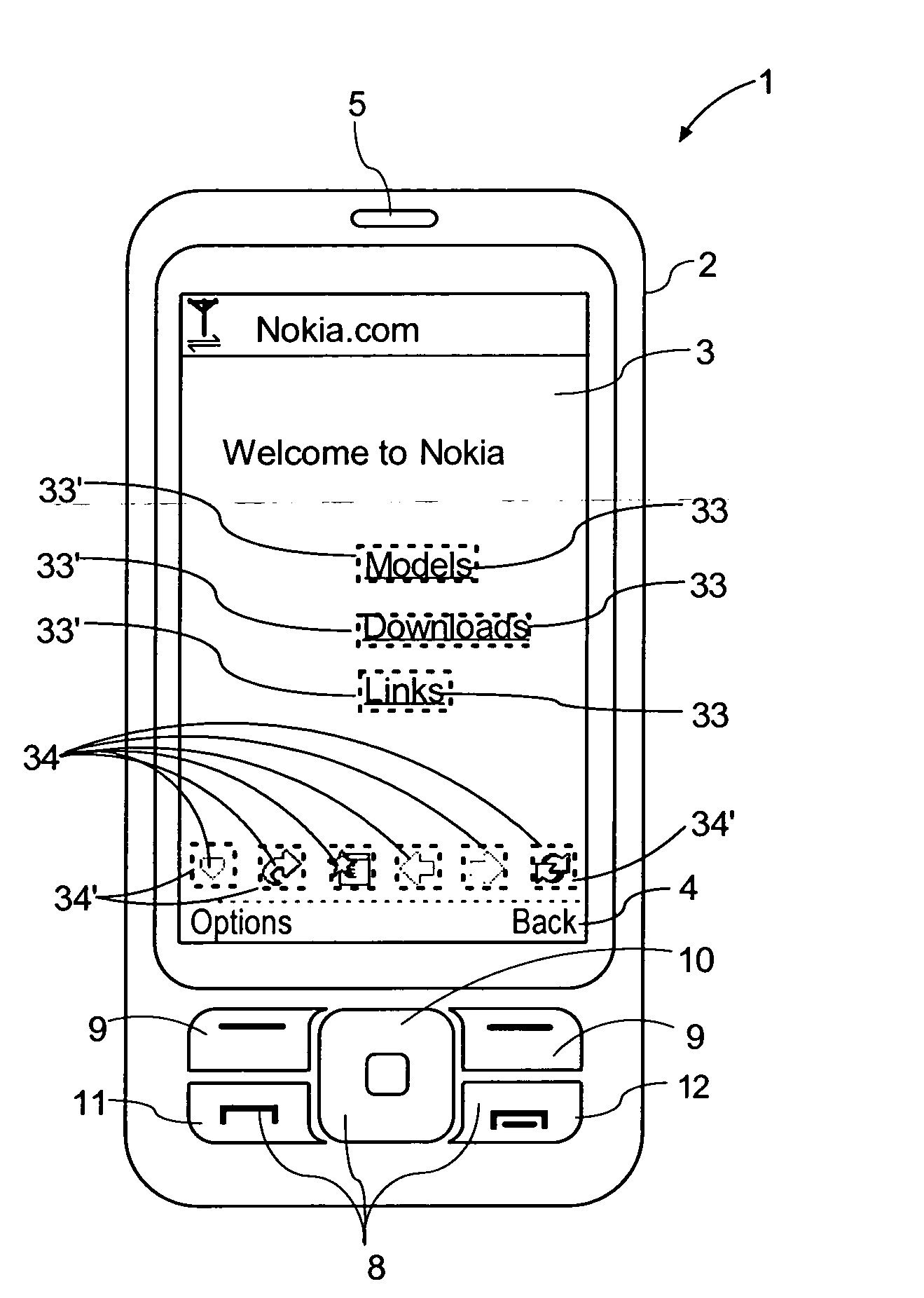
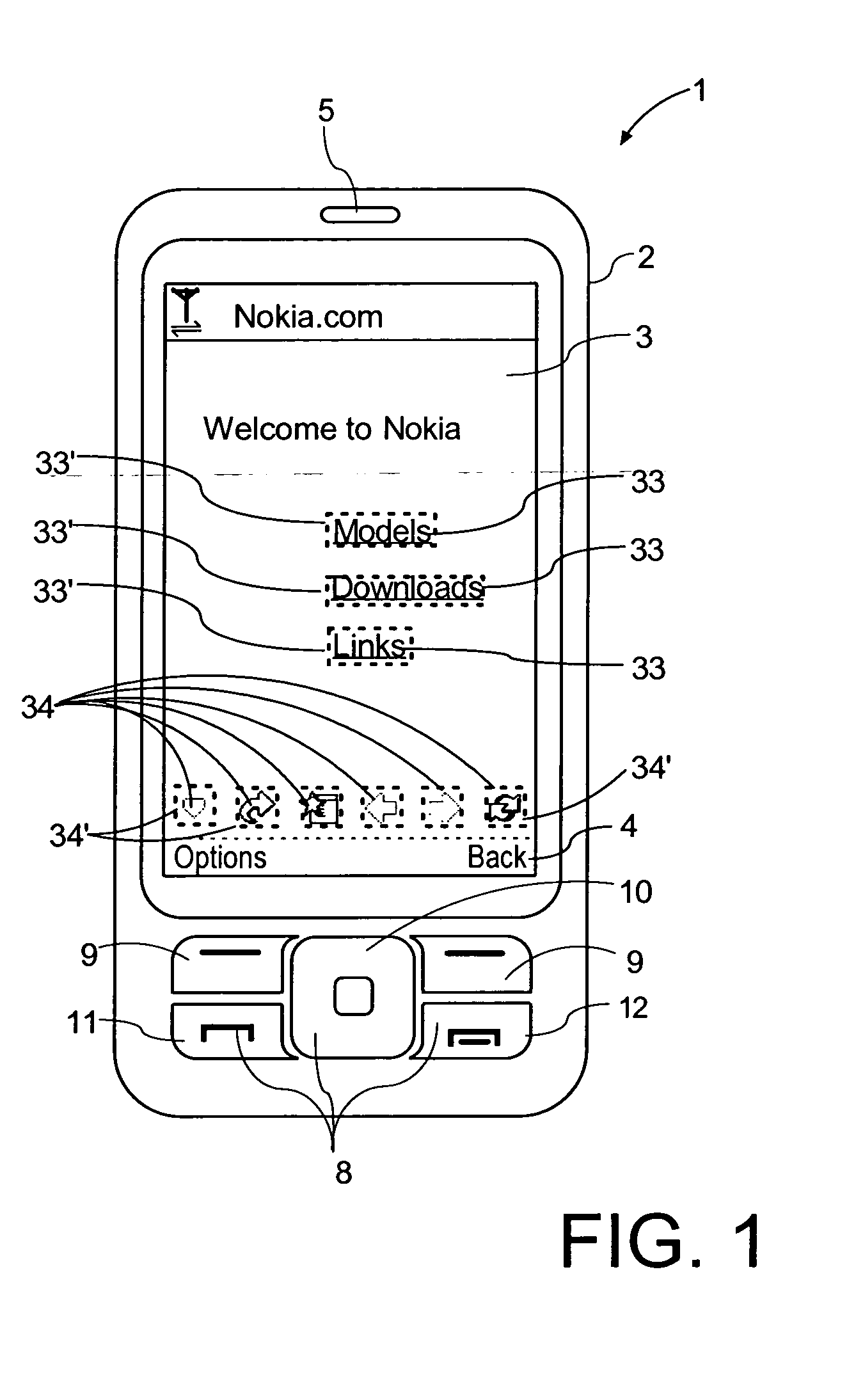
Tactile Touch Screen
InactiveUS20100315345A1Increased and lowered frictionIncreased and lowered and roughnessInput/output processes for data processingTouch SensesDisplay device
A touchscreen including a touch sensitive layer wherein the user perceived surface roughness or friction coefficient is variable and dynamically controlled. The level of user perceived surface roughness or friction coefficient is related to the information that is displayed at the position at which an object touches the touch sensitive layer. The surface roughness is not locally changed but rather for a complete portion of the touchscreen or for the whole touchscreen simultaneously. Because the modulation of user experience surface roughness or friction coefficient is faster than the user interaction, the user will experience that the surface roughness of certain areas of the display is different from other areas, depending on the information that is being shown, although in fact the surface roughness or friction coefficient is uniform over the whole portion or the whole display at any given point of time.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Nanoparticle additives and lubricant formulations containing the nanoparticle additives
ActiveUS20080161213A1Reduce frictionReduce wearMaterial nanotechnologyCerium oxides/hydroxidesNanoparticleBase oil
A method for reducing a friction coefficient adjacent a lubricated surface, and a lubricant composition for reducing a friction coefficient between lubricated surfaces. The method includes providing an amount of metal-containing dispersed in a fully formulated lubricant composition containing a base oil of lubricating viscosity, wherein the nanoparticles have an average particles size ranging from about 1 to about 10 nanometers. The lubricant composition containing the metal-containing nanoparticles is applied to a surface to be lubricated.
Owner:AFTON CHEMICAL
Device and method for testing linear reciprocating sliding friction and abrasion
InactiveCN101556238AAdjustable sliding speedAdjustable loadUsing mechanical meansMaterial weighingPositive pressurePeak value
The invention discloses a device and a method for testing linear reciprocating sliding friction and abrasion; the device consists of a transducer, a workbench, a sample table, a dragging frame, a force sensor, a changeover switch, a counter, a locking device, a guideway, a baffle, a cable wire, a reducer, a peak value stabilizer, a control part and an auxiliary component; the equipment can automatically complete the abrasion test of an arranged period and can manually complete the test to friction coefficient. The testing method comprises the following steps of: leading the friction block and the sample to reciprocate to slide horizontally with constant pressure, obtaining an abrasion weight loss rate after abrading, keeping a certain positive pressure and leading the sliding block to move from stillness to uniform movement, thus obtaining the maximum static friction coefficient and the sliding friction coefficient. The device and the method can realize uniformly linear and reciprocating relative sliding abrasion in long unidirectional journey, test the maximum static friction coefficient between two bodies and the maximum static friction coefficient, the speed, the load and the adjustable journey with other materials, and can be widely applied to the detection of various samples of different materials and different structural forms.
Owner:725TH RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING INDAL CORP
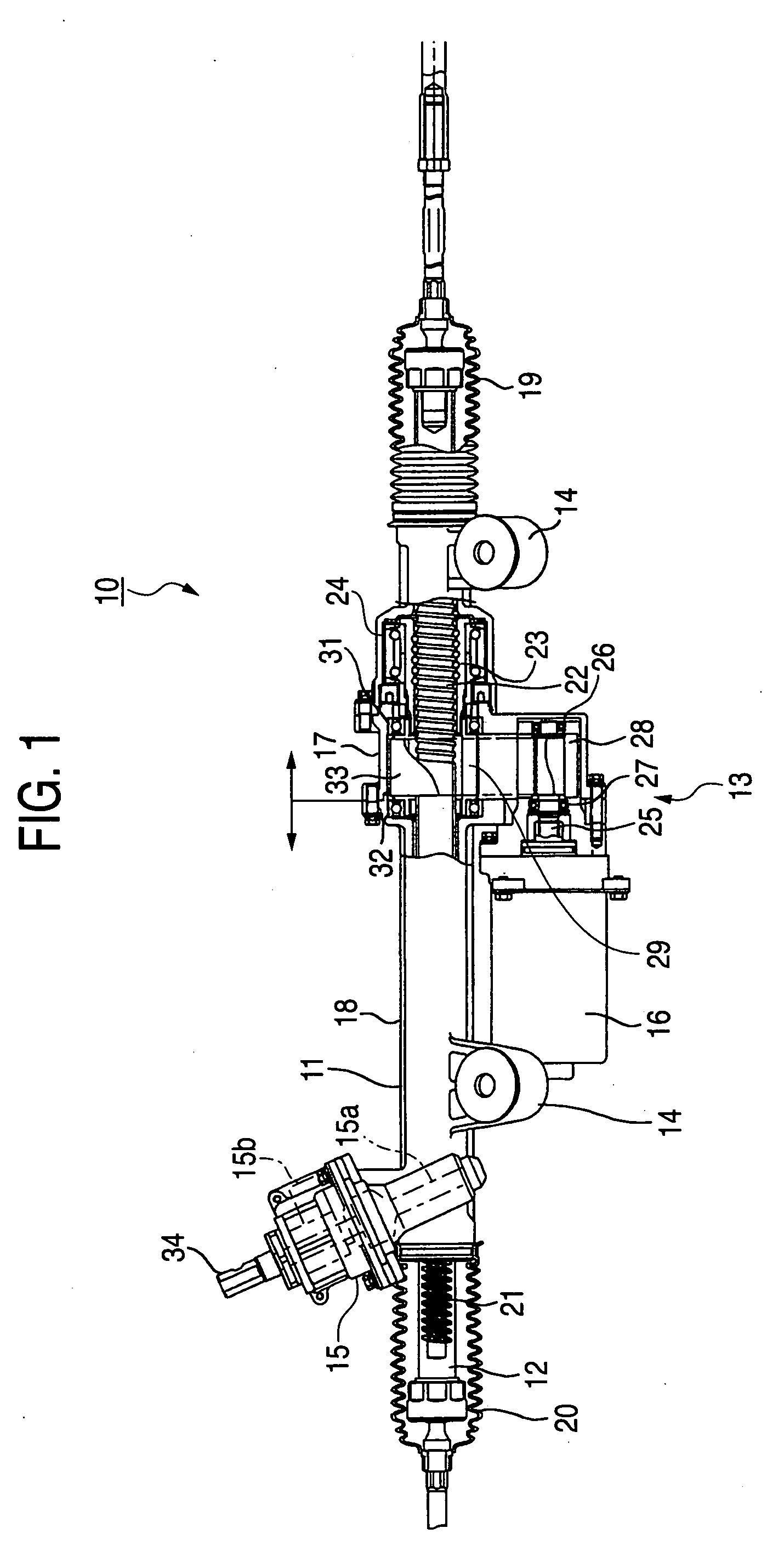
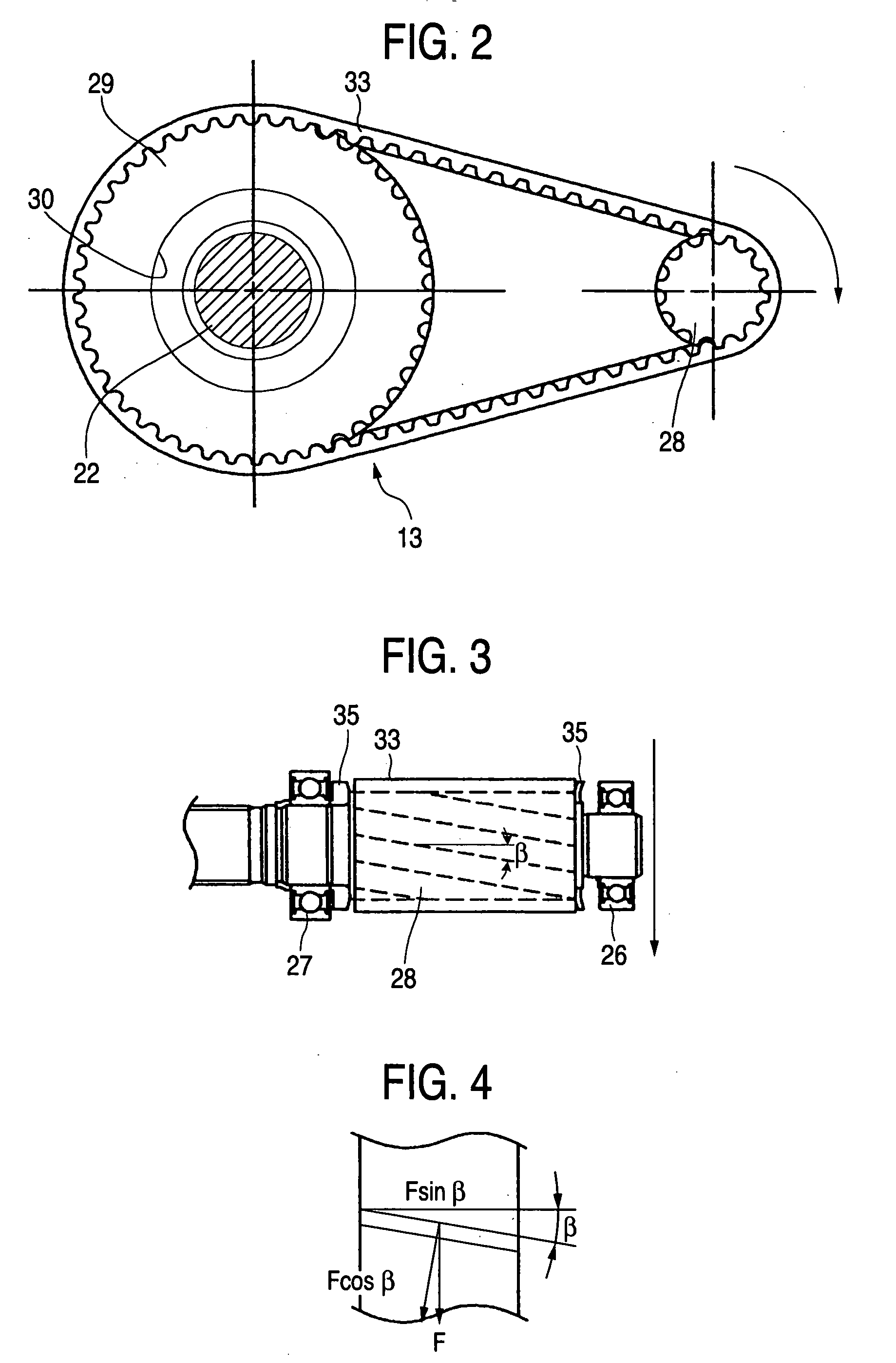
Belt speed reducing apparatus for electric power steering apparatus and electric power steering apparatus
ActiveUS20050121251A1Improve driving durabilityIncrease the angleToothed gearingsElectrical steeringElectric power steeringBelt speed
A belt speed reducing apparatus for an electric power steering apparatus includes a drive pulley having a first helical gear, a driven pulley having a second helical gear and a drive belt having a third helical gear in which a relationship of tan β<μ is established between a twist angle β of the respective helical gears and a friction coefficient μ between the first or the second helical gear and the third helical gear. Further, an electric power steering apparatus for adjusting a backlash between gears of a speed reducing apparatus brought in mesh with each other or adjusting a tension of a belt of a speed reducing apparatus.
Owner:NSK LTD +1
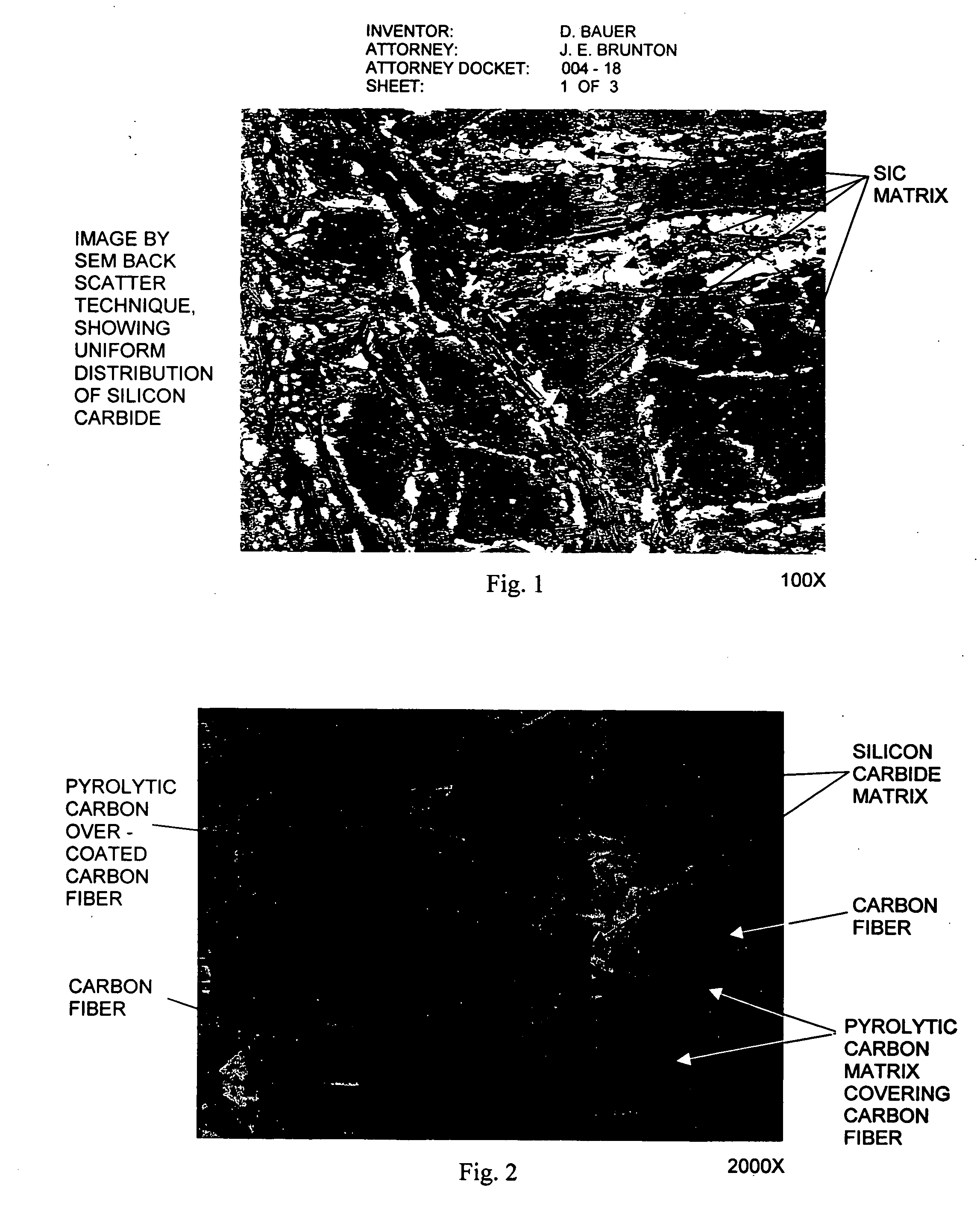
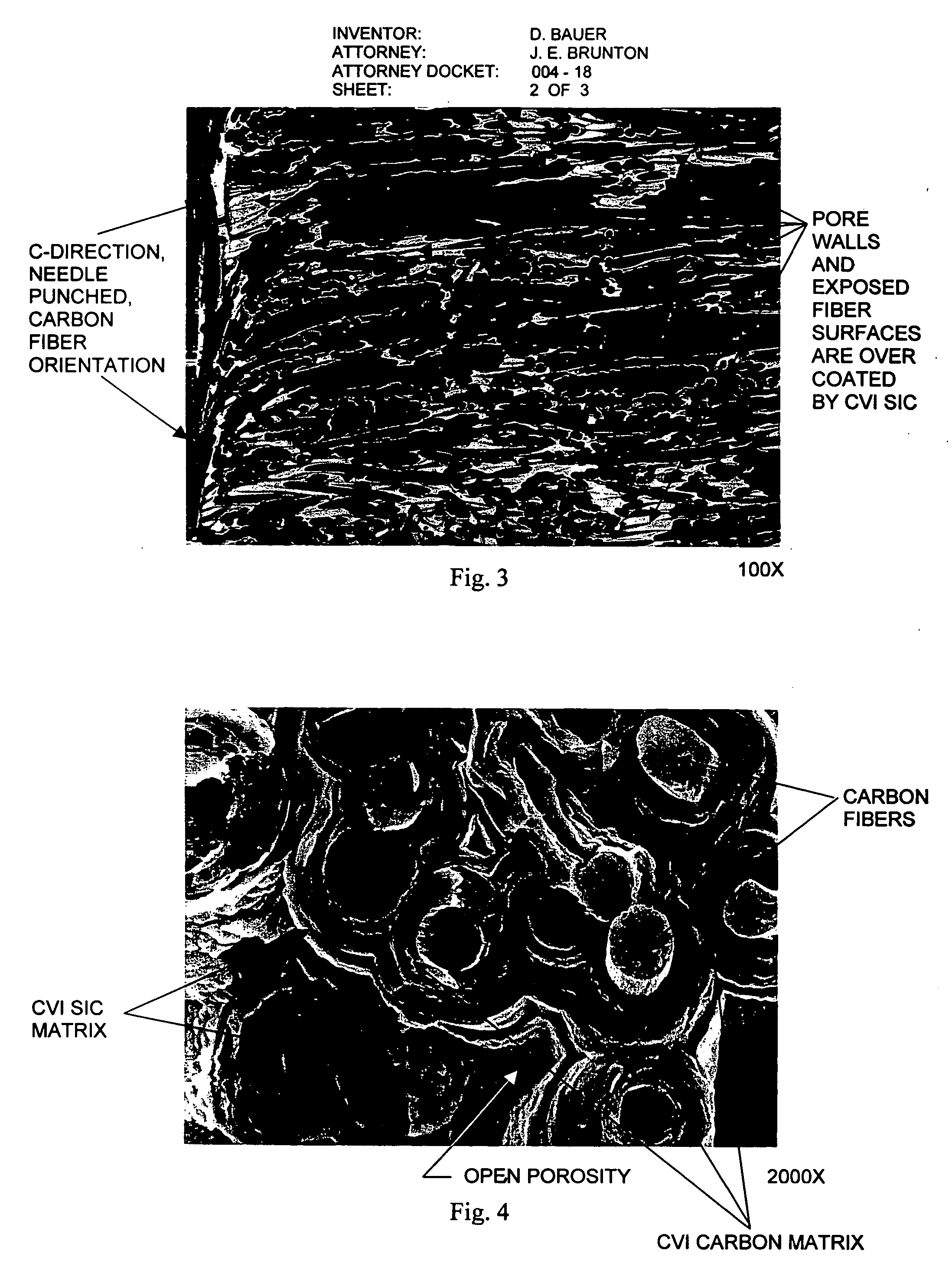
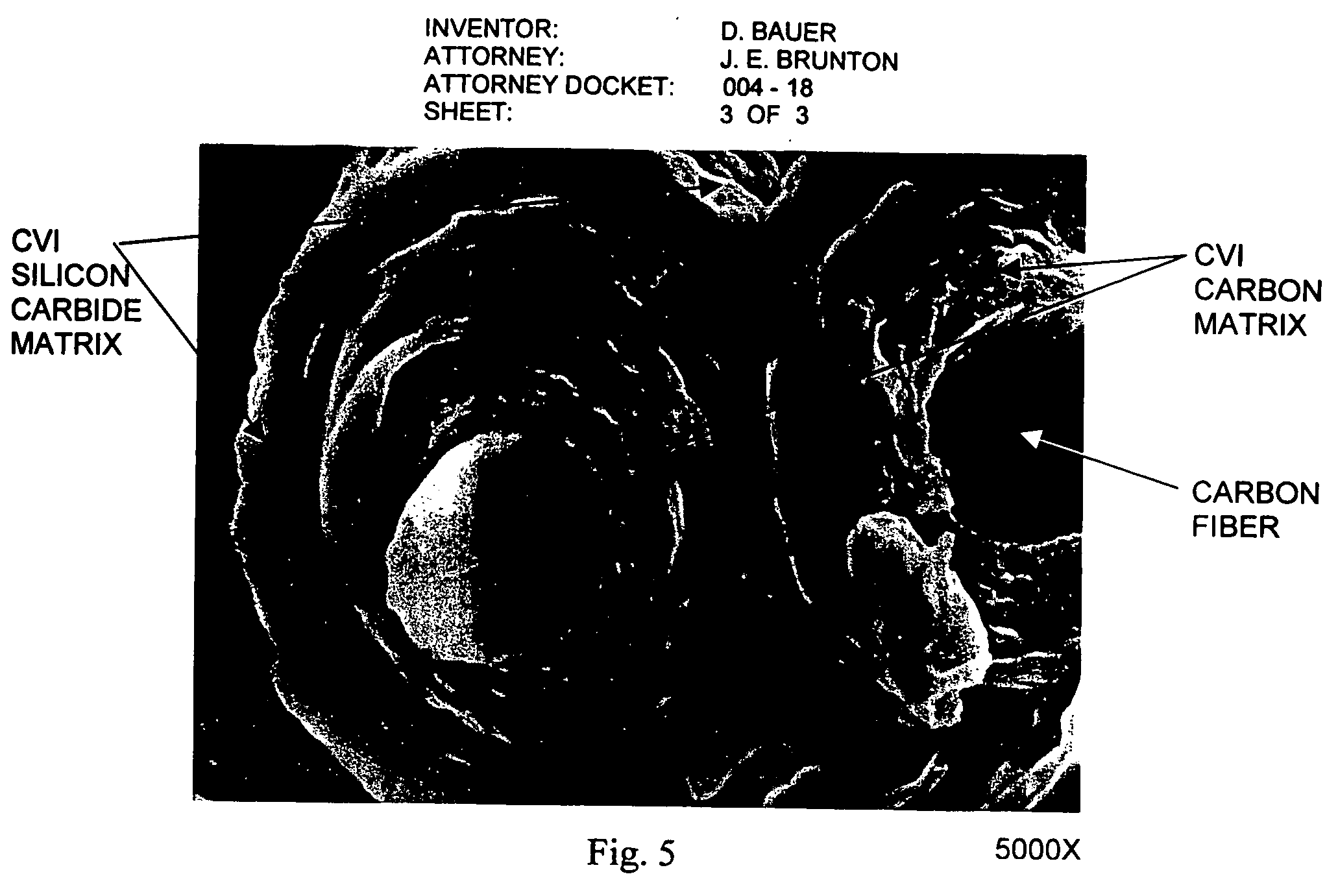
Carbon/ceramic matrix composites and method of making same
InactiveUS20060151912A1Improve performanceOptimization of coefficientWood working apparatusCeramic shaping apparatusCarbon compositesHeat treated
Owner:BAUER DIETER
Toner, method for manufacturing the toner, developer including the toner, container containing the toner, and image forming method and apparatus and process cartridge using the toner
An image forming method including forming an electrostatic latent image on an image bearing member; developing the electrostatic latent image with a developer including a toner to prepare a toner image on the image bearing member; transferring the toner image onto a receiving material; and cleaning the surface of the image bearing member with a cleaning blade; wherein a surface of the image bearing member has a friction coefficient of from 0.10 to 0.40, and wherein the toner has an average circularity of from 0.97 to 1.00 and includes toner particles and a particulate material having an average particle diameter of from 0.03 to 1 μm, wherein the particulate material is externally added to the toner particles by a wet method.
Owner:RICOH KK
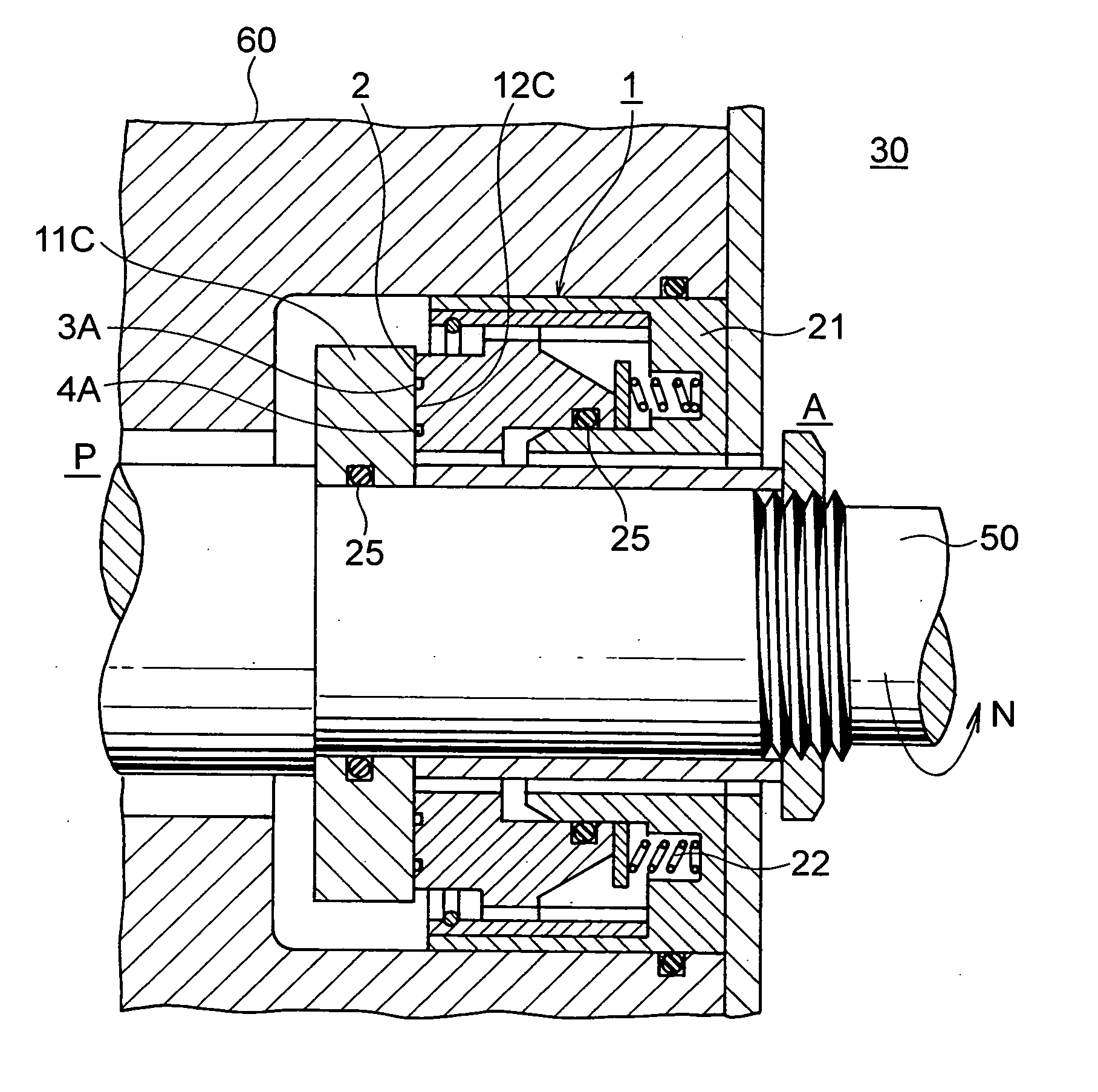
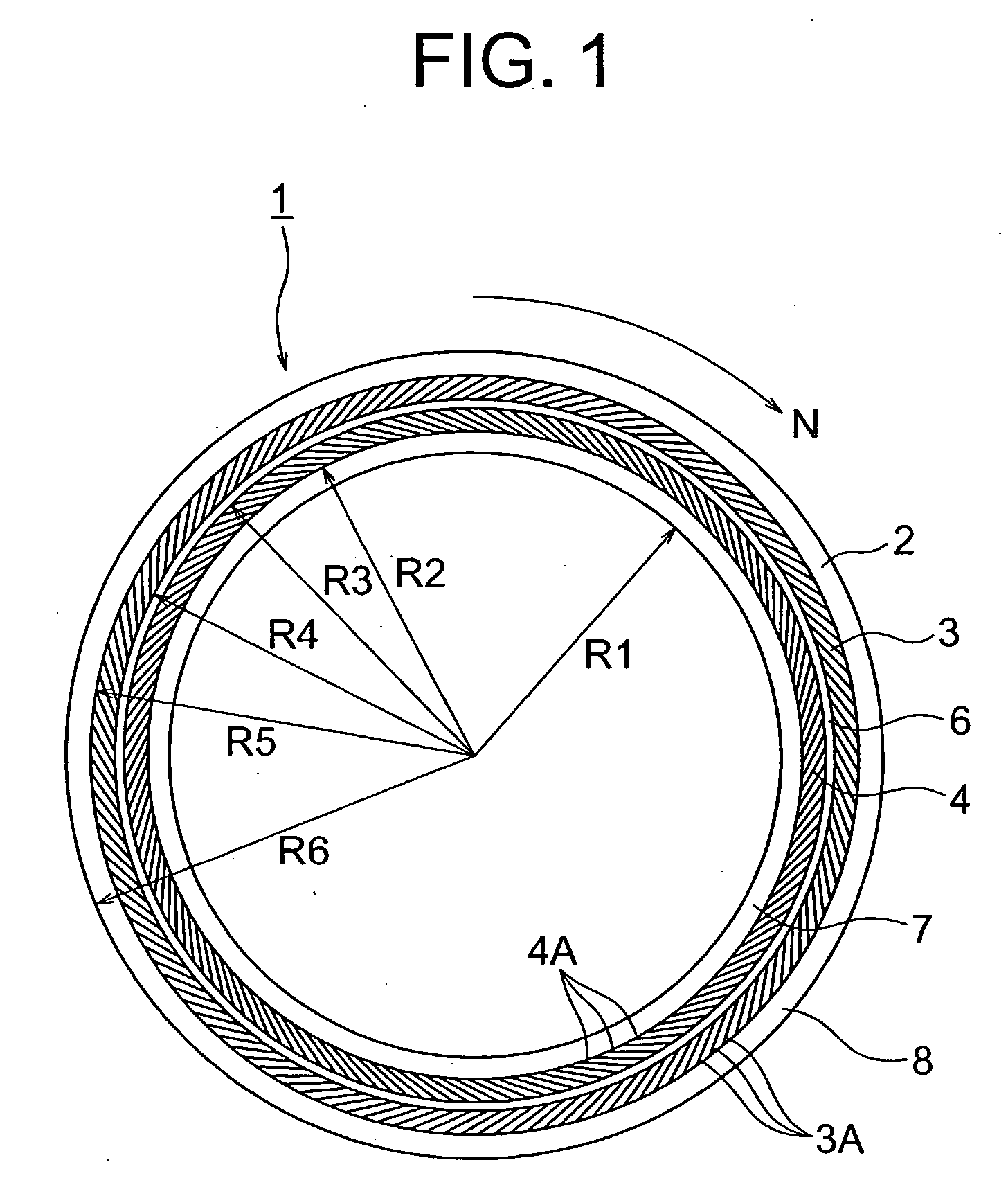
Sliding element
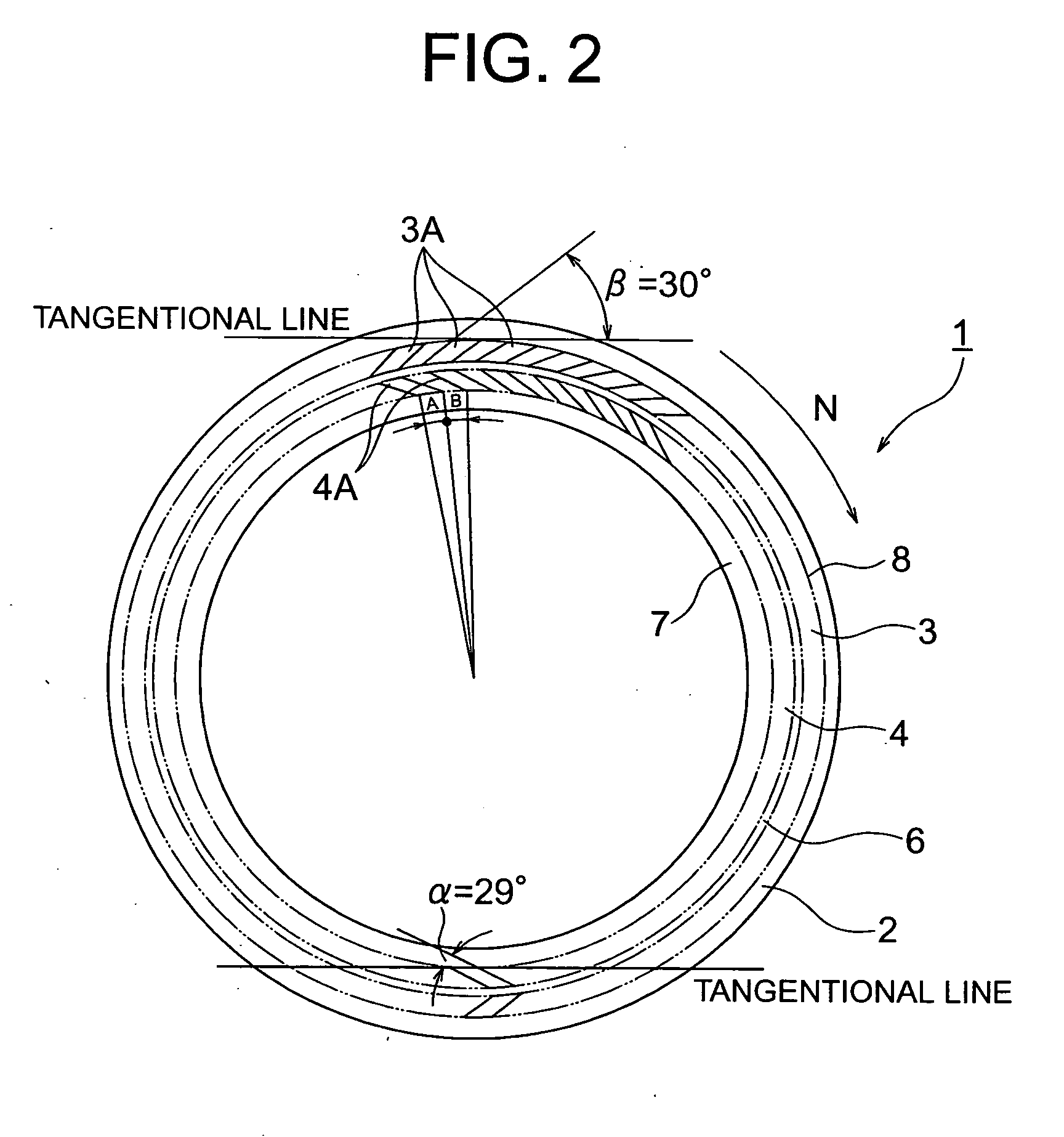
A primary objective of a sliding element of the present invention is to decrease a friction coefficient of the sliding face and to improve seal performance thereof. The sliding element comprises a first dam section (6) which is configured in an annular form on the sliding face (2), a second dimple section (3A) which has a form of a narrow groove and makes an inclination angle (α) being measured from the dam section (6) in a direction of rotation pointing toward the sealed fluid, a suction means (3) which includes an annularly arranged array of the second dimple sections (3A), a first dimple section (4A) which has a form of a narrow groove and makes an inclination angle (α) being measured from the dam section (6) in a direction of rotation pointing an opposite direction relative to the suction means (3), a discharge means (4) which includes an annularly arranged array of the first dimple sections (4A), and a seal face (7) which is disposed in a peripheral surface adjacent to the discharge means (4) and in the opposite side relative to the dam section (6).
Owner:EAGLE INDS
Tube for installing an optical fiber unit having a lubricous surface
InactiveUS20070098340A1Easy to installHigh strengthOptical fibre/cable installationFibre mechanical structuresEngineeringLubricant
Disclosed is a tube for installing an optical fiber unit having lubricous surface, which is installed in a communication pipe. The tube for installation includes an inner layer having lubricant components to decrease friction against an optical fiber unit, and an outer layer provided around the inner layer and composed of polymer having a lower friction coefficient than polyethylene so as to decrease friction when the tube is installed in the communication pipe. The tube is easier to install than the conventional one due to decreased friction against the communication pipe.
Owner:LG CABLE LTD (KR)
Environmental ceramic base friction material free of copper or metal and preparation method of material
InactiveCN103881657AGood mechanical skeleton performanceStable coefficient of frictionOther chemical processesFriction liningSulfurMetallic sulfide
The invention discloses an environmental ceramic base friction material free of copper or metal and a preparation method of the material. The environmental ceramic base friction material is characterized by comprising the following components by weight percent: 6-12% of phenolic resin, 2-10% of ceramic fiber, 2-8% of inorganic fiber, 2-10% of rubber, 4-12% of graphite, 10-25% of potassium titanate lamella, 3-15% of mineral fiber, 4-20% of metal sulfur compound, 6-20% of grinding aid and 5-20% of filler. The prepared friction material has excellent friction and wear properties, high heat-conducting property, excellent high-temperature decline property, stable friction coefficient, and excellent noise performance.
Owner:YANTAI SHENGRUI BRAKE SYST
Graphene-nano polytetrafluoroethylene composite filler as well as preparation method and application thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of friction material, and in particular relates to a graphene-nano polytetrafluoroethylene composite filler with a function of reducing friction, as well as a preparation method and the application of the composite filler. The composite filler comprises the following main components in parts by weight: 1 part of modified graphene and 1-20 parts of modified nano polytetrafluoroethylene; the preparation method of the composite filler comprises the following steps: separately reacting graphene and nano polytetrafluoroethylene with amination reagent and carboxylation reagent to obtain the modified graphene and the modified nano polytetrafluoroethylene; carrying condensation reaction so that the modified graphene and the modified nano polytetrafluoroethylene are connected with each other by a covalent bond to obtain the graphene-nano polytetrafluoroethylene composite filler. The function of friction reduction of the graphene and the function of lubrication of the nano polytetrafluoroethylene are utilized at the same time; after the composite filler is added to a polymer material, the friction coefficient and the wear rate of the material can be reduced, and the mechanical property of the material can be improved.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Method for sterilizing a medical device having a hydrophilic coating
InactiveUS20020037943A1Reduce coefficient of frictionReduce the risk of infectionLavatory sanitoryCatheterHydrophilic coatingMedical device
A method for sterilizing a medical device comprising a hydrophilic coating using radiation said method comprising the steps of bringing the medical device-having such coating in contact with an aqueous liquid for wetting the hydrophilic coating, said liquid comprising a solution of a hydrophilic polymer and sterilizing the device by applying a sufficient amount of radiation provides coated devices showing a significantly increased and prolonged water retention and lower friction coefficient when wet.
Owner:COLOPLAST AS
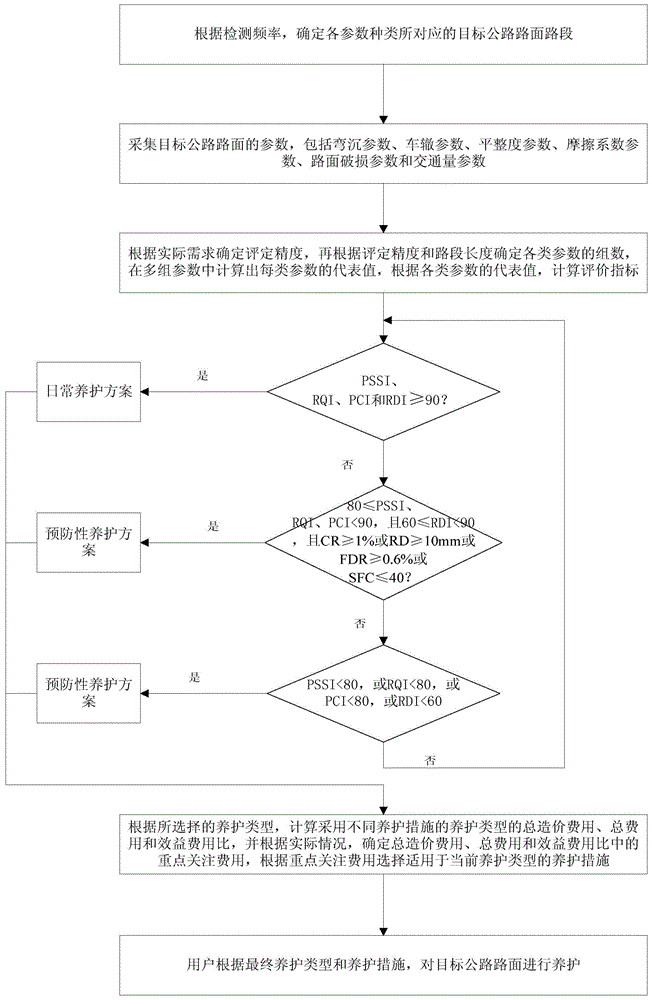
Modification scheme decision-making system and method for bituminous pavement
InactiveCN104463348AEasy to useSmall amount of calculationForecastingResourcesPavement maintenanceImage resolution
Owner:辽宁省交通科学研究院有限责任公司
Spherical calcium carbonate and method for producing thereof
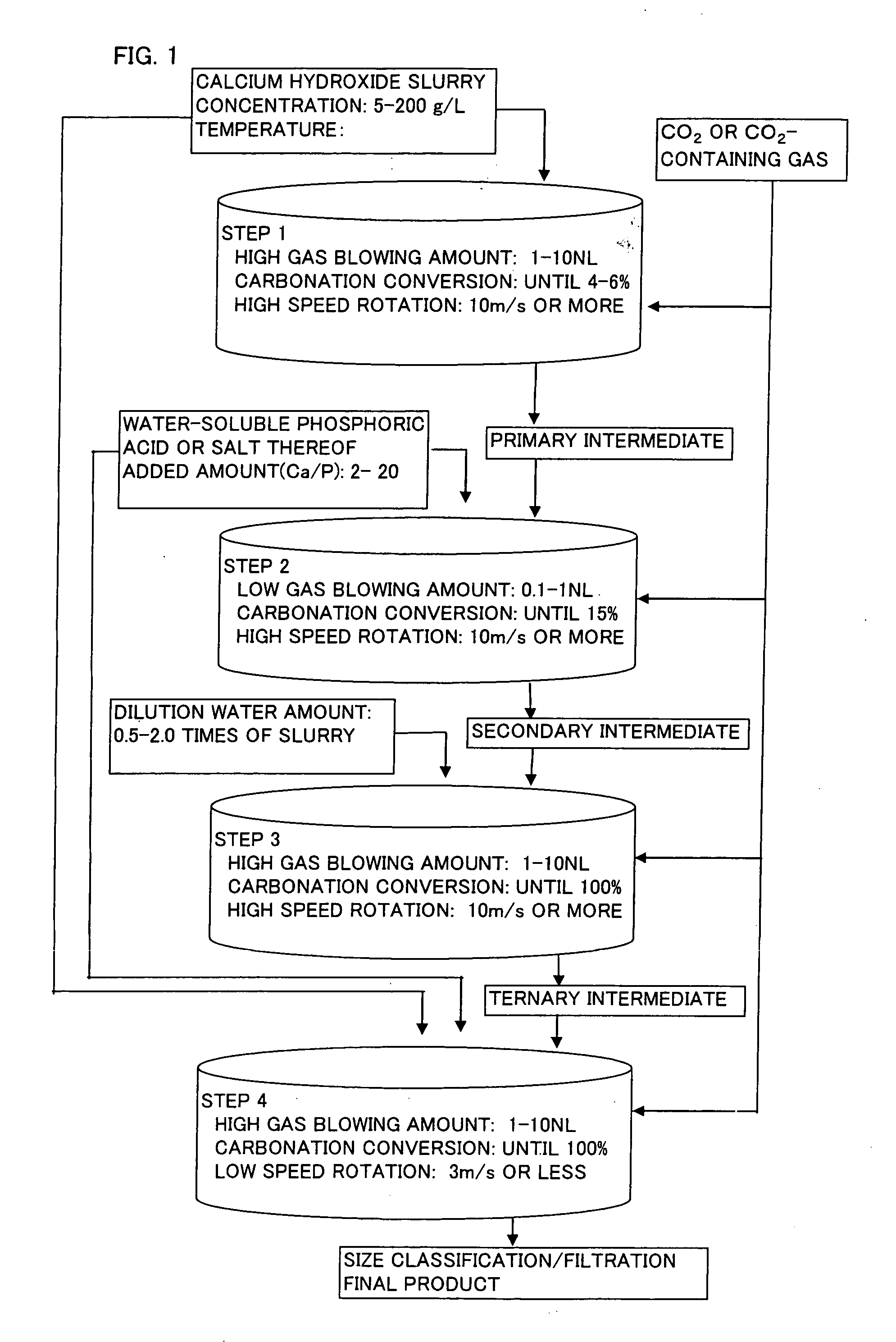
InactiveUS20060165583A1Inferior physical propertyLow blowing rateCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesCosmetic preparationsCalcium hydroxideO-Phosphoric Acid
When spherical calcium carbonate is produced by blowing a carbon dioxide gas or a carbon dioxide-containing gas into an aqueous suspension containing calcium hydroxide to react them, after start of the reaction, an aqueous solution or suspension of a water-soluble phosphoric acid compound or a water-soluble salt thereof is added to the reaction mixture when carbonation ratio reaches 2 to 10%, and the reaction is further allowed to continue at a low gas blowing rate of 1.0 NL / minute or lower (step (a)). Subsequently, an aqueous suspension containing calcium hydroxide and an aqueous solution or suspension of a water-soluble phosphoric acid compound or a water-soluble salt thereof are added to the reaction mixture, and a carbon dioxide gas or a carbon dioxide-containing gas is introduced to allow to react and thereby produce spherical calcium carbonate having a mean particle diameter of 10 μm or larger. This production method is performed under high velocity revolution from the start of the reaction to the end of the step (a) This method provides calcite type spherical calcium carbonate showing high brightness and small friction coefficient, and having a shape comparatively close to a true sphere and a mean particle diameter of 10 μm or larger.
Owner:OKUTAMA IND
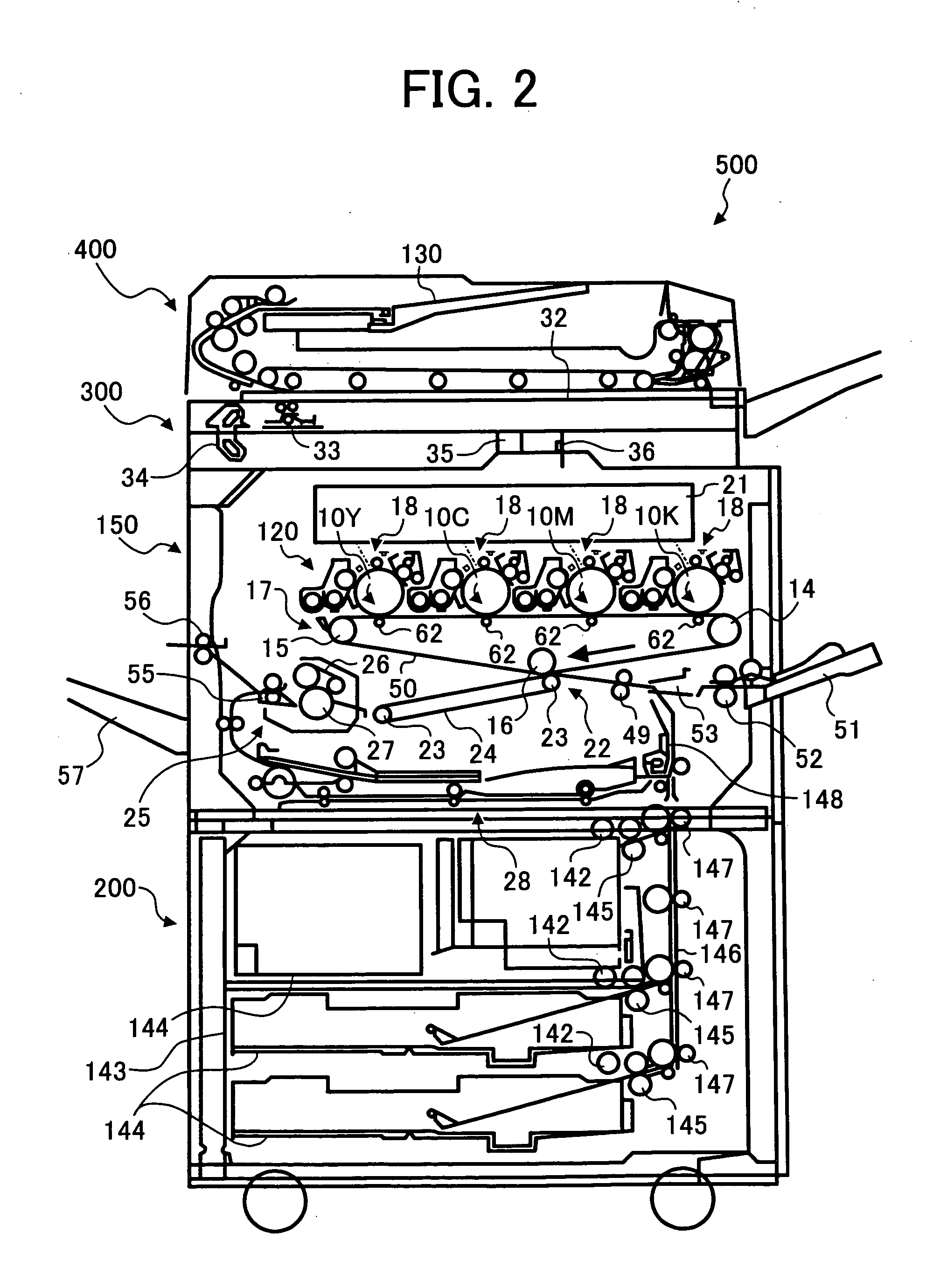
Image heating apparatus
An image heating apparatus comprising first and second belts for forming a nip for heating an image on a recording material; a first pressing pad for pressing the first belt at the nip; a first roller, provided spaced from the first pressing pad with a gap therebetween, for pressing the first belt at the nip; a second pressing pad, provided opposed to the first pressing pad, for pressing the second belt at the nip; a second roller, provided opposed to the first roller and contacted to the second pressing pad, for pressing the second belt at the nip, the second roller having a friction coefficient which is smaller than that of the first roller.
Owner:CANON KK
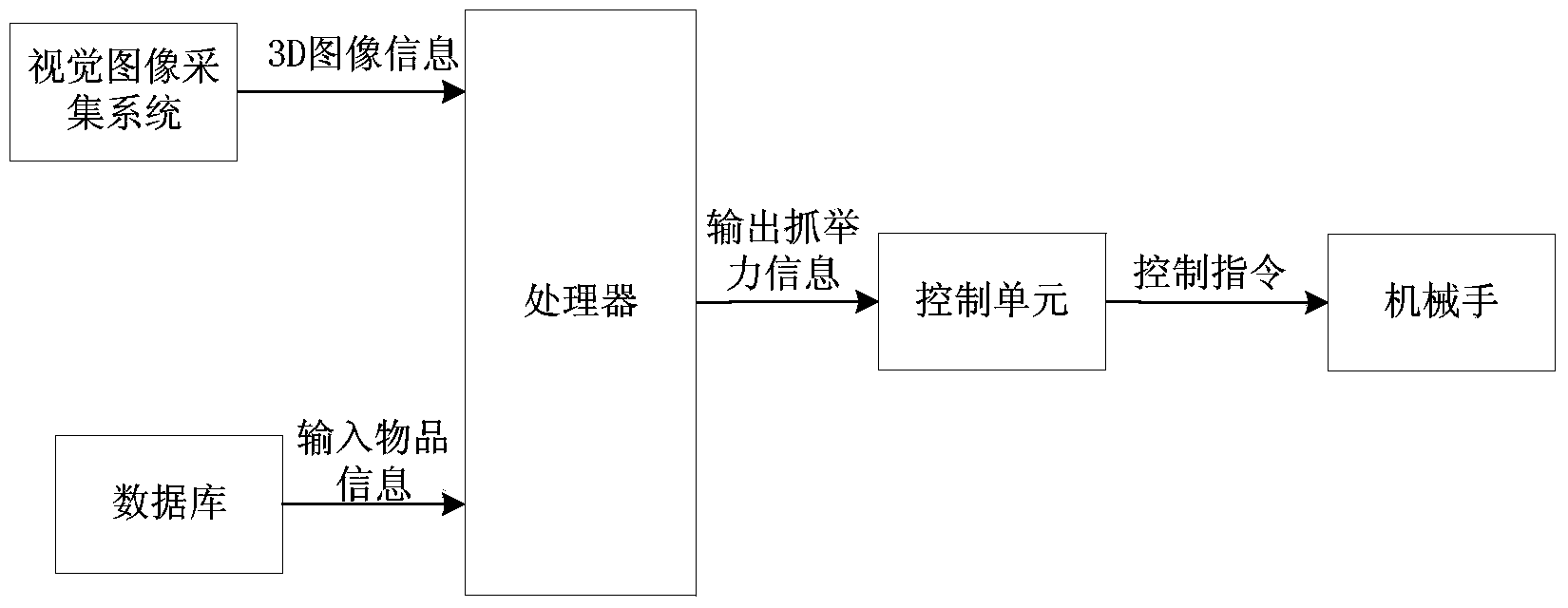
Method for intelligently adjusting manipulator and grasping force on basis of visual image analysis
InactiveCN103753585AAccurate Discrimination RatePrecise calculation of grip forceManipulatorImaging analysisManipulator
The invention relates to a method for regulating a manipulator and grasping force thereof. The manipulator comprises a vision image acquisition system and a database. The vision image acquisition system takes and acquires 3D (three-dimensional) entitative images of objects to be grasped by the manipulator, simultaneously scans dimension information of the acquired objects, acquires the volumes of the acquired objects and transmits the volumes of the acquired objects to a central processing unit; image data of various objects and parameters of the density, the roughness and friction coefficients of materials of the various objects are stored in the database; the central processing unit compares the acquired 3D entitative images to the image data in the database, judges the acquired 3D entitative images, determines the types, the dimensions and the volumes of the grasped objects, calls out the parameters of the density, the roughness and the friction coefficients of the corresponding materials of the grasped objects and outputs grasping and lifting force information to a control unit according to the parameters, and the control unit controls the grasping force and lifting force of the manipulator. The method has the advantages that the three-dimensional entitative images are acquired, and accordingly the grasping force required to be outputted by the manipulator can be accurately computed.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
Nano-carbon-reinforced wear-resistant composite material
The invention belongs to the technical field of materials, and specifically relates to a nano-carbon-reinforced wear-resistant composite material. The nano-carbon-reinforced wear-resistant composite material comprises the following components in percentage by mass: 55-99% of metal powder, 0.1-35% of ceramic powder, and 0.01-15% of nano-carbon, wherein the metal powder is used as a composite material matrix; the ceramic powder is used as a wear-resistant filling material; and the nano-carbon comprises single-wall carbon nano-tubes, multi-wall carbon nano-tubes and other materials, and is mainly used for improving the heat-conducting performance, strength, toughness, wear resistance and other performances of the composite material. The wear-resistant composite material disclosed by the invention can keep a stable friction coefficient and a low wear rate under the conditions of a heavy load, a high speed, and long-time braking.
Owner:SUZHOU FIRST ELEMENT NANO TECH
Chemical modifications to polymer surfaces and the application of polymer grafting to biomaterials
InactiveUS20050237480A1Numerous polymerizationQuality improvementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansOptical partsPolymeric surfacePolymer science
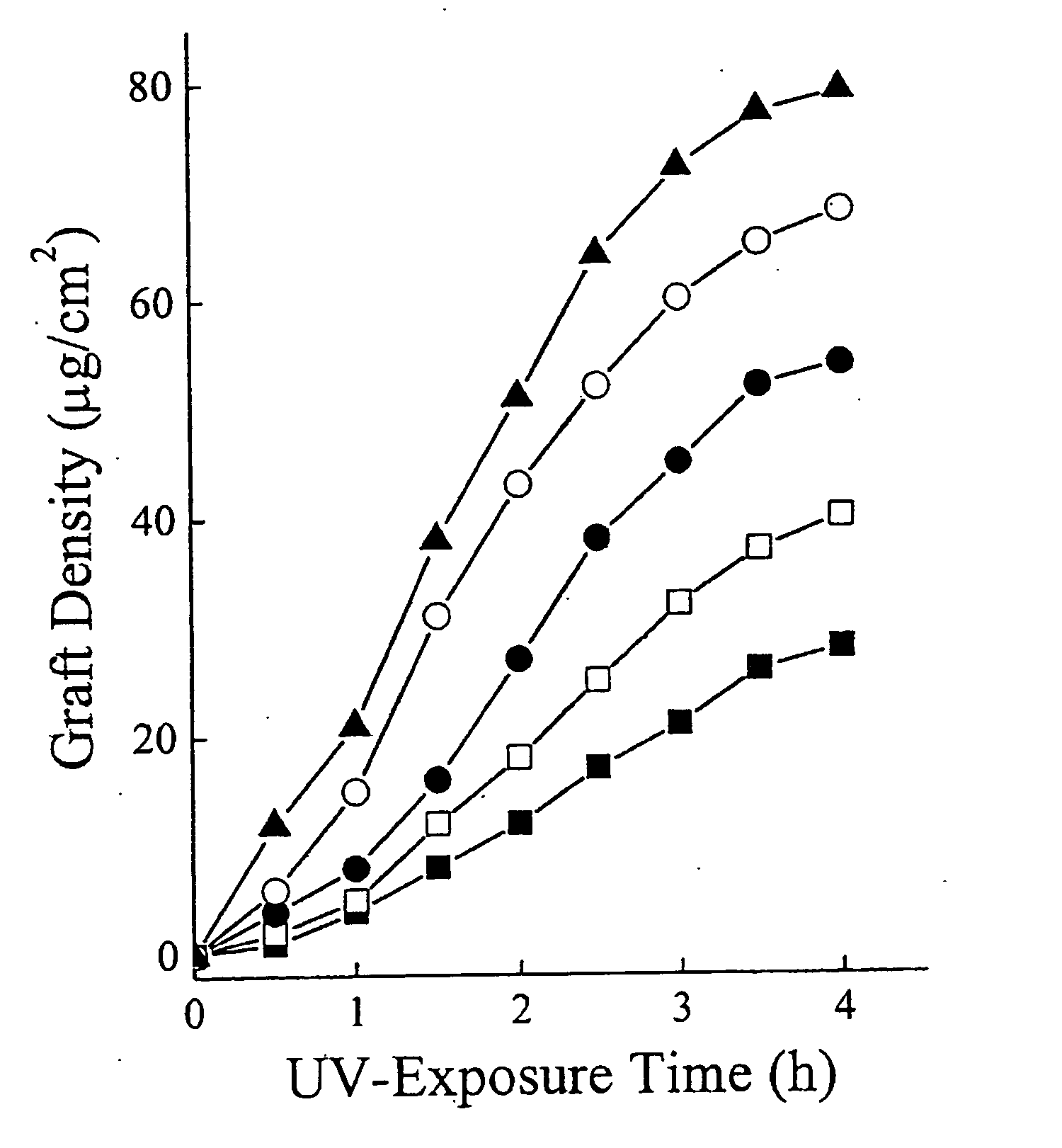
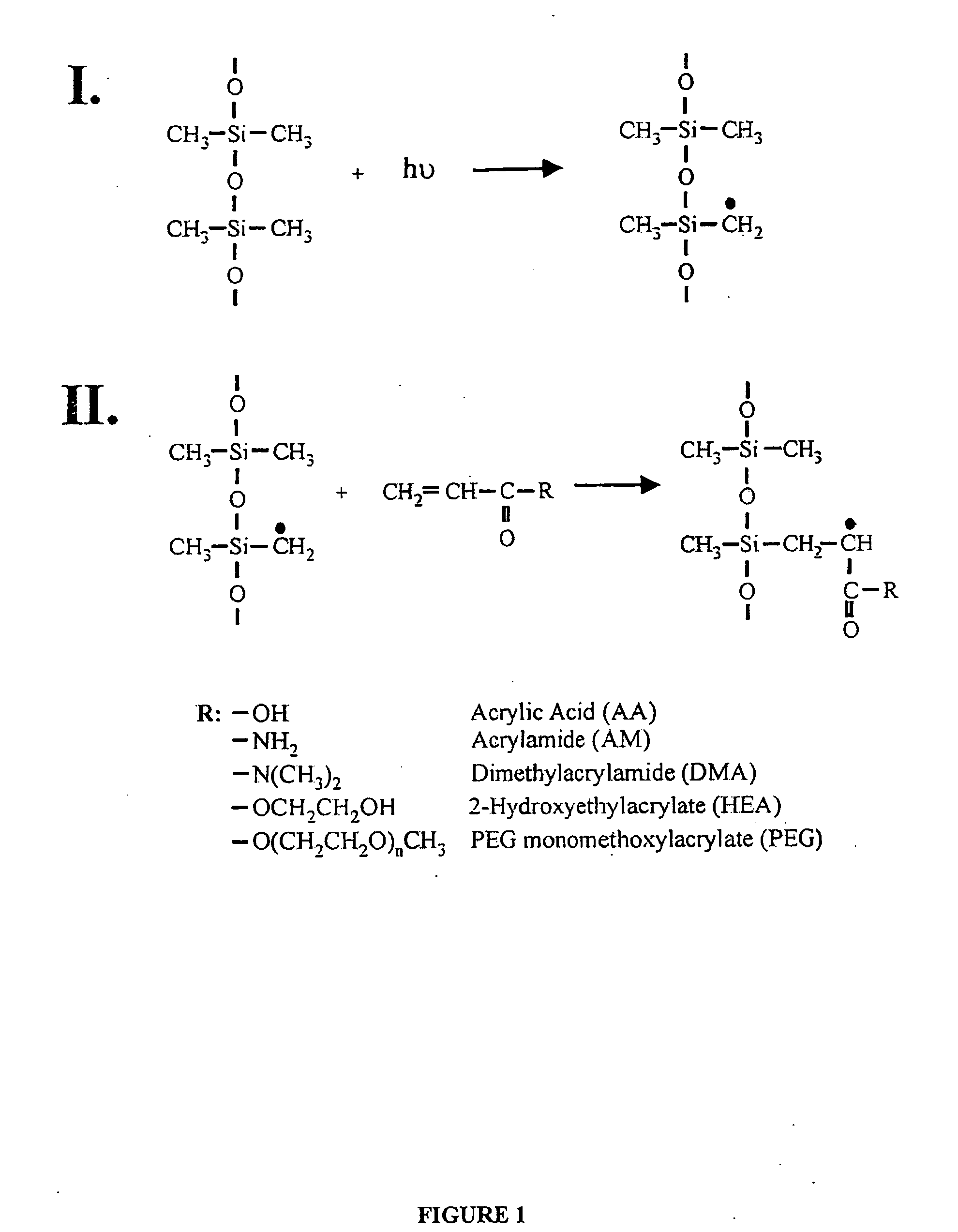
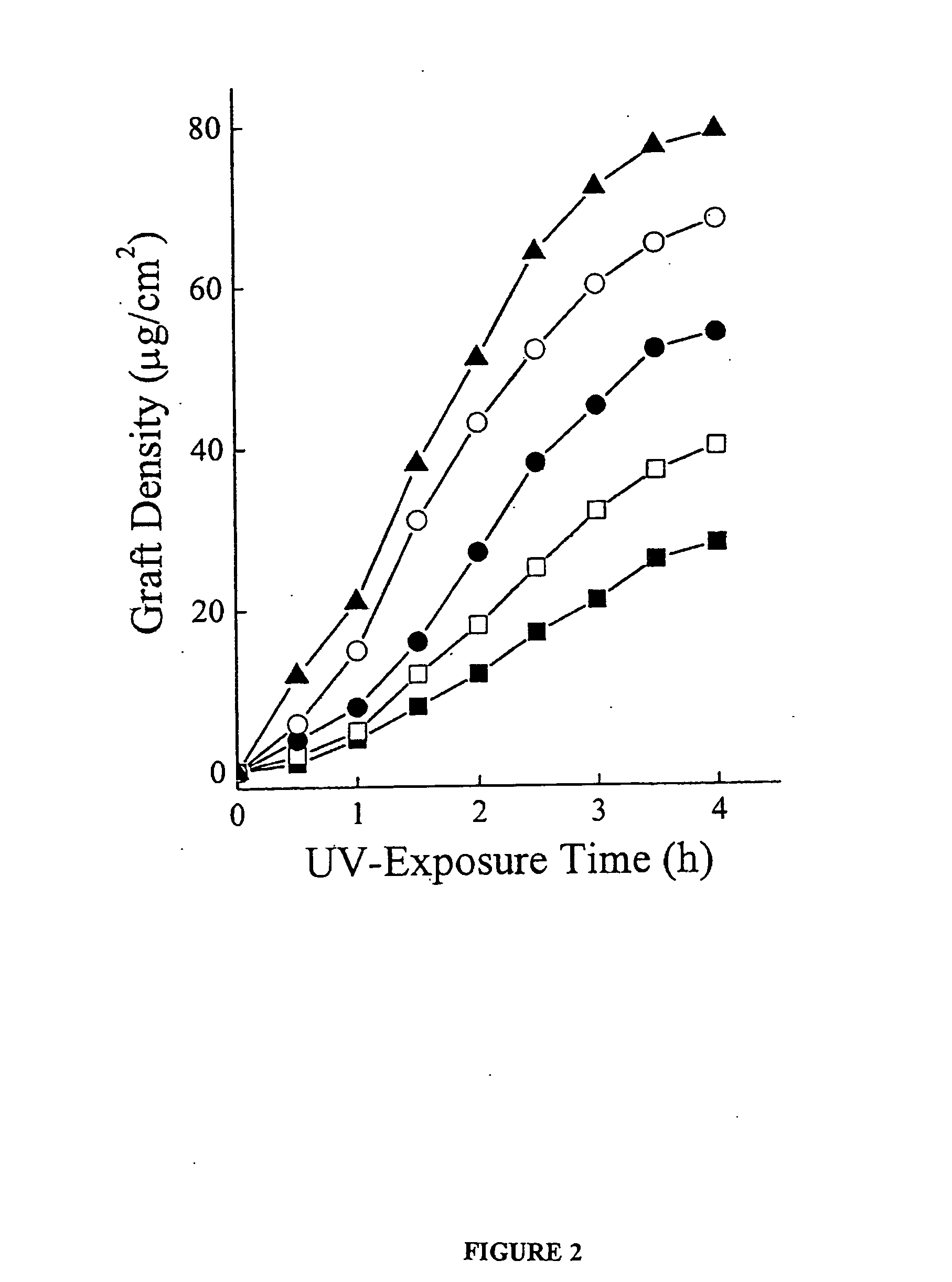
Polymer-based biomaterials are popular due to ease of fabrication and low costs. However, many polymer substrates have undesirable surface properties. The invention provides a procedure to covalently apply a graft polymer to the surface of a polymer substrate by ultraviolet graft polymerization. The graft polymer is formed from monomers such as PEG, AA, monomethoxy acrylate PEG, HEMA, or DMA. Also, mixed monomers may be used to create the graft and the surface properties of the graft may be tailored for different properties, including hydrophobicity, friction coefficient, electroosmotic mobilities and electrophoretic separations. The invention has particular utility in tailoring surface chemistries in ocular lenses and polymer microdevices. I.II.R:—OHAcrylic Acid(AA)—NH2Acrylamide (AM)—N(CH3)2Dimethylacrylamide (DMA)—OCH2CH2OH2-Hydroxyethylacrylate (HEA)—O(CH2CH2O)nCH3PEG monomethyoxylacrylate (PEG)
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Methods and systems for improved drilling operations using real-time and historical drilling data
ActiveUS9022140B2Easy to operateOptimized for speedEarth drilling toolsMathematical modelsLithologyReal-time data
Methods and systems are described for improved drilling operations through the use of real-time drilling data to predict bit wear, lithology, pore pressure, a rotating friction coefficient, permeability, and cost in real-time and to adjust drilling parameters in real-time based on the predictions. The real-time lithology prediction is made by processing the real-time drilling data through a multilayer neural network. The real-time bit wear prediction is made by using the real-time drilling data to predict a bit efficiency factor and to detect changes in the bit efficiency factor over time. These predictions may be used to adjust drilling parameters in the drilling operation in real-time, subject to override by the operator. The methods and systems may also include determining various downhole hydraulics parameters and a rotary friction factor. Historical data may be used in combination with real-time data to provide expert system assistance and to identify safety concerns.
Owner:RESOURCE ENERGY SOLUTIONS
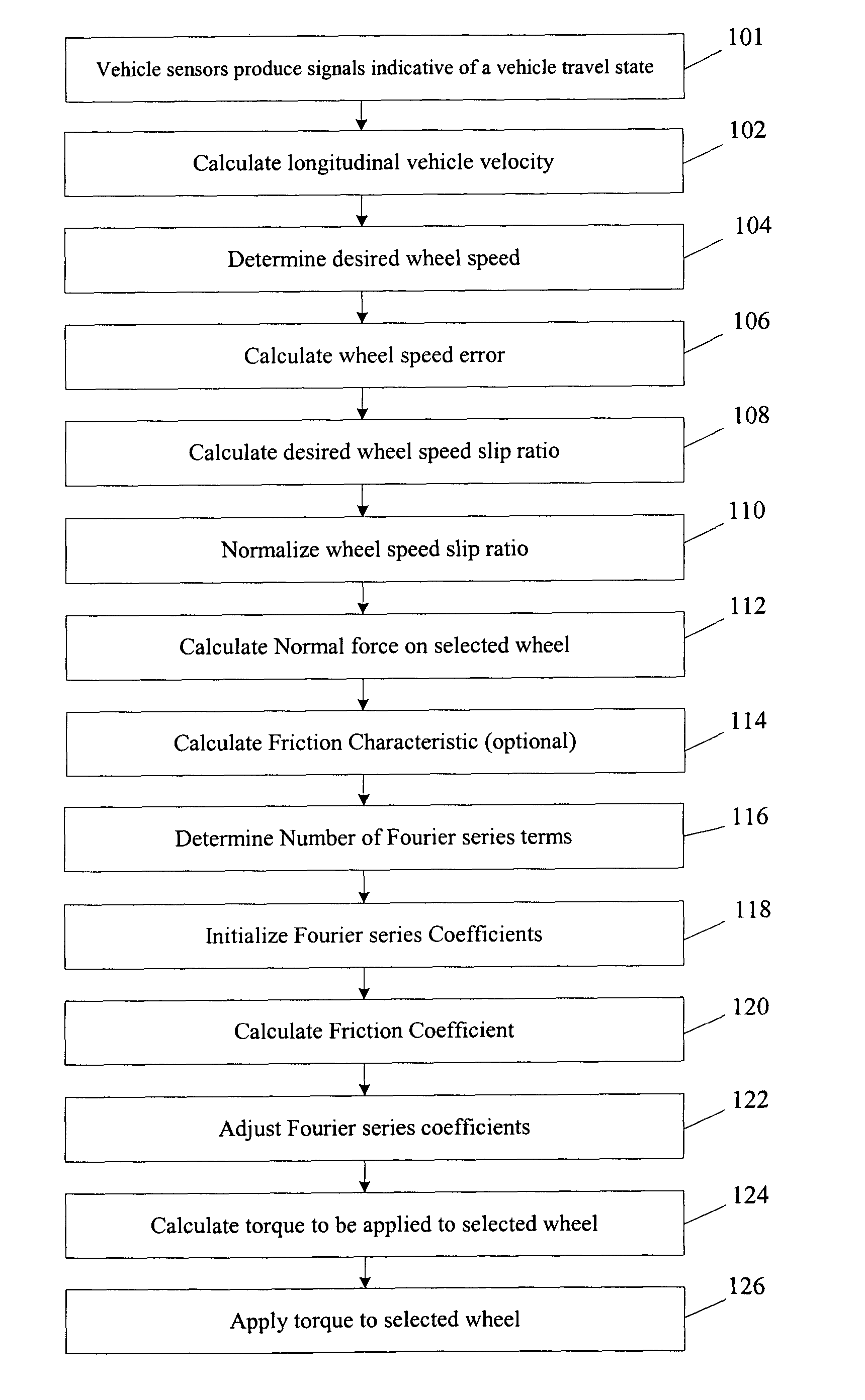
Method for estimating a friction coefficient
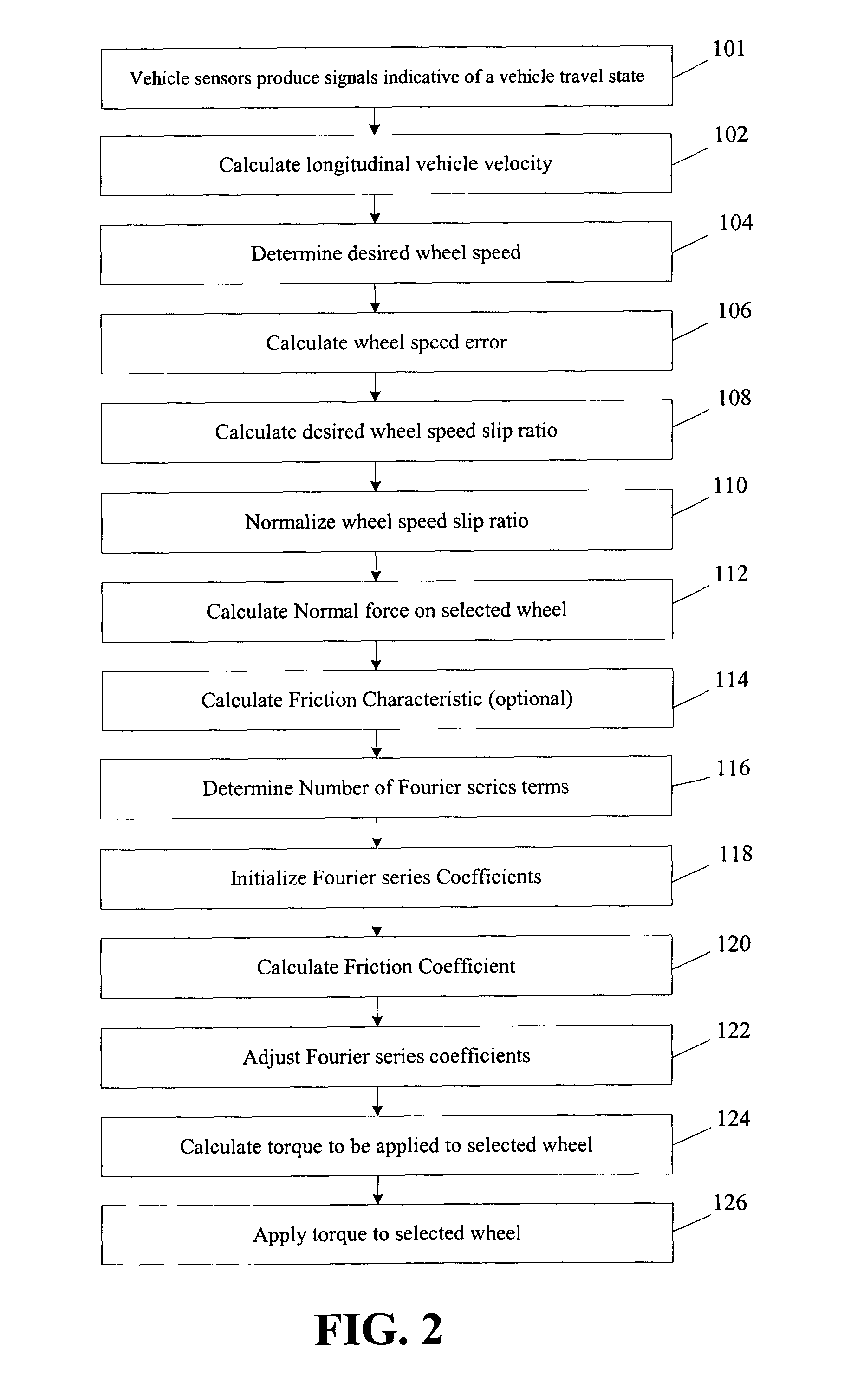
InactiveUS20050038589A1Reduce the differenceDigital data processing detailsAutomatic initiationsAccelerometerDrive wheel
A method and a system for estimating a friction coefficient between a driven wheel and a surface. The method uses a Fourier series to calculate the friction coefficient. More specifically, a desired wheel slip ratio is calculated using received sensor readings related to a system state and a desired wheel speed determined from various system conditions or user inputs. A Fourier series is used to estimate the friction coefficient. The method is generally cycled many times each second to allow for varying road conditions by adjusting the Fourier series coefficients after each cycle. The system generally includes a wheel speed sensor and an accelerometer providing signals to a processor or various modules to perform the above method.
Owner:VISTEON GLOBAL TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com